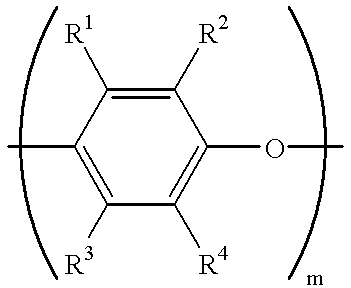
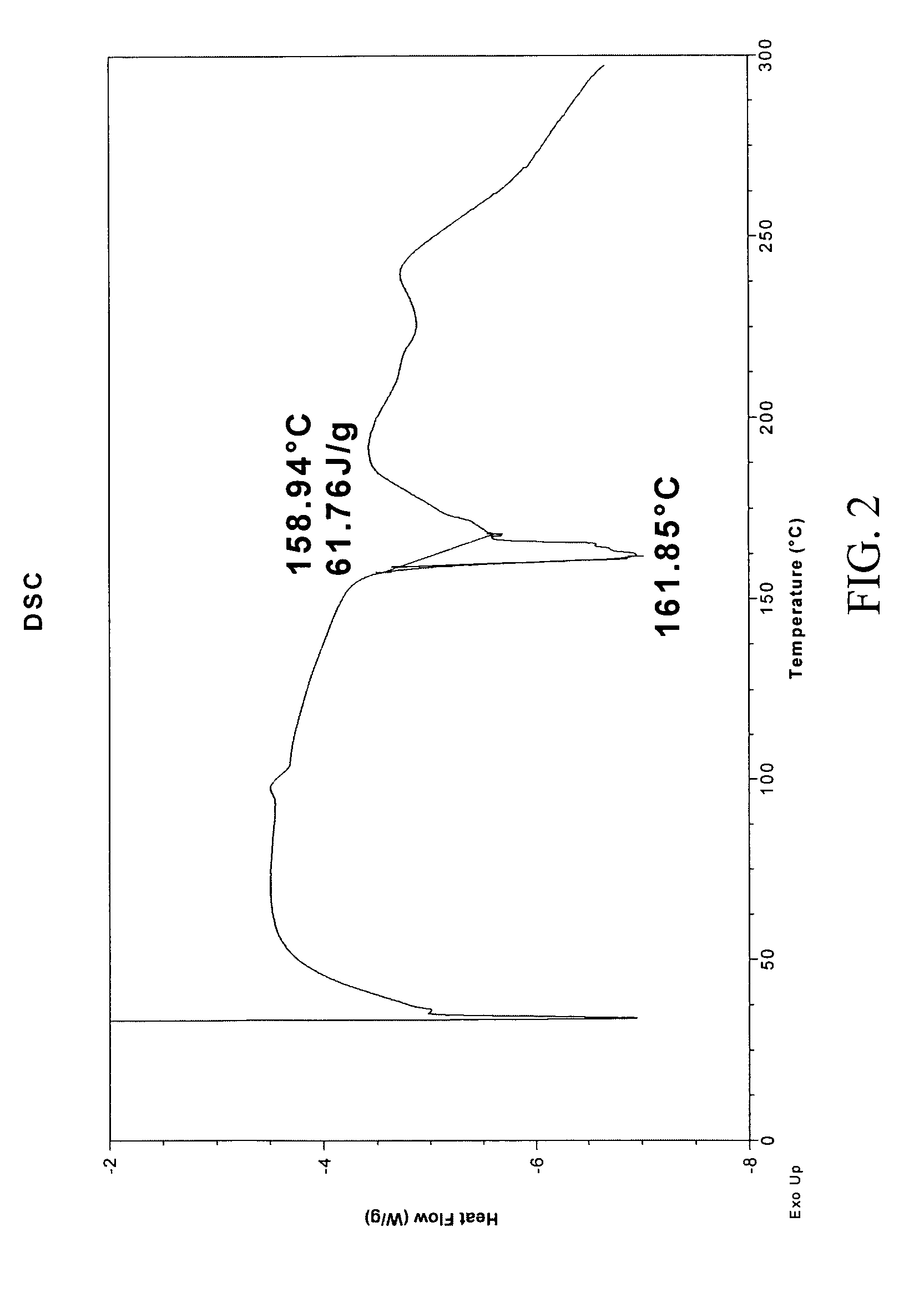
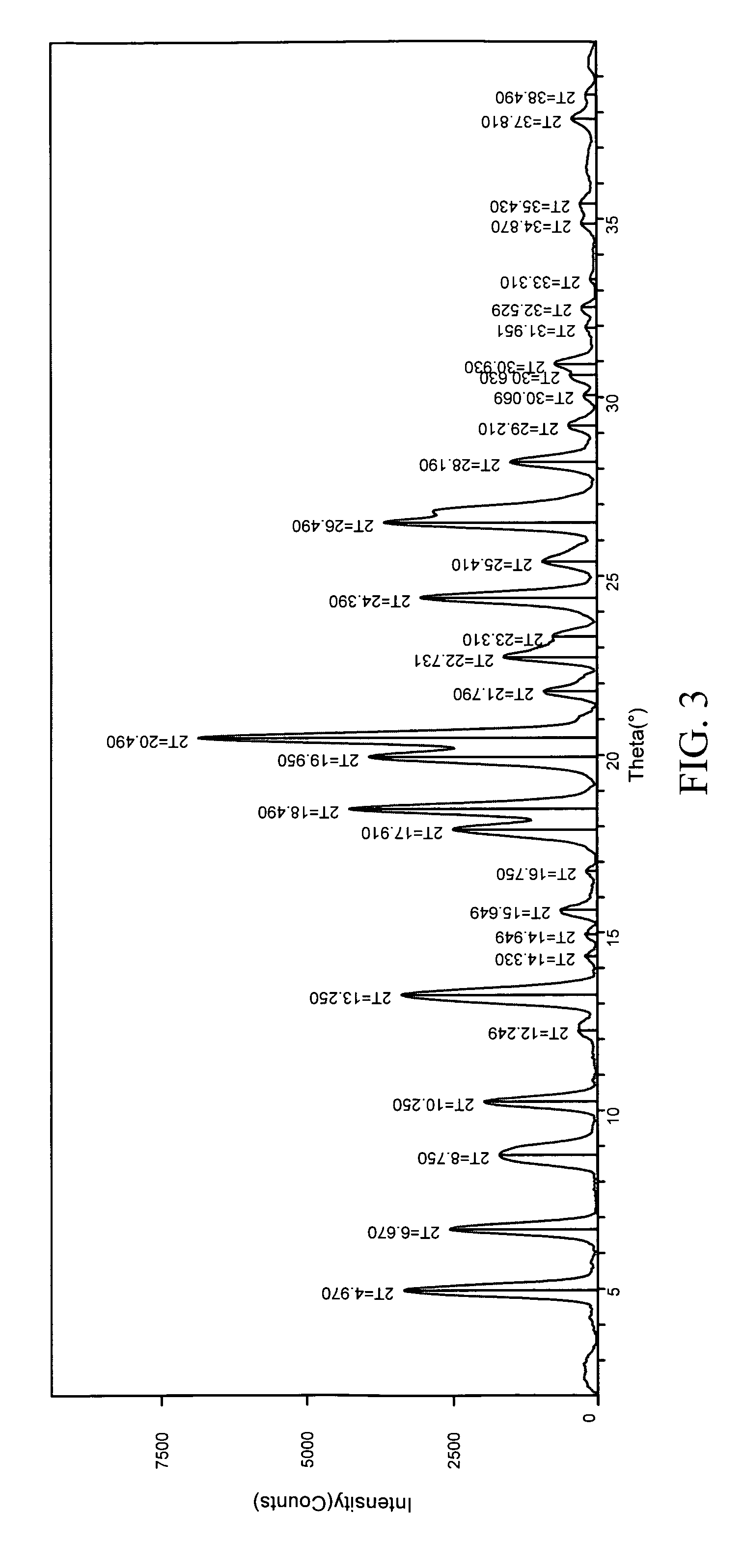
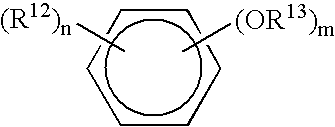
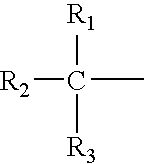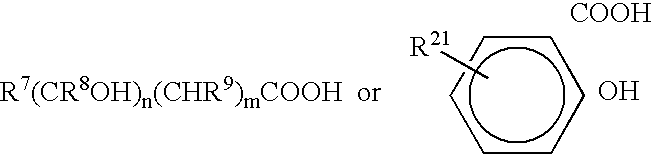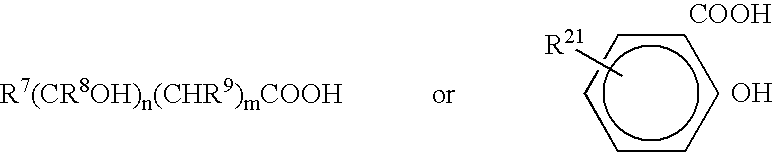Patents
Literature
38700 results about "Ether" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
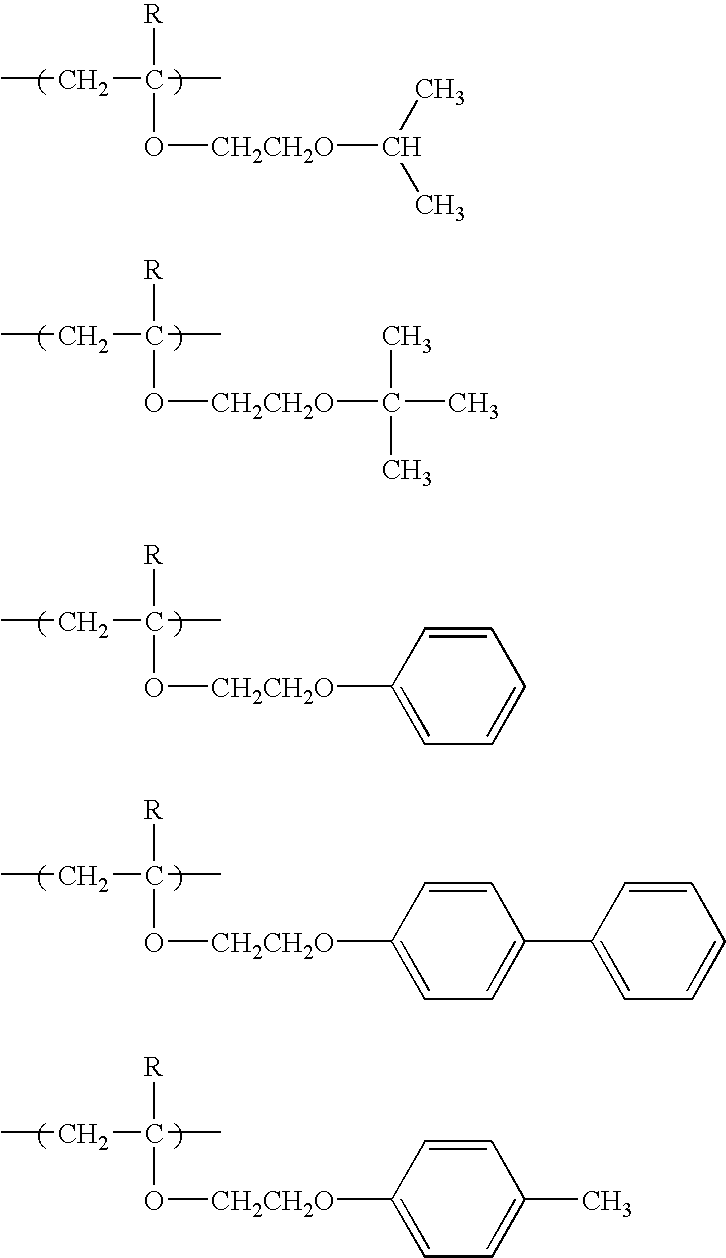
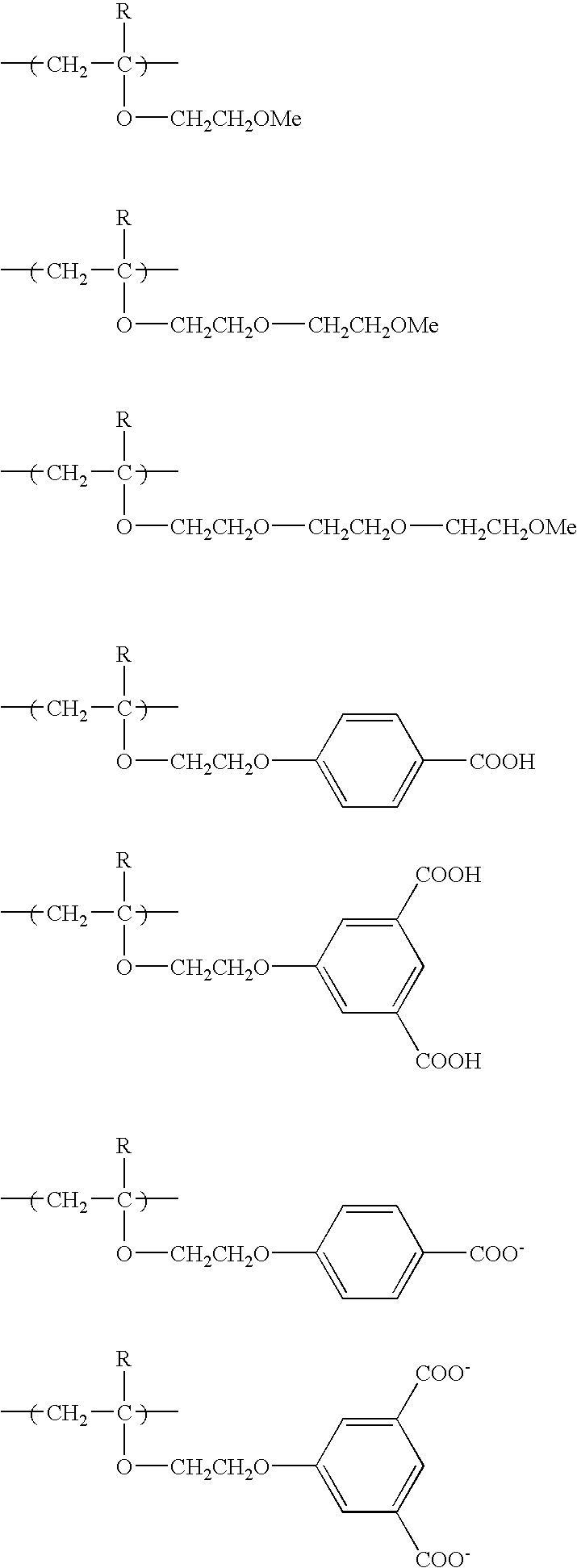
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups, as opposed to esters. They have the general formula R–O–R′, where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (CH₃–CH₂–O–CH₂–CH₃). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.
Precursor source mixtures
A precursor source mixture useful for CVD or ALD of a film comprising: at least one precursor composed of an element selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr, Be, Mg, Ti, Zr, Hf, Sc, Y, La, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Re, Fe, Ru, Os, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, B, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, As, P, Sb and Bi, to which is bound at least one ligand selected from the group consisting of hydride, alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkenyl, aryl, alkyne, carbonyl, amido, imido, hydrazido, phosphido, nitrosyl, nitryl, nitrate, nitrile, halide, azide, alkoxy, siloxy, silyl, and halogenated, sulfonated or silyated derivatives thereof, which is dissolved, emulsified or suspended in an inert liquid selected from the group consisting of aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, acids, phenols, esters, amines, alkylnitrile, halogenated hydrocarbons, silyated hydrocarbons, thioethers, amines, cyanates, isocyanates, thiocyanates, silicone oils, nitroalkyl, alkylnitrate, and mixtures thereof. The precursor source mixture may be a solution, emulsion or suspension and may consist of a mixture of solid, liquid and gas phases which are distributed throughout the mixture.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
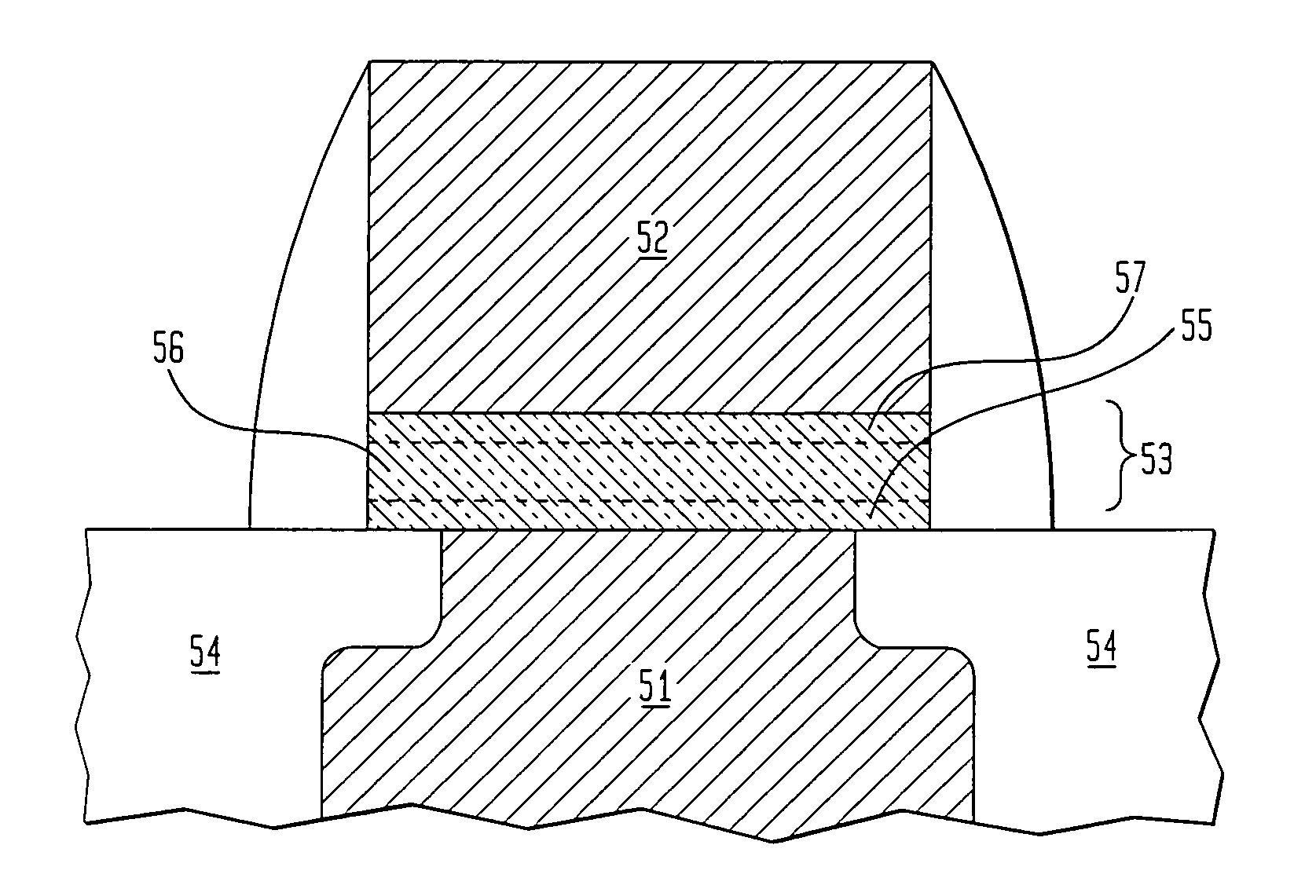
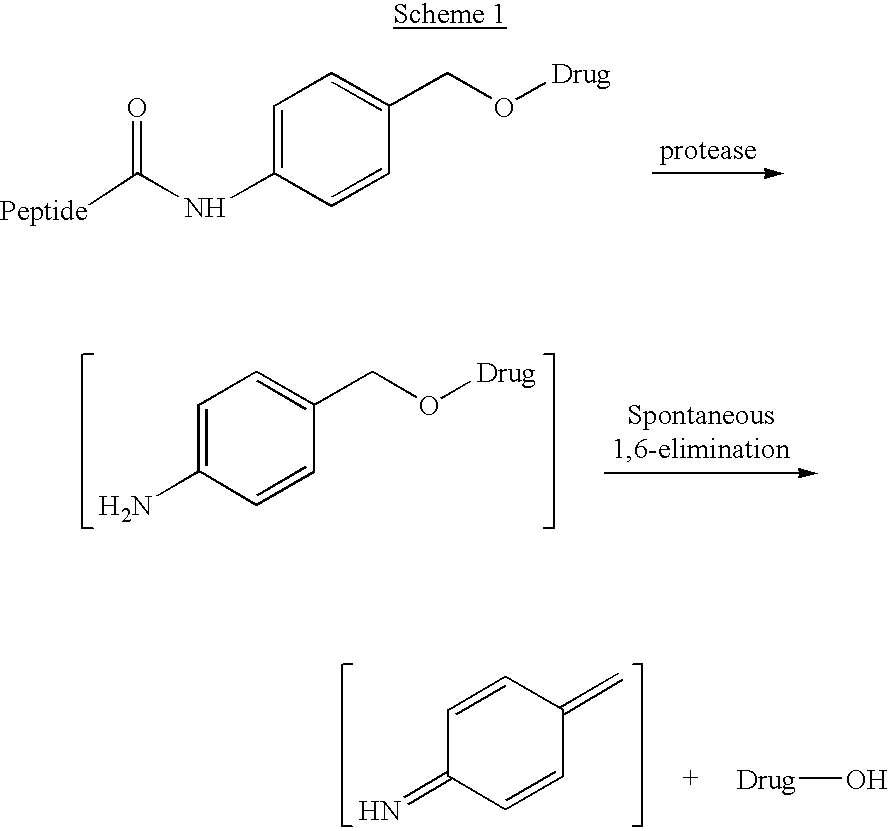
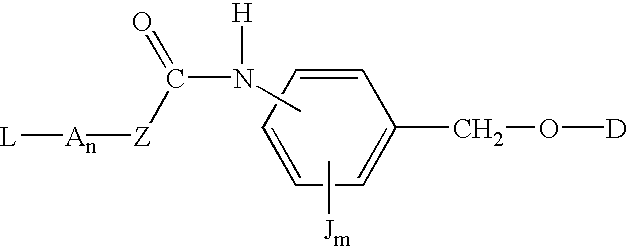
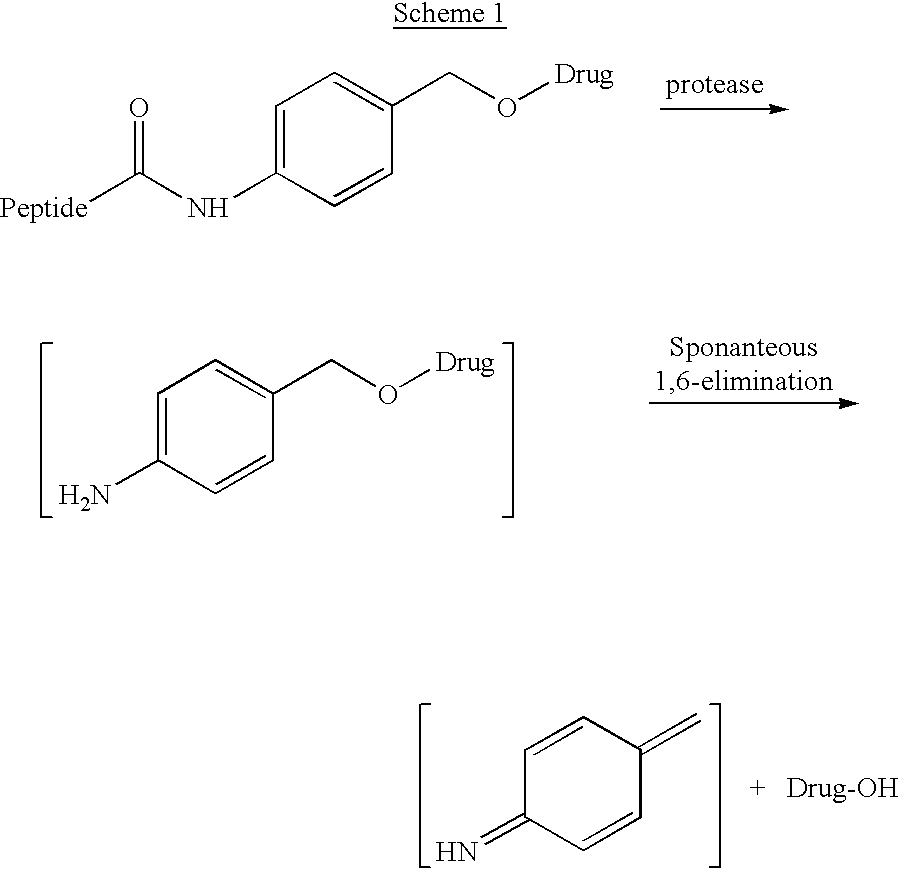
P-amidobenzylethers in drug delivery agents
InactiveUS20030130189A1Decrease in drug activityImprove stabilityTetrapeptide ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsEtherDiluent
Compounds of the formulas LAn-Z-X-WwD and BZ-X-WwD wherein: D is a drug moiety; L is a ligand; B is a blocking group; A is an optional acyl unit; Z is an amino acid or a peptide; X is an aminobenzyl ether self-immolative spacer group; W is an optional second self-immolative group; n is an integer of 0 or 1; and w is an integer of 0 or 1, and compositions of said compounds with pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, diluent and / or excipient, and methods of delivery the drug D via the compounds.
Owner:SEAGEN INC
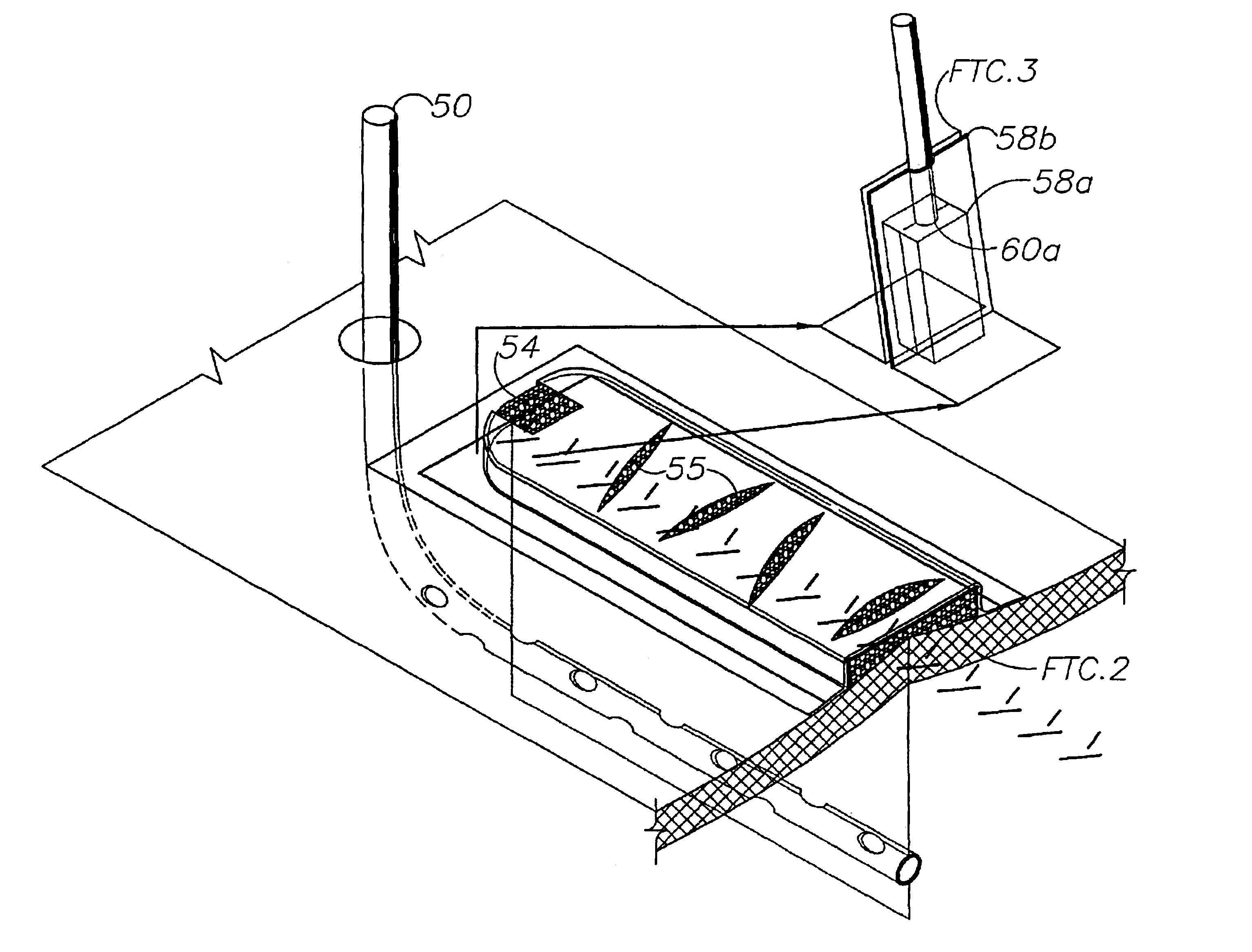
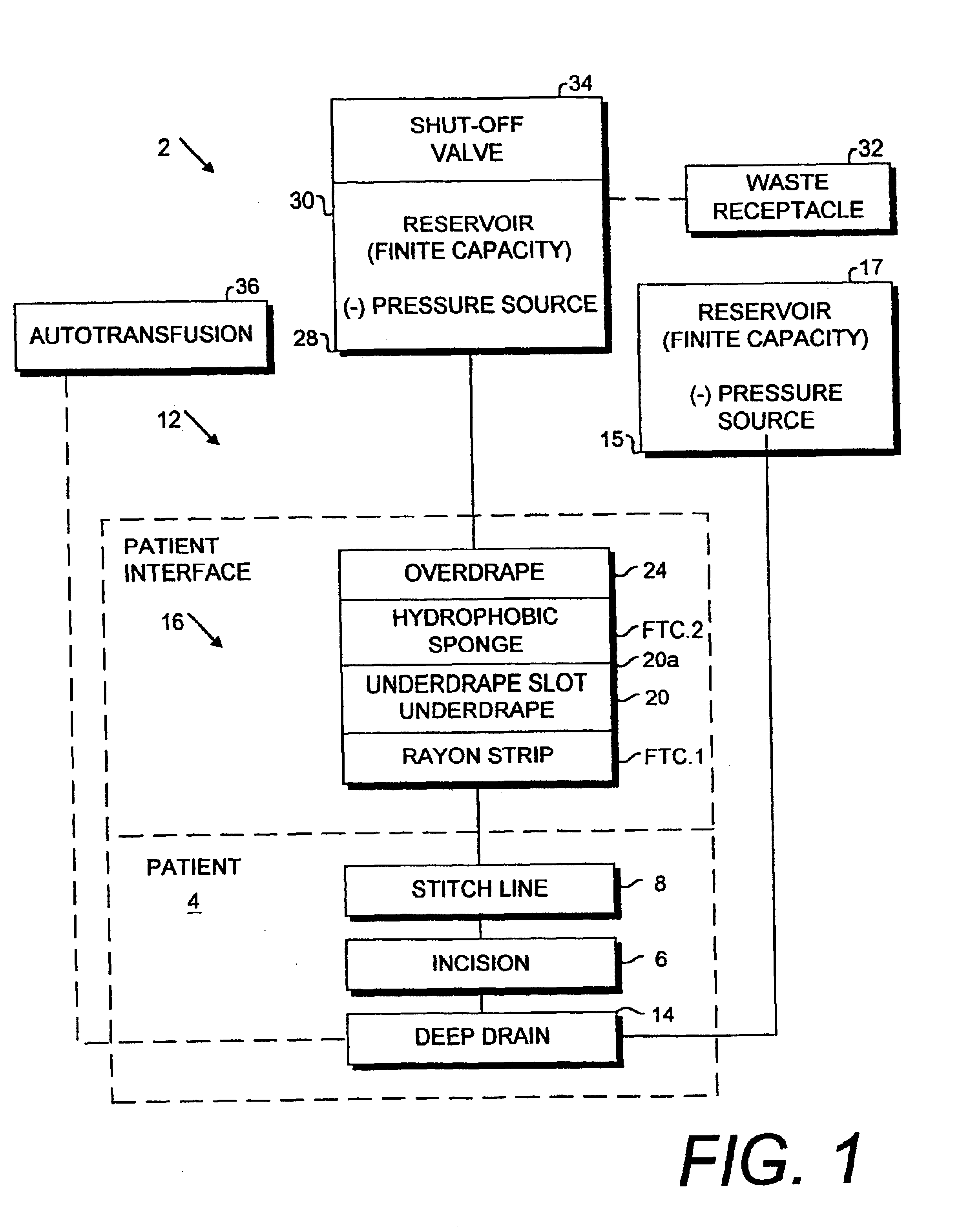
Tissue closure treatment system and method with externally-applied patient interface
A tissue closure treatment system and method are provided with an external patient interface. A first fluid transfer component FTC.1 comprises a strip of porous material, such as rayon, with liquid wicking properties. FTC.1 can be placed directly on a suture line for transferring fluid exuded therethrough. An underdrape is placed over FTC.1 and includes a slot exposing a portion of same. FTC.2 comprises a suitable hydrophobic foam material, such as polyurethane ether, and is placed over the underdrape slot in communication with FTC.1. Negative pressure is applied to FTC.2 through a connecting fluid transfer component FTC.3. A negative pressure source can comprises a manual device or a power-operated suction device. The tissue closure method includes a manual operating mode using a manual suction device with an automatic shut off for discontinuing suction when a predetermined volume of fluid has been drained. An automatic operating mode utilizes a microprocessor, which can be preprogrammed to respond to various patient and operating conditions. The method proceeds through several phases with different components in place and different patient interface functions occurring in each.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Process for preparing olefin polymerization ball type catalytic component and carrier
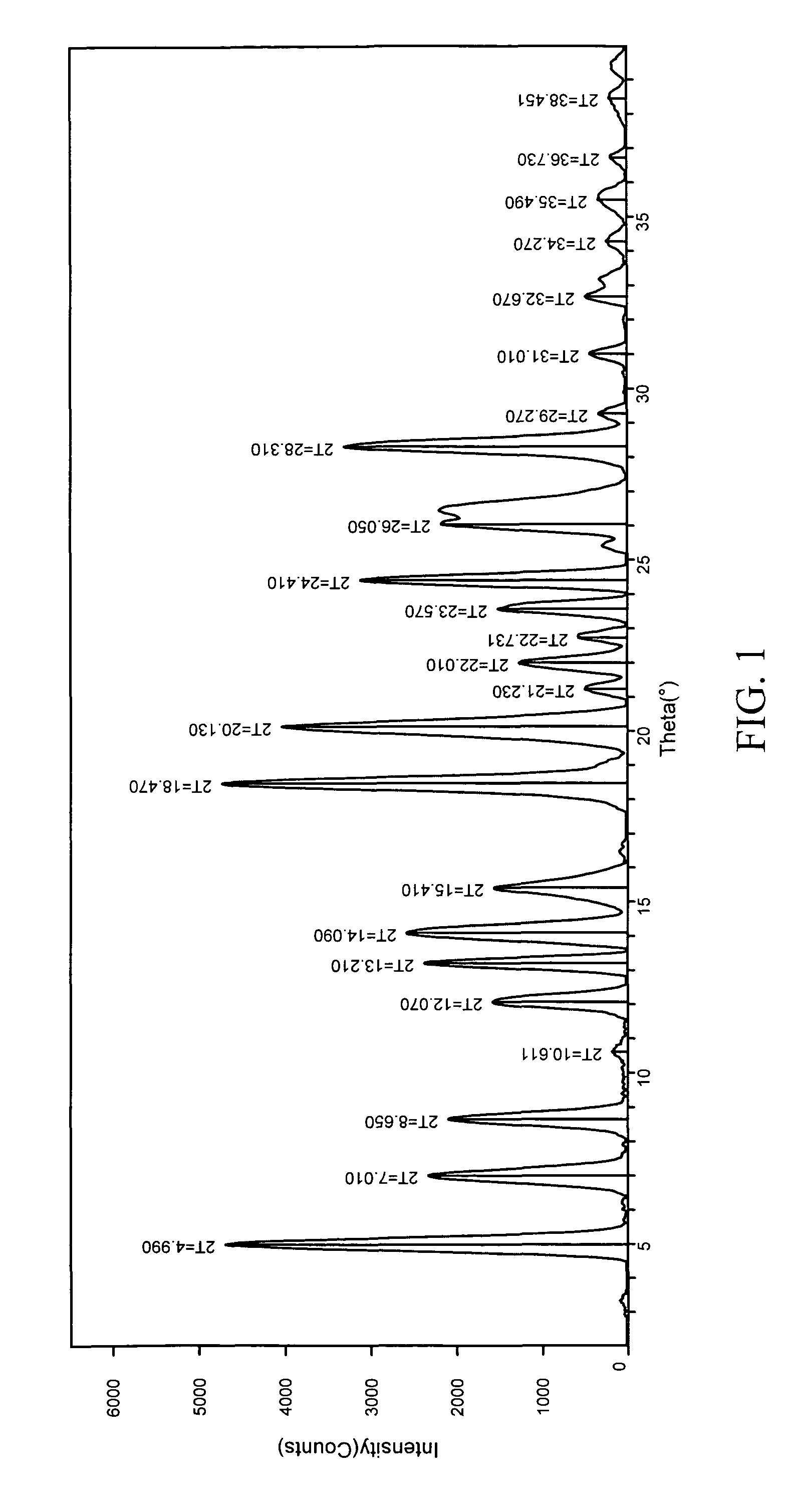
The spherical catalyst carrier is prepared with alcoholated magnesium chloride containing double-ether compound in emulsifying pelletizer. Liquid titanium halide compound is carried onto the spherical catalyst carrier to form spherical solid catalyst component in the presence of electron donor. In the X-ray diffraction spectrogram, the spherical solid catalyst component has diffraction peak in 13.3 deg of 2theta angle, strongest diffraction peak in 26.5 deg of 2theta angle and no characteristic diffraction peak of alpha-anhydrous MgCl2 in 15 deg of 2theta angle. The catalyst of the presentinvention has very high activity and may be used to produce polymer with good form, high apparent density and less fine powder. The catalyst is used in homopolymerization and copolymerization of olefin and suitable for various polymerization process.
Owner:YINGKOU XIANGYANG CATALYST
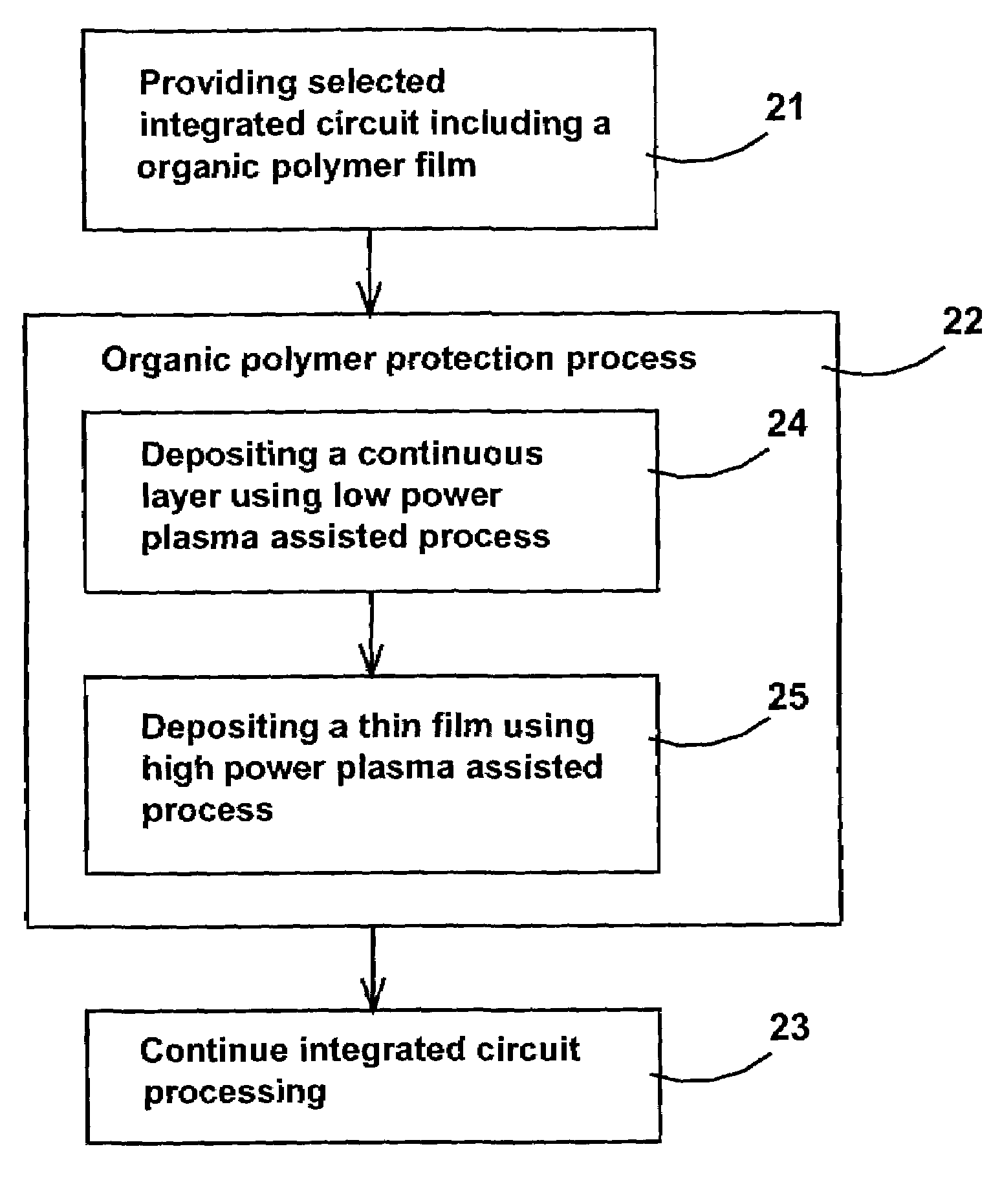
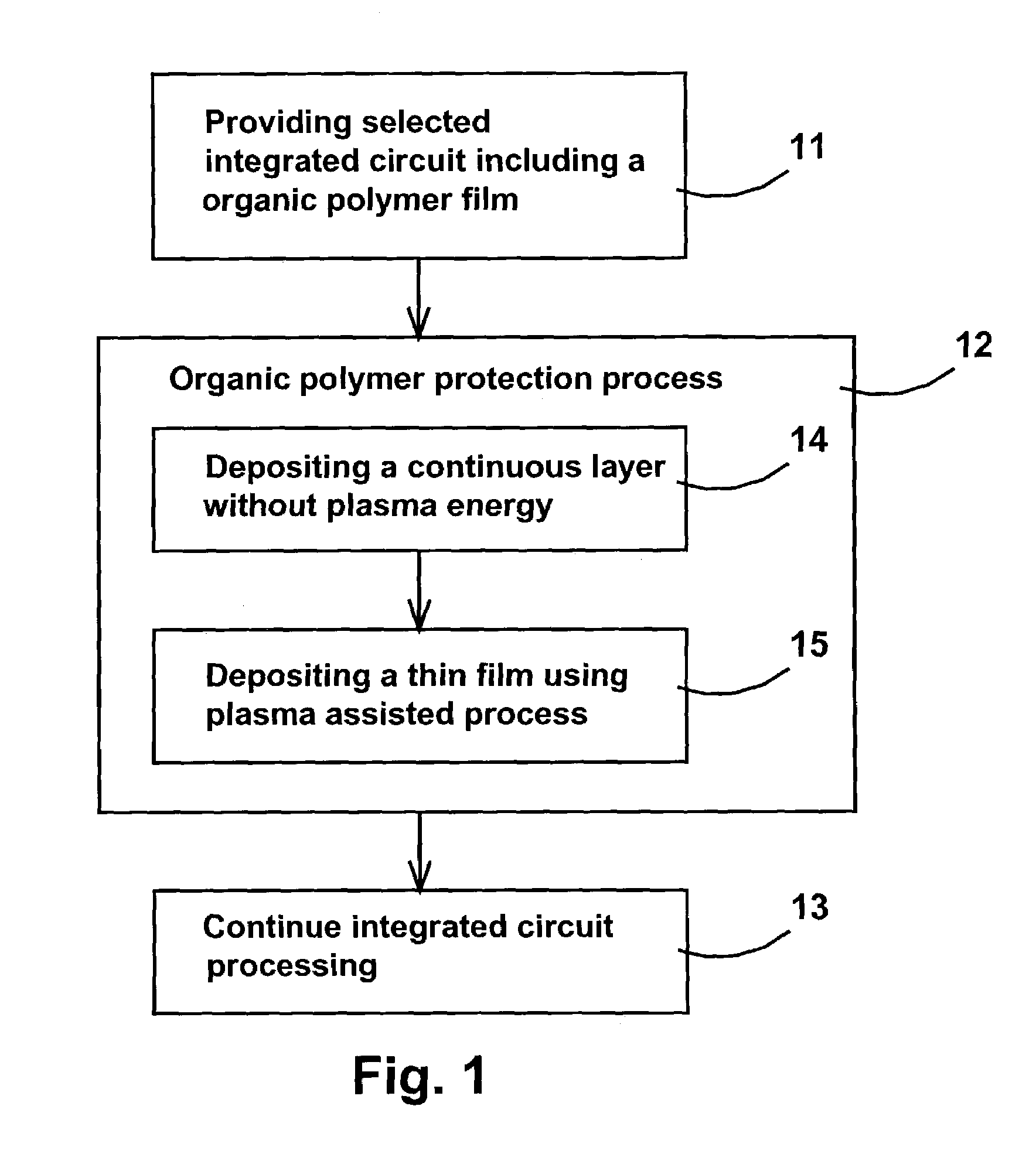
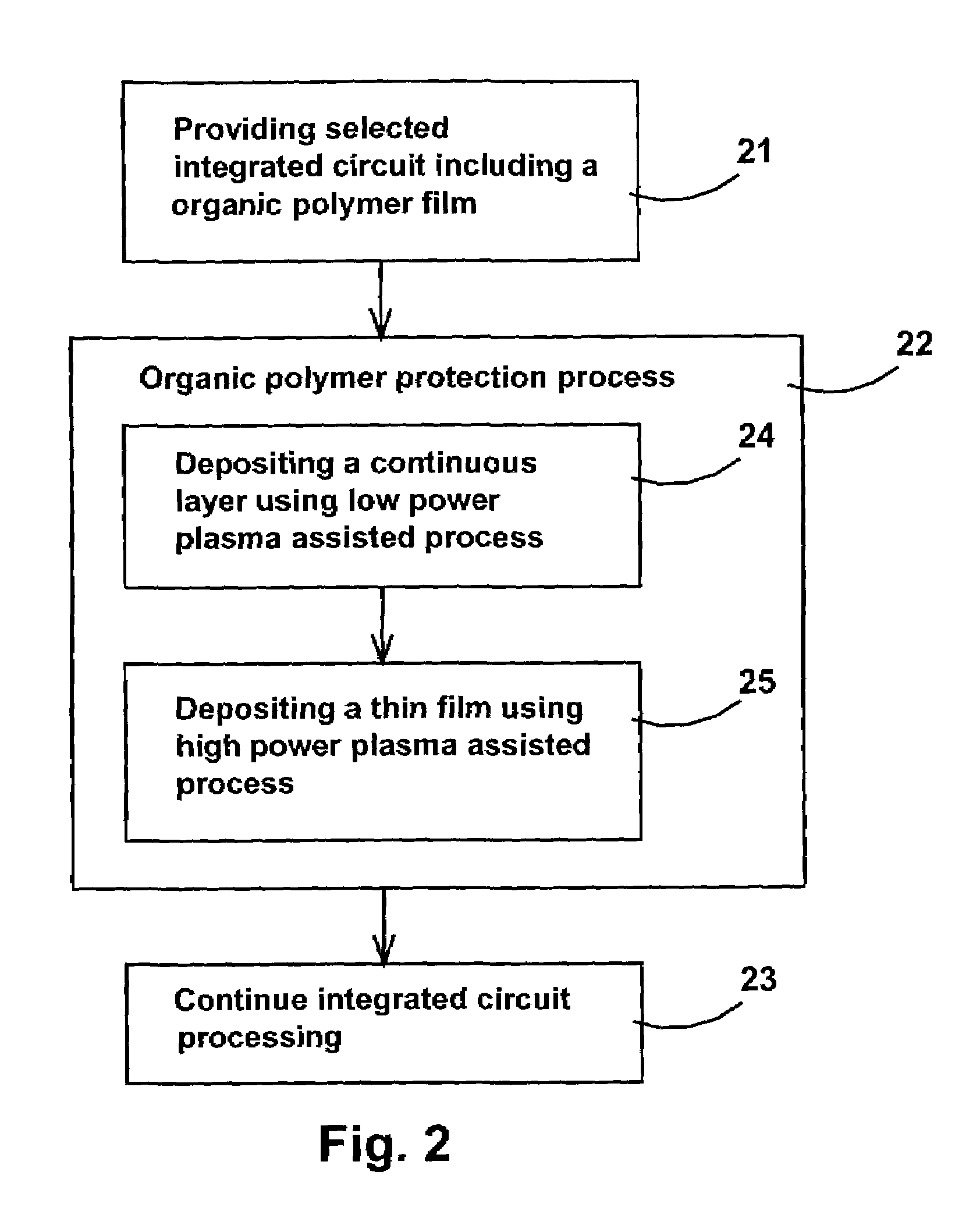
Method to plasma deposit on organic polymer dielectric film
ActiveUS7163721B2Without sacrificing qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon nitrideEther
A method for protecting an organic polymer underlayer during a plasma assisted process of depositing a subsequent film on the organic polymer underlayer is disclosed. The method provides the deposition of a protective continuous layer using organic polymer damage-free technique in order to not damage the organic polymer underlayer and to protect the organic polymer underlayer during the plasma assisted process of depositing a subsequent film. The organic polymer damage-free technique is a non-plasma process, using only thermal energy and chemical reactions to deposit the continuous layer. The organic polymer damage-free technique can also be a plasma assisted process using a reduced plasma power low enough in order to not damage the organic polymer underlayer. This method is applicable to many organic polymer underlayers such as organic polymer is aromatic hydrocarbon, polytetrafluoroehtylene (PTFE), parylene, benzocyclobutene-based polymers (BCB), polyimide, fluorinated polyimide, fluorocarbon-based polymers, poly(arylene ether)-based polymers (PAE), cyclohexanone-based polymers, and to many plasma assisted deposition processes such as plasma enhanced CVD deposition, plasma enhanced ALD deposition and plasma enhanced NLD deposition of silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, nitrided diffusion barrier such as TiN, TaN, WN, TiSiN, TaSiN, WSiN.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
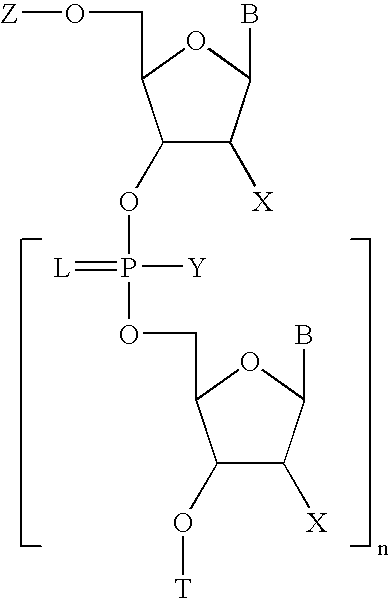
Methods for synthesis of oligonucleotides
Improved methods for synthesis of oligonucleotides and other phosphorus-linked oligomers are disclosed. The methods include the use of aromatic solvents, alkyl aromatic solvents, halogenated aromatic solvents, halogenated alkyl aromatic solvents, or aromatic ether solvents to achieve deprotection of protected hydroxyl groups.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using a fluorinated surfactant
InactiveUS20070015866A1Low toxicityGood chemical stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsFibre treatmentEmulsion polymerizationEther
The present invention provides an aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers including gaseous fluorinated monomers using a perfluoro ether surfactant as an emulsifier. The perfluoro ether surfactants correspond to formula (I) Rf—O—CF2CF2—X (I) wherein Rf represents a linear or branched perfluoroalkyl group having 1, 2, 3 or 4 carbon atoms and X represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof. In a further aspect, the invention also provides an aqueous fluoropolymer dispersion comprising the perfluoro ether surfactant and the use of such dispersion in the coating or impregnation of substrates.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
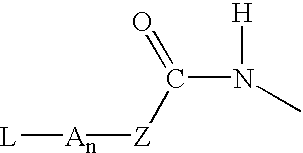
p-Amidobenzylethers in drug delivery agents
Compounds of the formulaeLAn-Z-X—WwD and BZ-X—WwDwherein: D is a drug moiety; L is a ligand; B is a blocking group; A is an optional acyl unit; Z is an amino acid or a peptide residue; X is an aminobenzyl ether self-immolative spacer group; W is an optional second self-immolative group; n is an integer of 0 or 1; and w is an integer of 0 or 1, and compositions of said compounds with pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, diluent and / or excipient, and methods of delivery the drug D via the compounds.
Owner:SEAGEN INC
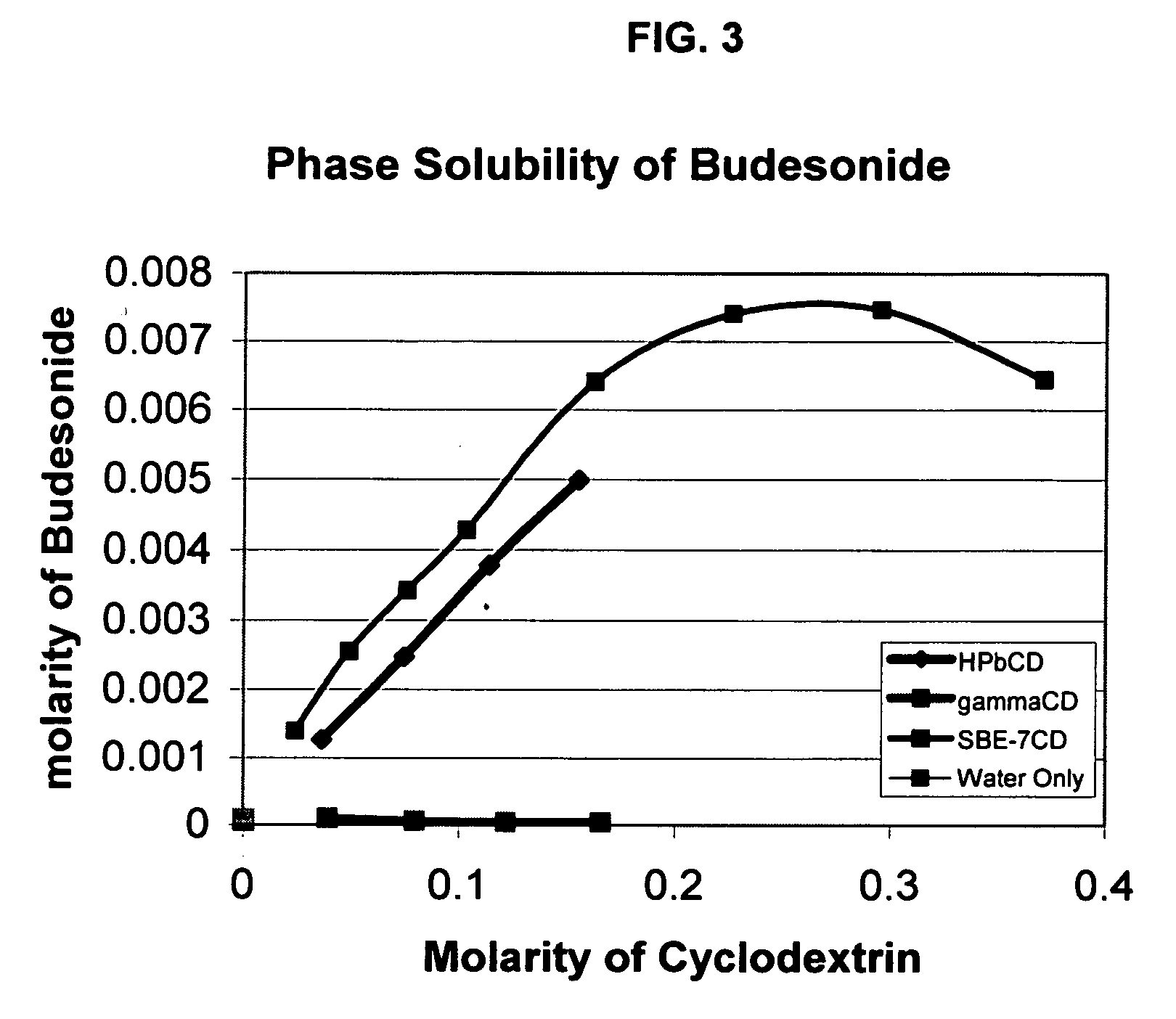
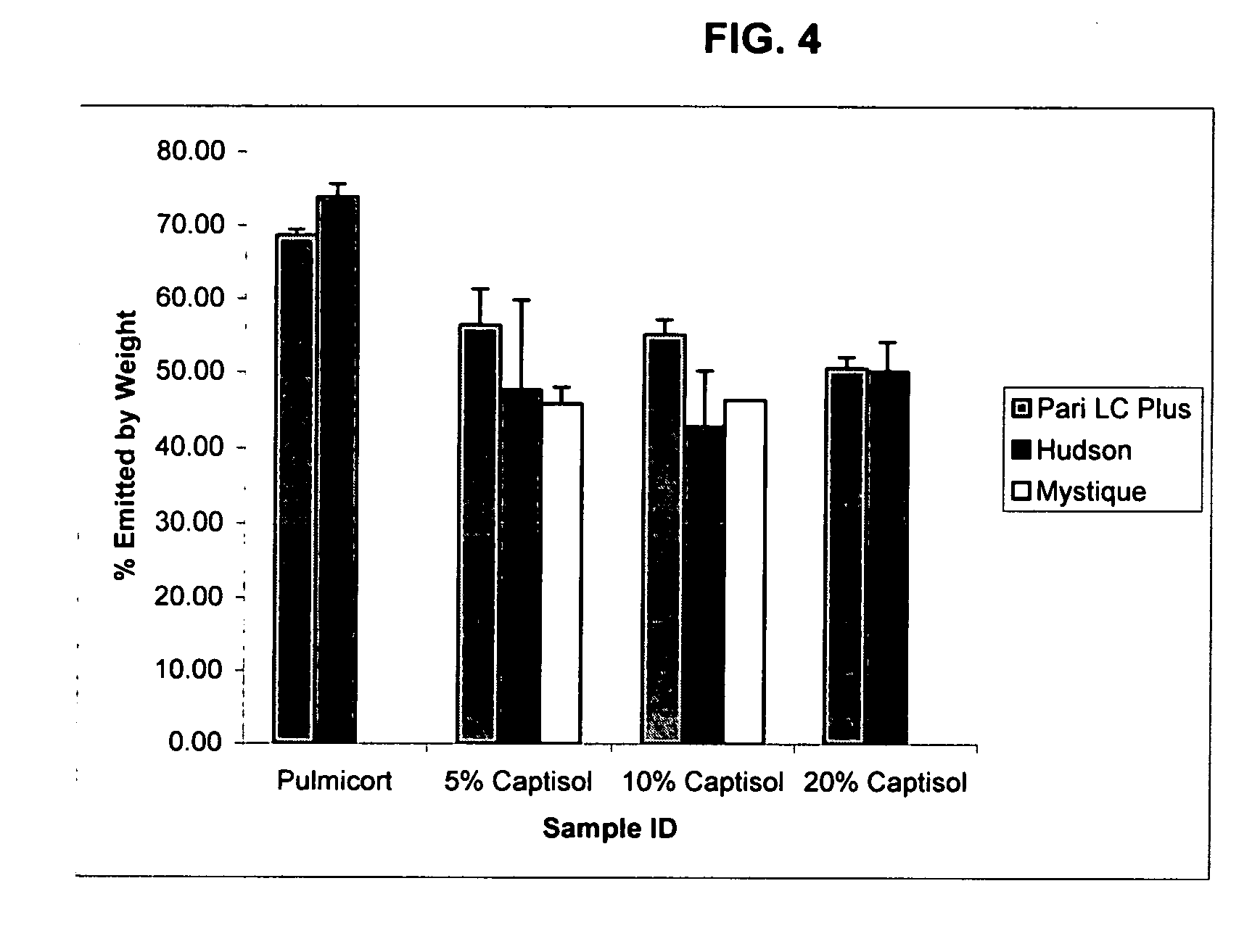
Inhalant formulation containing sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin and corticosteroid prepared from a unit dose suspension
InactiveUS20070020196A1Reduce the degradation rateIncrease productivityBiocideDispersion deliveryNebulizerCyclodextrin
An inhalable unit dose liquid formulation containing SAE-CD and corticosteroid is provided. The formulation is adapted for administration to a subject by nebulization with any known nebulizer. The formulation can be included in a kit. The formulation is administered as an aqueous solution or concentrated composition. The formulation is employed in an improved nebulization system for administering corticosteroid by inhalation. SAE-CD present in the formulation significantly enhances the chemical stability of corticosteroid, such as budesonide. A method of administering the formulation by inhalation is provided. The formulation can also be administered by conventional nasal delivery apparatus. The formulation is prepared by mixing SAE-CD, in solid or liquid (dissolved) form, with an inhalable suspension-based unit dose formulation.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Continuous process for the preparation of polytrimethylene ether glycol
InactiveUS6720459B2Liquid-gas reaction as foam/aerosol/bubblesOrganic compound preparationGas phaseEther
The invention is a continuous process for the preparation of polytrimethylene ether glycol from 1,3-propanediol reactant. In addition, the invention is directed to a continuous multi-stage process comprising reacting at least one reactant in a liquid phase in an up-flow column reactor, and forming a gas or vapor phase by-product wherein the gas or vapor phase by-product is continuously removed at the top and at least one intermediate stage.
Owner:DUPONT CA +1
Poly(arylene ether)-containing thermoset composition, method for the preparation thereof, and articles derived therefrom
InactiveUS6627704B2Fast curingReduce sensitivitySynthetic resin layered productsPolyether coatingsHeat resistanceEther
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Sealants and potting formulations including mercapto-terminated polymers produced by the reaction of a polythiol and polyvinyl ether monomer
Sealant and potting formulations are provided which are prepared from components including ungelled mercapto-terminated polymer(s) prepared by reacting reactants comprising polyvinyl ether monomer(s) and polythiol material(s); curing agent(s) reactive with a mercapto group of the mercapto-terminated polymer; and additive(s) selected from the group consisting of fillers, adhesion promoters, plasticizers and catalysts.
Owner:PRC DE SOTO INT INC
Lead free reduced ricochet limited penetration projectile
A frangible projectile with a specific gravity similar to a lead projectile. The projectile comprises 34-94%, by weight, binder. The binder comprises poly ether block amide resin. The projectile further comprises 6-66%, by weight, ballast. The ballast comprises at least one member selected from a group consisting of tungsten, tungsten carbide, molybdenum, tantalum, ferro-tungsten, copper, bismuth, iron, steel, brass, aluminum bronze, beryllium copper, tin, aluminum, titanium, zinc, nickel silver alloy, cupronickel and nickel. The projectile can be prepared with a particularly preferred specific gravity of 5-14 and more preferably 11-11.5.
Owner:ACCUTEC USA
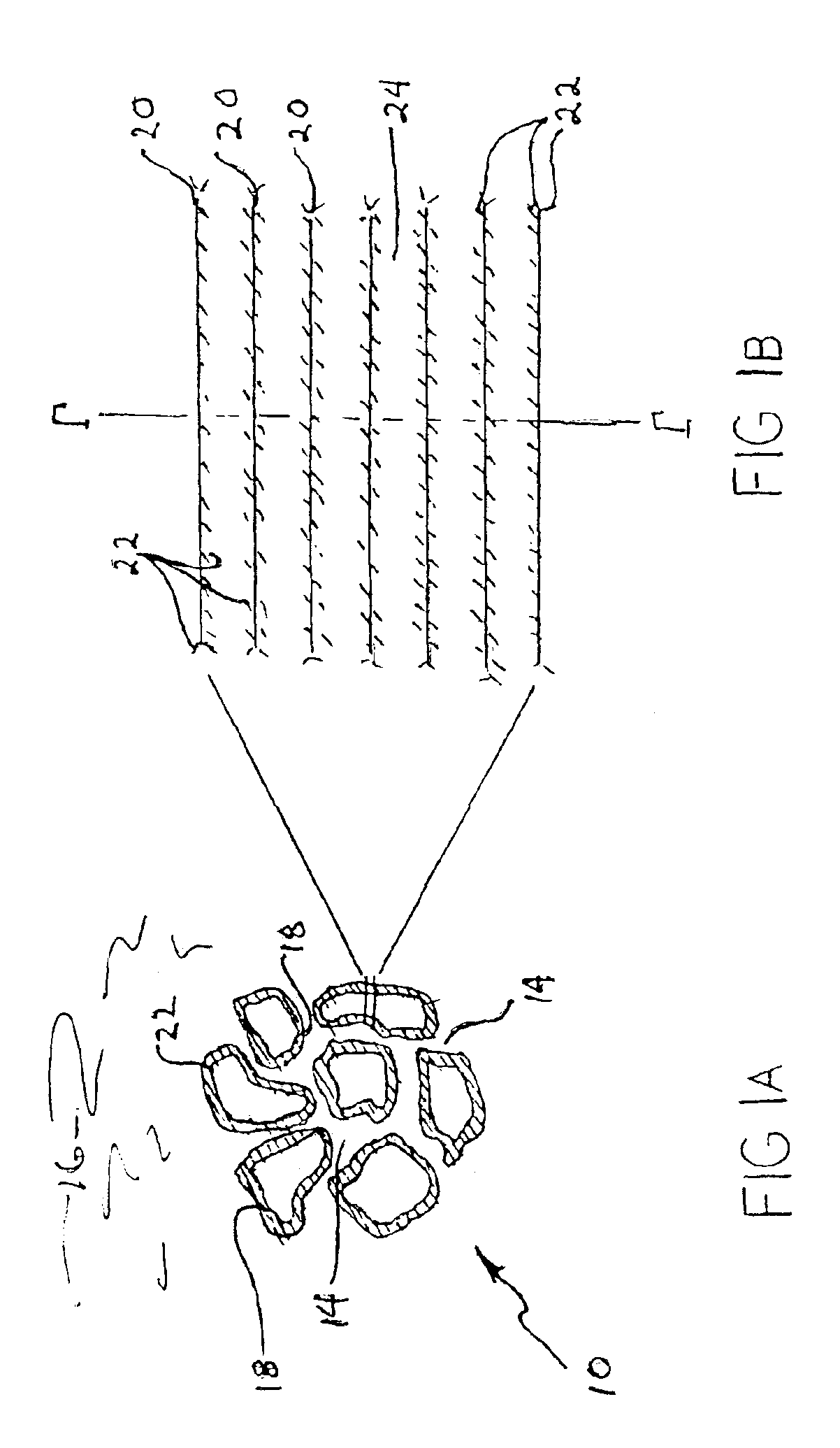
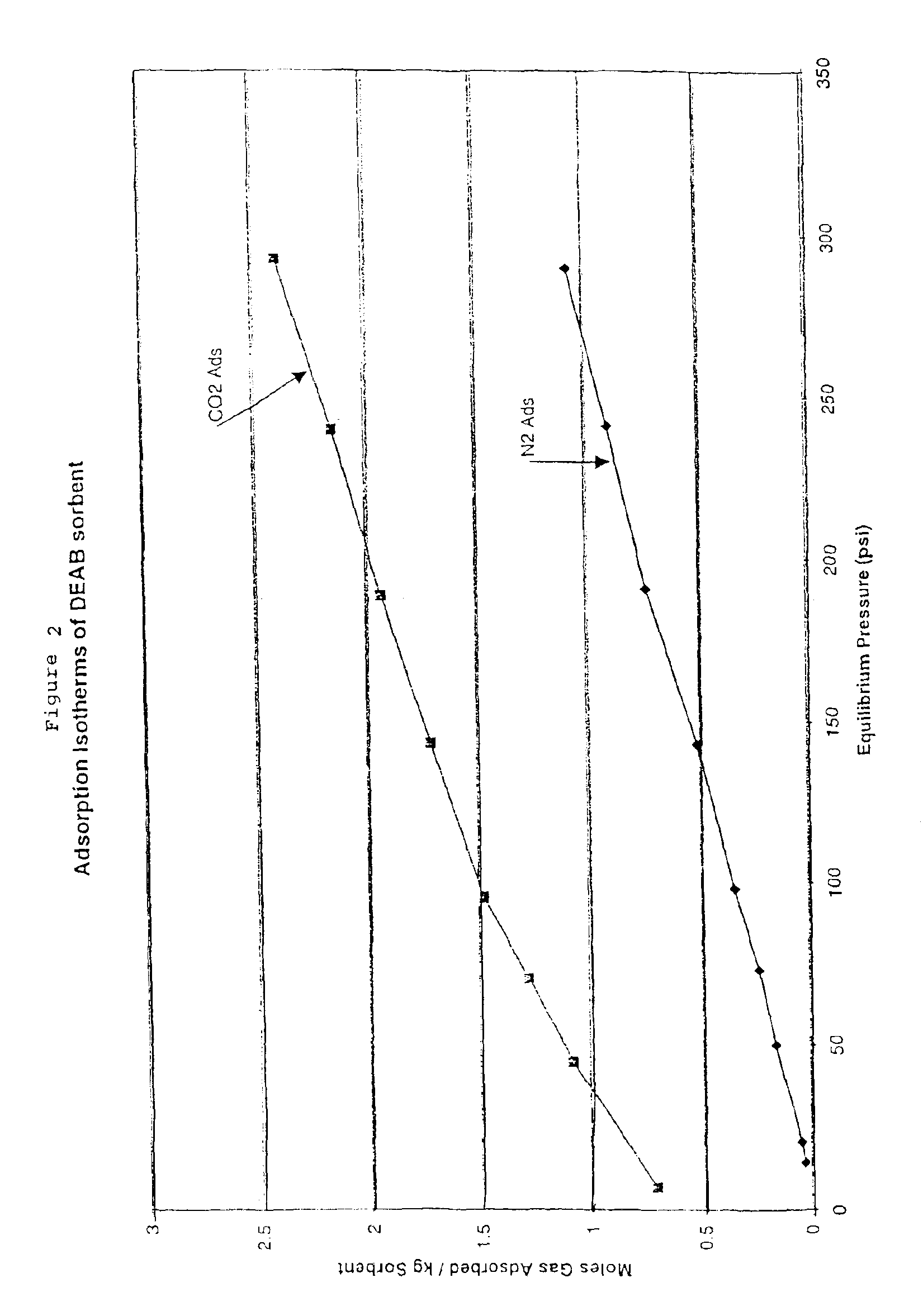
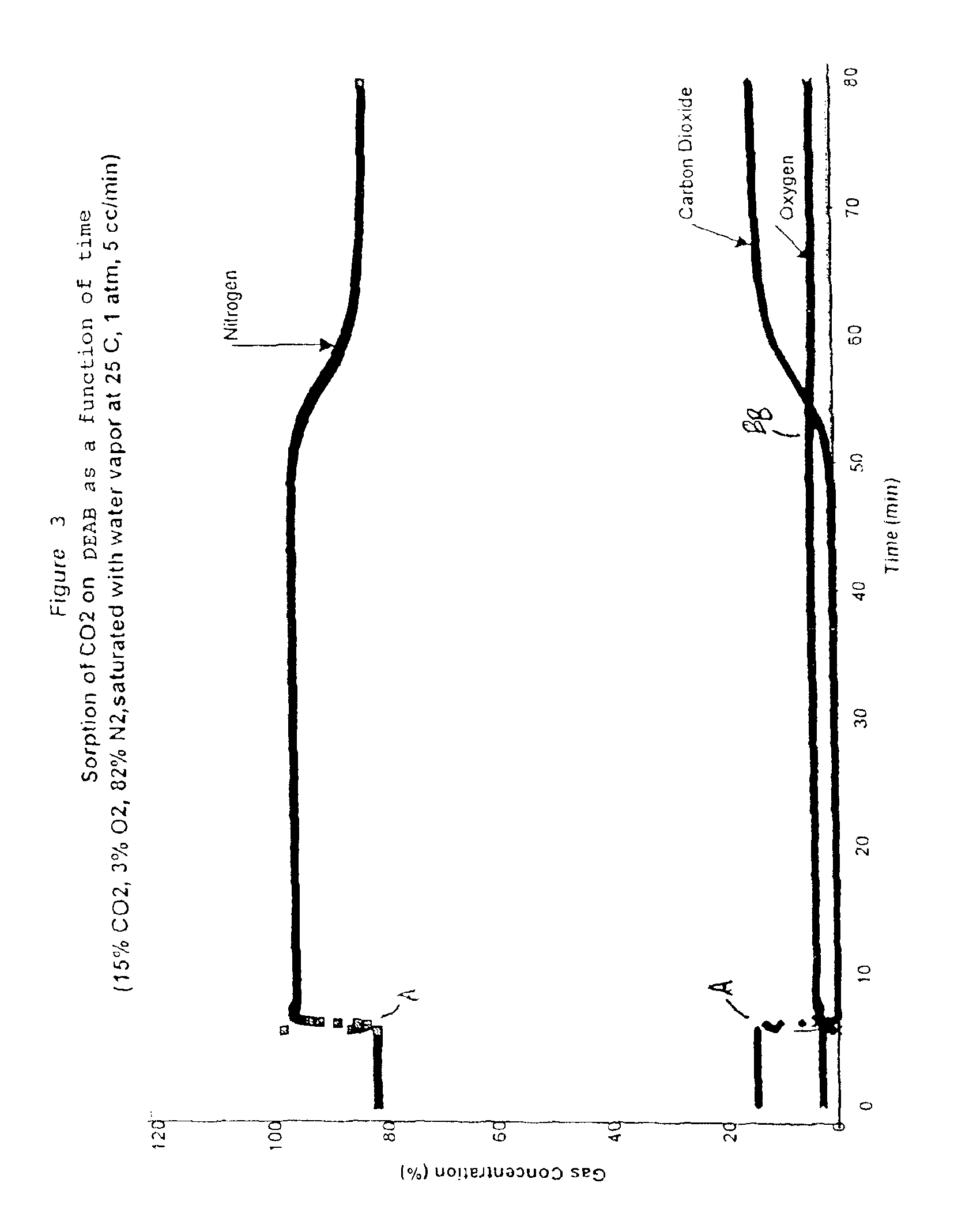
Solid sorbents for removal of carbon dioxide from gas streams at low temperatures
InactiveUS6908497B1Promote regenerationRegeneration process is inexpensiveGas treatmentOther chemical processesGas solidSorbent
New low-cost CO2 sorbents are provided that can be used in large-scale gas-solid processes. A new method is provided for making these sorbents that involves treating substrates with an amine and / or an ether so that the amine and / or ether comprise at least 50 wt. percent of the sorbent. The sorbent acts by capturing compounds contained in gaseous fluids via chemisorption and / or physisorption between the unit layers of the substrate's lattice where the polar amine liquids and solids and / or polar ether liquids and solids are located. The method eliminates the need for high surface area supports and polymeric materials for the preparation of CO2 capture systems, and provides sorbents with absorption capabilities that are independent of the sorbents' surface areas. The sorbents can be regenerated by heating at temperatures in excess of 35° C.
Owner:ENERGY U S DEPARMENT OF
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphonic acid, phosphinic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, sp2 amine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, s-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, n-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, o-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES +2
Reactive diluent and curable resin composition
InactiveUS20030199655A1Effect is not sufficientLow water resistanceFatty acid chemical modificationFatty acids production/refiningVinyl etherHydrogen atom
The present invention provides a reactive diluent composition which overcomes drawbacks of both the radical-cure and the cationic-cure reactive diluents and can be applied in a broad variety of uses such as paints, inks, adhesives, pressure sensitive adhesives, surface-modifiers, and molding materials; a curable resin composition containing the same; an activated energy ray-curable resin composition; and an activated energy ray-curable ink composition for ink-jet printing. A reactive diluent composition comprising a vinyl ether group-containing (meth)acrylic ester represented by the following general formula (1): CH2=CR<1>-COO-R<2>-O-CH=CH-R<3> (1) wherein R<1 >represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group; R<2 >represents an organic residue of 2 to 20 carbon atoms; R<3 >represents a hydrogen atom or an organic residue of 1 to 11 carbon atoms and a hydroxyl group-containing polymerizable compound and / or divinyl ether.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Antimicrobial compositions and methods
Antimicrobial compositions, especially those useful when applied topically, particularly to mucosal tissues (i.e., mucous membranes), including, in particular, an antimicrobial lipid component, such as a fatty acid ester, fatty ether, or alkoxide derivative thereof. The compositions can also include an enhancer component, a surfactant, a hydrophobic component, and / or a hydrophilic component. Such compositions provide effective topical antimicrobial activity and are accordingly useful in the treatment and / or prevention of conditions that are caused, or aggravated by, microorganisms (including viruses).
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Masonry cement having higher strength and water retention
InactiveCN101182139AHigh strengthSolve the difficult problem of preparing high-strength grade building mortarSolid waste managementCelluloseLower grade
The invention discloses a masonry cement with high strength and water retention. According to the weight percentage, the masonry cement consists of 21-98.99 percent of porland cement clinker, 0-50 percent of blending materials, 1-12 percent of gypsum, 0.01-2 percent of cellulose ether and 0-15 percent of other additives. With the cellulose ether of high water retention material added, the water retention of the masonry cement is greatly improved. At the same time, through breaking through the limitation that the using amount of the blending materials in the original masonry cement is not less than 50 percent, the using amount of the blending materials is lowered to be 50 percent below to improve the strength of novel masonry cement. The strength of the prepared masonry cement is high, and the masonry cement with the strength grades of 12.5, 22.5, 52.5R, 62.5, 62.5R, etc. can be made. The hard problems of using low-grade blending materials to produce masonry cement with high water retention and using low- grade strength masonry cement of 12.5 and 22.5 to produce high-grade strength building mortar are solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Poly(arylene ether)-containing thermoset composition, method for the preparation thereof, and articles derived therefrom
InactiveUS20010053820A1Fast curingReduce sensitivitySynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingHeat resistanceEther
A thermosetting composition comprises a capped poly(arylene ether), an alkenyl aromatic monomer, and an acryloyl monomer. The composition provides good flow properties and fast curing rates. After curing, the composition exhibits good stiffness, toughness, heat resistance, and dielectric properties.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
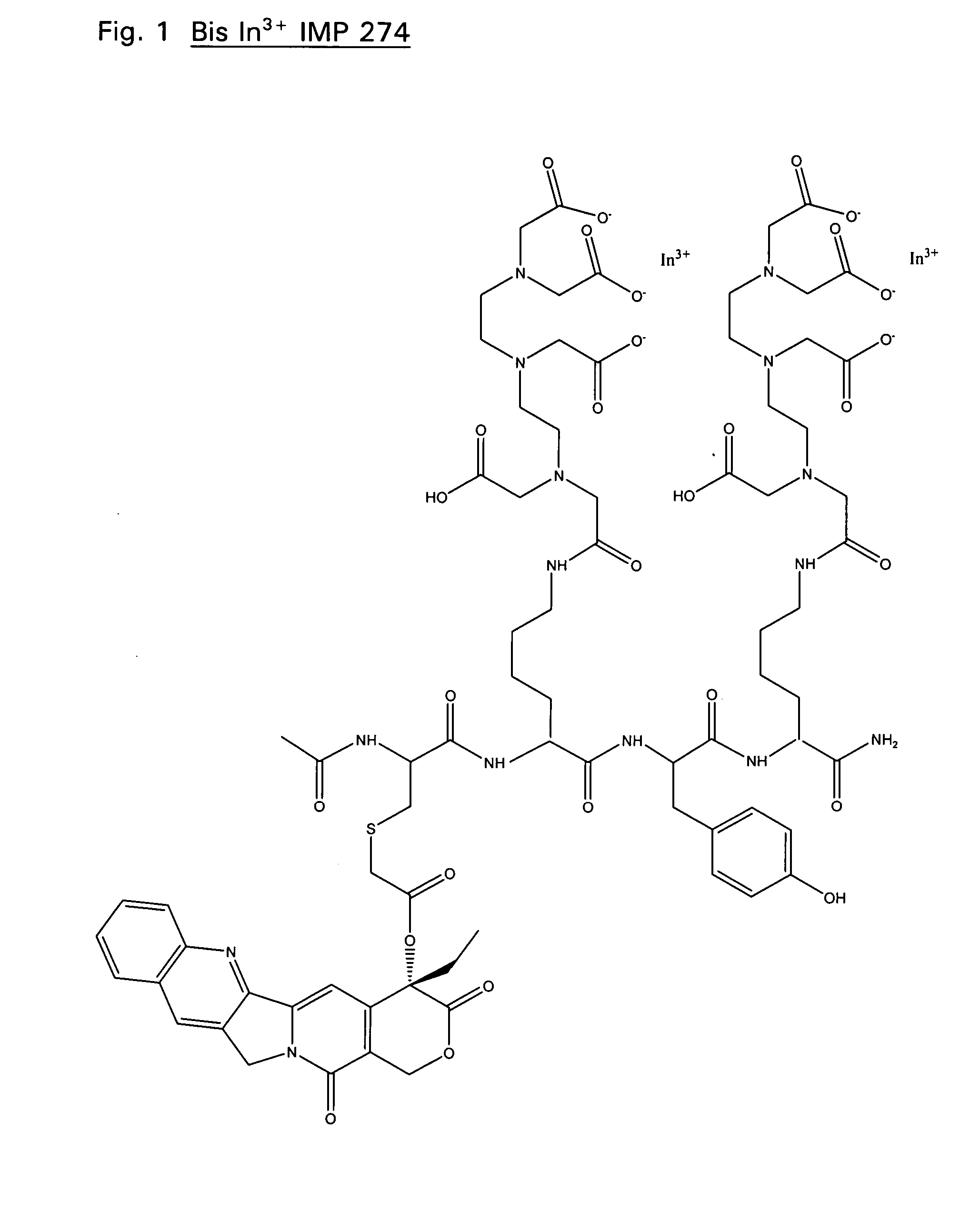
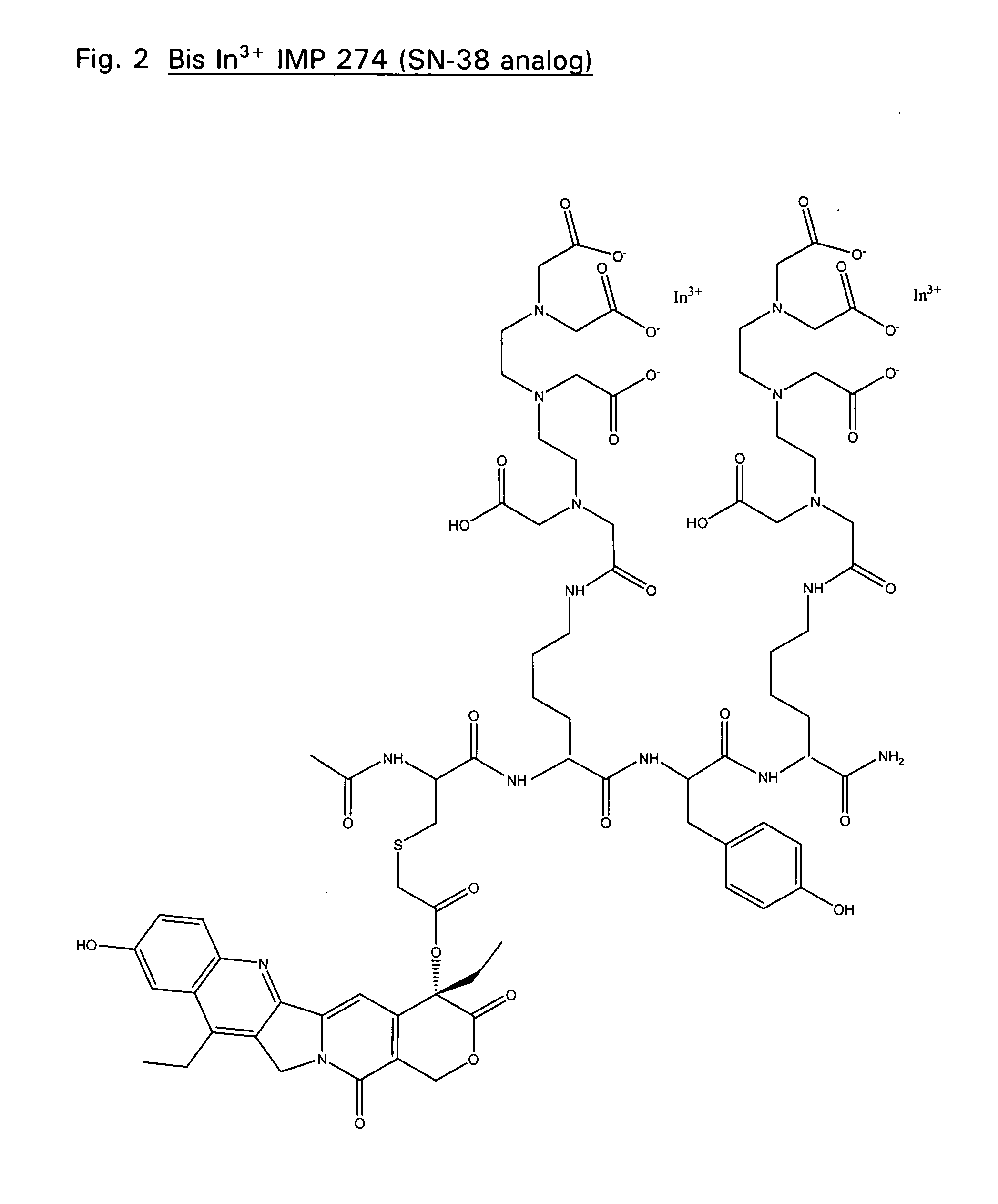
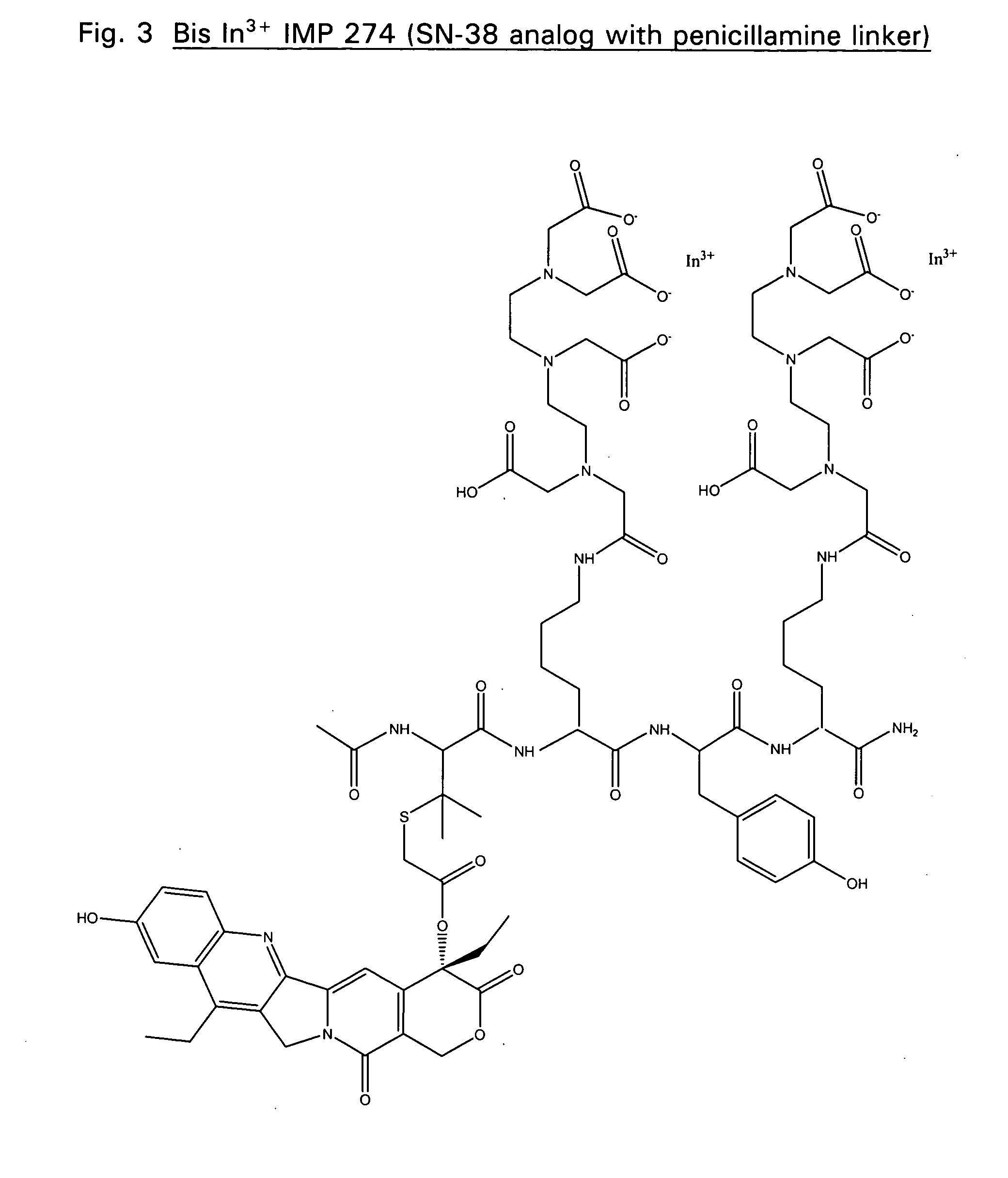
Therapeutic and diagnostic conjugates for use with multispecific antibodies
InactiveUS20050002945A1Low toxicityPromote localizationAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsSemicarbazoneEther
Disclosed are compounds that include two or more haptens conjugated by a spacer or a carrier. The haptens may include diethylenetriaminepentaacetate (DTPA), histimine-succinyl-glutamine (HSG), or combinations of DTPA and HSG. The compound also includes an effector molecule which may be conjugated to one or more of the haptens, the spacer / carrier, or both. The effector molecule may be conjugated by a number of linkages including an ester linkage, an imino linkage, an amino linkage, a sulfide linkage, a thiosemicarbazone linkage, a semicarbazone linkage, an oxime linkage, an ether linkage, or combinations of these linkages. Also disclosed are methods of synthesizing the compounds and / or precursors of the compounds.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
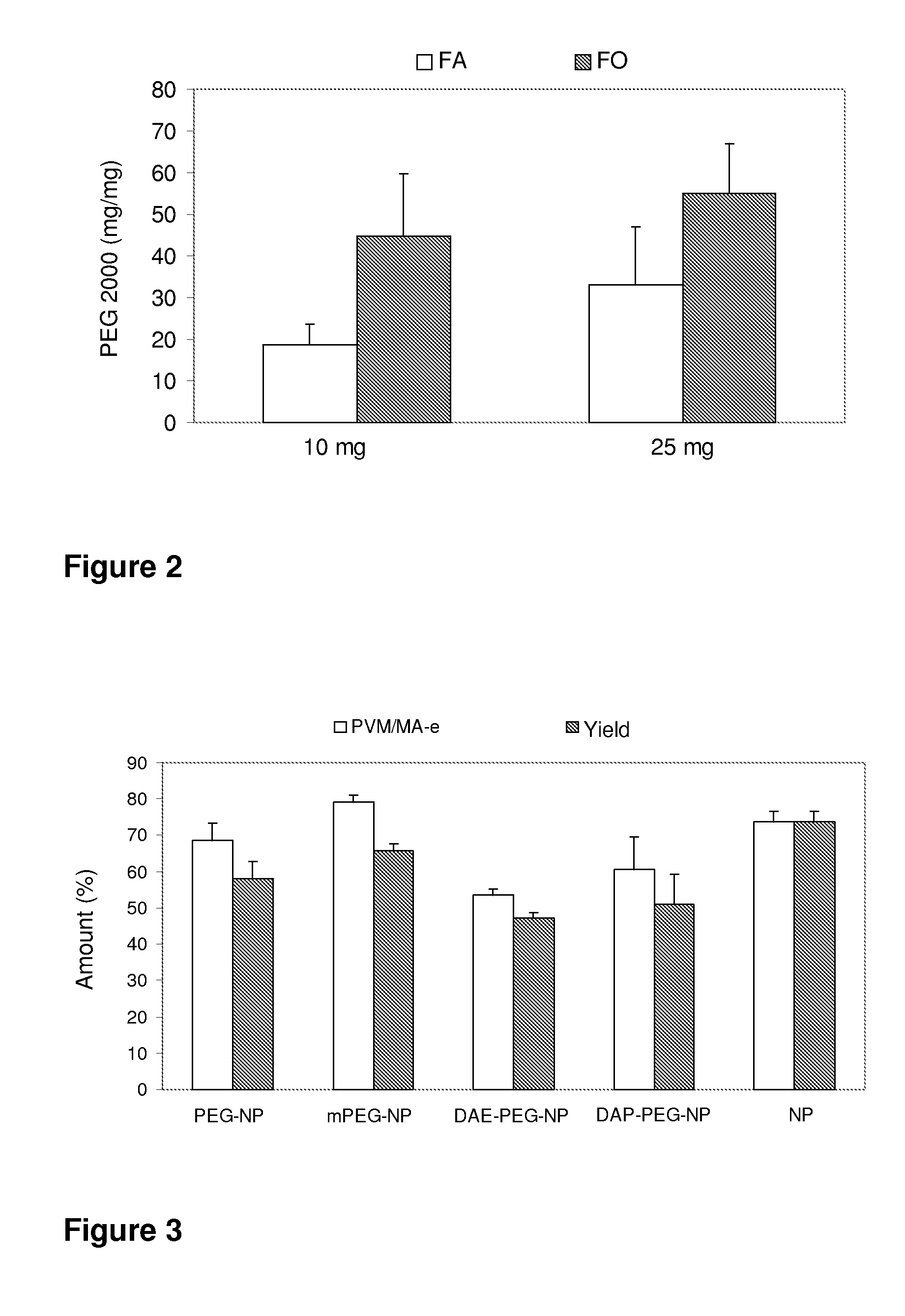
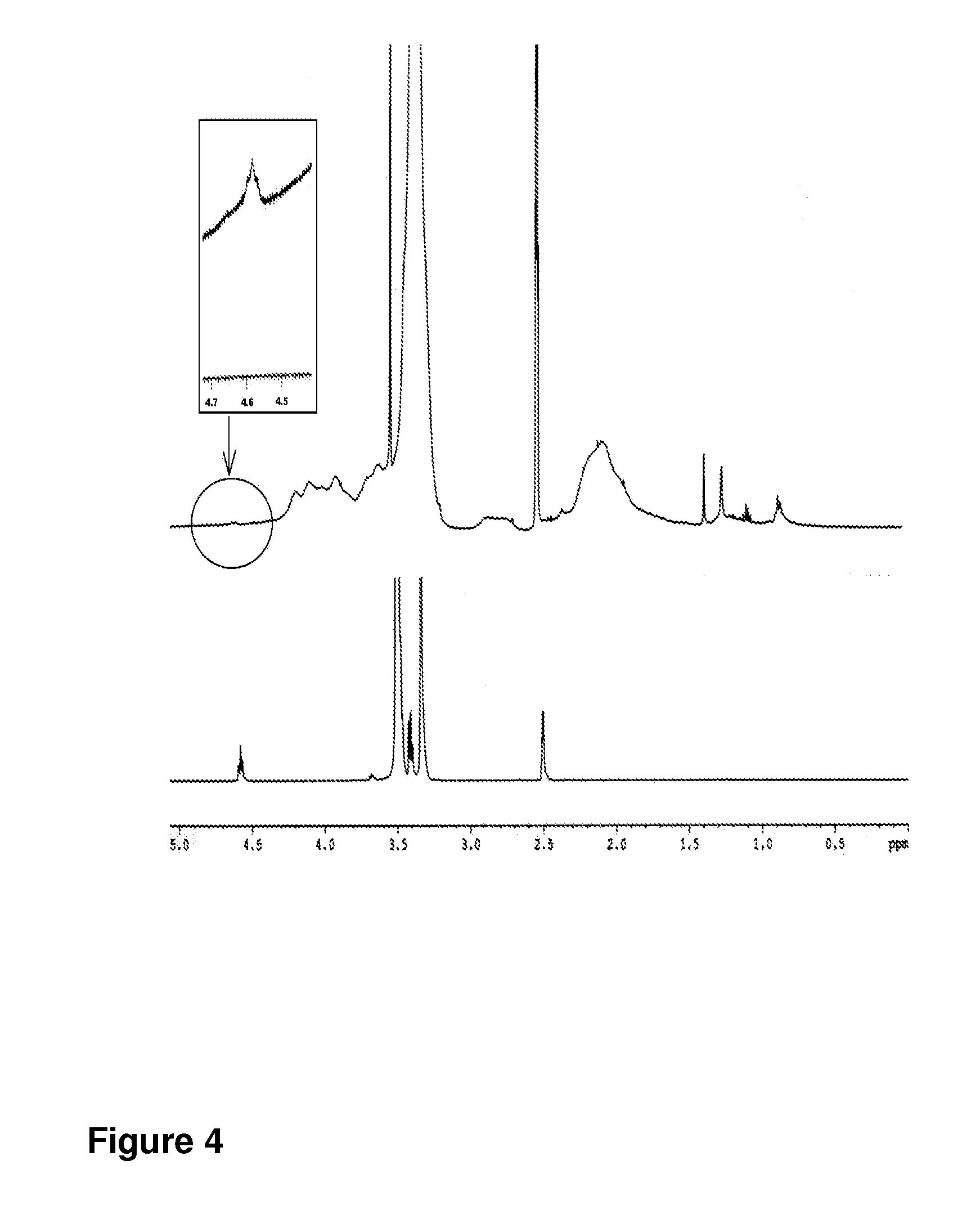
Pegylated nanoparticles
ActiveUS8628801B2Good bioadhesionStrong specificityPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsZeta potentialOrganic synthesis
The present invention relates to nanoparticles comprising a biodegradable polymer, preferably the vinyl methyl ether and maleic anhydride (PVM / MA) copolymer, and a polyethylene glycol or derivatives thereof. These nanoparticles are easy to produce and provide excellent bioadhesion, size and zeta potential characteristics making them suitable for the administration of active molecules. The selection of the type of polyethylene glycol used in their production allows suitably modulating the characteristics of these nanoparticles, which can be advantageously used according to the type of drug to be carried and / or the method of administration of the pharmaceutical formulation. pegylation is carried out by simple incubation for a short time period of the two macromolecules in question, without needing to have to resort to the use of organic solvents with high toxicity or long and laborious organic synthesis processes. Furthermore, the pegylation process can be associated to the process of encapsulating the biologically active molecule.
Owner:INNOUP FARMA
Aqueous dispersion of epoxy resin and blend of epoxy resin-polyoxyalkylene amines
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 06364 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 25, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 25, 1998 PCT Filed Nov. 14, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 25988 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 18, 1998A blend of epoxy-amine adducts are useful as emulsifiers of aqueous epoxy resin dispersions comprises (A-1) one or more epoxy-amine adduct(s) obtained by the reaction of (i) one or more aromatic, cycloaliphatic or novolac epoxy compound(s) and (ii) one or more amine-terminated polyalkylene glycol(s) having a molecular weight of from 700-5000 and an ethyleneoxide content of at least 60% by weight in an equivalent ratio of amine-terminated polyalkylene glycol(s) to epoxy compound(s) of from 0.01:1 to 0.9:1; (A-2) one or more epoxy-amine adduct(s) derived from the reaction of (i) one or more aliphatic epoxy compound(s) and (ii) one or more amine-terminated polyalkylene glycol(s) having a molecular weight of from 700-5000 and an ethyleneoxide content of at least 60% by weight in an equivalent ratio of amine-terminated polyalkylene glycol(s) to epoxy compound(s) of from 0.01:1 to 0.9:1; (B-1) aromatic, cycloaliphatic or novolac polyglycidyl ethers; (B-2) optionally, polyglycidyl esters of aromatic or cycloaliphatic polycarboxylic acids; and (C) optionally, at least one of reactive thinners, pigments, filler or other addtitives.
Owner:SIKA CHEM
Substituted nucleosides, preparation thereof and use as inhibitors of RNA viral polymerases
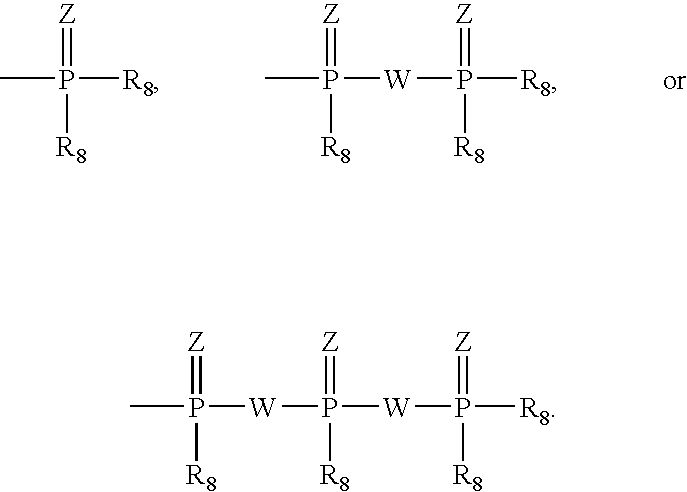
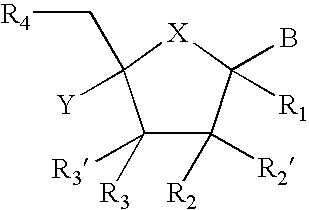
Provided are compounds represented by: X is O, S or NR6, R1 is H or (CH2)mR5, R2, R2', R3 and R3' are independently NO2, N3 or (CH2)mR5, OH R4 is H, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)nR7, R5 is H, halo, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)mR7, R6 and R6a are individually H, alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, aryl or substituted aryl, R7 is: R8 is H, F, SR9 or OR9, R9 is H, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl or hydroxyprotecting group, Y is H, CH3 or (CH2)mR5, Z is O or S W is CH2, CF2, CHF or O, m is 0-4, B is adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil, thymine, modified purines and pyrimidines substituted pyridines, five membered heterocycles substituted by at least one of amines, substituted amines, amides, substituted amides, esters, halogens, alkyls, ethers; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and prodrugs thereof. These ring systems may be substituted.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
Polytrimethylene ether glycol and polytrimethylene ether ester with excellent quality
A process is provided comprising contacting 1,3-propanediol with a suitable polymerization catalyst to produce polytrimethylene ether glycol or random polytrimethylene ether ester, wherein the 1,3-propanediol comprises about 10 microg / g or less peroxide compounds, based on the weight of 1,3-propanediol, and about 100 microg / g or less carbonyl compounds based on the weight of the 1,3-propanediol. Preferably, the 1,3-propanediol comprises about 100 microg / g or less of monofunctional alcohol compounds based on the weight of the PDO. In addition, polytrimethylene ether glycol and random polytrimethylene ether ester prepared by the process.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
Ink composition, method of producing ink composition, method of applying liquid using the ink composition and apparatus therefor
An ink composition comprising at least a block polymer compound having a polyalkenyl ether main chain, a solvent and a pigment, wherein particles composed of the block polymer compound and the pigment have an average particle size of not more than 80 nm and the particles in the composition have a dispersion index of not more than 0.15.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Reactive diluent and curable resin composition
InactiveUS6767980B2Effect is not sufficientLow water resistanceFatty acid chemical modificationFatty acids production/refiningVinyl etherHydrogen atom
The present invention provides a reactive diluent composition which overcomes drawbacks of both the radical-cure and the cationic-cure reactive diluents and can be applied in a broad variety of uses such as paints, inks, adhesives, pressure sensitive adhesives, surface-modifiers, and molding materials; a curable resin composition containing the same; an activated energy ray-curable resin composition; and an activated energy ray-curable ink composition for ink-jet printing.A reactive diluent composition comprisinga vinyl ether group-containing (meth)acrylic ester represented by the following general formula (1):wherein R<1 >represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group; R<2 >represents an organic residue of 2 to 20 carbon atoms; R<3 >represents a hydrogen atom or an organic residue of 1 to 11 carbon atoms anda hydroxyl group-containing polymerizable compound and / or divinyl ether.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Sheets having a starch-based binding matrix
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix, optionally reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, a cellulosic ether, optionally fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the cellulosic ether to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and cellulosic ether form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Antimicrobial compositions and methods
InactiveUS20050058673A1Effective topical antimicrobial activityReduce usageAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsEtherFatty acid ester
Antimicrobial compositions, especially those useful when applied topically, particularly to mucosal tissues (i.e., mucous membranes), including a fatty acid ester, fatty ether, or alkoxide derivative thereof. The compositions can also include an enhancer component, a surfactant, a hydrophobic component, and / or a hydrophilic component. Such compositions provide effective topical antimicrobial activity and are accordingly useful in the treatment and / or prevention of conditions that are caused, or aggravated by, microorganisms (including viruses).
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Systems and methods for forming refractory metal oxide layers
InactiveUS20050009266A1Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseEther
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal oxide layers, such as tantalum pentoxide layers, on substrates by using vapor deposition processes with refractory metal precursor compounds and ethers.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
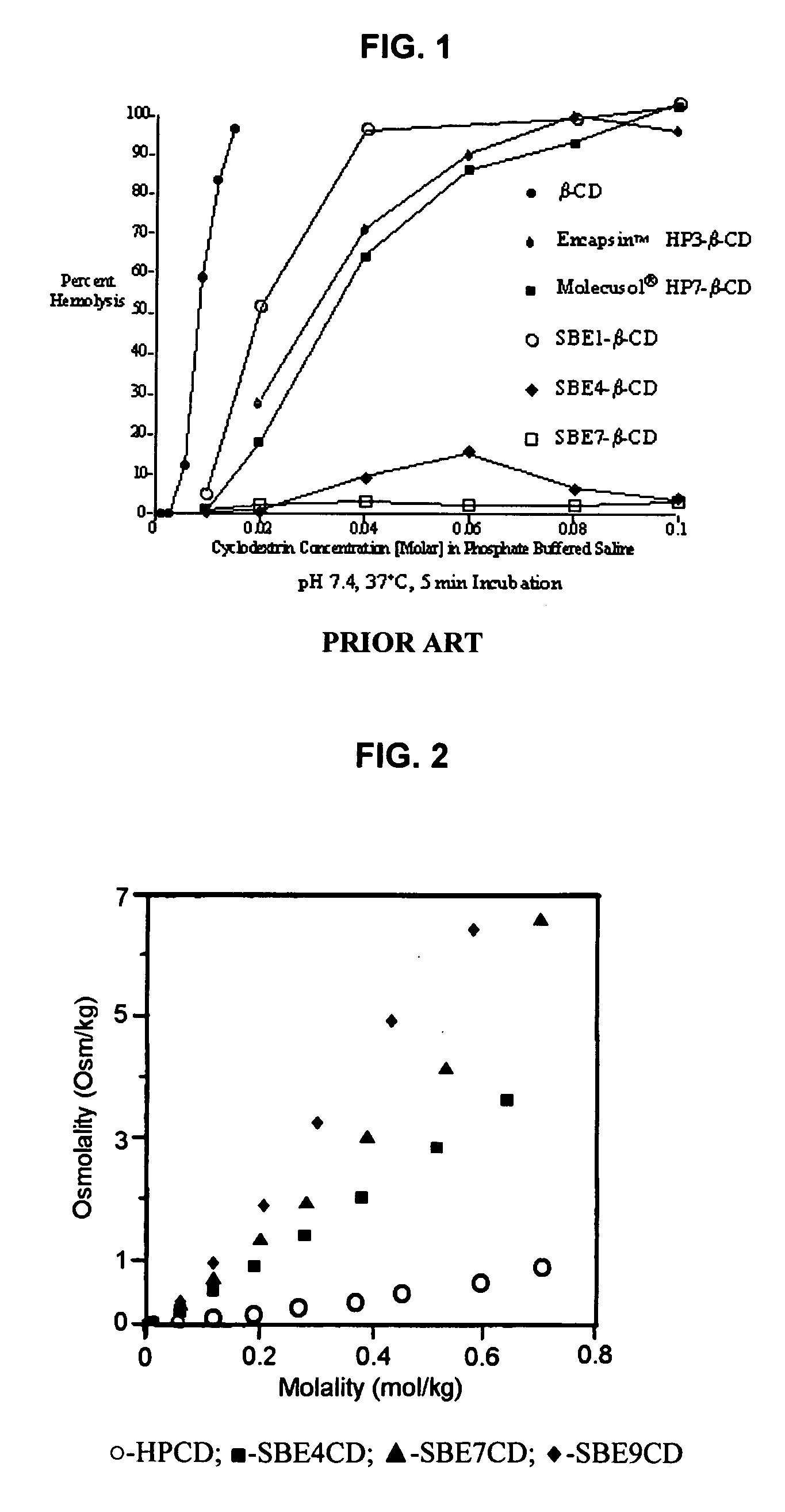
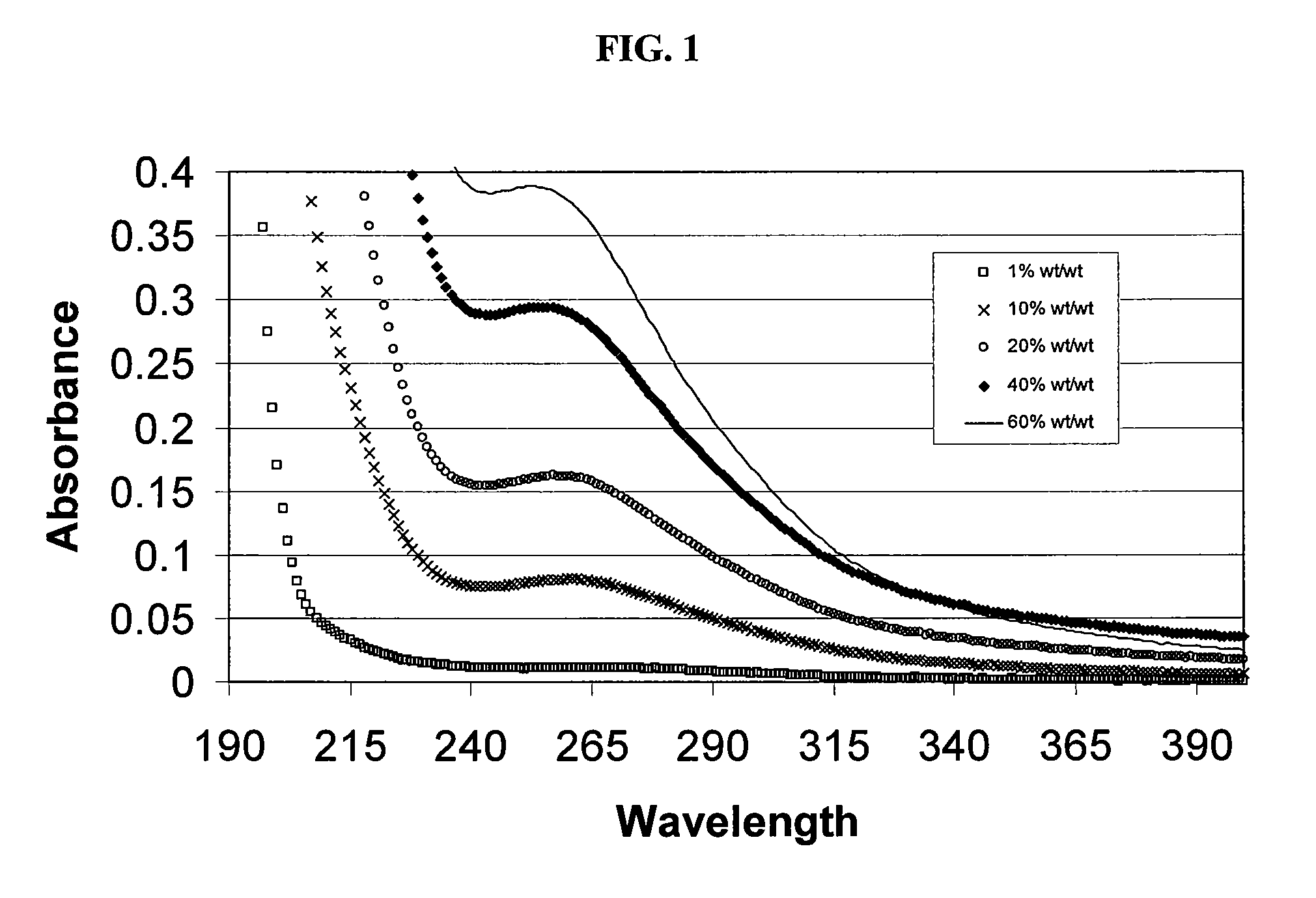
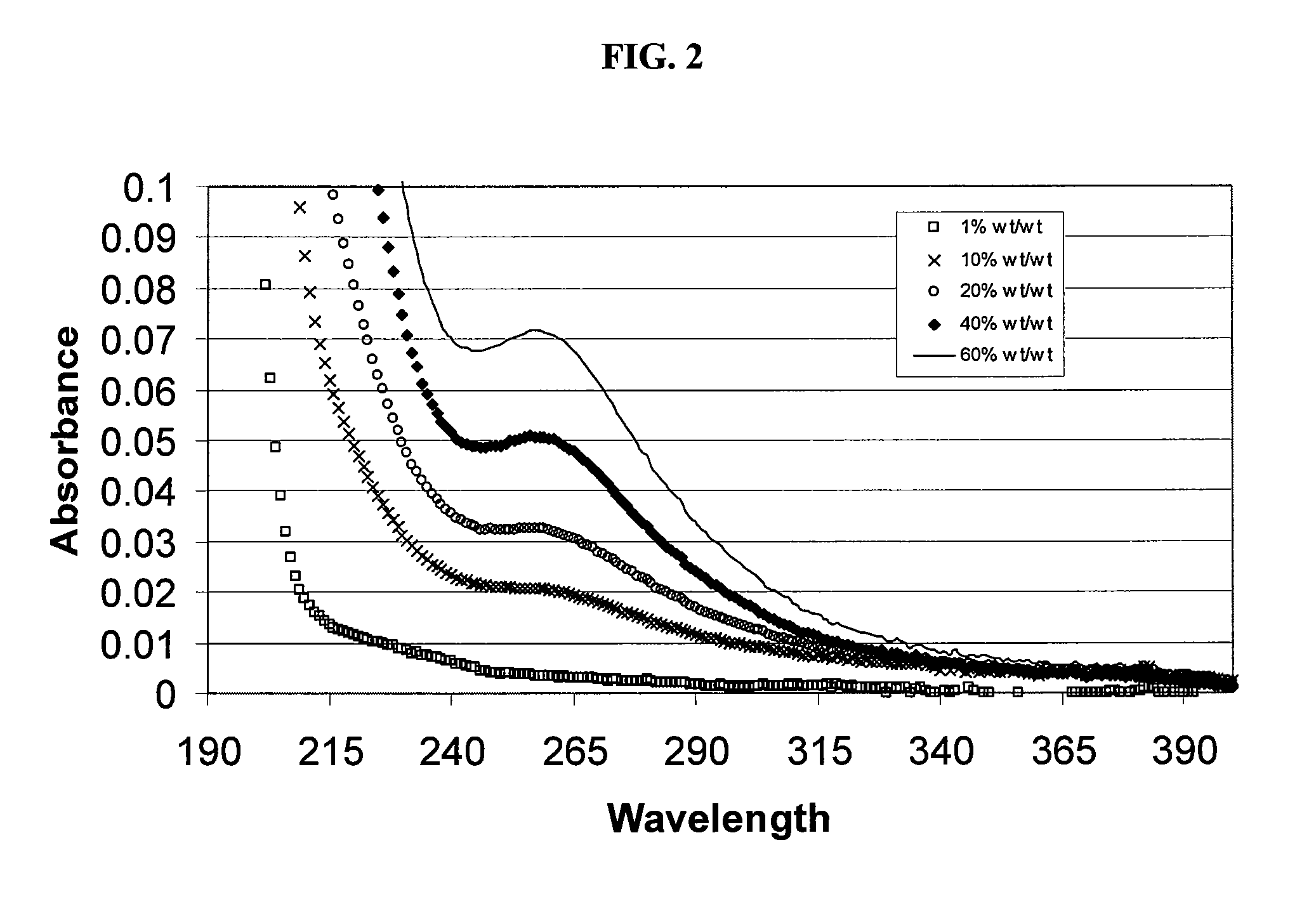
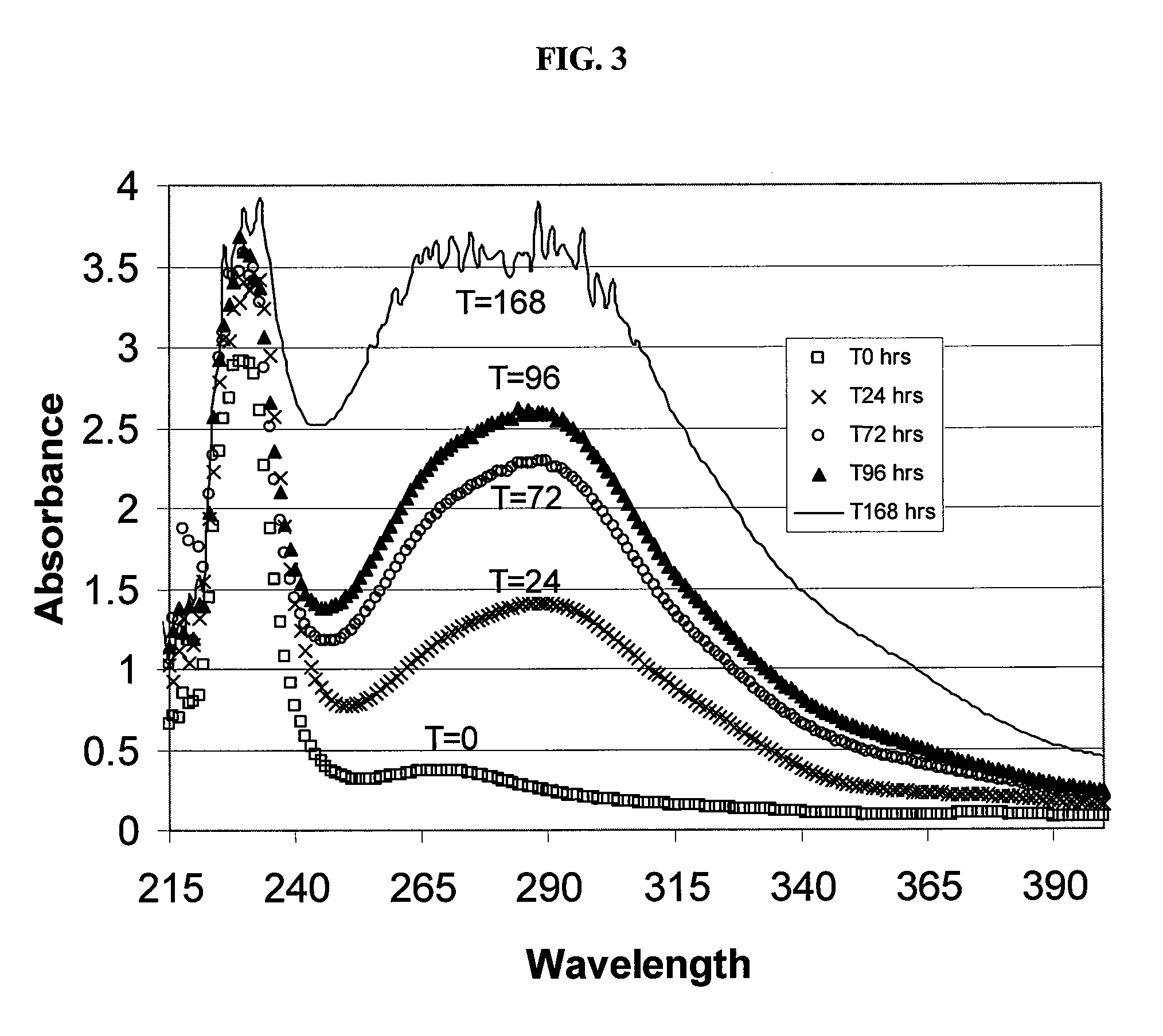
Sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin compositions
ActiveUS7635773B2Well mixedReduce the amount requiredOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPhosphateEther
SAE-CD compositions are provided, along with methods of making and using the same. The SAE-CD composition comprises a sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin and less than 100 ppm of a phosphate, wherein the SAE-CD composition has an absorption of less than 0.5 A.U. due to a drug-degrading agent, as determined by UV / vis spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 245 nm to 270 nm for an aqueous solution containing 300 mg of the SAE-CD composition per mL of solution in a cell having a 1 cm path length.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com