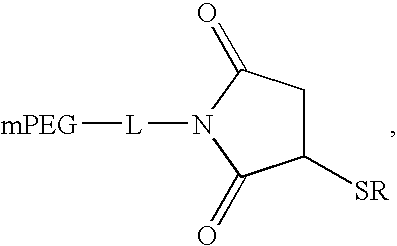
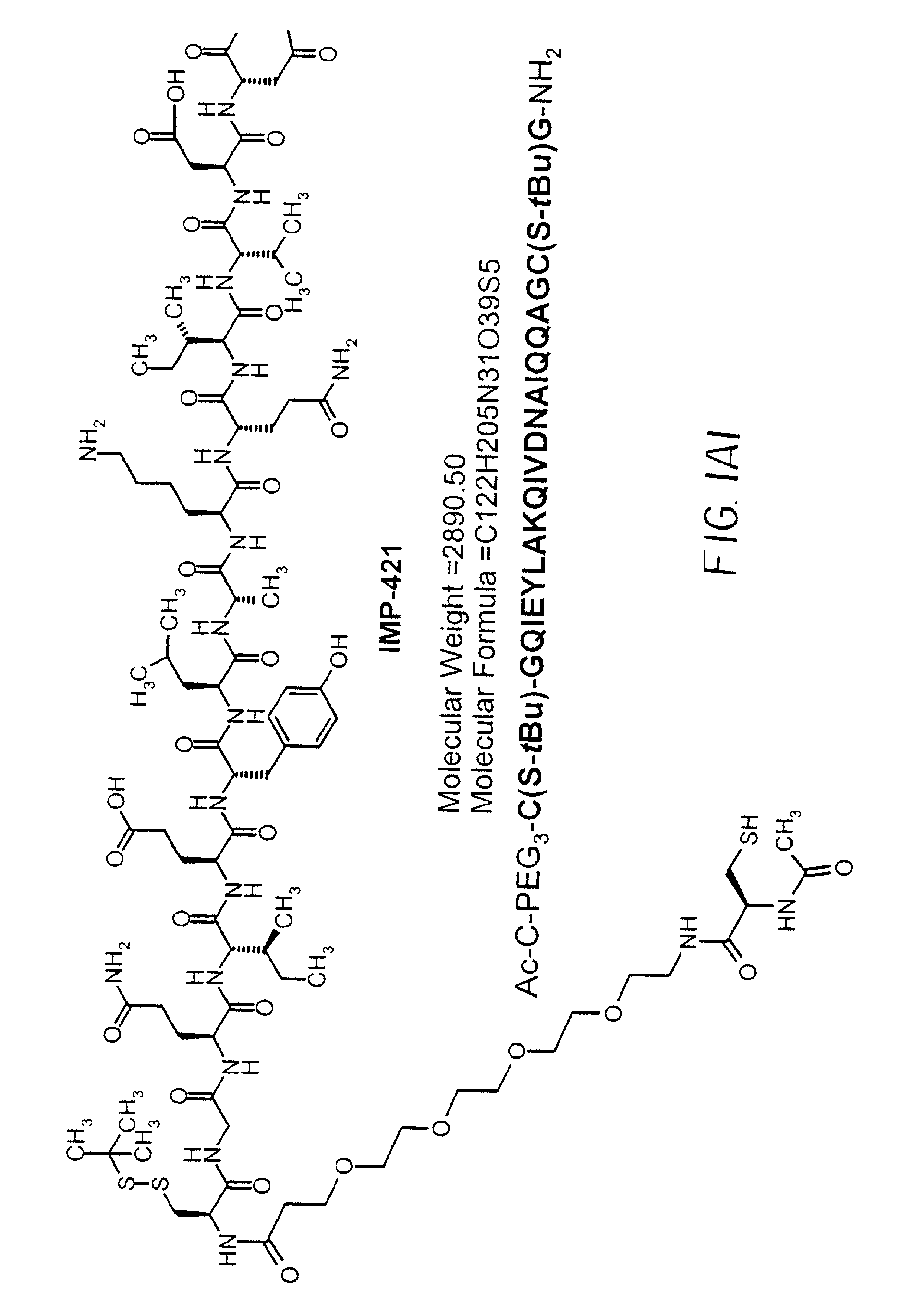
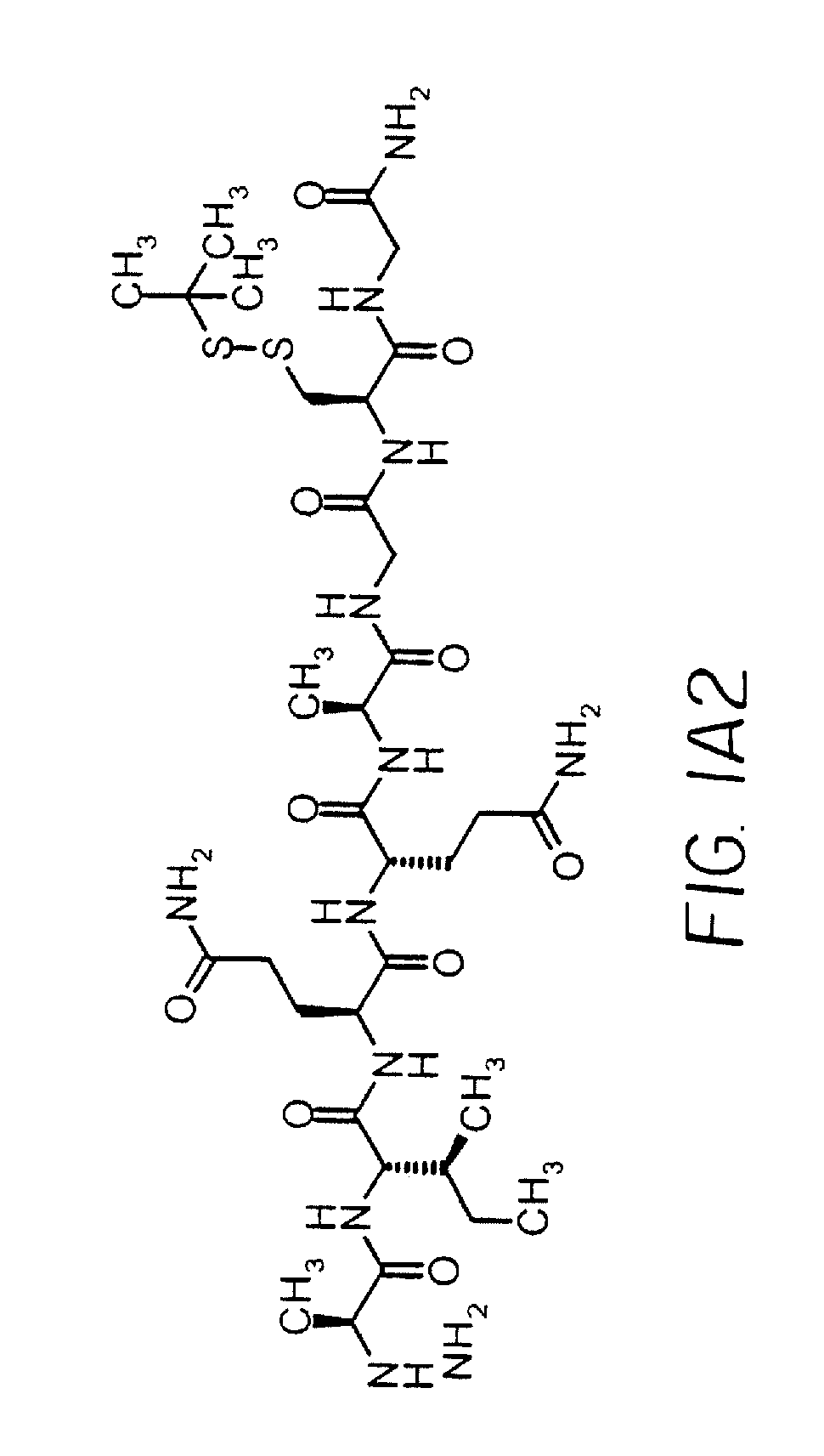
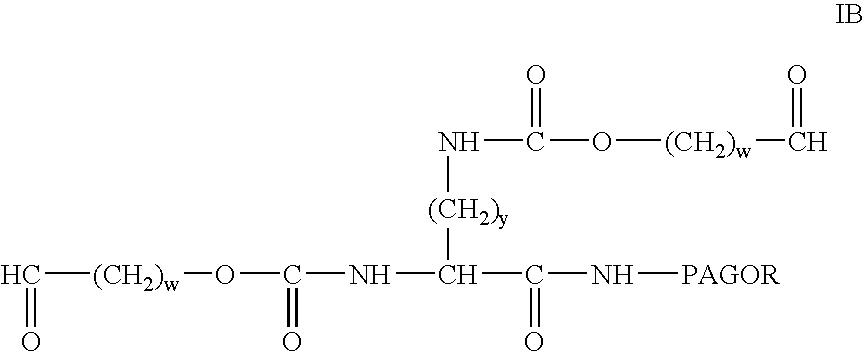
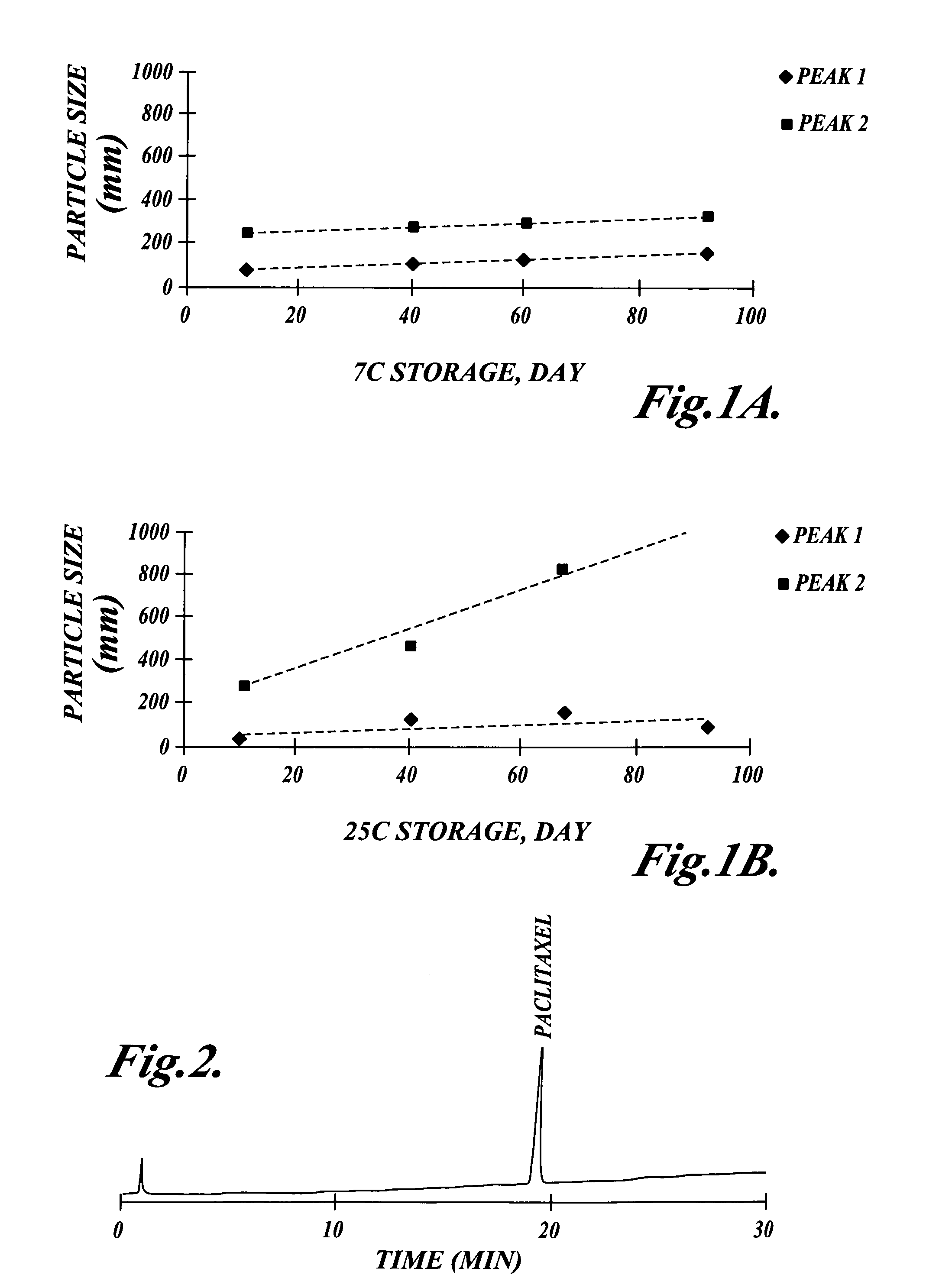
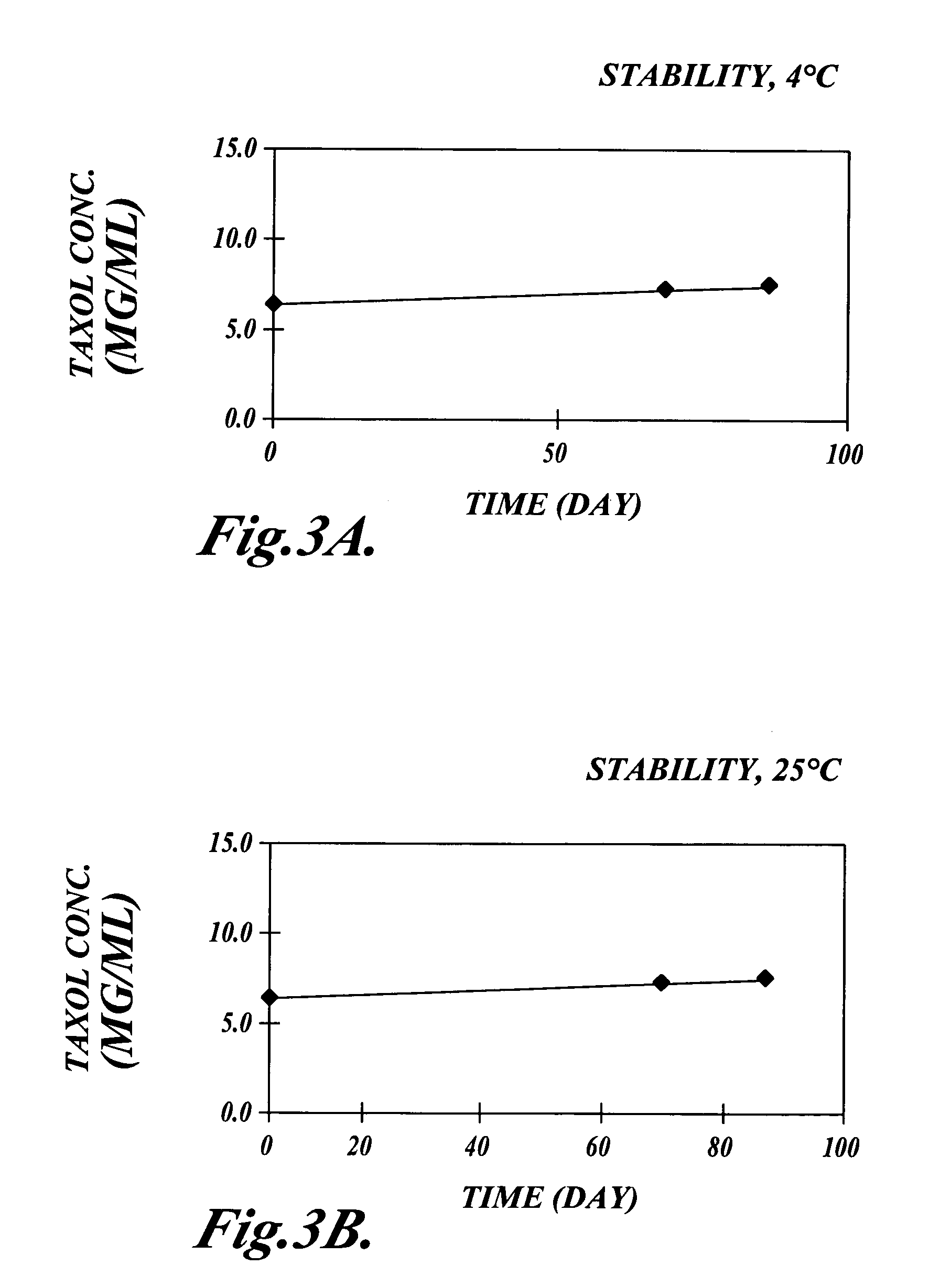
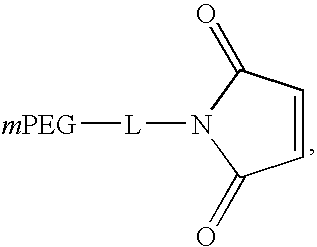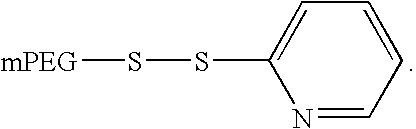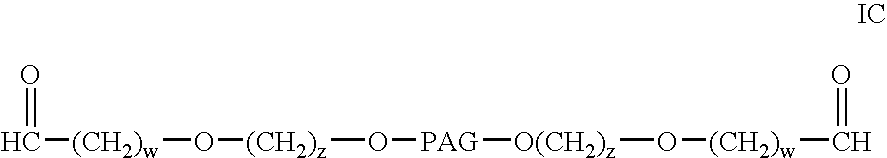Patents
Literature
900 results about "PEGylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
PEGylation (often styled pegylation) is the process of both covalent and non-covalent attachment or amalgamation of polyethylene glycol (PEG, in pharmacy called macrogol) polymer chains to molecules and macrostructures, such as a drug, therapeutic protein or vesicle, which is then described as PEGylated (pegylated). PEGylation is routinely achieved by the incubation of a reactive derivative of PEG with the target molecule. The covalent attachment of PEG to a drug or therapeutic protein can "mask" the agent from the host's immune system (reducing immunogenicity and antigenicity), and increase its hydrodynamic size (size in solution), which prolongs its circulatory time by reducing renal clearance. PEGylation can also provide water solubility to hydrophobic drugs and proteins. Having proven its pharmacological advantages and acceptability, PEGylation technology is the foundation of a growing multibillion-dollar industry.
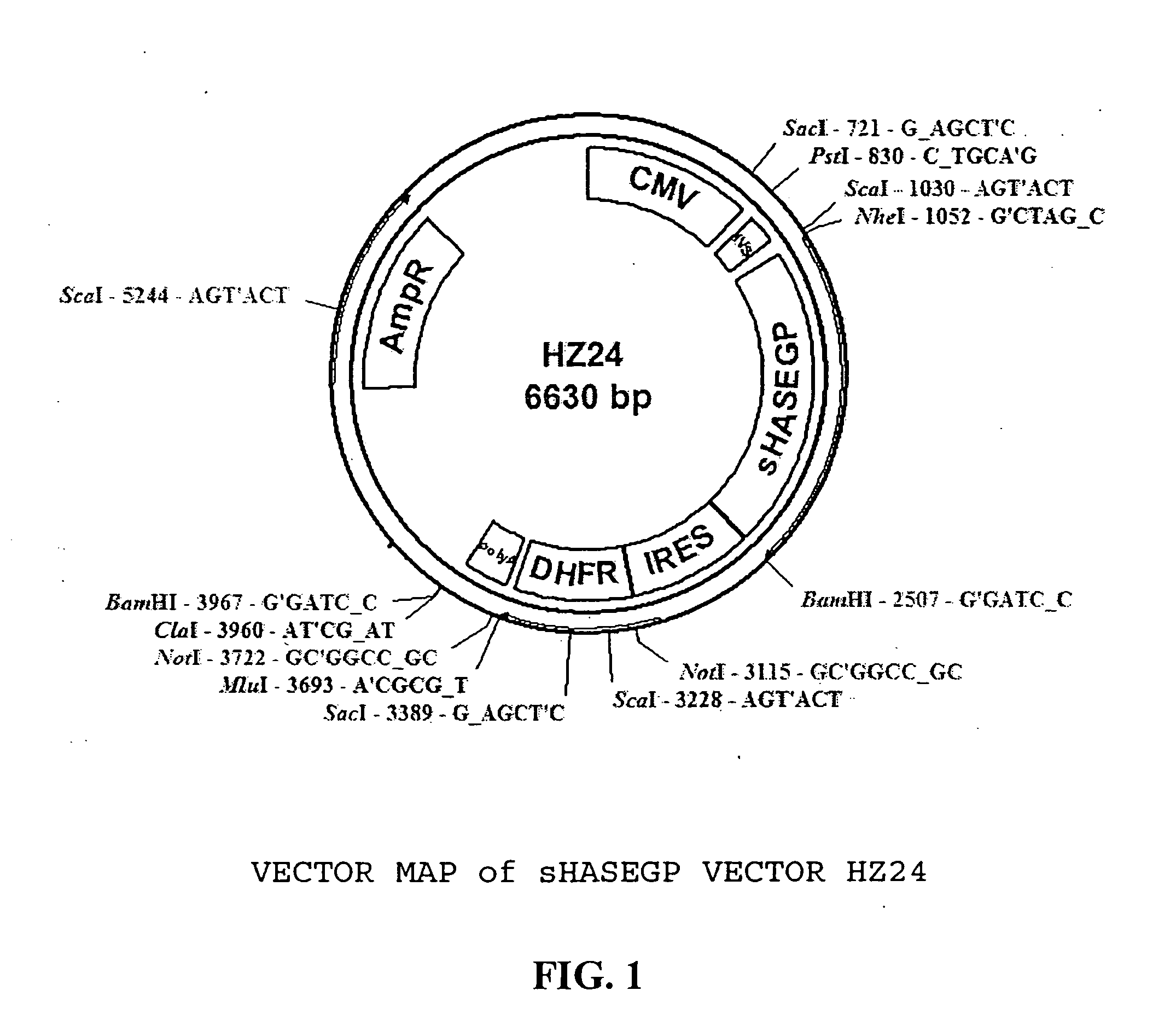
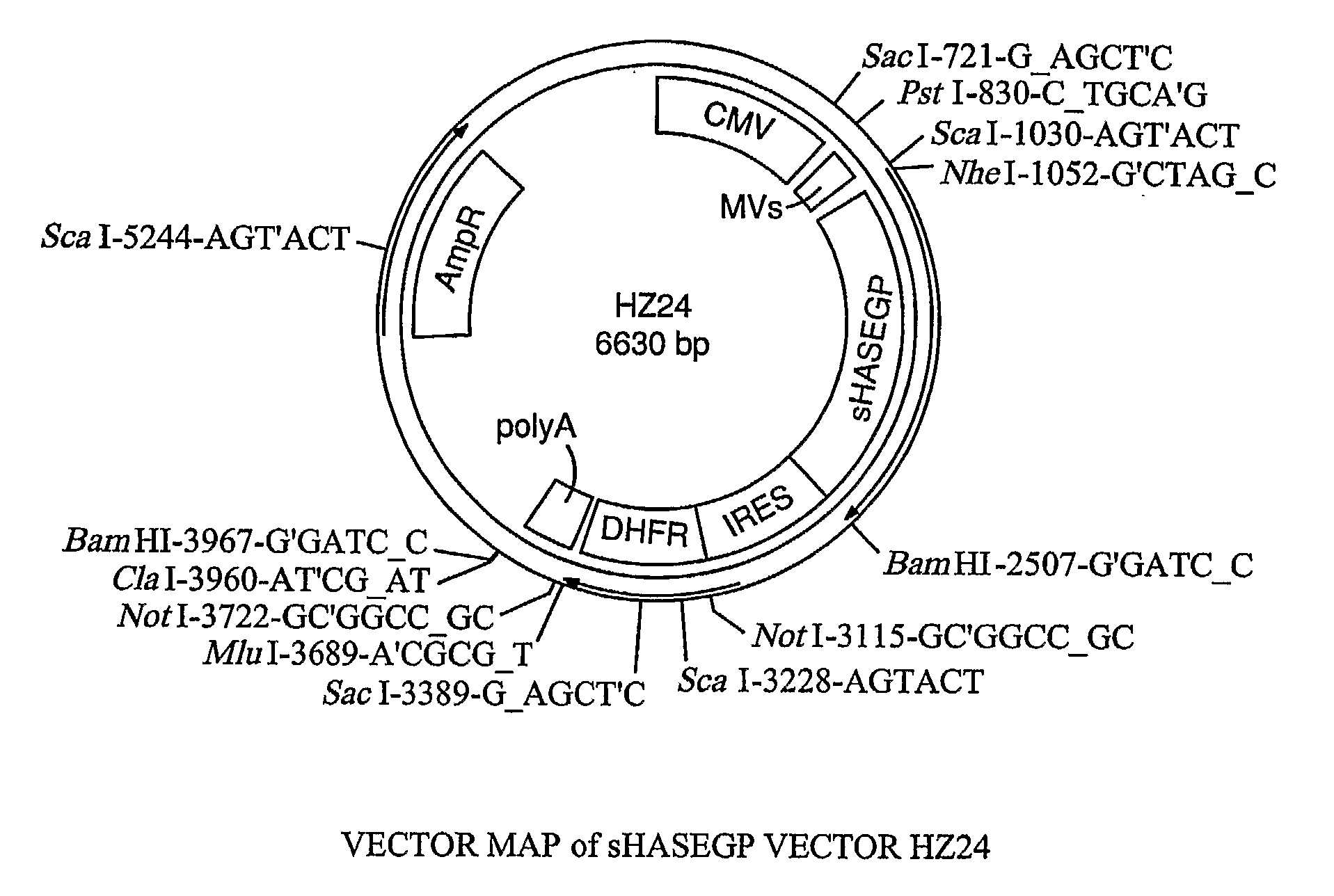
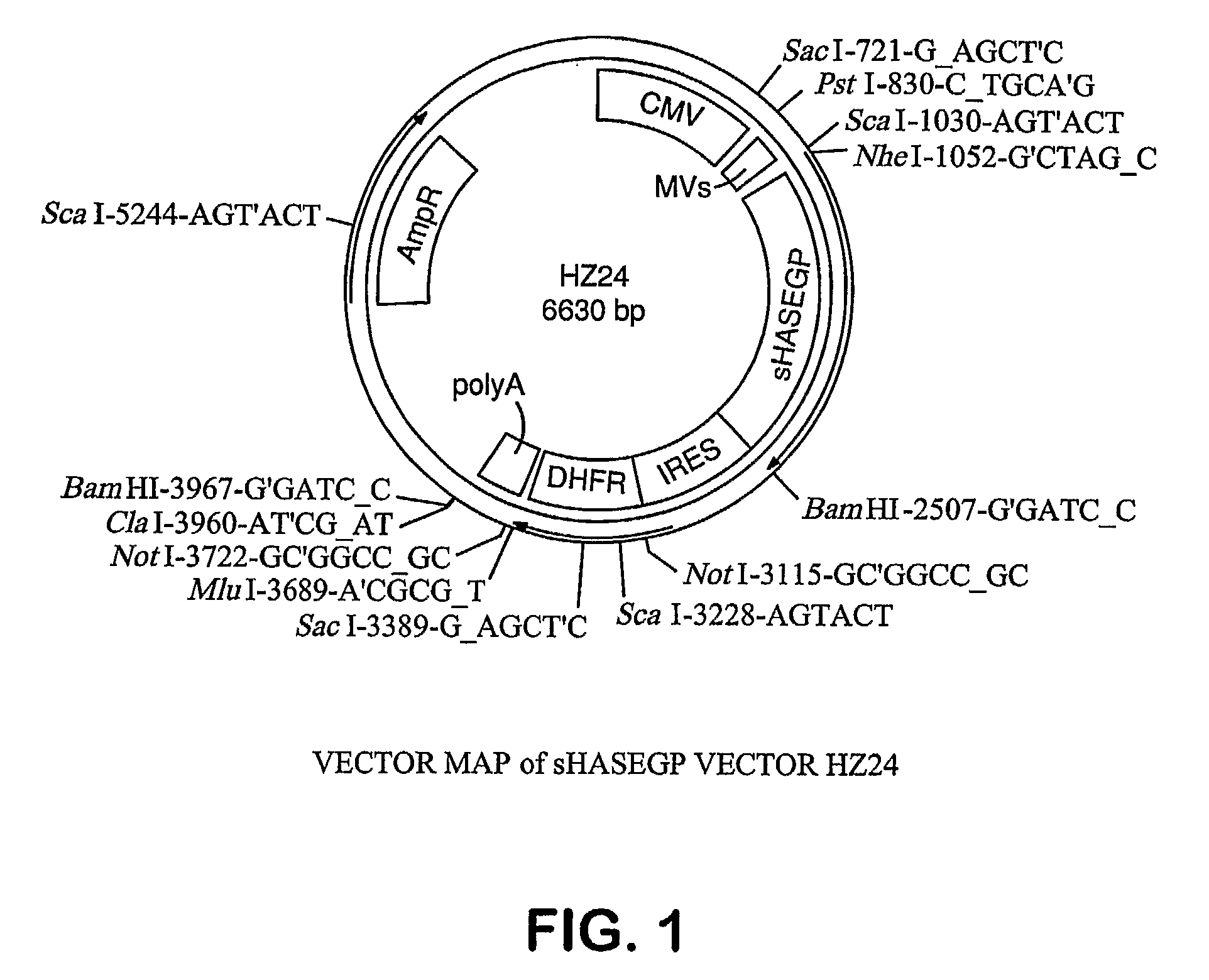
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminogly ycanases
PendingUS20060104968A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsSenses disorderNervous disorderHyaluronidaseRecombinant glycoprotein
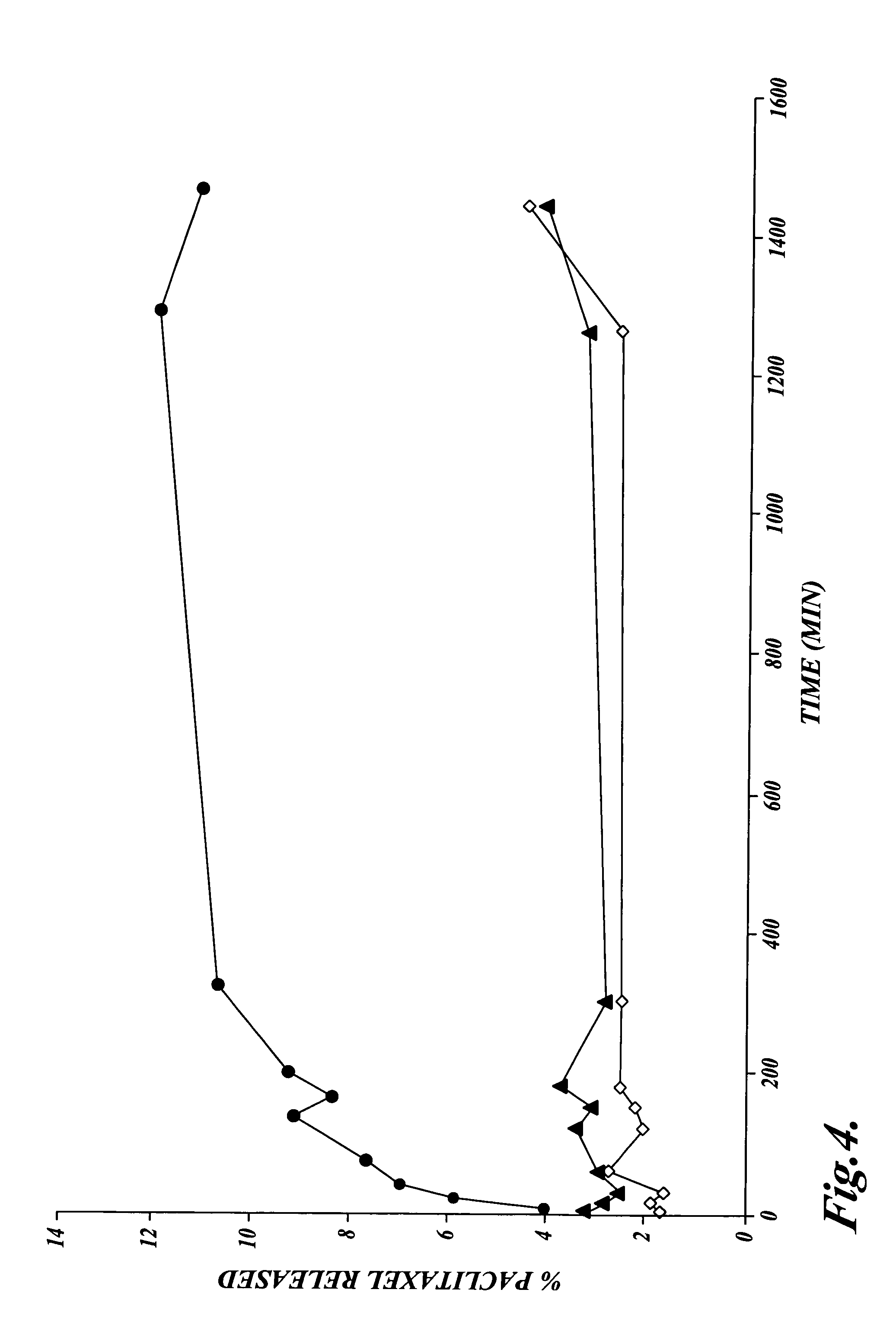
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Methods for rational pegylation of proteins
The present invention relates to the use of simulation technology to rationally optimize the locations and sizes of attached polymeric moieties for modification of therapeutic proteins and the proteins generated from this method.
Owner:XENCOR
Methods for making proteins containing free cysteine residues
The present invention relates to novel methods of making soluble proteins having free cysteines in which a host cell is exposed to a cysteine blocking agent. The soluble proteins produced by the methods can then be modified to increase their effectiveness. Such modifications include attaching a PEG moiety to form pegylated proteins.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Reversible pegylated drugs
ActiveUS20060171920A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeProvide benefitsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphate9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl
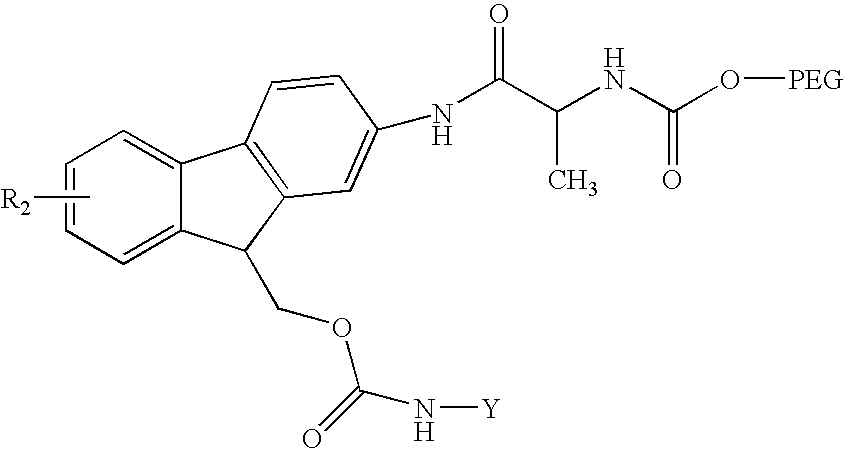
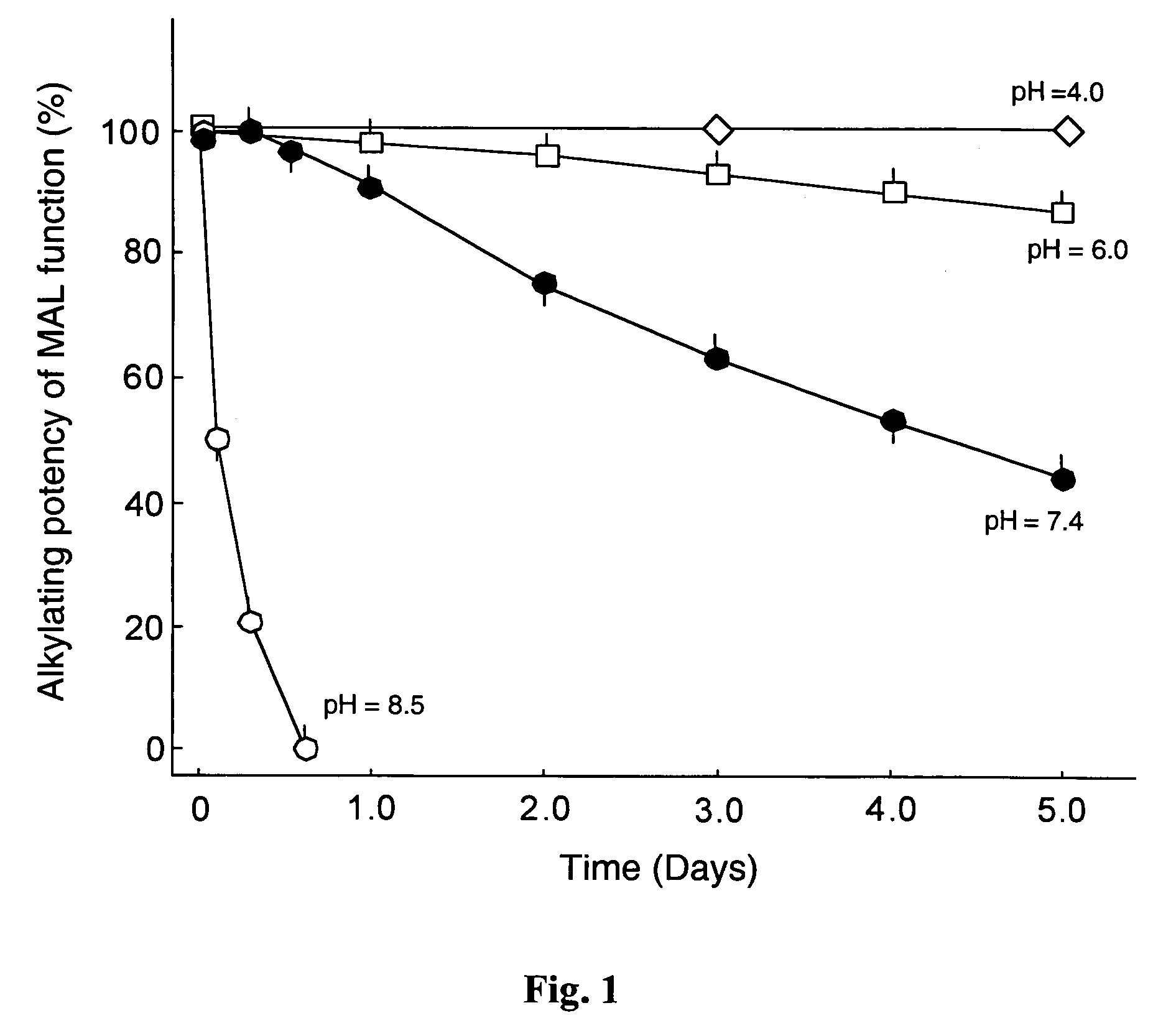
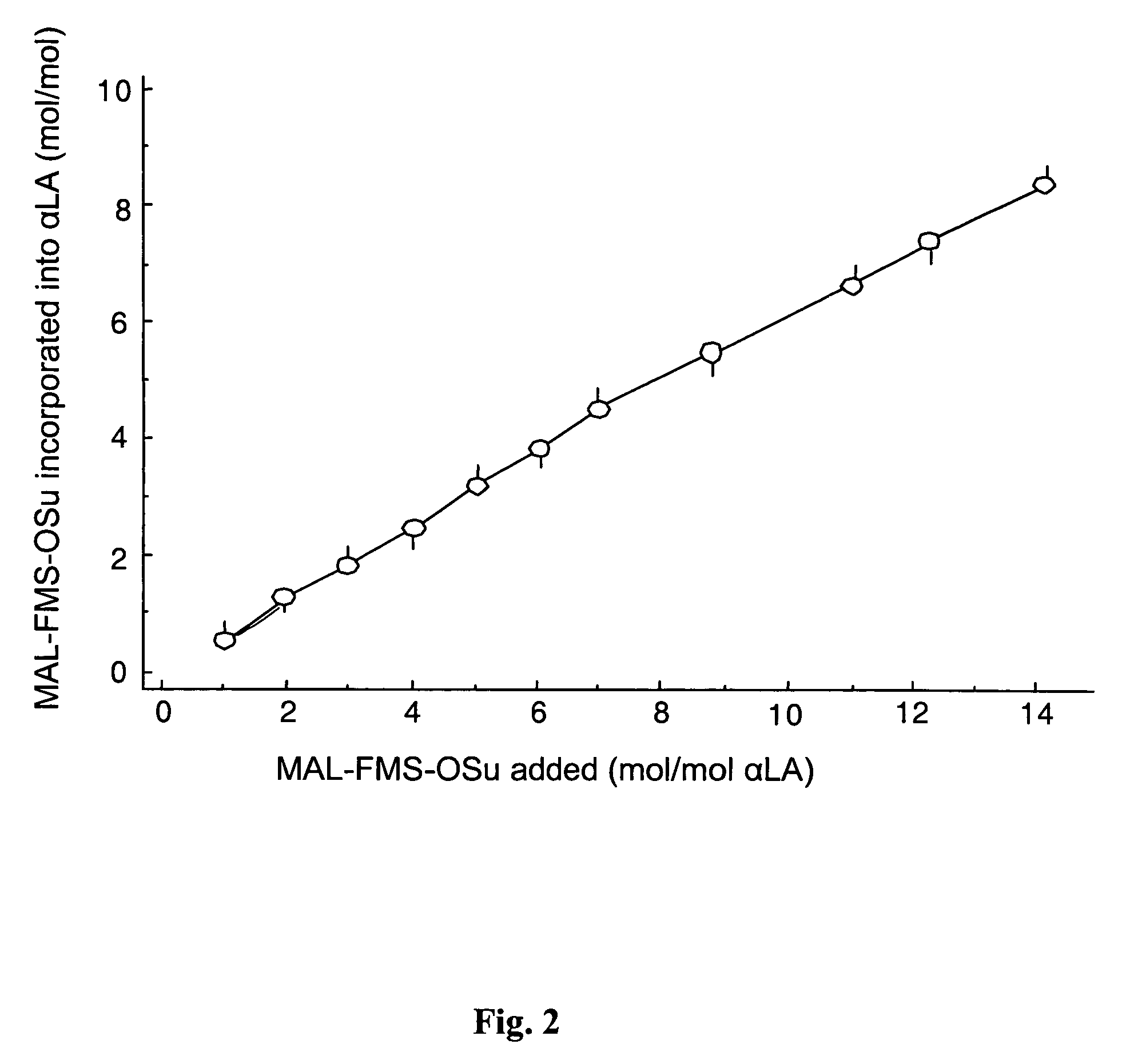
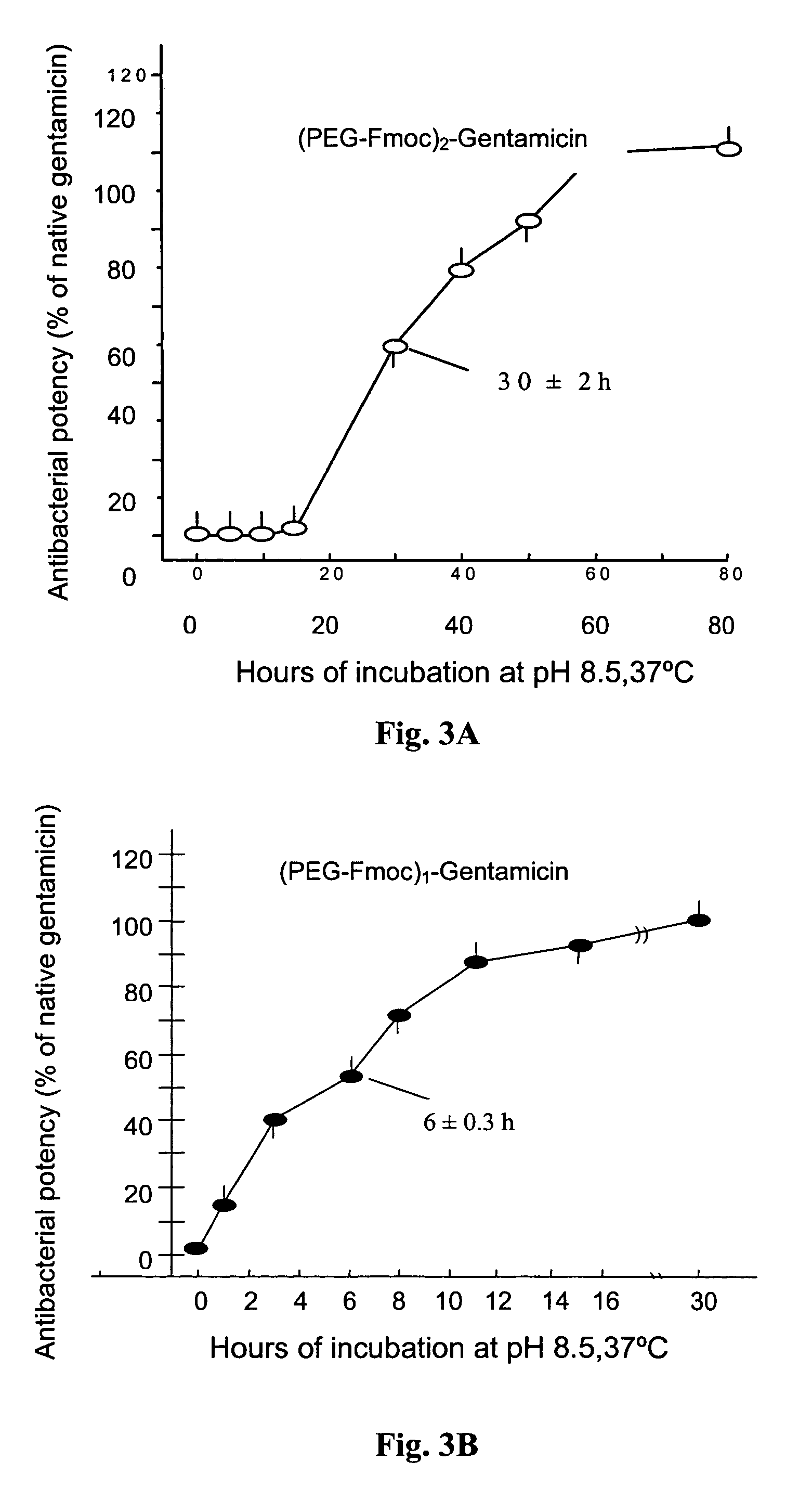
Reversible pegylated drugs are provided by derivatization of free functional groups of the drug selected from amino, hydroxyl, mercapto, phosphate and / or carboxyl with groups sensitive to mild basic conditions such as 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) or 2-sulfo-9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (FMS), to which group a PEG moiety is attached. In these pegylated drugs, the PEG moiety and the drug residue are not linked directly to each other, but rather both residues are linked to different positions of the scaffold Fmoc or FMS structure that is highly sensitive to bases and is removable under physiological conditions. The drugs are preferably drugs containing an amino group, most preferably peptides and proteins of low or medium molecular weight. Similar molecules are provided wherein a protein carrier or another polymer carrier replaces the PEG moiety.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Reversible pegylated drugs
ActiveUS7585837B2Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeLoss of biological and pharmacological potenciesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphate9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl
Reversible pegylated drugs are provided by derivatization of free functional groups of the drug selected from amino, hydroxyl, mercapto, phosphate and / or carboxyl with groups sensitive to mild basic conditions such as 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) or 2-sulfo-9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (FMS), to which group a PEG moiety is attached. In these pegylated drugs, the PEG moiety and the drug residue are not linked directly to each other, but rather both residues are linked to different positions of the scaffold Fmoc or FMS structure that is highly sensitive to bases and is removable under physiological conditions. The drugs are preferably drugs containing an amino group, most preferably peptides and proteins of low or medium molecular weight. Similar molecules are provided wherein a protein carrier or another polymer carrier replaces the PEG moiety.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
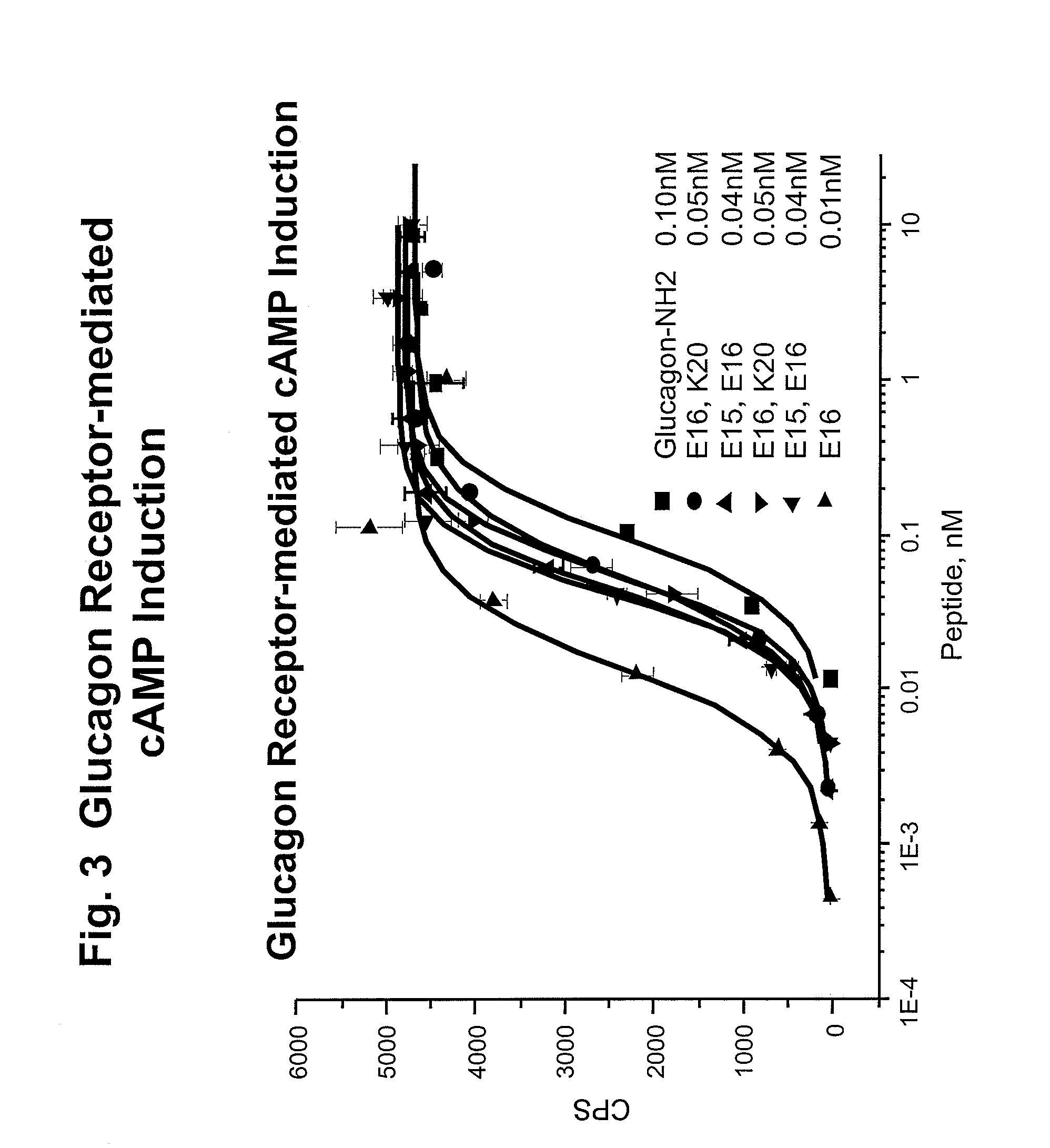
Glucagon/glp-1 receptor co-agonists
InactiveUS20100190701A1High activityEnhanced biophysical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityCarboxylic acid
Modified glucagon peptides are disclosed having enhanced potency at the glucagon receptor relative to native glucagon. Further modification of the glucagon peptides by forming lactam bridges or the substitution of the terminal carboxylic acid with an amide group produces peptides exhibiting glucagon / GLP-1 receptor co-agonist activity. The solubility and stability of these high potency glucagon analogs can be further improved by modification of the polypeptides by pegylation, substitution of carboxy terminal amino acids, or the addition of a carboxy terminal peptide selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 26 (GPSSGAPPPS), SEQ ID NO: 27 (K-RNRNNIA) and SEQ ID NO: 28 (KRNR).
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
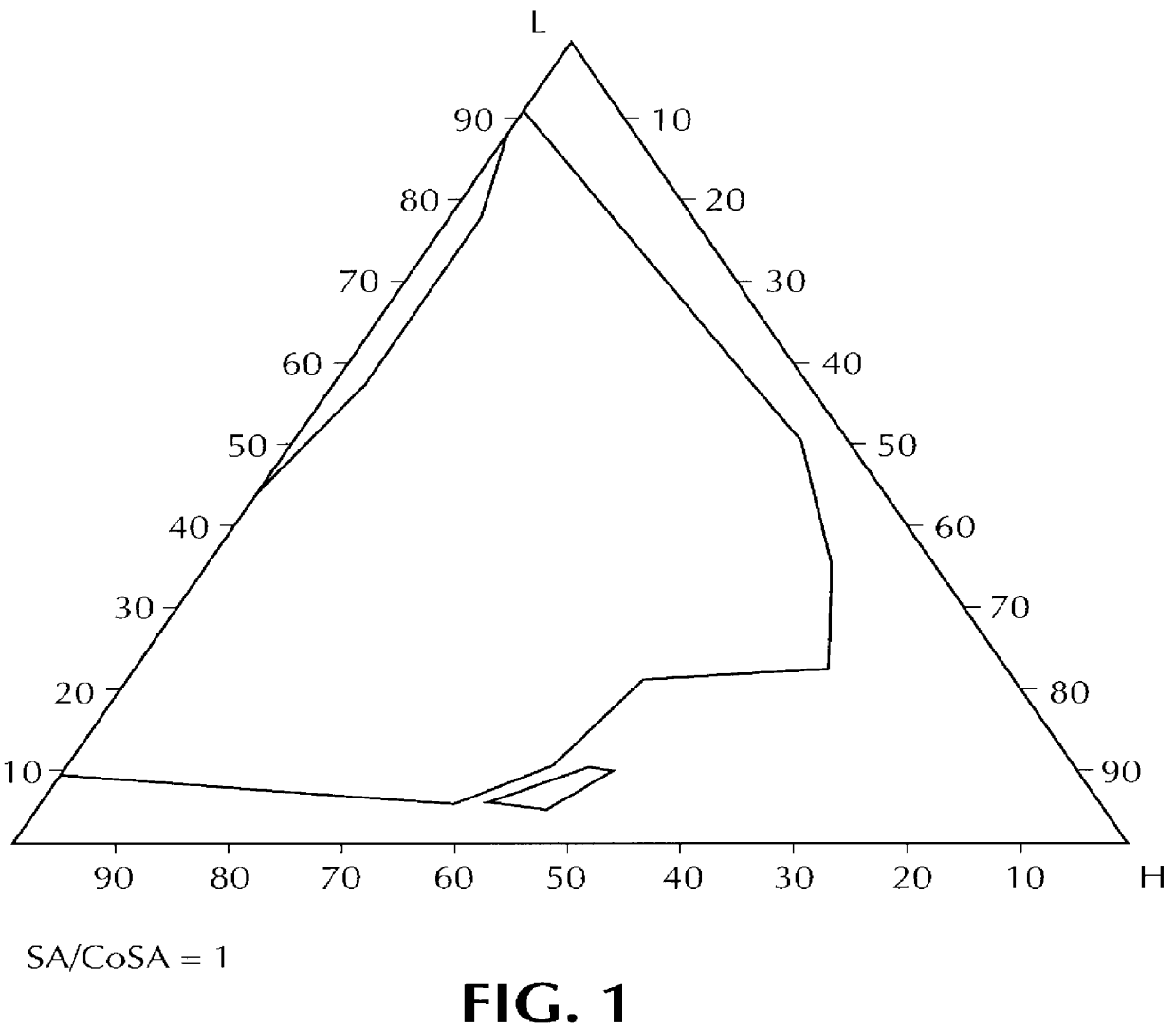
Orally administrable composition capable of providing enhanced bioavailability when ingested
InactiveUS6054136AImprove solubilityImprove bioavailabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFatty acid esterIngestion
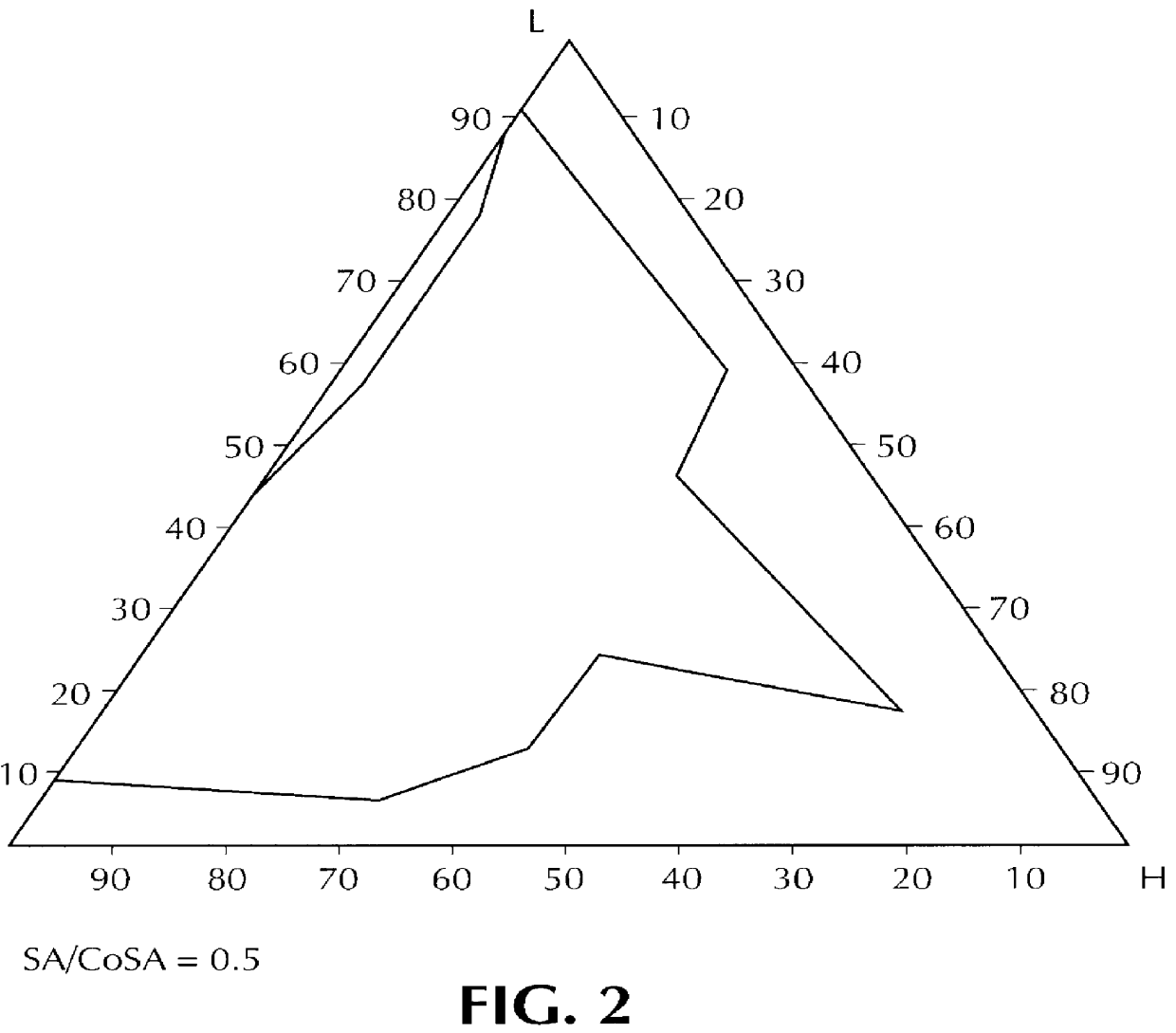
Composition for pharmaceutical or cosmetic use, capable of forming a microemulsion, comprising at least: an active principle, a lipophilic phase consisting of a mixture of fatty acid esters and glycerides, a surfactant (SA), a cosurfactant (CoSA), a hydrophilic phase, characterized: in that the lipophilic phase consists of a mixture of C8 to C18 polyglycolized glycerides having a hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) of less than 16, this lipophilic phase representing from 30 to 75% of the total weight of the composition; in that the surfactant (SA) is chosen from the group comprising saturated C8-C10 olyglycolized glycerides and oleic esters of polyglycerol, this surfactant having an HLB of less than 16; in that the cosurfactant (CoSA) is chosen from the group comprising lauric esters of propylene glycol, oleic esters of polyglycerol and ethyl diglycol; in that the SA / CoSA ratio is between 0.5 and 6; and in that the hydrophilic phase of the final microemulsion is supplied after ingestion by the physiological fluid of the digestive milieu.
Owner:GATTEFOSSE HLDG
Pegylated nanoparticles
ActiveUS8628801B2Good bioadhesionStrong specificityPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsZeta potentialOrganic synthesis
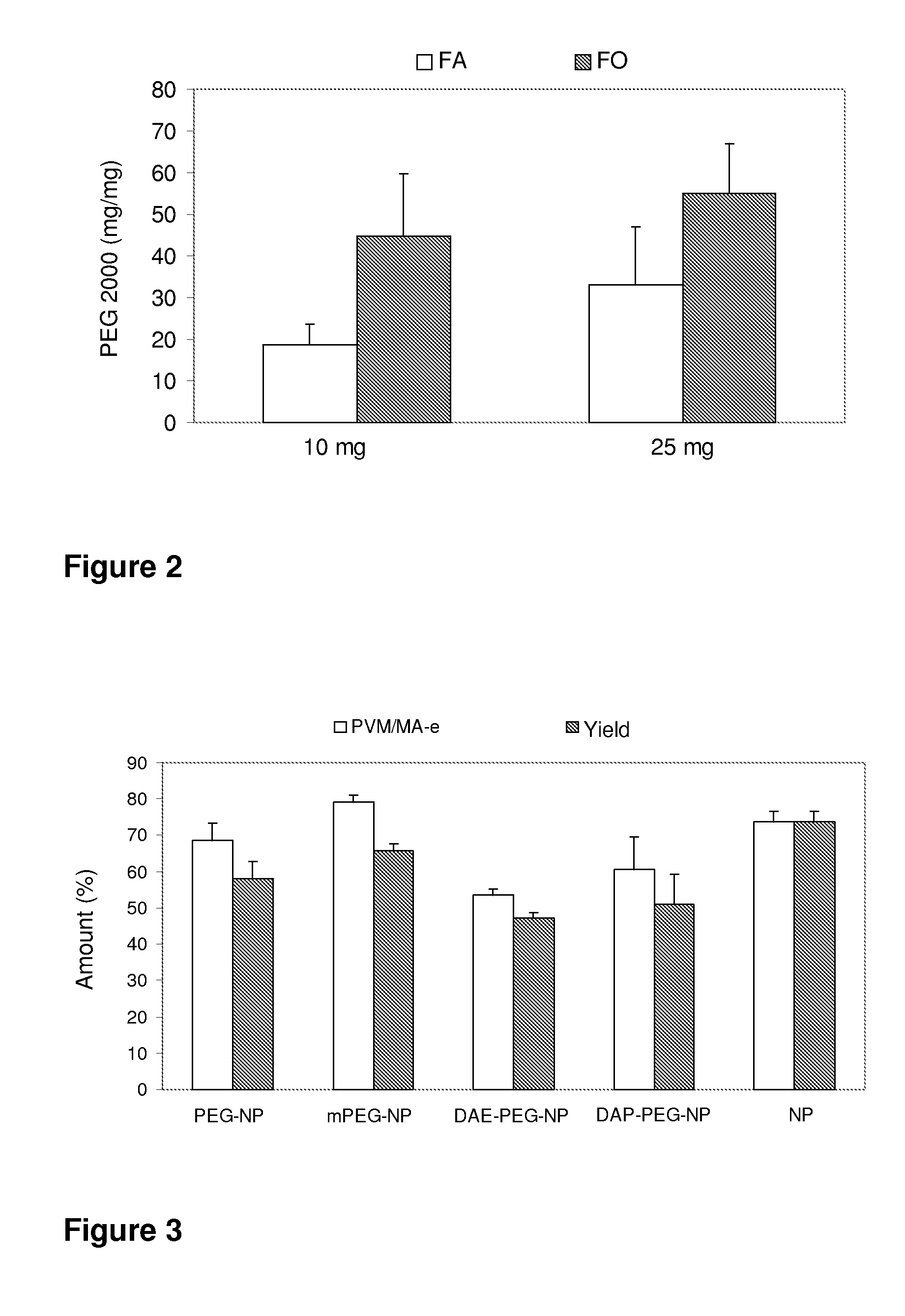
The present invention relates to nanoparticles comprising a biodegradable polymer, preferably the vinyl methyl ether and maleic anhydride (PVM / MA) copolymer, and a polyethylene glycol or derivatives thereof. These nanoparticles are easy to produce and provide excellent bioadhesion, size and zeta potential characteristics making them suitable for the administration of active molecules. The selection of the type of polyethylene glycol used in their production allows suitably modulating the characteristics of these nanoparticles, which can be advantageously used according to the type of drug to be carried and / or the method of administration of the pharmaceutical formulation. pegylation is carried out by simple incubation for a short time period of the two macromolecules in question, without needing to have to resort to the use of organic solvents with high toxicity or long and laborious organic synthesis processes. Furthermore, the pegylation process can be associated to the process of encapsulating the biologically active molecule.
Owner:INNOUP FARMA
PYY agonists and use thereof
InactiveUS20060178501A1Reduces caloric intakeLose weightHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsAgonistPEGylation
Owner:PFIZER INC
Pegylated interleukin-10
InactiveUS7052686B2Minimize disruptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticInterleukin 10White blood cell
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) conjugated via a linker to one or more polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecules at a single amino acid residue of the IL-10, and a method for preparing the same, are provided. The method produces a stable mono-pegylated IL-10, which retains IL-10 activity, where pegylation is selective for the N-terminus on one subunit of IL-10 with little or no formation of monomeric IL-10. The method also provides a substantially homogenous population of mono-PEG-IL-10.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
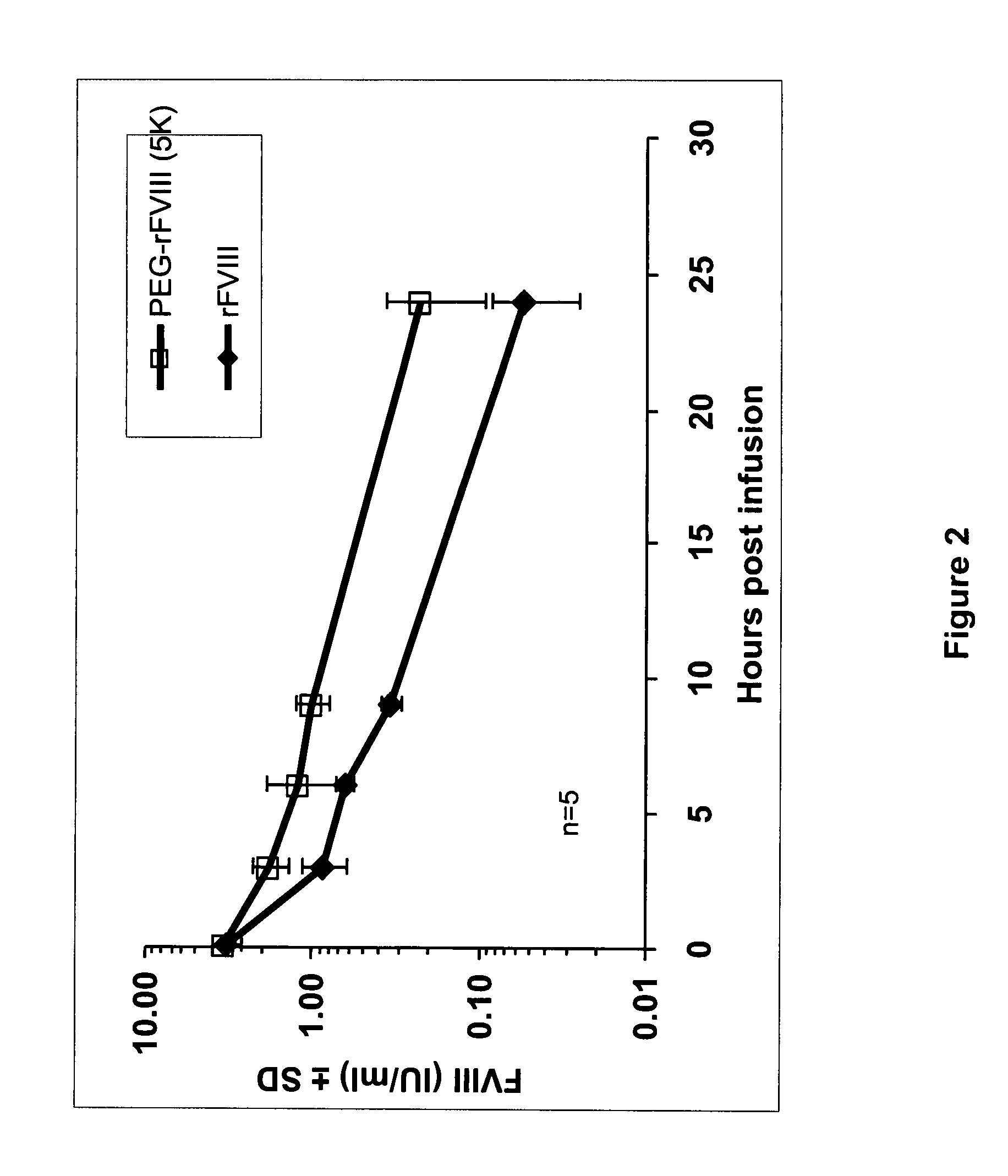
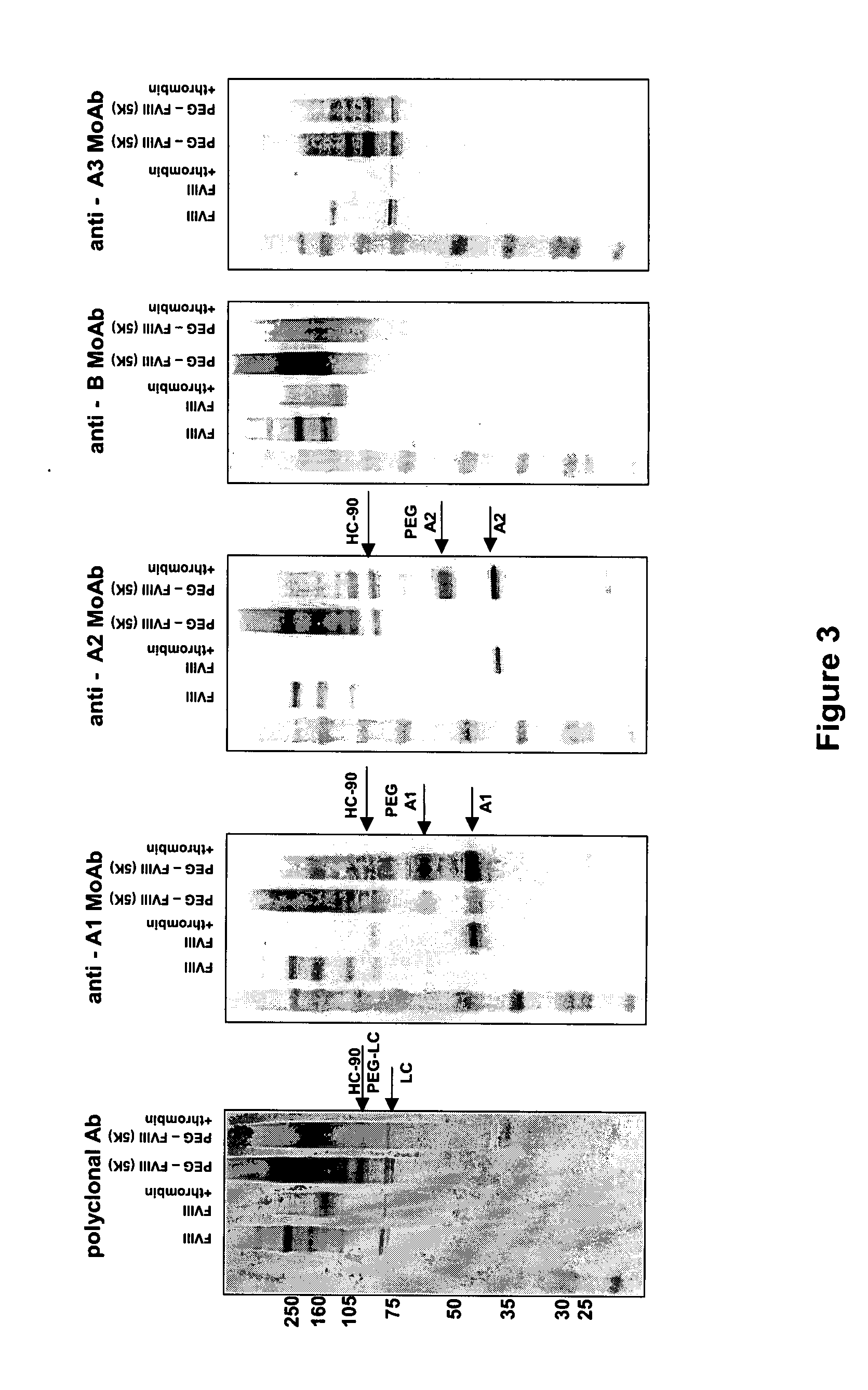
Pegylated factor VIII
The invention is a proteinaceous construct comprising a Factor VIII molecule having at least a portion of the B domain intact, which is conjugated to a water-soluble polymer such as polyethylene glycol having a molecular weight of greater than 10,000 Daltons. The construct has a biological activity of at least 80% of the biological activity of native Factor VIII, and the in vivo half-life of the construct is increased by at least 1.5 fold as compared to the in vivo half-life of native factor FVIII.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
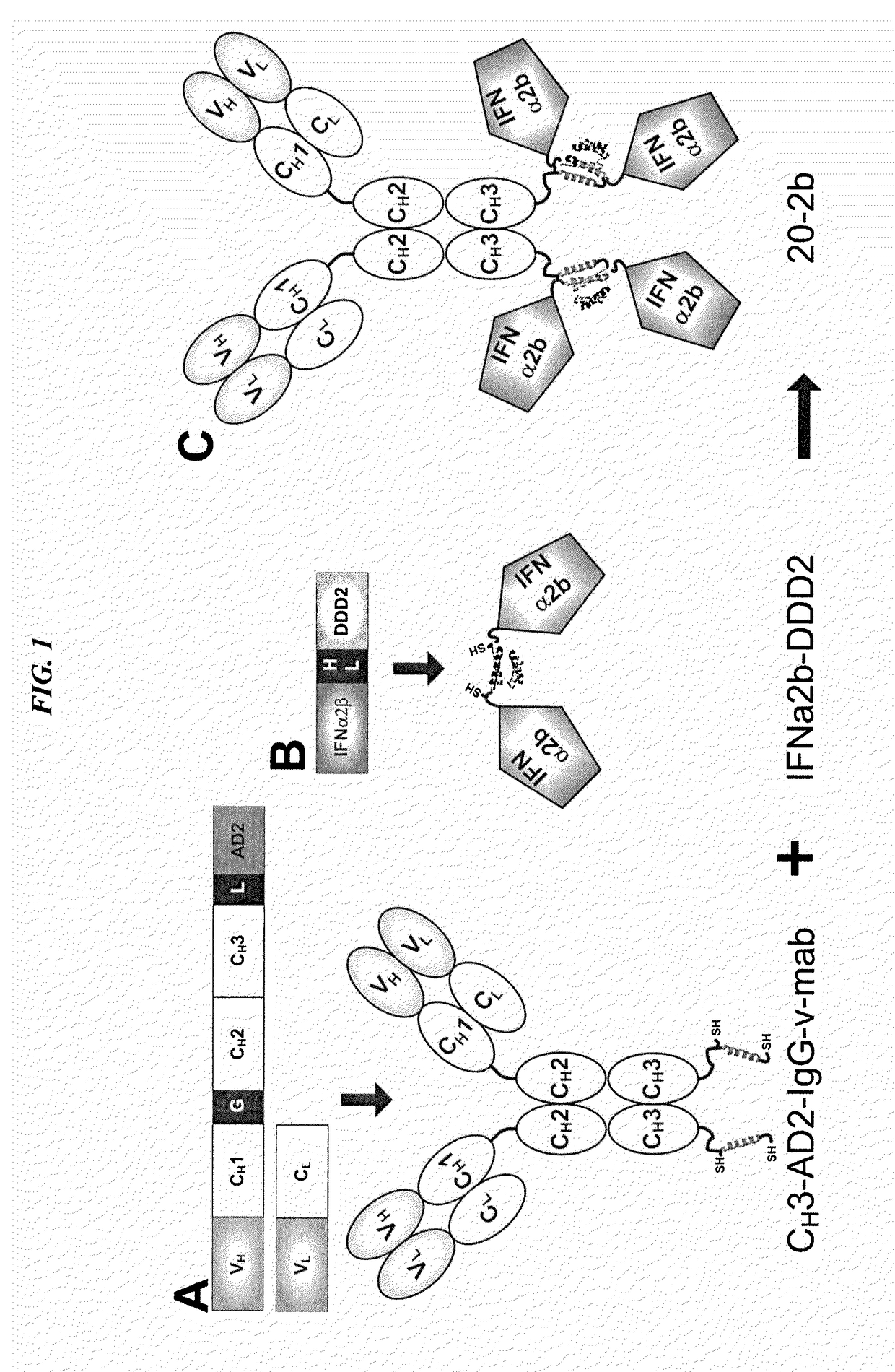
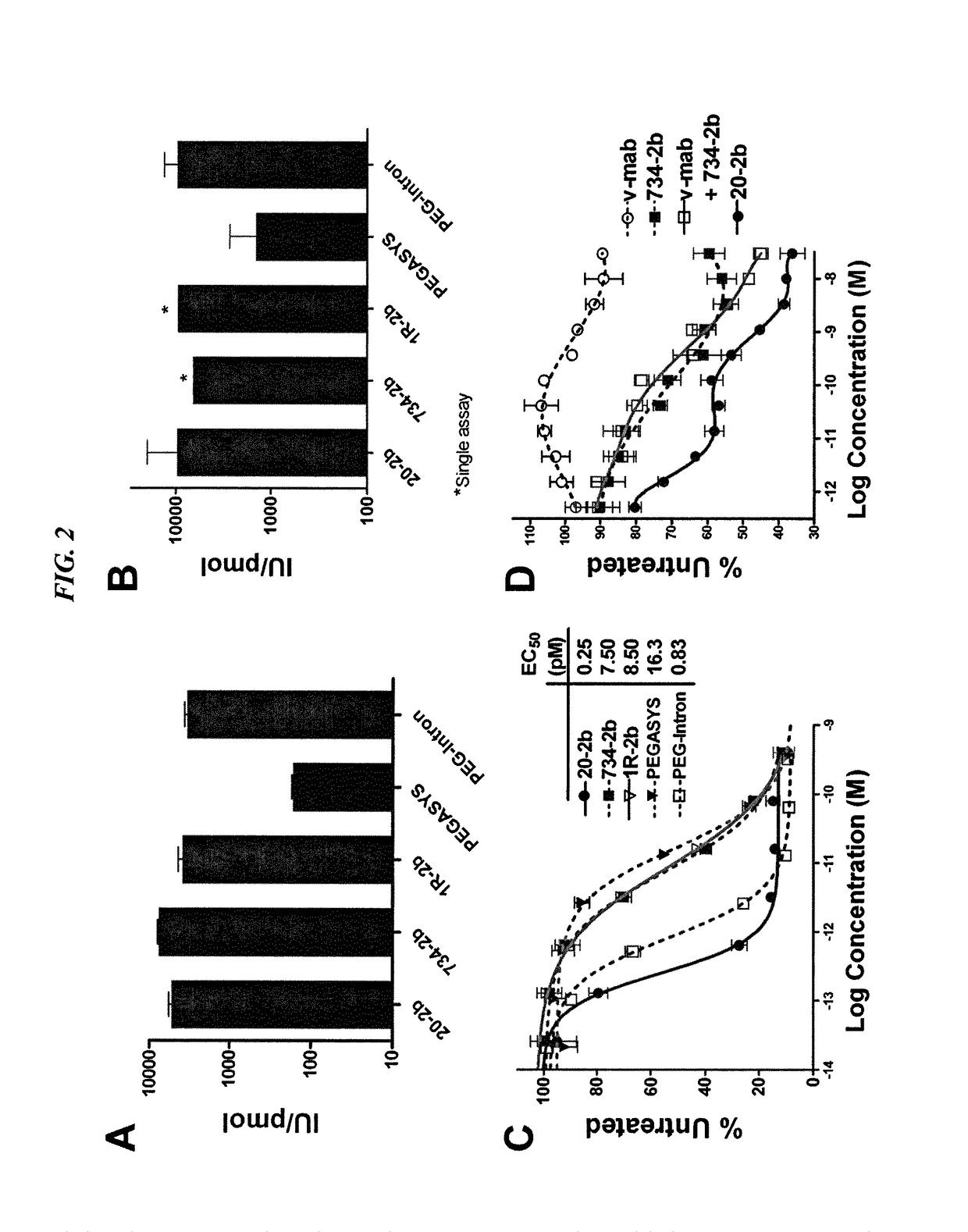
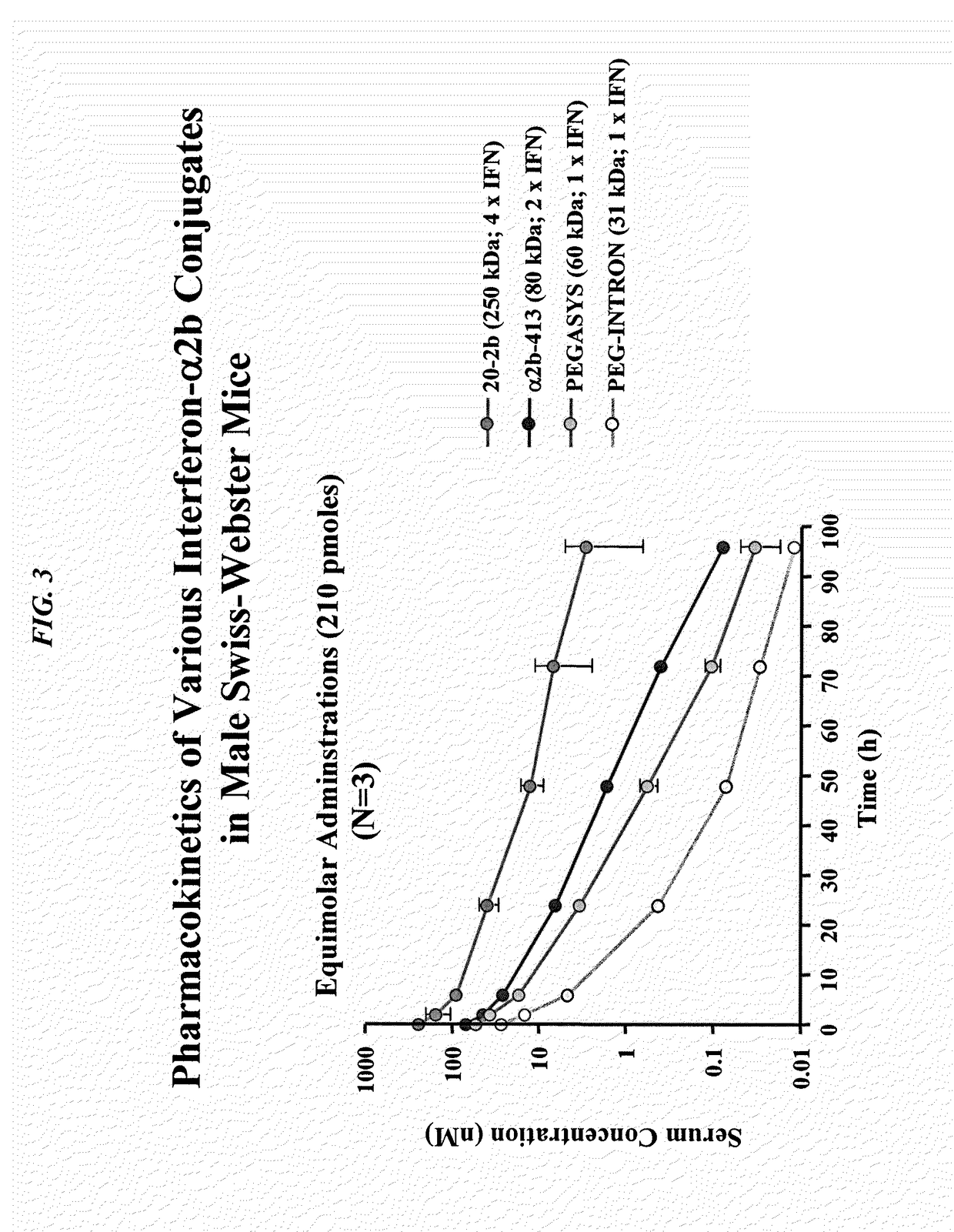
Modular method to prepare tetrameric cytokines with improved pharmacokinetics by the dock-and-lock (DNL) technology
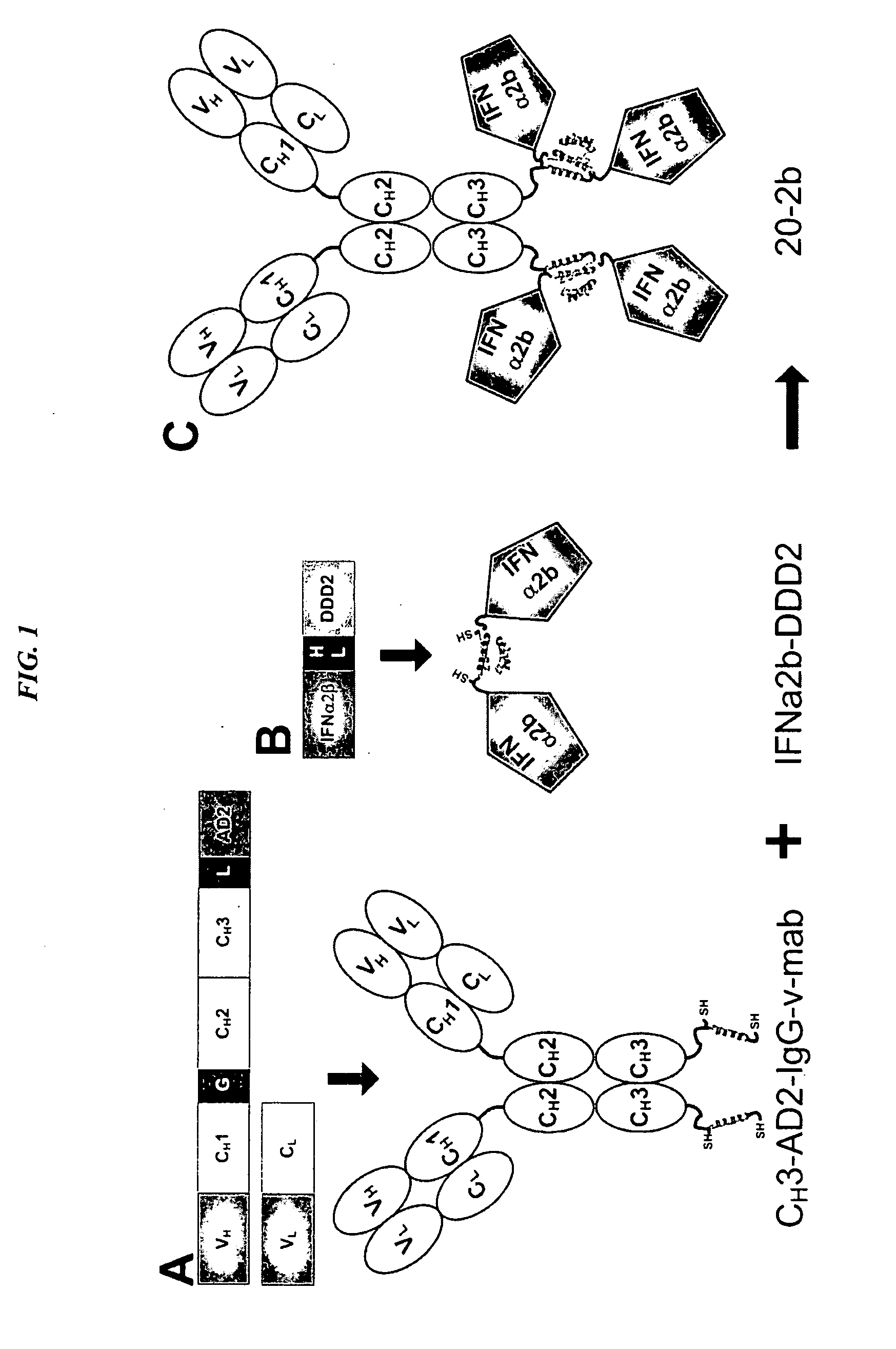
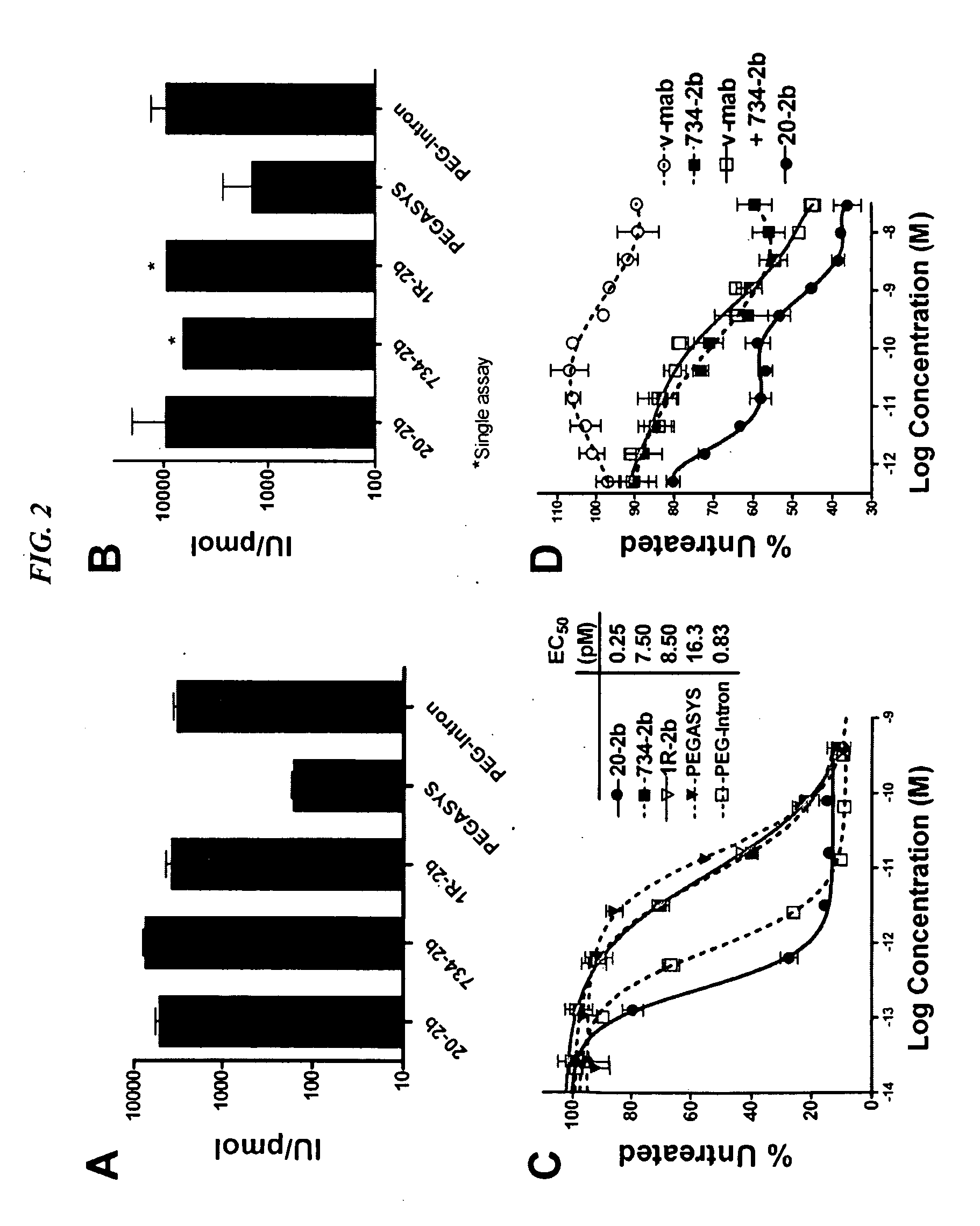
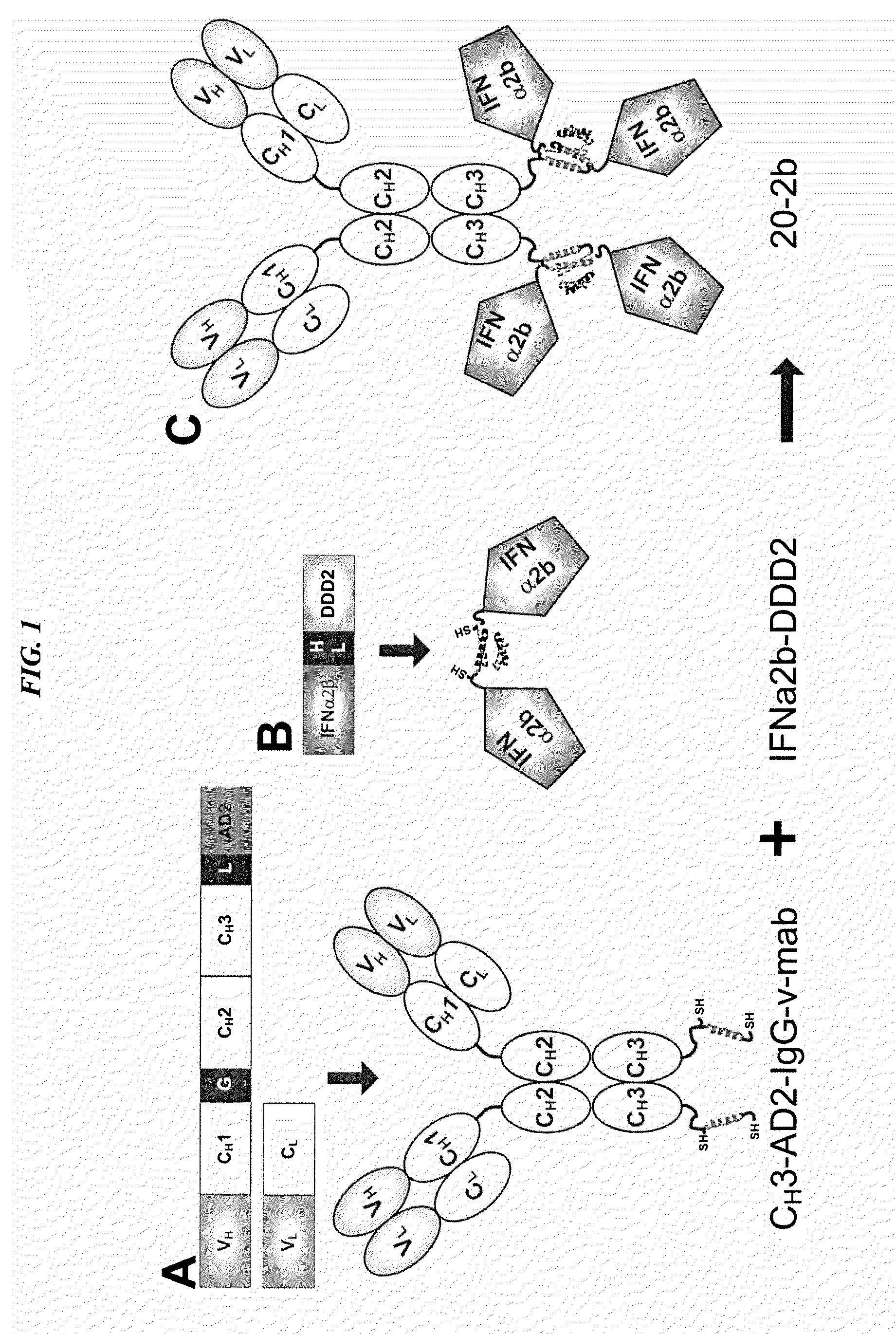
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming cytokine-antibody complexes using dock-and-lock technology. In preferred embodiments, the cytokine-MAb DNL complex comprises an IgG antibody attached to two AD (anchor domain) moieties and four cytokines, each attached to a DDD (docking and dimerization domain) moiety. The DDD moieties form dimers that bind to the AD moieties, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of DDD to AD. The cytokine-MAb complex exhibits improved pharmacokinetics, with a significantly longer serum half-life than either naked cytokine or PEGylated cytokine. The cytokine-MAb complex also exhibits significantly improved in vitro and in vivo efficacy compared to cytokine alone, antibody alone, unconjugated cytokine plus antibody or cytokine-MAb DNL complexes incorporating an irrelevant antibody. In a most preferred embodiment the complex comprises an anti-CD20 IgG antibody conjugated to four IFN-α2b moieties, although other antibodies and cytokines have been used to form effect DNL complexes.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Modular Method to Prepare Tetrameric Cytokines with Improved Pharmacokinetics by the Dock-and-Lock (DNL) Technology
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming cytokine-antibody complexes using dock-and-lock technology. In preferred embodiments, the cytokine-MAb DNL complex comprises an IgG antibody attached to two AD (anchor domain) moieties and four cytokines, each attached to a DDD (docking and dimerization domain) moiety. The DDD moieties form dimers that bind to the AD moieties, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of DDD to AD. The cytokine-MAb complex exhibits improved pharmacokinetics, with a significantly longer serum half-life than either naked cytokine or PEGylated cytokine. The cytokine-MAb complex also exhibits significantly improved in vitro and in vivo efficacy compared to cytokine alone, antibody alone, unconjugated cytokine plus antibody or cytokine-MAb DNL complexes incorporating an irrelevant antibody. In a most preferred embodiment the complex comprises an anti-CD20 IgG antibody conjugated to four IFN-α2b moieties, although other antibodies and cytokines have been used to form effect DNL complexes.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
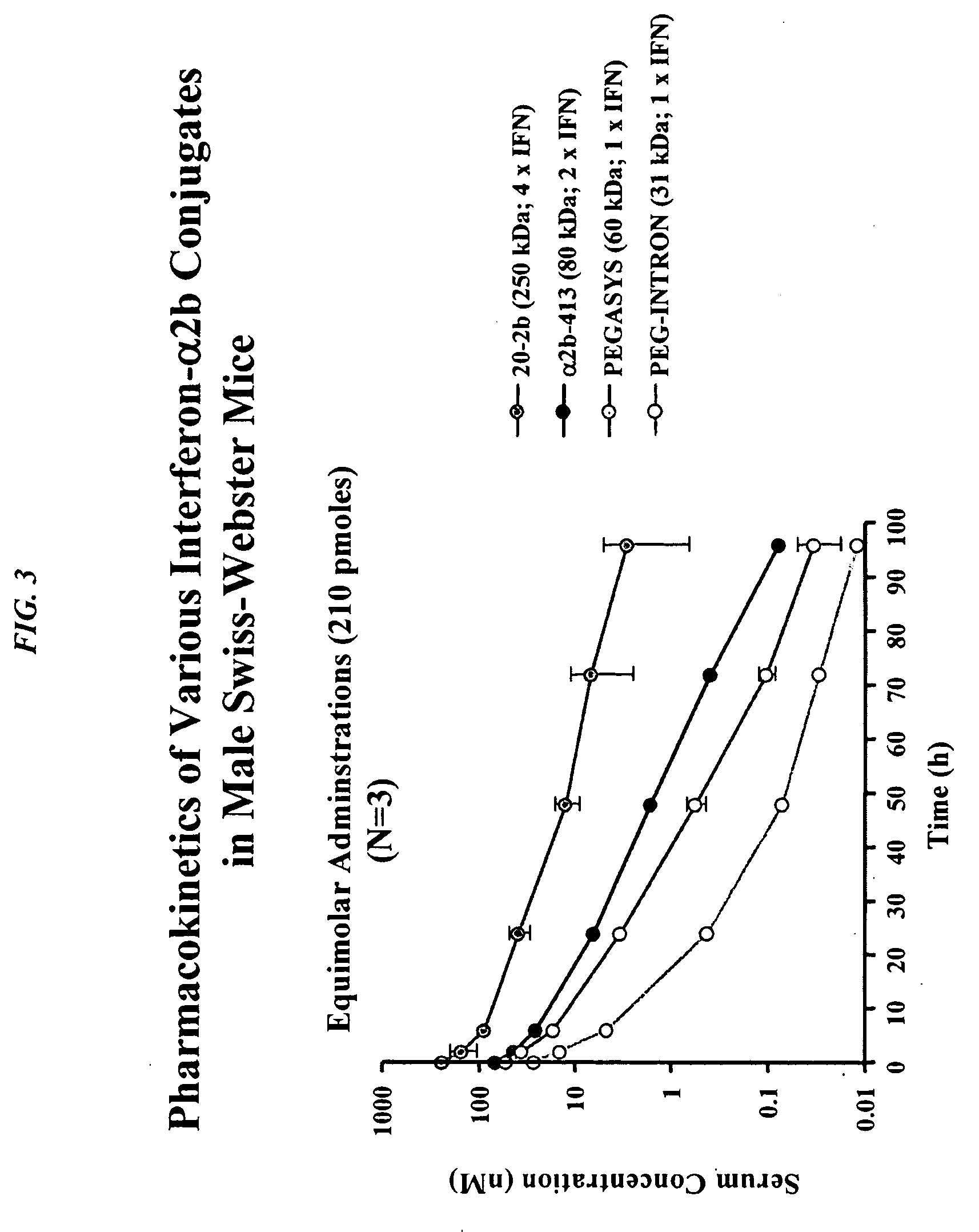
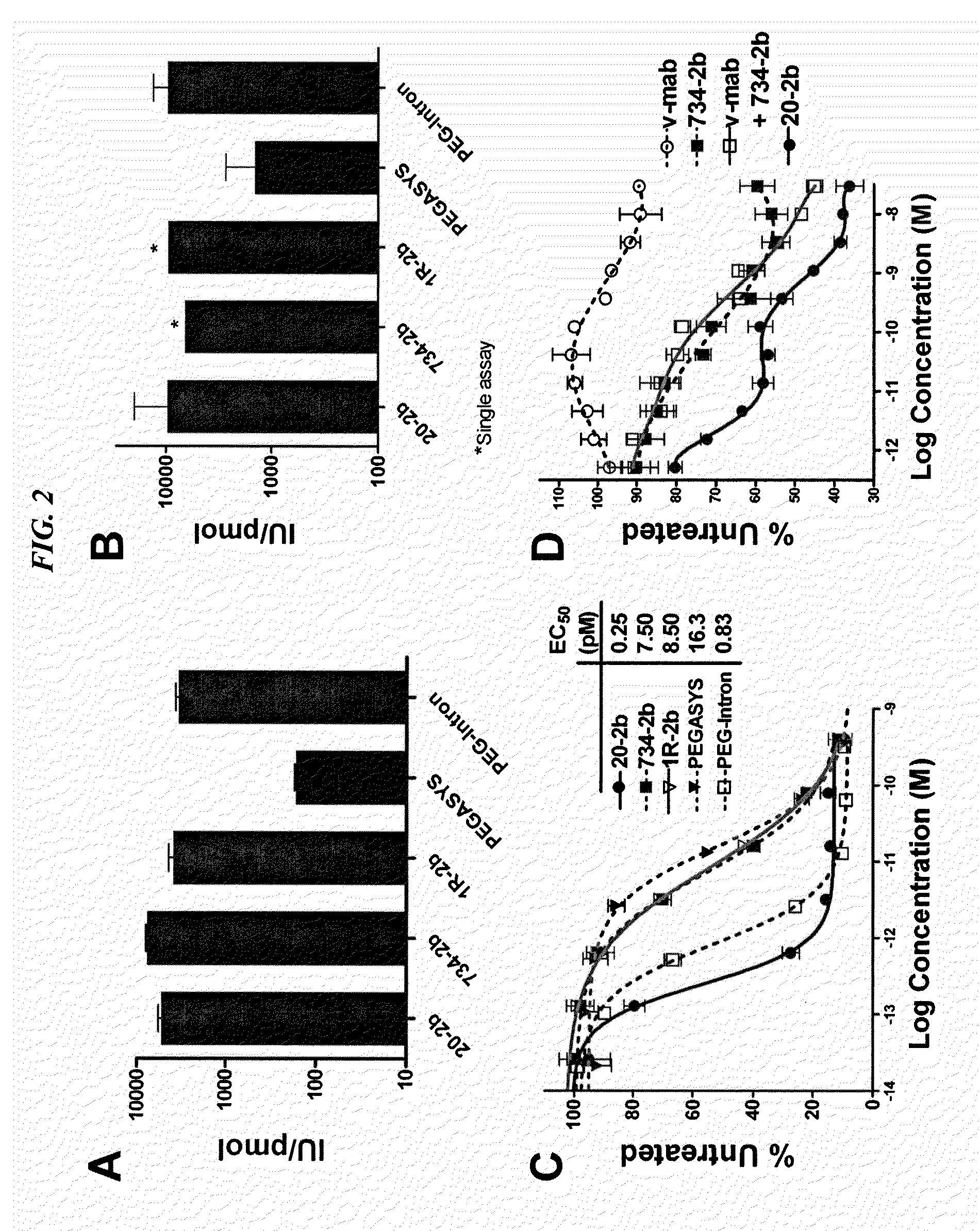
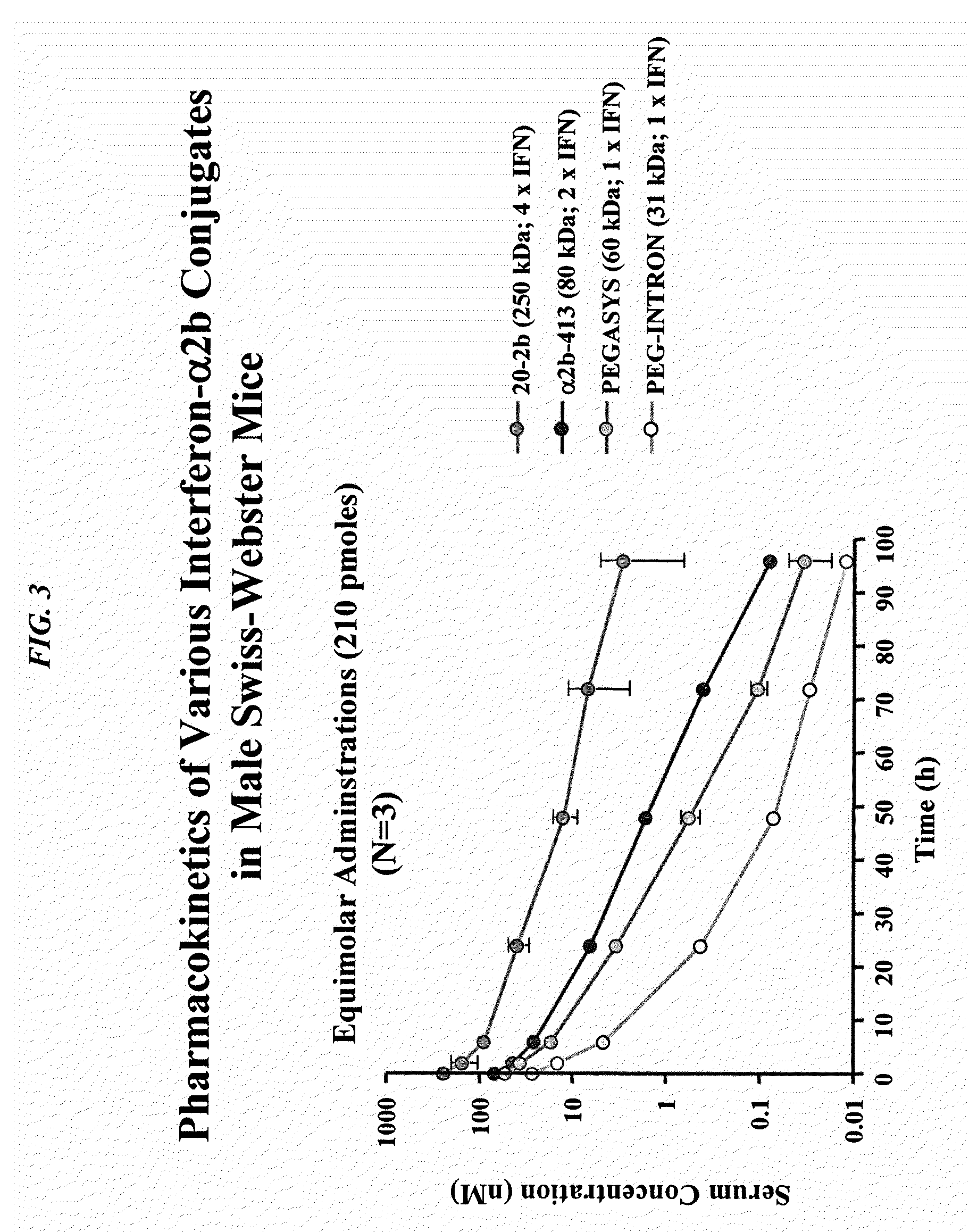
Dimeric alpha interferon pegylated site-specifically shows enhanced and prolonged efficacy in vivo
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming PEGylated complexes of defined stoichiometry and structure. In preferred embodiments, the PEGylated complex is formed using dock-and-lock technology, by attaching a therapeutic agent to a DDD sequence and attaching a PEG moiety to an AD sequence and allowing the DDD sequence to bind to the AD sequence in a 2:1 stoichiometry, to form PEGylated complexes with two therapeutic agents and one PEG moiety. In alternative embodiments, the therapeutic agent may be attached to the AD sequence and the PEG to the DDD sequence to form PEGylated complexes with two PEG moieties and one therapeutic agent. In more preferred embodiments, the therapeutic agent may comprise any peptide or protein of physiologic or therapeutic activity, preferably a cytokine, more preferably interferon-α2b. The PEGylated complexes exhibit a significantly slower rate of clearance when injected into a subject and are of use for treatment of a wide variety of diseases.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases and Methods of Preparing and Using Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases
InactiveUS20090123367A1Facilitated DiffusionEnhance convective transportBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHyaluronidaseNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME +6
Tetrameric cytokines with improved biological activity
ActiveUS8034352B2Keep for a long timeLow toxicityMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igeHalf-life
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming cytokine-antibody complexes using dock-and-lock technology. In preferred embodiments, the cytokine-MAb DNL complex comprises an IgG antibody attached to two AD (anchor domain) moieties and four cytokines, each attached to a DDD (docking and dimerization domain) moiety. The DDD moieties form dimers that bind to the AD moieties, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of DDD to AD. The cytokine-MAb complex exhibits improved pharmacokinetics, with a significantly longer serum half-life than either naked cytokine or PEGylated cytokine. The cytokine-MAb complex also exhibits significantly improved in vitro and in vivo efficacy compared to cytokine alone, antibody alone, unconjugated cytokine plus antibody or cytokine-MAb DNL complexes incorporating an irrelevant antibody. In more preferred embodiment the cytokine is G-CSF, erythropoietin or INF-α2b.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
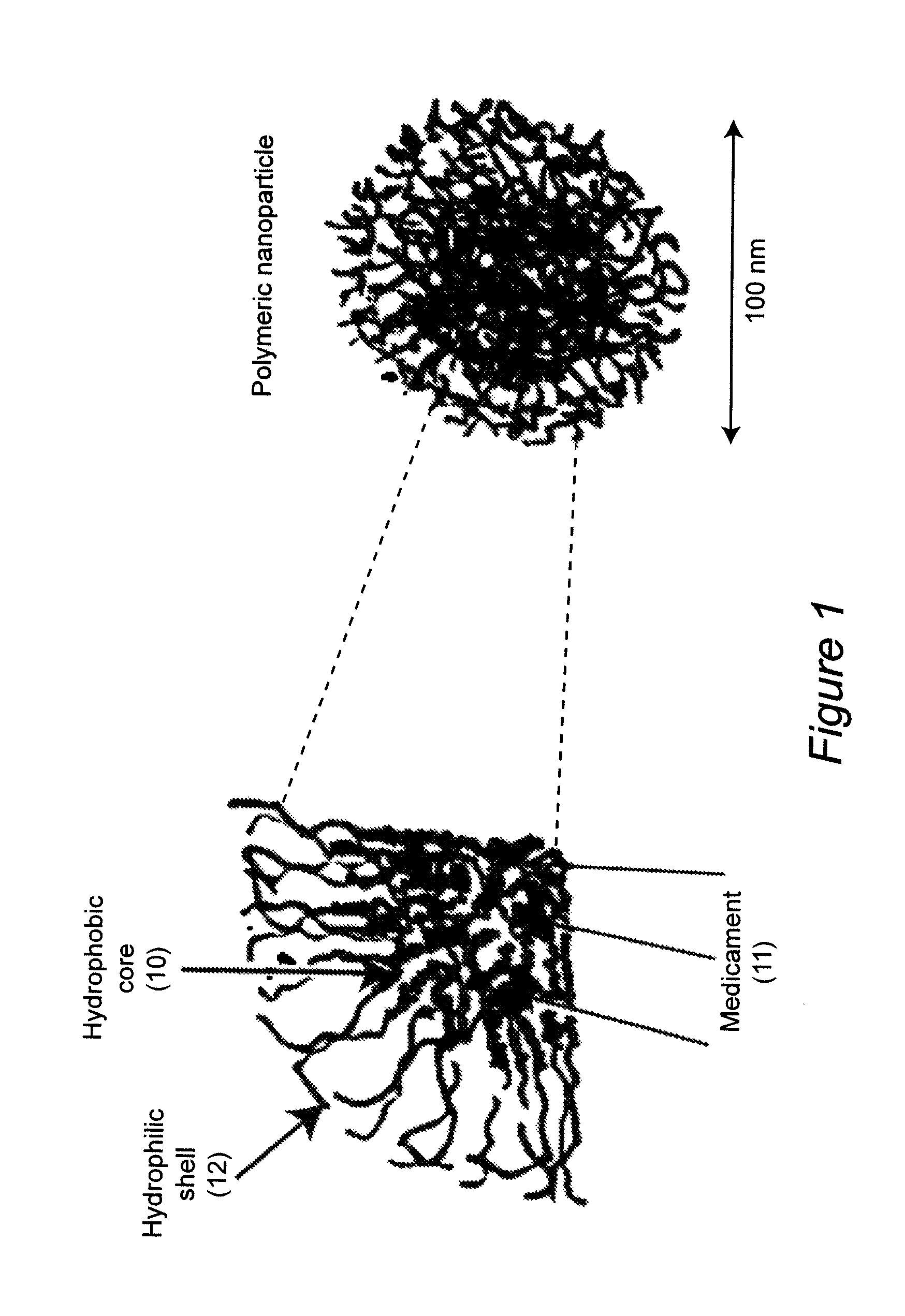
Water-dispersible oral, parenteral, and topical formulations for poorly water soluble drugs using smart polymeric nanoparticles
ActiveUS8313777B2Control releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryNervous disorderWater dispersibleSmart polymer
Polymeric nanoparticles with a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic shell are formed from: 1) N-isopropyl acrylamide (NIPAAM), at a molar ratio of about 50% to about 90%, and preferably 60% for specific delivery routes such as oral or parenteral; either water-soluble vinyl derivatives like vinylpyrolidone (VP) or vinyl acetate (VA), or water insoluble vinyl derivatives like methyl methacrylate (MMA) or styrene (ST), at a molar ratio of about 10% to about 30%; and acrylic acid (AA), at a molar ratio of about 10% to about 30%. The formed nanoparticles may be optionally surface functionalized using reactive groups present in AA, including PEGylation, or conjugation of moieties such as chemotherapeutics, contrasting agents, antibodies, radionucleides, ligands, and sugars, for diagnostic, therapeutic, and imaging purposes. The polymeric nanoparticles are preferably dispersed in aqueous solutions. The polymeric nanoparticles incorporate one or more types of medicines or bioactive agents in the hydrophobic core; on occasion, the medicine or bioactive agent may be conjugated to the nanoparticle surface via reactive functional groups. The polymeric nanoparticles are capable of delivering the said medicines or bioactive agents through oral, parenteral, or topical routes. The polymeric nanoparticles allow poorly water soluble medicines or bioactive agents, or those with poor oral bioavailability, to be formulated in an aqueous solution, and enable their convenient delivery into the systemic circulation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods for the purification of polypeptide conjugates
InactiveUS20100035299A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsPolymer sciencePolypropylene glycol
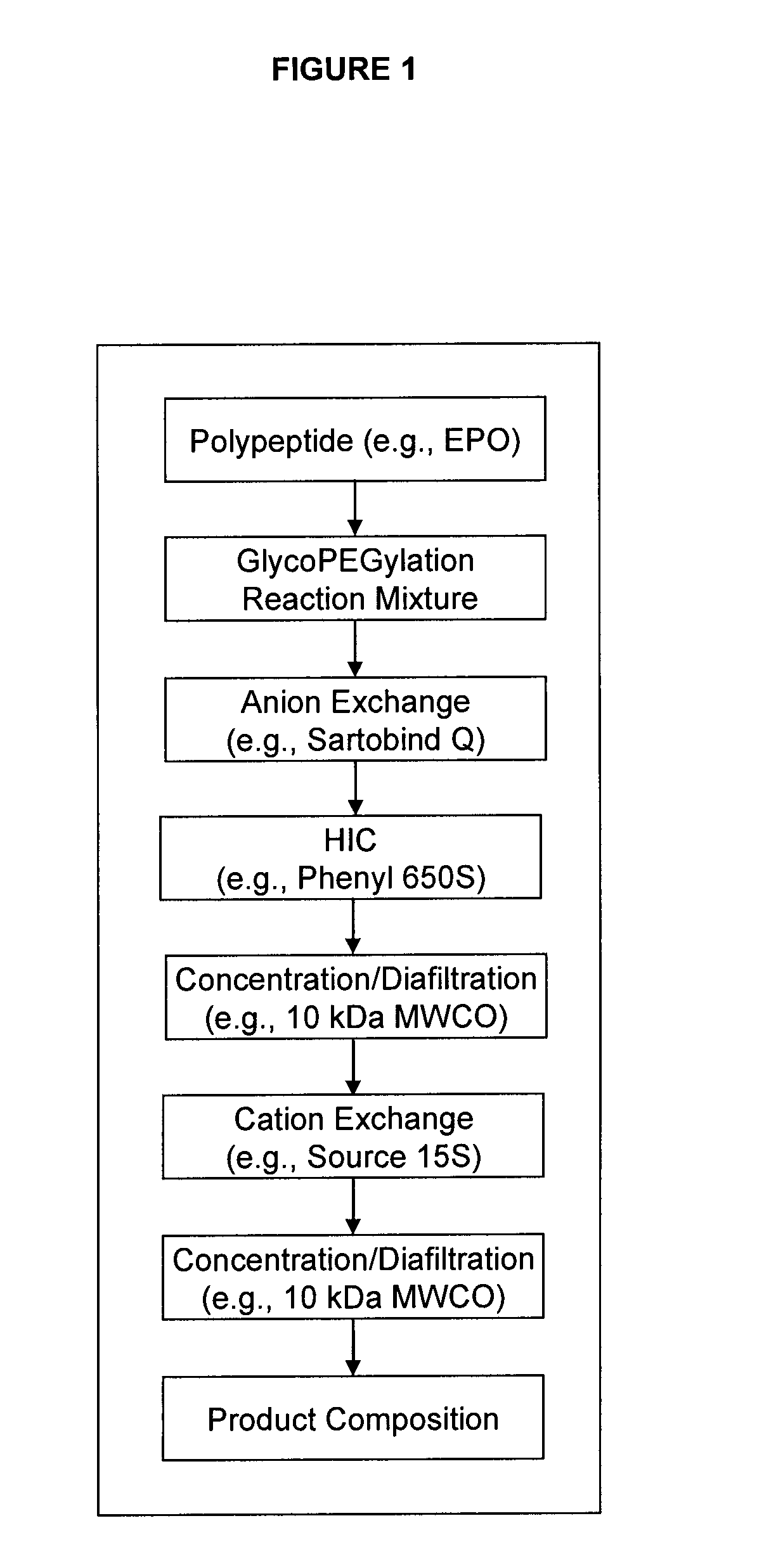
The present invention provides processes for the manufacturing of polypeptide conjugates. In particular, the invention provides methods for the purification of polypeptide conjugates, which include at least one polymeric modifying groups, such as a poly(alkylene oxide) moiety. Exemplary poly(alkylene oxide) moieties include poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and poly(propylene glycol). In an exemplary process, hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) is used to resolve different glycoforms of glycoPEGylated polypeptides.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Matrix composed of a naturally-occurring protein backbone cross linked by a synthetic polymer and methods of generating and using same
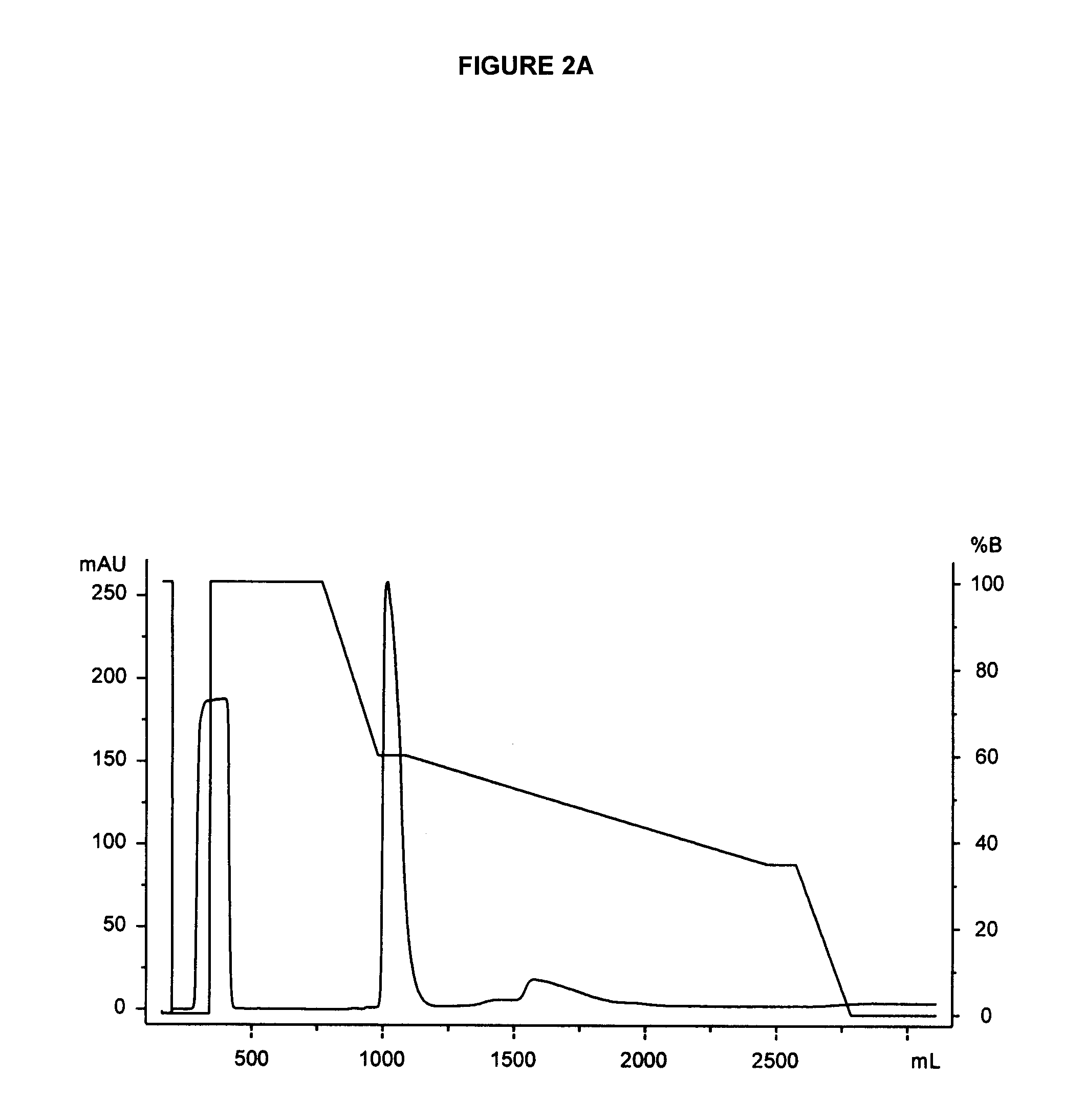
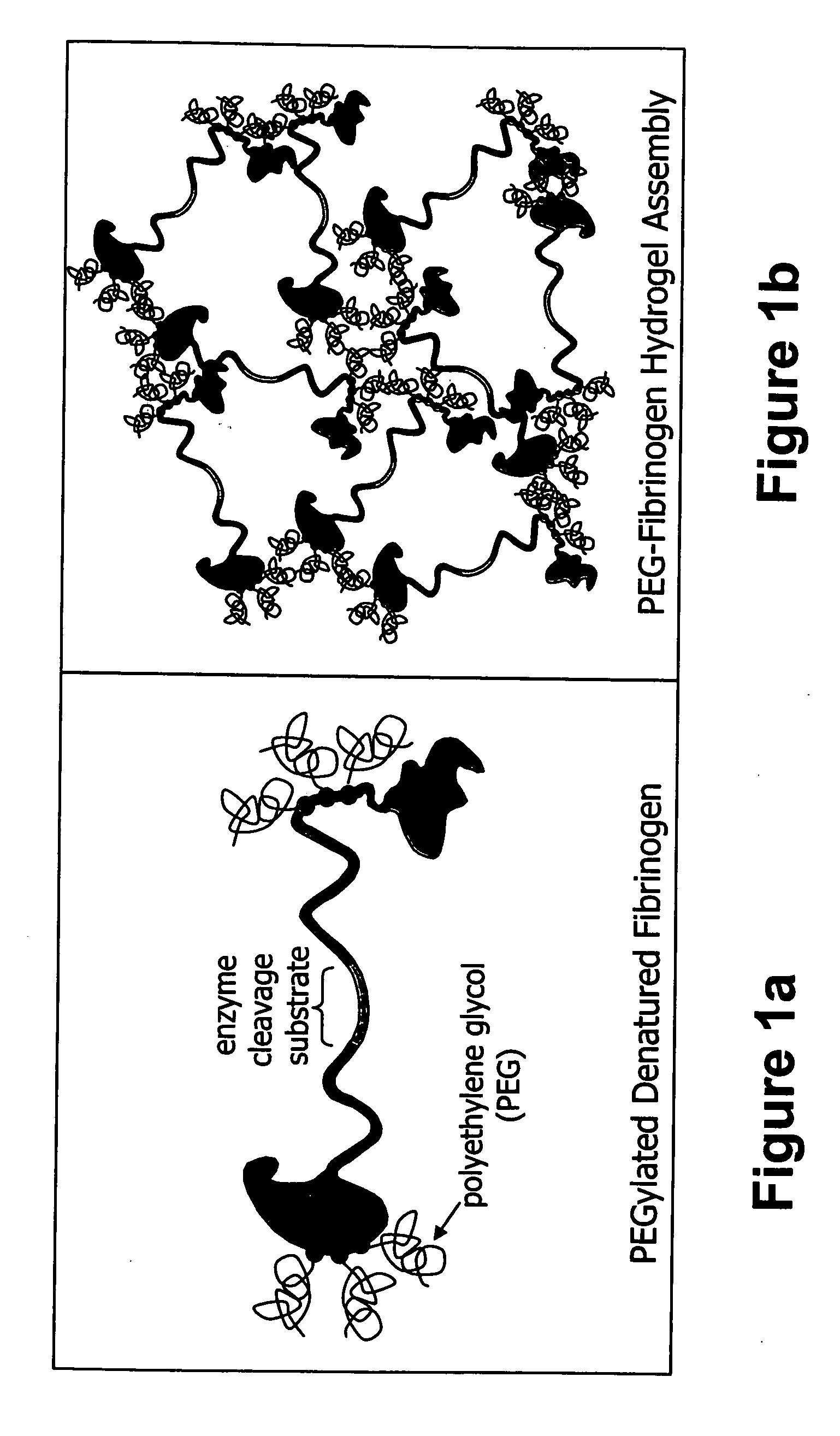
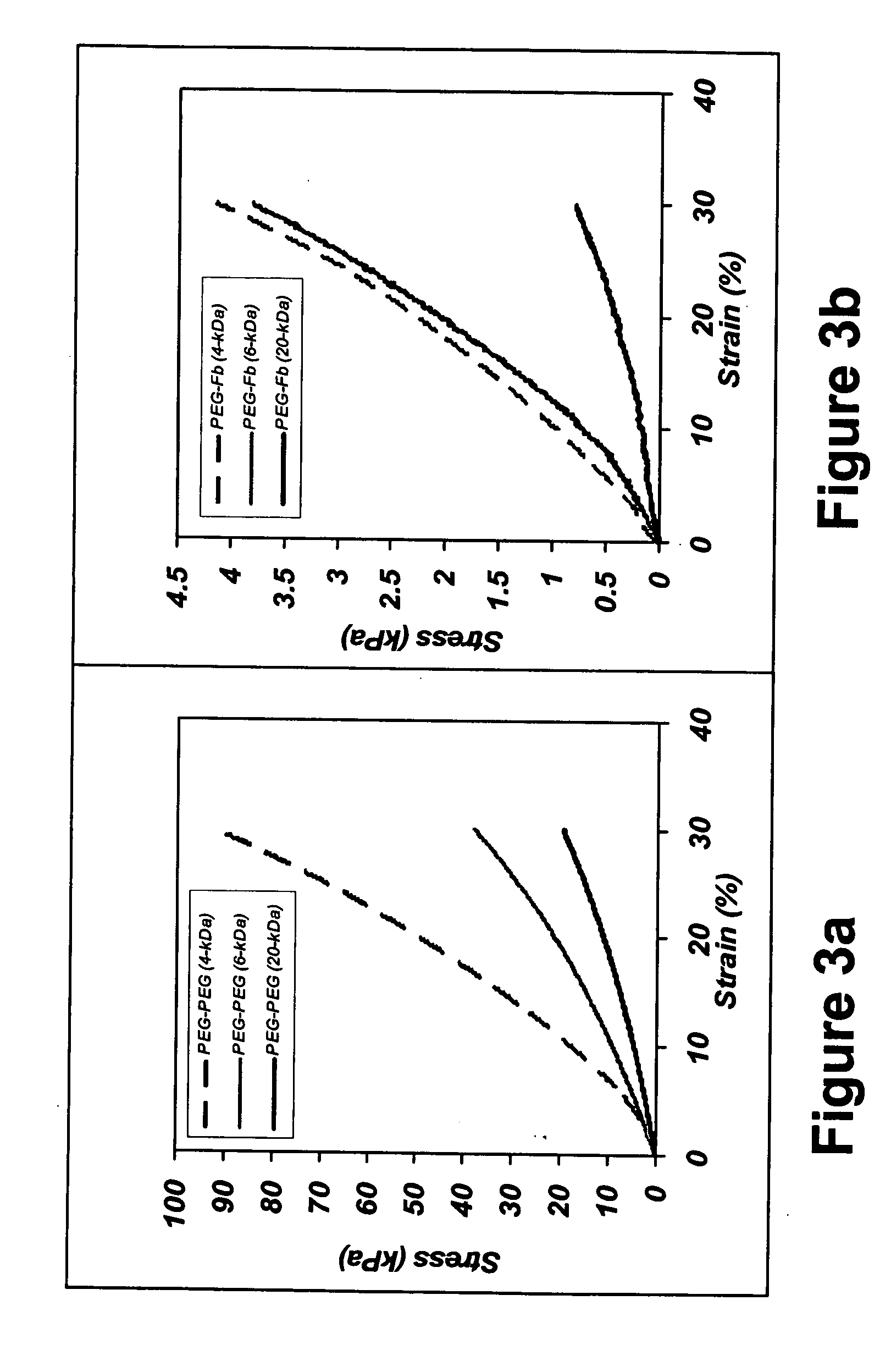
The present invention relates to biodegradable scaffolds composed of a naturally-occurring protein backbone cross-linked by a synthetic polymer. Specifically, the present invention provides PEGylated-fibrinogen scaffold and methods of generating and using same for treating disorders requiring tissue regeneration.
Owner:REGENTIS BIOMATERIALS
Pegylated factor VII glycoforms
InactiveUS20050113565A1Improve functional propertiesFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIIOligosaccharide
The invention concerns a preparation comprising a plurality of Factor VII polypeptides or Factor VII-related polypeptides, wherein the polypeptides comprise asparagine-linked and / or serine-linked oligosaccharide chains, and wherein at least one oligosaccharide group is covalently attached to at least one polymeric group.
Owner:KLAUSEN NIELS +3
Remodeling and Glycopegylation of Fibroblast Growth Factor (Fgf)
InactiveUS20080176790A1Improve pharmacokineticsCost effectiveOrganic active ingredientsFungiMutantPolynucleotide
The present invention relates to mutants of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF), particularly FGF-20 and FGF-21, which contain newly introduced N-linked or O-linked glycosylation site(s). The polynucleotide coding sequences for the mutants, expression cassettes comprising the coding sequences, cells expressing the mutants, and methods for producing the mutants are also disclosed. Further disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the mutants and method for using the mutants.
Owner:89BIO LTD +1
Pegylated interleukin-10
InactiveUS20060210534A1Minimize disruptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticInterleukin 10White blood cell
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) conjugated via a linker to one or more polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecules at a single amino acid residue of the IL-10, and a method for preparing the same, are provided. The method produces a stable mono-pegylated IL-10, which retains IL-10 activity, where pegylation is selective for the N-terminus on one subunit of IL-10 with little or no formation of monomeric IL-10. The method also provides a substantially homogenous population of mono-PEG-IL-10.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Di-aliphatic substituted pegylated lipids
The disclosure relates to di-aliphatic substituted PEGylated lipids and to methods of their preparation. The disclosure also relates to lipid conjugates containing di-aliphatic substituted PEGylated lipids, and to the use of di-aliphatic substituted PEGylated-lipid conjugates in drug delivery.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD +1
Controlled release delivery device for pharmaceutical agents incorporating microbial polysaccharide gum
The present invention provides a controlled release device for sustained or pulsatile delivery of pharmaceutically active substances for a predetermined period of time. This invention further provides such device in which sustained or pulsatile delivery is obtained by the unique blend and intimate mixture of pharmaceutically active substances with a microbial polysaccharide and uncrosslinked linear polymer and optionally a crosslinked polymer and / or lipophillic polymer and / or saturated polyglycolyzed glyceride. The invention also provides a process for the manufacture of such devices and pharmaceutical compositions containing the same.
Owner:INTELLIPHARMACEUTICS
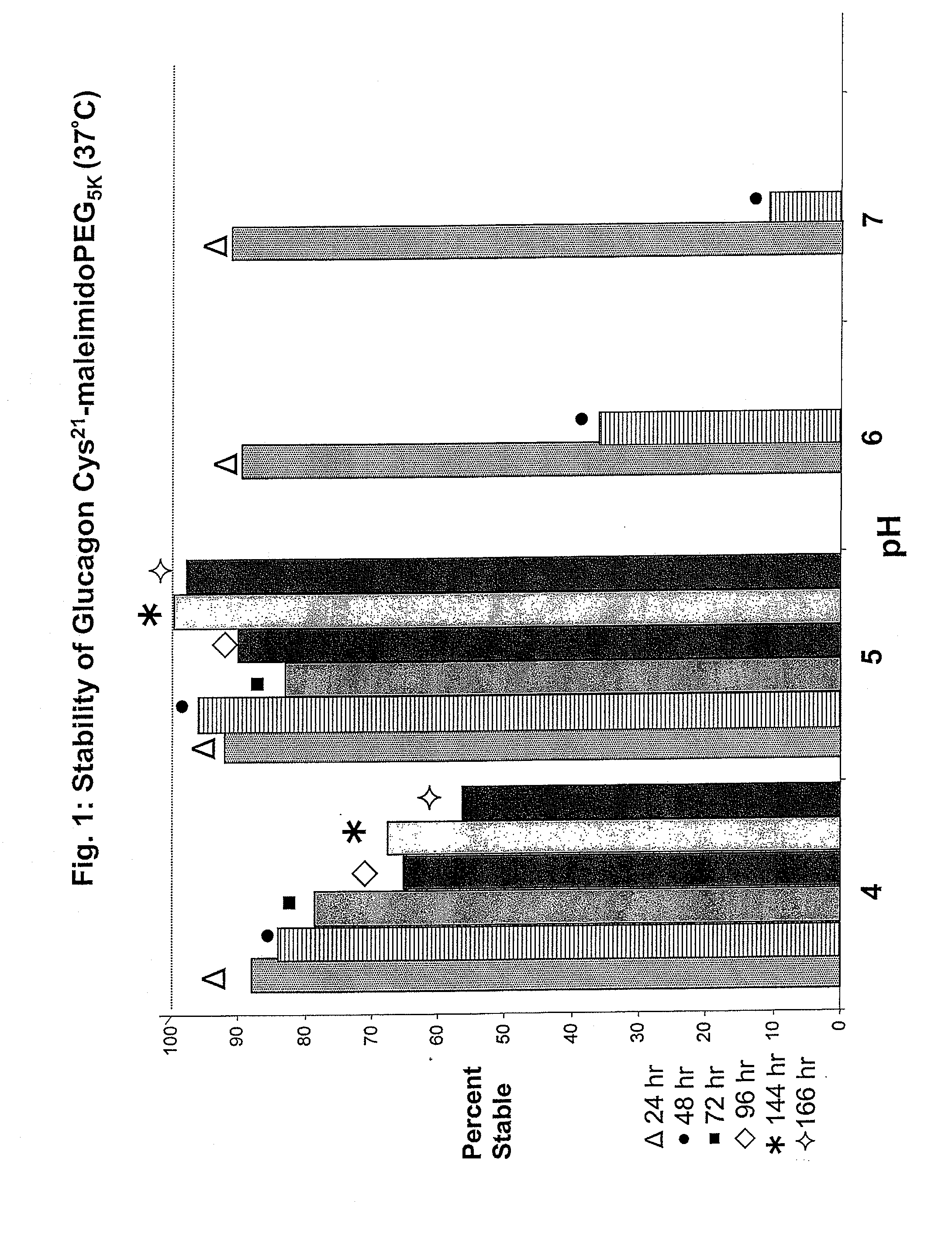
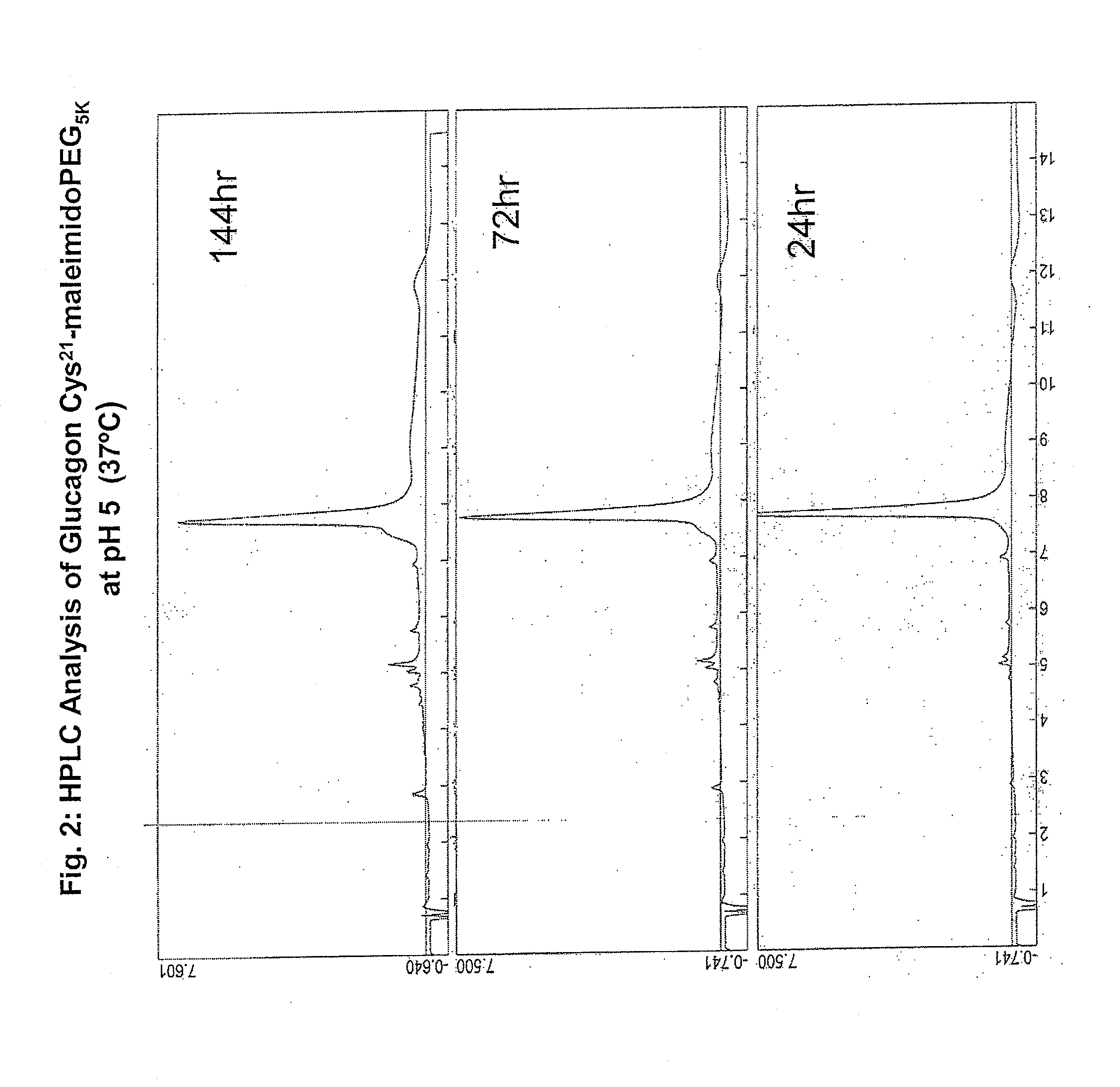
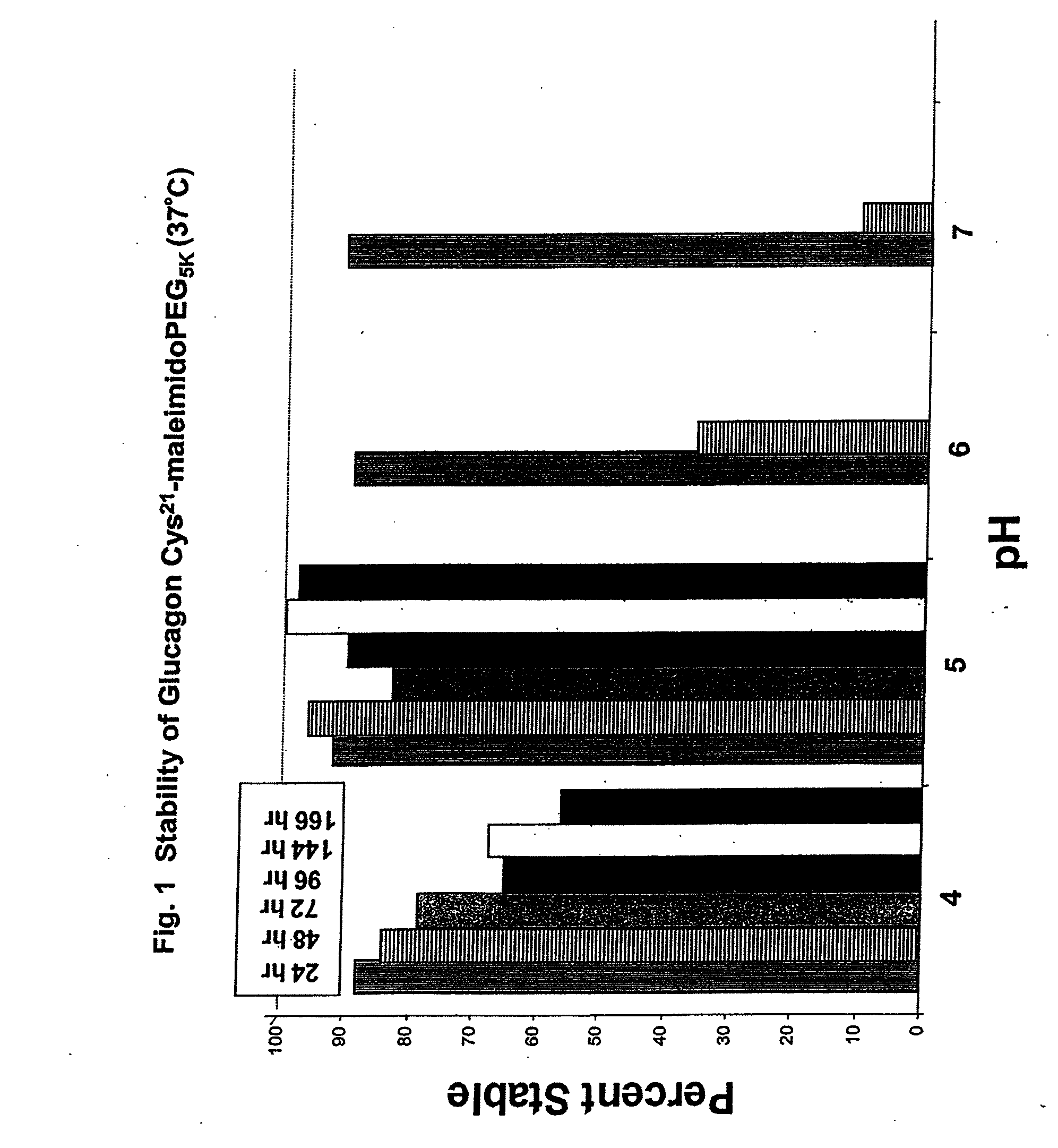
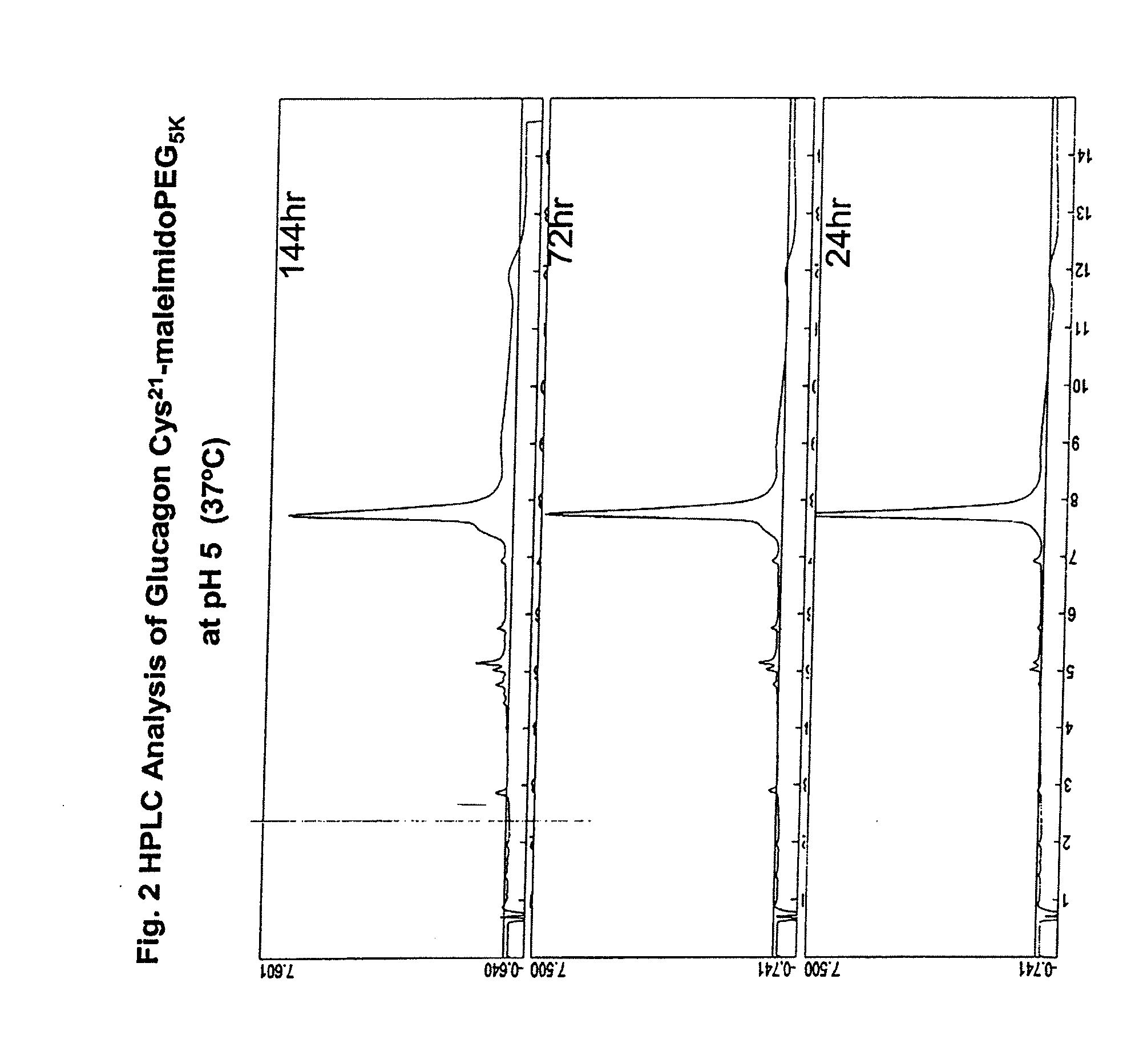
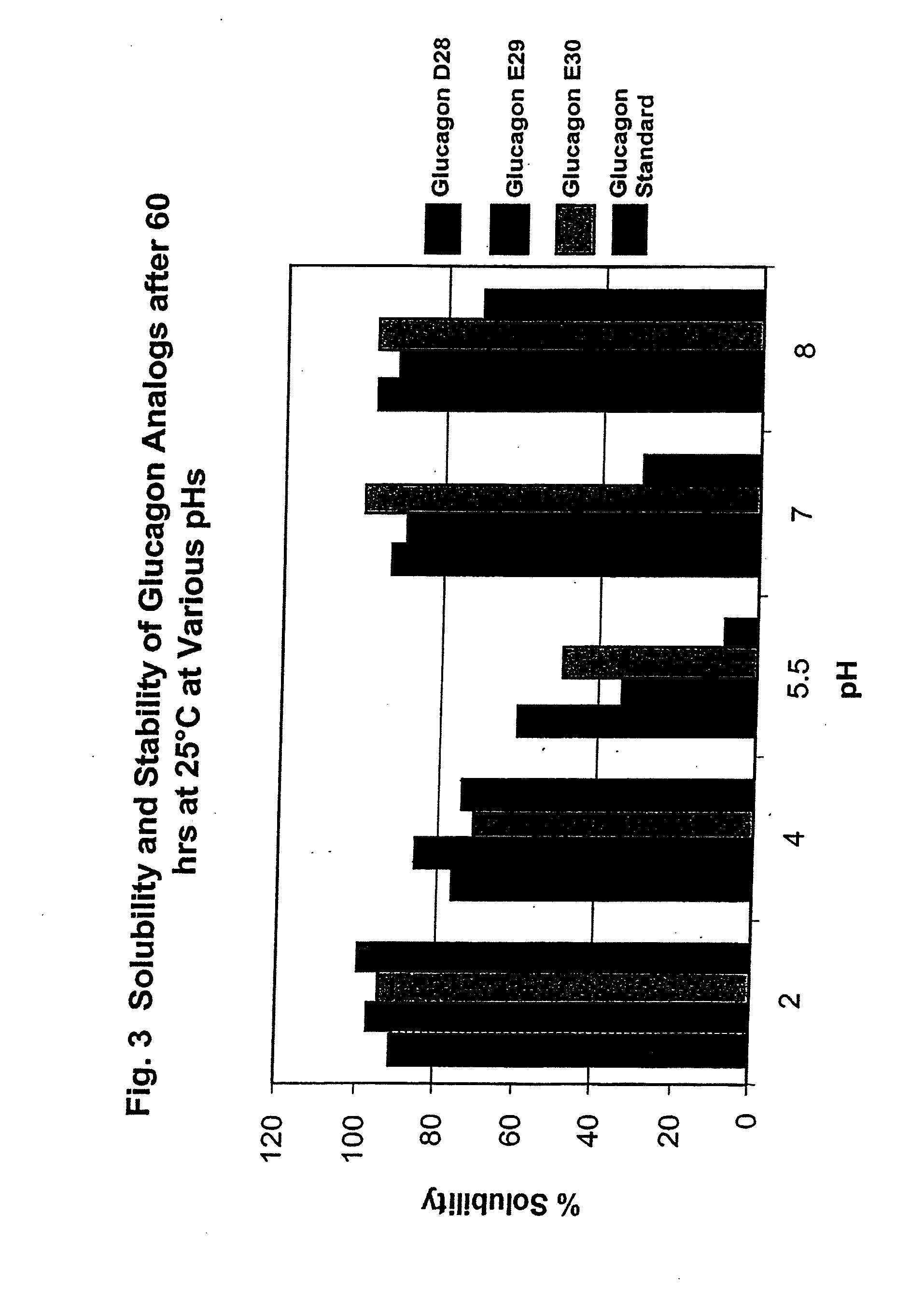
GLUCAGON ANALOGS EXHIBITING ENHANCED SOLUBILITY AND STABILITY IN PHYSIOLOGICAL pH BUFFERS
ActiveUS20110190200A1Rapidly increasing glucose levelNormalizing blood glucose levelAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionHalf-life
Modified glucagon peptides are disclosed having improved solubility and / or half-life while retaining glucagon agonist activity. The glycogen peptides have been modified by substitution of native amino acids with, and / or addition of, charged amino acids to the carboxy terminus of the peptide. The modified glucagon agonists can be further modified by pegylation, or the addition of a carboxy terminal peptide selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 20, SEQ ID NO: 21, SEQ ID NO: 23, or both to further enhance the solubility of the glucagon agonist analogs.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
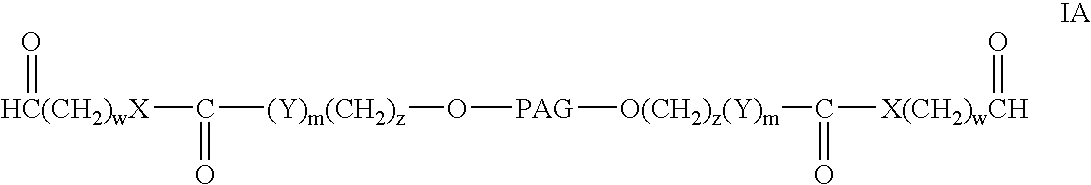
Bifunctional polyethylene glycol derivatives
InactiveUS20040115165A1Linkage stabilityDifficult to purifyOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProtein insertionActive protein
The present invention provides novel heterobifunctional and monobifunctional polyethylene glycol derivatives for the pegylation of therapeutically active proteins. The heterobifunctional PEGs which bear two different functional groups as well as the monobifunctional PEGs which contain two similar functional groups, may be used for cross-linking purposes. The cross-linking may be intramolecular between two areas within the same molecule or intermolecular between two separate molecules. The pegylated protein conjugates that are produced, retain a substantial portion of their therapeutic activity and are less immunogenic than the protein from which the conjugate is derived. New syntheses for preparing such bifunctional derivatives are described.
Owner:SUN BIO INC
Emulsion vehicle for poorly soluble drugs
An emulsion of α-tocopherol, stabilized by biocompatible surfactants, as a vehicle or carrier for therapeutic drugs, which is substantially ethanol free and which can be administered to animals or humans via various routes is disclosed. Also included in the emulsion is PEGylated vitamin E. PEGylated α-tocopherol includes polyethylene glycol subunits attached by a succinic acid diester at the ring hydroxyl of vitamin E and serves as a primary surfactant, stabilizer and a secondary solvent in emulsions of α-tocopherol.
Owner:IGDRASOL
Soluble hyaluronidase glycoprotein (sHASEGP), process for preparing the same, uses and pharmaceutical compositions comprising thereof
ActiveUS20090214505A1Extended half-lifeOptimize allocationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
Provided are soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGP's), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. Sialated and pegylated forms of the sHASEGPs also are provided. Methods of treatment by administering sHASEGPs and modified forms thereof also are provided.
Owner:HALOZYME
Use of Pegylated IL-10 to Treat Cancer
InactiveUS20080081031A1Improved modulator of tumor growthReducing and inhibiting growth of tumorPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemAbnormal tissue growthOncology
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com