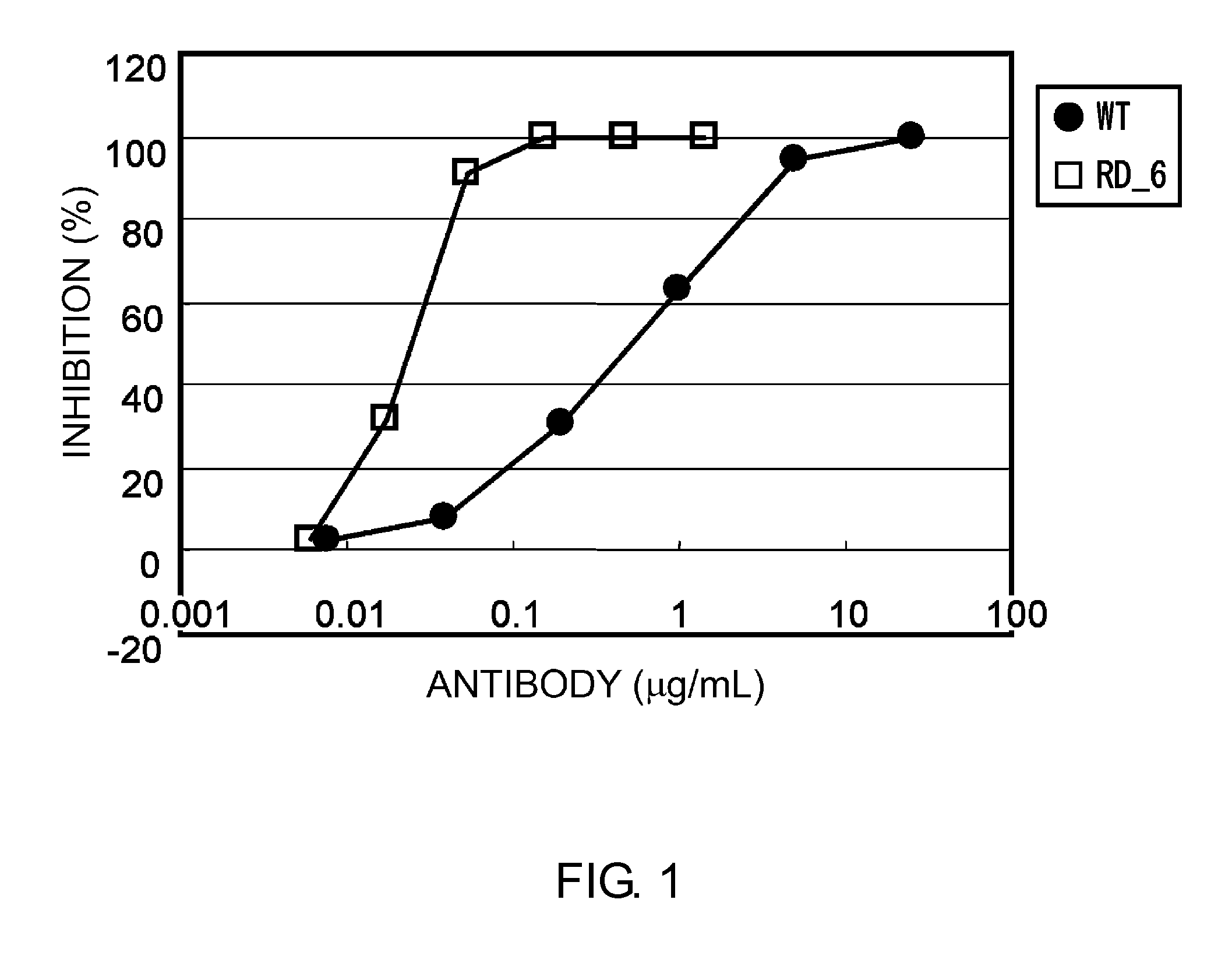
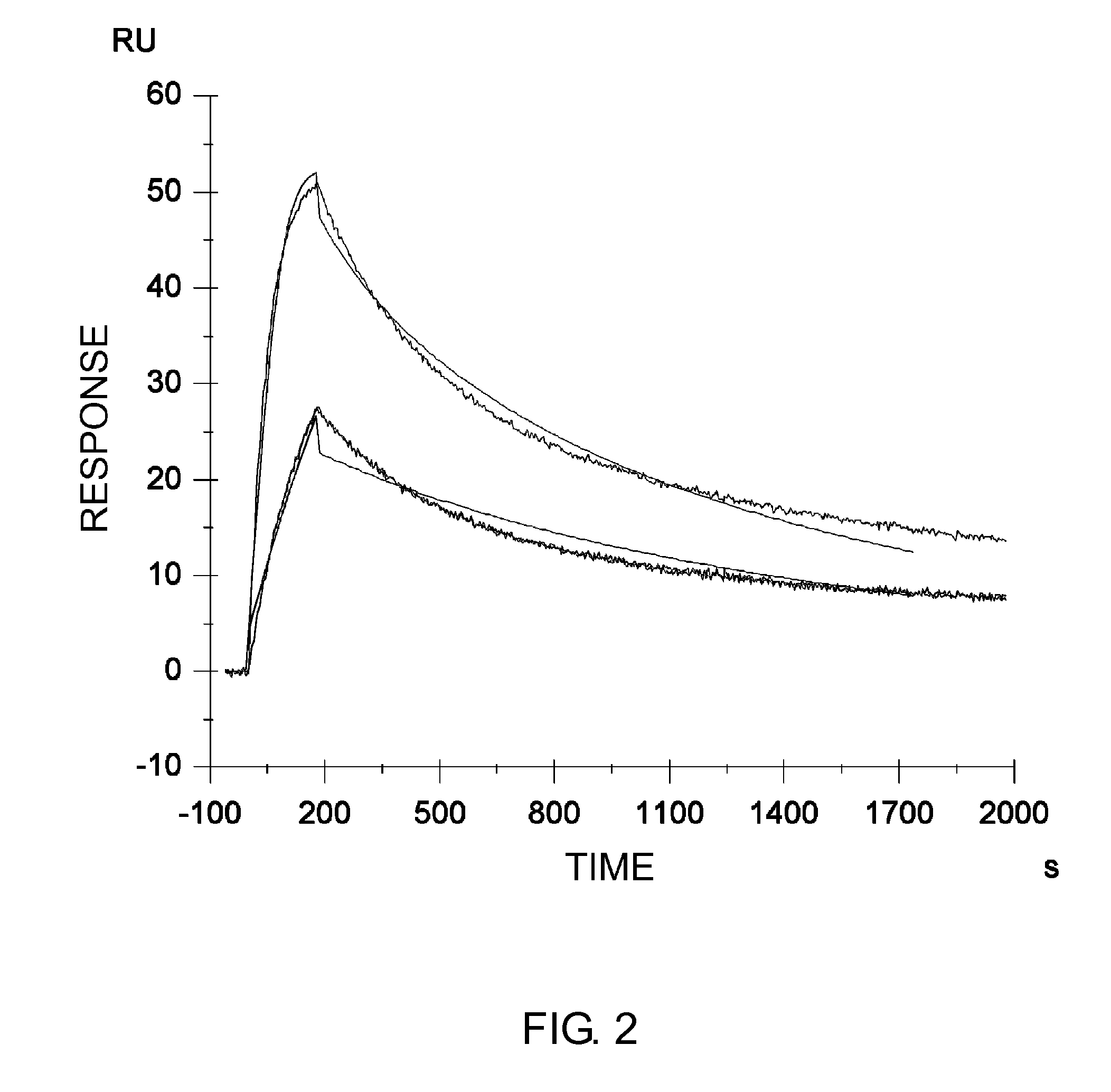
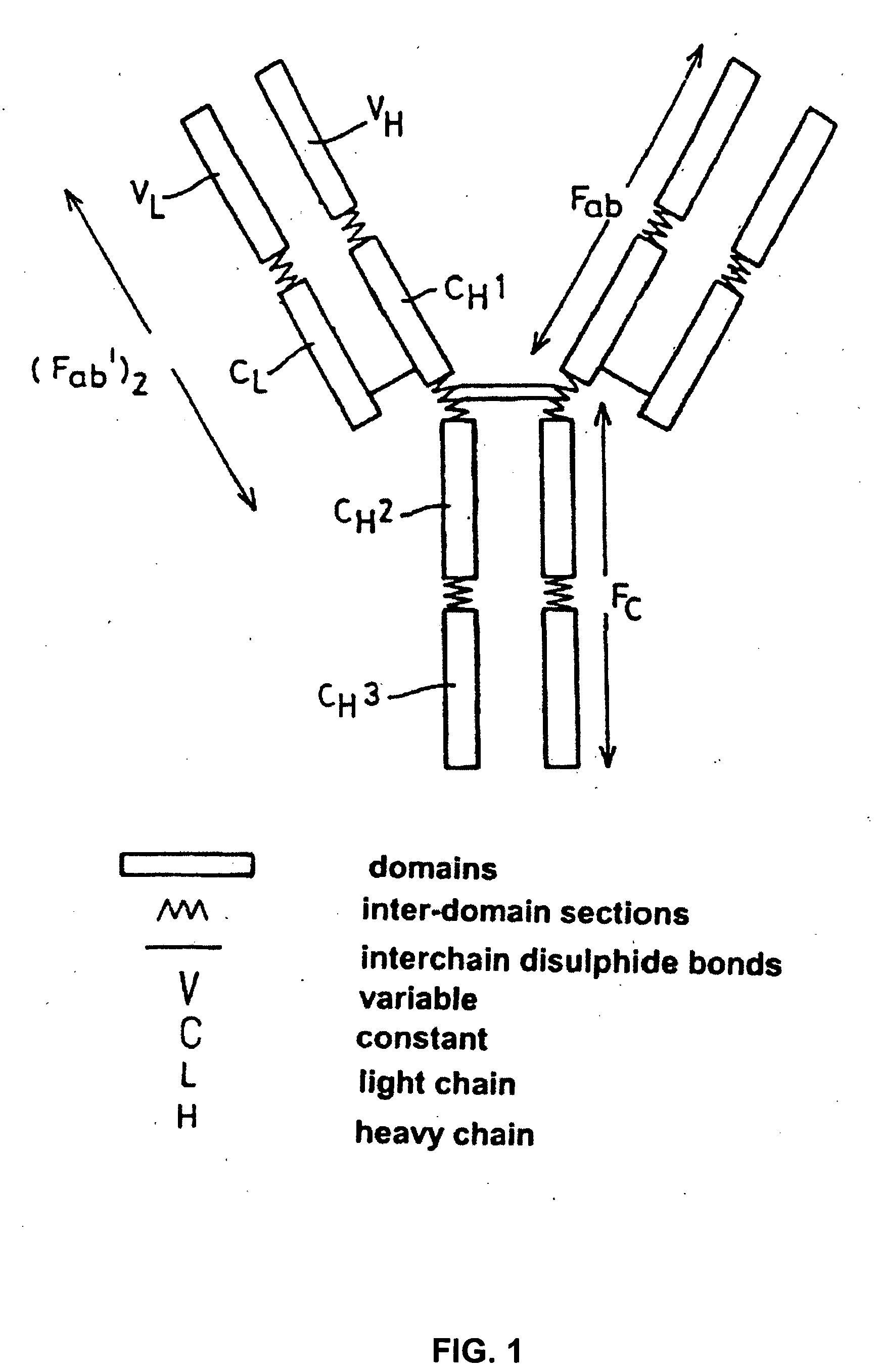
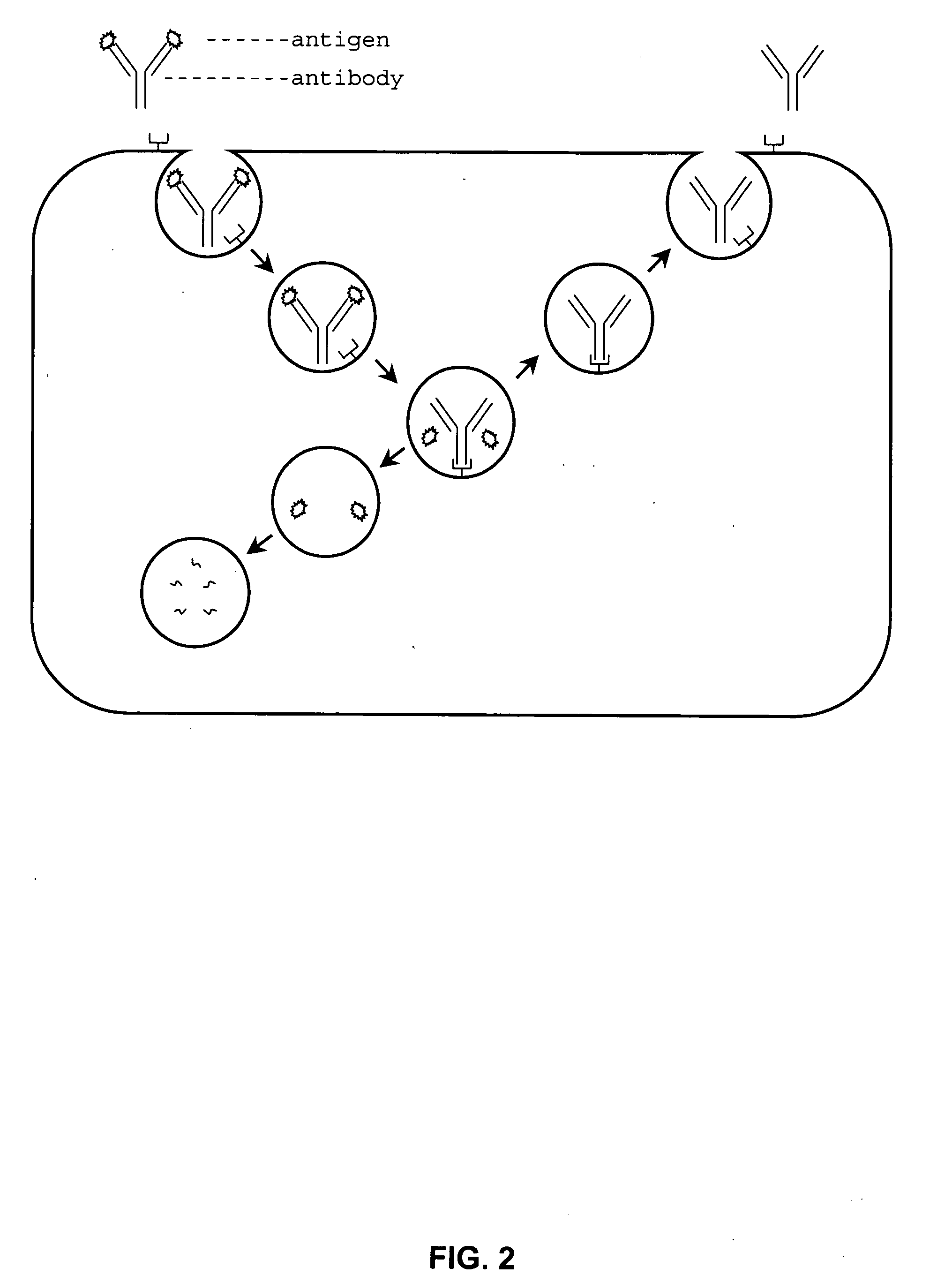
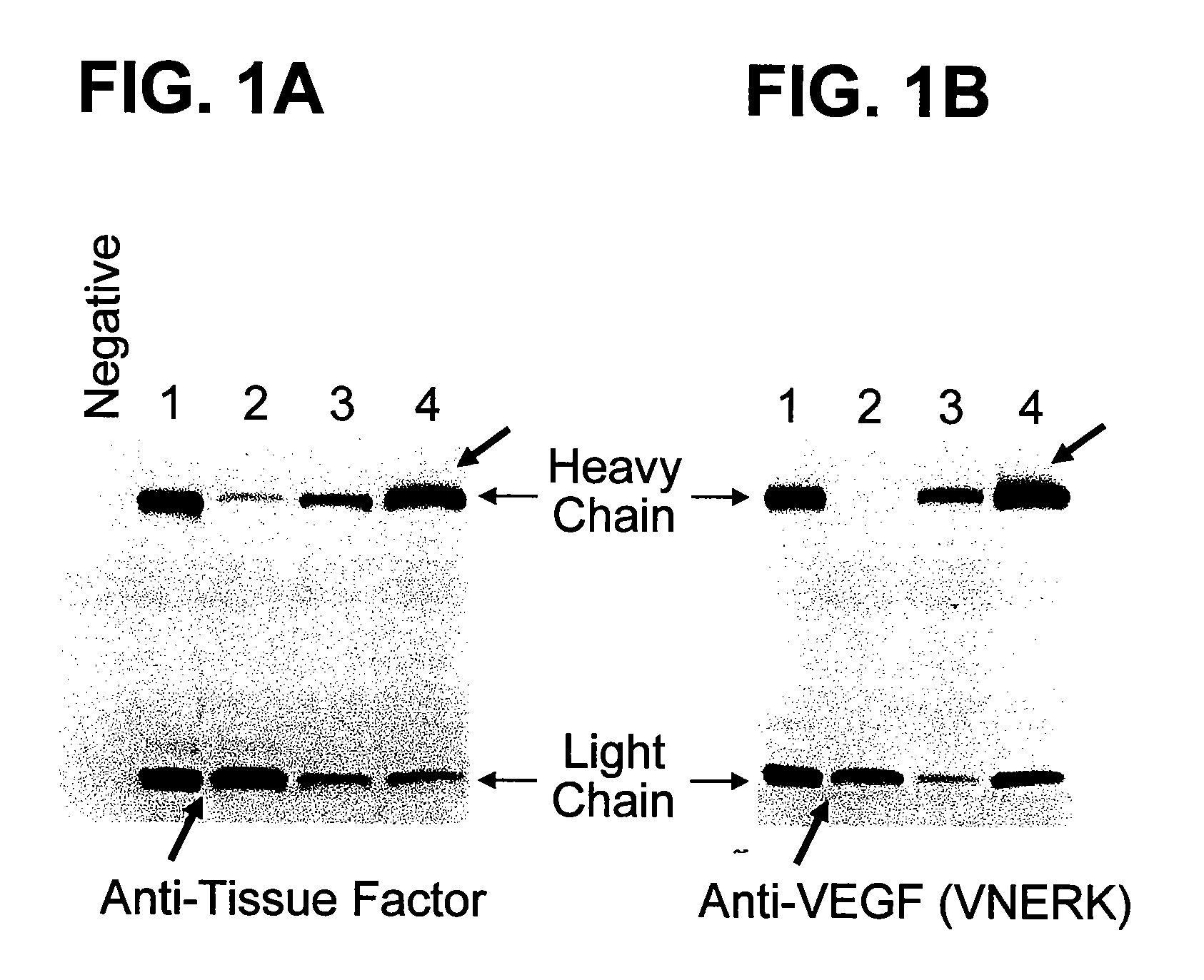
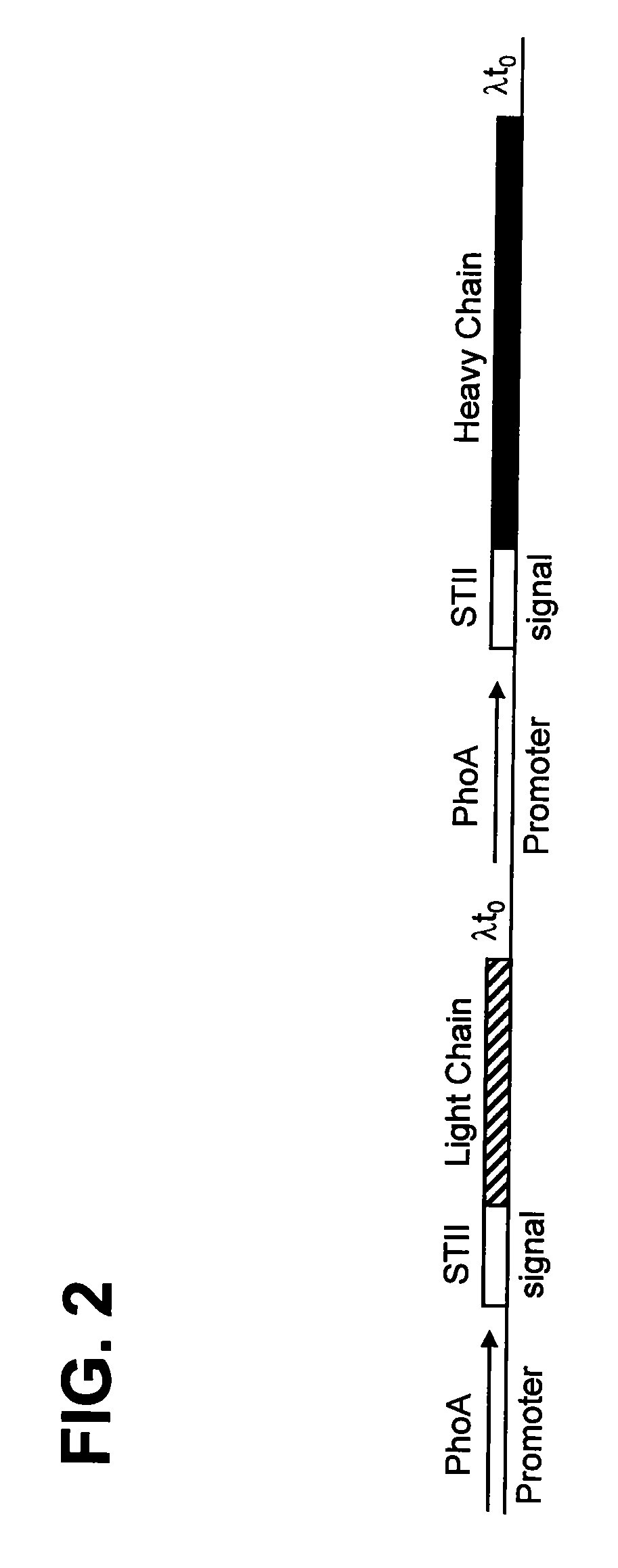
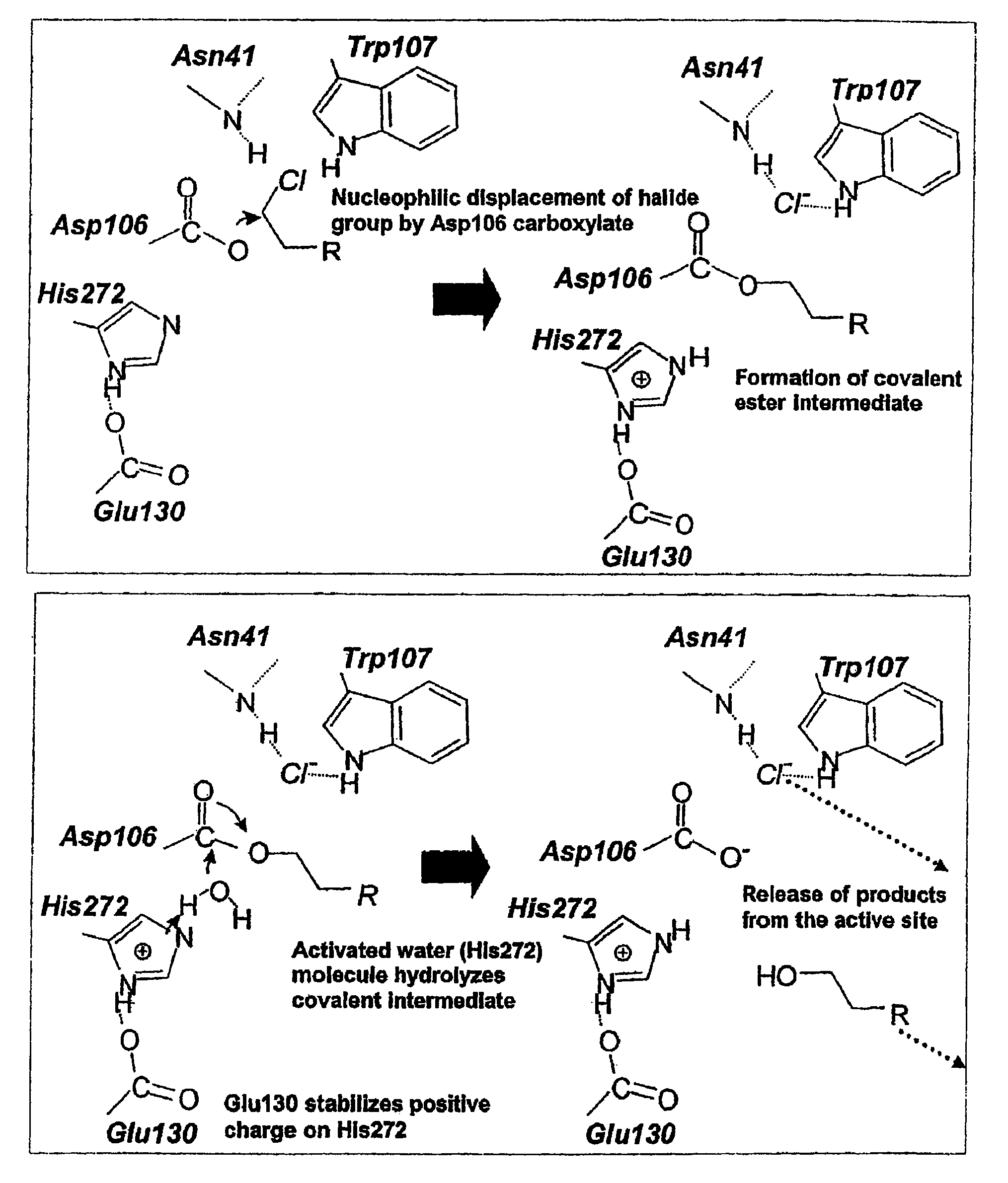
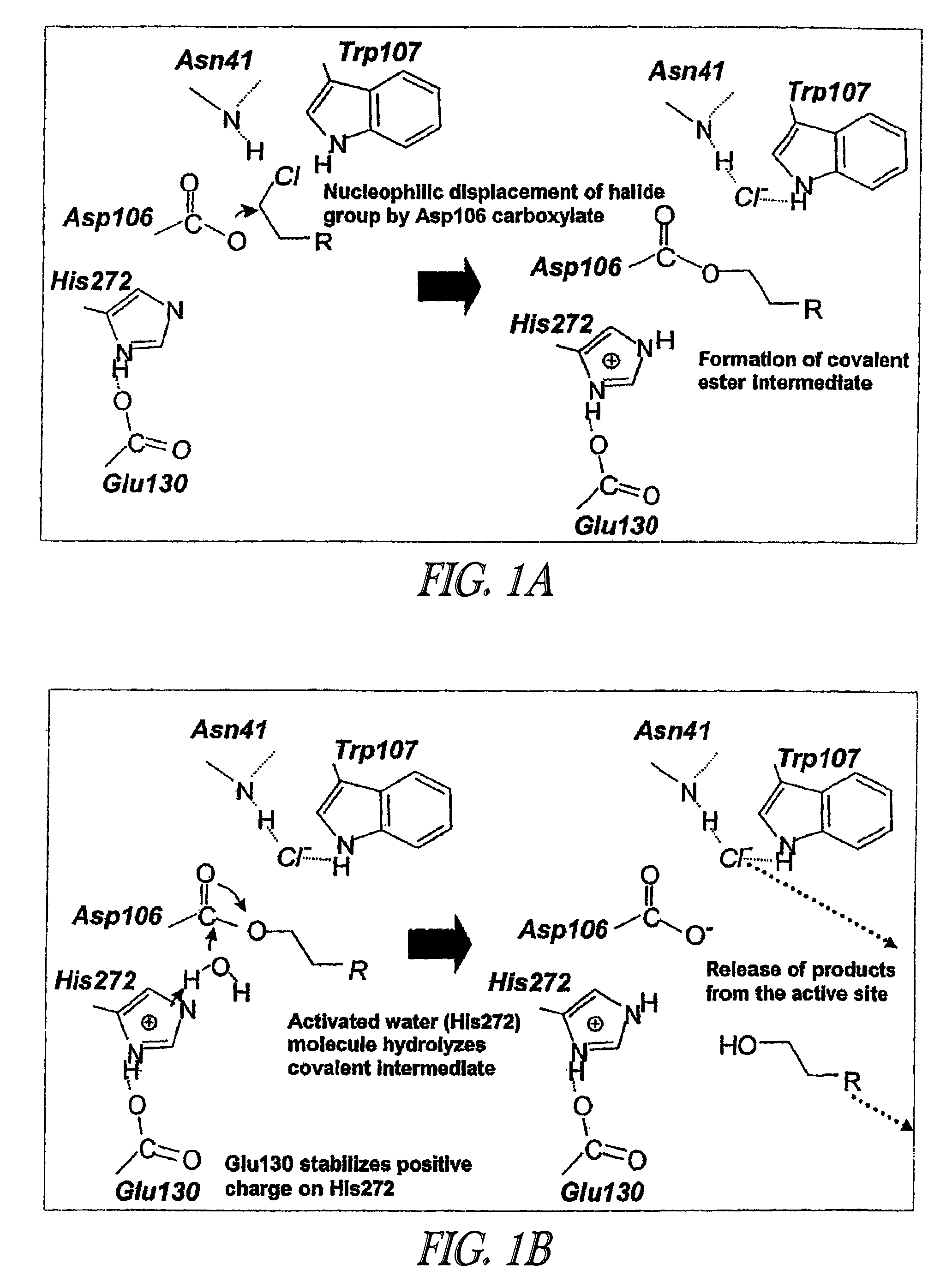
Patents
Literature
819 results about "Amino acid substitution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
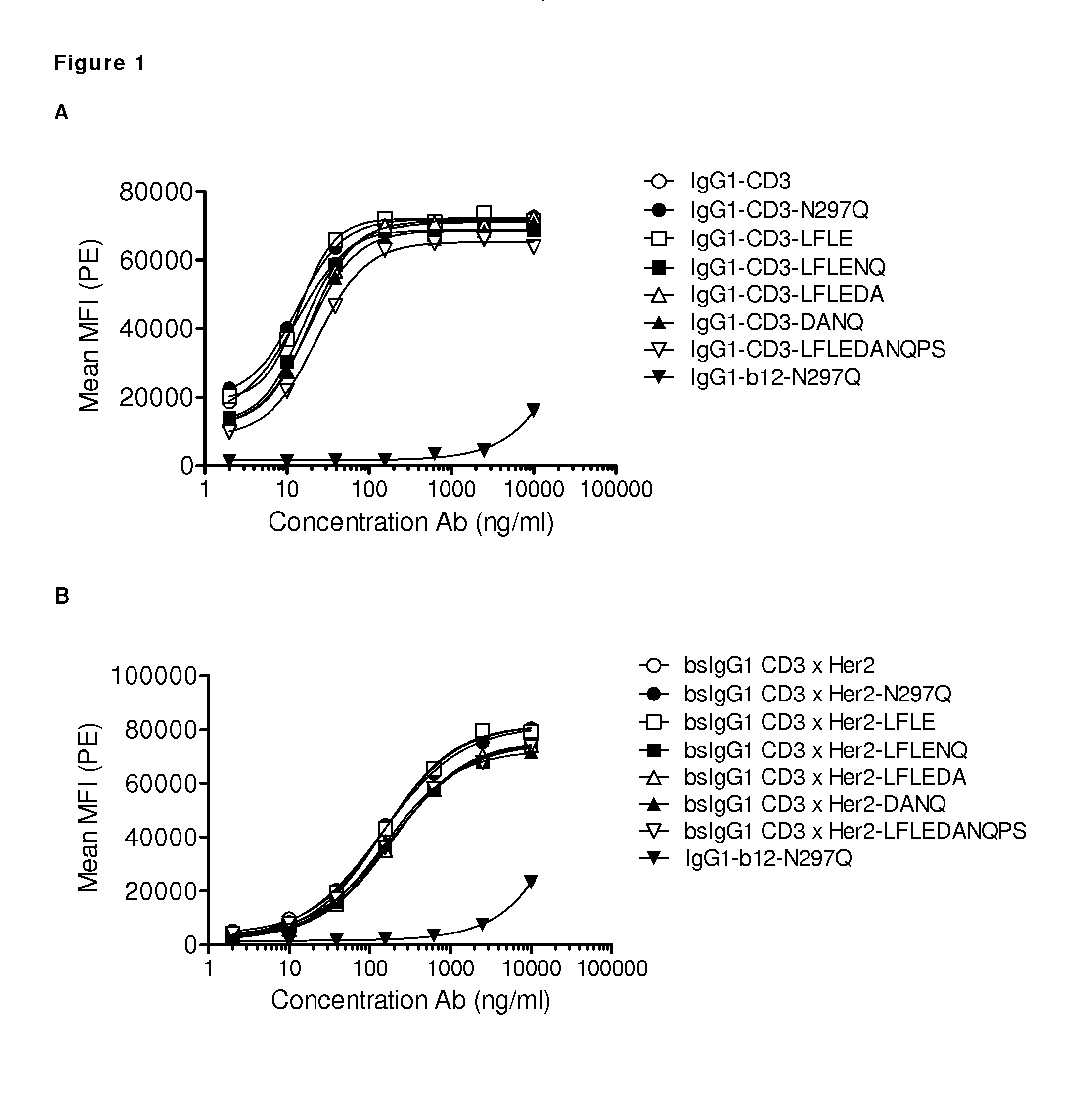
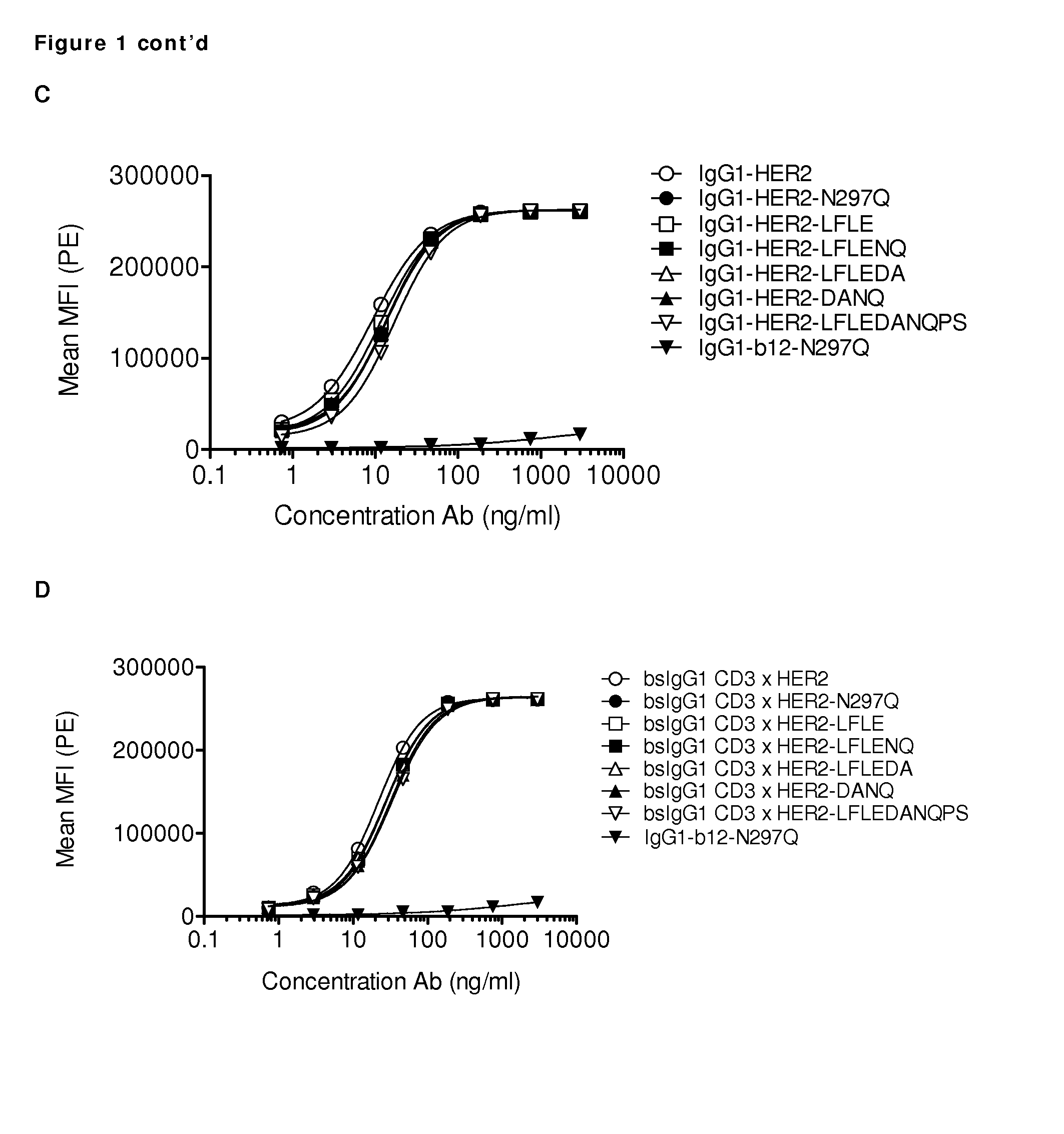
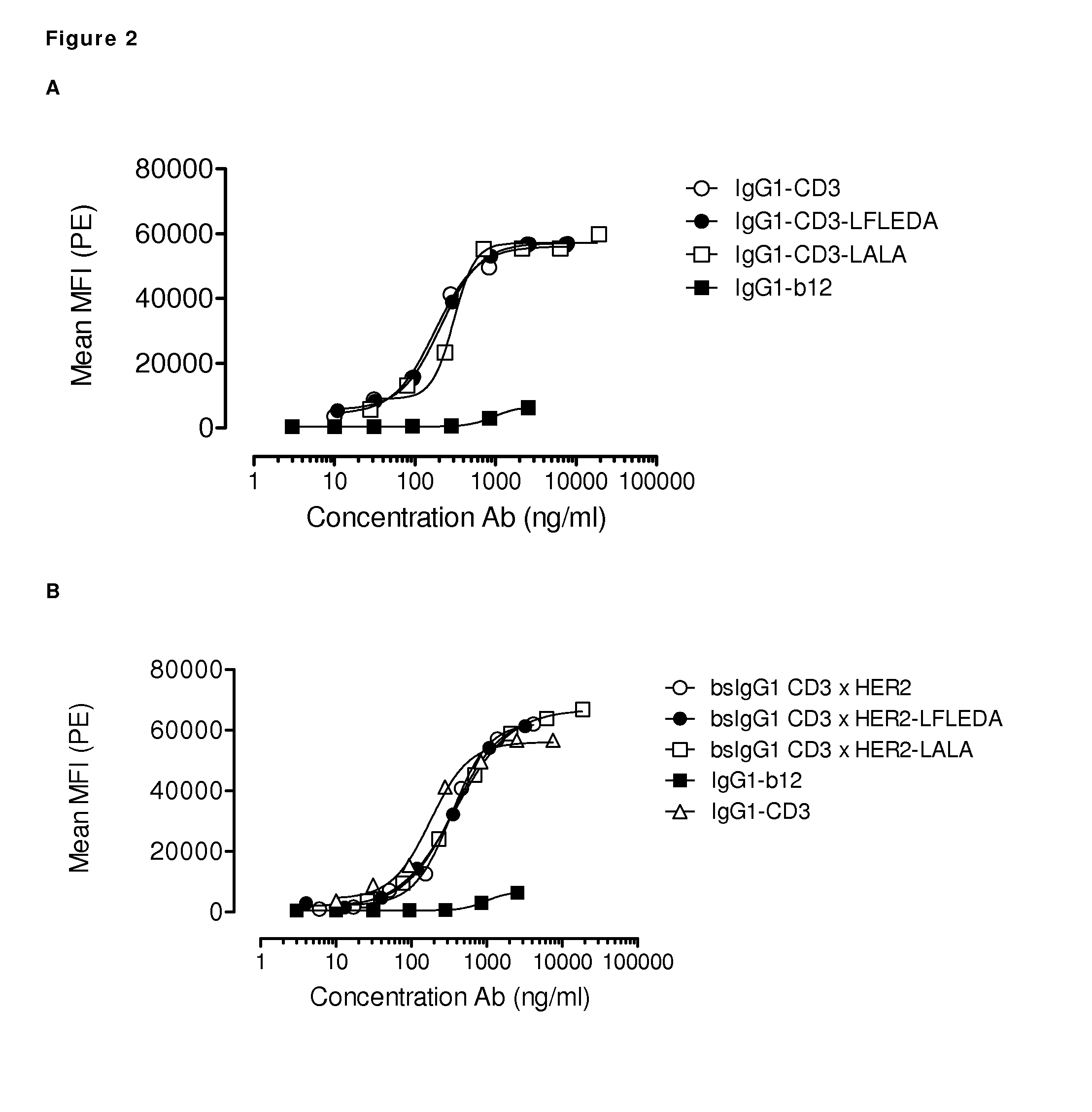
Amino Acid Substitution. The naturally occurring or experimentally induced replacement of one or more AMINO ACIDS in a protein with another. If a functionally equivalent amino acid is substituted, the protein may retain wild-type activity.
Polypeptide variants
InactiveUS7297775B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAmino acid substitutionComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
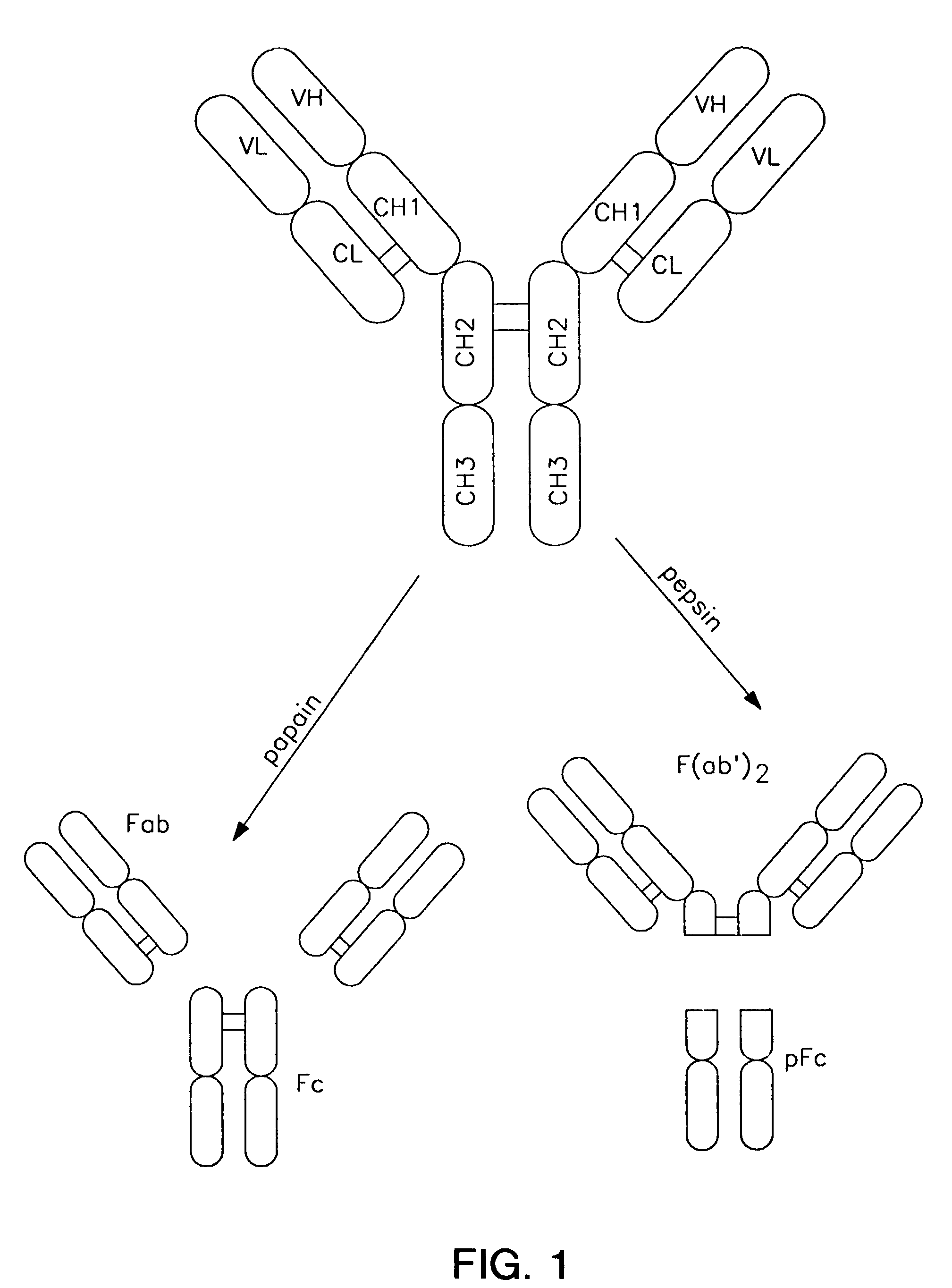
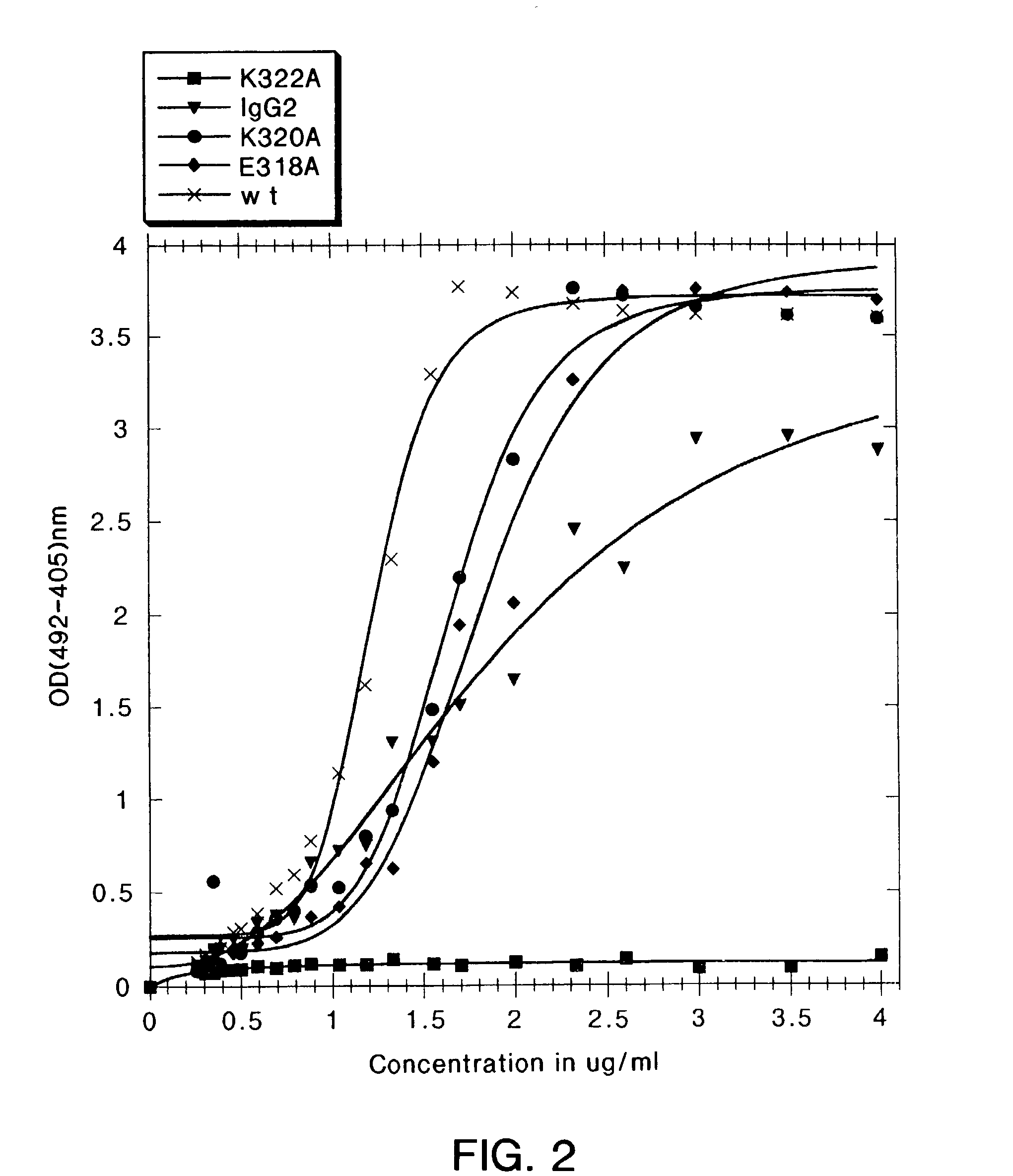
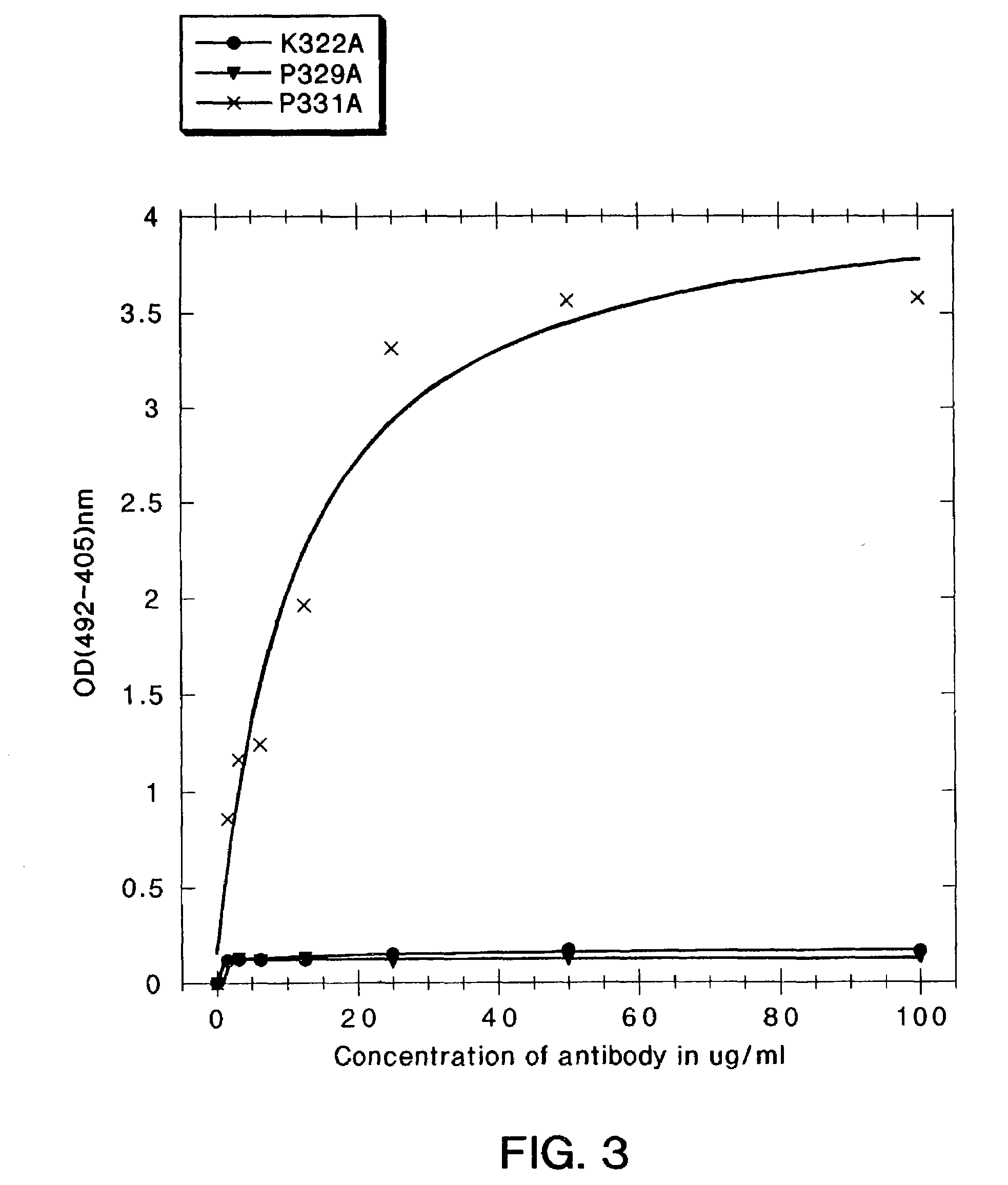
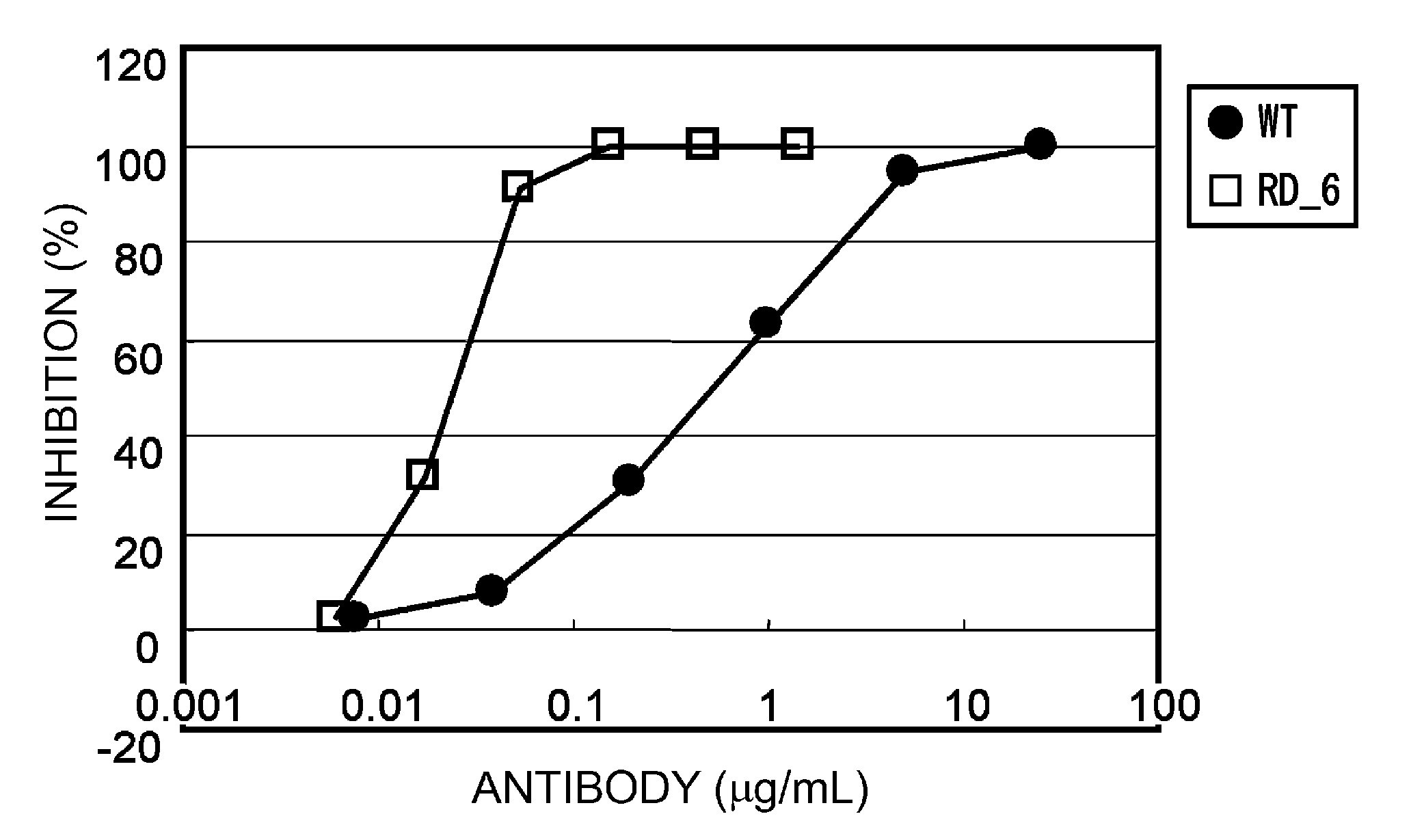
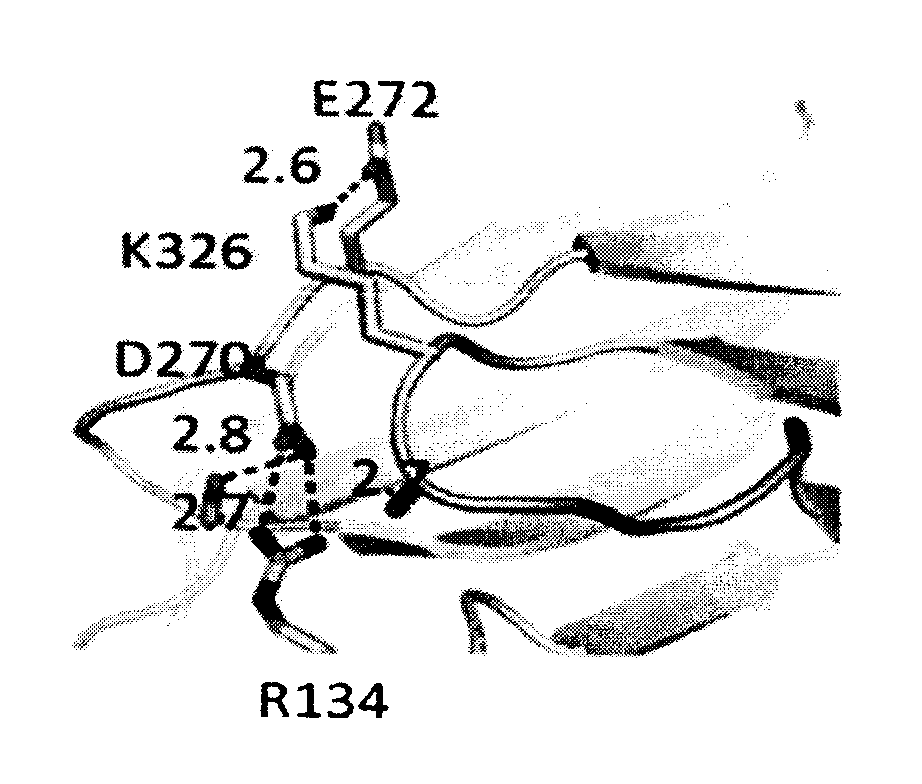
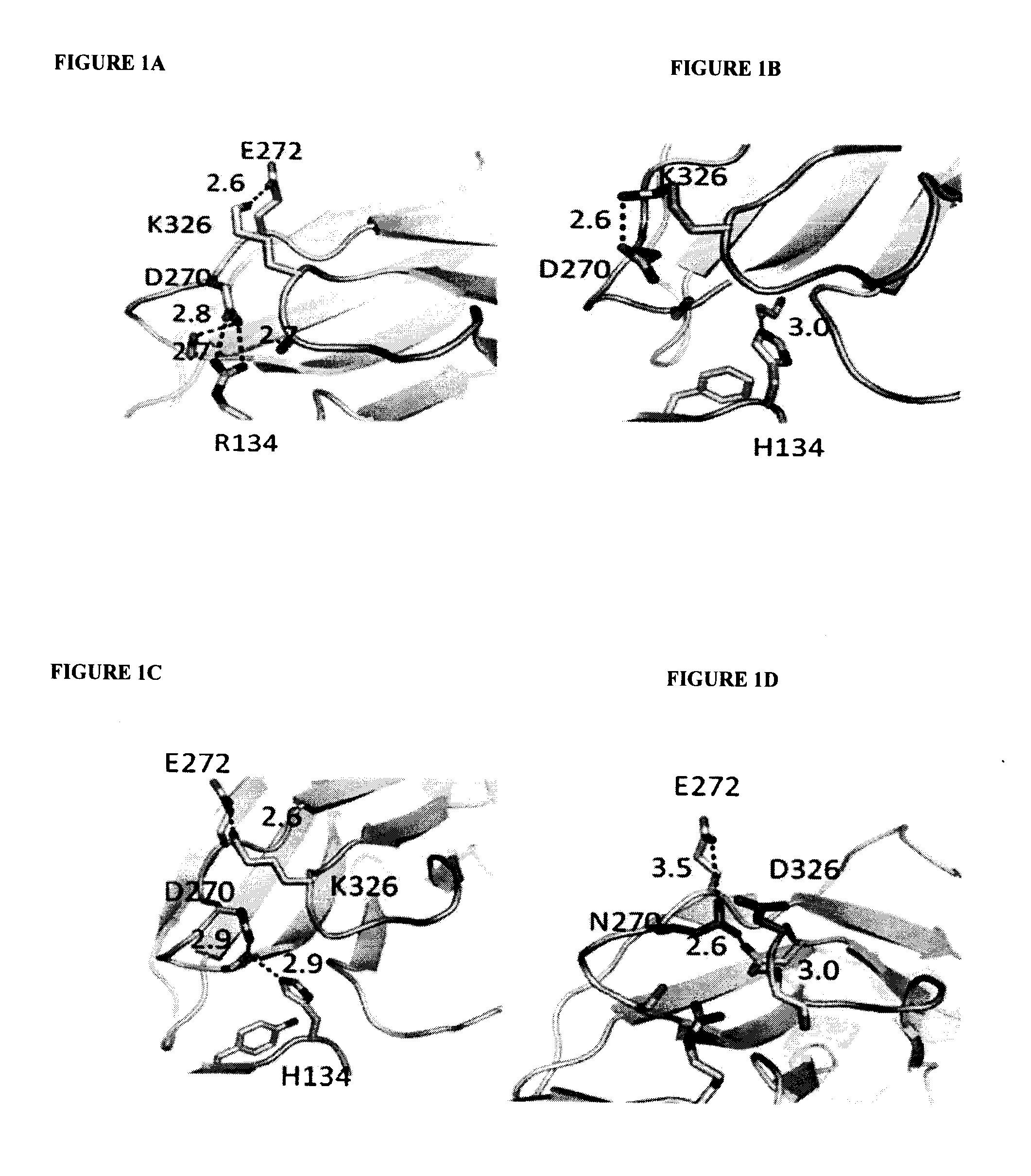
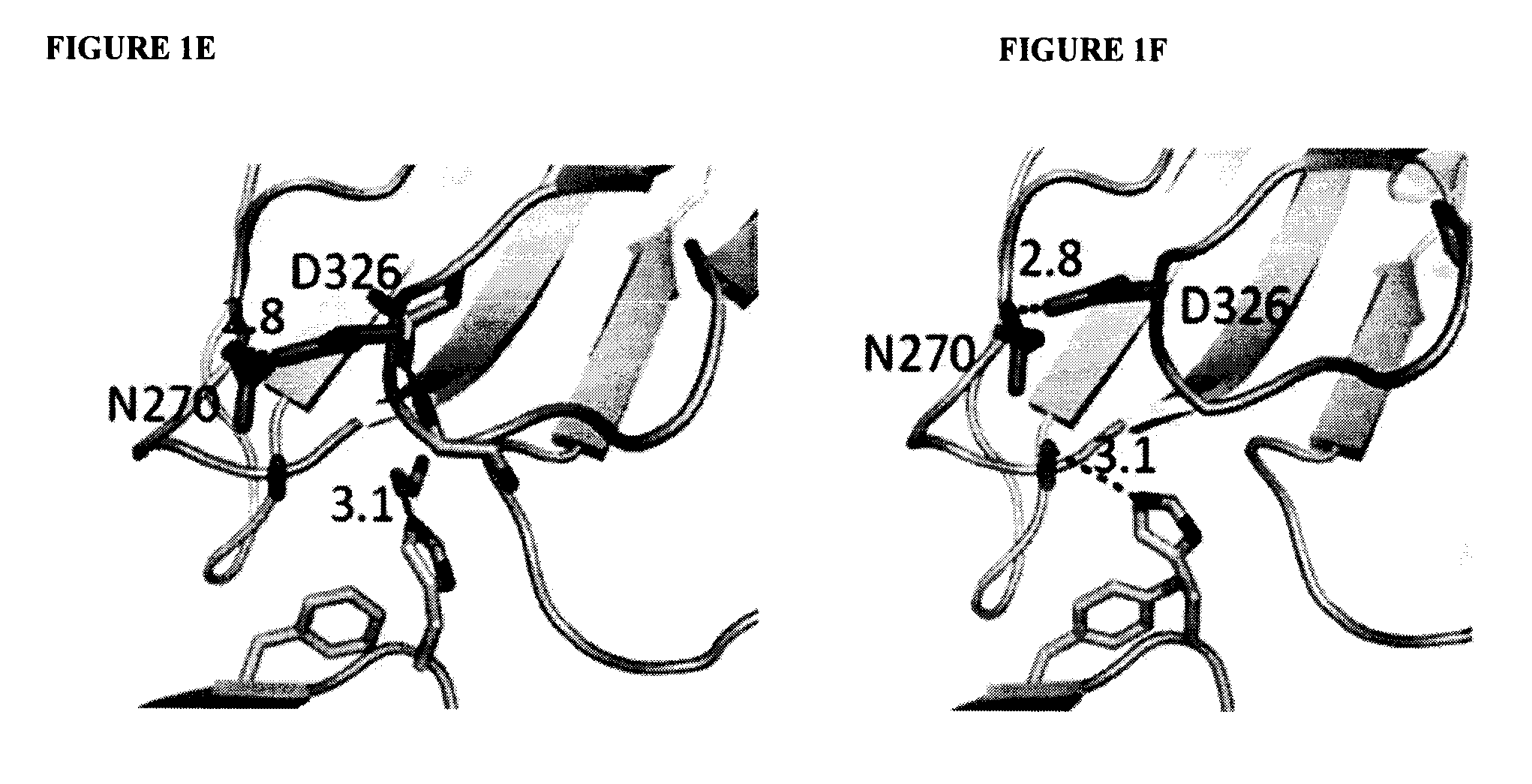
A variant of a polypeptide comprising a human IgG Fc region is described, which variant comprises an amino acid substitution at one or more of amino acid positions 270, 322, 326, 327, 329, 331, 333 or 334 of the human IgG Fc region. Such variants display altered effector function. For example, C1q binding and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity may be altered in the variant polypeptide. The application also discloses a variant of a parent polypeptide comprising a human IgG Fc region, which variant has a better binding affinity for human C1q than the parent polypeptide.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method of Modifying Isoelectric Point of Antibody Via Amino Acid Substitution in CDR
ActiveUS20110076275A1Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activityImprove retentionSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAmino acid substitution
The present inventors provide methods for modifying the isoelectric point of an antibody while retaining its antigen-binding activity, comprising modifying the charge of at least one exposable amino acid residue on the surface of the complementarity determining region (CDR). The present invention also provides methods for purifying multispecific antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point, and methods for improving the plasma pharmacokinetics of antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point. The present invention further provides antibodies with a modified isoelectric point, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies as an active ingredient, and methods for producing the antibodies and compositions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Alteration of FcRn binding affinities or serum half-lives of antibodies by mutagenesis
ActiveUS20050276799A1Reducing FcRn binding affinityReduced half-lifeImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunoglobulins against virusesSerum igeHalf-life
The present invention provides for a modified antibody of class IgG, in which at least one amino acid from the heavy chain constant region selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues 250, 314, and 428 is substituted with another amino acid which is different from that present in the unmodified antibody, thereby altering the binding affinity for FcRn and / or the serum half-life in comparison to the unmodified antibody.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Amino acid substituted-cresyl violet, synthetic fluorogenic substrates for the analysis of agents in individual in vivo cells or tissue
InactiveUS6235493B1Organic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementAmino acid substitutionTissue sample
The present invention concerns a method to detect the presence of an enzyme in in vivo or in vitro tissue or cell, which method comprises:(a) obtaining a tissue or cell sample to be analyzed;(b) contacting the tissue or cell sample with a substrate of the structure selected from the group consisting of:X=H or one or more natural or synthetic amino acids with or without amino blocking groups,Y=H or one or more natural or synthetic amino acids with or without amino blocking groups,wherein X and Y are the same or different and are amino acid sequences of between about 1 to 1,000,000 amino acids wherein each amino acid is the same or a different amino acid, with the proviso that at least one of X or Y is at least one amino acid;(c) when an enzyme is present in the tissue or cell sample which degrades X, Y and combinations thereof, fluorescent cresyl violet is released in the tissue sample producing a color change;(d) detecting the presence and amount of the enzyme present by the detection and quantification of the fluorescence produced; and(e) optionally comparing the fluorescence to a pre-calibrated fluorescence scale to quantify the fluorescence present. A diagnostic kit for use and a method to prepare amino acid cresyl violet derivatives are described.
Owner:MP BIOMEDICALS
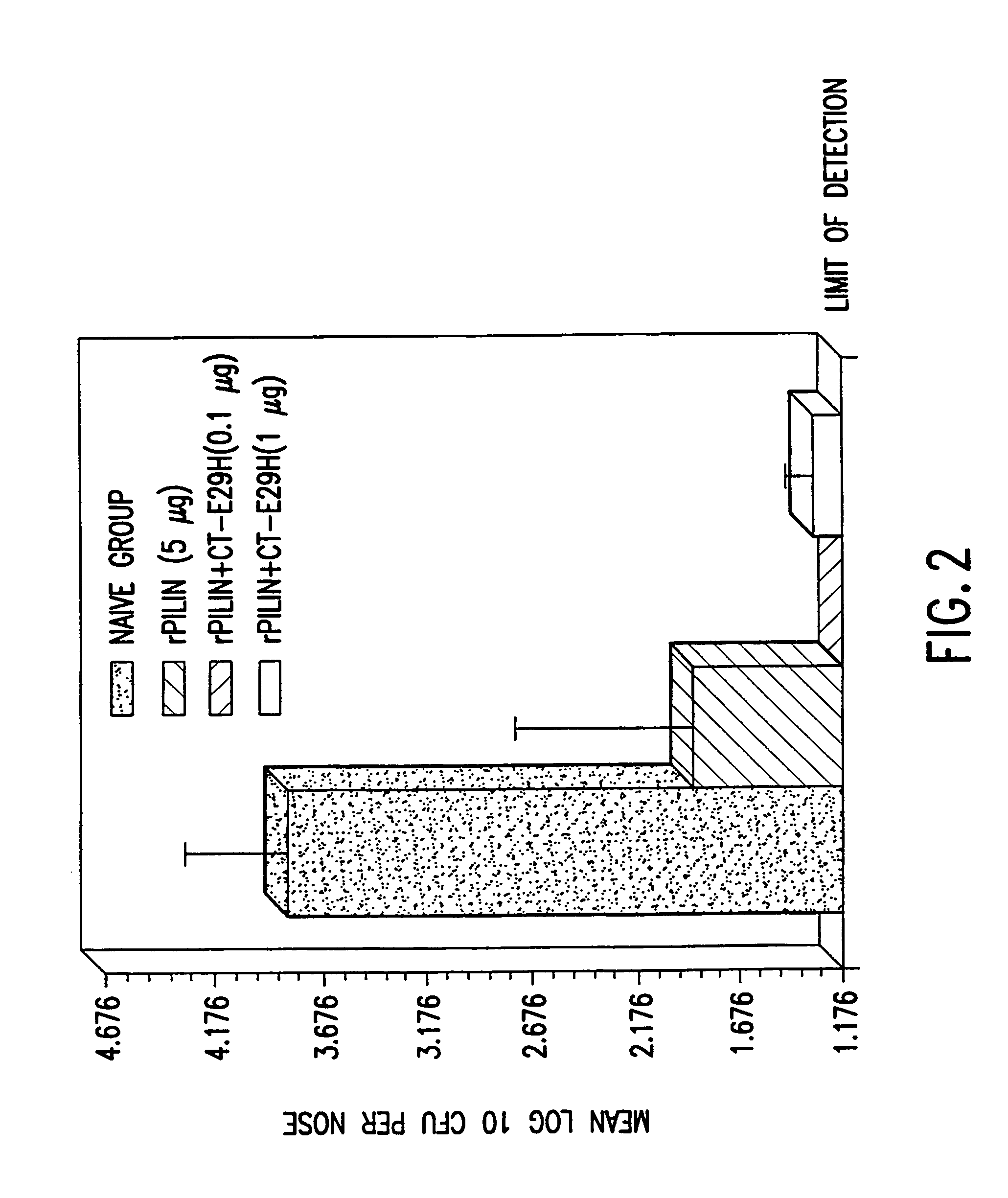
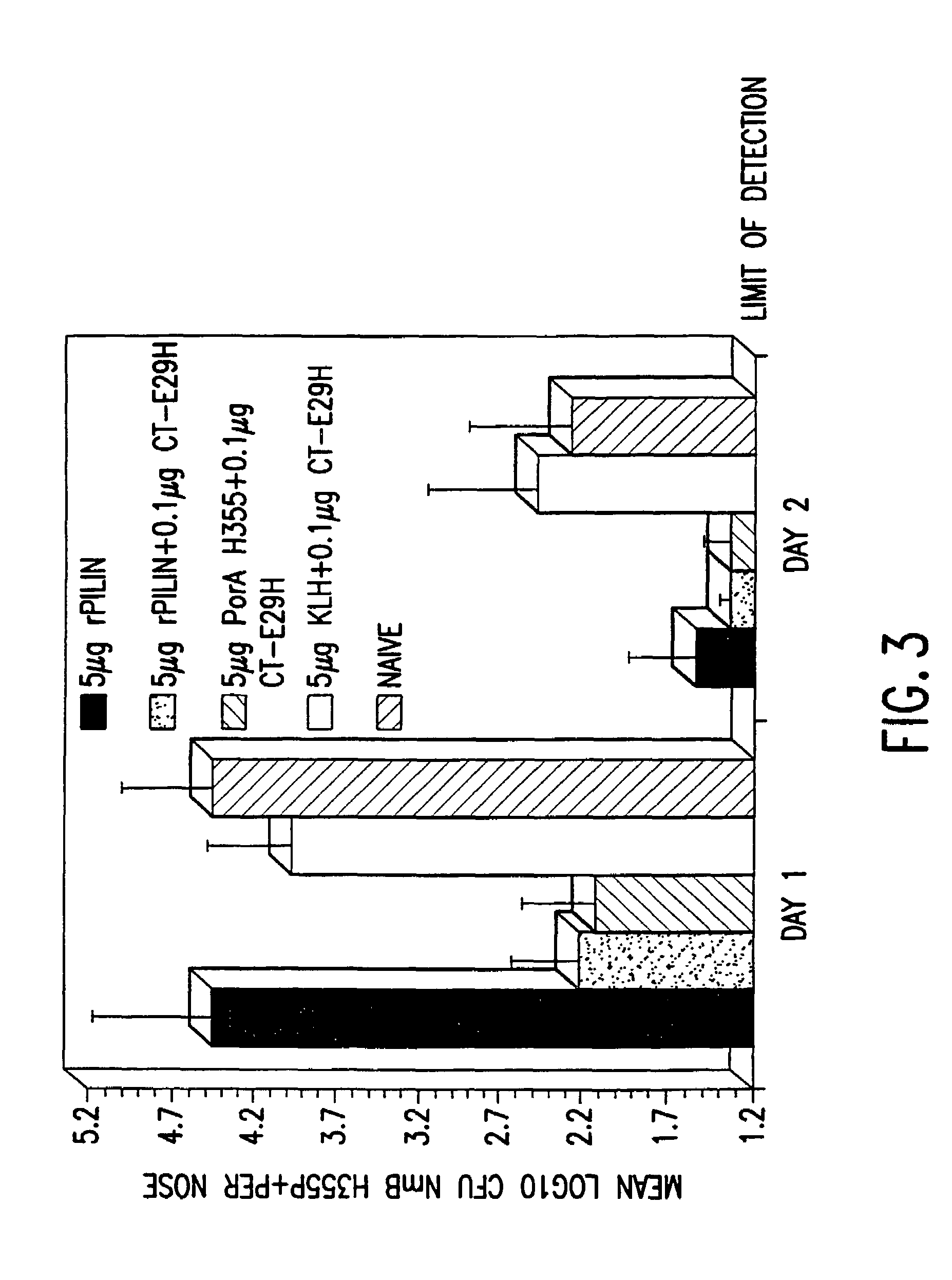
Mutant cholera holotoxin as an adjuvant
InactiveUS7384640B1Low toxicityEnhance immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaAntigenAdjuvant
A mutant cholera holotoxin featuring a point mutation at amino acid 29 of the A subunit, wherein the glutamic acid residue is replaced by an amino acid other than aspartic acid, is useful as an adjuvant in an antigenic composition to enhance the immune response in a vertebrate host to a selected antigen from a pathogenic bacterium, virus, fungus or parasite. In a particular embodiment, the amino acid 29 is histidine. The mutant cholera holotoxin may contain at least one additional mutation in the A subunit at a position other than amino acid 29. The antigenic composition may include a second adjuvant in addition to the mutant cholera holotoxin.
Owner:UNIFORMED SERVICES UNIV OF HEALTH SCI UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE +1
Mutant forms of cholera holotoxin as an adjuvant
InactiveUS7332174B2No loss in adjuvanting propertyLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsFungiAntigenAdjuvant
Mutant cholera holotoxins having single or double amino acid substitutions or insertions have reduced toxicity compared to the wild-type cholera holotoxin. The mutant cholera holotoxins are useful as adjuvants in antigenic compositions to enhance the immune response in a vertebrate host to a selected antigen from a pathogenic bacterium, virus, fungus, or parasite, a cancer cell, a tumor cell, an allergen, or a self-molecule.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP +1
Mutant forms of cholera holotoxin as an adjuvant
InactiveUS7285281B2No loss in adjuvanting propertyLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsFungiAdjuvantCancer cell
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO FOUND +1
T cell receptor-like antibodies specific for a wti peptide presented by hla-a2
The present invention provides antigen binding proteins that specifically bind to Wilms' tumor protein (WT1), including humanized, chimeric and fully human antibodies against WT1, antibody fragments, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), fusion proteins, and conjugates thereof. The antigen binding proteins and antibodies bind to HLA-A0201-restricted WT1 peptide. Such antibodies, fragments, fusion proteins and conjugates thereof are useful for the treatment of WT1 associated cancers, including for example, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, chronic myelocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid / myelogenous leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). In more particular embodiments, the anti-WT1 / A antibodies may comprise one or more framework region amino acid substitutions designed to improve protein stability, antibody binding and / or expression levels.
Owner:EUREKA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Antibodies with Enhanced or Suppressed Effector Function
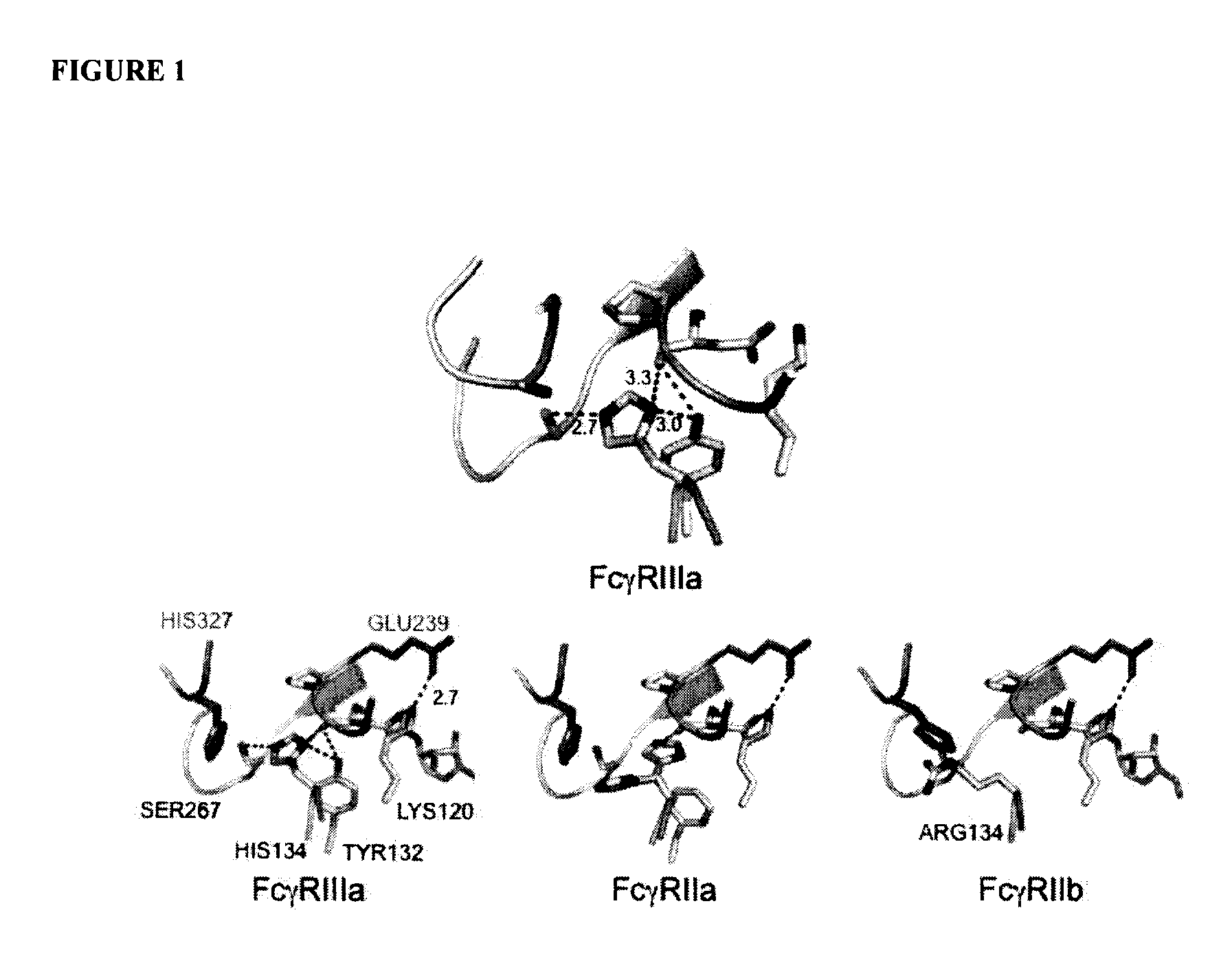
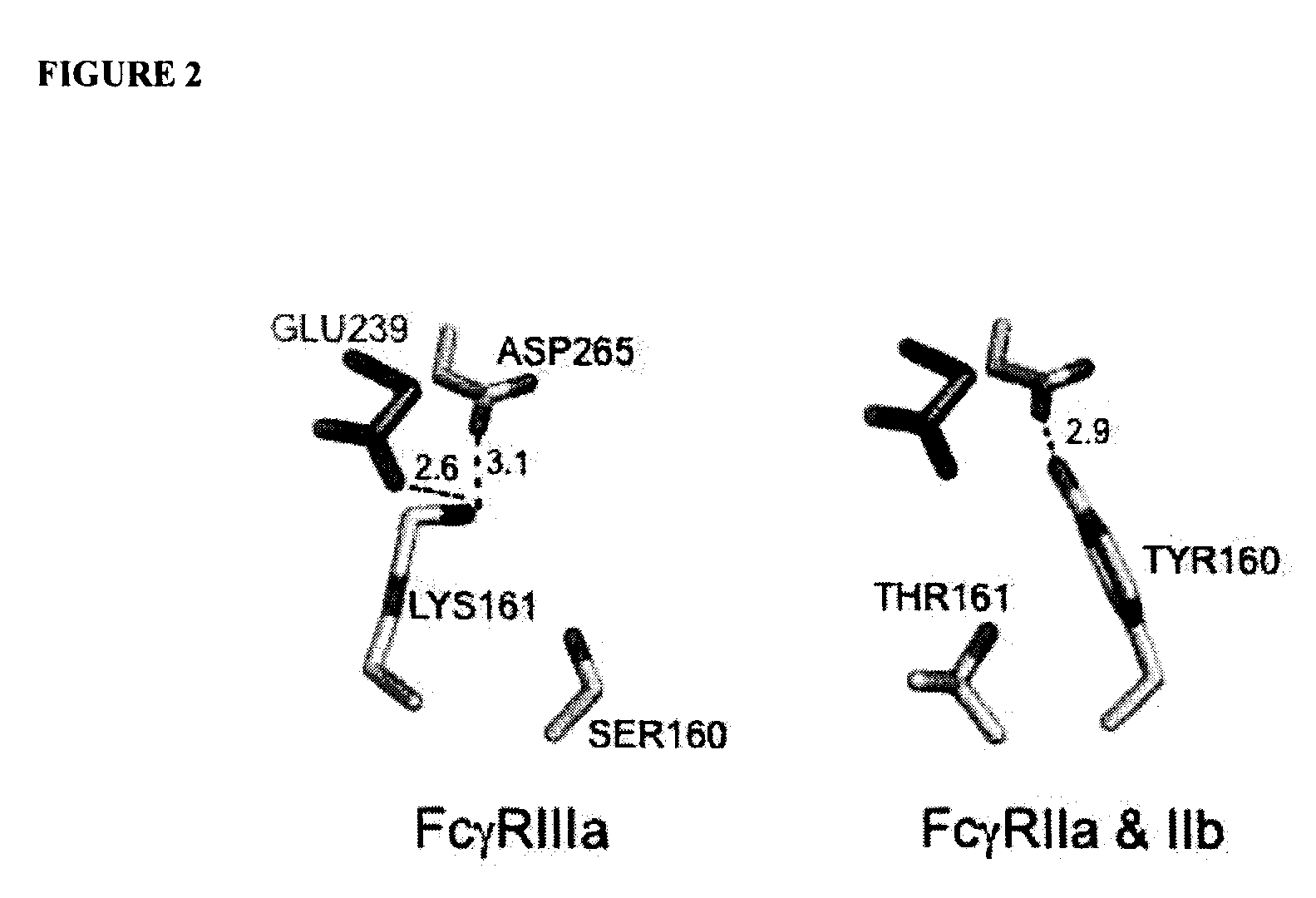
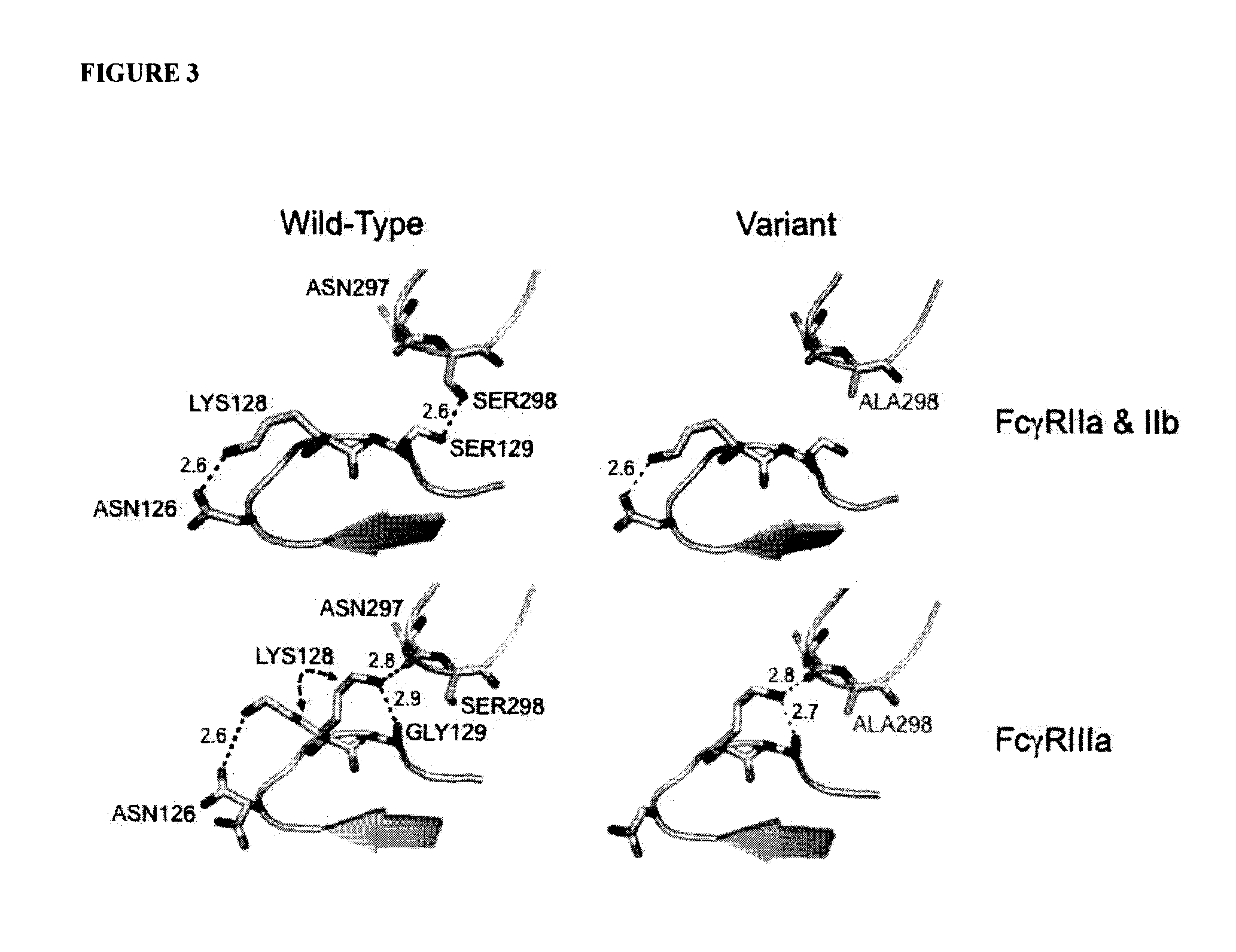
ActiveUS20130089541A1Inhibition is effectiveStrong specificityAntipyreticAnalgesicsFc receptorFc(alpha) receptor
Rationally designed antibodies and polypeptides that comprise multiple Fc region amino acid substitutions that synergistically provide enhanced selectivity and binding affinity to a target Fc receptor are provided. The polypeptides are mutated at multiple positions to make them more effective when incorporated in antibody therapeutics than those having wild-type Fc components.
Owner:ZYMEWORKS INC
Covalent tethering of functional groups to proteins and substrates therefor
ActiveUS20060024808A1Rapidly and efficiently loaded into and washedStable rateMethine/polymethine dyesBacteriaAmino acid substitutionTethering
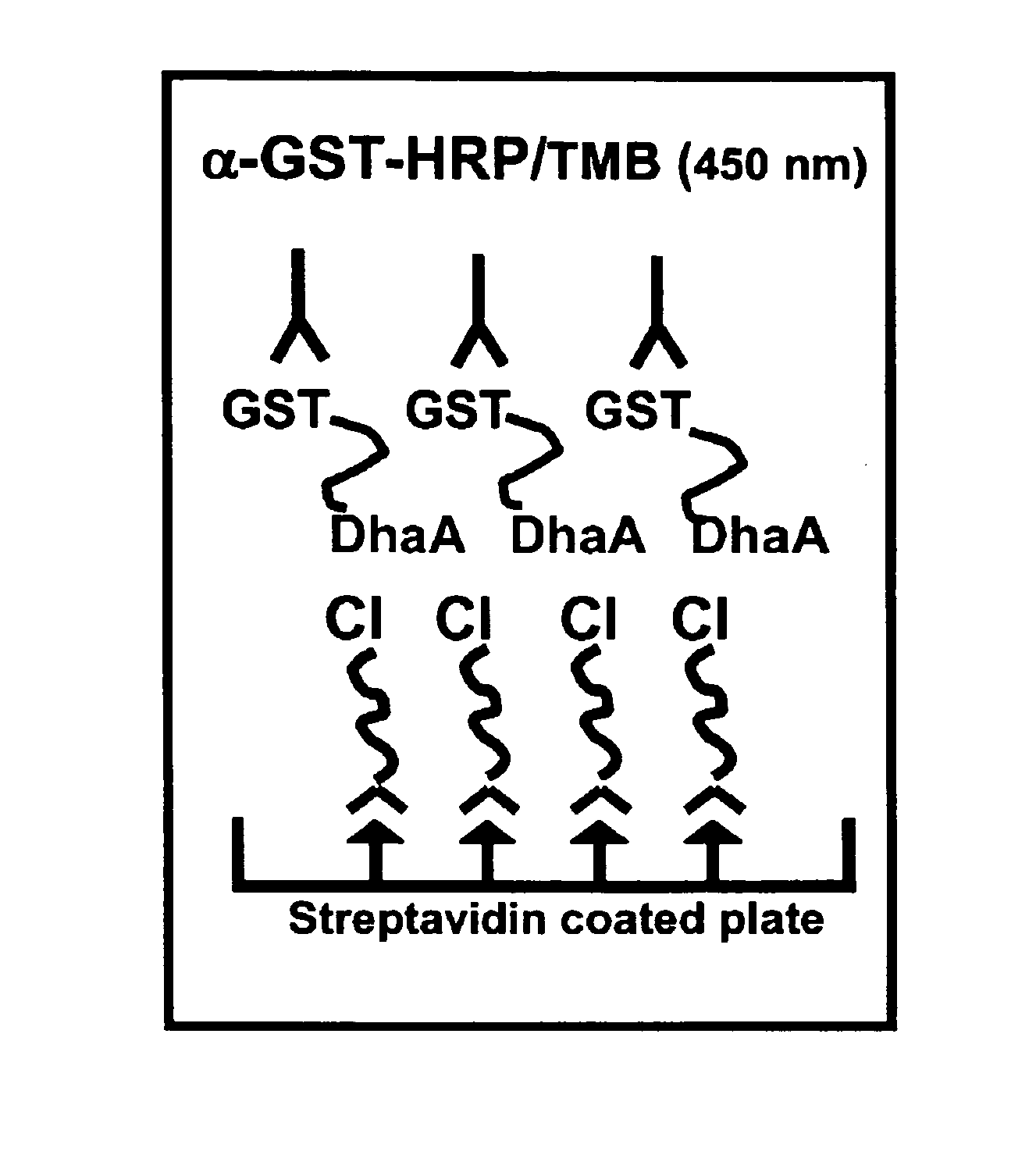
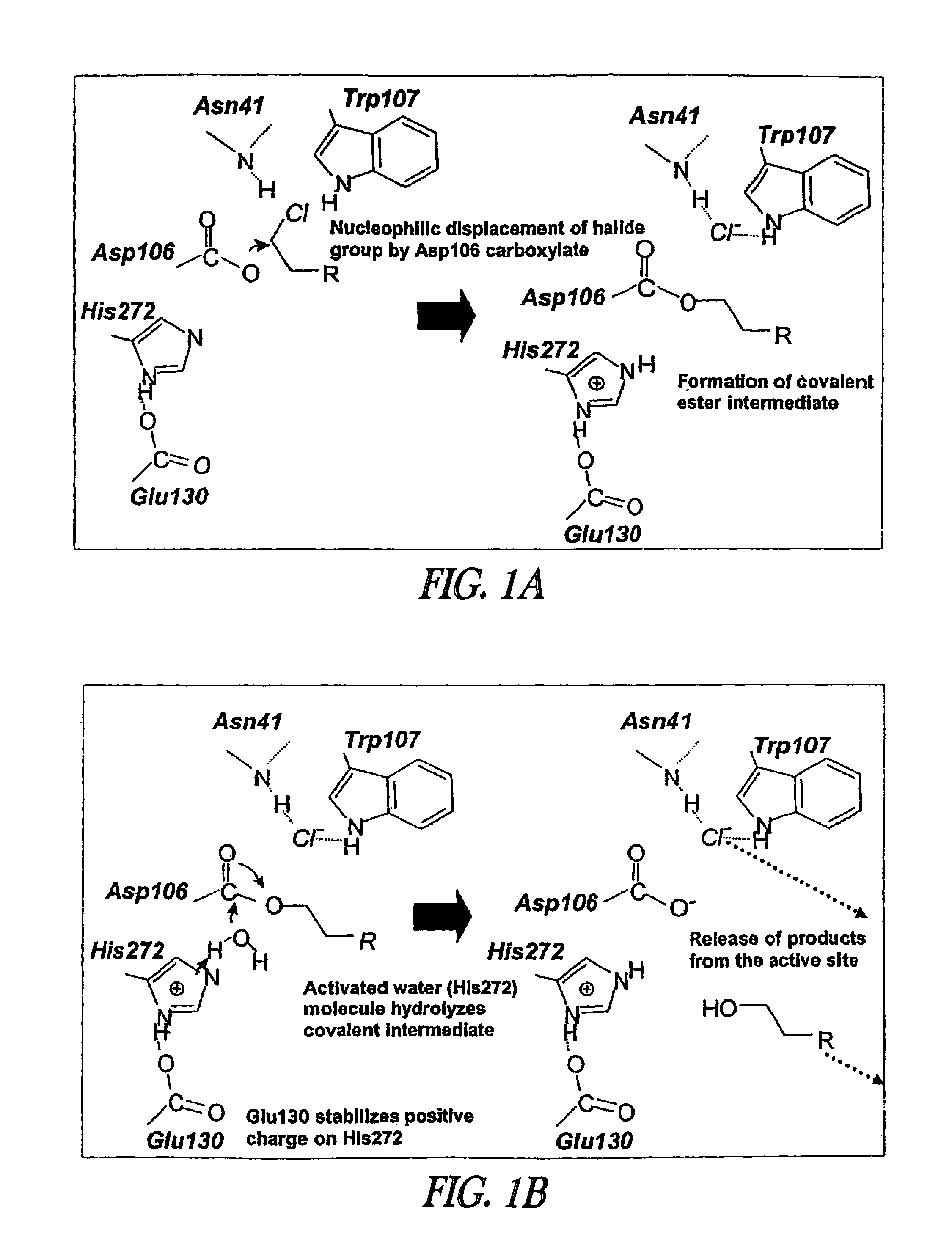
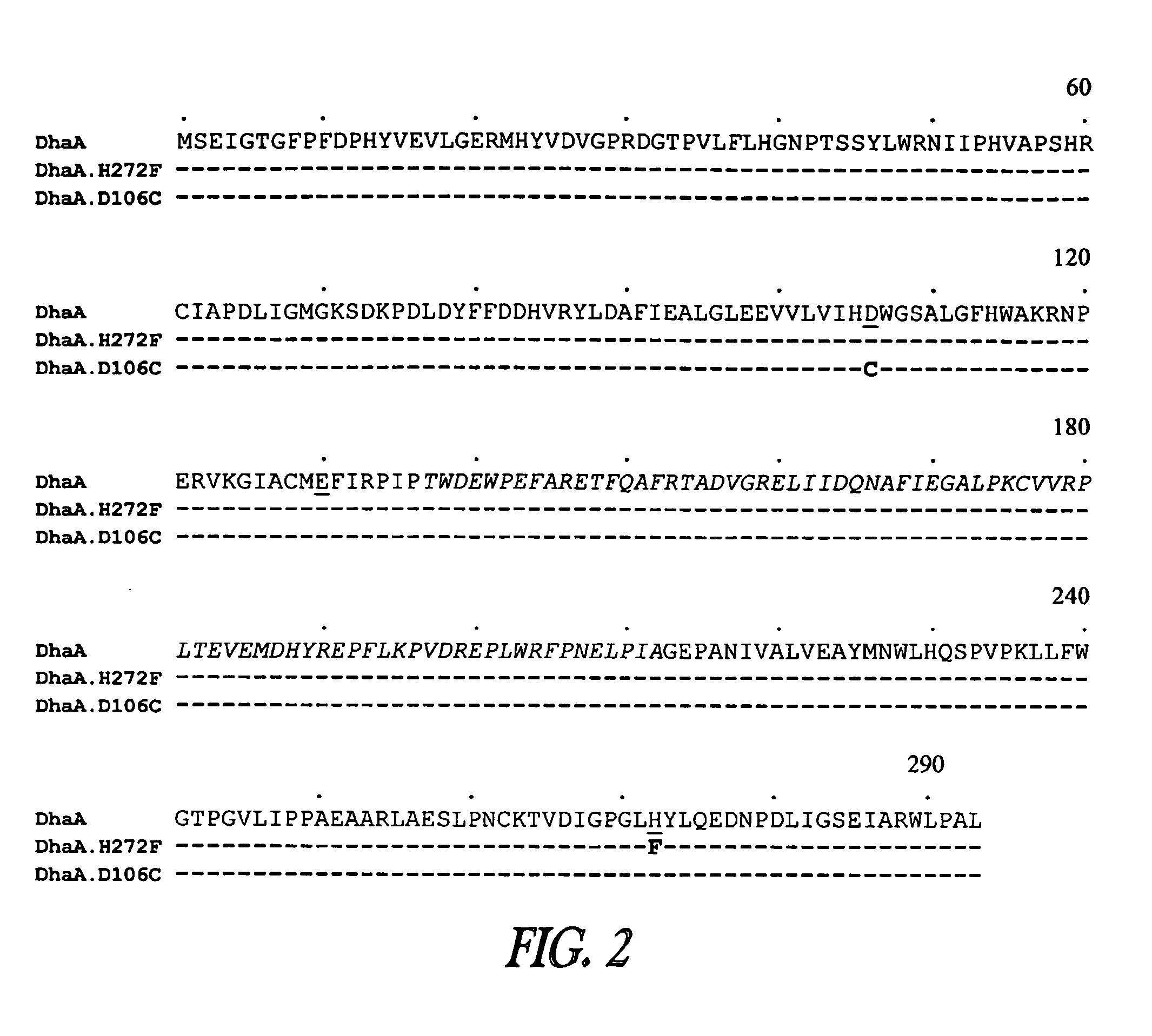
A mutant hydrolase optionally fused to a protein of interest is provided. The mutant hydrolase is capable of forming a bond with a substrate for the corresponding nonmutant (wild-type) hydrolase which is more stable than the bond formed between the wild-type hydrolase and the substrate and has at least two amino acid substitutions relative to the wild-type hydrolase. Substrates for hydrolases comprising one or more functional groups are also provided, as well as methods of using the mutant hydrolase and the substrates of the invention. Also provided is a fusion protein capable of forming a stable bond with a substrate and cells which express the fusion protein.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
Alteration of FcRn binding affinities or serum half-lives of antibodies by mutagenesis
InactiveUS7361740B2Function increaseExtended half-lifeImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunoglobulins against virusesSerum igeHalf-life
The present invention provides for a modified antibody of class IgG, in which at least one amino acid from the heavy chain constant region selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues 250, 314, and 428 is substituted with another amino acid which is different from that present in the unmodified antibody, thereby altering the binding affinity for FcRn and / or the serum half-life in comparison to the unmodified antibody.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Substrates for covalent tethering to proteins
ActiveUS20050272114A1Efficient loadingLoad is outside loadMaterial nanotechnologyHydrolasesAmino acid substitutionWild type
A mutant hydrolase optionally fused to a protein of interest is provided. The mutant hydrolase is capable of forming a bond with a substrate for the corresponding nonmutant (wild-type) hydrolase which is more stable than the bond formed between the wild-type hydrolase and the substrate and has at least two amino acid substitutions relative to the wild-type hydrolase. Substrates for hydrolases comprising one or more functional groups are also provided, as well as methods of using the mutant hydrolase and the substrates of the invention. Also provided is a fusion protein capable of forming a stable bond with a substrate and cells which express the fusion protein.
Owner:PROMEGA
Human Coagulation Factor VII Polypeptides
InactiveUS20090055942A1Prolong half-life in vivoPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationFactor VIIClotting factor
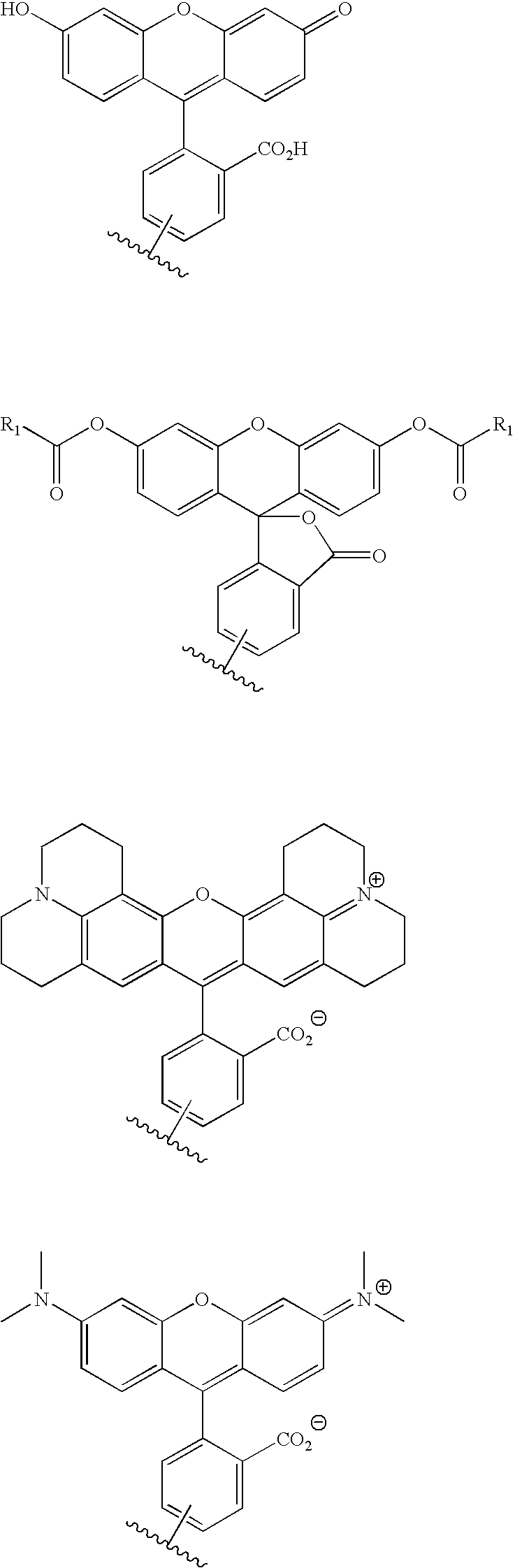
The present invention relates to novel human coagulation Factor Vila variants having substitutions of one or more amino acids at a position selected from the group consisting of position 172, 173, 175, 176, 177, 196, 197, 198, 199, 200, 203, 235, 237, 238, 239, 240, 286, 287, 288, 289, 290, 291, 292, 293, 294, 295, 297, 299, 319, 320, 321, 327, 341, 363, 364, 365, 366, 367, 370, 373 corresponding to amino acid positions of SEQ ID NO:1 and wherein said Factor VII polypeptide exhibits increased resistance to inactivation by an endogenous inhibitor of said FVII polypeptide relative to wild-type human FVIIa.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Method of immobilizing a protein or molecule via a mutant dehalogenase that is bound to an immobilized dehalogenase substrate and linked directly or indirectly to the protein or molecule
ActiveUS7429472B2Rapidly and efficiently loaded into and washedStable rateMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionWild type
A mutant hydrolase optionally fused to a protein of interest is provided. The mutant hydrolase is capable of forming a bond with a substrate for the corresponding nonmutant (wild-type) hydrolase which is more stable than the bond formed between the wild-type hydrolase and the substrate and has at least two amino acid substitutions relative to the wild-type hydrolase. Substrates for hydrolases comprising one or more functional groups are also provided, as well as methods of using the mutant hydrolase and the substrates of the invention. Also provided is a fusion protein capable of forming a stable bond with a substrate and cells which express the fusion protein.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
Antibodies and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS20080187966A1Speed up the processIncrease productionImmunoglobulins against growth factorsRecombinant DNA-technologyDisulfide bondingAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides methods for producing humanized antibodies and increasing the yield of antibodies and / or antigen binding fragments when produced in cell culture. In one aspect of the invention, at least one framework region amino acid residue of the variable domain is substituted by a corresponding amino acid from a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain. In another aspect, an amino acid is placed at a position proximal to a cys residue that participates in an intrachain variable domain disulfide bond that corresponds to an amino acid found at that position in a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Covalent tethering of functional groups to proteins and substrates therefor
ActiveUS7425436B2Rapidly and efficiently loaded into and washedStable rateMethine/polymethine dyesBacteriaTetheringAmino acid substitution
A mutant hydrolase optionally fused to a protein of interest is provided. The mutant hydrolase is capable of forming a bond with a substrate for the corresponding nonmutant (wild-type) hydrolase which is more stable than the bond formed between the wild-type hydrolase and the substrate and has at least two amino acid substitutions relative to the wild-type hydrolase. Substrates for hydrolases comprising one or more functional groups are also provided, as well as methods of using the mutant hydrolase and the substrates of the invention. Also provided is a fusion protein capable of forming a stable bond with a substrate and cells which express the fusion protein.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
Methods of identifying and creating rubisco large subunit variants with improved rubisco activity, compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20080256666A1Increased Rubisco activityImprove productivitySugar derivativesUnicellular algaeRuBisCO activityAmino acid substitution
Methods for identifying one or more amino acid substitutions in a Rubisco large subunit polypeptide (variant) that confer increased Rubisco activity in a unicellular photosynthetic organism and transferring those substitutions to a Rubisco large subunit polypeptide of a higher plant cell are described herein. Methods and compositions for modulating plant productivity using the modified Rubisco large subunit polypeptide variants are provided. The Rubisco large subunit sequences are used in a variety of methods including increasing plant productivity in a plant. Transformed plants, plant cell, tissues, seed, and expression vectors are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Methods for antibody engineering
ActiveUS20060099204A1Reducing binding activity of antibodyAffecting activity of antibodyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntigenAmino acid substitution
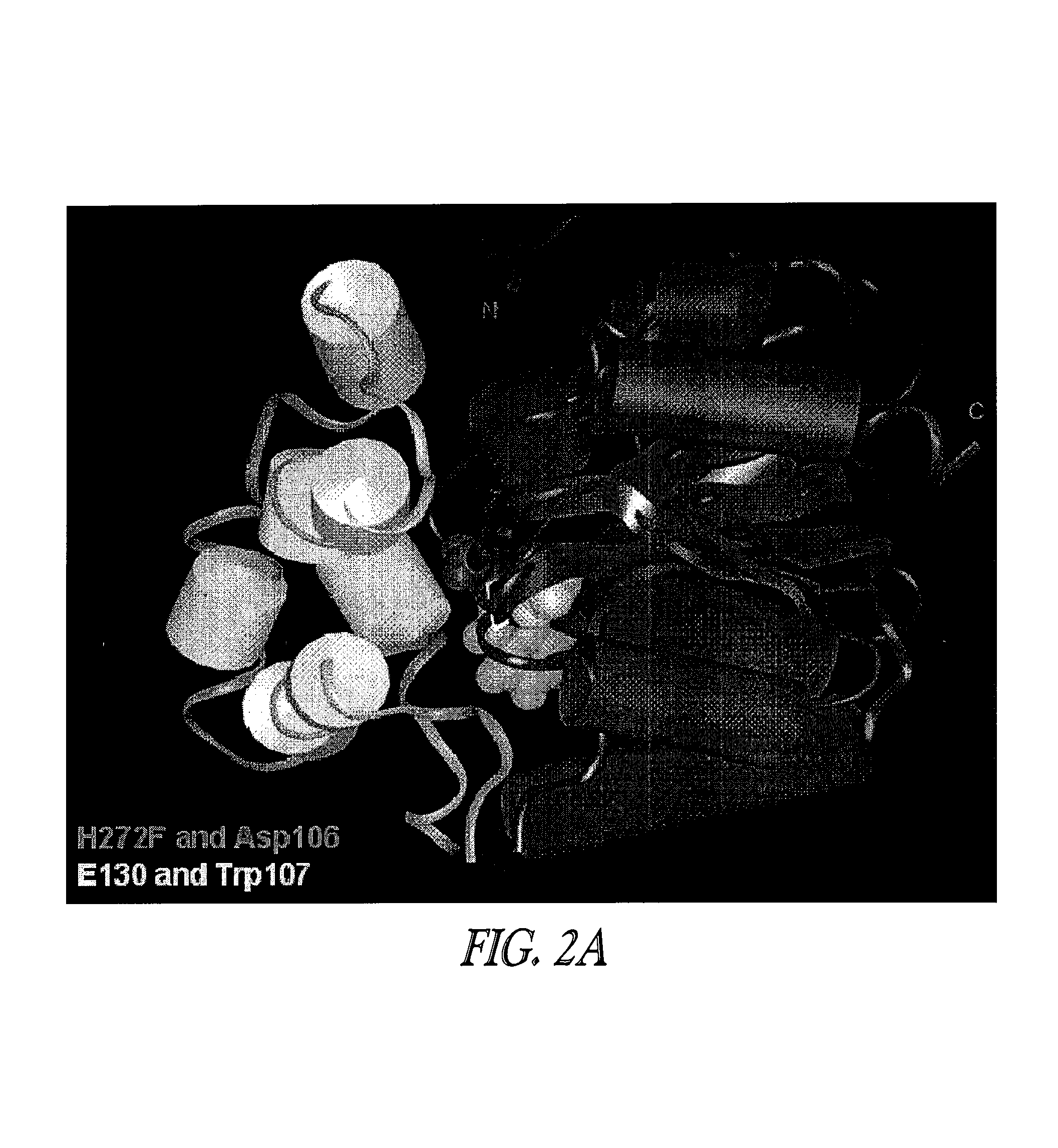
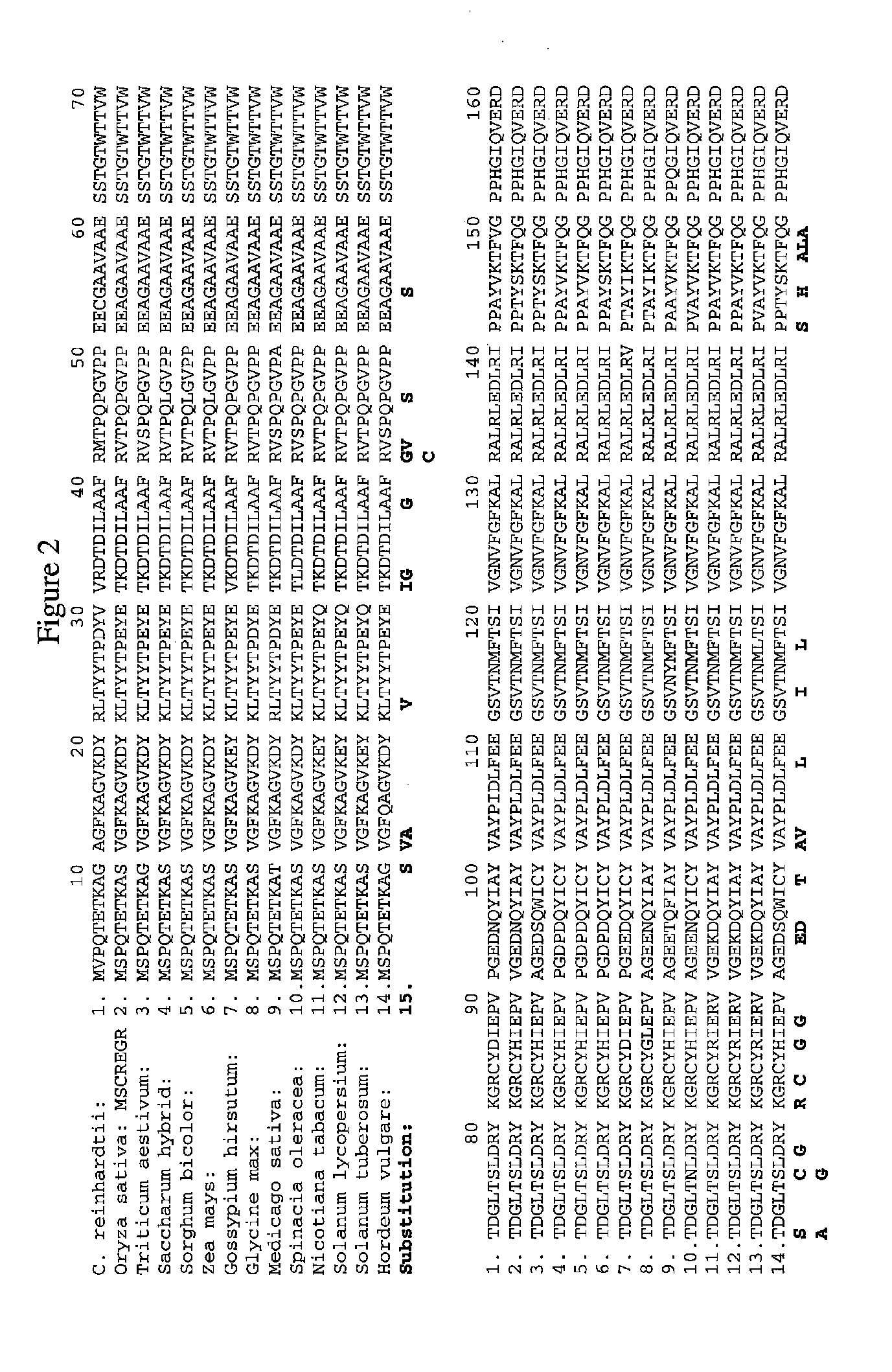
The invention provides a method for identifying positions of an antibody that can be modified without significantly reducing the binding activity of the antibody. In many embodiments, the method involves identifying a substitutable position in a parent antibody by comparing its amino acid sequence to the amino acid sequences of a number of related antibodies that each bind to the same antigen as the parent antibody. The amino acid at the substitutable position may be substituted for a different amino acid without significantly affecting the activity of the antibody. The subject methods may be employed to change the amino acid sequence of a CDR without significantly reducing the affinity of the antibody of the antibody, in humanization methods, or in other antibody engineering methods. The invention finds use in a variety of therapeutic, diagnostic and research applications.
Owner:EPITOMICS INC
Method of modifying isoelectric point of antibody via amino acid substitution in CDR
ActiveUS9096651B2Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activityGood treatment effectImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsComplementarity determining regionAmino acid substitution
Methods are described for modifying the isoelectric point of an antibody while retaining its antigen-binding activity, comprising modifying the charge of at least one exposable amino acid residue on the surface of the complementarity determining region (CDR). The disclosure also provides methods for purifying multispecific antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point, and methods for improving the plasma pharmacokinetics of antibodies with a modified isoelectric point. The disclosure further provides antibodies with a modified isoelectric point, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies as an active ingredient, and methods for producing the antibodies and compositions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
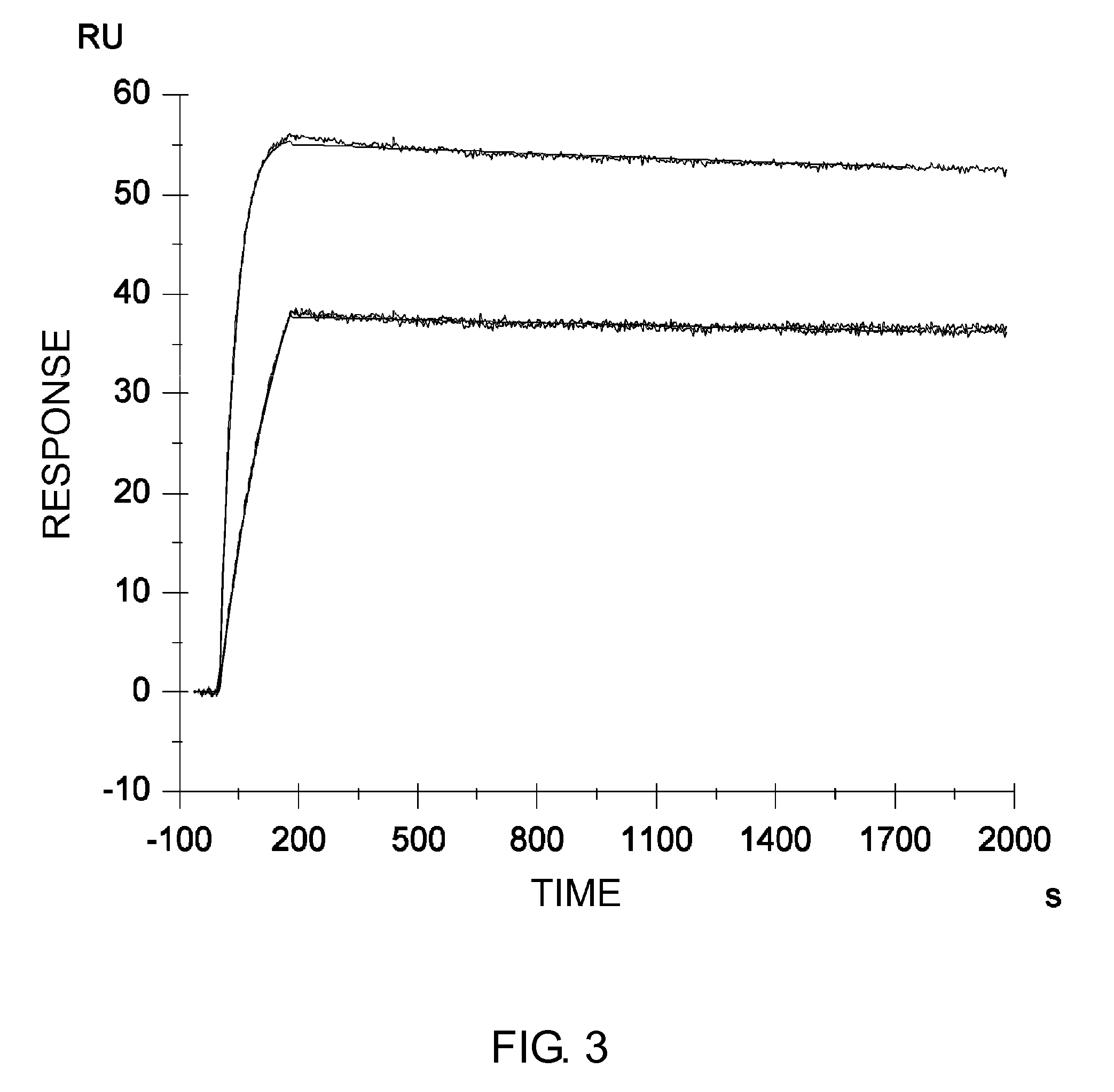
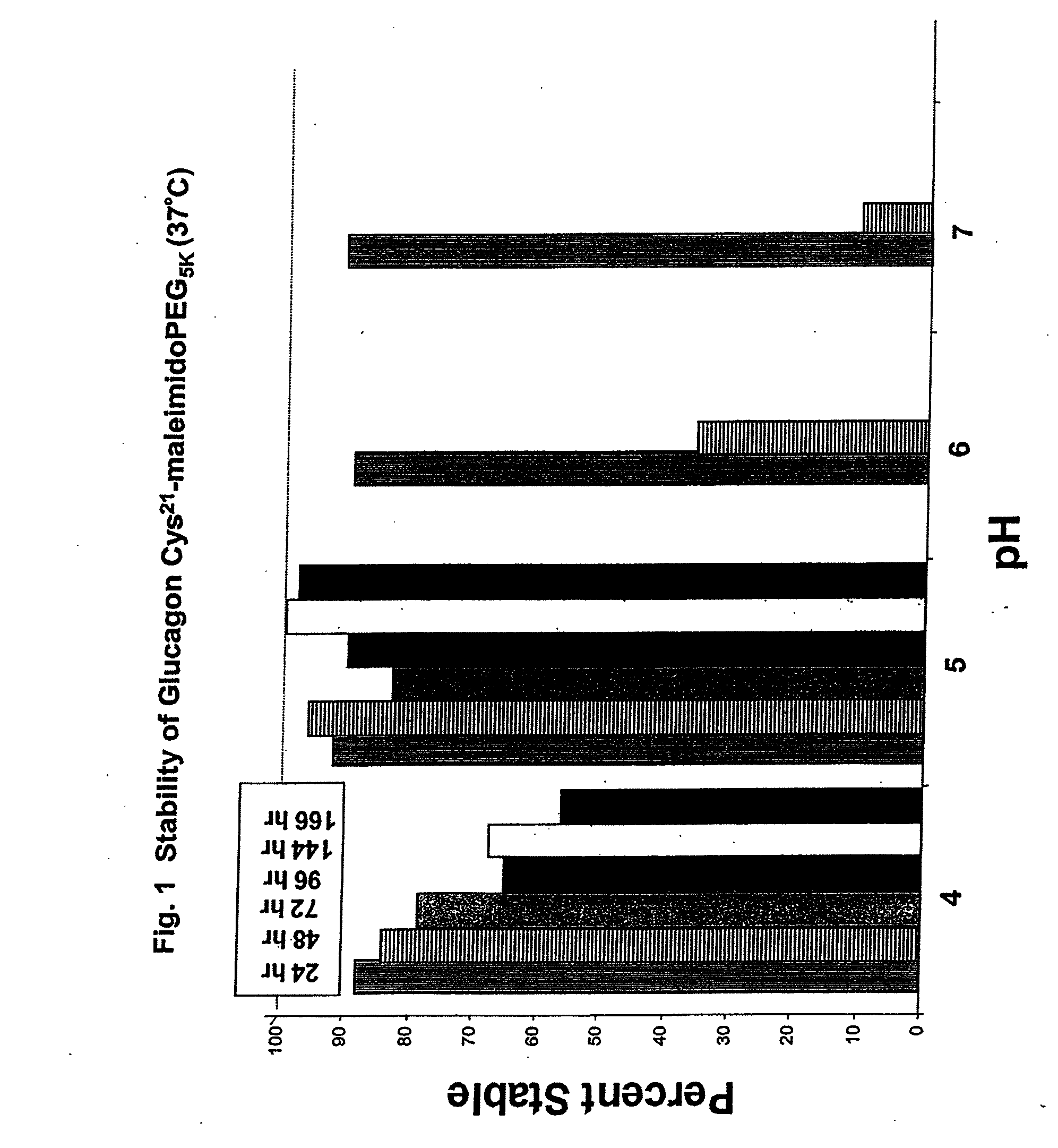
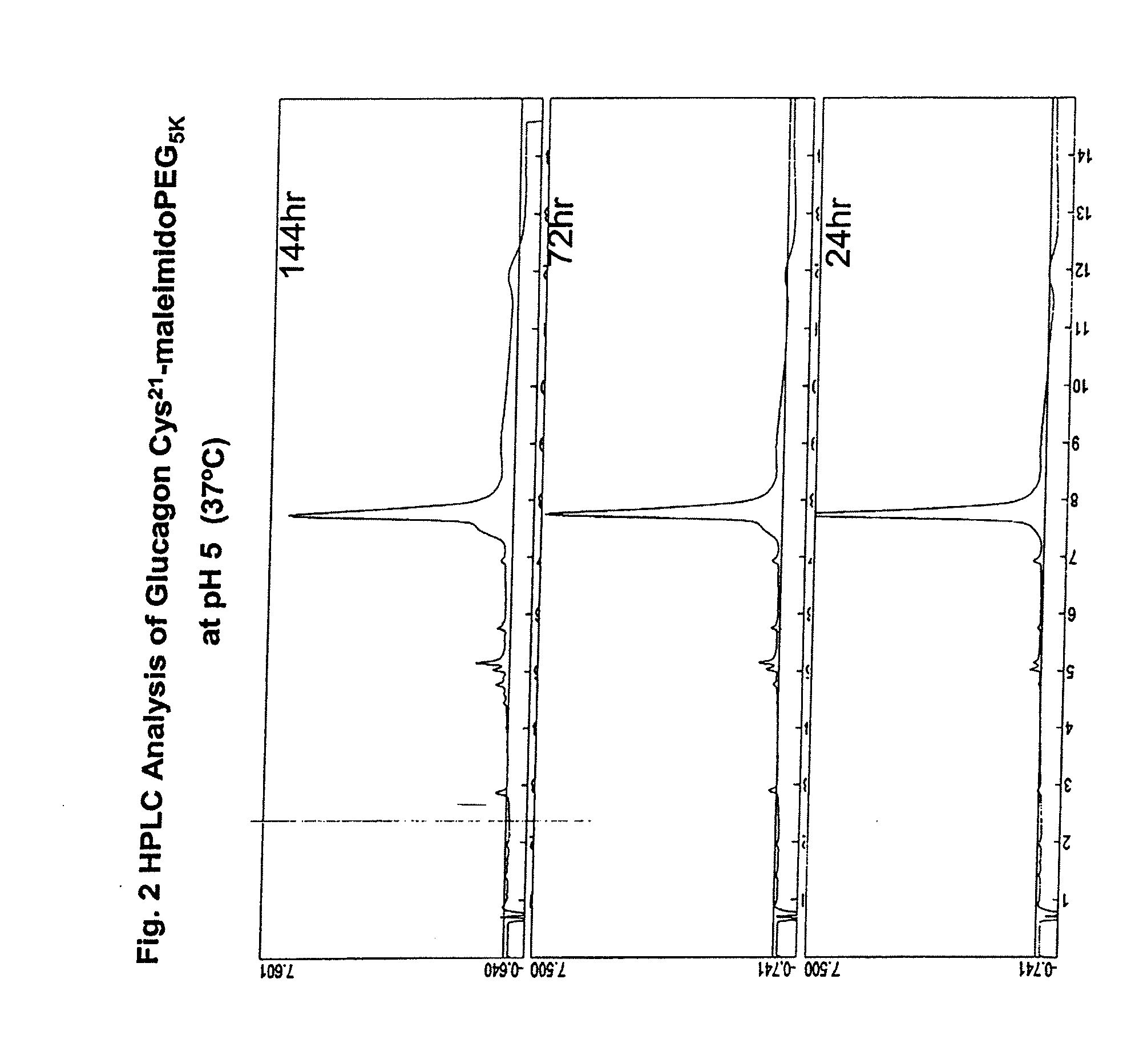
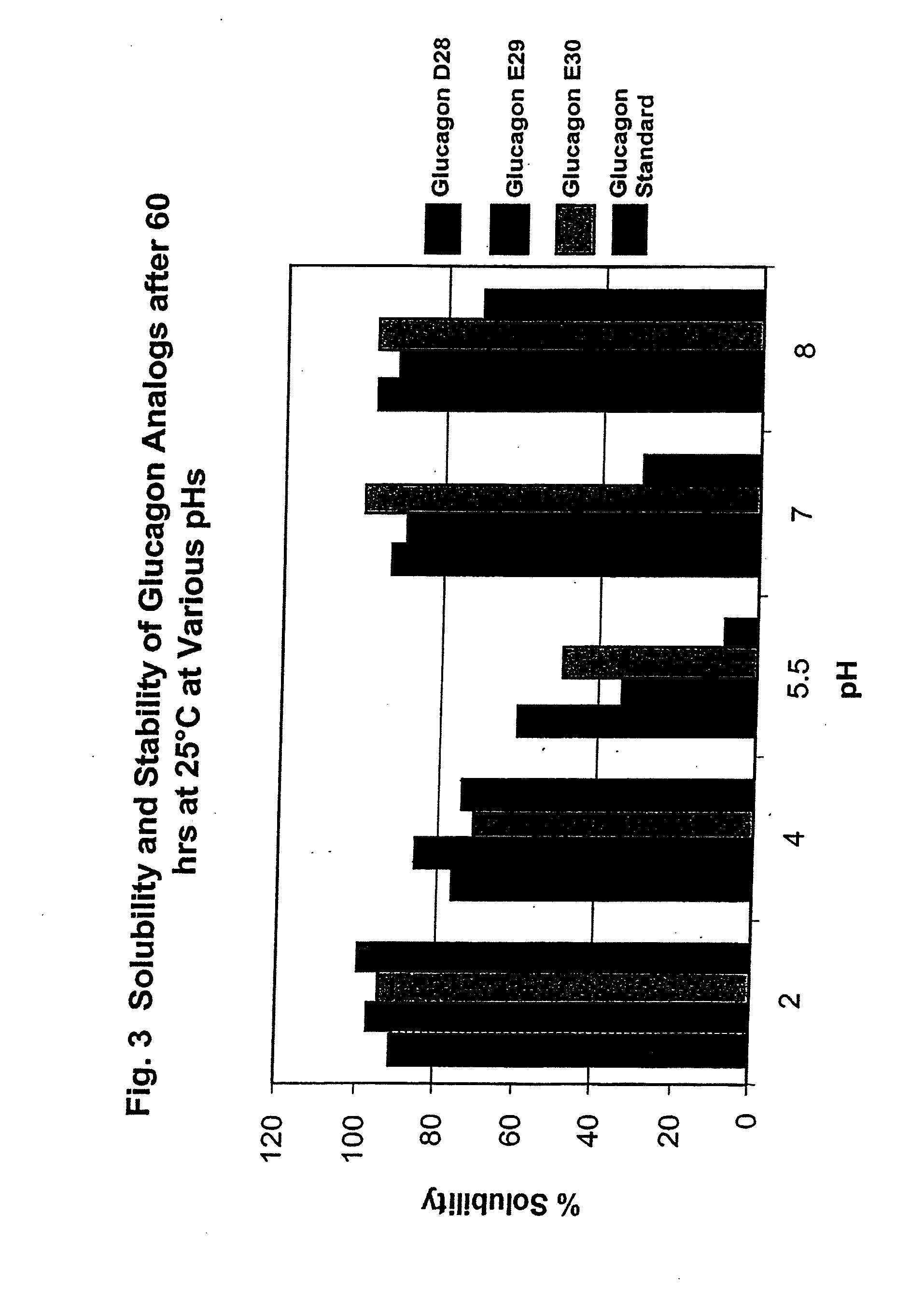
GLUCAGON ANALOGS EXHIBITING ENHANCED SOLUBILITY AND STABILITY IN PHYSIOLOGICAL pH BUFFERS
ActiveUS20110190200A1Rapidly increasing glucose levelNormalizing blood glucose levelAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionHalf-life
Modified glucagon peptides are disclosed having improved solubility and / or half-life while retaining glucagon agonist activity. The glycogen peptides have been modified by substitution of native amino acids with, and / or addition of, charged amino acids to the carboxy terminus of the peptide. The modified glucagon agonists can be further modified by pegylation, or the addition of a carboxy terminal peptide selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 20, SEQ ID NO: 21, SEQ ID NO: 23, or both to further enhance the solubility of the glucagon agonist analogs.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Epitope analogs
InactiveUS20060057673A1Similar and improved immunological propertyTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionAmino acid
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Anti-CD19 Antibodies
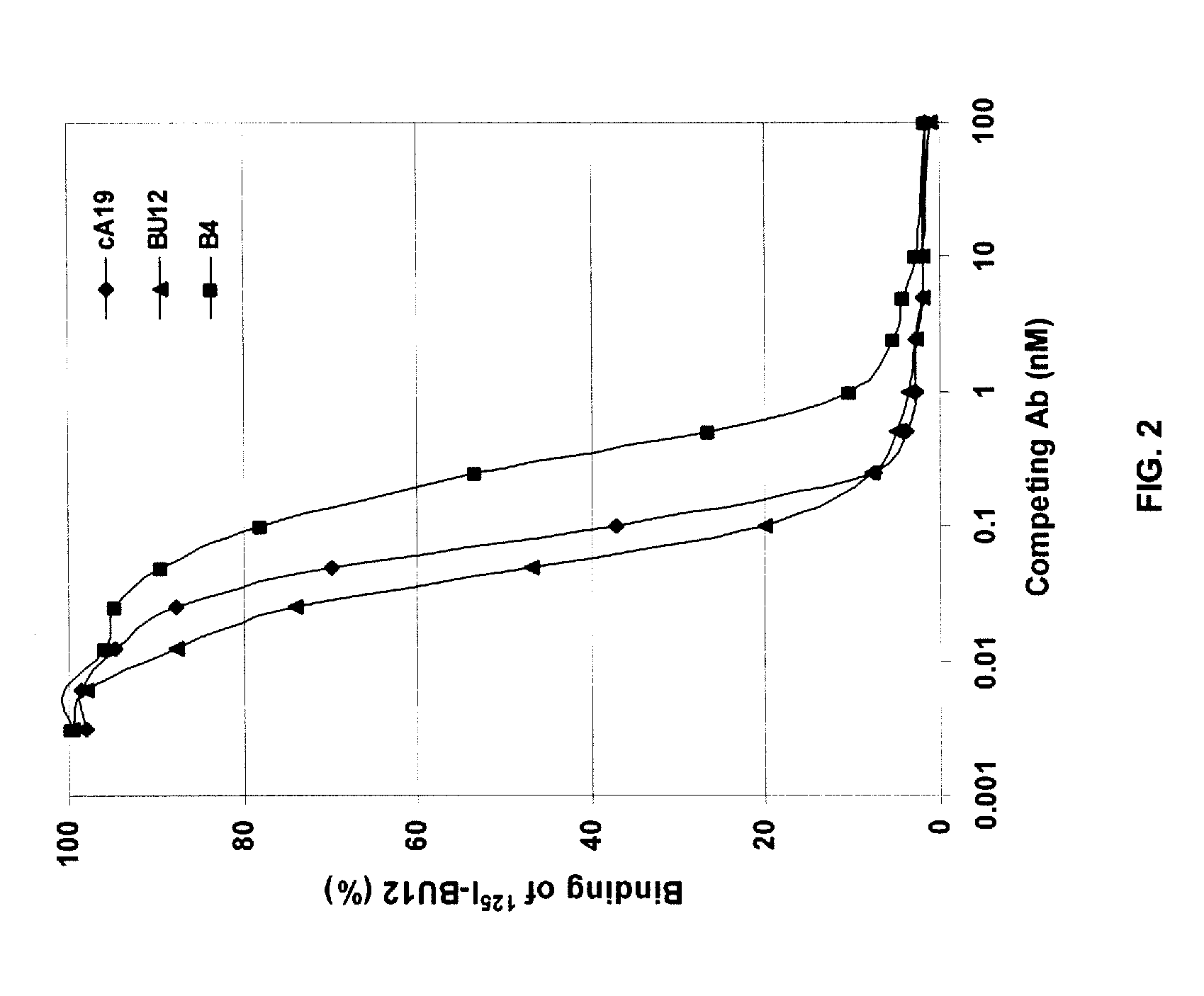
The present invention provides humanized, chimeric and human anti-CD19 antibodies, anti-CD19 antibody fusion proteins, and fragments thereof that bind to a human B cell marker. Such antibodies, fusion proteins and fragments thereof are useful for the treatment and diagnosis of various B-cell disorders, including B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases. In more particular embodiments, the humanized anti-CD19 antibodies may comprise one or more framework region amino acid substitutions designed to improve protein stability, antibody binding and / or expression levels. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the substitutions comprise a Ser91Phe substitution in the hA19 VH sequence.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
SSX-2 peptide analogs
InactiveUS20060063913A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionAmino acid
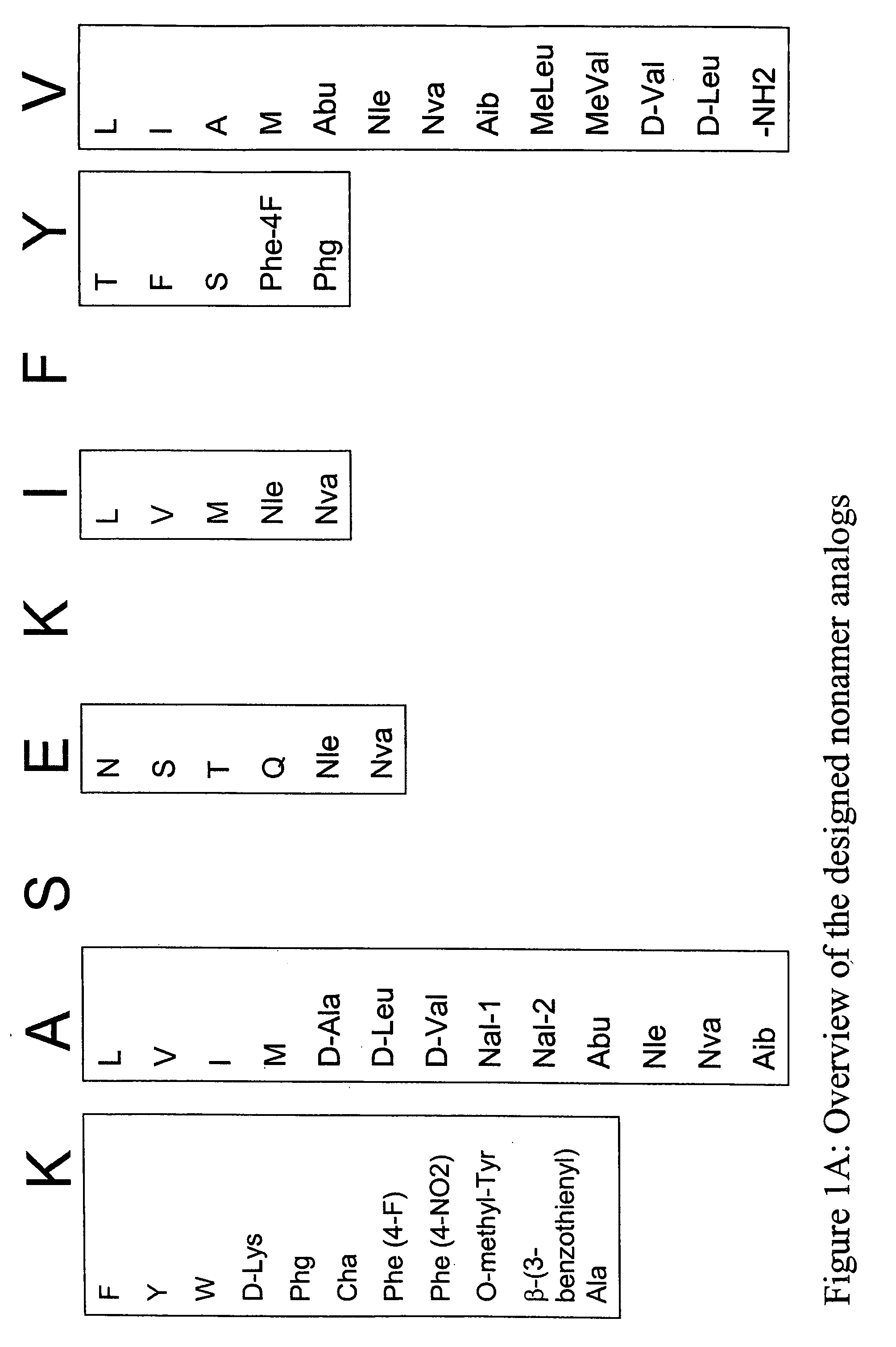
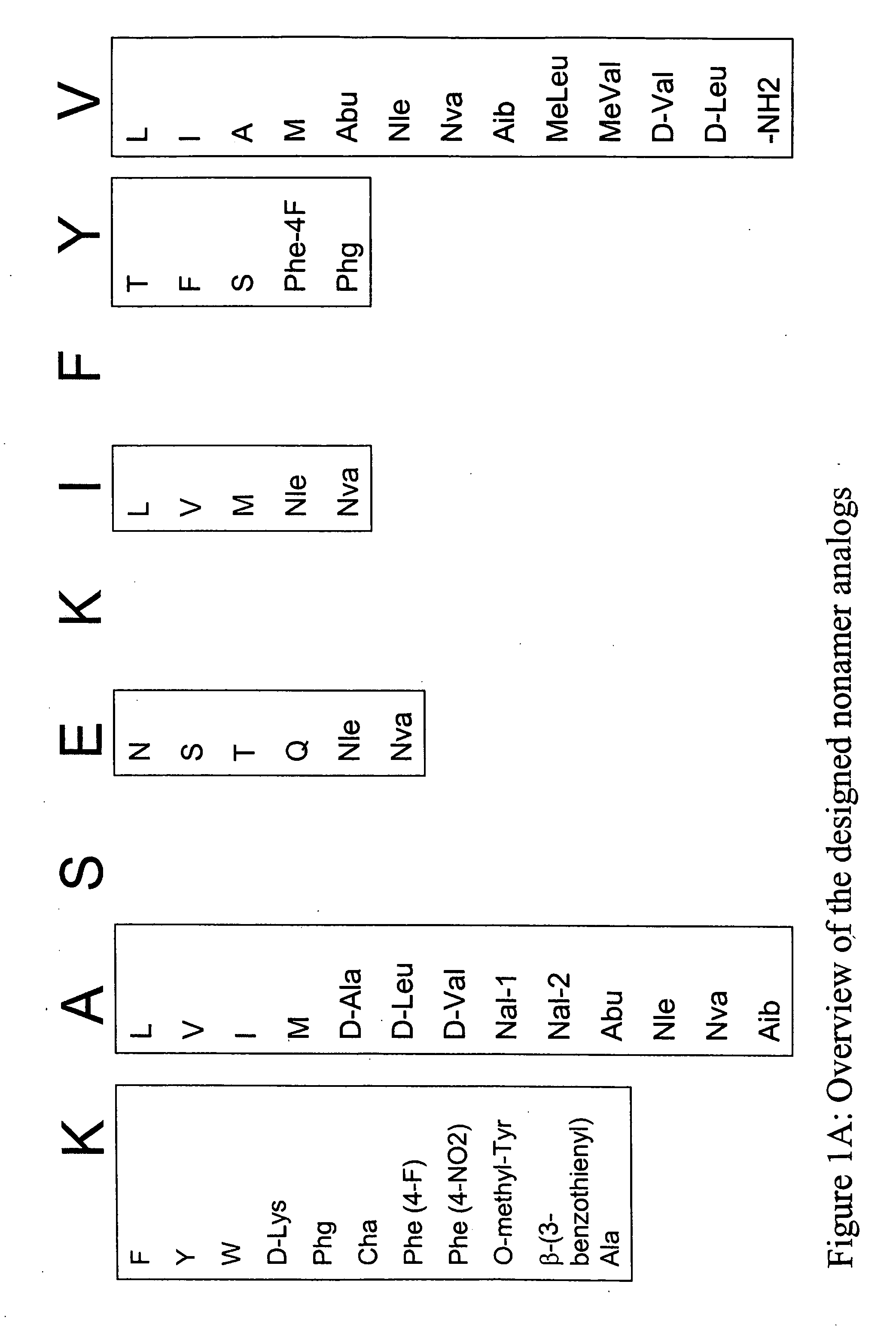
Some embodiments relate to analogs of peptides corresponding to class I MHC-restricted T cell epitopes and methods for their generation. These analogs can contain amino acid substitutions at residues that directly interact with MHC molecules, and can confer improved, modified or useful immunologic properties. Additionally classes of analogs, in which the various substitutions comprise the non-standard residues norleucine and / or norvaline, are disclosed.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Method for altering antibody light chain interactions
InactiveUS6485943B2Increase productionEasy to controlPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesHeavy chainAmino acid substitution
A method for recombinant antibody subunit dimerization including modifying at least one codon of a nucleic acid sequence to replace an amino acid occurring naturally in the antibody with a charged amino acid at a position in the interface segment of the light polypeptide variable region, the charged amino acid having a first polarity; and modifying at least one codon of the nucleic acid sequence to replace an amino acid occurring naturally in the antibody with a charged amino acid at a position in an interface segment of the heavy polypeptide variable region corresponding to a position in the light polypeptide variable region, the charged amino acid having a second polarity opposite the first polarity. Nucleic acid sequences which code for novel light chain proteins, the latter of which are used in conjunction with the inventive method, are also provided.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants
InactiveUS20050202419A1Improve abilitiesImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesOxygenaseHeme
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have an improved ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. These variants also have an improved thermostability as compared to the cytochrome P450 BM-3 F87A mutant. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain mutants having I58V, F87A, H100R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, N239H, S274T, L324I, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Soluble heavy-chain only antibodies
ActiveUS20130323235A1Efficient expressionEfficient routingHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAmino acid substitutionGene
The present invention provides a high affinity, antigen-specific, soluble heavy chain-only antibody which: lacks hallmark camelid-related amino acid substitutions and has FR2 substitutions which are not found in antibodies which comprise heavy and light chain; shows increased net hydrophobicity within CDR1 and an increased number of charged amino acids present in CDR3; and comprises one or more amino acid substitutions within the framework β-pleated sheet leading to increased net hydrophobicity within FR1 and increased number of charged amino acids present in FR3. Also provided are VH domains having the same properties, gene segments for their production, methods for their production, transgenic animals and uses of the antibody of the VH domains in therapy.
Owner:HARBOUR ANTIBODIES BV +1
Inert format
ActiveUS20150337049A1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibacterial agentsAmino acid substitutionAmino acid
Described herein are, proteins comprising amino acid substitutions in at least one of a first and a second polypeptide chain. Furthermore, is described the uses and methods related to said proteins.
Owner:GENMAB AS
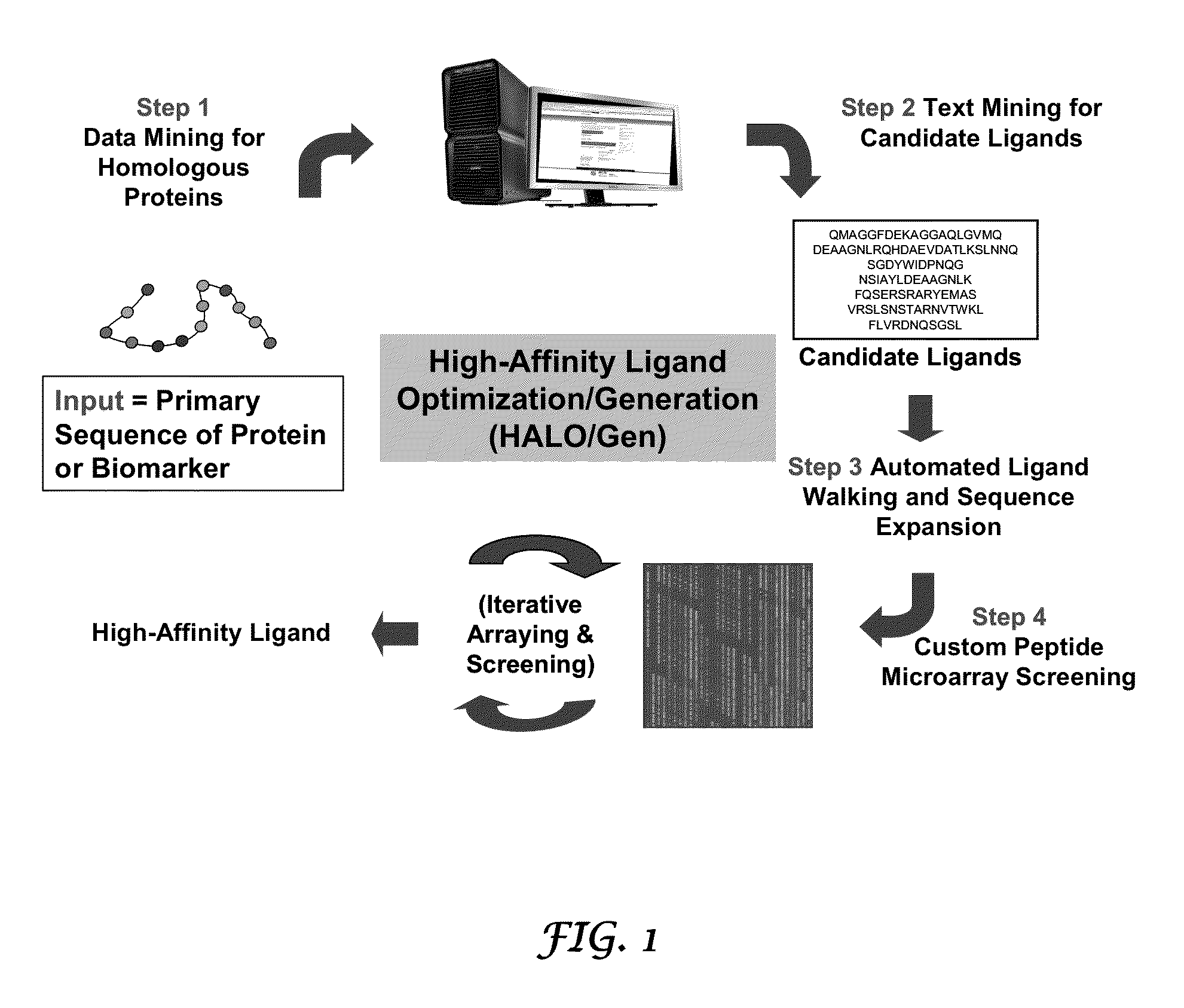
Methods for discovering molecules that bind to proteins
InactiveUS20130053541A1Inhibit functionPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningProtein targetPeptide ligand
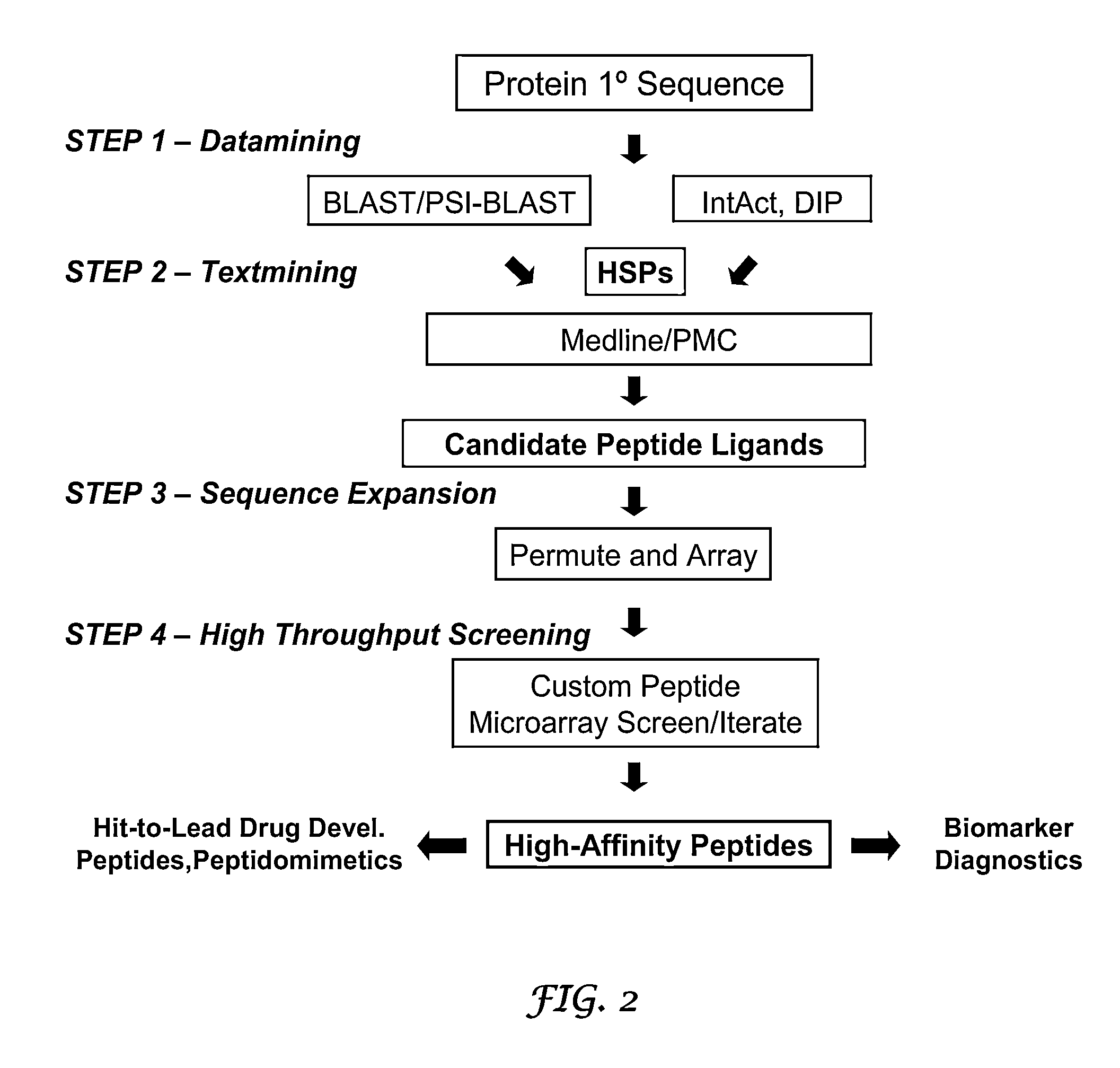
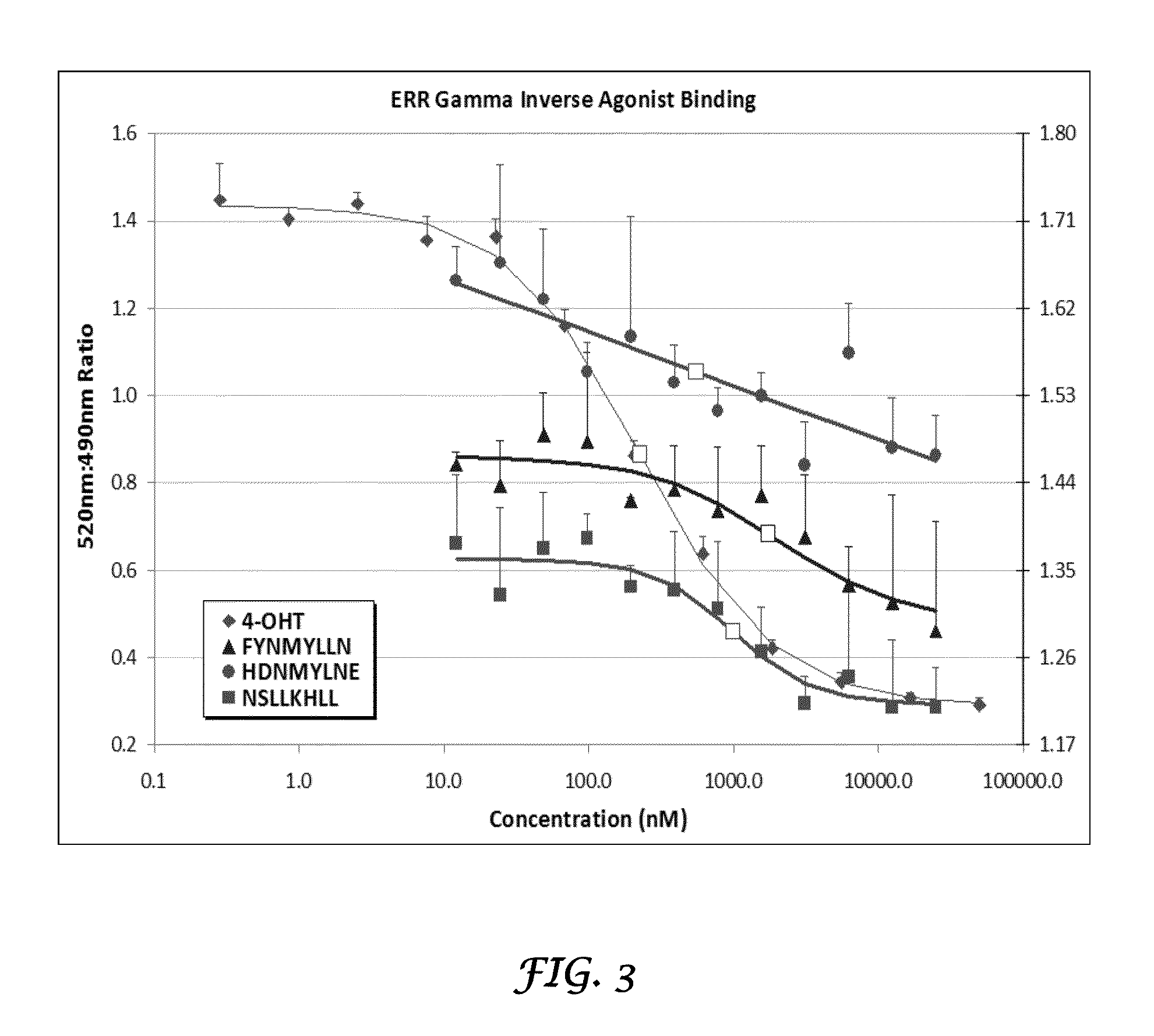
Methods and systems for the discovery of high-affinity peptide ligands and the resulting compositions are described herein. The amino acid sequence of a target protein is used to identify one or more homologous proteins of the target protein. Publications and databases are textmined to retrieve the sequences of peptide ligands that bind to the homologues or the target protein. Complementary proteins, which are proteins that bind to the target or homologous proteins or to DNA, and their target protein- or DNA-binding regions may also be identified. These candidate ligands are predicted to have a high probability of binding to the target protein or the DNA. The library of candidate peptide ligands is modulated by substituting native amino acid residues with suitable amino acids, thus increasing the explored protein space in a knowledge-based manner. Peptides designed in the modulation step are experimentally screened to identify high-affinity binding ligands, and further optimized through iterative application of the modulation and screening steps.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Cartilage particle tissue mixtures optionally combined with a cancellous construct
Mixtures, such as gels or pastes, comprising freeze-milled cartilage particles and exogenous growth factors are used for repairing chondral defects. Such mixtures may be applied to constructs comprising cancellous bone for implantation at the defect site. Suitable growth factors include variants of FGF-2, particularly variants that include a sole amino acid substitution for asparagine at amino acid 111 of the β8-β9 loop of the FGF-2 peptide. Such FGF-2 variants are released slowly and continuously at a constant rate from cartilage pastes. In other embodiments, the amino acid substituted for asparigine is glycine. Other variants that may be used include FGF-9 variants having truncated chains and a sole amino acid substitution in the β8-β9 loop of the FGF-9 peptide either for tryptophan at amino acid 144 or for asparagine at amino acid 143.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC +1
Antibodies with Enhanced or Suppressed Effector Function
InactiveUS20130108623A1Increase free energyLow affinitySugar derivativesAntipyreticFc receptorAntiendomysial antibodies
Rationally designed antibodies and polypeptides that comprise two Fc region amino acid substitutions that synergistically provide enhanced selectivity and binding affinity to a target Fc receptor are provided. The polypeptides comprise Fc region mutations at two positions that synergistically make the polypeptides more effective when incorporated in antibody therapeutics than those having wild-type Fc components.
Owner:ZYMEWORKS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com