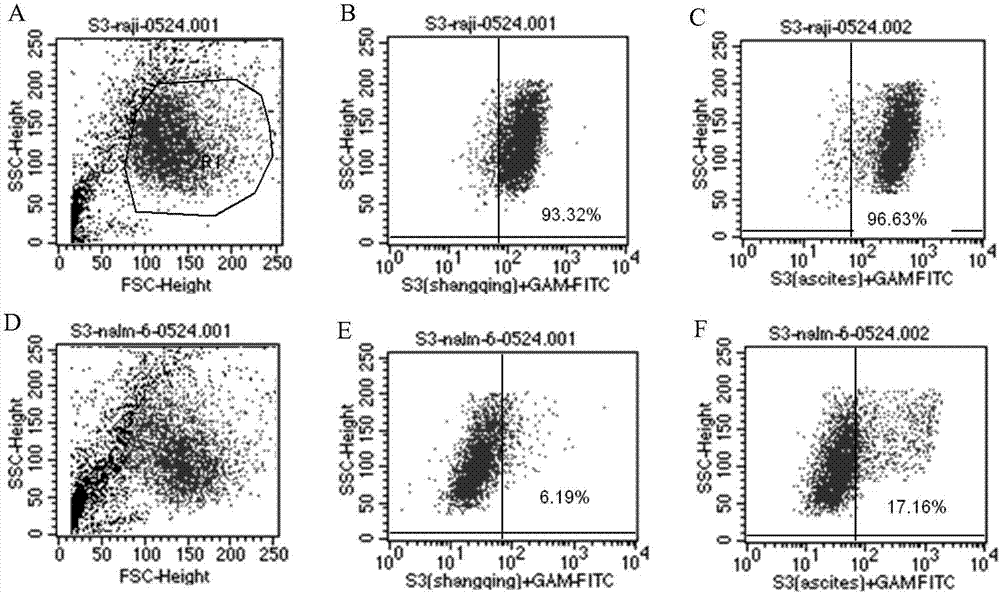
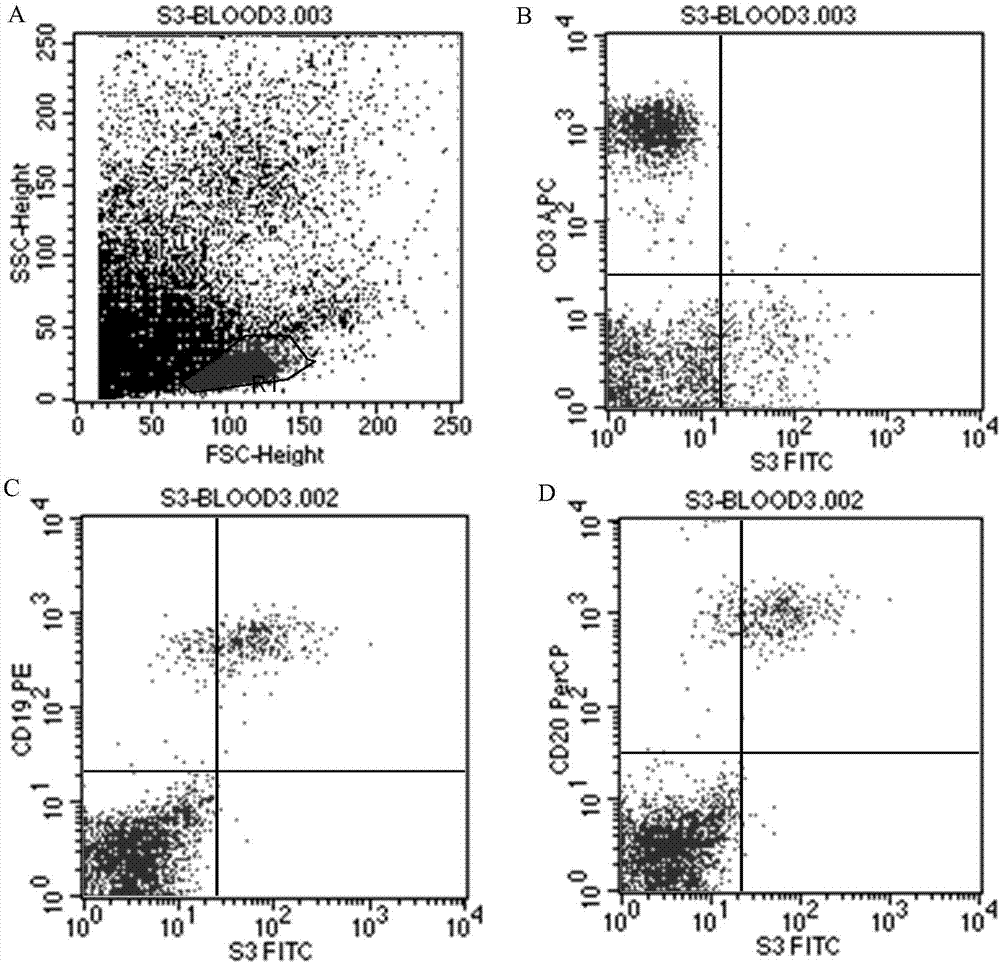
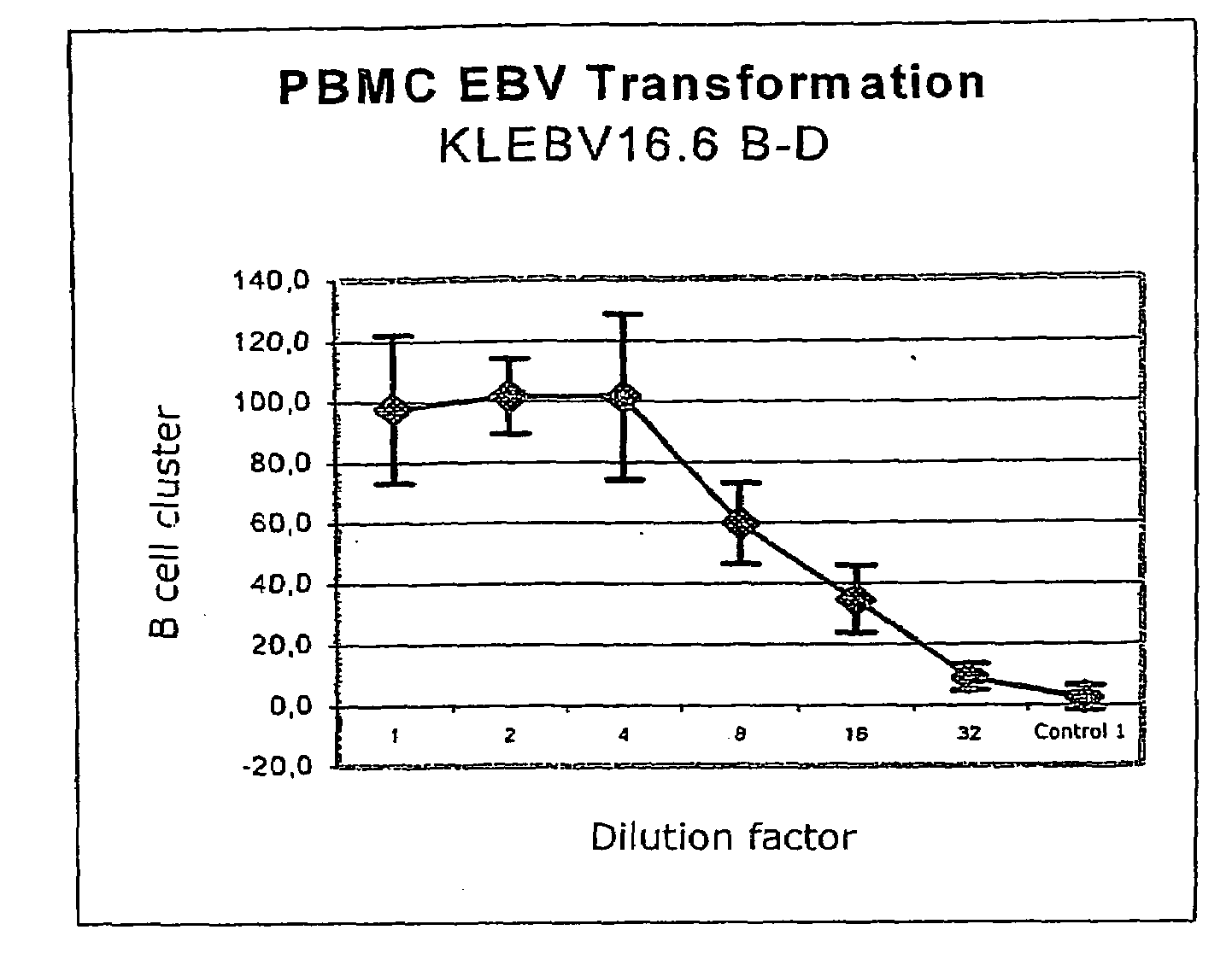
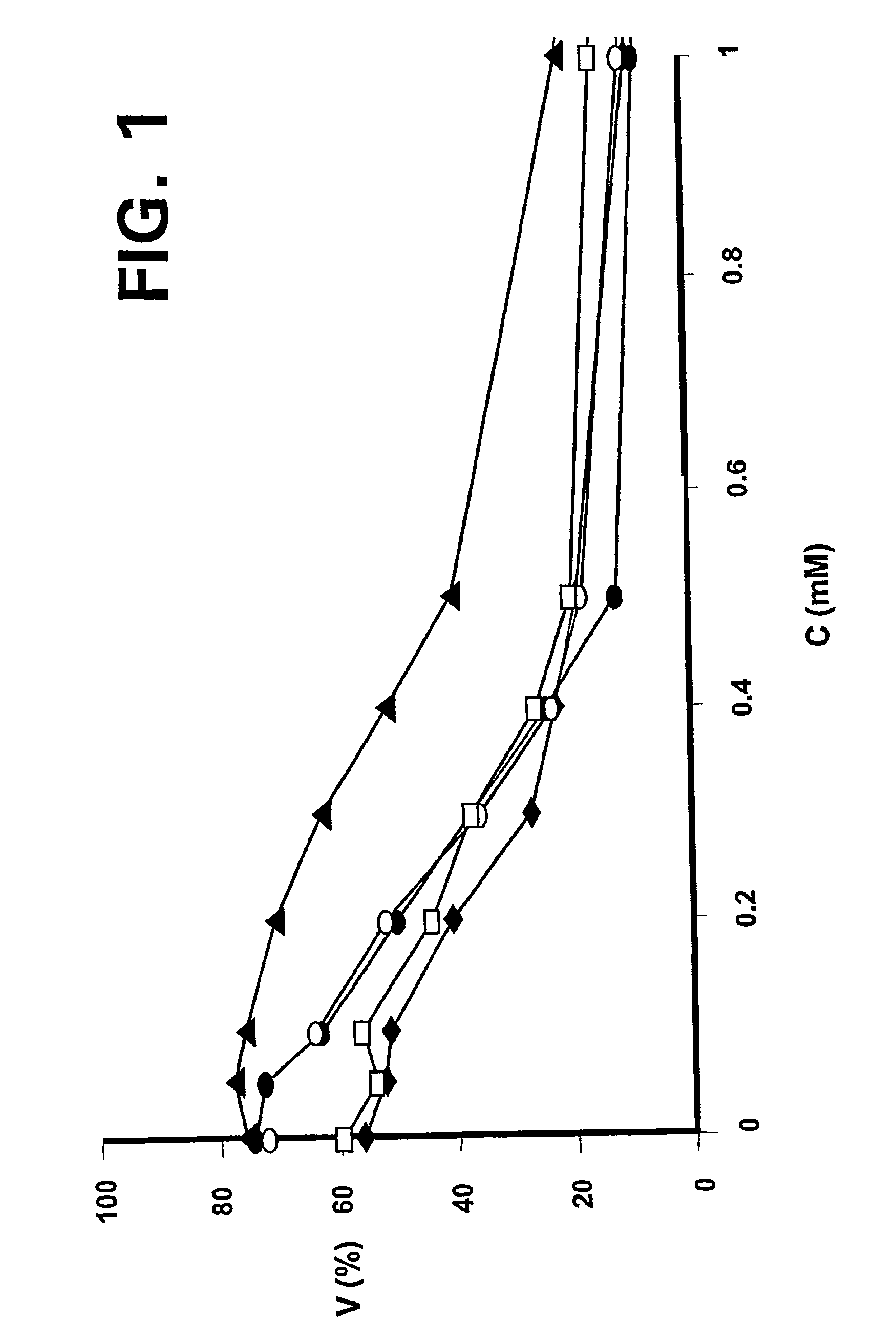
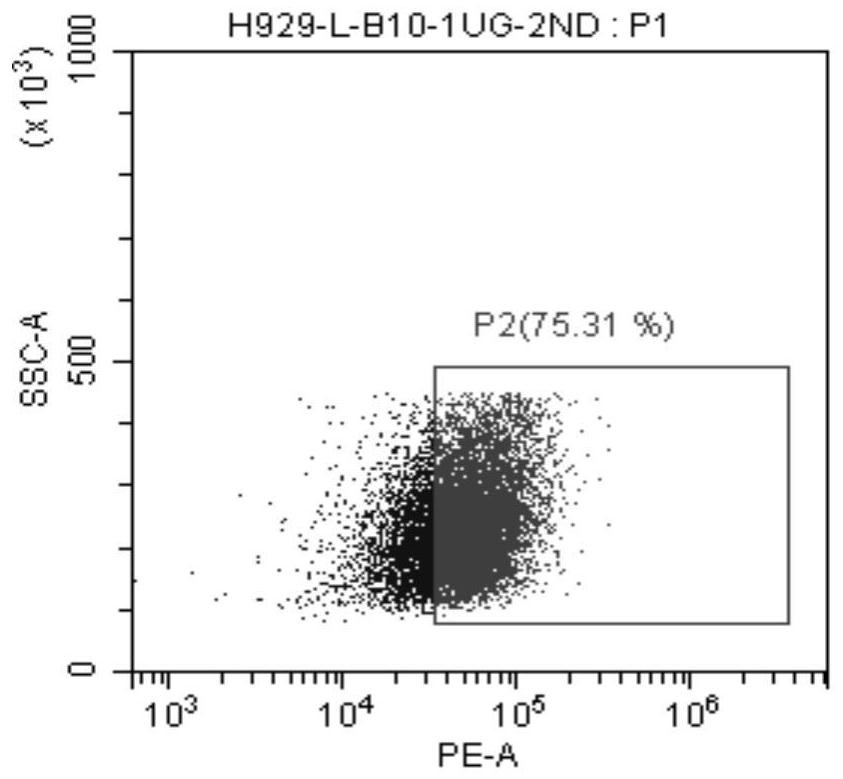
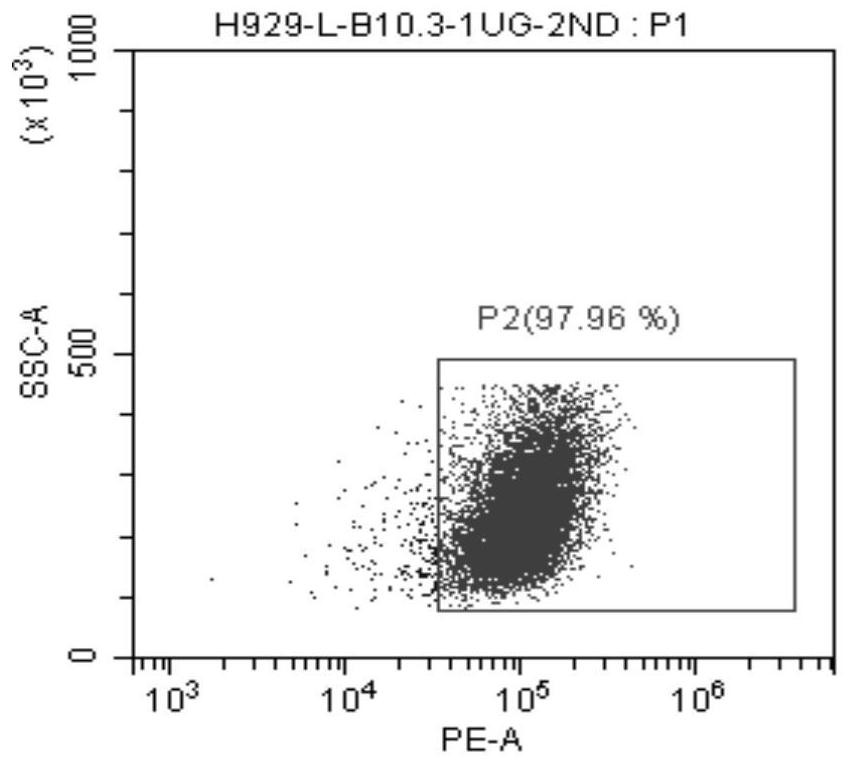
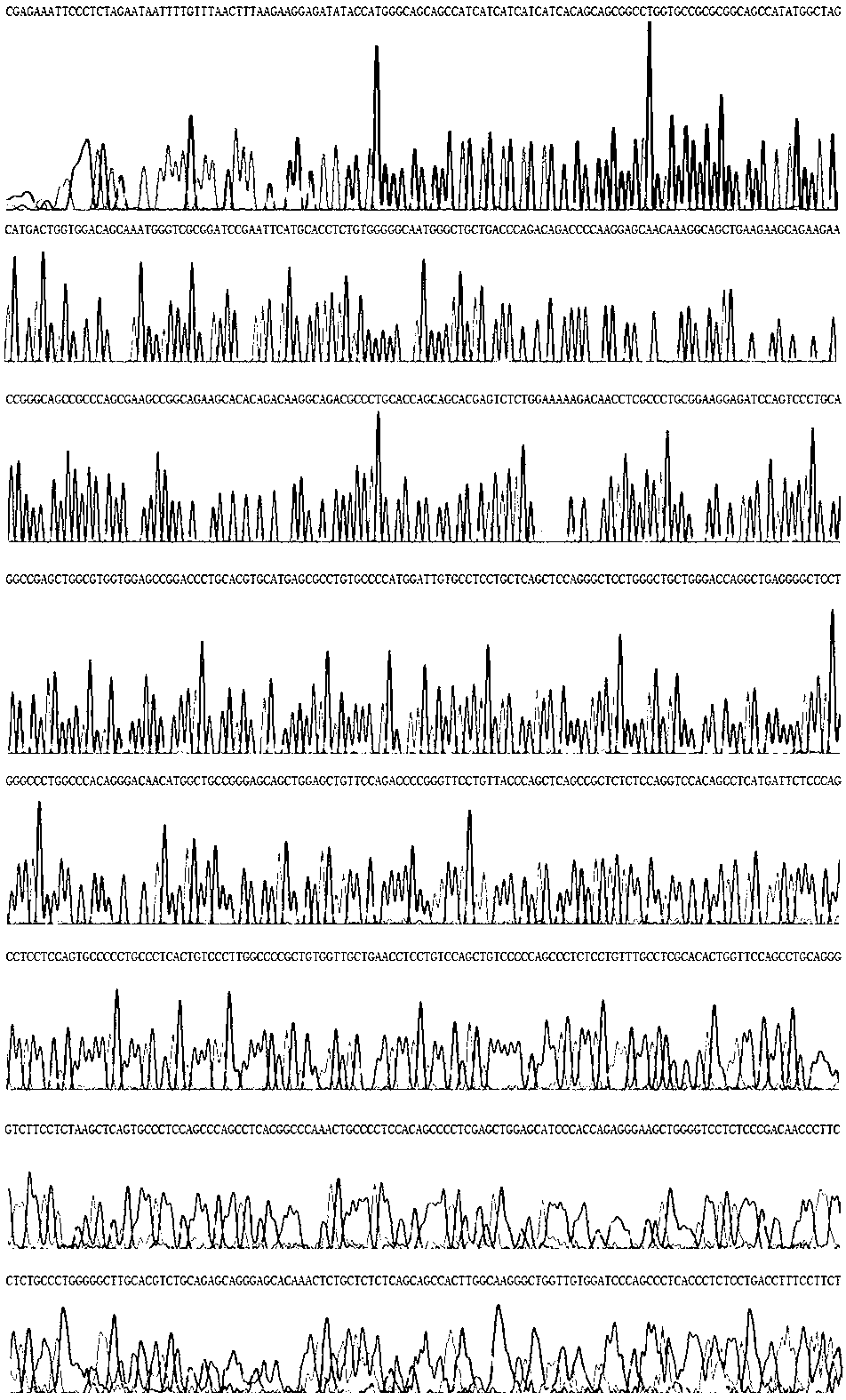
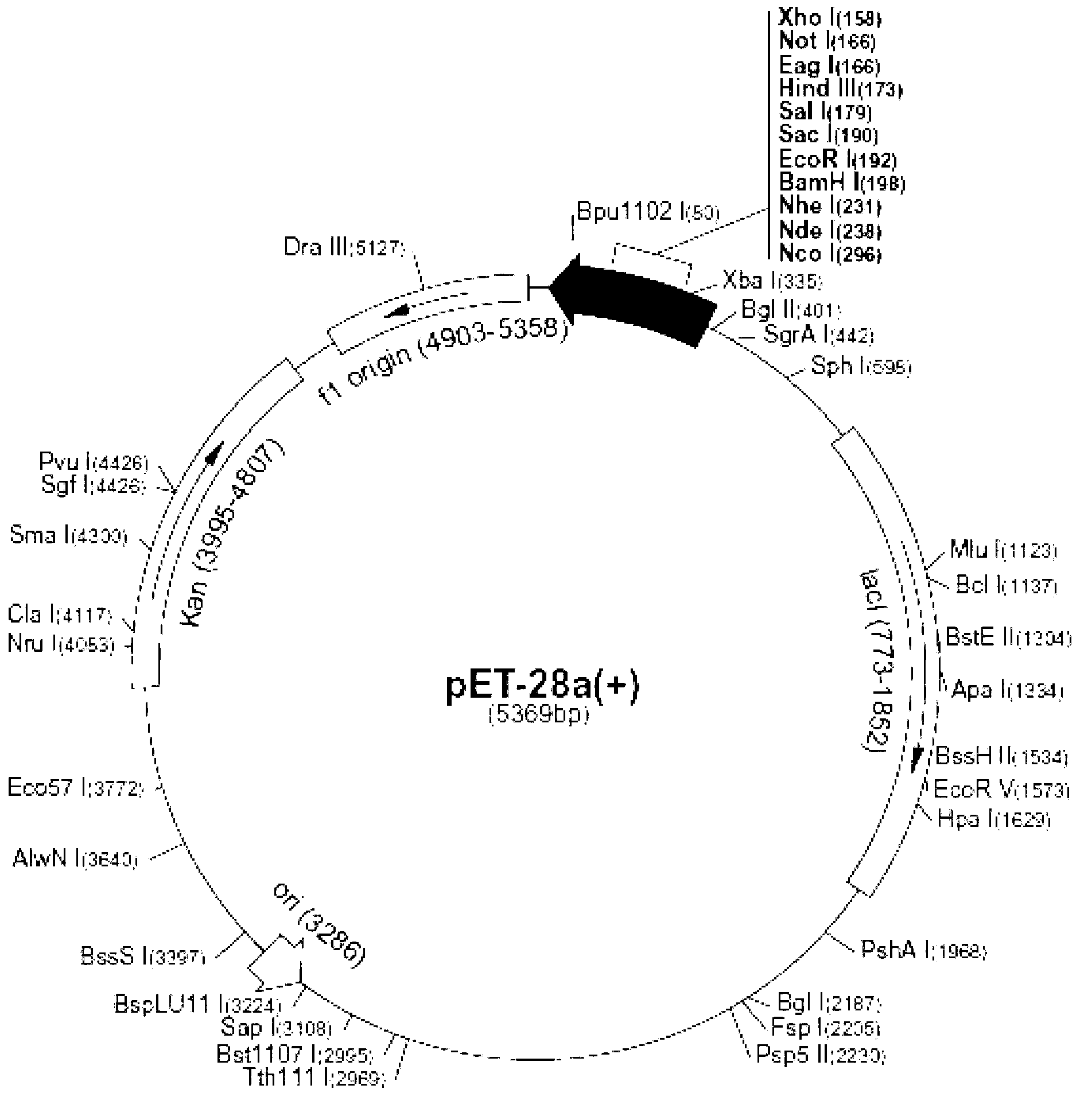
Patents
Literature
67 results about "Human b cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Human B Cells. Different subsets of human B cells are found in the blood with each population classified according to their maturation stage. In a typical adult, approximately 2% of circulating B cells are of the immature type, still undergoing development to become a naïve B cell capable of recognizing antigen.
Chimeric antibody with specificity to human B cell surface antigen
A chimeric antibody with human constant region and murine variable region, having specificity to a 35 kDA polypeptide (Bp35(CD20)) expressed on the surface of human B cells, methods of production, and uses.
Owner:ROYALTY PHARMA FINANCE TRUST
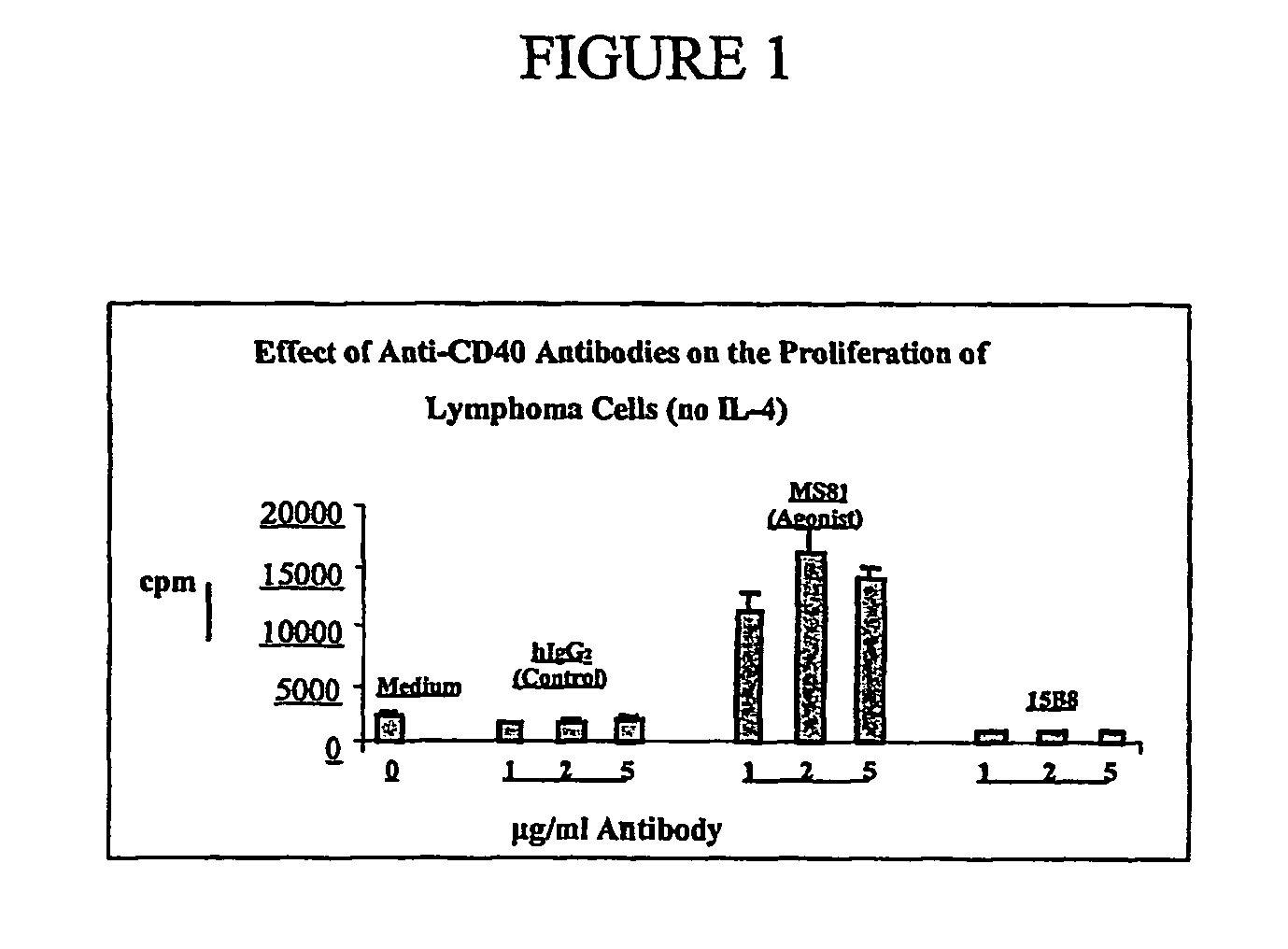
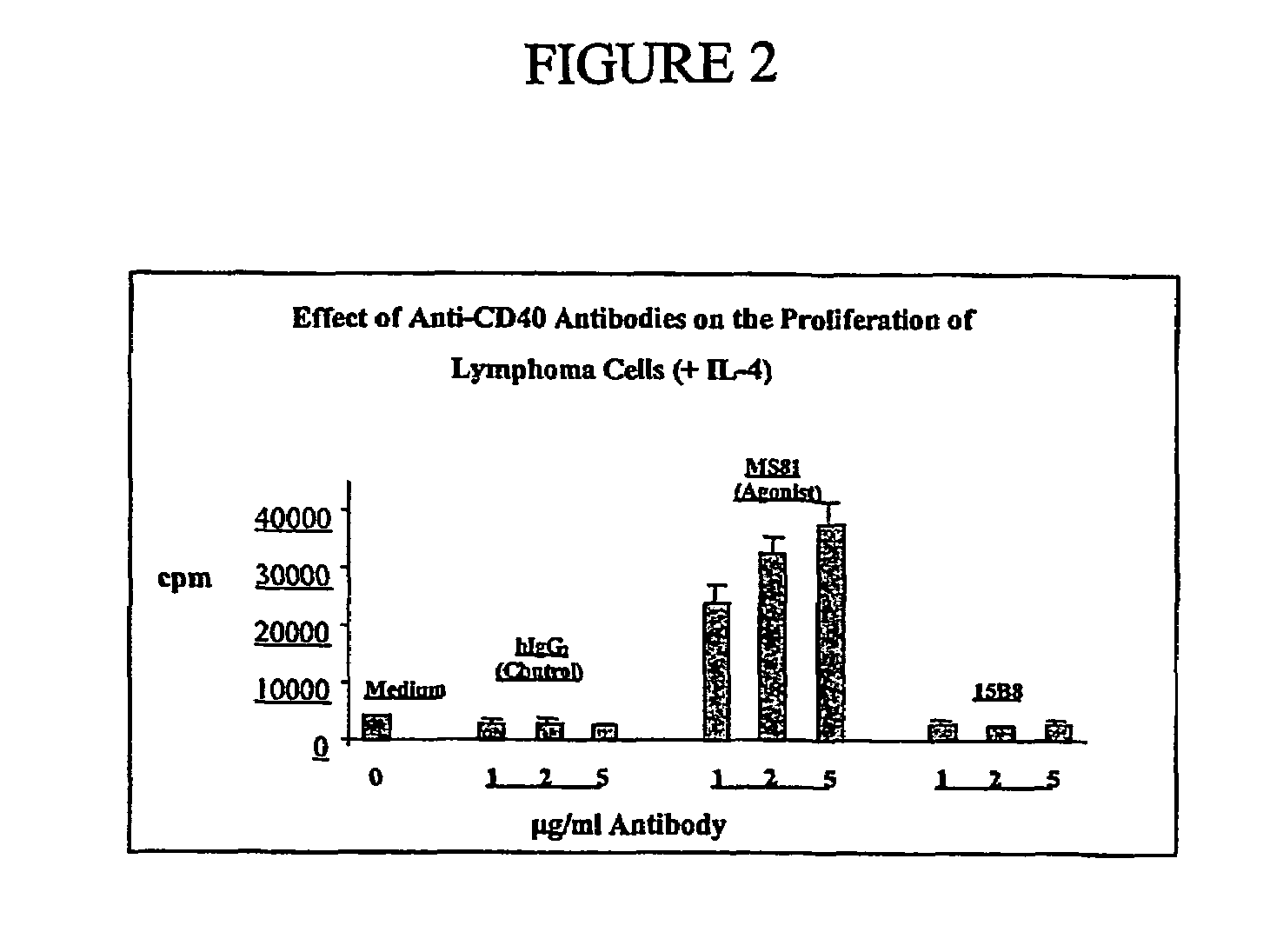
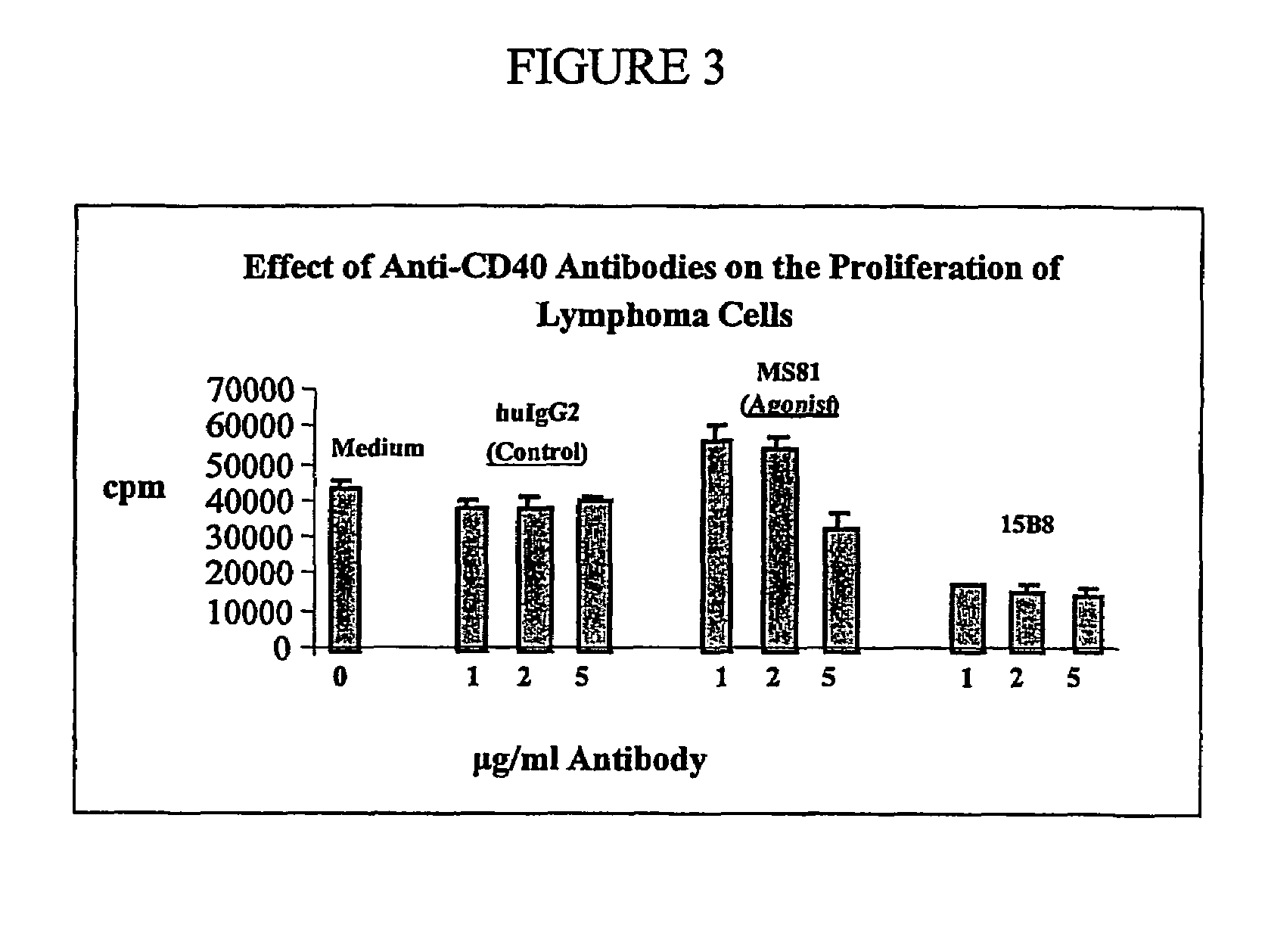
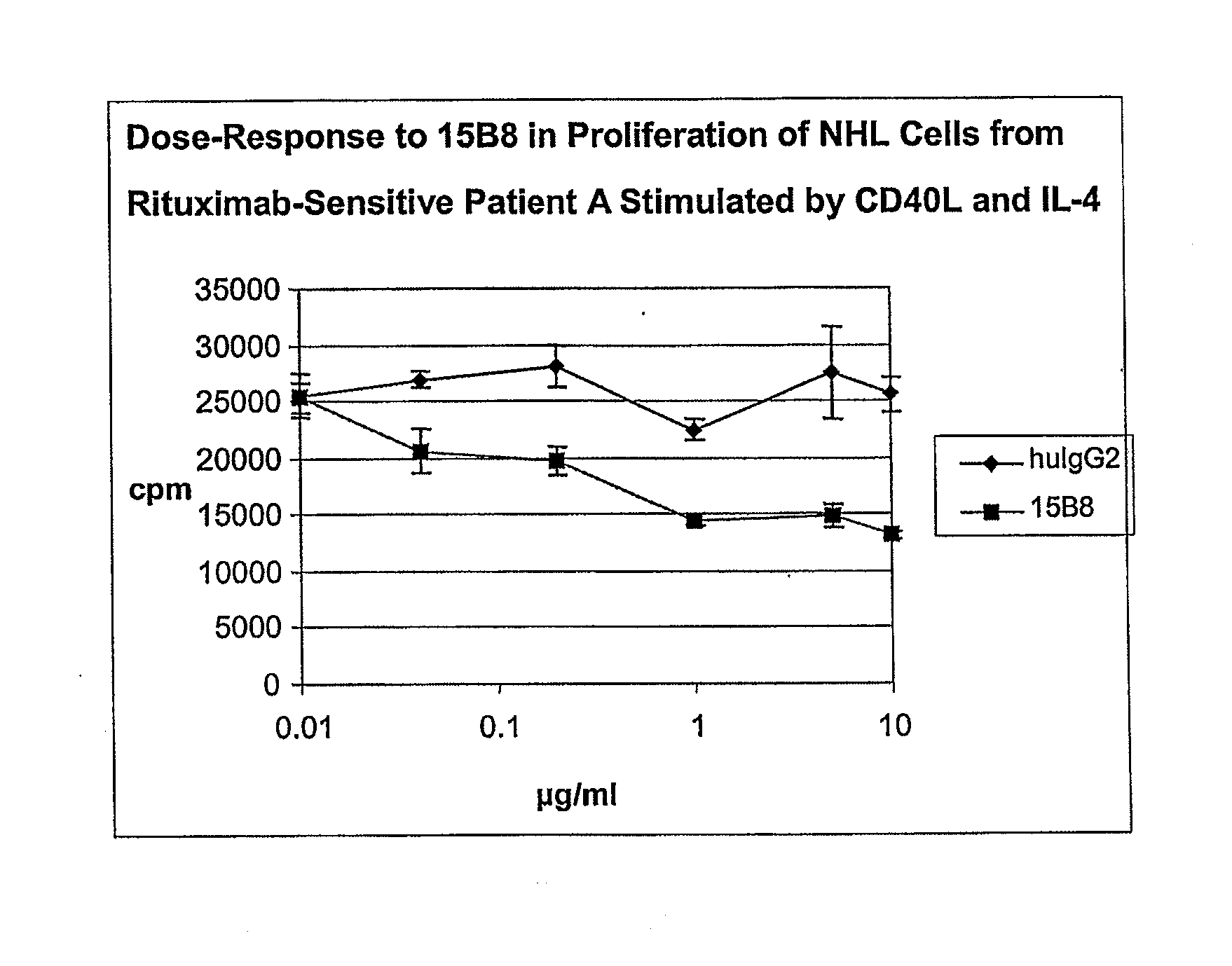
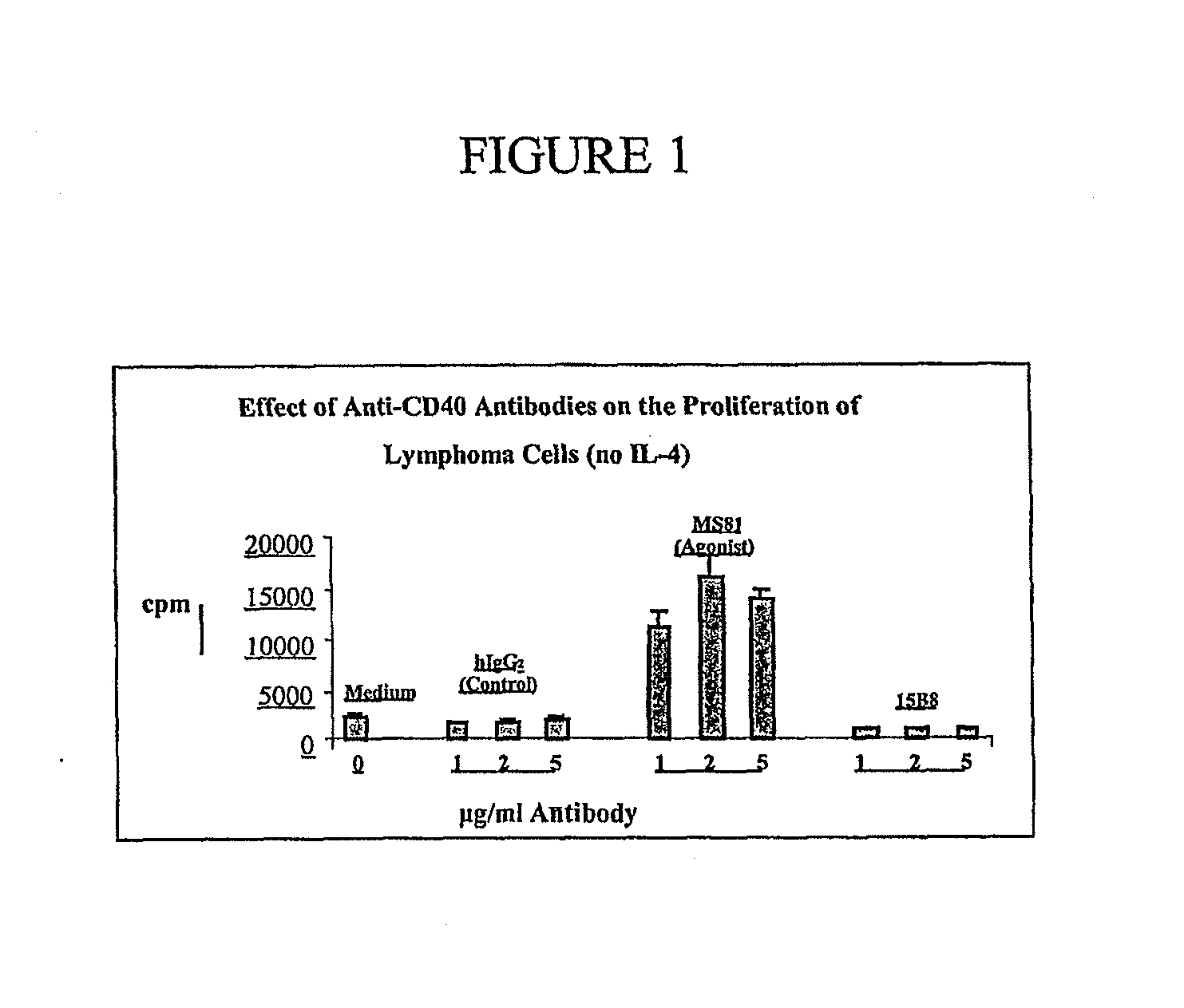
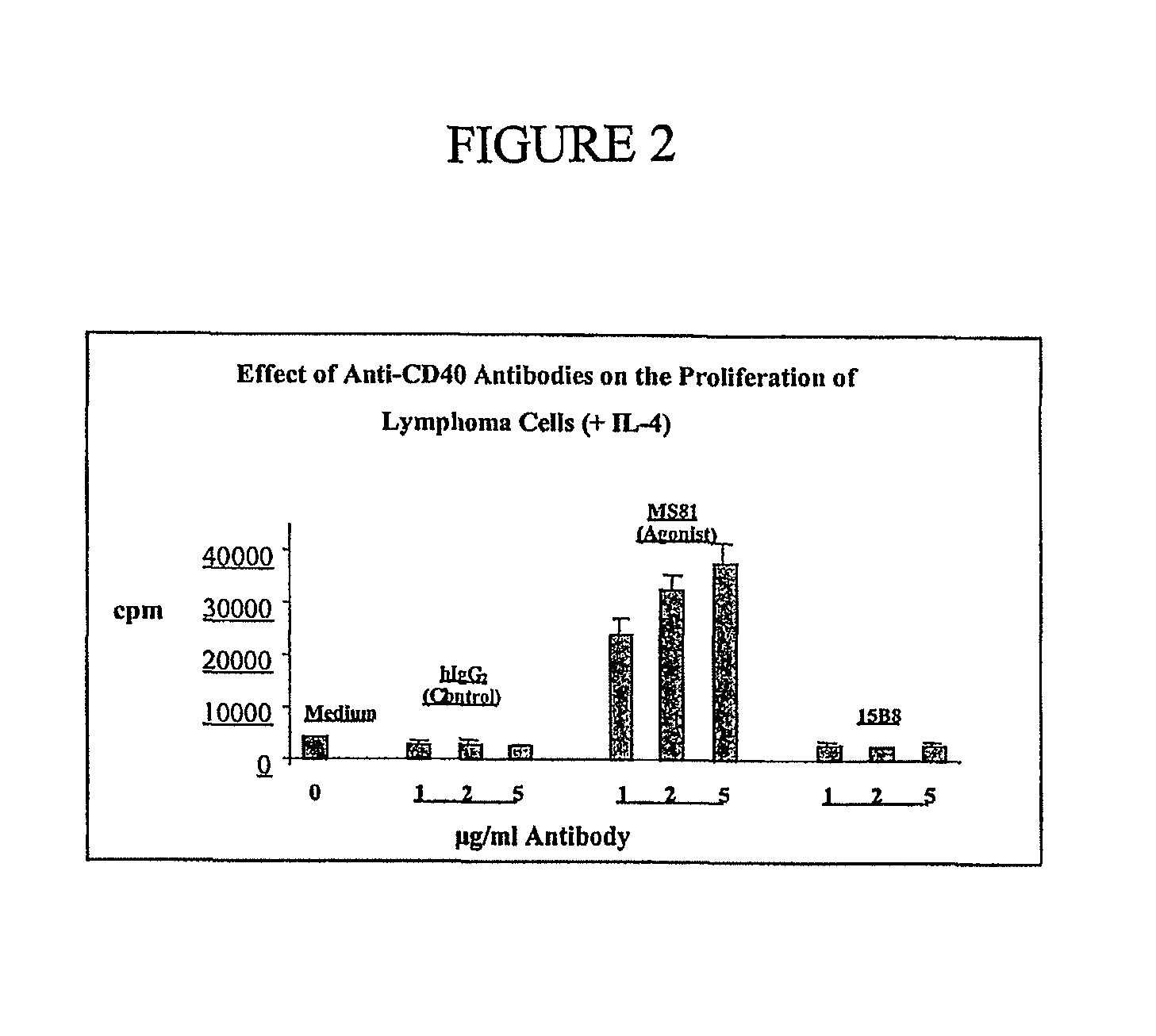
Method for treating an IgE-mediated disease in a patient using anti-CD40 monoclonal antibodies
InactiveUS6899879B2Inhibition of differentiationInhibit growthOrganic active ingredientsVirusesDiseaseEpitope
Methods for preventing or treating an IgE-mediated allergic disease in a patient are presented, the methods comprising administration of a monoclonal antibody capable of binding to a human CD40 antigen located on the surface of a human B cell, wherein binding of the antibody to the CD40 antigen prevents the growth or differentiation of the B cell. Monoclonal antibodies useful in these methods, and epitopes immunoreactive with such monoclonal antibodies are also presented.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Anti-cd20 antibodies and fusion proteins thereof and methods of use
InactiveUS20070020259A1Useful in diagnosisUseful in treatmentAntipyreticAnalgesicsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides humanized, chimeric and human anti-CD20 antibodies and CD 20 antibody fusion proteins that bind to a human B cell marker, referred to as CD20, which is useful for the treatment and diagnosis of B-cell disorders, such as B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases, and methods of treatment and diagnosis.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Chimeric antibody with specificity to human B cell surface antigen
A chimeric antibody with human constant region and murine variable region, having specificity to a 35 kDA polypeptide (Bp35(CD20)) expressed on the surface of human B cells, methods of production, and uses.
Owner:ROBINSON RANDY +2
Anti-CD19 Antibodies
The present invention provides humanized, chimeric and human anti-CD19 antibodies, anti-CD19 antibody fusion proteins, and fragments thereof that bind to a human B cell marker. Such antibodies, fusion proteins and fragments thereof are useful for the treatment and diagnosis of various B-cell disorders, including B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases. In more particular embodiments, the humanized anti-CD19 antibodies may comprise one or more framework region amino acid substitutions designed to improve protein stability, antibody binding and / or expression levels. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the substitutions comprise a Ser91Phe substitution in the hA19 VH sequence.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Methods of therapy for B-cell malignancies using antagonist anti-CD40 antibodies
InactiveUS7288252B2Little or no agonist activityNervous disorderVirusesAntigenAntigen Binding Fragment
Methods of therapy for B-cell malignancies are provided. The methods comprise administering a therapeutically effective amount of an antagonist anti-CD40 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof to a patient in need thereof. The antagonist anti-CD40 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof is free of significant agonist activity when the antibody binds a CD40 antigen on a normal human B cell, exhibits antagonist activity when the antibody binds a CD40 antigen on a malignant human B cell, and can exhibit antagonist activity when the antibody binds a CD40 antigen on a normal human B cell. Antagonist activity of the anti-CD40 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof beneficially inhibits proliferation and / or differentiation of malignant human B cells.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Method for Accelerating Somatic Mutations and use Thereof in Proteomics
The invention relates to a method of accelerating the induction of somatic mutations in vitro. The inventive method comprises the expression of at least one cDNA expressing a modified version of the AID gene in the cells to be mutated, in culture conditions and a medium that are suited thereto, said modified version resulting from an AID gene in which the three hydrophobic amino acids, leu189, phe193 and leu196, have been replaced by means of alanine mutations in each case. The invention can be used to induce mutations in Burkitt's lymphoma BL2. The invention can also be used to induce mutations in the immunoglobulin genes of immortalised antibody-producing cells, such as mouse hybridoma cells, human hybridoma cells or human B-cell lines immortalised by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Owner:INST NECKER
Preparation method of human cytokine-induced killer cells
InactiveCN102732481APromote proliferationRaise the ratioBlood/immune system cellsHybrid peptidesPeripheral blood mononuclear cellCytotoxicity
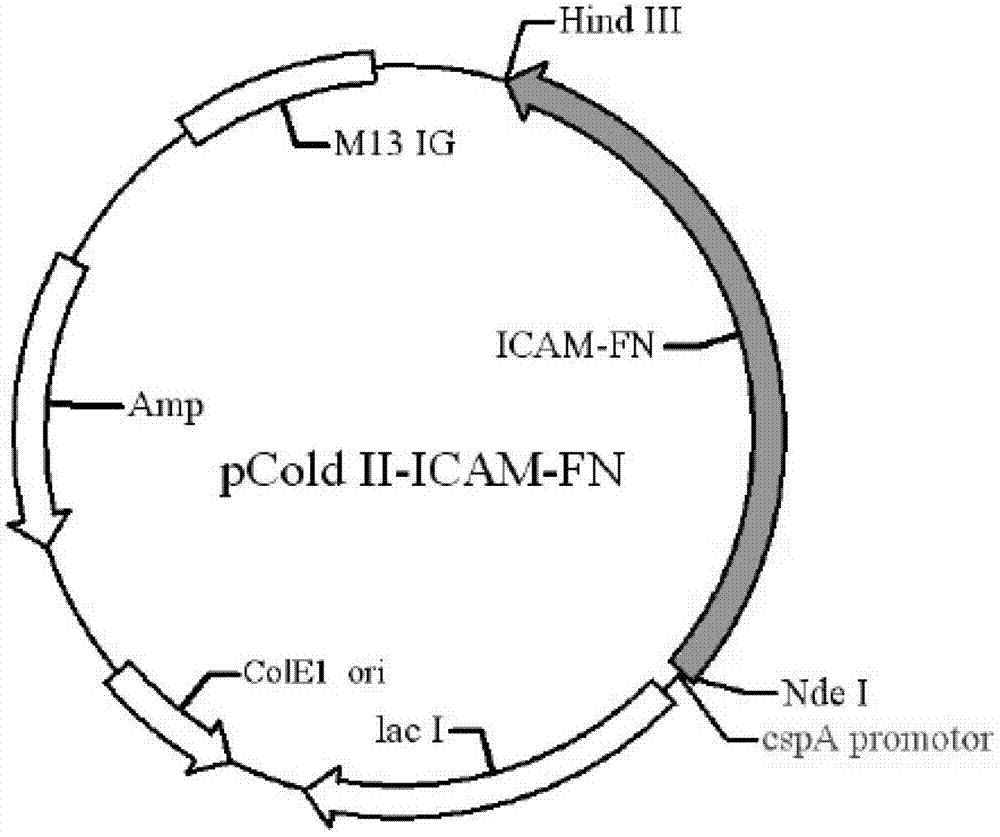
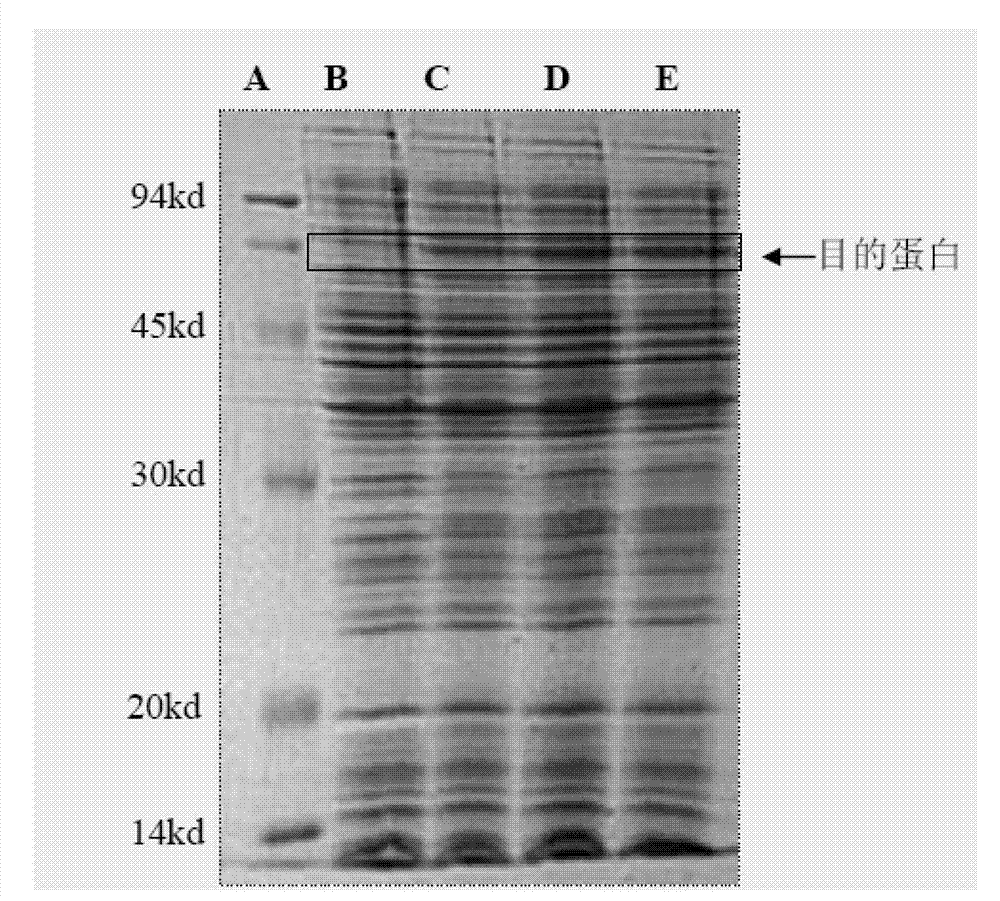
The invention discloses a preparation method of human cytokine-induced killer cells, comprising the following steps: coating a cell culture flask with a coating buffer containing effective amount of fusion protein and human CD3 monoclonal antibody before culturing precursor cells of human CIK cells, and adding the human CD3 monoclonal antibody in the whole process of inducing and culturing the human CIK cells, wherein the fusion protein is human intercellular adhesion molecule-1 functional domain and human fibronectin functional domain fusion protein, and the concentration of the human CD3 monoclonal antibody in the cell culture solution is lower than the concentration of the human CD3 monoclonal antibody in the coating buffer. According to the invention, ex-vivo expansion efficiency of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the proportion of CD3 / CD56 double positive cells in the CIK cells are significantly raised, the cytotoxicity activity of the CIK cells is enhanced, thus the effect of cellular immunity treatment is raised.
Owner:SHENZHEN YOUNGCELL BIO TECH
ULBP antibodies
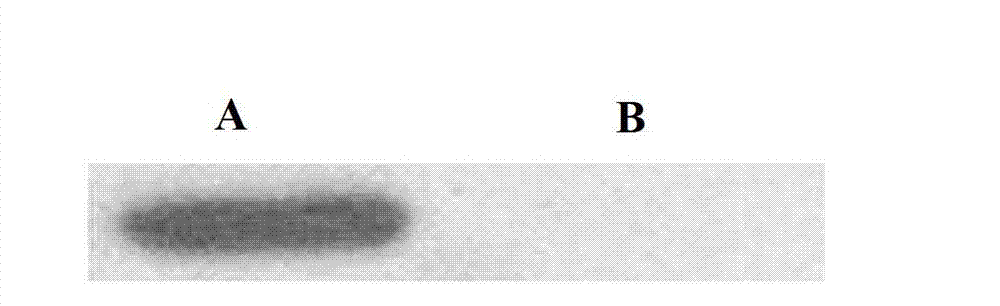
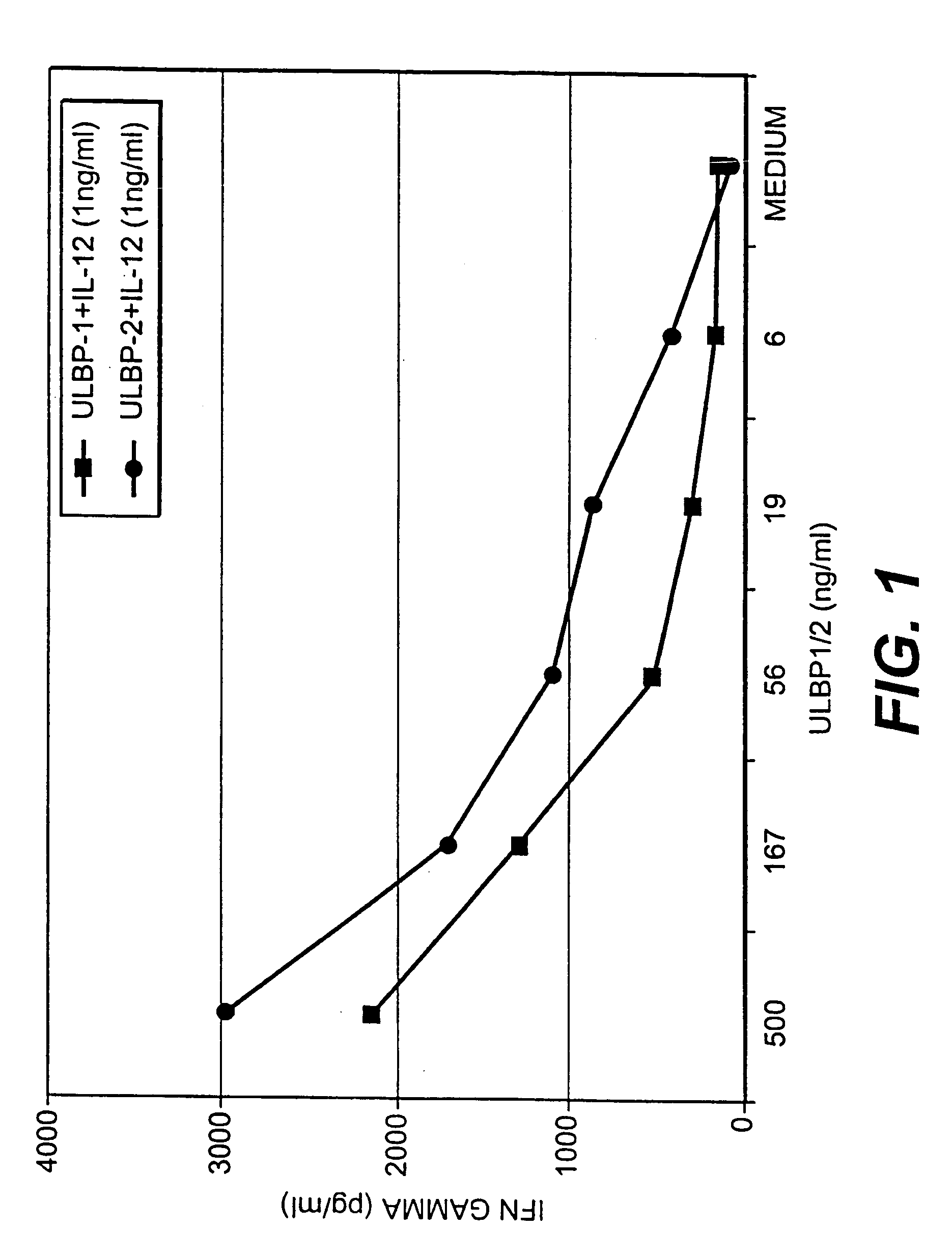
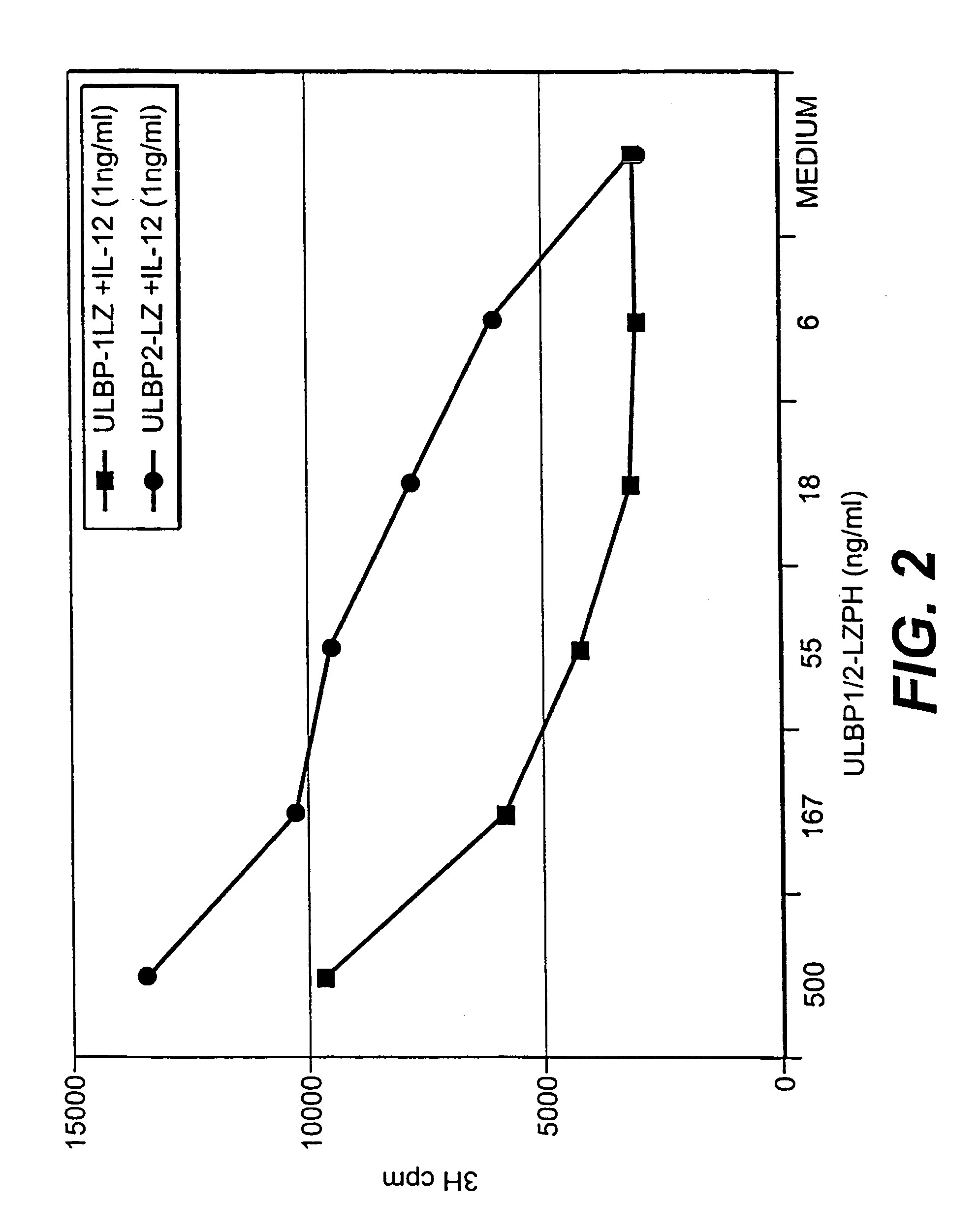
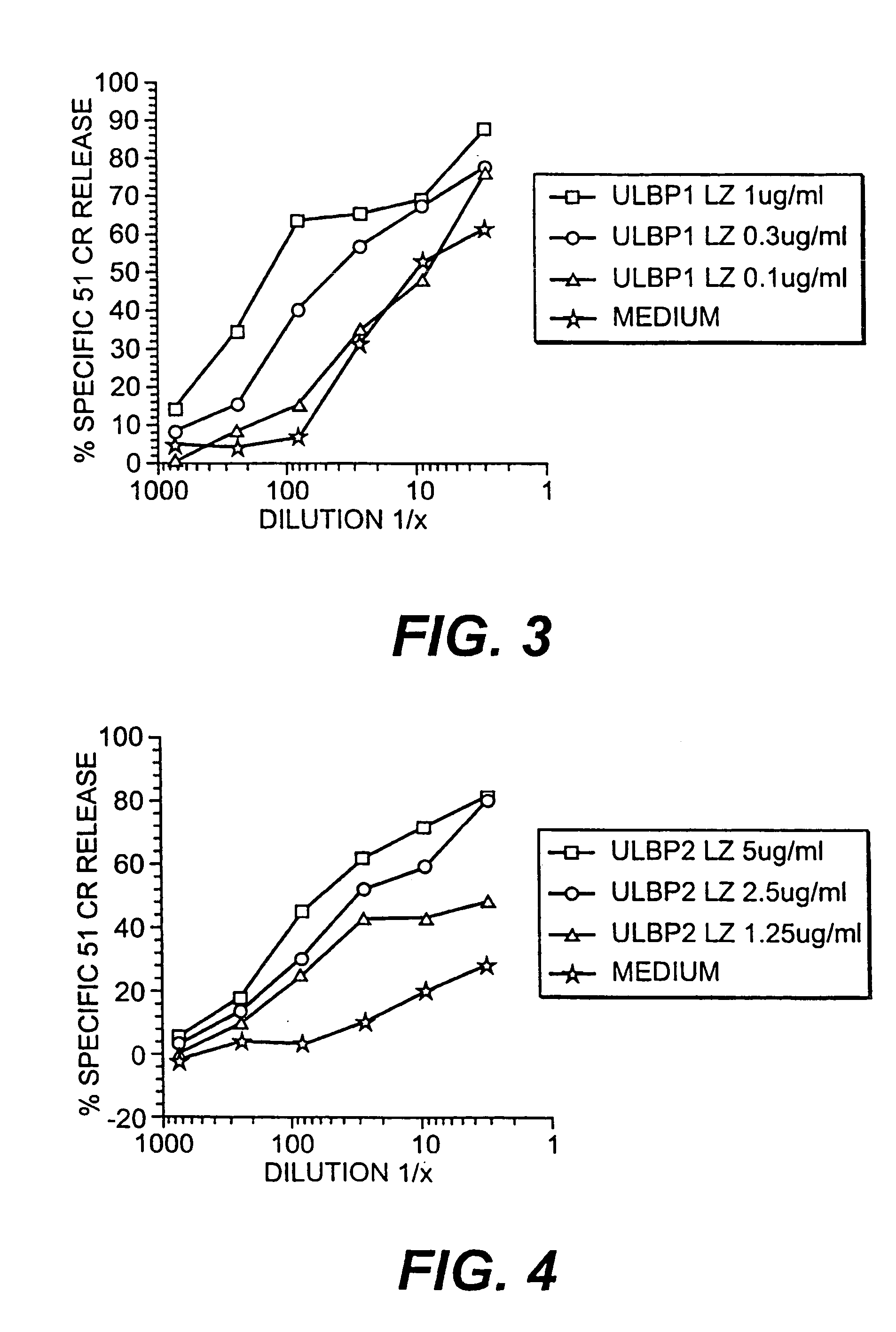
The invention is directed to purified and isolated novel ULBP polypeptides, the nucleic acids encoding such polypeptides, processes for production of recombinant forms of such polypeptides, antibodies generated against these polypeptides, fragmented peptides derived from these polypeptides, and the uses of the above. ULBP polypeptide can be found on the surface of human B cell lymphomas. Mammalian forms of ULBP polypeptide in isolated or purified forms are provided. In addition, isolated nucleic acids encoding ULBP polypeptides and expression vectors comprising a cDNA encoding ULBP polypeptides are provided. The ULBP polypeptides can be isolated or synthesized and used to prepare antibodies, and in particular monoclonal antibodies, against the polypeptides. The antibodies, in turn, are useful for detecting the presence of ULBP polypeptides in human cell samples, which can be correlated with the existence of a malignant condition in a patient. ULBP polypeptides stimulate IFN-γ production, NK cell proliferation, and CTL activity.
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
Method of promoting b-cell proliferation and activation with CD40 ligand and cyclosporin
InactiveUS6465251B1Efficient inductionModulate immune responseDead animal preservationArtificial cell constructsAntigenCyclosporins
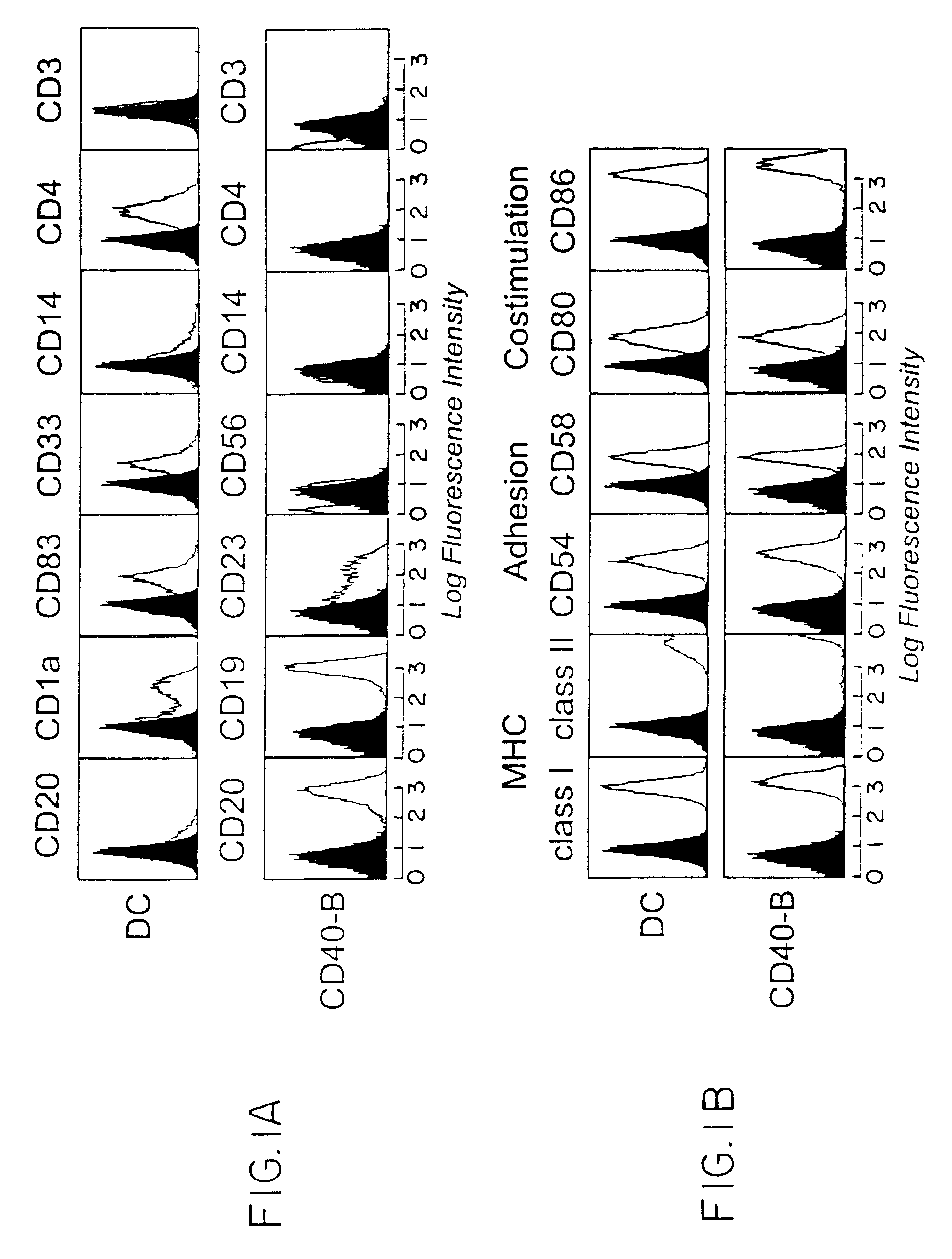
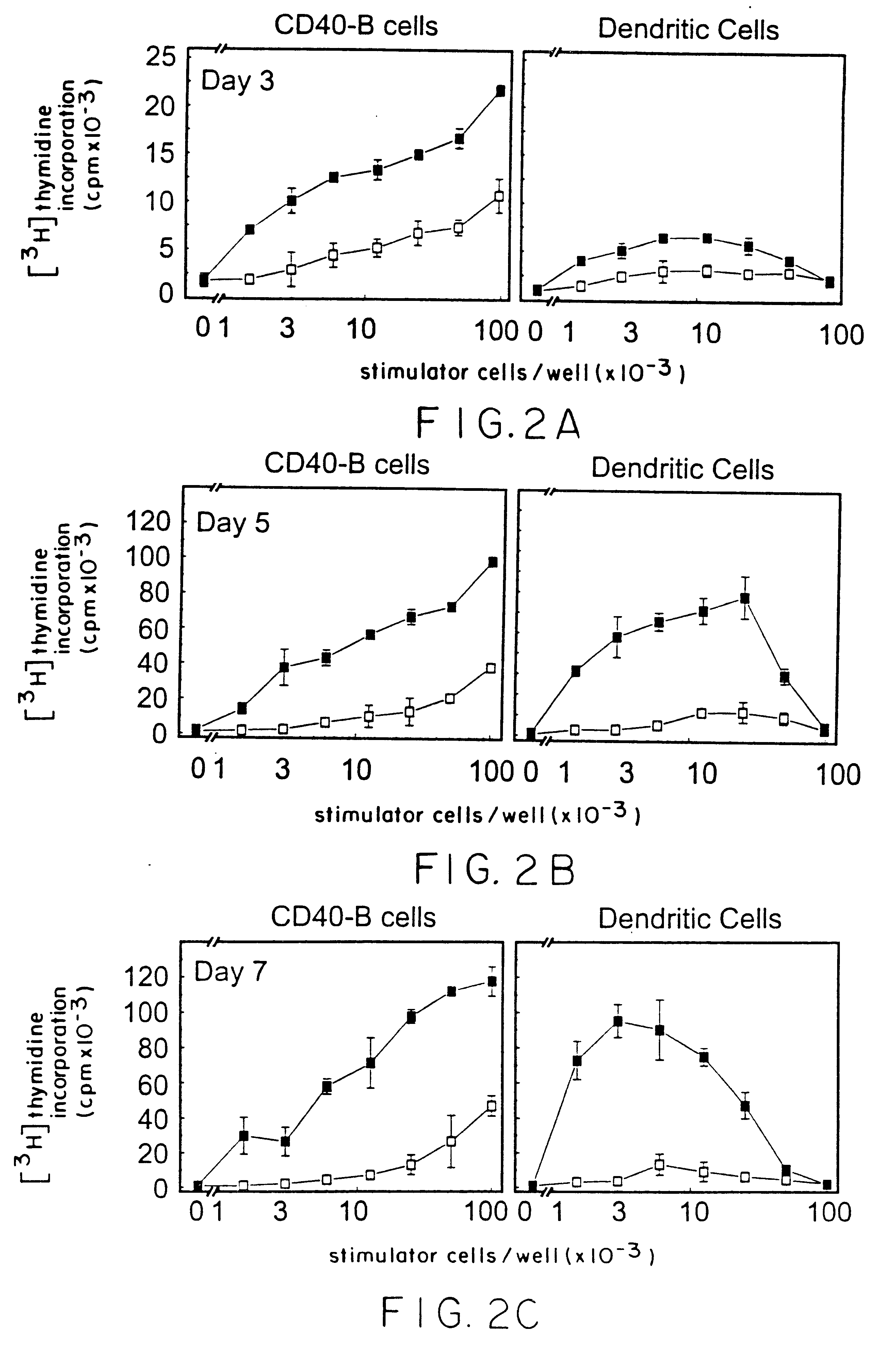
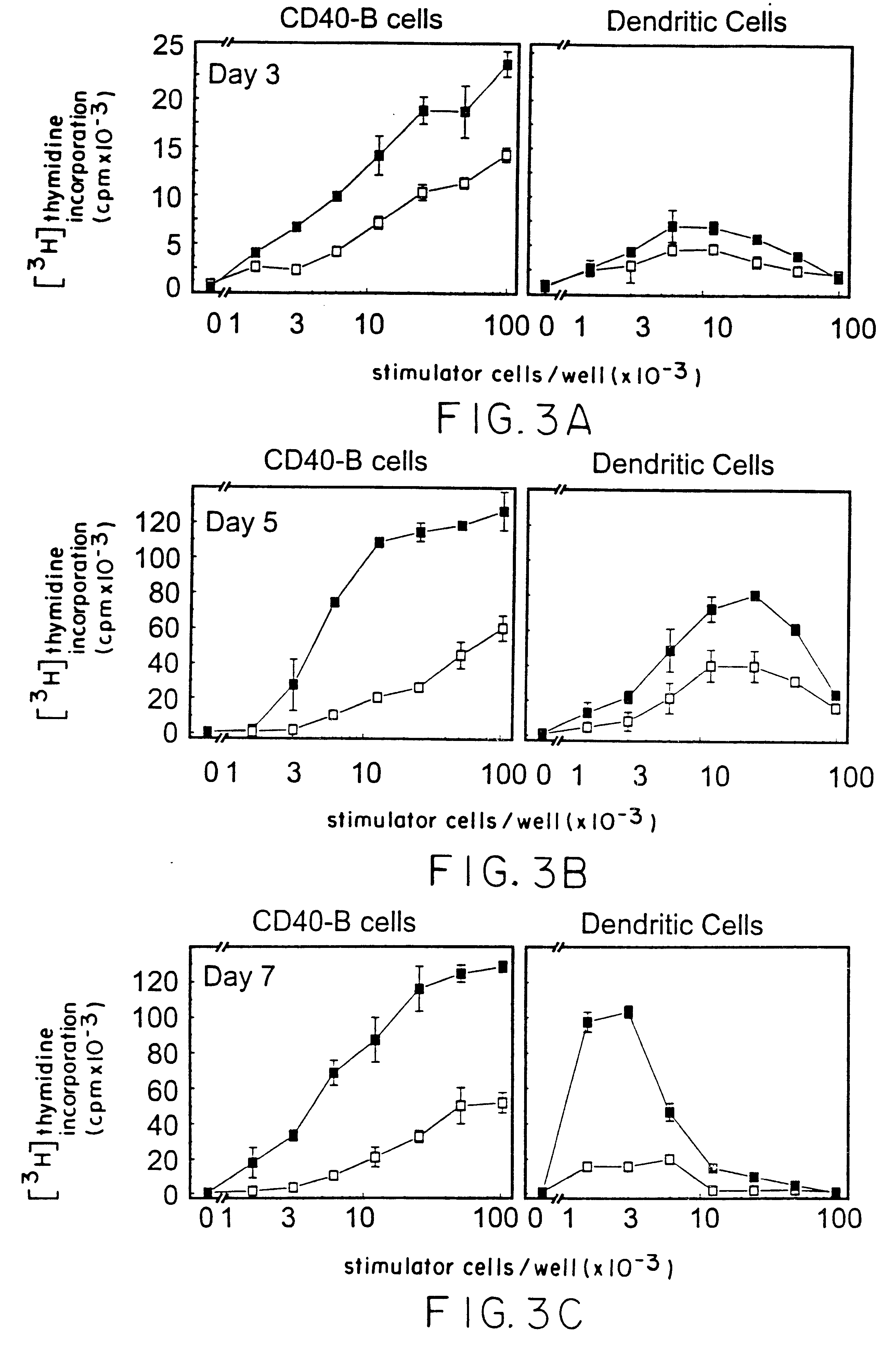
We teach a strategy to obtain large quantities of desired APCs, activated B cells, which are superior in their capacity to present tumor protein antigen in a multiadministration protocol. Human B cells can be obtained from peripheral blood in large numbers. These cells can be activated in vitro by coculture with CD40L (CD40-B cells) and an immunosuppressive agent such as cyclosporin A. They can expanded up to 1x103 to 1x104 fold in 2 weeks or 1x105 to 1x106 fold in 2 months. We demonstrate these cells are most efficient APCs comparable to DCs in stimulating allogeneic CD4+ CD45RA+, CD4+ CD45RO+, and CD8+ T cells. In contrast to DCs, CD40-B cells are fully functional even in the presence of immunosuppressive cytokines such as IL-10 and TGFbeta.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
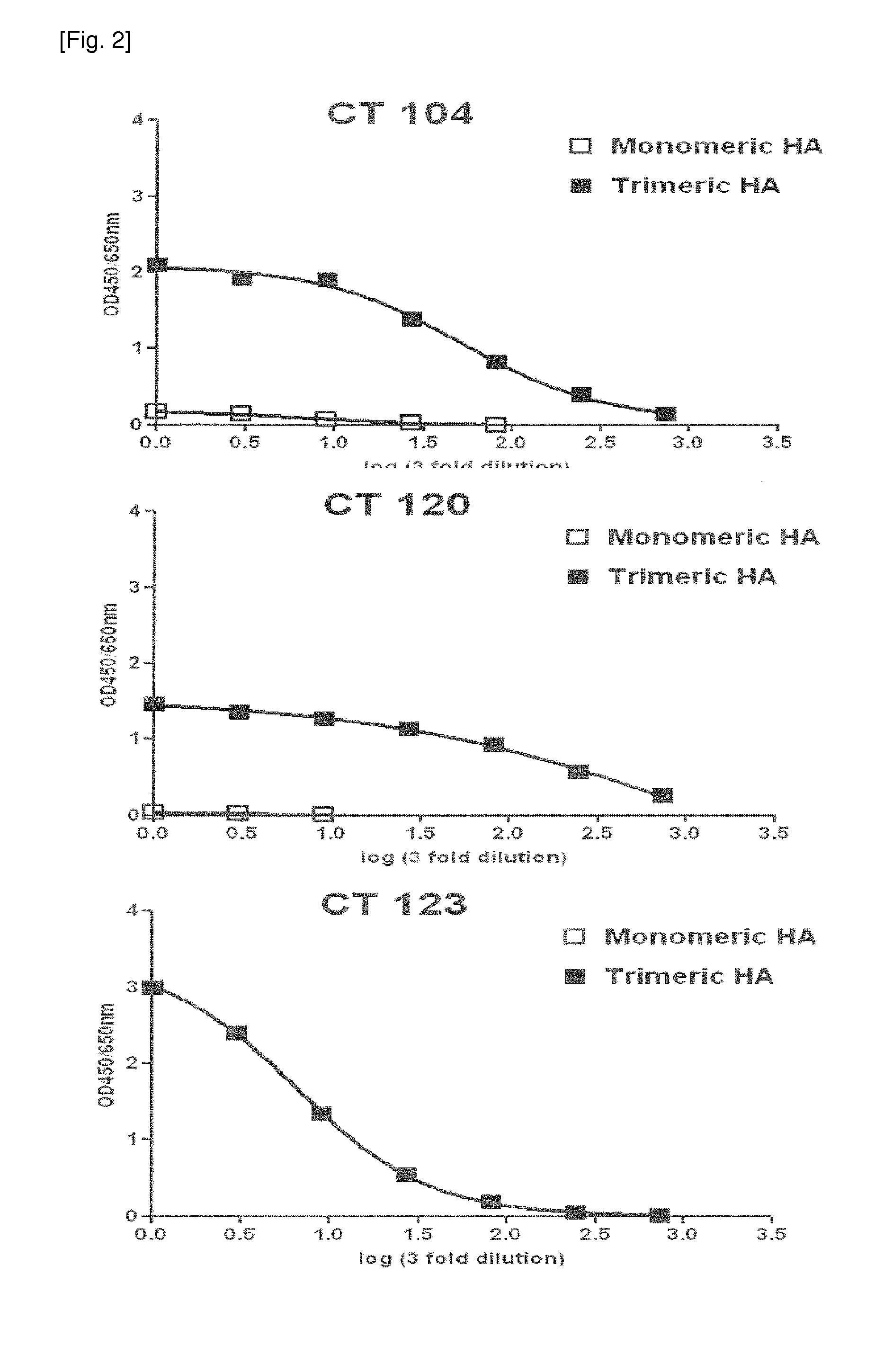
Human monoclonal antibodies derived from human b cells and having neutralizing activity against influenza a viruses
ActiveUS20130004505A1Prevention and treatmentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementVirologyInfluenza a
The present invention relates to human monoclonal antibodies derived from human B cells present in the blood of patients who had recovered from infection with influenza A viruses, wherein the monoclonal antibodies have neutralizing activity against influenza A viruses. The anti-influenza A virus monoclonal antibody of the present invention has binding and neutralizing activities against at least one influenza A virus selected from the group consisting of influenza A virus H1, H2 and H5 subtypes, and thus it is useful for the prevention and treatment of a disease caused by the influenza A virus and is also useful for diagnosis of influenza A virus infection.
Owner:CELLTRION INC
Methods of therapy for b-cell malignancies using antagonist Anti-cd40 antibodies
Methods of therapy for B-cell malignancies are provided. The methods comprise administering a therapeutically effective amount of an antagonist anti-CD40 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof to a patient in need thereof. The antagonist anti-CD40 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof is free of significant agonist activity when the antibody binds a CD40 antigen on a normal human B cell, exhibits antagonist activity when the antibody binds a CD40 antigen on a malignant human B cell, and can exhibit antagonist activity when the antibody binds a CD40 antigen on a normal human B cell. Antagonist activity of the anti-CD40 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof beneficially inhibits proliferation and / or differentiation of malignant human B cells.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Anti-cd20 monoclonal antibodies
InactiveUS20110263825A1High binding affinityInhibit cell activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsImmunological disordersAntigenCD20
It is intended to provide a monoclonal antibody having a growth inhibitory activity against a cell having a human CD20 antigen which is produced by using, as immunogens, a human B cell line expressing the human CD20 antigen and a cell line originating in a non-human animal, which is different from an animal to be immunized and has been transformed with human CD20 DNA, and a monoclonal antibody obtained by chimerization or humanization of the above-described monoclonal antibody. These monoclonal antibodies show biological activities suitable for using as drugs.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
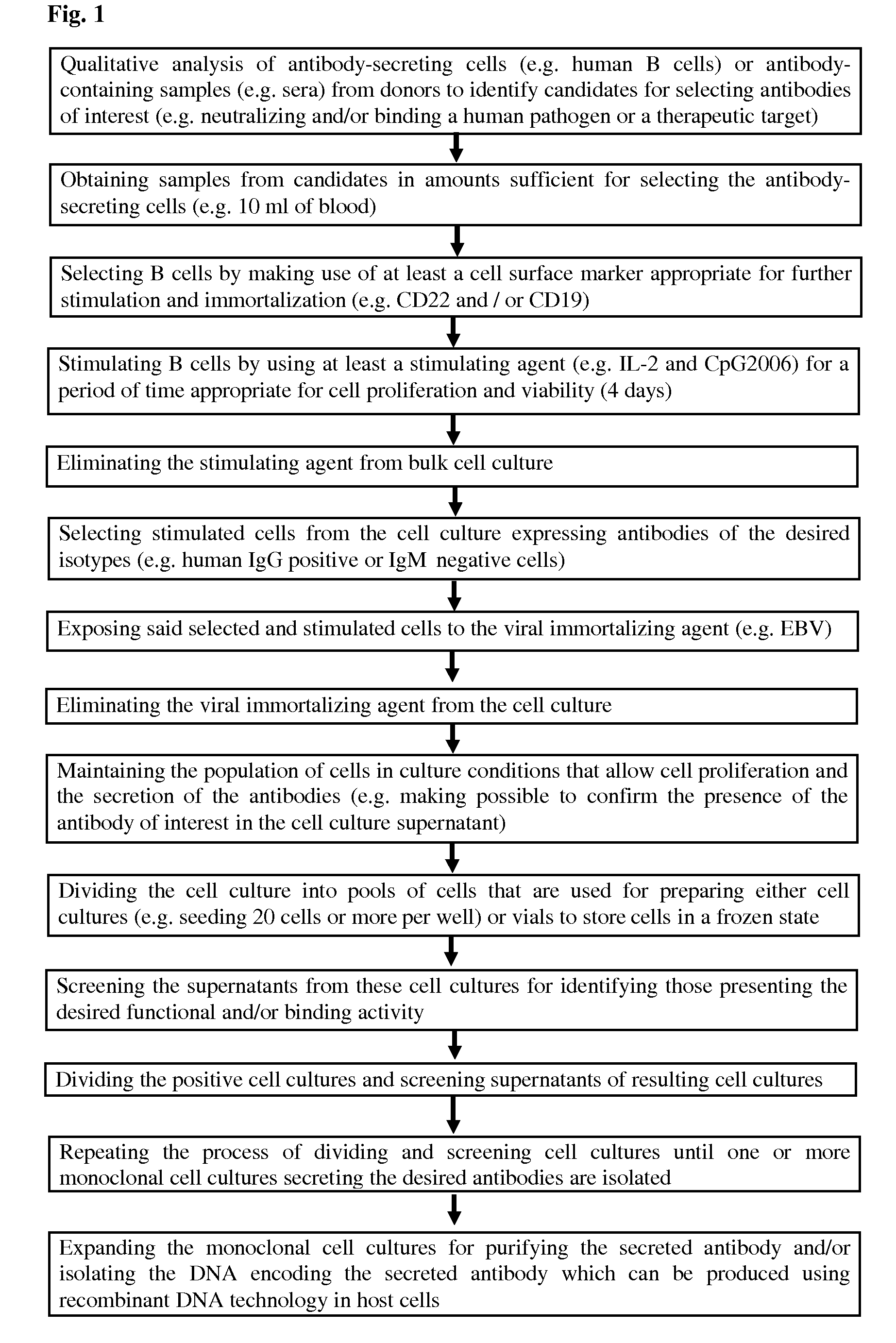
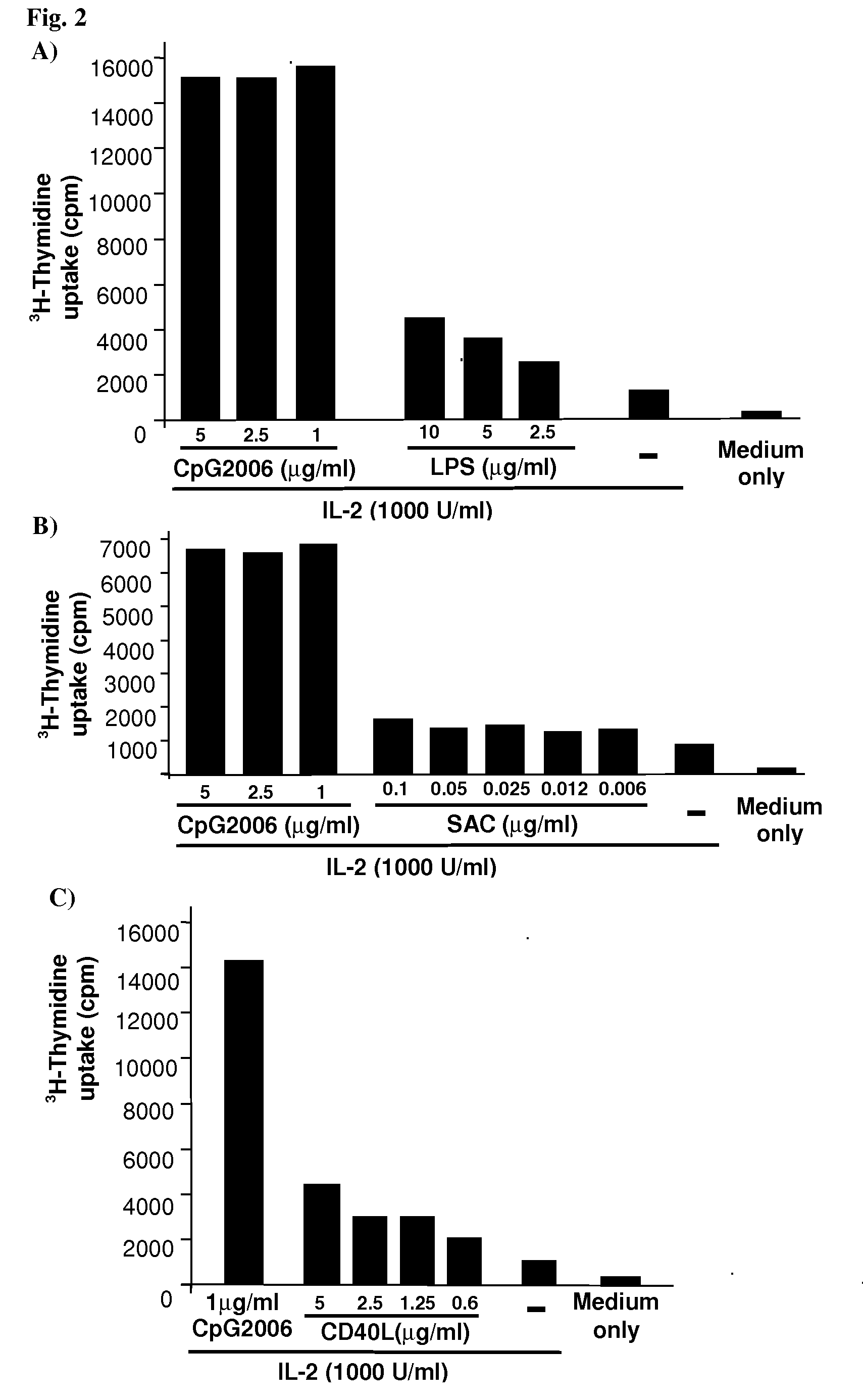
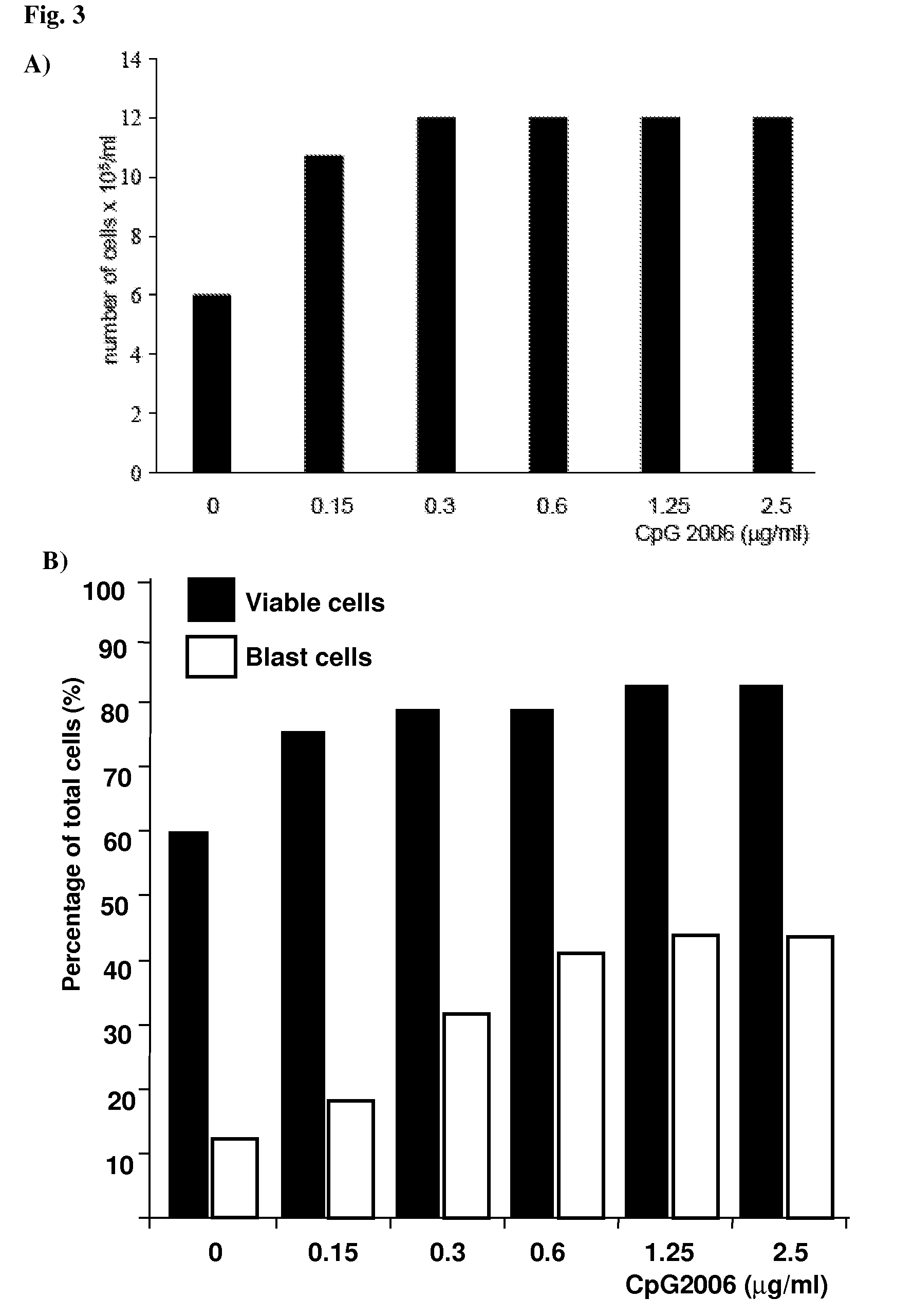
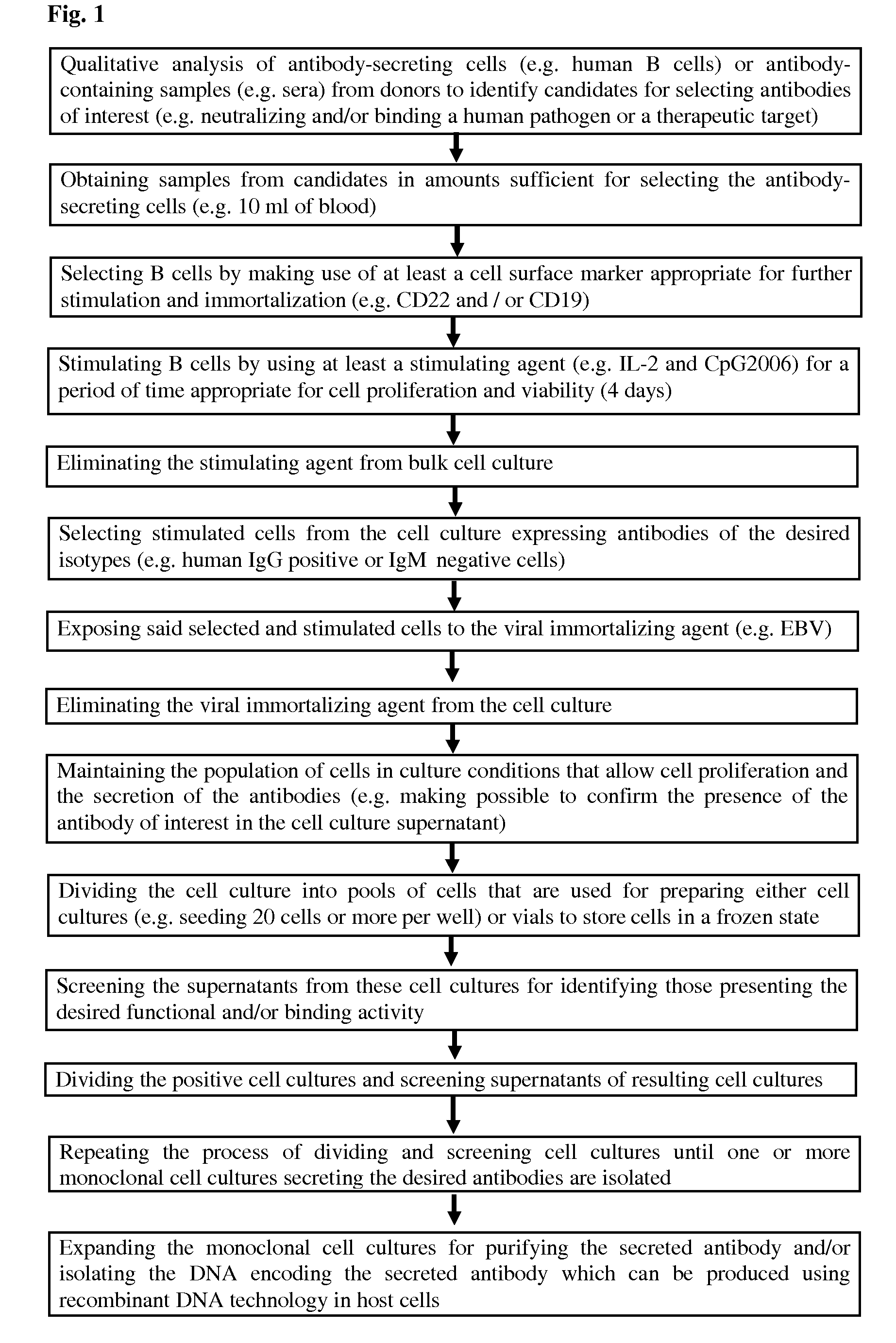
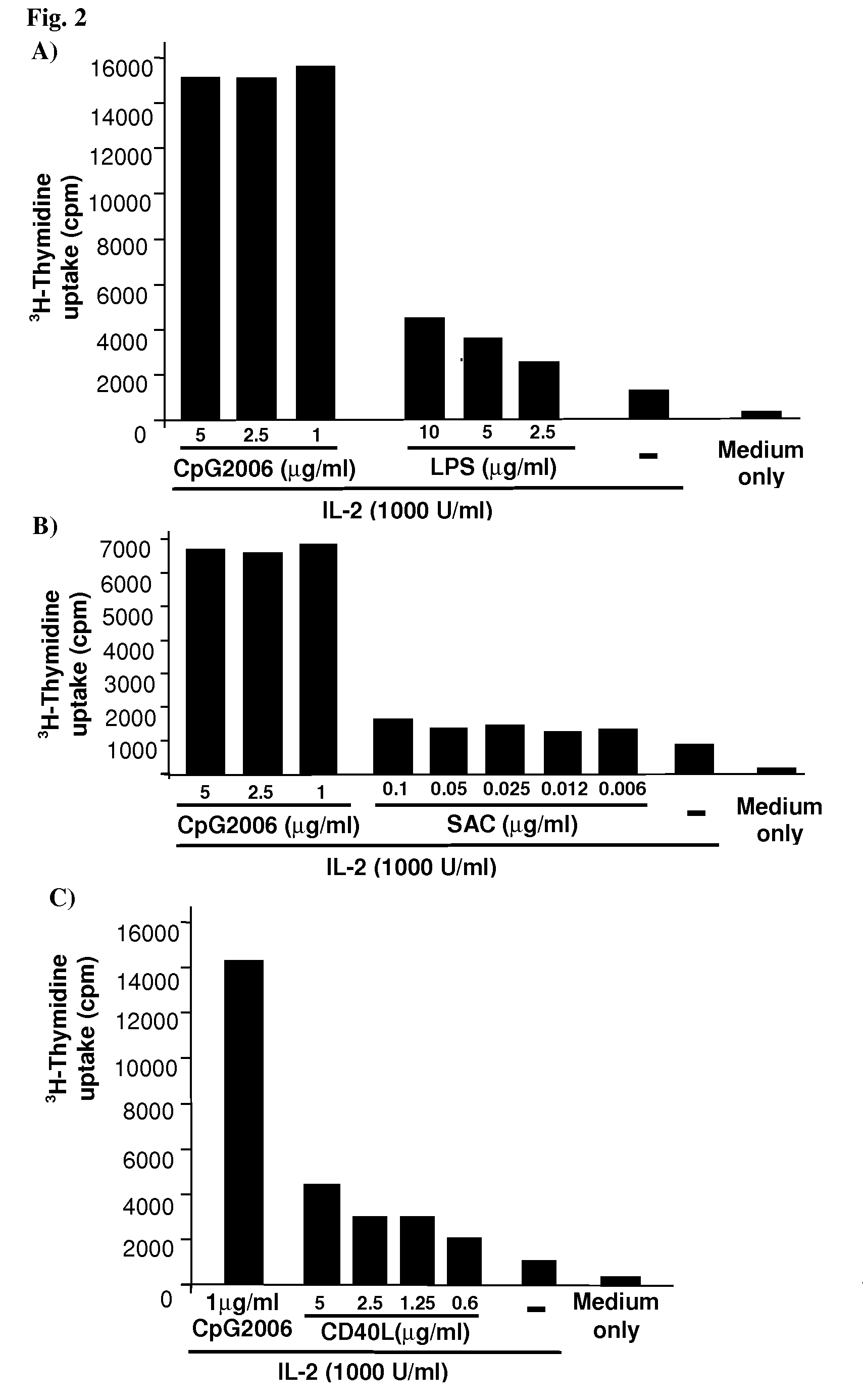
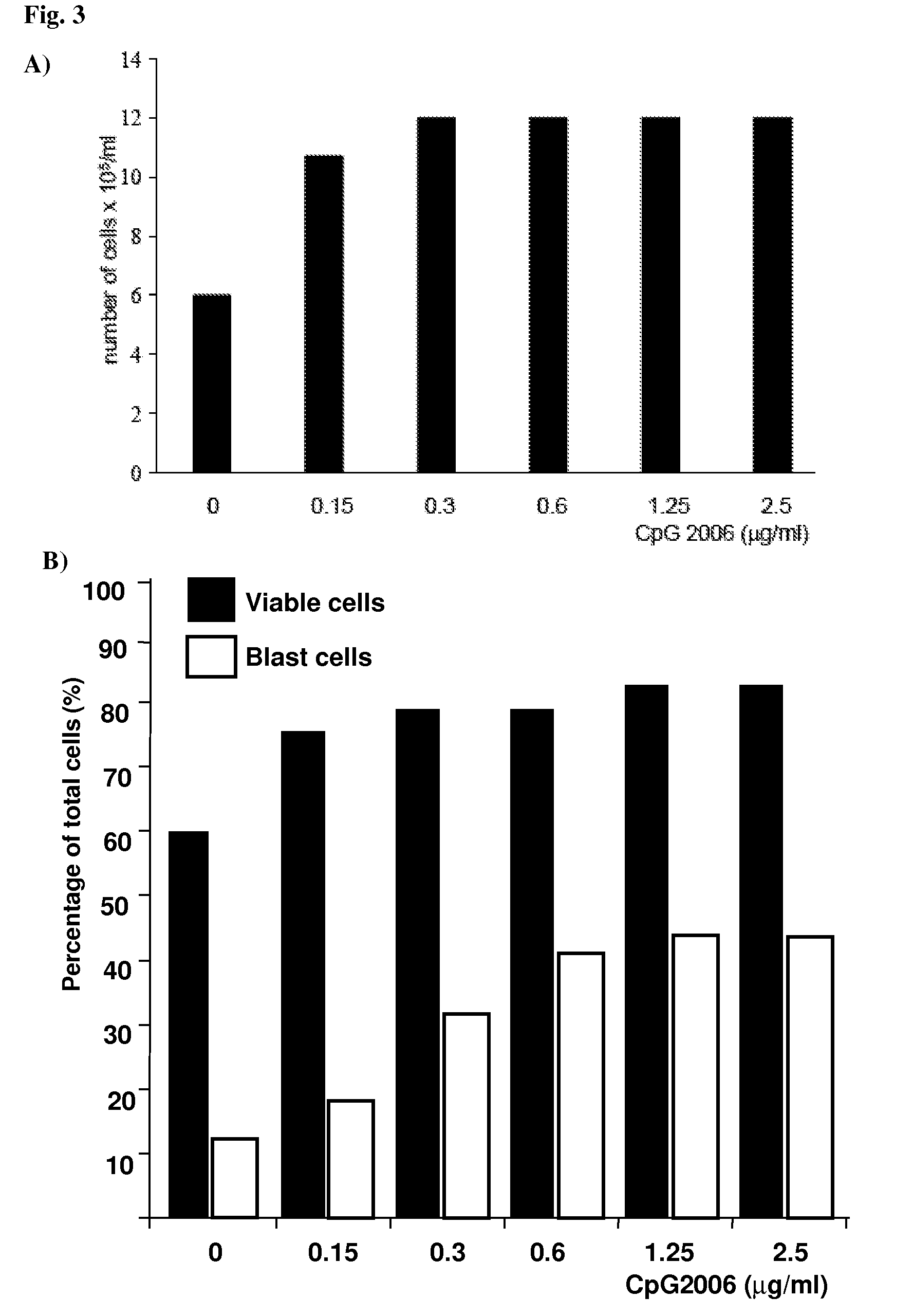
Methods for Obtaining Immortalized Antibody Secreting Cells
InactiveUS20090270268A1Good reproducibilityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHuman cytomegalovirusAntibody-Secreting Cells
The present Invention provides novel methods for immortalizing cells that secrete antibodies of one or more specific isotypes. Polyclonal, oligoclonal, and monoclonal populations of cells obtained using the methods of the Invention can be screened on the basis of the functional and / or binding activities of the antibodies they secrete, for example directed to antigens of human or viral origin having medical interest, in cell culture conditions. Using these methods, human B cells that secrete antibodies binding human Cytomegalovirus, Herpes Simplex Virus, or HSP60 protein have been efficiently immortalized with Epstein-Barr virus.
Owner:RIBOVAX BIOTECHNOLOGIES SA
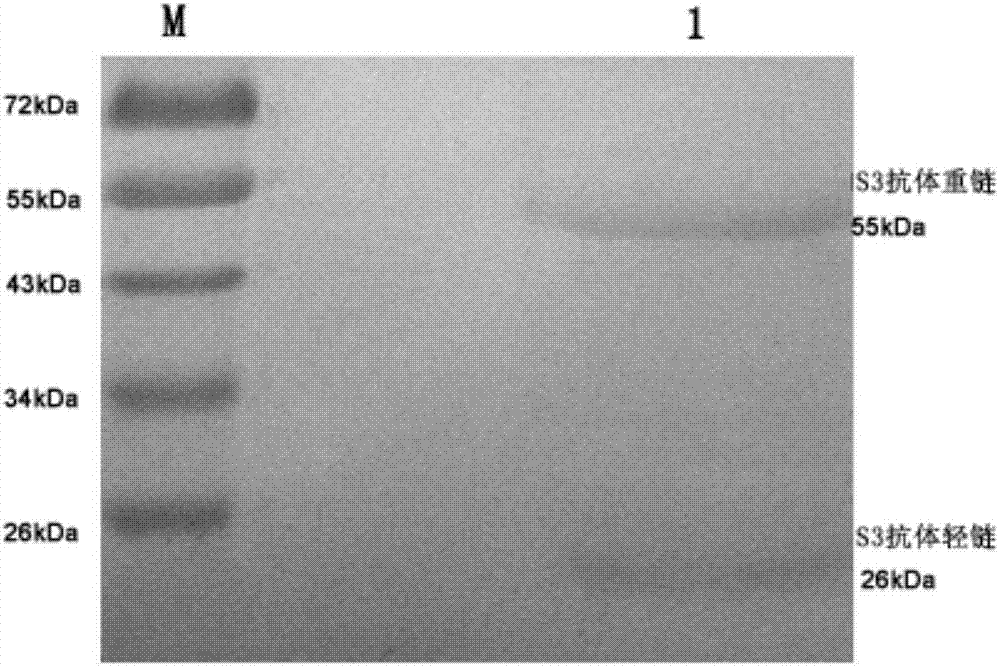
Antibody for resisting human CD79a extracellular terminal protein, coding gene and application
ActiveCN107488230AEfficient identificationHigh internalization rateOrganic active ingredientsTetrapeptide ingredientsDiseaseSequence analysis
The invention discloses an antibody for resisting human CD79a extracellular terminal protein, a coding gene and application. The antibody is characterized in that a human B cell lymphoma Raji cell line is used as an immunogen for immunizing mice; splenocyte is obtained and then is fused with a mouse myeloma cell to obtain a hybridoma cell; a monoclonal antibody for specifically aiming at the human CD79a extracellular terminal protein is obtained via screening; an amino acid sequence of the monoclonal antibody is obtained by sequence analysis; variable region sequence with a heavy chain and a light chain and CDR (Complementarity-Determining Region) sequences with light chains and heavy chains are obtained via analyzing; an chimeric antibody expressed via cloning can be used for effectively and specifically recognizing the human CD79a extracellular terminal protein; in addition, when the antibody acts on human B lymphocyte, the internalization rate is high; the antibody has a good prospect for preparing a targeted drug of targeted B lymphocyte and can be used for treating diseases associated with the B lymphocyte.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Isolation Of Allergen-Specific Immunoglobulin Genes From Human B-Cells From Atopy Sufferers
ActiveUS20100035241A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene repertoireGenetic Materials
A process is disclosed which enables the establishing of comprehensive immunoglobulin-specific reaction profiles of subjects with disorders of the immune function by the individual V gene repertoire of Ig-expressing B cells. The process comprises the isolation of B cells from body fluids, the isolation of individual B cells and their genetic material, the amplification of nucleic acids coding the variable regions of an antibody expressed by a B cell, the recombinant preparation of antibodies by expressing the amplificates, and the determination of the binding
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Therapeutic use of riboside of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide (acadesine)
The present disclosure relates to a method of treatment of a human patient suffering from a B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders such as B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL), splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL), and Waldenström syndrome (WS), by the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside (acadesine) or its precursors (eg. its mono-, di- and tri-5′-phosphates). This makes acadesine and its bioprecursors (eg. its mono-, di- and tri-5′-phosphates) useful as therapeutic agents for B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders in humans. The surprising feature that T cells are virtually not affected means that the side effect (immunosuppression) is minor, what represents a therapeutical advantage of acadesine over cladribine, fludarabine and other nucleosides known in the art.
Owner:ADVANCELL ADVANCED IN VITRO CELL TECH
Human monoclonal antibodies derived from human B cells and having neutralizing activity against influenza A viruses
The present invention relates to human monoclonal antibodies derived from human B cells present in the blood of patients who had recovered from infection with influenza A viruses, wherein the monoclonal antibodies have neutralizing activity against influenza A viruses. The anti-influenza A virus monoclonal antibody of the present invention has binding and neutralizing activities against at least one influenza A virus selected from the group consisting of influenza A virus H1, H2 and H5 subtypes, and thus it is useful for the prevention and treatment of a disease caused by the influenza A virus and is also useful for diagnosis of influenza A virus infection.
Owner:CELLTRION INC
In vitro germinal centers
ActiveUS20100184148A1Artificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingArtificial immune systemLymphocyte
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR VAX DESIGN
In vitro germinal centers
ActiveUS8003387B2Artificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingArtificial immune systemLymphocyte
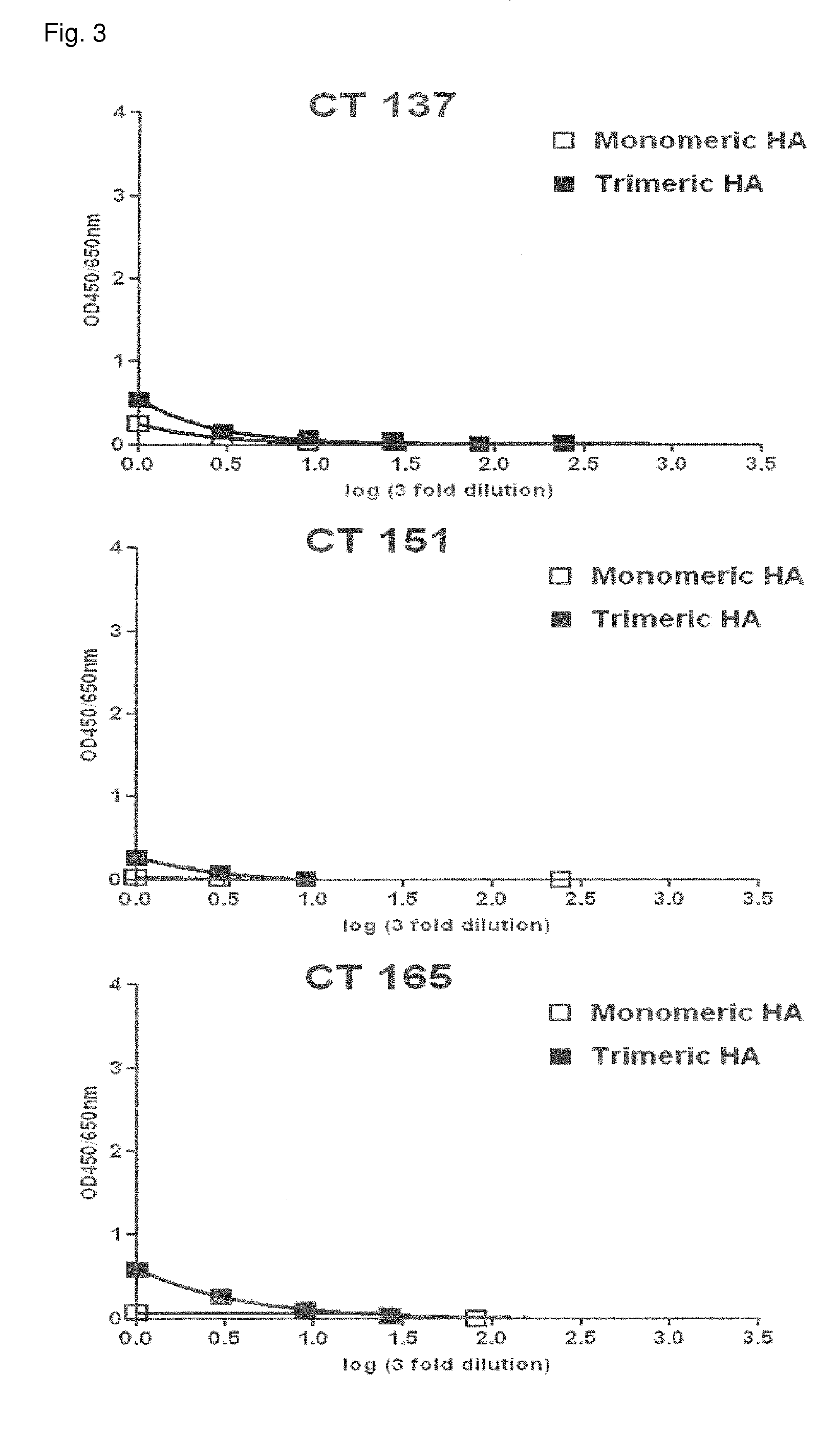
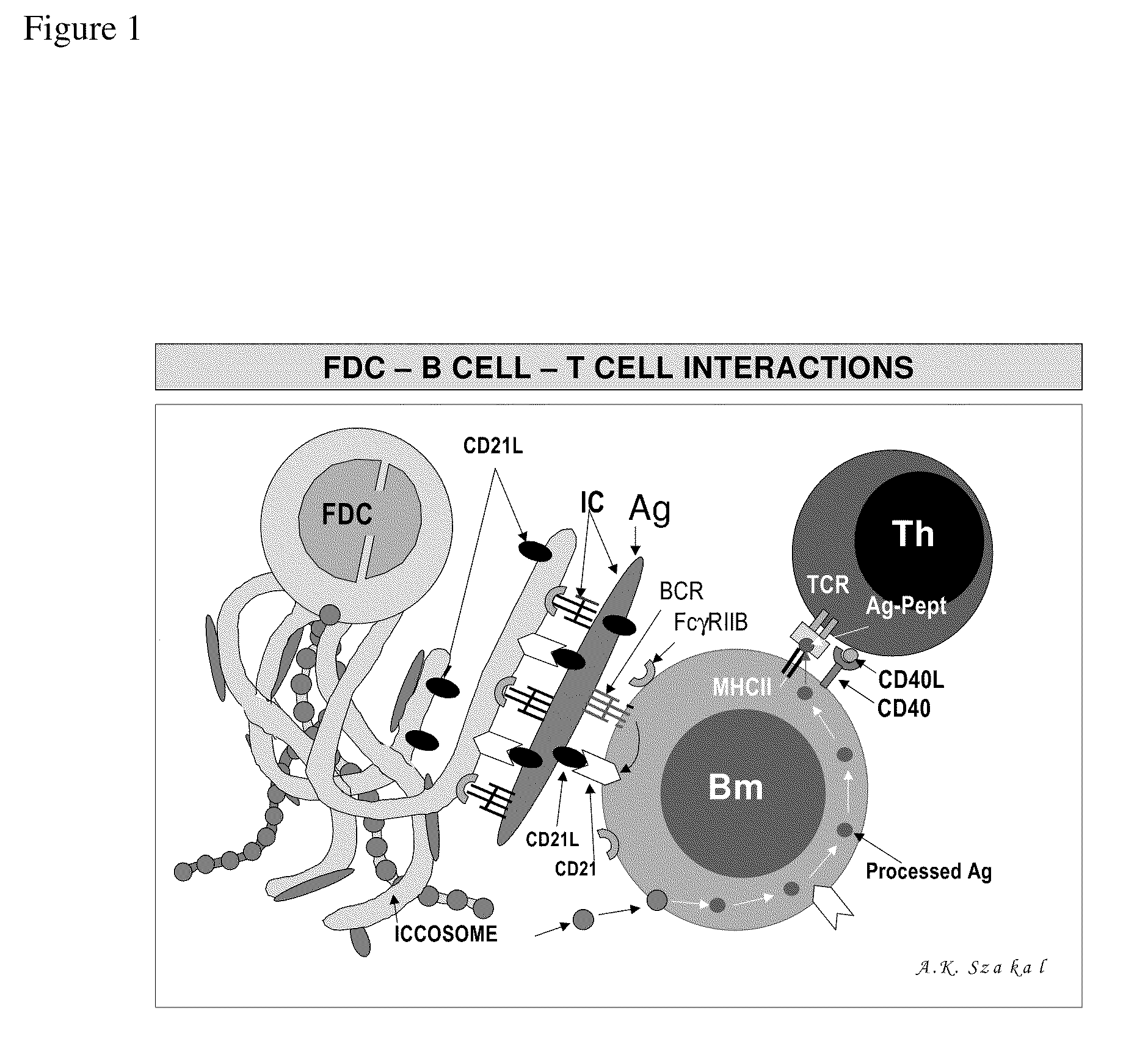
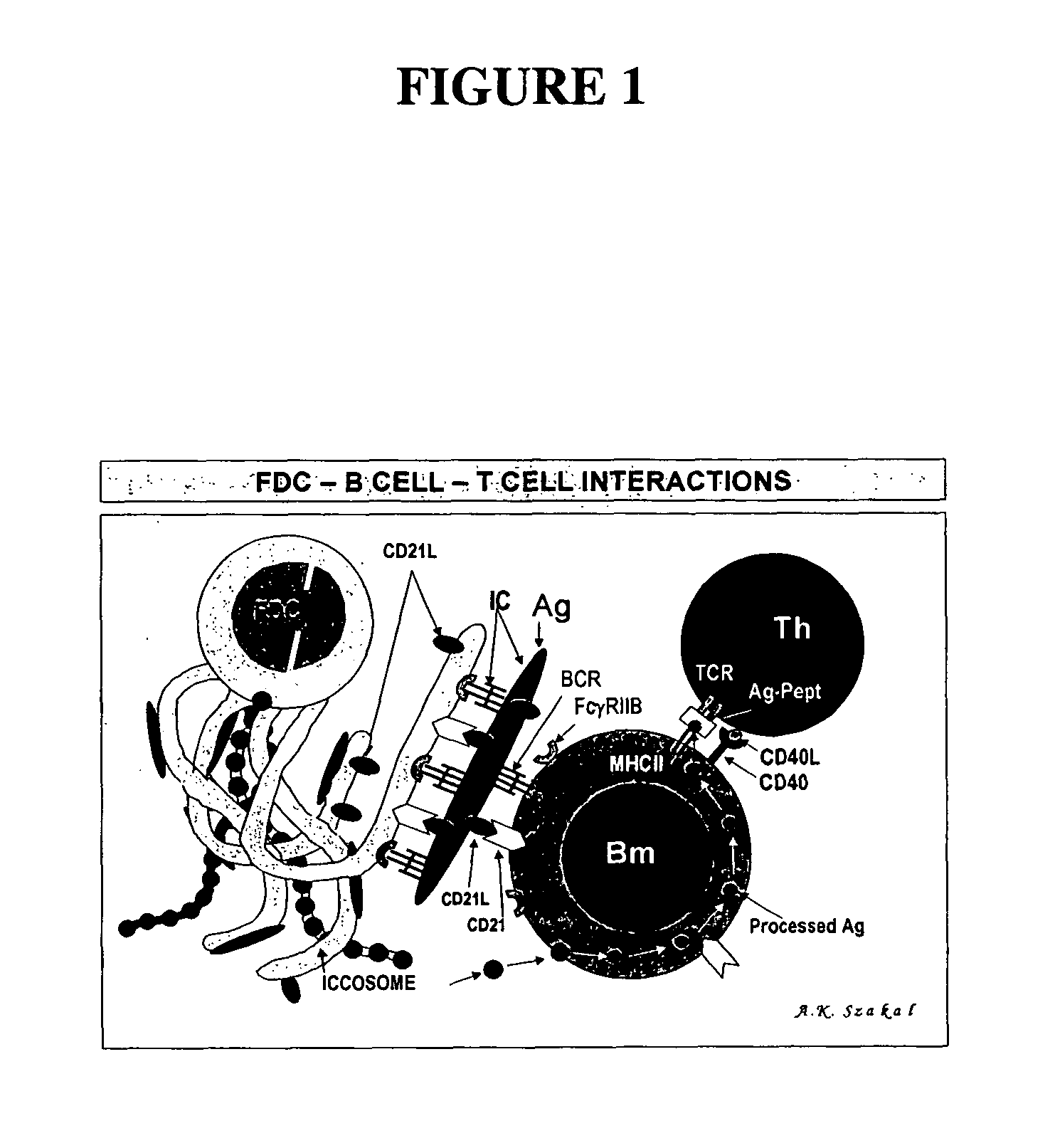
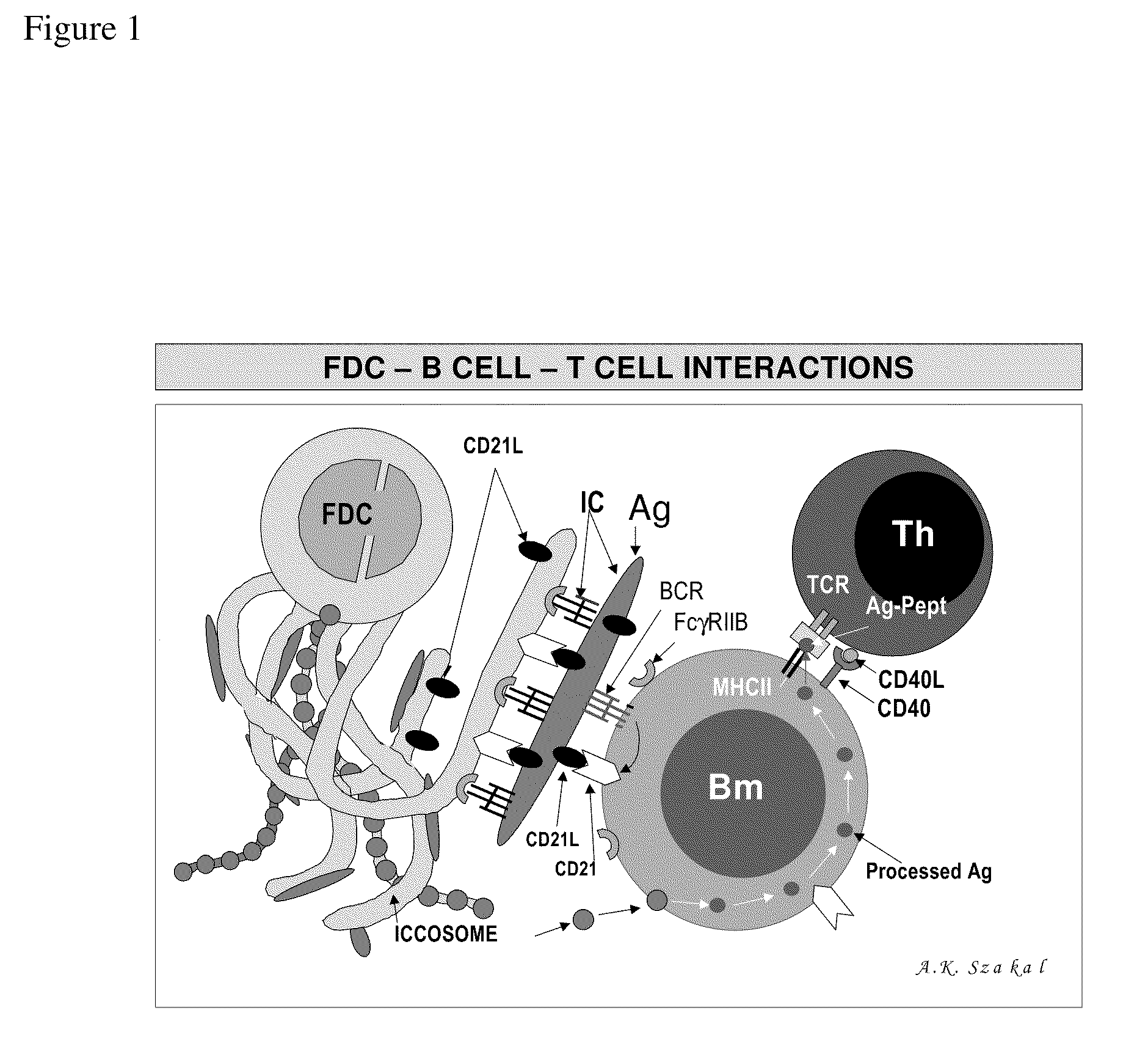
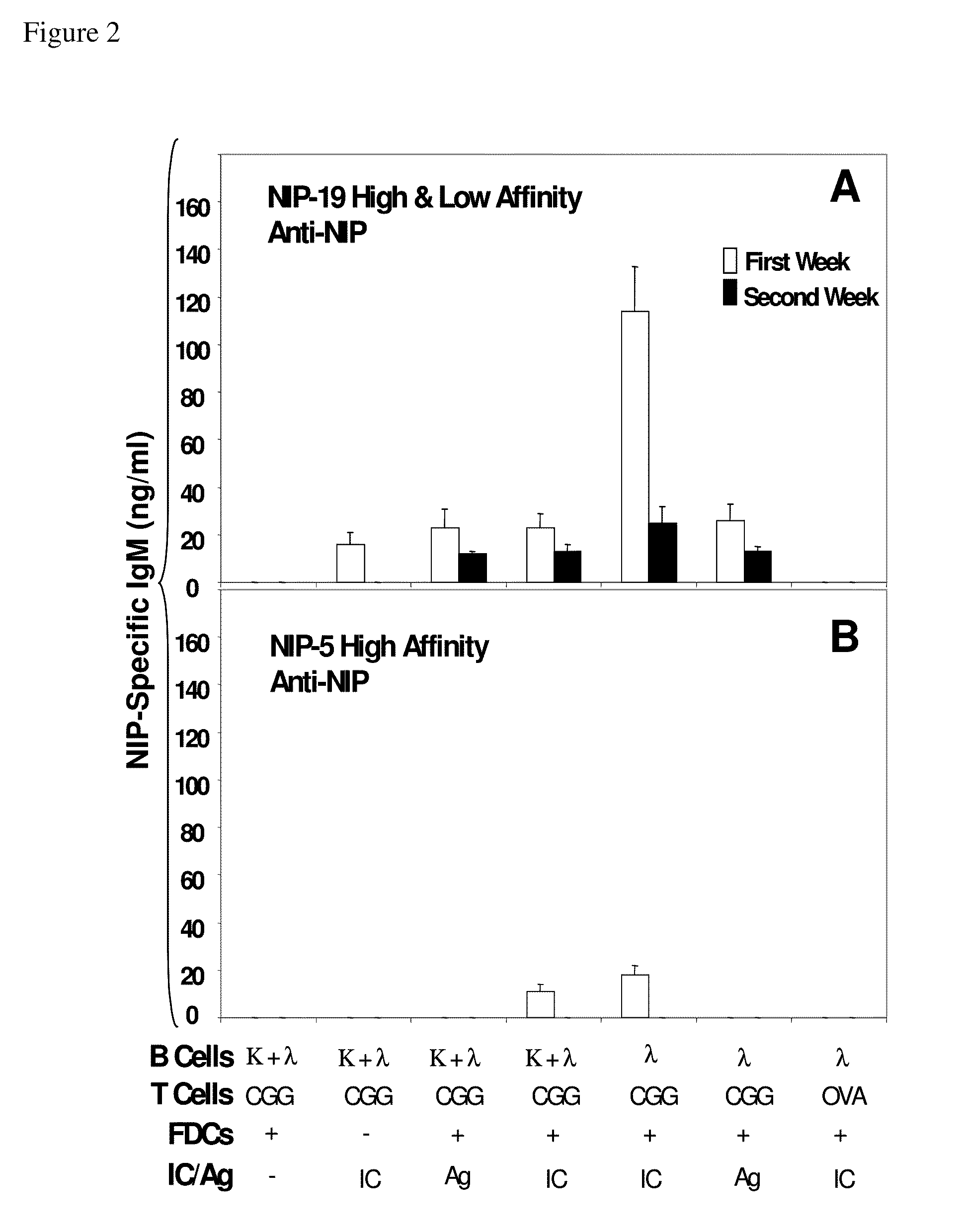
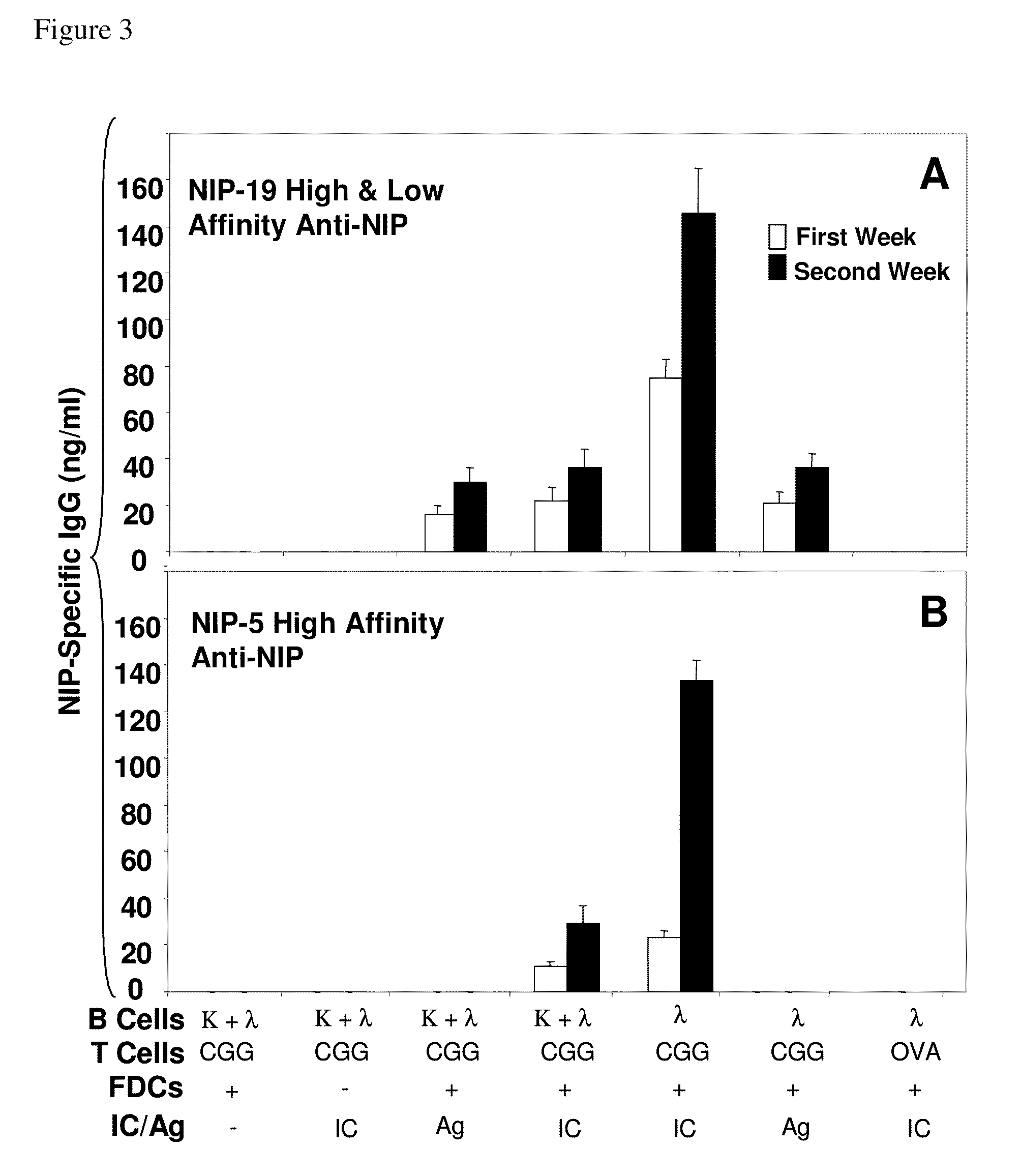
The present invention incorporates germinal centers (GCs) into three-dimensional (3D) engineered tissue constructs (ETCs). In an embodiment, we have incorporated the GC in the design of an artificial immune system (AIS) to examine immune responses to vaccines and other compounds. Development of an in vitro GC adds functionality to an AIS, in that it enables generation of an in vitro human humoral response by human B lymphocytes that is accurate and reproducible, without using human subjects. The invention also permits evaluation of, for example, vaccines, allergens, and immunogens, and activation of human B cells specific for a given antigen, which can then be used to generate human antibodies. In an embodiment of the present invention the function of the in vitro GC is enhanced by placing FDCs and other immune cells in a 3D ETC; FDCs appear more effective over a longer time (antibody production is sustained for up to about 14 days.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV +1
In vitro germinal centers
ActiveUS8003385B2Artificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingArtificial immune systemLymphocyte
The present invention incorporates germinal centers (GCs) into three-dimensional (3D) engineered tissue constructs (ETCs). In an embodiment, we have incorporated the GC in the design of an artificial immune system (AIS) to examine immune responses to vaccines and other compounds. Development of an in vitro GC adds functionality to an AIS, in that it enables generation of an in vitro human humoral response by human B lymphocytes that is accurate and reproducible, without using human subjects. The invention also permits evaluation of, for example, vaccines, allergens, and immunogens, and activation of human B cells specific for a given antigen, which can then be used to generate human antibodies. In an embodiment of the present invention the function of the in vitro GC is enhanced by placing FDCs and other immune cells in a 3D ETC; FDCs appear more effective over a longer time (antibody production is sustained for up to about 14 days.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR VAX DESIGN
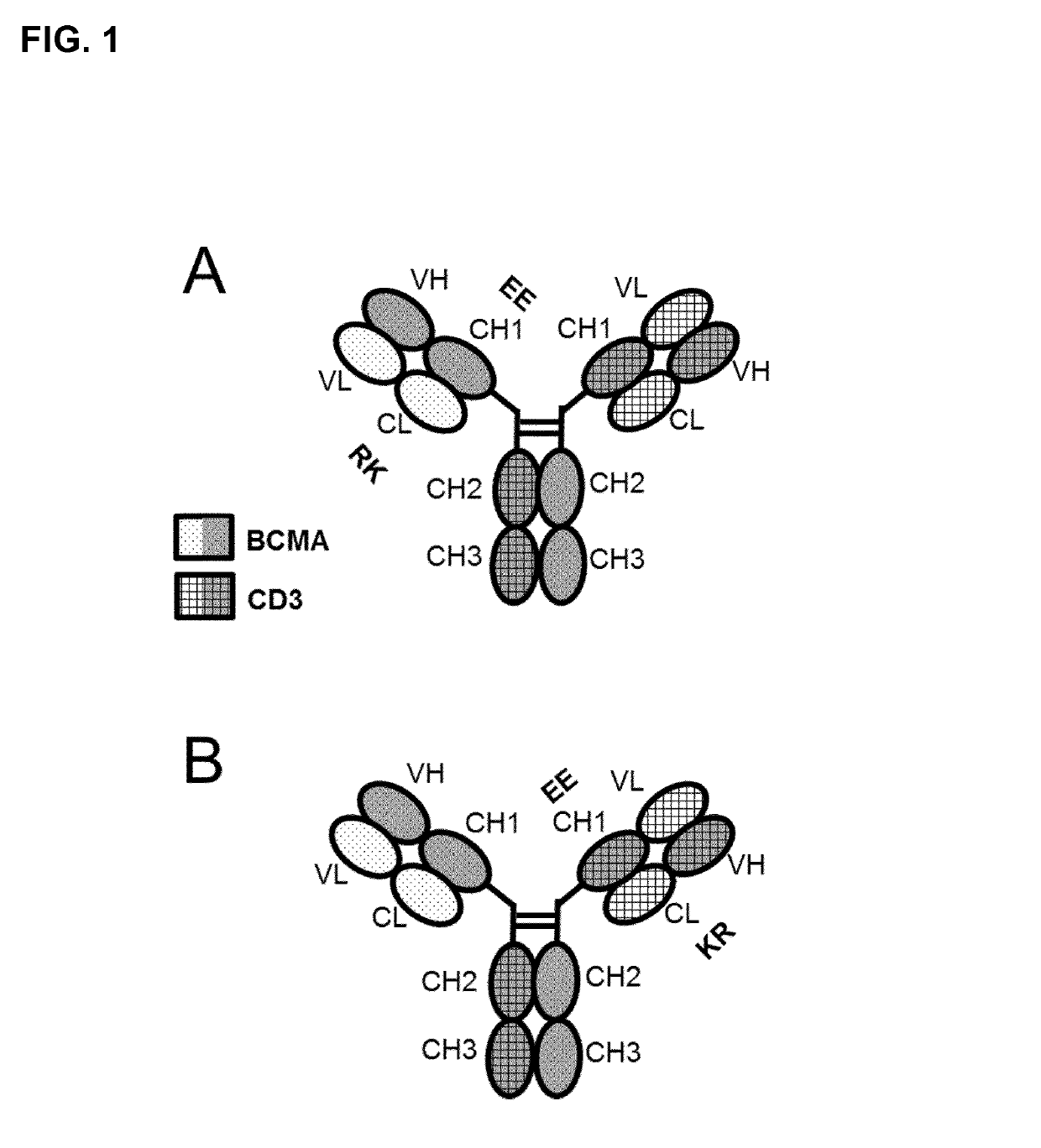
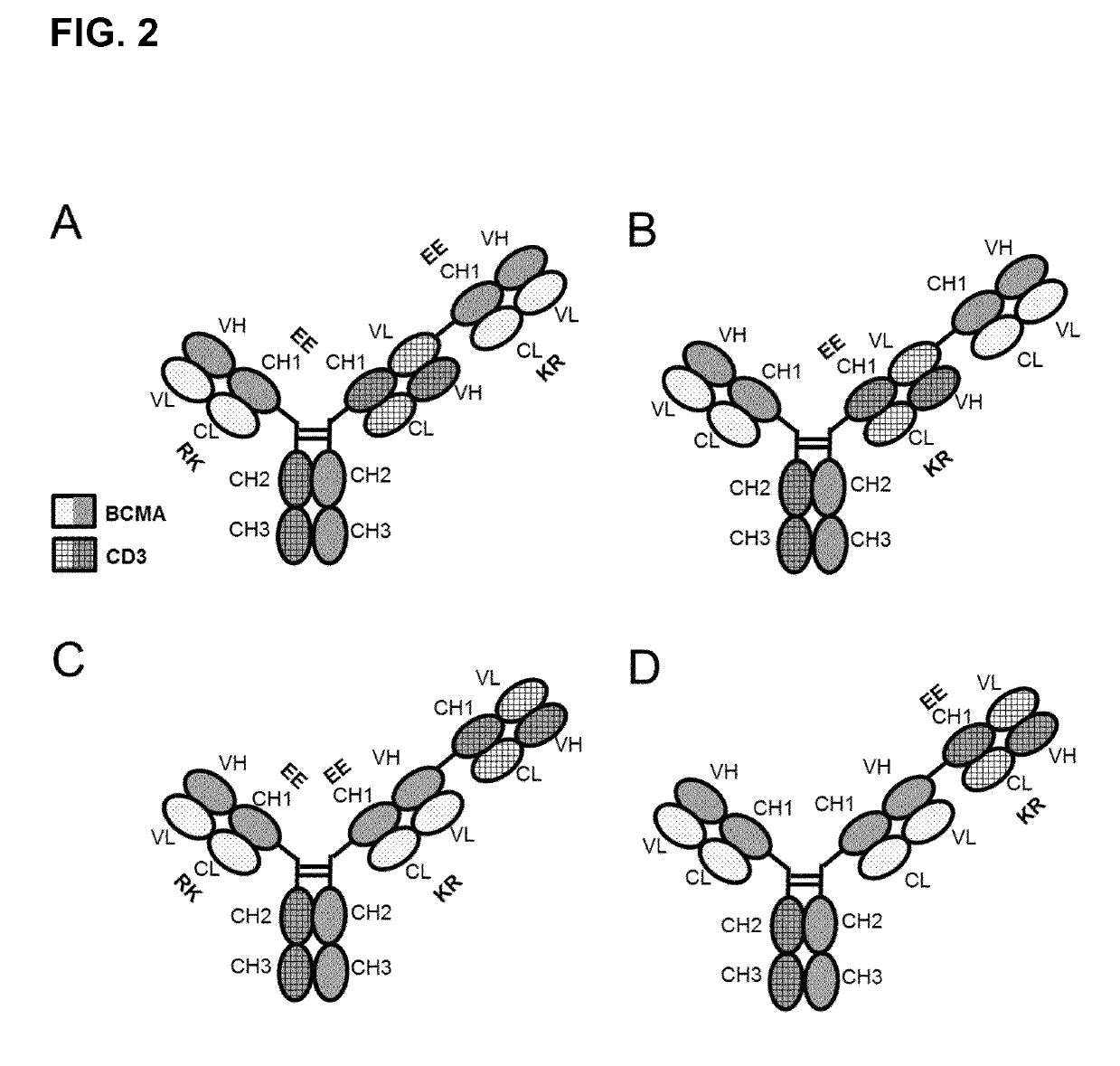
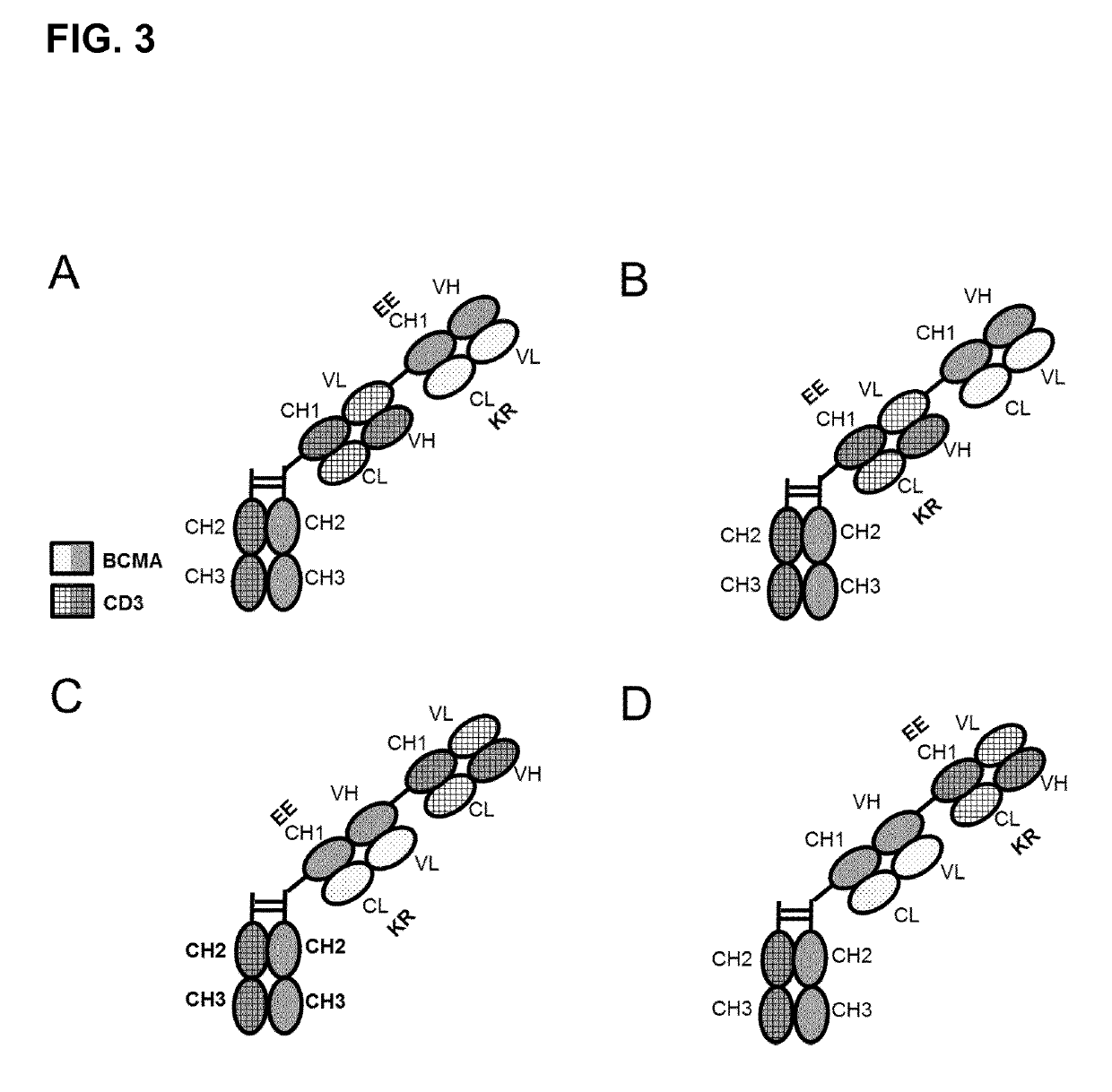
Bispecific antibodies against CD3ϵ and BCMA
ActiveUS10253104B2Minimizing ADCC/CDCMediates its tumor cell killing efficacyHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenArginine
A bispecific bi- or trivalent antibody specifically binding to the two targets which are extracellular domain of human B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) and human CD3ε, wherein the variable domains VL and VH in a light chain and the respective heavy chain are replaced by each other, characterized in comprising a constant domain CL wherein the amino acid at position 124 is substituted independently by lysine (K), arginine (R) or histidine (H) (numbering according to Kabat), and in the respective constant domain CH1 the amino acid at position 147 and the amino acid at position 213 is substituted independently by glutamic acid (E), or aspartic acid (D) (numbering according to EU index of Kabat). Also the manufacture and use of said antibody.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO +1
Methods for obtaining immortalized antibody secreting cells
InactiveUS8338172B2Good reproducibilityImprove throughputImmunoglobulins against virusesArtificial cell constructsHuman cytomegalovirusAntibody-Secreting Cells
The present Invention provides novel methods for immortalizing cells that secrete antibodies of one or more specific isotypes. Polyclonal, oligoclonal, and monoclonal populations of cells obtained using the methods of the Invention can be screened on the basis of the functional and / or binding activities of the antibodies they secrete, for example directed to antigens of human or viral origin having medical interest, in cell culture conditions. Using these methods, human B cells that secrete antibodies binding human Cytomegalovirus, Herpes Simplex Virus, or HSP60 protein have been efficiently immortalized with Epstein-Barr virus.
Owner:RIBOVAX BIOTECHNOLOGIES SA
12 amino acid analog epi-position of human b cell specificity membrane molecule CD20 and polypeptide epi-position vaccine configurated by said analog epi-position
InactiveCN1786021AEfficient killingReduce the burden onPeptidesAntibody ingredientsChemical synthesisCD20
The present invention discloses a simulation epitope of 12 amino acids of human cell B specificity expression membrane molecule CD 20 and its polypeptide epitope vaccine constructed by using said simulation spitope. Said invention also provides a method for screening simulation epitope of CD 20 molecule by using Rituximab as ligand, and provides its amino acid sequence, Gln-Asp-Lys-Leu-Th-Gln-Try-Pro-Lys-Try-Leu-Glu. Said invention also provides a method for chemically-synthesizing simulation epitope of 12 amino acids and making it be chemically-coupled with keyhole limpet hemo cyanin (KLH) to obtain the successfully-constructed vaccine. Besides, said invention also provides the concrete application of said vaccine.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Artificial single-chain deoxynucleotide having therapeutic effect to human B cell tumour
Owner:CHANGCHUN HUAPU BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Anti-CD19 Antibodies
ActiveUS20110052489A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionAutoimmune disease
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Preparation method and application of BCMA antibody
ActiveCN113061185AIncreased apparent affinityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAutoimmune conditionSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a BCMA antibody. The specific single-chain antibody resisting the human B cell surface antigen BCMA is screened from a single-chain antibody library of a non-immune fully human source sequence through genetic engineering and phage surface display library technology. A plurality of Fab clones with remarkably improved binding capacity are obtained through affinity maturation modification, and the affinity of the Fab clones with human BCMA is between 0.26 nM and 0.31 nM. The apparent affinity measured by a flow cytometry is improved by 61-97 times compared with the apparent affinity of a parent antibody, and it is proved that the anti-human BCMA antibody and the optimized mutant have good BCMA binding capacity. The invention provides a human BCMA specific antibody candidate molecule for research and development of an anti-tumor antibody drug aiming at a BCMA target, development of a CAR-T reagent and prevention and treatment of other diseases such as B cell related inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:EXCYTE LLC
Anti-malignant lymphoma fusion protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103172748AGood prospects for tumor treatmentPrevent proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMalignant lymphomaMutated protein
The invention provides an anti-malignant lymphoma fusion protein. The anti-malignant lymphoma fusion protein comprises an inhibitor SARI (Suppressor of AP-1 Regulated by Interferon) of a human activator protein-1 and a mutant protein msBAFF of human B cell activating factor BAFF, wherein the msBAFF is a mutant which is formed after amino acids at the 217-224 loci of the human BAFF are replaced by two glycines. The invention further provides a preparation method of the fusion protein. After the recombinant fusion protein of the invention is obtained through a genetic engineering strategy, vitro anti-tumor effect detection is performed and shows that the tumor growth can be effectively inhibited in cells and animals.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
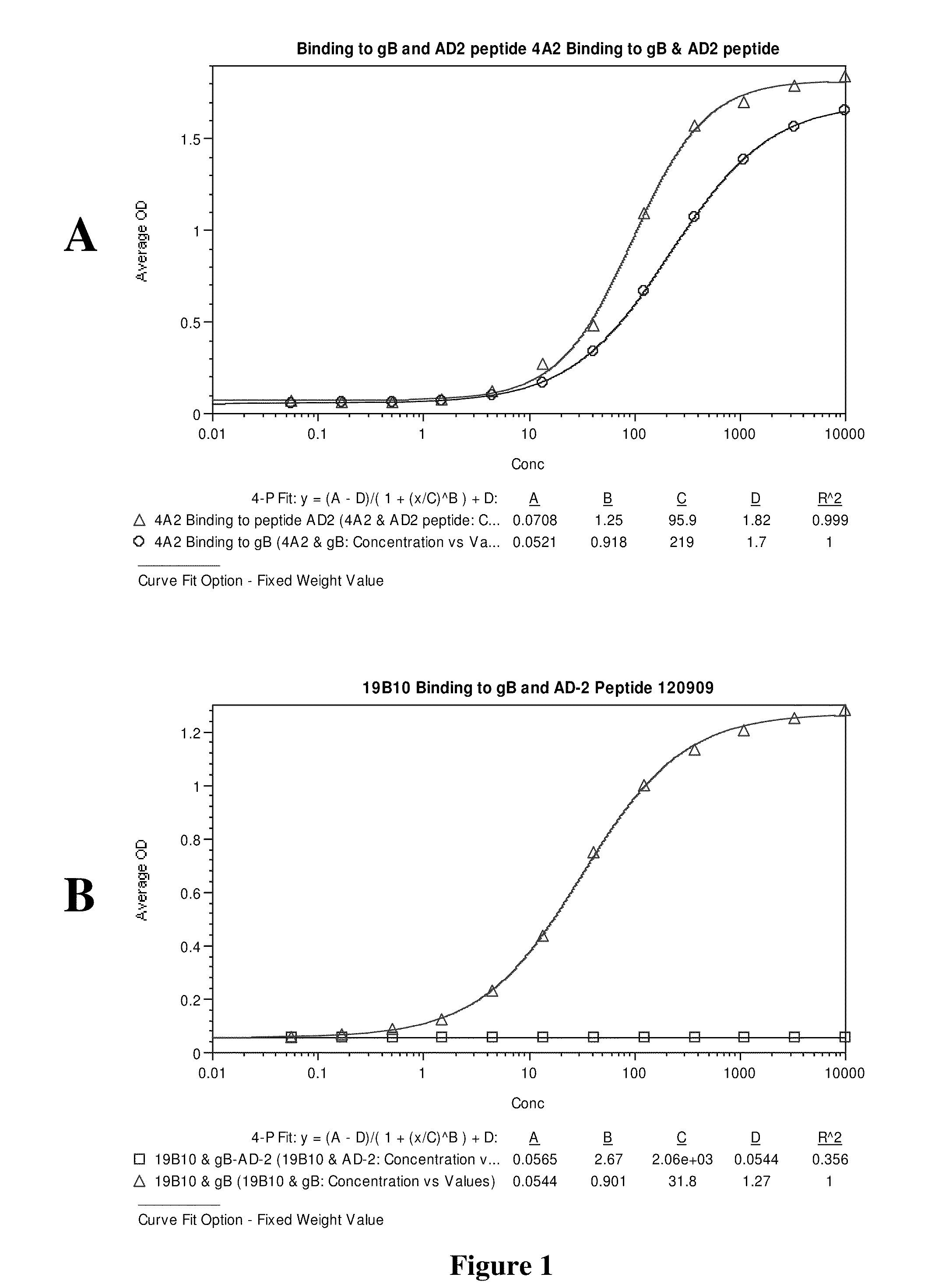
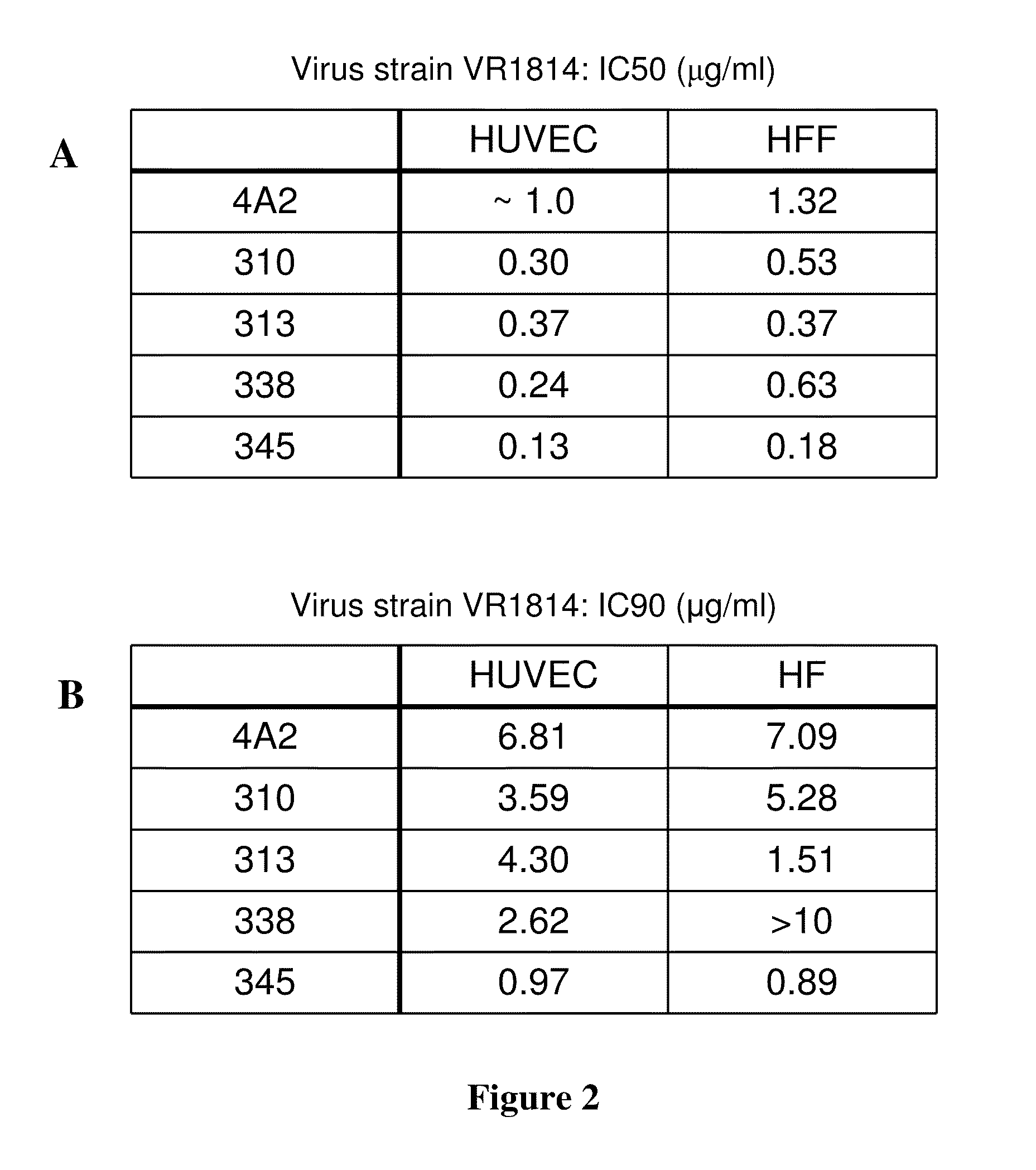
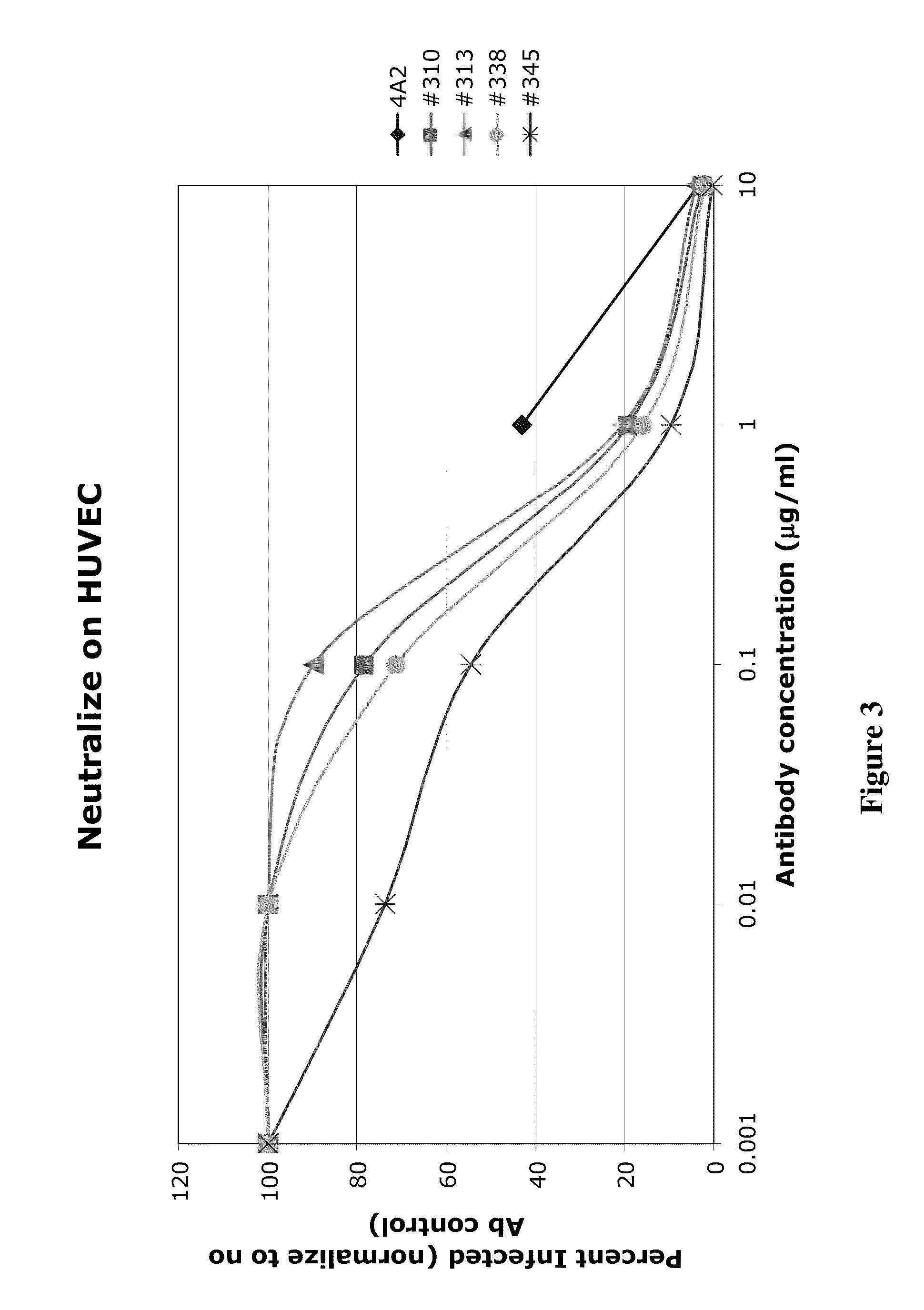
High affinity human antibodies to human cytomegalovirus (CMV) gb protein
ActiveUS20120020980A1High affinityNeutralizing abilityMicroorganismsGenetic material ingredientsCmv infectionsProtein antibody
Antibodies to human Cytomegalovirus (CMV) gB protein have been isolated from human B cells. The affinities of these antibodies are higher than the best previously reported antibodies. Since high affinity is critical to prevention of virus transfer across the placenta, the invention antibodies are useful as therapeutic and prophylactic agents to prevent or ameliorate effects on the fetus of CMV infection during pregnancy.
Owner:TRELLIS BIOSCIENCE LLC
Construction and expression of recombinant human B cell stimulating factor (rhBLyS) expression vector, and monoclonal antibody preparation and use
InactiveCN1401776AImproving immunogenicityEasy to filterBacteriaAntibody ingredientsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
A recombinant plasmid vector containing human B lymphocyte stimulating factor (hBlyS) gene, the construction and expression of said expression vector, the process for preparing its monoclonal antibody and the application of said monoclonal antibody in preparing the medicines to treat B lymphocyte cancer and self-immunopathy and the test reagent for the BlyS concentration in human plasma are disclosed.
Owner:张志方 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com