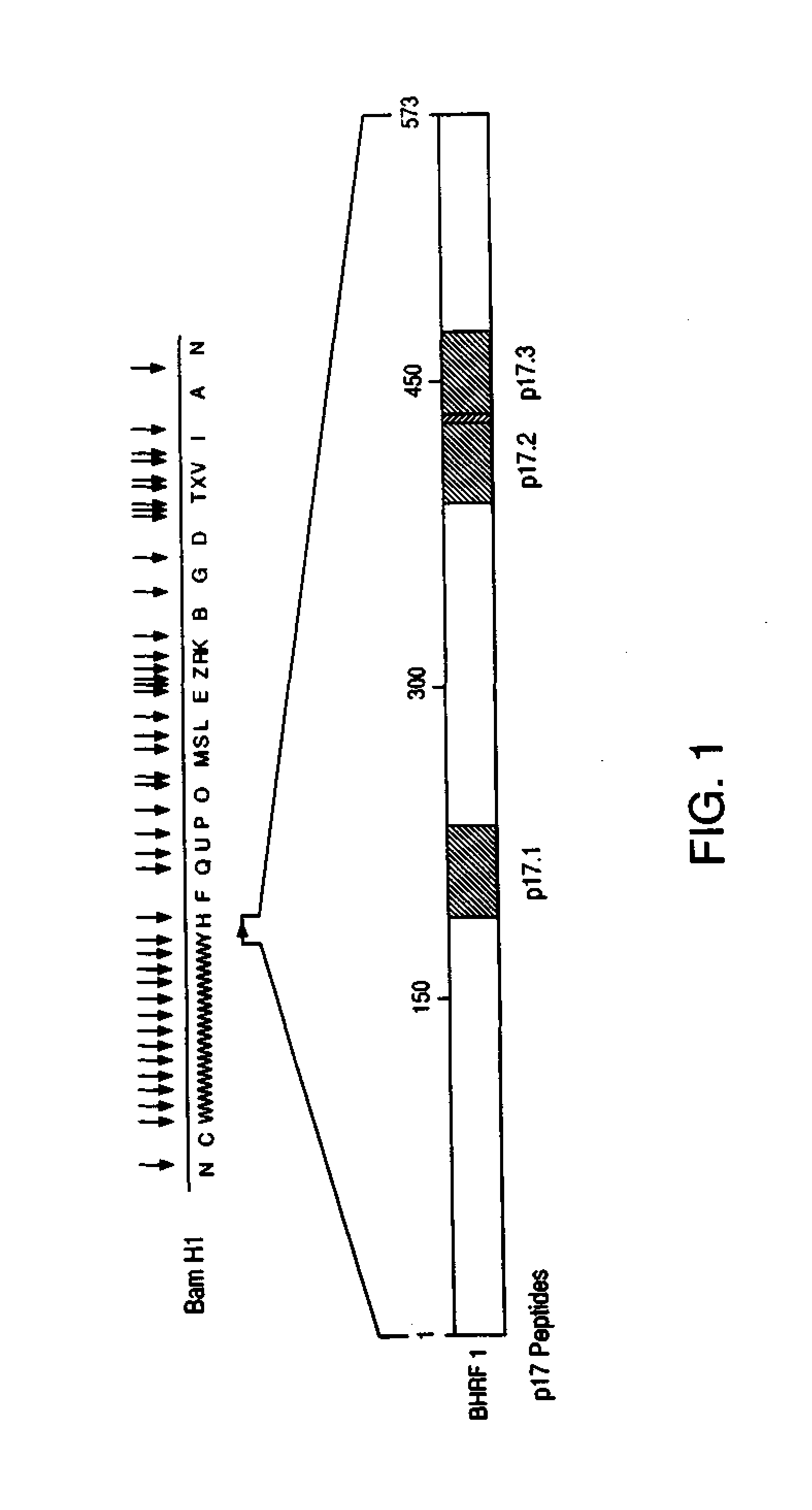
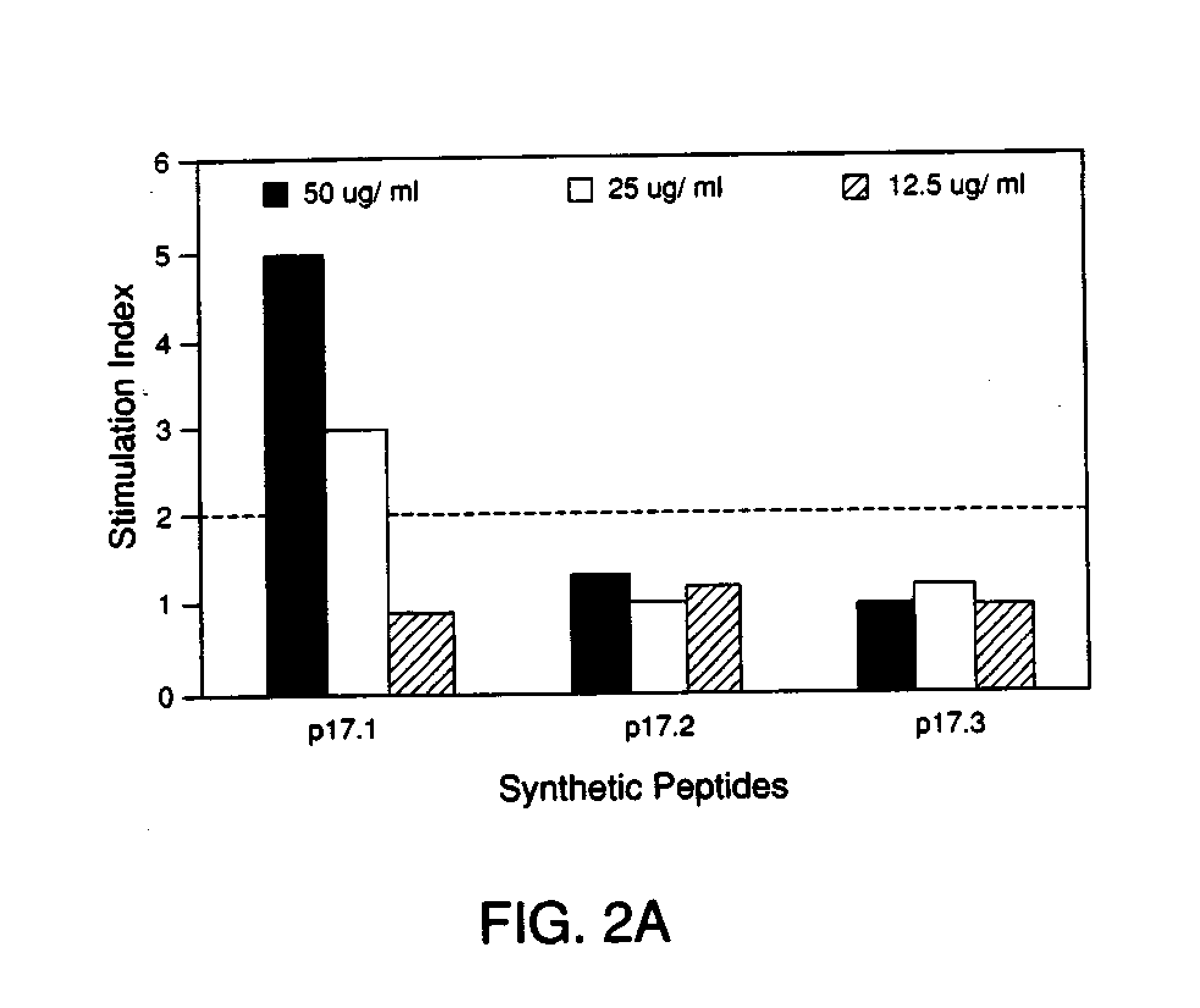
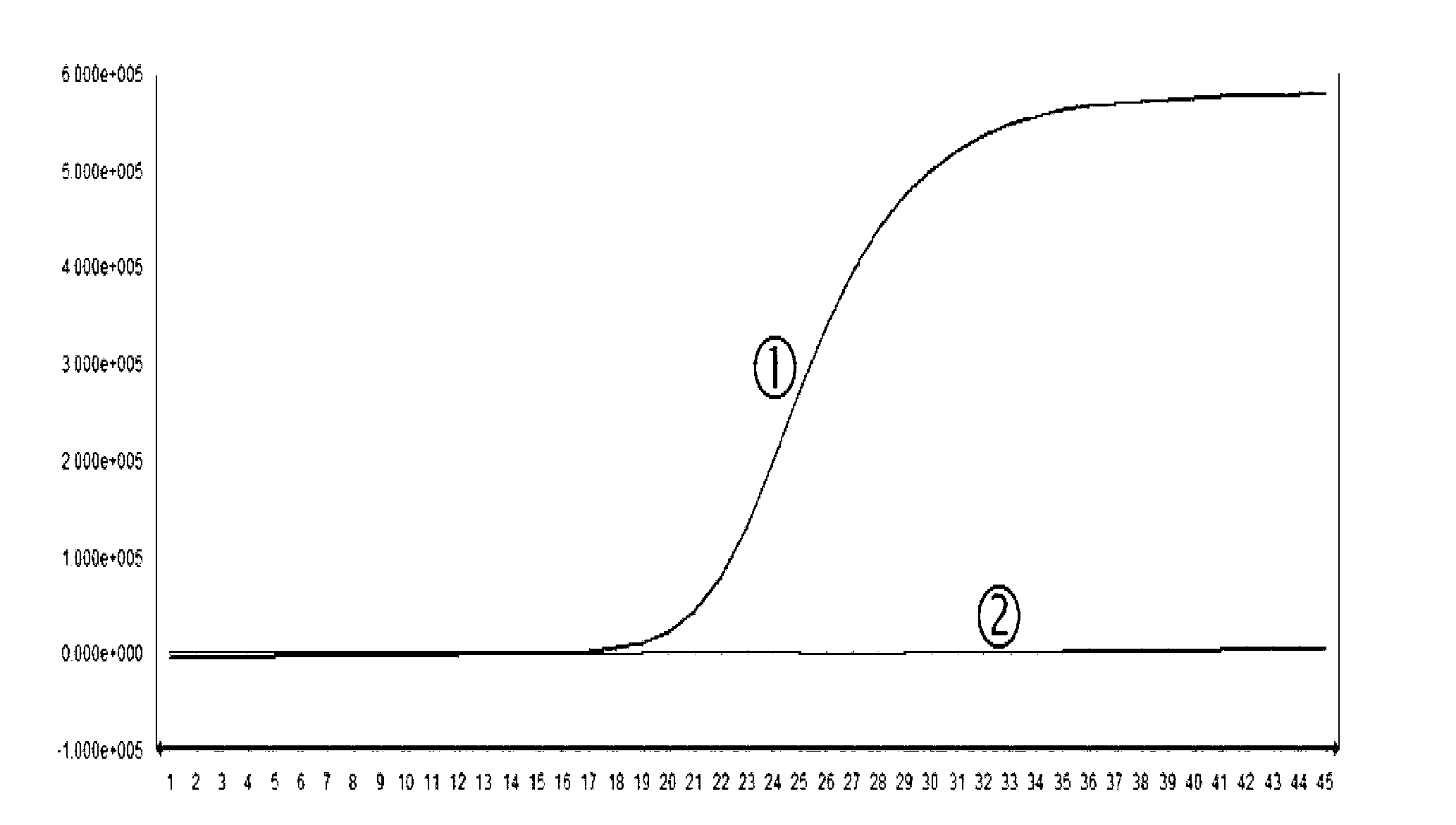
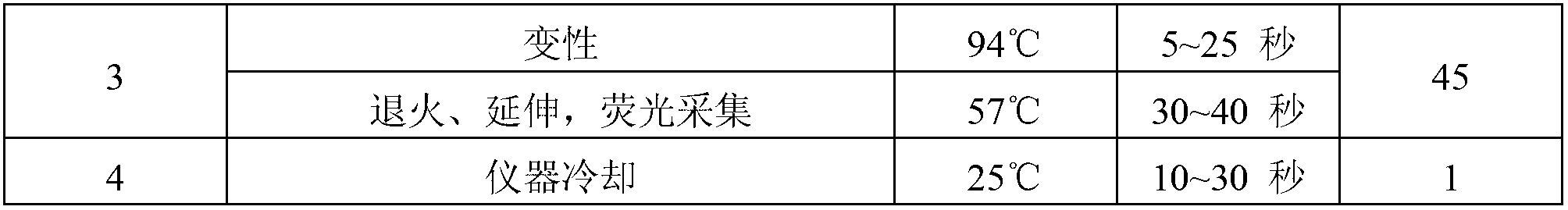
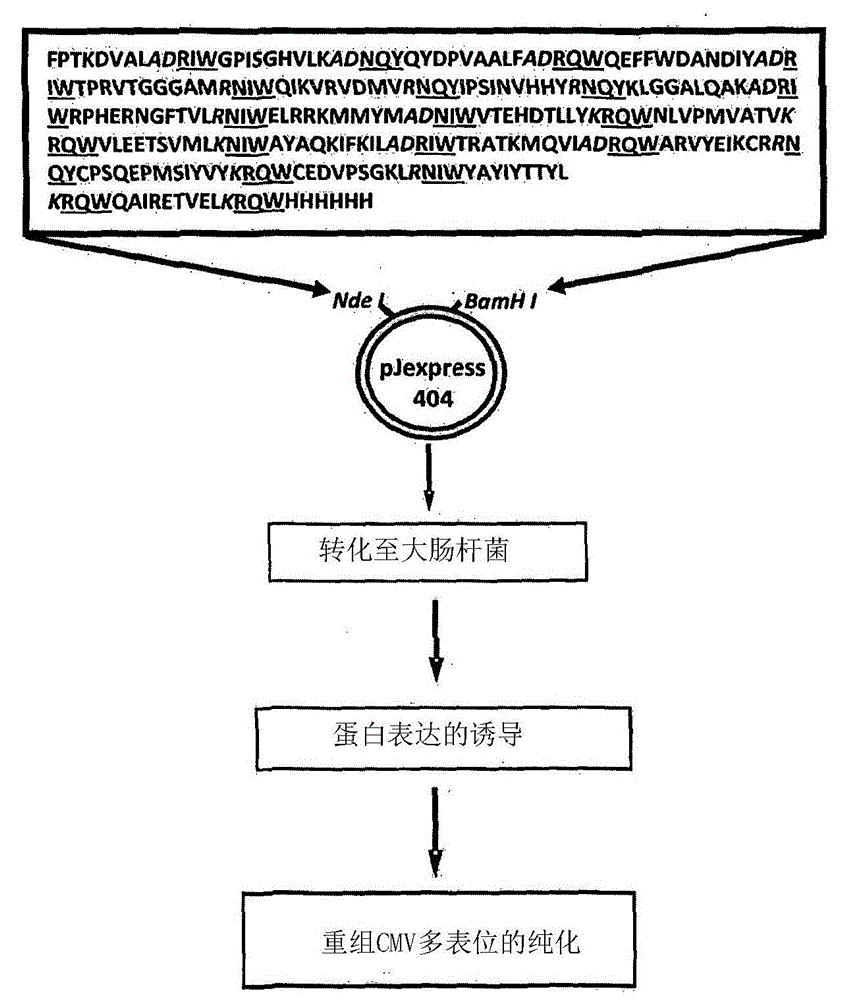
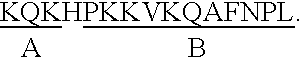Patents
Literature
96 results about "Barr virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
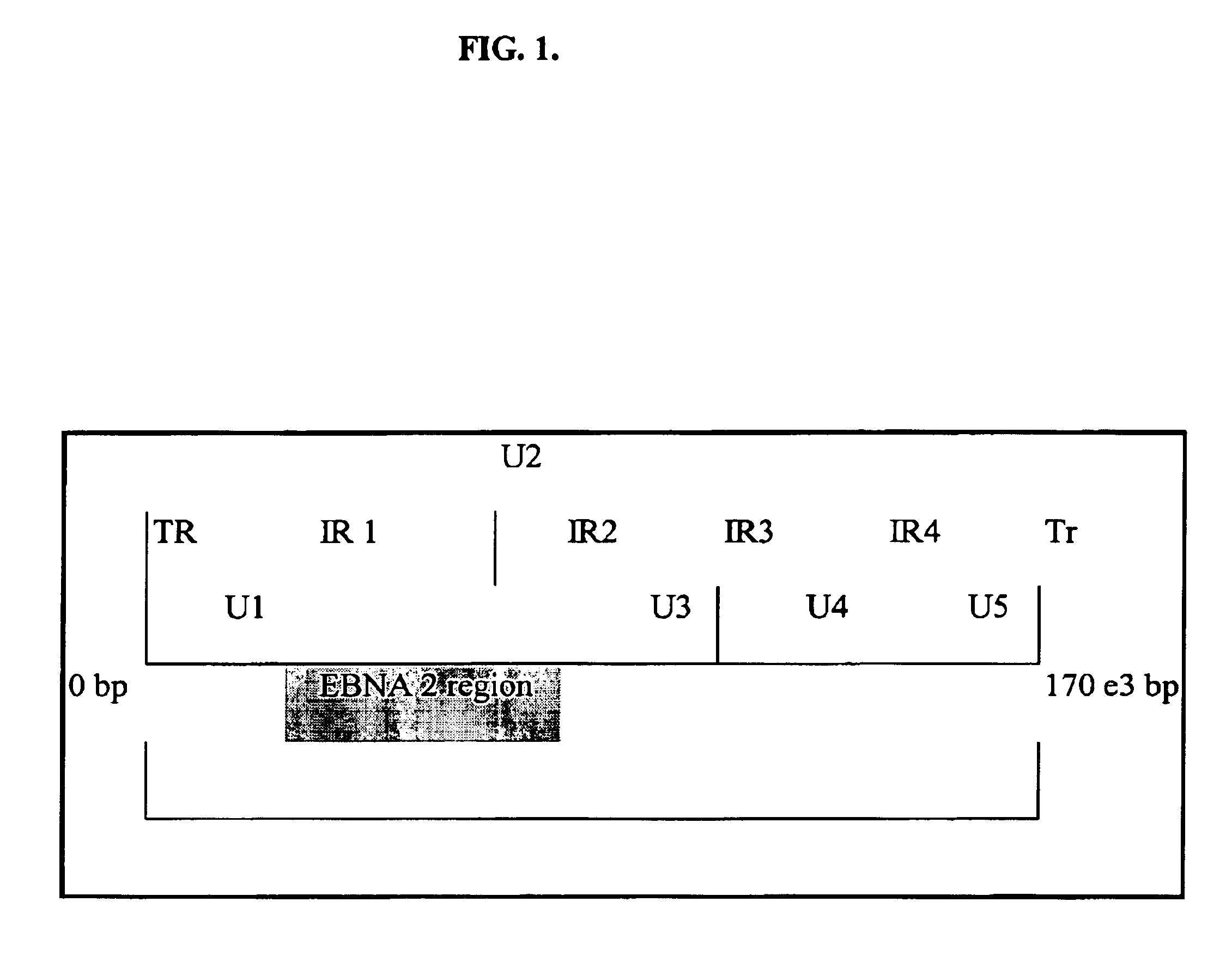
Epstein–Barr virus. The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV, sometimes abbreviated as EPV), formally called Human gammaherpesvirus 4, is one of eight known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans.
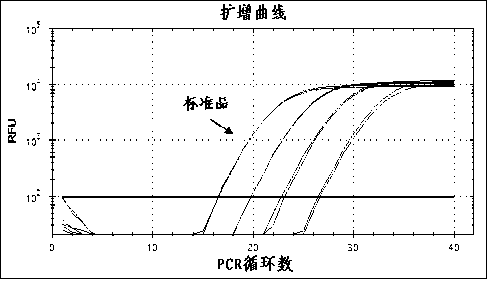
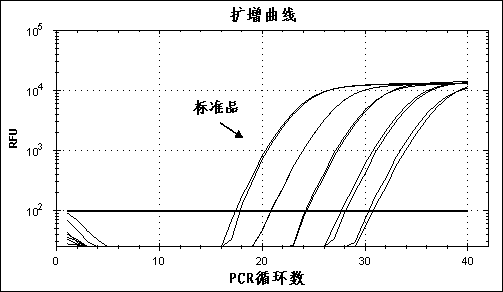
Quantitative epstein barr virus PCR rapid assay
InactiveUS6790952B2Sensitive and accurateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEpstein bar virusNucleotide
The present invention provides novel compositions comprising Epstein-Barr virus-specific oligonucleotides that are useful as primers to amplify particular regions of the genome during enzymatic nucleic acid amplification. The invention also provides a rapid, sensitive and specific method for the detection and quantitation of the virus which may be present in a clinical specimen, using the virus-specific primers and enzymatic nucleic acid amplification; hybridization of amplified target sequences, if present, with one or more Epstein-Barr virus-specific oligonucleotide probes which are labeled with a detectable moiety; and detection of the detectable moiety of labeled oligonucleotide probe hybridized to amplified target sequences of Epstein-Barr virus DNA.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL RES FOUND
Method for the induction and expansion of natural killer cells derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells
ActiveUS20150152387A1Improve efficiencyImprove efficacyBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsNatural Killer Cell FunctionNatural killer cell
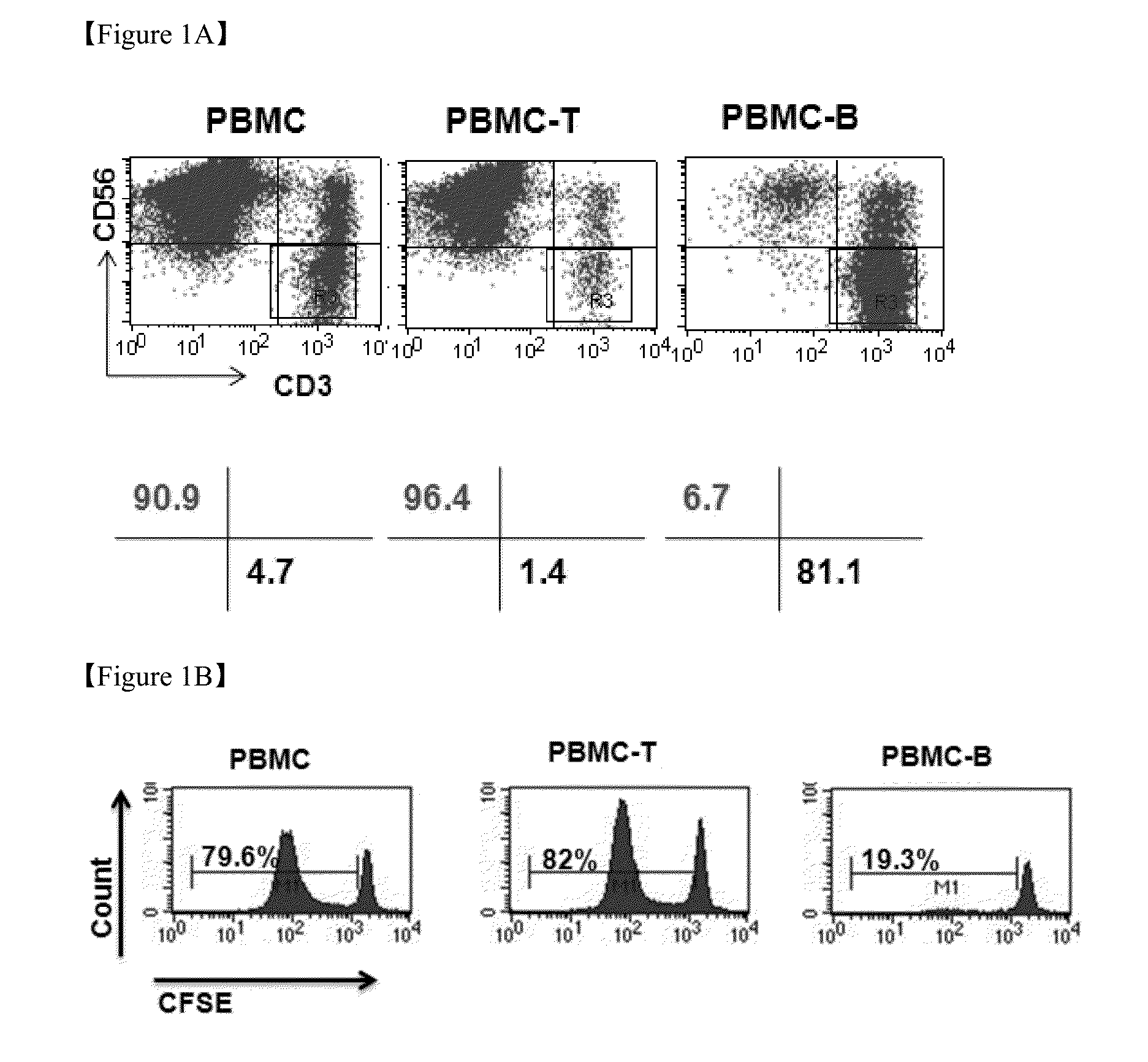
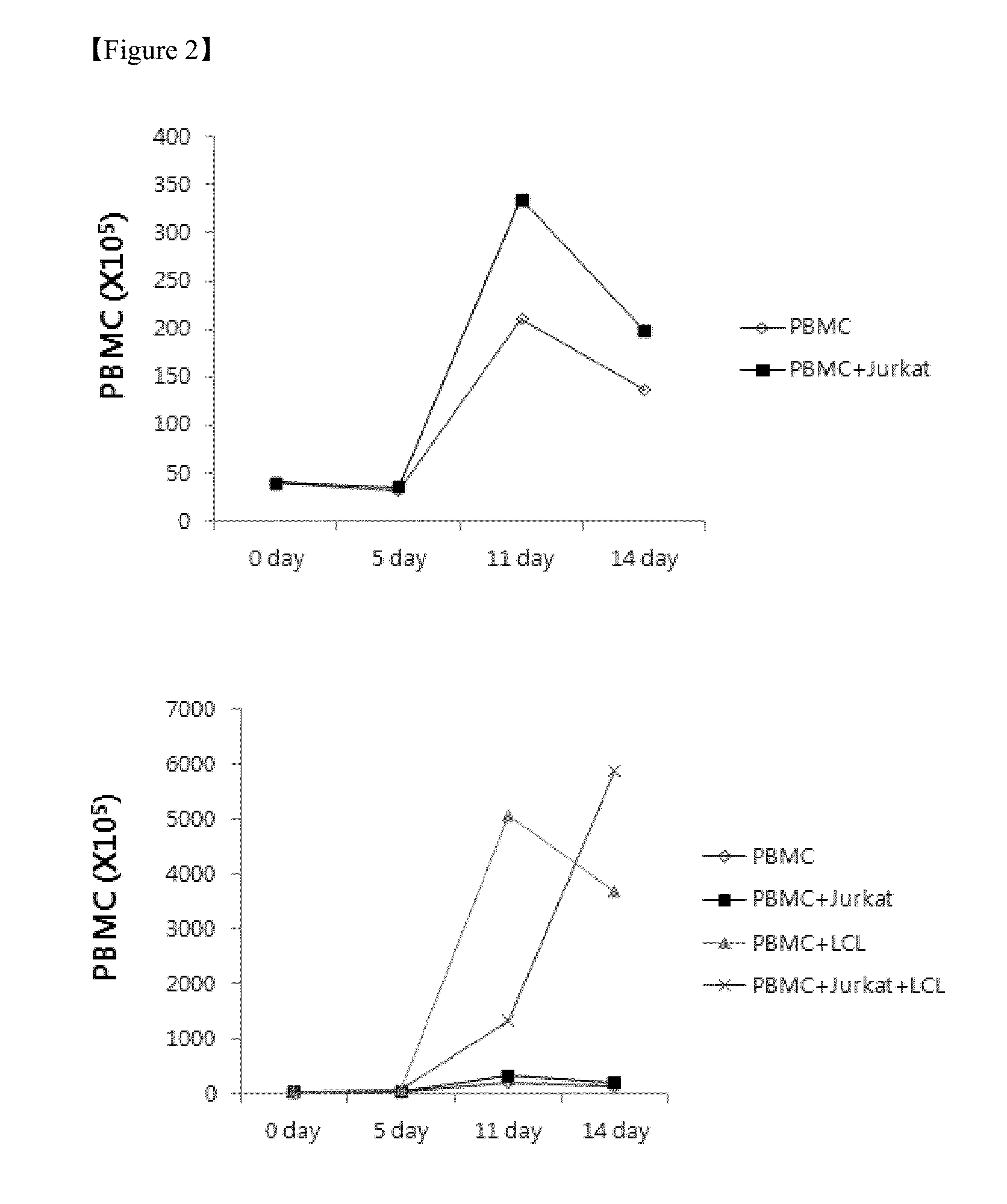
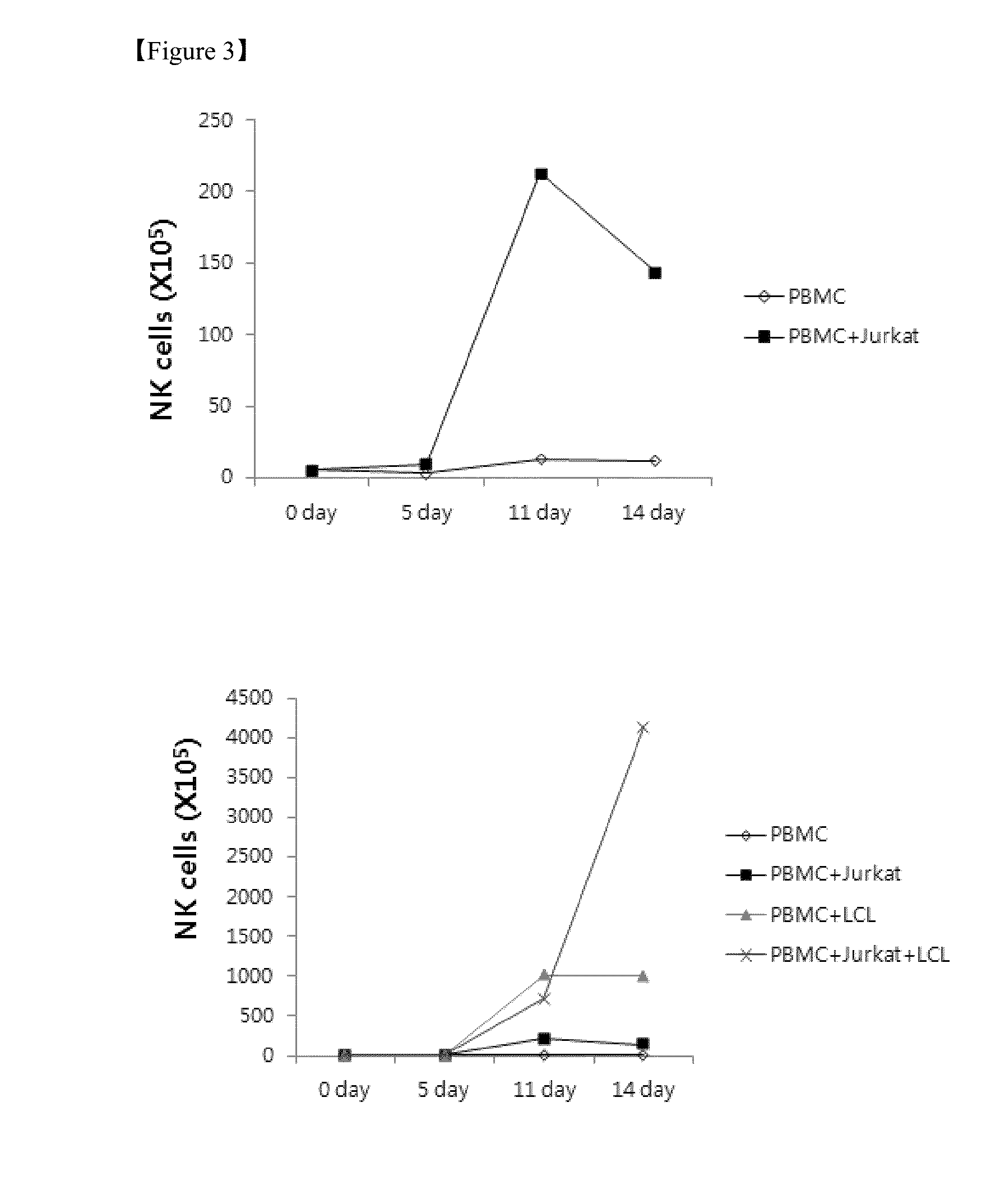
The present invention relates to a method for inducing and expanding natural killer cells derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells, which comprises co-culturing, as feeder cells, irradiated Jurkat cells and irradiated Epstein-Barr virus transformed lymphocyte continuous line (EBV-LCL) cells in the presence of cytokines, along with peripheral blood mononuclear cells. According to the present invention, a large quantity of natural killer cells can be induced and proliferated from a small quantity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells even without the use of high-cost equipment or various kinds of expensive cytokines, thereby making it possible to significantly improve the efficiency and efficacy of the prevention and treatment of cancer using the natural killer cells.
Owner:NKMAX CO LTD
Methods and kits for diagnosis, prognosis or monitoring of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated cancer
InactiveUS20080206749A1Lower Level RequirementsEliminate false positive caseMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteriuriaNon invasive
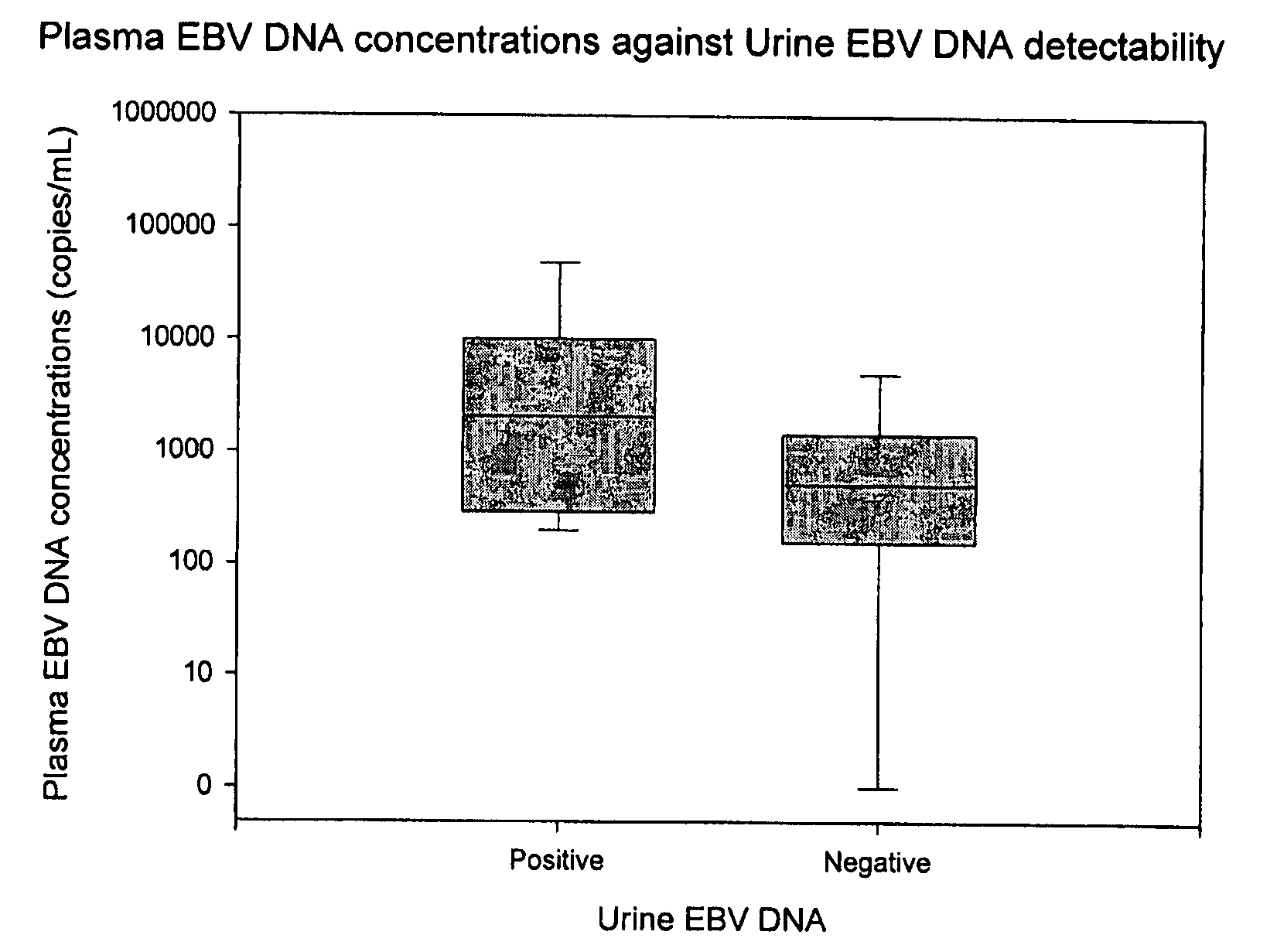
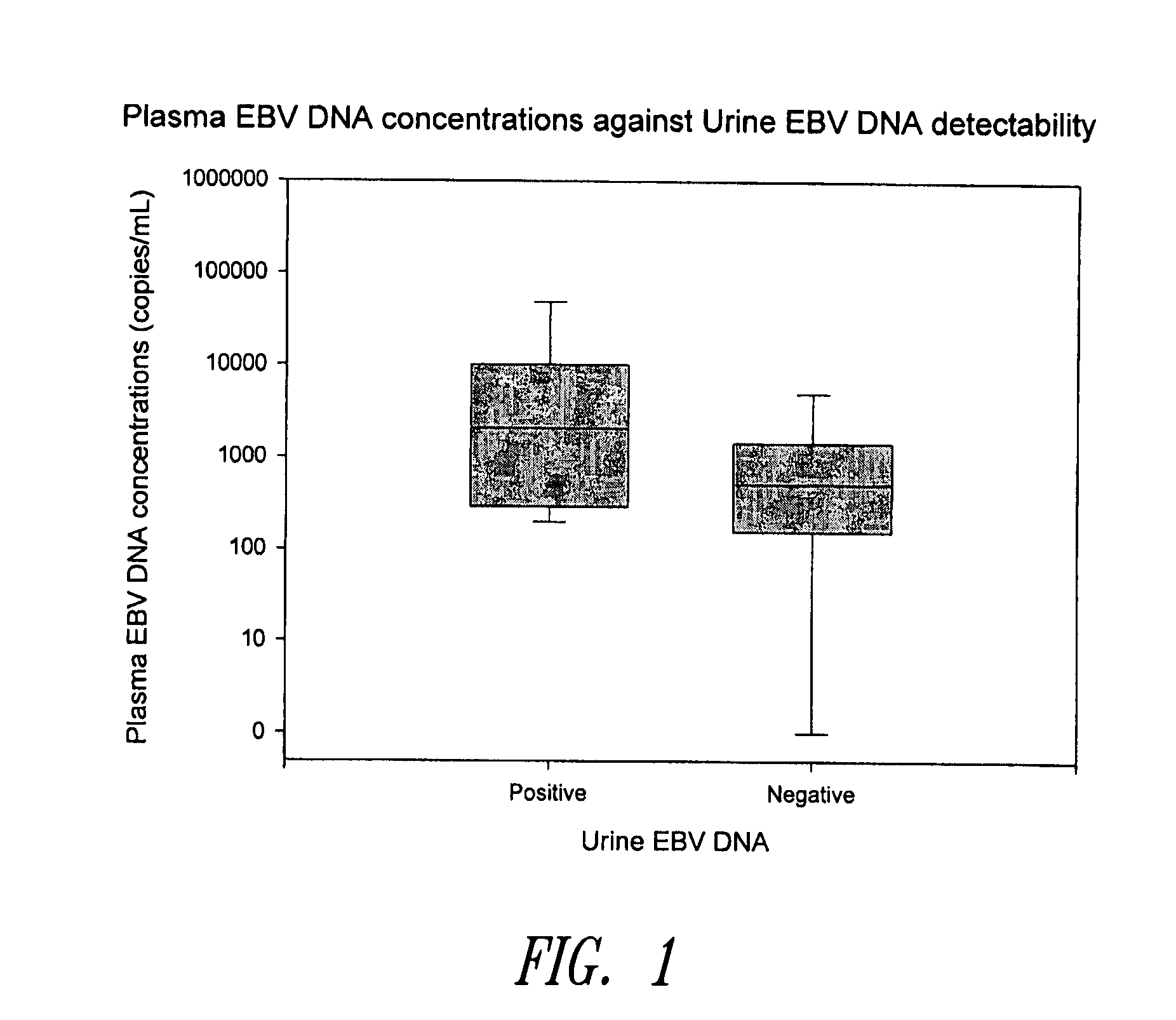
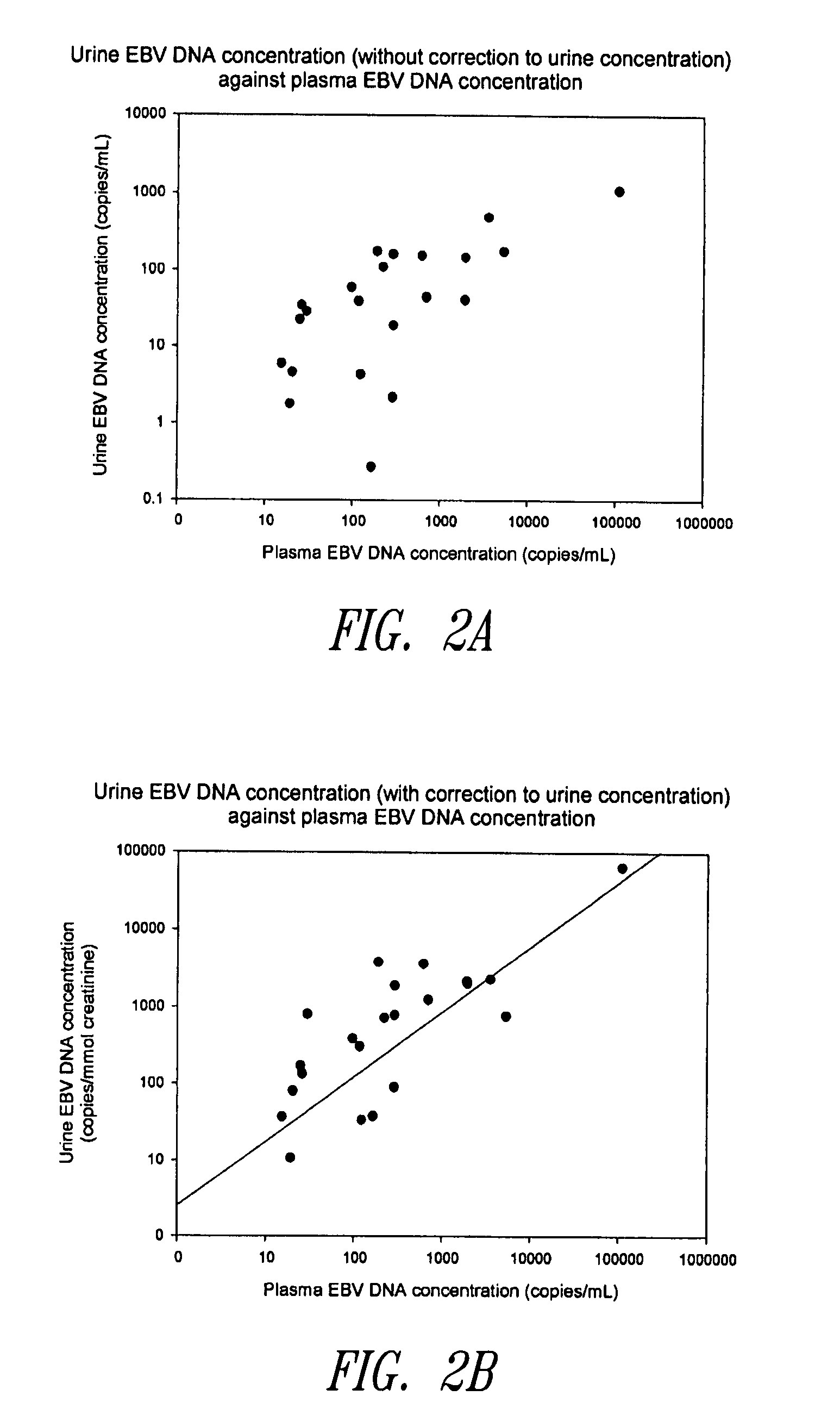
Disclosed is a non-invasive method for diagnosis, prognosis or monitoring of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated cancer by detecting and / or quantifying EBV associated nucleic acid fragments in a urine sample from an individual. Kits for diagnosis, prognosis or monitoring of cancer are also disclosed.
Owner:HONG KONG THE CHINESE UNIV OF
Cytotoxic t-cell epitope peptides that specifically attack epstein-barr virus-infected cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090305324A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsEpitopeNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
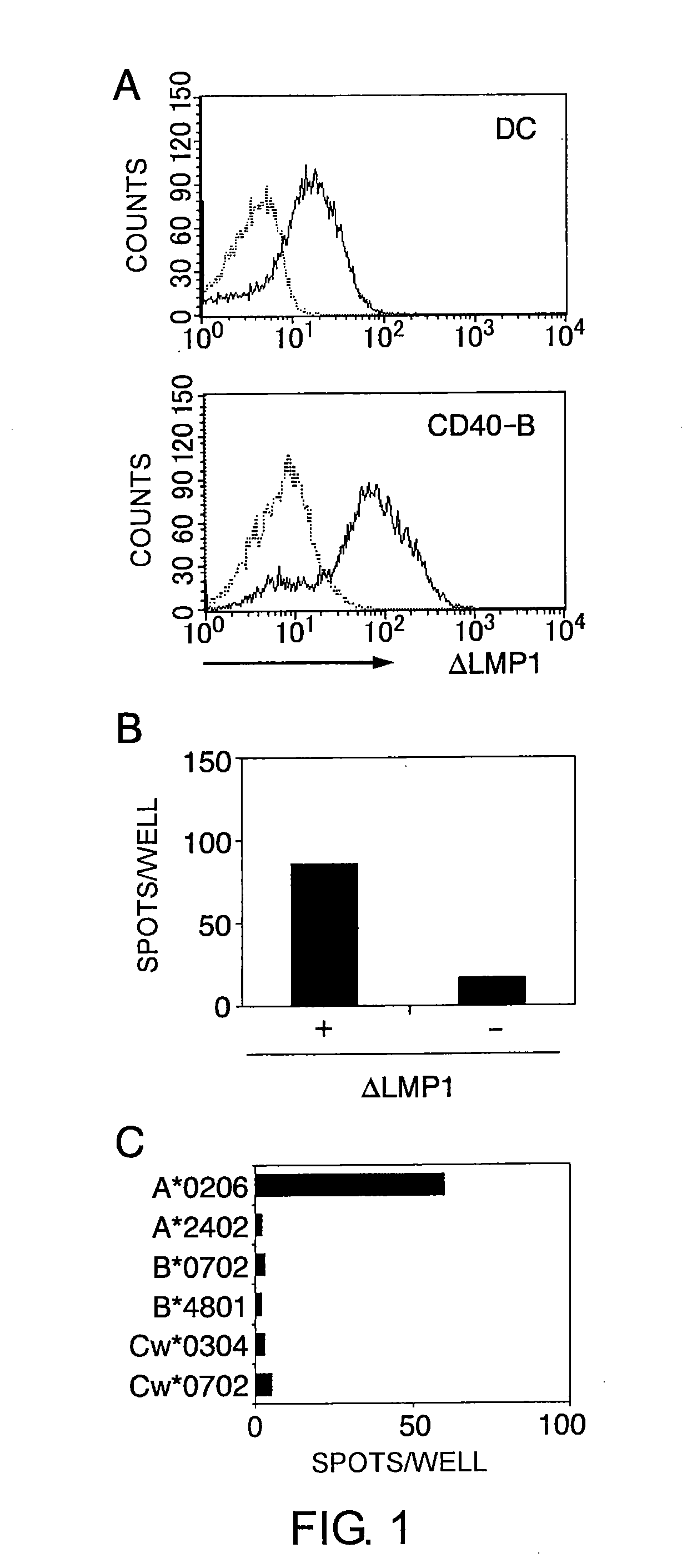
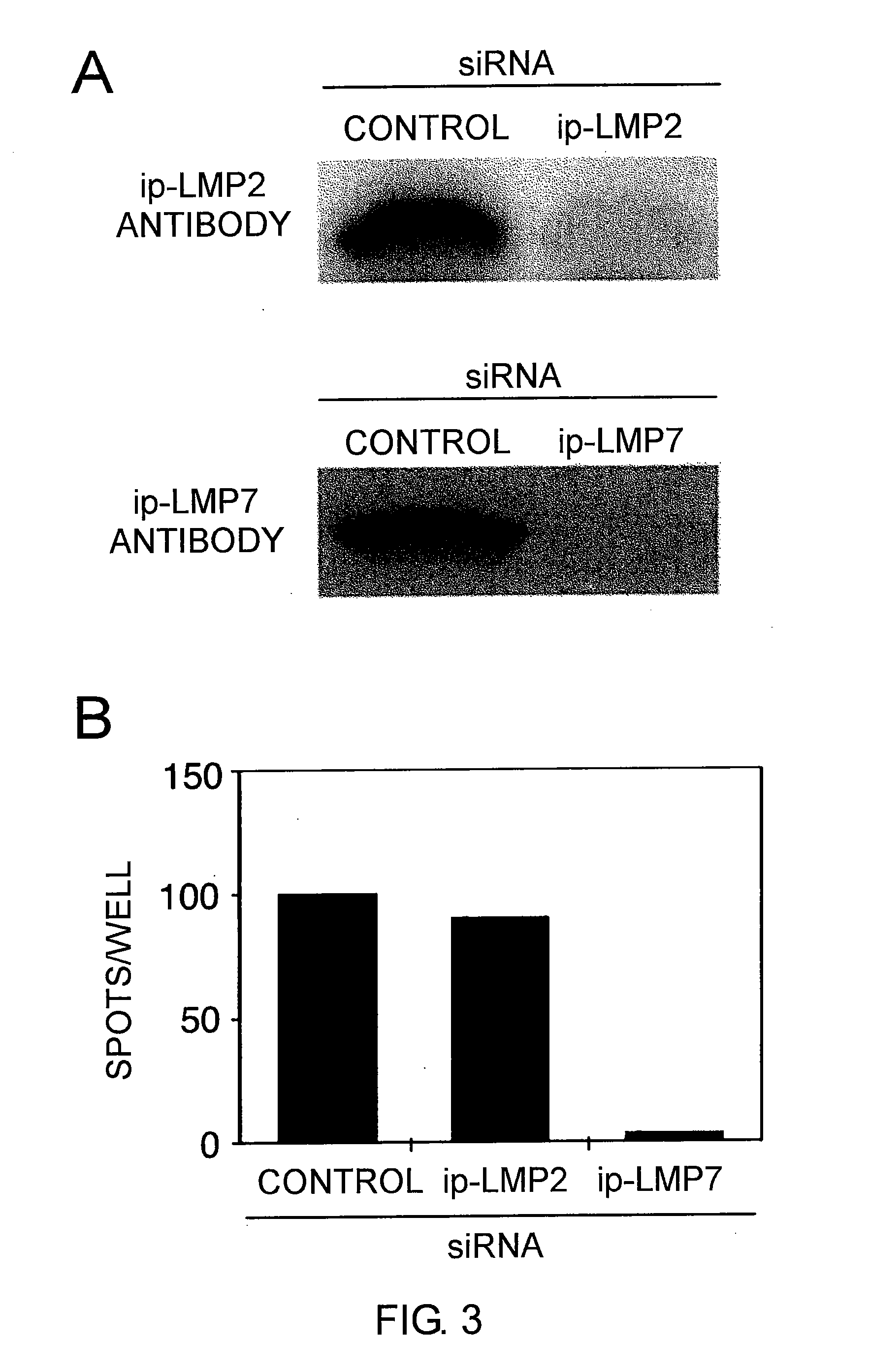
The present inventors introduced mRNAs for the Epstein-Barr virus proteins LMP1 and EBNA1 into antigen-presenting cells, and as a result, demonstrated that the cells induced Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T cells. The present inventors also demonstrated that the cytotoxic T cells recognized epitope peptides presented via HLA-A*0206, HLA-Cw*0303, or HLA-Cw*0304, inhibited the outgrowth of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells, and lysed Epstein-Barr virus-infected NK lymphomas and NK cells.
Owner:AICHI PREFECTURE +1
Reprogramming immortalized b cells
ActiveUS20120058562A1High reprogramming efficiencySave stepsGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsLymphocyteB cell
Methods and composition for providing induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods including reprogramming B lymphocytes transformed by episomal vectors such as Epstein-Barr virus-based vectors are described. Furthermore, the invention provides induced pluripotent stem cells essentially free of exogenous elements and having B cell immunoglobin variable region rearrangement.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
CTL epitopes from EBV
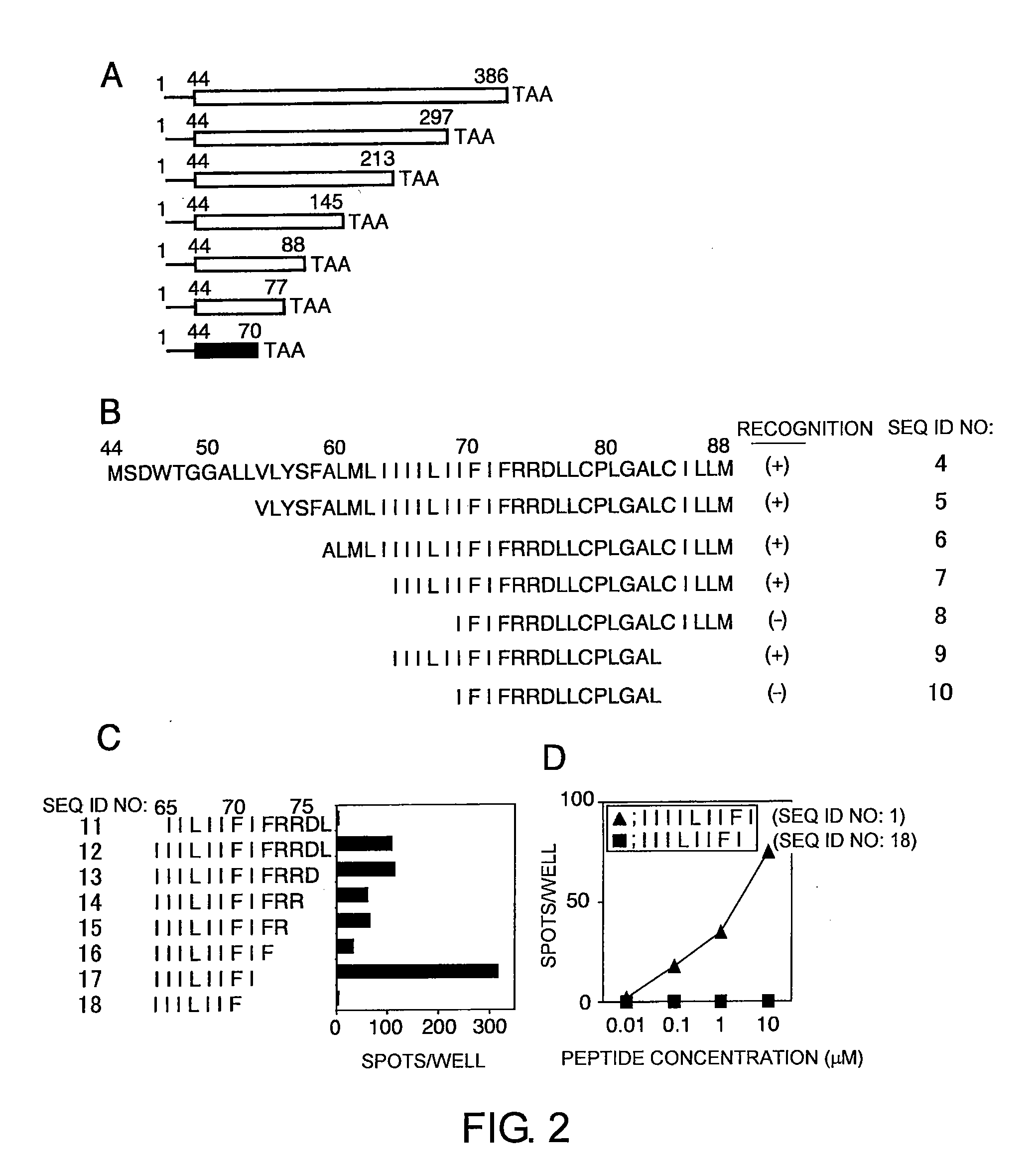
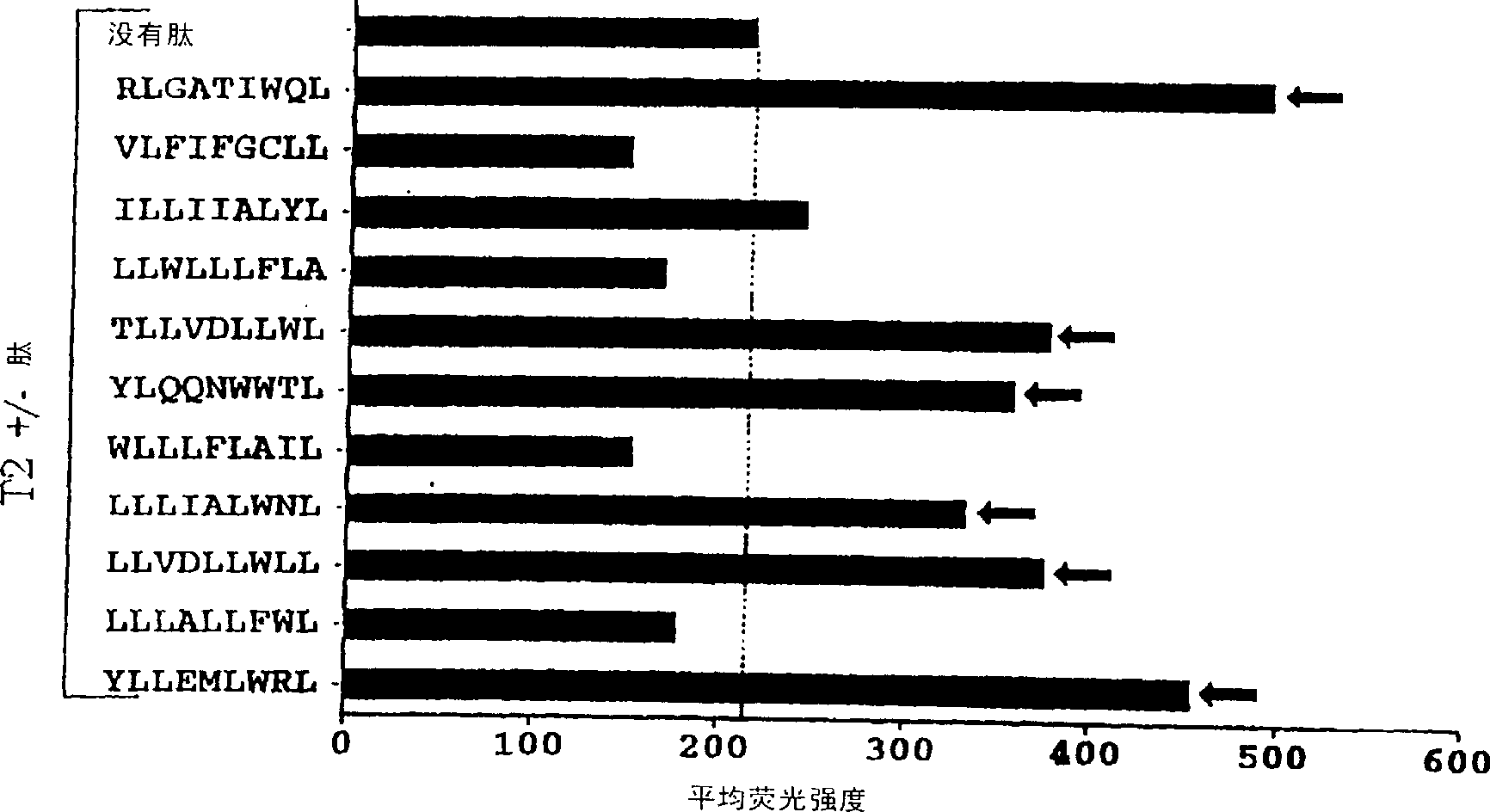
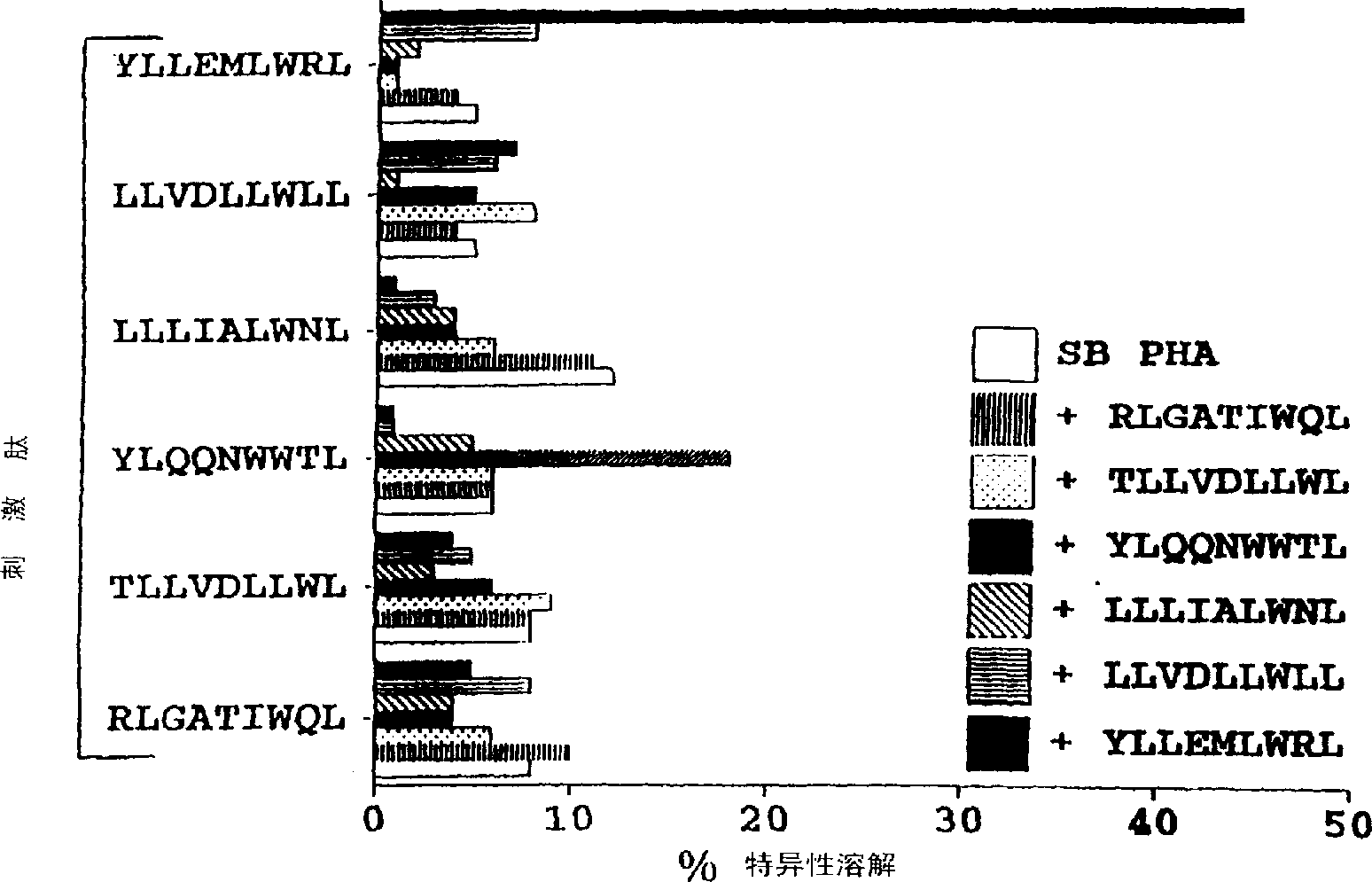
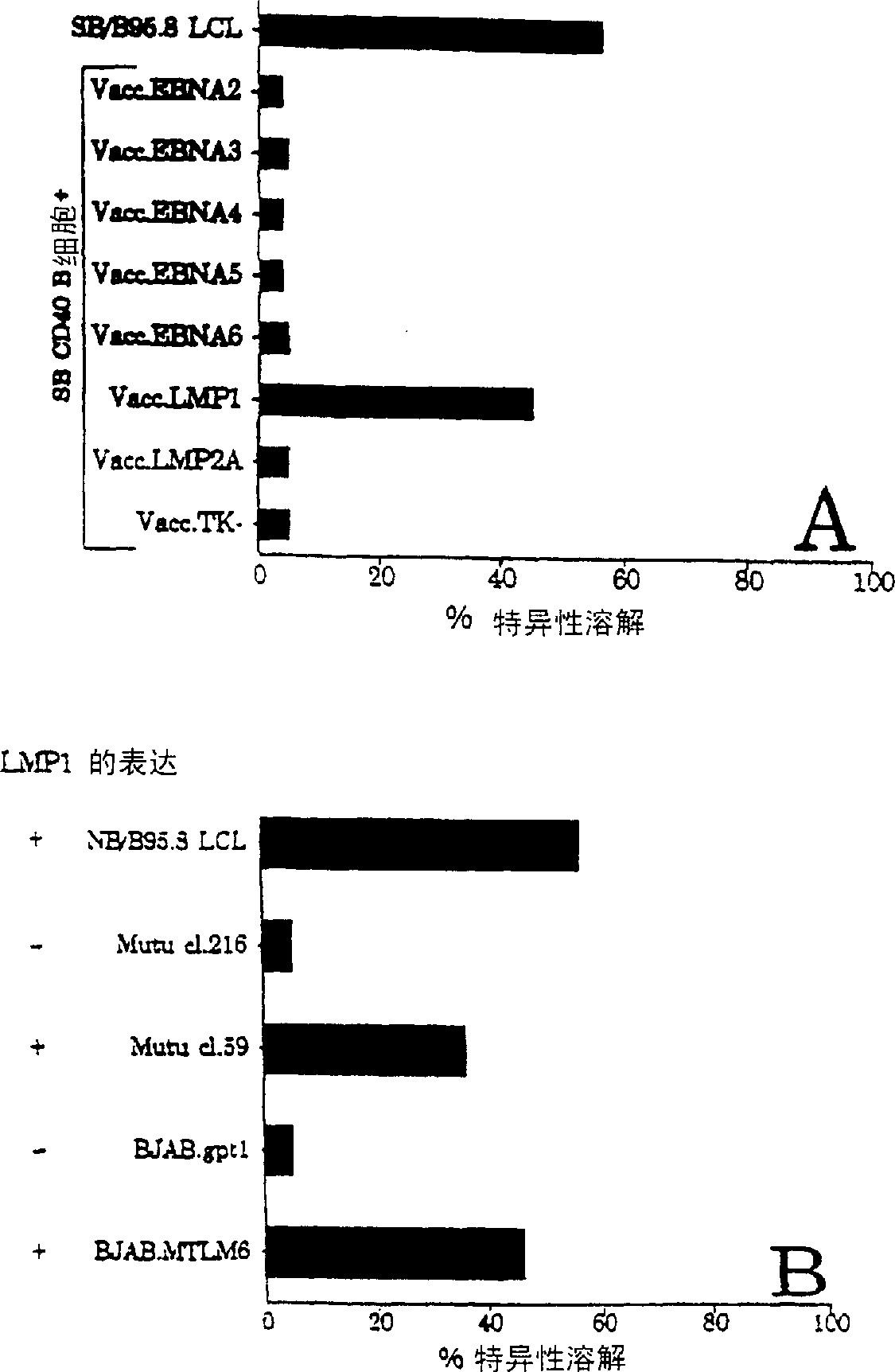
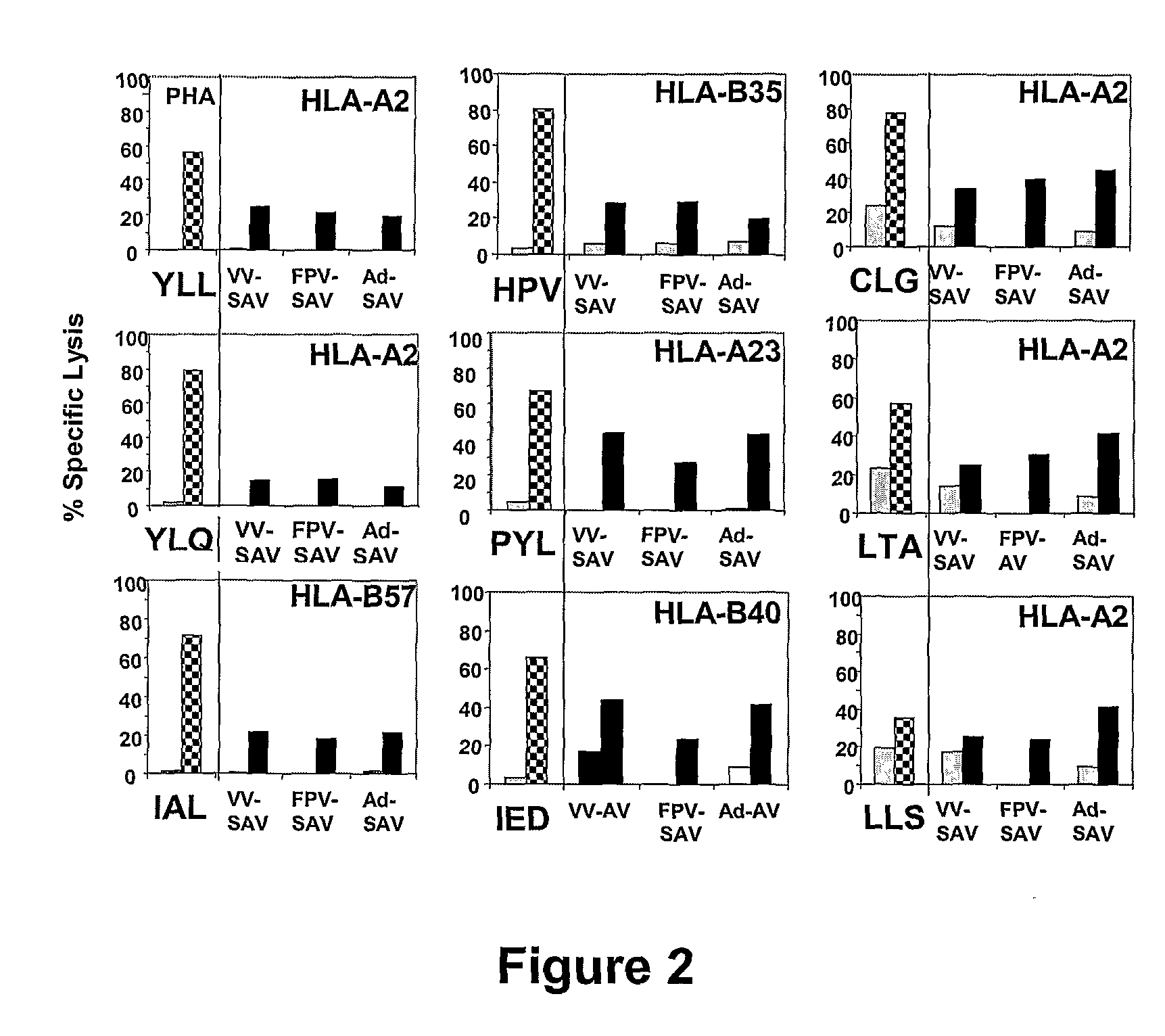
The present invention provides cytotoxic Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) T-cell epitopes derived from EBV structural antigens. Preferred epitopes include YLLEMLWRL (SEQ ID NO:1), YFLEILWGL (SEQ ID NO:32), YLLEILWRL (SEQ ID NO:33), YLQQNWWTL (SEQ ID NO:6), LLLALLFWL (SEQ ID NO:2), LLVDLLWLL (SEQ ID NO:3), LLLIALWNL (SEQ ID NO:4), WLLLFLAIL (SEQ ID NO:5), TLLVDLLWL (SEQ ID NO:7), LLWLLLFLA (SEQ ID NO:8), ILLIIALYL (SEQ ID NO:9), VLFIFGCLL (SEQ ID NO:10), RLGATIWQL (SEQ ID NO:11), ILYFIAFAL (SEQ ID NO:15), SLVIVTTFV (SEQ ID NO:17), LMIIPLINV (SEQ ID NO:20), TLFIGSHVV (SEQ ID NO:24), LIPETVPYI (SEQ ID NO:26), VLQWASLAV (SEQ ID NO:27) and QLTPHTKAV (SEQ ID NO:29). The present invention also provides methods of treating or preventing EBV infection in subjects which involve administration of EBV cytotoxic T-cell epitopes.
Owner:COUNCIL OF THE QUEENSLAND INST OF MEDICAL RES
New medicinal application of iridoid glycoside
ActiveCN104510747AReduce loadLower lung indexAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsViral MyocarditisInflammation
The invention belongs to the field of medicines and particularly relates to a new application of an iridoid glycoside compound, genipin-1-[beta]-D-gentiobioside, and a composition composed by compounding the genipin-1-[beta]-Dgentiobioside with other components as effective components for preparing antiviral drugs, antibacterial drugs, fever alleviating drugs, inflammation resistant drugs and anti-oxidizing drugs. The iridoid glycoside compound and the composition can be used for treating acute respiratory infection, flu, pneumonia, viral hepatitis type B, herpes zoster, herpes viral keratitis, viral myocarditis, Epstein-Barr virus infection, retrovirus infectious diseases and bacterial infectious diseases.
Owner:樊向德 +1
Methods to prevent vertical transmission of infectious diseases
InactiveUS20080269205A1Prevent vertical transmissionPrevent the spread of diseaseAntiviralsRadiation therapyEscherichia coliMonilinia laxa
The present invention presents a method of preventing vertical transmission of an infectious disease comprising: (a) applying a photosensitizing composition to host tissues of birth canal of a mother during the intrapartum period; and (b) applying light to the host tissues after the step (a) at a wavelength absorbed by the photosensitizing composition so as to inhibit or eliminate infectious disease microorganisms that come into contact with the host tissues. The infectious disease may be caused by human immunodeficiency virus type 1, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, Group B Streptococcus, cytomegalovirus, Listeria monocytogenes, Chiamydia trachomatis, Escherichia coli, herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus, Toxoplasma gondii, human papilloma virus, and Candida.
Owner:ONDINE INT
Protective antigen of Epstein Barr Virus
The present invention relates to the identification of a subunit vaccine to prevent or treat infection of Epstein Barr Virus. In particular, EBNA-1 was identified as a vaccine antigen. In a specific embodiment, a purified protein corresponding to EBNA-1 elicited a strong CD4+ T cell response. The responsive CD4+ T cell are primarily TH1 in function. EBNA-1 is an attractive candidate for a protective vaccine against EBV, and for immunotherapy of EBV infection and neoplasms, particularly with dendritic cells charged with EBNA-1.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Immunoreactive peptides from epstein-barr virus
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Herpes virus EBV (Epstein-Barr Virus) detection kit
ActiveCN103060473AEasy to operateSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEBV InfectionsPotassium
The invention provides a herpes virus EBV (Epstein-Barr Virus) detection kit. The kit comprises a nucleic acid releasing agent and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) reaction solution, wherein the nucleic acid releasing agent comprises 0.01-0.5 mM / L of surfactin, 20-300 mM / L of potassium chloride, 0.01-2% of sodium dodecyl sulphate and 0.05-1% of ethanol; and the PCR reaction solution comprises an upstream primer and a downstream primer used for target polynucleotide amplification, and a probe used for target polynucleotide detection. The detection result of the method for releasing nucleic acid by the nucleic acid releasing agent in the kit disclosed by the invention has no obvious difference with the detection result of a boiling method, a strong protein denaturing agent is used during nucleic acid extraction in the kit disclosed by the invention for rapidly breaking the coat protein structure of a pathogen and releasing the nucleic acid of the pathogen, and release and extraction for DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) can be rapidly finished without heating; the sensitivity of the EBV detection of the kit disclosed by the invention can achieve 400 copies / ml, and the quantitative linear range is 400-4.00E+09 copies / ml; by applying the kit, rapid and accurate detection can be performed on EBV-DNA in the unknown samples of blood plasma, throat swab, peripheral blood and the like, and reliable experimental basis is provided for diagnosing EBV infection.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
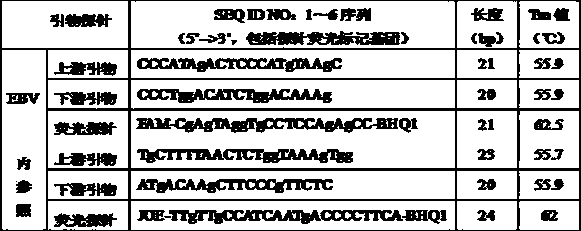
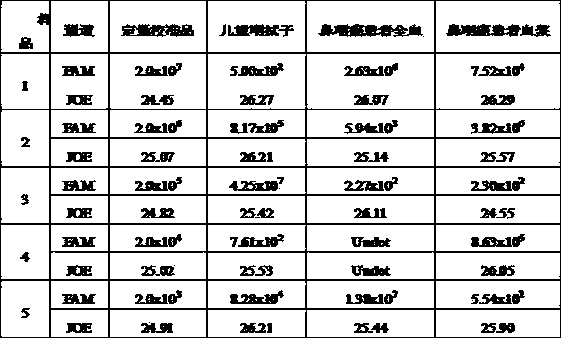
Reference-containing high-sensitivity fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kit for Epstein-Barr virus
ActiveCN103642945AHigh detection sensitivityAvoid misdiagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementFluoProbesViral nucleic acid
The invention relates to a kit for quantitative detection of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nucleic acid by using a fluorescent polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology. A pair of primers is used for amplifying an EBV specific nucleic acid sequence and EBVDNA is quantitatively detected through a fluorescence probe and meanwhile, an internal reference DNA is detected by using a human endogenous gene specificity primer and the fluorescence probe. By adopting the kit, existence of the EBV and internal reference nucleic acid is simultaneously detected by a single-tube double-wavelength fluorescent PCR technology, the EBVDNA in whole blood, plasma and a nasopharyngeal secretion sample can be quantitatively detected, and the whether a PCR inhibitor or template loss caused by a misoperation in detection exists in the sample is judged by the detection result of the internal reference nucleic acid. Thus, the kit is simple, convenient and fast in operation, can provide sensitive and accurate quantitative result, and can be widely applied to quantitative detection of clinical EBV virus infection.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGYAO MED TECH DEV CO LTD +1
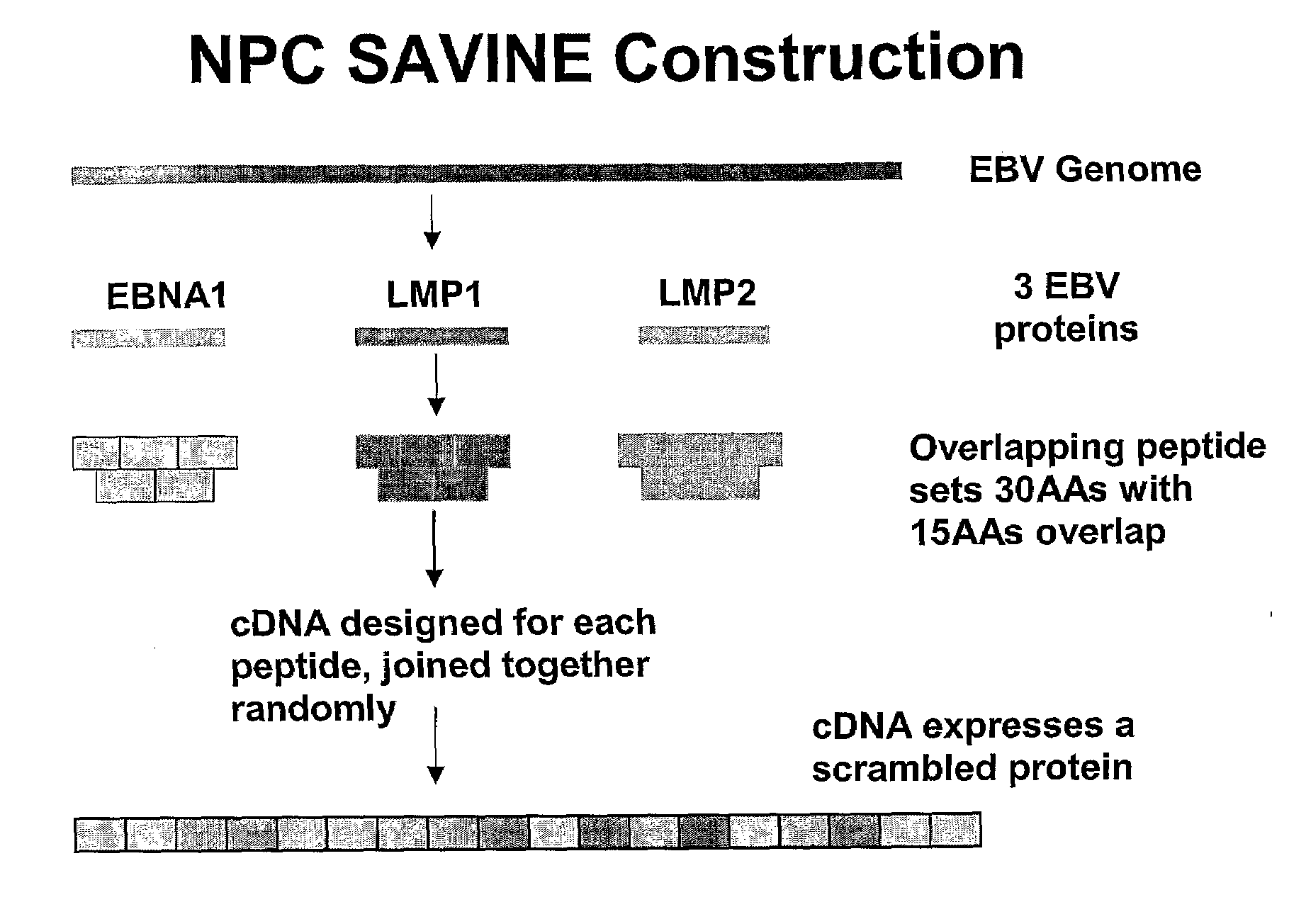
Treatment of epstein-barr virus-associated diseases
InactiveUS20090202584A1Improve stabilityImprove translationSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsVirologyDisease cause
The present invention relates to a vaccine for the treatment or prevention of an EBV-associated disease in a subject, wherein said vaccine comprises a synthetic polypeptide comprising a plurality of different segments of at least one parent EBV polypeptide, and wherein the segments are linked together in a different relationship relative to their linkage in the at least one parent EBV polypeptide.
Owner:SAVINE THERAPEUTICS
Diagnostics and therapy of epstein-barr virus in autoimmune disorders
InactiveUS7192715B2Encourage autoimmunityVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune responses
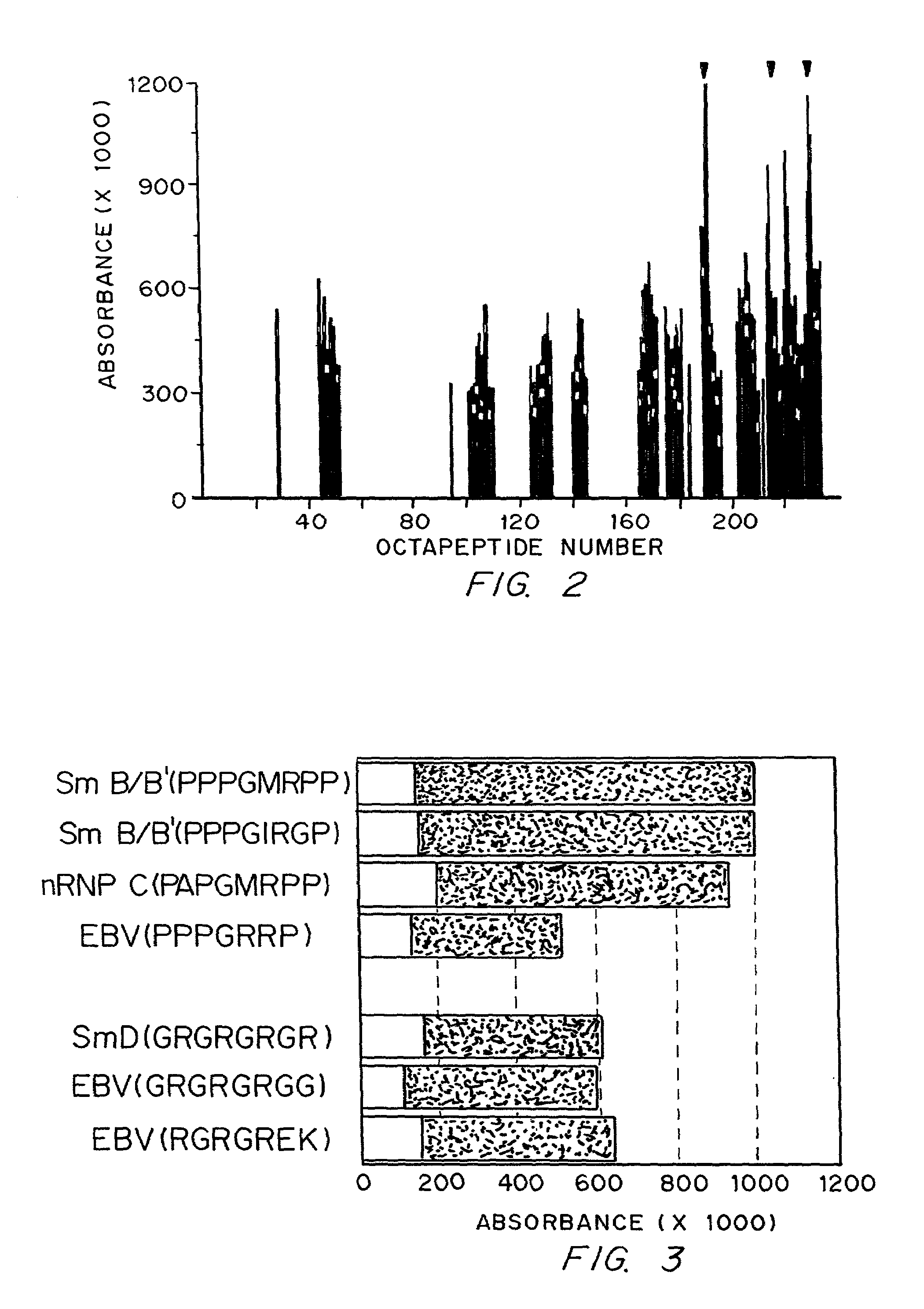
Data consistent with autoimmune disease being caused by Epstein-Barr virus are shown. Based on this evidence, an effective vaccine would prevent the autoimmune disease in those vaccinated, modified or administered so that the vaccine is not itself capable of inducing autoimmune disease. In the case of anti-Sm, structures to be avoided in an Epstein-Barr virus-derived vaccine have been identified. Differences have been identified in the immune responses to Epstein-Barr infection between individuals who develop a specific autoimmune disease and those who do not. These differences are used to distinguish those who are at greater risk for developing specific autoimmune diseases from those who are a lesser risk. Assuming Epstein-Barr virus causes autoimmune disease and that Epstein-Barr virus remains latent in the patient for life, reactivation of the virus from the latent state is important in generating or maintaining the autoimmune response that culminates in autoimmune disease. Cells infected with latent virus may also encourage autoimmunity. Based on the understanding that reactivation or latency are important to produce or sustain autoimmunity, then therapies directed against Epstein-Barr virus will also be effective therapies for the autoimmune manifestations of disease for which Epstein-Barr virus is responsible.
Owner:HARLEY JOHN B +1
Process, vectors and engineered cell lines for enhanced large-scale transfection
ActiveUS8637315B2Enhanced transfectionHigh expressionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesValproic AcidHamster
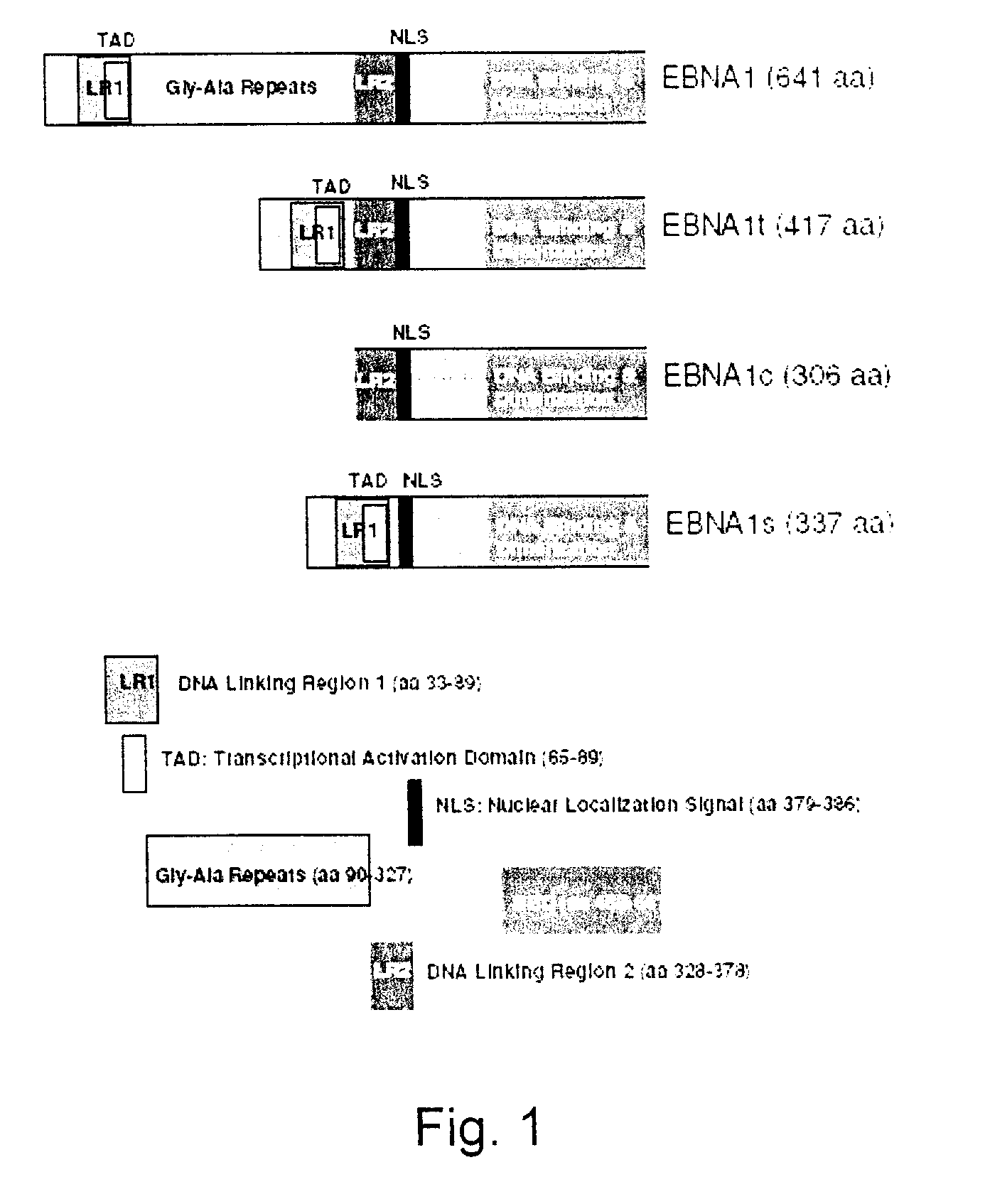
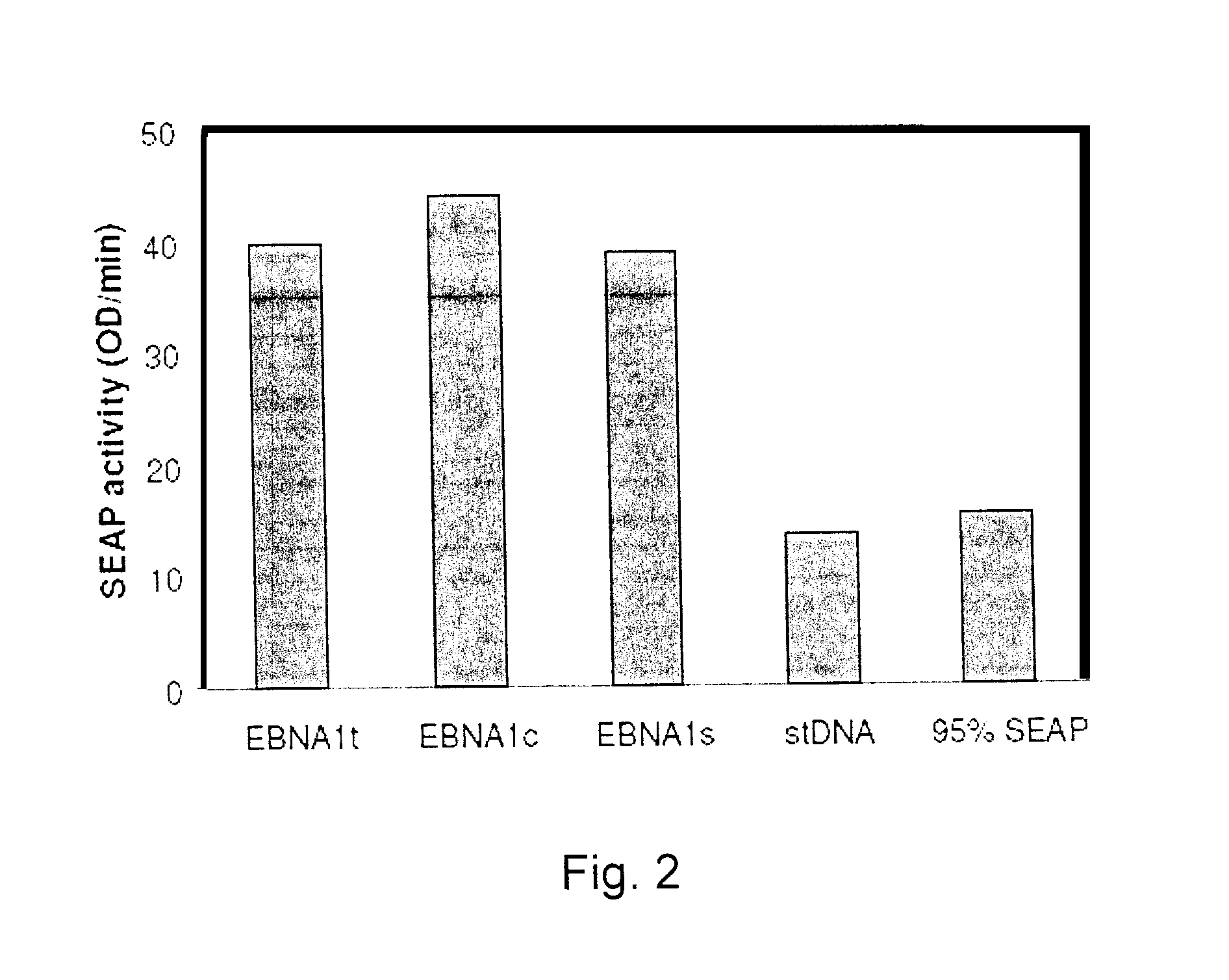
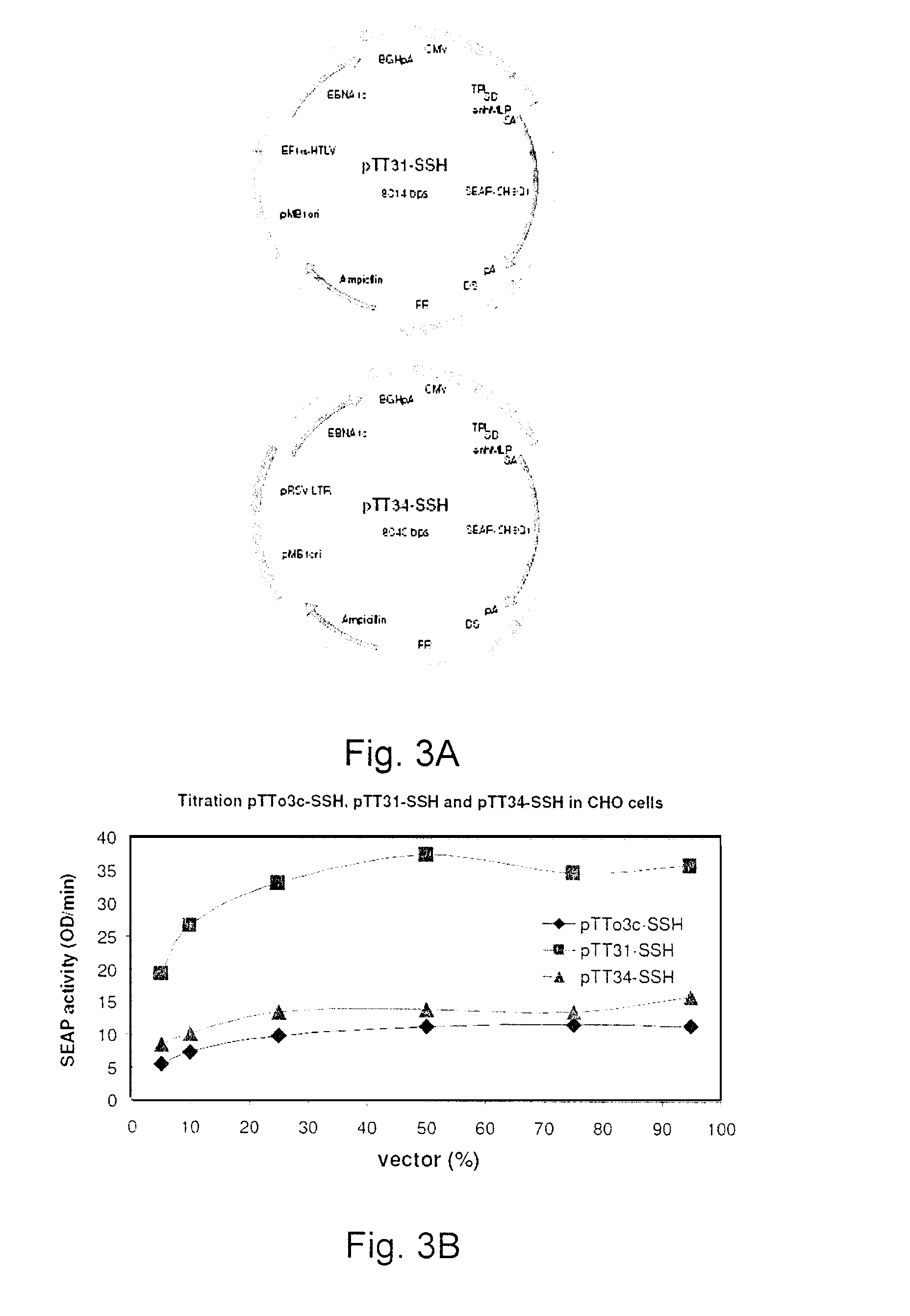
Processes vectors and engineered cell lines for large-scale transfection and protein production in mammalian cells, especially Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells are described in which transfection efficiencies are realized through the use of a single vector system, the use of functional oriP sequences in all plasmids, the use of codon-optimized Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA1) constructs the use of a fusion protein between a truncated Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigenen-1c (EBNA1c) protein and a herpes simplex virus protein VP16, the use of a 40 kDa fully deacetylated poly(ethylenimine) as a transfection reagent, the use of co-expression of a fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and / or the use of protein kinase B to potentiate heterologous gene expression enhancement by valproic acid (VPA).
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Molecular target for diagnosing and treating nasopharyngeal cancer related with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection and application thereof
InactiveCN102174516AAccurately reflect retention and lossPrevent proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsEBV InfectionsNasopharyngeal carcinoma
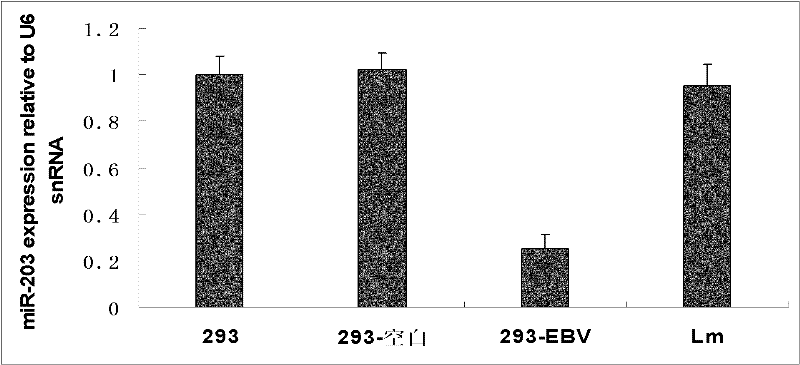
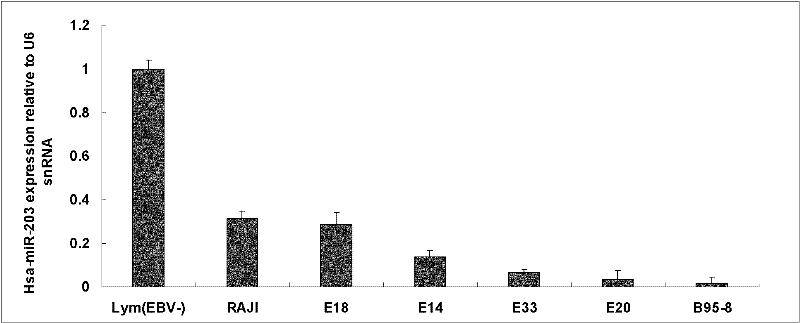
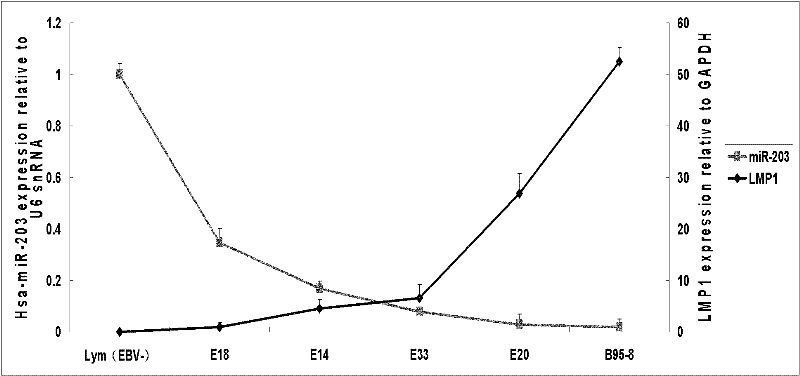
The invention discloses a molecular target hsa-miR203 for diagnosing and treating nasopharyngeal cancer related with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection and application thereof. The microRNA can accurately reflect the conditions of retention and loss of EBV viruses in cells and tissues, and further can be used for diagnosing the nasopharyngeal cancer related with the EBV infection; and meanwhile, target genes E2F3, CCNG1 and the like controlled by the hsa-miR203 obviously inhibit the proliferation and conversion capacities of the cells, so the hsa-miR203 can be used for treating the nasopharyngeal cancer related with the EBV infection. Therefore, the hsa-miR203 has important scientific research theory and clinical application value, and provides new clue and proof for diagnosis, treatment or prognosis of EBV related tumors.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Compositions and methods for modulating the activity of epstein-barr nuclear antigen 1
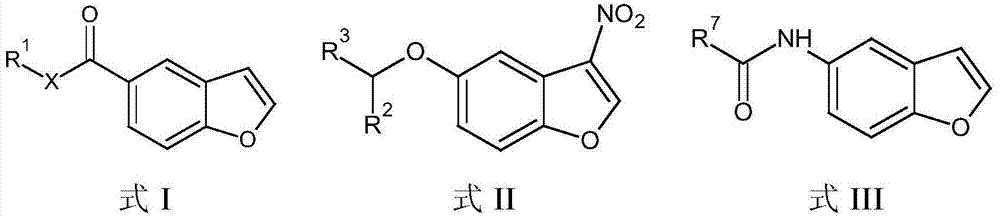
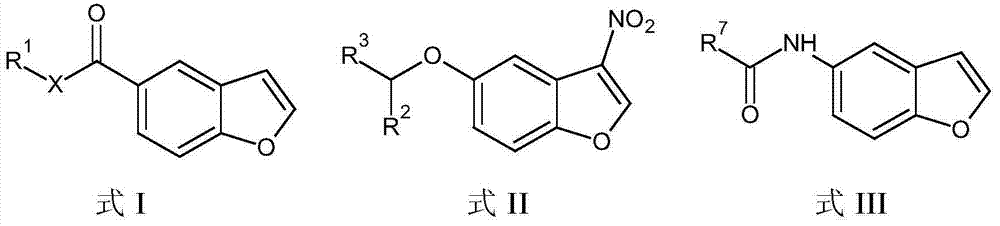
InactiveCN103717757AOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementEpstein bar virusPharmaceutical drug
The present invention embraces compounds that modulate the activity of Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 (BBNA1 ) protein and use thereof in methods for treating latent Epstein-Barr virus infection. R7 is a substituted or unsubstituted phenyl, pyridyl, or pyrimidinyl group. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of the invention in admixture with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier is also provide as are methods for modulating the activity of Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 (EBNA1 ) protein and treating a latent EpsteinBarr virus infection with a composition of the present invention.
Owner:WISTAR INSTITUTE
Cytotoxic t-cell epitope peptide and use thereof
InactiveCN107709351AMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansImmunotherapeutic agentEBV Infections
The present invention provides a cytotoxic T-cell (cytotoxic T lymphocyte, abbreviated hereinafter as CTL) epitope peptide specific to the Epstein-Barr virus (described hereinafter as EBV), a vaccinefor treating or preventing EBV infection or EBV-positive cancer using this peptide, a passive immunotherapeutic agent for EBV, and a method for assaying CTL specific to EBV. The present invention alsoprovides an HLA-A*24:02-restricted epitope peptide comprising an IYTEVRELV sequence (SEQ ID NO: 43) from a cytoskeleton-associated protein (cytoskeleton-associated protein 4: CKAP4 hereinafter, alsoknown as: CLIMP-63, ERGIC-63, P63). The peptide-specific cytotoxic T-cells (CTL hereinafter) can attack malignant tumor cells that express a high level of CKAP4.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
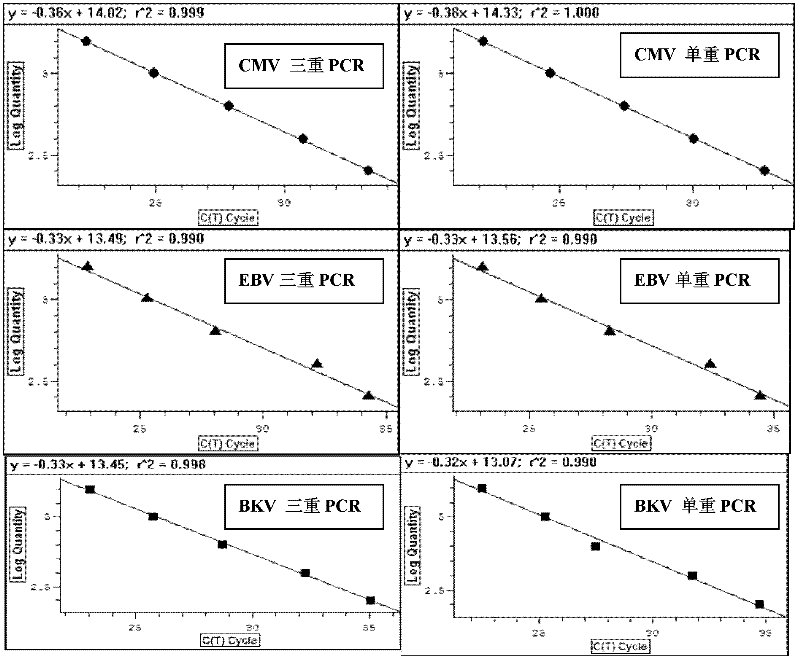
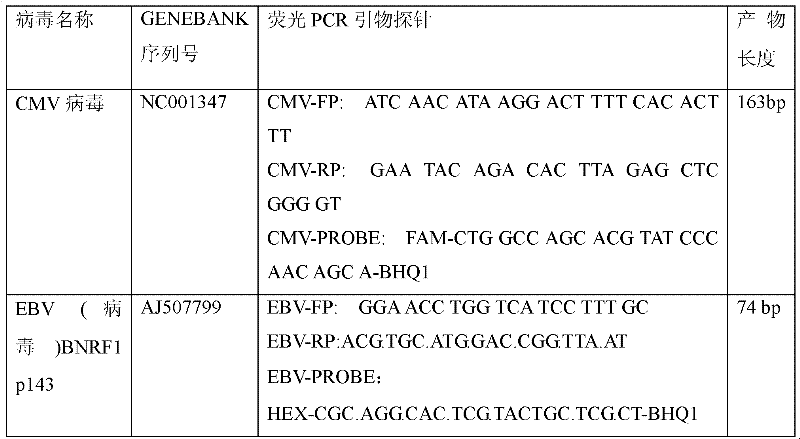
Treble real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for simultaneously detecting epstein-barr virus (EBV), polyma virus (BKV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) of people and kit
ActiveCN102363818AOptimize the PCR systemEasy procedureMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescencePcr method
The invention discloses a treble real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for simultaneously detecting an epstein-barr virus (EBV), a polyma virus (BKV) and a cytomegaloviruses (CMV) of people and a kit, which belong to medical molecular biological detection techniques. Three sets of primers and probes of the three viruses, which are designed by self, are adoptedto simultaneously detect a specimen to be detected. Experiments show that through adopting the three sets of probes and primers to simultaneously amplify a template to be detected or a manually-configured verification standard substance, the stocks of the three viruses in the specimen can be reflected peculiarly and correctly, and the three viruses cannot interfere with one another.
Owner:同昕生物技术(北京)有限公司
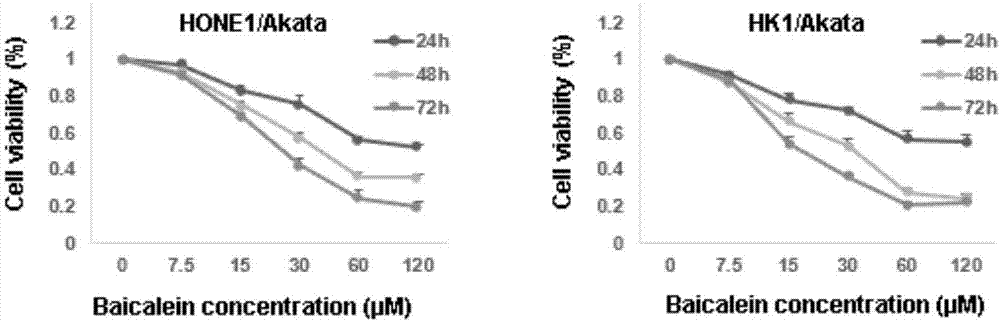
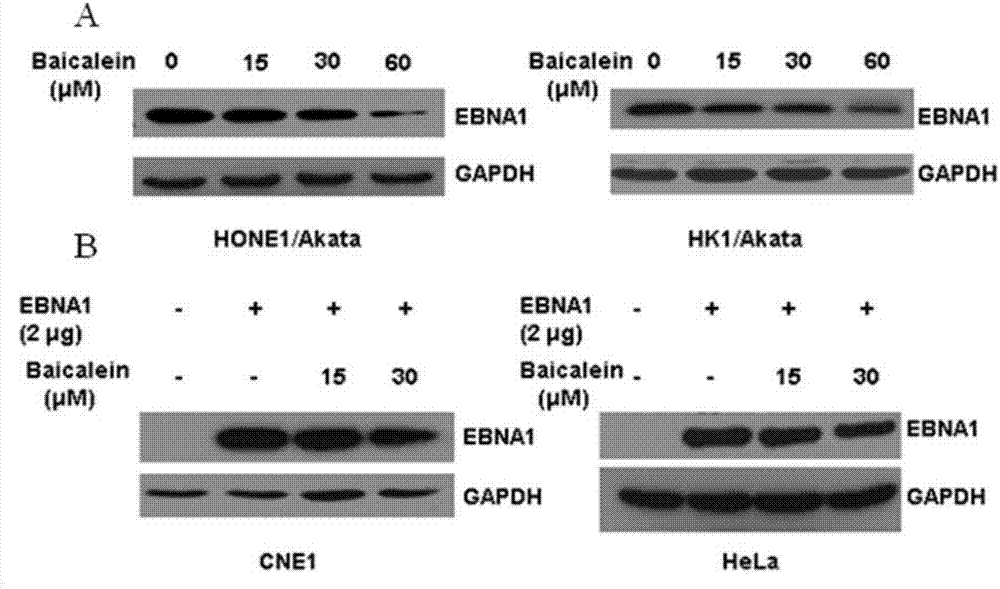
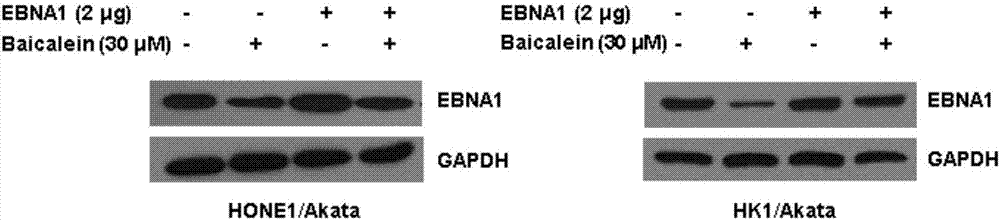
Application of baicalein to preparation of drug for preventing and/or treating nasopharyngeal carcinoma
InactiveCN107334763AConvenient treatmentHelps treat precancerous lesionsOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsNasopharyngeal CancersBaicalein
The invention discloses an application of baicalein to the preparation of a drug for preventing and / or treating nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The application firstly proves that baicalein can remarkably inhibit a viral protein EBNA1 on which an Epstein-Barr virus exists, and a cell can become a normal cell due to tumor virus loss caused by overlow existing quantity of the protein in the cell. Baicalein can be favorably used for treating precancerous lesion, the conversion of severe rhinitis to nasopharyngeal carcinoma is effectively stopped, and the application has important significance for treating the precancerous lesion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and reducing the occurrence rate and fatality rate of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Quantitative fluorescent multiplex PCR test kit for Epstein-Barr virus, and application thereof in nasopharyngeal carcinoma screening
InactiveCN102839222ATo achieve the purpose of high-throughput screening NPCAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMultiplexPromoter
The invention relates to a quantitative fluorescent multiplex PCR test kit for Epstein-Barr virus, and the kit comprises the following reagents: a, specific primer pairs for amplifying mutations of key target genes in the Epstein-Barr virus; and b, specific probes for the mutations of key target genes in the Epstein-Barr virus, wherein the mutations are P-thr, V-val and V-leu in the coding region of EBNA-1 gene, promoters Cp, Fp and Zp of the EBNA-1 gene, and XhoI-loss, 30bp Deletion and Ser 366 Thr of LMP1 gene. The test kit is advantageous in that: the aim of precise prediction of the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in high risk population can be achieved; the main carcinogenic mutations can be well known for the combination of population screening and population intervention for nasopharyngeal carcinoma; and the kit has the advantages of high in sensitivity, fast in test, and low in cost, having broad market prospect.
Owner:广州市第十二人民医院
An epstein-barr-virus vaccine
InactiveCN103328003AViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesMembrane lipidsEpstein–Barr virus vaccine
The present invention relates to a vaccine comprising a particle, said particle comprising (i) at least one Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) structural polypeptide, (ii) at least one EBV lytic polypeptide, (iii) membrane lipids, said particle being devoid of EBV DNA, wherein (a) the B-cell transformation capacity of one or more EBV polypeptides required for B-cell transformation as comprised in said particle is disabled while their immunogenicity is maintained; and / or (b) said particle is devoid of one or more EBV polypeptides required for B-cell transformation. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for generating a particle, to a cell obtained in the method of the invention, a kit comprising the vaccine or the particle generated according to the method of the invention. Also, the invention relates to the use of the vaccine or the particle generated according to the method of the invention for generating CD8+ cells specific for an EBV antigen.
Owner:亥姆霍兹慕尼黑中心德国研究健康与环境有限责任公司
Improved human herpesvirus immunotherapy
An isolated protein comprises respective amino acid sequences of each of a plurality of CTL epitopes from two or more different herpesvirus antigens and further comprises an intervening amino acid or amino acid sequence between at least two of said CTL epitopes comprising proteasome liberation amino acids or amino acid sequences and, optionally, Transporter Associated with Antigen Processing recognition motifs. The isolated protein is capable of rapidly expanding human cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) in vitro and eliciting a CTL immune response in vivo upon administration to an animal as an exogenous protein. Typically, the isolated protein comprises no more than twenty (20) CTL epitopes derived from cytomegalovirus and / or Epstein-Barr virus antigens.
Owner:COUNCIL OF THE QUEENSLAND INST OF MEDICAL RES
Epitope of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2b and its application
The invention relates to the preparation and application of EB virus latent membrane protein 2B cell epitope recombinant protein. The invention discloses three B cell epitopes screened on the basis of full-length Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2. The invention also discloses the coding nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the B cell epitope. The invention also discloses the use of the B cell epitope in preventing, treating and diagnosing Epstein-Barr virus infection and related diseases. The protein of the invention has strong immunogenicity and antigenicity, and has good application prospect.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
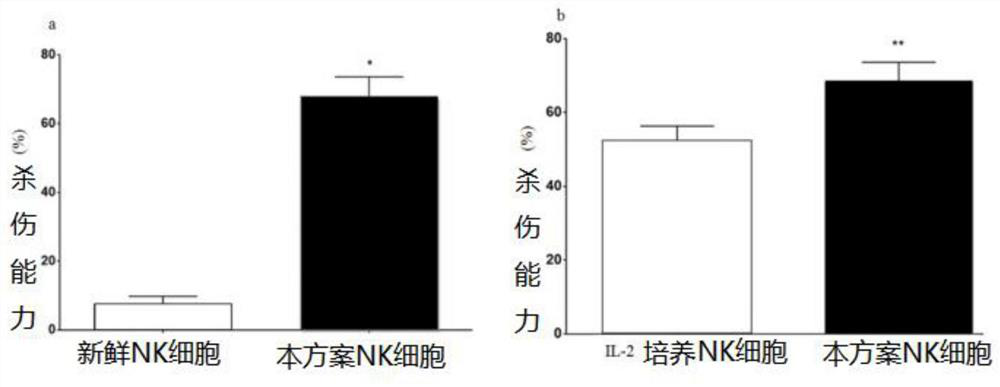
Peripheral blood-based LCL-NK cell co-culture method, cell and product
ActiveCN112852728AImprove efficiencyGood application effectCulture processBlood/immune system cellsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellLysis
The invention provides a peripheral blood-based LCL-NK cell co-culture method, whichcomprises the following steps: preparing and obtaining the PBMC from the peripheral blood, and preparing the LCL cells from the PBMC, wherein the LCL cells are obtained by culturing PBMC (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) in supernate containing EBV (electron barr virus); the EBV supernate is obtained by carrying out culture passage on B958 cells, then carrying out starvation lysis and then separating; and co-culturing the cells in a culture system formed by PBMC, LCL cells, cell factors and a culture solution. According to the culture method provided by the scheme, the purity of a cell product is effectively improved, and the culture efficiency, the NK cell killing property and the like are remarkably improved.
Owner:JIANGSU MOBILI BIOTECH CO LTD
Immunoreactive peptides from Epstein-Barr virus
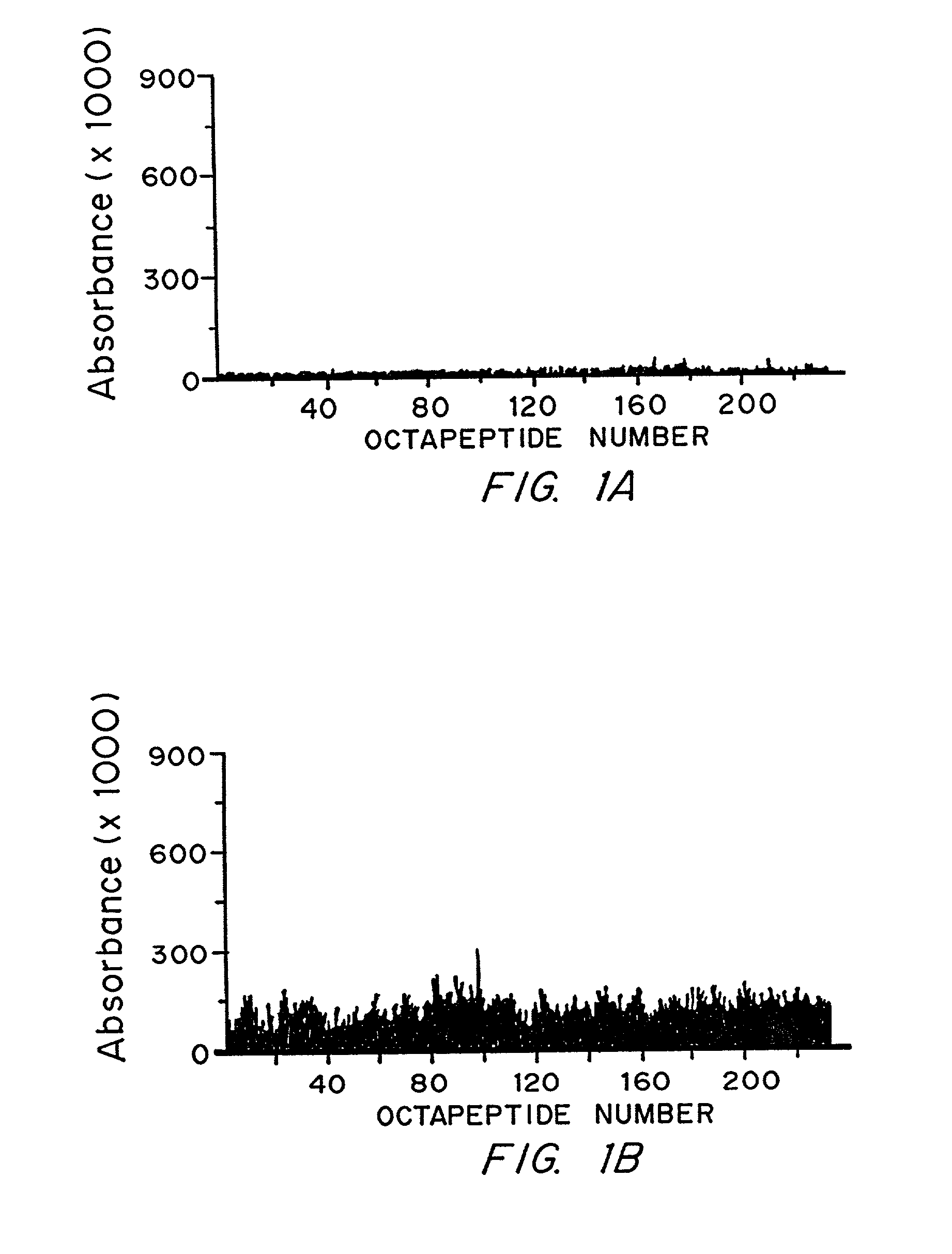
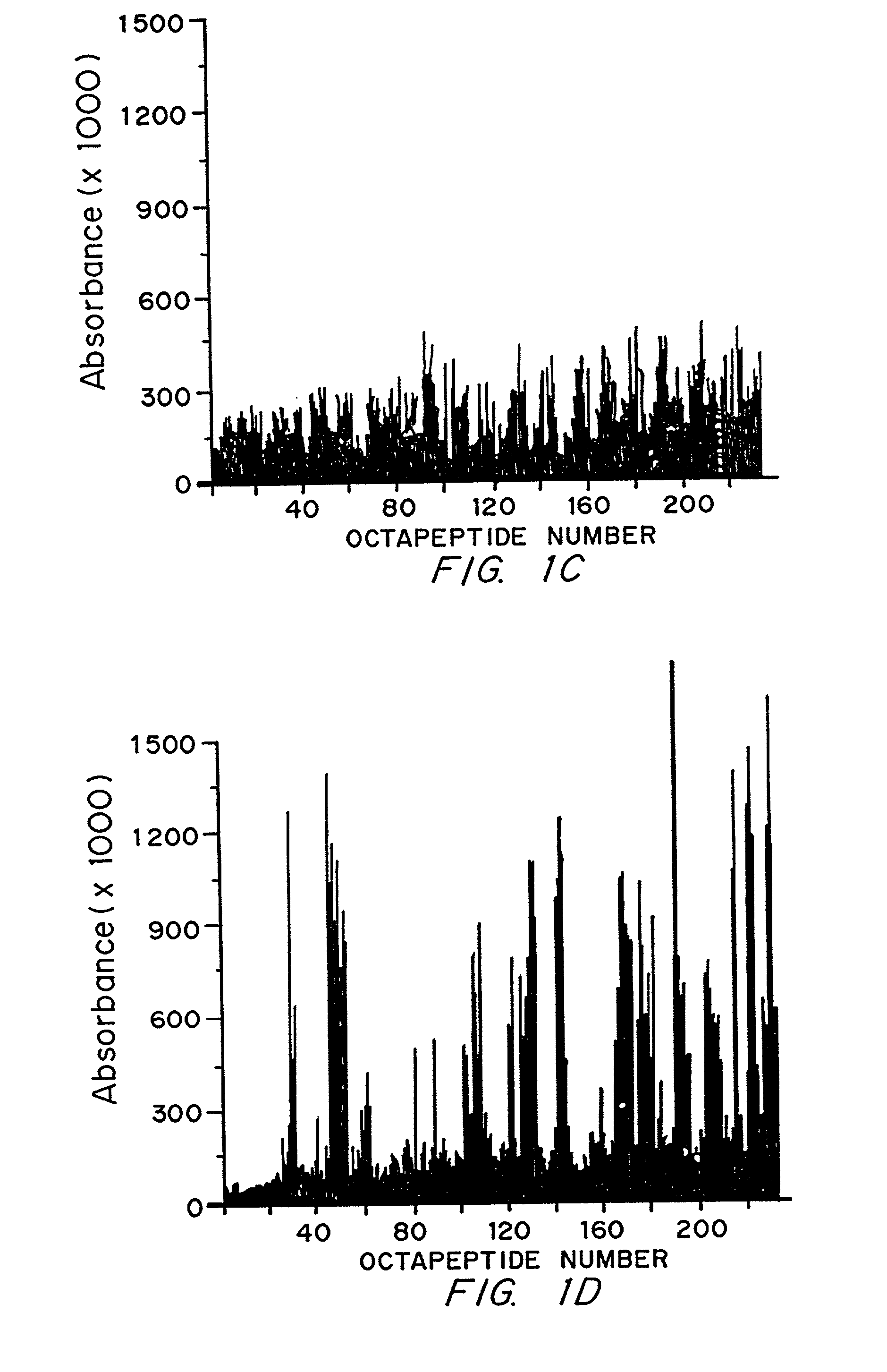
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) specific polypeptides consisting of a series of one to 1000 peptide units selected from the group consisting of peptide units Φ, Γ, Δ and Ω, wherein Φ is 25 amino acids or less and has the formula (αETFTETWNRFITHTEβ) (SEQ ID NO:1), Γ is 25 amino acids or less and has the formula (αGMLEASEGLDGWIHQβ) (SEQ ID NO:2), Δ is 25 amino acids or less and has the formula (αHQQGGWSTLIEDNIβ) (SEQ ID NO:3), Ω is 25 amino acids or less and has the formula (αKQKHPKKVKQAFNPLβ) (SEQ ID NO:4), α and β are each independently from 0 to 5 naturally occurring amino acids, and the polypeptide is capable of binding antibody in a specimen from an individual with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated disease are disclosed. Also disclosed are the use of these polypeptides for the production of polypeptide-specific antibodies and the diagnosis and treatment of EBV-associated disease.
Owner:ORTHO DIAGNOSTICS +1
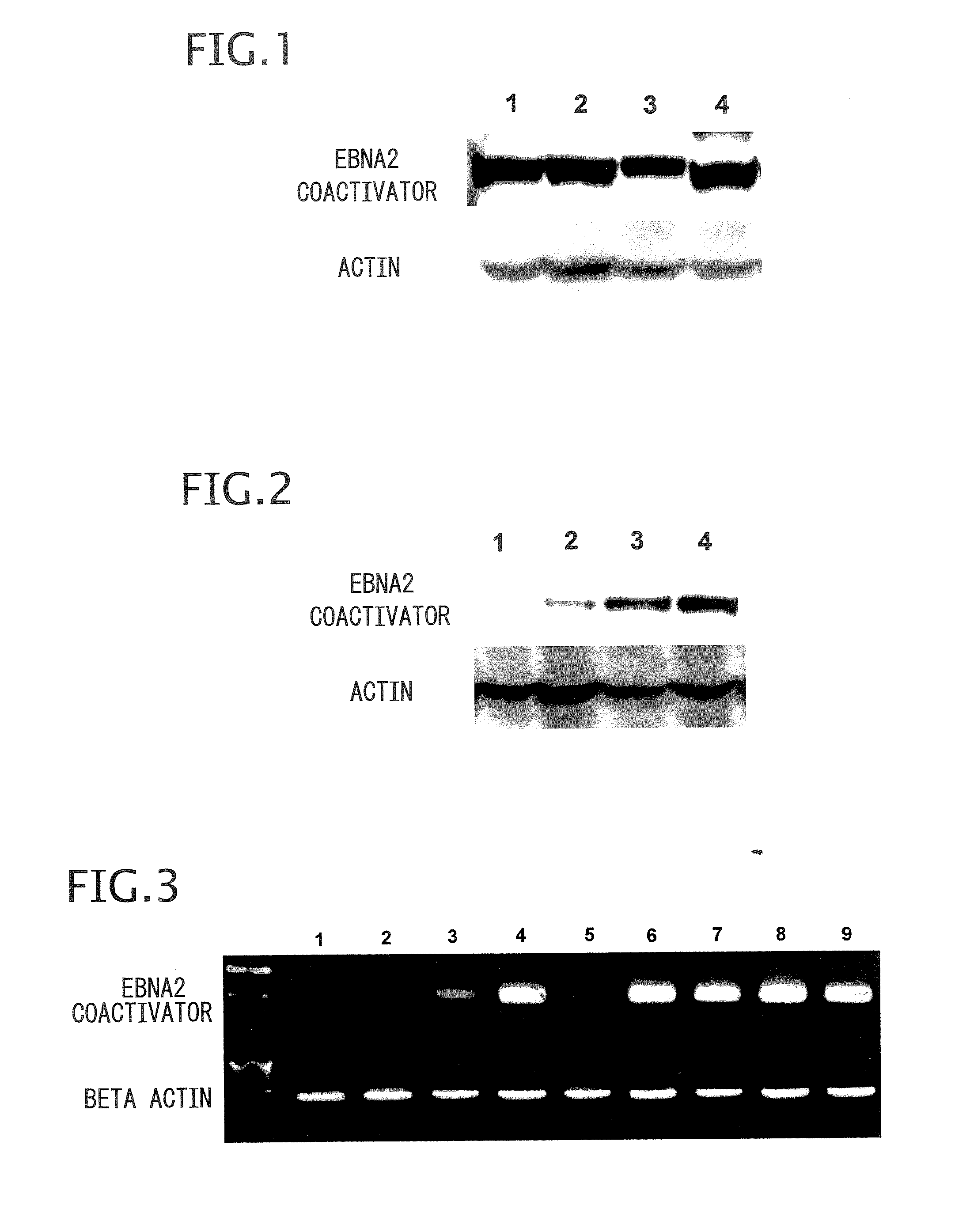
Method and composition for detecting cancer by means of detection of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 coactivator P100
ActiveUS7939269B2Microbiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsEpstein-Barr Virus Nuclear AntigensAntigen
Owner:TOSOH CORP
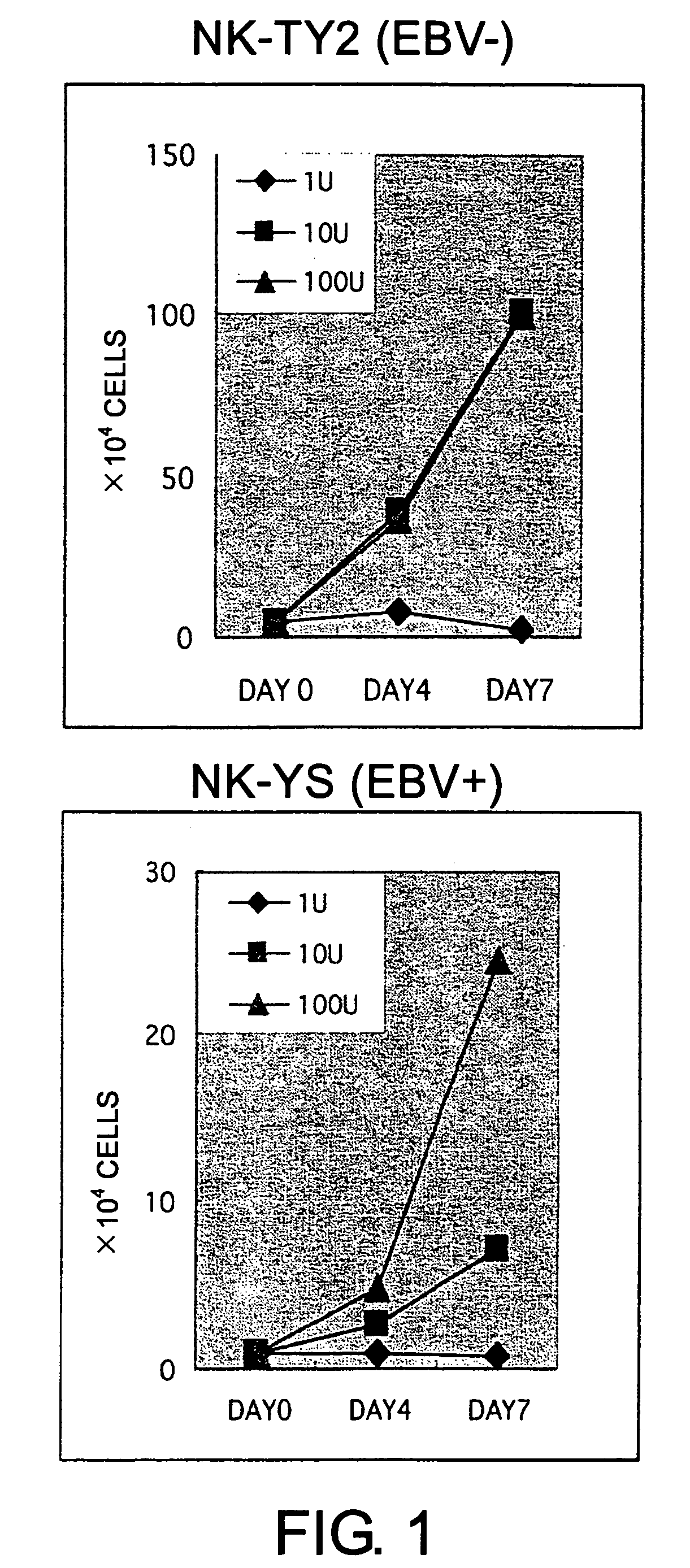
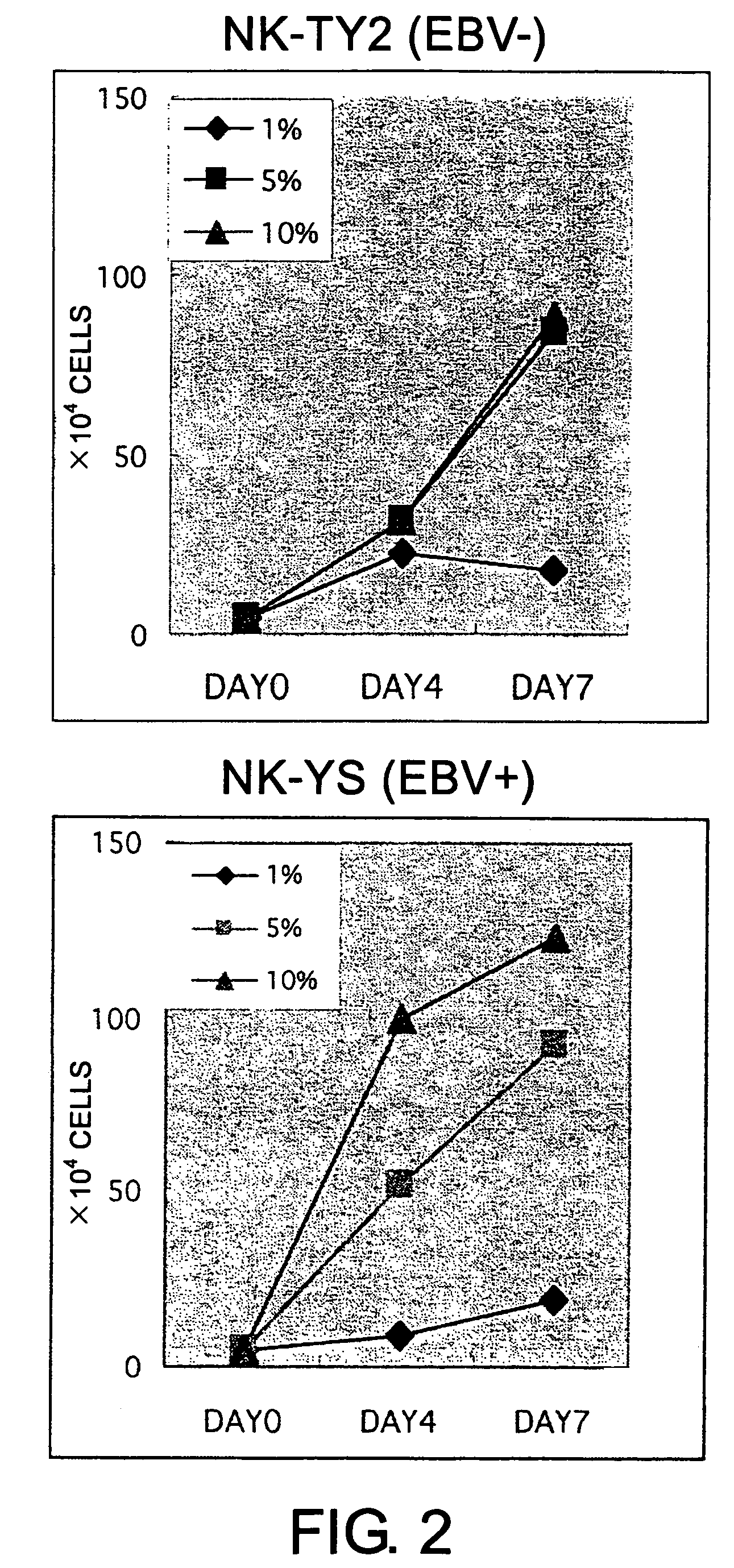
Epstein-Barr virus-negative NK cell line
ActiveUS7781210B2High sensitivity measurementEasy to measureGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementEpstein bar virusNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The present invention provides Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-negative NK cell lines. The NK cell lines of the present invention are useful for screening factors associated with the proliferation and expression functions of NK cells and to discover factors produced by the NK cells. In addition, the cell lines are immortalized despite the fact that they are EBV-negative. Thus, unknown mechanisms of oncogenesis may be elucidated through an understanding of the mechanisms underlying the immortalization of the cell lines of the present invention.
Owner:JUNJIRO TSUCHIYAMA
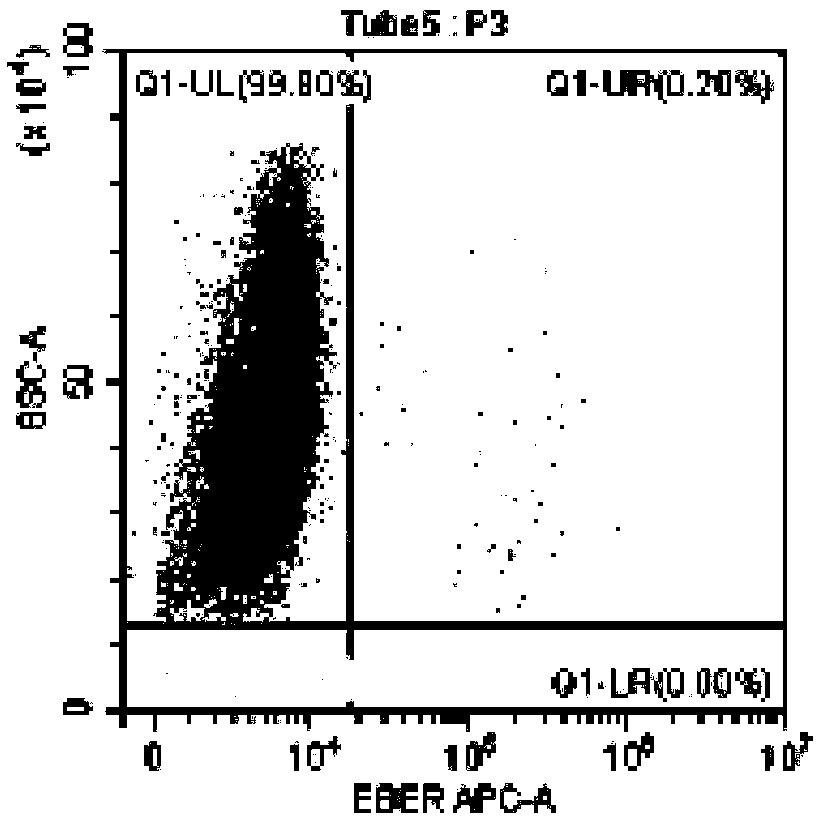
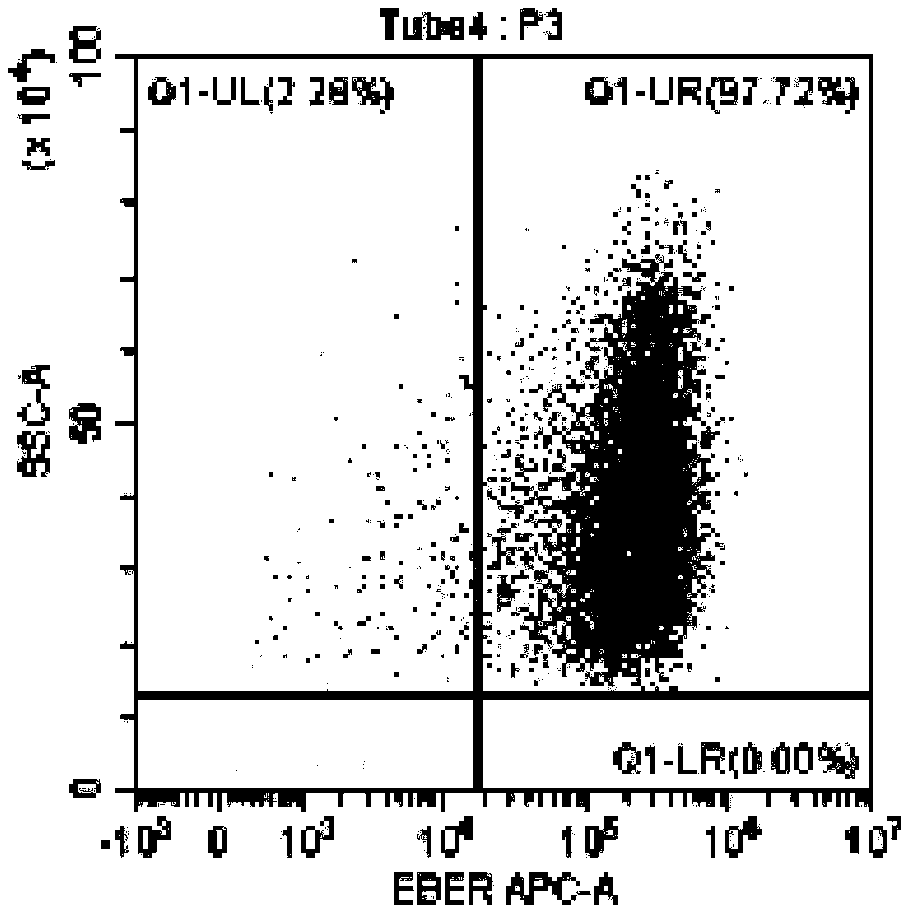
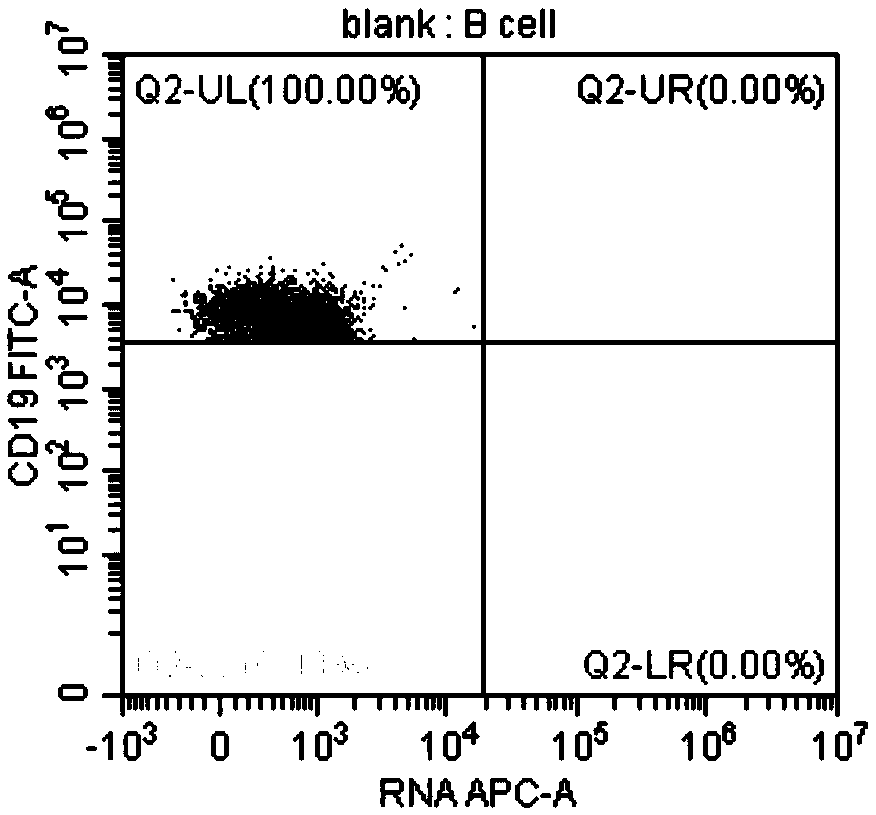
Method for identifying lymphocyte subpopulations infected by EB (epstein-barr) virus and proportion of injected cells in lymphocyte subpopulations and application of method
InactiveCN109136333APrecision therapyEffective treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementInfected cellDisease
The invention provides a method for identifying lymphocyte subpopulations infected by an EB (epstein-barr) virus and a proportion of injected cells in the lymphocyte subpopulations and application ofthe method, and relates to the technical field of medical test. According to the method, a probe is mixed with a mononuclear cell extracted from preprocessed peripheral blood, and after hybridization,a flow cytometry measurement method is adopted to acquire and analyze to identify the lymphocyte subpopulations infected by the EB virus and the proportion of the injected cells in the lymphocyte subpopulations. The method has the advantages that the type of cells infected by the EBV (epstein-barr virus) can be found out accurately, the proportion of the infected cells in the lymphocyte subpopulations can be found out, according to the type of the cells infected by the EBV and the proportion of the infected cells, a targeted therapeutic schedule can be beneficially made to effectively and accurately treat diseases caused by EBV injection, and accordingly the method plays important roles in implement of accurate therapy and prognosis improvement of a patient.
Owner:北京倍科为生物技术有限公司
Method for treating epstein-barr virus—positive cancer with immunotherapy
InactiveUS10342865B2Reduce the amount requiredReduced activityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiviralsDiseasePrognosis biomarker
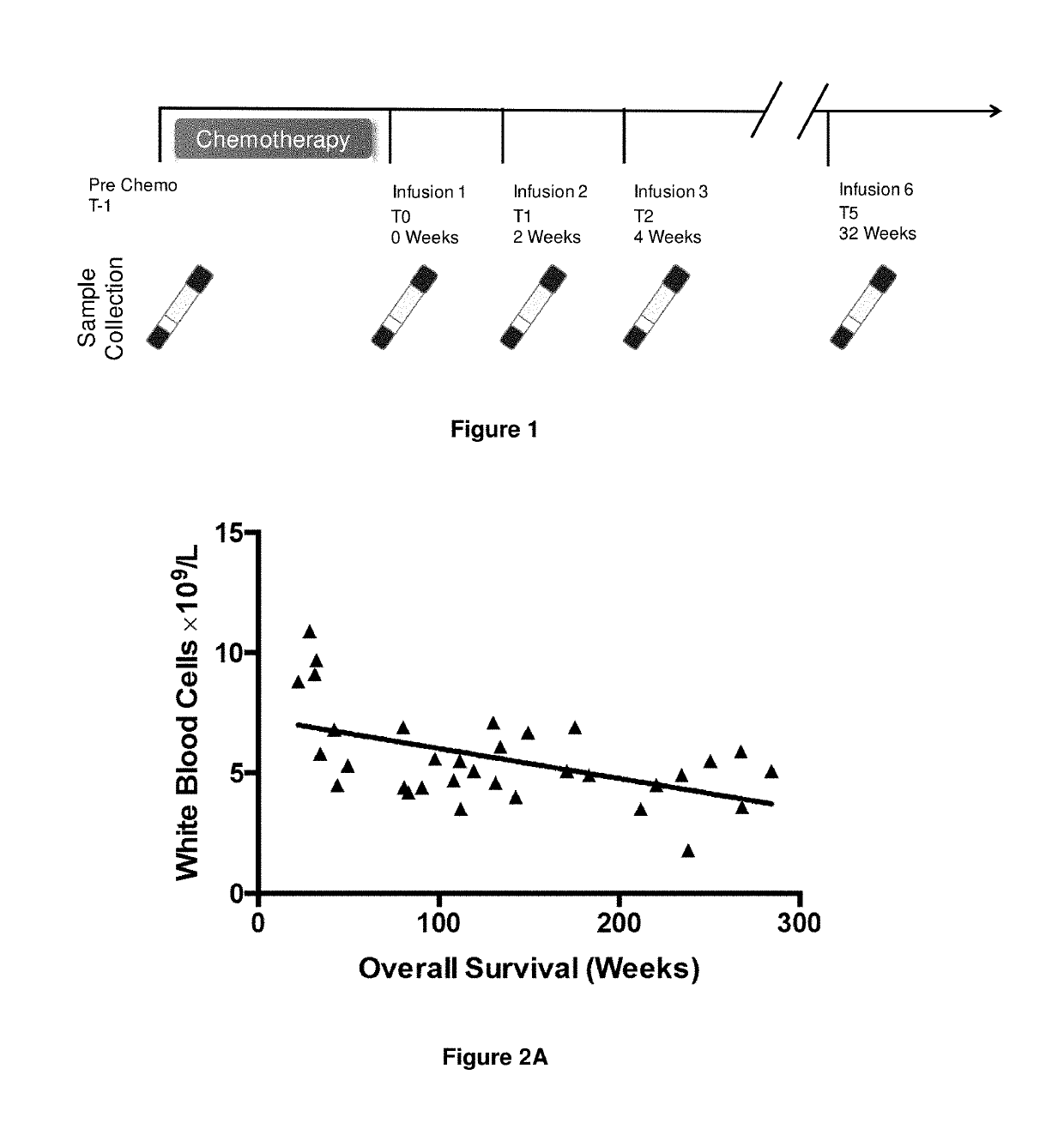
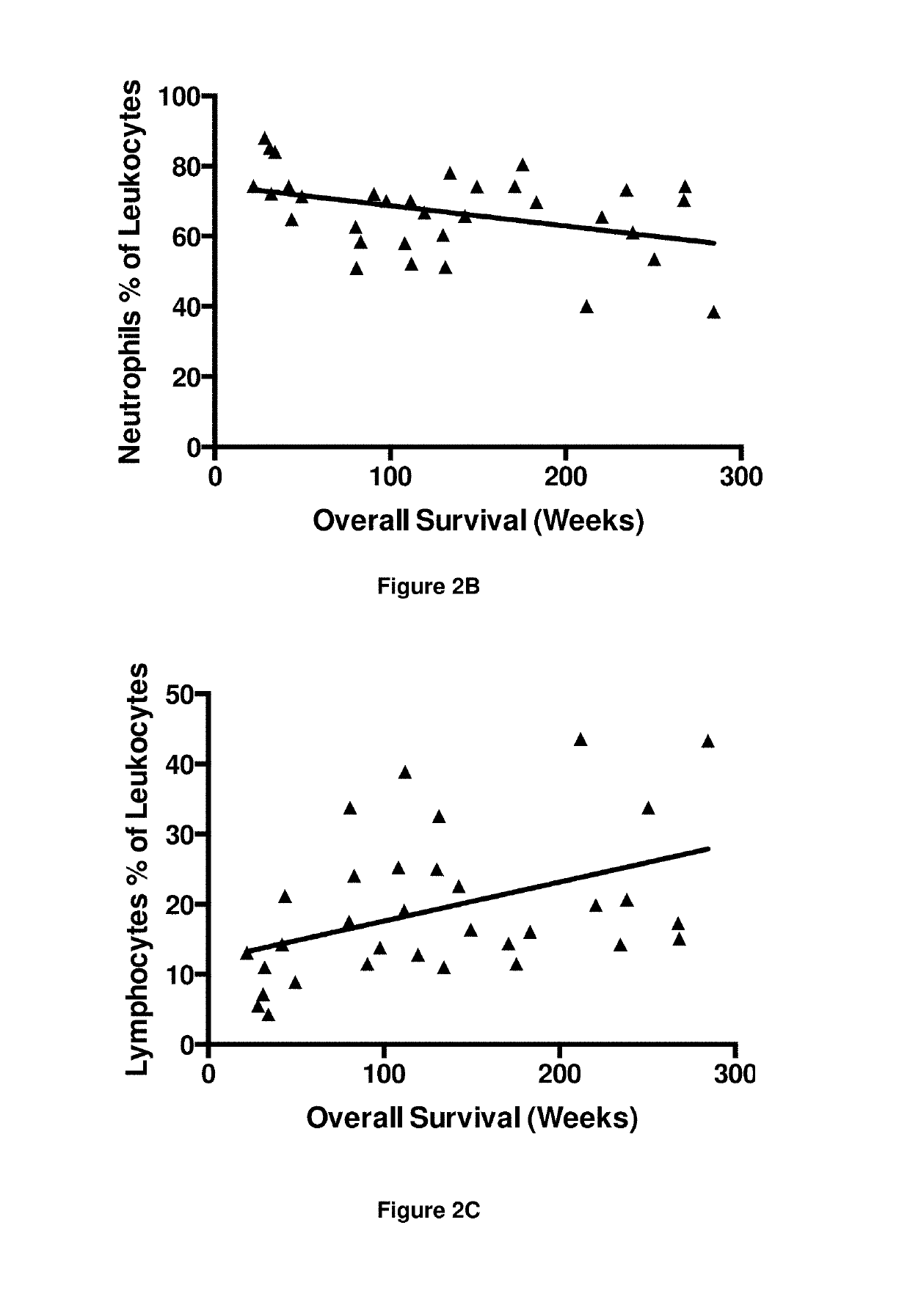
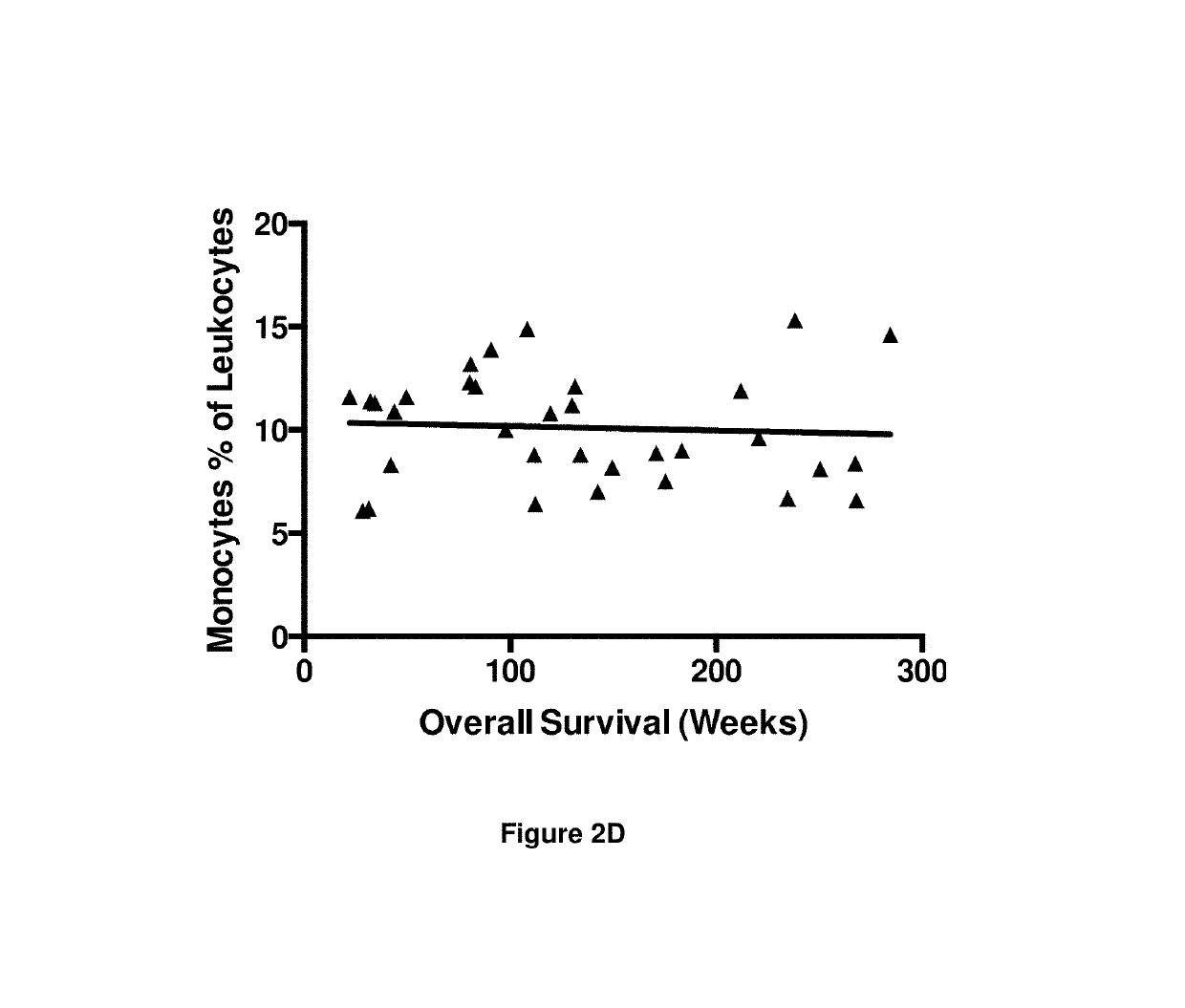
A method for predicting whether a patient will be a long-term survivor on treatment of a disease by adoptive cell transfer (ACT), is disclosed comprising: (i) analyzing a blood-derived sample obtained from the patient for one or more prognostic markers of long-term survival on treatment of a disease by ACT, and; (ii) based on the analysis of step (i), predicting whether the patient will be a long-term survivor on treatment of the disease by ACT. Also disclosed are methods for treating a patient by ACT, methods for selecting a patient for treatment by ACT, and methods for selecting a patient for treatment of a disease by ACT.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com