Patents
Literature
392 results about "Vaccine antigen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antigen Vaccines. Antigen vaccines use tumor-specific antigens (proteins displayed on a tumor cell) to stimulate the immune system. By injecting these antigens into the cancerous area of the patient, the immune system will produce an increased number of antibodies or cytotoxic T lymphocytes, also known as killer T cells,...
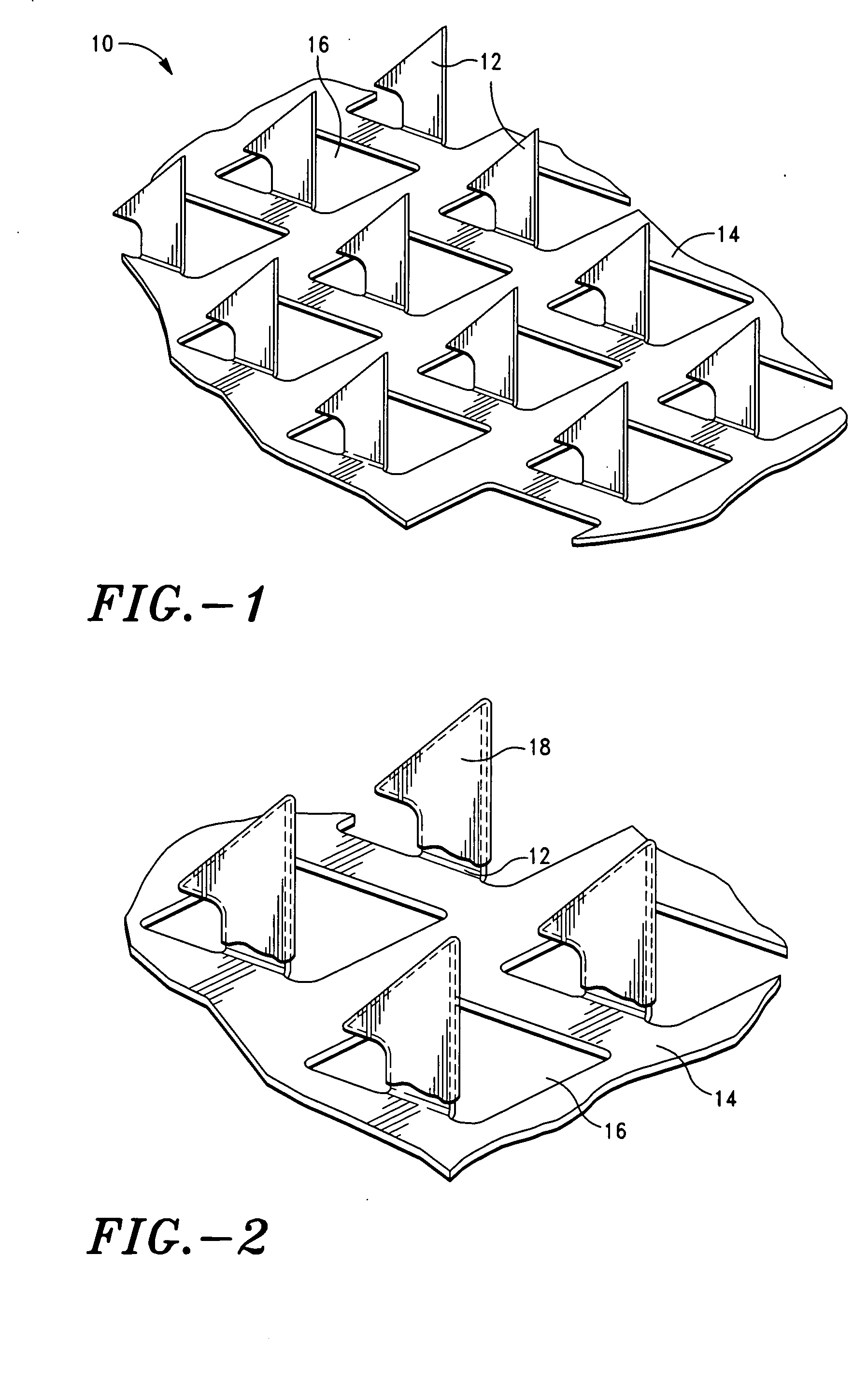
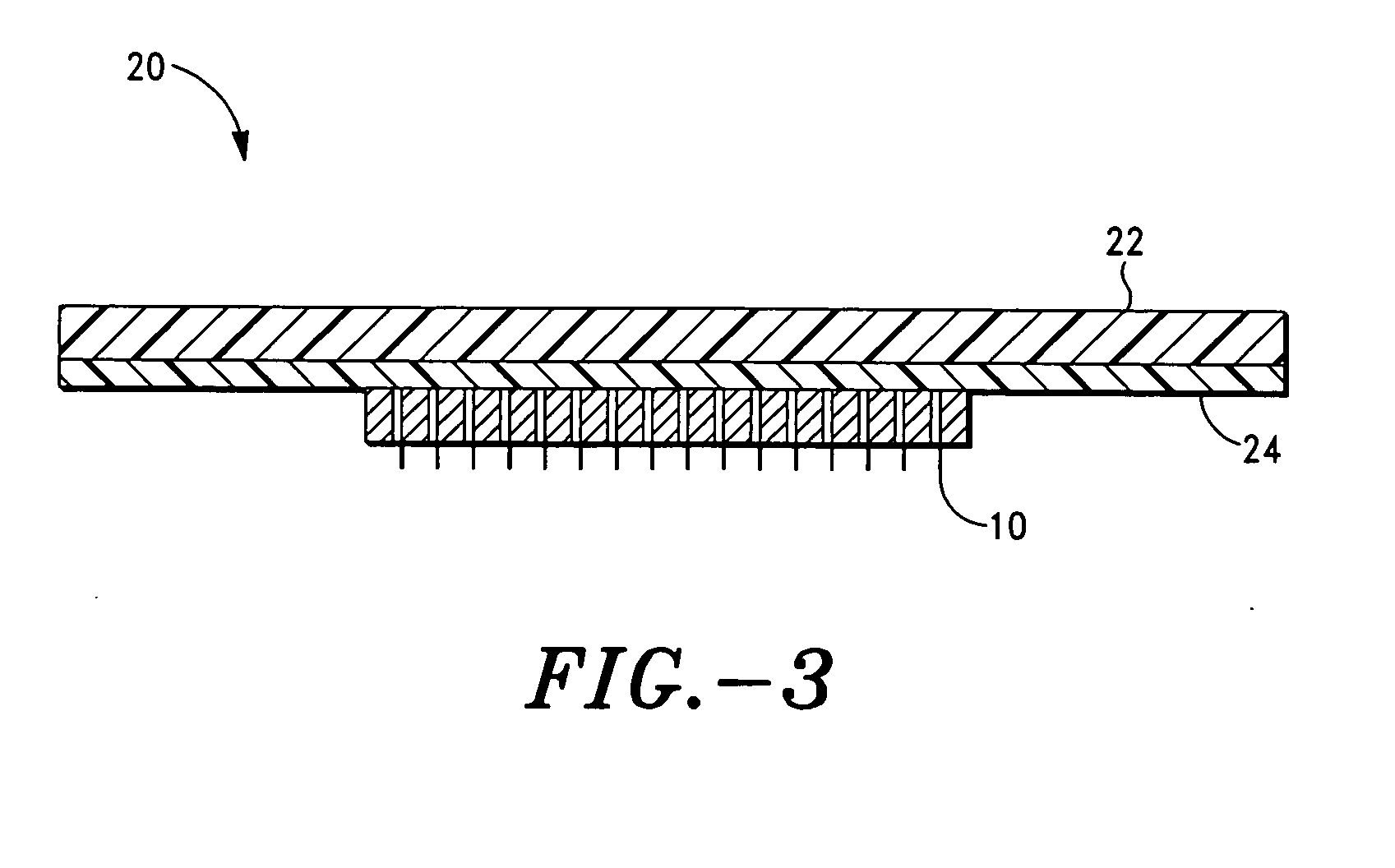
Microprojection array immunization patch and method
InactiveUS20050025778A1Adequate buffering capacityIncrease concentrationMicroneedlesSurgeryCurative effectVaccine antigen
Microprojection members (10) having a reservoir containing an antigenic agent and methods of using such members to vaccinate mammals (e.g., humans) are disclosed. The microprojection members are used to transdermally deliver an antigenic agent (e.g., a vaccine antigen) with substantially reduced skin reactions. This is achieved by delivering an induction amount and thereafter delivering one or more subsequent booster amounts. The induction amount is relatively larger than the booster amount. This technology has broad applicability for a wide variety of therapeutic vaccines to improve efficacy and convenience of use.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Novel, non-antigenic, mucosal adjuvant formulation which modulates the effects of substances, including vaccine antigens, in contact with mucosal body surfaces
InactiveUS20030104010A1Antibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseMucosal adjuvantVaccine antigen
Adjuvant for mucosal vaccines which modulates the effects of substances, including vaccine antigens in contact with mucosal body surfaces.
Owner:BIOTEC PHARMACON
Pharmaceutical proteins, human therapeutics, human serum albumin, insulin, native cholera toxic b submitted on transgenic plastids
InactiveUS20030204864A1Eliminate needLarge biomassBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliInsulin-like growth factor
Transgenic chloroplast technology could provide a viable solution to the production of Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I), Human Serum Albumin (HSA), or interferons (IFN) because of hyper-expression capabilities, ability to fold and process eukaryotic proteins with disulfide bridges (thereby eliminating the need for expensive post-purification processing). Tobacco is an ideal choice because of its large biomass, ease of scale-up (million seeds per plant), genetic manipulation and impending need to explore alternate uses for this hazardous crop. Therefore, all three human proteins will be expressed as follows: a) Develop recombinant DNA vectors for enhanced expression via tobacco chloroplast genomes b) generate transgenic plants c) characterize transgenic expression of proteins or fusion proteins using molecular and biochemical methods d) large scale purification of therapeutic proteins from transgenic tobacco and comparison of current purification / processing methods in E. coli or yeast e) Characterization and comparison of therapeutic proteins (yield, purity, functionality) produced in yeast or E. coli with transgenic tobacco f) animal testing and pre-clinical trials for effectiveness of the therapeutic proteins. Mass production of affordable vaccines can be achieved by genetically engineering plants to produce recombinant proteins that are candidate vaccine antigens. The B subunits of Enteroxigenic E. coli (LTB) and cholera toxin of Vibrio cholerae (CTB) are examples of such antigens. When the native LTB gene was expressed via the tobacco nuclear genome, LTB accumulated at levels less than 0.01% of the total soluble leaf protein. Production of effective levels of LTB in plants, required extensive codon modification. Amplification of an unmodified CTB coding sequence in chloroplasts, up to 10,000 copies per cell, resulted in the accumulation of up to 4.1% of total soluble tobacco leaf protein as oligomers (about 410 fold higher expression levels than that of the unmodified LTB gene). PCR and Southern blot analyses confirmed stable integration of the CTB gene into the chloroplast genome. Western blot analysis showed that chloroplast synthesized CTB assembled into oligomers and was antigenically identical to purified native CTB. Also, GM1,-ganglioside binding assays confirmed that chloroplast synthesized CTB binds to the intestinal membrane receptor of cholera toxin, indicating correct folding and disulfide bond formation within the chloroplast. In contrast to stunted nuclear transgenic plants, chloroplast transgenic plants were morphologically indistinguishable from untransformed plants, when CTB was constitutively expressed. The introduced gene was stably inherited in the subsequent generation as confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analyses. Incrased production of an efficient transmucosal carrier molecule and delivery system, like CTB, in transgenic chloroplasts makes plant based oral vaccines and fusion proteins with CTB needing oral administration a much more practical approach.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV +1
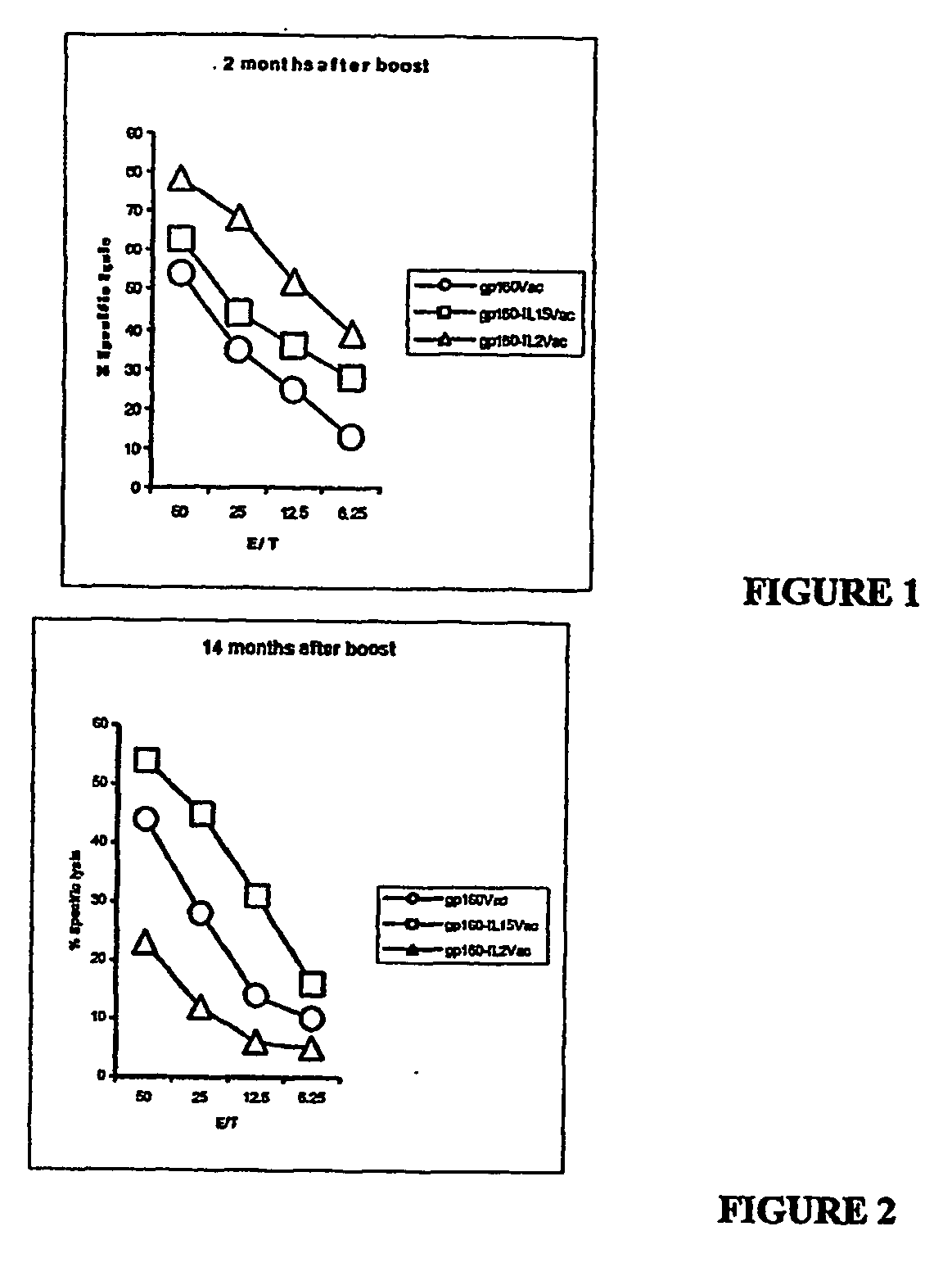
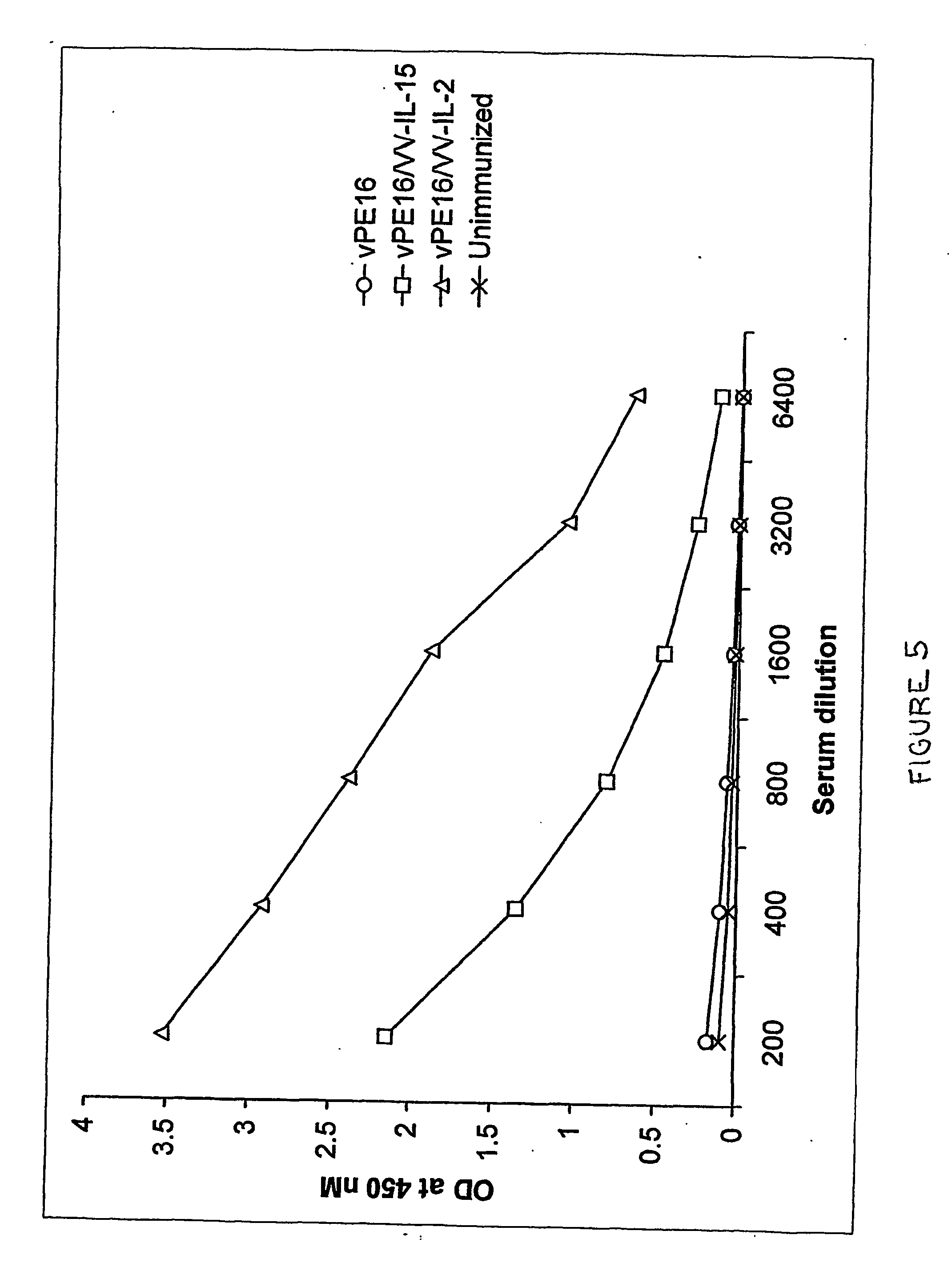
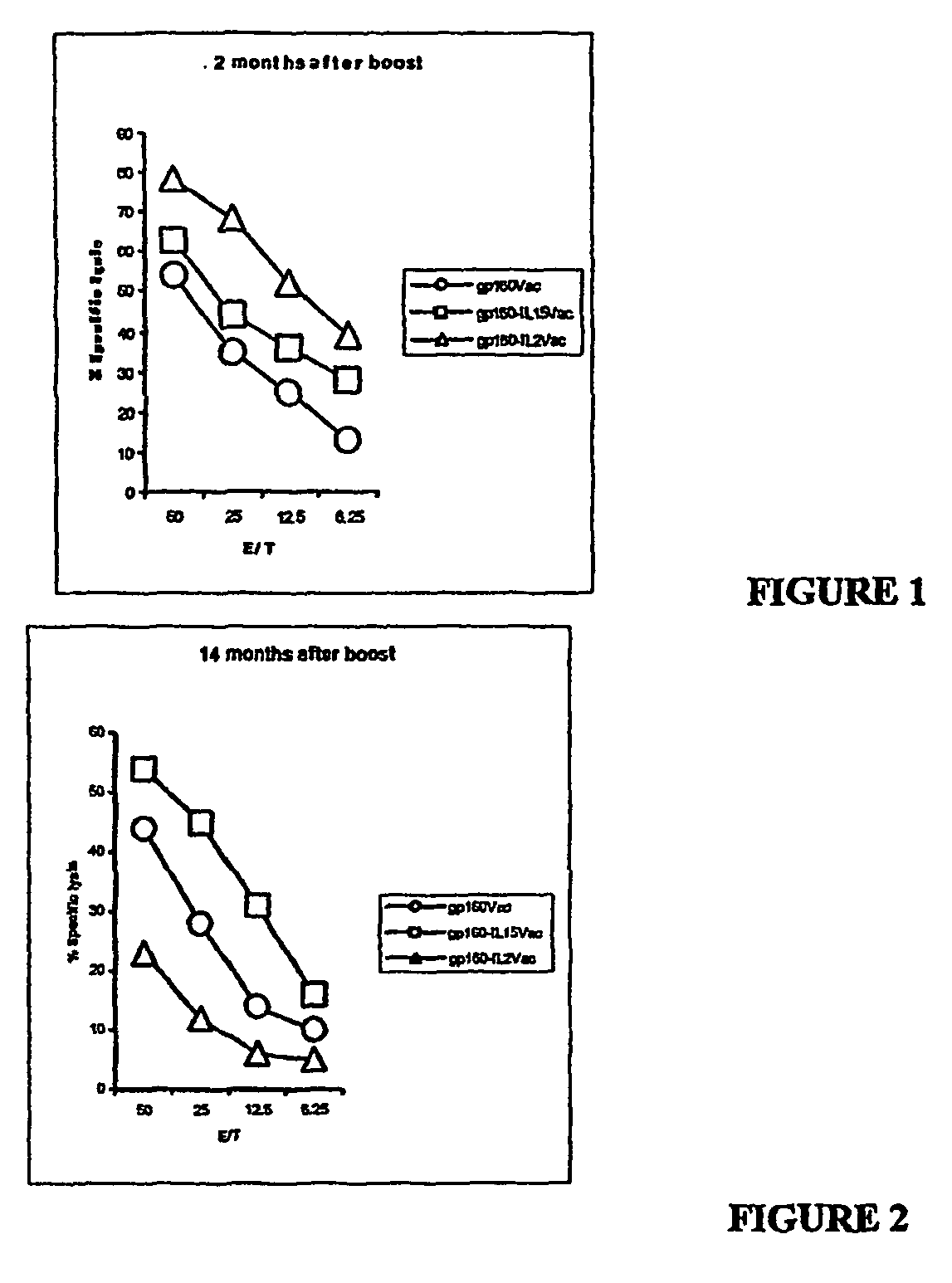
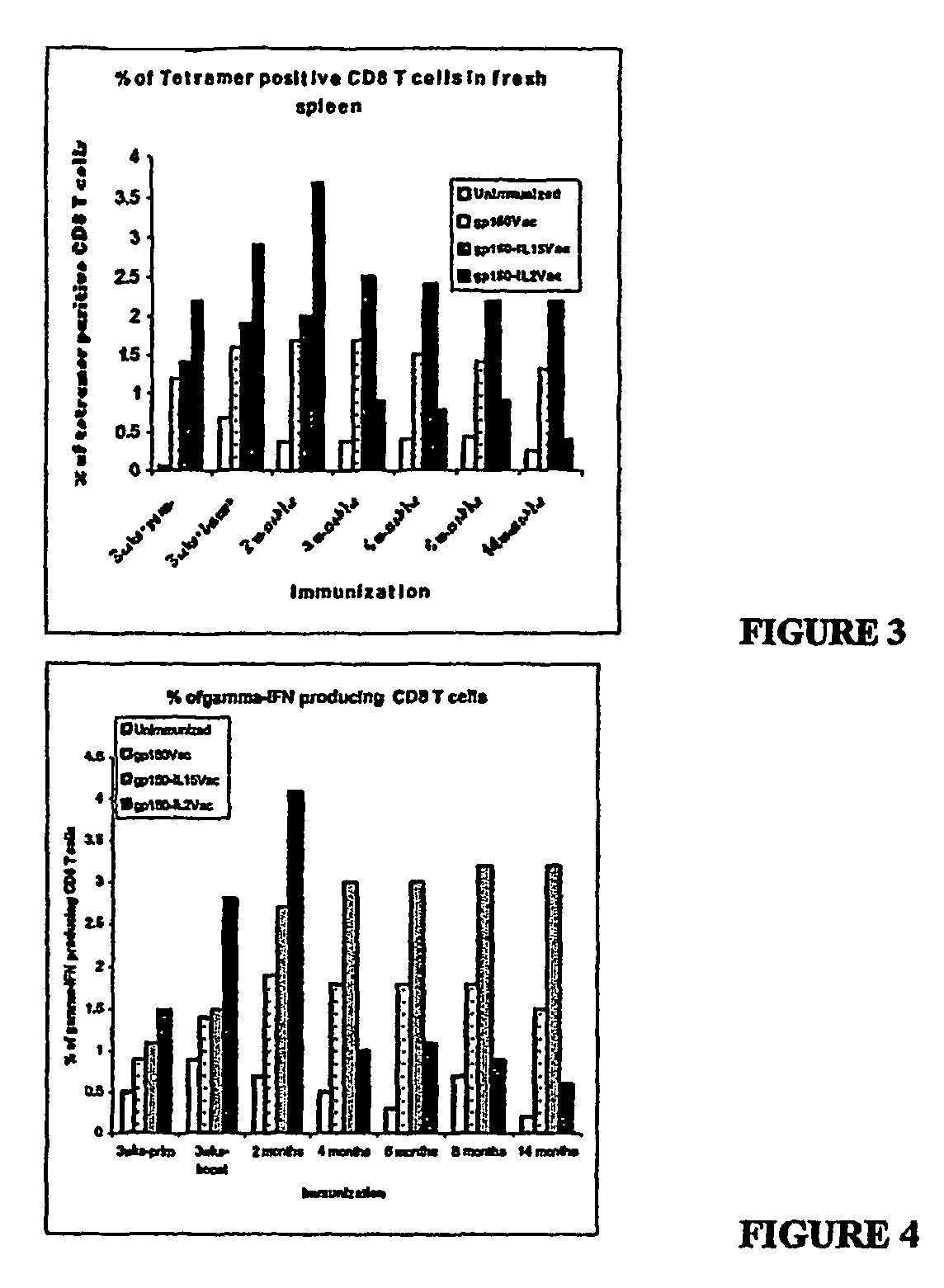
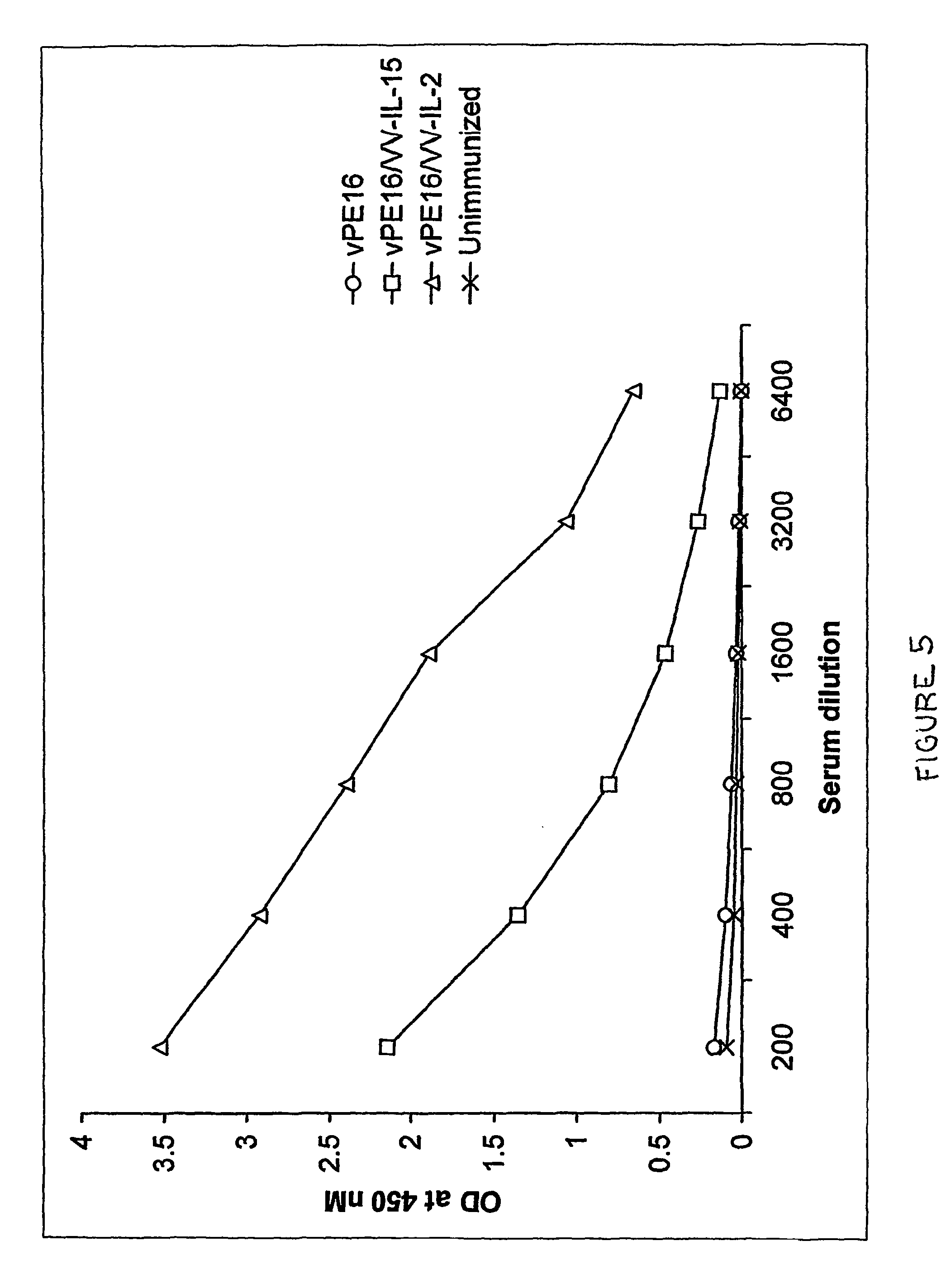
Recombinant vaccine viruses expressing il-15 and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20060147419A1Stimulates proliferationStimulates differentiationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAdjuvantMammal
The invention is directed to compositions capable of augmenting the immunogenicity of a vaccine. The composition, or adjuvant, is administered to a mammal in need thereof in sequential or concurrent combination with a vaccine antigen. In one preferred aspect, the adjuvant is provided in the form of a recombinant poxvirus vector, such as a vaccinia virus vector, which comprises a nucleic acid sequence encoding IL-15.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Use of consensus sequence as vaccine antigen to enhance recognition of virulent viral variants
ActiveUS20090186045A1Reduce probabilitySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsVaccine antigenPhases of clinical research
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Lipid nanoparticle vaccine adjuvants and antigen delivery systems
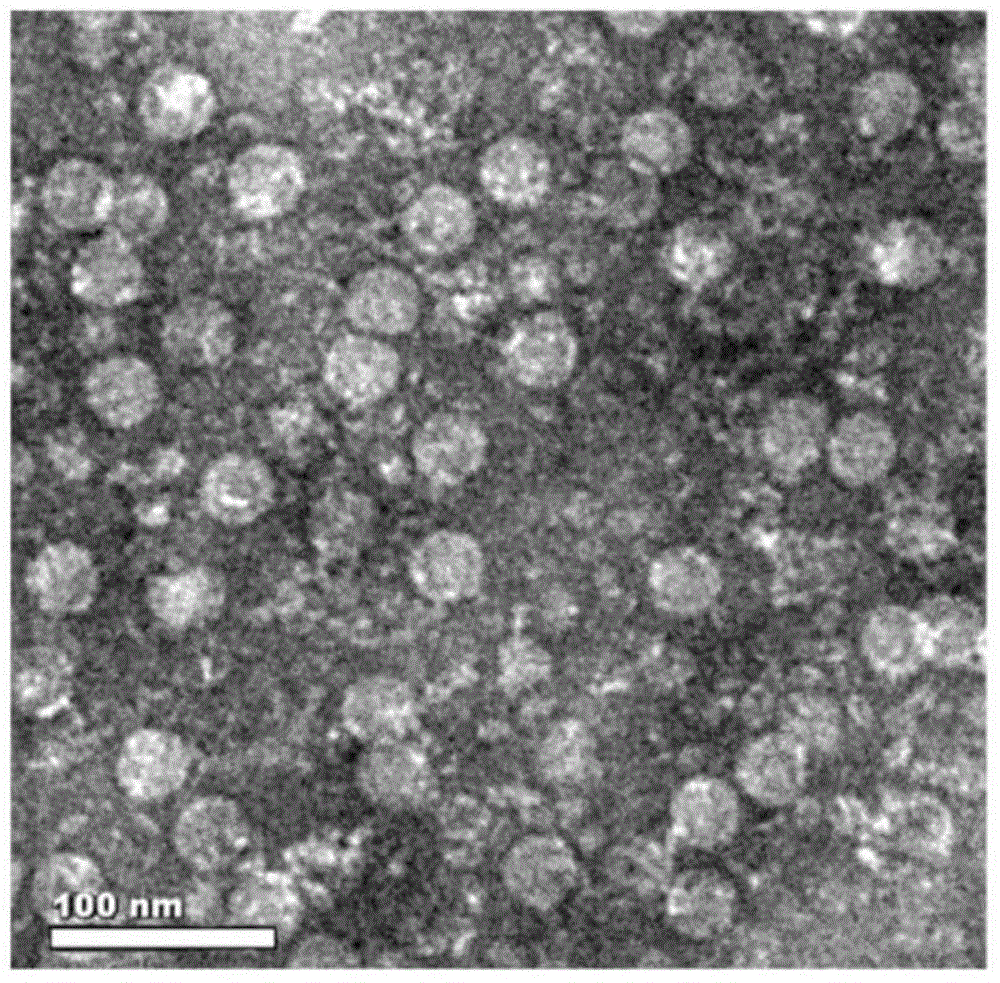
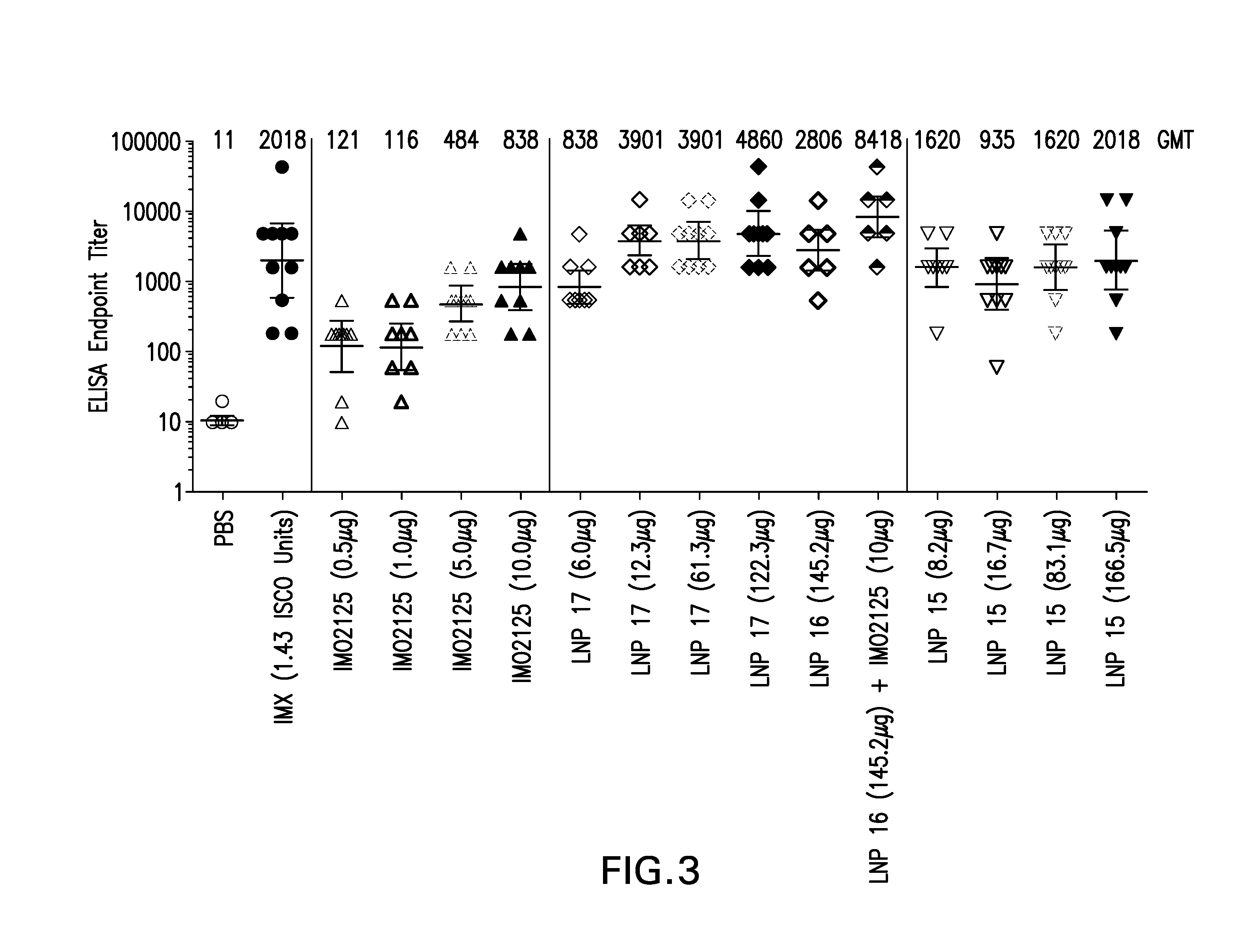
The instant invention provides for novel lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations, containing cationic lipids, for use as vaccine adjuvants and / or as antigen delivery systems. It is an object of the instant invention to provide LNP formulations that demonstrate enhancements in humoral and cellular immunogenicity of vaccine antigens, particularly subunit vaccine antigens, when utilized alone or in combination with immunostimulatory agents (e.g. small molecule or oligonucleotide TLR agonists). The instant invention further identifies physical and chemical properties of the LNP formulations that can be manipulated to enhance antigen efficiency and adjuvant tolerability in vivo.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
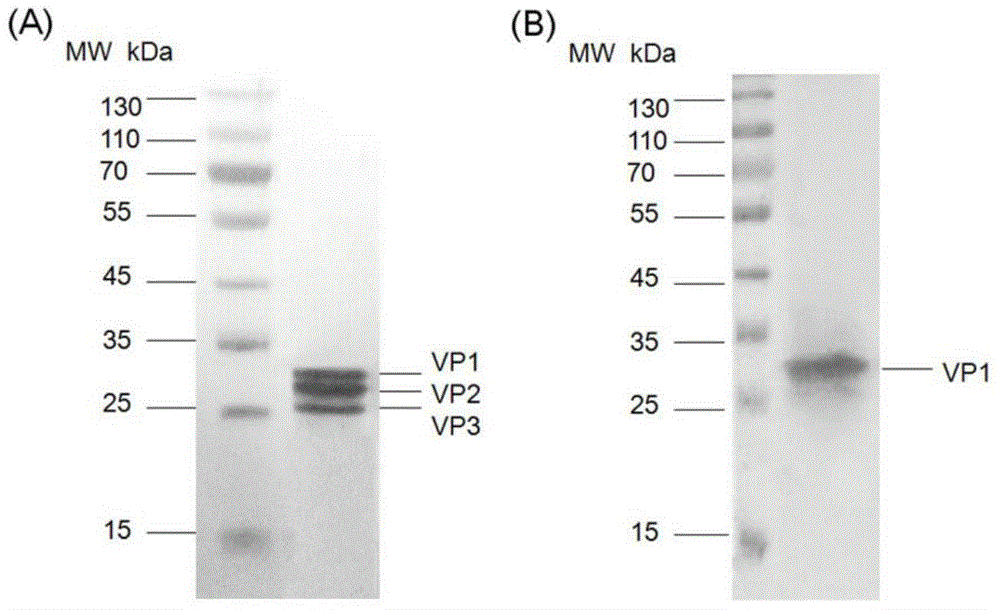
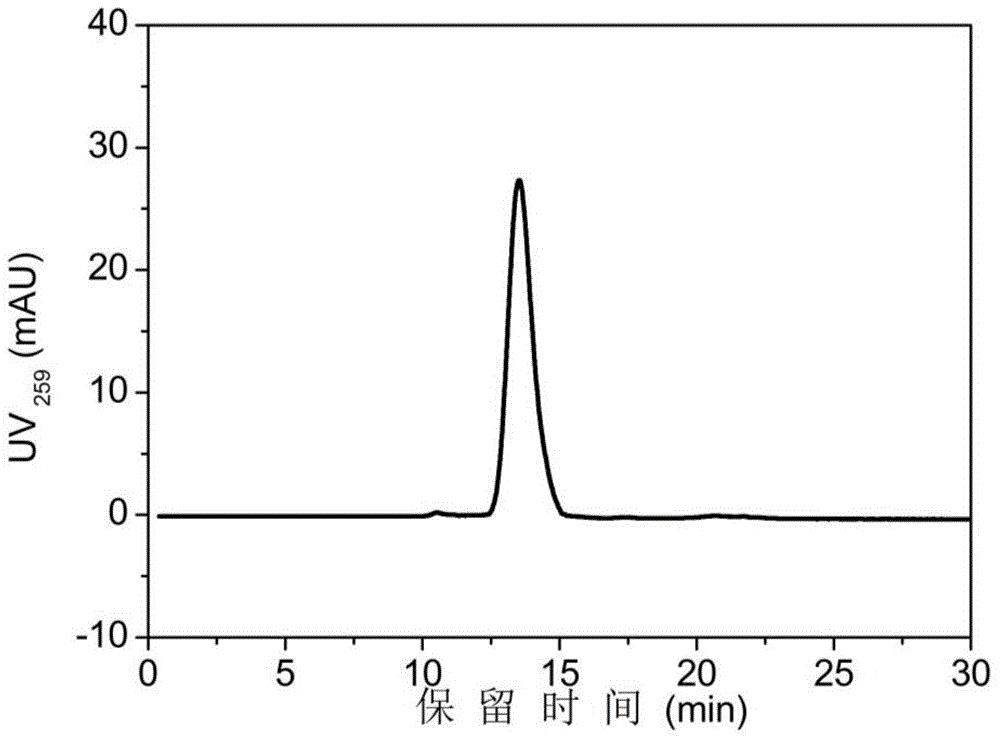
Method for rapidly, accurately and repeatedly determining foot-and-mouth disease vaccine antigen 146S
InactiveCN104634891AGood repeatabilityReduce mistakesComponent separationChromatographic separationPhosphate
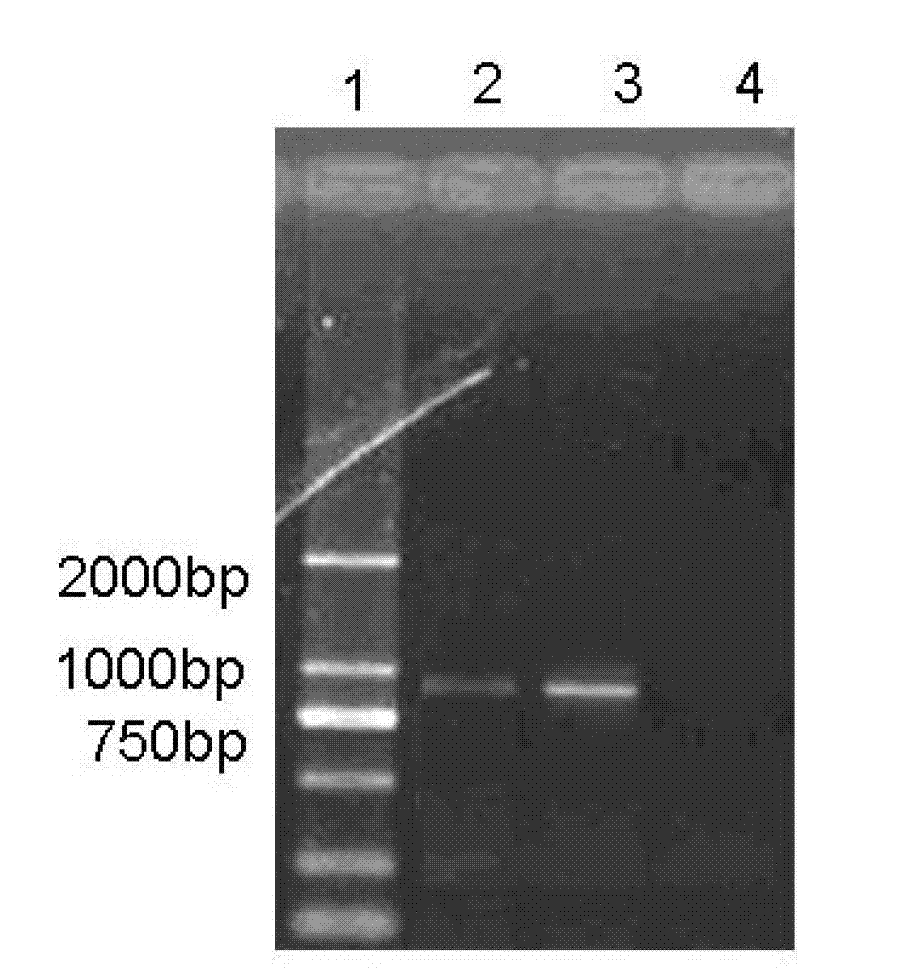
The invention discloses a method for rapidly, accurately and repeatedly determining foot-and-mouth disease vaccine antigen 146S. A size exclusion high-efficiency liquid-phase chromatographic column in a molecular weight separation range of 2*10<4> to 1*10<7>Da is adopted to carry out the chromatographic separation on a detected sample on a high-efficiency liquid-phase chromatography. The operation pressure of the chromatography is 1.0MPa to 2.5MPa, the flow rate in the chromatographic column is 0.5 to 1.0 ml / min, a flow phase is phosphate buffer (pH 7.0 to 7.5) containing 0.1M sodium sulfate, and the column temperature is 15 to 25 DEG C. An ultraviolet and laser detector is used for detecting an optical signal of effluent at an outlet of the size exclusion high-efficiency liquid-phase chromatographic column, and a peak area of a sample can be analyzed by virtue of a computer software system of the high-efficiency liquid-phase chromatography. A standard curve of the absorption peak area and 146S concentration is established by virtue of a relation between the ultraviolet absorption peak and the concentration of different 146S standard products of different concentrations. Chromatograph is carried out on the detected sample through the size exclusion high-efficiency liquid-phase chromatographic column. The ultraviolet absorption peak area is measured, and the concentration of 146S in the detected sample can be acquired according to the standard curve.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
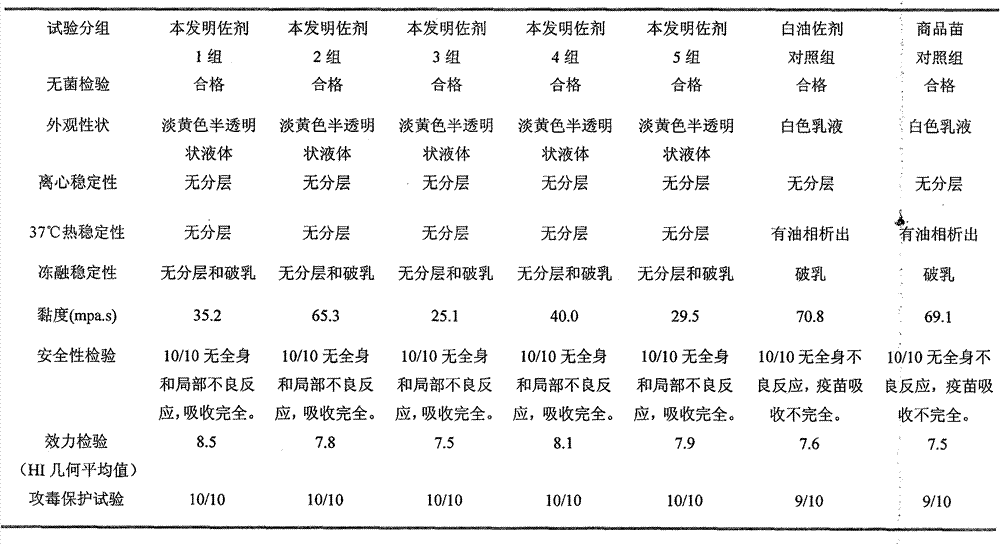
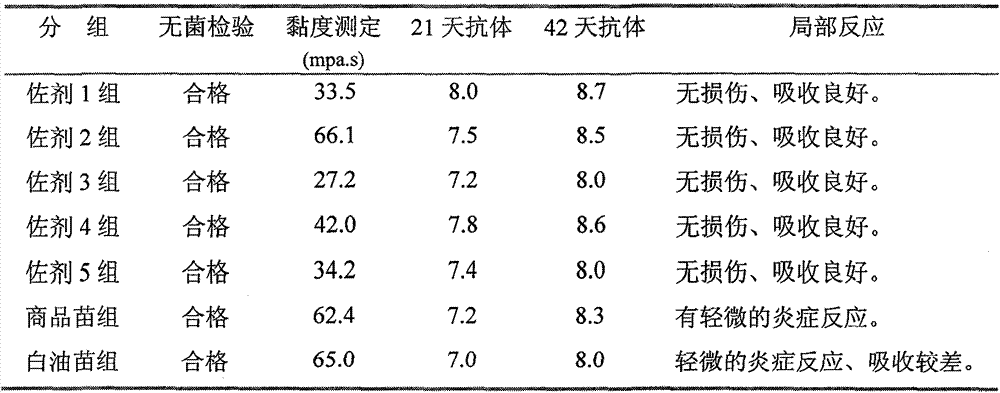
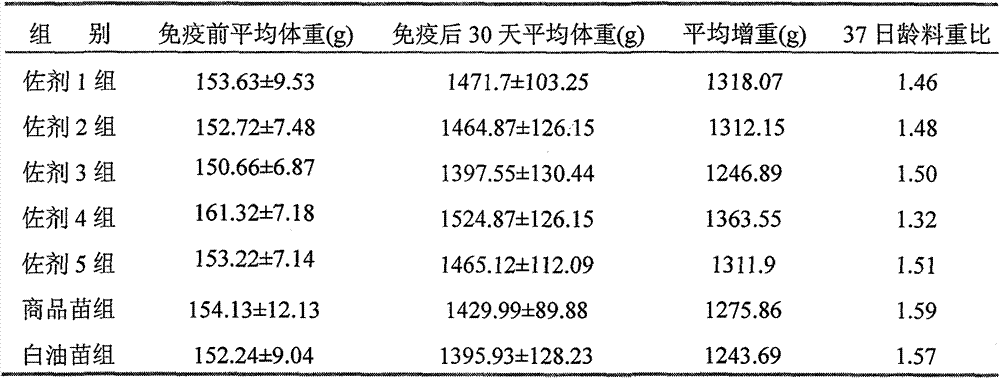
Vaccine composition for preventing and treating porcine circovirus type 2, haemophilus parasuis and mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103083655ASimplified immunization programReduce manufacturing costAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseCircovirus
The invention provides a vaccine composition for preventing and treating porcine circovirus type 2, haemophilus parasuis and mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection. The vaccine composition comprises an inactivated porcine circovirus type 2 antigen, inactivated haemophilus parasuis, inactivated mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and a vaccine adjuvant. The vaccine composition disclosed by the invention can realize the aim of preventing three diseases including a porcine circovirus disease, mycoplasma pneumonia, a haemophilus parasuis disease by one injection of the vaccine; the content of antigen is 1 / 2 of the content of a common single-vaccine antigen when the vaccine composition disclosed by the invention is prepared by mixing the three antigens; and compared with the existing condition that three injections of single vaccine are injected to prevent three infectious diseases, the technical scheme disclosed by the invention is economical and practical, reduces the production cost, simplifies an immune procedure and reduces the epidemic prevention cost.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Method for introducing and expressing genes in animal cells, and live invasive bacterial vectors for use in the same
A method for introducing and expressing genes in animal cells is disclosed comprising infecting said the animal cells with live invasive bacteria, wherein bacteria contain a eukaryotic expression cassette encoding said gene. The gene may encode, e.g., a vaccine antigen, an therapeutic agent, an immunoregulatory agent or a anti-sense RNA or a catalytic RNA.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Novel vaccine for preventing COVID-19 and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111939250AHighly conservativeAntibody induction ability is weakSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideReceptor
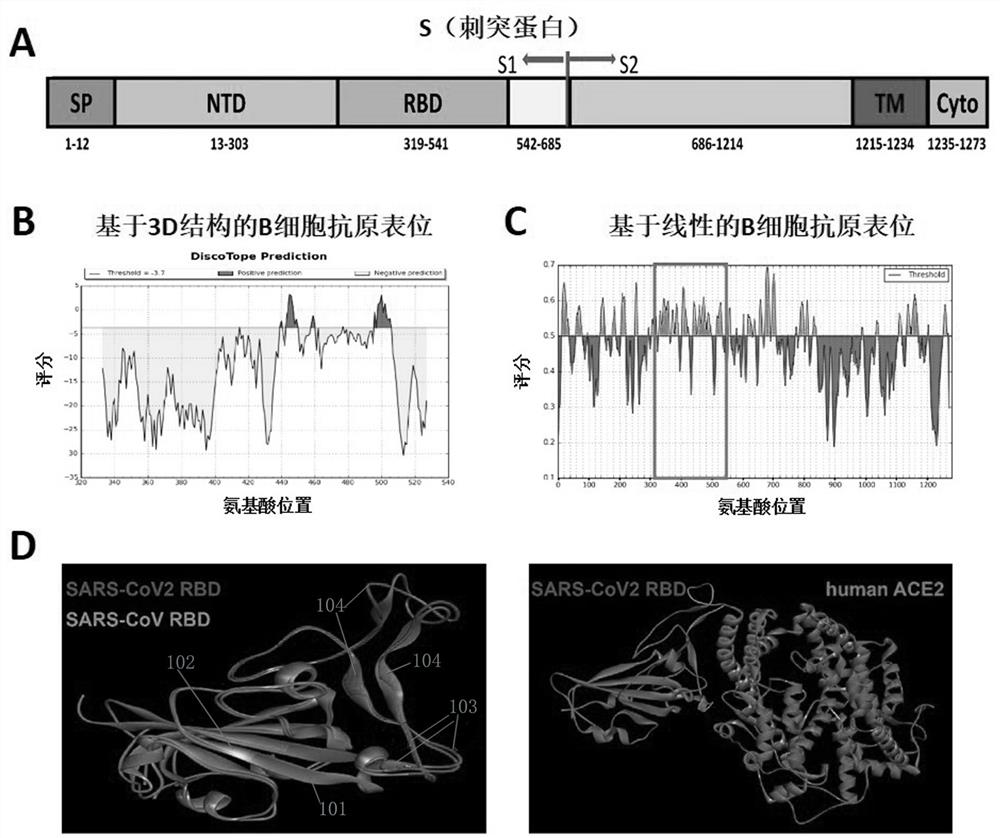
Provided is a novel vaccine for preventing COVID-19, the nucleotide sequence of an antigen of the novel vaccine is SEQ NO: 1, the amino acid sequence of the antigen of the novel vaccine is SEQ NO: 2,and the antigen of the vaccine comprises two functional parts: an S protein receptor binding structural domain capable of inducing a specific neutralizing antibody and a T cell related N protein truncated peptide fragment capable of inducing and activating effector T cells; The vaccine disclosed by the invention has the characteristics that the T cell related N protein truncated peptide fragment has weak capability of inducing the generation of the N protein antibody, so that a vaccine inoculator and a COVID-19 infected patient can be identified by using the N protein antibody, and the vaccineantigen does not induce the generation of the N protein antibody, so that lung injuries can be reduced, and the vaccine is safer. The cell vaccine disclosed by the invention is low in manufacturing cost, and can induce generation of virus-specific neutralizing antibodies and T cell immune response.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Lipidated Imidazoquinoline Derivatives
The compounds of the subject invention are adjuvant molecules that comprise a imidazoquinoline molecule covalently linked to a phospho- or phosphonolipid group. The compounds of the invention have been shown to be inducers of interferon-a, IL-12 and other immunostimulatory cytokines and possess an improved activity profile in comparison to known cytokine inducers when used as adjuvants for vaccine antigens.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Large-scale preparation method for foot-and-mouth disease totivirus marked vaccine with high yield, high purity and high safety and product thereof
ActiveCN104491855AMark stableEnsure safetyMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsSucroseUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a large-scale preparation method for foot-and-mouth disease totivirus marked vaccine with high yield, high purity and high safety and a product thereof. The method comprises the following steps: a)collecting a virus solution; b)performing deep filtration on a membrane, performing ultrafiltration and performing enzymolysis on nuclease; c)purifying through a strong anion exchange adsorption bed or an adsorption film; d)depositing by PEG, extracting by chloroform-isoamyl aleohl; e)inactivating; F)performing density gradient centrifugation on an inactivation liquid through cane sugar and purifying; g)performing ultrafiltration dialysis and aseptic filtration; and h)reserving a stock solution or emulsifying. The provided foot-and-mouth disease totivirus marked vaccine antigen is uniform and complete foot-and-mouth virus particle, The vaccine is injected into body, so animal infection and immunization can be completely distinguished, does not contain foot-and-mouth disease virus non-structural protein and other virus particle, and does not contain animal-based foreign protein, polypeptide and oligopeptides, animal latent anaphylactic reaction, carcinogenesis and latent risk such as mad cow disease for causing animal infectious diseases due to vaccine injection can be effectively reduced, and the vaccine has no influence on animal food safety and trade.
Owner:吕宏亮 +2
Preparation of nose-spraying flu immunization pentavalent or multivalent inactivated vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN101732711ANo side effectsAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesVirus-like particleMultivalent Vaccine
The invention discloses a nose-spraying flu immunization pentavalent or multivalent inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof. The vaccine is inactivated vaccine antigen of totivirus, lytic virus, viron or virus-like particles, flue multivalent vaccine antigen is flue pentavalent, namely H1N1, H3N2, B, H5N1 and A (H1N1) or multivalent vaccine antigen combined on the basis at will, or flue multivalent vaccine antigen obtained by containing all the combination of the HA selecting from H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, H6, H7, H8, H9, H10, H11, H12, H13, H14, H15 and H16 and the NA selecting from N1, N2, N3, N4, N5, N6, N7, N8 and N9 subtypes on the basis. The content of flu multivalent inactivated vaccine antigen HA in the vaccine of the invention is 1.0-15.0 Mug / 0.2ml / per person, and the vaccine of the invention can effectively prevent routine human flue, high pathogenicity H5N1 avian-human flu, influenza A (H1N1) and infection of other subtype influenza viruses.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Special diluent for swine mycoplasmal pneumonia vaccines and preparation method of special diluent
ActiveCN103071151AStrengthen cellsEnhance humoral immune stimulationAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCholesterolVaccine antigen
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Recombinant helicobacter pylori protein vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107298716ARetain the infrastructureRetain activityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAdjuvantVaccine antigen
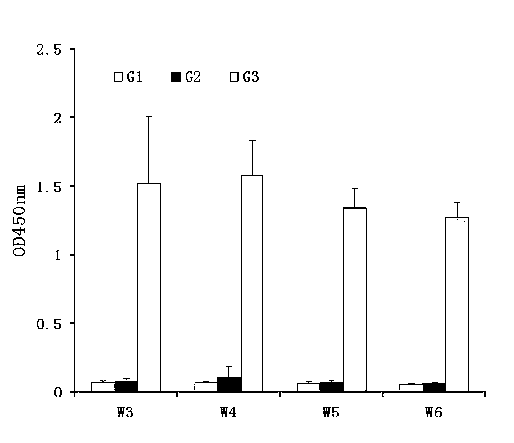
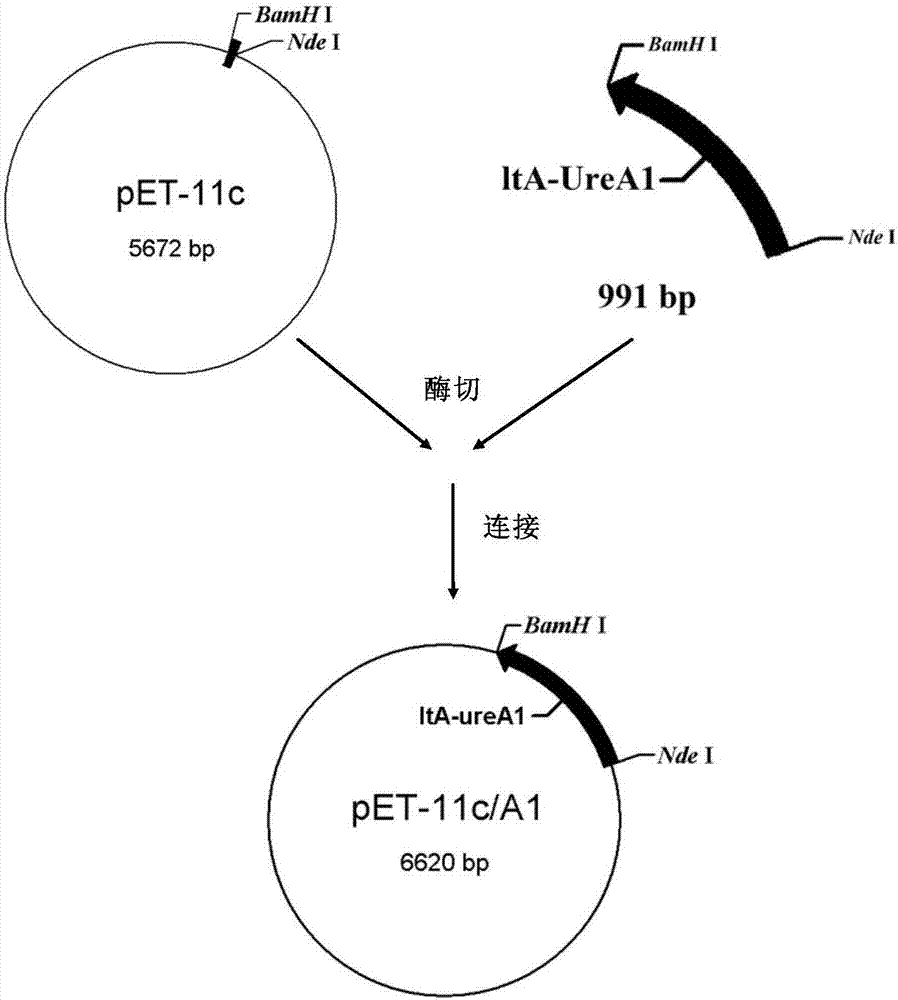
The invention discloses a recombinant helicobacter pylori protein vaccine and a preparation method thereof. The active ingredient recombinant fusion protein of the vaccine consists of recombinant LTAl-Ureal protein and LTB protein, the amino acid sequence of the recombinant LTAl-Ureal protein is shown as Seq ID No.1, the amino acid sequence of the LTB protein is shown as Seq ID No.2. Epitope-containing gene segments of Hp urease A subunit is inserted in an LTA subunit-encoded gene, a toxic part-containing segment is replaced to prepare a recombinant plasmid so as to express and obtain recombinant fusion protein polymer as a vaccine antigen, the fusion antigen and LTB protein pentamer are combined to form a hexamer structure, so that not only can the structure basis and activity of an LT mucosa adjuvant be remained, but also the toxicity can be removed, the immune response of organism muscosa can be effectively induced through immunity of mucosa path, to generate specific IgA antibody. The recombinant helicobacter pylori protein vaccine provides a vaccine manner for preventing and treating infection of helicobacter pylori.
Owner:成都亿妙生物科技有限公司
Method for introducing and expressing genes in animal cells, and live invasive bacterial vectors for use in the same
A method for introducing and expressing genes in animal cells is disclosed comprising infecting the animal cells with live invasive bacteria, wherein the bacteria contain a eukaryotic expression cassette encoding the gene. The gene may encode, e.g., a vaccine antigen, a therapeutic agent, an immunoregulatory agent or an anti-sense RNA or a catalytic RNA.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
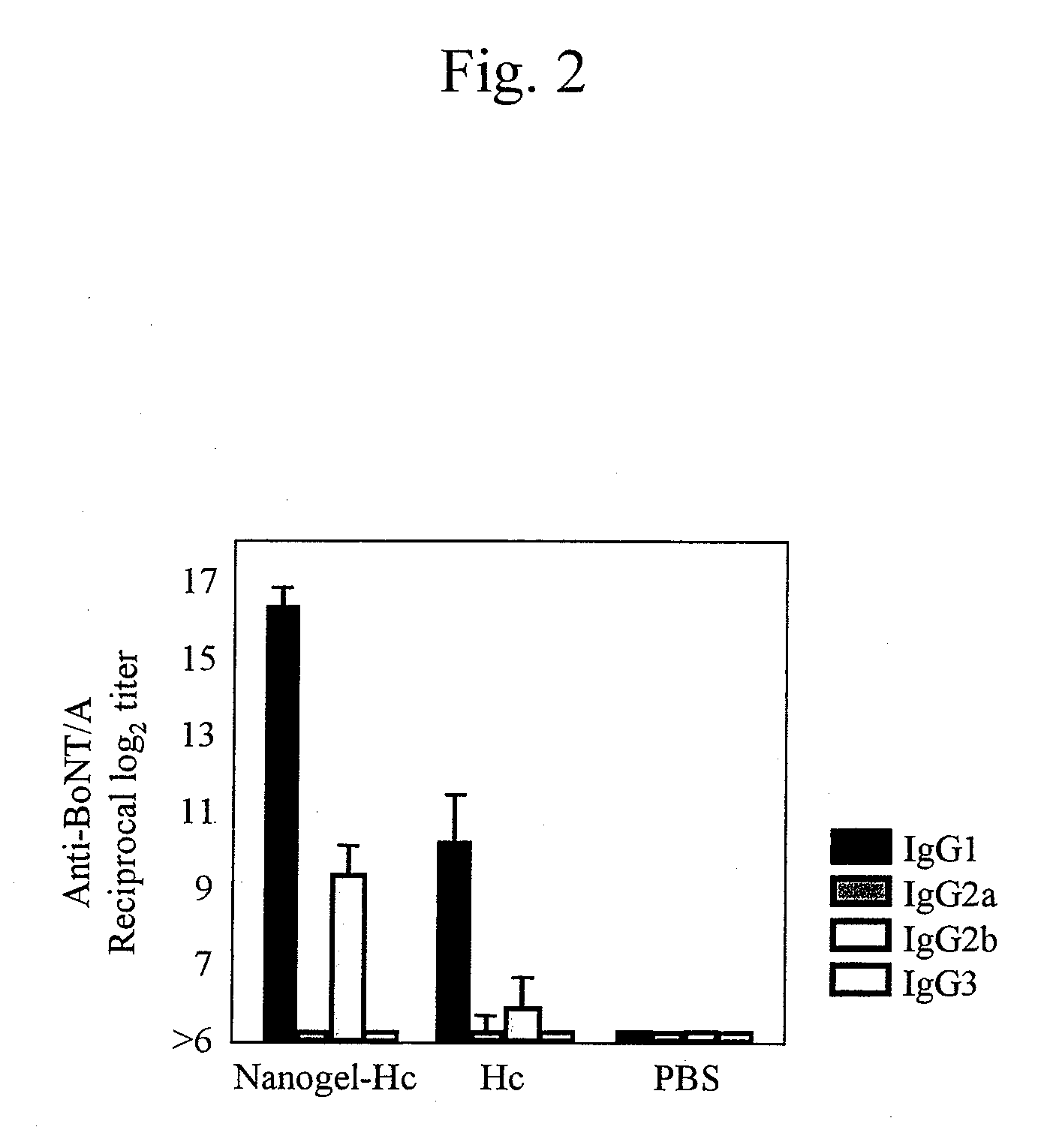
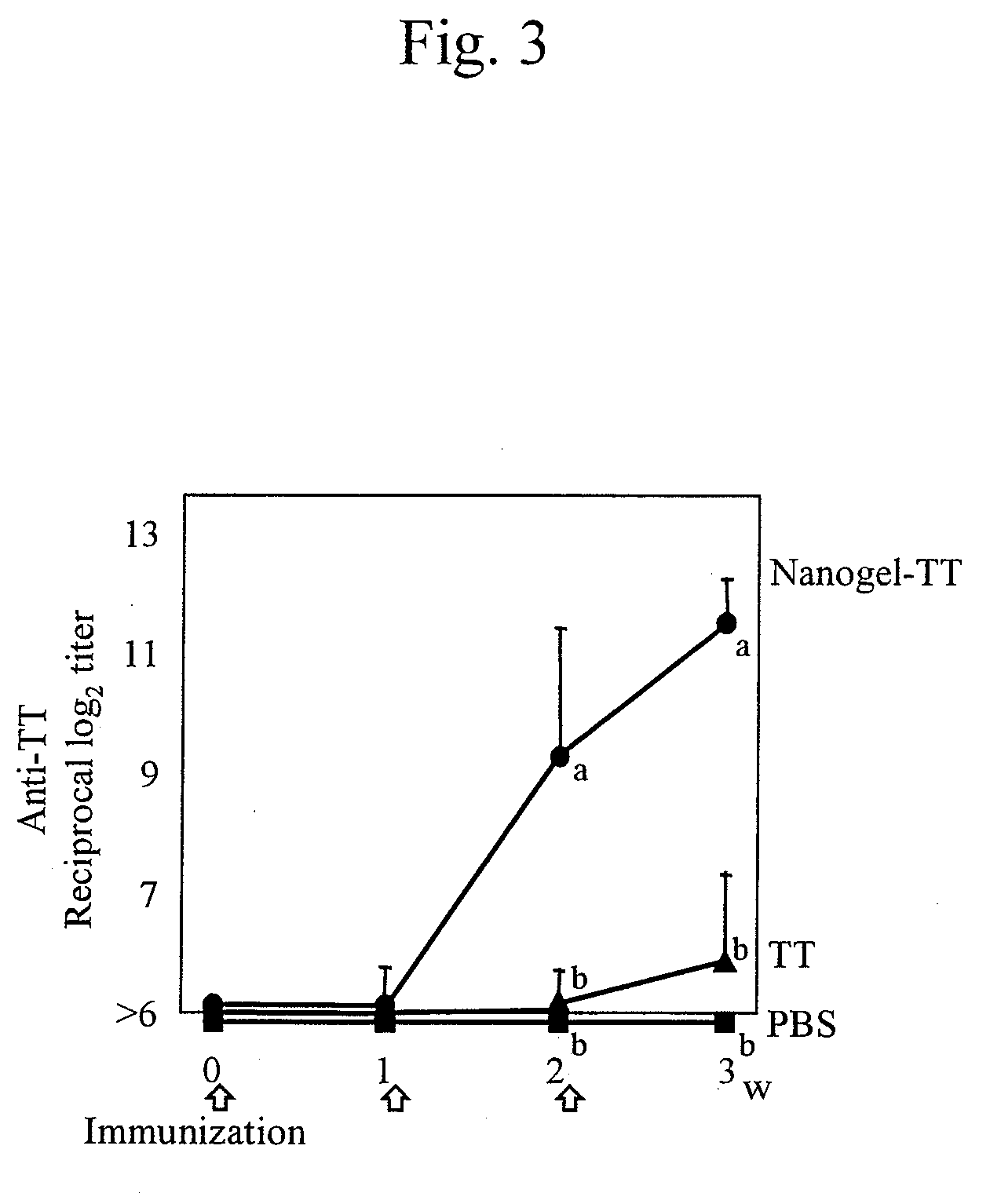
Mucosal vaccine using cationic nanogel
InactiveUS20110206729A1Effectively induces systemic and mucosal immune responseEfficient deliveryAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMedicineCholesterol
A mucosal vaccine for the prevention or treatment of microbial infections is described that is capable of inducing vaccine antigen-specific immune responses in an organism without the addition of a mucosal adjuvant. The mucosal vaccine comprises a composite of a nanogel comprising a hydrophilic polysaccharide having a cationic functional group and a hydrophobic cholesterol added thereto as a side chain and a vaccine antigen. The vaccine is administered via a mucosal route.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO MEDICAL & DENTAL UNIV
Genetic engineering subunit vaccine for porcine circovirus as well as preparation method and application of genetic engineering subunit vaccine
PendingCN108619503AReduce virus contentHigh antigen purityViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsSolubilityEscherichia coli
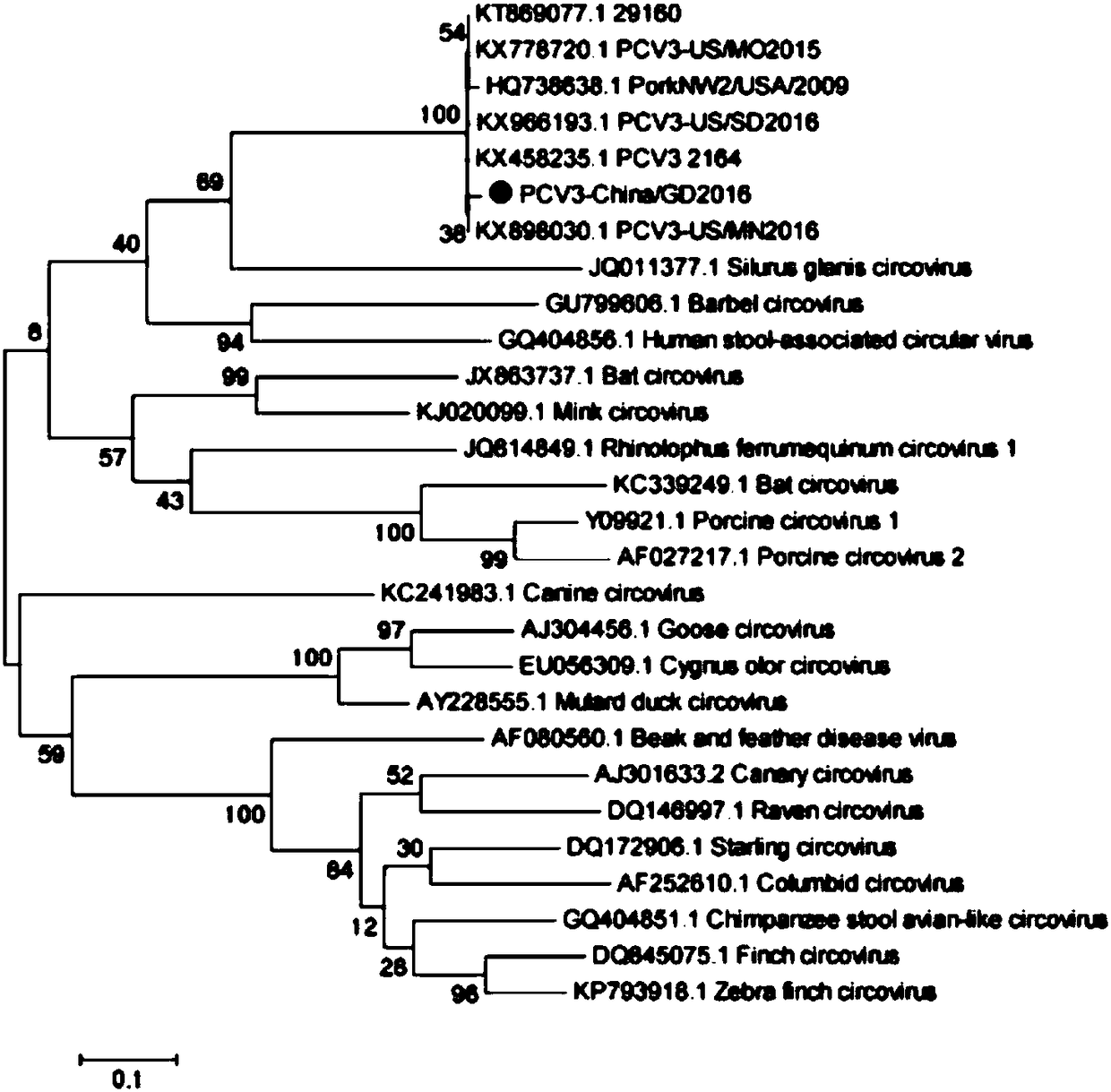
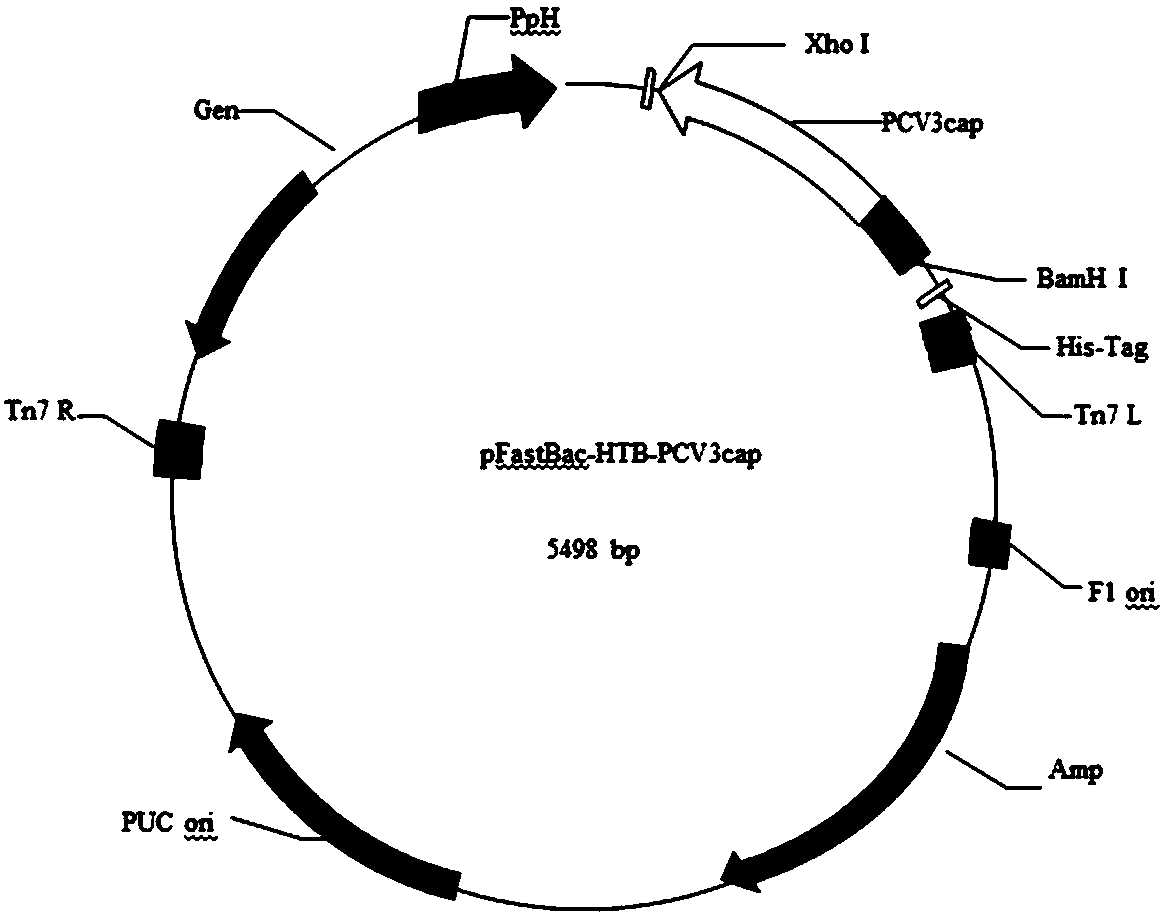
The invention discloses a genetic engineering subunit vaccine for a porcine circovirus as well as a preparation method and application of the genetic engineering subunit vaccine. By cloning the nucleocapsid protein of the novel porcine circovirus 3 (PCV3), a PCV-Cap protein with higher purity is successfully expressed by using an escherichia coli or baculovirus expression system. The subunit vaccine for the PCV3 is successfully developed for the first time by using the PCV-Cap protein; the prepared vaccine is high in antigen purity, good in safety and strong in immunogenicity, and has no pathogenicity to pigs and other animals; the antigen has good solubility in a neutral PH buffer solution; furthermore, the preparation method is simple and low in cost, thus being suitable for large-scaleindustrial production; an effective and powerful means is provided for the prevention and control of novel PCV, and the genetic engineering subunit vaccine has a wide application prospect in the fieldof the prevention and control of the PCV3.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation method and application of novel oil-free adjuvant
ActiveCN103083659AImprove product qualityReduce manufacturing costAntibacterial agentsAntiviralsImmune effectsAdjuvant
The invention relates to a preparation method of a novel oil-free adjuvant (adjuvant 605) compound and an application of the novel oil-free adjuvant in veterinary vaccines. The adjuvant prepared by using the method provided by the invention is capable of completely taking the place of mineral oil adjuvants and alumina gel adjuvants for inactivated vaccine production; the adjuvant can be completely absorbed by organisms within short time without residual; the adjuvant is low in side reaction, and capable of improving the safety of vaccines, and simultaneously simplifying the vaccine production process and reducing the vaccine production cost. The adjuvant prepared by using the method provided by the invention can be also taken as live vaccine diluting protection liquid, and has the characteristics of protecting the biological activity of the vaccine antigen, enhancing the immune effect of the vaccine, prolonging the persistent period of the vaccine antibody and the like.
Owner:BEIJING HUAXIA XINGYANG BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Lipidated imidazoquinoline derivatives
The compounds of the subject invention are adjuvant molecules that comprise a imidazoquinoline molecule covalently linked to a phospho- or phosphonolipid group. The compounds of the invention have been shown to be inducers of interferon-a, IL-12 and other immunostimulatory cytokines and possess an improved activity profile in comparison to known cytokine inducers when used as adjuvants for vaccine antigens.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Use of hyaluronic acid polymers for mucosal delivery of vaccine and adjuvants
InactiveUS20050226937A1Efficient methodImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsAdjuvantVaccine antigen
Compositions are provided which include hyaluronic acid derivatives in combination with vaccine antigens, and optionally adjuvants, for mucosal delivery. Also provided are methods of making the compositions, as well as methods of immunization using the same.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Immune response induction method
InactiveUS20050031587A1High activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsAdjuvantVaccine antigen
The present invention proposes a method of inducing both vaccine antigen-specific antibody in blood and vaccine antigen-specific antibody secreted at the mucosal surface using vaccine antigen and adjuvant of said vaccine antigen.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
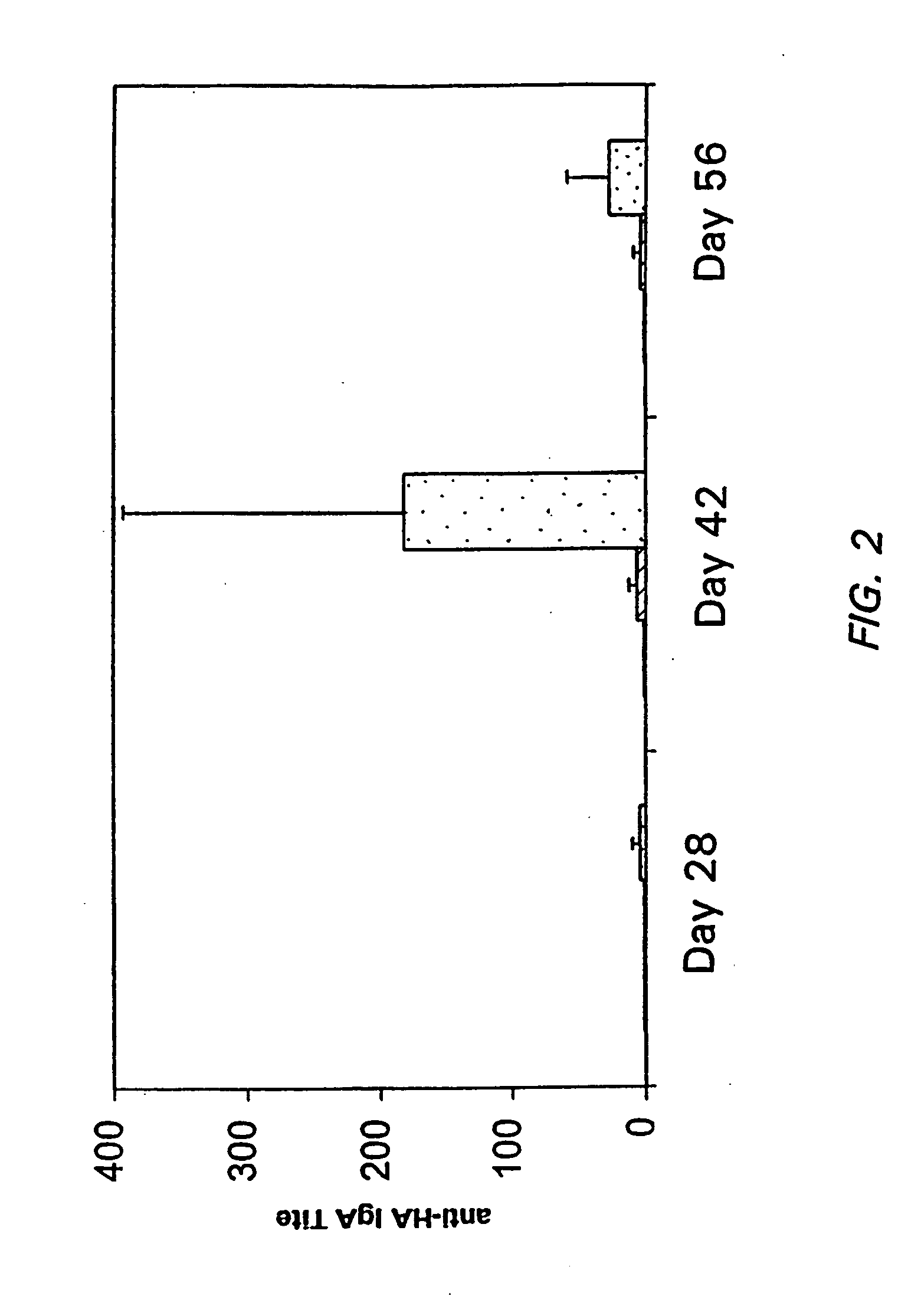
Japanese encephalitis particle vaccine and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102127554AImprove the level ofStrong immune memoryViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesHepatitis B virus core AntigenEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a vaccine embedded with virus-like particles expressing multi-epitope antigen for Japanese encephalitis, and a preparation method and application thereof. The antigen of the vaccine is virus-like particles formed through spontaneous assembly of hepatitis B virus core antigen embedded with neutralizing antigen epitope expressing Japanese encephalitis virus and cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) antigen epitope, and is prepared through soluble expression of escherichia coli and purification. The Japanese encephalitis virus-like particle antigen is properly diluted with physiological saline, or is compatible with immunologic adjuvants to be prepared into the Japanese encephalitis particle vaccine. Animal experiments show that: the vaccine is safe and high-efficiency; mice inoculate with the vaccine generate high-level neutralizing antigen for the Japanese encephalitis virus to protect the mice against the attack of strong Japanese encephalitis virus by 100 percent.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Hepatitis b virus surface antigen as a mucosal immunostimulator and the resulting formulations
InactiveUS20050025780A1Enhance immune responseViral antigen ingredientsReverse transcribing DNA virusesHeterologous AntigensAdjuvant
The invention relates to a mucosal surface antigen which is used to promote and increase in the immune response against co-administered antigens in the formulations out line in the invention. Said novel formulations are obtained from the dual use of the surface antigen as an immunostimulatory agent and, at the same time, as a vaccine antigen. In this way it is possible to obtain multiple formulations of the hepatitis B surface antigen and heterologous antigens, with immunogenicity levels similar to those obtained following parenteral administration and with a reduction in components that can dispense with the use of nasal adjuvants, thereby converting same antigens into elements that can promote an increase in the response to the other co-administered antigens. Said novel use of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen and the resulting antigen formulations can be used in the pharmaceutical industry as therapeutic and preventive vaccine formulations.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
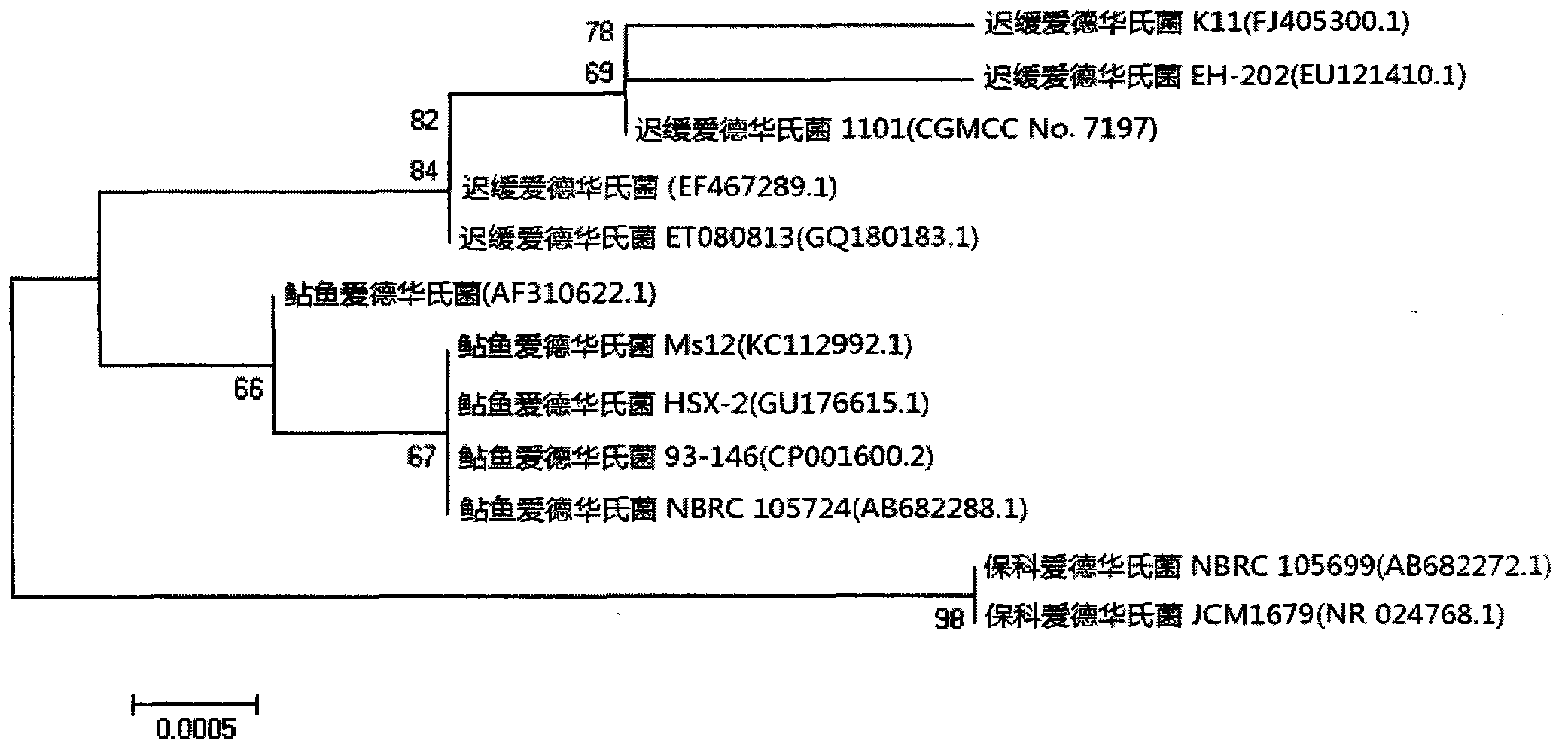
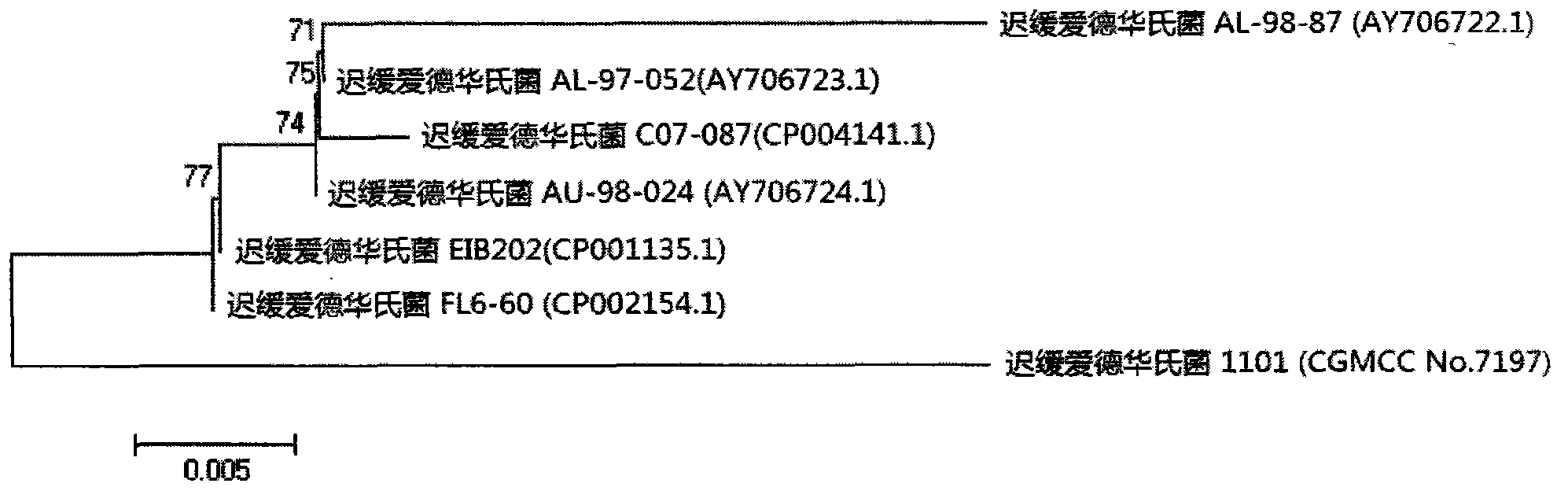
Velogenic Edwardsiella tarda vaccine strain and application thereof
ActiveCN103255089AStrong drug resistanceReduce lossesAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesProtective antigen
The invention relates to an Edwardsiella tarda strain and an application method thereof. The Edwardsiella tarda strain is separated from a turbot adult fish body and is a wild strain with strong virulence, and the preservation number of the Edwardsiella tarda strain is CGMCC No.7197. Preparation modes of an antigen of the Edwardsiella tarda strain comprise any one or more than one of an inactivated thallus, a bacteruak ghost ingredient, an attenuated strain, a protective antigen, an antigen subunit and an expression product of an antigen determinant or an antigen gene expression carrier; the produced vaccine can be a single ingredient of the antigen prepared by utilizing the Edwardsiella tarda strain and can also be a combined vaccine produced by mixing the antigen prepared by utilizing the Edwardsiella tarda strain with antigens of other bacteria, and the prepared single or combined vaccine antigen is added with an adjuvant to produce the vaccine; and an inoculation mode of the vaccine in immunization application can adopt injection immunization, wound immunization, immersion bath immunization or oral administration immunization.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
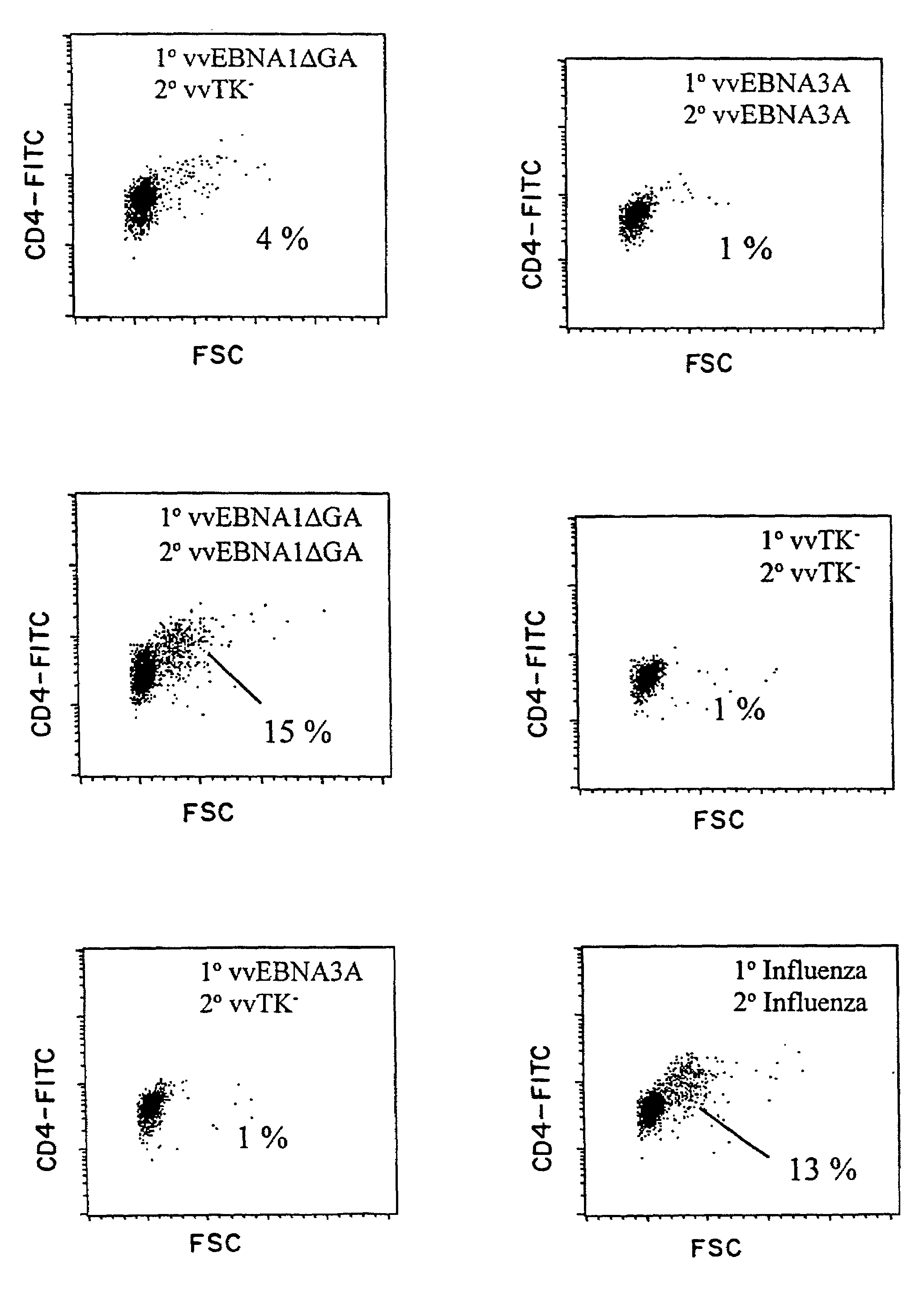
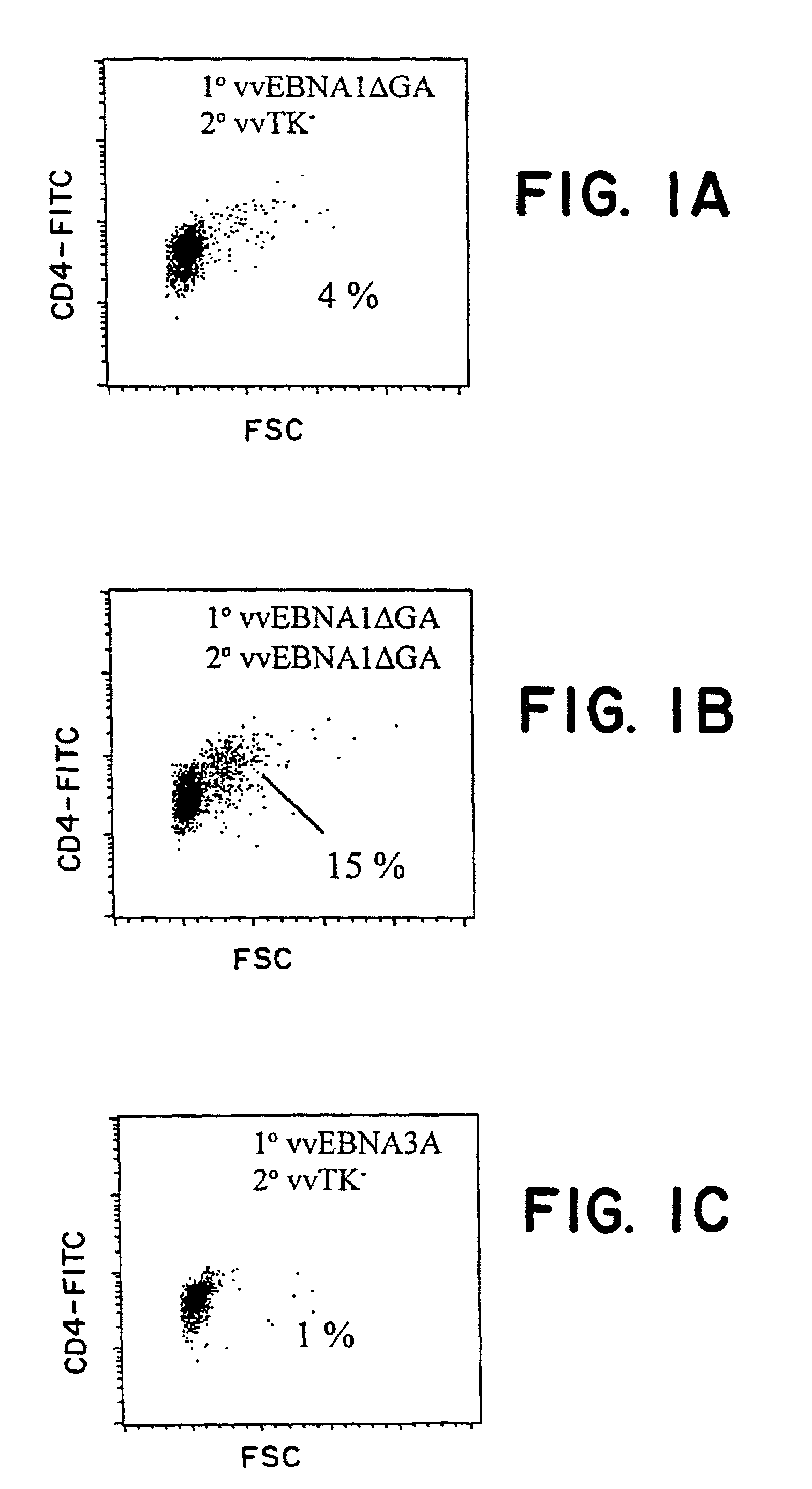
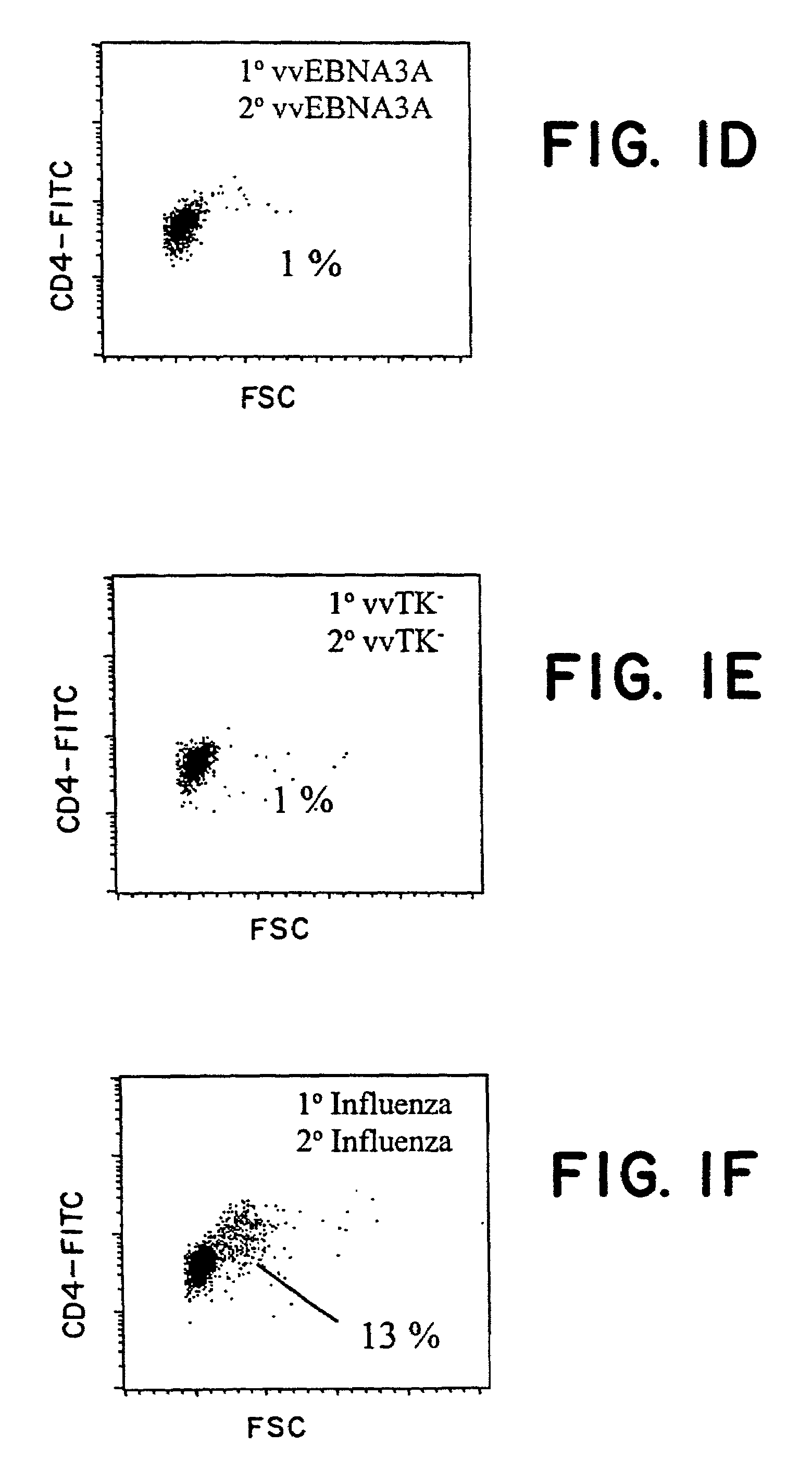
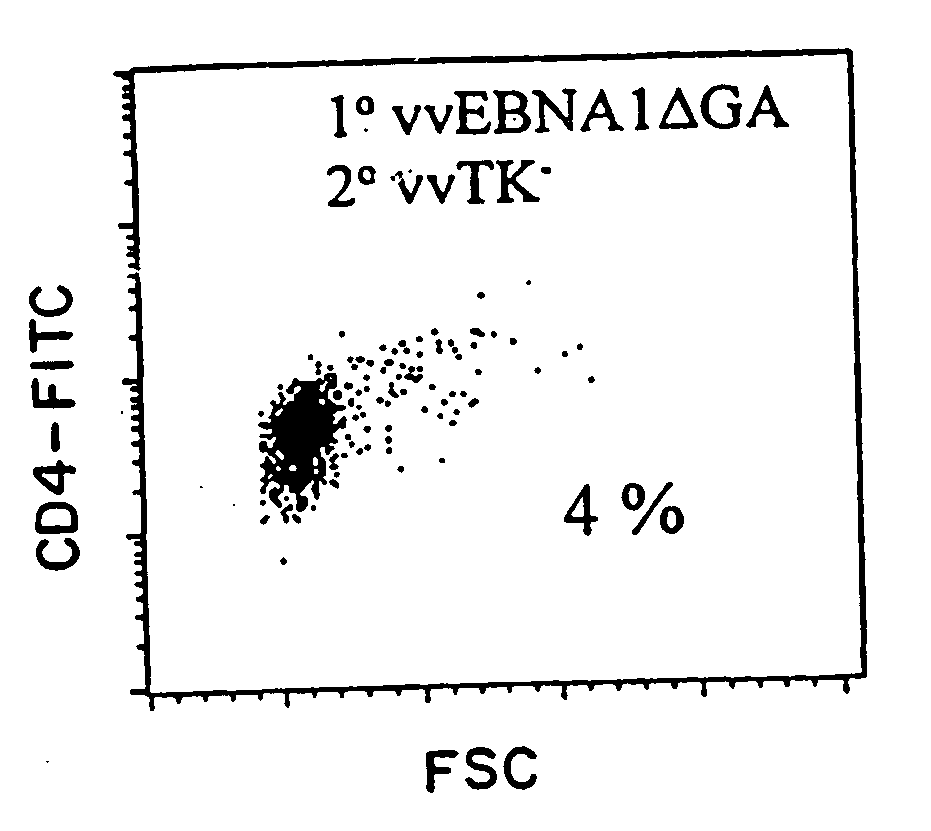
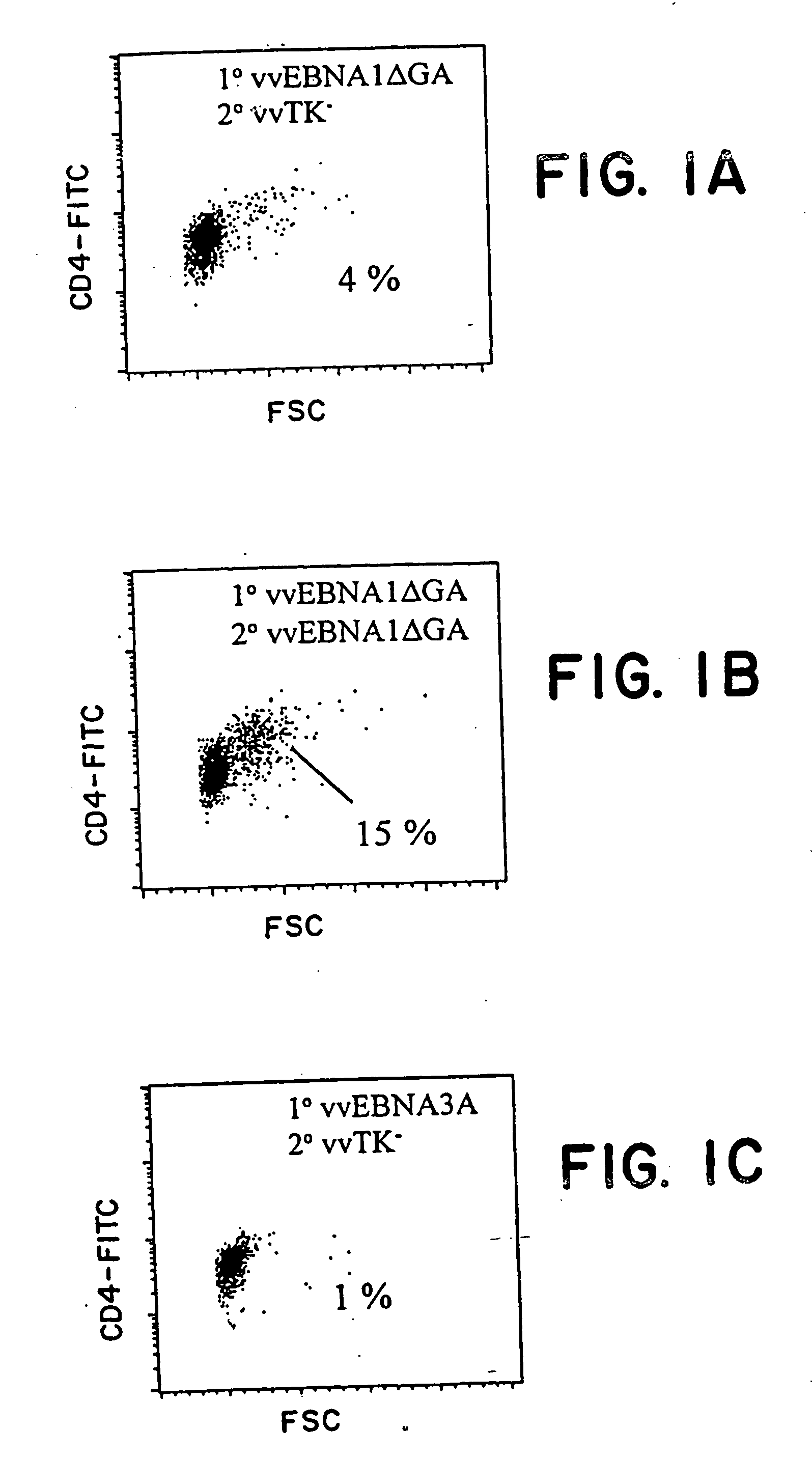
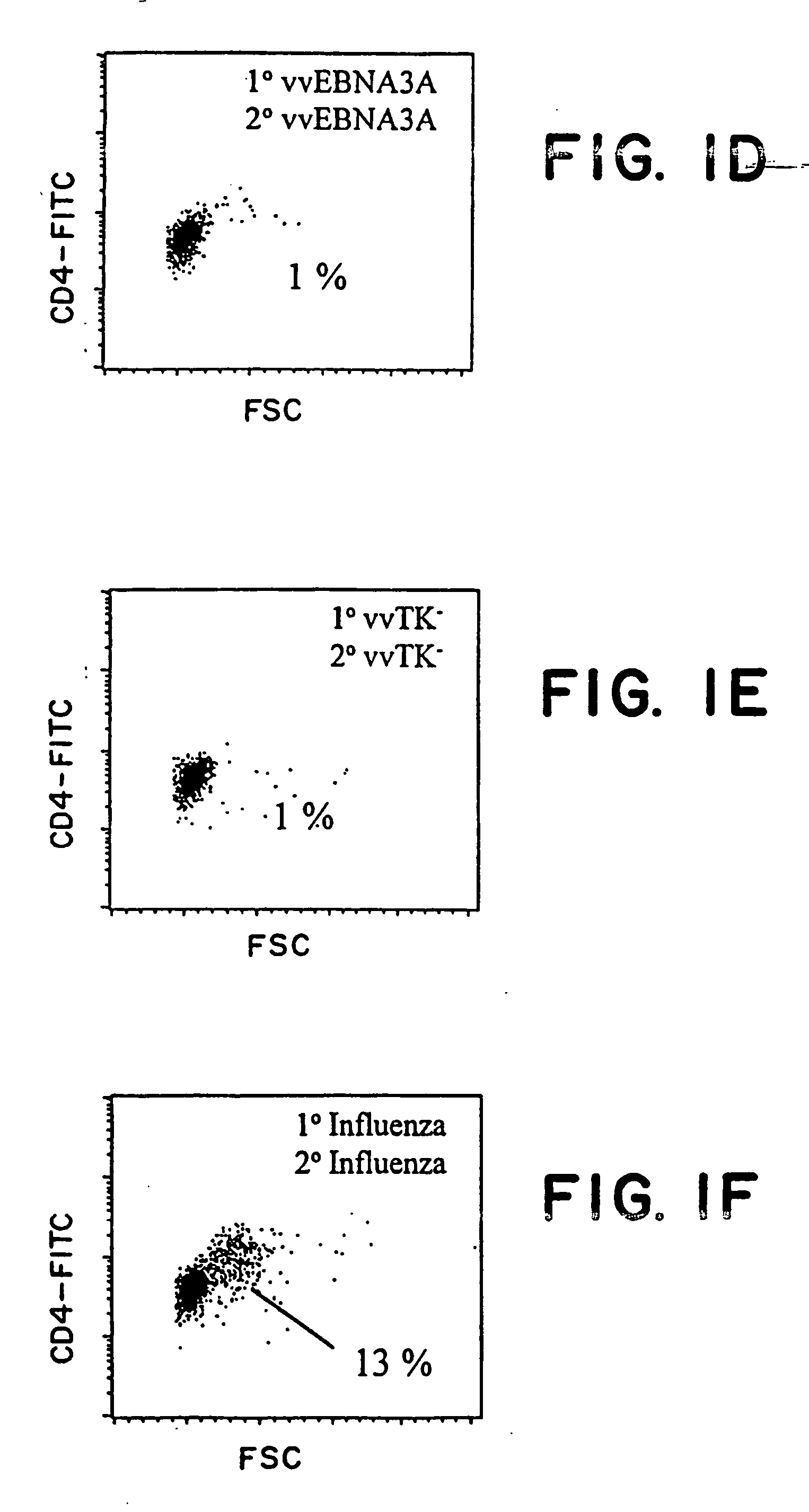
Protective antigen of Epstein Barr Virus
The present invention relates to the identification of a subunit vaccine to prevent or treat infection of Epstein Barr Virus. In particular, EBNA-1 was identified as a vaccine antigen. In a specific embodiment, a purified protein corresponding to EBNA-1 elicited a strong CD4+ T cell response. The responsive CD4+ T cell are primarily TH1 in function. EBNA-1 is an attractive candidate for a protective vaccine against EBV, and for immunotherapy of EBV infection and neoplasms, particularly with dendritic cells charged with EBNA-1.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Protective antigen of epstein barr virus
The present invention relates to the identification of a subunit vaccine to prevent or treat infection of Epstein Barr Virus. In particular, EBNA-1 was identified as a vaccine antigen. In a specific embodiment, a purified protein corresponding to EBNA-1 elicited a strong CD4+ T cell response. The responsive CD4+ T cell are primarily TH1 in function. EBNA-1 is an attractive candidate for a protective vaccine against EBV, and for immunotherapy of EBV infection and neoplasms, particularly with dendritic cells charged with EBNA-1.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Recombinant vaccine viruses expressing IL-15 and methods using the same
InactiveUS8663622B2Stimulates proliferation and differentiationImprove immunityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAdjuvantRecombinant vaccines
The invention is directed to compositions capable of augmenting the immunogenicity of a vaccine. The composition, or adjuvant, is administered to a mammal in need thereof in sequential or concurrent combination with a vaccine antigen. In one preferred aspect, the adjuvant is provided in the form of a recombinant poxvirus vector, such as a vaccinia virus vector, which comprises a nucleic acid sequence encoding IL-15.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
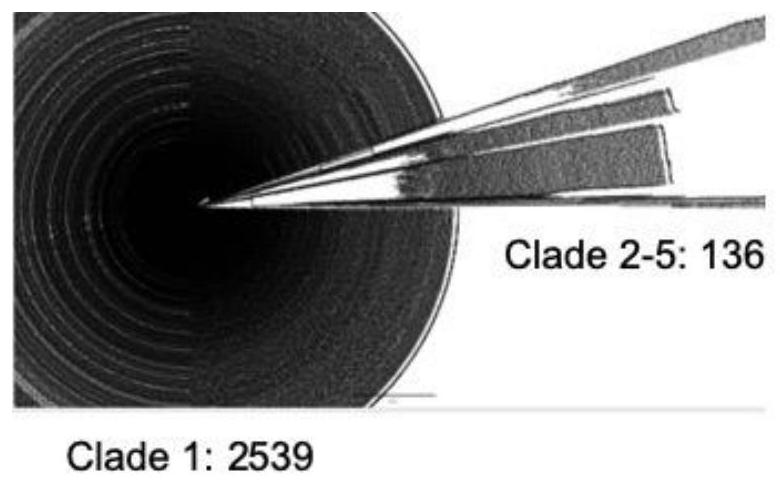
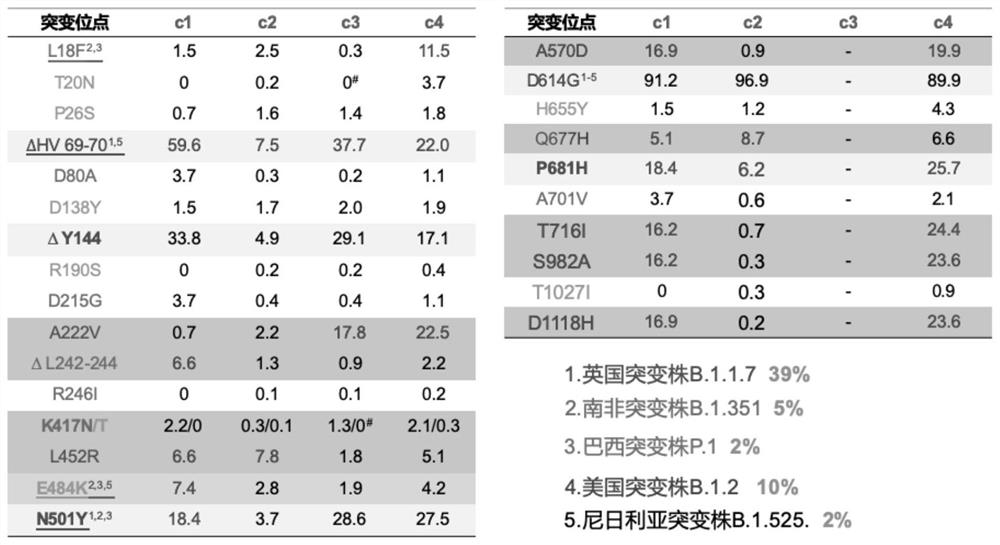
Novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein and subunit vaccine thereof
InactiveCN113234170AIntegrity guaranteedPromote formationSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVaccine antigenTGE VACCINE
The invention provides a novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein and a subunit vaccine thereof. The novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein is characterized in that a furin cleavage site 682-RRAR-685 between an S1 subunit and an S2 subunit of the novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein is replaced with a flexible protein linker; the linker is (GGCAGCGCCAGC), or (GGCGGCGGCAGC)n, or (GGCGGCGGCGGCAGC)n, or (GGC)n, or the linker is GSAS or (GGGS)n or (GGGGS)n or (G) n, n is greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 3, and n is an integer; and the amino acid sequence of the novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 or as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4. The S protein has great potential as a vaccine antigen for coping with an SARS-CoV-2 mutant strain.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
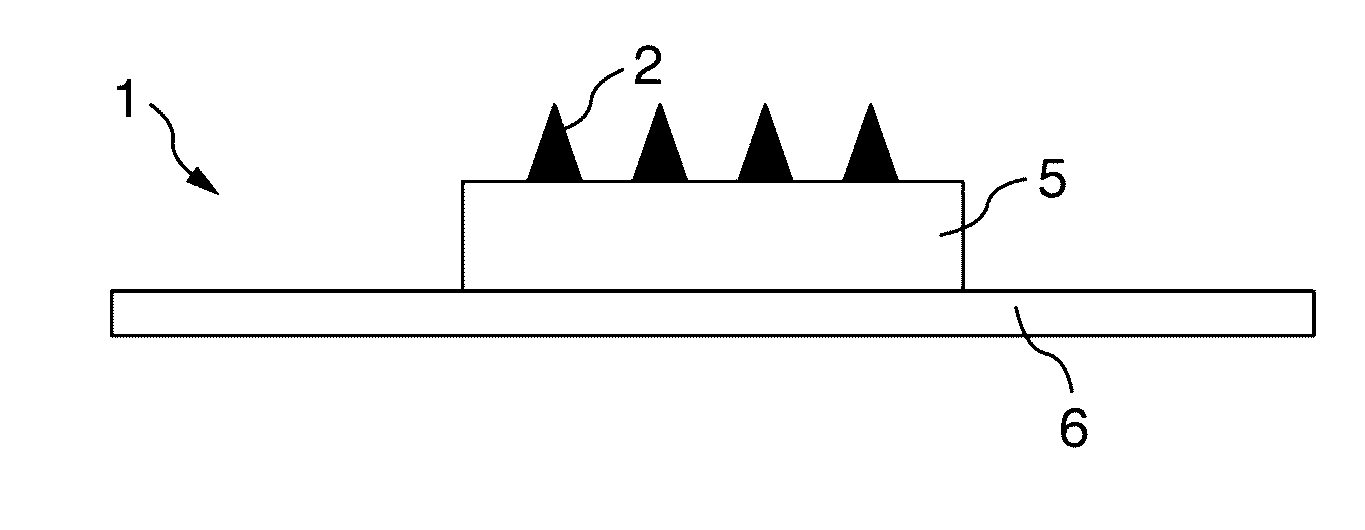
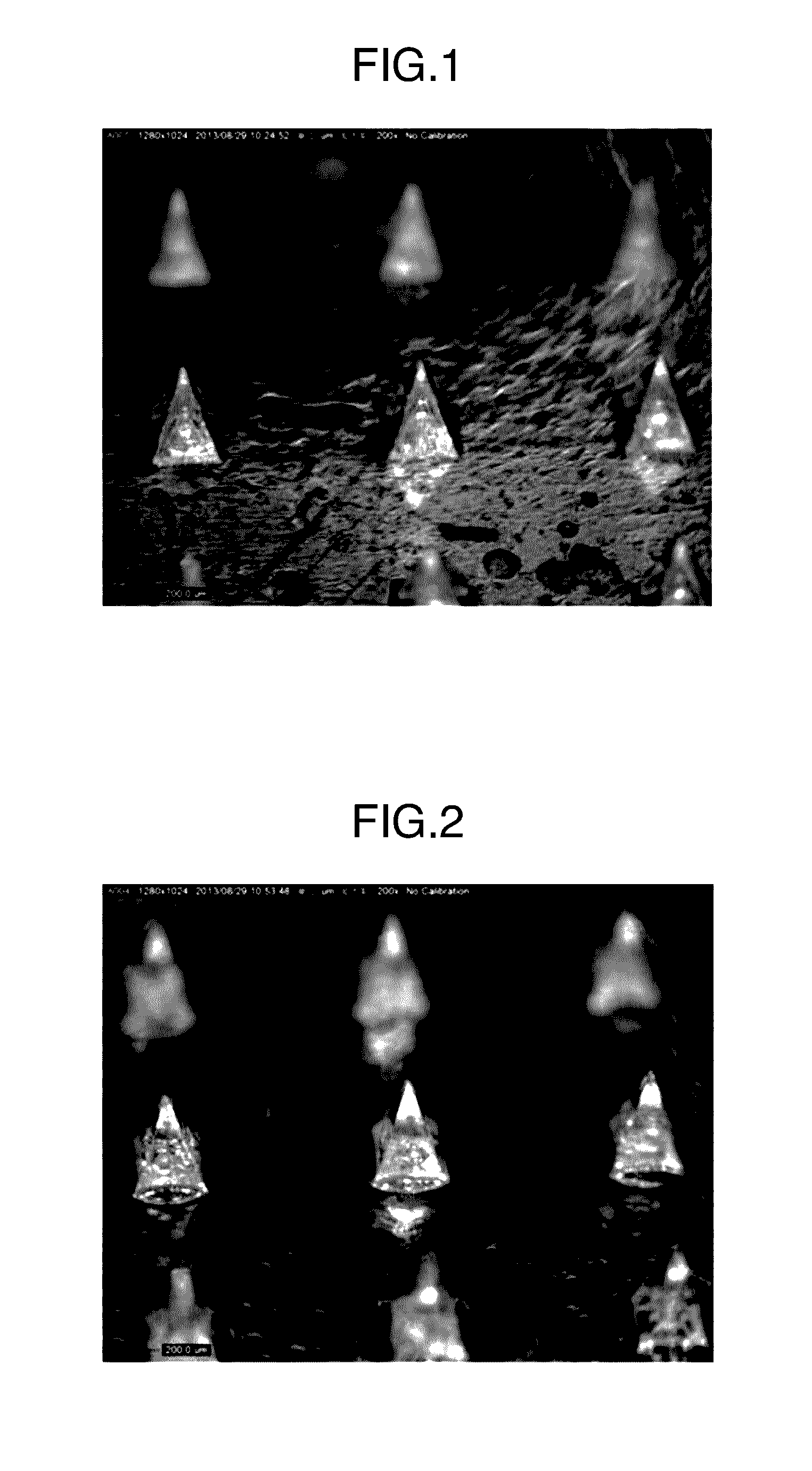
Microneedle
InactiveUS20160310412A1Improve stabilityBacterial antigen ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseCyclodextrinAlcohol sugars
In order to configure a microneedle to be more suitable for administering a vaccine antigen, the present invention is a formulation having a dissolving-type microspike which is used as a microneedle in which a vaccine antigen is stabilized, and which includes a vaccine antigen, an ionic polymer base material, and at least one species selected from the group consisting of a non-reducing sugar, a sugar alcohol, cyclodextrin, and a surfactant.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com