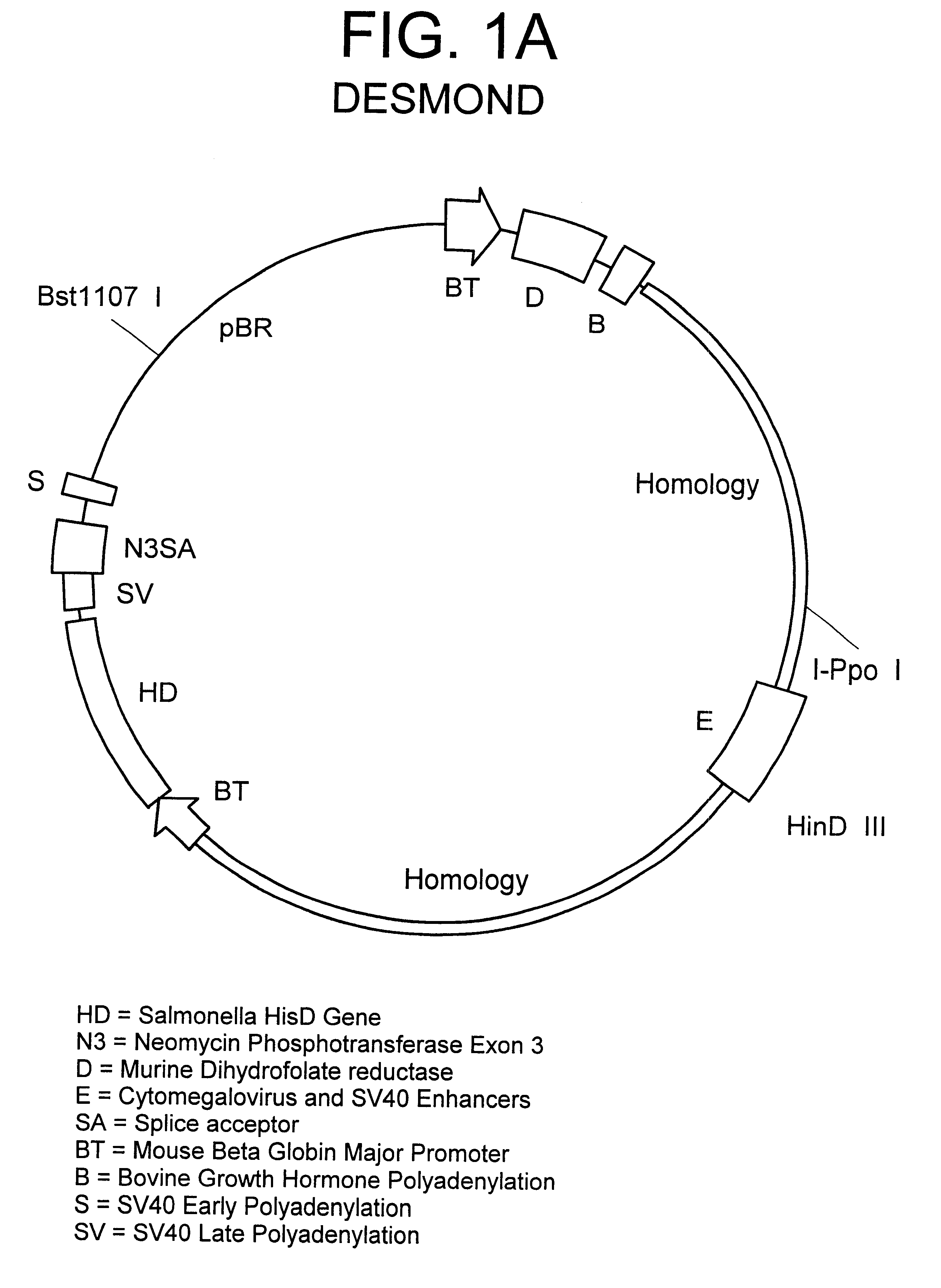
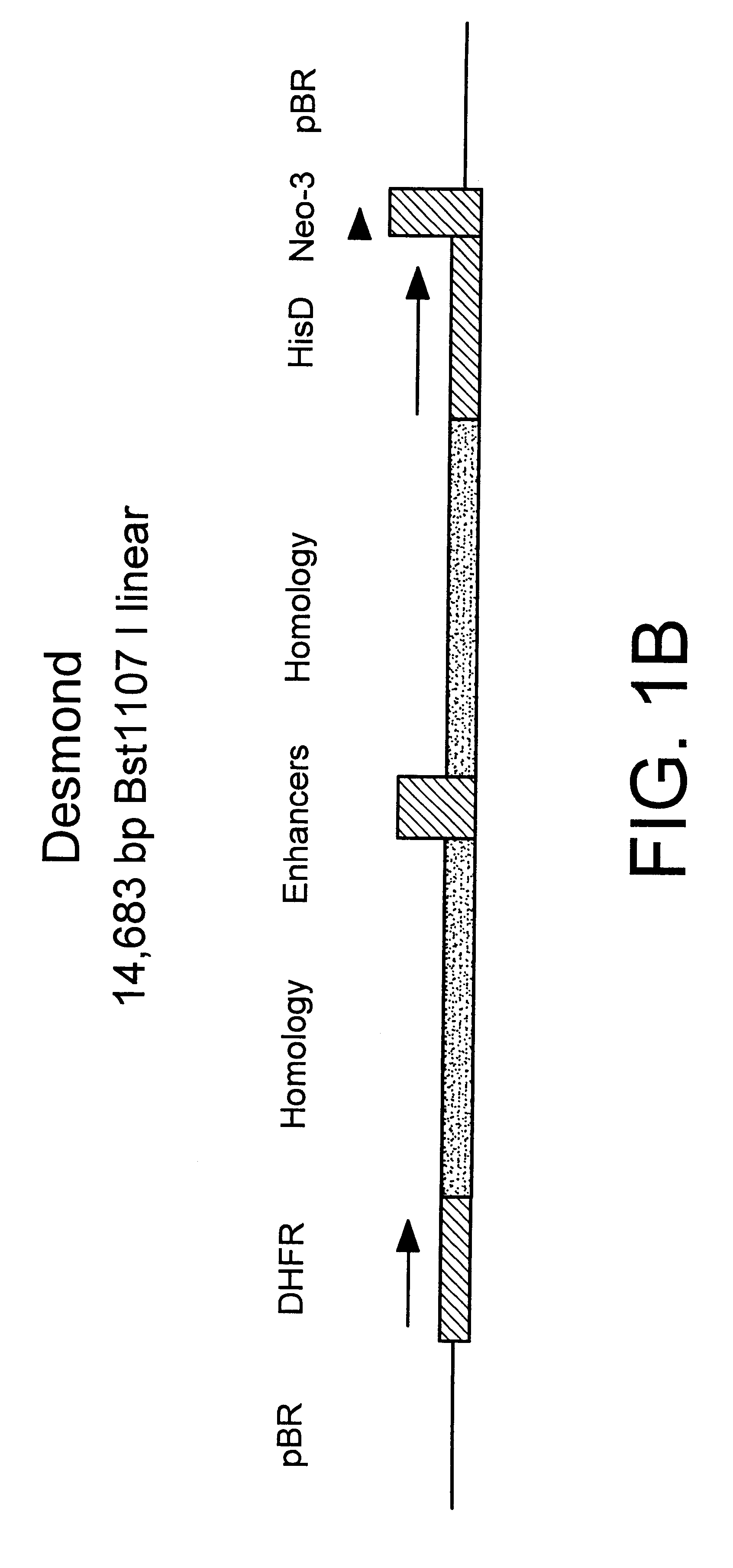
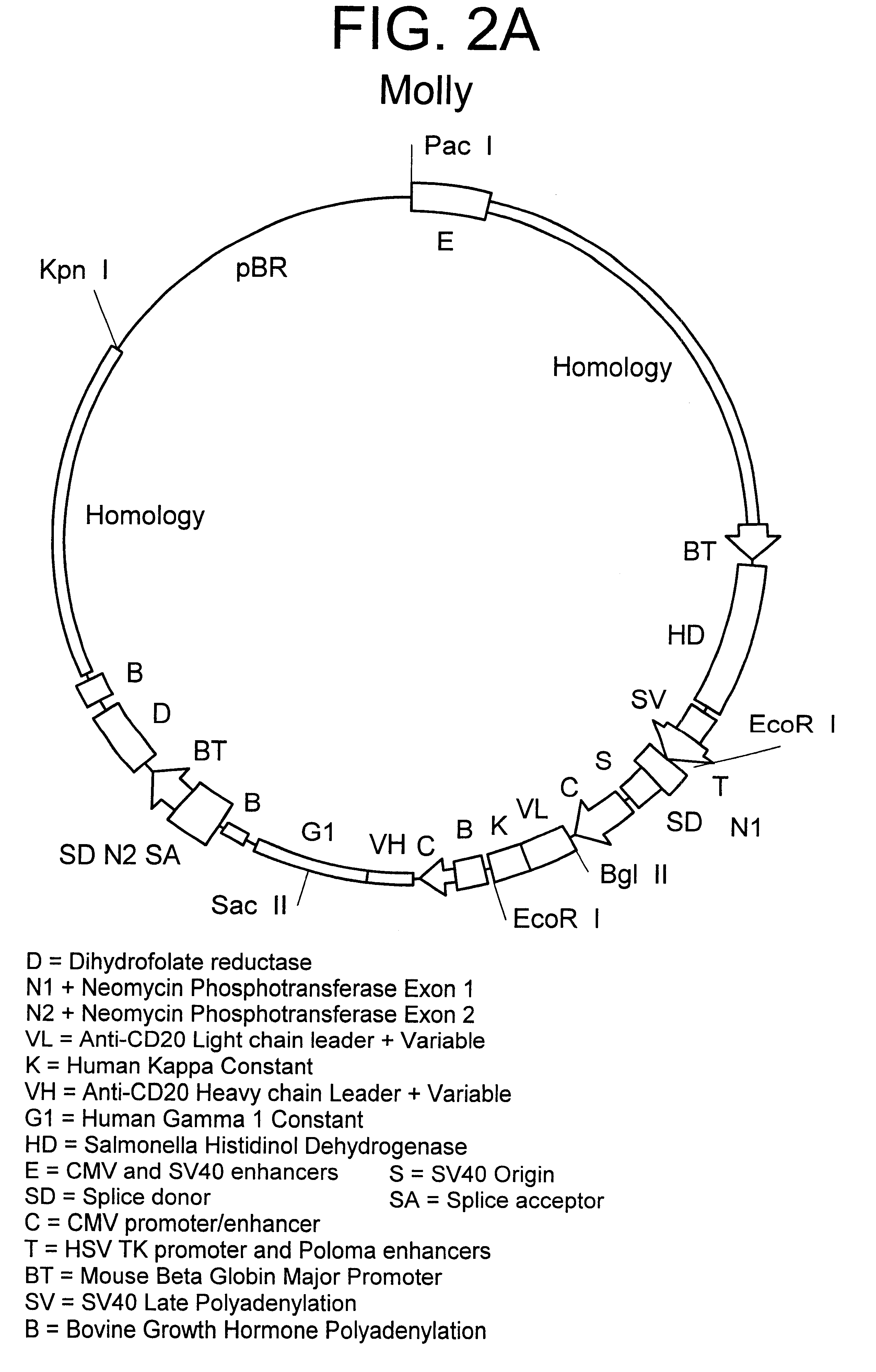
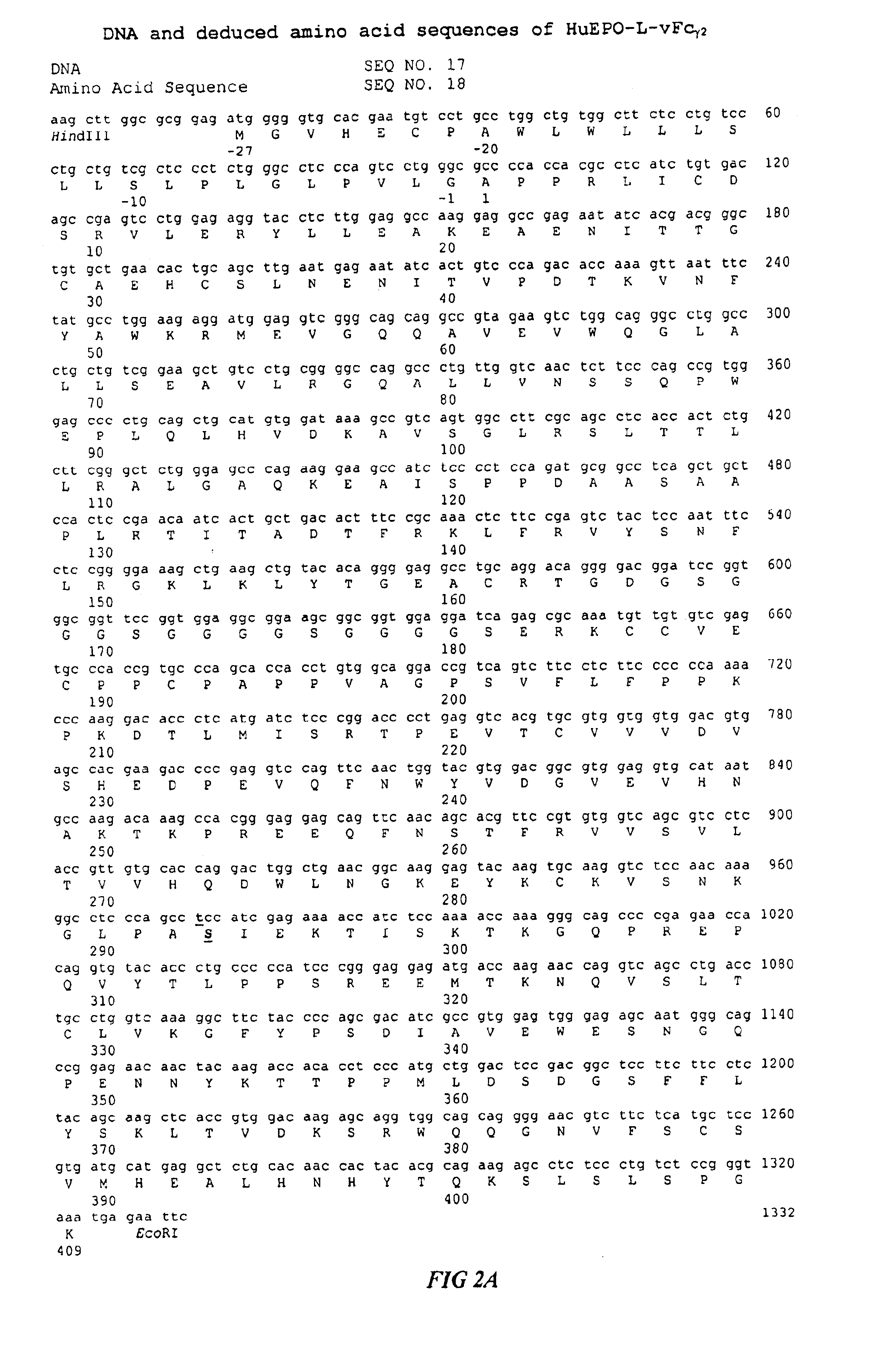Patents
Literature
25711 results about "Protein C" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein C, also known as autoprothrombin IIA and blood coagulation factor XIV, is a zymogen, the activated form of which plays an important role in regulating anticoagulation, inflammation, cell death, and maintaining the permeability of blood vessel walls in humans and other animals. Activated protein C (APC) performs these operations primarily by proteolytically inactivating proteins Factor Vₐ and Factor VIIIₐ. APC is classified as a serine protease as it contains a residue of serine in its active site. In humans, protein C is encoded by the PROC gene, which is found on chromosome 2.
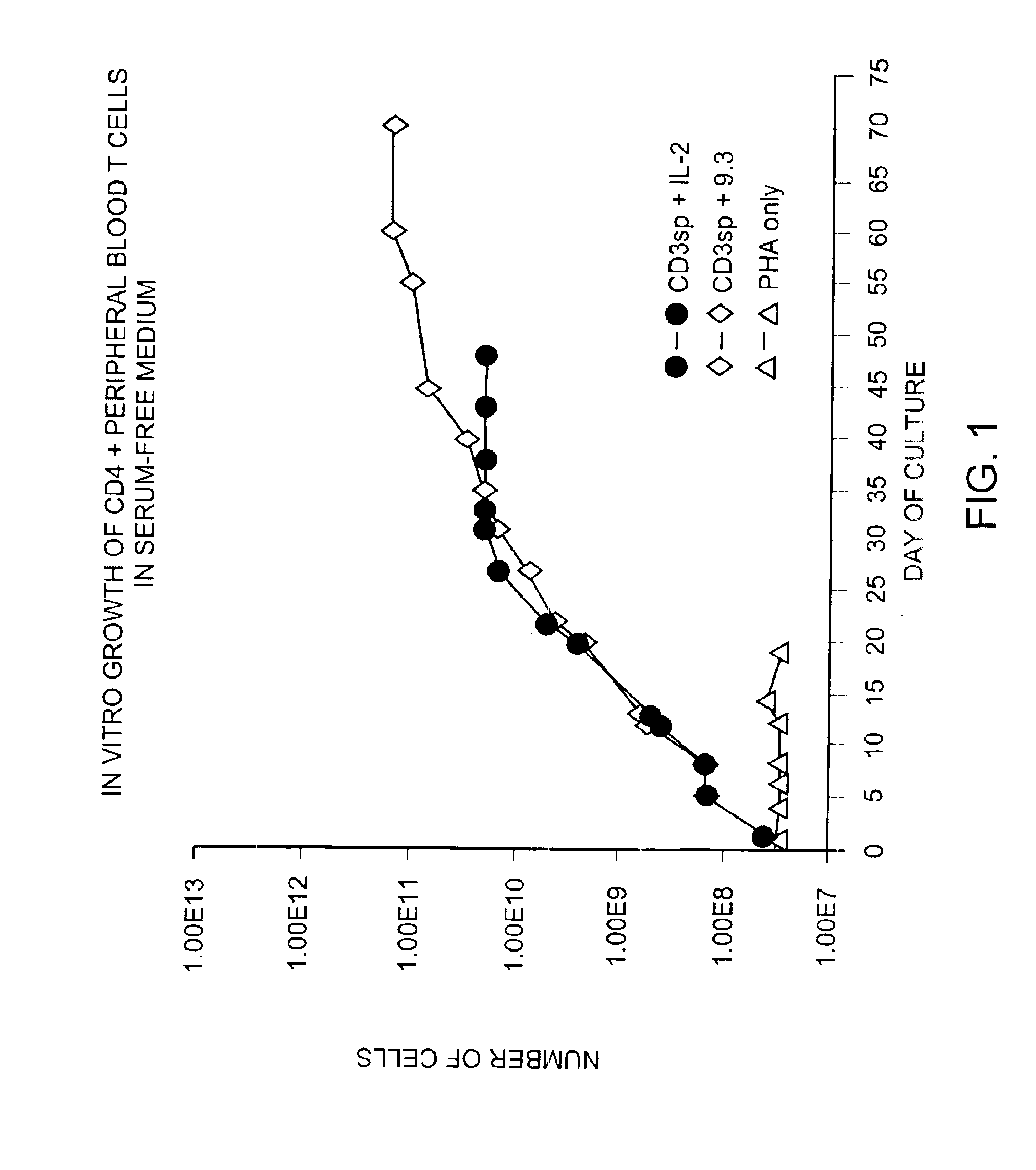
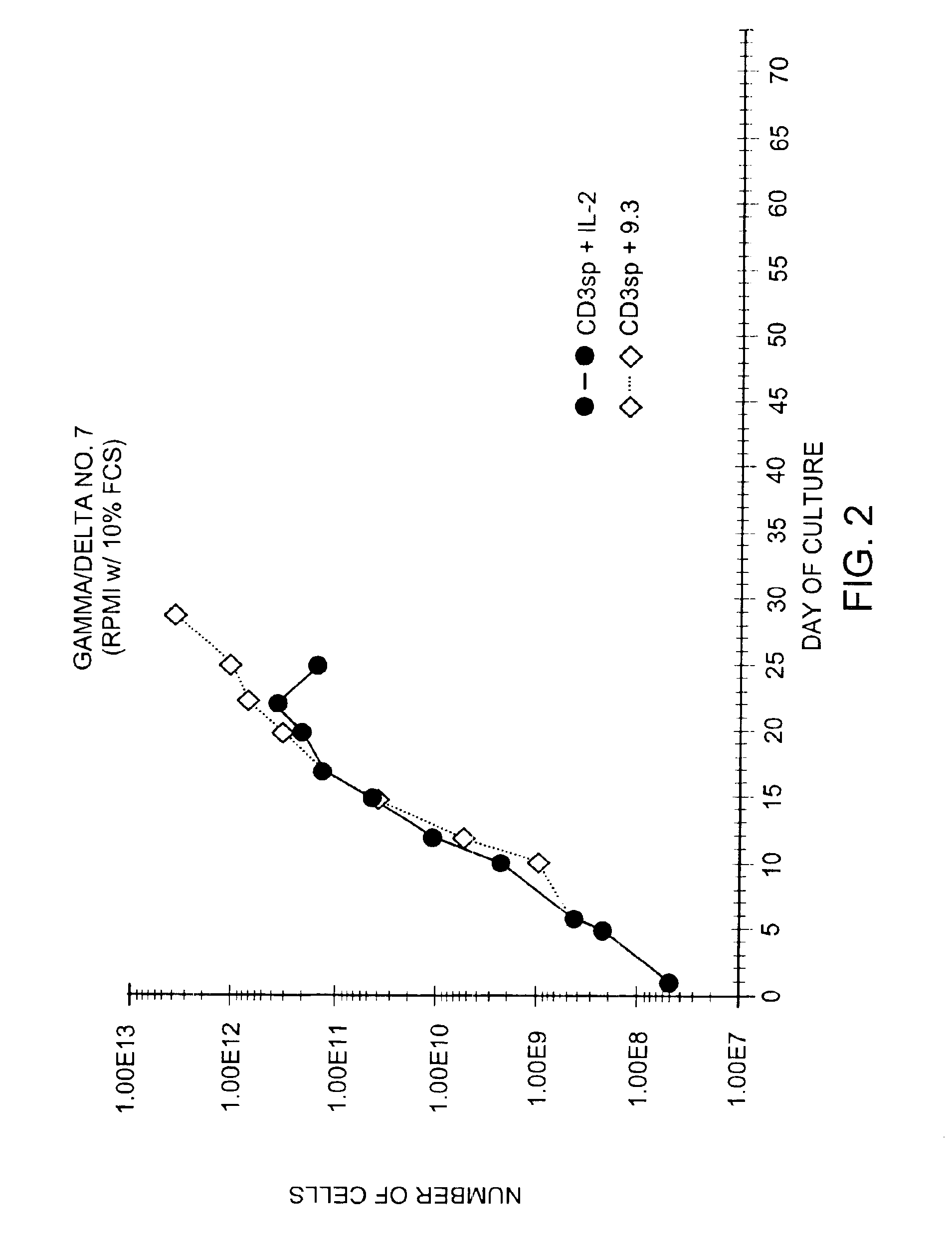
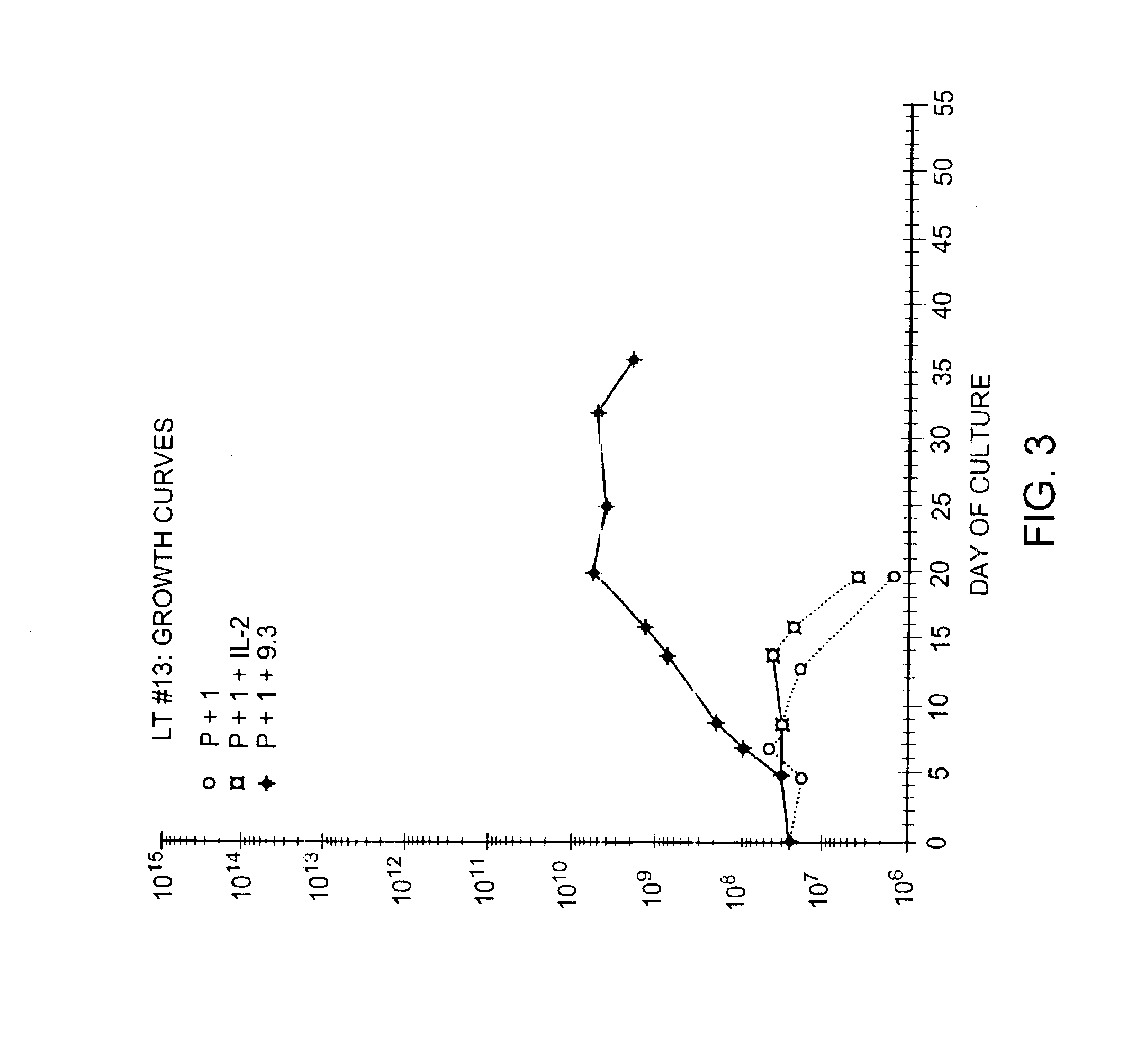
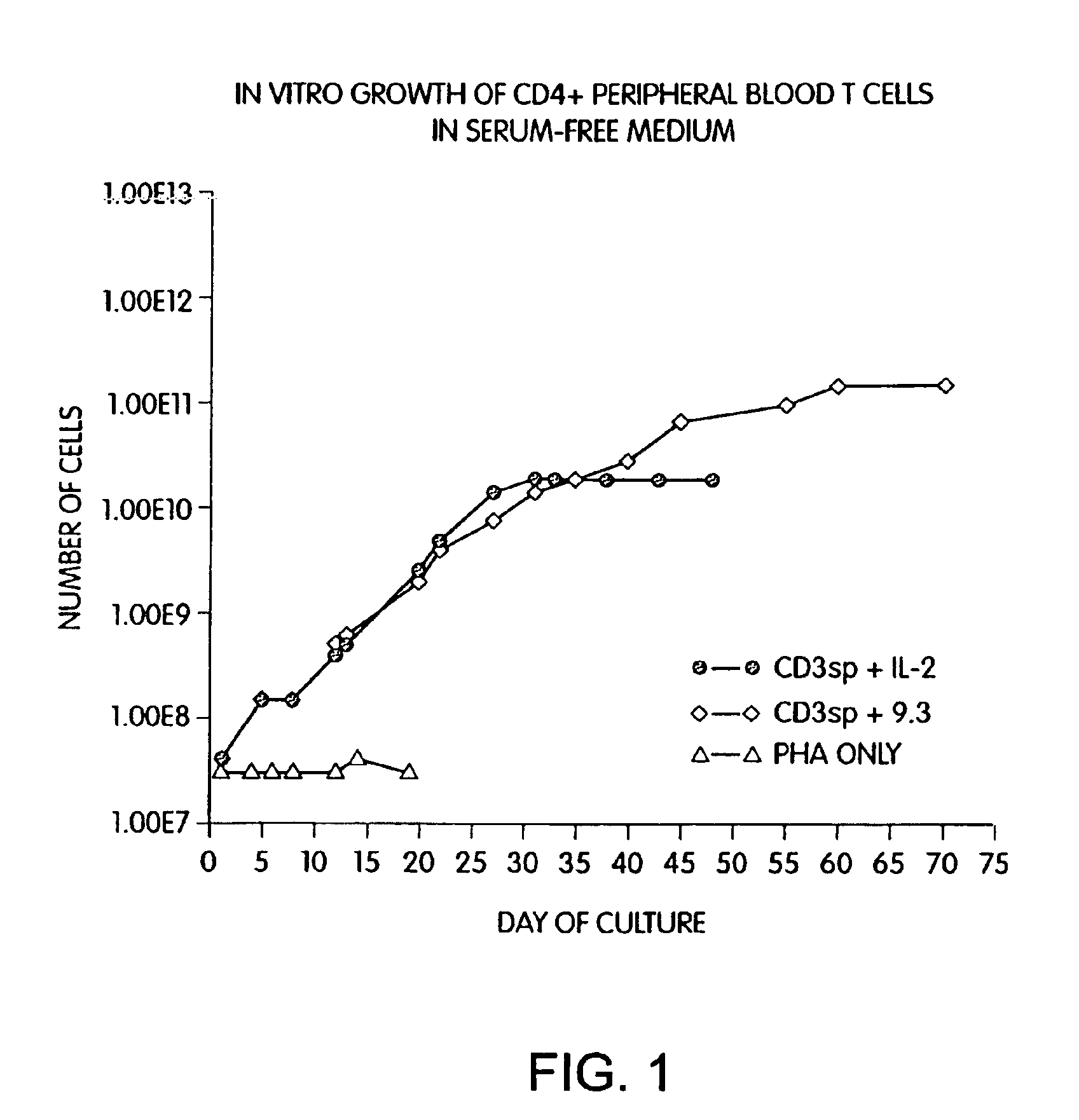
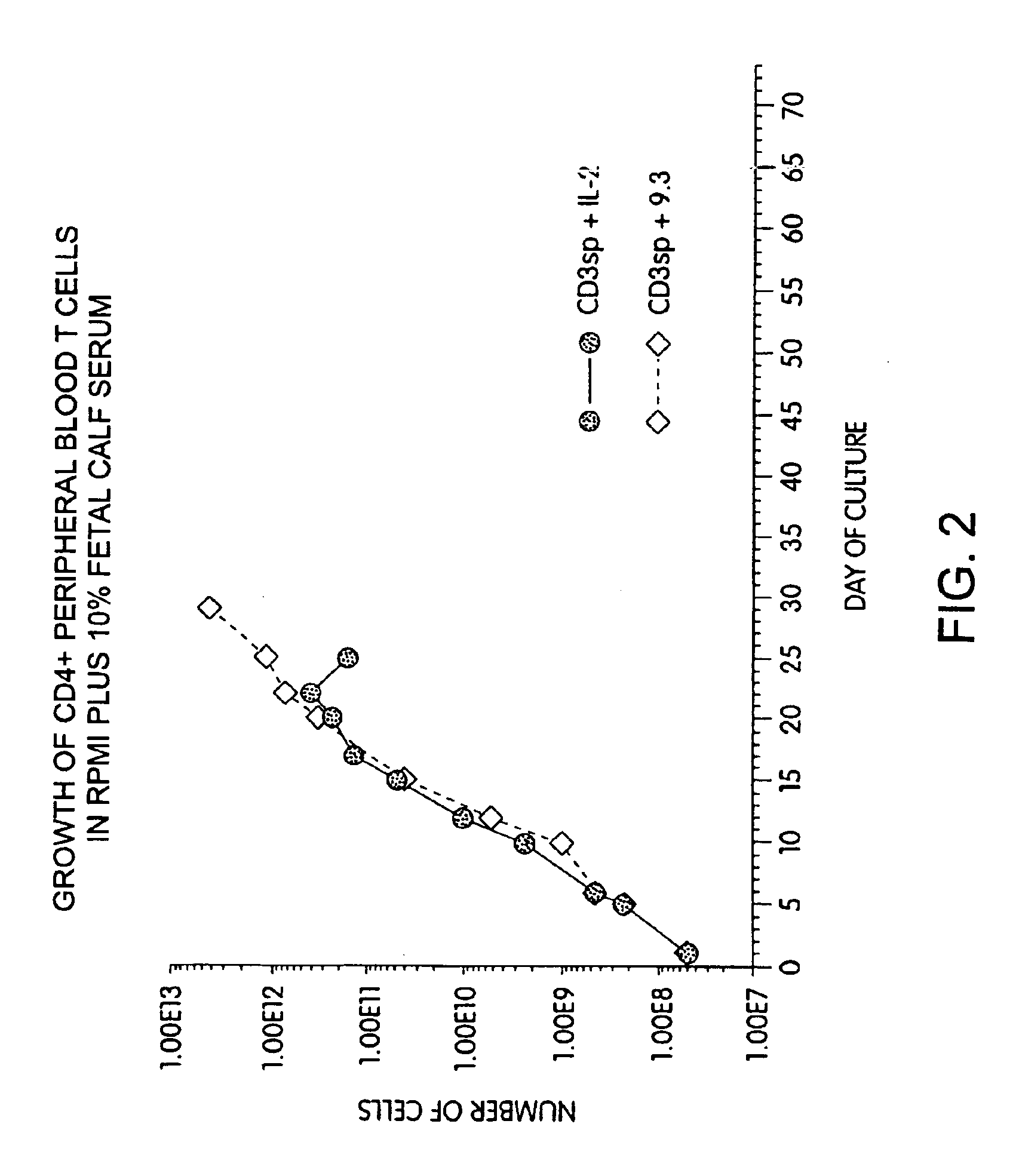
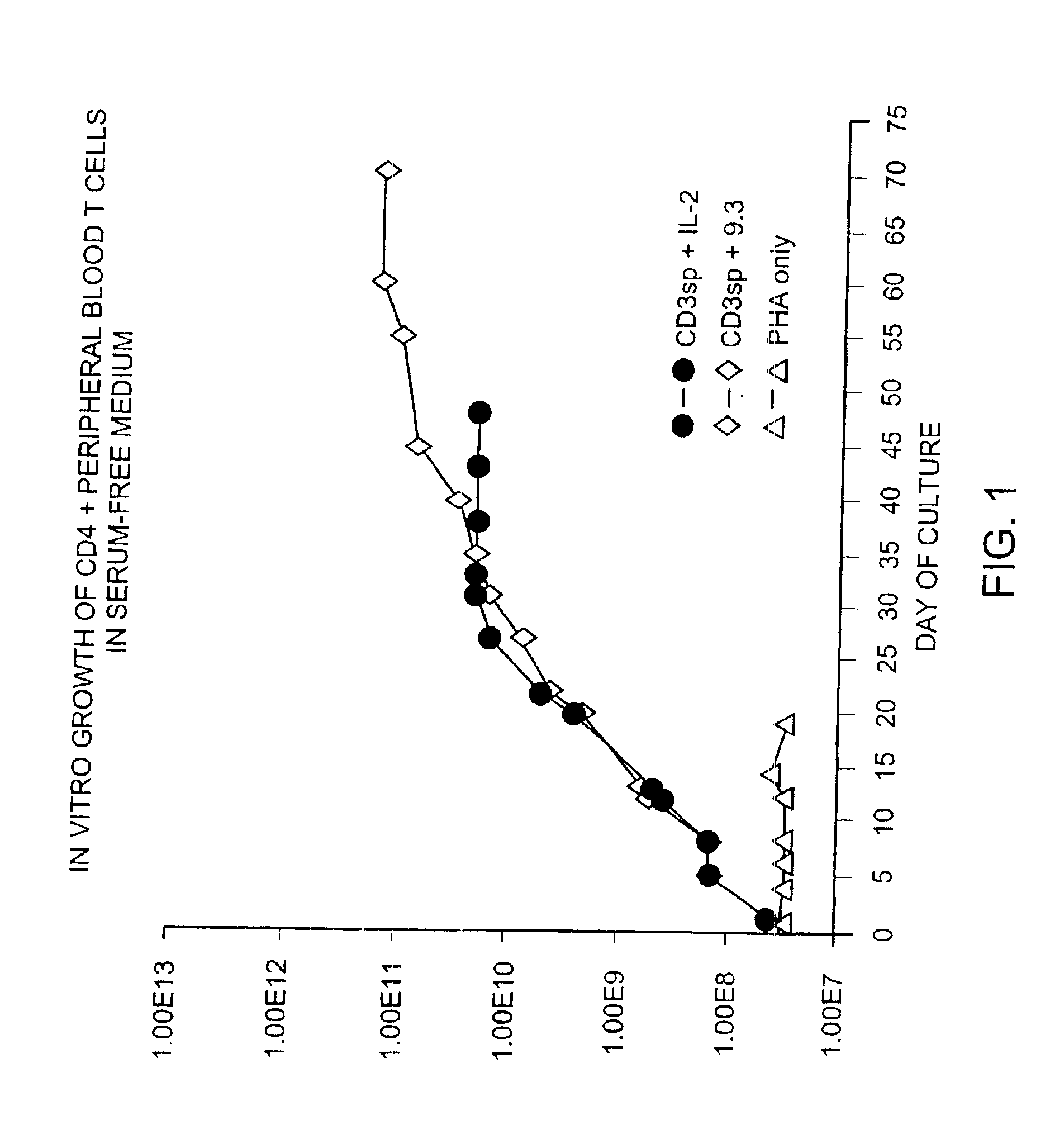
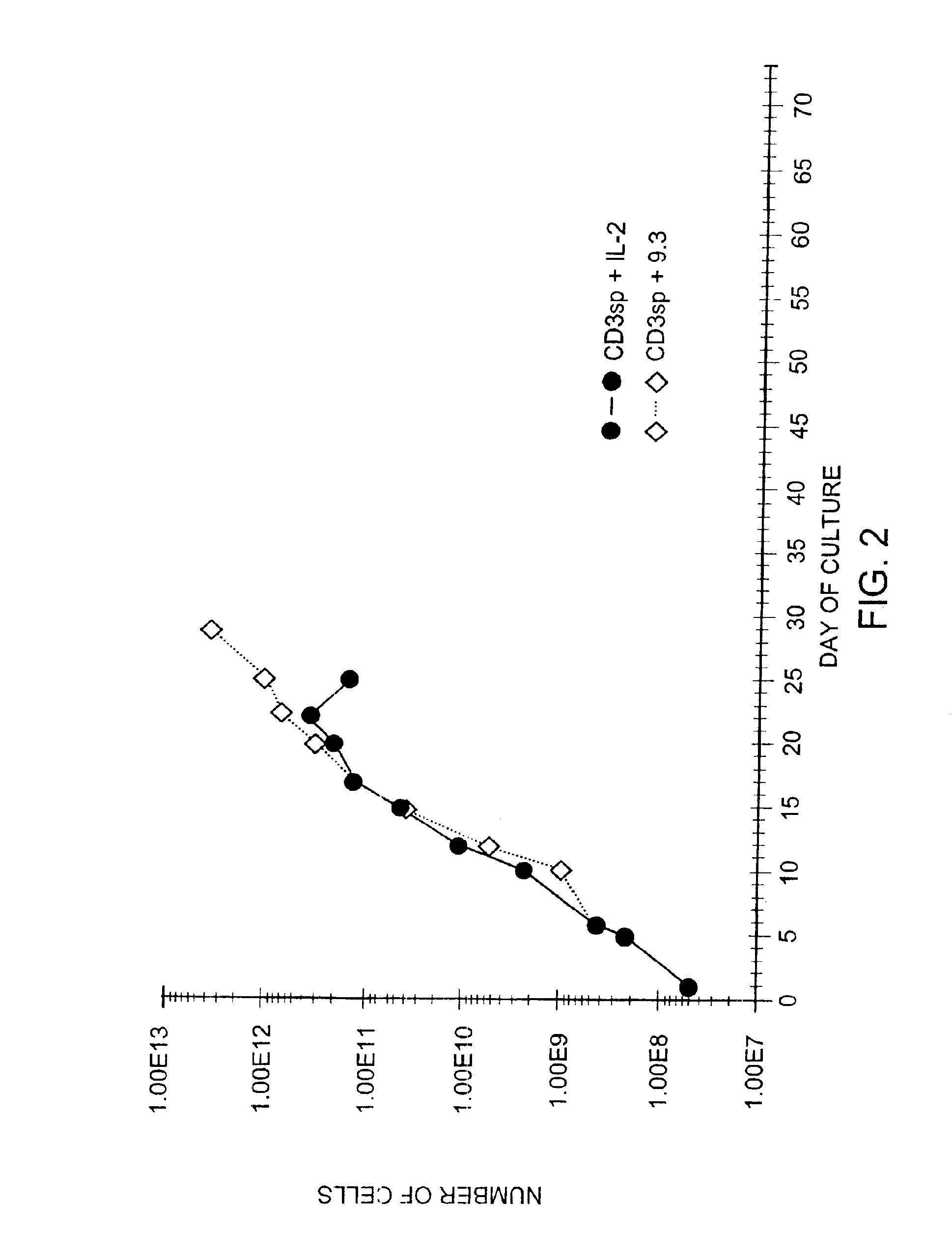
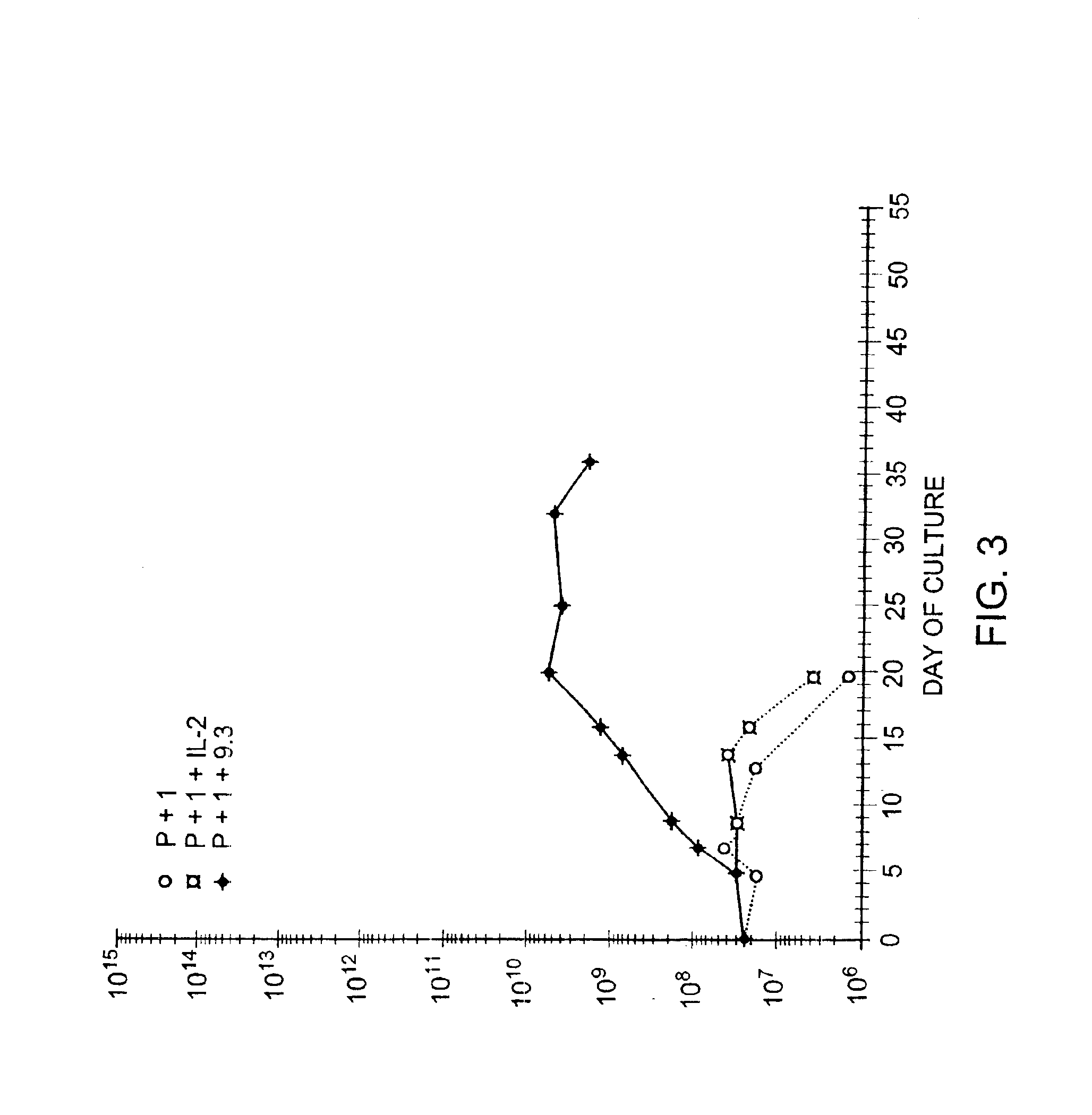
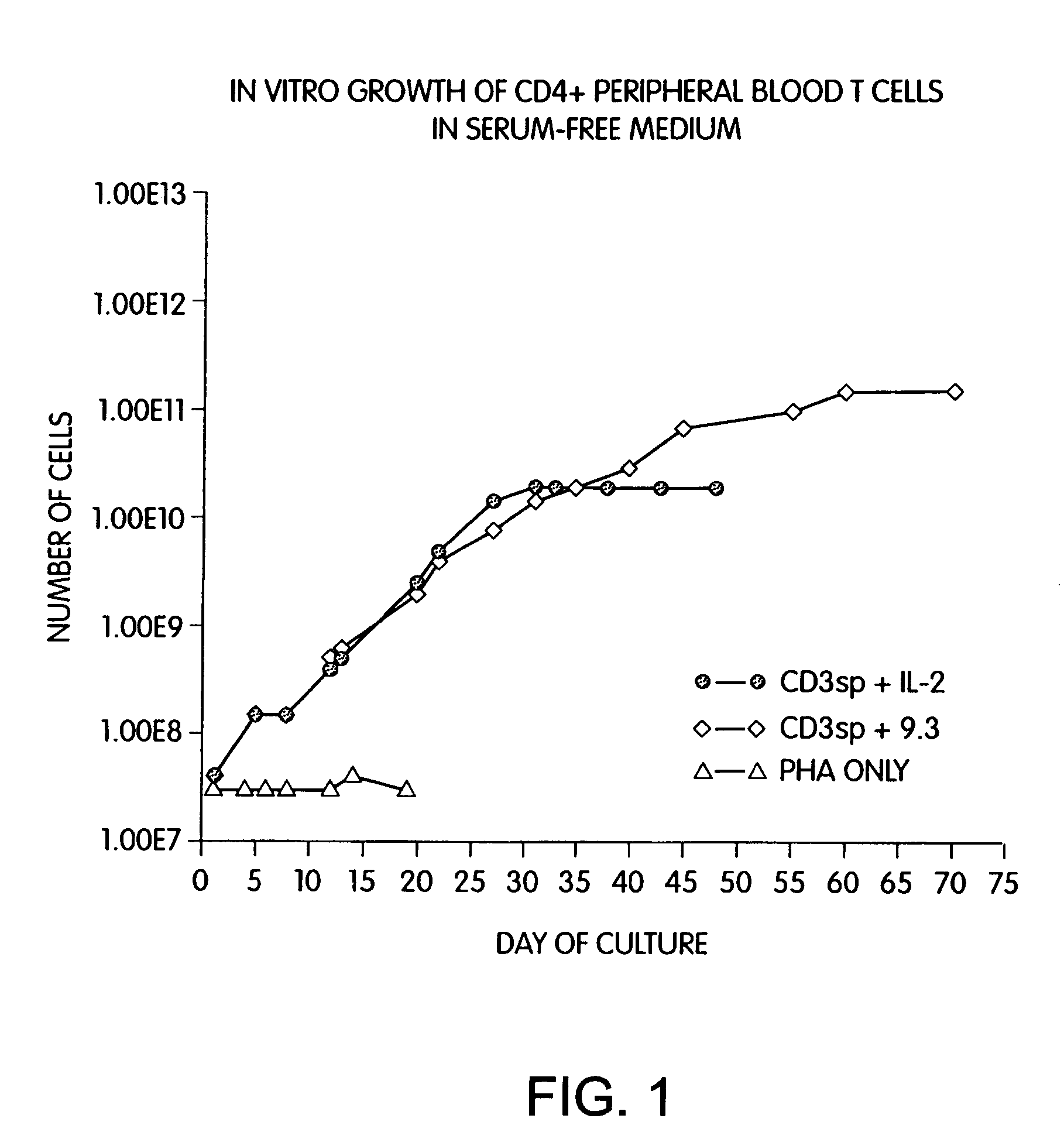
Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells
InactiveUS6905681B1Increase the number ofVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
Owner:GENETICS INST INC +2
Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells
InactiveUS6887466B2Expanding population of cellIncrease the number ofVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
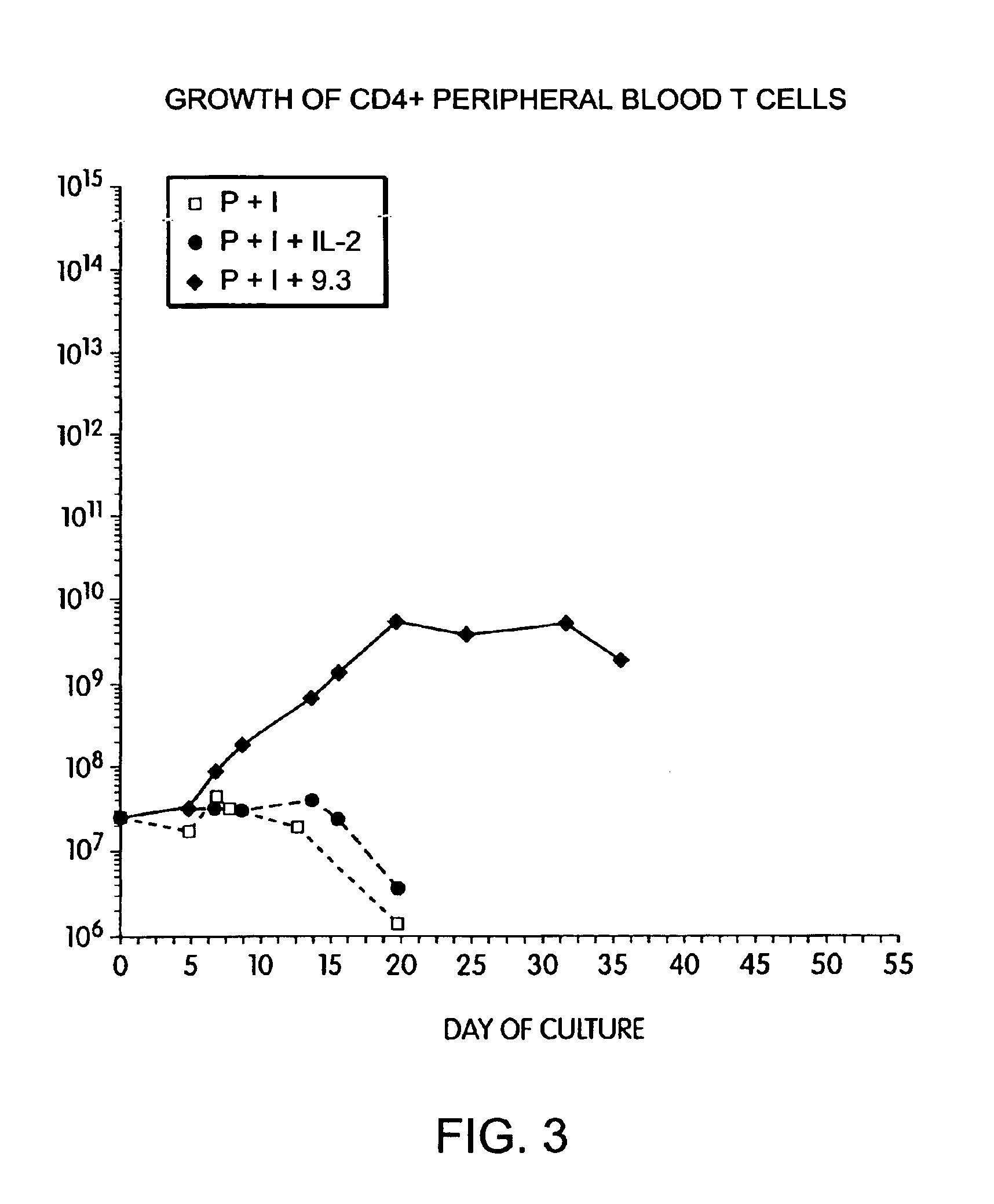
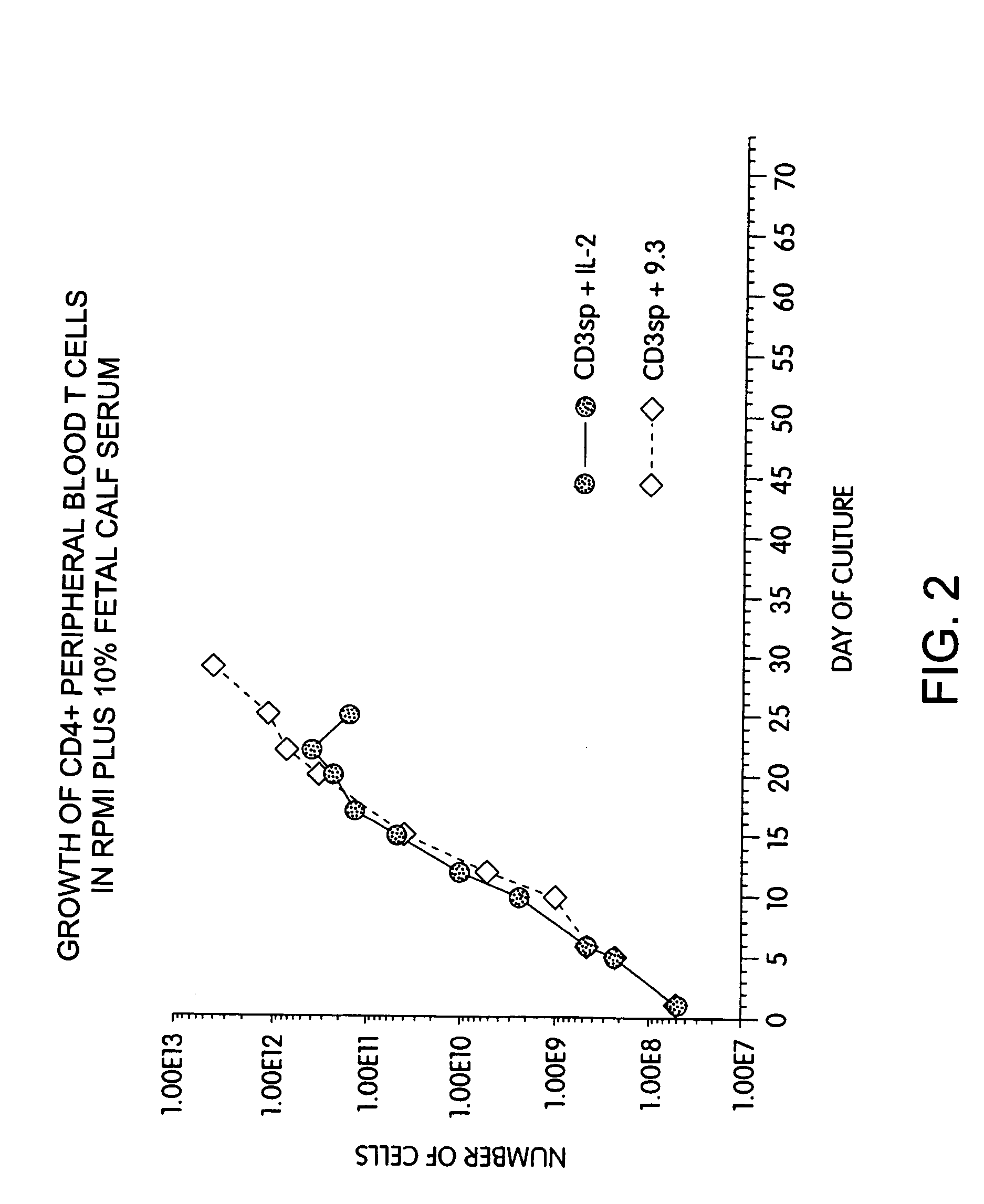
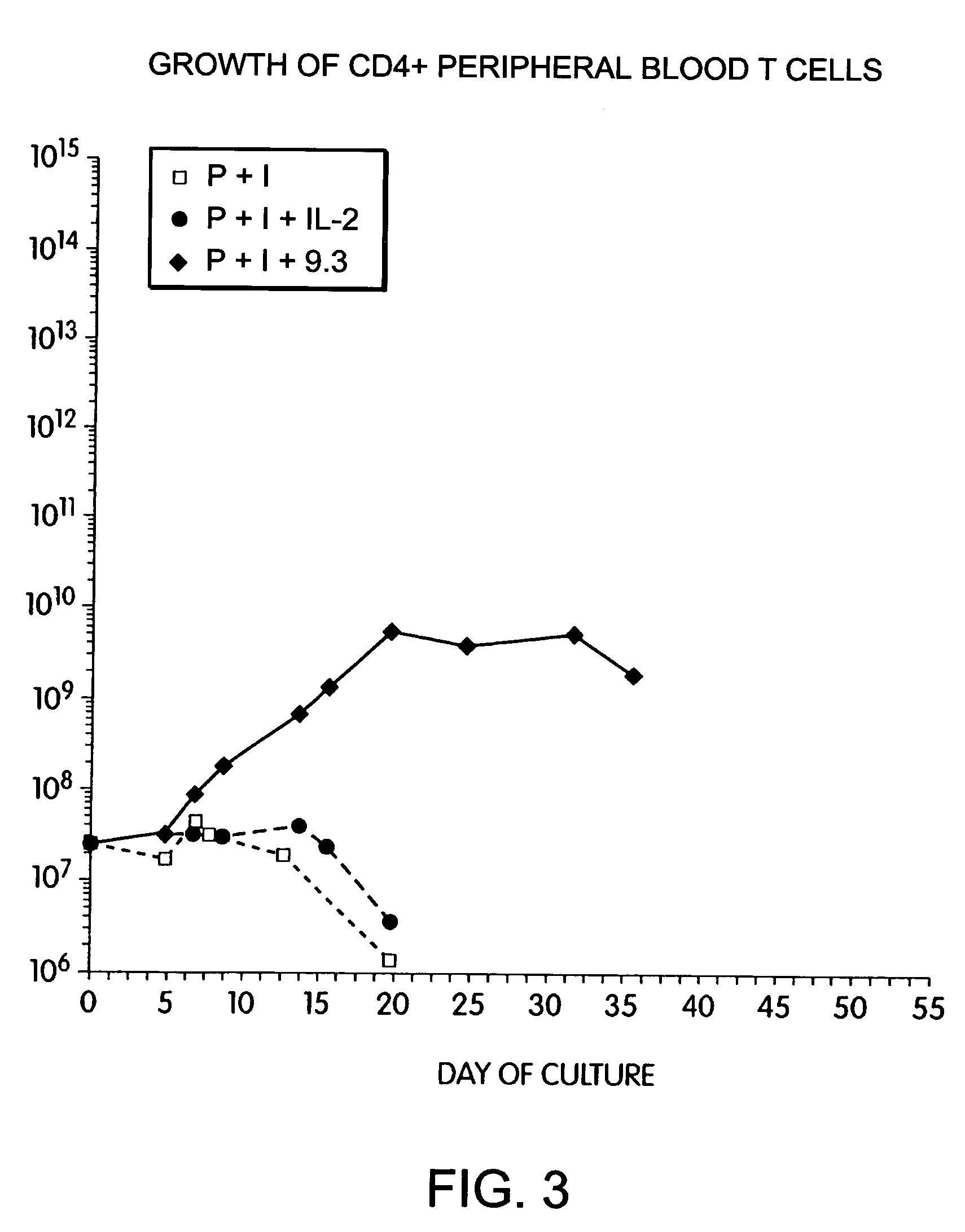
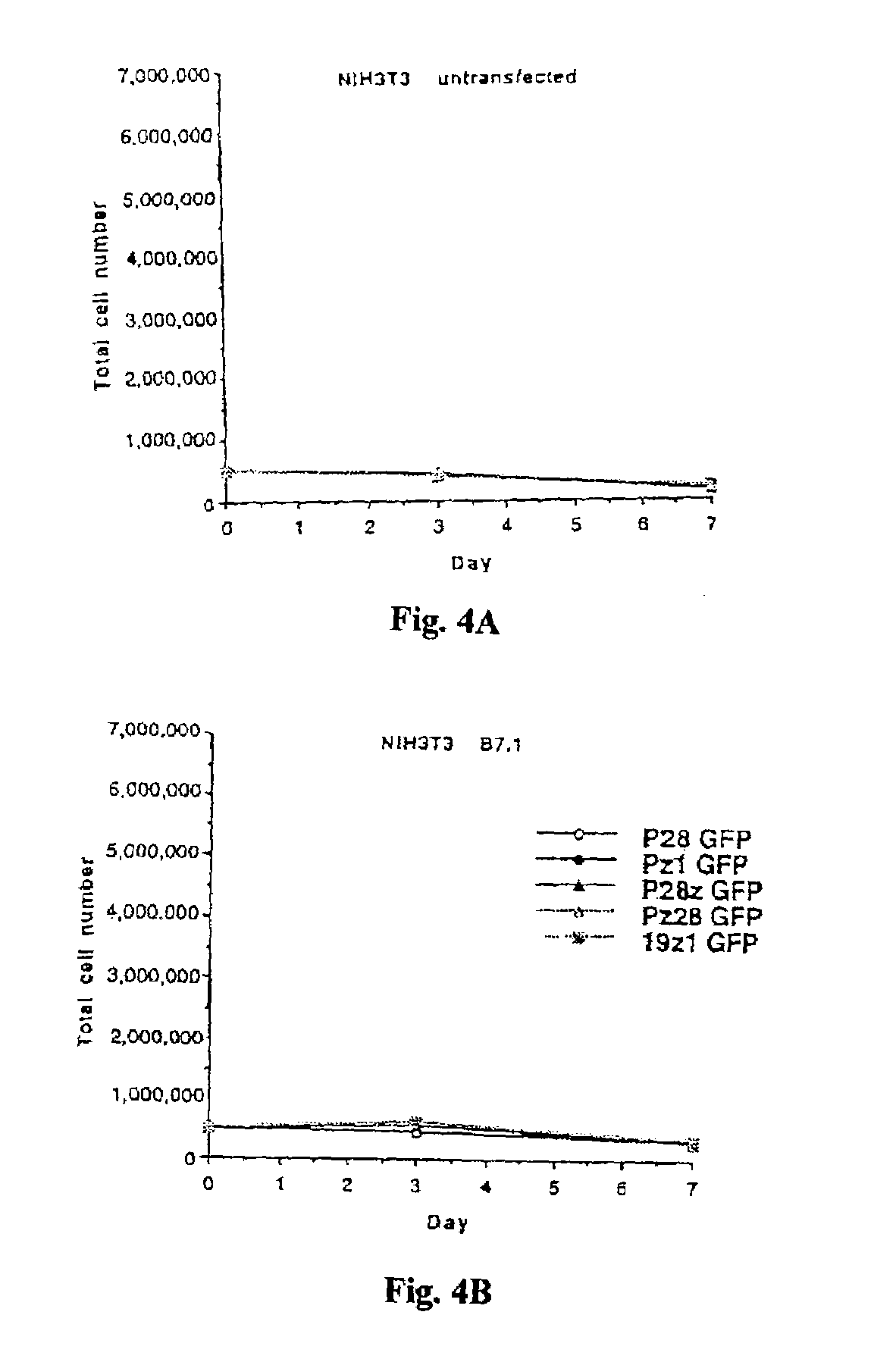
Methods for inducing a population of T cells to proliferate by activating the population of T cells and stimulating an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule are described. T cell proliferation occurs in the absence of exogenous growth factors or accessory cells. T cell activation is accomplished by stimulating the T cell receptor (TCR) / CD3 complex or the CD2 surface protein. To induce proliferation of an activated population T cells, an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells, such as CD28, is stimulated with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule. The T cell population expanded by the method of the invention can be genetically transduced and used for immunotherapy or can be used in methods of diagnosis.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC +2
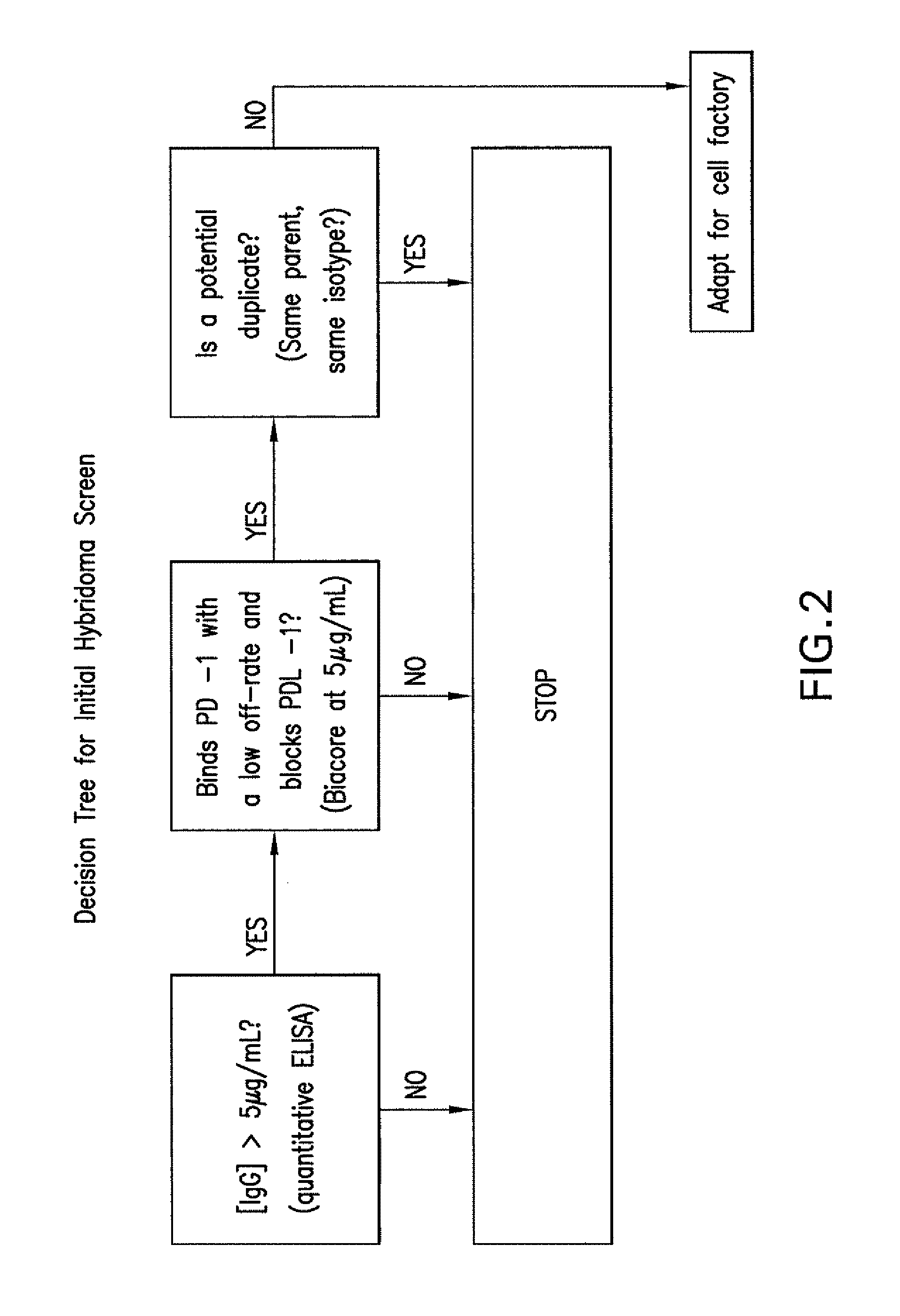
PD-1 binding proteins
ActiveUS8168757B2Regulating T cell responsesImprove immunityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody ingredientsHost immunitySignalling pathways
The present invention features PD-1 binding proteins, a subset of which inhibits binding of PD-L1 to the PD-1 receptor. These binding proteins can be employed to modulate the immune system through the manipulation of the PD-1 signaling pathway, enhancing host immunity to treat infections and cancer.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells
InactiveUS7175843B2Increase the number ofBiocideCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
Owner:GENETICS INST LLC +2
Methods of treating HIV infected subjects
InactiveUS6905680B2Expanding population of cellIncrease the number ofVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
Methods for inducing a population of T cells to proliferate by activating the population of T cells and stimulating an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule are described. T cell proliferation occurs in the absence of exogenous growth factors or accessory cells. T cell activation is accomplished by stimulating the T cell receptor (TCR) / CD3 complex or the CD2 surface protein. To induce proliferation of an activated population T cells, an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells, such as CD28, is stimulated with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule. The T cell population expanded by the method of the invention can be genetically transduced and used for immunotherapy or can be used in methods of diagnosis.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC +2
Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells
InactiveUS7144575B2Increase the number ofBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
Methods for inducing a population of T cells to proliferate by activating the population of T cells and stimulating an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule are described. T cell proliferation occurs in the absence of exogenous growth factors or accessory cells. T cell activation is accomplished by stimulating the T cell receptor (TCR) / CD3 complex or the CD2 surface protein. To induce proliferation of an activated population T cells, an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells, such as CD28, is stimulated with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule. The T cell population expanded by the method of the invention can be genetically transduced and used for immunotherapy or can be used in methods of diagnosis.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +2
Nucleic acids encoding chimeric T cell receptors
ActiveUS7446190B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCytotoxicityBiological activation
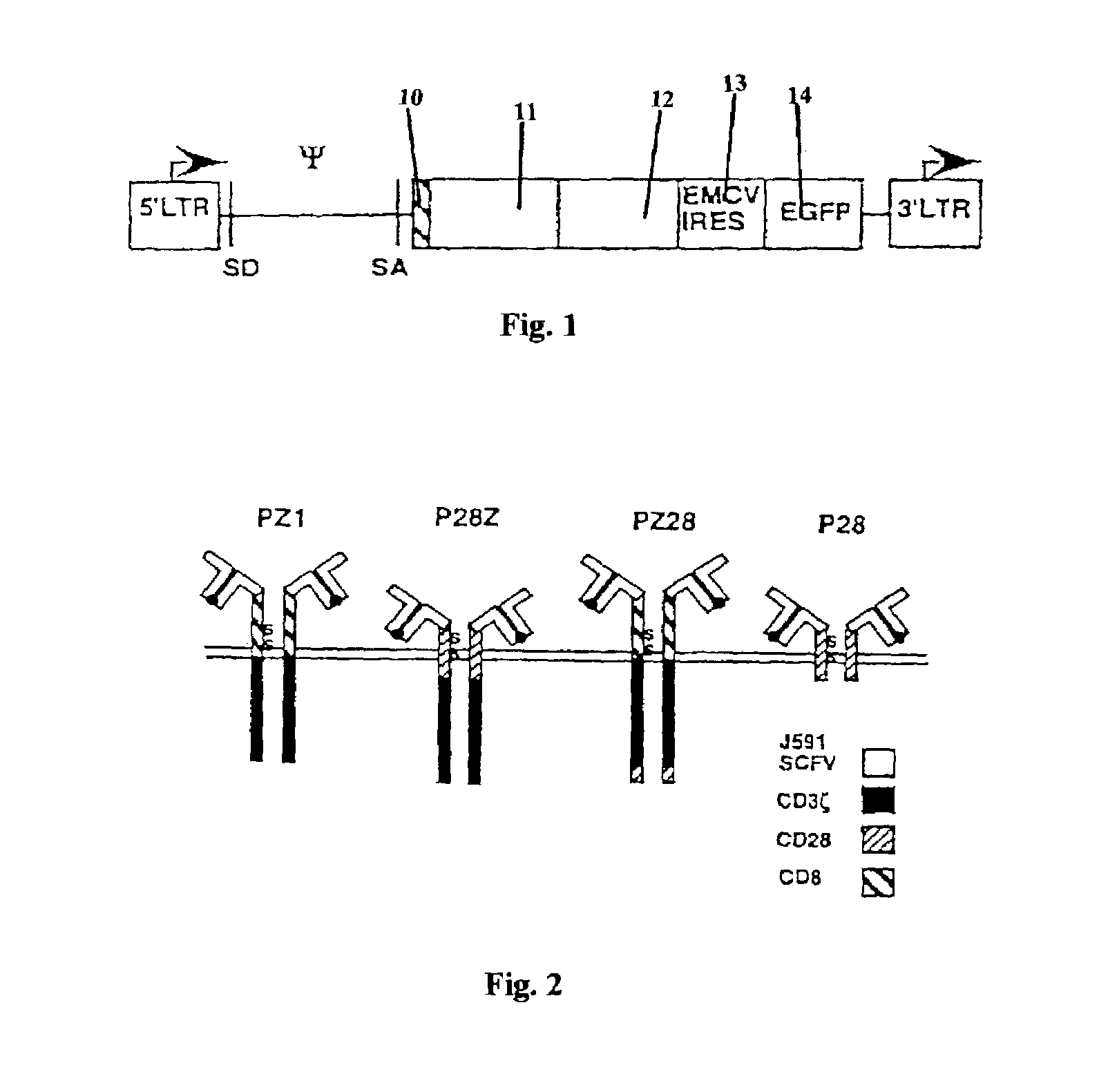
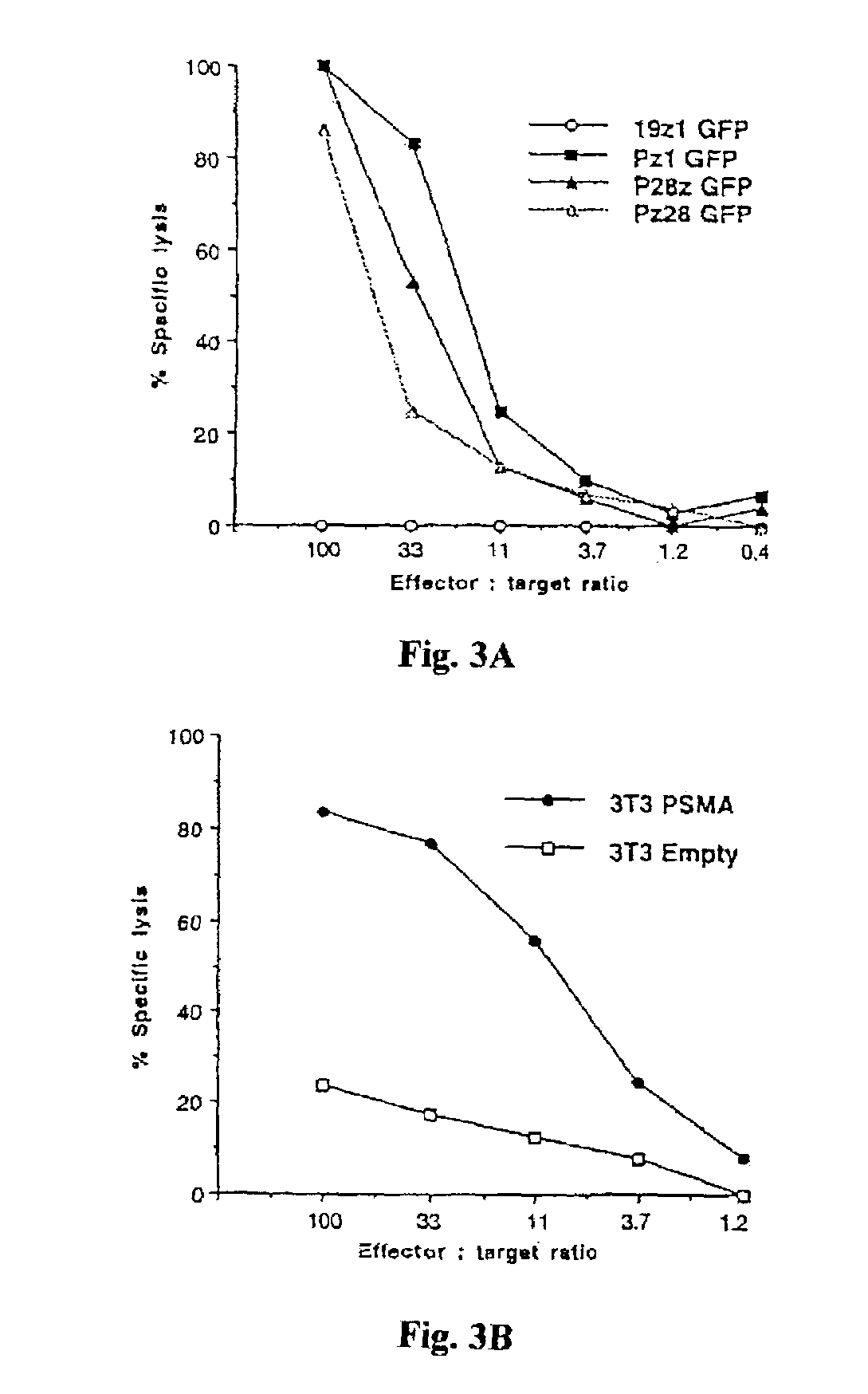
Chimeric T cell receptors (TCR) are provided that combine, in a single chimeric species, the intracellular domain of CD3 ζ-chain, a signaling region from a costimulatory protein such as CD28, and a binding element that specifically interacts with a selected target. When expressed, for example in T-lymphocytes from the individual to be treated for a condition associated with the selected target, a T cell immune response is stimulated in the individual to the target cells. The chimeric TCR's are able to provide both the activation and the co-stimulation signals from a single molecule to more effectively direct T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity against the selected target and T-lymphocyte proliferation.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
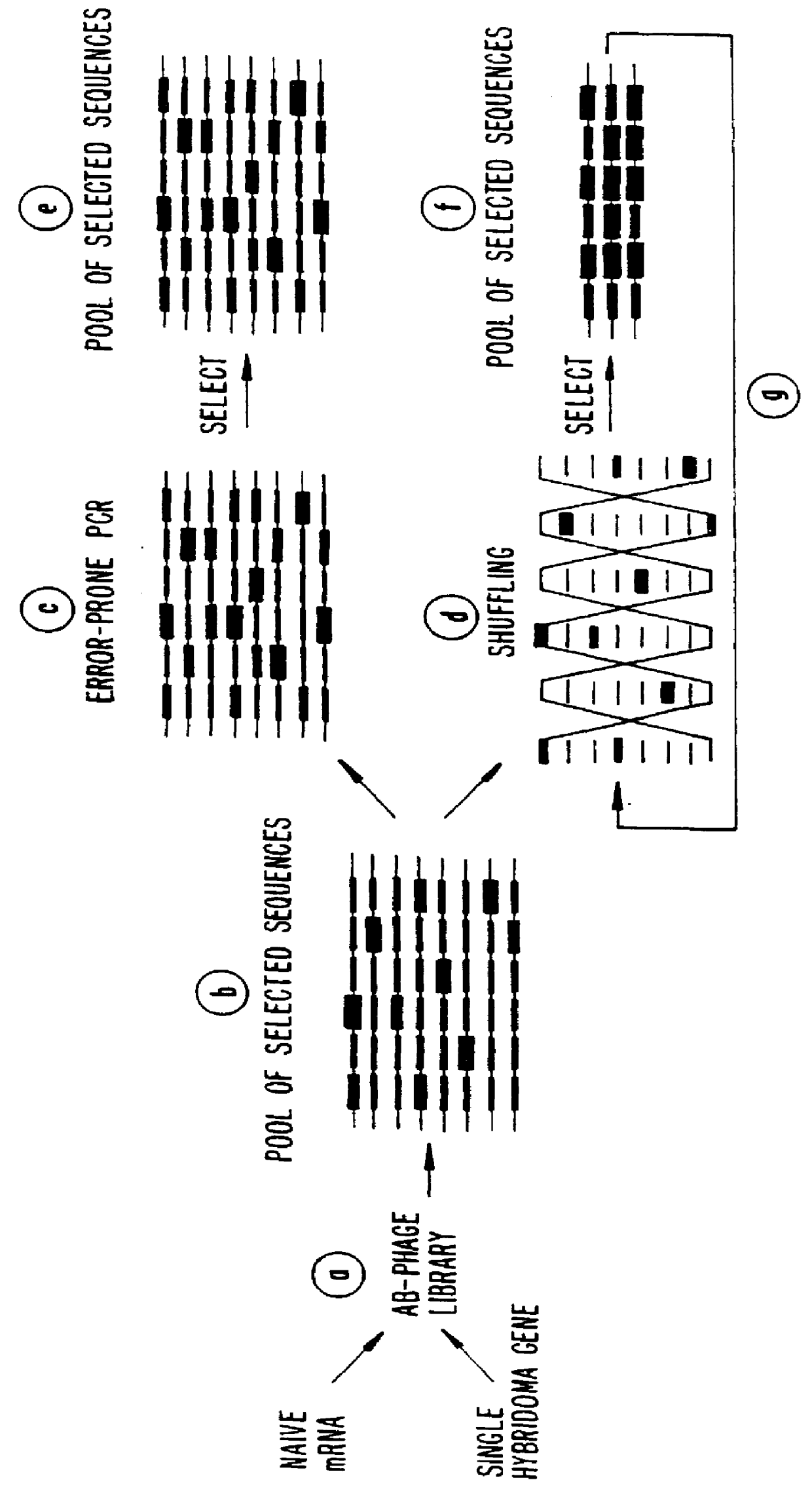
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
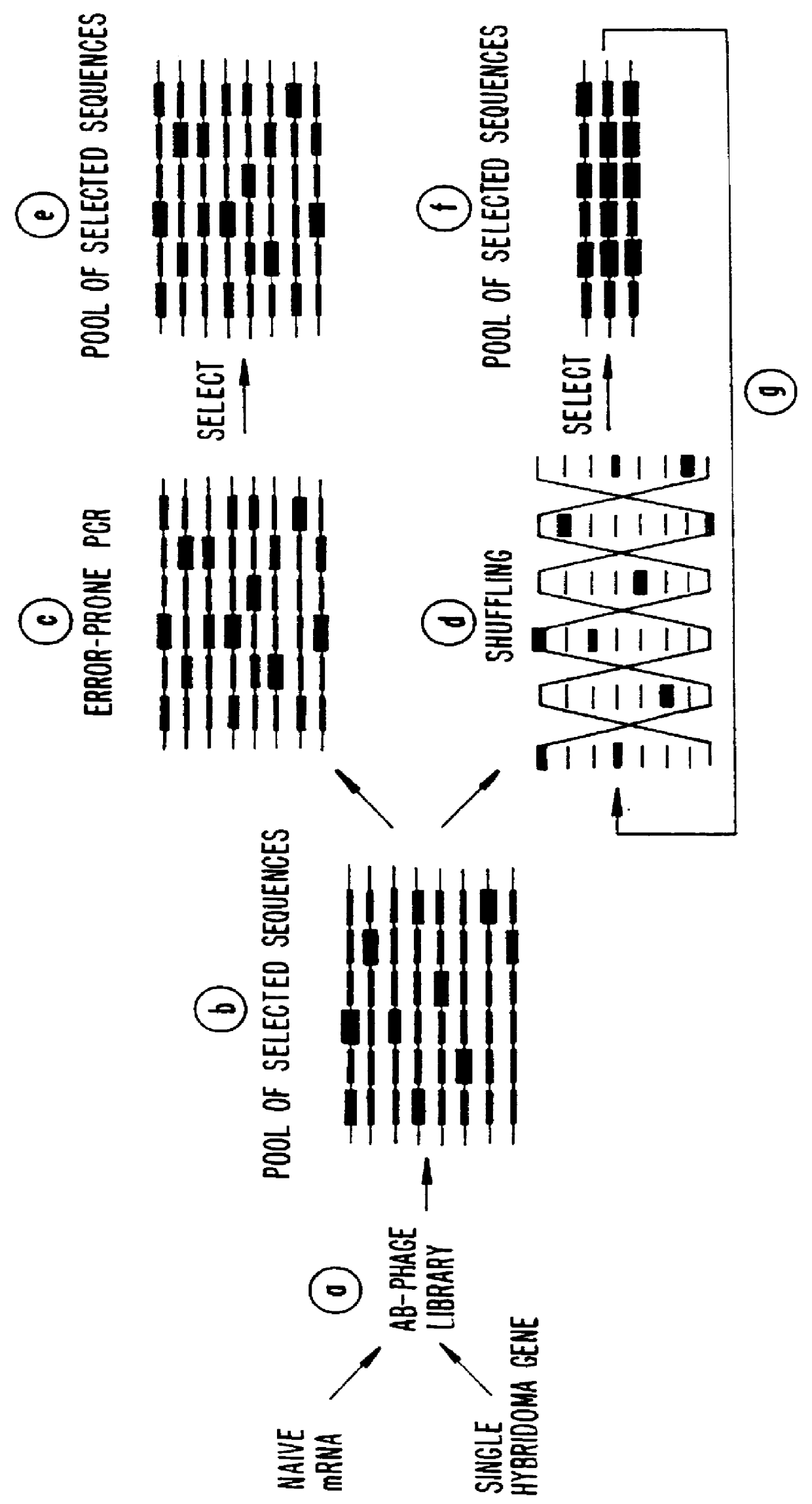
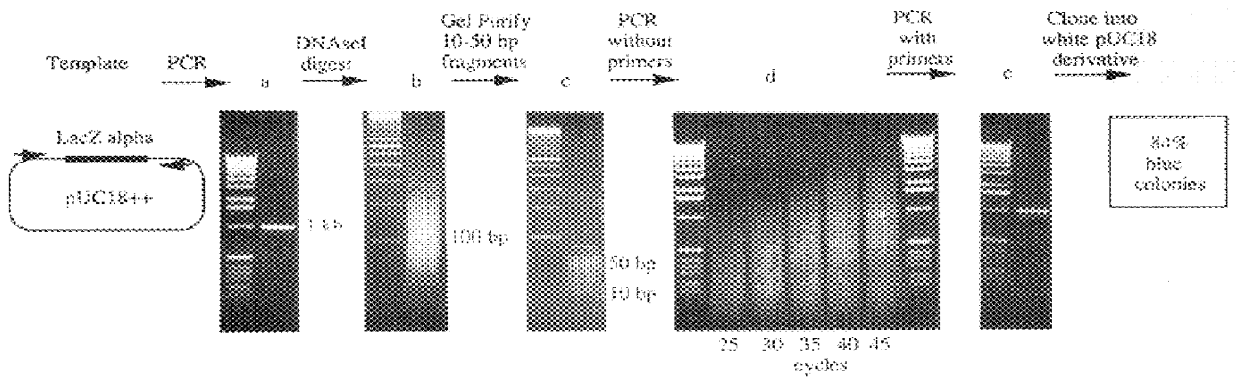
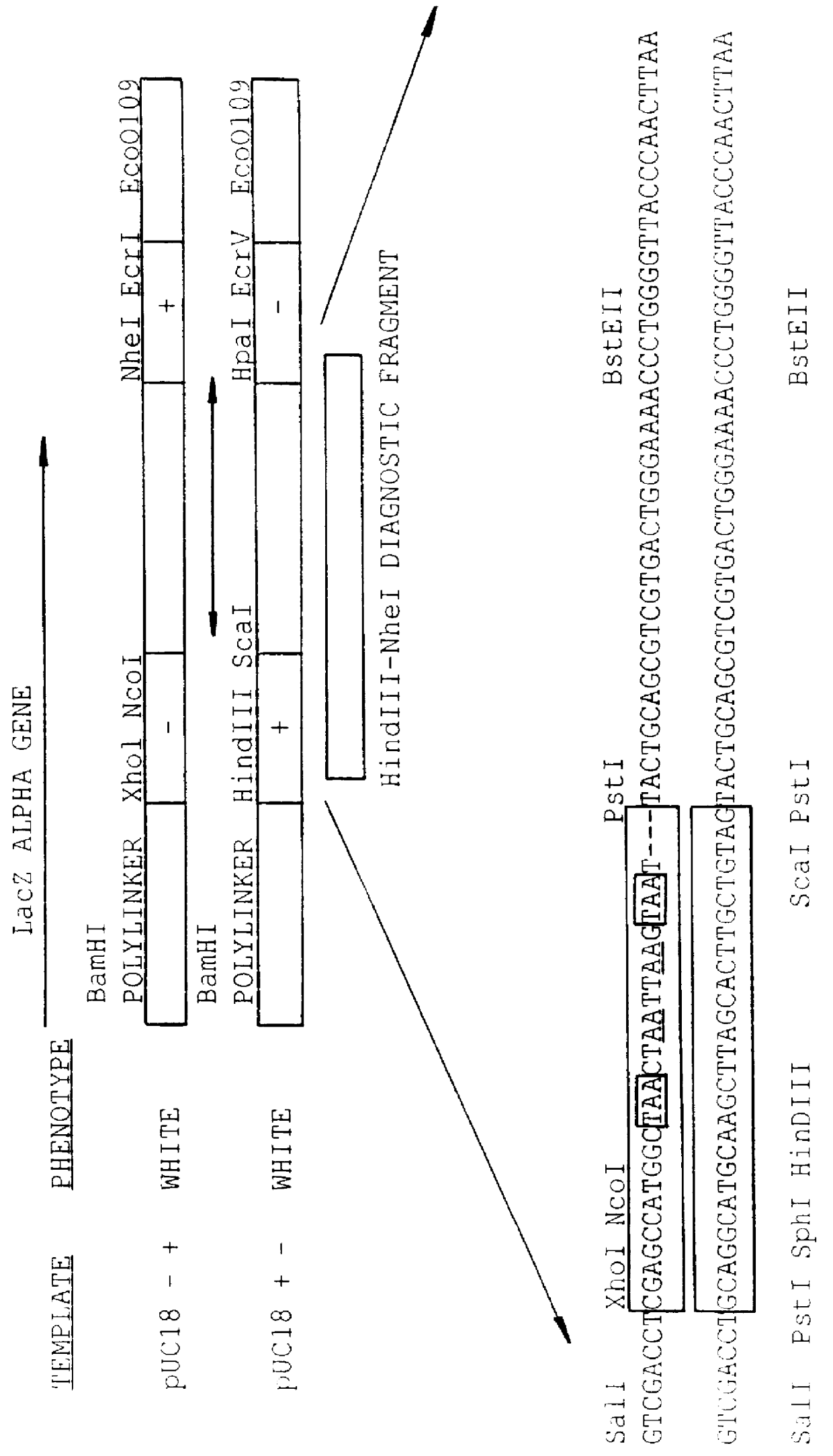
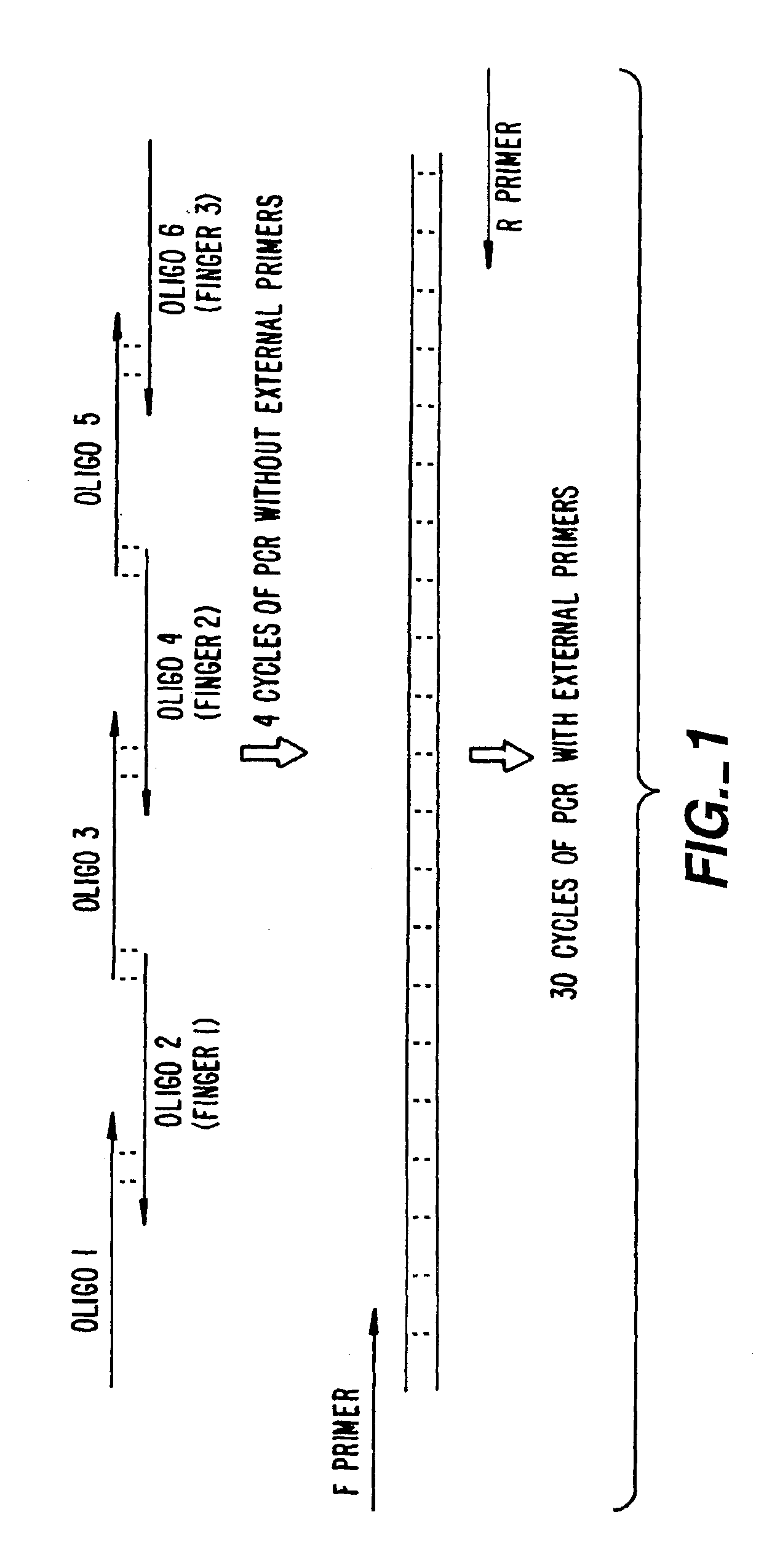
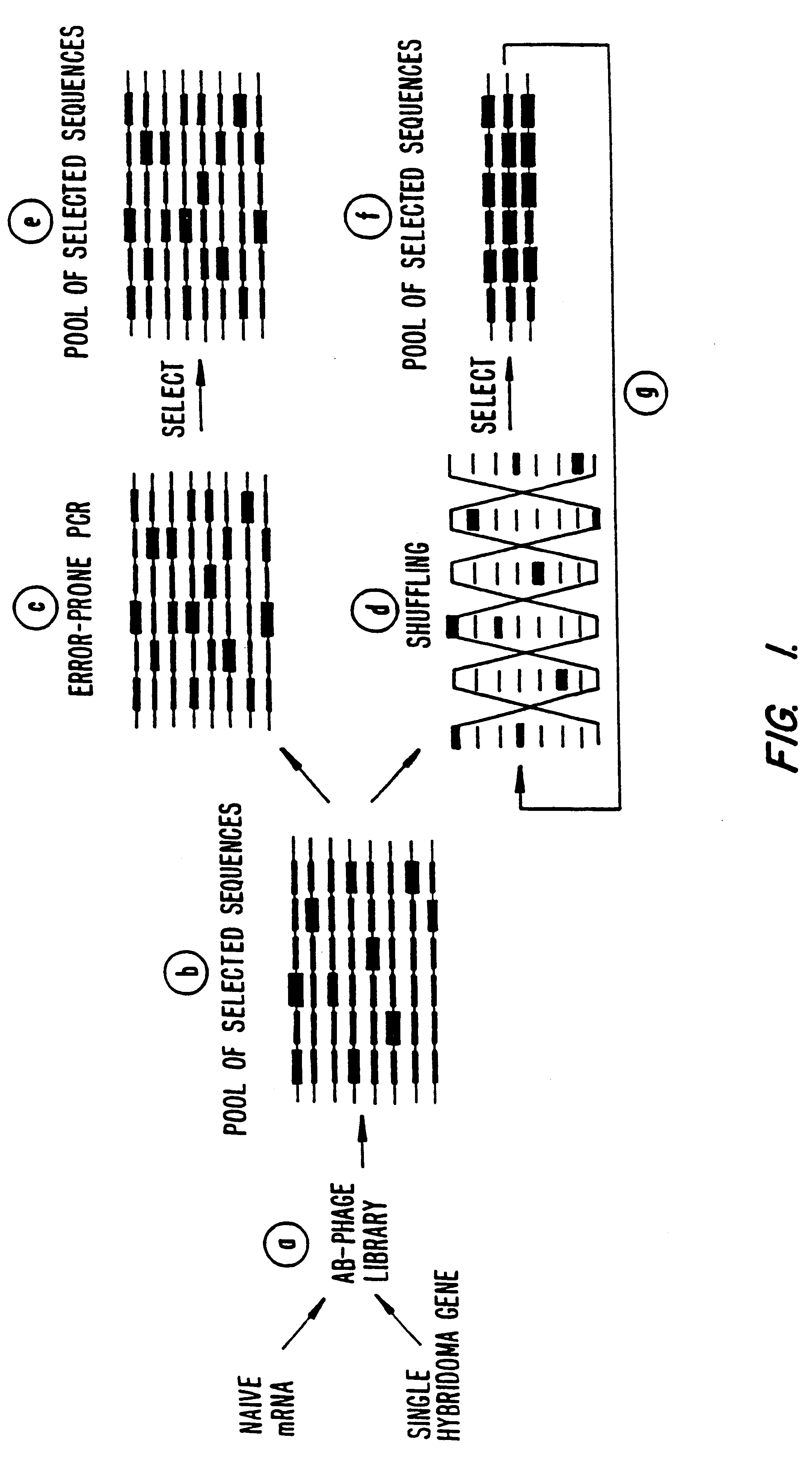
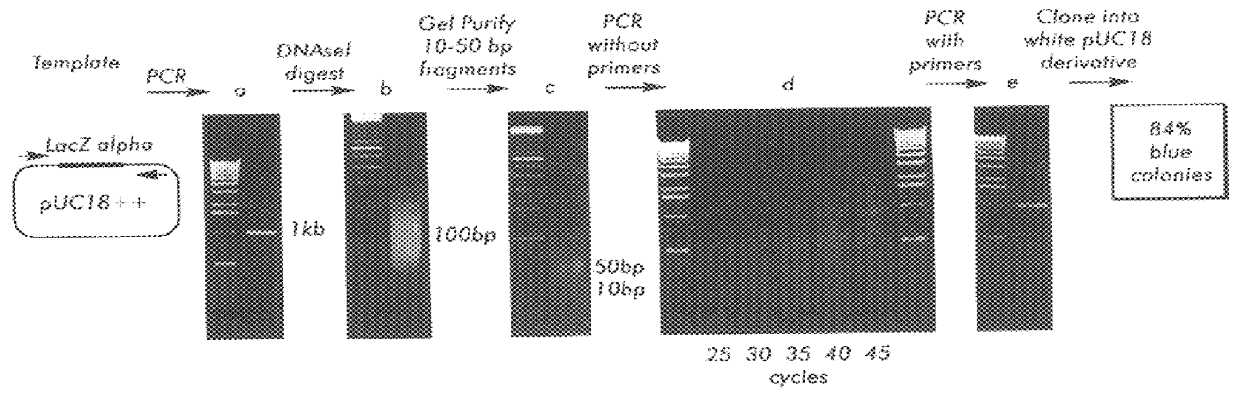
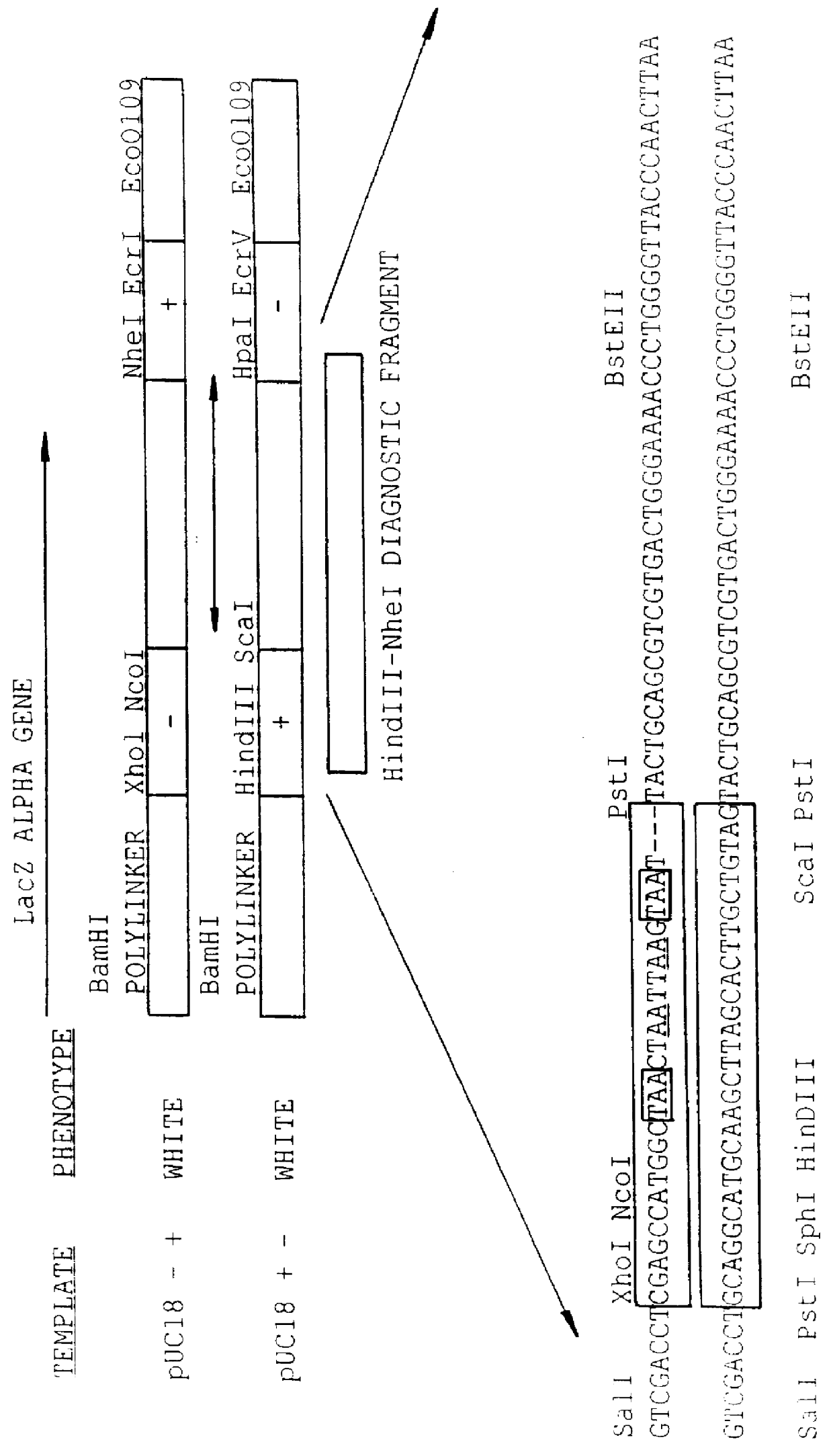
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Regulation of endogenous gene expression in cells using zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS7013219B2Fusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsZinc fingerGene expression
The present invention provides methods for modulating expression of endogenous cellular genes using engineered zinc finger proteins.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Nucleic acid encoding poly-zinc finger proteins with improved linkers
InactiveUS7153949B2Enhanced affinity and specificityImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainNucleotide
Polynucleotides encoding chimeric proteins, and methods for their production and use are disclosed. The chimeric proteins comprise a flexible linker between two zinc finger DNA-binding domains, wherein the linker contains eight or more amino acids between the second conserved histidine residue of the carboxy-terminal zinc finger of the first domain and the first conserved cysteine residue of the amino-terminal zinc finger of the second domain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6165793ALess immunogenicDirected macromolecular evolutionImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
CE7-specific redirected immune cells
Genetically engineered, CE7-specific redirected immune cells expressing a cell surface protein having an extracellular domain comprising a receptor which is specific for CE7, an intracellular signaling domain, and a transmembrane domain, and methods of use for such cells for cellular immunotherapy of CE7+ neuroblastoma are disclosed. In one embodiment, the immune cell is a T cell and the cell surface protein is a single chain FvFc:ζ receptor where Fv designates the VH and VL chains of a single chain monoclonal antibody to CE7 linked by peptide, Fc represents a hinge —CH2—CH3 region of a human IgG1, and ζ represents the intracellular signaling domain of the zeta chain of human CD3. DNA constructs encoding a chimeric T-cell receptor and a method of making a redirected T cell expressing a chimeric T cell receptor by electroporation using naked DNA encoding the receptor are also disclosed.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
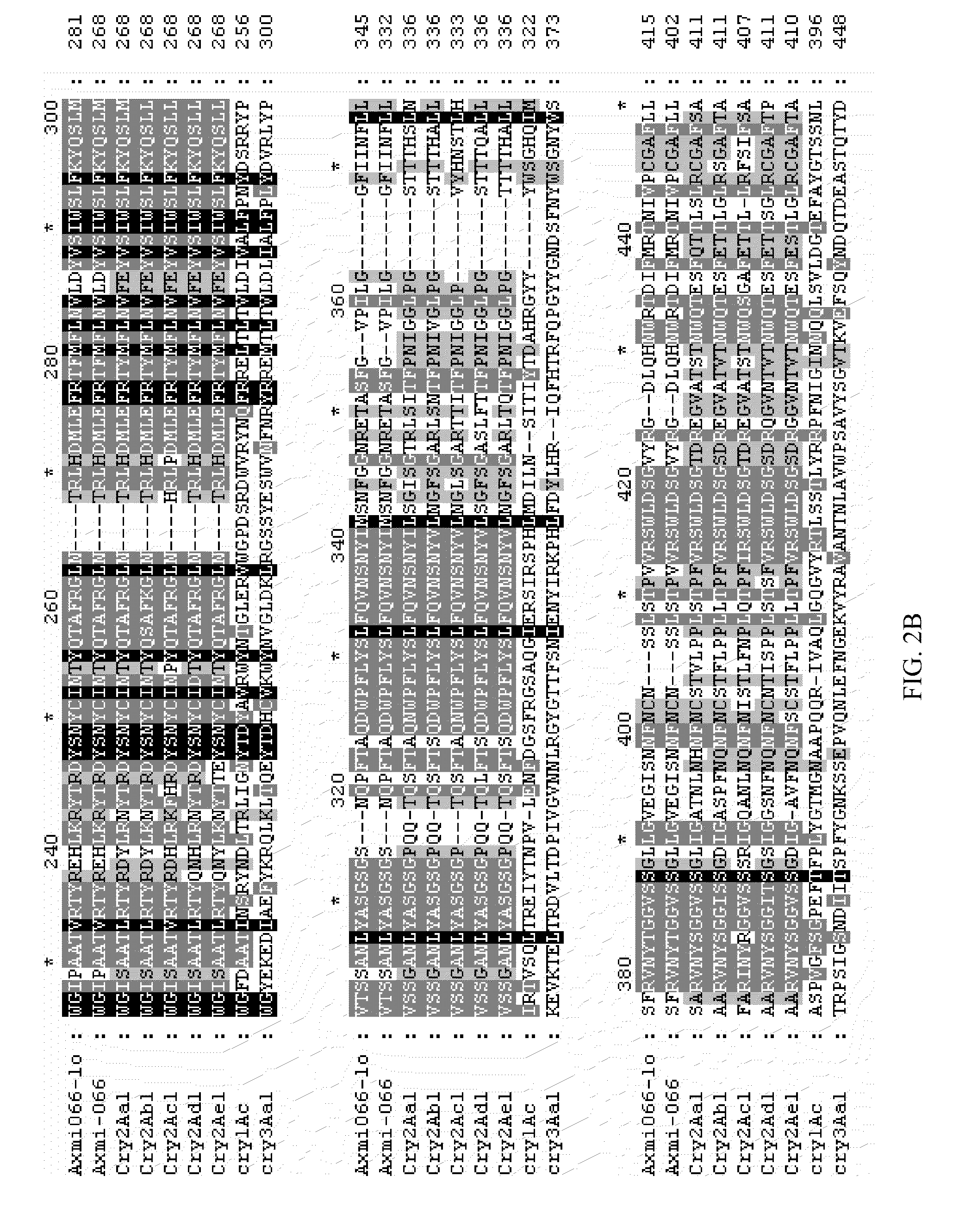
Axmi-066 and axmi-076: delta-endotoxin proteins and methods for their use
InactiveUS20090144852A1Increase productionIncrease resistanceBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDelta endotoxinDNA construct
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for pesticidal polypeptides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:5, 2, or 10, the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:4, 1, 3, 4, 6, 9, or 11, or the nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession No. B-50045, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
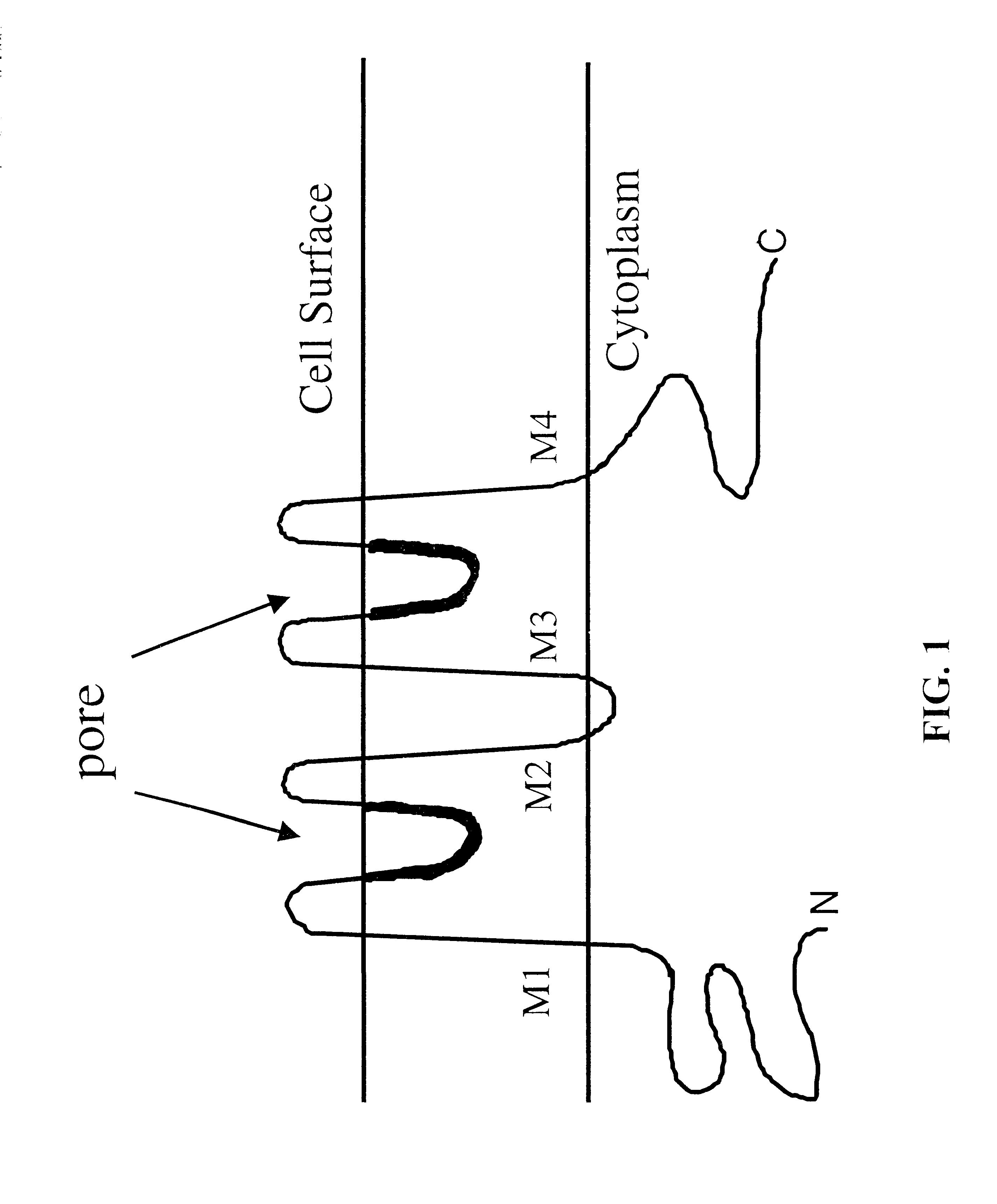
Nucleic acids and polypeptides of invertebrate TWIK channels and methods of use
Tandem pore domain weak inward rectifying K+ (TWIK) channel nucleic acids and proteins that have been isolated from Drosophila melanogaster and Leptinotarsa are described. The TWIK channel nucleic acids and proteins can be used to genetically modify metazoan invertebrate organisms, such as insects, coelomates, and pseudocoelomates, or cultured cells, resulting in TWIK channel expression or mis-expression. The genetically modified organisms or cells can be used in screening assays to identify candidate compounds which are potential pesticidal agents or therapeutics that interact with TWIK channel proteins. They can also be used in methods for studying TWIK channel activity and identifying other genes that modulate the function of, or interact with, the TWIK channel gene.
Owner:EXELIXIS PHARMA
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
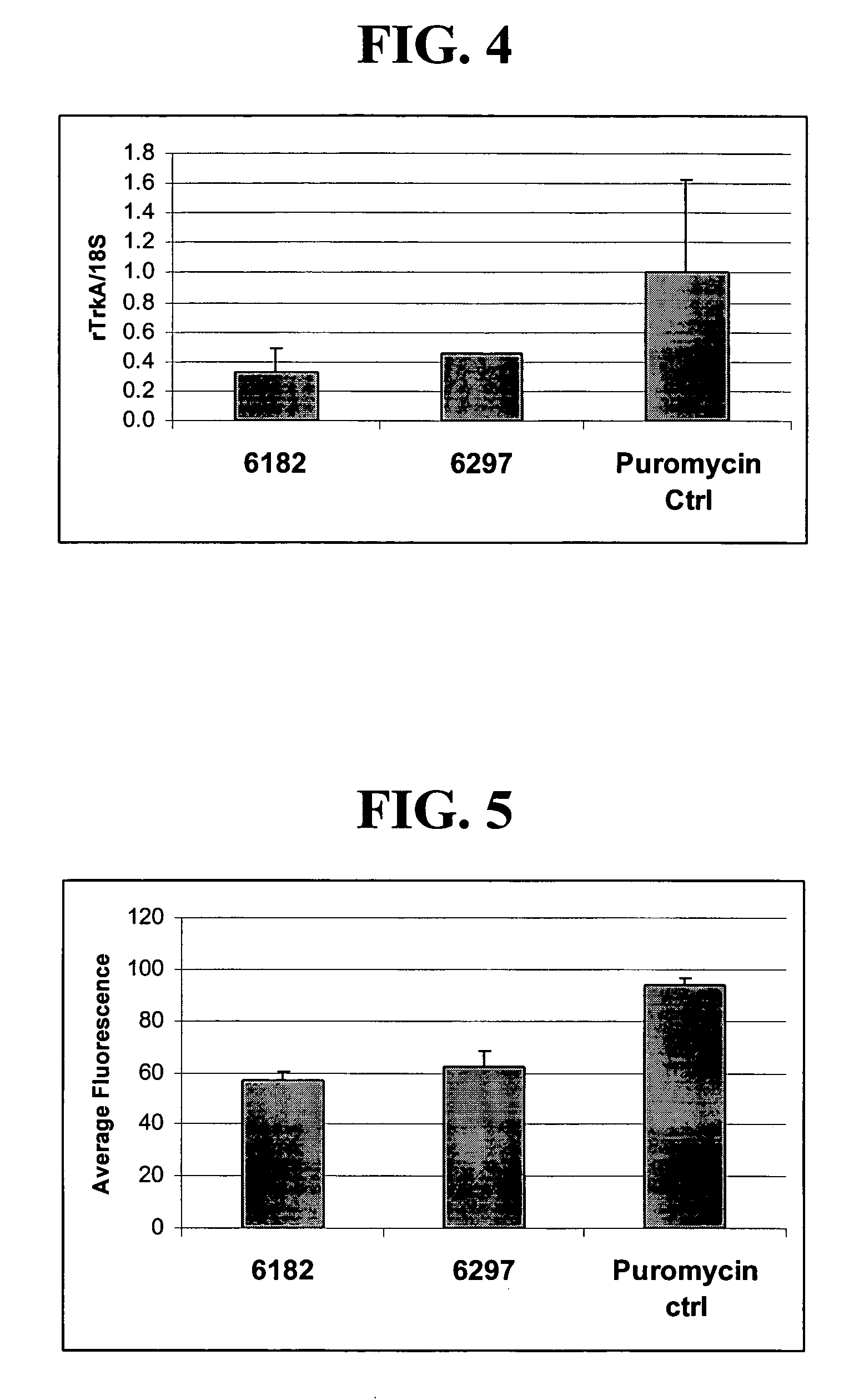
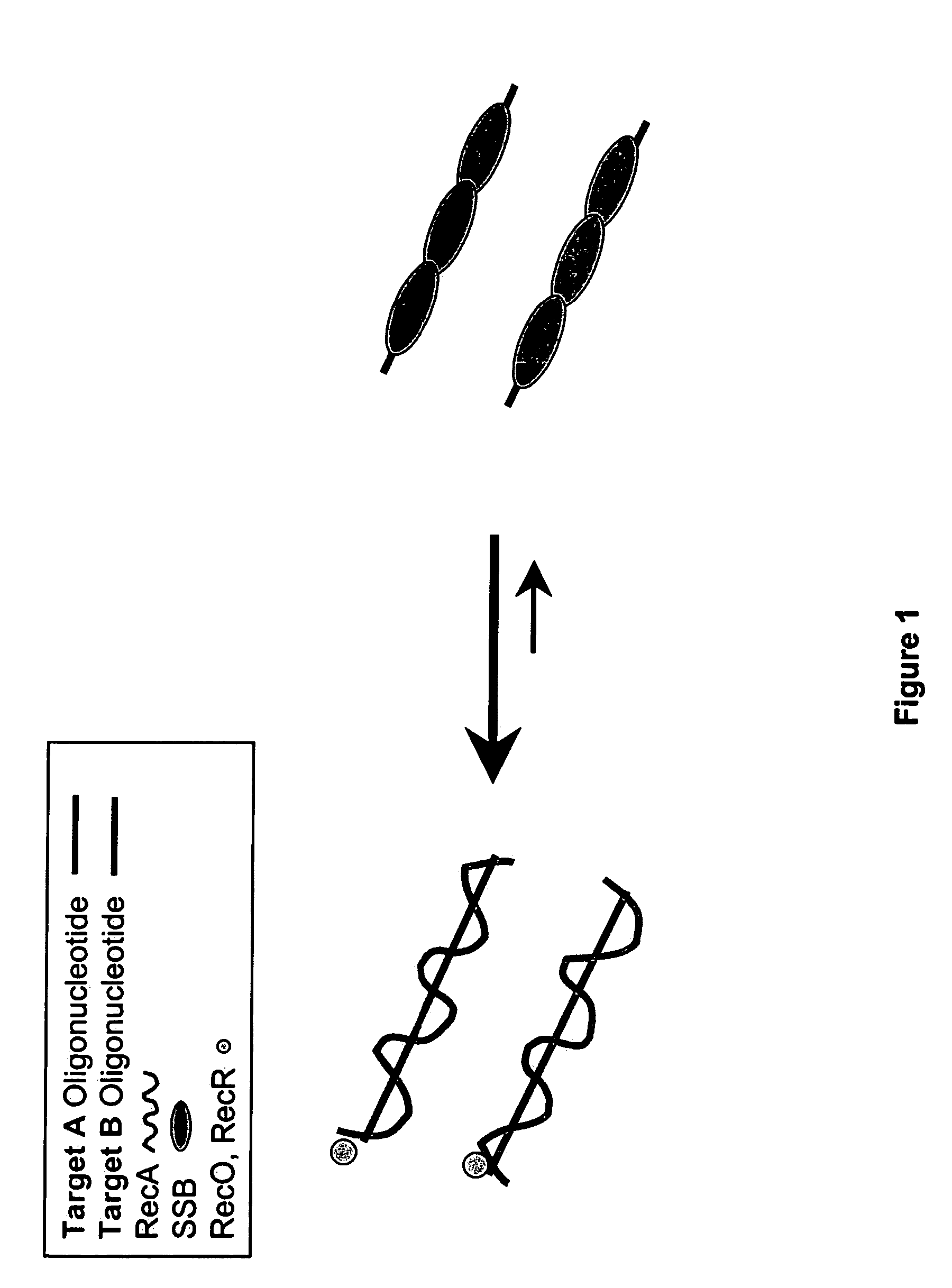
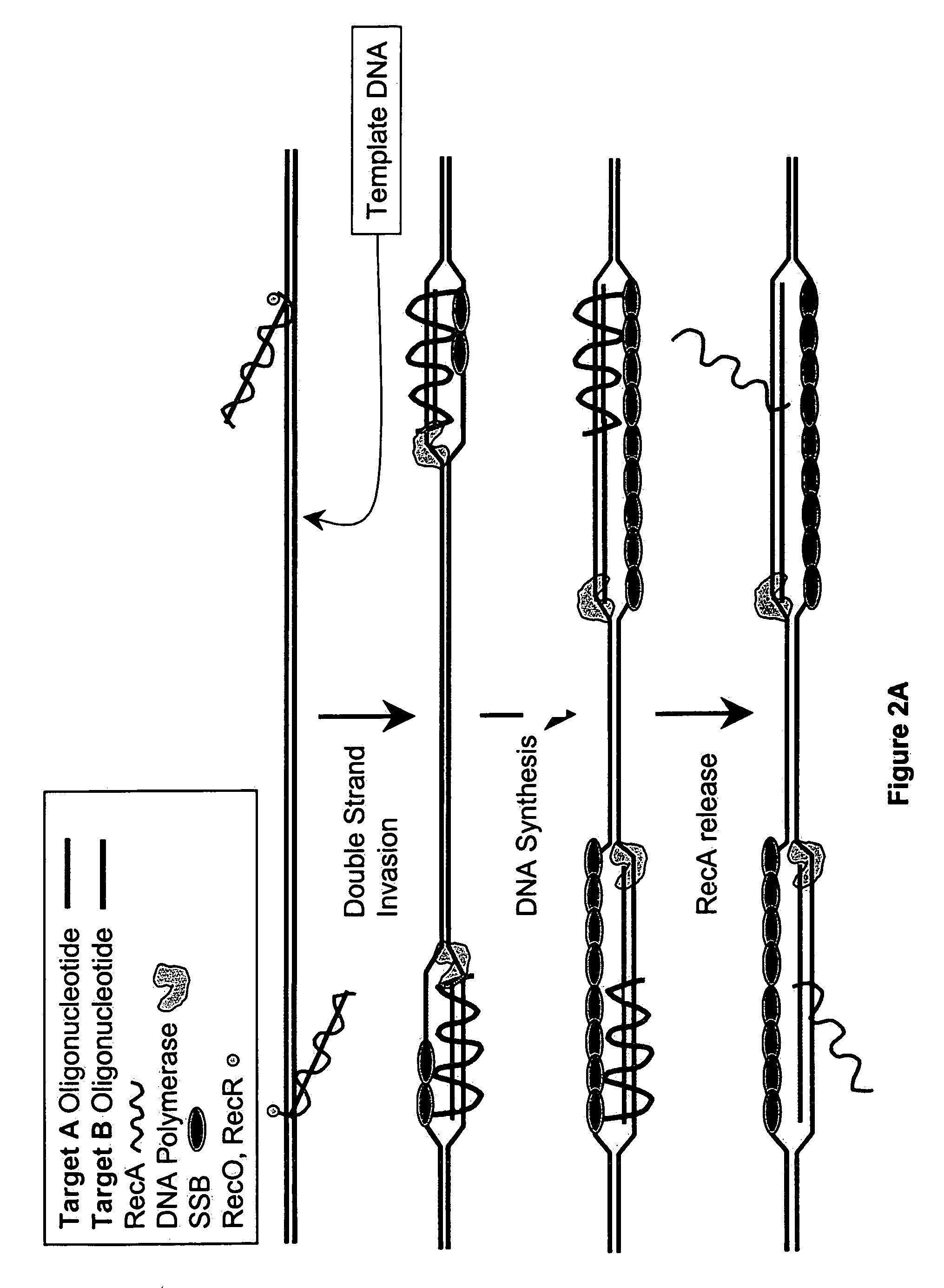
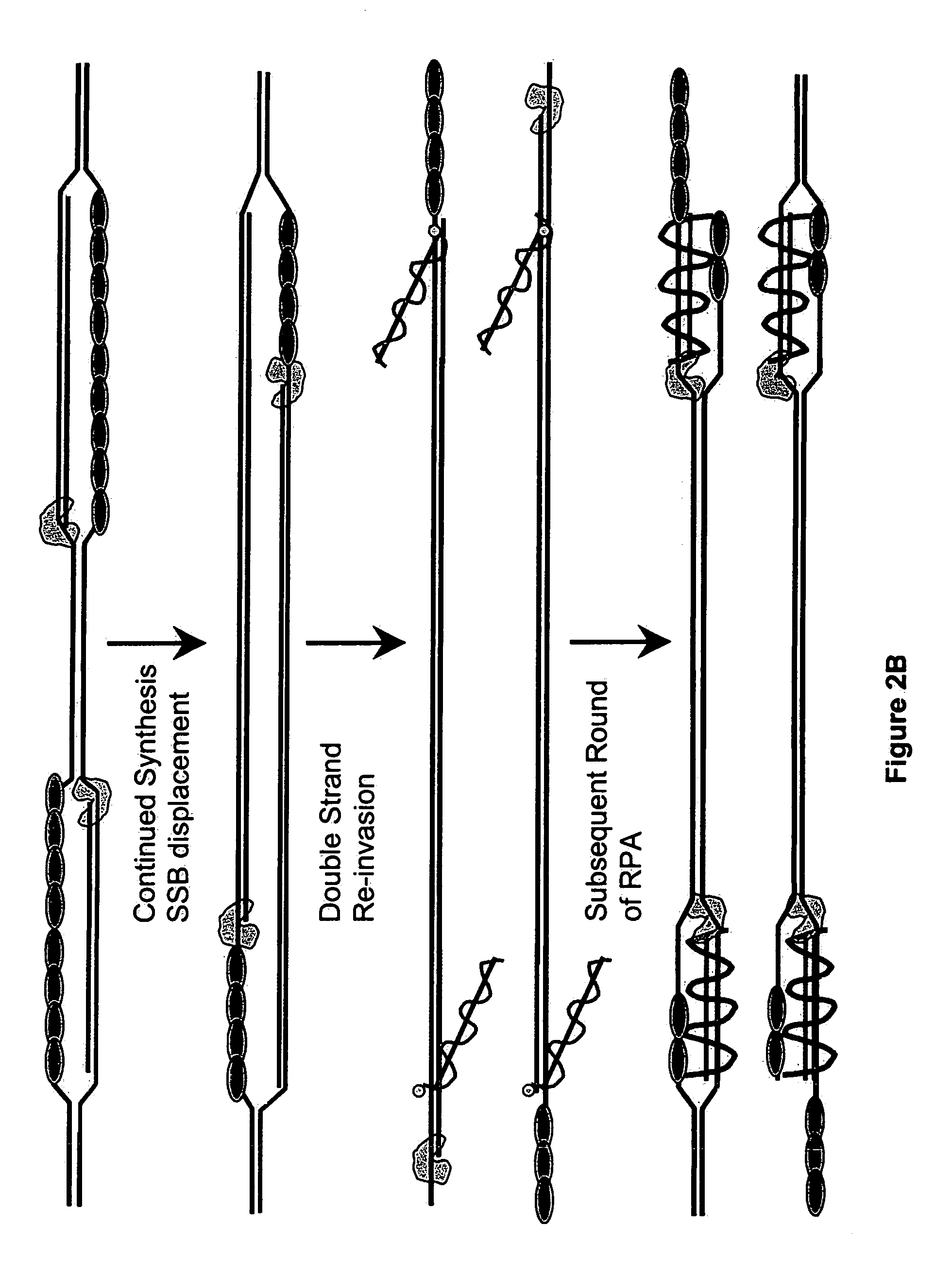
Recombinase polymerase amplification
ActiveUS7399590B2HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinase Polymerase AmplificationSingle strand
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
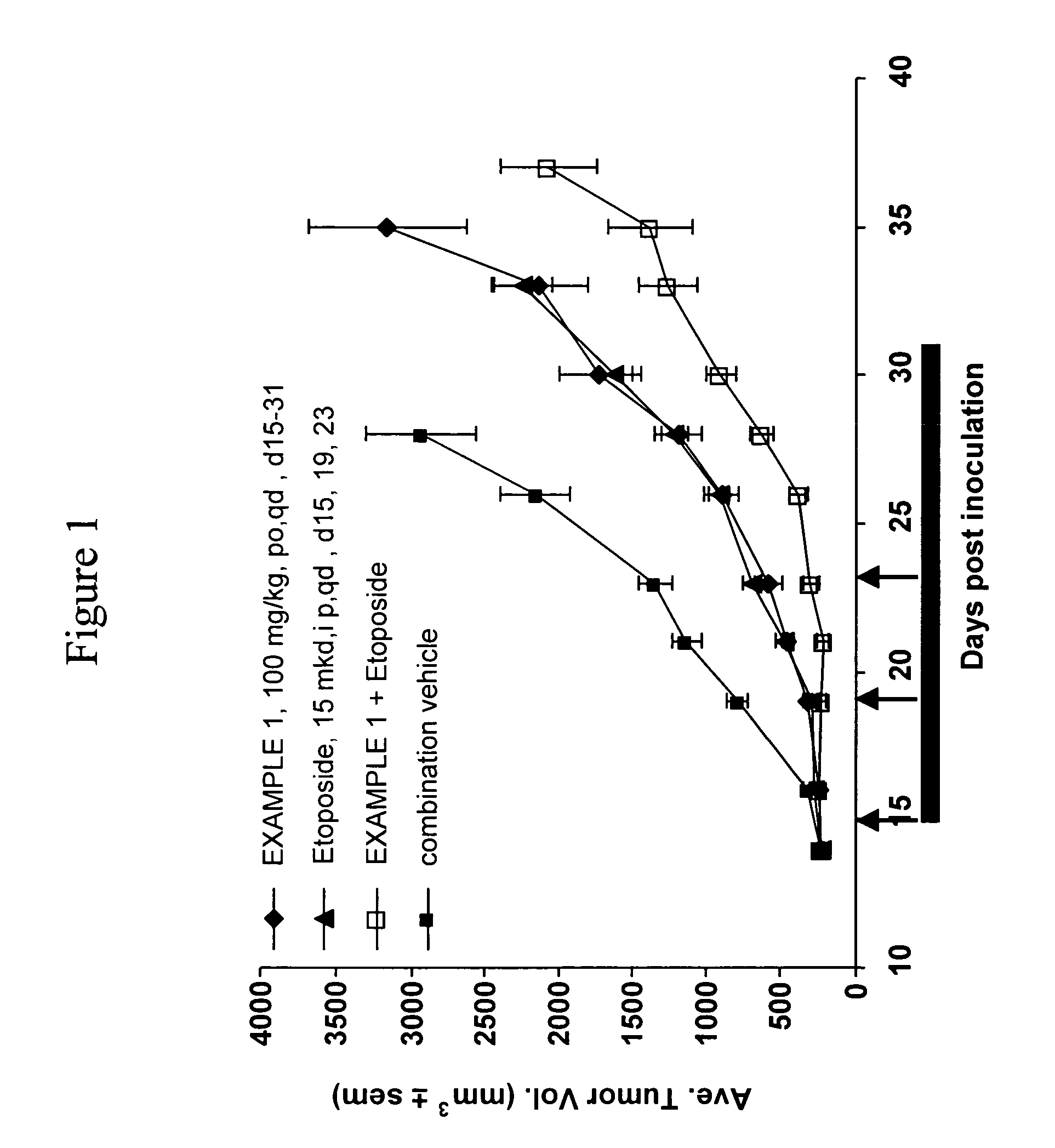
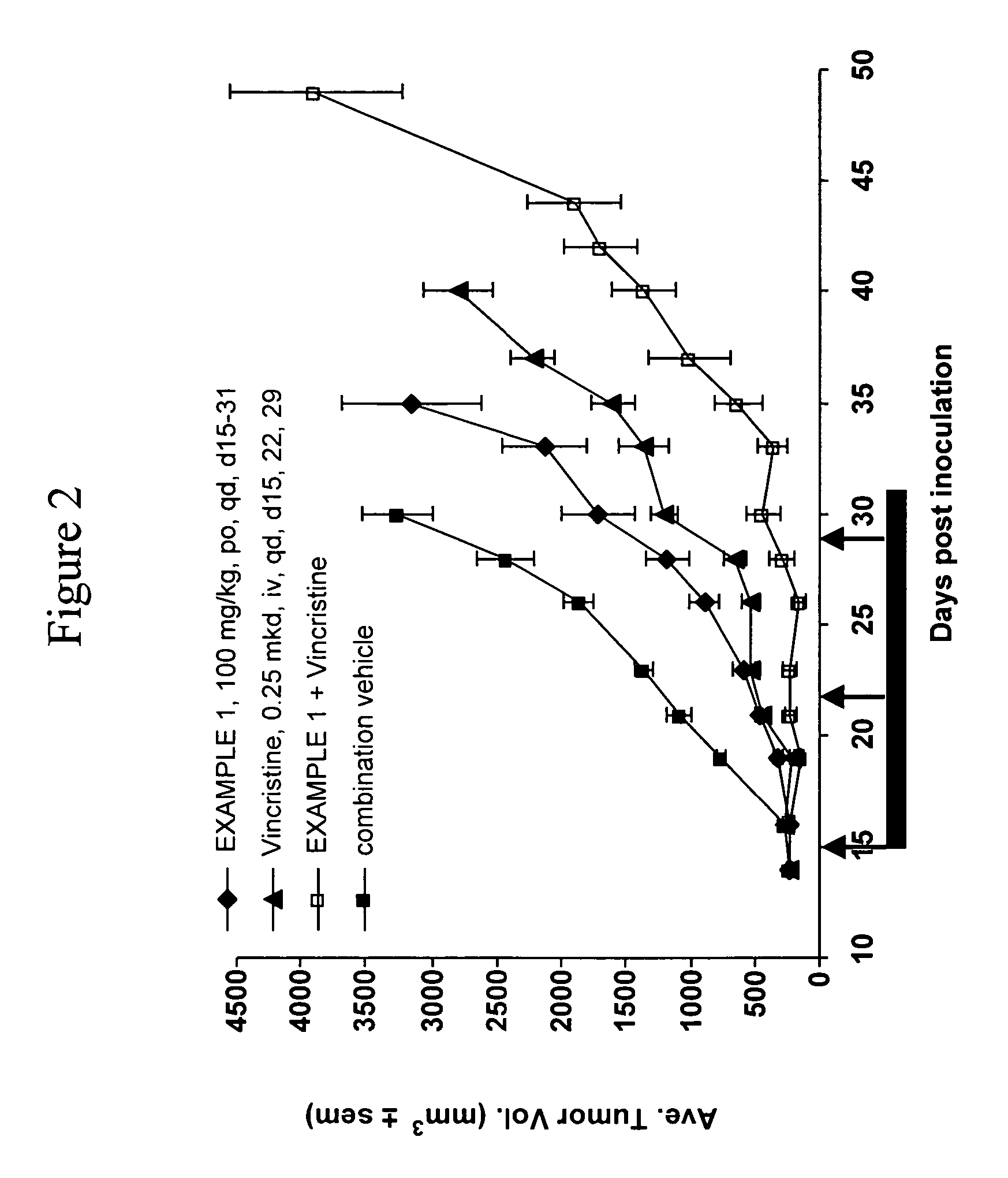
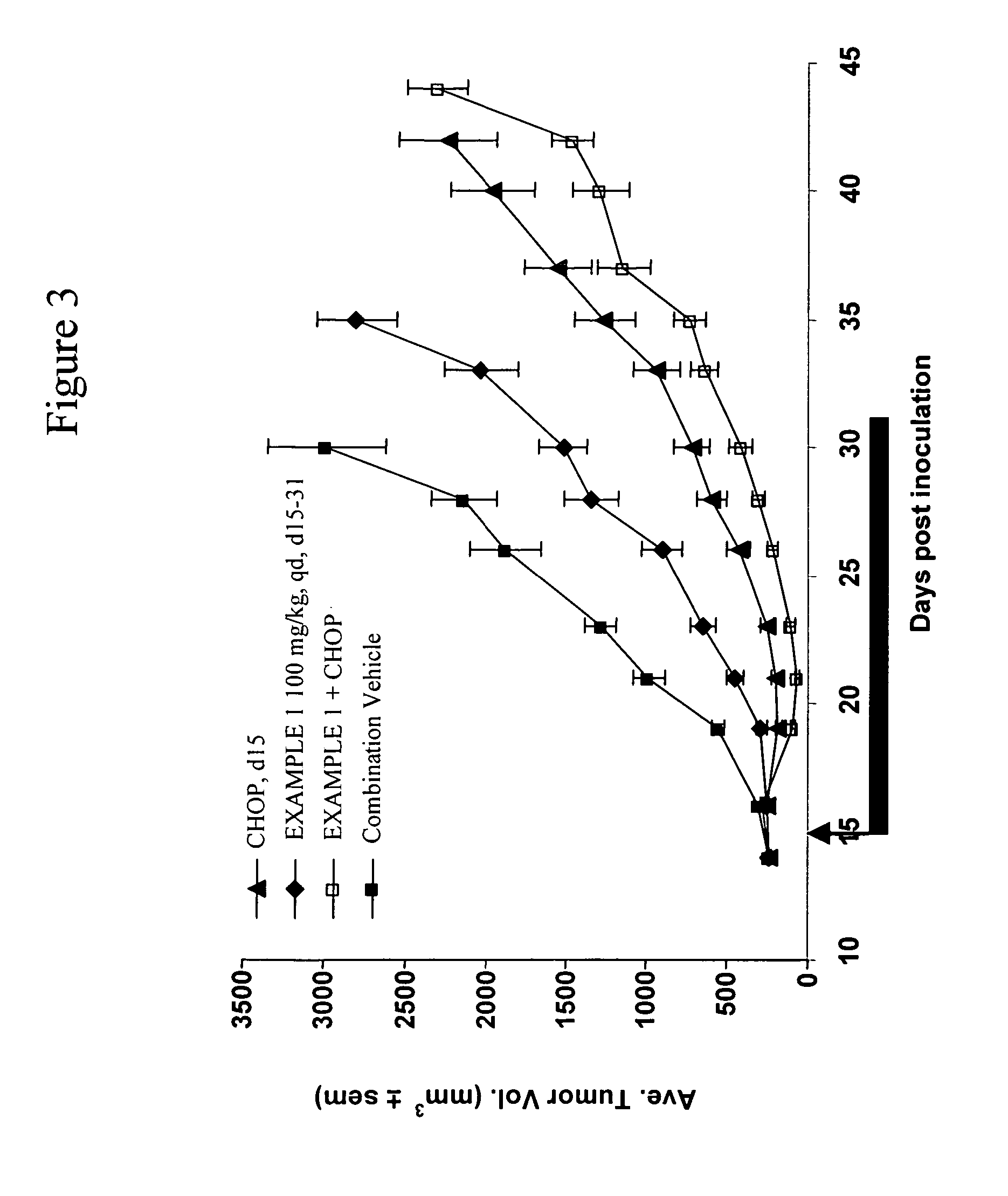
Fc fusion proteins of human erythropoietin with increased biological activities
InactiveUS6900292B2Improve biological activityExtended serumPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSide effectHalf-life
Fc fusion proteins of human EPO with increased biological activities relative to rHuEPO on a molar basis are disclosed. The HuEPO-L-vFc fusion protein comprises HuEPO, a flexible peptide linker of about 20 or fewer amino acids, and a human IgG Fc variant. The Fc variant is of a non-lytic nature and shows minimal undesirable Fc-mediated side effects. A method is also disclosed to make or produce such fusion proteins at high expression levels. Such HuEPO-L-vFc fusion proteins exhibit extended serum half-life and increased biological activities, leading to improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, thus fewer injections will be needed within a period of time.
Owner:LONGBIO PHARM (SUZHOU) CO LTD
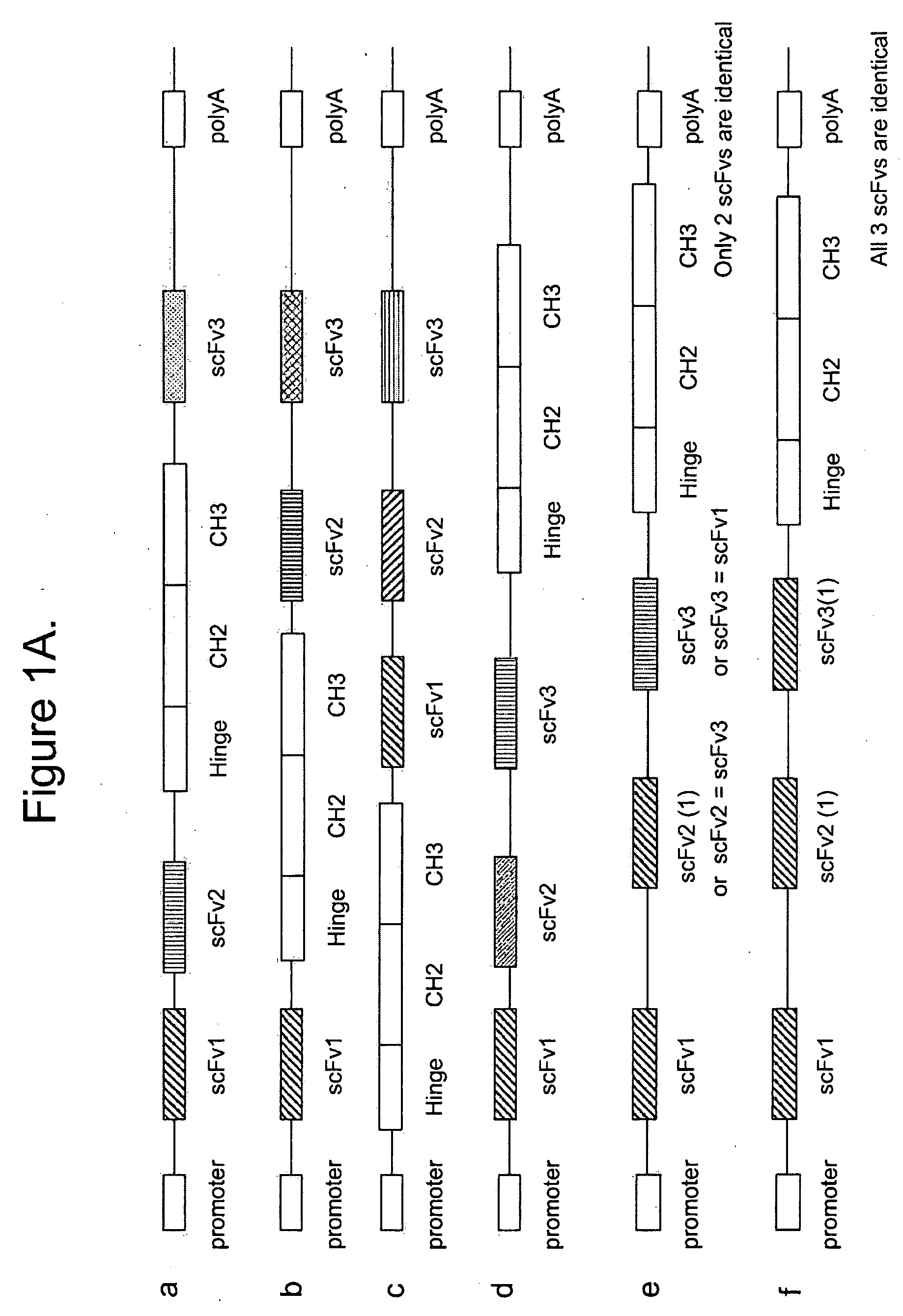
Multispecific epitope binding proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090155275A1Stimulate immune responseEnhanced interactionAntipyreticAnalgesicsEpitopeDisease
The present invention relates to multispecific epitope binding proteins, methods of making, and uses thereof in the prevention, management, treatment or diagnosis of acute or chronic diseases.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Modified polynucleotides for the production of secreted proteins
Owner:MODERNATX INC
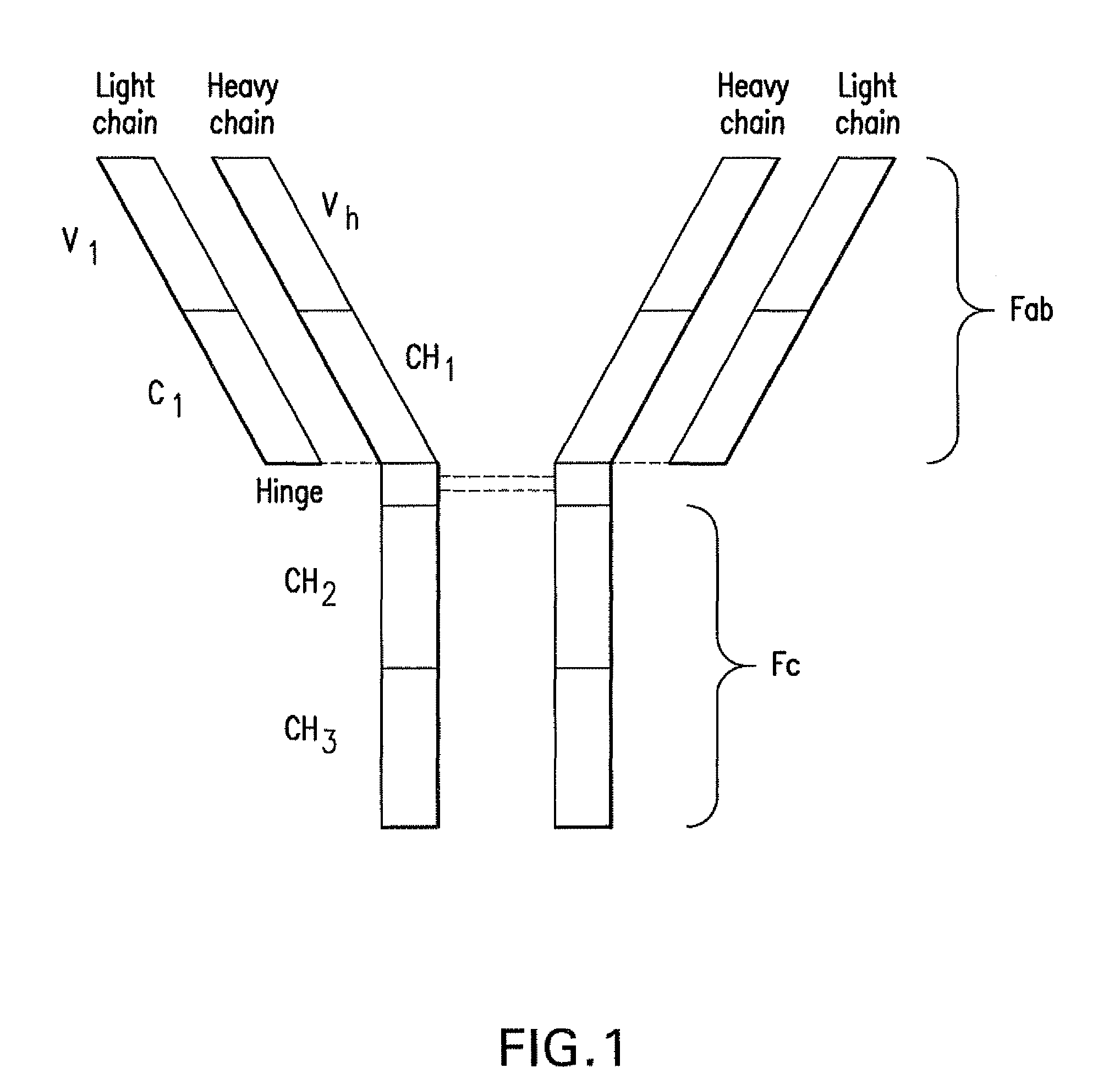
Antibody
InactiveUS20070274985A1Generate efficientlyEffective isolationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansNatural antibodySingle-Chain Antibodies
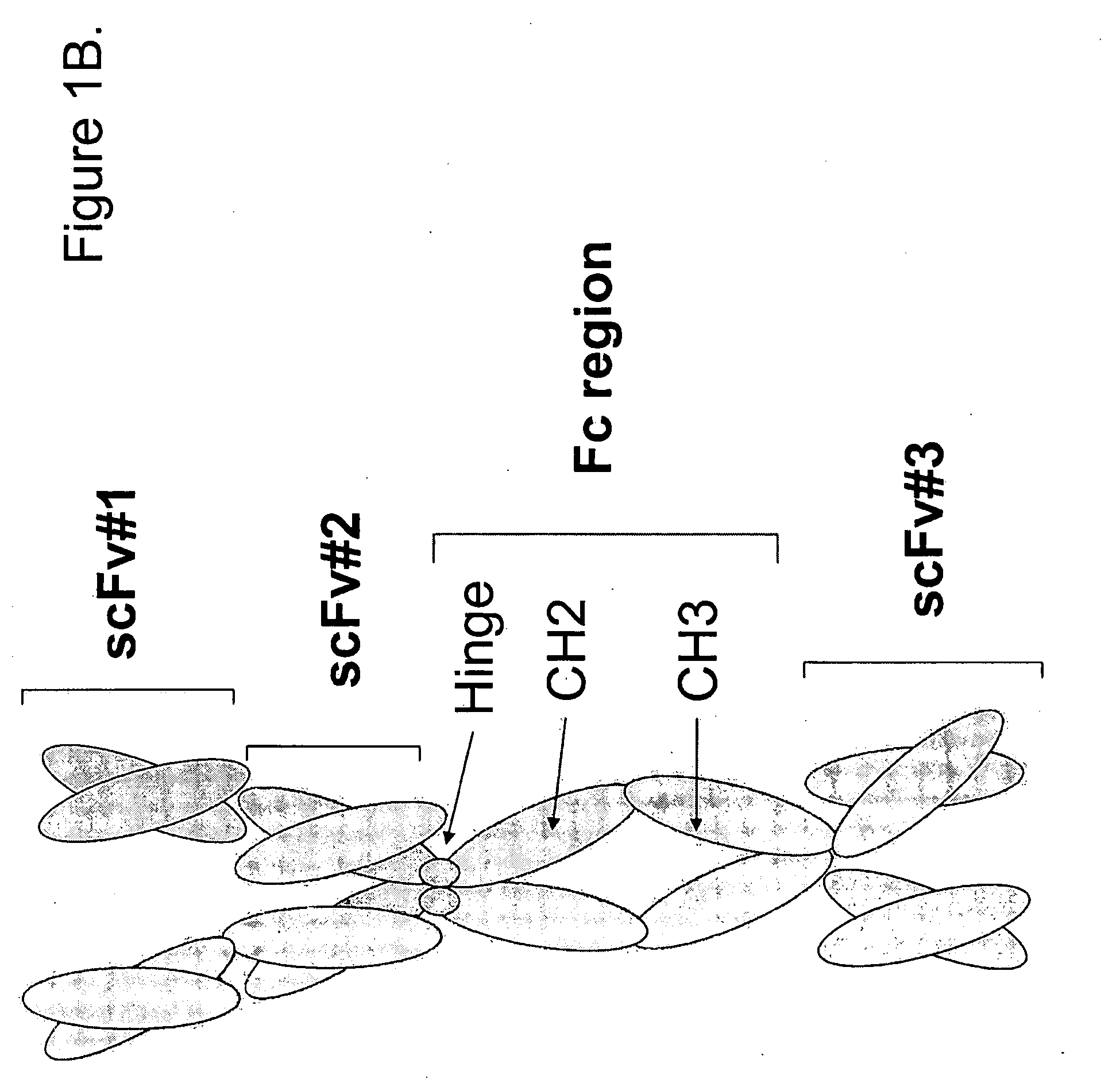
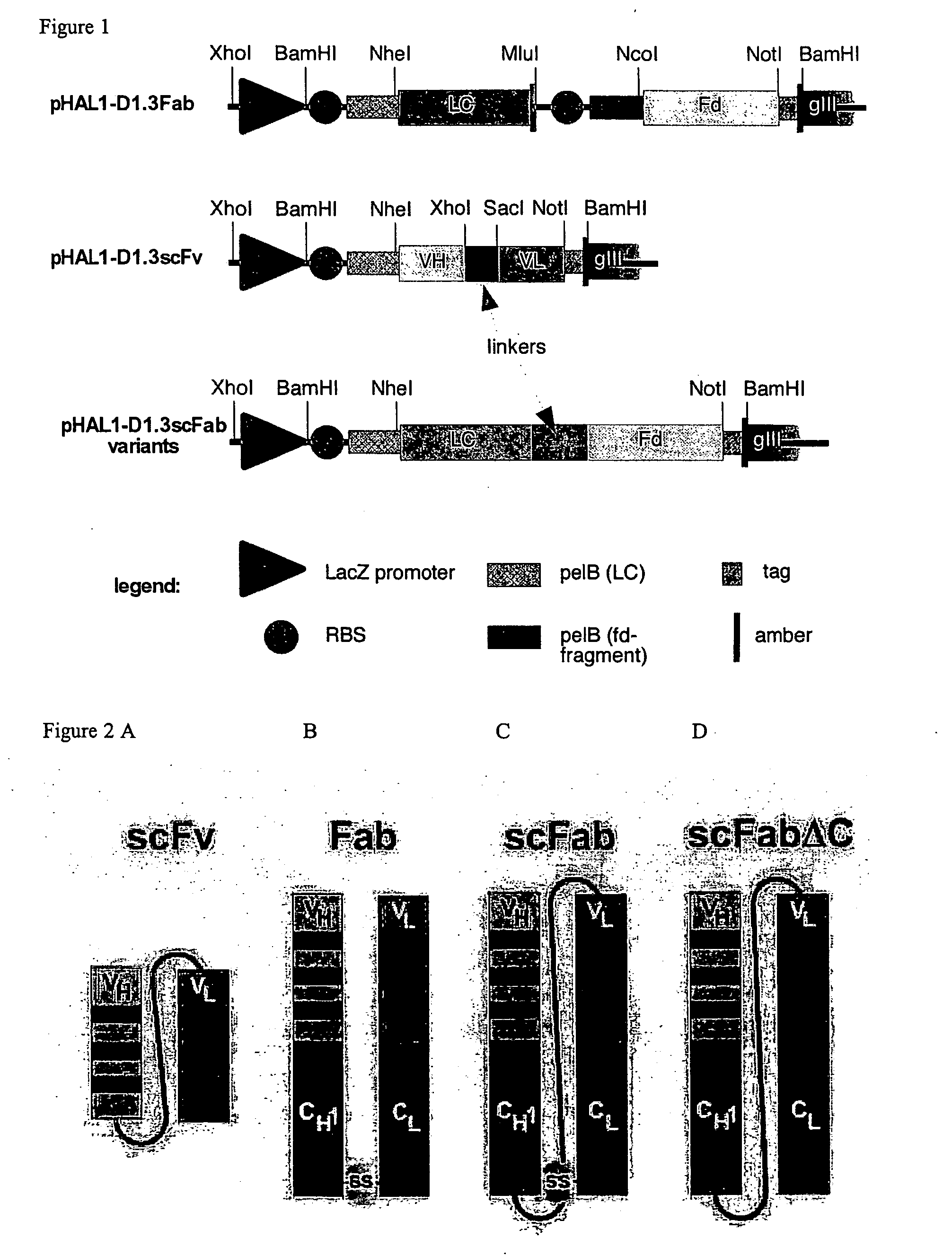
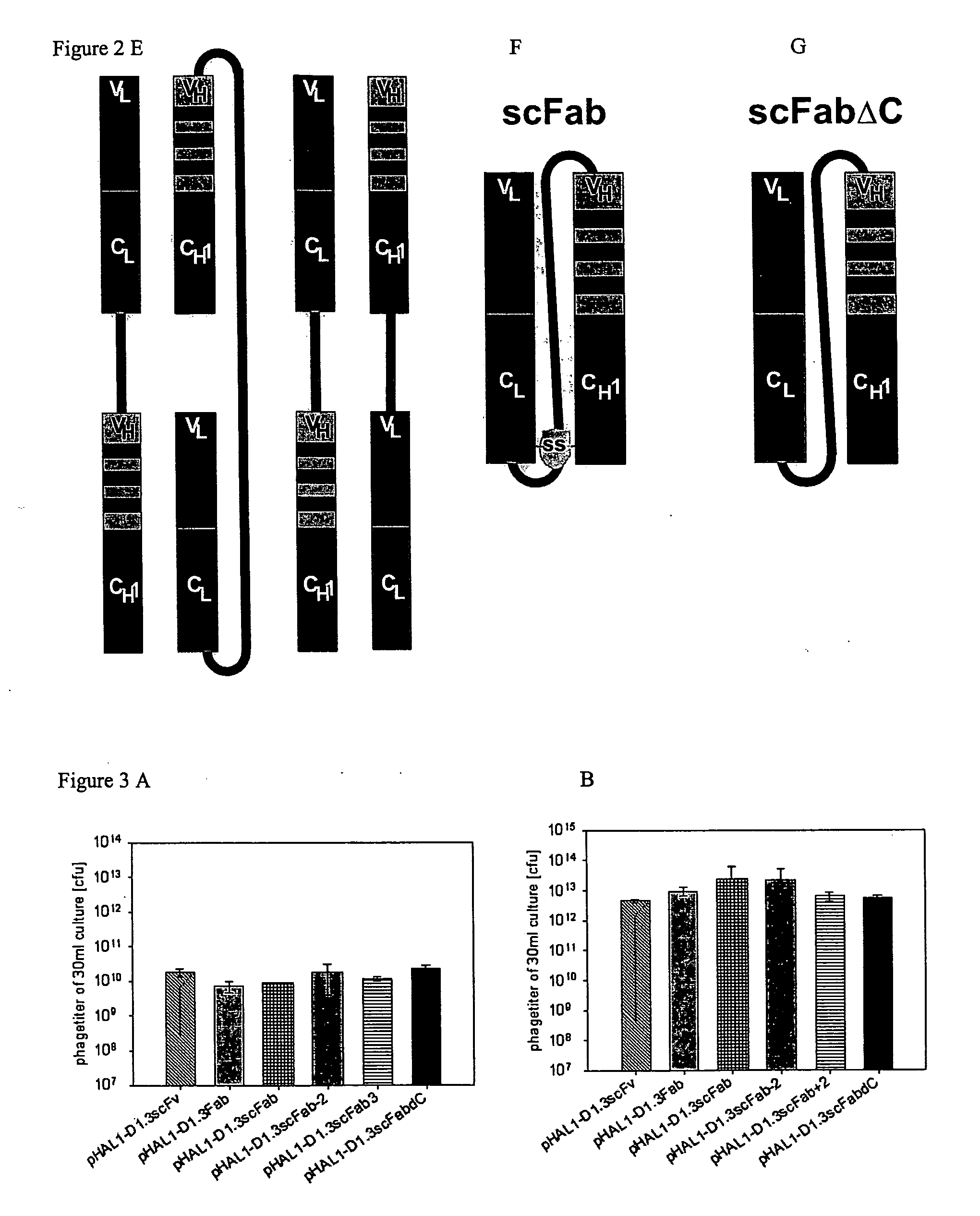
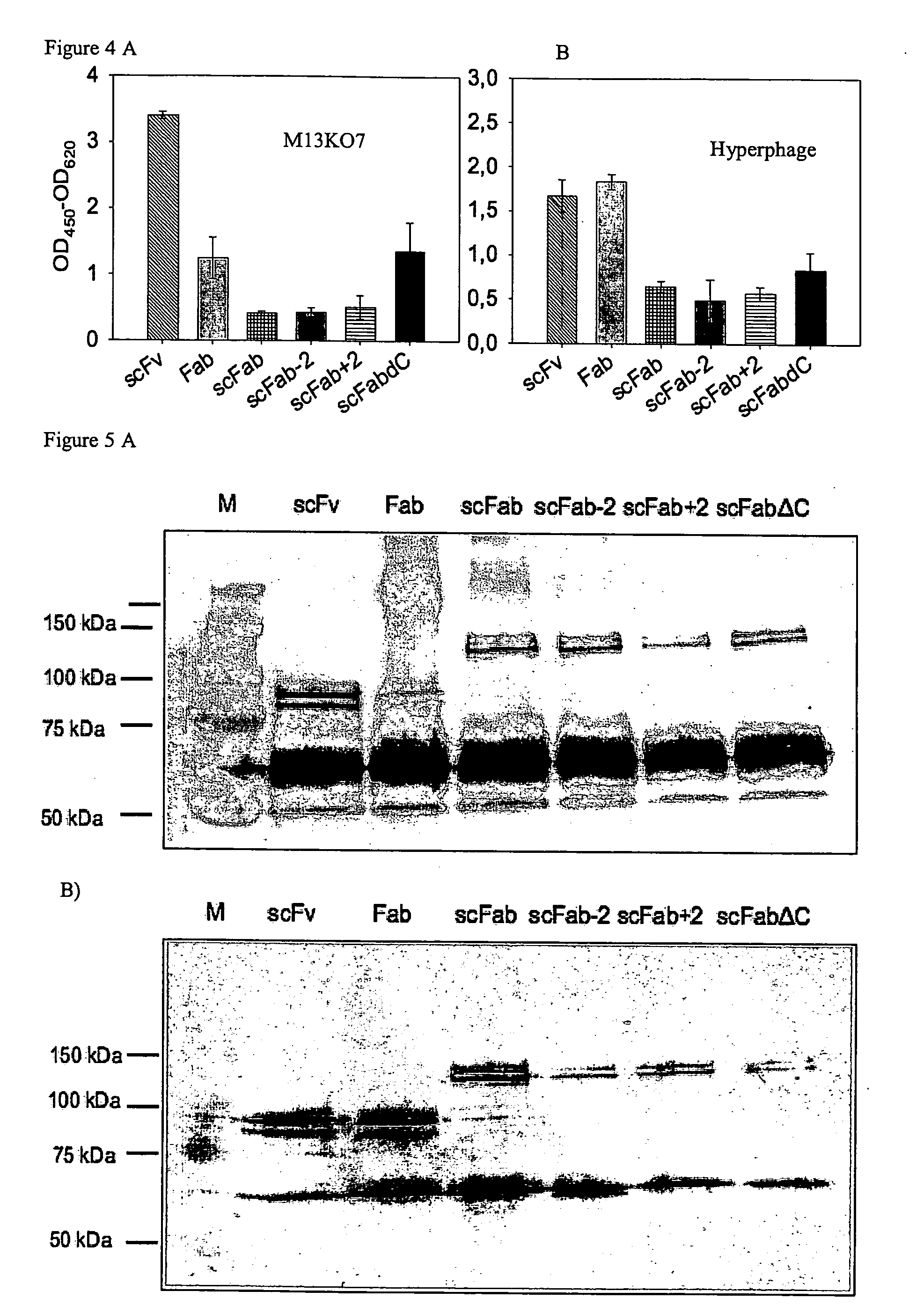
The present invention refers to synthetic antibody molecules which comprise domains from naturally occuring antibodies, e.g. domains derivable from IgG, preferably of human origin, in a novel arrangement. Single chain molecules are provided which are suitable for expression in micro-organisms in their active conformation, which single chain molecules generally comprise a VL domain, a CL domain, and a VH domain, a CH1 domain, linked by a linker arranged between VUCL and VH / CH1. Accordingly, these antibody molecules can be termed single chain Fabs (scFabs). These antibody molecules are single chain proteins, which can also be associated to dimers, including heteromeric antibodies, wherein at least two single chain antibody molecules are associated.
Owner:TECH UNIV BRAUNSCHWEIG
Tumour necrosis factor antibodies
InactiveUS6451983B2Enhance or inhibit TNF alpha activityInduction of endothelial procoagulant activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman tumorSingle-Chain Antibodies
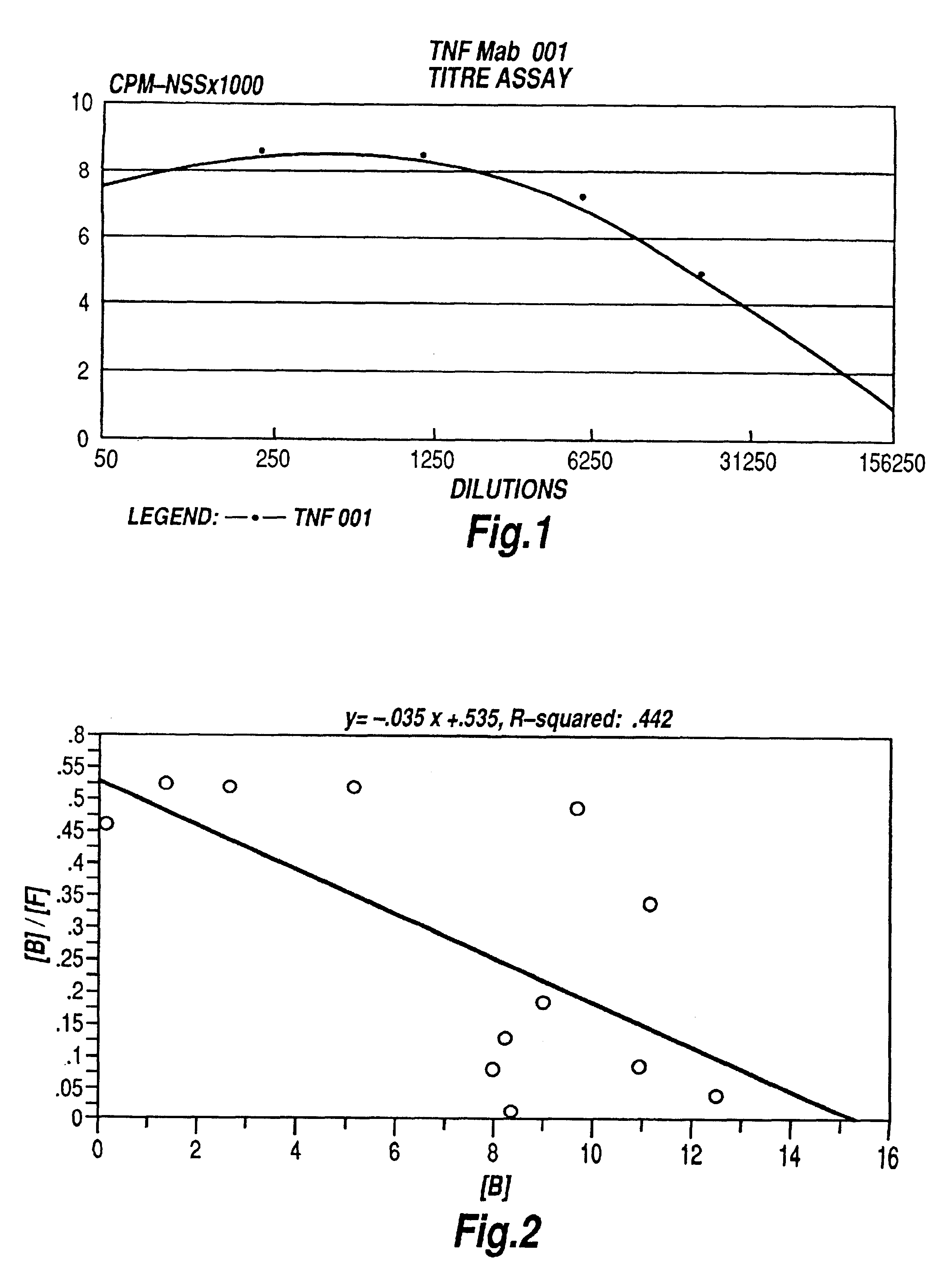
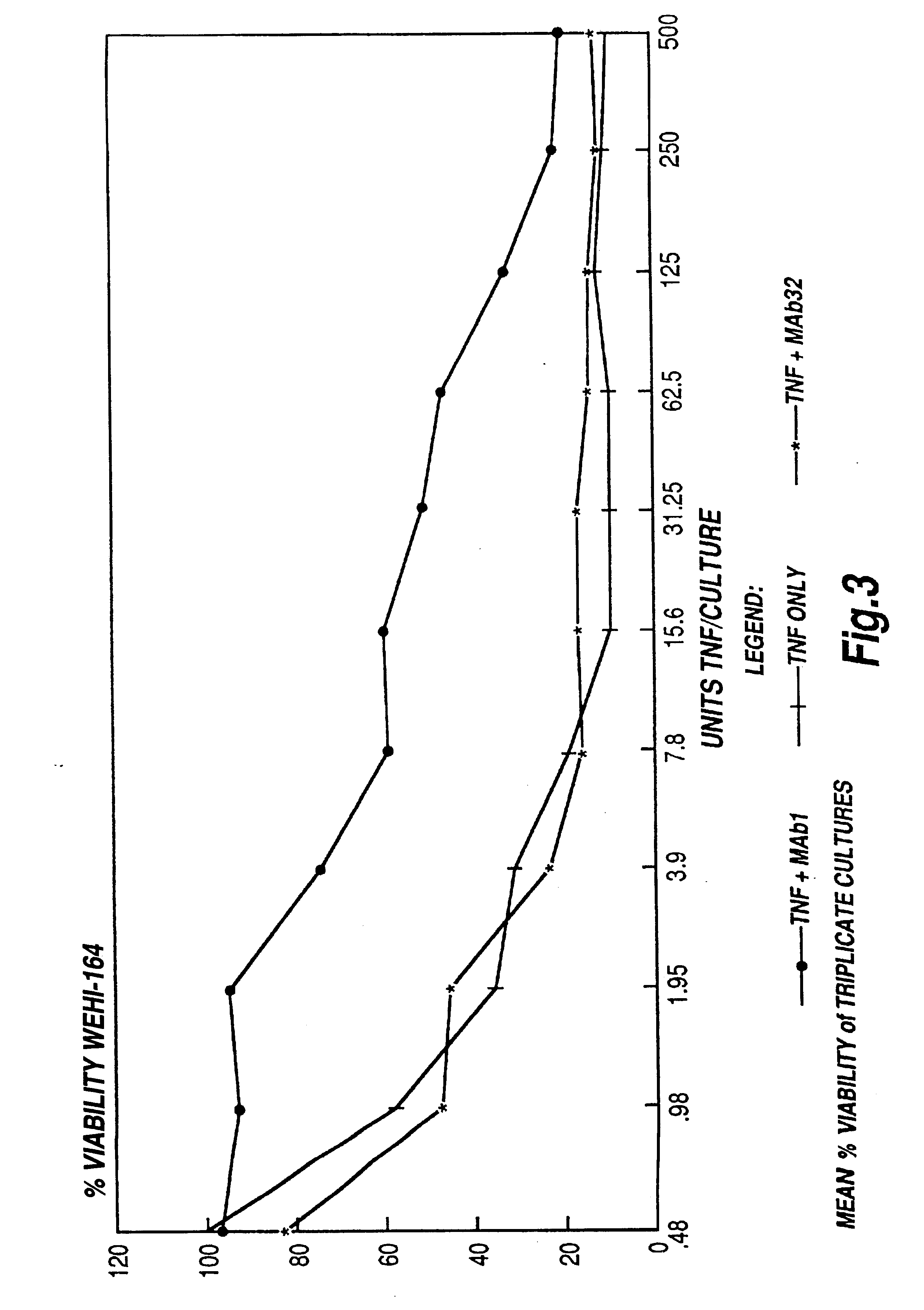
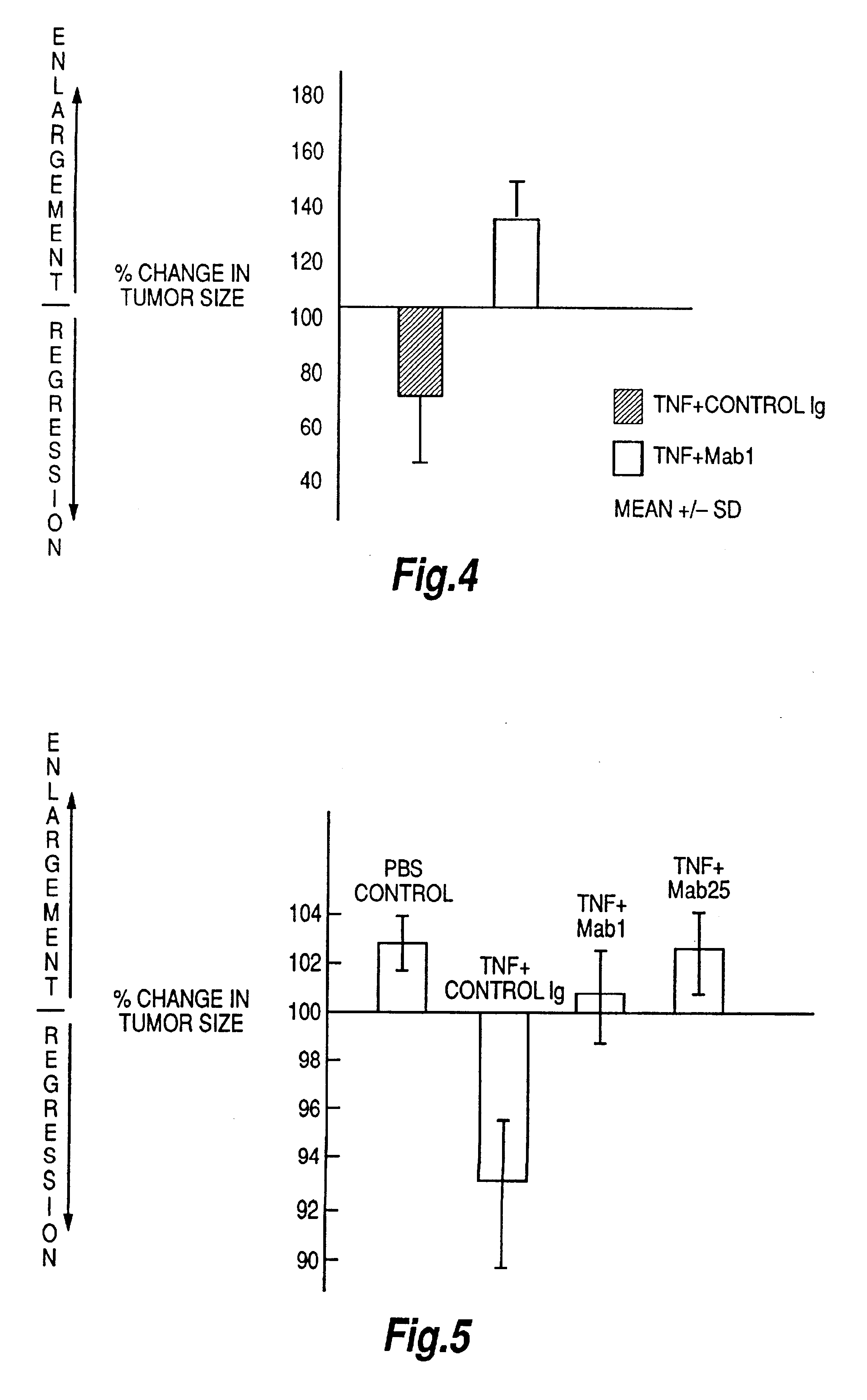
The present invention relates to ligands which bind to human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) in a manner such that upon binding of these ligands to TNF the biological activity of TNF is modified. In preferred forms the ligand binds to TNF in a manner such that the induction of endothelial procoagulant activity of the TNF is inhibited; the binding of TNF to receptors on endothelial cells is inhibited; the induction of fibrin deposition in the tumor and tumor regression activities of the TNF are enhanced; and the cytotoxicity and receptor binding activities of the TNF are unaffected or enhanced on tumor cells. The ligand is preferably an antibody, F(ab) fragment, single domain antibody (dABs) single chain antibody or a serum binding protein. It is preferred, however, that the ligand is a monoclonal antibody or F(ab) fragment thereof.
Owner:CEPHALON AUSTRALIA
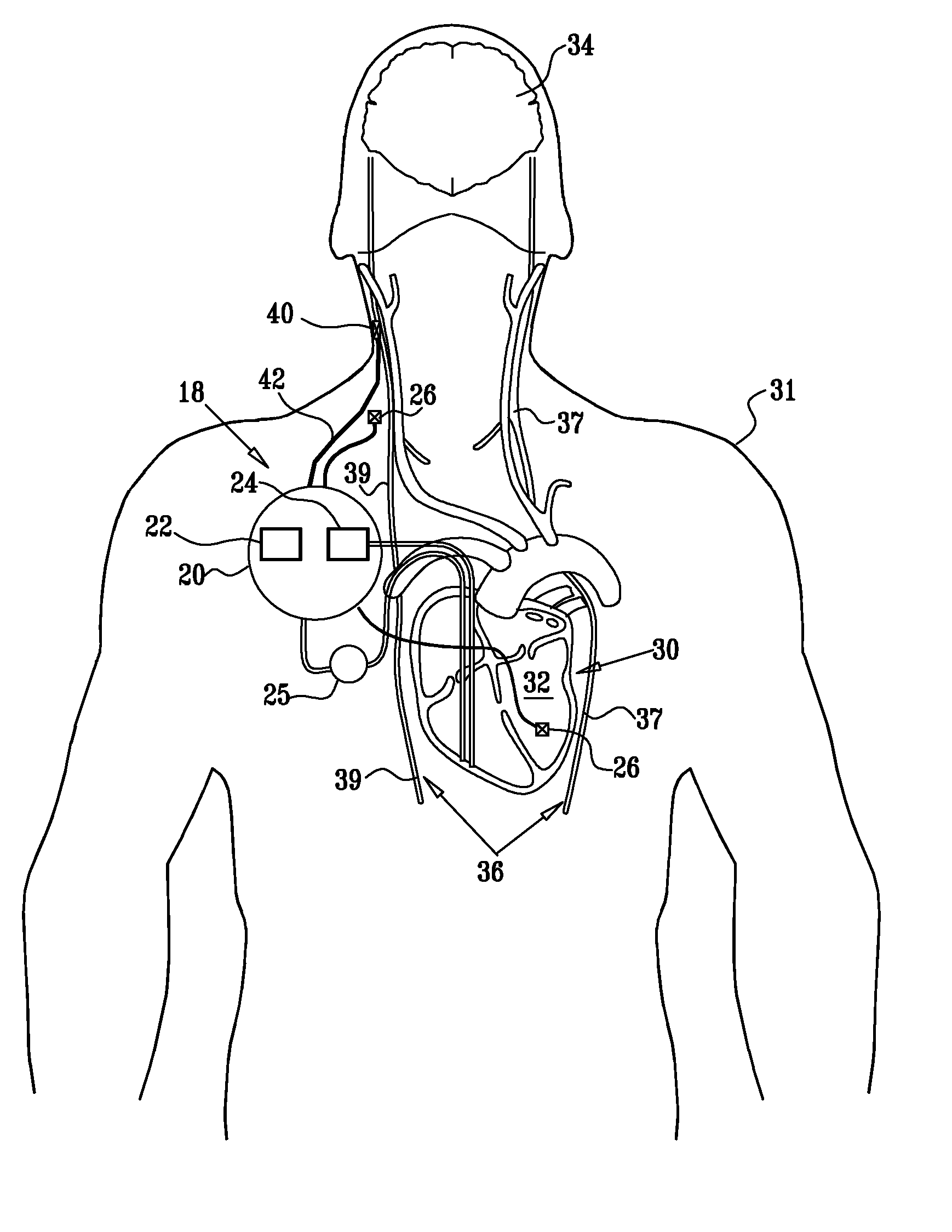
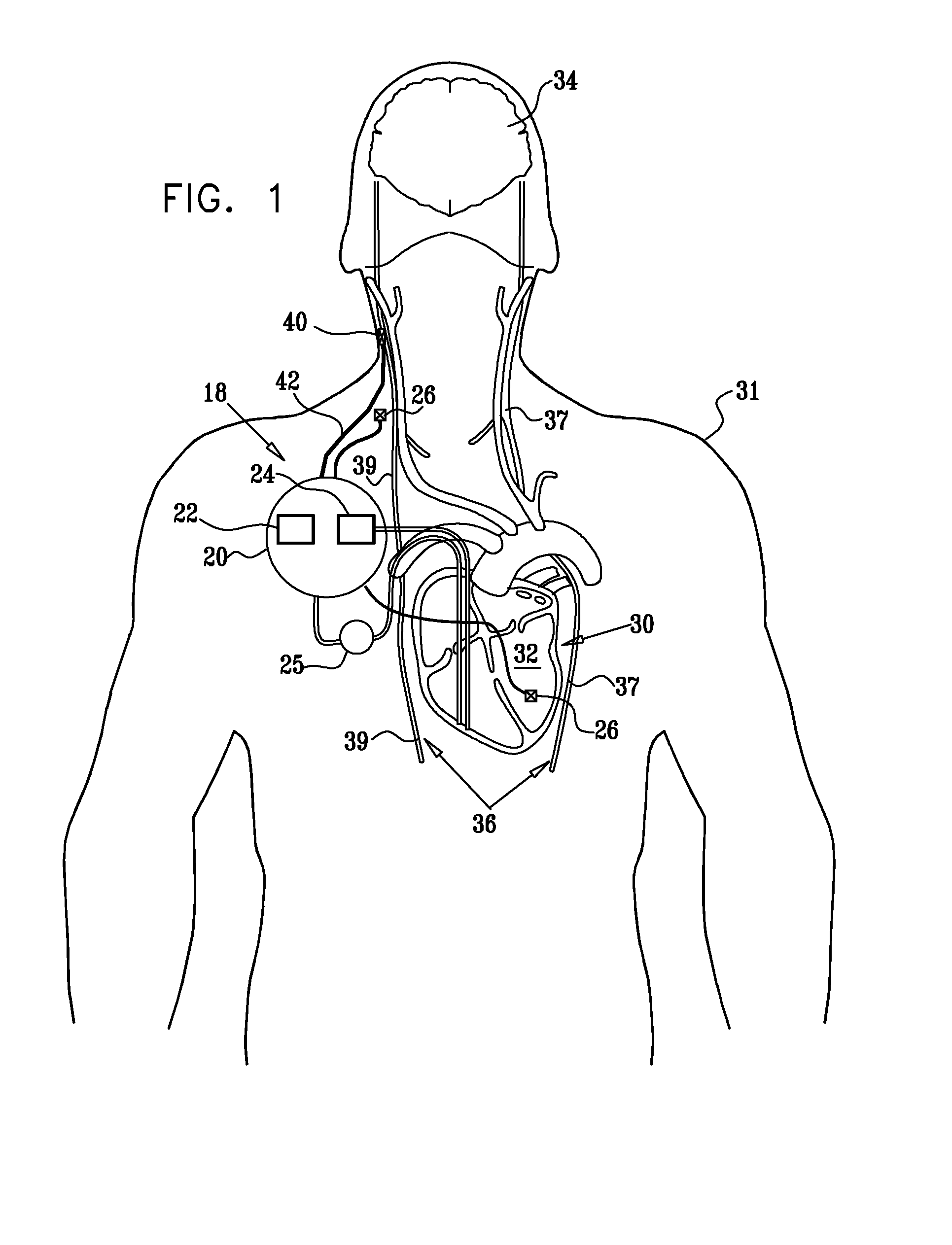
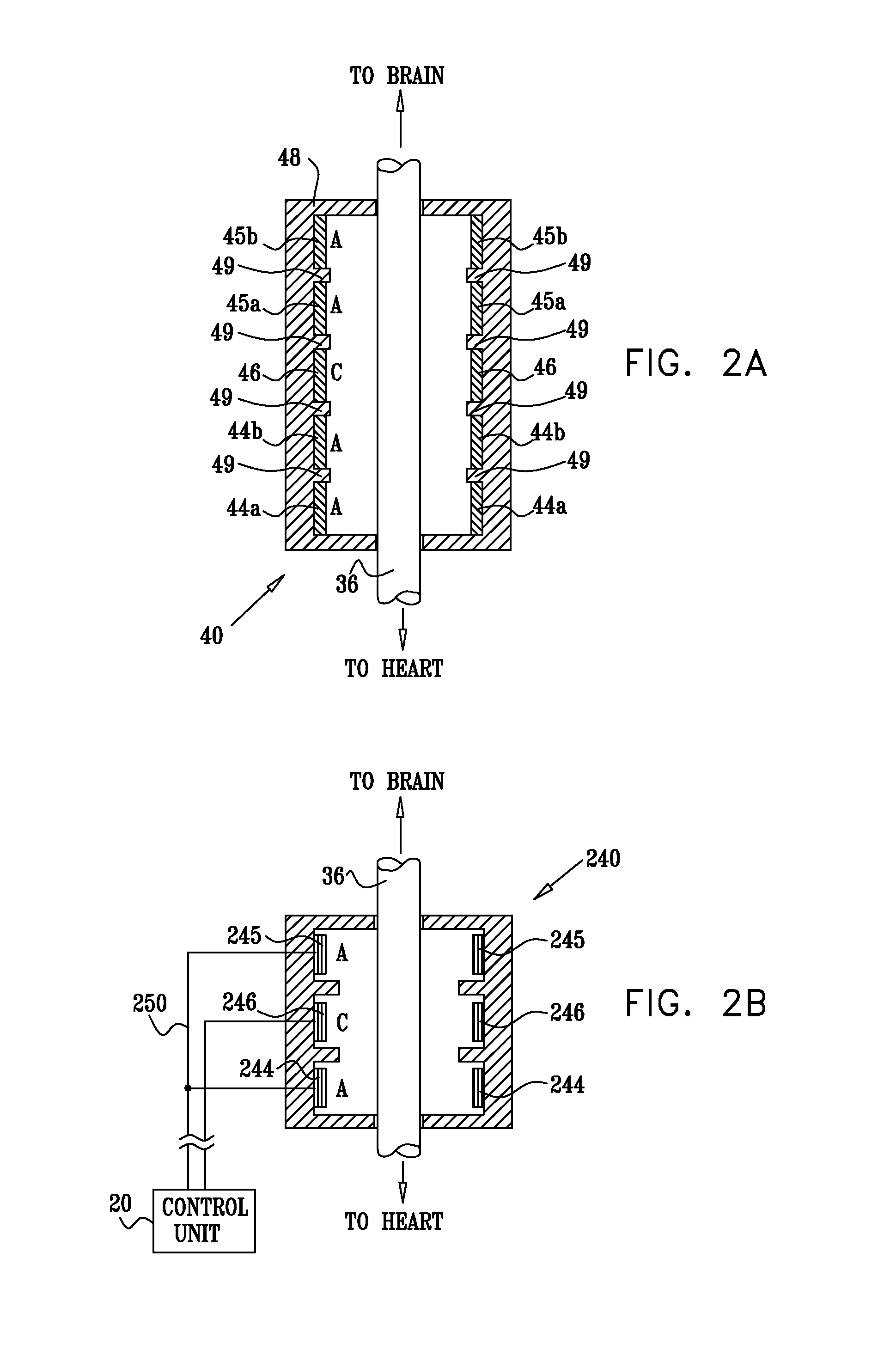
Nerve stimulation techniques
InactiveUS20110224749A1Minimize any unintended side effect of the signal applicationSuppresses afferent action potentialHeart stimulatorsMedicineCytokine
A method is provided for treating heart failure in a subject in need of such treatment, including applying a stimulating current to parasympathetic nervous tissue of the subject, selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve and an epicardial fat pad. The stimulating current is configured to inhibit release of at least one proinflammatory cytokine sufficiently to the treat heart failure of the subject. A level of the at least one proinflammatory cytokine is measured. Optionally, the stimulating current is configured to change a level of Connexin 43 of the subject, and the level of Connexin 43 is also measured. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Antibody for 4-1BB
The present invention includes the receptor protein 4-1BB and the cDNA gene encoding for receptor protein 4-1BB. The nucleotide sequence of the isolated cDNA is disclosed herein along with the deduced amino acid sequence. The 4-1BB protein and fragments and derivatives can be used: 1) as a probe to isolate ligands to receptor protein 4-1BB, 2) to stimulate proliferation of B-cell's expressing 4-1BB, or 3) to block 4-1BB ligand binding. A monoclonal antibody against 4-1BB was developed which specifically recognizes an epitope on the extracellular domain of receptor protein 4-1BB. The monoclonal antibody can be used enhance T-cell proliferation and activation by treating T-cells that have expressed receptor protein 4-1BB with the monoclonal antibody. The effectiveness of the treatment was enhanced when conducted in the presence of protein tyrosinase kinase. A fusion protein for detecting cell membrane ligands to receptor protein 4-1BB was developed. It comprises the extracellular portion of the receptor protein 4-1BB and a detection protein bound to the portion of the receptor protein 4-1BB.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
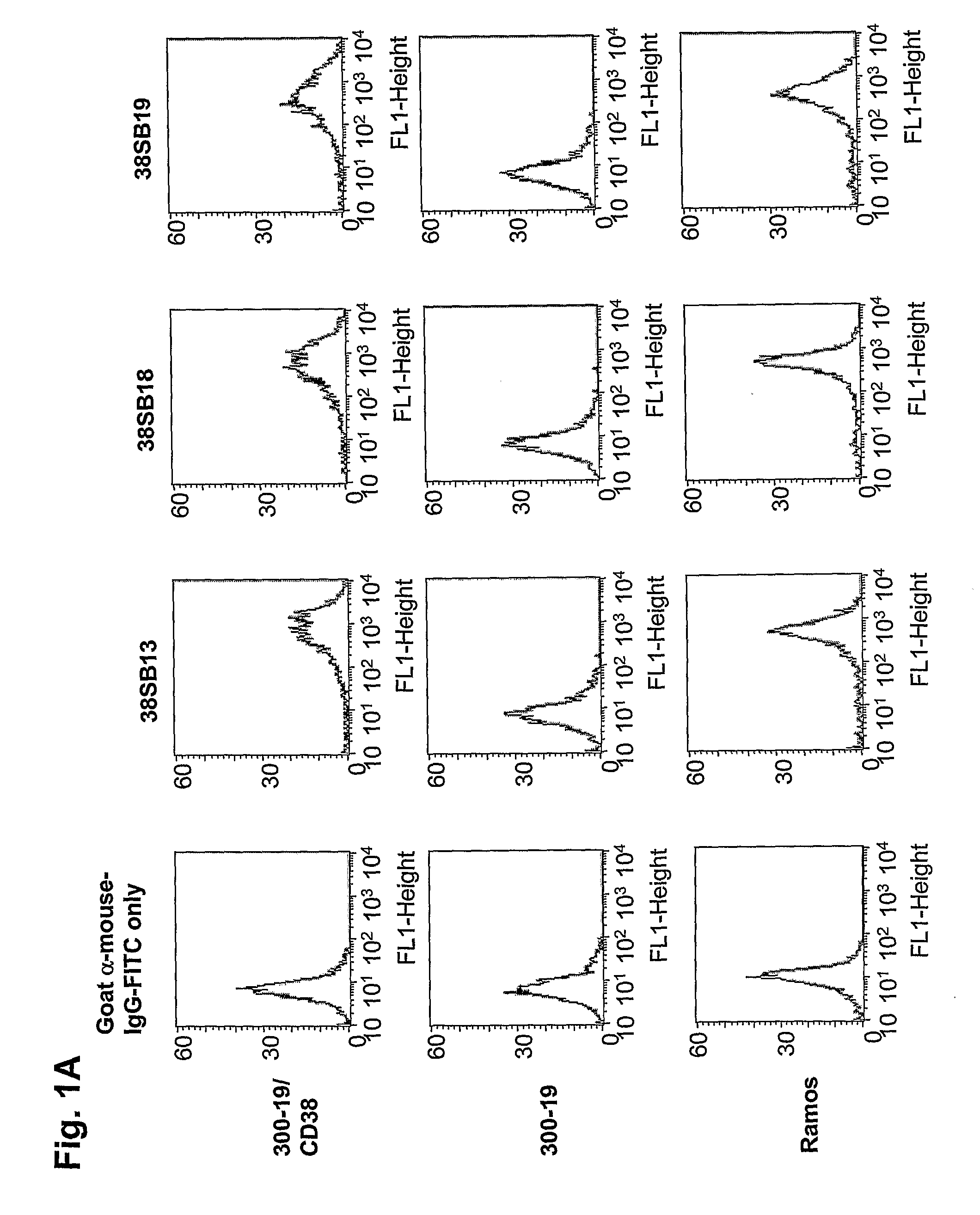
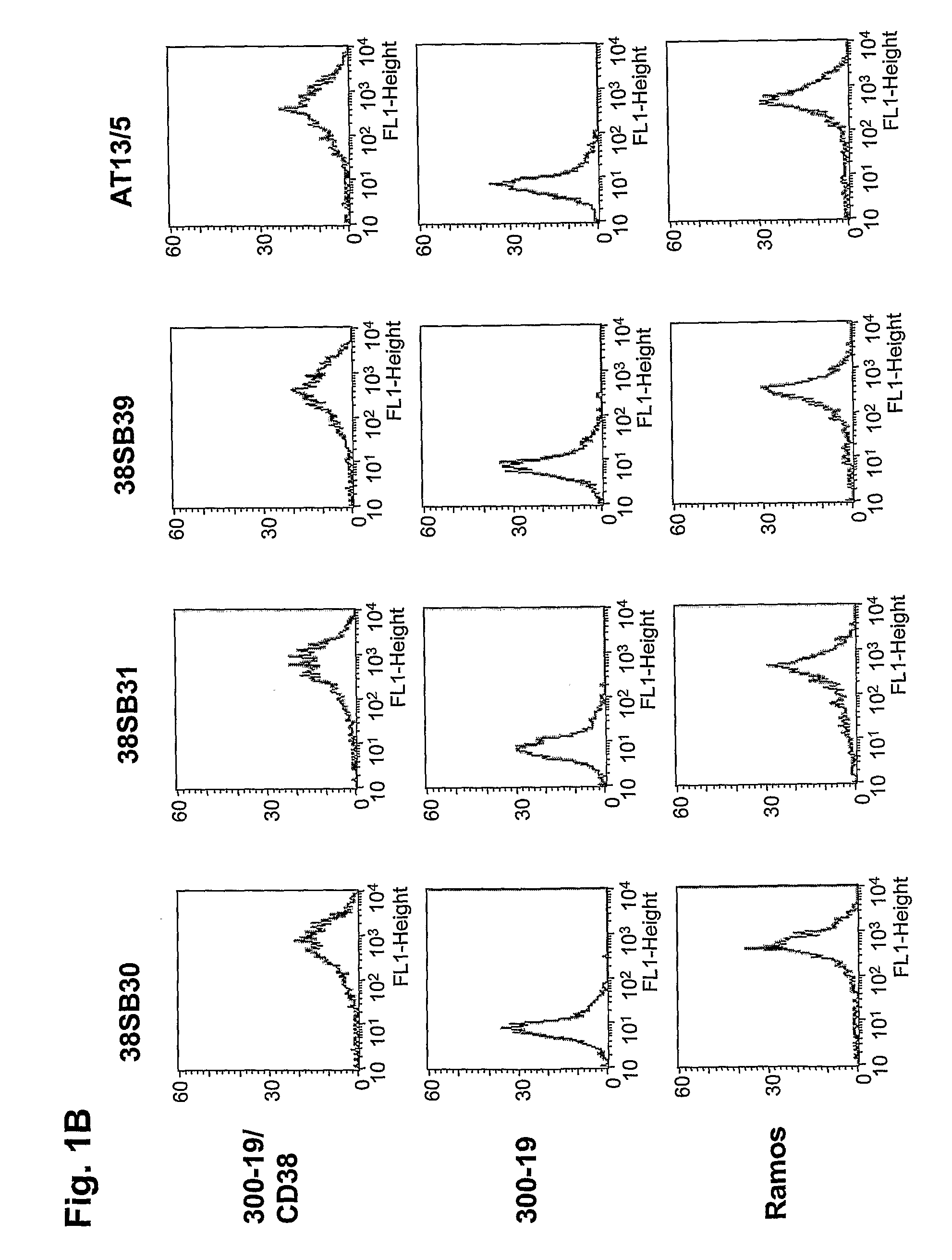
Novel Anti-cd38 antibodies for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20090304710A1Improve propertiesLess immunogenicSenses disorderAntipyreticComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
Antibodies, humanized antibodies, resurfaced antibodies, antibody fragments, derivatized antibodies, and conjugates of same with cytotoxic agents, which specifically bind to CD38, are capable of killing CD38+ cells by apoptosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and / or complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Said antibodies and fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of tumors that express CD38 protein, such as multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, or acute lymphocytic leukemia, or the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, erythematosus, and asthma. Said derivatized antibodies may be used in the diagnosis and imaging of tumors that express elevated levels of CD38. Also provided are cytotoxic conjugates comprising a cell binding agent and a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic compositions comprising the conjugate, methods for using the conjugates in the inhibition of cell growth and the treatment of disease, and a kit comprising the cytotoxic conjugate. In particular, the cell binding agent is a monoclonal antibody, and epitope-binding fragments thereof, that recognizes and binds the CD38 protein.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS US LLC
Method for producing immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in plants and their use
The immunoglobulins of the present invention are useful therapeutic immunoglobulins against mucosal pathogens such as S. mutans. The immunoglobulins contain a protection protein that protects the immunoglobulins in the mucosal environment. The invention also includes the greatly improved method of producing immunoglobulins in plants by producing the protection protein in the same cell as the other components of the immunoglobulins. The components of the immunoglobulin are assembled at a much improved efficiency. The method of the invention allows the assembly and high efficiency production of such complex molecules. The invention also contemplates the production of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in a variety of cells, including plant cells, that can be selected for useful additional properties. The use of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins as therapeutic antibodies against mucosal and other pathogens is also contemplated.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
Method for preparing thrombin for use in a biological glue
InactiveUS6472162B1Derive fast acting, stable autologous thrombinSimple preparatory procedureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue sealantDonors plasma
A sterile method for preparing stable thrombin component from a single donor's plasma in which the thrombin component and the clotting and adhesive proteins component are harvested simultaneously from the same donor plasma in less than one hour. The combined components provide an improved biological hemostatic agent and tissue sealant by virtue of its freedom from the risk of contaminating viruses or bacteria from allogenic human or bovine blood sources. The thrombin provides polymerization of the clotting and adhesive proteins in less than five seconds, and is sufficiently stable to provide that fast clotting over a six hour period. Further, the clotting times can be predictably lengthened by diluting the thrombin with saline.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Method for integrating genes at specific sites in mammalian cells via homologous recombination and vectors for accomplishing the same
InactiveUS6413777B1Reduce in quantityImprove the level ofPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMammalReactive site
A method for achieving site specific integration of a desired DNA at a target site in a mammalian cell via homologous recombination is described. This method provides for the reproducible selection of cell lines wherein a desired DNA is integrated at a predetermined transcriptionally active site previously marked with a marker plasmid. The method is particularly suitable for the production of mammalian cell lines which secrete mammalian proteins at high levels, in particular immunoglobulins. Novel vectors and vector combinations for use in the subject cloning method are also provided.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Hemostatic sandwich bandage
The present invention relates to a haemostatic multilayer bandage that comprises preferably a thrombin layer between two fibrinogen layers. The dressing may contain other resorbable materials such as glycolic acid or lactic acid based polymers or copolymers. The inventive haemostatic bandage is useful for the treatment of wounded tissue.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com