Patents
Literature
169 results about "Drosophila melanogaster" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Drosophila melanogaster is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is known generally as the common fruit fly (though inaccurately) or vinegar fly. Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, D. melanogaster continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. As of 2017, eight Nobel prizes had been awarded for research using Drosophila.
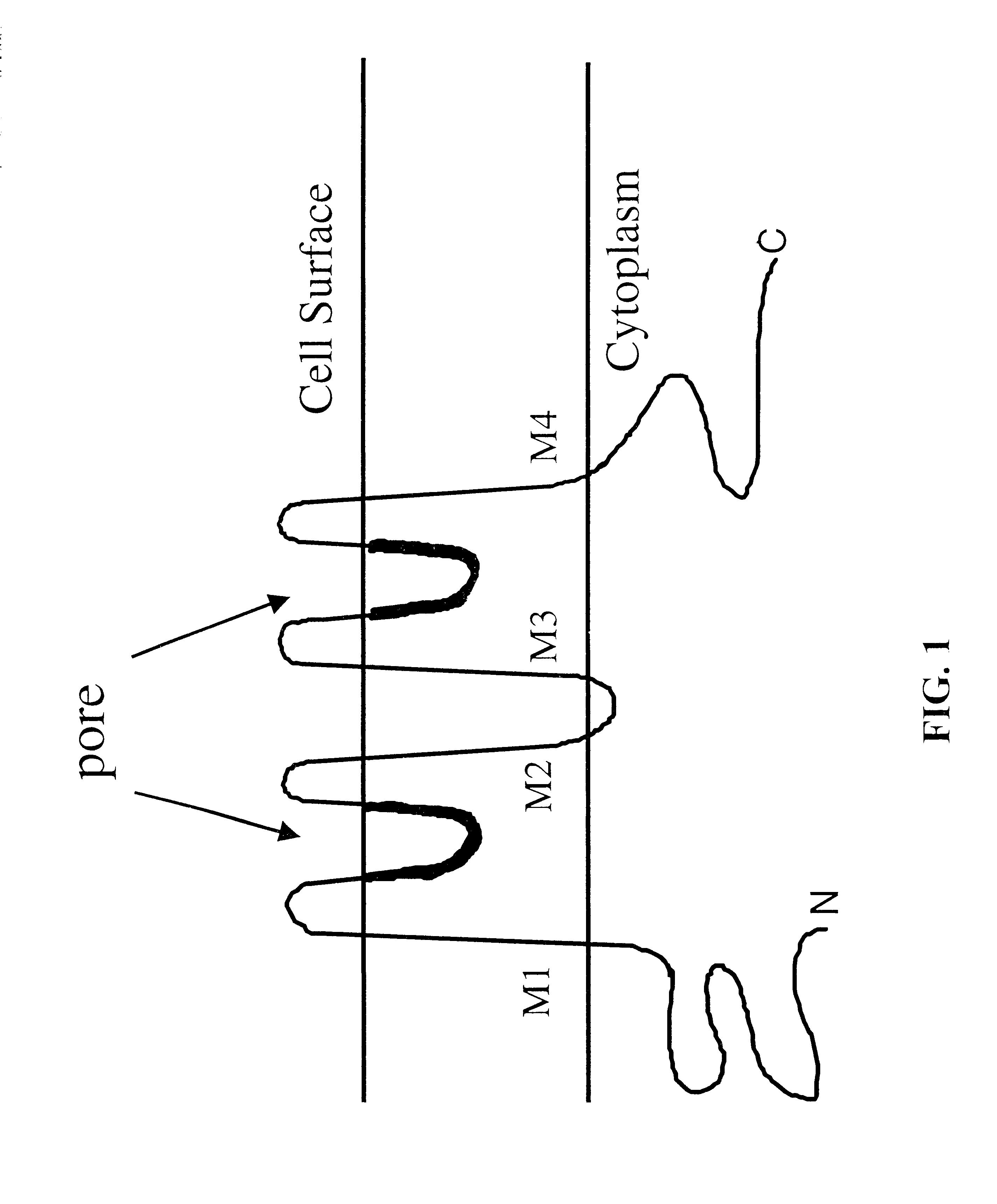
Nucleic acids and polypeptides of invertebrate TWIK channels and methods of use
Tandem pore domain weak inward rectifying K+ (TWIK) channel nucleic acids and proteins that have been isolated from Drosophila melanogaster and Leptinotarsa are described. The TWIK channel nucleic acids and proteins can be used to genetically modify metazoan invertebrate organisms, such as insects, coelomates, and pseudocoelomates, or cultured cells, resulting in TWIK channel expression or mis-expression. The genetically modified organisms or cells can be used in screening assays to identify candidate compounds which are potential pesticidal agents or therapeutics that interact with TWIK channel proteins. They can also be used in methods for studying TWIK channel activity and identifying other genes that modulate the function of, or interact with, the TWIK channel gene.
Owner:EXELIXIS PHARMA
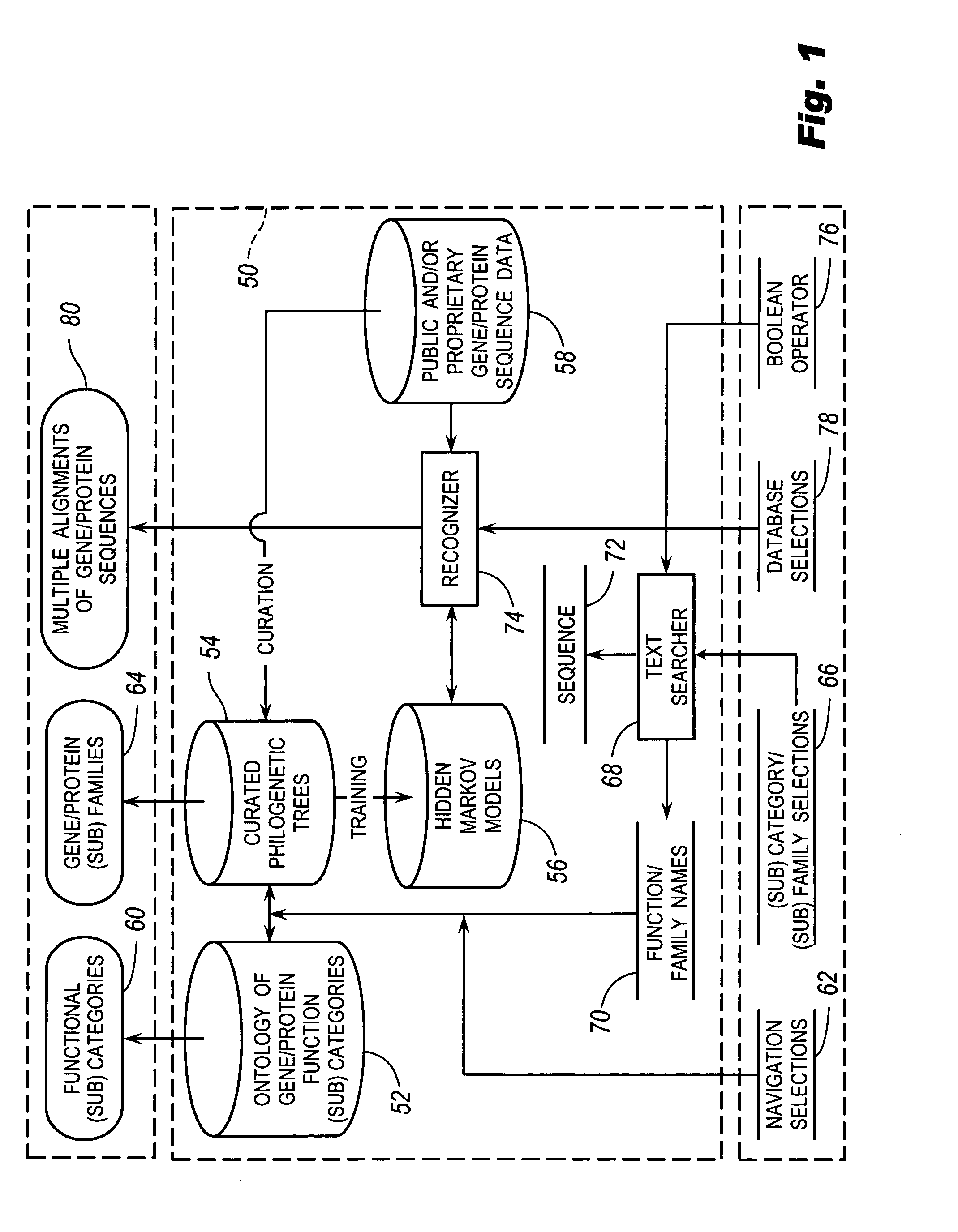
Browsable database for biological use
The browsable database can allow for high-throughput analysis of protein sequences. One helpful feature may be a simplified ontology of protein function, which allows browsing of the database by biological functions. Biologist curators may have associated the ontology terms with Hidden Markov Models (HMMs), rather than individual sequences, so that they can be applied to additional sequences. To ensure accurate functional classification, HMMs may be constructed not only for families, but for curator-defined subfamilies, whenever family members have divergent functions or nomenclature. Multiple sequence alignments and phylogenetic trees, including curator-assigned information, can be available for each family. Various versions of the browsable database may include training sequences from all organisms in the GenBank non-redundant protein database, and the HMMs can be used to classify gene products across the entire genomes of human, and Drosophila melanogaster.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
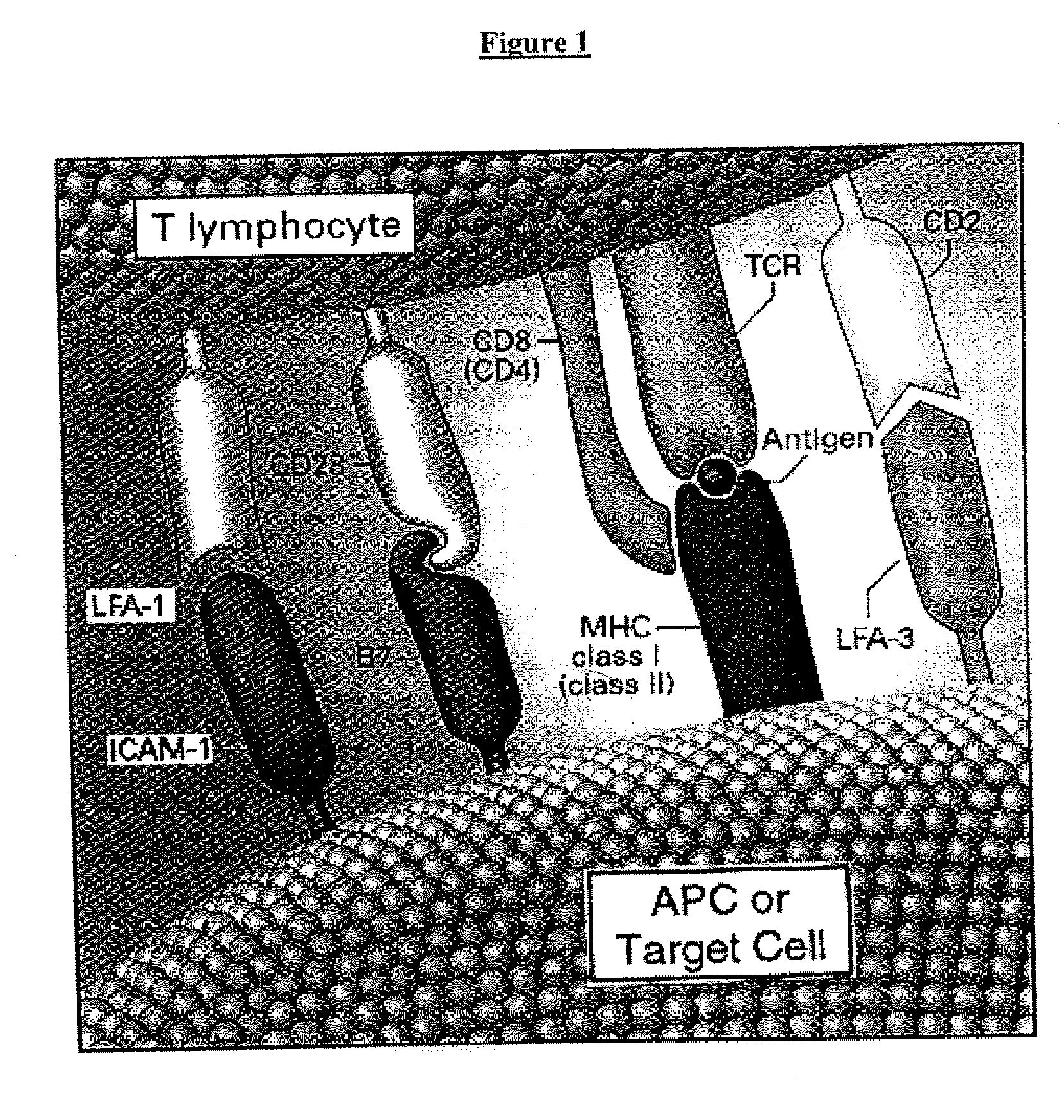
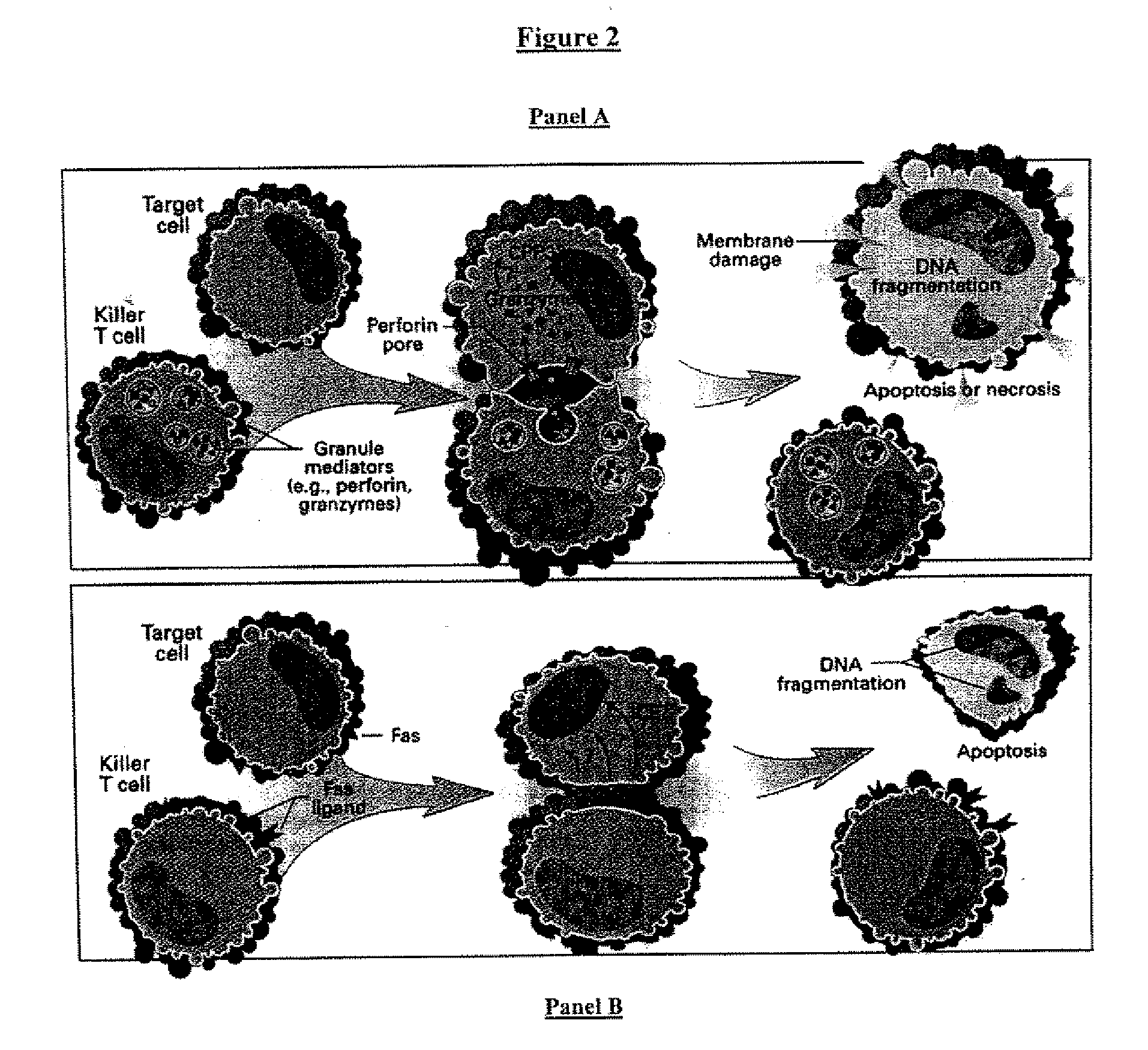
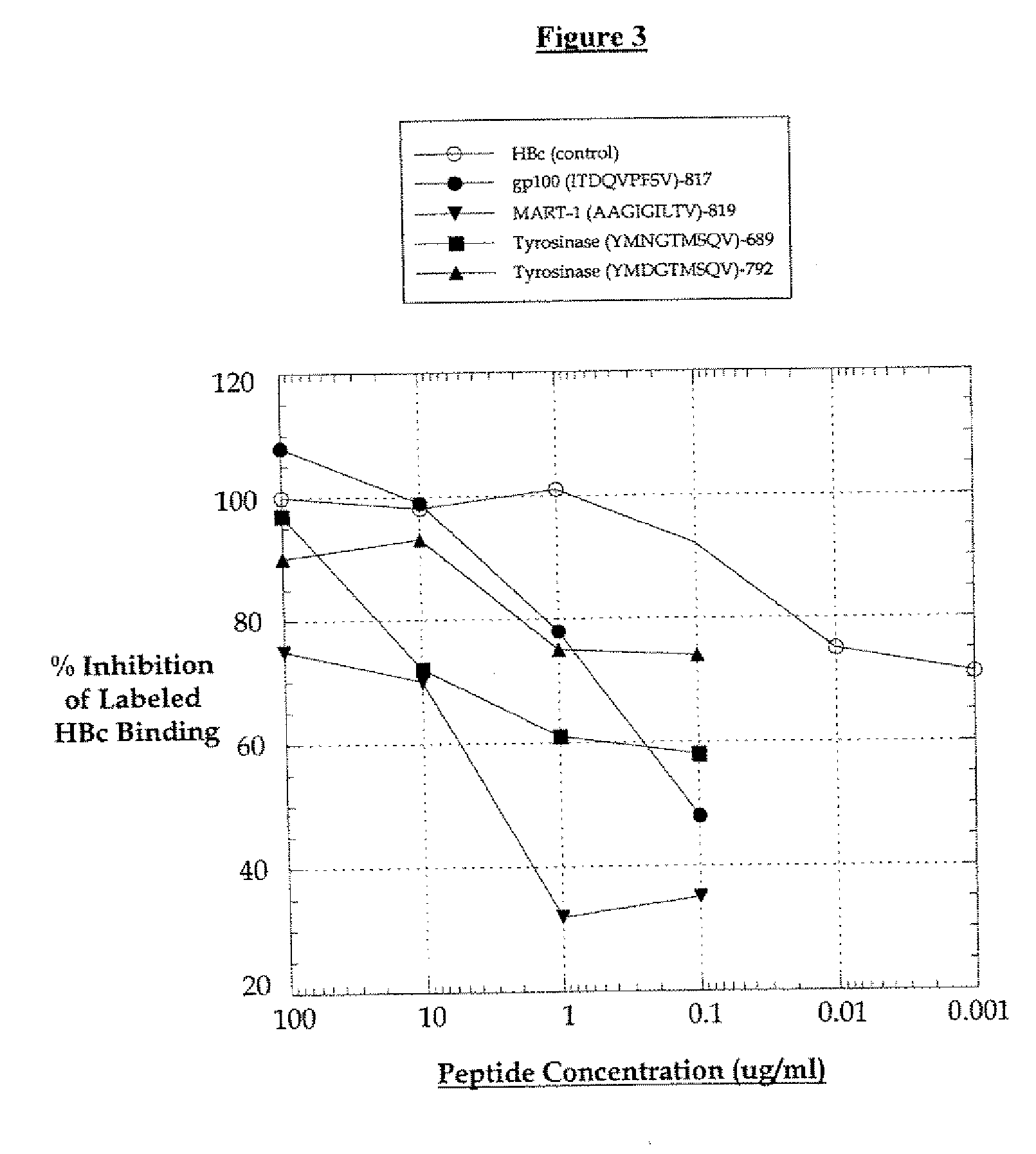
A cell therapy method for the treatment of tumors
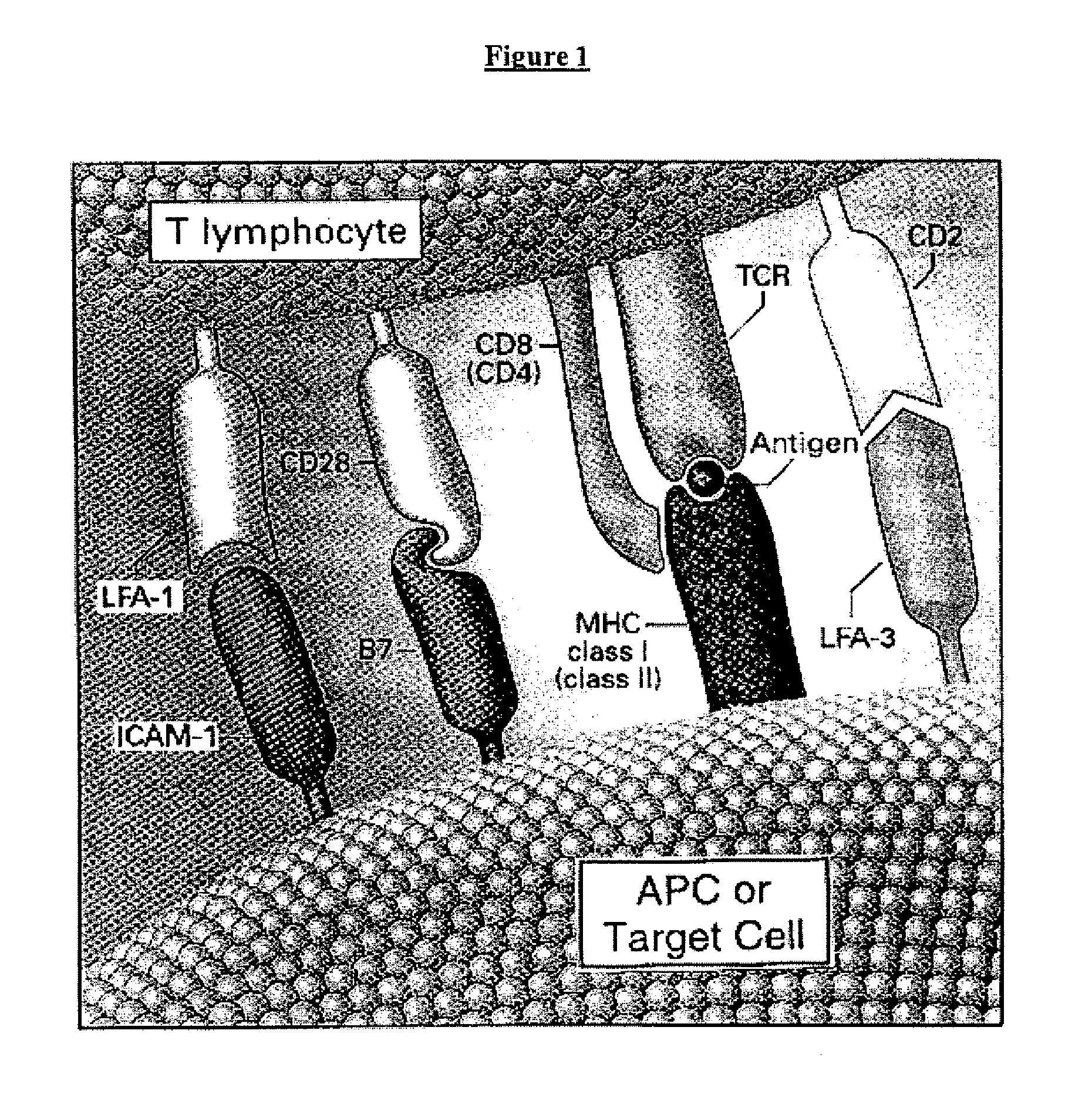
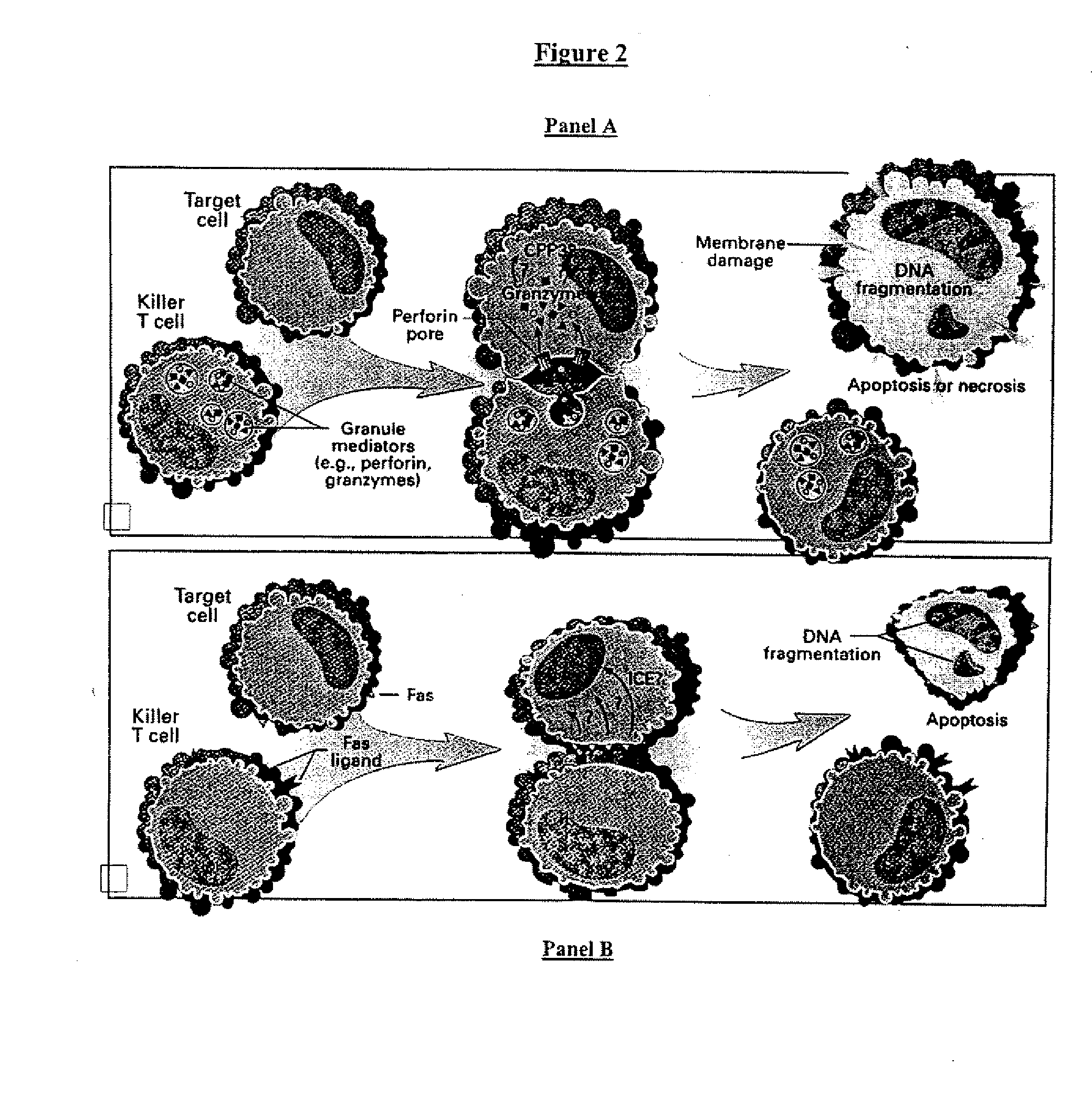
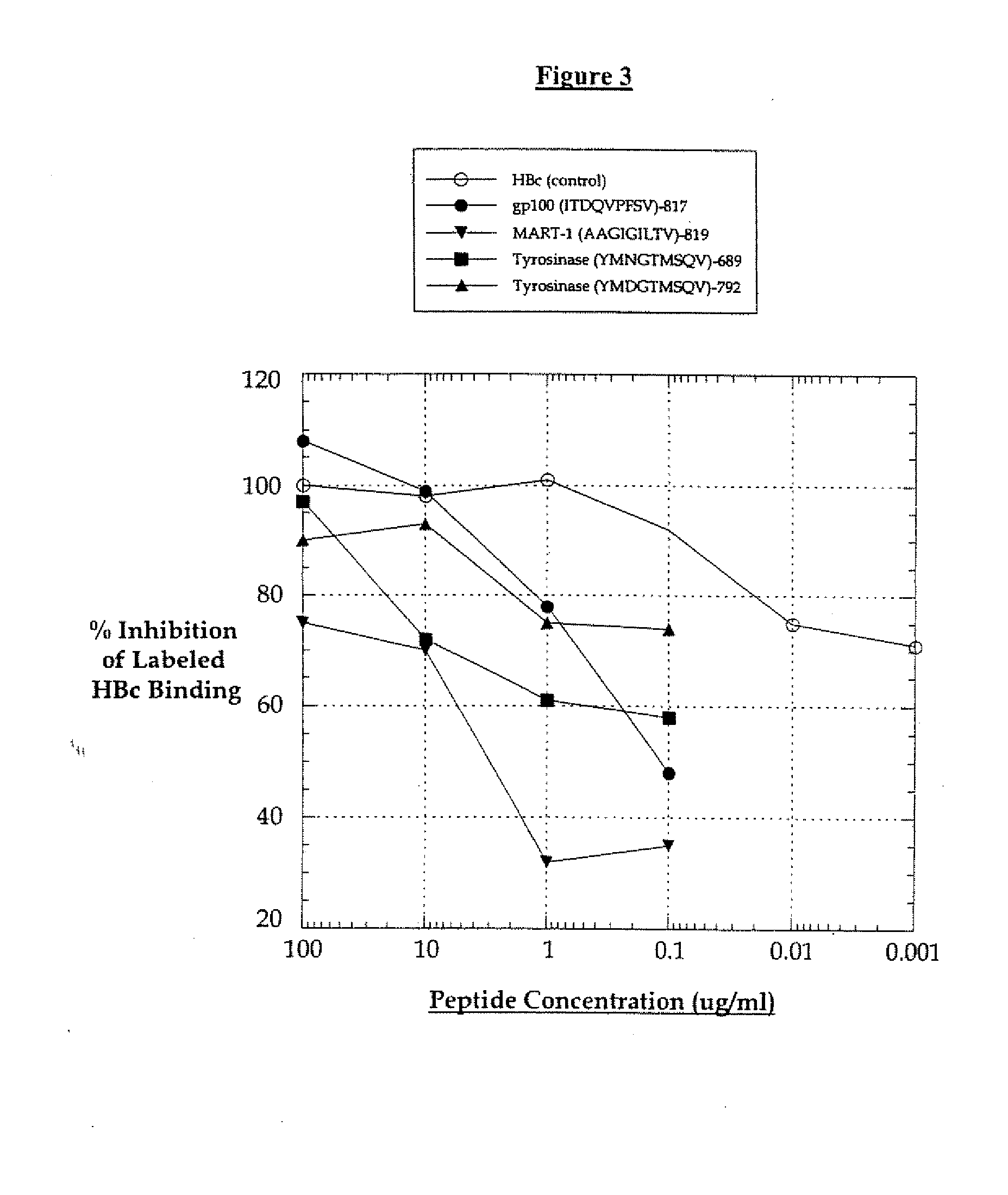
T cell responses are often diminished in humans with a compromised immune system. We have developed a method to isolate, stimulate and expand naïve cytotoxic T lymphocyte precursors (CTLp) to antigen-specific effectors, capable of lysing tumor cells in vivo. This ex vivo protocol produces fully functional effectors. Artificial antigen presenting cells (AAPCs; Drosophila melanogaster) transfected with human HLA class I and defined accessory molecules, are used to stimulate CD8+ T cells from both normal donors and cancer patients. The class I molecules expressed to a high density on the surface of the Drosophila cells are empty, allowing for efficient loading of multiple peptides that results in the generation of polyclonal responses recognizing tumor cells endogenously expressing the specific peptides. The responses generated are robust, antigen-specific and reproducible if the peptide epitope is a defined immunogen. This artificial antigen expression system can be adapted to treat most cancers in a significant majority of the population.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA INC
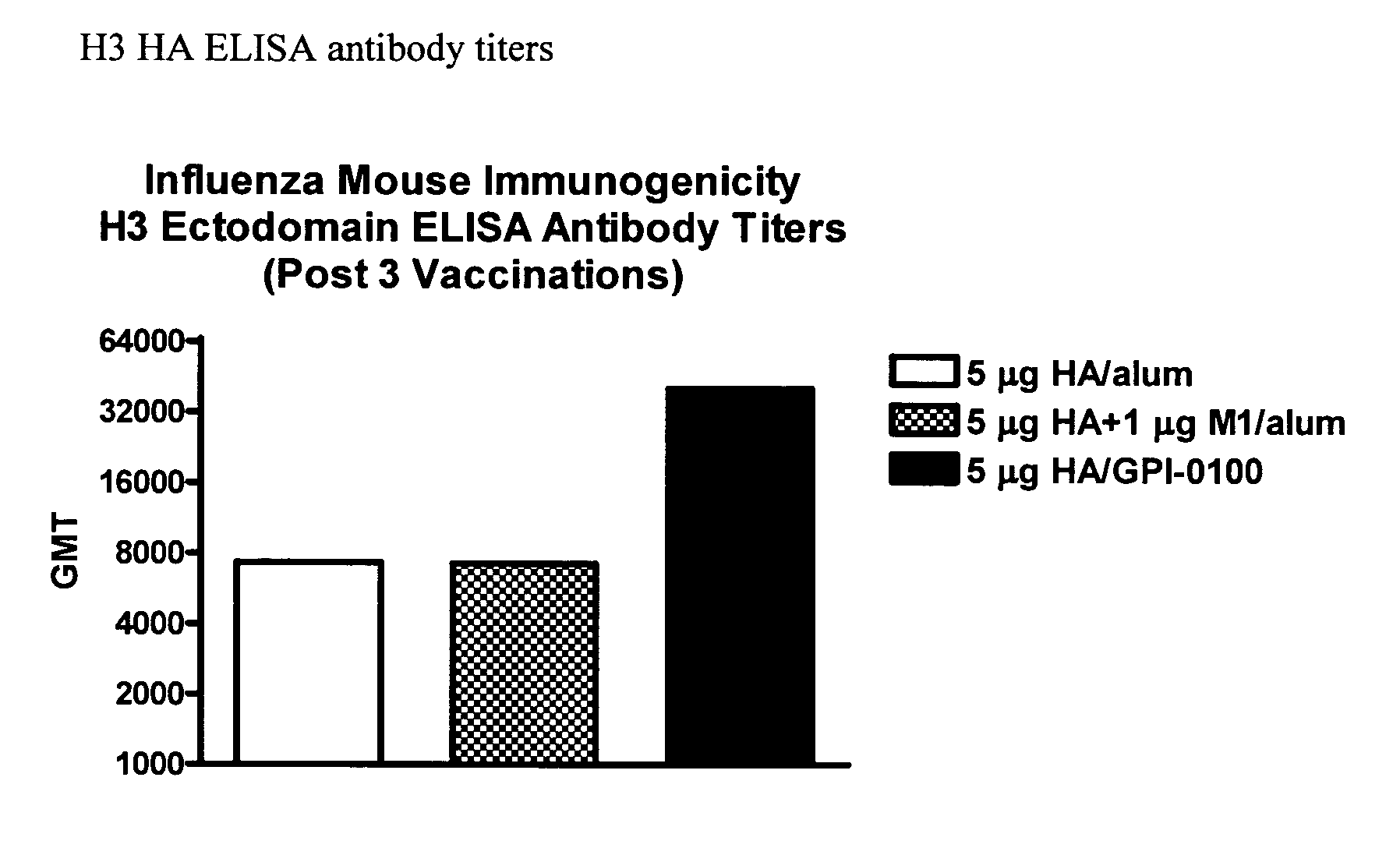
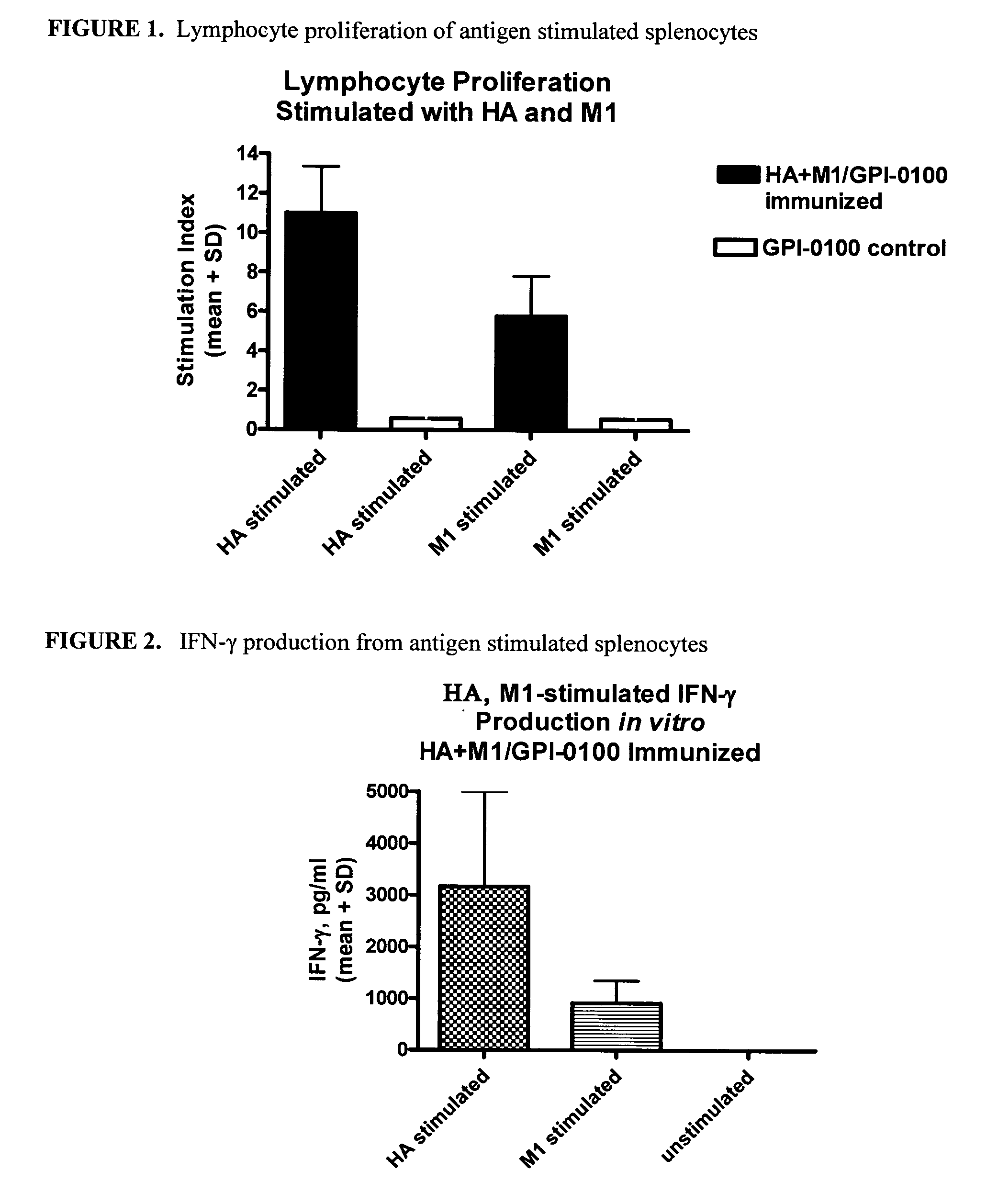
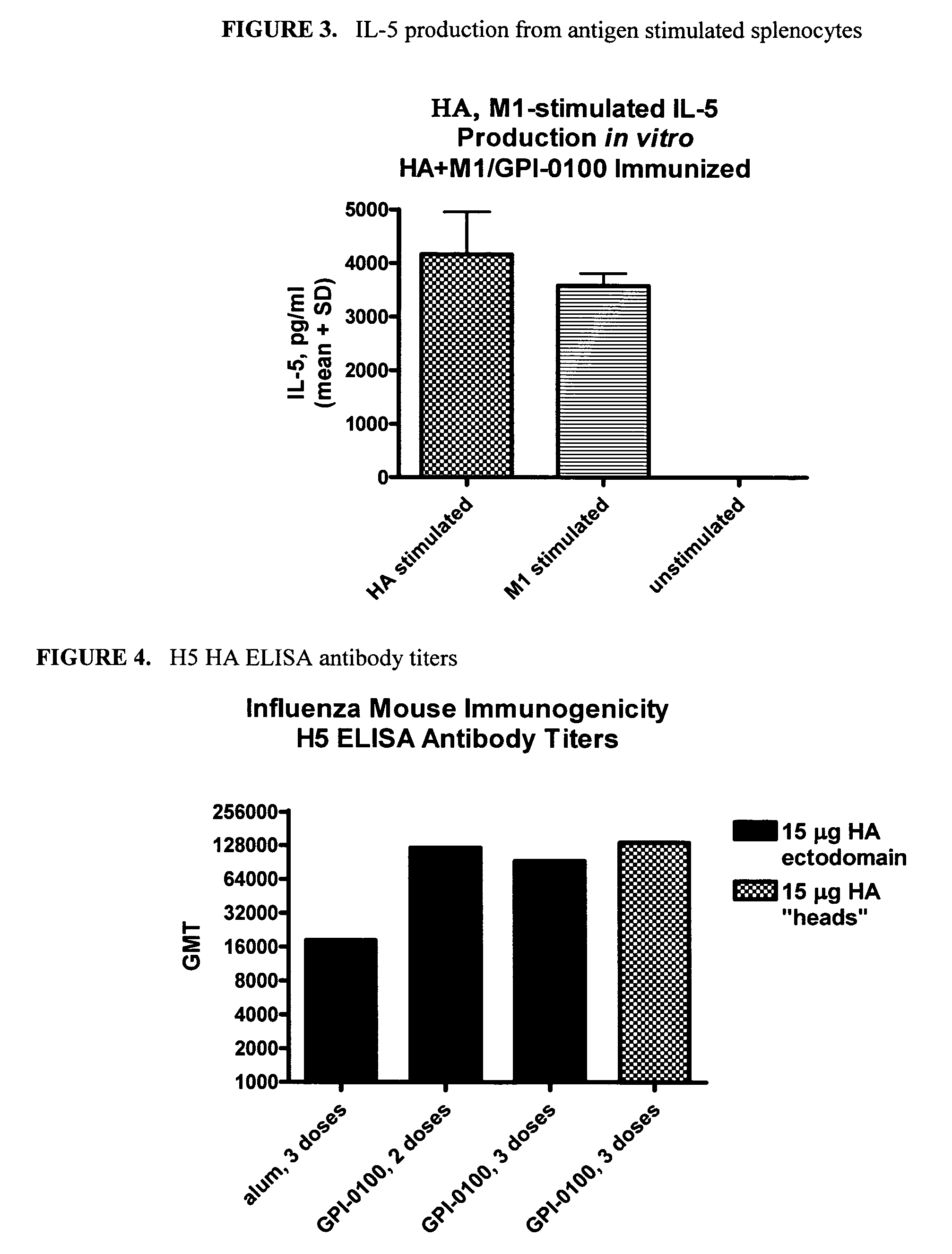
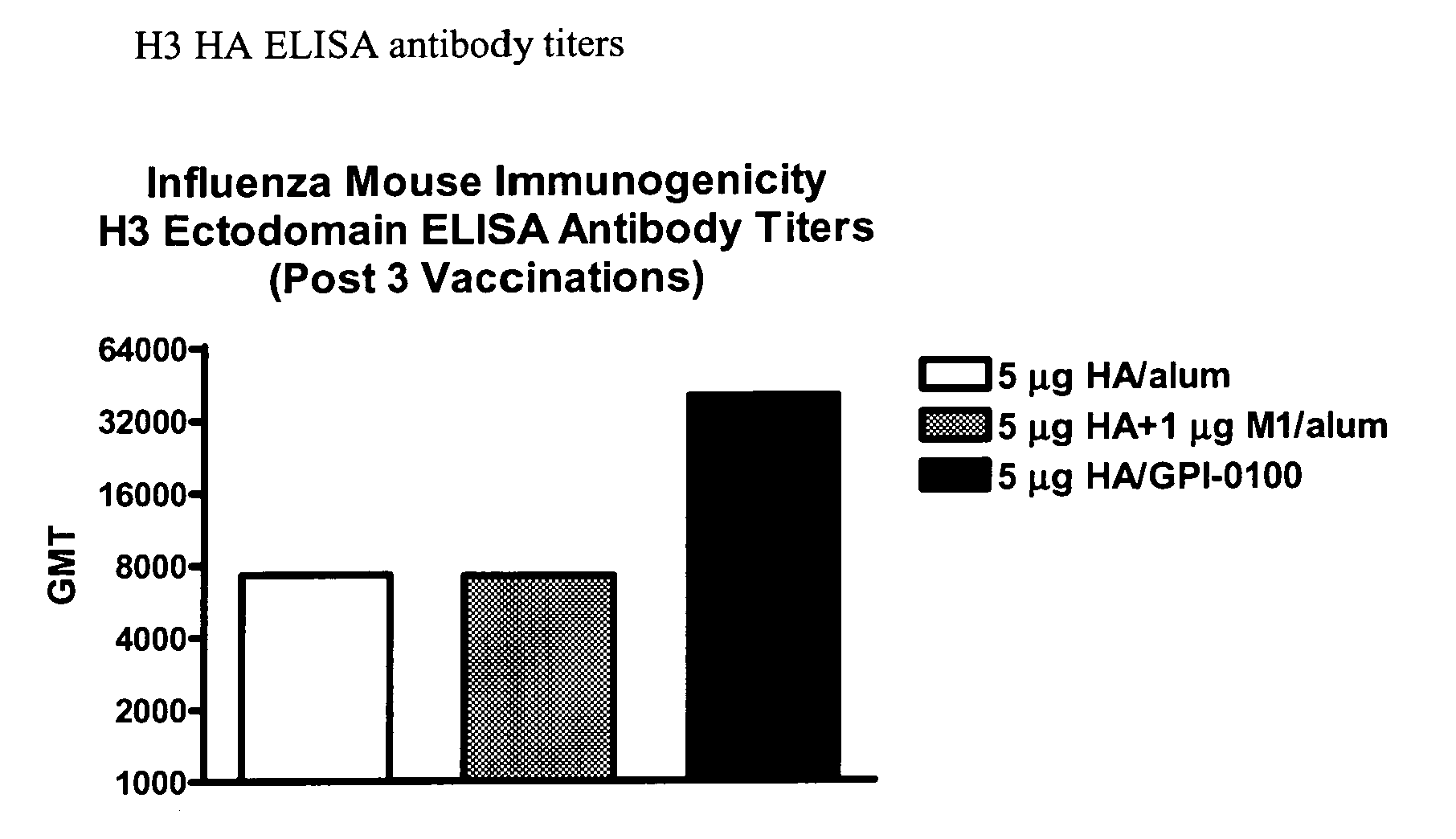
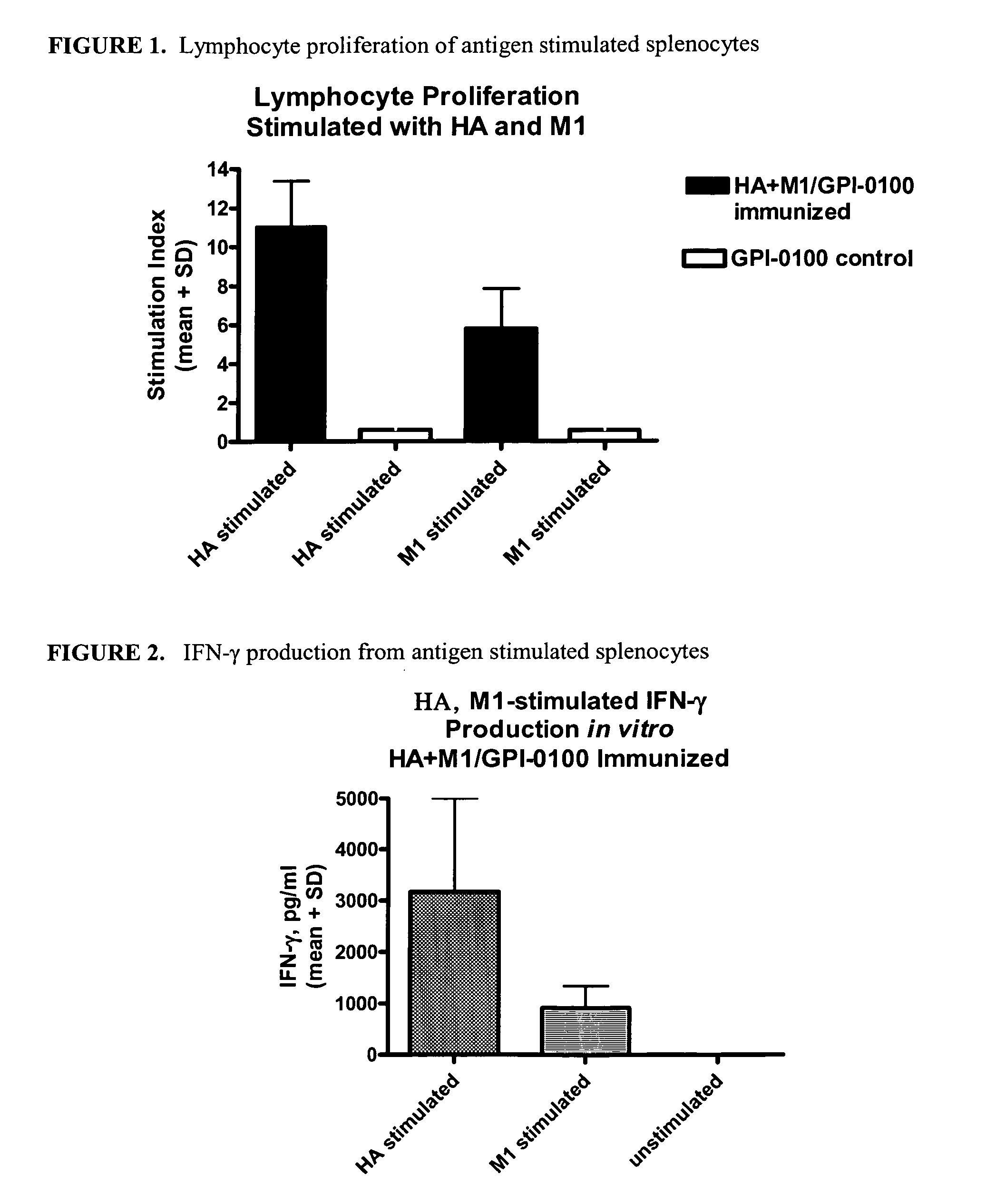
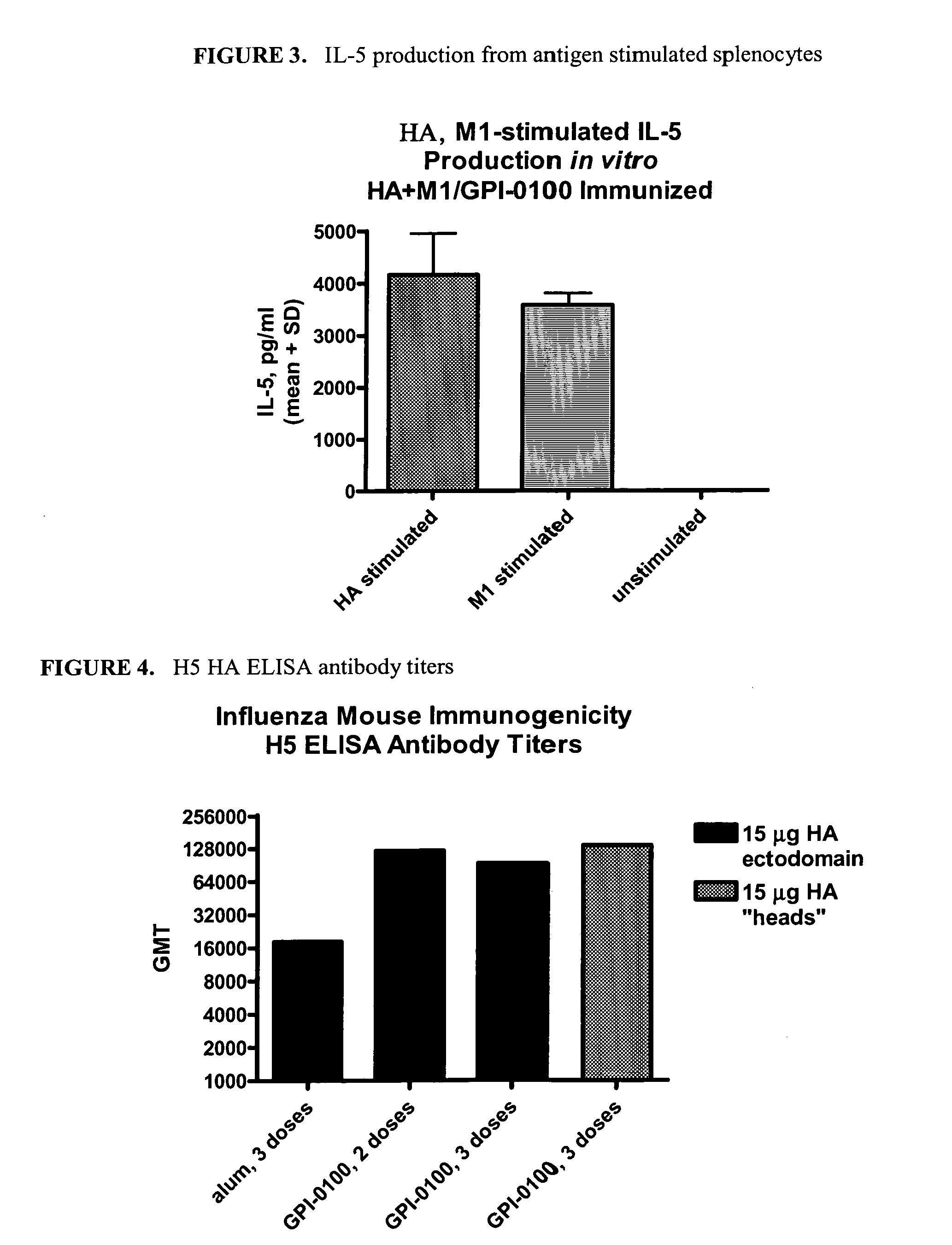
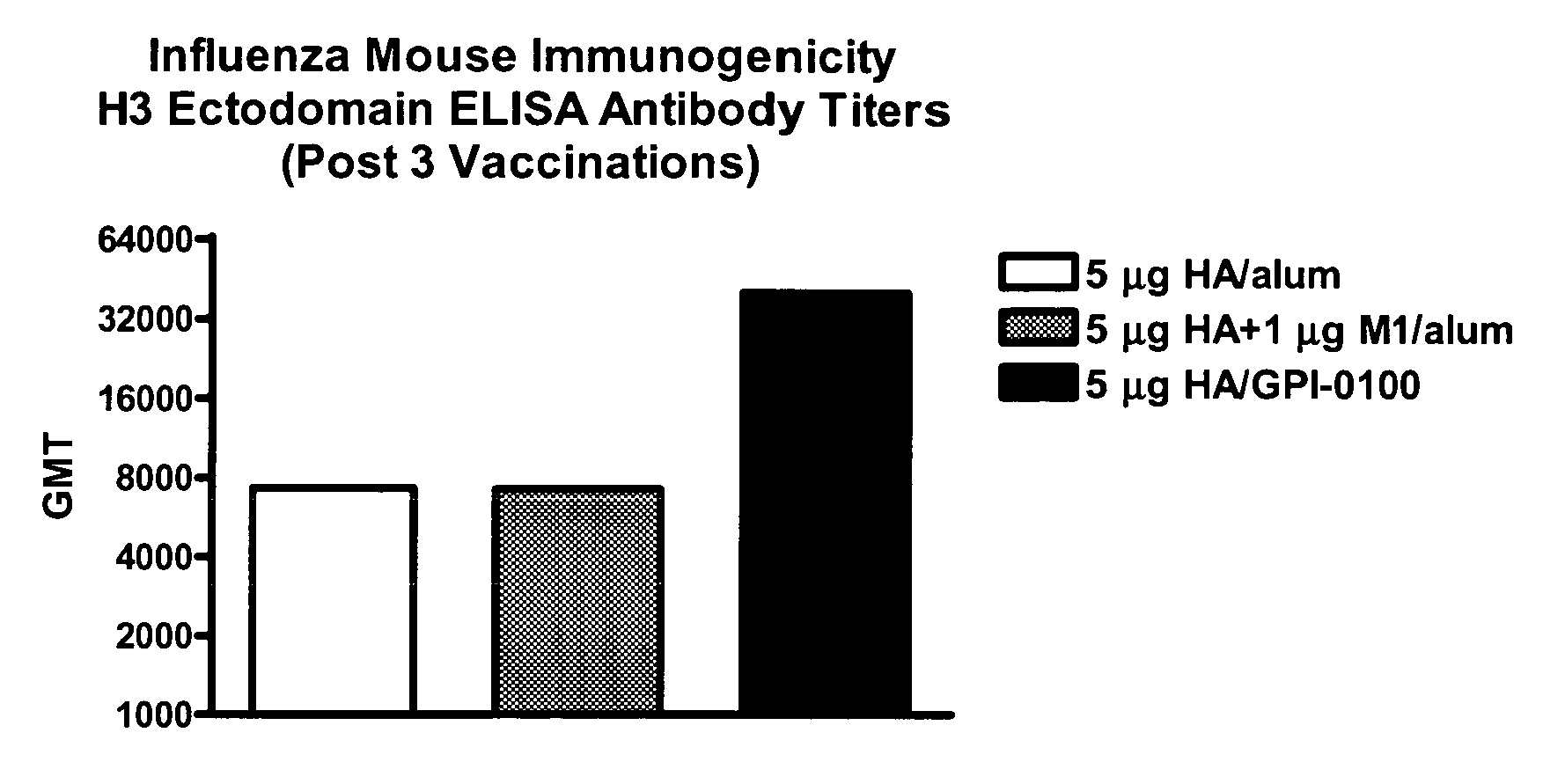
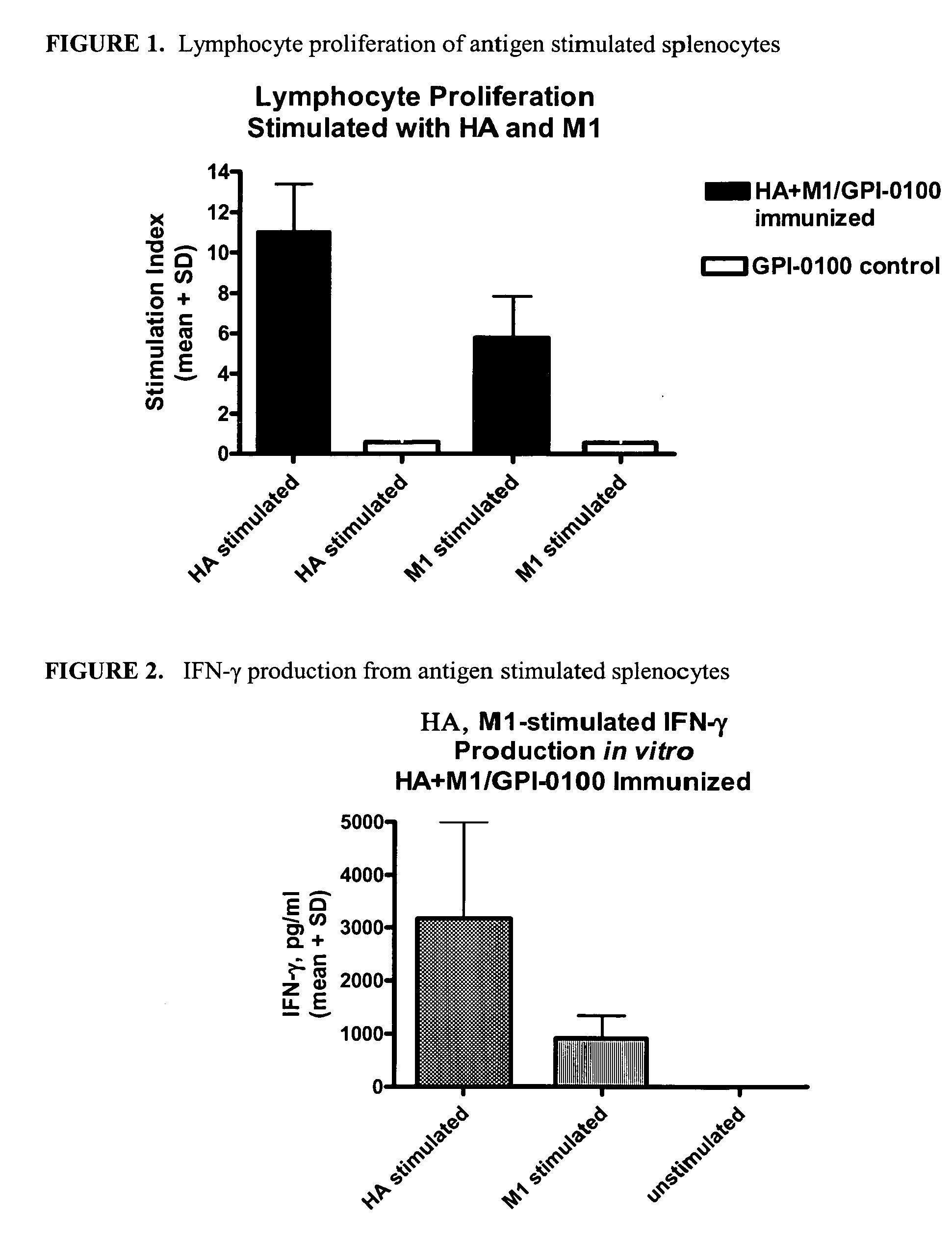
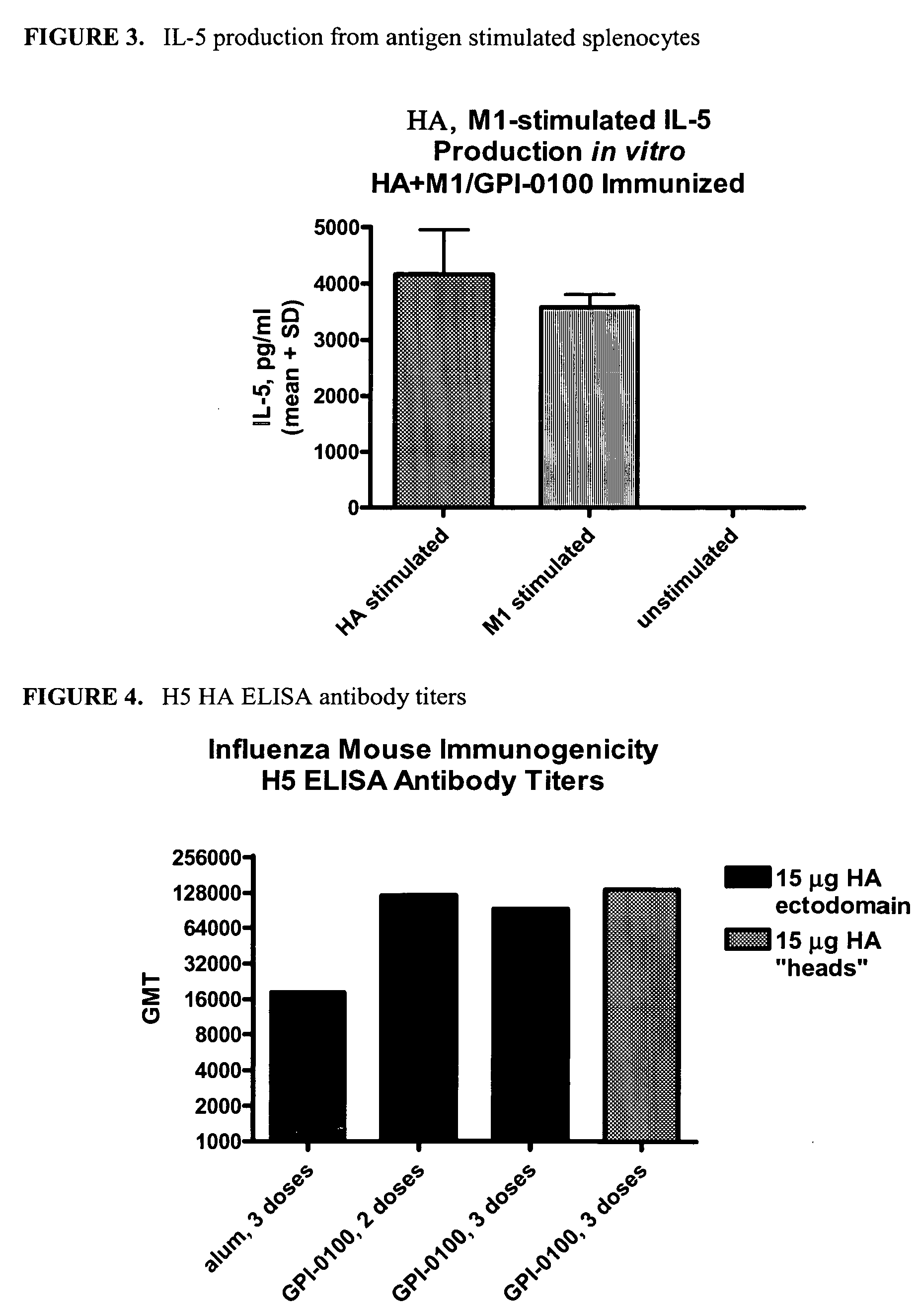
Influenza recombinant subunit vaccine
InactiveUS20070042002A1Improving immunogenicityImprove efficacySsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesAdjuvantEnation
The invention provides influenza proteins, including subunit proteins and immunogenic compositions that can be utilized, with or without adjuvants, as vaccines to protect against influenza infection in animal models and humans. The recombinant proteins are expressed from transformed insect cells that contain integrated copies of the appropriate expression cassettes in their genome. The invention uses a Drosophila melanogaster expression system to provide high yields of recombinant subunit proteins with native-like conformation.
Owner:HAWAII BIOTECH INC
Nucleic acids proteins of a D. melanogaster insulin-like gene and uses thereof
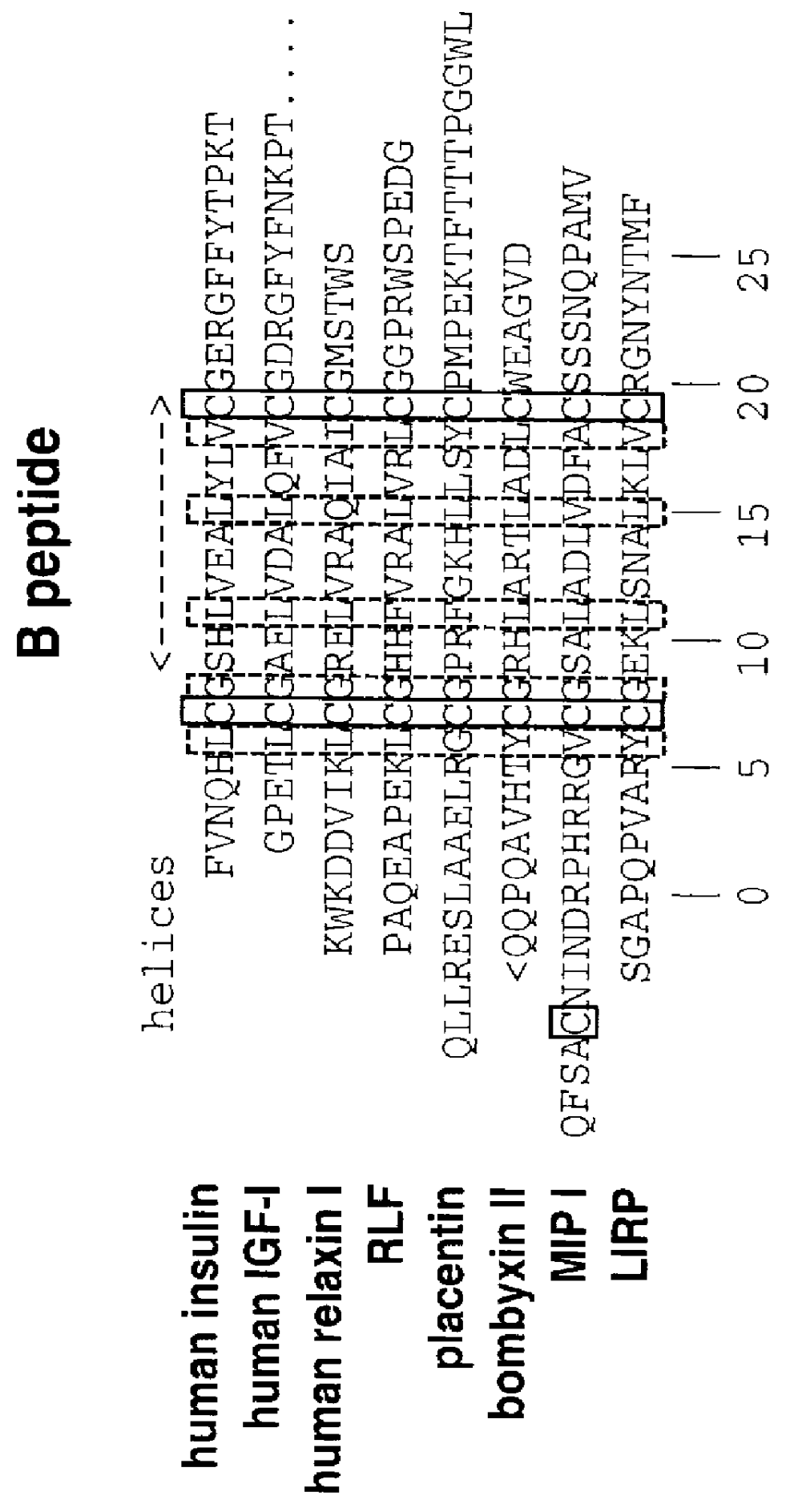
The present invention relates to a D. melanogaster insulin-like gene and methods for identifying insulin-like genes. The methods provide nucleotide sequences of a D. melanogaster insulin-like gene, amino acid sequences of the encoded proteins, and derivatives (e.g., fragments) and analogs thereof. The invention further relates to fragments (and derivatives and analogs thereof) of insulin-like proteins which comprise one or more domains of an insulin-like protein. Antibodies to an insulin-like protein, and derivatives and analogs thereof, are provided. Methods of production of an insulin-like protein (e.g., by recombinant means), and derivatives and analogs thereof, are provided. Further, methods to identify the biological function of a D. melanogaster insulin-like gene are provided, including various methods for the functional modification (e.g., overexpression, underexpression, mutation, knock-out). Still further, methods to identify a D. melanogaster gene which modifies the function of, and / or functions in a signaling pathway with, an insulin-like gene are provided. The invention further provides uses of Drosophila insulin-like nucleic acids and proteins, e.g., as a media additive, and as a pesticide.
Owner:LEPTIN MARIA
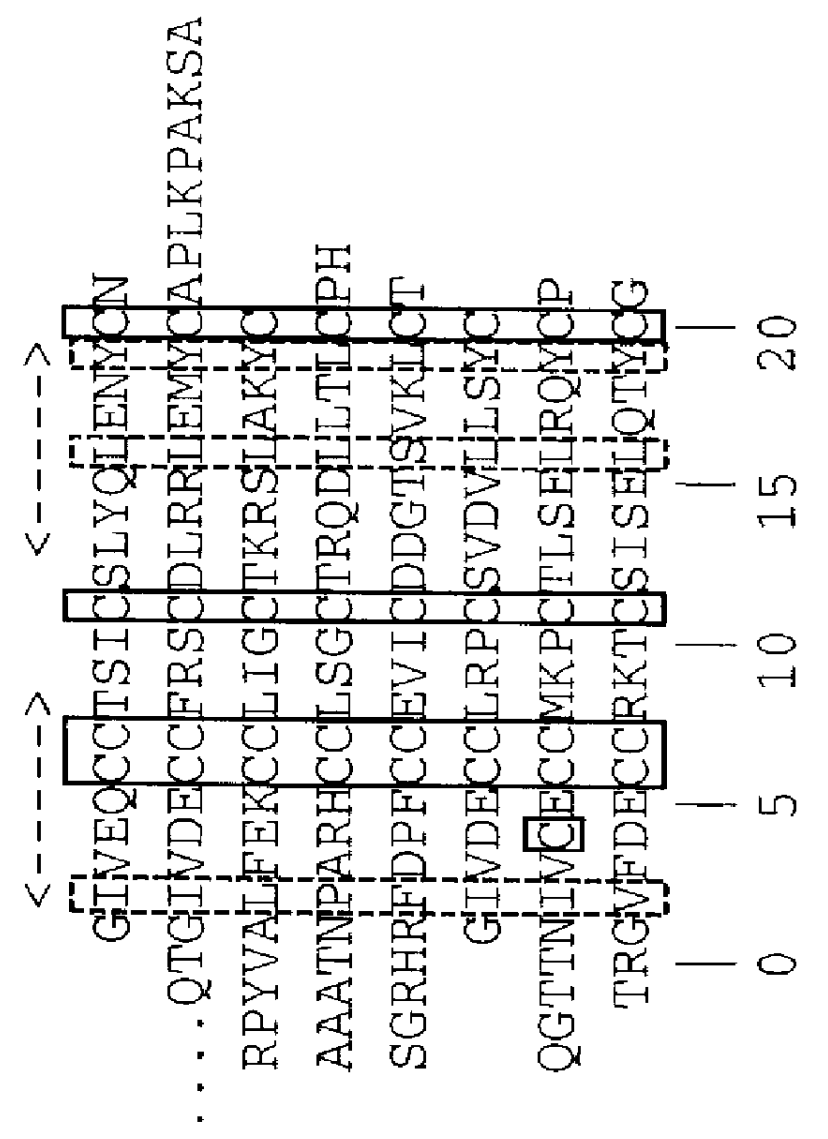
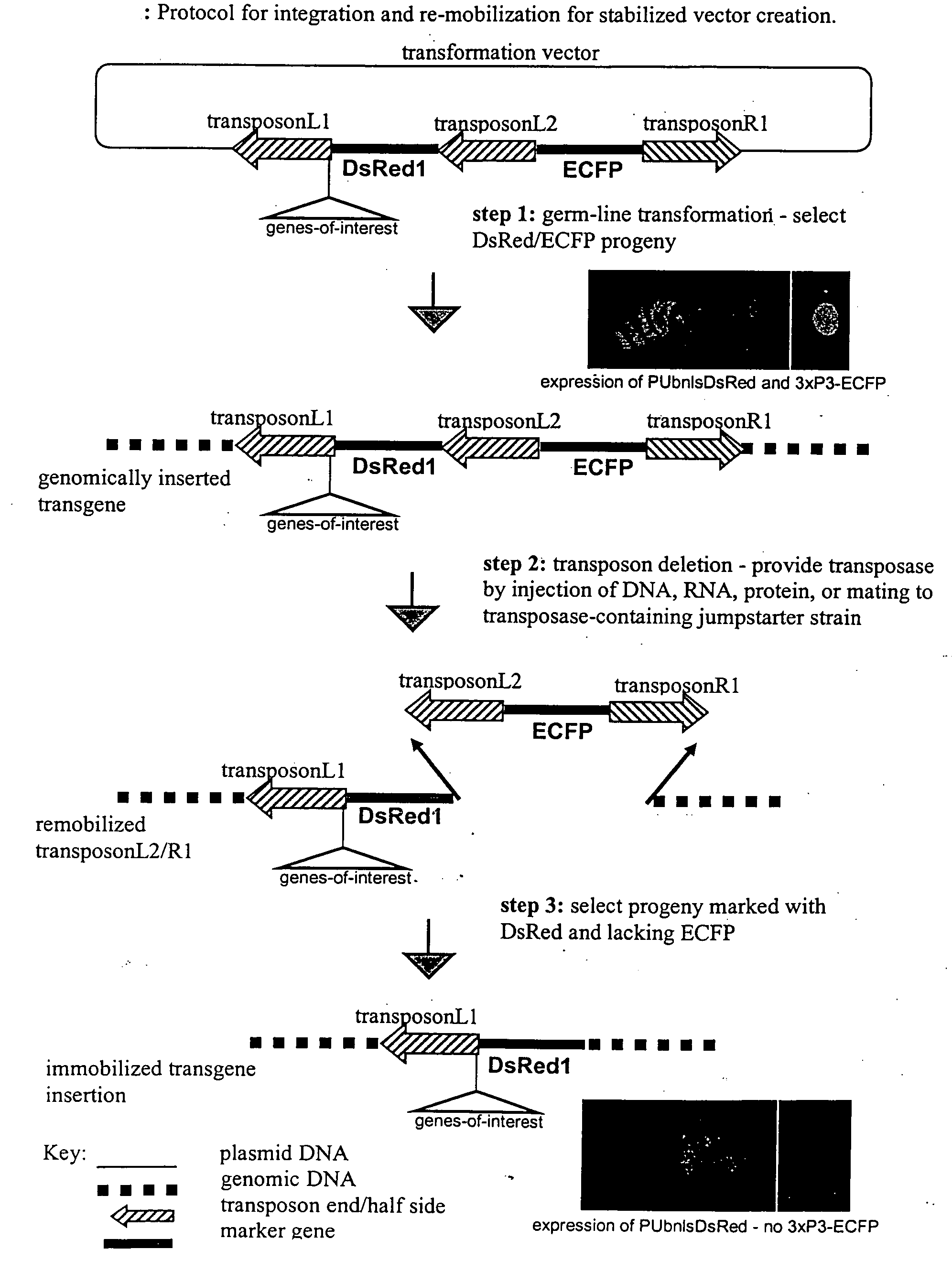
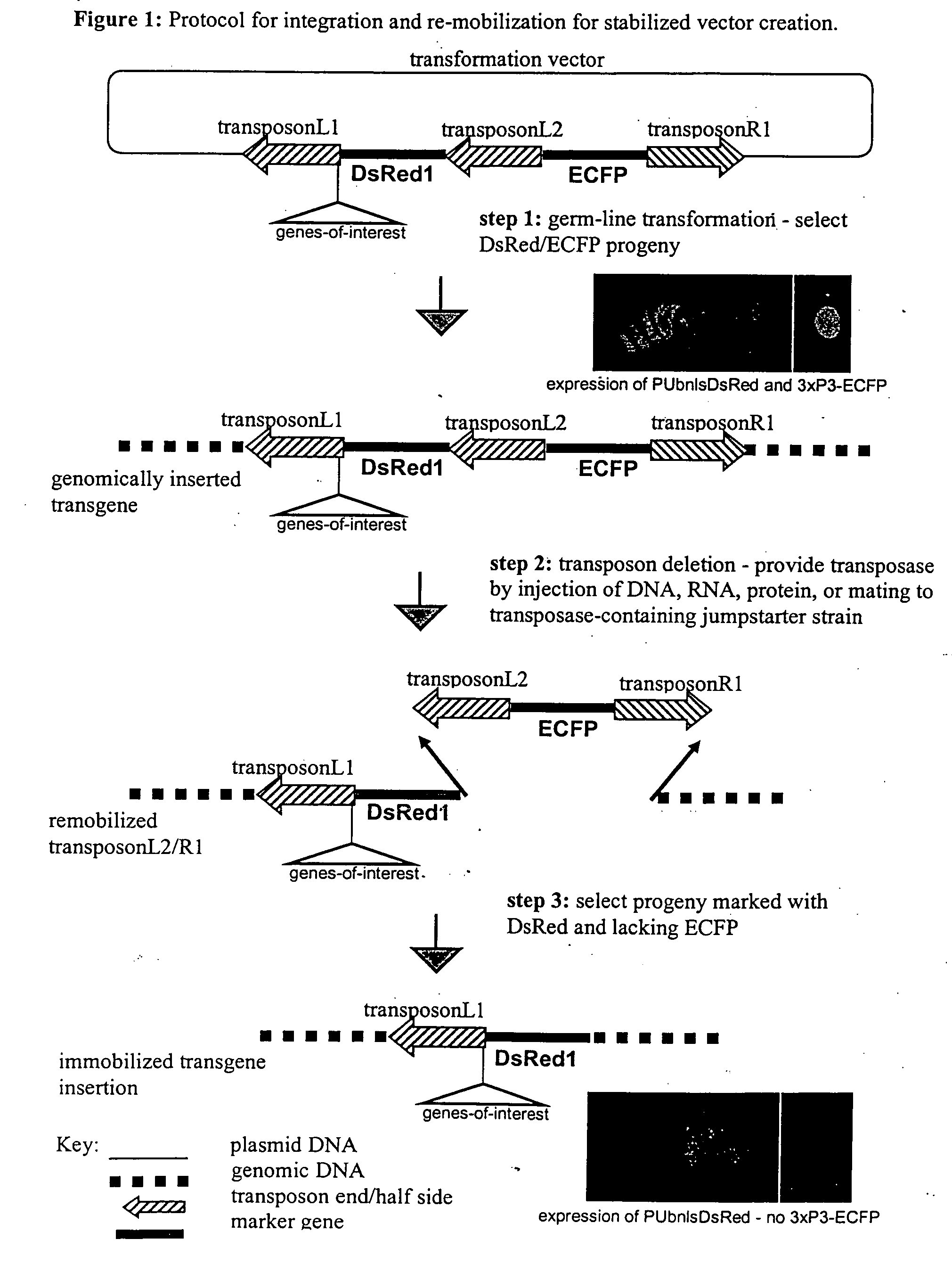
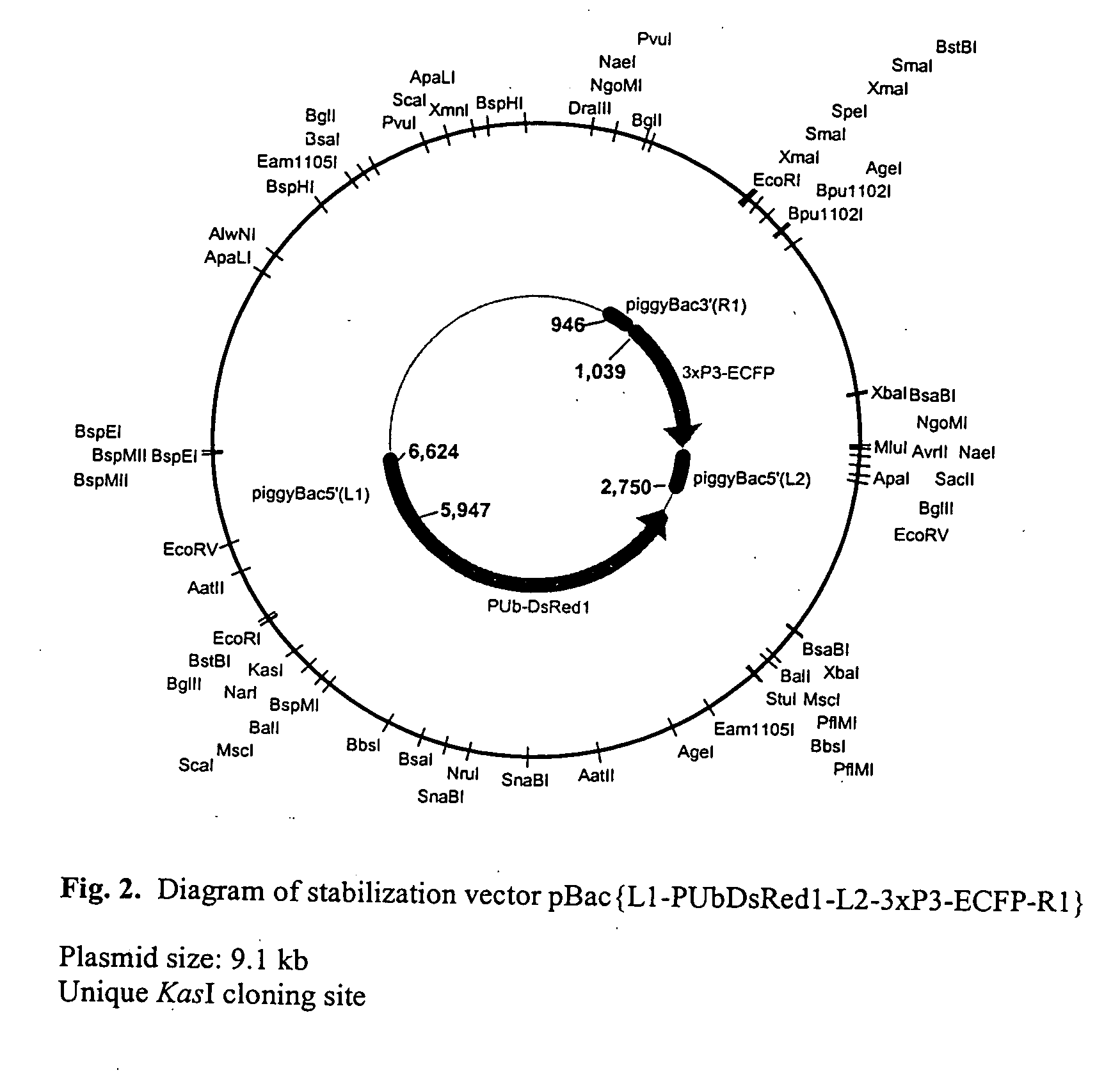
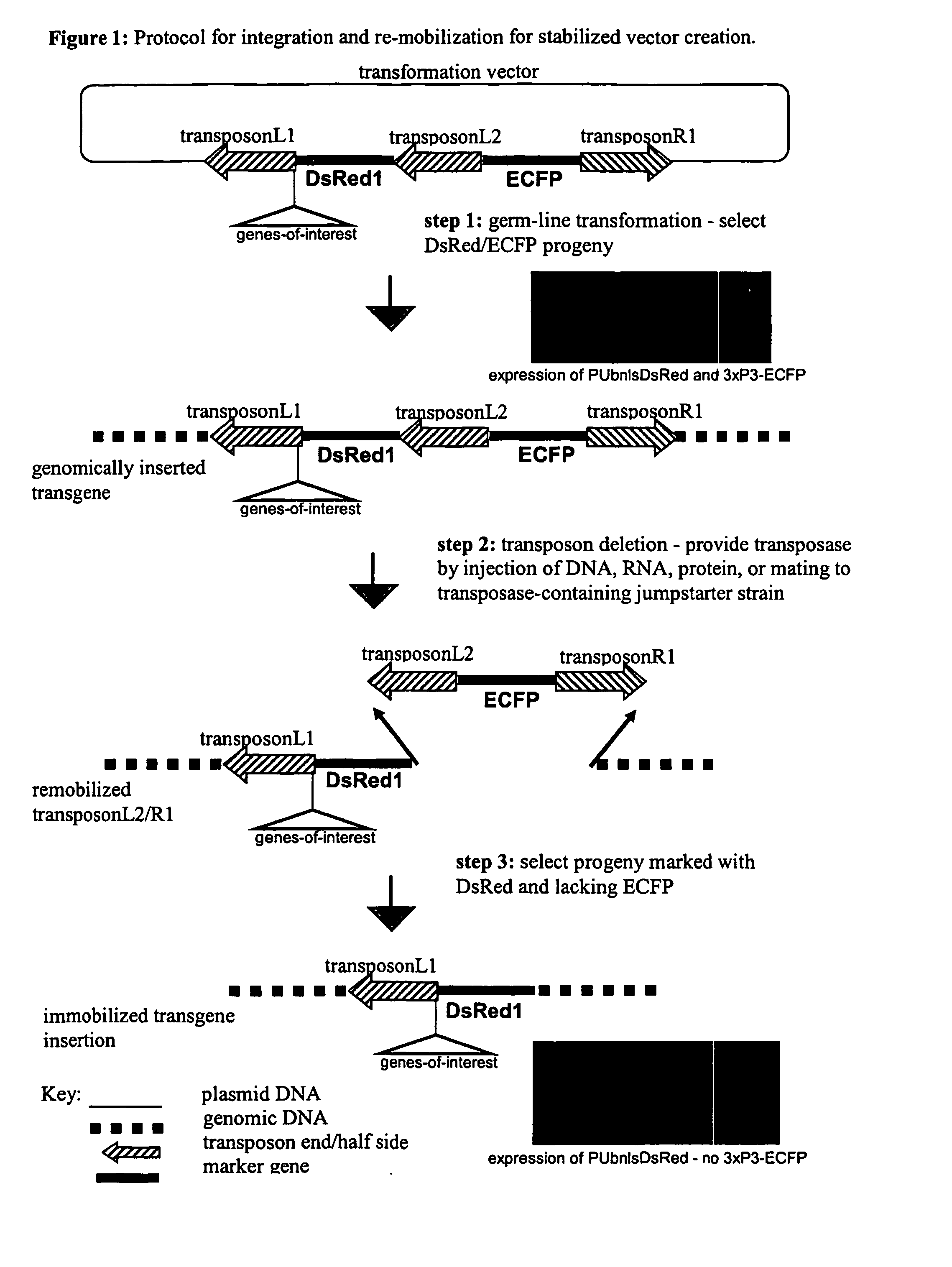
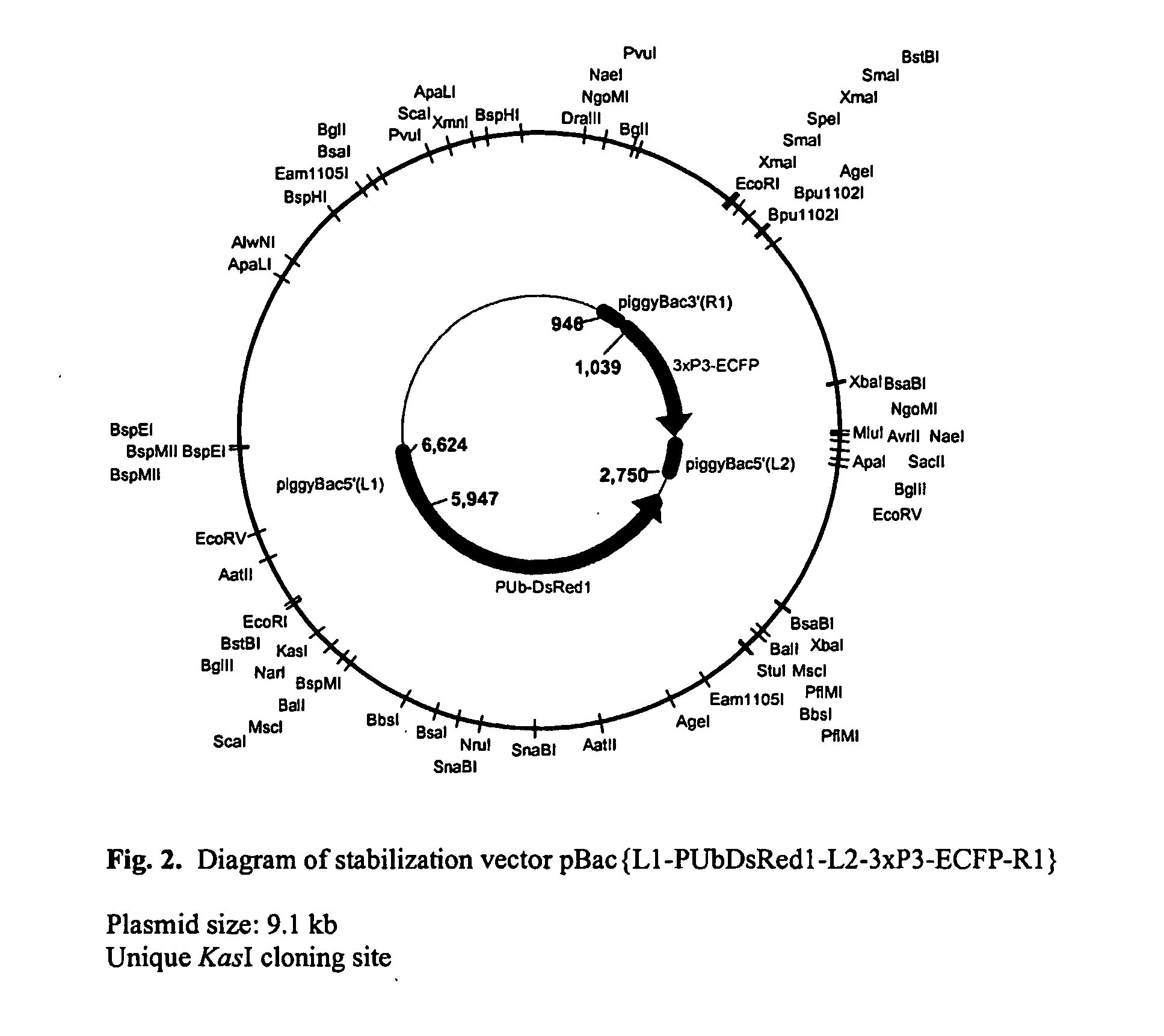
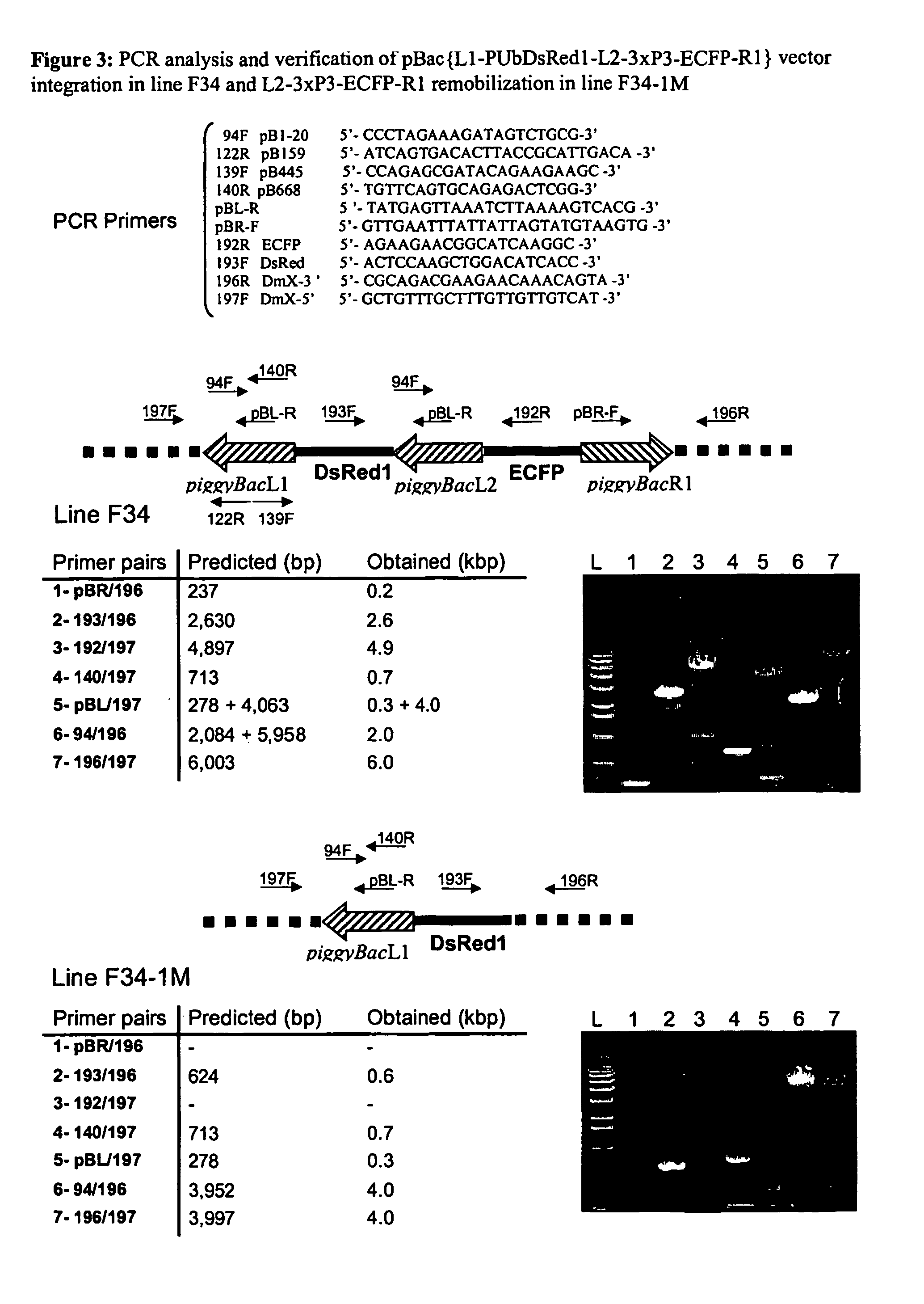
Systems for gene targeting and producing stable genomic transgene insertions
InactiveUS20090083870A1Improve stabilityStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorInstabilityTransgene
The novel germ-line transformation systems disclosed in this patent application allow the physical deletion of transposon DNA following the transformation process, and the targeting of transgene integrations into predefined target sites. In this way, transposase-mediated mobilization of genes-of-interest is excluded mechanistically and random genomic integrations eliminated. In contrast to conventional germ-line transformation technology, our systems provide enhanced stability to the transgene insertion. Furthermore, DNA sequences required for the transgene modification (e.g. transformation marker genes, transposase or recombinase target sites), are largely removed from the genome after the final transgene insertion, thereby eliminating the possibility for instability generated by these processes. The RMCE technology, which is disclosed in this patent application for invertebrate organisms (exemplified in Drosophila melanogaster) represents an extremely versatile tool with application potential far beyond the goal of transgene immobilization. RMCE makes possible the targeted integration of DNA cassettes into a specific genomic loci that are pre-defined by the integration of the RMCE acceptor plasmid. The loci can be characterized prior to a targeting experiment allowing optimal integration sites to be pre-selected for specific applications, and allowing selection of host strains with optimal fitness. In addition, multiple cassette exchange reactions can be performed in a repetitive way where an acceptor cassette can be repetitively exchanged by multiple donor cassettes. In this way several different transgenes can be placed precisely at the same genomic locus, allowing, for the first time, the ability to eliminate genomic positional effects and to comparatively study the biological effects of different transgenes.
Owner:HORN CARSTEN +1
Influenza recombinant subunit vaccine
InactiveUS20080008725A1Avoids potential degradationAvoiding lysis of the host cellsSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAdjuvantEnation
The invention provides influenza proteins, including subunit proteins and immunogenic compositions that can be utilized, with or without adjuvants, as vaccines to protect against influenza infection in animal models and humans. The recombinant proteins are expressed from transformed insect cells that contain integrated copies of the appropriate expression cassettes in their genome. The invention uses a Drosophila melanogaster expression system to provide high yields of recombinant subunit proteins with native-like conformation.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Influenza recombinant subunit vaccine
InactiveUS20070042001A1Avoids potential degradationAvoiding lysis of the host cellsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesAdjuvantEnation
The invention provides influenza proteins, including subunit proteins and immunogenic compositions that can be utilized, with or without adjuvants, as vaccines to protect against influenza infection in animal models and humans. The recombinant proteins are expressed from transformed insect cells that contain integrated copies of the appropriate expression cassettes in their genome. The invention uses a Drosophila melanogaster expression system to provide high yields of recombinant subunit proteins with native-like conformation.
Owner:HAWAII BIOTECH INC
A bayberry orchard Drosophila elanogaster artificial breeding method, and method for breeding parasitic wasp with the same
InactiveCN102578052ARealize continuous feedingAchieve biological controlAnimal husbandryDrosophila dunniParasitoid wasp
The invention discloses a bayberry orchard Drosophila elanogaster artificial breeding method, and a method for breeding parasitic wasp with the same, belonging to artificial breeding technology of natural enemy insects. The method successively propagates Pachycrepoideus vindemmiae capable of controlling bayberry orchard Drosophila elanogaster through the steps of Drosophila elanogaster breeding to obtain pupae, egg laying of Pachycrepoideus vindemmiae on the pupae, development and eclosion of parasitic wasp, and adult wasp breeding. The method is simple and convenient, and is especially suitable for large-scale indoor breeding of Pachycrepoideus vindemmiae to give large amount of wasps for test or release in bayberry orchard. Non-professional breeding personnel can grasp operation skill in short time. The breeding method has low land occupation and cost.
Owner:TECH EXTENSION CENT FOR FORESTRY & SPECIALTY FOREST PROD
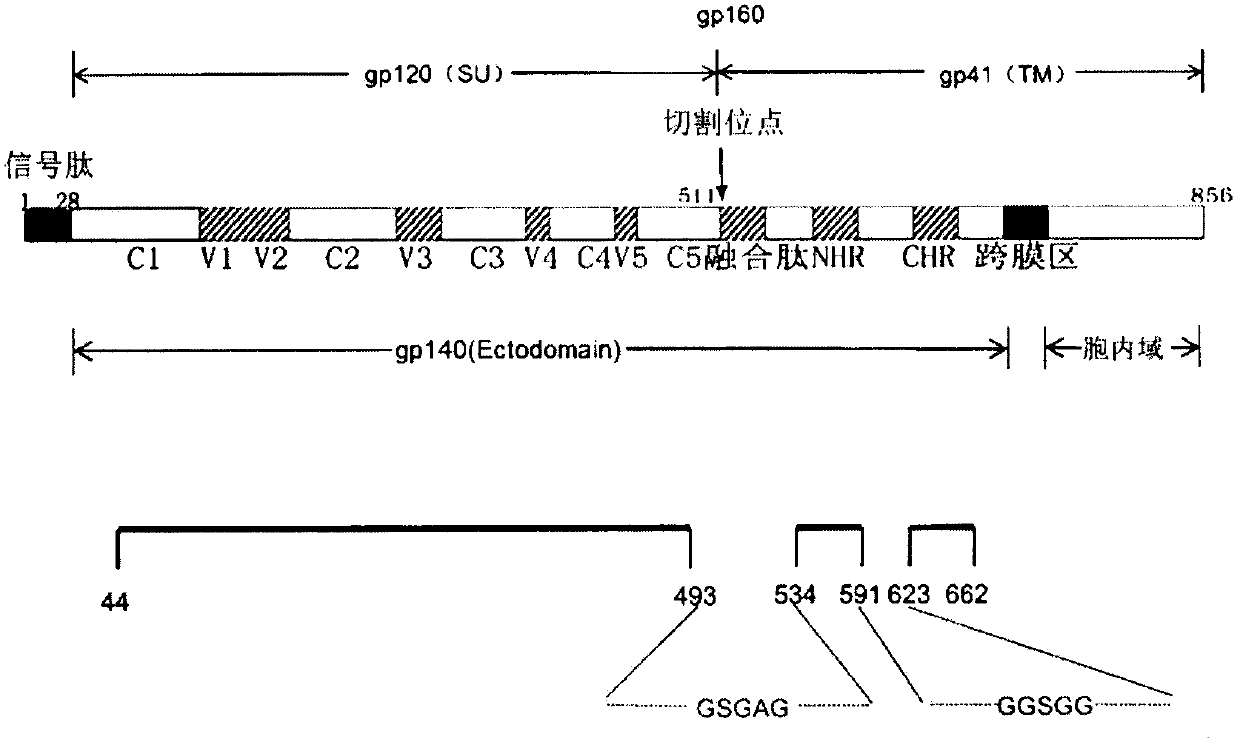
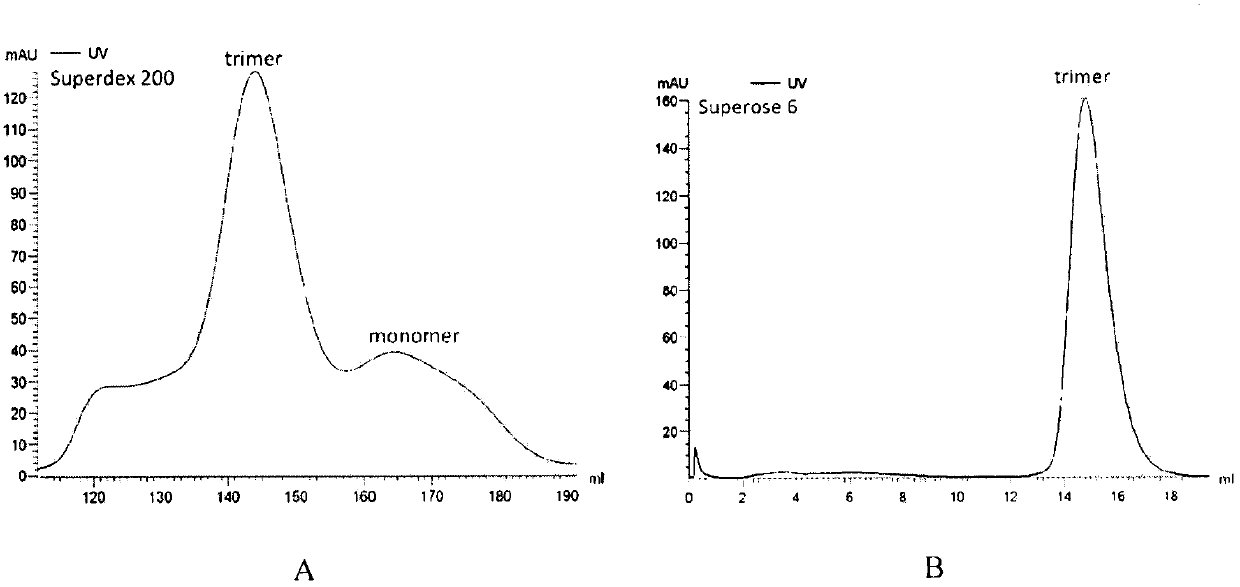
Potential preparation method for highly-efficient recombinant HIV-1 CRF07-BC gp140 immunogen
InactiveCN103992396AImprove uniformityHigh antigen reactivityVirus peptidesDepsipeptidesAntigenEndotoxin removal
The invention discloses a potential preparation method for a highly-efficient recombinant HIV-1 CRF07-BC gp140 immunogen. The immunogen is designed based on the structure of HIV-1 envelope protein crystals which have been published internationally and obtained in our lab. The specific method uses an overlap extension PCR technology to obtain gp140 gene segments, and comprises the steps that target genes are cloned into an eukaryotic expression vector pMT, endotoxin is removed through extraction of a large amount of plasmids, the gp140 gene segments and resistance screening plasmids pCoBlast are co-transfected into drosophila melanogaster Schneider2 (S2) cells together, blasticidin (Blasticidin S) is used for positive clone screening, S2 cell lines for stably and efficiently secreting and expressing gp140 are screened, and after enlarged cultivation and through two steps of purification of nickel column affinity chromatography and gel filtration chromatography, the gp140 with high purity can be obtained. A series of biochemical and biophysical technologies indicate that the gp140 is uniform in polymeric states, and high in antigenic reactivity, and is quite fittingly used as the immunogen for the research and the development of AIDS subunit vaccines or multivalent combined vaccines.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Cell therapy method for the treatment of tumors
T cell responses are often diminished in humans with a compromised immune system. We have developed a method to isolate, stimulate and expand naïve cytotoxic T lymphocyte precursors (CTLp) to antigen-specific effectors, capable of lysing tumor cells in vivo. This ex vivo protocol produces fully functional effectors. Artificial antigen presenting cells (AAPCs; Drosophila melanogaster) transfected with human HLA class I and defined accessory molecules, are used to stimulate CD8+ T cells from both normal donors and cancer patients. The class I molecules expressed to a high density on the surface of the Drosophila cells are empty, allowing for efficient loading of multiple peptides that results in the generation of polyclonal responses recognizing tumor cells endogenously expressing the specific peptides. The responses generated are robust, antigen-specific and reproducible if the peptide epitope is a defined immunogen. This artificial antigen expression system can be adapted to treat most cancers in a significant majority of the population.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA INC
Compound for trapping and killing drosophila melanogaster
The invention provides a compound for trapping and killing drosophila melanogaster. The compound is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials according to ratio: 40-60wt% of Chinese herbal medicine asarum powder, 1-3wt% of brown sugar, 5-10wt% of millet wine, 5-10wt% of rice vinegar and 20-40wt% of water. The compound does not pollute the environment, has no toxic and side effect to human, livestock and fertilization insects, the pesticide effect is long and can be kept for about three months, the cost is low and the compound is cheap.
Owner:范宇
System for gene targeting and producing stable genomic transgene insertions
InactiveUS20060218652A1Improve stabilityEnhance cassette exchange efficiencyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesInstabilityEukaryotic plasmids
The novel germ-line transformation systems disclosed in this patent application allow the physical deletion of transposon DNA following the transformation process, and the targeting of transgene integrations into predefined target sites. In this way, transposasemediated mobilization of genes-of-interest are excluded mechanistically and random genomic integrations eliminated. In contrast to conventional germ-line transformation technology, our systems provide enhanced stability to the transgene insertion. Furthermore, DNA sequences required for the transgene modification (e.g. transformation marker genes, transposase or recombinase target sites), are largely removed from the genome after the final transgene insertion, thereby eliminating the possibility for instability generated by these processes. The RMCE technology, which is disclosed in this patent application for invertebrate organisms (exemplified in Drosophila melanogaster) represents an extremely versatile tool with application potential far beyond the goal of transgene immobilization. RMCE makes possible the targeted integration of DNA cassettes into a specific genomic loci that are pre-defined by the integration of the RMCE acceptor plasmid. The loci can be characterized prior to a targeting experiment allowing optimal integration sites to be pre-selected for specific applications, and allowing selection of host strains with optimal fitness. In addition, multiple cassette exchange reactions can be performed in a repetitive way where an acceptor cassette can be repetitively exchanged by multiple donor cassettes. In this way several different transgenes can be placed precisely at the same genomic locus, allowing, for the first time, the ability to eliminate genomic positional effects and to comparatively study the biological effects of different transgenes.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
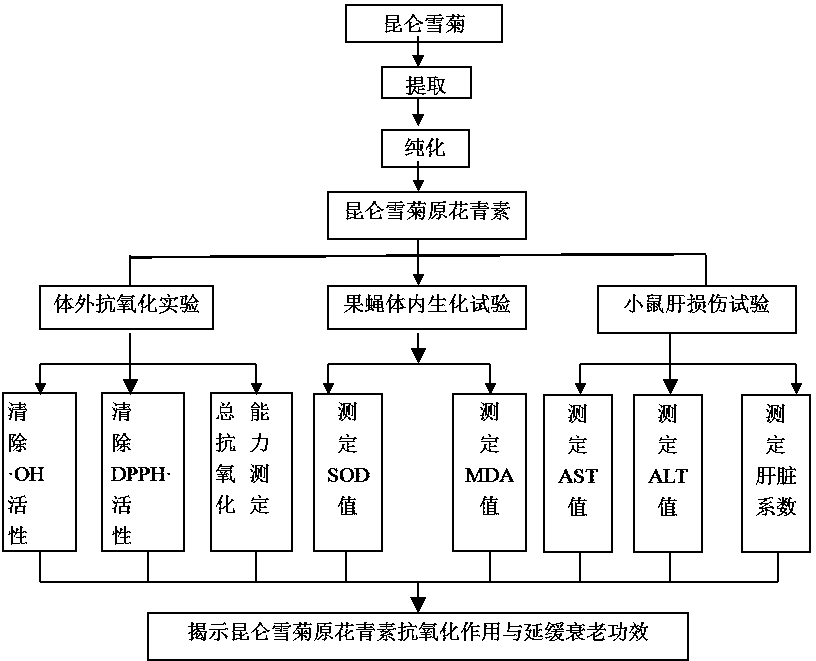
Method for extracting coreopsis tinctoria procyanidins and application of coreopsis tinctoria procyanidins in delaying senescence
InactiveCN104173401AExploring the protective effectHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDrosophila ornatifronsCoreopsis
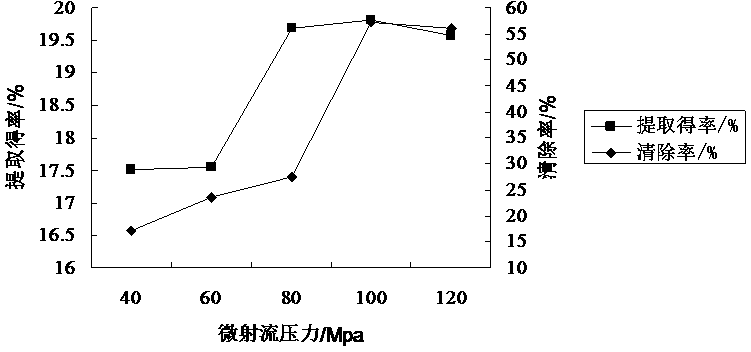
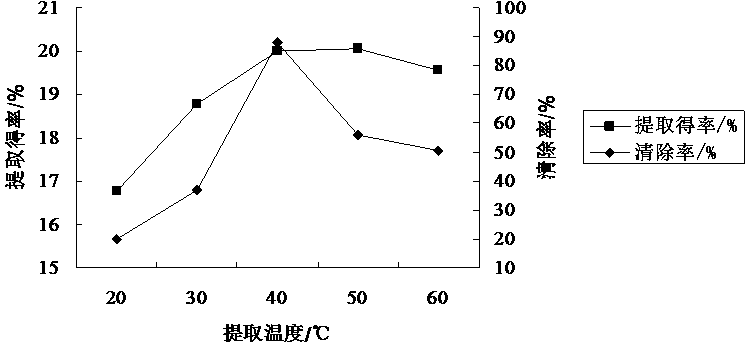
The invention discloses a method for extracting coreopsis tinctoria procyanidins and an application of the coreopsis tinctoria procyanidins in delaying senescence. The method comprises the following steps: extracting coreopsis tinctoria procyanidins from the raw material coreopsis tinctoria which grows 2600m over the sea level by adopting a dynamic high-pressure microfluidization assisted extraction technology for 30 minutes with 70% ethanol at the extracting pressure of 120MPa and the extracting temperature of 50 DEG C, and treating the coreopsis tinctoria twice by means of microjet pressure. The total antioxidation activity of the prepared procyanidins is higher than that of ascorbic acid, and has an effect of delaying senescence of drosophila melanogaster by combining results of drosophila melanogaster surviving experiments and in-vivo biochemical index detection; liver injury experiments in mice indicate that the procyanidins extracted from coreopsis tinctoria is capable of reducing the activities of ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase) in serum and playing a certain role in protecting CC14 caused liver injury in mice. According to the application, the procyanidins extracted from coreopsis tinctoria have an excellent effect of delaying senescence, and has a wide practical value.
Owner:新疆泸疆生物科技有限公司
Card for fast testing residual pesticide
InactiveCN101693916ASensitive detectionImprove anti-interference abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAcetylcholine esteraseBio engineering
A card for fast testing residual pesticide belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and comprises two layers of plastic plates, wherein one of the plastic plates is provided with a sampling hole and an observation hole, one face of the plastic plate is provided with water-absorbing paper and an enzyme bar for fixing drosophila melanogaster acetylcholine esterase, the water-absorbing paper opposites the sampling hole, the enzyme bar opposites the observation hole, and the water-absorbing paper is connected with the enzyme bar. A base sheet for fixing indoxyl acetic ester is bonded on the other plastic plate at the position corresponding to the enzyme bar, and a baffle is arranged between the base sheet and the enzyme bar. When the sample and the indoxyl acetic ester in the enzyme bar pre-react, the baffle is drawn out to make the enzyme bar and the base sheet contact. The card for fast testing residual pesticide has the advantages of wide application range, delicate testing and fast and simple operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
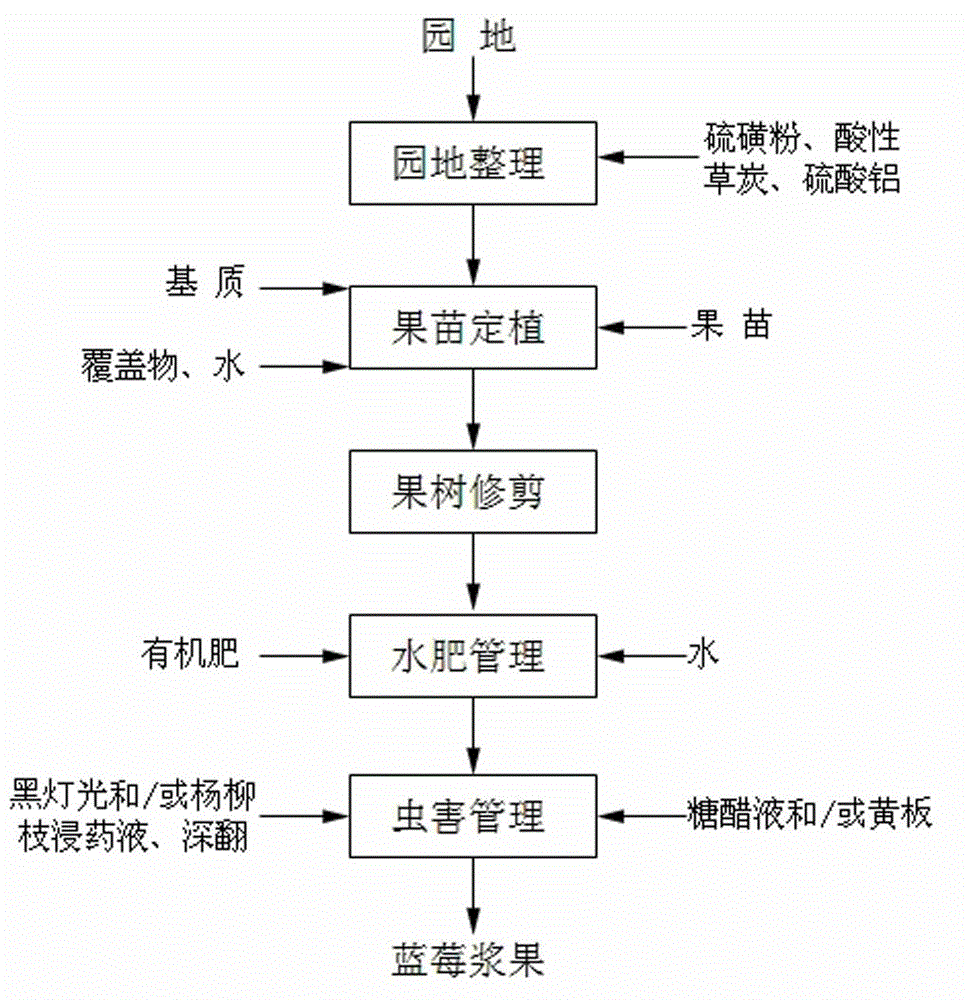
Method for cultivating organic blueberries in low-latitude and high-altitude areas
ActiveCN104855208AGuaranteed survival rateThe purpose of guaranteeing organic cultivationCultivating equipmentsMulchTillage
The invention discloses a method for cultivating organic blueberries in low-latitude and high-altitude areas. The method comprises the steps as follows: selecting fields with the slope gradient not higher than 10 degrees, the soil PH value being 4.0-6.0 and the organic matter content being not lower than 5%, and carrying out field soil preparation with the deep tillage depth being 20-25 cm in the year before field planting; selecting blueberry seedlings to perform field planting in winter or in rainy seasons of the next year, then covering a moist soil surface with a mulching material and performing filed planting on seedlings which are sufficiently watered; performing fruit tree pruning twice including pruning after fruit picking, and pruning and disbranching in winter; adopting drop irrigation or irrigation to maintain the maximum water-holding capacity of the soil to be 60-70%, and applying organic fertilizer in twice every year, wherein applying organic fertilizer after blueberry harvest and before spring-growth on the moist soil surface, and applying fertilizer heavily while ditching to realize water and fertilizer management; trapping the adults and larva of scarabs by adopting light and / or trapping and killing by using willow leaves impregnated with pesticide and performing deep ploughing to enable the larva of scarabs to be exposed to the sun; trapping and killing drosophila melanogasters with sweet lure or yellow sticky boards. The method for cultivating organic blueberries in low-latitude and high-altitude areas has the characteristics that the management is simple and convenient, damage caused by diseases is less, good harvest and high quality of the blueberries are achieved, and the blueberries obtained by adopting the method are purely natural and pollution-free.
Owner:禹城市盛之源农业科技有限公司
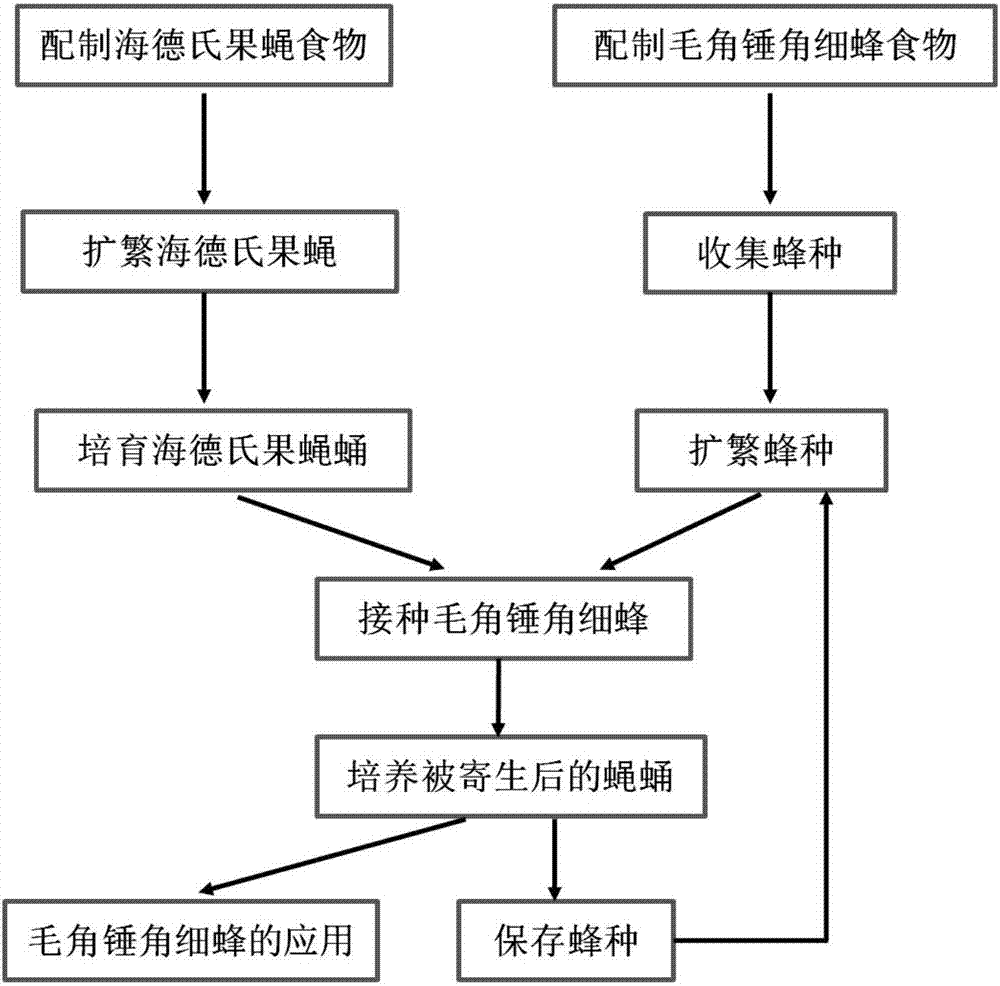
Pupal parasitized wasp artificial breeding production method capable of enhancing drosophila biological control effects
ActiveCN107439491AImprove rationalityEfficient use ofAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsDrosophila hydeiOrganism
The invention relates to the field of agricultural pest biological control and aims at providing a pupal parasitized wasp artificial breeding production method capable of enhancing drosophila biological control effects. The method comprises collecting drosophila melanogaster pupas with parasitized trichopria drosophilae perkins, performing eclosion for continuous three generations for parasitizing drosophila hydei pupas, and collecting wasp species; inoculating and breeding drosophila hydei, parasitizing and breeding the drosophila hydei pupas with queen parasite wasps, and collecting hatched parasite wasps for storage and reservation. The pupal parasitized wasp artificial breeding production method capable of enhancing the drosophila biological control effects controls the parasite time of the trichopria drosophilae perkins during production and inoculation processes, avoids low parasitic rate caused by over-short parasite time or low yield rate caused by excessive parasitism, facilitates reasonable inoculation and utilization of the parasite wasps through cultivation of the trichopria drosophilae perkins, is applicable to large-scale continuous production, optimizes dominant host selection and wasp breeding technology, achieves high-quality, efficient and large-scale propagation of the trichopria drosophilae perkins and lays a good foundation for propagation and utilization of the trichopria drosophilae perkins.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
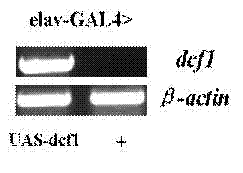
Construction method of human dcf1 gene transgenic drosophila melanogaster model
InactiveCN102766635AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDrosophila ornatifronsNeuro-degenerative disease
The present invention relates to a construction method of a human dcf1 gene transgenic drosophila melanogaster model. According to the invention, a drosophila melanogaster transgenic vector pUAST-dcf1 is constructed; a human dcf1 transgenic UAS drosophila melanogaster strain is obtained through microinjection; and human dcf1 transgenic drosophila melanogaster strains, with balance gene and genetic stability, of w, UAS-dcf1 / Cyo and Tm6B / Tm2 are obtained through hybrid and backcross of the human dcf1 transgenic UAS drosophila melanogaster strain with Double Balance drosophila melanogasters of w, B1 / Cyo and Tm6B / Tm2. The present invention utilizes microinjection gene engineering technology and drosophila melanogaster hybridization technology to construct the human dcf1 gene transgenic drosophila melanogaster model, and provides materials and new ideas for research on relative neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
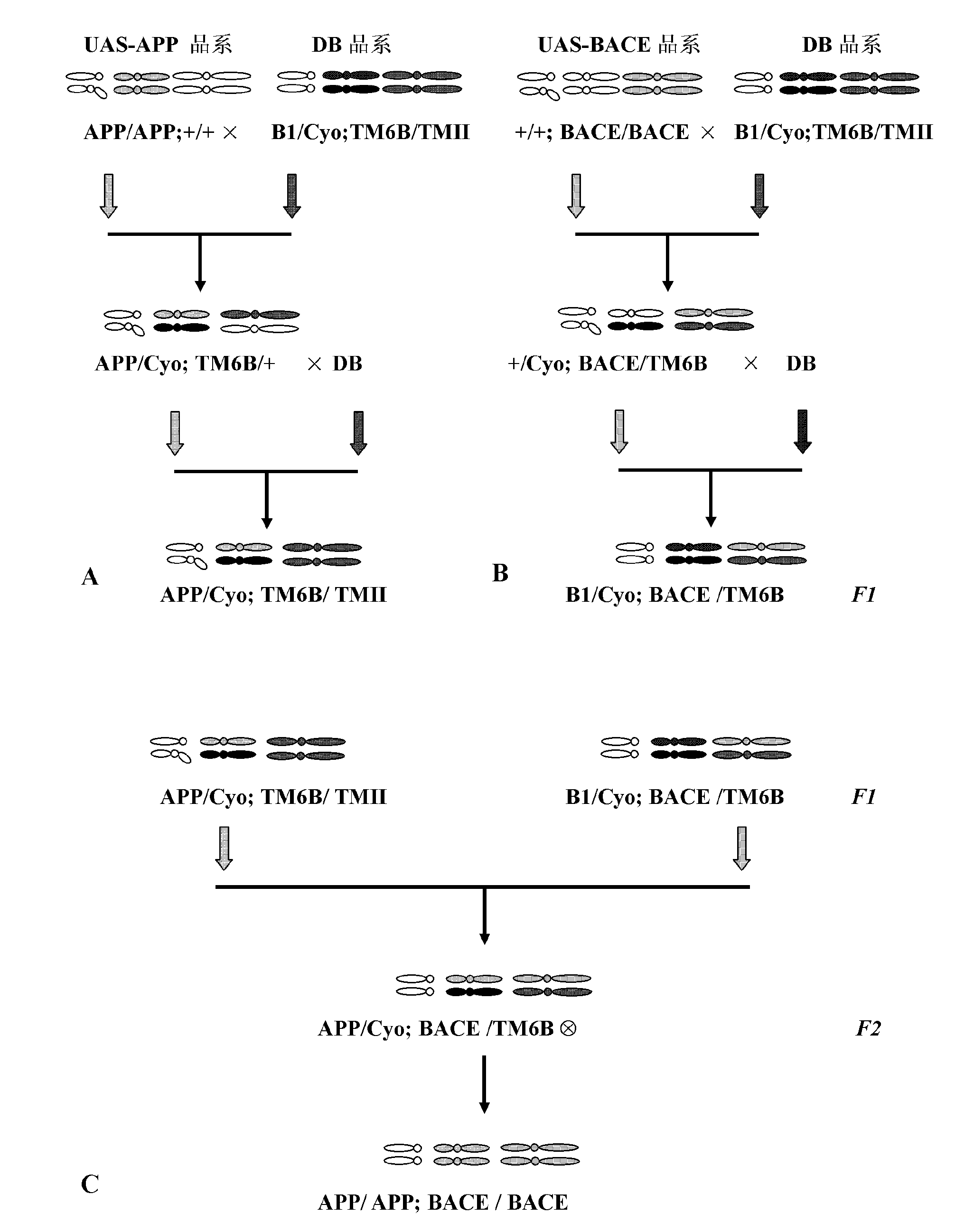
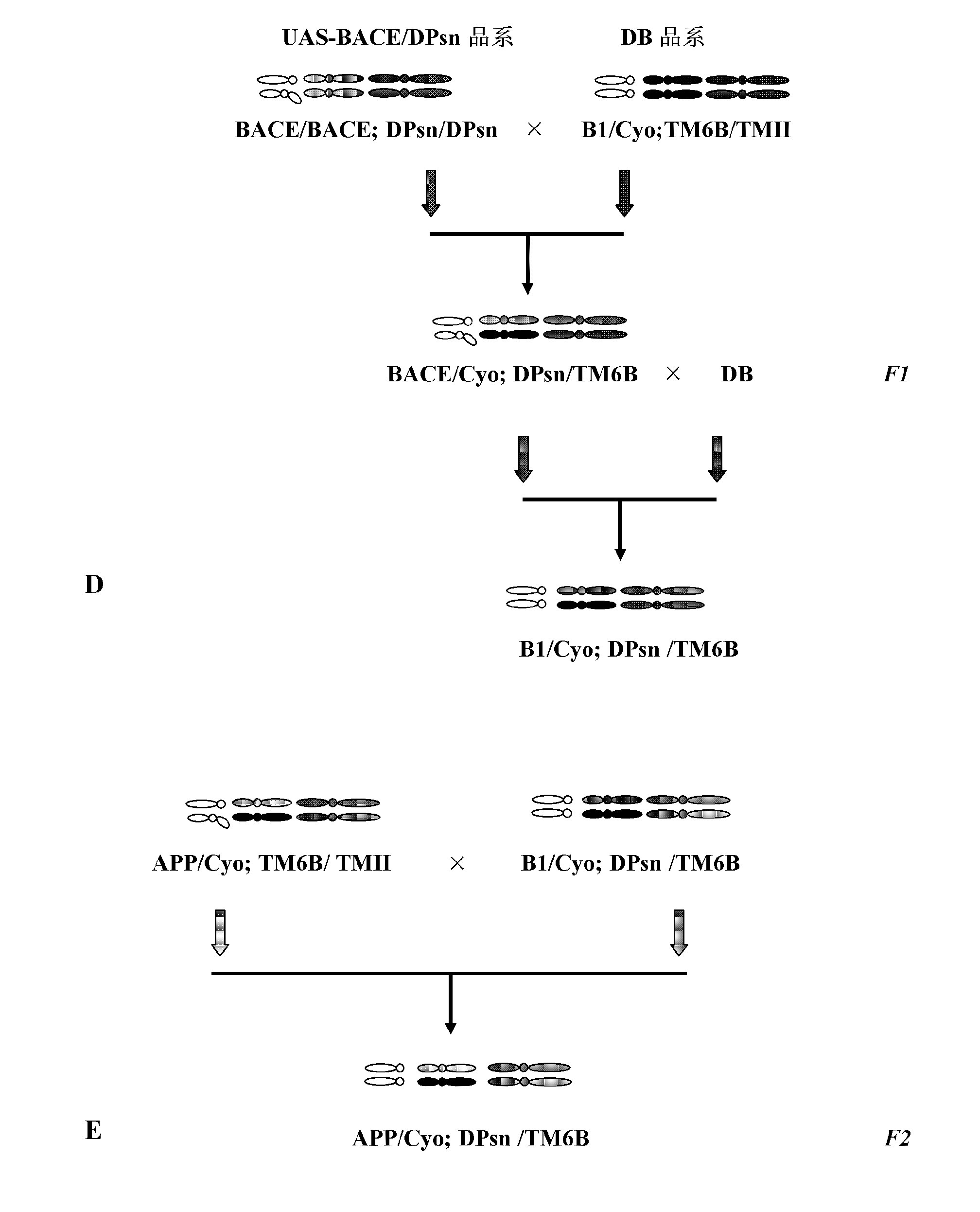
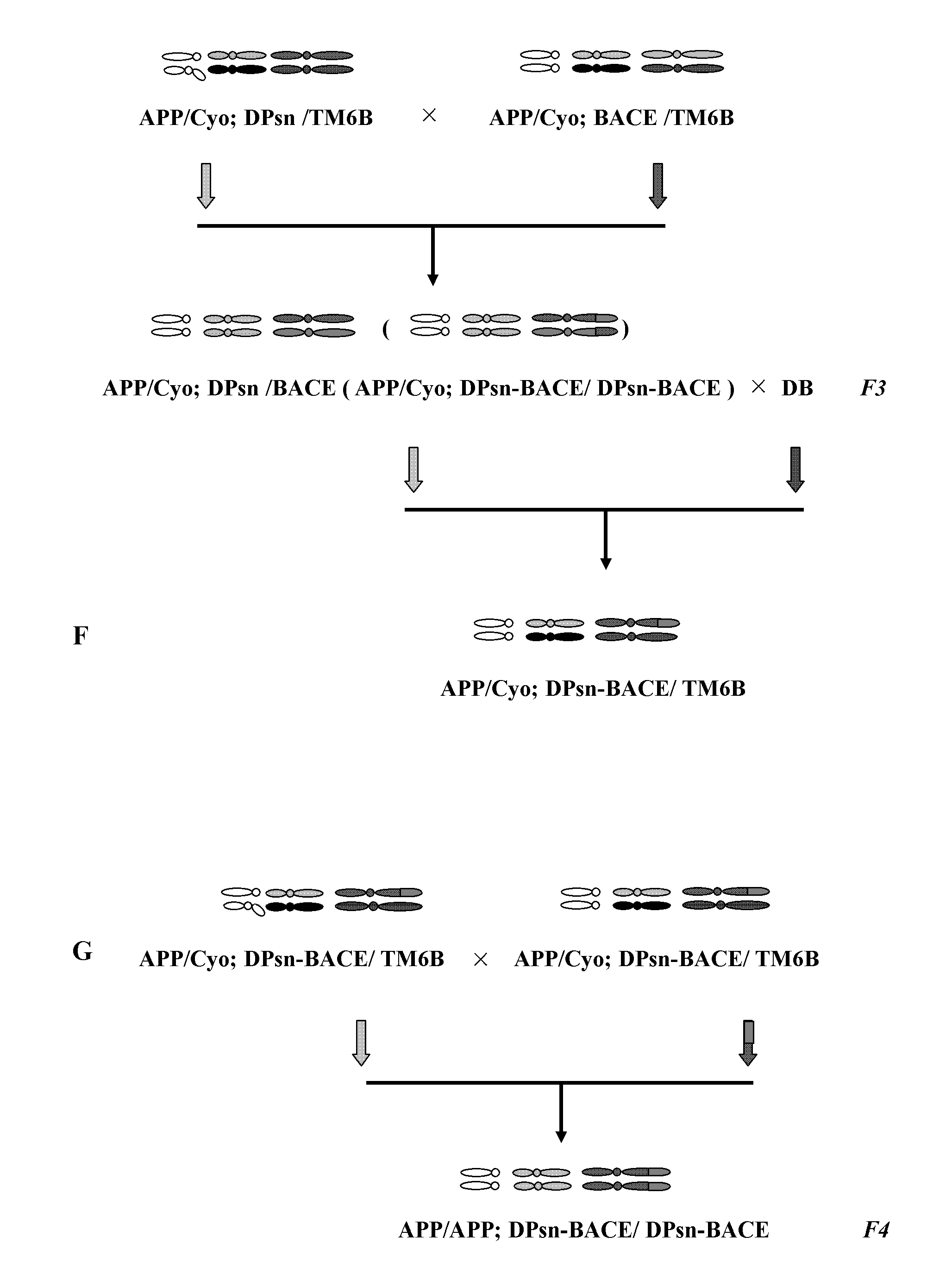
Anti-Alzheimer's Transgenic Drosophila Model and Its Application in Drug Screening
The invention relates to establishment and application of a model for screening medicines for treating Alzheimer disease, and aims to provide a transgenic Dosophila melanogaster model for studying molecular pathway of pathogenesis progress of Alzheimer disease and drug screening. The invention obtains stable heritable novel Drosophila melanogaster variety by successive crossing of available transgenic Drosophila melanogaster. The novel disease model can simulate the in vivo generation and metabolism processes of major pathogenic genes of Alzheimer disease, and reproduce the pathogenesis process of the disease. The Drosophila melanogaster model provided by the invention is proven by a variety of indicators closely related to the symptoms of disease, including survive curve, mobility and learning and memory indexes and in vivo experiments, to be distinctly different from other Alzheimer disease Dosophila melanogaster models in all respects.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
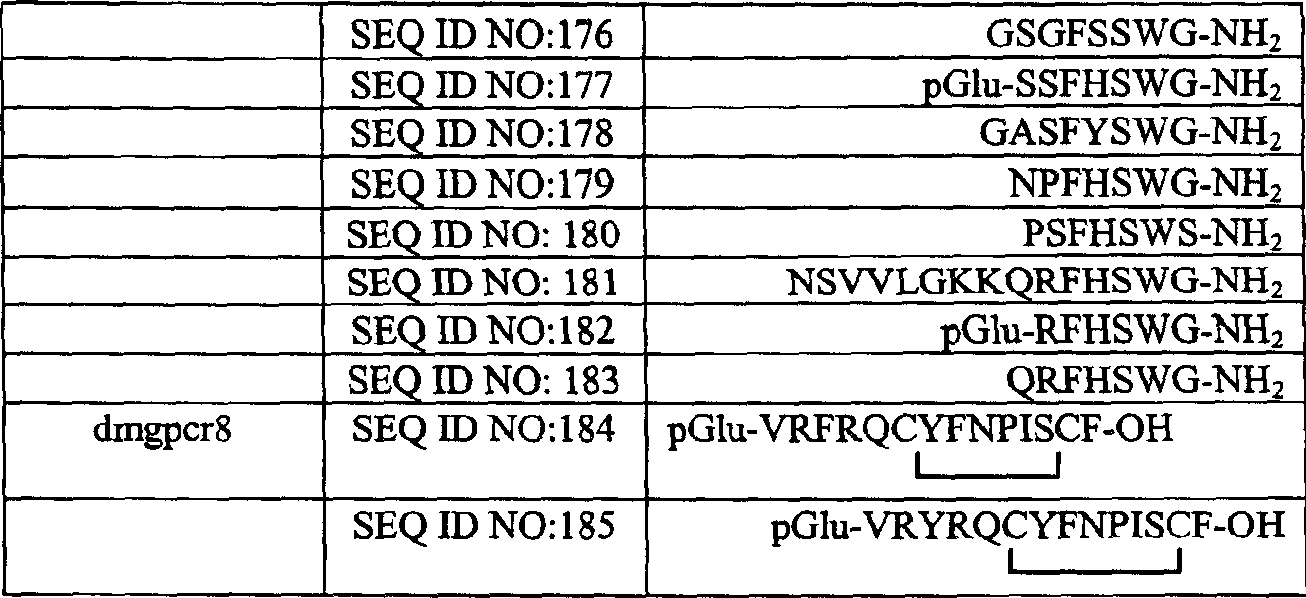
Drosophila g protein coupled receptors, nucleic acids, and methods related to the same
The present invention provides Drosophila melanogaster GPCR (DmGPCR) polypeptides and polynucleotides which identify and encode such a DmGPCR. In addition, the invention provides expression vectors, host cells, and methods for its production. The invention also provides methods for the identification of homologues in other species and of DmGPCR agonists / antagonists useful as potential insecticides. The invention further provides methods for binding a DmGPCR, methods for identifying modulators of DmGPCR expression and activity, methods for controlling a population of insects with a DmGPCR antibody, a DmGPCR antisense polynucleotide, a DmGPCR binding partner or modulator, and methods of preventing or treating a disease or condition associated with an ectoparasite. Specifically, this invention discloses the matching of the orphan Drosophila short neuropeptide F receptor with its cognate peptide ligands.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
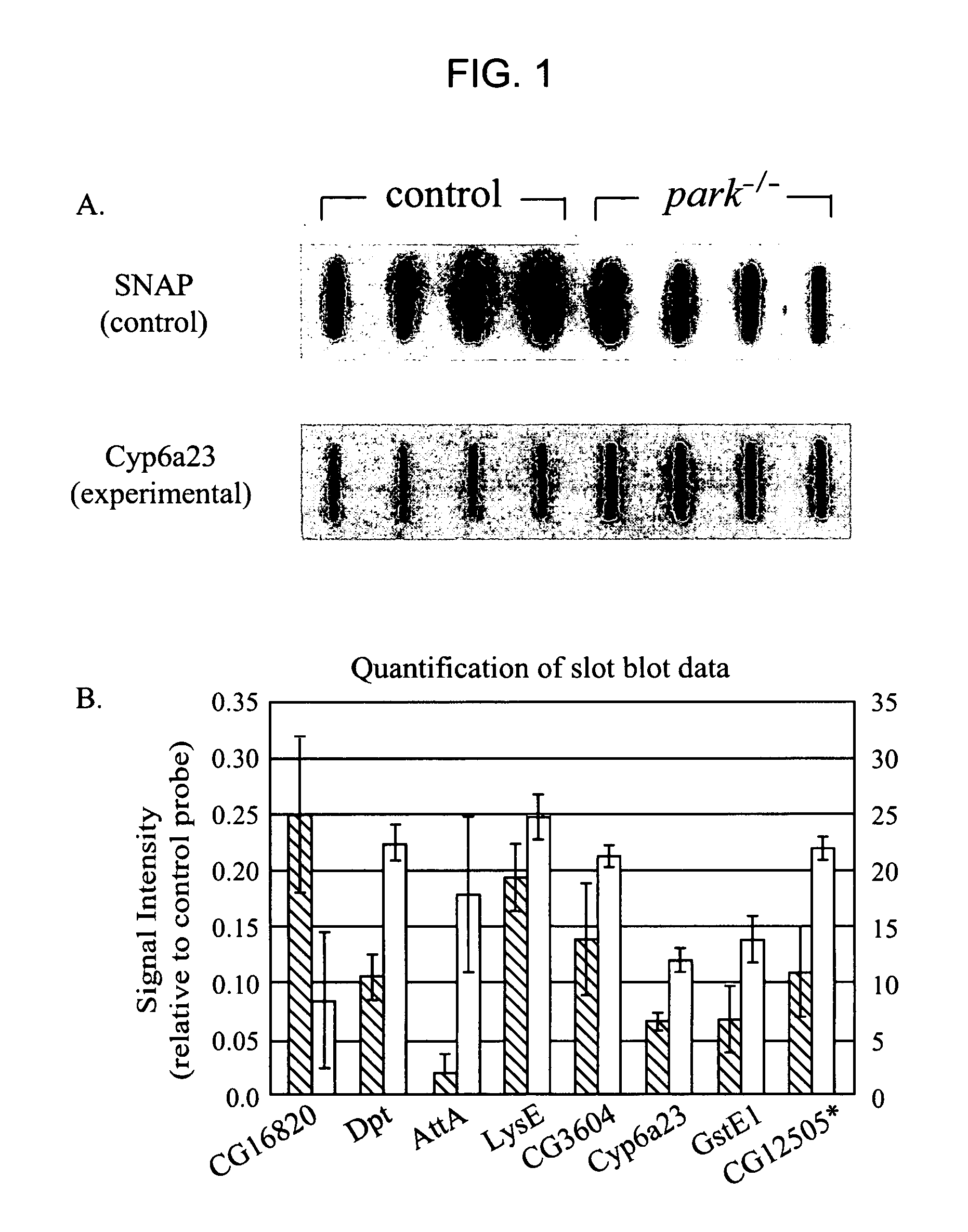
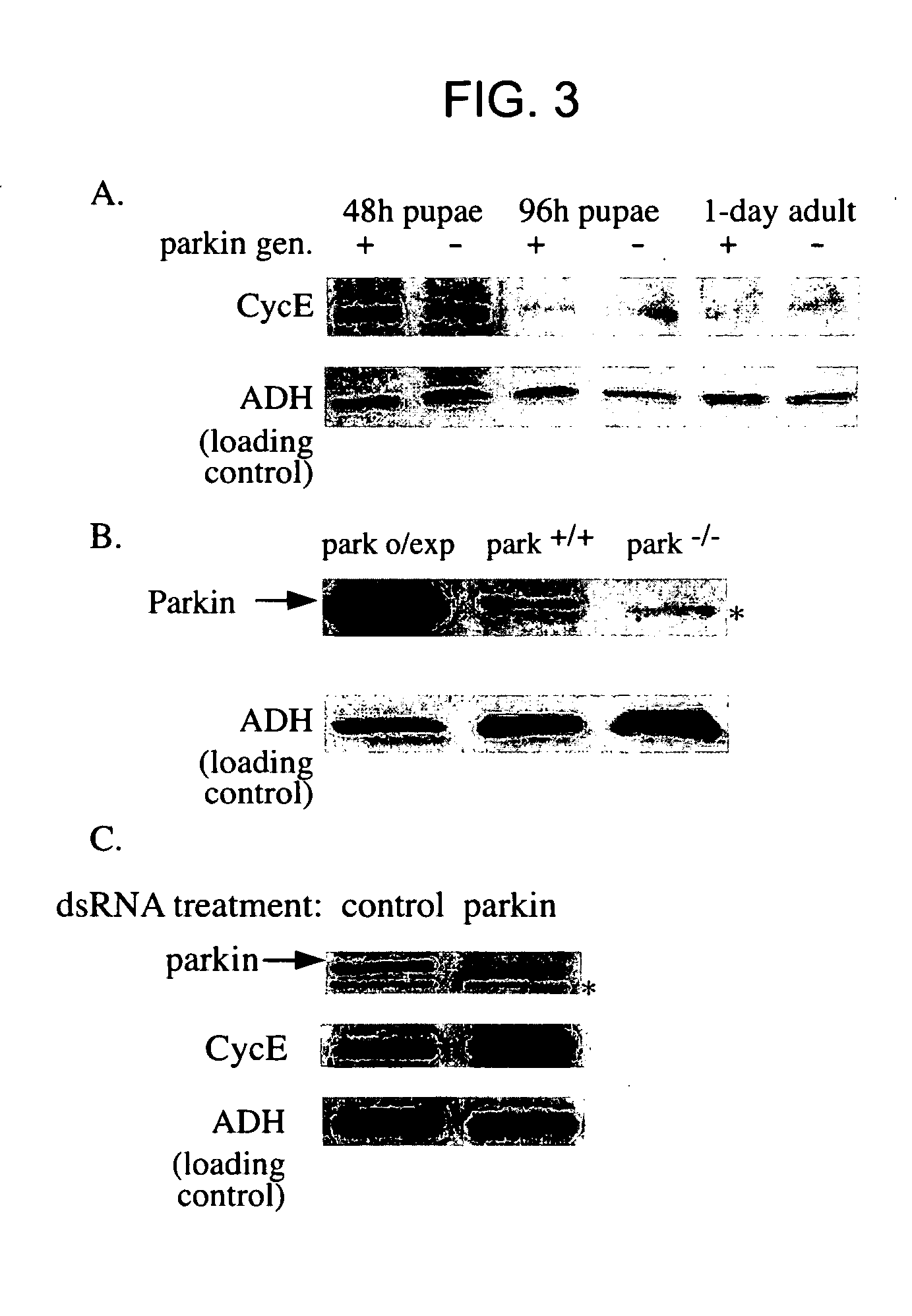
Transgenic Drosophila having a disrupted Parkin gene and exhibits reduced climbing ability
InactiveUS6943278B2LigasesVector-based foreign material introductionNeuronal degenerationNeuronal disease
The present invention relates to animal models for neuronal function, e.g., spontaneous changes in motor ability related to neuronal degeneration. For example, the present invention provides a Drosophila melanogaster model for Parkinson's disease. The present invention also provides methods for generating genetically based neuronal disease models, identifying genes that affect neuronal function and methods for identifying compounds having activity with respect to neurological function.
Owner:GENEXEL
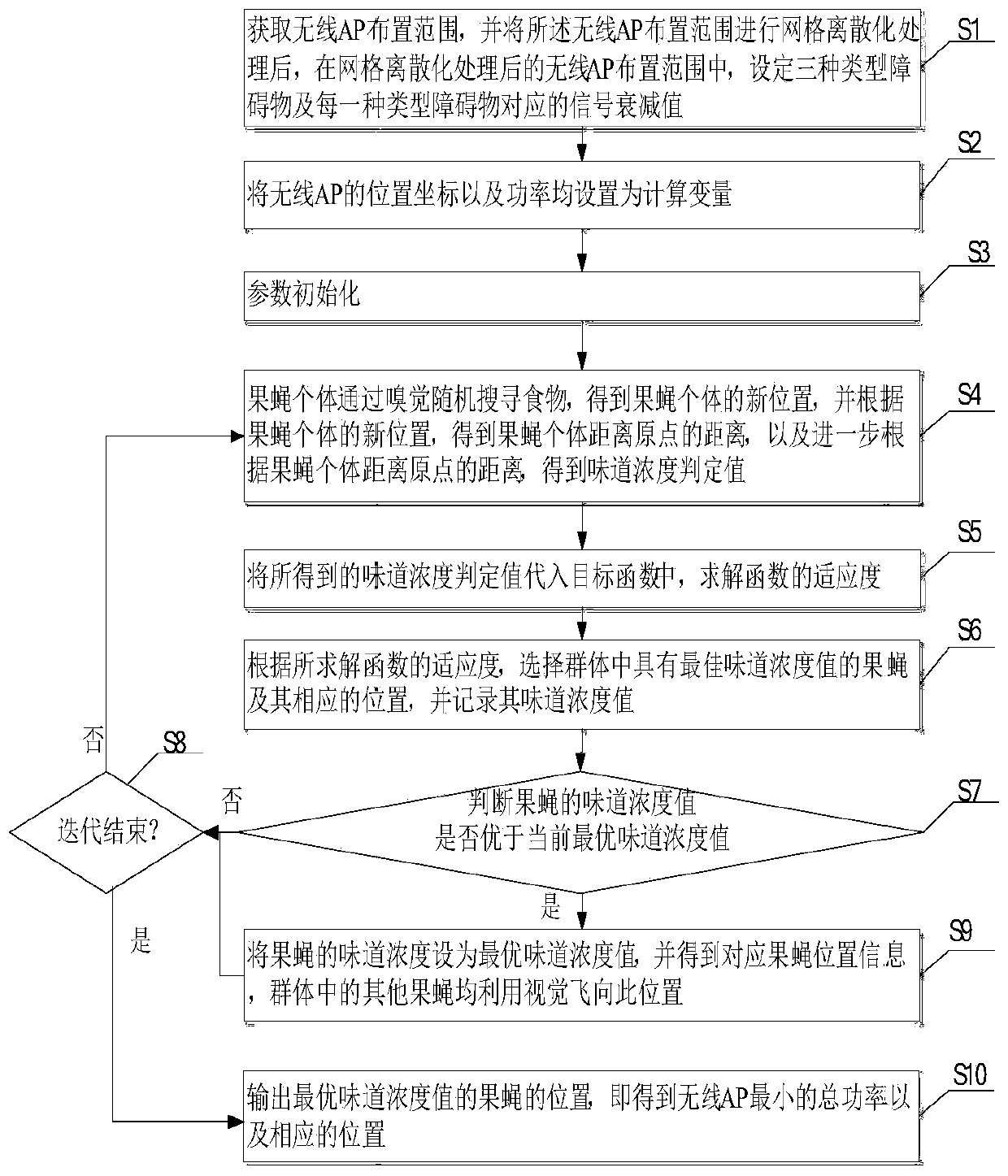
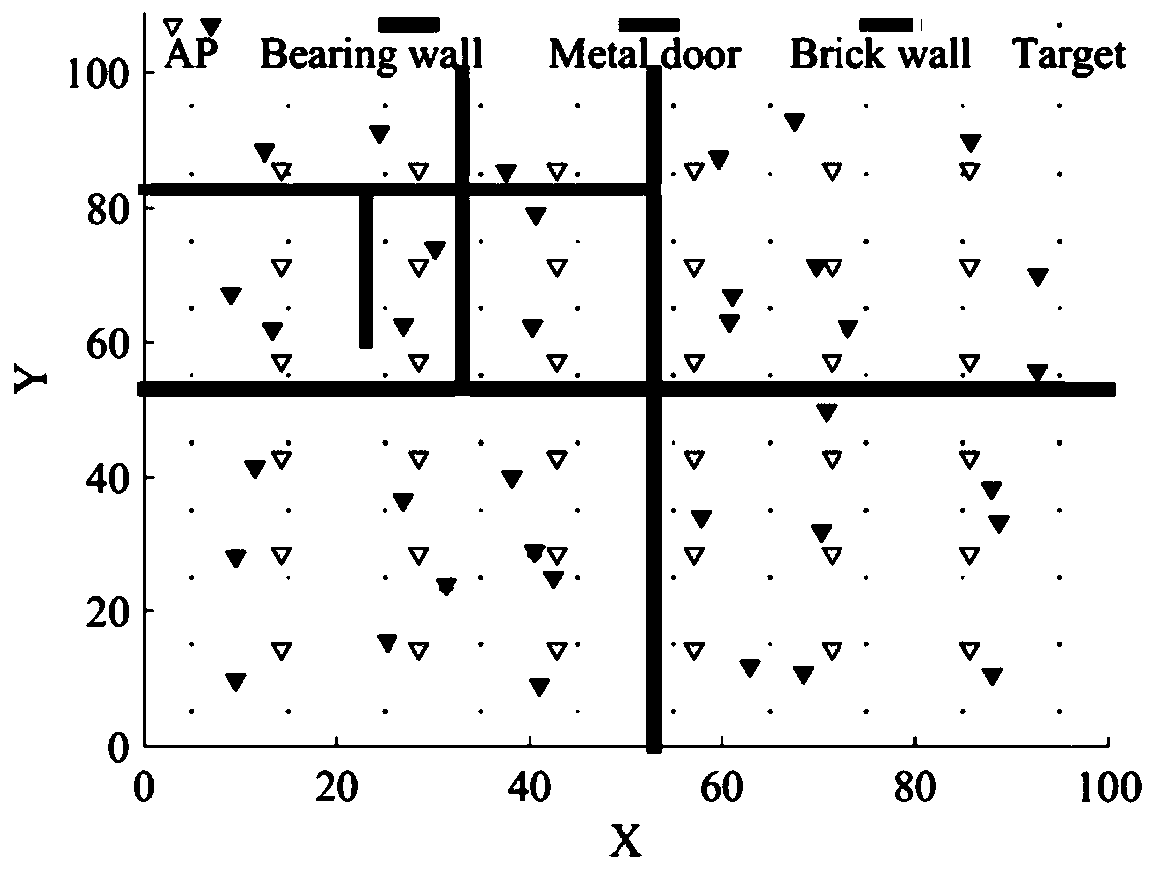
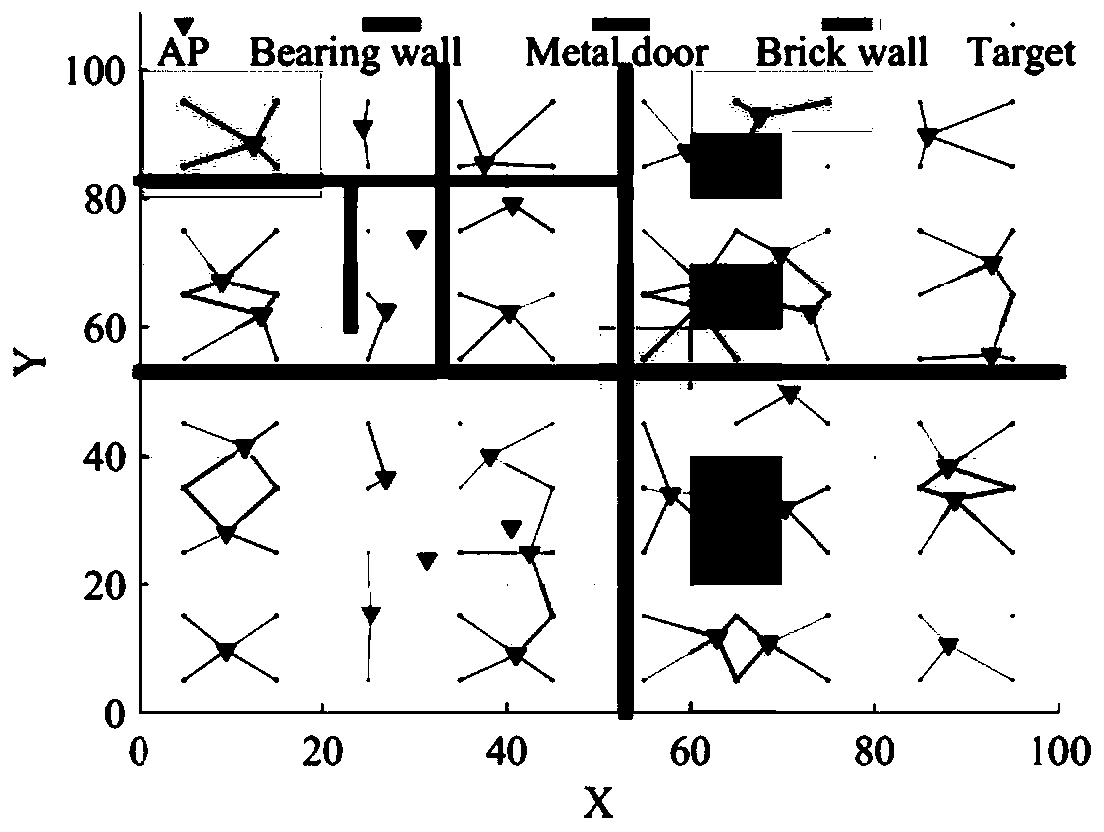
Wireless AP deployment optimization method based on fruit fly optimization in non-uniform environment
ActiveCN110430579ASolve analysisTroubleshooting Deployment DeviationsNetwork planningHigh level techniquesUltrasound attenuationMetapopulation
The invention provides a wireless AP deployment optimization method based on fruit fly optimization in a non-uniform environment, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a wireless AP deploymentrange, processing the wireless AP deployment range, and setting three types of obstacles and signal attenuation values; setting calculation variables as position coordinates and power of the wirelessAP; initializing a drosophila population and parameters; acquiring a new position of the drosophila melanogaster individual, a distance from the new position to an original point and a taste concentration judgment value; substituting into a target function to solve the fitness; according to the fitness, selecting the drosophila melanogaster with the optimal taste concentration value and the position of the drosophila melanogaster; judging whether the taste concentration of the selected drosophila melanogaster is superior to the current optimal taste concentration value or not; and updating the position of the fruit fly with the optimal taste concentration value, and continuing iteration until the iteration is finished to obtain the minimum total power of the wireless AP and the corresponding position. By implementing the method and the device, a non-uniform propagation environment is formed, and the wireless AP deployment position and the power are jointly optimized, so that the problems of wireless AP analysis and deployment deviation in a non-uniform environment in the prior art are solved.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
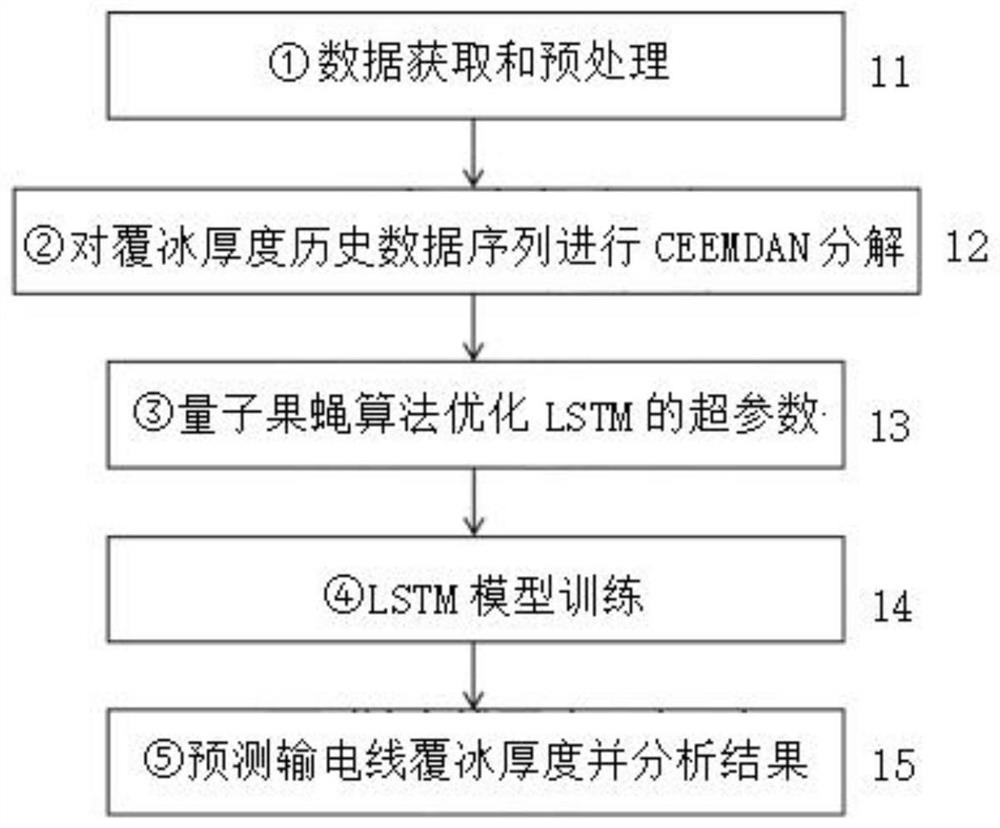
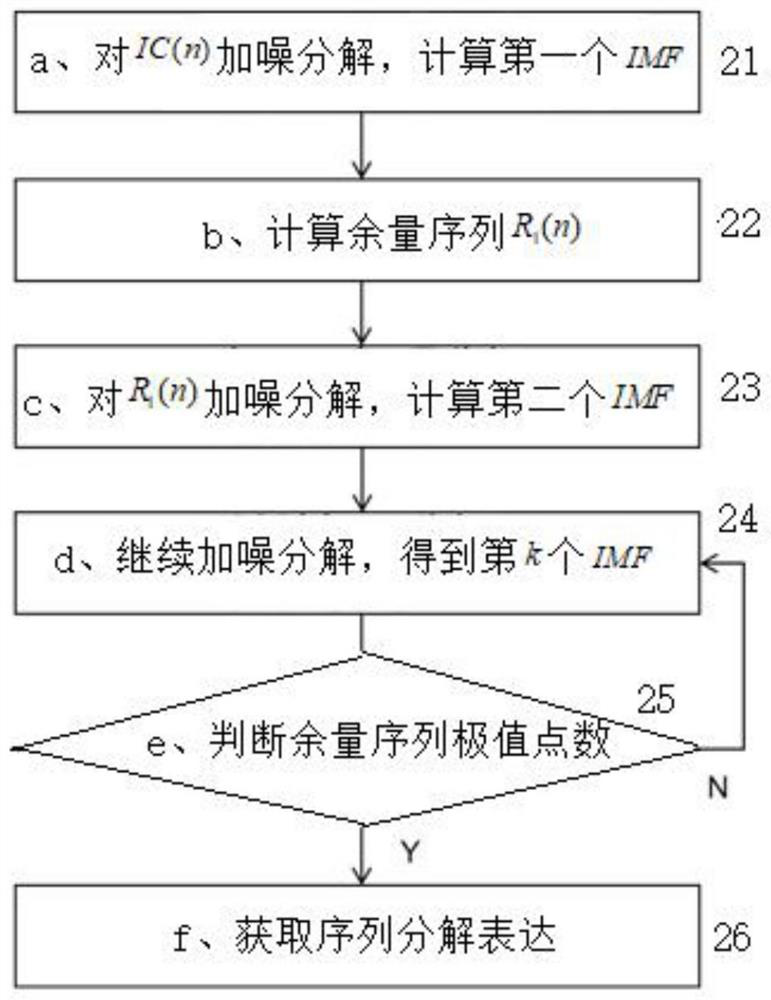
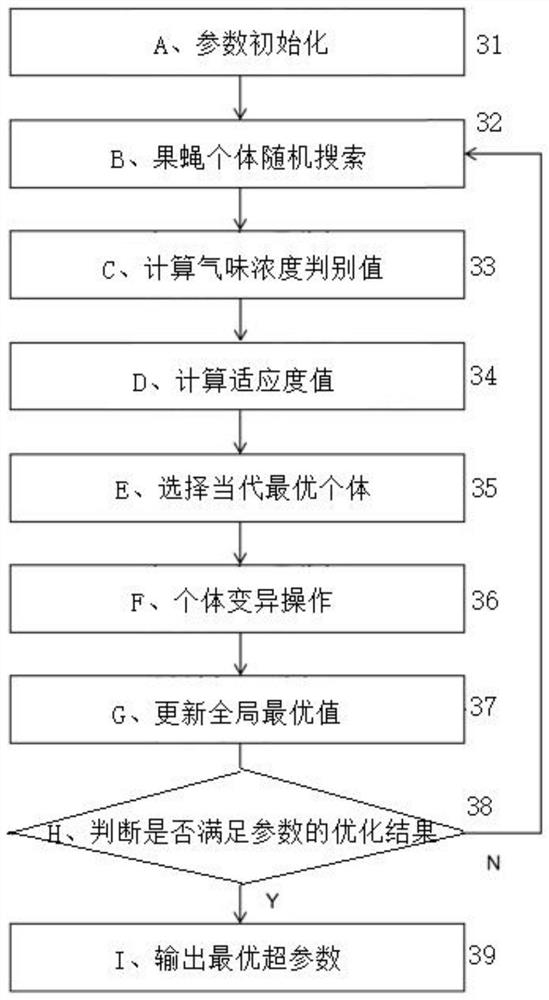
Power transmission line icing thickness prediction method based on CEEMDAN-QFOA-LSTM
ActiveCN112116162AAvoid estimation processingClear classificationQuantum computersForecastingData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses a power transmission line icing thickness prediction method based on CEEMDAN-QFOA-LSTM, and relates to the field of combination of power transmission line state evaluation anddeep learning. The method comprises the following steps o: (1) carrying out data acquisition and preprocessing; (2) carrying out CEEMDAN decomposition on an icing thickness historical data sequence (12); (3) optimizing hyper-parameters of the LSTM by a quantum drosophila melanogaster algorithm; (4) carrying out LSTM model training (14); and (5) predicting the icing thickness of a power transmission line and analyzing a result (15). According to the method, the CEEMDAN decomposition algorithm is used, a sequence which is difficult to directly predict is converted into a plurality of predictablecomponent sequences; a neural network can more accurately grasp the law of the sequence according to multi-dimensional feature information obtained through decomposition; a QFOA optimization algorithm is used for obtaining the hyper-parameters, a complex manual parameter adjustment process is avoided, and a network model is trained more effectively; the used LSTM neural network does not have theproblem of gradient disappearance of a general network, so that optimal convergence of the model is ensured, and the problem of short-term and long-term time sequence prediction is effectively solved.
Owner:CENT CHINA BRANCH OF STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Method for identifying cancer drug candidates in drosophila
ActiveUS20130136694A1Microbiological testing/measurementIn-vivo testing preparationsEpitheliumCancer drugs
Owner:HAMPSON RICHARD
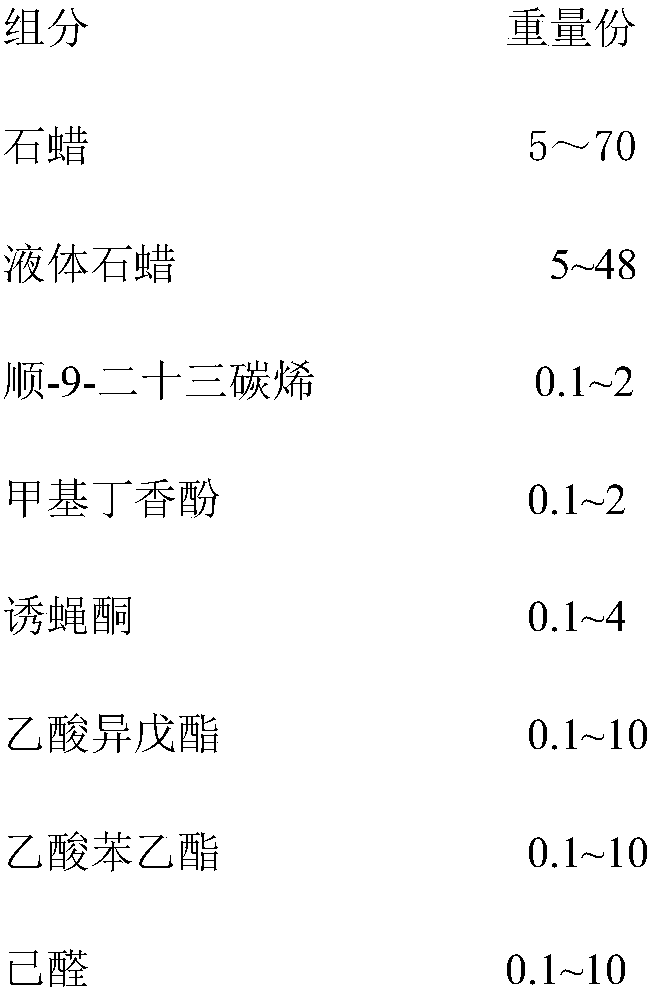
Waterproof drosophila melanogaster attractant controlled release formulation, preparation method and application
The invention discloses a waterproof drosophila melanogaster attractant controlled release formulation, a preparation method and application. The controlled release formulation comprises paraffin, liquid paraffin, cis-9-tricosene, methyleugenol, cuelure, isoamyl acetate, phenethyl acetate and hexanal. The provided attractant controlled release formulation can be used in a smearing way, can also beused by being mixed with a poison bait, or is used as a lure material matched with a sticky coloured card or a fly-killer lamp. The method effectively prolongs the effective life of a drosophila melanogaster attractant, and the satisfactory attraction effect is maintained for more than one month even under the severe rainy condition in the South.
Owner:WUHAN HANTE ENVIRONMENT SCI & TECH
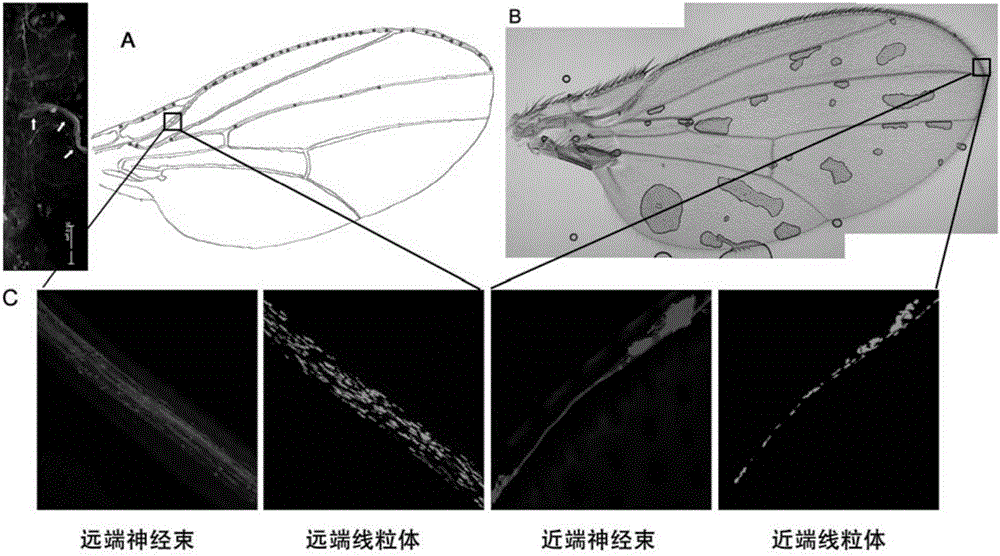
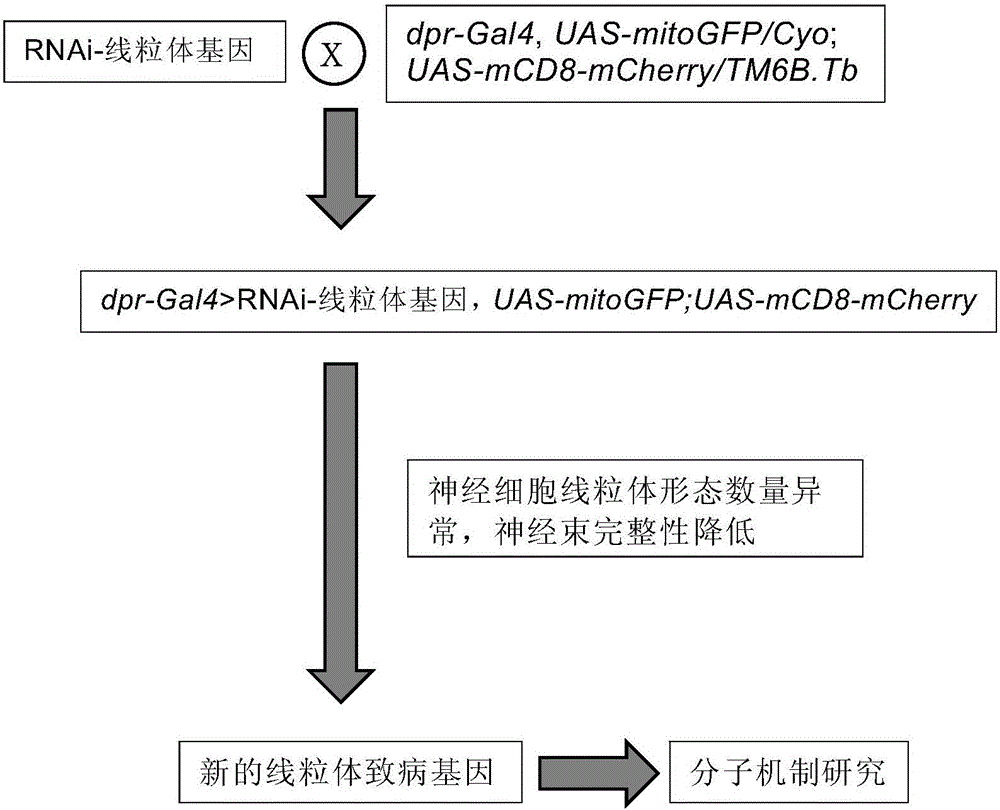
Building method of Drosophila melanogaster model for screening and researching mitochondria disease virulence gene, and application of same
The invention provides a building method of a Drosophila melanogaster model for screening and researching mitochondria disease virulence gene, and an application of the same. In the method, first fluorescent protein is represented by a mitochondria in a wing nerve cell in a Drosophila melanogaster model; second fluorescent protein is represented by in a wing nerve cell film in the Drosophila melanogaster model; the mitochondria is labeled via the first fluorescent protein positioned by the mitochondria; the nerve cell is labeled by the second fluorescent protein positioned by the nerve cell film; and research to mitochondria functions in a nervous system can be achieved in vivo. The Drosophila melanogaster transgene model built by the method can simply and conveniently screen and research mitochondria disease virulence genes; and demands for high flux, strong economic property and short time during mitochondria disease virulence gene screening can be met.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods of Controlling Insects
Methods of controlling insects include applying at least one spinosyn compound to a locus of a neonicotinoid-resistant insect, such as a strain of Drosophila melanogaster resistant to a neonicotinoid compound. The spinosyn compound may be a mixture of spinosyn A and spinosyn D. The spinosyn compound may cause up to approximately ten times increased mortality in the neonicotinoid-resistant insect compared to an insect susceptible to a neonicotinoid compound.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
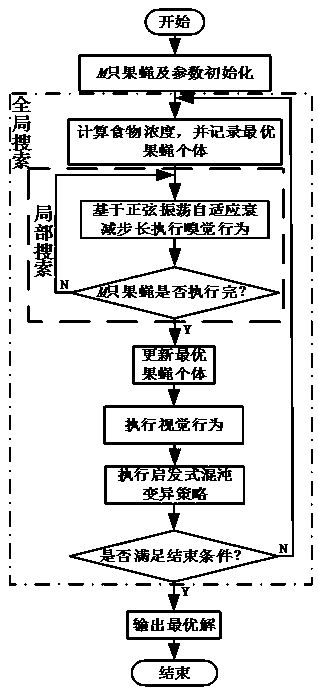
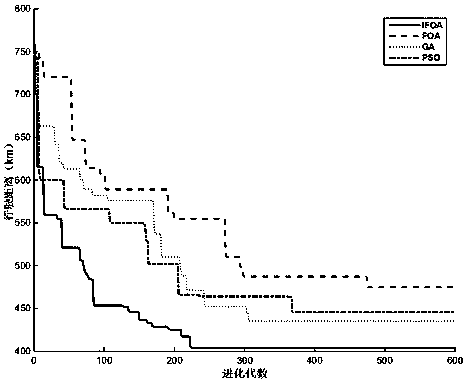
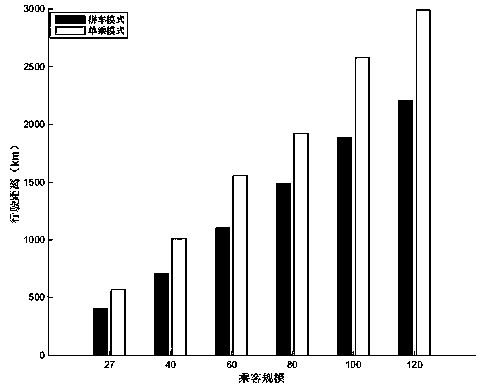
Multi-vehicle cooperative carpooling path optimization method based on improved fruit fly algorithm
PendingCN110084390AReduce seat vacancyImprove operational efficiencyReservationsForecastingLocal optimumUltrasound attenuation
The invention discloses a multi-vehicle cooperative carpooling path optimization method based on an improved fruit fly algorithm in the technical field of intelligent transportation. The key points ofthe technical scheme are as follows: through a step length sine attenuation strategy, an algorithm can carry out breadth exploration on a solution space with a large step length in the early evolution stage and carry out deep development with a small step length in the later evolution stage, and meanwhile, due to the fact that the step length is attenuated in a sine oscillation manner, the performance of the algorithm can be well considered in global and local optimization; and through a chaotic variation strategy, diversity of populations is improved, and the capability of jumping out of local optimum is further improved. The improvement measures further improve the solving performance of the drosophila melanogaster algorithm. The efficiency of citizen carpooling travel is effectively improved, expenses are saved for passengers, benefits are increased for drivers, and more importantly, the emission of automobile exhaust is reduced, and the air quality is improved.
Owner:HENAN INST OF SCI & TECH
Methods and compositions for screening for modulators of parkinson's disease
InactiveUS20060101527A1Enhancing Parkinson 's disease phenotypeSuppressing Parkinson 's disease phenotypeGenetic engineeringMaterial analysisDisease phenotypeMammal
Methods and compositions for identifying an agent (e.g., a gene product or small molecule compound) that modulates a Parkinson's disease phenotype are provided. In practicing the subject methods, a non-mammalian animal model, such as Drosophila melanogaster, that includes a mutant parkin gene and at least one other mutant gene are evaluated for a Parkinson's disease phenotype. Also provided are kits, and systems for practicing the subject methods, as well as methods of use of agents identified in the screening method of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
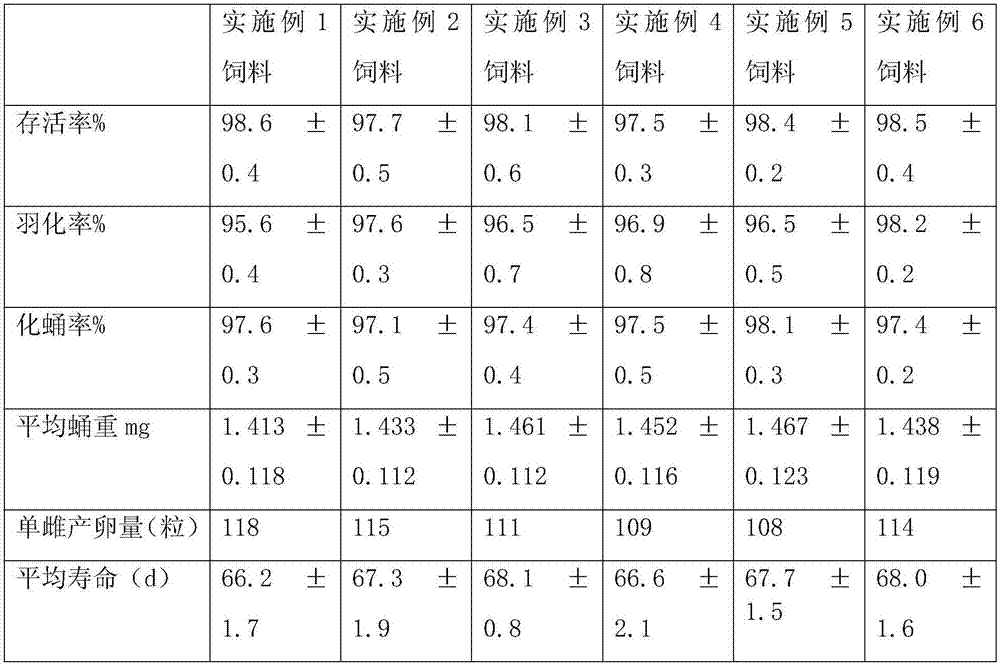
High-nutrition artificial feed for drosophila melanogaster and preparation method of artificial feed
InactiveCN106974140AGood regulationPromote rapid growthFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSemenWheat Brans
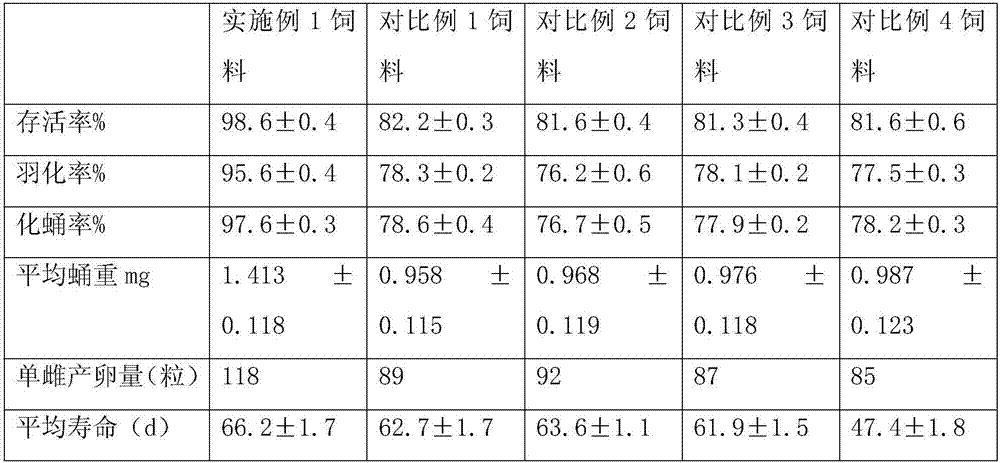
The invention provides high-nutrition artificial feed for drosophila melanogaster. The artificial feed is prepared from components of raw materials in parts by weight as follows: 50-80 parts of banana paste, 40-60 parts of mango paste, 40-60 parts of yellow peach paste, 10-20 parts of wheat bran powder, 20-30 parts of royal jelly, 10-20 parts of soybean meal, 1-2 parts of chitosan, 2-4 parts of a semen coicis extract, 10-20 parts of yeast powder, 5-10 parts of agar, 0.5-1.5 parts of a preservative and 100-200 parts of water. The novel high-nutrition feed prepared with the preparation method according to the proportion is used for feeding test drosophila melanogaster all the year round, meanwhile, the survival rate, pupation rate, eclosion rate and single-female egg laying quantity of the test drosophila melanogaste fed with the synthetic feed are all superior to those of drosophila melanogaster fed with natural feed, and the average pupal weight of male and female drosophila melanogaster is larger than that of drosophila melanogaster fed with the natural feed.
Owner:广东人为峰健康管理科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com