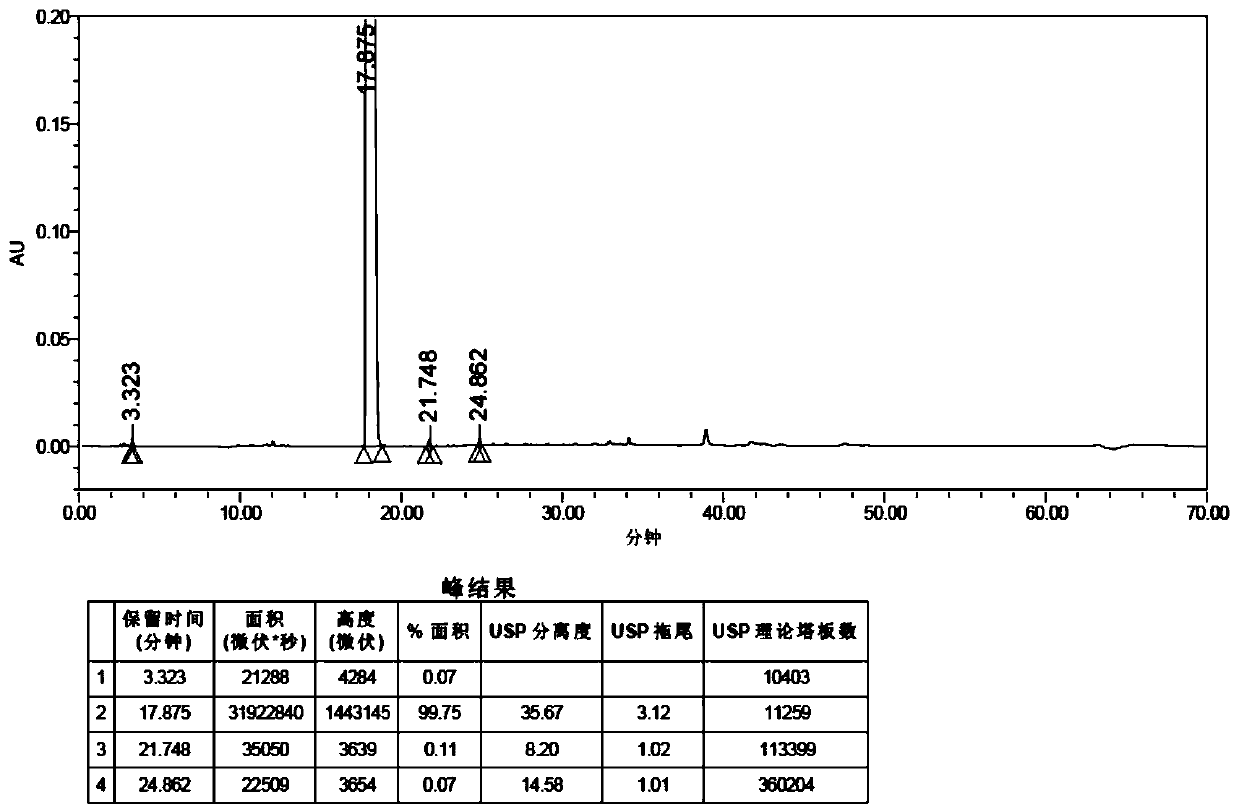
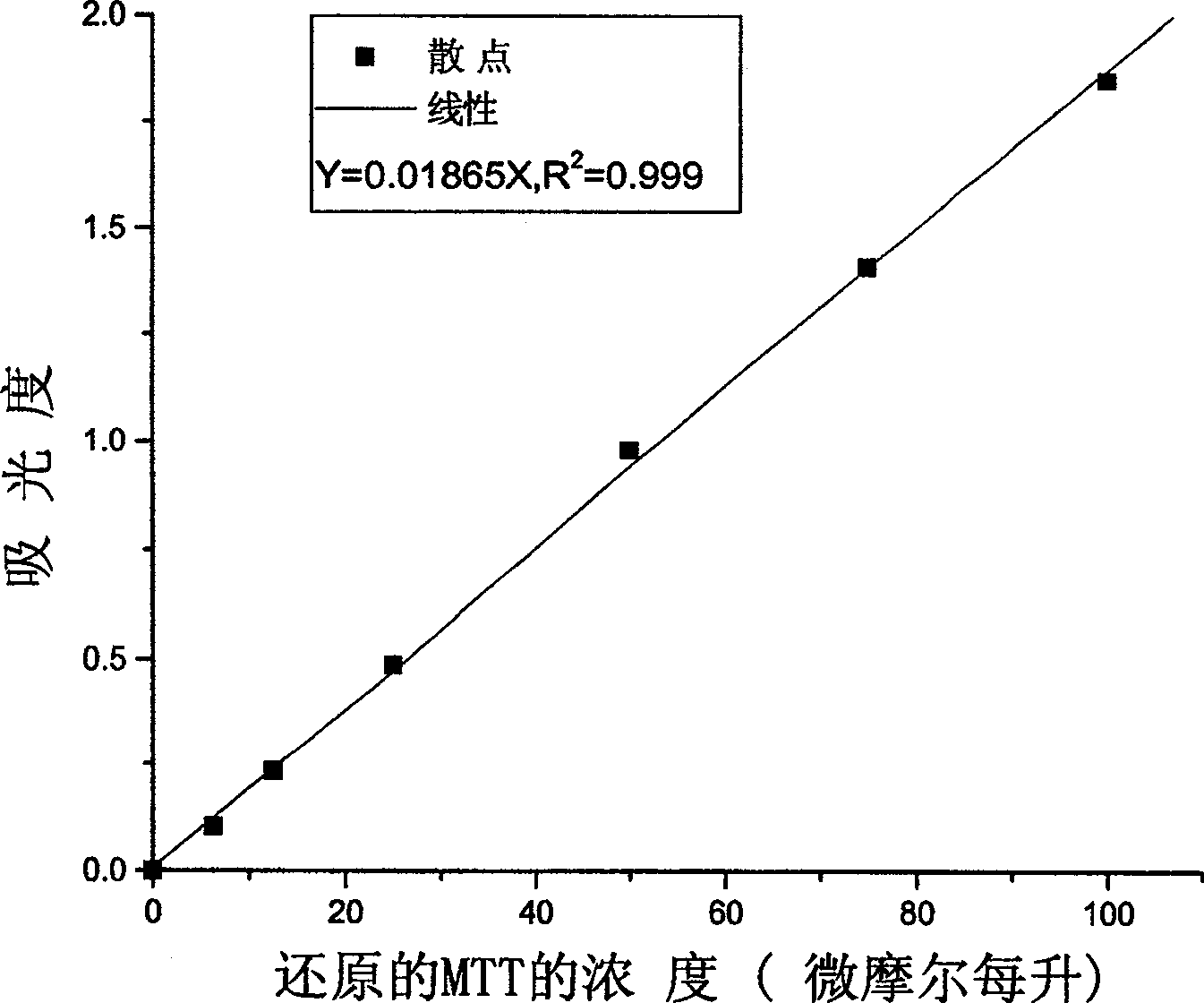
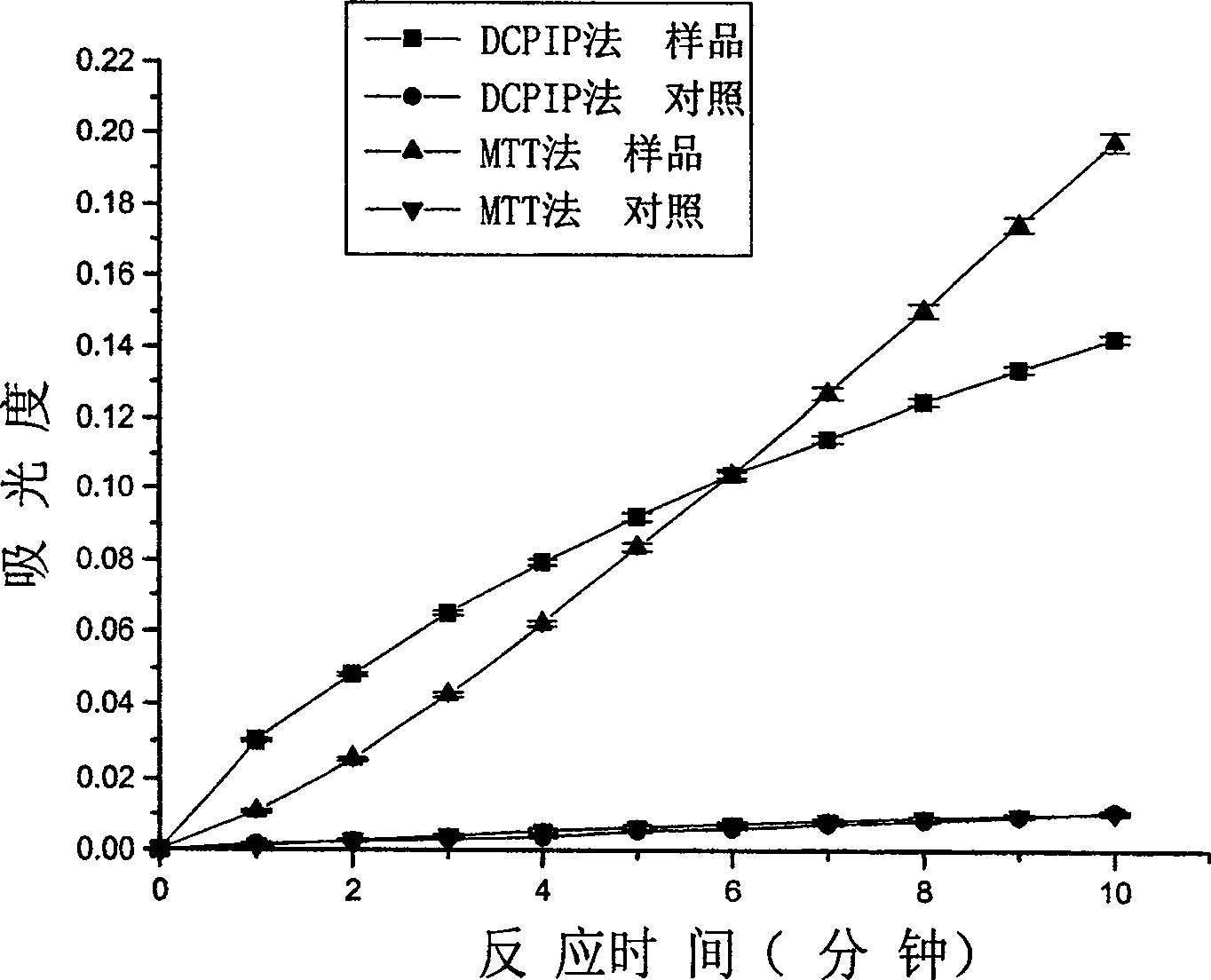
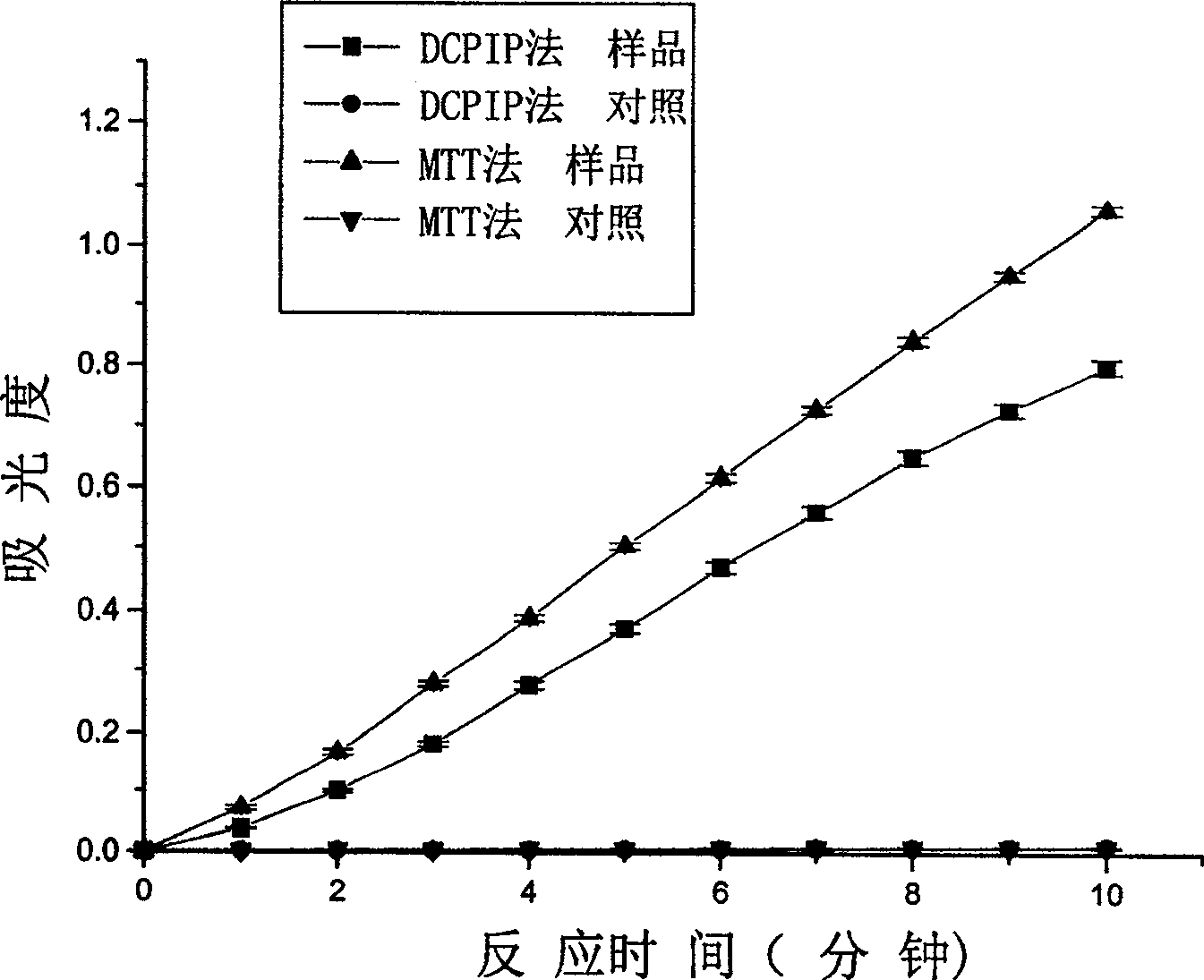
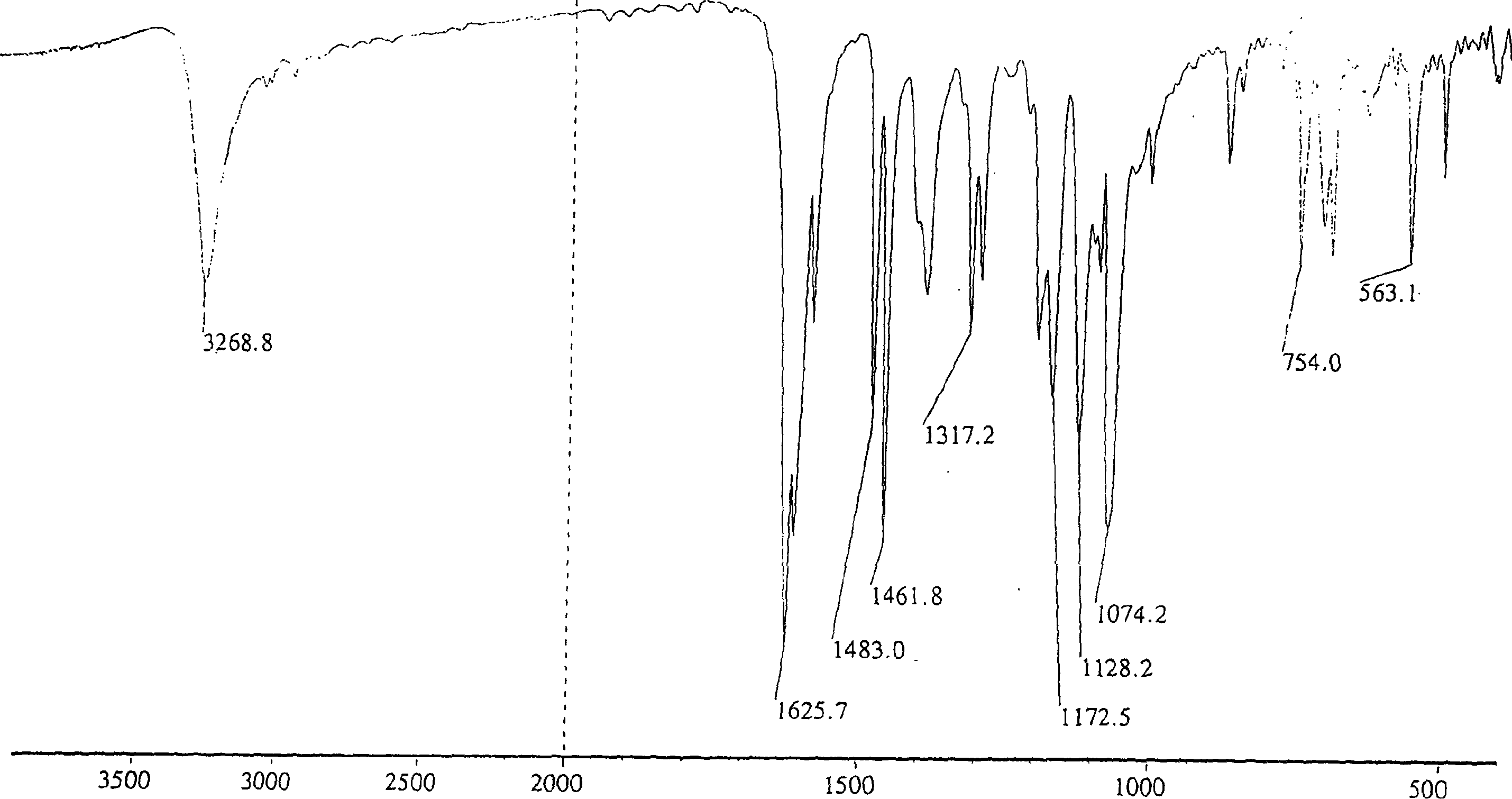
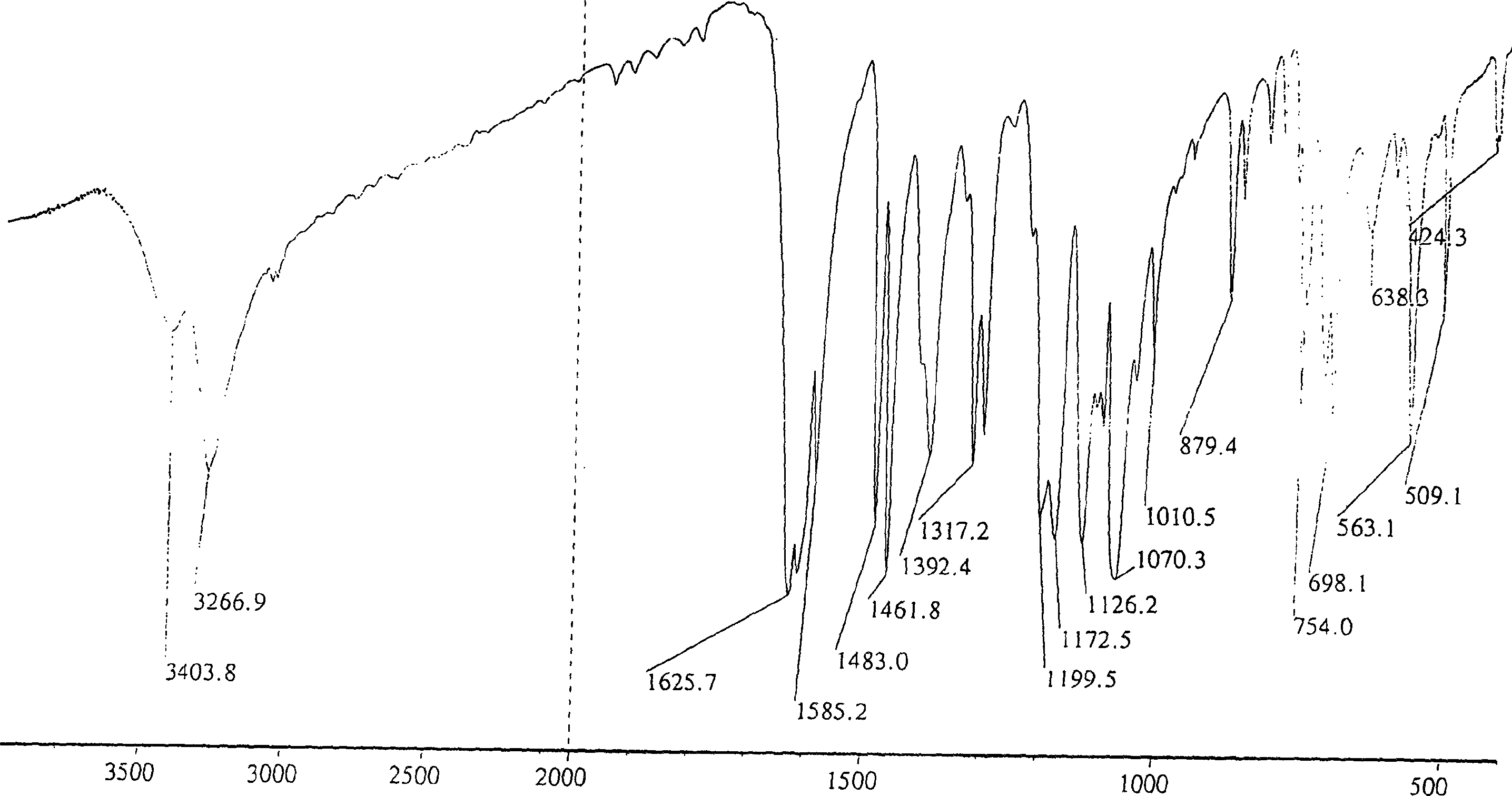
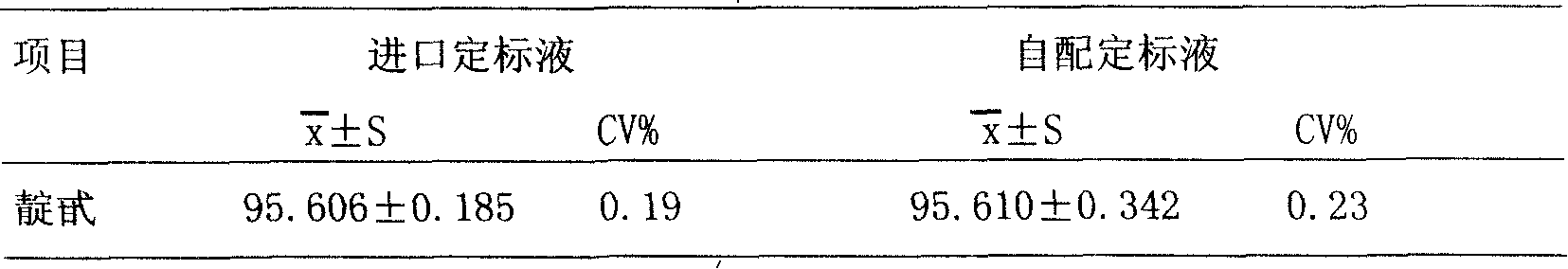
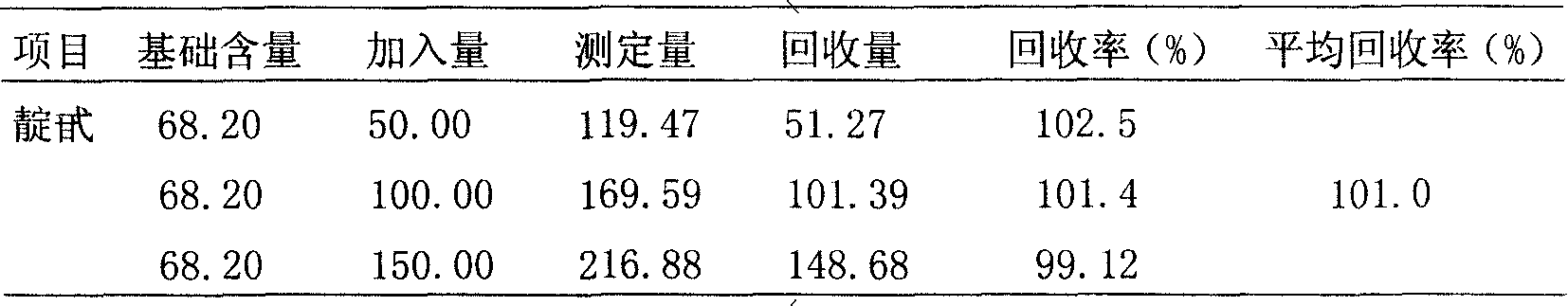
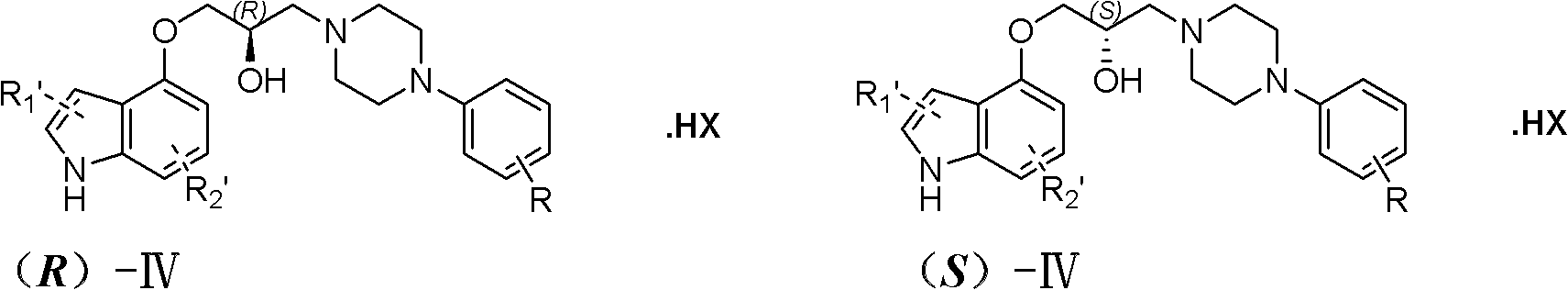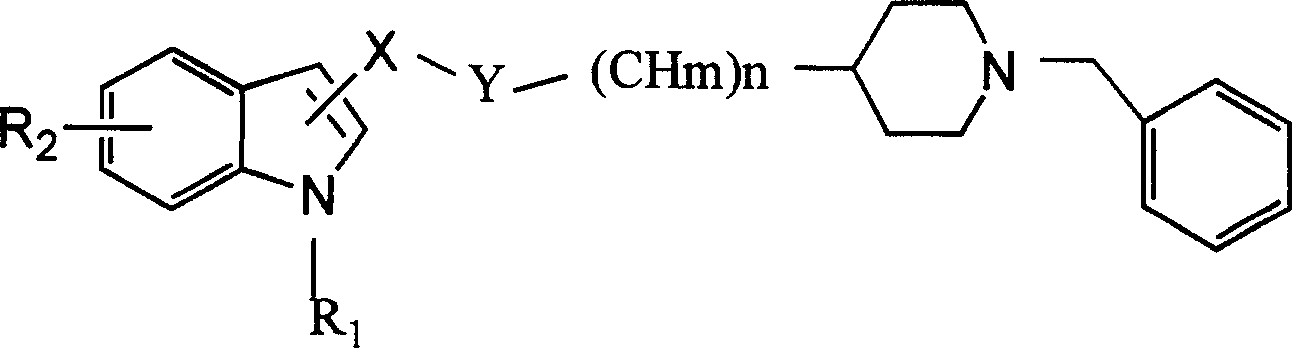Patents
Literature
34 results about "Indoxyl" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, indoxyl is a nitrogenous substance with the chemical formula: C₈H₇NO. Indoxyl is isomeric with oxindol and is obtained as an oily liquid. Indoxyl is obtained from indican, which is a glycoside. The hydrolysis of indican yields β-D-glucose and indoxyl.
Potentially fluorogenic compounds and plating media containing same
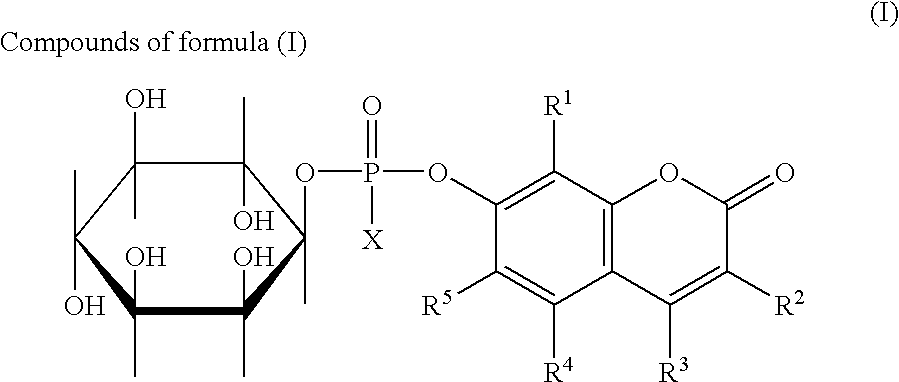
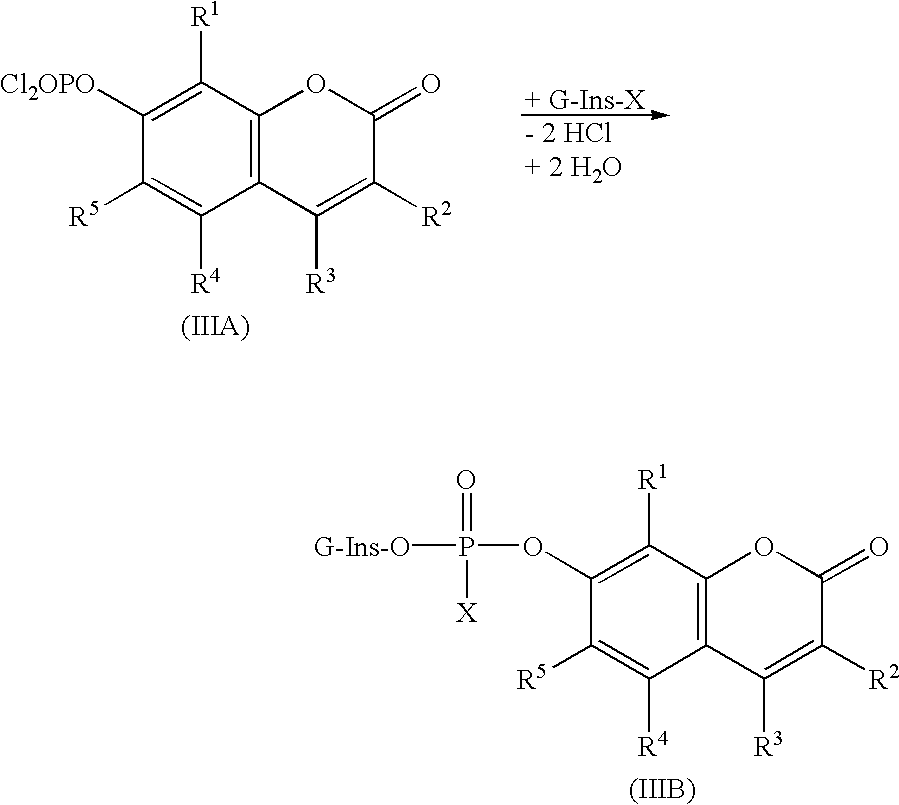
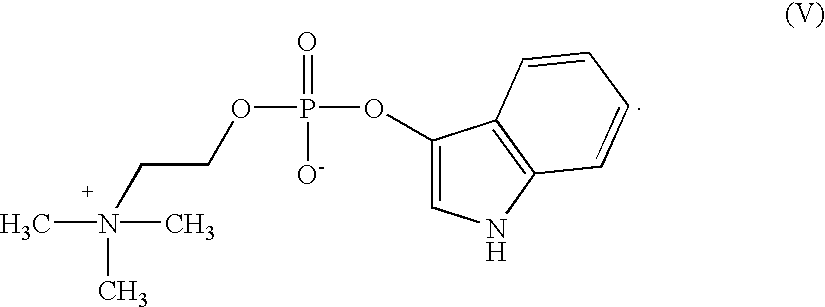
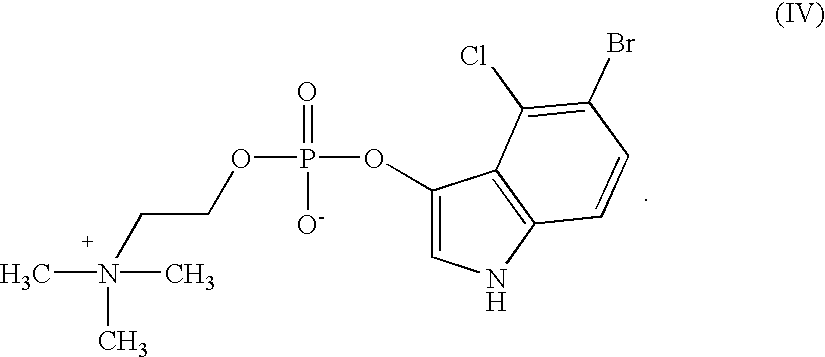
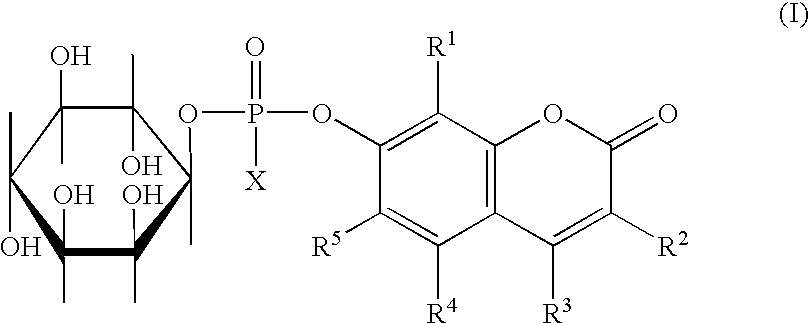
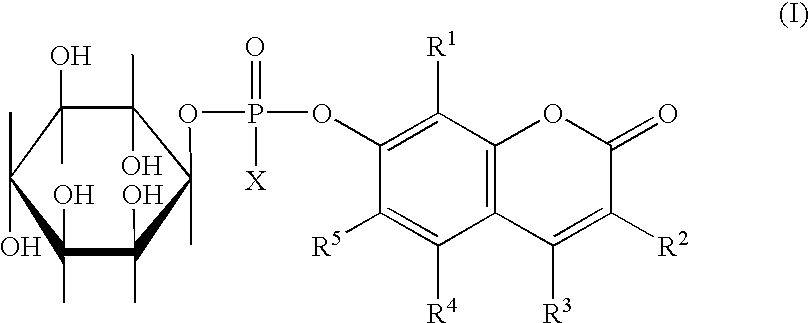
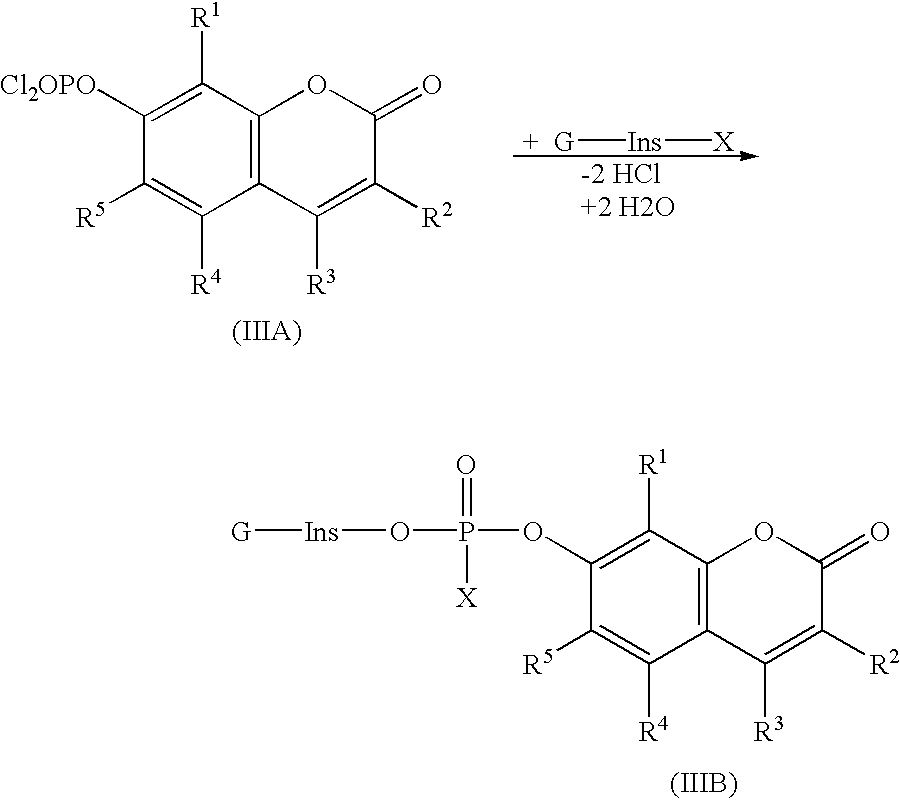
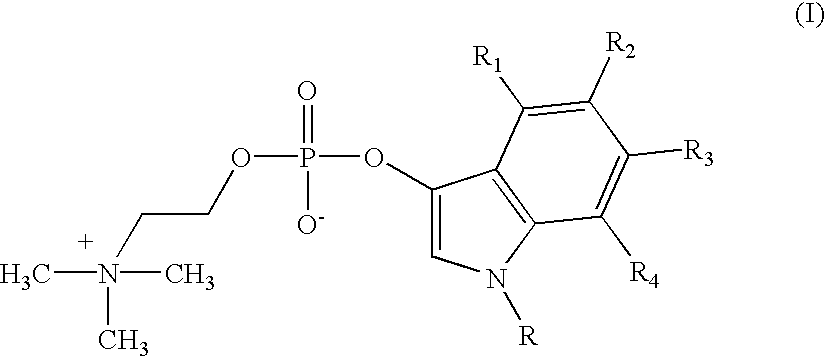
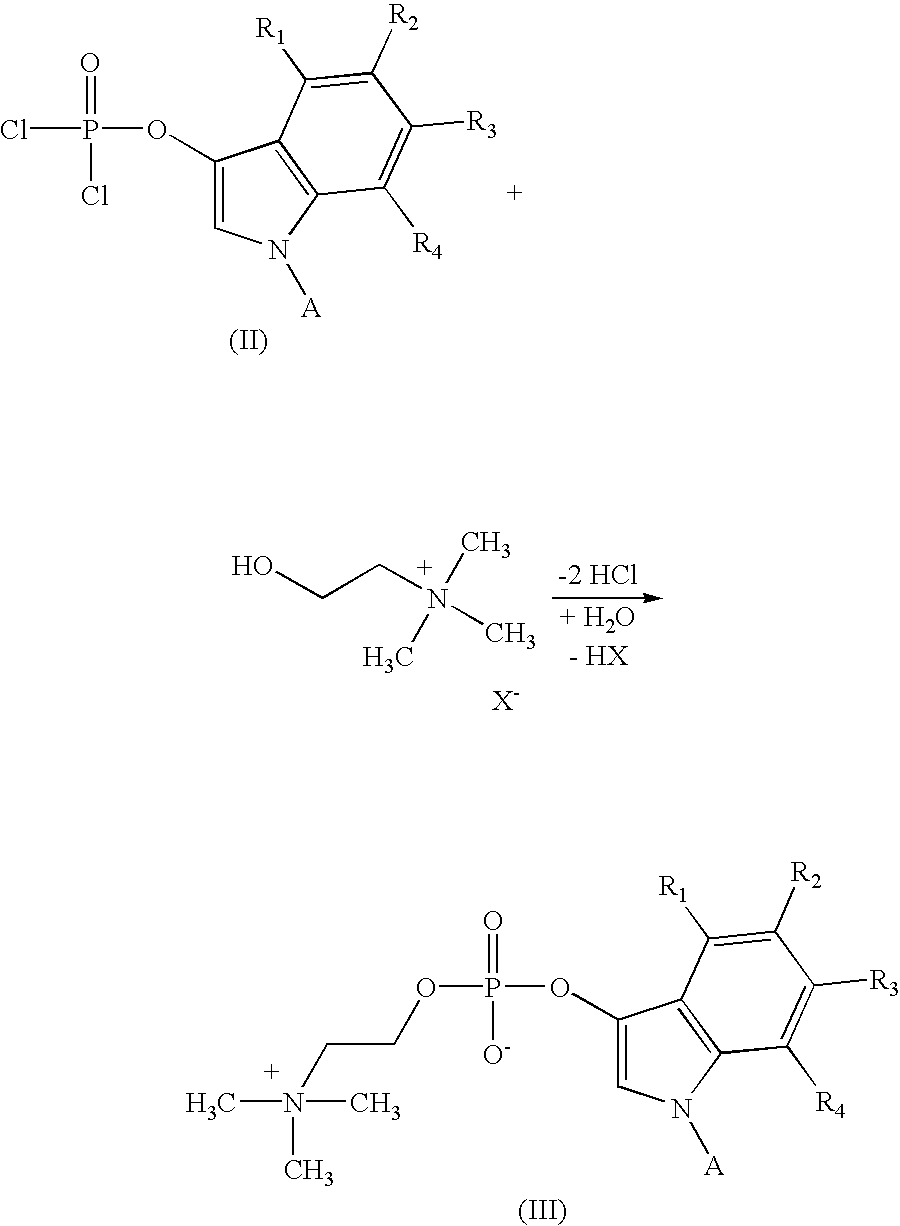
Compounds of formula (I)in which R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are hydrogen atoms or chromogenic substituents and X is hydroxyl, OR6 wherein R6 is selected from the group consisting of C1-C4 alkyl, or O-Me+ wherein Me+ is a cation derived from an organic or inorganic base; these compounds do not exhibit significant fluorescence but are capable of being cleaved by phosphatidyl-inositol-specific phospholipase C, an enzyme which is indicative of bacterial activity; the umbelliferyl moity resulting from such cleavage is a strong fluorogen thus providing effective test methods for various pathogenic bacteria, such as Listeria, Staphylococcus and Clostridium species. Also disclosed are plating media for detection of microorganisms that are capable of metabolic generation of a phosphatidyl inositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC). The plating medium can be in a dry, liquid, or semi-liquid form, depending upon its water content, and comprise at least one compound capable of forming an aqueous gel when in contact with water; at least one nutrient capable of supporting growth of said microorganism; and at least one indicator compound of formula I and / or IV, notably 4-methylumbelliferyl myo-inositol-1-phosphate or salts thereof and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoxyl myo-inositol-1-phosphate or salts thereof. PI-PLC generated by the microorganisms of interest leads to cleavage of the indicator compounds causing formation of fluorescence and / or color suitable for identification of type and count of such hygienically and pathologically important microorganisms as Listeria species.
Owner:BIOSYNTH
Detection of microbial metabolites
InactiveUS6660494B2Easy to detectAvoid disadvantagesBacteriaMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiotechnologyMetabolite
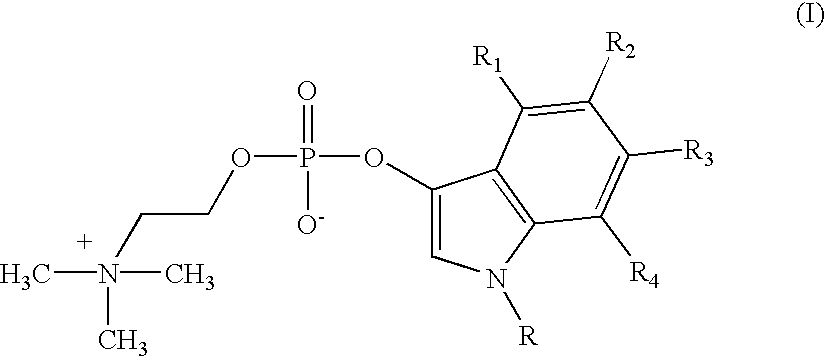
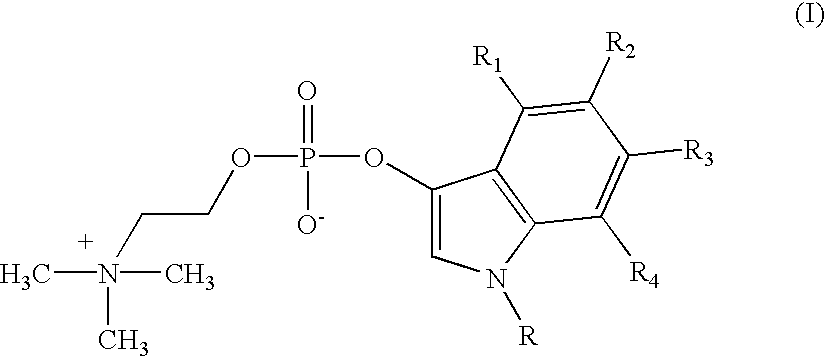
Chromogenic 3-Indoxyl choline phosphate compounds of formula (I):wherein R is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and C1-4 alkyl, such as methyl, ethyl, propyl and butyl while R<1>, R<2>, R<3>, and R<4 >are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro, carboxy, amino, amino substituted with one or two C1-4 alkyl groups, aminomethyl, hydroxy, C1-4 alkoxy, carboxyalkyl, and sulphonyl. These compounds are capable of being cleaved by lecithinase C leading to products which are calorimetrically detectable. The invention provides safe and sensitive detection of potentially pathogenic bacterial activity of such microbes as Clostridium perfringens, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus anthracis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Listeria monocytogenes, Heliobacter pylori, Legionella pneumophila, and others in material which may contain such activity typically including physiological samples, goods for consumption, such as food and beverages, and any other potentially infected objects or articles.
Owner:BIOSYNTH
Solid-phase synthesis of asymmetric indocyanine dyes
Solid-phase synthesis of asymmetric indocyanine dye is carried out by preparing methine-electrophilic agent with polyethylene as carrier, reacting carried electrophilic agent with nucleophilic 1-bit substitute 2-methyl indole or its derivative to obtain carried semi-dicyan dye, attacking 1-bit substitute 2-methyl indole or its derivative with nucleophilic carbon atom to carried semi-dicyan dye and nucleophilic reacting to obtain the final product. It costs low and has short production period, high purity and no need for chromatography separation.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Detection of microbial metabolites with a 3-indoxyl-myo-inositol-1-phosphate compound
InactiveUS6068988ADisadvantageous effect stabilityGood colorSugar derivativesHydrolasesPhosphoric acidBacillus cereus
A method of detecting a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C enzyme by means of a substrate which is cleaved by said enzyme and yields a dye when the chromophoric portion of the substrate is dimerized and oxidized; the invention teaches using in such method, as a novel substrate, a 3-indoxyl-myo-inositol-1-phosphate compound of formula (I) wherein R is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and C1-4 alkyl, while R1, R2, R3, and R4 are radicals selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro, carboxy, amino, alkyl-substituted amino and sulphonyl; or of a salt of said formula I compound. The invention provides for a safe and sensitive method of detection of potentially pathogenic bacterial activity of such microbes as Bacillus cereus, B. Thuringiensis, Staphy lococcus aureus and various Listeria strains in potentially infected materials including physiological samples or consumable goods such as foods and beverages.
Owner:BIOSYNTH
Novel potentially fluorogenic compounds and plating media containing same
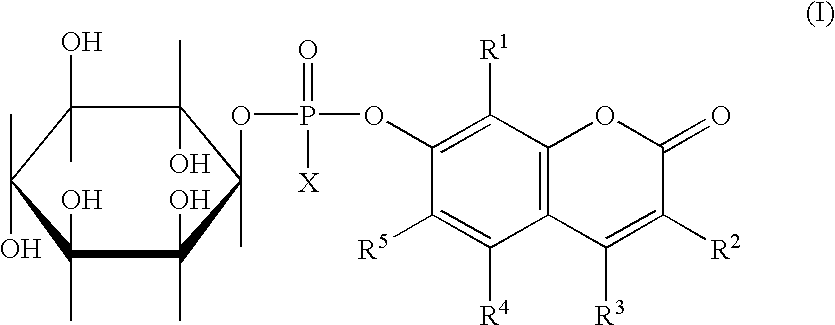
Compounds of formula (I) in which R1,R2,R3,R4 and R5 are hydrogen atoms or chromogenic substituents and X is hydroxyl, OR6 wherein R6 is selected from the group consisting of C1-C4 alkyl, or O-Me+ wherein Me+ is a cation derived from an organic or inorganic base; these compounds do not exhibit significant fluorescence but are capable of being cleaved by phosphatidyl-inositol-specific phospholipase C, an enzyme which is indicative of bacterial activity; the umbelliferyl moity resulting from such cleavage is a strong fluorogen thus providing effective test methods for various pathogenic bacteria, such as Listeria, Staphylococcus and Clostridium species. Also disclosed are plating media for detection of microorganisms that are capable of metabolic generation of a phosphatidyl inositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC). The plating medium can be in a dry, liquid, or semi-liquid form, depending upon its water content, and comprise at least one compound capable of forming an aqueous gel when in contact with water; at least one nutrient capable of supporting growth of said microorganism; and at least one indicator compound of formula I and / or IV, notably 4-methylumbelliferyl myo-inositol-1-phosphate or salts thereof and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoxyl myo-inositol-1-phosphate or salts thereof. PI-PLC generated by the microorganisms of interest leads to cleavage of the indicator compounds causing formation of fluorescence and / or color suitable for identification of type and count of such hygienically and pathologically important microorganisms as Listeria species.
Owner:BIOSYNTH
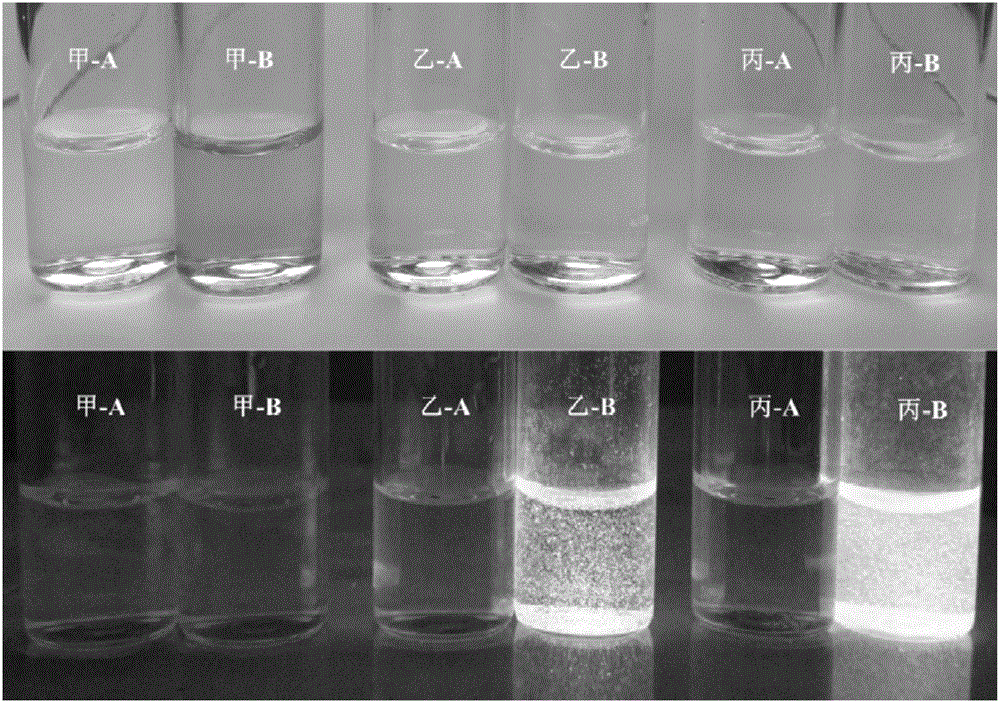
Synthesis method of glucoside based on indoxyl derivative and 2-(benzothiazol-2'-yl)phenol derivative
ActiveCN106432369AEasy to operateHigh yieldSugar derivativesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroorganismIndoxyl
The invention discloses a synthesis method of glucoside based on an indoxyl derivative and a 2-(benzothiazol-2'-yl)phenol derivative. The general formula of a synthetic equation of the synthesis method is as shown in the description; the Ar-OH represents aromatic phenol or a ketonic compound thereof, and is used as a glycosyl receptor in a glycosylation reaction; the G-X represents halogenated sugar, and is used as a glycosyl donor in the glycosylation reaction. According to the synthesis method of the glucoside based on the indoxyl derivative and the 2-(benzothiazol-2'-yl)phenol derivative, a 1-acetylindolin-3-one derivative is selected and used as an intermediate; a novel synthesis method is researched and developed to prepare the glucoside based on the indoxyl derivative; a novel glycosidase fluorescence probe based on a BTP ((2-benzothiazol-2'-yl)phenyl) derivative is synthesized by applying the method; meanwhile, the application effects of the glucoside based on the indoxyl derivative and the glycosidase fluorescence probe are investigated. The glucoside based on the indoxyl derivative and the 2-(benzothiazol-2'-yl)phenol derivative can be used as glycosidase substrates, and is used for the positioning analytic detection and screening on the corresponding glycosidase, a microorganism using the corresponding glycosidase as a characteristic target, and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY +1
Detection of microbial metabolites
InactiveUS20020151725A1Easy to detectAvoid disadvantagesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesBacillus perfringens
Chromogenic 3-Indoxyl choline phosphate compounds of formula (I): wherein R is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and C1-4 alkyl, such as methyl, ethyl, propyl and butyl while R1, R2, R3, and R4 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro, carboxy, amino, amino substituted with one or two C1-4 alkyl groups, aminomethyl, hydroxy, C1-4 alkoxy, carboxyalkyl, and sulphonyl. These compounds are capable of being cleaved by lecithinase C leading to products which are calorimetrically detectable. The invention provides safe and sensitive detection of potentially pathogenic bacterial activity of such microbes as Clostridium perfringens, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus anthracis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Listeria monocytogenes, Heliobacter pylori, Legionella pneumophila, and others in material which may contain such activity typically including physiological samples, goods for consumption, such as food and beverages, and any other potentially infected objects or articles.
Owner:BIOSYNTH
Preparation method of erasable neutral ink
InactiveCN105670385ANovel methodRaw material safety and environmental protectionInksVitamin CIndoxyl
The invention discloses a preparation method of erasable neutral ink, which belongs to the technical field of ink preparation. The present invention extracts vitamin C from orange peel, and compound-coats it with gelatin and gum arabic to prepare microcapsules, uses indoxyl as the ink dye, and supplements surfactants, thickening rheological agents, etc. to improve the stability and fluidity of the ink. Denaturation, thereby obtaining the preparation method of erasable neutral ink. The invention is easy to operate, uses gelatin and gum arabic to compound vitamin C to make vitamin C microcapsules, uses indoxyl as ink dye, and the raw materials are safe and environmentally friendly, so that the finally prepared erasable neutral ink has higher thixotropy , stability and fluidity, smooth writing feel, clear lines, and easy to erase, has broad application prospects.
Owner:张静
Card for fast testing residual pesticide
InactiveCN101693916BNo pesticide residueSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementIndoxylAcetylcholine esterase
A card for fast testing residual pesticide belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and comprises two layers of plastic plates, wherein one of the plastic plates is provided with a sampling hole and an observation hole, one face of the plastic plate is provided with water-absorbing paper and an enzyme bar for fixing drosophila melanogaster acetylcholine esterase, the water-absorbing paper opposites the sampling hole, the enzyme bar opposites the observation hole, and the water-absorbing paper is connected with the enzyme bar. A base sheet for fixing indoxyl acetic ester is bonded on the other plastic plate at the position corresponding to the enzyme bar, and a baffle is arranged between the base sheet and the enzyme bar. When the sample and the indoxyl acetic ester in theenzyme bar pre-react, the baffle is drawn out to make the enzyme bar and the base sheet contact. The card for fast testing residual pesticide has the advantages of wide application range, delicate testing and fast and simple operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Indole hemicyanine fluorescent probe, preparation method and application to detection of cyanide ions
ActiveCN110041305ATo achieve specific identificationInhibit transferOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceIndoxylCyanide ion
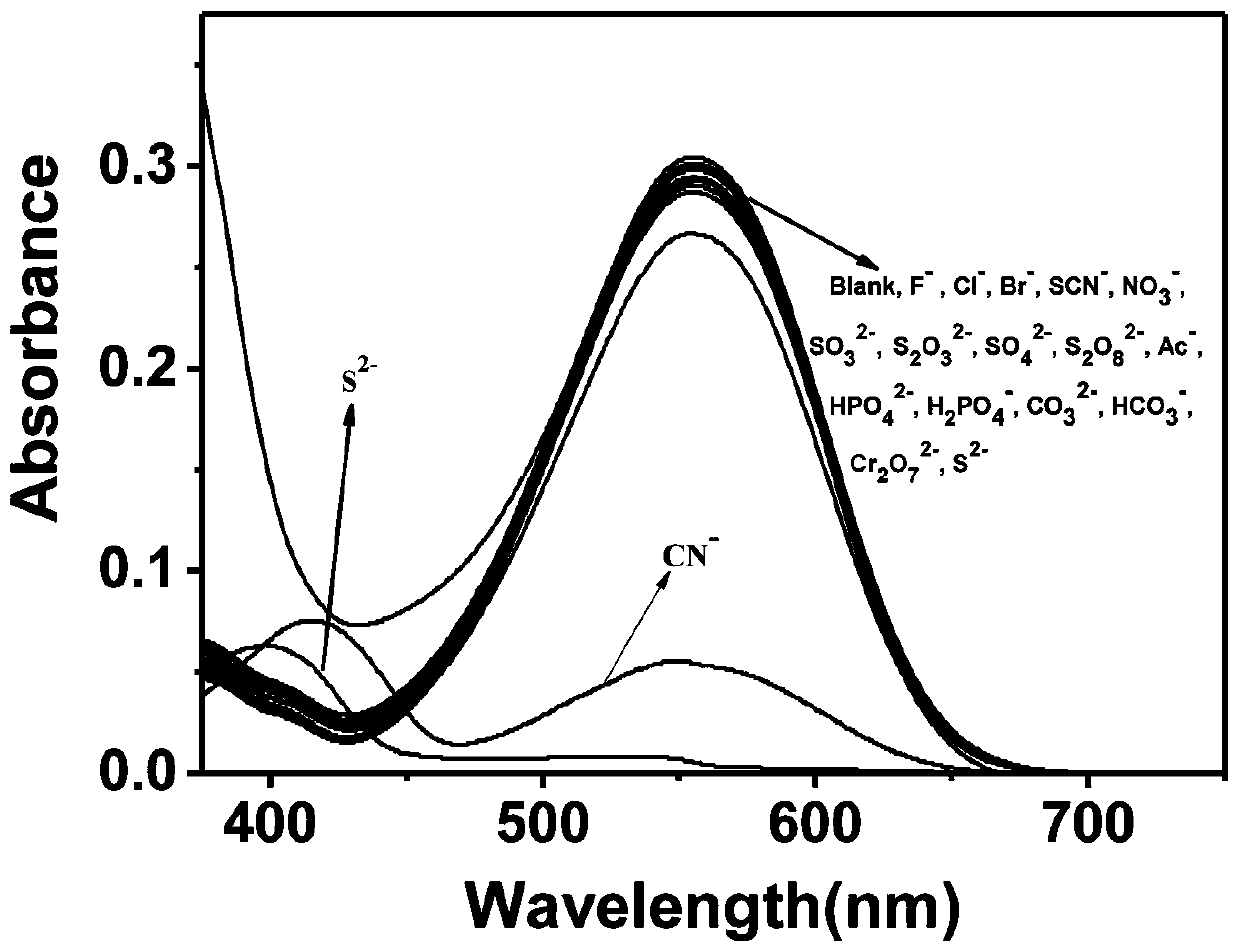
The invention provides an indole hemicyanine fluorescent probe, a preparation method and application to detection of cyanide ions and particularly relates to a probe, i.e., 2-(2-(2-chloro-7-diethylaminoquinoline-3-yl)vinyl-N,3,3-trimethyl-3H-indole (QIE). The probe is prepared by taking 2-chloro-7-diethylaminoquinoline-3-formaldehyde and N,2,3,3-tetramethyl-3H-indole as raw materials and carryingout condensation. After the cyanide ions react with the QIE, a solution becomes colorless from purple when being observed by naked eyes; the solution becomes bright yellow green fluorescence from darkpurple fluorescence under the action of an ultraviolet lamp with 365 nm. The lowest detection limit for detecting the cyanide ions through an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry is 1.05*10<-6> mol / L and the lowest detection limit for detecting the cyanide ions through a fluorescence spectrophotometry is 4.16*10<-8> mol / L. The qualitative and quantitative detection of micro / trace cyanide ions ofsamples with different sources is realized through double channels including the ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry and the fluorescence spectrophotometry.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
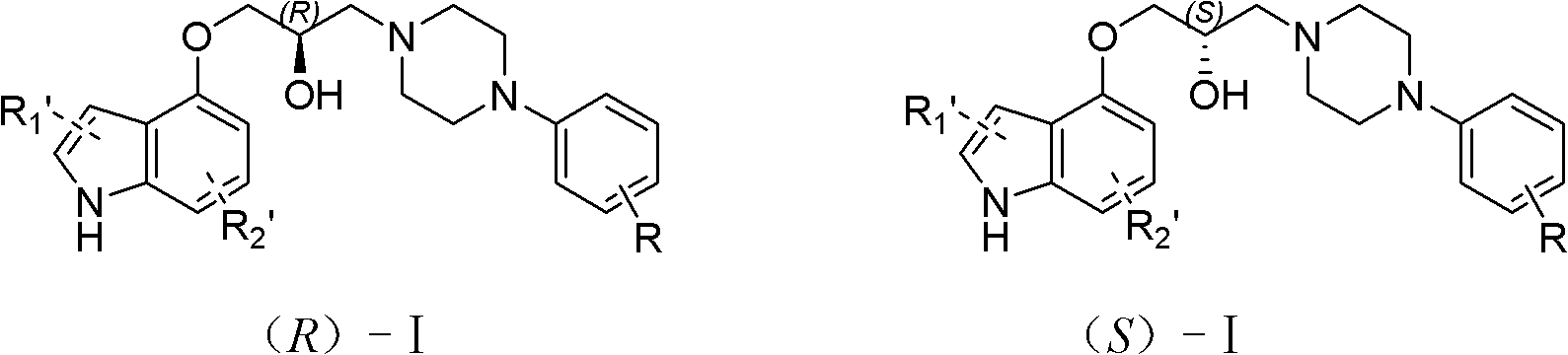
1-(4-indoxyl)-3-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazidine)-2-propanol optical isomer, derivative and salt thereof and preparation and application of optical isomer
InactiveCN102807522AEffective diastoleDiastoleOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAdjuvantPhosphate
The invention relates to a 1-(4-indoxyl)-3-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazidine)-2-propanol optical isomer, a derivative and a salt thereof and a preparation method and an application of the optical isomer. The 1-(4-indoxyl)-3-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazidine)-2-propanol optical isomer is characterized by being an optical isomer shown as a structural general formula (R)-I or formula (S)-I, wherein the substituents of R1' and R2' are hydrogen; or the optical isomer is a free alkali or salt shown as a structural general formula (R)-I or formula (S)-I, wherein the substituents of R1' and R2' are alkyl, alkoxyl, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy, substituted aryloxy or halogen, and the substituent of R in the formula is halogen, alkoxy or alkyl. The 1-(4-indoxyl)-3-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazidine)-2-propanol optical isomer is suitable for preparing a medicament for treating hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia; the conventional medicament excipients can be added for preparing oral dosage forms such as syrup, capsules, tablets and particles; and the medicament excipients can include solid carriers such as lactose, starch, glucose, methylcellulose, magnesium stearate, dicalcium phosphate and mannite, or oral excipients such as ethanol, glycerol and water, or adjuvants such as flavoring agents and sweeteners, or the conventional technical mixtures known by technological personnel in other preparation fields.
Owner:广州医学院
Preparation method for continuously synthesizing indigo
InactiveCN101591287AImprove conversion rateReduce consumptionOrganic chemistryBis-indole indigosNitrogen gasSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method for continuously synthesizing indigo, which comprises the following steps: at certain temperature, introducing nitrogen gas to liquid metallic sodium; reacting the nitrogen gas with the liquid metallic sodium in an ammonia-sodium synthesizing tower to generate sodium amide; adding the sodium amide into alkali according to certain mixture ratio; continuously or intermittently adding the mixture into a blending reactor; at certain temperature and pressure, taking the alkali as solvent and the sodium amide as a condensation agent; continuously adding anilino group acetate; cyclically synthesizing the anilino group acetate into oxyindole phenate; continuously discharging and diluting the oxyindole phenate by water; and continuously oxidizing the diluted oxyindole phenate by an oxidation reaction device to obtain indigo blue. The preparation method improves the reaction yield and the quality of products, shortens the reaction period, reduces the generation of contaminants, reduces the equipment investment and the labor intensity of workers, improves the working environment and greatly reduces the energy consumption and material consumption.
Owner:JIANGSU TAIFENG CHEM
Method for synthesizing 5-bromine-4-chlorine-1-acetyl-3-indoxyl
PendingCN110683981ASimple processMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryMethylanilineAcetic anhydride
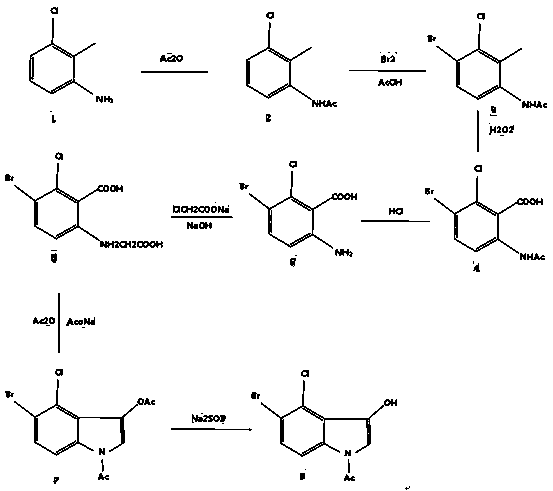
The invention discloses a 5-bromine-4-chlorine-1-acetyl-3-indoxyl synthesis process method. According to the method, 3-chlorine-2-methylaniline which is very easy to obtain is adopted as an initial raw material, and 5-bromine-4-chlorine-1-acetyl-3-indoxyl is prepared through seven steps of acetylation of acetic anhydride, bromine addition, oxidation of hydrogen peroxide, hydrolysis under an acidiccondition, a nucleophilic reaction of chloroacetic acid, cyclization of acetic anhydride, selective hydrolysis of sodium sulfite, and the like. The 5-bromine-4-chlorine-1-acetyl-3-indoxyl is furtheradopted as indoxyl for producing chromogen and is indirectly condensed with an enzyme substrate to prepare an indole developing substrate. The method is simple and practical in process, reaction conditions of the method are very mild, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the process is safe and environment-friendly, and industrialization is easy.
Owner:湖南恒泰生物医药有限公司
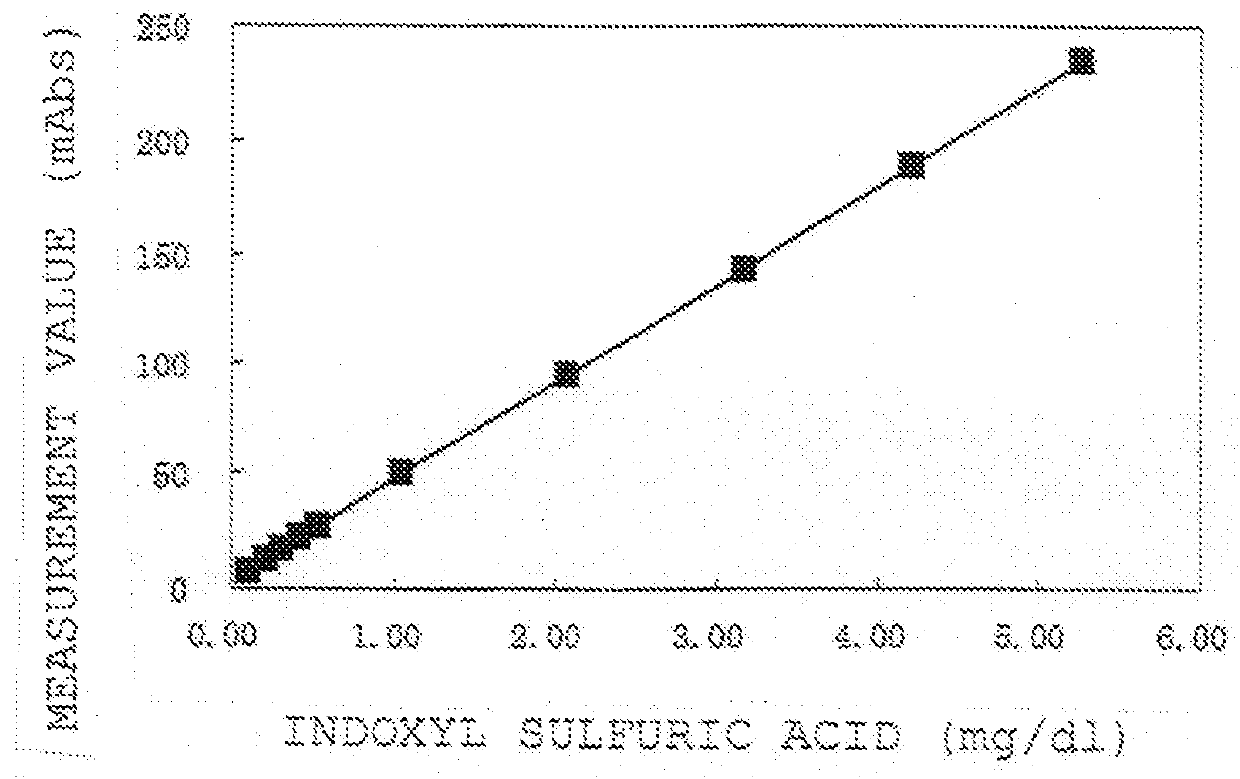
Method for measuring indoxyl sulfuric acid
ActiveUS20160032354A1High sensitivityEasy to detectHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementFormazanIndoxyl
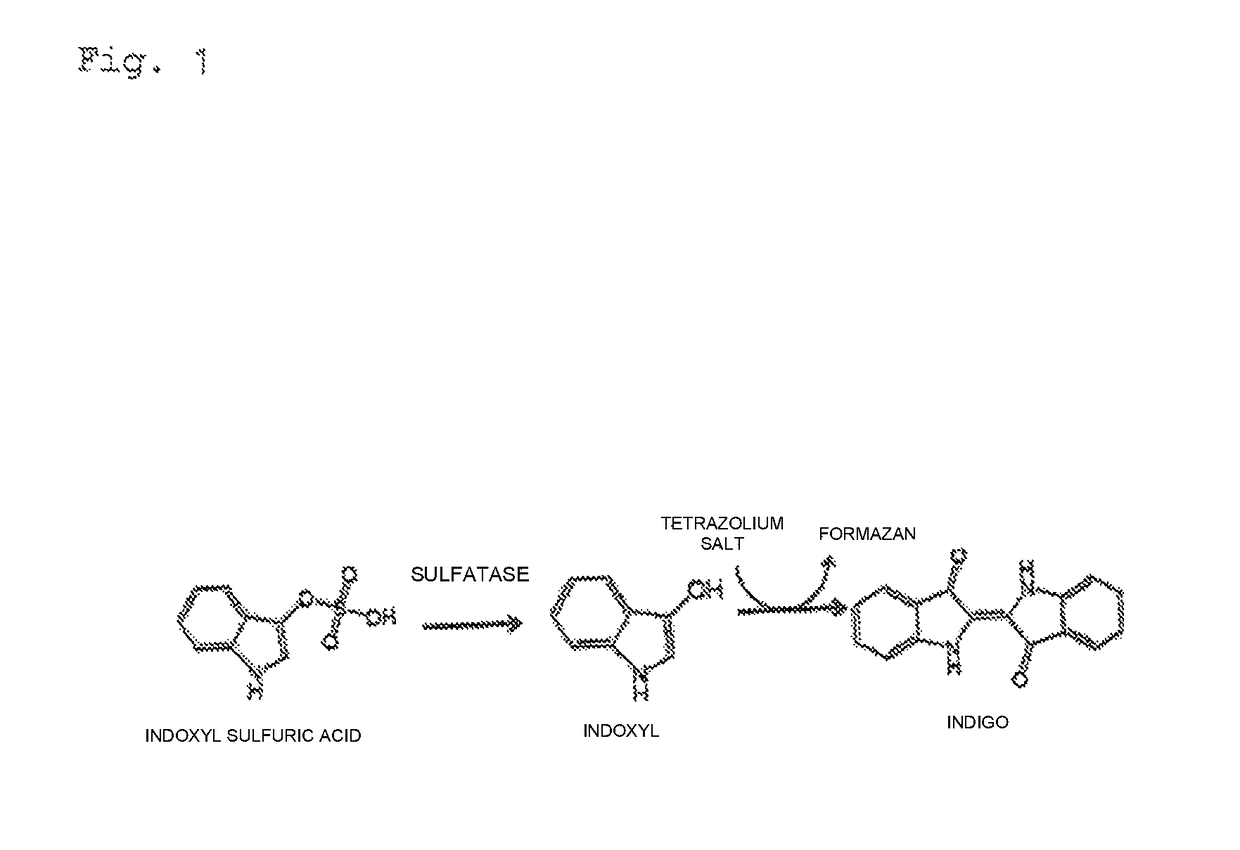
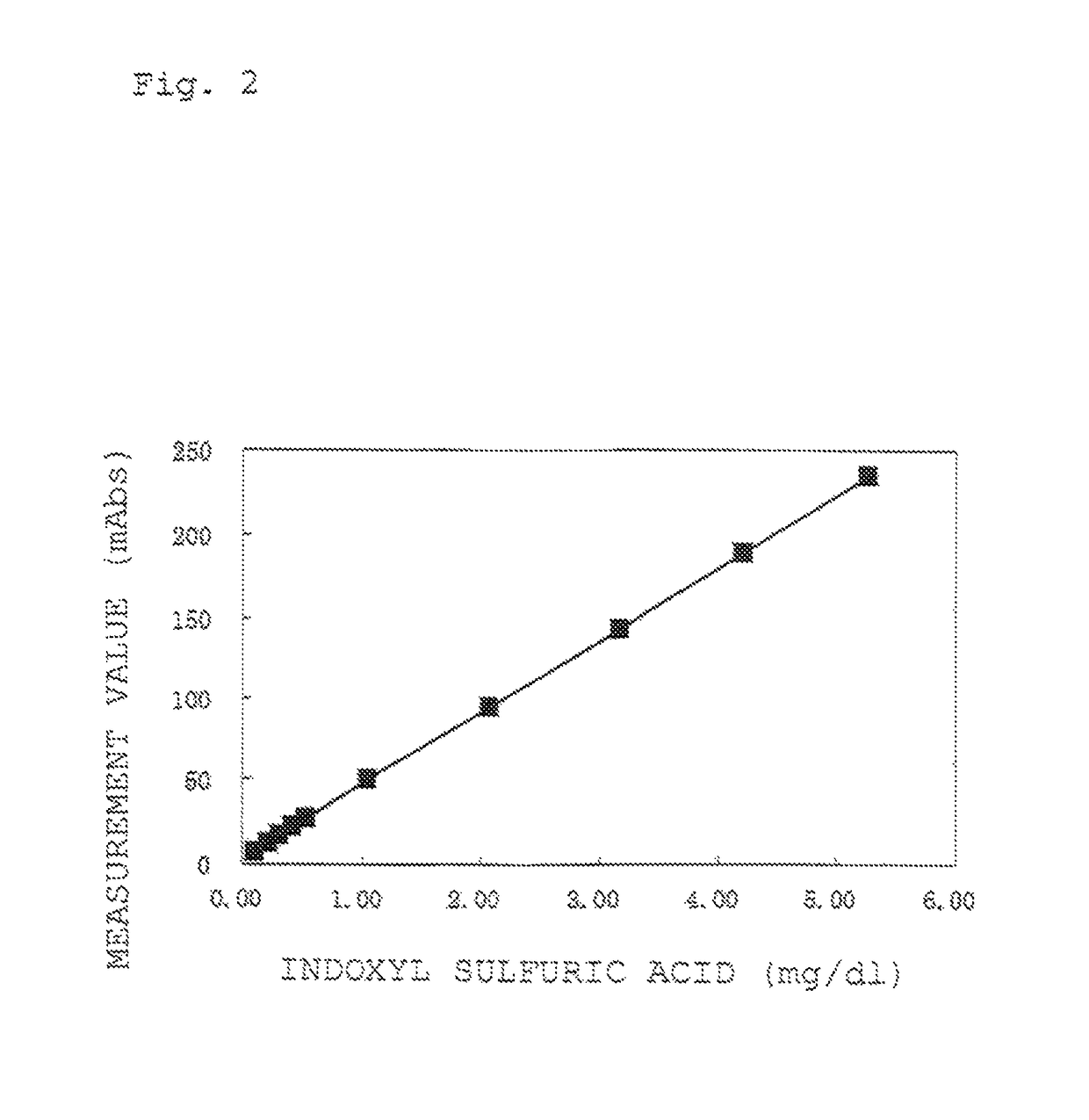
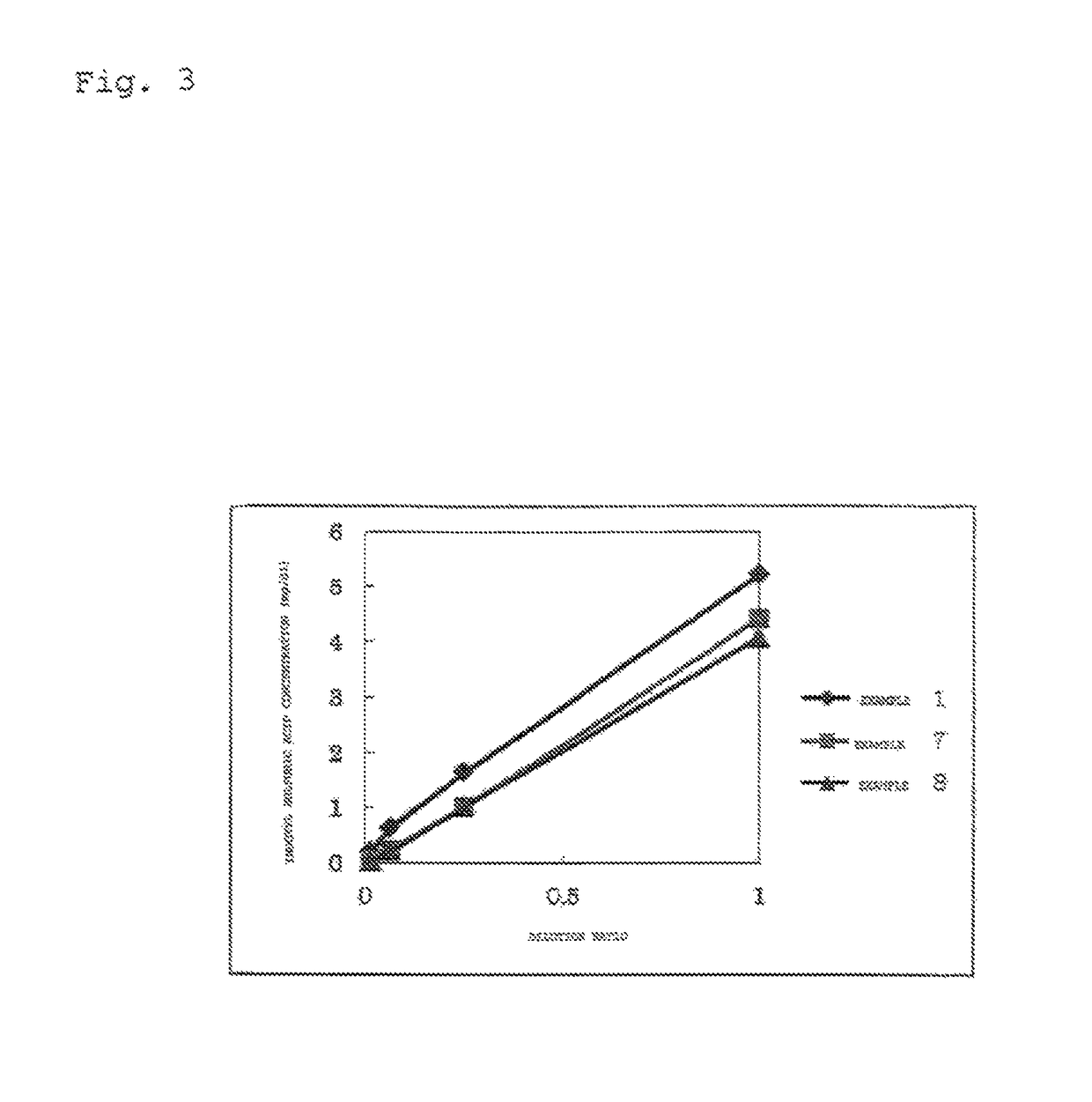
It is an object of this invention to provide a simple measurement method capable of detecting indoxyl sulfuric acid in a sample rapidly and at high sensitivity. By causing sulfatase and tetrazolium salt to act on indoxyl sulfuric acid in a sample to generate a formazan dye, and then calculating the generation amount of the formazan dye, indoxyl sulfuric acid in the sample can be measured more simply, more rapidly, and at higher sensitivity as compared with former methods.
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Preparation method for continuously synthesizing indigotin
The invention discloses a preparation method for continuously synthesizing indigotin, which comprises the steps that: liquid sodium metal reacts with ammonia gas at a certain temperature to produce sodium amide; the sodium amide is added to molten anhydrous alkali in a certain proportion, and then the mixture of the sodium amide and the anhydrous alkali is continuously added to a mixing reactor; anilino acetate is continuously added to the mixing reactor taking the anhydrous alkali as a solvent and the sodium amide as a condensing agent; and the anilino acetate is cyclized into hydroxyindole phenolate at certain temperature and pressure, and then the hydroxyindole phenolate is continuously oxidized to produce the indigotin. The alkali is potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide or a mixture of the potassium hydroxide and the sodium hydroxide. The method has the advantages of improving the reaction yield and the product quality, shortening the reaction period, reducing the generation of pollutants, reducing the equipment investment and the employee labor intensity, improving the working environment, and greatly reducing the energy consumption and the production cost.
Owner:JIANGSU TAIFENG CHEM
Synthesis of psuedo indoxyl derivatives
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
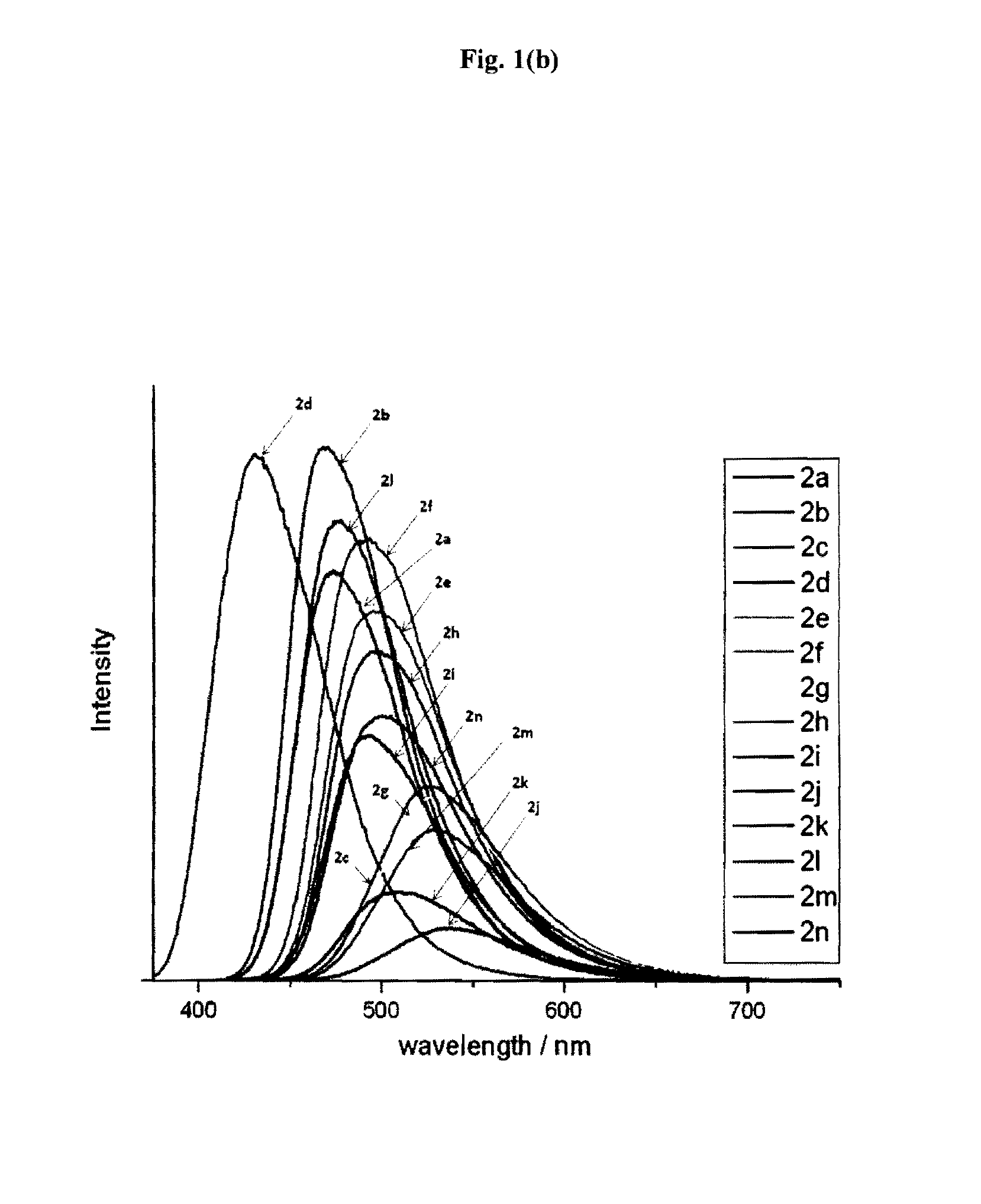
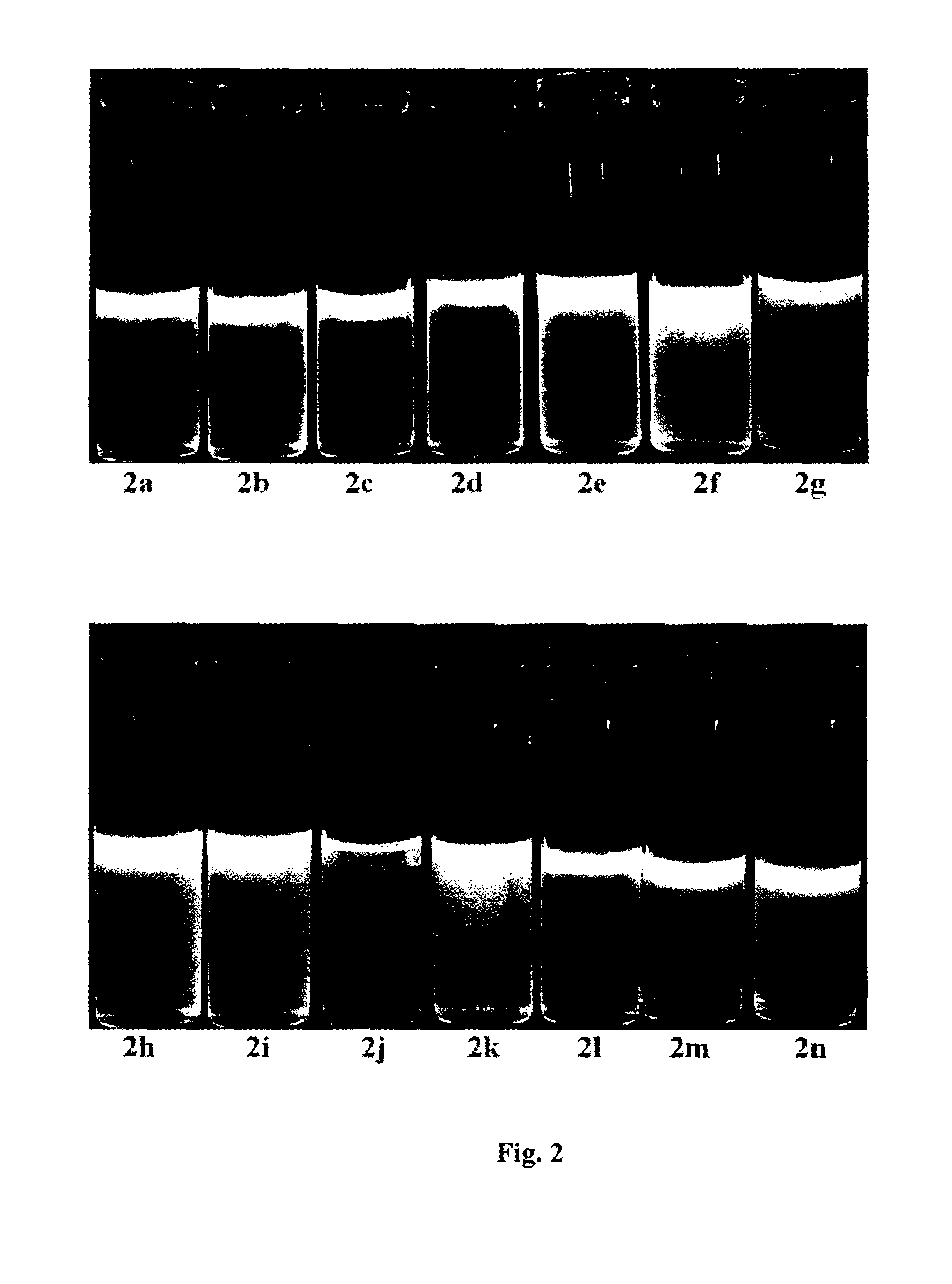
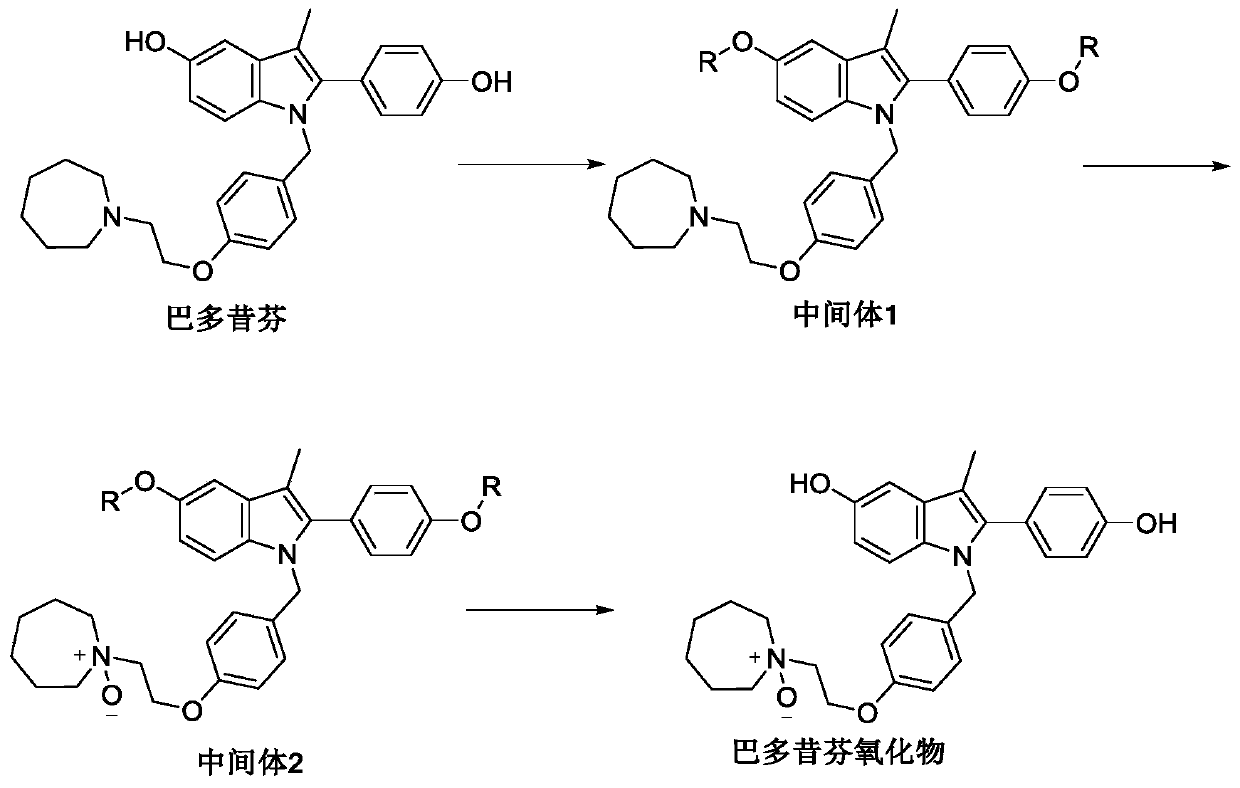
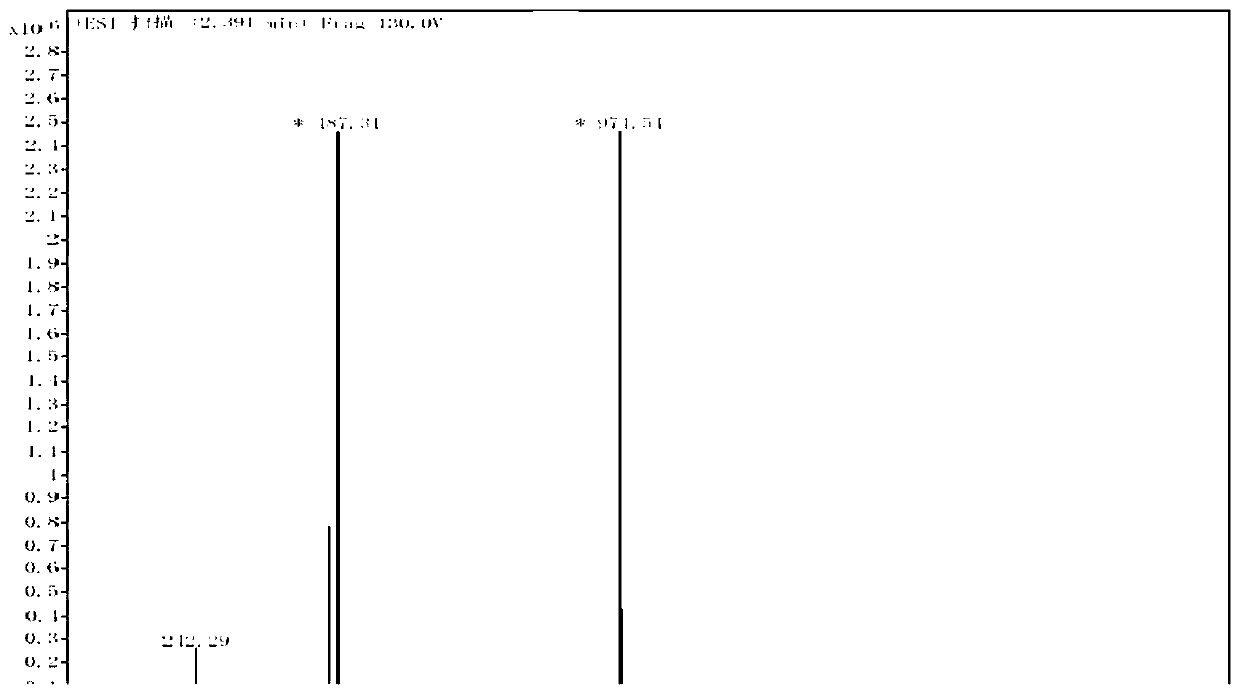
Preparation method of bazedoxifene oxide
InactiveCN111018770AEffective quality controlSolve the problem of quality controlOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionPhenyl groupPhenol
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a preparation method of bazedoxifene oxide, wherein the preparation method comprises the steps: by using bazedoxifene free alkali as a raw material, dissolving in a first benign solvent, adding an organic alkali, and adding a silane protecting group to protect two phenolic hydroxyl groups, and thus obtaining anintermediate 1; dissolving the intermediate 1 in a second benign solvent, and adding an oxidant for oxidation to obtain an intermediate 2; and dissolving the intermediate 2 in a third benign solvent,and adding a protecting group removing reagent to remove two molecular silane protecting groups, and thus obtaining the bazedoxifene oxide. According to the preparation method of the bazedoxifene oxide provided by the invention, a preparation method of 1-[4-[2-(azacycloheptan-1-yl)ethoxy]benzyl]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1H-indole-5-phenol-N-oxide is provided, and the preparation method has important significance in effectively controlling the quality of bazedoxifene.
Owner:北京鑫开元医药科技有限公司
Spectrophotometry for testing activity of pyruvic acid dehydrogenase system
InactiveCN100523784CLow priceSmall standard errorMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsThiamine pyrophosphatePotassium ferricyanide
A spectrophotometric method for the determination of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. This method uses a spectrophotometer, in the presence of substrate sodium pyruvate and cofactors magnesium chloride, thiamine pyrophosphate, using phenazine dimethyl sulfate as electron transporter, thiazole blue as electron acceptor, thiazole blue Reducted by pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1) product hydroxyethyl-pyrophosphate thiamine, the maximum absorption peak of thiazole blue changes from wavelength 400-430 nanometers to 540-640 nanometers, by measuring the wavelength 540-640 nanometers light absorption The amount of increase determines the reduction of thiazolium blue and defines the activity of the enzyme. The reagents used in this method are more economical, more stable, and more sensitive than the 2,6-dichloroindoxyl method and the potassium ferricyanide method. The influence of reagents is not conducive to the determination of E1 activity in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. This method is not only suitable for the determination of purified pyruvate dehydrogenation activity, but also for pyruvate dehydrogenation in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex after mitochondria extraction. Hydrogenase activity assay.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
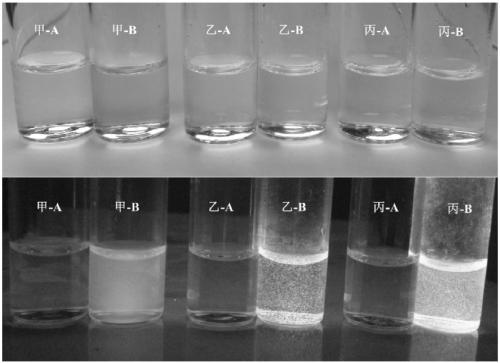
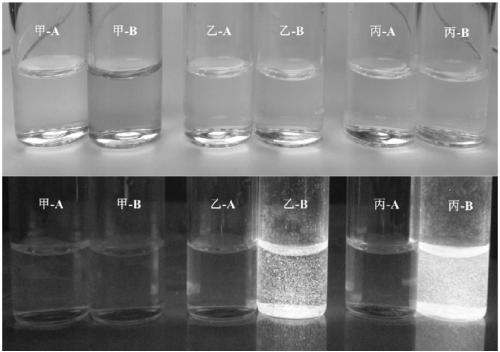
Catalyst for aqueous-phase preparation of indole nitrogen arylide and preparation method of indole nitrogen arylide
InactiveCN102806104BSimple compositionLow priceOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsArylIndoxyl
The invention discloses a catalyst for aqueous-phase preparation of indole nitrogen arylide. The catalyst comprises oxides of copper salt or copper, ligands and surface active agents according to the molar ratio of 1:(0.5-50):(0.5-50). The invention further discloses a method utilizing the catalyst to realize aqueous-phase preparation of the indole nitrogen arylide. The method includes steps of adding the catalyst, indoles or indole derivatives, iodo-arylide and alkali into water to realize nitrogen arylation reaction; and treating after the nitrogen arylation reaction so as to obtain the indole nitrogen arylide. The catalyst for the aqueous-phase preparation of the indole nitrogen arylide is cheap and environment-friendly, is simple in composition, wide in application range and easy to use, and can be used for industrialization production. Reaction conditions required by the catalyst for preparing the indole nitrogen arylide are easy to control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kind of synthetic method of the glycoside based on indoxyl derivative, 2-(benzothiazol-2'-yl)phenol derivative
ActiveCN106432369BEasy to operateHigh yieldSugar derivativesFluorescence/phosphorescenceThiazoleIndoxyl
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY +1
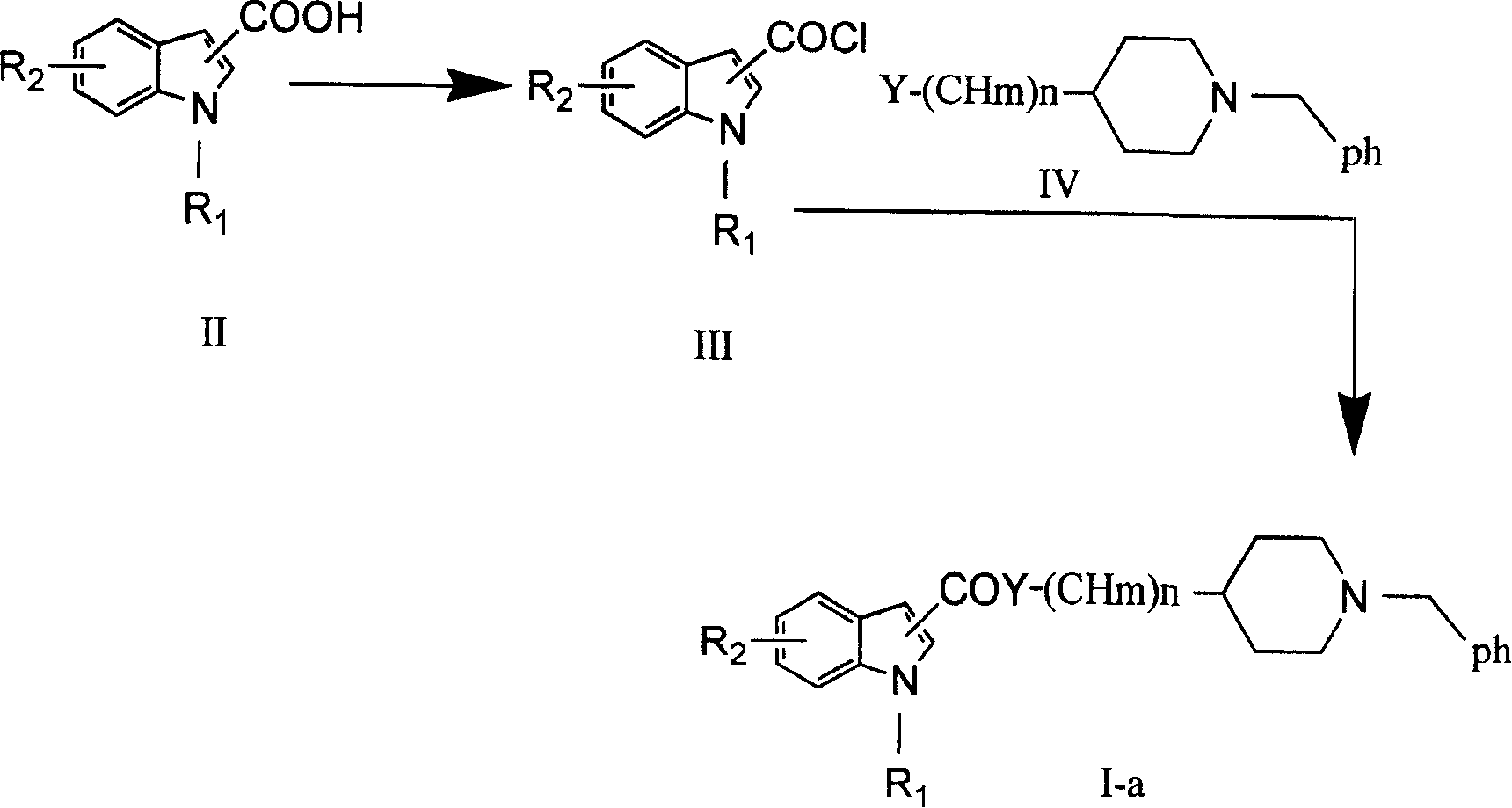
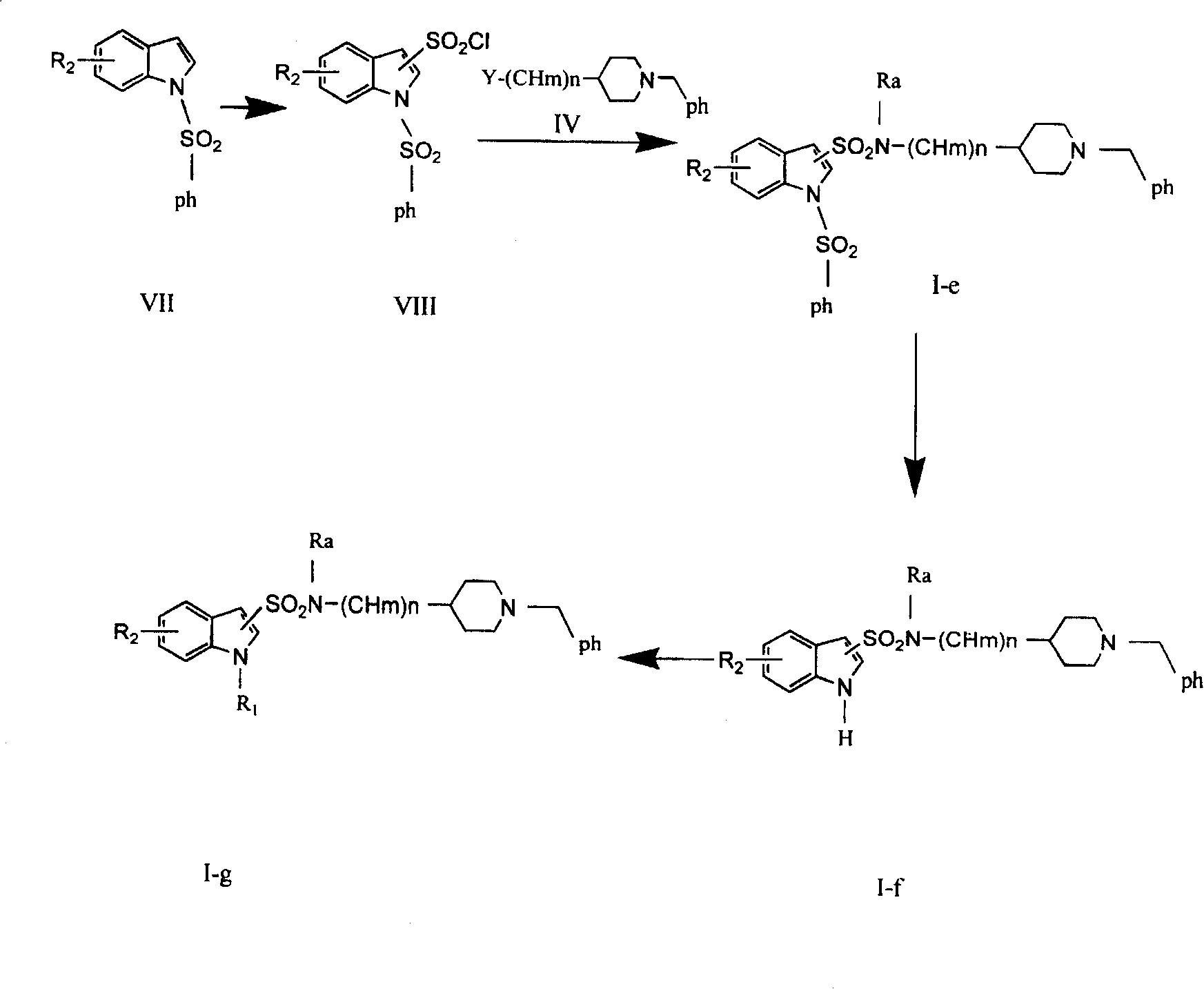
Indolylpiperidine compound and preparation process and use thereof
The present invention provides a kind of indoxyl piperidine compound. The pharmacological tests show that said kind of compound can be used as inhibitor of acetylcholin esterase, can competitively inhibit the activity of acetylcholin esterase, can delay hydrolysis of acetylcholin so as to raise the action of acetylcholin in synapsis and attain the goal of curing presenile dementia.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Usage of indophenol salt in direct dyeing in situ
InactiveCN1204202CImprove protectionConducive to market competitionIndole-indigosDyeing processIndoxylIndigo dye
The invention relates to a 3-indoxyl salt that can be oxidized to indigo directly to dye textile materials instead of indigo and indigo white in situ, the preparation method of the indoxyl salt, and the indoxyl salt to be oxidized in situ to form The use of indigo to directly dye textile materials. The invention can simplify the repeated reduction-oxidation process of converting indoxyl salt into indigo in the traditional process into one step. This simplifies the process, saves the alkali and hydrosulfite consumed in multiple reduction-oxidation processes, saves manpower and material resources, thereby improving the utilization rate of equipment, reducing costs, and is conducive to environmental protection and market competition.
Owner:北京慧聚英力医药化学技术发展有限公司 +2
Calibration reagent and preparation method for indican test
ActiveCN101210878AGood precisionGood correlationColor/spectral properties measurementsIndoxylPhosphate
The invention discloses indoxyl-Beta-glucoside calibration solution, which comprises (by weight parts) disodium hydrogen phosphate 9-12, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1-4, sodium chloride 70-90, and potassium chloride 1-4. The experimental observation and clinical applications indicate that the inventive calibration solution has similar performance and test effect as the imported reagent and can replace the imported reagent for clinical applications.
Owner:北京迈达康医疗设备制造有限公司
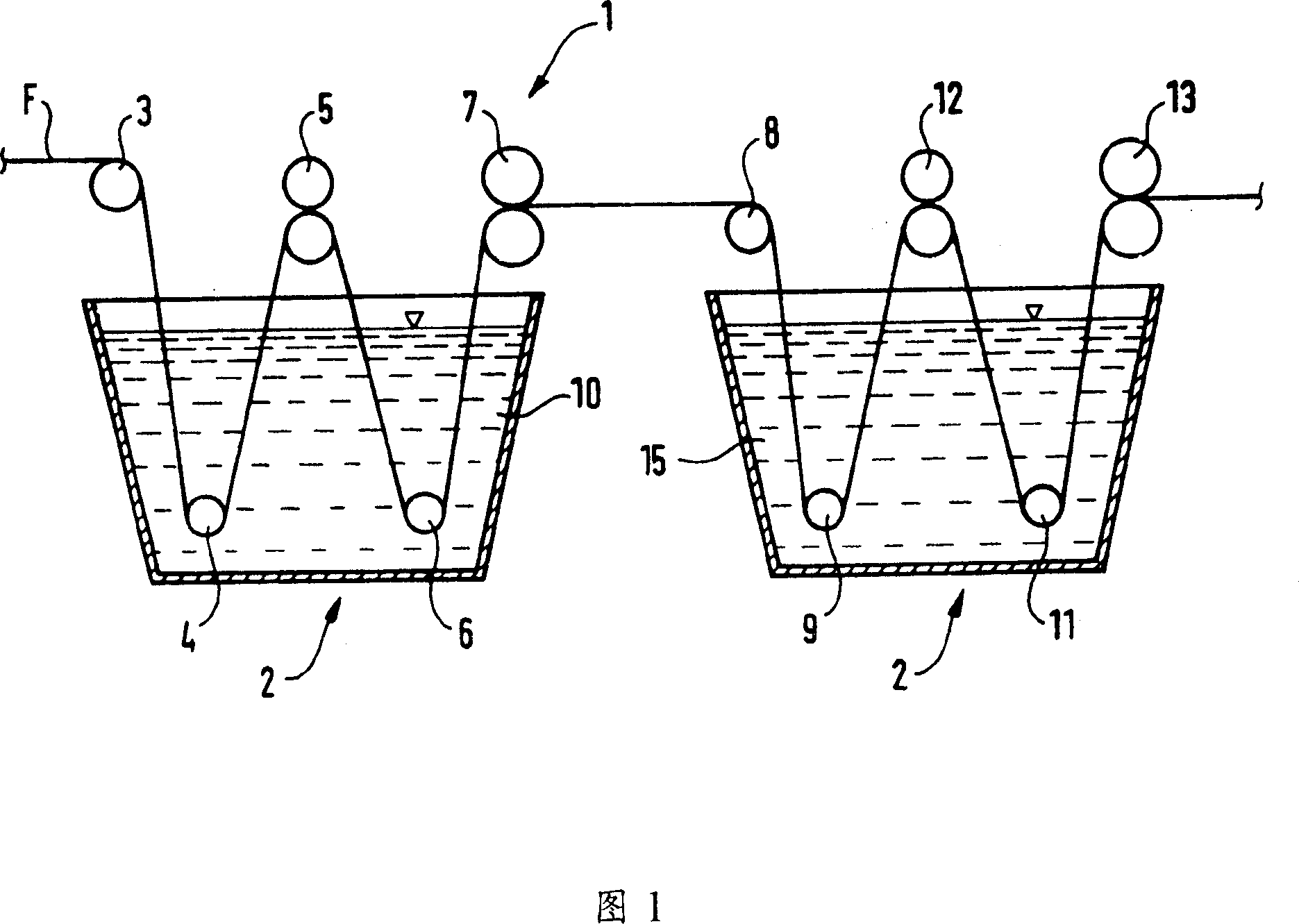
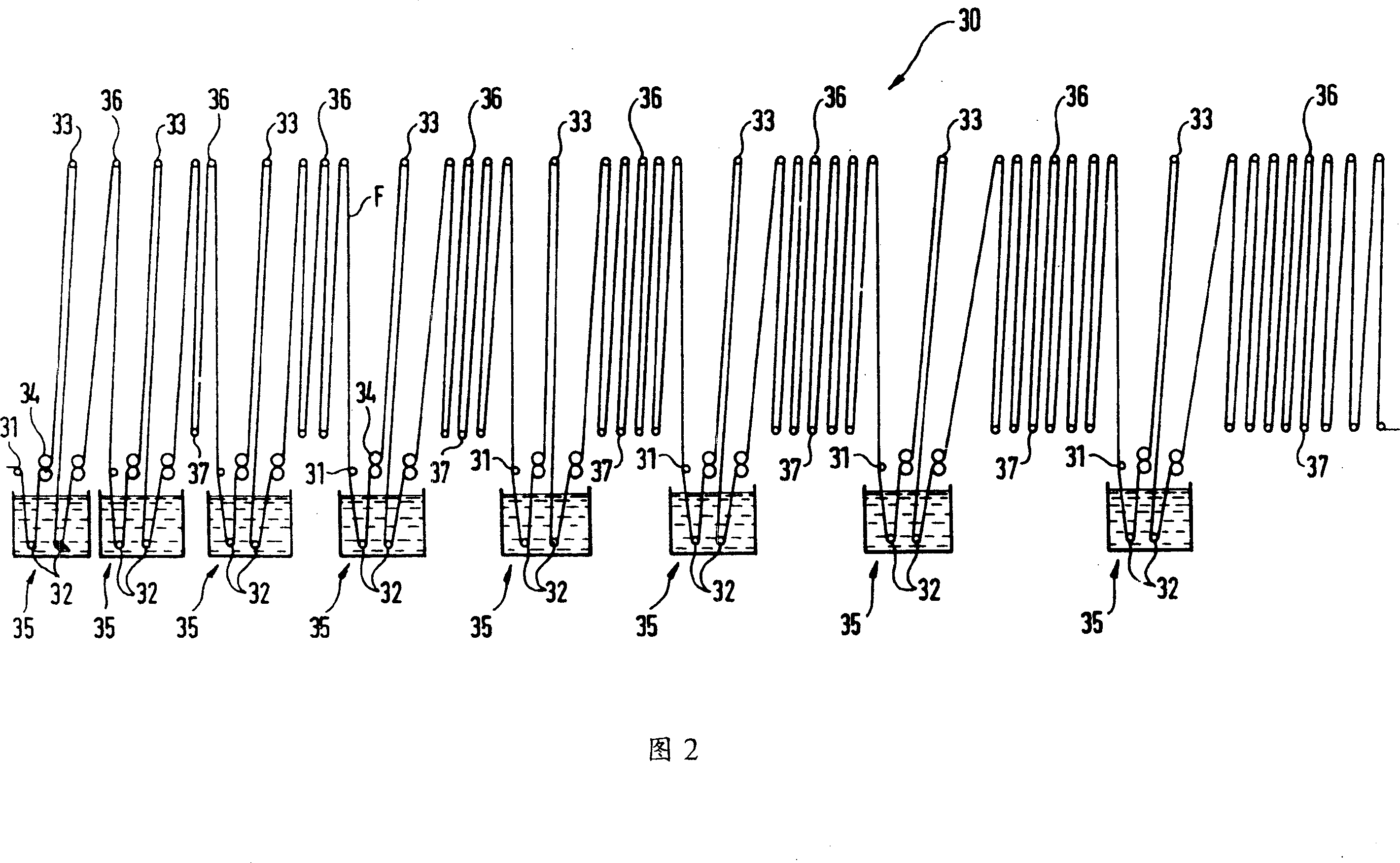
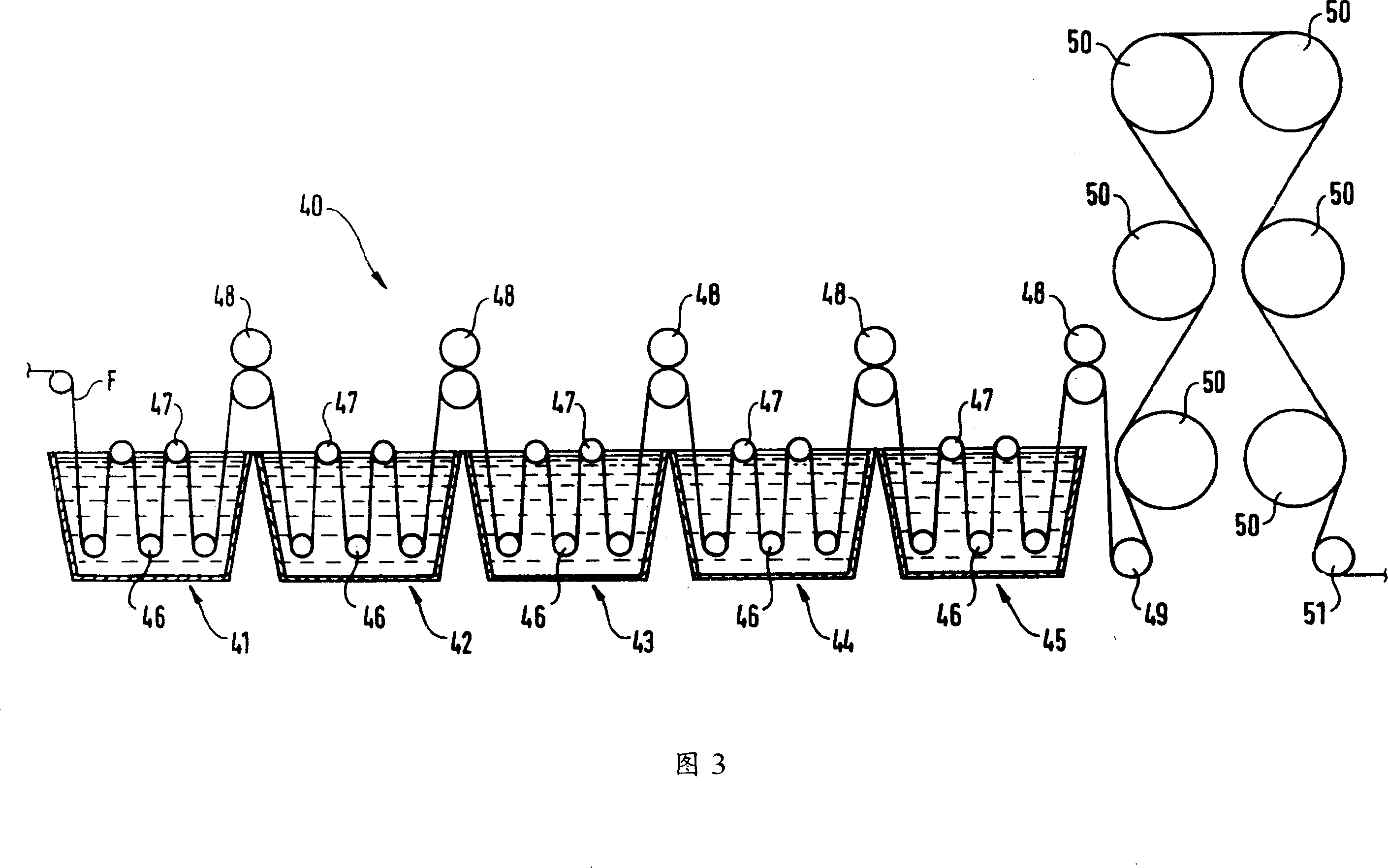
Byeing method spinning material using 3-indoxyl indigo blue and equipment utilizing said method
InactiveCN1330824CEliminate agingAchieve penetrationFibre treatmentTextile treatment machine partsYarnEnvironmental engineering
A method for dyeing textile material using indigo with the help of 3-indole-oxyl includes such steps as passing yarn through pre-washing unit, passing the yarn through 9 serially communicated tanks containing 3-indde-oxyl solution for dyeing, passing the yarn through the washing and pre-drying unit composed of a series of tanks, passing the yarn through sizing unit for sizing it with indigo dye, passing the yarn through dryer containing rollers, and winding yarn to obtain warp yarn.
Owner:弗兰科伊斯·格鲍德 +1
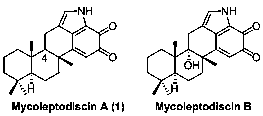
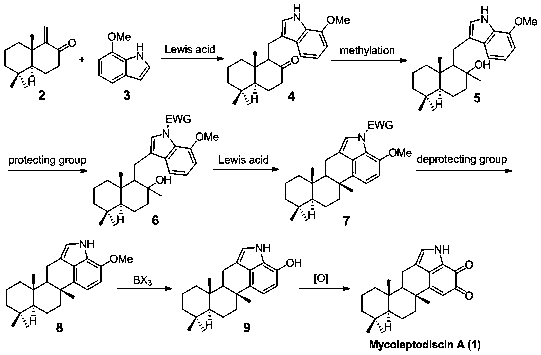
A kind of synthetic method of mycoleptodiscin A
ActiveCN108659094BFew reaction stepsSuitable for industrial productionSteroidsBulk chemical productionChemical synthesisKetone
The invention relates to a synthetic method for marine natural product mycoleptodiscin A, and belongs to the field of chemical synthesis. The method comprises the following steps: ketene sesquiterpene2 and 7-methoxyindole 3 are used as starting raw materials, the ketone sesquiterpene 2 and the 7-methoxyindole 3 are subjected to coupling to form sesquiterpene indole 4, the sesquiterpene indole 4 is methylated to form sesquiterpene indolol 5, the sesquiterpene indolol 5 reacts with an electron-withdrawing protecting group, protection is performed on -NH to form N-EWG protected sesquiterpene indole 6, the N-EWG protected sesquiterpene indole 6 is subjected to a cyclization reaction to form pentacyclic sesquiterpene indole 7, the pentacyclic sesquiterpene indole 7 is subjected to removal of N-EWG protection to form -NH pentacyclic sesquiterpene indole 8, the -NH pentacyclic sesquiterpene indole 8 is subjected to demethylation to form -NH pentacyclic sesquiterpene indoxyl 9, and finally the -NH pentacyclic sesquiterpene indoxyl 9 is subjected to an oxidation reaction to form the final natural product mycoleptodiscin A. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of having few reaction steps, simple operation and good product selectivity and being suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:威海创惠环保科技有限公司
New tower type oxidation technology for indigo blue
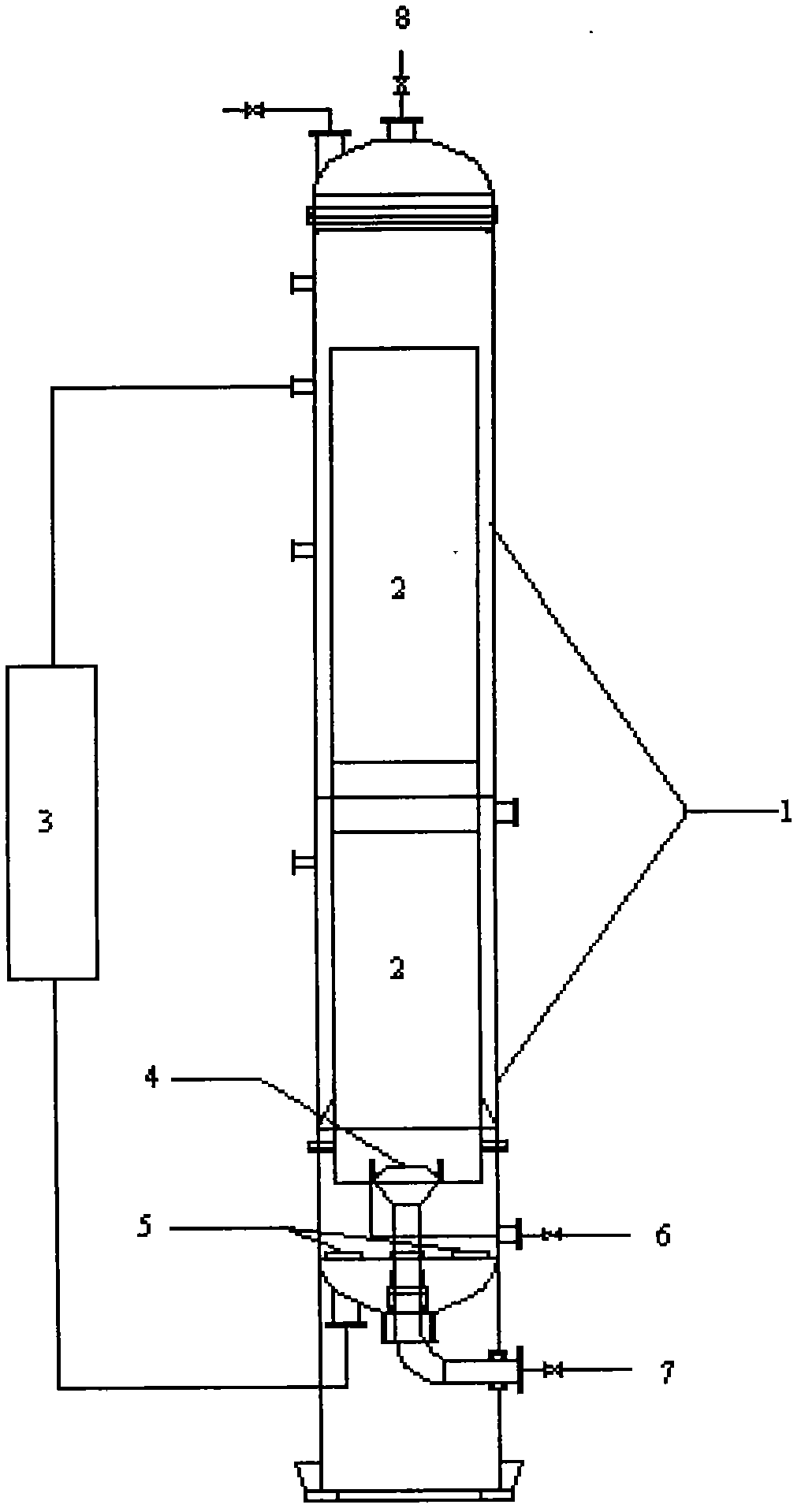
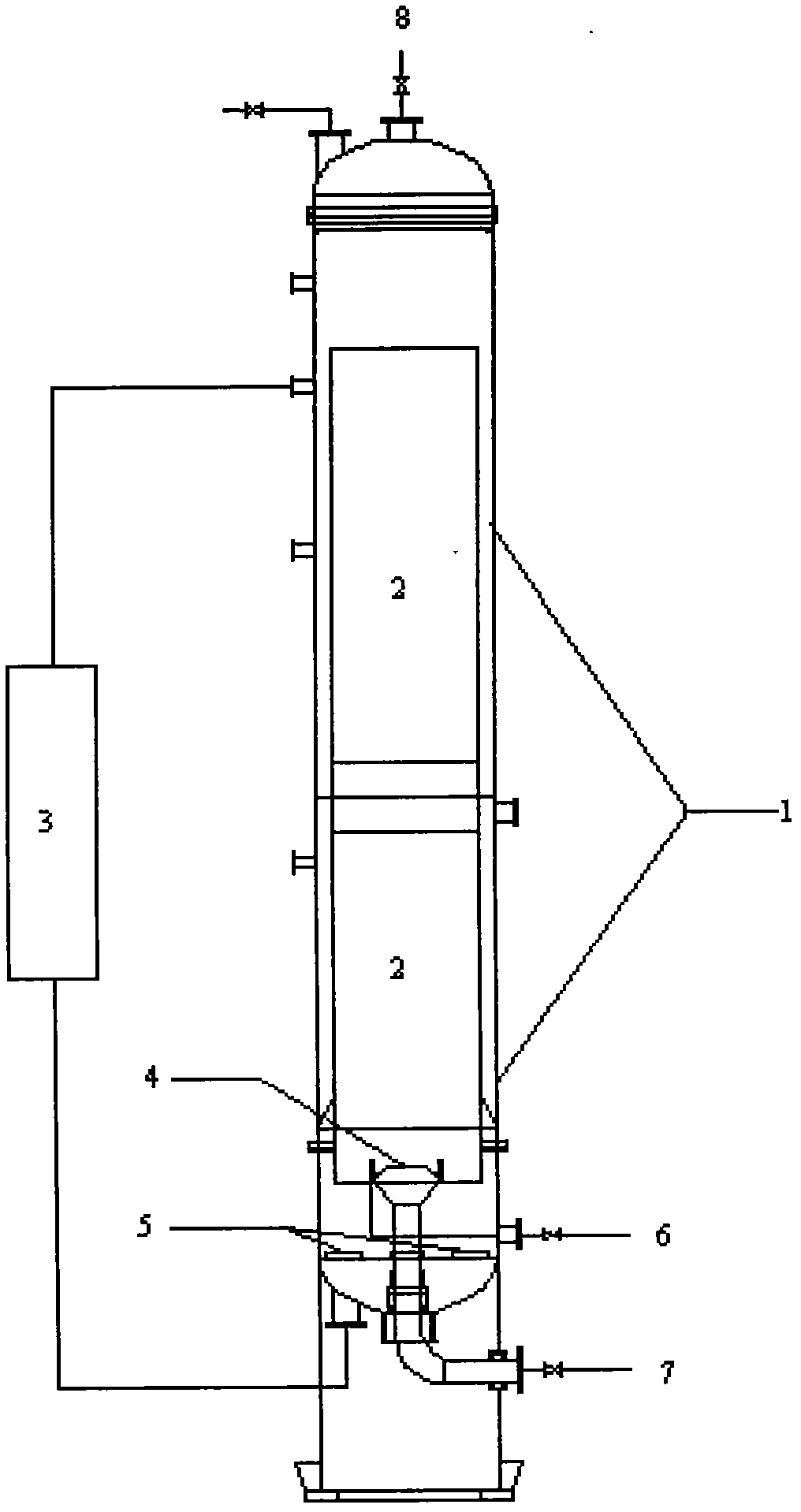
The present invention relates to a new technology for direct oxidation of a 3-indoxyl salt into indigo blue in a novel efficient ultrasonic circulation type reactor by using air or oxygen-containing gas. According to the present invention, the new technology and the new equipment are combined, such that concentration of the existing oxide material can be substantially increased, yield and purity of the reaction can be ensured well, significant effects of energy saving and consumption reduction are provided, and indigo production with characteristics of large scale, continuality and automation can be achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU TAIFENG CHEM +2
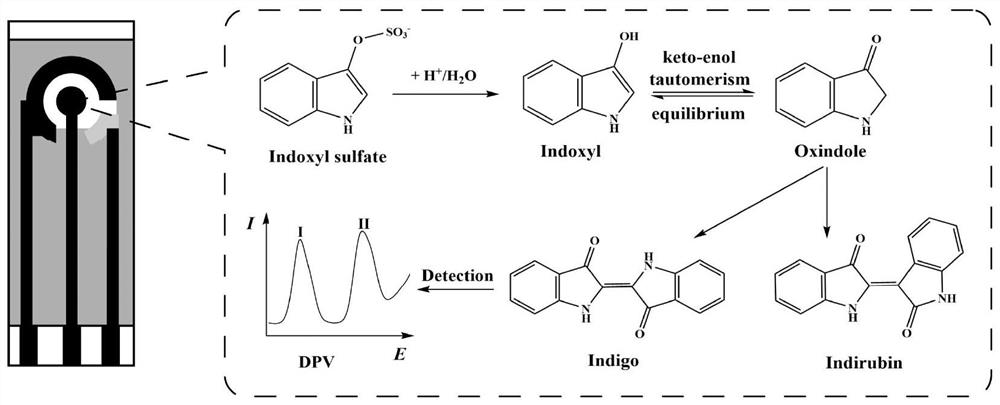
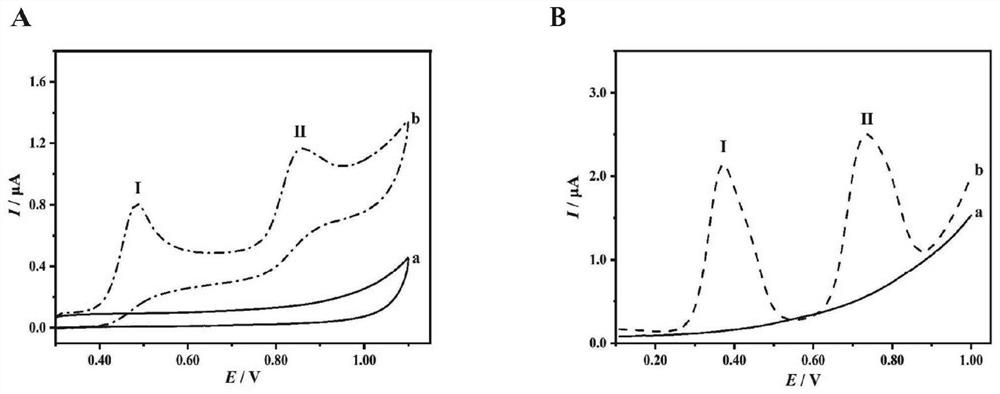
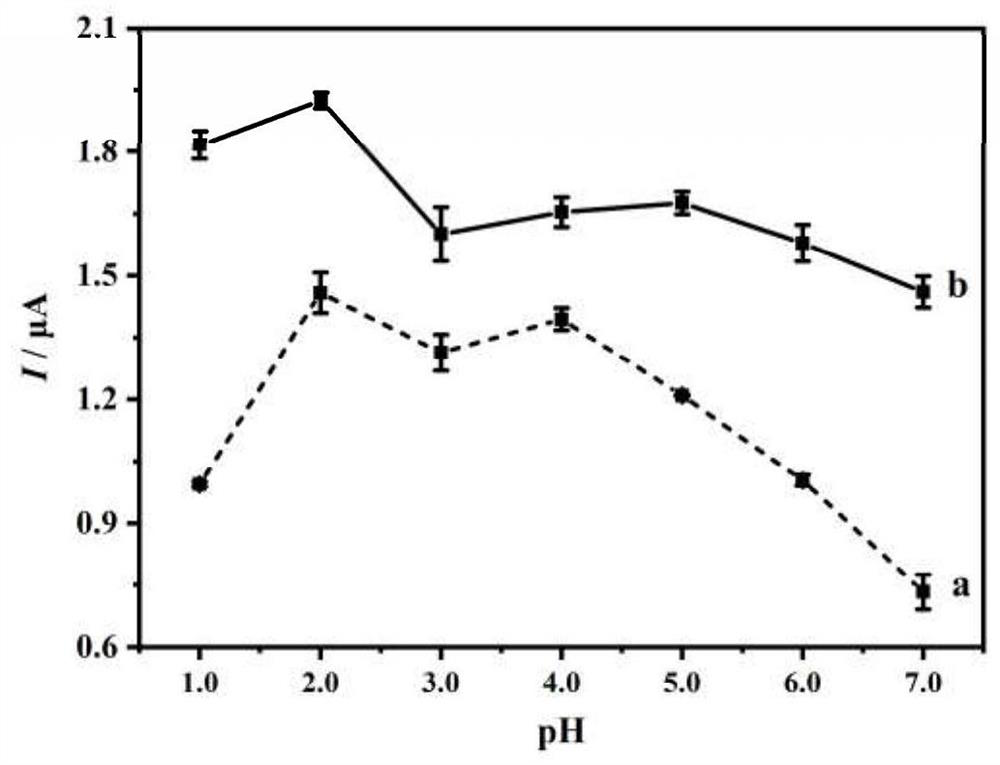
Electrochemical method for rapidly detecting plasma indoxyl sulfate
PendingCN113702463AEasy to operateReduce manufacturing costMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical responseDisease
The invention discloses an electrochemical method for rapidly detecting plasma indoxyl sulfate. According to the method, the modification-free silk-screen printing carbon electrode is adopted, the differential pulse voltammetry can effectively reduce the background current, electrochemical detection is carried out by adopting the differential pulse voltammetry, and according to the linear relation between an electrochemical response signal and the concentration of a to-be-detected substance, rapid quantitative detection of the indoxyl sulfate in the plasma is achieved. Instruments and equipment used in the method are small, the screen-printed carbon electrode has the advantages of simple design, low price, disposable use, less sample consumption, miniaturization and the like, the electrochemical detection method is simple, convenient and rapid, has good repeatability, stability and accuracy, can realize rapid quantitative detection of indoxyl sulfate in plasma, the method is helpful to understand the metabolic condition of the indoxyl sulfate in gestational diabetes mellitus, and provides laboratory basis for the occurrence mechanism, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of the disease and complications thereof.
Owner:重庆医科大学国际体外诊断研究院
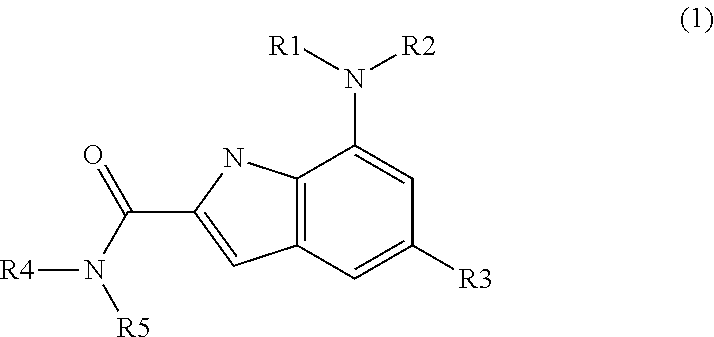
Indole amide compound as inhibitor of necrosis
ActiveUS20160194313A1Necrosis inhibitory efficacyAvoid blockingAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseIndoxyl
The present invention relates to an indole amide compound represented by formula (1), a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or isomer thereof, a composition for prevention or treatment of necrosis and necrosis-associated diseases, and a method for preparing the composition, the composition comprising the indole compound or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt or isomer thereof as an active ingredient.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
New tower type oxidation technology for indigo blue
The present invention relates to a new technology for direct oxidation of a 3-indoxyl salt into indigo blue in a novel efficient ultrasonic circulation type reactor by using air or oxygen-containing gas. According to the present invention, the new technology and the new equipment are combined, such that concentration of the existing oxide material can be substantially increased, yield and purity of the reaction can be ensured well, significant effects of energy saving and consumption reduction are provided, and indigo production with characteristics of large scale, continuality and automation can be achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU TAIFENG CHEM +2
Method for measuring indoxyl sulfuric acid
ActiveUS10150983B2Easy to detectQuick measurementHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementFormazanIndoxyl
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com