Patents
Literature
117 results about "Hydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
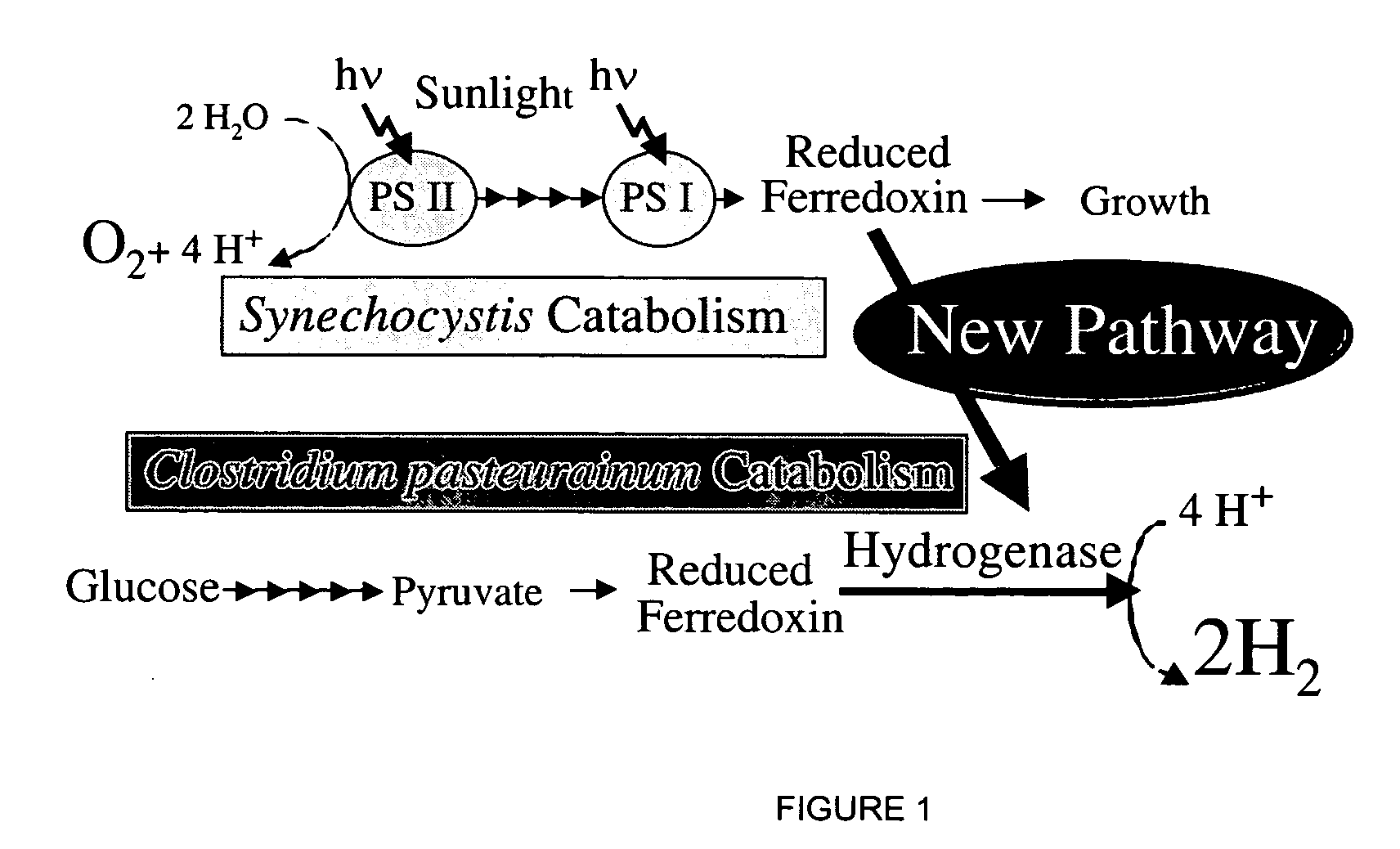
A hydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyses the reversible oxidation of molecular hydrogen (H₂), as shown below...
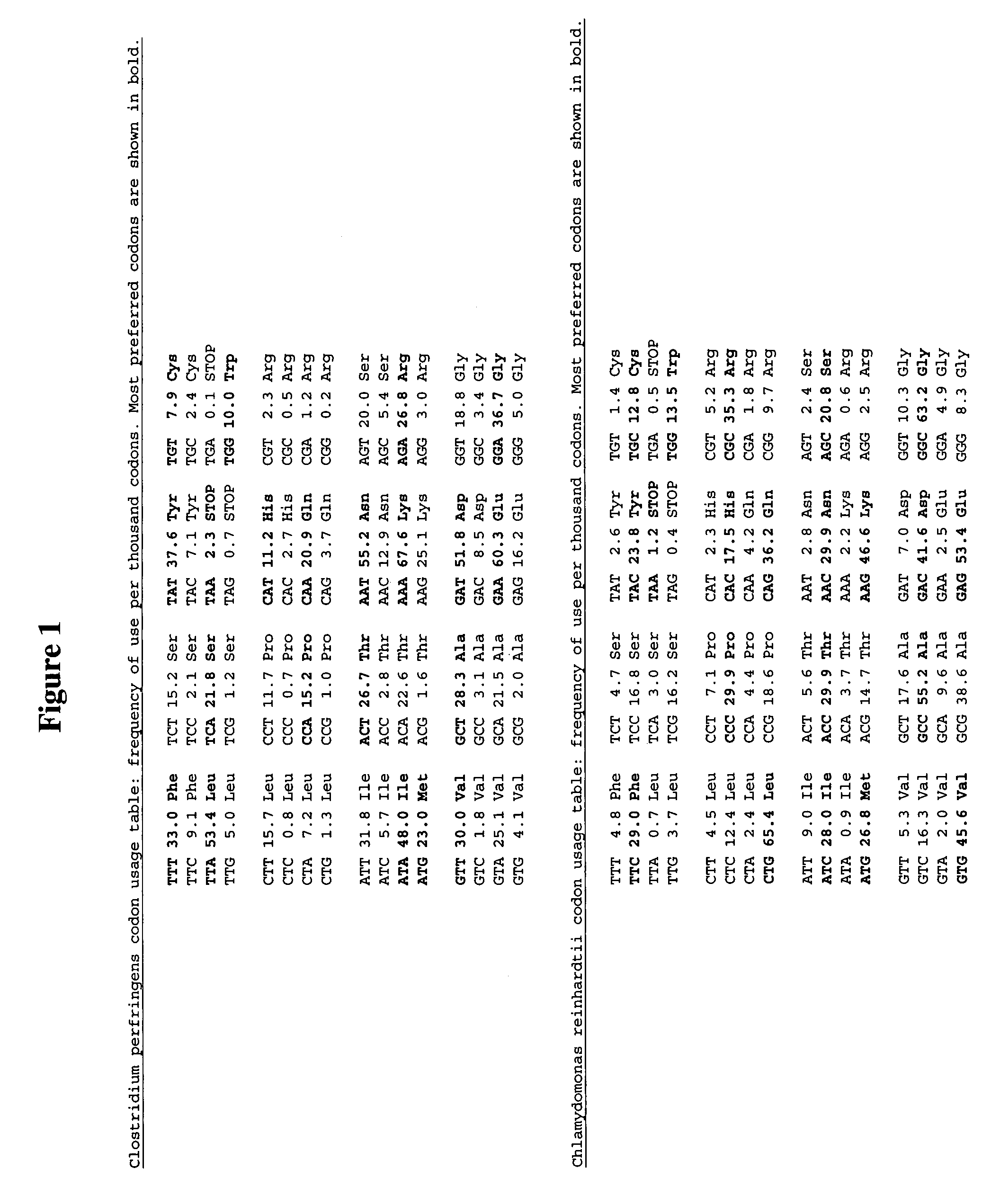
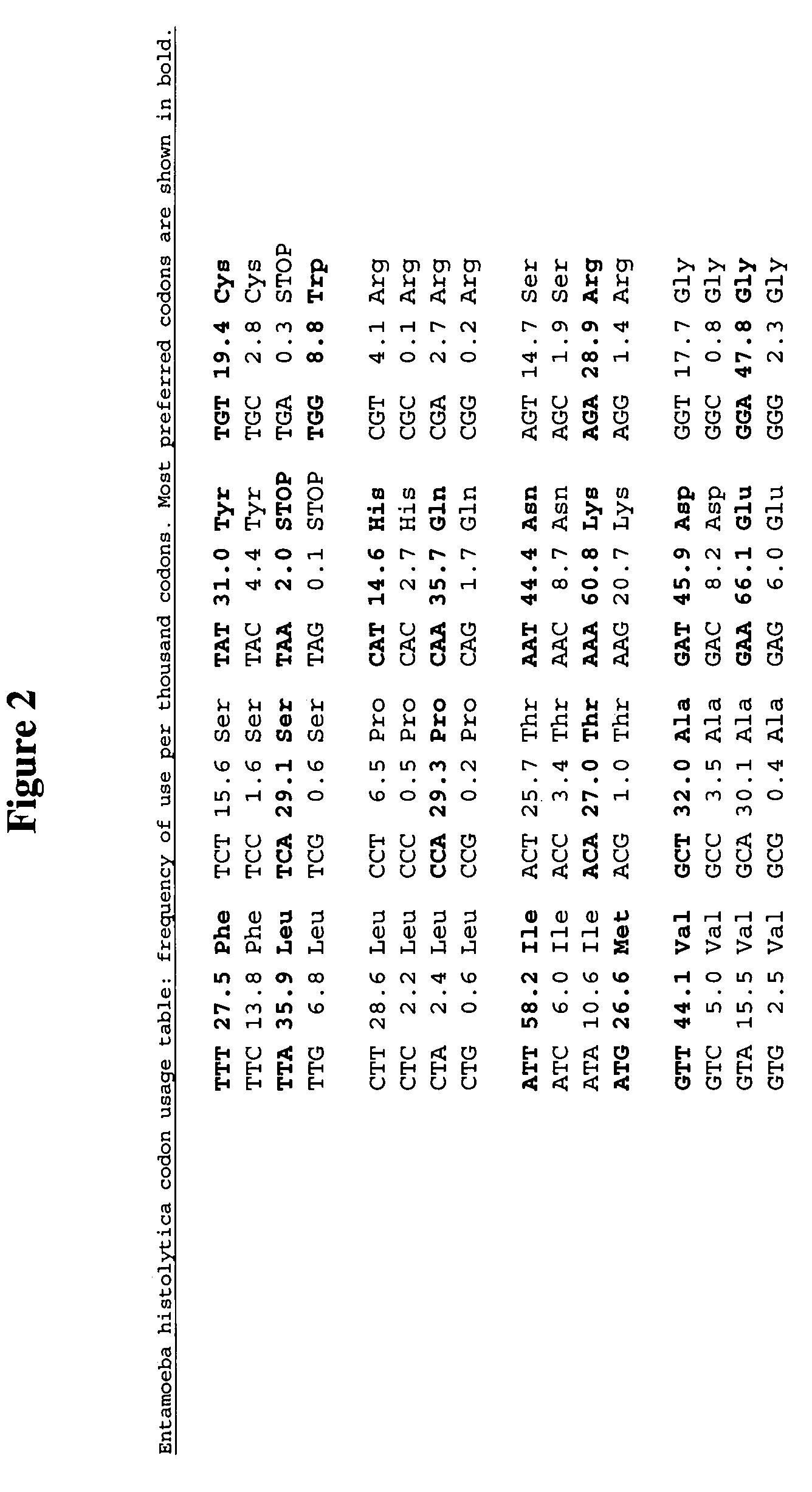
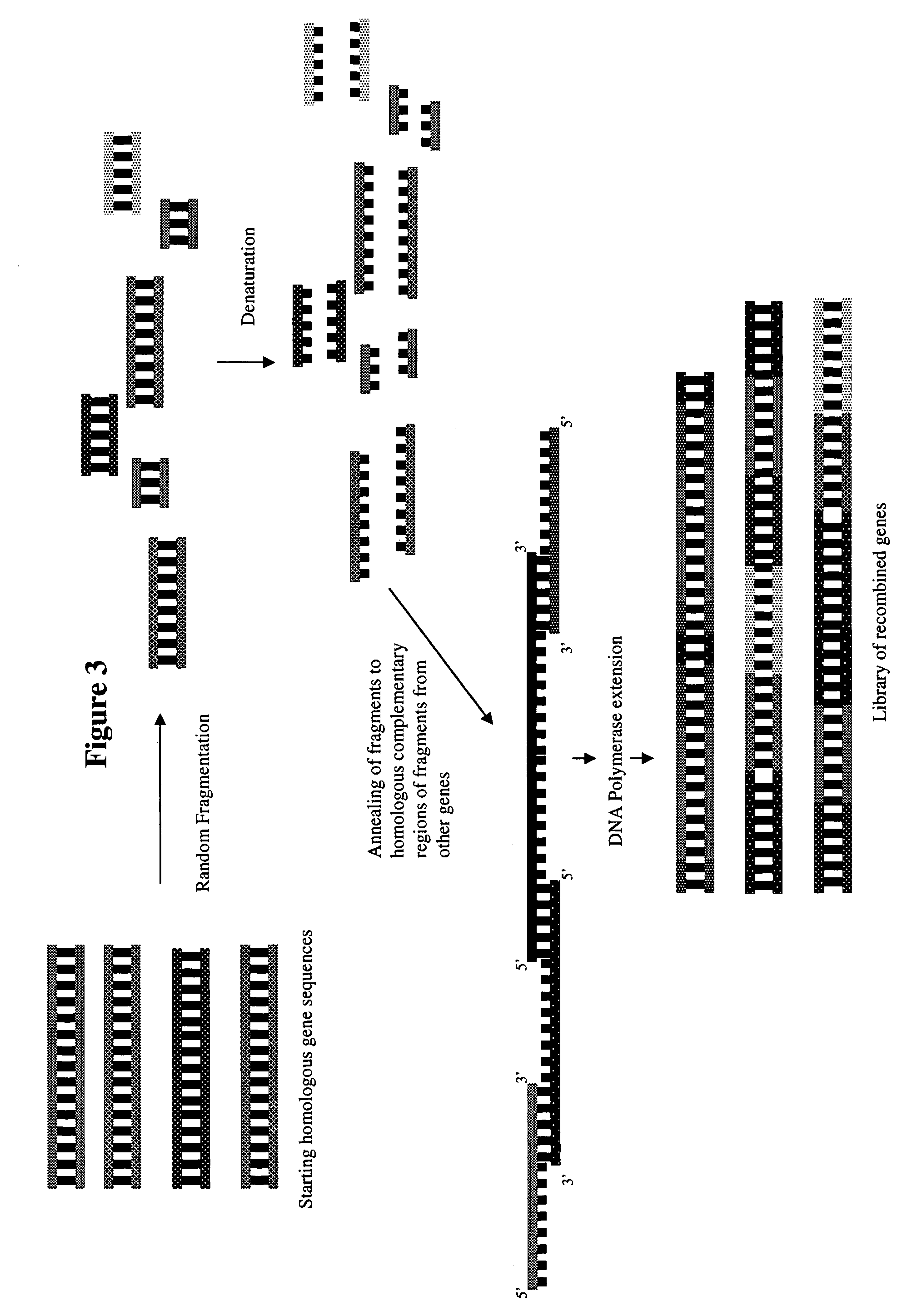
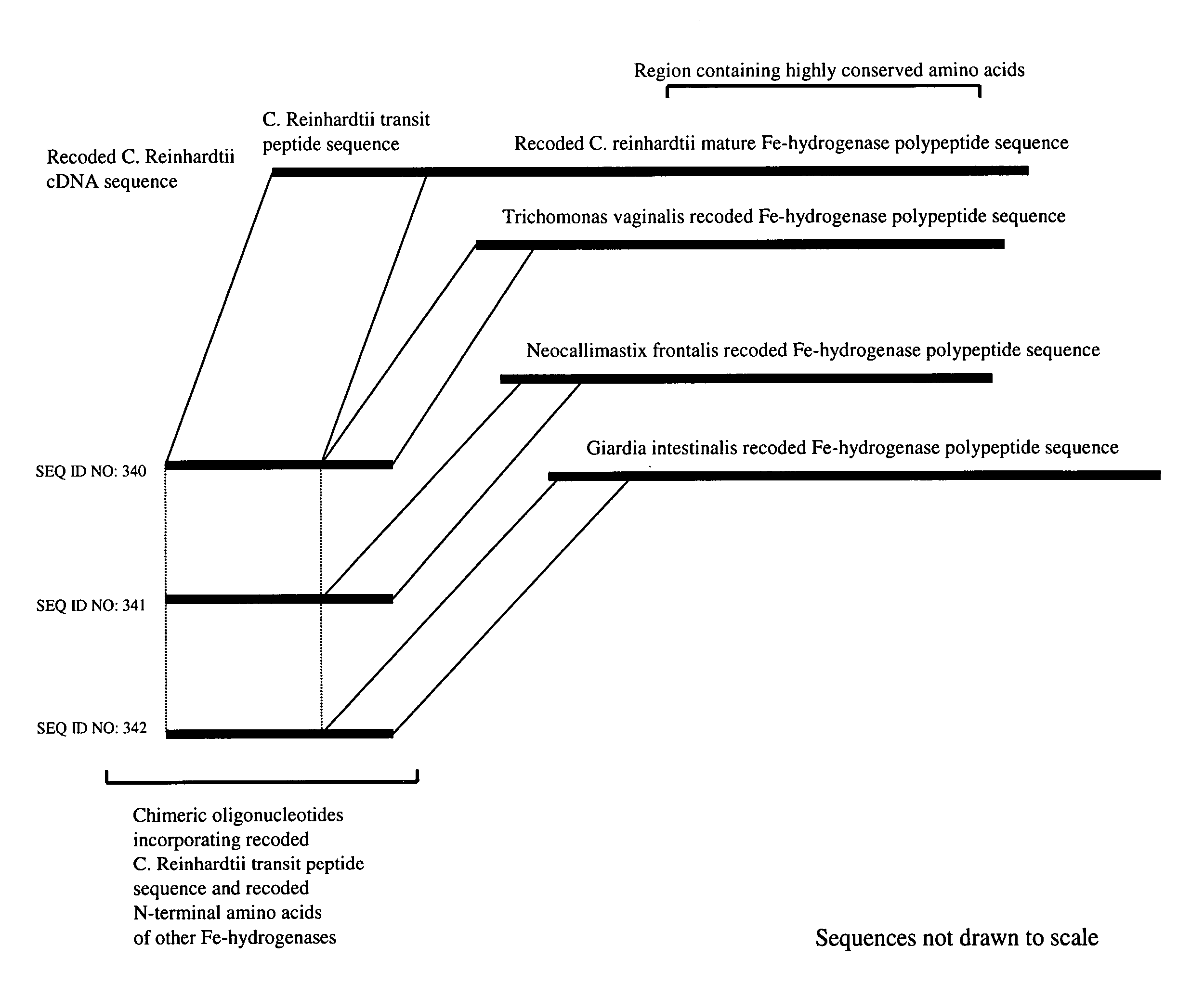
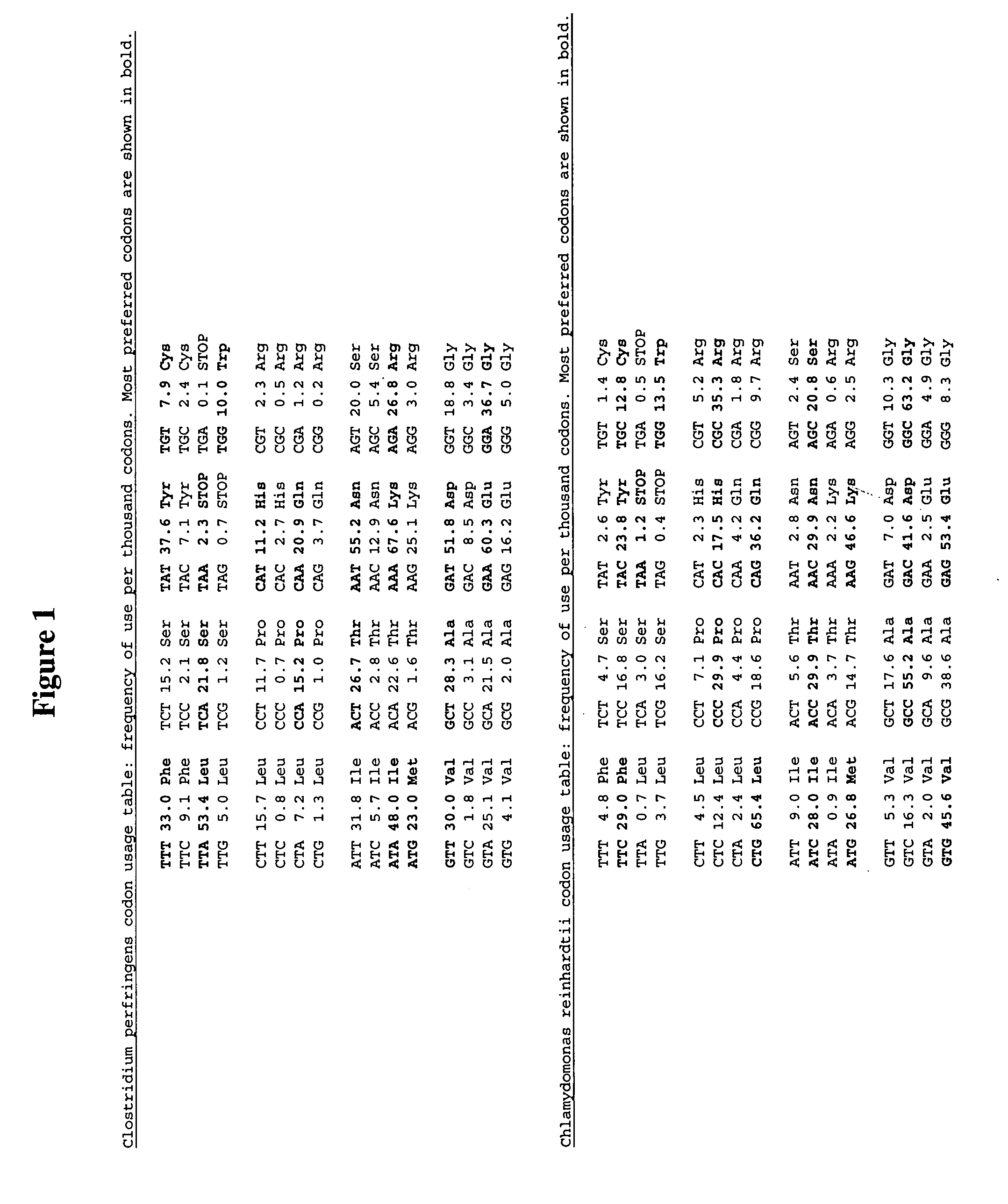
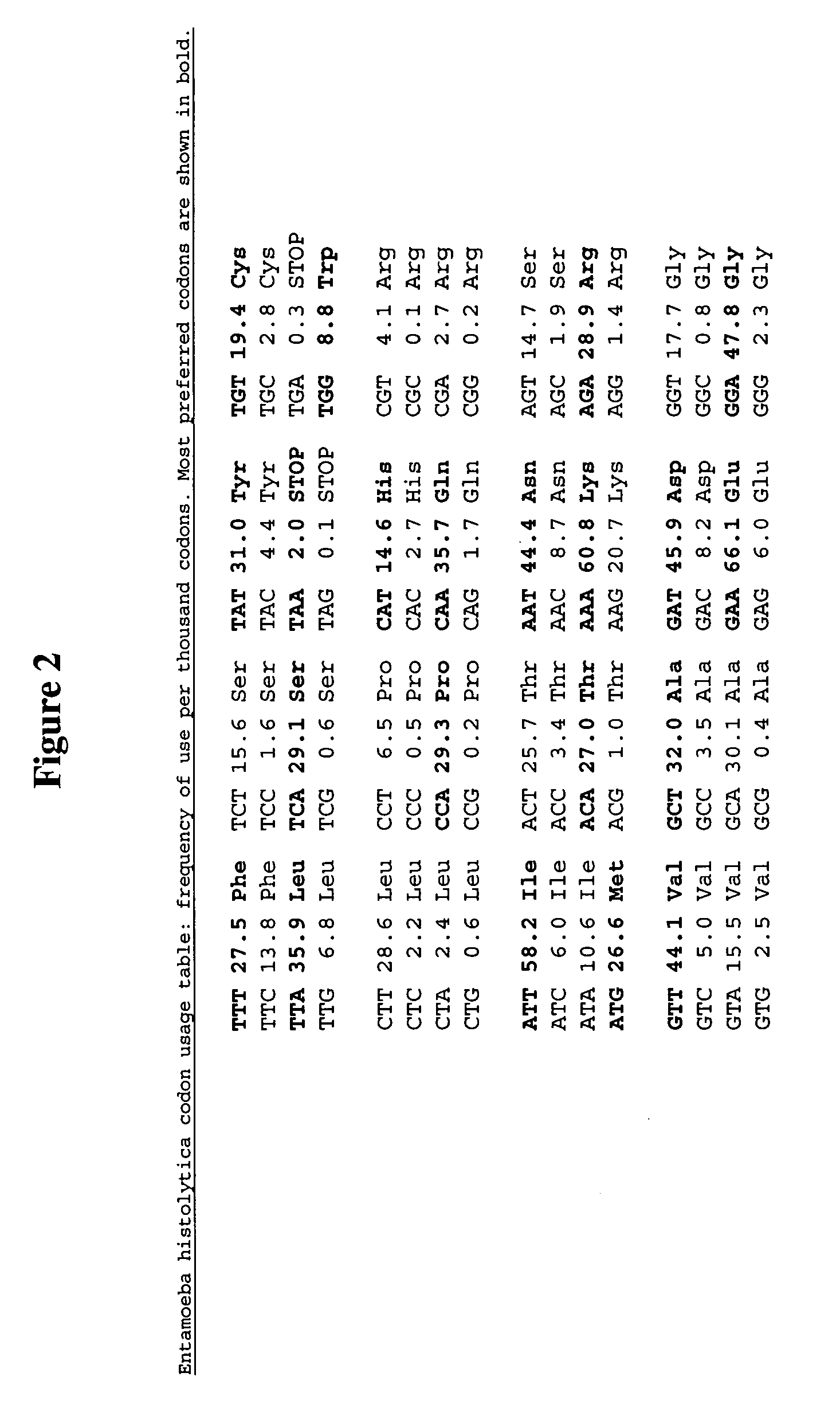
Methods and compositions for evolving hydrogenase genes
ActiveUS7135290B2Improve abilitiesIncrease ratingsMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides methods and compositions for engineering microbes to generate Hydrogen. Some methods of the invention involve recoding of hydrogenase genes followed by subjecting the recoded genes to annealing-based recombination methods. The invention further provides methods of mating organisms that are transformed with recoded and recombined hydrogenase genes with other organisms containing different genome sequences.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Highly efficient hydrogen production method using microorganism
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH +1
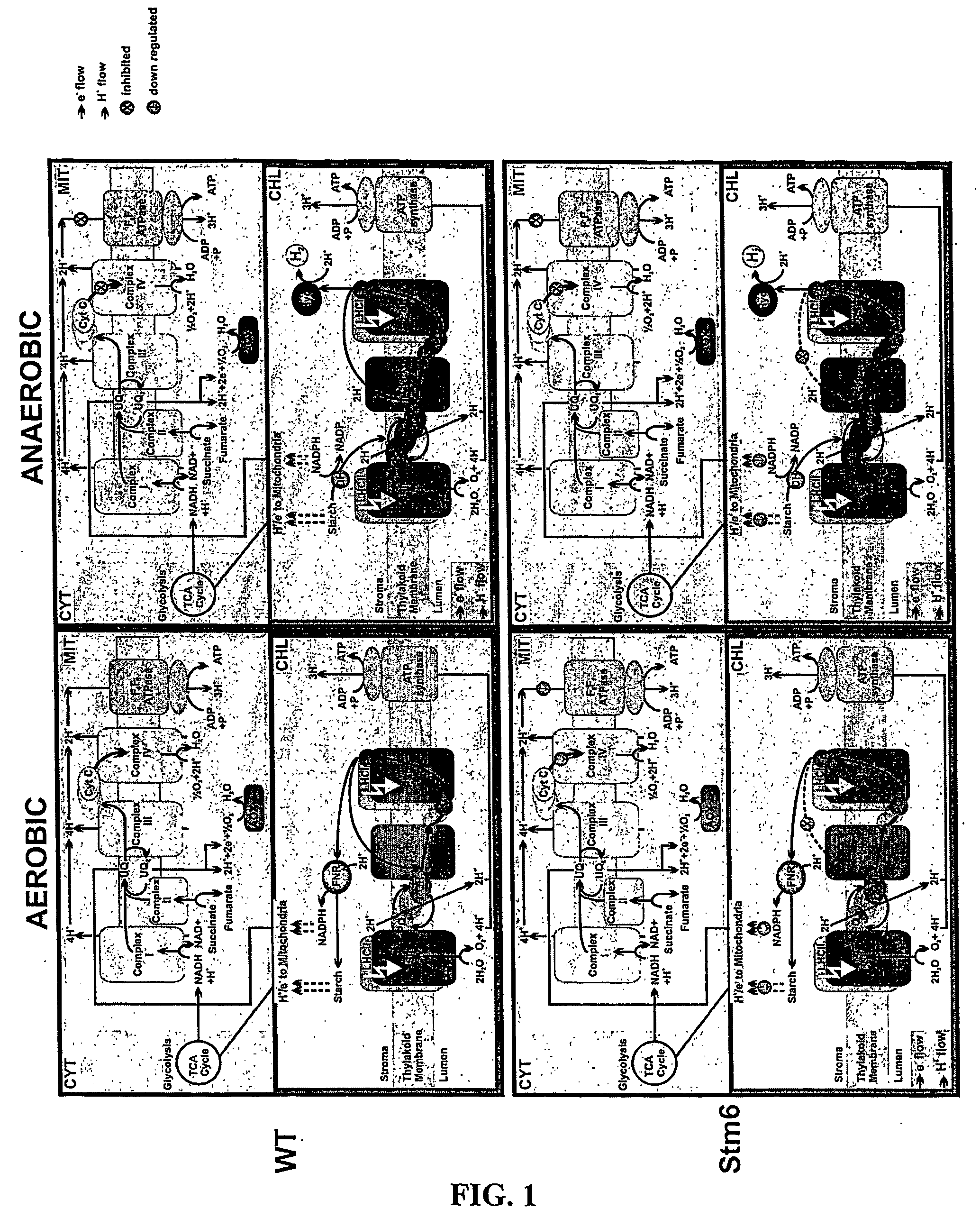
Photosynthetic hydrogen production
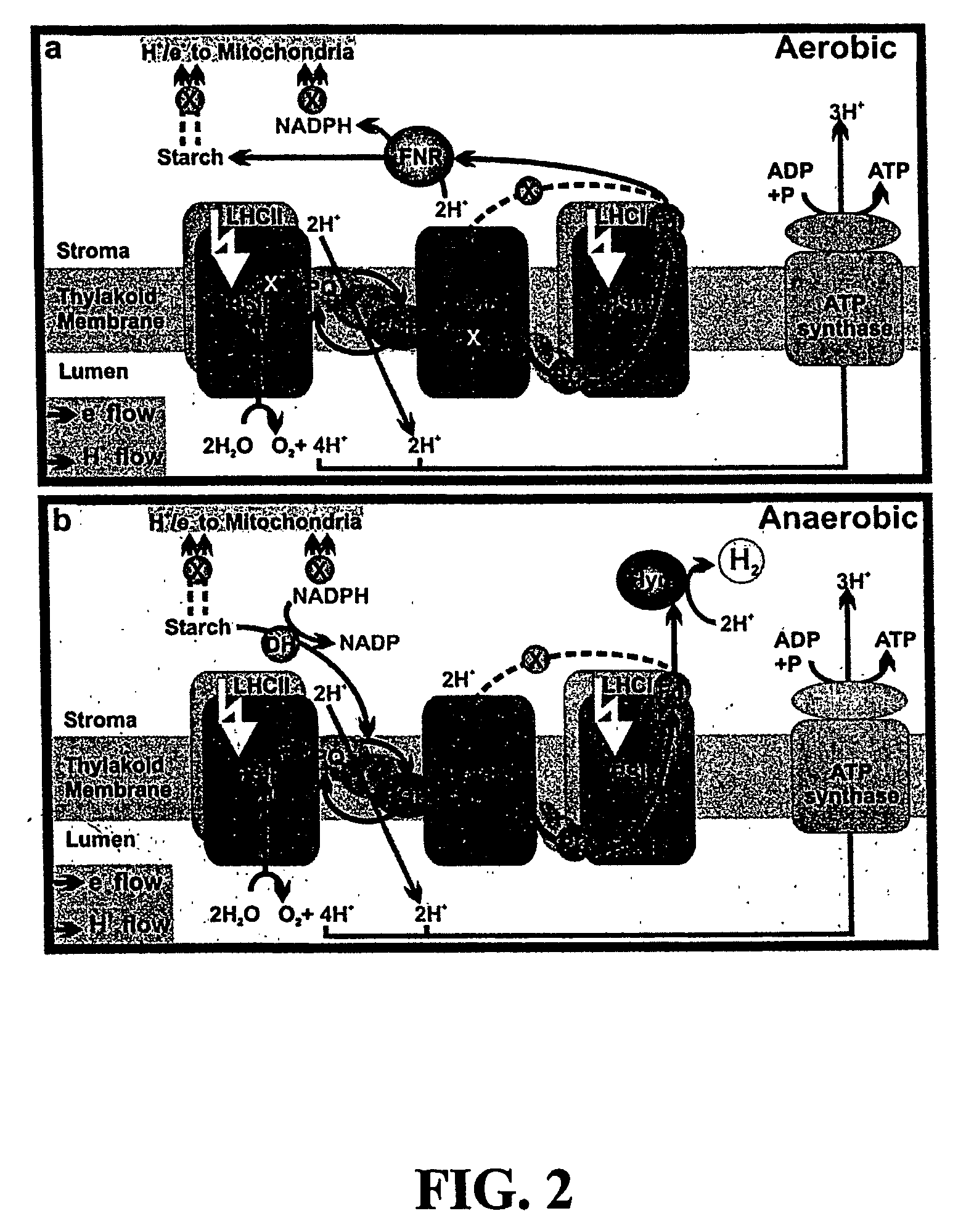
A process for the production of hydrogen, comprising the steps of: (i) providing a photosynthetic microorganism having electron transfer capability through a photosynthetic “light” reaction pathway and through a respiratory electron transfer chain involving an oxidative phosphorylation pathway, and which expresses a hydrogenase, wherein regulation of the oxidative phosphorylation pathway is disrupted with the result that electron flow along the respiratory electron transfer chain toward cytochrome oxidase (complex IV) is reduced; ii) culturing the microorganism under microoxic and illuminated conditions; and (iii) collecting evolved hydrogen.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Cell-free extracts and synthesis of active hydrogenase
ActiveUS7351563B2Lower energy requirementsMore economicallySugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismCell free
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Green algae biological fuel cell generating power on basis of photosynthesis
InactiveCN102075113ABiochemical fuel cellsLight radiation electric generatorMitochondrial electron transportCell system
The invention relates to a microbial fuel cell, in particular to a green algae biological fuel cell generating power on the basis of photosynthesis, which comprises a transparent cathode cell of green algae culture solution and an anode cell containing rich oxygen or oxidant solution, wherein the cathode cell and the anode cell are isolated by a proton exchange membrane; the cathode and anode of the cell are fixed in the cathode cell and the anode cell respectively; the cathode cell is isolated from the air to create an anaerobic environment in the cathode cell, hydrogen-generating green algae is used a system green algae material, an indirect-process hydrogen generation regulating technique is adopted, an electronic transfer mediator is added into the system to enable electrons which aregenerated by photosynthesis to be combined with the electronic mediator through an electron transport chain before reaching hydrogenase, the electronic mediator releases electrons at a cathode electrode, and the electrons are transferred to the anode to combine with protons passing through the proton exchange membrane and oxidant in the cathode cell to form water. In the invention, optical energycan be converted into electric energy by coupling the photosynthesis of microalgae and a cell system, and a novel biological fuel cell is provided.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cell-free extracts and synthesis of active hydrogenase
ActiveUS20060281148A1Lower energy requirementsMore economicallyBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismCell free
Enzymatically active hydrogenase is synthesized in a cell-free reaction. The hydrogenases are synthesized in a cell-free reaction comprising a cell extract derived from microbial strains expressing at least one hydrogenase accessory protein. In some embodiments, the extracts are produced under anerobic conditions.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Cecropin A-magainin hybrid gene engineering bactericidal peptide
InactiveCN1896107AReduce manufacturing costLow priceAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyYeast
An eka-cecropinA-magainin heterozygous gene engineering antibacterial peptide is prepared by adopting No.1-7 amino acid residue on N end of cecropinA CA and No.2-12 amino acid residue on N end of magainin M, design synthesizing heterozygous peptide CA(1-7)-M(2-12) gene by codon, connecting with carrier pPICZ alpha-A, mutating by point mutation technology to obtain mutant pPICZ alpha-CA-Mu-1, pPICZ alpha-CA-Mu-2 and pPICZ alpha-CA-Mu-3, converting SMD1168, and expressing CecA-Mag heterozygous antibacterial peptide to make into use under alcohol hydrogenase starter regulation.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Highly efficient hydrogen production method using microorganism
ActiveUS20060128001A1Highly efficient biological hydrogen generation capabilityIncrease the number ofFungiBacteriaMicroorganismCompound (substance)
It is intended to obtain anaerobic microbial cells in an amount sufficient for hydrogen generation reaction, impart a hydrogen generation function to an aerobic microorganism within a short time and provide an industrial advantageous method of producing hydrogen. The above object can be established by providing a highly efficient microbial hydrogen production method characterized by comprising culturing a microorganism having a formate dehydrogenase gene and a hydrogenase gene under aerobic conditions, culturing the resulting microbial cells under anaerobic conditions in a liquid culture medium containing a formic acid compound, and then using the thus obtained cells for hydrogen generation.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH +1
Hydrogen production using hydrogenase-containing oxygenic photosynthetic organisms
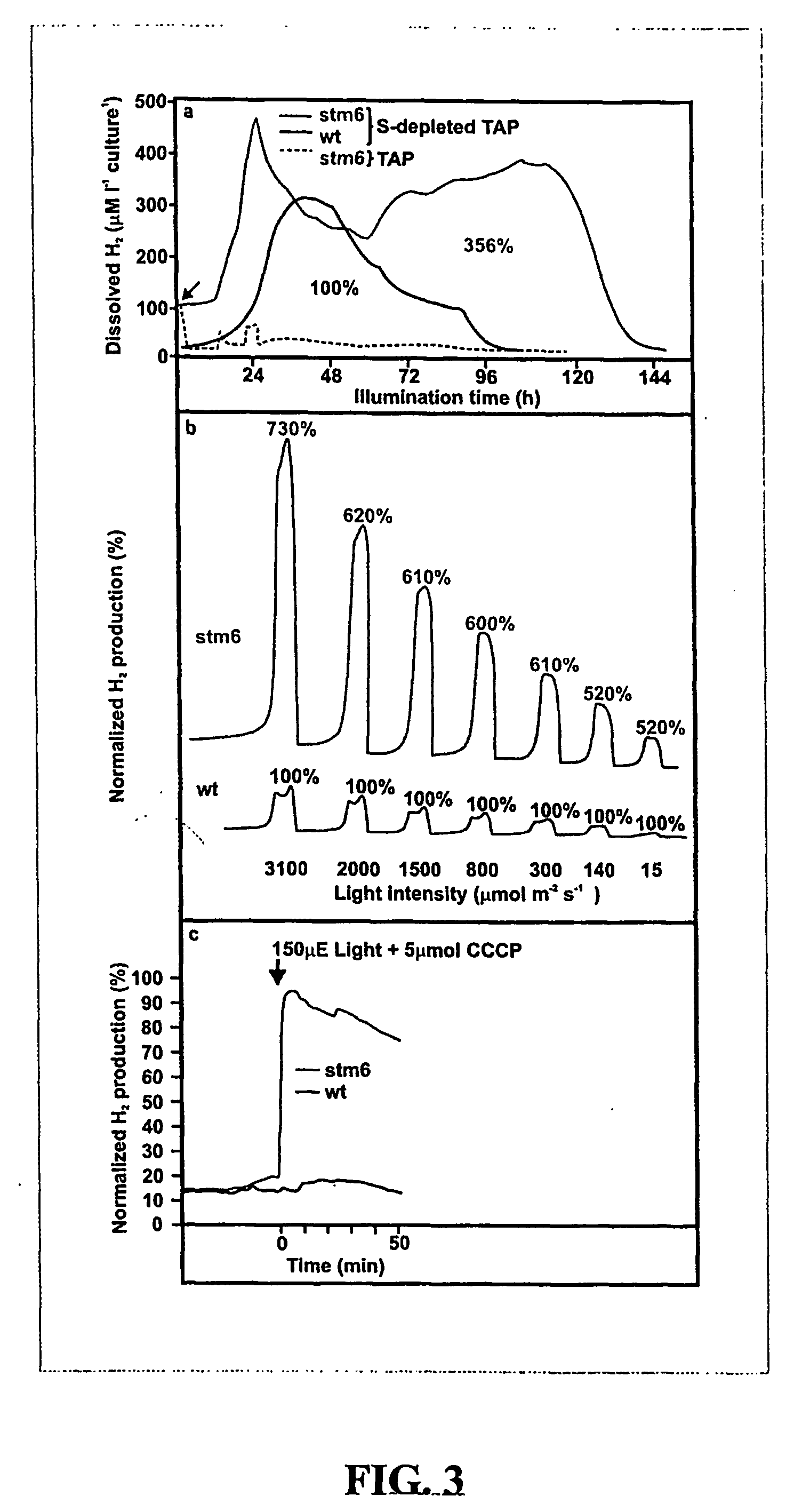
A reversible physiological process provides for the temporal separation of oxygen evolution and hydrogen production in a microorganism, which includes the steps of growing a culture of the microorganism in medium under illuminated conditions to accumulate an endogenous substrate, depleting from the medium a nutrient selected from the group consisting of sulfur, iron, and / or manganese, sealing the culture from atmospheric oxygen, incubating the culture in light whereby a rate of light-induced oxygen production is equal to or less than a rate of respiration, and collecting an evolved gas. The process is particularly useful to accomplish a sustained photobiological hydrogen gas production in cultures of microorganisms, such as Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Method for improving fermentation productivity of carotenoid
InactiveCN104846049AImprove fermentation yieldPromote absorptionMicroorganism based processesFermentationDismutaseContinuous fermentation
The invention discloses a method for improving the fermentation productivity of carotenoid, which is realized by the following steps: rhodotorula mucilaginosa is used as fermentation strains of the carotenoid, and the rhodotorula mucilaginosa is inoculated into a culture medium according to the inoculum size of 2%-10%; a ferrous ion solvent is added into the culture medium, wherein the volume of addition of the ferrous ion solvent is that the molarity relative to the culture medium is between 0.05-0.5mmol / L, and the fermentation temperature is kept at 27-33 DEG C; after the fermentation lasts for 32-40 hours, the temperature is lowered to 20-25 DEG C for continuous fermentation; the fermentation lasts for 24-46 hours. By adding ferrous ions, the capability of beta-carotene for converting into the high antioxygen carotenoid is greatly improved, the insufficience of quantity of beta-carotene dioxygen dismutase and beta-carotene hydrogenase is made up; the beta-carotene is converted into the high antioxygen carotenoid; by the method, the fermentation yield is improved by 30-34%.
Owner:WEIHAI LIDA BIOTECH
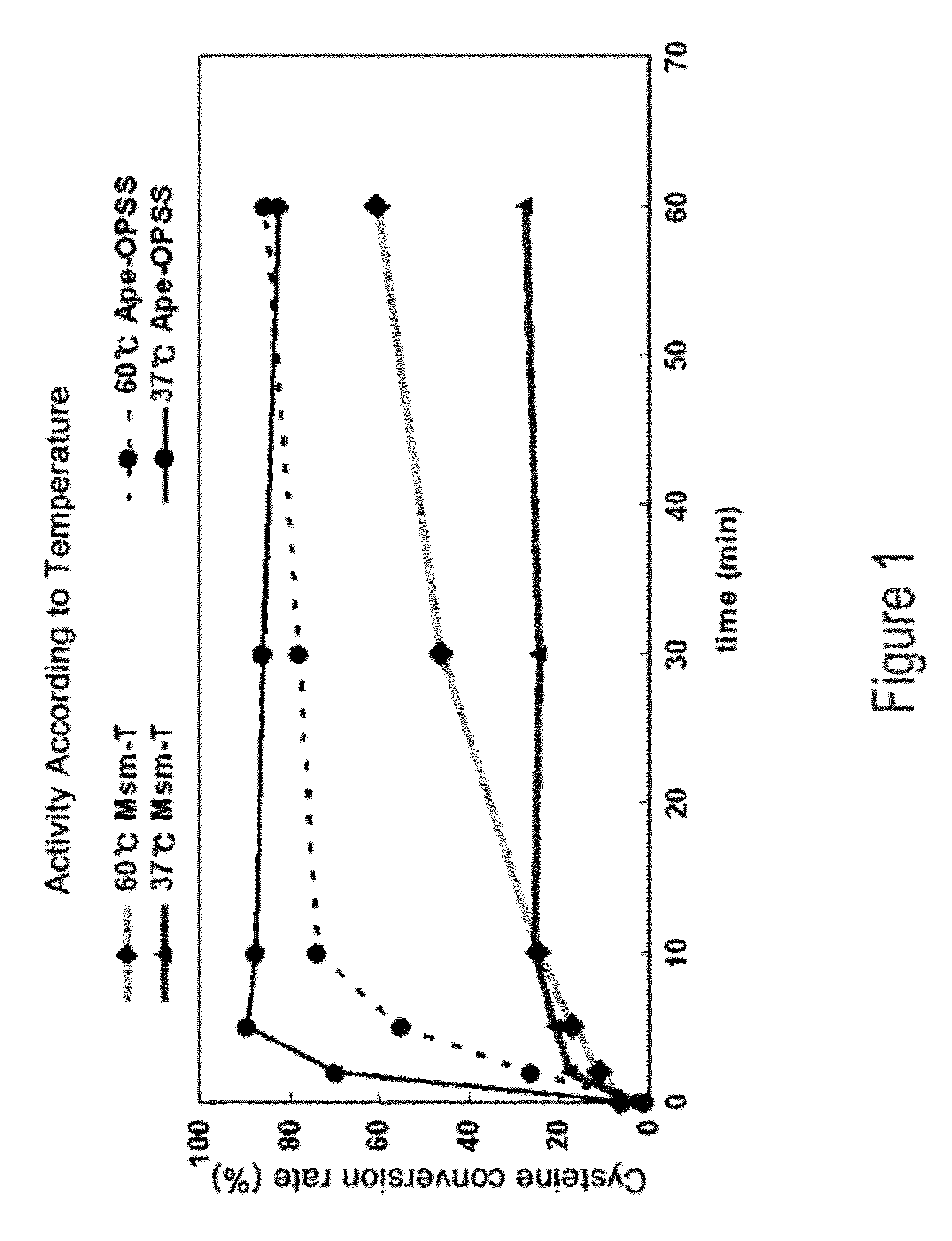
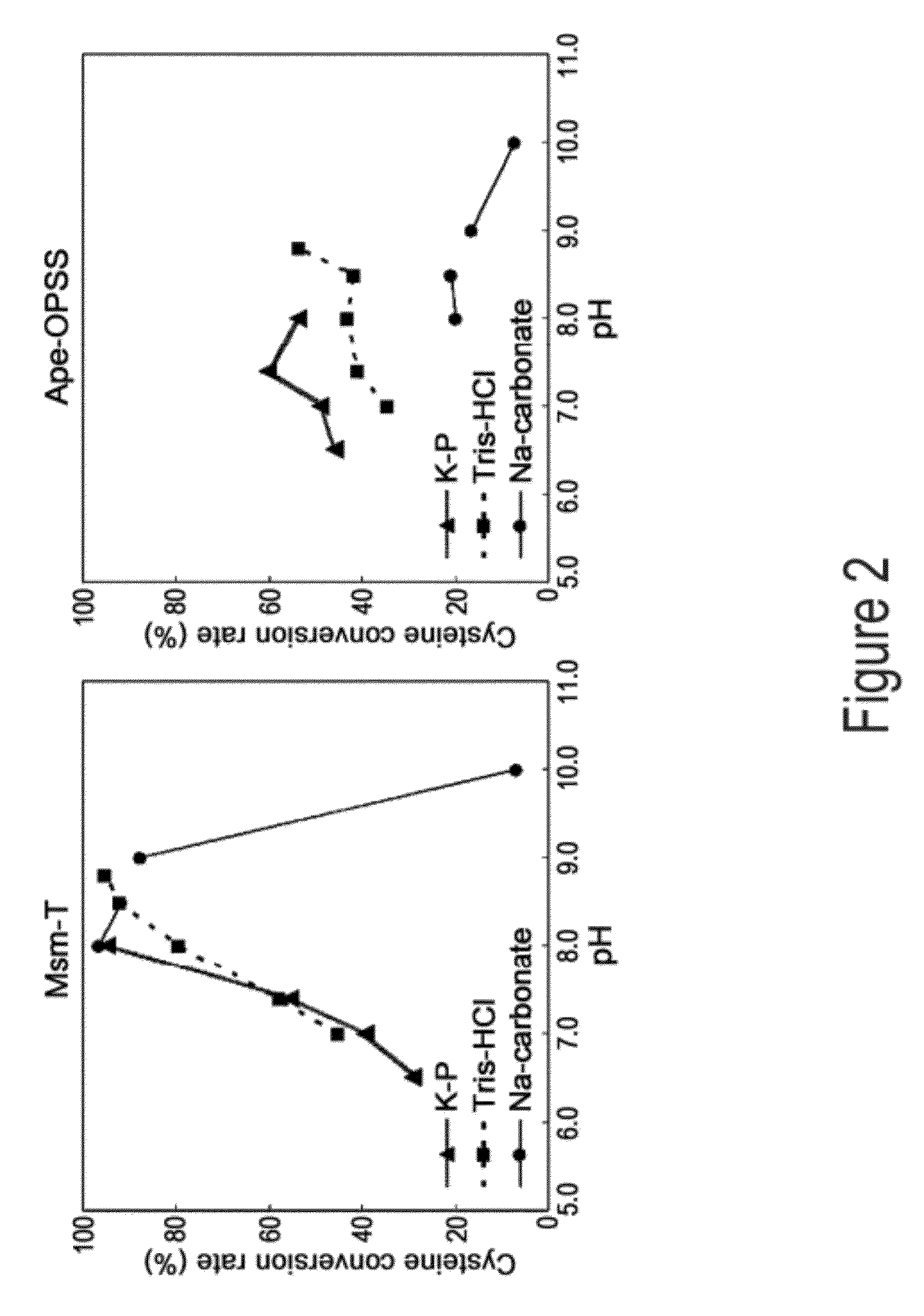
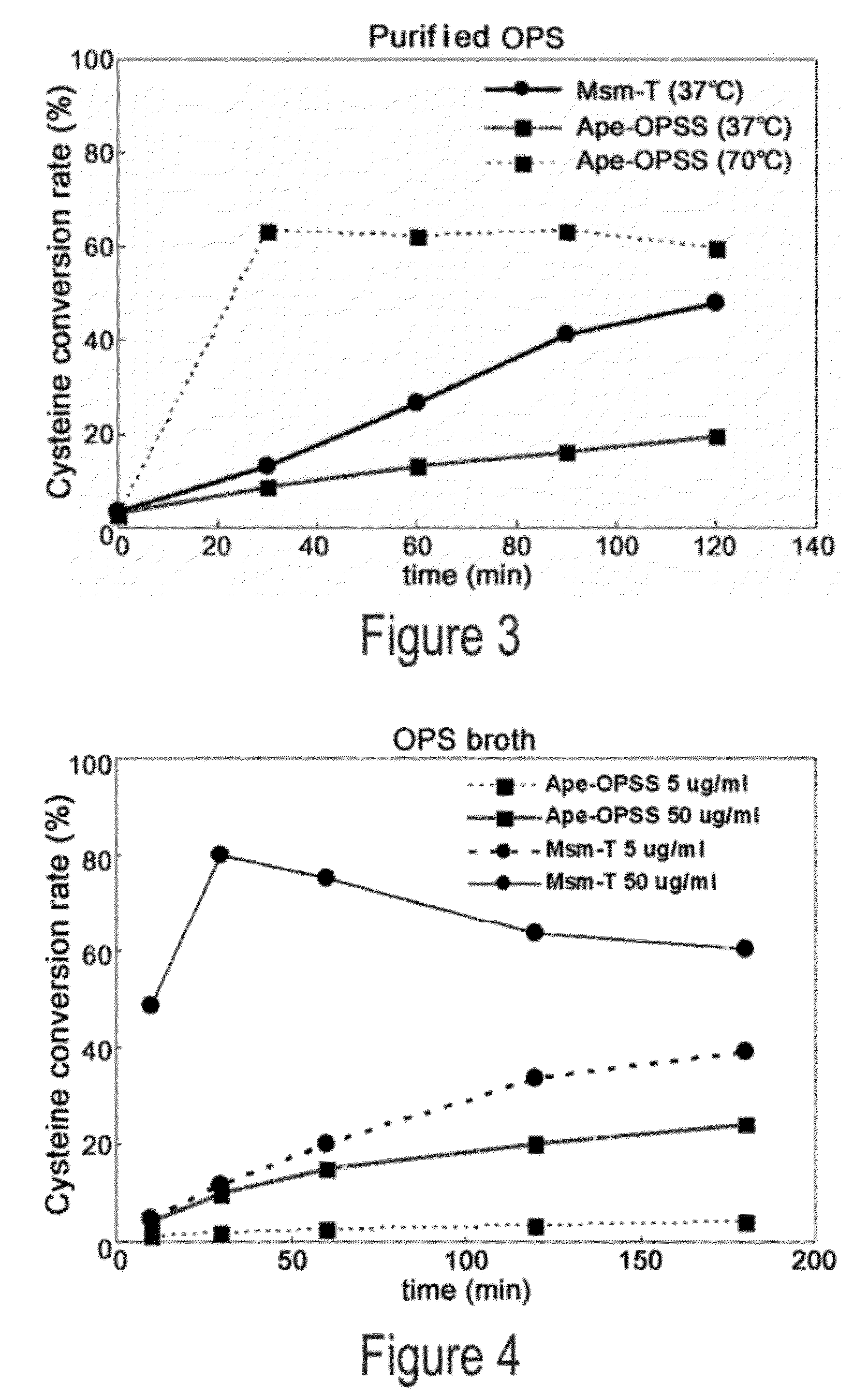
O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase mutants and method for production of cysteine using the same
ActiveUS9127324B2Improve enzymatic activityHigh yieldSugar derivativesBacteriaMycobacterium smegmatisO-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase
Disclosed is an O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase (OPSS) mutant which has a Mycobacterium smegmatis-derived amino acid sequence corresponding to that of SEQ ID NO: 1 which is devoid of three to seven C-terminal amino acid residues. Also, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the OPSS mutant, an expression vector carrying the nucleic acid molecule, and a transformant transformed with the expression vector are disclosed. In addition, a method is provided for producing cysteine in which O-phospho-L-serine (OPS) is reacted with a sulfide in the presence of the OPSS mutant. The OPSS mutant has improved enzymatic activity and can be applied to the environmentally friendly production of L-cysteine through a simple enzymatic conversion reaction.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Fe-hydrogenase model compound, its preparation method, photo-catalytic hydrogen production system containing it, and hydrogen preparation method of system
ActiveCN102924532AHigh catalytic activityLarge TON valueOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIron organic compoundsSolvent(Fe) hydrogenase
The invention discloses an Fe-hydrogenase model compound, its preparation method, a photo-catalytic hydrogen production system containing it, and a hydrogen preparation method of the system. The Fe-hydrogenase model compound can be used for the photocatalytic hydrogen production system, and has a high catalytic activity. The photo-catalytic hydrogen production system containing the Fe-hydrogenase model compound comprises the Fe-hydrogenase model compound, a photo-sensitizer, an electronic donor, a proton source and a solvent; the catalytic activity of the system can be stably maintained for a plurality of hours under an illumination condition; the system can be constructed in pure water, or in a mixed system of water and an organic solvent, and the TON value of the system is large; and the photo-sensitizer used in the system comprises CdSe quantum dot, CdTe quantum dot, Ru(III) tri(terpyridine) and zinc porphyrin, so the cost of the system is reduced. Hydrogen can be generated through using visible light having a wavelength lambda of above 400nm to irradiate the system.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nano-iron-loaded biochar, preparation method of nano-iron-loaded biochar, and application of nano-iron-loaded biochar in dark fermentation hydrogen production process
InactiveCN107858379AEasy reunionAchieve releaseFerric oxidesCarbon preparation/purificationDark fermentationBiochar
The invention relates to nano-iron-loaded biochar, a preparation method of the nano-iron-loaded biochar, and an application of the nano-iron-loaded biochar in a dark fermentation hydrogen production process. Ferrite and soluble starch are taken as raw materials which are subjected to reaction under proper conditions and are dried and charred to obtain the nano-iron-loaded biochar, wherein the maincomponent of the nano-iron-loaded biochar is Fe2O3 / C, and the particle diameter range of the nano-iron-loaded biochar is 2-150nm. The biochar is of an amorphous structure, and Fe2O3 is of a mesoporous structure. By adding the iron-loaded biochar to an anaerobic fermentation system, a synergistic strengthening effect of iron and biochar in the dark fermentation hydrogen production process is realized, so that the hydrogen yield and the process stability are improved. Fe2O3 can not only release iron ions to enhance the activity of fermentative hydrogen producing bacterium hydrogenase but also increase the transfer rate of electrons; and furthermore, the biochar in nano-particles can enrich microorganisms, improve the concentration of hydrogen producing bacteria, buffer acid accumulation andrelieve ammonia inhibition.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
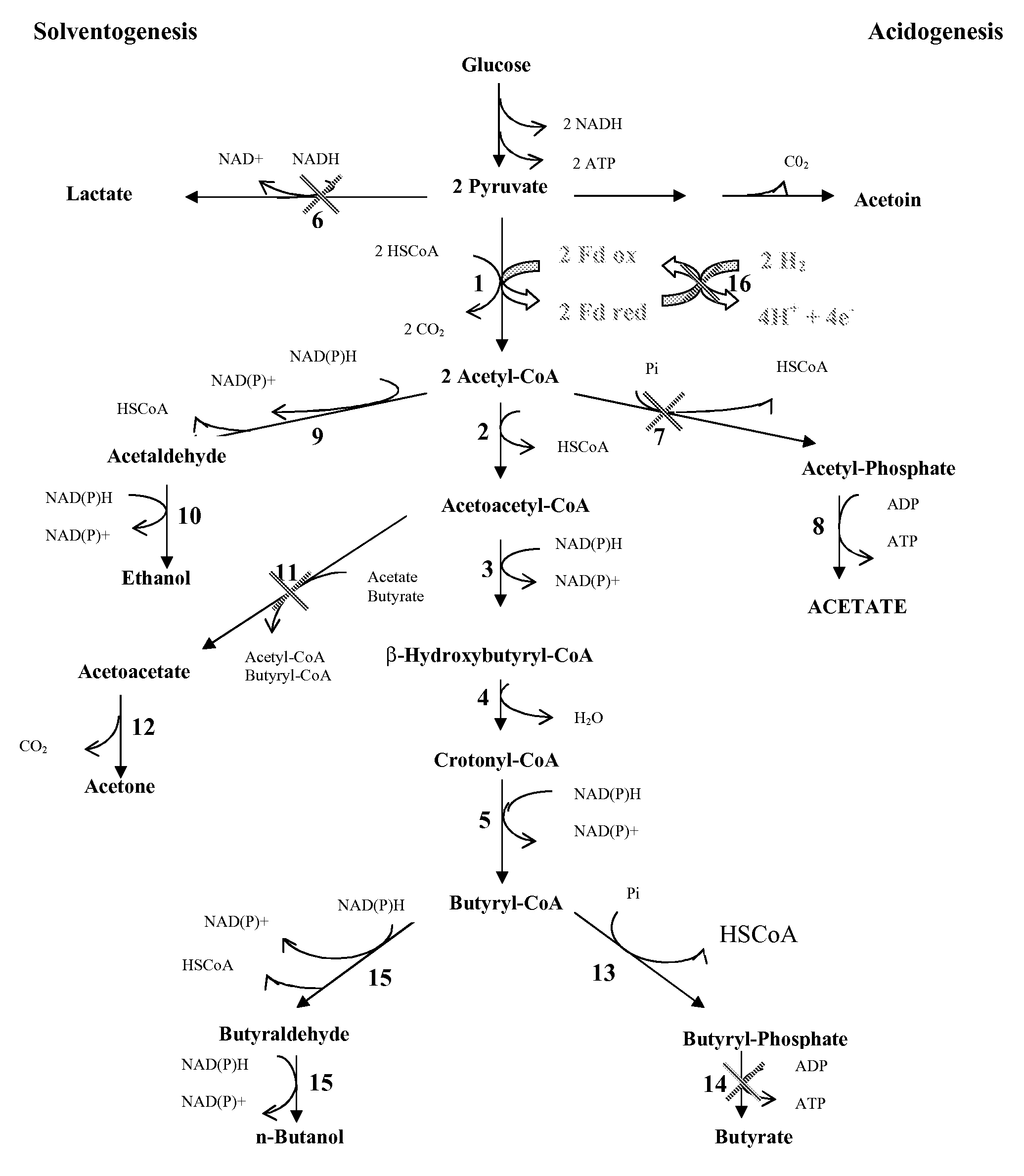
PROCESS FOR THE BIOLOGICAL PRODUCTION OF n-BUTANOL WITH HIGH YIELD
The present invention provides a method for the biological production of n-butanol at high yield from a fermentable carbon source. In one aspect of the present invention, a process for the conversion of glucose to n-butanol is achieved by the use of a recombinant organism comprising a host C. acetobutilicum transformed i) to eliminate the butyrate pathway ii) to eliminate the acetone pathway iii) to eliminate the lactate pathway and iv) to eliminate the acetate pathway. In another aspect of the present invention, the hydrogen flux is decreased and the reducing power redirected to n-butanol production by attenuating the expression of the hydrogenase gene. Optionally the n-butanol produced can be eliminated during the fermentation by gas striping and further purified by distillation.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
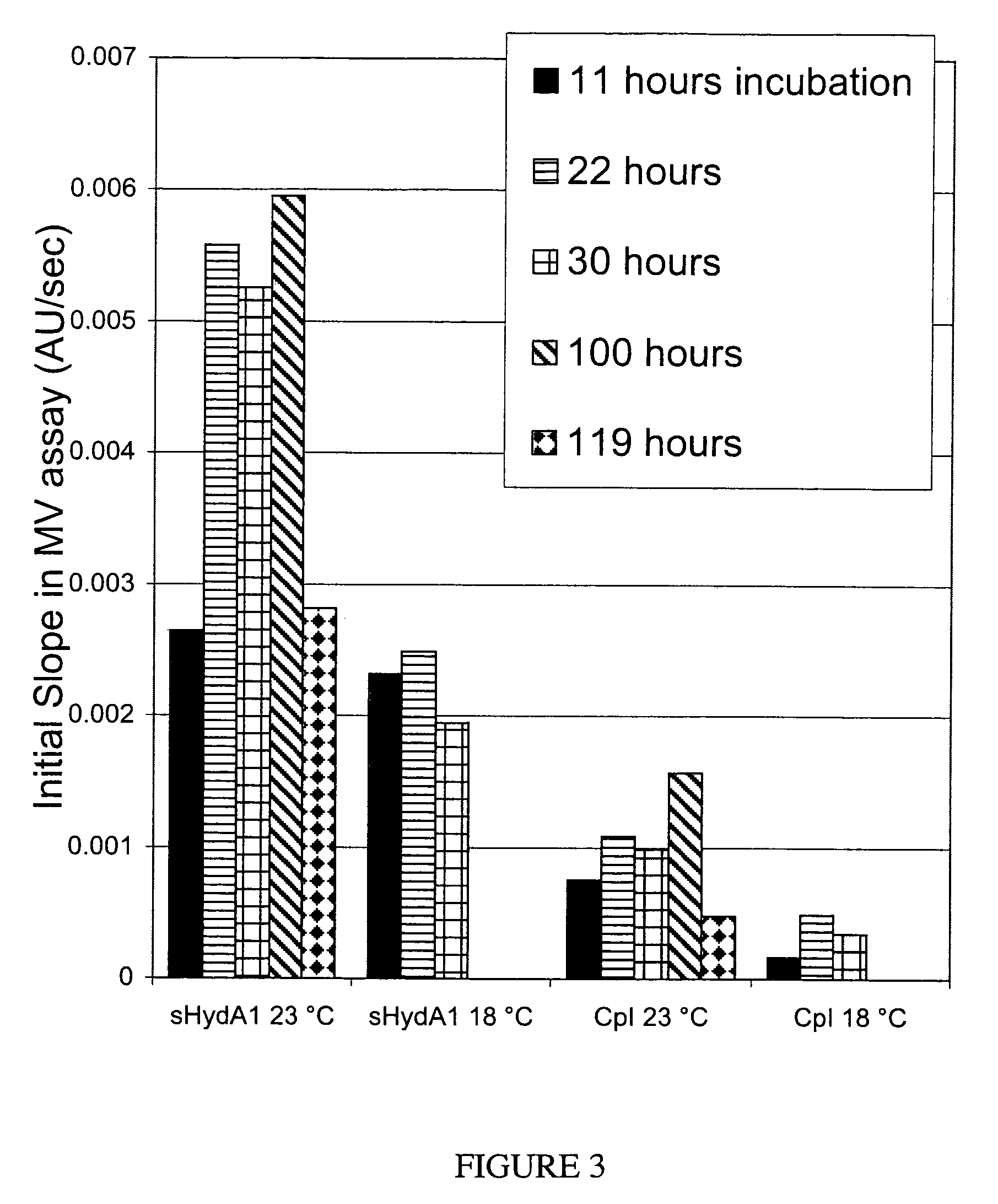
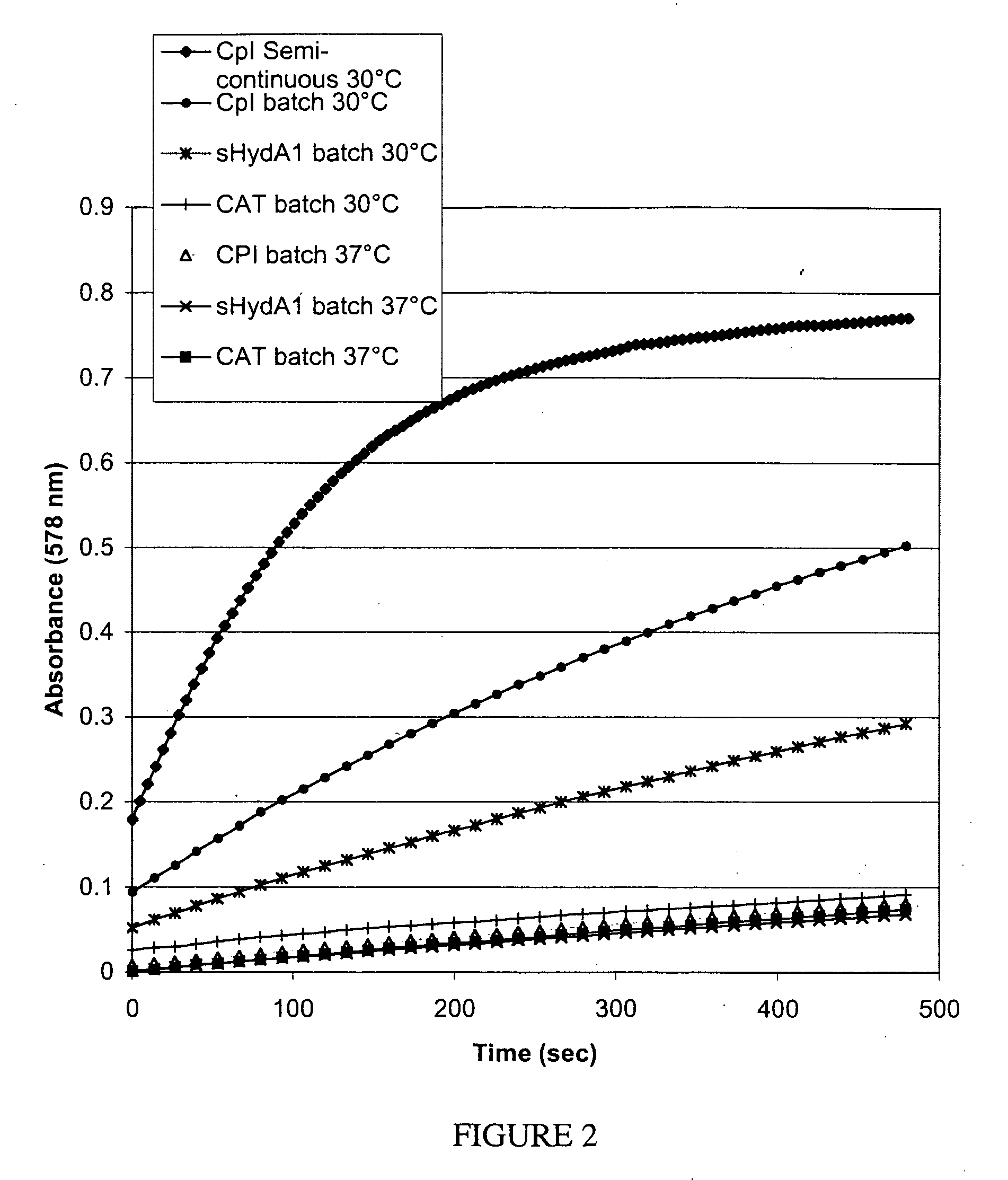
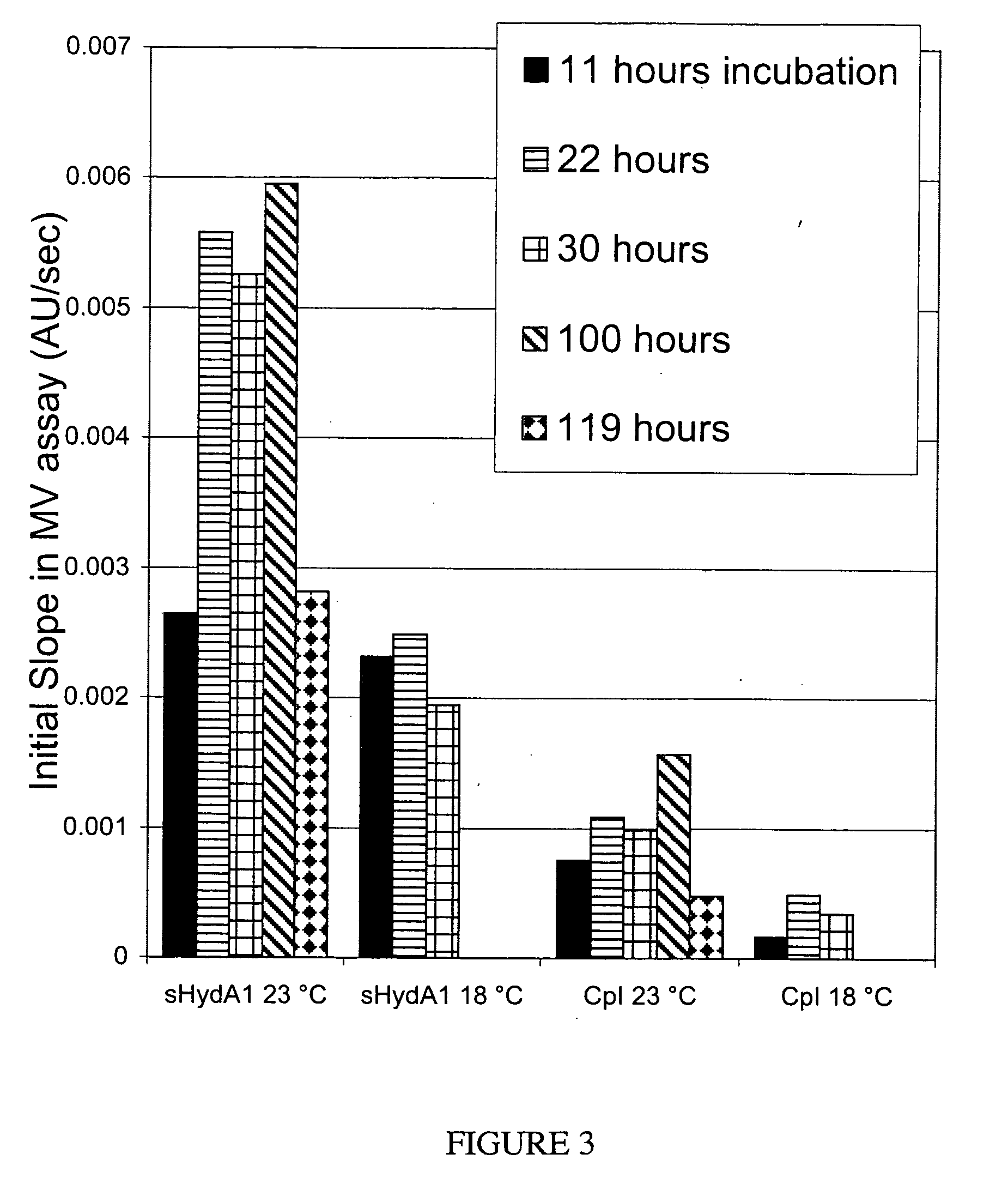
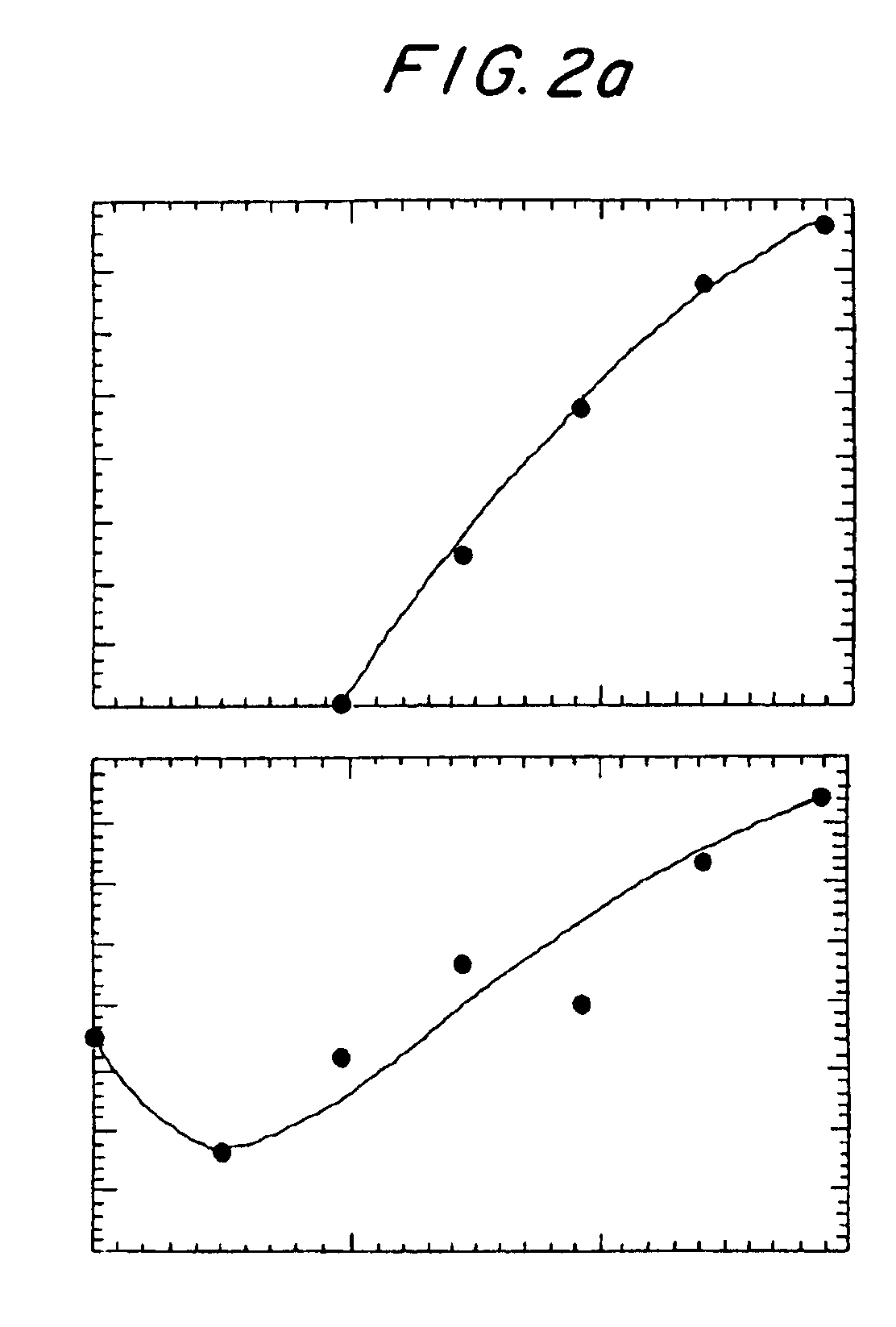
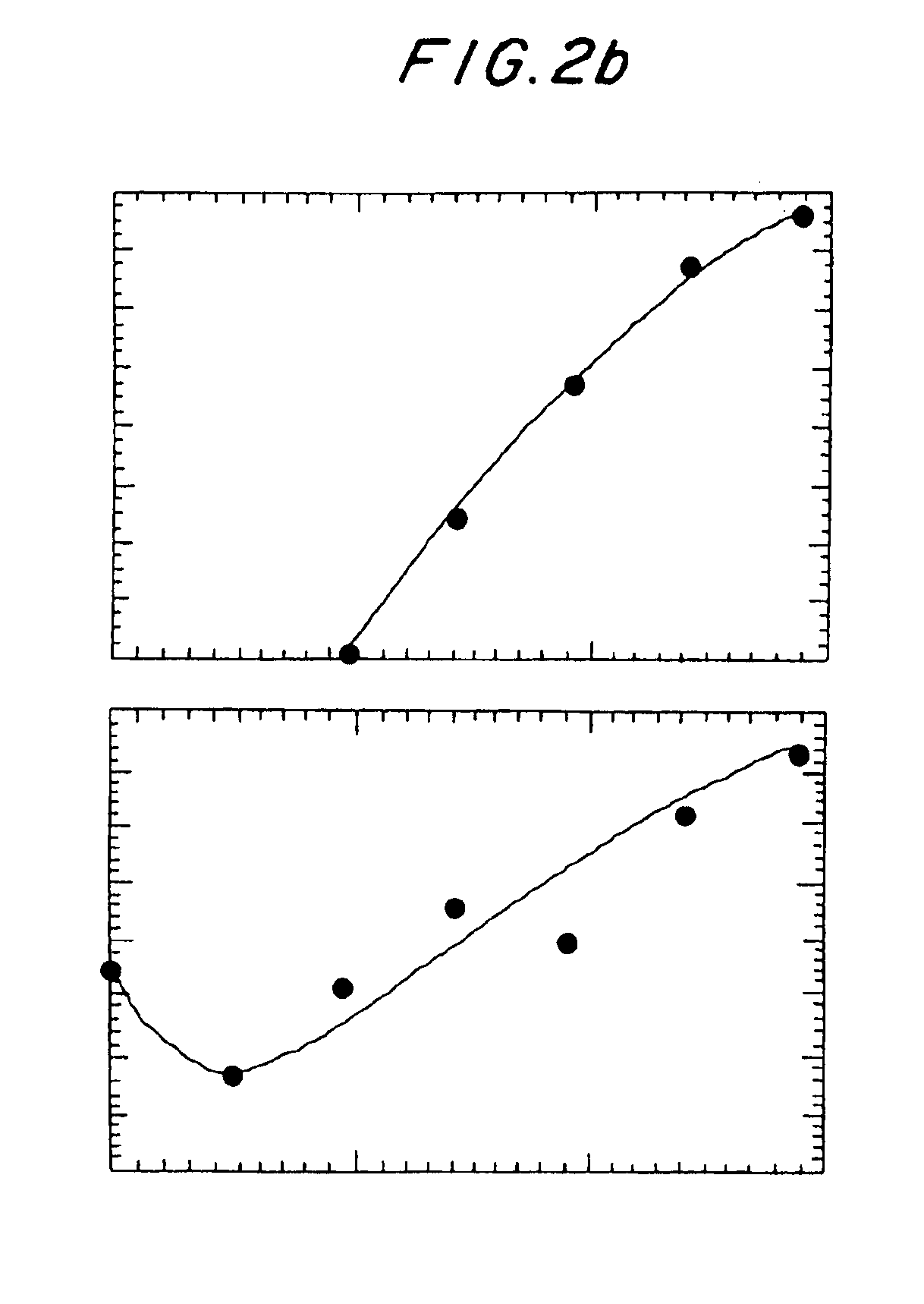
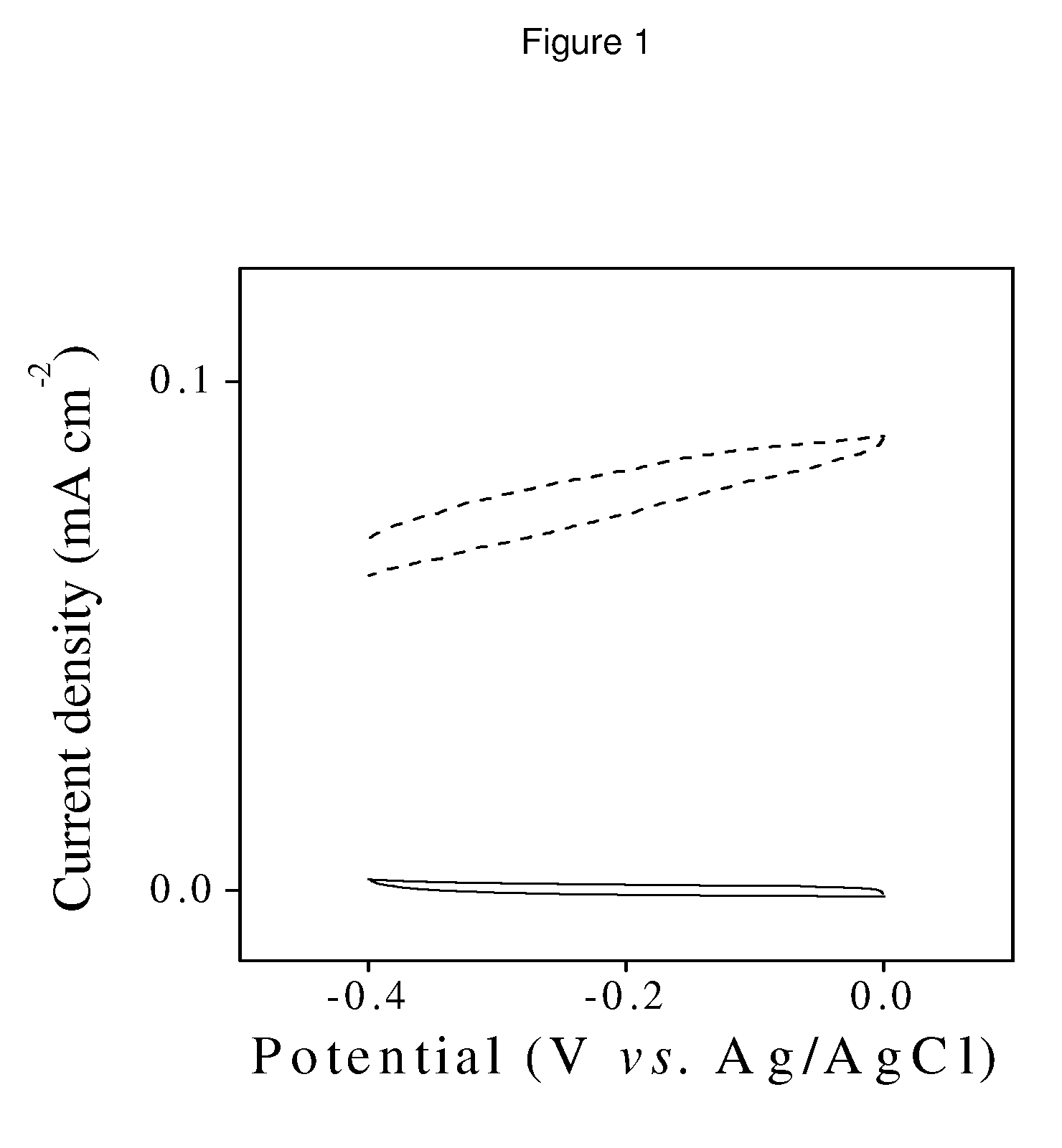
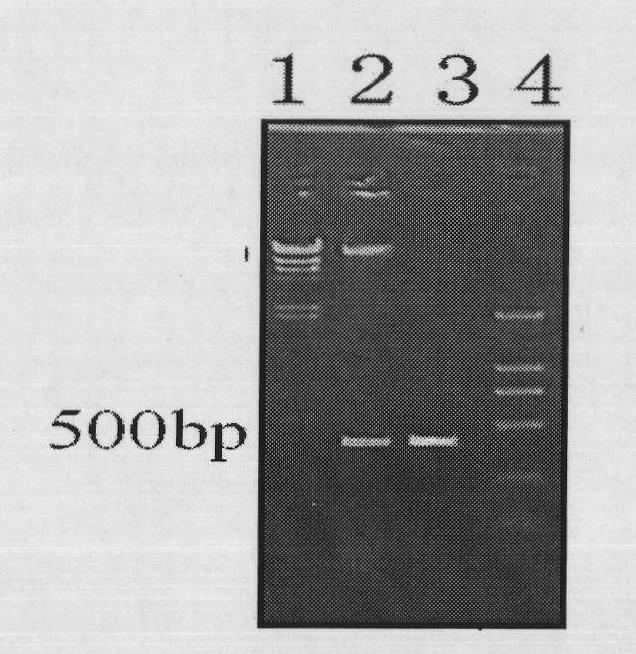
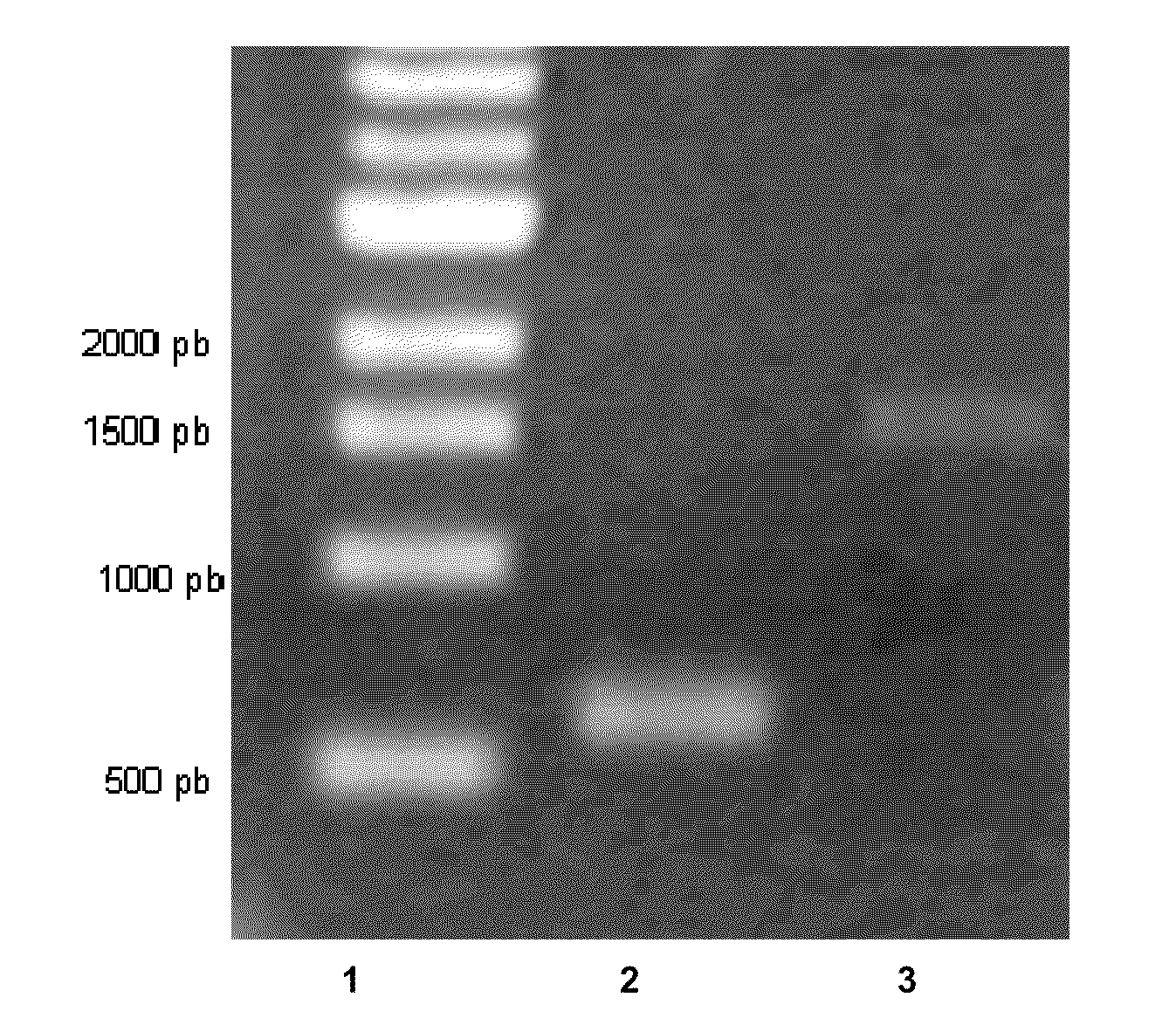
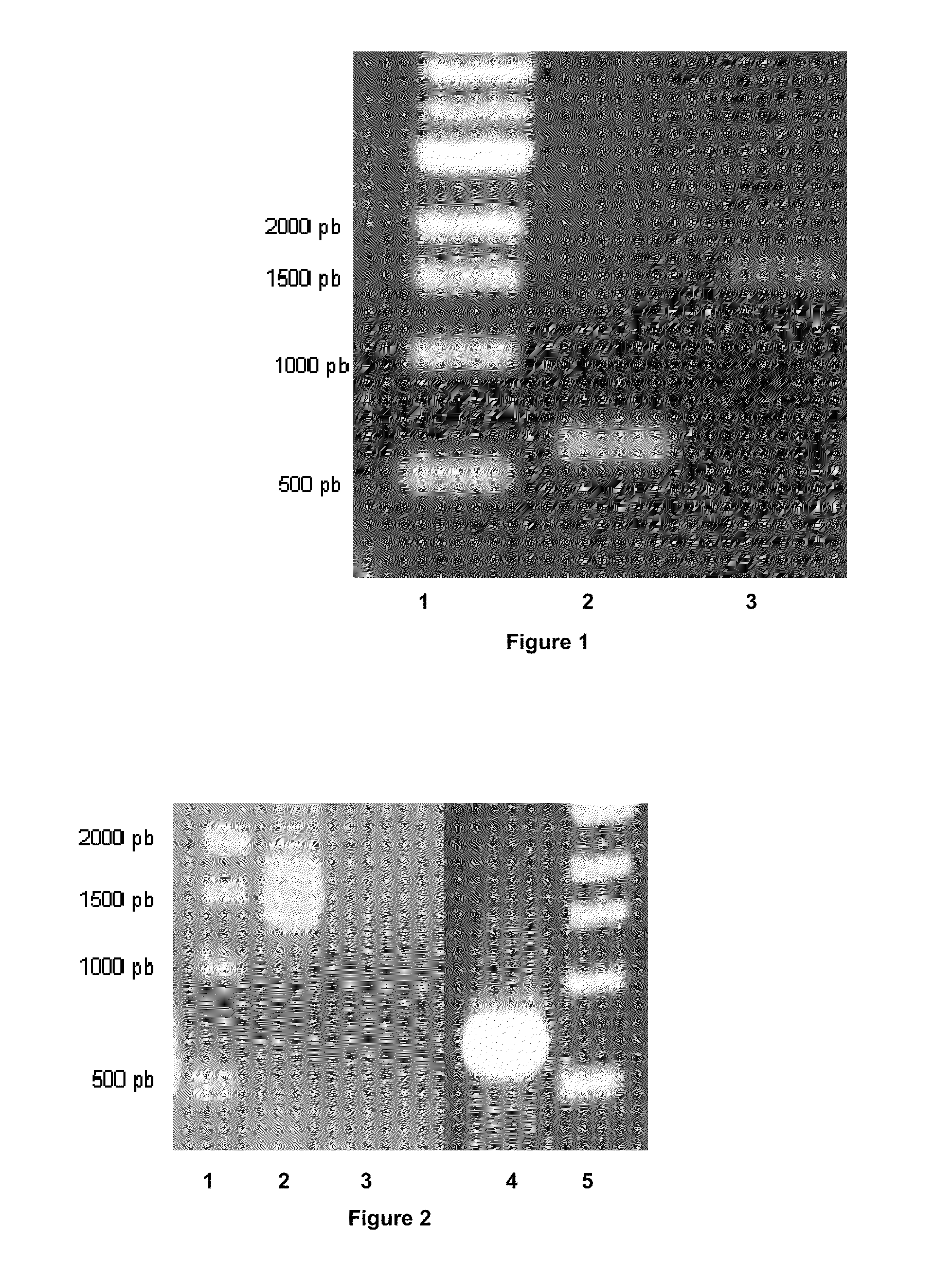
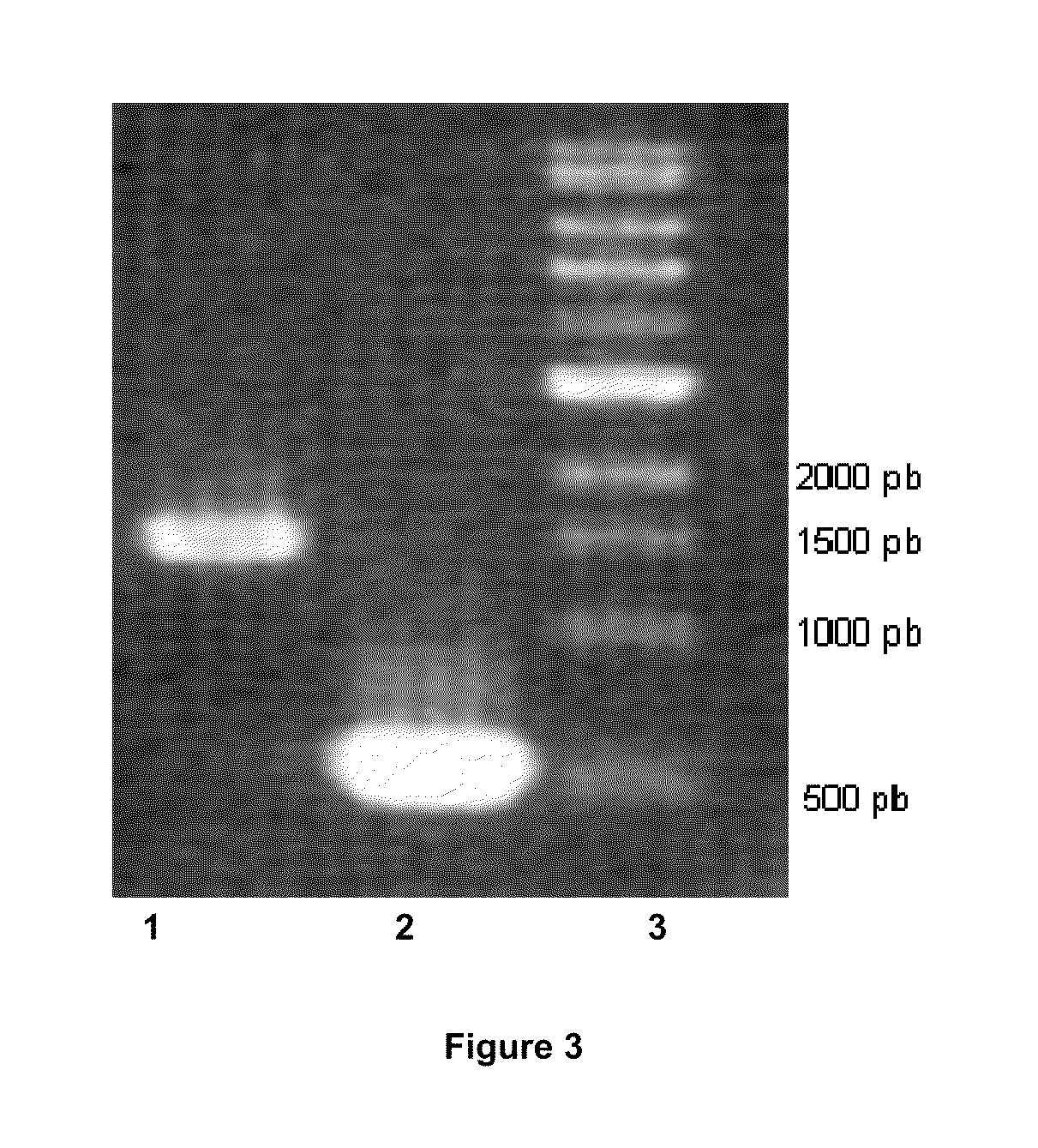
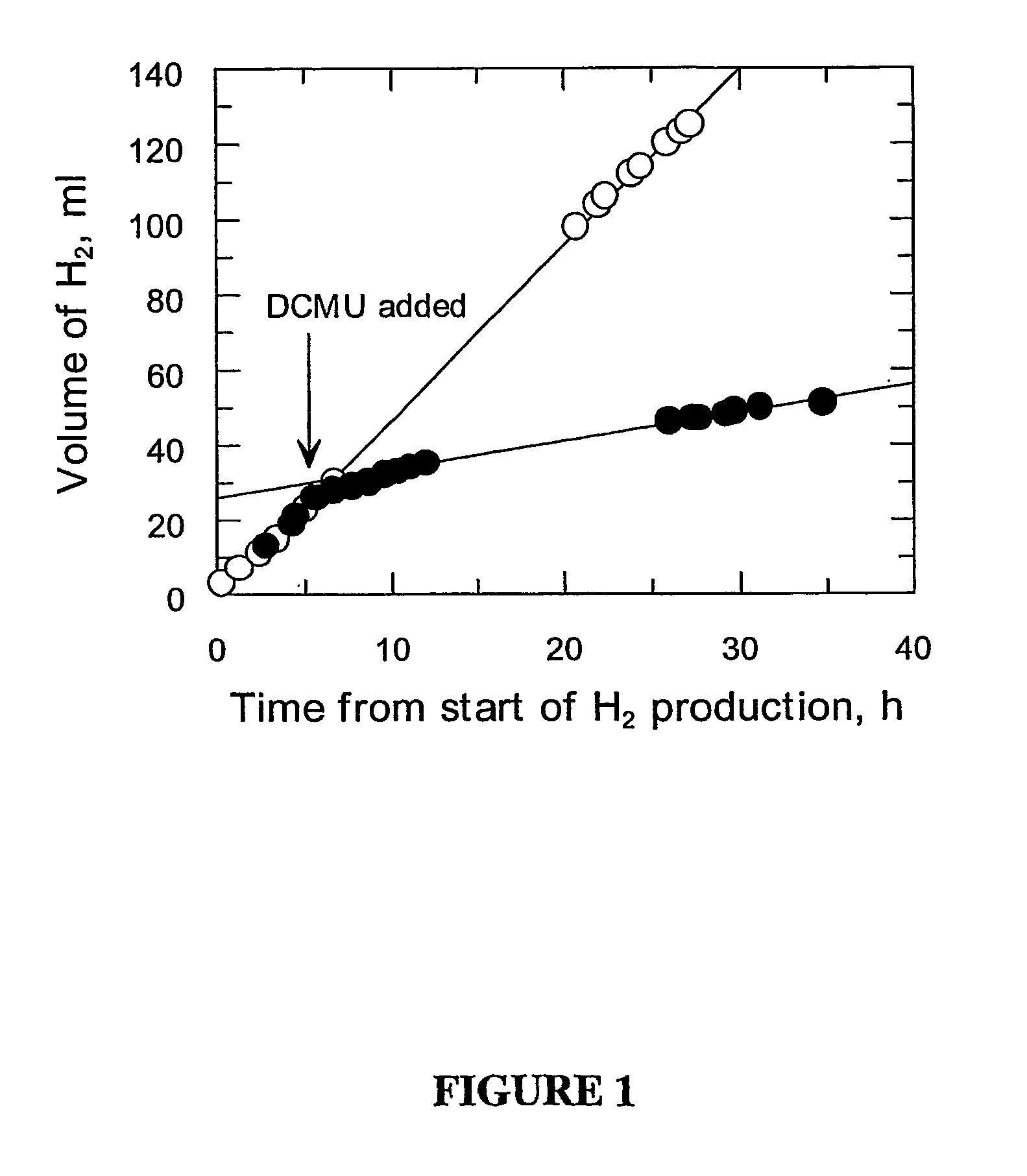
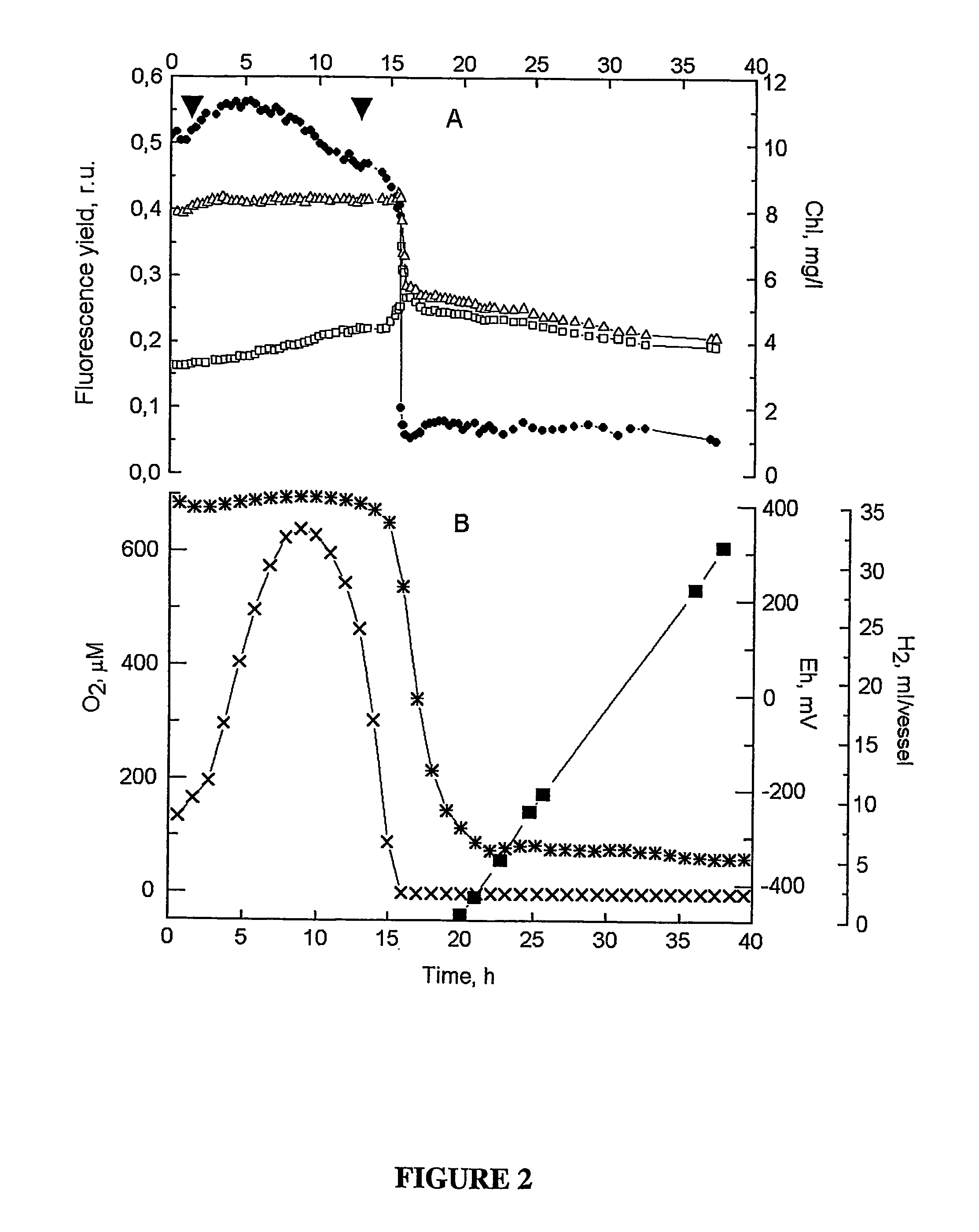
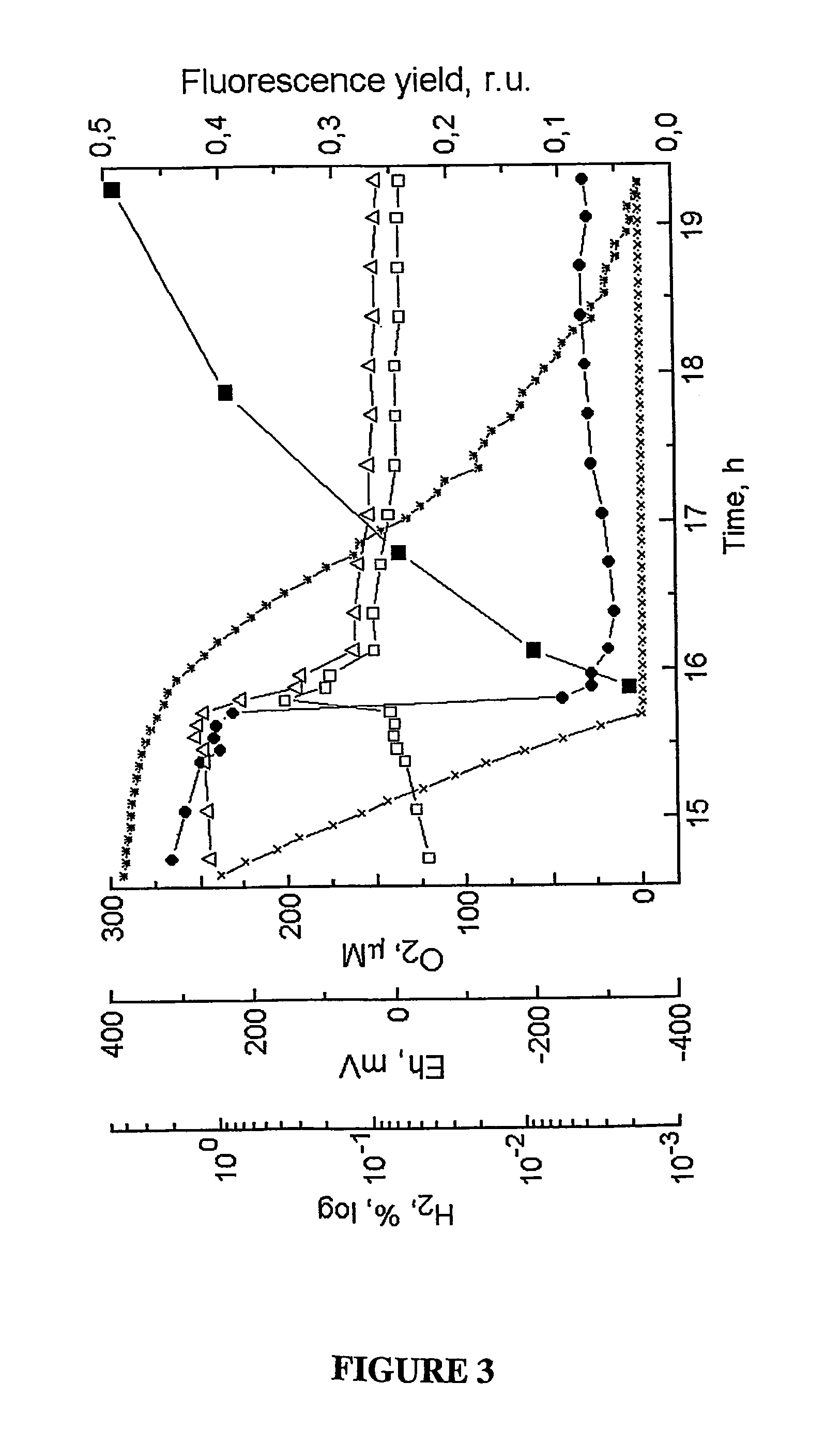
[NiFe]-hydrogenases having an improved resistance to dioxygen, process for obtaining them and their applications
The invention relates to [NiFe]-hydrogenases having an improved resistance to dioxygen, said [NiFe]-hydrogenases may be obtained by:—providing an initial polynucleotide comprising a sequence encoding a large subunit of a [NiFe]-hydrogenase, said large subunit comprising the following peptide motifs: •L1: RGXE, wherein X=L, I, F, V or M•L2: [R / K]X1C[G / R]X2C, wherein Xi is any amino acid residue, X2=L, V, I or M; L1 and L2 being separated by 16 any amino acid residues; •L3: X1X2X3X4X5X6X7X8X9X10X11X12[D / S / E], wherein X1=D, S, N or E, X2=H, D, S, N or L, X5=H, S, A, Q or W, X6=F, T, Y or G, X9=L, F, M or Y, the other Xn being any amino acid residue; •L4: D[P / I / S]CX1X2CX3X4[H / R], wherein X2=A, S, V, G or T, X1, X3 and X4 are any amino acid residue • and optionally comprising a motif LO: R[I / V / A]EG[H / D / A].—modifying said initial polynucleotide in order to substitute at least one of the residues X2 of motif L2 and Z or X4 of motif L3 and Z or X9 of motif L3 of said large subunit by a methionine.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Biological electrode with the hydrogenase enzyme, method of obtaining same and applications thereof
InactiveUS20090142649A1Easy transferFacilitates direct transfer of electronCellsCell electrodesFuel cellsElectrochemical cell
The present invention relates to biological electrodes modified with hydrogenase enzymes (anodes), by means of which it is possible to produce electrical energy from hydrogen in a typical fuel cell configuration. Likewise, using these hydrogenase-modified electrodes (cathodes), it is possible to produce hydrogen from water in a typical electrochemical cell configuration. The methods of making the biological electrodes of the present invention and applications thereof are also described.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Protein cage-stabilized pickering emulsions and the use thereof
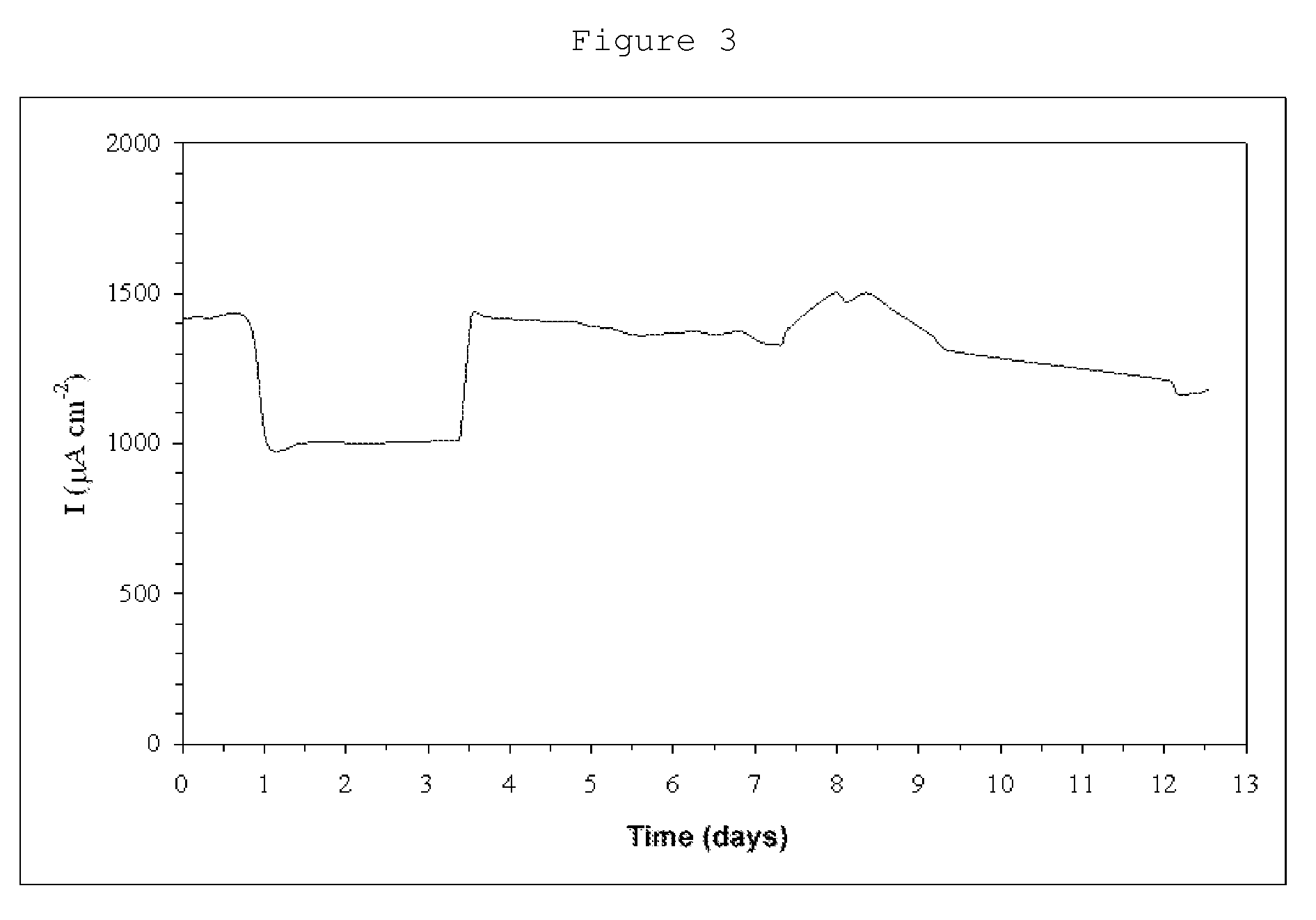
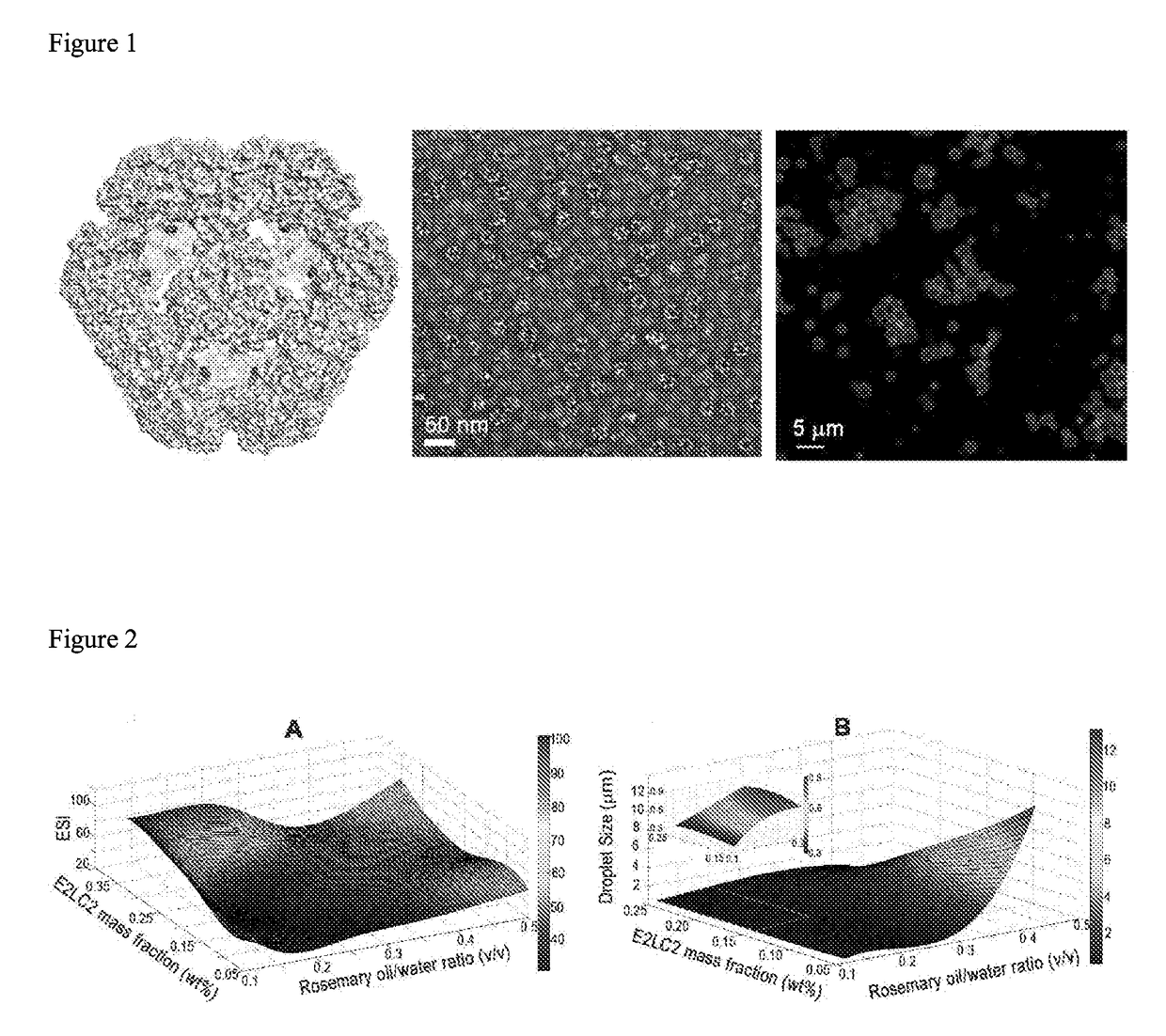
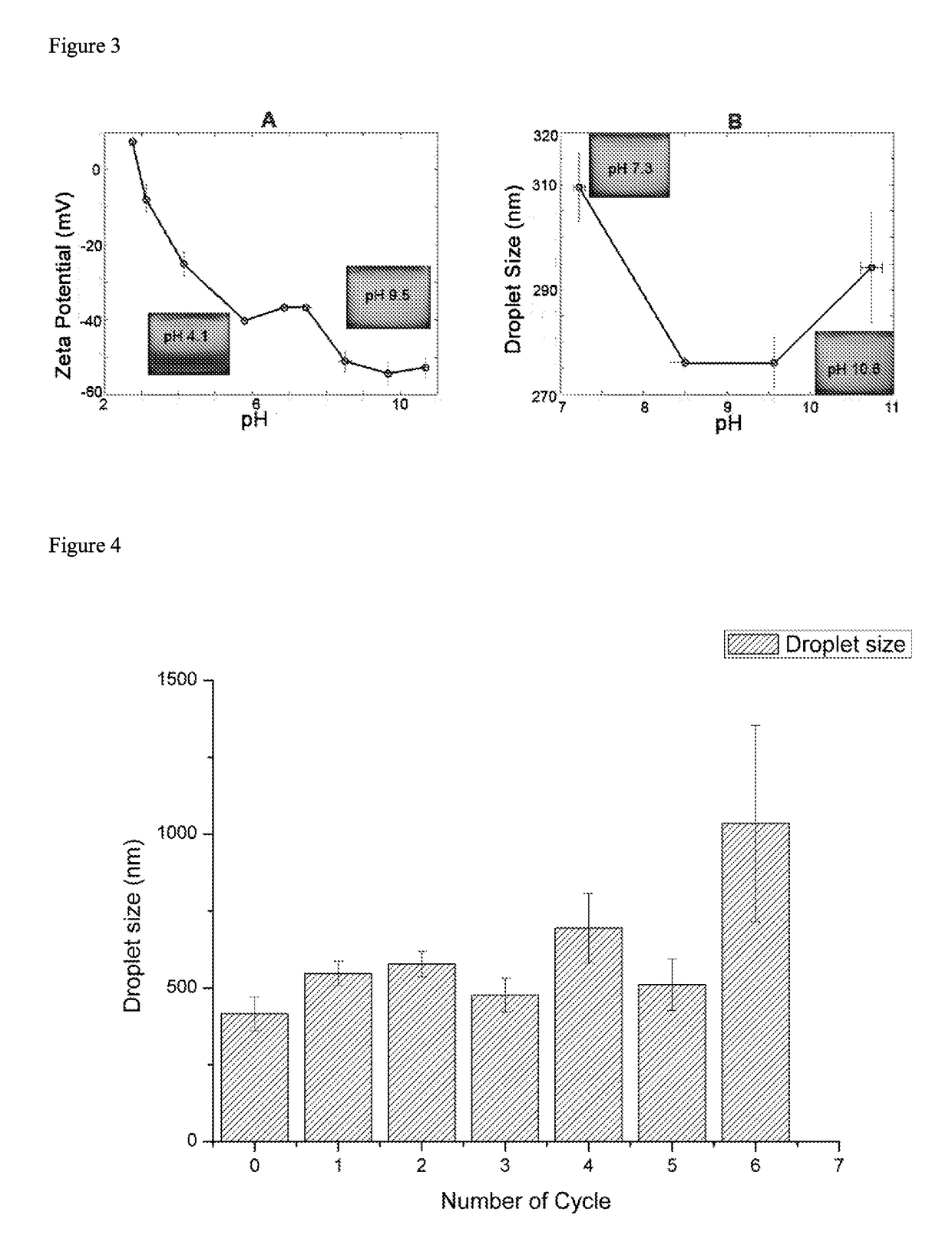
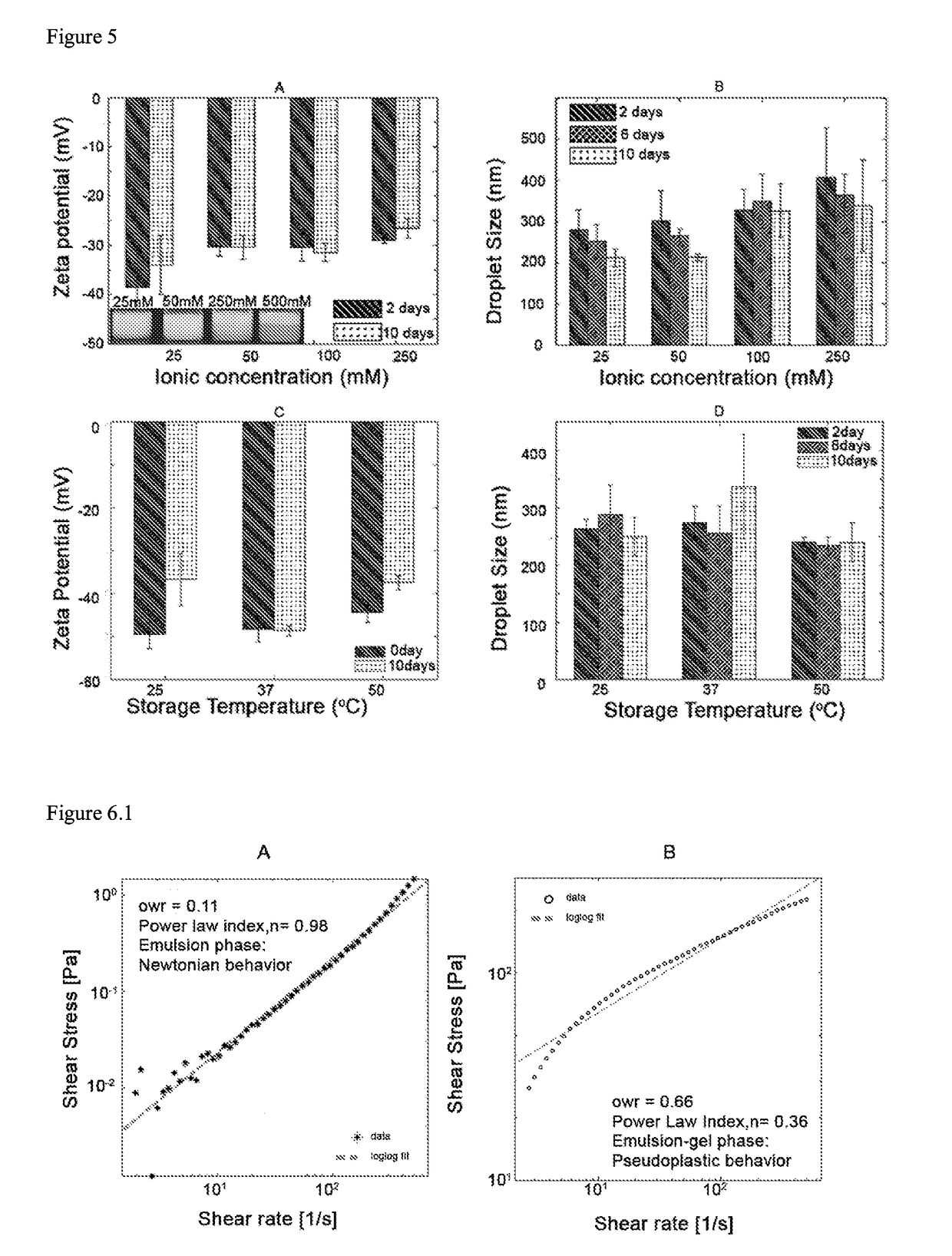
The present invention relates to a Pickering emulsion comprising an aqueous phase, an oil phase and a nanoparticle, wherein the nanoparticle is a protein cage. The protein cage is preferably a Bacillus stearothermophilus E2 protein of pyruvate hydrogenase multi-enzyme complex or an E2LC2 protein. Preferably the aqueous or oil phase of the Pickering emulsion comprises an agent, or the protein cage is coupled to or loaded with an agent, wherein the agent is a therapeutic, nutritional, nutraceutical or cosmetic agent. The invention further includes use of the Pickering emulsions disclosed herein in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, or food applications, or as a controlled release delivery system, and use of protein cages as emulsifiers in Pickering emulsions.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
Methods and compositions for evolving hydrogenase genes
InactiveUS20070009942A1Improve abilitiesIncrease ratingsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
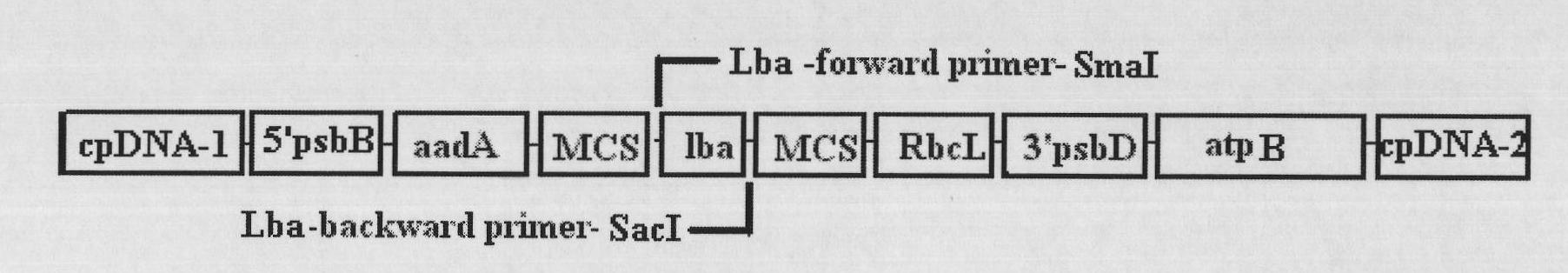
Method for improving yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes
InactiveCN101845461AIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesChlamydomonas reinhardtiiChloroplast
The invention belongs to a biological hydrogen production technology, particularly to a method for improving the yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes. Traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production has the disadvantages that chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogenase is sensitive to oxygen and is easily inhabited by the oxygen to inactivate; and the hydrogen production effect of chlamydomonas is limited. The invention discloses application of soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes in chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production, the soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes lba are constructed in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast expression vector, and the expression vector is transformed into chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast, so that the lba genes are expressed in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. The decrease of the oxygen content in a closed culture system of the transformed chlamydomonas reinhardtii is markedly quicker than that of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii of the untransformed genes, the oxygen content can be kept at a lower level, and the hydrogen yield is markedly increased; the method is applicable for all microalgae for hydrogen production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Process for the biological production of n-butanol with high yield
The present invention provides a method for the biological production of n-butanol at high yield from a fermentable carbon source. In one aspect of the present invention, a process for the conversion of glucose to n-butanol is achieved by the use of a recombinant organism comprising a host C. acetobutylicum transformed i) to eliminate the acetate pathway ii) to eliminate the butyrate pathway iii) to eliminate the lactate pathway and iv) to eliminate the acetone pathway. In another aspect of the present invention, the hydrogen flux is decreased and the reducing power redirected to n-butanol production by interrupting the expression of the hydrogenase gene. Optionally the n-butanol produced can be eliminated during the fermentation by gas striping and further purified by distillation.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
Method for maintaining continuous hydrogen production after chlorella cell death
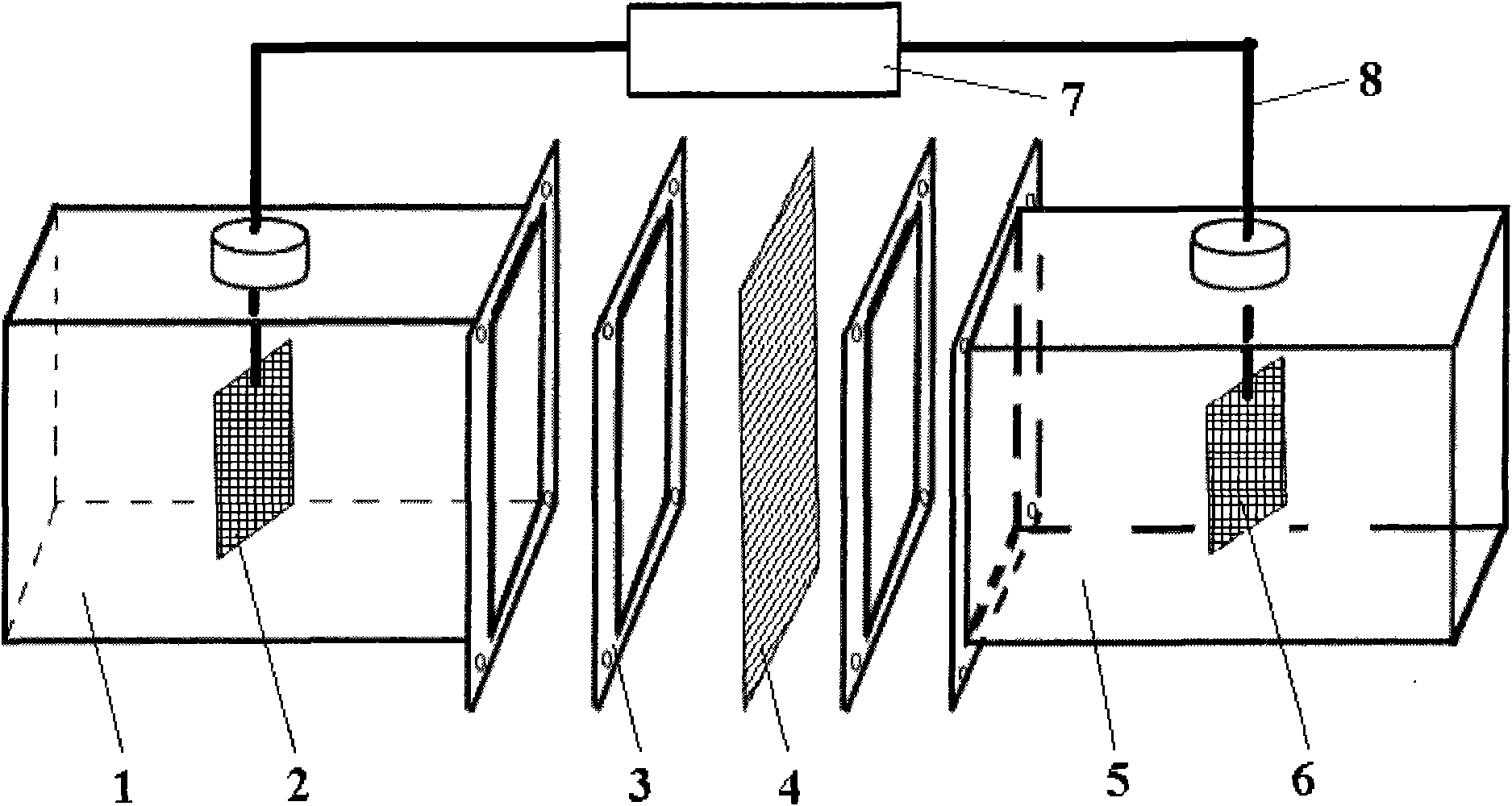
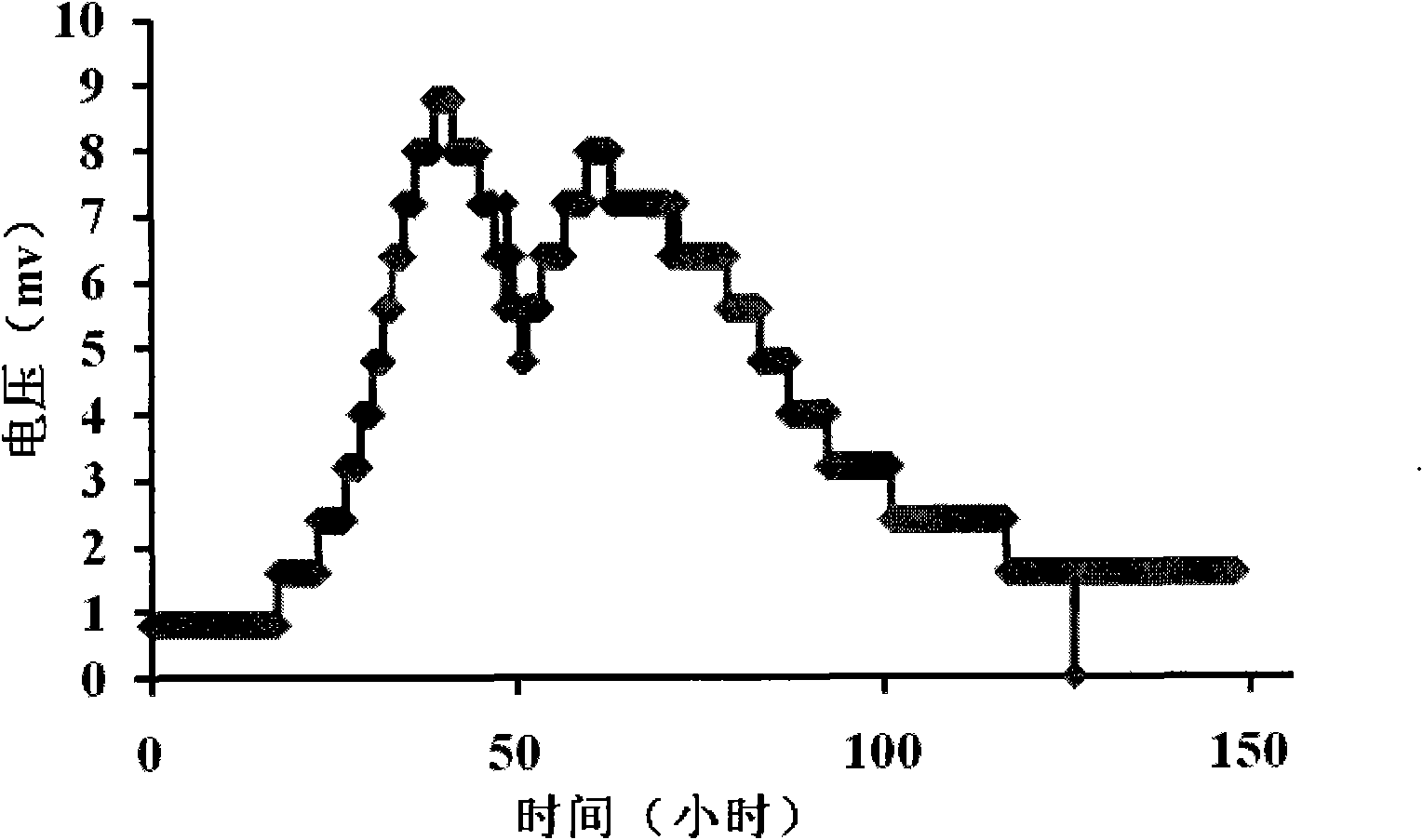
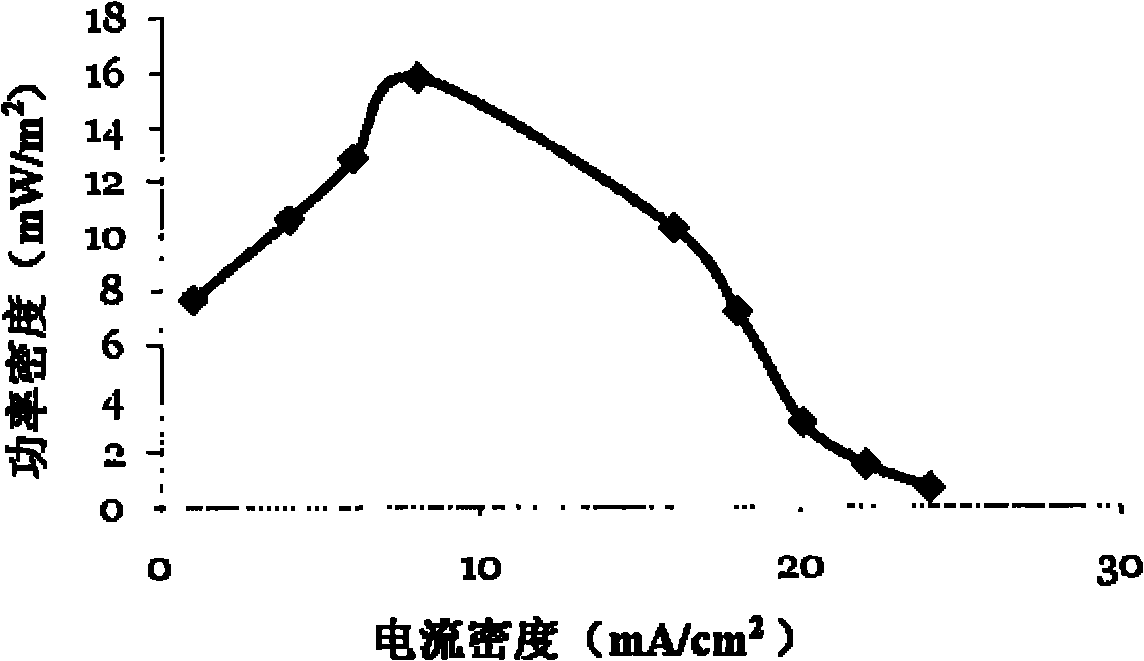
ActiveCN110144368ASolve the costSolving activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiological bodyBiotechnology
The invention relates to a method for maintaining continuous hydrogen production after chlorella cell death. The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a method for maintaining continuous hydrogen production after chlorella cell death. The invention aims to introduce a power supply system into the living environment of chlorella, and to realize high-efficiency and continuous hydrogen production in an anaerobic environment by utilizing hydrogenase in the chlorella body. The method comprises the following steps: taking chlorella pyrenoidosa as a basic organism, and constructing an integrated artificial hydrogen production system by using a biological enzyme-hydrogenase in the chlorella body through an external conductive medium pyrrole and an electronsupply system. The method enables the biological enzyme to be efficiently and fully utilized, not only can maintain the activity of life body of chlorella cells, but also can continue to utilize active substances in the body of the chlorella cells after the life body is dead, so that the chlorella pyrenoidosa can continuously and efficiently produce hydrogen in an anaerobic environment for more than two months.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
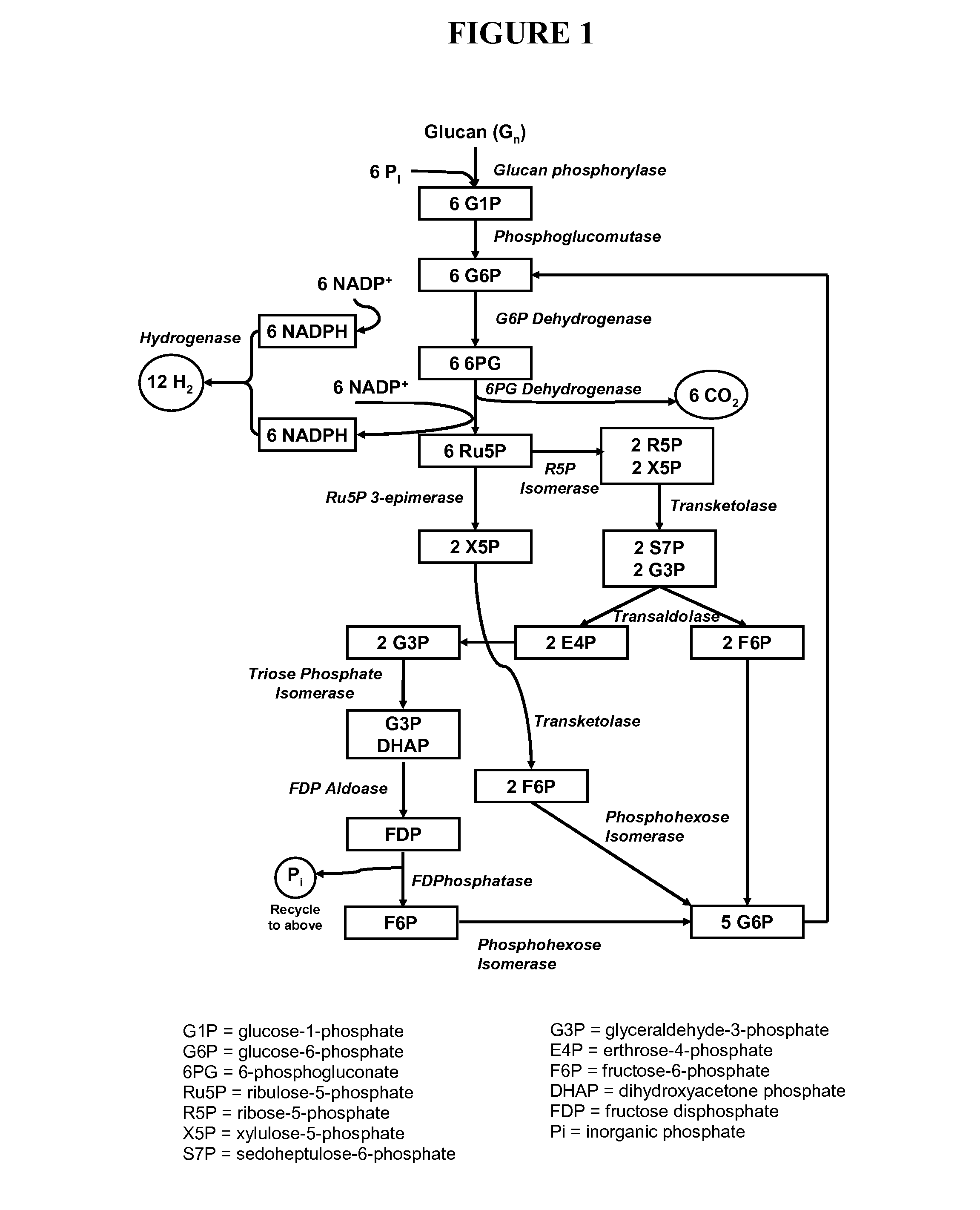
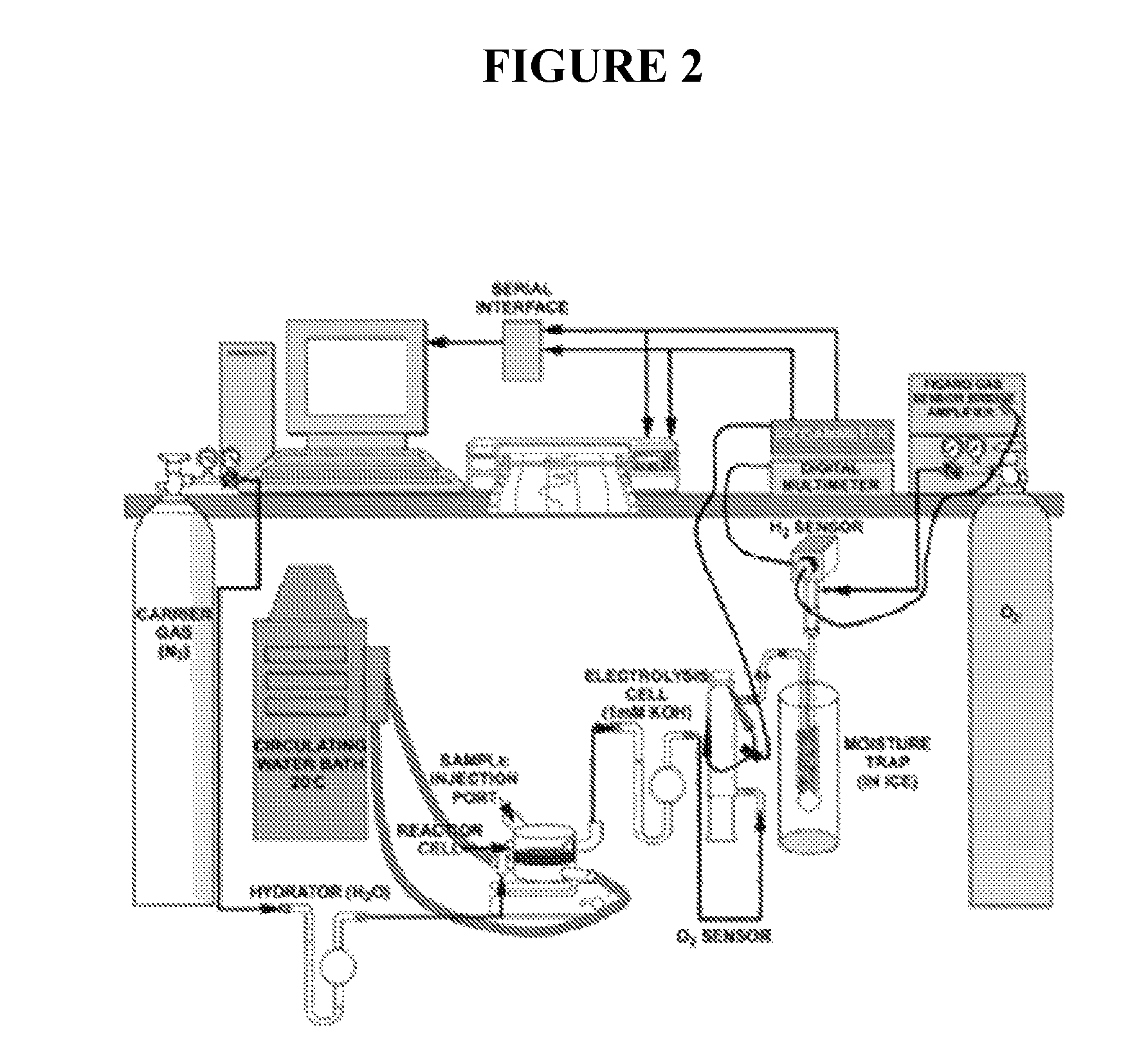
Biohydrogen production by an artificial enzymatic pathway
The present invention comprises an in vitro enzymatic process that effectively converts renewable polysaccharides into high yields of hydrogen at mild conditions, using only enzymes and water. The process comprises a number of enzymes: (1) phosphorylases, (2) phosphoglucomutases, (3) hydrogenases, and (4) enzymes involved in the pentose-phosphate pathway. Preferred embodiments of the process produce only hydrogen and carbon dioxide as net products, translating into an inexpensive method of generating hydrogen in very large quantities from low-cost feedstocks.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
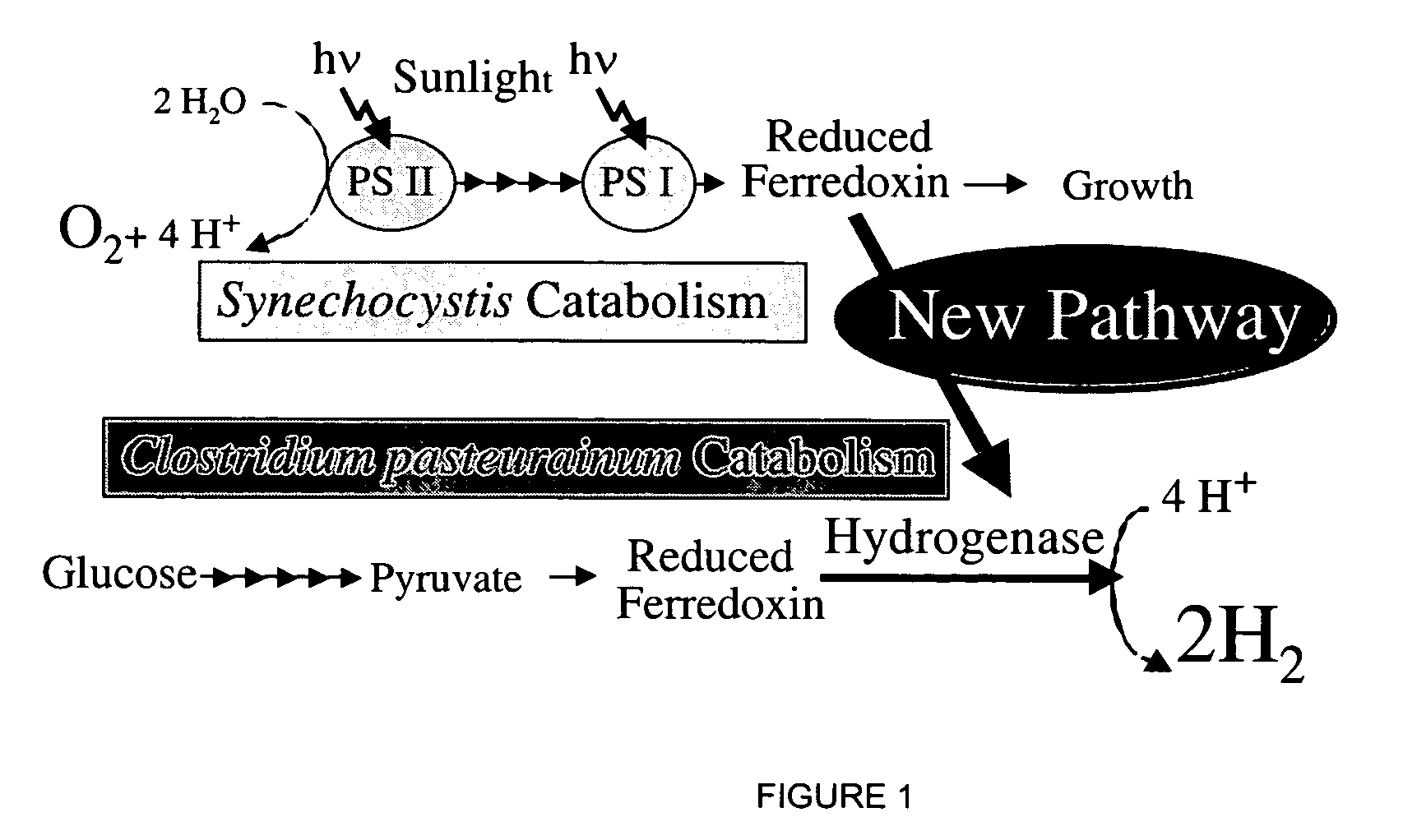
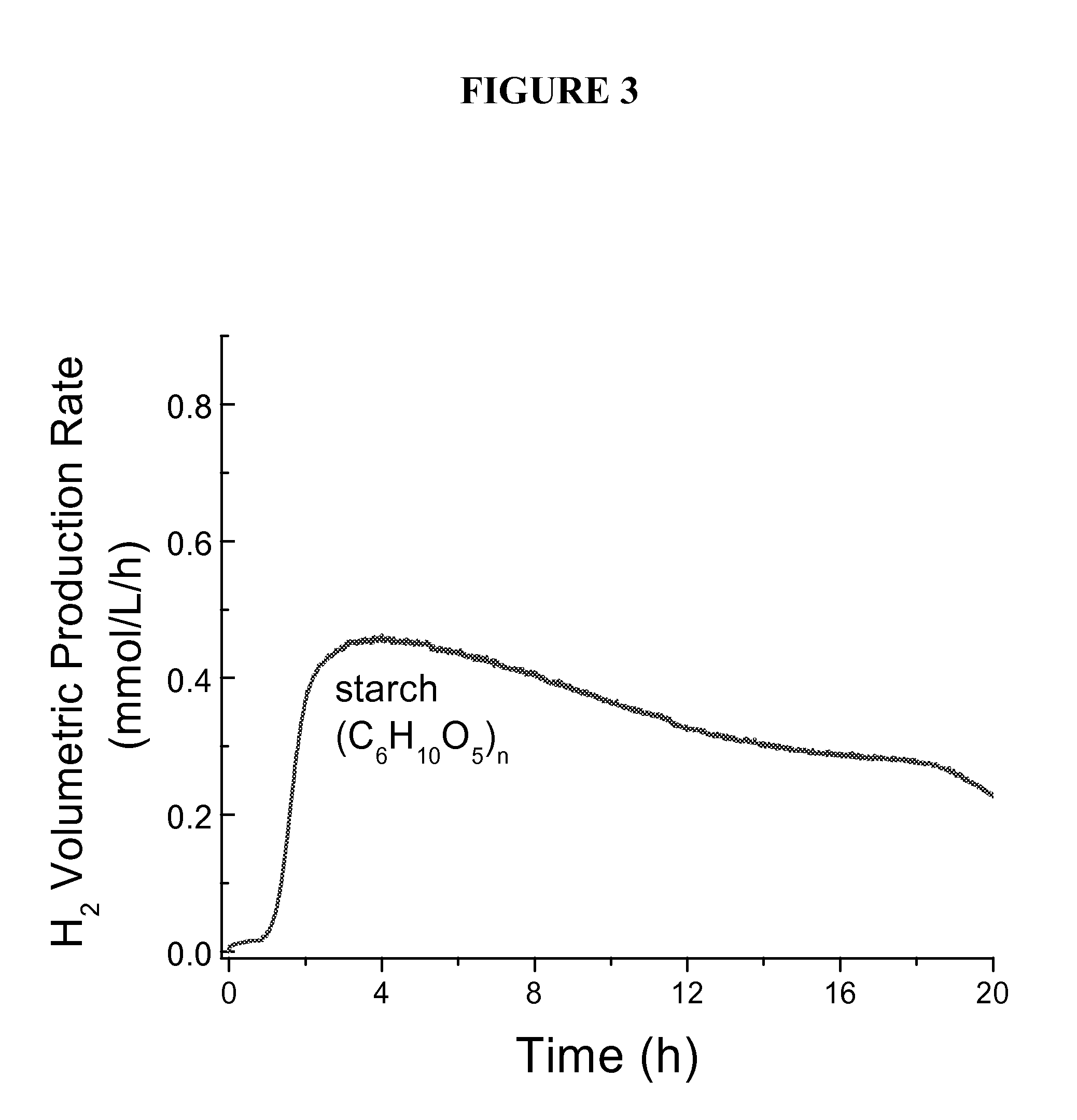
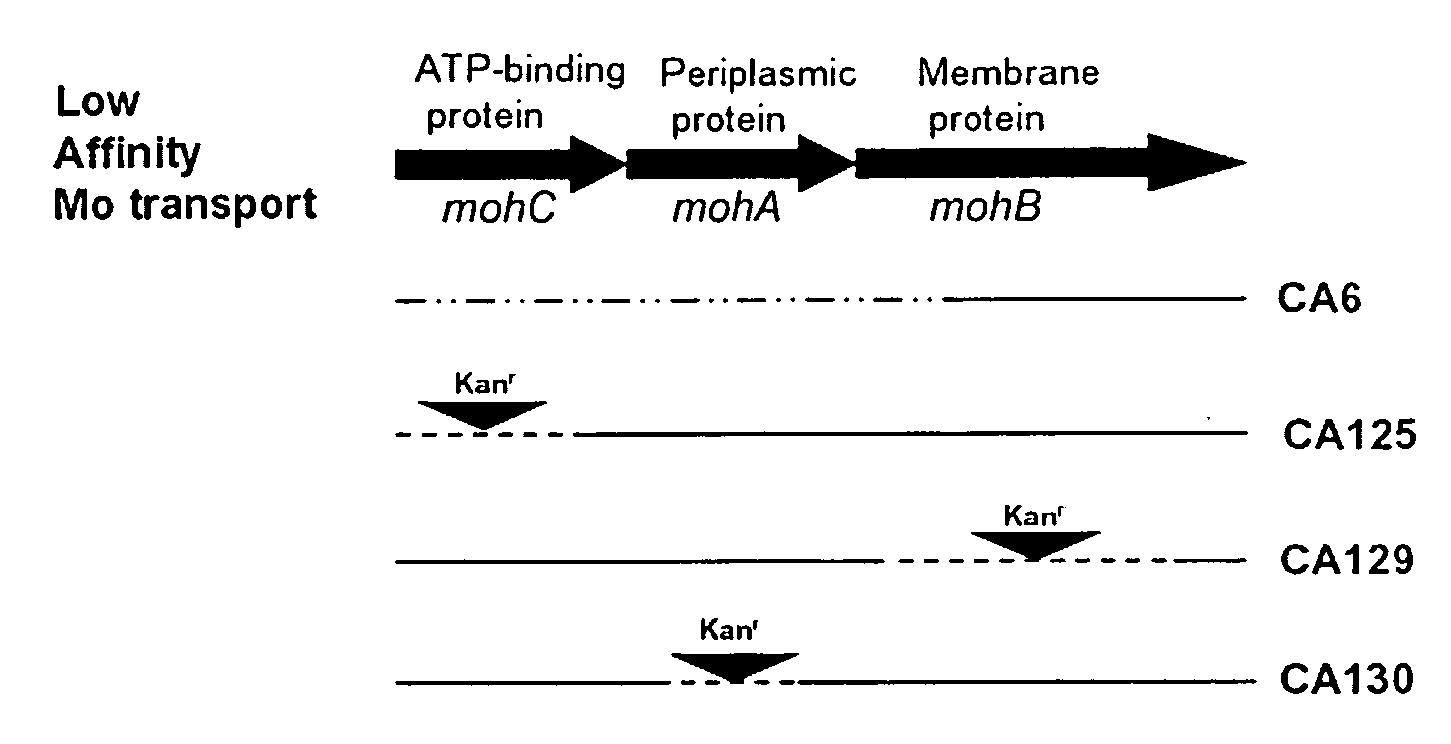
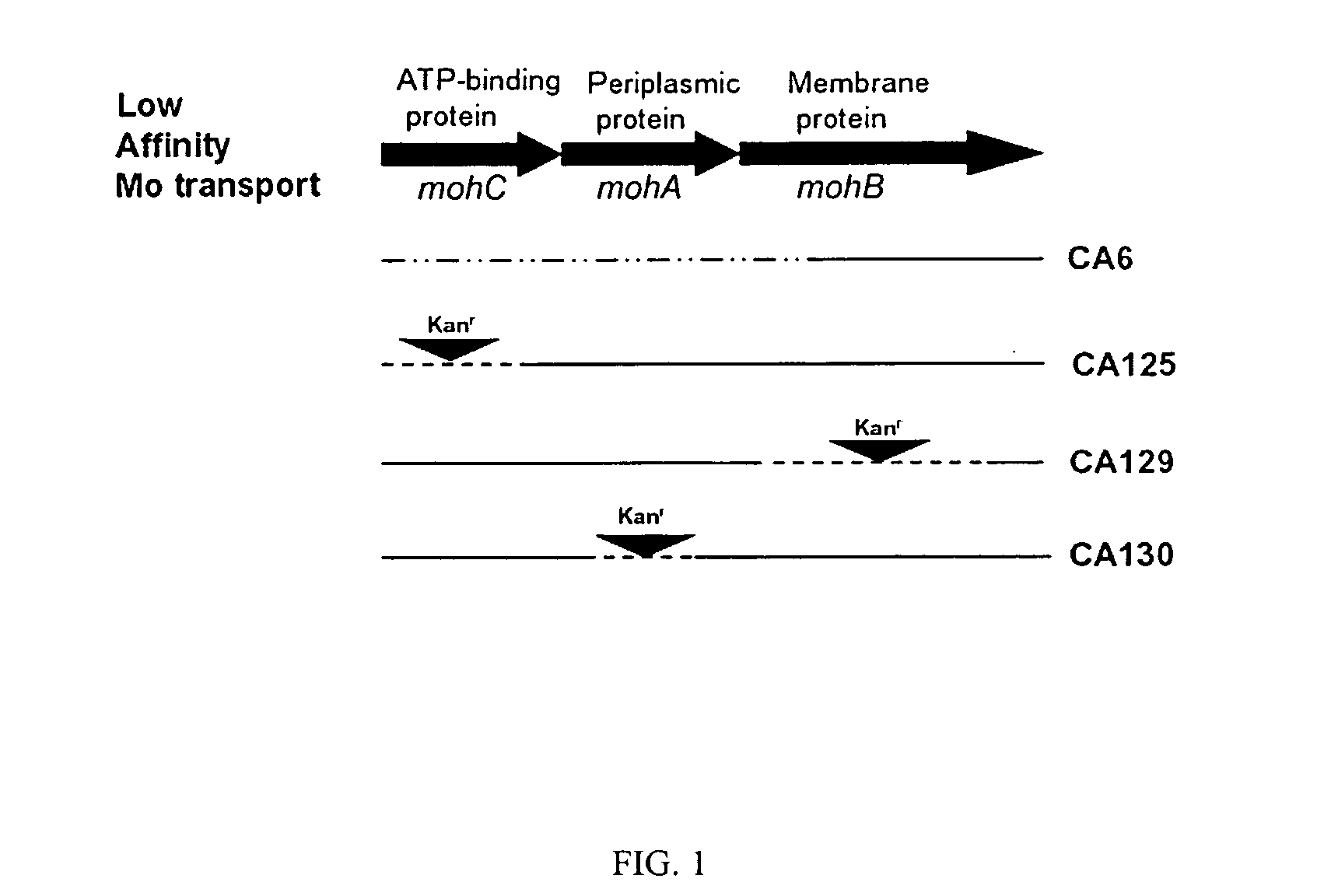
Method of identifying hydrogen evolving diazotrophic bacteria
MohC is required for expression of uptake hydrogenase in A. vinelandii and inactivation of this gene results in H2 evolution via nitrogenase 3. Since MohC− mutants are tungsten tolerant under nitrogen-fixing conditions, tungsten can be used to select spontaneous tungsten-tolerant mutants of nitrogen-fixing bacteria that are genetically uncharacterized. A major advantage of producing H2 via nitrogenase 3 is that carbon substrates used to culture the nitrogen-fixing bacteria harboring this nitrogenase are derived from plant sources.
Owner:BISHOP PAUL E +3
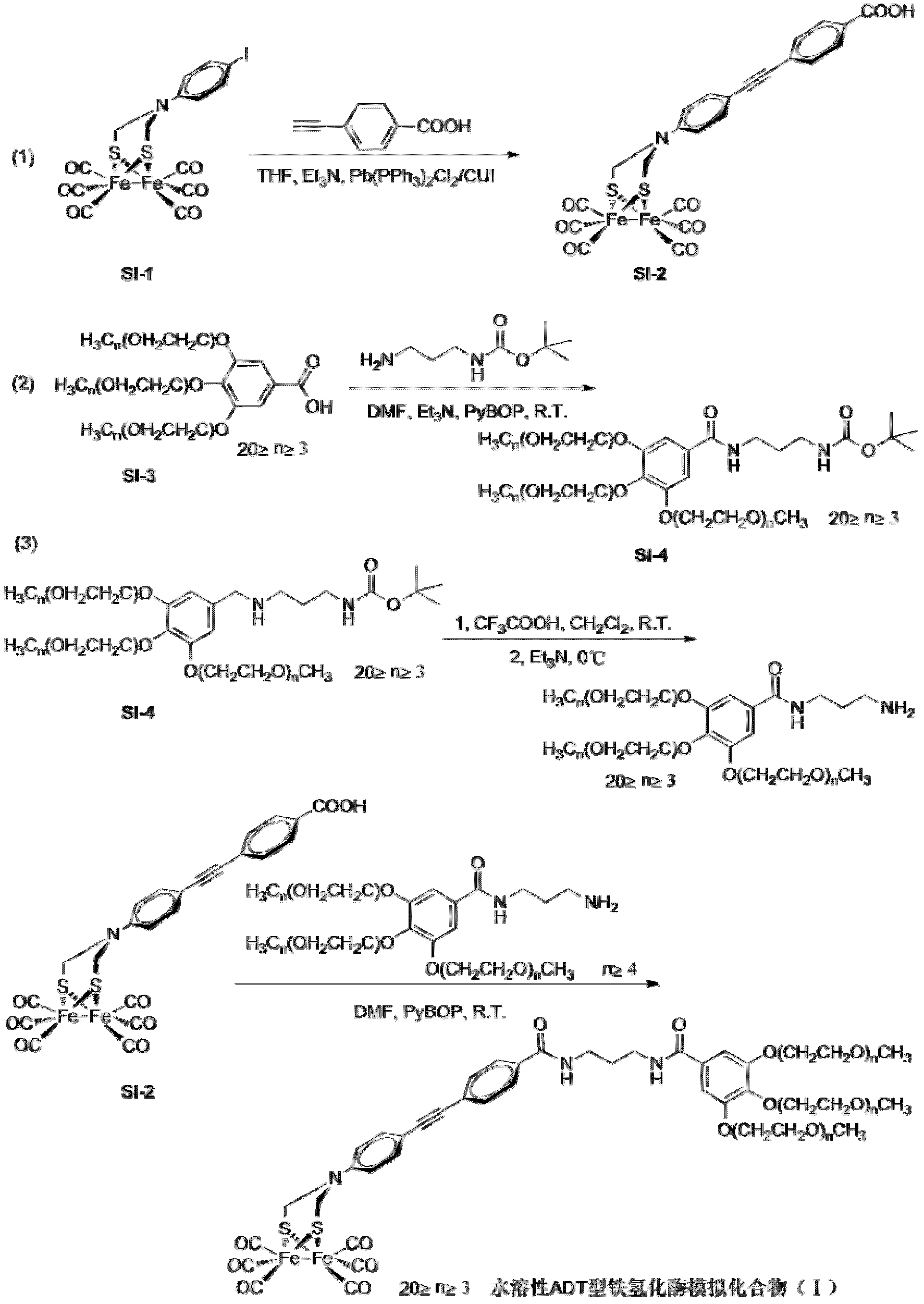
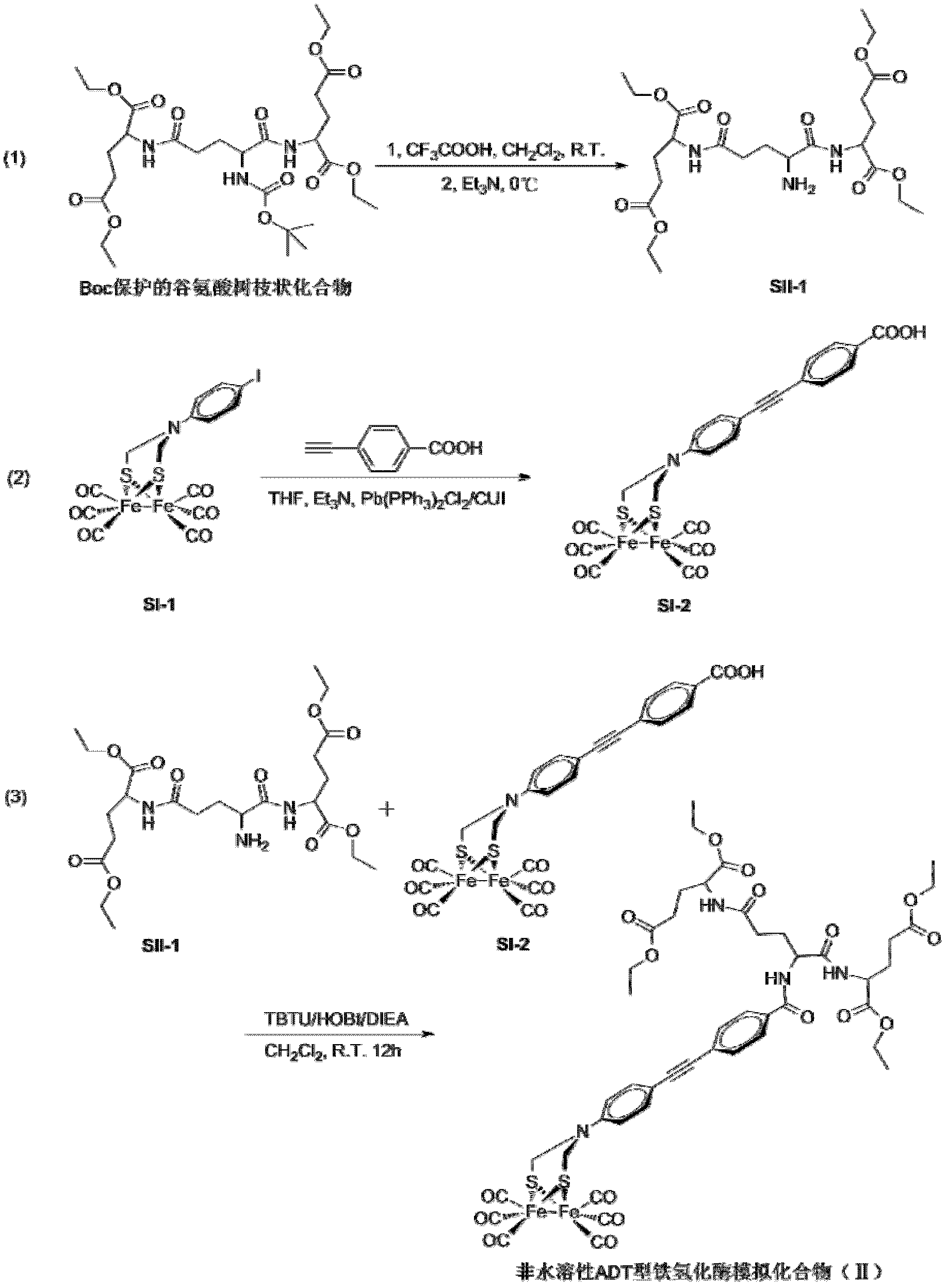
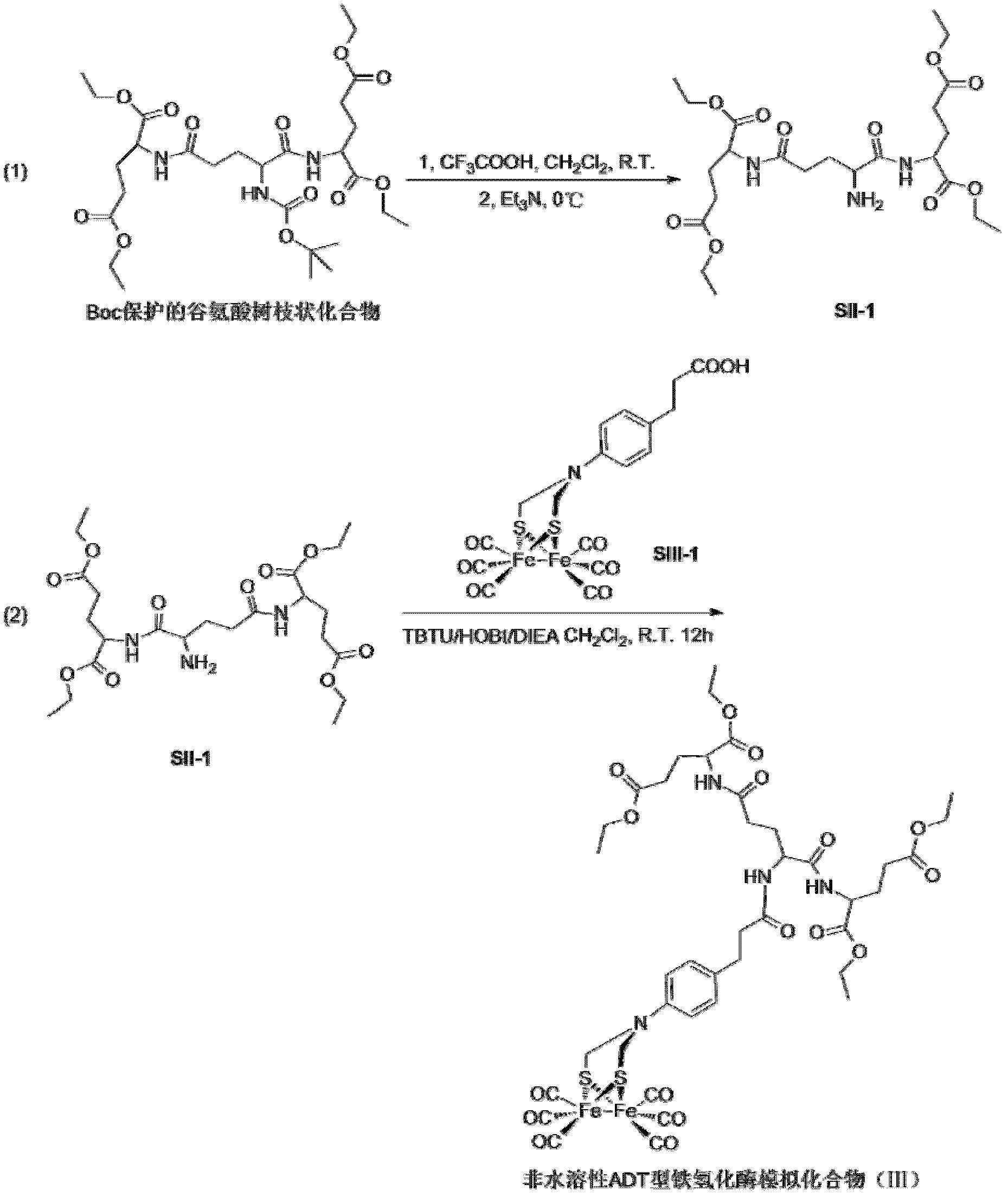
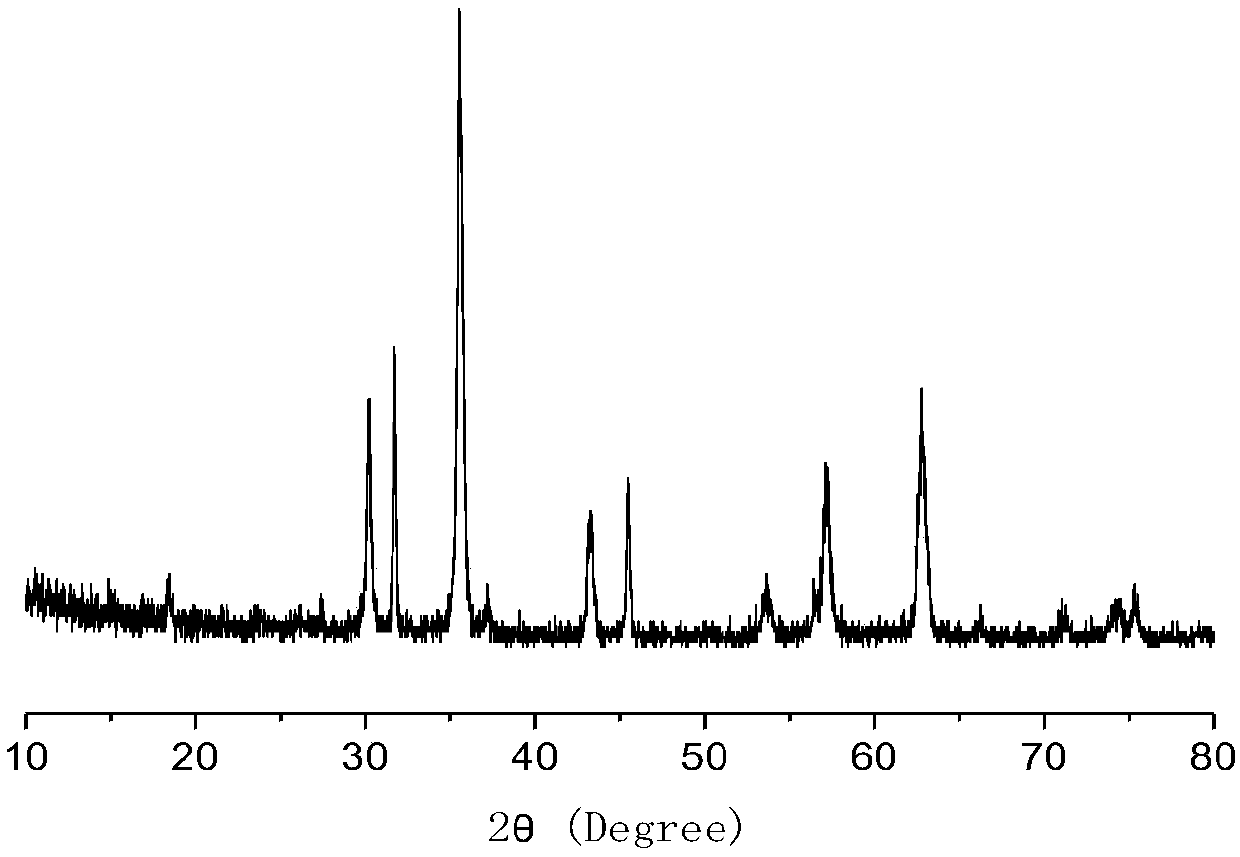
Artificial simulation hydrogenase of aromatic ether dendritic polymer and application of artificial simulation hydrogenase
ActiveCN102875820AEasy to synthesizeEasy to prepare in large quantitiesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen productionProtonEther
The invention discloses an artificial simulation hydrogenase of an aromatic ether dendritic polymer. The artificial simulation hydrogenase has the following two molecular structures of a molecular structure (I) and a molecular structure (II), wherein X is the aromatic ether dendritic polymer and has a structural formula shown in the description, R1, R2, R3 and R4 are carbonyl, isocyano, triphenylphosphino, trimethylphosphino, triethylphosphino, tributylphosphino or tripyzzolephosphino. Compared with natural hydrogenase, the artificial simulation hydrogenase of the aromatic ether dendritic polymer disclosed by the invention has good stability and is convenient to store; the artificial simulation hydrogenase is firstly used as a proton reduction catalyst for hydrogen production by water decomposed under catalysis of visible light; during hydrogen production, the catalyst has a stable property and a rather high hydrogen production catalytic activity; so far, the artificial simulation hydrogenase is an artificially synthesized artificial simulation hydrogenase with a highest catalytic activity.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
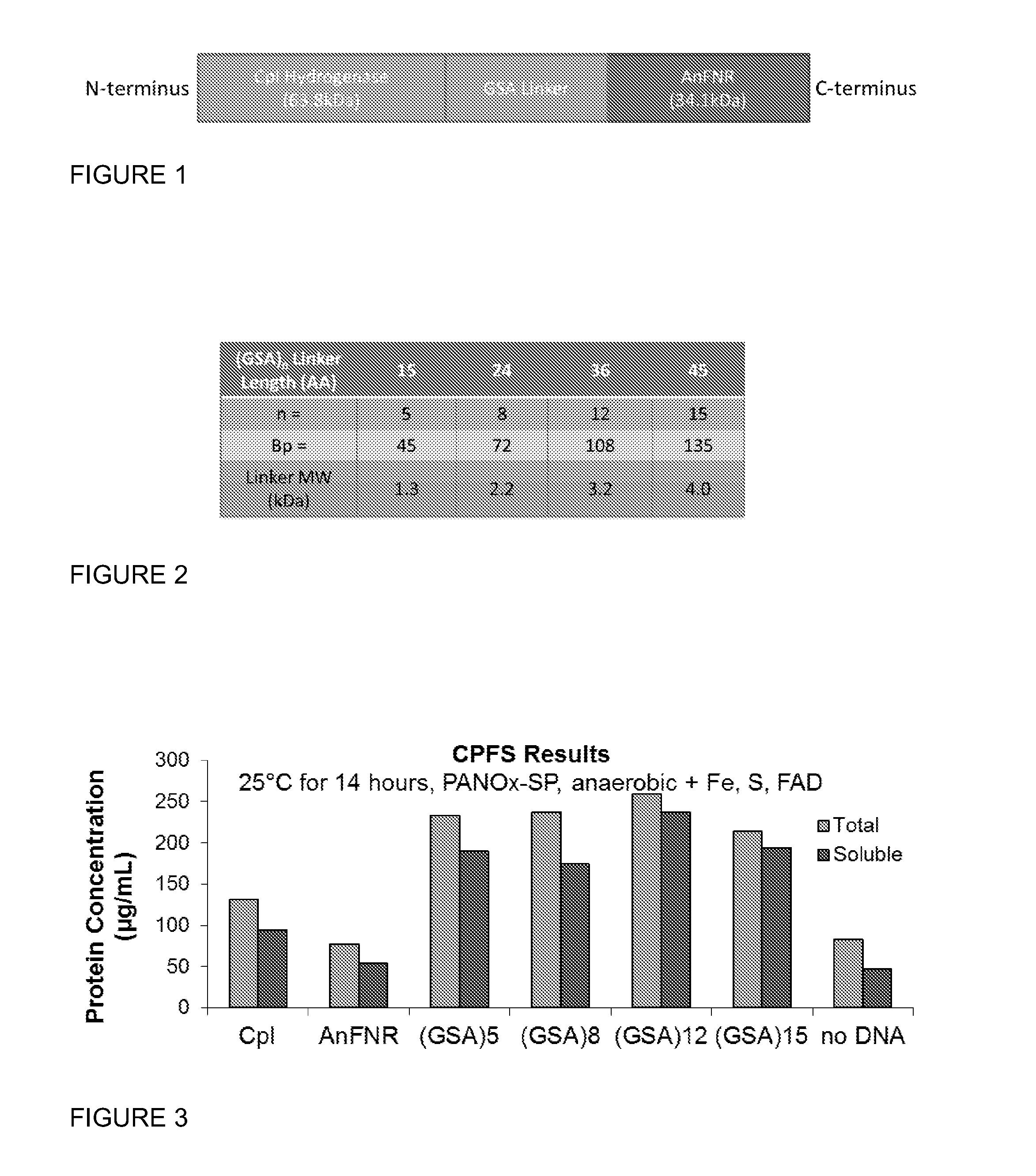
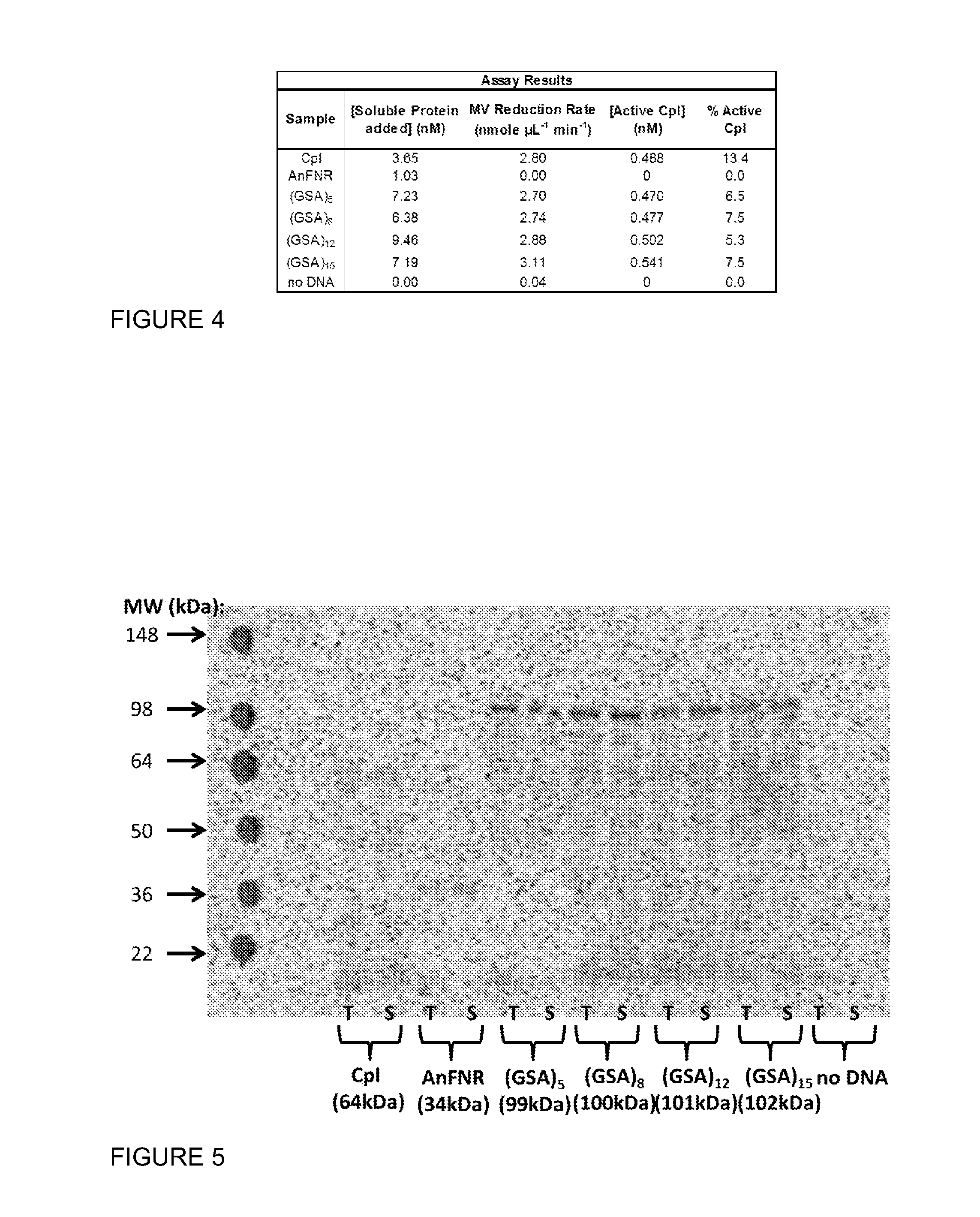
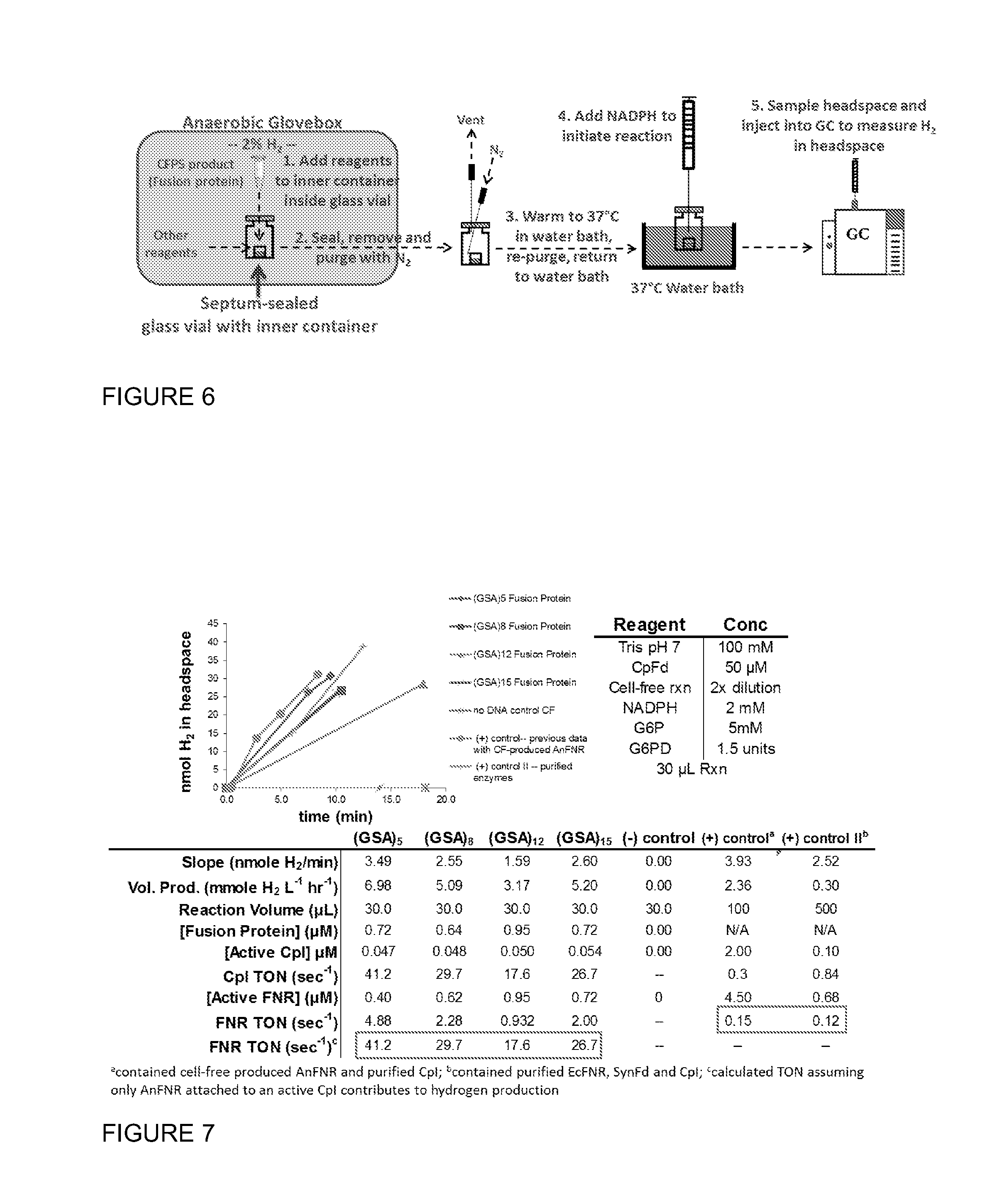
Hydrogenase Fusion Protein for Improved Hydrogen Production
ActiveUS20130273628A1Facilitates electron transferElectron transfer directSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFerredoxin—NADP(+) reductaseElectron transfer
Compositions of a fusion protein comprising a spatially tethered ferredoxin-NADP-reductase (FNR) and an active [FeFe] hydrogenase, genetic sequences encoding such fusion proteins, and methods of use thereof are provided. The fusion proteins of the invention link an FNR polypeptide to an active [FeFe] hydrogenase through a polypeptide linker. The fusion protein facilitates improved electron transfer through a ferredoxin, and allows direct electron transfer from NADPH to the hydrogenase.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Microorganism for converting carbon dioxide to aliphatic carboxylic acids via formic acid intermediate
The invention relates to a micro-organism comprising a hydrogenase enzyme system which is capable of converting carbon dioxide into formic acid and a second enzyme system which is capable of converting formic acid into aliphatic carboxylic acids having a chain length of five or more carbon atoms. Also described are various methods for producing oil, as well as other aspects of the invention.
Owner:VERDANT BIOPRODS
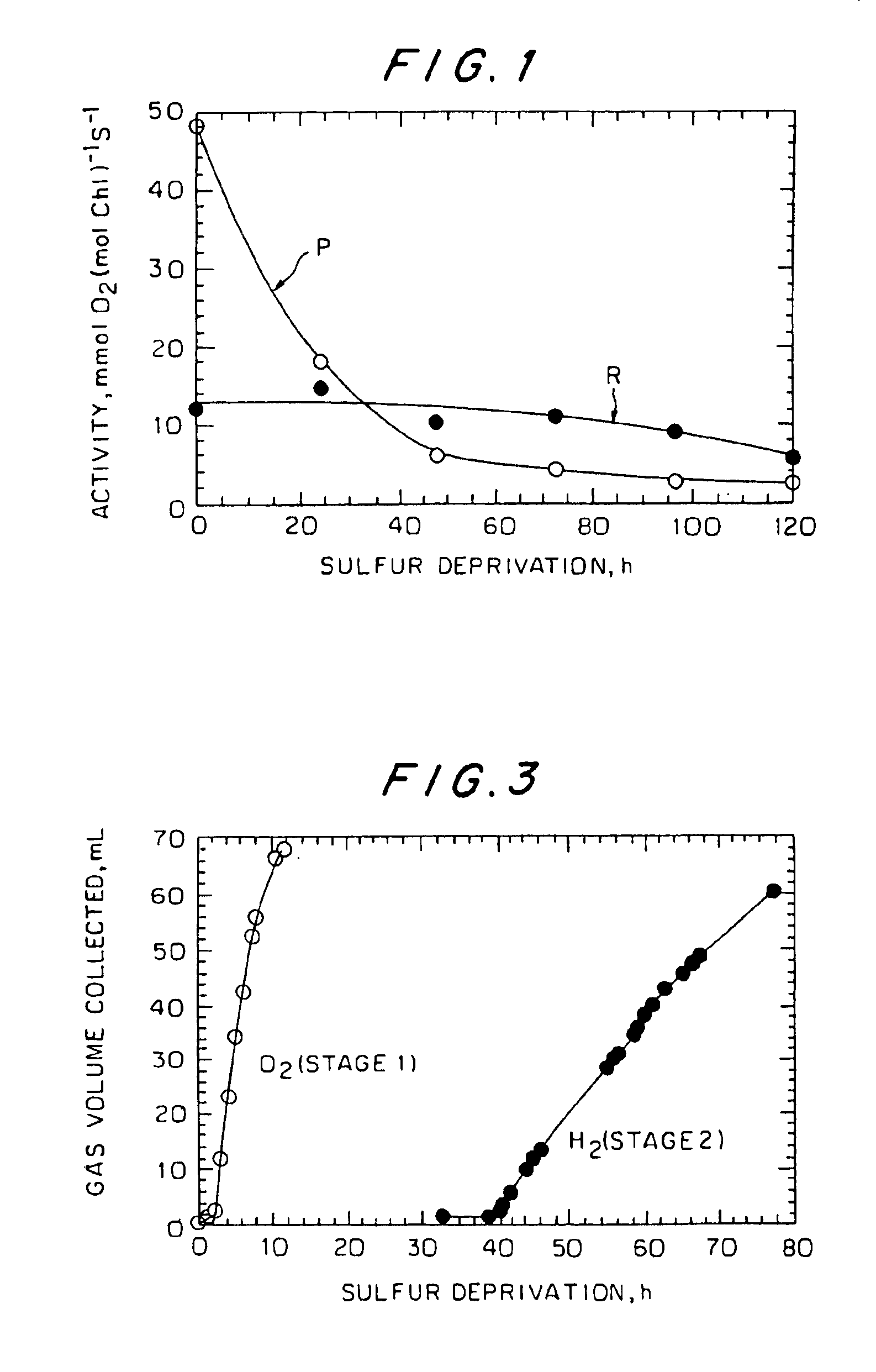
Fluorescence technique for on-line monitoring of state of hydrogen-producing microorganisms
In situ fluorescence method to monitor state of sulfur-deprived algal culture's ability to produce H2 under sulfur depletion, comprising: a) providing sulfur-deprived algal culture; b) illuminating culture; c) measuring onset of H2 percentage in produced gas phase at multiple times to ascertain point immediately after anerobiosis to obtain H2 data as function of time; and d) determining any abrupt change in three in situ fluorescence parameters; i) increase in Ft (steady-state level of chlorophyll fluorescence in light adapted cells); ii) decrease in Fm, (maximal saturating light induced fluorescence level in light adapted cells); and iii) decrease in ΔF / Fm′=(Fm′−Ft) / Fm′ (calculated photochemical activity of photosystem II (PSII) signaling full reduction of plastoquinone pool between PSII and PSI, which indicates start of anaerobic conditions that induces synthesis of hydrogenase enzyme for subsequent H2 production that signal oxidation of plastoquinone pool asmain factor to regulate H2 under sulfur depletion.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Fluorescence technique for on-line monitoring of state of hydrogen-producing microorganisms
In situ fluorescence method to monitor state of sulfur-deprived algal culture's ability to produce H2 under sulfur depletion, comprising: a) providing sulfur-deprived algal culture; b) illuminating culture; c) measuring onset of H2 percentage in produced gas phase at multiple times to ascertain point immediately after anerobiosis to obtain H2 data as function of time; and d) determining any abrupt change in three in situ fluorescence parameters; i) increase in Ft (steady-state level of chlorophyll fluorescence in light adapted cells); ii) decrease in Fm′, (maximal saturating light induced fluorescence level in light adapted cells); and iii) decrease in ΔF / Fm′=(Fm′−Ft) / Fm′ (calculated photochemical activity of photosystem II (PSII) signaling full reduction of plastoquinone pool between PSII and PSI, which indicates start of anaerobic conditions that induces synthesis of hydrogenase enzyme for subsequent H2 production that signal oxidation of plastoquinone pool asmain factor to regulate H2 under sulfur depletion.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Rhodobacter capsulatus and application thereof
ActiveCN103667109AReduce nitrogen fixationReduce carbon sequestrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesNormal growth
The invention discloses rhodobacter capsulatus and an application thereof. The invention provides rhodobacter capsulatus BN-W-6 which has a collection number of CGMCC No.8311 and belongs to photosynthetic bacteria. The rhodobacter capsulatus is fermented by adding an energy source after enlargement cultivation to obtain fermentation products including chlorophyll a, carotenoid, ketone-carotenoid, hydrogenase, catalase and the like. Biological enzymes generated by the fermentation products of the rhodobacter capsulatus in a pond can ensure that macroscopic algae are gradually decomposed, the products including chlorophyll a, carotenoid and the like can absorb illumination wavebands necessary for growth of the macroscopic algae to make the macroscopic algae shrunk and agglomerated until death, and the dead macroscopic algae can not influence bottom matters, thereby achieving the aims of controlling rampant growth of algae and not influencing the normal growth of sea cucumbers. The fermentation broth of the rhodobacter capsulatus provided by the invention can be used for inhibiting and removing the macroscopic algae, so that the culture density is increased, the culture environment is improved, and the aim of improving the pond culture output of aquatic organisms is achieved.
Owner:大连市水产技术推广总站 +1
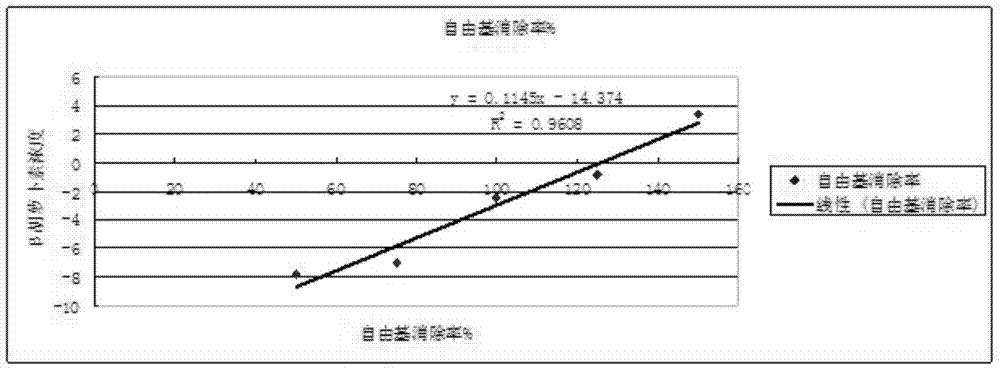
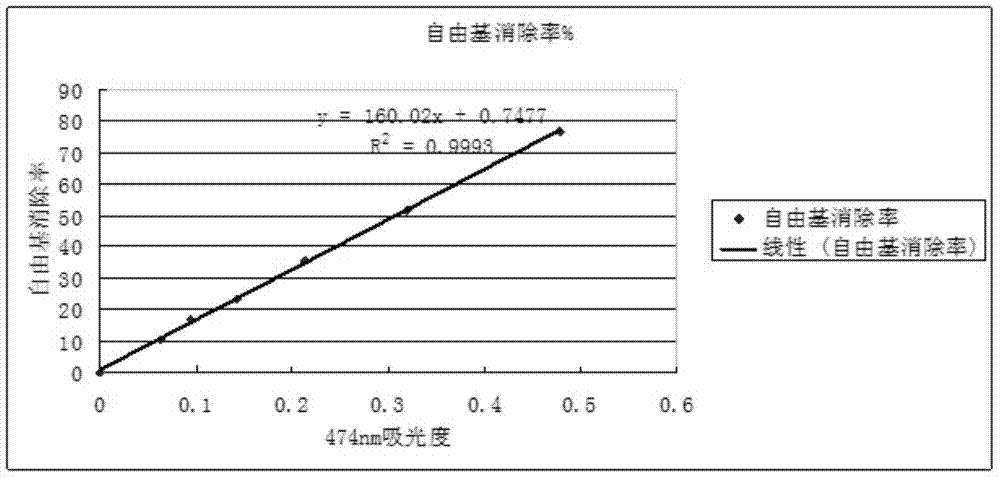
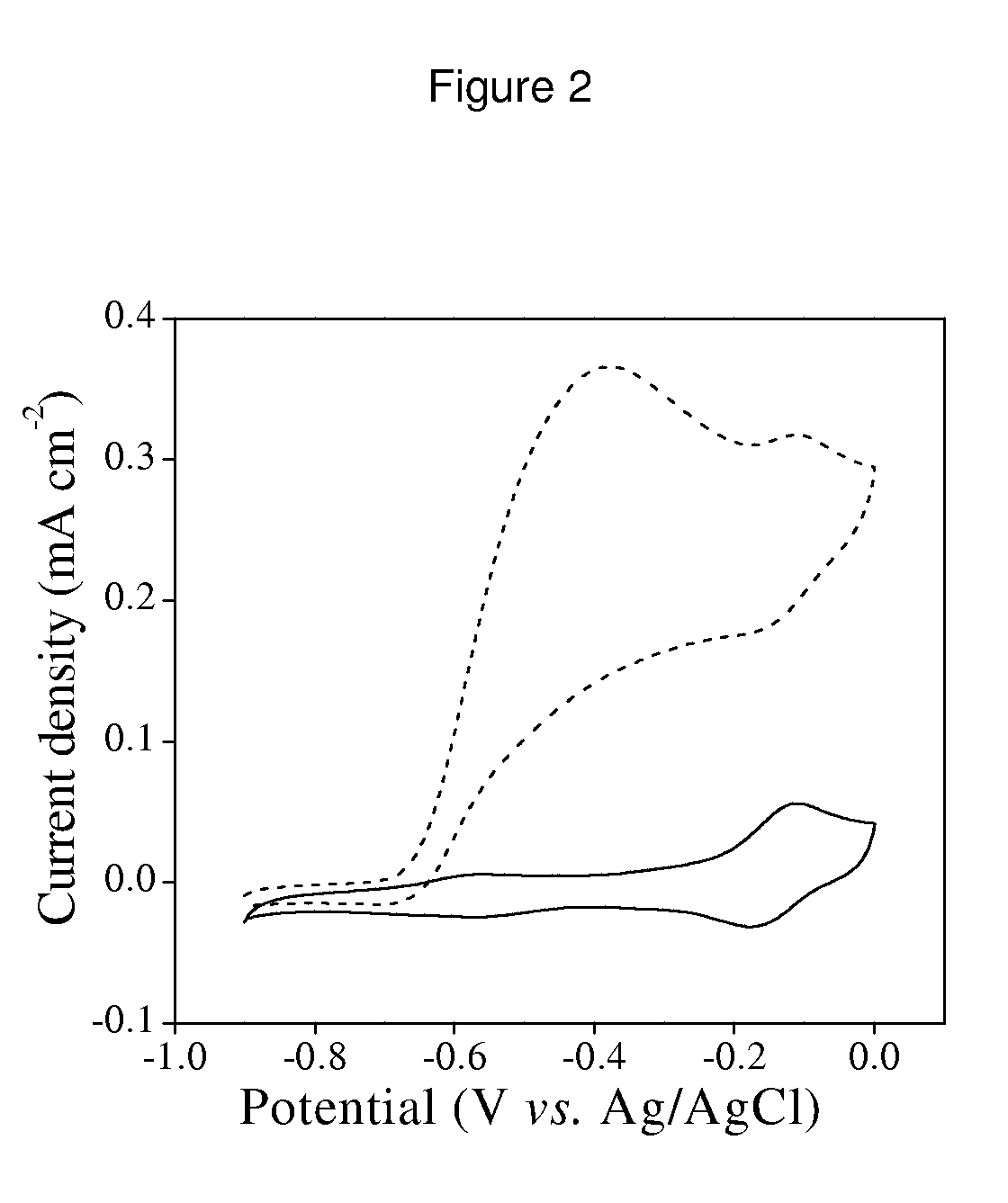
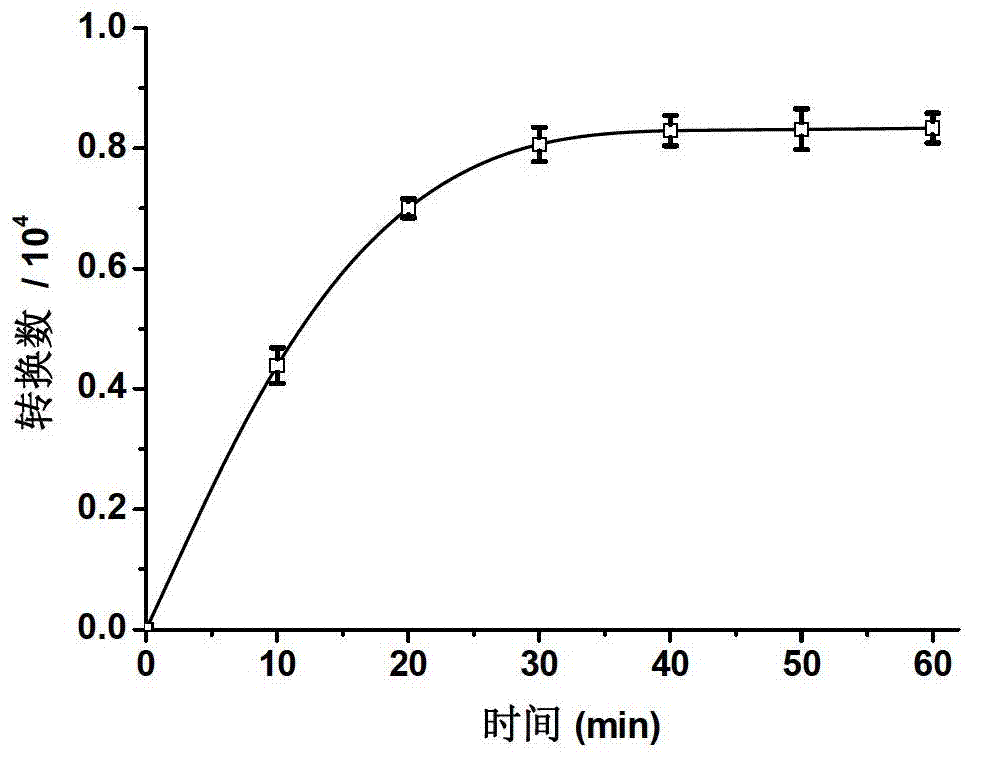
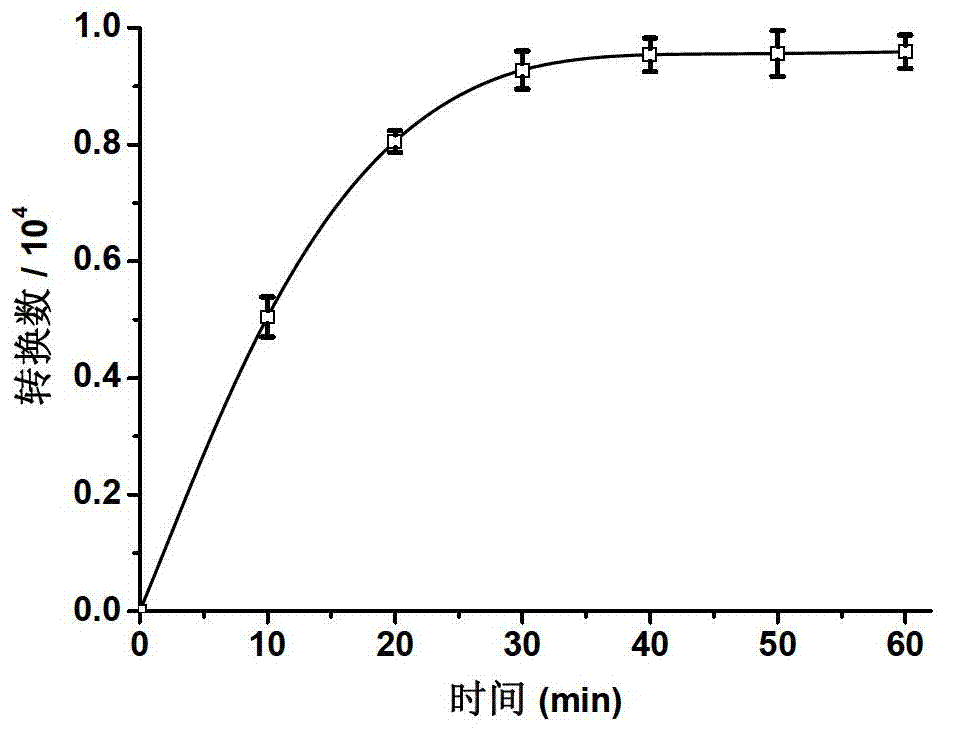
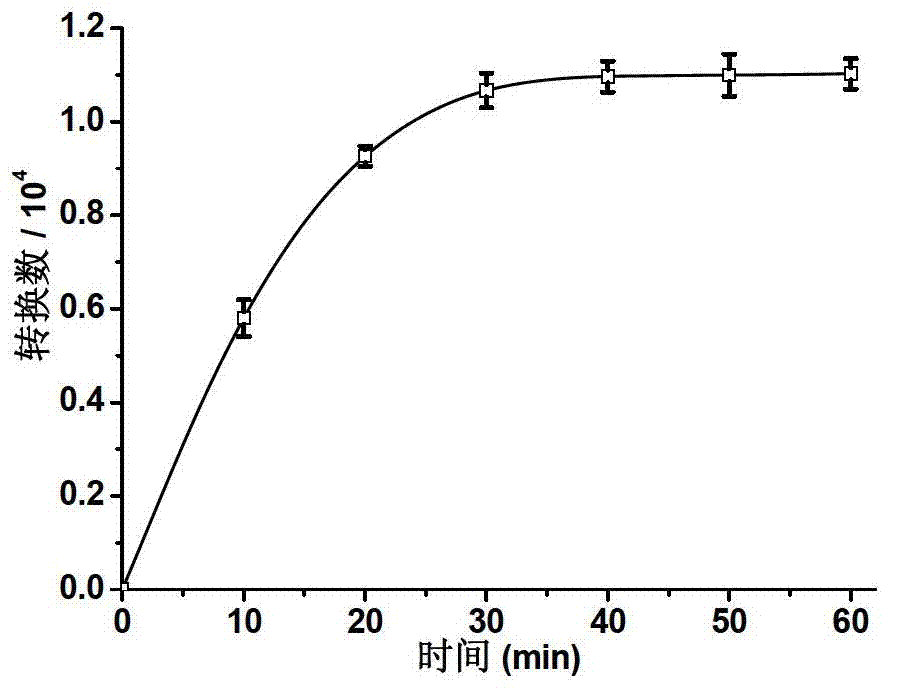
[ferronickel]hydrogenase model compound containing dppf skeleton and O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107353312ACatalytic hydrogen production performanceEasy to prepareOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen productionChemical structureSynthesis methods
The invention provides a [ferronickel]hydrogenase model compound containing dppf skeleton and O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand. The [ferronickel]hydrogenase model compound is a bimetallic complex formed by connection of 1, 1'-bis(diphenylphosphine)ferrocene (dppf) structural unit and the O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand with metal nickel atom, and has a chemical structure shown as the specification, wherein R can be methyl, ethyl, benzyl or phenethyl. The synthesis method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, mild reaction conditions, simple post-treatment and high yield, etc., is suitable for synthesis of a variety of [ferronickel]hydrogenase model compounds containing 1, 1'-bis(dialkylphosphine)ferrocene skeleton and O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand, and the model compounds have good catalytic hydrogen production performance, thus having potential industrial application value.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![[NiFe]-hydrogenases having an improved resistance to dioxygen, process for obtaining them and their applications [NiFe]-hydrogenases having an improved resistance to dioxygen, process for obtaining them and their applications](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/3a535feb-5f56-4792-8a9b-d47a7baed501/US08377671-20130219-D00001.png)
![[NiFe]-hydrogenases having an improved resistance to dioxygen, process for obtaining them and their applications [NiFe]-hydrogenases having an improved resistance to dioxygen, process for obtaining them and their applications](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/3a535feb-5f56-4792-8a9b-d47a7baed501/US08377671-20130219-D00002.png)
![[NiFe]-hydrogenases having an improved resistance to dioxygen, process for obtaining them and their applications [NiFe]-hydrogenases having an improved resistance to dioxygen, process for obtaining them and their applications](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/3a535feb-5f56-4792-8a9b-d47a7baed501/US08377671-20130219-D00003.png)




![[ferronickel]hydrogenase model compound containing dppf skeleton and O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand and preparation method thereof [ferronickel]hydrogenase model compound containing dppf skeleton and O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f1ac7628-ed2e-46cd-938e-834fc50ded94/170712113644.png)
![[ferronickel]hydrogenase model compound containing dppf skeleton and O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand and preparation method thereof [ferronickel]hydrogenase model compound containing dppf skeleton and O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f1ac7628-ed2e-46cd-938e-834fc50ded94/170712113649.png)
![[ferronickel]hydrogenase model compound containing dppf skeleton and O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand and preparation method thereof [ferronickel]hydrogenase model compound containing dppf skeleton and O-alkyldithiophosphate ligand and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f1ac7628-ed2e-46cd-938e-834fc50ded94/BDA0001347976140000031.png)