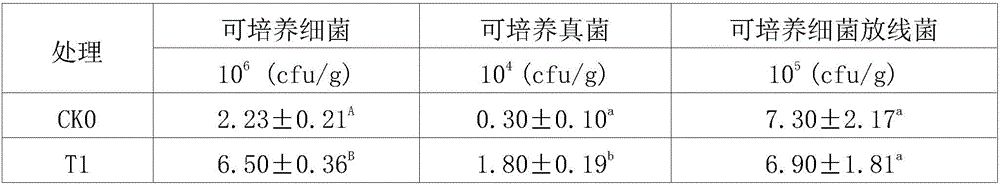
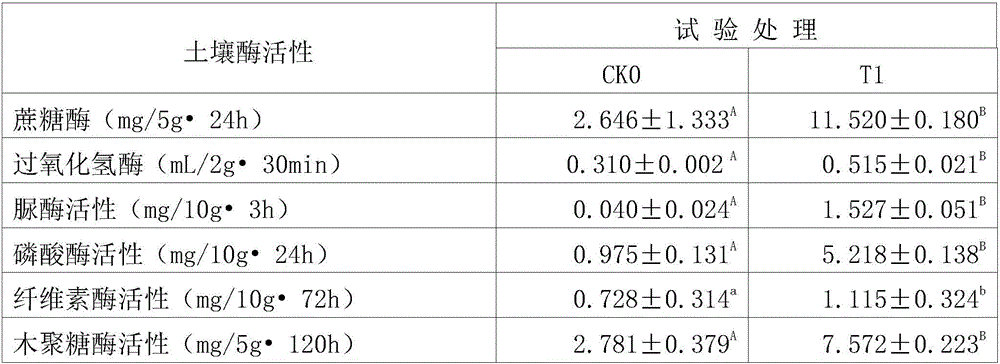
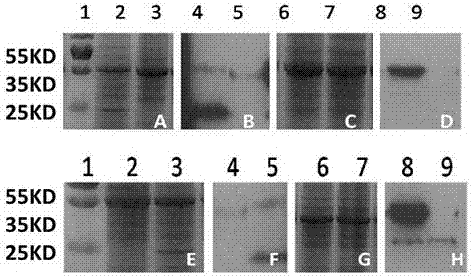
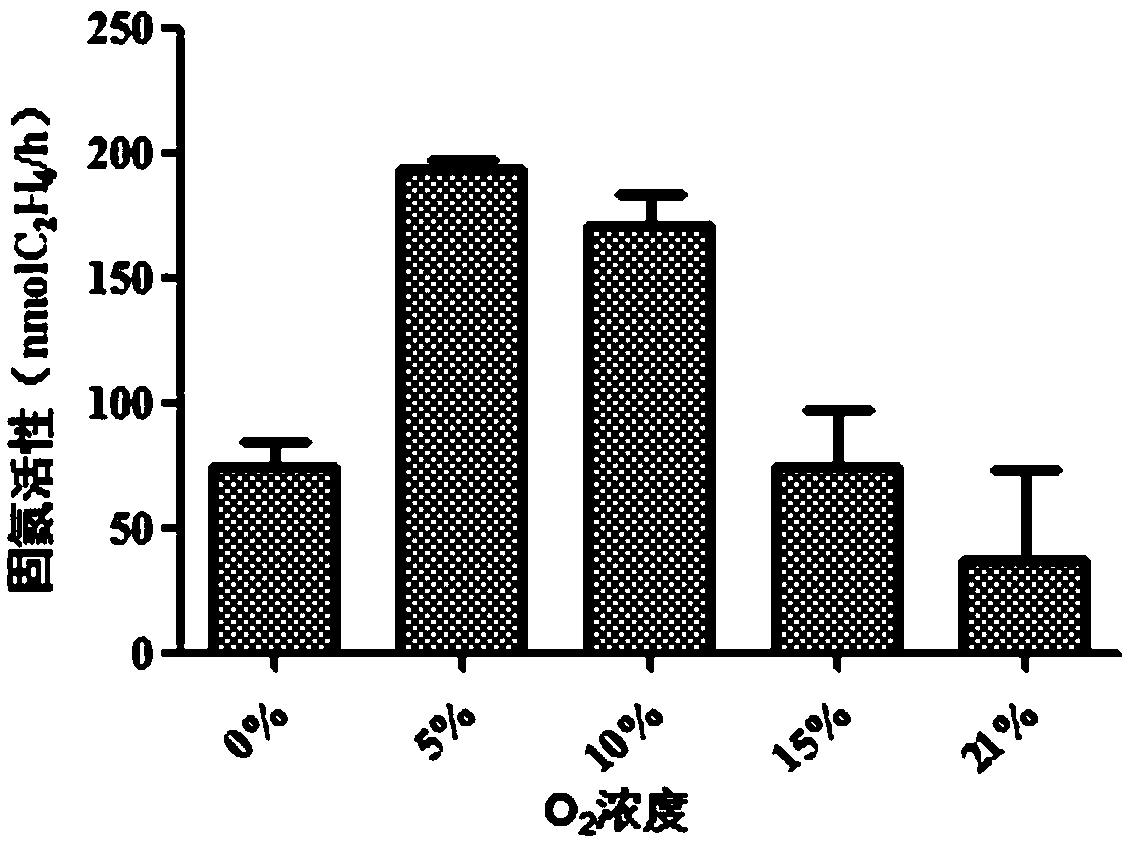
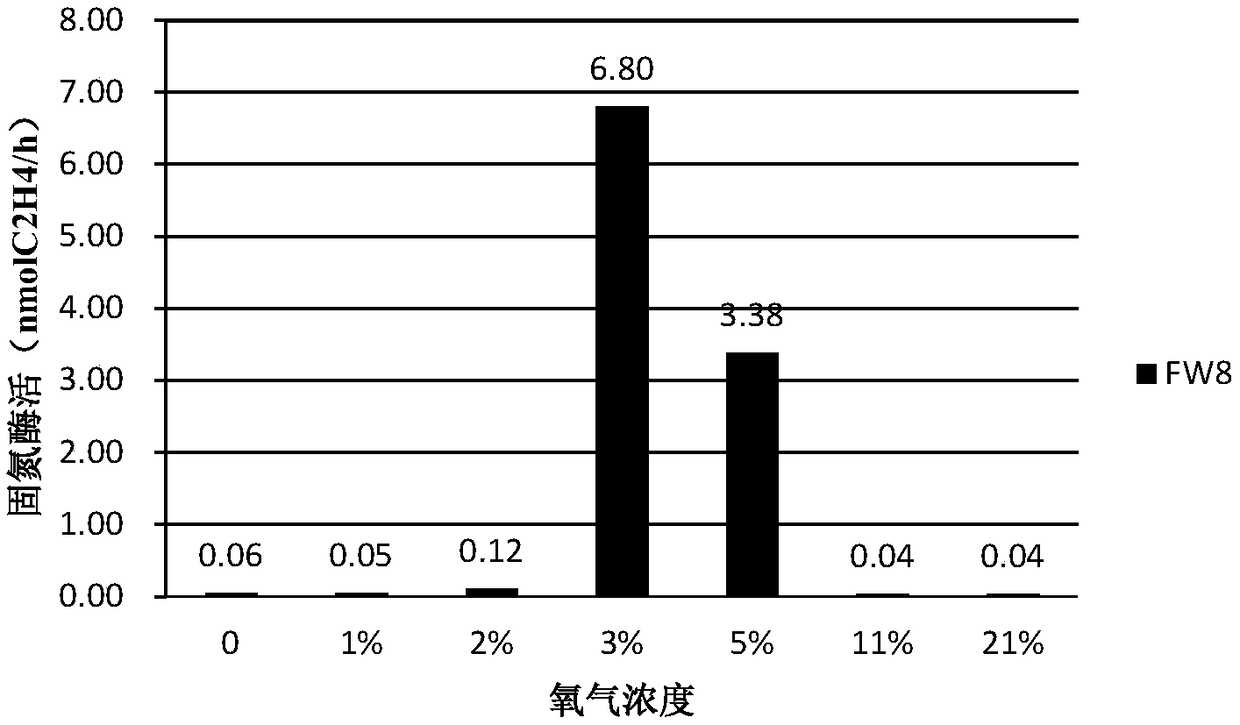
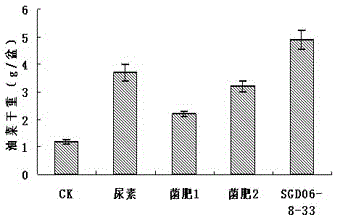
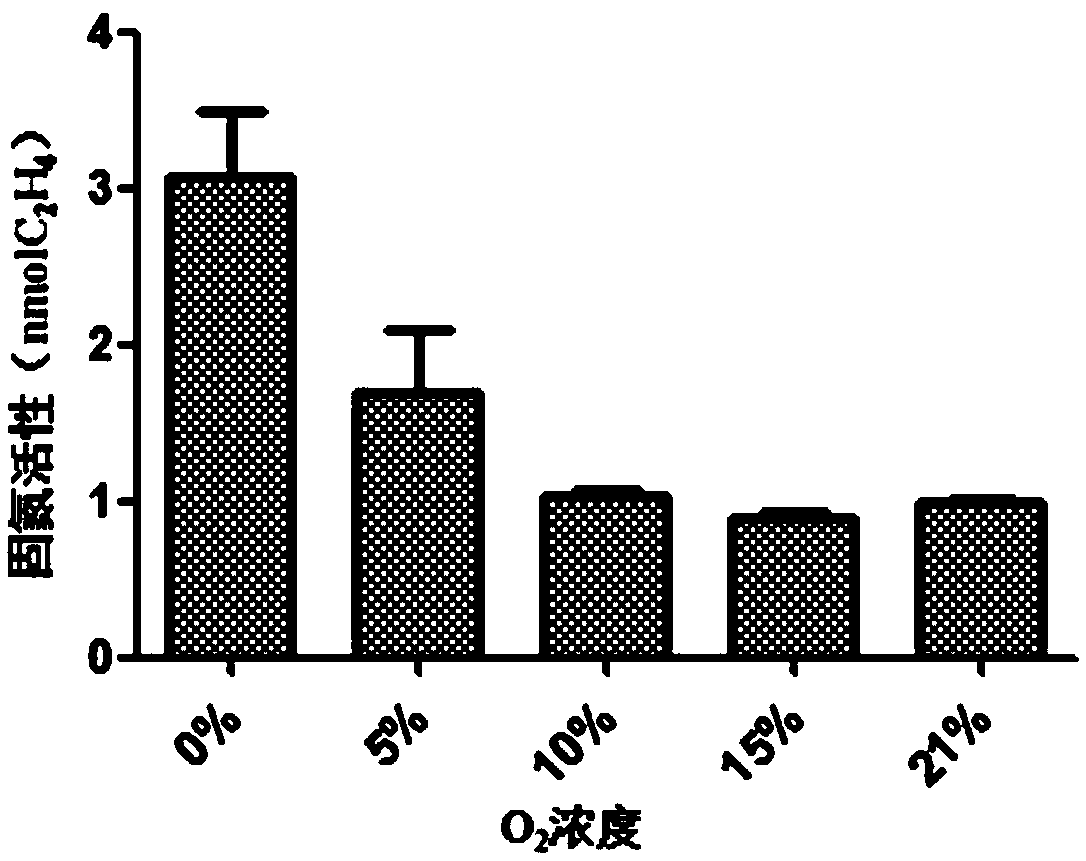Patents
Literature
101 results about "Nitrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nitrogenases are enzymes (EC 1.18.6.1EC 1.19.6.1) that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). These enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitrogen (N₂) to ammonia (NH₃). Nitrogenases are the only family of enzymes known to catalyze this reaction, which is a key step in the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation is required for all forms of life, with nitrogen being essential for the biosynthesis of molecules (nucleotides, amino acids) that create plants, animals and other organisms. They are encoded by the Nif genes or homologs. They are related to protochlorophyllide reductase.
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus with free living nitrogen fixation and phosphorus and potassium dissolving capability and application of acinetobacter calcoaceticus
ActiveCN103789223AGuaranteed stabilityStable genetic traitsBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to acinetobacter calcoaceticus X.L.Zhu.SGD07-3-16 with free living nitrogen fixation capability. The acinetobacter calcoaceticus is preserved in China general microbiological culture collection center, and the preservation number of the acinetobacter calcoaceticus is CGMCCNo.5455. The acinetobacter calcoaceticus is high in nitrogenase activity and phosphorus and potassium dissolving capability, and has ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid) deaminase activity, a certain amount of indoleacetic acid can be generated, and the generation of siderophore is avoided; when an acinetobacter calcoaceticus-containing liquid or solid microbial agent is used for inoculating crops such as corns, oilseed rapes and leaf mustard, the growth of the crops can be remarkably promoted, and the yield of the crops can be increased.
Owner:西安金博瑞生态科技有限公司
Nitrogen-fixing Paenibacillus sp. 1-33 and application thereof
ActiveCN102352331AGood inhibitory effectReduce usageBiocidePlant growth regulatorsOrganismPathogenic fungus
The invention provides a Paenibacillus sp. strain 1-33 with nitrogen-fixing capability, the collection number of which is CGMCC No.4964. The Paenibacillus sp. 1-33 has a nitrogenase-structured gene nifH, and the acetylene reduction method determines that the nitrogenase activity of the Paenibacillus sp. 1-33 is 565.94nmolC2H4 / (mg protein h) negative 1. The nitrogen-fixing Paenibacillus sp. strain1-33 provided by the invention has a remarkable inhibition effect on a variety of plant pathogenic fungi, and nitrogen-fixing microorganism fungicide or bioorganic fertilizer prepared with the strain1-33 can remarkably promote the germination and growth of plant seeds, and can be popularized to use in agricultural production to effectively reduced the usage of urea.
Owner:HUBEI FORBON TECH
Brevibacterium halotolerans and application thereof in ecological restoration of soils
ActiveCN106434496AIncrease nitrogenase activityImprove fertilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAzotobacter chroococcumMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a brevibacterium halotolerans with relatively high azotase activity and application thereof in ecological restoration. The brevibacterium halotolerans GDSD21 is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the collection number of CGMCC No.12402. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are separated from rhizosphere soils of field-crop roots, further strains with relatively high azotase activity are screened, and finally the efficient nitrogen-fixing bacterium brevibacterium halotolerans GDSD21 is screened. The azotase activity of the brevibacterium halotolerans GDSD21 is obviously higher than that of common production strain azotobacter chroococcum ACCC11103 for microbial fertilizers, and the brevibacterium halotolerans GDSD21 has extensive application prospects in soil improvement, increasing of the soil fertility, ecological restoration of a virgin land, and production of industrialized seedling-rearing inoculation agents, nitrogen-fixing microbial agents and bio-organic fertilizers for vegetables.
Owner:北京复天科技有限公司 +1
Nitrogen fixing Paenibacillus 1-43 and application thereof
ActiveCN102352332BHas the ability to fix nitrogenBiocidePlant growth regulatorsOrganismMicrobiological culture
The invention provides Paenibacillus sp. strain 1-43 which has nitrogen fixing capability and conservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 4965. The strain contains a nitrogenase structure gene nifH, and has the nitrogenase activity of 904.49 nmol C2H4 / (mg protein h)<-1> measured by an acetylene reduction method. The nitrogen fixing Paenibacillus strain 1-43 has an obvious inhibition action on multiple plant pathogenic bacteria; and the nitrogen fixing microorganism agent or biological organic fertilizer prepared from the strain 1-43 has an obvious promotion action on the germination and growth of plant seeds, can be popularized and used in agricultural production, and can effectively reduce the use amount of urea.
Owner:HUBEI FORBON TECH
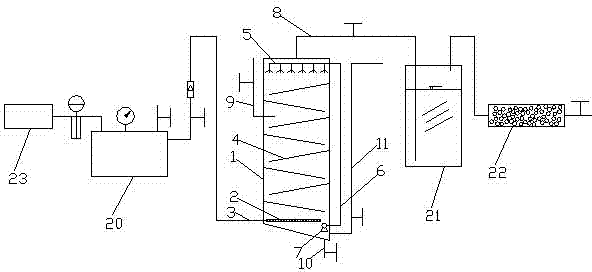
A method for nitrogen fixation using organic wastewater for anaerobic fermentation of straw
InactiveCN102286540ANitrogen fixation process is simpleAvoid contamination damageTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesEnergy based wastewater treatmentBacterial pigmentNitrogen atmosphere
The invention belongs to the technical field of comprehensively utilization of sources and in particular relates to a method for performing nitrogen fixation for straw anaerobic fermentation by utilizing organic wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: using a nitrogen product, which is obtained through performing deoxygenation on air by use of a deoxidation reactor, as an initial nitrogen source; (2) inoculating photosynthetic bacteria in organic wastewater, performing illuminating culture in the nitrogen atmosphere, centrifuging the cultured liquid, taking the supernatant, namely an organic nitrogen product; and (3) inactivating the organic nitrogen product to be used as the nitrogen source, and adding the nitrogen source into straw to perform anaerobic fermentation. In themethod, photosynthetic bacteria are utilized to ensure that the nitrogen fixation function of the nitrogenase of nutrients in the organic wastewater is utilized to convert the nitrogen in the air to bacterial protein and bacterial pigment under anaerobic and illuminating conditions, thus the elemental nitrogen in the air is converted and fixed in an organic state, then the nitrogen is used as thenitrogen source to be supplied in a straw anaerobic fermentation process, the organic wastewater can be utilized again and the pollutions and damages caused by the direct discharge of the organic wastewater can be avoided.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus megatherium T317, microbial agent and preparation method of microbial agent
ActiveCN106011002AHigh sporulationGood qualityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAcetic acidMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial agents, in particular to bacillus megatherium T317, a microbial agent and a preparation method of the microbial agent. The bacillus megatherium T317 is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the collection number is CCTCCM 2015753. The preparation method of the microbial agent comprises the following steps of (1) separating and sieving; (2) purifying and storing; (3) solid fermenting and culturing; (4) preparation of microbial agent, so as to obtain the microbial agent of the bacillus megatherium T317. The microbial agent has the advantages that the bacillus megatherium T317 is used as an original strain, and the nitrogenase activity and the auxin secreting capability are measured; the bacillus megatherium T317 has higher nitrogenase activity and IAA (indole acetic acid) secreting capability, the nitrogenase activity of bacillus megatherium T317 is 800-900nmol / (mL h), and the IAA secreting amount is 300-400mg / L in the growth and metabolism process.
Owner:DONGGUAN BAODE BIOLOGICAL ENG
Nitrogen-fixing Paenibacillus sp. 1-49 and application thereof
InactiveCN102352333AGood inhibitory effectReduce usagePlant growth regulatorsBiocideOrganismPathogenic fungus
The invention provides a Paenibacillus sp. strain 1-49 with nitrogen-fixing capability, the collection number of which is CGMCC No.4966. The Paenibacillus sp. 1-49 has a nitrogenase-structured gene nifH, and the acetylene reduction method determines that the nitrogenase activity of the Paenibacillus sp. 1-49 is 969. 49nmolC2H4 / (mg protein h) negative 1. The nitrogen-fixing Paenibacillus sp. strain 1-49 provided by the invention has a remarkable inhibition effect on a variety of plant pathogenic fungi, and nitrogen-fixing microorganism fungicide or bioorganic fertilizer prepared with the strain 1-49 can remarkably promote the germination and growth of plant seeds, and can be popularized to use in agricultural production to effectively reduced the usage of urea.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
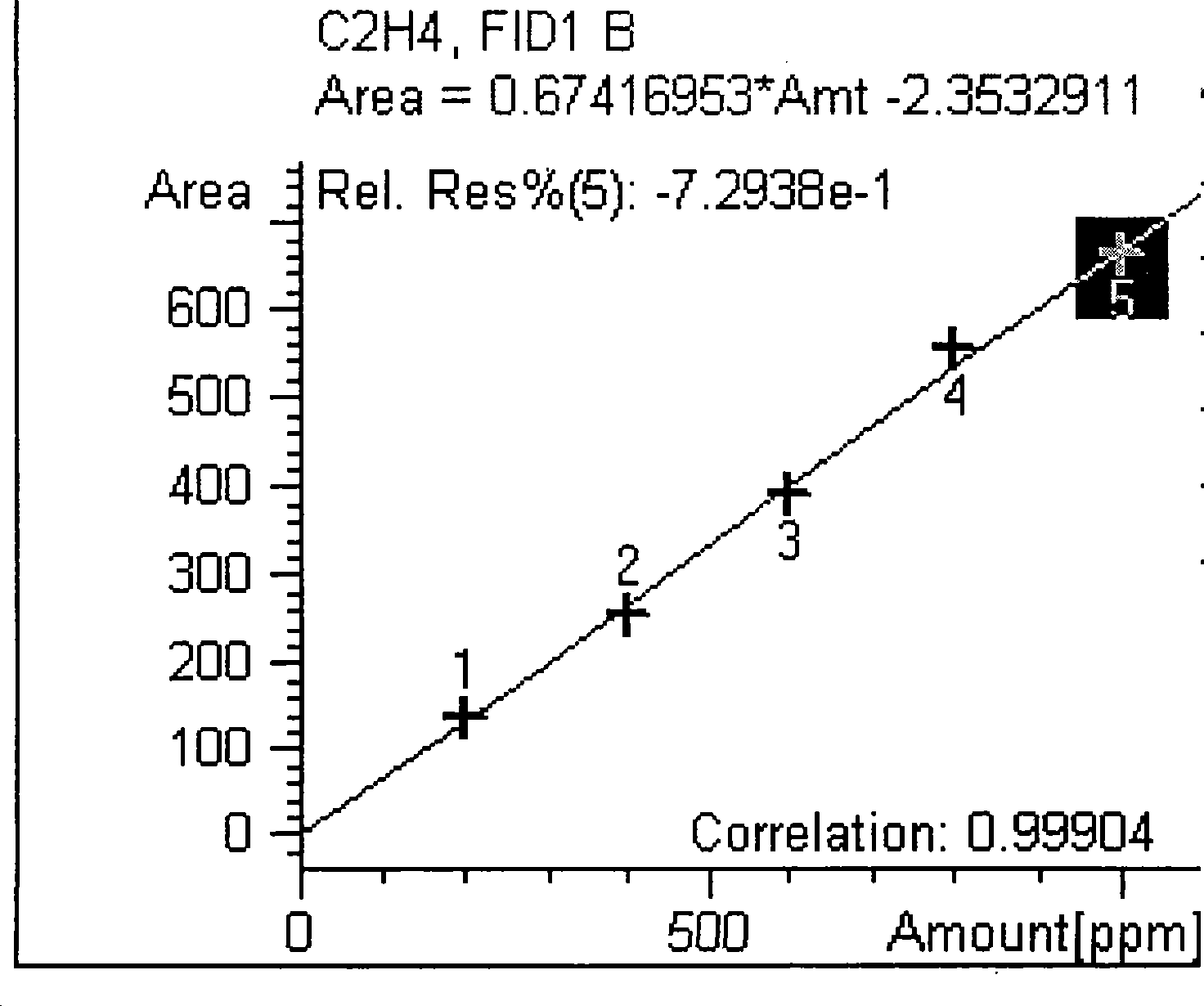
Method for measuring nitrogenase activity of azotobacteria in sugarcane
InactiveCN101381763ASimple compositionEasy to prepareComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementSucroseSaccharum
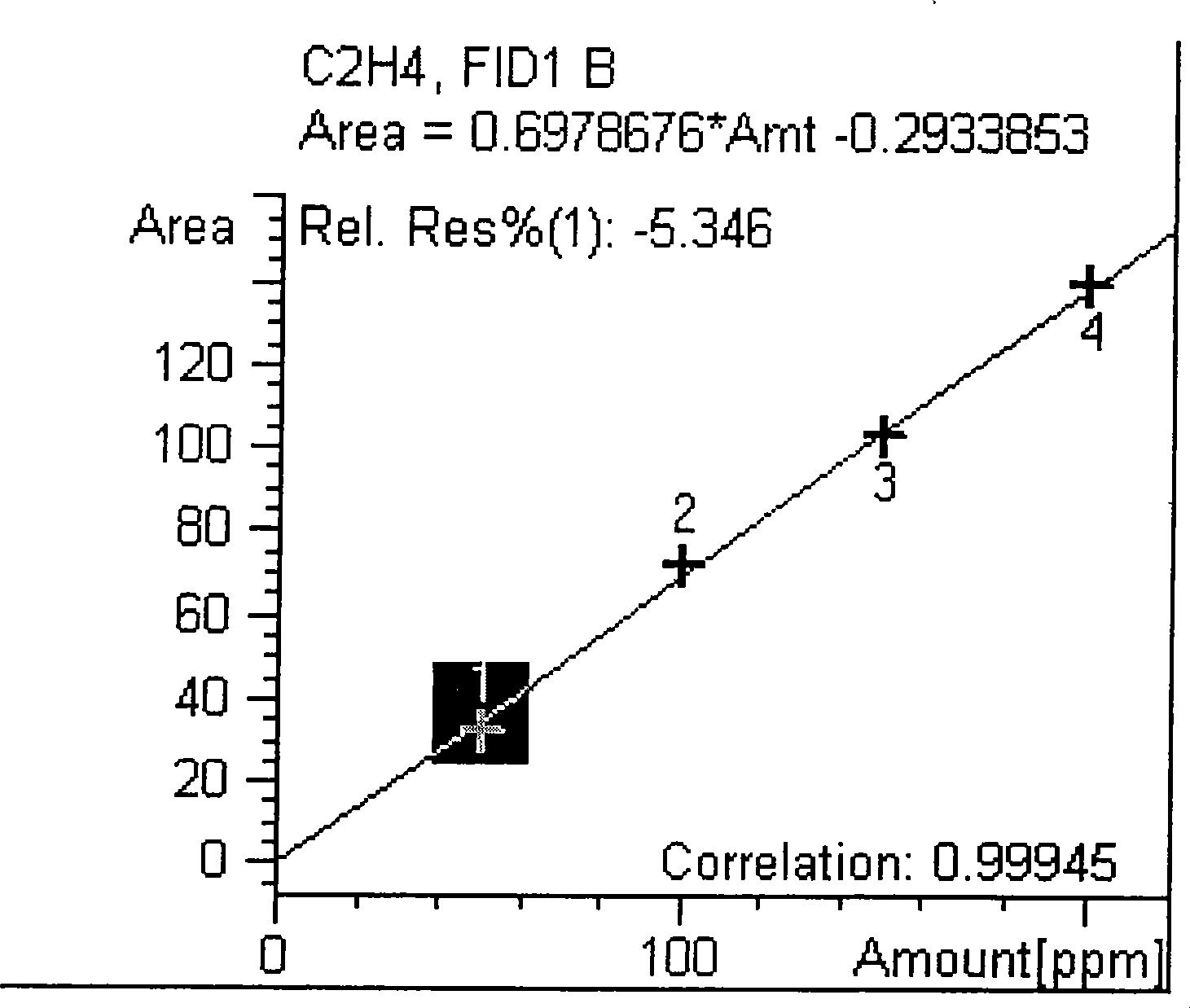
The invention discloses a method for determining the nitrogenase activity of azotobacteria in sugar cane. The method comprises the following steps: distilled water and the cane sugar are prepared into a culture medium which contains 10 percent of the cane sugar and the pH value of which is 5.8, and the culture medium is named as SH culture medium for short; and the nitrogenase activity value of a sample is calculated through the steps of sampling, sample treatment, incubation, manufacture of a standard curve for determining the content of ethylene, determination of the content of the ethylene, calculation of the nitrogenase activity and so on. The method has the advantages that: firstly, the SH culture medium is simple in compositions, is easy to prepare and has low cost; secondly, the selectivity of the SH culture medium on the azotobacteria in the sugar cane is small; and thirdly, the SH culture medium can more accurately reflect the difference of the nitrogenase activity of different varieties.
Owner:广西壮族自治区甘蔗研究所
Azotification method by use of organic wastewater
InactiveCN102351309ANitrogen fixation process is simpleReduce manufacturing costNitrogen purification/separationTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesCentrifugationWastewater
The invention belongs to the technical field of wastewater recovery and utilization, and relates to an azotification method by the use of organic wastewater. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) adding organic wastewater into a reactor after sterilization of the organic wastewater; (2) inoculating photosynthetic bacteria into the reactor; (3) allowing nitrogen to enter into the bottom of the reactor until the air pressure in the reactor reaches 0.1MPa; (4) carrying out light culture on the organic wastewater for at least 96 hours; (5) carrying out centrifugation and dehydration on a liquid in the reactor after culture so as to obtain a solid organic nitrogenous product. In the invention, photosynthetic bacteria is utilized to transform aerial nitrogen into microbial protein and microbial pigment by the nitrogen fixation of their own nitrogenase under the anaerobic light condition, so as to transform and fix aerial simple substance nitrogen into a organic form and provide suitable nitrogen source form.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
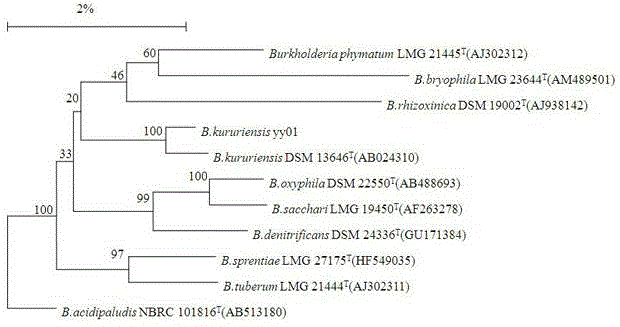
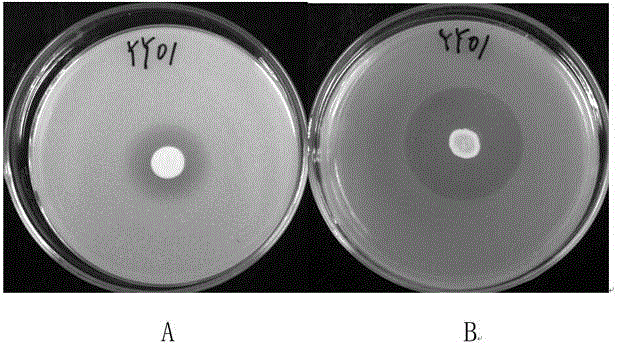
Burkholderia kururiensis strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104911122AImprove effectivenessIncrease nitrogenase activityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and specifically discloses a Burkholderia kururiensis strain and application thereof. The strain is Burkholderia kururiensis yy01, and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 17, 2015, and has preservation No. CGMCC No. 10631. The strain yy01 has both efficient releasing of phosphorus and potassium and high nitrogenase activity, increases the effectiveness of insoluble phosphorous and potassium in soil and convert free nitrogen in the air into ammonia for absorption and utilization by crops, and has significant growth-promoting effect on rice, tobacco and other crops.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
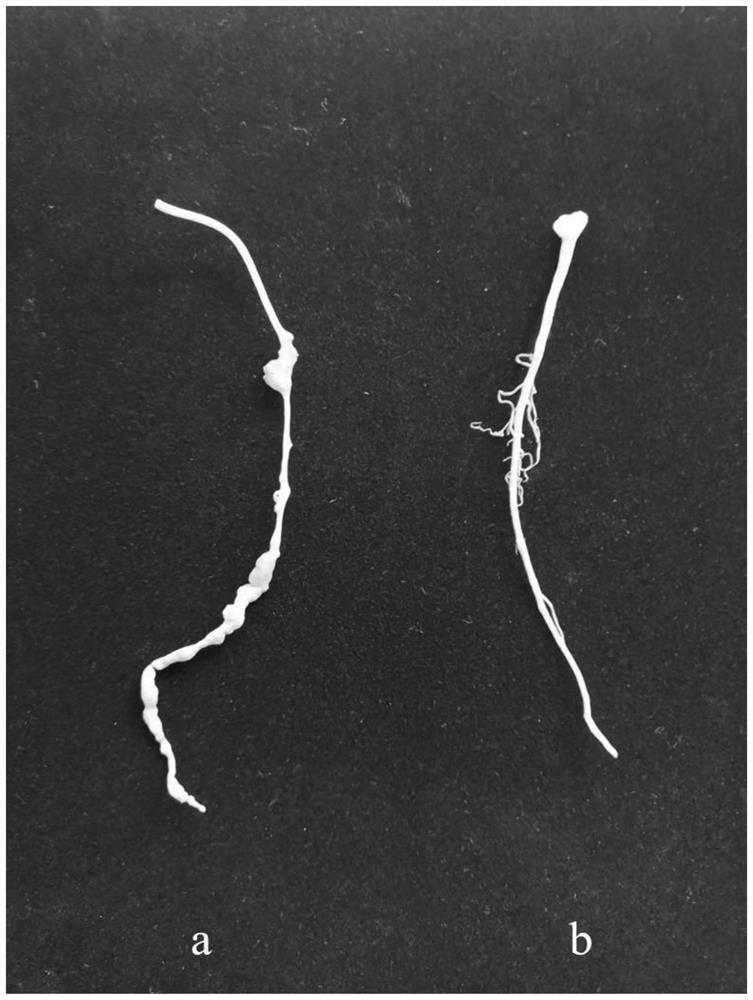
Ecological cultivation method for intercropping atractylodes macrocephala koidz and soybeans
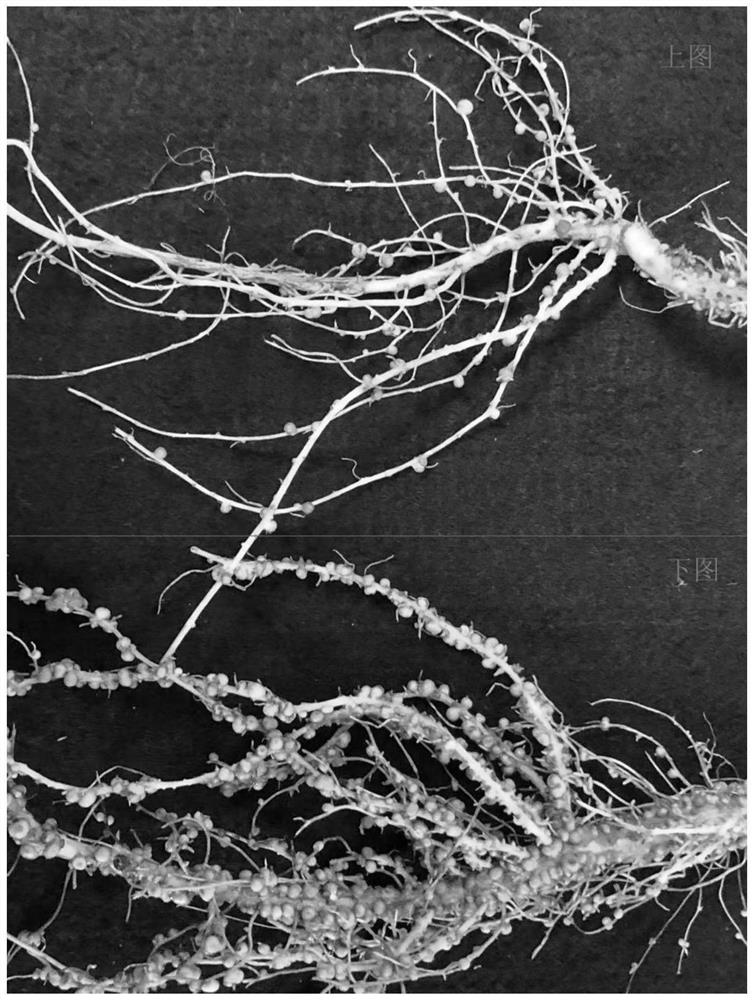
ActiveCN112753516AStrong nitrogen fixation abilityImprove the ecological environmentBiocideBio-organic fraction processingEnvironmental resource managementPlant nodule
The invention discloses an ecological cultivation method for intercropping atractylodes macrocephala koidz and soybeans, and belongs to the technical field of atractylodes macrocephala koidz cultivation. The cultivation method comprises the following steps of soil preparation and soil improvement, seed selection and disinfection, fertilization and bedding, soybean seedling raising, transplanting, field management and orderly harvesting. According to the ecological cultivation method, the atractylodis macrocephala koidz and the soybeans are intercropped, soybean root nodules have high nitrogen fixation capacity, and soil can be continuously fertilized in the growth process. The invention provides a method for infecting the root system of the atractylodes macrocephala koidz through exogenous (soybean, wild soybean and peanut) rhizobium for the first time. According to the method, the atractylodes macrocephala koidz obtains natural nitrogen fixation capacity, the input of nitrogen fertilizer is greatly reduced, and the requirement of the atractylodes macrocephala koidz for the nitrogen fertilizer can be met; in addition, soil conditioner, slow-release biological organic fertilizer and root nodule biological composite liquid are combined, so that soil-borne pathogenic bacteria in soil can be effectively killed, heavy metal in the soil is passivated, the activity of nitrogenase in the soil is improved, the planting cost is effectively reduced, and the purposes of safety, high quality and high yield of the atractylodes macrocephala koidz are achieved.
Owner:湖北省农业科学院中药材研究所
Gene capable of keeping efficient nitrogen fixing capability of strain
ActiveCN104862315AEfficient nitrogen fixation capacityEfficient nitrogen fixation activityBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionActivity regulationNitrogen
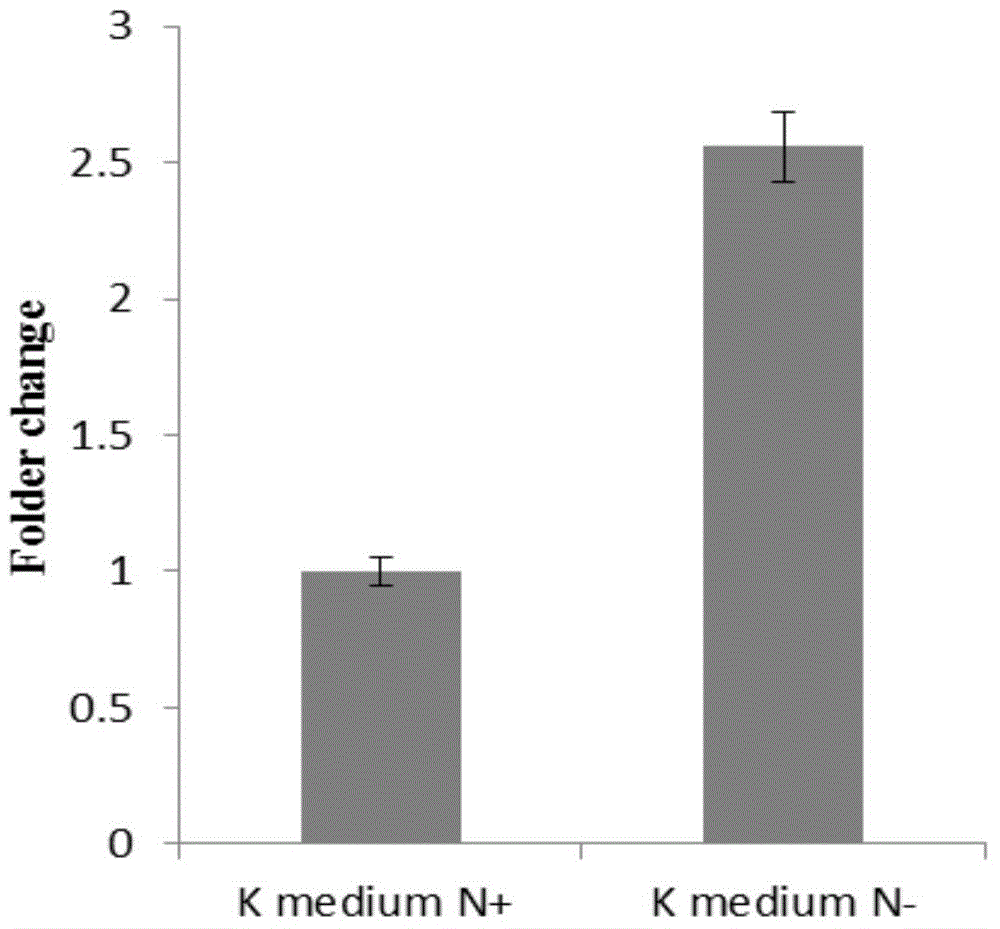
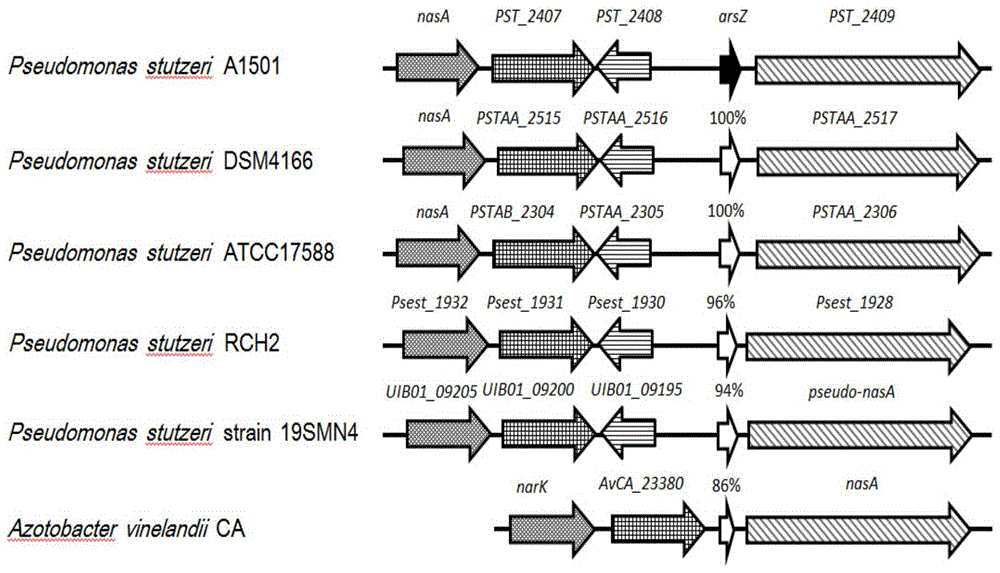
The invention discovers a transcriptional functional non-coding RNA gene having the capability of keeping nitrogen fixing activity of a strain for the first time. The invention discovers that the gene can specifically respond to an external nitrogen signal, participate in the nitrogen fixing enzymatic activity regulation of nitrogen fixing pseudomonas stutzeri and keep the efficient nitrogen fixing capability of the strain, thereby being applicable to obtaining a gene engineering strain having efficient nitrogen fixing capability.
Owner:北京绿氮生物科技有限公司
Method for expression of nitrogenase gene in eukaryotic cells
The present invention relates to a method for expression of nitrogenase gene in eukaryotic cells, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The method includes the following steps: 1, amplification of a nitrogenase gene fragment; 2, construction of a recombinant vector, to be more specific, the nitrogenase gene fragment is connected with a virus transformation vector; 3, transfection of the eukaryotic cells by the recombinant vector constructed by the step 2; and 4, screening of plant cells for expression of the nitrogenase gene. The expression of the nitrogenase gene in plants can be realized, and a foundation is laid for autonomic nitrogen fixation of the plants.
Owner:杭州禾骑士未来生物科技有限公司
Method for enriching and separating dominant nitrogen fixing bacteria from petroleum-contaminated soil
ActiveCN108707571AIncrease nitrogenase activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMolten stateNitrogenase
The invention provides a method for enriching and separating dominant nitrogen fixing bacteria from petroleum-contaminated soil, and belongs to the technical field of microbial isolation and culture.The method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting the petroleum-contaminated soil; adding glucose for induction; measuring the nitrogenase activity of a sample by an acetylene reduction process; selecting the sample with high nitrogen fixing activity or large quantity of nitrogen fixing bacteria; preparing a suspension, and performing gradient dilution; (2) preparing a nitrogen-free solid medium; adding suspensions different in dilution in a molten state of the medium; mixing uniformly and transferring into an anaerobic tube to prepare a thin-layer medium; culturing with 0-2% oxygen concentration, wherein if a colony grows on the surface or the inside of the medium, the dominant nitrogen fixing bacteria enriched in the petroleum-contaminated soil are separated and obtained. According to the method disclosed by the invention, with the imbalance of carbon nitrogen ratio and by adding a quick-acting carbon source, indigenous nitrogen fixing bacteria are activated and enriched; meanwhile, by adopting the nitrogen-free medium and culturing with 0-2% oxygen concentration, the nitrogenase expression is promoted so as to obtain dominant nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the petroleum-contaminated soil; thus, the method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Special boron/molybdic fertilizer for peanut and prepn. thereof
InactiveCN1834067AIncrease productionImprove qualityUrea compound fertilisersPotassium fertilisersPotassiumMonopotassium phosphate
This invention relates to agricultural fertilizers, mainly boron-molybdenum special fertilizers for peanut growth and their preparation method. Lack of boron or molybdenum may cause abnormal growth of peanuts, increase of empty peanut grains and quality declination. This invention provides a kind of boron-molybdenum special fertilizer for peanut cultivation, which comprises two components. Component 1 includes urea, potassium dihydrophosphate, potassium chloride, borax, ammonium molybdate, acetyisalicylic acid and triacontanol. Component 2 includes sodium alginate, xanthan gum and quicklime. The boron-molybdenum peanut special fertilizer is intended for southern earth which is seriously short of boron and molybdenum. According to many years' experience, by fertilized with this kind of fertilizer, activity of nitrate reductase and nodule nitrogenase in peanut leaves can be significantly promoted, nitrogen absorption, transportation and distribution can be enhanced, chlorophyll content and photosynthesis intensity in peanut leaves can be raised, peanut weight can be increased and both the quality and the yield can be promoted. The peanut yield can be increased by 10~18% per unit of area.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Rhizobium and application thereof
InactiveCN103898009AIncrease biomassAchieve high yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesContinuous croppingRoot nodule
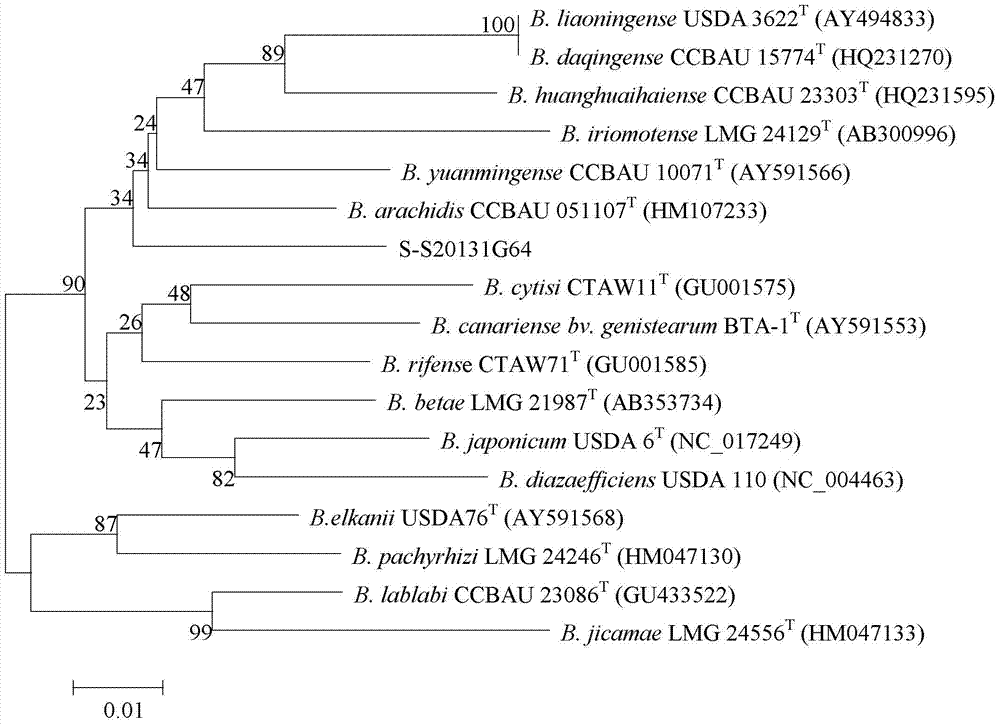
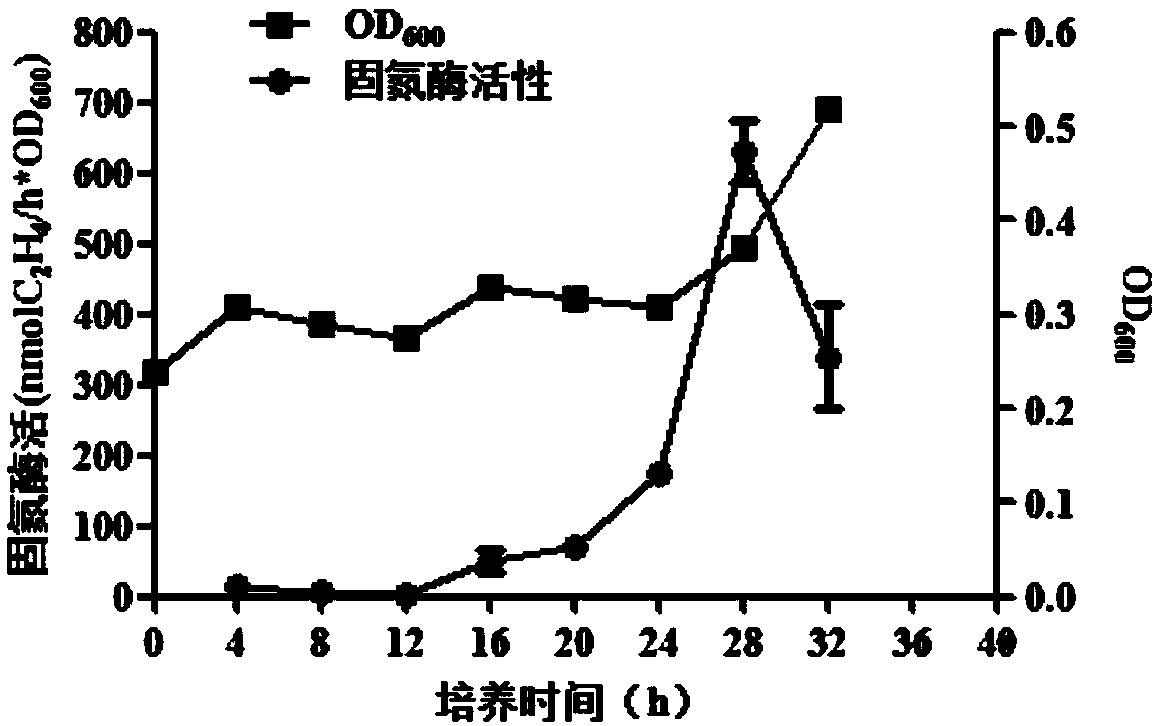
The invention discloses rhizobium and application thereof. The invention aims to solve the problem that the conventional rhizobium inoculated by soybean is low in competitive nodulation capacity and nitrogenase activity under long-term continuous cropping conditions. The rhizobium refers to bradyrhizobium hailunense (Bradyrhizobium hailunense) S-S20131G64 and is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the collection address is 3#, courtyard No.1, Beichen west road in Chaoyang District in Beijing, the collection date is 10th, January in 2014, and the collection number is CGMCC No.8693. The application refers to application in long-term soybean continuous cropping soil. The rhizobium has the high-efficiency nodulation characteristic, the soybean biomass can be improved, the nitrogen nutrition of soybeans is improved, and the rhizobium is applied to long-term soybean continuous cropping soil districts in Heilongjiang Province. The invention is applied to the field of agriculture.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Nitrogen-fixing bacterium PJ 12 capable of degrading petroleum and tolerating petroleum and application of nitrogen-fixing bacterium PJ 12
ActiveCN108424864AIncrease nitrogenase activityHas the ability to degradeBacteriaWater contaminantsAlkaneMicroorganism
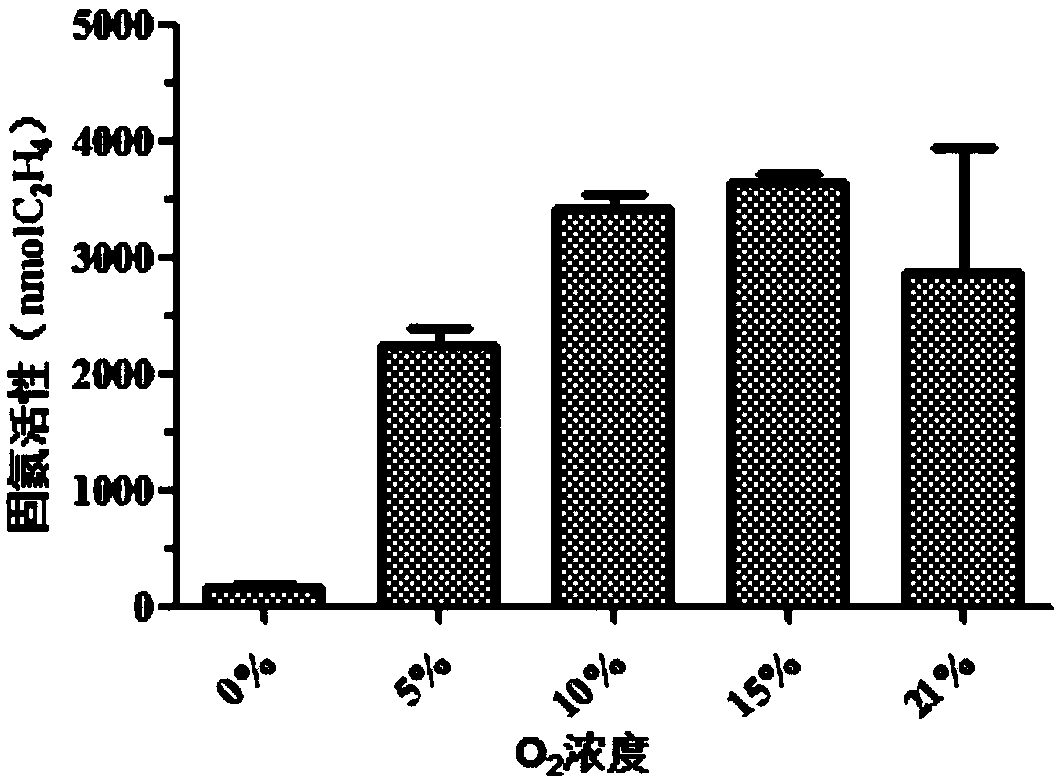
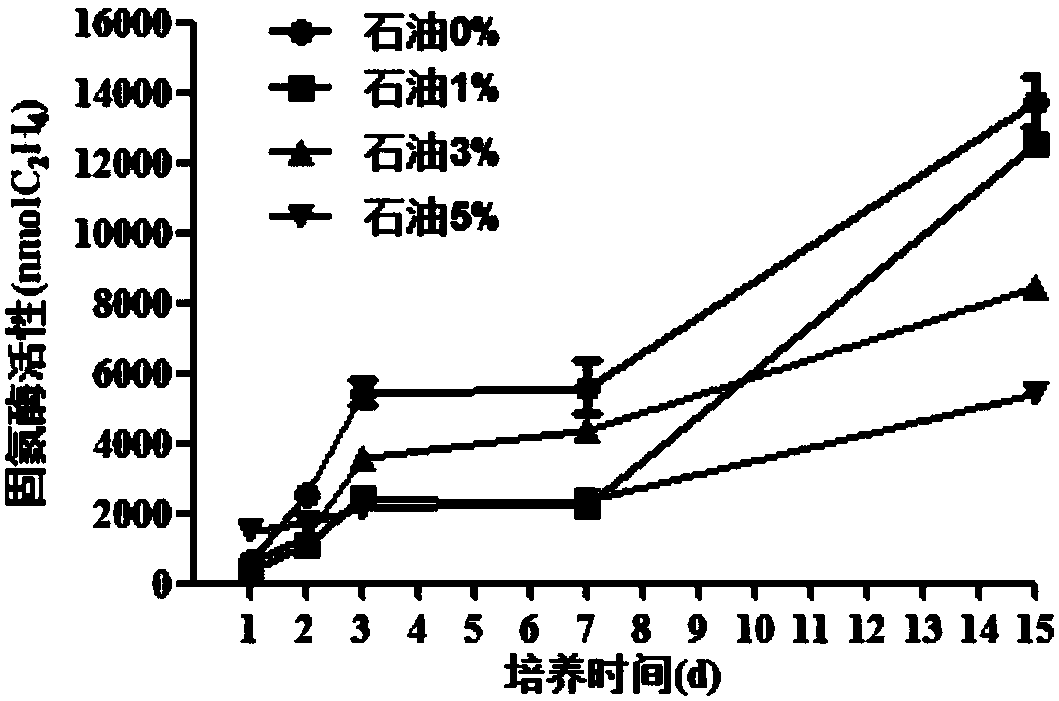
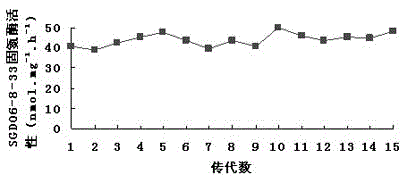
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms and particularly relates to a nitrogen-fixing bacterium PJ 12 capable of degrading petroleum and tolerating petroleum and an application of the nitrogen-fixing bacterium PJ 12, and the conservation number is CGMCC No.14659. The activity analysis of nitrogenase proves that a provided bacterial strain has a stronger activity of nitrogenase, and the activity of the dinitrogenase is higher under the condition of 5-21% oxygen concentration. The activity of the dinitrogenase is still kept at the petroleum concentration of 1%-5%. More than that, the provided bacterial strain further has the capability of degrading long-chain alkane, the degrading capability is up to 37-100%, and the provided bacterial strain has an excellent positive application prospect on balancing nitrogen and degrading petroleum pollutants in the remediation of petroleum polluted soil in the future.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A kind of Agrobacterium with autogenous nitrogen fixation, phosphorus and potassium decomposing ability and its application
InactiveCN103789224BGuaranteed stabilityStable genetic traitsBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present invention relates to a strain of Agrobacterium with the ability to self-generate nitrogen fixation, phosphorus and potassium solubilization, which is classified as Agrobacterium r sp. Microbiology Center, the deposit number is CGMCC No.5457. The strain has high nitrogenase activity, high ability to decompose phosphorus and potassium, can produce a certain amount of indole acetic acid and siderophore, and has no ACC deaminase activity. Inoculating crops such as corn, rapeseed and mustard with the liquid or solid bacterial agent containing the strain can obviously promote their growth and increase the yield of the crops. The method has simple process, abundant sources of raw materials, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Method of transferring rhizobium japonicum to corn root system
InactiveCN103947443AEasy to operateLow costPlant genotype modificationHorticultureRoot noduleRhizobium japonicum
The invention relates to a cultivating technology in the crop field, and in particular to a method of transferring rhizobium japonicum to a corn root system with an ultra-distant compound type breeding technique. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out sexual propagation (hybridization) between corn and soybean; transferring dinitrogenase of the soybean to the corn, and enabling a root system of the grass family plant corn to form nodules. As the corn is ultra distant from the soybean, the corn and the soybean cannot be carried out with cross pollination, so at first, vegetative propagation (grafting) must be carried out, in order to close the genetic relationship and make the sexual propagation possible; the key of the compound breeding technique is firstly ensuring that the corn and the soybean are grafted successfully, in particular grated in the seedling phase, as the seedlings at this time communicate with each other most actively, and variation is most possible. But, the seedlings just come up out the ground are extremely fragile, and the plants are tender and small, so that the grafting is very difficult, and has not yet been successful in the foreign countries.
Owner:王孚望
Bacillus megaterium B16, inoculant and inoculant preparation method
ActiveCN106167770APromote growthGood economic valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus megateriumNitrogenase
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial inoculants, in particular to a bacillus megaterium B16, an inoculant and an inoculant preparation method. The bacillus megaterium B16 is preserved in China Center for Type Collection with a preservation number of CCTCCM 2015750. The invention takes bacillus megaterium B16 as the starting strain to determine its nitrogenase activity and auxin secreting ability, and finds that the strain B16 has efficient nitrogenase activity and IAA secreting ability. The strain can supplement the nitrogen element needed in the growing process of paddy rice, corn and other graminaceous crops by free living nitrogen fixation, and also is a functional microbial strain capable of secreting indoleacetic acid to promote plant growth, thus having considerable economic value in the field of microbial fertilizer application. The bacillus megaterium B16 can be prepared into three B16 inoculants, i.e. liquid inoculant, powdery inoculant and particle inoculant, thereby providing convenience for putting it into agricultural production application.
Owner:DONGGUAN BAODE BIOLOGICAL ENG
Bionic peat coal, artificial wet land plate and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN101215193ARich in organic matterImprove ventilation and water permeabilityOrganic fertilisersBiological water/sewage treatmentMarshConstructed wetland
The invention provides bionic peat and artificial marsh plates and a method for preparation thereof. The bionic peat is prepared as the following steps: adding plant nodule nitrogenase and uricase or hydrogen peroxidase into biomass waste to produce humifying accelerants as allantoin, allantoic acid and the like, humifying for 4-20 days at the temperature of 15-75 DEC G to obtain the bionic peat, then compressing the bionic peat, binders and water-loss reducer via a molding press, thereby obtaining the bionic peat and artificial marsh plates. The bionic peat of the invention has the advantages of abundant organic content, looseness and porousness, perfect breathing hydraulic permeability, large specific surface area and strong suction-chelation ability, and by application of the bionic peat the invention is capable of reducing consumption and loss amount of fertilizer, easing contaminations of water nitrate, nitrite and high-density metal and mitigating eutrophication caused by accumulation of water nitrogen, phosphorus and the like. And after degrading the bionic peat and 'artificial marsh' plates can further be used for improvement of land and the like by means of biochemistry and the like.
Owner:上海臻衍生物科技有限公司
Recombinant strain of bacillus subtilis
ActiveUS20200032237A1Promoting acetylglucosamine synthesisEasy to useOxidoreductasesLigasesQuinoneCarbon metabolism
The invention relates to a recombinant strain of Bacillus subtilis, wherein pyruvate carboxylase BalpycA, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ferredoxin dehydrogenase gor, isocitrate NAD+ dehydrogenase icd, malate quinone dehydrogenase mqo, pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase porAB and nitrogenase ferritin cyh are integrated and expressed in the recombinant strain. The invention also discloses use of the recombinant strain in fermentation production of acetylglucosamine. The recombinant Bacillus subtilis of the invention eliminates the central carbon metabolism overflow of the Bacillus subtilis and balances the intracellular reducing force, and the fermentation yield of acetylglucosamine is greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nitrogen-fixing Paenibacillus sp. 1-49 and application thereof
InactiveCN102352333BEnhanced inhibitory effectReduce usageBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyPlanting seed
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
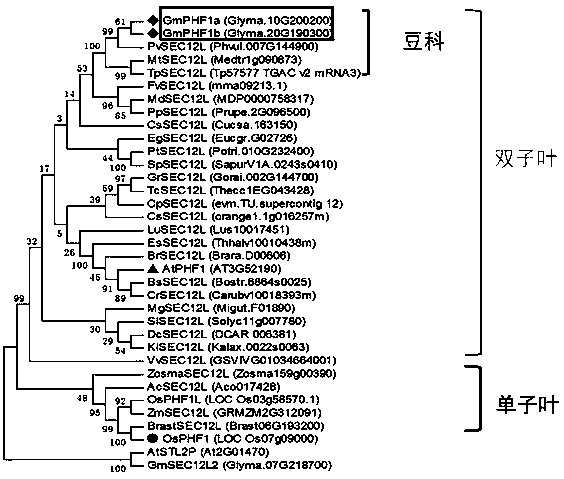
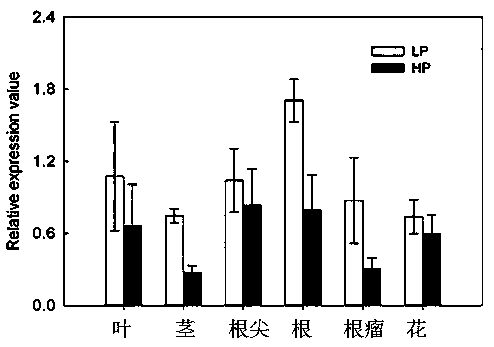
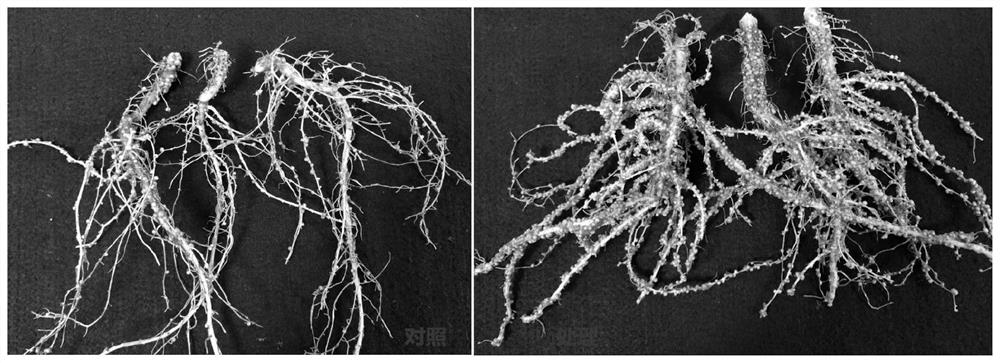
Application of transport assistance factor GmPHF1b of phosphate transporter
InactiveCN108841832AIncrease the number of nodulesWeight increasePlant peptidesFermentationPlant nodulePhosphate Transporters
The invention provides application of a transport assistance factor GmPHF1b of a phosphate transporter, and particularly relates to application of a GmPHF1b gene in promotion of obtaining of phosphorus by leguminous plants so as to promote nodulation and nitrogen fixation and in cooperation of nitrogen and phosphorus to achieve collaborative efficiency. Homologous comparison clones a gene GmPHF1bexpressed in a leaf, a stem, a root, a root nodule and a flower and verifies that a protein encoded by the gene GmPHF1b cooperates with a phosphate transporter GmPT5 / GmPT7 for controlling obtaining ofnodule phosphorus; overexpression of GmPHF1b obviously increases the number of root nodules of soybeans and the weight of the root nodules and improves the activity of the nitrogenase of the root nodules, so that the contents and the biomasses of nitrogen and phosphorus are increased, and the yield of the soybeans is finally increased.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Microbial agent for promoting root nodule number increase and root nodule nitrogenase activity increase of leguminous crops and application of microbial agent
PendingCN113980854APromotes hypernodulationPromote growthBacteriaFabaceae cultivationBiotechnologyEnterobacter species
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a microbial agent for promoting root nodule quantity increase and root nodule nitrogenase activity increase of leguminous crops and application of the microbial agent. The microbial agent is prepared by respectively fermenting and culturing four microbial bacteria, namely bacillus amyloliquefaciens, brevibacillus laterosporus, bacillus mucilaginosus and enterobacter ludwigii, concentrating, mixing and compounding. The microbial agent can effectively promote the number of root nodules with nitrogenase activity and increase of nitrogenase activity, promote crop growth and improve crop yield and product quality.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Pseudomonas stutzeri mutant strain as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111286481AImprove expression levelIncrease nitrogenase activityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and relates to a mutant strain as well as a construction method and application thereof. The pseudomonas stutzeri mutant strain is pseudomonas stutzeri DSM4166-TP (nifR), is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 20, 2019, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.19081. The pseudomonas stutzeri mutant strain has a preservation number of CGMCC No.19081. The pseudomonas stutzeri mutant strain has the beneficial effects that compared with the existing wild type DSM4166 strain, the pseudomonas stutzeri mutant strain has the advantages that the nitrogenase synthesis gene expression level is greatly improved, and the activity of the produced nitrogenase is also greatly higher than that of the wild type DSM4166 strain. The pseudomonas stutzeri mutant strain disclosed by the invention can be industrially produced on a large scale and has a wide commercial value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Organic pinellia ternata cultivation method capable of avoiding insect killing and weeding
InactiveCN111183861AHigh yieldTake advantage ofRoot crop cultivationHorticulture methodsPinelliaNitrogenase
The invention discloses an organic pinellia ternata cultivation method capable of avoiding insect killing and weeding, and relates to the technical field of agricultural planting. The organic pinelliaternata cultivation method comprises land preparation, planting, field management and harvesting. By use of the pinellia ternata planting method, extra addition of a chemical bactericide, a chemicalinsecticide and a chemical herbicide is not required in the planting process of the pinellia ternata, the planting cost is effectively reduced, besides, compound probiotic organic fertilizer is combined with a soil conditioner, and the activity of soil nitrogenase can be effectively improved, so that the organic fertilizer and nitrogen in the air can be fully utilized, the requirement of the pinellia ternata for the nitrogen element can be well met, and the high yield of the pinellia ternata can be achieved.
Owner:安徽焦半夏生态农业发展有限公司
Method for rapidly evaluating nitrogen fixing capacity of root nodule nitrogen fixation symbionts of leguminous plants
ActiveCN105296605AEasy to operateHigh quality total RNAMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant noduleNitrogenase
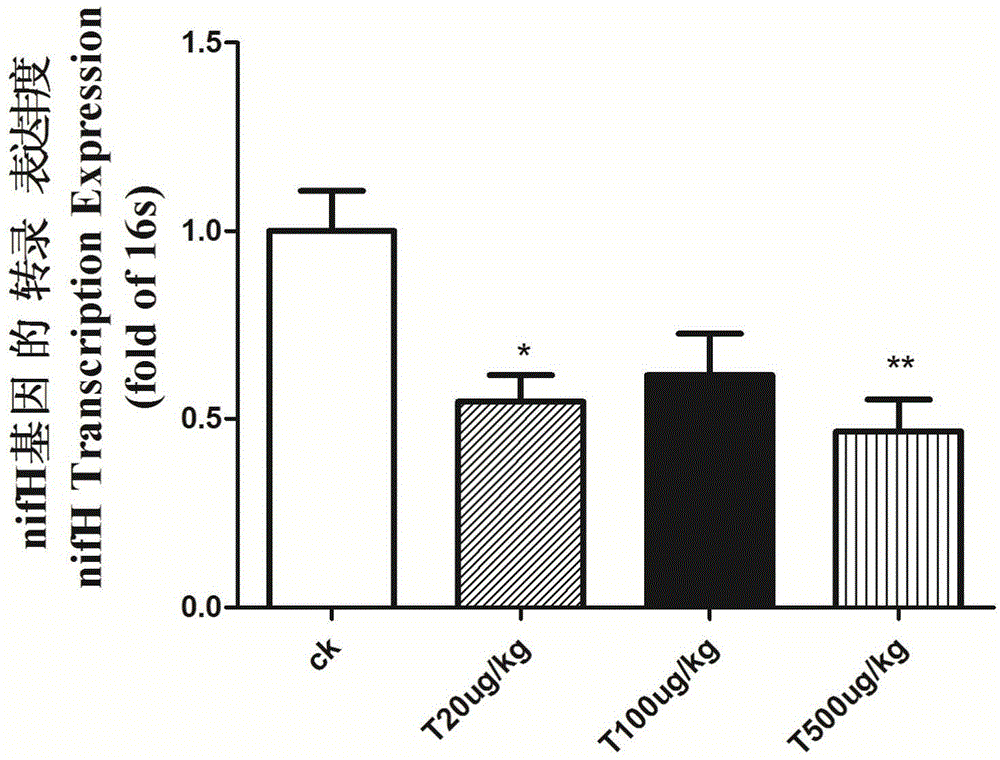
The invention relates to a method for rapidly evaluating nitrogen fixing capacity of root nodule nitrogen fixation symbionts of leguminous plants. The method mainly includes steps: 1) co-extraction of plant-rhizobium transcript information; 2) in-situ testing of nitrogenase expression; 3) evaluation of the nitrogen fixing capacity of soybean root nodule nitrogen fixation symbionts according to relative transcription abundance of nitrogenase gene nifH. The method has the advantages that firstly, operation steps are simple and convenient; secondly, the method can be used for real-time rapid field detection of nitrogen fixing level.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preventing and controlling aspergillus flavus and toxin thereof and increasing quantity of nitrogenase active root nodules at roots of leguminous crops and application of method
ActiveCN114097459APromote production increaseIncrease the number of nodules with nitrogenase activityBacteriaFabaceae cultivationPlant noduleNitrogenase
The invention relates to a method for preventing and controlling aspergillus flavus and toxin thereof and increasing the number of nitrogenase active root nodules of leguminous roots. Comprising the following steps: obtaining bacillus amyloliquefaciens, brevibacillus laterosporus, bacillus mucilaginosus and enterobacter ludwigii which have prevention and control effects on aspergillus flavus and toxins thereof; after two or three of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, brevibacillus laterosporus and bacillus mucilaginosus are mixed with enterobacter ludwigii, the mixture is applied to the field of leguminous crops, and the number of root nodules with nitrogenase activity at the roots of the leguminous crops is increased. The strain is used for increasing the number of nitrogenase active root nodules at the roots of leguminous crops such as peanuts and reducing the levels of aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin, and is simple to use, remarkable in yield increasing benefit and ecological benefit and easy to popularize and apply.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacillus megaterium D122, Bacillus megaterium D122 agent, and Bacillus megaterium D122 agent preparation method
ActiveCN106167771AReduce mortalityLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAcetic acid
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial agents, specifically to Bacillus megaterium D122, a Bacillus megaterium D122 agent, and a Bacillus megaterium D122 agent preparation method. According to the present invention, the Bacillus megaterium D122 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection and has the preservation number of CCTCCM 2015751; the preparation method comprises: (1) separating and screening; (2) purifying and preserving; (3) culturing with a culture medium; and (4) D122 agent preparation to obtain the Bacillus megaterium D122 agent; and the Bacillus megaterium D122 has functions of nitrogenase activity and auxin indoleacetic acid secretion.
Owner:DONGGUAN BAODE BIOLOGICAL ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com