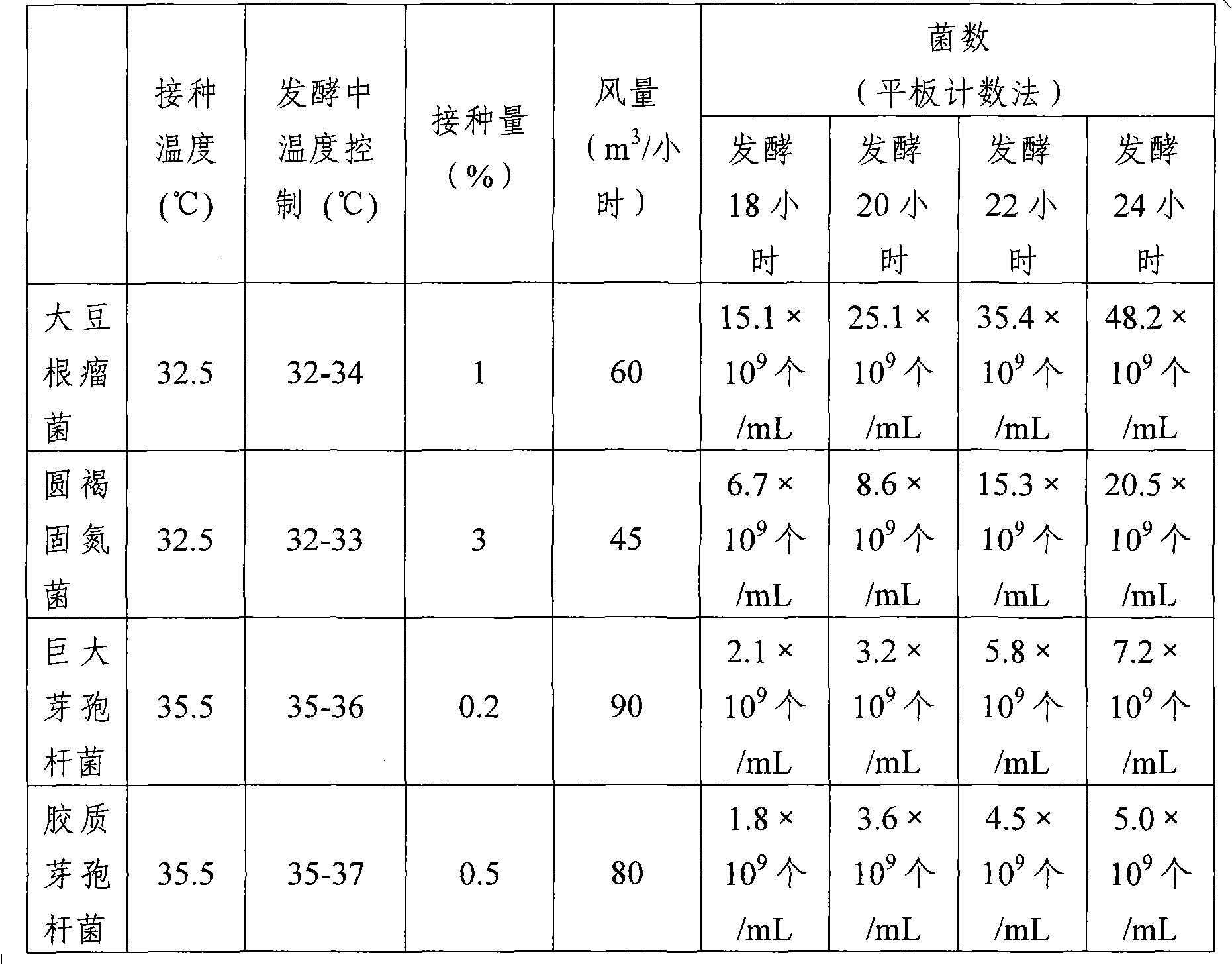
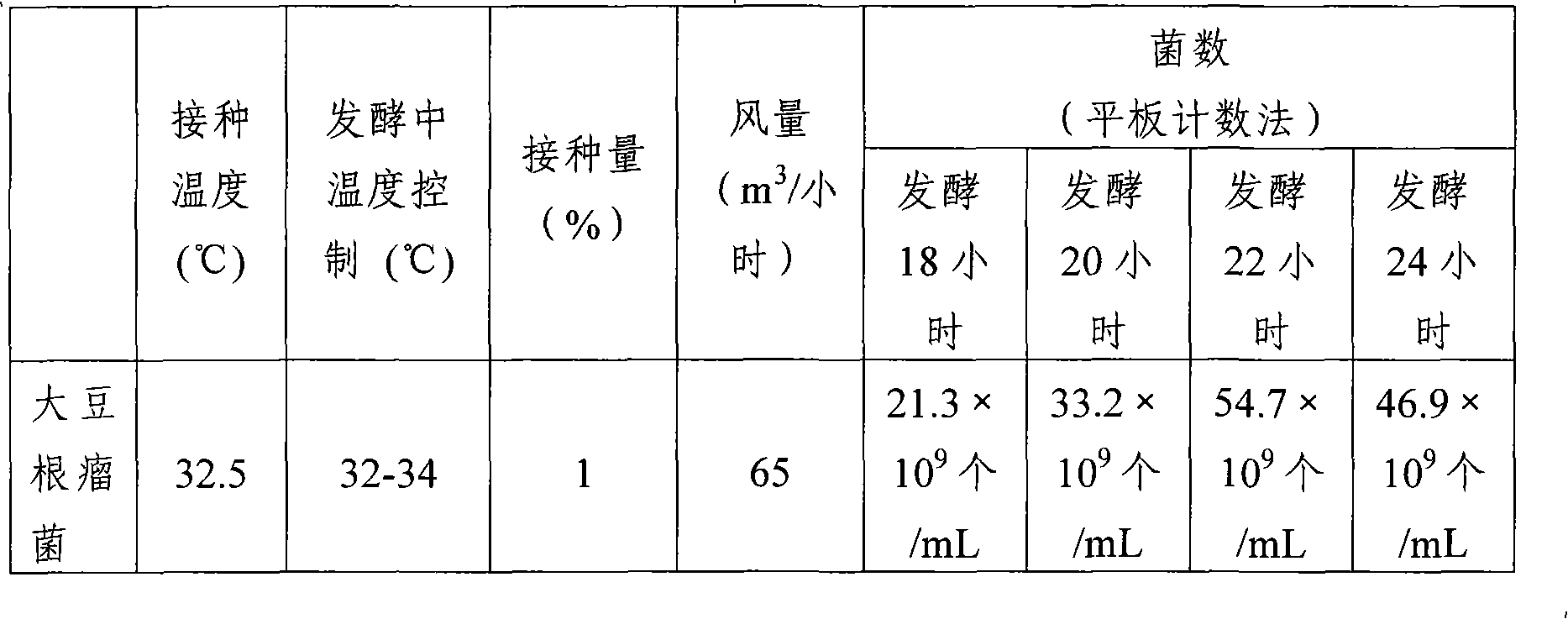
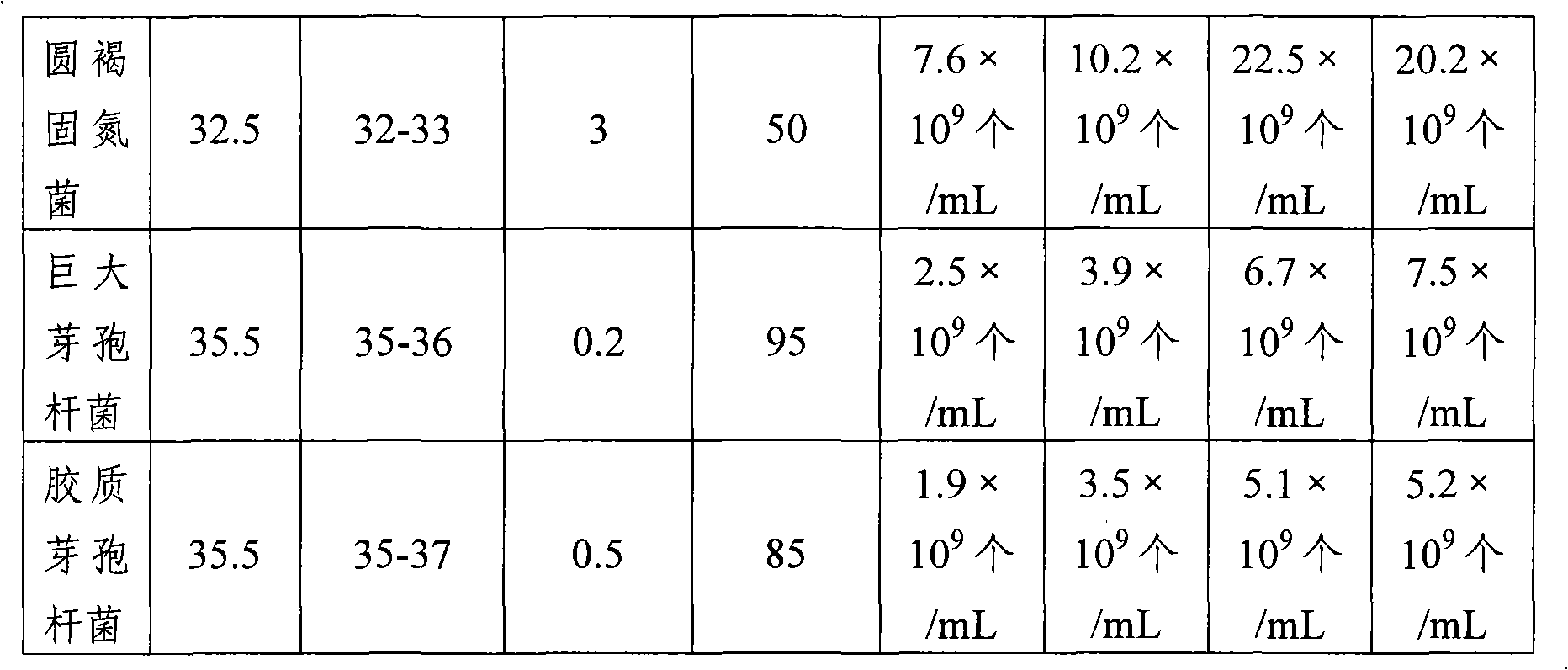
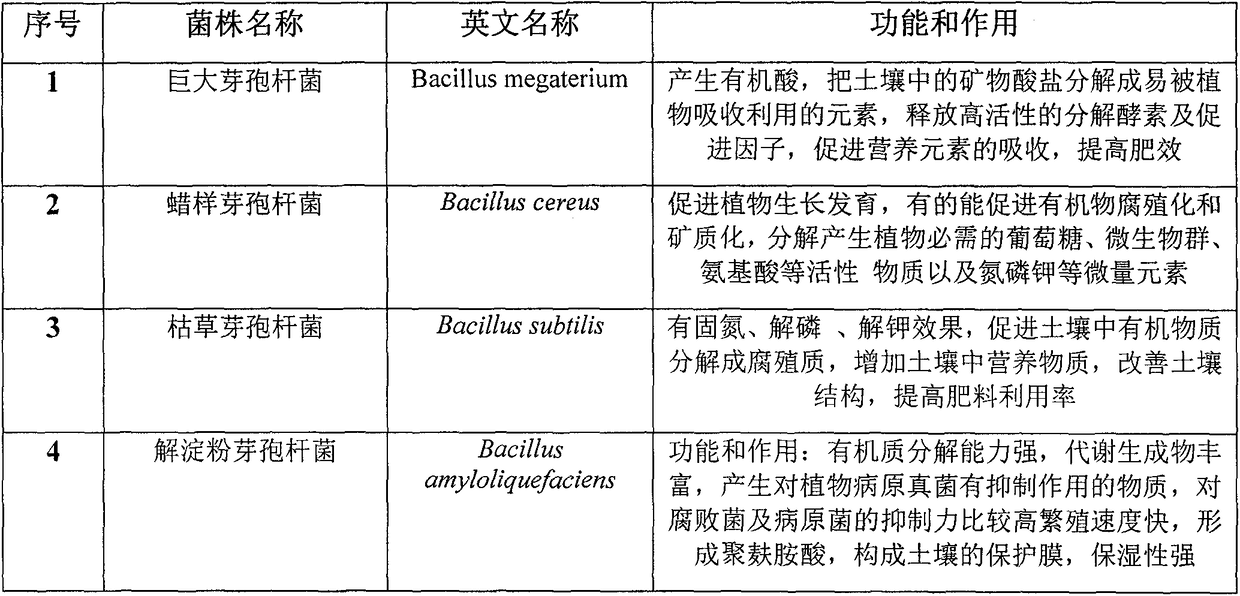
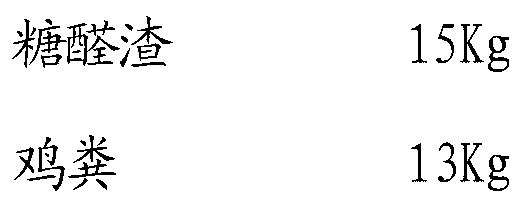Patents
Literature
58 results about "Rhizobium japonicum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rhizobium japonicum Buchanan 1926 Rhizobacterium japonicum Kirchner 1896. Bradyrhizobium japonicum is a species of legume-root nodulating, microsymbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The species is one of many Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria commonly referred to as rhizobia.
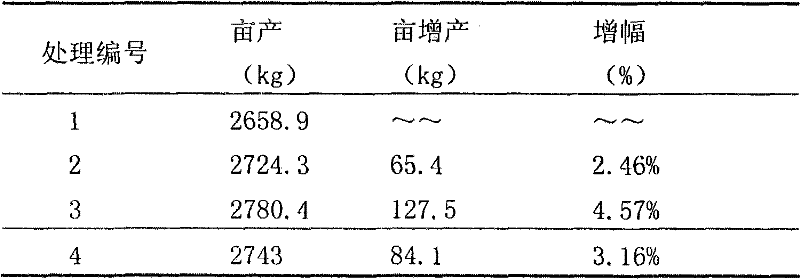
Complex microbial inoculum 707 and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101914447APromote growthImprove qualityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDiseaseBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to a complex microbial inoculum 707 and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological materials of the application of plant biological regulators to crop planting. The preparation method of the complex microbial inoculum 707 comprises the following step of: performing the cultivation of one-level strains and second-level and third-level fermentation on strains comprising 45 to 55 percent of bacillus subtilis, 5 to 10 percent of bacillus licheniformis, 5 to 10 percent of bacillus megaterium, 5 to 10 percent of candida utilis, 5 to 10 percent of rhizobium japonicum, 5 to 10 percent of bacillus mucilaginosus and 5 to 10 percent of lactobacillus plantarum, so that the microbial content of fermentation liquor reaches 6-10*10<9> per milliliter to obtain the complex microbial inoculum 707. Through long-term field verification, the complex microbial inoculum 707 has the advantages of reasonable formula and stable effect, can promote the growth of crops, improve fruit quality, promote early ripening, increase yield, improve the utilization rate of fertilizers and improve the ecological environment of soil, and has certain effect on disease prevention and disease resistance.
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
Composite microbial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102199050AImprove the preservation effectImprove sexual functionOrganic fertilisersBacillus megateriumNutrient solution
The invention relates to the field of microbiology, and specifically relates to a composite microbial fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The composite microbial fertilizer is composed of a composite microbial fermentation broth and an embedding medium, wherein a volume ratio of the composite microbial fermentation broth to the embedding medium are in a range of 1:5 to 1:4. The compositemicrobial fermentation broth is compounded of a co-culture comprising Candida utilis, lactic streptococci, lactobacillus acidophilus and bacillus subtilis, and a single nutrient solution comprising Bradyrhizobium japonicum, Azospirillum lipoferum, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus mucilaginosus and Azotobacter chrococcum. In the invention, composite microbes processed by embedding can be stored stably for more than 60 days and a count of the composite microbes is always more than 2 billion per gram, thus the composite microbial fertilizer comprising the composite microbes has a long effective time and can improve a planting capacity of soil.
Owner:沈阳科丰牧业科技有限公司
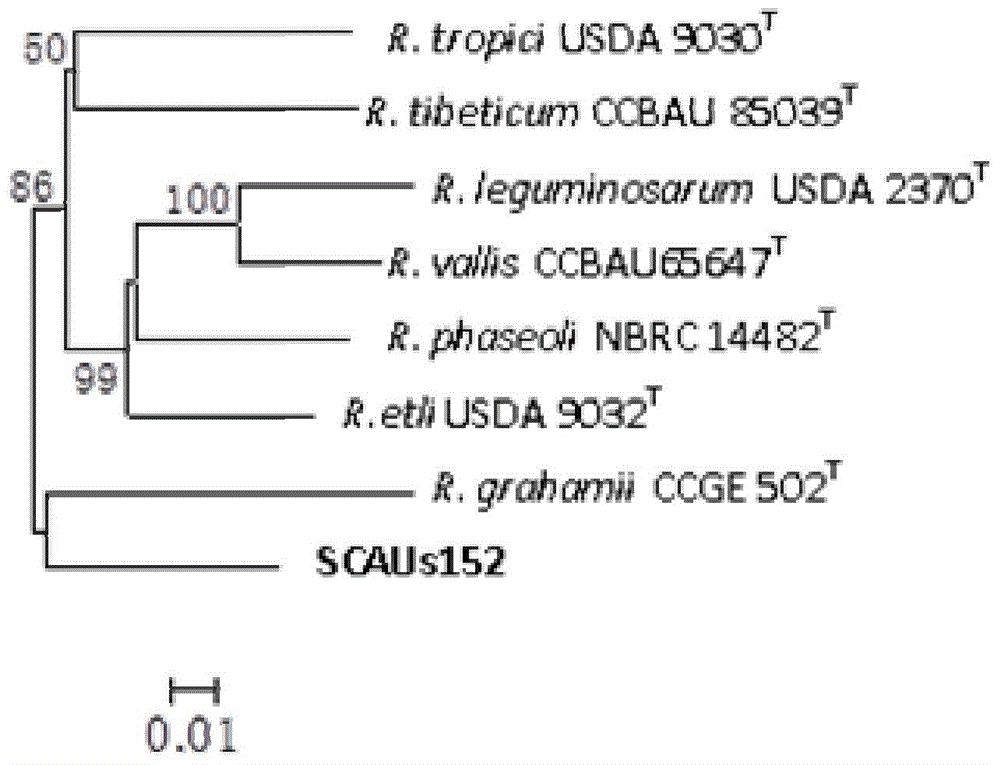
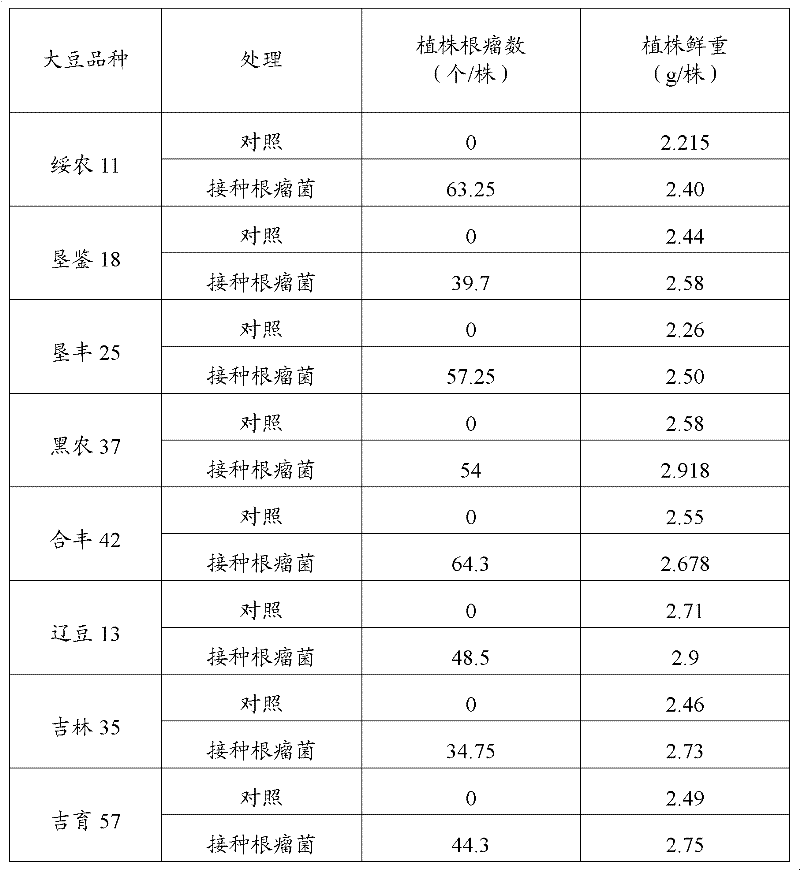
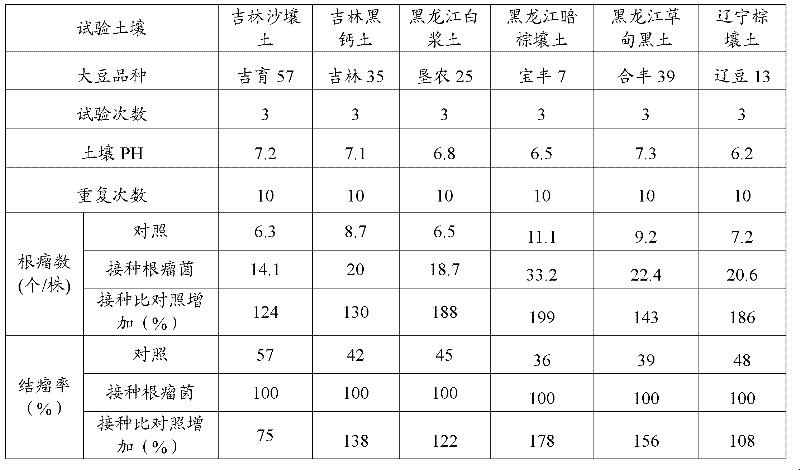
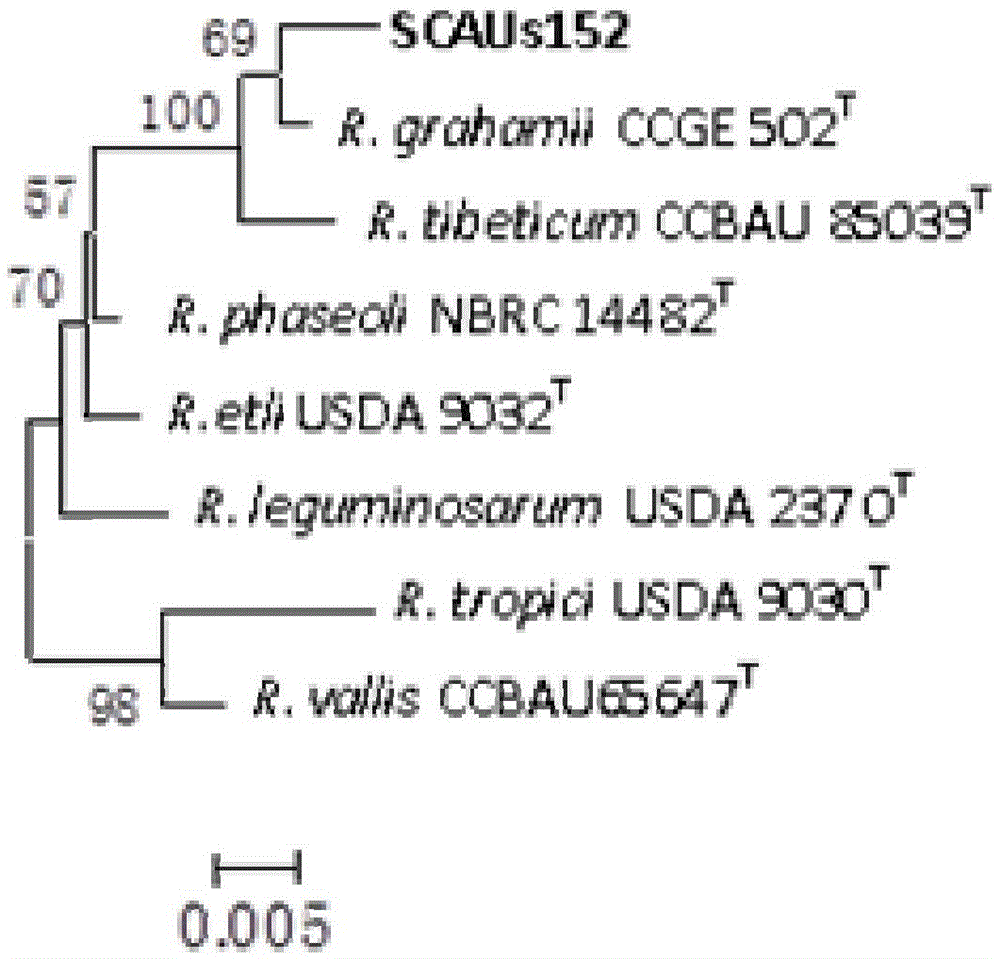
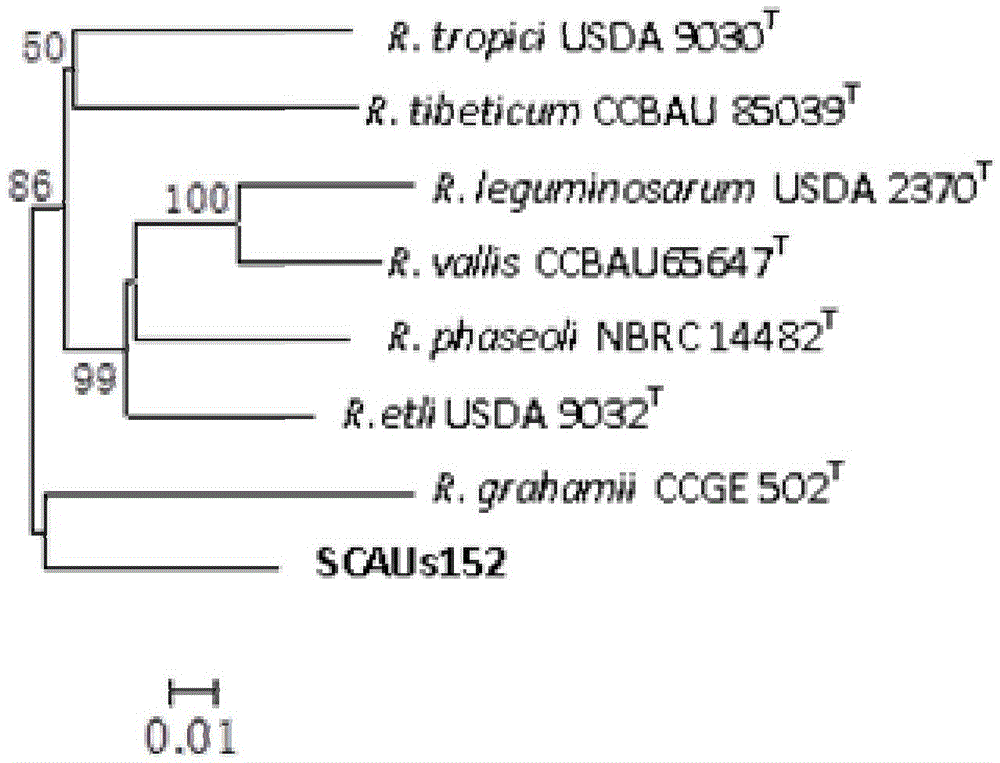
Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 and application thereof
InactiveCN103952341AStrong stress resistanceHas the ability to secrete IAABiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyPlant nodule
The invention discloses an Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 and application thereof. The strain is a new strain which is separated and purified from fresh soybean root nodules and belongs to Rhizobium. The strain is collected to China Center for Type Culture Collection of Wuhan University on March 14th, 2014, and the collection number is CCTCC NO.M2014085. The strain is applied to production of Sichuan soybeans. The Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 is a favorable broad-spectrum Rhizobium japonicum strain with high symbiotic fixation capacity, wide application range of Sichuan soybean species, IAA (indoleacetic acid) secretion capacity, capacities for dissolving inorganic phosphorus, organic phosphorus and potassium and high stress tolerance. The strain has favorable matching affinity with Sichuan dominant bean species, and can enhance the soybean yield by more than 23% in different ecological regions where no nitrogen fertilizer is applied and the Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 is inoculated, which is much different from the regions where the Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 is not inoculated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
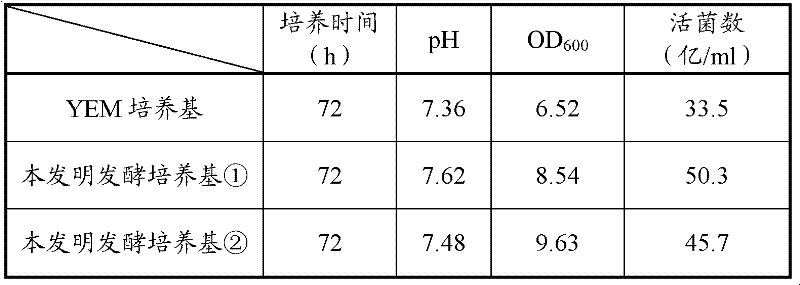
Bradyrhizobium japonicum capable of effectively fixing nitrogen and culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN102174436AWide variety of sourcesLow pricePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyEthylene glycol toxicity
The invention relates to bradyrhizobium japonicum capable of effectively fixing nitrogen and a culture method and application thereof. The bradyrhizobium japonicum CGMCC No.4346 is cultured by the steps of strain activation, seed culture, fermentation culture and the like. The invention has the following beneficial effects: sorbitol and diethylene glycol are utilized to replace the carbon source, mannitol in the traditional YEM (yeast extract mannitol) culture medium, and when the improved fermentation culture medium is adopted for culturing, the viable count of the fermentation liquor is higher than that of the YEM culture medium; compared with the rhizobium inoculants which are not inoculated on the soy beans, the bradyrhizobium japonicum agent ensures the theoretical yield of the soy beans to be increased by 16.7-17.2%, the crude fat content to be increased by 0.65-1.21% and the protein content to be increased by 1.29-1.60% after being inoculated on the soy beans, thus being an excellent strain for production of rhizobium japonicum and inoculation of the soy beans; and the culture method is simple and practical, and the raw materials have wide sources and low price and are suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Agricultural composite microbial preparation and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101585736AShorten fermentation timeReduce the number of bacteriaFertilising methodsOrganic fertilisersNutrientAgricultural science
The invention discloses an agricultural composite microbial preparation, respective zymocyte solutions of soja bean legume bacteria, round brown azotobacteria, bacillus megaterium and colloidal substance bacillus are respectively adsorbed on the adsorbing agent according to the proportionality of 15-20 % by weight to prepare soja bean legume bacteria, round brown azotobacteria, bacillus megaterium and colloidal substance bacillus, which are compounded to the agricultural composite microbial preparation; the invention adopts the composition of four kinds of bacterial seeds, also considers the requirement ofnitrogen, phosphor and kalium nutrients for plant, it is proved by the field experiment, the obvious yield increasing and quality raising actions for multiple corps are provided; the method accelerates the growth respectively adopting the controls of air flow of microorganism, temperature and inoculating amount during fermentation, enables the fermentation periods of the four kinds of composite bacterial series to be shortened, thereby fermenting at the same time and the terminating at the same time.
Owner:嵇书琼
Organic fertilizer containing medical dregs and biological germs and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103274875AReduce pests and diseasesReduce usageFertilizer mixturesSodium BentoniteEcological environment
The invention discloses an organic fertilizer containing medical dregs and biological germs and a preparation method thereof. The organic fertilizer containing medical dregs and biological germs, provided by the invention, comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15 parts of Chinese prickly meal, 10 parts of bean meal, 15 parts of plant ash, 20 parts of medicine residue, 15 parts of corm pulp, 10 parts of bone meal, 10 parts of bentonite and 5 parts of biological germ; and the biological germ is either any one of or the mixture of more than one of bacillus megatherium, rhizobium japonicum, basil rhizobia and EM flora. According to the organic fertilizer provided by the invention, the Chinese prickly meal and the medicine residue are added in the active ingredients, the Chinese prickly meal has an insecticidal property, and the medicine dregs has medical value, so that the synergistic effect of the two can reduce crop diseases and insect pests, reduce the usage of pesticide, and preserve the ecological environment. After using the organic fertilizer containing medical dregs and biological germs, the applicant found that the production of sweet potato increases more than 24 percent a year, the nutrient substance in the organic fertilizer is provided to the plants, the production cost is low, and the method can be widely used in agricultural field.
Owner:SHANDONG YIFENGYUAN BIOTECH
Organic fertilizer containing medical dregs and microelements and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103274863AReduce pests and diseasesReduce usageBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationEcological environmentInsect pest
The invention discloses an organic fertilizer containing medical dregs and microelements and a preparation method thereof. The organic fertilizer containing medical dregs and microelements, provided by the invention, comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15 parts of Chinese prickly meal, 10 parts of bean meal, 15 parts of plant ash, 20 parts of medicine residue, 15 parts of corm pulp, 10 parts of bone meal, 10 parts of bentonite, 4.5 parts of biological germ and 0.5 part of micronutrients fertilizer; and the biological germ is either any one of or the mixture of more than one of bacillus megatherium, rhizobium japonicum, basil rhizobia and EM flora. According to the organic fertilizer provided by the invention, the Chinese prickly meal and the medicine residue are added in the active ingredients, the Chinese prickly meal has an insecticidal property, and the medicine dregs has medical value, so that the synergistic effect of the two can reduce crop diseases and insect pests, reduce the usage of pesticide, and preserve the ecological environment. After using the organic fertilizer containing medical dregs and microelements, the applicant found that the production of sweet potato increases more than 24 percent a year, the nutrient substance in the organic fertilizer is provided to the plants, the production cost is low, and the method can be widely used in agricultural field.
Owner:SHANDONG YIFENGYUAN BIOTECH
Breeding of functional biocontrol bacterial fertilizer microorganisms and preparation of bacterial fertilizer series products
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bacterial fertilizer or a bacterial product. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: uniformly mixing a type A microbial agent and a type B microbial agent in the ratio of 1 to (0.1 to 10); adding the uniformly-mixed microbial agent into a pesticide residue culture medium to obtain the bacterial fertilizer or thebacterial product. Active components of the microbial agent consist of rhizobium japonicum, bacillus megaterium, bacillus cereus, bacillus subtilis, bacillus mucilaginosus, lactobacillus buchneri, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, paenibacillus polymyxa, bacillus pumillus, bacillus licheniformis, trichoderma harzianum, etc. The microbial agent and pesticide residues are mixed uniformly to obtain the bacterial fertilizer or the bacterial product. The bacterial fertilizer or the bacterial product can be applied to the facilitation of crop growth or the improvement of crop yield or the improvement of planting soil, as well as the improvement of crop disease resistance. The product can be combined with different bacterial fertilizer carriers to form a solid bacterial fertilizer, a dry or gel starchbacterial fertilizer, a liquid bacterial fertilizer, a pesticide residue waste bacterial fertilizer, a grass charcoal bacterial fertilizer, a peat bacterial fertilizer, a hibernated bacterial fertilizer, as well as a pig, cattle, sheep and chicken manure excrement bacterial fertilizer, and to form seed coatings.
Owner:天津市天大天福生物技术有限公司
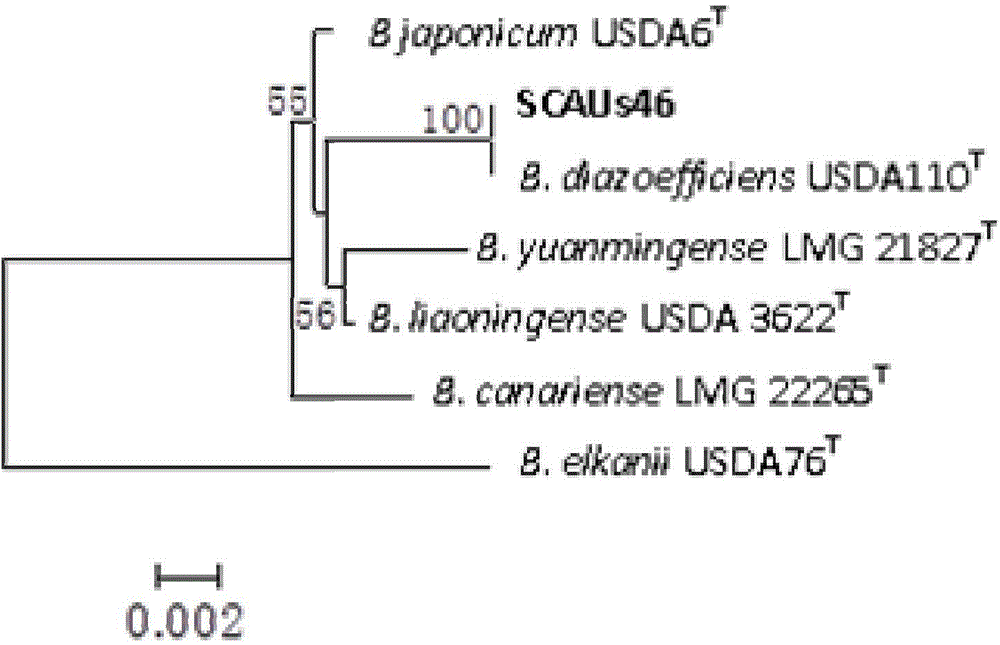
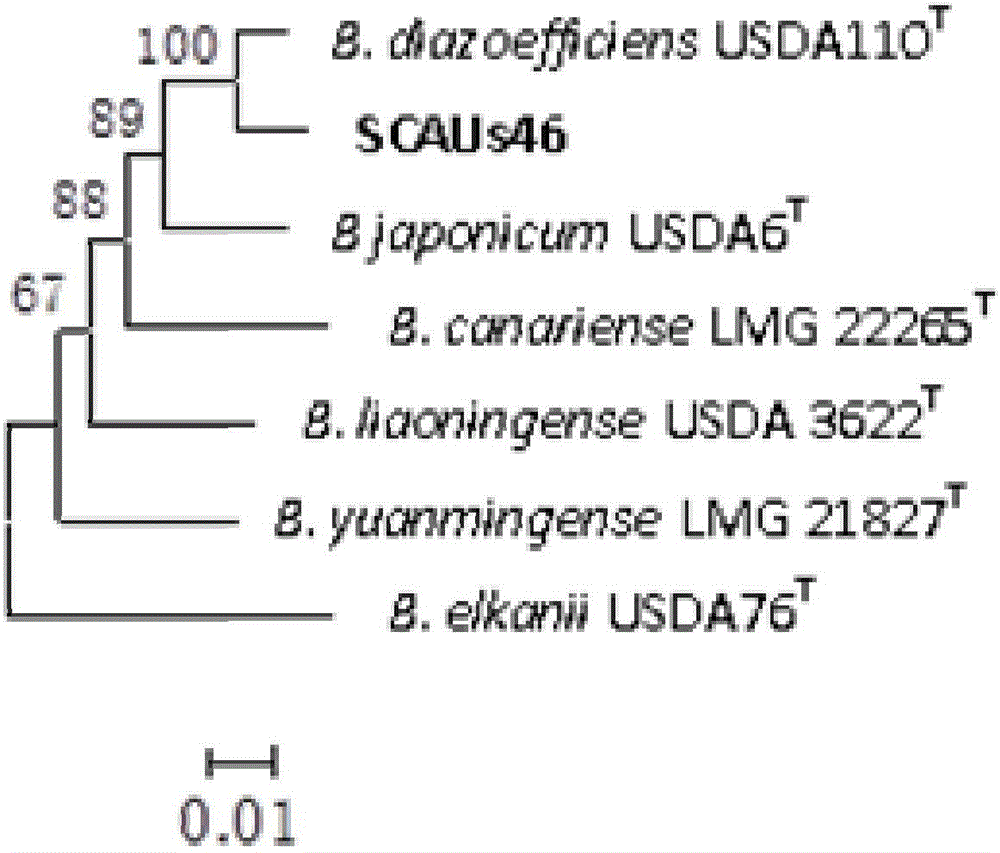
Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens strain SCAUs46 and application thereof
InactiveCN103952344AStrong stress resistanceHas the ability to secrete IAABacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleRhizobium japonicum
The invention discloses a Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens SCAUs46 and application thereof. The strain is separated and purified from fresh soybean root nodules, and is collected to China Center for Type Culture Collection of Wuhan University on March 14th, 2014; and the collection number is CCTCC NO.M2014083, and the classification designation is Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens. The strain is applied to production of Sichuan soybeans. The Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens SCAUs46is a favorable broad-spectrum Rhizobium japonicum strain with high symbiotic fixation capacity, wide application range of Sichuan soybean species, IAA (indoleacetic acid) secretion capacity, capacities for dissolving inorganic phosphorus, organic phosphorus and potassium and high stress tolerance. The strain has favorable matching affinity with Sichuan dominant bean species, and can enhance the soybean yield by more than 22% in different ecological regions where no nitrogen fertilizer is applied and the SCAUs46 is inoculated, which is much different from the regions where the SCAUs46 is not inoculated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum and production method thereof
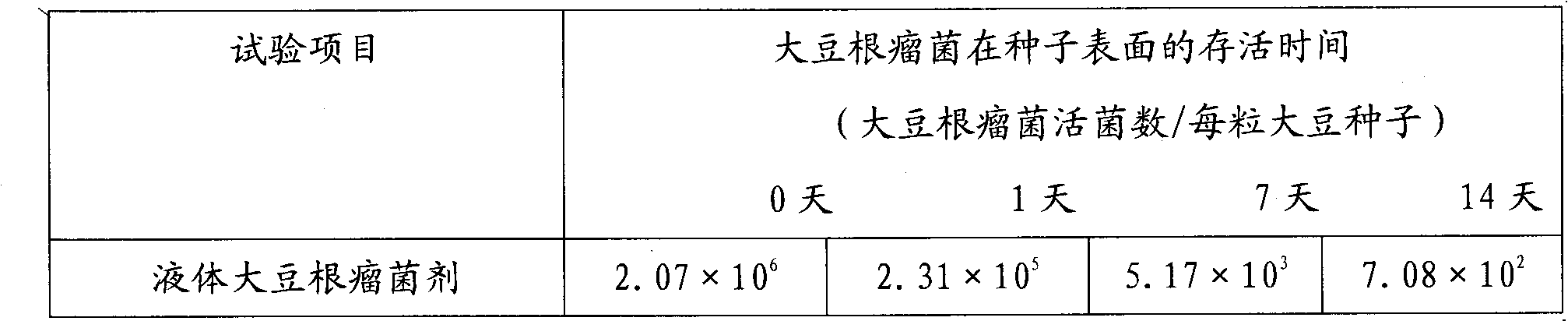
InactiveCN101818119AServe as nutritionPlay a role in film formationMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationCarboxymethyl celluloseSodium molybdate
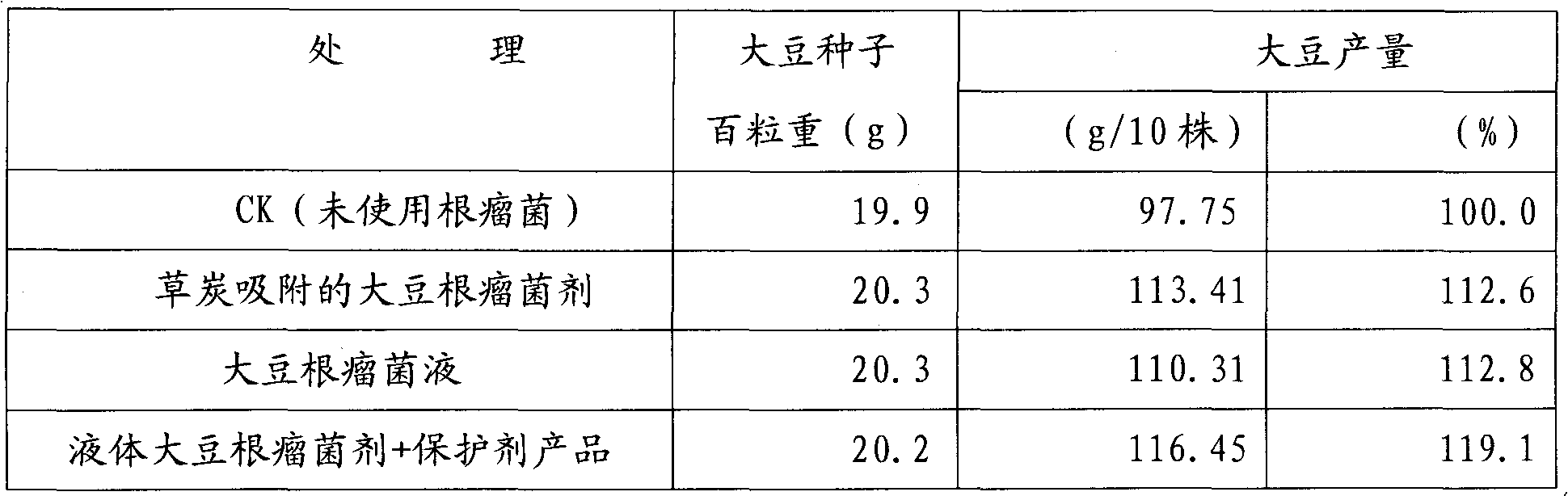
The invention relates to a nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum and a production method thereof. The nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum is prepared by selecting the raw materials of PVP (Polyvinylpyrrolidone) K30, PVP S630, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, peptone, bovine serum albumin and sodium molybdate and reacting under a certain reaction condition; the nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum, a liquid rhizobium japonicum agent and soybean seeds are mixed and stirred according to a certain proportion; and after the soybean seeds are coated and stored for two days, each soybean seed can ensure 100,000 live rhizobium japonicums. The invention has wide needed raw material sources, simple production process and low cost, can play roles of nutrition, film formation and protection in the rhizobium japonicum, and can ensure that the liquid rhizobium japonicum agent is preserved for one year at normal temperature; the live bacterium quantity is not smaller than 2,000,000,000 / ml, and the nitrogen fixing activity is not reduced.
Owner:哈尔滨奥龙奇康科技发展有限公司
Mutant of rhizobium japonicum SMH12 and application of mutant
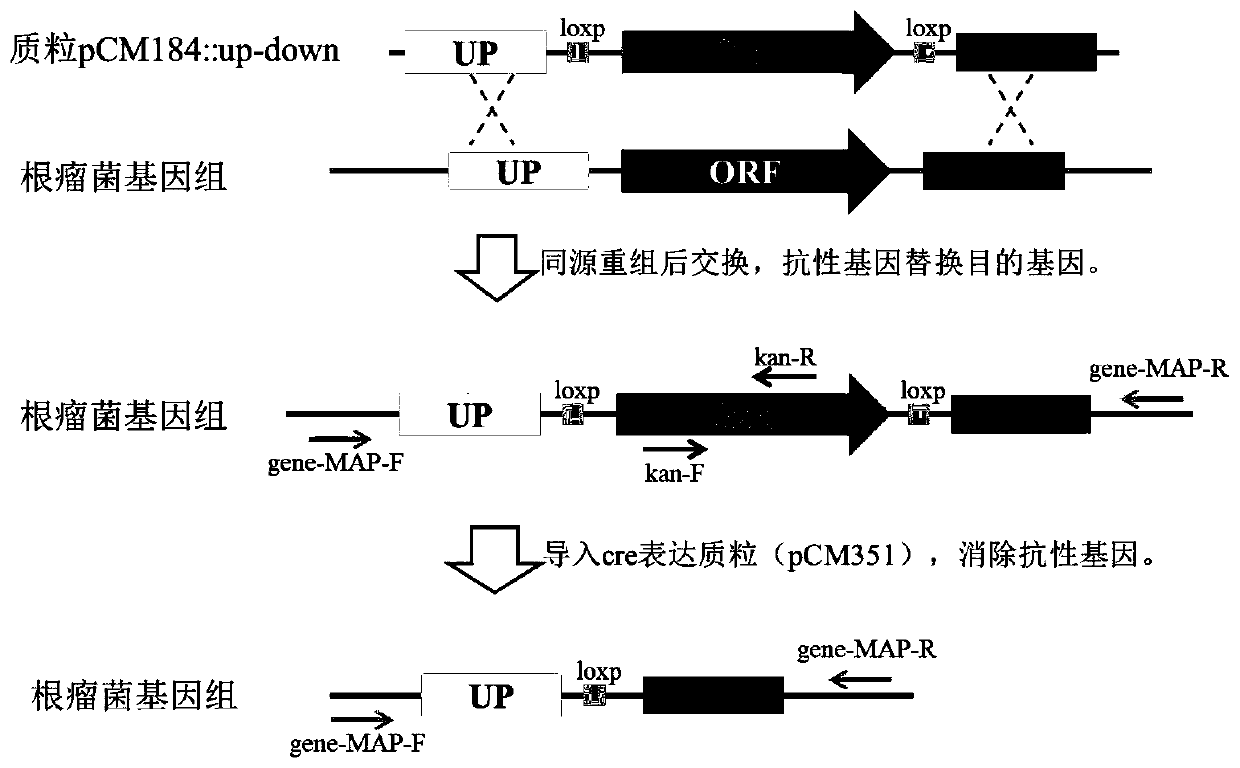
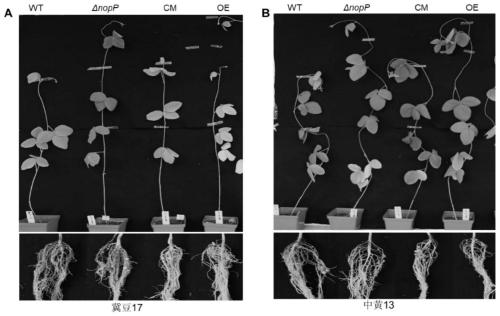
ActiveCN111286513ANodulation Restriction LiftedDecreased defense responseBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a mutant of rhizobium japonicum SMH12 and application of the mutant. The nopP gene deletion mutant is constructed by utilizing a CreloxP system double-exchange replacement method. By taking fast-growing rhizobium SMH12 genome DNA as a template and adopting a nopP-up-F / R primer pair and a nopP-down-F / R primer pair, a nopP homologous exchange upper arm and a nopP homologous exchange lower arm are respectively amplified, a product is connected with a digested pCM351 vector in two steps after being subjected to double enzyme digestion, plasmid transformation is obtained, and the mutant can be obtained. Therefore, the rhizobium target gene mutant is constructed and obtained. After the nopP gene is mutated or deleted, the defense reaction of leguminous plants is inhibitedor eliminated, so that rhizobium infection and nitrogen fixation are promoted. The improved rhizobium can improve the growth and nitrogen fixation capacity of leguminous crops, reduce nitrogen fertilizer application in agricultural production and generate huge economic and ecological benefits.
Owner:华创佳农生物科技(武汉)有限公司
Organic fertilizer containing furfural slag and biological bacteria, as well as preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103274860AReduce contentReduce alkalinityBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationBiotechnologyBacillus megaterium
The invention discloses an organic fertilizer containing furfural slag and biological bacteria, as well as a preparation method thereof. The organic fertilizer containing furfural slag and biological bacteria comprises components in parts by weight as follows: 15 parts of furfural slag, 13 parts of chicken manure, 5 parts of amino acid, 15 parts of humic acid, 12 parts of bone powder, 20 parts of xylogen, 15 parts of bentonite and 5 parts of biological bacteria; the furfural slag is waste furfural slag generated in a furfural slag production process; and the biological bacteria are a mixture of one or more than two of bacillus megatherium, rhizobium japonicum, purple perilla rhizobium and an EM (effective microorganism) flora. According to the organic fertilizer containing furfural slag and biological bacteria, as well as the preparation method thereof, a large amount of furfural slag is added in the effective components, so that contents of CO3<2->and HCO3<-> in the soil can be reduced, physical and chemical properties of soil are effectively improved, and alkalinity of soil is reduced; and further, the content of the furfural slag in the organic fertilizer is higher, during application, Cl<-> can be further reduced, contents of elements such as organic matters, potassium, nitrogen and the like in salinity soil are increased, and the elements and other nutritional ingredients in the organic fertilizer are combined to promote growth of crops.
Owner:SHANDONG YIFENGYUAN BIOTECH
Constructing method of nifA gene-introduced rhizobium japonicum genetic engineering bacterial strain HD-SFH-01
InactiveCN101880676AIncrease productionIncreased number of nodulesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a constructing method of a nifA gene-introduced rhizobium japonicum genetic engineering bacterial strain HD-SFH-01, belonging to a constructing method of a rhizobium japonicum genetic engineering bacterial strain and solving the problems of less increase on soybean nodule quantity and little soybean yield increase after the traditional rhizobium japonicum genetic engineering bacterial strain is inoculated to a soybean seedling. The method comprises the steps of: extracting rhizobium japonicum genome DNA for carrying out PCR amplification to obtain a target gene nifA, purifying and then connecting with a TA clone carrier pMD18-T to obtain a connecting product and then converting into escherichia coli; carrying out multiple enzyme digestion, connection and verification to obtain a recombinant prokaryote expression carrier pTR-Plac-nifA; and converting the recombinant prokaryote expression carrier pTR-Plac-nifA into soybean indigenous rhizobium. The bacterial strain HD-SFH-01 is inoculated into the soybean seedling, the rhizobium quantity is increased, and the soybean yield is increased by 3.80 percent.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Organic fertilizer containing pepper meal and biological germs and preparation method thereof
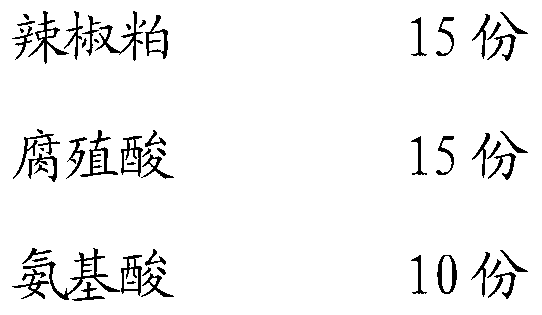
ActiveCN103274865AImprove physical and chemical propertiesPromote growthBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationSodium BentoniteSludge
The invention discloses an organic fertilizer containing pepper meal and biological germs and a preparation method thereof. The organic fertilizer containing pepper meal and biological germs, provided by the invention, comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15 parts of pepper meal, 15 parts of humic acid, 10 parts of amino acid, 5 parts of cigarette foam, 30 parts of bacterial sludge, 10 parts of starch dregs, 10 parts of bentonite and 5 parts of biological germ; and the biological germ is either any one of or the mixture of more than one of bacillus megatherium, rhizobium japonicum, basil rhizobia and EM flora. The active ingredient pepper meal of the organic fertilizer, provided by the invention, comprises capsorubin, carotene, zeaxanthine, VC and capsaicin, the mixed use of the pepper dregs with humic acid and bacterizl sludge can improve the physicochemical property of the soil, promote the microorganism in the soil to convert the organic fertilizer into components that the crop can absorb, and remarkably improve the manufacturing efficiency of the crop. After using the organic fertilizer containing pepper meal and biological germs, the applicant found that the production of potato increases more than 11 percent a year, and the pollution of the organic fertilizer to the environment is decreased.
Owner:SHANDONG YIFENGYUAN BIOTECH
Organic fertilizer containing furfural residues and trace elements and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103265386AReduce contentReduce alkalinityBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationBacillus megateriumPotassium
The invention discloses an organic fertilizer containing furfural residues and trace elements and a preparation method thereof. The organic fertilizer comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15 parts of furfural residues, 13 parts of chicken manure, 5 parts of amino acid, 15 parts of humic acid, 12 parts of bone meal, 20 parts of lignin, 15 parts of bentonite, 4.5 parts of biological bacterium and 0.5 part of trace element fertilizer, wherein the furfural residues are furfural waste residues generated in the furfural production process; and the biological bacterium is any one of or the mixture of more than any two of bacillus megaterium, rhizobium japonicum, rhizobium astragali and EM (effective microorganisms). The organic fertilizer and the preparation method have the advantages that the contents of CO3<2-> and HCO3<-> in soil can be reduced by adding lots of furfural residues to the active components, thus effectively improving the physical and chemical properties of soil and reducing the alkalinity of soil; and as the content of the furfural residues in the organic fertilizer is higher, Cl<-> can be reduced and the contents of such elements as organic matters, potassium and nitrogen in salinity soil can be increased by applying the organic fertilizer so that the elements promote growth of crops together with other nutrients in the organic fertilizer.
Owner:SHANDONG YIFENGYUAN BIOTECH
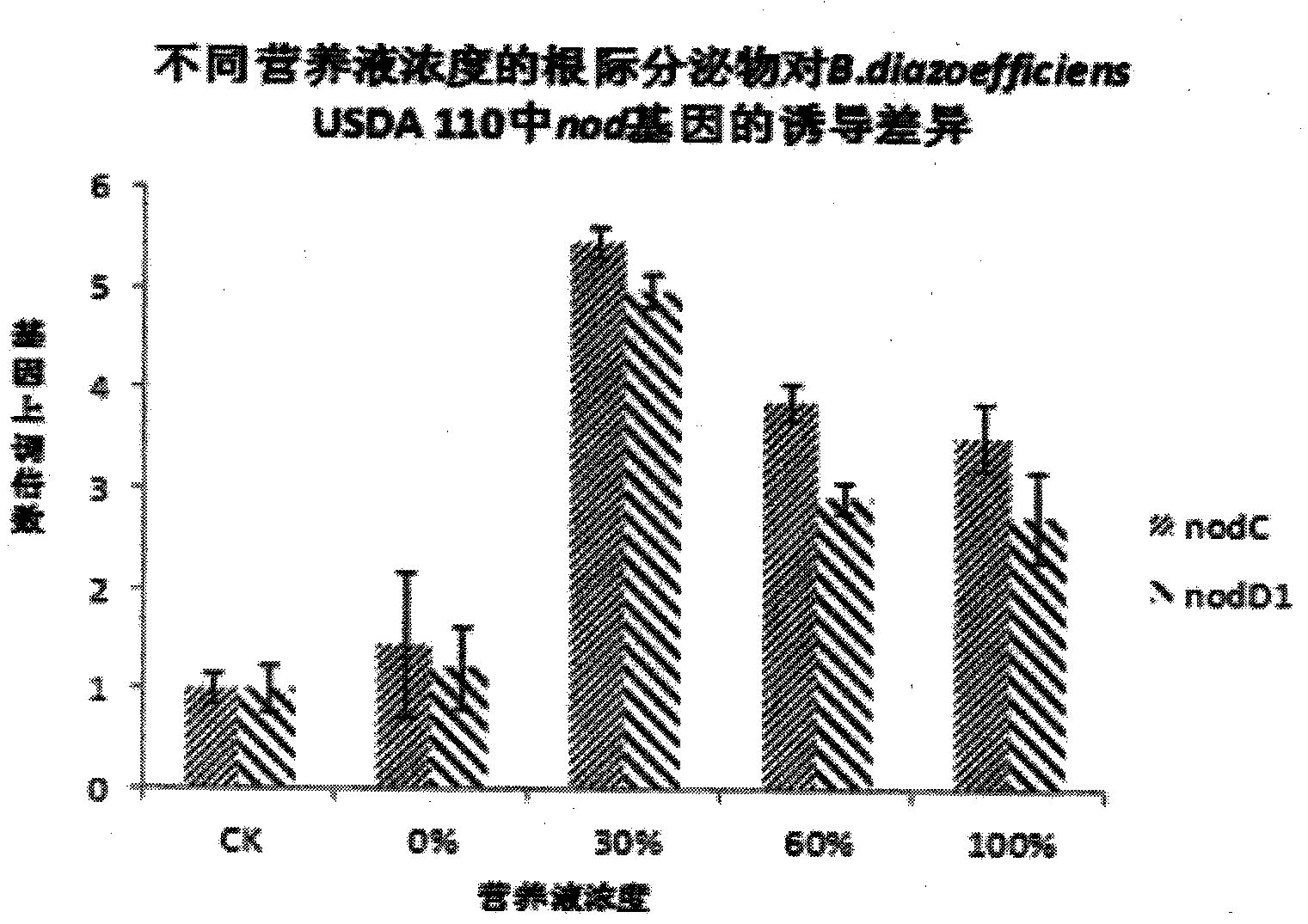
Preparation method of soybean root exudate for efficiently promoting competitive nodulation of rhizobium japonicum
ActiveCN104351047AEnhance nodulation geneThe effect of promoting competitive nodulationPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsRhizobium japonicumNutrient solution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a soybean root exudate for efficiently promoting competitive nodulation of rhizobium japonicum, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: (1) sterilizing the surface of a soybean seed; (2) moving the sterilized soybean seed into a YMA agar watch glass under the aseptic condition to germinate, moving to a nitrogen-free Rigaud-Puppo nutrient solution of which the concentration is 30%, to culture after the seed is germinated, and collecting the soybean root exudate on the 12 day of culturing, so as to obtain the soybean root exudate for efficiently promoting competitive nodulation of the rhizobium japonicum. The preparation method has the advantages: the best concentration of the nitrogen-free Rigaud-Puppo nutrient solution is confirmed to be 30%, the soybean root exudate collected on the 12 day of culturing remarkably improves the expression of a nodulation gene of the rhizobium japonicum, and the effect of efficiently promoting competitive nodulation of the soybean is further reflected.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
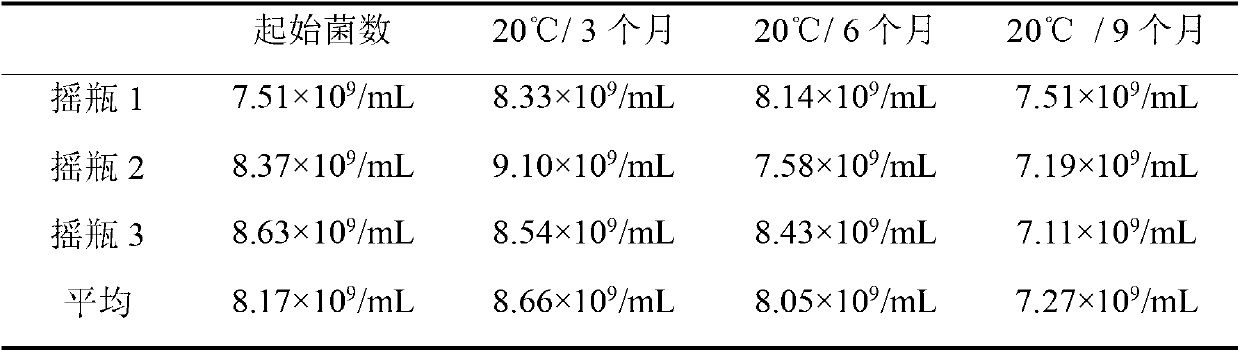
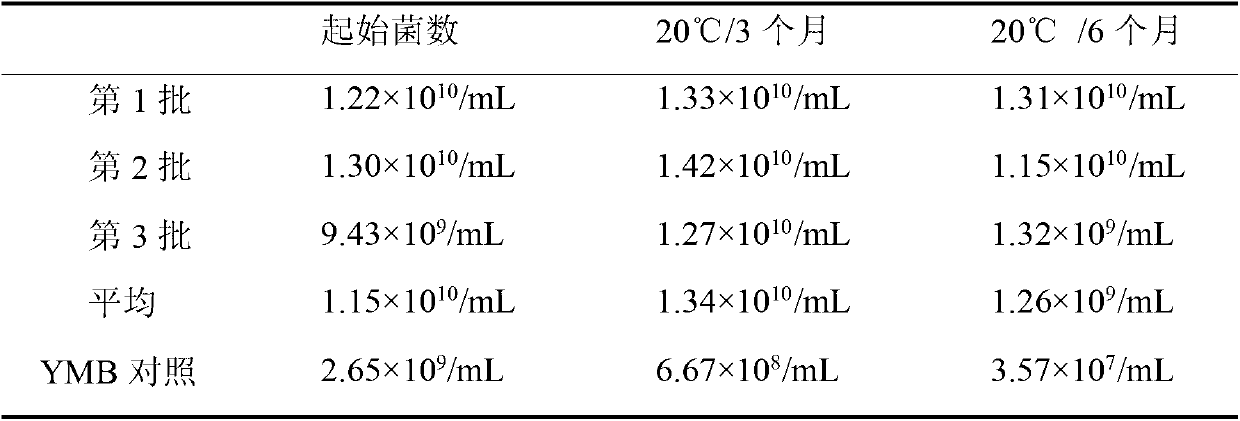
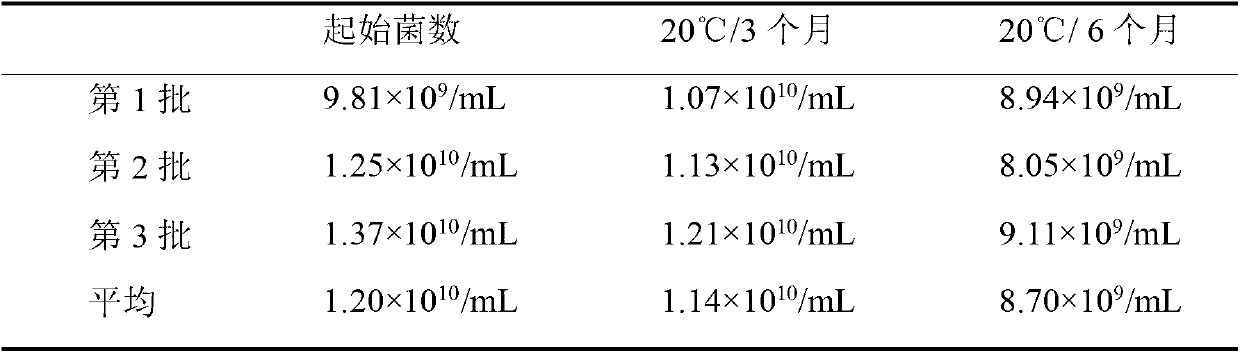
Rhizobium japonicum culture medium and method for preparing liquid rhizobium japonicum agent by adopting rhizobium japonicum culture medium
The invention relates a rhizobium japonicum culture medium and a method for preparing a liquid rhizobium japonicum agent by adopting the rhizobium japonicum culture medium and aims at solving the problem that an existing liquid rhizobium japonicum agent is unbalanced in nutrition and low in thallus activity and rhizobium japonicum prepared by means of a fermentation technology cannot stably survive at the room temperature. The rhizobium japonicum culture medium is an aqueous solution prepared by glycerin, mannitol, glucose, rhamnose, fructose, alpha-oxoglutarate, yeast powder, serine, arginine, NH4C1, K2HPO4, KH2PO4, MgSO4*7H2O, CaCl2*2H2O, FeSO4*7H2O, NaCl, Na2MoO4*2H2O and biotin, and can be obtained by controlling fermentation tank conditions. The viable count of microbial inoculum of the rhizobium japonicum culture medium preserved at 20 DEG C for 12 months can still reach to more than 100 hundred millions per milliliter.
Owner:黑龙江省华龙生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of alfalfa rhizobia immobilized embedded granule formation and application thereof
InactiveCN106754500AEasy to addNo loss of activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh activityDrug biological activity
The invention discloses preparation and application of a novel alfalfa rhizobia immobilized embedded granule formation, and belongs to the field of agricultural microbe application. An immobilized cell technology is a method for immobilizing microbial cells in some special materials, preparing granules to form a limited space, enabling the thallus to keep biological activity in a certain time and realizing proliferation. At present, the alfalfa rhizobia is widely applied to the fields such as medicines, foods, fermentation industry, wastewater treatment and the like, preliminary study in a rhizobium japonicum embedding aspect is realized, while the preparation and application of the alfalfa rhizobia embedded immobilized granules is still a blank at present. According to the novel alfalfa rhizobia immobilized embedded granules developed in the invention, the alfalfa rhizobia is conveniently added by alfalfa cultivation enterprises, and the activity of fungicides is not lost in the compounding, processing, granulating and transportation and storage processes. Therefore, alfalfa rhizobia bacterial manure can be easily used by farmer households, and the main technical bottleneck difficulty of a high-tolerance high-activity alfalfa rhizobia seed embedding technique is broken.
Owner:DAQING BRANCH OF HEILONGJIANG ACAD OF SCI
Seed coating agent for promoting germination and seedling formation of leguminous seeds in saline-alkali soil and preparation method of seed coating agent
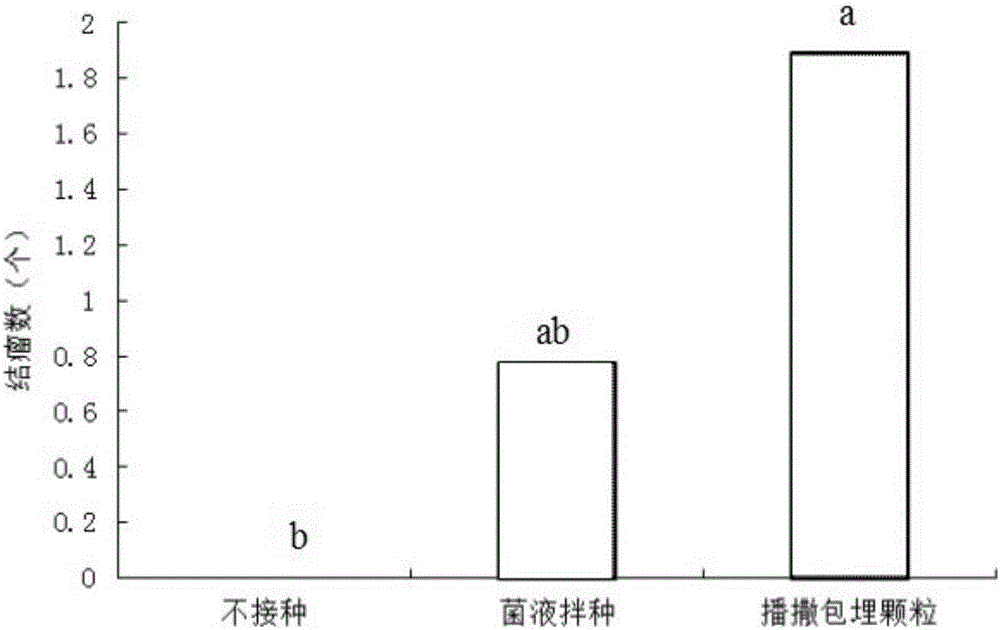
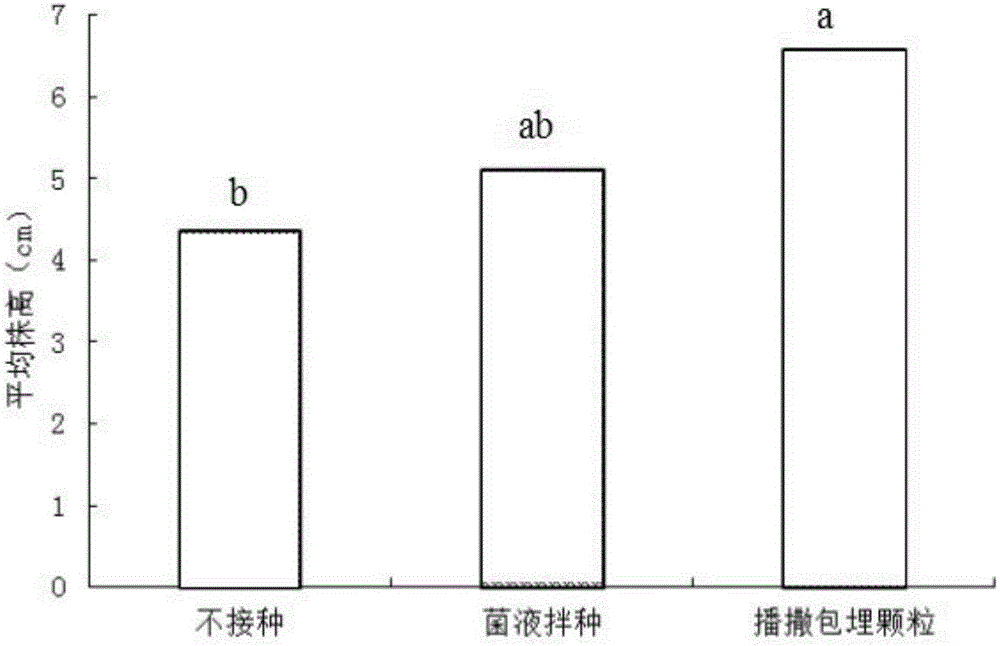
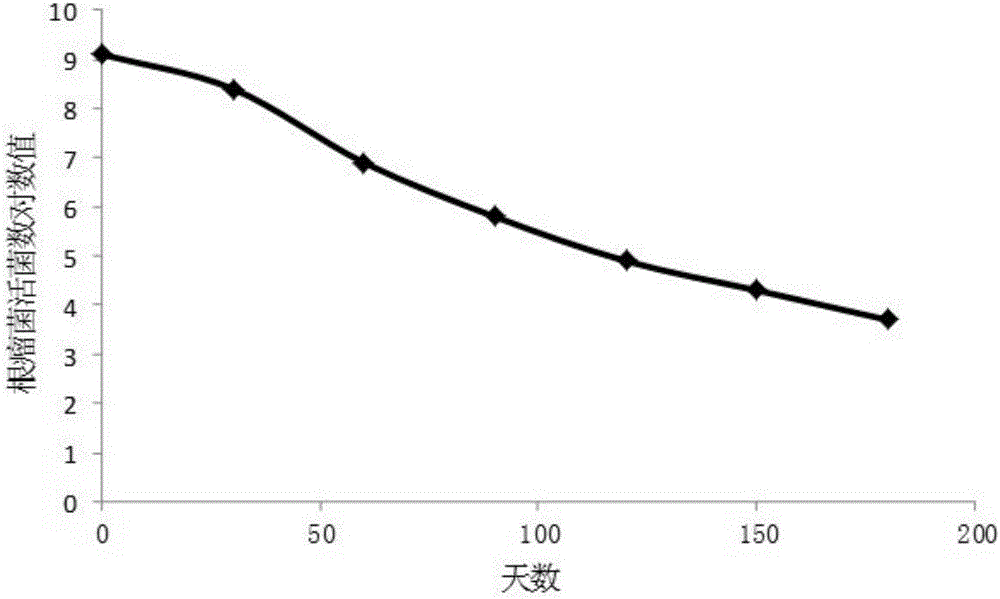
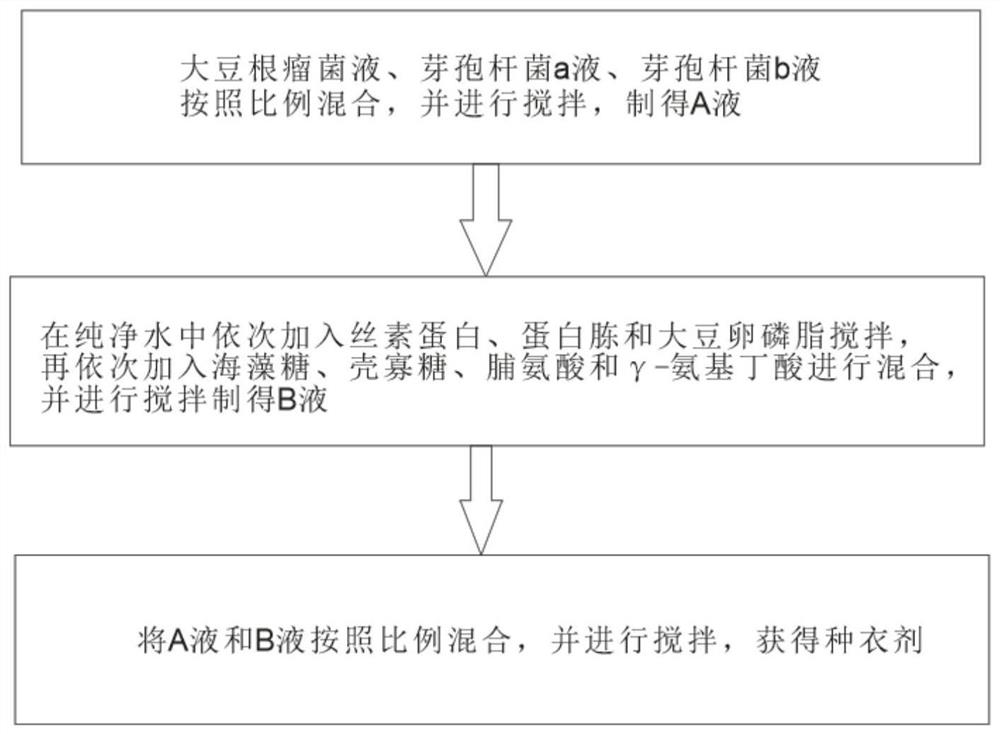
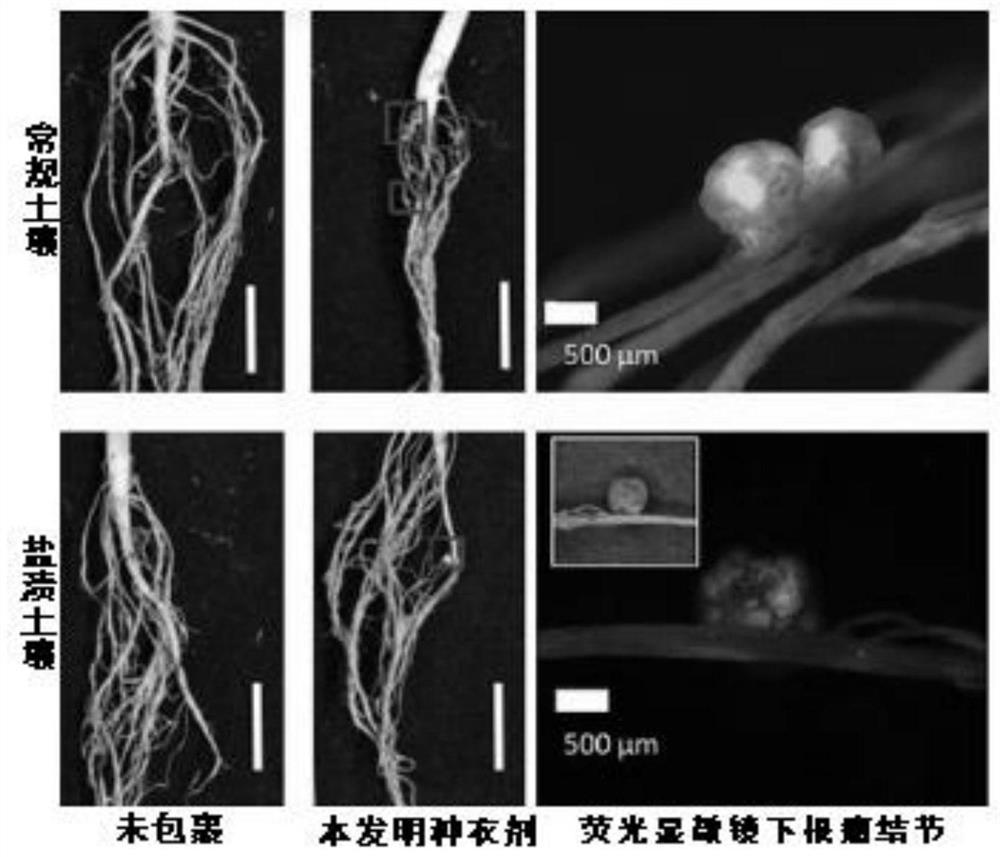
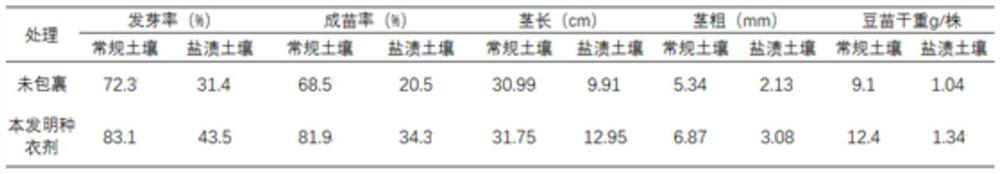
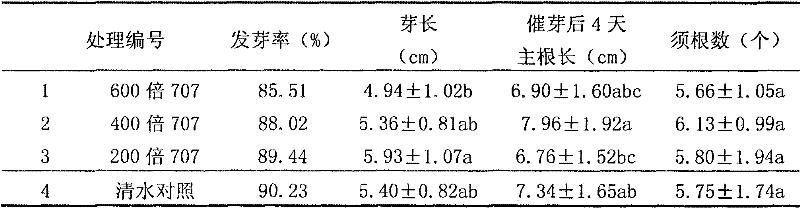
PendingCN113693082AGood physical propertiesPromote germination and growthBiocideAnimal repellantsAlkali soilRhizobium japonicum
The invention discloses a seed coating agent for promoting germination and seedling formation of leguminous seeds in saline-alkali soil and a preparation method of the seed coating agent. The seed coating agent mainly comprises a soybean rhizobium solution, a bacillus liquid a, a bacillus liquid b, silk fibroin, peptone and the like. A film is formed outside the seeds before sowing, so that the seeds are helped to resist abiotic stress outside soil, and a protective layer can be formed around rhizosphere during seedling growth, so that the harm of abiotic stress to the seedlings is further reduced, and the leguminous seeds can grow healthily.
Owner:SHENZHEN BATIAN ECOTYPIC ENG
Environment-friendly biological agent for treating organic garbage and preparation method of biological agent
InactiveCN112111425AThe reaction site is simpleDo resource processingFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyOligosaccharide
The invention relates to an environment-friendly biological agent for treating organic garbage and a preparation method of the environment-friendly biological agent. The environment-friendly biological agent, in parts by weight, comprises 8-13 parts of bacillus licheniformis powder, 10-15 parts of bacillus pumilus powder, 13-16 parts of nitrobacteria powder, 8-10 parts of lactic acid bacteria powder, 7-10 parts of bacillus megaterium powder, 8-12 parts of bacillus subtilis powder, 9-14 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens powder, 5-8 parts of saccharomyces cerevisiae powder, 1-5 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus powder, 1-5 parts of rhizobium japonicum powder, 2-4 parts of azotobacter chroococcum powder, 3-7 parts of thermomonospora fusca powder, 1-3 parts of lactobacillus delbrueckii, 1-3 parts of cellulase, 0.5-2 parts of ligninase, 0.01-0.05 part of 90% amino-oligosaccharin and 0.05-1 part of brassinolide. The biological agent can be applied to treatment of different organic solid wastes, has low requirements on working conditions, can start self-fermentation at normal temperature, does not need high-temperature and high-pressure catalysis, greatly shortens the treatment period to24 hours to one week, and is environment-friendly and harmless; and a final treatment product is biological bacterial fertilizer, so that waste is turned into wealth.
Owner:上海玖霖环保科技有限公司
Complex microbial inoculum 707 and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101914447BPromote growthImprove qualityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBacillus licheniformisDisease
The invention relates to a complex microbial inoculum 707 and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological materials of the application of plant biological regulators to crop planting. The preparation method of the complex microbial inoculum 707 comprises the following step of: performing the cultivation of one-level strains and second-level and third-level fermentation on strains comprising 45 to 55 percent of bacillus subtilis, 5 to 10 percent of bacillus licheniformis, 5 to 10 percent of bacillus megaterium, 5 to 10 percent of candida utilis, 5 to 10 percent of rhizobium japonicum, 5 to 10 percent of bacillus mucilaginosus and 5 to 10 percent of lactobacillus plantarum, so that the microbial content of fermentation liquor reaches 6-10*10<9> per milliliter to obtain the complex microbial inoculum 707. Through long-term field verification, the complex microbial inoculum 707 has the advantages of reasonable formula and stable effect, can promote the growth of crops, improve fruit quality, promote early ripening, increase yield, improve the utilization rate of fertilizers and improve the ecological environment of soil, and has certain effect on disease prevention and disease resistance.
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
Construction method of genetic engineering strains for improving quantity of soybean nodules
InactiveCN102660573AIncrease productionIncrease nitrogenase activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleCulture expansion
The invention relates to a construction method of genetic engineering strains for improving quantity of soybean nodules. The construction method aims at solving the problems that when the conventional rhizobium japonicum genetic engineering strains are inoculated to soybean seedlings, the root nodule quantity of soybean plants and the yield increase of soybeans are small compared with those of the original starting strains. The construction method comprises the following steps of: performing activation and culture expansion on sinorhizobium fredii to extract genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by virtue of a homologous sequence cloning method to obtain target gene dct A; performing sequencing identification on the target gene; constructing a prokaryotes expression vector pTR-Plac-dct A; and converting the prokaryotes expression vector into the sinorhizobium fredii to obtain the gene engineering strains. The quantity of the root nodules on the soybean plant with the transformed gene engineering strains is increased by 53.73%, and the yield of the soybeans is increased by 62.02%.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
R gene for controlling soybean-rhizobium matching property as well as protein and application thereof
ActiveCN112626080AImprove symbiotic nitrogen fixationReduce the number of nodulesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyR gene
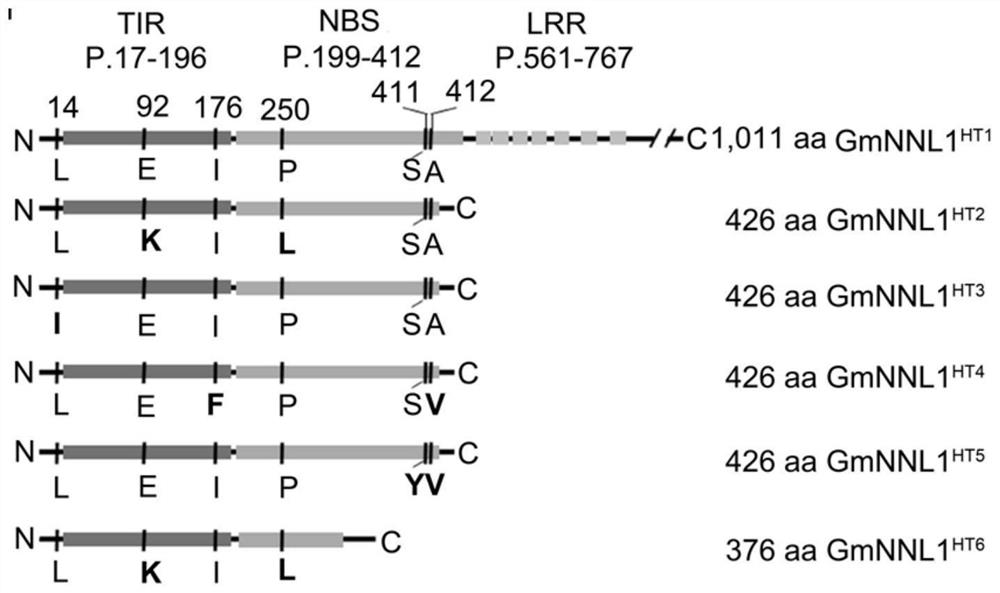
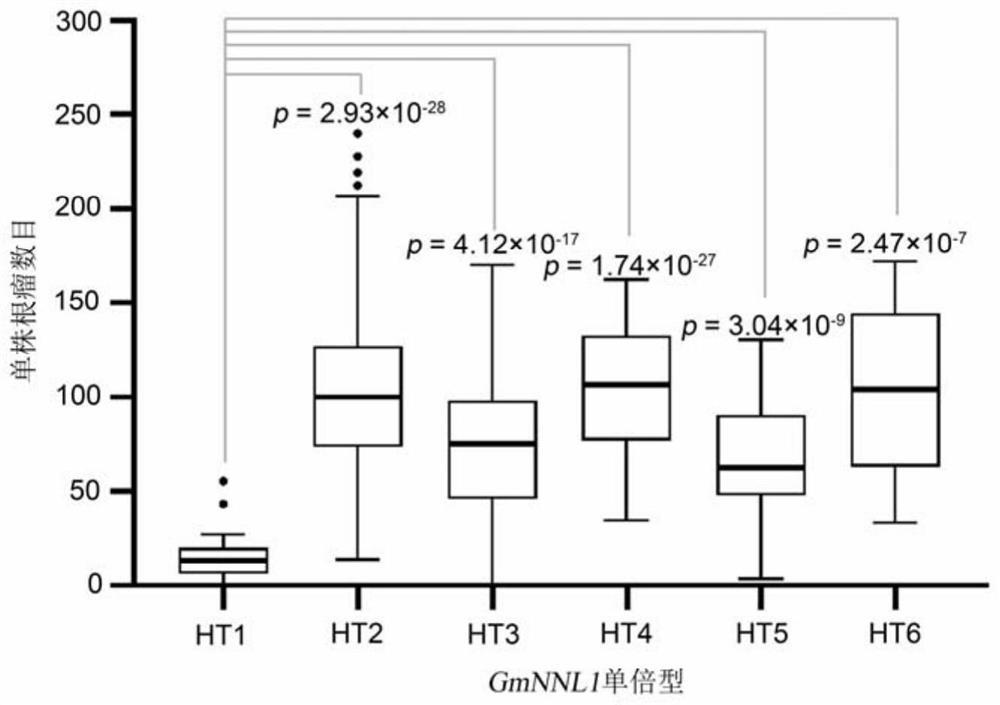
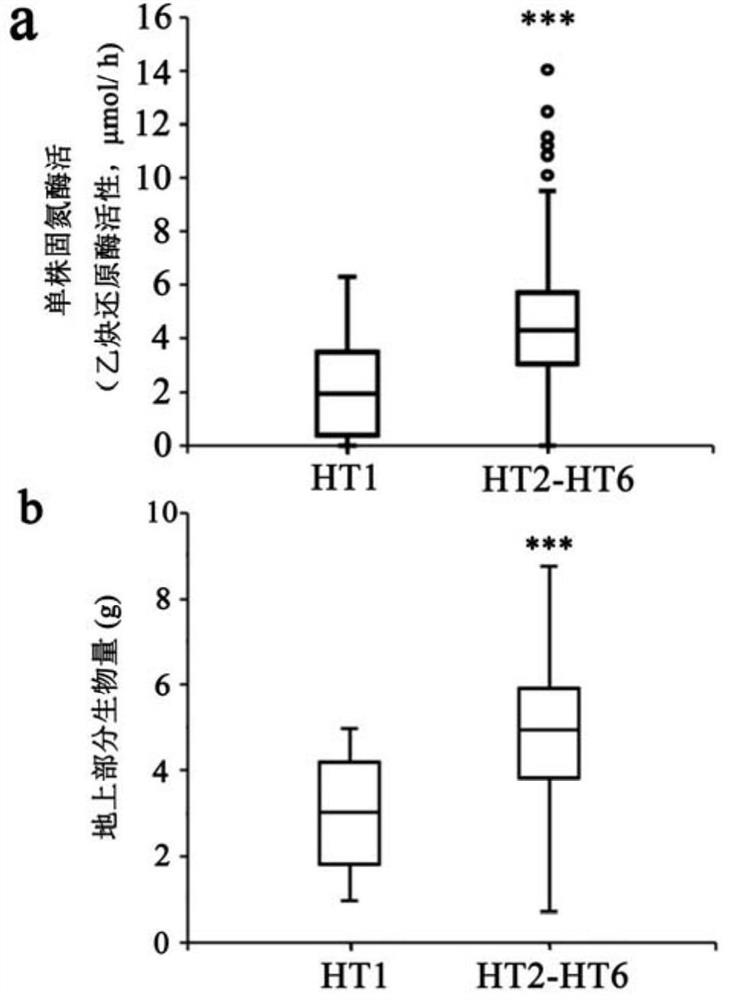
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to application of a new gene, in particular to an R gene for controlling soybean-rhizobium matching property as well as protein and application of the R gene. The GmNNL1 genome sequence of the gene GmNNL1 disclosed by the invention in the HENGFENG WUDOU of a soybean line is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2 and the coded amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3. The R gene GmNNL1 of the soybean is an effective gene capable of regulating and controlling the nodulation quantity of specific rhizobium on the soybean, and can regulate and control the nodulation quantity by directly identifying the haplotype of slow-growing rhizobium specific effect protein NopP to limit the symbiotic nodulation of indigenous rhizobium, so that the soybean preferentially nodulates with artificially applied efficient rhizobium inoculant; and the symbiotic nitrogen fixation capability can be improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY +1
Method for extracting rhizobium japonicum exopolysaccharides
InactiveCN110698568AHigh removal rateImprove the efficiency of protein removalAnimal scienceRhizobium japonicum
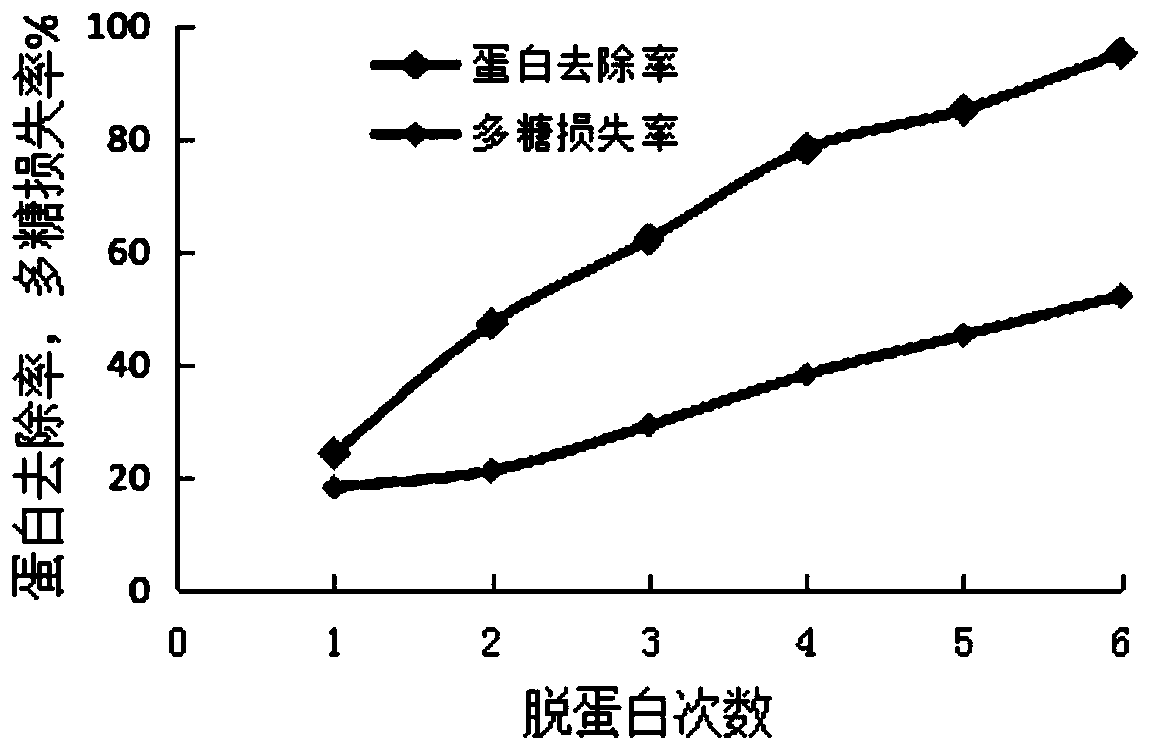
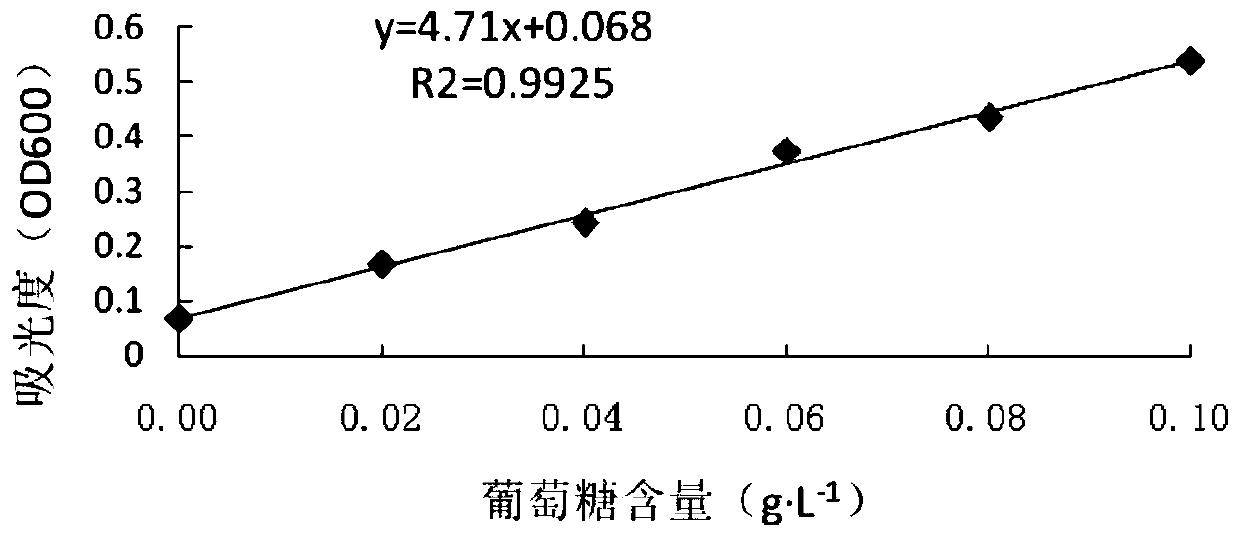
The invention discloses a method for extracting rhizobium japonicum exopolysaccharides, belongs to the technical field of rhizobium japonicum exopolysaccharides extraction, and aims to solve the technical problem that the effect of removing protein from rhizobium exopolysaccharides is not ideal. According to the method, serine protease and a Sevage method are adopted for deproteinization treatmentto treat crude exopolysaccharides of rhizobium HH103, the protein removal rate is obviously increased along with increase of the deproteinization frequency, and a linear trend is formed.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of transferring rhizobium japonicum to corn root system
InactiveCN103947443AEasy to operateLow costPlant genotype modificationHorticultureRoot noduleRhizobium japonicum
The invention relates to a cultivating technology in the crop field, and in particular to a method of transferring rhizobium japonicum to a corn root system with an ultra-distant compound type breeding technique. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out sexual propagation (hybridization) between corn and soybean; transferring dinitrogenase of the soybean to the corn, and enabling a root system of the grass family plant corn to form nodules. As the corn is ultra distant from the soybean, the corn and the soybean cannot be carried out with cross pollination, so at first, vegetative propagation (grafting) must be carried out, in order to close the genetic relationship and make the sexual propagation possible; the key of the compound breeding technique is firstly ensuring that the corn and the soybean are grafted successfully, in particular grated in the seedling phase, as the seedlings at this time communicate with each other most actively, and variation is most possible. But, the seedlings just come up out the ground are extremely fragile, and the plants are tender and small, so that the grafting is very difficult, and has not yet been successful in the foreign countries.
Owner:王孚望
Environment-friendly multifunctional composite soybean seed coating agent and processing technique thereof
InactiveCN103539578AIncrease productionImprove qualityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyAlkaloid
The invention discloses an environment-friendly multifunctional composite soybean seed coating agent, belongs to the technical field of agriculture, and is used for solving the problem of lack of environment-friendly multifunctional composite soybean seed coating agent products at present. The seed coating agent is composed of 70-83.9% of microorganism compound bacterium agent, 1-10% of metal microelement liquid, 5-15% of film-forming agent, 0.1%-5% of food-grade brilliant blue and 0.1-1% of total alkaloid of sophora flavescens by weight, wherein the microorganism compound bacterium agent is composed of 20% of rhizobium japonicum GIM 1.93 fermentation broth, 10% of bacillus CGMCC 1.7195 fermentation broth, 10-20% of bacillus CGMCC 1.1870 fermentation broth, 10-20% of bacillus mucilaginosus CCTCC 10013 fermentation broth, 10-20% of bacillus subtilis CGMCC 1.2397 fermentation broth and 10-20% of bacillus CGMCC 1.2397 fermentation broth by weight. The seed coating agent is capable of improving the adaptability of crops to biotic and abiotic stress, improving own immunity of crops, enhancing the nitrogen fixing capacity of root nodules of bean or pea family, improving the yield structure of crops, increasing the yield, and the like.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
A kind of nitrogen-fixing bacteria rhizobium strain scaus152 and its application
The invention discloses an Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 and application thereof. The strain is a new strain which is separated and purified from fresh soybean root nodules and belongs to Rhizobium. The strain is collected to China Center for Type Culture Collection of Wuhan University on March 14th, 2014, and the collection number is CCTCC NO.M2014085. The strain is applied to production of Sichuan soybeans. The Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 is a favorable broad-spectrum Rhizobium japonicum strain with high symbiotic fixation capacity, wide application range of Sichuan soybean species, IAA (indoleacetic acid) secretion capacity, capacities for dissolving inorganic phosphorus, organic phosphorus and potassium and high stress tolerance. The strain has favorable matching affinity with Sichuan dominant bean species, and can enhance the soybean yield by more than 23% in different ecological regions where no nitrogen fertilizer is applied and the Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 is inoculated, which is much different from the regions where the Azorhizobium strain SCAUs152 is not inoculated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Saline-alkali soil resistant nitrogen fixation rhizobium japonicum and application thereof
ActiveCN114456981AHigh nitrogen contentIncrease productionPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant noduleEcological environment
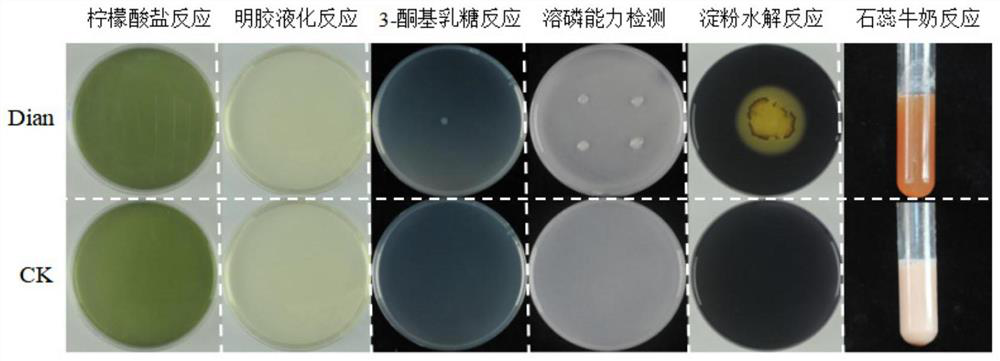
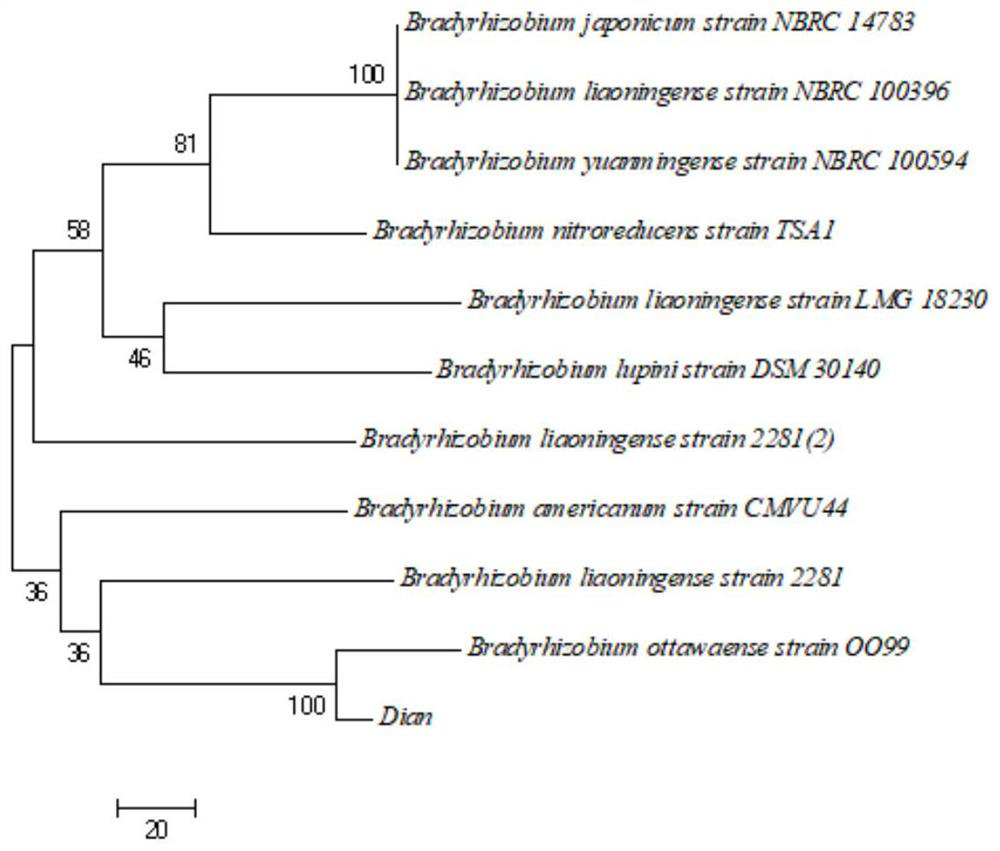
The invention discloses a nitrogen-fixing bradyrhizobium japonicum strain resistant to saline-alkali soil and application of the bradyrhizobium japonicum strain. According to the invention, a strain of bradyrhizobium taihuae Dian strain is obtained through separation and is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on January 11, 2022, and the preservation number is GDMCC No: 62202. Researches show that the strain has the characteristics of high nodulation rate and strong nitrogen fixation capability, and can optimize the micro-ecological environment of alkaline soil crop root growth; the Dian strain is adopted to treat plants, soybean nodulation and nitrogen fixation can be effectively promoted, plant nitrogen nutrition is increased, plant growth is promoted, and the biomass, root nodule number and nitrogen content of soybean plants can be remarkably improved. The strain is especially suitable for cultivation and production of soybeans in stony desertification areas, expands a strain resource library of nitrogen-fixing rhizobium, is beneficial to promoting nodulation and nitrogen fixation of plants, and increases nitrogen nutrition of the plants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation process of organochlorine pesticide contaminated soil remediation microbial agent
InactiveCN112011492APromote decompositionPromote degradationFungiAgriculture tools and machinesMicrobial agentPesticide contamination
The invention relates to the field of environmental protection, in particular to a preparation process of an organochlorine pesticide contaminated soil remediation microbial agent. The composite soilremediation microbial agent is prepared by taking rhizobium which is preferably selected from rhizobium japonicum as a main component, and taking nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphate solubilizing bacteria, potassium solubilizing bacteria, trichoderma and the like as auxiliary materials. The microbial agent has a very good decomposition effect on organochlorine pesticides, has the advantages which are not possessed by a single bacterial colony, and has a more beneficial effect on degradation of the organochlorine pesticides. The composite microbial agent provided by the invention takes crop waste residues wheat bran and corn straw as carrier materials, and also has the effect of fertilizing soil. The composite microbial agent has relatively high degradation capacity on pollutants, and can play a role respectively in the presence of multiple pollutants. According to the invention, a complex and stable composite microbial ecological system capable of playing multiple functions is formed through the symbiotic relationship of multiple microbial agents.
Owner:森科环保新材料(广州)有限公司
Method for mutually promoting growth of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
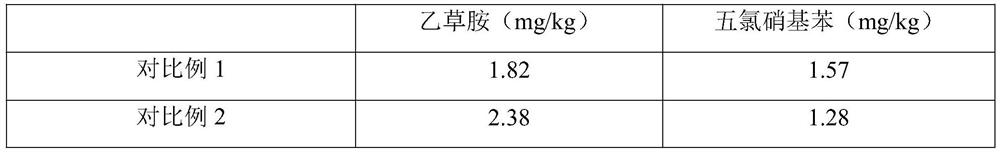
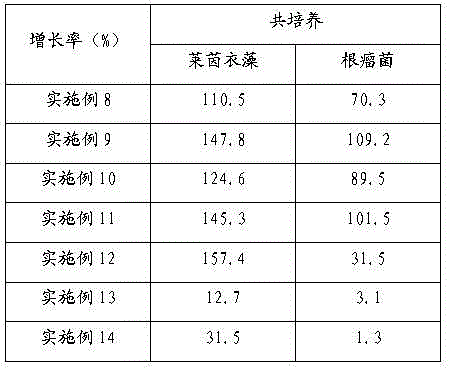
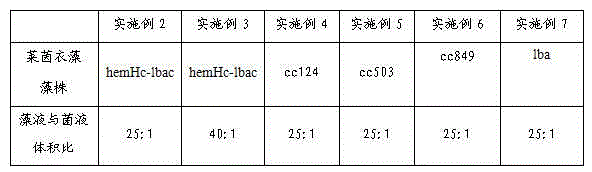
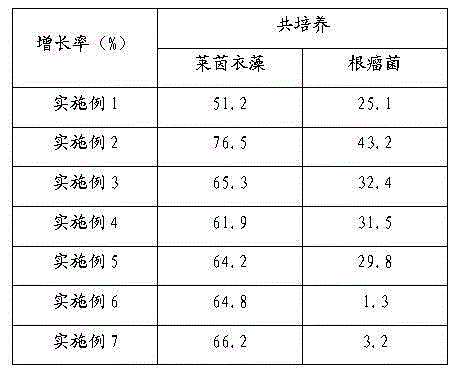
InactiveCN104017763AIncrease productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeChlamydomonas reinhardtiiEcological environment
The invention relates to the technical field of biological hydrogen production and particularly relates to a method for mutually promoting growth of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.. The method comprises the following steps: respectively co-culturing Bradyrhizobium japonicum (hereinafter referred to as rhizobia) and another three strains, namely Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain cc124 (hereinafter referred to as 124), algal strains cc503 (hereinafter referred to as 503) and transgenic Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hemHc-lbac (hereinafter referred to as hemHc-lbac) in a normal culture medium and a sulfur-deficient culture medium, the results show that the growth of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Bradyrhizobium japonicum can be promoted and the Bradyrhizobium japonicum gathers around the Chlamydomonas cell and grows prior to the hydrogen production decrescence, which indicates that a phenomenon of a periodical reciprocal symbiosis exists between Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and rhizobia. The method disclosed by the invention provides an experimental basis and a new idea for further broadening the host range of rhizobia, promoting the biomass accumulation of large-scale cultivation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, producing a renewable biological energy source and improving the ecological environment.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com