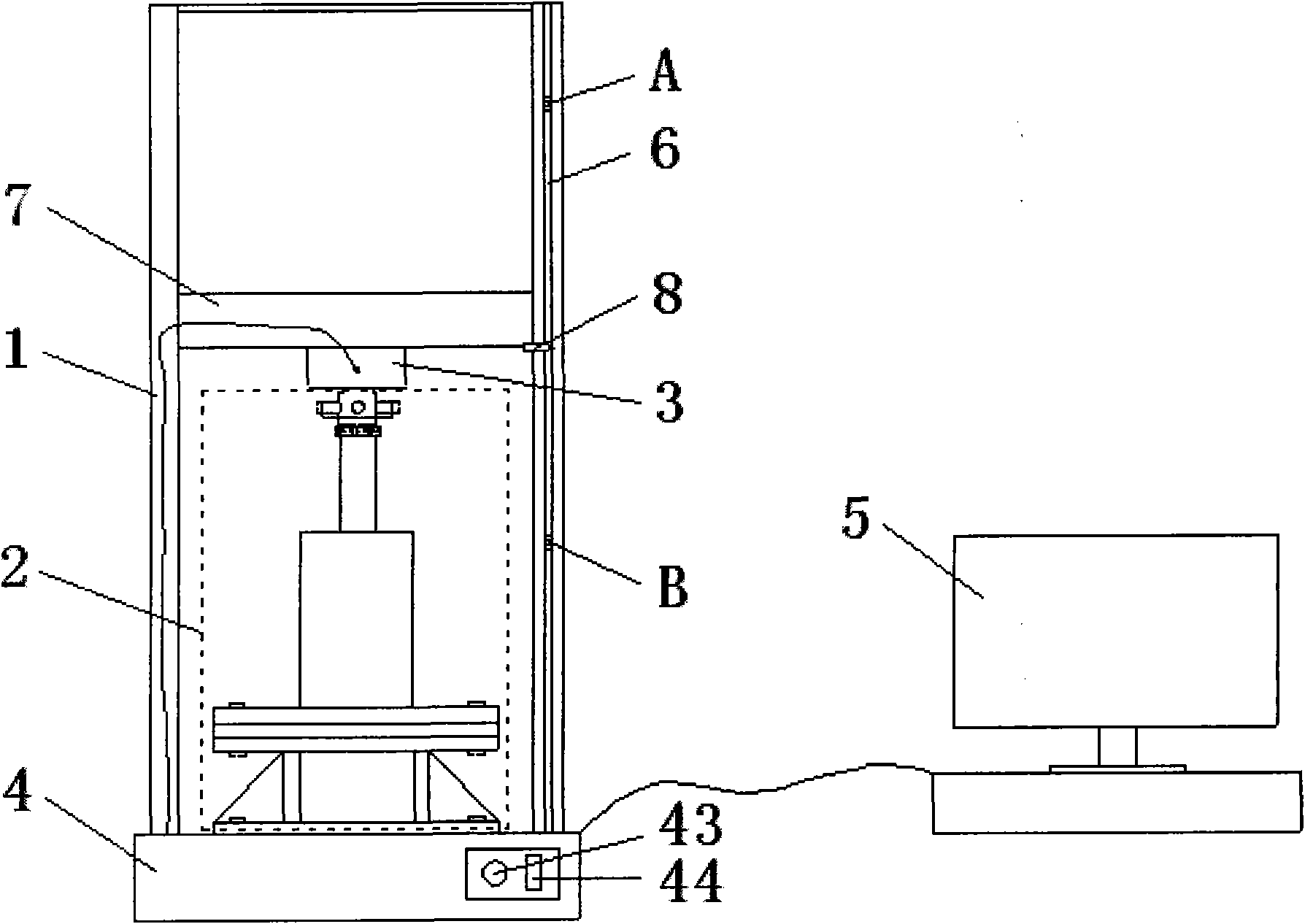
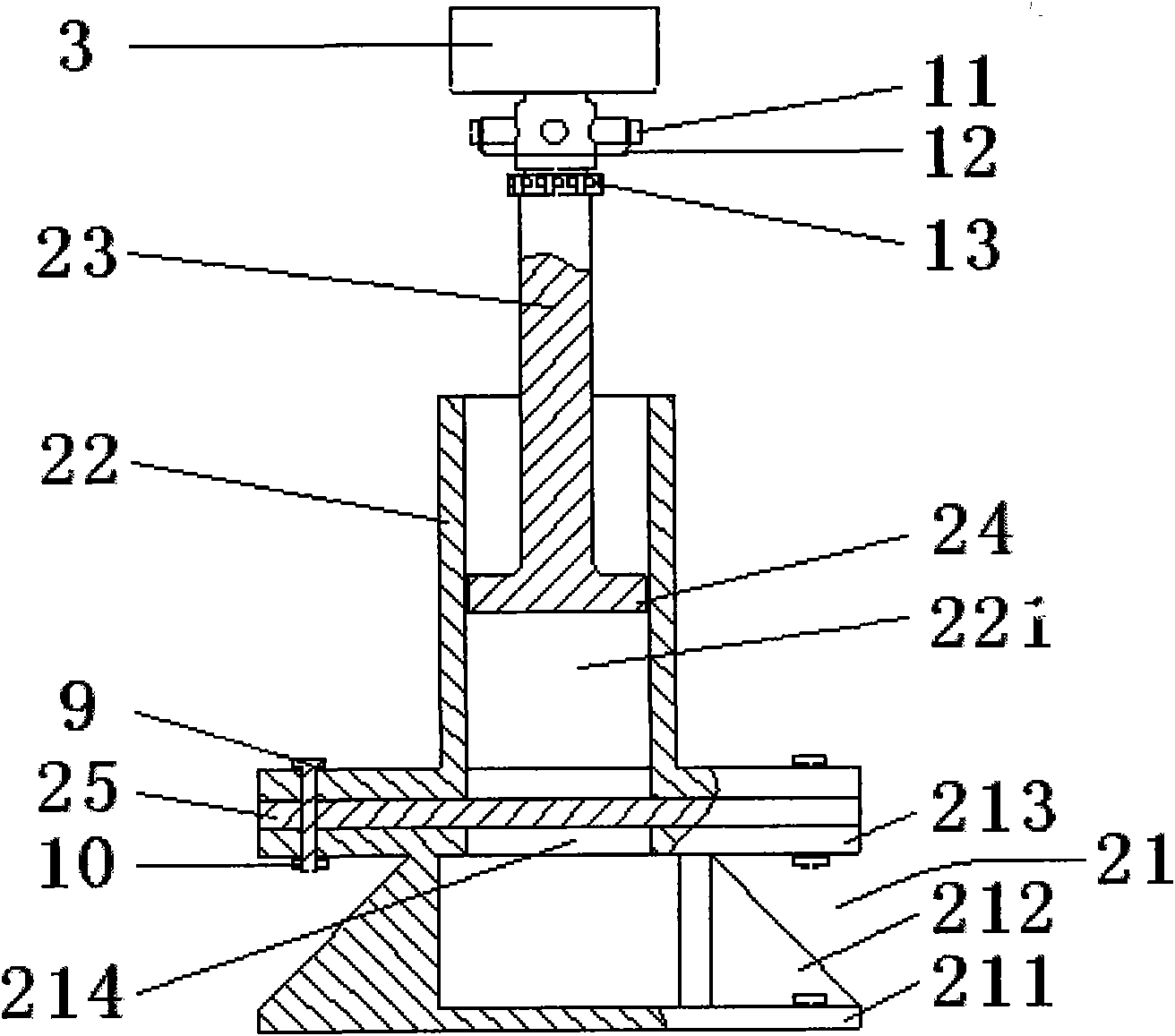
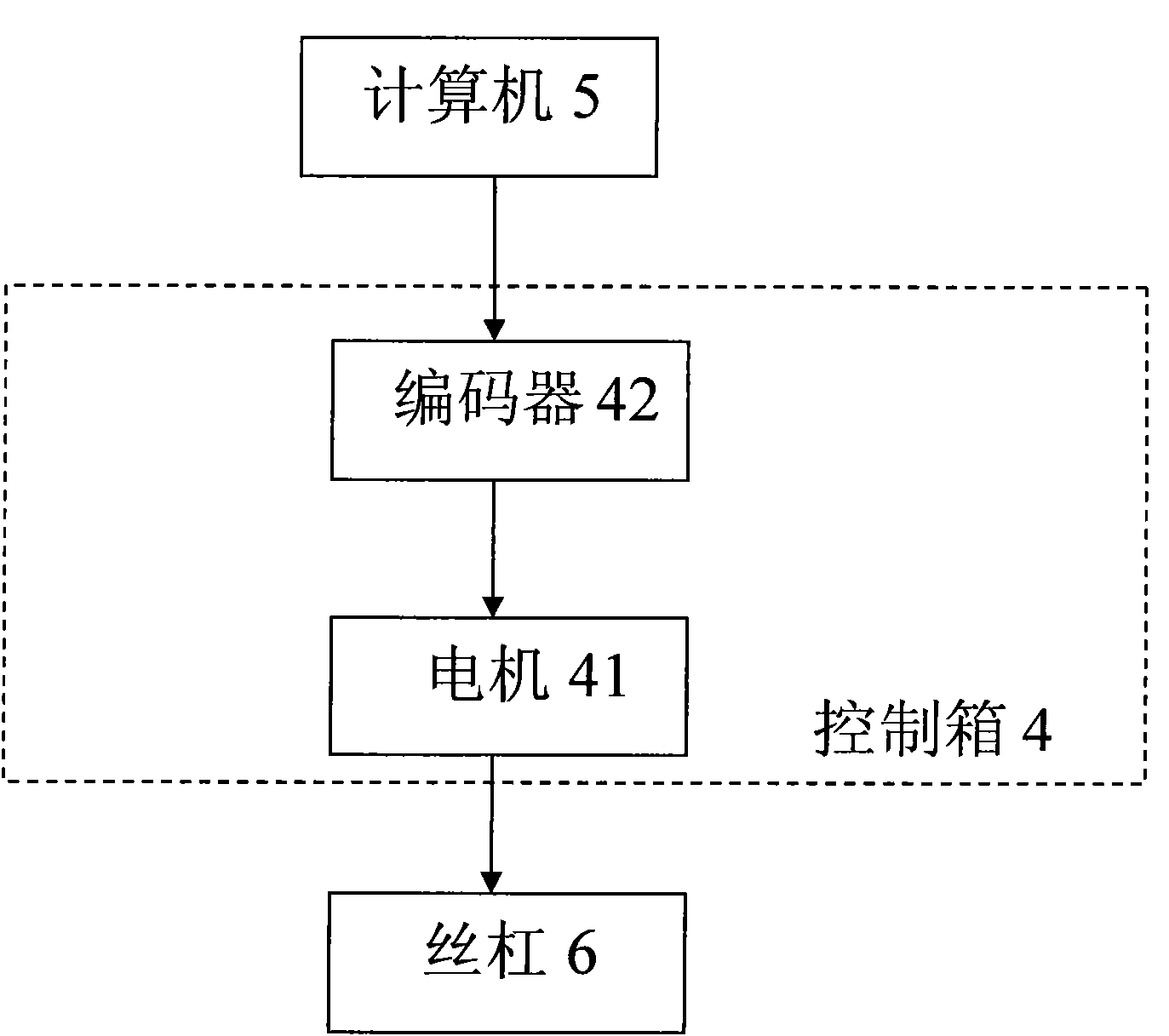
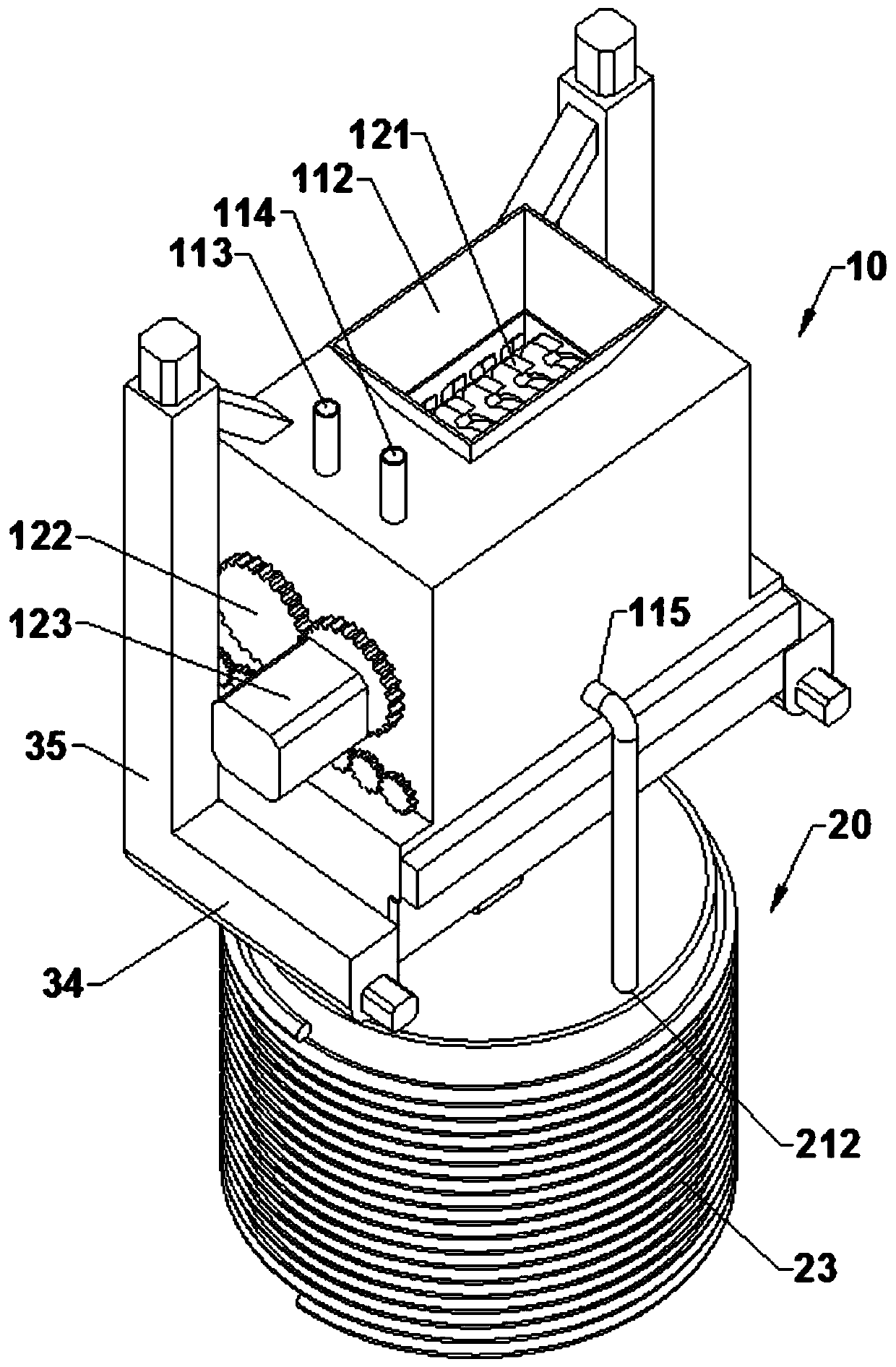
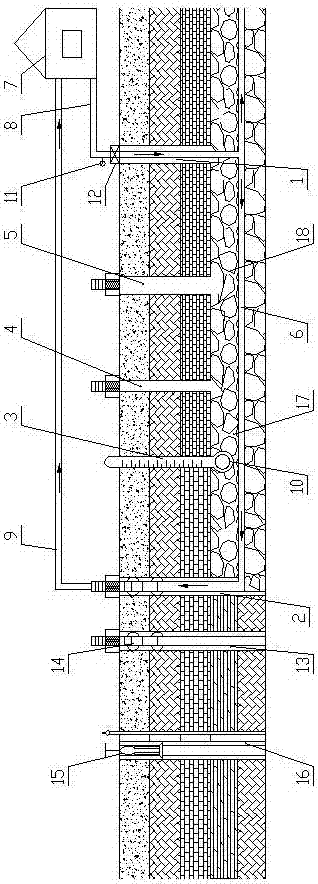
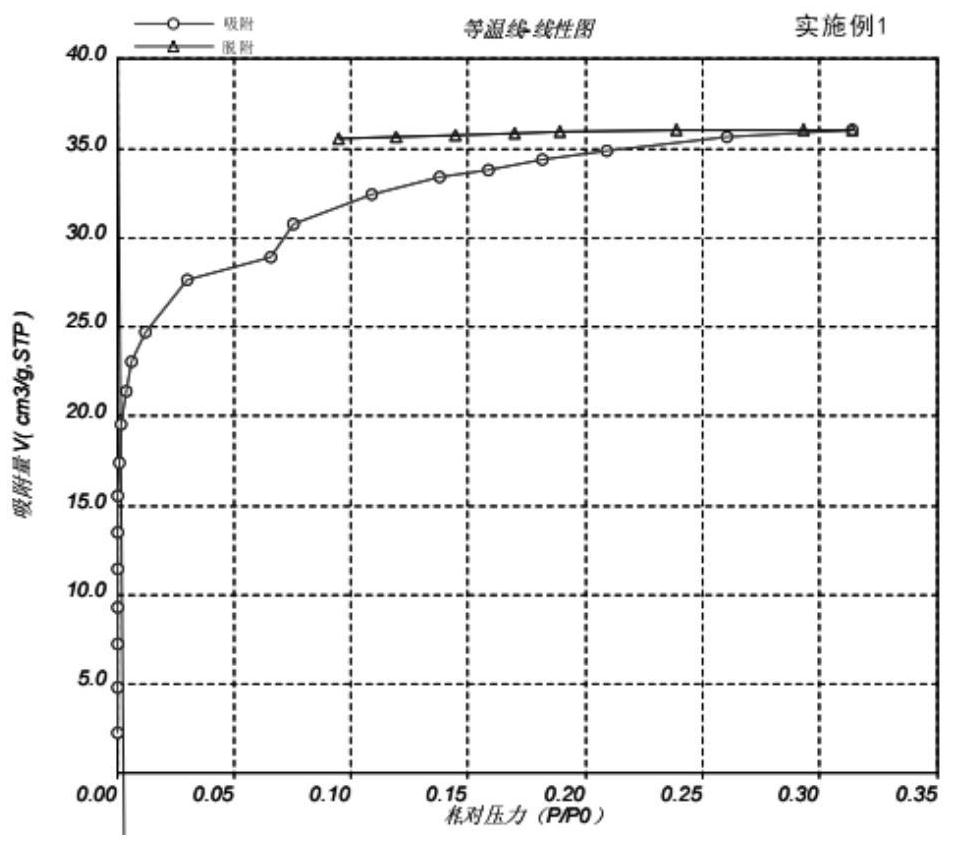
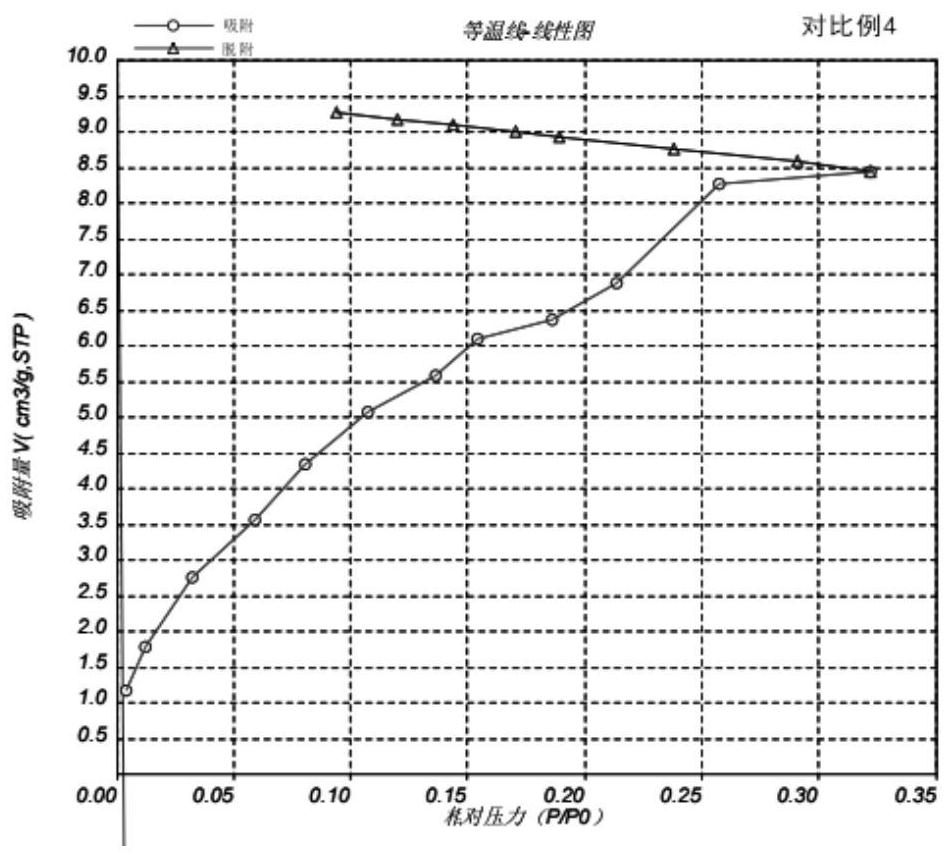
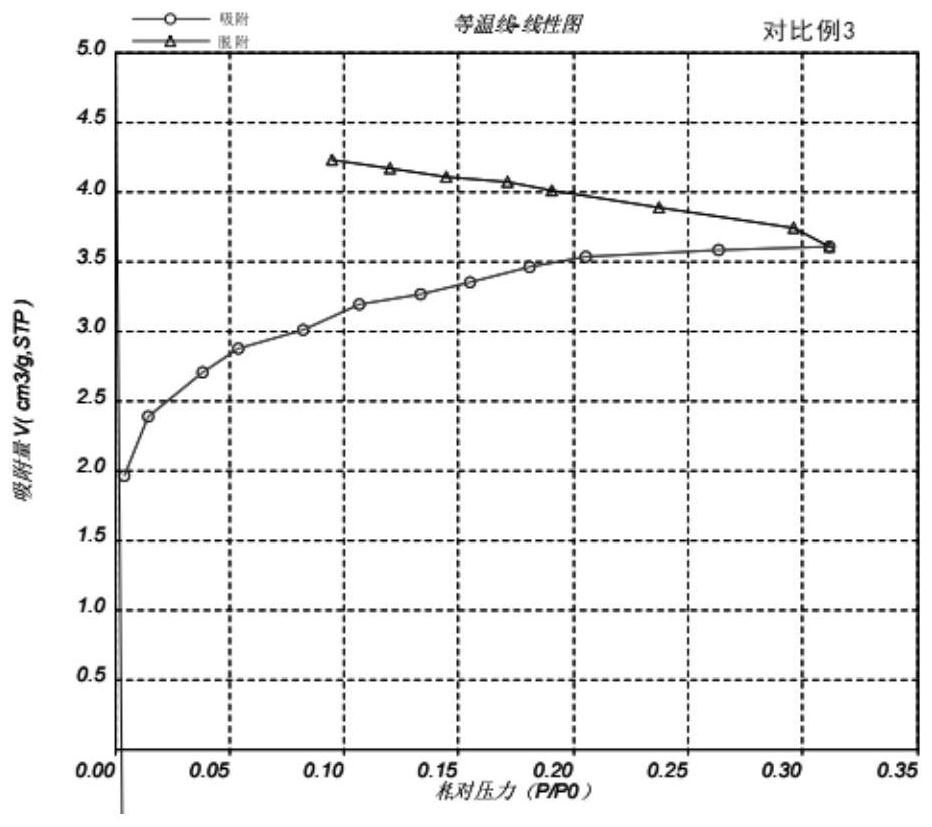
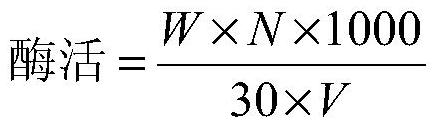Patents
Literature
335 results about "Straw" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cryopreservation straw is a small storage device used for the cryogenic storage of liquid samples, often in a biobank or other collection of samples. Their most common application is for storage of sperm for in-vitro fertilization.
In-Vitro fertilization systems with spermatozoa separated into X-chromosome and Y-chromosome bearing populations
ActiveUS20060281176A1Promote divisionQuality improvementAnimal reproductionDead animal preservationX chromosomeBiology
An IVF system for successfully utilizing spermatozoa separated into X-chromosome bearing and into Y-chromosome bearing population for insemination. The IVF system includes fertilization medium that can shorten the time from insemination to cleavage and a portable incubator for the transportation of maturing oocytes and inseminated oocytes comprising a straw (19) and an incubation element (20) that can be sealed with a cap (22).
Owner:XY
Ferment fungi biological organic fish guano, and its prodn. method
InactiveCN1757616APromote reproductionFast growthBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationNitrogen fertilizerAnimal feces
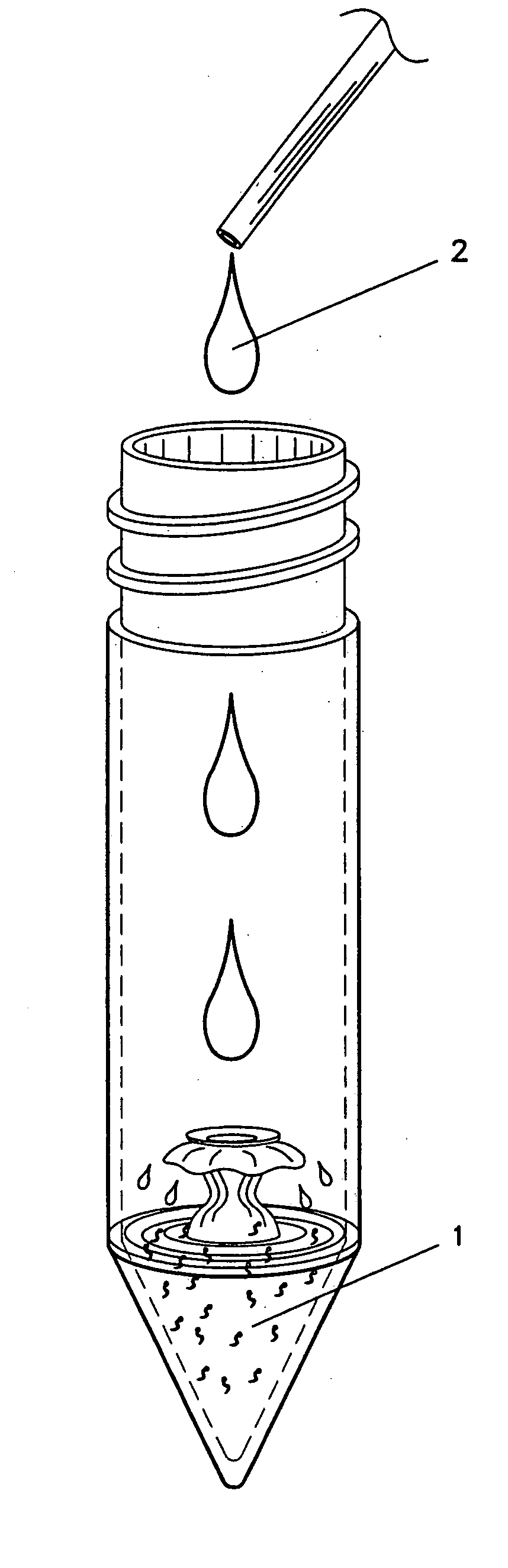
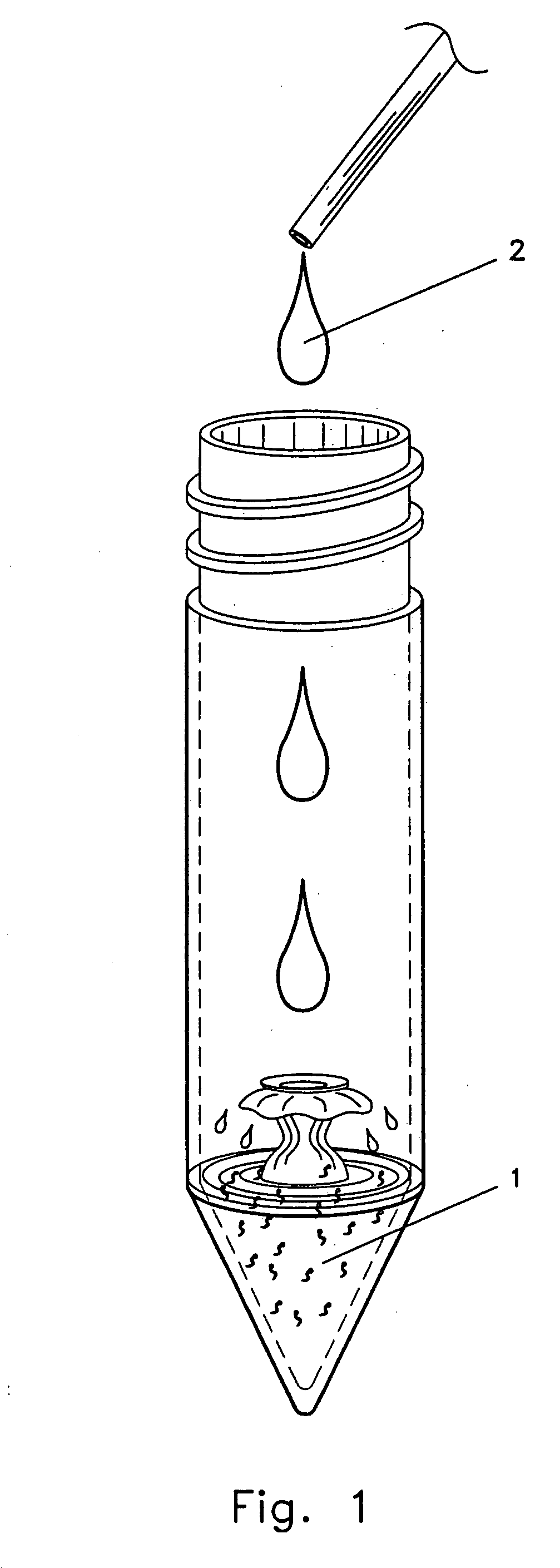
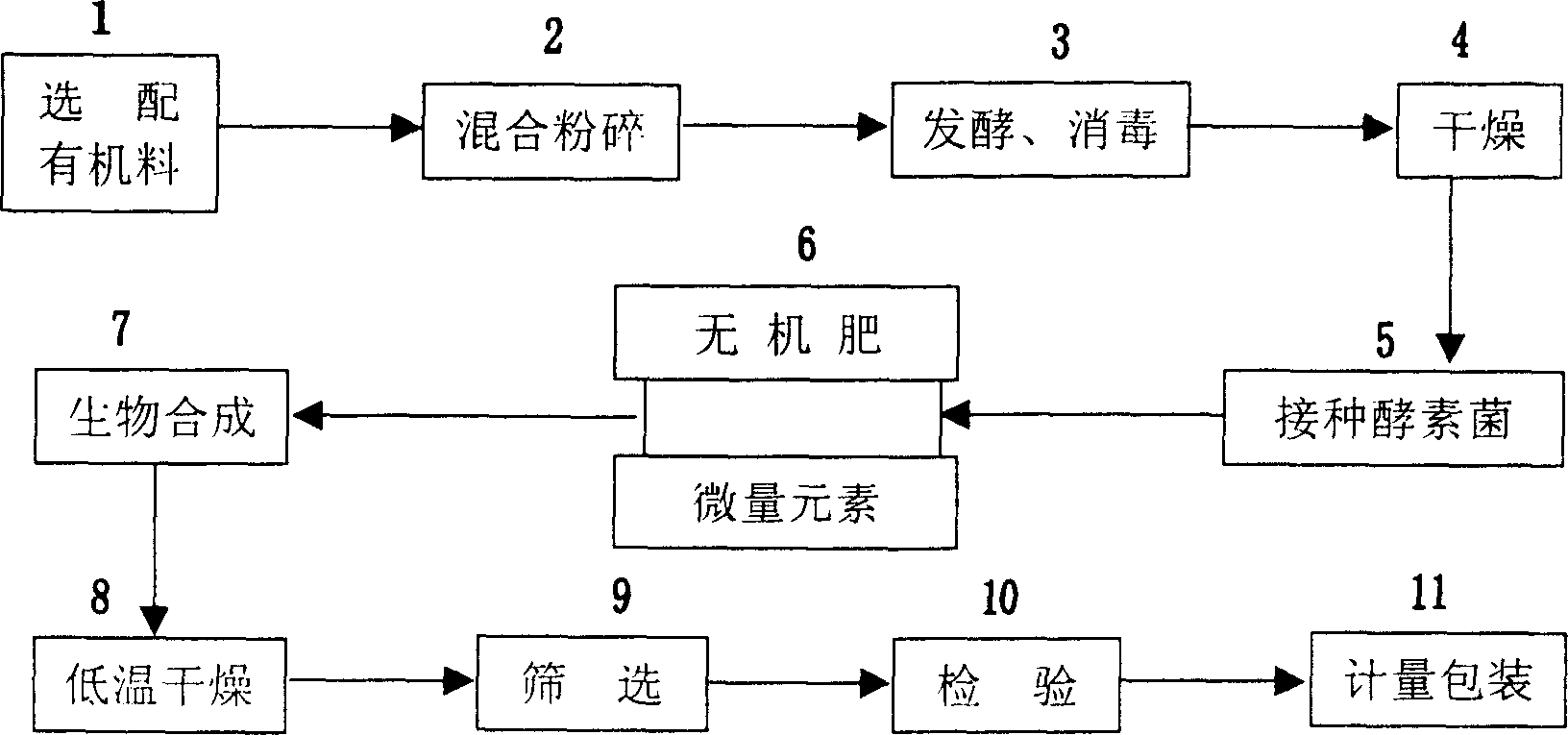
A biologic organic fertilizer for culturing fish is prepared from ferment bacteria, inorganic N and / or P fertilizer, organic substance (straw, stalk, city garbage, and droppings and dung of fowls and animals), and trace elements chosen from Cu, Fe, Mn, Si, Co, Zn and B through proportional mixing, inoculating ferment bacteria, biologic synthesis, low-temp drying and examining. Its advantages are high growth speed and quality of fish, high effect to improve water quality and low cost.
Owner:武汉合缘绿色生物股份有限公司
Biological modified straw adsorbent, and reparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102847516ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getWide variety of sourcesOther chemical processesWaste water treatment from animal processingSorbentDyeing wastewater
The invention discloses a biological modified straw adsorbent, and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the steps of: crushing the straw to prepare a straw powder; mixing the straw powder with a synergistic agent and water, and inoculating microbial strain for modification to conduct fermentation; and after the fermentation, taking out the modified straw powder and drying to prepare the adsorbent. The microbial strain is Trichoderma viride CGMCC3.5455, Trichoderma koningii CGMCC3.2774, Aspergillus niger CGMCC3.4309, Rhizopus stolonifer CICC40317, and Trichoderma koningii CICC 40108. The invention uses straw powder as a carbon source to conduct solid fermentation, so as to produce the adsorbent. The production process does not produce wastewater, waste gas or waste residue, and is energy-saving and environment-friendly. The prepared adsorbent has strong capacity, and can be used for treatment of tanning wastewater and dyeing wastewater.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Method for breeding procambarus clarkii spring seedlings in pond
InactiveCN104206329AIncreased burrow areaIncrease feed areaClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaStrawProcambarus clarkii
The invention provides a method for breeding procambarus clarkii spring seedlings in a pond. A pot bottom-shaped pond structure is replaced by a structure formed by a circular groove and a shallow, so that the enlargement of a burrowing breeding area of crawfish, the complete freezing-drying of the pond, the enlargement of a feeding area and the like are facilitated; a step-by-step precipitation method is used for guiding the burrowing overwintering and reproduction of the crawfish, and straws are used for preserving heat and protection against cold; aquatic plants are arranged in two stages, corrugated clay tile shelters are arranged among the aquatic plants, so that the perching area of the crawfish is enlarged, and fresh and tender green feeds are provided; fertilizers are applied to cultivate sufficient natural bait organisms in three stages to ensure the fertility of water in the pond, so that the rapid growth of the aquatic plants is facilitated, and sufficient high-quality natural biologic baits are cultivated for feeding the crawfish; the above measures have the advantages of strengthening the physique of the crawfish, increasing the overwintering survival rate of the crawfish, reducing the probability of cannibalization of the seedlings, increasing the proportion of the spring seedlings, improving the specification uniformity of the seedlings and the like, and are significant for improving the unit breeding yield and economic benefits of the pond.
Owner:MINGGUANG YONGYAN AQUATIC GROUP CORP
Straw biological organic manure and production process thereof
The invention relates to a straw biology organic fertilizer and the manufacture method that could effectively solves the fully use of straw, fertilizing, and good harvest problem. The method is mixing straw powder, dejection, shale powder, fused calcium magnesium phosphate, mixed cake, bran powder, urea, and other assistant material and compounding enzyme nutrient solution. The method is that adding dejection, shale powder, fused calcium magnesium phosphate, mixed cake, bran powder, urea, and assistant material to the smashed straw, mixing with enzyme nutrient solution taking fermenting, deodorizing, detoxicating, graining, drying, filtering, and packaging. The invention has good effect, easy method, plenty resource, wide application, and has great prospect.
Owner:曹明军
Straw in-situ decomposition microbial agent and application thereof
InactiveCN103642721AIncrease enzyme activityQuick destructionBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaCelluloseMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a straw in-situ decomposition microbial agent. Active ingredients of the microbial agent are formed by mixing clostridium xylanolyticum, xylan monad cellulolyticus, pseudomonas and bacillus subtilis in a CFU (Colony Forming Unit) ratio of (25-35): (25-30):(20-30):(15-20). Experiments prove that the microbial agent provided by the invention has degradation rate for straws, which can reach 70%-80% in a culture medium, and can reach over 50% when the straws are returned to the field for 20 days. The microbial agent disclosed by the invention is low in cost and simple to prepare. The microbial agent disclosed by the invention breaks through the limit that natural cellulose cannot be efficiently decomposed by purifying bacteria and clastic enzymes thereof, provides a key technology for straw in-situ rapid decomposition, and has a wide application prospect in the field of returning straws to the field and decomposing a lignocelluloses material.
Owner:MOUNT EMEI GREEN LAND ECOLOGICAL AGRI DEV LIMITED
Vaginitis test kit and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102321731AEasy to operateImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBacterial vaginosisFacultative anaerobic organism
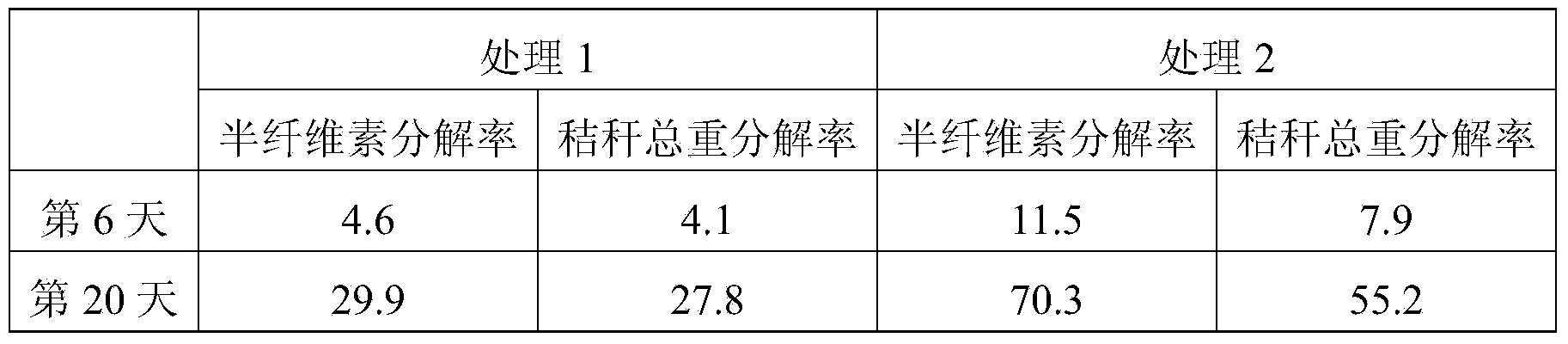
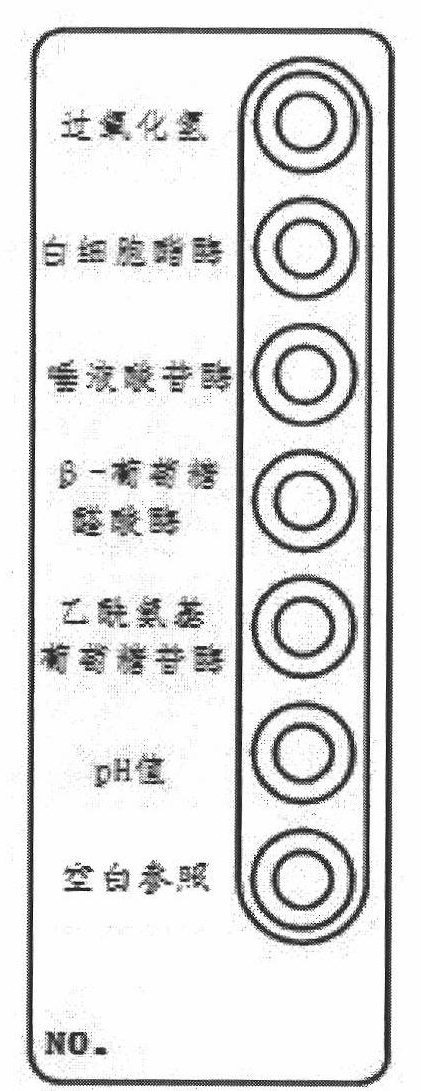
The invention discloses a vaginitis test kit which comprises a reaction device, a sampling test tube, a straw, joint test diluent, joint test chromogenic reagent, joint test stop solution, a user manual and a joint test colourimetric card, wherein a hydrogen peroxide reaction hole, a leukocyte esterase reaction hole, a sialic acid glucoside enzyme reaction hole, a beta- glucuronic acid enzyme reaction hole, a P glucosidase reation hole and a pH value hole; relevant reaction bases are arranged in the reaction holes; reach reaction base comprises a corresponding reaction substrate curing layer,a chromogenic promotional layer and a chemical inert carrier layer. The invention also provides a preparation method of the test kit and the preparation method of a novel chemical carrier. The test kit can be used for distinguishing bacterial vaginosis and vaginitis, and can further identify aerobic / anaerobic bacteria, facultative anaerobic bacteria and other flora in vaginal secretion. The method is simple and quick to operate, has high accuracy, and is applicable to clinical practice, particularly hospital outpatient practice.
Owner:JIANGSU BIOPERFECTUS TECH CO LTD
Large scale stalk anaerobic fermentation technique and apparatus
InactiveCN101407826ASmooth entryIncrease contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingAnaerobic bacteriaNitrogen source
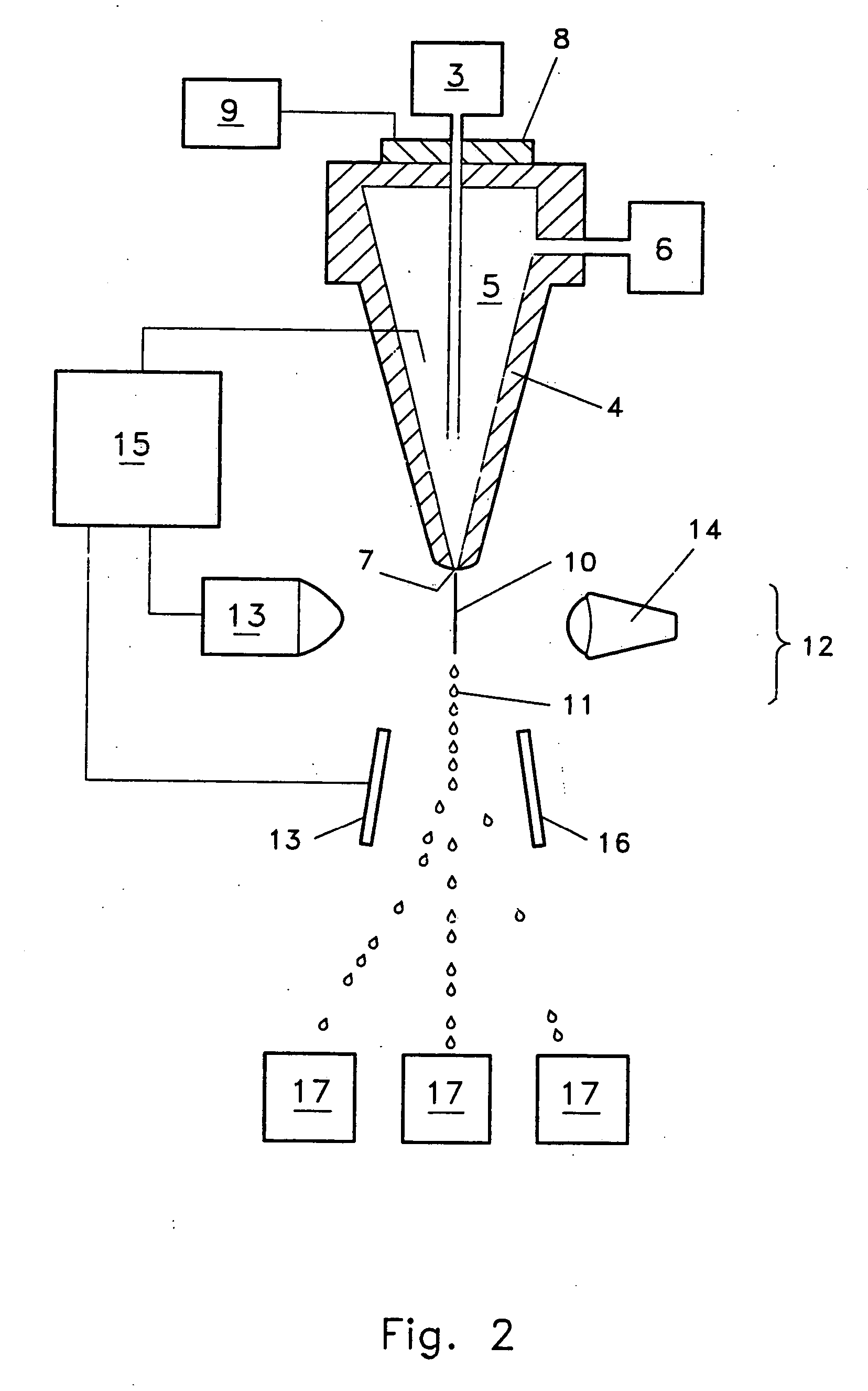
The invention relates to a large-scale anaerobic fermentation technique of straws and a device thereof. The fermentation technique includes biological pretreatment, anaerobic fermentation and anaerobic bacteria separation of the straws for separating an anaerobic bacteria liquid used for another circulation. The anaerobic fermentation device for implementing the method is composed of a feed device, an anaerobic generator and an anaerobic bacteria separator. The technique and the device do not need nitrogen source during the fermentation process of the straws and realize continuous feed and discharge during the anaerobic process of the straws; the molecular structure of the straws is changed through the mode of biochemistry; a large amount of straw lignin hard to be anaerobically digested is converted into a carbon source which is easily biodegraded; and a waxiness component for protecting the straws is decomposed, thus being capable of leading the anaerobic bacteria to successfully enter the inside of the straws, improving the speed of the degraded straws and being capable of realizing the production with low cost and large scale.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for culturing biofloc and method for applying biofloc to aquaculture
InactiveCN105366820AEasy to get materialsReasonable nutritional compositionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStrawSuspended matter
The invention discloses a method for culturing biofloc and a method for applying the biofloc to aquaculture, and belongs to the technical field of aquaculture. Straw is crushed, and evenly mixed with corn starch and water, the mixture is cut up to solid particles of 0.45 mm to 0.55 mm after being puffed, and the solid particles and aquaculture water are mixed according to the volume ratio of (1-1.2):1; bacillus is added to the aquaculture water, so that the viable count is (2-5)*1,010 cfu / L; suspended solids in a culturing unit are collected, and the biofloc is obtained; when aquaculture is carried out, 0.3-0.5 kg of biofloc is added to each stere of culture pond water, the biofloc is sprayed into the aquaculture water, and the volume ratio of the biofloc to water in a culture pond is kept to range from 10% to 15% in the culture period. A carbon source is obtained through biochemical treatment on the straw, the culturing cost of the biofloc is reduced, the biofloc is promoted to fast grow, and the biofloc with the grain size of 500 micrometers to 1,000 micrometers is obtained. The quality of the aquaculture water is adjusted, and the utilization rate of bait is increased.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV +2
Biological material vitrified frozen vector and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101386814ARich sourcesLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVitrificationCryopreservation
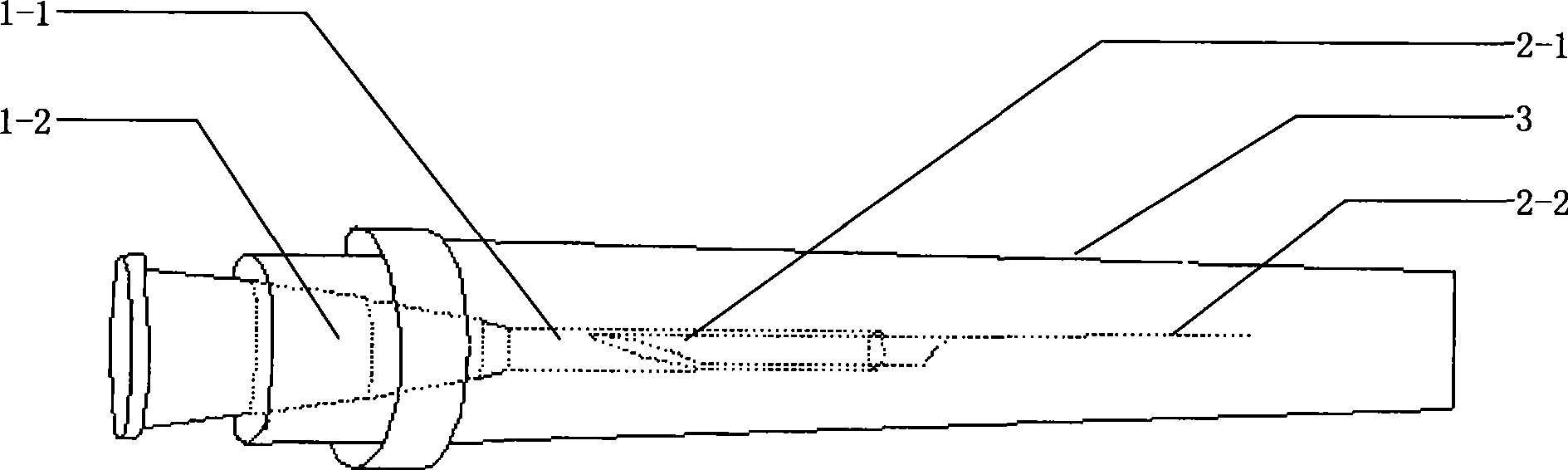
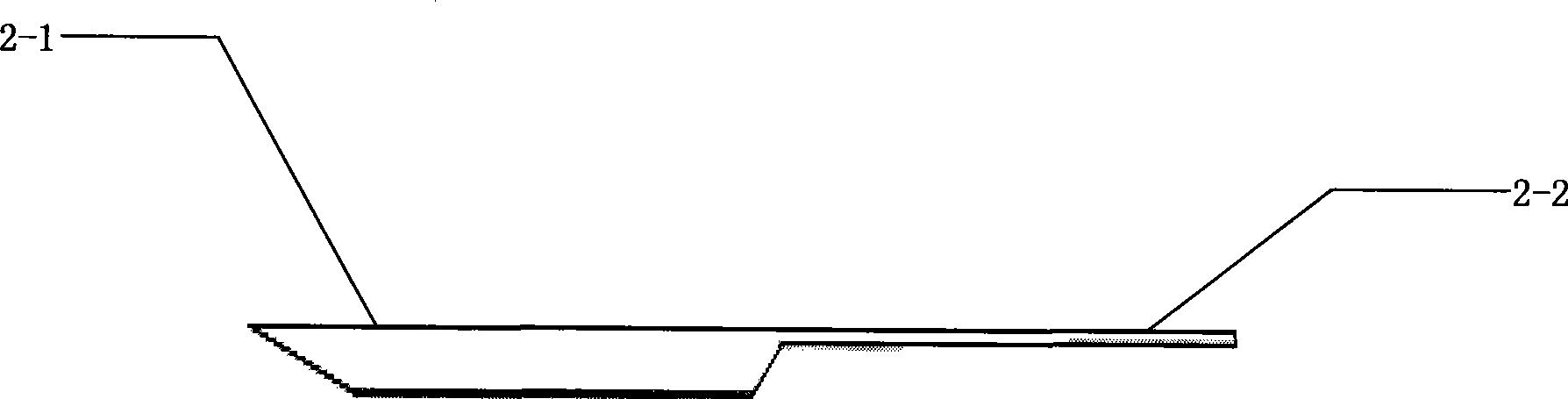
The invention discloses a biomaterial vitrified freezing vector and a preparation method thereof. The biomaterial vitrified freezing vector provided by the invention comprises a syringe needle (1) and a wheat flake (2), wherein the syringe needle (1) consists of a needle (1-1) and a needle seat (1-2); the wheat flake (2) is an open finely-drawn straw; one end (2-1) of the wheat flake (2) is sleeved in an inner cavity of the needle (1-1); and the straw wall on the other free end (2-2) of the wheat flake (2) is partially lost, and the cross section of the residual straw wall is one fifth to one third of the circumference. The invention also provides the preparation method for the biomaterial vitrified freezing vector. The biomaterial vitrified freezing vector has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, short time consumption, low cost and so on, is suitable to be used by genocentric labs of various hospitals and various research units, and has important significance in promoting the development of the vitrified freezing technology in the medical field and the cryopreservation research on ovum, embryo, ovarium tissues and so on.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Bacillus subtilis RB and application thereof
InactiveCN102732463AAdaptableEasy to handleBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaLivestock manureMicrobiological culture
The present invention discloses Bacillus subtilis RB, which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), wherein the preservation number is CGMCGNO.6268. The strain provides high utilization rates for cellulose, hemicellulose and protein in livestock manure or crop straws, has strong sludge treatment capacity and strong adaptability, and can be used for treatments of sludge and decomposition of livestock manure or crop straws, wherein the product has high amino acid content, and can be used as fertilizer so as to achieve utilization of waste into treasure and provide wide application prospects.
Owner:CHONGQING RUIBAO AGRI IND GROUP
Method and device for simulating straw compression molding
InactiveCN101975721AEasy to operateSimple structurePreparing sample for investigationUsing mechanical meansWater contentForming processes
The invention relates to a method and a device for simulating straw compression molding. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) performing defoliation and hair root removal treatment on selected straw; and taking a small amount of straw as a sample after cutting short and drying; 2) measuring and analyzing hemicellulose, cellulose, acid washing lignin, coarse ash and water content of the sample in the step 1); 3) air-drying remaining straw in the step 1); 4) cutting the straw in the step 3) short according to the diameter of a compression tube; 5) performing rehydration treatment on the straw in the step 4); 6) editing an 'open' compression method and a 'closed' compression method according to the varietal characteristics, measured in the step 1), of the straw to be compressed by BlueHill2 software; 7) performing an 'open' compression test and a 'closed' compression test; and 8) when the compression processes are finished completely, respectively recording and storing the displacement and the load in the processes of the 'open' compression test and the 'closed' compression test accruing to a sampling frequency set in the step 6); and calculating stress, strain, straw density and compression ratio energy consumption. The method and the device can be used in a simulation research of a straw compression molding process.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for preparing magnetic biochar by one-step method
InactiveCN112263989AImprove the level of resource utilizationImprove economyOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesActivated carbonIron salts
The invention discloses a method for preparing magnetic biochar by a one-step method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, straw pretreatment: drying and crushing plant straws, and screeningparticles with the particle size of 60-30 meshes for later use; S2, iron salt dipping: adding an iron salt solution into the straw particles in the step S1 for dipping, adjusting the pH value to 10-11with an alkali solution, and then carrying out heat preservation dipping; S3, high-temperature pyrolysis: performing suction filtration on the impregnated particles in the step S2, drying, and transferring into an atmosphere furnace for high-temperature pyrolysis to obtain a magnetic biochar crude product; and S4, post-treatment: carrying out suction filtration, cleaning and drying on the magnetic biochar crude product obtained by pyrolysis in S3 to obtain a magnetic activated carbon finished product. According to the method for preparing the magnetic biochar through the one-step method, plant straw serves as a raw material, pyrolysis and magnetization can be achieved through one step to prepare the magnetic activated carbon, the method is simple, and large-scale production is easy to achieve.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Integrated device for preparing biochar through co-pyrolysis of sludge and straw
PendingCN111410970AReduce complex preparation stepsShorten the timeRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingStrawSludge
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochar, and provides an integrated device for preparing biochar through co-pyrolysis of sludge and straw, which comprises a crushing device and a carbonizing device, the crushing device comprises a crushing bin, a feeding storage bin, a crushing mechanism and a first sieve plate; and the carbonizing device comprises a carbonizing bin and a stirringmechanism. According to the device, preparation steps and preparation equipment for preparing the biochar through sludge and straw heat supply are simplified, the time for connecting all procedures isshortened, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing feed from organic perishable wastes to breed black soldier flies
ActiveCN111066733AMeet the requirements of farmingImprove efficiencyFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceStraw
The invention discloses a method for preparing feed from organic perishable wastes to breed black soldier flies. According to the method, the organic perishable wastes are adopted as a feed raw material, and together with multiple optimally designed auxiliary materials and composite bacteria, efficient breeding of the black soldier flies is achieved. By adopting the breeding method disclosed by the invention, requirements of black soldier fly breeding can be met, the food taking efficiency of black soldier fly larvae can be improved, the survival rate of the black soldier fly larvae can be increased, nutrient components in the organic perishable wastes are sufficiently utilized, and rapid conversion and utilization can be achieved. The method reuses waste resources such as the organic perishable wastes, straw and bean dregs and is simple to operate, low in cost, low in carbon, good in environment protection and high in economic value, and a basic scheme is provided for on-scale and industrial breeding of the black soldier flies.
Owner:李路胜
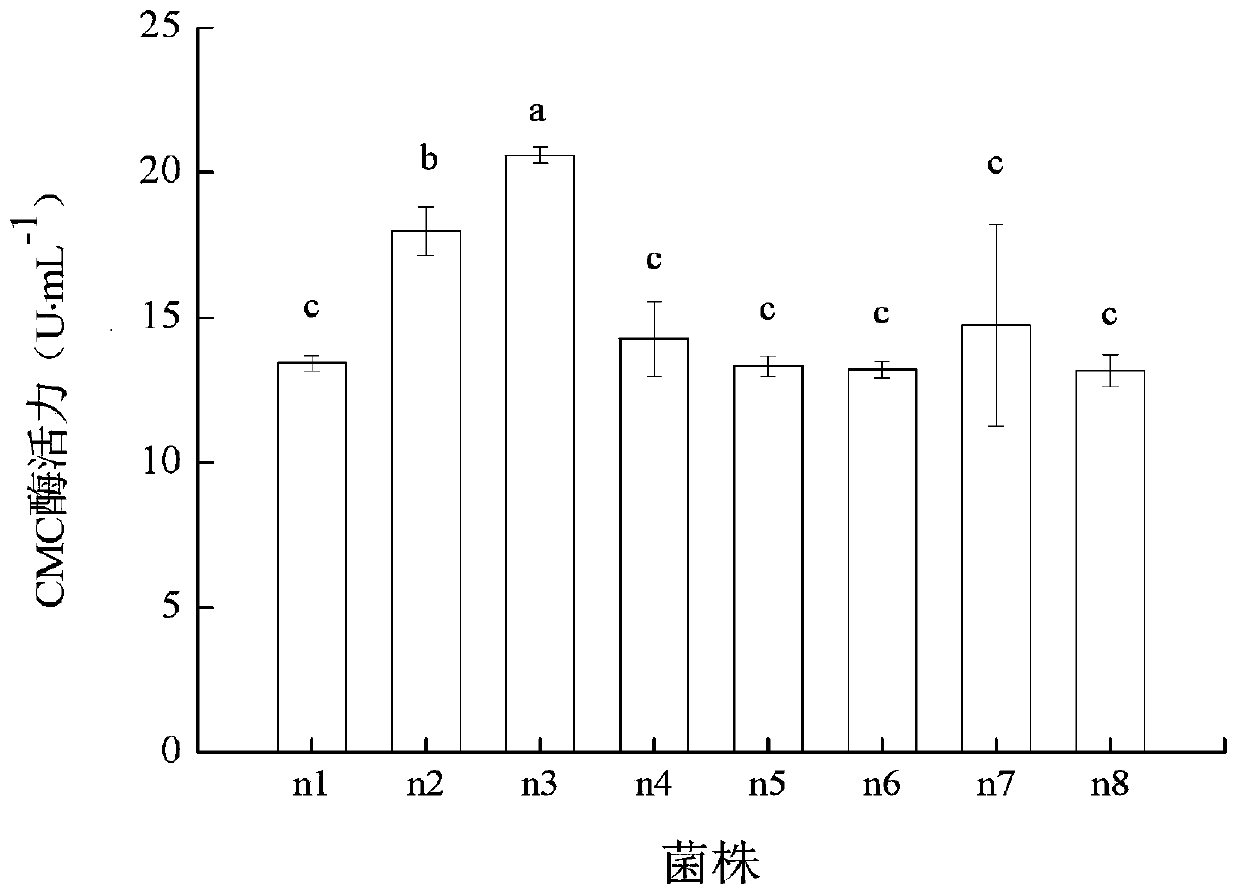
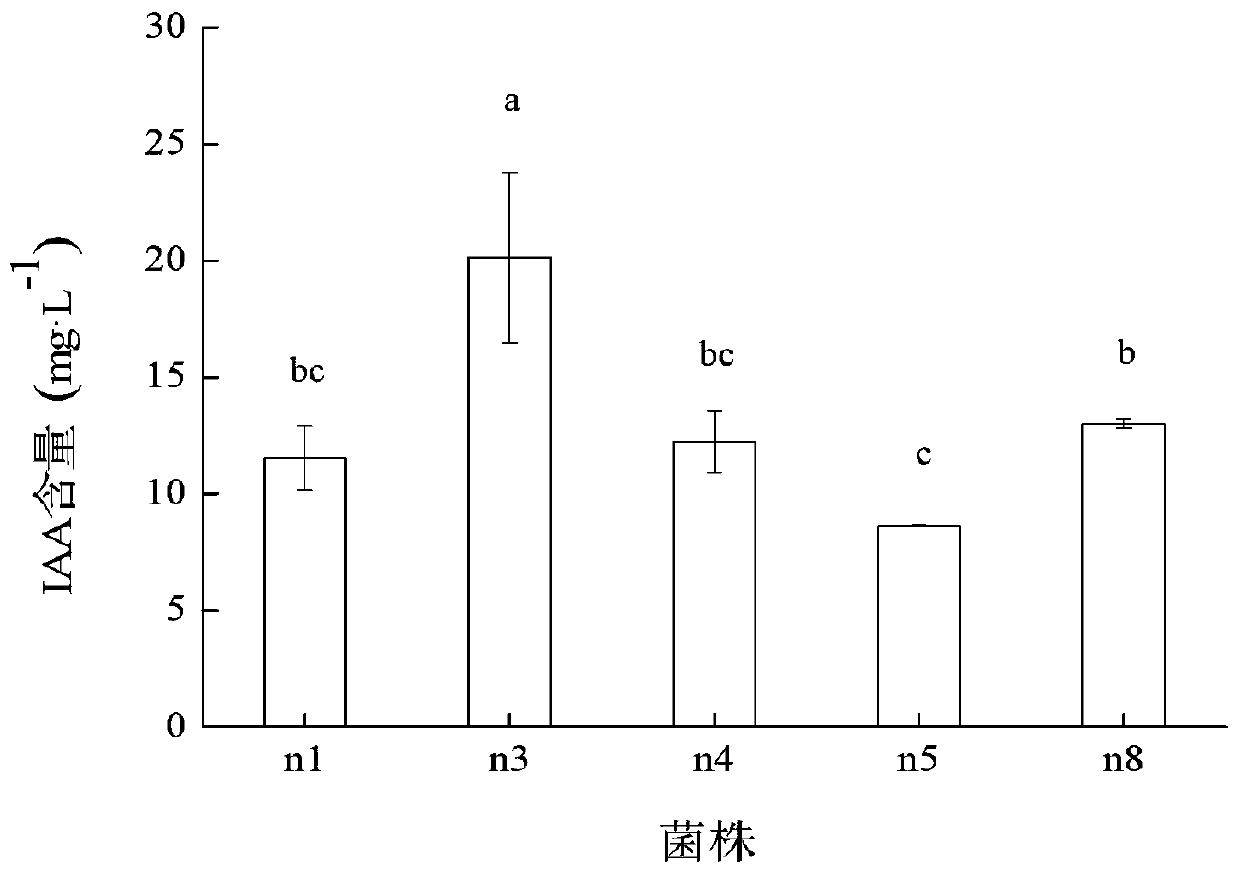
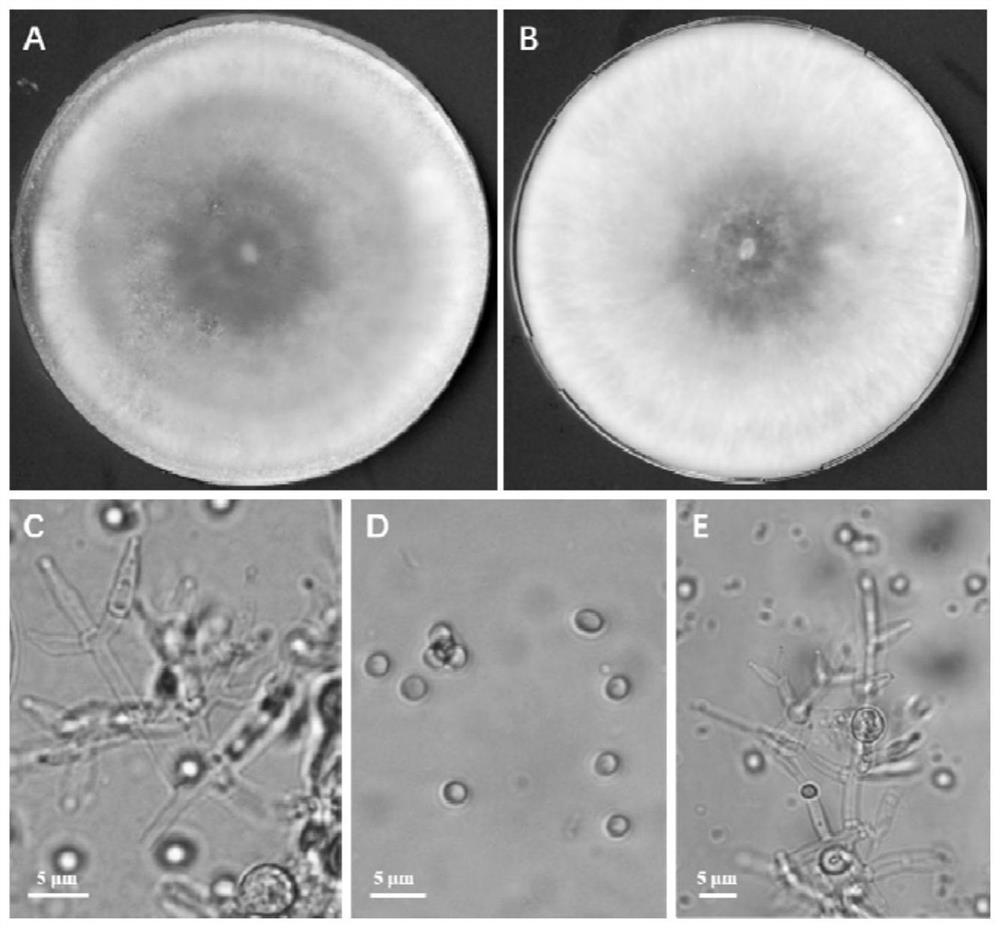
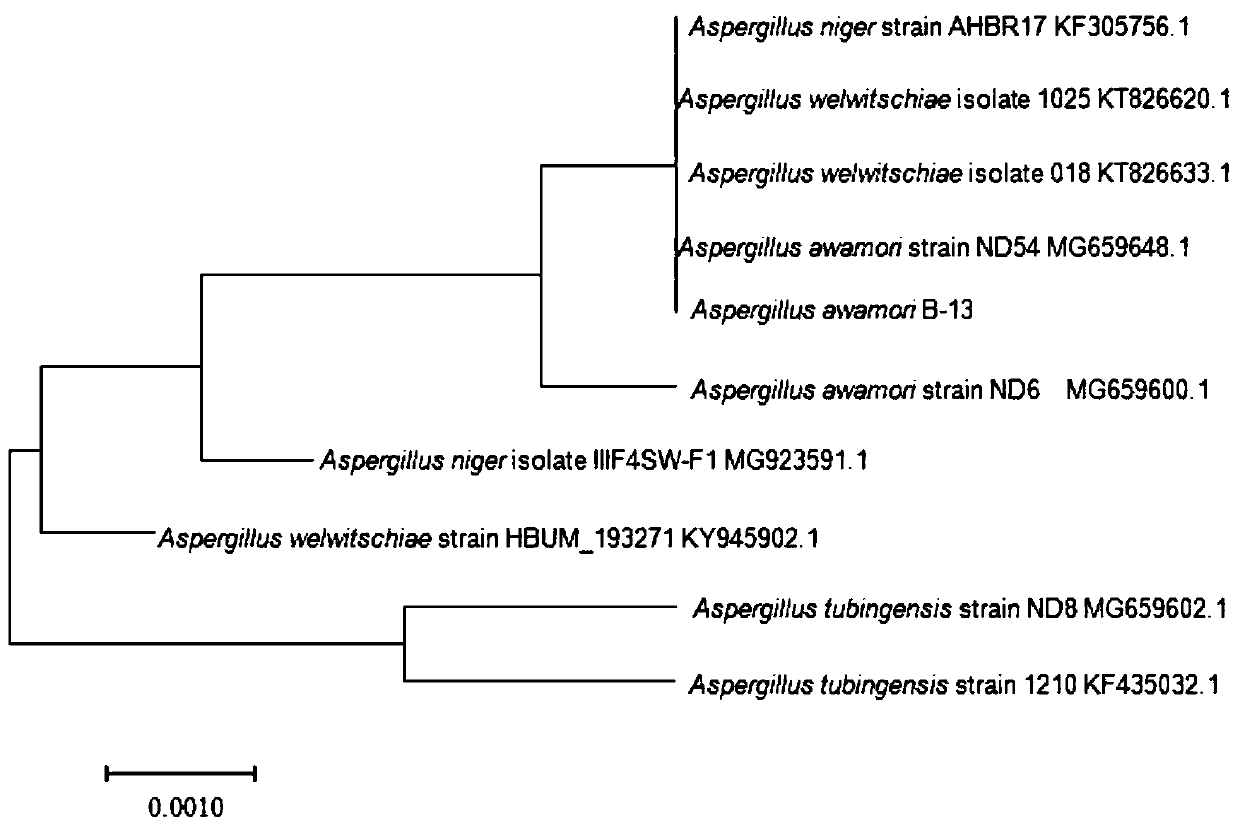
Cellulose degrading bacterium n3 for producing IAA and application thereof
The invention provides a cellulose degrading bacterium n3 for producing IAA and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms. The cellulose degrading bacterium n3 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 18613. The cellulose degrading bacterium n3 has high CMC enzyme production capacity and can produce IAA, the highest CMC enzyme activity can reach 24.96 U / mL, and the highest secretion amount of IAA can reach 19.07 mg / L. Therefore, the cellulose degrading bacterium n3 can be usedfor preparing a straw decay-promoting microbial inoculum capable of producing IAA and / or CMC enzymes or having a growth-promoting function, so that the cellulose degrading bacterium n3 is applied to straw decay promotion and crop growth promotion, and the efficiency of straw returning to the field and the crop yield are improved.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
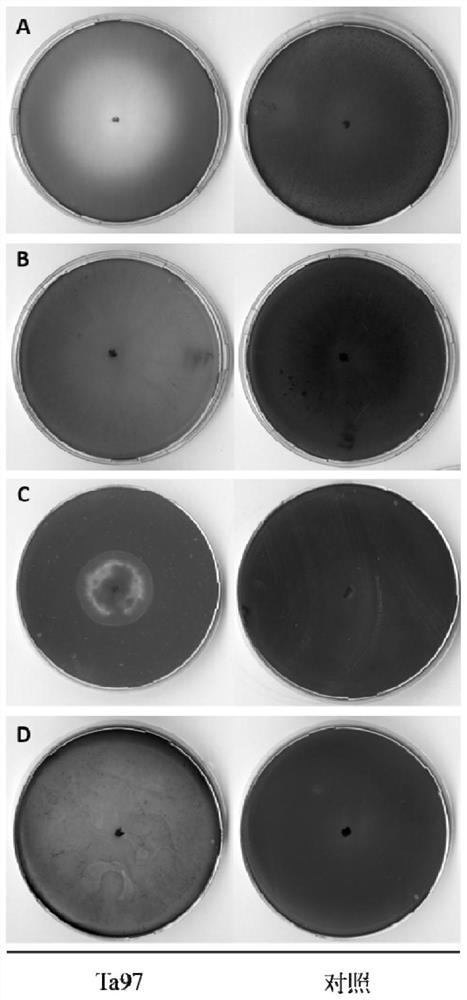
Trichoderma afroharzianum Ta97 and application thereof in straw returning
ActiveCN112322501APromote degradationFully degradedBio-organic fraction processingFungiBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention provides Trichoderma afroharzianum Ta97 and application thereof in straw returning. The strain is classified and named as Trichoderma afroharzianum in Latin, the strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 14th, 2020, the preservation unit is called CGMCC for short, the address is Courtyard 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.19930. The invention further discloses the application of the Trichoderma afroharzianum Ta97 in the straw returning. The Trichoderma afroharzianum Ta97 is applied to the straw returning, in a laboratory test, the average weight loss rate of straw reaches 80.40% within 30 days, and in a field test, the straw can be fully degraded within 30 days to reach the fourth level of decomposition, nutrition is provided for growth of next-stubble crops, and the purposes of straw returning cyclic utilization and fertilizer cost saving are achieved.
Owner:BIOTECH CENT OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and application of complex microbial agent for straw degradation
InactiveCN110699289APromote degradationImprove antagonistic abilityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention belongs to the technical field of vegetable straw recovery treatment and relates to a preparation method and application of a complex microbial agent for straw degradation. The method includes steps: S1, collecting vegetable straw, cutting into fragments, and smashing to obtain a straw waste material A; S2, well mixing the straw waste material A, culture soil, a nitrogen source and water to obtain a mixture B; S3, taking the mixture B, performing inoculation of EM bacterial fluid, saccharomycete fluid, bacillus subtilis fluid and trichoderma harzianum fluid, stirring, mixing, andfermenting for 3-5 days to obtain the complex microbial agent. The invention further provides a straw organic fertilizer and a straw returning treatment method. The complex microbial agent for strawdegradation has advantages that antagonism of dominant growth florae can be improved, flora and microbial diversity is improved, and great straw degradation effects and low production cost are realized.
Owner:WEIFANG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lowline embryo freezing liquid, freezing method and unfreezing method
InactiveCN104206376AImprove freezing effectSimple and fast operationDead animal preservationAnimal scienceSucrose
The invention discloses a lowline embryo freezing liquid, a freezing method and an unfreezing method and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and embryonic heredity. The lowline embryo freezing liqui comprises ethanediol, cane sugar and DMSO. The freezing method comprises the following steps: freezing an obtained embryo for pre-treating, putting the embryo in a tube and freezing the embryo. The unfreezing method comprises the following steps: retaining a straw in air for 5-10 seconds, putting the straw in water bath at the temperature of 35-38 DEG C for 10-15 seconds, detecting the embryo, transferring the embryo in WM1 liquid drops, transferring into another hole liquid drops containing the same solution, then respectively transferring to WM2 and liquid drop containing HM with the concentration being 800 microliter per hole and retaining for 5 minutes each time; and washing the embryo by a culture solution for three times, continuously observing the development condition of the embryo in the culture solution or transplanting the embryo to a receptor cow after being subjected to estrus synchronization. The freezing liquid, the freezing method and the unfreezing method have the good freezing effect, are strong in operability, convenient to operate and suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:南宁培元基因科技有限公司
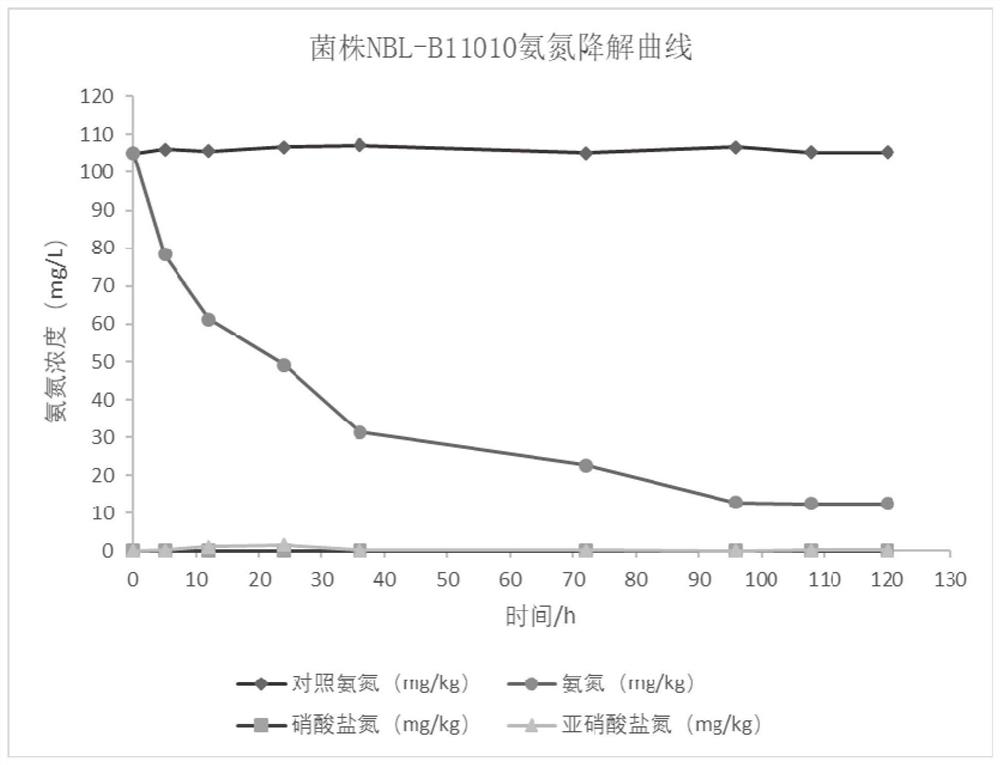
Cellulose degradation strain with sewage ammonia nitrogen degradation capacity and application thereof
ActiveCN112175877AReduce the concentration of ammonia nitrogenGood cellulase activityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsCelluloseMicroorganism
The invention provides a cellulose degradation strain with sewage ammonia nitrogen degradation capacity, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain is Bacillus Velezensis strainNBL-B11010. The strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on August 31, 2020, and the preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO: M 2020458. The strain is obtained from a farmland rotten straw material through screening, purification, identification and other technologies, safety tests and fermentation conditions of the strain are studied, straw degradation efficiency andsewage ammonia nitrogen degradation efficiency are measured, it is shown that the strain is a beneficial strain with efficient cellulose degradation and sewage ammonia nitrogen degradation capacity, and has good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG BEE LAN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Isolation of RNA
InactiveUS20110313145A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStrawTotal rna
Disclosed herein are methods for purification of RNA from a sample. The RNA can be total RNA or mRNA. The method involves preparing the sample in a solution of lysis buffer and depositing into a first end of a lysis straw such that the sample solution flows through the matrix of the lysis straw and is eluted from the opposite end of the lysis straw, and depositing the eluted material into a first end of a solid phase extraction (SPE) straw, such that the deposited solution flows through the matrix of the SPE straw towards the opposite end of the SPE straw, and eluting the RNA from the SPE straw by depositing a solution of elution buffer, into the first end of the SPE straw, such that the deposited solution flows through the matrix of the SPE straw and is eluted from the opposite end of the SPE straw, wherein purified RNA from the sample is present in the eluate of the SPE straw. When the RNA is total RNA, and the sample is a cell sample, and step b) requires adding a precipitating solution to the eluted material from step a), and depositing the solution into the first end of the SPE straw, wherein the straw comprises silica microspheres, such that the deposited solution flows through the matrix of the SPE straw toward the opposite end of the SPE straw. When the RNA is mRNA and step b) further comprises depositing the solution into the first end of the solid phase extraction (SPE) straw, wherein the straw comprises oligo-dT. Pressure (e.g., at least 10 psi pressure) and heat (e.g., about 60° C.) can be applied to the samples, and / or eluates and / or straws. Examples of lysis buffers, loading buffers and elution buffers are provided. Also disclosed are the specific straws and porous polymer monolith matrix components.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA +1
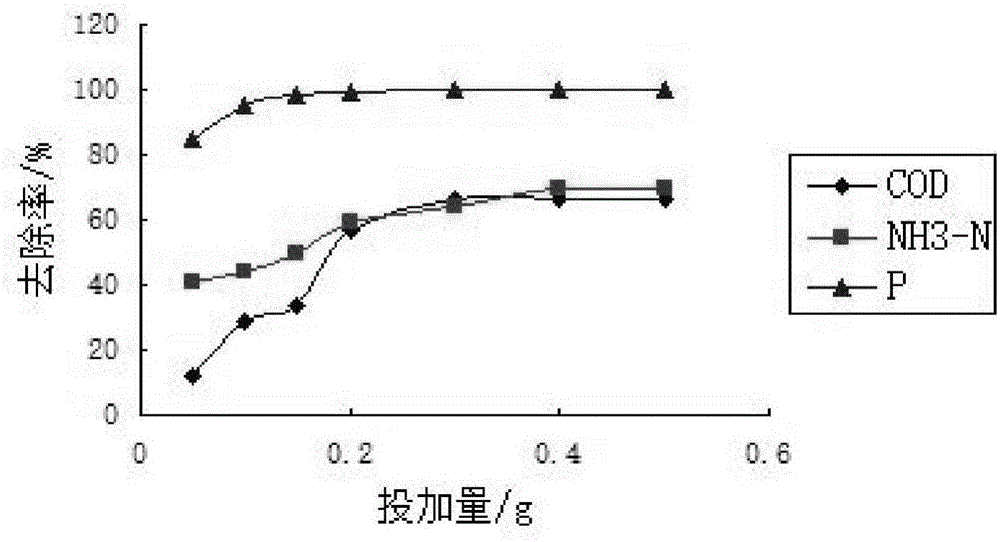
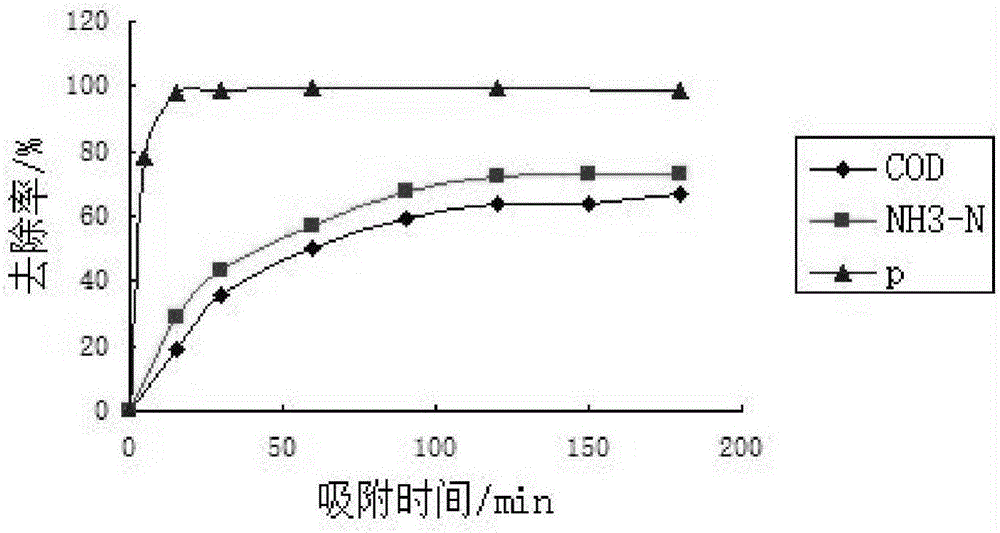
Preparation method and application of porous bio-carrier adsorption material
InactiveCN106140086AReduce the burden onLarge specific surface areaOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesChemical oxygen demandRoom temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous biological carrier adsorption material and its application. The wheat straw powder a, attapulgite powder b and limonite powder c are uniformly mixed and then granulated by adding water, and the particle diameter is controlled at 6-6. 10mm, and then dried at 105°C to obtain pellets; the obtained pellets were placed in a high-temperature tube furnace, sintered at high temperature, and cooled to obtain a limonite-based Fe / C porous biological carrier adsorption material. The porous biological carrier adsorption material of the present invention can be used to treat the secondary effluent of the city, to COD, NH 3 ‑N and total P have better adsorption removal effect.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Application of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide in freezing long-term storage of livestock semen
InactiveCN109997844AMaintain fertilization capacityGood effectDead animal preservationFrozen storageBiology
The invention discloses a protective agent applied to frozen storage of livestock semen. The protective agent can remarkably improve the survival rate of livestock sperms, and the main substance of the protective agent is ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide. The preparation method is mainly characterized in that the ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide is used as the protective agent for long-term preservation of straw frozen semen of pigs, sheep and cattle, for artificial insemination, and for insemination after long-distance transportation of the semen subjected to ultralow temperature refrigeration for the first time at home and abroad. The survival rate, the acrosome integrity and plasma membrane integrity of sperms of pigs, sheep and cattle after freezing and thawing are notably improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Straw degrading bacteria and separation and screening method
ActiveCN112080450AImprove degradation efficiencyBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention provides straw degrading bacteria and a separation and screening method, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: screening microorganismsin soil with straw returned to the field for many years by taking lignin as a target to obtain lignin degrading single bacteria, and screening cellulose degrading single bacteria; and forming a floraby the screened cellulose degrading bacteria and lignin degrading bacteria with high straw degrading efficiency to obtain the flora with high degrading efficiency, mixing and fermenting strains to prepare a microbial agent, and screening a combination with high degrading efficiency in a field test.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Straw biological decomposition method by adoption of lactobacillus casei decomposition accelerator and application thereof in recarburization and fertilization in saline-alkali soil
InactiveCN105036824AIncreased content of water-stable aggregatesBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationCation-exchange capacityAlkali soil
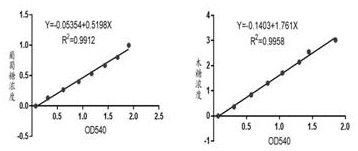
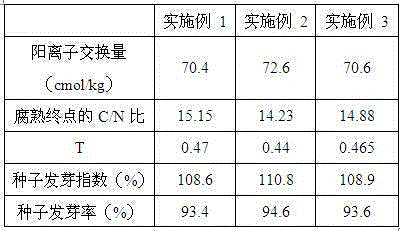
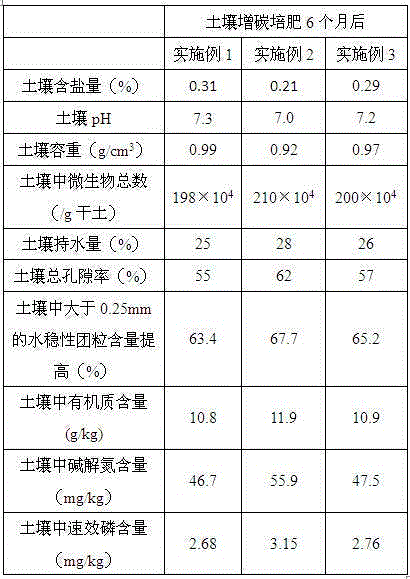
The invention provides a straw biological decomposition method by the adoption of a lactobacillus casei decomposition accelerator. The method comprises the step of adding the lactobacillus casei decomposition accelerator, the decomposition accelerator is composed of, by mass, 3-7 parts of complex microbial inoculants, 24-36 parts of radix ophiopogonis, 15-26 parts of rape flower pollen and 22-33 parts of scenedesmus quadricauda breb, according to the straw which is subjected to the decomposition treatment by means of the straw decomposition method, the cation exchange capacity is 70.4-72.6 cmol / kg, when the decomposition is finished, C / N is 14.23-15.15, T is 0.44-0.47, the germination index of seeds is 108.6-110.8%, and the germination rate of the seeds is 83.4-94.6%. The invention further provides the application of the method in recarburization and fertilization in saline-alkali soil, by means of the application, the soil salinity and soil pH can be reduced remarkably, the soil structure can be improved, the soil pores can be increased, the organic contents in the soil can be improved, and the soil fertility can be enhanced.
Owner:WEIFANG YOURONG IND
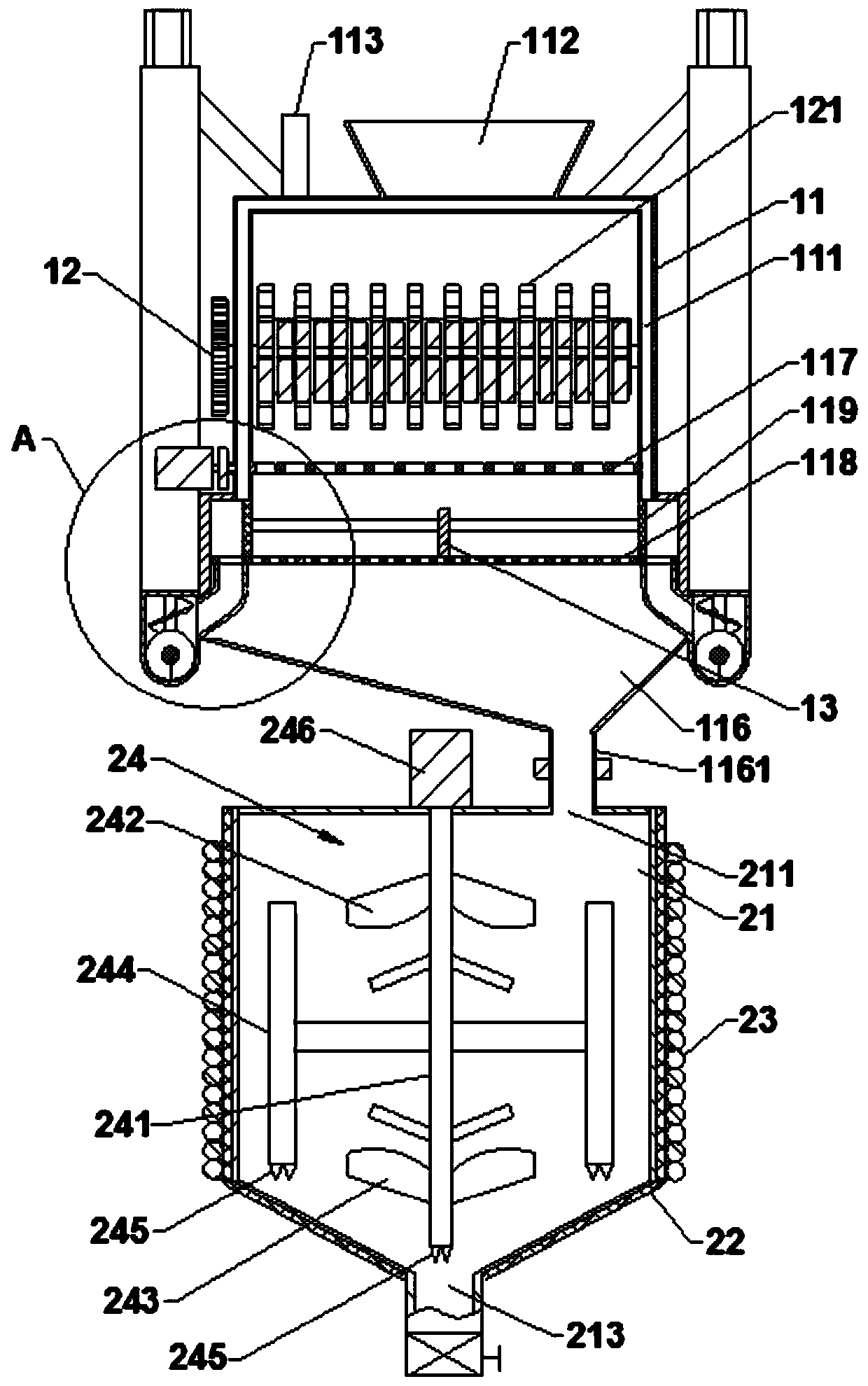
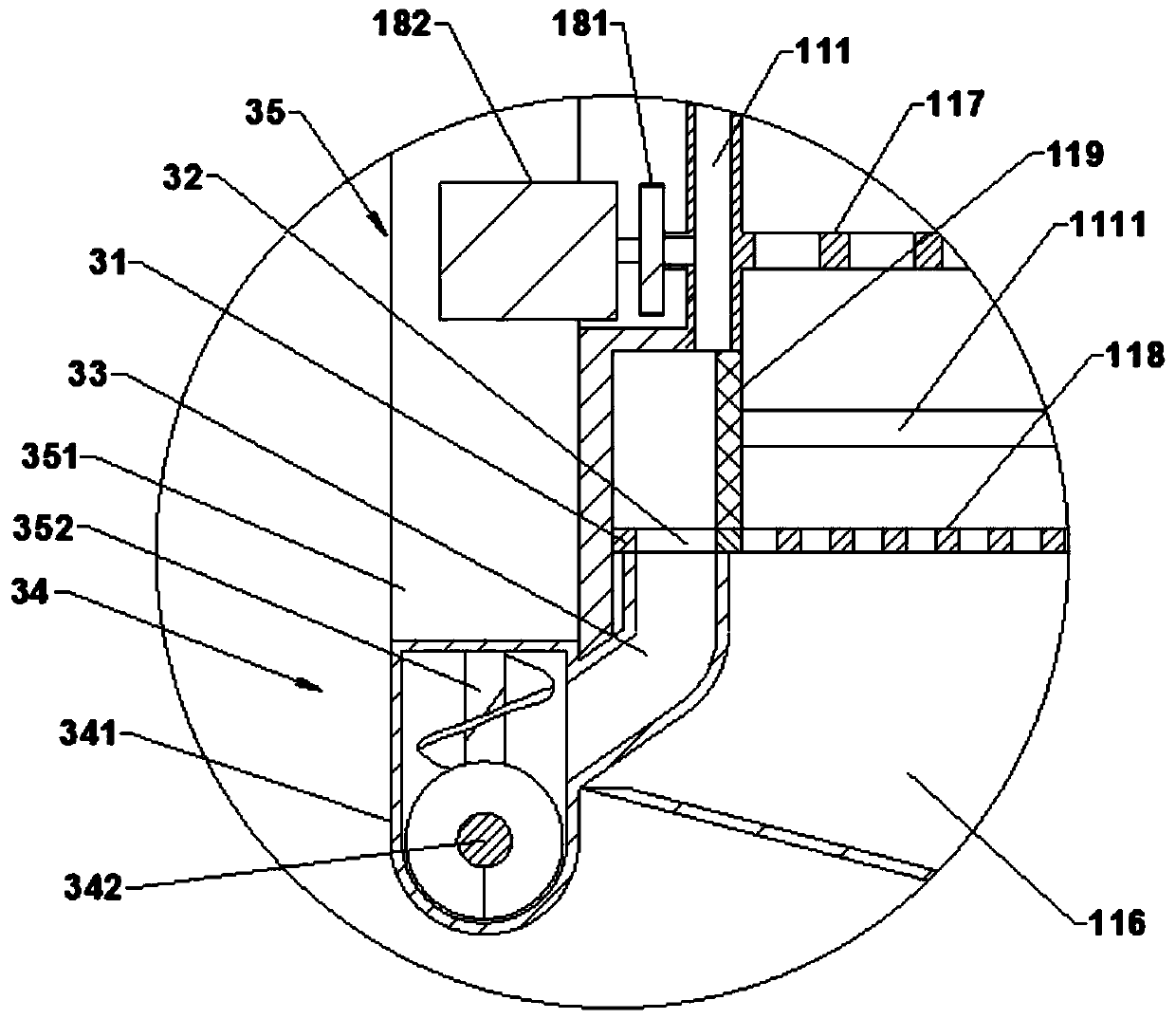
Straw and mushroom matrix compression forming machine
The invention provides a straw and mushroom matrix compression forming machine and belongs to the technical field of cultivation of edible mushrooms. The straw and mushroom matrix compression forming machine mainly comprises a bed, a discharging device, a compactor and a die. A raw material hopper and the discharging device part are arranged at the head part of one end of the bed. The compactor part is arranged at the tail part of the other end of the bed. The die capable of reciprocating is arranged at the middle part of the bed. The straw and mushroom matrix compression forming machine has simple and compact structure and is easy to operate. Straw culture materials can be compressed into one fifth of the original volume of the straw culture materials, so that the output in unit area is possibly improved for over five times; and compressed material blocks can be stacked and is developed toward the space and a mushroom bed does not need to be set up.
Owner:山西省农业科学院试验研究中心
Biological gas production system for filling straws in mine goaf and gas production process thereof
PendingCN107177497AEfficient use ofReduce land subsidenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWater dischargeTemperature monitoring
The invention provides a biological gas production system for filling straws in a mine goaf. The biological gas production system comprises a hot water entering well, a water returning well, a temperature monitoring well, an exogenous bacterium injection and bacterium colony monitoring well and a biological gas collection and conveying well which are formed above the mine goaf and are communicated with the ground, wherein heat insulation pipelines, which are made of stainless steel or an aluminum alloy material, are paved on the ground in the goaf in a crisscrossing manner; a residual heat water discharge pipe of a thermal power plant penetrates through the hot water entering well and stretches into the goaf to be connected with water inlets of the heat insulation pipelines; water outlets of the heat insulation pipelines are connected with a water returning pipe; the water returning pipe upward penetrates through the water returning well, and then is returned back to the thermal power plant; and the goaf is internally filled with crushed straws. The invention further discloses a gas production process of the biological gas production system for filling the straws in the mine goaf. According to the biological gas production system and the gas production process, provided by the invention, a good space advantage of the mine goaf is utilized, and the aim of green mining of mines is realized; and meanwhile, the straws are converted into a clean energy source by utilizing a biotechnology, and energy consumption and emission reduction are realized.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
High-activity straw biochar and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of biochar preparation methods, and particularly discloses a preparation method of high-activity straw biochar, which comprises the following steps: S1 to S2, activating straws, and S3, pyrolyzing the activated straws to obtain the high-activity straw biochar. The high-activity straw biochar prepared by the invention can improve the yield, specific surface area and porosity of a biochar product, and is a low-cost, ecological and environment-friendly preparation process.
Owner:INST OF PLANT NUTITUION & RESOURCE ENVIRONMENT HENAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Heavy metal soil remediation method
InactiveCN111744953AImprove stabilityHigh organic contentContaminated soil reclamationMagnetotactic bacteriumSoil science
The invention discloses a remediation method for heavy metal soil. The method comprises the following steps: 1, mixing magnetotactic bacteria with soil with the soil surface thickness of 10-15 cm, forming a magnetic field is arranged on the soil surface, culturing that magnetotactic bacteria for 20-30 days, modifying straw ropes, burying the modified straw ropes under the ground by 40-50 cm; after15-45 days, moving out the straw ropes, adding a soil conditioner to the treated soil to remediate the soil, planting hyperaccumulator plants in the improved soil, and removing the plants two years later. According to the remediation method for the heavy metal soil, magnetotactic bacteria and modified straw ropes are used for conducting surface layer remediation and deep layer remediation on thesoil respectively, hyper-accumulation plants are used for absorbing the balance heavy metal in the soil, and the effect of deep remediation of the heavy metal soil is achieved.
Owner:河南省科学院地理研究所
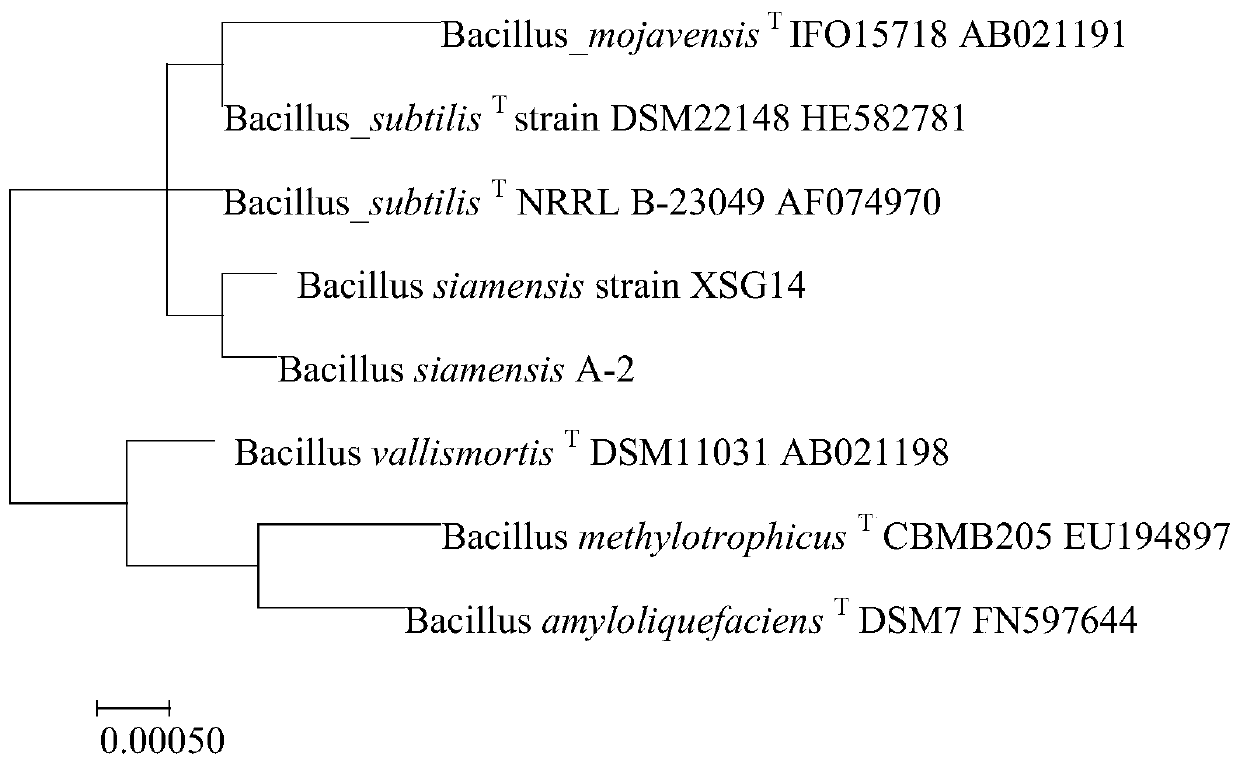
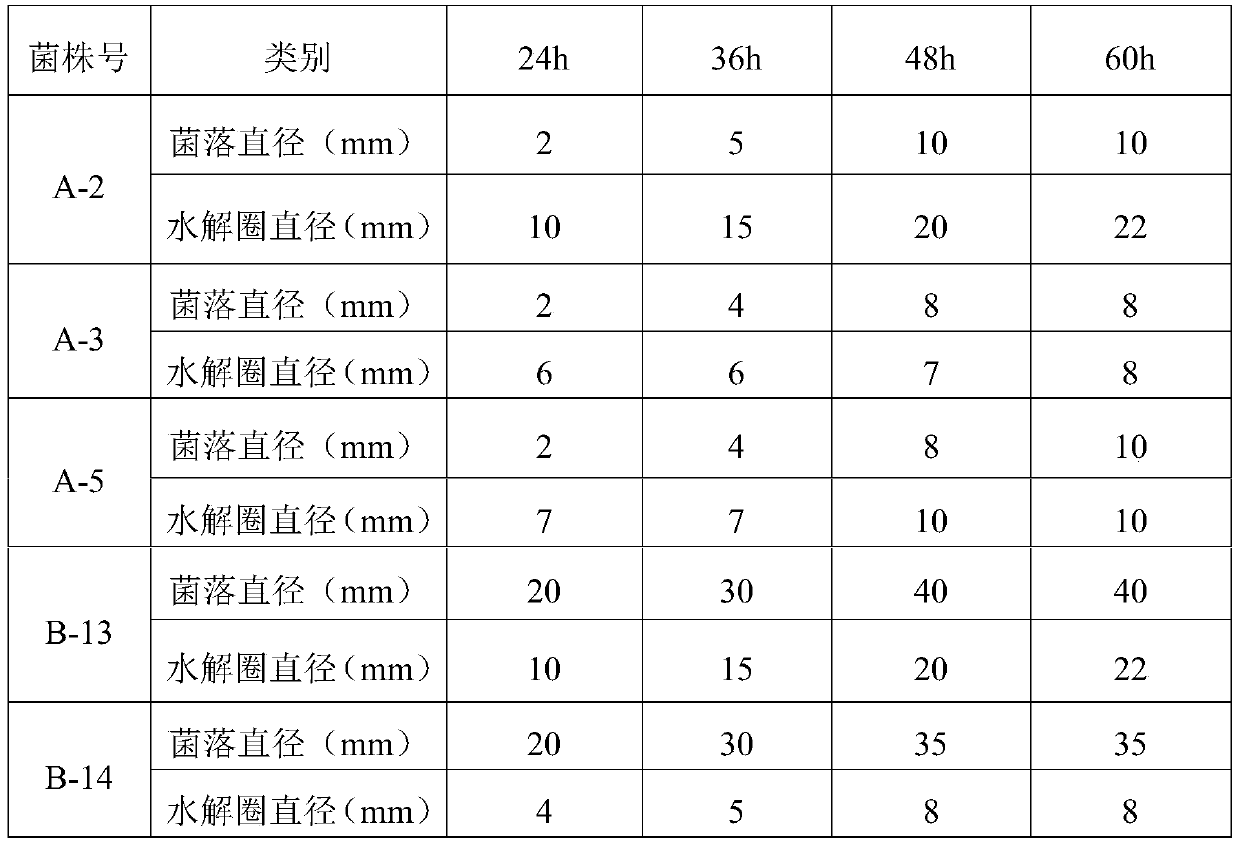
Bacillus siamensis, microbial agent containing bacillus siamensis and application thereof
ActiveCN111073839APromote absorptionImprove physical and chemical propertiesBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention provides a microorganism, a microbial agent containing the microorganism, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The microorganism is bacillus siamensis which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, under the preservation number of CGMCC No. 18688, from October 15, 2019 on. The microorganism provided by the invention has relatively good ability to decompose cellulose, and can be effectively applied in straw composting so as to obviously accelerate temperature rise rate in an early stage of composting, raise fermentation temperature, increase straw weight loss rate after the composting, decrease C / N content and achieve high compost maturity; and thus, the microorganism is suitable for large-scale application.
Owner:SINOCHEM AGRI LINYI R&D CENT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com