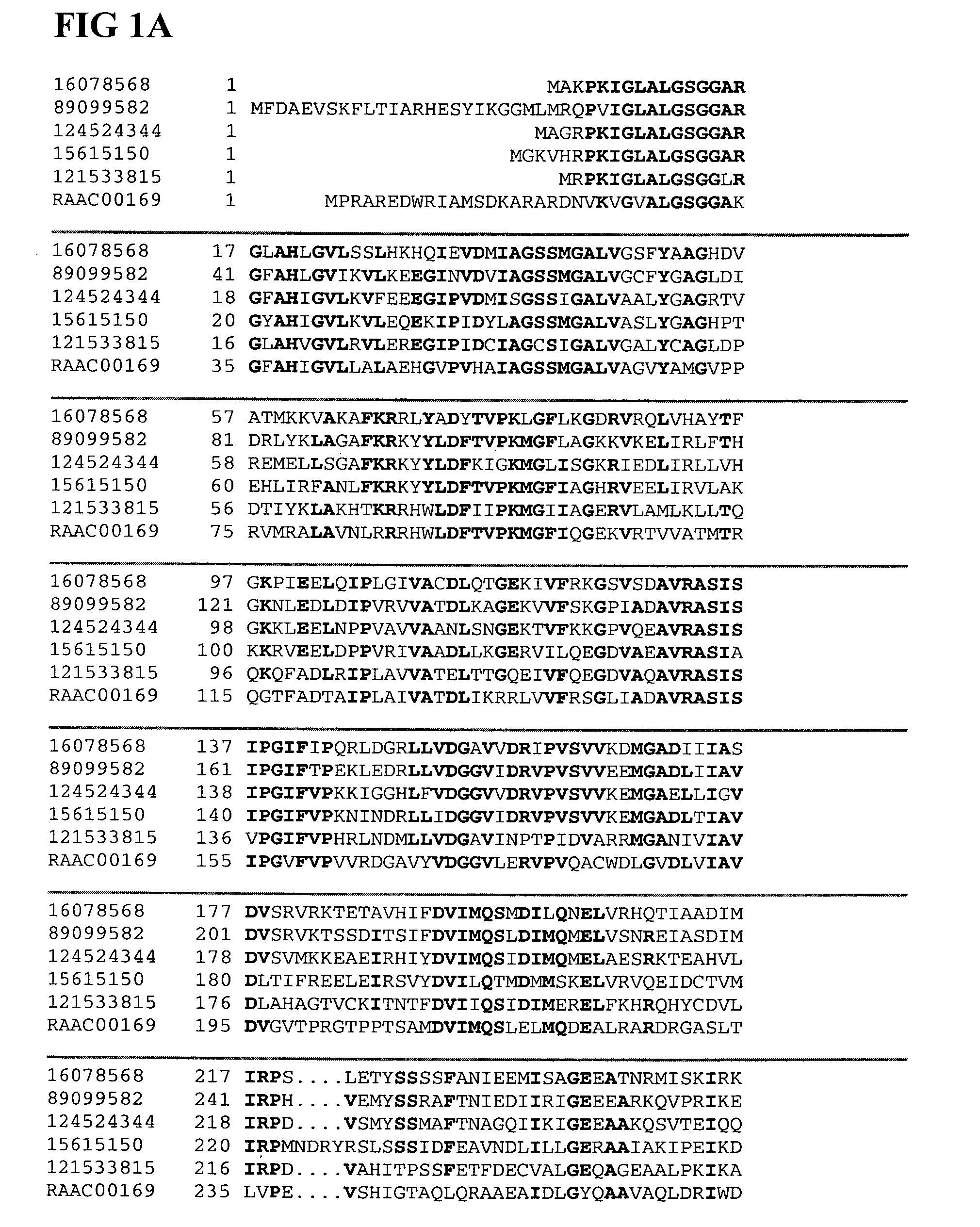
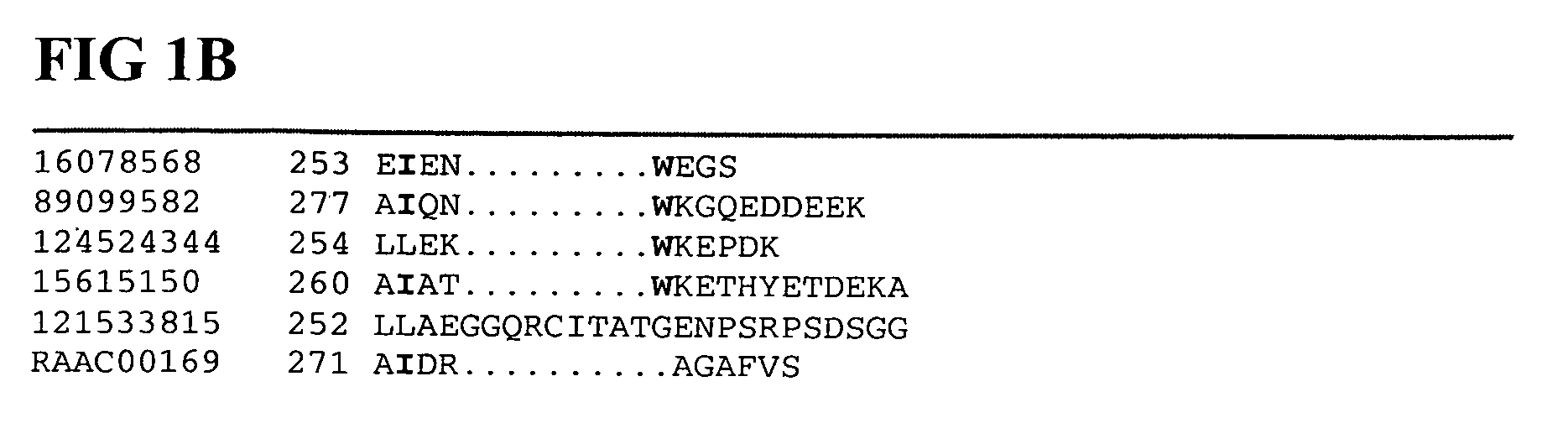
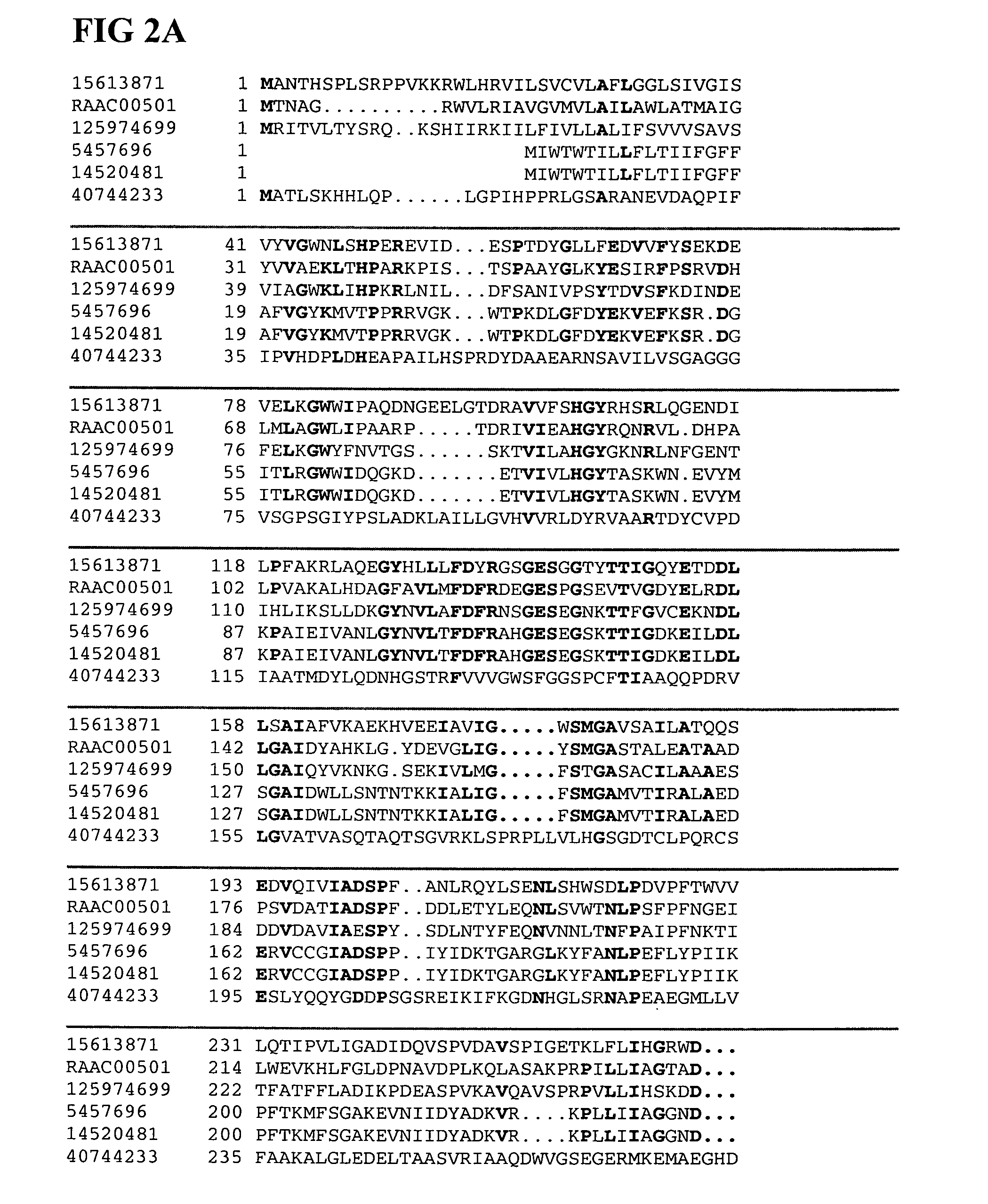
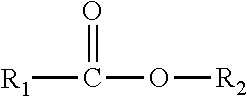
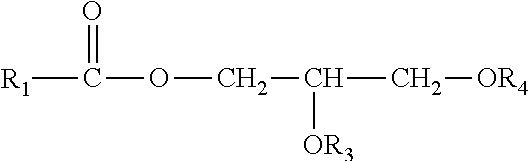
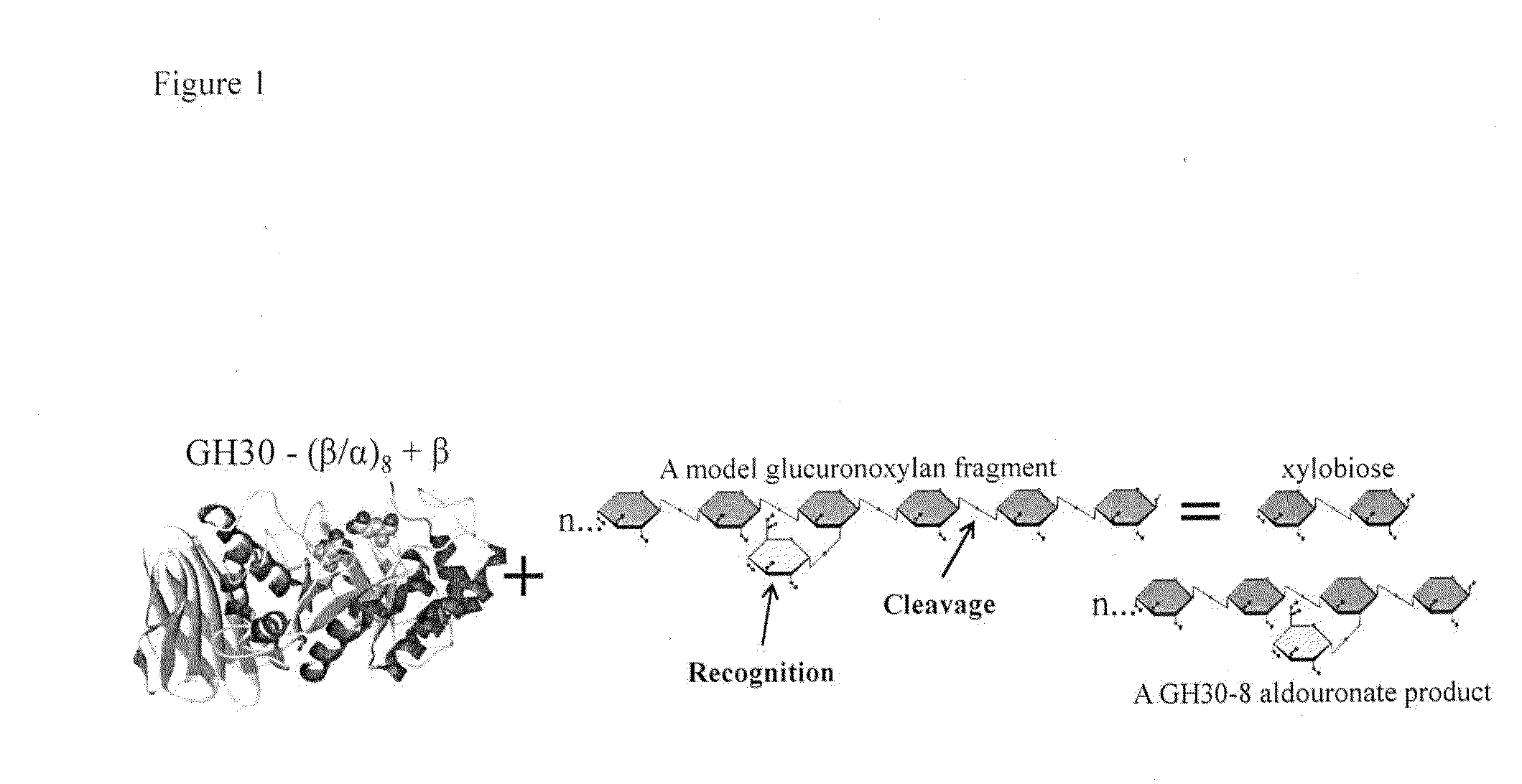
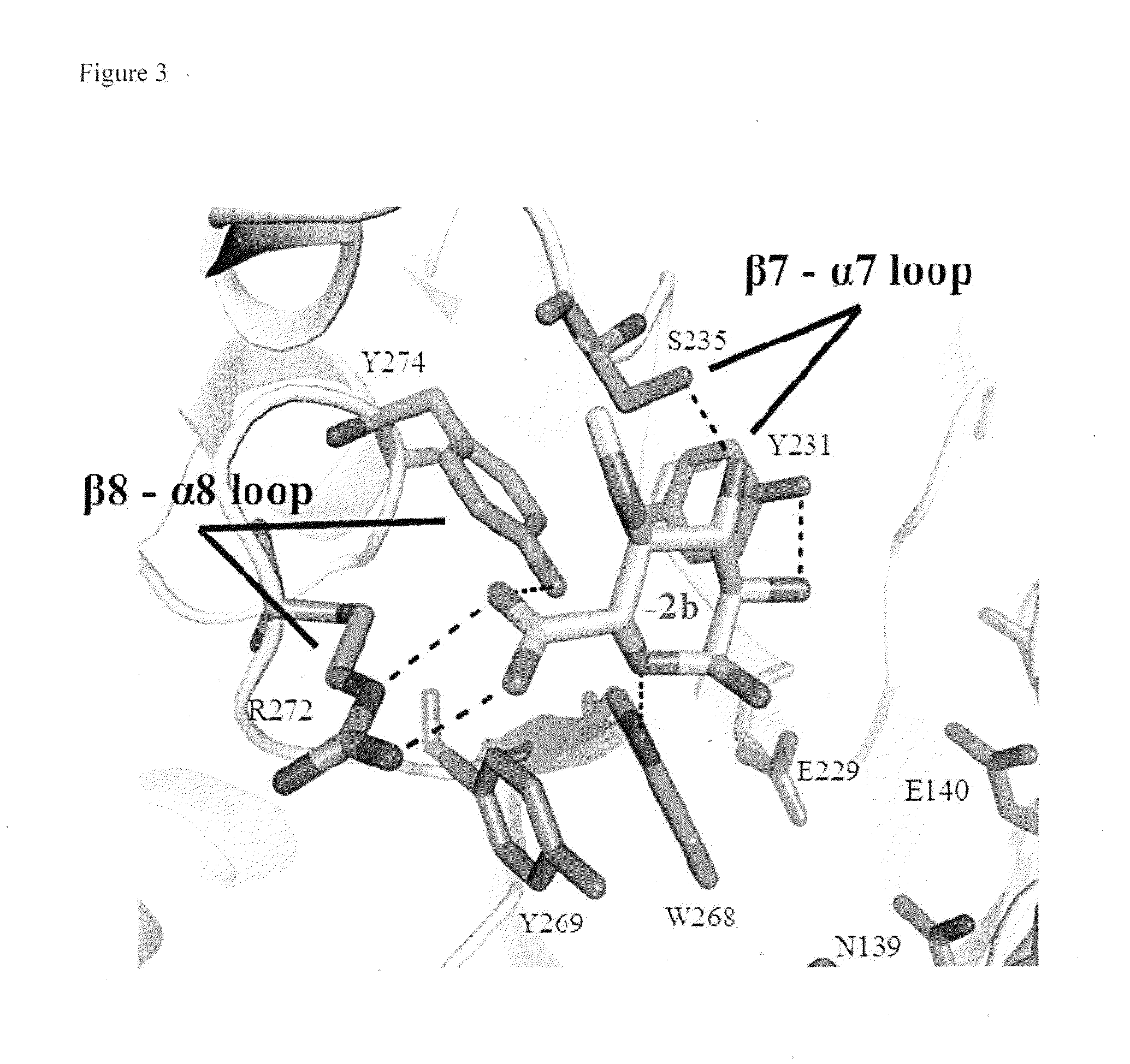
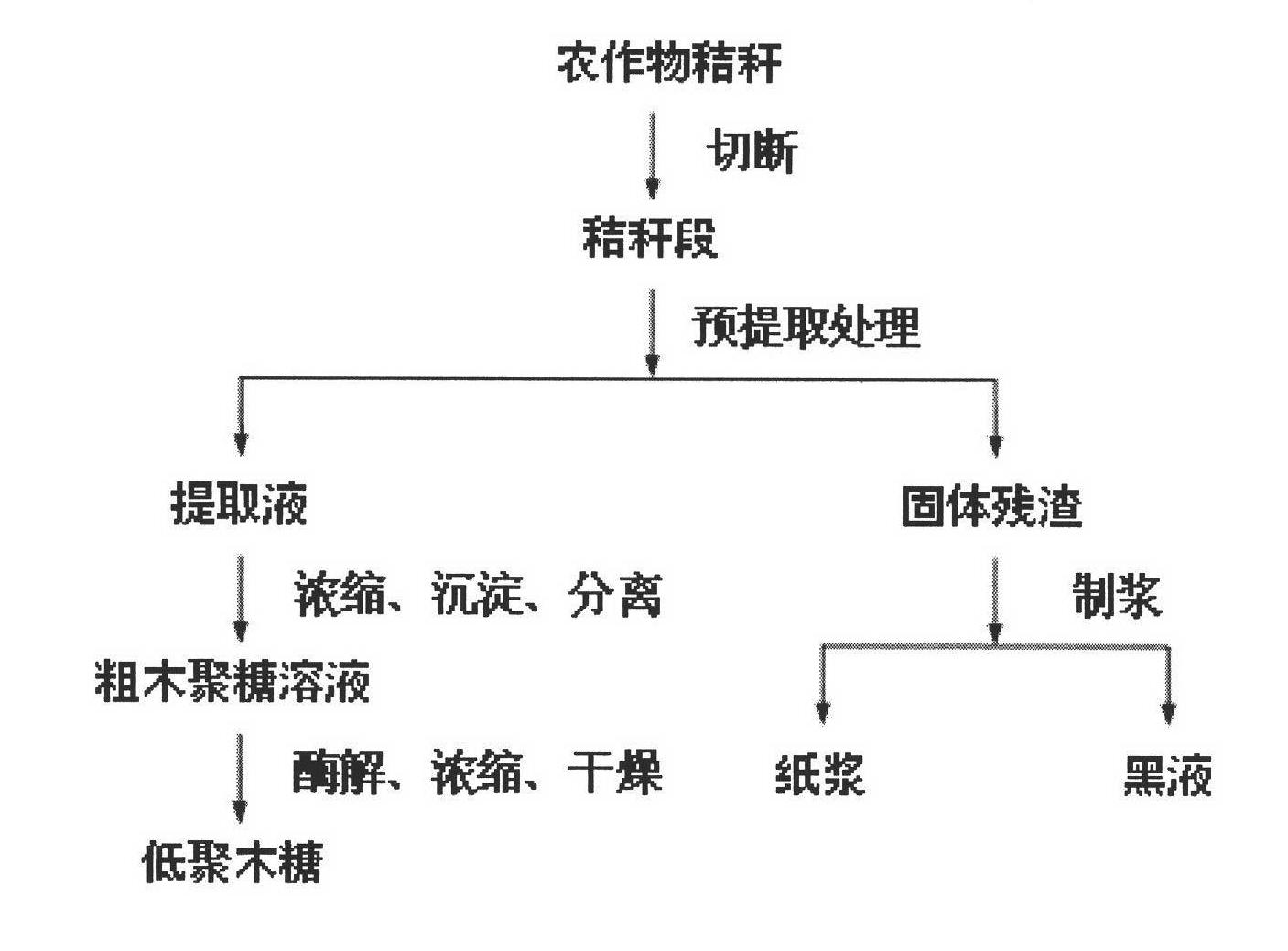
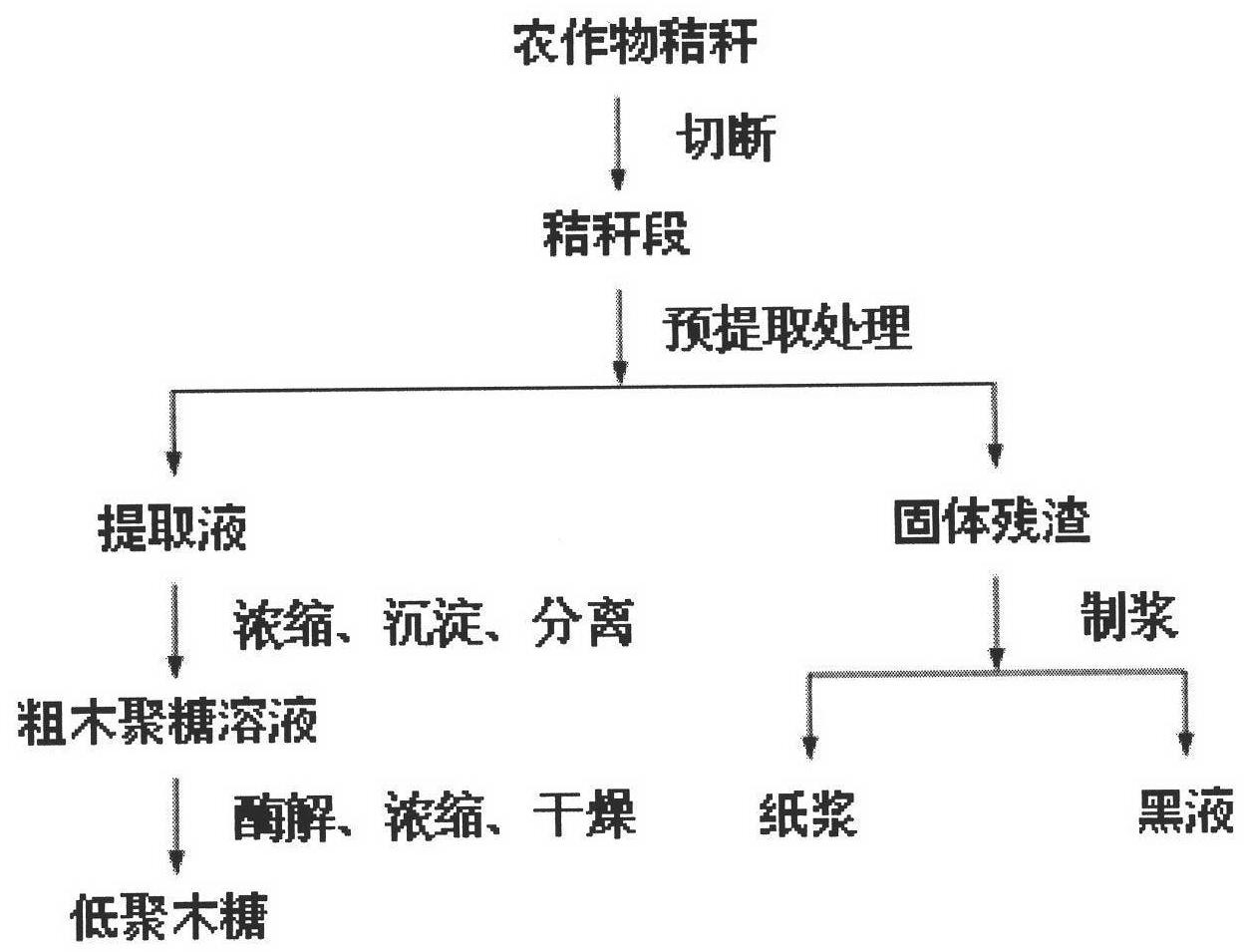
Patents
Literature
678 results about "Xylan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
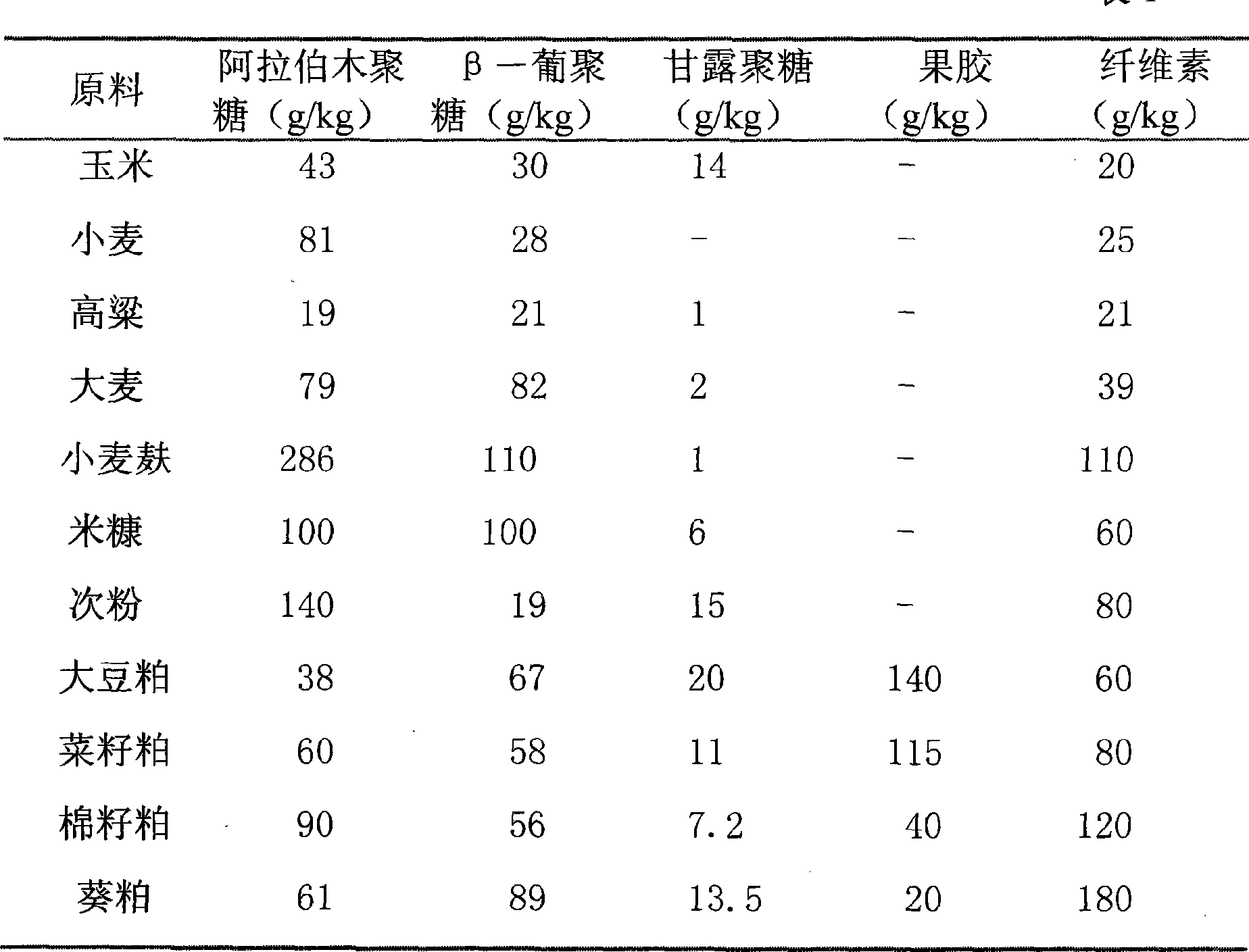
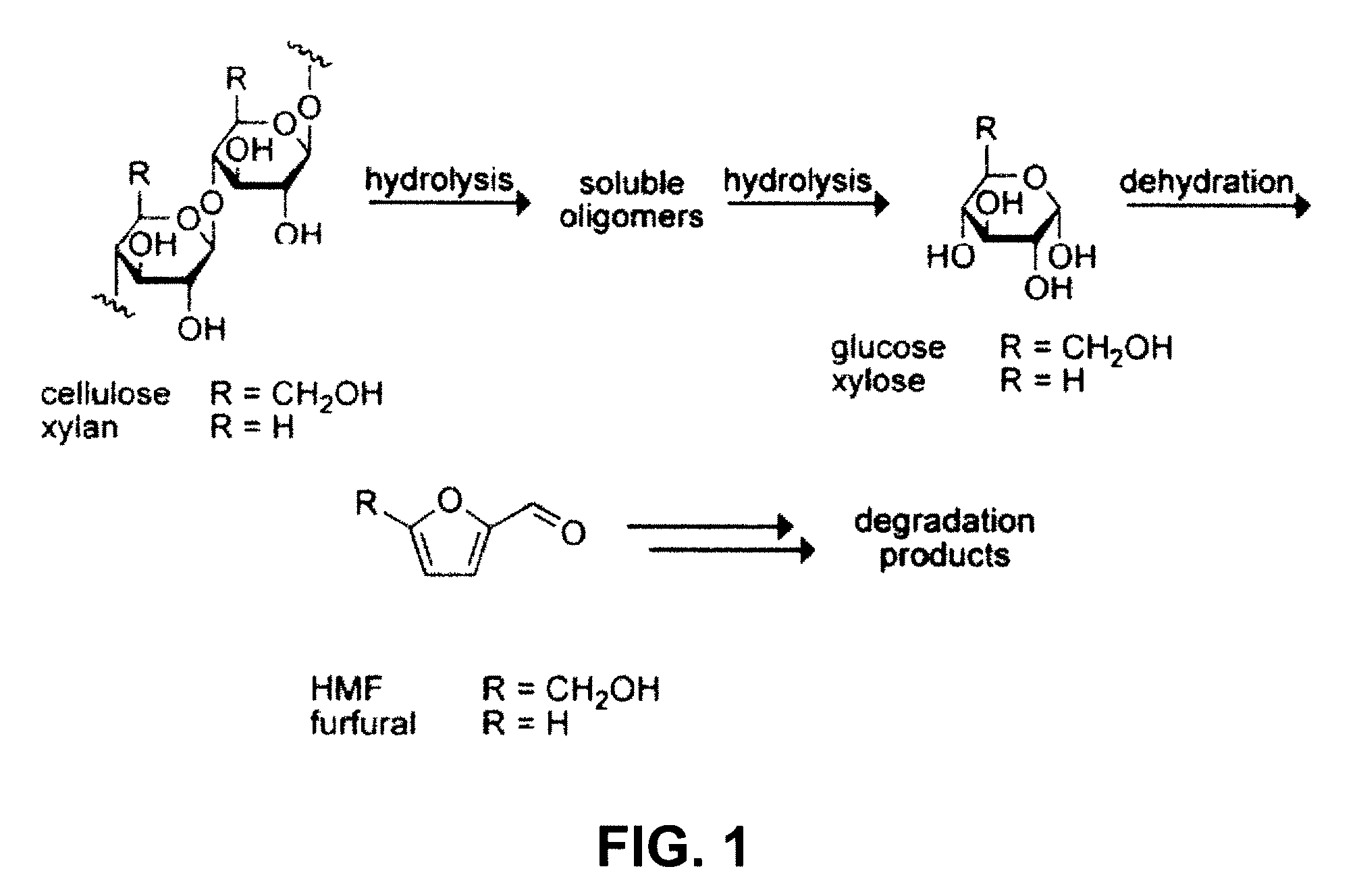
Xylan (/ˈzaɪlən/) (CAS number: 9014-63-5) is a group of hemicelluloses that represents the third most abundant biopolymer on Earth. It is found in plants, in the secondary cell walls of dicots and all cell walls of grasses.
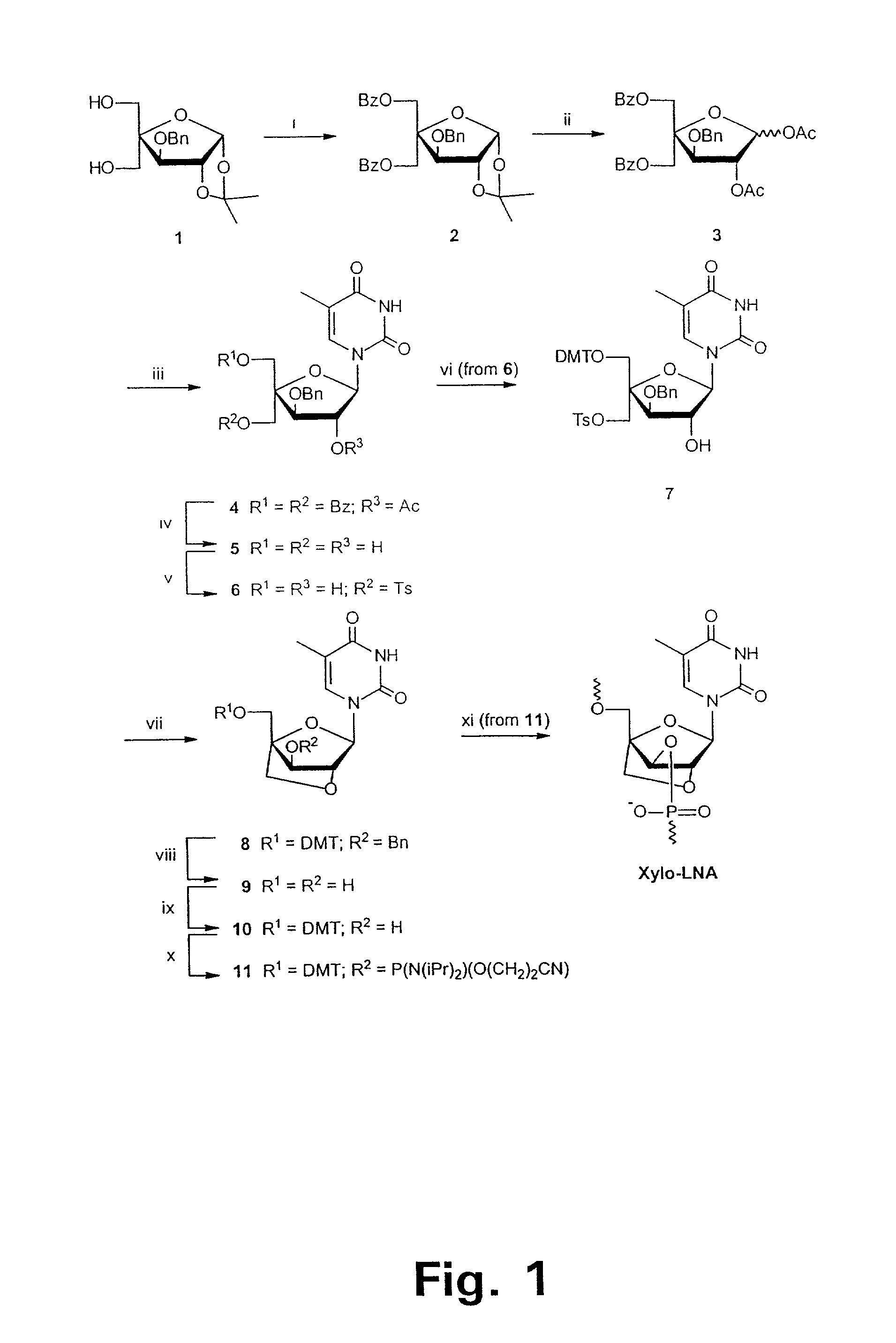
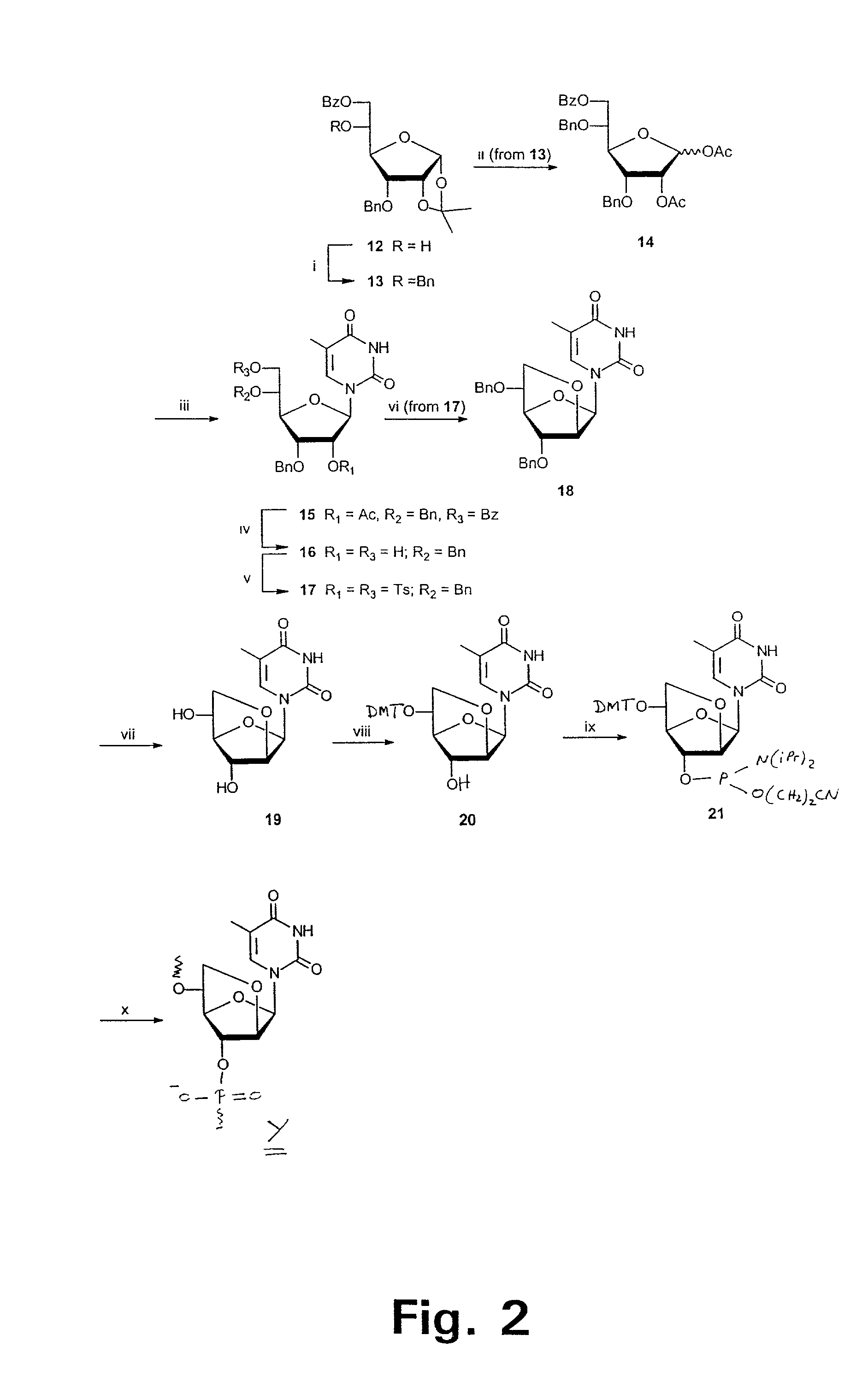
Xylo-LNA analogues
Based on the above and on the remarkable properties of the 2′-O,4′-C-methylene bridged LNA monomers it was decided to synthesise oligonucleotides comprising one or more 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer(s) as the first stereoisomer of LNA modified oligonucleotides. Modelling clearly indicated the xylo-LNA monomers to be locked in an N-type furanose conformation. Whereas the parent 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleosides were shown to adopt mainly an N-type furanose conformation, the furanose ring of the 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl monomers present in xylo-DNA were shown by conformational analysis and computer modelling to prefer an S-type conformation thereby minimising steric repulsion between the nucleobase and the 3′-O-phopshate group (Seela, F.; Wömer, Rosemeyer, H. Helv. Chem. Acta 1994, 77, 883). As no report on the hybridisation properties and binding mode of xylo-configurated oligonucleotides in an RNA context was believed to exist, it was the aim to synthesise 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer and to study the thermal stability of oligonucleotides comprising this monomer. The results showed that fully modified or almost fully modified Xylo-LNA is useful for high-affinity targeting of complementary nucleic acids. When taking into consideration the inverted stereochemistry at C-3′ this is a surprising fact. It is likely that Xylo-LNA monomers, in a sequence context of Xylo-DNA monomers, should have an affinity-increasing effect.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Process for manufacturing high purity xylose
InactiveUS20050203291A1Low costAvoid timeSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHigh concentrationChromatographic separation
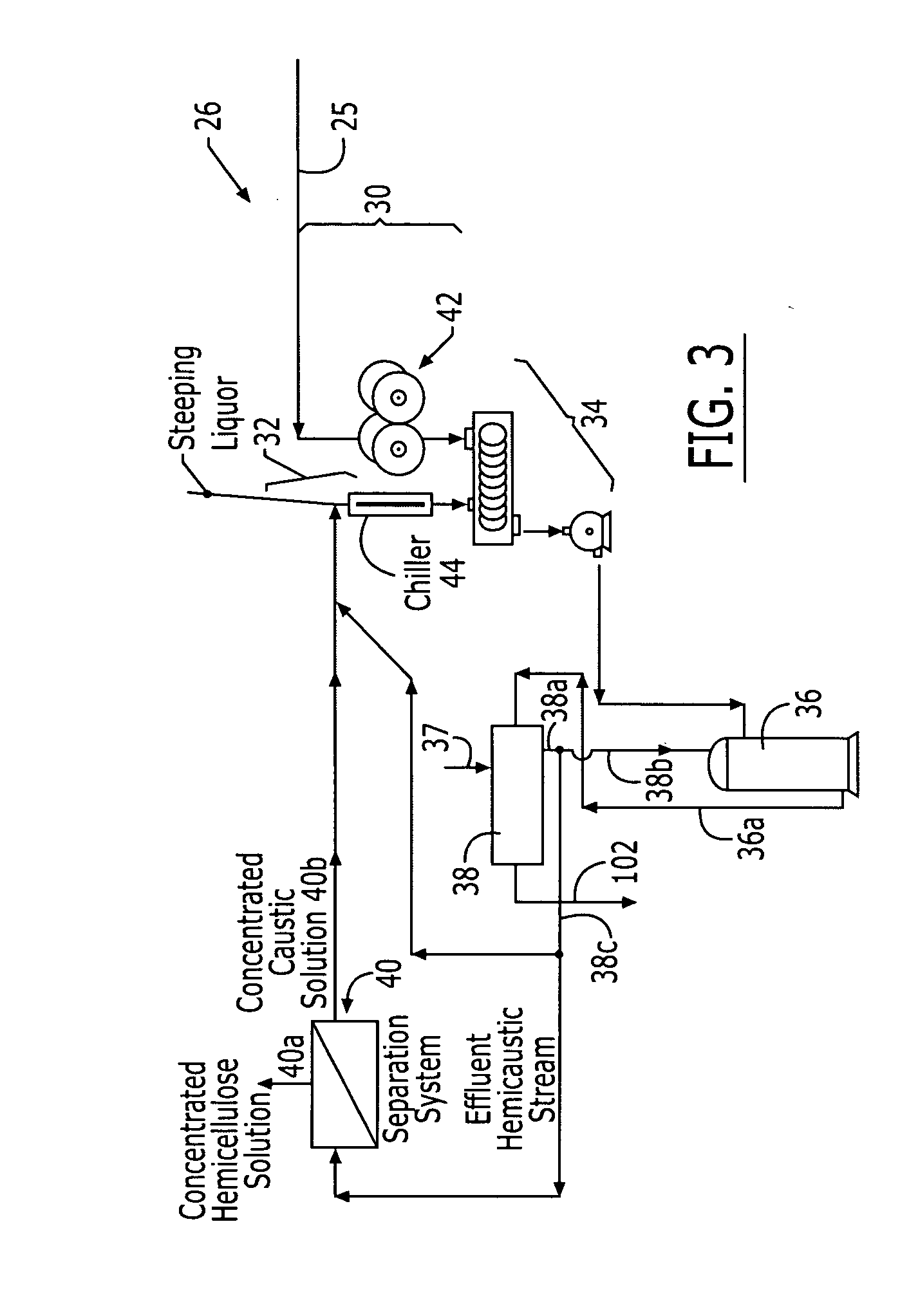
A process for manufacturing xylose by extracting hemicellulose from a cellulosic material, such as by a cold caustic extraction method, concentrating the extract, such as by nanofiltration, into a hemicaustic stream containing hemicellulose with greater than about 85 wt % xylan content, and subsequently hydrolysing the xylan from the hemicaustic stream to xylose. The high concentration of xylan within the concentrated hemicaustic stream enables hydrolyzation of the xylan to food-grade xylose and, optionally, hydrogenation of the xylose to xylitol without the need of a chromatographic separation step as previously required.
Owner:RAYONIER PERFORMANCE FIBERS
Modulation of plant xylan synthases
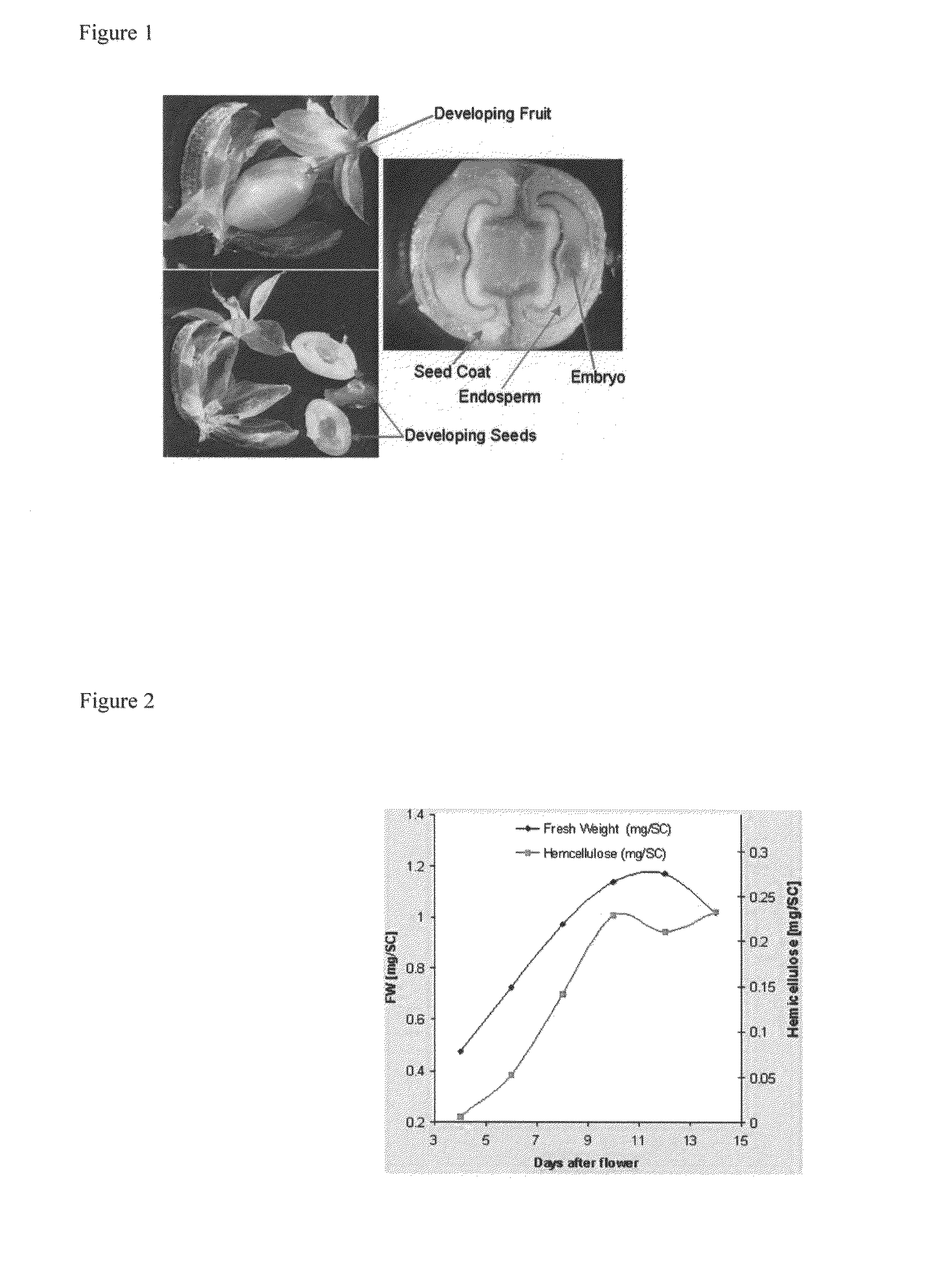
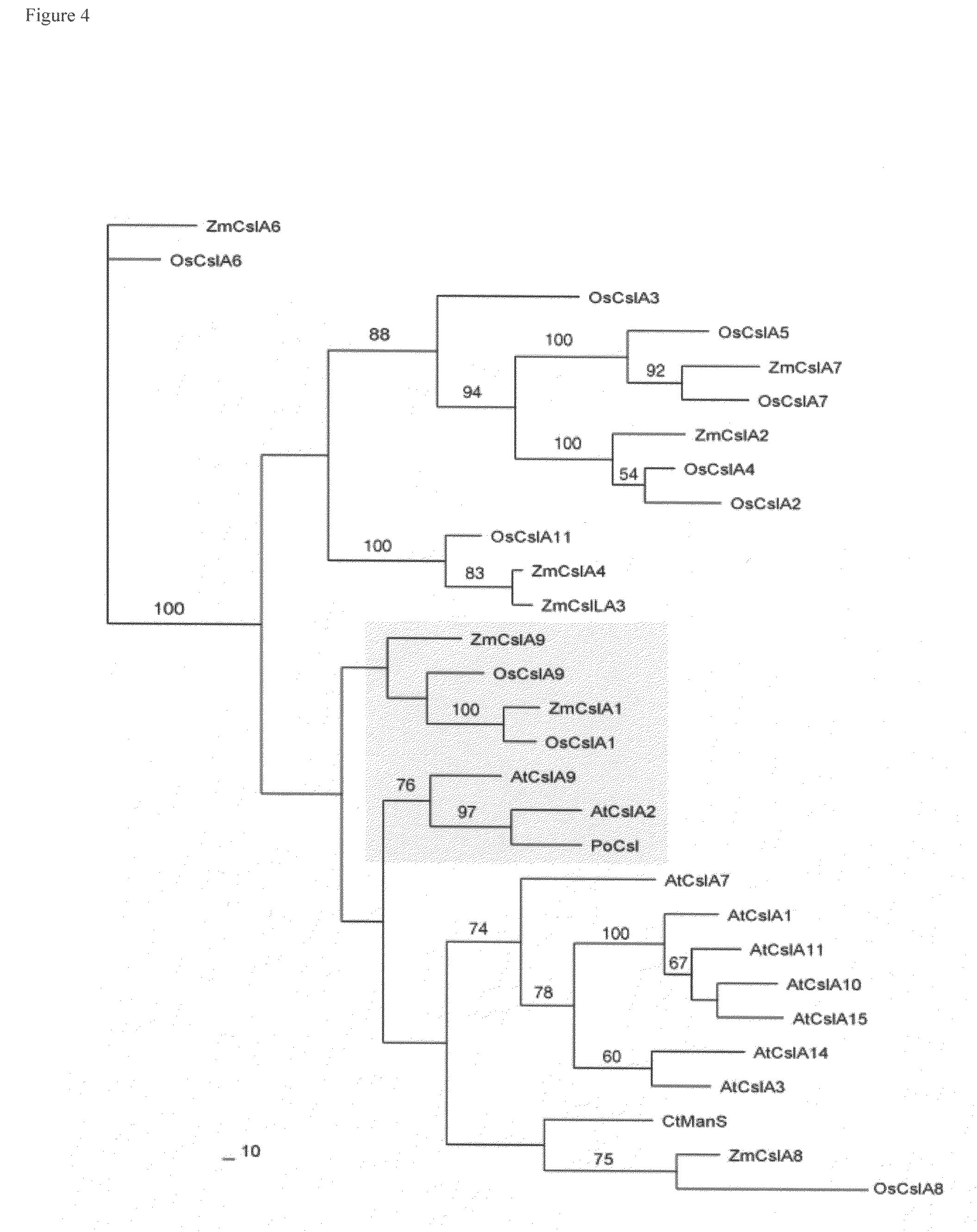
The present invention provides compositions and methods for manipulation of plant arabinoxylose and plant xylan synthases. Compositions include novel nucleotide sequences encoding xylan synthases and biologically active variants thereof. The invention also includes the discovery xylan synthase activity is a property of CslA polypeptides. Further provided are methods for xylose manipulation using the sequences disclosed herein. One method comprises stably incorporating into the genome of a plant cell, a CslA encoding nucleotide sequence operably linked to a heterologous promoter and regenerating a stably transformed plant. Methods for enhancing digestibility of plants and improving gum production in plants are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Premix feed with probiotics for laying hen
InactiveCN101485397AInhibition of reproductionReduce generationAnimal feeding stuffSodium bicarbonateSodium Bentonite
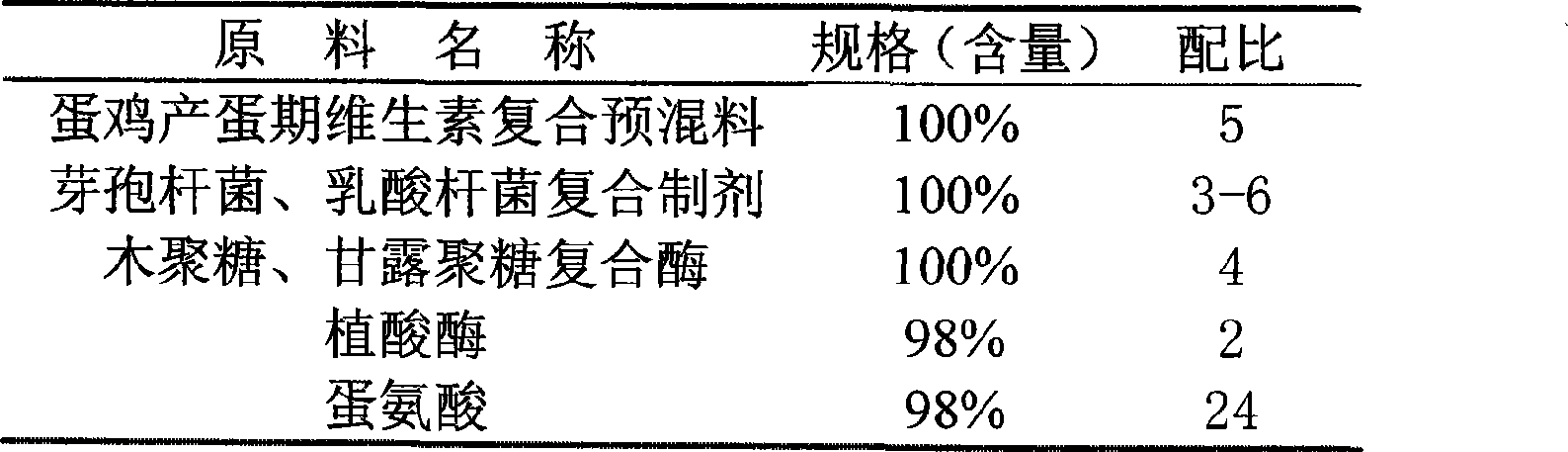
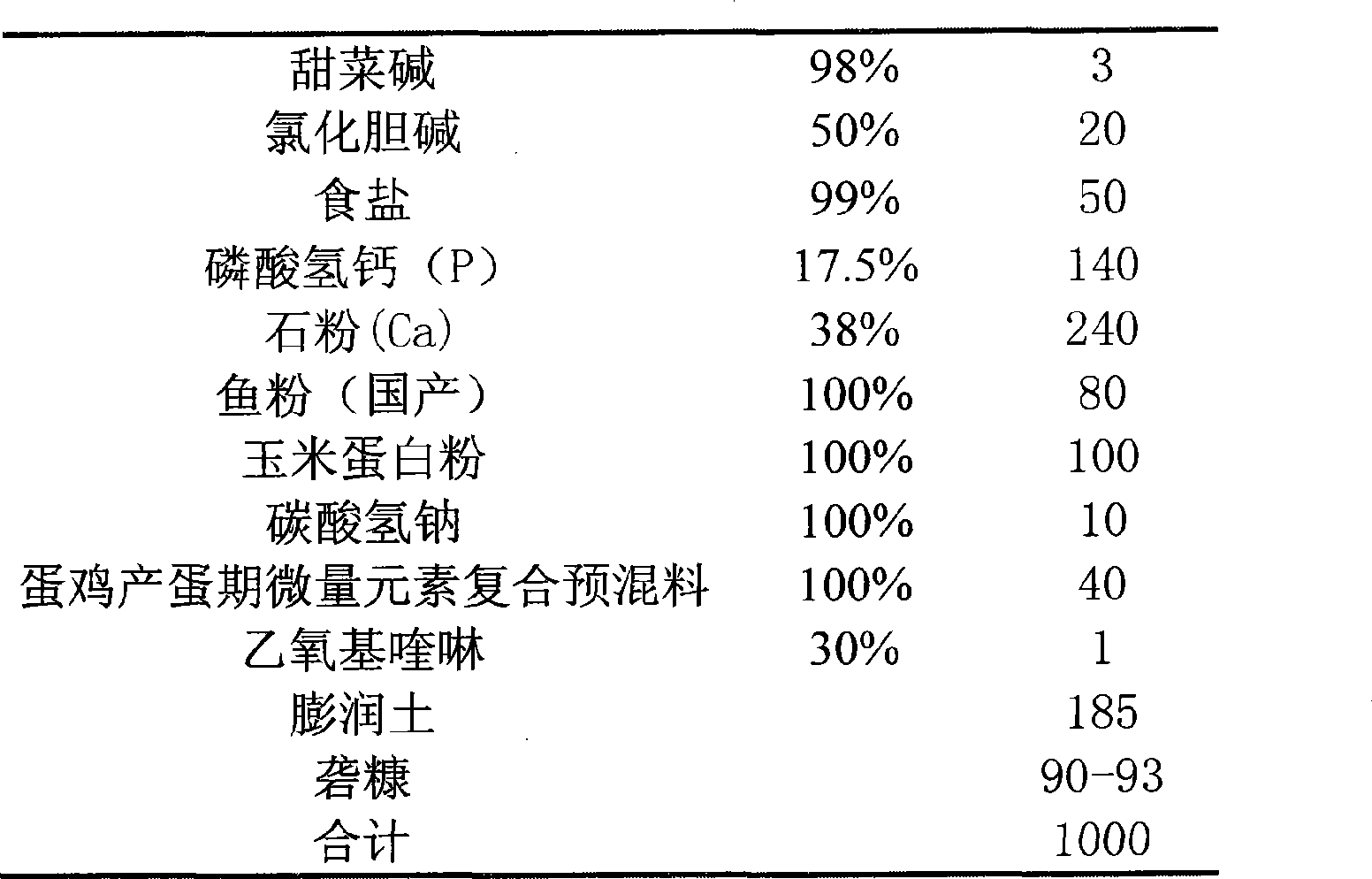
The invention discloses probiotic type premix feed for laying hens, which is prepared from vitamin compound premix feed for the laying hens in laying period, a bacillus and lactobacilli compound preparation, xylan and mannan complex enzyme, phytase, methionine, lycine, choline chloride, common salt, calcium hydrophosphate, stone dust, fish meal, corn gluten meal, sodium bicarbonate, trace element compound premix feed for the laying hens in the laying period, ethoxyquinoline, bentonite, and rice chaff by mixing in proportion. Compared with the common compound feed for the laying hens, the compound feed prepared by the premix feed reduces discharge of harmful substances such as nitrogen and phosphorus in chicken manure by more than 20 percent, reduces the concentration of harmful gases such as ammonia in a hen house by more than 40 percent, improves the feed utilization rate by 5 to 10 percent and the laying rate by 3 to 5 percent, averagely prolongs the laying period by 25 days, and reduces feeding cost by 5 to 8 percent and the death-cull rate of the laying hens.
Owner:山东众成饲料科技有限公司
Thermophilic and thermoacidophilic biopolymer-degrading genes and enzymes from alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius and related organisms, methods
Isolated and / or purified polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences encoding polypeptides from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius are provided. Further provided are methods of at least partially degrading, cleaving, or removing polysaccharides, lignocellulose, cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, starch, chitin, polyhydroxybutyrate, heteroxylans, glycosides, xylan-, glucan-, galactan, or mannan-decorating groups using isolated and / or purified polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences encoding polypeptides from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Biomass hydrolysis
ActiveUS20110065159A1Facilitate enhanced yield of glucoseImprove glucose yieldSugar derivativesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCelluloseHydrolysate
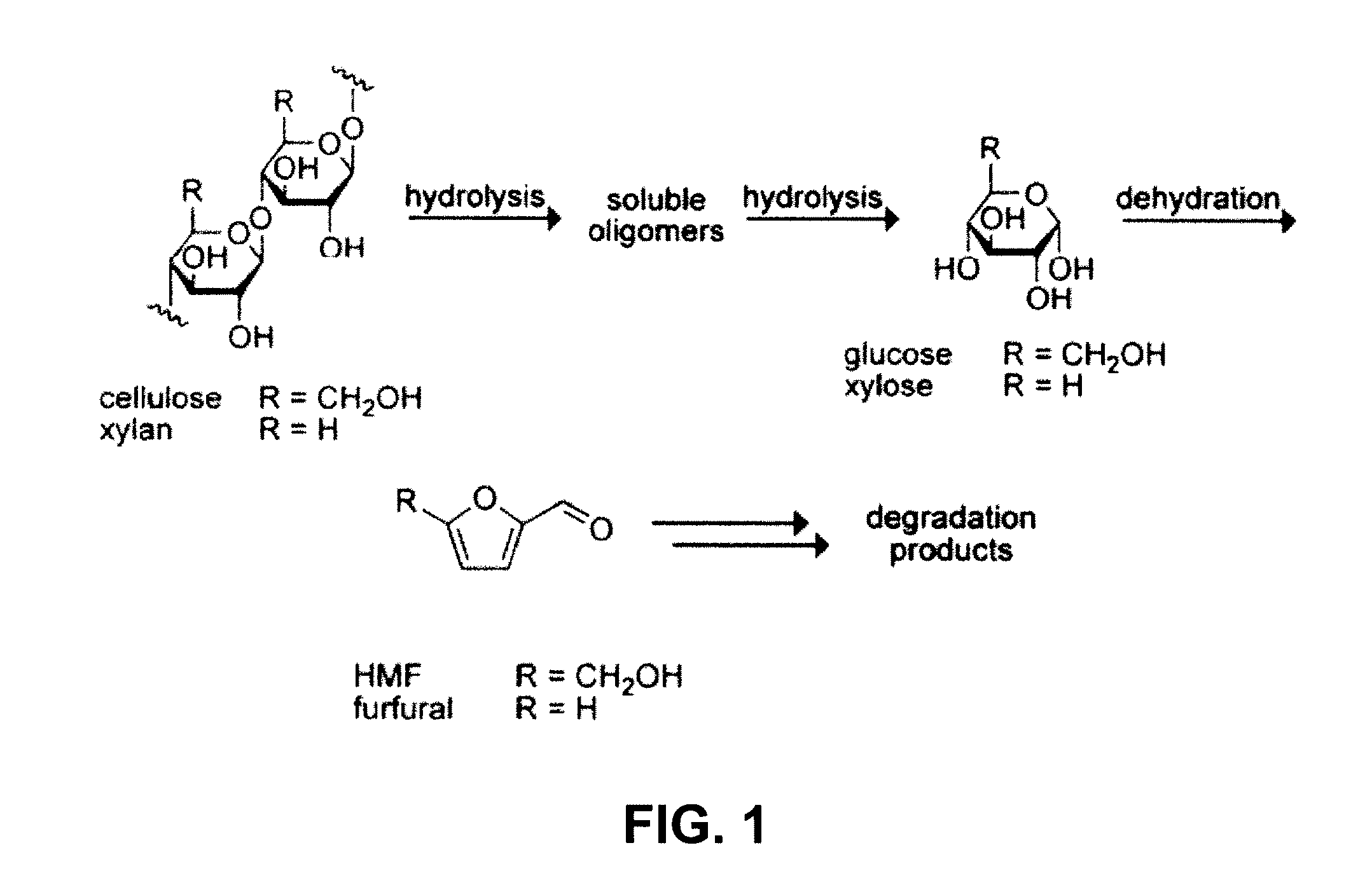
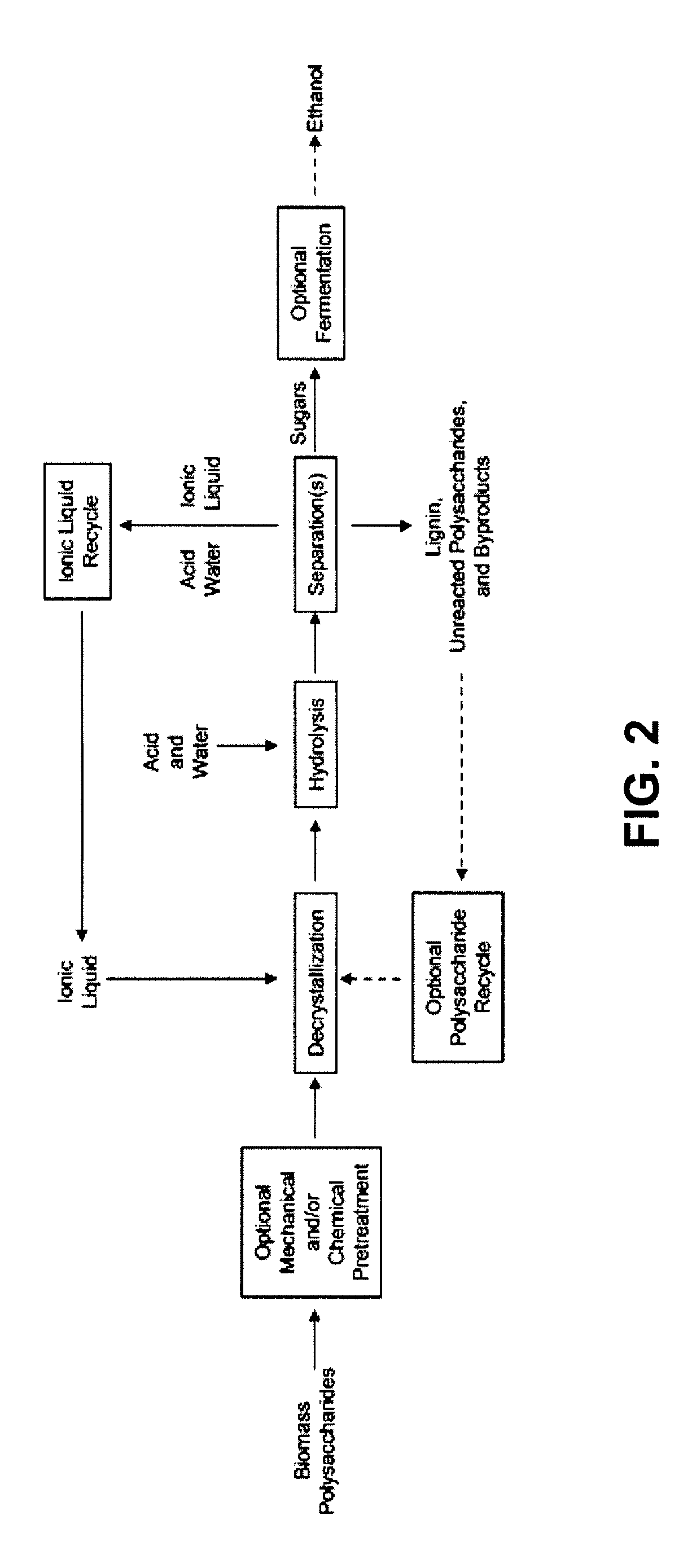
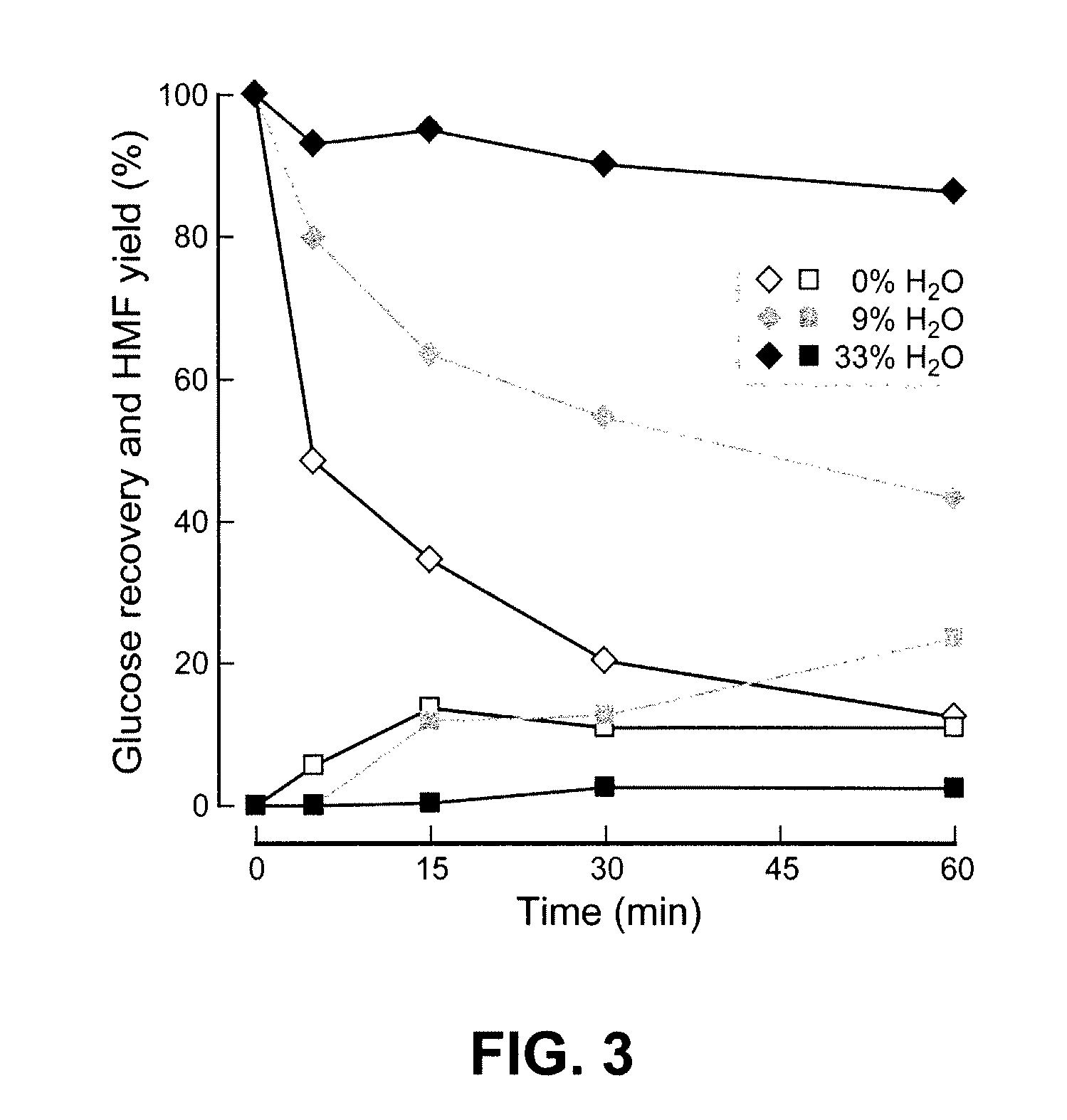
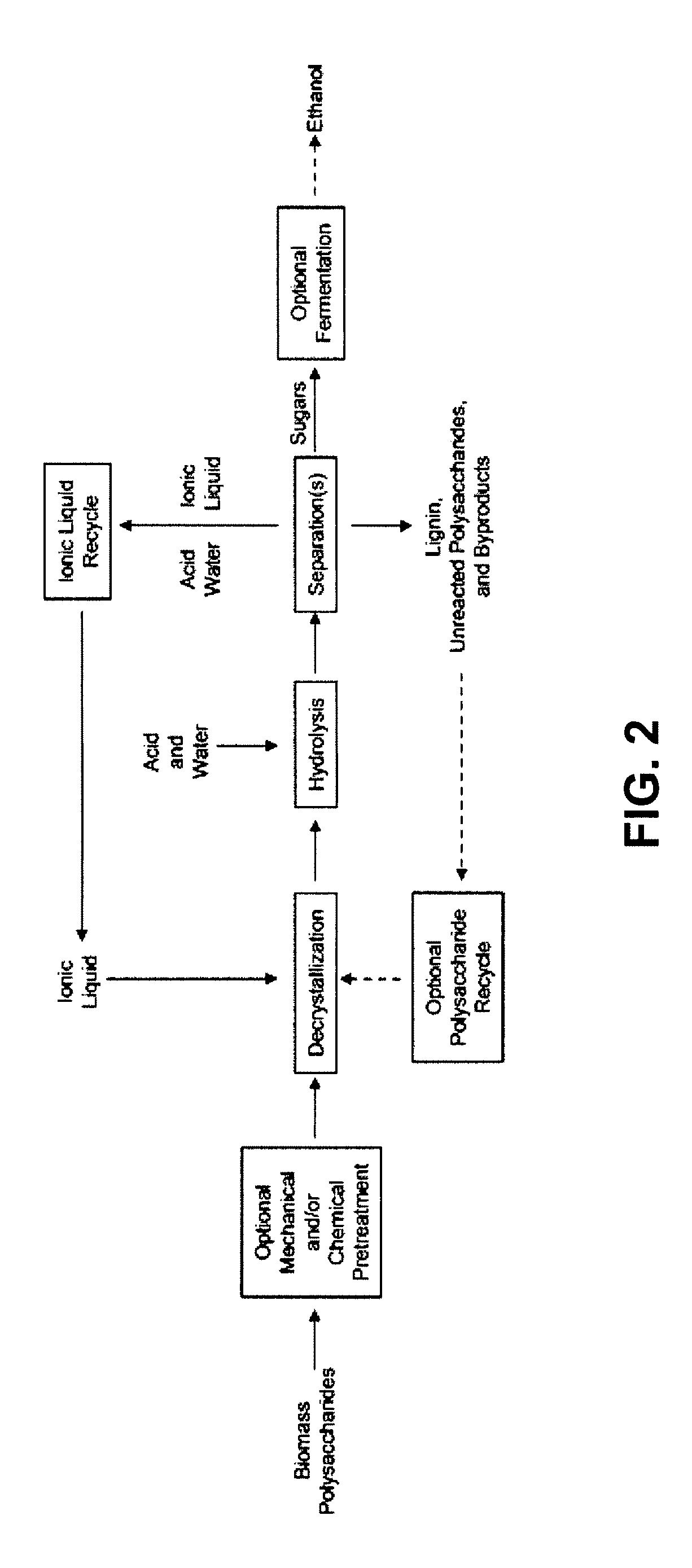
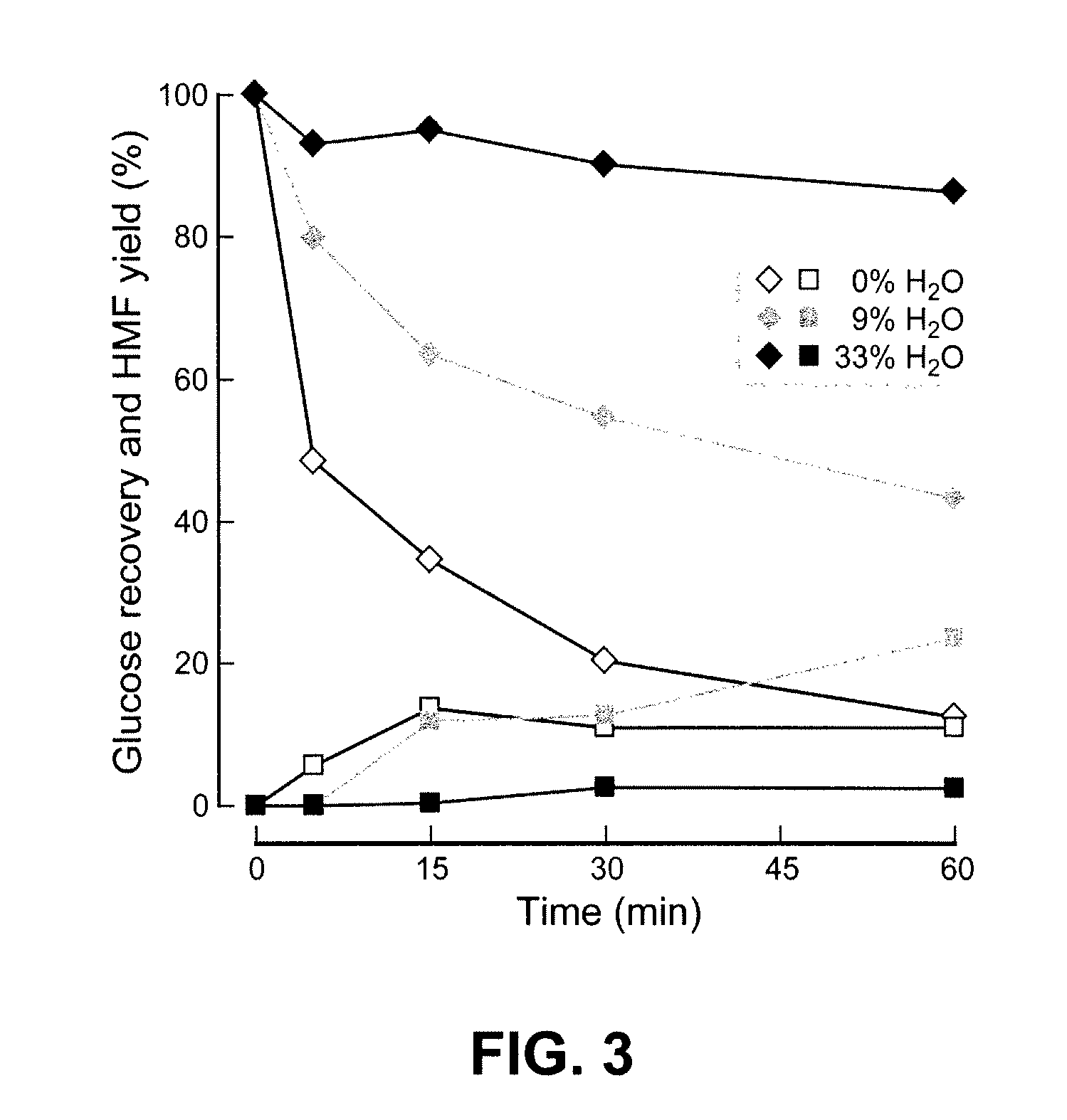
High-yielding method for chemical hydrolysis of lignocellulose into monosaccharides. The process of the invention can additionally be applied to cellulose, xylan and related biomass polysaccharides, such as galactan, mannan, or arabinan. The method is employed for hydrolysis of a biomass polysaccharide substrate. The process is carried out in an ionic liquid in which cellulose is soluble in the presence of catalytic acid at a temperature sufficiently high to initiate hydrolysis. Water is added to the reaction mixture after initiation of hydrolysis at a rate controlled to avoid precipitation yet avoid undesired sugar dehydration products such ad HMF. Hydrolysis product is useful as feedstock for fermentations including fermentation processes for ethanol, butanol and other fuels.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Thermal and acid tolerant beta xylosidases, arabinofuranosidases, genes encoding, related organisms, and methods
ActiveUS20100311110A1Decreasing proteolysisAllow stabilizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementXylanNucleic acid sequencing
Isolated and / or purified polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences encoding polypeptides from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius and variations thereof are provided. Further provided are methods of at least partially degrading xylotriose, xylobiose, and / or arabinofuranose-substituted xylan using isolated and / or purified polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences encoding polypeptides from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius and variations thereof.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Process of producing xylose and dissolving pulp
ActiveUS20110192560A1High yieldReduce the amount requiredPretreatment with water/steamWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsChromatographic separationXylan
The present invention relates to a process for the production of xylose and dissolving pulp from xylan-containing biomass, such as hardwood. The invention is based on prehydrolysis of the xylan-containing biomass with SO2 in specified conditions, followed by chromatographic fractionation, nanofiltration or precipitation crystallization of the xylose-containing prehydrolyzate to obtain a xylose product having a xylose content of at least 55% on DS. The dissolving pulp obtained from the process can be used for example for the production of viscose.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Biomass hydrolysis
ActiveUS8722878B2Reduce formationHigh yieldSugar derivativesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCelluloseXylan
High-yielding method for chemical hydrolysis of lignocellulose into monosaccharides. The process of the invention can additionally be applied to cellulose, xylan and related biomass polysaccharides, such as galactan, mannan, or arabinan. The method is employed for hydrolysis of a biomass polysaccharide substrate. The process is carried out in an ionic liquid in which cellulose is soluble in the presence of catalytic acid at a temperature sufficiently high to initiate hydrolysis. Water is added to the reaction mixture after initiation of hydrolysis at a rate controlled to avoid precipitation yet avoid undesired sugar dehydration products such ad HMF. Hydrolysis product is useful as feedstock for fermentations including fermentation processes for ethanol, butanol and other fuels.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for separating xylose from lignocelluloses rich in xylan, in particular wood
InactiveUS20050065336A1Many solutionsHigh cellulose yieldSugar derivativesXylose productionXylanPre treatment
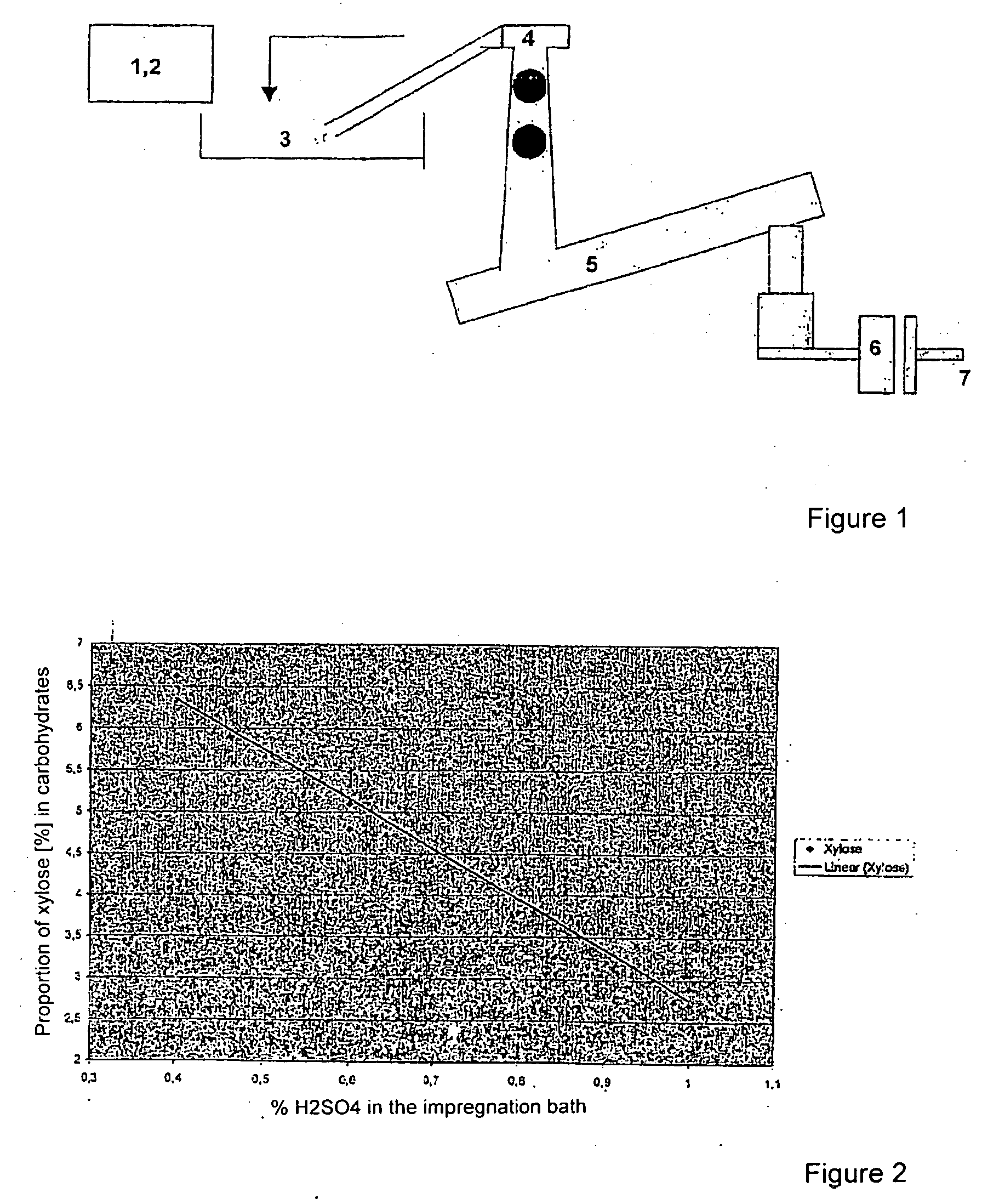
The invention is directed to a method for separating xylose from lignocelluloses rich in xylan, particularly wood, and for obtaining pulp, characterized by the following steps: (1) pretreating wood chips through mechanical destruction of the original structure; (2) impregnating the obtained wood mass with diluted mineral acid; (3) carrying out prehydrolysis of the obtained wood mass modified by the process under the influence of steam at an elevated temperature to hydrolyze the obtained hemicelluloses; and (4) removing the hemicelluloses from the residual pulp by washing, filtering and / or centrifuging while obtaining an aqueous solution rich in xylose. The combination of method steps according to the invention makes it possible to achieve high α-cellulose contents with very low proportions of xylose, that is, highly pure chemical pulp qualities, while at the same time enabling a virtually quantitative separation of the valuable xylose.
Owner:RHODIA ACETOW AG
Enzyme and microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose
InactiveCN101560488AImprove degradation rateLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroides xylanisolvensFlavobacterium aquatile
The invention discloses a microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose and application thereof. The active component of the microbial inoculum consists of Alcaligenes faecalis, Bacteroides xylanisolvens, Clostridium xylanolyticum, Clostridium lentocellum, Flavobacterium aquatile, and Pseudomonas stutzeri. Experiments prove that the microbial inoculum has high degradation rate to the lignocellulose, and the degradation rate can reach between 60 and 70 percent. The microbial inoculum has low cost and simple preparation, breaks through the limitation that a purification bacterium and a clastic enzyme thereof cannot decompose the lignocellulose efficiently, provides a key technique for decomposing, saccharifying biomass containing cellulose and converting the biomass into an energy source, and has extensive application prospect in the field of decomposing the lignocellulose.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Xylanases, Nucleic Acids Encoding Them and Methods For Making and Using Them
ActiveUS20110016545A1Low cost processingLow-cost and efficientImmobilised enzymesNon-fibrous pulp additionIncrease phCell wall
The invention relates to enzymes having xylanase, mannanase and / or glucanase activity, e.g., catalyzing hydrolysis of internal β-1,4-xylosidic linkages or endo-β-1,4-glucanase linkages; and / or degrading a linear polysaccharide beta-1,4-xylan into xylose. Thus, the invention provides methods and processes for breaking down hemicellulose, which is a major component of the cell wall of plants, including methods and processes for hydrolyzing hemicelluloses in any plant or wood or wood product, wood waste, paper pulp, paper product or paper waste or byproduct. In addition, methods of designing new xylanases, mannanases and / or glucanases and methods of use thereof are also provided. The xylanases, mannanases and / or glucanases have increased activity and stability at increased pH and temperature.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Thermophilic and thermoacidophilic biopolymer-degrading genes and enzymes from alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius and related organisms, methods
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
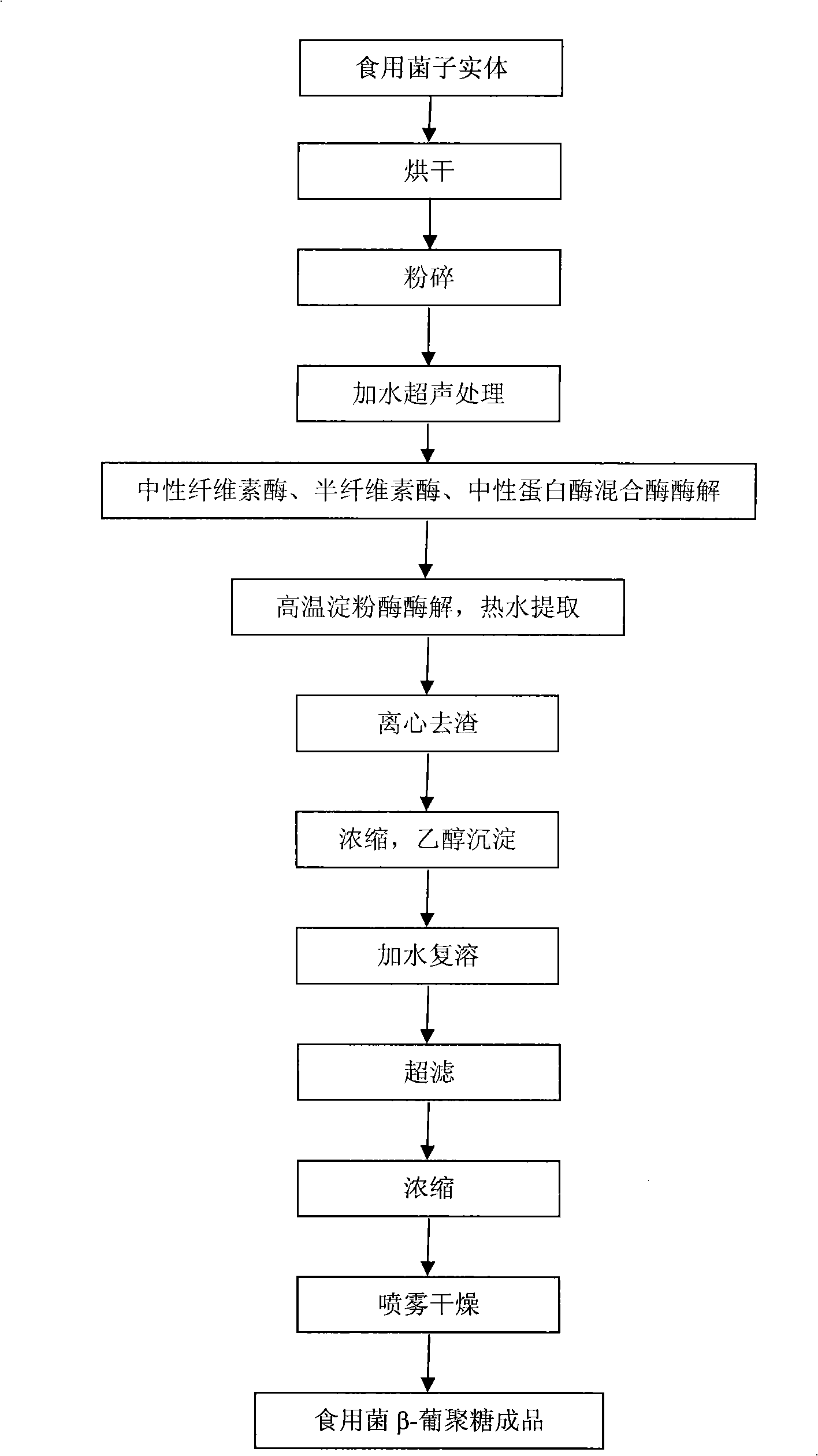
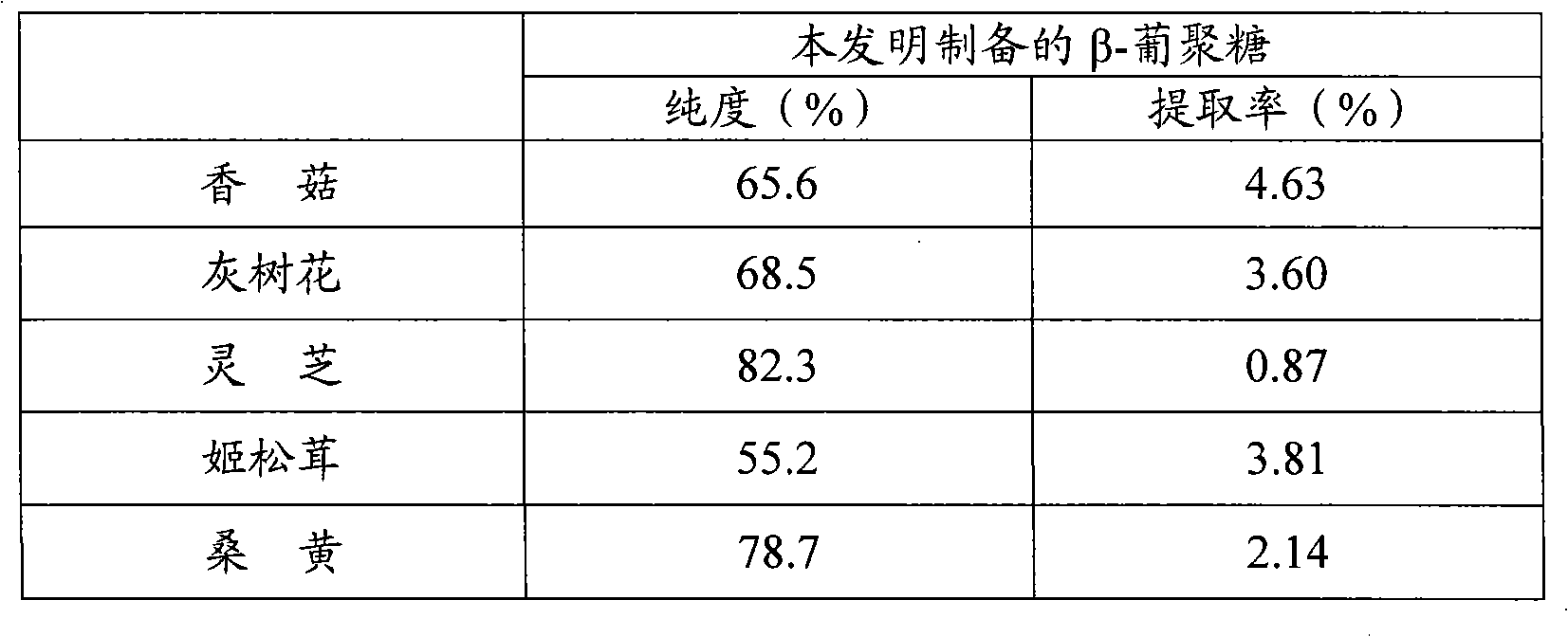
Preparation of edible fungus beta-dextran
The invention provides a preparation method of edible fungi Beta-glucan. In the method, ultrasonic pretreatment, neutral cellulose, hemi-cellulase, the cellulase enzyme digested by a neutral protease mixed enzyme, hemicellulose (like xylan, gelose and a plurality of heteroglycans) and proteins (and peptides) are mainly adopted; a high-temperature amylase is added for the enzyme digestion of the amyloid simultaneously when hot water is extracted; and a target is obtained through a sequent ethanol deposition and the edible fungi Beta-glucan with better activity is further obtained through the hyperfiltration of a film with an interception of 10,000. The preparation method has the advantages that: the product purity of the edible fungi Beta-glucan by adopting the method is high (55.2 to 82.3 percent); the preparation process does not have the residues of poisonous and harmful chemical reagents; the product is safe; the technical condition is moderate and is easy to be operated; and the preparation method is suitable for preparing all the edible fungi Beta-glucan and is suitable for commercial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for extracting xylan from woody fiber material
A process for extracting xylan from wooden fibre material features that under the catalysis of microwave, the alkali solution containing hydrogen peroxide in directly sued to treat raw material for performing extraction of xylane and bleaching it at same time. Its advantages are high speed, less consumption of alkali, and high extracting rate. The resultant xylan solution can be deposited in organic solvent or superfilted and dried to obtain light-color xylan product.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF BOTANY THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Perhydrolase providing improved specific activity
An acetyl xylan esterase variant having perhydrolytic activity is provided for producing peroxycarboxylic acids from carboxylic acid esters and a source of peroxygen. More specifically, a Thermotoga maritima acetyl xylan esterase gene was modified using error-prone PCR and site-directed mutagenesis to create an enzyme catalyst characterized by an increase in specific activity. The variant acetyl xylan esterase may be used to produce peroxycarboxylic acids suitable for use in a variety of applications such as cleaning, disinfecting, sanitizing, bleaching, wood pulp processing, and paper pulp processing applications.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Cellulose fibre, textile assistant for union biochemical pretreatment, perparing method and use
The invention relates to the method to use special biology enzyme (pectic enzyme, fibrin enzyme, lipase, albumen enzyme, lacquer enzyme, xylan enzyme, polysaccharide enzyme, and catalase) and environment-friendly effective surfactant to produce aid fitting the biochemical pretreatment of fibrin fiber, and its fabric, and its processing technology. The aid for short flow of zoology pretreatment made of a host of biology enzyme and environment-friendly surfactant can fit the short flow of zoology pretreatment of fibrin fiber and its fabric. The invention advances the quality of the production. At the same tie, it reduces pollution to the environment, and it achieves the process of pretreatment of fibrin fiber and its fabric with the interreaction with biology enzyme and surfactant. Moreover, thep rocess does little harm to the fiber and it has an effective removement of residue. Additionally, it is friendly to the environment.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Glycosyl hydrolase xylanases, compositions and methods of use for efficient hydrolysis and processing of xylan
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Method for extracting beta- glucosans from bran of corn
The invention provides a method for extracting beta- glucosans by taking bran of corn as material. The method comprises the bran of corn is mixed with water and then extracted respectively by alkali liquor and amylase for centrifugal separation; supernate is added with acid for precipitation to separate and remove protein and concentrated by a spiral-wound film; the mixed solution is precipitated by ammonium sulphate solution, and the precipitated product is dissolved in the water and then concentrated by the spiral-wound film and dried to obtain highland barley beta- glucosans. A horizontal spiral unloading sedimentation centrifugal device is adopted to effectively improve the yield of the beta- glucosans; the ammonium sulphate solution is adopted to selectively sedimentate the beta- glucosans, so as to effectively remove other heteroglycans such as pentosan, xylan and the like in the material, and effectively improve the purity of the beta- glucosans; by adopting the spiral-wound film concentration technique, the water-quality standard of a great deal of produced industrial sewage is higher than tap water, and the industrial sewage can be recycled, so that the aim of energy-saving and emission-reduction can be achieved, and the economic benefit and social benefit of the enterprise can be improved.
Owner:TIBET TIANMAILI HEALTH PROD CO LTD
A kind of method for preparing xylo-oligosaccharide and paper pulp
ActiveCN102277761AImprove fiber qualityImprove physical performance indicatorsPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsPulping with inorganic basesFiberOligosaccharide
The invention discloses a method for preparing oligosaccharide and paper pulp, belonging to the technical fields of pulping and the comprehensive utilization of pulping. The method comprises the steps of: using crop straws as raw materials, pre-treating the raw materials to obtain a pre-extracting solution, concentrating the pre-extracting solution by a membrane separation method, then obtaining a crude xylan solution via precipitation and centrifugal separation, and then preparing oligosaccharide via enzymolysis, vacuum concentration and frozen-drying. The pre-treated solid residues are stewed via an alkaline process so as to prepare unbleached paper pulps of which the indexes such as fiber length, whiteness, fracture length, tear resistance, folding strength and the like are all improved. The generated black liquid has the characters of low viscosity and high heat productivity. The method for preparing oligosaccharide and paper pulp integrates the comprehensive utilization method with the biomass transformation method on the premise of optimizing the traditional alkaline chemical pulping technique to prepare products with high additional values, namely oligosaccharide, thereby increasing the quality of the paper pulp and the extraction, vaporization and combustion performances of the black liquid.
Owner:CHINA NAT PULP & PAPER RES INST CO LTD
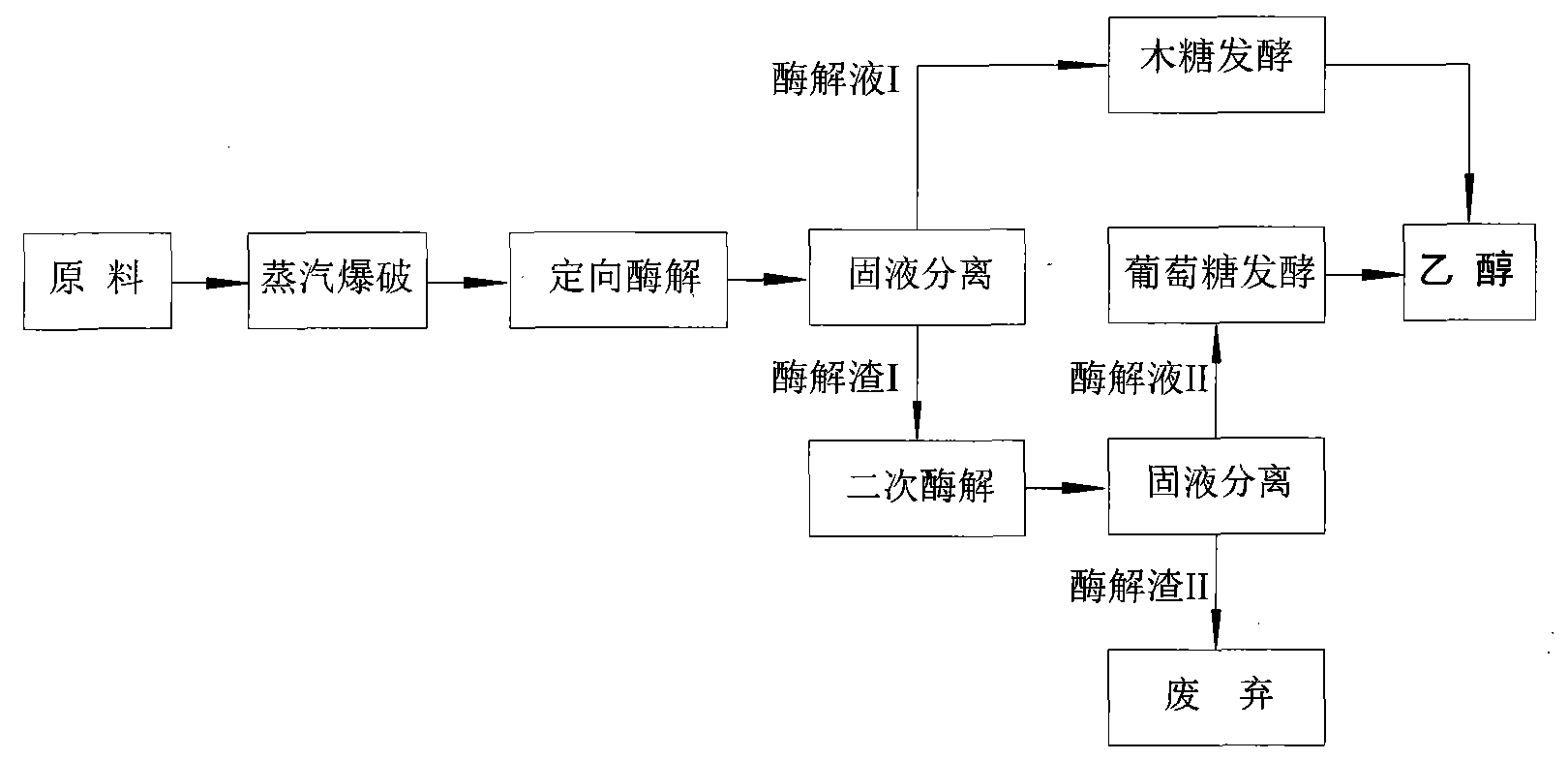
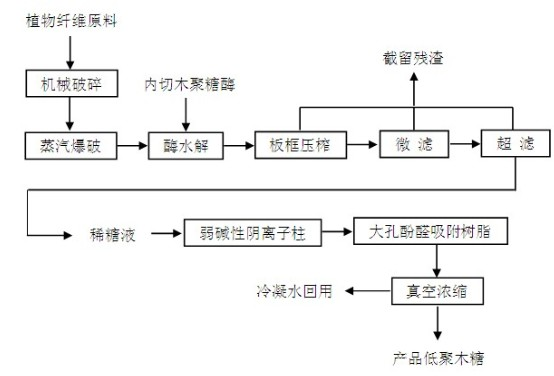
Method for performing steam explosion of wood fiber raw material, directional enzymatic dissociation and alcoholic fermentation
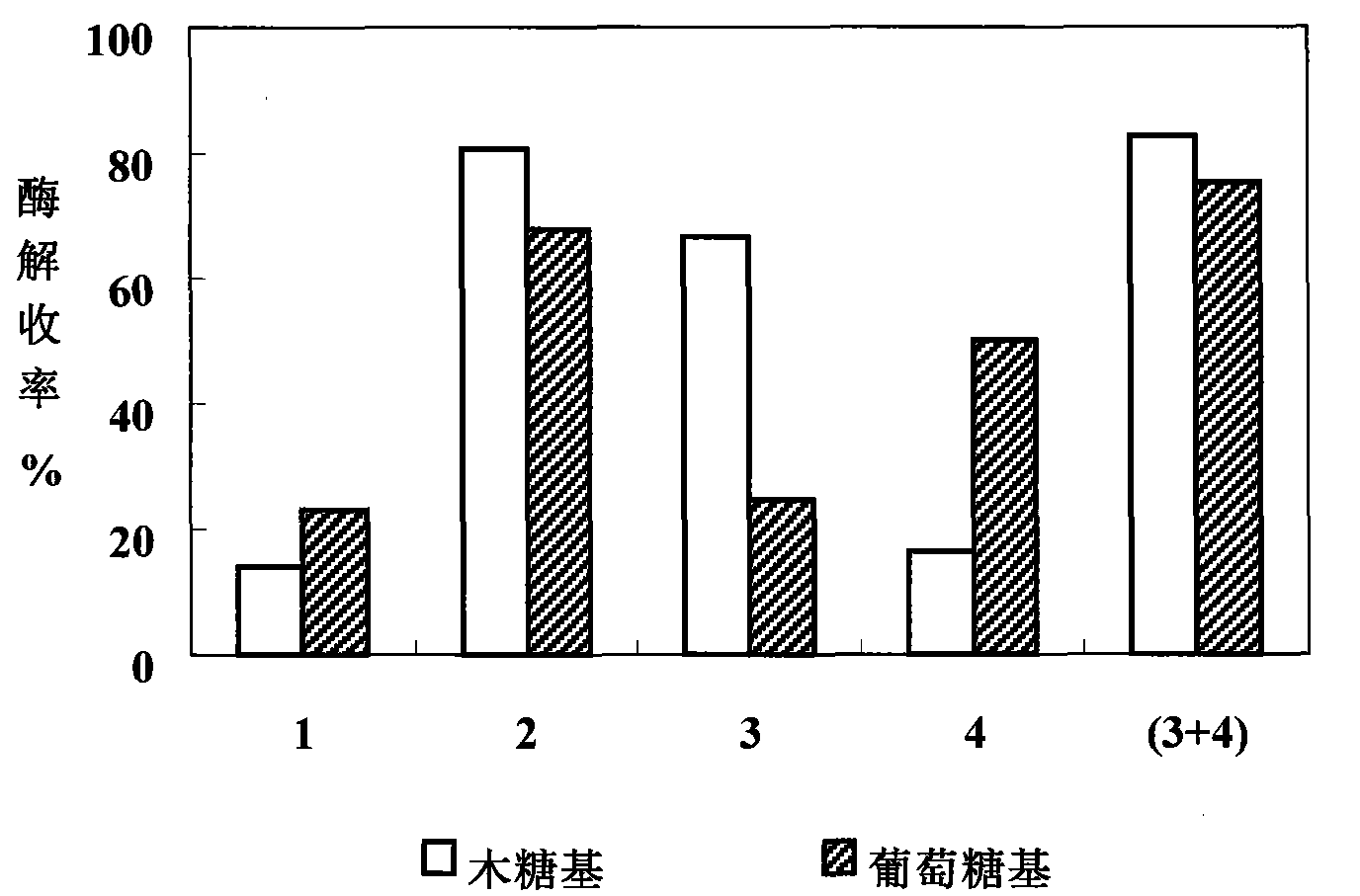
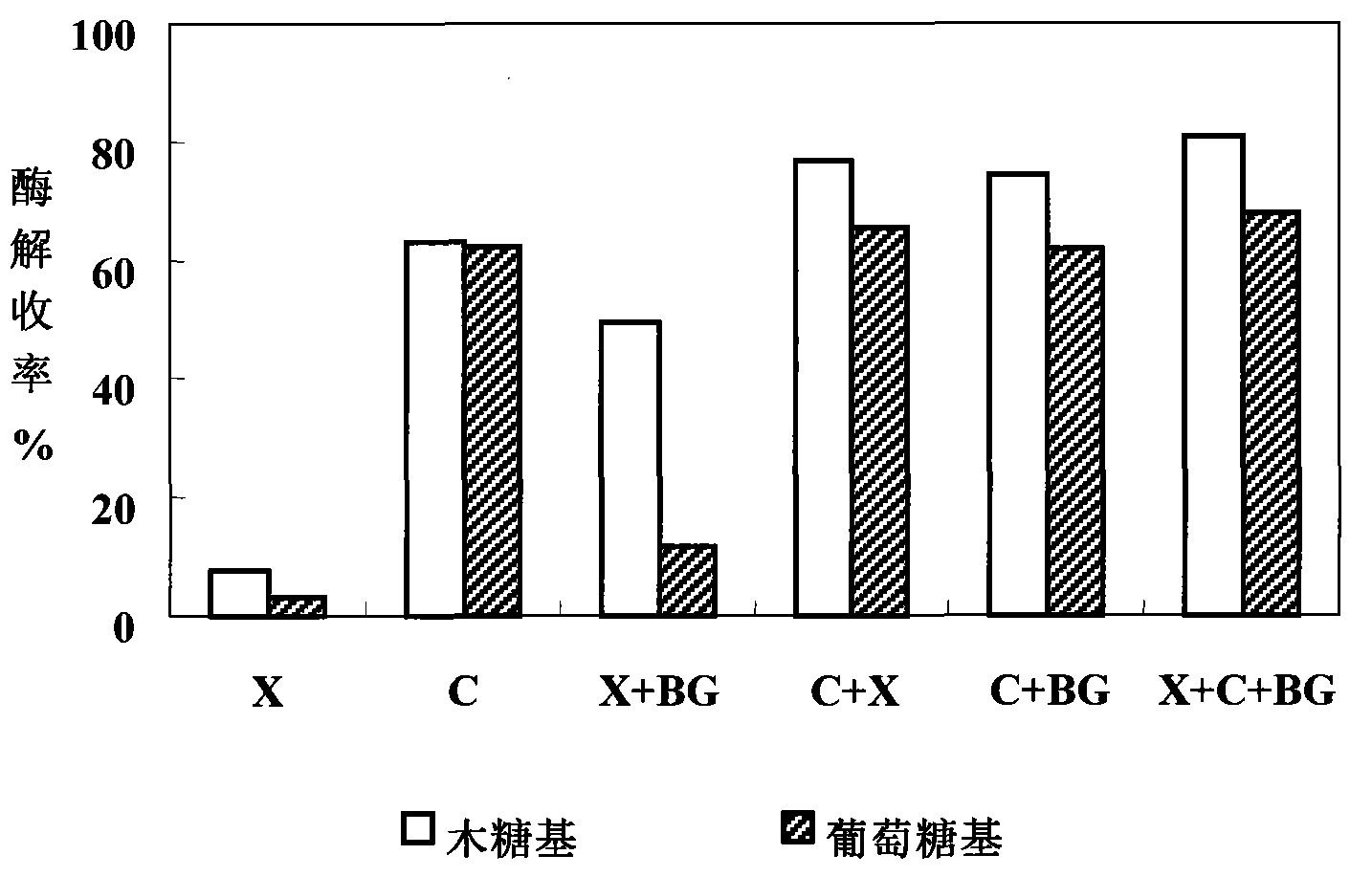
The invention relates to a method for performing steam explosion of wood fiber raw materials, directional enzymatic dissociation and alcoholic fermentation. The method is characterized in that steam explosion, directional enzymolysis of xylan, solid-liquid separation, extensive enzymolysis of cellulose, anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of xylose and anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of glucose areadopted. The new secondary enzymolysis technology is adopted and beta-glucosidase and little cellulose are introduced in xylanase so as to obviously improve the xylan directional enzymolysis and separation effect of raw materials. Therefore, the invention provides a new method for the effective separation of xylose and glucose in the wood fiber raw materials and the efficient alcoholic fermentation and significantly reduces the production cost for the fermentation of the ethanol in wood fiber raw materials.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
High temperature and strong alkali resistant xylanase improved gene, genetic engineering bacterial strain thereof and preparation method thereof
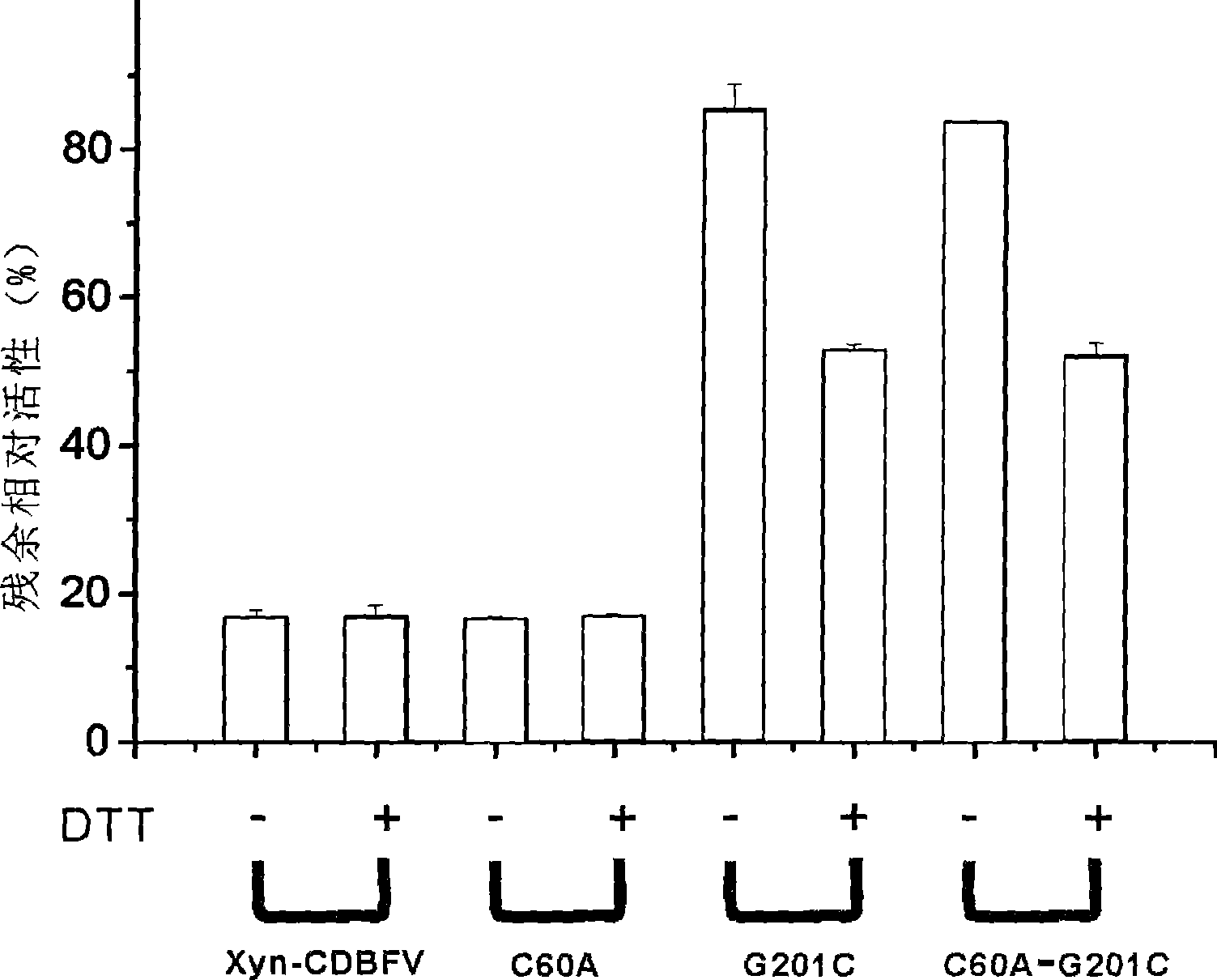
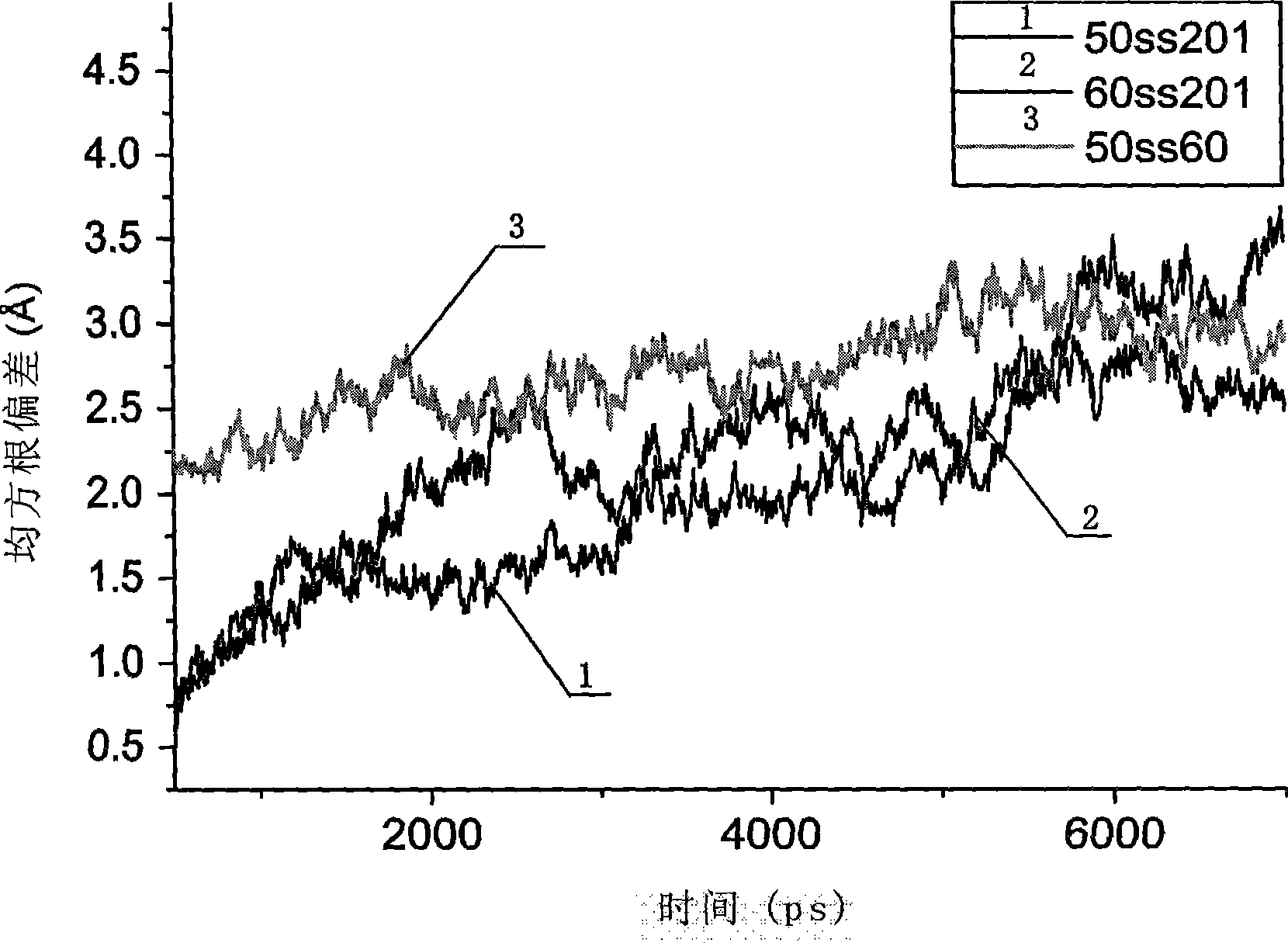
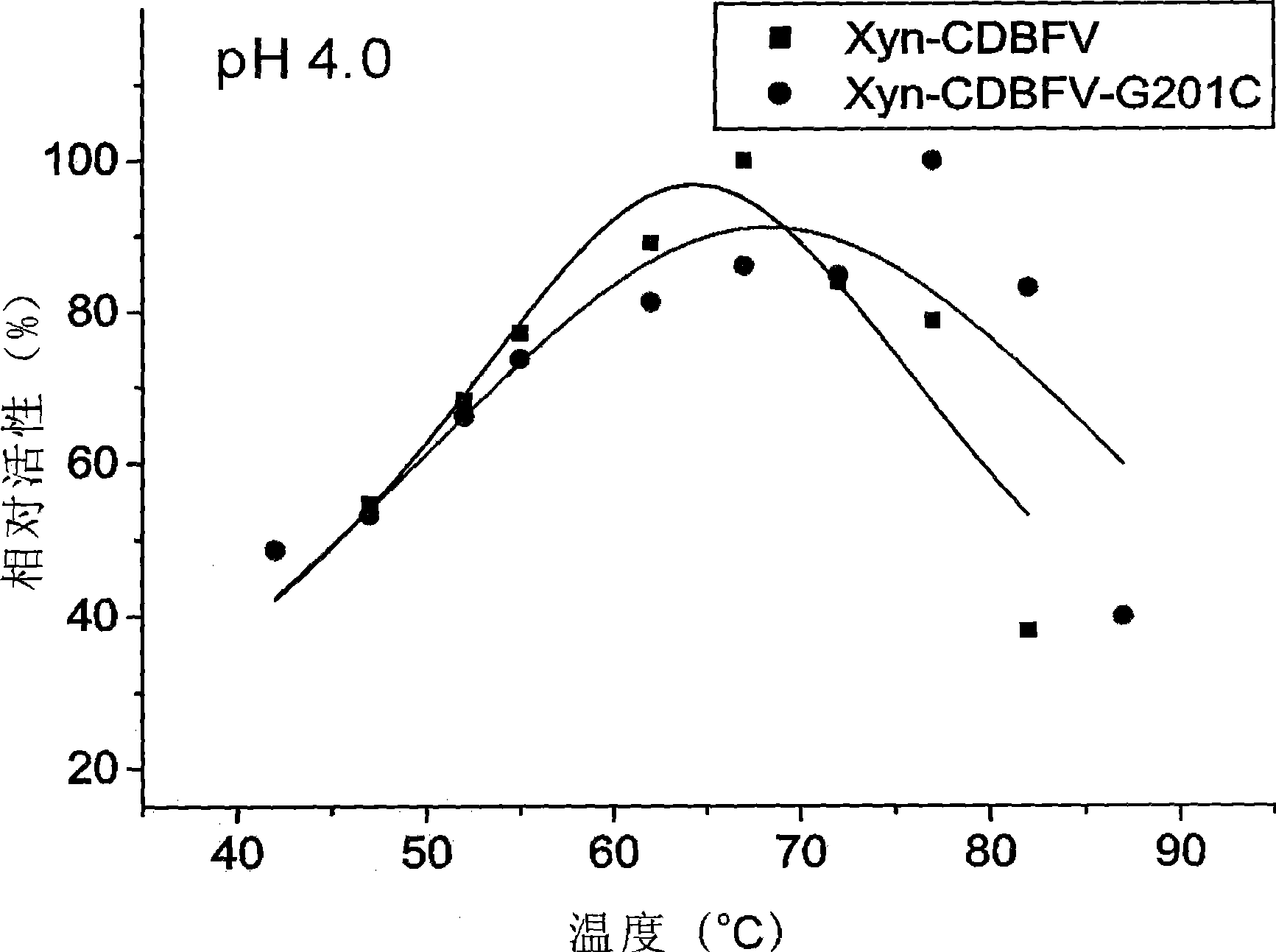
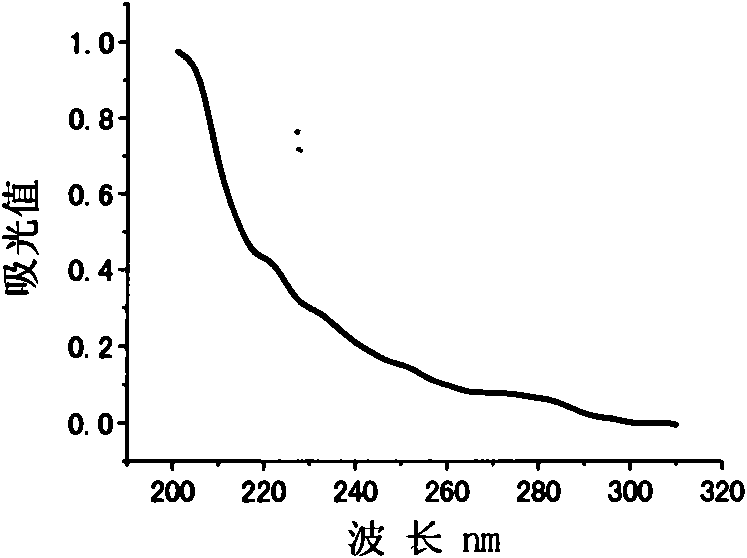
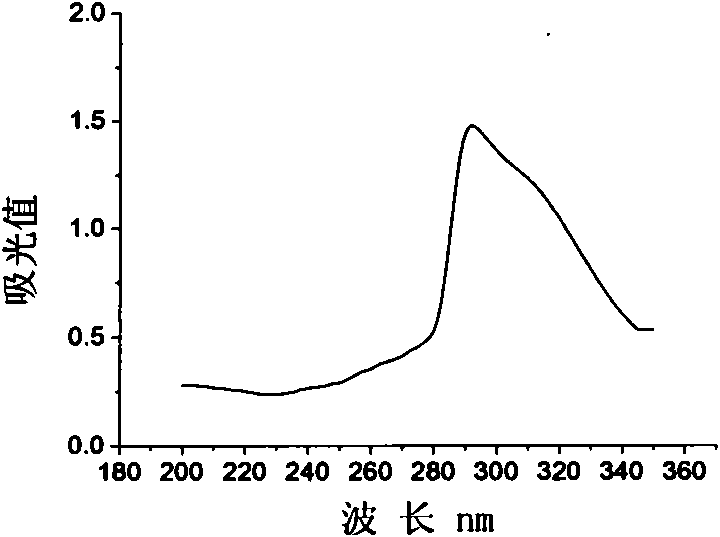
ActiveCN101392266AImprove thermal stabilityEasy extractionFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisXylanase
The invention provides a modified coding gene of xylanase that has high activity in the condition of high temperature and strong alkali, a recombinant plasmid thereof, a yeast recombination genetic engineering strain containing the gene and a preparation method of the gene. Compared with the original xylanase, the modified xylanase is mutated into cysteine from glycin of the 201 site of amino acid sequence of the original xylanase; and the modified xylanase has higher heat stability, after being processed for 10 minutes at the temperature of 75 DEG C, the residual activity of the modified xylanase reaches 80 percent, while that of the original xylanase is only 15 percent. The activity of the modified xylanase is 1.5 to 2 times of that of the original xylanase at the environment with high temperature and strong alkali and can decompose xylan for a long time at high temperature. The invention also provides the Pichia pastoris yeast recombination genetic engineering strain containing the modified gene. The modified xylanase can be widely applied to industries of paper making, feedstuff and food.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Method for preparing sulfated bagasse xylan
The invention discloses a method for preparing sulfated bagasse xylan. The method comprises the following steps of: dehydrating and cooling pyridine; dripping chlorosulfonic acid into the pyridine, wherein the volume ratio of the pyridine to the chlorosulfonic acid is between 15 and 25; when white solid appears in the reaction flask, adding anhydrous formamide to help dissolving, and continuing stirring for 1 to 2 hours; transferring the obtained solution into a constant-temperature water bath kettle, adding amino-sulfonic acid and bagasse xylan into the water bath kettle, and esterifying for 2.5 to 4 hours, wherein the ratio of the volume of the chlorosulfonic acid to the mass of the xylan is 1.2-2.0:0.7-1.5; adding excessive acetone and standing for 2 hours; pouring out the supernatant and adding the mixed solution of 75 to 90 volume percent methanol and water; depositing and then filtering; collecting the deposit and washing for multiple times; washing the deposit with the aqueous solution of ethanol at least once; washing and dehydrating with acetone; and drying in vacuum at 50 DEG C for 6 hours. The method has the characteristics of high substitution degree, high utilization rate of raw materials, easy control on synthesis process, simple post-treatment process and stable product quality; moreover, the prepared sulfated bagasse xylan has high water solubility.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Production method for xylose by enzyme process
The technical scheme for xylose preparation with enzyme comprises: using CGMCC1476 as a Aspergillus niger strain to ferment and prepare excision xylanase that has high activity and needs mild reaction condition; enzymolyzing specially corn core and zylan in straw materail; refining to prepare single-xylose with purity more than 90%. This invention has no pollution to environment and conversion more than 80%.
Owner:JINAN GUOLI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
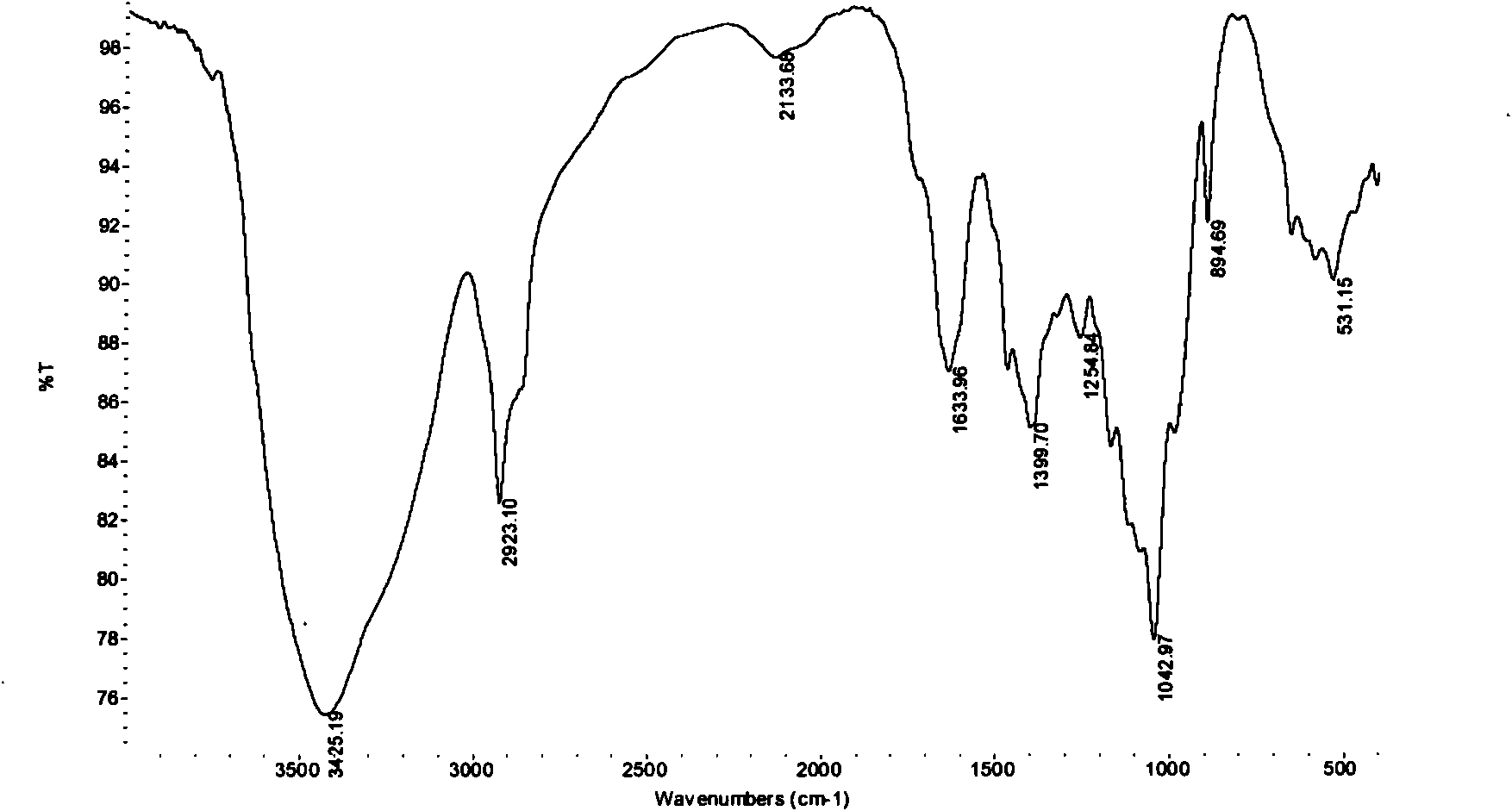
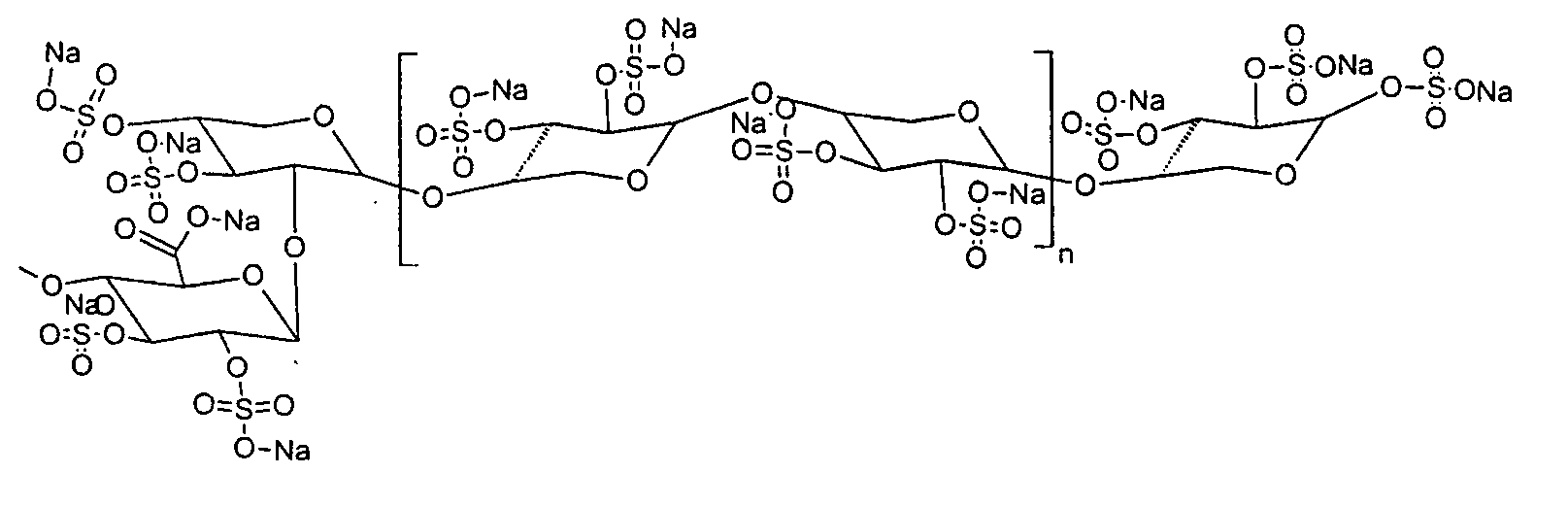
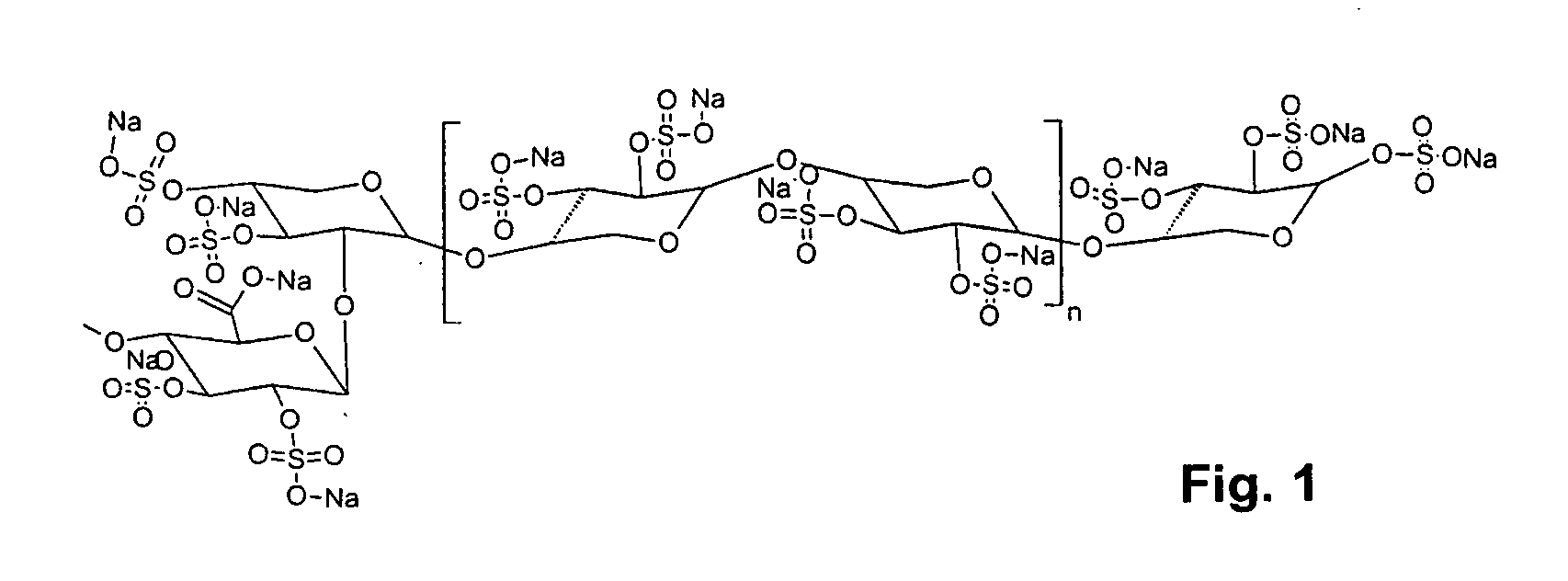
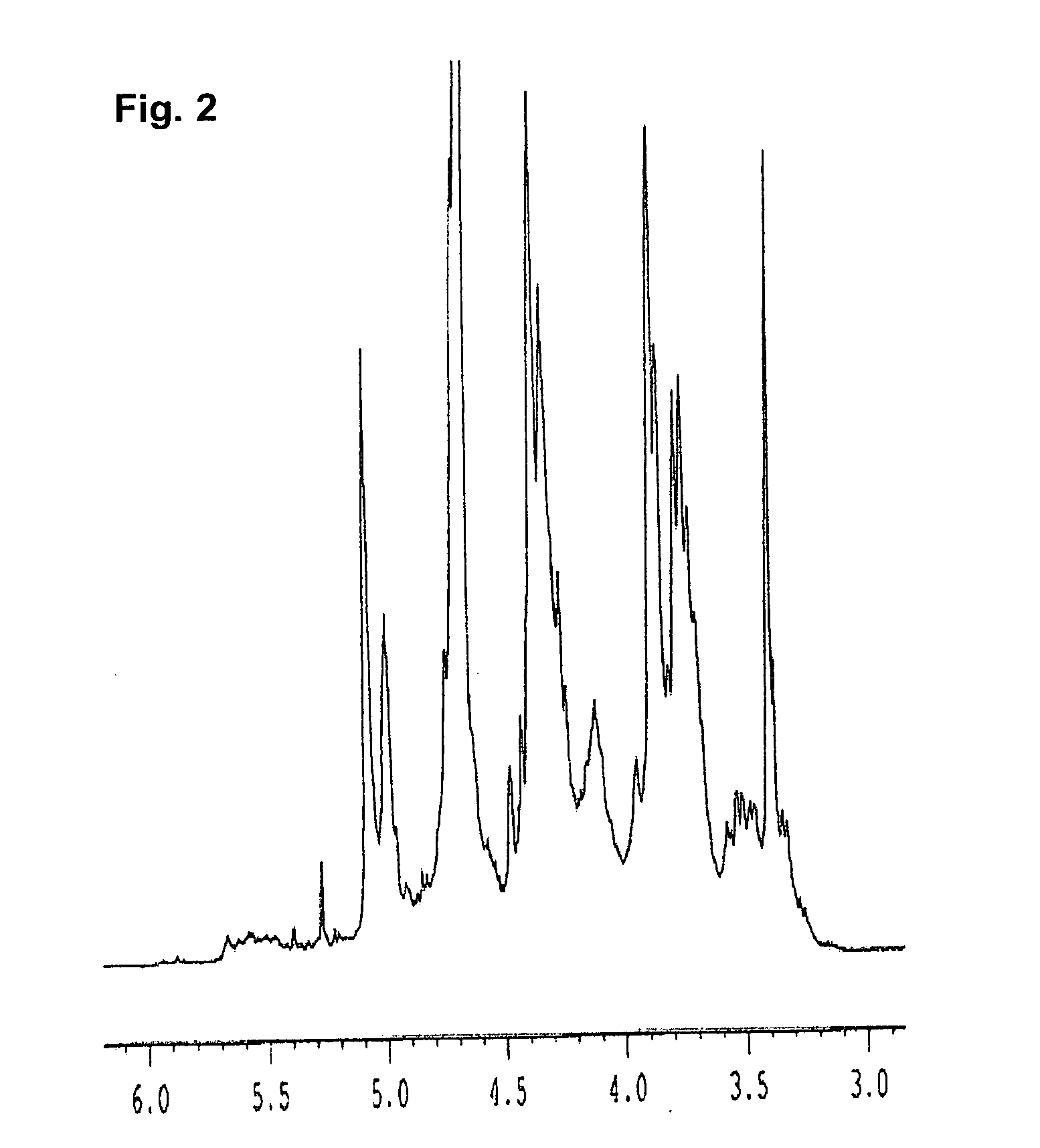
Sulfated polysaccharide compound and the preparation and use thereof
The present invention relates to a sulfated polysaccharide compound and the preparation and use thereof, and in particular to a narrow distribution low molecular weight, highly sulfated pentosan (in this instance a xylan) referred to as glucuronoxylan sulfate (GXS). The invention has been developed primarily for use in the treatment of various clinical conditions. However, it will be appreciated that the invention is not restricted this particular field of use.
Owner:PARNELL TECH
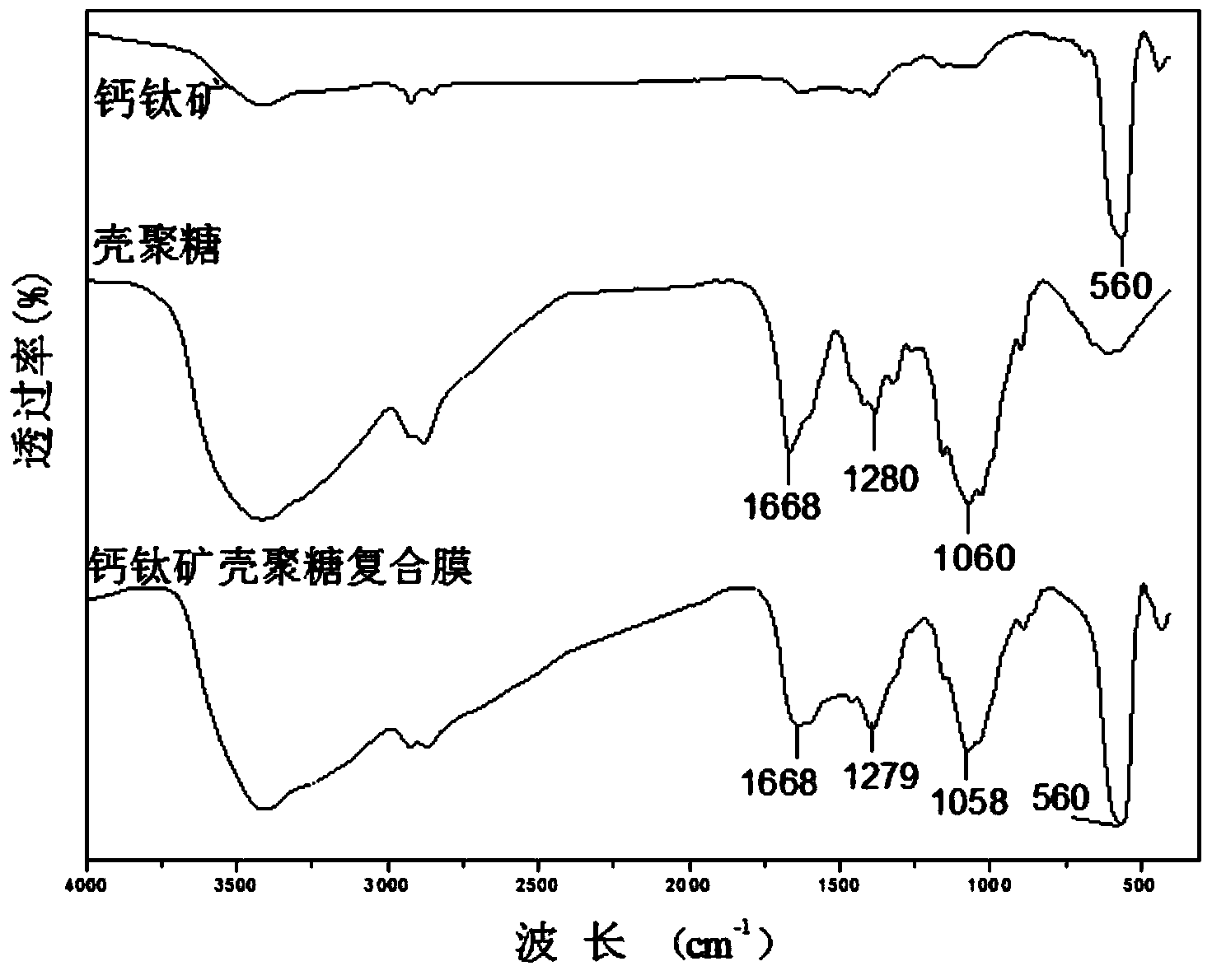
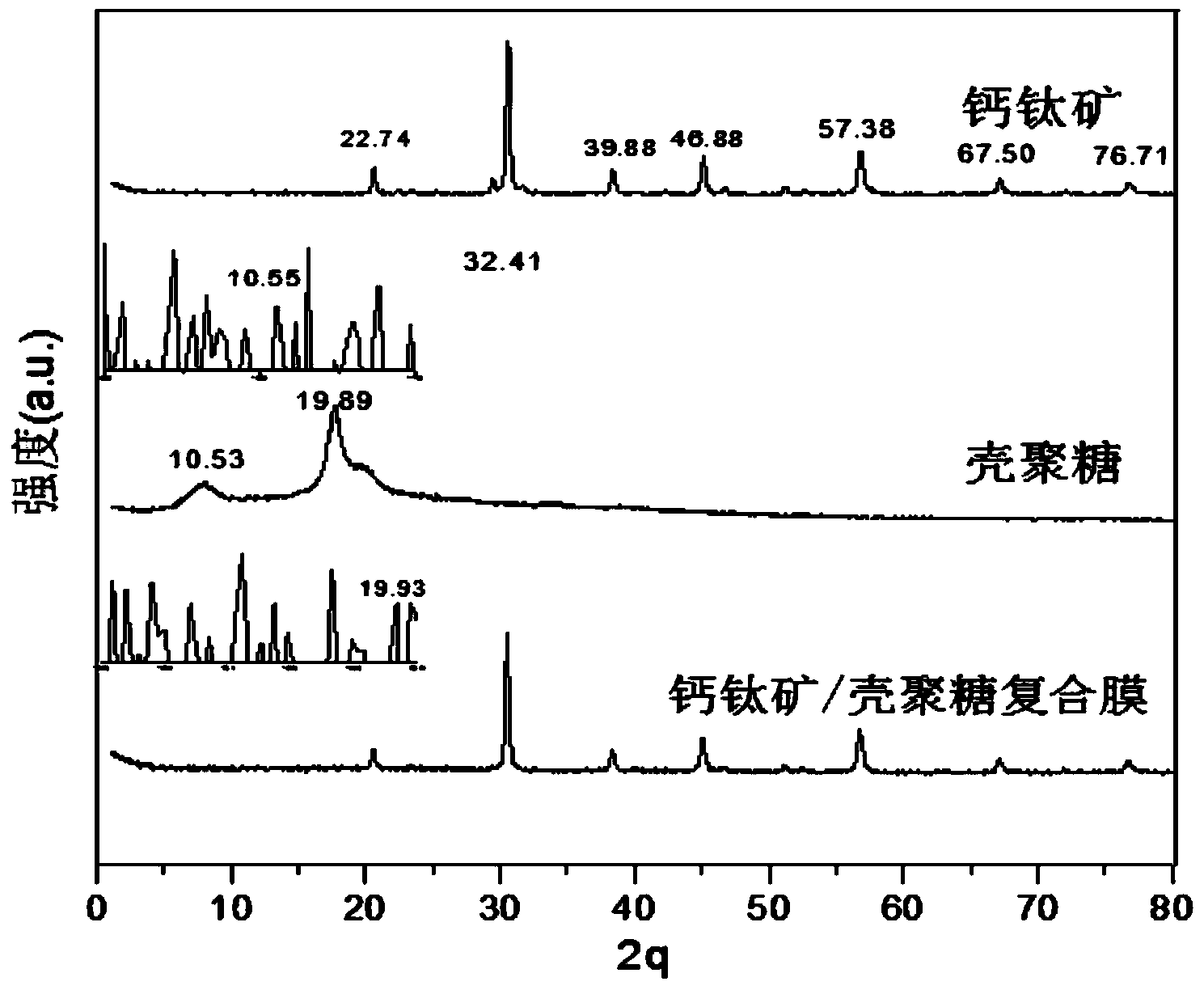
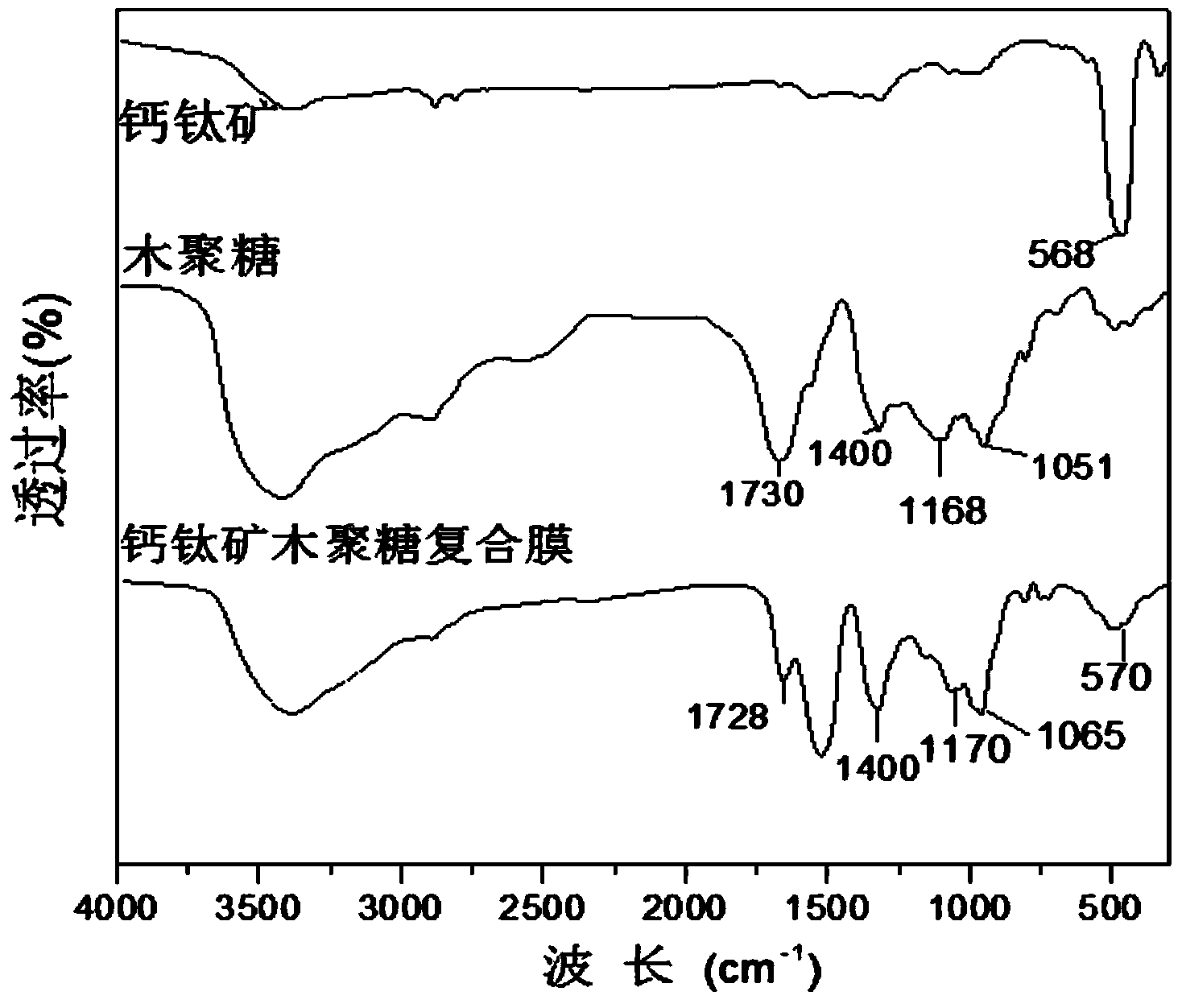
Method for degrading methyl orange by use of perovskite/polysaccharide composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN103936097AGood catalytic degradation effectShorten the timeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPhotocatalytic degradationMethyl orange
The invention discloses a method for degrading methyl orange by use of perovskite / polysaccharide composite photocatalyst. The method comprises the following steps: preparing perovskite by utilizing nitrate of La, Cu and Fe, adding the perovskite and chitosan into an acetic acid solution, and performing ultrasonic treatment; drying to form a film to obtain a perovskite / chitosan composite photocatalyst; or adding xylan into distilled water, adding sodium hypophosphite and citric acid solution, adding perovskite, performing ultrasonic treatment, dehydrating, crosslinking to form a film, and washing with ethanol to obtain a perovskite / xylan composite photocatalyst; adding the composite photocatalytic material into the methyl orange solution, respectively reacting for 470-490 minutes at normal temperature in ultraviolet radiation. The polysaccharide used in the method is formed by compounding the catalyst and polysaccharide respectively with chitosan and xylan, the methyl orange photocatlytic degrading capability of the polysaccharide can be improved. The polysaccharide has the advantages of high catalytic efficiency, strong photo-response performance, regeneration, recycling and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Composite biological enzyme preparation for deweighting treatment of domestic sludge, and production and application method thereof
InactiveCN102351321AStable structurePrevents oxidative deactivationBiological sludge treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentManganese peroxidaseNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a composite biological enzyme preparation for the deweighting treatment of domestic sludge, and a production and application method thereof. The invention is characterized in that 100-500 kilograms of composite biological enzyme for the deweighting treatment of domestic sludge are used for 100 thousand tons of municipal domestic sewage, wherein the composite biological enzyme for the deweighting treatment of domestic sludge comprises 25-30 parts of protease, 20-25 parts of one or more of laccase, polyphenol oxidase and manganese peroxidase, 17-21 parts of one or more of xylanase, pentosanase and mannase, 20-25 parts of one or more of cellulase, pectinase and hemicellulase, 10-15 parts of lipase and 12-16 parts of amylase. Compared with the prior art, the invention removes hydrogen sulfide gas and undesirable odor thereof, simultaneously eliminates the inhibiting effect of H2S on the nitrification process, effectively reduces nitrate and ammonia, decomposes proteins, starch, fat, food oil, xylan, cellulose and other organic substances, converts suspended substances, accumulated waste and soluble organic substances in the sludge into carbon dioxide, nitrogengas, oxygen gas, water and sulphate, reduces the TSS (Total Suspended Solids), COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) and BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand), greatly decreases the yield of the sludge, and has the advantages of no poison, no corrosiveness and no secondary pollution production.
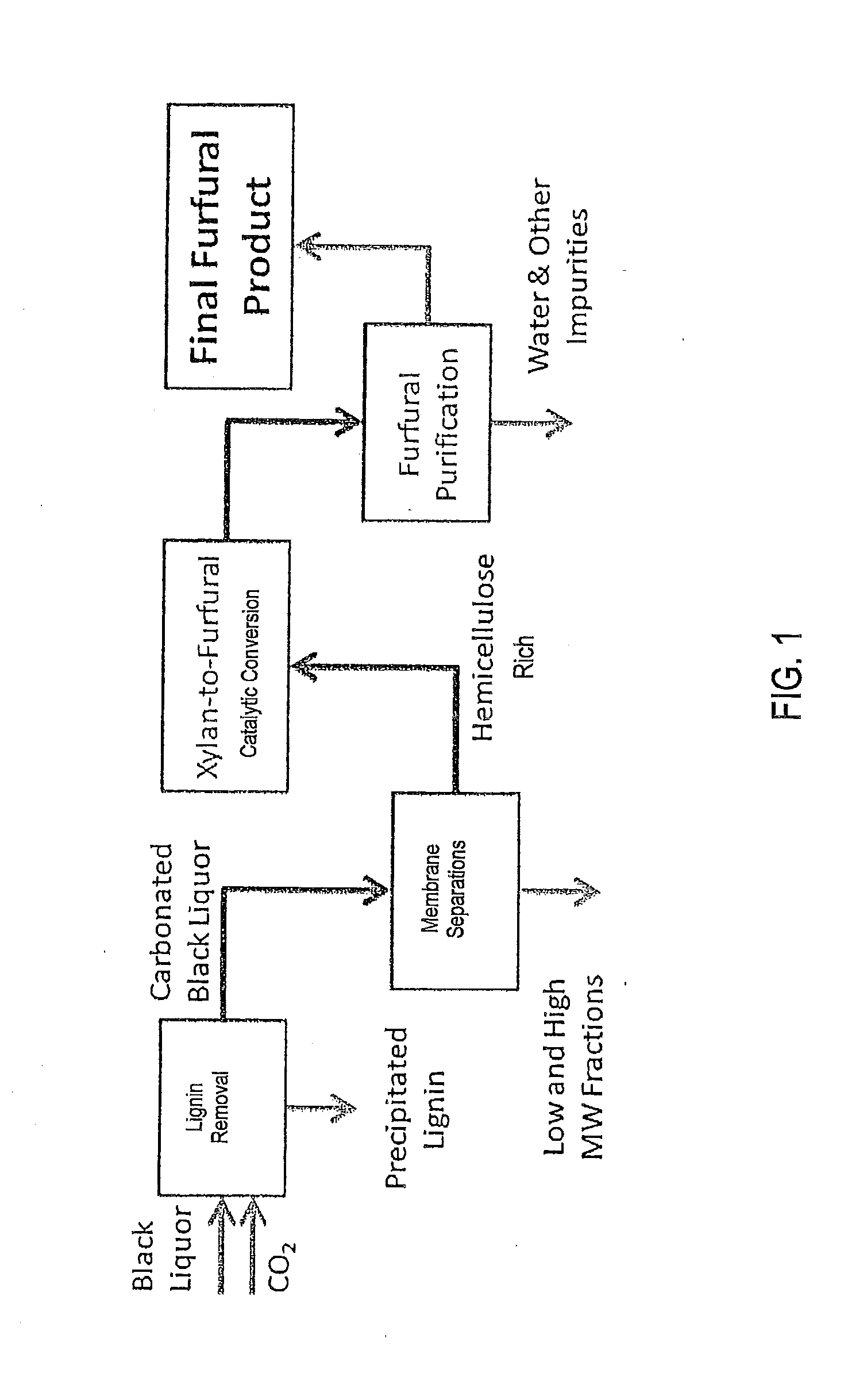
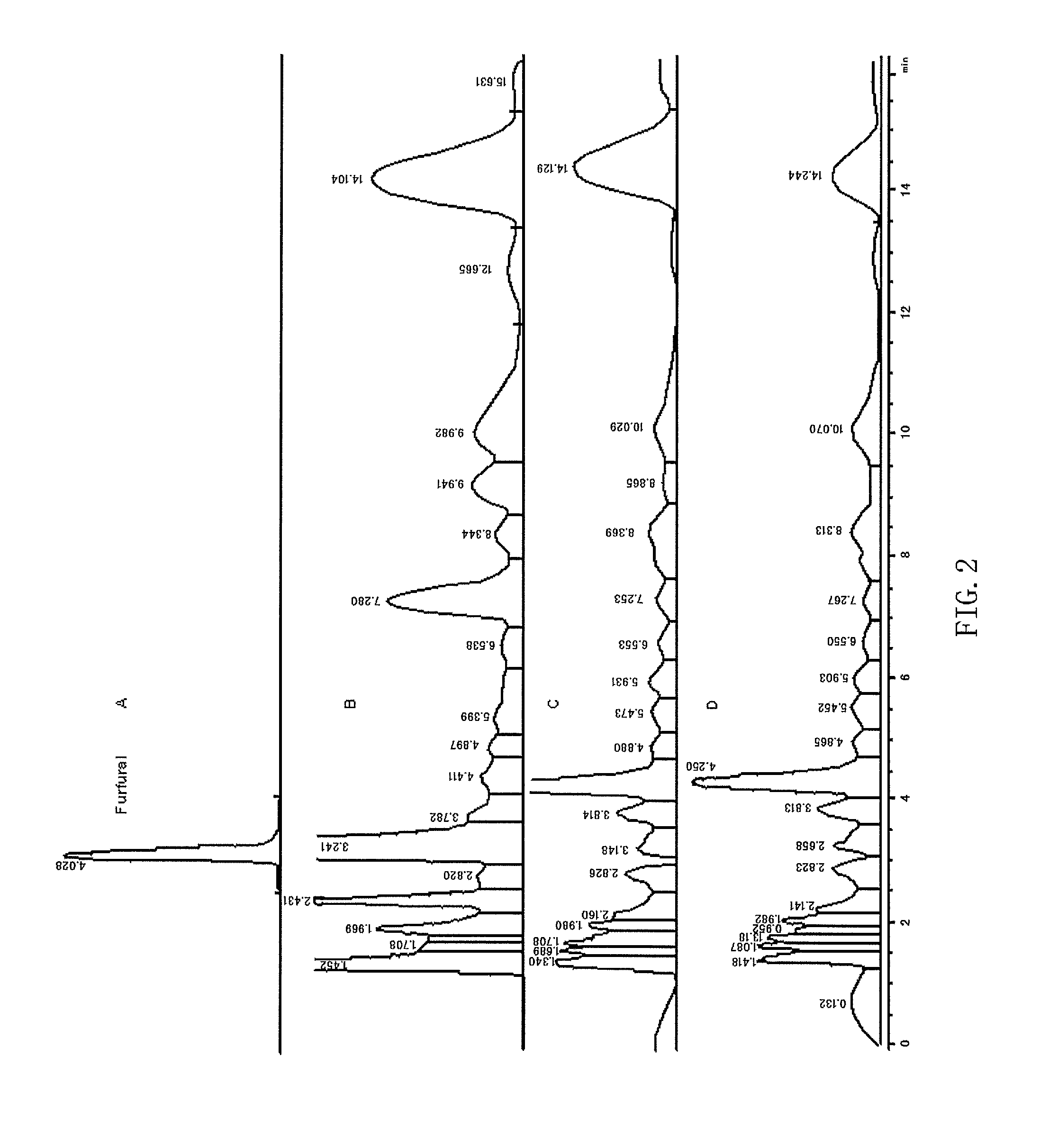
Process for producing furfural from black liquor
A process for making furfural using papermaking black liquor from the kraft pulping process as a feed material. First, the lignin is removed from the black liquor by carbonizing the black liquor to a pH below pH 10 to insolubilize the lignin, neutralize NaOH and other inorganic components of the black liquor. The next step is to treat the carbonated black liquor that contains the hemicellulose to remove the high molecular weight components. In a preferred embodiment the treatment uses multiple sequential steps. The first step of the treatment is to use ultrafiltration, centrifugation or dissolved-air floatation to separate the high molecular weight components. The second filtration is to pass the hemicellulose containing black liquor stream through a nanofilter to remove low molecular weight components. The conversion of xylans in the hemicellulose-containing mixture to furfural is accomplished using a catalytic process. The xylans are converted to pentose sugars and then converted to furfural. The furfural is formed at a low concentration and then further concentrated.
Owner:LIQUID LIGNIN
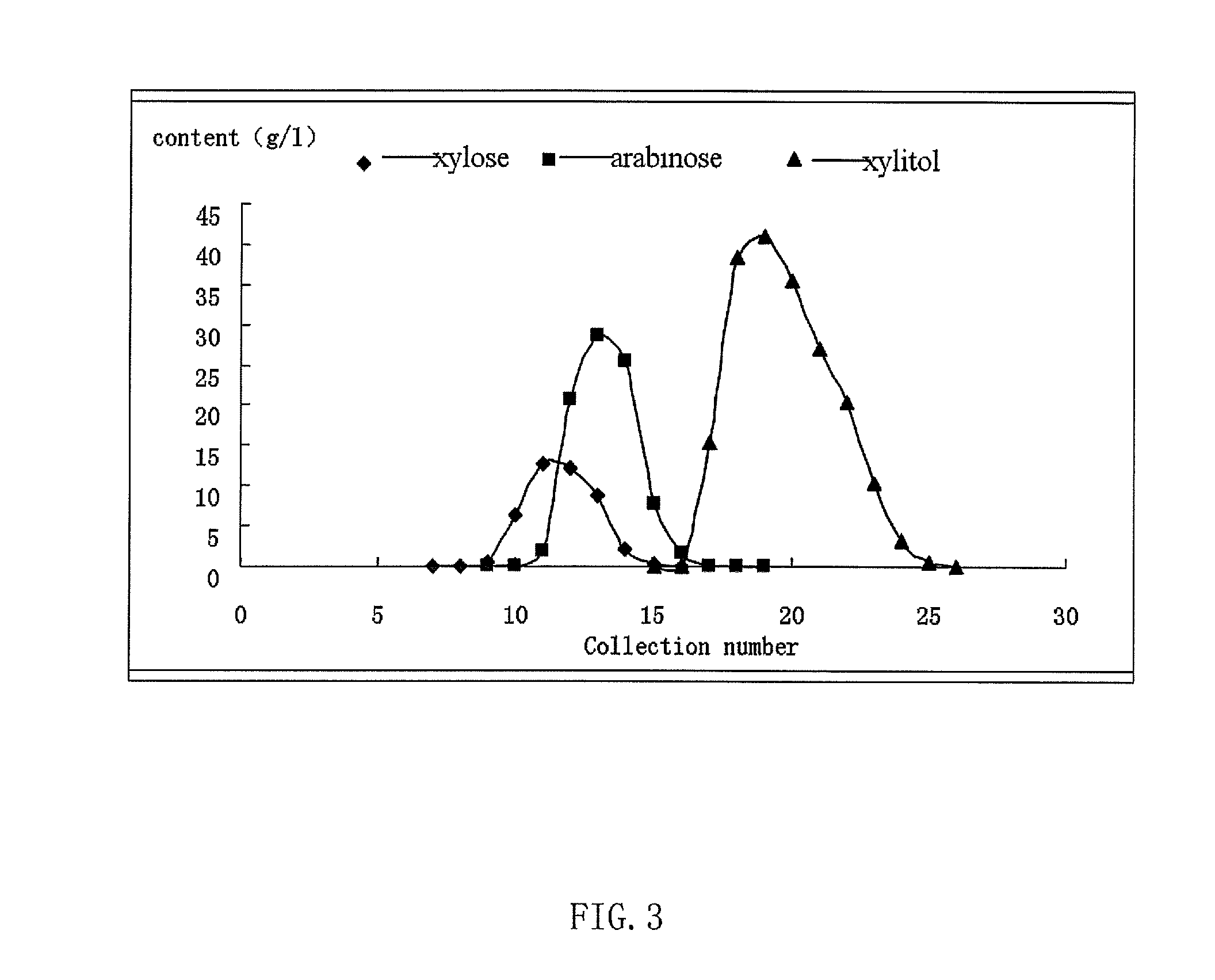
Method of producing xylitol and arabinose at same time from hemicellulose hydrolysates
InactiveUS20120021467A1Low costEliminate disadvantagesMicroorganismsFermentationIssatchenkia occidentalisHydrolysate
The present invention relates to a method of producing xylitol and arabinose at same time from hemicellulose hydrolysates, material rich in xylan is hydrolyzed by acid or enzymes to obtain hydrolysate mostly containing xylose and arabinose, then inoculated in Issatchenkia orientalis S-7 and / or Issatchenkia occidentalis LJ-3 to eliminate the inhibitor of microbes, after that / or at the same, inoculated a yeast of Candida tropicalis which can consume the glucose, transform the xylose to xylitol and can not consume the arabinose, and fermented, then fermented liquor containing xylitol and arabinose is obtained. After separation, xylitol with purity more than 99% and arabinose with high purity are obtained. After concentration and crystallization respectively, crystalline xylitol and crystalline arabinose are obtained respectively.
Owner:THOMSON BIOTECH XIAMEN PTE
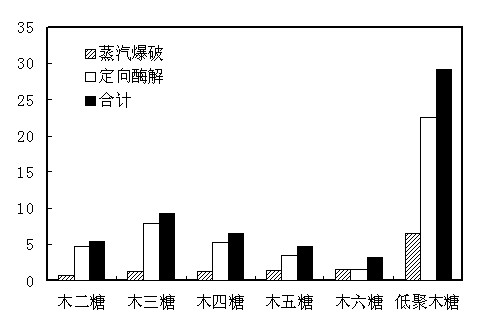
Method for preparing xylo-oligosaccharides by adopting steam explosion and oriented enzymolysis
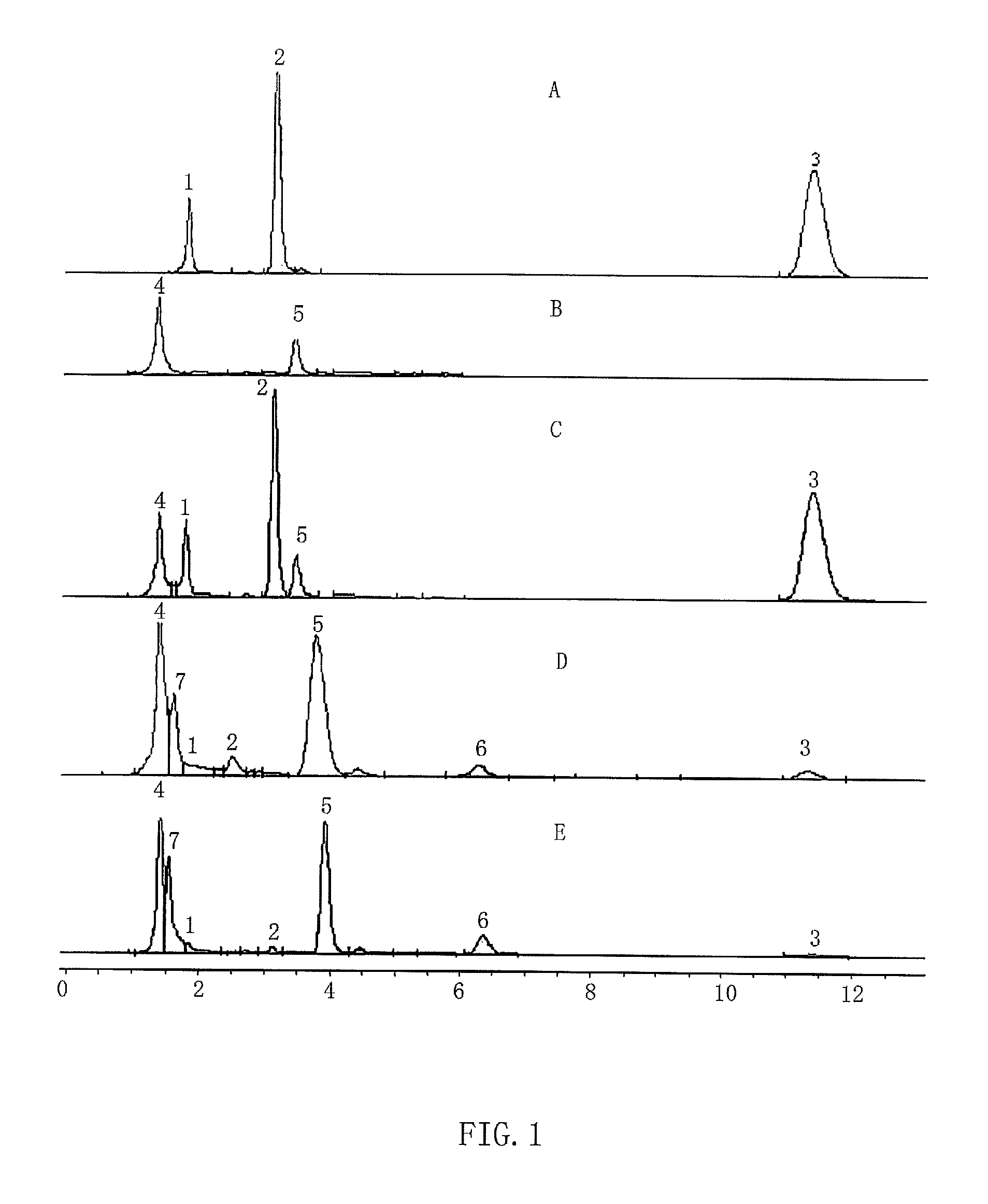
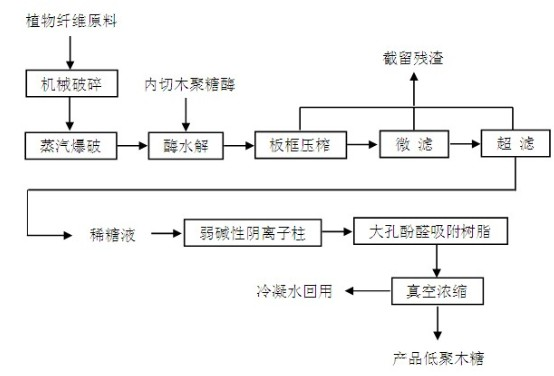
The invention discloses a method for preparing xylo-oligosaccharides by adopting steam explosion and oriented enzymolysis. The method comprises the following steps of plant fiber raw material chopping, steam explosion, endo-xylanase oriented enzymolysis, filter pressing by an enzymolysis system, micro-filtration, ultrafiltration, separation and extraction, anion exchange resin refining, macroporous phenolic aldehyde absorbent resin refining and decompressed evaporation concentration. The method for preparing xylo-oligosaccharides, provided by the invention, realizes that steam explosion and oriented enzymolysis are organically combined to substitute the traditional acid or alkali extraction method or single steam explosion method, thereby not only effectively degrading and dissolving out xylan in raw materials, but also overcoming the defects of more consumption and various impurities of acid or alkali chemicals, particularly overhigh content of noxious substances and high cost for following separating and refining in other processes, realizing no waste water emission in the production process, greatly simplifying the extraction process of the xylan, saving the operation labor hour, and remarkably improving the environment friendless and the economic benefit of production of xylo-oligosaccharides.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com