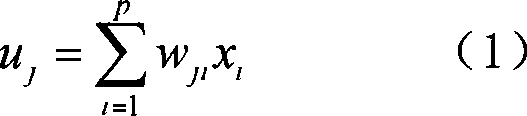Patents
Literature
1056 results about "Biochemical oxygen demand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) is the amount of dissolved oxygen needed (i.e. demanded) by aerobic biological organisms to break down organic material present in a given water sample at certain temperature over a specific time period. The BOD value is most commonly expressed in milligrams of oxygen consumed per litre of sample during 5 days of incubation at 20 °C and is often used as a surrogate of the degree of organic pollution of water.
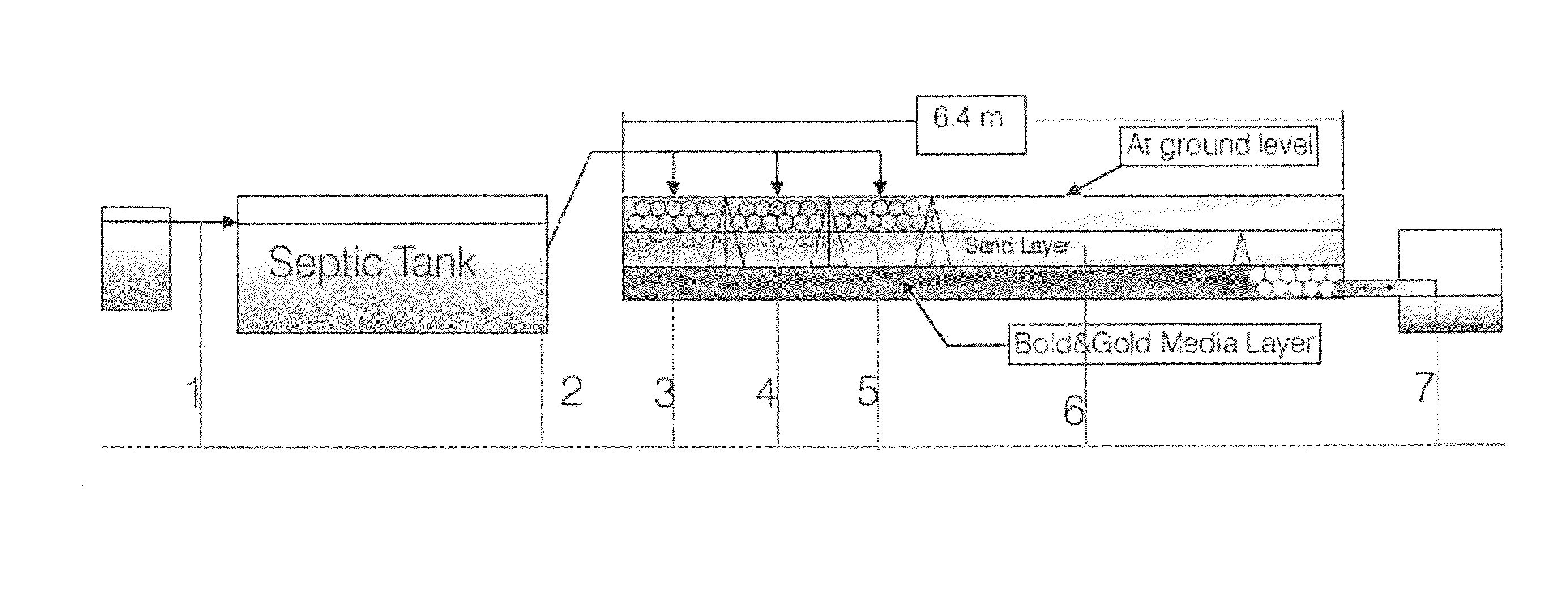
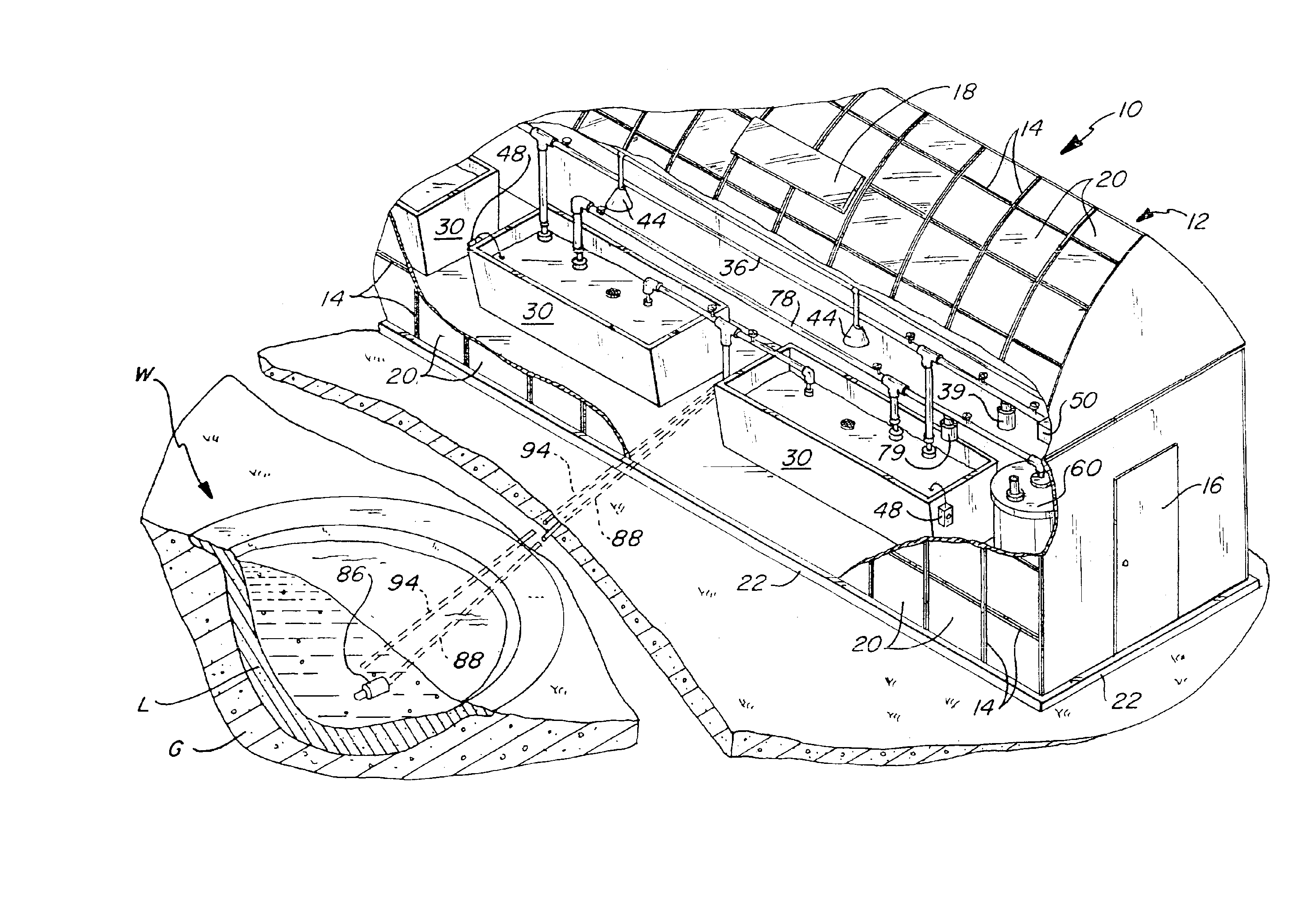
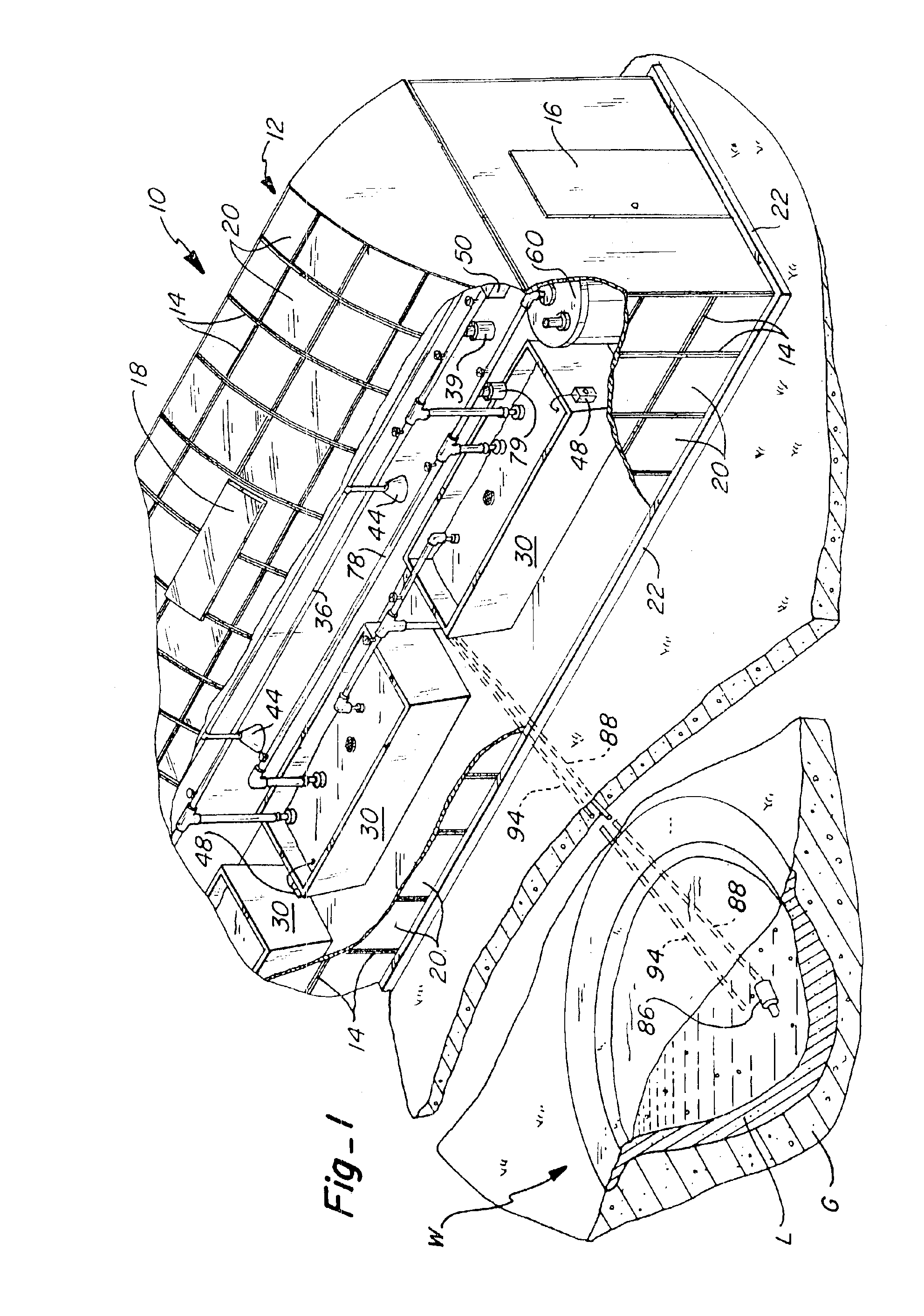
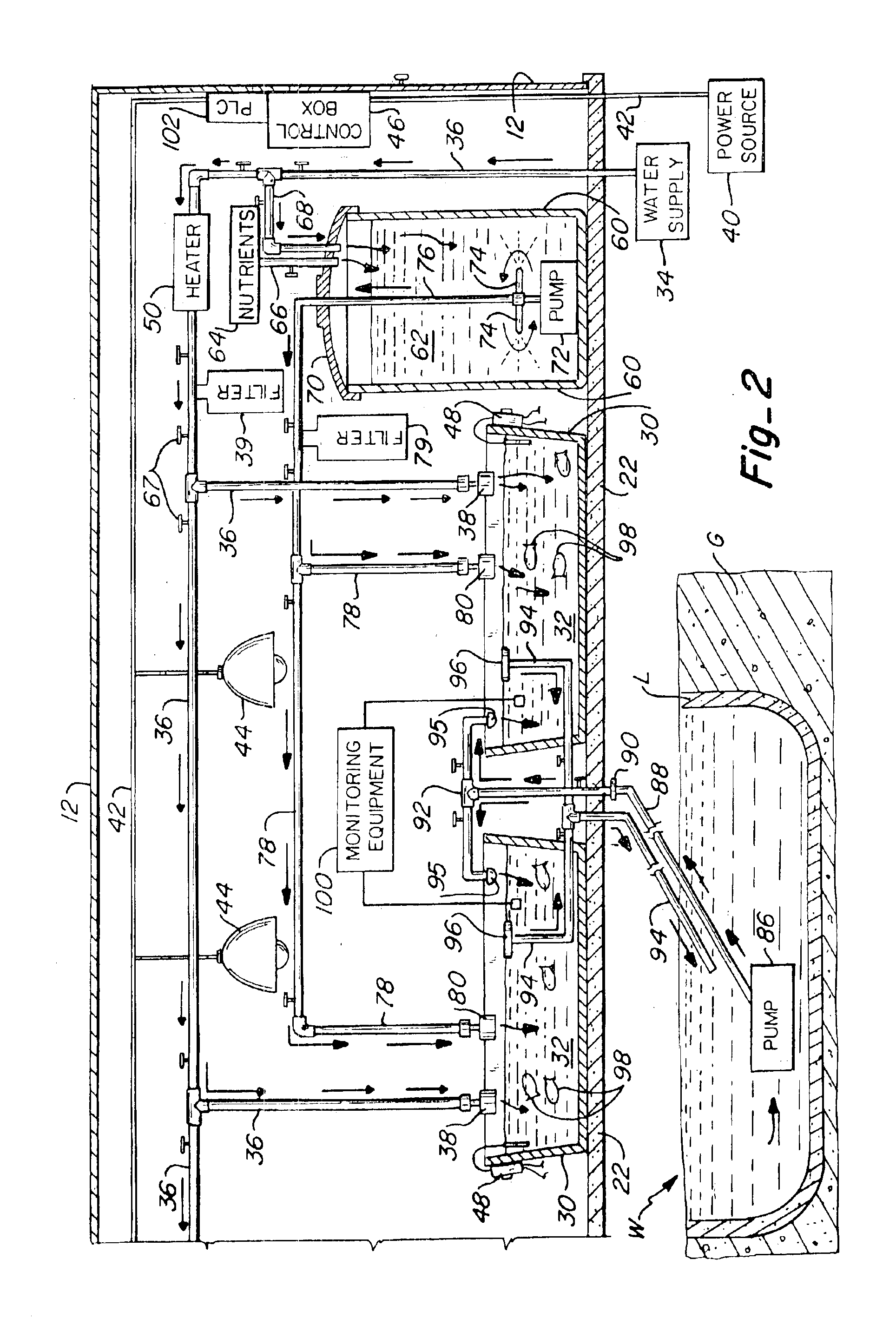
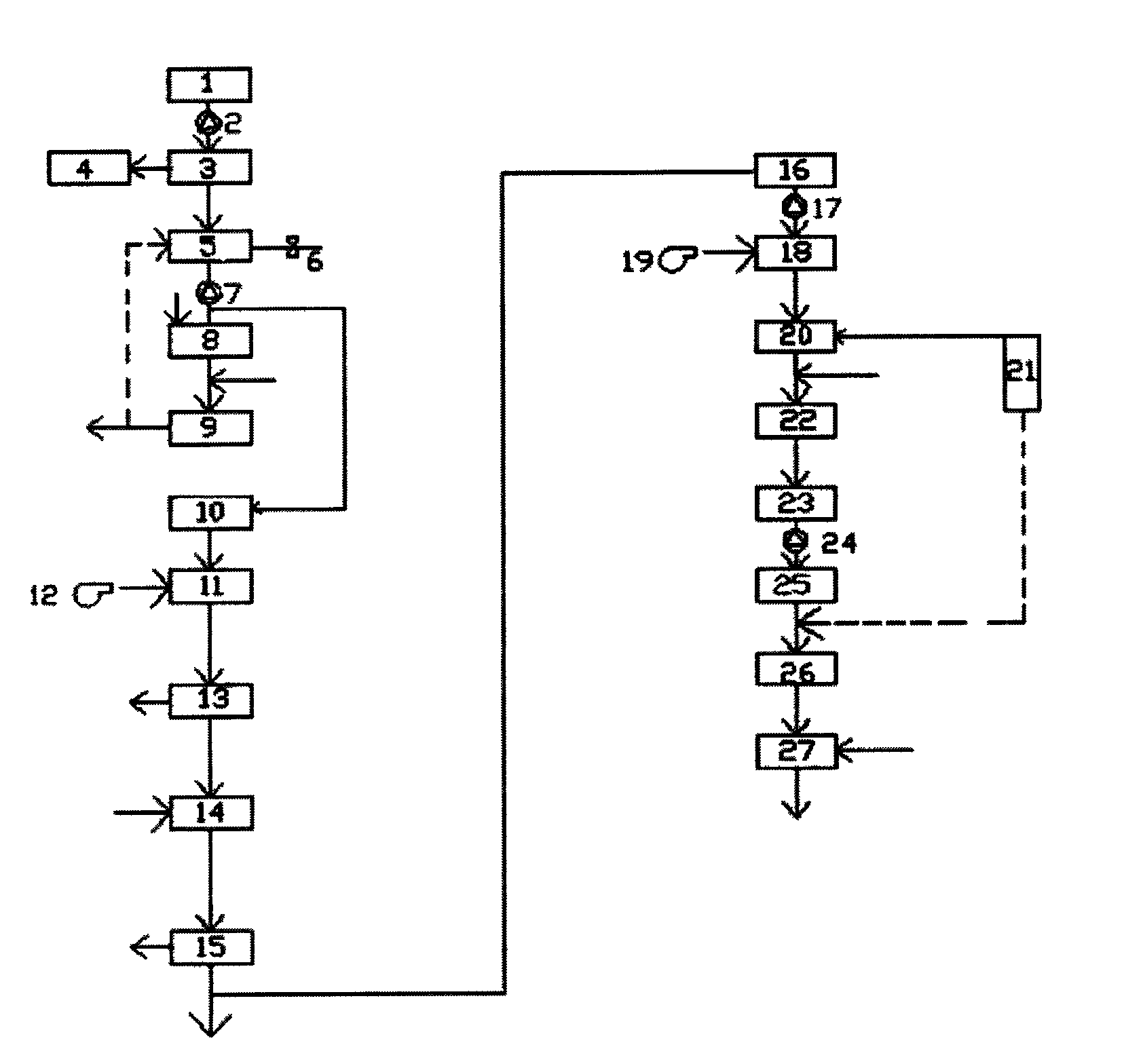
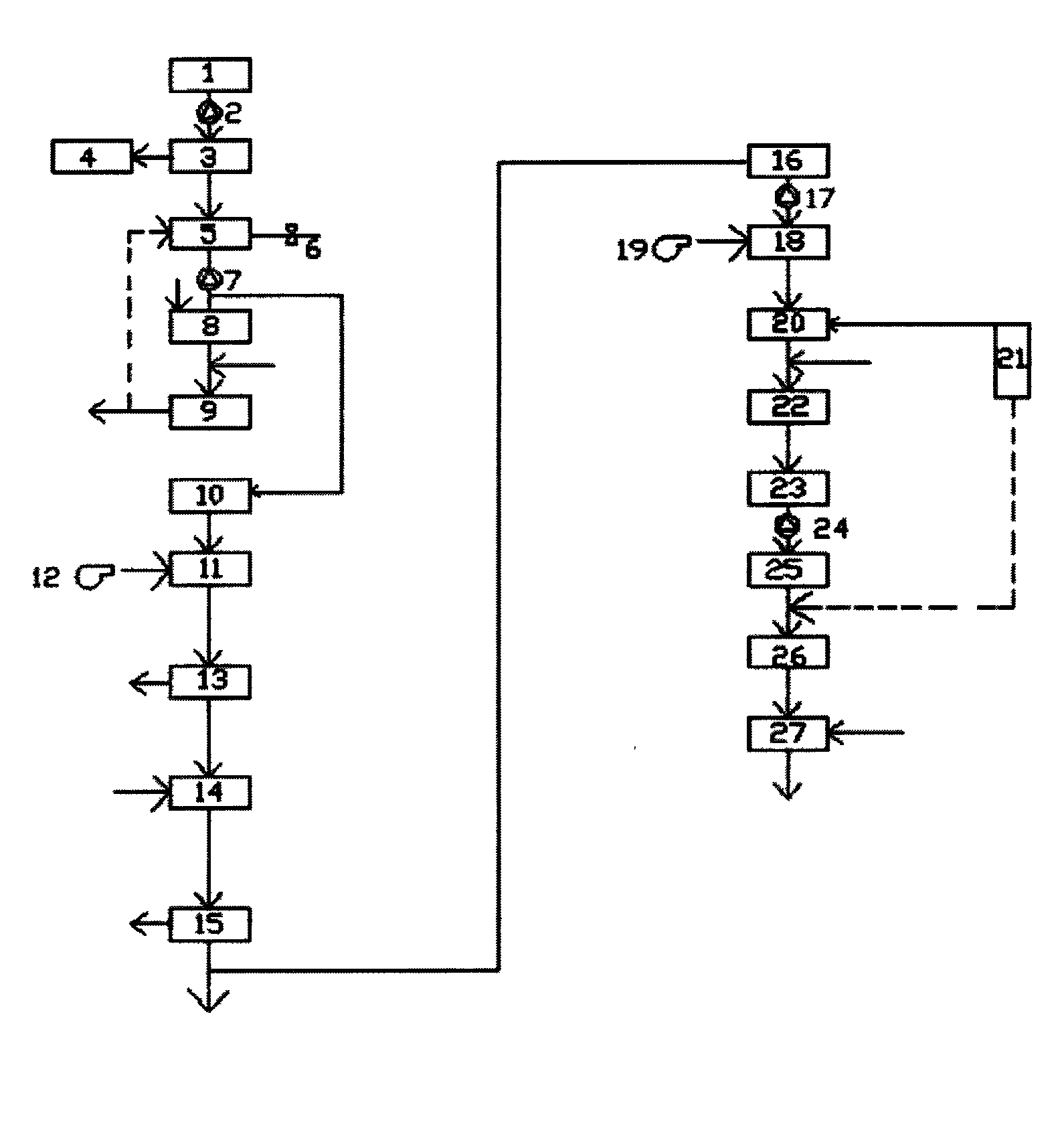
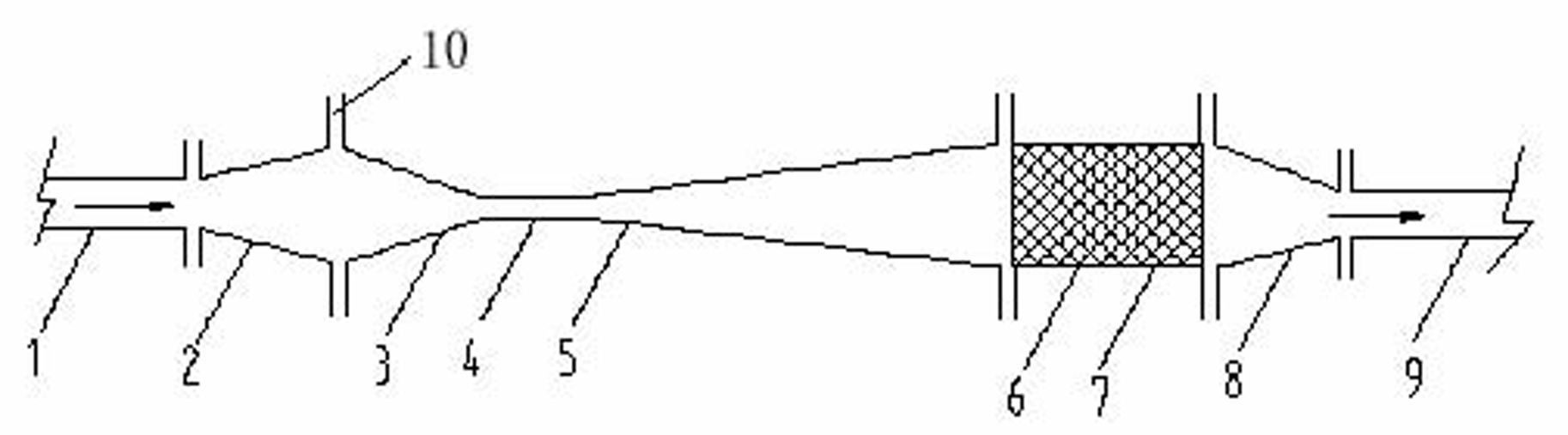
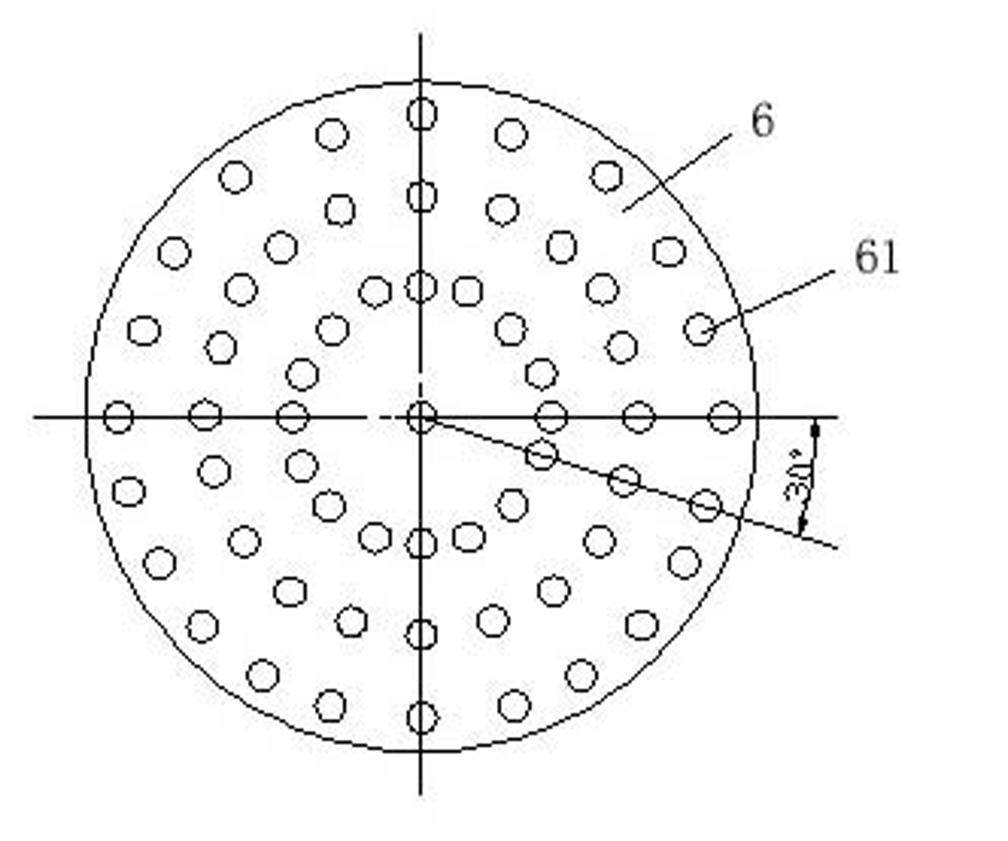
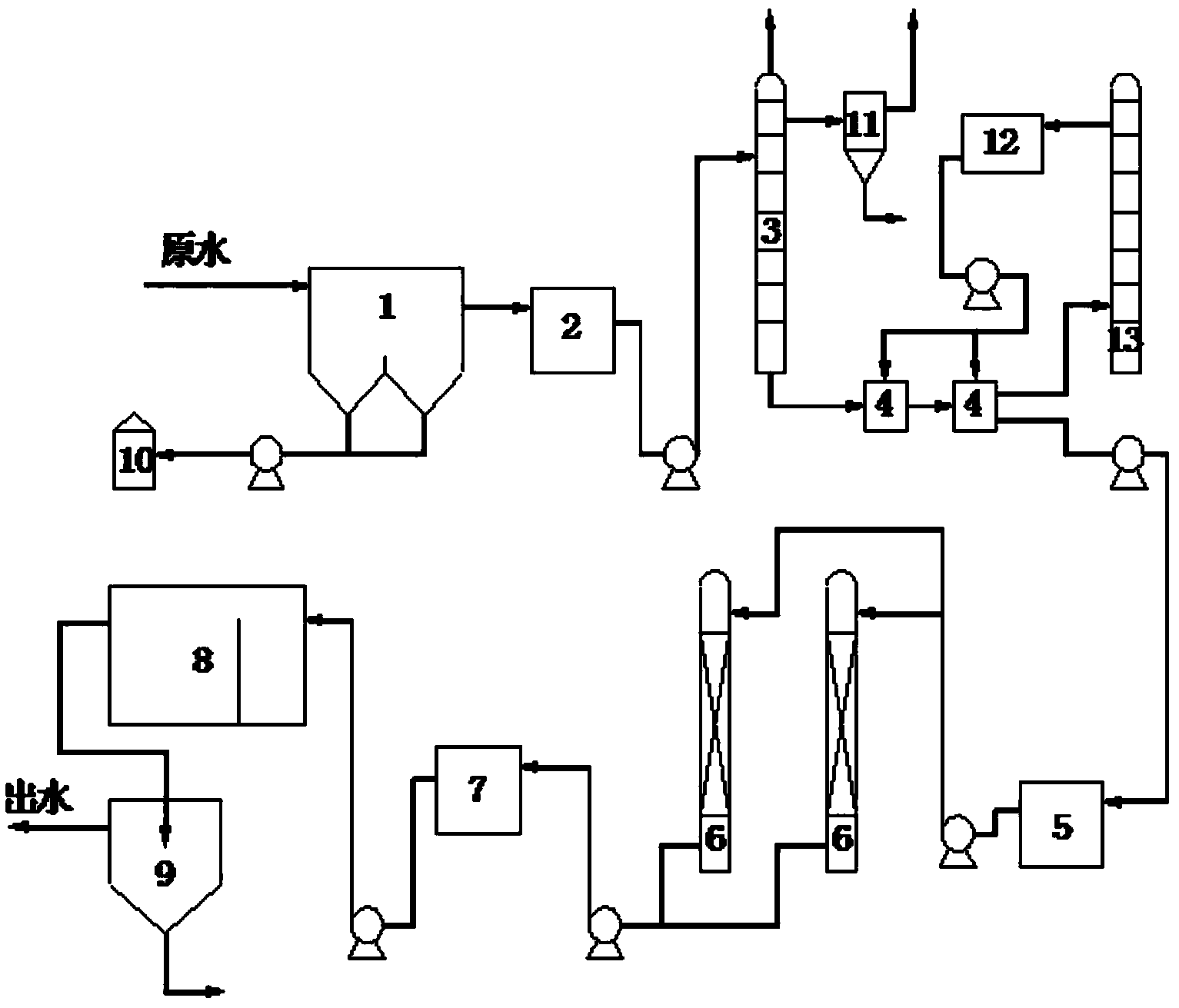
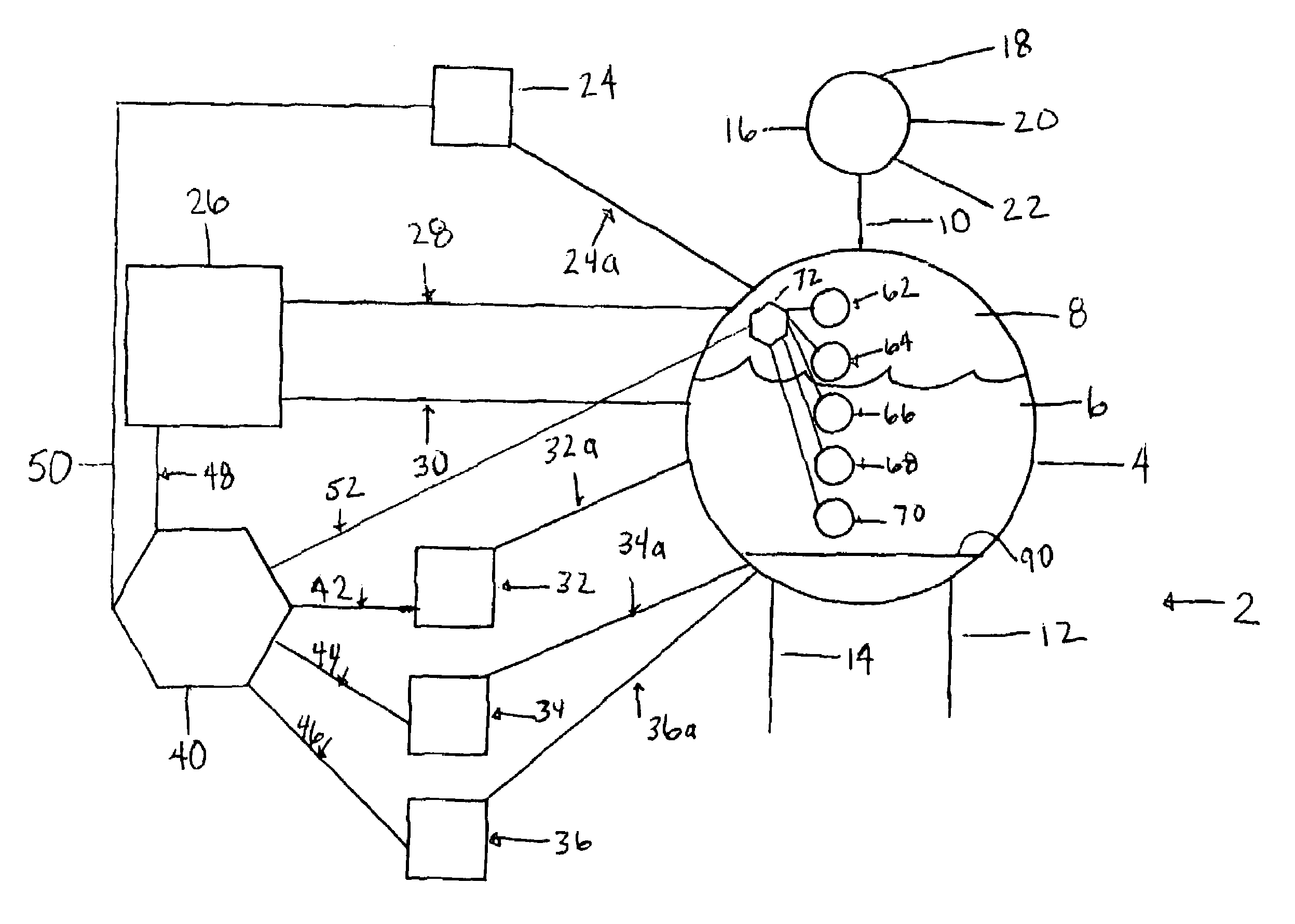
Subsurface upflow wetland system for nutrient and pathogen removal in wastewater treatment systems
ActiveUS8252182B1Low maintenance burdenHigh benefit cost ratioWater cleaningContaminated soil reclamationFecesTotal suspended solids
Methods and systems for a subsurface upflow wetland for wastewater treatment that includes a series of parallel treatment cells, each cell including from bottom to top, a layer of gravel, a layer of sand over the gravel to remove pathogens from a septic effluent, a pollution control medium above the sand layer to remove nutrients, total suspended solid, and biochemical oxygen demand and a growth media mixture layered on top of the pollution control media to grow plants, and a gravity distribution system to distribute effluent to the series of parallel treatment cells. The pollution control medium includes at least one recycled material and at least one naturally occurring material. In an embodiment it includes recycled tire crumb, sand and limestone or recycled tire crumb, compost, sand and limestone.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
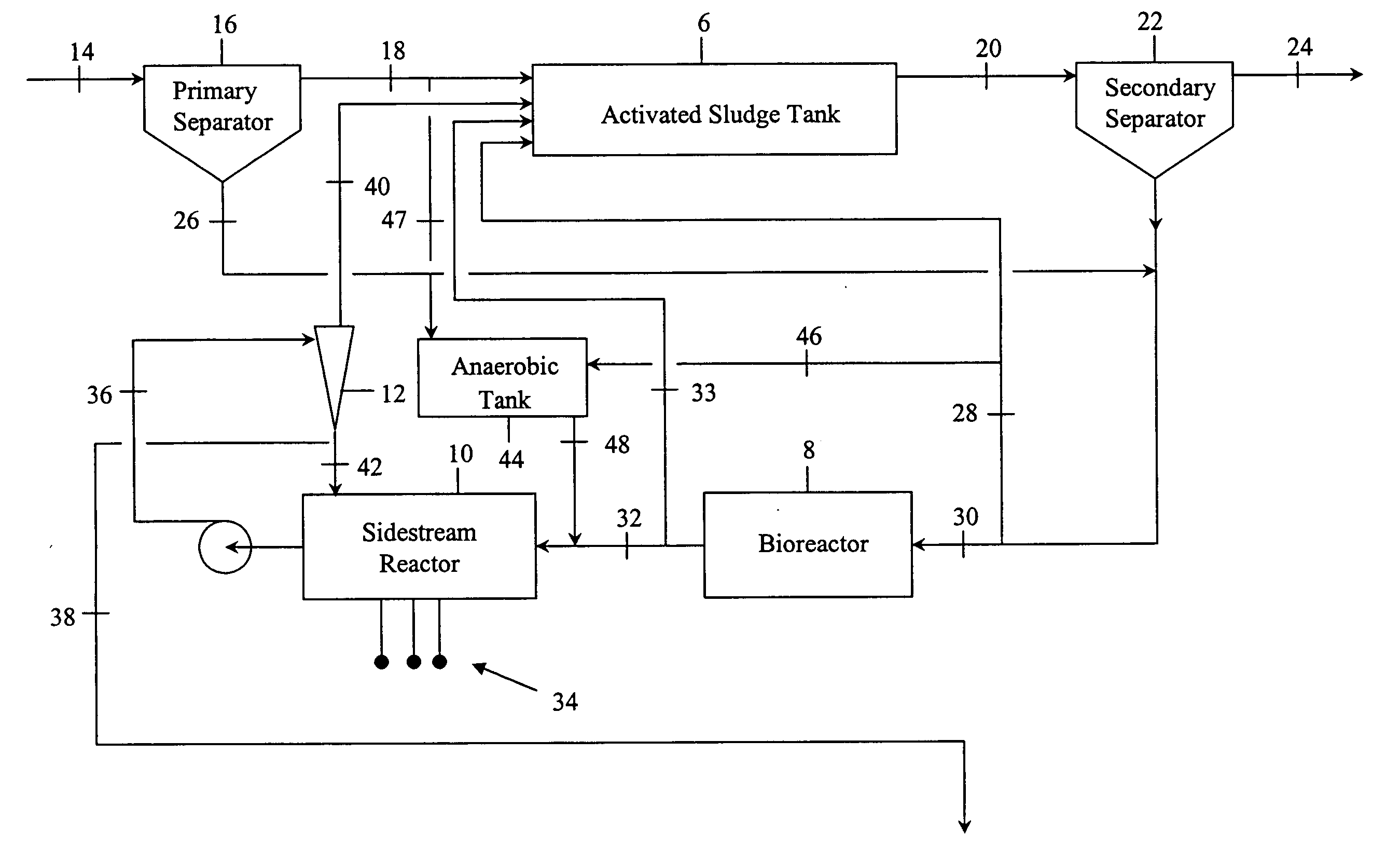
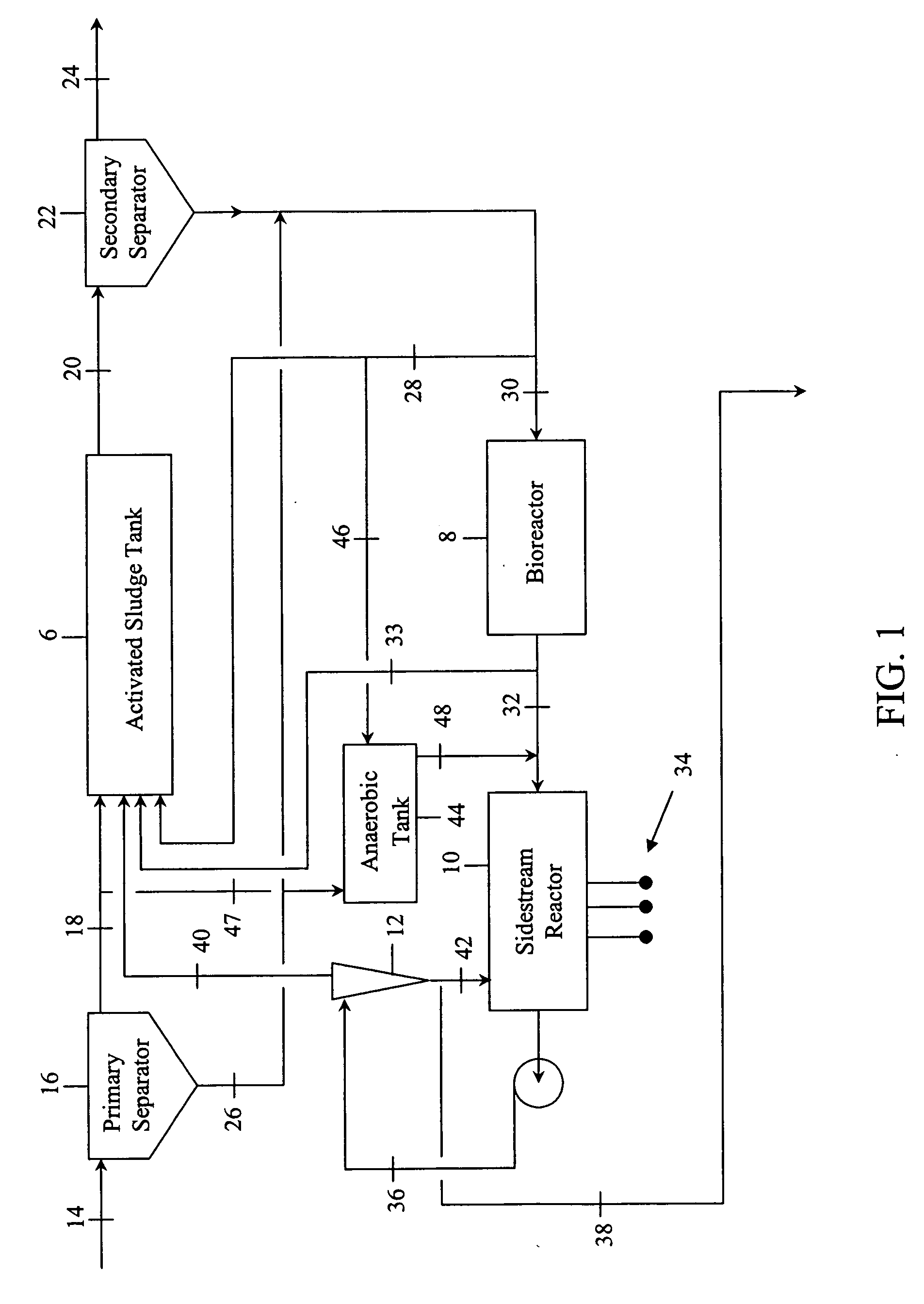
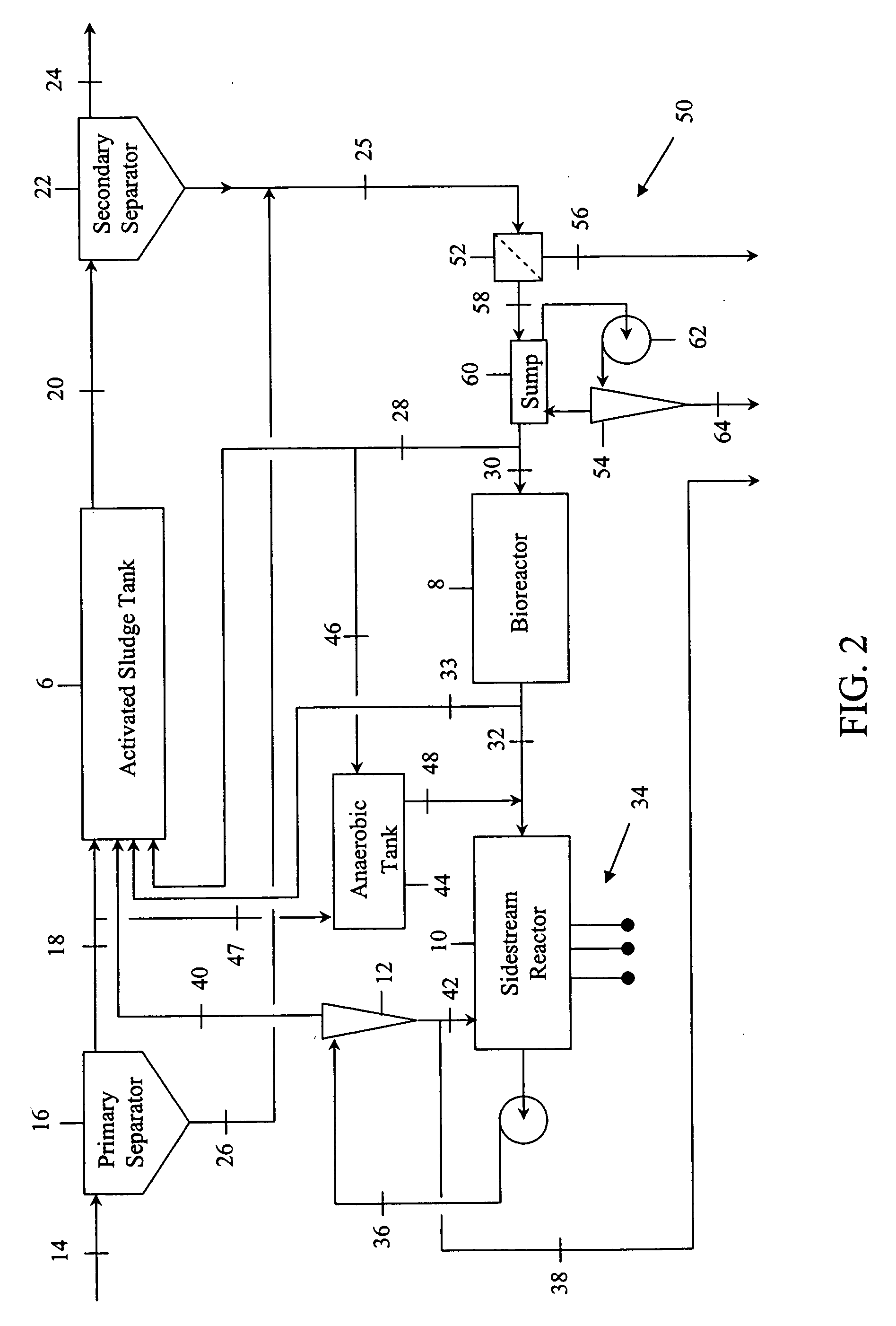
Process to enhance phosphorus removal for activated sludge wastewater treatment systems
InactiveUS20070000836A1Water/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater treatment parameter controlActivated sludgePhosphate
Contaminated wastewaters comprising biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), nitrogen and phosphorus are treated by an activated sludge process. The process utilizes an activated sludge tank, a solid-liquid separator, and a bioreactor to significantly reduce, or eliminate, waste activated sludge (WAS) within a sludge stream. A sidestream reactor is employed downstream from the bioreactor to remove soluble phosphates left in the sludge stream by the low WAS process. Within the sidestream reactor, a source of multivalent metal ions is added to a slightly alkaline sludge stream to precipitate the phosphates. The solid phosphates have a specific gravity higher than that of the organic matter in the sludge stream and may be separated from the sludge stream based upon differential settling velocity.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Extensive wastewater treatment capture agent
InactiveCN104071880ASimple application processQuick resultsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationChemical adsorptionSewage
The invention discloses an extensive wastewater treatment capture agent. The capture agent is prepared from an organic coagulant, an inorganic coagulant, a coagulant aid, a binder and a modifier. The colloid charge balance in sewage is broken by ionization of the capture agent in water, and pollutants are subjected to physical and chemical adsorption and subjected to consolidation settlement, so as to achieve the target of reducing chemical oxygen demand (COD), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and storativity (SS). The extensive wastewater treatment capture agent is simple in application process, quick to take effect, wide in adaptability and broad in market prospect.
Owner:NANCHANG GERUN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI &TECH CO LTD
System and method for remediation of waste
InactiveUS6896804B2Improve scalabilityEfficient and cost-effectiveWater treatment parameter controlAlgae productsHuman wasteGreenhouse
A system and method are provided for aerobic treatment of waste, such as animal or human waste. The method includes the continual introduction of microalgae. The high amounts of oxygen produced by the microalgae satisfies the biochemical oxygen demand in the treatment process and also allows oxidation of undesirable contaminants. Delivery of the microalgae at a desired rate is achieved by incorporation of a series of electrical and mechanical devices housed within a greenhouse type structure which optimizes growth conditions for the microalgae, and also allows the system to be automated.
Owner:AGSMART
Textile dyeing wastewater advanced treatment recycling technology
InactiveCN102145965AReduce chromaImproved BioprocessingMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationTextile fiberChemical treatment
The invention discloses a textile dyeing wastewater advanced treatment recycling technology. The technology comprises the following steps: filtering to remove textile fibers; cooling; neutralizing, degrading organic matters and decomposing, replacing or degrading (cracking) the chormophoric groups of the organic matters to reduce the chroma of the wastewater; performing biochemical treatment with the biomembrane; precipitating to ensure that the precipitated sludge enters a sludge treatment system and the supernatant enters a flocculation pool; performing chemical treatment, namely adding a medicament in the flocculation pool to remove the suspended matter (SS), CODcr (chemical oxygen demand), BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) and chroma of the water; performing secondary precipitation to ensure that the free SS is precipitated and the wastewater is decolored further; separating to remove and degrade the chloride ions of the reuse water; performing secondary biochemical treatment to further reduce the concentrations of the SS, CODcr and BOD in wastewater; performing ozone oxidation treatment, decoloring, degrading organic matters; performing chemical treatment to remove insoluble dye materials and SS and reduce the COD and chroma; and performing secondary filtration, and forming an ozone / activated carbon system to ensure that the hydroxyl radicals of activated carbon are used and the organic reaction in wastewater is adopted to decolor and degrade organic matters. The invention overcomes the defects of the existing physical method, chemical method and chemical method treatment technologies; and the technology has been used in many enterprises, and the good treatment effects are obtained.
Owner:李斌 +2
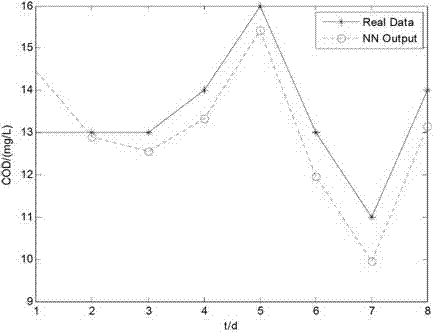
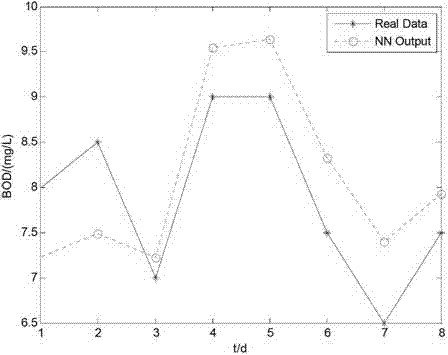
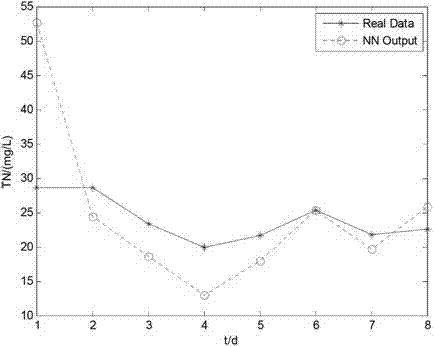
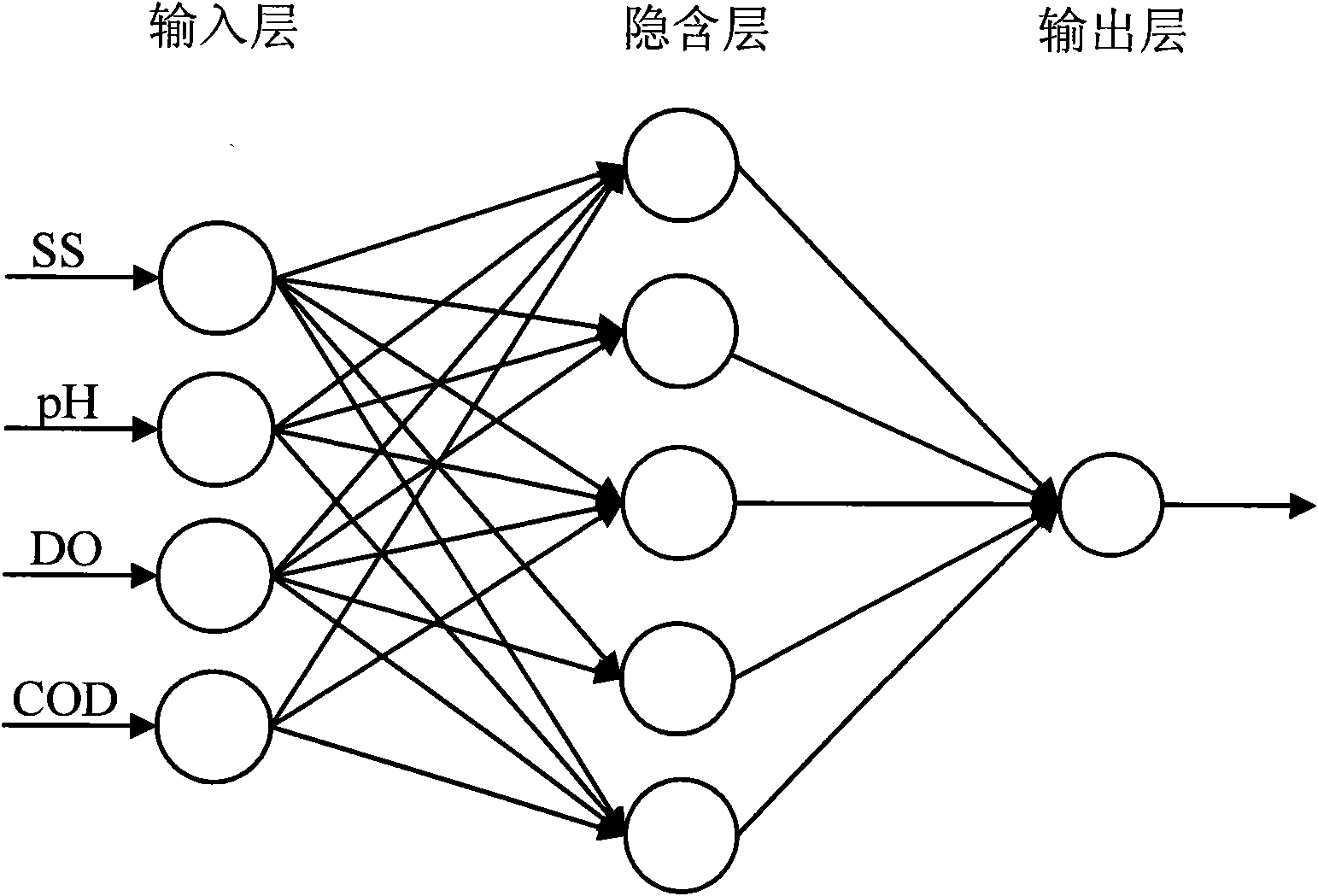
Sewage-disposal soft measurement method on basis of integrated neural network
ActiveCN102854296APrediction is accurateAccelerated trainingBiological neural network modelsTesting waterWater qualityEngineering
The invention discloses a sewage-disposal soft measurement method on the basis of an integrated neural network, and belongs to the field of sewage disposal. A sewage disposal process is high in nonlinearity, time-varying characteristics and complexity, and measurement for key water quality indexes is crucially significant in control of water pollution. In order to improve precision of simultaneous soft measurement for various key water quality parameters in a sewage-disposal soft measurement process by the sewage-disposal soft measurement method, an integrated neural network model is provided for measuring COD (chemical oxygen demand) of outlet water, BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) of the outlet water and TN (total nitrogen) of the outlet water, coupling relation between the three key water quality parameters is sufficiently utilized in the model, the integrated neural network model contains three feedforward neural sub-networks, and the various neural sub-networks are trained by particle swarm optimization, so that the optimal structure of each neural sub-network can be obtained. The COD of the outlet water, the BOD of the outlet water and the TN of the outlet water are predicted by the trained neural network finally, and prediction results are accurate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
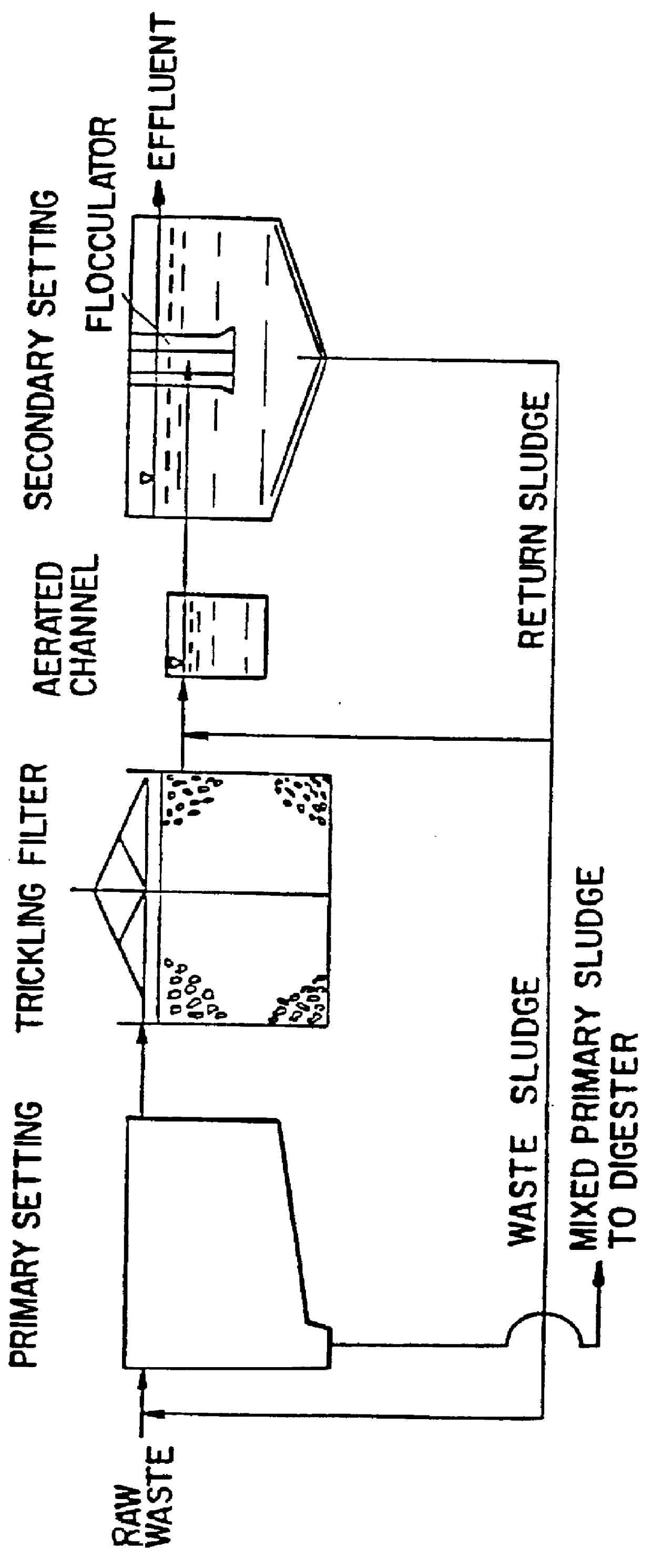
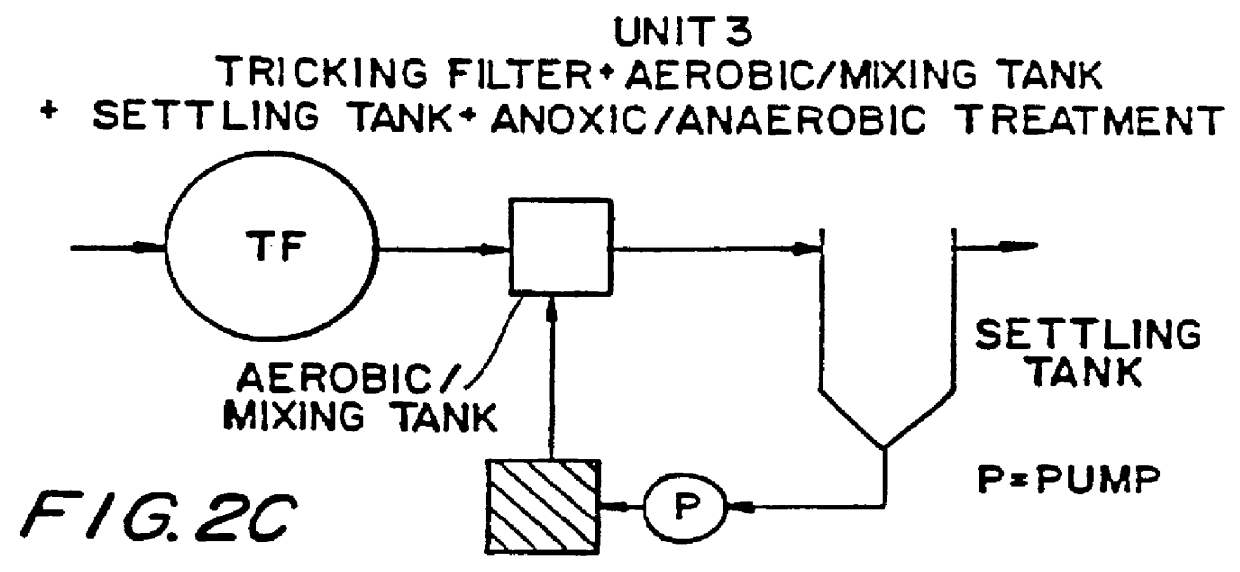
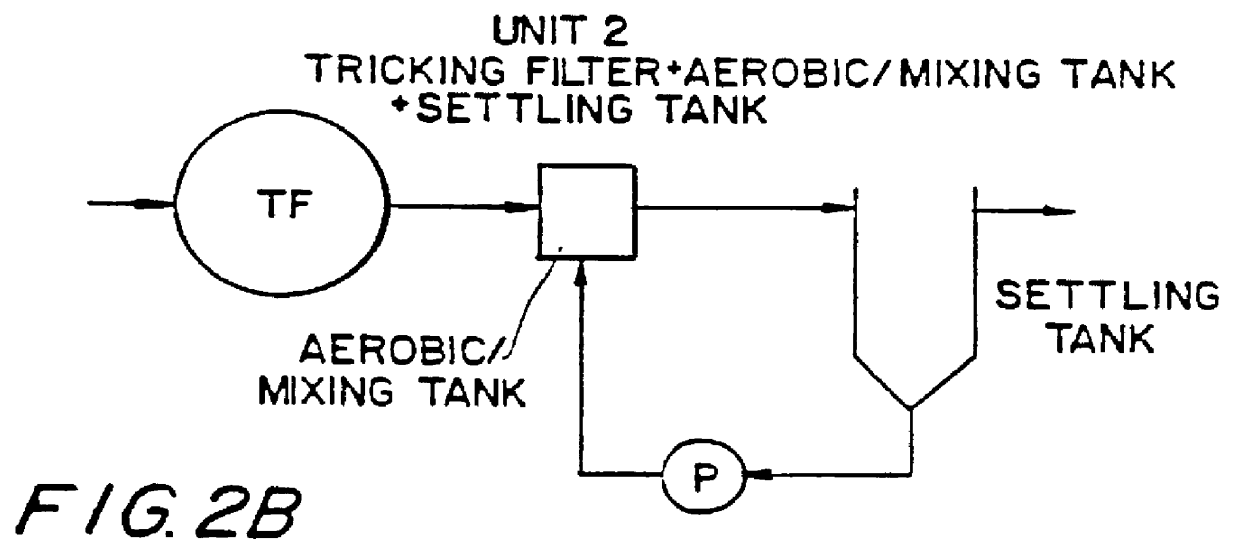
Wastewater treatment process
InactiveUS6113788AImprove efficiencyFacilitated releaseTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesSludgePhosphate
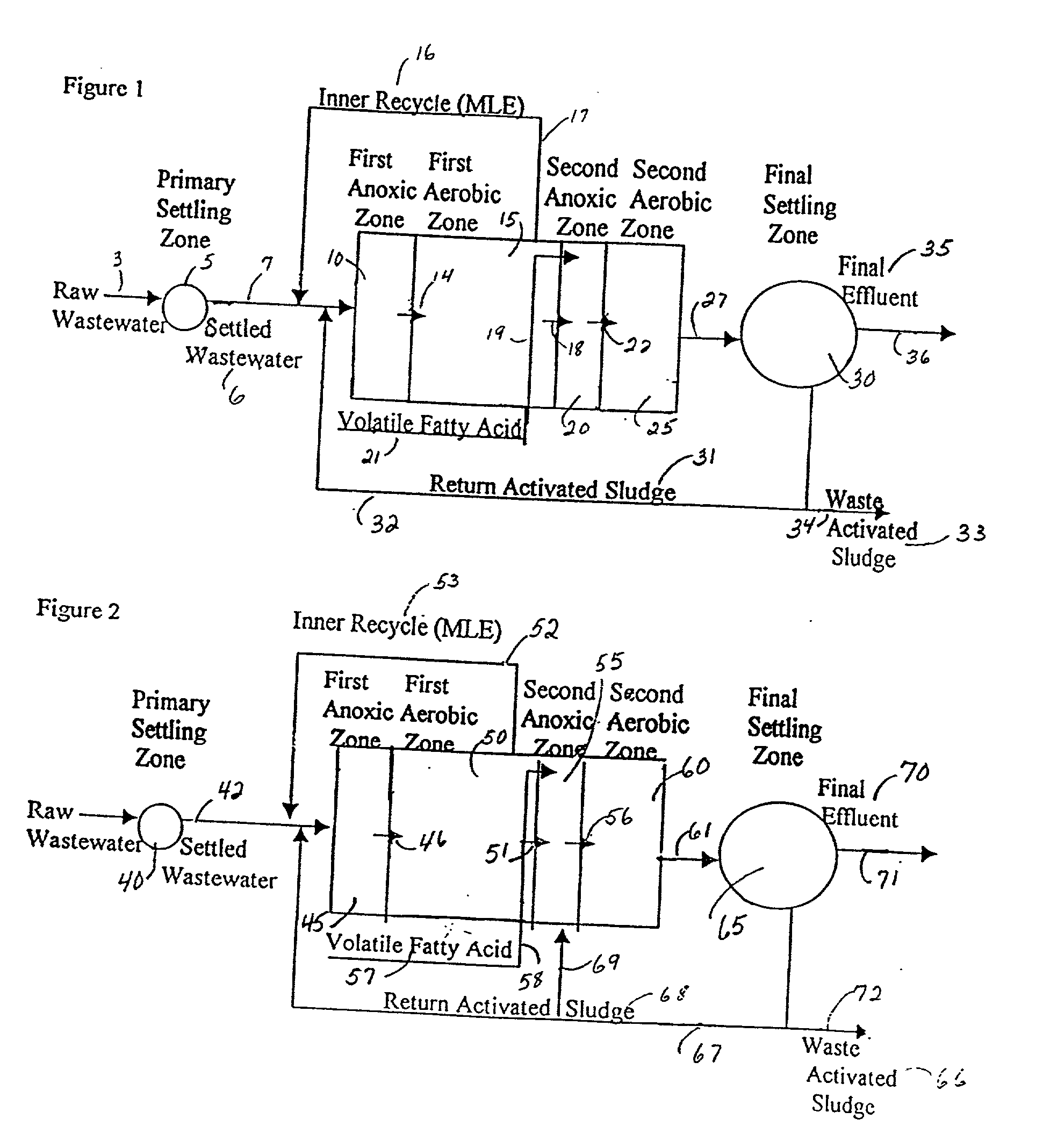
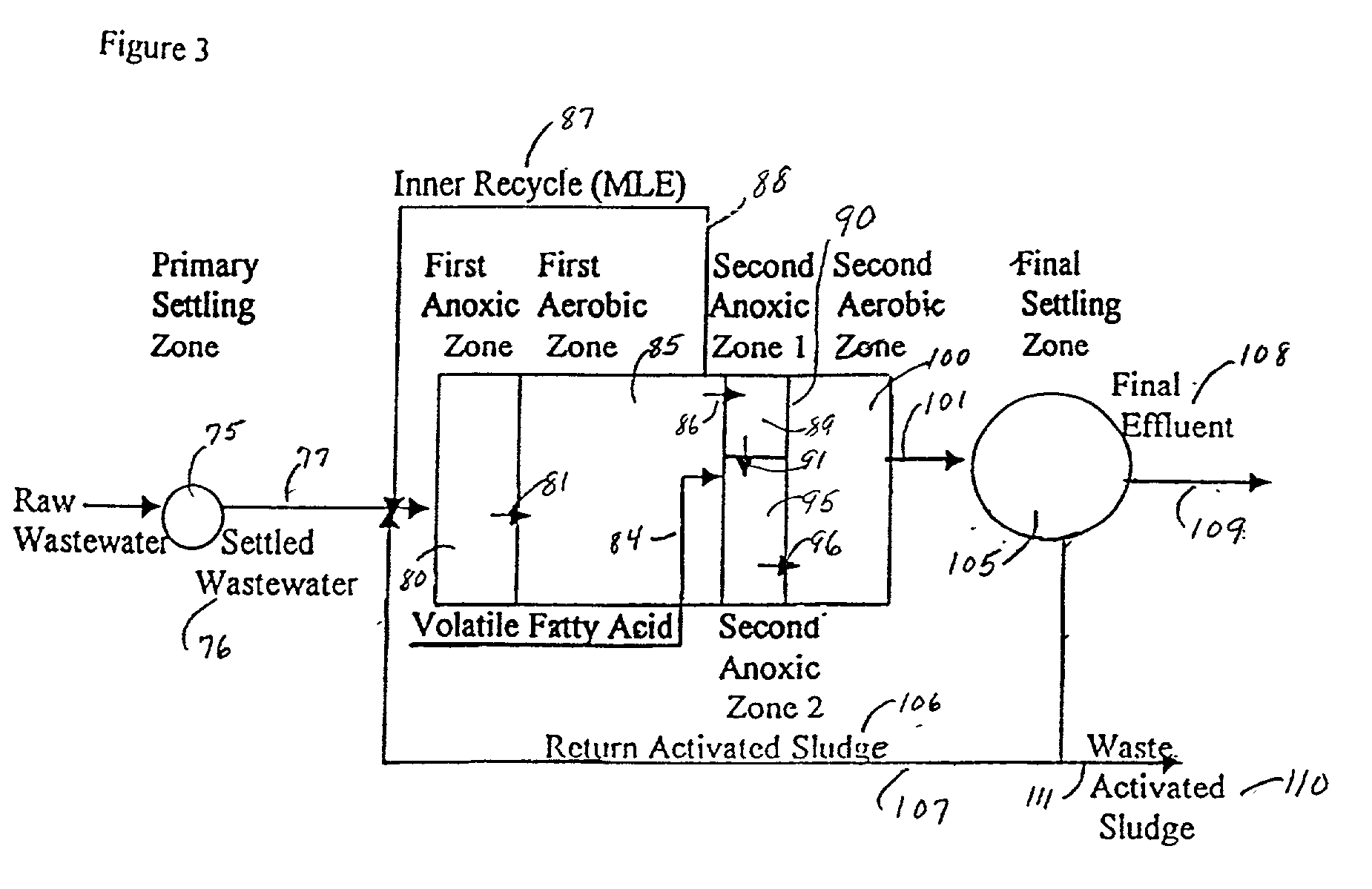
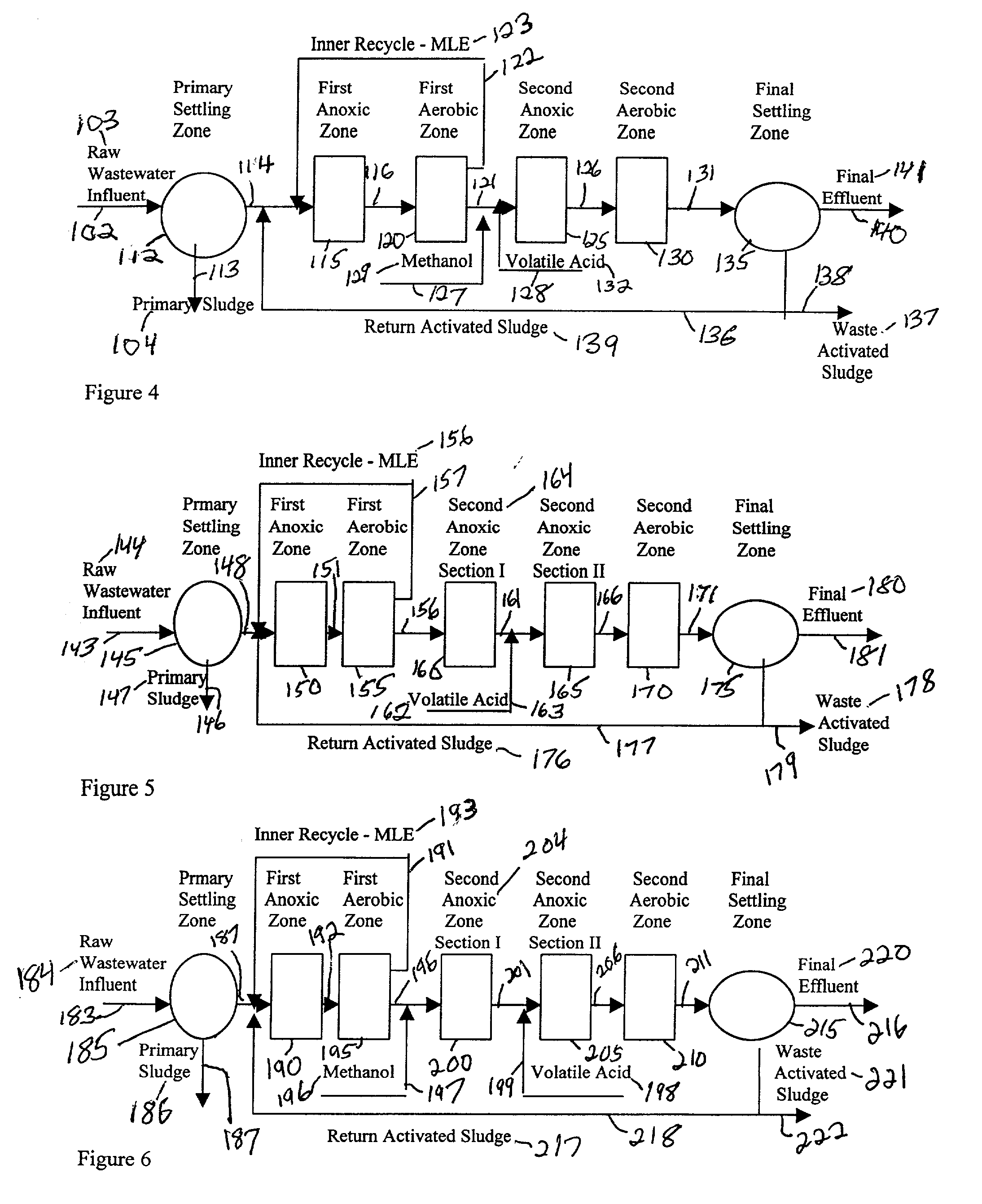
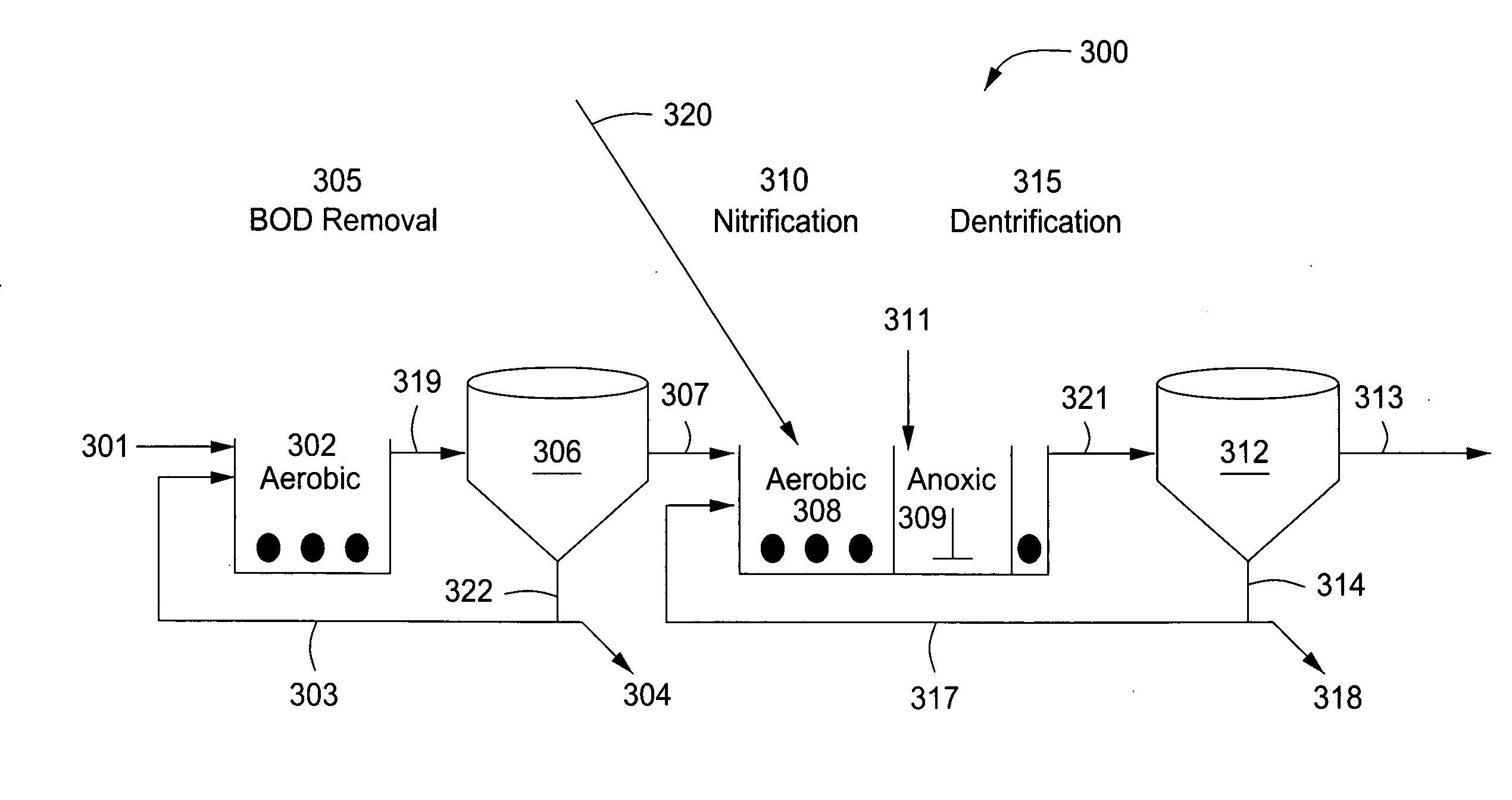
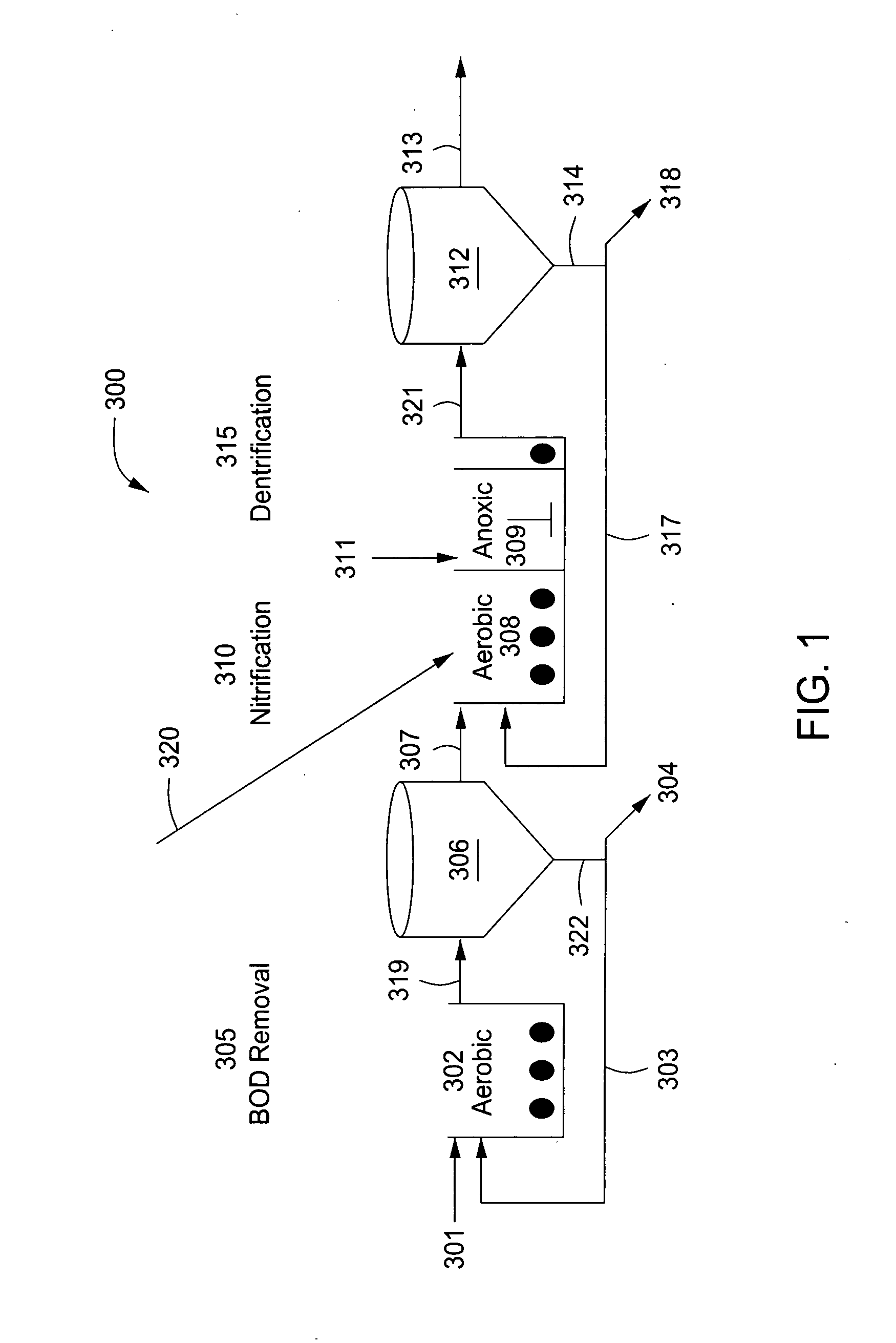
A wastewater treatment process having improved solids separation characteristics and reduced biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) in the purified wastewater comprising the steps of: passing wastewater through a main aerobic biological oxidation zone and therein oxidizing a portion of the BOD a portion of the ammonia nitrogen content (NH3-N); passing the effluent from said aerobic biological oxidation zone to an aerobic / mixing zone and therein mixing said effluent with effluent from the anoxic / anaerobic zone; passing the effluent from said aerobic / mixing zone to a settling zone and therein separating purified wastewater having reduced BOD and suspended solids, and sludge containing suspended solids; passing a portion of the sludge formed in the settling zone and volatile acids to an anoxic / anaerobic zone and therein increasing the extracellular polymer content of said sludge, the release of phosphorus into solution and the reduction of nitrate nitrogen to molecular nitrogen gas; and recycling an effective amount of the effluent from said anoxic / anaerobic zone to said aerobic / mixing zone. In an alternative embodiment, a volatile acid is added to a zone to which no additional oxygen has been added that is in the flow path from the main aerobic biological oxidation zone or, alternatively, it may be added to the anoxic / anaerobic zone and the thus-treated effluent is passed to the aerobic / mixing zone wherein phosphate is removed from the effluent.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
Wastewater treatment process
InactiveUS20010045390A1Improve efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeVolatile fatty acids
Owner:KIM SUNGTAI +2
Complex monitor for automatically monitoring multiple parameters of water on line
InactiveCN102661923AEconomic savingsNo secondary pollutionColor/spectral properties measurementsMaterial electrochemical variablesPrincipal component analysisUv vis absorbance
The invention discloses a method for automatically monitoring water quality indexes on line and a device for implementing the method. A method of combining an ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy and various sensors is adopted, dozens of water quality indexes including chemical oxygen demand and ammonia nitrogen can be measured at one time, measurement indexes can be configured in a building block mode according to requirements, and chemical agents are not required. According to the device, the constructed digital optical fiber spectrometer is taken as a core, ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrum data of a water sample is processed in a mode of sequentially combining wavelet de-noising, principal component analysis and a support vector machine, and water quality indexes such as chemical oxygen demand and biochemical oxygen demand of water are acquired. Various physical and electrochemical sensors acquire water quality indexes such as ammonia nitrogen, dissolved oxygen and conductivity. All hardware and software for implementing the method is put in a cabinet to form the device, and the device analyzes the introduced water sample under the control of an embedded industrial control computer system, and automatically monitors the water quality indexes in real time.
Owner:SICHUAN BELAM TECH
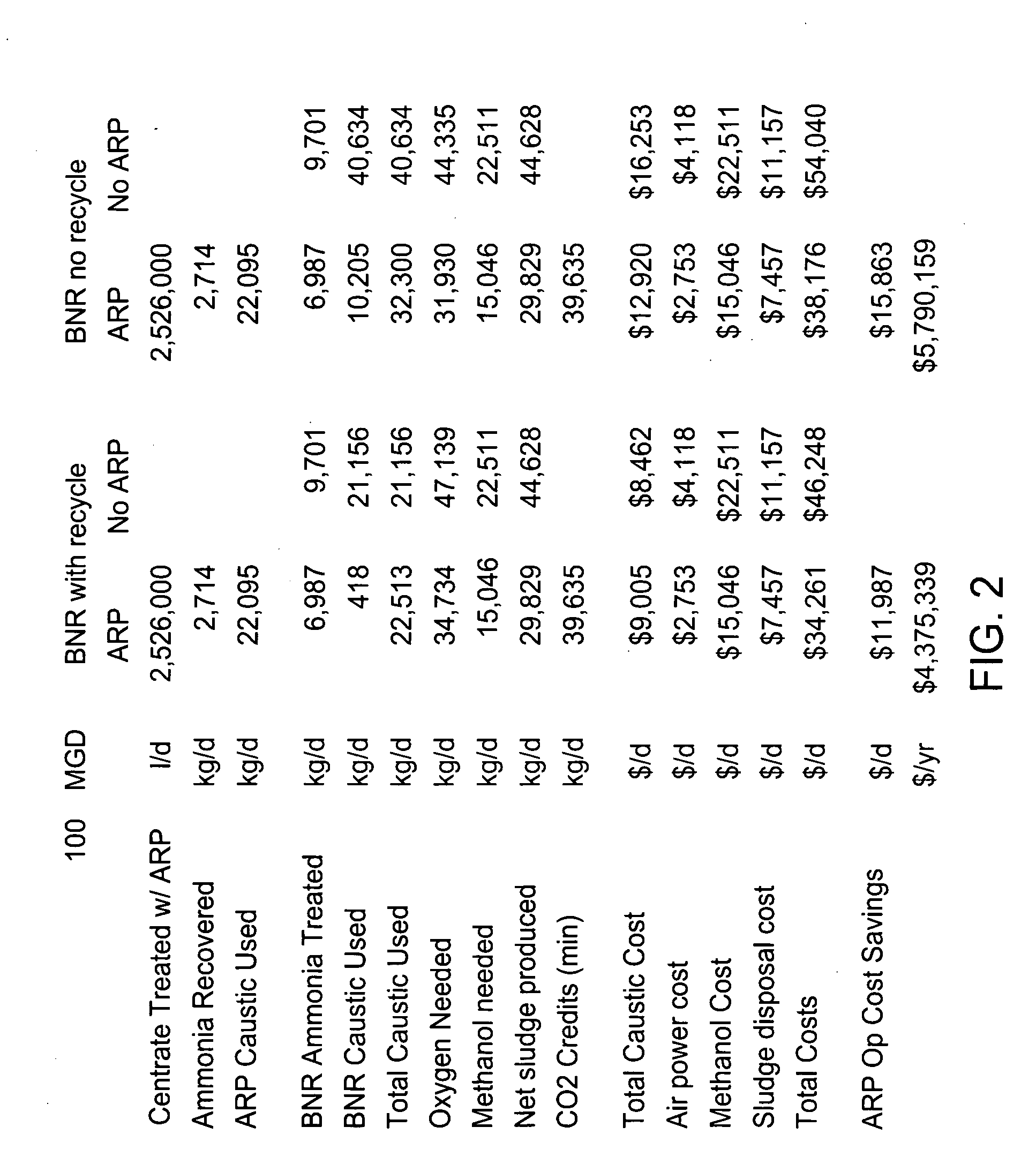
Integrating recycle stream ammonia treatment with biological nutrient removal
InactiveUS20080156726A1Reducing negative environmental impactReduce operating costsLiquid degasificationWater contaminantsRecovery methodAlkalinity
Embodiments include a method and apparatus for recovering ammonia and nitrogen from a waste stream. Embodiments further include recovering ammonia using an ammonia recovery process and a biological nitrogen recovery process. In some embodiments, a return stream from the ammonia recovery process may be used to provide alkalinity, carbon substrate, and / or biological oxygen demand to the biological nitrogen recovery process. In some embodiments, a hydrothermal sludge process may be used to further treat the waste stream and provide additional return to the ammonia recovery system. Other embodiments include an ammonia recovery system for conducting the ammonia recovery process, a biological nitrification and / or denitrification system for conducting the biological nitrogen recovery process, and an optional hydrothermal sludge processing system.
Owner:FASSBENDER ALEXANDER G
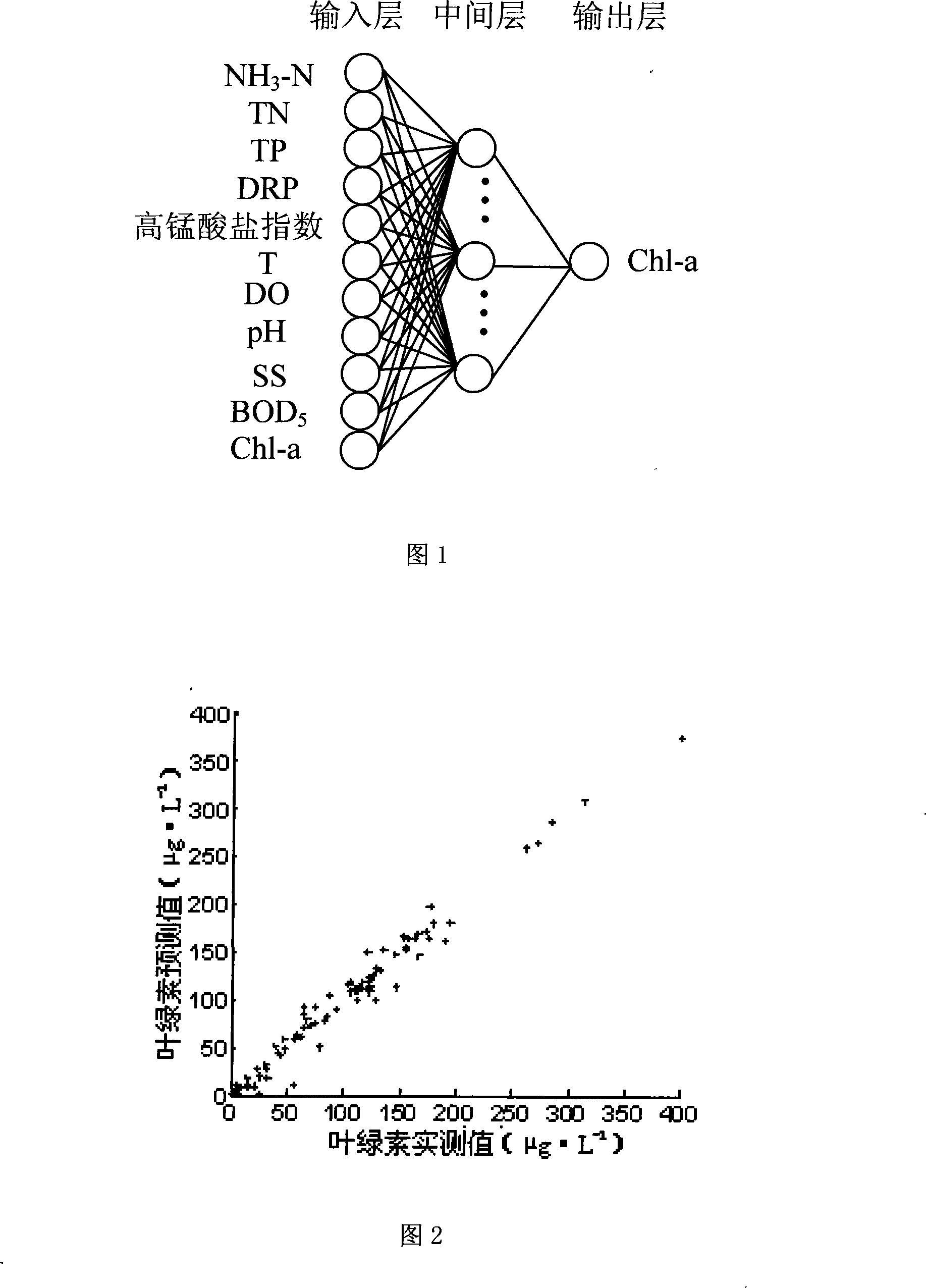
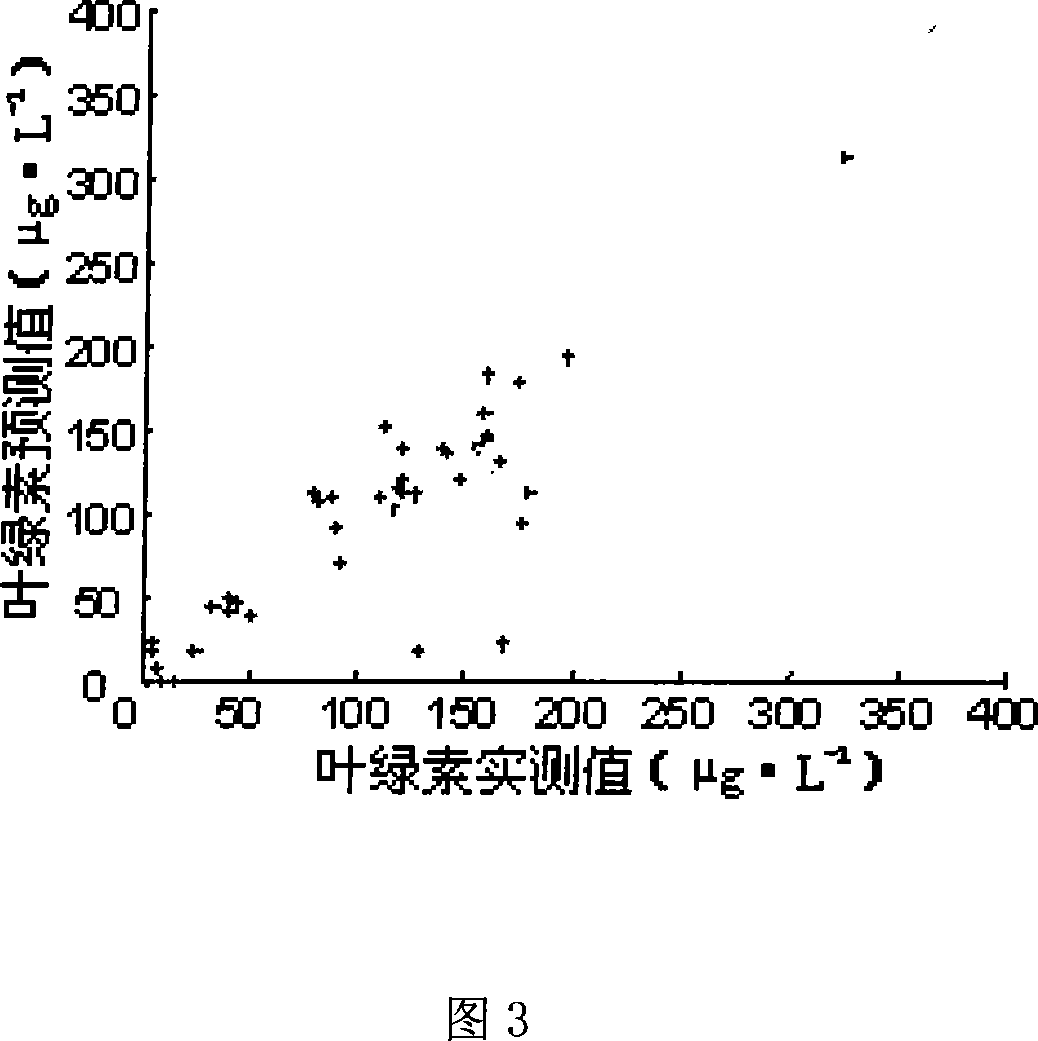
Method for predicting chlorophyll a concentration in water based on BP nerval net
ActiveCN101158674AReduce in quantityReduce consumptionGeneral water supply conservationTesting waterWater basedPredictive methods
The invention relates to a density forecast method of the chlorophyll a stemmed from a water body of the BP neural network. The density forecast method comprises the following steps: (1) the chlorophyll a in the tested water body and the value of other correlative water quality index which influences the chlorophyll a are acquired as the examination data. (2) The neural network of an error back propagation is established. (3) The neural network is trained and tested. (4) The neural network which passes the test is utilized to forecast the chlorophyll a in the water body. Other water qualities which influence the chlorophyll a are: Ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, orthophosphate, permanganate index, temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH, suspension, five-day biochemical oxygen demand. The step (1) also comprises a normalization process. The data of the chlorophyll a and other ten water quality indexes are between -1 and +1 after the data of the chlorophyll a and other ten water quality indexes are normalized. The neural network comprises an input layer, an intermediate layer and an output layer. The invention can establish a forecast model related to the chlorophyll a, just needing the experiment which has the limited times. The chlorophyll in the river can be accurately and quickly forecasted through the computer simulation experiment and the science forecast.
Owner:TIANJIN MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN & RES INST
Device for degrading waste water organic matters by combined type hydraulic power cavitation
InactiveCN102531146ABOD/COD improvementImprove subsequent biochemical effectsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationHigh concentrationShock wave
The invention relates to a device for degrading waste water organic matters by combined type hydraulic power cavitation. The device comprises a Venturi tube component and a sieve mesh plate component which are connected in series and communicated with each other, wherein the water inlet end of the Venturi tube component is connected with a high-pressure pump waste water device; and the water outlet end of the sieve mesh plate component is connected with a water outlet pipeline. According to the device, due to the adoption of the structure, ultra-high pressure and high temperature which are similar to the condition of 'wet air oxidation' are generated and accompanied with strong shock waves and jet flows at the moment of collapsing cavitation bubbles after cavitation by utilizing the hydraulic power cavitation principle, so that part of organic matters in waste water are decomposed into CO2, H2O and inorganic oxides to degrade chemical oxygen demands (COD) and biochemical oxygen demands (BOD). The device is suitable for the pretreatment of the high-concentration organic waste water which is insusceptible to biochemical degradation, and the pH value of the waste water is not limited.
Owner:深圳市宇力科技有限公司 +2
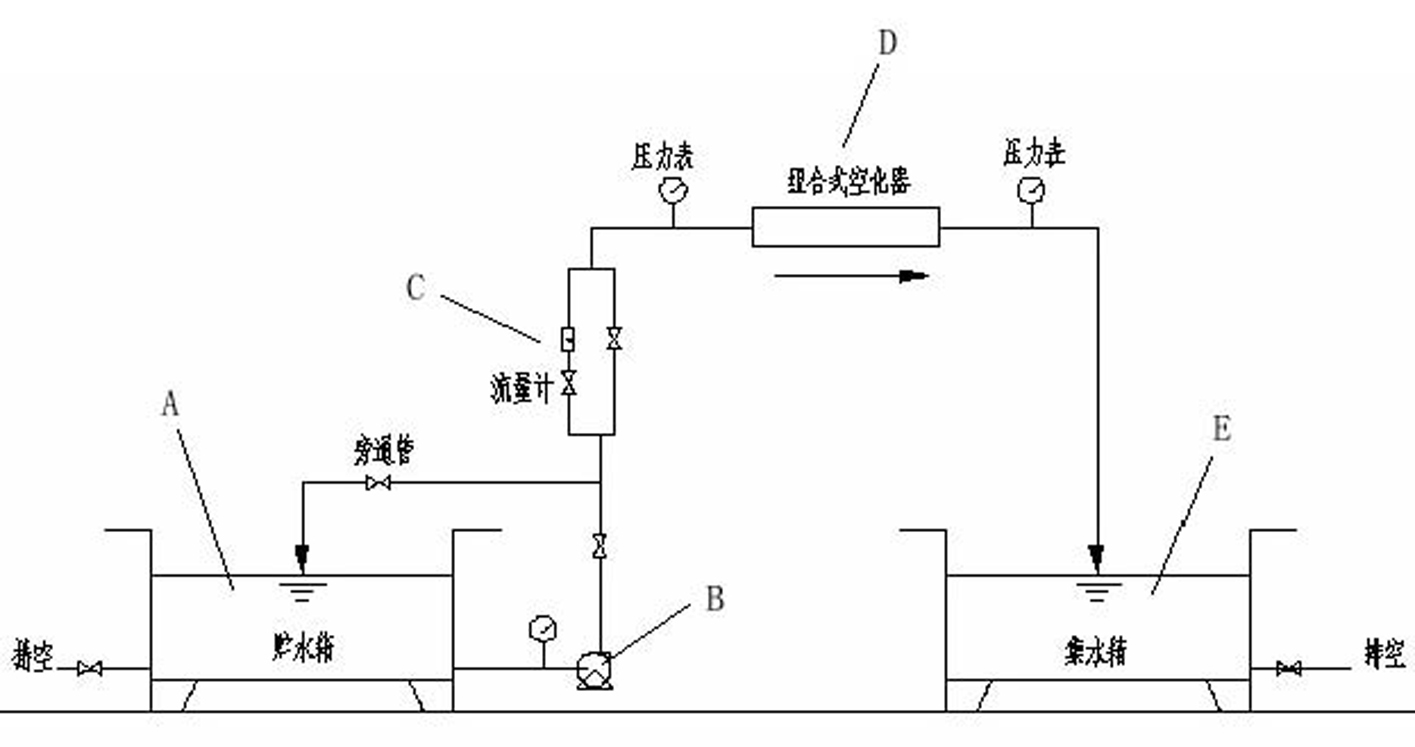
Portable water quality monitoring system
InactiveUS7666285B1Reliable and inexpensiveInexpensive and reliableImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsWater qualityEngineering
A disposable microsensor is designed, fabricated and tested for standard BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) measurements. A transparent Cyclic Olefin Copolymer (COC) substrate is used for sensor fabrication. Standard lithographic procedures in addition to techniques like screen printing and electroplating are used to fabricate the sensor. A microbial strain of Trichosporon Cutaneum is immobilized over one pair of sensor electrodes while the other is used as a reference. Depending on the respiratory activities of the microbial strain in different samples, the BOD values of the samples can be measured in terms of difference between the output signals. The sensor layer is attached to an injection-molded passive microfluidic channel on the top. Advantages of the BOD microsensor include, but are not limited to, fast BOD measurement, disposability because of its low cost, chemically inert polymer substrate, flow-through sample injection scheme and integration of on-chip optics.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
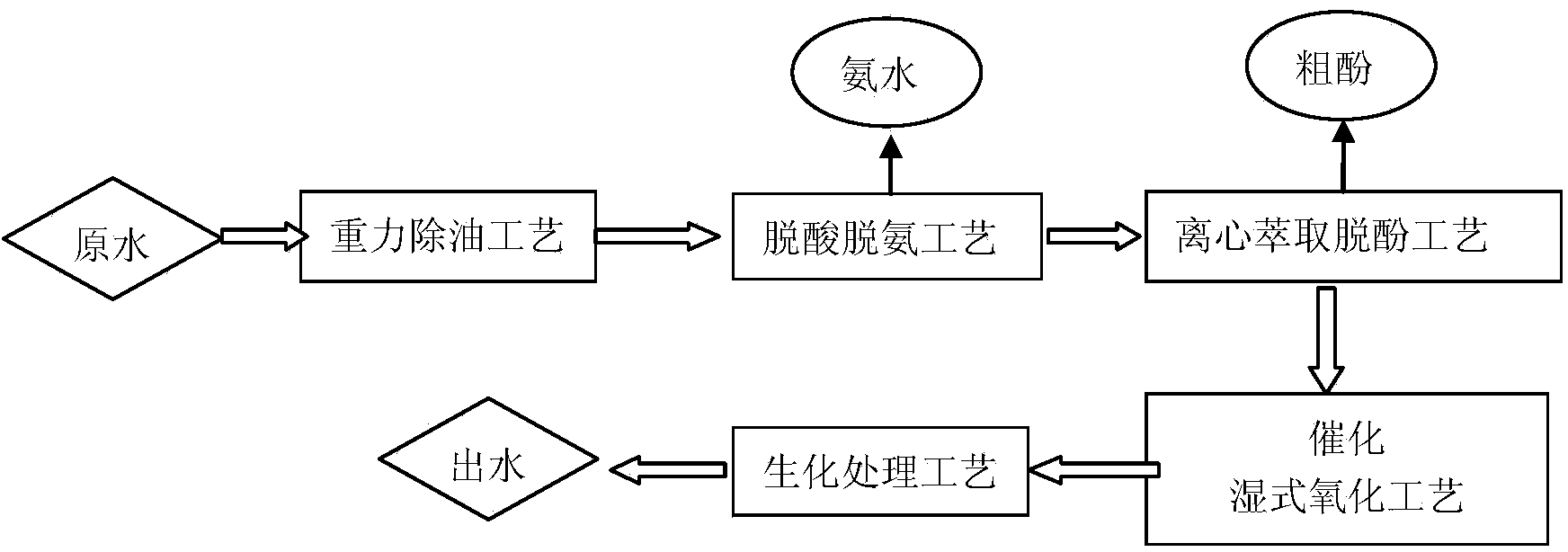
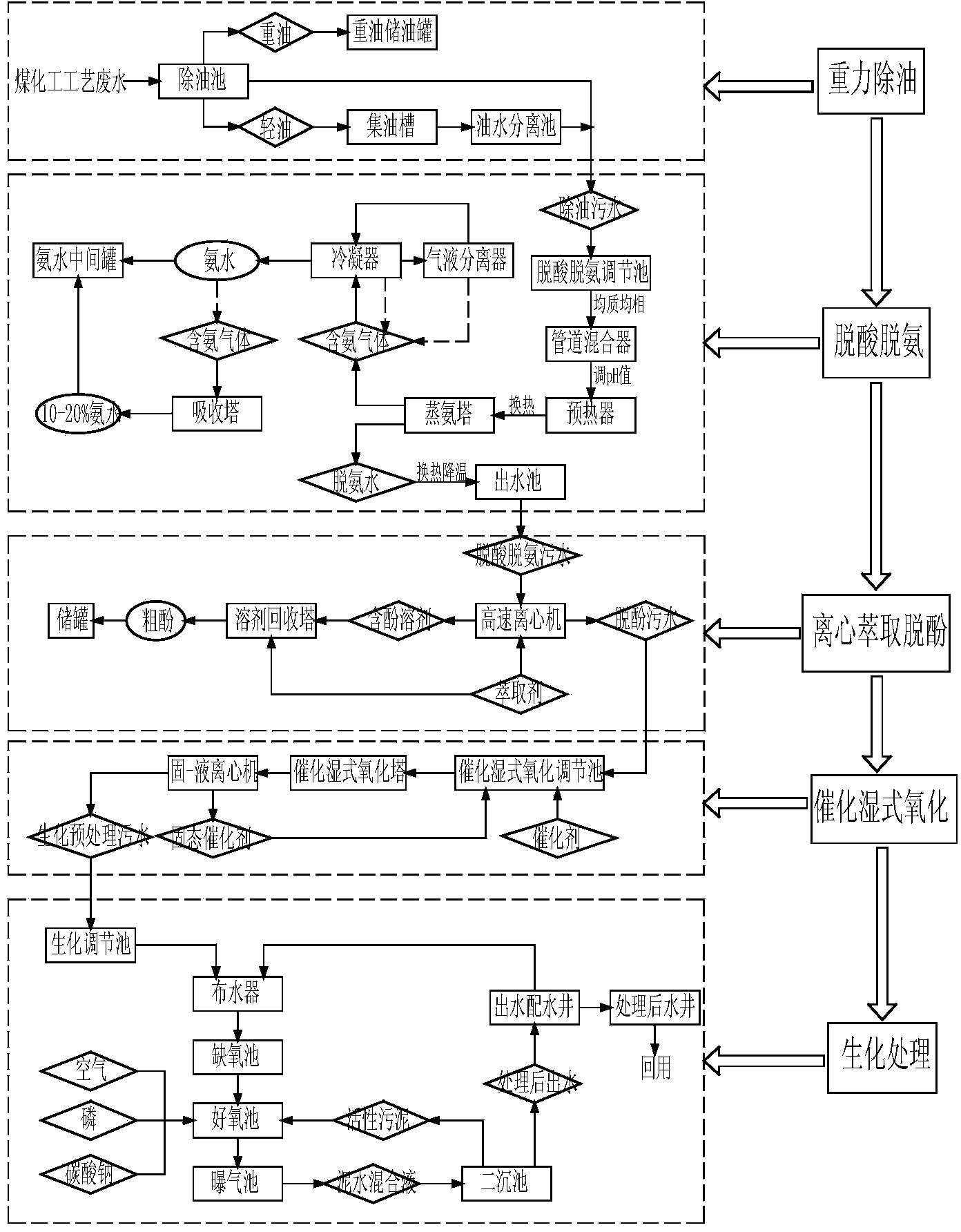
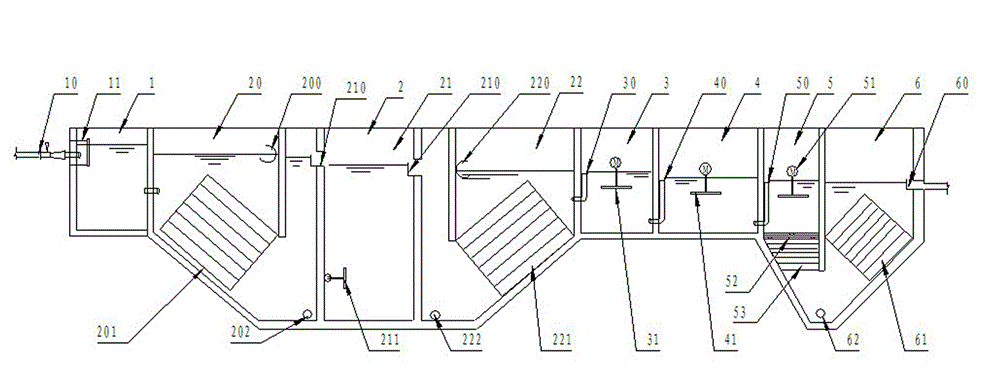
Advanced treatment process of coal chemical industry wastewater
ActiveCN103880242AAchieve water balanceMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical industryEmission standard
The invention relates to an advanced treatment process and device of coal chemical industry wastewater. The process comprises the following steps: removing oil, performing deacidification and deamination, performing centrifugal extraction and dephenolization, performing catalytic wet oxidation and performing biochemical treatment. The device comprises an oil removal pool, a deacidification and deamination regulating reservoir, an ammonia still, a high speed centrifuge, a catalytic wet oxidation regulating reservoir, a catalytic wet oxidation tower, a biochemical regulating reservoir and an A / O biochemical system which are connected with one another sequentially. The indirect emission standard requirements in the national coking chemical industrial pollutant discharge standard (GB16171-2012) can be met after main pollutants such as chemical oxygen demand (COD), oil, ammonia nitrogen and phenol in coal chemical industry wastewater are treated, and ammonia water and crude phenol can be recovered. Compared with the prior art, the advanced treatment process of coal chemical industry wastewater has the beneficial effects that sewage produced in coal chemical industry is treated with a clear target on the basis of characteristics of the coal chemical industry production process, so that the indirect emission standard requirements are met, available resources in the sewage are recovered, and sewage resource treatment is really realized.
Owner:SINOSTEEL ANSHAN RES INST OF THERMO ENERGY CO LTD
Low-cost domestic sewage treatment agent
InactiveCN103663577AGood effectLow production costWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationWater/sewage treatment by sorptionEcological environmentPollution
The invention discloses a low-cost domestic sewage treatment agent. The low-cost domestic sewage treatment agent contains polymerized ferric chloride, polyacrylamide, polyethyleneimine, bentonite, sodium chloride, lime, an adsorbate, sodium carbonate and a pH regulator. The treatment agent has the advantages that domestic sewage can be treated effectively, the cost is low, the effect is good, the pollution to ecological environment caused by the domestic sewage is alleviated, the removal ratio of suspended solids in the sewage reaches 98.3%, the BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) removal ratio is 95.2%, the COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) removal ratio is 96.8%, and the chroma is 5.
Owner:杭州浩蓝环境工程技术有限公司
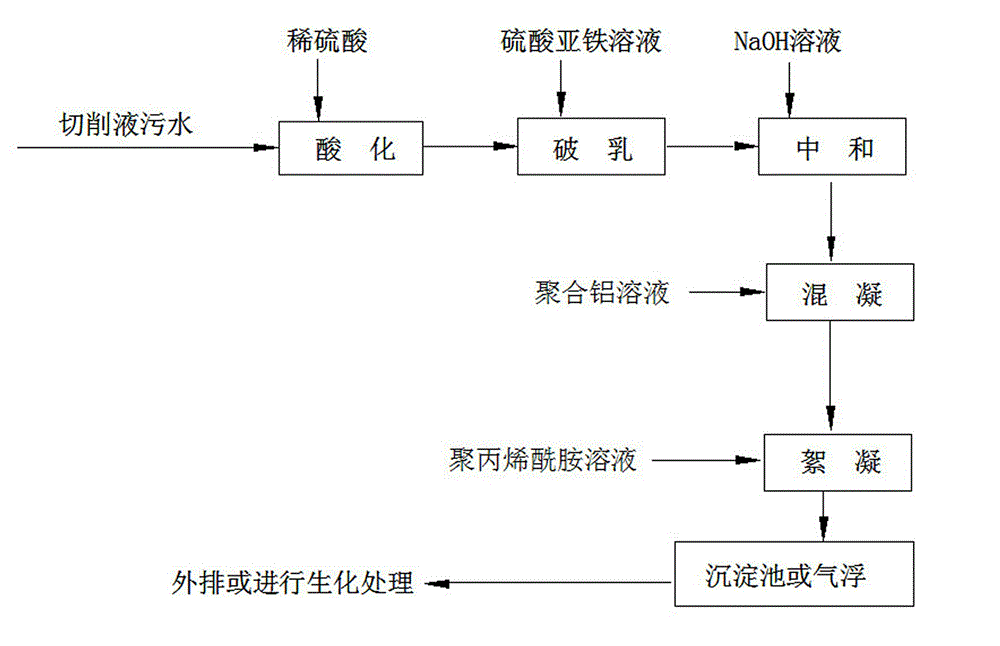
Demulsifying and flocculating treatment method of machining cutting fluid sewage water
InactiveCN102910765ALower surface potentialReduce repulsionMultistage water/sewage treatmentPollutionPolyacrylamide
The invention discloses a demulsifying and flocculating treatment method of machining cutting fluid sewage water, comprising the following steps: conveying cutting fluid sewage water in an acidification pool and adding diluted sulfuric acid for acidification; adjusting the pH to be 3.5-5.5; then conveying in a demulsifying device and adding ferrous sulfate solution for demulsification and precipitation; then conveying in a neutralization pond and adding NaOH solution for neutralization; conveying in a coagulating basin after neutralization and adding a coagulating agent for coagulation; then adding polyacrylamide to a flocculation tank; flowing down by a sieve body through the square rectifying plate of the flocculation tank after flocculating; depositing through the sloped tube stuffing body of a flocculation precipitation pool; discharging out supernatant fluid from a water collection weir; and removing precipitated sludge floccule. The method has the characteristics of integrating oil removal, demulsifying and flocculating, and being thorough for pollution control, good in application effect and economic and efficient; the effluent COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) of cutting fluid sewage water treated through the method can be decreased to below 500mg / L; and the method can be widely applied to sewage water treatment in machining industry.
Owner:安徽新天安全环境科技有限公司
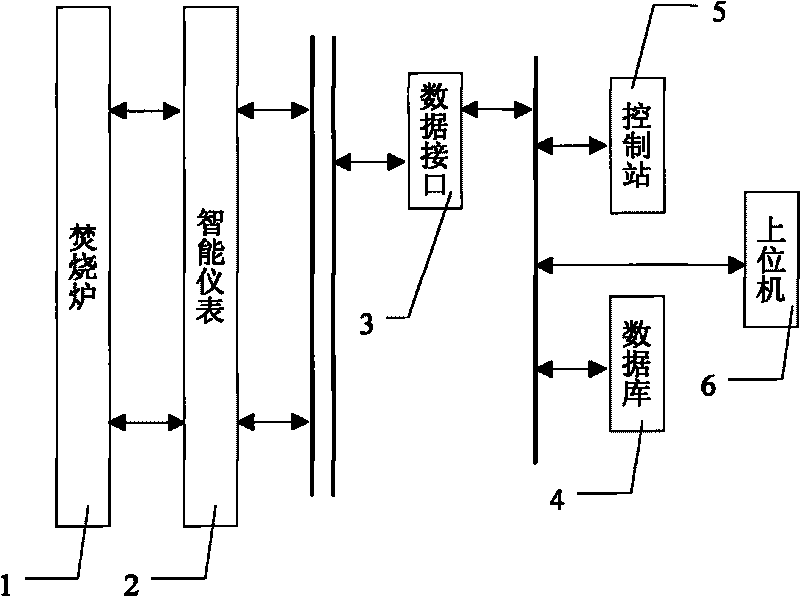
System and method for minimizing chemical oxygen demand (COD) discharge of pesticide production waste liquid incinerator
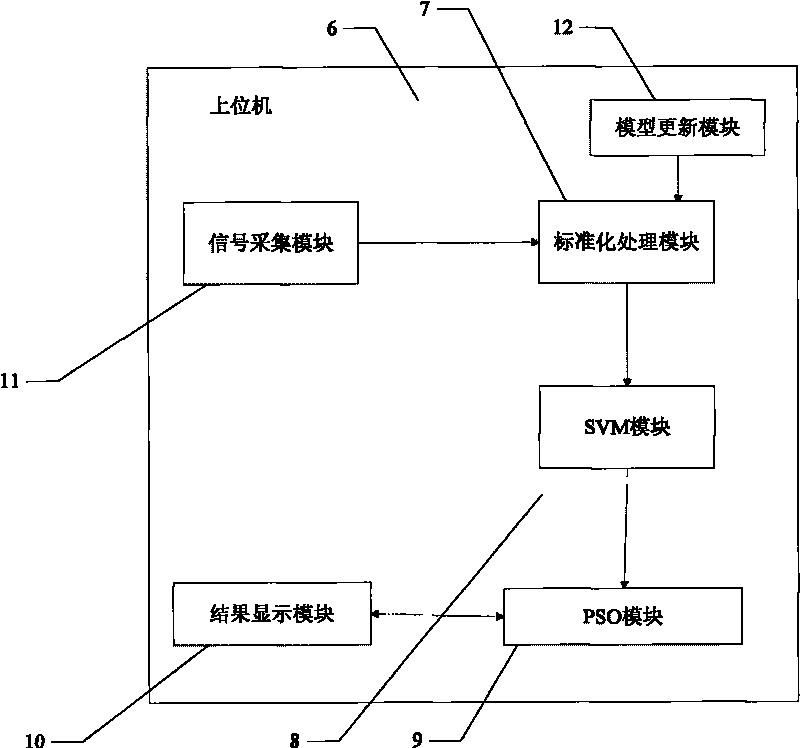
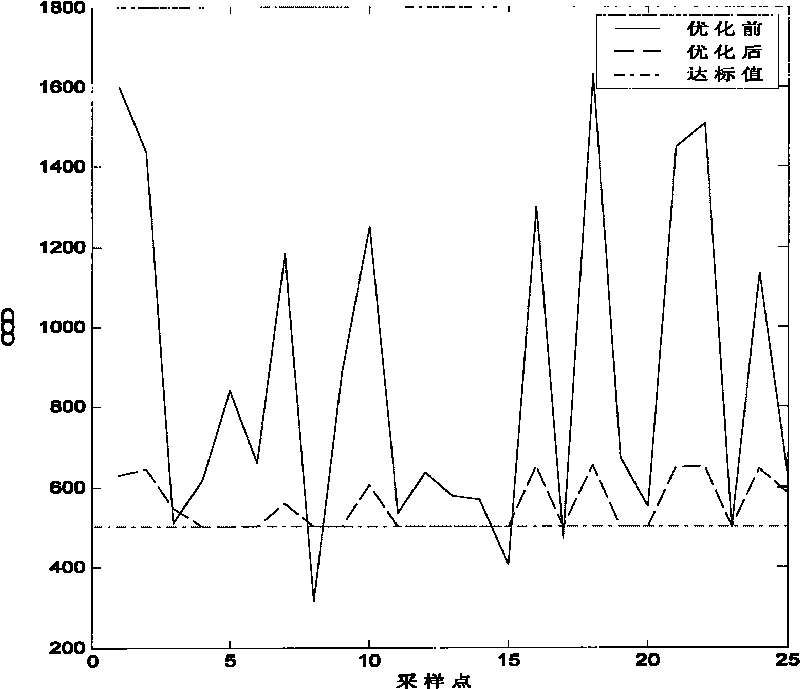
InactiveCN101763084ASmall operand variable valueTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlLiquid wasteEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a system for minimizing chemical oxygen demand (COD) discharge of a pesticide production waste liquid incinerator, comprising a field intelligent instrument connected with the pesticide production waste liquid incinerator, a DCS system and a host computer. The host computer comprises a standardized processing module for collecting training samples TX of key system variables from a database and the chemical oxygen demand data Y corresponding to the training samples TX and standardized processing the training samples TX, a support vector machine (SVM) module for soft-sensor modeling and a particle swarm algorithm module for solving the following minimum problem with the pgK obtained when iteration is ended being the operating variable with minimum chemical oxygen demand. The invention also discloses a method for minimizing the chemical oxygen demand (COD) discharge of the pesticide production waste liquid incinerator. The invention provides a system and a method for minimizing the chemical oxygen demand (COD) discharge of the pesticide production waste liquid incinerator, which can measure the COD online and effectively monitor whether the COD exceeds standard.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
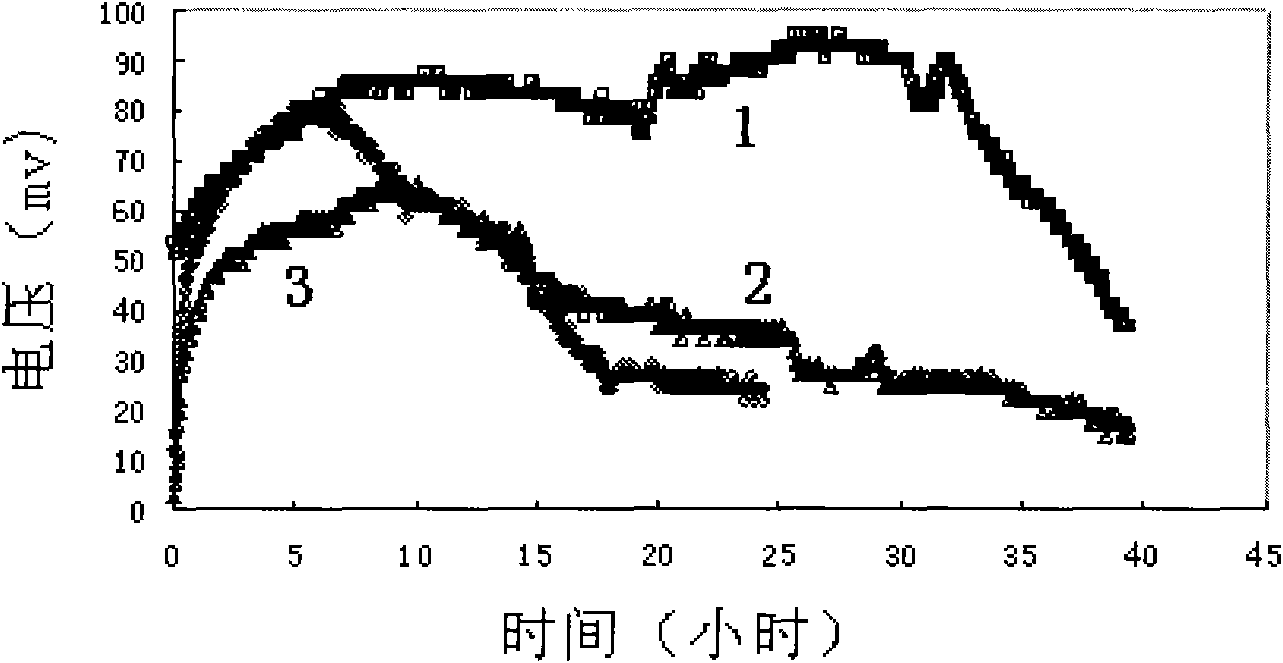
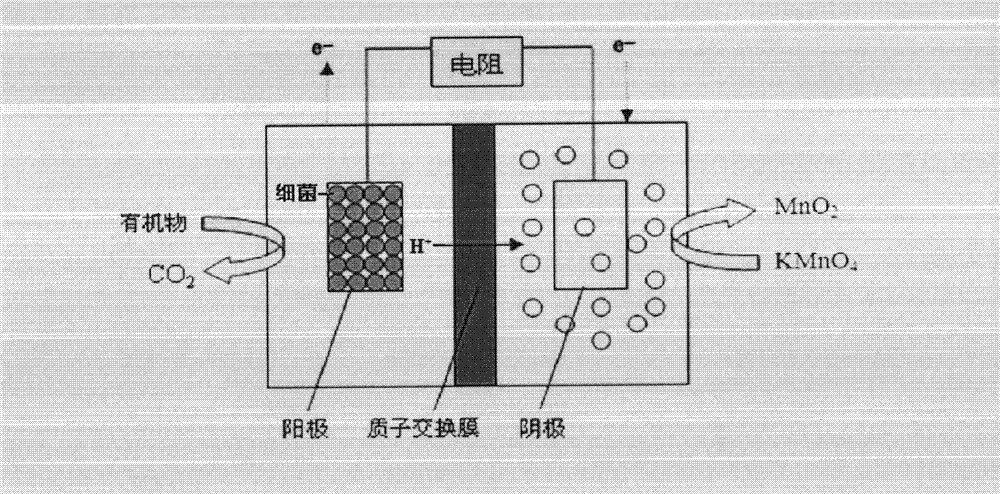
Measuring method of biochemical oxygen demand and BOD sensor and applications
ActiveCN101620201ASolve problems requiring complex aeration operationsReduce manufacturing costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiochemical fuel cellsFuel cellsMeasuring output
The invention discloses a measuring method of biochemical oxygen demand and a BOD sensor and applications. The measuring method comprises the following steps of: constructing a unilocular air cathode no-amboceptor microbial fuel cell, adding a sample into the microbial fuel cell; measuring output voltage generated by the microbial fuel cell and calculating electrical quantity value; and substituting the electrical quantity value into a liner equation and calculating the BOD value and the like. The invention provides the specific BOD sensor and applications thereof for implementing the method; the lowest detection limit of the measuring method is 0.2mg / L, the measuring range of BOD is 5 to 50mg / L, and the relative error with the detection result of a culture method at the temperature of 20 plus or minus 1 DEG C for 5 days is less than 4.0%. The invention has simple and programmable operation process, stable and fast measuring process, can realize online detection, has low cost and is suitable for promotion and application commonly.
Owner:福建省致青生态环保有限公司
Biomass treatment of organic waste or water waste
InactiveUS20080023397A1Water treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsDecompositionControl system
A method, system, apparatus and program for effecting thef decomposition of organic waste material comprises: providing a treatment tank for decomposition of organic waste material, the treatment tank containing an active biomass comprising at least one bacteria that decomposes organic material; providing at least two inlets to the treatment tank, a first inlet comprising an inlet for organic material and a second inlet comprising an inlet for an aqueous stream; a processor that receives and stores information on: the status of chemical oxygen demand of the active biomass; and the oxygen provision capability of a first organic material that can be fed into the treatment tank through the first inlet; a mass flow control system controlled by the processor which feeds the at least one organic material through the first inlet at a rate based at least in part upon the status of chemical oxygen demand in the treatment tank as recognized by the processor.
Owner:NBE
Supercritical dissolved air cavitation equipment and method for reinforcing sludge reduction by adopting same
InactiveCN103408212AAchieve the purpose of reducingReduce outputSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by oxidationMunicipal sewageSewage sludge treatment
The invention provides supercritical dissolved air cavitation equipment and a method for reinforcing sludge reduction by adopting the same, belonging to the technical field of municipal sewage sludge treatment. The equipment is characterized in that when sludge flows through a shrinking spray pipe at a high speed, air is injected into a dissolved air cavitation cavity from an air suction pipe to be mixed with the sludge, then the air and the sludge enter a primary diffusion pipe and a secondary diffusion pipe in sequence and then are sprayed into an oxidation reaction kettle from cavitation nozzles, and finally the sludge subjected to dissolved air cavitation treatment is discharged from a sludge output pipe. The supercritical dissolved air cavitation equipment can operate in combination with a biochemical reaction tank, a reflux and excess sludge tank or a sludge homogenization tank. The equipment and the method have the beneficial effects that as a target vortex cavitation generator is combined with the oxidation reaction kettle, the conditions of supercritical wet oxidation reaction are achieved, the refractory organics in the sludge are directly decomposed into CO2, H2O and the like, and refractory organic macromolecular chains are broken into micromolecular chains and are further oxidized into fatty acids, so that the BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) / COD (chemical oxygen demand) ratio is increased, and favorable conditions are created for subsequent biochemical reaction, thus reducing the sludge; and after the equipment and the method are used by sewage plants, the sludge yield is reduced by 60-70%.
Owner:DONGGUAN YUANKONG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Comprehensive treatment method of high-sulphur high-COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) caustic sludge waste liquid
ActiveCN103045288AReduce CODMild operating conditionsOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationLiquid wasteHigh concentration
The invention relates to a comprehensive treatment method of high-sulphur high-COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) caustic sludge waste liquid. The comprehensive treatment method comprises the steps of: 1, acidizing high-sulphur high-COD caustic sludge waste liquid by using an N2 / SO2 mixed gas, when the pH value of the waste liquid reaches 2-6, stopping acidizing; 2, sending tail gas discharged in the acidizing process in the step 1 to a sulphur production device for preparing sulphur; 3, settling the waste liquid generated in acidizing treatment in the step 1and recovering an oil phase; 4, further reducing the COD of the waste liquid by adopting an extraction method when the COD of the waste liquid after the oil phase is separated in the step 3 is always high; and 5, regenerating the waste liquid extracted in the step 4 by using lime. The comprehensive treatment method is low in investment, is mild in operation conditions, is capable of recycling the caustic sludge waste liquid, avoiding the impact of the high-concentration wastewater on a wastewater treatment field, is also capable of recovering sulfide and crude carbolic acid from the caustic sludge waste liquid, and has a certain economic benefit.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
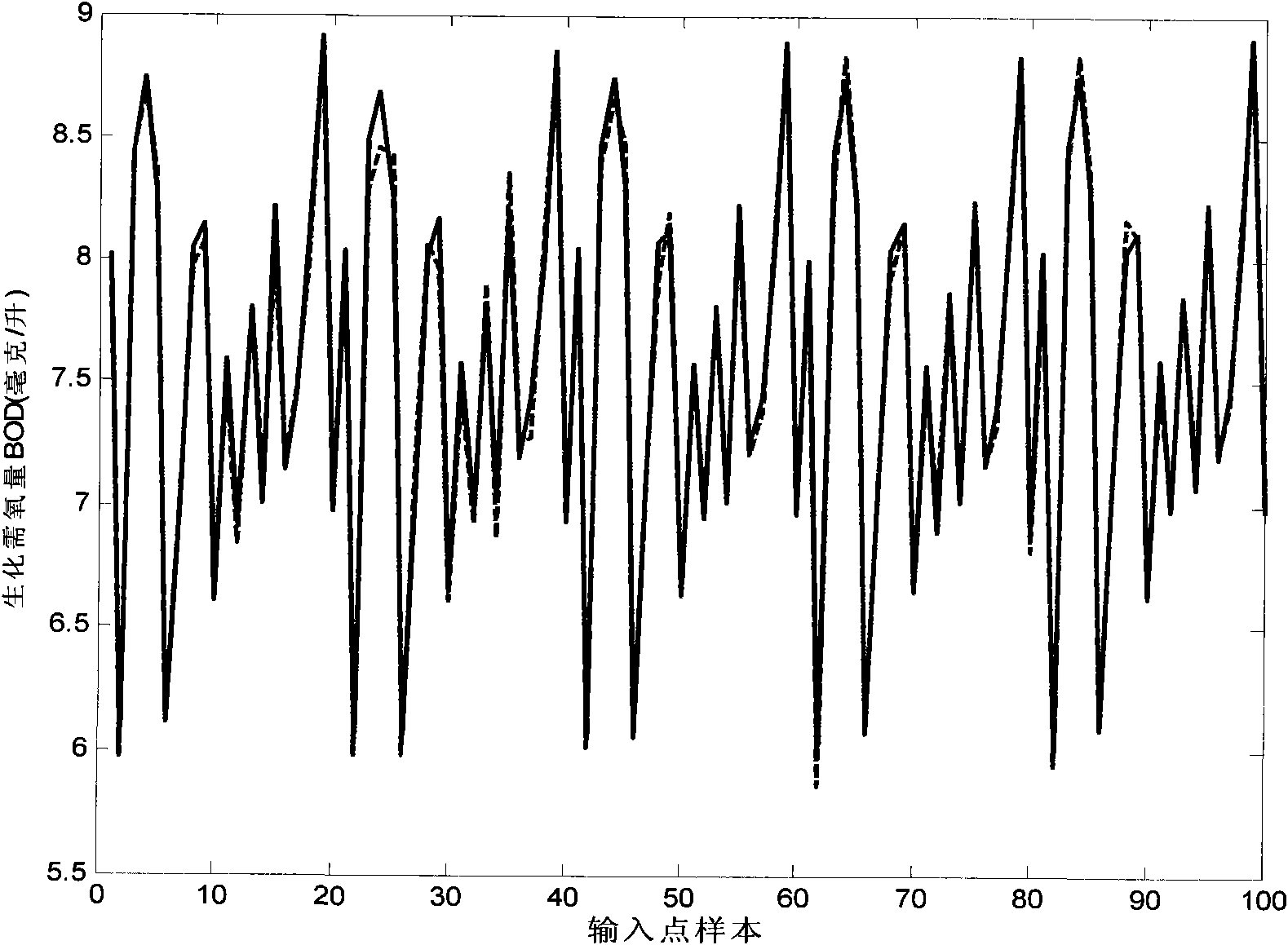
Biochemical oxygen demand BOD soft measurement method based on elastic radical basis function neural network
ActiveCN101957356AGuaranteed uptimeSave investment costBiological neural network modelsTesting waterMathematical modelWater quality
The invention discloses a biochemical oxygen demand BOD soft measurement method based on elastic radical basis function neural network, belonging to the technical field of detection. The sewage processing process has severe production condition and serious random disturbance, has the characteristics of strong nonlinearity, large time varying and serious lag and is hard to build a precise mathematical model by mechanism analysis. The invention utilizes the liveness function of an RBF neuron to judge the activeness of the neuron, and divides the neuron with strong activeness; then, joint strength between the hidden layer neuron and the output layer neuron of an RBF neuron network is analyzed by calculating a mutual information dependency function so as to revise the neural network structureaccording to the mutual information intensity; and finally, the parameter of the neural network is adjusted until the network structure satisfies the requirement on processing information. The invention improves the quality and the efficiency of sewage processing, lowers sewage processing cost and provides in-time water quality and relevant parameter monitoring for realizing closed loop control for the sewage processing process so as to accelerate sewage treatment plants to efficiently and stably operate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
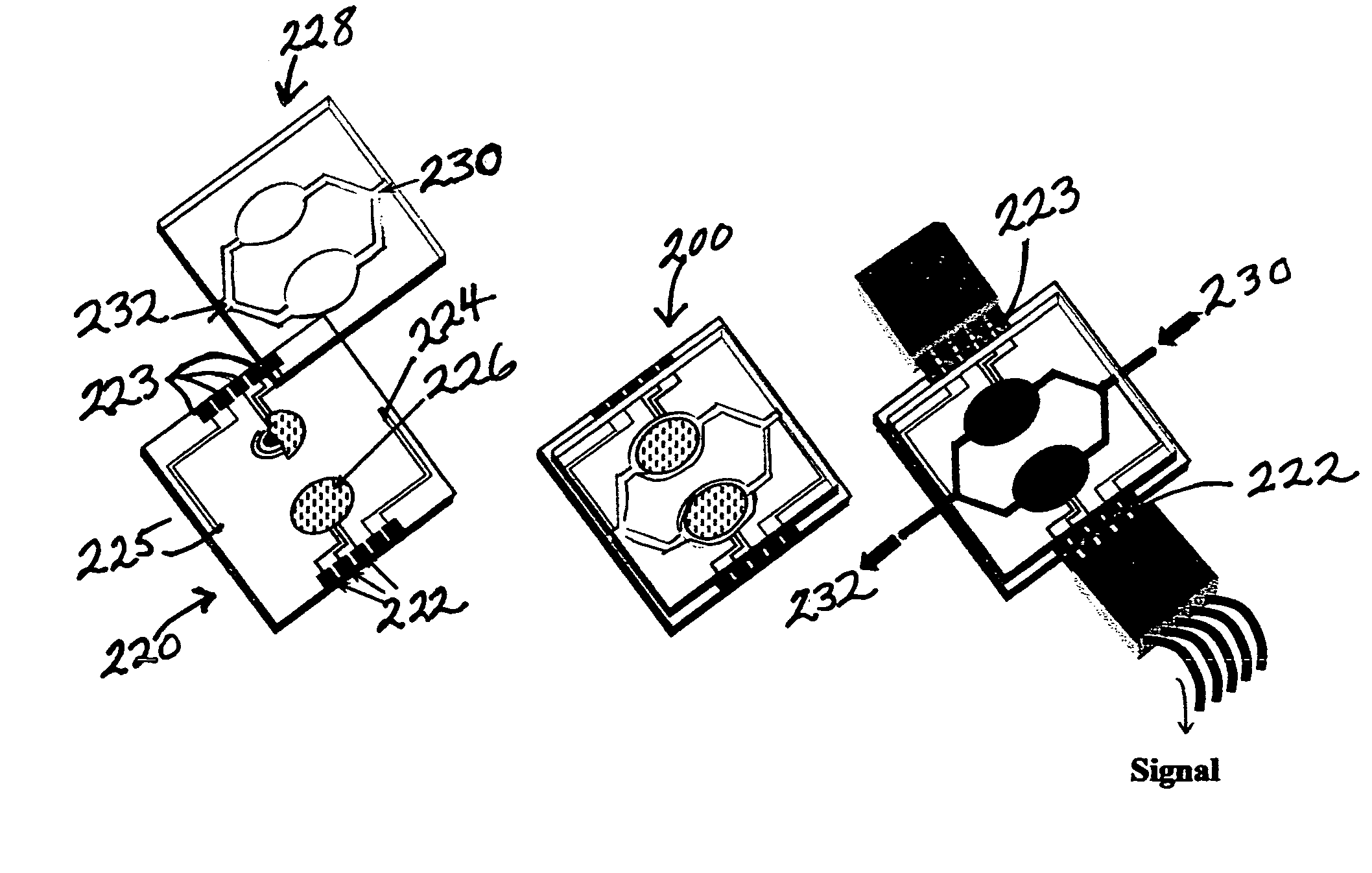
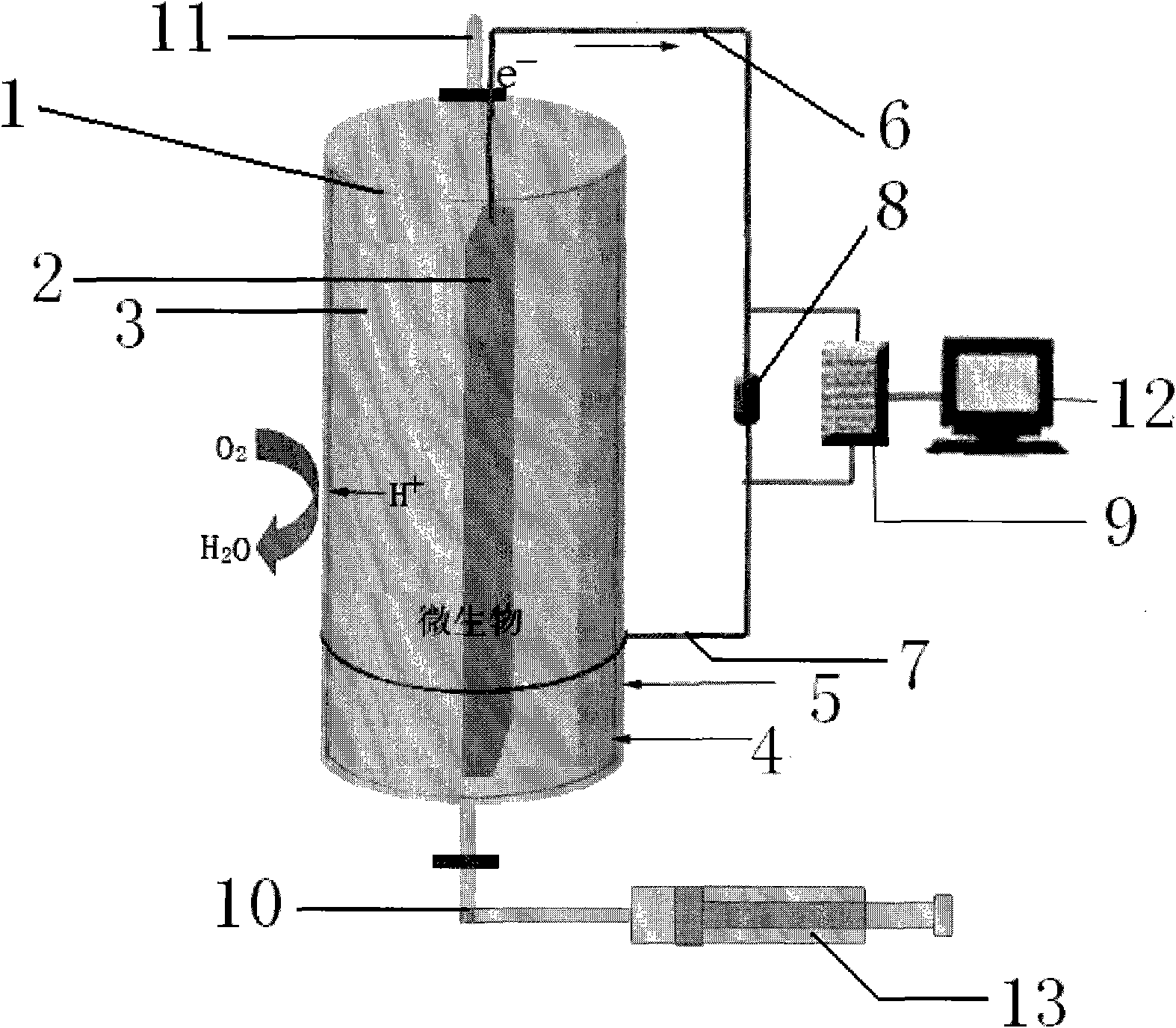
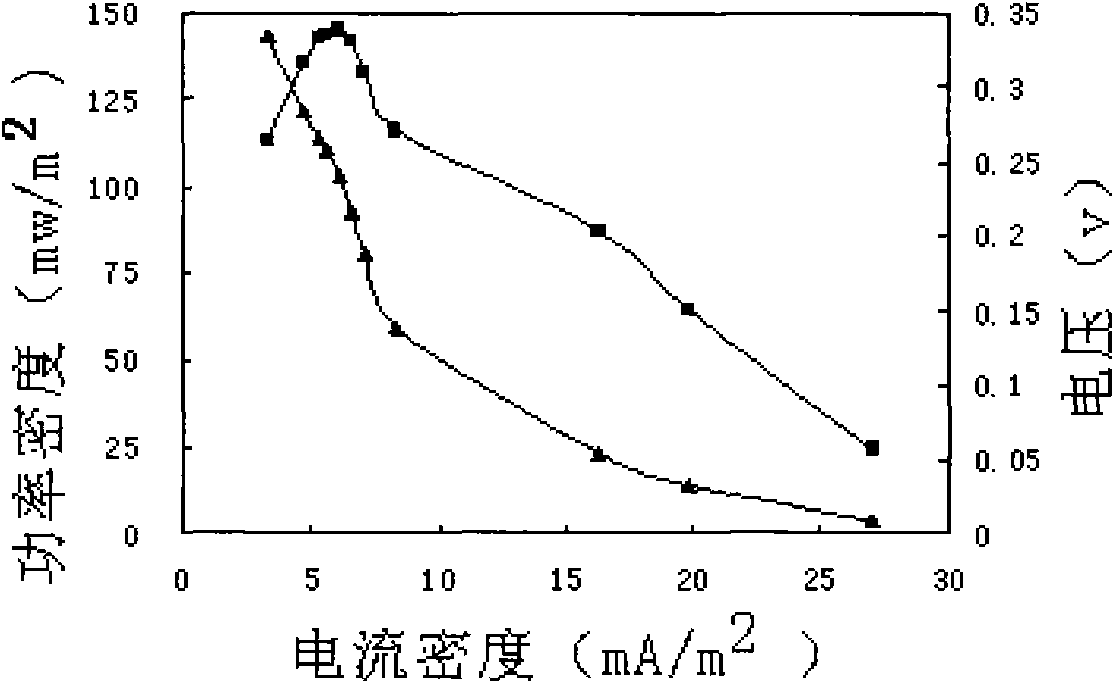
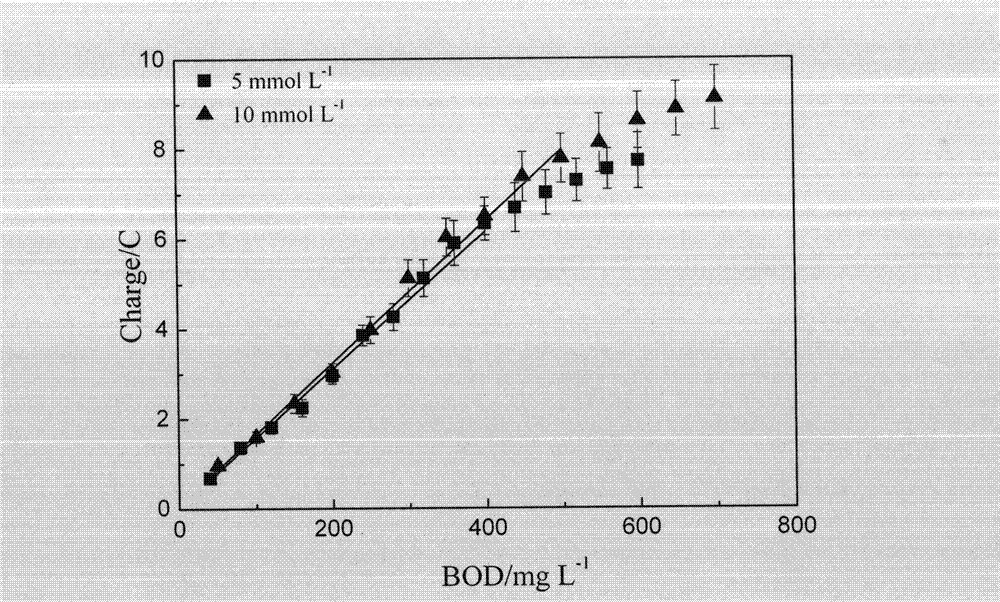
Method for constructing dual-chamber microbial fuel cell-type BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) sensor by using potassium permanganate as cathode electron acceptor
InactiveCN103207230AImprove performanceQuick checkMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWater qualityEngineering
The invention provides a method for constructing a dual-chamber microbial fuel cell (MFC)-type BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) sensor by using potassium permanganate as cathode electron acceptor, which belongs to the field of waste water quality monitoring. The method specially comprises the steps of constructing a dual-chamber MFC reactor; enriching electricigenic microorganisms on an MFC anode plate, and adjusting an external resistor to obtain maximum MFC output power; respectively adding different concentrations of artificial sewage and potassium permanganate solution into an anode chamber and a cathode chamber of the MFC, calculating the generated electricity of the MFC corresponding to different BOD concentrations according to MFC output current and detection time; and processing the generated electricity and BOD by linear fitting to obtain a sensor detection limit and a linear equation. After a to-be-tested solution with unknown BOD value is added into the anode chamber of the MFC, the generated electricity of the MFC is calculated according to the MFC output current and the detection time; and the BOD value of the to-be-tested solution can be calculated according to the known linear equation. The MFC-type BOD sensor using potassium permanganate as cathode electron acceptor has the advantages that the BOD detection range is widened to be 500mg / L; the detection time is shortened by 50% or more; and the detection relative error is less than 10%. Accordingly, the MFC-type BOD sensor has a high application value.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Processing process of albiotic residue
InactiveCN101323862AIncrease gas production rateIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelHigh concentrationSludge
The invention discloses a processing technology of the waste dregs of lincomycin. The technology comprises the steps that: the waste dregs of the lincomycin, the bacterial liquid of EM and the culture solution of alcohol yeast are mixed according to the proportion of 100: (0.5 to 1.5): (3 to 5) and stirred uniformly, and solid anaerobic fermentation is carried out for over 96 hours to remove antibiotics left in the waste dregs; the ferment material is diluted by water and prepared into 10 to 30 percent of a suspension which is uniformly stirred, and sheared and broken mechanically at high speed, reticular mycelium is cut into 'bacillus' shape by observation under a microscope, and by chemical detection: chemical oxygen demand (COD for short) is over 5000; a sheared solution is mixed with the high concentration organic wastewater of lincomycin by the proportion of 10 to 40: 100 put into a jar to carry out anaerobic fermentation and produce biogas. The method is practical, the gas production rate thereof is improved by over 30 percent, the indexes of an anaerobic system, such as the removal rate of COD, PH, degradation rate and sludge discharge, etc. are not affected, and facilities run normally.
Owner:南阳普康药业有限公司
Processing method for resource recovery of acidic dye waste water
InactiveCN102050535AGreening the production processIncrease average reuse rateMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSolubilityFiltration
The invention discloses a processing method for resource recovery of acidic dye waste water. The method comprises the following steps: adding the acidic dye waste water subjected to filtration and impurity removal into a reactor and evenly stirring; oxidizing dissoluble organic matters in the dye waste water by using an oxidant or a mixture of the oxidant and a catalyst, and removing the corresponding components through generating suspended matters; carrying out absorption and separation process of a absorbent so that the decoloration rate of a water sample is up to 25-60%, and the total organic carbon-removing rate reaches 30-85%; and reusing the treated waste water serving as a reaction solvent in the dye production technology process and then obtaining the qualified product. The processing method for the resource recovery of the dye waste water has the advantages of high oxidization efficiency, cheap catalysis price and the like, and is simple to operate; and by using the processing method, the average utilization of the waste water is improved, the resource recycle of the dye waste water with a high-acid value and high chemical oxygen demand (COD) is achieved, so that greening is achieved in the whole dye production technology process, and the industrial application prospect is wide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Biomass treatment of organic waste or water waste
InactiveUS7481940B2Water treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsControl systemDecomposition
A method, system, apparatus and program for effecting the decomposition of organic waste material comprises: providing a treatment tank for decomposition of organic waste material, the treatment tank containing an active biomass comprising at least one bacteria that decomposes organic material; providing at least two inlets to the treatment tank, a first inlet comprising an inlet for organic material and a second inlet comprising an inlet for an aqueous stream; a processor that receives and stores information on: the status of chemical oxygen demand of the active biomass; and the oxygen provision capability of a first organic material that can be fed into the treatment tank through the first inlet; a mass flow control system controlled by the processor which feeds the at least one organic material through the first inlet at a rate based at least in part upon the status of chemical oxygen demand in the treatment tank as recognized by the processor.
Owner:NBE
Method for extracting tea seed oil by using enzymatic hydrolysis method
ActiveCN102061217AHigh purityLight colorFatty-oils/fats productionOil and greaseEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for extracting tea seed oil by using an enzymatic hydrolysis method, which comprises the following steps of: airing, unshelling, husking and pulverizing tea seeds; carrying out enzymolysis on the tea seeds in the material-liquid ratios of 1:3 to 1:5 at the extraction temperature of 40-60 DEG C for 1-5h with the enzyme quantity of 40-600U under the pH natural condition; centrifugally layering; adding an organic solvent into centrifugal liquid and extracting; and rotating and evaporating to obtain an oil sample. By adopting the scheme, the method has the advantages of low temperature for equipment operation, low energy consumption, high purity of extracted oil, low content of phospholipid, low acid value and low peroxide value, shallow color, low BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) and COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) values, easiness of treatment and less pollution, and the oil yield ratio is up to 23.1 percent.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Method for extracting tea oil by microwave-assisted aqueous enzymatic method
InactiveCN101967423AImprove qualityImprove extraction efficiencyFatty-oils/fats productionWater bathsFatty acid
The invention discloses a method for extracting tea oil by a microwave-assisted aqueous enzymatic method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) hulling tea seeds, drying the hulled tea seeds for 0.5 to 2 hours at 60 to 105 DEG C, and performing crushing; (2) weighing tea seed kernels obtained by the crushing, performing microwave treatment for 50 to 90 seconds, adding the treated tea seed kernels into 0.05 to 1 mol / L alkaline salt solution according to the weight / volume (w / v) of 1:3-6, performing water bath for 30 minutes at 90 DEG C, performing centrifugation and extracting upper-layer oil; (3) adjusting the pH value of a part of de-oiled mixed solution to be 4.0 to 4.5 by using acid solution, heating complex enzyme with the v / w of 0.5 to 4 percent, performing thermal treatment for 2 to 6 hours at 40 to 50 DEG C, adjusting the pH to be 8 to 9 by using alkaline solution, performing the centrifugation and extracting the upper-layer oil; and (4) combining the oil obtained in the steps (2) and (3) and performing vacuum drying. The method of the invention is simple, the extraction conditions are moderate, required equipment is relatively less and the production cost is low; over 36 percent of tea oil can be obtained at low temperature without any organic solvent; the obtained tea oil does not contain any trans fatty acid and foreign toxic residue, and has light color, a low acid value and a high nutritional value; tea saponin, proteins, carbohydrate and other nutrition in residues are easy to extract and utilize; and with a biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) value and a chemical oxygen demand value, wastewater produces less pollution and is easy to treat.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Treatment method of landfill leachate
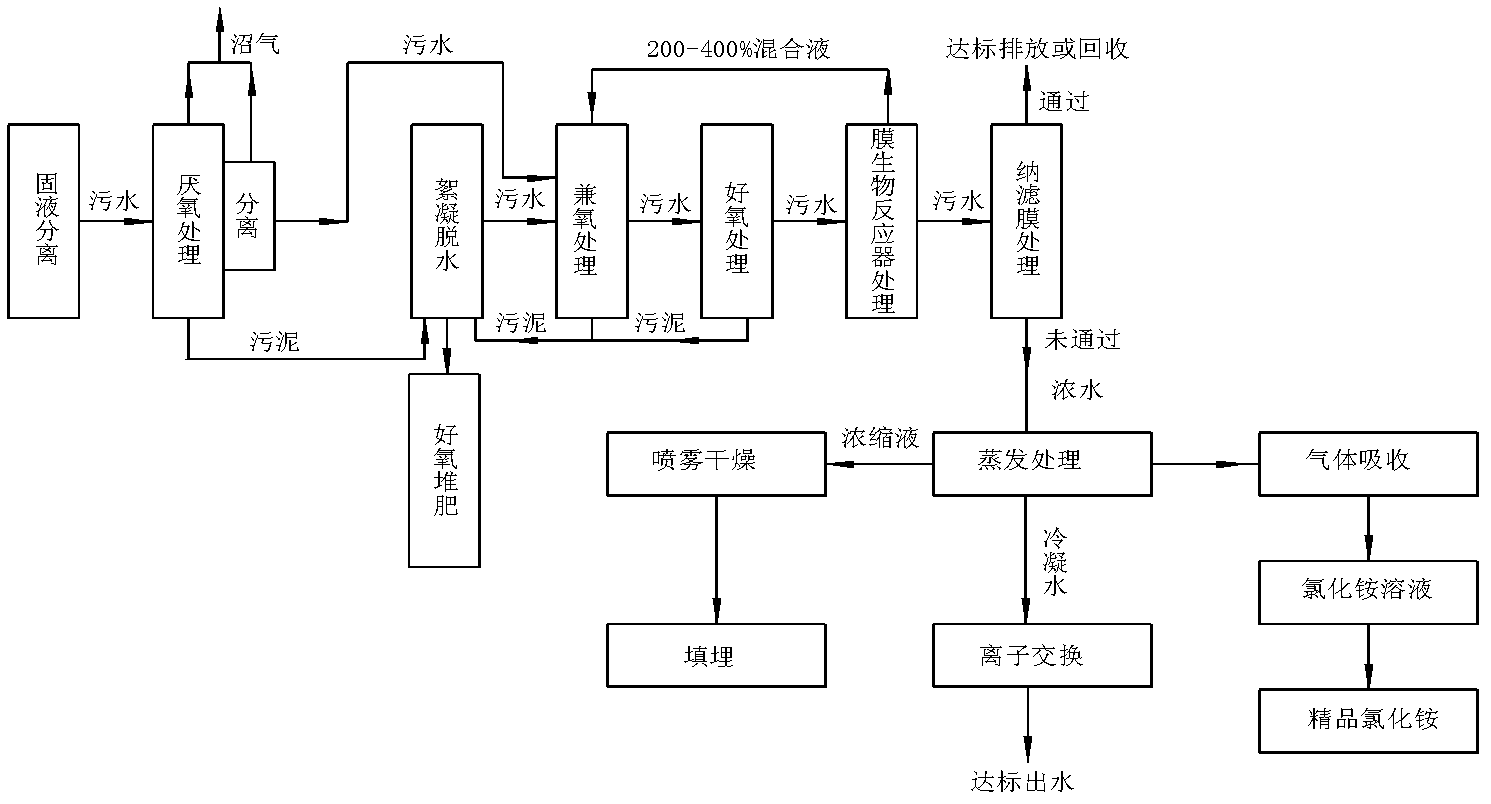
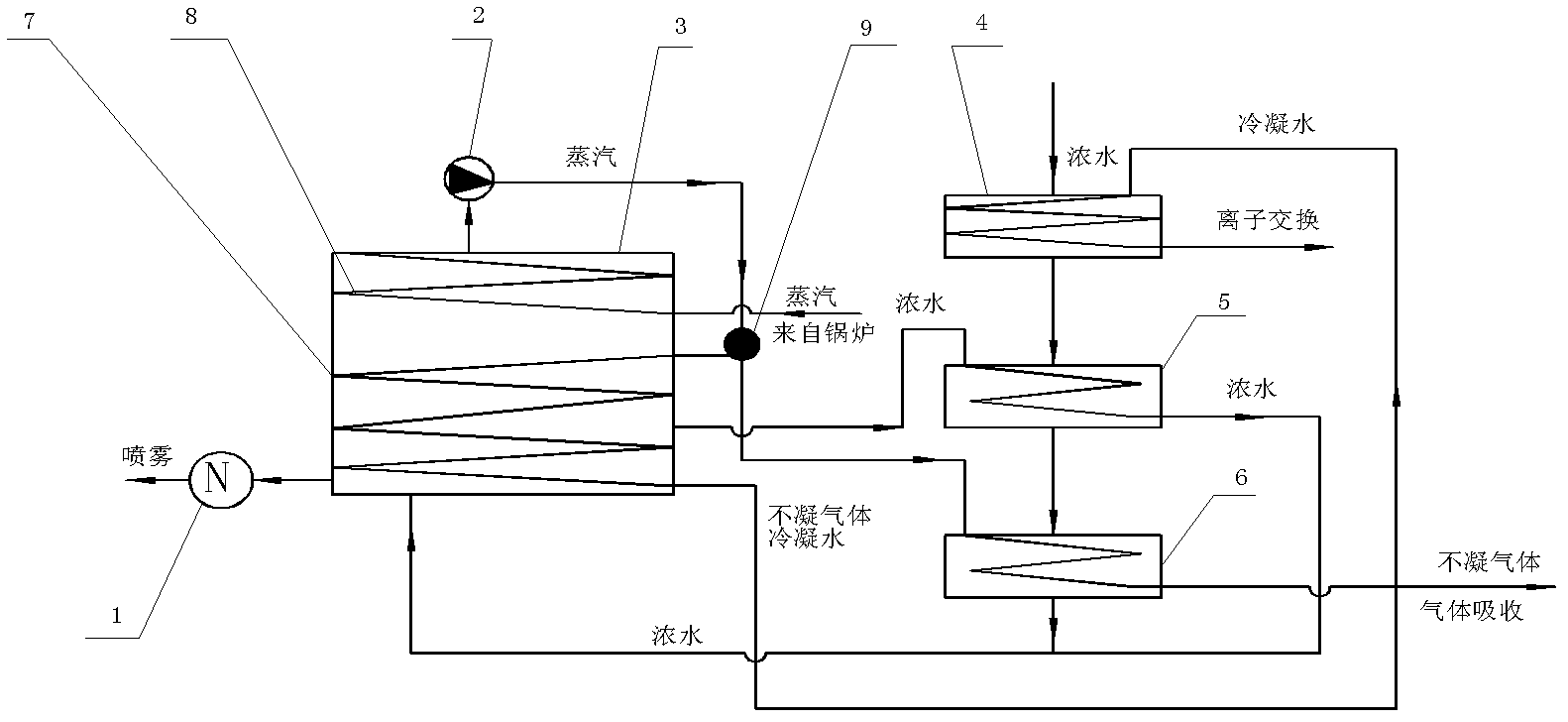
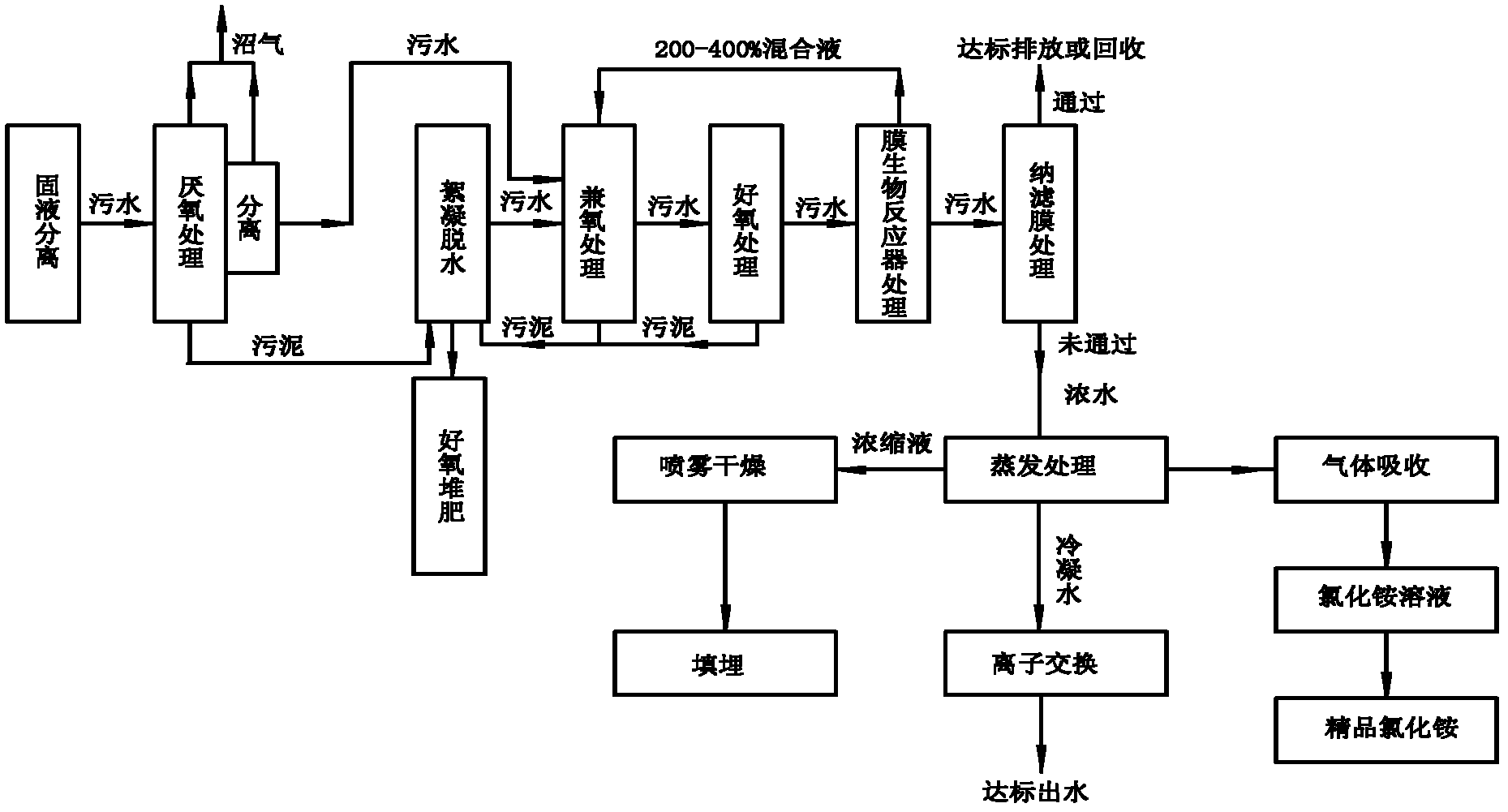
ActiveCN102557339AHarmlessImplement resourcesSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningBio-organic fraction processingEvaporationIon exchange
The invention relates to a treatment method of a landfill leachate, which comprises the step of treating the landfill leachate by adopting a multi-stage processing method of solid-liquid separation, anaerobic treatment, aerobic treatment, membrane bioreactor treatment, nanofiltration membrane, evaporation, ion exchange and spray drying. Due to the adoption of the treatment method, the problem that the future trouble of difficult treatment is finally generated due to higher and higher ammonia nitrogen and chemical oxygen demand COD in the landfill leachate caused by recharging is solved.
Owner:北京昊业怡生科技有限公司
Device and method for on-line measuring biochemical oxygen demand in sample
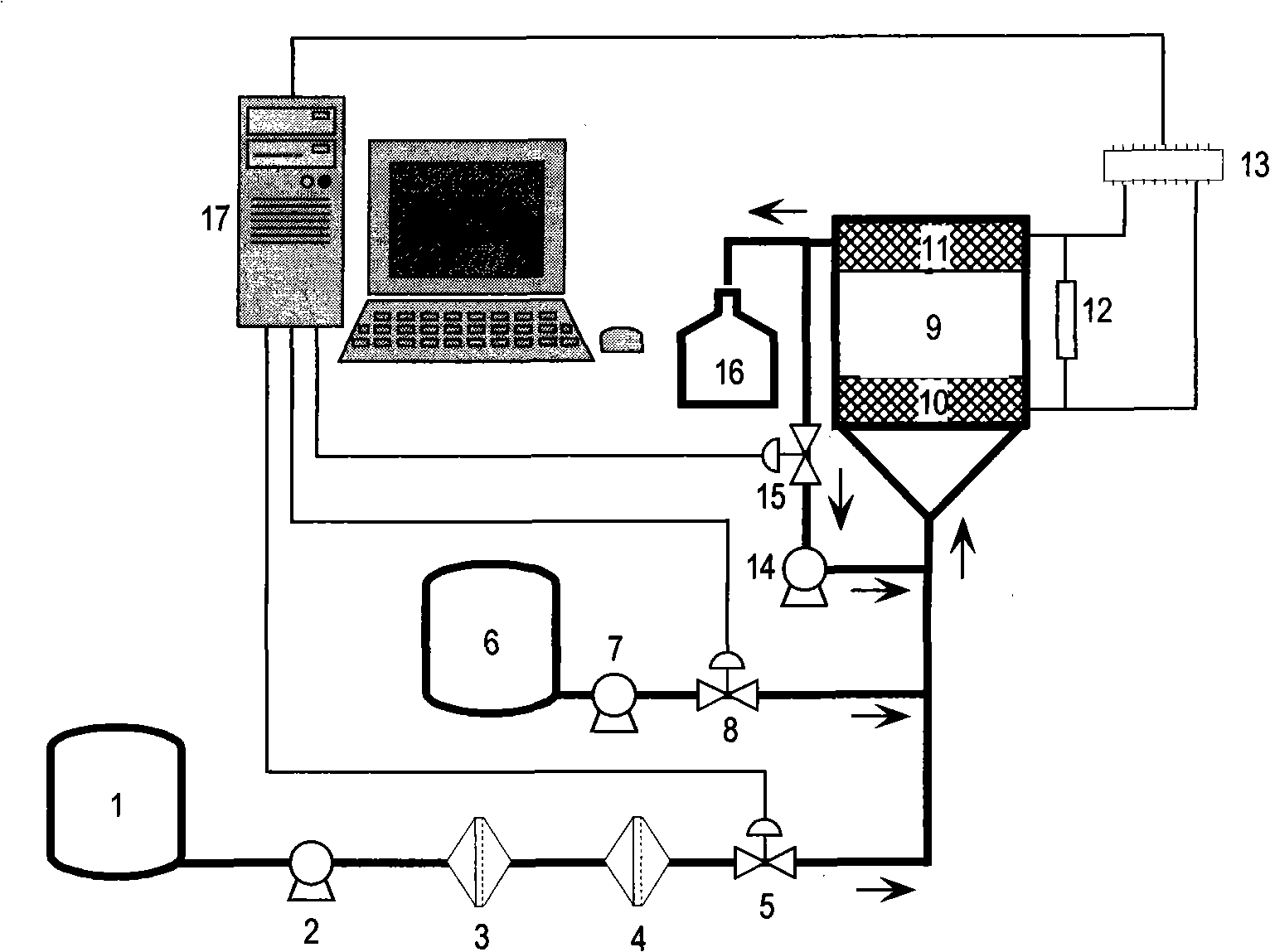
InactiveCN101315347AReduce manufacturing costLower runMaterial electrochemical variablesComputer control systemMicrobial fuel cell
The invention relates to a device and a method for carrying out on-line detection of the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) in a water body sample by utilizing a microbiological fuel cell. The detection device has the advantages of real-time and on-line continuous detection function, simple operation, long continuous working time, and lower use and maintenance costs. The upwelling microbiological fuel cell is taken as the core, a BOD sample enters the microbiological fuel cell directly or after being diluted, and a linear relation exists between the coulomb yield of the microbiological fuel cell and the BOD content of the sample, thereby obtaining the BOD content of the sample through detecting the electrical signal generated by the microbiological fuel cell and through analyzing the obtained data by a computer control system. The detection method includes detecting the oligotrophic BOD concentration with the BOD concentration value in the sample less than critical value, and the eutrophic BOD concentration with the BOD concentration value in the sample larger than critical value; the detection of the eutrophic BOD concentration can be completed by adopting a buffer solution dilution method or a pulse integration method.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com