Patents
Literature
2191results about "Biochemical fuel cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
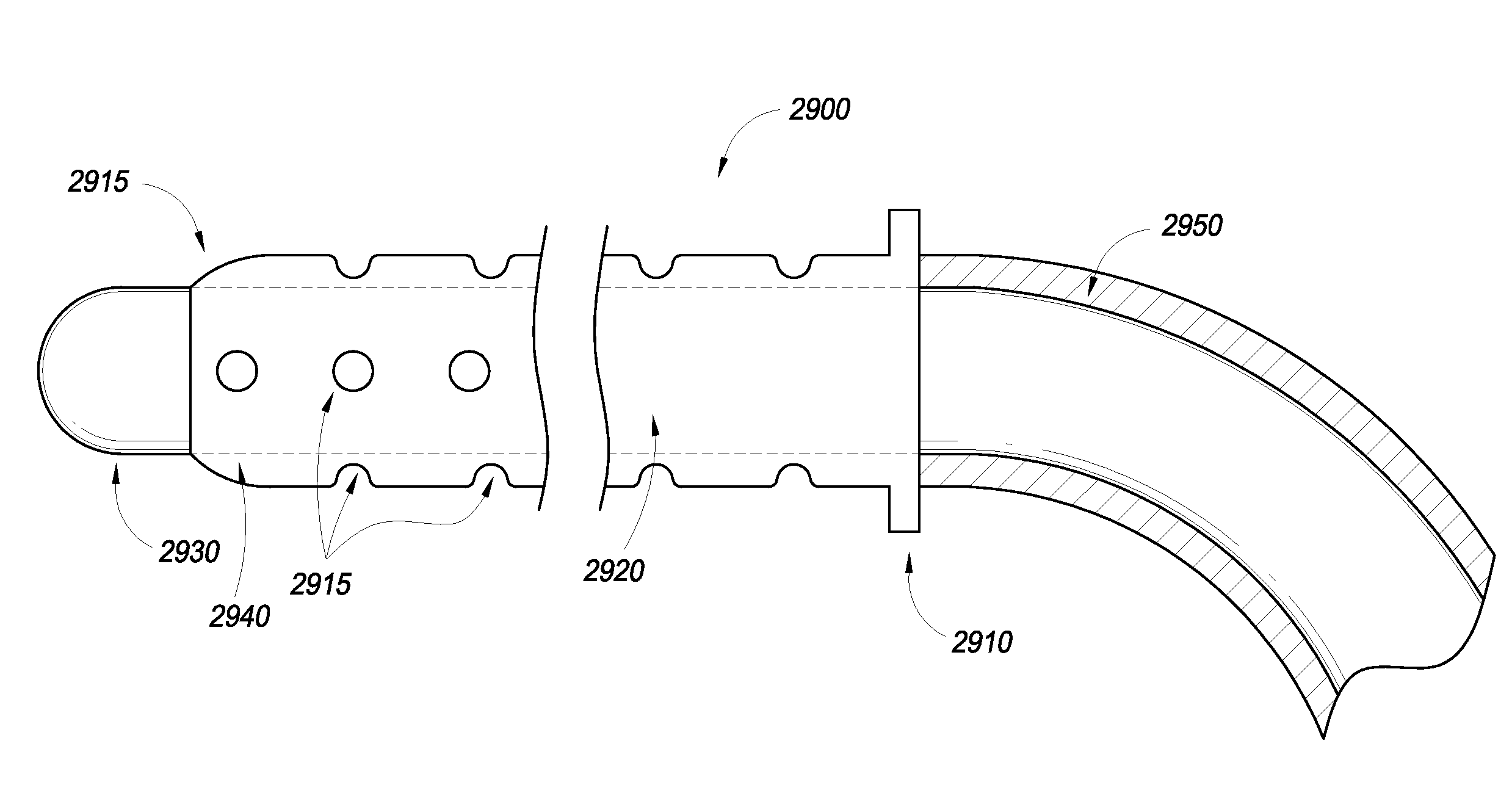
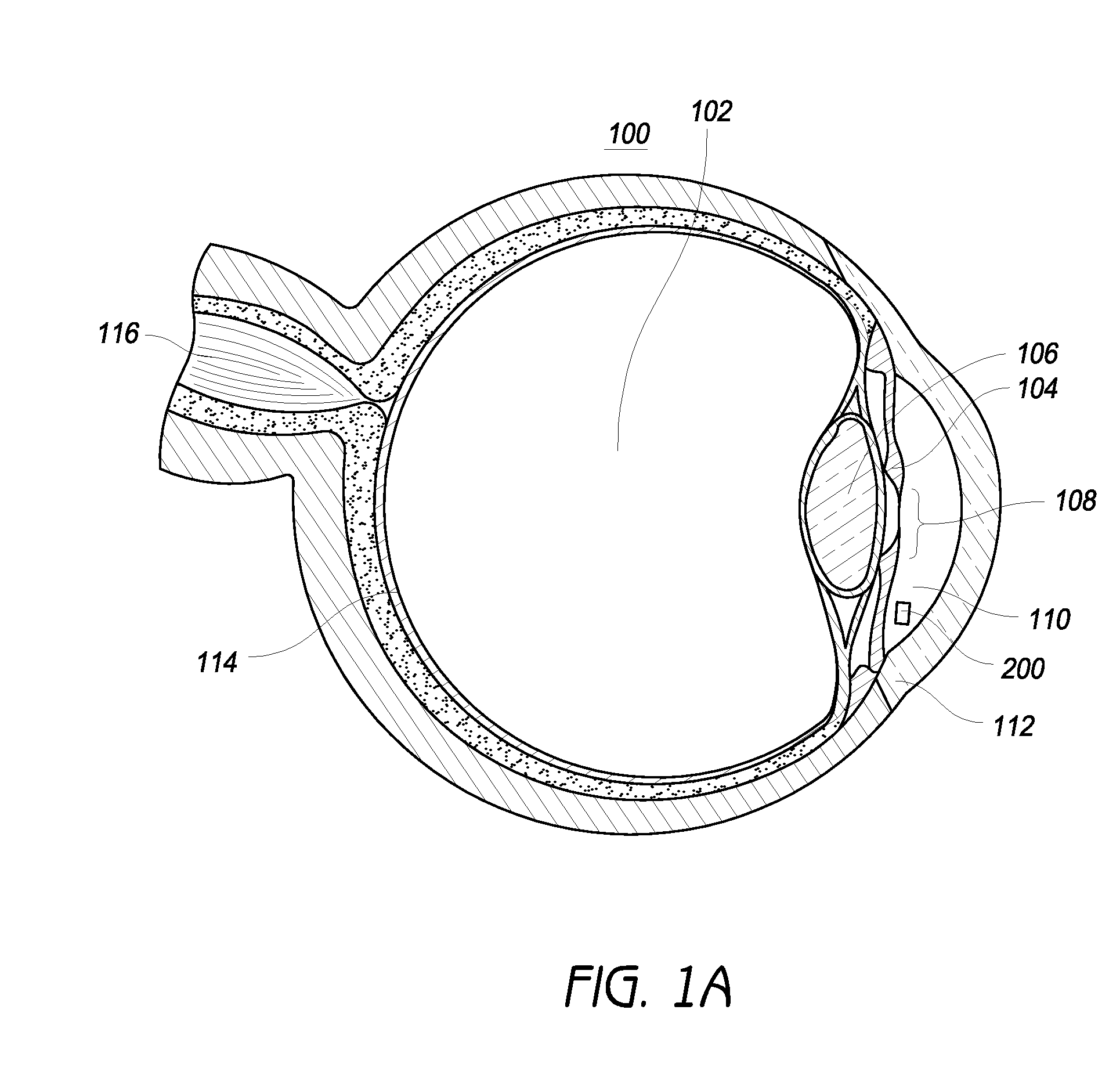
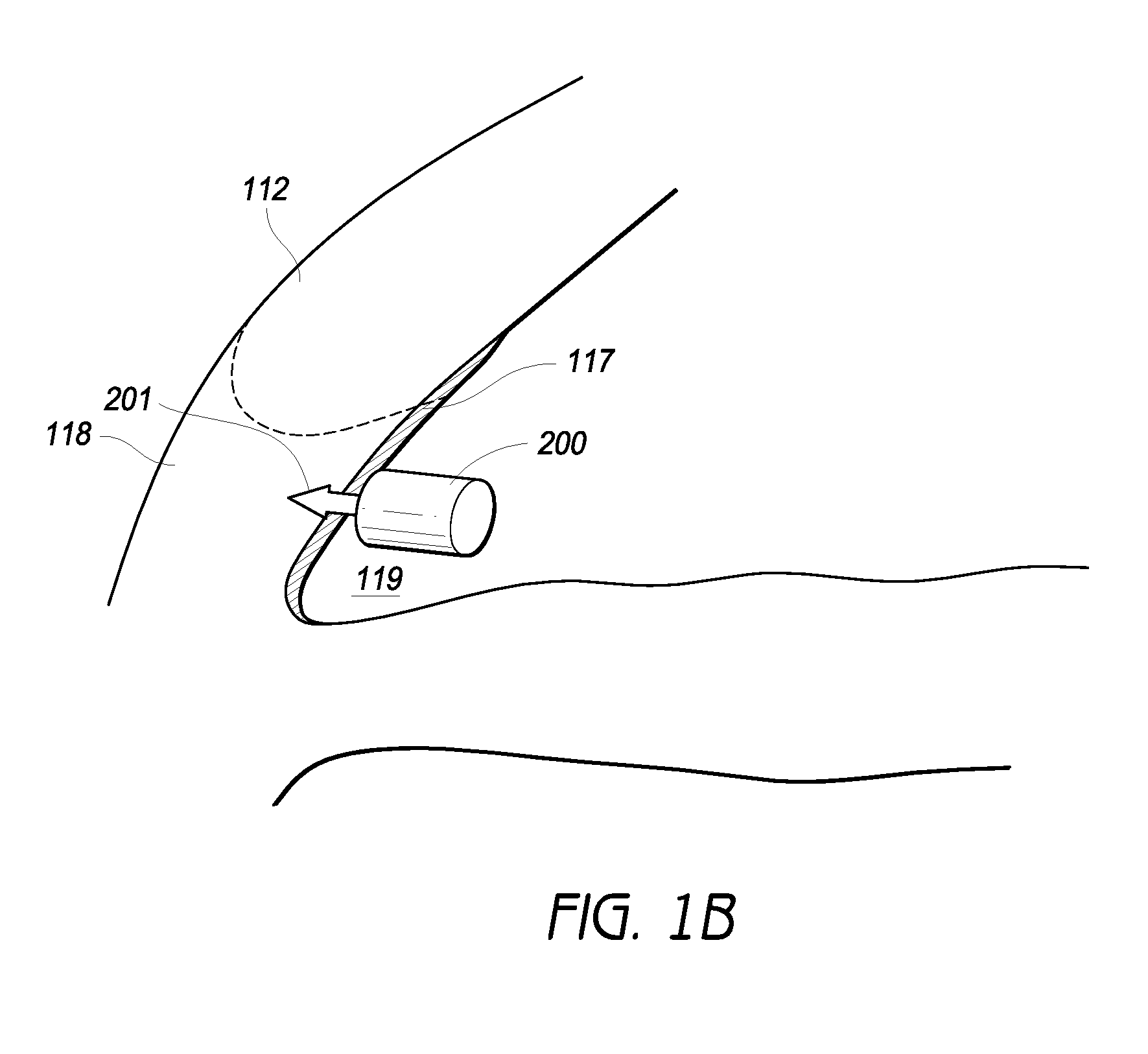
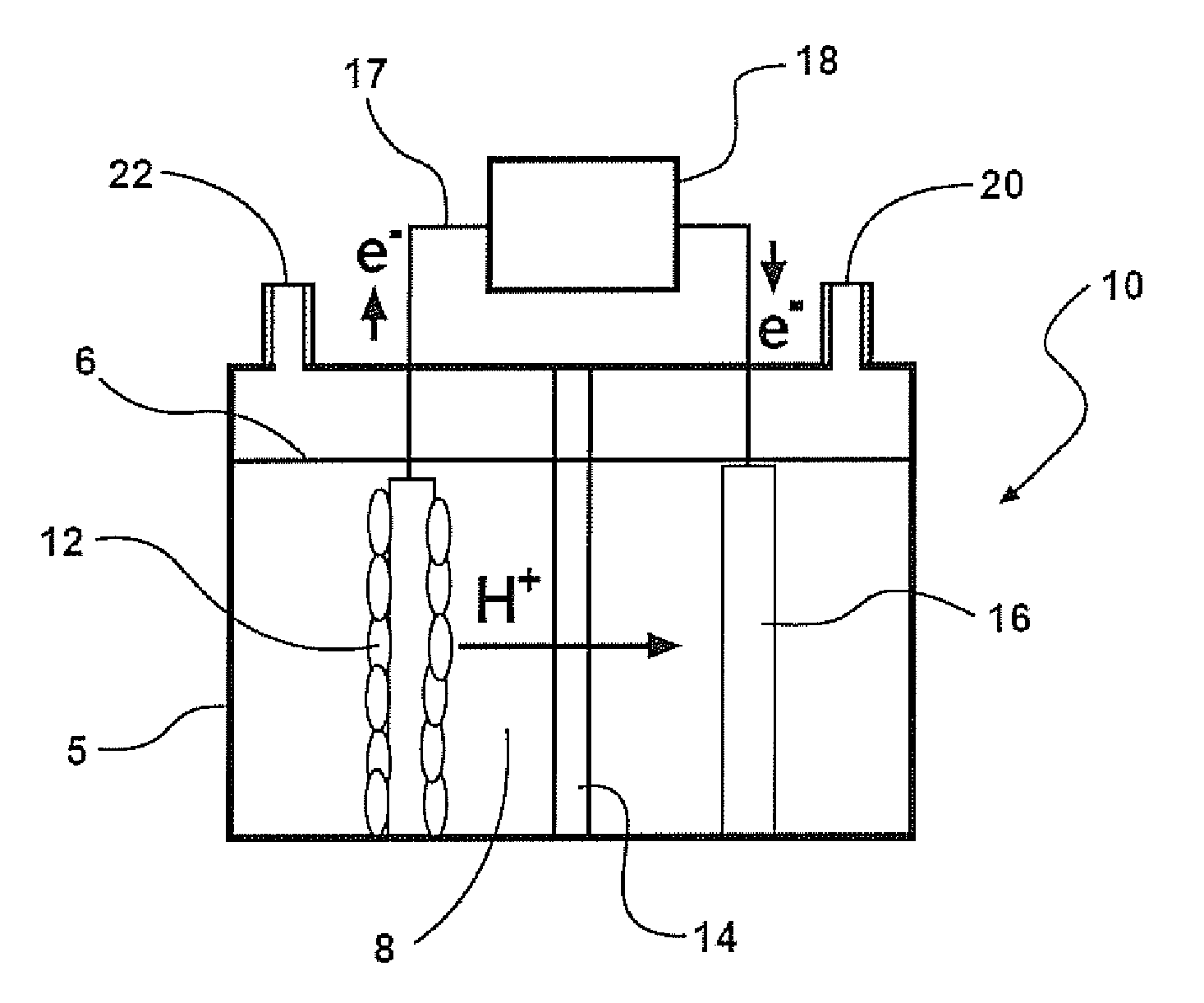
Intraocular physiological sensor
An implantable intraocular physiological sensor for measuring intraocular pressure, glucose concentration in the aqueous humor, and other physiological characteristics. The implantable intraocular physiological sensor may be at least partially powered by a fuel cell, such as an electrochemical glucose fuel cell. The implantable intraocular physiological sensor may wirelessly transmit measurements to an external device. In addition, the implantable intraocular physiological sensor may incorporate aqueous drainage and / or drug delivery features.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Materials and configurations for scalable microbial fuel cells
ActiveUS20070259217A1Raise the potentialTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesActive material electrodesElectricityMicrobial fuel cell
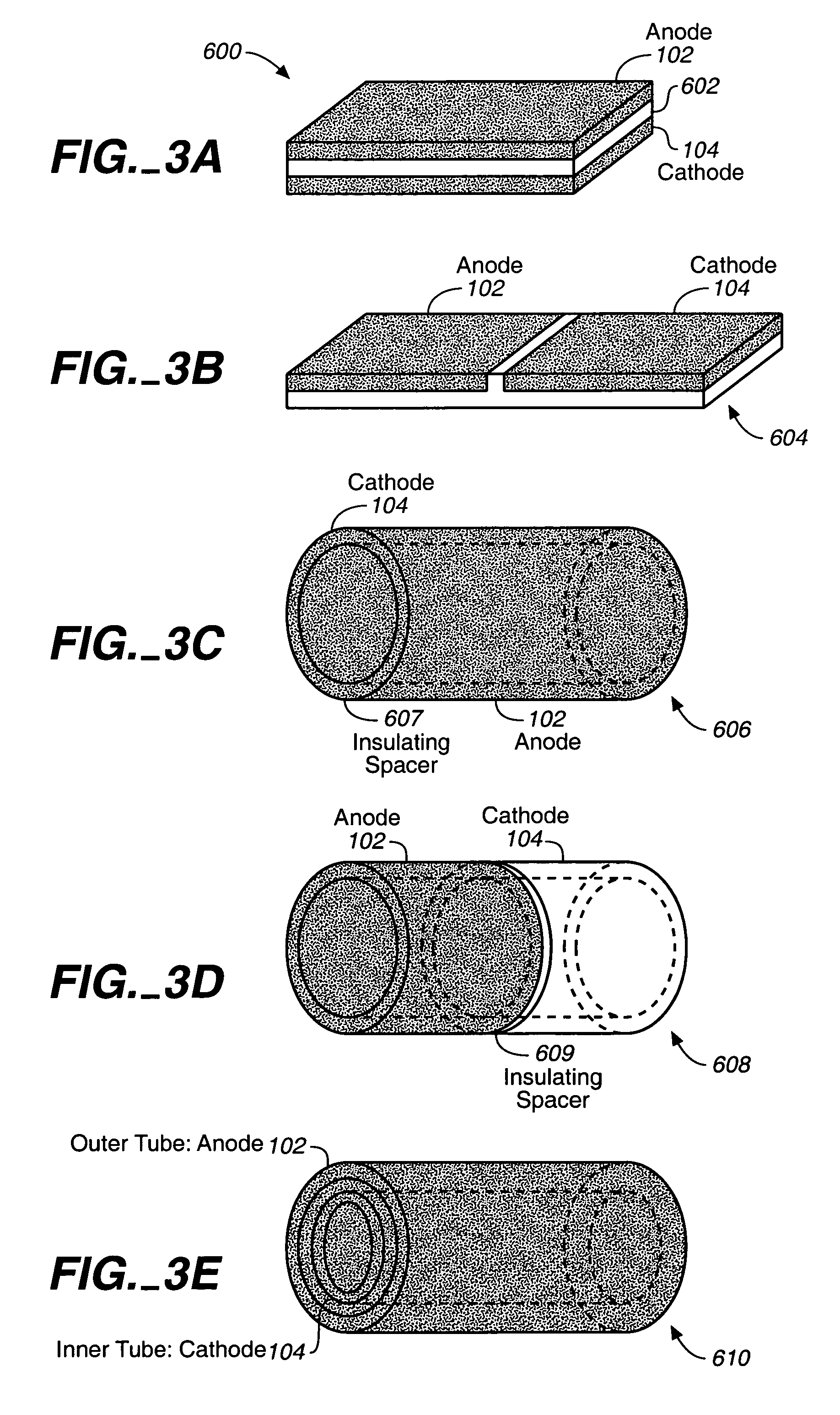
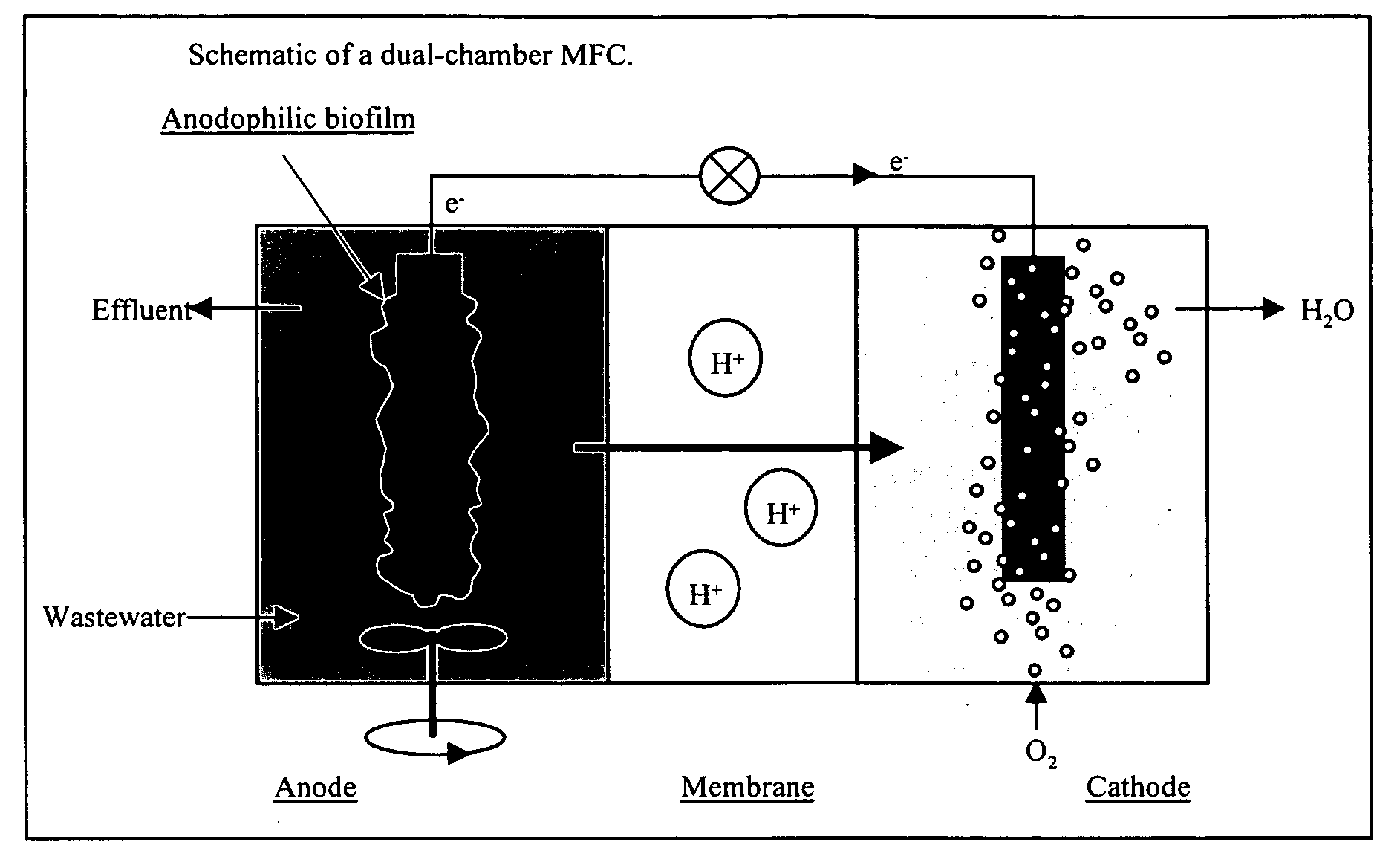
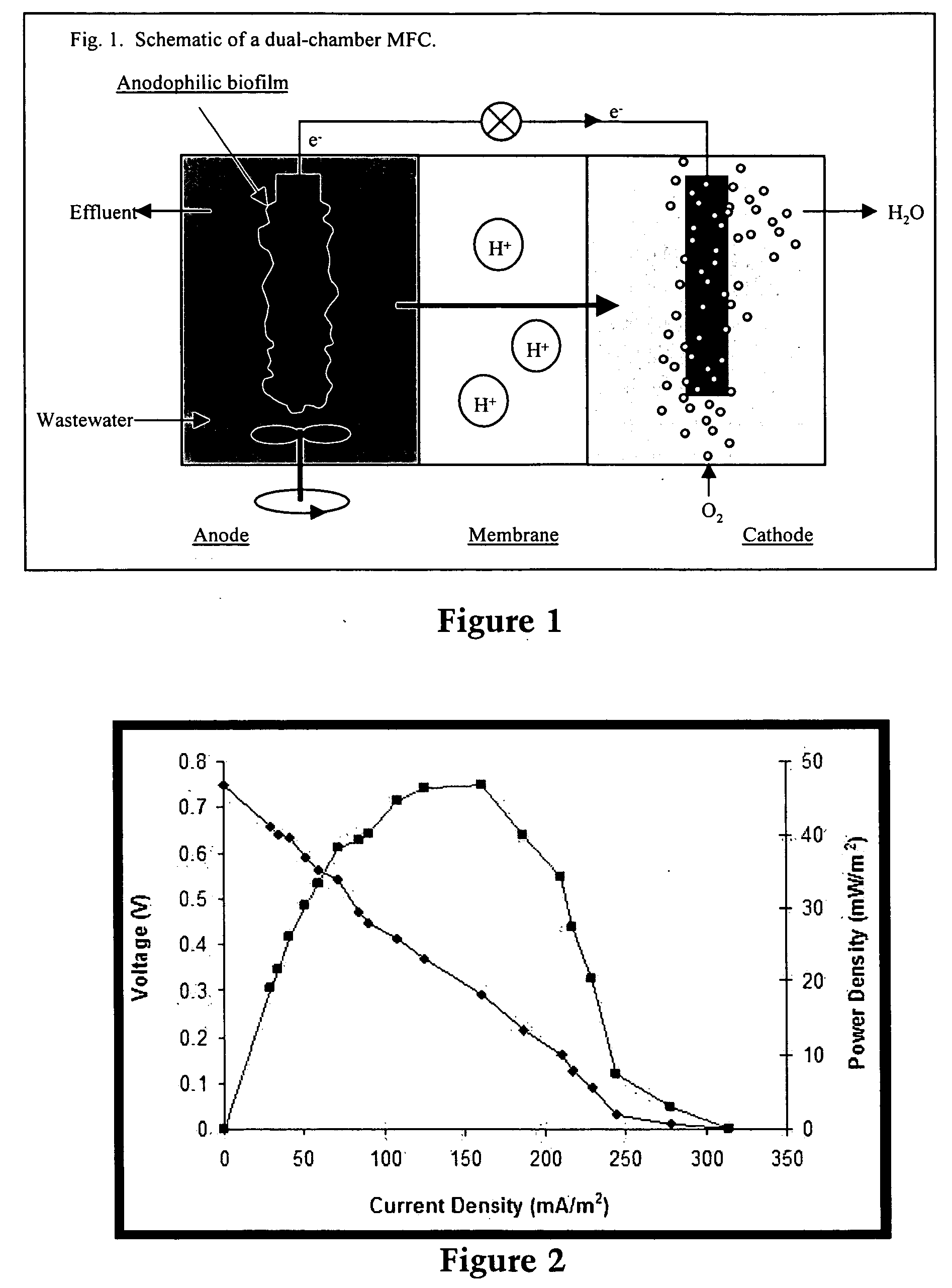
Devices for production of electricity and / or hydrogen gas are provided by the present invention. In particular, microbial fuel cells for production of electricity and modified microbial fuel cells for production of hydrogen are detailed. A tube cathode is provided which includes a membrane forming a general tube shape. An anode is provided which has a specific surface area greater than 100 m2 / m3. In addition, the anode is substantially non-toxic to anodophilic bacteria. Combinations of particular anodes and cathodes are included in microbial fuel cells and modified microbial fuel cells.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method and apparatus for sustainable energy and materials
A process for the production of hydrogen from anaerobically decomposed organic materials by applying an electric potential to the anaerobically decomposed organic materials, including landfill materials and sewage, to form hydrogen, and for decreasing the time required to treat these anaerobically decomposed organic materials. The organic materials decompose to volatile acids such as acetic acid, which may be hydrolyzed by electric current to form hydrogen. The process may be continuously run in sewage digestion tanks with the continuous feed of sewage, at landfill sites, or at any site having a supply of anaerobically decomposed or decomposable organic materials.
Owner:MCALISTER TECH LLC +1
Bio-electrochemically assisted microbial reactor that generates hydrogen gas and methods of generating hydrogen gas
ActiveUS20060011491A1Provide supportGrowth inhibitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityHydrogen
Systems and processes for producing hydrogen using bacteria are described. One detailed process for producing hydrogen uses a system for producing hydrogen as described herein, the system including a reactor. Anodophilic bacteria are disposed within the interior of the reactor and an organic material oxidizable by an oxidizing activity of the anodophilic bacteriais introduced and incubated under oxidizing reactions conditions such that electrons are produced and transferred to the anode. A power source is activated to increase a potential between the anode and the cathode, such that electrons and protons combine to produce hydrogen gas. One system for producing hydrogen includes a reaction chamber having a wall defining an interior of the reactor and an exterior of the reaction chamber. An anode is provided which is at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber and a cathode is also provided which is at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber. The cathode is spaced apart at a distance in the range between 0.1-100 centimeters, inclusive, from the anode. A conductive conduit for electrons is provided which is in electrical communication with the anode and the cathode and a power source for enhancing an electrical potential between the anode and cathode is included which is in electrical communication at least with the cathode. A first channel defining a passage from the exterior of the reaction chamber to the interior of the reaction chamber is also included.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
Substrate-enhanced microbial fuel cells
A microbial fuel cell configuration of the invention includes a substrate particularly formulated for a microbial fuel cell configured to produce electricity and / or a modified microbial fuel cell configured to produce hydrogen. A substrate formulation according to one embodiment includes a solid biodegradable organic material in a package porous to bacteria. A microbial fuel cell provided according to embodiments of the present invention includes an anode, a cathode, an electrically conductive connector connecting the anode and the cathode, a housing for an aqueous medium, the aqueous medium in contact with the anode, and a solid form of a biodegradable organic substrate disposed in the aqueous medium, the solid form of a biodegradable organic substrate formulated to support electron generation and transfer to the anode by anodophilic bacteria over a selected minimum period of time.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Immobilized enzymes in biocathodes
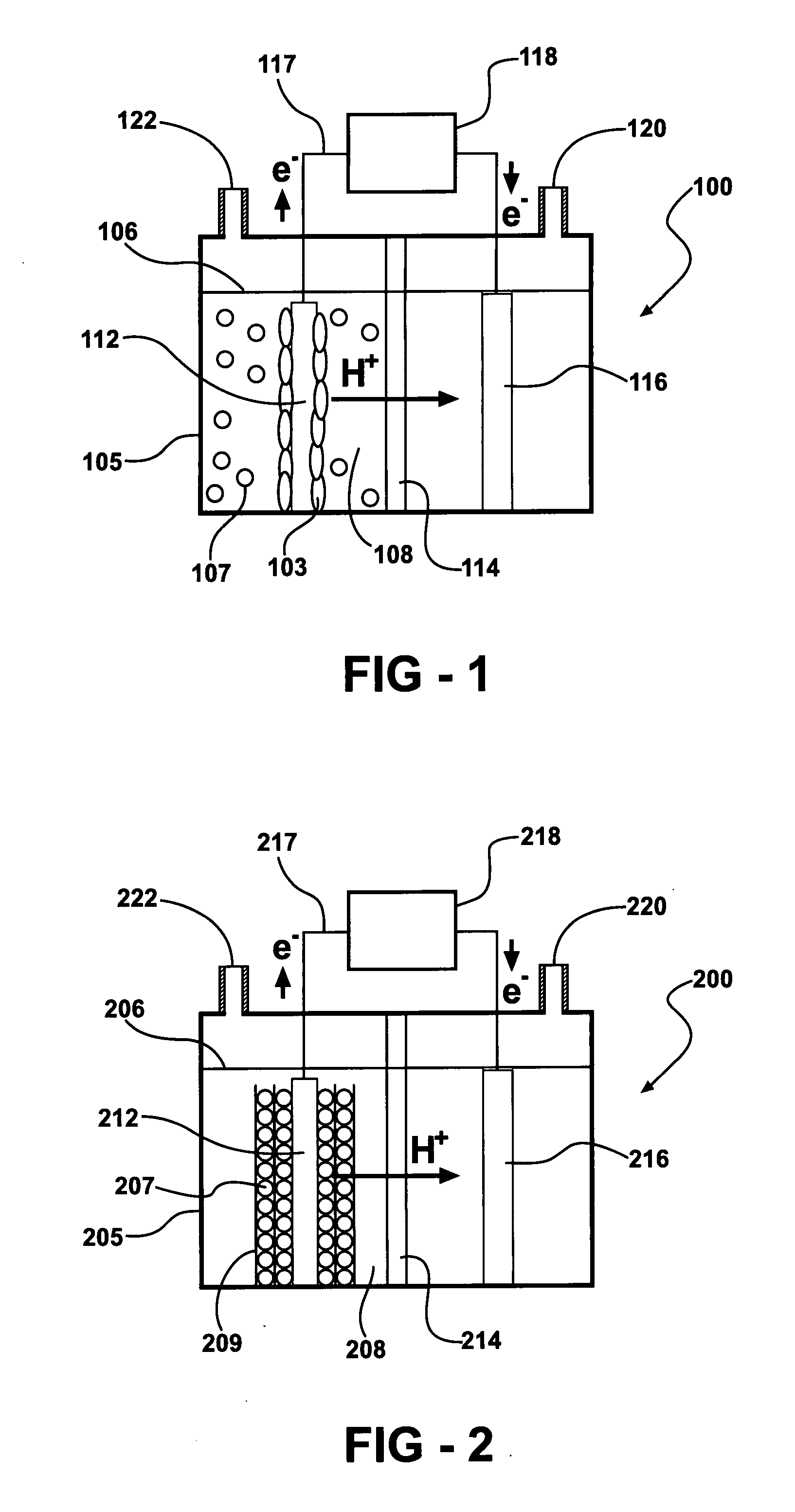
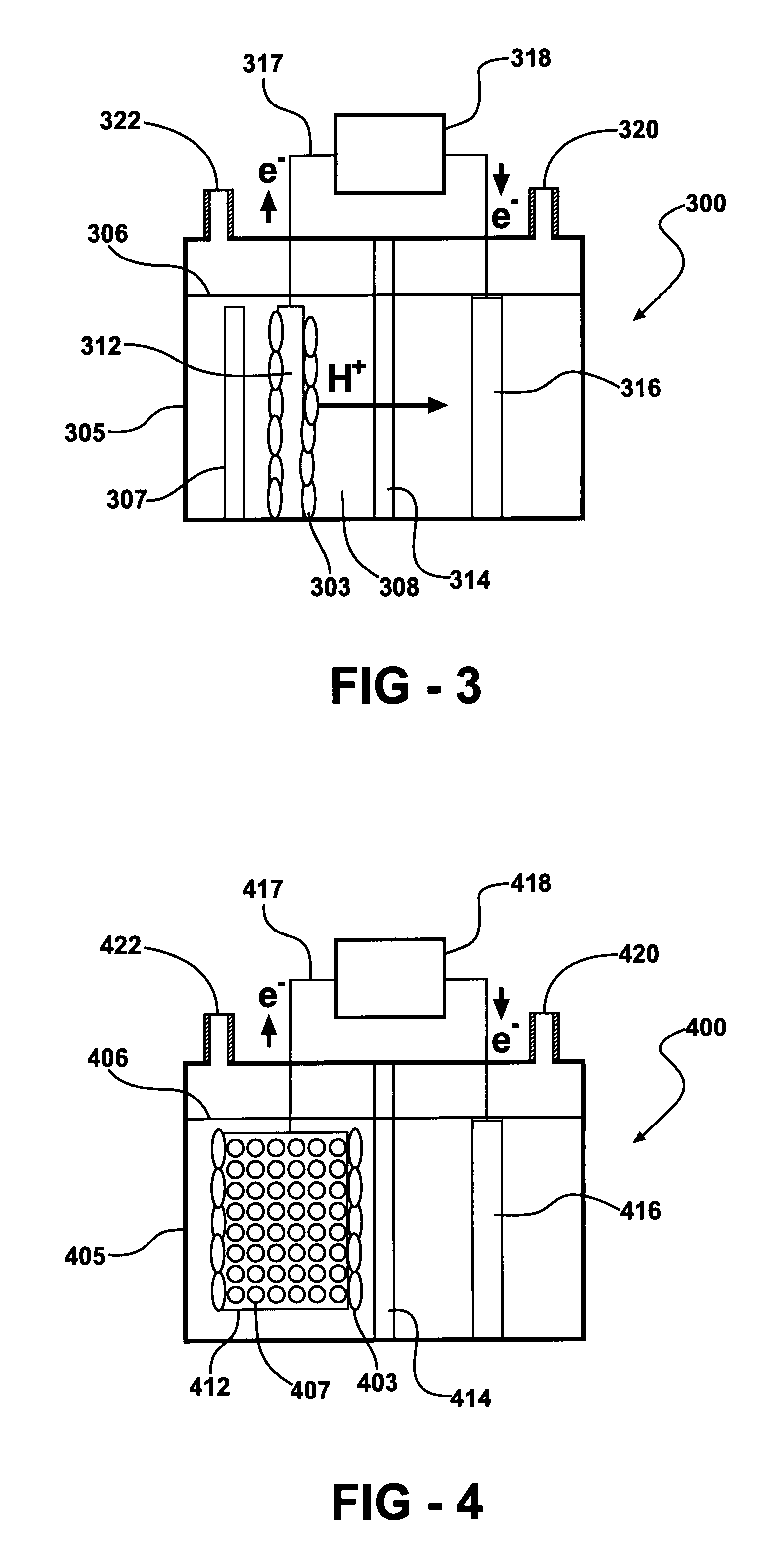
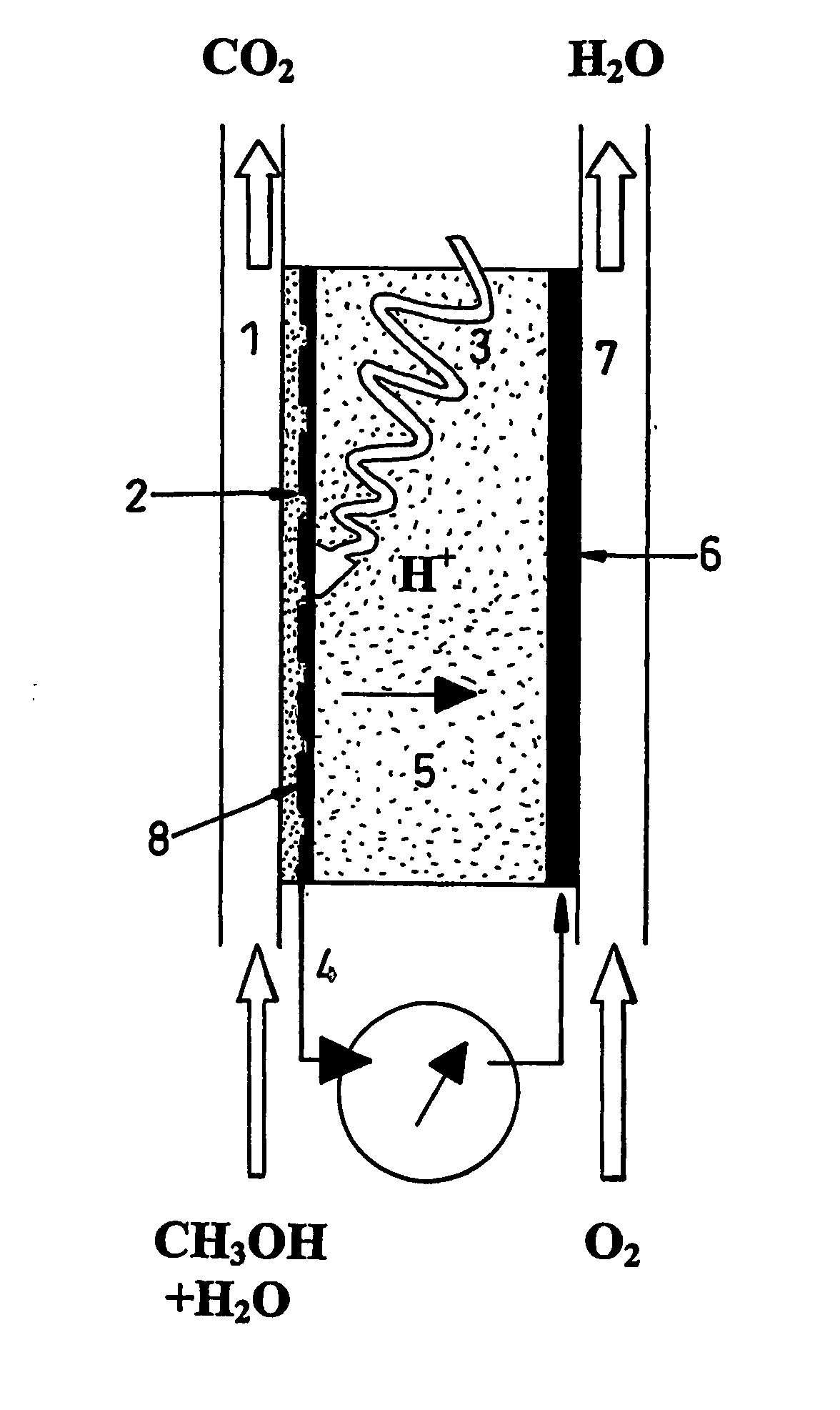
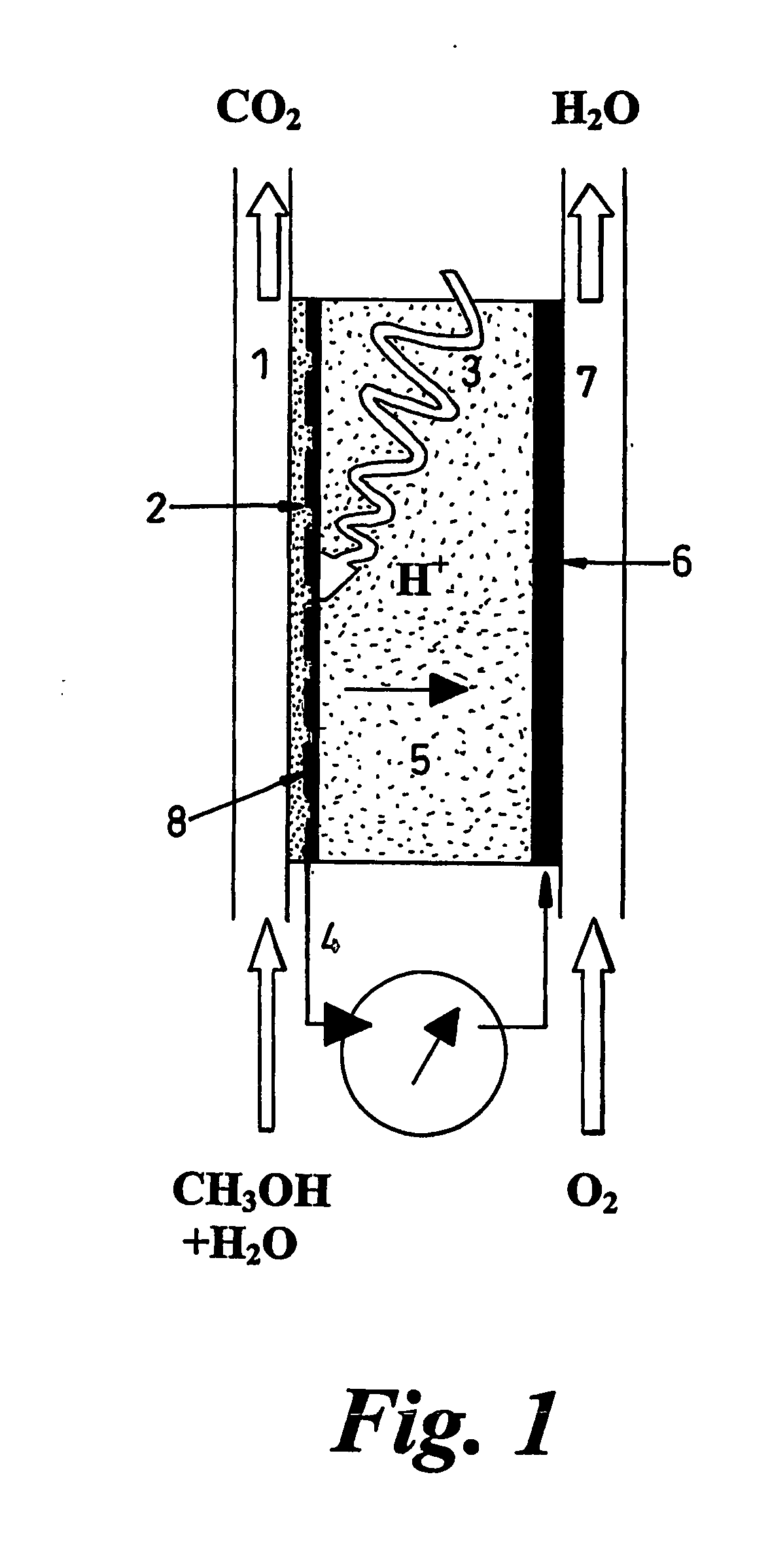
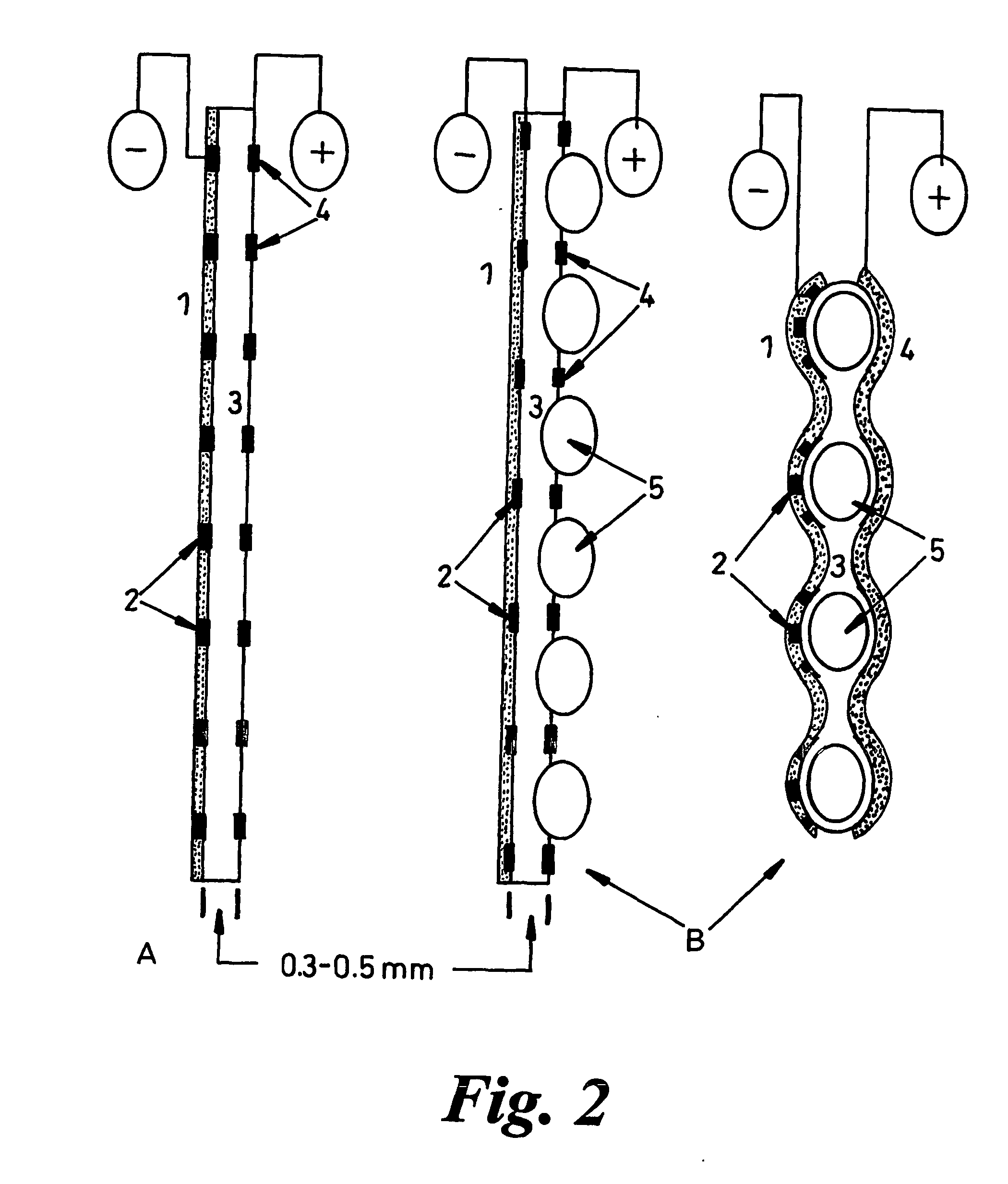
Disclosed is an improved biofuel cell having a cathode comprising a dual function membrane, which contains an oxygen oxidoreductase enzyme immobilized within a buffered compartment of the membrane and an electron transport mediator which transfers electrons from an electron conducting electrode to the redox reaction catalyzed by the oxygen oxidoreductase enzyme. The improved biofuel cell also has an anode that contains an oxidoreductase enzyme that uses an organic fuel, such as alcohol, as a substrate. An electric current can flow between the anode and the cathode.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Electrodes and methods for microbial fuel cells
InactiveUS20080292912A1Raise the potentialImprove performanceTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesCell electrodesMicrobial fuel cellFuel cells
Methods of improving a performance parameter of a microbial fuel cell are provided according to embodiments of the present invention which include heating an electrode and exposing the heated electrode to ammonia gas to produce a treated electrode characterized by an increased positive surface charge on the electrode surface. Improved performance parameters include increased maximum power density, increased coulombic efficiency, increased volumetric power density and decreased microbial fuel cell operation time to achieve maximum power density
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Implantable biofuel cell system based on nanostructures
InactiveUS20050118494A1Increase powerImprove power densityMaterial nanotechnologyFuel cell auxillariesCarbon nanotubeMolecular level
A bio-implantable electrochemical cell system for active implantable medical devices. In one embodiment, the fuel cell includes an electrode structure consisting of immobilized anode and cathode enzymes deposited on nanostructured high-surface-area metal nanowires or carbon nanotube electrodes. The anode enzyme comprises immobilized glucose oxidase and the cathode enzyme comprises immobilized laccase. Glucose is oxidized at the surface of the anode and oxygen is reduced at the surface of the cathode. The coupled glucose oxidation-oxygen reduction reactions provide a self-generating current source. In another embodiment, the nanowires or carbon nanotubes, along with the adjacent surface anode and cathode electrodes, are coated with immobilized glucose oxidase and immobilized laccase containing biocolloidal substrates, respectively. This results in the precise construction of an enzyme architecture with control at the molecular level, while increasing the reactive surface area and corresponding output power by at least two orders of magnitude.
Owner:NANOSOLUTIONS
Conversion systems for biomass
ActiveUS20100064746A1Efficient and economical and convenient to moveEasy to transportBio-organic fraction processingBiofuelsBiomass transportationPetroleum
The efficient production of ethanol from low-cost biomass (e.g., corn, sugar beets, sugar cane, switchgrass and / or paper) has become increasingly important in making ethanol competitive with gasoline and decreasing the United States' dependence on foreign oil. For example, to reduce the cost of transporting biomass to ethanol production facilities, mobile systems for producing ethanol from biomass are provided. Also provided are small-scale ethanol production facilities. For example, instead of transporting biomass to the production facility, the facility is transported to the biomass or is located nearby the source of the biomass. The ethanol production facilities or components thereof may be transported via land, water, or air. Production of other products, such as hydrocarbons, natural gas, hydrogen gas, plastics, polymers, and proteins, can also be made by the methods and facilities. Any product described herein can be made in finished form or un-finished form and moved, e.g., to a fixed facility, e.g., fixed production facility.
Owner:XYLECO INC
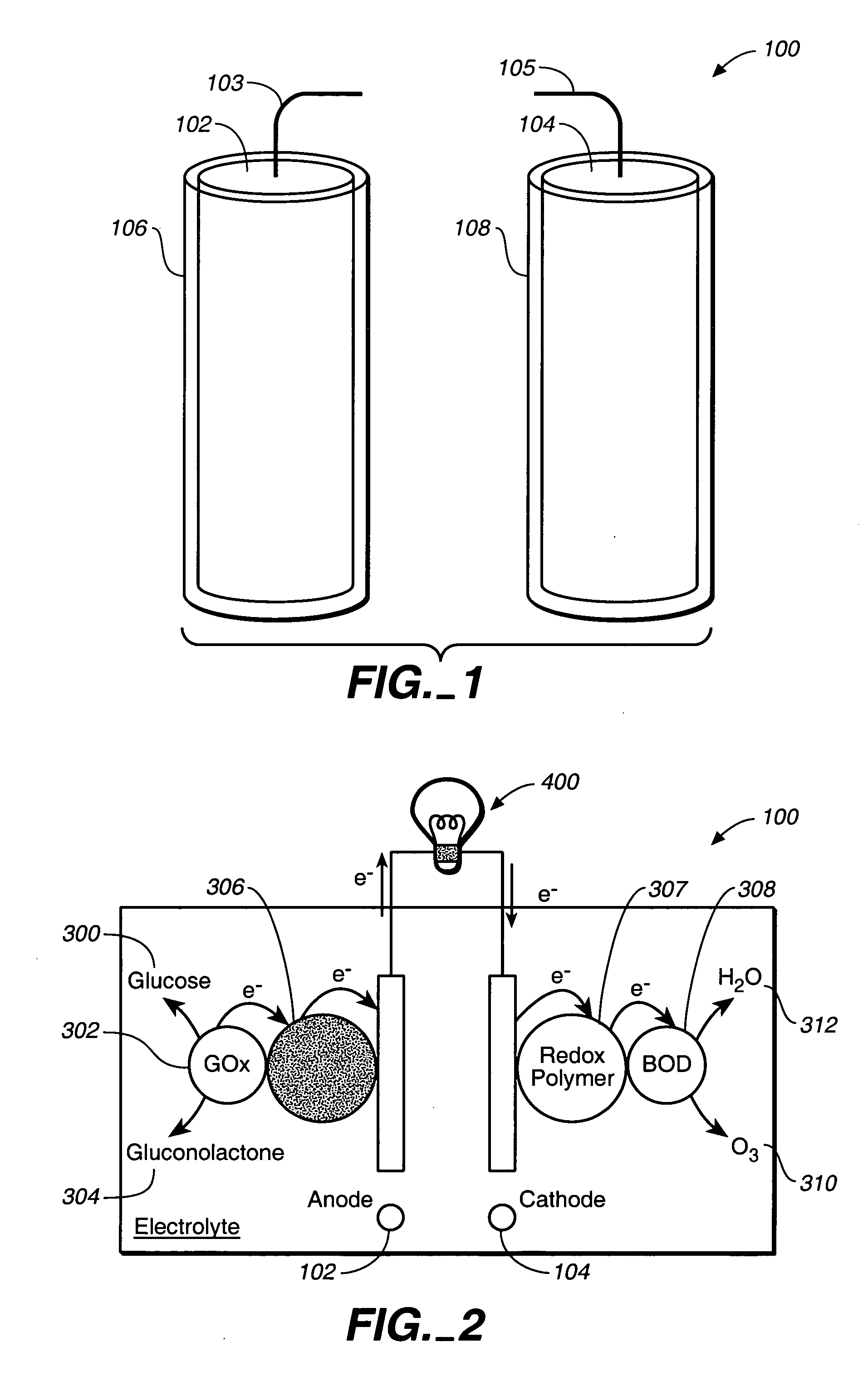
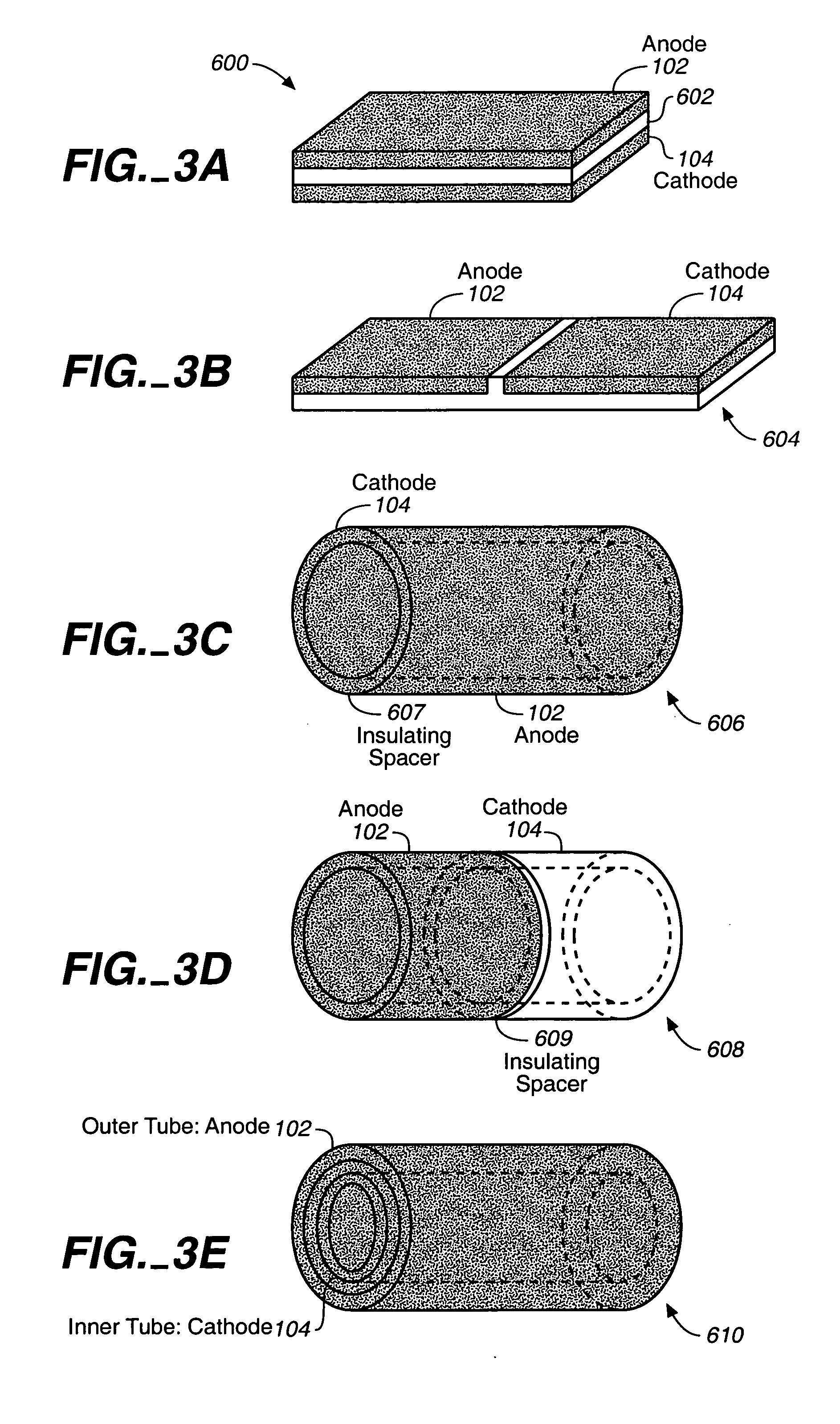
Miniature biological fuel cell that is operational under physiological conditions, and associated devices and methods
InactiveUS7368190B2Reduce physical sizeReduced dimensionMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementOperabilityRedox polymers
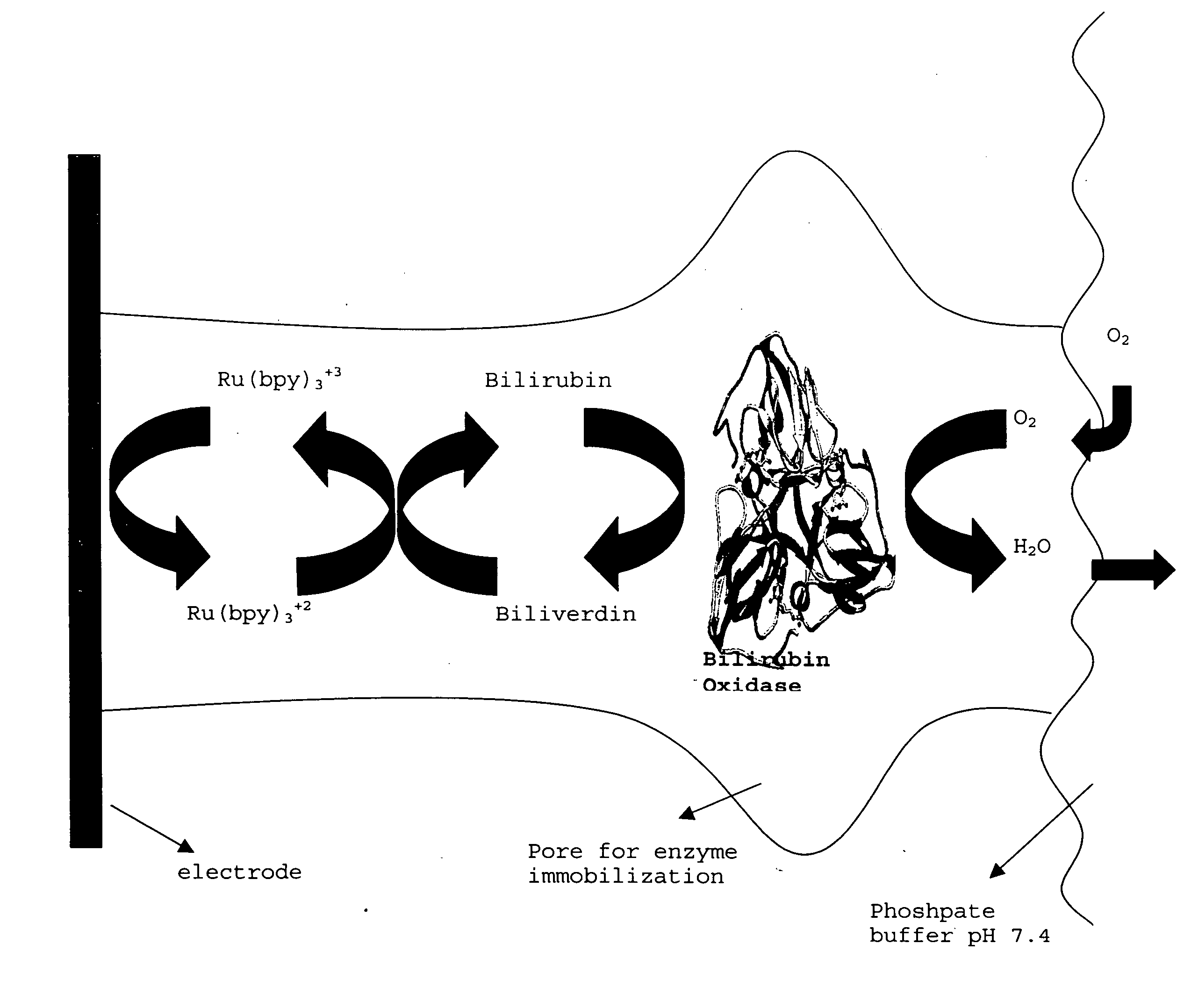
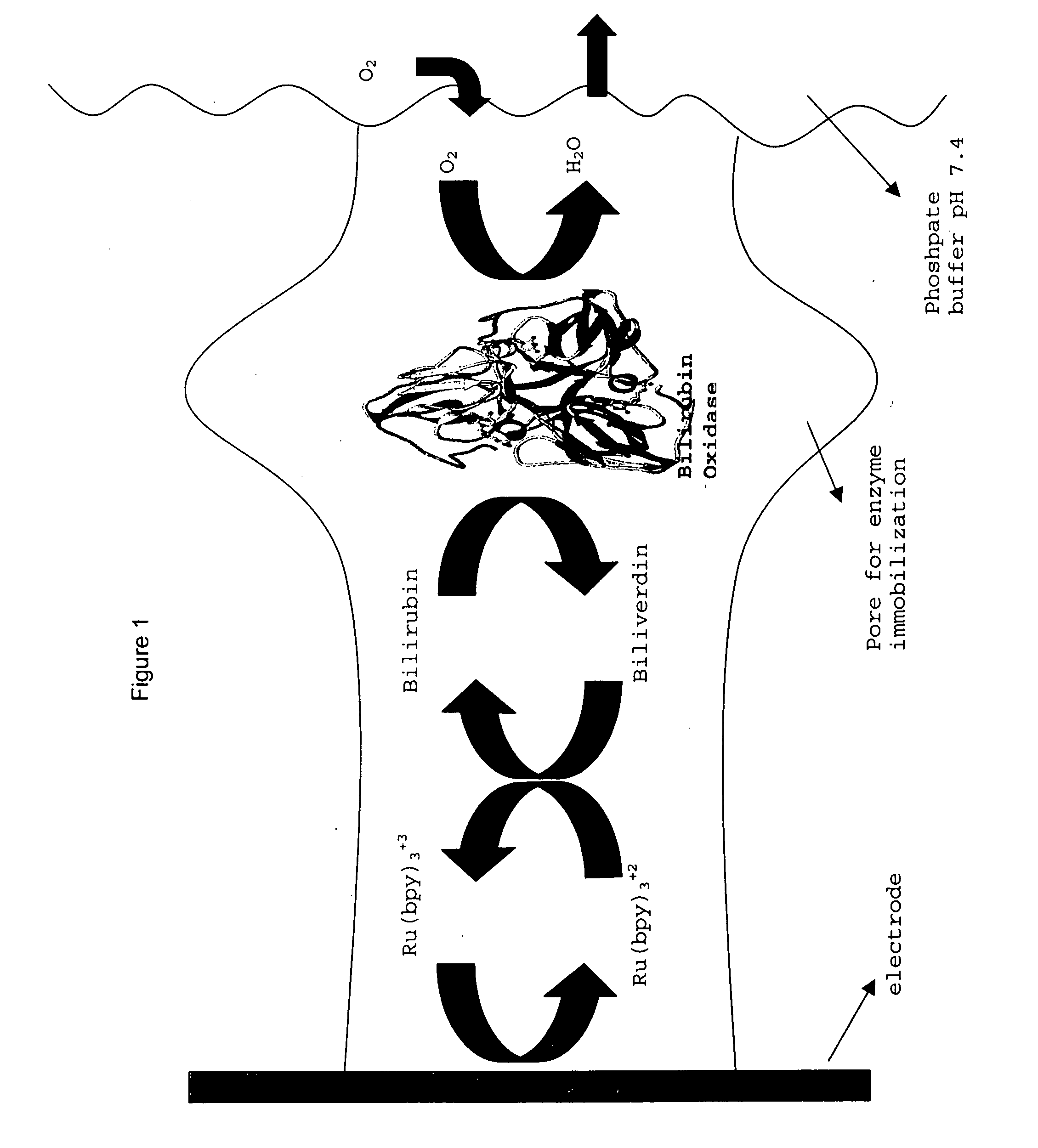
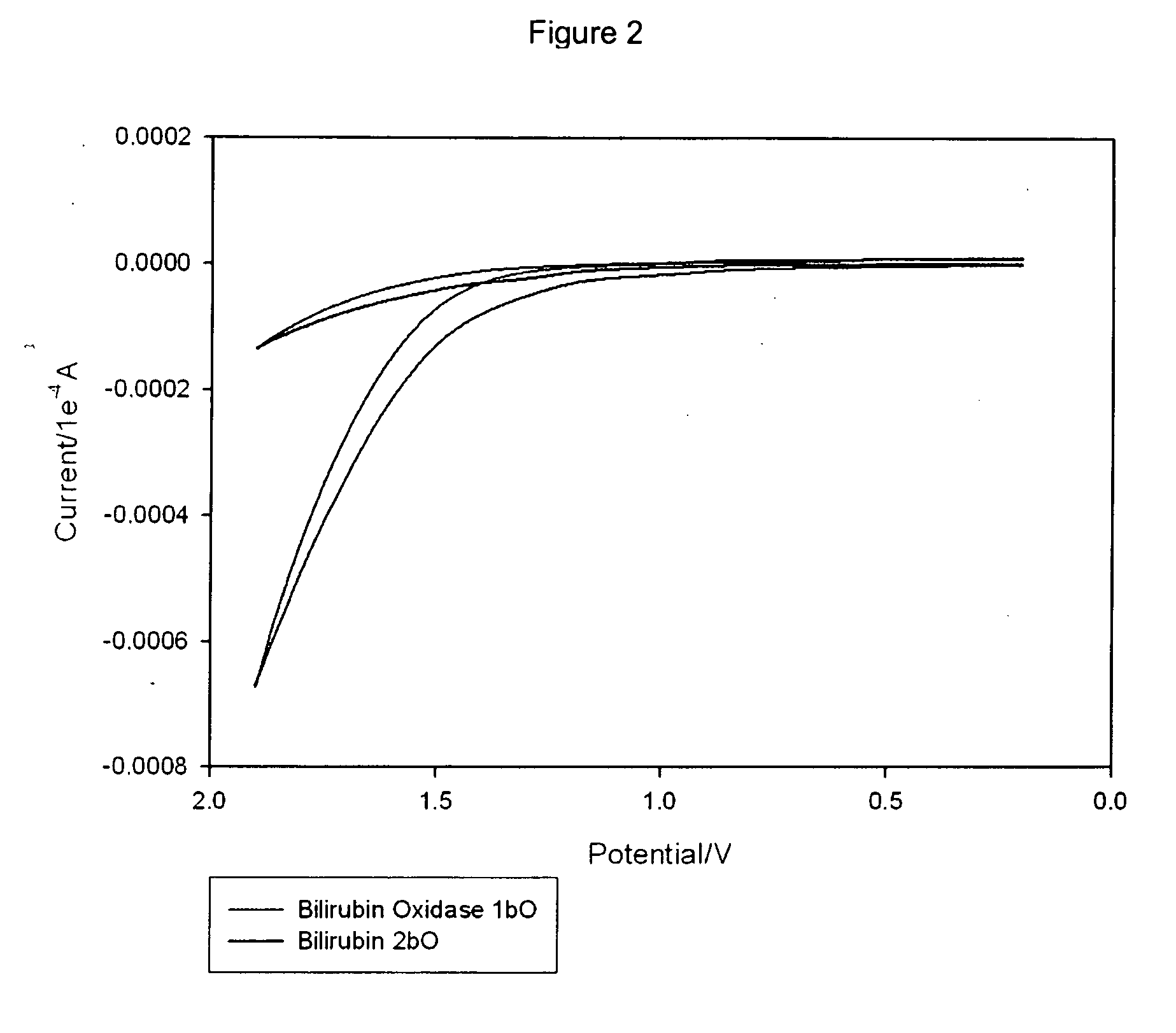
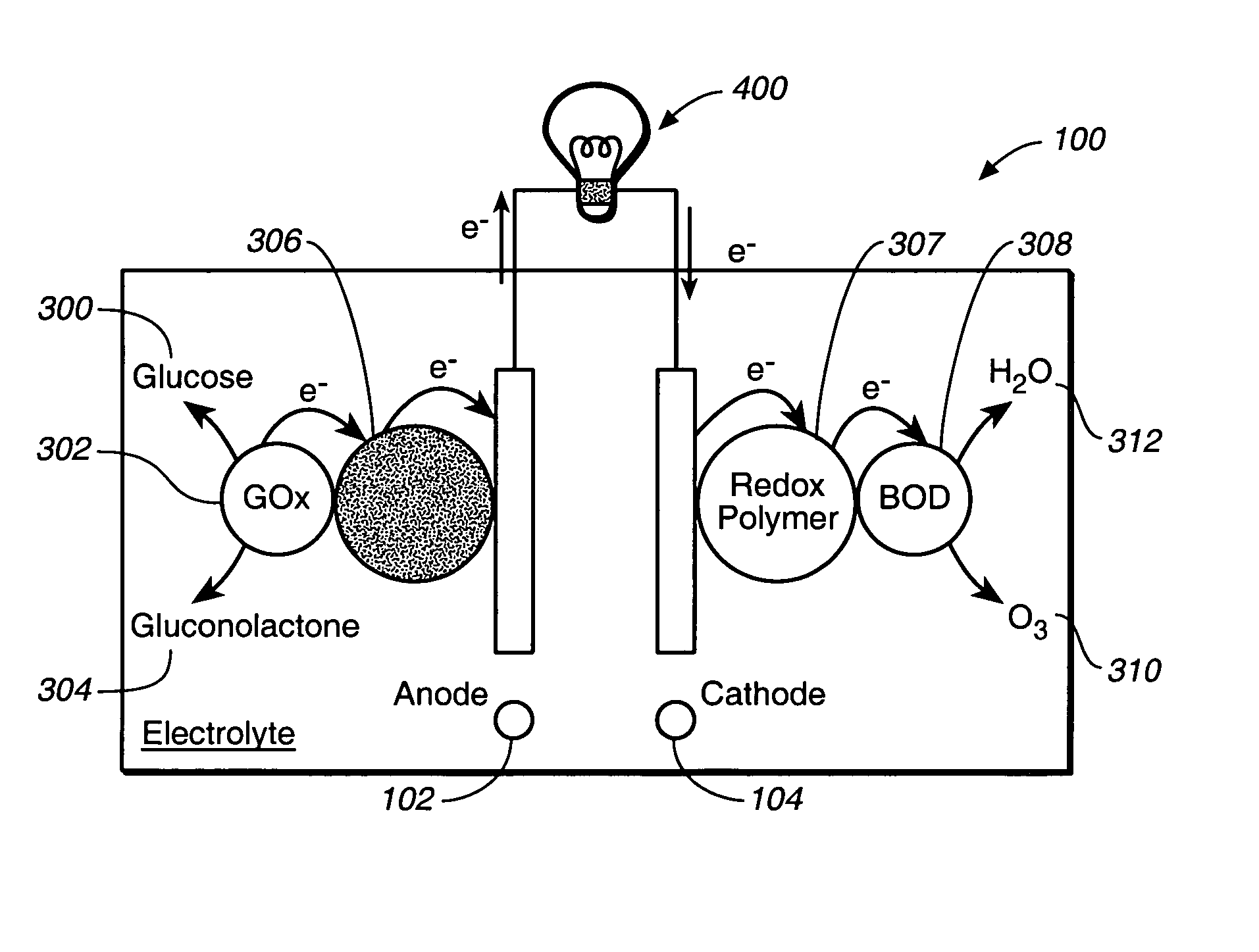
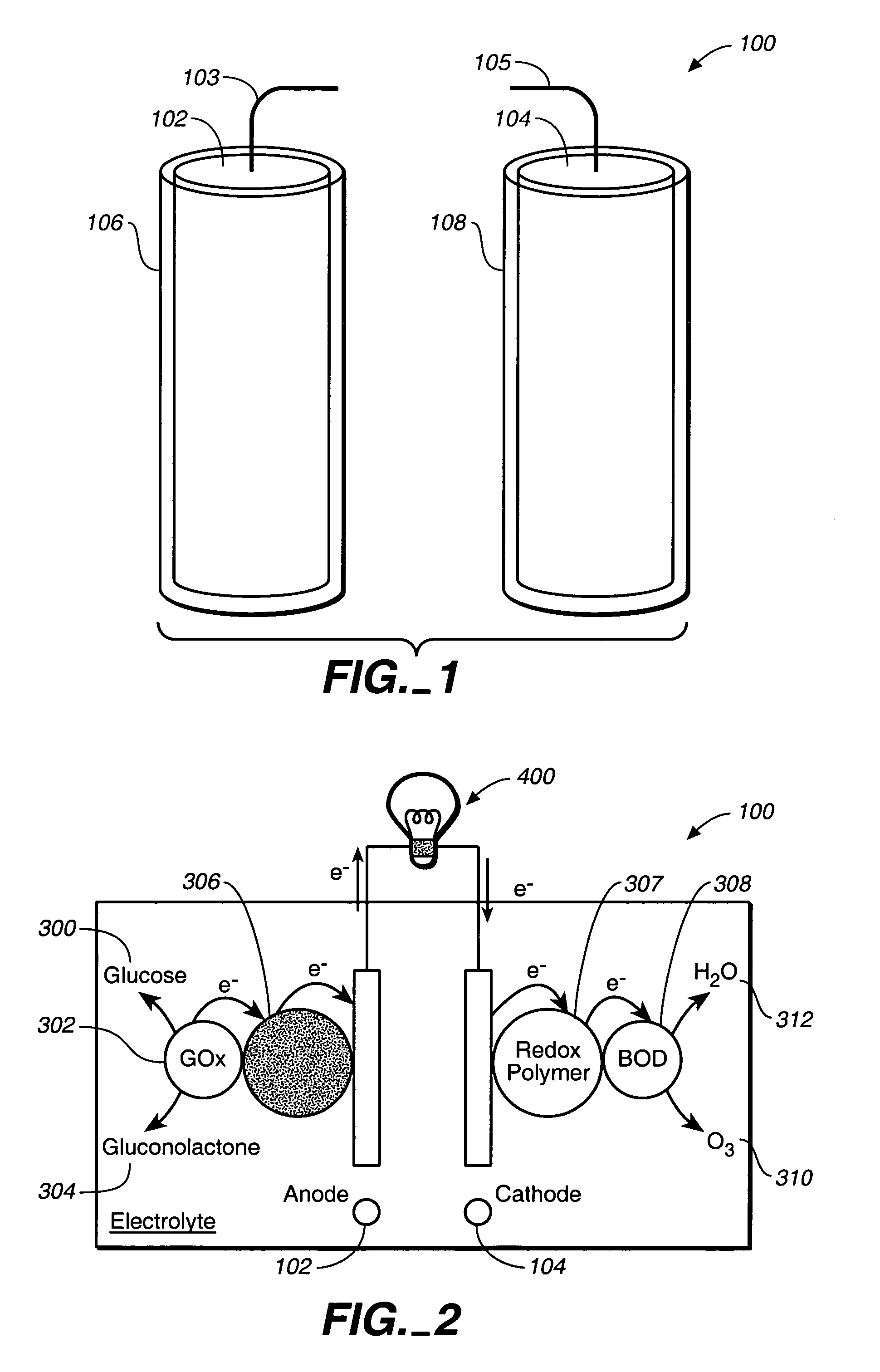
A fuel cell is provided with an anode and a cathode. The anode is in electrical communication with an anode enzyme and the cathode is in electrical communication with a cathode enzyme. The anode enzyme is preferably an oxidase or a dehydrogenase. The cathode enzyme is a copper-containing enzyme, such as a laccase, an ascorbate oxidase, a ceruloplasmine, or a bilirubin oxidase. Preferably, the cathode enzyme is operable under physiological conditions. Redox polymers serve to wire the anode enzyme to the anode and the cathode enzyme to the cathode. The fuel cell can be very small in size because it does not require a membrane, seal, or case. The fuel cell can be used in connection with a biological system, such as a human, as it may operate at physiological conditions. By virtue of its size and operability at physiological conditions, the fuel cell is of particular interest for applications calling for a power source implanted in a human body, such as a variety of medical applications.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Photo-catalytic reactor
ActiveUS20060246342A1Reduce deliveryEasy to demonstrateDeferred-action cellsFuel cells groupingElectron holePhotocatalytic reaction
A photocatalytic reactor, capable of generating an electric current by consumption of a fuel containing organic material, comprises a direct oxidation fuel cell including an anode and a cathode. The anode is a photocatalysis-assisted anode which comprises a photocatalyst on a surface of an electrically-conductive substrate so arranged as to be receptive to light. A light-transmissive proton-conductive membrane is arranged between the anode and the cathode, such that light passes through said membrane as a final stage in the optical path to the photocatalyst. The photocatalyst promotes oxidation of organic material and generates electron-hole pairs. The reactor, configured to support multiple cells in a stacked array, is provided with inlet(s) for introducing said fuel and connector(s) for connection to an external electrical circuit.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF ABERDEEN REGENT WALK
Upflow microbial fuel cell (UMFC)
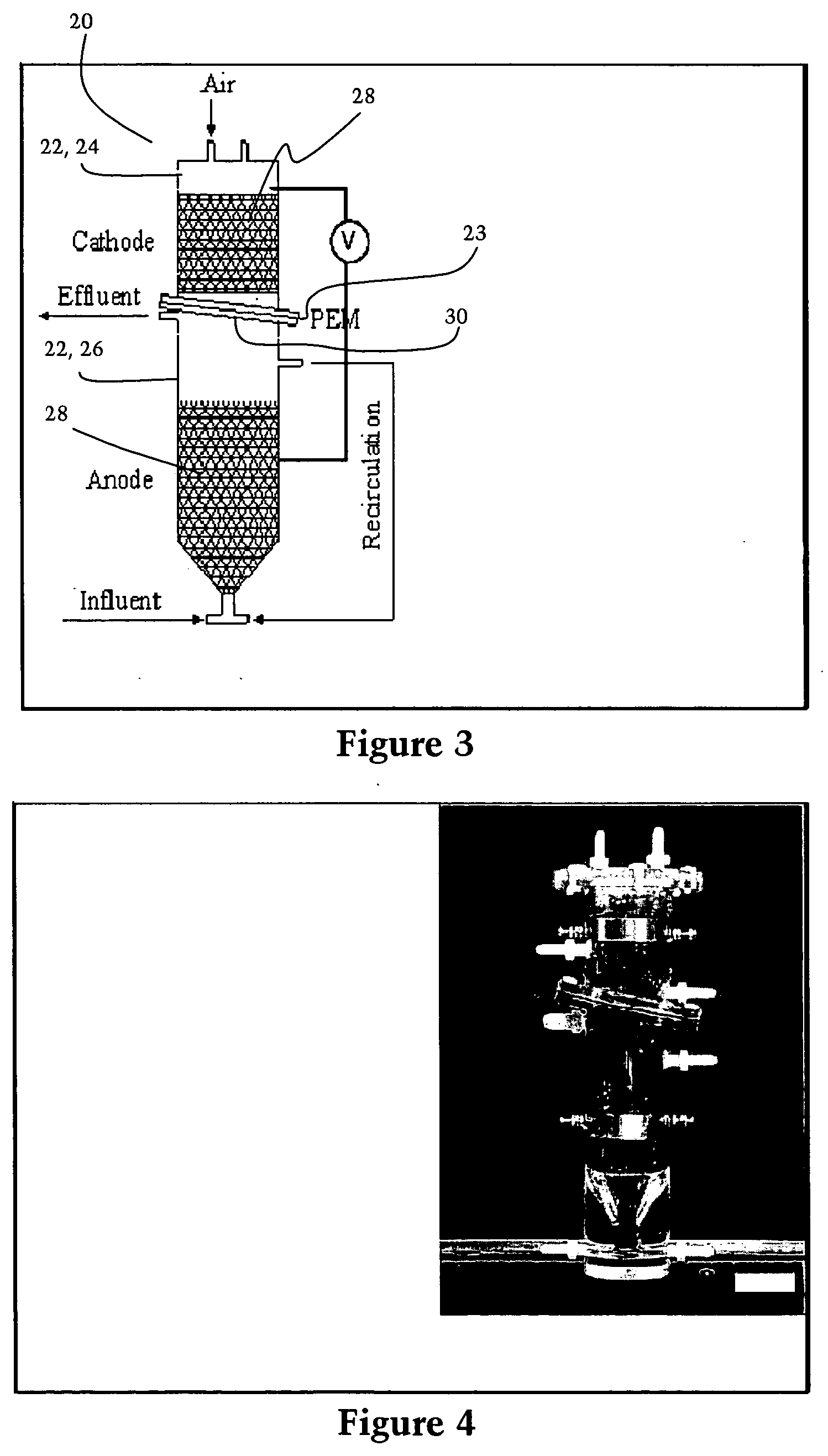
InactiveUS20060147763A1Reduce dependenceReduce the amount requiredCell electrodesFuel cell auxillariesMicrobial fuel cellElectricity
An upflow microbial fuel cell in one embodiment is comprised of a generally cylindrical cathode chamber containing a cathode sitting atop a generally cylindrical anode chamber containing an anode, with a proton exchange membrane separating the two chambers, so that as influent is passed upwardly through the anode chamber electricity is created in a continuous process not requiring mixing such as with a mechanical mixer or the like. Electrodes are connected to each of the anode and the cathode for harvesting the electricity so created. Effluent may be recirculated through the anode chamber by a second inlet and outlet therein. A multiphase fuel cell includes a plurality of electrode couples arranged in a single chamber with an influent inlet near its bottom and an effluent outlet near its top, with the electrode couples connected in series to generate electricity at higher voltages. In another embodiment, the cathode chamber—preferably U-shaped—is positioned inside the anode chamber.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Miniature biological fuel cell that is operational under physiological conditions, and associated devices and methods
InactiveUS20080044721A1Reduce physical sizeReduced dimensionMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementOperabilityRedox polymers
A fuel cell is provided with an anode and a cathode. The anode is in electrical communication with an anode enzyme and the cathode is in electrical communication with a cathode enzyme. The anode enzyme is preferably an oxidase or a dehydrogenase. The cathode enzyme is a copper-containing enzyme, such as a laccase, an ascorbate oxidase, a ceruloplasmine, or a bilirubin oxidase. Preferably, the cathode enzyme is operable under physiological conditions. Redox polymers serve to wire the anode enzyme to the anode and the cathode enzyme to the cathode. The fuel cell can be very small in size because it does not require a membrane, seal, or case. The fuel cell can be used in connection with a biological system, such as a human, as it may operate at physiological conditions. By virtue of its size and operability at physiological conditions, the fuel cell is of particular interest for applications calling for a power source implanted in a human body, such as a variety of medical applications.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Device for the determination of glycated hemoglobin
InactiveUS20060205029A1Retain and improve accuracySpeed the ultimate determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementTotal hemoglobinCathode reaction
A method of determining the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in a blood sample is disclosed wherein at least one of the assay steps is performed electrochemically. The method includes determining the total amount of hemoglobin in a sample by electrochemically measuring, in an oxygen electroreduction reaction at a cathode, the amount of oxygen in the sample. Because the amount of oxygen dissolved in the sample is known, the total hemoglobin is determined by subtracting the amount of free oxygen from the total oxygen measured, recognizing the fast equilibrium Hb+O2⇄HbO2. This can be followed by determining the amount of glycated hemoglobin in the sample. The cathode reaction is accomplished by contacting the sample with an enzyme, the enzyme being a copper-containing enzyme having four copper ions per active unit. The family of these enzymes includes, for example, laccases and bilirubin oxidases. A device associated with such a process or method is also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
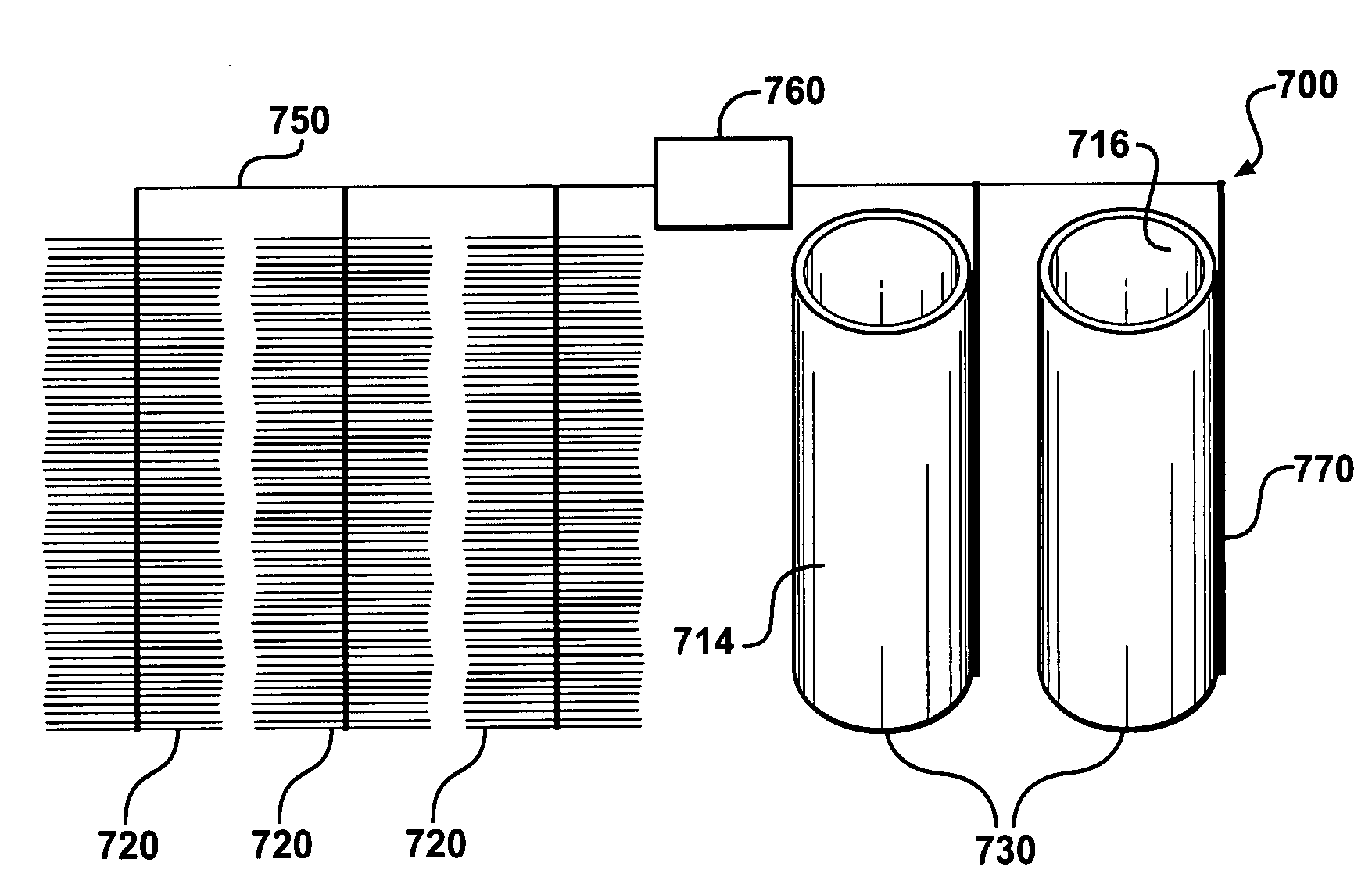
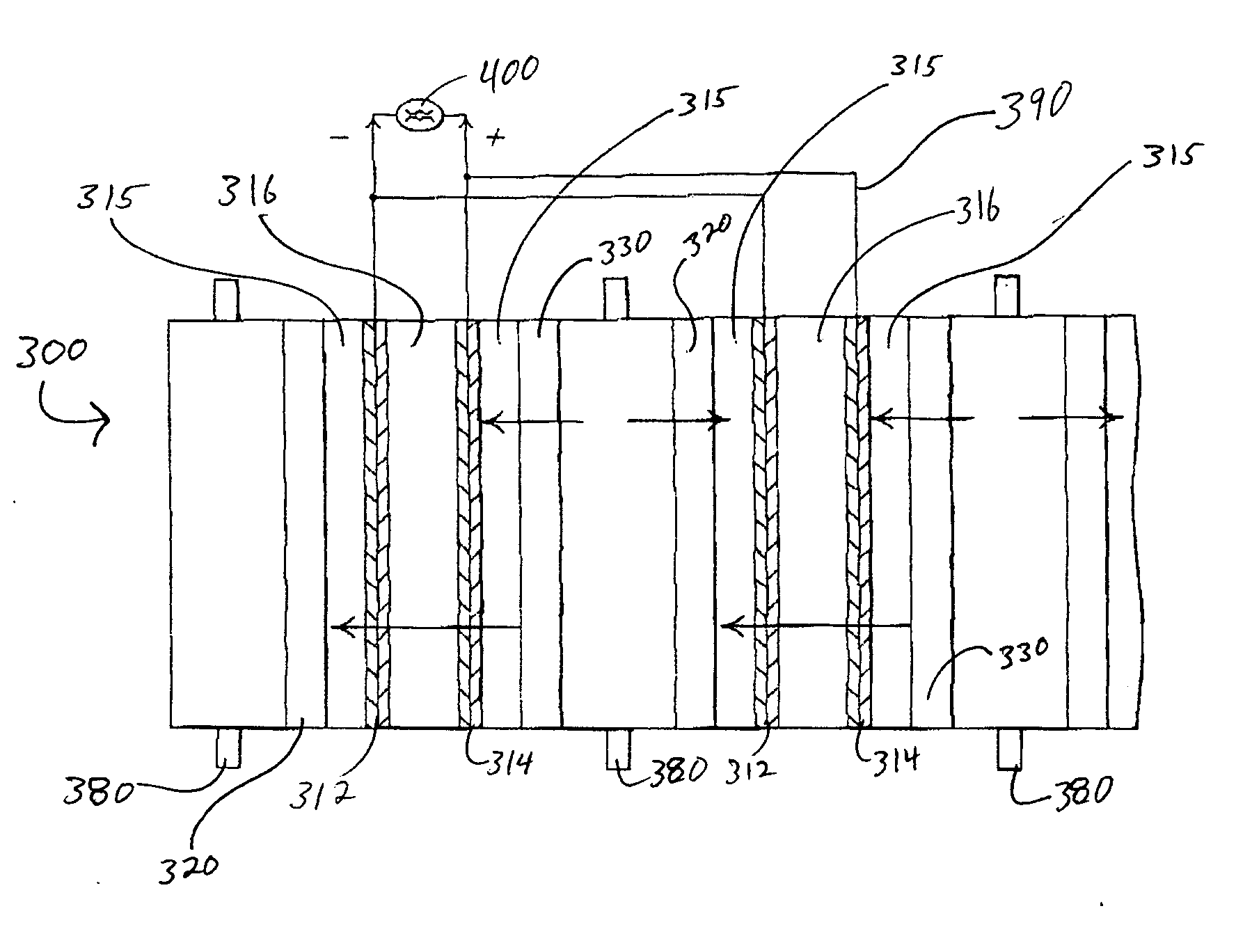
Scalable microbial fuel cell with fluidic and stacking capabilities
A fuel cell having: a proton exchange membrane; anode and cathode housings containing chambers; a three-dimensional anode and cathode. Each housing may have a feed passage, a waste passage, and two through passages. The anode feed passage and the anode waste passage are each coupled to the anode chamber and to one of the cathode through passages and vice versa. The anode chamber may have bacteria capable of donating electrons to the anode upon exposure to a fuel. Solutions may be circulated through the passages and chambers.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Biological fuel cell and methods
InactiveUS20060159981A1Active material electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsFuel cellsOxidation-Reduction Agent
A fuel cell has an anode and a cathode with anode enzyme disposed on the anode and cathode enzyme is disposed on the cathode. The anode is configured and arranged to electrooxidize an anode reductant in the presence of the anode enzyme. Likewise, the cathode is configured and arranged to electroreduce a cathode oxidant in the presence of the cathode enzyme. In addition, anode redox hydrogel may be disposed on the anode to transduce a current between the anode and the anode enzyme and cathode redox hydrogel may be disposed on the cathode to transduce a current between the cathode and the cathode enzyme.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
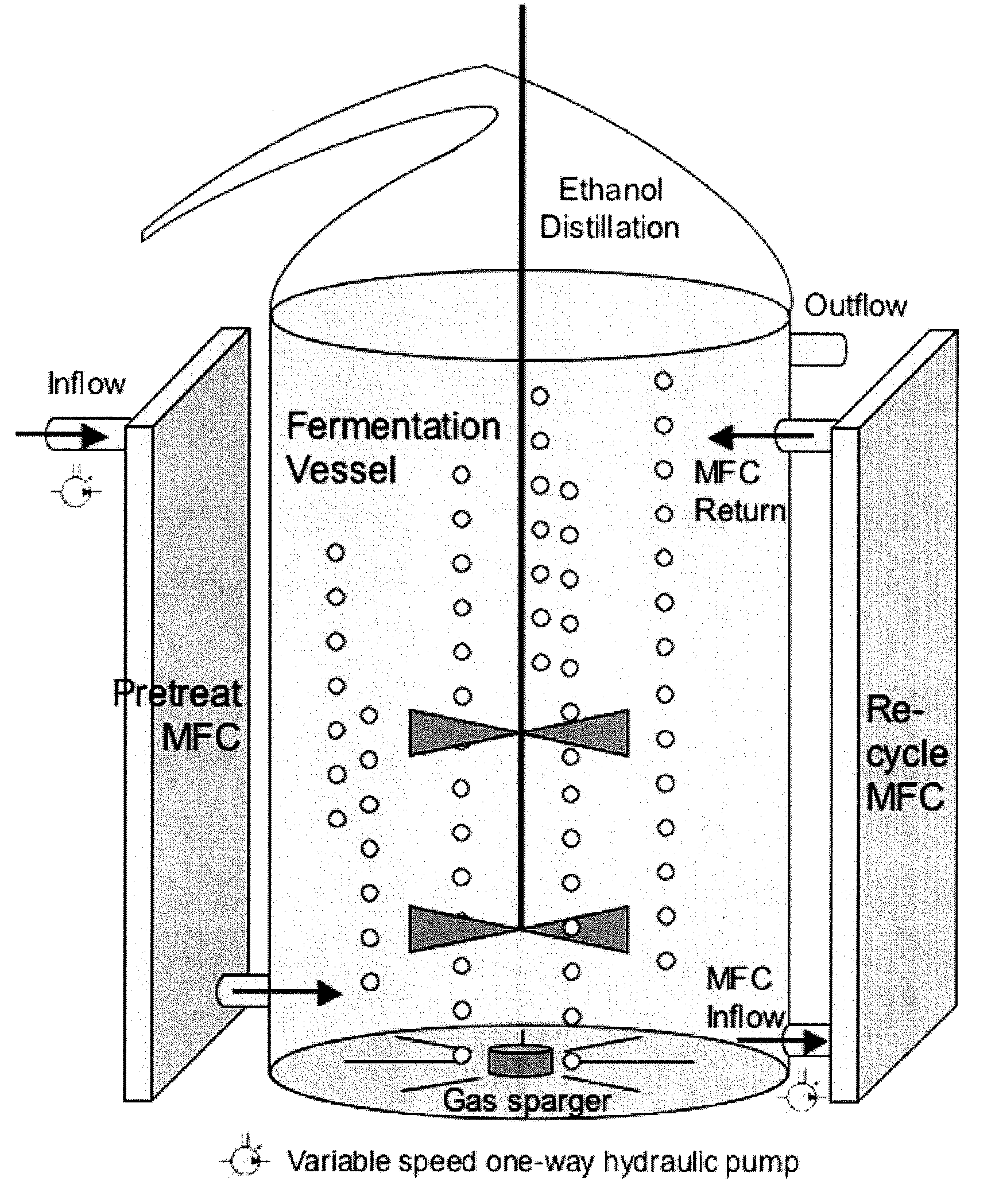
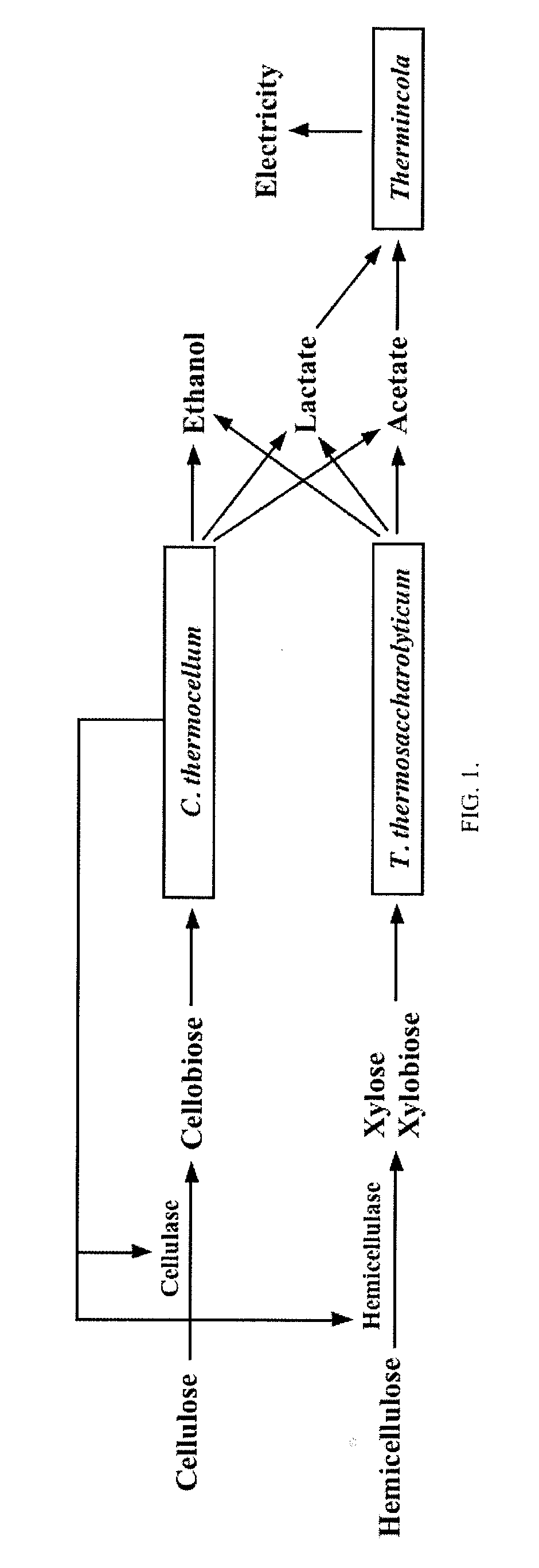
Apparatus and methods for the production of ethanol, hydrogen and electricity
InactiveUS20090017512A1Improve reaction speedLess expensiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBacteriaMicrobial fuel cellElectricity
The compositions, methods and apparatus of the present invention allow the production of electricity, ethanol and hydrogen, and combinations thereof. In some embodiments, the invention provides a process for generating electricity or hydrogen comprising supplying a microbial catalyst and a fuel source to a microbial fuel cell or a bio-electrochemically assisted microbial reactor (BEAMR), respectively, under thermophilic conditions. In other embodiments, the invention provides a process of generating ethanol and electricity or ethanol and hydrogen comprising supplying a microbial catalyst and a fuel source to a fermentation vessel in operable relation with a microbial fuel cell or a BEAMR system, respectively, wherein the microbial catalyst has a cellulolytic activity, an ethanologenic activity, and an electricigenic activity. Other embodiments include compositions and apparati for practicing the invention.
Owner:MFC TECH LLC
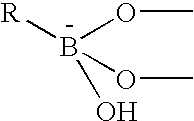
Biosensor carrying redox enzymes
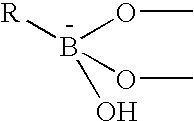
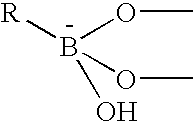
The present invention concerns an electrode carrying immobilized redox enzymes such that electric charge can flow between an electron mediator group to the enzyme cofactor by the use of boronic acid or a boronic acid derivative that acts as a linker moiety between the cofactor and the electron mediator group. The invention also concerns devices and systems that make use of the electrode of the invention, such as bio-sensors and fuel cells, the electrode being one of the components thereof.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
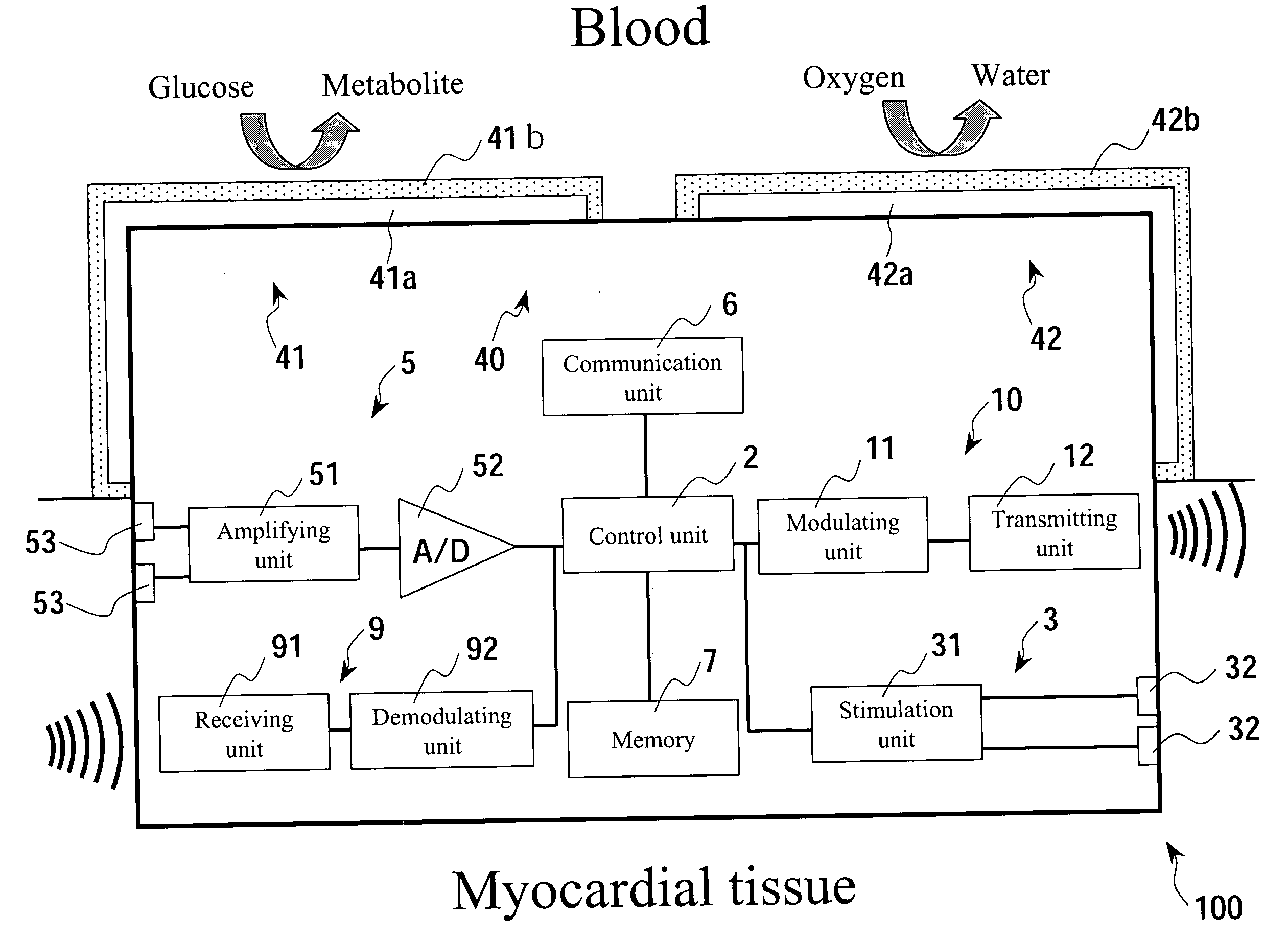
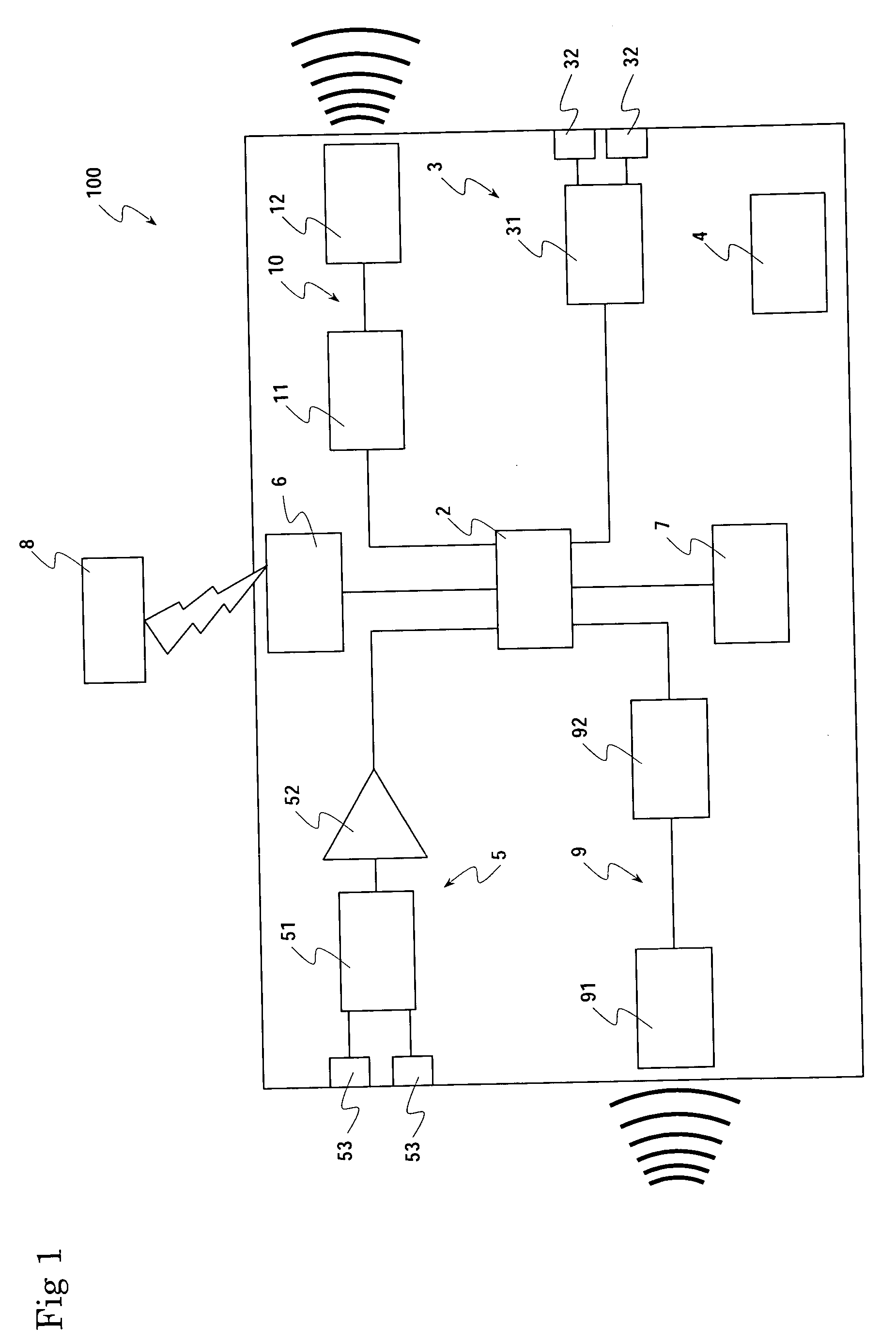
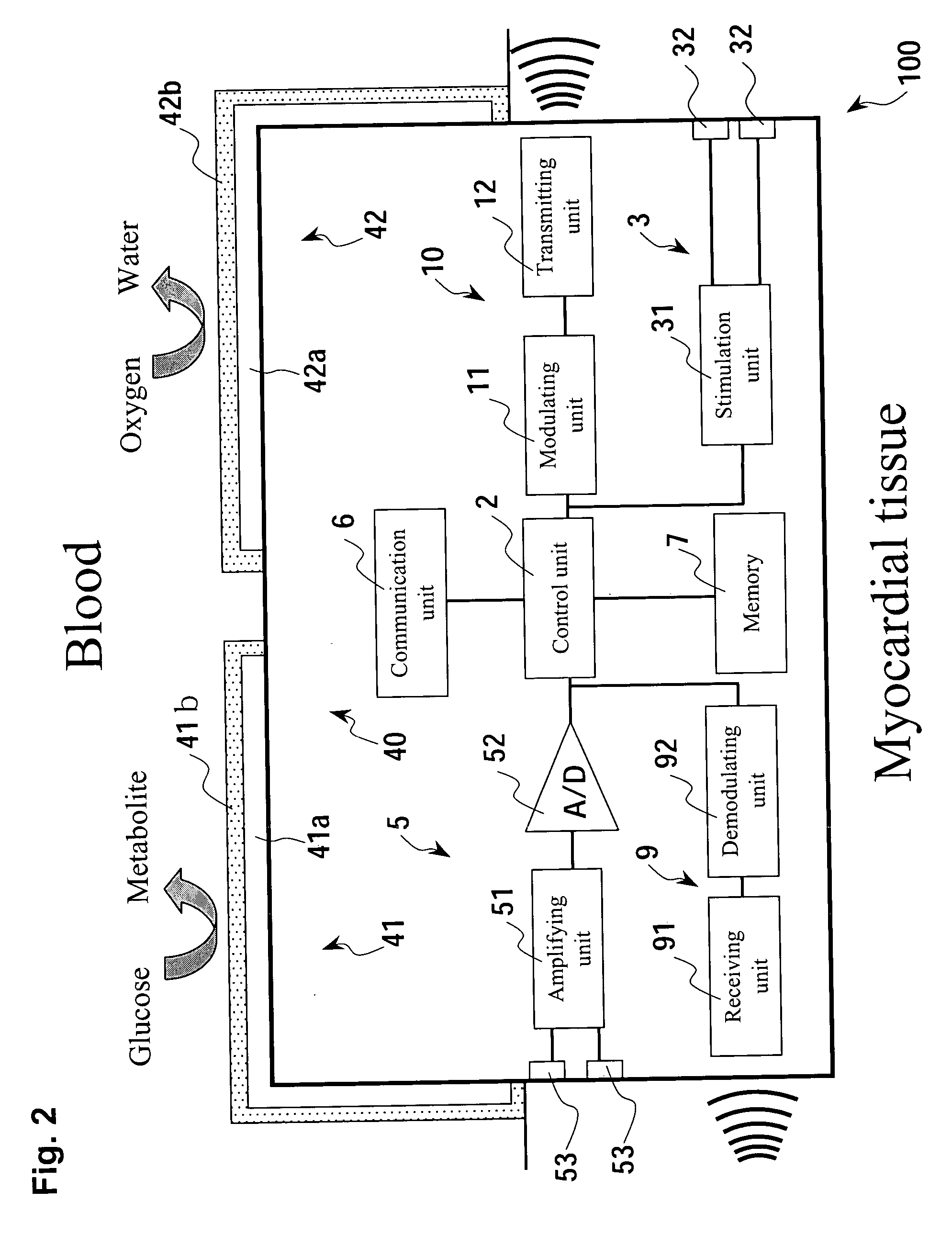
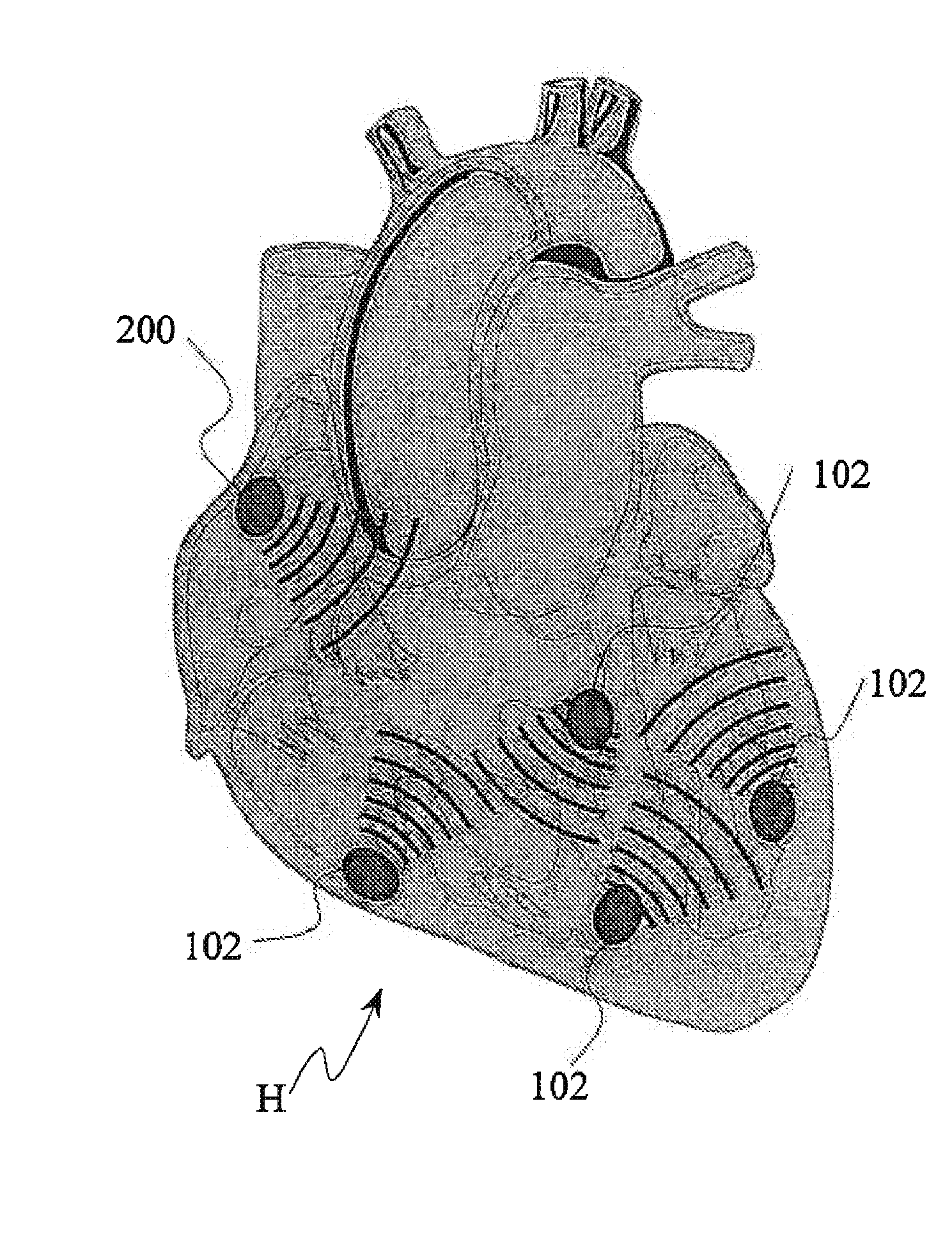
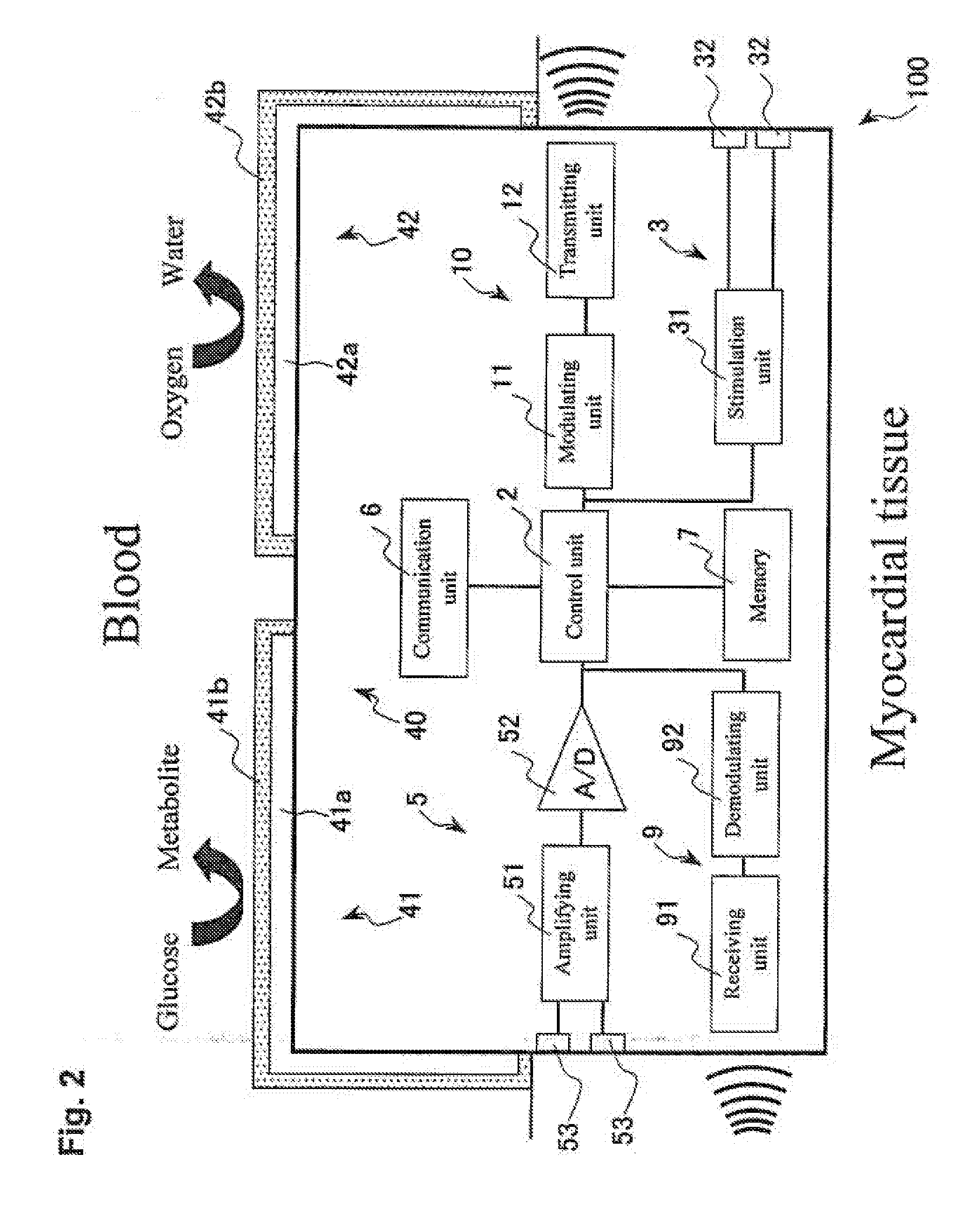
Micro integrated cardiac pacemaker and distributed cardiac pacing system
ActiveUS20050288717A1Suppress generationSuppresses detectionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl signalCardiac pacemaker electrode
A micro integrated cardiac pacemaker includes a control unit for outputting a control signal according to cardiograph information, heart stimulating means for stimulating heart tissue in response to the control signal, cardiograph information extracting means for extracting cardiograph information and outputting it to the control unit, and a power supply unit for supplying drive power. The power supply unit is a biological fuel cell that takes out electrons by oxidation of a biological fuel. The biological fuel cell includes an anode and a cathode. An oxidase of a biological fuel and a mediator are immobilized on the cathode. Blood and / or body fluid are used as an electrolytic solution, and a biological fuel and oxygen in the blood and / or the fluid are used. The biological fuel cell is attached to the end of a catheter and implanted into the heart, and the catheter is withdrawn, without incising the breast.
Owner:FUJIKIN INC +1
Enzyme electrode
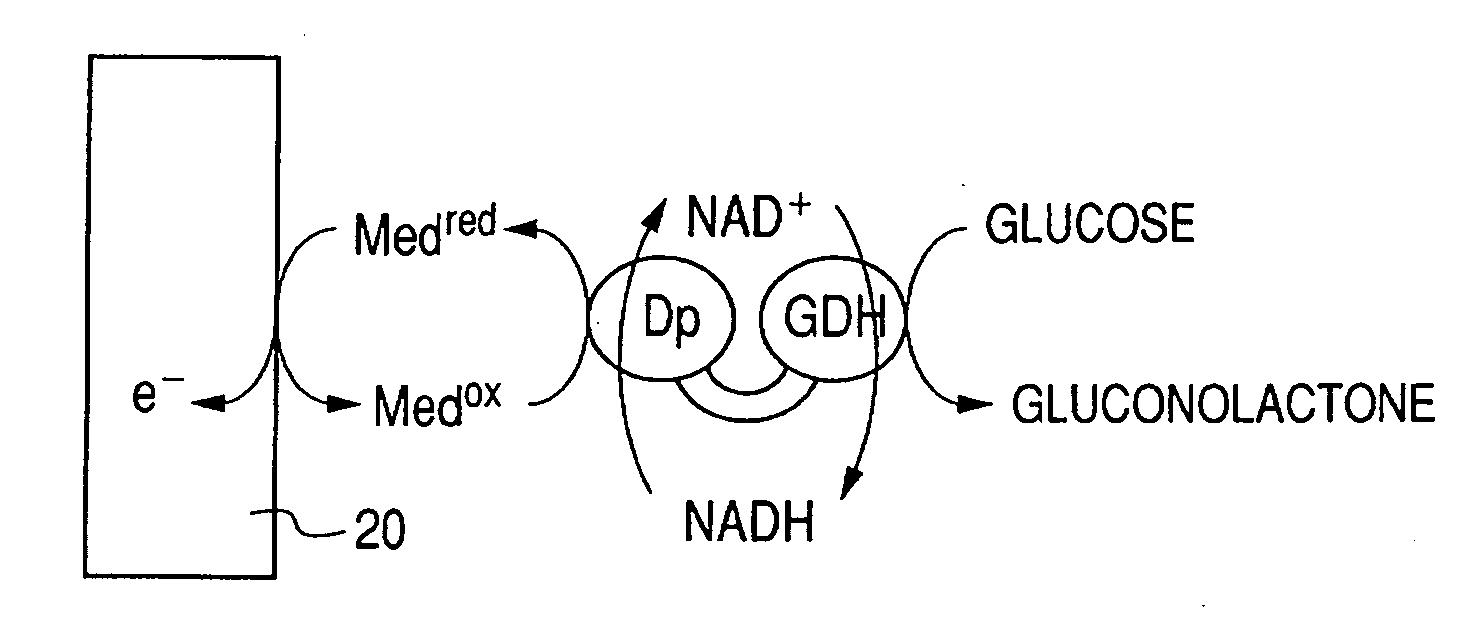
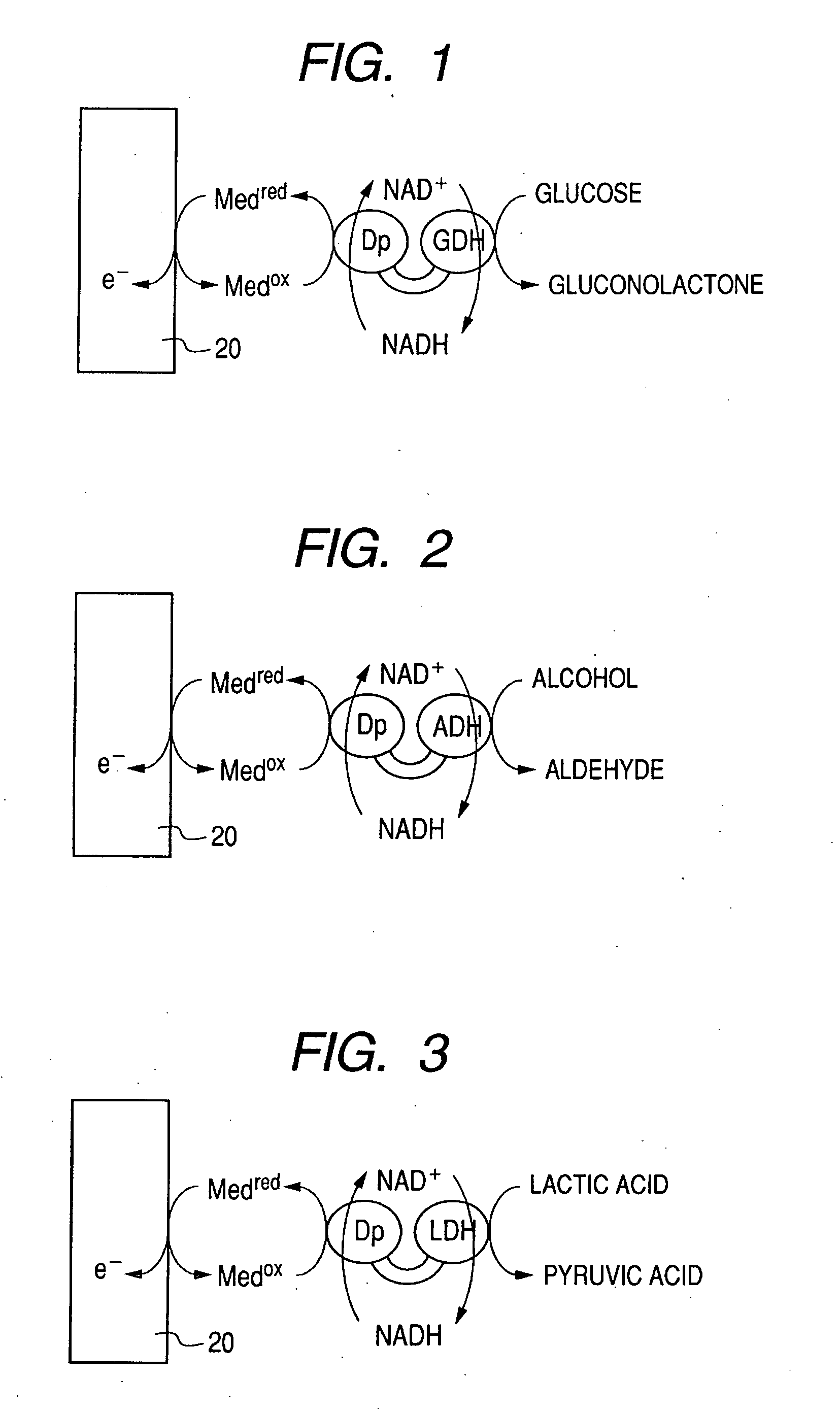
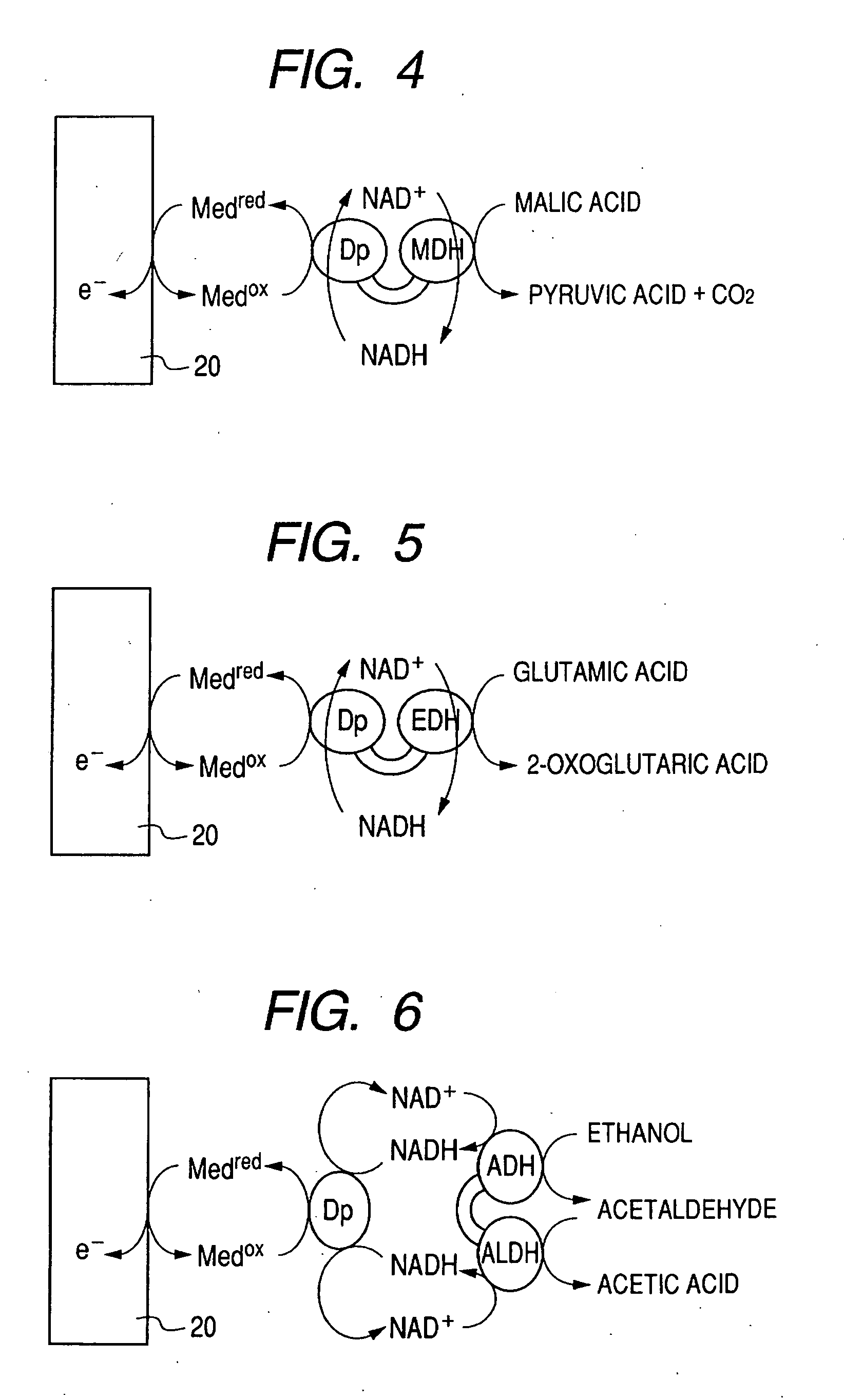
InactiveUS20070131546A1Small distanceLarge current valueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical responseElectron transfer mediator
There is provided with an enzyme electrode which can be used as a sensor with high sensitivity, a biofuel cell with high output, and an electrochemical reaction device with high reaction efficiency. The enzyme electrode has a conductive base plate, a fusion protein immobilized to the conductive base plate and an electron transfer mediator, wherein the fusion protein is a fusion protein of a enzyme 1 to catalyze a chemical reaction for producing a reaction product 1 from a reaction substrate 1 and a enzyme 2 to catalyze a chemical reaction for producing a reaction product 2 from a reaction substrate 2, and at least one chemical substance of the reaction product 1 is identical to at least one chemical substance of the reaction substrate 2.
Owner:CANON KK
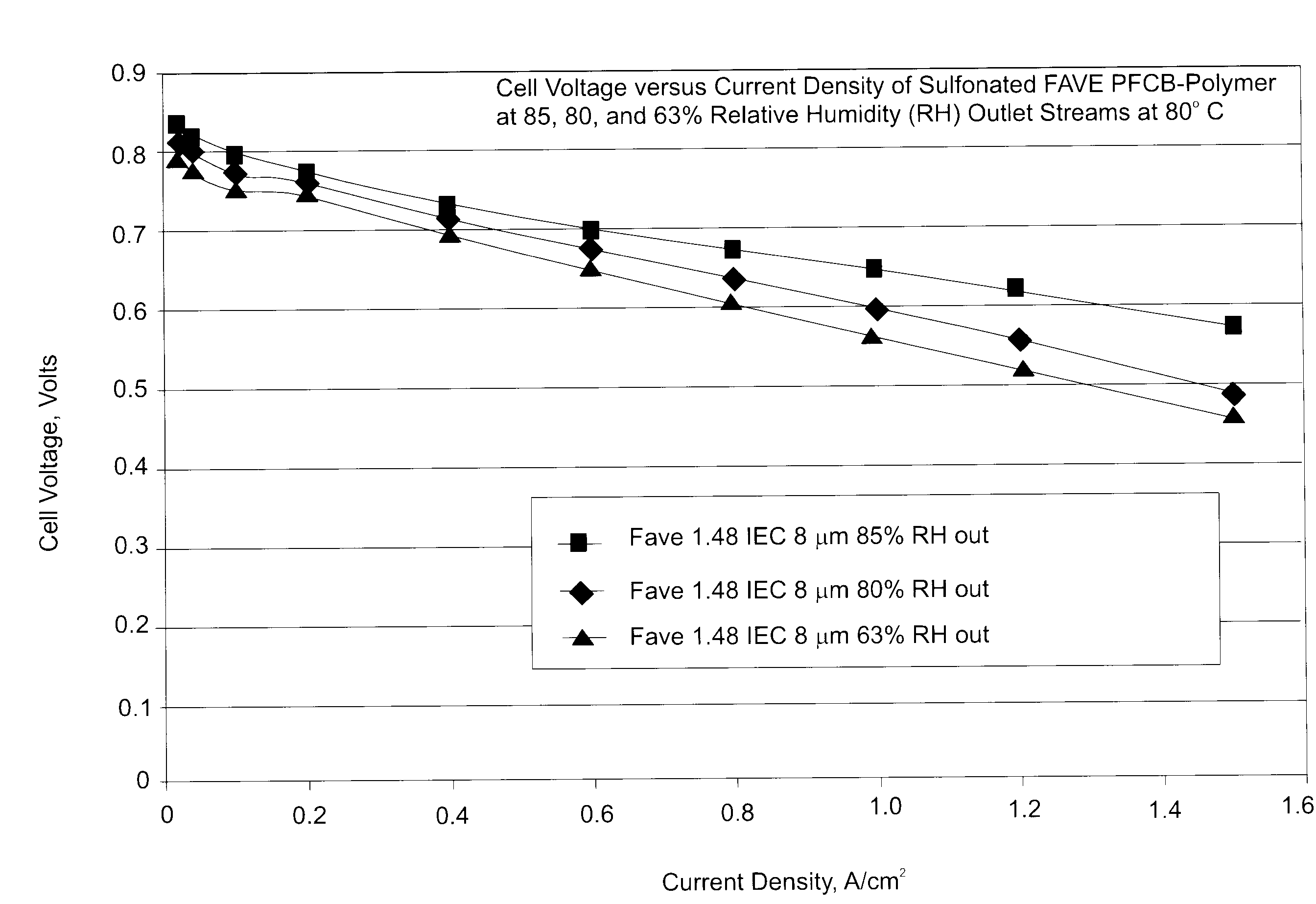
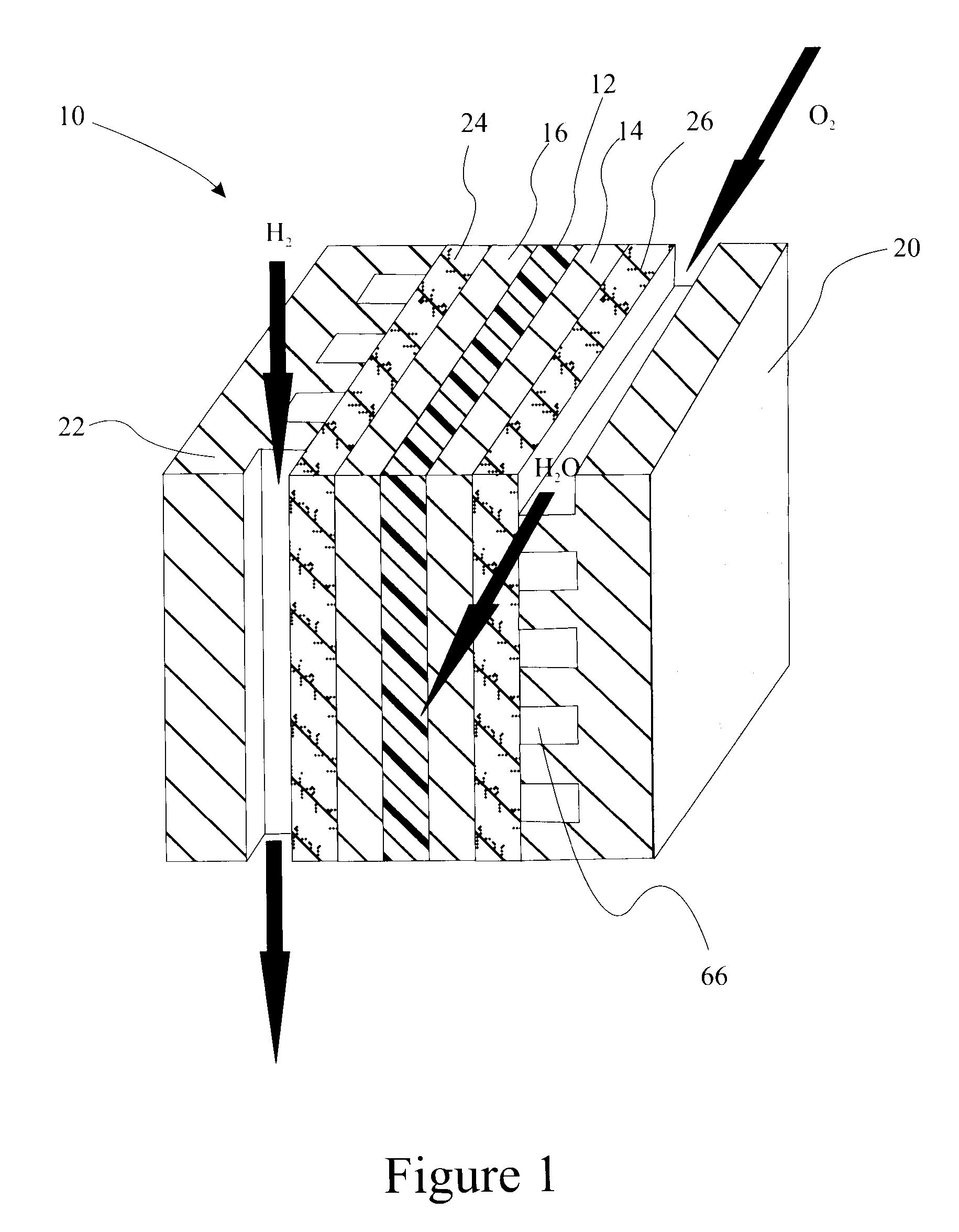
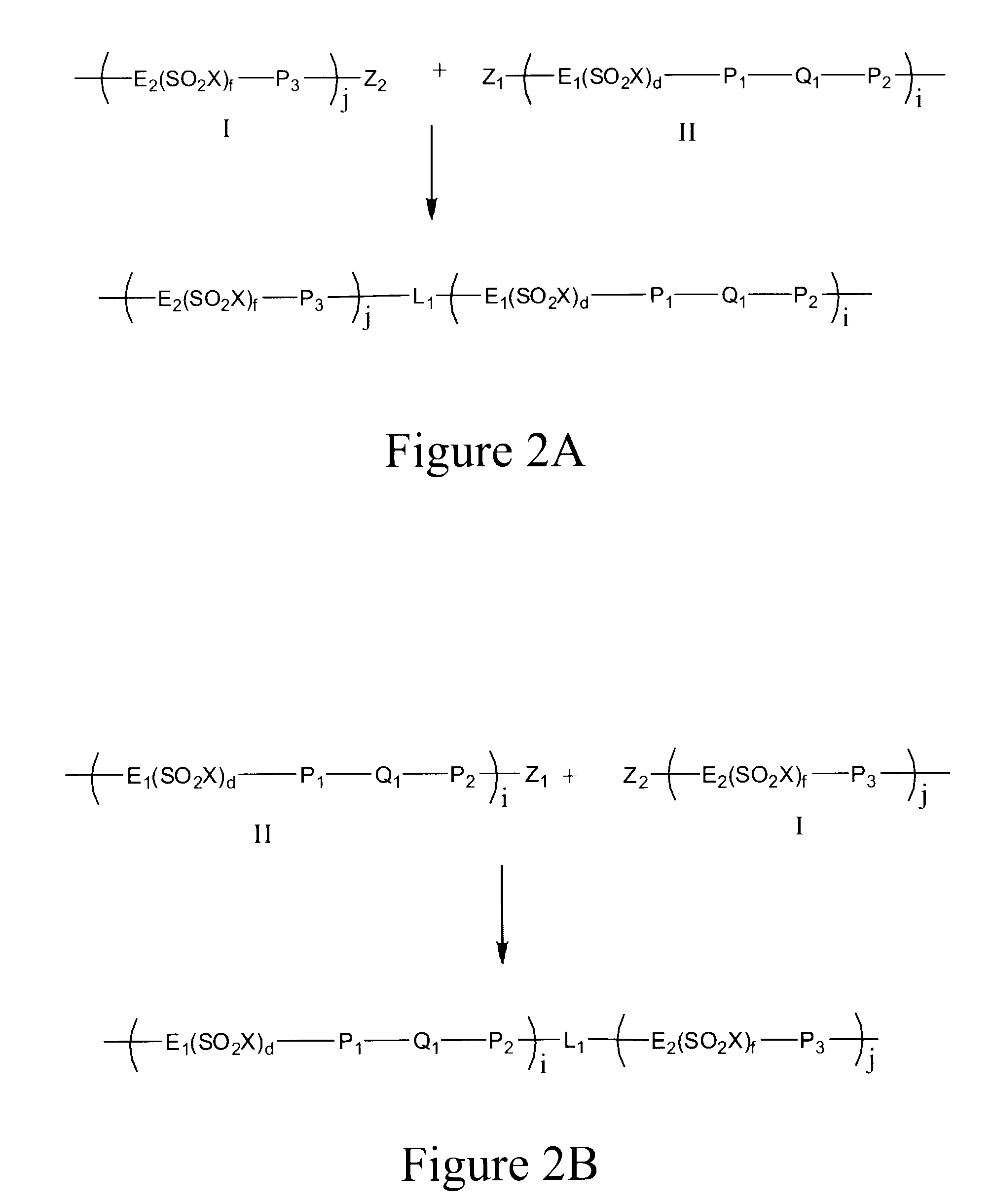
Sulfonated-polyperfluoro-cyclobutane-polyphenlene polymers for PEM fuel cell applications
ActiveUS20090281270A1Solve problemsCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsFuel cellsElectrical conductor
A polymer for ion conductor applications includes a polymer segment having a perfluorocyclobutyl moiety and a polymer segment not having such a moiety. One of these polymer segments is sulfonated to improve ionic conductivity. Fuel cells incorporating the ion conducting polymers are provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Highly efficient hydrogen production method using microorganism
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH +1
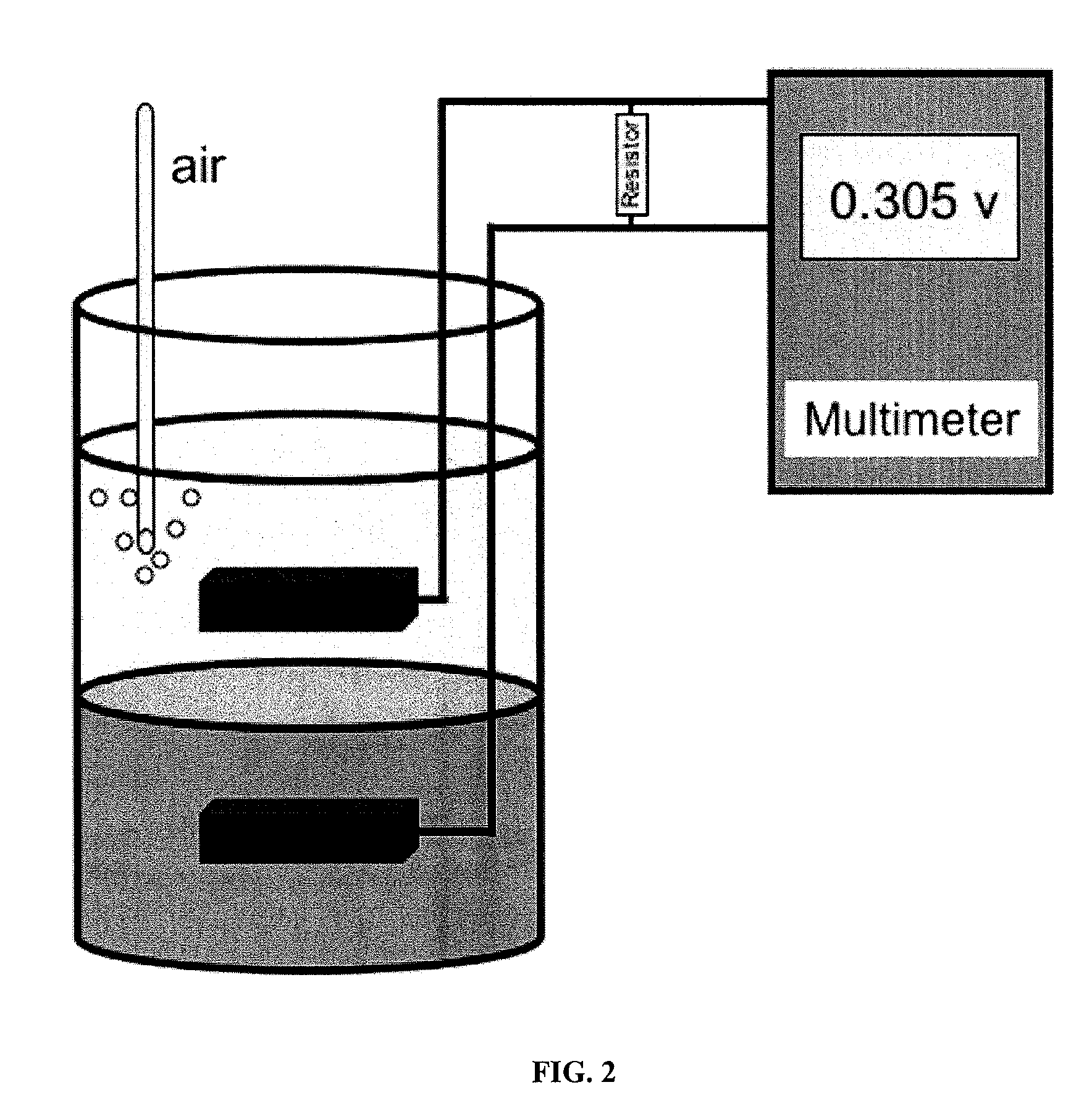
Method and apparatus for generating power from voltage gradients at sediment-water interfaces
A method and apparatus for generating power from voltage gradients at sediment-water interfaces or within stratified euxinic water-columns is provided. Natural voltage gradients typically exist at and about sediment-water interfaces or in isolated water bodies. One electrode (anode) is positioned in the sediment or water just below the redox boundary and the other electrode (cathode) is positioned in the water above the redox boundary over the first electrode. The anode is lower in voltage than the cathode. Current will flow when the electrodes are connected through a load, and near-perpetual generating of worthwhile power may be sustained by the net oxidation of organic matter catalyzed by microorganisms.
Owner:NAVY SEC OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES +1
Polyfluorinated boron cluster anions for lithium electrolytes
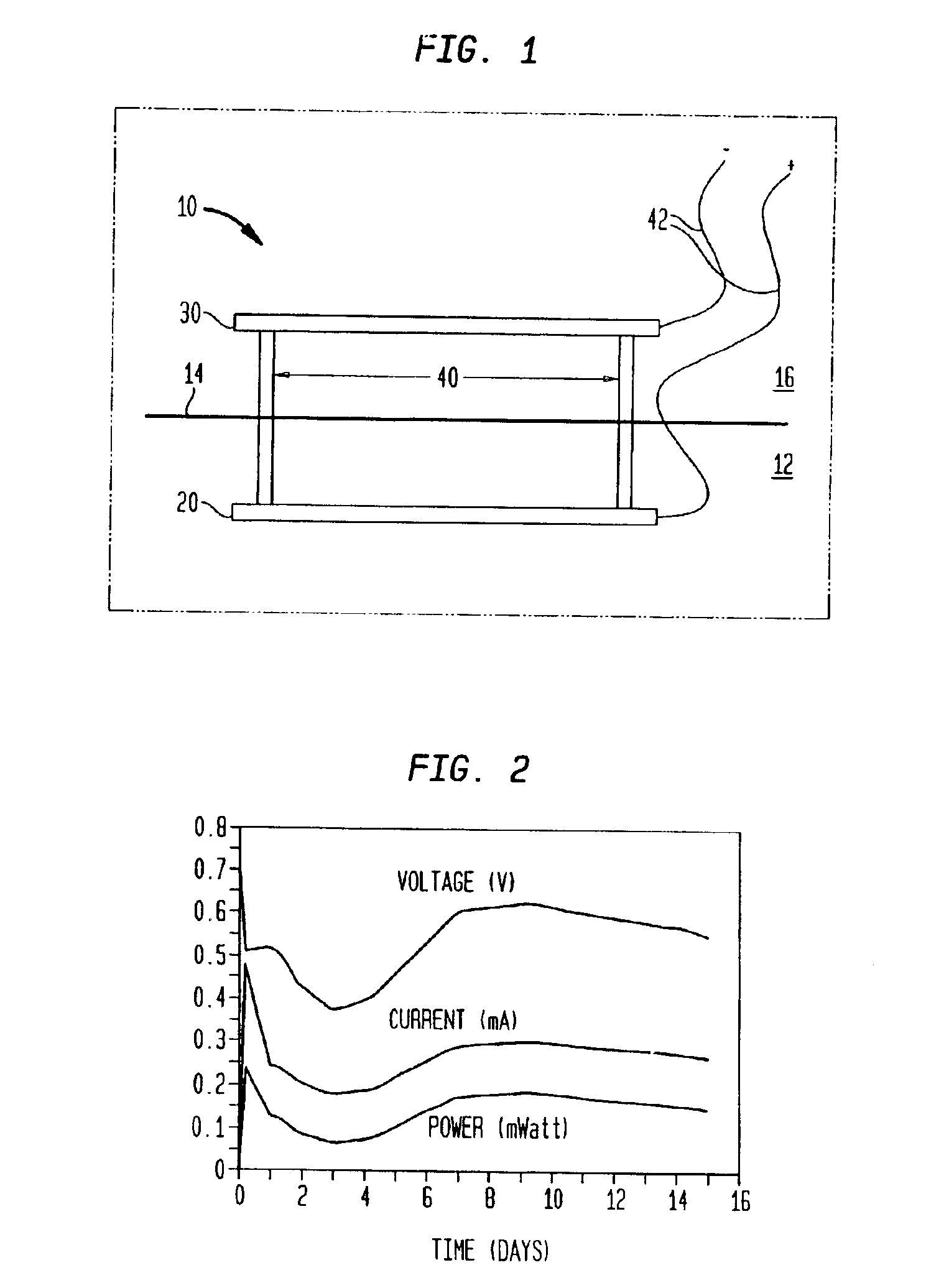
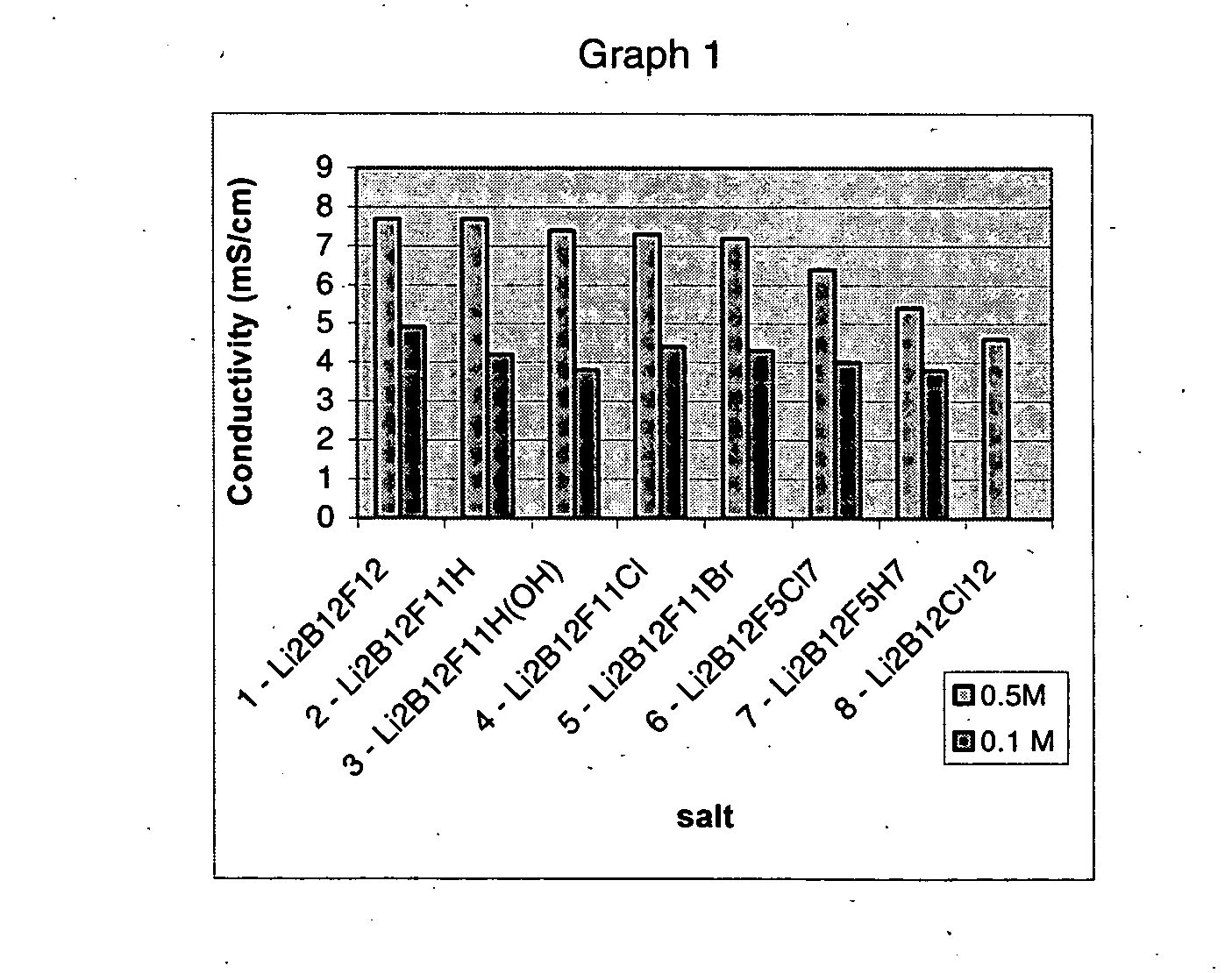
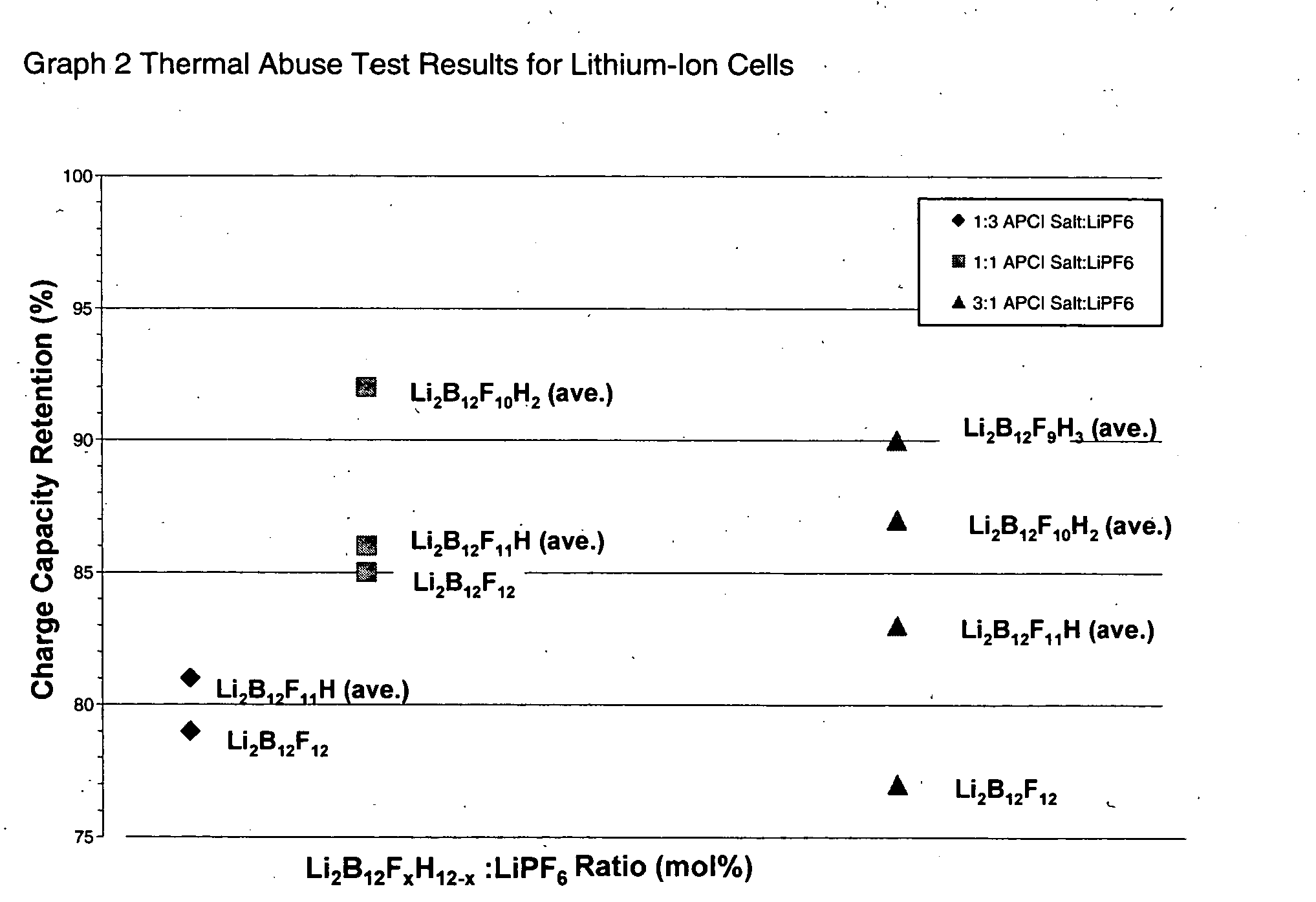
ActiveUS20050064288A1Low viscosityLower impedanceOrganic electrolyte cellsBiochemical fuel cellsBoron clustersElectrolyte composition
The present invention relates to an improvement in lithium secondary batteries comprised of a negative electrode, a positive electrode, a separator, and a lithium-based electrolyte carried in an aprotic solvent and to the electrolyte compositions. The improvement resides in the use of a lithium salt of the formula: Li2B12FxZ12-x wherein x greater than or equal to 4 and Z represents H, Cl, and Br.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Electrode for use in oxygen reduction
ActiveUS20070243449A1High valenceFuel and primary cellsOrganic chemistryFuel cellsStructural formula
The present invention is usable in oxygen electrodes and air electrodes for air cells, fuel cells, electrochemical sensors and like electrochemical devices. The present invention provides a very stable oxygen-reducing electrode that can achieve electrochemical reduction of oxygen at a noble potential. The oxygen-reducing electrode of the present invention contains a cobalt tetrapyrazinoporphyrazine derivative represented by the following Structural Formula (1) as a catalytic component.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Cardiac pacing system and distributed cardiac pacing system
InactiveUS20080319502A1Television system detailsColor television detailsCardiac pacemaker electrodeControl signal
A micro integrated cardiac pacemaker includes a control unit for outputting a control signal according to cardiograph information, heart stimulating means for stimulating heart tissue in response to the control signal, cardiograph information extracting means for extracting cardiograph information and outputting it to the control unit, and a power supply unit for supplying drive power. The power supply unit is a biological fuel cell that takes out electrons by oxidation of a biological fuel. The biological fuel cell includes an anode and a cathode. An oxidase of a biological fuel and a mediator are immobilized on the cathode. Blood and / or body fluid are used as an electrolytic solution, and a biological fuel and oxygen in the blood and / or the fluid are used. The biological fuel cell is attached to the end of a catheter and implanted into the heart, and the catheter is withdrawn, without incising the breast.
Owner:FUJIKIN INC +1
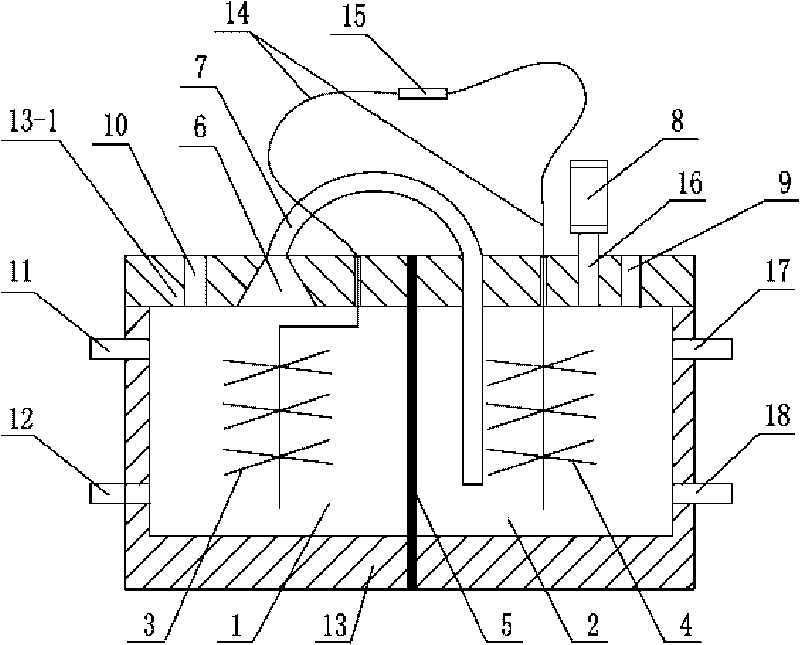
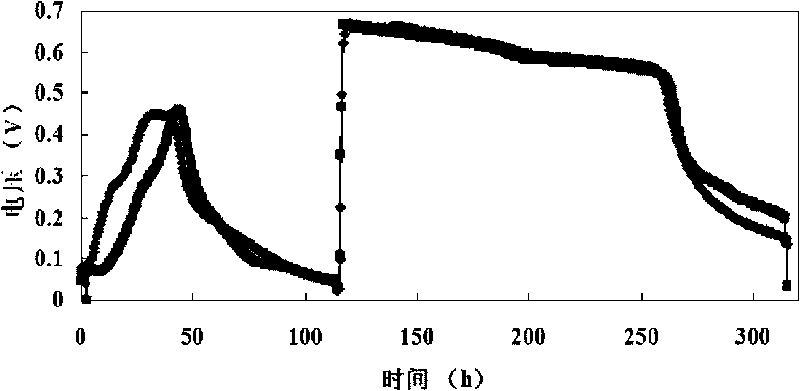
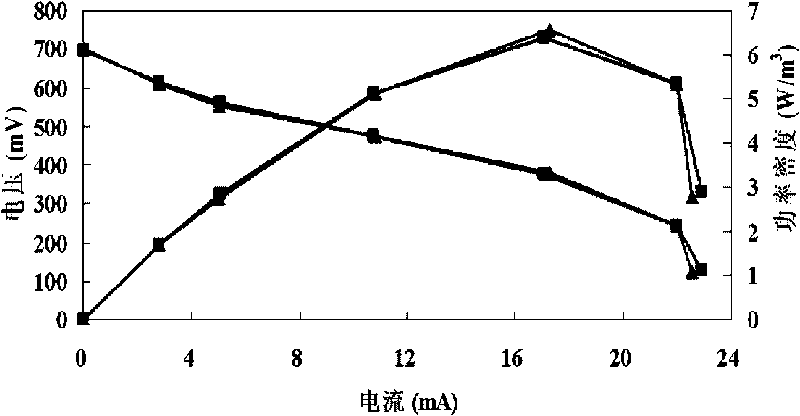
Double-chamber alga microbial fuel cell and method thereof for treating waste water and realizing zero carbon emission
ActiveCN101719555AAchieving zero emissionsAchieving zero carbon emissionsCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsPhotosynthesisZero emission
The invention discloses a double-chamber alga microbial fuel cell and a method thereof for treating waste water and realizing zero carbon emission, which relates to a microbial fuel cell and a method for treating waste water. The invention solves the problem that the traditional microbial fuel cell can generate a large amount of CO2 in the process of treating waste water. In the invention, a cation exchange membrane is vertically arranged in a box body of a reactor; an anode chamber and a cathode chamber are formed in the box body of the reactor; an anode is arranged in the anode chamber; a cathode is arranged in the cathode chamber; leads are connected with the anode and the cathode; one end of a gas duct is hermetically connected with a gas collecting chamber, and the other end of the gas duct is arranged at the bottom of the cathode chamber; and a gas collecting device is hermetically installed at a gas outlet. The method comprises the following steps: (1) starting the reactor; and (2) introducing the waste water into the cathode chamber and the anode chamber, catabolizing organic matters by microbes at room temperature, simultaneously obtaining electrical energy, and introducing the CO2 generated in the anode chamber into the cathode chamber to be used by the alga at the cathode for photosynthesis. The invention realizes zero emission of CO2 and simultaneously can recover electrical energy, thereby really changing waste into resources.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Cathodes for microbial electrolysis cells and microbial fuel cells
An apparatus is provided according to embodiments of the present invention which includes a reaction chamber having a wall defining an interior of the reaction chamber and an exterior of the reaction chamber; exoelectrogenic bacteria disposed in the interior of the reaction chamber; an aqueous medium having a pH in the range of 3-9, inclusive, the aqueous medium including an organic substrate oxidizable by exoelectrogenic bacteria and the medium disposed in the interior of the reaction chamber. An inventive apparatus further includes an anode at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber; and a brush or mesh cathode including stainless steel, nickel or titanium, the cathode at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Mixed reactant molecular screen fuel cell
InactiveUS20050058875A1Eliminate the problemReduce decreaseSolid electrolytesFuel cells groupingFuel cellsElectrolyte
In one aspect, the present invention provides a fuel cell having a first membrane selective to a fuel, a second membrane selective to an oxidant, and a mixed reactant flow provided to the screens. The invention further includes an anode, a cathode and a semi-permeable electrolyte fluidly separating the same.
Owner:JEROME ALLAN
Conversion systems for biomass
ActiveUS8318453B2Efficient and economical and convenient to moveEasy to transportBio-organic fraction processingBiofuelsHydrocotyle bowlesioidesBiomass transportation
The efficient production of ethanol from low-cost biomass (e.g., corn, sugar beets, sugar cane, switchgrass and / or paper) has become increasingly important in making ethanol competitive with gasoline and decreasing the United States' dependence on foreign oil. For example, to reduce the cost of transporting biomass to ethanol production facilities, mobile systems for producing ethanol from biomass are provided. Also provided are small-scale ethanol production facilities. For example, instead of transporting biomass to the production facility, the facility is transported to the biomass or is located nearby the source of the biomass. The ethanol production facilities or components thereof may be transported via land, water, or air. Production of other products, such as hydrocarbons, natural gas, hydrogen gas, plastics, polymers, and proteins, can also be made by the methods and facilities. Any product described herein can be made in finished form or un-finished form and moved, e.g., to a fixed facility, e.g., fixed production facility.
Owner:XYLECO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com