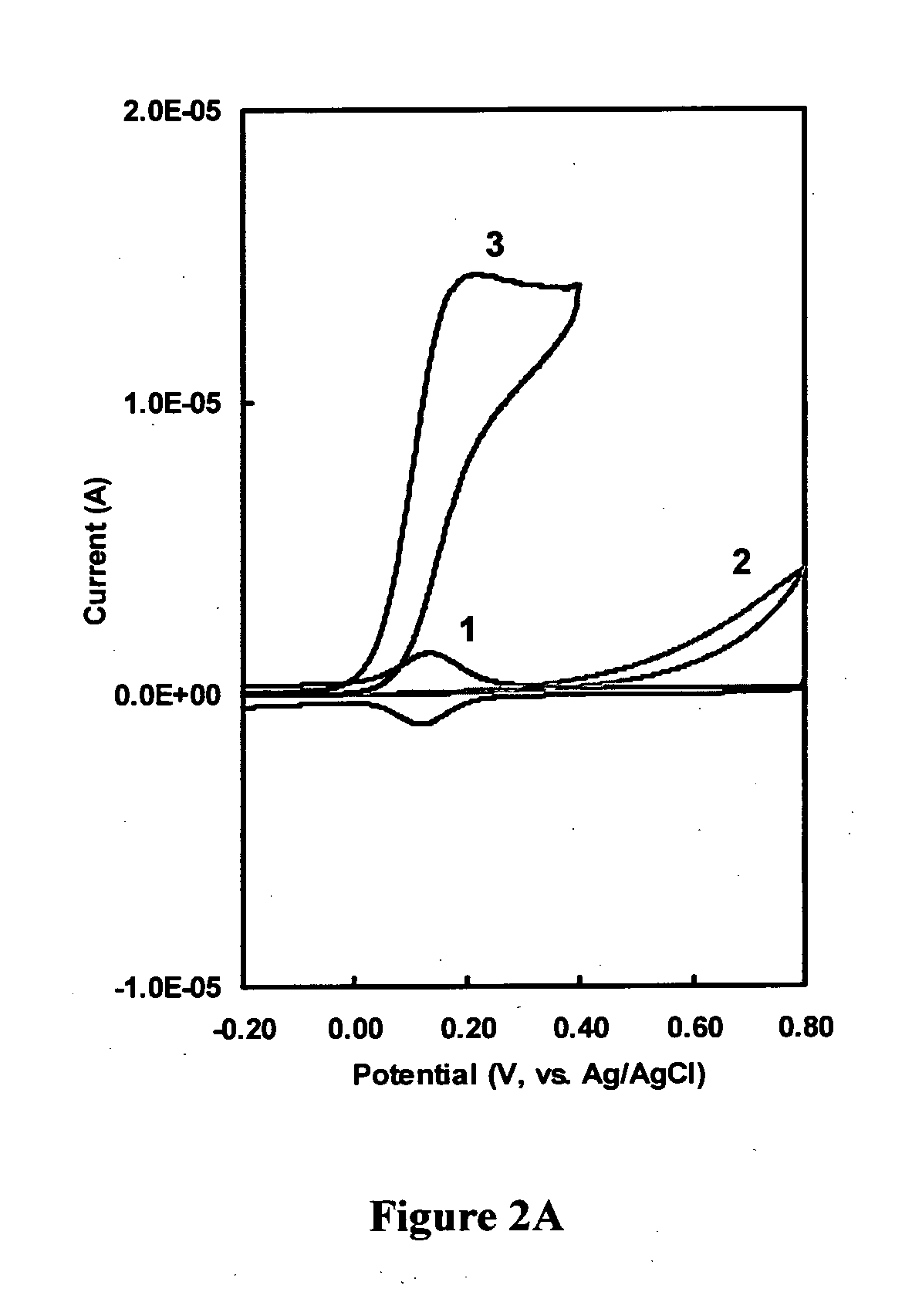
Patents
Literature
59 results about "Redox polymers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
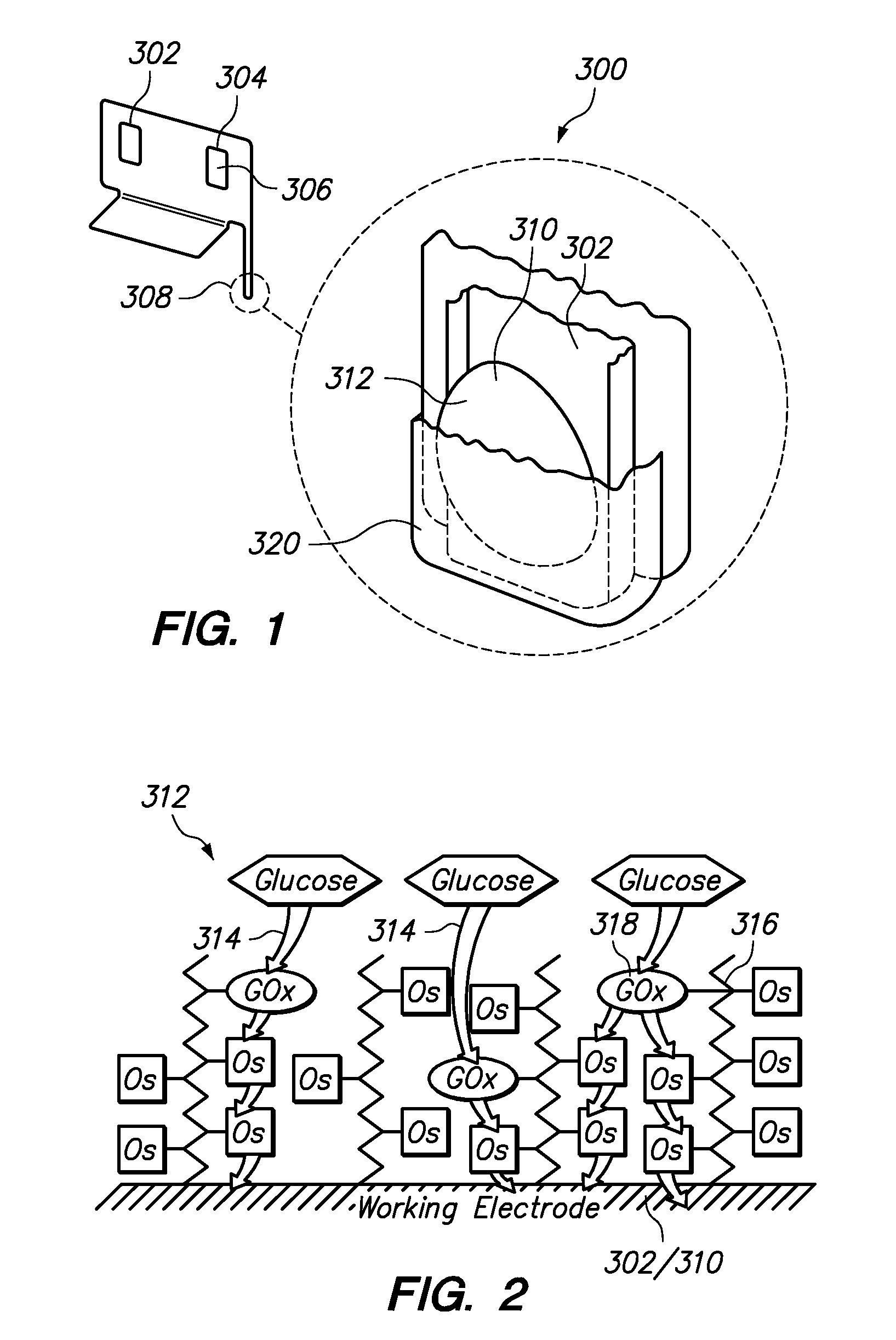
Enzymatic electrochemical detection assay using protective monolayer and device therefor
InactiveUS20060160100A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
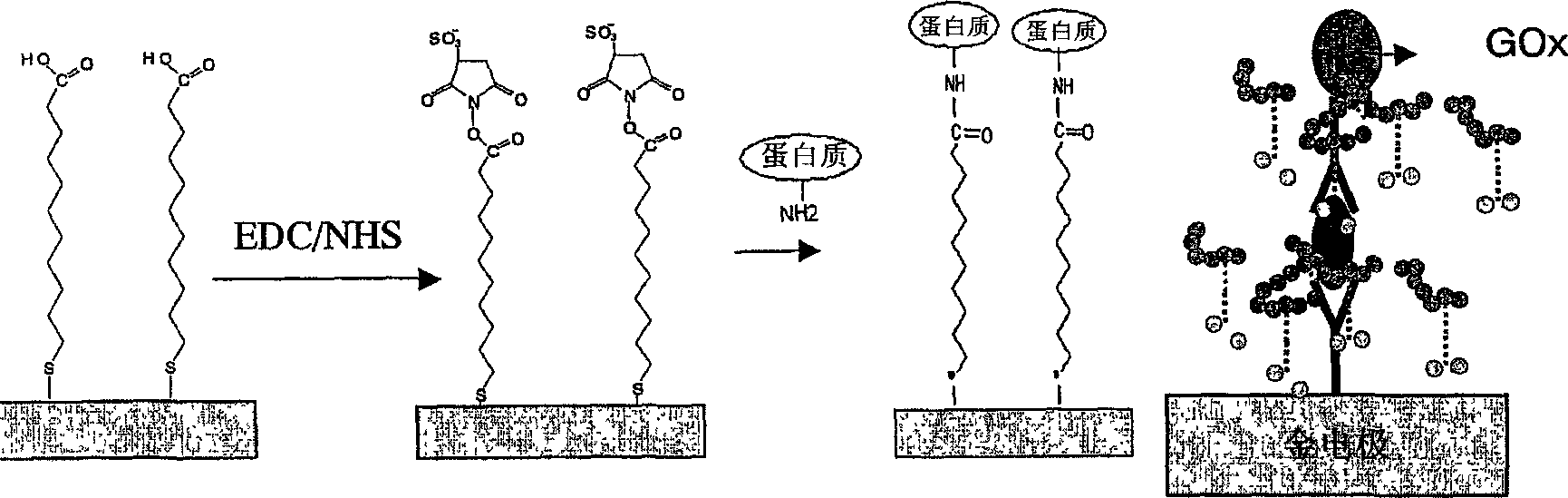
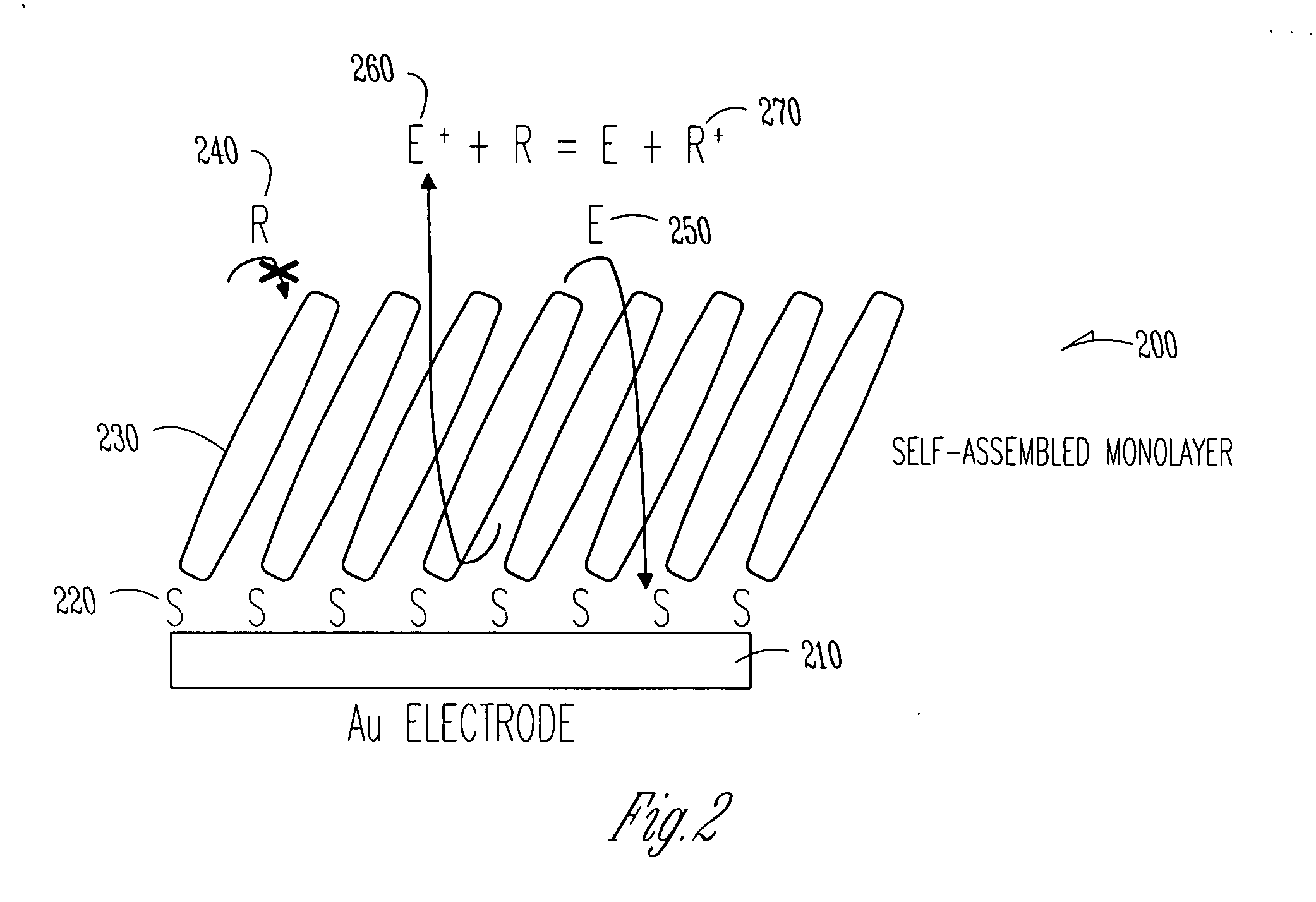
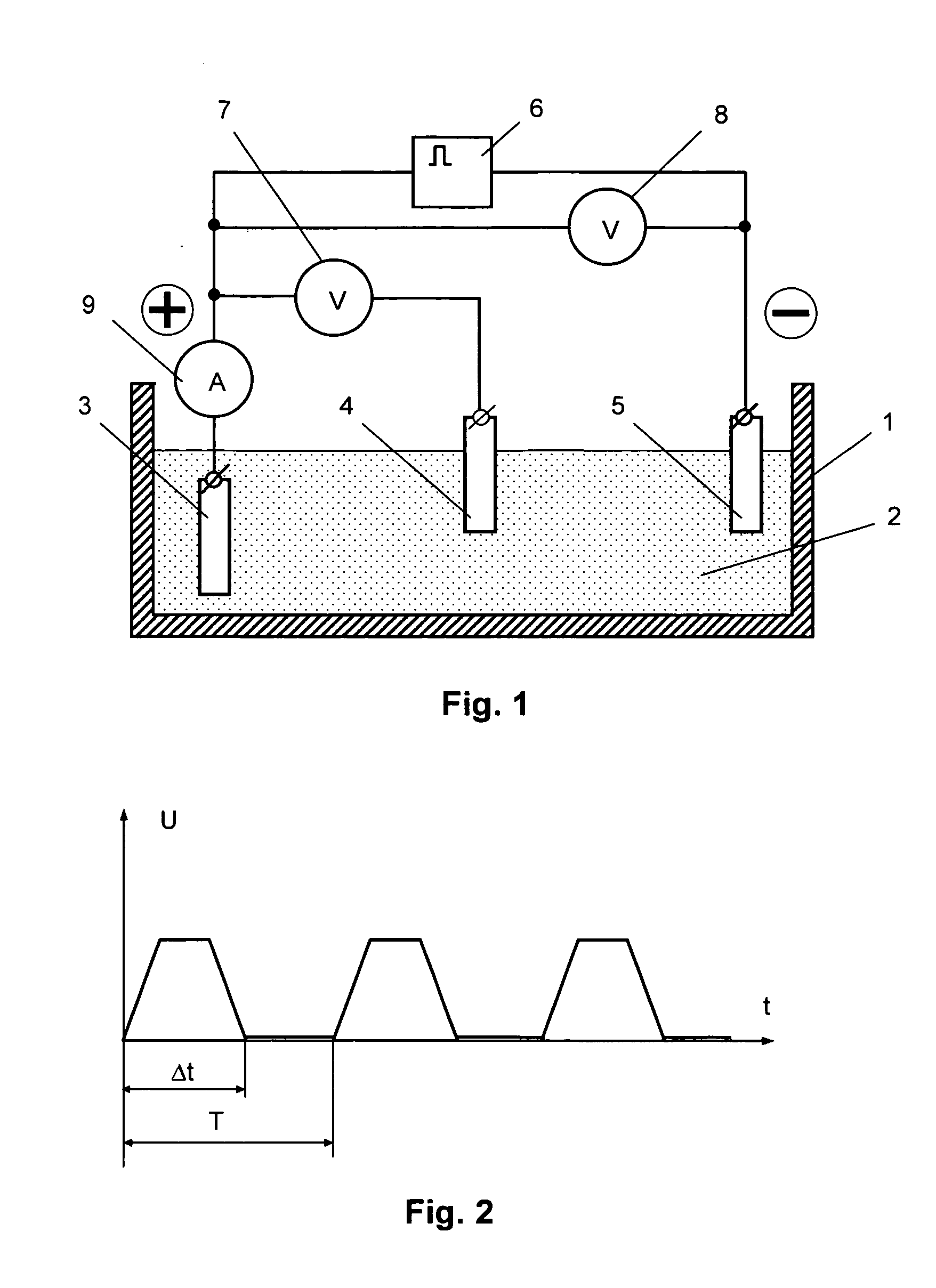
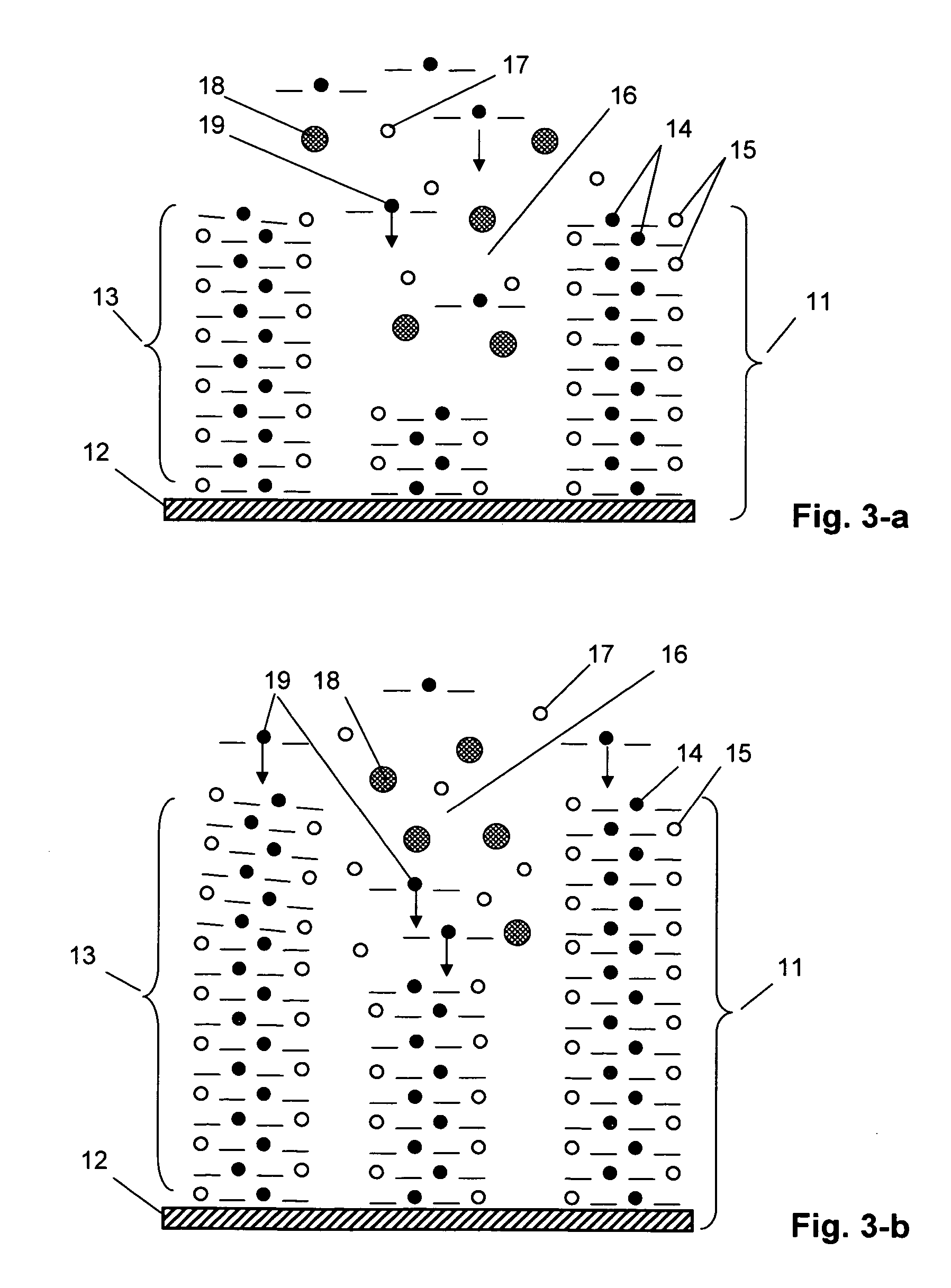
There is provided an electrochemical assay method for detecting a target molecule, for example a protein, in a sample, which involves the use of a protective monolayer and a redox polymer to form a bilayer immobilized on an electrode. The monolayer protects the electrode from non-specific adherence of reagents, particular proteins, to the electrode while simultaneously providing a surface that can be functionalized to immobilize a capture molecule and that can interact with the redox polymer.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
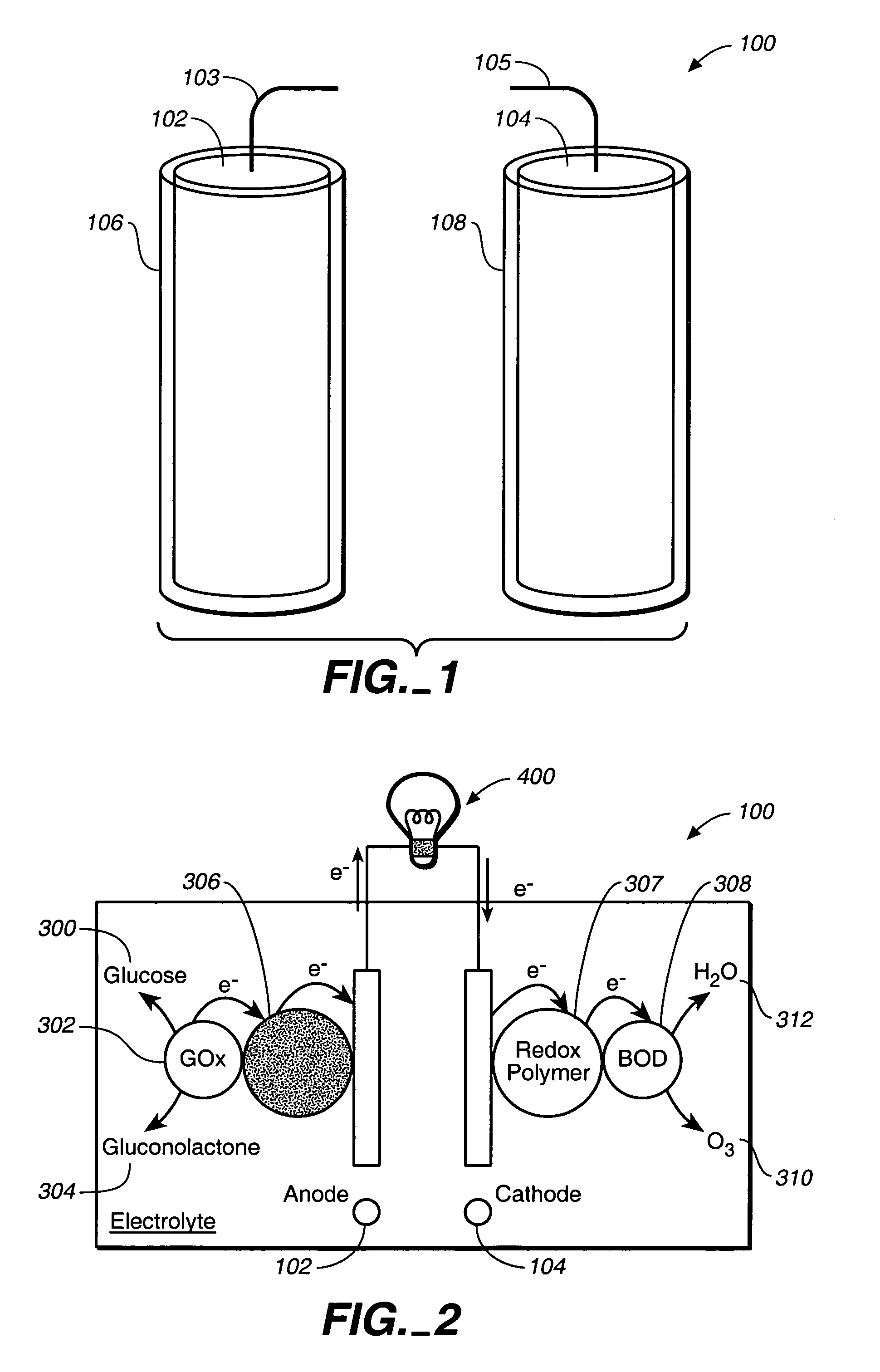
Miniature biological fuel cell that is operational under physiological conditions, and associated devices and methods
InactiveUS7368190B2Reduce physical sizeReduced dimensionMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementOperabilityRedox polymers
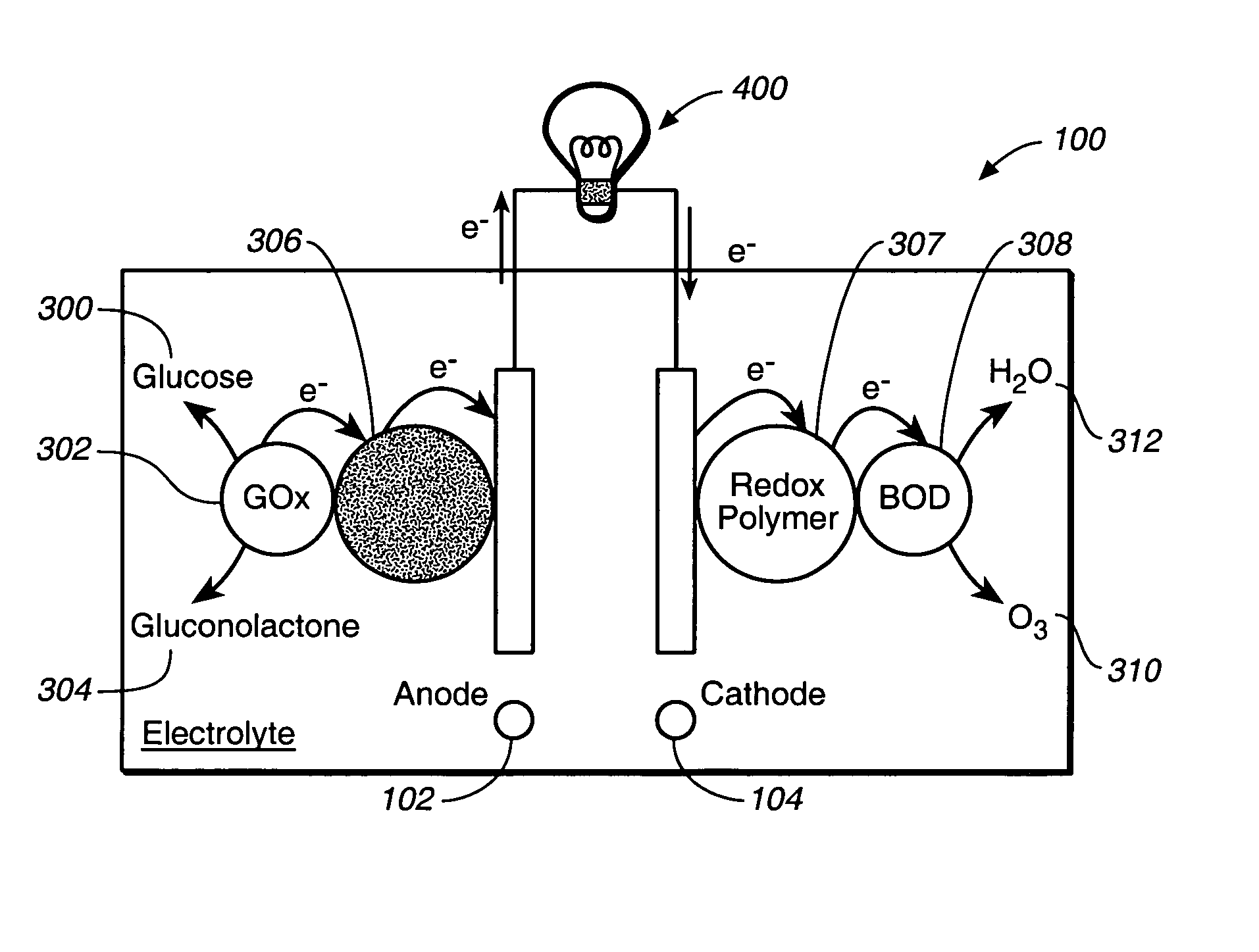
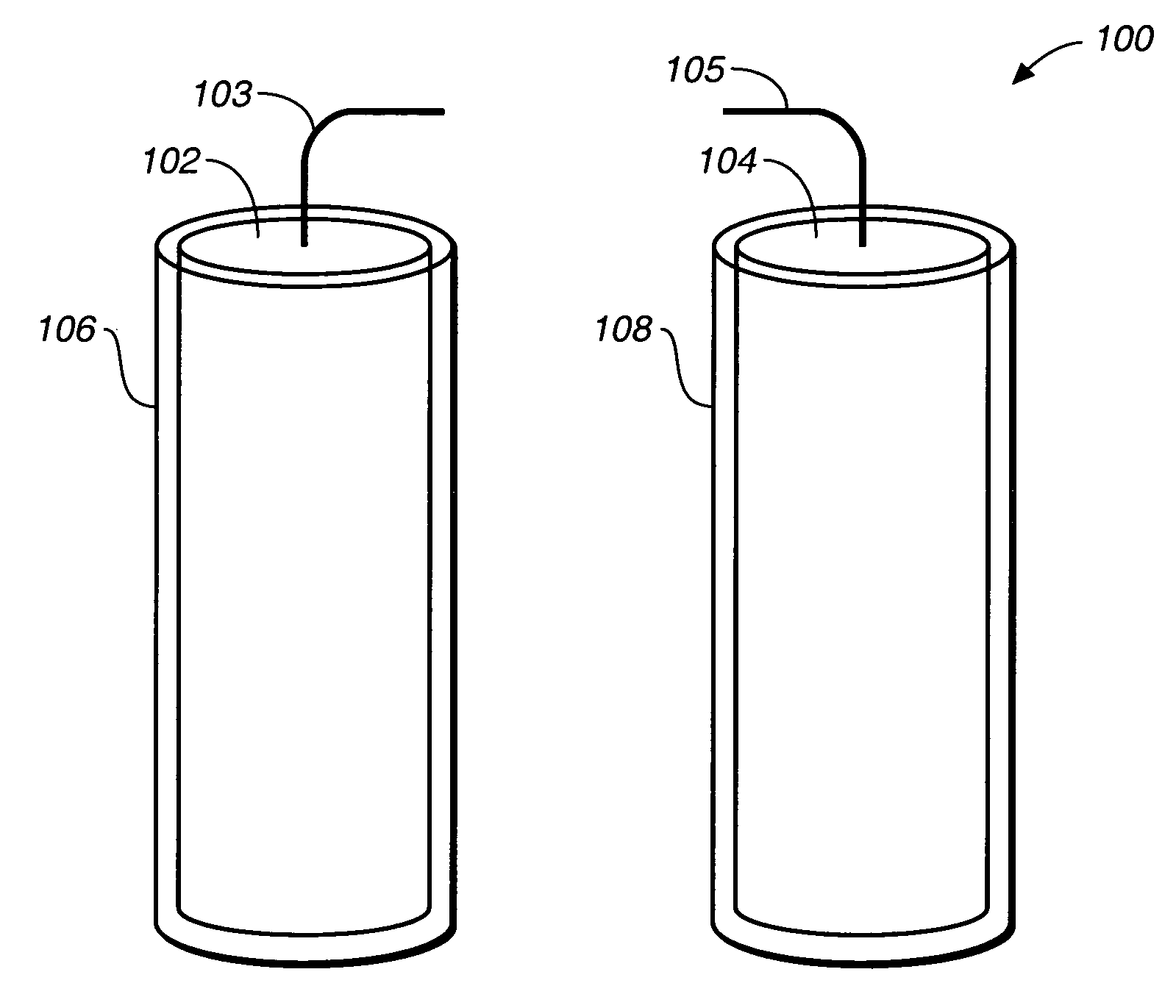
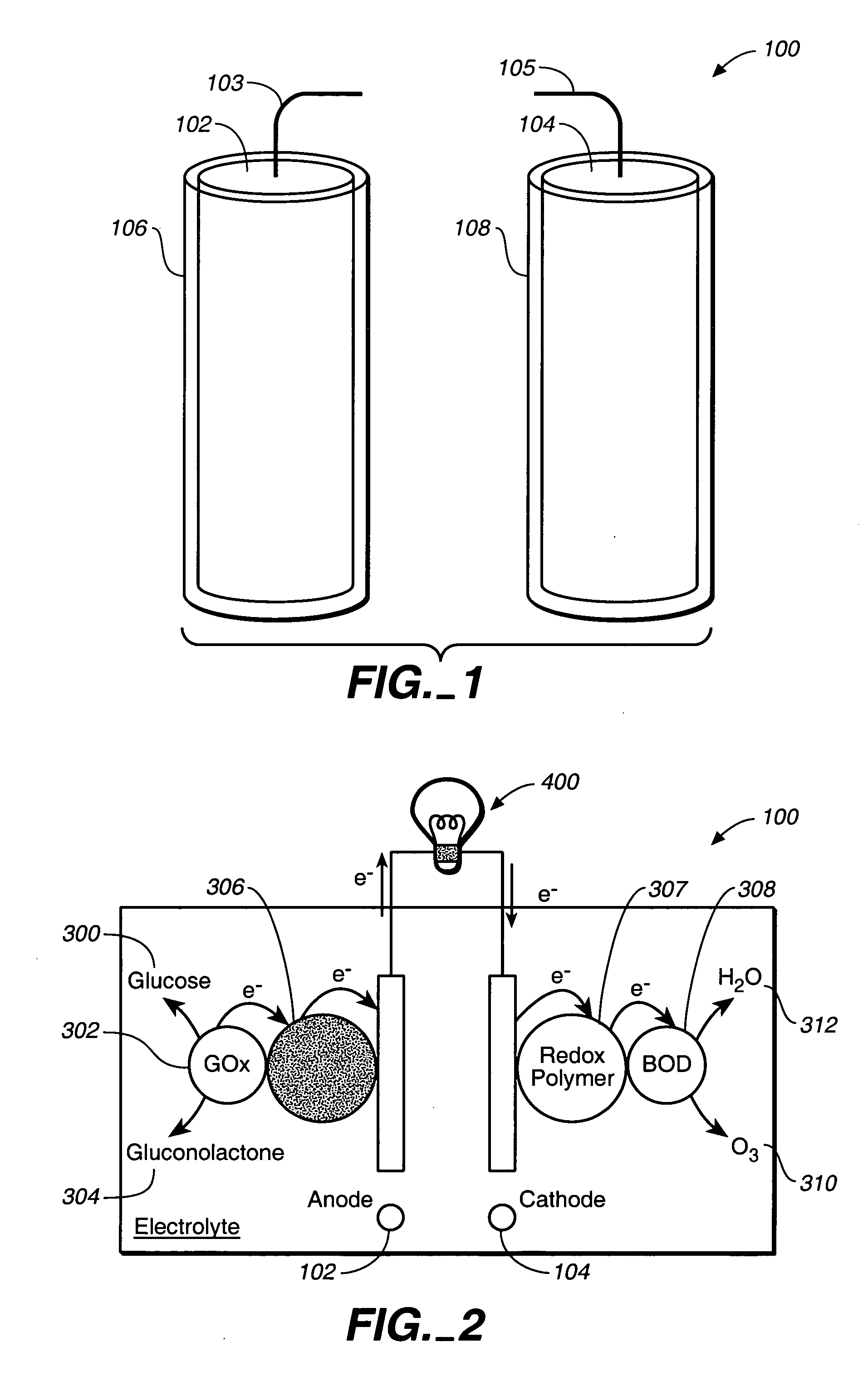
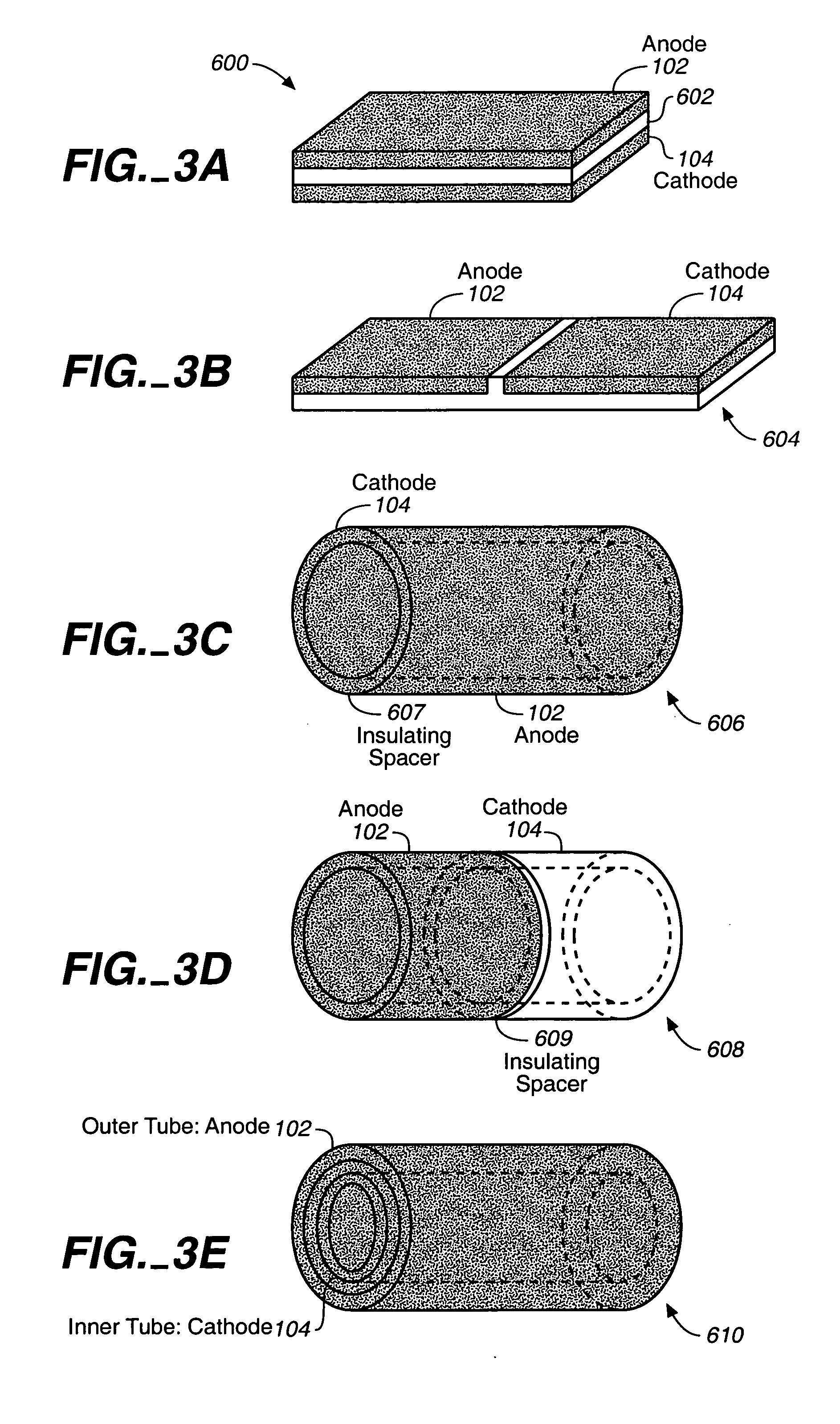
A fuel cell is provided with an anode and a cathode. The anode is in electrical communication with an anode enzyme and the cathode is in electrical communication with a cathode enzyme. The anode enzyme is preferably an oxidase or a dehydrogenase. The cathode enzyme is a copper-containing enzyme, such as a laccase, an ascorbate oxidase, a ceruloplasmine, or a bilirubin oxidase. Preferably, the cathode enzyme is operable under physiological conditions. Redox polymers serve to wire the anode enzyme to the anode and the cathode enzyme to the cathode. The fuel cell can be very small in size because it does not require a membrane, seal, or case. The fuel cell can be used in connection with a biological system, such as a human, as it may operate at physiological conditions. By virtue of its size and operability at physiological conditions, the fuel cell is of particular interest for applications calling for a power source implanted in a human body, such as a variety of medical applications.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
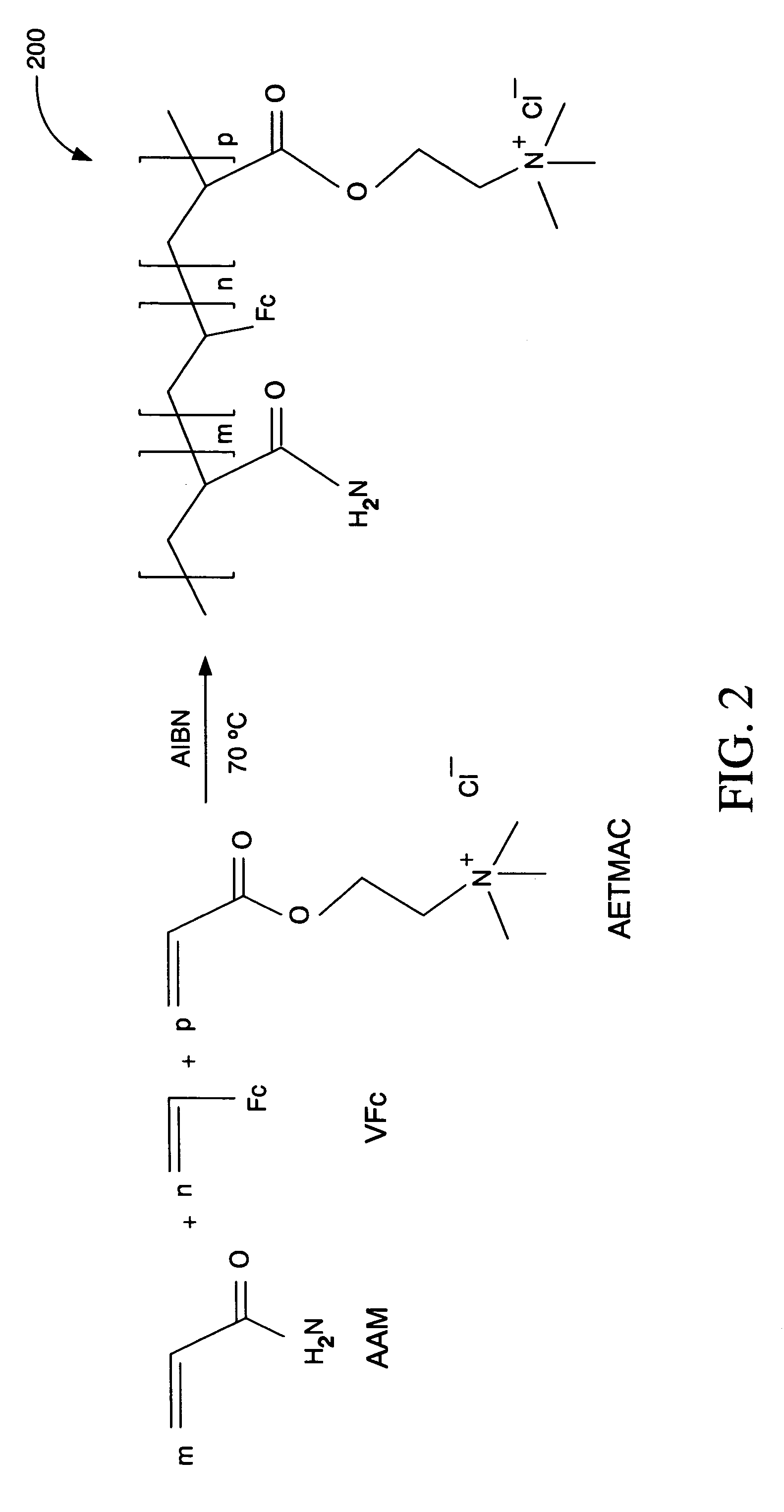
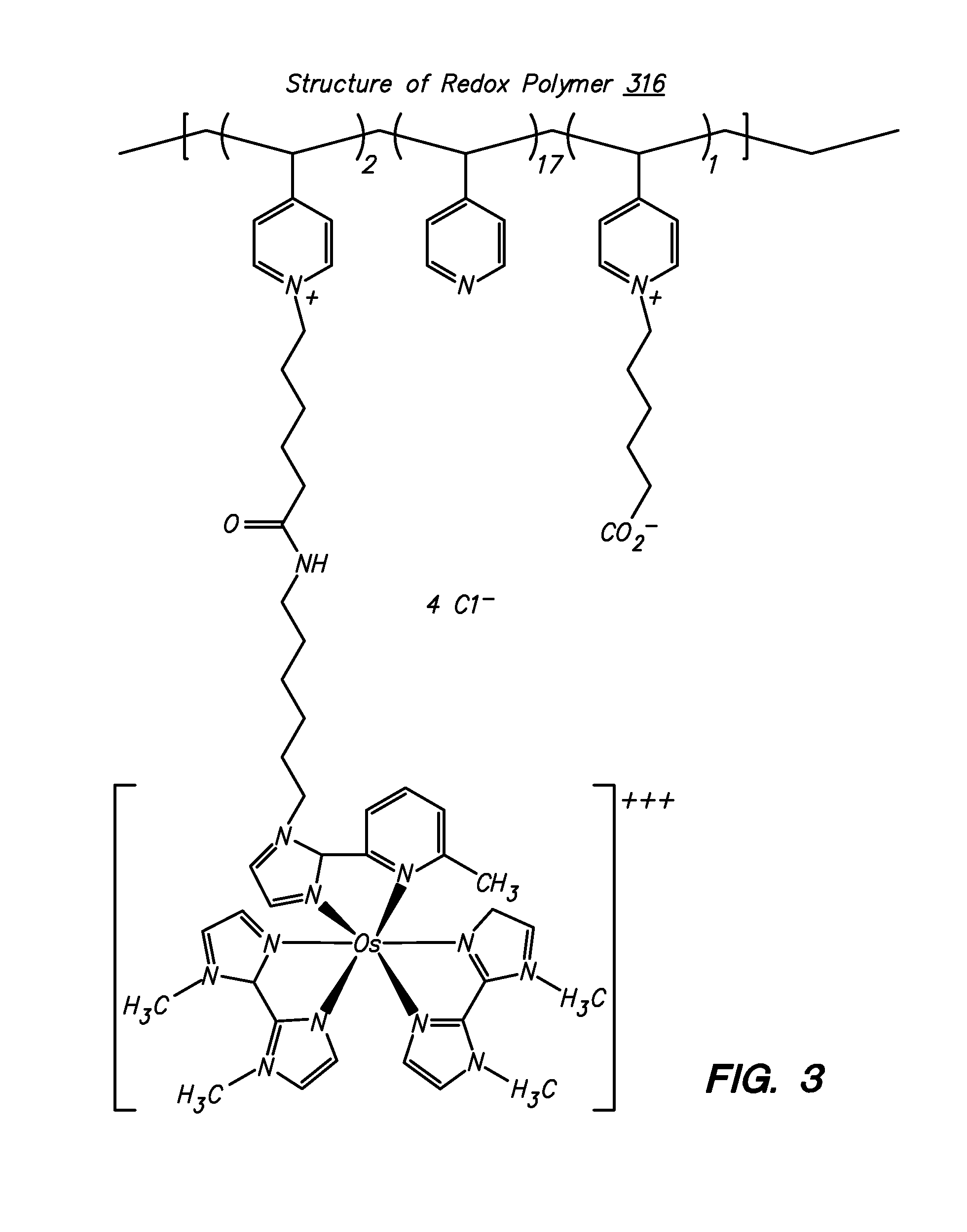
Ionic hydrophilic high molecular weight redox polymers for use in enzymatic electrochemical-based sensors
ActiveUS7351770B2Solve the lack of activityReduce leachingMicrobiological testing/measurementHydrophilic polymersFerrocene
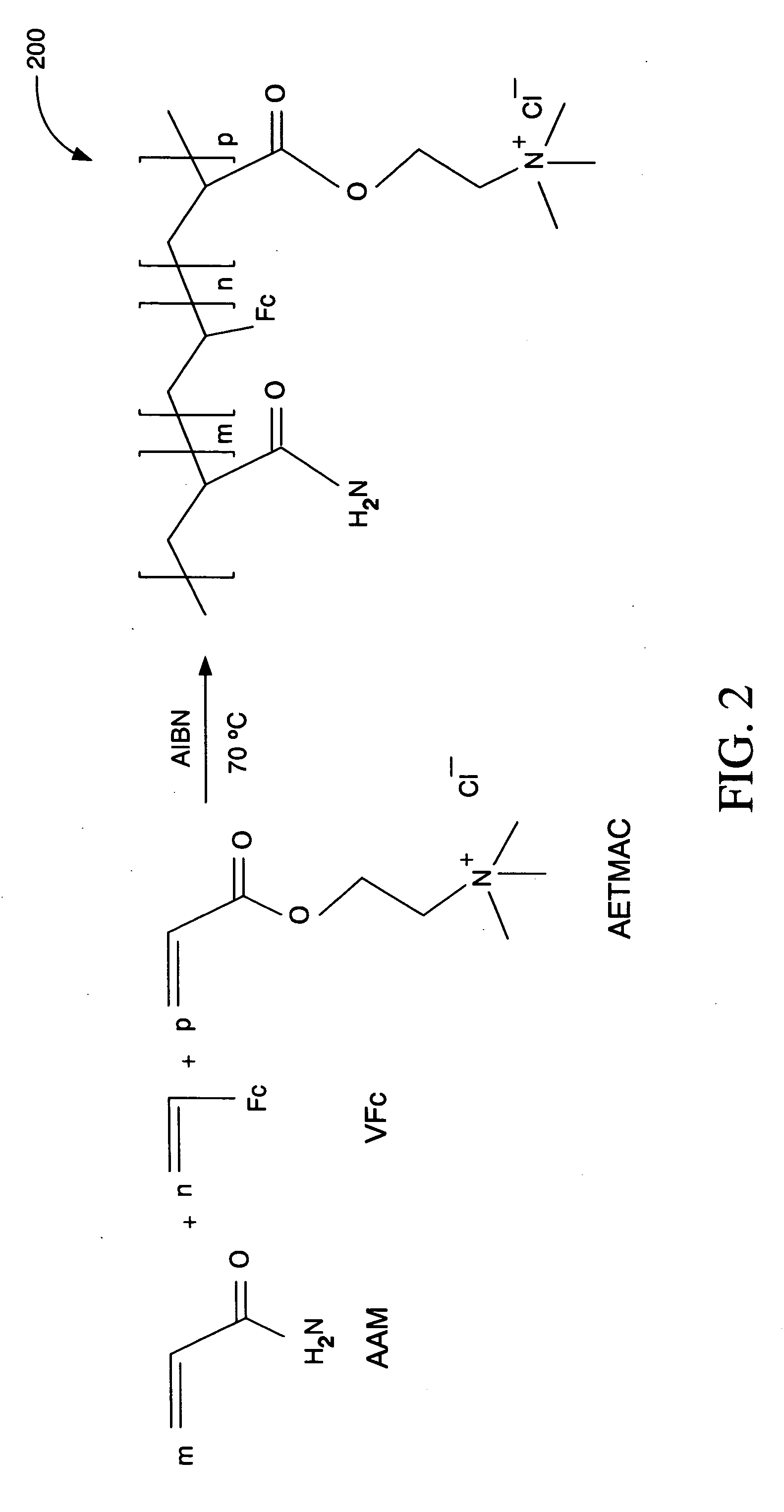
Ionic hydrophilic high molecular weight redox polymers for use in enzymatic electrochemical-based sensors include a hydrophilic polymer (such as a hydrophilic polymer backbone) with ionic portions (e.g., cationic monomers incorporated in the hydrophilic polymer backbone) and a plurality of attached redox mediators. The redox mediators can be, for example, covalently attached to the hydrophilic polymer in a pendant manner. An exemplary cationic hydrophilic high molecular weight redox polymer is synthesized by co-polymerization of a hydrophilic acrylamide monomer, [2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethyl ammonium chloride and vinyl ferrocene.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
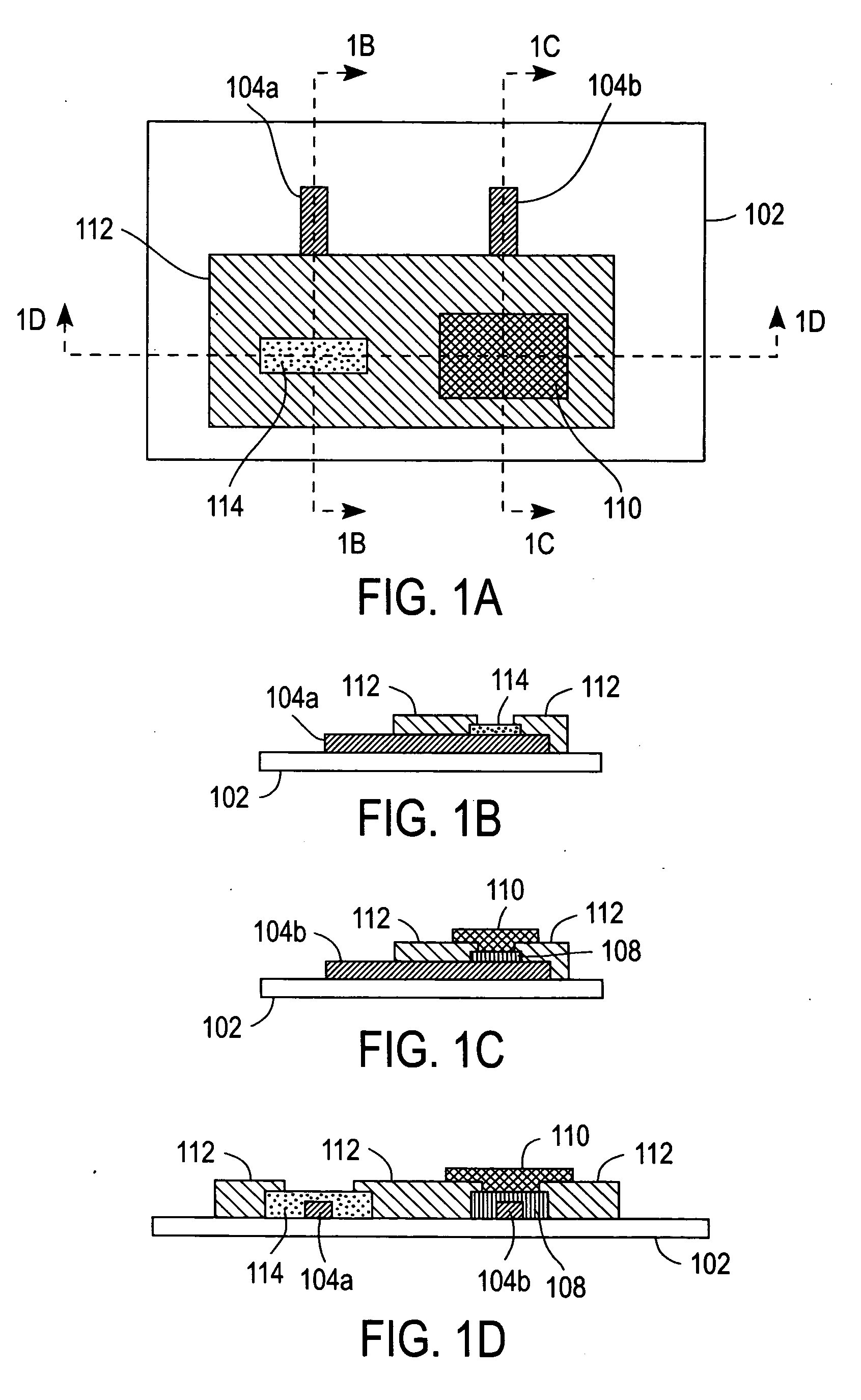
Electrochemical-based sensor with a redox polymer and redox enzyme entrapped by a dialysis membrane
ActiveUS7572356B2Rapid responseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox enzymesDialysis membranes
An electrochemical-based sensor includes an electrode with at least one electrode surface, a film disposed on the electrode surface, and a dialysis membrane disposed on the film. The film includes a redox enzyme and a hydrophilic redox polymer (i.e., a polymer with an attached redox mediator(s)). In addition, the dialysis membrane serves to entrap the redox polymer and redox enzyme in the vicinity of the electrode. Such entrapment is accomplished by employing a redox enzyme and a hydrophilic redox polymer of a sufficiently high molecular weight that they do not pass through the dialysis membrane.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Miniature biological fuel cell that is operational under physiological conditions, and associated devices and methods
InactiveUS20080044721A1Reduce physical sizeReduced dimensionMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementOperabilityRedox polymers
A fuel cell is provided with an anode and a cathode. The anode is in electrical communication with an anode enzyme and the cathode is in electrical communication with a cathode enzyme. The anode enzyme is preferably an oxidase or a dehydrogenase. The cathode enzyme is a copper-containing enzyme, such as a laccase, an ascorbate oxidase, a ceruloplasmine, or a bilirubin oxidase. Preferably, the cathode enzyme is operable under physiological conditions. Redox polymers serve to wire the anode enzyme to the anode and the cathode enzyme to the cathode. The fuel cell can be very small in size because it does not require a membrane, seal, or case. The fuel cell can be used in connection with a biological system, such as a human, as it may operate at physiological conditions. By virtue of its size and operability at physiological conditions, the fuel cell is of particular interest for applications calling for a power source implanted in a human body, such as a variety of medical applications.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
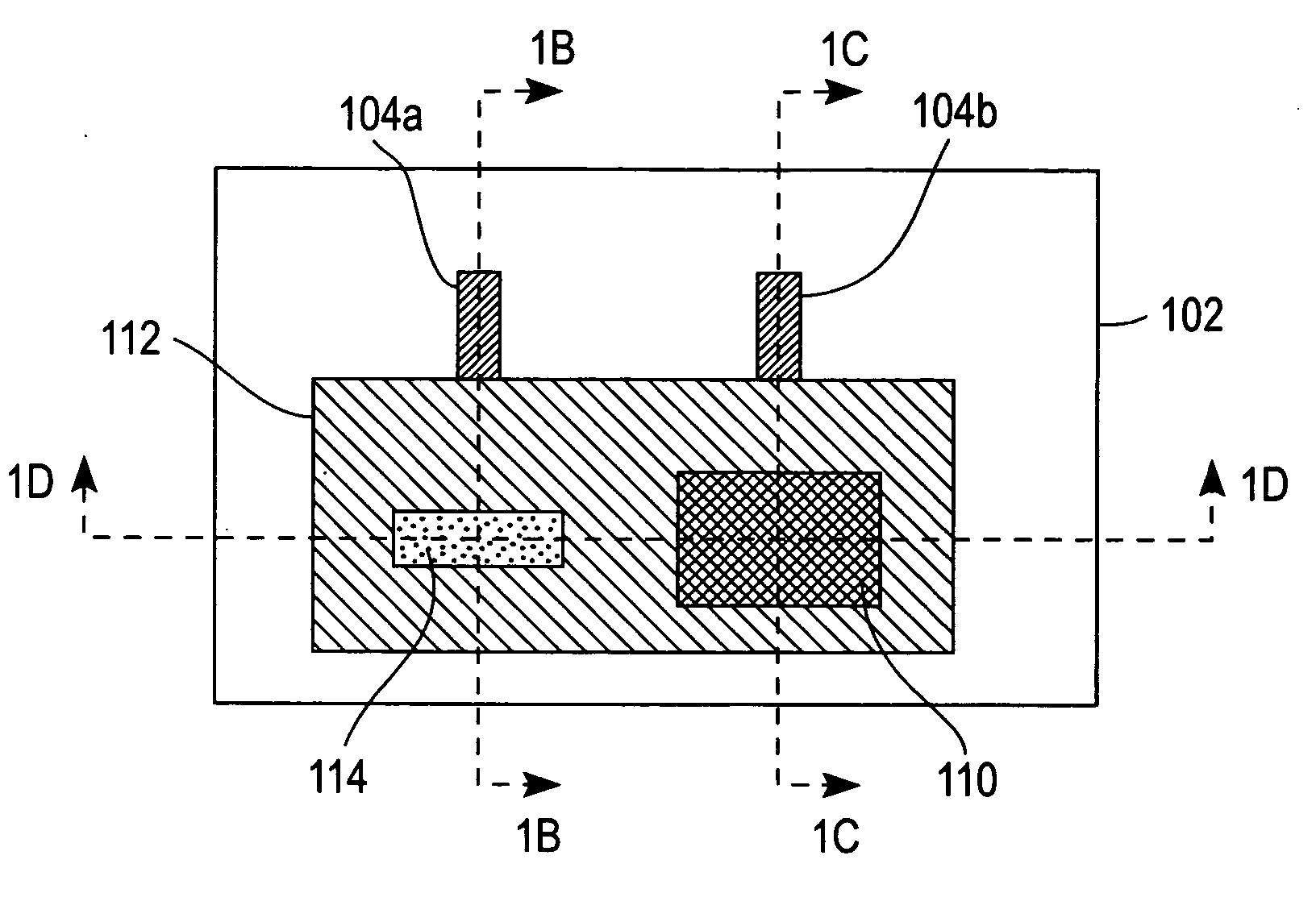
Redox polymers for use in analyte monitoring
InactiveUS8444834B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHigh rateElectrochemical biosensor
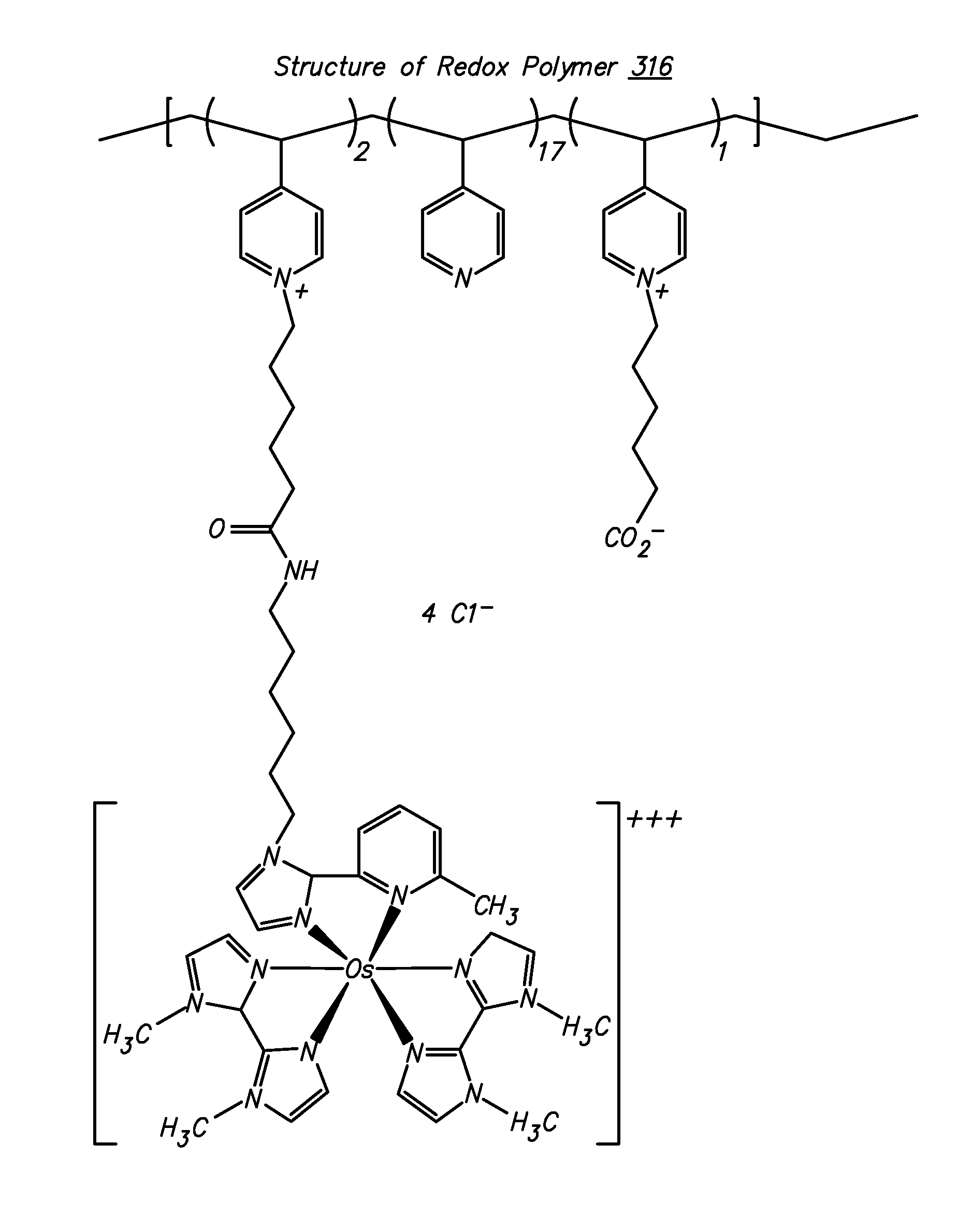
Polymers for use as redox mediators in electrochemical biosensors are described. The transition metal complexes attached to polymeric backbones can be used as redox mediators in enzyme based electrochemical sensors. In such instances, transition metal complexes accept electrons from, or transfer electrons to, enzymes at a high rate and also exchange electrons rapidly with the sensor. The transition metal complexes include at least one substituted or unsubstituted biimidazole ligand and may further include a second substituted or unsubstituted biimidazole ligand or a substituted or unsubstituted bipyridine or pyridylimidazole ligand.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
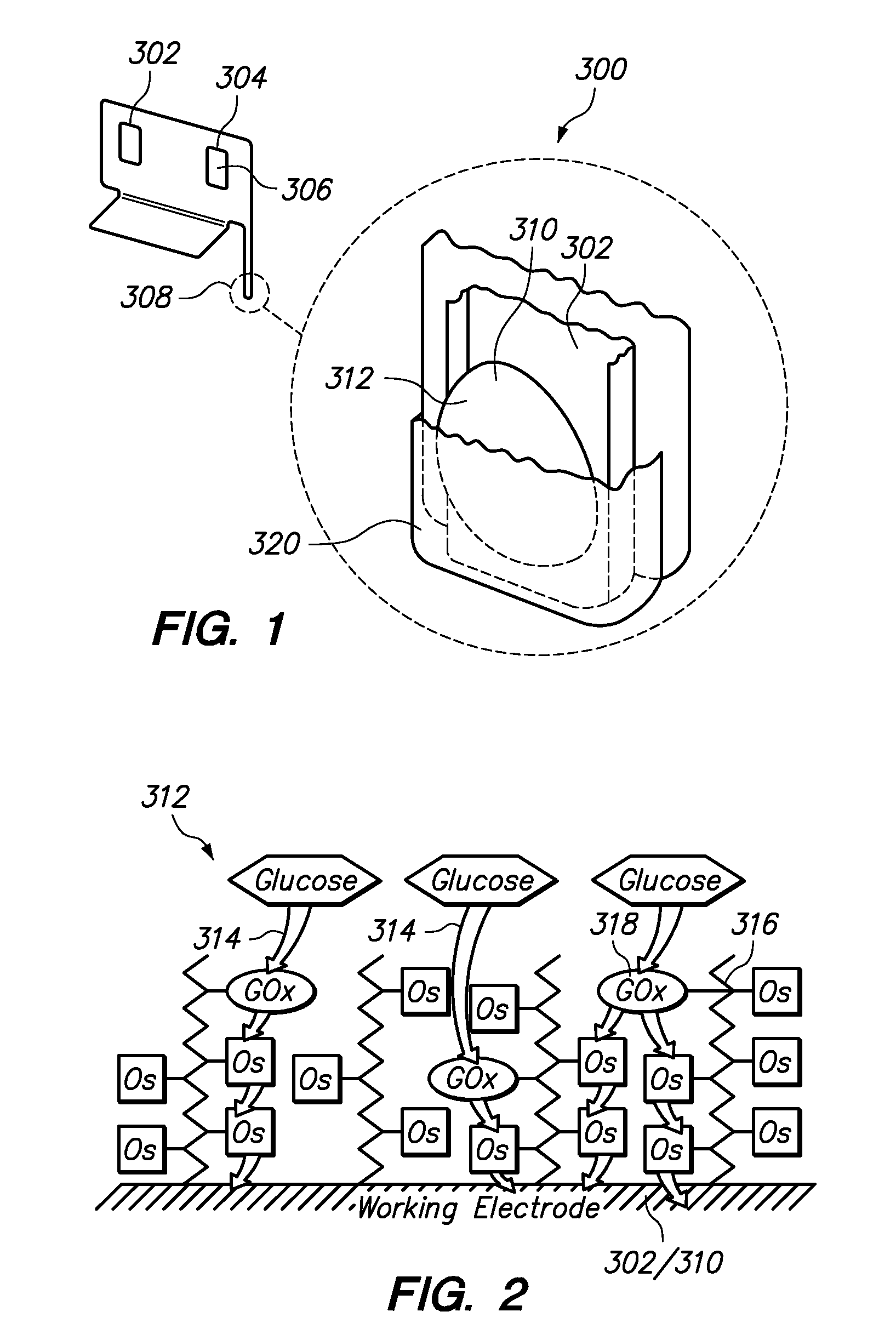
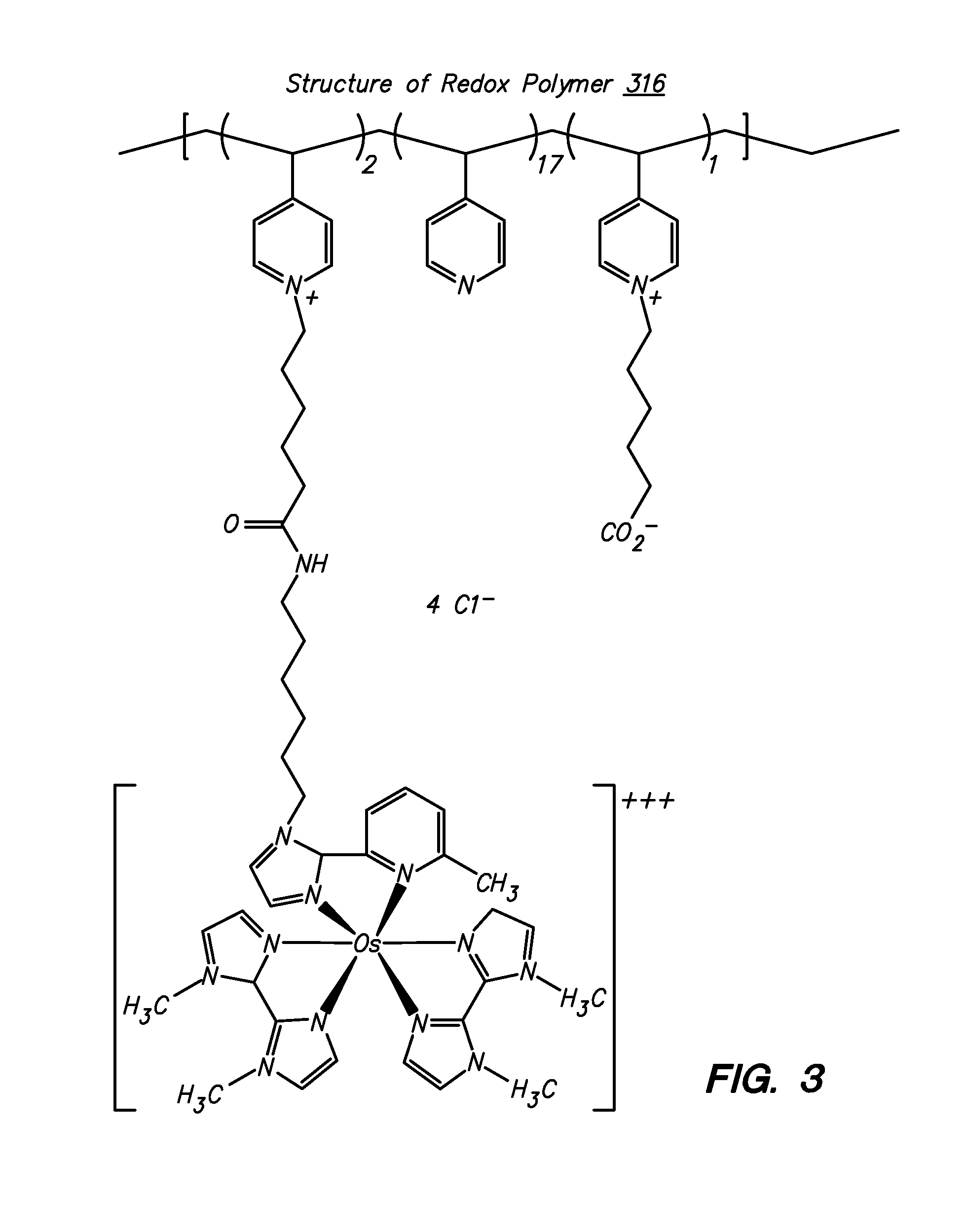
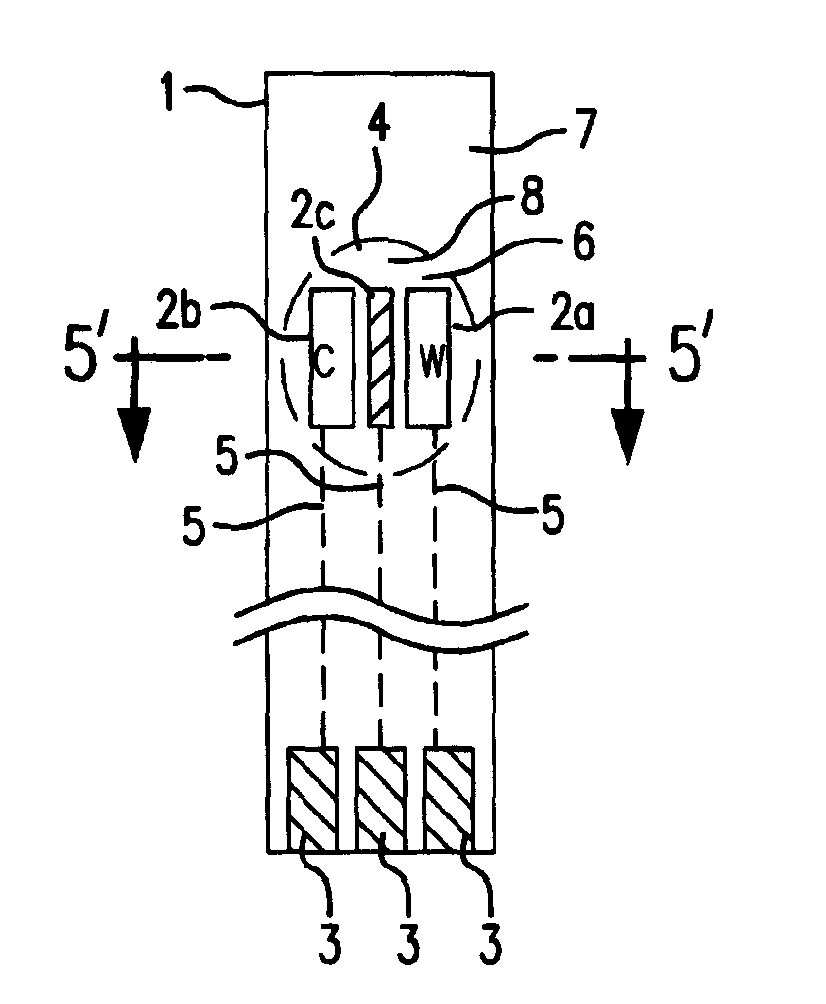
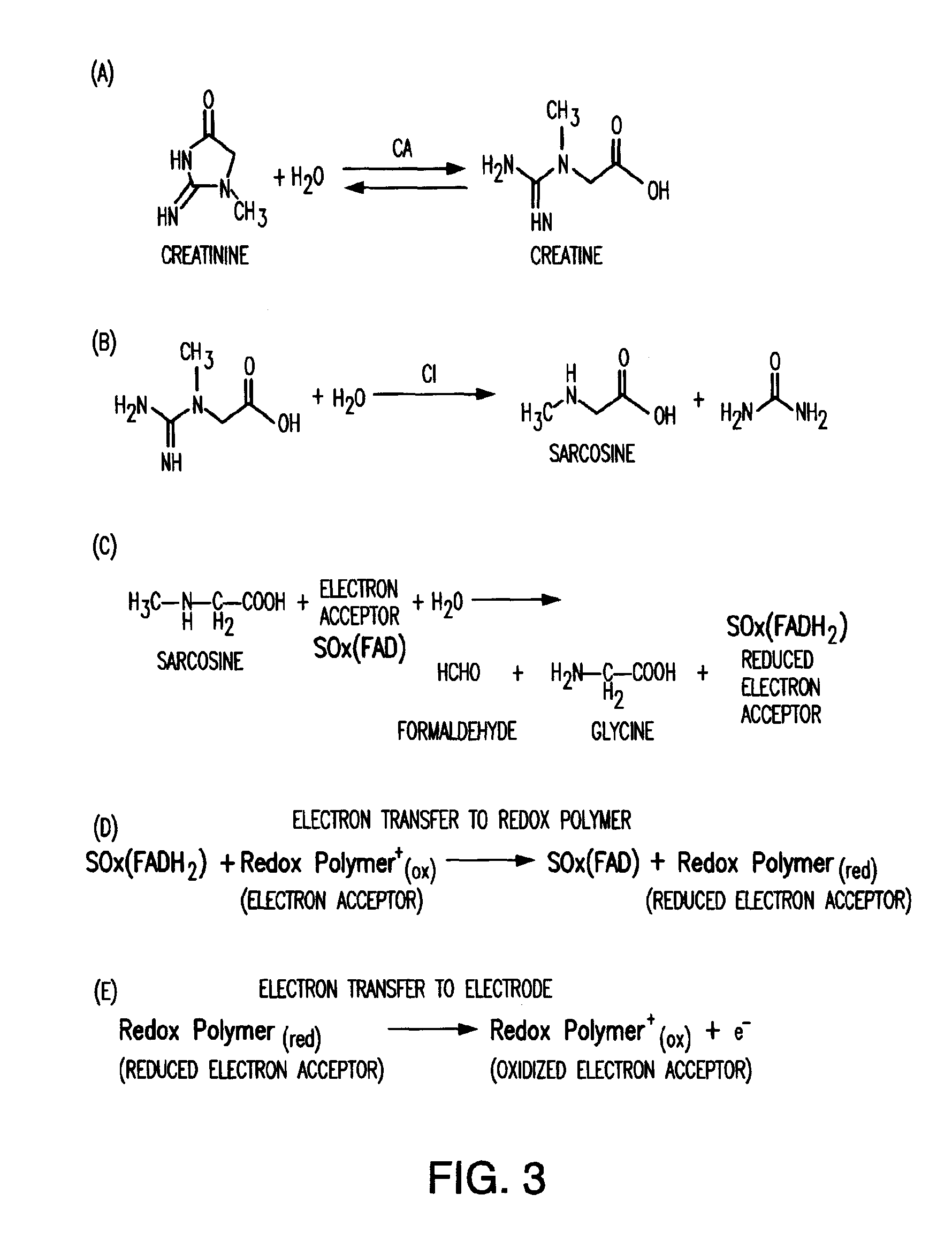
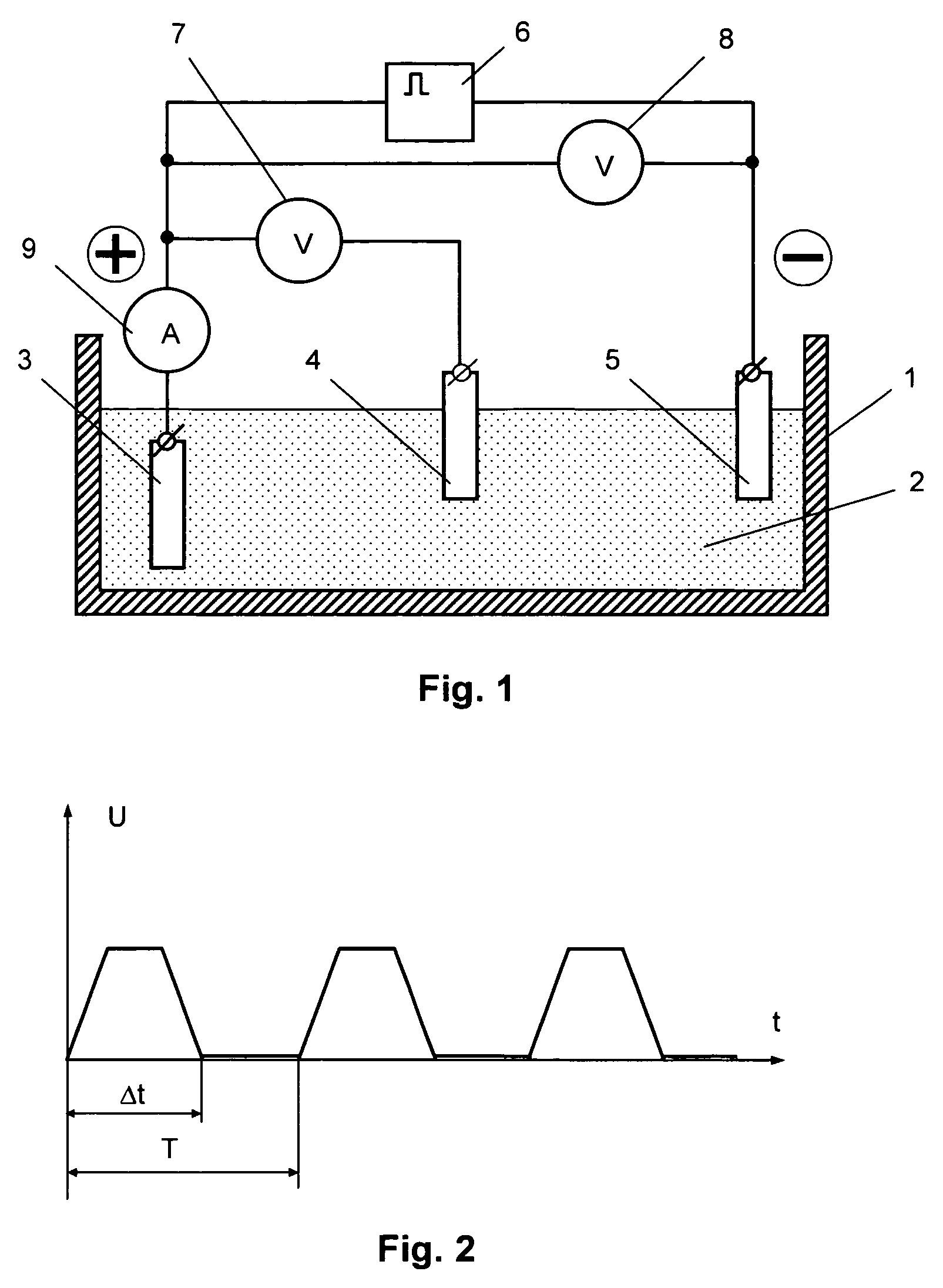
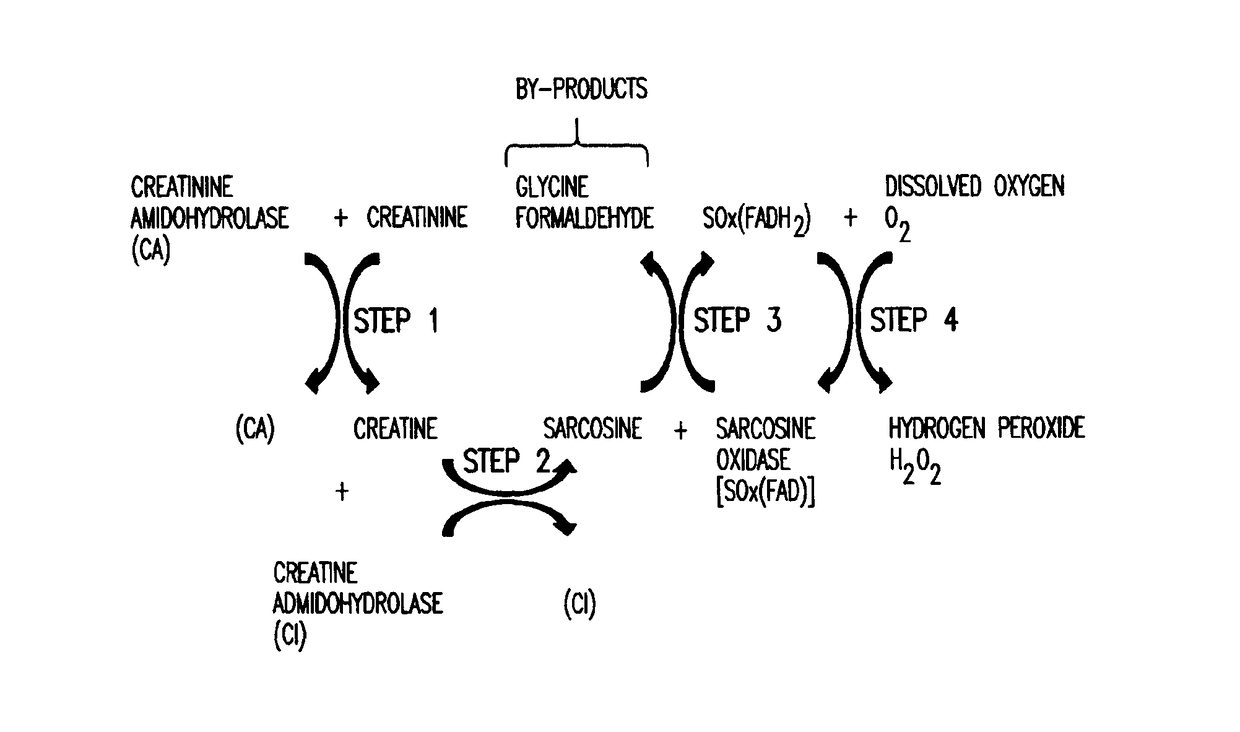
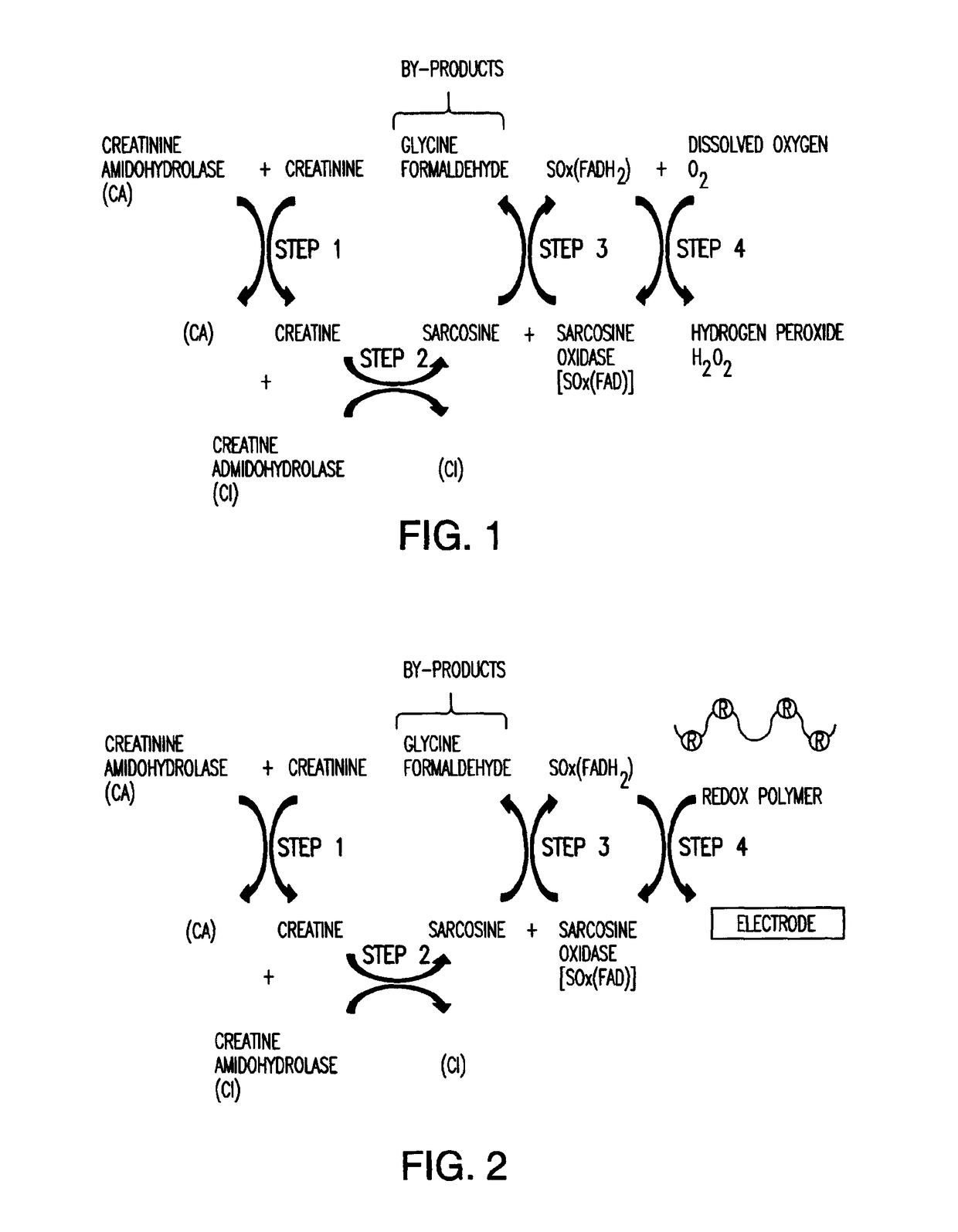
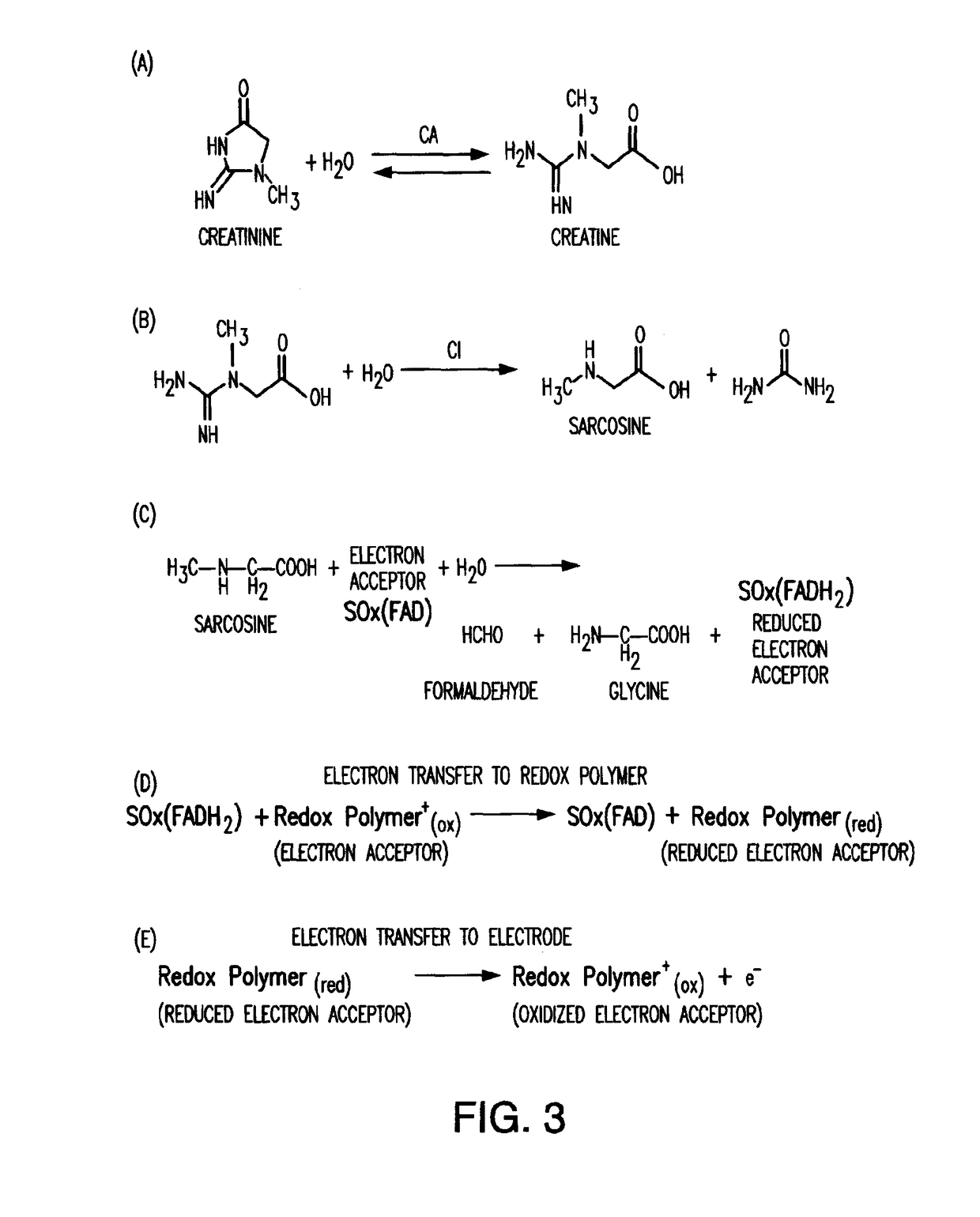
Amperometric Creatinine Biosensor With Immobilized Enzyme-Polymer Composition And Systems Using Same, And Methods
InactiveUS20120181189A1Reduced potential rangeIncreased current responseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCreatinine riseMedicine
An amperometric biosensor is provided for determination of creatinine in a sample fluid. The biosensor can be an enzyme-polymer composition having at least one redox polymer and a plurality of enzymes immobilized on an electrode surface. Methods of preparing the amperometric biosensor are included. In addition, methods and systems using the amperometric biosensor in measuring creatinine concentrations of a patient and treatments of a patient with monitoring of the progress of dialysis performed on the patient are also provided.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Electrode for energy storage devices and electrochemical supercapacitor based on said electrode
ActiveUS20070065719A1Extended service lifeImprove reliabilityHybrid capacitor electrodesLiquid electrolytic capacitorsPolymer scienceRedox polymers
An electrode comprises an electrically conductive substrate, a layer of energy accumulating redox polymer deposited onto the substrate, the redox polymer comprising a polymer metal complex with a substituted tetra-dentate Schiff's base selected from the group: poly-[Me(R, R′—Y)], wherein Me is a transition metal; Y is a bridge group binding the atoms of Nitrogen in the Schiff's base; R is an electron-donating substituent comprising a functional group (X)O—, —COO(X), where (X) is an alkali metal; R′ is Hydrogen or Halogen; and wherein the polymer metal complex has the following structure: The electrochemical capacitor comprises a case housing the above-described positive electrode and a negative electrode disposed inside the case, and an electrolyte filling the space between the electrodes.
Owner:POWERMERS
Light emitting device and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS6838836B2Low costIncrease productionDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesGeneral purposeConductive polymer
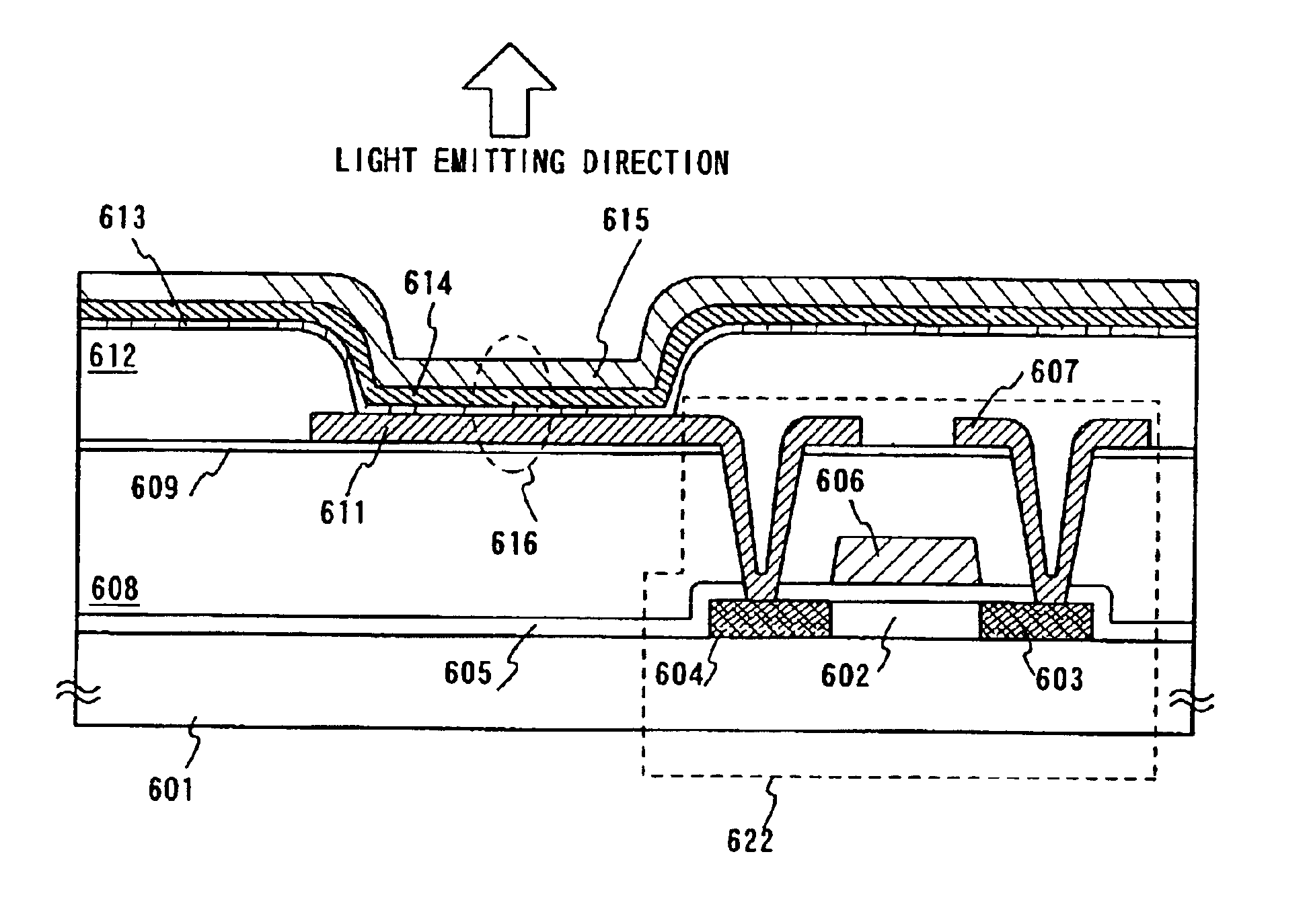
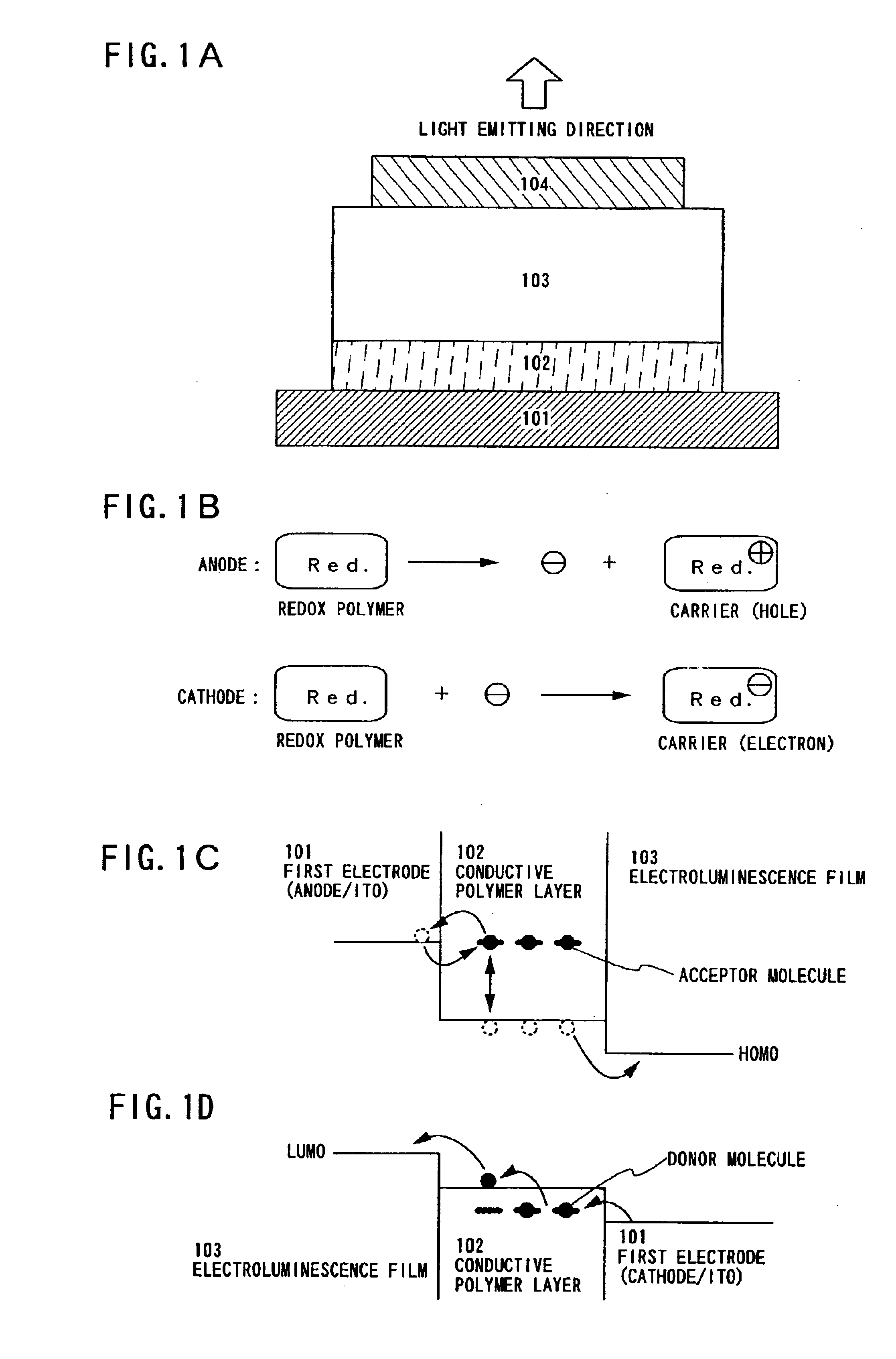
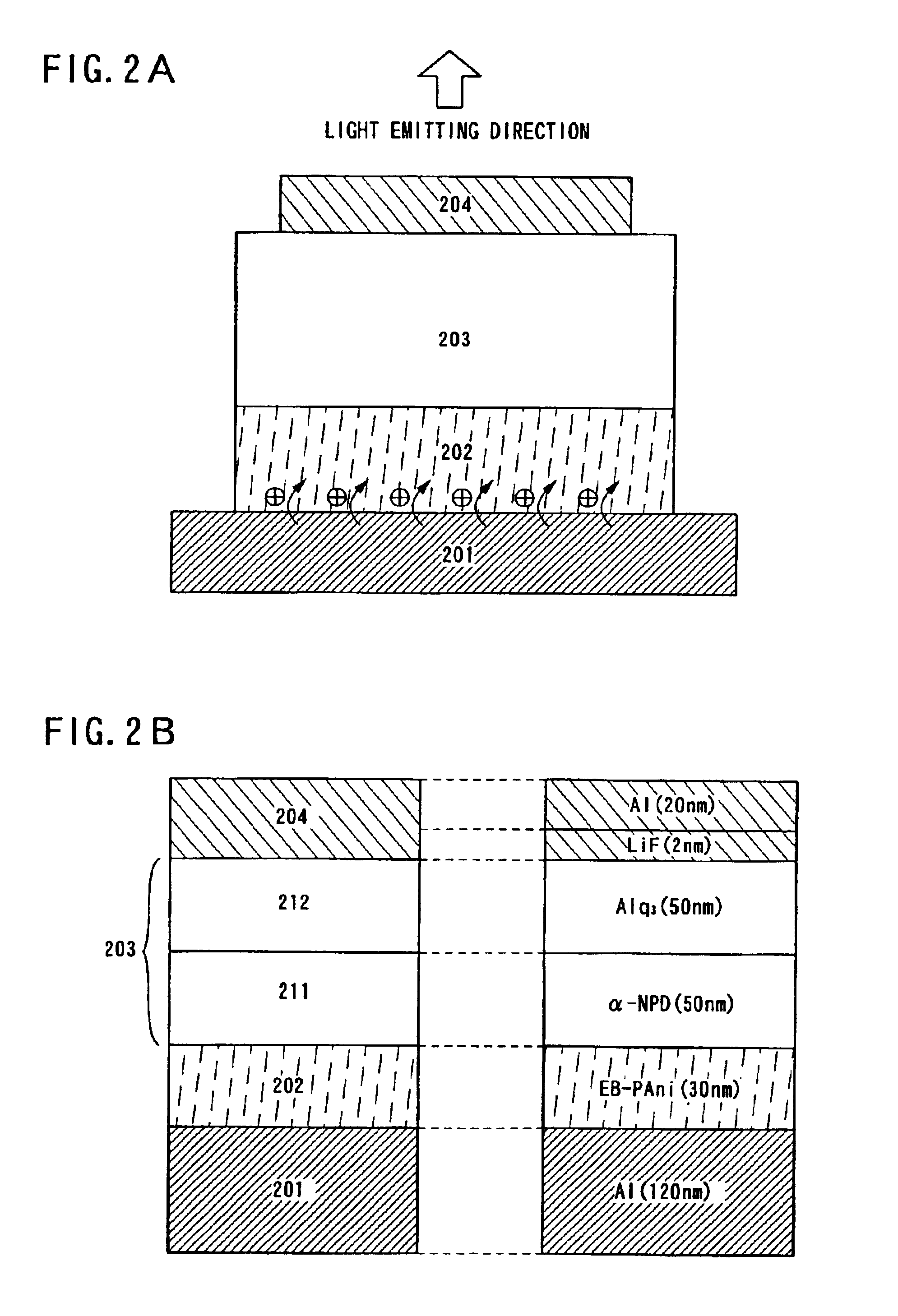
To provide a light emitting element having a top emission structure, which can be easily manufactured without considering an ionization potential of an electrode (particularly an electrode in contact with a substrate) and a manufacturing method therefor. A light emitting device having the top emission structure according to the present invention includes: a first electrode (101) formed of general-purpose metal (specifically, a wiring material such as Ti or Al) having a light-shielding property or reflectivity; a conductive polymer layer (102) formed by applying a conductive polymer material onto the first electrode (101); an electroluminescence film (103) formed in contact with the conductive polymer layer (102); and a light-transmissive second electrode (104) formed on the electroluminescence film 103, in which the conductive polymer layer (102) is formed of materials including a redox polymer etc., while being free of problems regarding work function (as shown in FIG. 1A).
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Redox polymers for use in analyte monitoring
InactiveUS20120132525A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorHigh rate
Polymers for use as redox mediators in electrochemical biosensors are described. The transition metal complexes attached to polymeric backbones can be used as redox mediators in enzyme based electrochemical sensors. In such instances, transition metal complexes accept electrons from, or transfer electrons to, enzymes at a high rate and also exchange electrons rapidly with the sensor. The transition metal complexes include at least one substituted or unsubstituted biimidazole ligand and may further include a second substituted or unsubstituted biimidazole ligand or a substituted or unsubstituted bipyridine or pyridylimidazole ligand.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Electrochemical-based sensor with a redox polymer and redox enzyme entrapped by a dialysis membrane
ActiveUS20060042944A1Rapid responseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox enzymesDialysis membranes
An electrochemical-based sensor includes an electrode with at least one electrode surface, a film disposed on the electrode surface, and a dialysis membrane disposed on the film. The film includes a redox enzyme and a hydrophilic redox polymer (i.e., a polymer with an attached redox mediator(s)). In addition, the dialysis membrane serves to entrap the redox polymer and redox enzyme in the vicinity of the electrode. Such entrapment is accomplished by employing a redox enzyme and a hydrophilic redox polymer of a sufficiently high molecular weight that they do not pass through the dialysis membrane.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
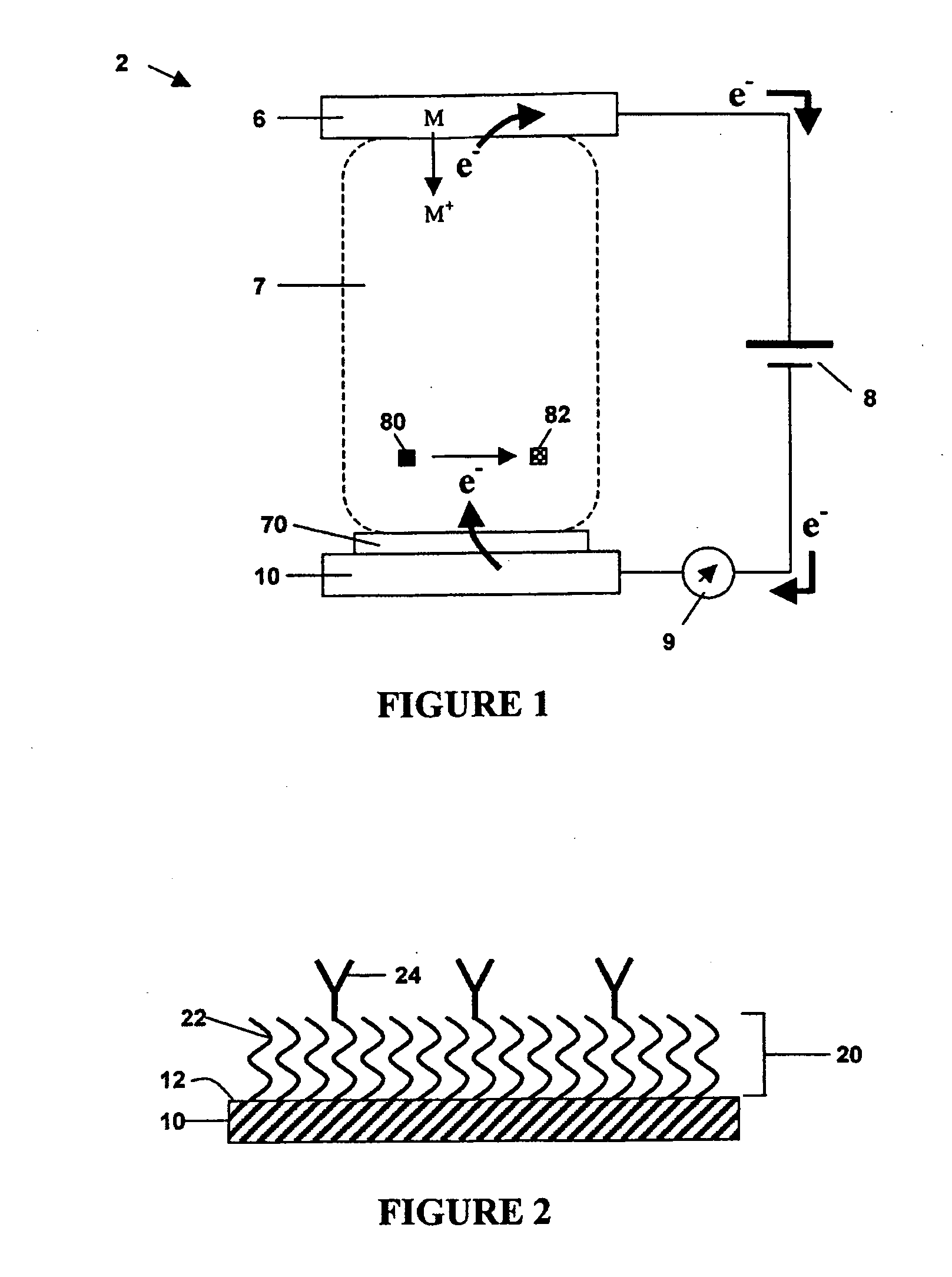
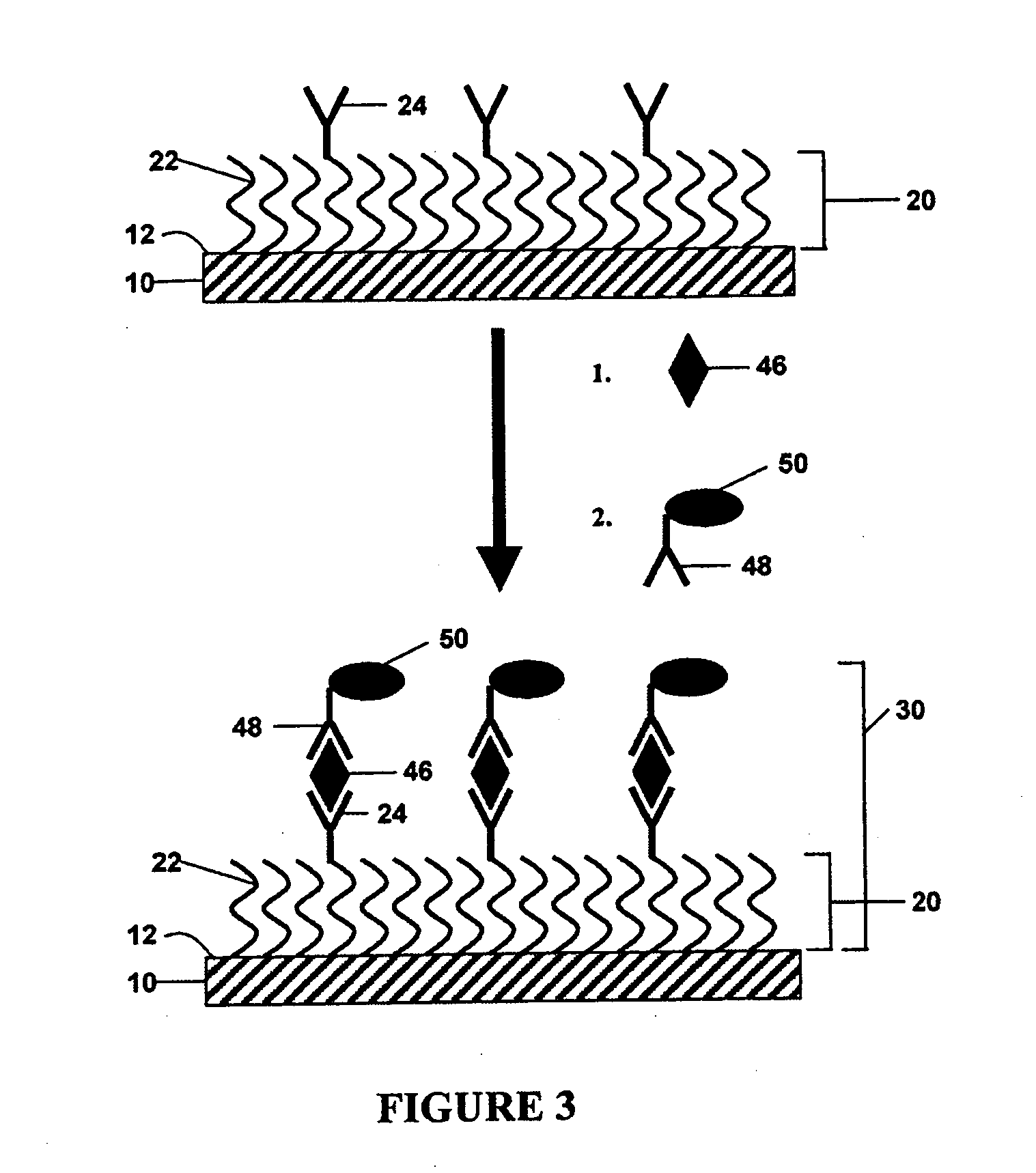
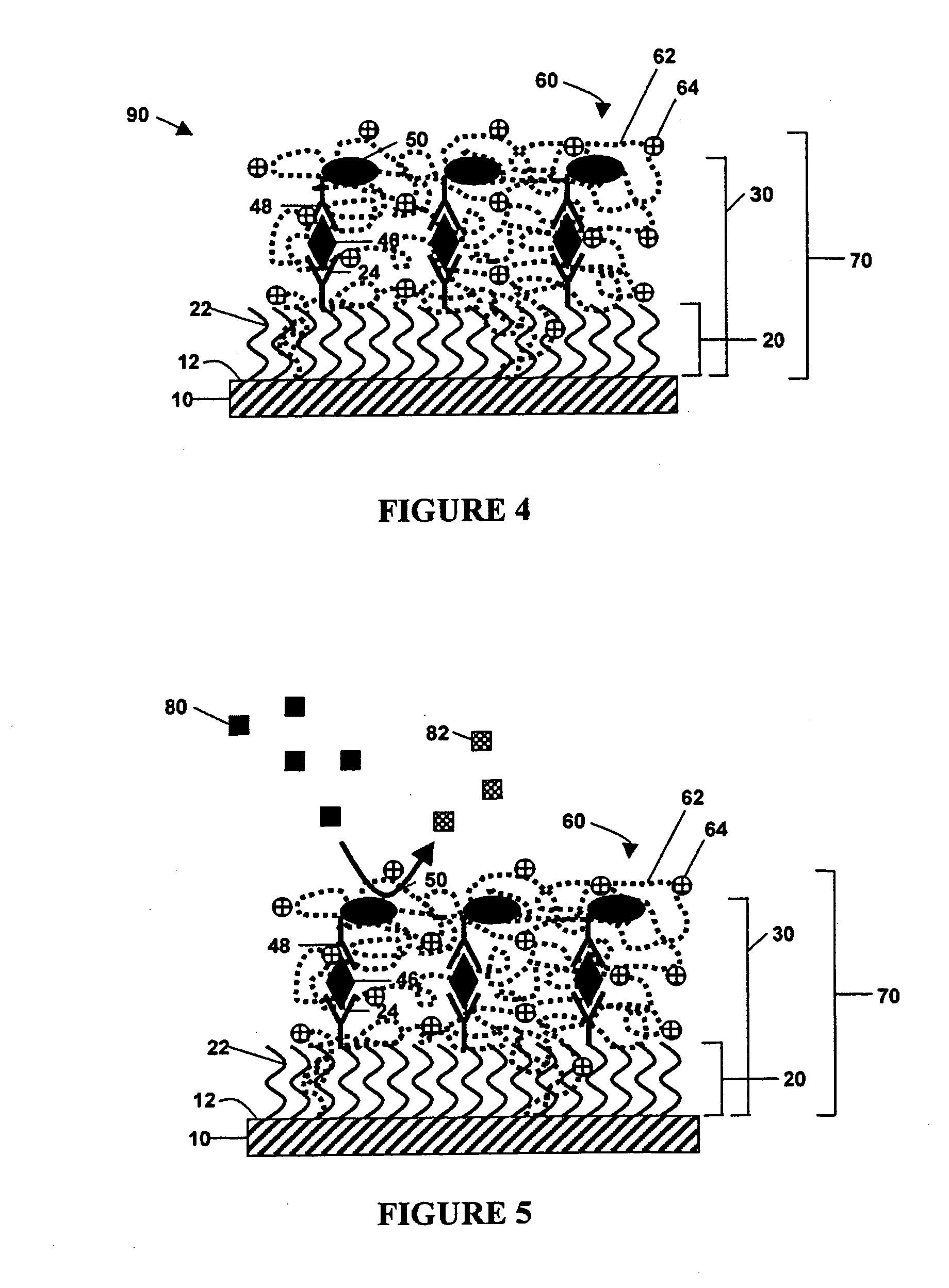
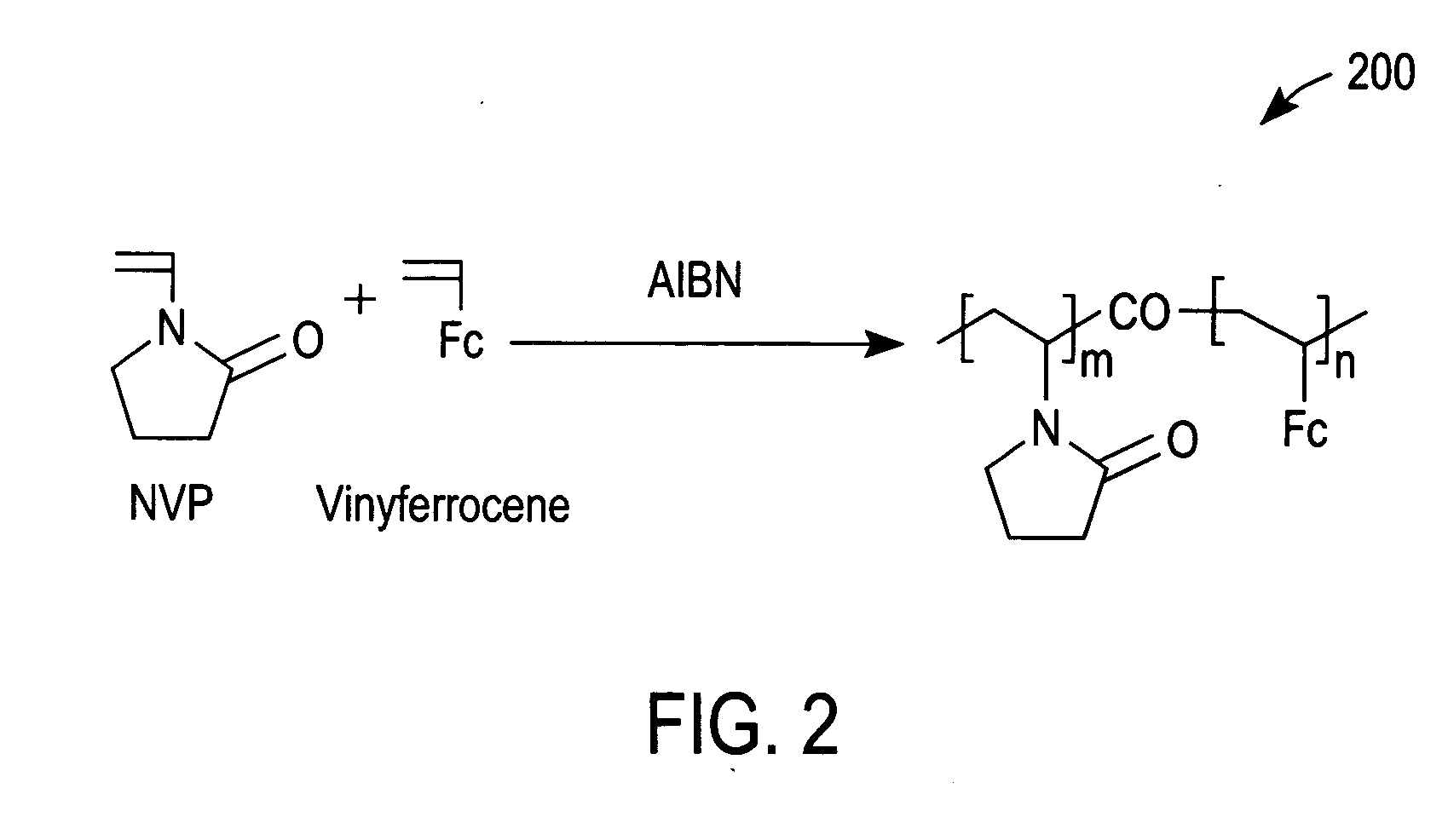
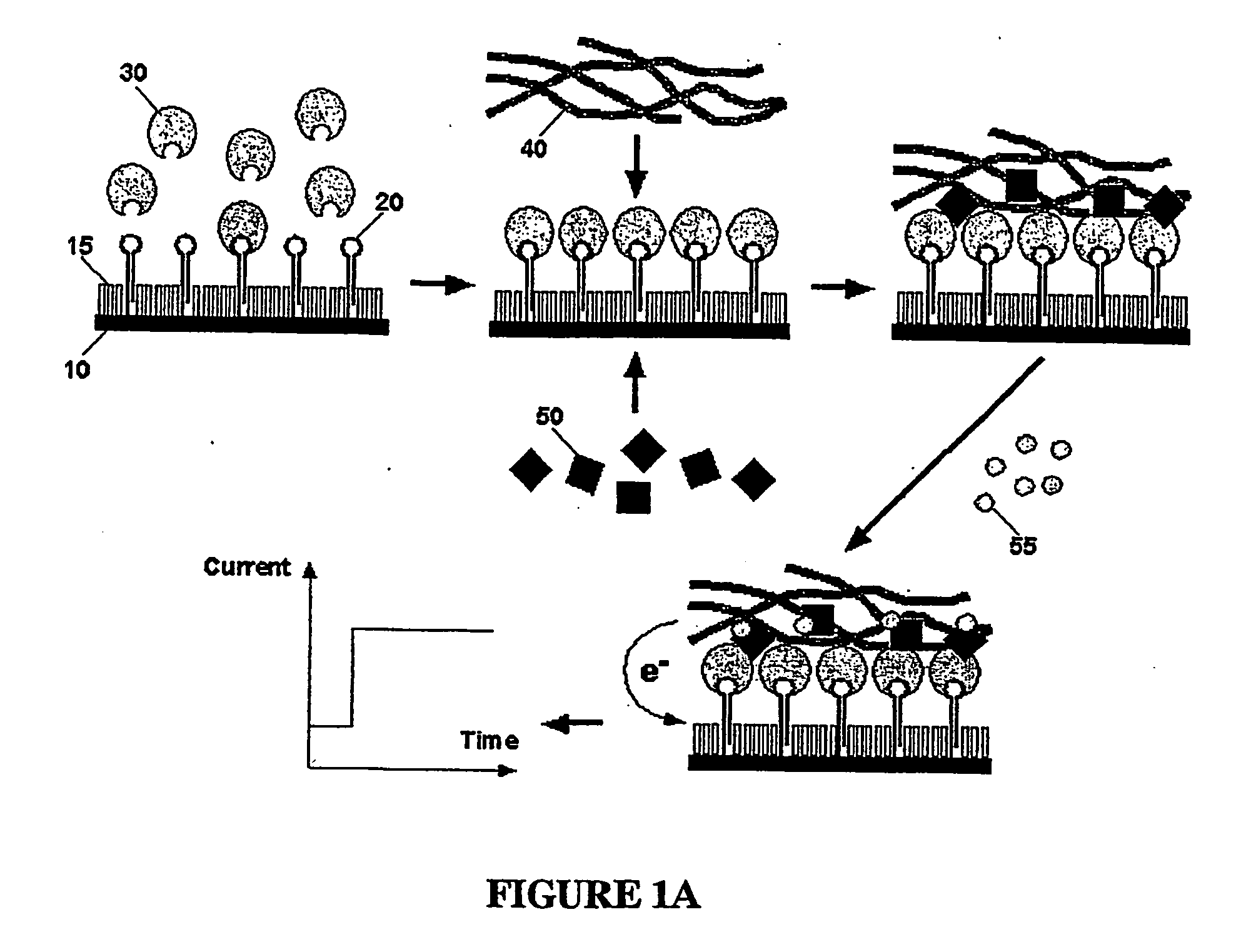
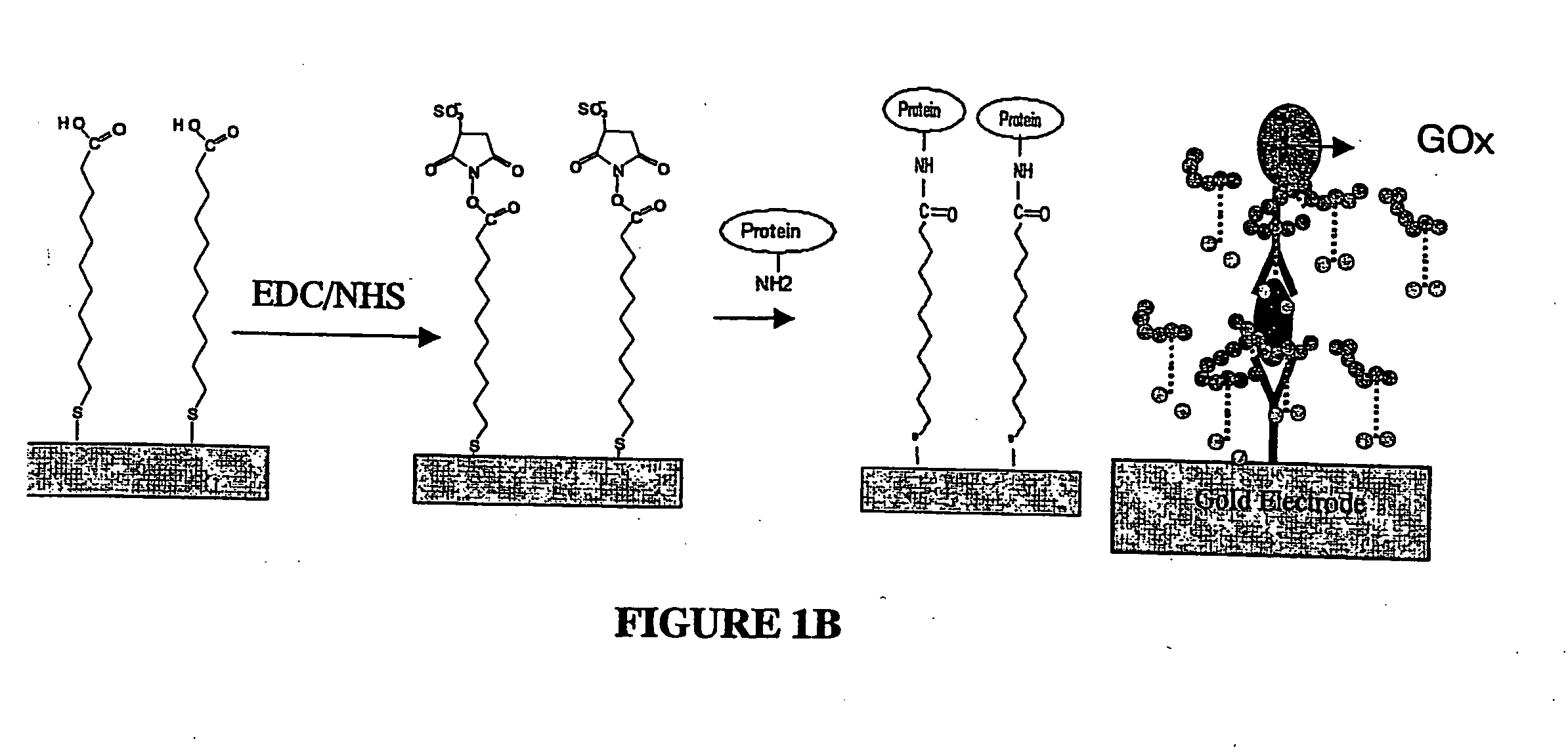
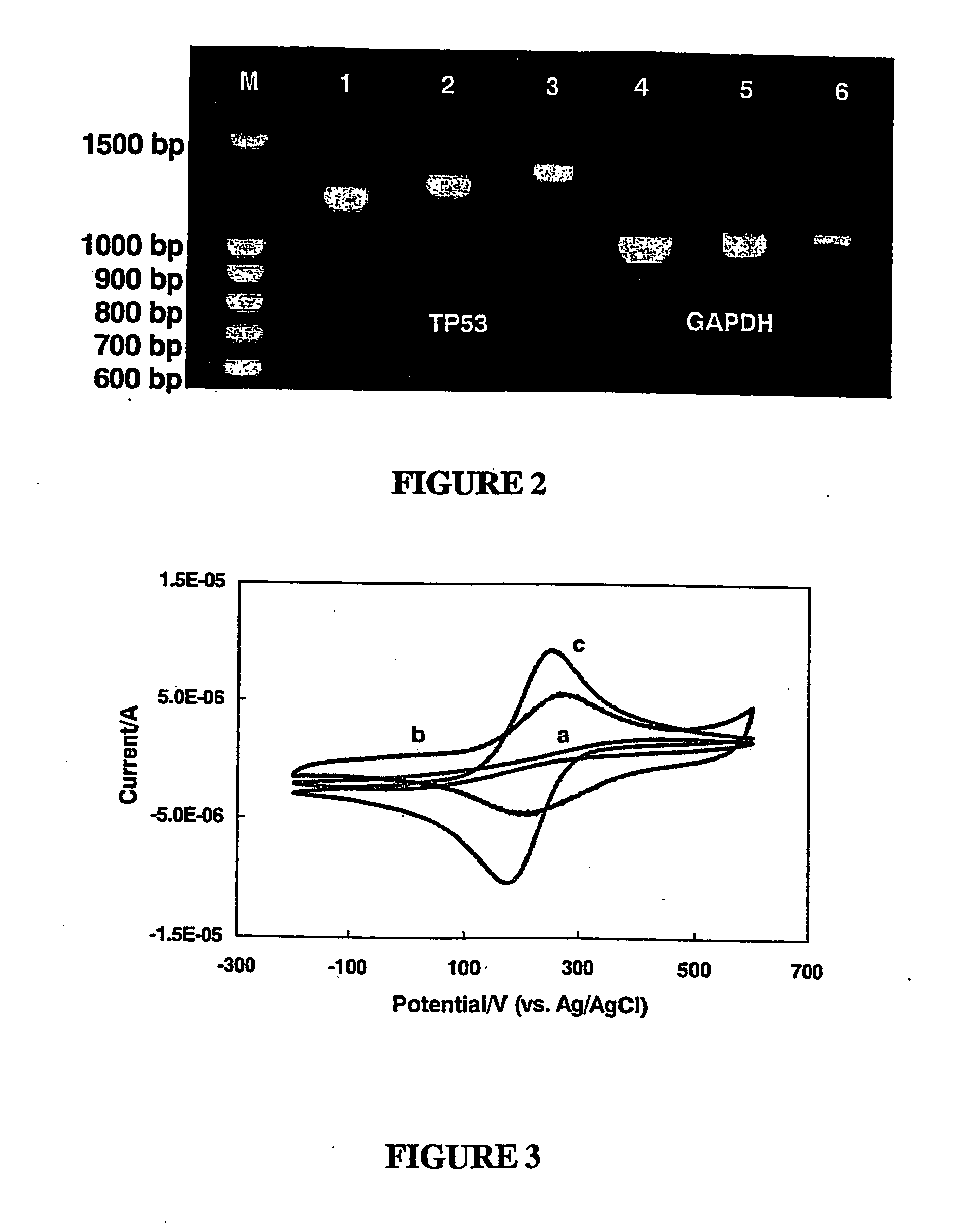
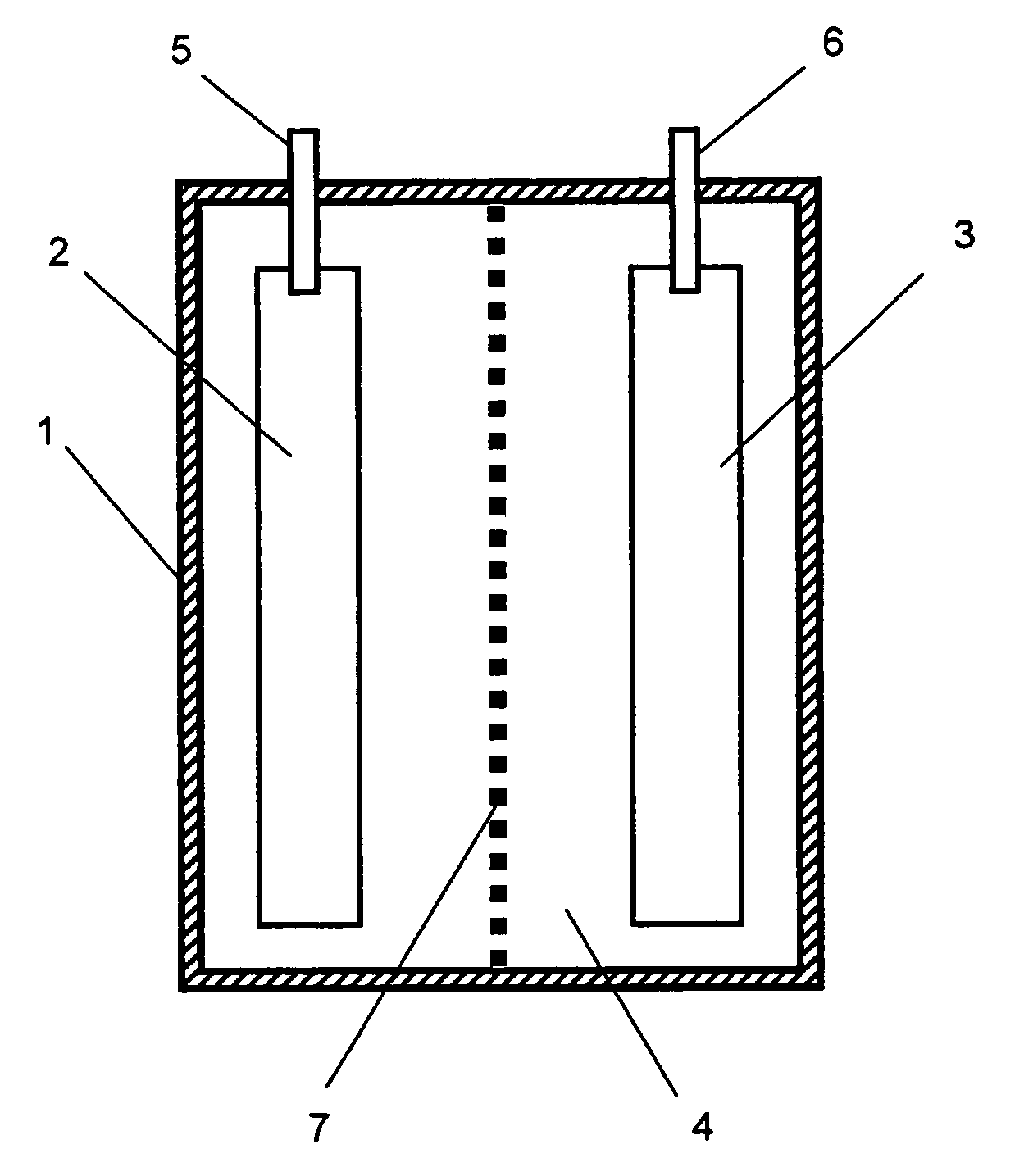
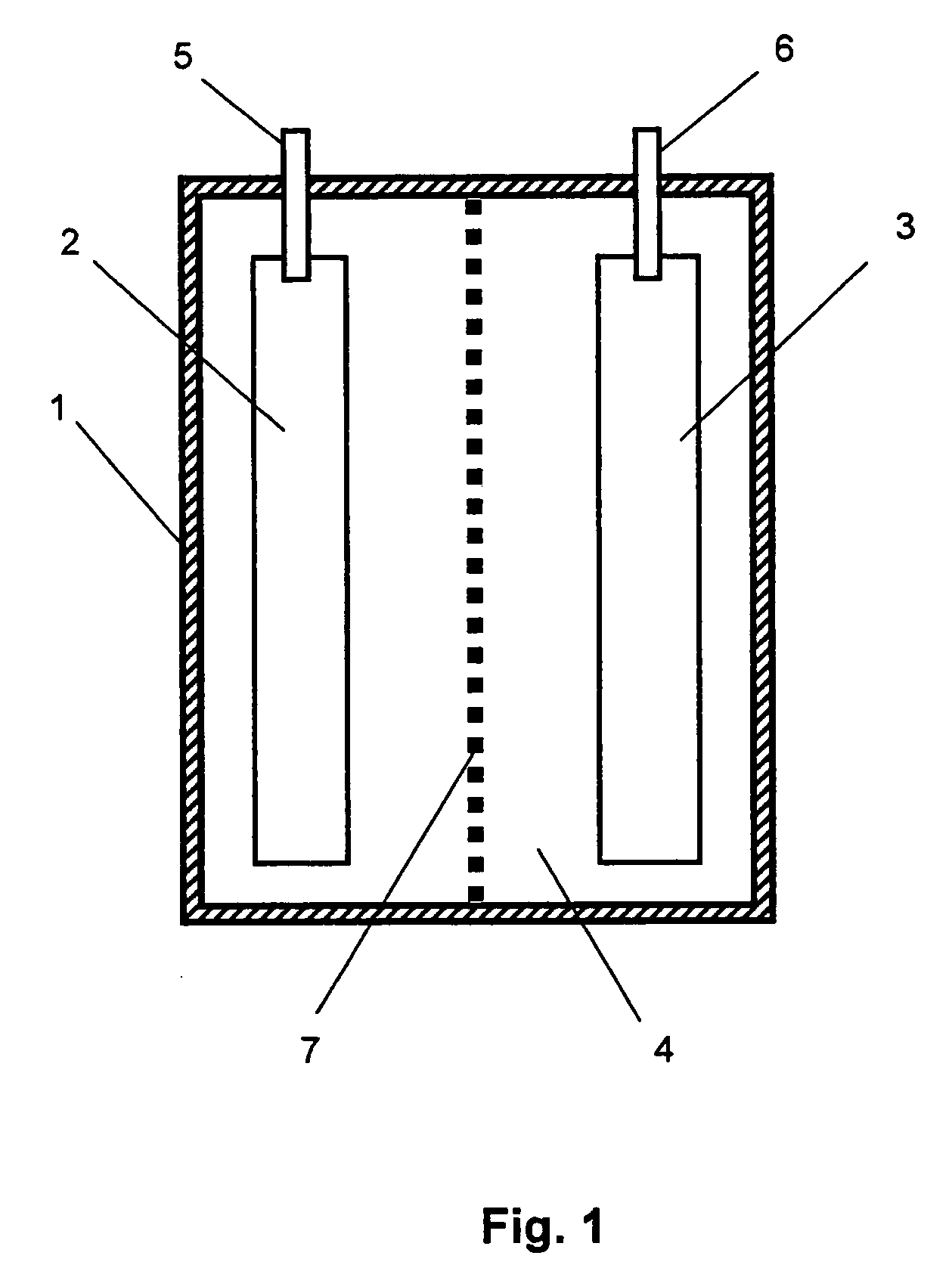
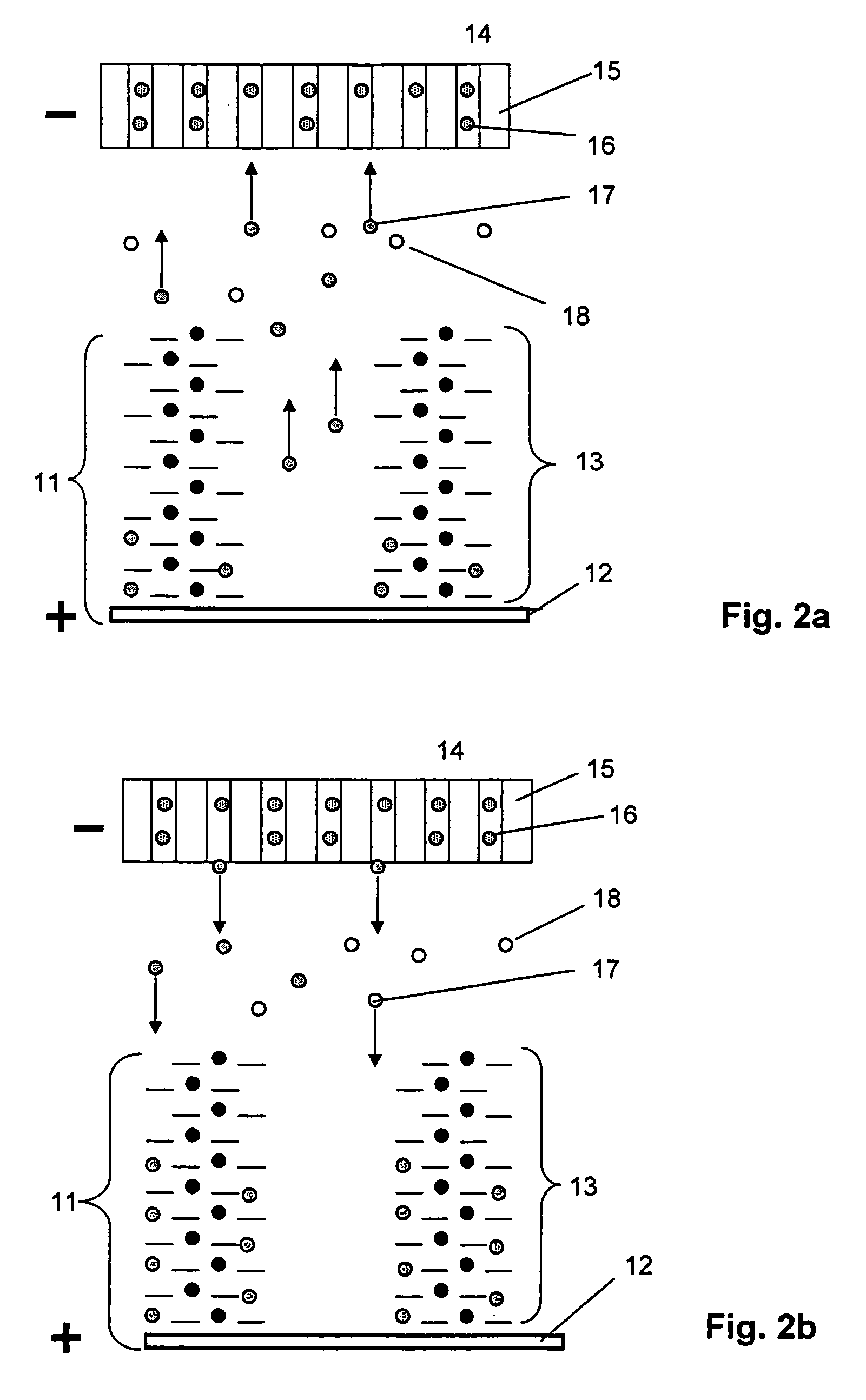
Method for detecting analytes by means of an analyte/polymeric activator bilayer arrangement
The invention relates to the field of analytical sensors. In particular, the invention relates to a method for the detection of analytes in a sample by means of an electrode arrangement, which is characterized by the formation of a conductive bilayer of analytes and an agent for increasing the conductivity of said analytes on the surface of an electrode. The invention is also directed to an electrode arrangement useful for performing such method as well as to the use of such electrode arrangement as biosensor. Also disclosed is a novel class of redox polymers that are suitable for being used in the electrochemical detection of analytes. A method of making this class of polymers is also disclosed.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Electrode for energy storage devices and electrochemical supercapacitor based on said electrode
ActiveUS7382603B2Increasing specific energy capacity of energyImprove stability and reliabilityElectrolytic capacitorsHybrid capacitor electrodesPolymer scienceRedox polymers
An electrode comprises an electrically conductive substrate, a layer of energy accumulating redox polymer deposited onto the substrate, the redox polymer comprising a polymer metal complex with a substituted tetra-dentate Schiff's base selected from the group: poly-[Me(R, R′-Schiff-Y)], wherein Me is a transition metal; Y is a bridge group binding the atoms of Nitrogen in the Schiff's base; R is an electron-donating substituent comprising a functional group (X)O—, —COO(X), where (X) is an alkali metal; R′ is Hydrogen or Halogen; and wherein the polymer metal complex has the following structure:The electrochemical capacitor comprises a case housing the above-described positive electrode and a negative electrode disposed inside the case, and an electrolyte filling the space between the electrodes.
Owner:POWERMERS
Method for detecting analytes by means of an analyte/polymeric activator bilayer arrangement
The invention relates to the field of analytical sensors. In particular, the invention relates to a method for the detection of analytes in a sample by means of an electrode arrangement, which is characterized by the formation of a conductive bilayer of analytes and an agent for increasing the conductivity of said analytes on the surface of an electrode. The invention is also directed to an electrode arrangement useful for performing such method as well as to the use of such electrode arrangement as biosensor. Also disclosed is a novel class of redox polymers that are suitable for being used in the electrochemical detection of analytes. A method of making this class of polymers is also disclosed.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Redox polymer nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060003457A1Overcomes shortcomingMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsAnalyteDiagnostic agent
The invention provides nanoparticles comprising one or more redox-active species, methods of making such nanoparticles, and methods for using such nanoparticles, for example, as diagnostic agents for the detection of various analytes.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
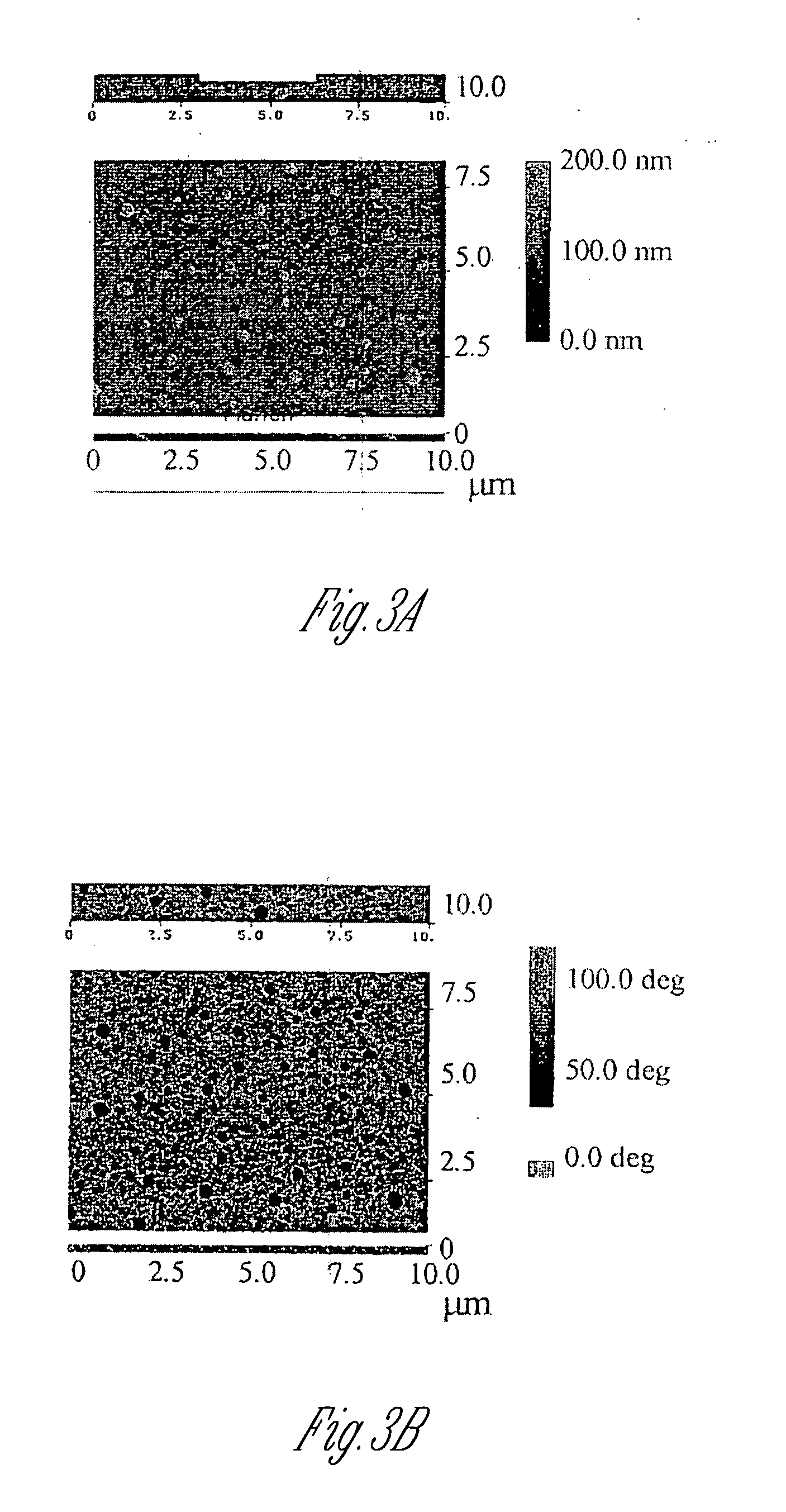
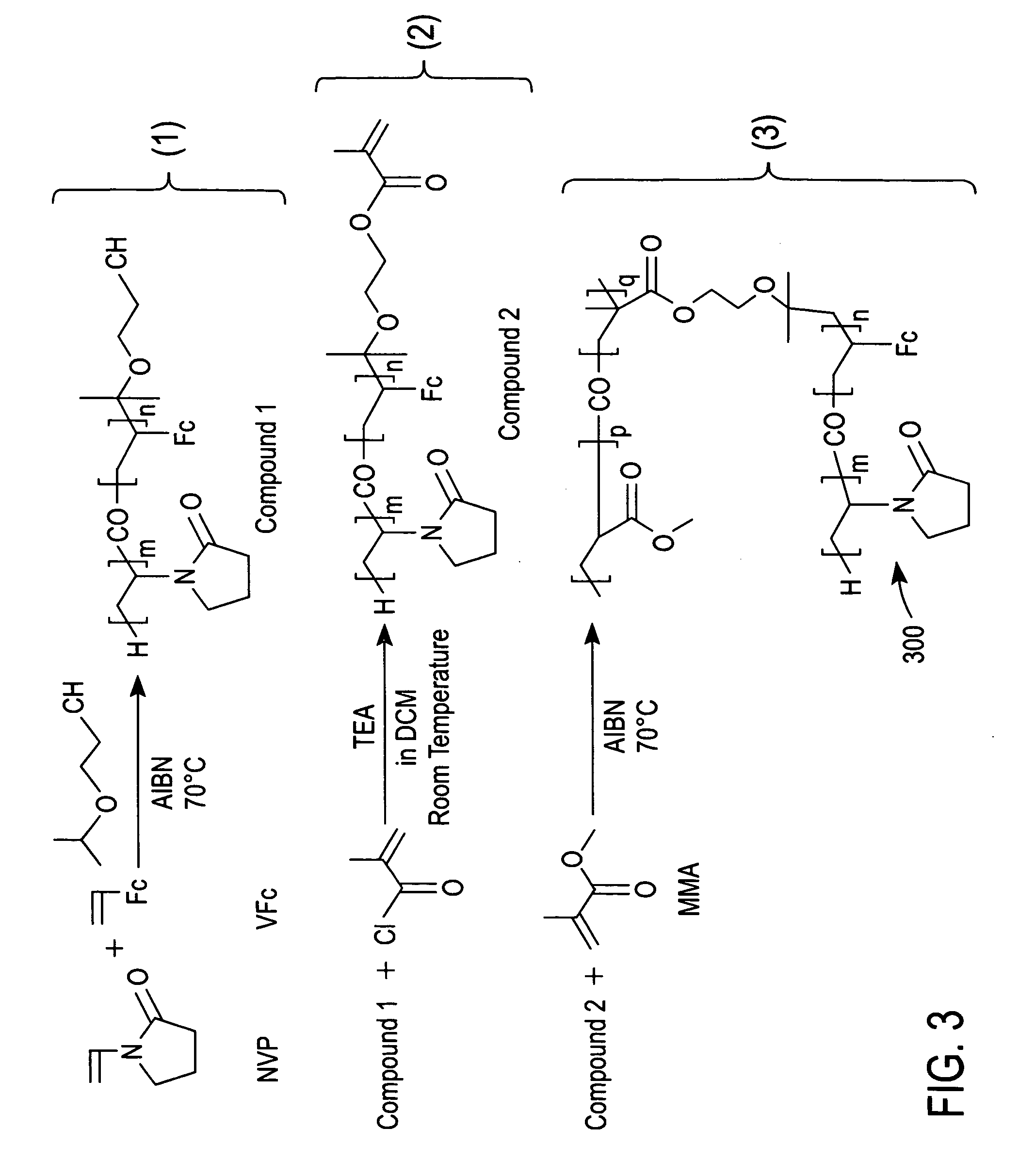
Redox polymers for use in electrochemical-based sensors
ActiveUS20060025550A1Adequate redox mediator activityAvoid leachingMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyPolymer scienceHydrophobic polymer
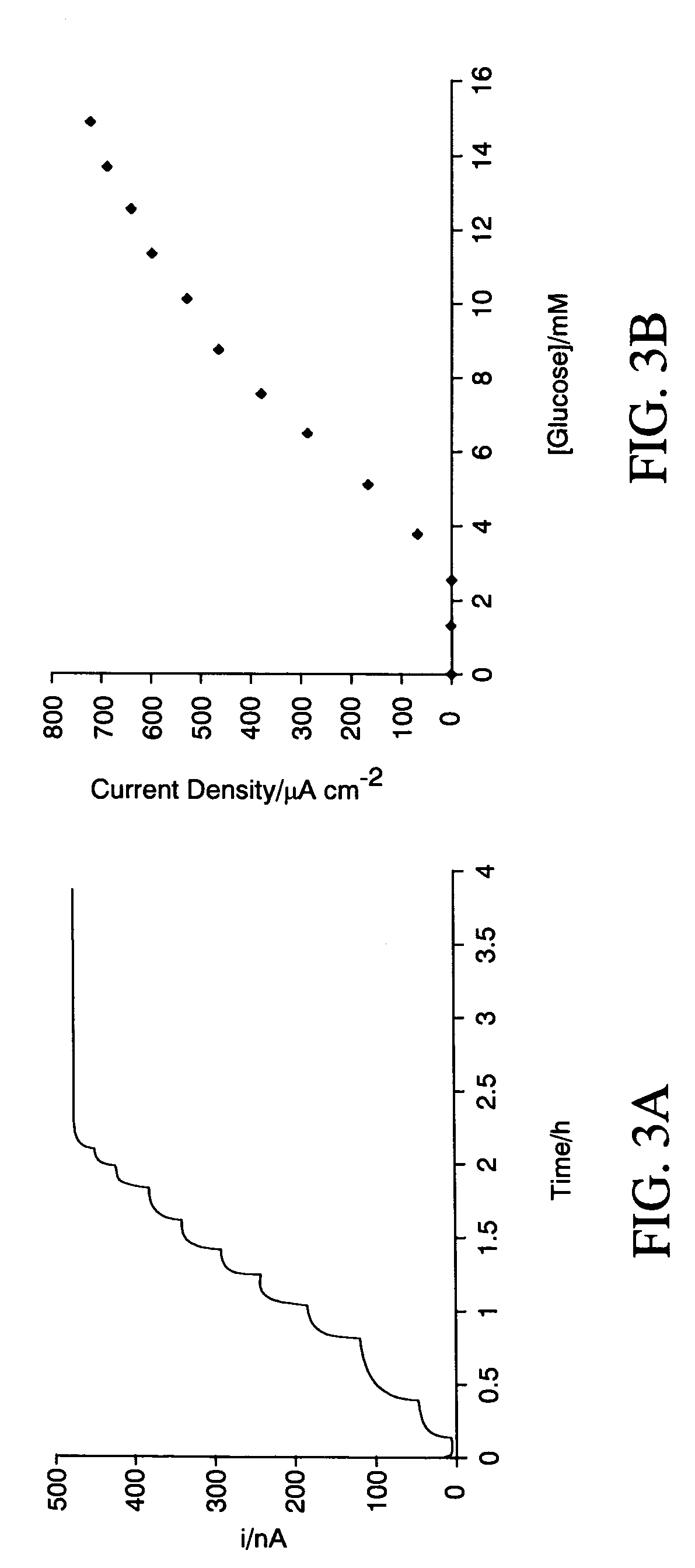
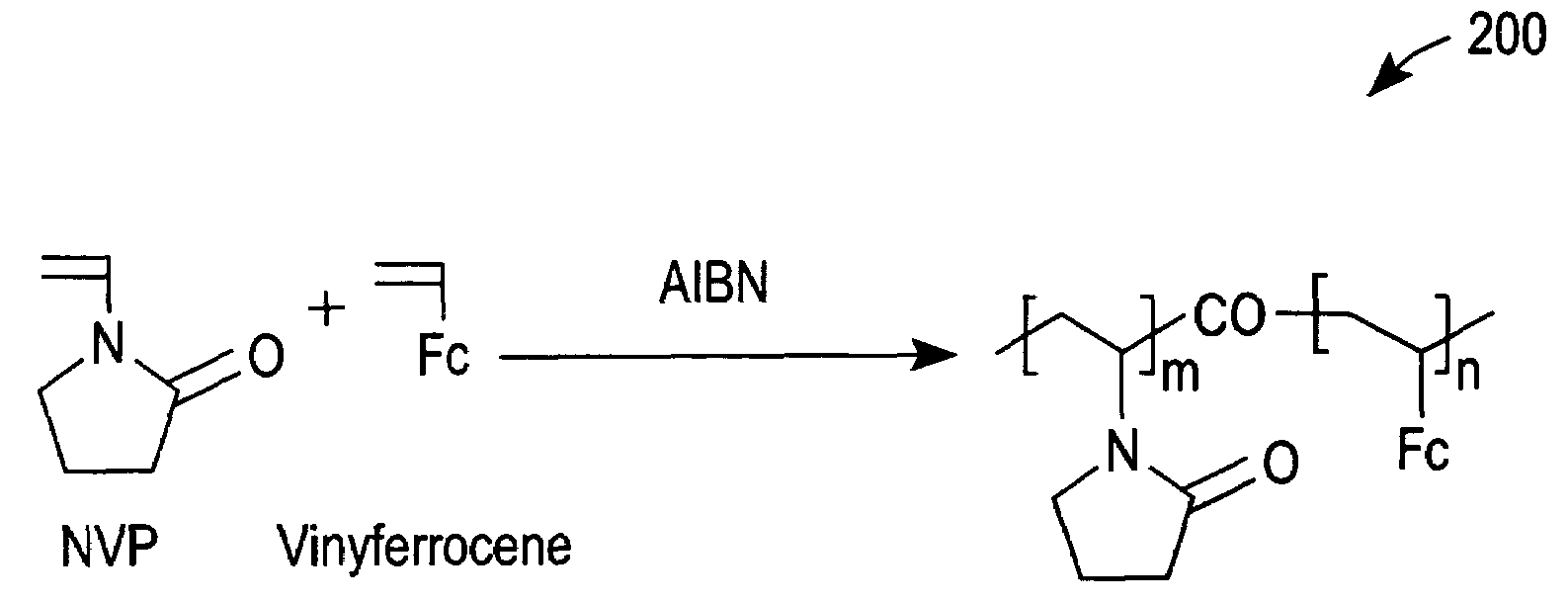
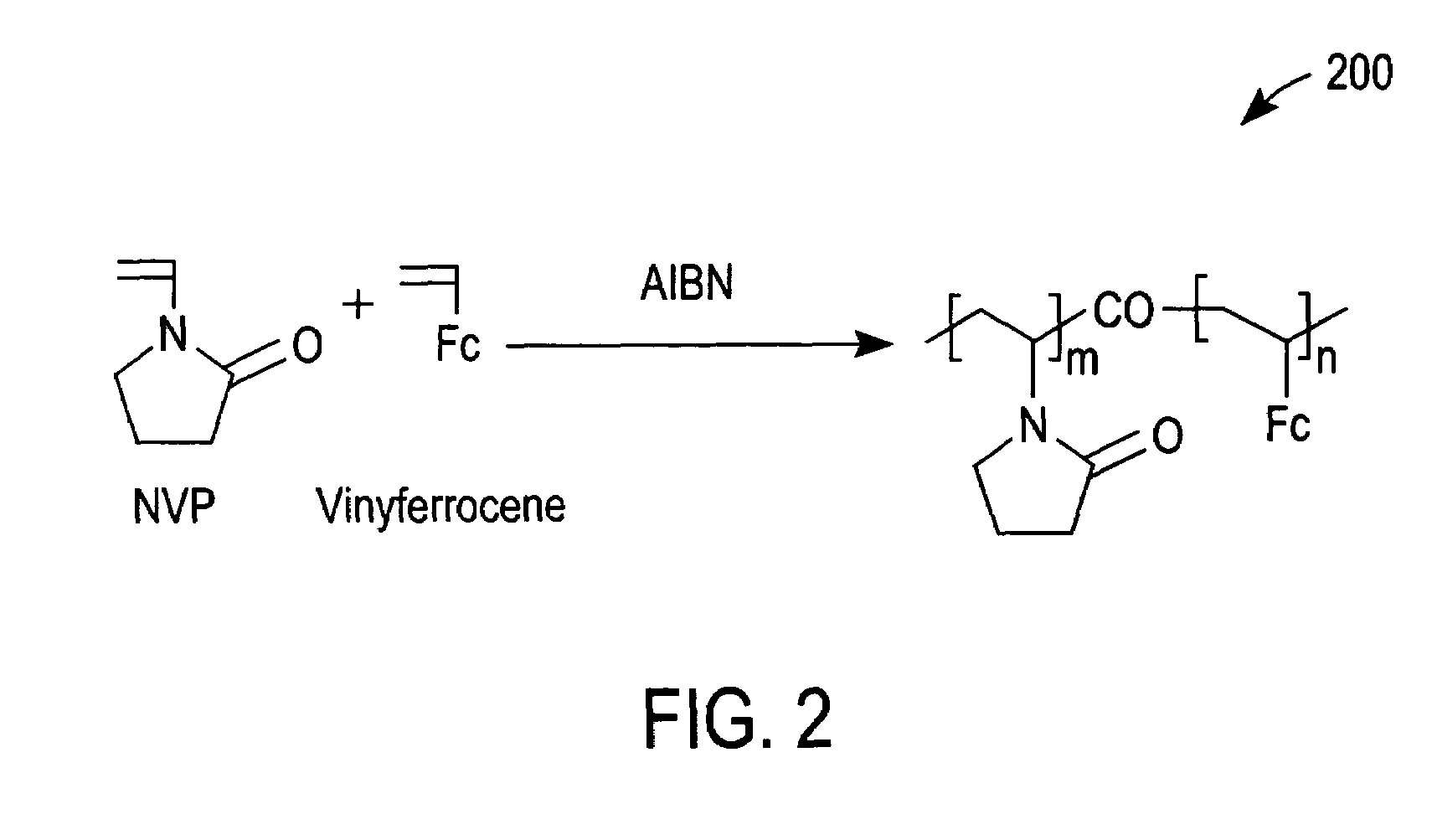
A redox polymer for use in an electrochemical-based sensor includes a hydrophobic polymer backbone (e.g., a hydrophobic poly(methyl methacrylate) polymer backbone) and at least one hydrophilic polymer arm (such as a hydrophilic oligo(N-vinylpyrrolidinone) polymer arm) attached to the hydrophobic polymer backbone. The redox polymer also includes a plurality of redox mediators (e.g., ferrocene-based redox mediators) attached to the at least one hydrophilic polymer arm.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Method of manufacture of an electrode for electrochemical devices
InactiveUS20050258042A1Quality improvementReduces probability of cross linkingElectrochemical processing of electrodesHybrid capacitor electrodesEthylenediamineSolvent
Deposition of a redox polymer of the poly-Me(R-Salen) type onto a conducting substrate by electrochemical polymerization is disclosed. Said polymerization occurs at a voltage applied between the substrate and a counter-electrode, both of which are submerged into the electrolyte. The electrolyte contains an organic solvent, compounds capable of dissolving in the solvent and forming electrochemically inactive ions at concentrations of no less than 0.01 mol / l within the range of potentials from −3.0 V to +1.5 V, and a metal complex poly-[Me(R-Salen)] dissolved at a concentration of no less than 5×10−5 mole / liter. Me is transition metal having at least two different degrees of oxidation, R is an electron-donating substituent, Salen is a residue of bis(salicylaldehyde)-ethylenediamine in Schiff' s base). Deposition of the redox occurs in the electrolyte where the cations of the compounds have a diameter larger than that of the electrolyte cations of energy storing device containing the electrode.
Owner:GEN3 PARTNERS INC
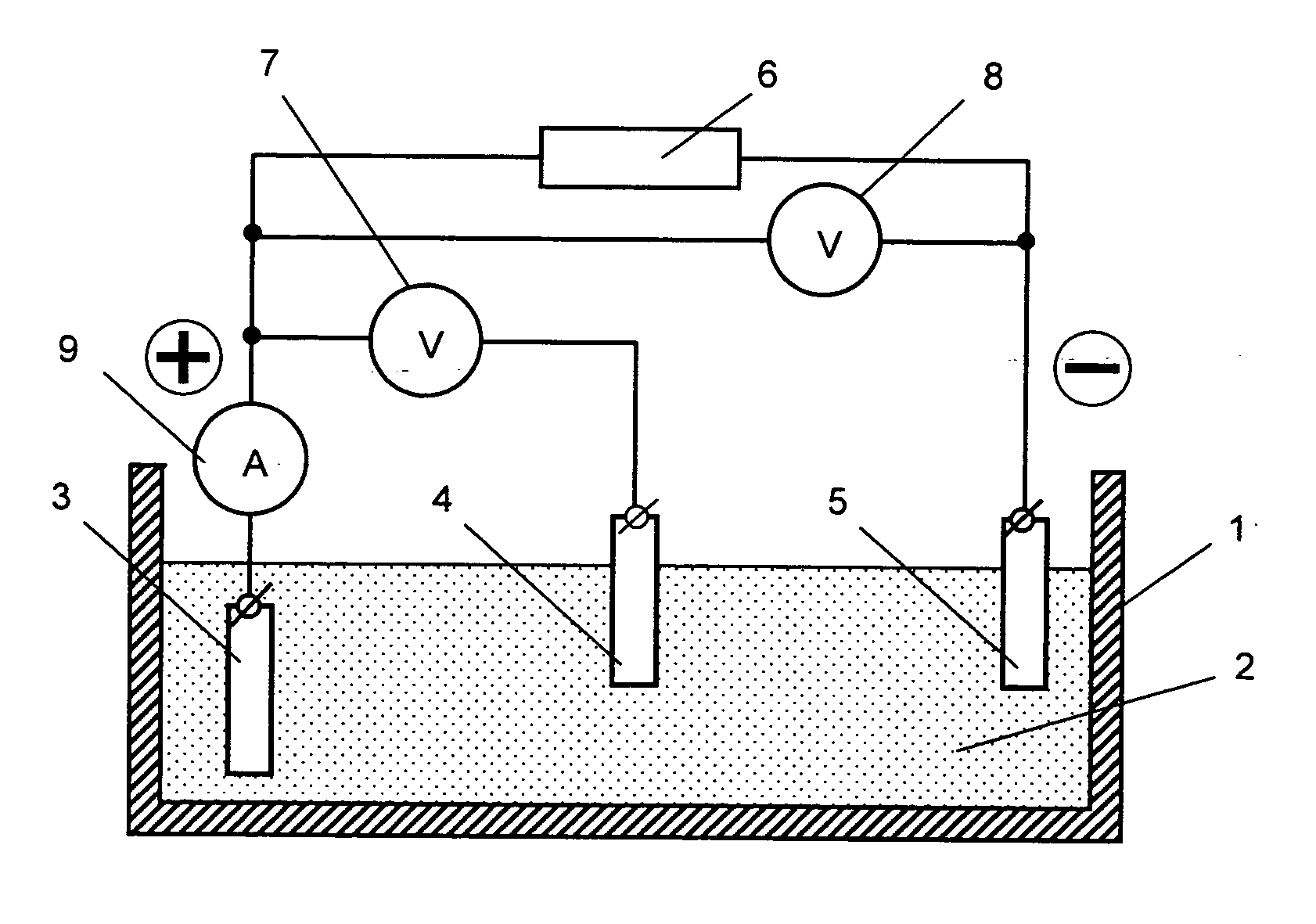
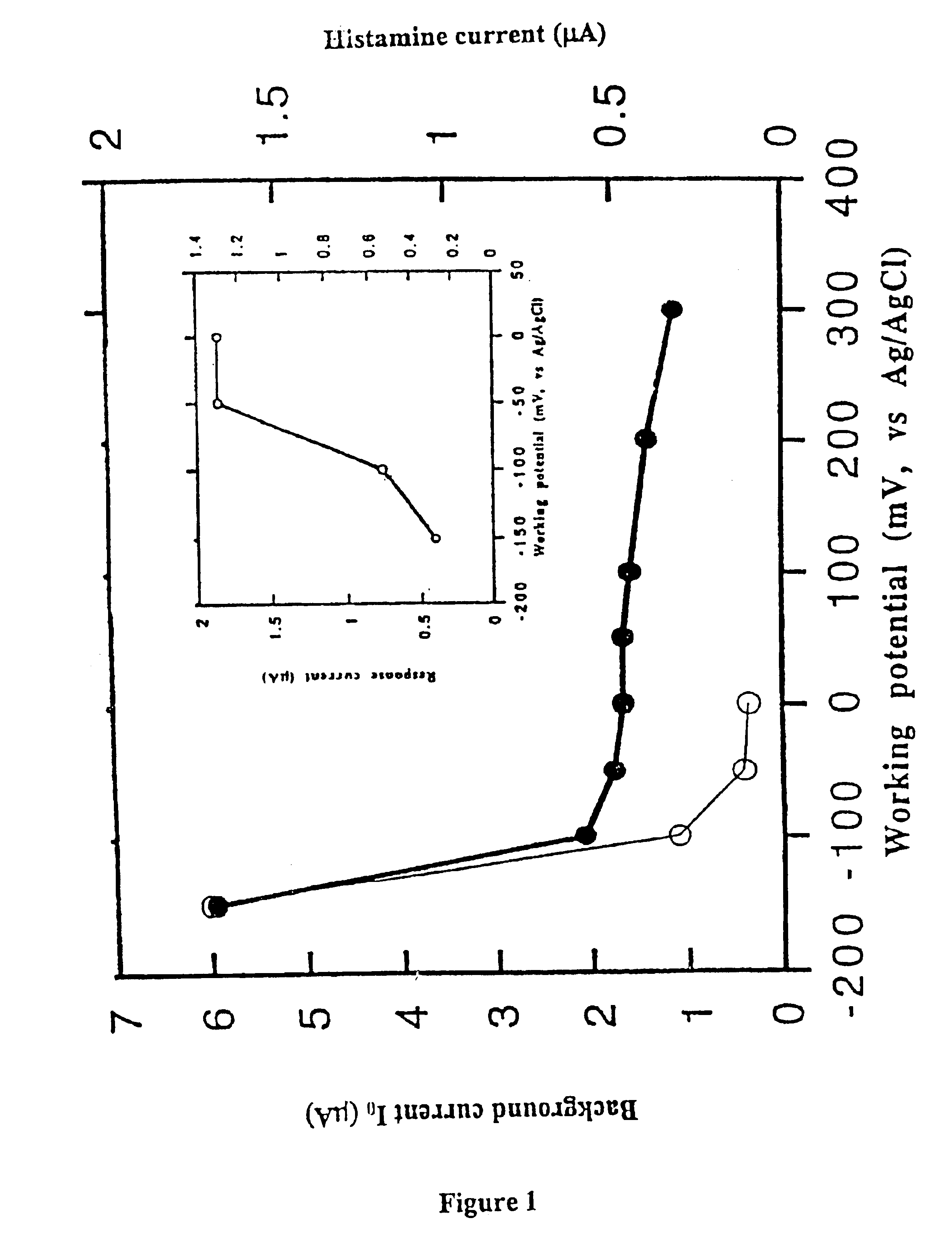
Biosensor
InactiveUS6897035B1Rapid and accurate and simple and handyRapid, accurate, simple and handy analytical instrumental toolMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPeroxidaseEnzyme system
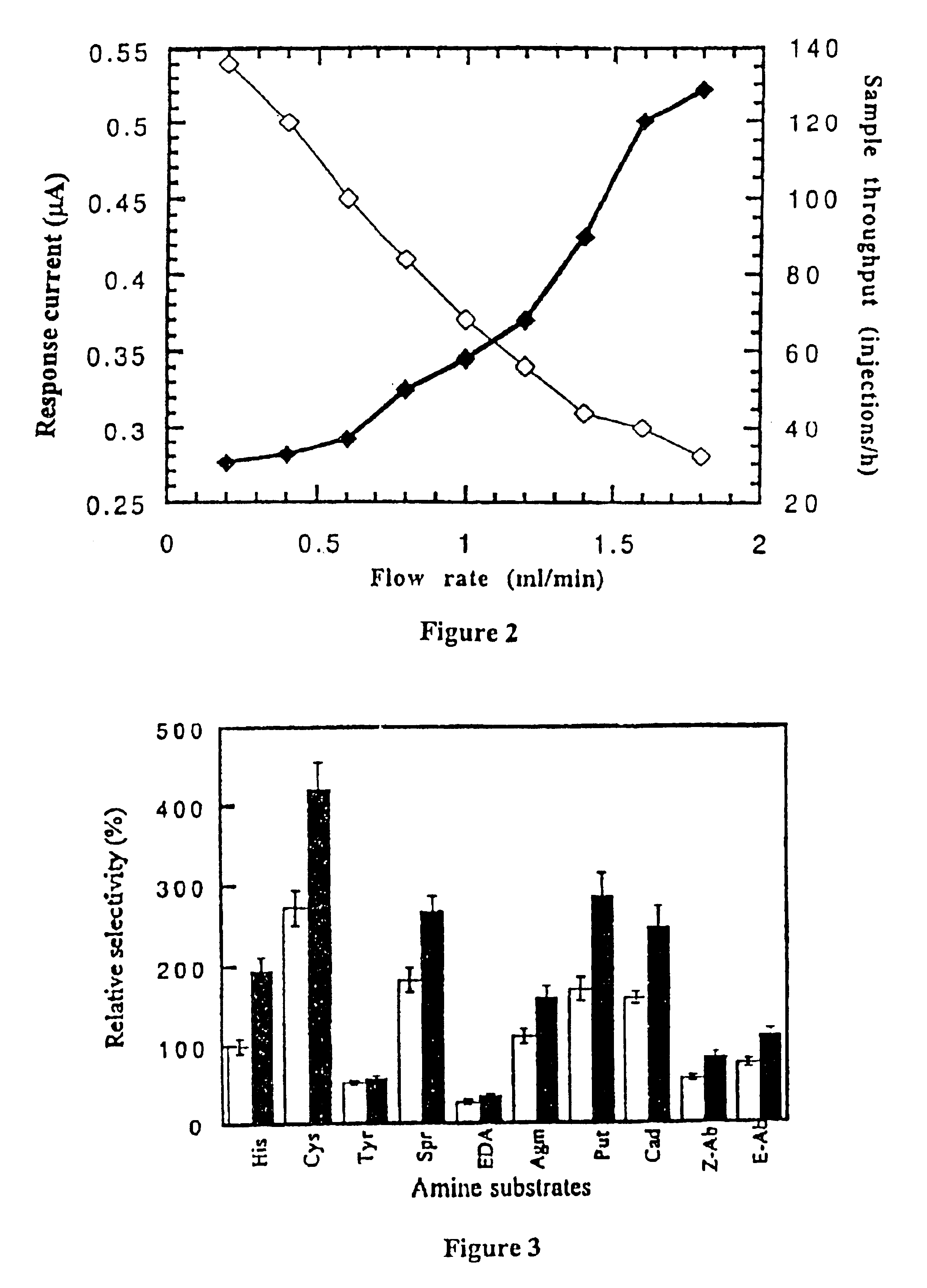
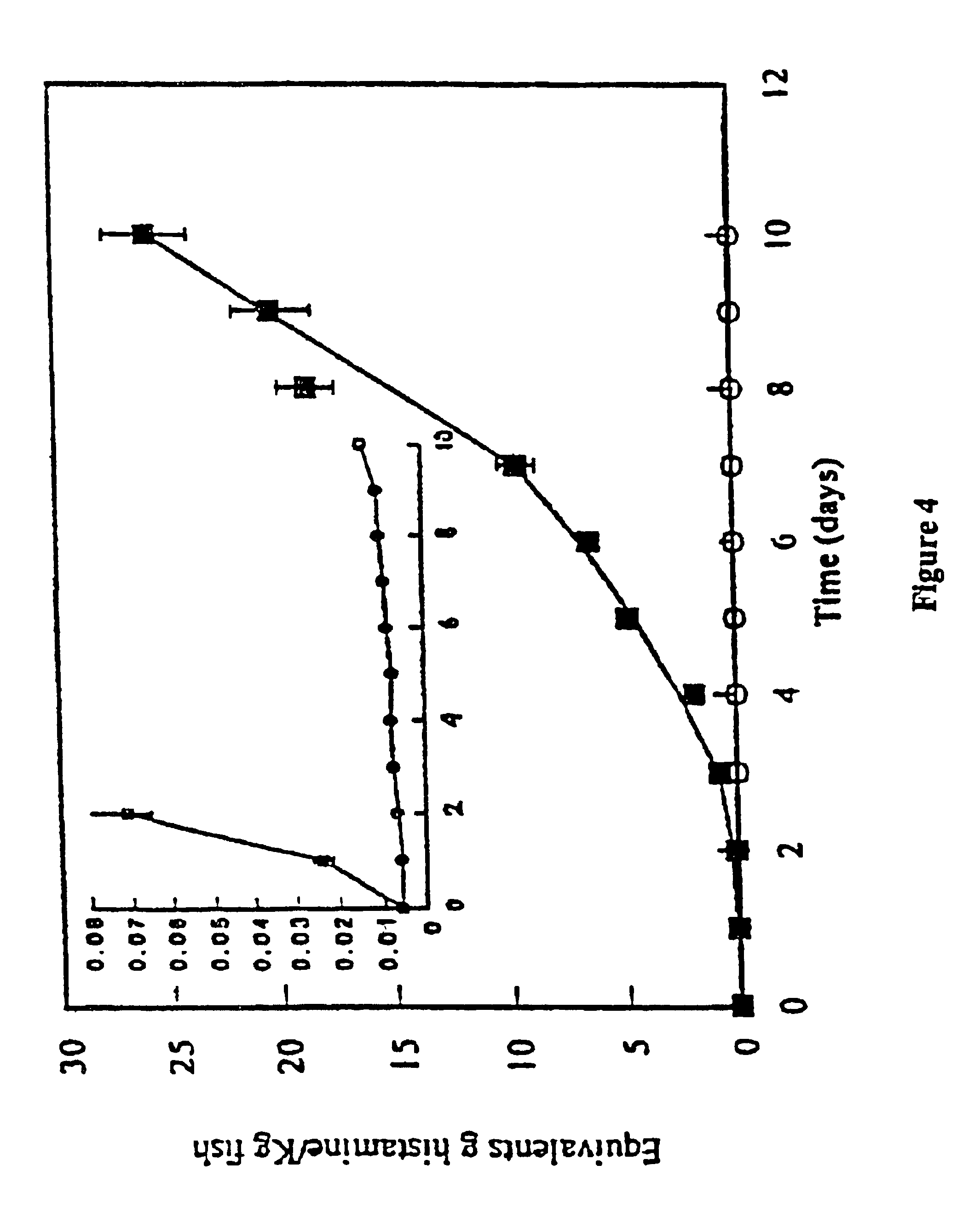
The present invention relates to a biosensor for the detection and / or the determination of freshness biomarkers, such as biogenic amines (preferably histamine) in food and beverage, comprising an electrode and a mono-enzyme system, such as an amine oxidase, or a bi-enzyme system of an amine oxidase and a peroxidase. The enzymes are optionally crosslinked into an osmium based redox polymer.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Ionic hydrophilic high molecular weight redox polymers for use in enzymatic electrochemical-based sensors
ActiveUS20060069211A1Solve the lack of activityReduce leachingMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
Ionic hydrophilic high molecular weight redox polymers for use in enzymatic electrochemical-based sensors include a hydrophilic polymer (such as a hydrophilic polymer backbone) with ionic portions (e.g., cationic monomers incorporated in the hydrophilic polymer backbone) and a plurality of attached redox mediators. The redox mediators can be, for example, covalently attached to the hydrophilic polymer in a pendant manner. An exemplary cationic hydrophilic high molecular weight redox polymer is synthesized by co-polymerization of a hydrophilic acrylamide monomer, [2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethyl ammonium chloride and vinyl ferrocene.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Thermally self-chargeable flexible energe storage device and method of forming and operating the same
ActiveUS20200295370A1Hybrid capacitor separatorsLead-acid accumulatorsPorous substratePolyelectrolyte
An energy storage device and method of forming and operating the same. In one embodiment, the energy storage device includes a positive electrode including a first redox polymer deposited on a first conductive porous substrate. The energy storage device also includes a solid-state polyelectrolyte separator operative as a voltage generator, and a negative electrode including a second redox polymer deposited on a second conductive porous substrate, thereby forming an electrochemical cell.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Devices and systems for elution of biomolecules
A device and a system for eluting biomolecules from biological sample by electroelution are provided. The device for electroelution of biomolecules from a biological sample is constituted with a housing configured to receive an electrolyte and the biological sample, at least two electrodes comprising conductive redox polymers operationally coupled to the housing, and a biomolecule impermeable layer disposed on at least one of the electrodes. The biomolecule impermeable layer disposed on at least one of the electrodes to prevent the biomolecules from reaching the electrode. A system is provided, wherein the system comprises a sample collection port, one or more reservoirs comprising a buffer, a solvent, a reagent or combinations thereof, an device for electroelution, and a controller.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Method for the manufacture of electrode for energy-storage devices
ActiveUS20050217998A1Quality improvementIncreased specific energy capacityElectrochemical processing of electrodesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsEthylenediamineSolvent
Application of a redox polymer of the poly-[Me(R-Salen)] type onto a conducting substrate is accomplished by the method of electrochemical polymerization. Said polymerization is accomplished by supplying a voltage between the substrate (that serves as an anode) and a counter electrode (that serves as a cathode), with both of them being submerged into the electrolyte containing an organic solvent and the compounds capable of dissolving in said solvent. The process is accompanied by the production of electrochemically inactive (at concentrations of no less than 0.01 mol / l) ions within the range of potentials from −3.0 V to +1.5 V, and metal complex [Me(R-Salen)] dissolved at a concentration of no less than 5·10−5 mol / l, (where: Me is a transition metal having at least two different degrees of oxidation, R is an electron-donating substituent, Salen is a residue of bis-(salicylaldehyde)-ethylenediamine in Schiff's base.
Owner:POWERMERS
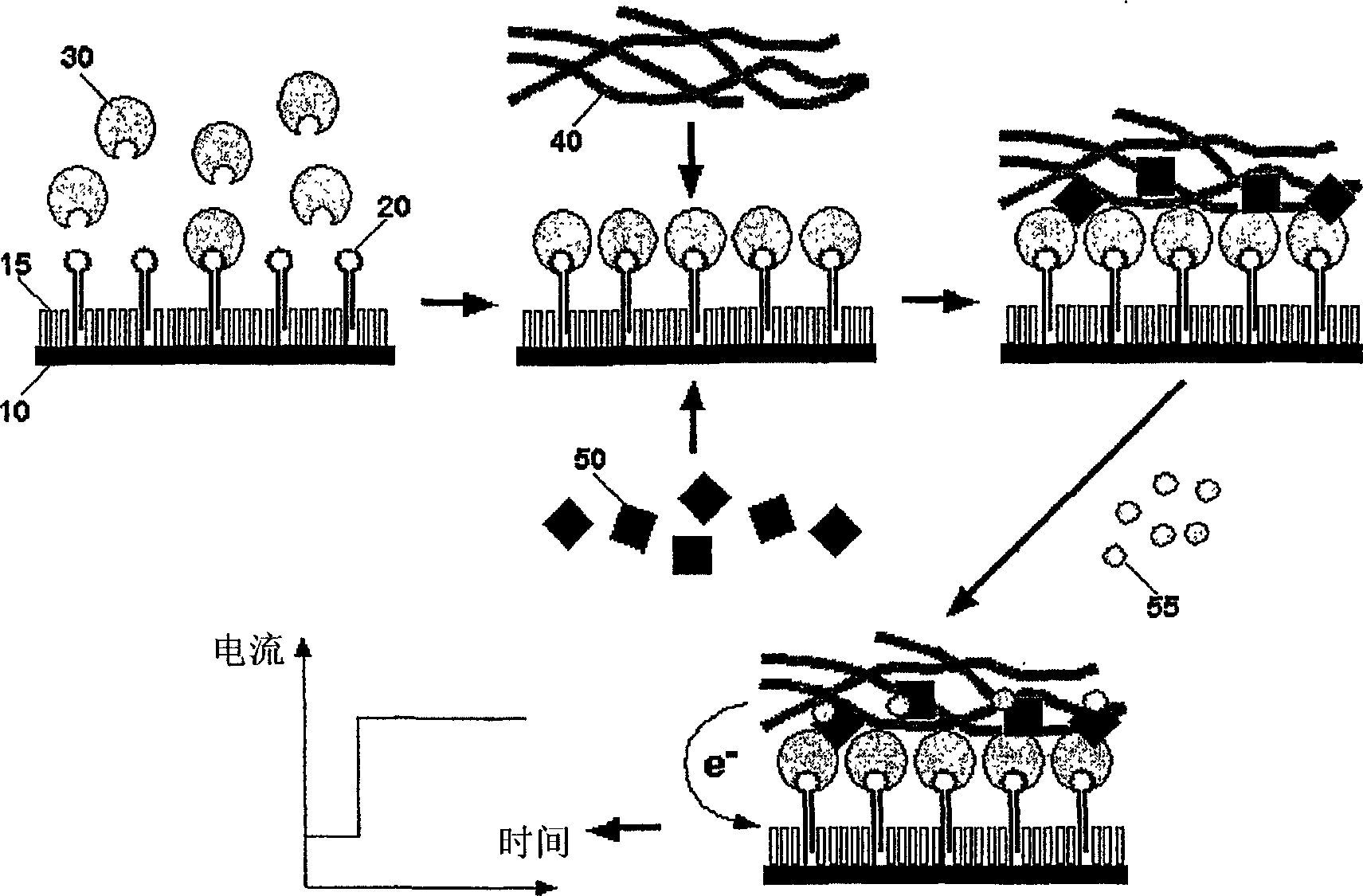
Immunoassay
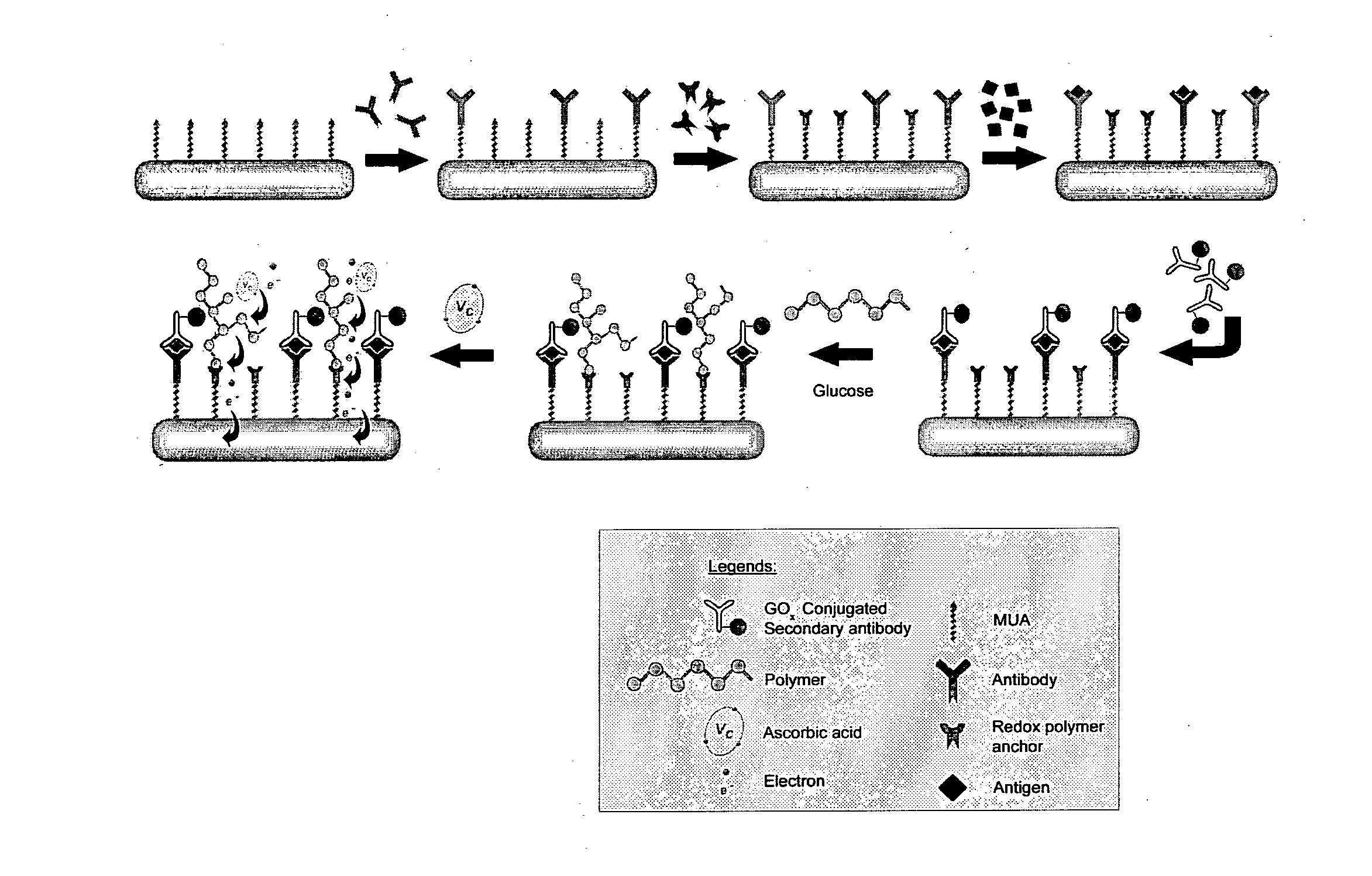
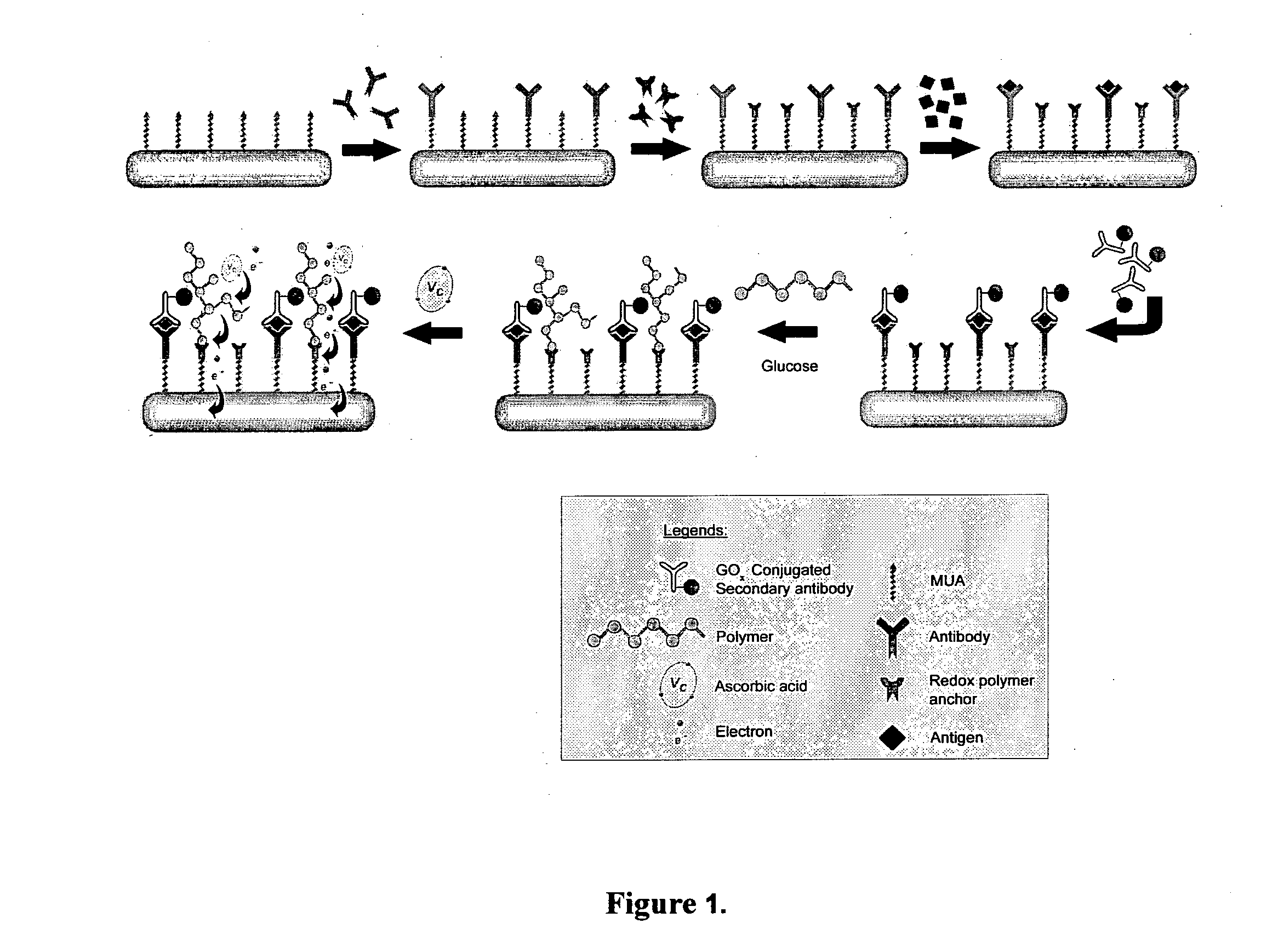
InactiveUS20110189705A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRedox enzymesAntigen binding
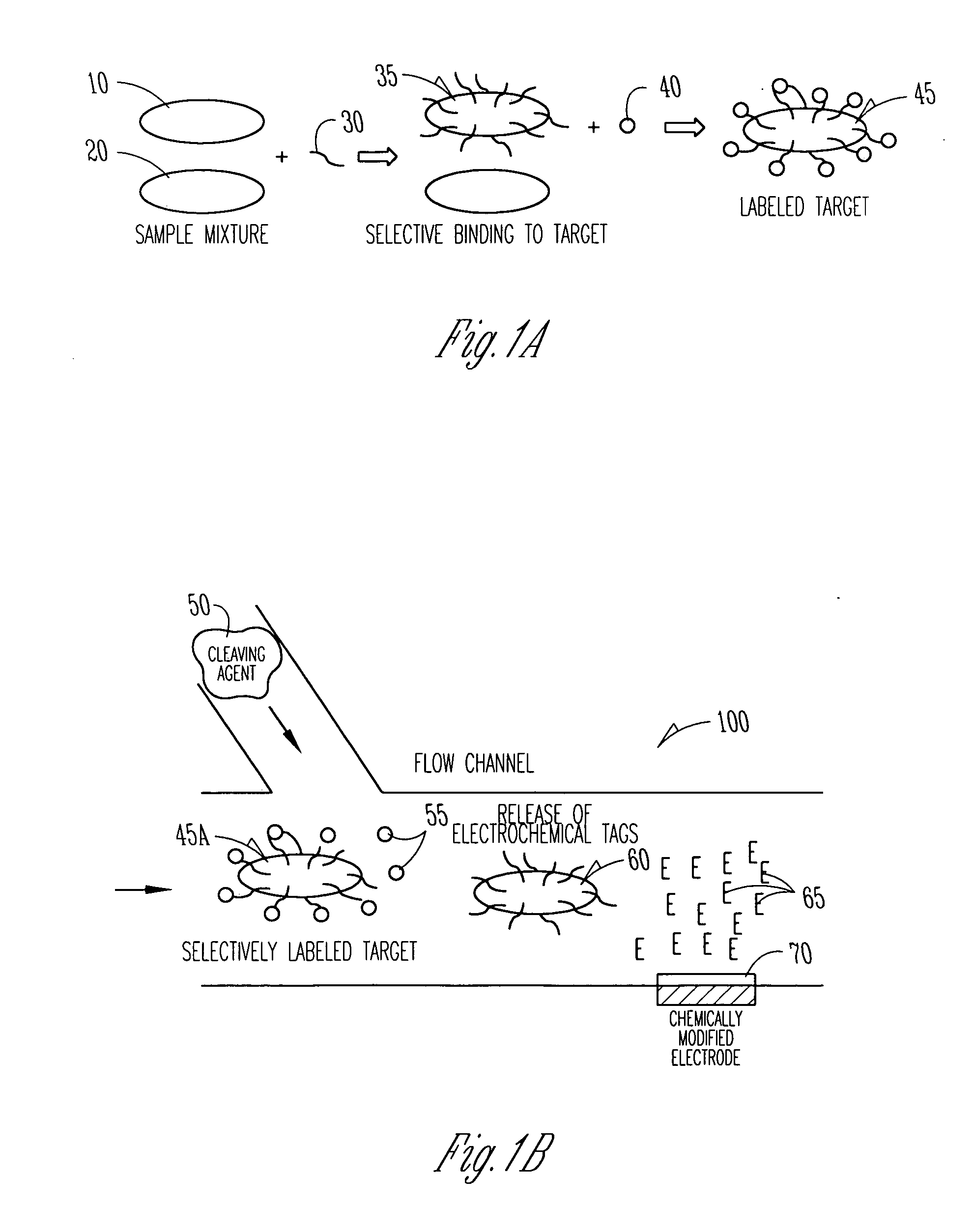
The invention provides a highly sensitive immunoassay for detection of a biological species. The immunoassay comprises exposing an electrode to an analyte liquid putatively containing the biological species so as to couple the biological species, if present in the analyte liquid, to a binding antibody on the electrode. The electrode comprises a binding antibody and an anchor group, each being coupled to an electrically conductive substrate, said binding antibody being capable of binding to the biological species and said anchor group being capable of binding to a redox polymer. The electrode is then exposed to an antibody-enzyme liquid comprising an antibody-enzyme species, said antibody-enzyme species comprising a detection antibody capable of binding to the biological species, said detection antibody being coupled to a redox enzyme, whereby, if the analyte liquid comprises the biological species, the redox enzyme couples to the electrode by means of the coupling of both the detection antibody and the binding antibody to the biological species. The electrode is then exposed to a polymer solution comprising the redox polymer and to an enzyme substrate, whereby if the redox enzyme is coupled to the anchor group on the electrode the redox polymer is reduced and couples to the anchor group on the electrode. A voltage is then applied between the electrode and a reference electrode and the electrode is exposed to an oxidisable species, whereby a magnitude of an electric current between said electrode and a reference electrode is indicative of the presence or absence of the biological species.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Electrochemical capacitor and method of use
InactiveUS7292431B2Restore characteristicElectrode manufacturing processesHybrid capacitor electrodesSolvent2-hydroxybenzaldehyde
The invention is an electrochemical capacitor with its electrodes made on a conducting substrate with a layer of a redox polymer of the poly[Me(R-Salen)] type deposited onto the substrate. Me is a transition metal (for example, Ni, Pd, Co, Cu, Fe), R is an electron-donating substituent (for example, CH3O—, C2H5O—, HO—, —CH3), Salen is a residue of bis(salicylaldehyde)-ethylendiamine in Schiff's base. The electrolyte comprises of an organic solvent, compounds capable of dissolving in such solvents with the resulting concentration of no less than 0.01 mol / l and dissociating with the formation of ions, which are electrochemically inactive within the range of potentials from −3.0 V to +1.5 V (for example, salts of tetramethyl ammonium, tetrapropyl ammonium, tetrabutyl ammonium), and a dissolved metal complex [Me(R-Salen)]. The method of using the capacitor contemplates periodically alternating the connection polarity of the electrodes, causing the electrochemical characteristics of the electrodes to regenerate.
Owner:POWERMERS
Method of Manufacture of an Energy Storage Device
InactiveUS20100188801A1Reduces probability of cross linkingIncrease capacityElectrochemical processing of electrodesLiquid electrolytic capacitorsEthylenediamineSalicylaldehyde
A method of preparing an energy-storage device is disclosed, which involves deposition of a redox polymer of the poly-Me(R-Salen) type onto a conducting substrate by electrochemical polymerization to prepare an electrode for use in the energy-storage device. Polymerization occurs at a voltage applied between the substrate and a counter-electrode, both of which are submerged in an electrolyte. The electrolyte contains an organic solvent, compounds capable of dissolving in the solvent and forming electrochemically inactive ions at concentrations of no less than 0.01 mol / L within the range of potentials from −3.0 V to +1.5 V, and a metal complex polymer represented by the formula poly-[Me(R-Salen)] dissolved at a concentration of no less than 5×10−5 mol / L, wherein Me is a transition metal having at least two different degrees of oxidation, R is an electron-donating substituent, and Salen is a residue of bis(salicylaldehyde)-ethylenediamine. Deposition of the redox polymer occurs in an electrolyte in which the cations have a diameter that is larger than the diameter of the cations of the electrolyte employed in the energy-storage device for which the electrode is manufactured.
Owner:LYUBOMIRSKIY ALEXANDER +7
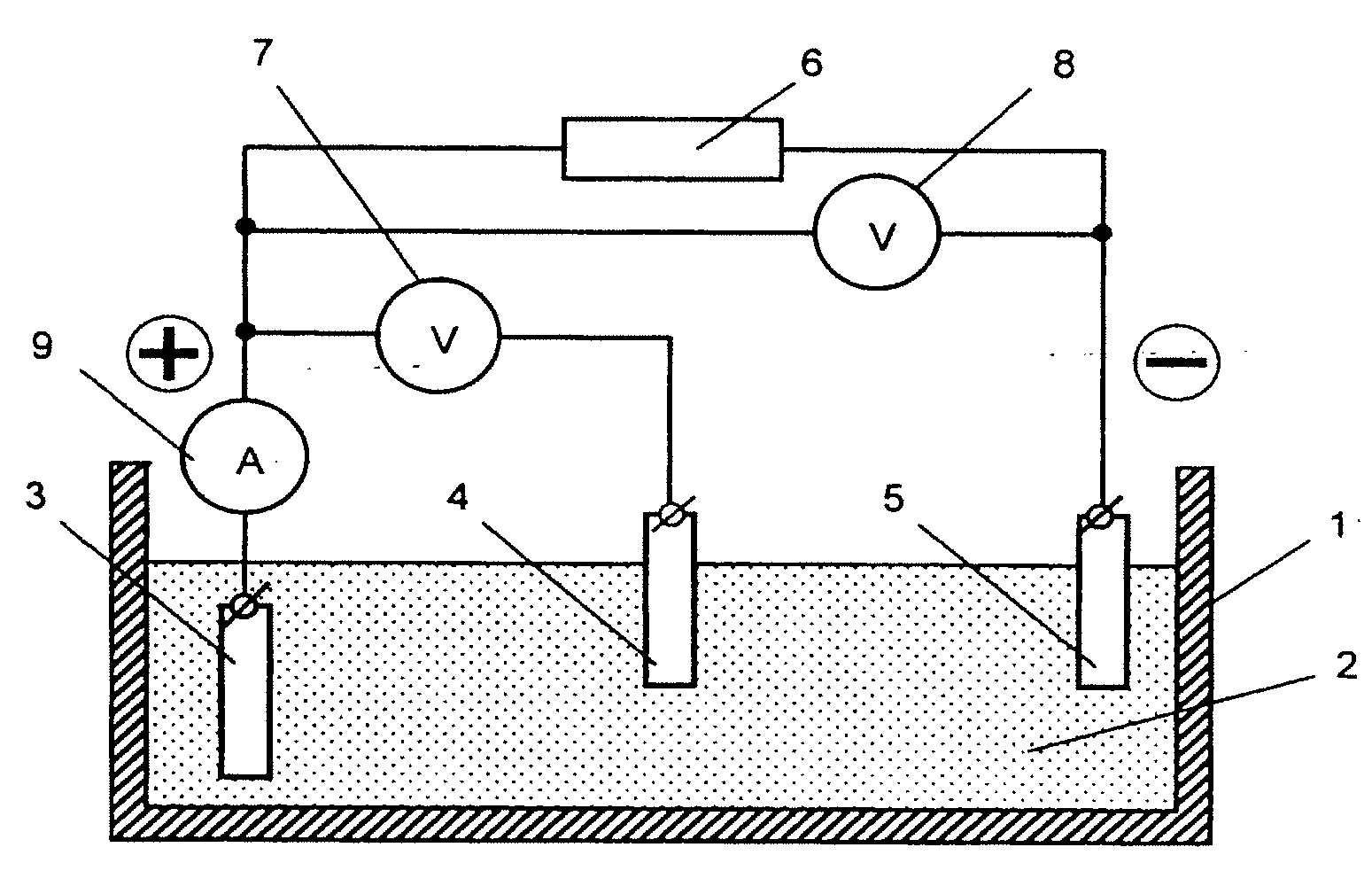
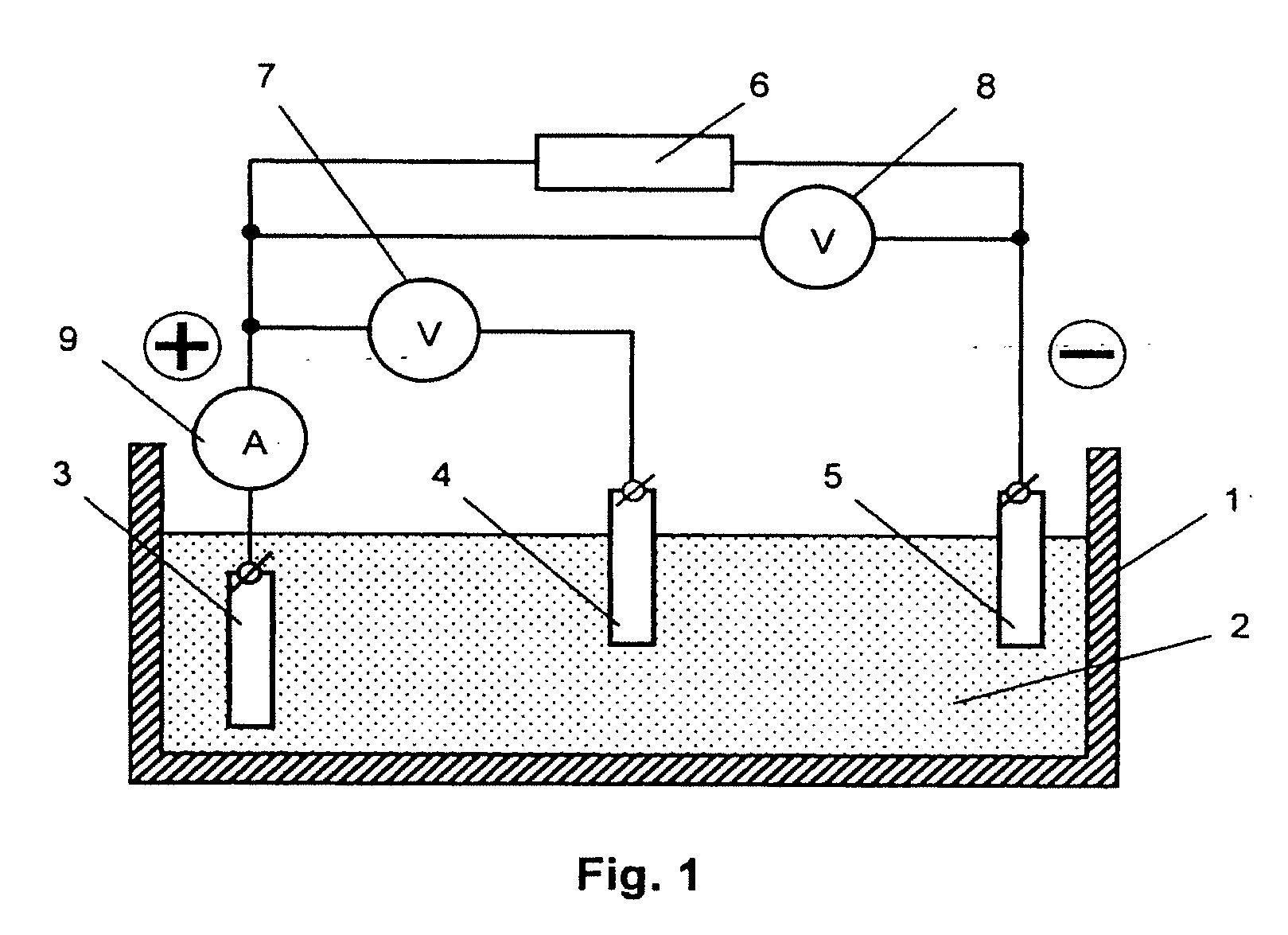
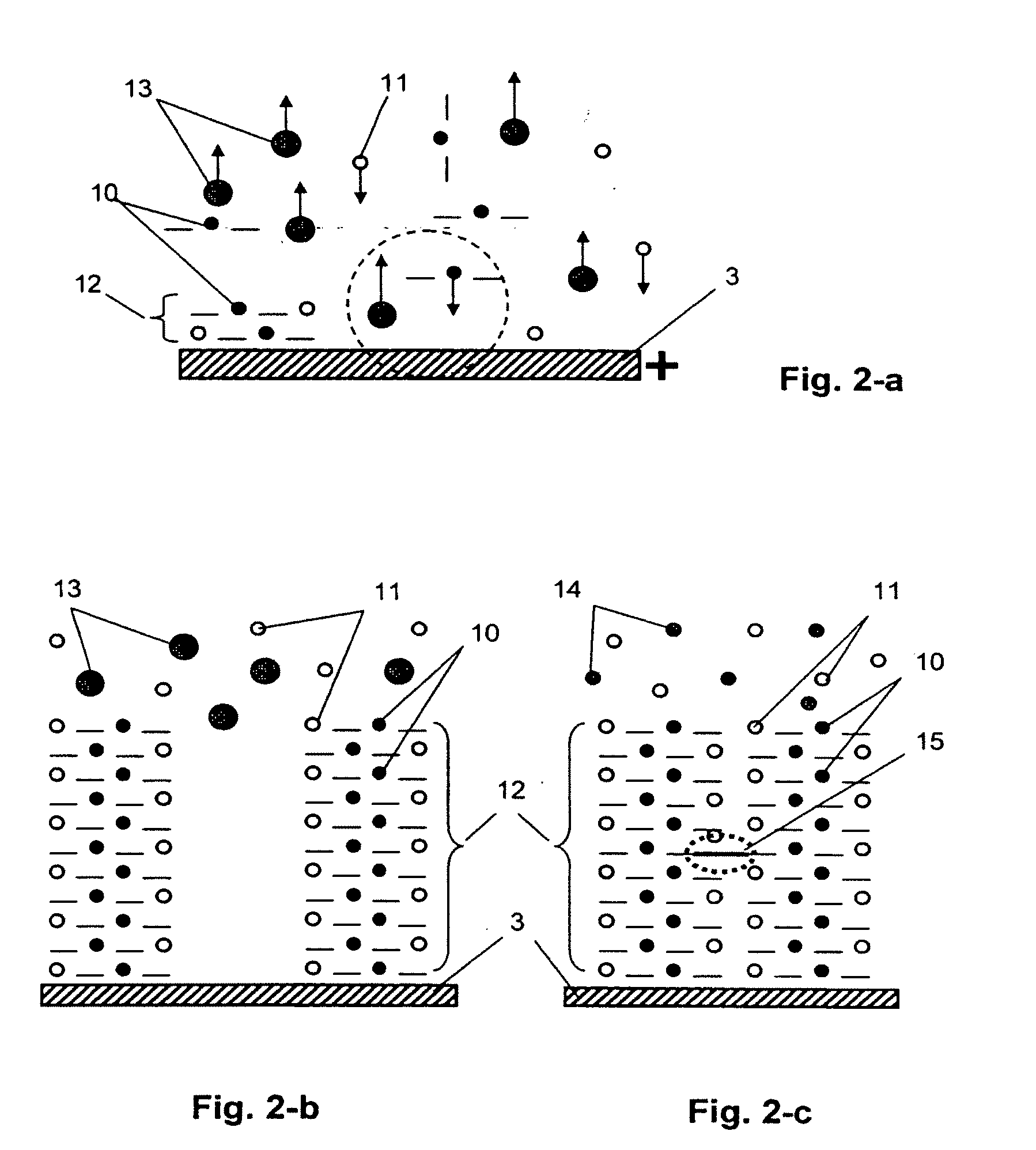
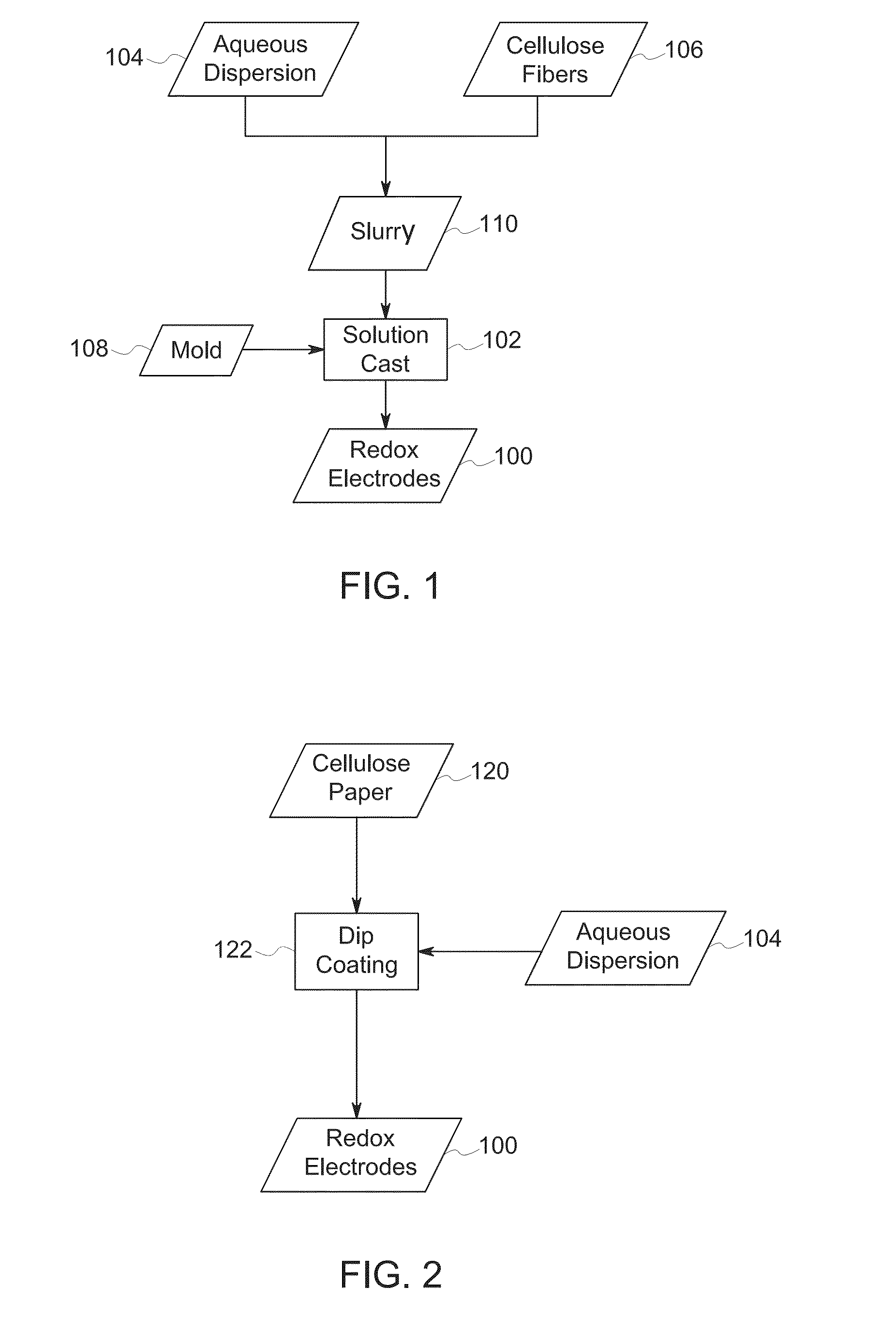
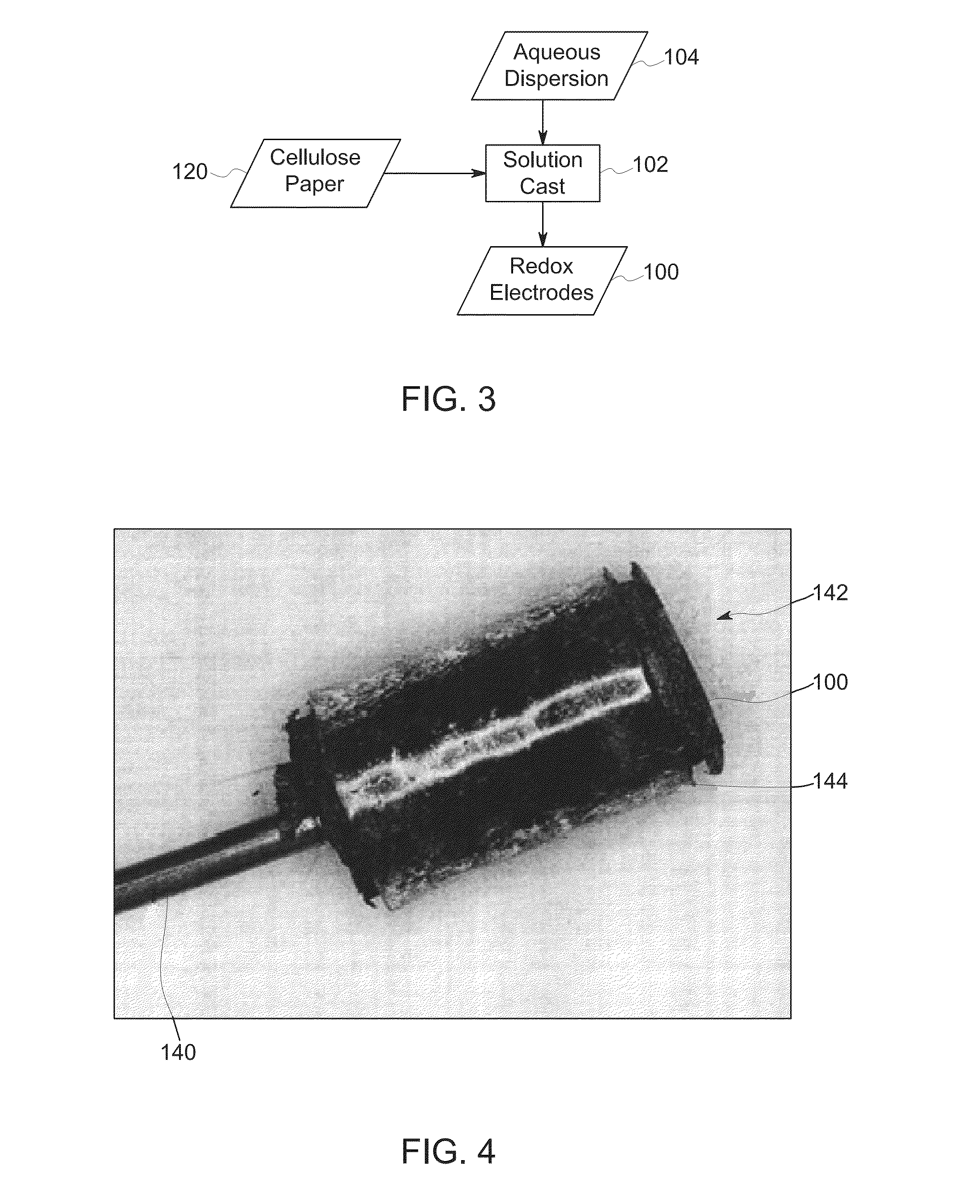
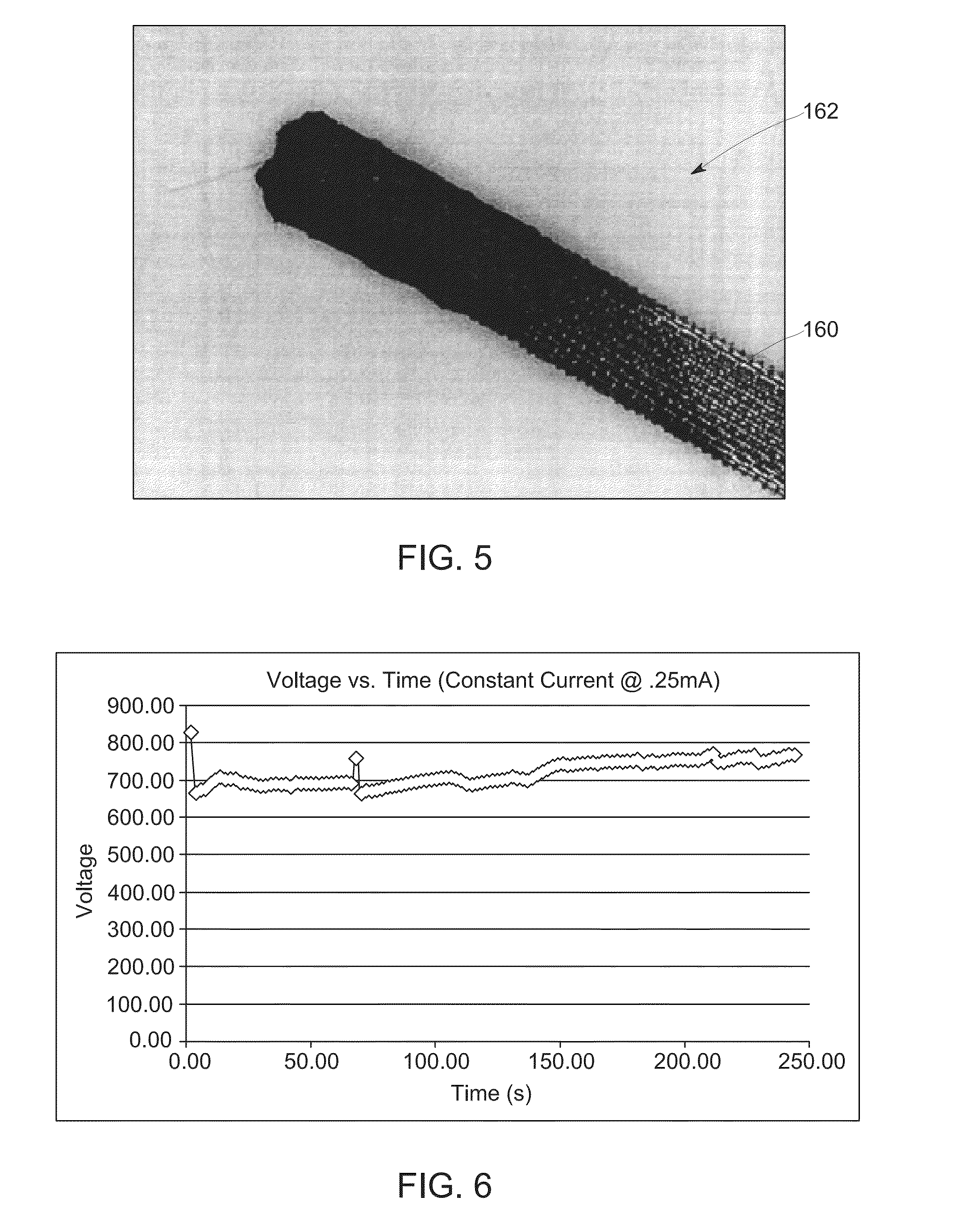
High capacity redox electrodes
The present disclosure relates to the manufacture and use of redox electrodes. In certain embodiments, the redox electrodes are manufactured using a hybrid material approach, such as using a redox polymer in combination with a support substrate, such as cellulose fibers or paper. In certain implementations, the redox electrodes are suitable for use at voltages greater than 25 V.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Redox Polymer Based Reference Electrodes Having An Extended Lifetime For Use In Long Term Amperometric Sensors
InactiveUS20120078070A1Considerable stabilityExtended service lifeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCatheterPower flowRedox
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Method for manufacturing an energy storage device
ActiveUS20070234537A1Hybrid capacitor electrolytesSolid electrolytic capacitorsCharge dischargeRedox polymers
The present invention relates to methods of manufacturing an electrochemical energy storage device, such as a hybrid capacitor. The method comprises saturating a porous electrically conductive material in a solution comprising an organic solvent and a metal complex or a mixture of metal complexes; assembling a capacitor comprising the positive electrode made of porous electrically conductive material saturated with a metal complex, a negative electrode, and a separator in a casing; introducing the electrolyte solution into the casing; sealing the casing; and subsequent charge-discharge cycling of the capacitor. The charge-discharge cycling deposits a layer of an energy-accumulating redox polymer on the positive electrode. The electrolyte solution for filling the hybrid capacitor contains an organic solvent, a metal complex, and substances soluble to a concentration of no less than 0.01 mol / L and containing ions that are electrochemically inactive within the range of potentials between −3.0 V to +1.5 V.
Owner:POWERMERS
Method for the manufacture of electrode for energy-storage devices
ActiveUS7563354B2Quality improvementIncreased specific energy capacityElectrochemical processing of electrodesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsEthylenediamineSalicylaldehyde
Application of a redox polymer of the poly-[Me(R-Salen)] type onto a conducting substrate is accomplished by the method of electrochemical polymerization. Said polymerization is accomplished by supplying a voltage between the substrate (that serves as an anode) and a counter electrode (that serves as a cathode), with both of them being submerged into the electrolyte containing an organic solvent and the compounds capable of dissolving in said solvent. The process is accompanied by the production of electrochemically inactive (at concentrations of no less than 0.01 mol / l) ions within the range of potentials from −3.0 V to +1.5 V, and metal complex [Me(R-Salen)] dissolved at a concentration of no less than 5-10−5 mol / l, (where: Me is a transition metal having at least two different degrees of oxidation, R is an electron-donating substituent, Salen is a residue of bis-(salicylaldehyde)-ethylenediamine in Schiff's base.
Owner:POWERMERS
Amperometric Creatinine Biosensor With Immobilized Enzyme-Polymer Composition And Systems Using Same, And Methods
InactiveUS20170260560A1Increase rangeImprove responseMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMedicineRedox
An amperometric biosensor is provided for determination of creatinine in a sample fluid. The biosensor can be an enzyme-polymer composition having at least one redox polymer and a plurality of enzymes immobilized on an electrode surface. Methods of preparing the amperometric biosensor are included. In addition, methods and systems using the amperometric biosensor in measuring creatinine concentrations of a patient and treatments of a patient with monitoring of the progress of dialysis performed on the patient are also provided.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com