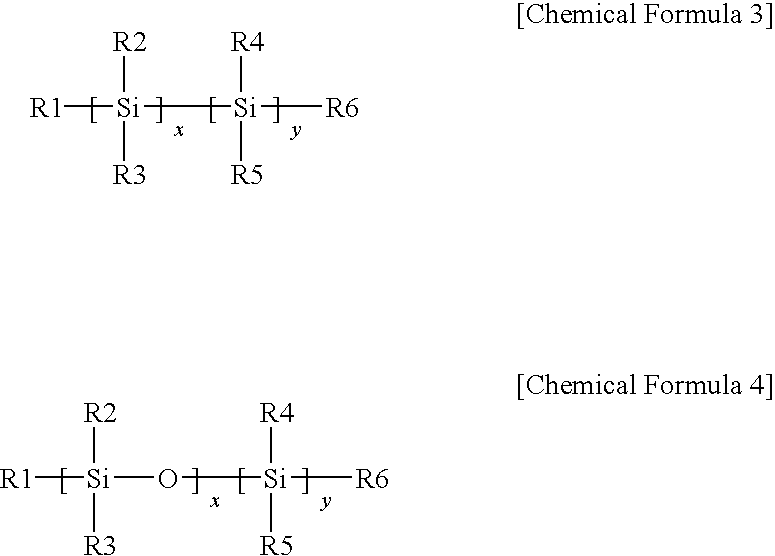
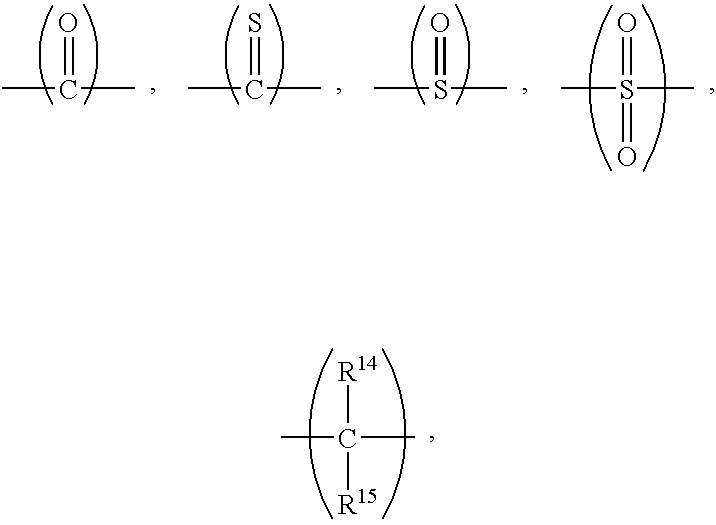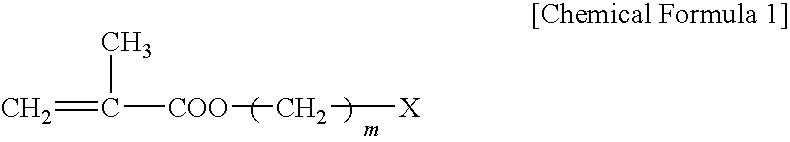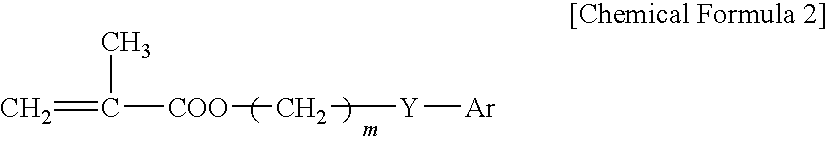Patents
Literature
6643 results about "Methyl methacrylate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an organic compound with the formula CH₂=C(CH₃)COOCH₃. This colorless liquid, the methyl ester of methacrylic acid (MAA), is a monomer produced on a large scale for the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).
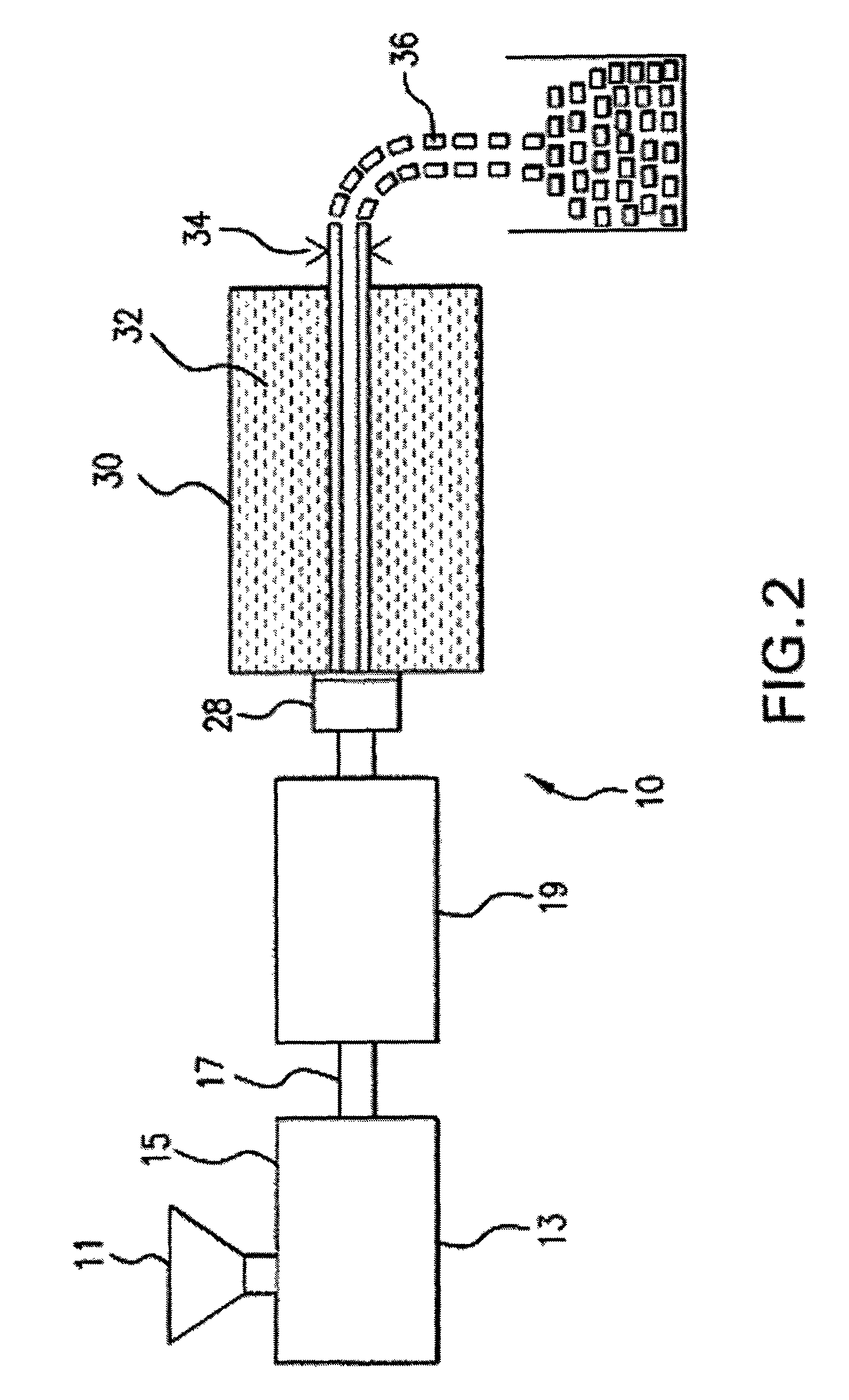
Method for making a chemical contrast pattern using block copolymers and sequential infiltration synthesis
ActiveUS20140346142A1Decorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusInorganic materialsAtomic layer deposition
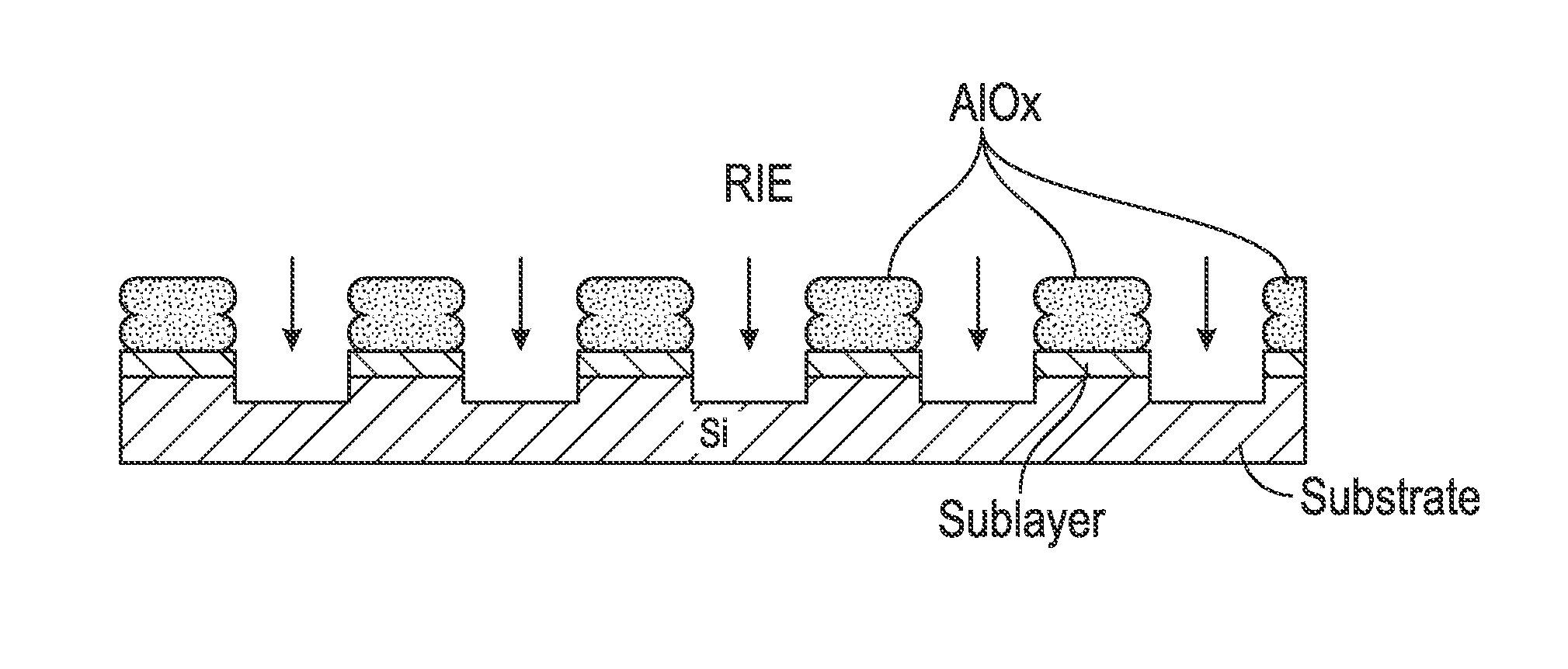
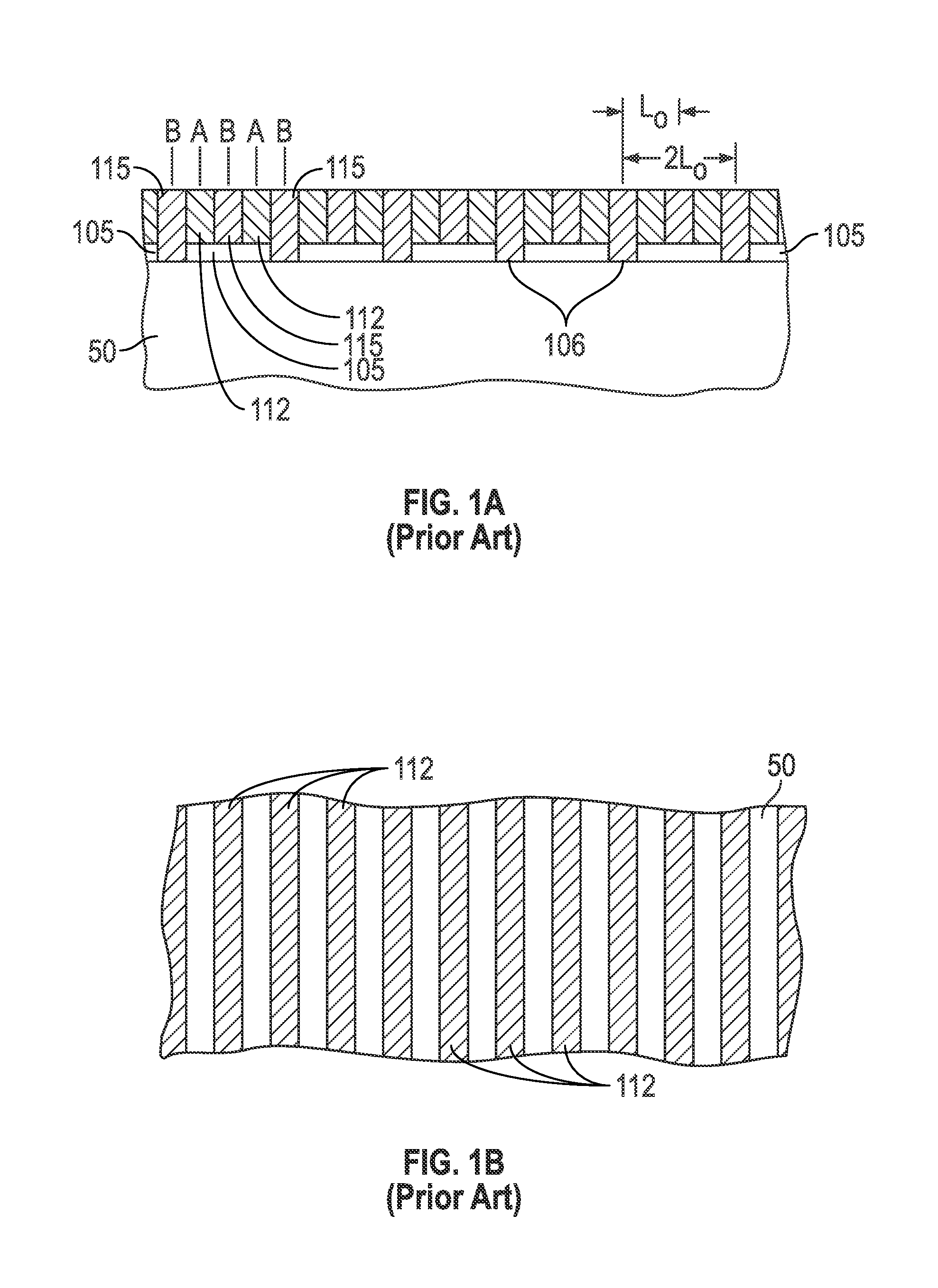
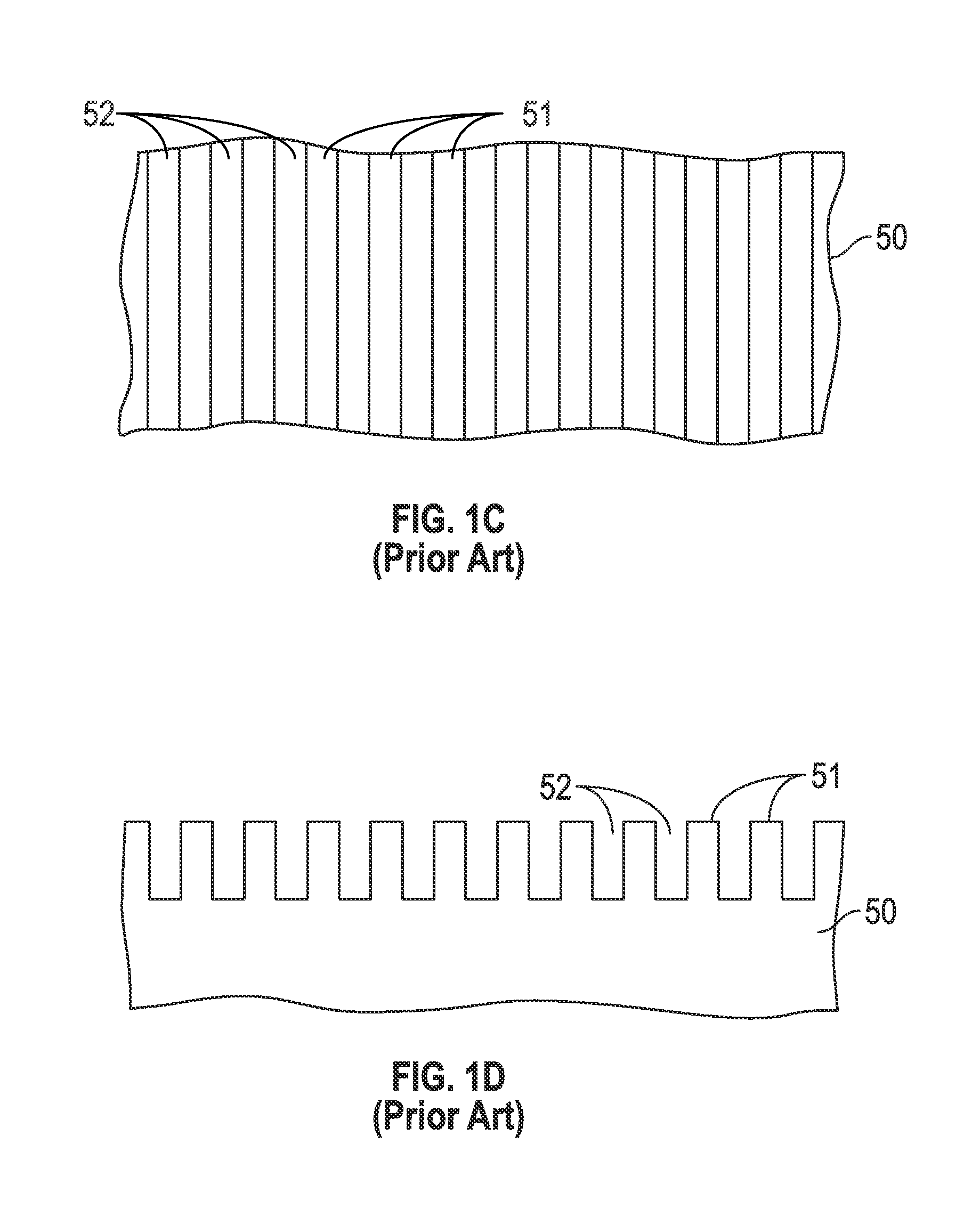
A method for making a chemical contrast pattern uses directed self-assembly of block copolymers (BCPs) and sequential infiltration synthesis (SIS) of an inorganic material. For an example with poly(styrene-block-methyl methacrylate) (PS-b-PMMA) as the BCP and alumina as the inorganic material, the PS and PMMA self-assemble on a suitable substrate. The PMMA is removed and the PS is oxidized. A surface modification polymer (SMP) is deposited on the oxidized PS and the exposed substrate and the SMP not bound to the substrate is removed. The structure is placed in an atomic layer deposition chamber. Alumina precursors reactive with the oxidized PS are introduced and infuse by SIS into the oxidized PS, thereby forming on the substrate a chemical contrast pattern of SMP and alumina. The resulting chemical contrast pattern can be used for lithographic masks, for example to etch the underlying substrate to make an imprint template.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Thermoset materials with improved impact resistance
The present invention relates to a thermoset material with improved impact resistance comprising:99 to 20% of a thermoset resin, and1 to 80% of an impact modifier comprising at least one copolymer comprising S-B-M, B-M and M-B-M blocks,wherein:each block is connected to the other by means of a covalent bond or of an intermediate molecule connected to one of the blocks via a covalent bond and to the other block via another covalent bond,M is a PMMA homopolymer or a copolymer comprising at least 50% by weight of methyl methacrylate,B is incompatible with the thermoset resin and with the M block and its glass transition temperature Tg is less than the operating temperature of the thermoset material, andS is incompatible with the thermoset resin, the B block and the M block and its Tg or its melting temperature is greater than the Tg of B.S is advantageously polystyrene and B polybutadiene. The thermoset resin advantageously originates from the reaction of a thermosetting epoxy resin and of a hardener.
Owner:ATOFINA
Polymer powders for SIB processes
A process of selective inhibition of bonding (SIB) to produce three-dimensional objects is used to obtain high-quality moldings. High-quality moldings can be produced by using pulverulent materials which have a median particle size of from 10 to 200 μm in which at least one polymer or copolymer selected from polyester, polyvinyl chloride, polyacetal, polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, polycarbonate, polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), PMMI, ionomer, polyamides, copolyester, copolyamides, terpolymers, or ABS, or a mixture of these, is present.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Pharmaceutical dosage form with multiple coatings for reduced impact of coating fractures
InactiveUS6893662B2Reduce the impactReduce impactPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsOral medicationActive agent
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition in a solid unit dosage form for oral administration in a human or lower animal comprising: a. a safe and effective amount of a therapeutically active agent; b. an inner coating layer selected from the group consisting of poly(methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate) 1:2, poly(methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate) 1:1, and mixtures thereof; and c. an outer coating layer comprising an enteric polymer or film coating material; wherein the inner coating layer is not the same as the outer coating layer; wherein if the inner coating layer is poly(methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate) 1:1 then the outer coating layer is not poly(methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate) 1:2 or is not a mixture of poly(methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate) 1:1 and poly(methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate) 1:2; and wherein the inner coating layer and the outer coating layer do not contain any therapeutically active agent. This invention further relates to a method of maintaining the desired site of delivery of a therapeutic agent in the gastrointestinal tract by administering the above compositions to a human or lower animal.
Owner:APTALIS PHARMA
Dental adhesive composition
This invention discloses a dental adhesive composition comprising (A) a polymerizable monomer comprising an acidic-group containing polymerizable monomer such as 11-methacryloyloxy-1,1-undecane dicarboxylic acid, (B) a mixed filler of a spherical filler substantially consisting of a non-crosslinking polymethyl methacrylate and a spherical filler substantially consisting of a non-crosslinking polyethyl methacrylate; and (C) a polymerization initiator; and a dental adhesive kit comprising the above dental adhesive composition in combination with a dental primer comprising (D) an acidic-group containing polymerizable monomer, (E) an aryl borate, (F) an organosulfinic acid salt and (G) water. The dental adhesive composition exhibits good operability and improved adhesion performance.
Owner:TOKUYAMA DENTAL CORP +1
Non-volatile dental compositions containing multifunctional acrylate compounds and lacking an oxygen-inhibited layer
Dental composite formulations containing an initiator and a multiacrylate compound are disclosed. The formulations lack methyl methacrylate, a volatile, irritating, and potentially hazardous material commonly found in dental formulations. The multiacrylate compound has at least three acrylate functionalities per molecule. The formulations cure to form a surface lacking an oxygen inhibition layer. The formulations can be used as dental sealants, dental coatings, and in fingernail / toenail repair applications.
Owner:BISCO
Cement compositions containing flexible, compressible beads and methods of cementing in subterranean formations
Cement compositions comprising flexible, compressible beads, processes for preparing such cement compositions, and methods of cementing in subterranean formations using such cement compositions. One or more flexible, compressible beads are mixed with the cement before pumping the cement into a well bore. The flexible, compressible beads are preferably composed of an elastomeric material such as a copolymer of methylmethacrylate and acrylonitrile; a terpolymer of methylmethacrylate, acrylonitrile, and dichloroethane; a styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer; and polystyrene. The flexible, compressible beads may be heated to expand the beads before mixing with the cement such that the ensuing cement composition will have a desired density. Non-flexible beads such as spherulites may also be added to the cement compositions.
Owner:REDDY B RAGHAVA +2
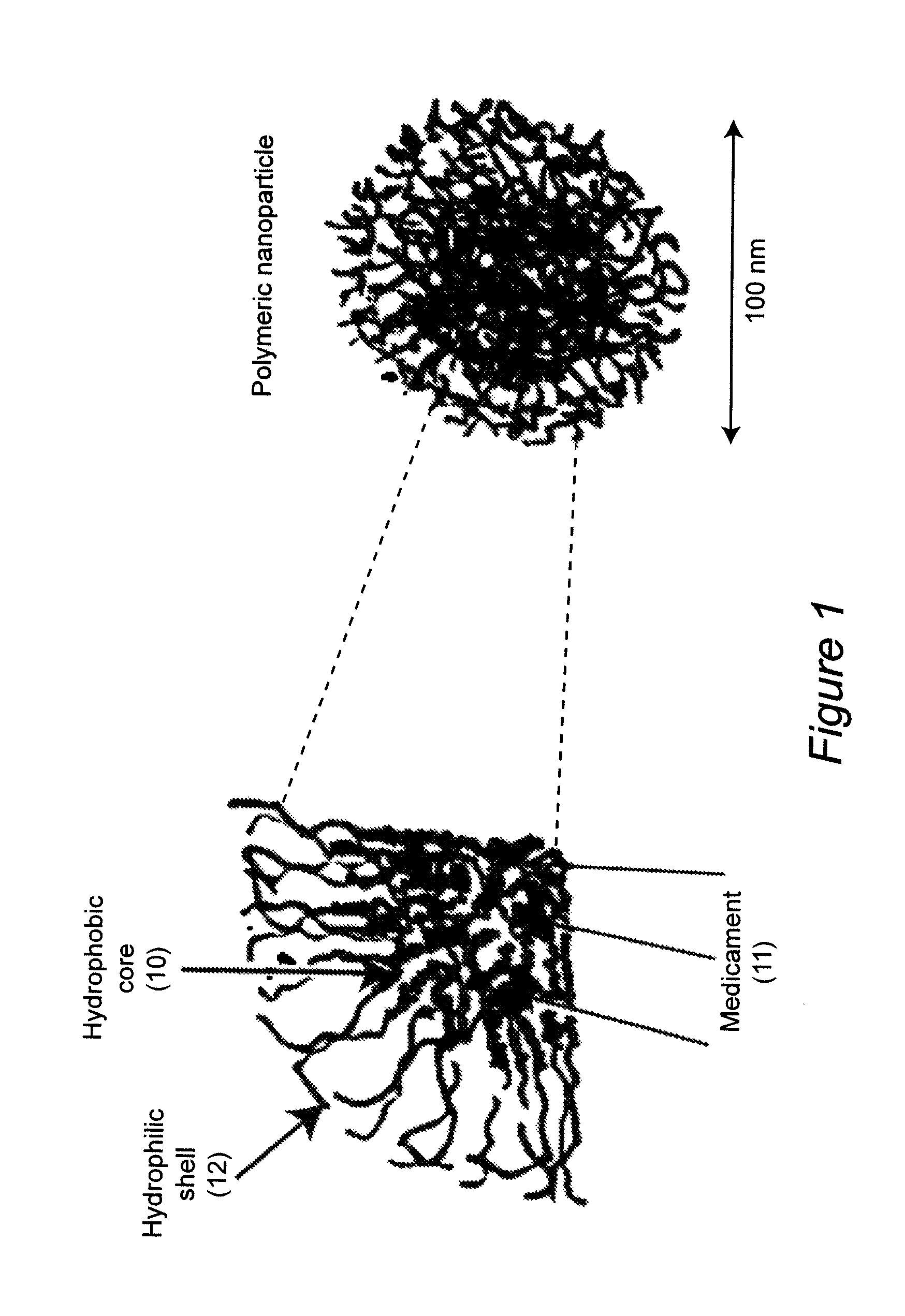
Water-dispersible oral, parenteral, and topical formulations for poorly water soluble drugs using smart polymeric nanoparticles
ActiveUS8313777B2Control releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryNervous disorderWater dispersibleSmart polymer
Polymeric nanoparticles with a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic shell are formed from: 1) N-isopropyl acrylamide (NIPAAM), at a molar ratio of about 50% to about 90%, and preferably 60% for specific delivery routes such as oral or parenteral; either water-soluble vinyl derivatives like vinylpyrolidone (VP) or vinyl acetate (VA), or water insoluble vinyl derivatives like methyl methacrylate (MMA) or styrene (ST), at a molar ratio of about 10% to about 30%; and acrylic acid (AA), at a molar ratio of about 10% to about 30%. The formed nanoparticles may be optionally surface functionalized using reactive groups present in AA, including PEGylation, or conjugation of moieties such as chemotherapeutics, contrasting agents, antibodies, radionucleides, ligands, and sugars, for diagnostic, therapeutic, and imaging purposes. The polymeric nanoparticles are preferably dispersed in aqueous solutions. The polymeric nanoparticles incorporate one or more types of medicines or bioactive agents in the hydrophobic core; on occasion, the medicine or bioactive agent may be conjugated to the nanoparticle surface via reactive functional groups. The polymeric nanoparticles are capable of delivering the said medicines or bioactive agents through oral, parenteral, or topical routes. The polymeric nanoparticles allow poorly water soluble medicines or bioactive agents, or those with poor oral bioavailability, to be formulated in an aqueous solution, and enable their convenient delivery into the systemic circulation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
High-quality transfer method of graphene prepared by chemical vapor deposition method
The invention relates to a high-quality transfer method of graphene prepared by a chemical vapor deposition method. The method comprises the following steps: a, spinning a polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) thin layer having even thickness on the surface of graphene prepared on a copper foil substrate with the chemical vapor deposition method; b, dissolving the copper foil; c, laminating; and d, and removing PMMA. By using the method provided by the invention, graphene can be stably, reliably and high-quality transferred, and the impurities in graphene are less, thereby ensuring the completeness and good property of prepared graphene not to be damaged and meeting the requirement of researching and applying graphene. After the method provided by the invention is adopted, complete and less-impurity-containing graphene can be stably, reliably and high-quality transferred, and thus a reliable guarantee for representation, research and application of graphene is provided.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
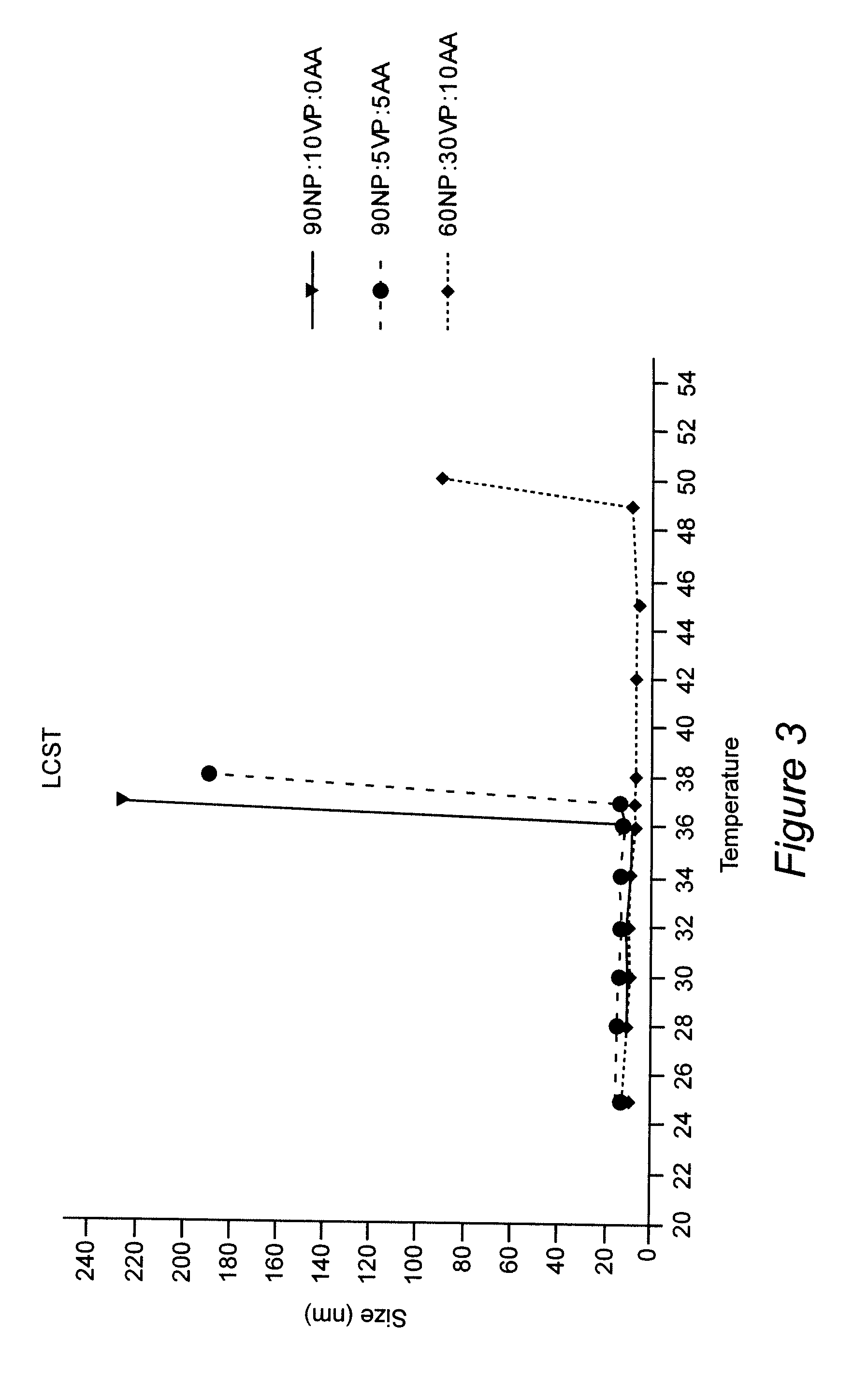
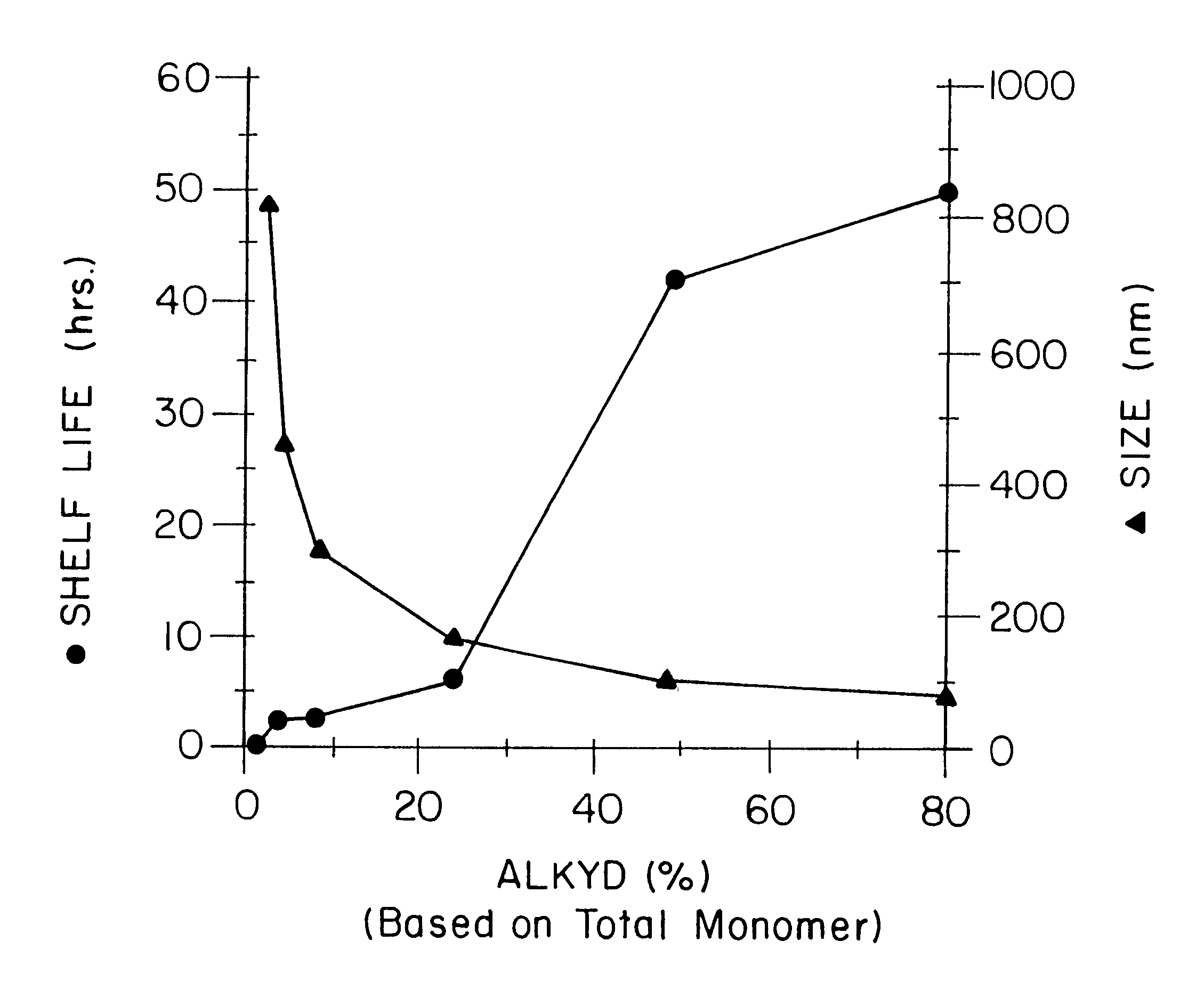
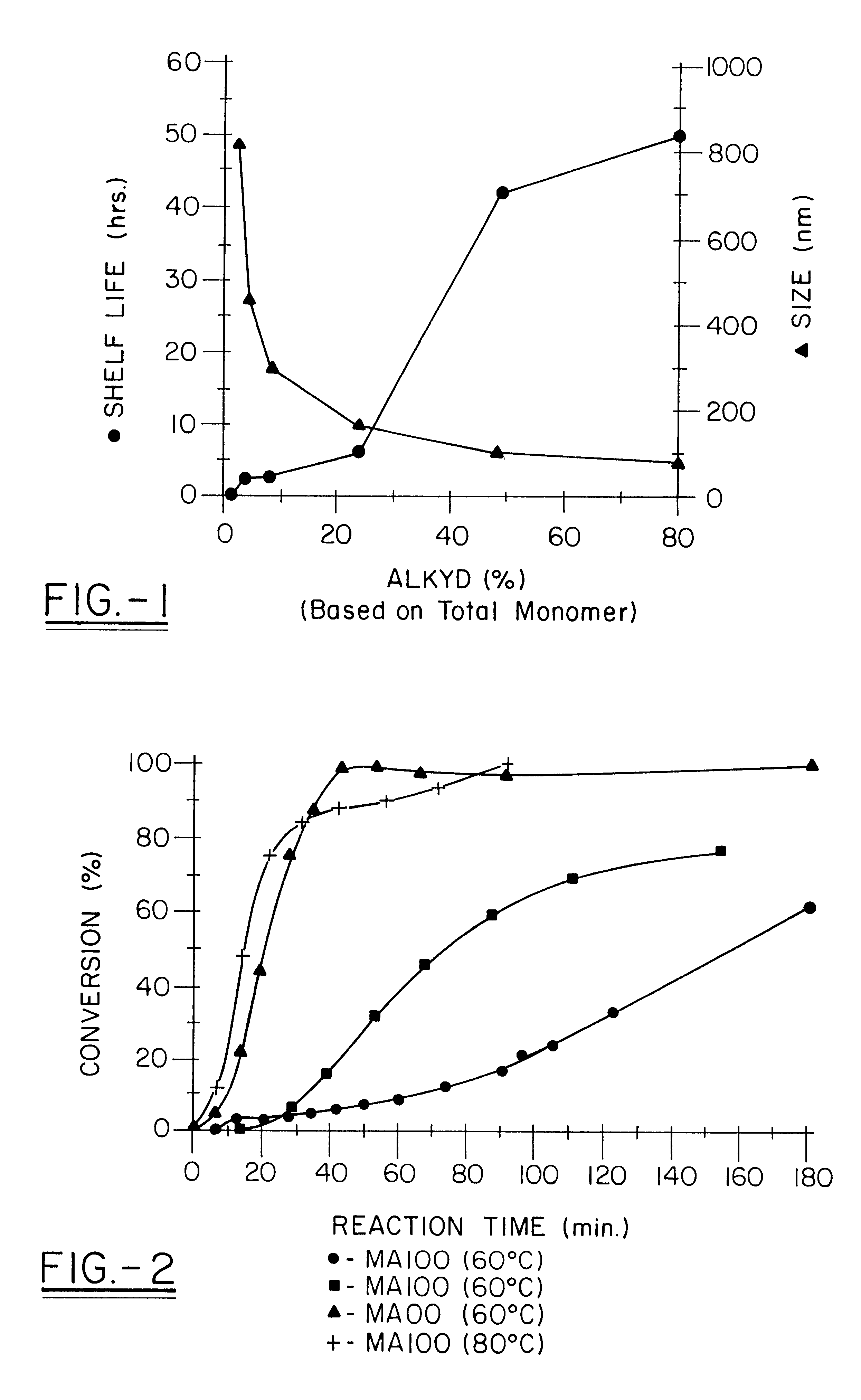
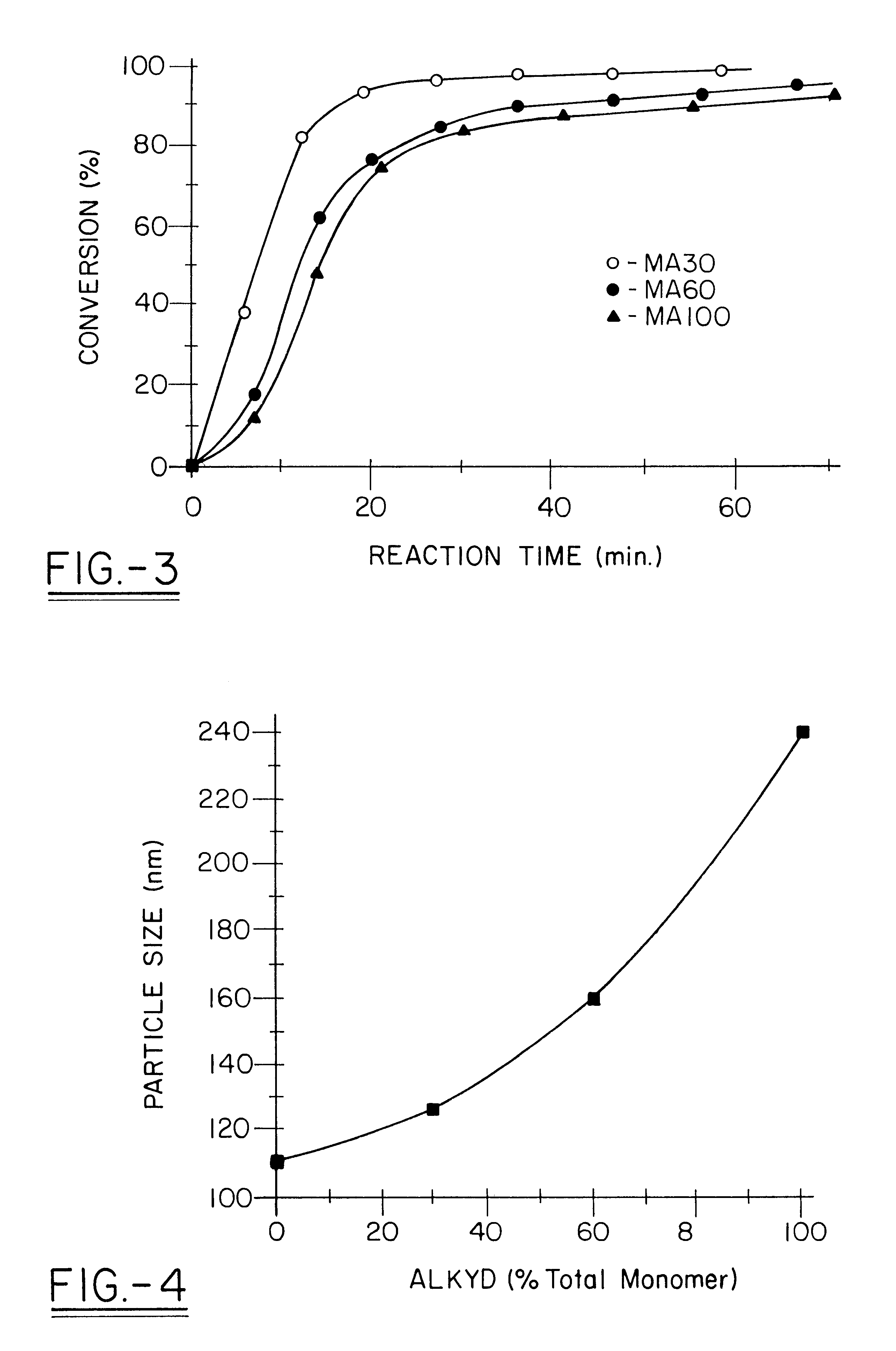
Water-borne alkyd coatings by miniemulsion polymerization
A distinctive graft copolymer is made by dissolving an alkyd resin in various vinyl monomers (methyl methacrylate, styrene, etc.). The monomer / alkyd solution is then miniemulsion polymerized to form a latex consisting of submicron particles of polymer with the alkyd grafted onto the polymer backbone. The latex can be applied to a substrate, which on drying forms a polymeric film with good film properties. The latex can be used in a latex paint formulation in place of an acrylate, acetate or styrene-divinyl benzene latex. In this way it is possible to produce water-borne alkyd coatings which combine the film hardness properties of an oil-based alkyd coating with easy application and cleanup. The coating will beneficially lack organic solvent exposure of typical standard latex coatings.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Functionalized vinyl polymer nanoparticles
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
Plastic body provided with a microstructured surface
InactiveUS20060121248A1Lamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticPoly methacrylate
The invention relates to a process for the production of a plastics article with a microstructured surface via production of a composite composed of a backing layer composed of a thermoplastic or thermoelastic with one or more structure layers, characterized in that the structure layer(s) is / are composed of from 1 to 100% by weight of a polymethacrylate moulding composition which comprises from 80 to 100% by weight of free-radical-polymerized methyl methacrylate units and from 0 to 20% by weight of other comonomers capable of free-radical polymerization, and which has an average (weight-average) molar mass Mw of from 30 000 g / mol to 70 000 g / mol and, where appropriate, is present in a. mixture with up to 99% by weight of a polymethacrylate moulding composition which is composed of from 80 to 100% by weight of free-radical-polymerized methyl methacrylate units and from 0 to 20% by weight of other comonomers capable of free-radical polymerization, and which has an average (weight-average) molar mass Mw of from 90 000 g / mol to 200 000 g / mol and the structure layer(s) obtain microstructuring via known structuring processes, after production of the composite. The invention further relates to the plastics articles themselves which are capable of production according to the invention, and also to their uses.
Owner:ROEHM GMBH & CO KG
Prepn of polyacrylonitrile-base high-performance raw carbon fiber
InactiveCN1417393AReduce gel particlesHigh strengthFibre chemical featuresMethyl methacrylateItaconic acid
The present invention relates to the preparation of high-performance polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber. Acrylonitrile, itaconic acid and methyl methacrylate in a certain weight proportion are reacted to obtain spinning dope, and the spinning dope is made into greign fiber of high-performance carbon fiber through filtering, solidification, water washing, drafting in hot water, oiling, drying and densifying, re-oiling, drying and densifying for the second time, steam drafting and drying setting. The present invention has the advantages of high drafting rate, homogeneous fibre structure, and small mechanical performance variation coefficient.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
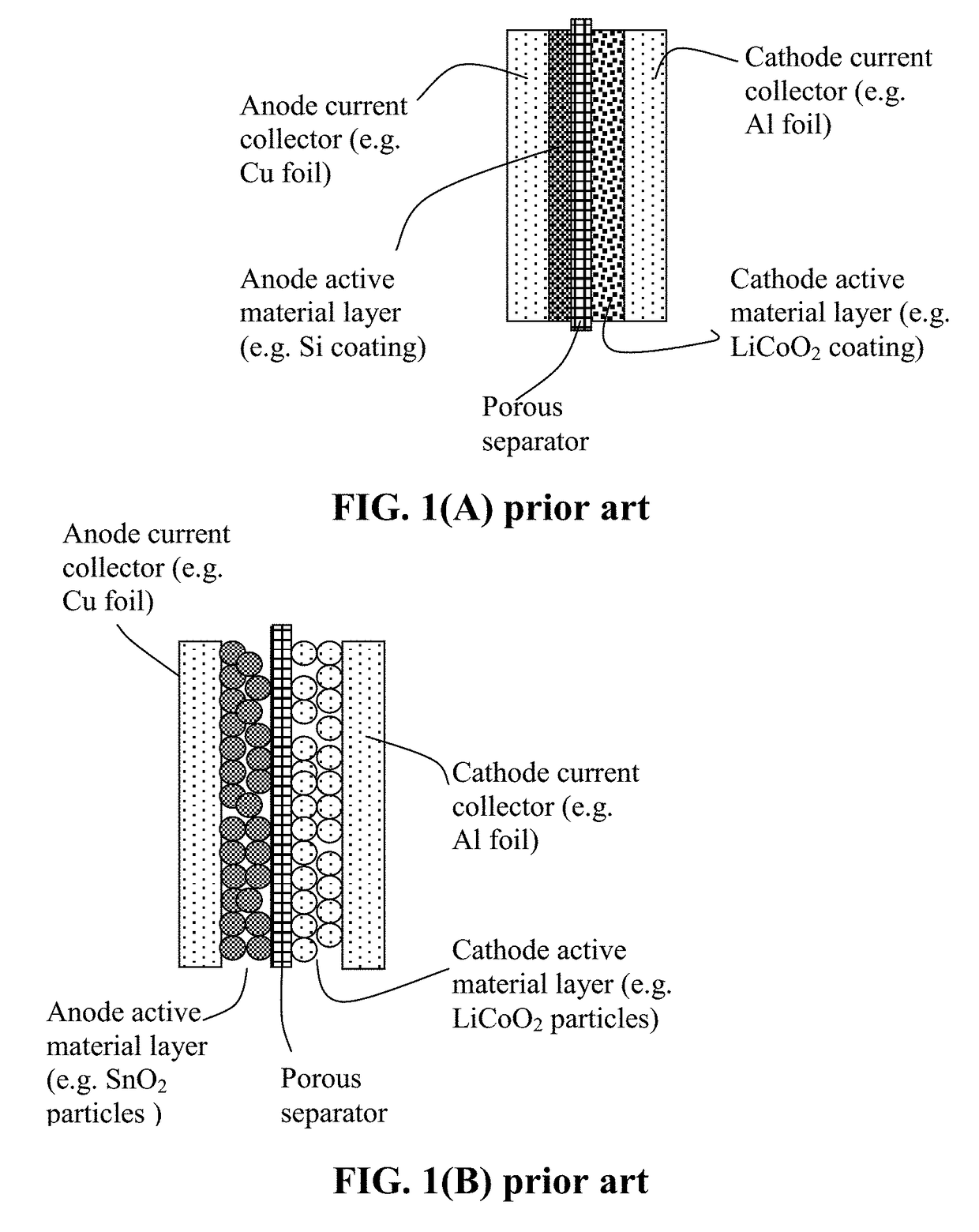
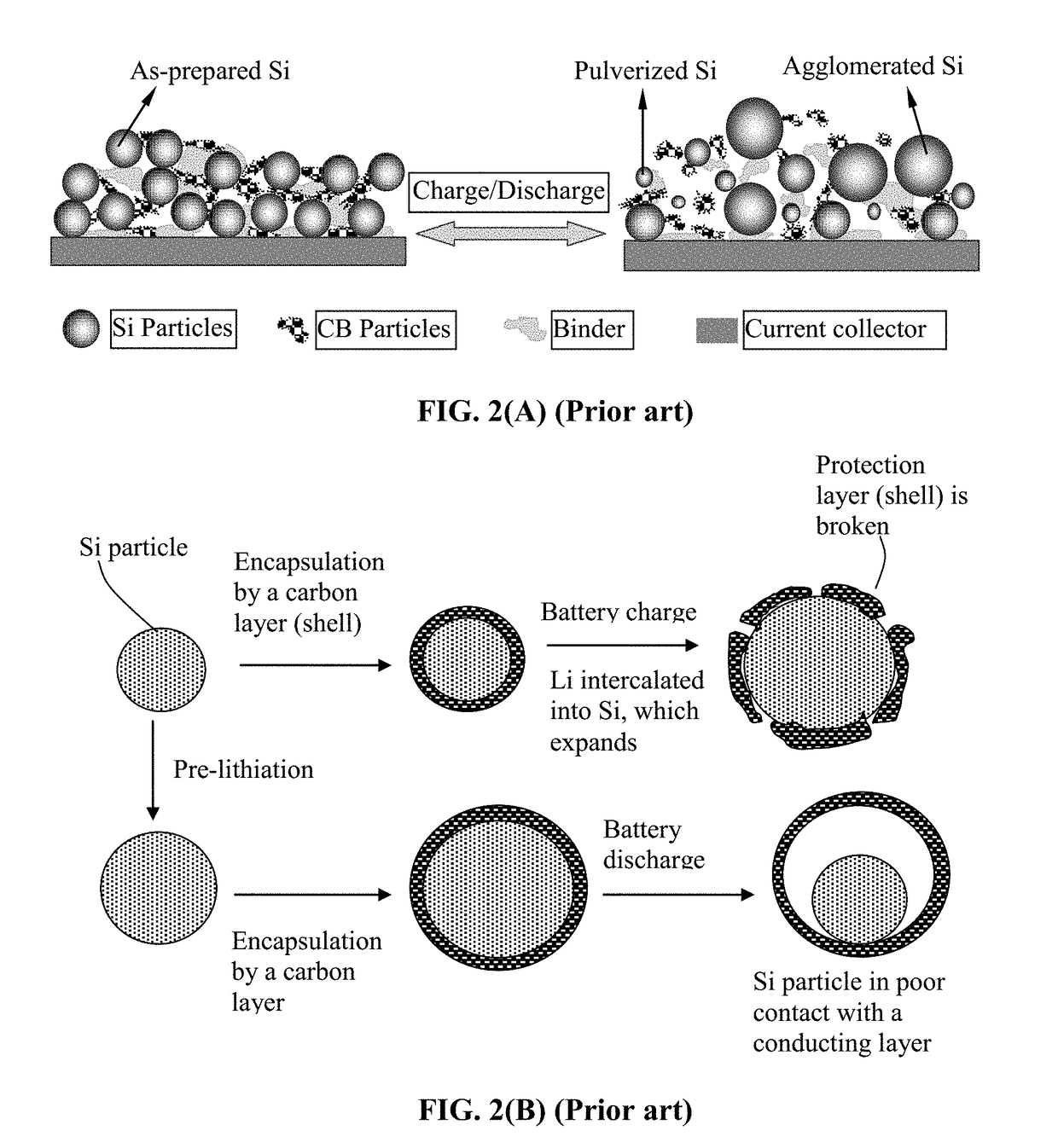
Encapsulated Anode Active Material Particles, Lithium Secondary Batteries Containing Same, and Method of Manufacturing
ActiveUS20180287142A1Improve lithium ion conductivitySolid electrolytesNegative electrodesParticulatesPolyethylene oxide
Provided is particulate of an anode active material for a lithium battery, comprising one or a plurality of anode active material particles being embraced or encapsulated by a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 5%, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−6 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 0.5 nm to 10 μm, wherein the polymer contains an ultrahigh molecular weight (UHMW) polymer having a molecular weight from 0.5×106 to 9×106 grams / mole. The UHMW polymer is preferably selected from polyacrylonitrile, polyethylene oxide, polypropylene oxide, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, polyacrylamide, poly(methyl methacrylate), poly(methyl ether acrylate), a copolymer thereof, a sulfonated derivative thereof, a chemical derivative thereof, or a combination thereof.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Thermoset composition, method, and article
InactiveUS20030215588A1Improve as-molded surface characteristics of polyReduce shrinkage on moldingSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingVinyl etherPolystyrene
A curable composition includes a functionalized poly(arylene ether), an alkenyl aromatic monomer, an acryloyl monomer, and a polymeric additive effective selected from polystyrene, poly(styrene-maleic anhydride), poly(styrene-methyl methacrylate), polybutene, poly(ethylene-butylene), poly(vinyl ether), poly(vinyl acetate), and combinations thereof. The composition exhibits low shrinkage on curing and improved surface smoothness. It is useful, for example, in the manufacture of automotive body panels.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Molding material containing a matting agent
The invention relates to a moulding composition, comprising a) 50 to 99.9% by weight of a matrix composed of a thermoplastic polymer and b) from 0.1 to 50% by weight of a matting agent in the form of a (meth)acrylate copolymer dispersed in the matrix, characterized in that the matting agent is a (meth)acrylate copolymer which has been prepared from the following monomers, b1) from 50 to 95% by weight of methyl methacrylate b2) from 5 to 50% by weight of C1-C6-alkyl acrylates b3) from 0.01 to less than 0.5% by weight of a crosslinking monomer and / or graft-linking agent having two or more ethylenically unsaturated radicals capable of free-radical polymerization, b4) from 0 to 20% by weight of one or more other, non-crosslinking ethylenically unsaturated monomers capable of free-radical polymerization, where the entirety of the constituents b1) and b2) and, where appropriate, b3) and / or b4) gives 100% by weight, and the glass transition temperature Tmg of the matting agent is at least 20° C.
Owner:ROEHM GMBH & CO KG
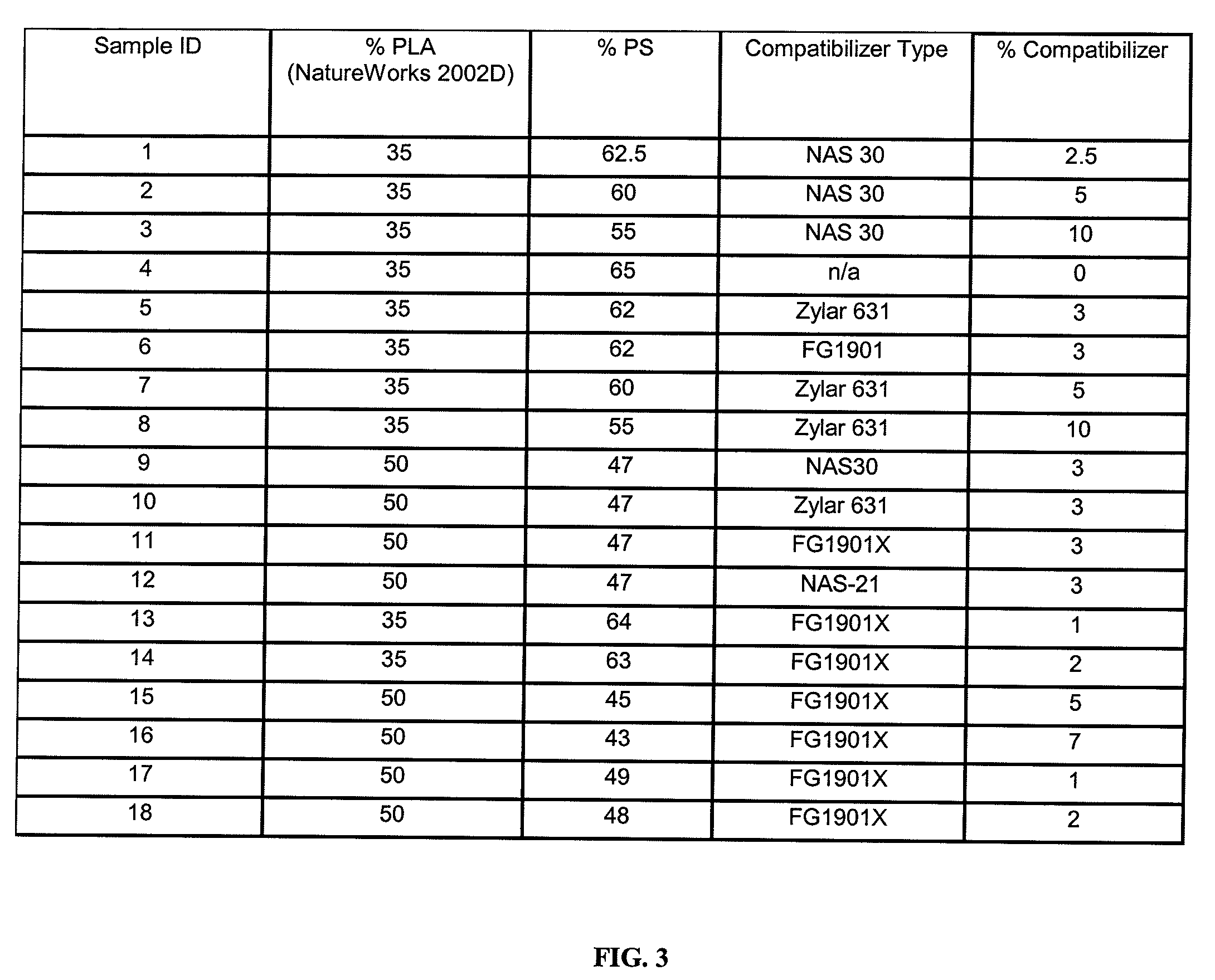
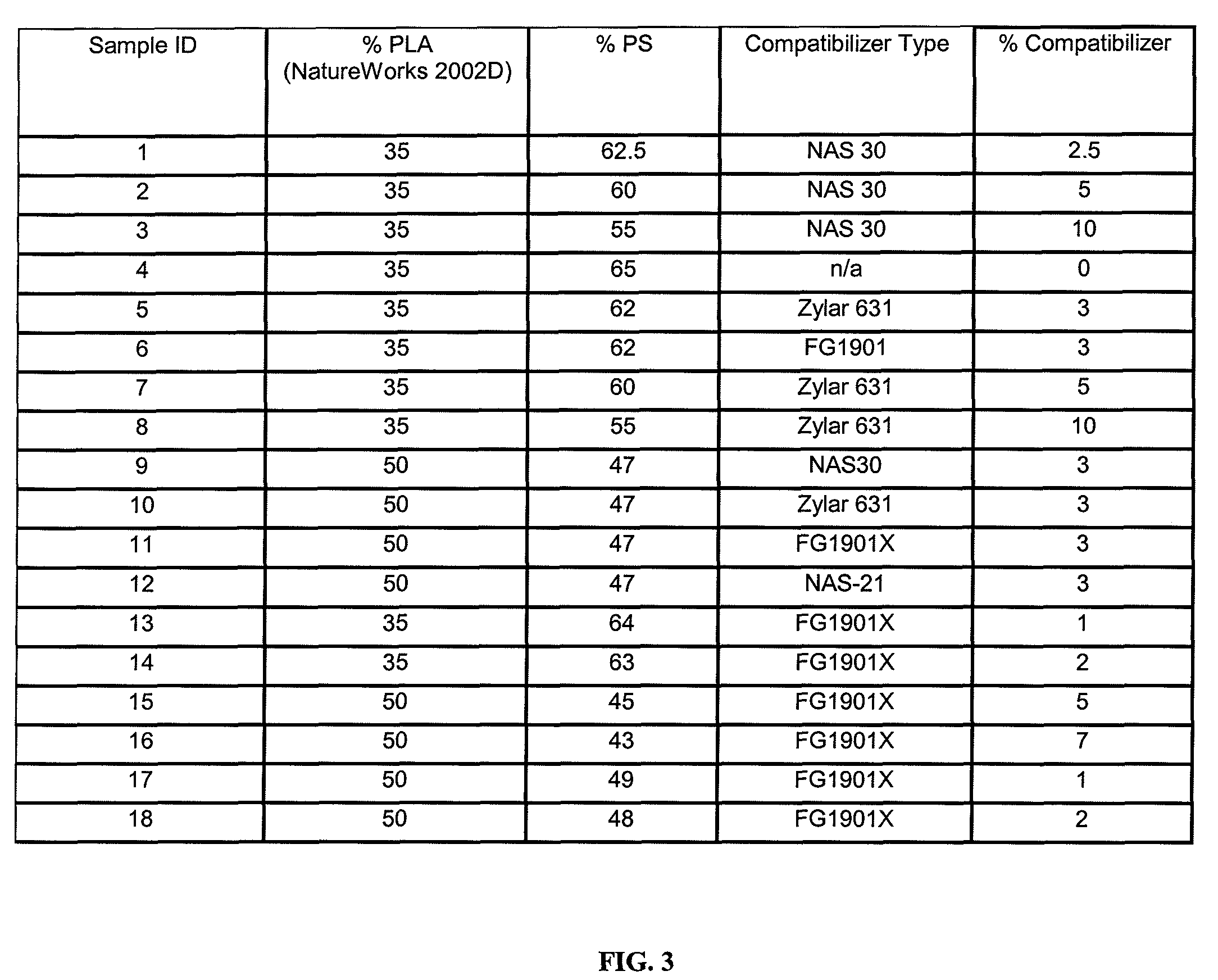
Polymer Blends Of Biodegradable Or Bio-Based And Synthetic Polymers And Foams Thereof
The present invention relates to compositions comprising blends of alkenyl aromatic polymers such as styrenic polymers (i.e. PS and HIPS) and bio-based or biodegradable polymers (i.e. PLA, PGA, PHA, PBS, PCL) compatibilized with styrene-based copolymers (i.e. styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene (SEBS) block copolymers, maleated SEBS, styrene-maleic anhydride (SMA) copolymer, styrene-methyl methacrylate (SMMA) copolymer) or a mixture of two or more styrene-based copolymers such as SEBS and SMA. These novel compositions can be extruded and thermoformed to produce very low density food service and consumer foam articles such as plates, hinged lid containers, trays, bowls, and egg cartons with good mechanical properties.
Owner:PACTIV LLC
Alumina carrier with composite pore structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102614934AExtend your lifeHigh selectivityCatalyst carriersMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPolymer scienceMicrosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method of an alumina carrier with a composite pore structure, which comprises the steps of mixing and roasting an aluminum-contained compound and a composite template, wherein the composite template comprises a mesoporous template selected from at least one of a polyethylene glycol-polypropylene glycol-polyethylene glycol triblock polymer, polyethylene glycol, dodecylamine, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, lauric acid, stearic acid and fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether and a macroporous particulate template selected from polystyrene microspheres with the particle size of greater than 50nm, polymethyl methacrylate microspheres, biomaterial particles, asphalt particles or heavy oil residues; and the weight ratio of the mesoporous template to the macroporous particulate template to the aluminum-contained compound (by alumina) is 0.1-2:0.1-0.7:1. The invention also discloses the alumina carrier simultaneously having mesoporous tunnels and macroporous tunnels prepared through the method, wherein mesopores account for 40-90% of the total pore volume, and macropores account for 10-60% of the total pore volume.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Ultraviolet curing paint and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102070981AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistancePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyether coatingsPolyesterPliability
The invention discloses an ultraviolet (UV) curing paint and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighting modified SiO2 sol to place in a container, adding water-soluble UV-cured resin, solvent and additive in turn, stirring for 10min, then adding photoinitiator, and stirring for 5min to obtain the UV curing paint, wherein the contents of the water-soluble UV-cured resin, the solvent, the additive and the photoinitiator are 10-60%, 7-33%, 0.1% and 2% respectively. The UV curing paint prepared by the method of the invention has the advantages of inorganic materials such as high hardness, high wear resistance, scratch resistance and good thermal stability and also has the advantages of organic materials such as adhesivity and relative flexibility; and the UV curing paint is suitable to be used as the protective coatings on the surfaces of all kinds of optical plastic products such as polyester which contains polycarbonate, polymethylmethacrylate, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and the like. By adopting the UV curing paint of the invention, the defects of the existing UV curing paint in the aspects of hardness, wear resistance, scratch resistance and light transmittance, can be overcomed to a certain extent.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUMAN CHEM
Method for modifying polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membrane by amphiphilic co-polymer
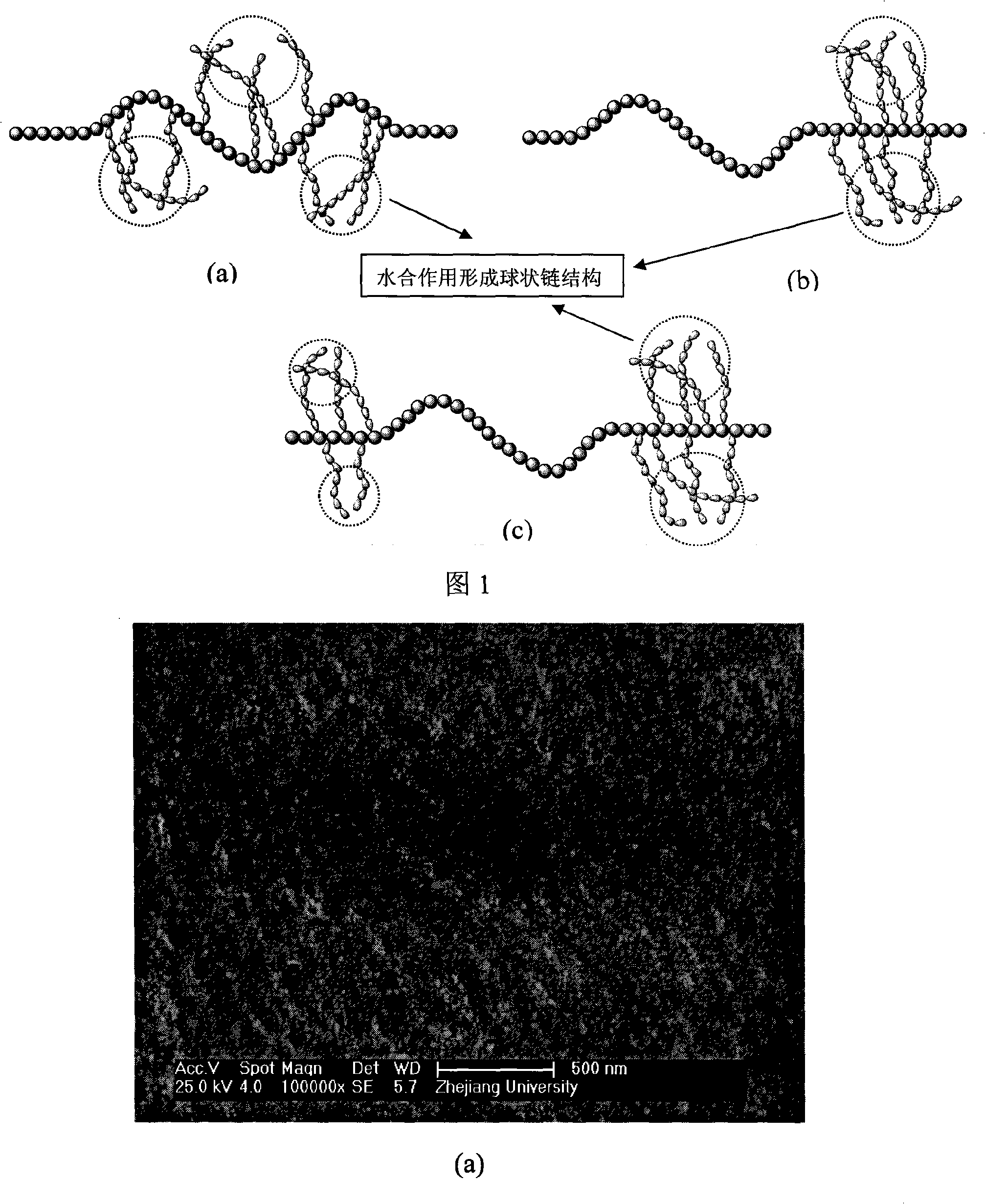
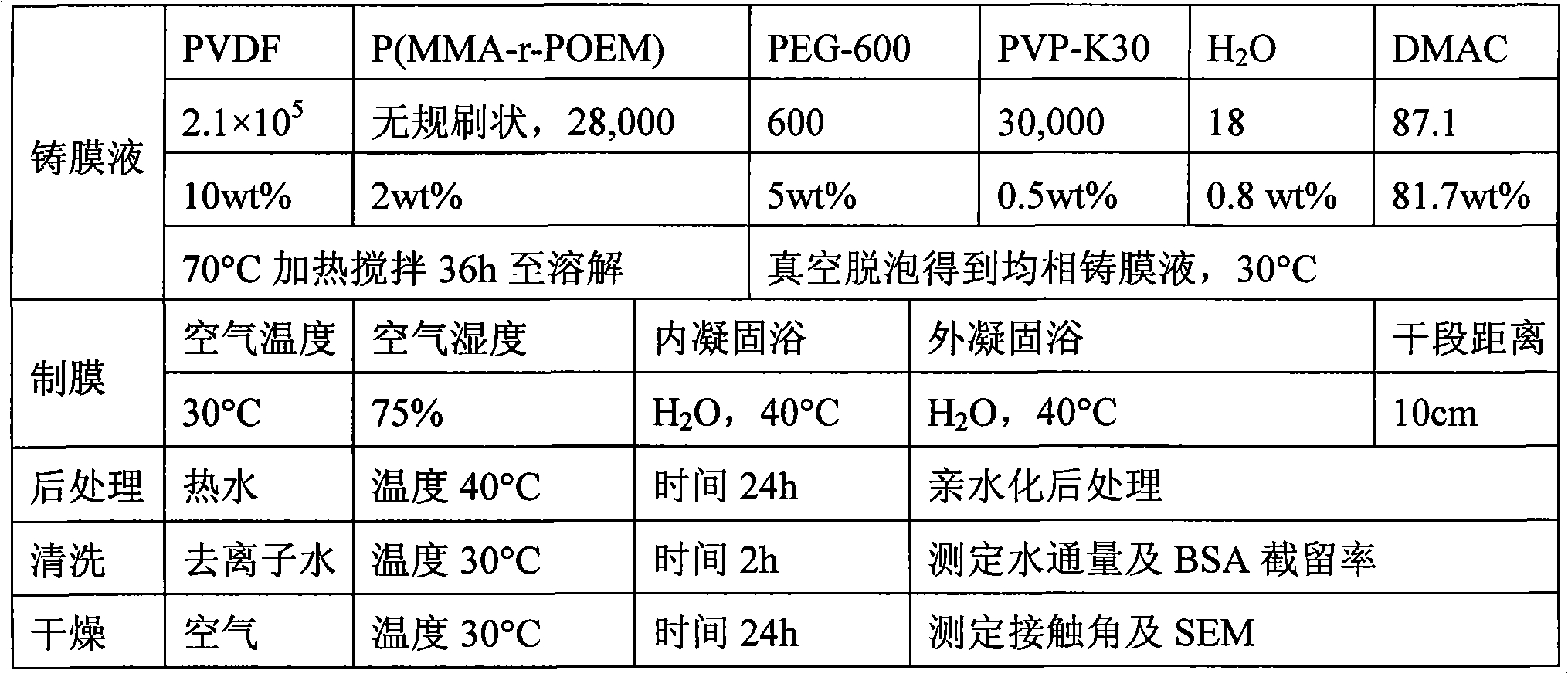
InactiveCN101264428AImprove hydrophilicityReduce energy consumptionSemi-permeable membranesUltrafiltrationDumbbell shaped
The invention discloses a method of producing the hyperfiltration membrane of amphiphilic copolymer modified polyvinylidene fluoride, comprising the following steps: 1) mixing polyvinylidene fluoride, poly (methyl methacrylate - monomethyl ether polyoxyethylene methyl methacrylate), additives, non-solvent and solvent to form the casting film solution; 2) making the casting film solution into the polyvinylidene fluoride membrane by using the film forming machine and then soaking in the coagulation bath; 3) conducting the posttreatment of hydrophilicity; 4)obtaining the hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membrane after cleaning and drying. The method is characterized in that the brush shape, chain ball shape or dumbbell shape amphiphilic copolymer are mixed with the polyvinylidene fluoride to produce the polyvinylidene fluoride hyperfiltration membrane with hydrophilicity, anti-pollution, large flux and high retention rate by adopting the solution phase conversion method. The method has the advantages that the obtained membrane is provided with dozens to hundreds nanometer of particular densified hydrogel surface layers, the contact angle of the membrane surface can be reduced below 60 degrees and can be lowered to 0 degree within tens of seconds, the water flux can reach 1000L / m<2> / h (0.1Mpa) or above, the retention rate of BSA can reach 90% or more and the recovery rate of water cleaning flux can reach 90% or higher.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Film coating process for aluminium alloy wheel hub
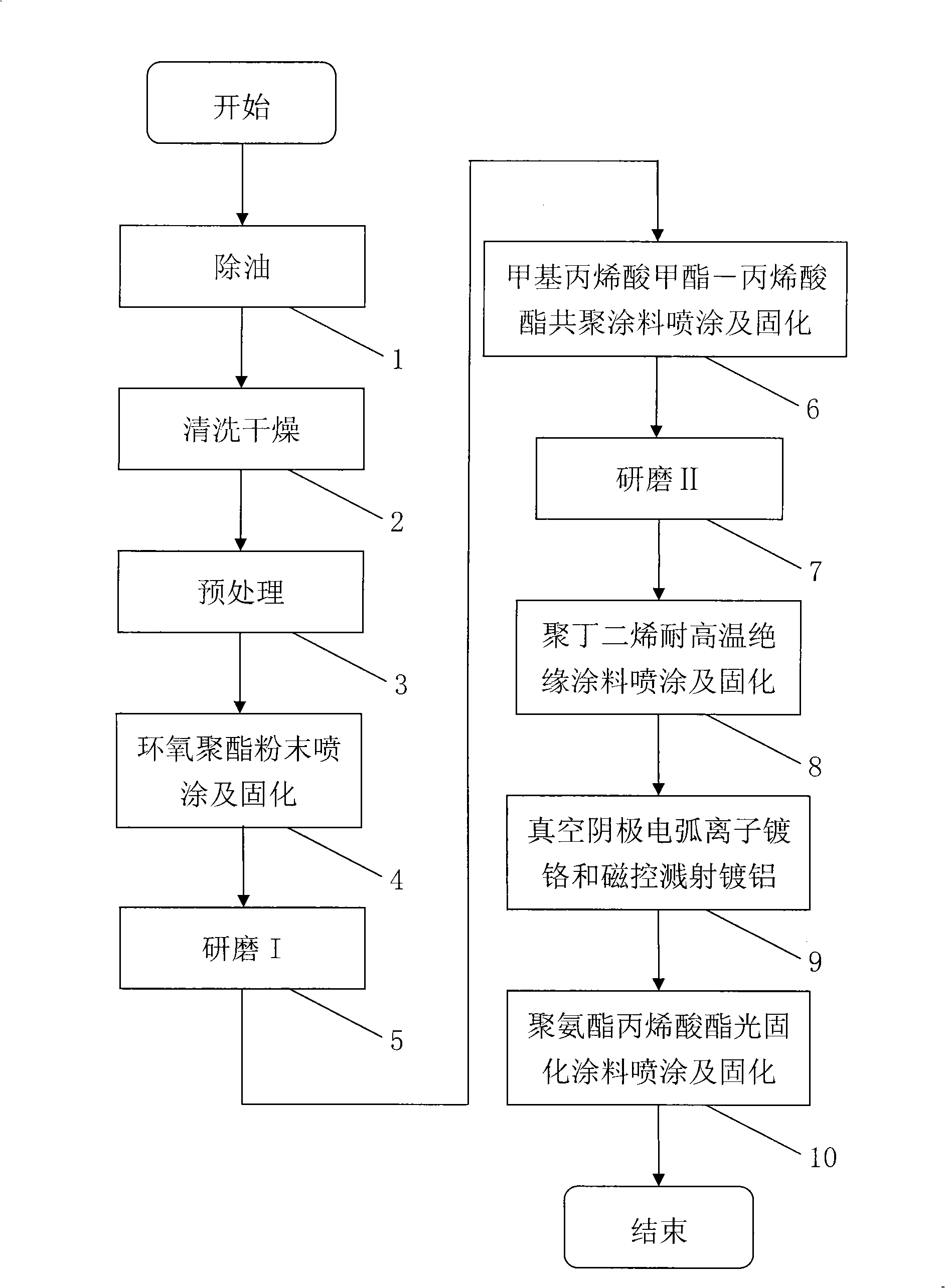
InactiveCN101343740AReduce pollutionReduce energy consumptionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPolyesterFilm coating
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy wheel hub coating technology. The aluminum alloy wheel hub coating technology comprises the procedures of oil removing, cleaning and drying, pre-treating, epoxy polyester powder spraying and solidifying, grinding I, methyl methacrylate-acrylate copolymer paint spraying and solidifying, grinding II, polybutadiene high temperature resistant insulating coating spraying and solidifying, vacuum cathode arc ion chromium plating and magnetism control sputtering aluminum plating, and polyurethane methacrylate light solidifying paint spraying and solidifying in sequence. The aluminum alloy wheel hub coating technology adopts dry electric plating to replace the traditional wet electric plating, the plating layer surface quality and the physical and chemical properties are approximately equivalent to the wet electric plated aluminum alloy wheel hub, the chromium consumption is reduced to about one fifth of the wet electric plating, the water consumption is reduced to about one seventh of the wet electric plating, precious nickel and copper are not utilized, the poisonous metal substance such as hexavalent chromium is not contained, the pollution to the environment is reduced, the energy, water and precious metal consumption is remarkably reduced, the technological flow is simplified, the production efficiency is enhanced, the heavy polishing working sequence is omitted, the working condition is remarkably improved, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:HUZHOU JINTAI PLATING IND
Saloon car bumper special material capable of direct spray coating
The invention discloses a special material for direct spray coating of a bumper, which is prepared by mixing of polypropylene, a rubber toughening agent, a crosslinking agent, grafted polypropylene, inorganic filler, black master bath, an antioxidant and a light stabilizer in proportion, preparation of the master bath, dynamic vulcanization, secondary extrusion, multi-monomer fusing and grafting, etc. The polarity of the special material for the bumper is changed by multi-monomer fusing and grafting modification of methyl methacrylate and so on, and the surface activity of the special material for the bumper is increased; and spray coating paint of the bumper comprises a plurality of chemical compositions, the appetency of various compositions and given functional groups is insufficient, a plurality of active functional groups are formed on the surface of the material by activation of a plurality of functional groups and can simultaneously form physical absorption or chemical bonding with the various chemical compositions in the paint, thereby the special material can perform direct spray coating without flame treating, achieves the optimum spray coating effect, and has good processing fluidity and high toughness.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation of monodisperse porous polymer microsphere
The invention provides a preparation method of a monodisperse porous polymer microsphere. After a second stage of swelling of two-stage seed swelling polymerization, remnant monomer separation technology is adopted to avoid the aggregation of the microspheres and the generation of secondary particles, thereby greatly improving the stability of preparing monodisperse porous polymer microsphere through the two-stage seed swelling polymerization. The two-stage seed swelling polymerization can stably prepare the following monodisperse porous polymer microspheres: P(St-co-DVB) (PSD for short) and P(St-co-DVB-co-MMA) (PSDA for short), wherein, St is referred to as styrene, DVB as divinybenzene, MMA as methyl methacrylate, AN as acrylonitrile and co as copolymerization. The monodisperse porous polymer microsphere PSDA prepared by the method can be seen in an attached drawing.
Owner:芜湖万隆新材料有限公司
Nanometer blocking agent for oil-based drilling fluid and preparation method of nanometer blocking agent
ActiveCN104194750ASimple operation processReduce API filtration lossDrilling compositionCross-linkEmulsion
The invention provides a nanometer blocking agent for an oil-based drilling fluid and a preparation method of the nanometer blocking agent. The nanometer blocking agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 10-40 parts of styrene, 20-60 parts of methyl methacrylate, 0.3-1.0 part of emulsifier, 130-150 parts of deionized water, 1.0-2.0 parts of cross-linking agent and 0.1-0.2 part of redox initiator. The preparation method of the nanometer blocking agent comprises the following steps of mixing the emulsifier, the cross-linking agent and deionized water and evenly stirring to obtain a mixture; adding styrene and methyl methacrylate into the mixture and emulsifying for 20-30 minutes to obtain a pre-emulsion; adding the redox initiator into the 20-35wt% pre-emulsion, raising the temperature to 60-80 DEG C, reacting for 20-30 minutes, dropwise adding the residual pre-emulsion and continuously reacting at 60-80 DEG C for 2-5 hours to obtain the nanometer blocking agent for the oil-based drilling fluid. Due to adoption of the nanometer blocking agent for the oil-based drilling fluid disclosed by the invention, the nanoscale microcrack can be effectively blocked and the problem that the well wall of a shale gas well easily collapses is solved and the nanometer blocking agent is simple in preparation method.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Branched (Meth)acrylate Copolymer with High Refractive Index and Method for Preparing the Same
Disclosed herein is a branched (meth)acrylate copolymer prepared by polymerizing a monomer mixture comprising (A) about 20 to about 99.999% by weight of a (meth)acrylate monomer having a refractive index higher than methyl methacrylate; (B) about 0 to about 79.999% by weight of a mono-functional unsaturated monomer; and (C) about 0.001 to about 10% by weight of a crosslinking monomer. The copolymer has a refractive index of about 1.495 to about 1.590.
Owner:LOTTE ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for preparing and transferring graphene transparent film
ActiveCN102719803AIncrease contactNo crackGrapheneChemical vapor deposition coatingElectrochemistryCvd graphene
The invention discloses a method for preparing and transferring a graphene transparent film. The technical problem required be solved is that impurities, cracks and bumps after the graphene transparent film is transferred are required to be reduced. The preparing and transferring method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of: carrying out chemical vapor deposition on the graphene film on a metal substrate, coating methyl methacrylate or photoresist to form a support layer; electrolyzing the graphene film and separating the metal substrate; and coating the methyl methacrylate or photoresist on the support layer, putting the support layer into acetone solution, and attaching the graphene film to an appointed substrate. Compared with the prior art, the film composed of the graphene film and the support layer is separated from the metal substrate by an electrochemical foaming method; the graphene film is transferred to an appointed substrate and then the graphene film well contacts the plane of the appointed substrate without the cracks by spin coating for second time; the metal substrate can be repeatedly used, and the cost of preparation of the graphene transparent film is reduced; the transferred graphene film is well contacted with the substrate, and the impurities are relatively few.
Owner:BTR NEW MATERIAL GRP CO LTD
Production of methyl a-methacrylate with methanal as raw material
InactiveCN101074192AImprove conversion rateReduce manufacturing costPreparation by aldehyde oxidation-reductionMethacrylateDivinylbenzene
Production of methyl-methyl acrylate from methanal is carried out by reacting methanal with propanal in diethylamine muriate solution at 40-45 degree to obtain methyl-acryl, mixing methyl-acryl with methanol in proportion of 30-50:1, adding them into reactor, adding into 2.0-4.0% catalyst, inducing into oxygen at 40-60 degree and flow 10 ml / min, reacting for 4-6 hrs and synthesizing to obtain final product. The catalyst carrier is styrene-divinylbenzene polymer organic resin, which consists of palladium 2-5 wt%, bismuth 0-3 wt%, lead 0.3-1 wt% and iron 0.3-1 wt%. It's cheap, has friendly reactive environment, better selectivity and conversion rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Polymer blends of biodegradable or bio-based and synthetic polymers and foams thereof
The present invention relates to compositions comprising blends of alkenyl aromatic polymers such as styrenic polymers (i.e. PS and HIPS) and bio-based or biodegradable polymers (i.e. PLA, PGA, PHA, PBS, PCL) compatibilized with styrene-based copolymers (i.e. styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene (SEBS) block copolymers, maleated SEBS, styrene-maleic anhydride (SMA) copolymer, styrene-methyl methacrylate (SMMA) copolymer) or a mixture of two or more styrene-based copolymers such as SEBS and SMA. These novel compositions can be extruded and thermoformed to produce very low density food service and consumer foam articles such as plates, hinged lid containers, trays, bowls, and egg cartons with good mechanical properties.
Owner:PACTIV CORP
Thermoplastic Resin Composition And Molded Article Comprising The Same
ActiveUS20070276090A1Increase resistanceHigh transparencyDyeing processRefractive indexAcrylic polymer
A thermoplastic resin composition comprising a polylactic acid polymer (A), an acrylic polymer (B) containing units of methyl methacrylate monomer, and a graft copolymer (C) obtained by graft-polymerizing a vinyl monomer onto a rubbery polymer, wherein the refractive index, Rc, of the graft copolymer (C) and the total refractive index, Rab, of the polylactic acid polymer (A) and the acrylic polymer (B) satisfy the following formula (1). −0.004≦−Rc−Rab≦+0.008 (1)
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
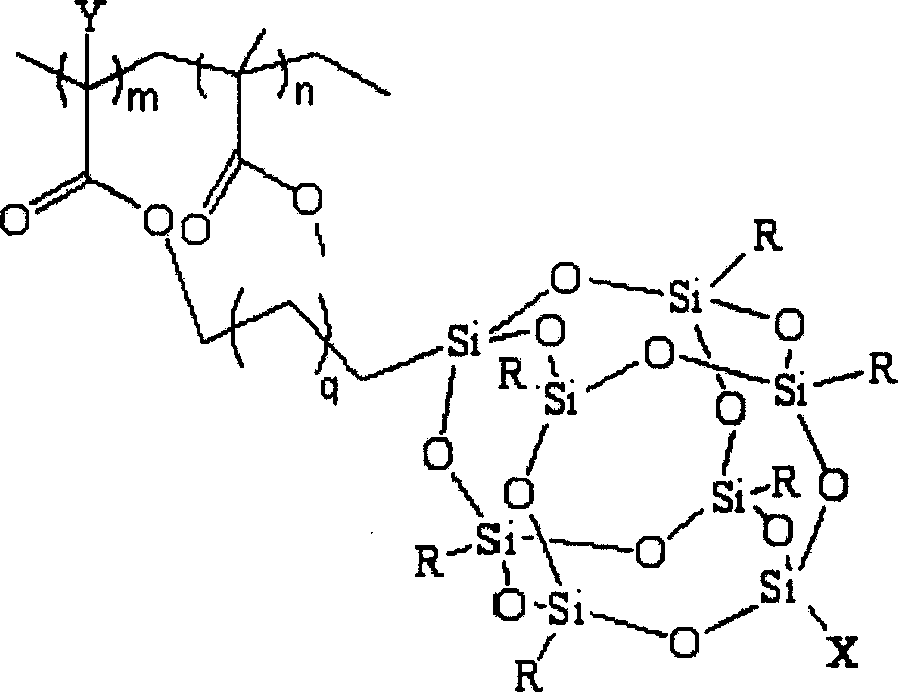
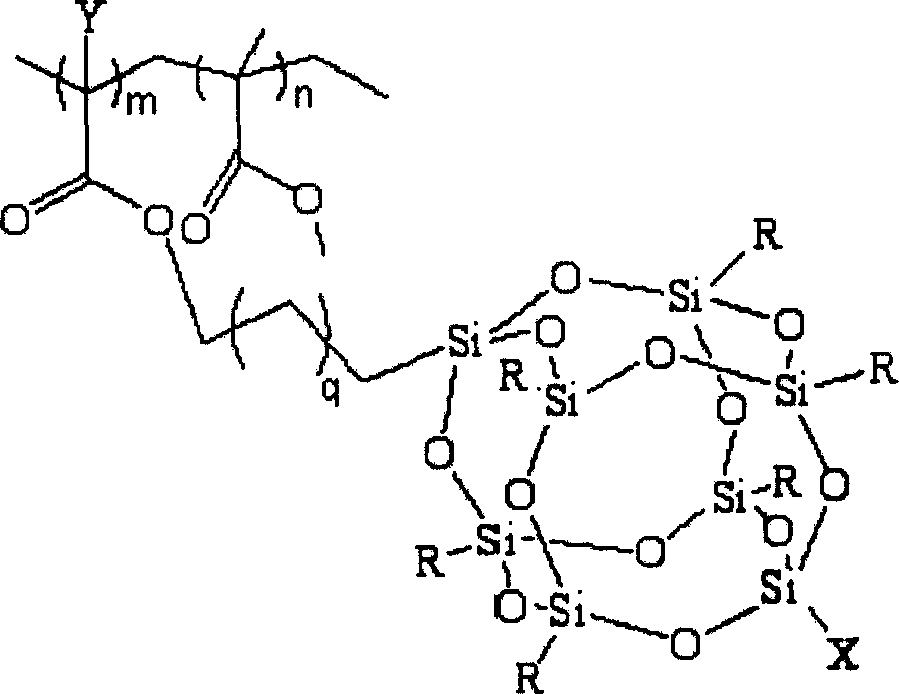
Fluoride POSS acrylic ester block multipolymer resin and its synthesis
InactiveCN101029137AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove hydrophobicityCyclohexanonePolymer science
A fluoride POSS acrylic resin block copolymer resin and its synthesis are disclosed. The molecular-weight of copolymer Mn is 20000-60000, Mn / Mw is 1.1-1.5, contact angle between coating and water is 85-120degree. The process is carried out by adding components into reactor to obtain methyl acrylate performed polymer with Br end capping, reacting with CuBr, PMDETA and F-POSS, removing catalyst from reactant, depositing while filtering by methanol, vacuum drying to constant weight to obtain the final product. The polymer powders can be dissolved into acetic ether, acetone, 1,2-dichloroethane, dioxane and cyclohexanone or their mixtures, then it can be used for coating or filming.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com