Patents
Literature
871 results about "Tensile strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tensile strain is the relative length of deformation exhibited by a specimen subjected to a tensile force.
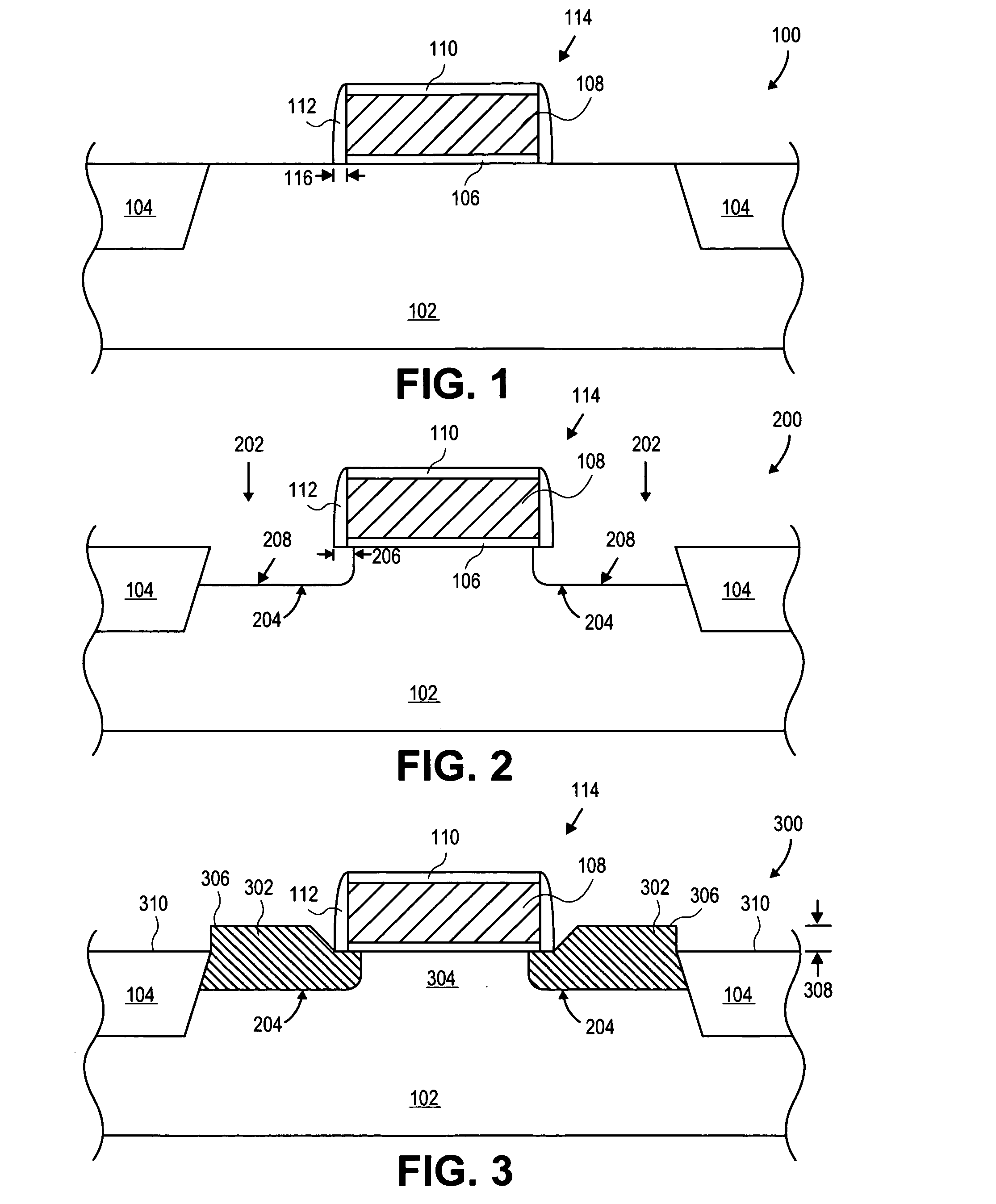
SiGe selective growth without a hard mask
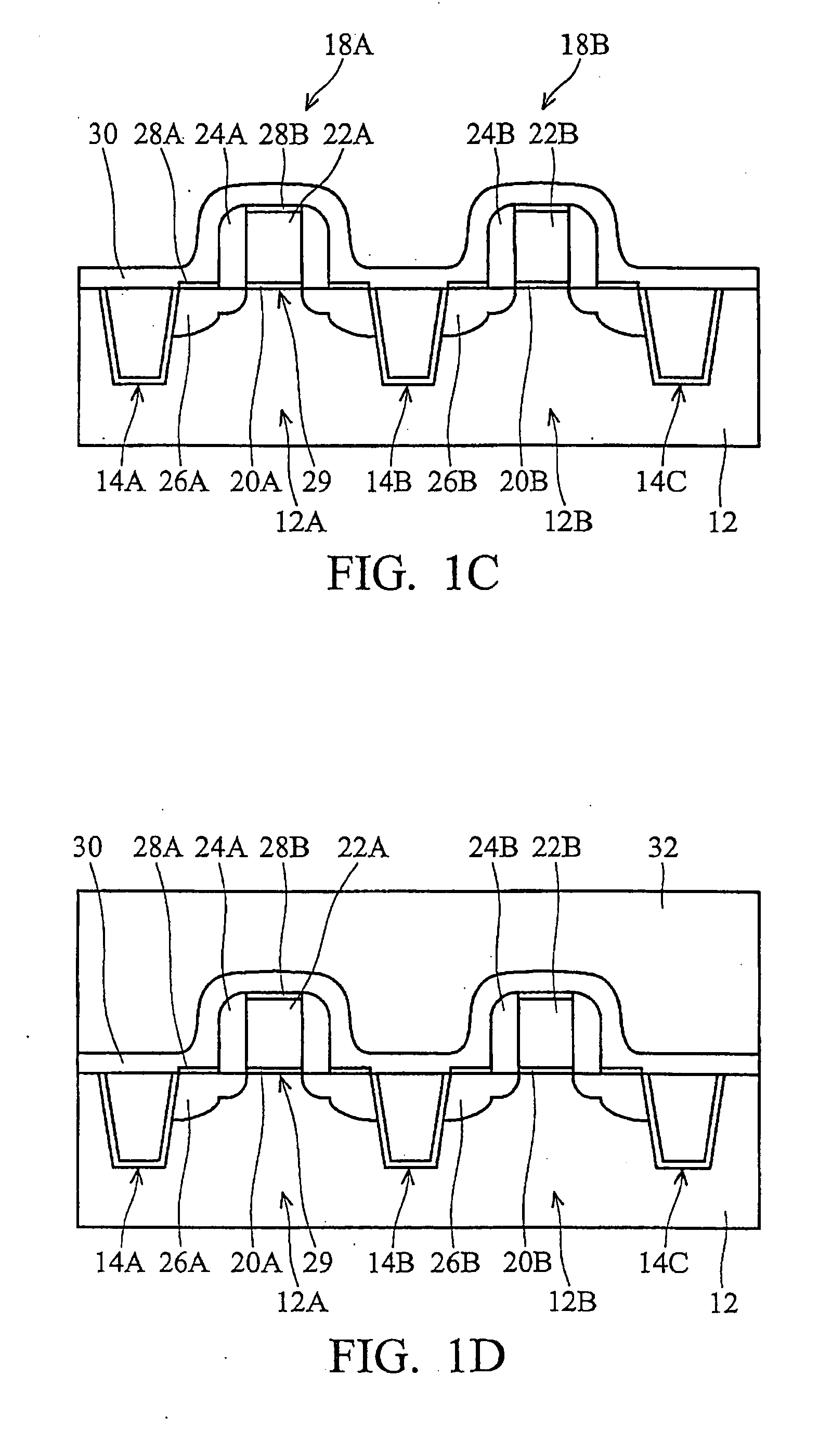
InactiveUS20080083948A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTensile strainCharge carrier mobility
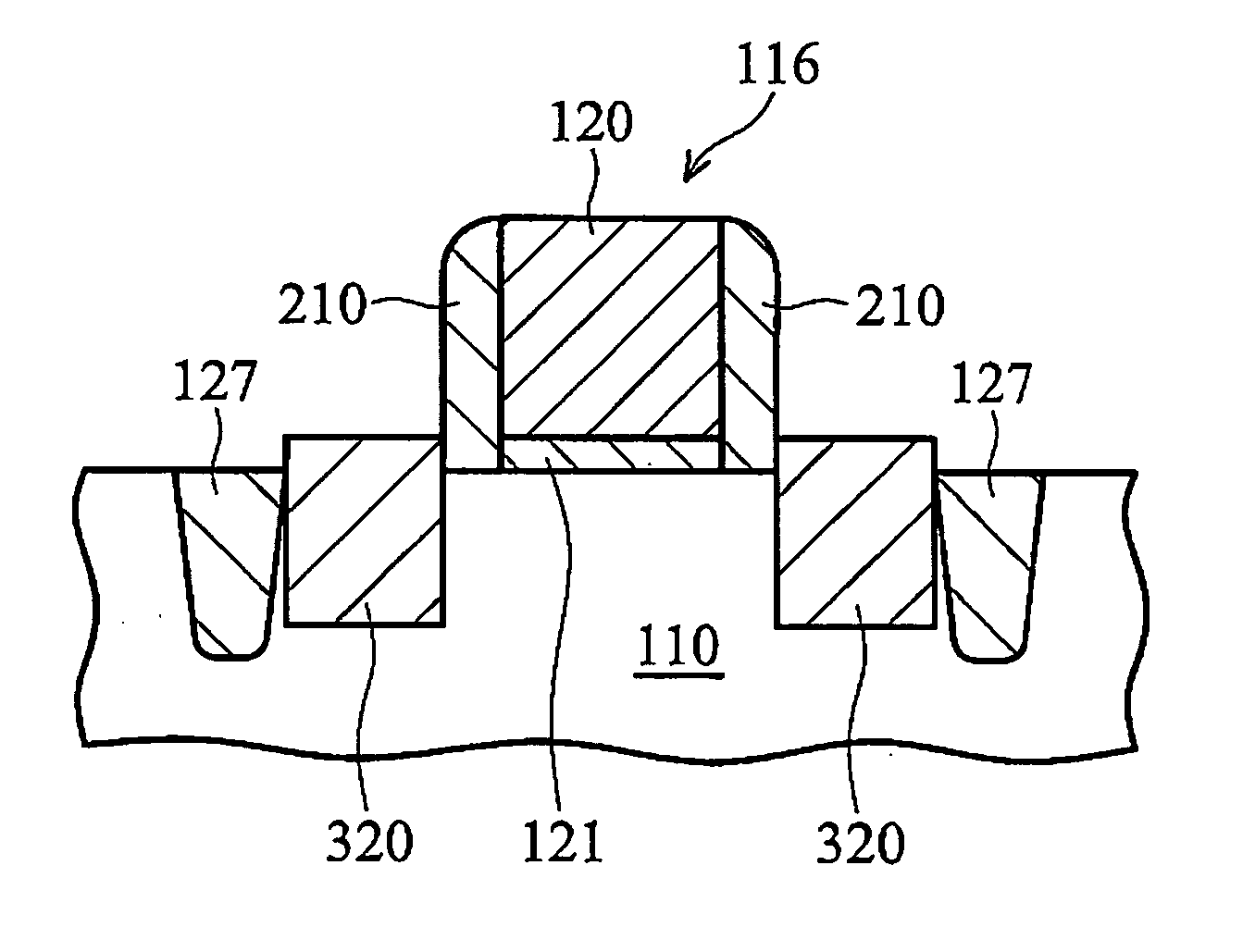
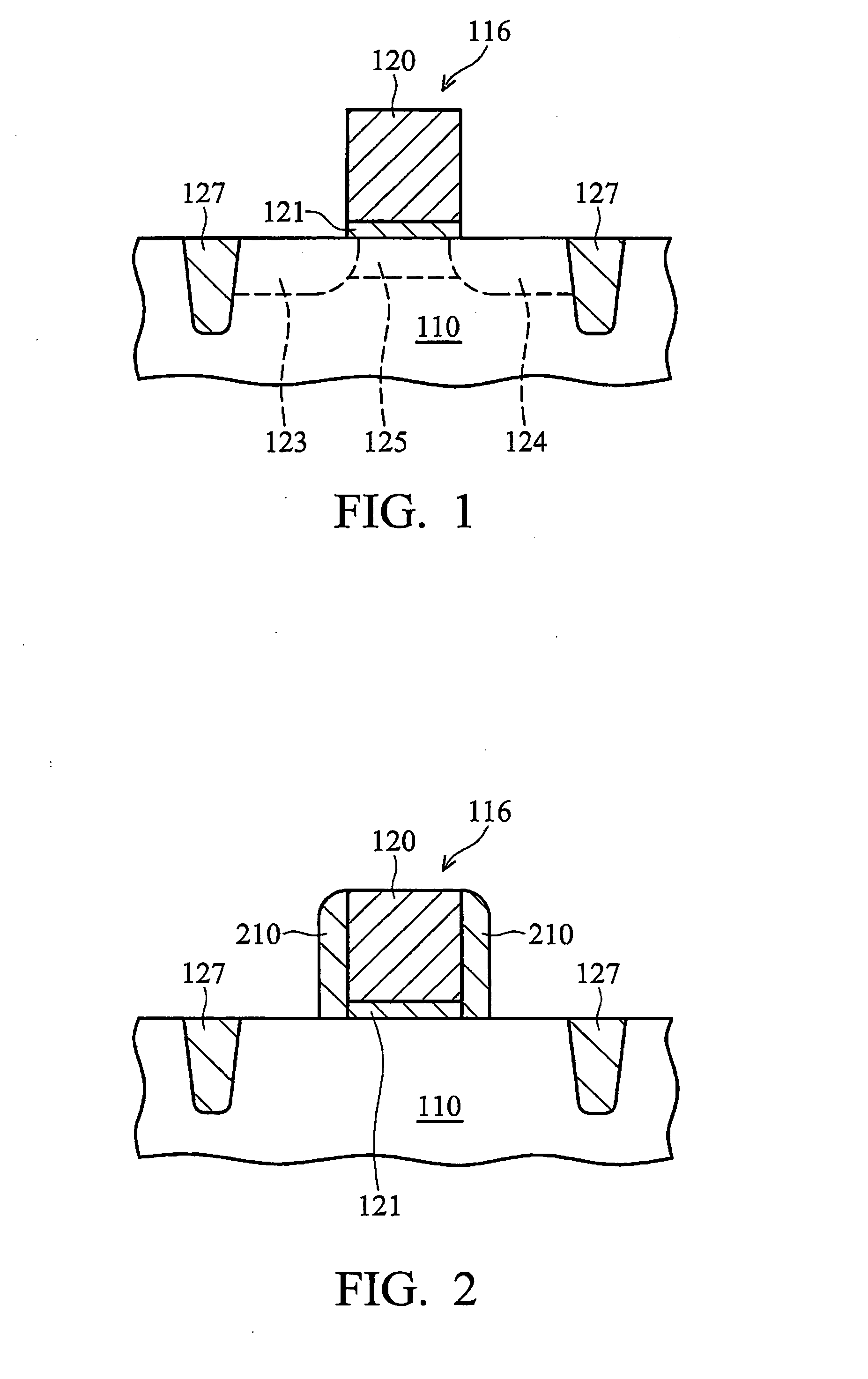
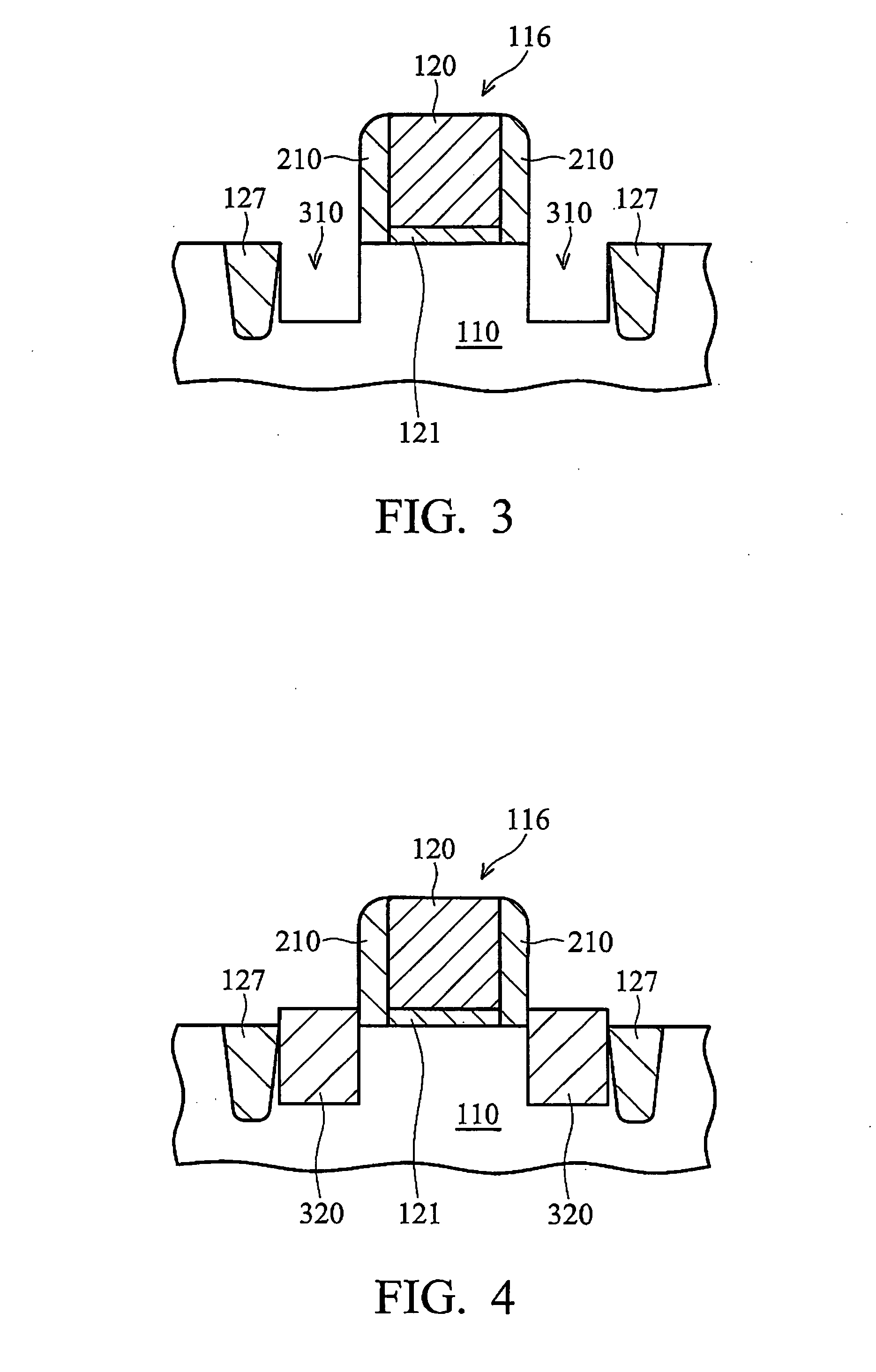
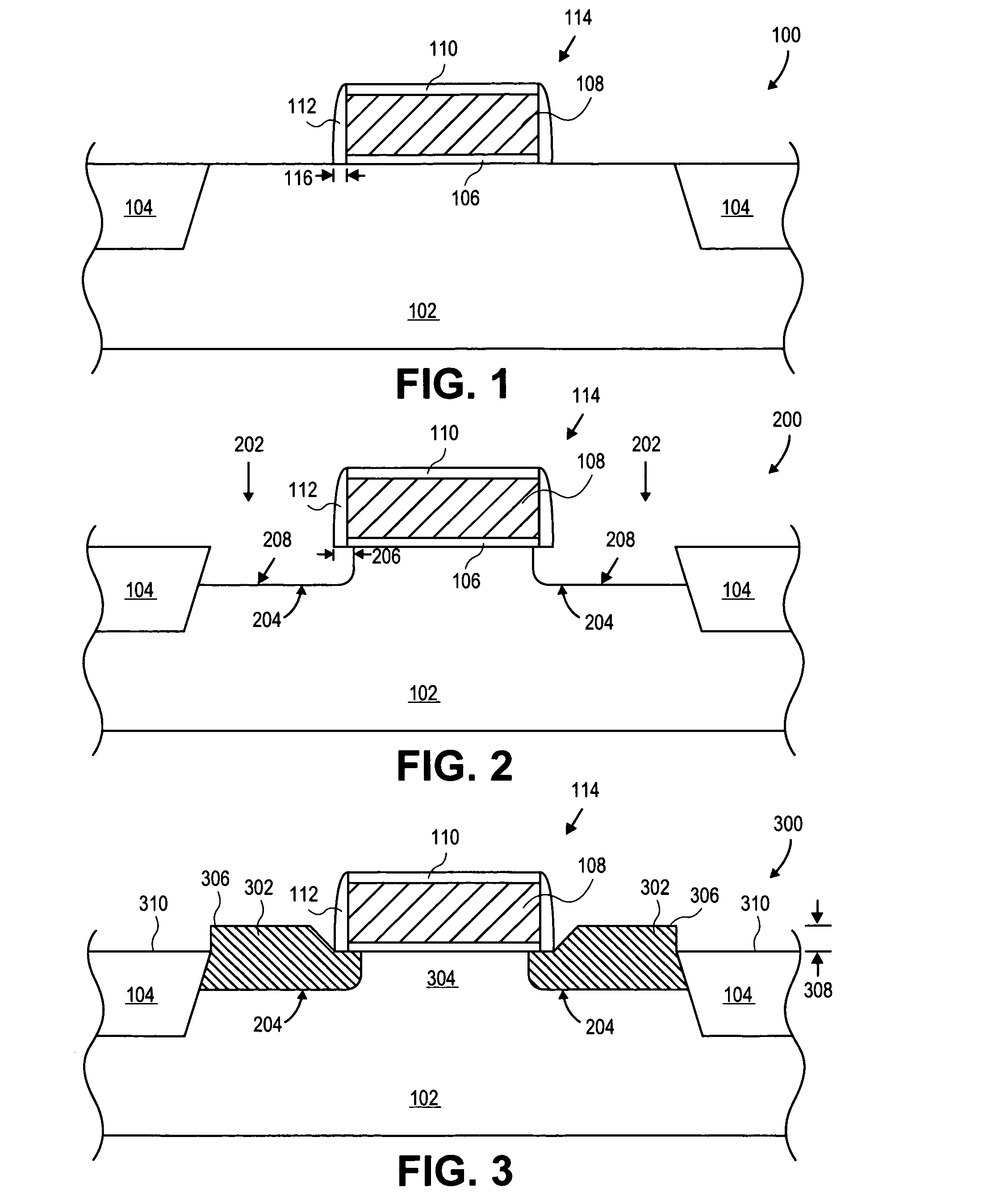
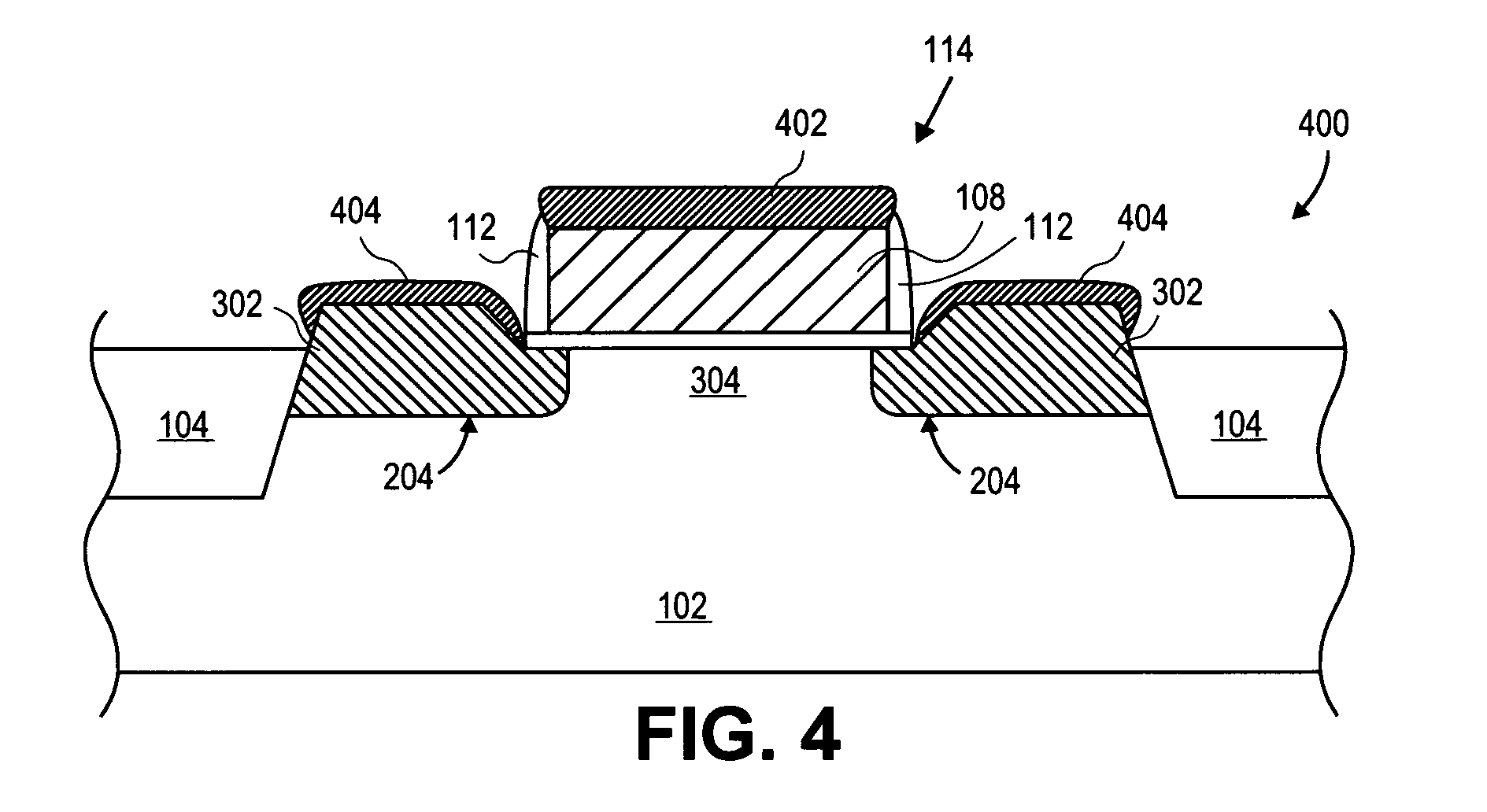
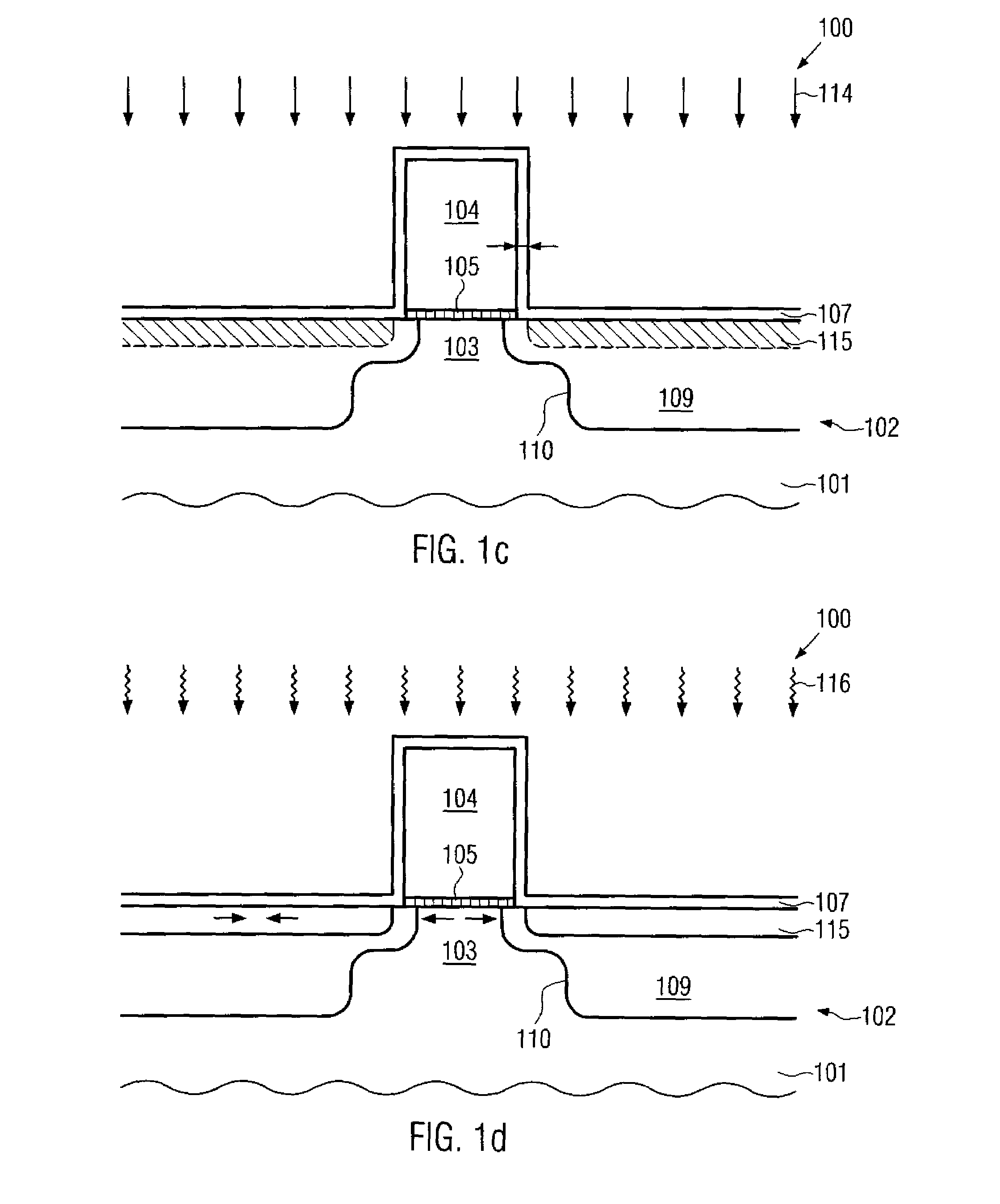
MOS transistors having localized stressors for improving carrier mobility are provided. Embodiments of the invention comprise a gate electrode formed over a substrate, a carrier channel region in the substrate under the gate electrode, and source / drain regions on either side of the carrier channel region. The source / drain regions include an embedded stressor having a lattice spacing different from the substrate. In a preferred embodiment, the substrate is silicon and the embedded stressor is SiGe or SiC. An epitaxy process that includes using HCl gas selectively forms a stressor layer within the crystalline source / drain regions and not on polycrystalline regions of the structure. A preferred epitaxy process dispenses with the source / drain hard mask required of conventional methods. The embedded SiGe stressor applies a compressive strain to a transistor channel region. In another embodiment, the embedded stressor comprises SiC, and it applies a tensile strain to the transistor channel region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
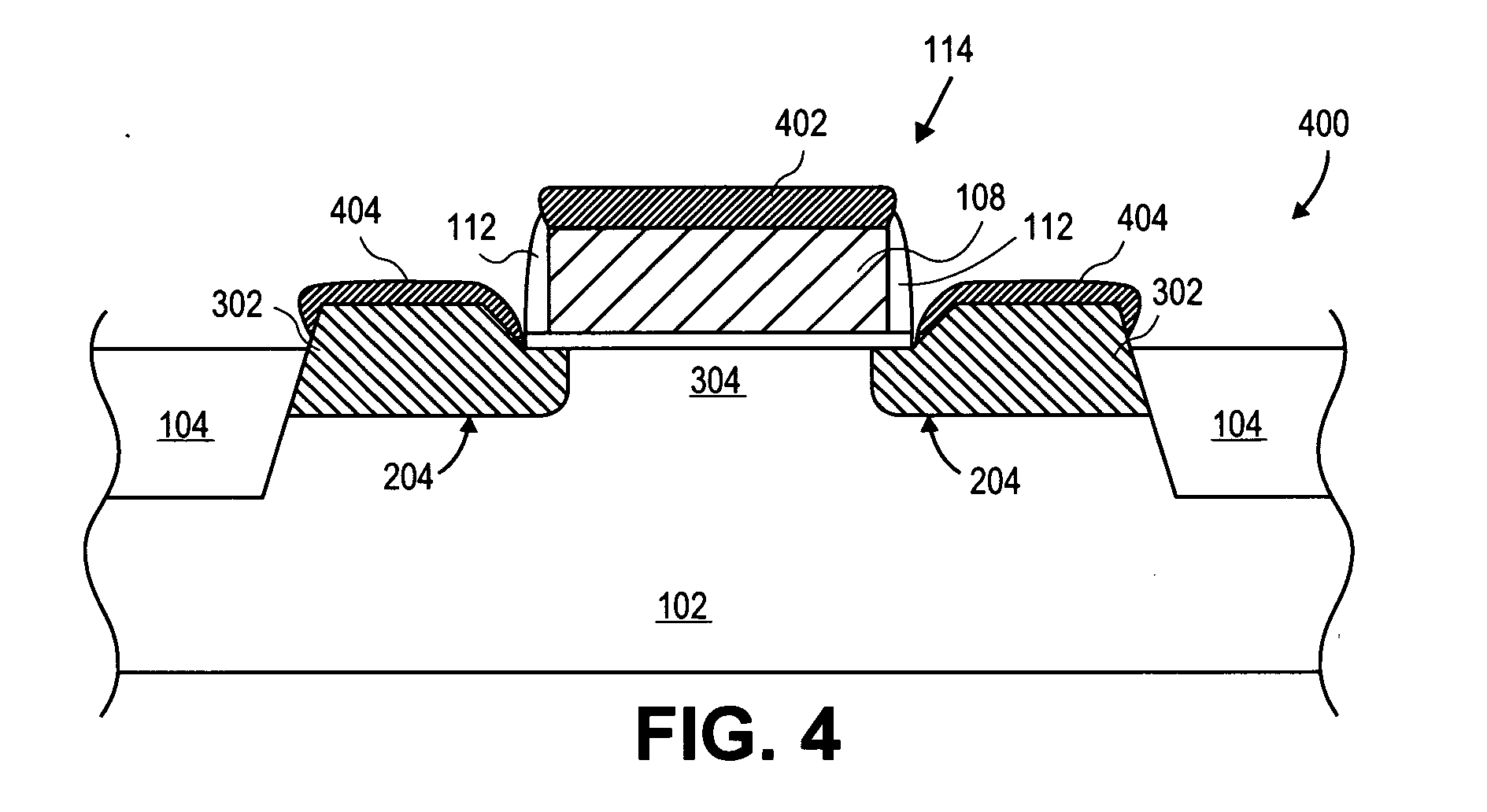
Method for forming an integrated circuit
ActiveUS7402872B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesContact resistanceEpitaxial silicon
A method is described for manufacturing an n-MOS semiconductor transistor. Recesses are formed in a semiconductor substrate adjacent a gate electrode structure. Silicon is embedded in the recesses via a selective epitaxial growth process. The epitaxial silicon is in-situ alloyed with substitutional carbon and in-situ doped with phosphorus. The silicon-carbon alloy generates a uniaxial tensile strain in the channel region between the source and drain, thereby increasing electron channel mobility and the transistor's drive current. The silicon-carbon alloy decreases external resistances by reducing contact resistance between source / drain and silicide regions and by reducing phosphorous diffusivity, thereby permitting closer placement of the transistor's source / drain and channel regions.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Temperature compensation for silicon MEMS resonator
Thermally induced frequency variations in a micromechanical resonator are actively or passively mitigated by application of a compensating stiffness, or a compressive / tensile strain. Various composition materials may be selected according to their thermal expansion coefficient and used to form resonator components on a substrate. When exposed to temperature variations, the relative expansion of these composition materials creates a compensating stiffness, or a compressive / tensile strain.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Strained channel FinFET
InactiveUS6897527B2High carrier mobilityImproving FinFET performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesTensile strainCrystalline materials
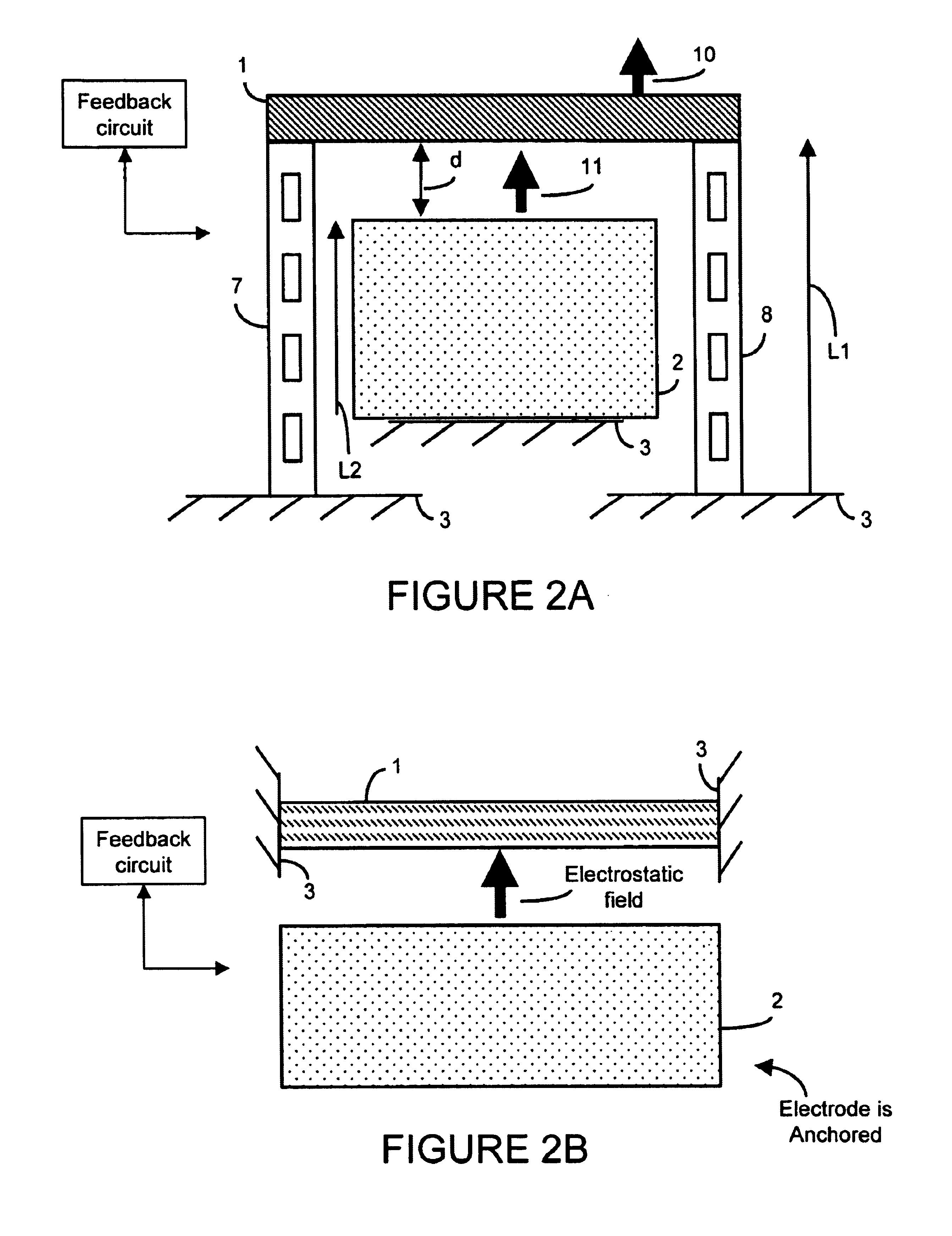
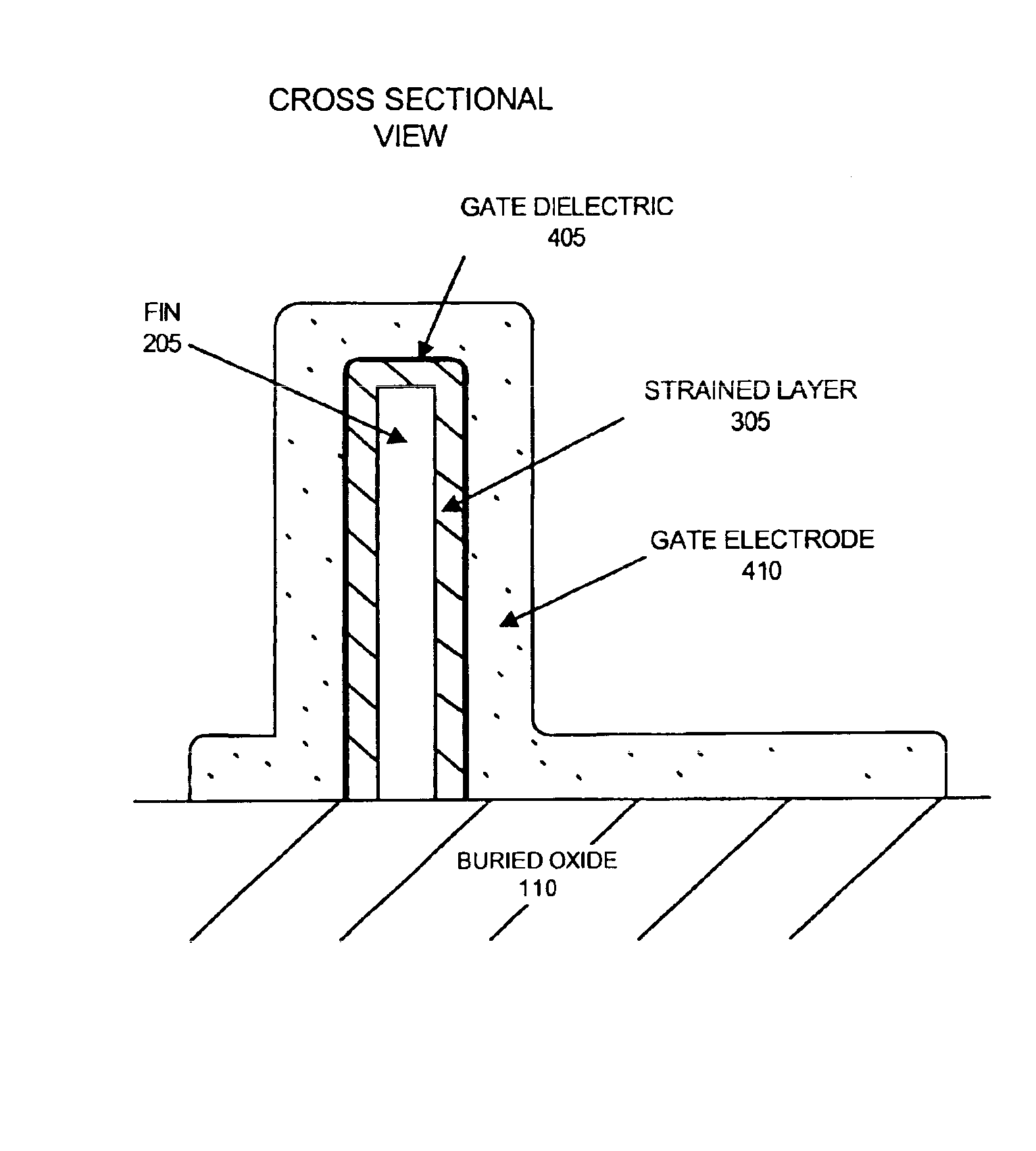
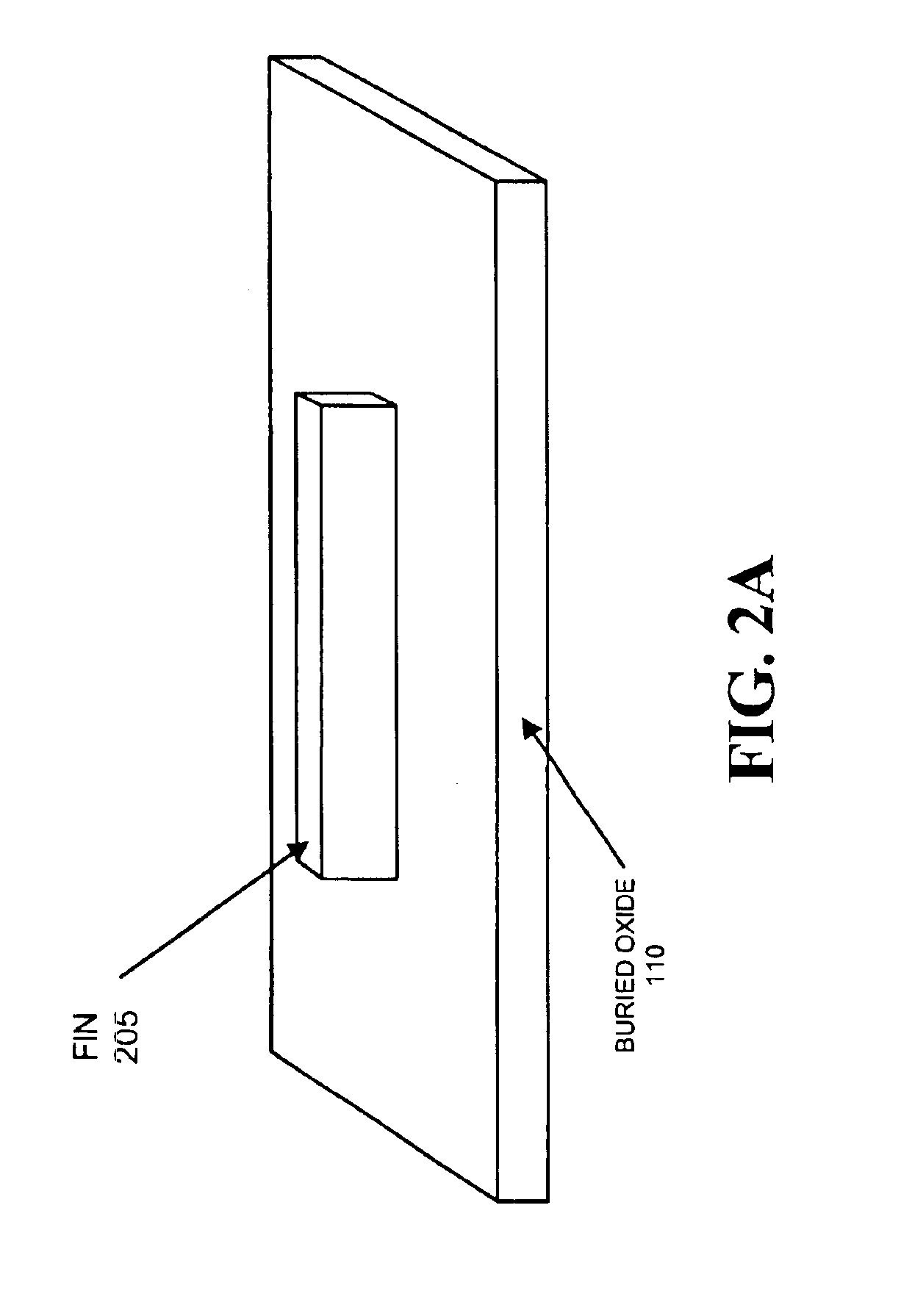
A semiconductor device includes a fin and a layer formed on at least a portion of the fin. The fin includes a first crystalline material. The layer includes a second crystalline material, where the first crystalline material has a larger lattice constant than the second crystalline material to induce tensile strain within the layer.
Owner:INNOVATIVE FOUNDRY TECH LLC
Formation of silicided surfaces for silicon/carbon source/drain regions
Formation of a silicide layer on the source / drain regions of a field effect transistor with a channel under tensile strain is disclosed. The strain is originated by the silicon / carbon source / drain regions which are grown by CVD deposition. In order to form the silicide layer, a silicon cap layer is deposited in situ by CVD. The silicon cap layer is then employed to form a silicide layer made of a silicon / cobalt compound. This method allows the formation of a silicide cobalt layer in silicon / carbon source / drain regions, which was until the present time not possible.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Laser sinter powder with a metal salt and a fatty acid derivative, process for its production, and moldings produced from this laser sinter powder
InactiveUS20050027050A1Improve the immunityMaintain good propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusFibre treatmentSelective laser sinteringPolyamide
The present invention relates to a sinter powder composed of polyamide which also comprises metal salts of weak acids, in particular metal carbonates, and fatty acid derivatives, in particular fatty acid esters or fatty acid amides, to a process for laser sintering, and also to moldings produced from this sinter powder. The moldings formed using the powder of the invention have marked advantages in appearance and in surface finish when compared with conventional products, especially when recyclability in the selective laser sintering (SLS) process is taken into account. Moldings produced from recycled sinter powder of the invention moreover also have markedly improved mechanical properties when compared with moldings based on recycled conventional nylon-12 powders, in particular in terms of modulus of elasticity and tensile strain at break. These moldings also have a density approaching that of injection moldings.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
High-strength and high-toughness reactive powder concrete of carbon doped nano-tube and preparation method of high-strength and high-toughness reactive powder concrete
The invention provides high-strength and high-toughness reactive powder concrete of a carbon doped nano-tube. The high-strength and high-toughness reactive powder concrete is prepared by taking cement, a carbon nano-tube, silica fume, a water reducing agent, silica sand, coal ash, quartz powder, steel fiber and water as raw materials, wherein all the components in the mixture are calculated in parts by mass: 1000-1200 parts of cement, 250-350 parts of silica fume, 250-350 parts of slag powder, 40-50 parts of water reducing agent, 1200-1400 parts of silica sand, 180-230 parts of water, 190-230 parts of steel fiber, 180-250 parts of coal ash, 80-120 parts of quartz powder, 0.1-5 parts of carbon-nano-tube dispersing agent and 1-10 parts of carbon nano-tube powder. The invention also provides a preparation method of the high-strength and high-toughness reactive powder concrete. The reactive powder concrete obtained by the invention has the high compression strength of 250-300MPa and breaking strength of 45-60MPa, which are higher than the 200-level related performances of the traditional RPC (Reactive Powder Concrete). Meanwhile, the initial cracking strength of the reactive powder concrete material prepared by using the carbon nano-tube is greatly improved and is up to 10MPa in a direct stretching state, and the tensile strain corresponding to peak stress is up to more than 0.5%, so that the toughness and strength of the traditional RPC material are greatly improved.
Owner:浙江固邦新材料有限公司
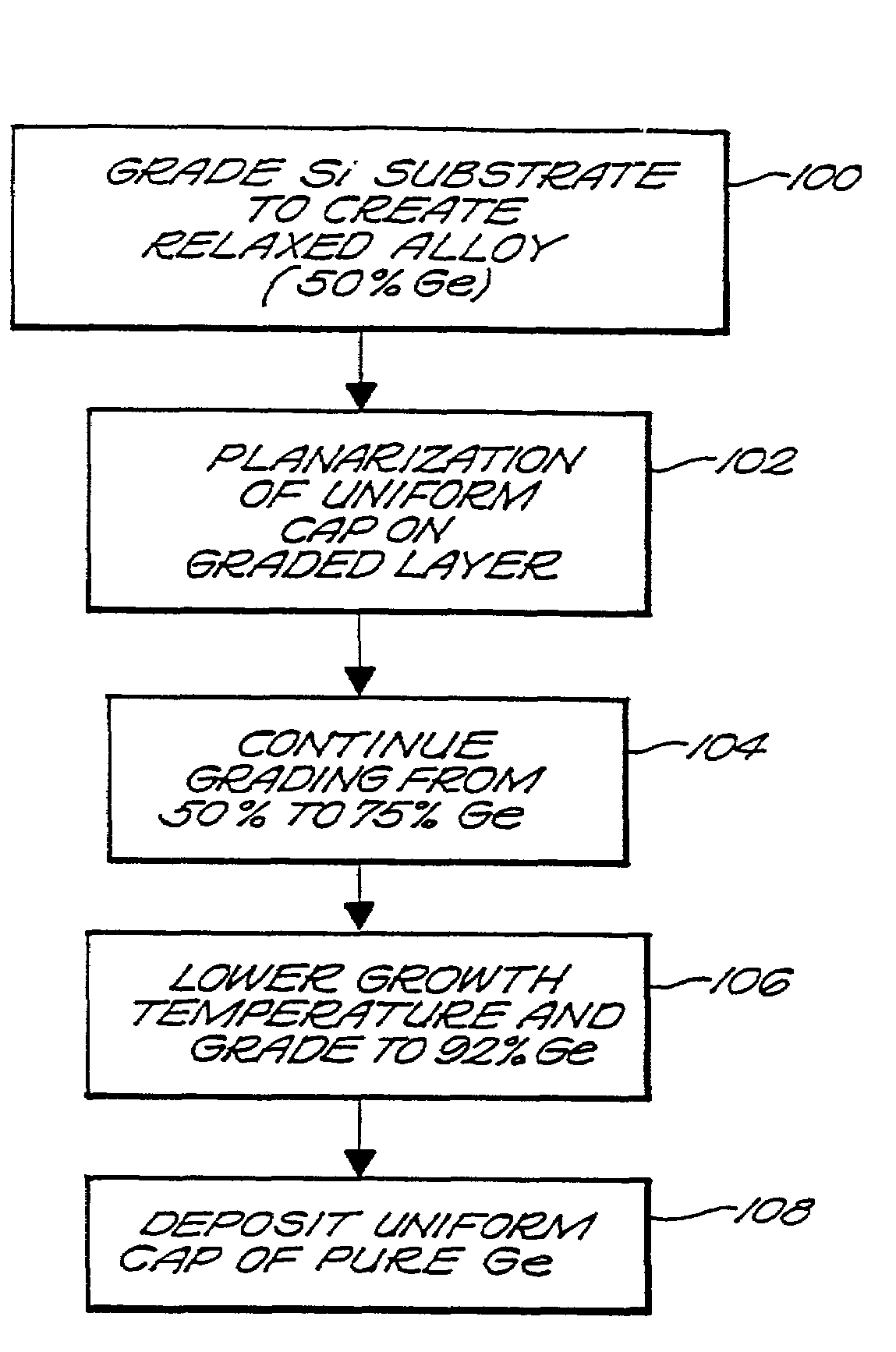
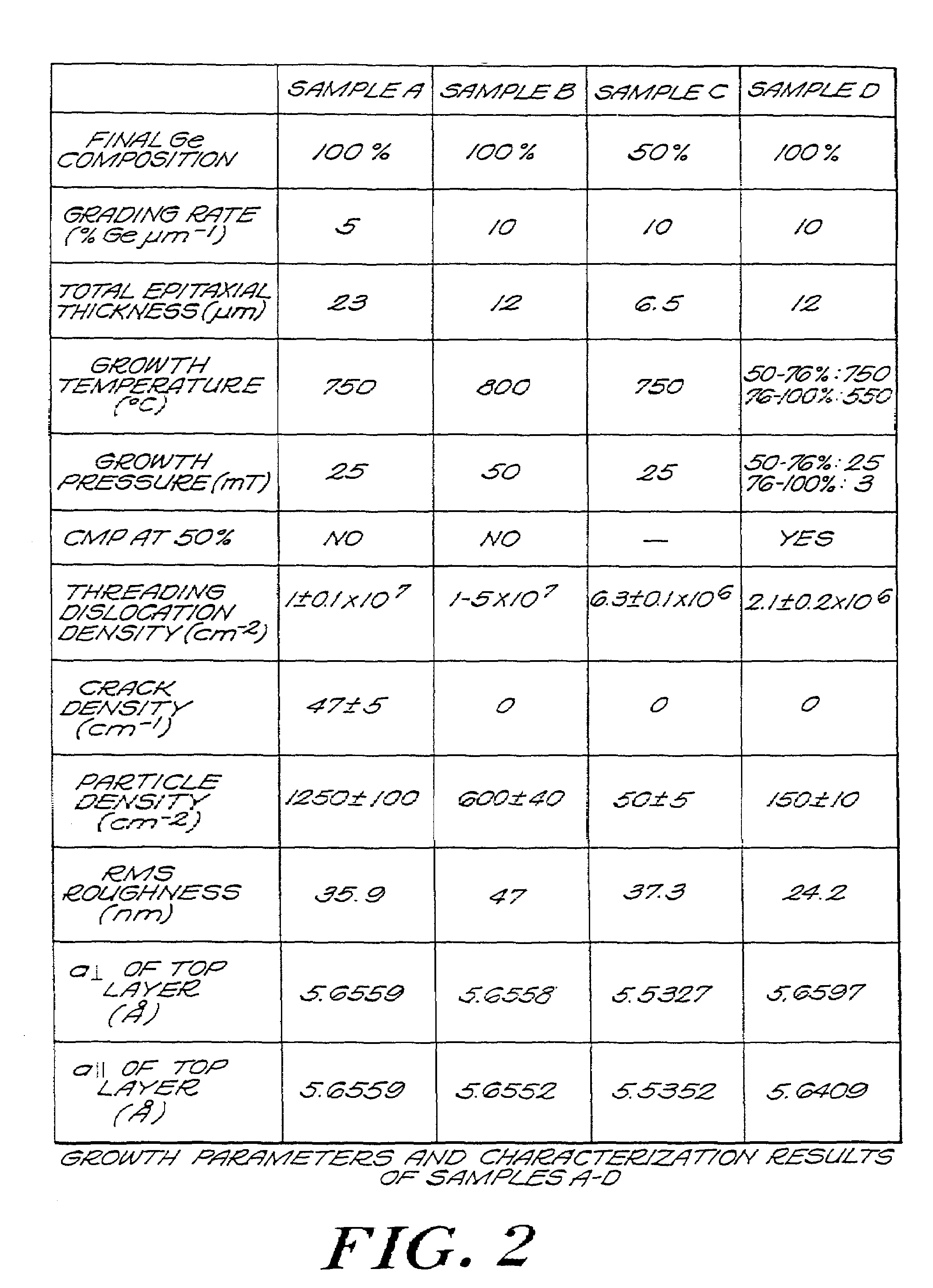
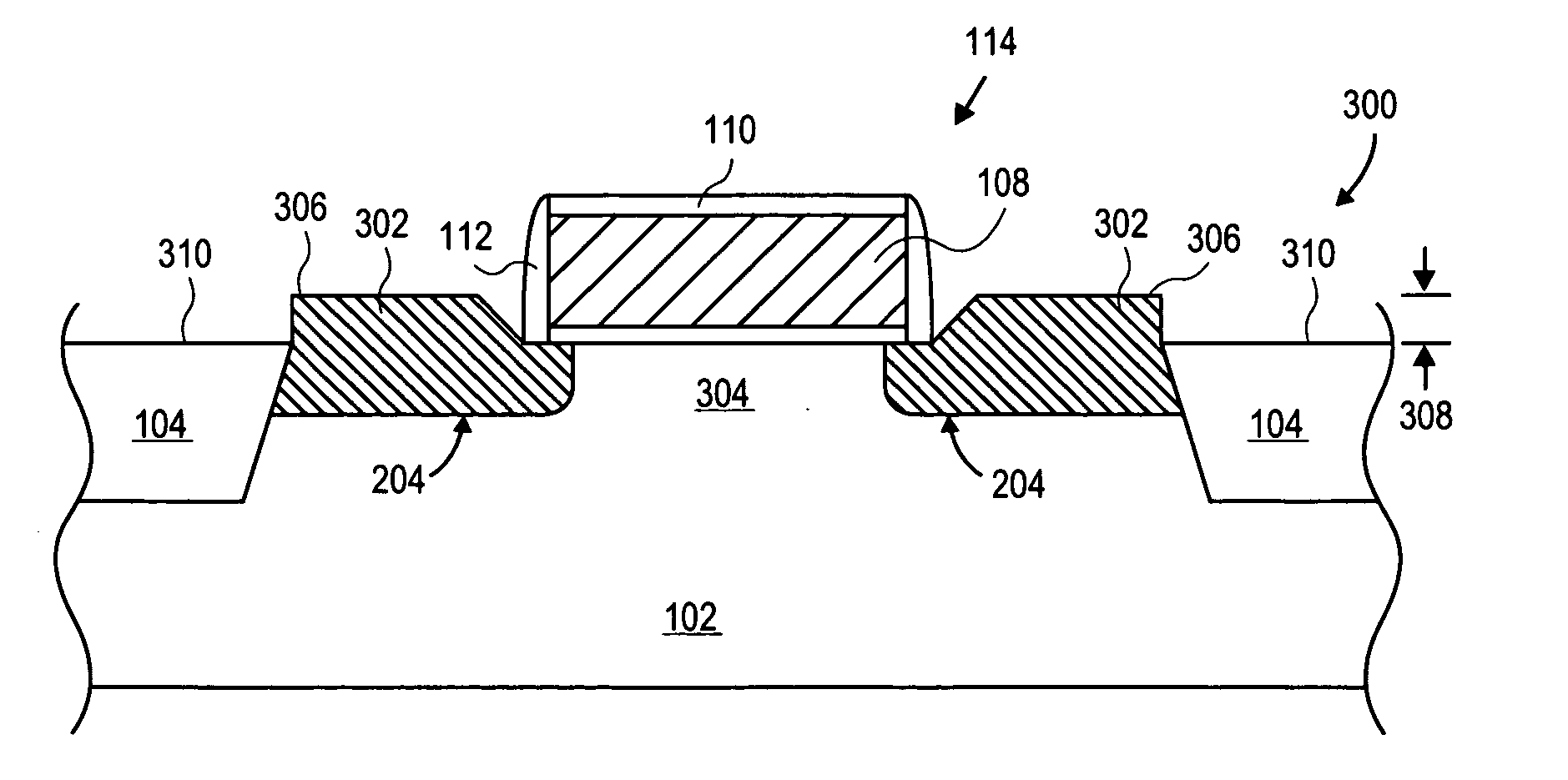
Controlling threading dislocation densities in Ge on Si using graded GeSi layers and planarization
InactiveUS7250359B2Dislocation increaseLight-sensitive devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTensile strainSemiconductor structure
A semiconductor structure including a semiconductor substrate, at least one first crystalline epitaxial layer on the substrate, the first layer having a surface which is planarized, and at least one second crystalline epitaxial layer on the at least one first layer. In another embodiment of the invention there is provided a semiconductor structure including a silicon substrate, and a GeSi graded region grown on the silicon substrate, compressive strain being incorporated in the graded region to offset the tensile strain that is incorporated during thermal processing. In yet another embodiment of the invention there is provided a semiconductor structure including a semiconductor substrate, a first layer having a graded region grown on the substrate, compressive strain being incorporated in the graded region to offset the tensile strain that is incorporated during thermal processing, the first layer having a surface which is planarized, and a second layer provided on the first layer. In still another embodiment of the invention there is provided a method of fabricating a semiconductor structure including providing a semiconductor substrate, providing at least one first crystalline epitaxial layer on the substrate, and planarizing the surface of the first layer.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for forming an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20060131665A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesContact resistanceEpitaxial silicon
A method is described for manufacturing an n-MOS semiconductor transistor. Recesses are formed in a semiconductor substrate adjacent a gate electrode structure. Silicon is embedded in the recesses via a selective epitaxial growth process. The epitaxial silicon is in-situ alloyed with substitutional carbon and in-situ doped with phosphorus. The silicon-carbon alloy generates a uniaxial tensile strain in the channel region between the source and drain, thereby increasing electron channel mobility and the transistor's drive current. The silicon-carbon alloy decreases external resistances by reducing contact resistance between source / drain and silicide regions and by reducing phosphorous diffusivity, thereby permitting closer placement of the transistor's source / drain and channel regions.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
High performance strained channel mosfets by coupled stress effects
InactiveUS20050260806A1Improve device performanceReduce performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETTensile strain
Strained channel transistors including a PMOS and NMOS device pair to improve an NMOS device performance without substantially degrading PMOS device performance and method for forming the same, the method including providing a semiconductor substrate; forming strained shallow trench isolation regions in the semiconductor substrate; forming PMOS and NMOS devices on the semiconductor substrate including doped source and drain regions; forming a tensile strained contact etching stop layer (CESL) over the PMOS and NMOS devices; and, forming a tensile strained dielectric insulating layer over the CESL layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
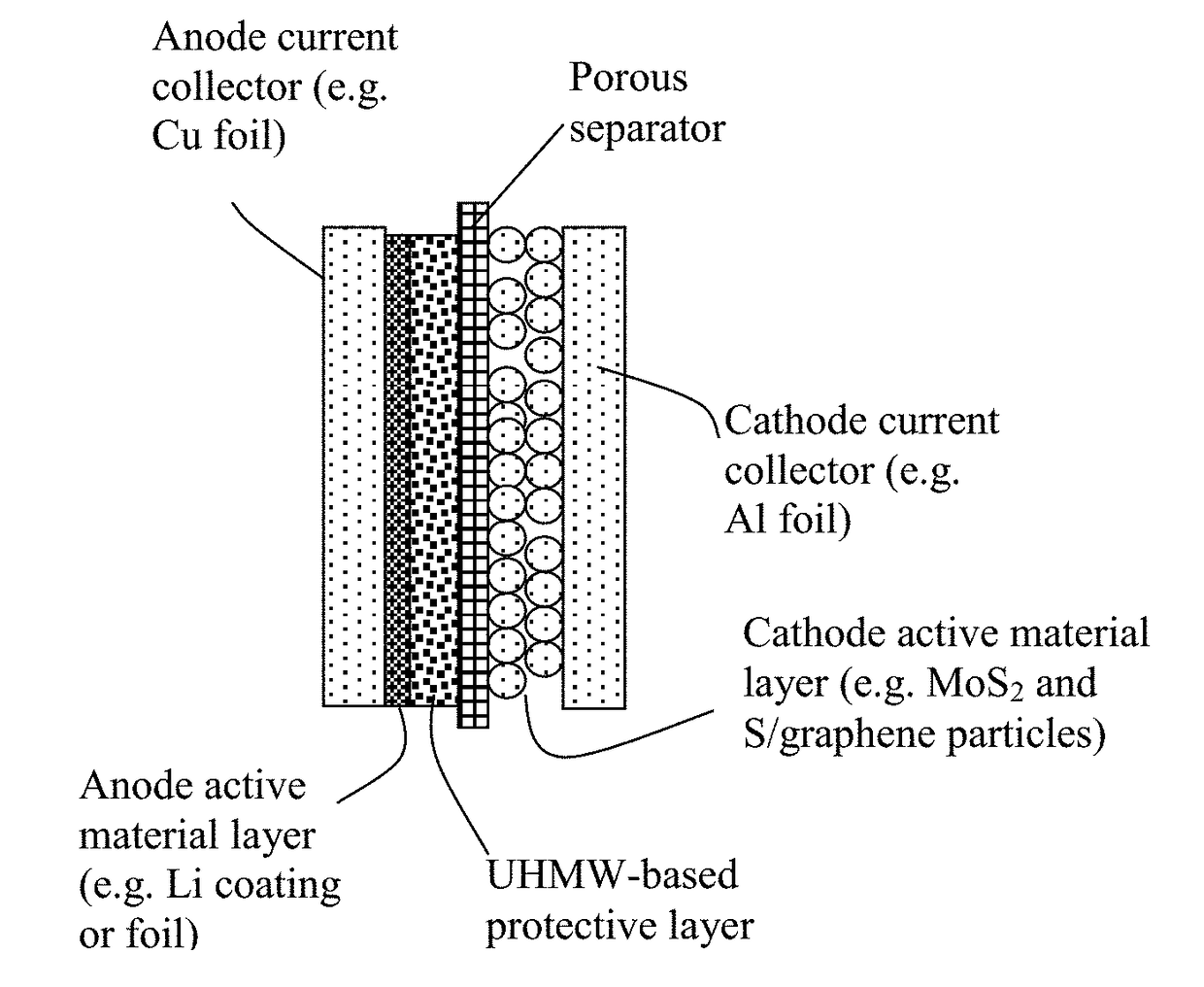
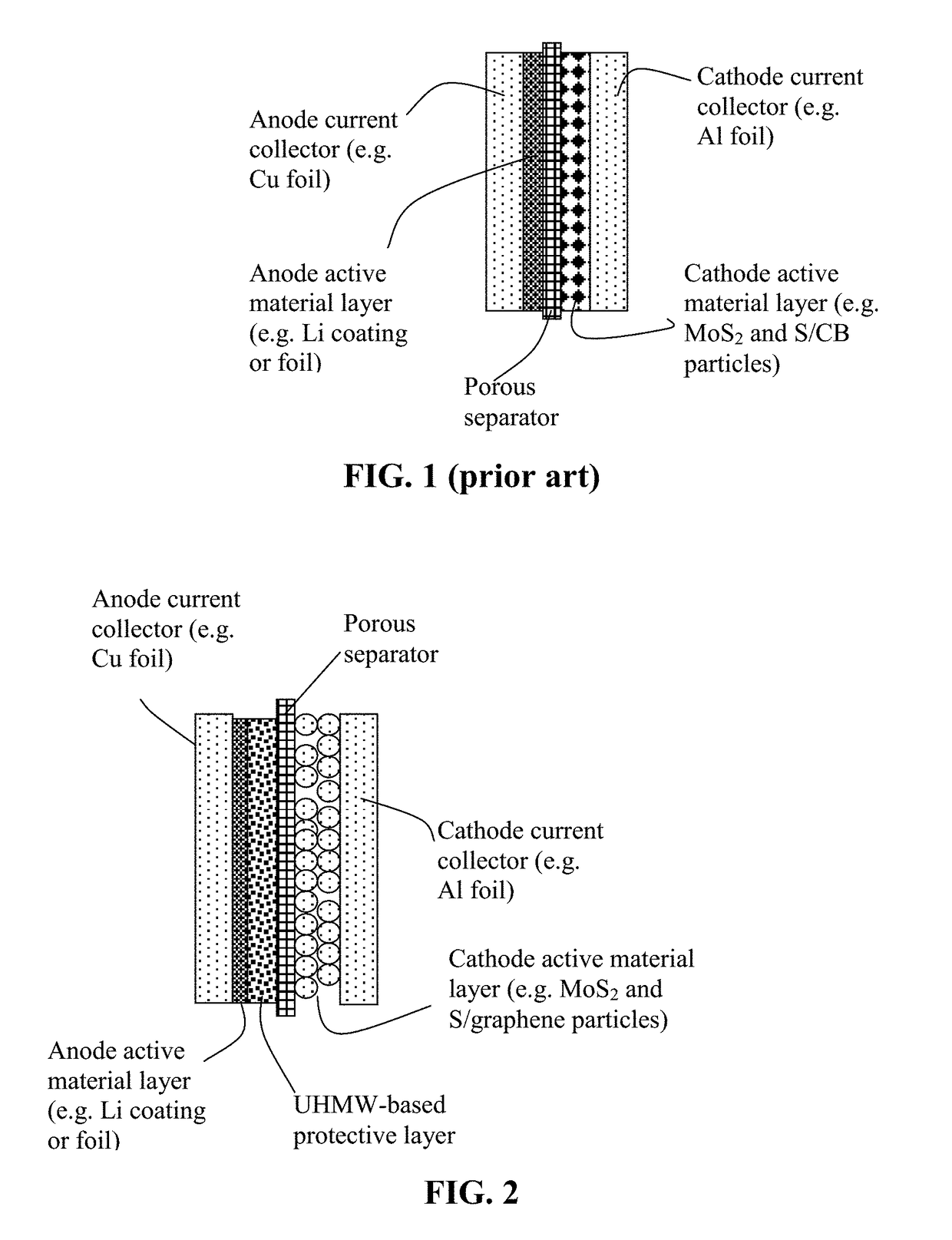
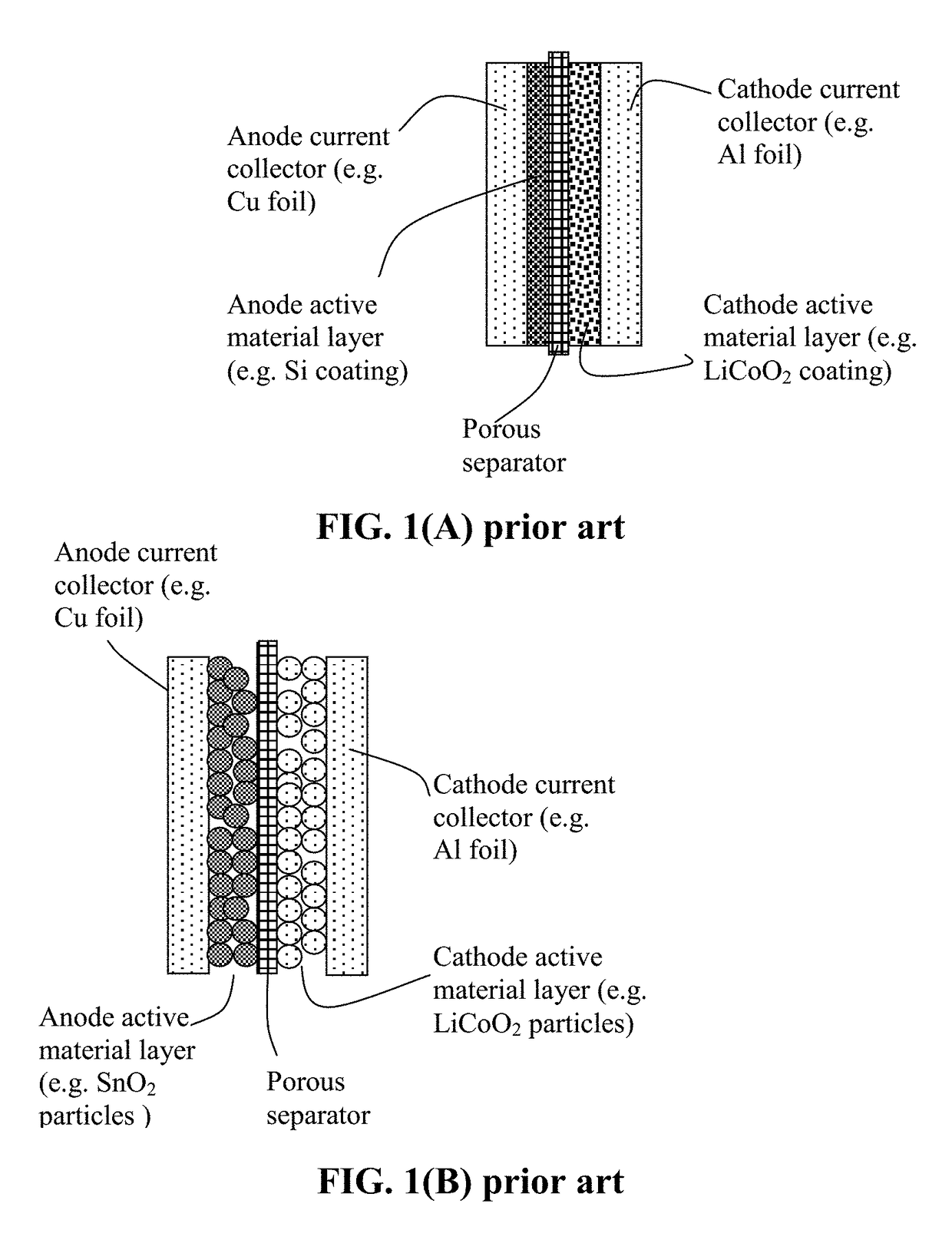
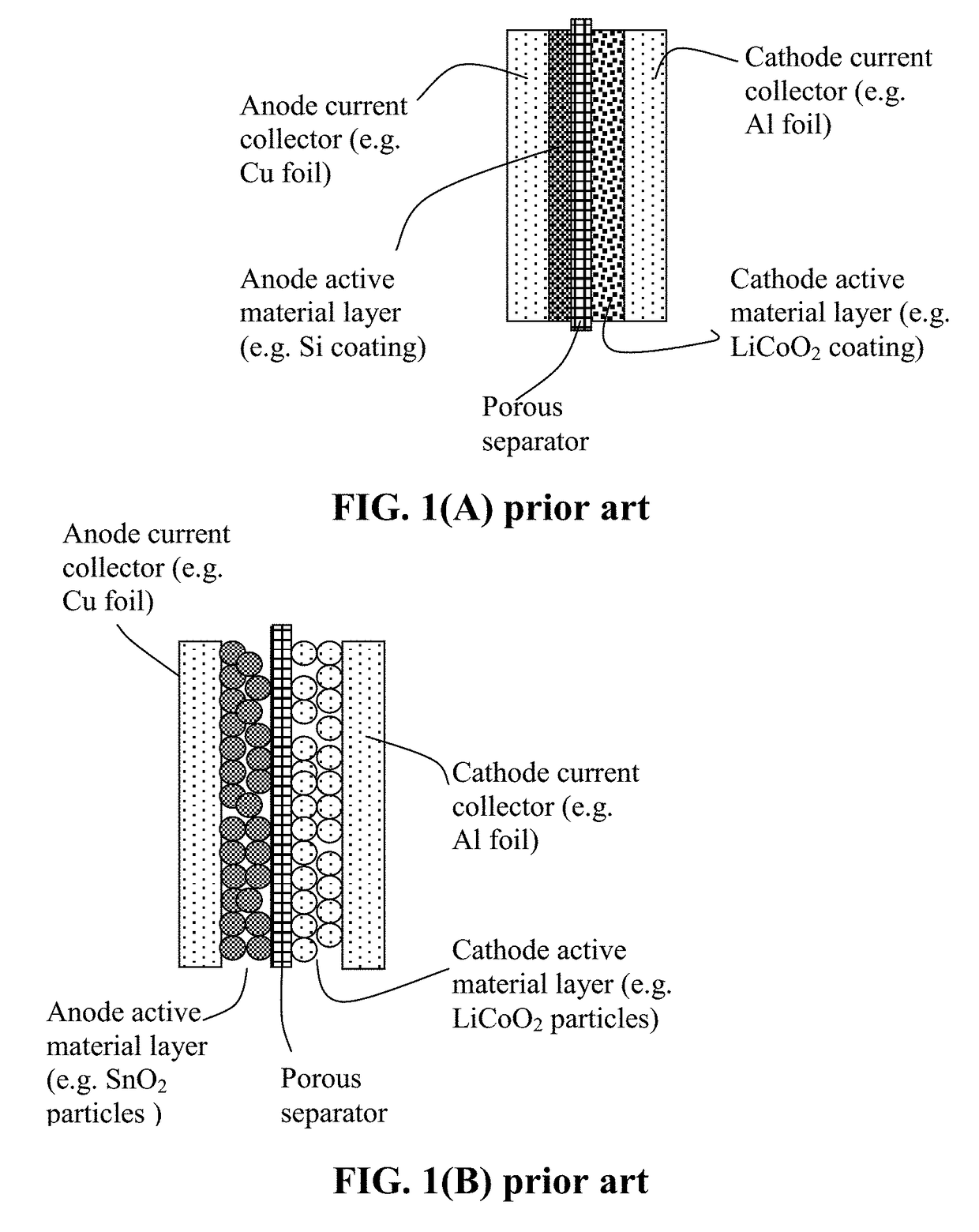
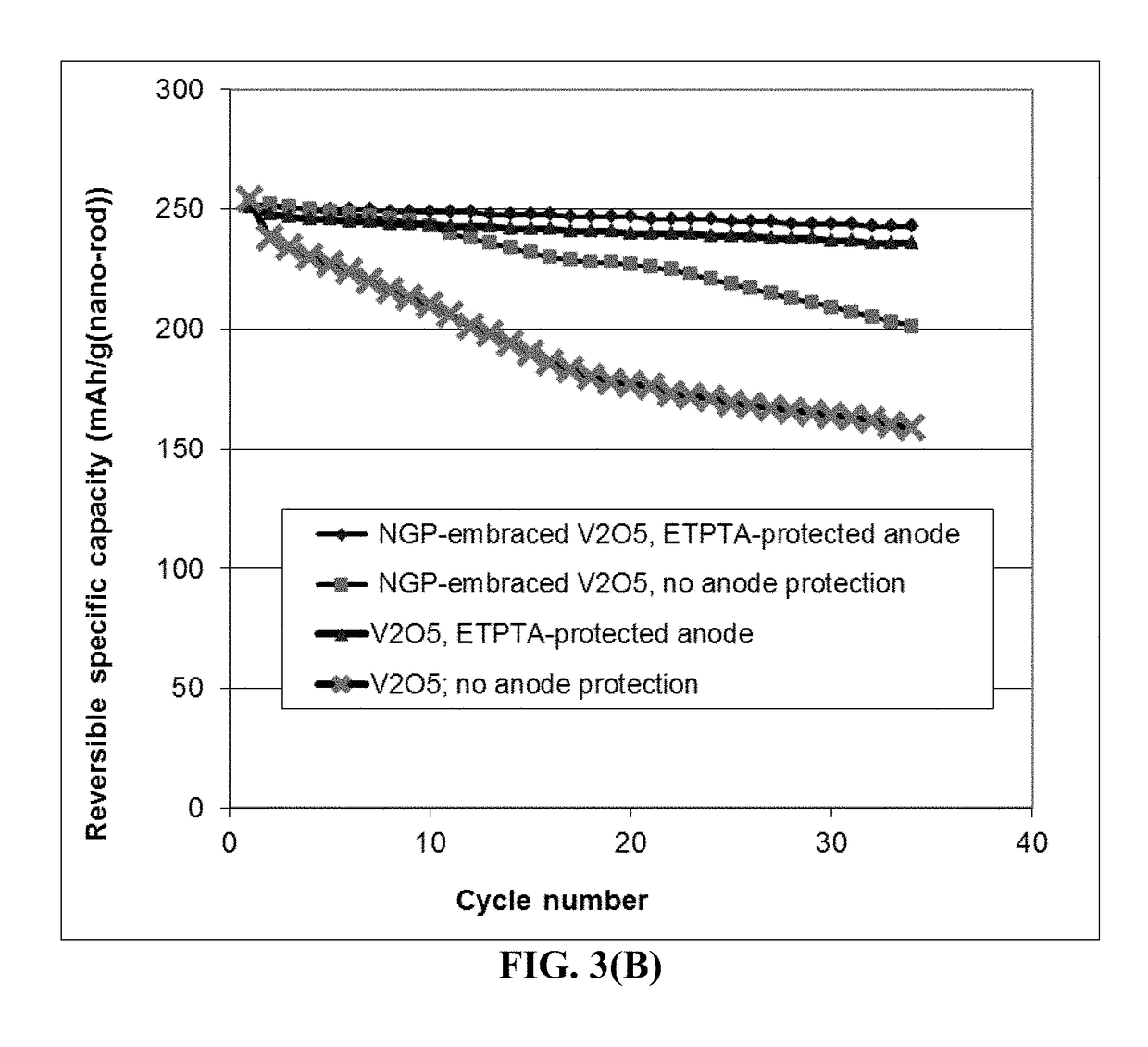
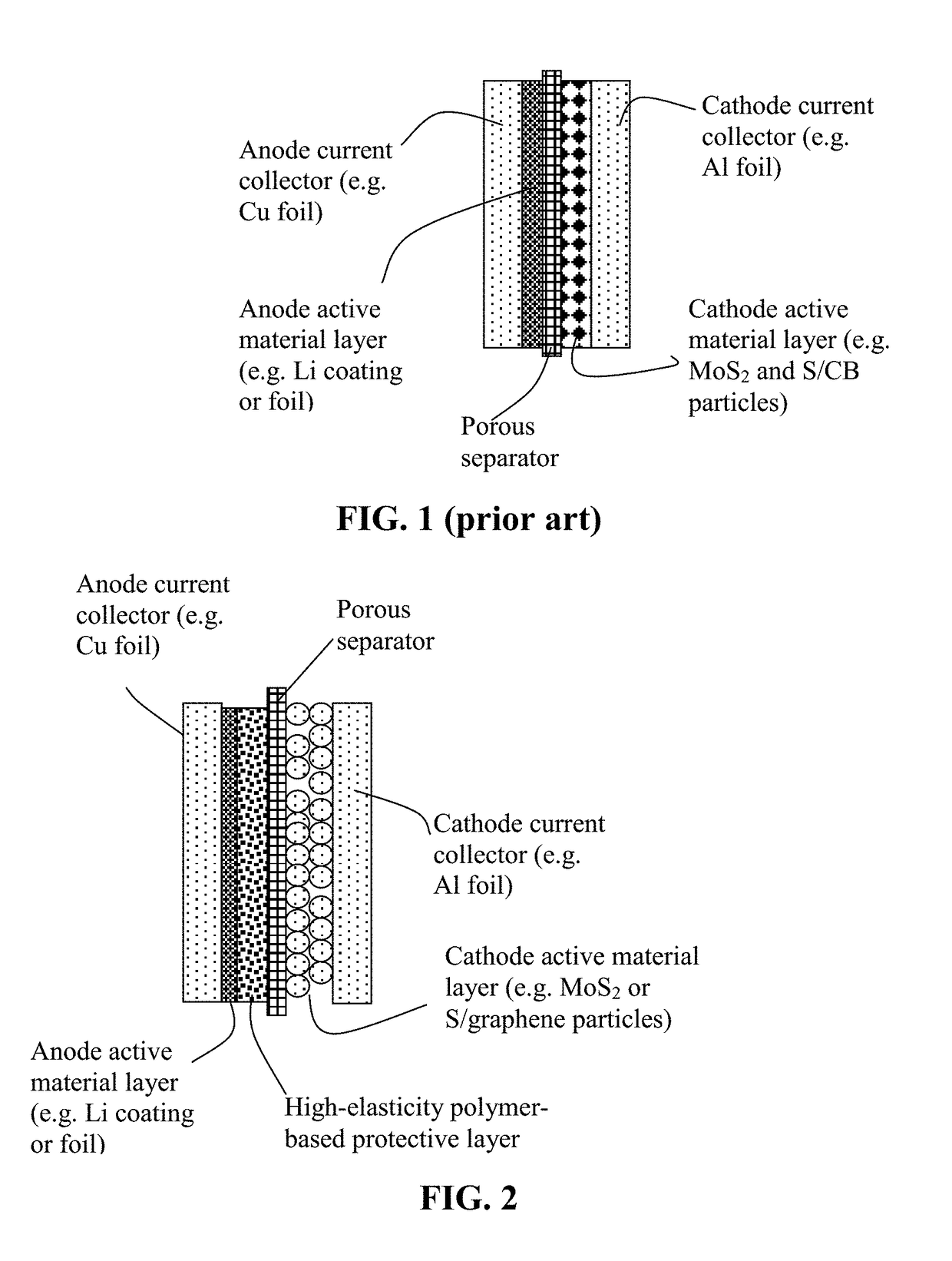
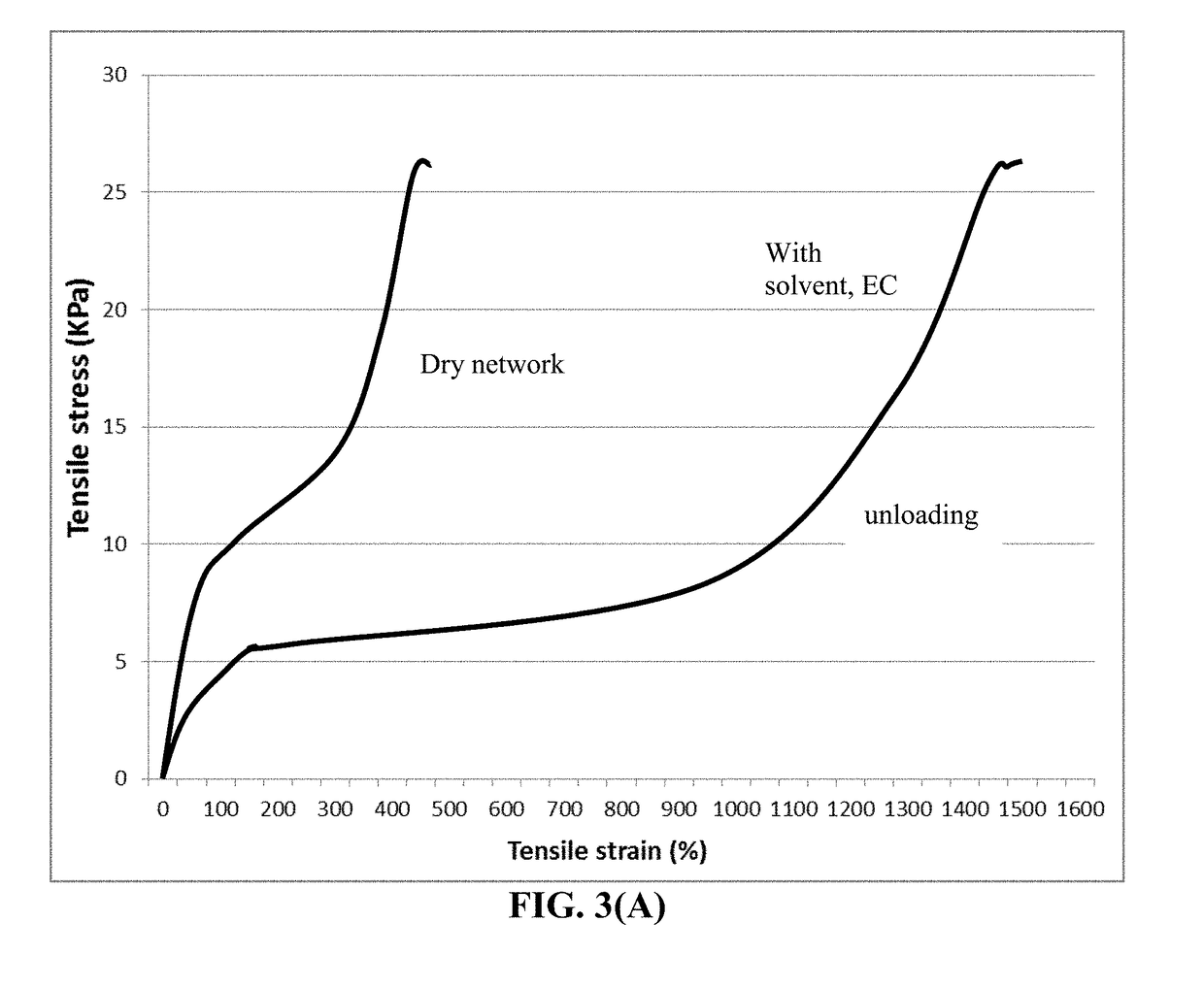
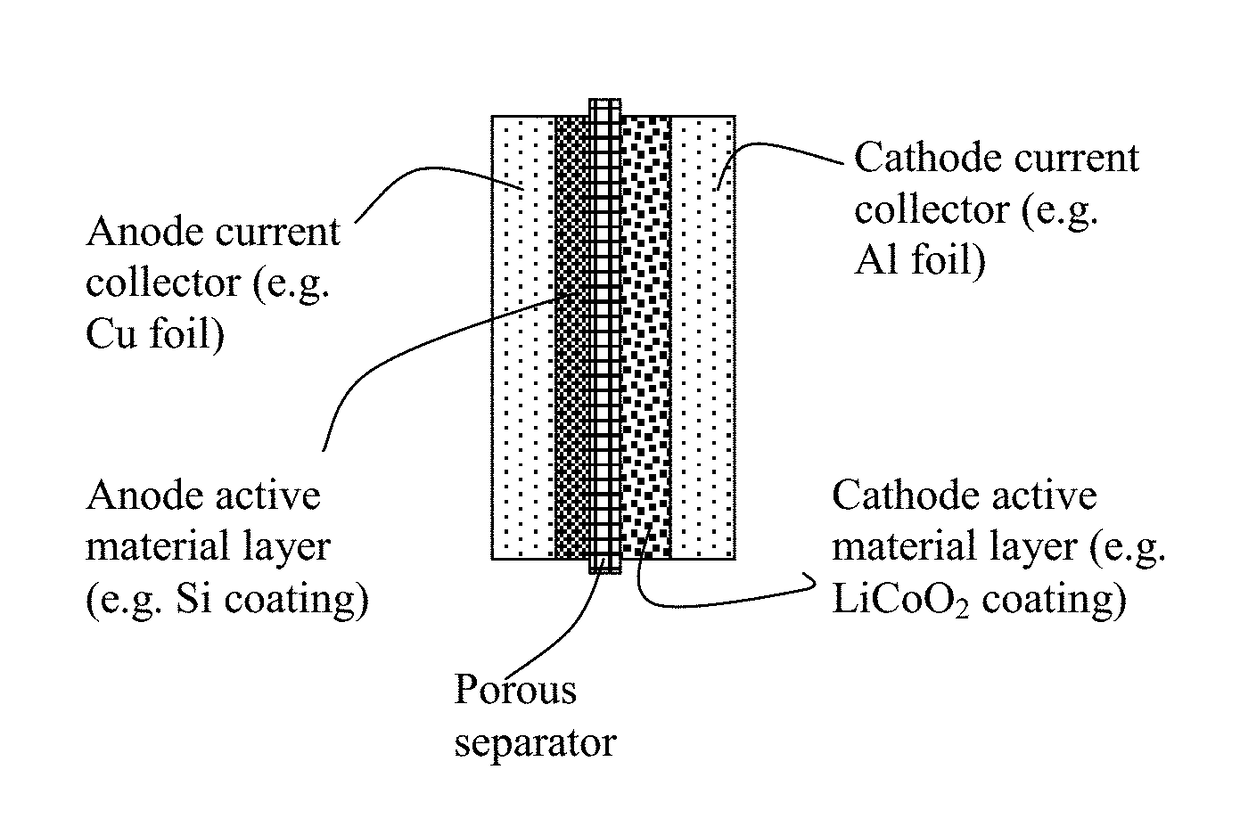
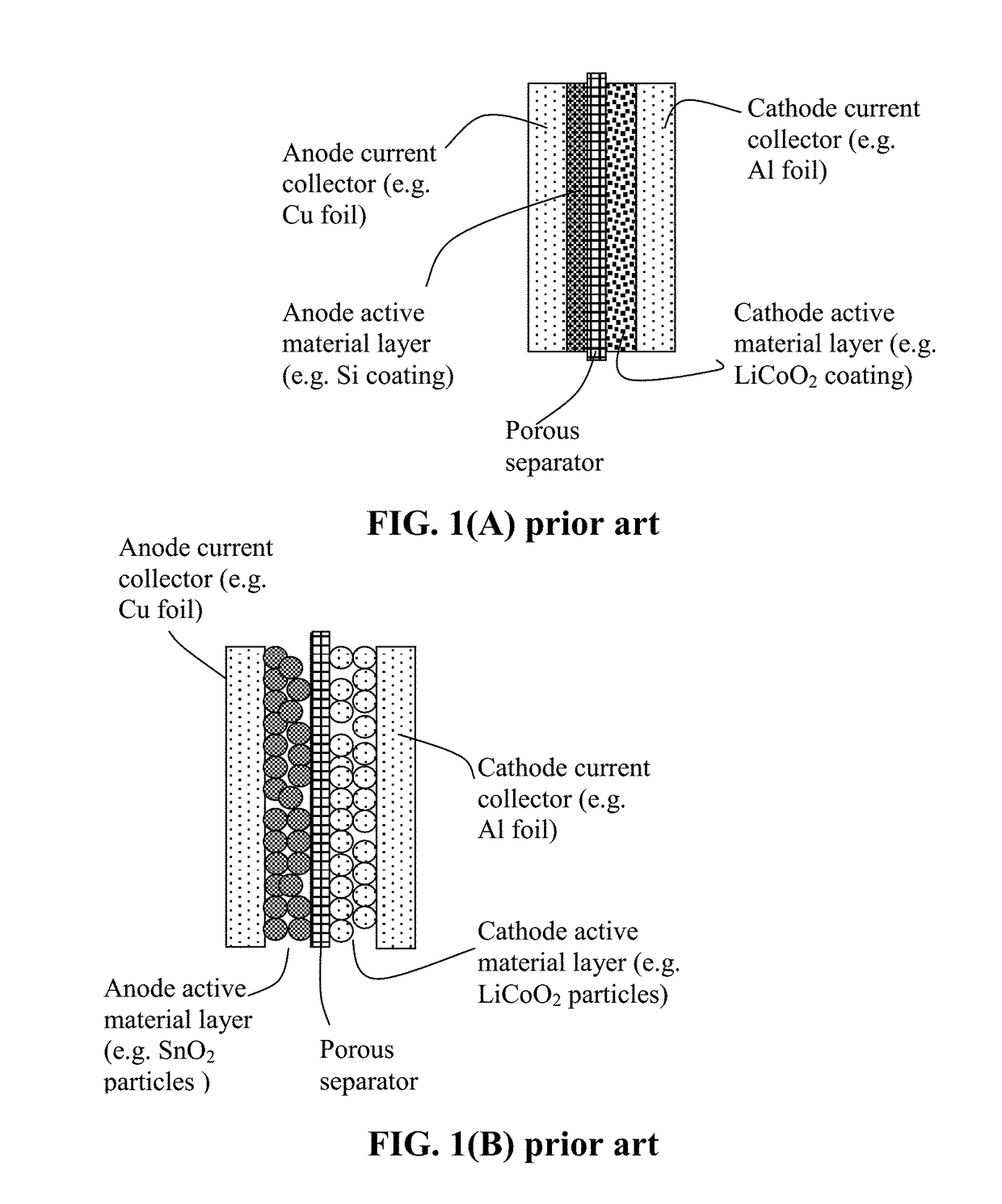
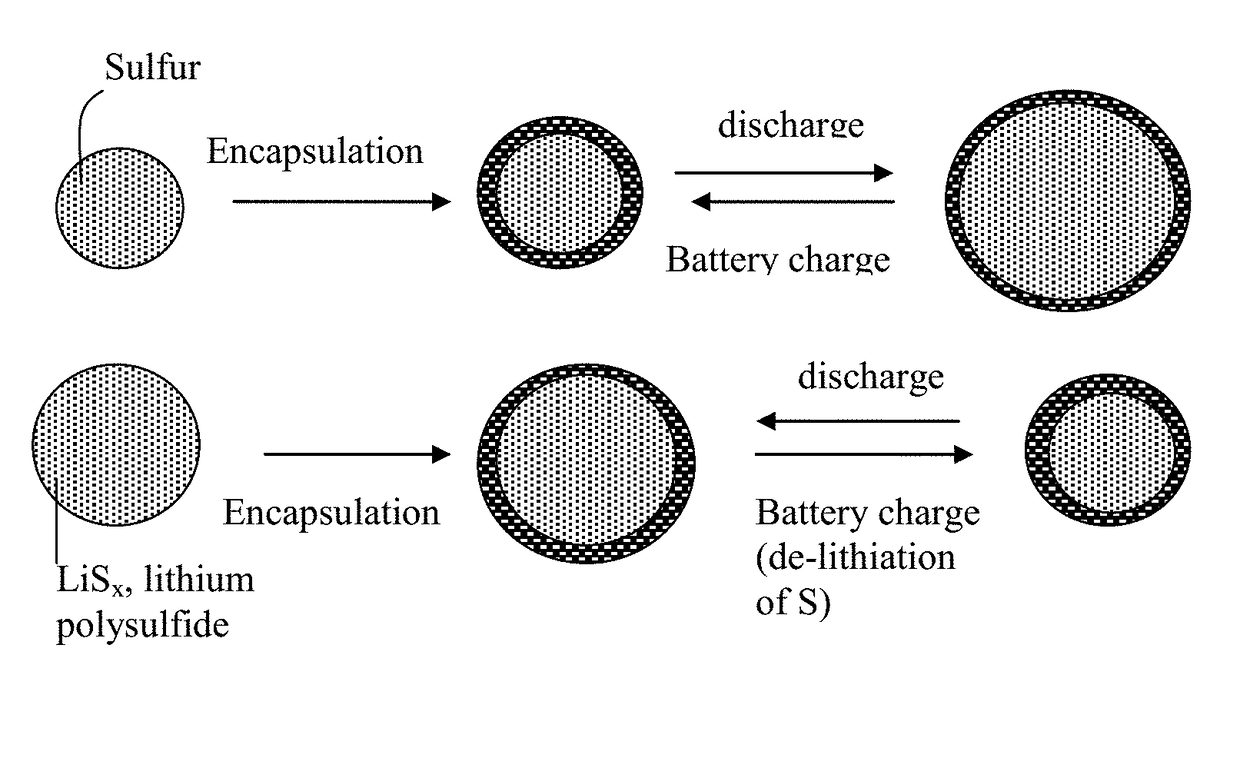
Lithium Metal Secondary Battery Containing an Anode-Protecting Polymer Layer and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20180294476A1Improve lithium ion conductivityReduce thicknessSolid electrolytesFuel and secondary cellsTensile strainLithium metal
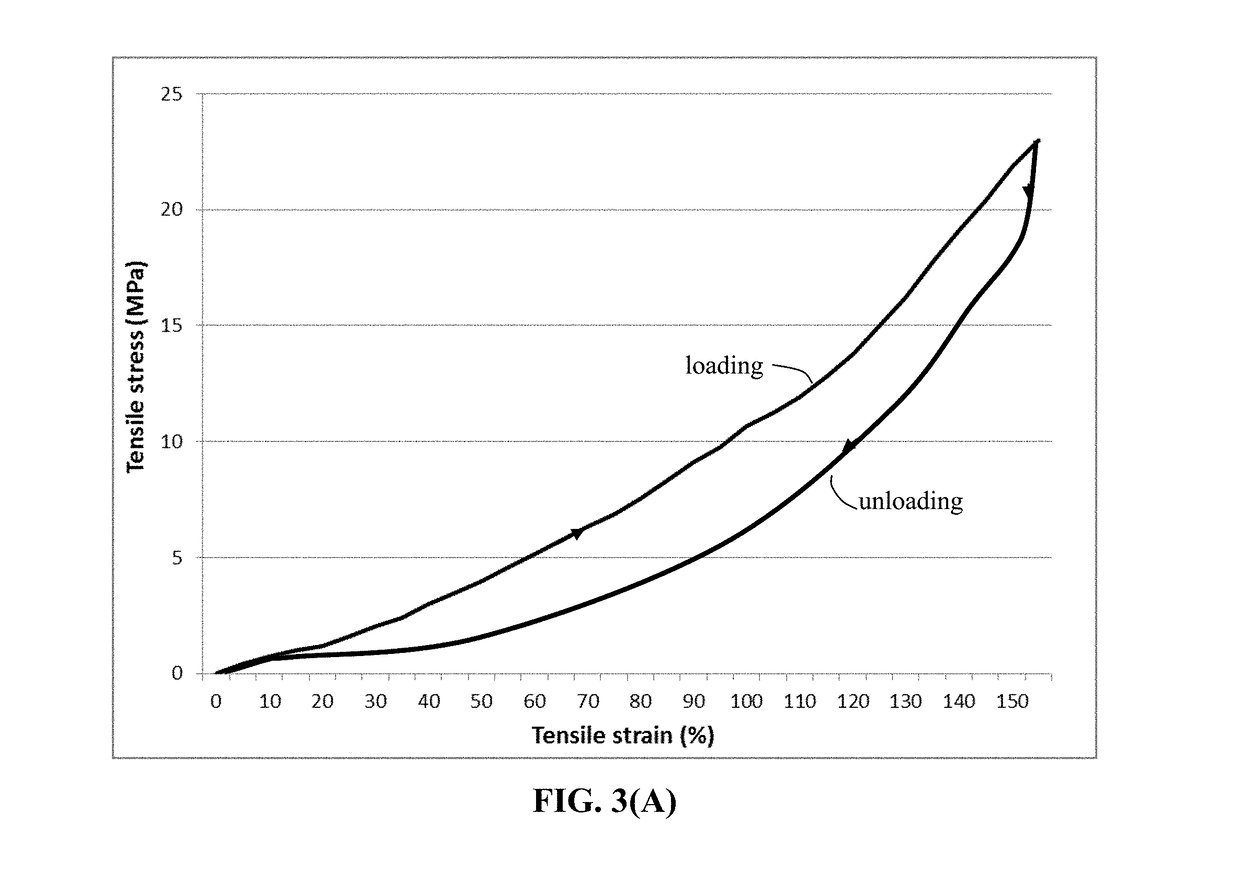
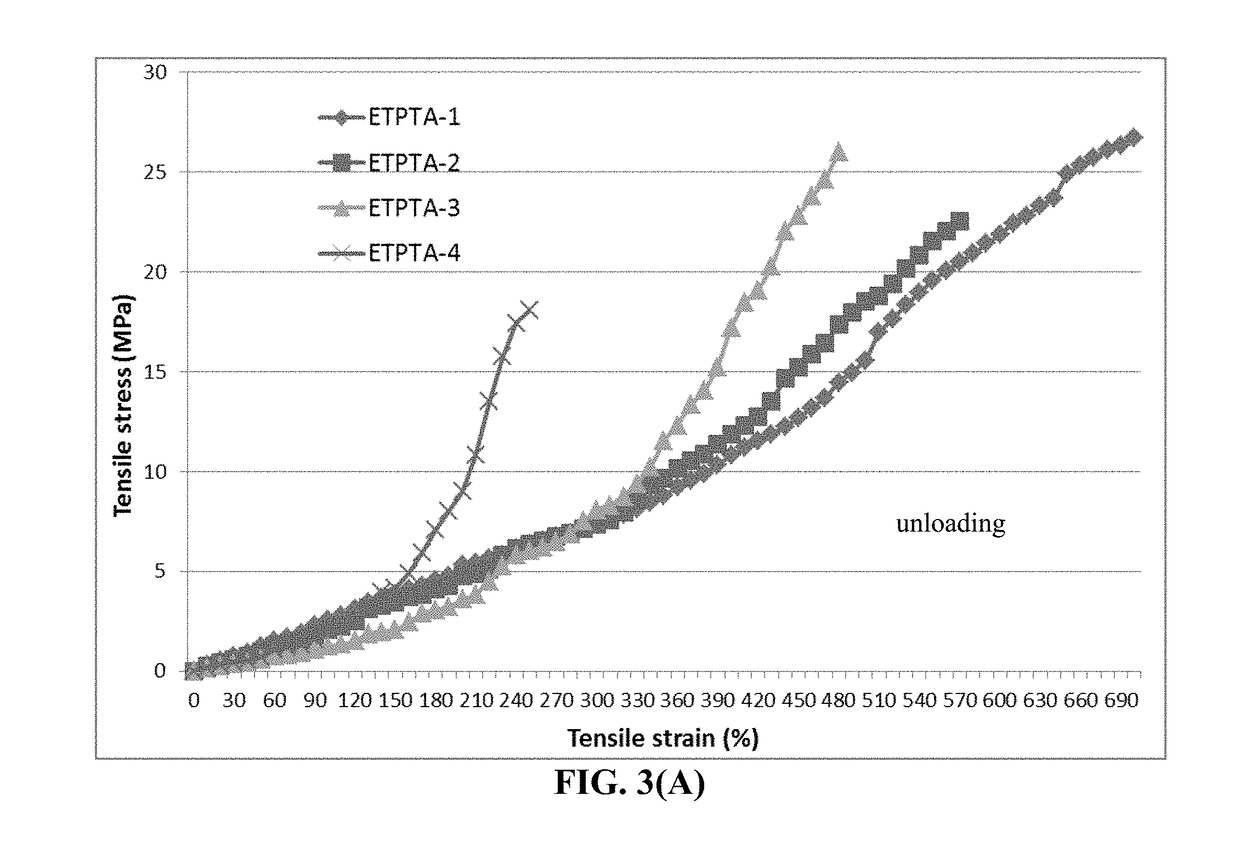
Provided is lithium secondary battery comprising a cathode, an anode, and an electrolyte or separator-electrolyte assembly disposed between the cathode and the anode, wherein the anode comprises: (a) a foil or coating of lithium or lithium alloy as an anode active material; and (b) a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 5%, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−6 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 1 nm to 10 μm, wherein the high-elasticity polymer contains an ultrahigh molecular weight polymer having a molecular weight from 0.5×106 to 9×106 g / mole and is disposed between the lithium or lithium alloy and the electrolyte or separator-electrolyte assembly.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Method And Apparatus For Protecting Against Ballistic Projectiles
InactiveUS20080307553A1Slow downAvoid relative motionPersonal protection gearArmour platesFiberElastic fibres
A composite material comprising a multitude of masses and fibers supported on a flexible substrate arranged in a manner to absorb energy from a ballistic projectile and thereby protect persons or property from ballistic injury or damage. An array of small, tough disc-like masses are suspended in a three dimensional cradle of high-tensile elastomeric fibers such that energy from an incoming ballistic projectile is first imparted to one or more masses and the motion of the masses are restrained by tensile strain of elastomeric fibers substantially in the direction of travel of the incoming projectile. The projectile is eventually decelerated to harmless velocity through a combination of transfer of momentum to the masses and the elastic and plastic tensile deformation of the fibers. One or more layers of the composite material can be assembled to form body protective armor (“bullet-proof vest”) or property protective armor, the number and characteristics of the layers being adjusted according to the specific ballistic threat anticipated.
Owner:ENERGY SCI
Polymer powder with phosphonate-based flame retardant, process for its production, and moldings produced from this polymer power
ActiveUS20050027047A1UL® classificationMaintain mechanical propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresPolymer sciencePolyamide
The present invention relates to a polymer powder composed of polyamide or of copolyamides, which also comprises flame retardant, in particular phosphonates, to a layer-by-layer process which selectively melts regions or selectively binds them, and also to moldings produced from this polymer powder. Compared with conventional products, the moldings constructed using the powder of the invention exhibit marked advantages in flammability and combustibility and drop behavior, particularly with respect to UL® (Underwriters Laboratories) classification. Furthermore, moldings produced from polymer powder of the invention have adequately good mechanical properties when compared with moldings based on polymer powders without flame retardant, in particular in terms of modulus of elasticity and tensile strain at break. In addition, these moldings also have a density close to that of injection moldings.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Performance enhancement in pmos and nmos transistors on the basis of silicon/carbon material
InactiveUS20100025771A1Improve production efficiencyImprove featuresTransistorSolid-state devicesTensile strainPerformance enhancement
A silicon / germanium material and a silicon / carbon material may be provided in transistors of different conductivity type on the basis of an appropriate manufacturing regime without unduly contributing to overall process complexity. Furthermore, appropriate implantation species may be provided through exposed surface areas of the cavities prior to forming the corresponding strained semiconductor alloy, thereby additionally contributing to enhanced overall transistor performance. In other embodiments a silicon / carbon material may be formed in a P-channel transistor and an N-channel transistor, while the corresponding tensile strain component may be overcompensated for by means of a stress memorization technique in the P-channel transistor. Thus, the advantageous effects of the carbon species, such as enhancing overall dopant profile of P-channel transistors, may be combined with an efficient strain component while enhanced overall process uniformity may also be accomplished.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
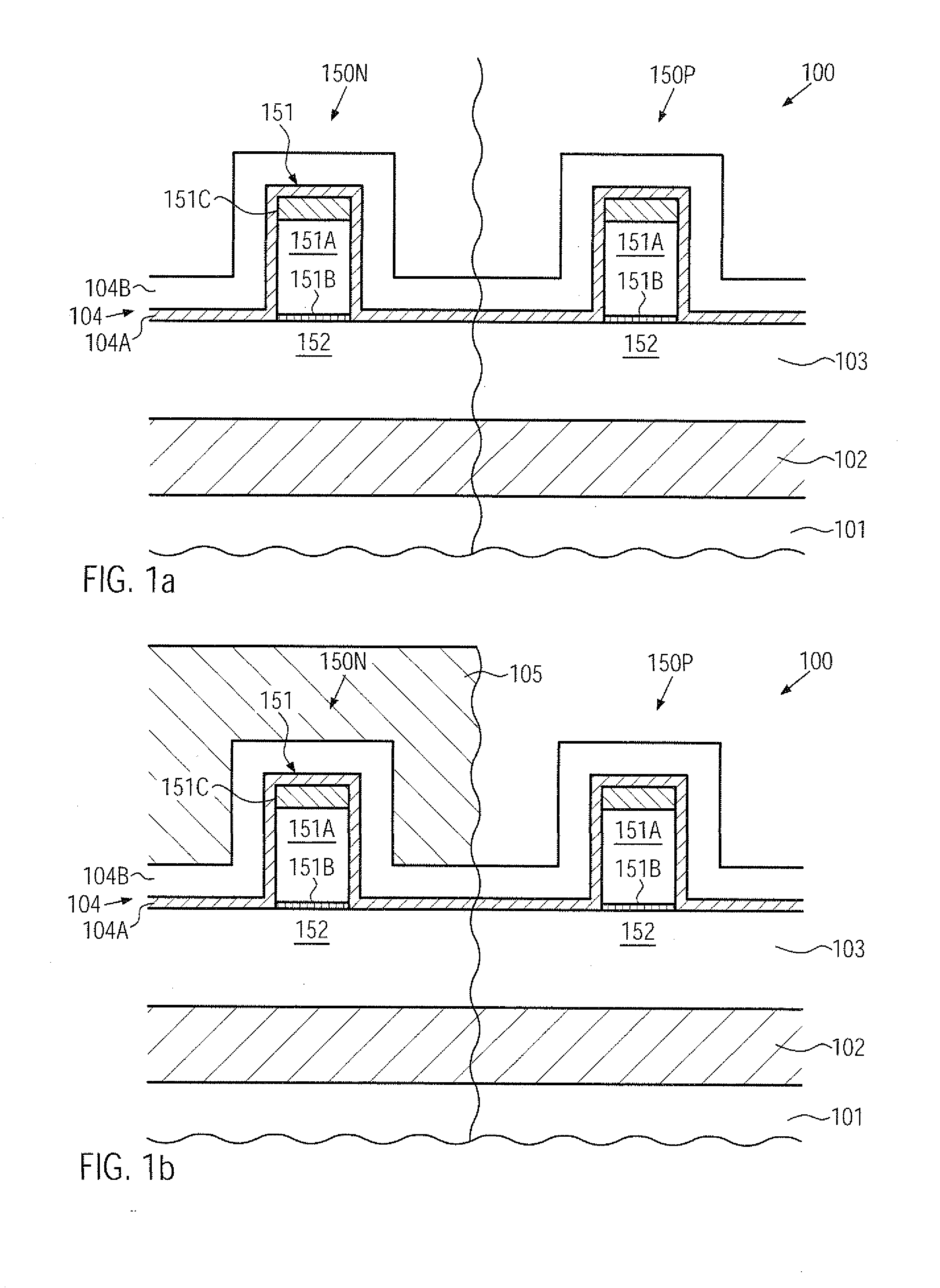
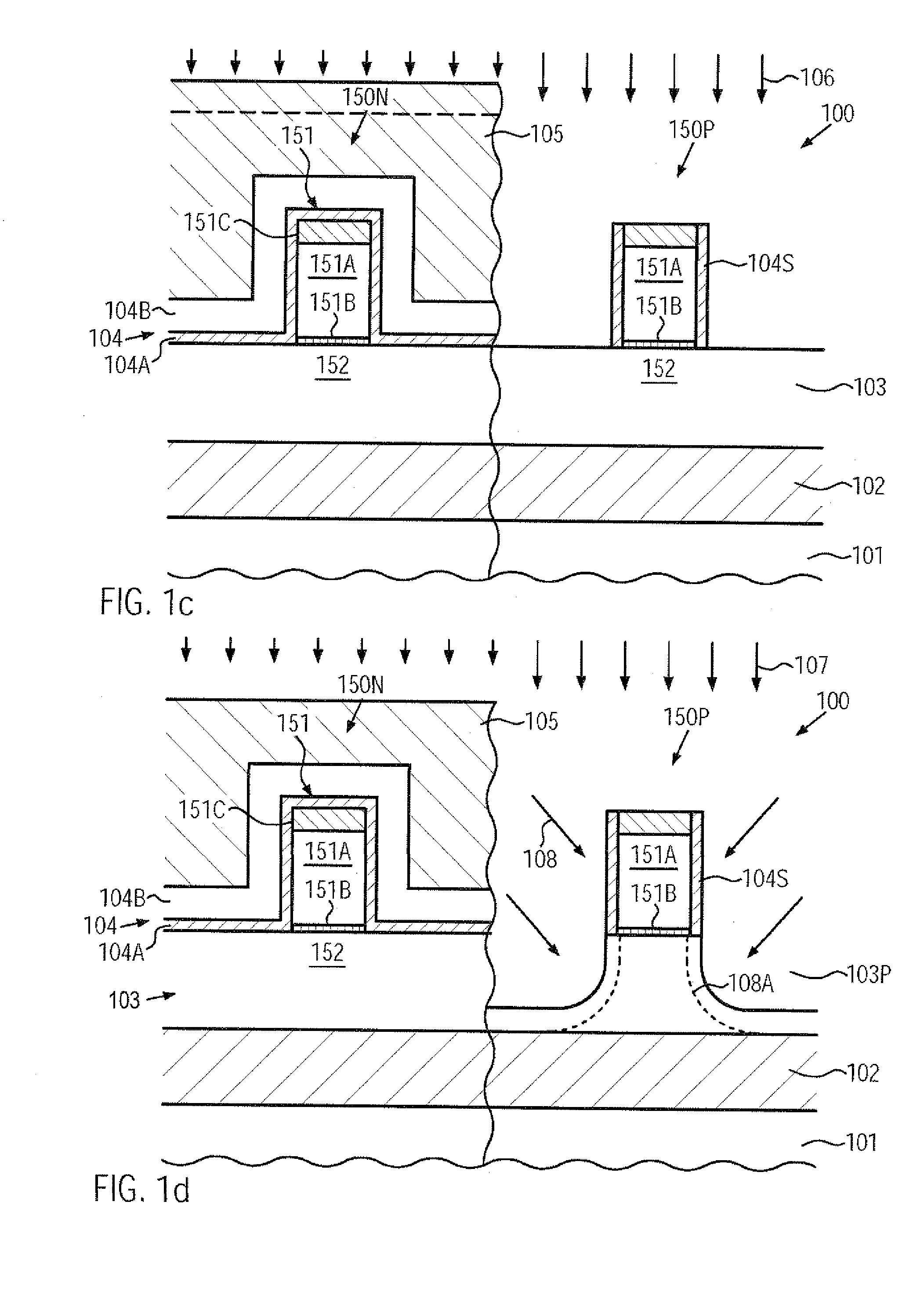
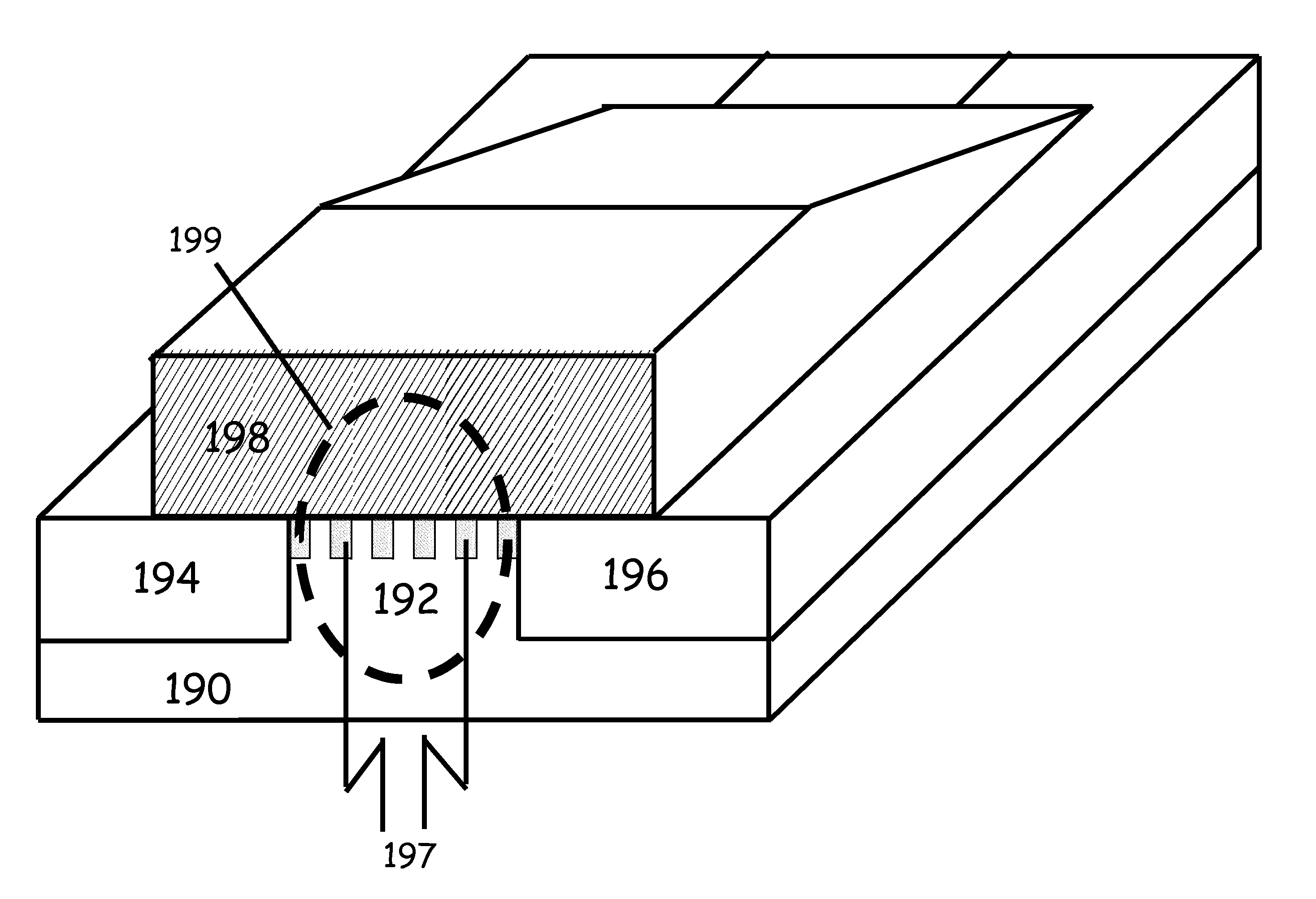
Transistor having an embedded tensile strain layer with reduced offset to the gate electrode and a method for forming the same
ActiveUS20070254461A1Increase strainIncrease flexibilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTensile strainSalicide
By incorporating carbon by means of ion implantation and a subsequent flash-based or laser-based anneal process, strained silicon / carbon material with tensile strain may be positioned in close proximity to the channel region, thereby enhancing the strain-inducing mechanism. The carbon implantation may be preceded by a pre-amorphization implantation, for instance on the basis of silicon. Moreover, by removing a spacer structure used for forming deep drain and source regions, the degree of lateral offset of the strained silicon / carbon material with respect to the gate electrode may be determined substantially independently from other process requirements. Moreover, an additional sidewall spacer used for forming metal silicide regions may be provided with reduced permittivity, thereby additionally contributing to an overall performance enhancement.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
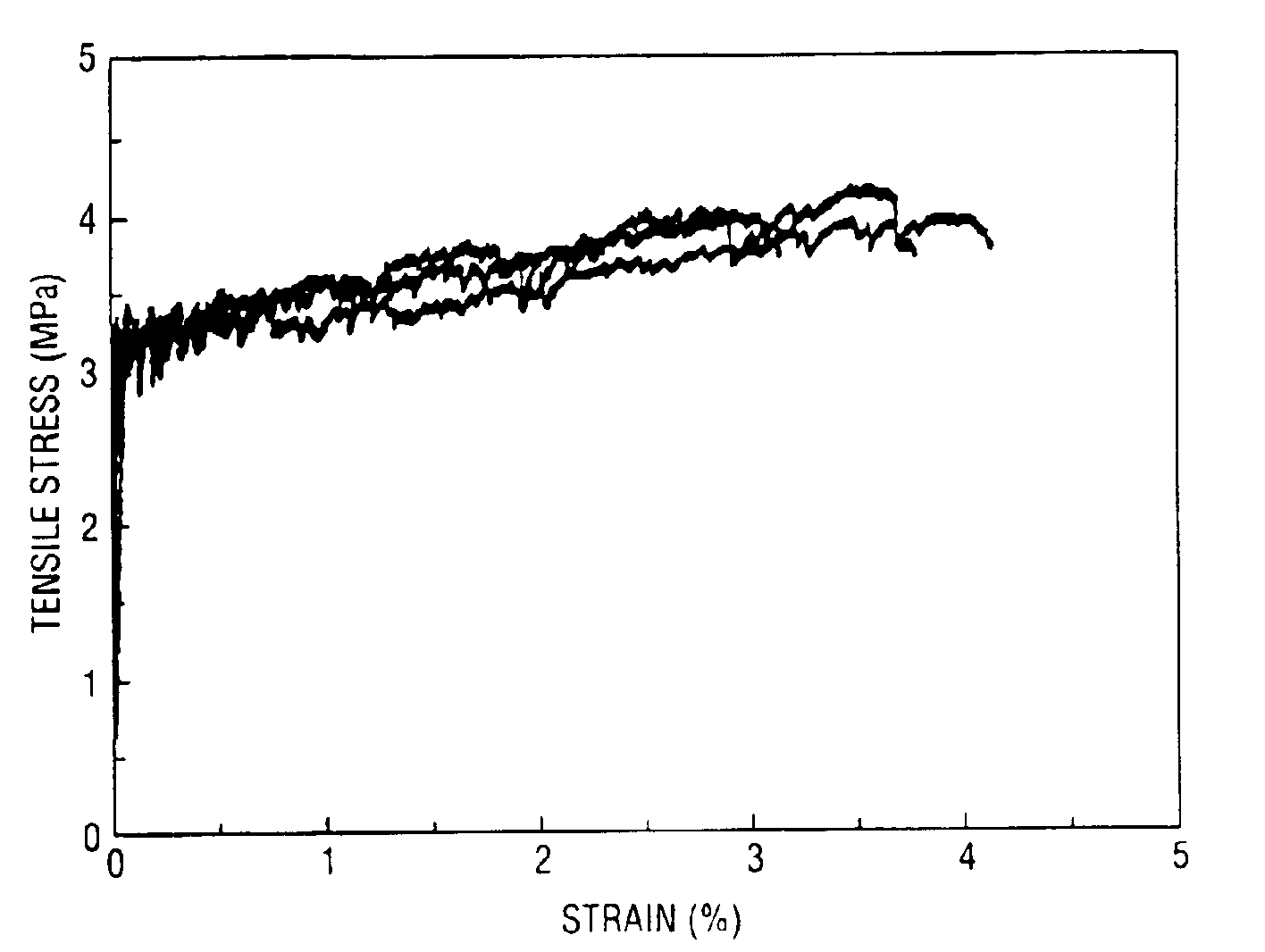
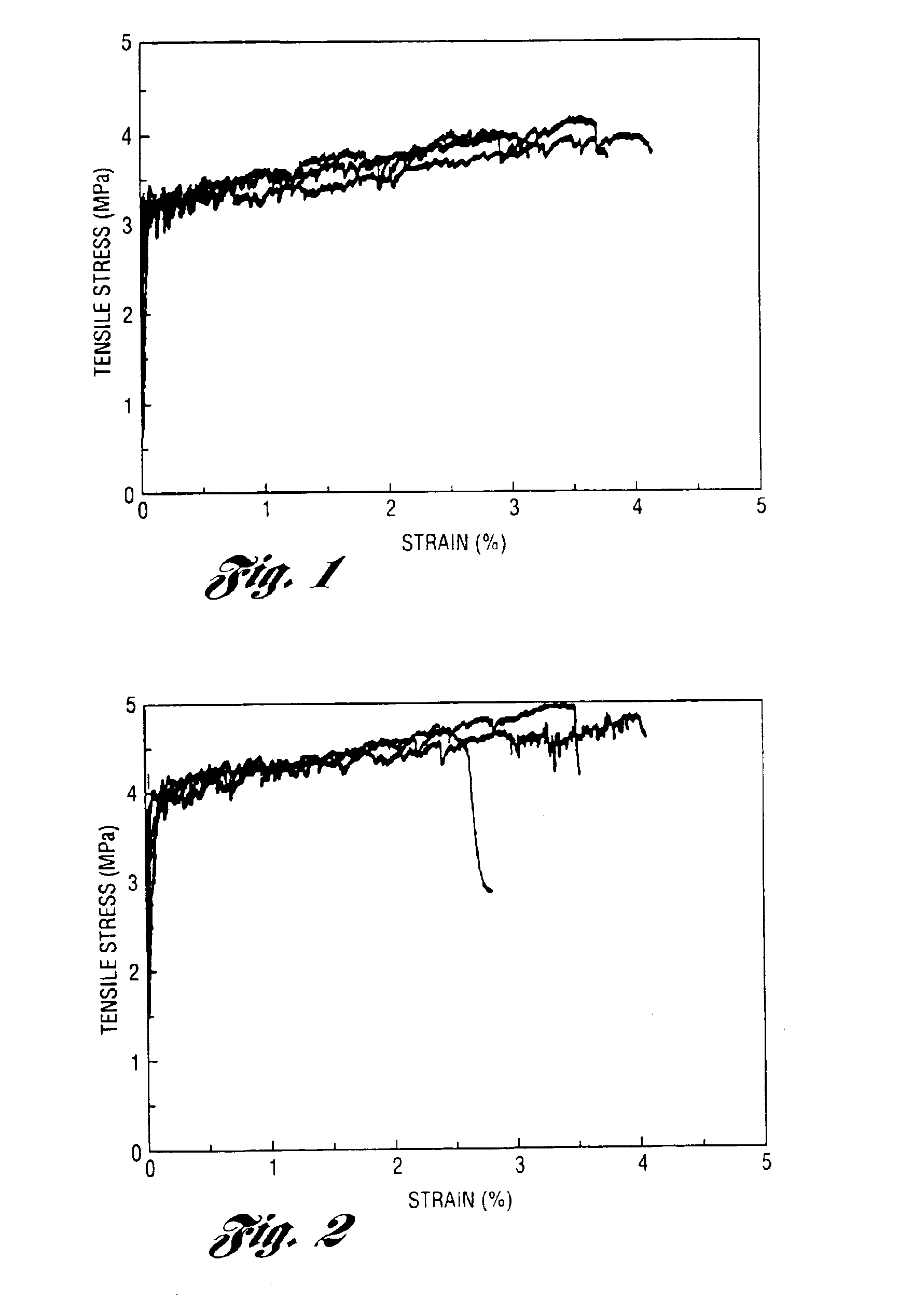
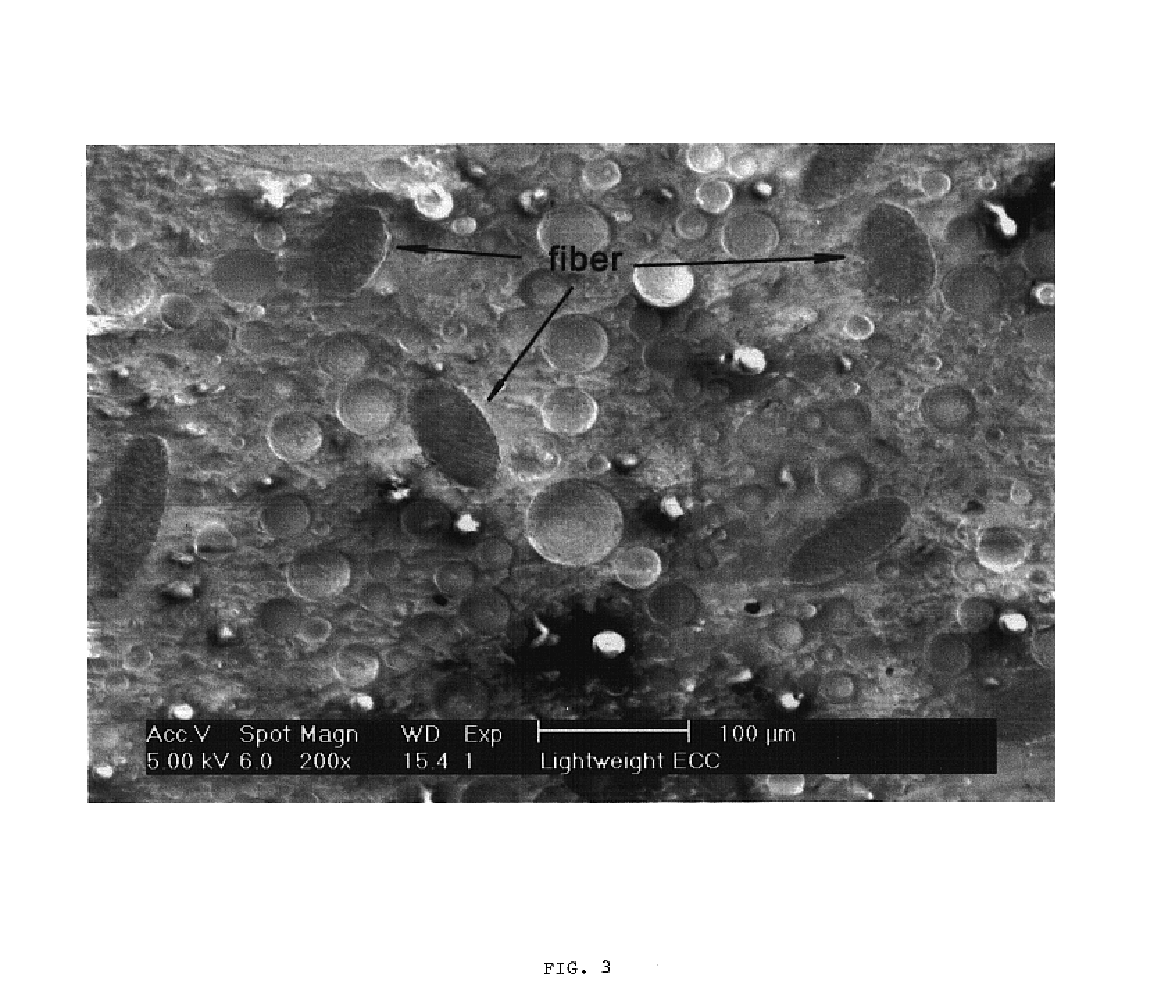
Lightweight strain hardening brittle matrix composites
Fiber reinforced lightweight concrete composites employ less than 4% by volume of reinforcing fibers in conjunction with small particulate lightweight aggregates or voids, and cure to composites which exhibit high tensile strain and strain hardening behavior. The composites are useful for numerous structures in civil engineering.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
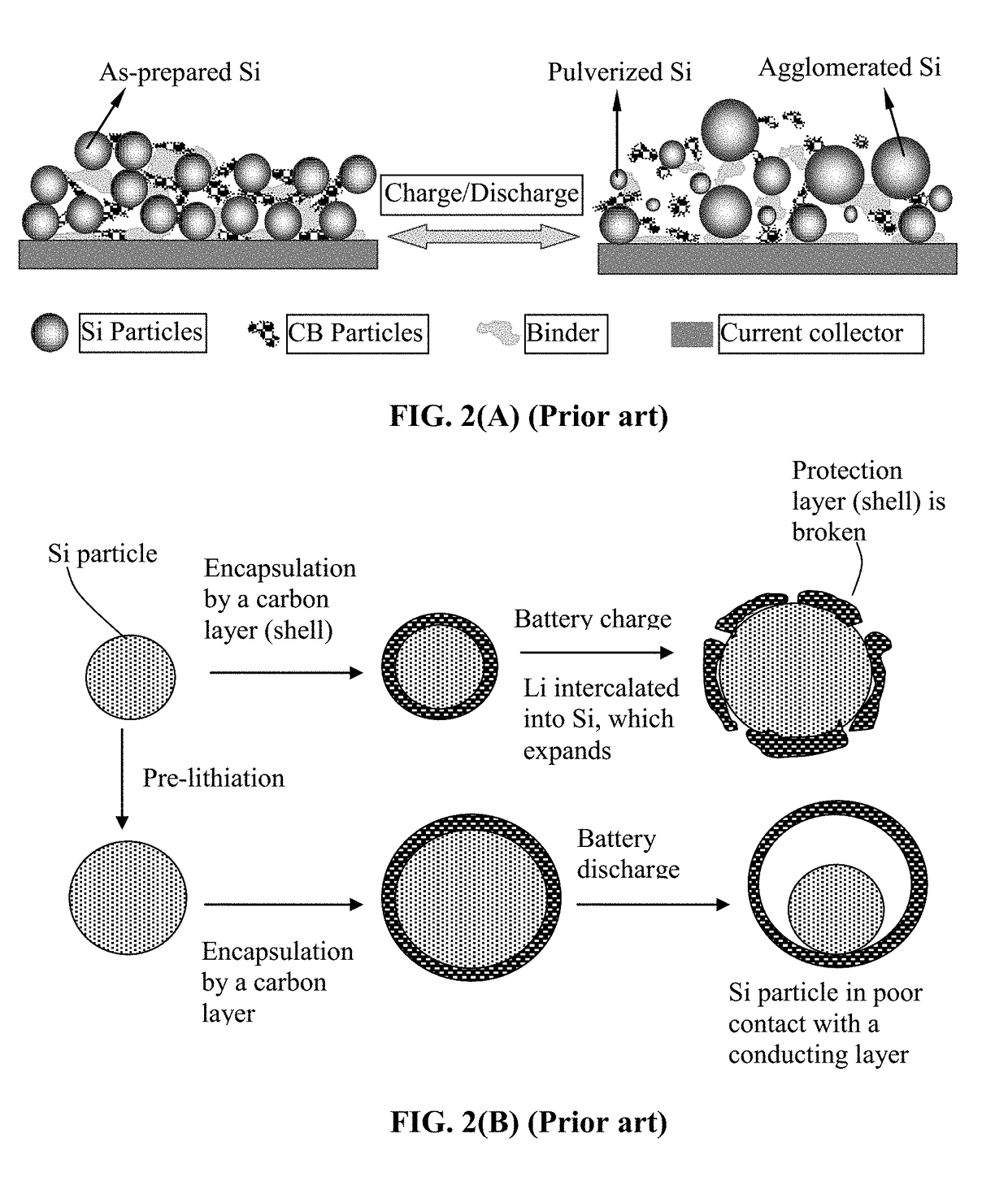
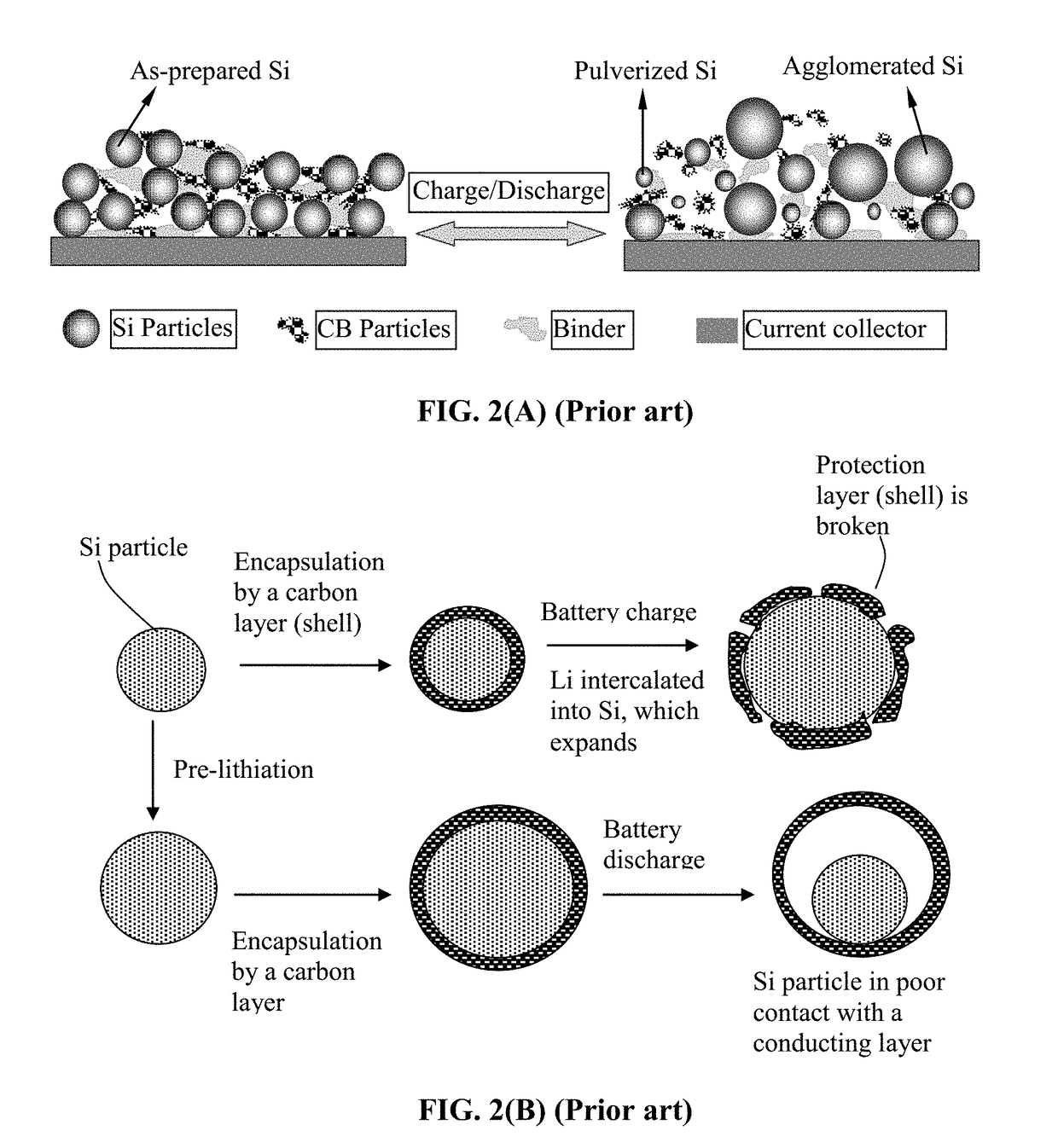
Lithium Secondary Batteries Containing Protected Particles of Anode Active Materials and Method of Manufacturing
ActiveUS20180241032A1Improve lithium ion conductivityIncrease elasticityFuel and secondary cellsSecondary cellsParticulatesTensile strain
Provided is anode active material layer for a lithium battery, comprising multiple particulates of an anode active material, wherein a particulate is composed of one or a plurality of particles of a high-capacity anode active material being embraced or encapsulated by a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 10% when measured without an additive or reinforcement, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10-5 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 0.5 nm (or a molecular monolayer) to 10 μm (preferably less than 100 nm), and wherein the high-capacity anode active material has a specific lithium storage capacity greater than 372 mAh / g (e.g. Si, Ge, Sn, SnO2, Co3O4, etc.).
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
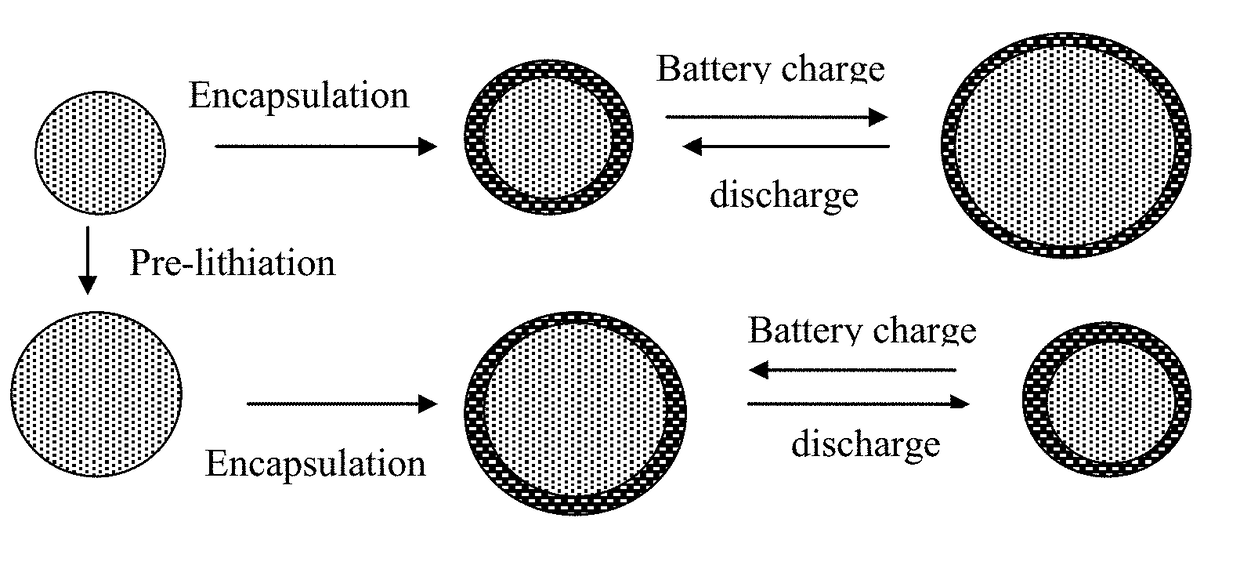
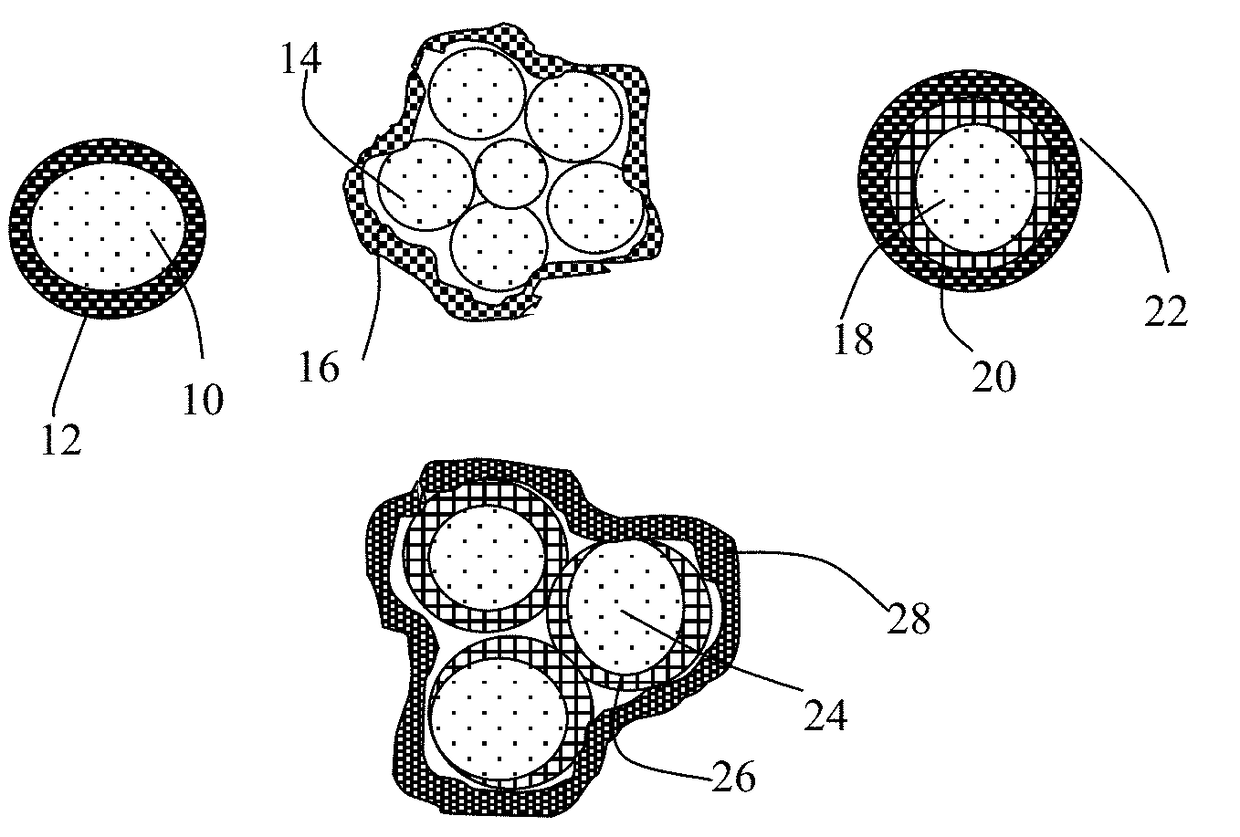
Encapsulated Anode Active Material Particles, Lithium Secondary Batteries Containing Same, and Method of Manufacturing
ActiveUS20180287142A1Improve lithium ion conductivitySolid electrolytesNegative electrodesParticulatesPolyethylene oxide
Provided is particulate of an anode active material for a lithium battery, comprising one or a plurality of anode active material particles being embraced or encapsulated by a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 5%, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−6 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 0.5 nm to 10 μm, wherein the polymer contains an ultrahigh molecular weight (UHMW) polymer having a molecular weight from 0.5×106 to 9×106 grams / mole. The UHMW polymer is preferably selected from polyacrylonitrile, polyethylene oxide, polypropylene oxide, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, polyacrylamide, poly(methyl methacrylate), poly(methyl ether acrylate), a copolymer thereof, a sulfonated derivative thereof, a chemical derivative thereof, or a combination thereof.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Lithium Anode-Protecting Polymer Layer for a Lithium Metal Secondary Battery and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20180301707A1Improve lithium ion conductivityIncrease elasticityFuel and secondary cellsCell electrodesCross-linkLithium metal
Provided is lithium secondary battery comprising a cathode, an anode, and an electrolyte or separator-electrolyte assembly disposed between the cathode and the anode, wherein the anode comprises: (a) a foil or coating of lithium or lithium alloy; and (b) a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer disposed between the foil / coating and the electrolyte (or separator-electrolyte assembly), having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 2%, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−6 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 1 nm to 10 μm, wherein the high-elasticity polymer contains a cross-linked network of polymer chains having an ether linkage, nitrile-derived linkage, benzo peroxide-derived linkage, ethylene oxide linkage, propylene oxide linkage, vinyl alcohol linkage, cyano-resin linkage, triacrylate monomer-derived linkage, tetraacrylate monomer-derived linkage, or a combination thereof in the cross-linked network of polymer chains.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
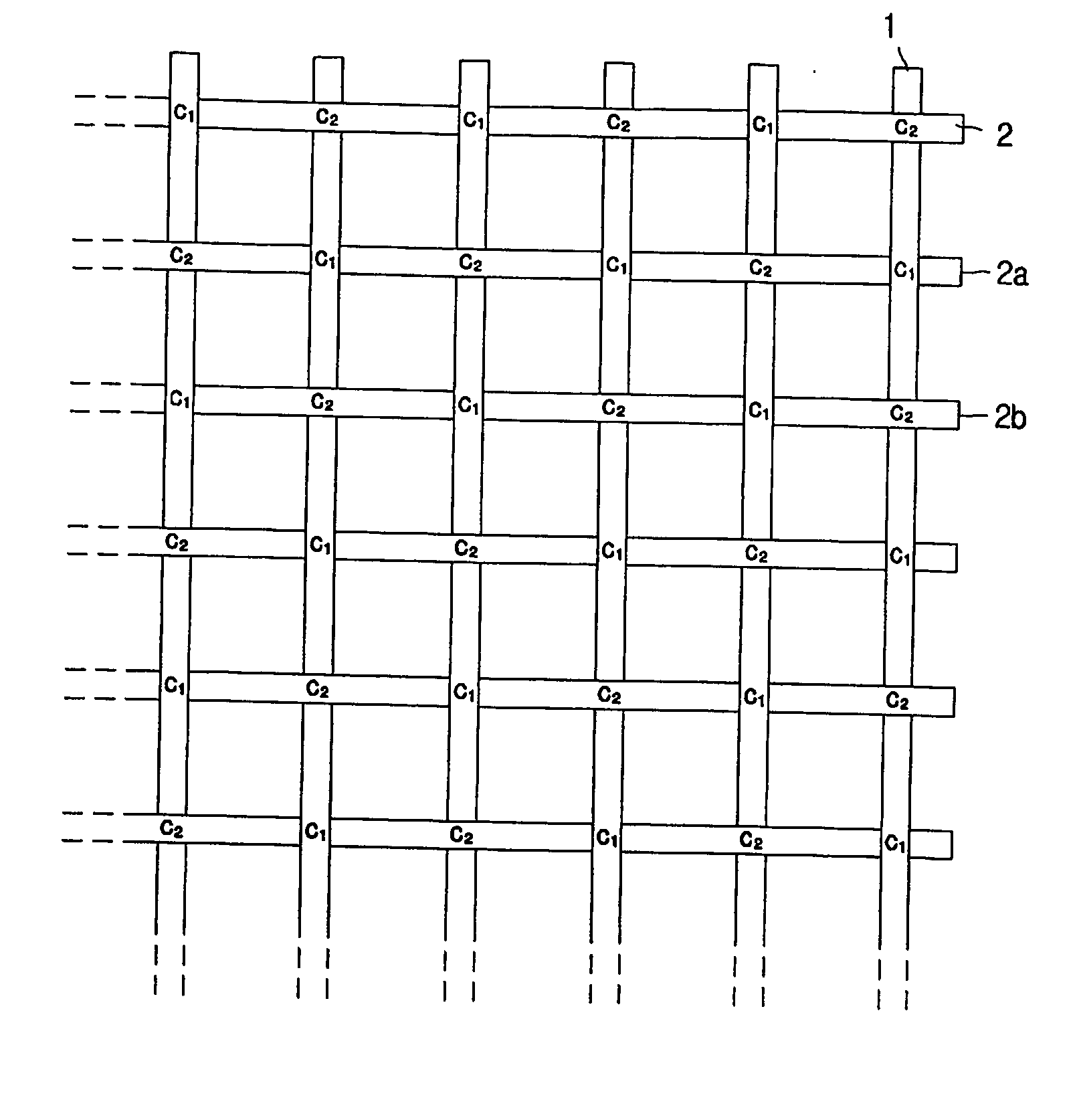
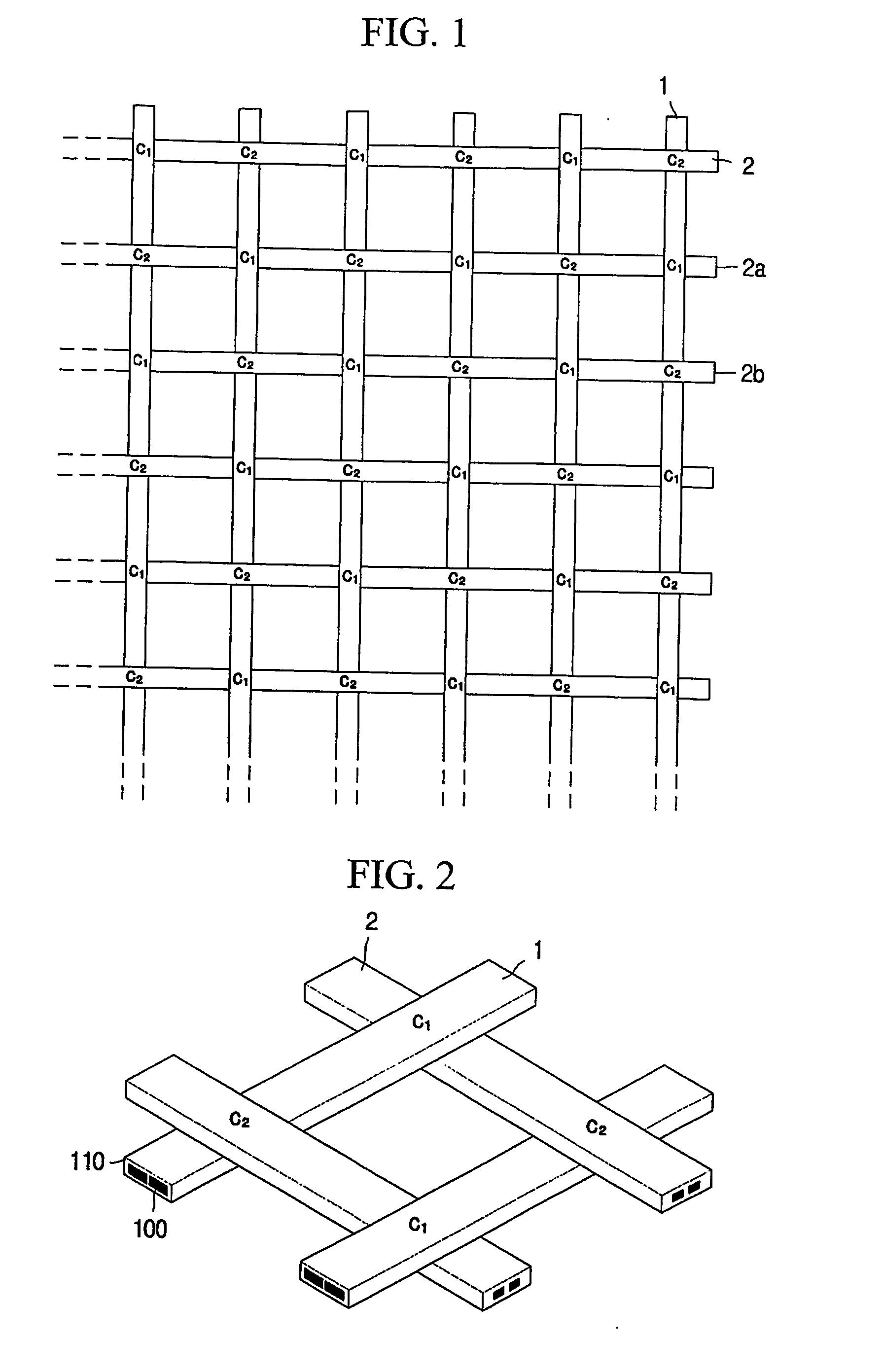
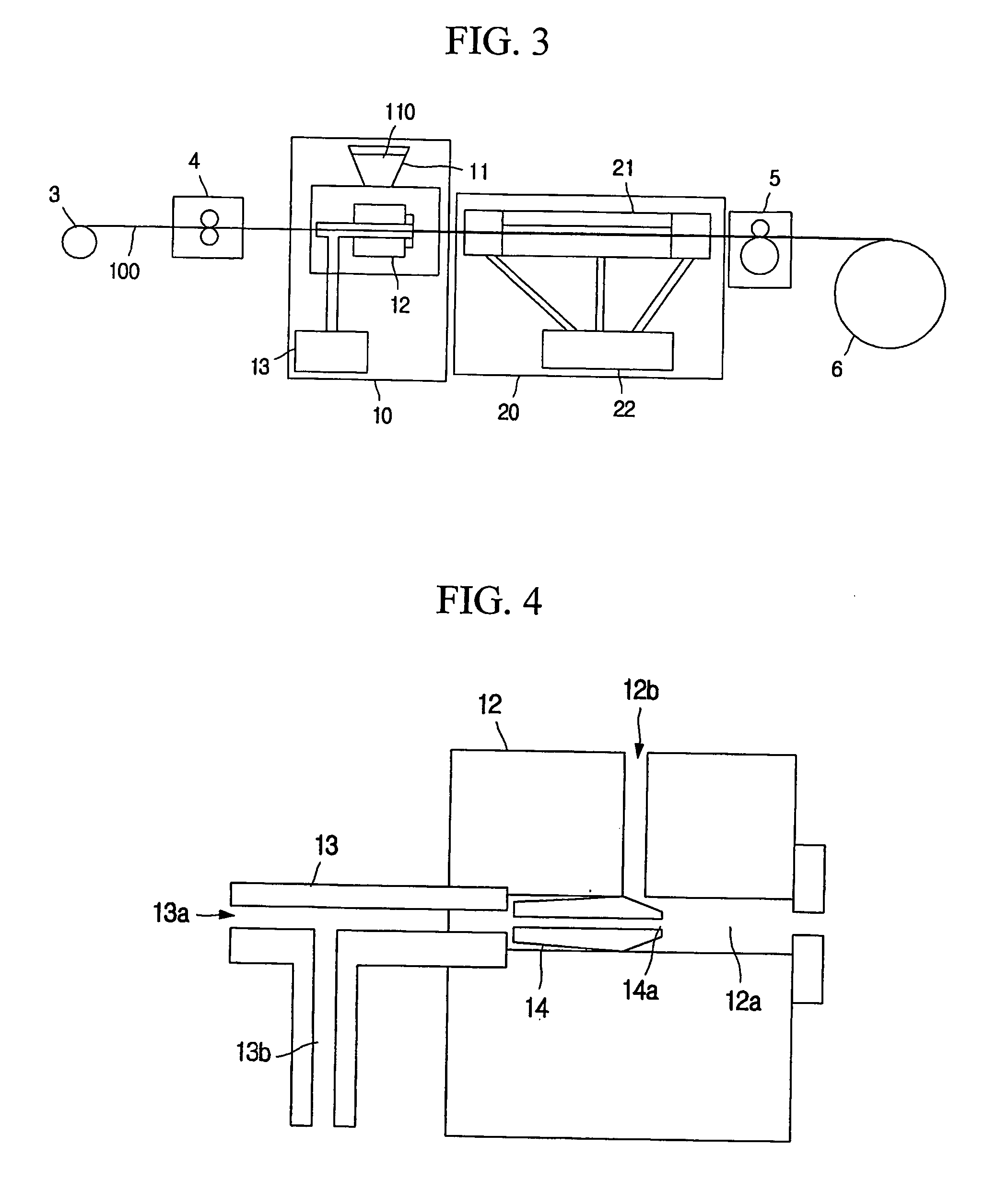
Geogrid composed of fiber-reinforced polymeric strip and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20060116040A1Increase resistance against vertical loadIncrease friction forceWarp knittingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesTensile strainGeogrid
A geogrid using fiber-reinforced polymeric strips and its producing method are disclosed. The geogrid of a lattice shape includes plural longitudinal fiber-reinforced polymeric strips longitudinally arranged in parallel at regular intervals and formed by reinforcing fiber in a thermoplastic polymer resin, and plural lateral fiber-reinforced polymer strip laterally arranged in parallel at regular intervals and formed by reinforcing fiber in a thermoplastic polymer resin. Each longitudinal fiber-reinforced polymer strip has at lease one first contact point crossed with the lateral fiber-reinforced polymer strip on the upper surface and at least one second contact point crossed with the lateral fiber-reinforced polymer strips on the lower surface. The contact points are fixed by welding the longitudinal and lateral fiber-reinforced polymer strips. The geogrid is excellent in installation capacity, frictional feature and shape stabilisation and shows high tensile strength and low tensile strain and low creep deformation.
Owner:SAMSANG CORP
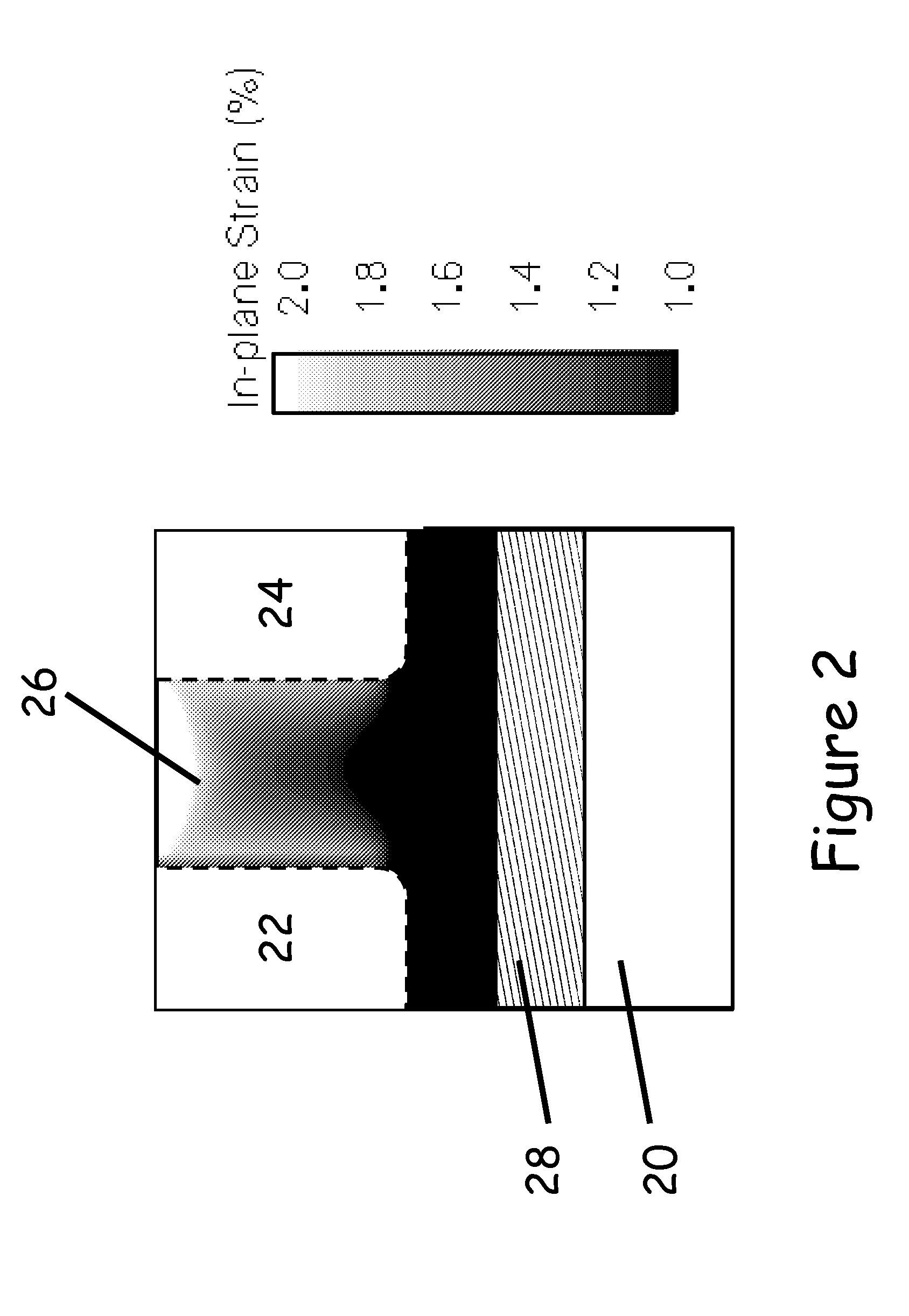
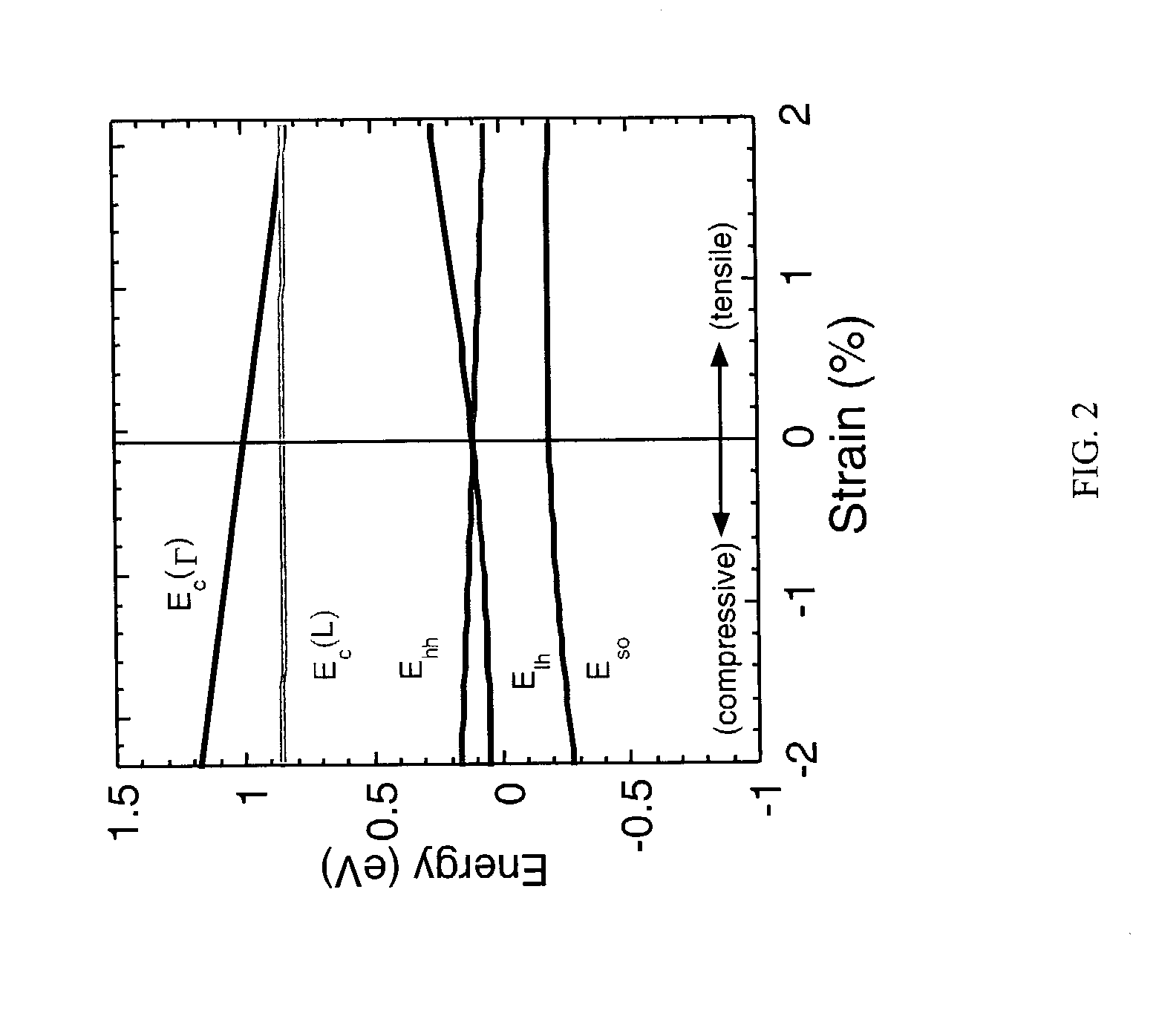
Tensile strained semiconductor photon emission and detection devices and integrated photonics system
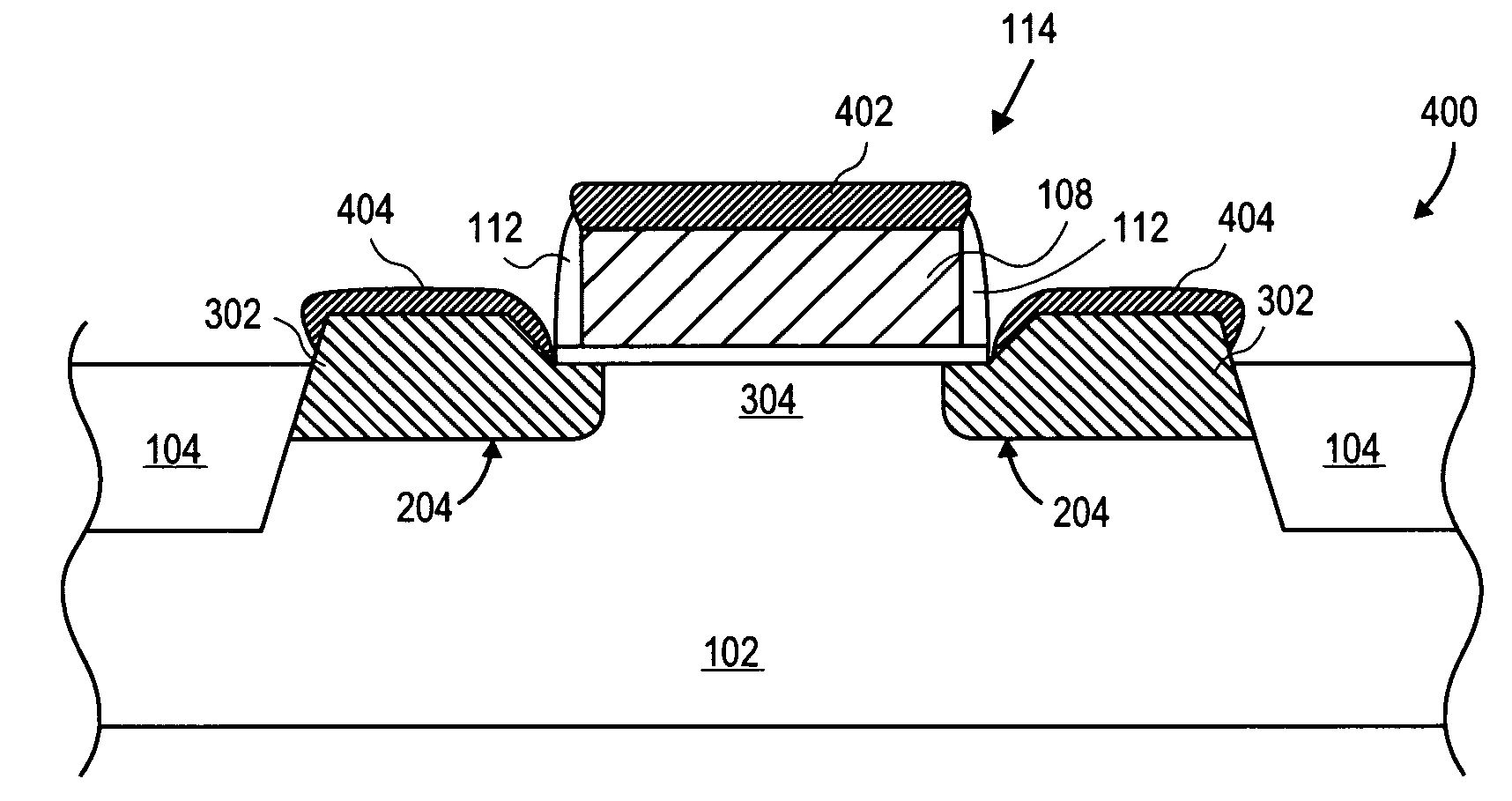
Tensile strained germanium is provided that can be sufficiently strained to provide a nearly direct band gap material or a direct band gap material. Compressively stressed or tensile stressed stressor materials in contact with germanium regions induce uniaxial or biaxial tensile strain in the germanium regions. Stressor materials may include silicon nitride or silicon germanium. The resulting strained germanium structure can be used to emit or detect photons including, for example, generating photons within a resonant cavity to provide a laser.
Owner:ACORN SEMI LLC
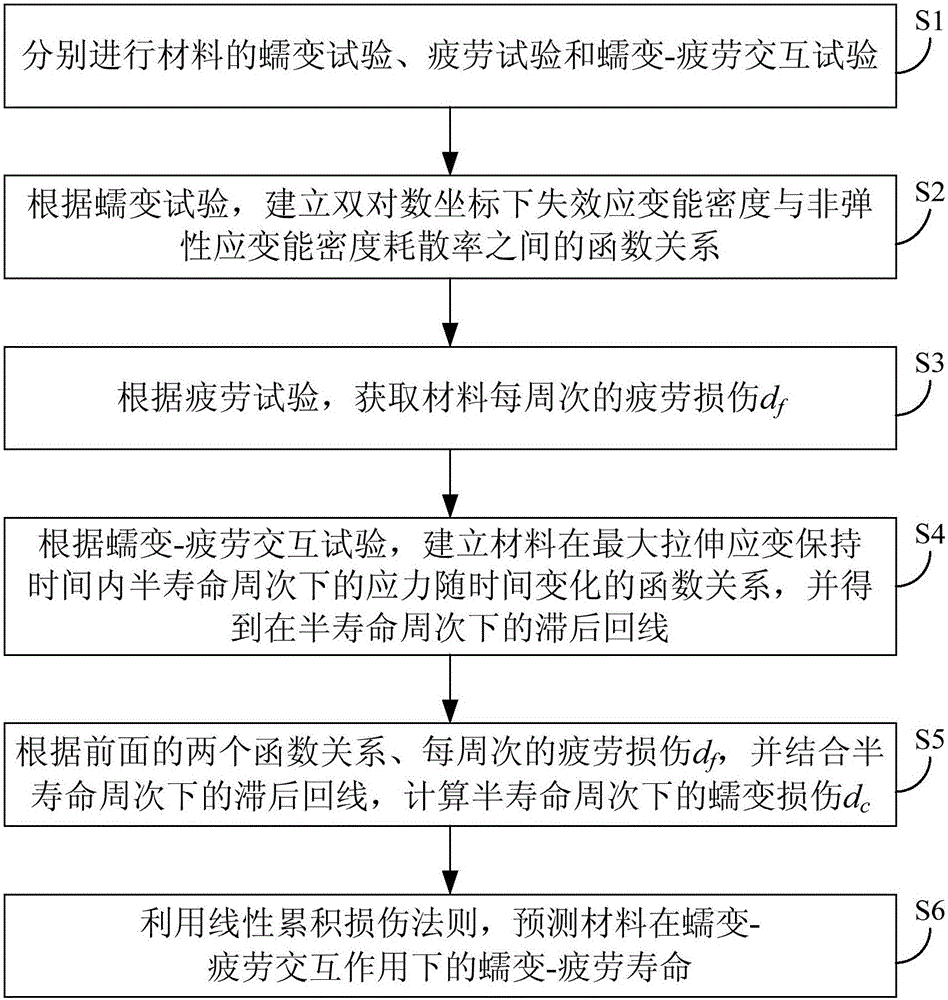
Forecasting method for creep-fatigue life of material
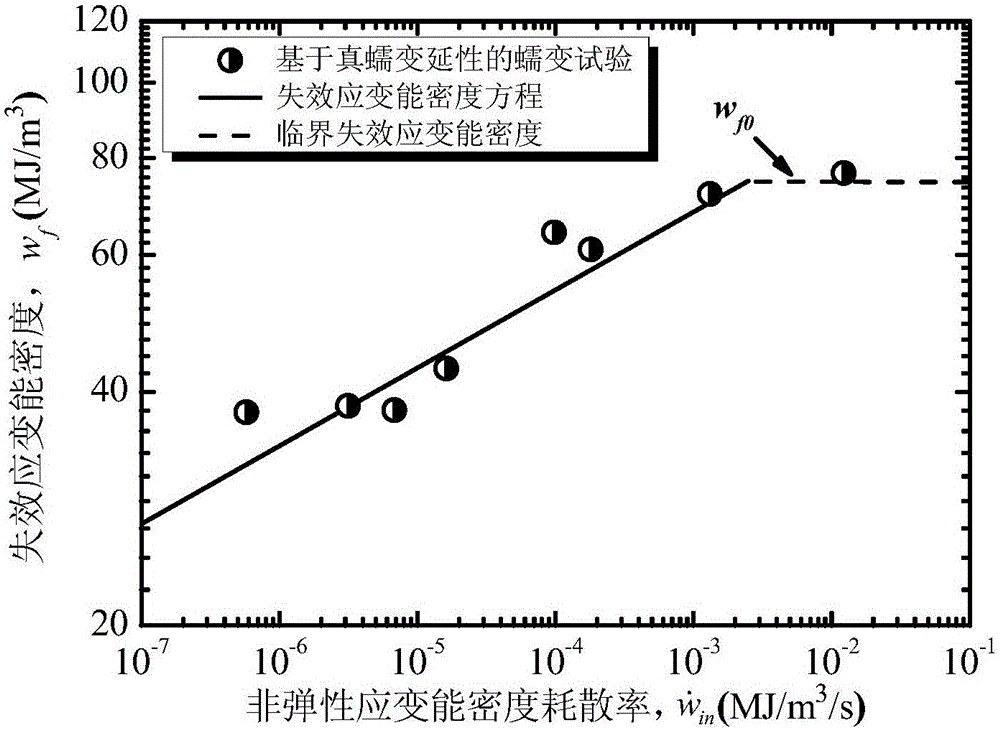
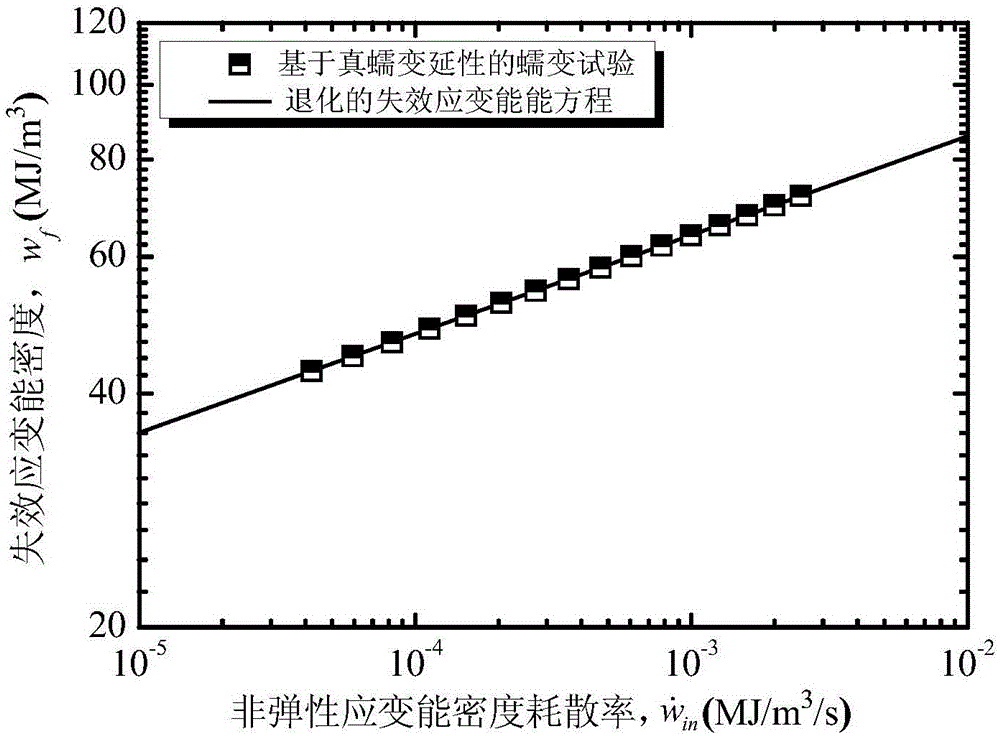
ActiveCN105158084ALife expectancyReal-time Damage DetectionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFatigue damageHysteresis
The invention provides a forecasting method for creep-fatigue life of a material. The method comprises the following steps: respectively performing a creep test, a fatigue test and a creep-fatigue interaction test for the material at a same test temperature; establishing a relation between the failure strain energy density wf and a non-elastic strain energy density dissipation rate of the material under a log-log coordinate according to the creep test; acquiring the fatigue damage df of the material per period according to the fatigue test; acquiring a hysteresis loop under a half-life period according to the creep-fatigue interaction test and establishing a function relation of the change of the stress Sigma (t) of the material under the half-life period within the maximum tensile strain maintaining time along with the change of time t; calculating the creep damage dc under the half-life period by combining with the hysteresis loop and based on the relation between wf and the function as shown in the specification and the relation of change of the fatigue damage df and the stress Sigma (t) along with the change of time t; and utilizing a linear accumulating damage rule to forecast the creep-fatigue life of the material under a creep-fatigue interaction. According to the method provided by the invention, the life of the material under the creep-fatigue interaction can be accurately forecasted.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ge photodetectors
InactiveUS20030235931A1Easy to operateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTensile strainPhotovoltaic detectors
A photodetector device includes a plurality of Ge epilayers that are grown on a substrate and annealed in a defined temperature range. The Ge epilayers form a tensile strained Ge layer that allows the photodetector device to operate efficiently in the C-band and L-band.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
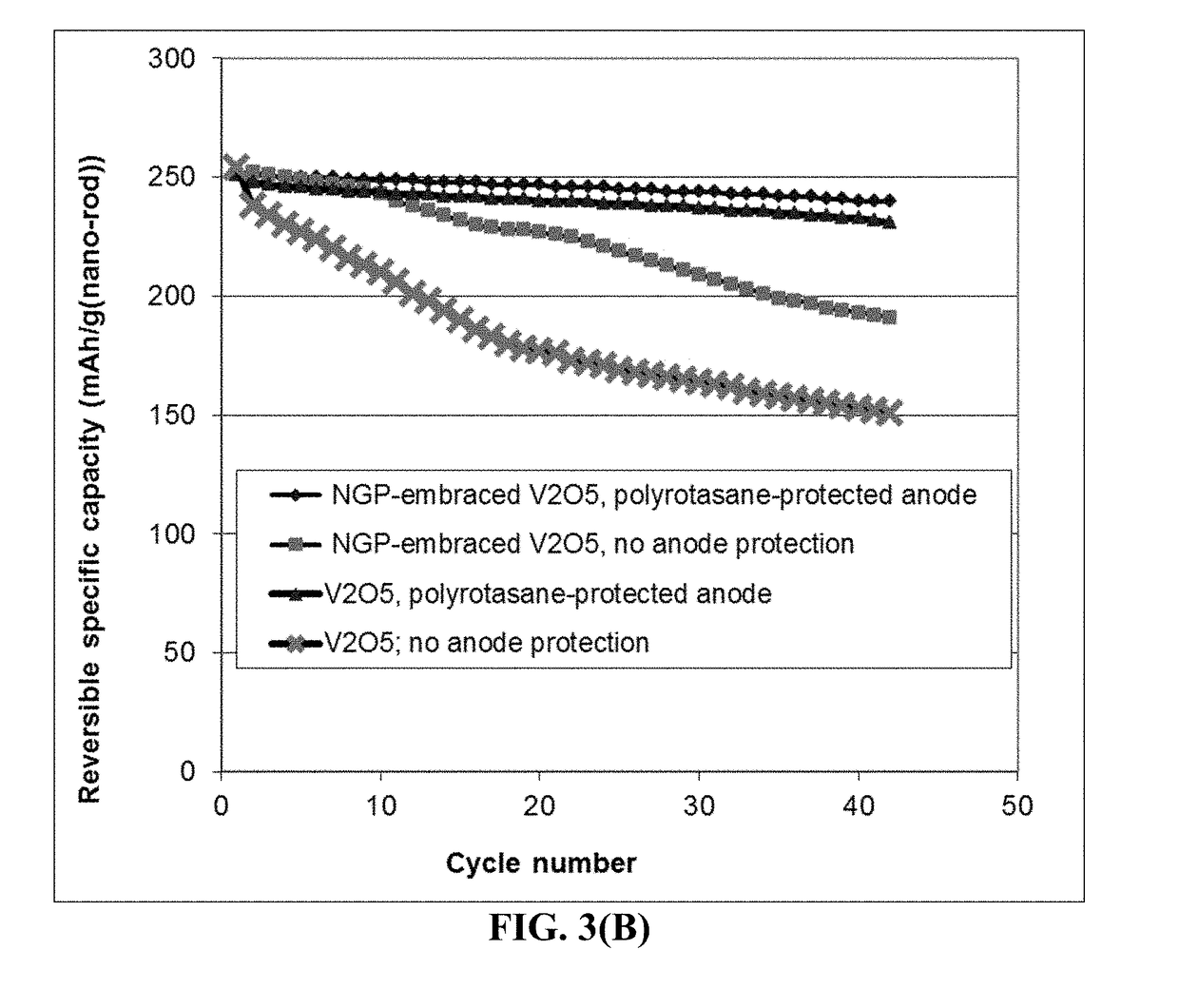
Anode-Protecting Layer for a Lithium Metal Secondary Battery and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20190051905A1Improve lithium ion conductivityReduce thicknessSolid electrolytesCell electrodesTensile strainPolyrotaxane
Provided is a lithium secondary battery, comprising a cathode, an anode, and a porous separator or electrolyte disposed between the cathode and the anode, wherein the anode comprises: (a) an anode active layer containing a layer of lithium or lithium alloy, in a form of a foil, coating, or multiple particles aggregated together, as an anode active material; and (b) a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer, disposed between the anode active layer and the porous separator or electrolyte; the polymer having a recoverable tensile strain from 2% to 1,500%, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−6 S / cm (typically up to 5×10−2 S / cm) at room temperature, and a thickness from 1 nm to 10 μm, wherein the high-elasticity polymer contains a polyrotaxane network having a rotaxane structure or a polyrotaxane structure at a crosslink point of the polyrotaxane network.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
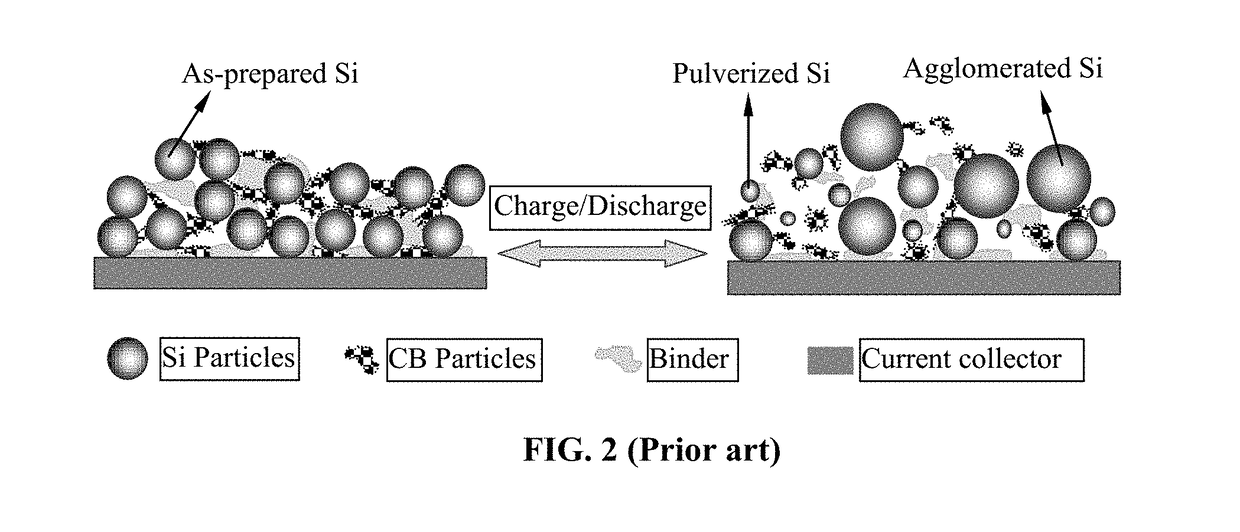
Polymer Binder for Lithium Battery and Method of Manufacturing
ActiveUS20180248173A1Increase elasticityIncrease strainSolid electrolytesFuel and secondary cellsTensile strainRoom temperature
Provided is an anode active material layer for a lithium battery. The anode active material layer comprises multiple anode active material particles and an optional conductive additive that are bonded together by a binder comprising a high-elasticity polymer having a recoverable or elastic tensile strain no less than 10% when measured without an additive or reinforcement in the polymer and a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−5 S / cm at room temperature. The anode active material preferably has a specific lithium storage capacity greater than 372 mAh / g (e.g. Si, Ge, Sn, SnO2, Co3O4, etc.).
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
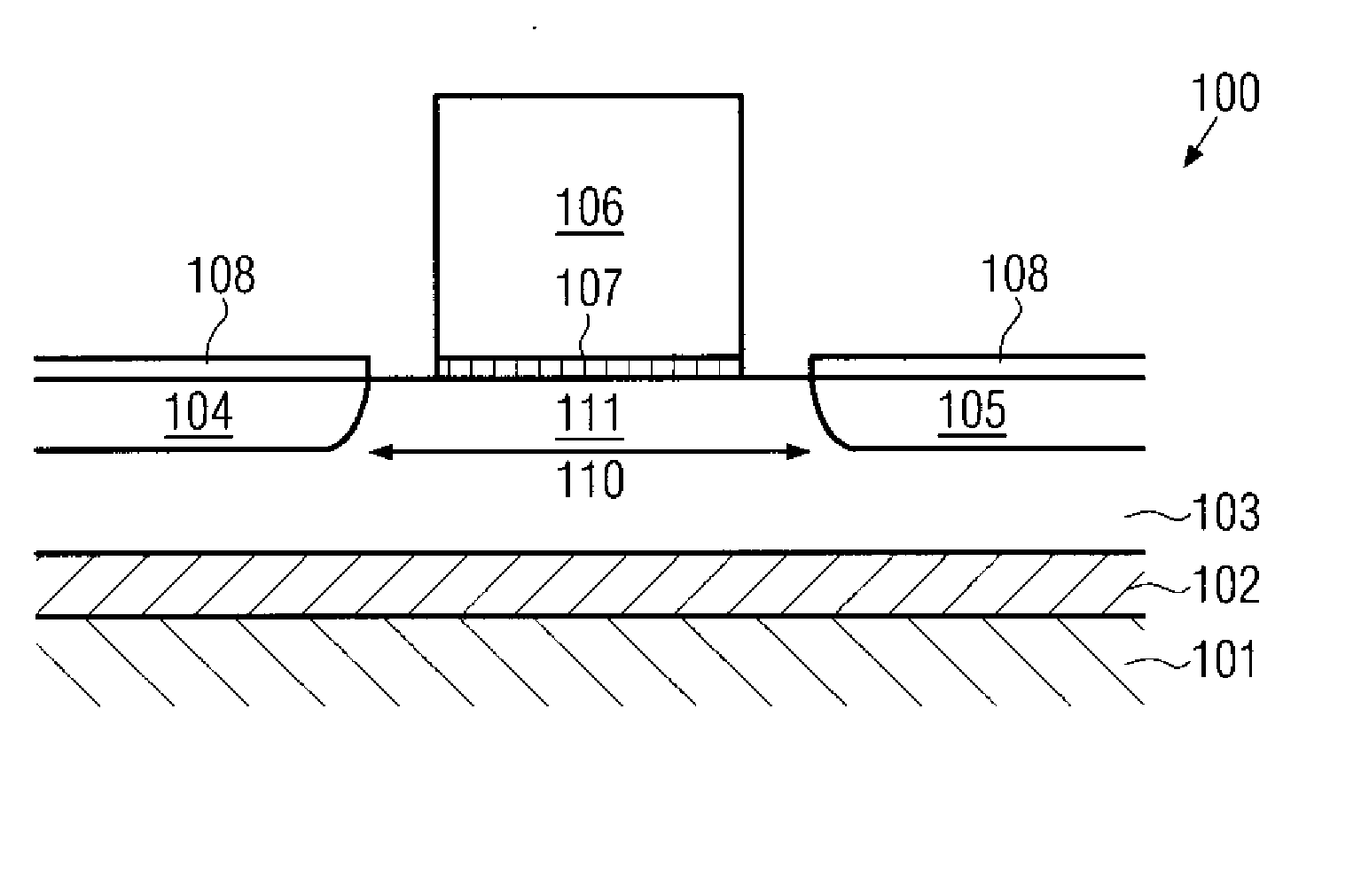
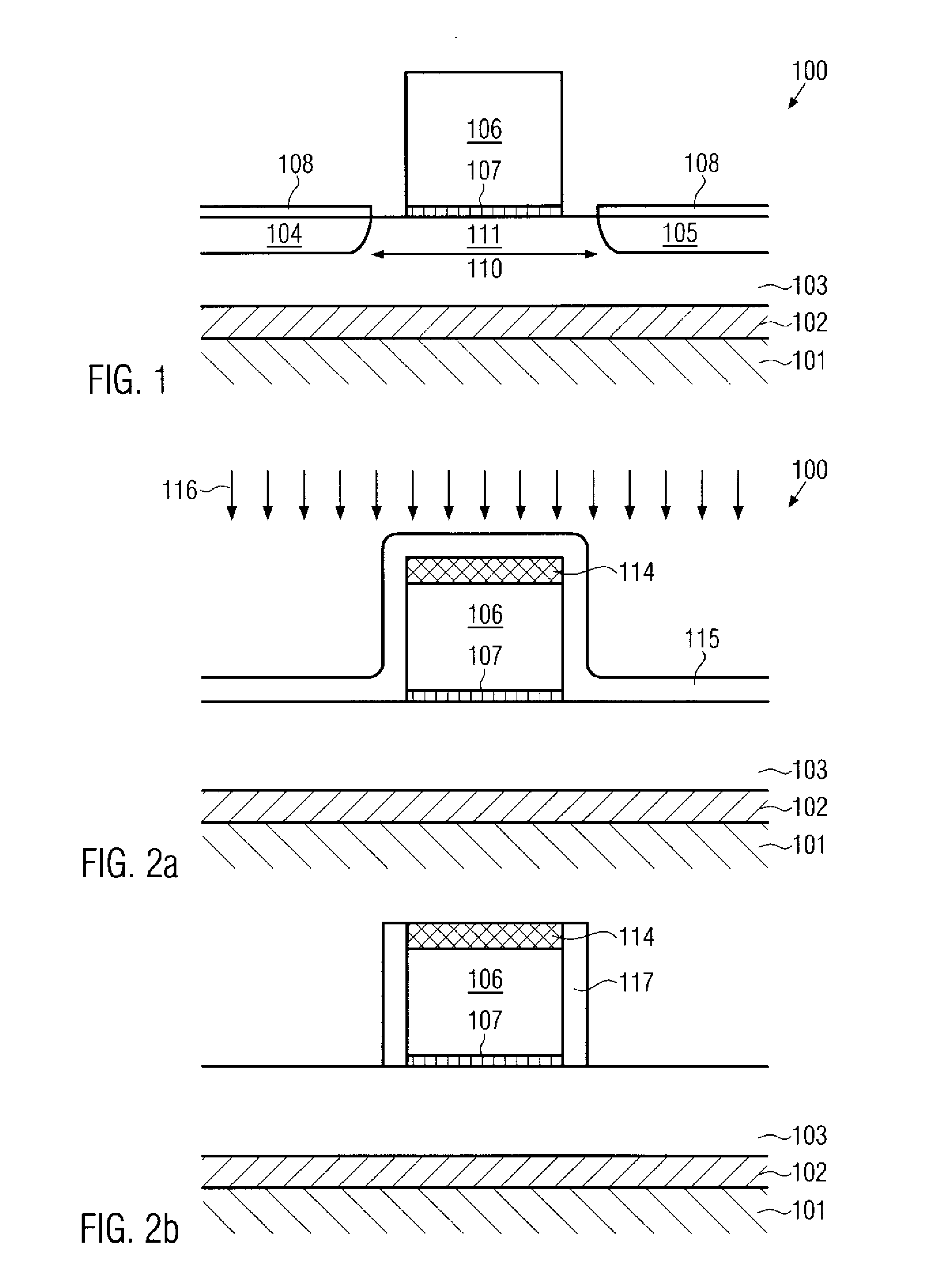
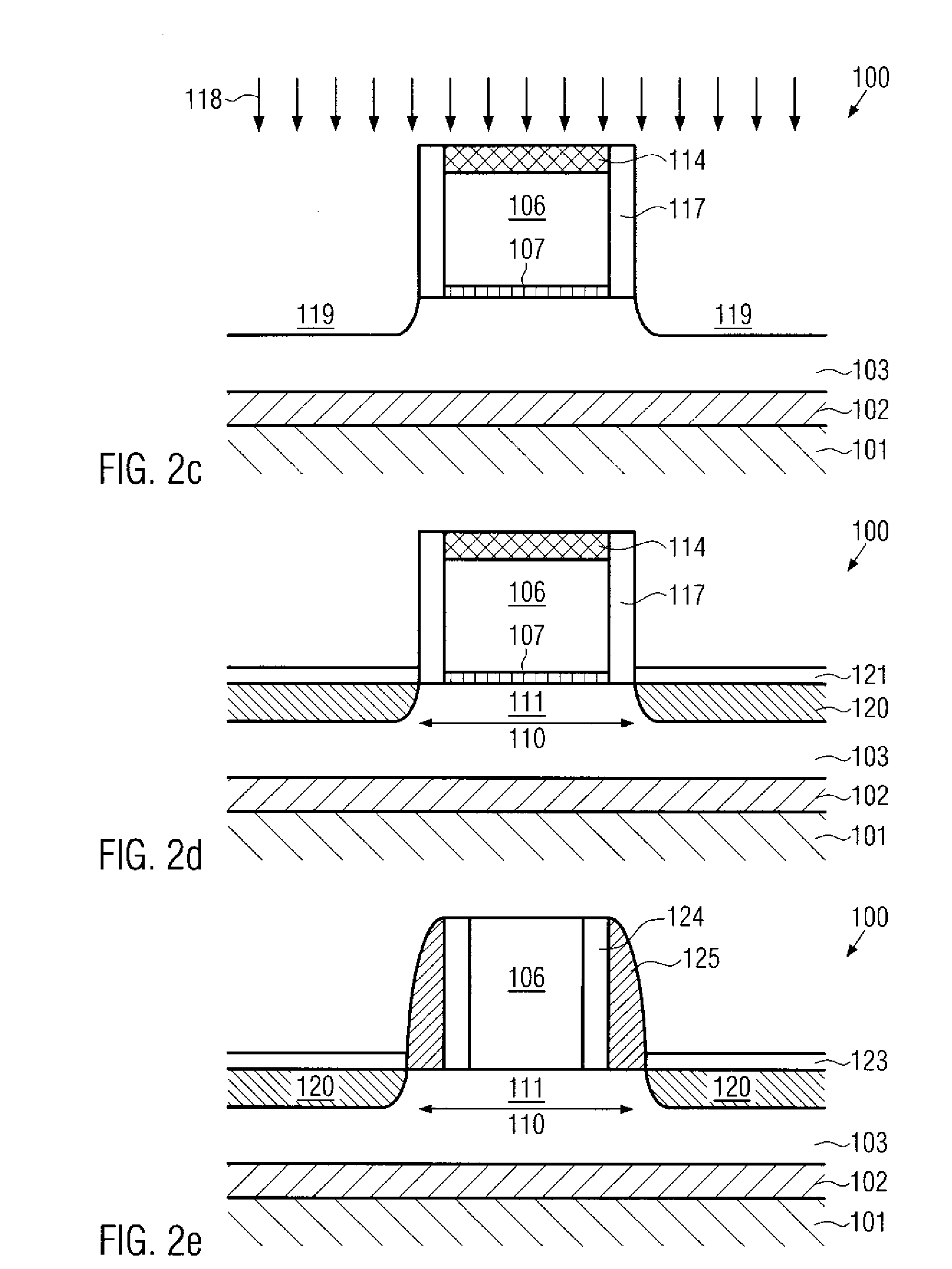
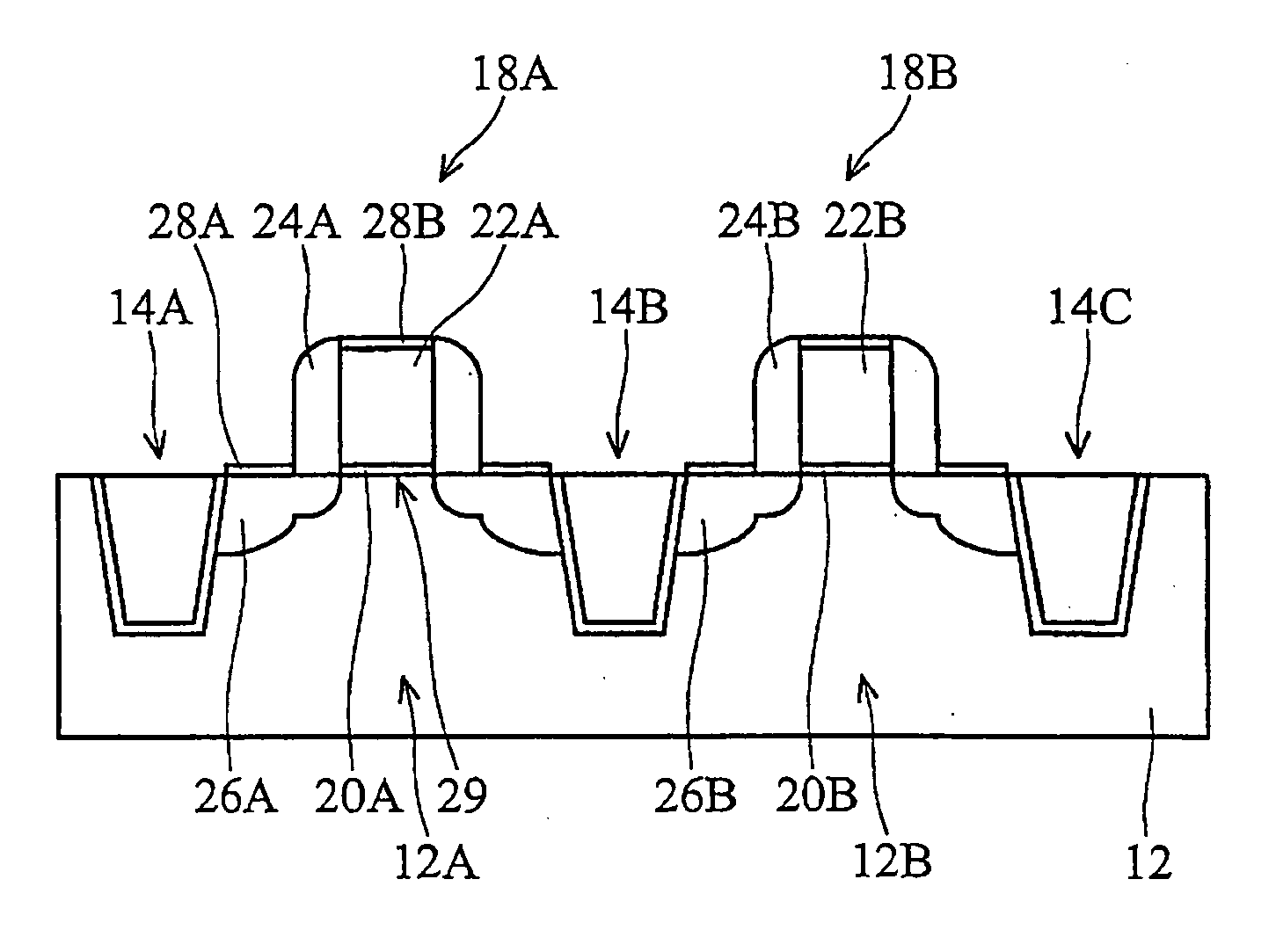
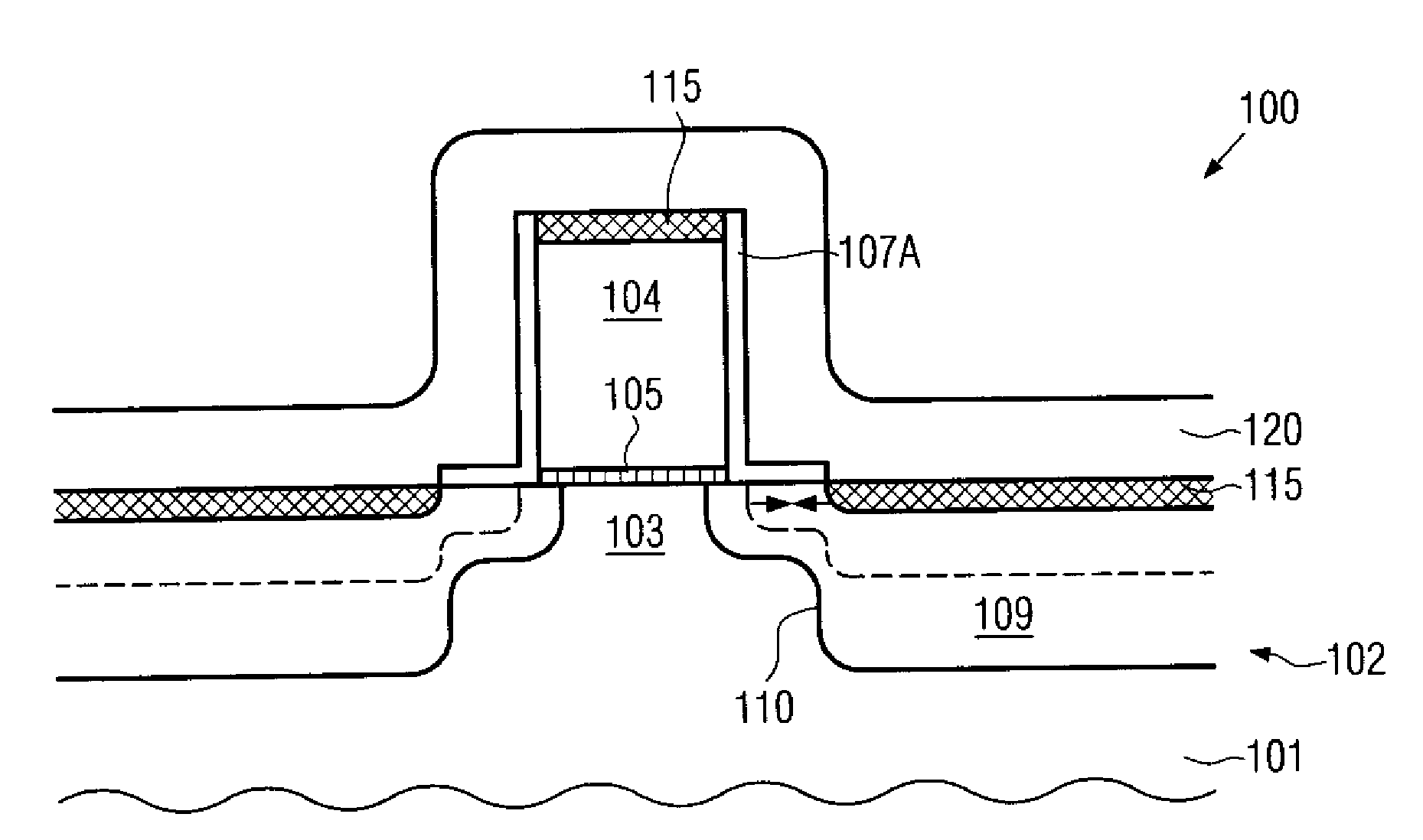
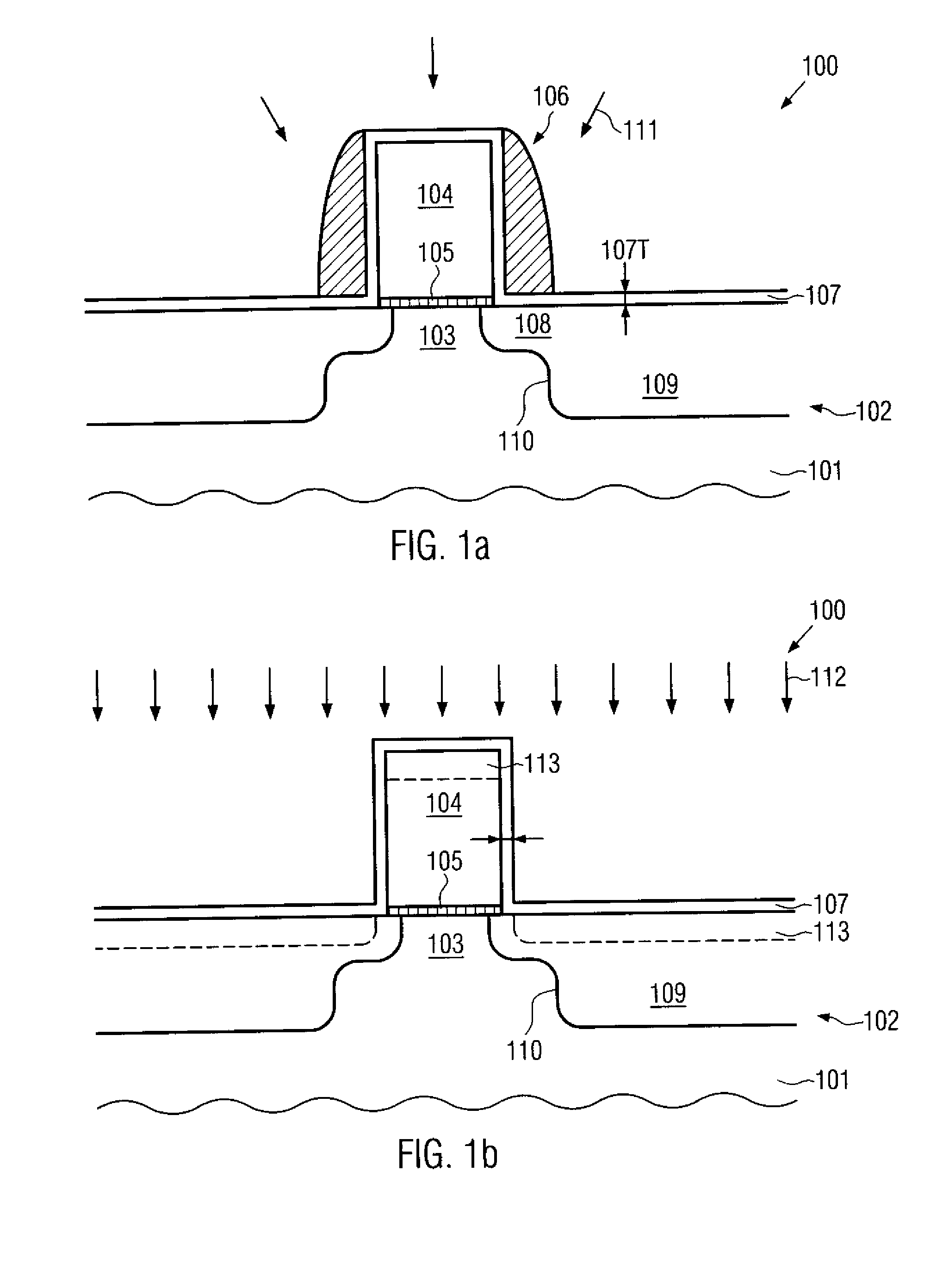
Silicon strain engineering accomplished via use of specific shallow trench isolation fill materials
InactiveUS7081395B2Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETThermal expansion
A method of forming a strained silicon layer created via a material mis-match with adjacent trench isolation (TI), regions filled with a dielectric layer comprised with either a higher, or lower thermal expansion coefficient than that of silicon, has been developed. Filling of trenches with a dielectric layer comprised with a higher thermal expansion coefficient than that of silicon results in a tensile strain in planar direction and compressive strain in vertical direction, in an adjacent silicon region. Enhanced electron mobility in channel regions of an N channel MOSFET device, and enhanced hole mobility and transit time in an N type base region of a vertical PNP bipolar device, is realized when these elements are formed in the silicon layer under tensile strain. Filling of trenches with a dielectric layer comprised with a lower thermal expansion coefficient than the thermal expansion coefficient of silicon results in a compressive strain in planar directions and tensile strain in vertical directions, in an adjacent silicon region. Enhanced hole mobility in channel regions of an P channel MOSFET device, and enhanced electron mobility and transit time in a P type base region of a vertical NPN bipolar device, is realized when these elements are formed in the silicon layer under compressive strain.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
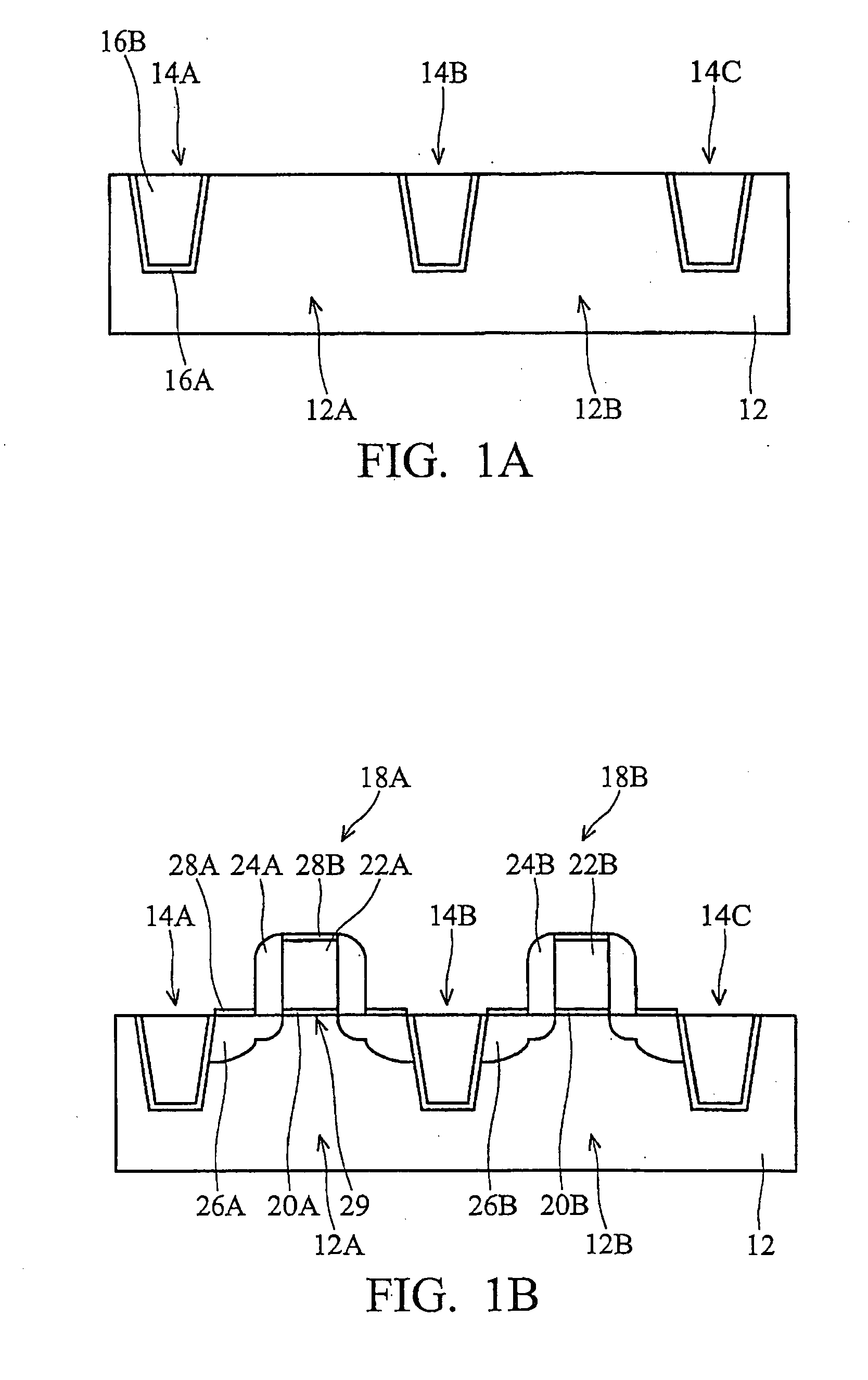
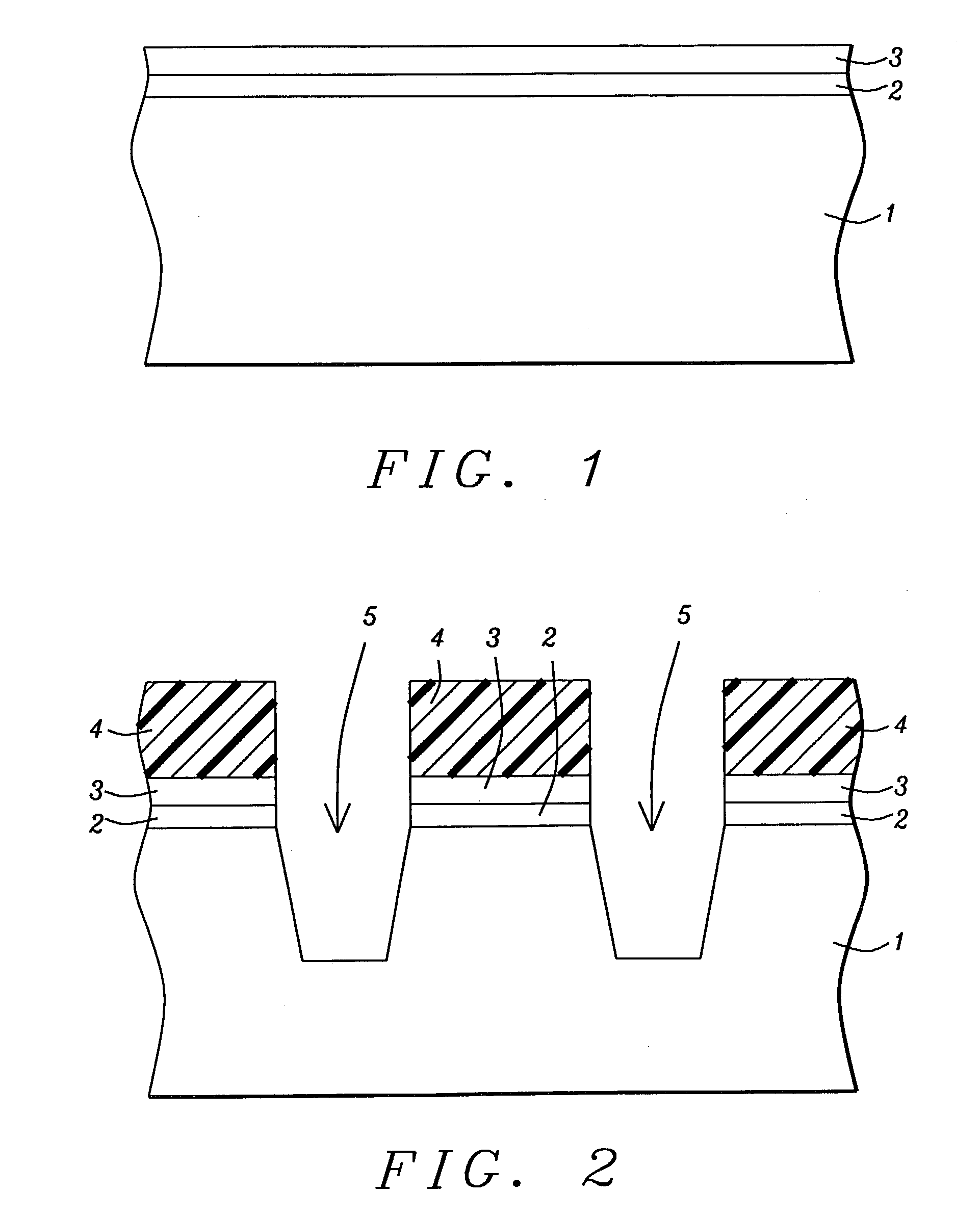
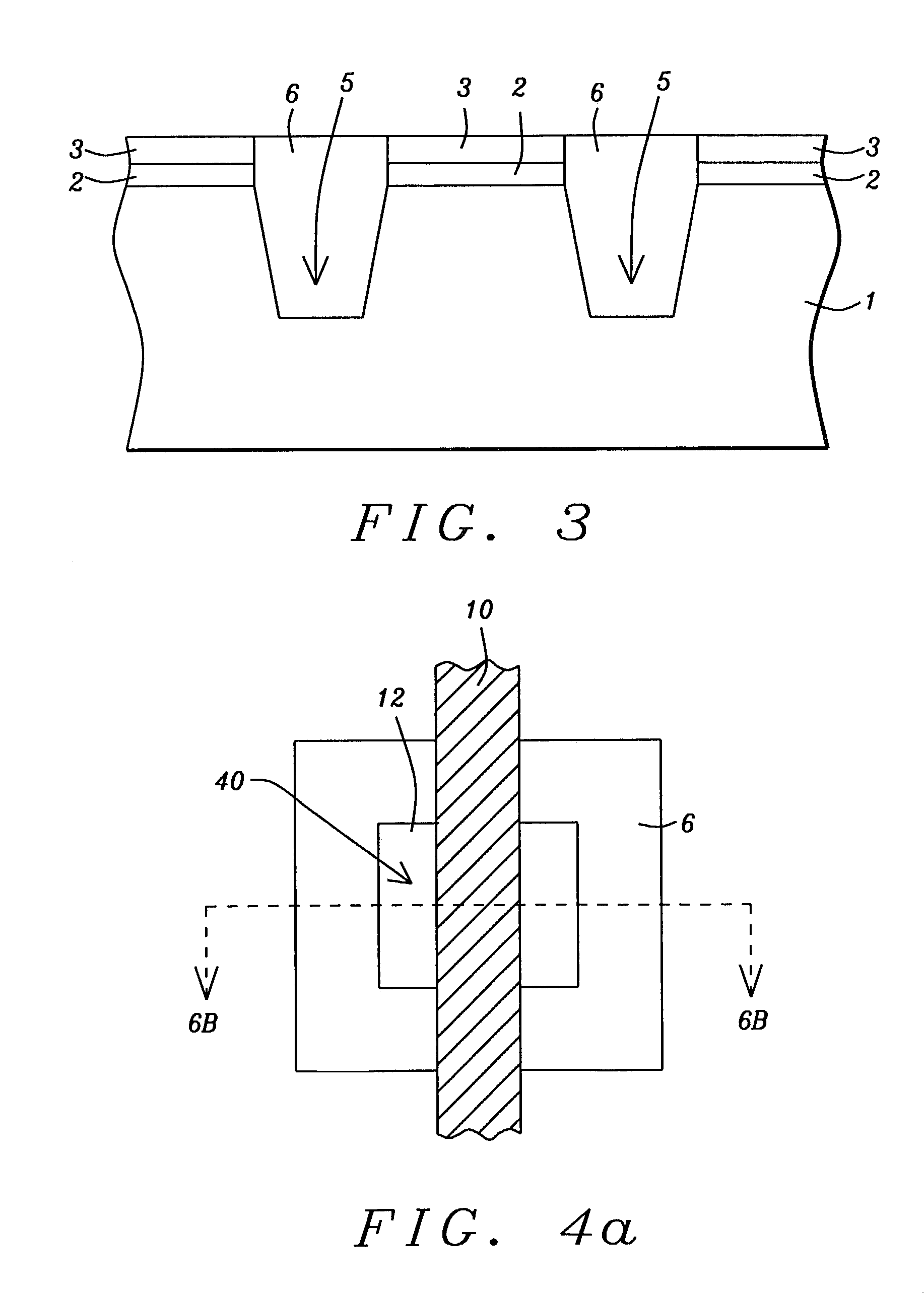
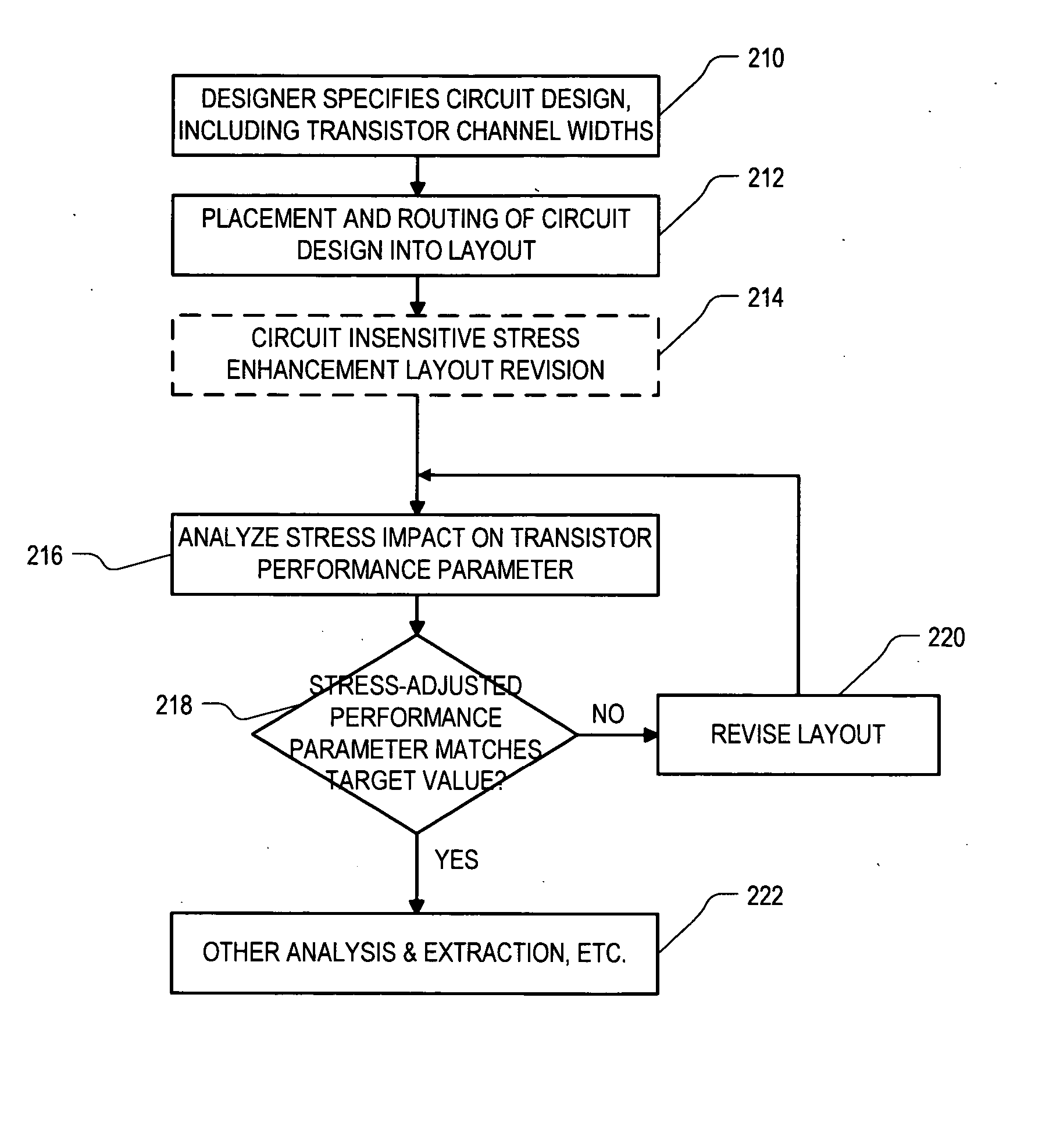
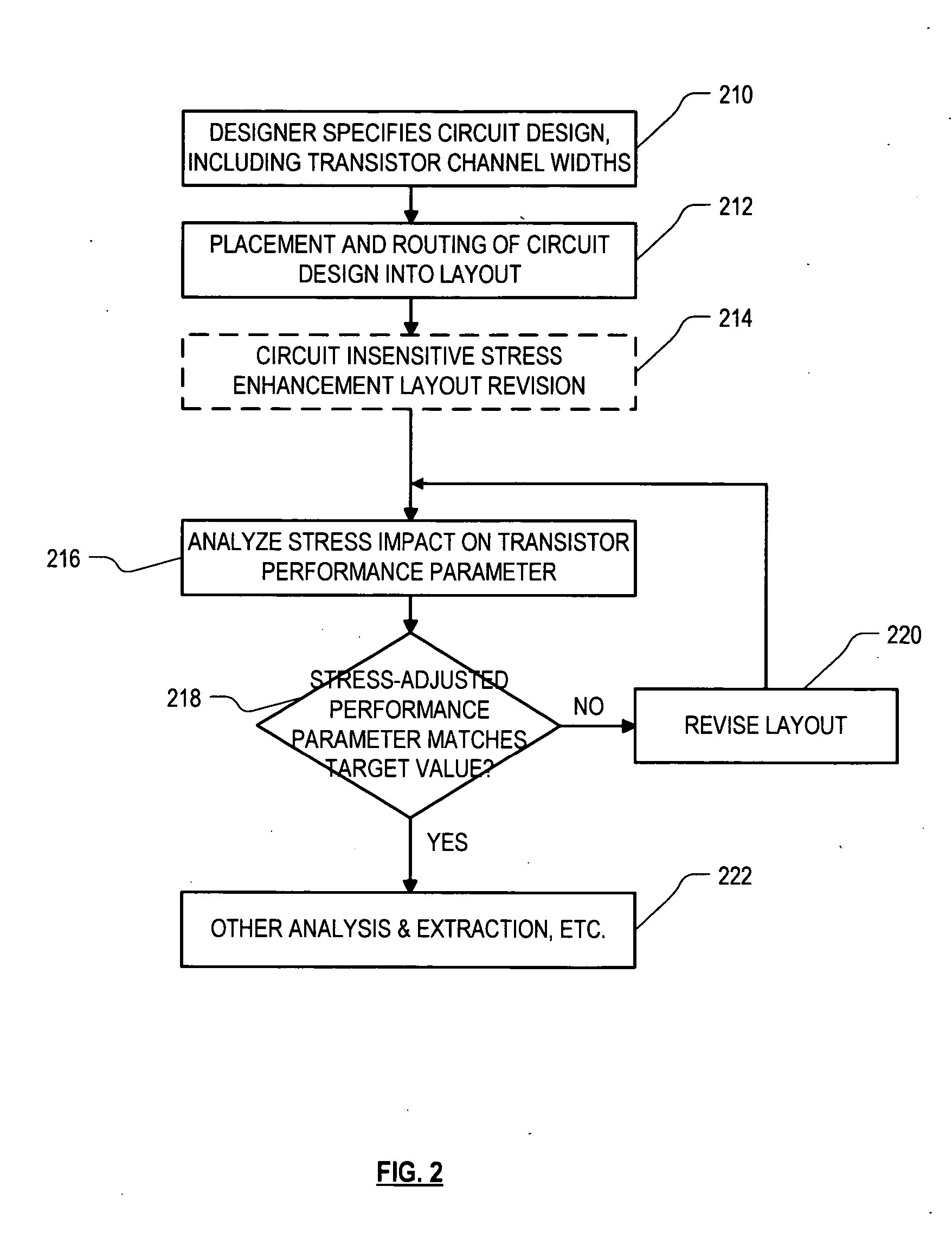
Stress-managed revision of integrated circuit layouts
ActiveUS20070204250A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designTensile strainDiffusion
Roughly described, methods and systems for improving integrated circuit layouts and fabrication processes in order to better account for stress effects. Dummy features can be added to a layout either in order to improve uniformity, or to relax known undesirable stress, or to introduce known desirable stress. The dummy features can include dummy diffusion regions added to relax stress, and dummy trenches added either to relax or enhance stress. A trench can relax stress by filling it with a stress-neutral material or a tensile strained material. A trench can increase stress by filling it with a compressive strained material. Preferably dummy diffusion regions and stress relaxation trenches are disposed longitudinally to at least the channel regions of N-channel transistors, and transversely to at least the channel regions of both N-channel and P-channel transistors. Preferably stress enhancement trenches are disposed longitudinally to at least the channel regions of P-channel transistors.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
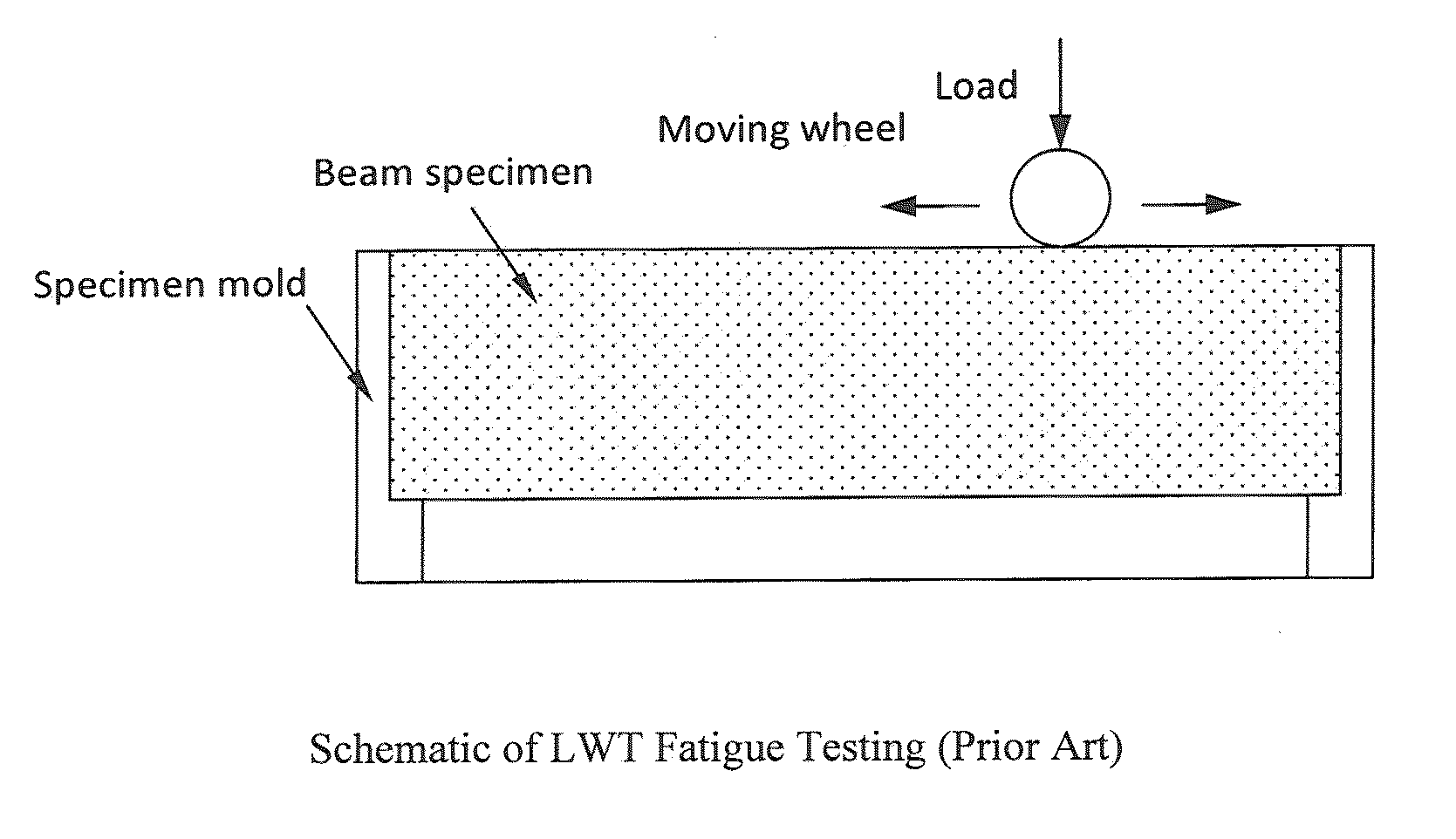
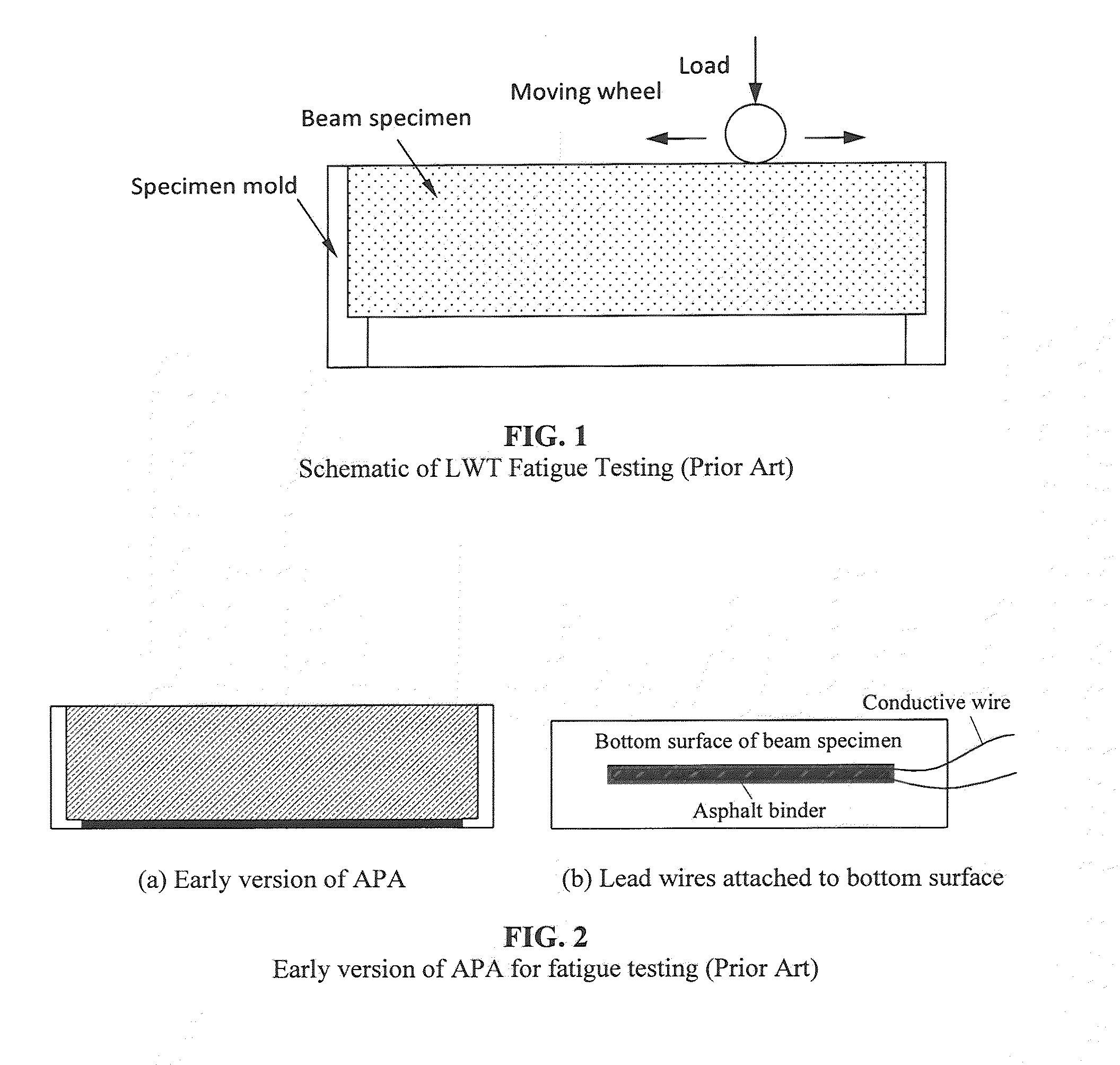
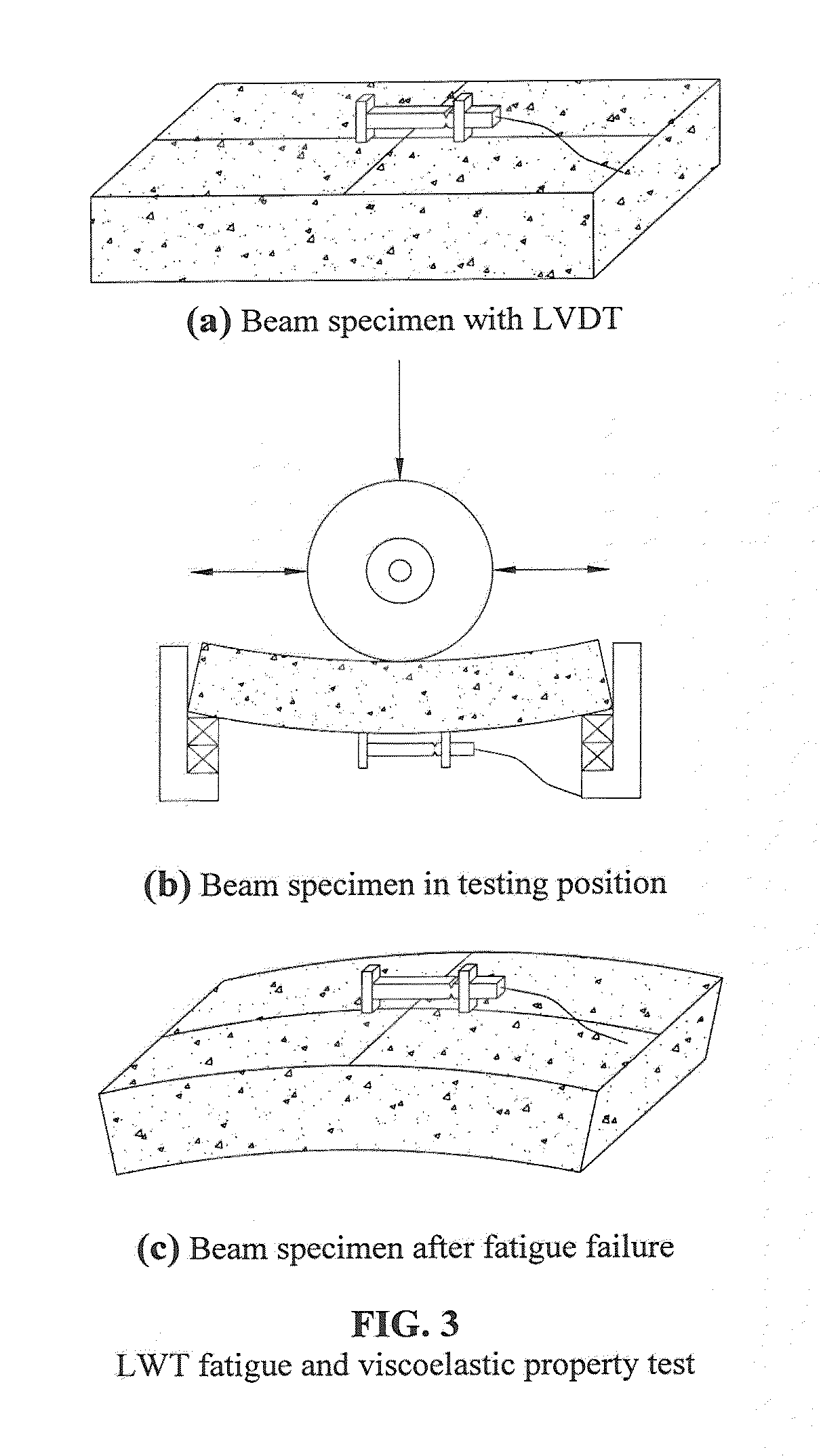
Method and apparatus for fatigue and viscoeleastic property testing of asphalt mixtures using a loaded wheel tester
InactiveUS20120253704A1Accurate measurementForce measurementWork measurementTensile strainTester device
A loaded wheel tester for testing asphalt mixtures comprises a loaded wheel tester having additional means for attachment to specimens under test to provide a measurement of tensile strain and for attachment between a frame of the loaded wheel tester and the loaded wheel to determine position of the loaded wheel over time. Output results demonstrate that viscoelastic and fatigue properties of asphalt mixtures are obtained in equivalent or improved format using a modified loaded wheel tester when compared with known pavement test apparatus and methods.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
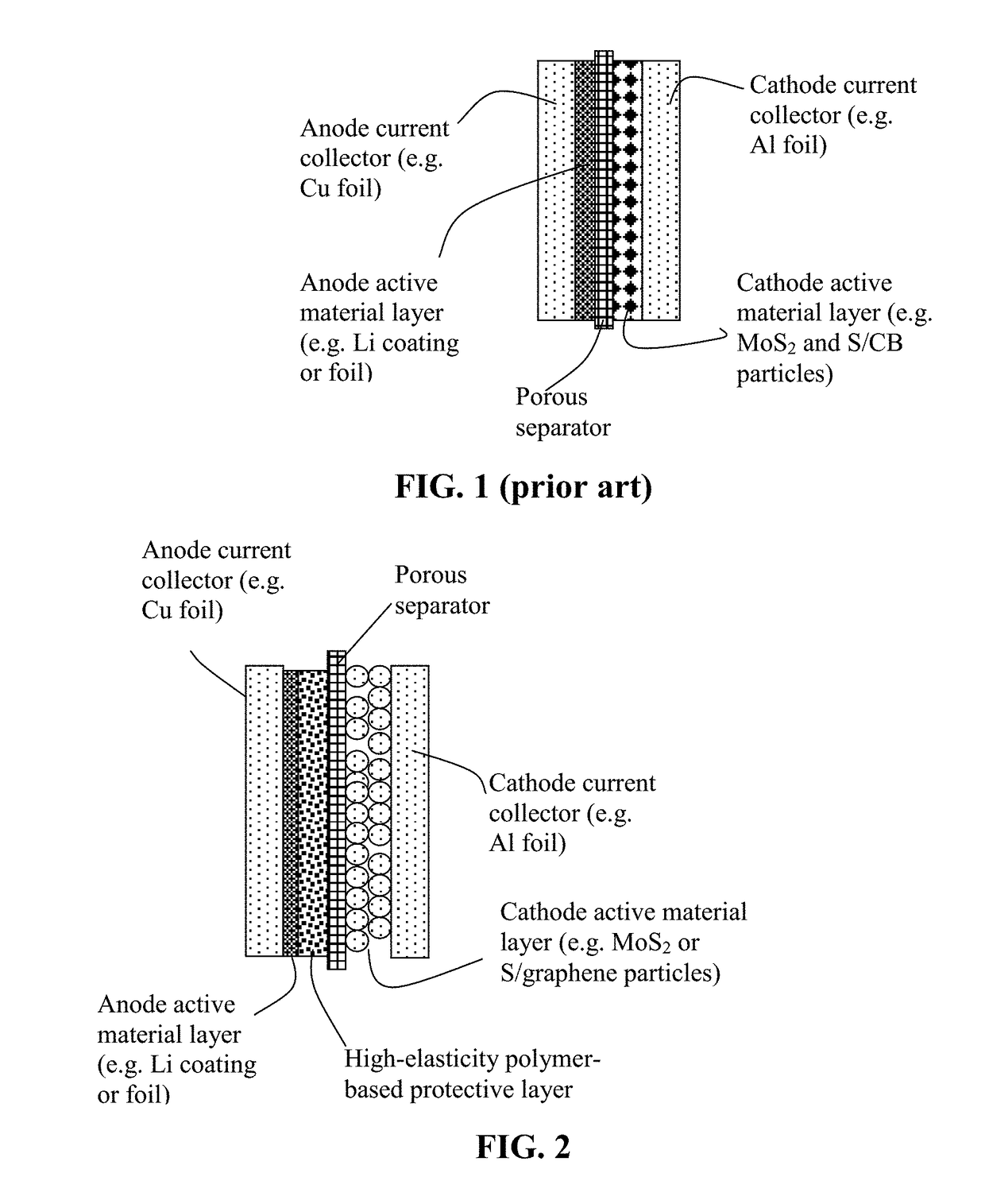
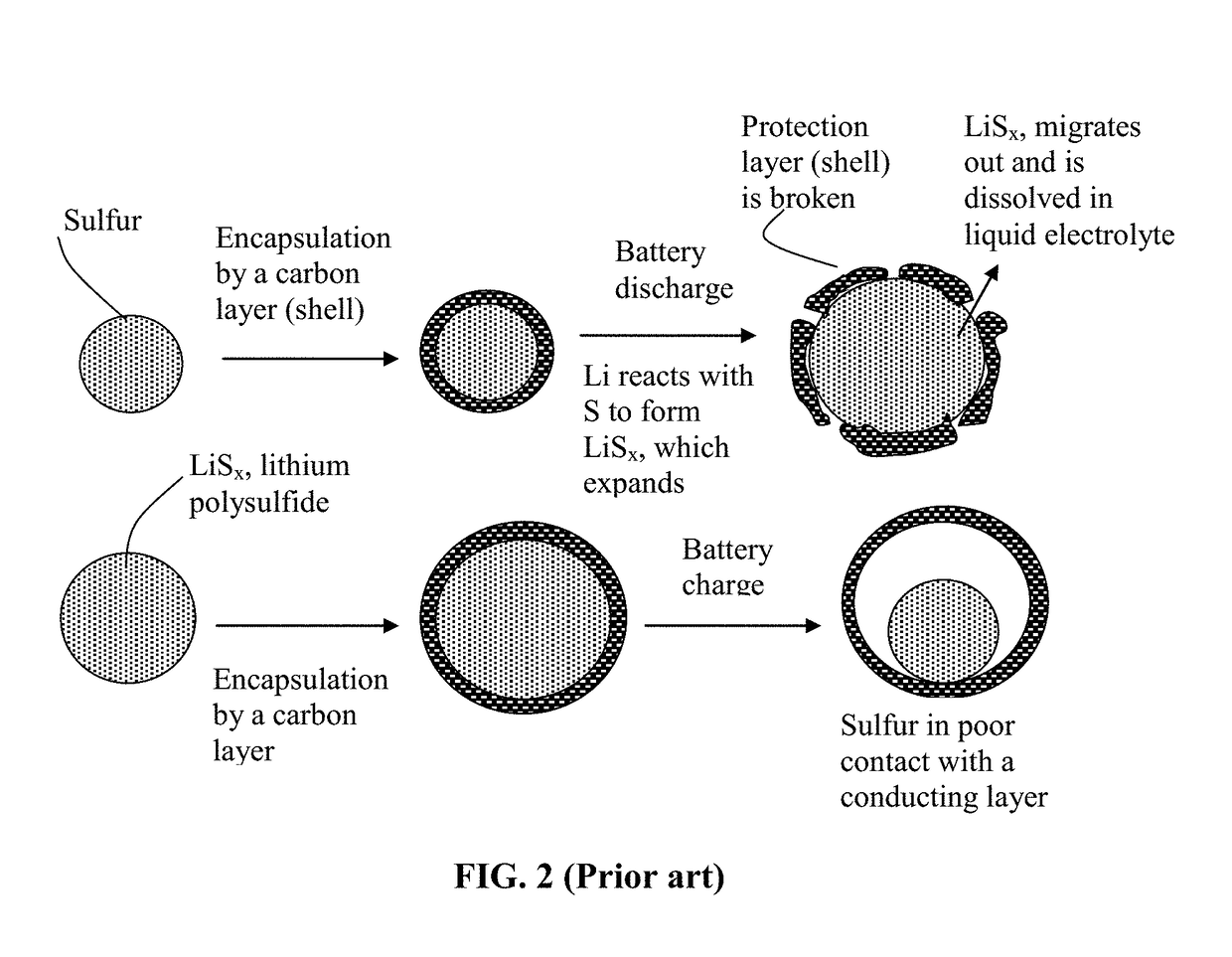
Alkali metal-sulfur secondary battery containing a protected sulfur cathode and manufacturing method
ActiveUS10084182B2Inhibited DiffusionReduce and eliminate effectFinal product manufacturePositive electrodesParticulatesConductive polymer
Provided is a rechargeable alkali metal-sulfur cell comprising an anode active material layer, an electrolyte, and a cathode active material layer containing multiple particulates of a sulfur-containing material selected from a sulfur-carbon hybrid, sulfur-graphite hybrid, sulfur-graphene hybrid, conducting polymer-sulfur hybrid, metal sulfide, sulfur compound, or a combination thereof and wherein at least one of the particulates is composed of one or a plurality of sulfur-containing material particles being embraced or encapsulated by a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 10% when measured without an additive or reinforcement, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−5 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 0.5 nm to 10 μm. This battery exhibits an excellent combination of high sulfur content, high sulfur utilization efficiency, high energy density, and long cycle life.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
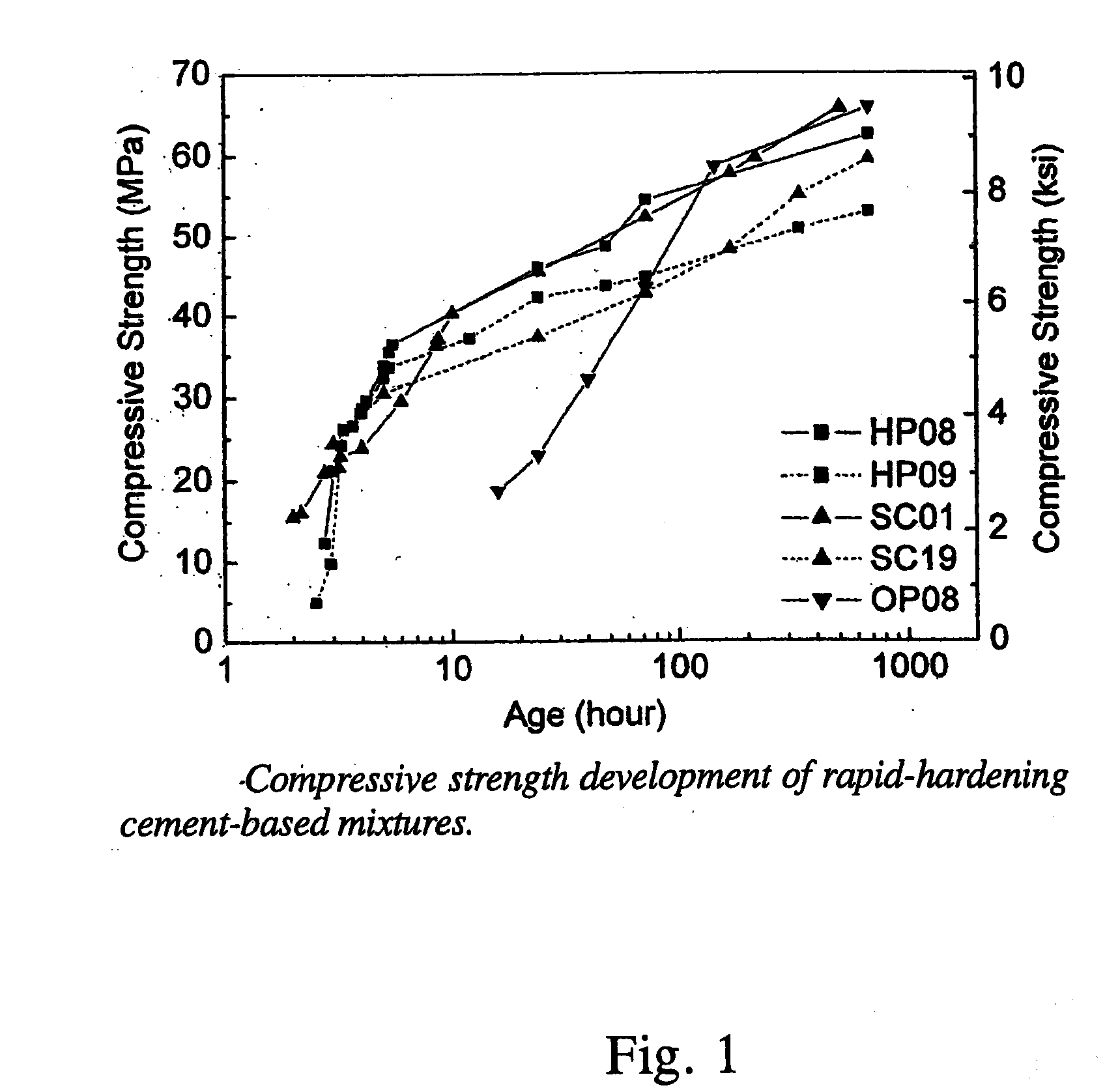
High Early Strength Engineered Cementitious Composites
ActiveUS20070181040A1High early-strengthLarge capacitySolid waste managementClimate change adaptationTensile strainCement composites
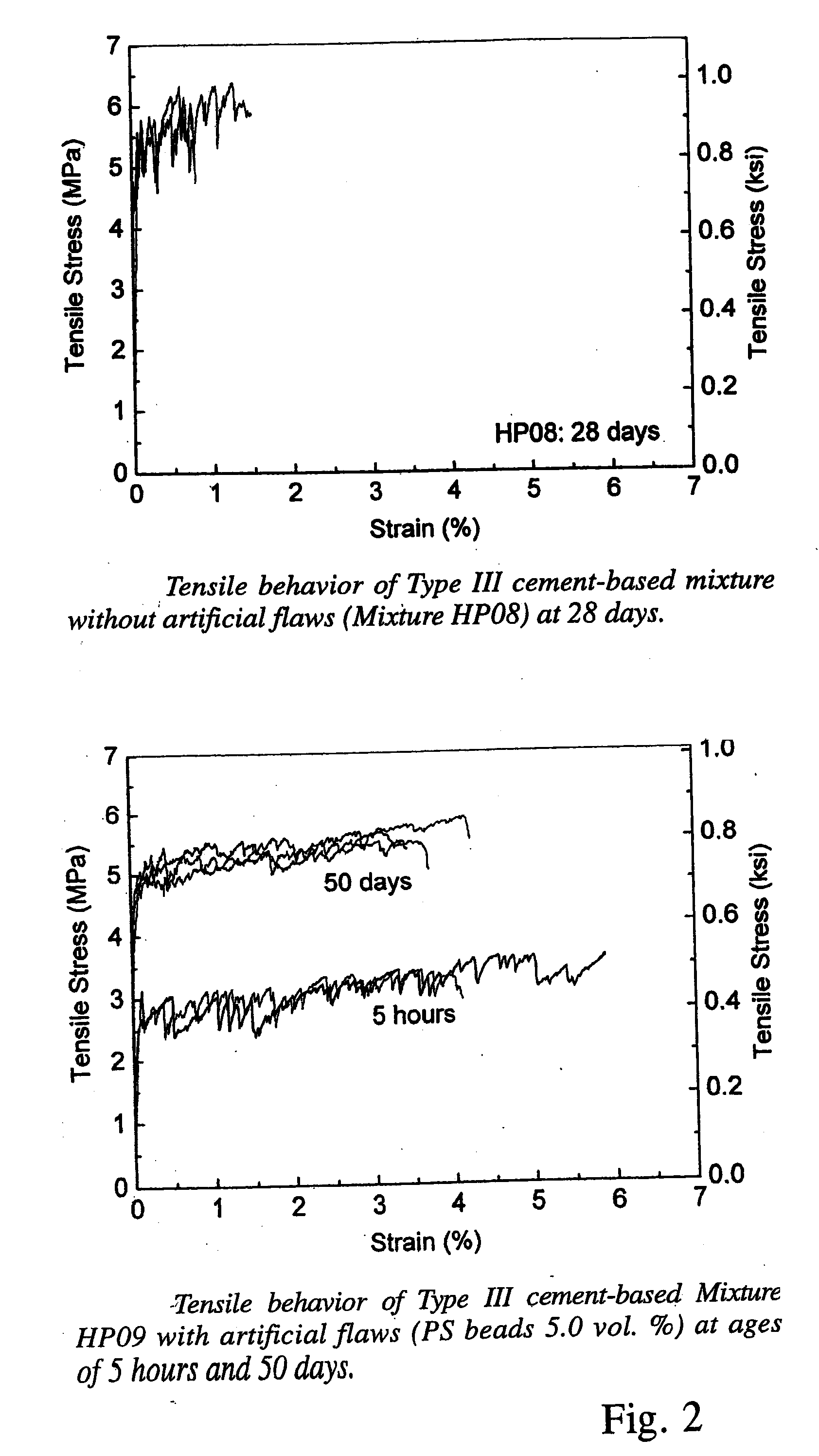
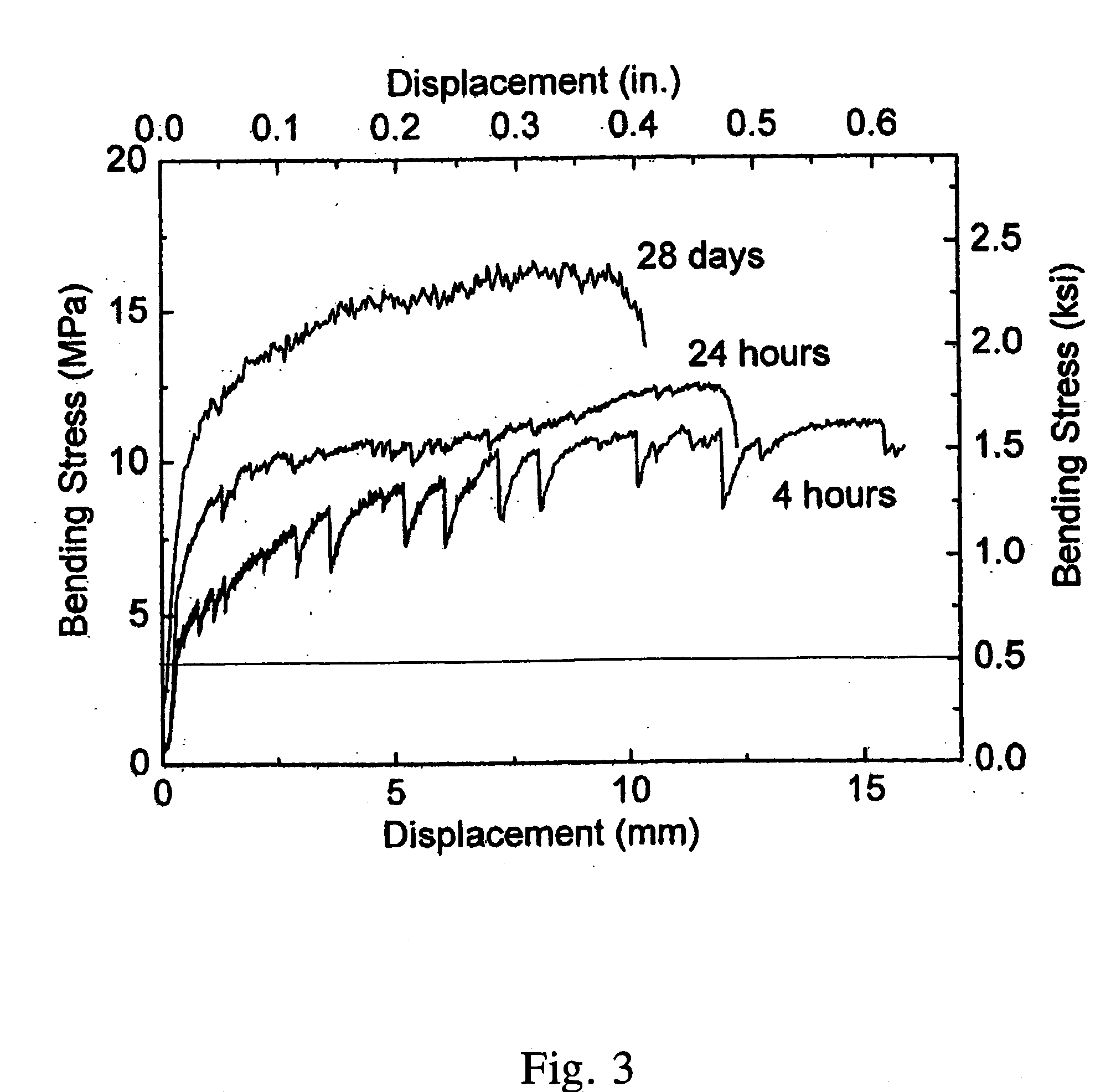
Rapid repair and retrofit of existing infrastructures demand durable high early strength materials that not only deliver sufficient strength within a few hours of placement but also significantly prolong the maintenance interval. The invention comprises a class of newly developed polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber-reinforced high early strength engineered cementitious composites (ECC) materials featuring extraordinary ductility. The tailoring of preexisting flaw size distribution through non-matrix interactive crack initiators in the composite matrix results in high tensile ductility. The resulting high early strength ECC materials are capable of delivering a compressive strength of 21 MPa (3.0 ksi) within 4 hours after placement and retaining long-term tensile strain capacity above 2%.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com