Forecasting method for creep-fatigue life of material
A technology for fatigue life prediction and creep, applied in the direction of applying stable tension/pressure to test material strength, etc., can solve the problems of unexplained creep effect from the mechanism, complicated steps, conservative ductility exhaustion model, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0130] The selected data are three papers published by Takahashi and Yaguchi [Y. Takahashi, Study on creep-fatigue evaluation procedures for high-chromium steels-Part I: Test results and life prediction based on measured stress relaxation, International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping. 85 (2008) 406-422]. Systematicevaluationofcreep-fatiguelifepredictionmethodsforvariousalloys,ProceedingsoftheASME2009PressureVesselsandPipingDivisionConference.(2009)1-10】、【K.Taguchi,E.Kanno,S.Ozaki,Applicationoftheoverstressconcepttoinelasticbehaviorandevaluationofcreep-fatiguedamageformodified9Cr-1MosteelInternationalJournalofPressureVesselsandPiping.44(1990)99-115】以及Asayama的报告【T.Asayama, Update and Improve Subsection NH-Alternative Simplified Creep-Fatigue Design Methods, STP-NU-041. (2011)]. First of all, these documents give the creep test data of Grade91 at 550 °C, 600 °C and 650 °C, that is, the linear material constant independent of temperature can be calculated, B 1 =2.23,n 1 =...
example 2
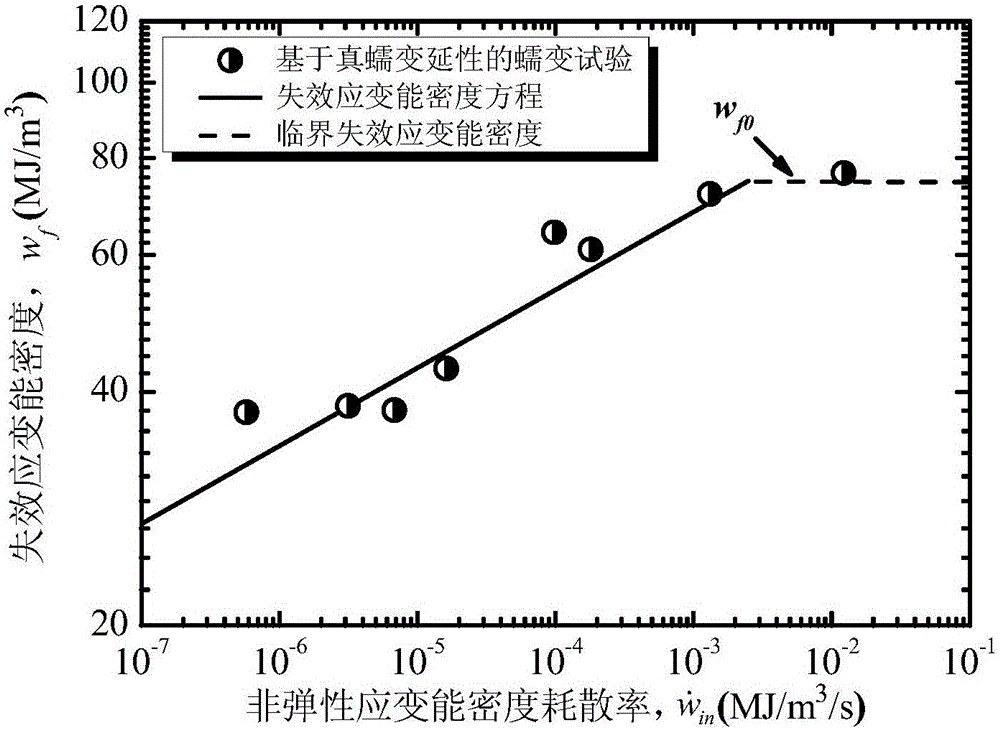
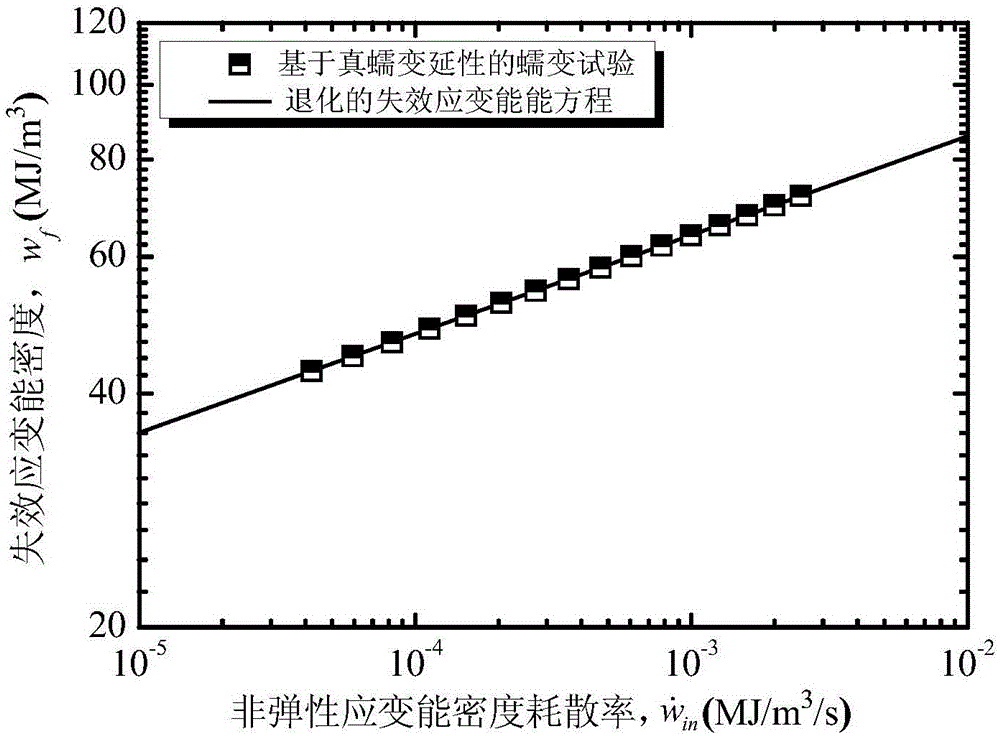
[0134] 选取数据为Chen,Pritchard和Kim发表的三篇论文【X.Chen,Hightemperaturecreep-fatiguebehaviorofalloy617andalloy230,UniversityofIllinoisatUrbana-Champaign.(2012)】、【P.G.Pritchard,L.Carroll,T.Hassan,Constitutivemodelingofhightemperatureuniaxialcreep-fatigueandcreep-ratchetingresponsesofAlloy617,ASME2013PressureVesselsandPipingConference .American Society of Mechanical Engineers.(2013)],【W.G.Kim, J.Y.Park, G.G.Lee, Temperature effect on the creep behavior of alloy 617 in air and helium environments. Nuclear Engineering and Design. 271(2014) 291-300]. First of all, these documents give Alloy creep test data at 850°C. Since only the material life at 850°C is studied, that is, using the degeneration formula (4), the temperature-related material constant D = 464.111 can be obtained; analysis 850 The functional relationship between the failure strain energy density and the inelastic strain energy density dissipation rate at ℃, it is found that there is a critical failure strain energy density w f0...
example 3
[0138] The selected data are two papers published by Conway and Kim [J.B.Conway, R.H.Stentz, J.T.Berling.Fatigue, tensile, and relaxation behavior of stainless steels, Mar-Test, Inc., Cincinnati, Ohio. (1975)], [V.K.Sikka, M.K.Booker. Assessment of tensile and creep data for Types 304 and 316 stainless steel, Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology. 99 (1977) 298-313]. First of all, these documents give the creep test data of 304SS at 650°C. Since only the material life at a temperature of 650°C is studied, that is, using the degeneration formula (4), the temperature-related material constant D=154.12 can be obtained; the analysis of 650 The functional relationship between the failure strain energy density and the inelastic strain energy density dissipation rate at ℃, it is found that there is no critical failure strain energy density; in the creep fatigue test at 650℃, the passing total strain ranges are 0.5% and 2.0%, respectively, Calculate the constants A=45.55 and B=129.19 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com