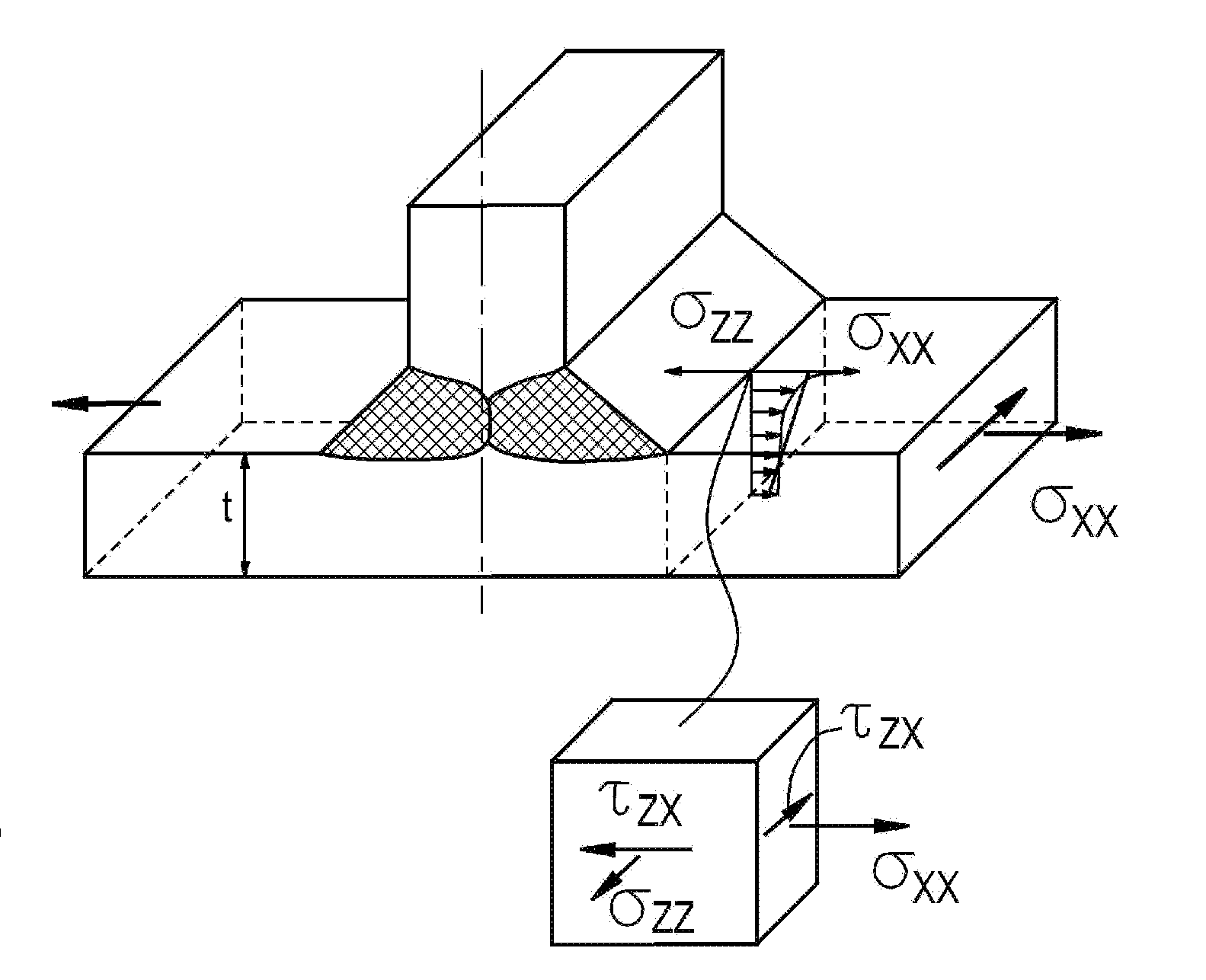
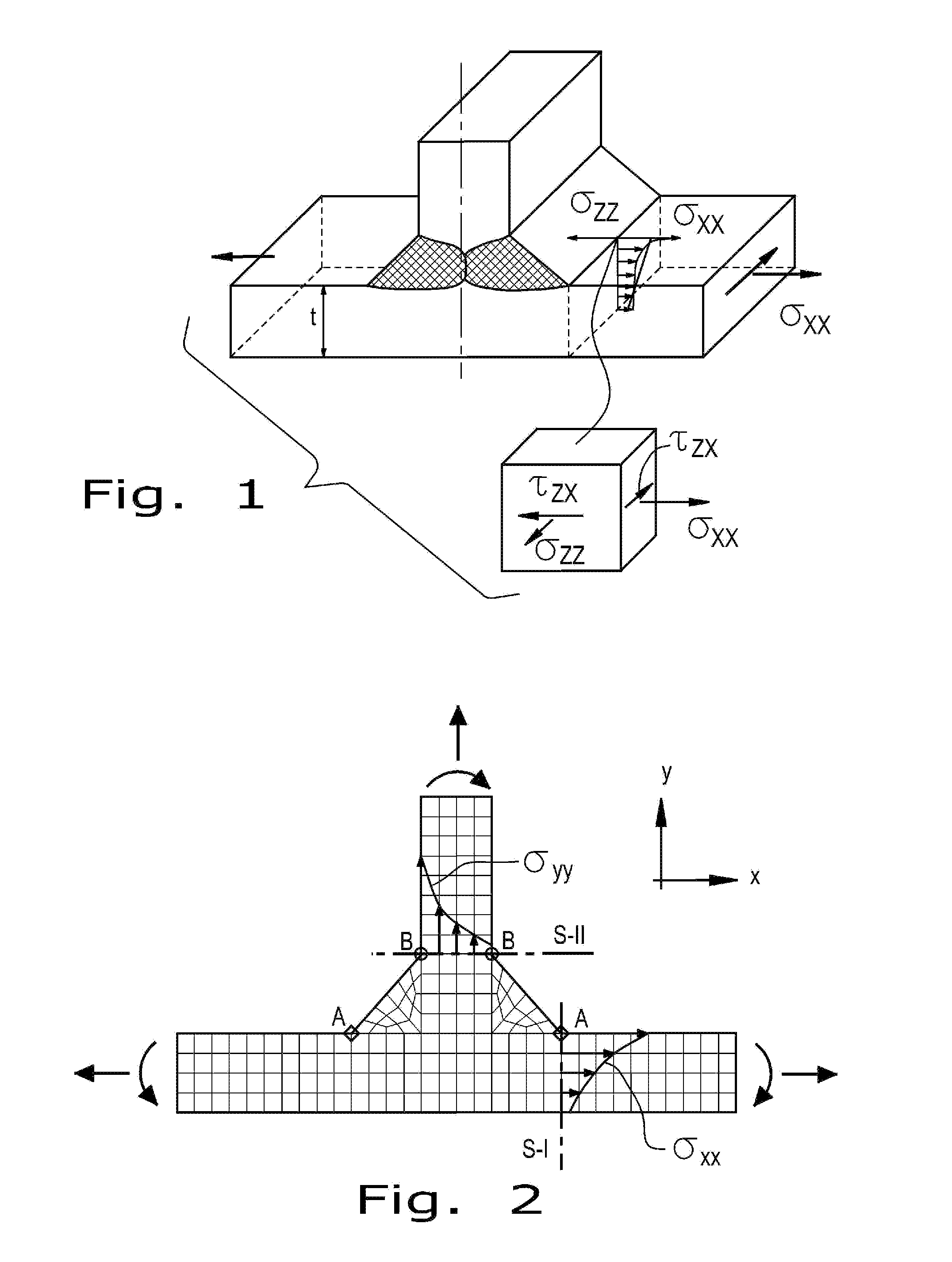
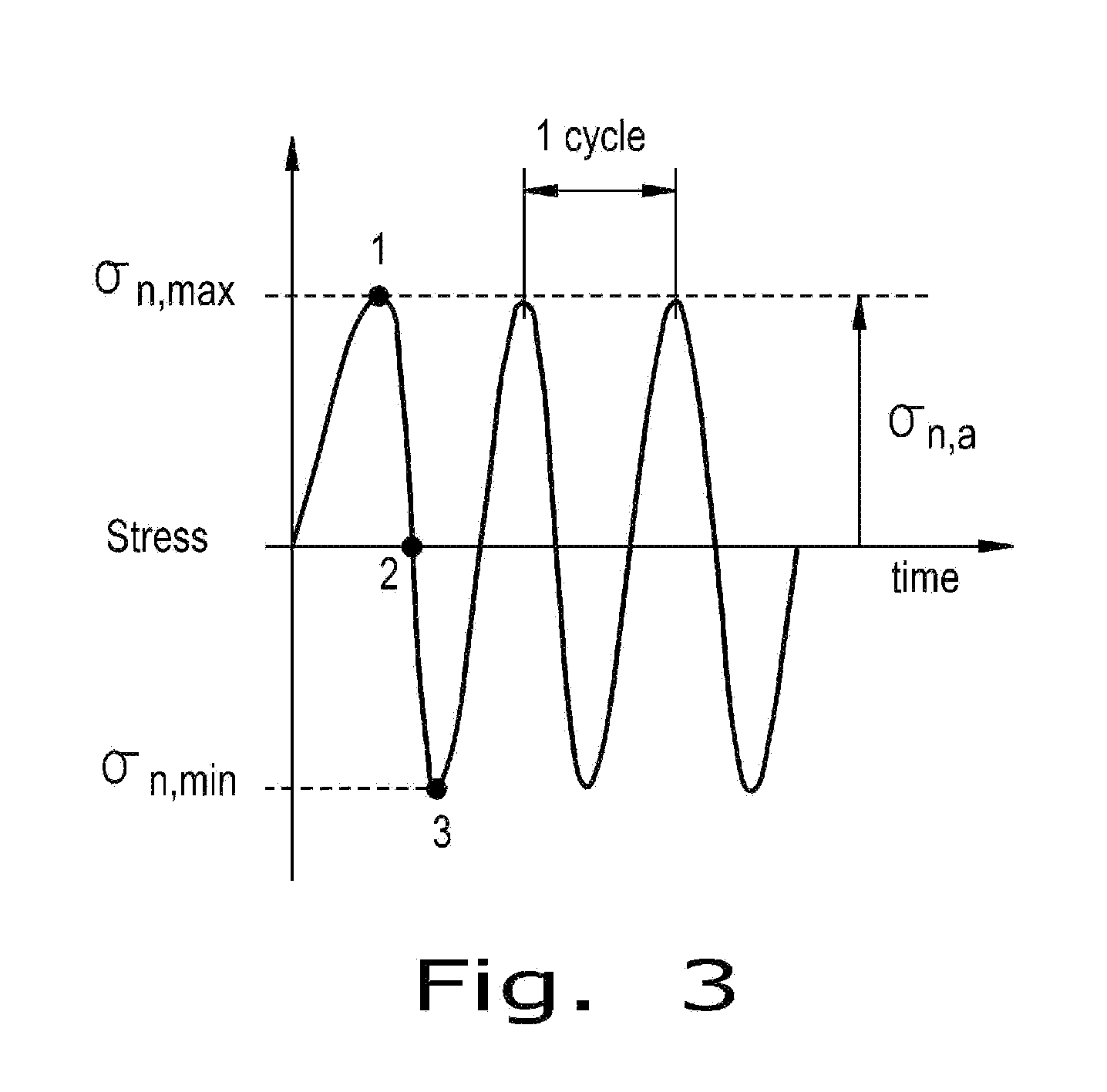
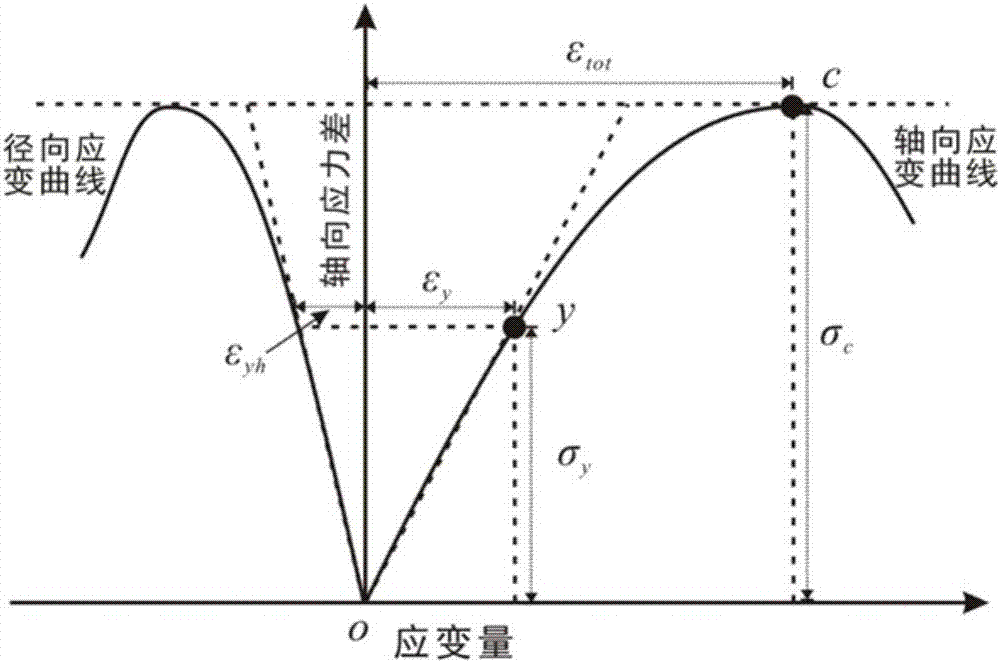
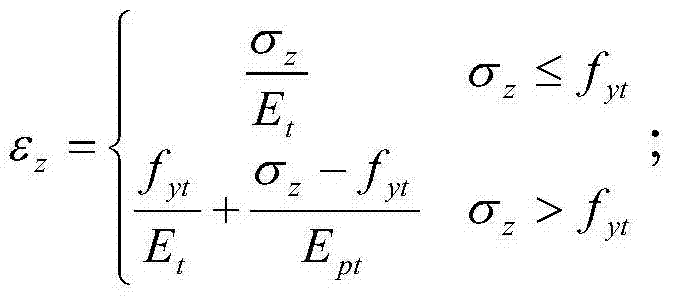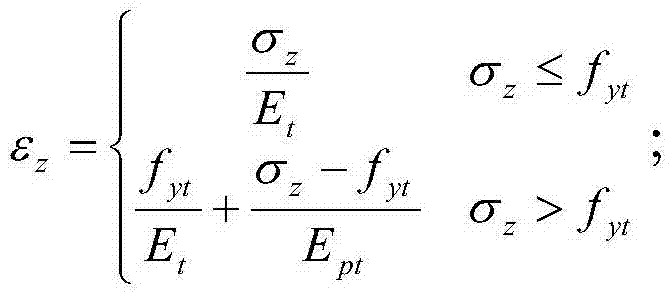Patents
Literature
100 results about "Total strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for the prediction of fatigue life for structures
A method of determining the fatigue life of a structure includes the steps of:associating a mathematical equation for total strain amplitude with the structure:Δɛ2=σf′E(2Nf)b+ɛf′(2Nf)c,where: Δε / 2=strain amplitude, σf′=fatigue strength coefficient associated with a material of the structure, b=fatigue strength exponent of the material, E=cyclic modulus of elasticity of the material, 2Nf=number of cycles, εf′=fatigue ductility coefficient of the material, and c=fatigue ductility exponent of the material;reducing the fatigue strength exponent (b) such that an elastic portion of a total strain amplitude curve associated with the equation has a reduced slope to account for variable amplitude loading for the structure;generating a total strain amplitude curve, based upon the mathematical equation:Δɛ2=σf′E(2Nf)breduced+ɛf′(2Nf)c,where (breduced) is now the reduced fatigue strength exponent; anddetermining a fatigue life of the structure, based on the total strain amplitude curve with the reduced fatigue strength exponent.
Owner:DEERE & CO
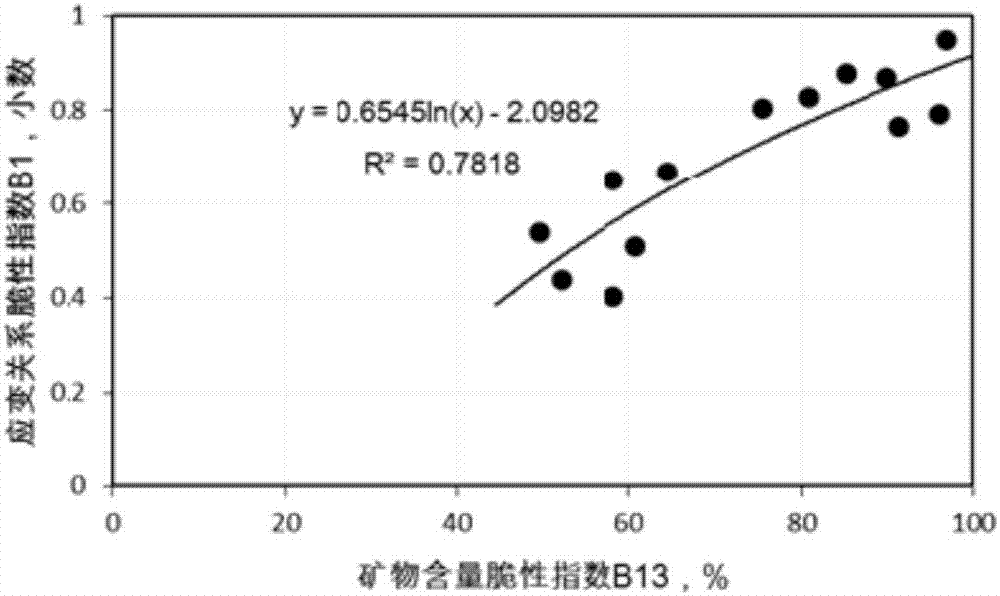
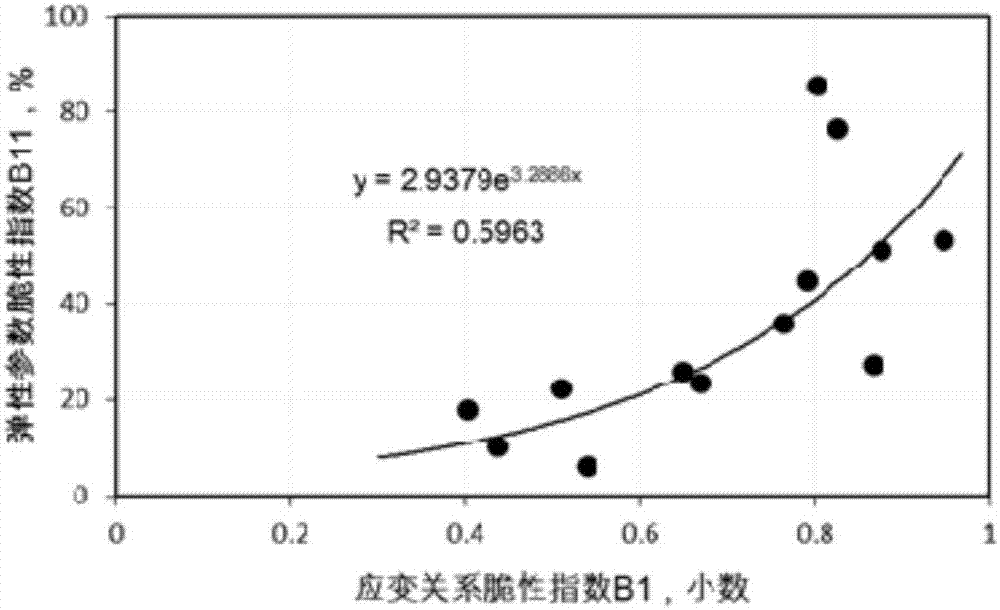
Acquisition method of brittleness index of rock and rock brittleness evaluation method
ActiveCN106872260AFragility Index CharacterizationEasy to readStrength propertiesStress–strain curveYoung's modulus
The invention discloses an acquisition method of a brittleness index of a rock and a rock brittleness evaluation method and relates to the field of brittleness evaluation of the rock. The acquisition method of the brittleness index comprises the following steps: calculating a normalized ratio of yield strain and total strain, a normalized ratio of yield strain and compressive strength, a normalized poisson ratio and a normalized Young modulus according to a resultant stress strain curve of the rock; and determining the brittleness index of the rock according to the normalized ratio of yield strain and total strain, the normalized ratio of yield strain and compressive strength, the normalized poisson ratio and the normalized Young modulus. The brittleness index comprehensively considers elastic and plastic characteristics of the rock and relatively comprehensively considers the whole process of peak-front stage stress-stain of the rock, and the required parameters are easily tested through a mechanical test. The rock brittleness evaluation method disclosed by the invention comprises the step of evaluating the brittleness of the rock by adopting the brittleness index of the rock. The evaluation method of the rock can relatively comprehensively represent the brittleness characteristic of the rock.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
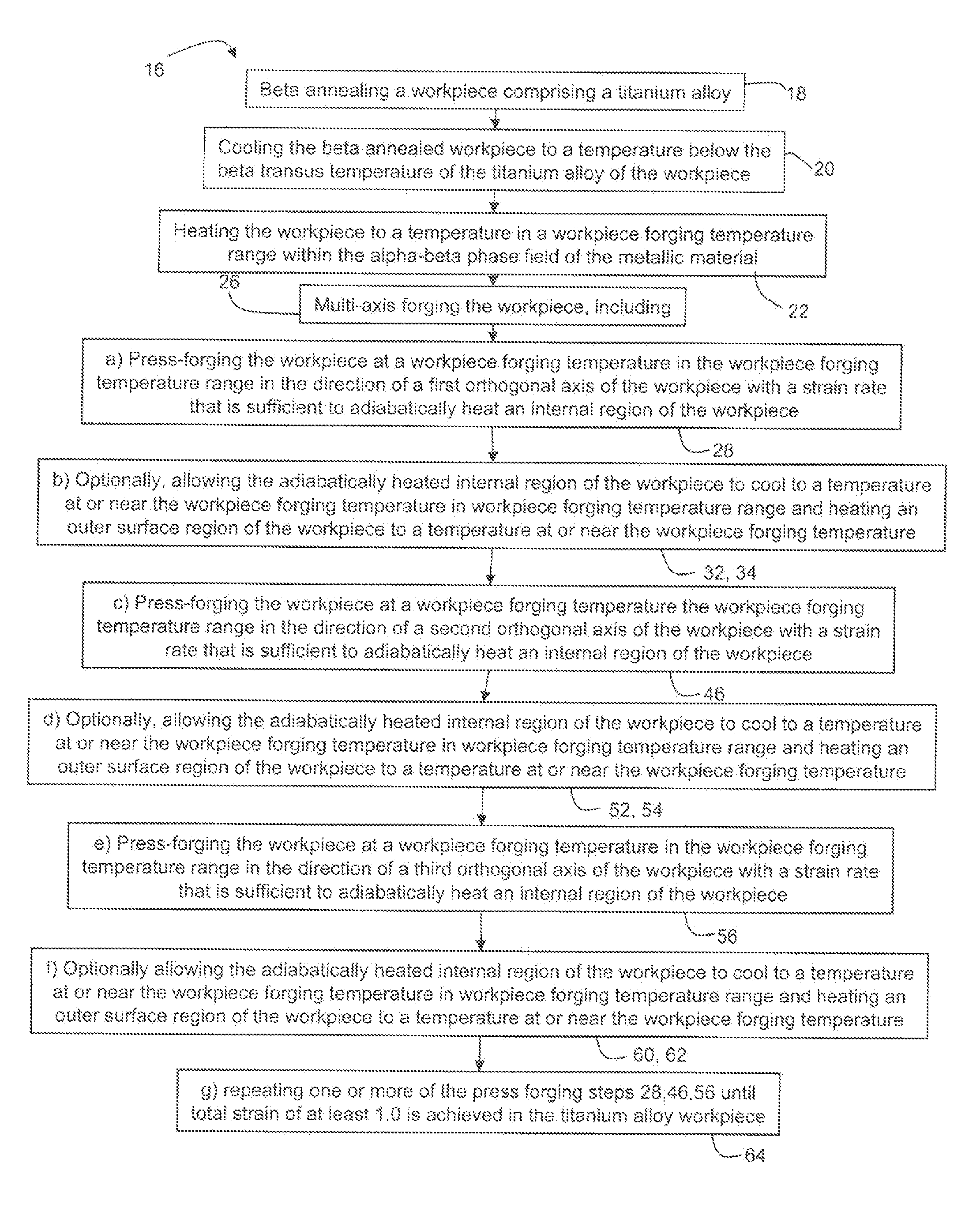
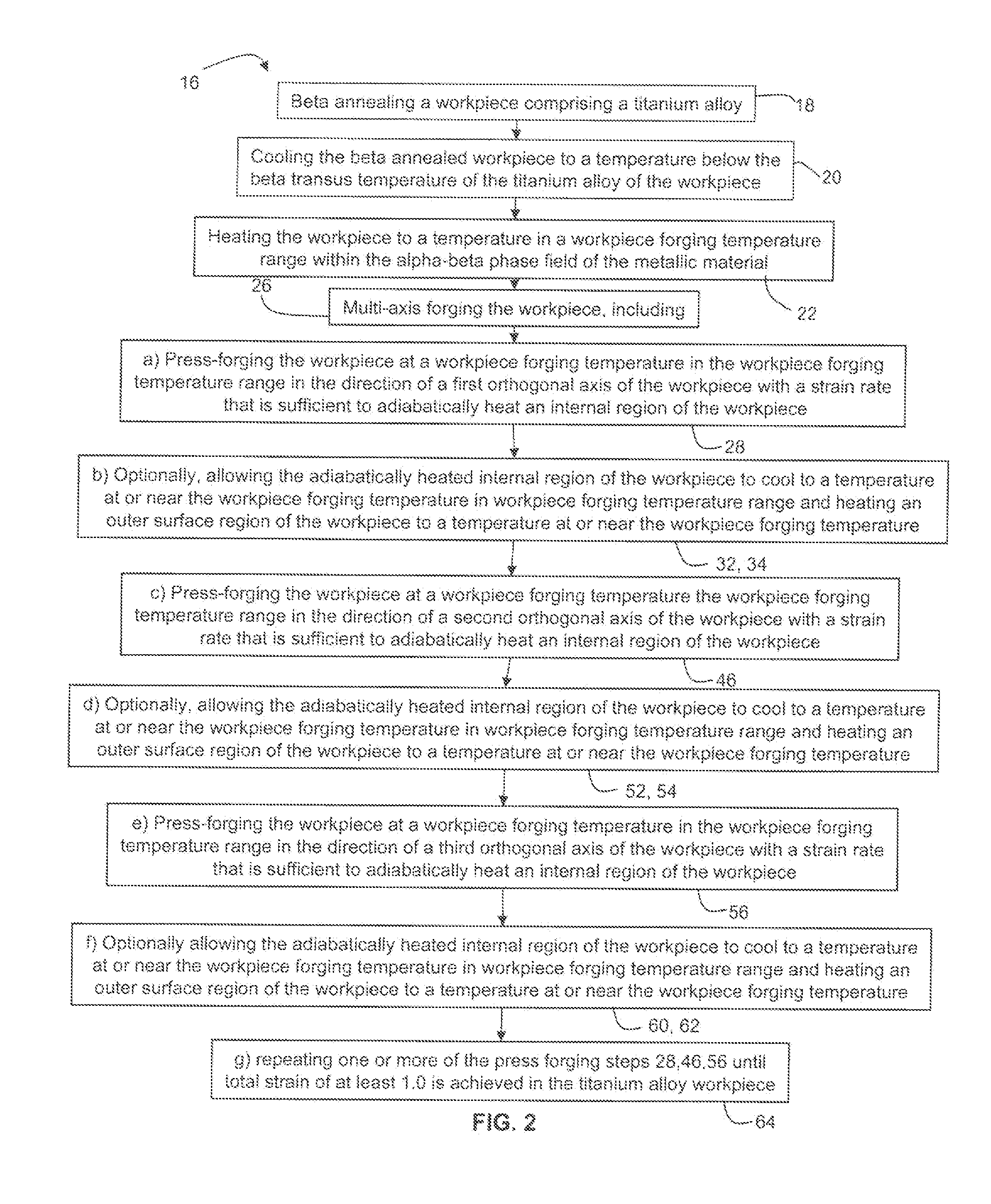
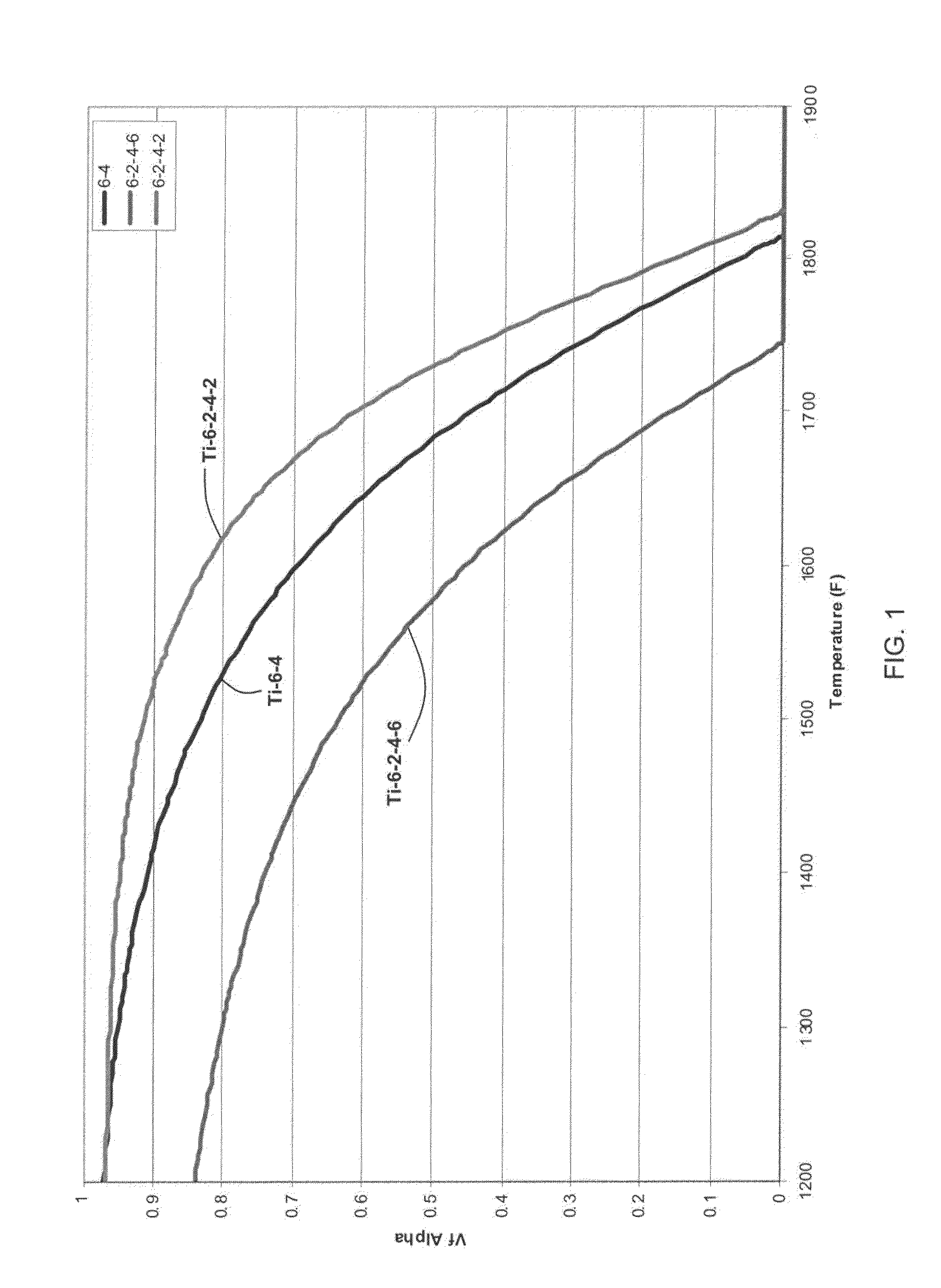
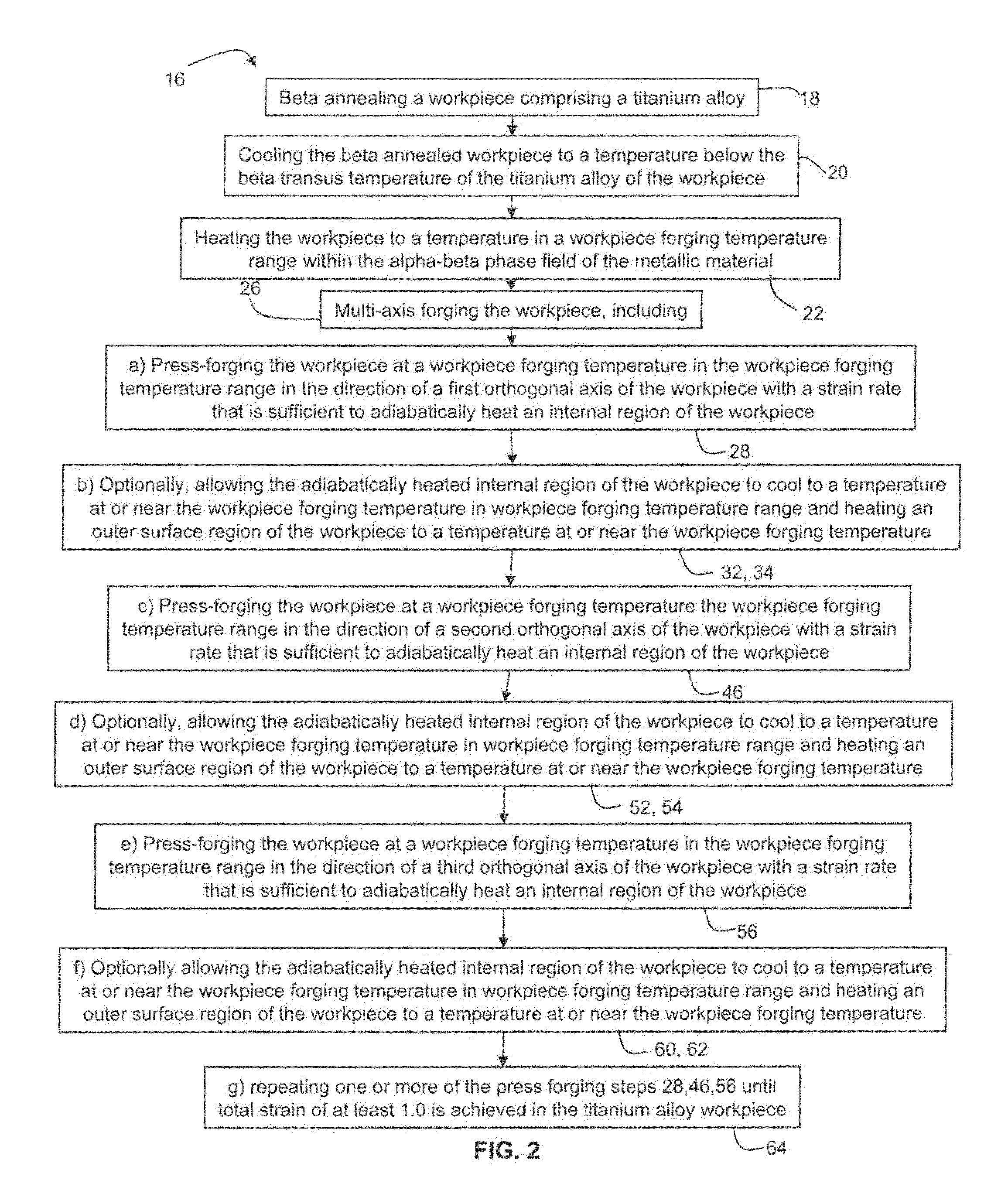
Methods for processing titanium alloys
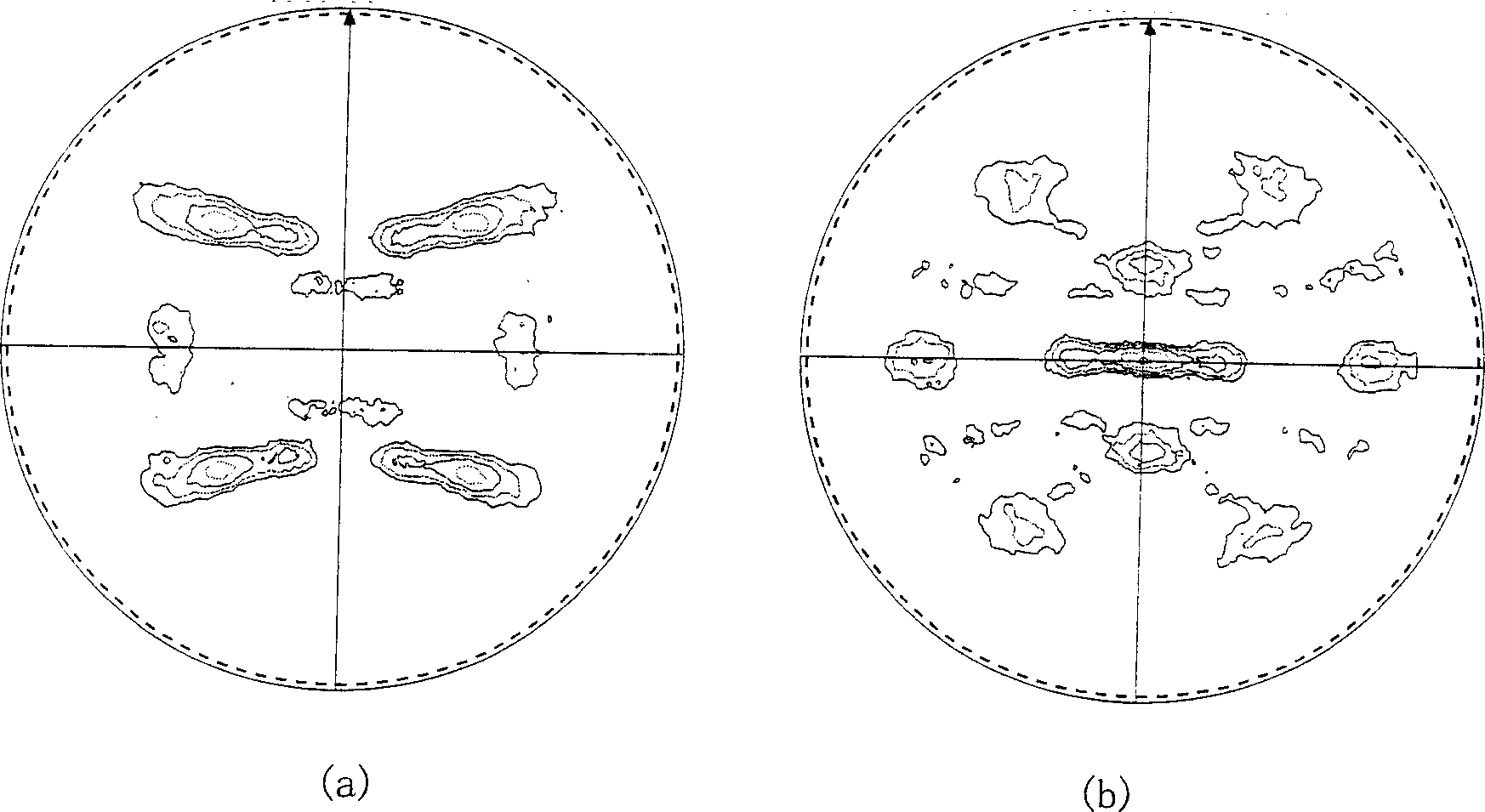
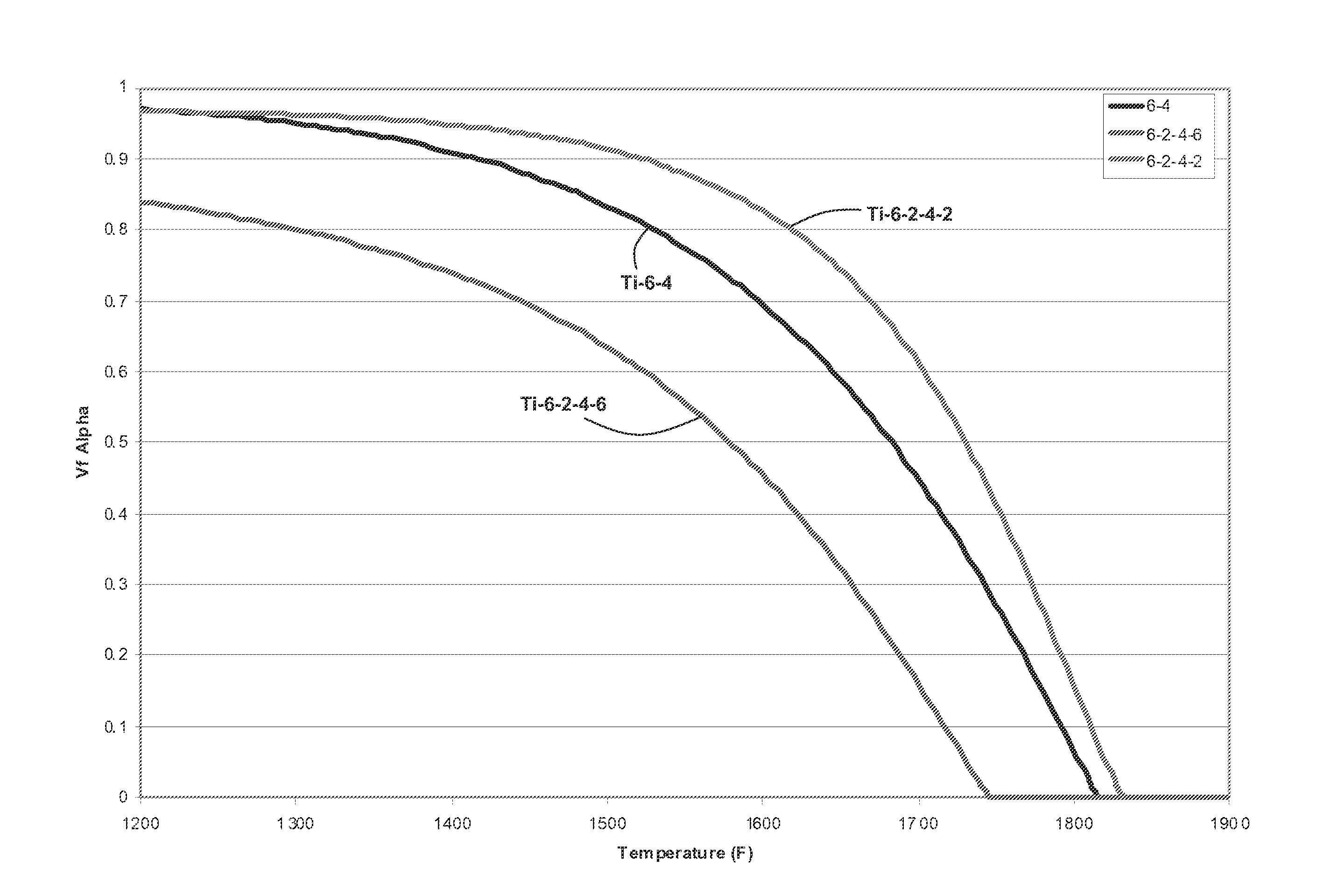
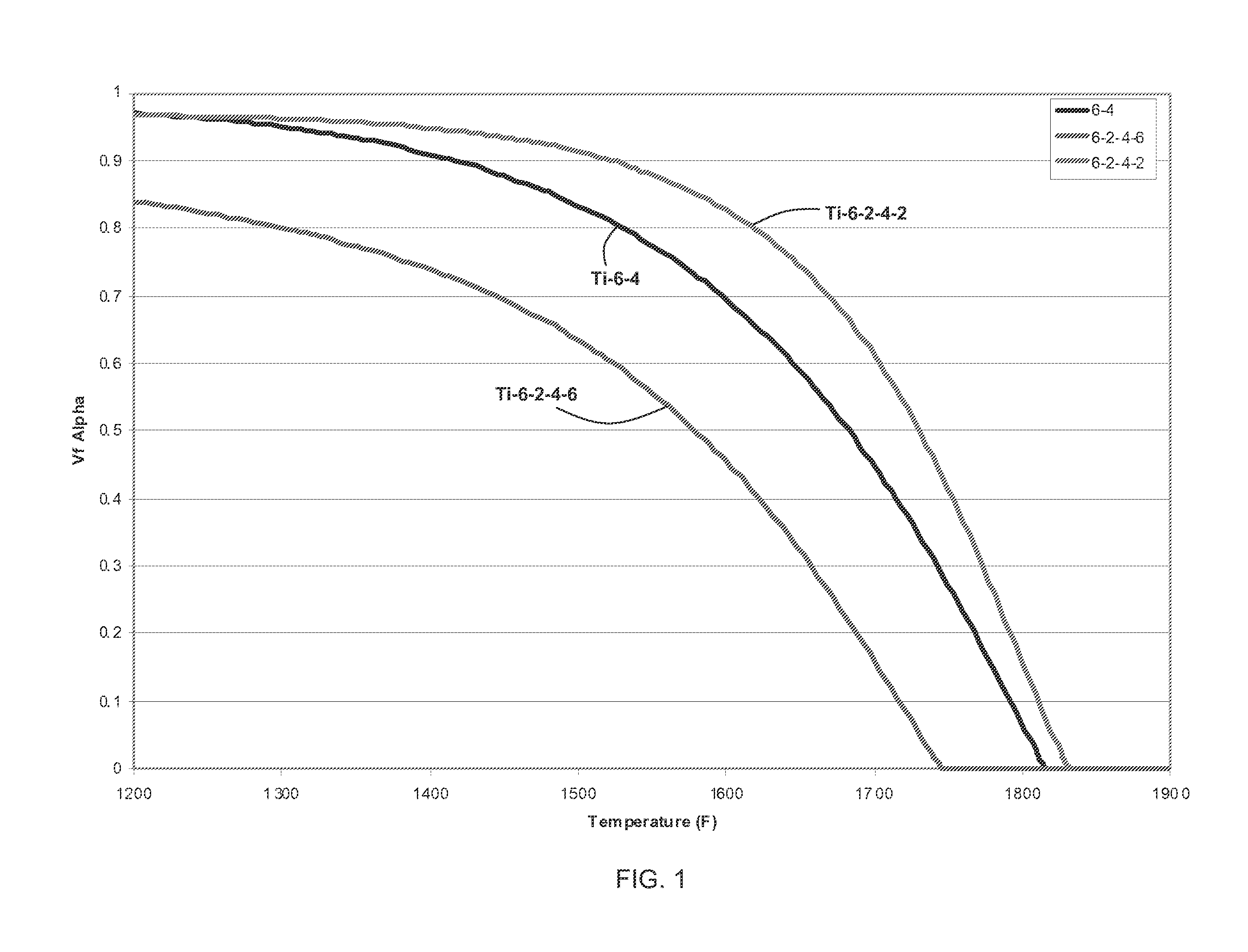
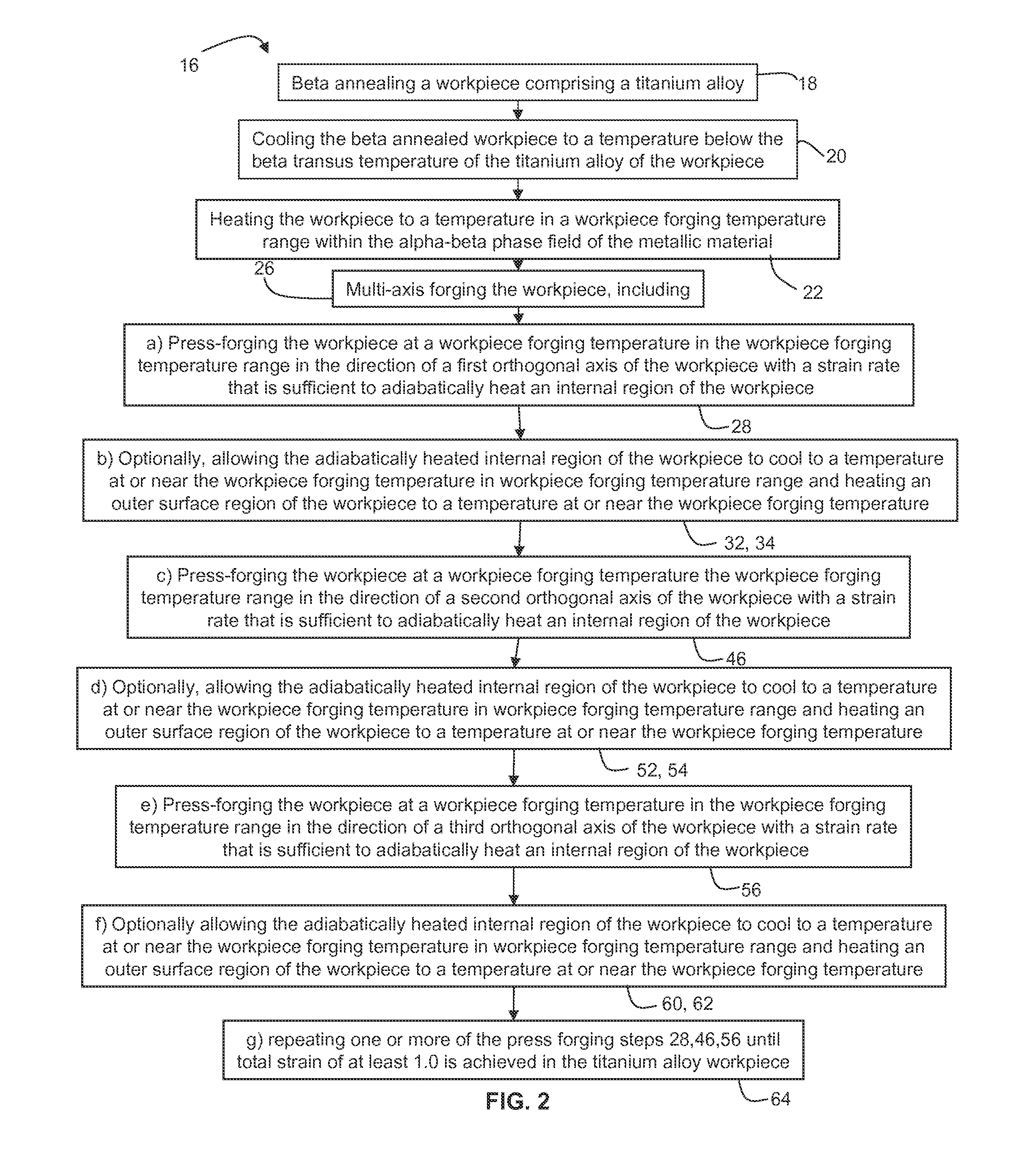
Methods of refining the grain size of a titanium alloy workpiece include beta annealing the workpiece, cooling the beta annealed workpiece to a temperature below the beta transus temperature of the titanium alloy, and high strain rate multi-axis forging the workpiece. High strain rate multi-axis forging is employed until a total strain of at least 1 is achieved in the titanium alloy workpiece, or until a total strain of at least 1 and up to 3.5 is achieved in the titanium alloy workpiece. The titanium alloy of the workpiece may comprise at least one of grain pinning alloying additions and beta stabilizing content effective to decrease alpha phase precipitation and growth kinetics.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES LLC
Dendrite-Reinforced Titanium-Based Metal Matrix Composites
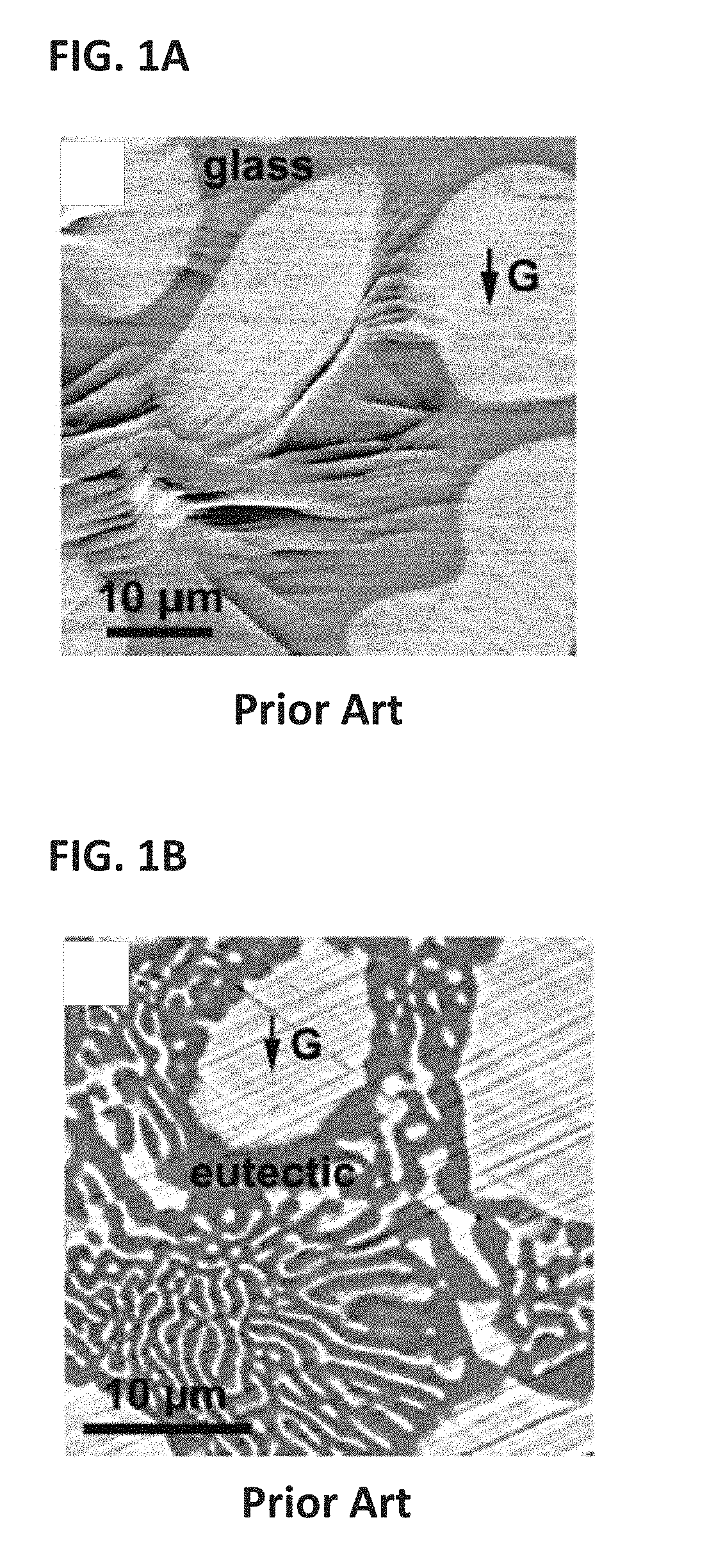
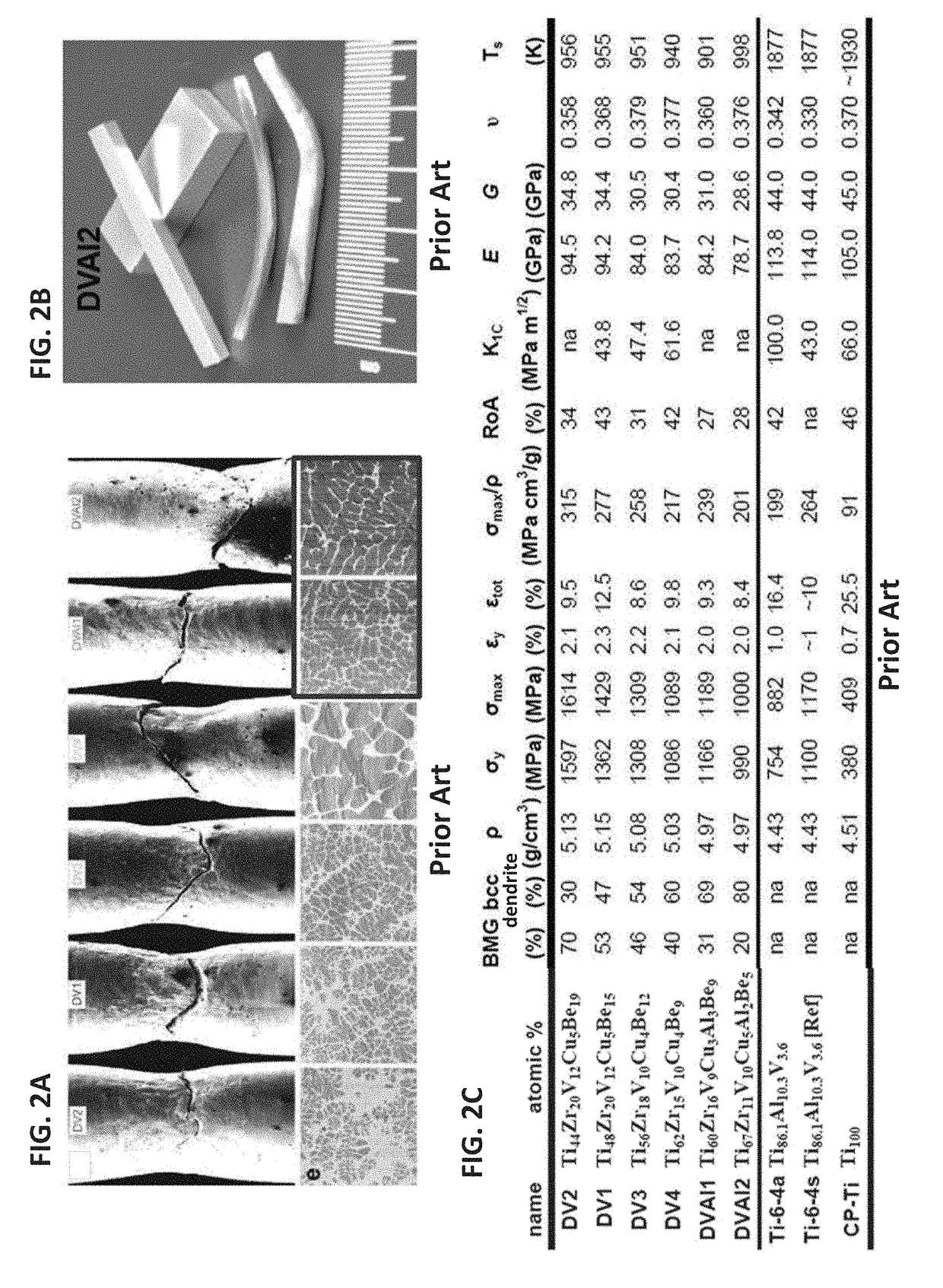
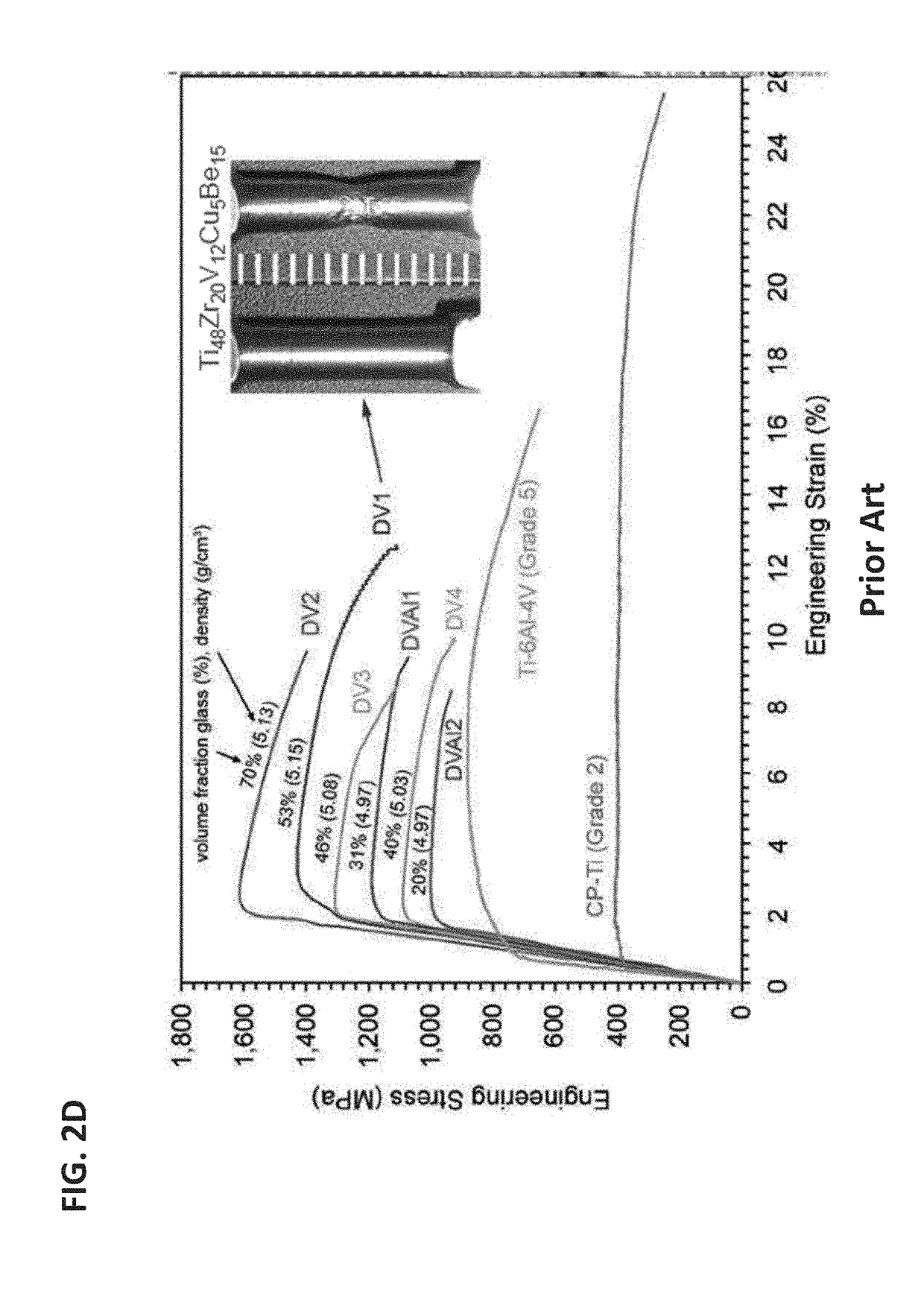
Ti-based metal matrix composites, methods of their additive manufacture, and parts manufactured therefrom and thereby are provided. Method include layer-by-layer additive manufacturing for fabricating Ti-based metal matrix composite parts thicker than 0.5 mm, in layers with thickness between 10-1000 micrometers. The parts formed may have one or more of the following properties: a tensile strength greater than 1 GPa, a fracture toughness greater than 40 MPa m1 / 2, a yield strength divided by the density greater than 200 MPa cm3 / g, and a total strain to failure in a tension test greater than 5%.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method of controlling grain size in forged precipitation-strengthened alloys and components formed thereby
ActiveUS8679269B2Significant control of average grain sizeAvoid grain growthBlade accessoriesReaction enginesAlloyPrecipitation
Components and methods of processing such components from precipitation-strengthened alloys so that the components exhibit desirable grain sizes following a supersolvus heat treatment. The method includes consolidating a powder of the alloy to form a billet having an average grain size. The billet is then forged at a temperature below the solvus temperature to form a forging having an average grain size of not coarser than the grain size of the billet. The billet is then forged at a total strain of at least 5%, after which at least a portion of the forging is heat treated at a temperature below the solvus temperature to pin grains within the portion. The entire forging can then be heat treated at a temperature above the solvus temperature of the alloy without coarsening the grains in the portion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
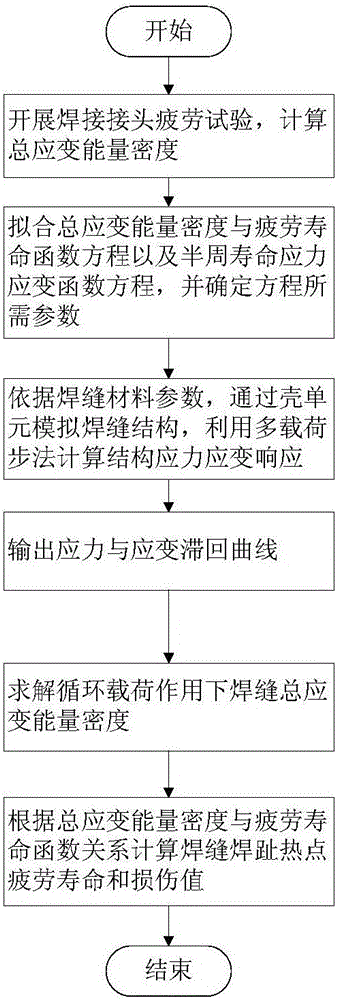
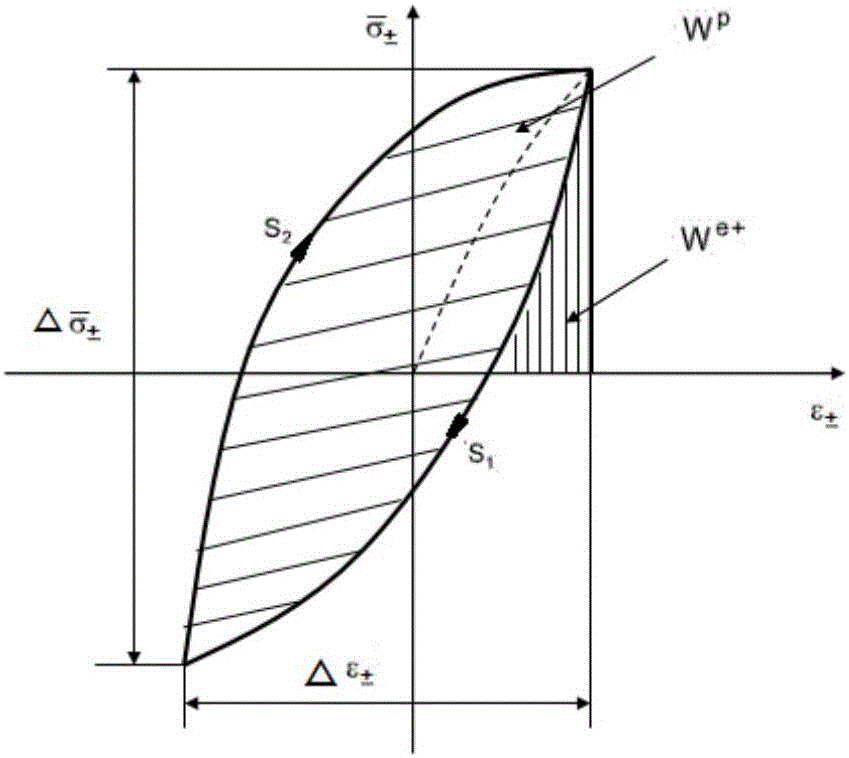
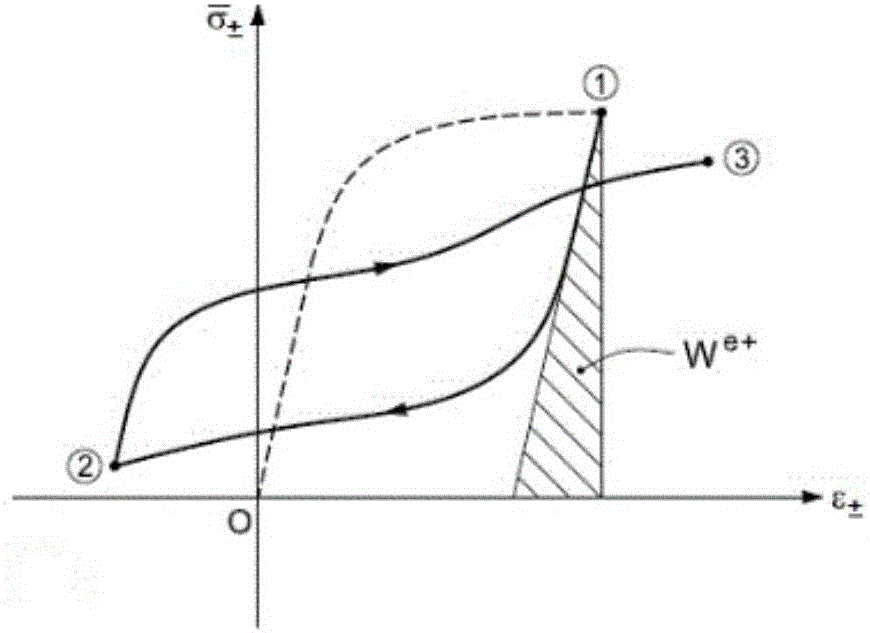
Weld seam fatigue life calculation method based on total strain energy density
ActiveCN106354898AImprove the accuracy of fatigue life calculationAvoid sureDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue IntensityFatigue damage
The invention discloses a weld seam fatigue life calculation method based on total strain energy density. The method mainly comprises the steps that 1, the weld-seam total strain energy density, a life function equation and a fatigue strength coefficient, a fatigue strength index, a cyclic strengthening coefficient and a cyclic strain hardening index which are needed by half-cycle life stress and a strain function equation are acquired through a welded joint fatigue test; 2, the weld seam structure is simulated through a shell unit module, the stress-strain response of the weld seam structure under the cyclic load action is calculated through a multi-load step method, and a stress-strain hysteretic curve is output; 3, the total strain energy density is calculated according to the stress-strain response, and the hot point fatigue life and a damage value of a weld toe of the weld seam are calculated by combining the energy density with the life function equation. According to the method, contribution of elastic-plastic stress and strain to the fatigue damage is comprehensively taken into account, scalar quantities are taken as damage parameters, the position and direction problems related to vectors are effectively avoided, the calculation precision is improved, and the time is saved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Biological-selenium-enriched multi-probiotics fermented rice milk and preparation method therefore
ActiveCN102613304AImprove gelatinizationIncrease profitMilk substitutesBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a biological-selenium-enriched multi-probiotics fermented rice milk and a preparation method therefore, belonging to the field of food processing. Grains such as rice or broken rice, seeds of Job's tears, oat, and millet are used as raw materials, and the raw materials adopt a certain proportion of milk powder according to a principle of nutrition complementation. A modernprocess is used for researching and developing a multi-strain fermented rice milk product which has the particular flavor and active ingredients of yoghourt and also has the functional factors and flavor of the grains. The rice milk does not have any thickening agent, the gelatinization degree of a product is changed through a screw extrusion technology, and a suitable enzymolysis technology of different grains as the raw materials is optimized. A multi-strain co-fermentation mode is adopted to increase the enrichment of biological selenium and promote the metabolic quantity of bacteriocins, and the total strain content of the product in the quality guarantee period is increased.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Split-pass open-die forging for hard-to-forge, strain-path sensitive titanium-base and nickel-base alloys
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES LLC
Split-pass open-die forging for hard-to-forge, strain-path sensitive titanium-base and nickel-base alloys
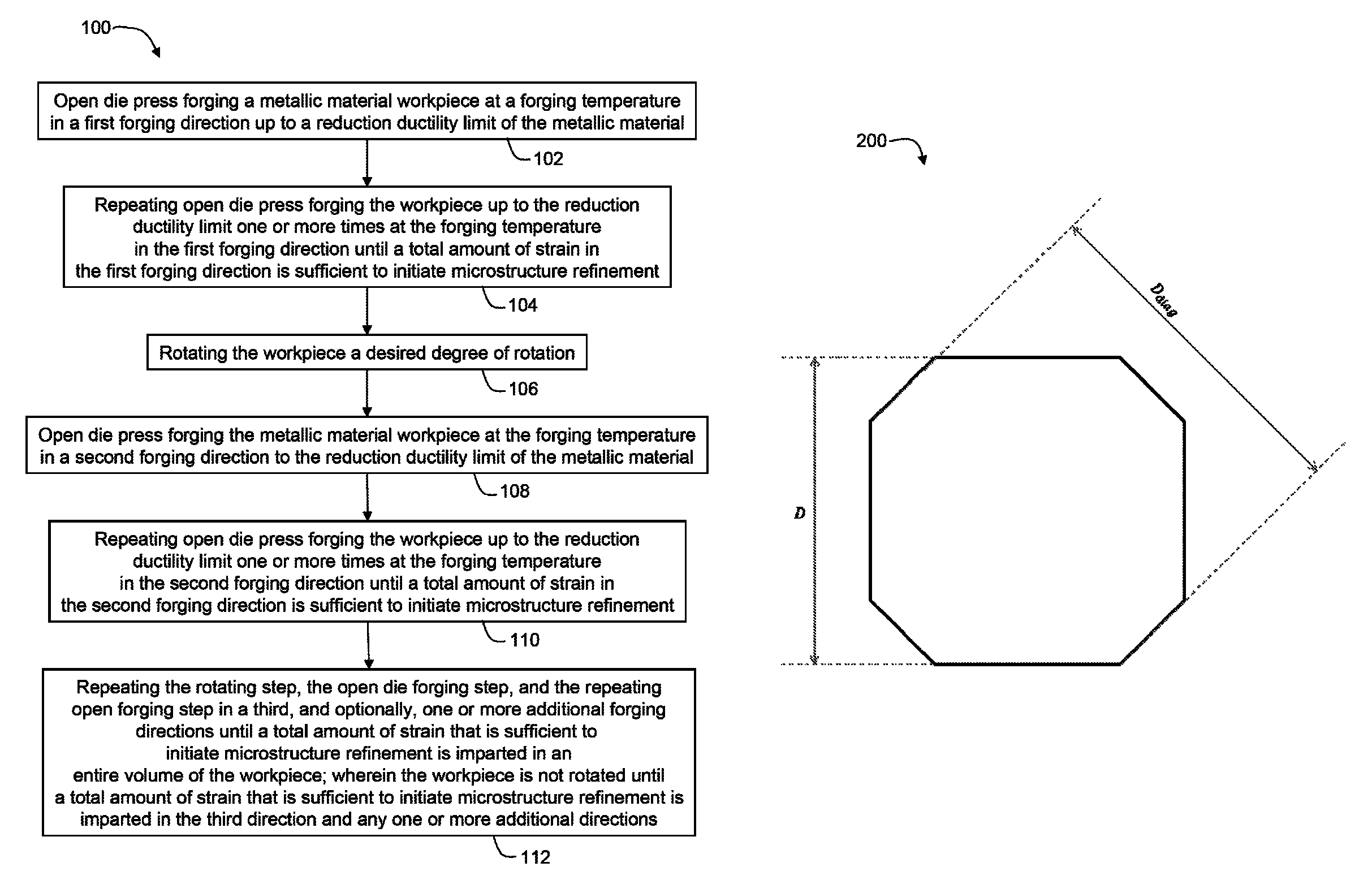
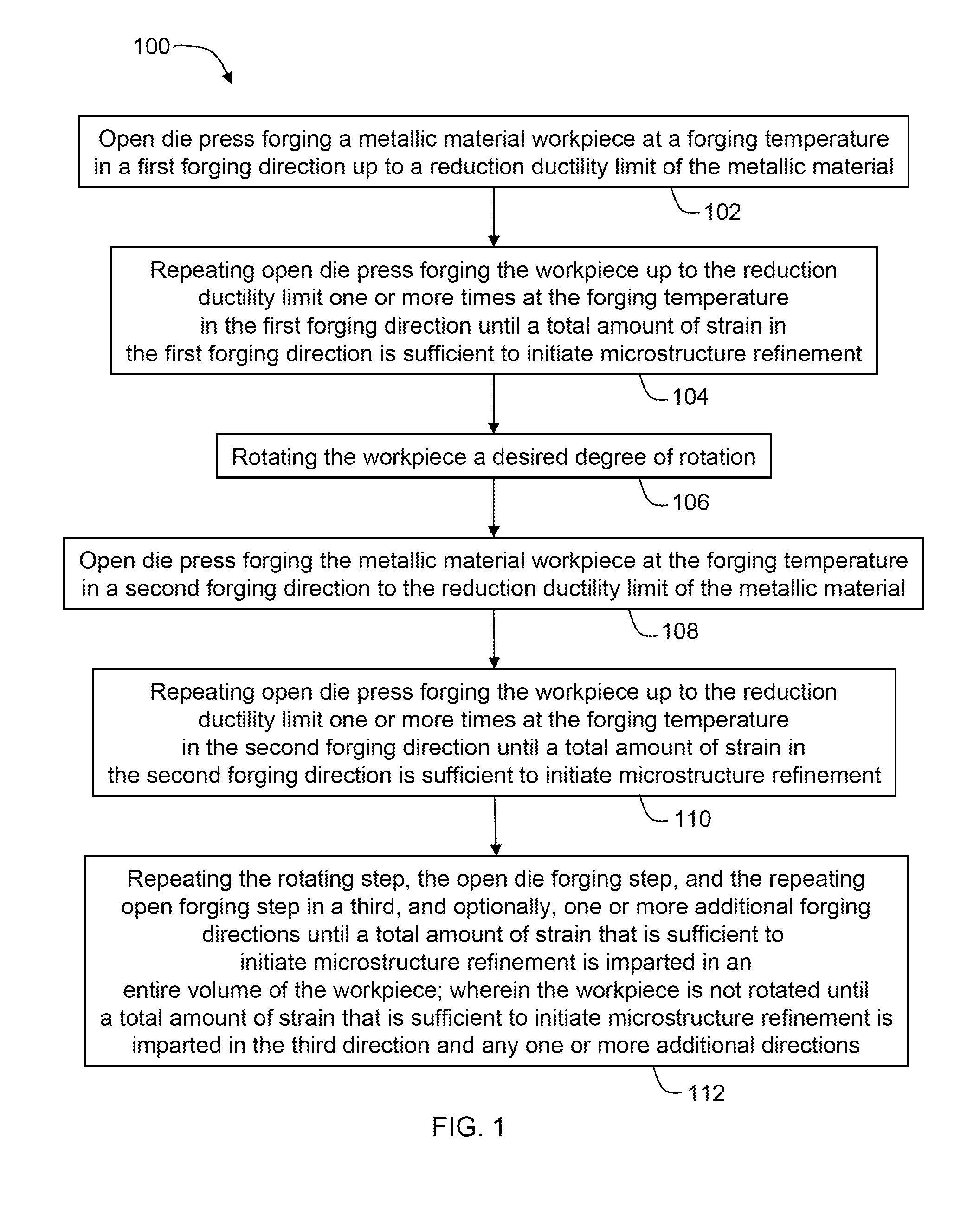
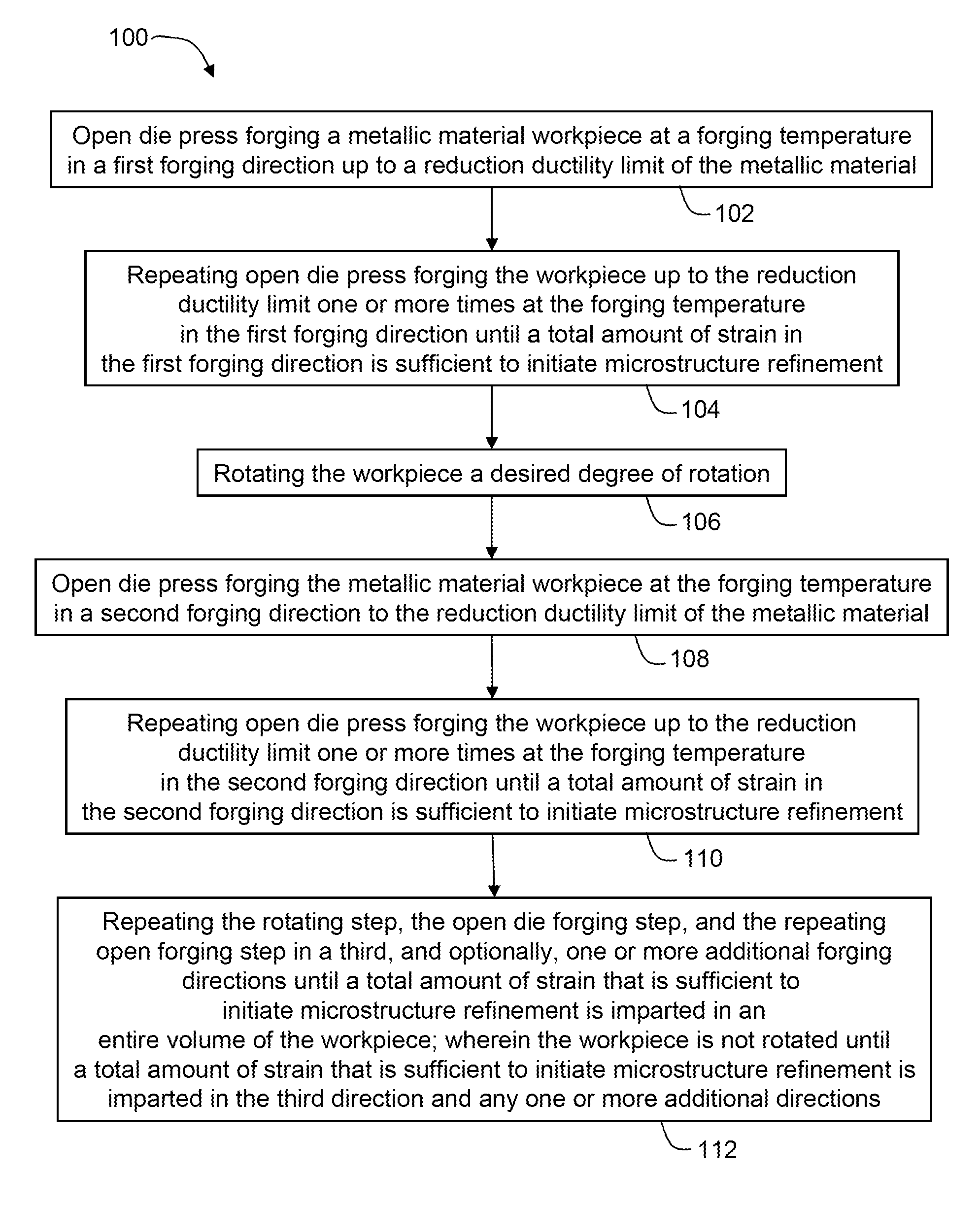
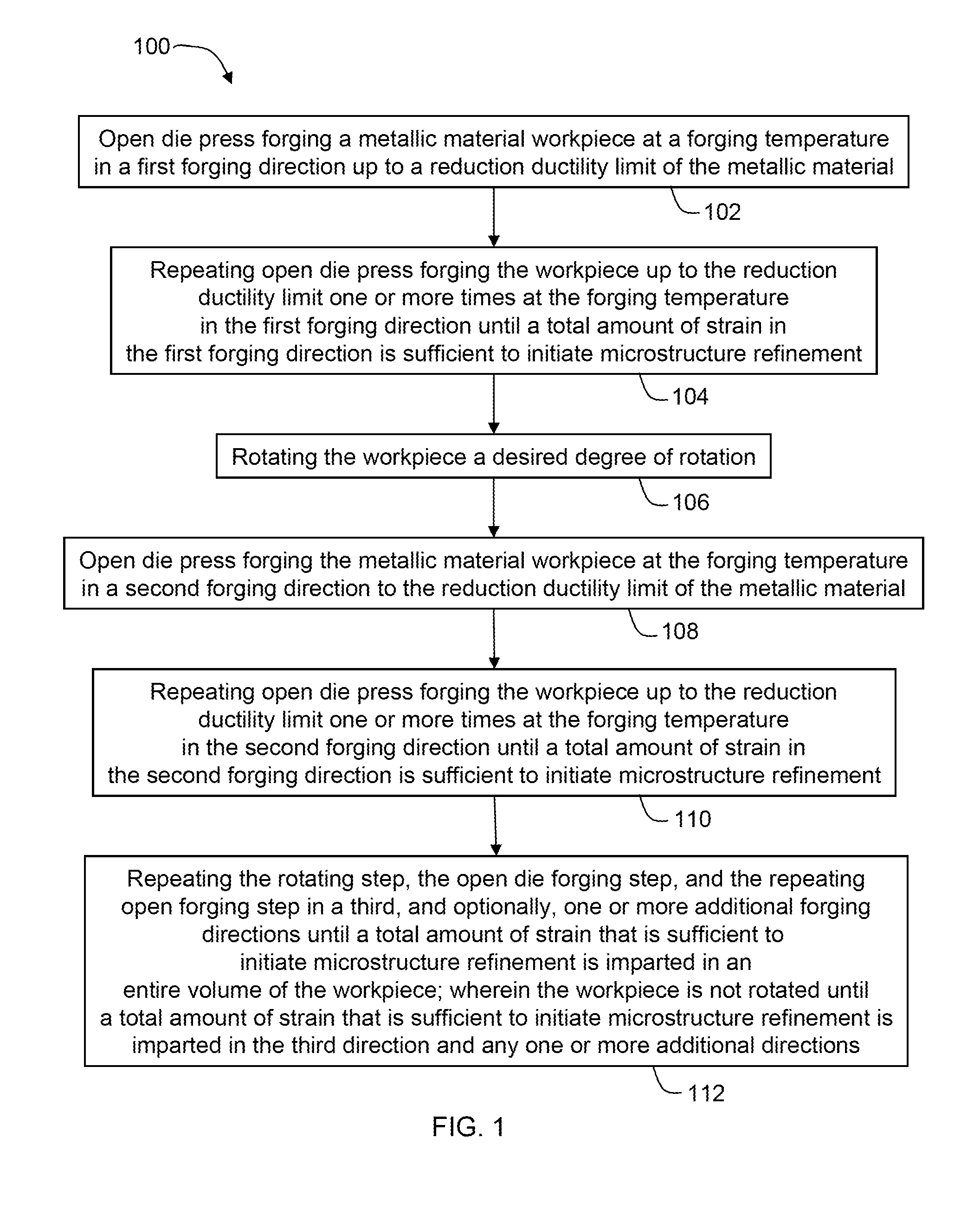
Split pass forging a workpiece to initiate microstructure refinement comprises press forging a metallic material workpiece in a first forging direction one or more times up to a reduction ductility limit of the metallic material to impart a total strain in the first forging direction sufficient to initiate microstructure refinement; rotating the workpiece; open die press forging the workpiece in a second forging direction one or more times up to the reduction ductility limit to impart a total strain in the second forging direction to initiate microstructure refinement; and repeating rotating and open die press forging in a third and, optionally, one or more additional directions until a total amount of strain to initiate microstructure refinement is imparted in an entire volume of the workpiece.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES LLC
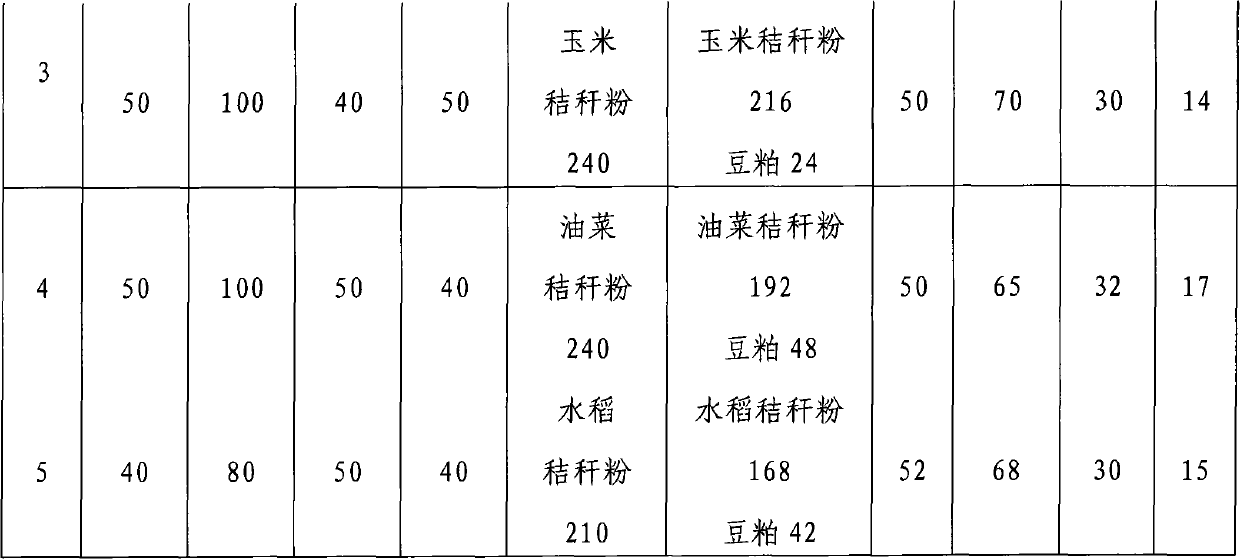
High-protein straw feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101816371AHigh protein contentPromote absorptionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyProtein structure
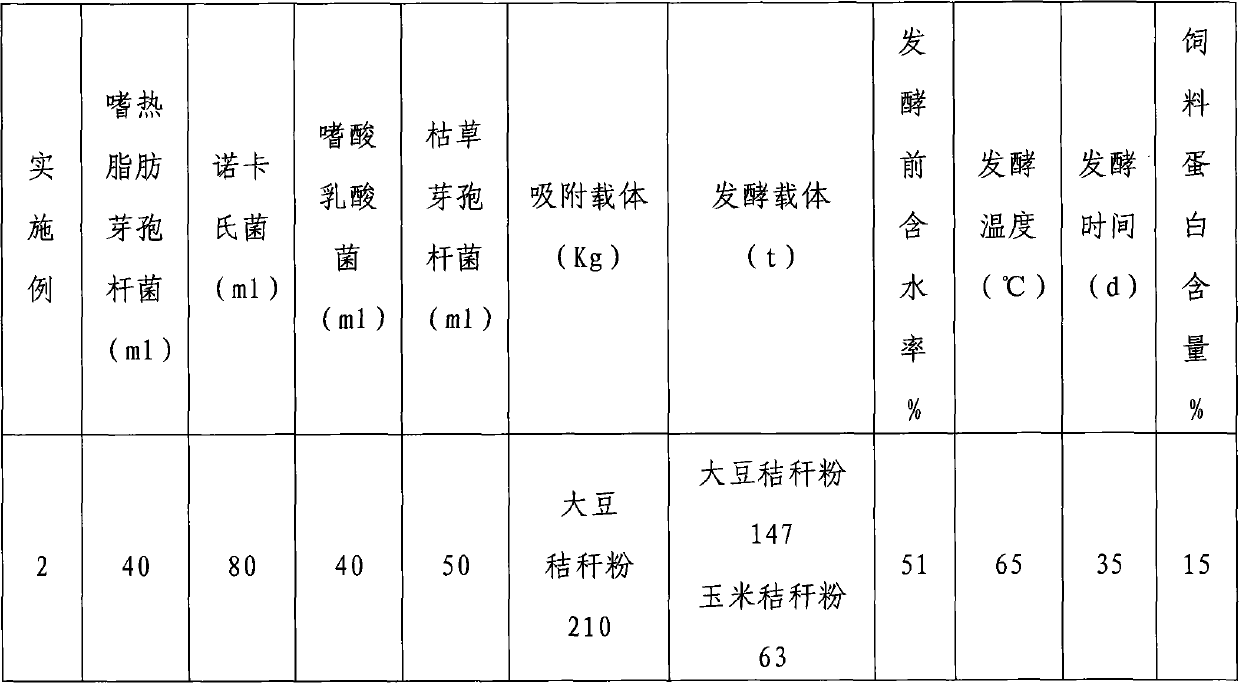
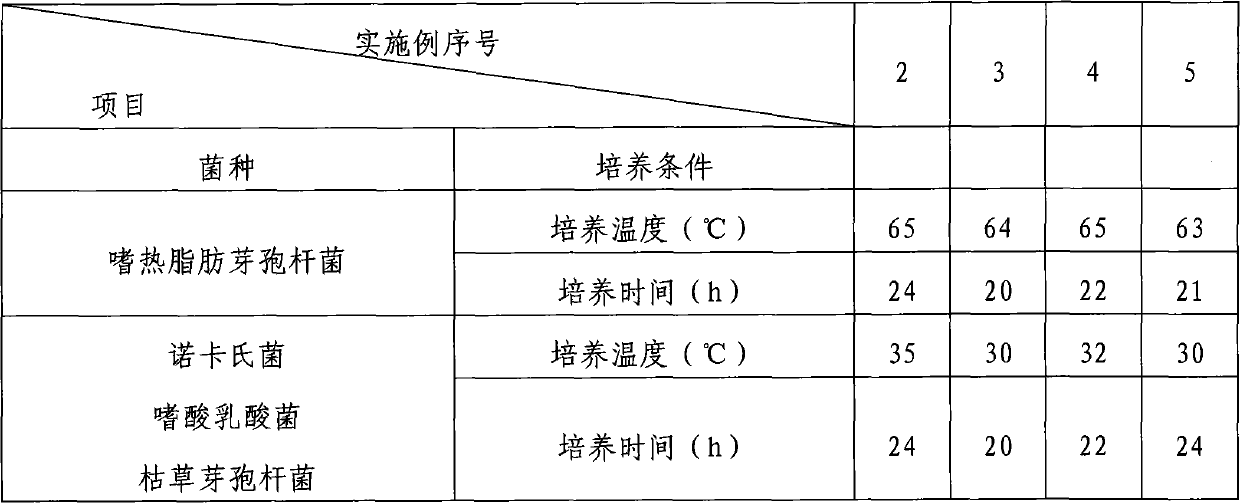
The invention discloses a high-protein straw feed, which comprises crop straw powder, actinomycetes, nocardia, lactobacillus acidophilusis and bacillus subtilis, the weight ratio of the strains is 0.8-1.2:1.6-2.4:0.8-1.2:1.8-1.2, and the weight ratio of the total strain amount to the crop straw powder is 1:1,000-1,200. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: respectively screening, separating, purifying, rejuvenating and culturing various strains, transplanting the strains into an industrial fermentation tank for fermentation, mixing in a ratio, and adsorbing by using an adsorptive support; and inoculating the obtained composite viable bacteria powder into crop straw powder or a mixture of the crop straw powder, staking and fermenting at the temperature of between 60 and 70 DEG C, uniformly turning once every two days, and obtaining the high-protein straw feed after 30 to 35 days. The high-protein straw feed has the advantages of improving protein content, optimizing protein structure, improving the absorption and nutrient conversion rate of the straw feed, and improving the immunity of livestock.
Owner:苏州荣基生态生物科技有限公司
Methods for processing titanium alloys
Methods of refining the grain size of a titanium alloy workpiece include beta annealing the workpiece, cooling the beta annealed workpiece to a temperature below the beta transus temperature of the titanium alloy, and high strain rate multi-axis forging the workpiece. High strain rate multi-axis forging is employed until a total strain of at least 1 is achieved in the titanium alloy workpiece, or until a total strain of at least 1 and up to 3.5 is achieved in the titanium alloy workpiece. The titanium alloy of the workpiece may comprise at least one of grain pinning alloying additions and beta stabilizing content effective to decrease alpha phase precipitation and growth kinetics.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES LLC
Value obtaining method-comprehensive method of additional effective damping ratios of energy dissipaters with energy dissipation and shock absorption structures
ActiveCN103838918AAdditional effective damping ratio accurateLow costSpecial data processing applicationsDamping ratioElastic plastic
The invention discloses a value obtaining method-comprehensive method of the additional effective damping ratios of energy dissipaters with energy dissipation and shock absorption structures. The method comprises the steps of extracting inter-floor shear force values Fit and inter-floor displacement values uit corresponding to seismic wave moment points after the energy dissipation and shock absorption structures are subjected to finite element elastic-plastic time-history analysis; obtaining total strain energy Wst of the energy dissipation and shock absorption structures at the seismic wave moment points and getting a maximum value max[Wst] of the total strain energy Wst; obtaining the sum Sigma Wcj of dissipative energy of all of energy dissipaters; performing calculation to obtain the additional effective damping ratios 8 a of the energy dissipaters with the energy dissipation and shock absorption structures; assessing whether the additional effective damping ratios 8 a of the energy dissipaters are larger than or equal to additional effective damping ratios set for performance objectives of the energy dissipation and shock absorption structures. In the method, the number and the positions of the energy dissipaters are constantly optimized in the accurate computation result obtaining process, the energy dissipaters are appropriate in selection and arrangement, the economic purpose is achieved while the requirement for dissipating seismic energy to the most extent is met, and the construction cost is reduced.
Owner:ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN RES INST OF GUANGDONG PROVINCE
Method of preparing High W content Ni-W alloy for high temp superconduct
This invention discloses a method for manufacturing high W-content Ni-W alloy substrates used on high-temperature superconductors. Low W-content (3-5 at. %) Ni-W alloy substrates have good cubic structure, but also have strong magnetism in liquid nitrogen temperature range and no mechanical strength. The method in this invention comprises the steps of: (1) mixing Ni powders and W powders with particle sizes of 3-6 mum, performing spark plasma sintering at 800-1300 deg.C, and keeping the temperature for 0-10 min, (2) cold-rolling the Ni-W sheets at room temperature with small pass strains of 3-8%, and performing intermediate annealing at 300-800 deg.C for 0.5-6 h when the strain is 30-80% until the total strain is more than 95%, and (3) annealing in a mixture of Ar and H2 at 1000-1400 deg.C for 0.5-3 h to obtain uniform Ni-W alloy substrates with W content in the range of 7.01-9.5 mol.%. The high W-content alloy substrates have such advantages as simple sintering process, low magnetism in liquid nitrogen temperature range and high mechanical strength.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods for processing titanium alloys
Methods of refining the grain size of a titanium alloy workpiece include beta annealing the workpiece, cooling the beta annealed workpiece to a temperature below the beta transus temperature of the titanium alloy, and high strain rate multi-axis forging the workpiece. High strain rate multi-axis forging is employed until a total strain of at least 1 is achieved in the titanium alloy workpiece, or until a total strain of at least 1 and up to 3.5 is achieved in the titanium alloy workpiece. The titanium alloy of the workpiece may comprise at least one of grain pinning alloying additions and beta stabilizing content effective to decrease alpha phase precipitation and growth kinetics.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES LLC
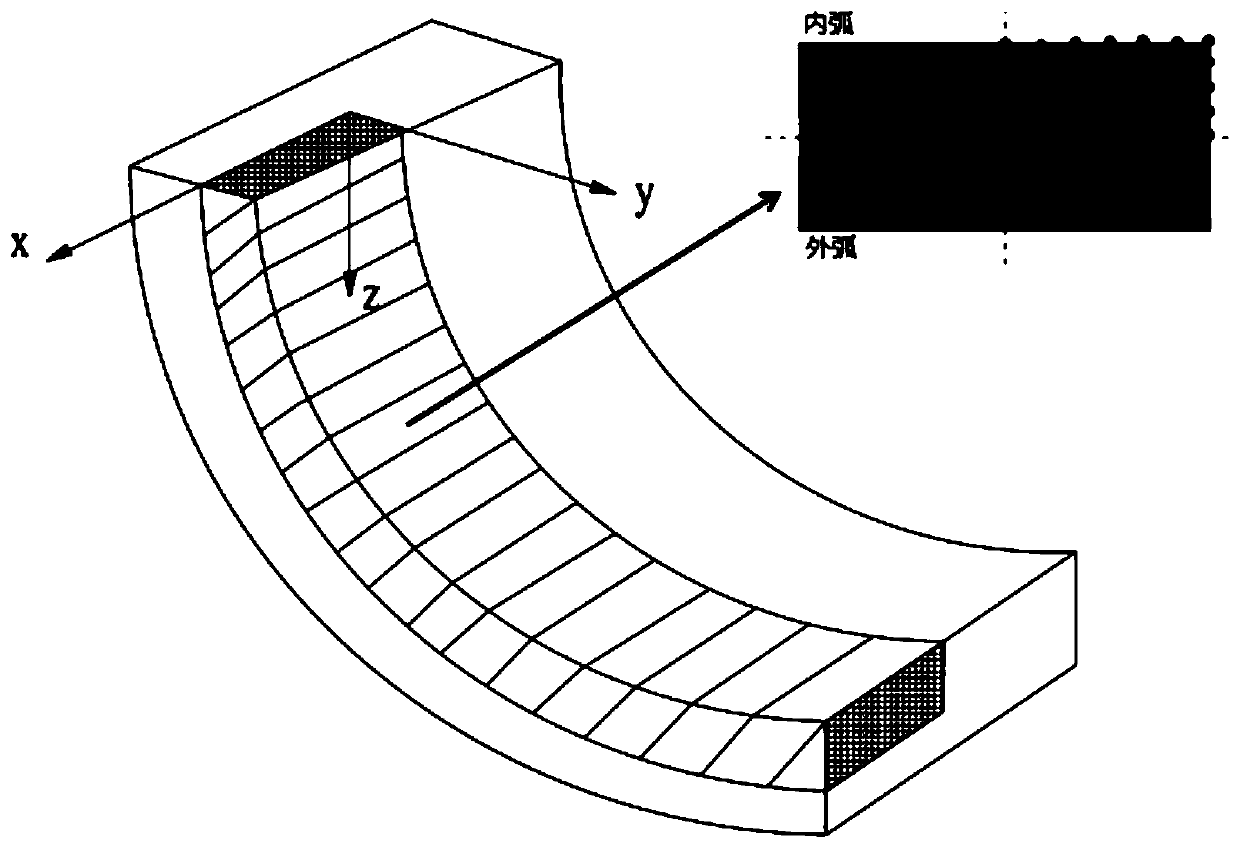
Rock uniaxial compression whole-process creep damage model construction method
ActiveCN110631908AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUniaxial compressionTemporal change
The invention discloses a rock uniaxial compression whole-process creep damage model construction method. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out a uniaxial compression test and a uniaxial compression creep test under the action of different axial stresses on a rock test piece to obtain the average compressive strength and creep curve of the rock, determining rock long-term strength and creep rupture time, determining a function expression of the deformation modulus changing along with time in the rock creep process, representing the elasticity modulus of the damaged rock material by the deformation modulus and determining an expression of a rock creep damage variable, determining a function expression of the creep damage model of the rock in the whole uniaxial compression process, and determining creep model parameters according to a rock uniaxial compression creep test result. The model built by the method can describe three stages of the whole process of instantaneous strain and creep generated in the rock loading process at the same time through a unified function expression, and therefore the defect that the existing model needs to manually divide the total strain generated in the rock creep process into four parts is overcome.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Online prediction and positioning method for internal crack of slab continuous casting
ActiveCN110568010AEasy to cutImprove accuracyMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentMaterials scienceContinuous casting
The invention relates to an online prediction and positioning method for an internal crack of slab continuous casting, and belongs to the technical field of continuous casting. A three-dimensional temperature field of a continuous casting blank is monitored online in real time; the bulging strain of each slicing unit and the total strain of the casting blank at each clamping roller in the monitoring area are calculated in real time according to present real-time casting blank three-dimensional temperature field information, casting equipment parameter information, production process parameterinformation and casting steel type parameter information and by means of a bulging strain model, a bending / straightening strain model and a non-centering strain model; and the critical strain of the casting blank is set according to the casting steel type, when the bulging strain of the slicing unit or the total strain of the casting blank in the monitoring area exceeds the ultra-high critical strain, an internal crack occurs, and the specific position of the internal crack of the casting blank is located. According to the method, the real-time online prediction accuracy for the internal crackof the slab continuous casting can be improved, the occurrence position of the internal crack can be located, then cutting of the casting blank is optimized, the detection time and cost are saved, and the qualified rate of products is increased.
Owner:CISDI ENG CO LTD +1
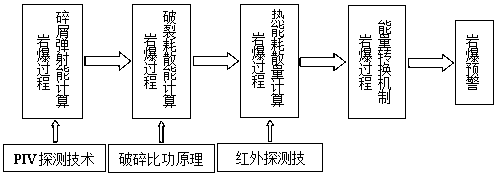
Rock burst destroying energy calculation method used for early warning of rock burst
InactiveCN109283073AReduce casualtiesReduce property damageMeasurement of explosion forceStrength propertiesCalculation methodsKinetic energy
A rock burst destroying energy calculation method used for early warning of a rock burst includes: calculating rock burst chipping ejection kinetic energy (E<k>) through partical image velocimetry (PIV) process , calculating the rock breaking consumption energy (E) through specific crushing energy principle, and calculating the heat energy dissipation quantity (E<h>) during the rock burst process by using an infrared detection system, thereby finally calculating the released total strain energy during the rock burst process, wherein the total strain energy (E<t>) is calculated according toE<t> = E<k> + E + E<h>. Compared with the prior art, with the dynamics process of generation of the rock burst being start point, the released total strain energy during the rock burst process is calculated by means of the PIV process, the specific crushing energy principle and the infrared detection system in the aspect of energy accumulation-release. The method is used for establishing a rockburst destroying energy rule and predicting and early-warning a rock burst, thereby reducing casualties and property loss.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
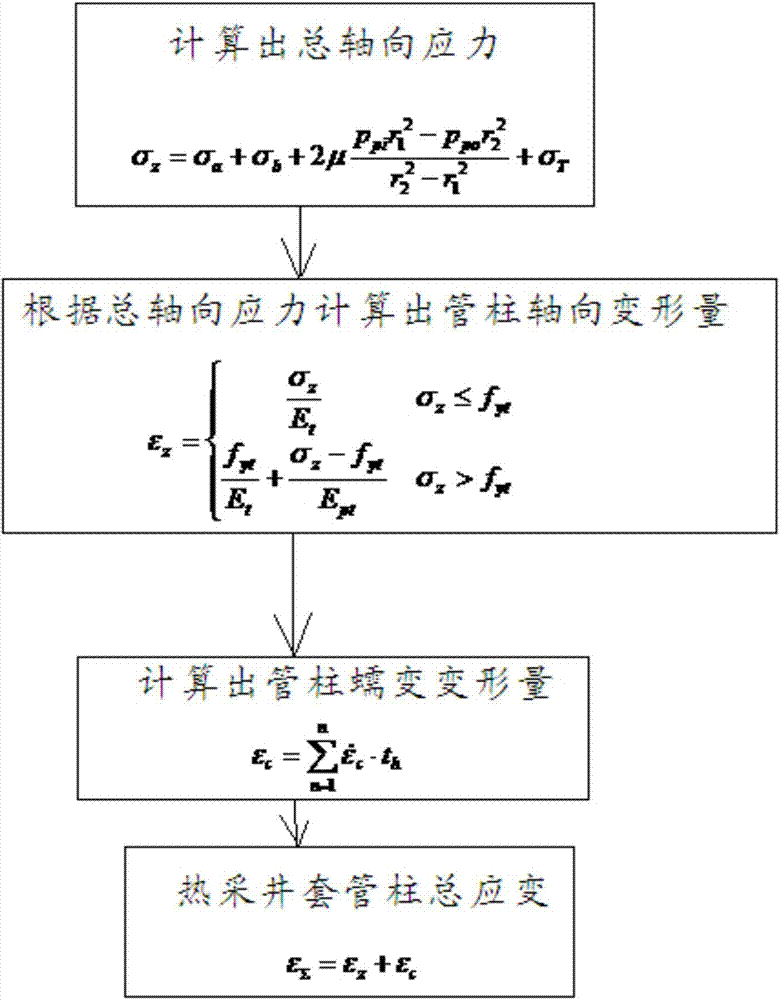
Thermal production well casing tubular column total strain calculating method
The invention discloses a thermal production well casing tubular column total strain calculating method, and belongs to the technical field of well drilling and oil recovery. The method comprises the following steps that the total axial stress is calculated; tubular column axial deformation is calculated through the total axial stress; tubular column creep deformation is calculated; the tubular column axial deformation and the tubular column creep deformation are added together to obtain thermal production well casing tubular column total strain. According to the thermal production well casing tubular column total strain calculating method, the thermal production well casing tubular column total strain is obtained, whether a thermal production well casing tubular column is in the pipe evenly-extending rate range or not can be accurately judged, and using safety is ensured.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Neutron diffraction measure method for CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 system microcrystalline glass residue stress
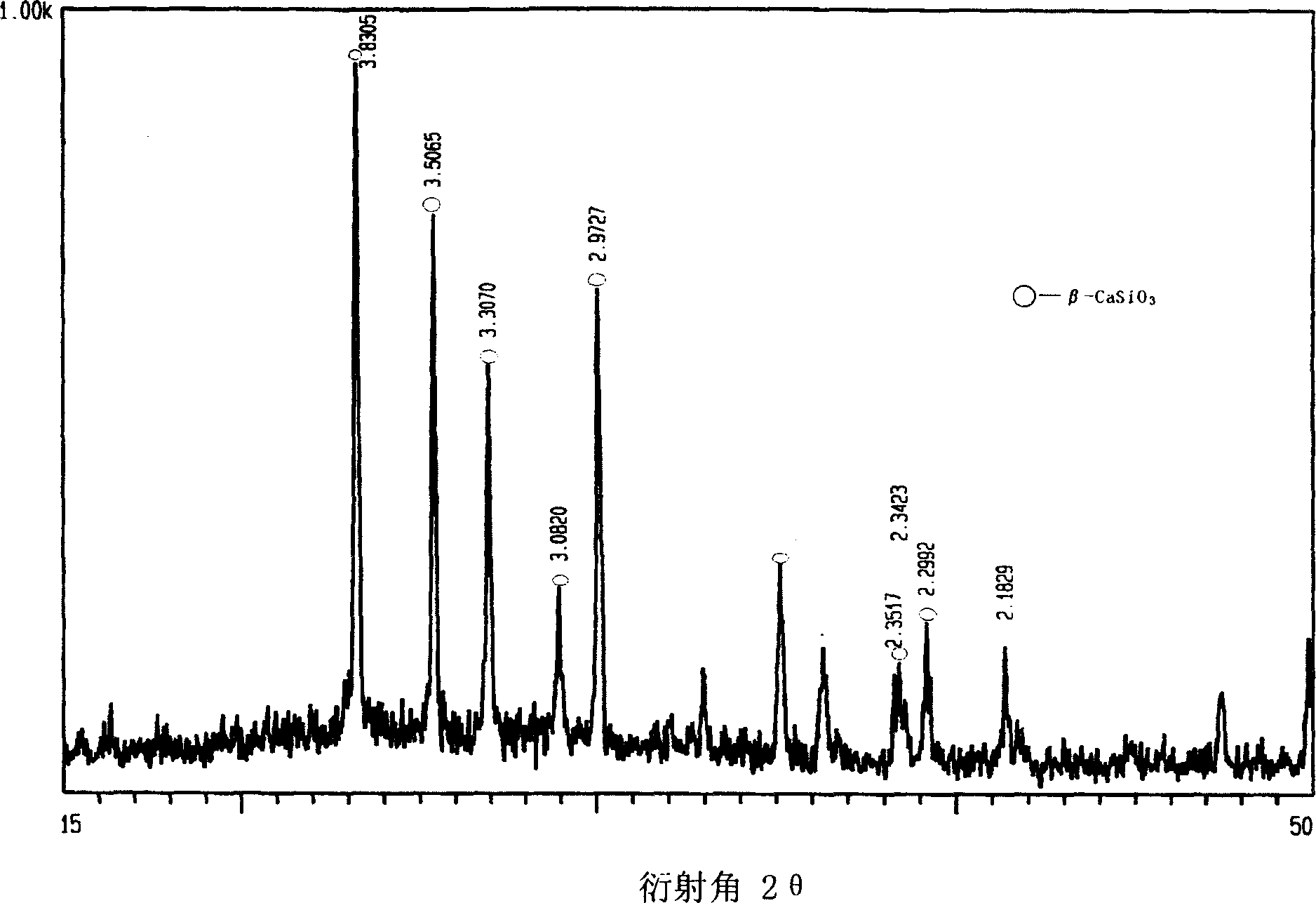
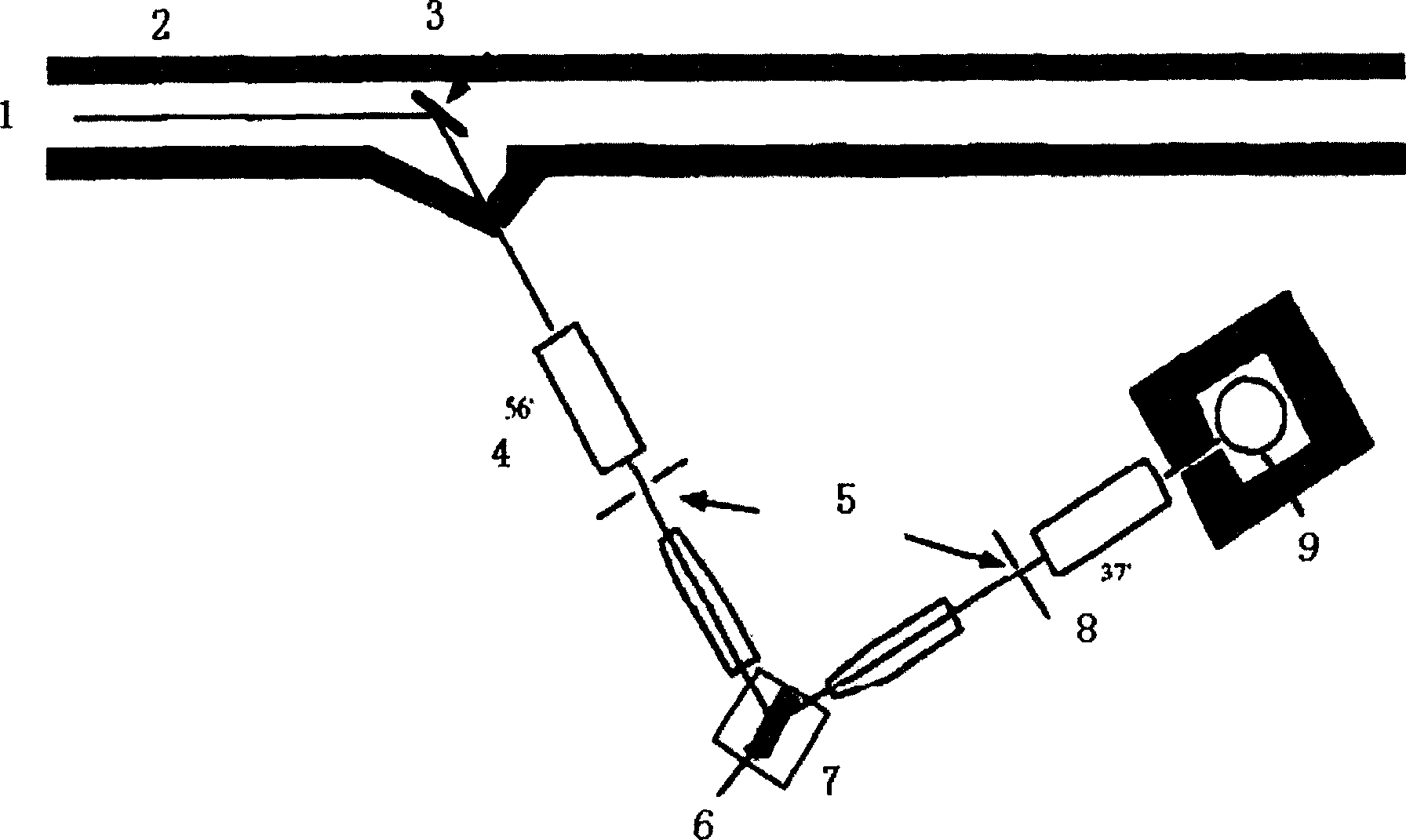
InactiveCN1828282AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationResidual strainYoung's modulus
Wherein, first preparing the glass-ceramic; adjusting the neutron monochromator to select opposite monochromatic neutron; irradiating sample surface with neutron beam with diffraction angle 2theta as 10-75Deg; taking strain detection crystal face with principal crystalline phase as beta-wollastonite and obtaining the average strain result as: ªŠ=1 / 3(ªŠ11+ªŠ22+ªŠ33), opposite volume mean strain as í¸=1 / V(íʪŠdV); calculating with formulaªÊ=E / 3(1-2ªÈ)í¸ (wherein, E: Young's modulus; ªÈ: Poisson's ratio), and then obtaining the total strain on three axial directions ªñ=ea+eb+ec; exactly, here, selecting E=70GPa and ªÈ=0.245; repeating former steps to obtain different residual strain values to draw distribution curve. This invention can obtain the inner strain of sample and fit to massive sample.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
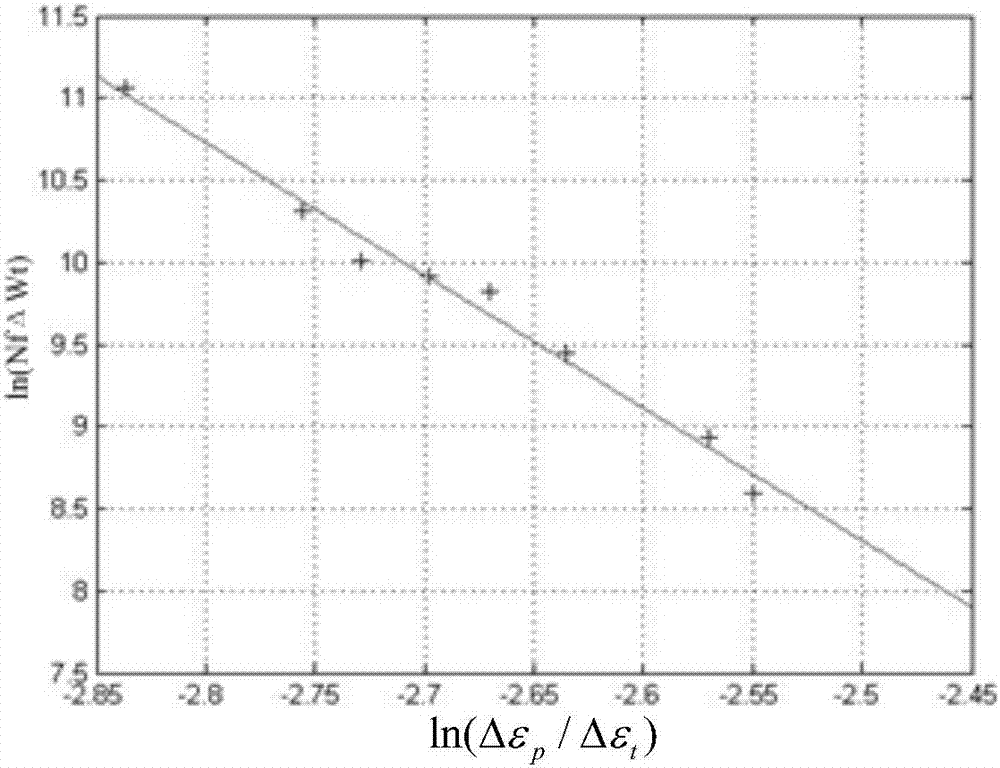
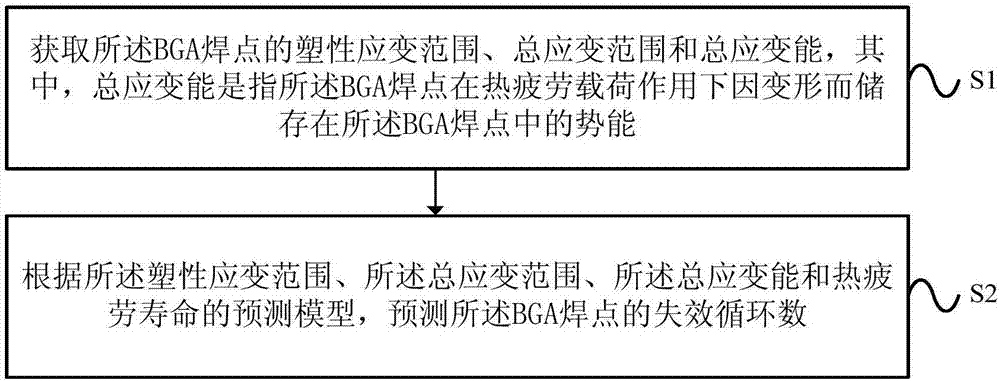
Predicting method and system for thermal fatigue life of BGA welding spots
ActiveCN107203666APredicted service lifeImprove versatilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsThermal fatigueEngineering
An embodiment of the invention provides a predicting method and system for the thermal fatigue life of BGA welding spots. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a plastic strain range, a total strain range and total strain energy of the BGA welding spots, wherein the total strain energy is potential energy which is stored in the BGA welding spots due to deformation under the thermal fatigue load effect of the BGA welding spots; and predicting the cycle to failure of the BGA welding spots according to the plastic strain range, the total strain range, the total strain energy and a predicting model for the thermal fatigue life. The system carries out the method. By the predicting method and system for the thermal fatigue life of the BGA welding spots provided by the embodiment, the service lives of the BGA welding spots can be simply, conveniently and rapidly predicted for the thermal fatigue life problem caused by temperature cycle, the universality is improved, and therefore, the engineering application value is high.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
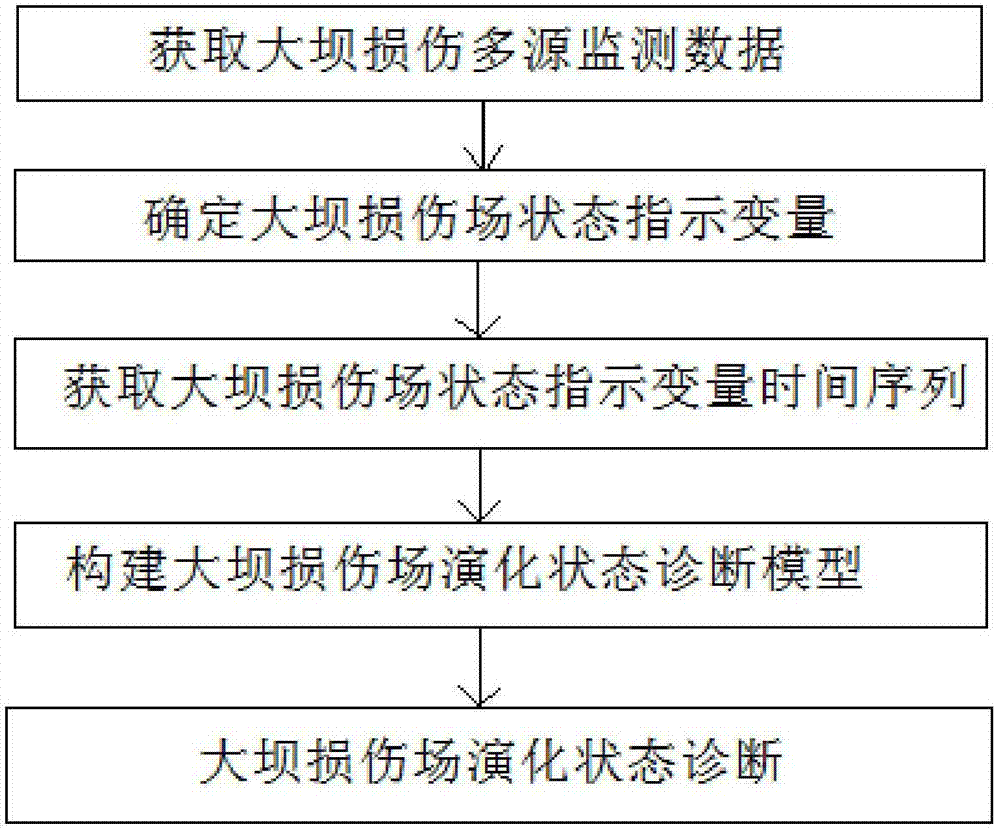
Diagnostic method of evolution state of damage field of concrete dam
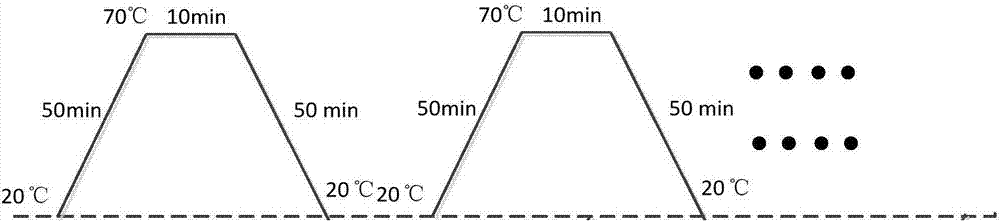
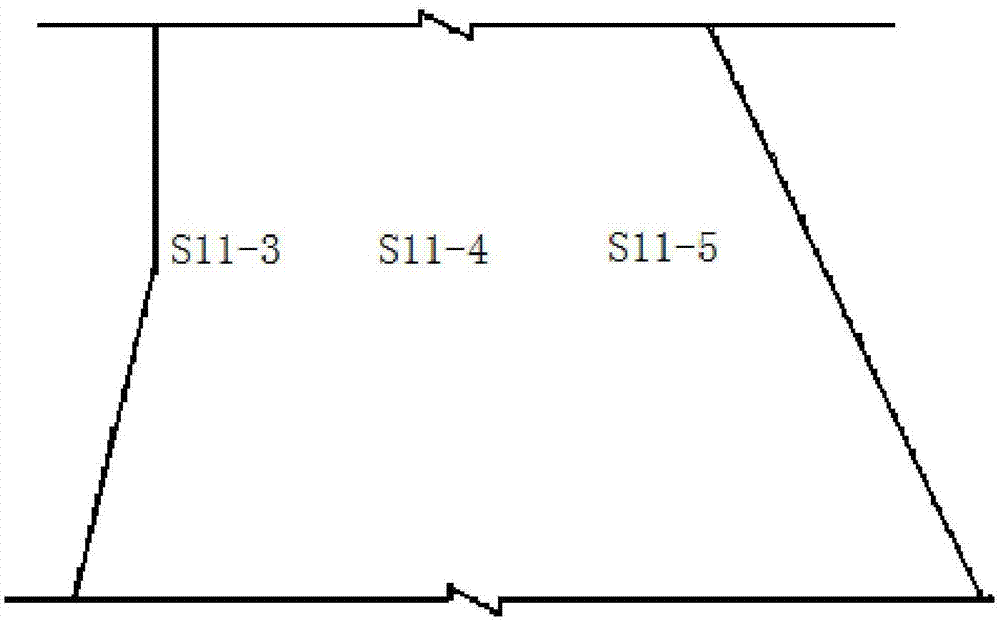
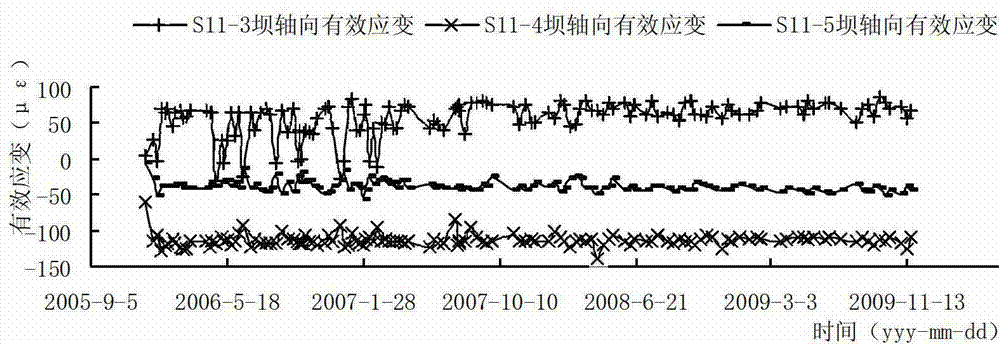
ActiveCN103162982AFully reflect the state of healthStructural/machines measurementStrain energyEngineering
The invention discloses a diagnostic method of an evolution state of a damage field of a concrete dam. The method includes the steps of (1) building a damage field indication variable based on entropy, and defining the entropy of a system as H=F(Q,qi,L,T); (2) calculating the damage field indication variable, and extracting sizes influenced by stress, strain and strainmeter of the damage field from a dam safety monitoring system, wherein the number of strainmeter groups is n, strain energy of a unit of a portion where an ith strainmeter group is located is qi (i=1,2,......,n), total strain energy Q of the area is obtained, and therefore an information entropy function H of a local area is shown in the description, (qi=0, lambada i ln lambada i= 0); and (3) expressing the entropy of the damage field of the concrete dam at a certain moment as F(H)=F(Hh)+F(HT)+F(Htheta) according to a time sequence of the damage field indication variable, and obtaining influence degrees of water pressure, temperature and aging for the damage field and changing trends of the damage field according to an entropy formula to achieve diagnosis and prediction for the damage field. The diagnostic method solves the problems that a traditional method can only diagnose a single measurement point and is lack of relevant diagnosis for changes of measured values of multiple measure points, and comprehensively reflects health states of the dam.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Online measurement method and measurement apparatus of residual stress of conductive thin film material
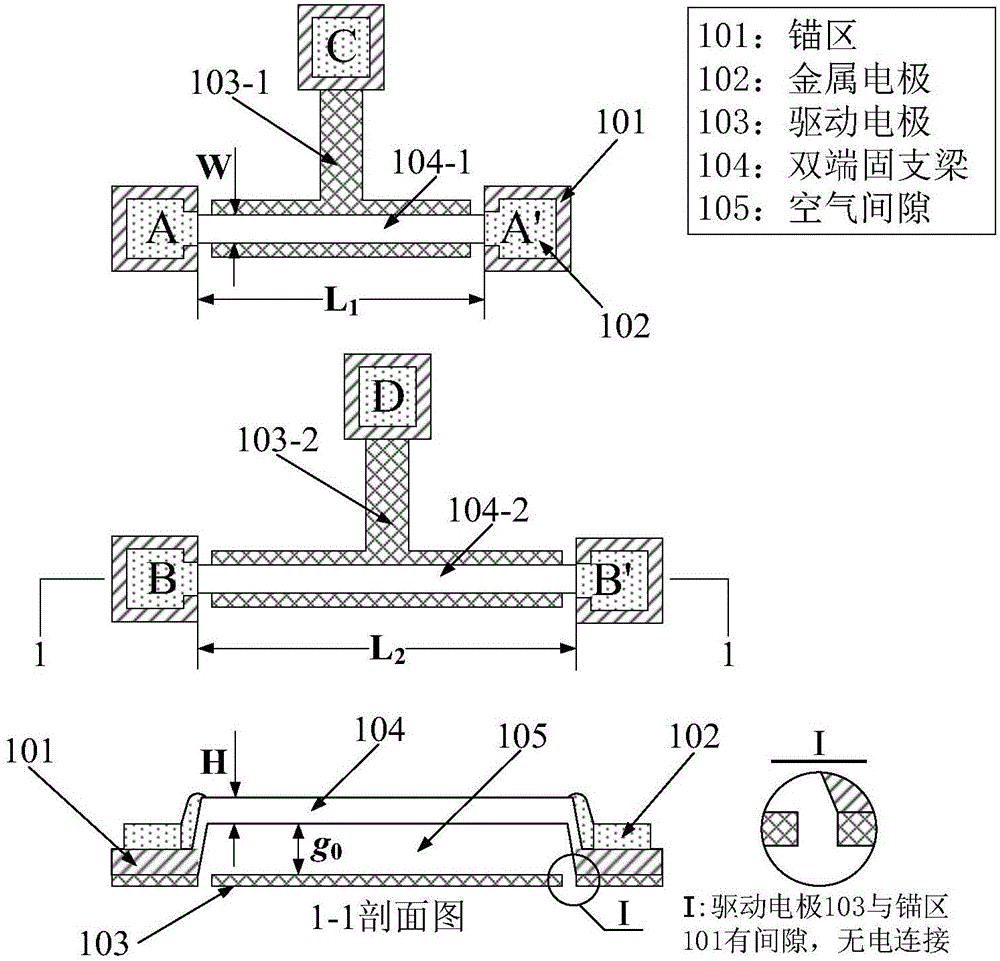
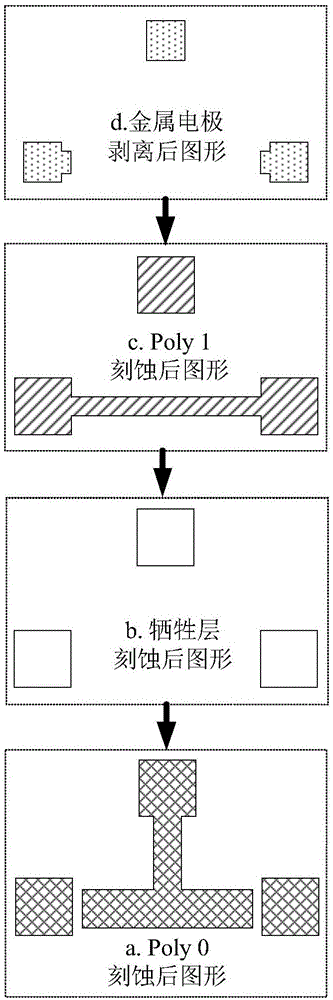
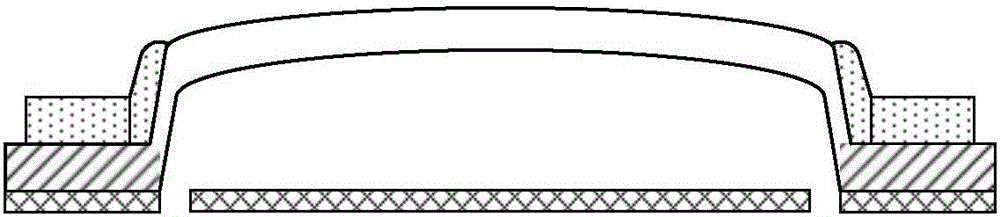
ActiveCN106248280ALower requirementEasy loadingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElectricityYoung's modulus
The invention brings forward an online measurement method of residual stress of a conductive thin film material, and a corresponding measurement apparatus. A measurement structure is designed by use of an electrostatic driving Pull-in principle, relevance of parameters of two measurement members is controlled through use of synchronous processing control, through limiting correlation parameters of total strain energy of the two measurement members, a partial differential equation set of the total strain energy is constrained accordingly, and values of unknown residual stress sigma 0 and a Young's modulus E of the two measurement members are obtained through a mode of solving the partial differential equation set. According to the invention, the problem of incapability of real-time measurement of the conductive thin film material under the condition of unknown material parameters, unknown residual stress size and unknown positivity and negativity (tensile stress or compression stress) is solved. The apparatus and method have the advantages of simple measurement structure, simple electric signal loading and measurement, stable calculation method and high measurement efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Mechanical response characteristic analysis method for pod rod coiling and folding process
ActiveCN113609595AThe coil deformation process is clear and clearGeometric CADSustainable transportationUltimate tensile strengthMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a mechanical response characteristic analysis method for a pod rod coiling and folding process, and belongs to the technical field of structural mechanical response characteristic analysis. The analysis method comprises the following steps of: S1, according to physical characteristics of a pod rod, establishing a coordinate system and defining required variables, and constructing and forming a pod rod structure model; S2, according to the geometrical characteristics of the cross section of the pod rod and the symmetry of the structure, carrying out region division on the pod rod structure model; S3, calculating the strain of each area of the pod rod in the coiling and folding process; S4, calculating the stress and strain of each composite material laying layer in the coiling and folding process of the pod rod; and S5, calculating the total strain energy of the pod rod in the folded state. According to the method, the characteristics of the composite material are considered, the mechanical response characteristics of each laying layer of the composite material and the total strain energy of the pod rod in the folded state are obtained, and a basis can be provided for preliminary design and strength checking of the pod rod.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method of controlling grain size in forged precipitation-strengthened alloys and components formed thereby
ActiveUS20120282106A1Significant control of average grain sizeAvoid grain growthBlade accessoriesReaction enginesAlloyHeat treated
Components and methods of processing such components from precipitation-strengthened alloys so that the components exhibit desirable grain sizes following a supersolvus heat treatment. The method includes consolidating a powder of the alloy to form a billet having an average grain size. The billet is then forged at a temperature below the solvus temperature to form a forging having an average grain size of not coarser than the grain size of the billet. The billet is then forged at a total strain of at least 5%, after which at least a portion of the forging is heat treated at a temperature below the solvus temperature to pin grains within the portion. The entire forging can then be heat treated at a temperature above the solvus temperature of the alloy without coarsening the grains in the portion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Heat treatment method of Fe-Mn-Al-C austenitic low-density steel
ActiveCN110205459AImprove work hardening abilityHigh tensile strengthPre deformationRoom temperature
The invention discloses a heat treatment method of a Fe-Mn-Al-C austenitic low-density steel. The heat treatment method comprises the following steps that (1), the pre-deformation treatment is carriedout on the Fe-Mn-Al-C austenitic low-density steel in the initial state, and the total strain capacity is controlled to be 4%-35%; and (2), the aging treatment is carried out on the Fe-Mn-Al-C austenitic low-density steel subjected to pre-deformation treatment, specifically, the aging treatment is one-step aging treatment or two-step aging treatment, wherein the one-step aging temperature is 600-700 DEG C, the heat preservation time is 10-60 min, and the cooling at room temperature is carried out; and the two-step aging is characterized in that the first-step aging temperature is 450-550 DEGC, the heat preservation time of the first-step aging is 0.5-4h, and after the completion of the first-step aging, the second-step aging temperature is reached through the rapid warming, the second-step aging temperature is 600-700 DEG C, the heat preservation time of the second-step aging is 10-40 min, and then the cooling at room temperature is carried out. According to the heat treatment method, the yield ratio of the Fe-Mn-Al-C austenitic low-density steel can be reduced, the use safety performance of the Fe-Mn-Al-C austenitic low-density steel is improved, and excellent comprehensive mechanical properties are obtained; and the method has important significance in practical application.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
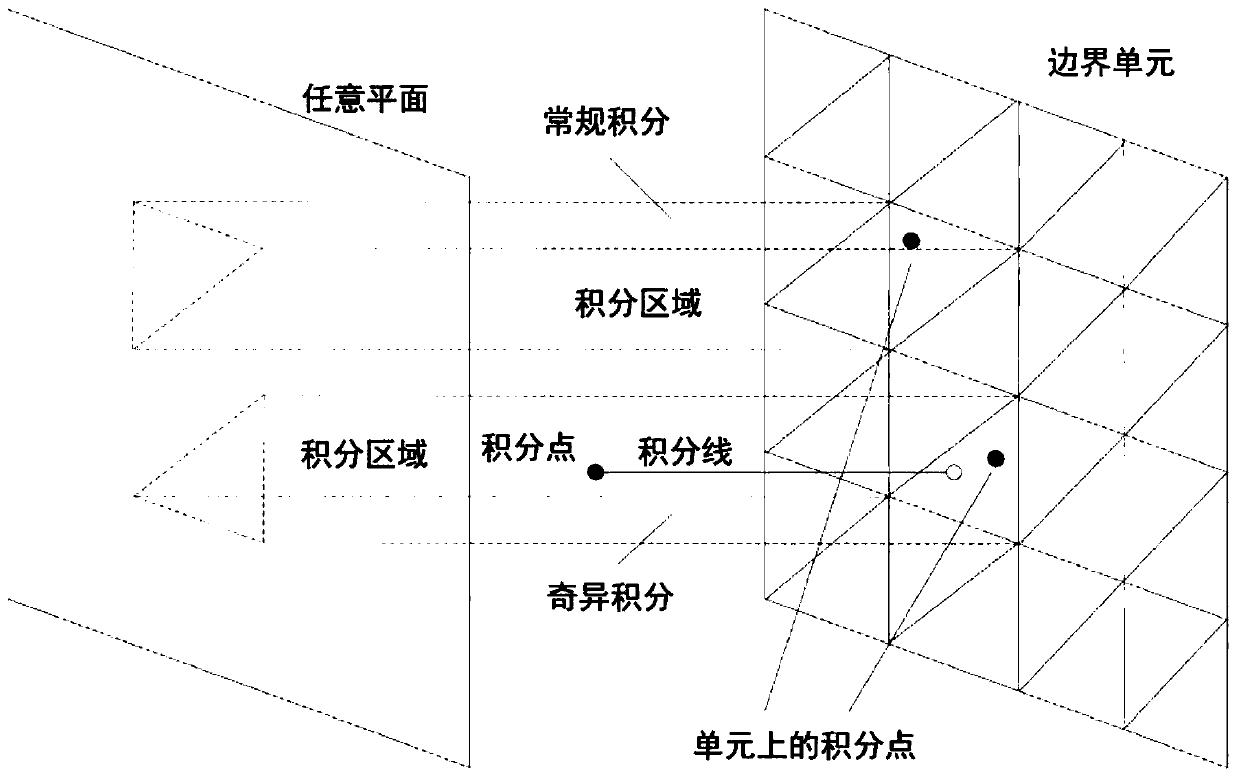
Method and device for solving static thermoelasticity problem of isotropic solid material
ActiveCN110705057AImprove accuracyImprove effectivenessDesign optimisation/simulationElastomerTypes of mesh
The invention provides a method and device for solving a static thermoelasticity problem of an isotropic solid material. The method comprises the steps of establishing a numerical model of a to-be-solved structure based on material parameters, gridding scores, grid types and boundary condition information of the actual to-be-solved structure, and adding the material parameters and the boundary condition information to nodes on each unit of the numerical model; establishing strain and stress equations including a relation equation between the total strain and stress of the isotropic elastomer material and a stress equation; further, establishing a displacement integral equation; establishing an internal stress integral equation; converting domain integrals in the displacement integral equation and the internal stress integral equation into boundary integrals; establishing a solving matrix throughout the integral equation, and performing discretization and integration to obtain a matrixequation; and then, obtaining change data of the boundary and the internal point of the model by utilizing a Gaussian elimination solution method, and taking the change data as change data of the boundary and the internal point of the to-be-solved structure.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
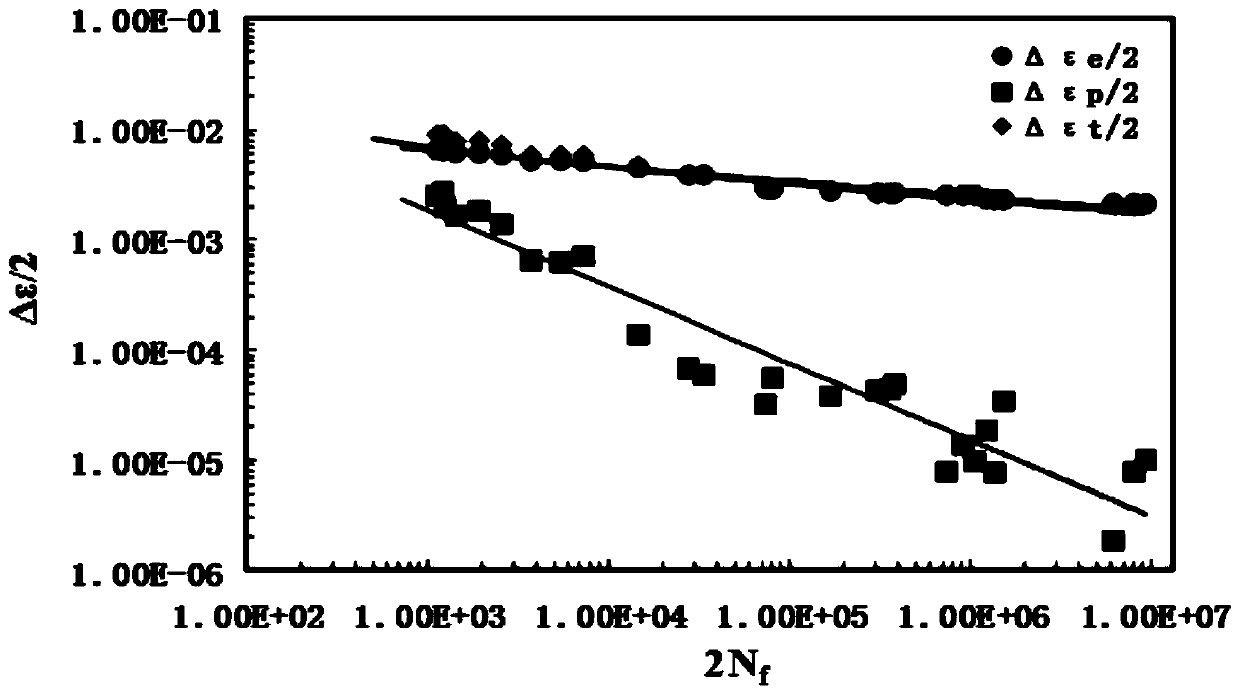
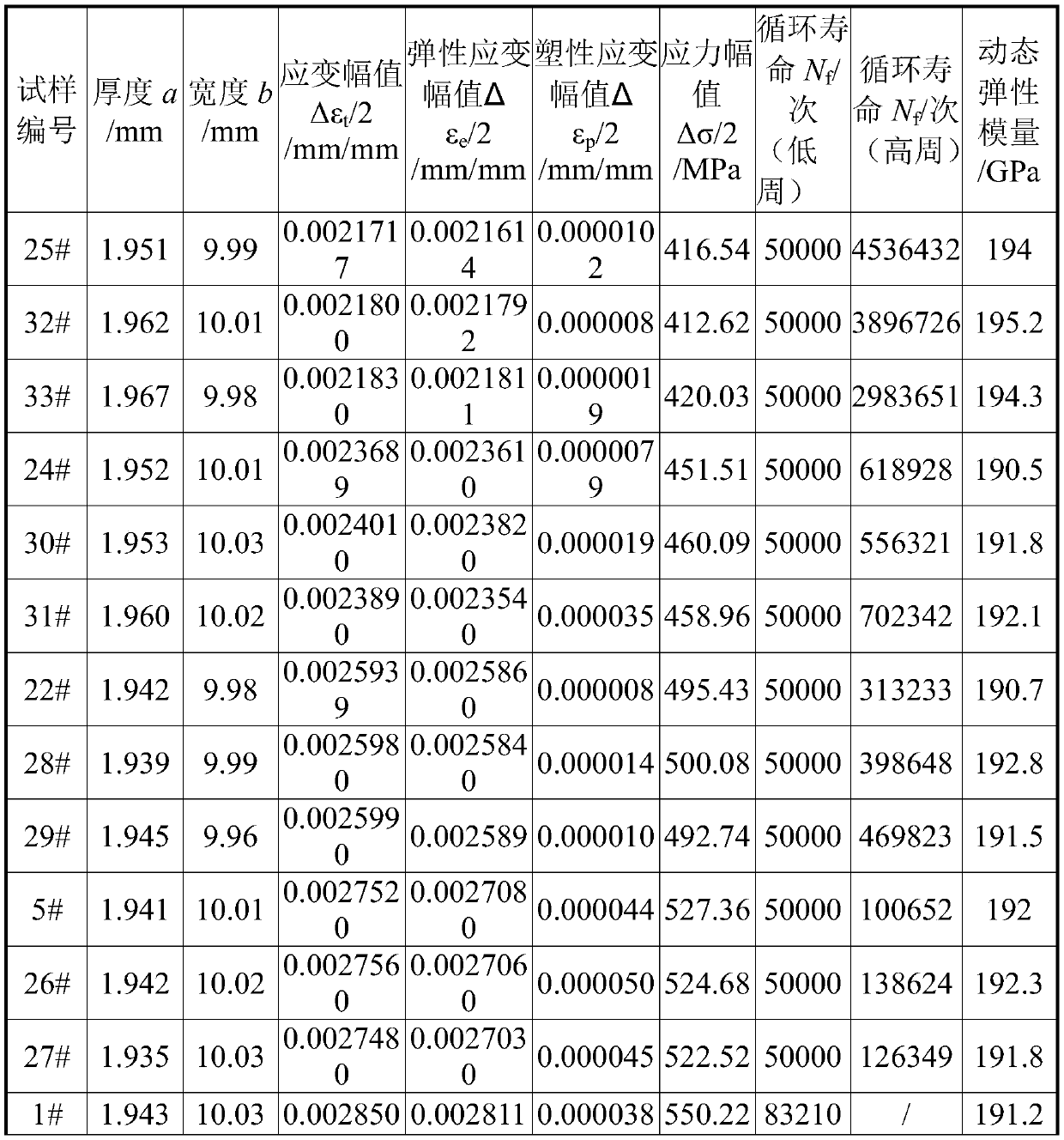
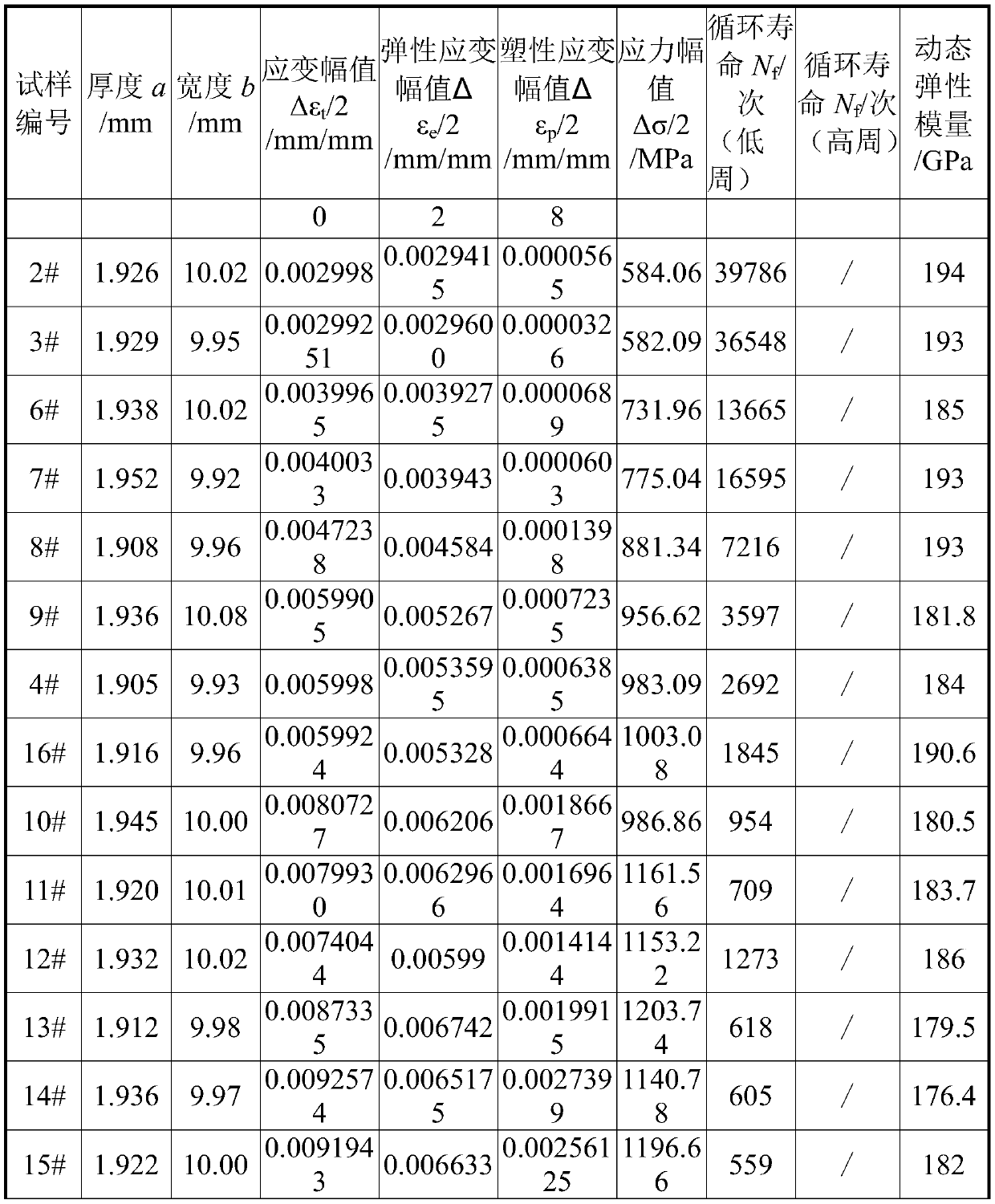
Uniform amplitude full-strain-life curve test method for metal material
ActiveCN110398430AImprove test efficiencyMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesMetallic materialsTransition point
The invention relates to a uniform amplitude full-strain-life curve test method for a metal material, and the method comprises the following steps of 1, performing processing and surface treatment ona sample; 2, performing a short-life fatigue test, and using an extensometer for strain control when the cycle life is less than 100,000 times, wherein the test frequency is 0.1Hz to 1Hz; 3, testing the cycle life under different strain amplitudes with a total strain amplitude greater than three per thousand, and controlling the test with the strain amplitudes, wherein the frequency is 0.1Hz and 1Hz; 4, determining a strain amplitude corresponding to the transition point of short-life fatigue to long-life fatigue in the range of one to three per thousand of the total strain amplitude; 5, performing long-life fatigue test, using the extensometer for strain control in the first stage within 50,000 times, wherein the test frequency is 10Hz to 25Hz, and selecting the stress amplitude corresponding to the cycle of 50,000 times as the stress control amplitude of the second stage; and 6, fitting the total strain-life formula. The full strain-life curve of the metal material can be obtained bythe method provided by the invention.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
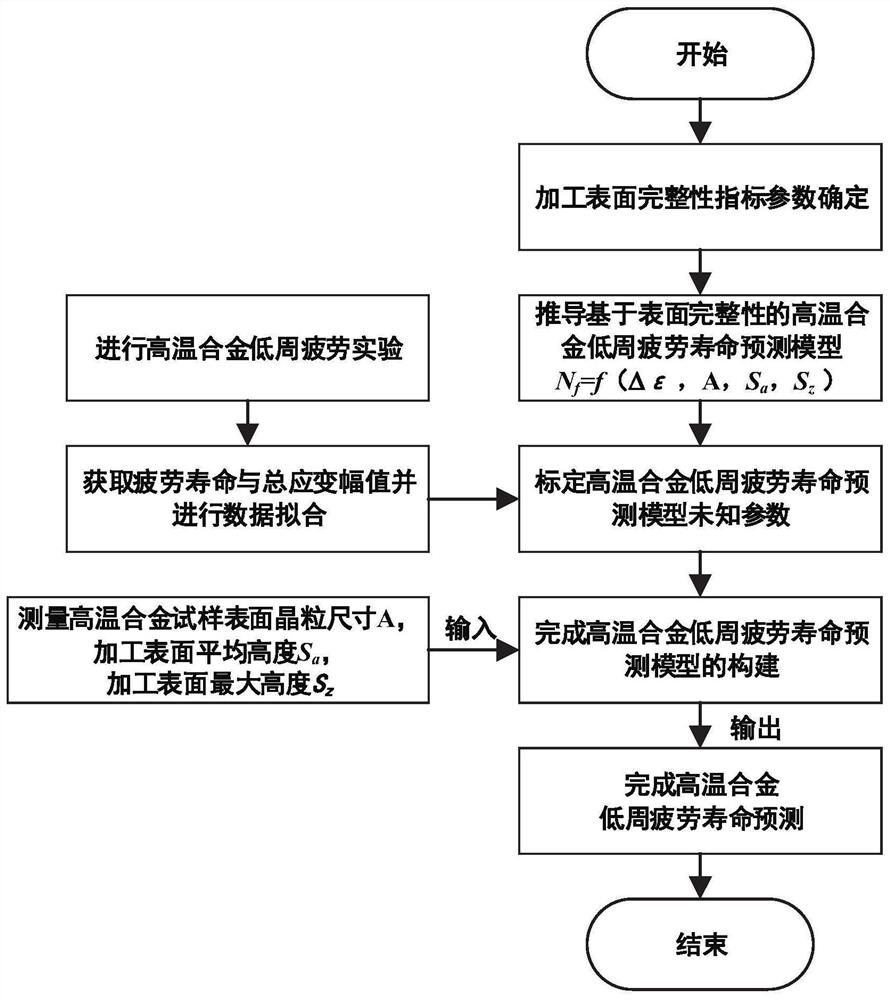
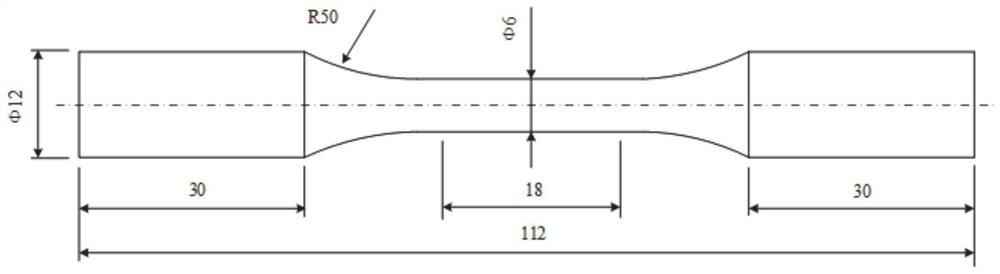
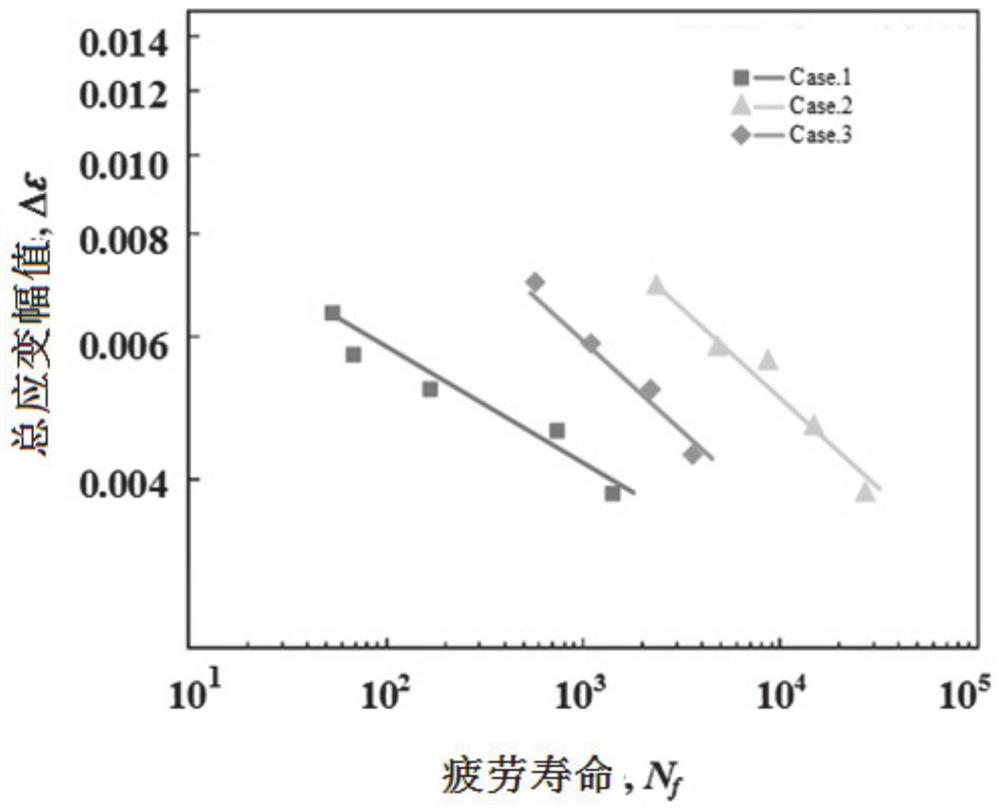
Low-cycle fatigue life prediction method based on high-temperature alloy machining surface integrity
PendingCN111678821AHigh precisionHigh fatigue life prediction accuracyWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationPattern recognitionMicron scale
The invention discloses a low-cycle fatigue life prediction method based on high-temperature alloy processing surface integrity, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out low-cycle fatigue test of a high-temperature alloy sample, obtaining the fatigue life and total strain amplitude data, and drawing a relation graph of the fatigue life and the total strain amplitude under a double logarithmic coordinate system; selecting a high-temperature alloy sample subjected to a low-cycle fatigue test, carrying out axial cutting sampling perpendicular to the sample, inlaying the sample into black inlaid resin, carrying out mechanical polishing to enable the roughness of the sampled surface to reach a micron level, and carrying out surface chemical corrosion to measure the average area root mean square of the surface; selecting a fatigue life test sample, and measuring the unevenness of the machined surface of the sample; and performing formula correction considering influence ofthe unevenness of the machined surface on the fatigue life prediction model, and establishing the high-temperature alloy sample low-cycle fatigue life prediction model based on the surface integrity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
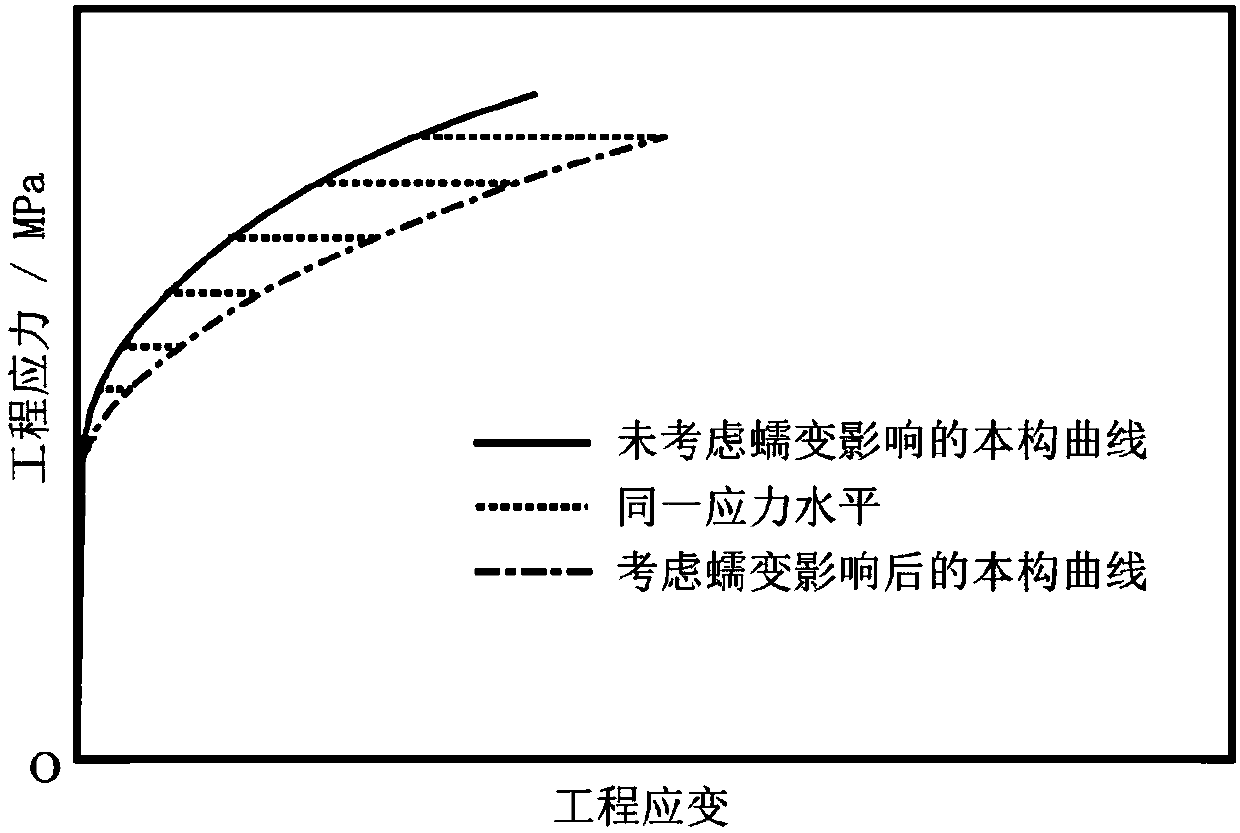
Obtaining method of austenite stainless steel constitutive curve considering room temperature creeping
ActiveCN107727497AImprove forecast accuracyPrediction is accurateMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesOriginal dataRoom temperature
The present invention relates to an austenite stainless steel processing technology. A purpose of the present invention is to provide an obtaining method of an austenite stainless steel constitutive curve considering room temperature creeping. The method comprises: obtaining the original data for constructing a constitutive curve through the tension load retention test of an austenite stainless steel material; and labeling points ([sigma]1, [epsilon]1), ([sigma]2, [epsilon]2), ..., ([sigma]n, [epsilon]n) respectively by using set stress [sigma] as horizontal ordinates and using the total strain [epsilon] as vertical coordinates, and establishing an [epsilon] change curve related to the stress [sigma] through fitting, wherein the curve is the austenite stainless steel constitutive curve considering the influence caused by room temperature creeping. Compared to the obtaining method in the prior art, the obtaining method of the present invention considers the influence of the room temperature creeping on the constitutive curve. According to the present invention, by defining the data determination method, the time calculation formula and the like, the prediction precision can be significantly improved and the prediction result is accurate when the finally-obtained constitutive curve is used in the stress-strain response theoretical calculation and simulation prediction of the austenite stainless steel material or structure in the late-stage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Technology for culturing and collecting seeding of Camptotheca acuminata Decne
InactiveCN1543770AImprove acquisitionDoes not inhibit growthHorticulture methodsGrowing seasonSeedling
Nyssaceae tree sapling cultivation and collection process comprises, using Nyssaceae seedling obtained from seeds of the same year as sprout source, transplanting seedling into land in early spring, adding nitrogen fertilizer, watering, collecting bough and leaflet of over ground portion, completing total-strain collection after the growing season ends. The invention increases the yield of plant material and the content of camptothecine.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com