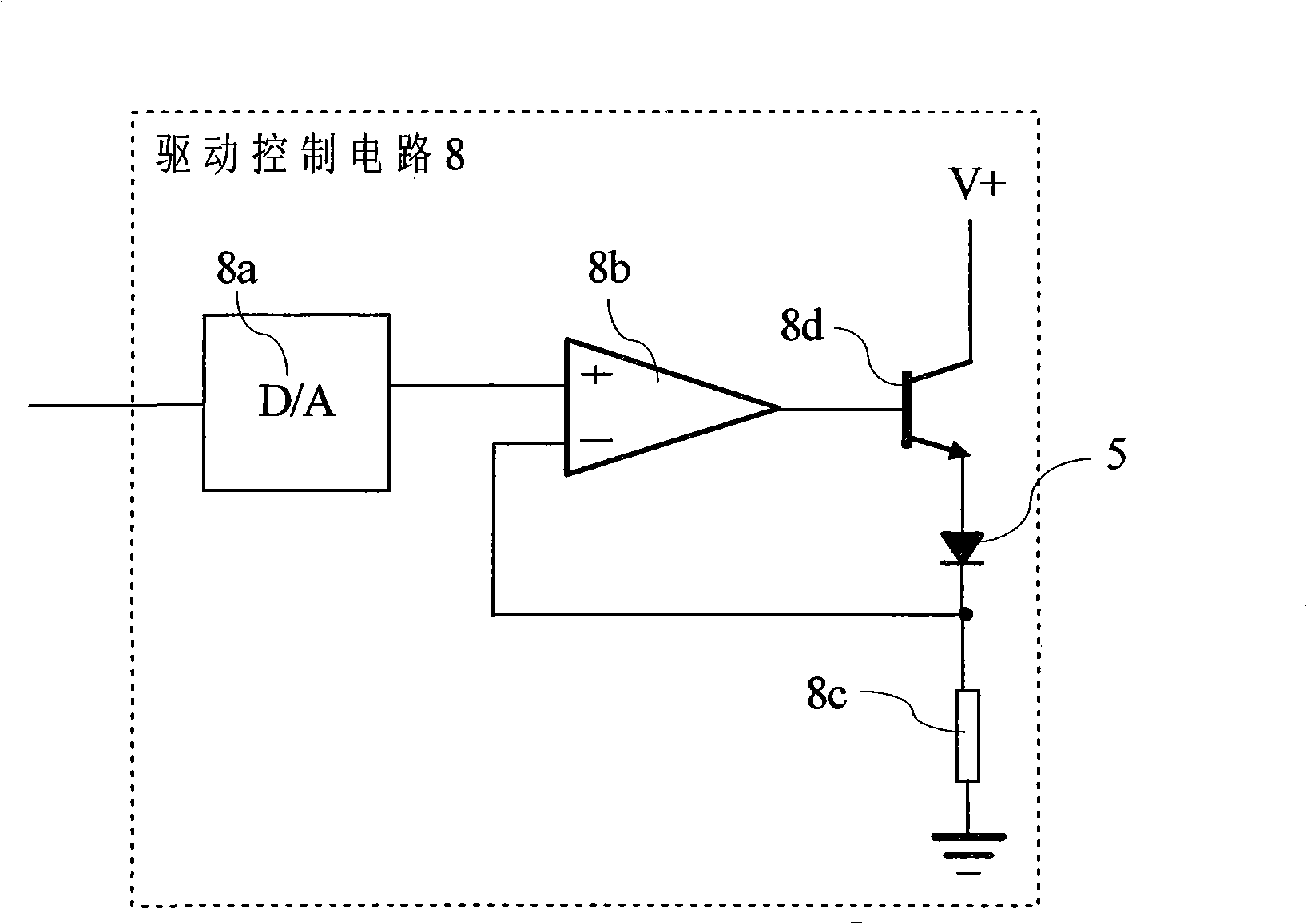
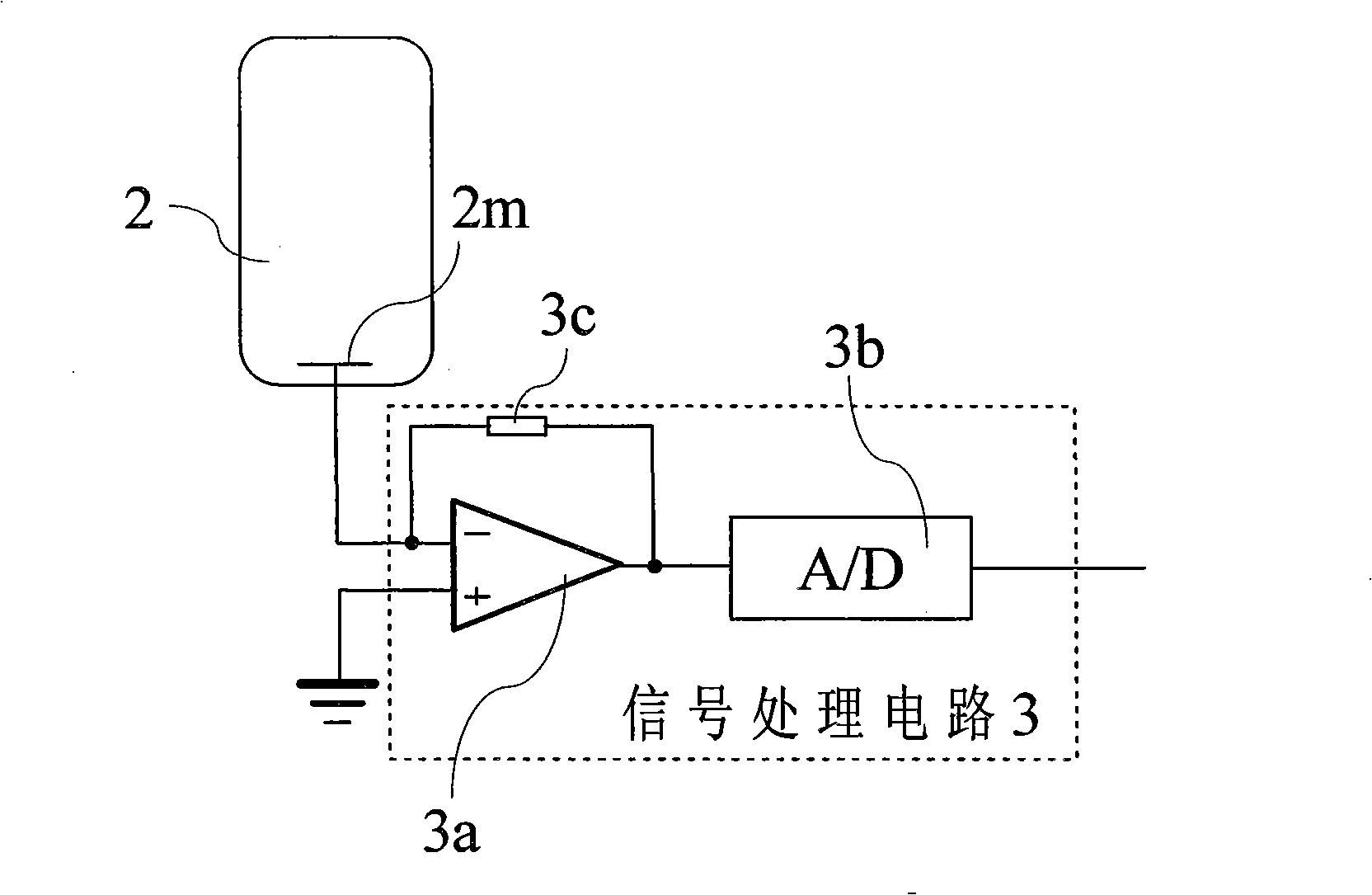
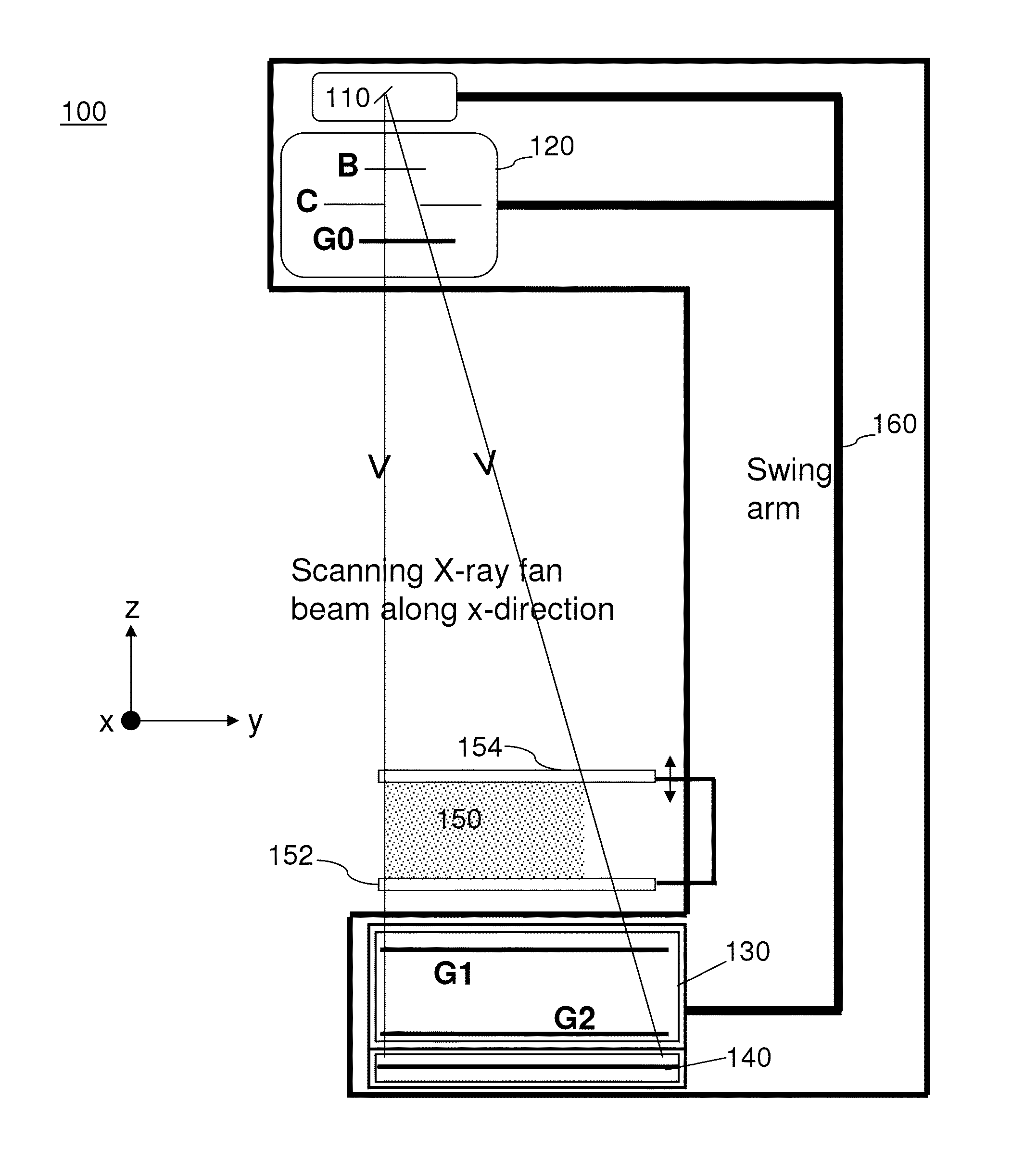
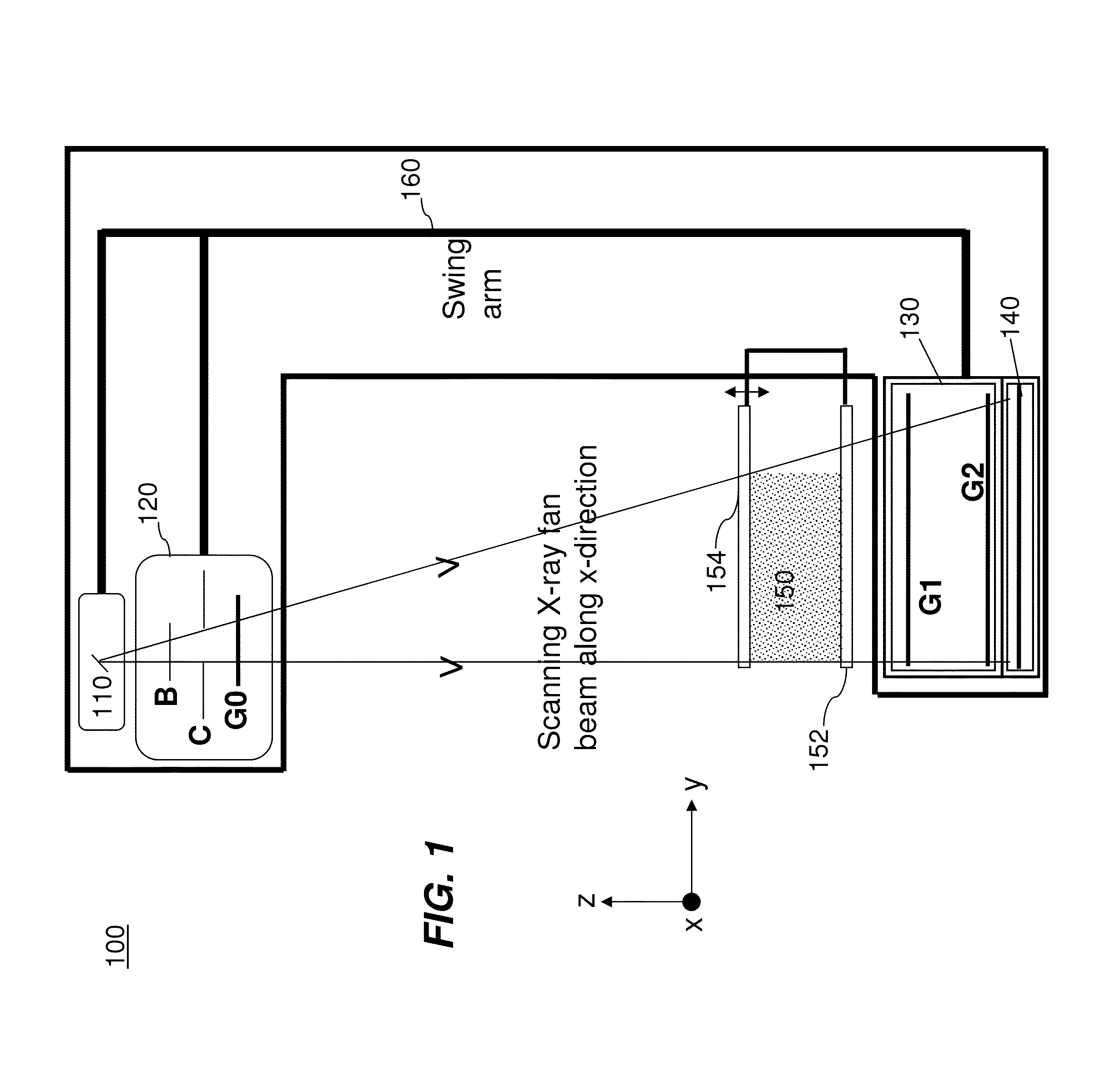
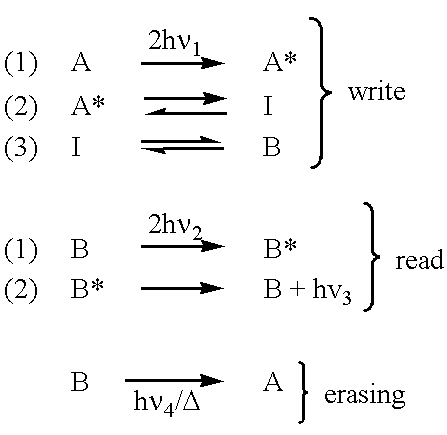Patents
Literature
849 results about "Monochromator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
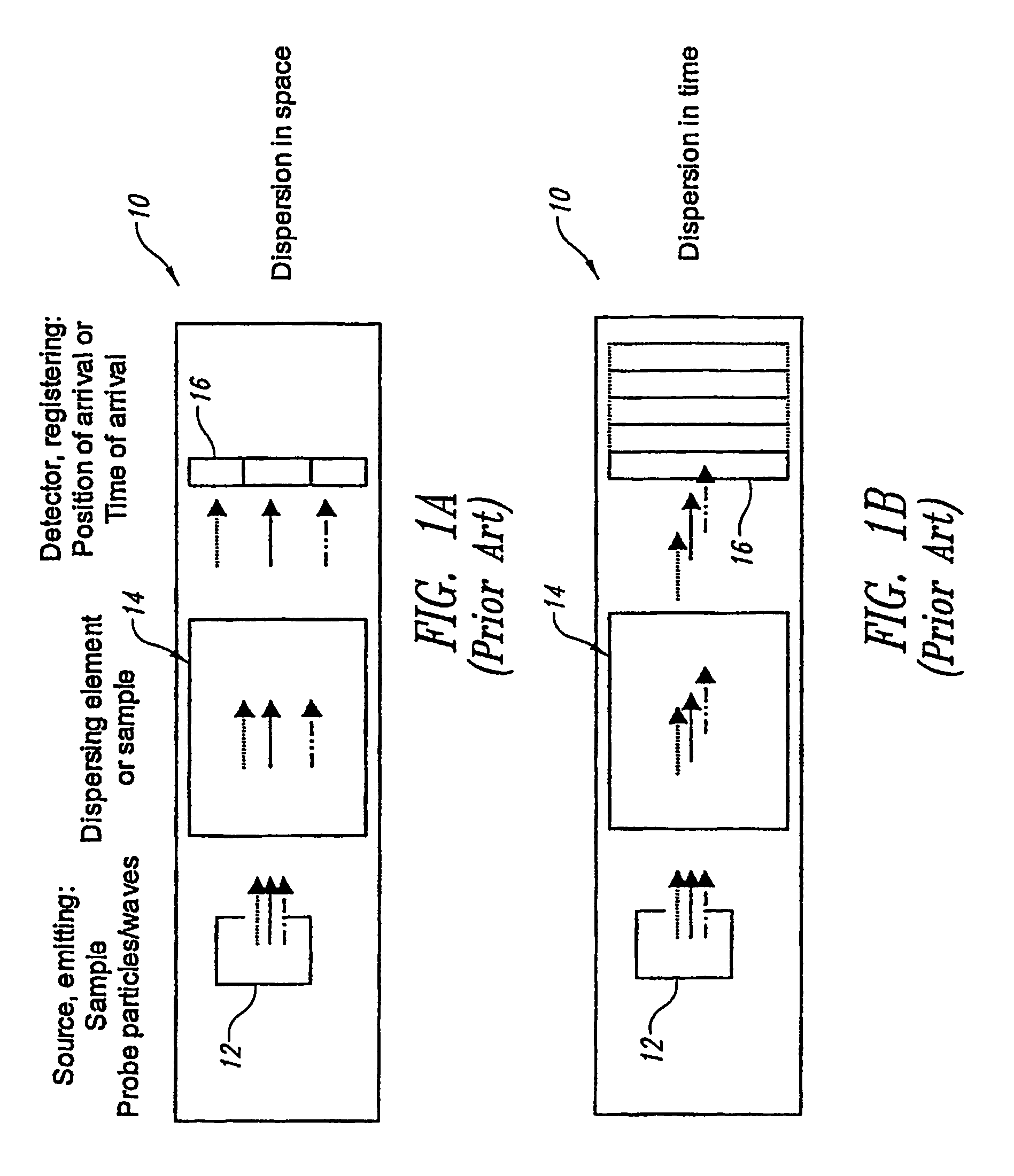
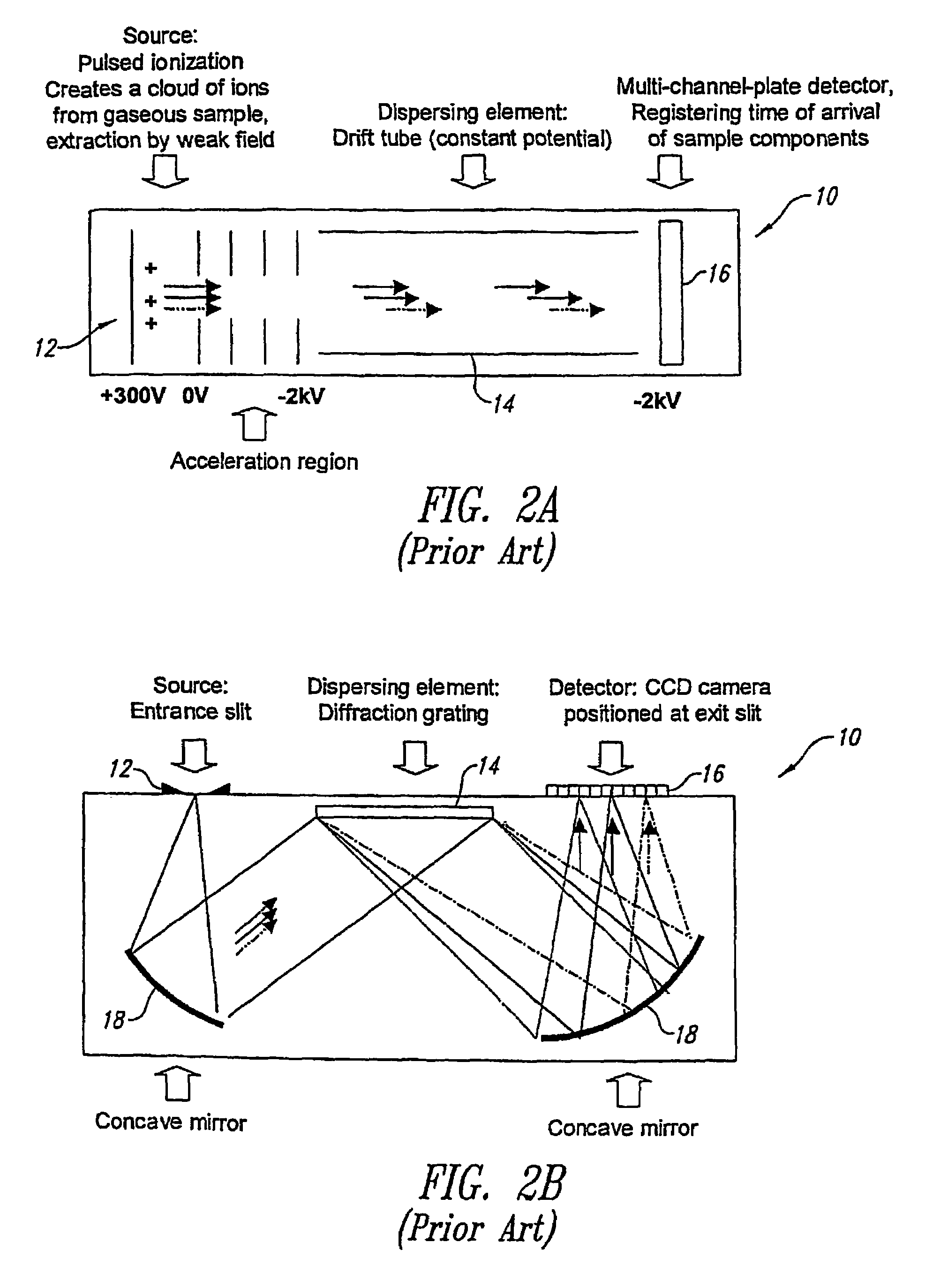
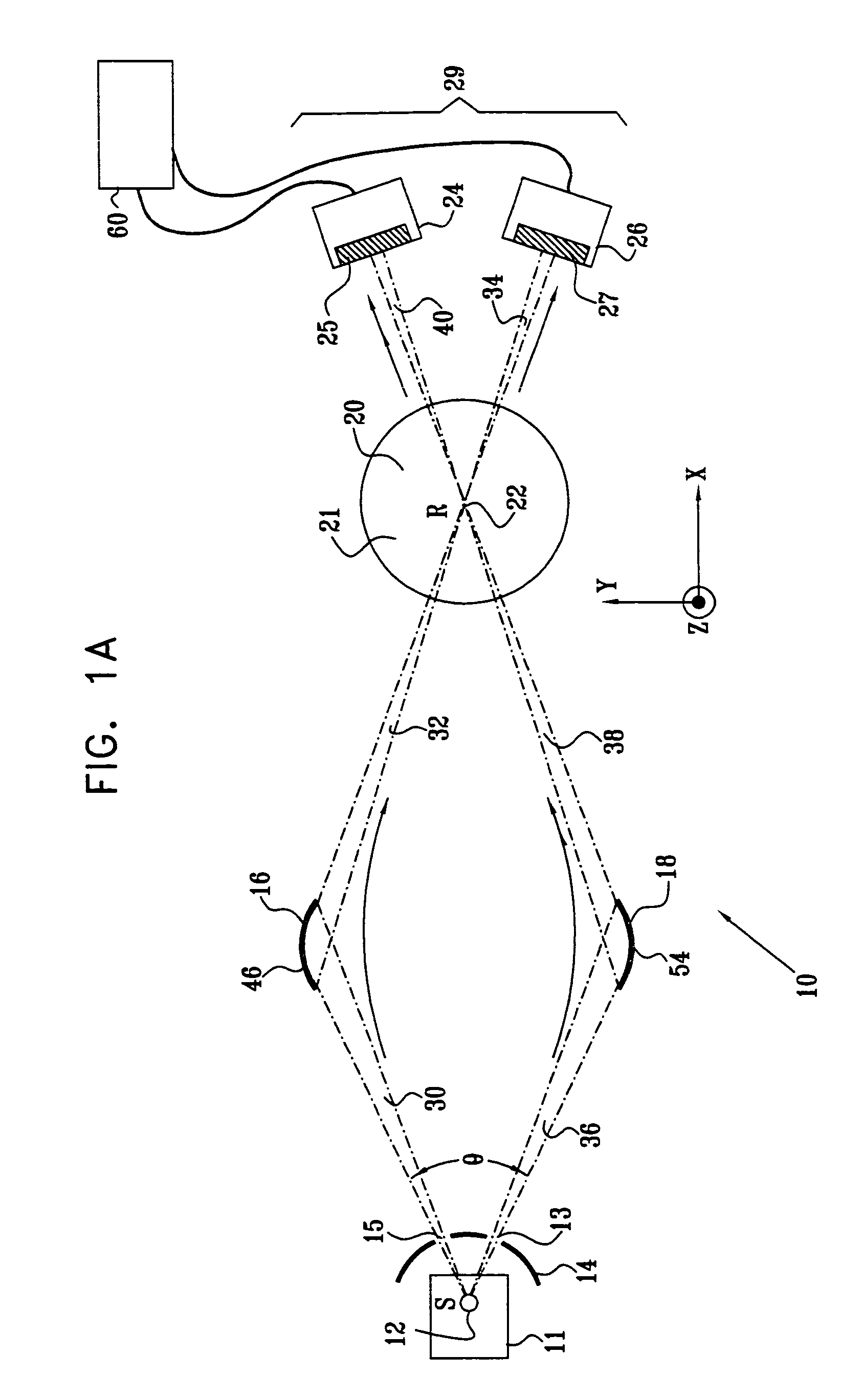
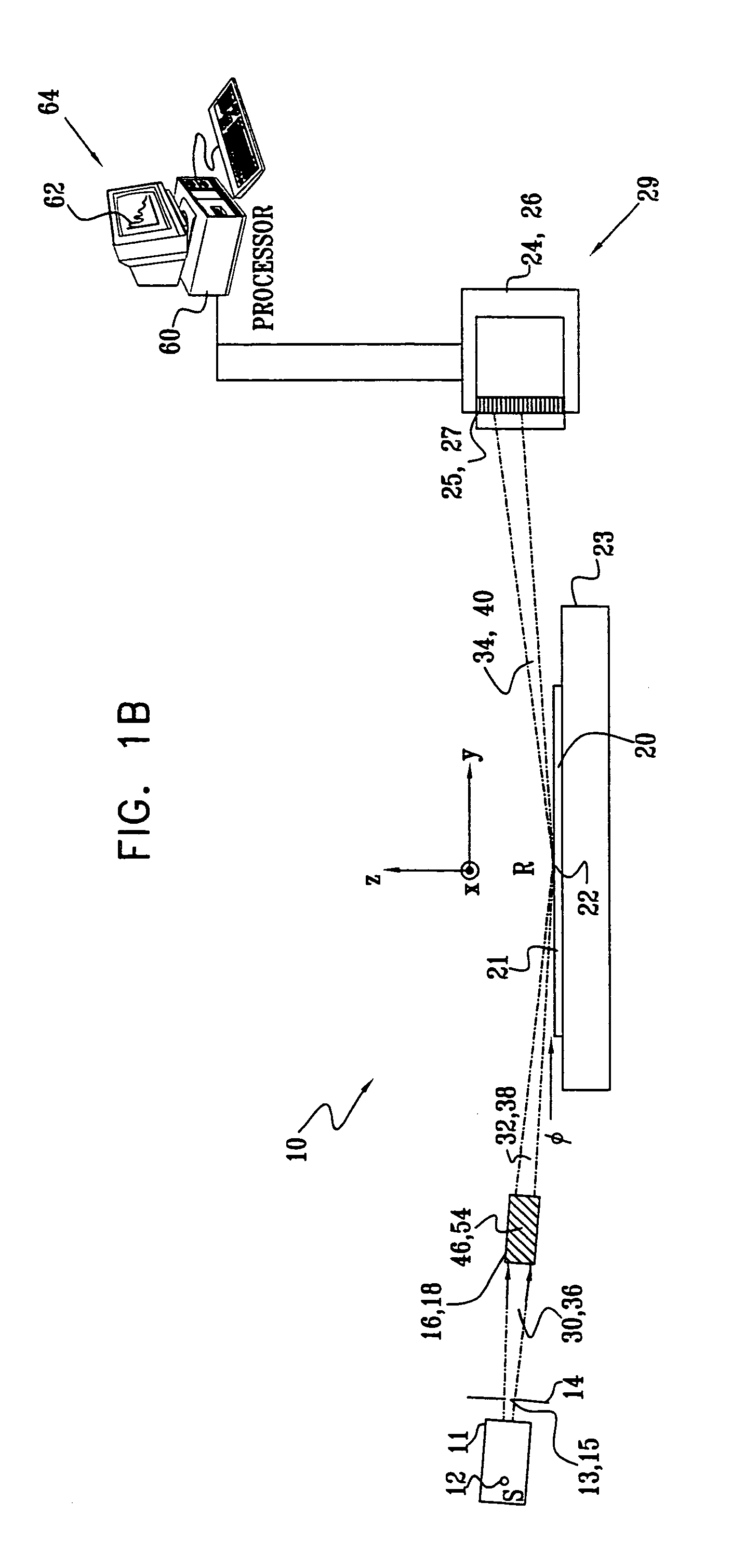
A monochromator is an optical device that transmits a mechanically selectable narrow band of wavelengths of light or other radiation chosen from a wider range of wavelengths available at the input. The name is from the Greek roots mono-, "single", and chroma, "colour", and the Latin suffix -ator, denoting an agent.
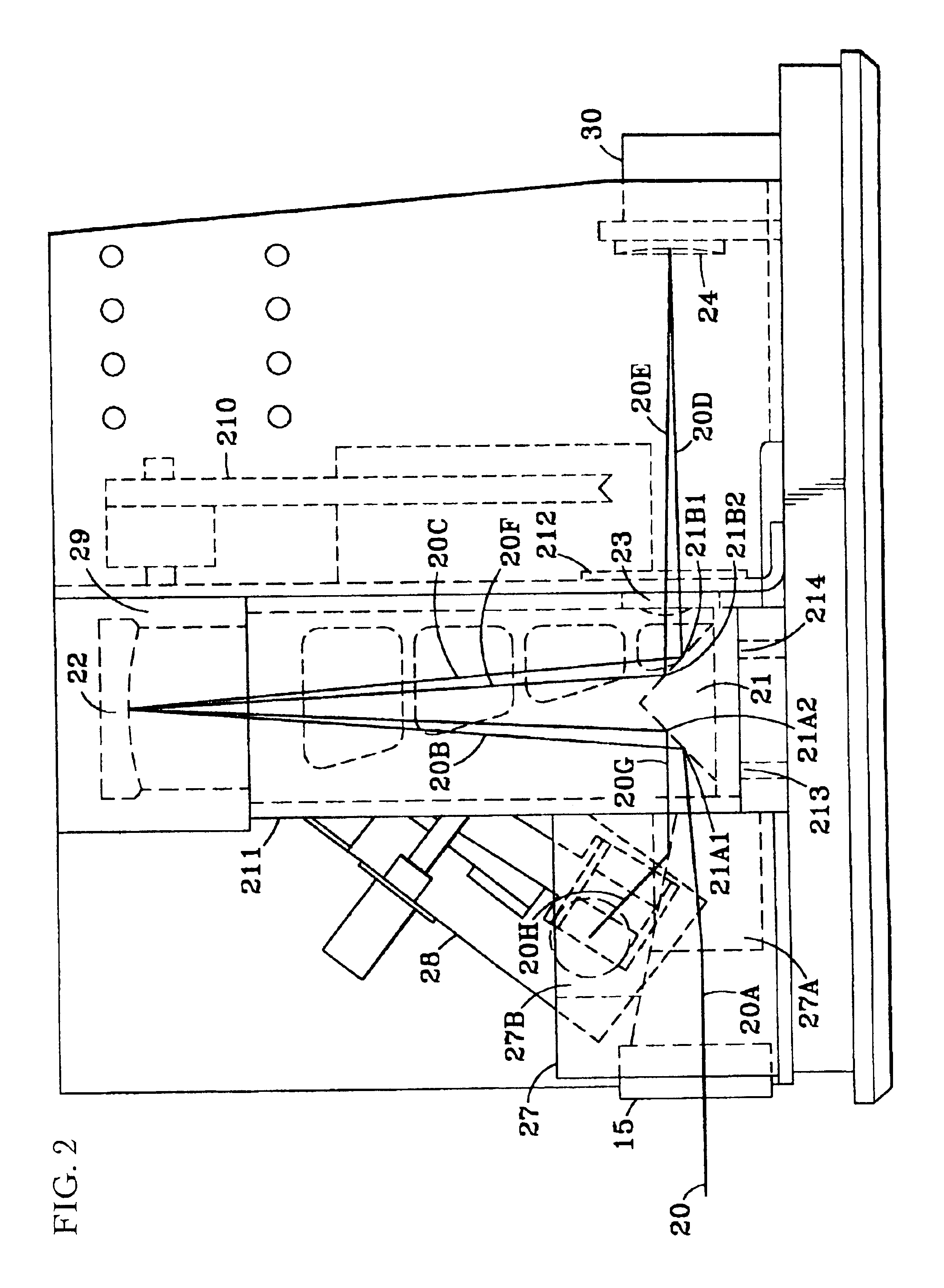
Fiber optic illumination and detection patterns, shapes, and locations for use in spectroscopic analysis
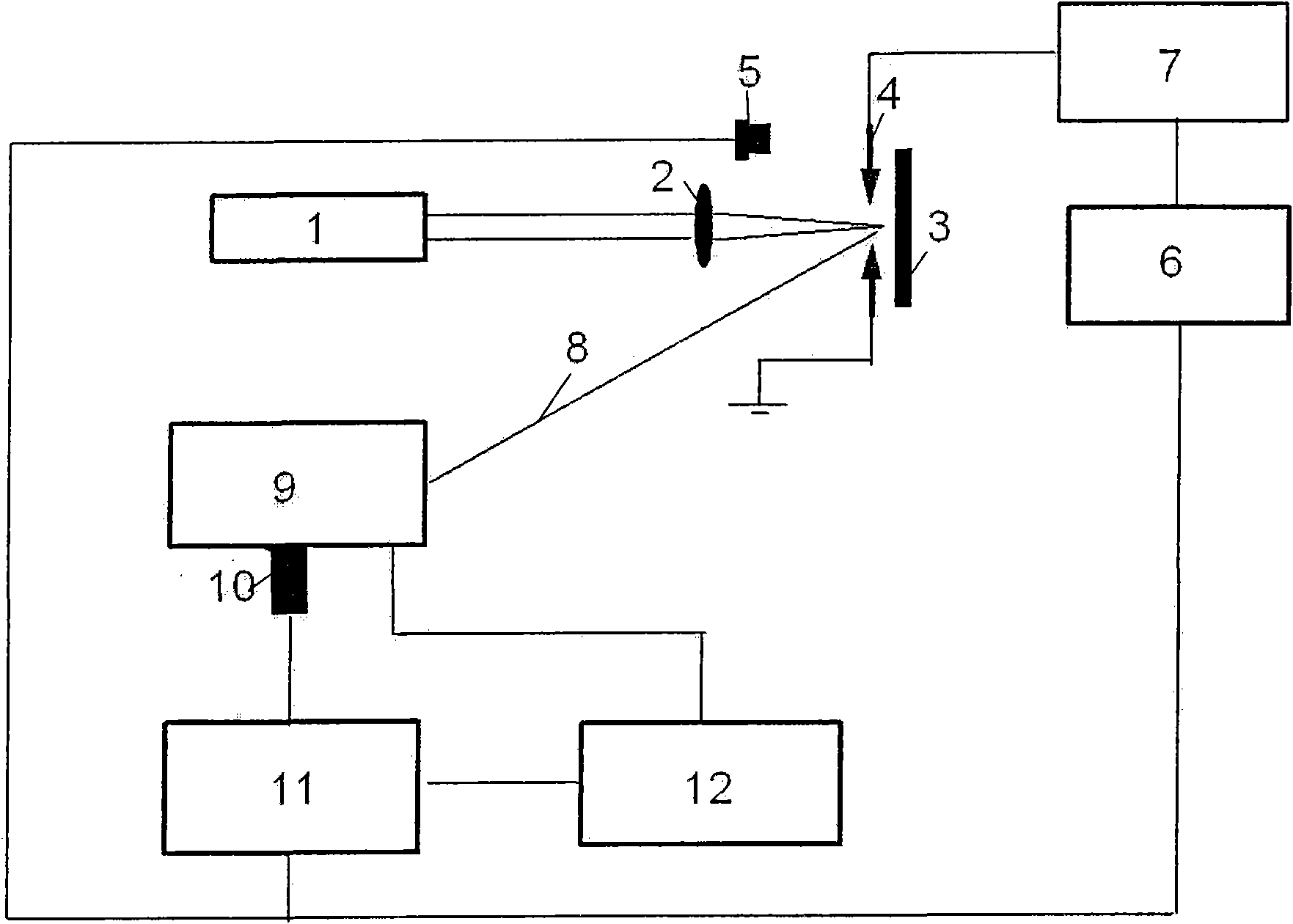
InactiveUS6411373B1Scattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberMonochromator
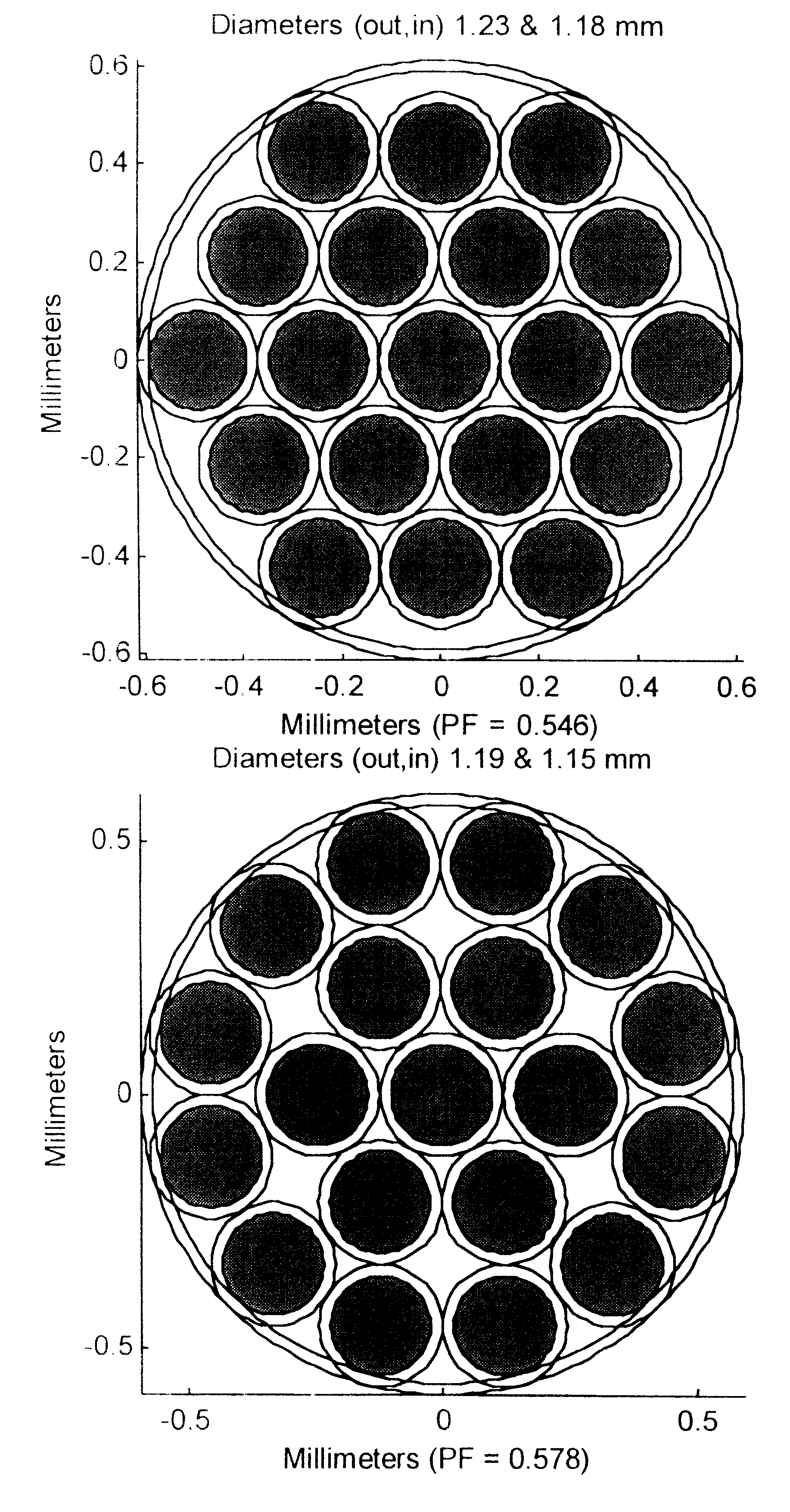
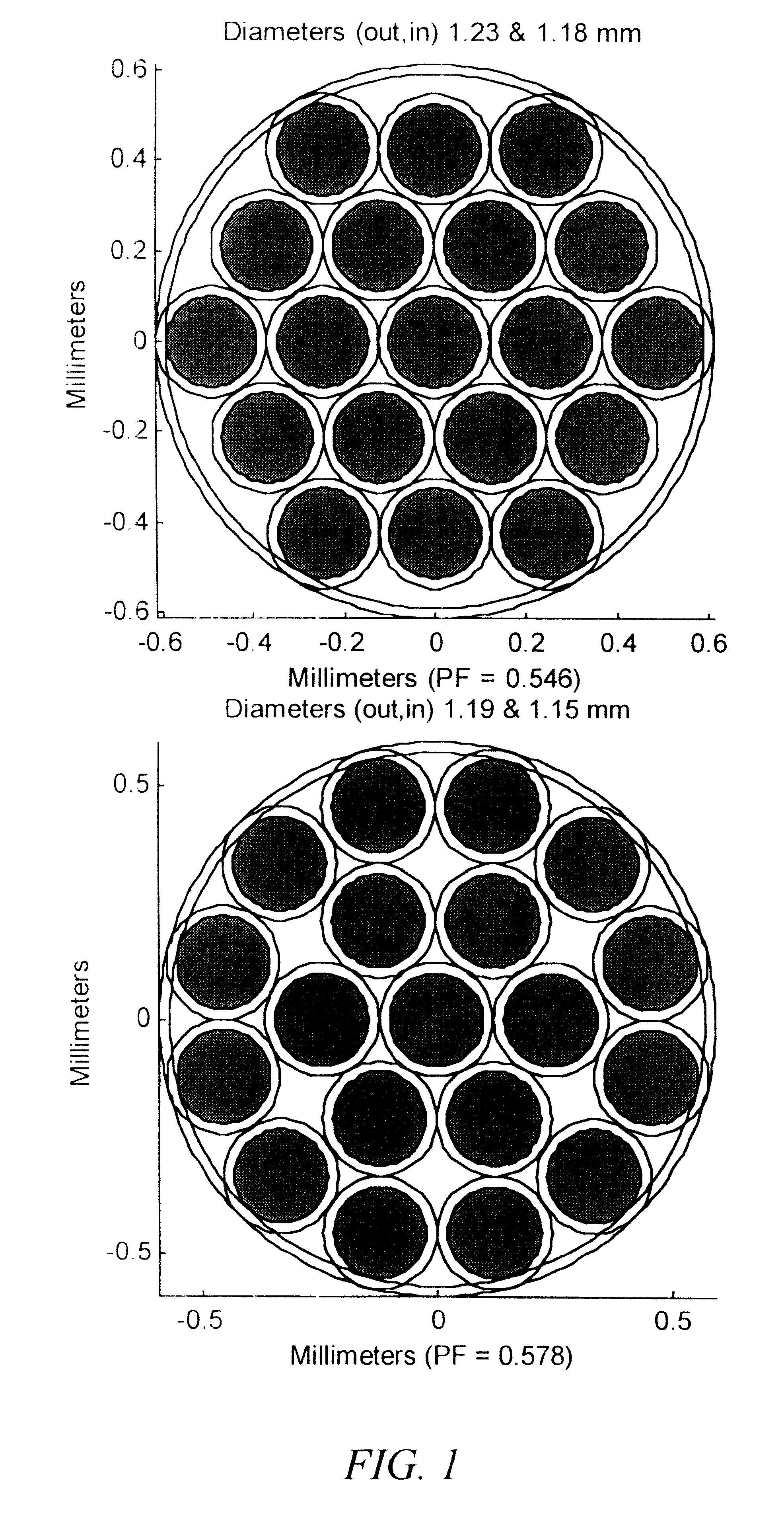
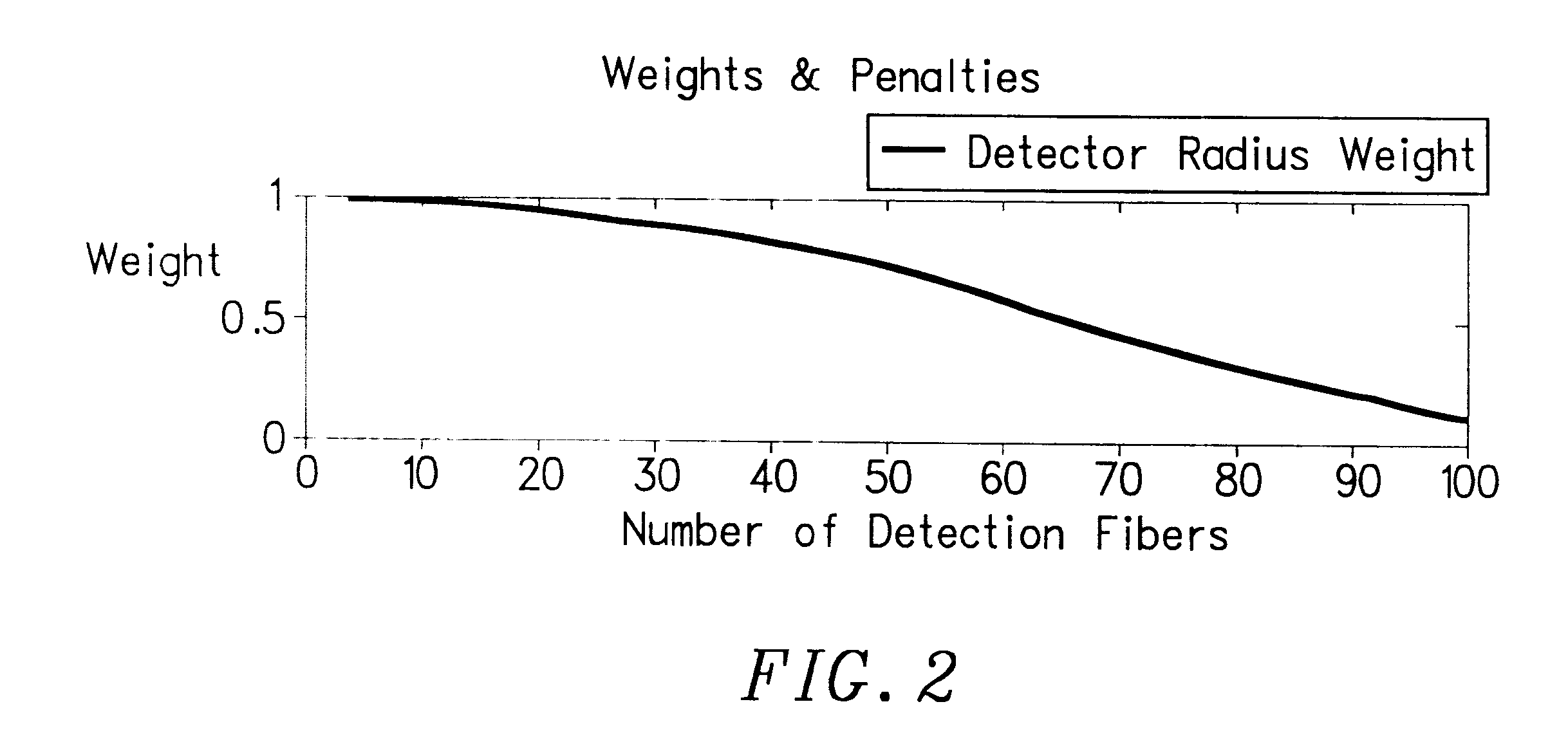
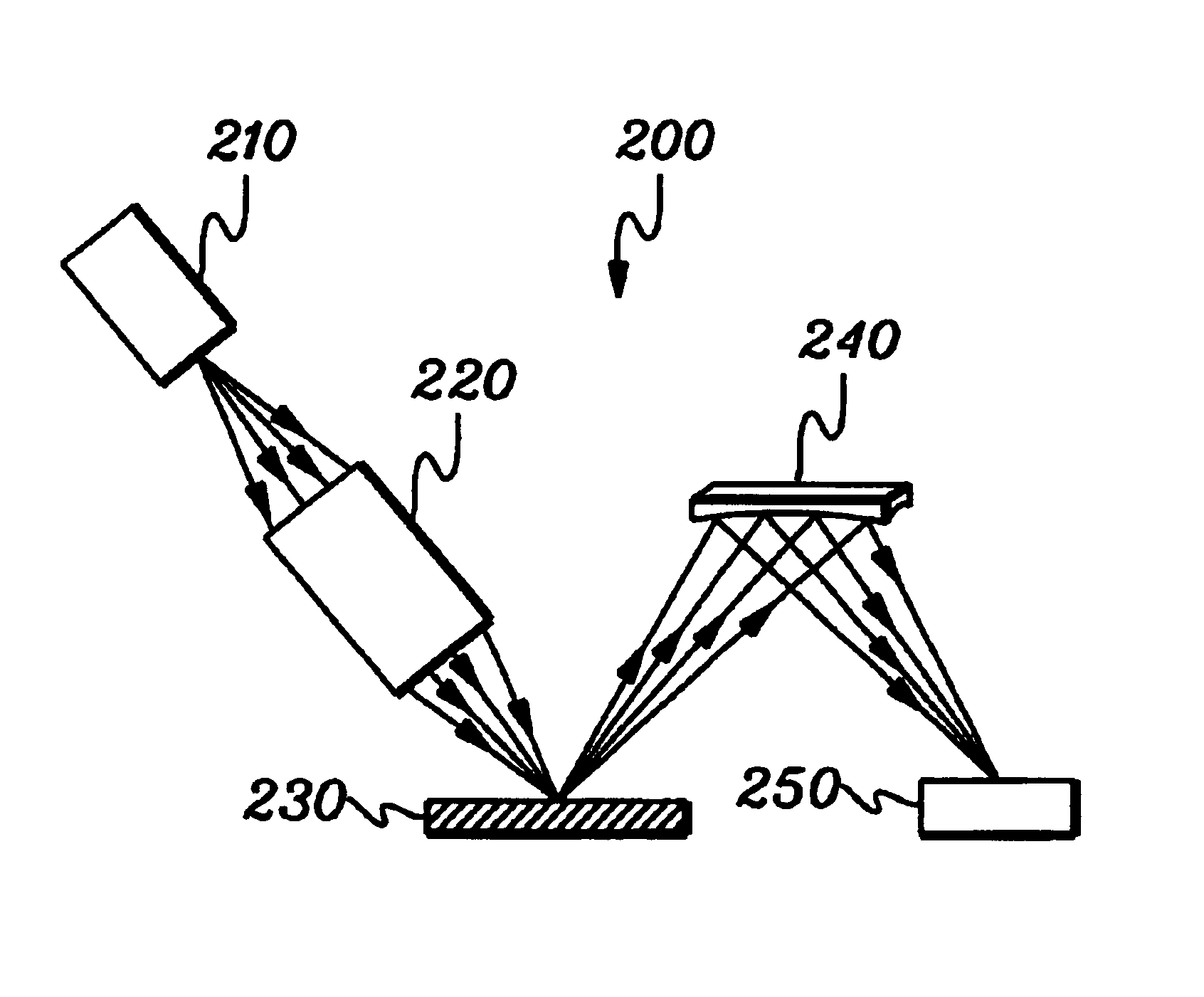
The invention provides a design process that is used in the determination of the pattern of detector and illumination optical fibers at the sampling area of a subject. Information about the system, specifically a monochromator (e.g. to determine the optimal number of fibers at an output slit) and the bundle termination at a detector optics stack (e.g. to determine the optimal number of fibers at the bundle termination), is of critical importance to this design. It is those numbers that determine the ratio and number of illumination to detection fibers, significantly limiting and constraining the solution space. Additional information about the estimated signal and noise in the skin is necessary to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio in the wavelength range of interest. Constraining the fibers to a hexagonal perimeter and prescribing a hex-packed pattern, such that alternating columns contain illumination and detection fibers, yields optimal results. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, two detectors share the totality of the detection fibers at the sampling interface. A third group of detection fibers is used for classification purposes.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Wavelength dispersive XRF system using focusing optic for excitation and a focusing monochromator for collection
InactiveUS6934359B2Overcomes shortcomingX-ray/infra-red processesX-ray spectral distribution measurementSoft x rayAnalyte
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy systems and methods are provided. One system includes a source of x-ray radiation and an excitation optic disposed between the x-ray radiation source and the sample for collecting x-ray radiation from the source and focusing the x-ray radiation to a focal point on the sample to incite at least one analyte in the sample to fluoresce. The system further includes an x-ray fluorescence detector and a collection optic comprising a doubly curved diffracting optic disposed between the sample and the x-ray fluorescence detector for collecting x-ray fluorescence from the focal point on the sample and focusing the fluorescent x-rays towards the x-ray fluorescence detector.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
Spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and elements for use therewith
InactiveUS6714298B2Good dispersionReduce dispersionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAngle of incidencePrism
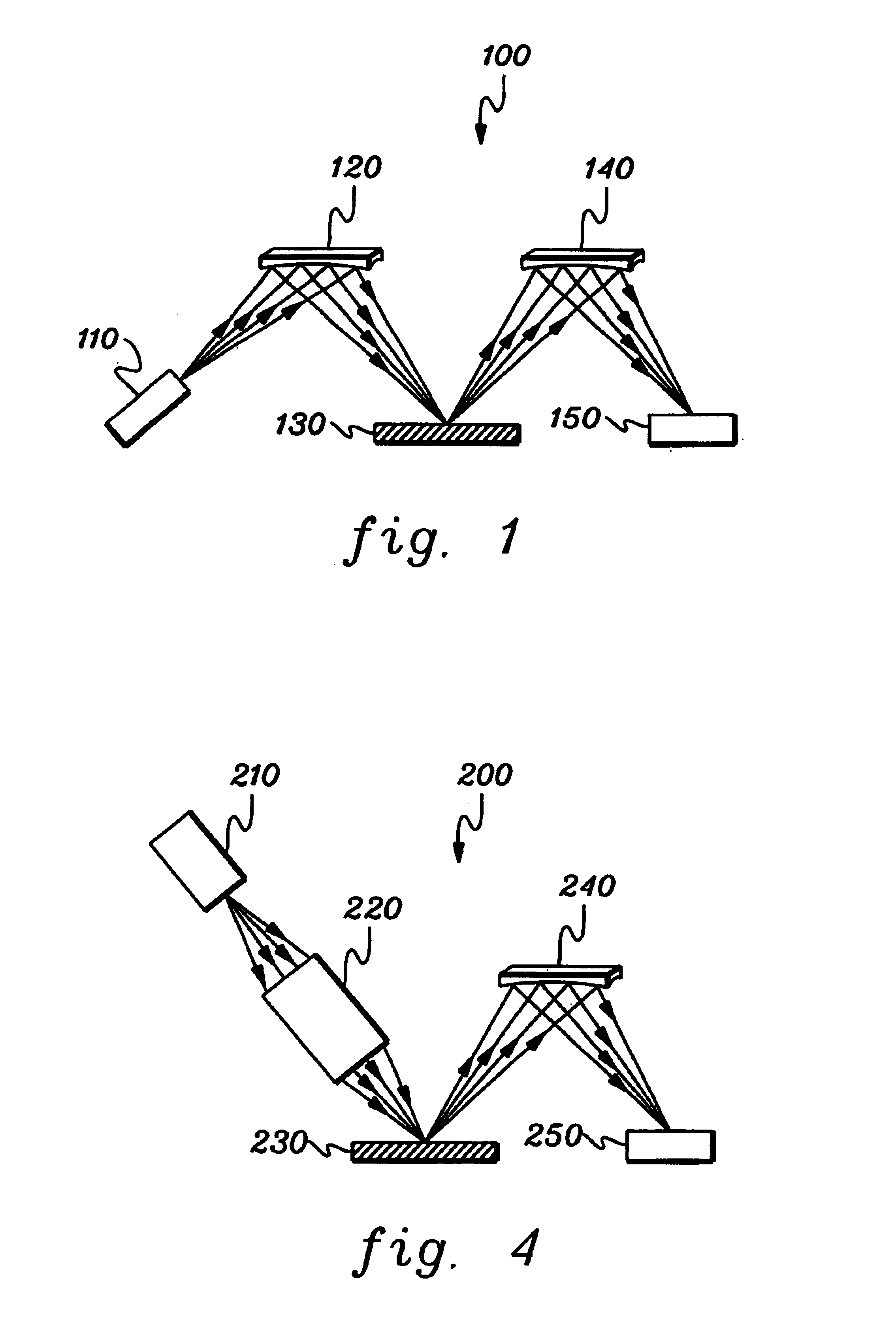
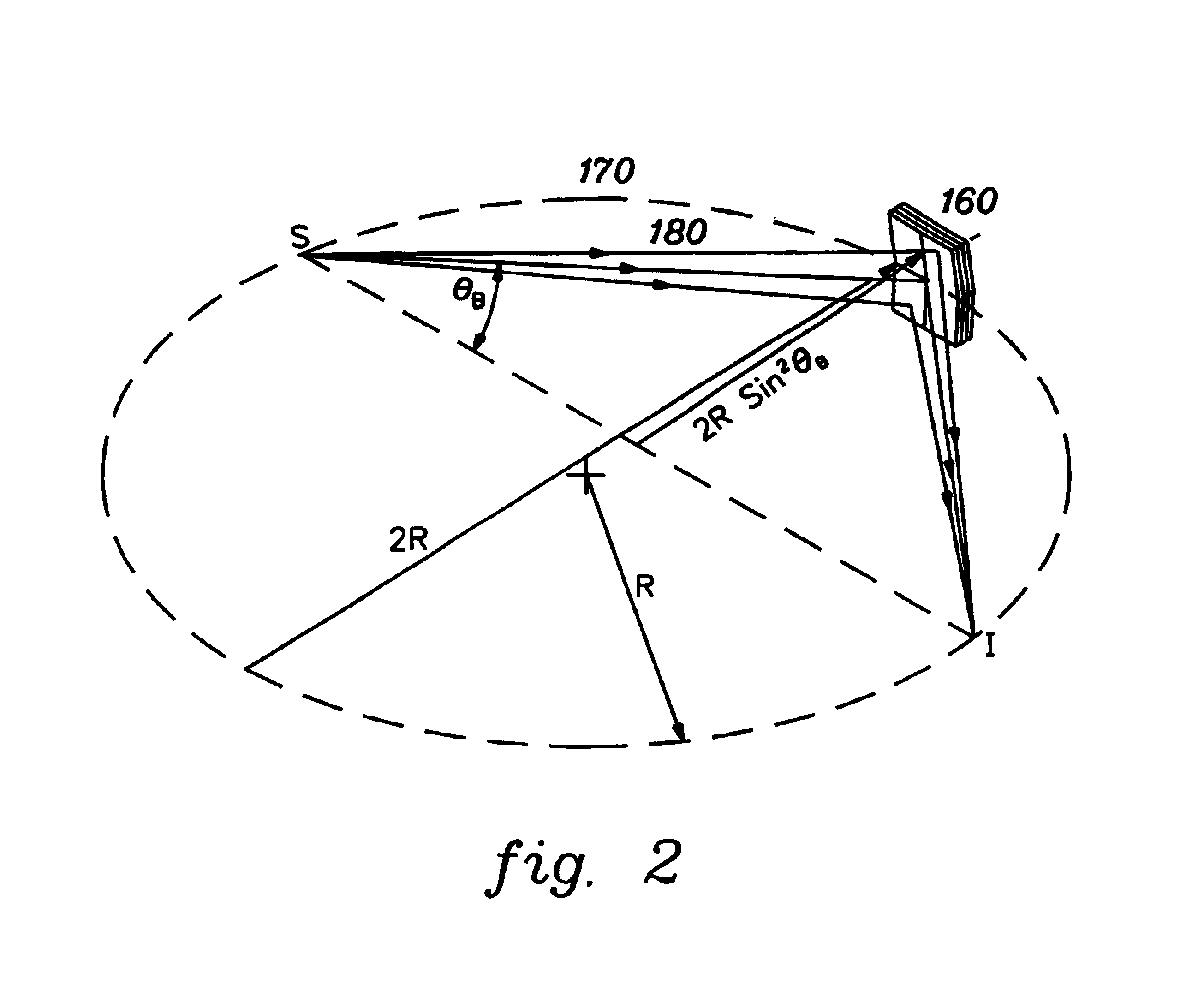
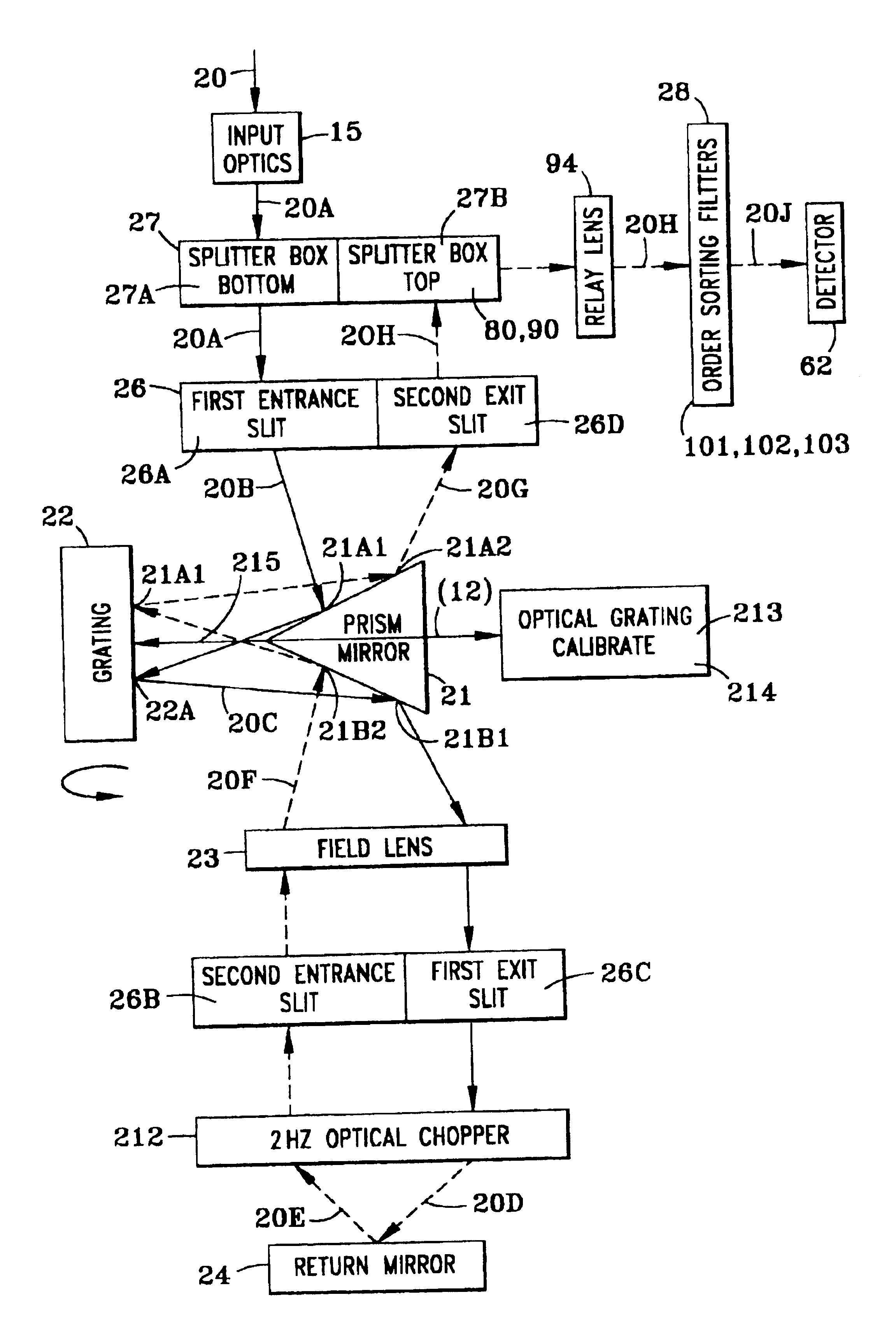
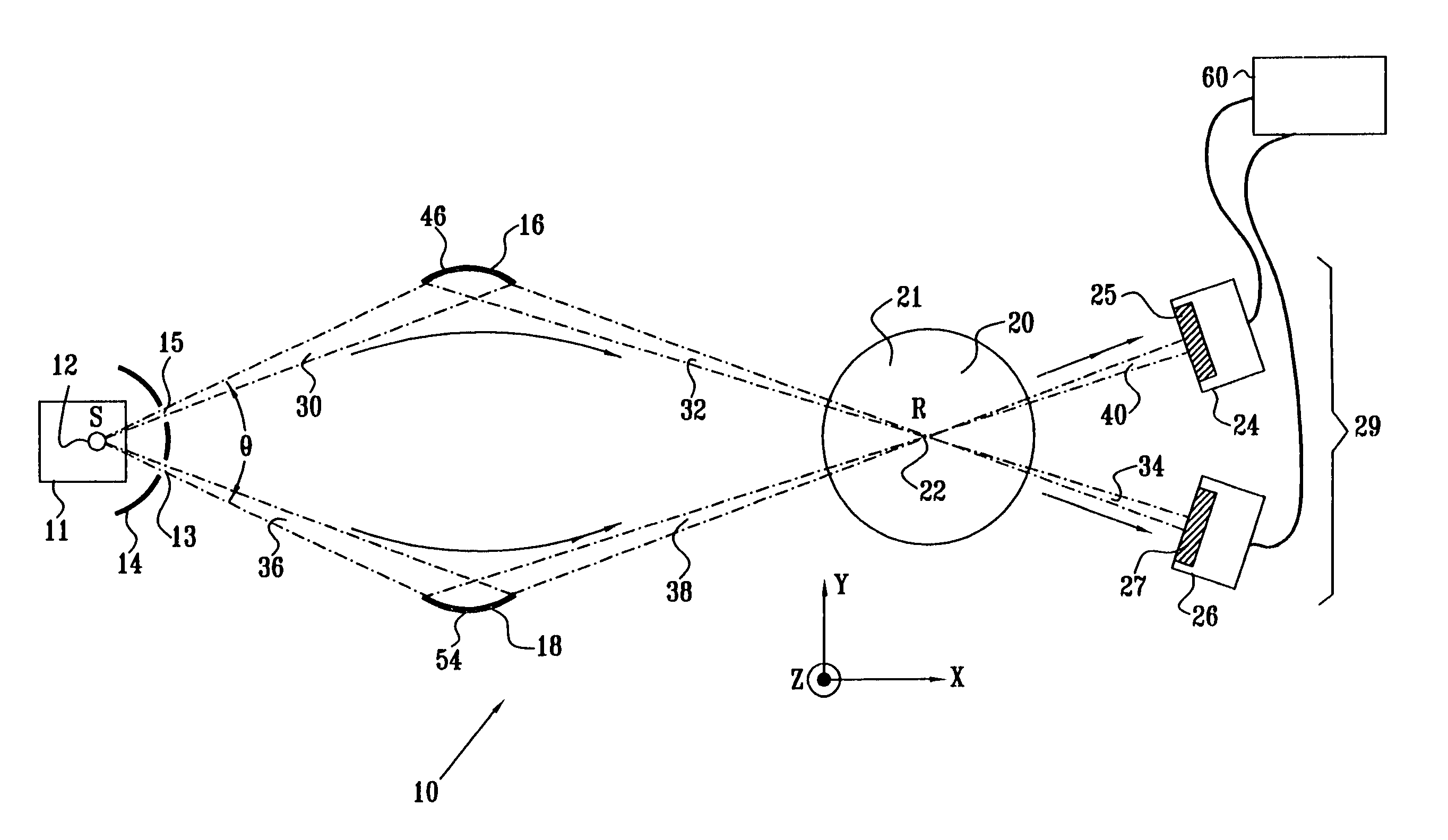
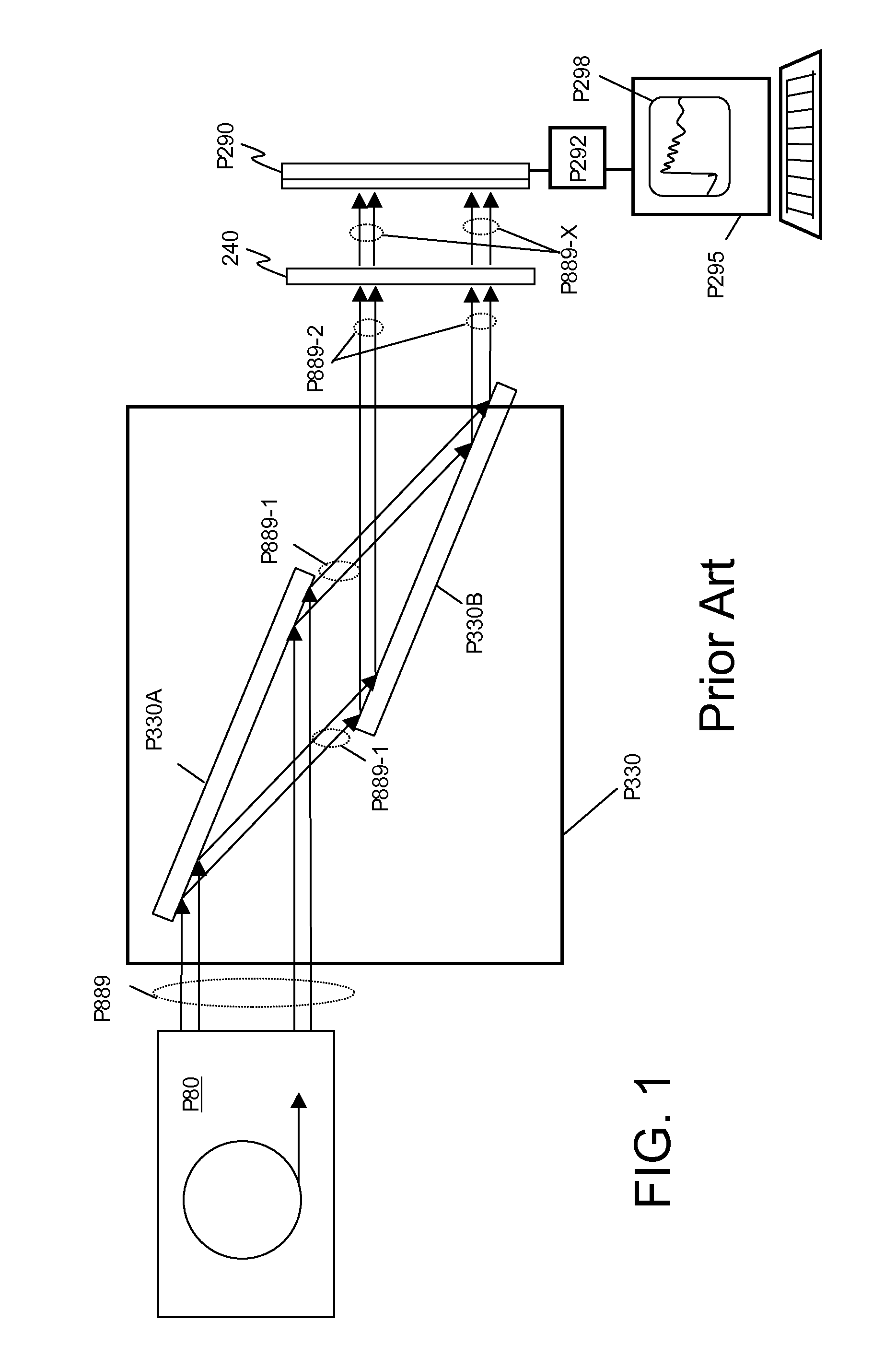
A spectrometer, or a spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and special optical elements. The special optical elements for use with the instrument are used for directing the optical beam and / or altering the form of the beam. The instrument has the potential, depending upon the totality of the optical components incorporated into the instrument, to be a monochromator, a spectroradiometer, a spectrophotometer and a spectral source. The spectral instrument may further be a part of the spectral system. The system may include the spectral instrument, a power module and means for remote control of the instrument. Such remote control may be by use of a personal computer or a control system dedicated to the control, measurement and analysis of the collected information. The multiple non-interfering beam paths are created using specially designed optical elements such as a diffraction grating, a splitter box, a zero back-lash drive system for movement of the grating element. The orientation of and a physical / spatial relationship between the field lenses, slits, return mirror, reflecting prism, turning lenses all define the multiple, preferably two paths. Particularly, there is a double pass through the grating to increase dispersion, reduce scatter while maintaining a perfect temperature independent spectral match for the second pass. Using the same grating twice reduces scatter by about a factor of 1000, increases the dispersion by a factor of two, and eliminates any temperature-related mechanical spectral drift which often is present with two separate monochromators. Because of the specially designed grating structure, the grating can cause the concurrent diffraction of a plurality of incident optical beams, each of which beams have different angles of incidence and different angles of reflection. The path of the incident and the reflected beam to and from the grating is "off-axis". That is, the beams going to and from the grating do not use the optical axis of the grating structure.
Owner:RYER DAMOND V
Transmission-based luminescent detection systems
InactiveUS20060019265A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl systemMonochromator
A luminescent detection system that employs transmission-based detection is provided for use with a chromatographic-based assay device. Unlike conventional systems, the detection system of the present invention is portable, simple to use, and inexpensive. For example, the system may be selectively controlled to reduce reliance on expensive optical components, such as monochromators or narrow emission bandwidth optical filters. In addition, the detection system is also capable of eliminating background interference from many sources, such as scattered light and autofluorescence, which have often plagued conventional fluorescent detection systems.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
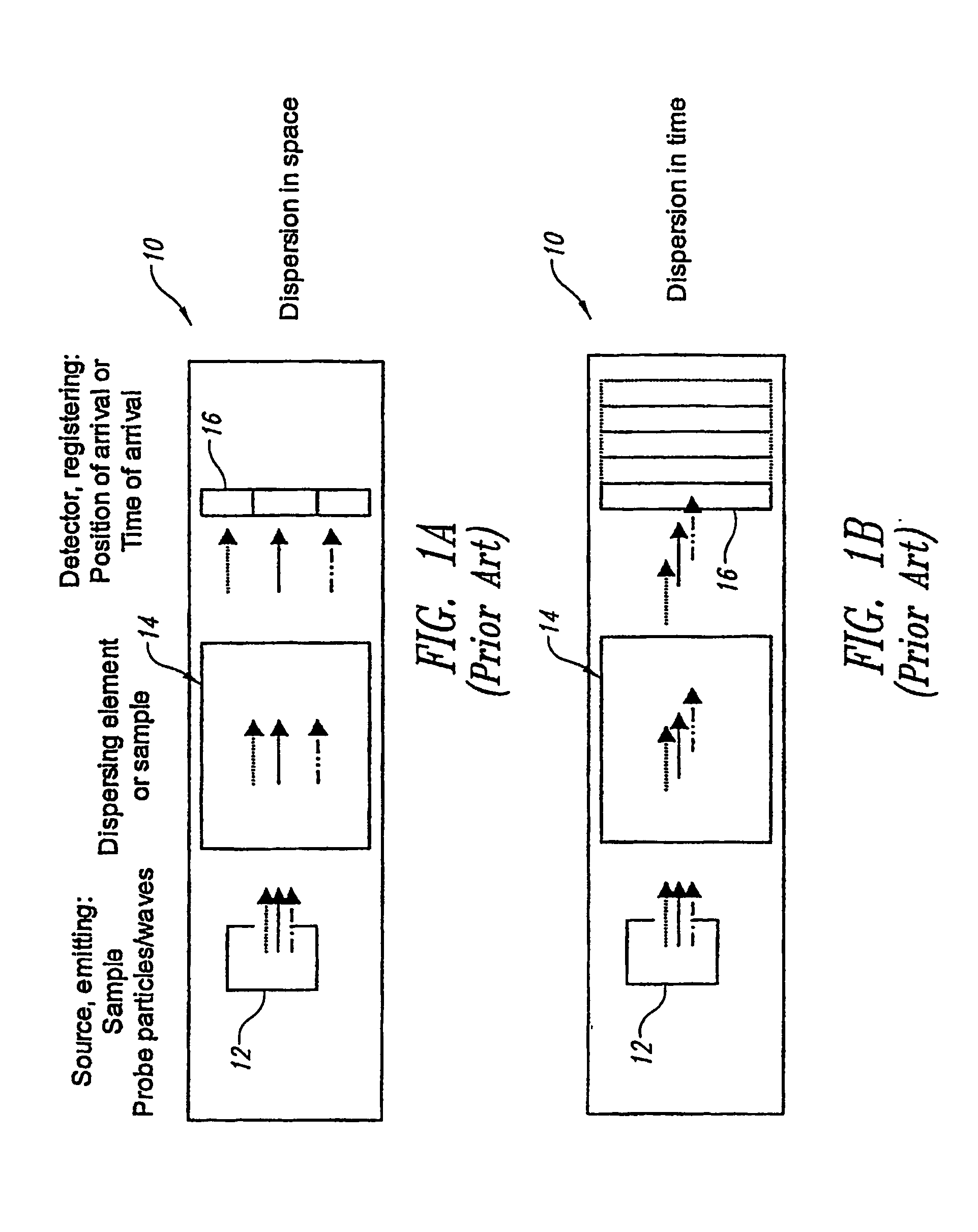
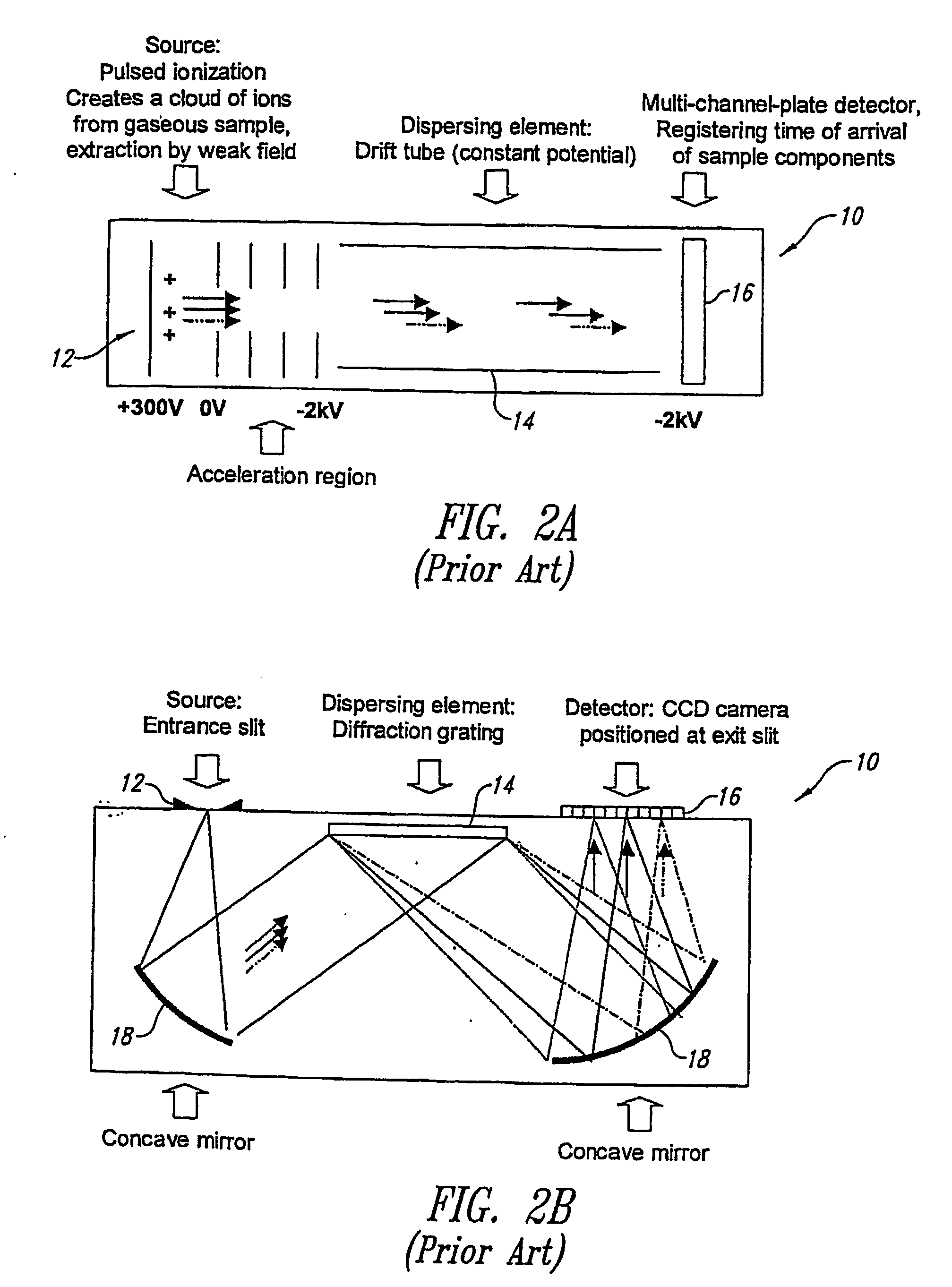
Analytical instruments using a pseudorandom array of sources, such as a micro-machined mass spectrometer or monochromator
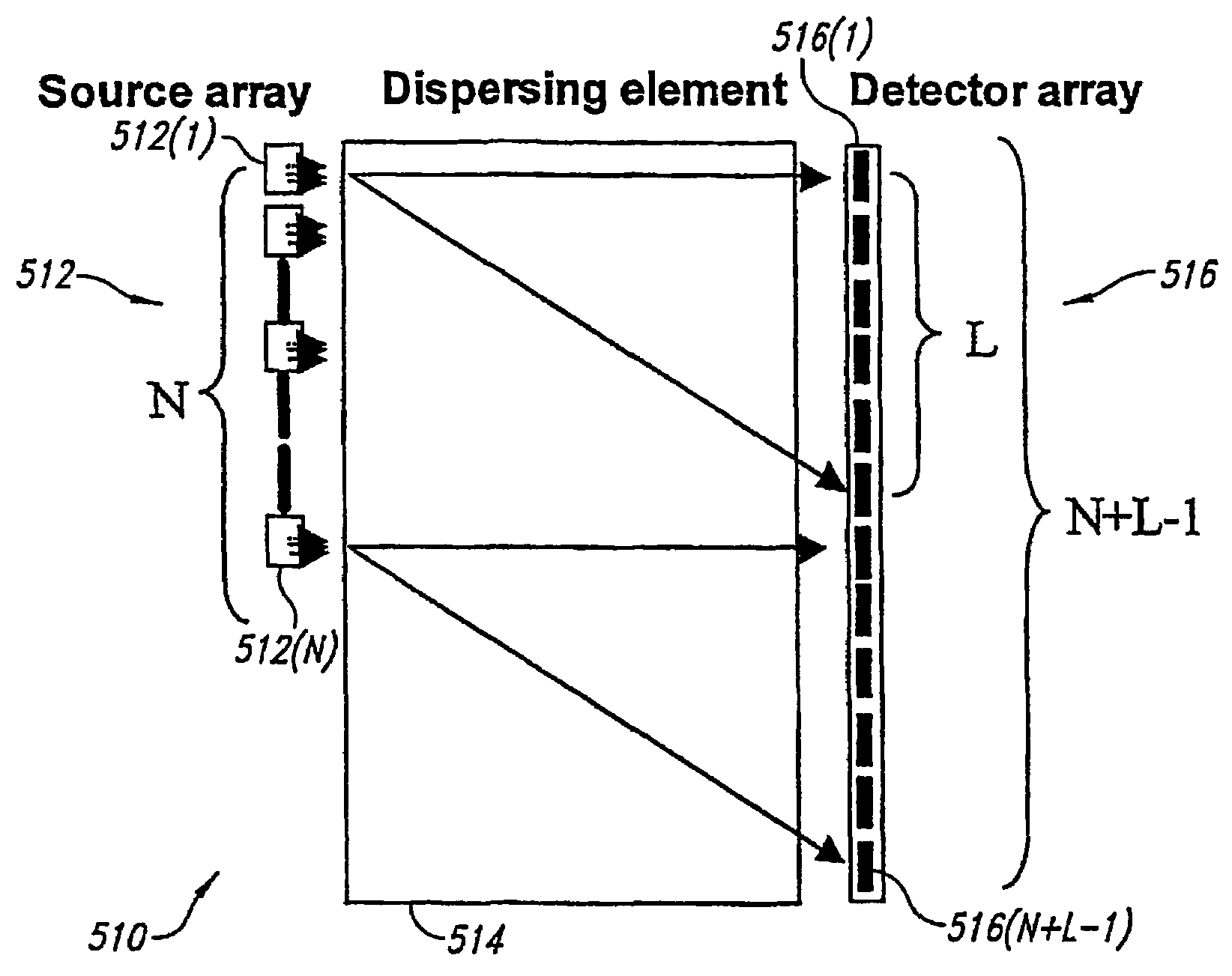
InactiveUS7339521B2Maximize signalEnhanced signalParticle separator tubesAntenna arraysSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal on
Novel methods and structures are disclosed herein which employ pseudorandom sequences to spatially arrange multiple sources in a pseudorandom source array. The pseudorandom source array can replace the single source in analytical instruments relying on spatial separation of the sample or the probe particles / waves emitted by the sources. The large number of sources in this pseudorandom source array enhances the signal on a position sensitive detector. A mathematical deconvolution process retrieves a spectrum with improved signal-to-noise ratio from the detector signal.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
X-ray apparatus with dual monochromators
ActiveUS7076024B2Increase powerConducive to accurate determinationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSoft x rayLight beam
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
High brightness X-ray absorption spectroscopy system
InactiveUS9448190B2Increase brightnessImprove thermal conductivityRadiation/particle handlingX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyDesign for X
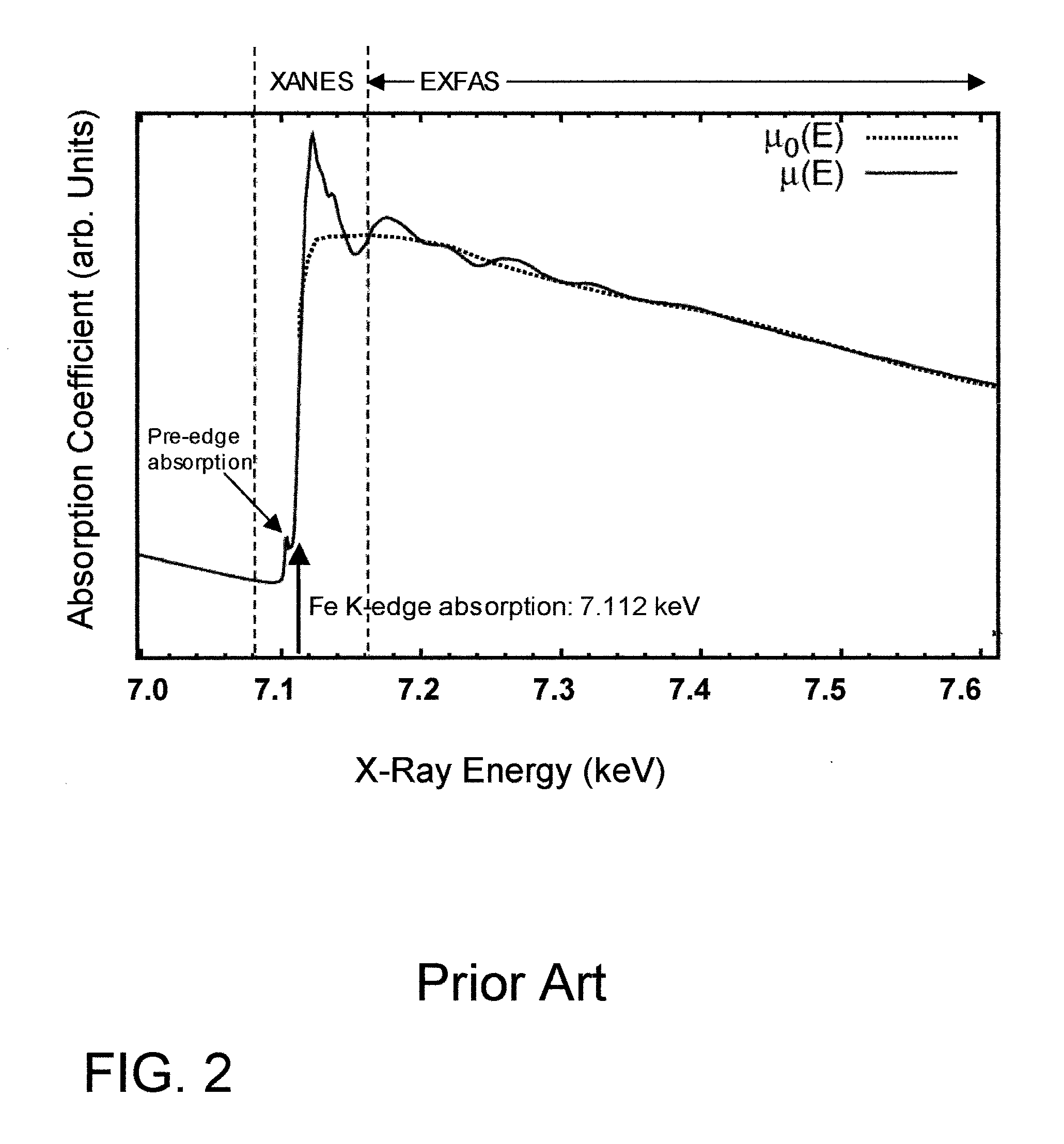
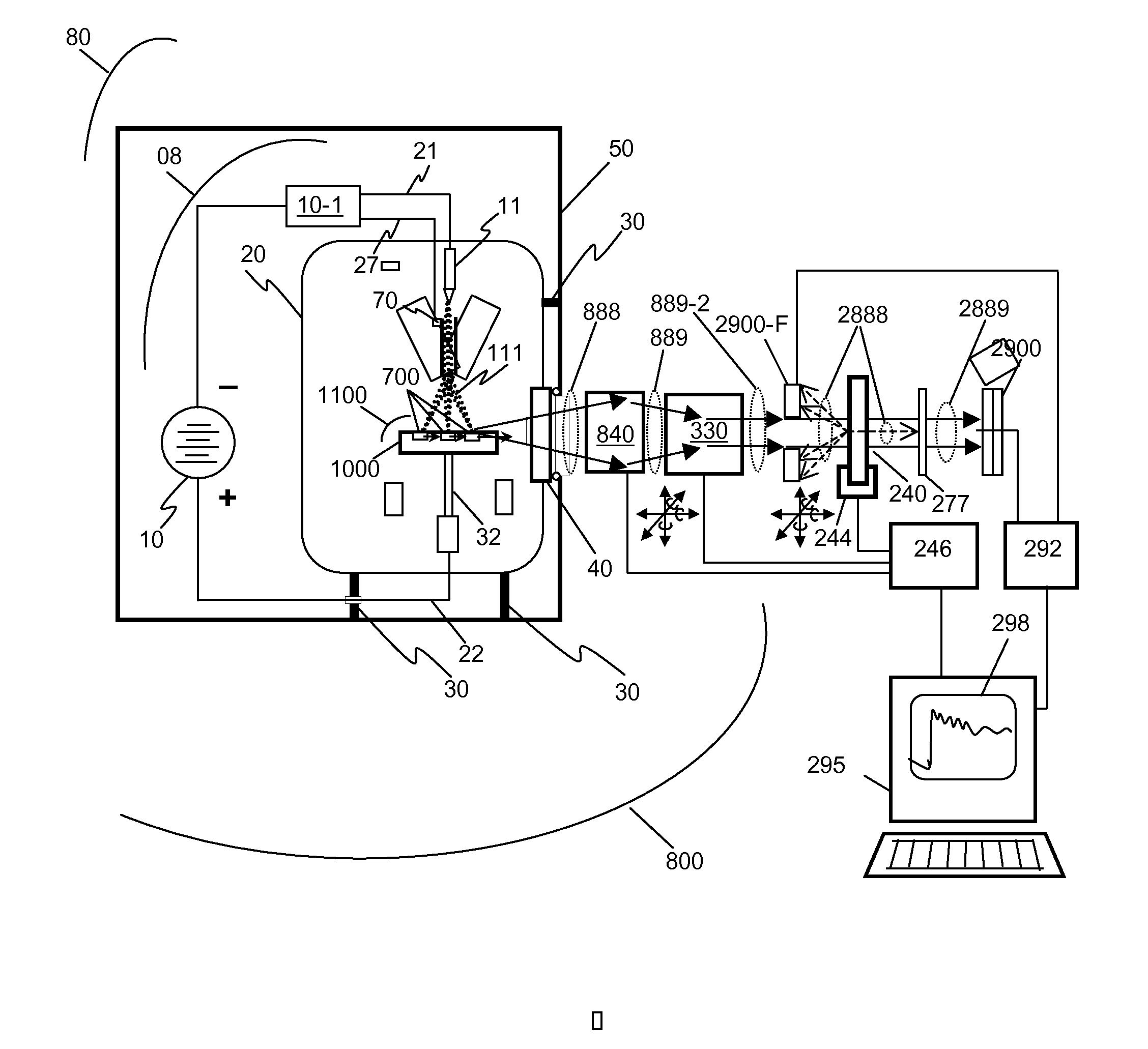
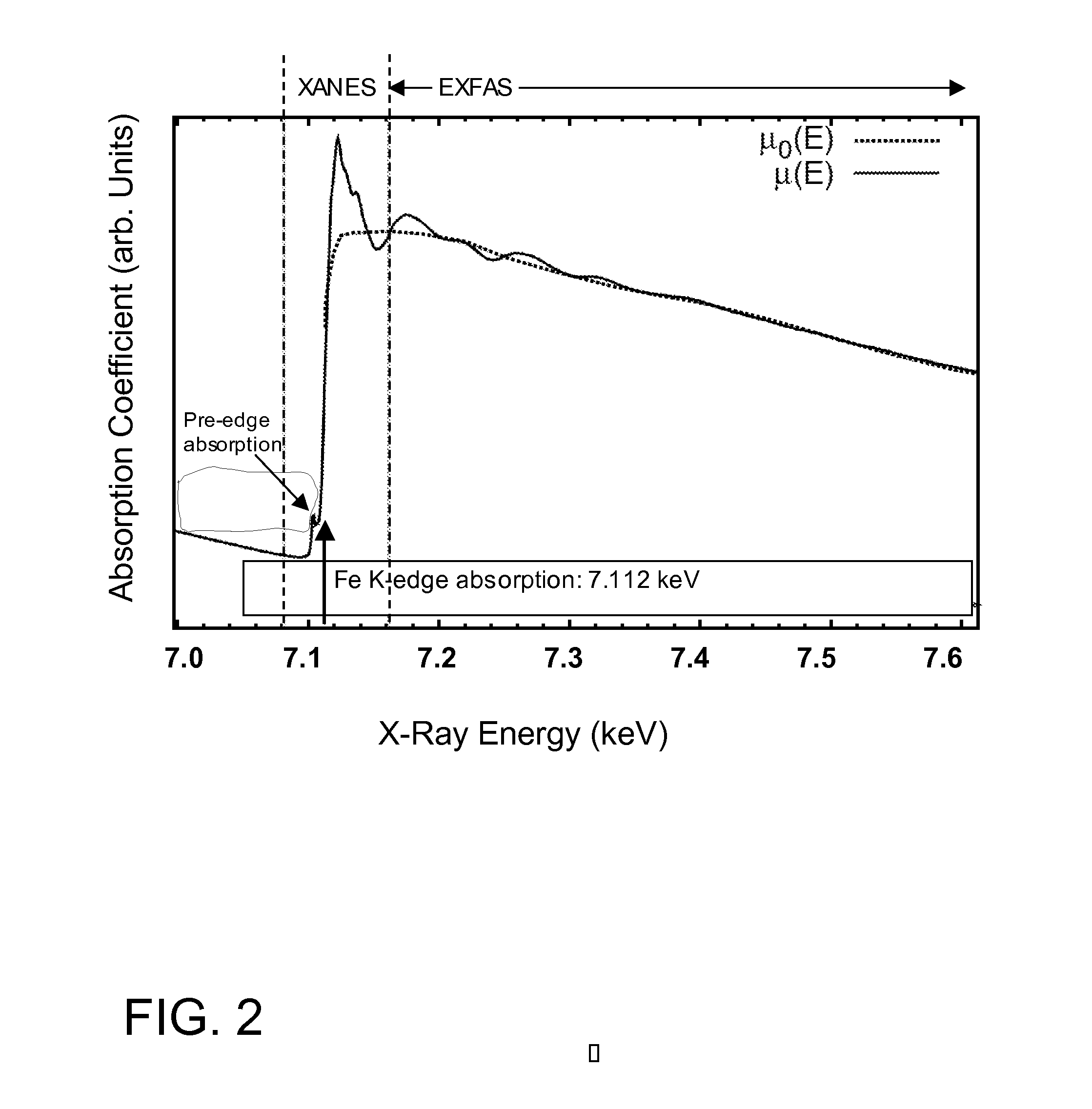
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements that have x-ray flux and flux density several orders of magnitude greater than existing compact systems. These are useful for laboratory or field applications of x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) or extended x-ray fine absorption structure (EXFAS) spectroscopy. The higher brightness is achieved by using designs for x-ray targets that comprise a number of aligned microstructures of x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment with higher electron density and / or higher energy electrons, leading to greater x-ray brightness and high flux. The high brightness x-ray source is then coupled to an x-ray reflecting optical system to collimate the x-rays, and a monochromator, which selects the exposure energy. Absorption spectra of samples using the high flux monochromatic x-rays can be made using standard detection techniques.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Two-photon, three-or four-dimensional, color radiation memory
InactiveUS6483735B1Large storageEasy to getNanoinformaticsRecording involving hole burningDetector arrayPrism
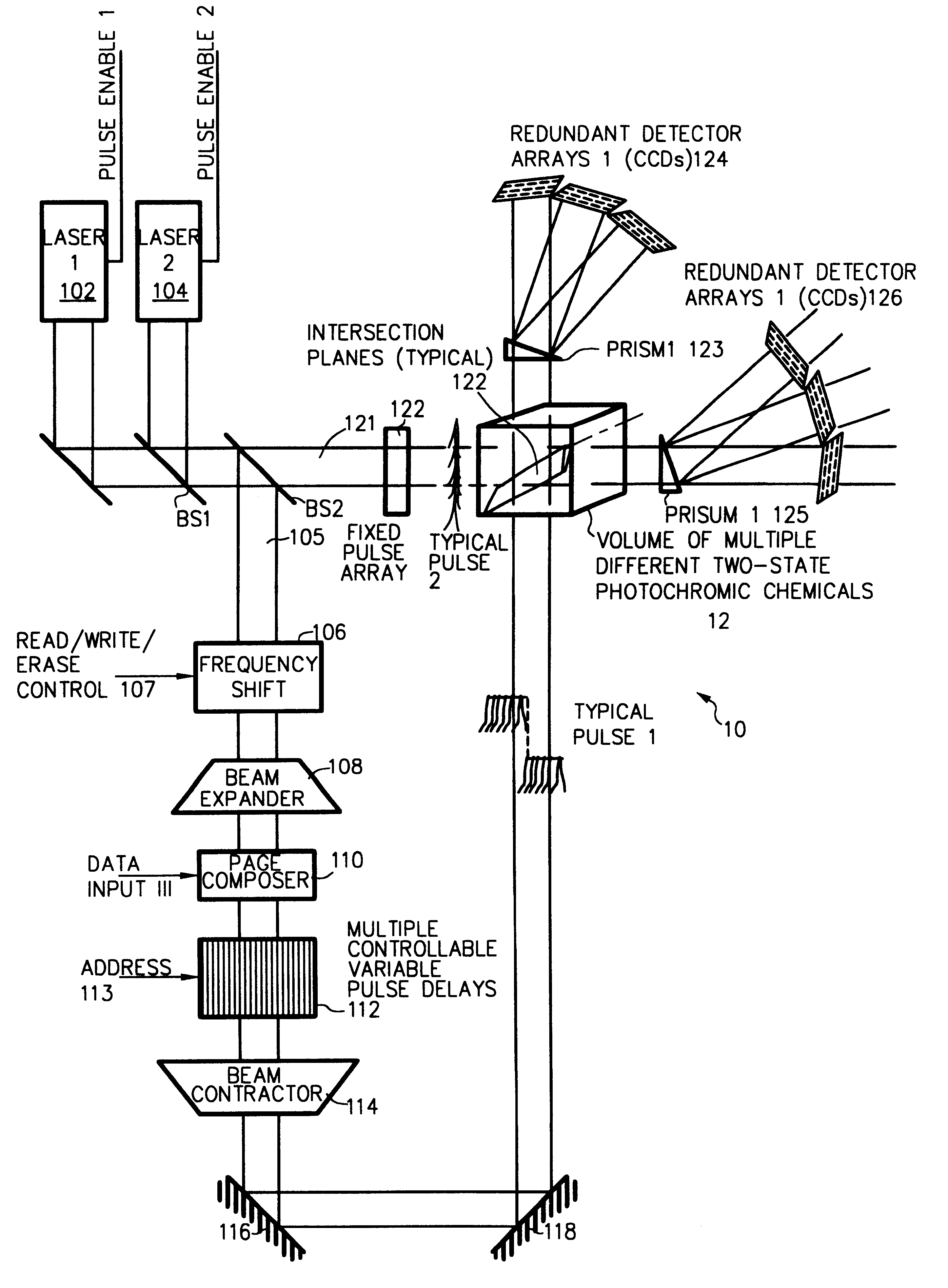
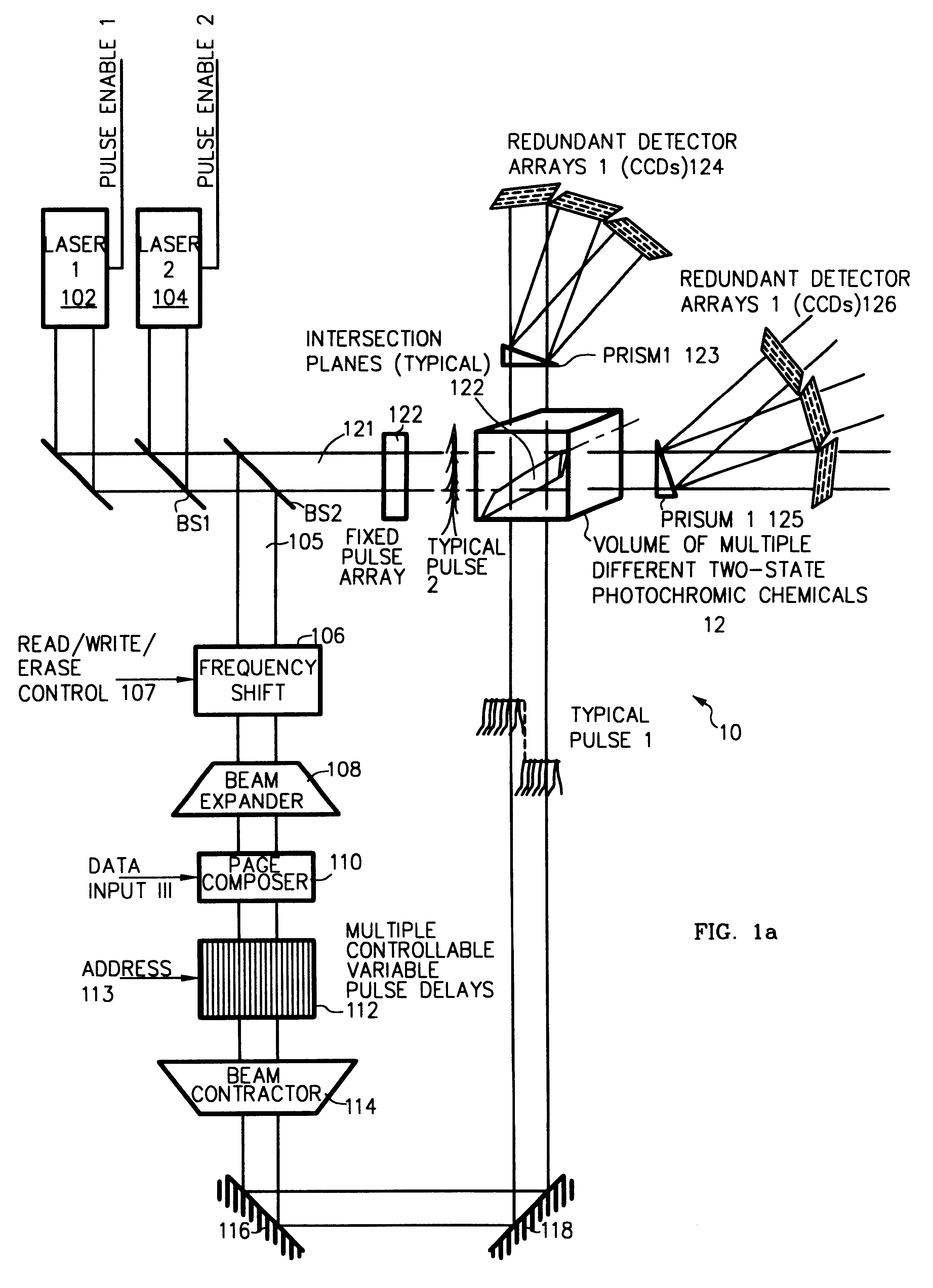
Three-, and four-dimensional ("3-D" and "4-D") volume radiation memories store multiple binary bits of information-typically about five to ten and more typically eight such bits-in the same physical volumes on several different photochromic chemicals co-located in the volume. Each of the multiple photochromic chemicals is individually selectively written with an individually associated pair of radiation beams of an appropriate combined frequency-i.e., a "color"-and energy by a process of two-photon ("2-P") absorption. All the multiple information bits that are stored within all the photochromic chemicals in each addressable domain are read in common, and induced to simultaneously fluoresce, again by process of 2-P absorption. The fluorescence of each of different photochromic chemical in each addressed domain-which fluorescence is selective in accordance with the written state of each such photochromic chemical-is separated from, and is separately detected from, the fluorescence of all other photochromic chemicals because it is of a unique color, and is spatially steered to an associated detector array, normally a Charge Coupled Device (CCD), by a monochromator, normally a prism. Exemplary fluorescent photochromic chemicals are spirobenzopyran, rhodamine, cumarin and anthracene. Suitable groups of photochromic chemicals are formed from individual photochromic chemicals exhibiting narrow, sharp, separate spectra of absorption and of emission suitably distinct from each other, and where no chemical's fluorescent emission energy overlaps the absorption energies of any other chemicals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High brightness x-ray absorption spectroscopy system
InactiveUS20150357069A1Increase brightnessImprove thermal conductivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementHigh energyDesign for X
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements that have x-ray flux and flux density several orders of magnitude greater than existing compact systems. These are useful for laboratory or field applications of x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) or extended x-ray fine absorption structure (EXFAS) spectroscopy.The higher brightness is achieved by using designs for x-ray targets that comprise a number of aligned microstructures of x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment with higher electron density and / or higher energy electrons, leading to greater x-ray brightness and high flux.The high brightness x-ray source is then coupled to an x-ray reflecting optical system to collimate the x-rays, and a monochromator, which selects the exposure energy. Absorption spectra of samples using the high flux monochromatic x-rays can be made using standard detection techniques.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Spectrometer and method for correcting the same
InactiveCN101354287AImprove performanceGood response linearityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicrocontrollerSignal processing circuits
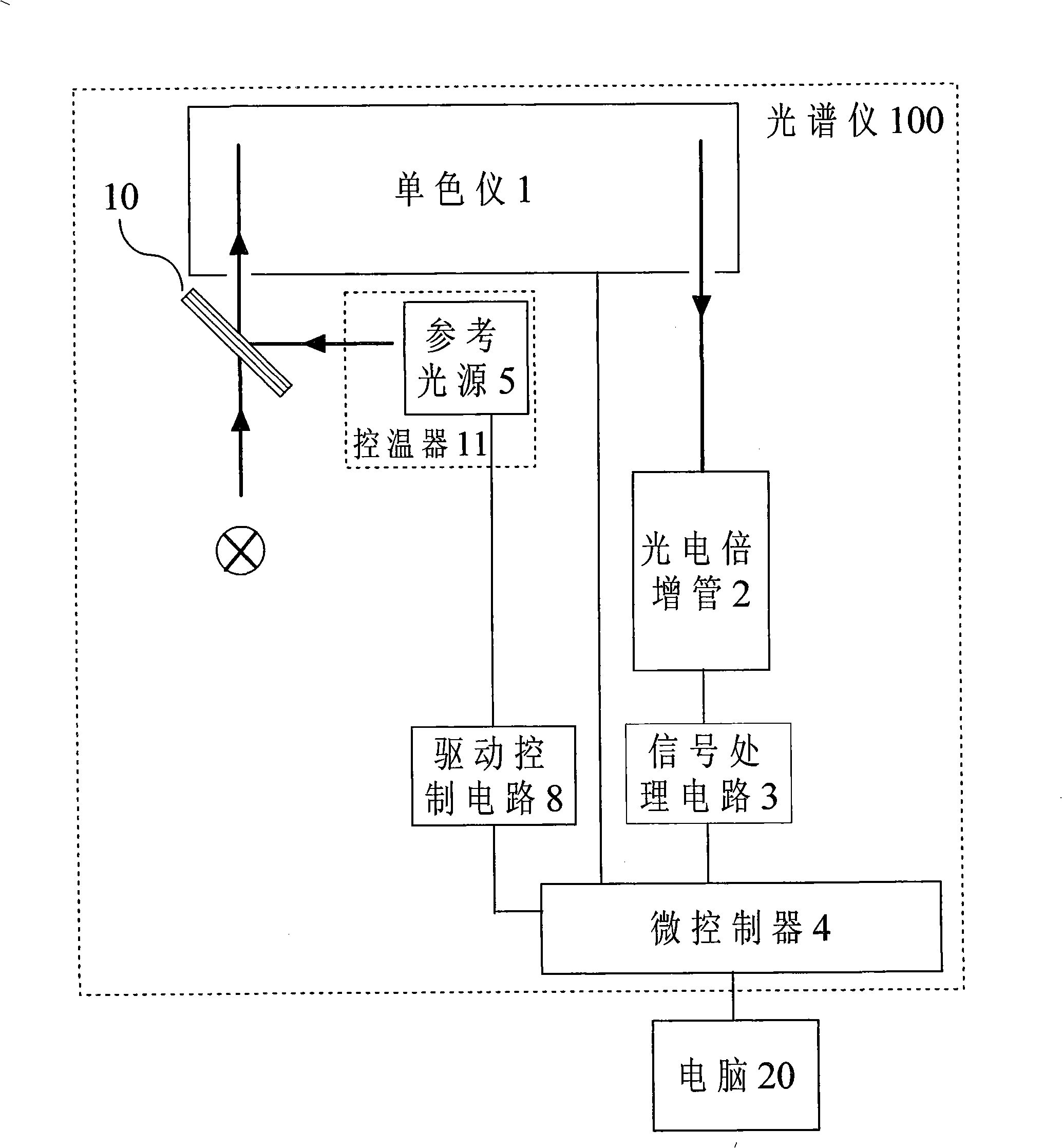
The invention relates to an optical spectrometer and a calibration method thereof. The optical spectrometer comprises a monochromator used for dividing the measured light into monochromatic lights, a photomultiplier used for receiving the monochromatic lights; the monochromator and the photomultiplier are optically connected. The photomultiplier is electrically connected with a microcontroller by a signal processing circuit. The optical spectrometer is characterized by further comprising a reference light source used for creating reference light; the reference light source which is alight-emitting diode is connected with the micro-controller. Compared with the prior art, the optical spectrometer and the calibration method thereof have the advantages as follows: 1. reasonable design, simple structure and large measuring dynamic range are ensured; 2. the absolute sensitivity of the photomultiplier is reasonably calibrated, therefore, the response linearity of the optical spectrometer is good; 3. thermostatic control is carried out to a reference detector, the reference light source and the photomultiplier, thus effectively enhancing the work stability of the optical spectrometer; and 4. the performance of the optical spectrometer is substantially enhanced under the condition that a small amount of cost is increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU EVERFINE PHOTO E INFO
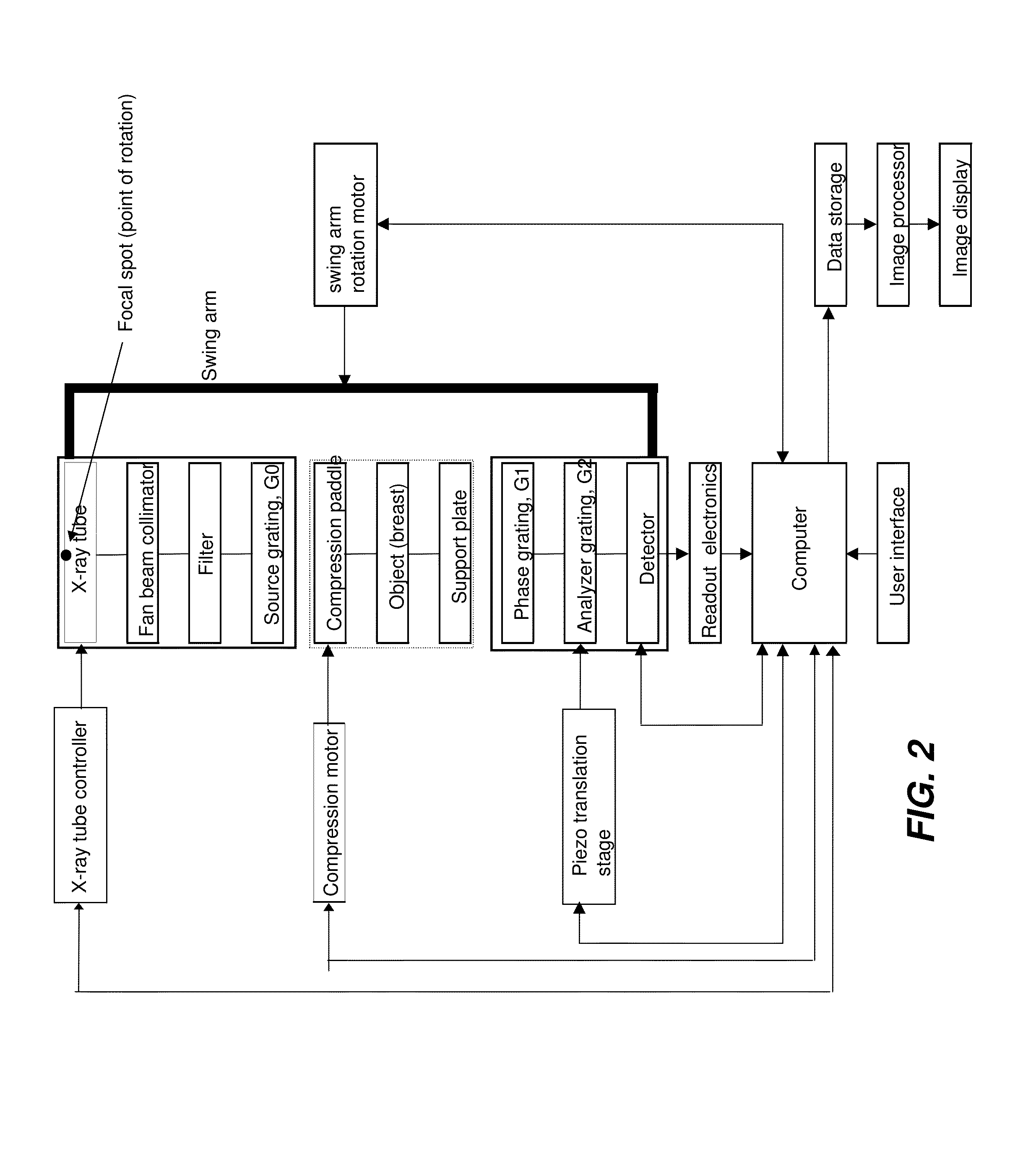
Hybrid slot-scanning grating-based differential phase contrast imaging system for medical radiographic imaging
InactiveUS20130259194A1Imaging devicesPatient positioning for diagnosticsDigital mammographyBeam shaping
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital mammography system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly including a filter or a tunable monochromator, a collimator, a source grating, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating, and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector; where the source grating, the phase grating, and the analyzer grating are aligned in such a way that the grating bars of these gratings are parallel to each other.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
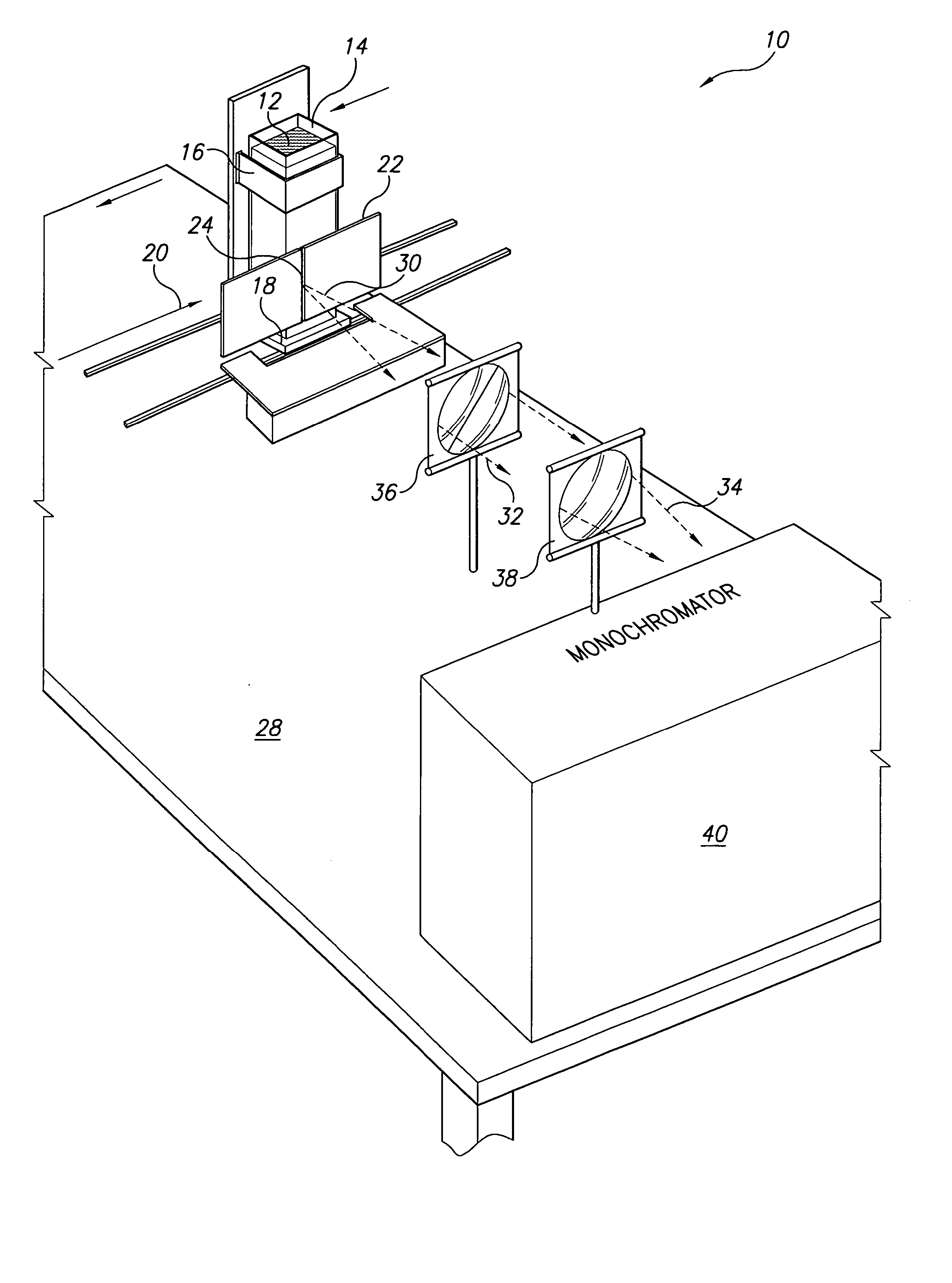
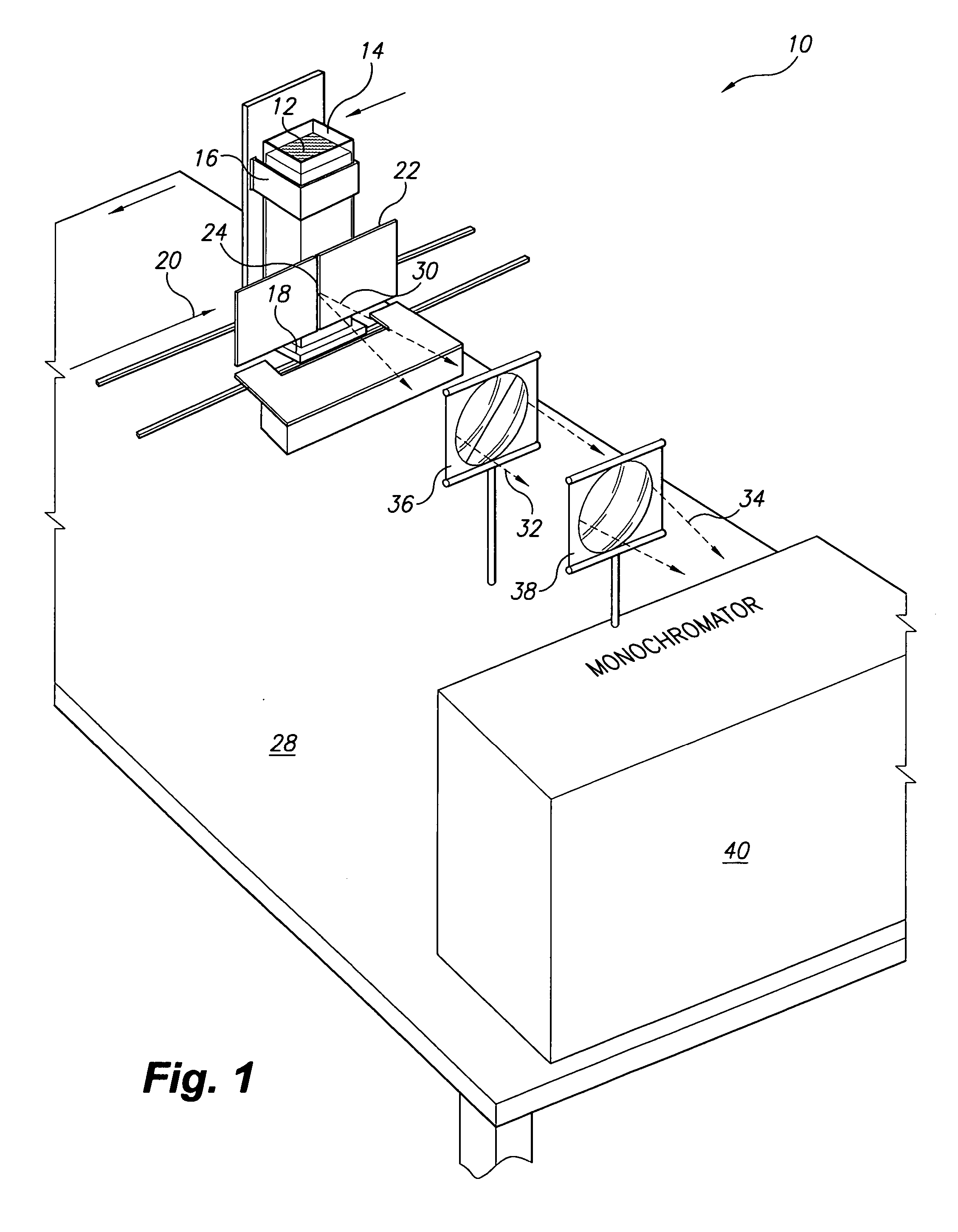
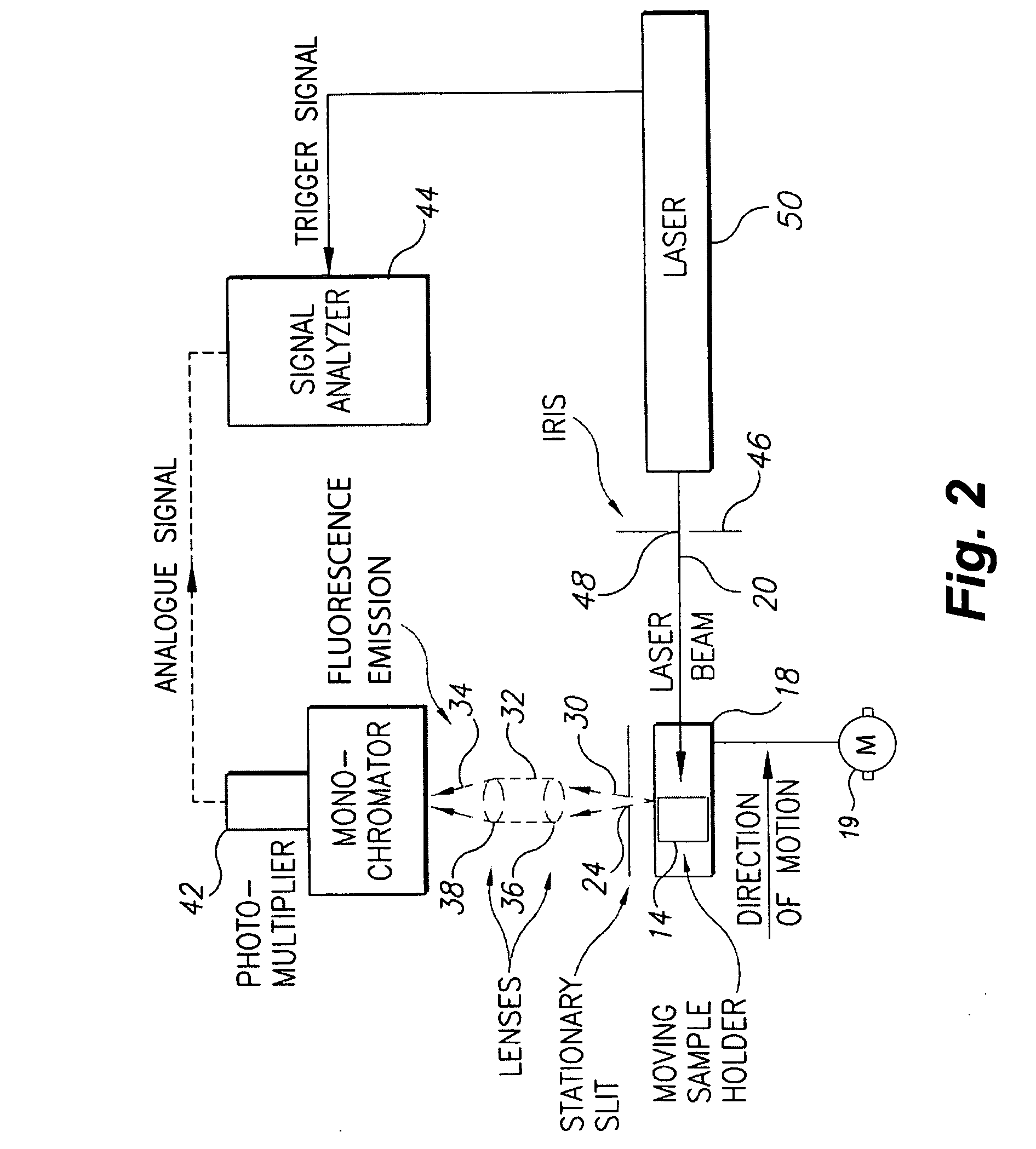
Apparatus and method for measuring concentrations of fuel mixtures using depth-resolved laser-induced fluorescence
InactiveUS20070237679A1Readily apparentSpectrum investigationChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEmission spectrumLaser-induced fluorescence
The apparatus for measuring concentrations of fuel mixtures using depth-resolved laser-induced fluorescence is a fluorometer equipped with a sample container holder that is movable in the path of the beam from the light source. Fluorescent emissions from the sample mixture pass at 90° to the excitation light path through a slit that is narrow enough that the emission intensity is effectively produced by a thin layer of the sample and focused on a monochromator, with successive thin layers receiving nonuniform excitation radiation due to reduction of intensity along the excitation light source path with increasing depth penetration and due to reabsorption of emitted fluorescence from adjacent layers. The method has a first mode in which the emission spectrum is scanned at a fixed depth, and a second mode in which the sample is moved relative to the emission monochromator slit to vary the depth while keeping the emission wavelength fixed.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
X-ray beam device
ActiveUS8422633B2Improve throughputIncreased collecting angleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayCatoptrics
The invention refers to an X-ray beam device for X-ray analytical applications, comprising an X-ray source designed such as to emit a divergent beam of X-rays; and an optical assembly designed such as to focus said beam onto a focal spot, wherein said optical assembly comprises a first reflecting optical element, a monochromator device and a second reflecting optical element sequentially arranged between said source and said focal spot, wherein said first optical element is designed such as to collimate said beam in two dimensions towards said monochromator device, and wherein said second optical element is designed such as to focus the beam coming from said monochromator device in two dimensions onto said focal spot.
Owner:XENOCS
Analytical instruments using a pseudorandom array of sources, such as a micro-machined mass spectrometer or monochromator
InactiveUS20050119868A1Maximize signalImprove signal-to-noise ratioAntenna arraysParticle separator tubesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal on
Novel methods and structures are disclosed herein which employ pseudorandom sequences to spatially arrange multiple sources in a pseudorandom source array. The pseudorandom source array can replace the single source in analytical instruments relying on spatial separation of the sample or the probe particles / waves emitted by the sources. The large number of sources in this pseudorandom source array enhances the signal on a position sensitive detector. A mathematical deconvolution process retrieves a spectrum with improved signal-to-noise ratio from the detector signal.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
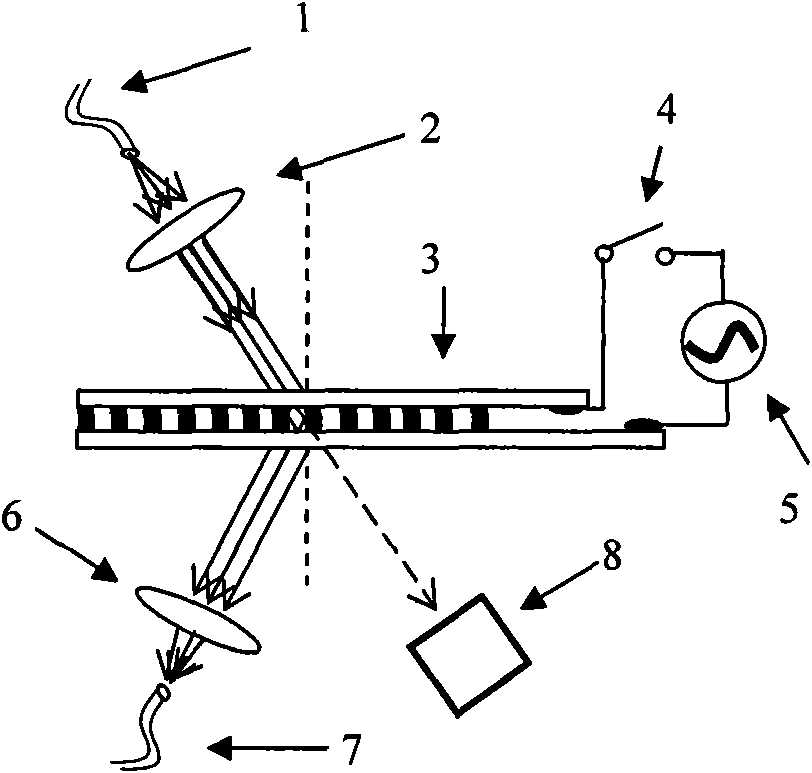
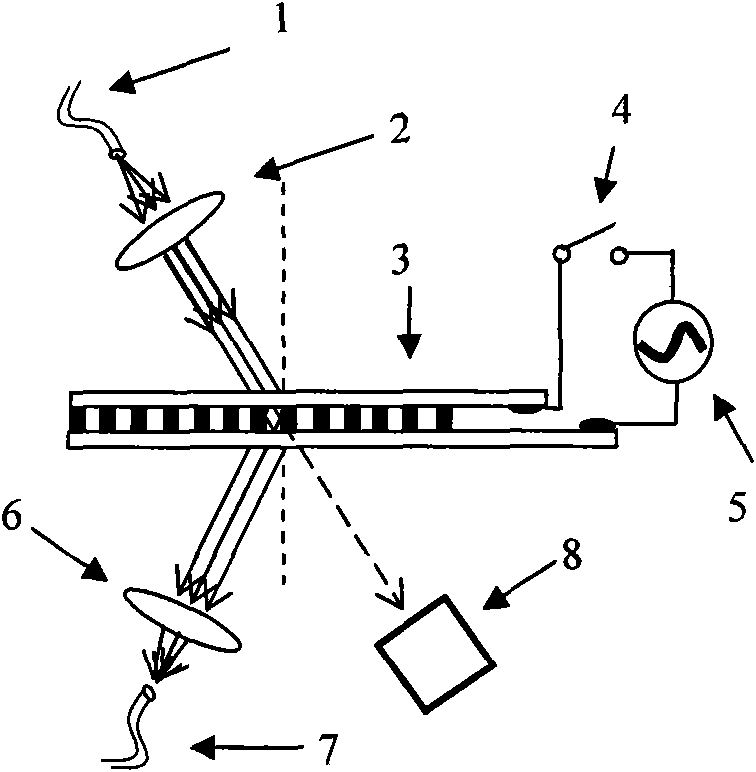
Bragg body grating monochromator prepared from electric tuning holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal (HPDLC)
InactiveCN101793555ARealize intelligent controlSmall sizeSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsDiffraction gratingsFiberBeam splitter
The invention belongs to the field of electrooptical functional materials and optical communication, in particular to a Bragg body grating monochromator prepared from an electric tuning holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal (HPDLC). The Bragg body grating monochromator comprises an input fiber-optical splice, a collimating lens, an HPDLC Bragg body grating, an electric driving control switch, a driving signal source, an output focus lens, an output fiber-optical splice and a transmitting light absorbing tube. By replacing a conventional plane grating by a high-efficiency Bragg body grating prepared from the holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal (HPDLC), the invention realizes the electric tuning with wavelength selection without a mechanical tuning mechanism of a conventional plane grating monochromator and simultaneously can realize the miniaturization and computer control. The invention avoids the problems that the diffraction efficiency of the plane (scoring) grating is seriously reduced caused by moldy surface due to the dampness or unclean surface, can prolong the service life of a system, can be used as an electric tuning variable beam splitter or an optical switch or applied to the field of optical communication.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
X-ray beam device
ActiveUS20100272239A1Reduce divergenceImprove throughputHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSoft x rayX-ray
The invention refers to an X-ray beam device for X-ray analytical applications, comprising an X-ray source designed such as to emit a divergent beam of X-rays; and an optical assembly designed such as to focus said beam onto a focal spot, wherein said optical assembly comprises a first reflecting optical element, a monochromator device and a second reflecting optical element sequentially arranged between said source and said focal spot, wherein said first optical element is designed such as to collimate said beam in two dimensions towards said monochromator device, and wherein said second optical element is designed such as to focus the beam coming from said monochromator device in two dimensions onto said focal spot.
Owner:XENOCS
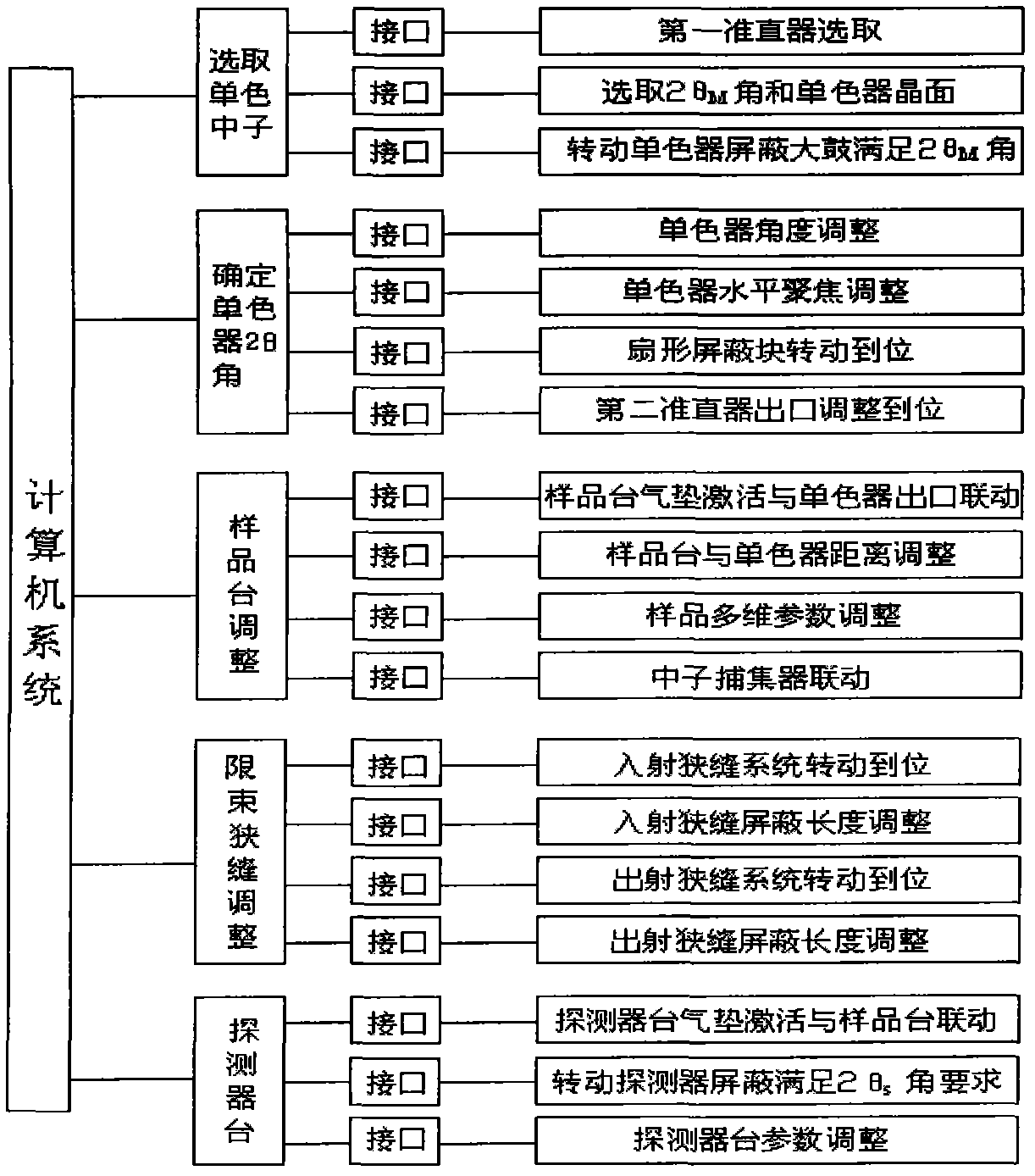
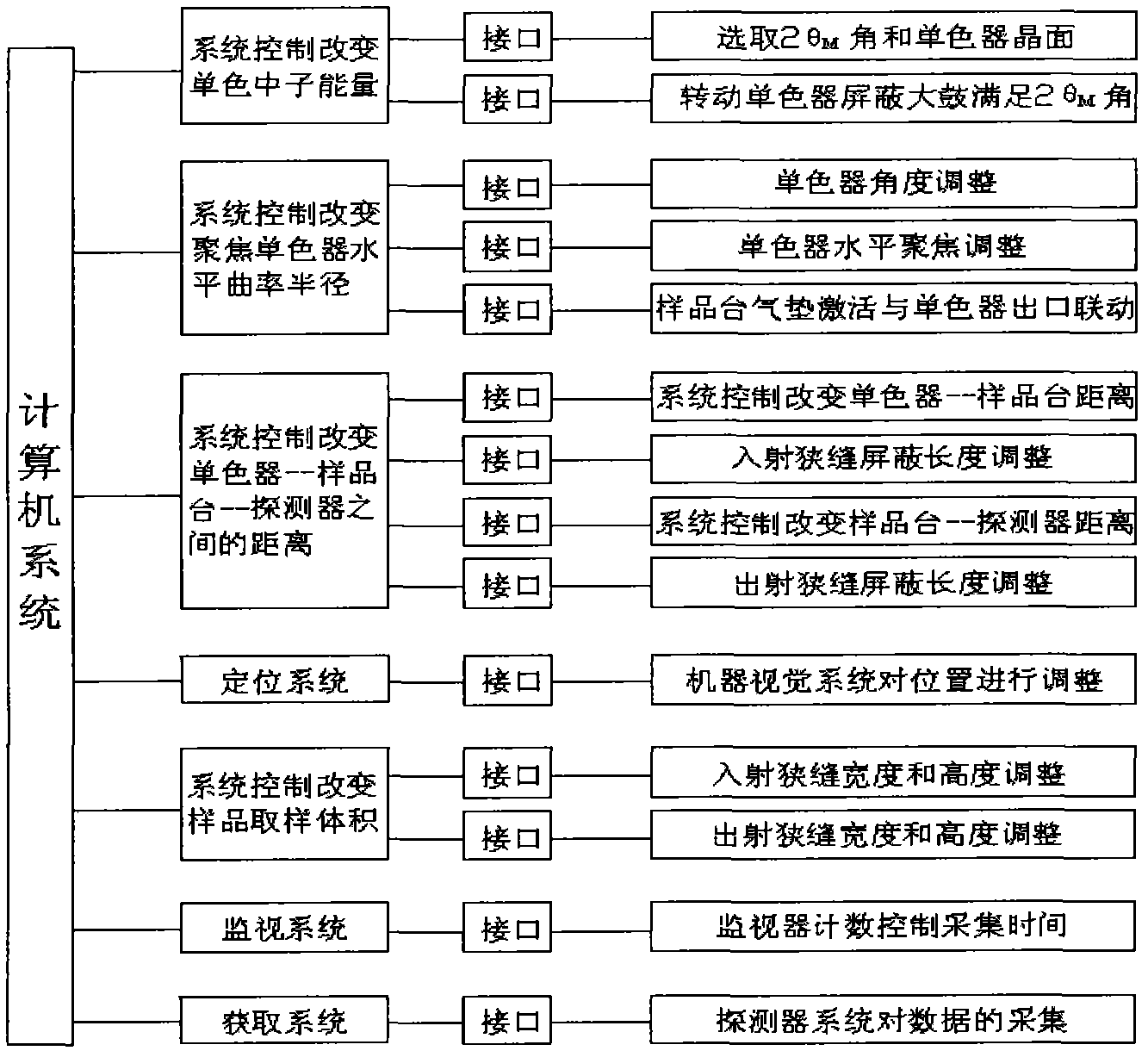
Neutron diffraction residual stress determination device and method
ActiveCN102435623AReduce absorptionNo need to overcome Coulomb barrierMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayNeutron diffraction
The invention discloses a neutron diffraction residual stress determination device and a method. The device is characterized by using the reactor neutron source, carrying out monochromatization by a monochromator to obtain a required monochromatic neutron beam at a certain wavelength, and using the neutron beam to detect the residual stress. According to the invention, because the neutrons are uncharged, and when the neutrons interact with substance, the neutrons have no effect with extranuclear electons, charge Coulombian force obstacle has no need to overcome, thus low energy neutrons can enter in atoms; the neutron absorption of great majority of materials is low, thus the penetration depth of incoming neutron beam is deep. Simultaneously by collimator and slit collimation, the limitedneutron beam has high space resolution ratio, a three-dimensional lossless and deep stress test of a test piece is realized by translation of three directions which are vertical to each other and rotation around testing central point, and the defect that an X-ray and a synchrotron radiation residual stress determination device can only losslessly determine the residual stress of the crystal material surface and subsurface is overcome.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
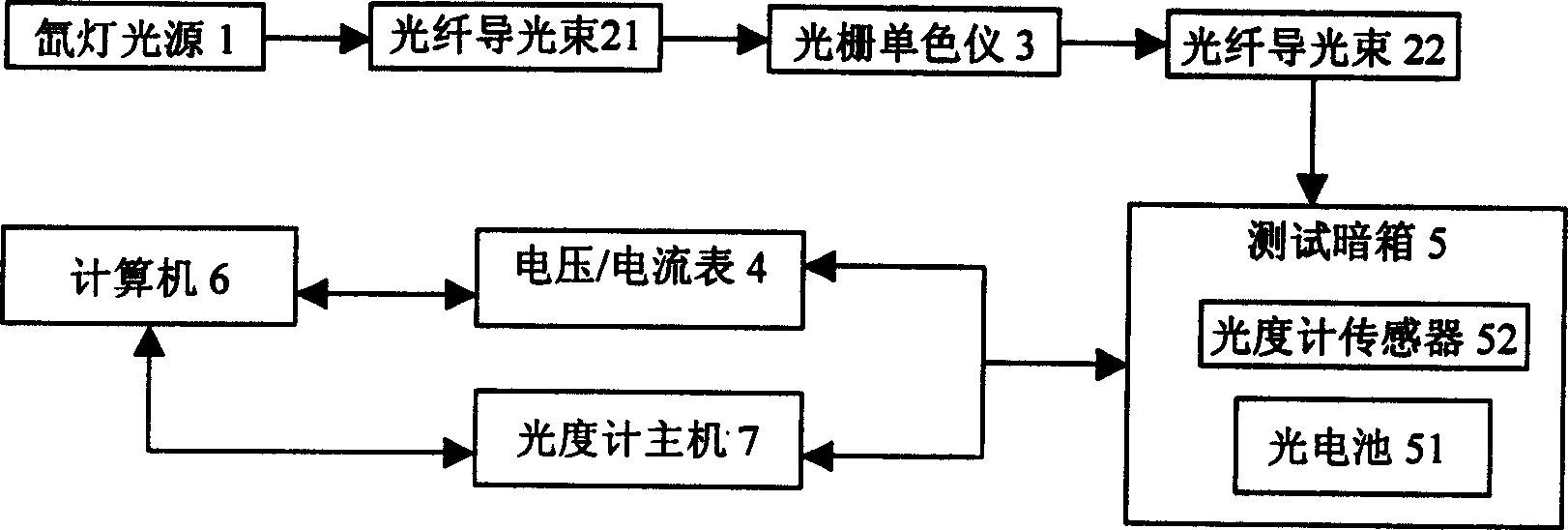
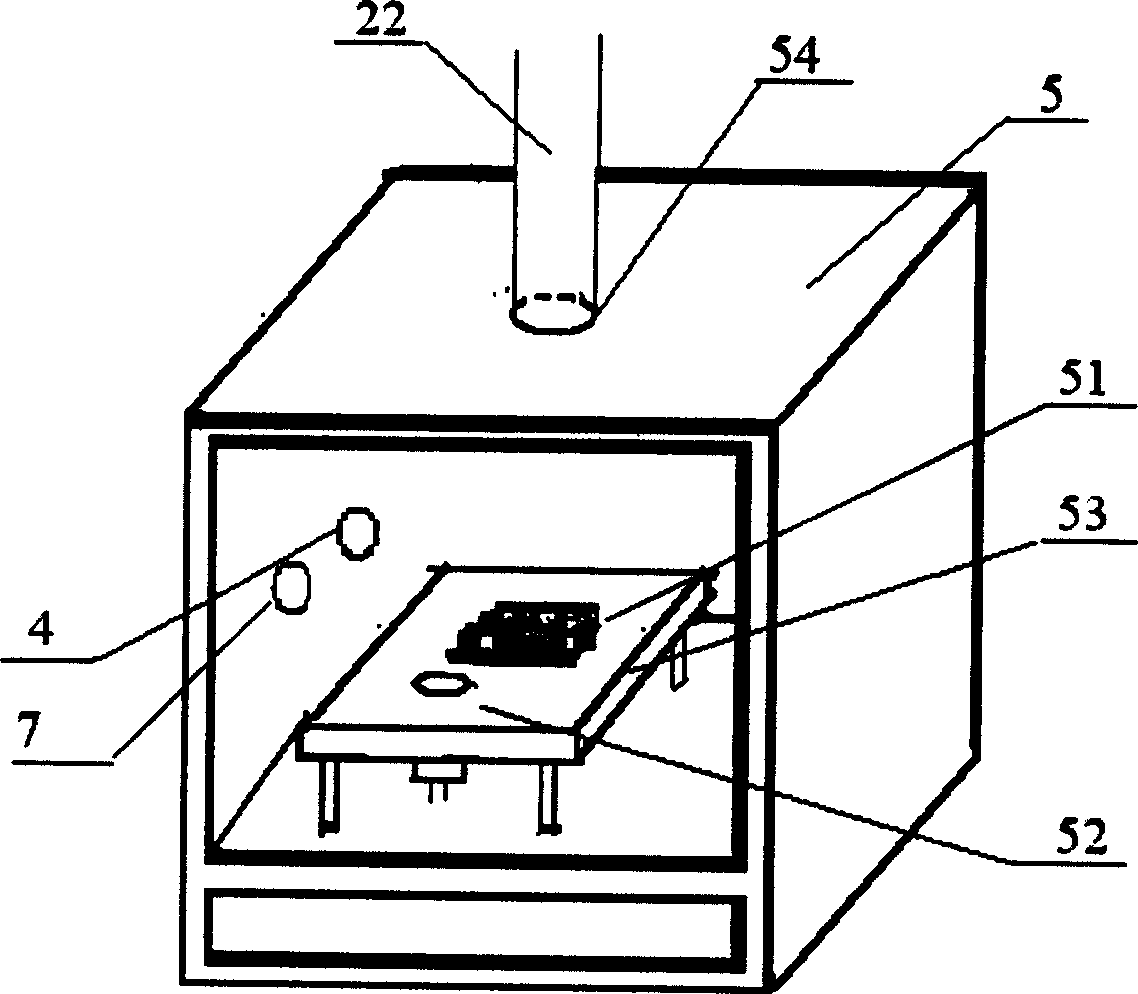
Integrated assayer for photoelectric performance
InactiveCN1564005AIllumination can be adjustedIncrease light intensityPhotovoltaic monitoringMaterial analysis by optical meansCombined testCurrent meter
The testing device is in use for measuring photoelectric properties of photovoltaic conversion materials and parts. In the device, xenon lamp simulates sunlight source. Optical fiber (21) of guiding light beam connects grating monochromator with xenon lamp, and optical fiber (22) of guiding light beam connects grating monochromator with testing dark box, where there are photocell and sensor of photometer inside. Output end of photocell is connected to voltage / current meter. Output end of sensor of photometer is connected to photometer. Output ends of photometer and voltage / current meter through data acquisition interface is connected to computer for in site measuring luminous intensity irradiated on photocell. Sensor of photometer is placed on the position the photocell located.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Normal-temperature normal-pressure femto-second CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Spectroscopy) time-resolved spectrum measuring system
InactiveCN101819064ASimple and fast operationImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringNonlinear opticsFemto second laser
The invention relates to a normal-temperature normal-pressure femto-second CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Spectroscopy) time-resolved spectrum measuring system which relates to the technical field of nonlinear optics and solves the problem of multiple limiting factors of traditional femto-second CARS time-resolved spectrum measuring experiment. Beams output by a femto-second laser are adjusted through a series of reflectors and optical delay lines by the system to form three bundles of beams which have approximate energy and are respectively positioned on three peaks of a square on the vertical direction of the beams, the beams are focused to a sample pool and then emit a new beam along a specific angle, i.e. a CARS signal, the CARS signal is filtered through a filter plate, then received by a probe and input to a monochromator, the data acquisition of an electrical signal converted by a photomultiplier is carried out by utilizing BOCCAR, and the data are input to a computer for data processing. The invention can carry out femto-second CARS time-resolved spectrum measurement under the experimental conditions of normal temperature and normal pressure and is applicable for the femto-second CARS spectrum measurement of gas samples and liquid samples in a static sample pool.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Testing device and method for defocused spot and color bias of optical system
InactiveCN102053010AHigh measurement accuracyHigh magnificationTesting optical propertiesImaging qualityOptical axis
The invention relates to a testing device and method for the defocused spot and the color bias of an optical system, wherein the device comprises a monochromator, a target wheel, a collimator, a rotary table, a CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) micro-measuring unit and an acquisition and control computer; the monochromator, the target wheel, the collimator and the CCD micro-measuring unit are sequentially positioned on the same optical axis; the rotary table is used for arranging the tested optical system and the CCD micro-measuring unit; and the rotary table, the monochromator and the CCD micro-measuring unit are all connected with the acquisition and control computer. The invention can be used for effectively testing the defocused-spot diameters and the color biases of various optical systemswithin different wavelength ranges and well ensures the imaging quality of the optical systems.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
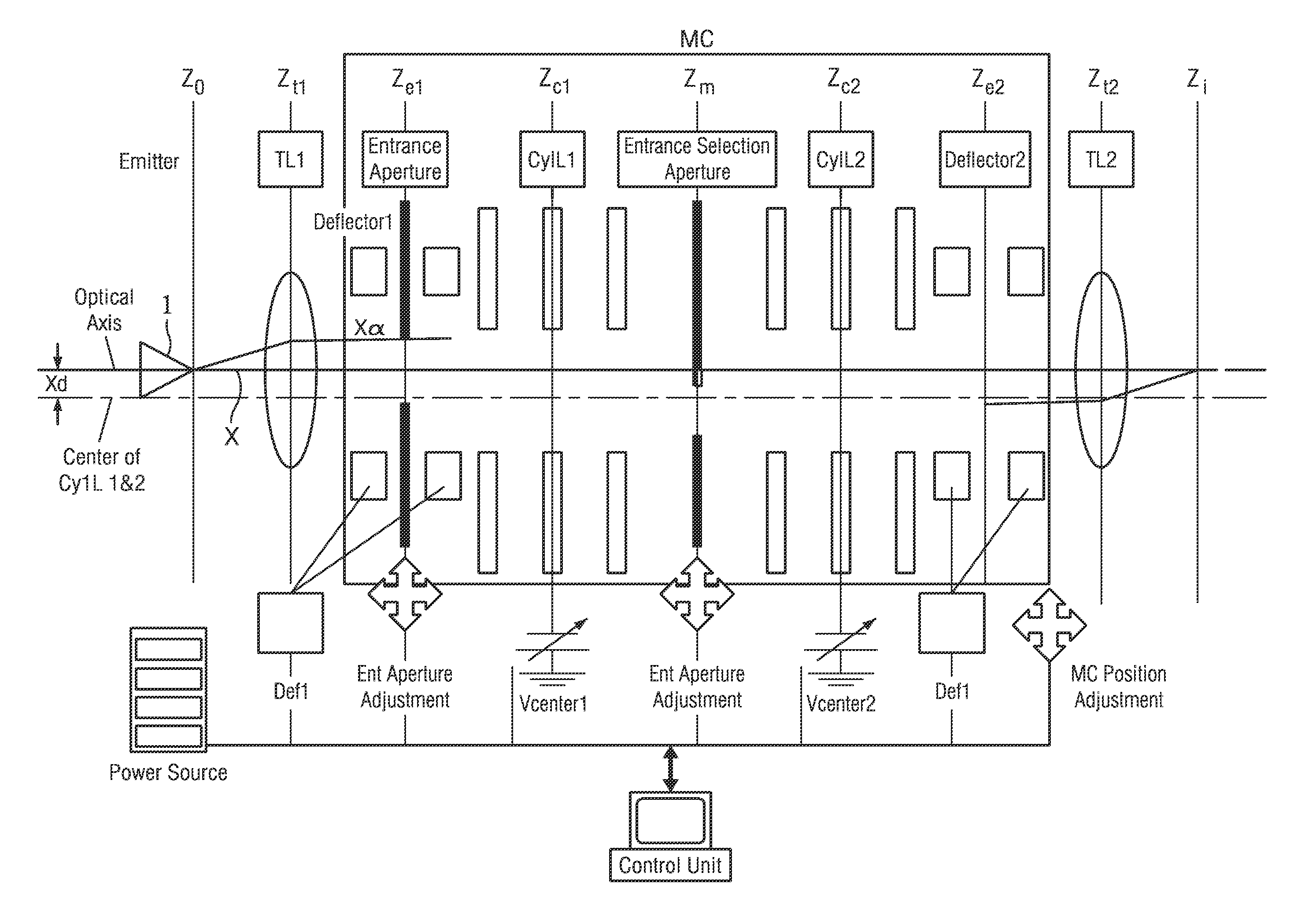
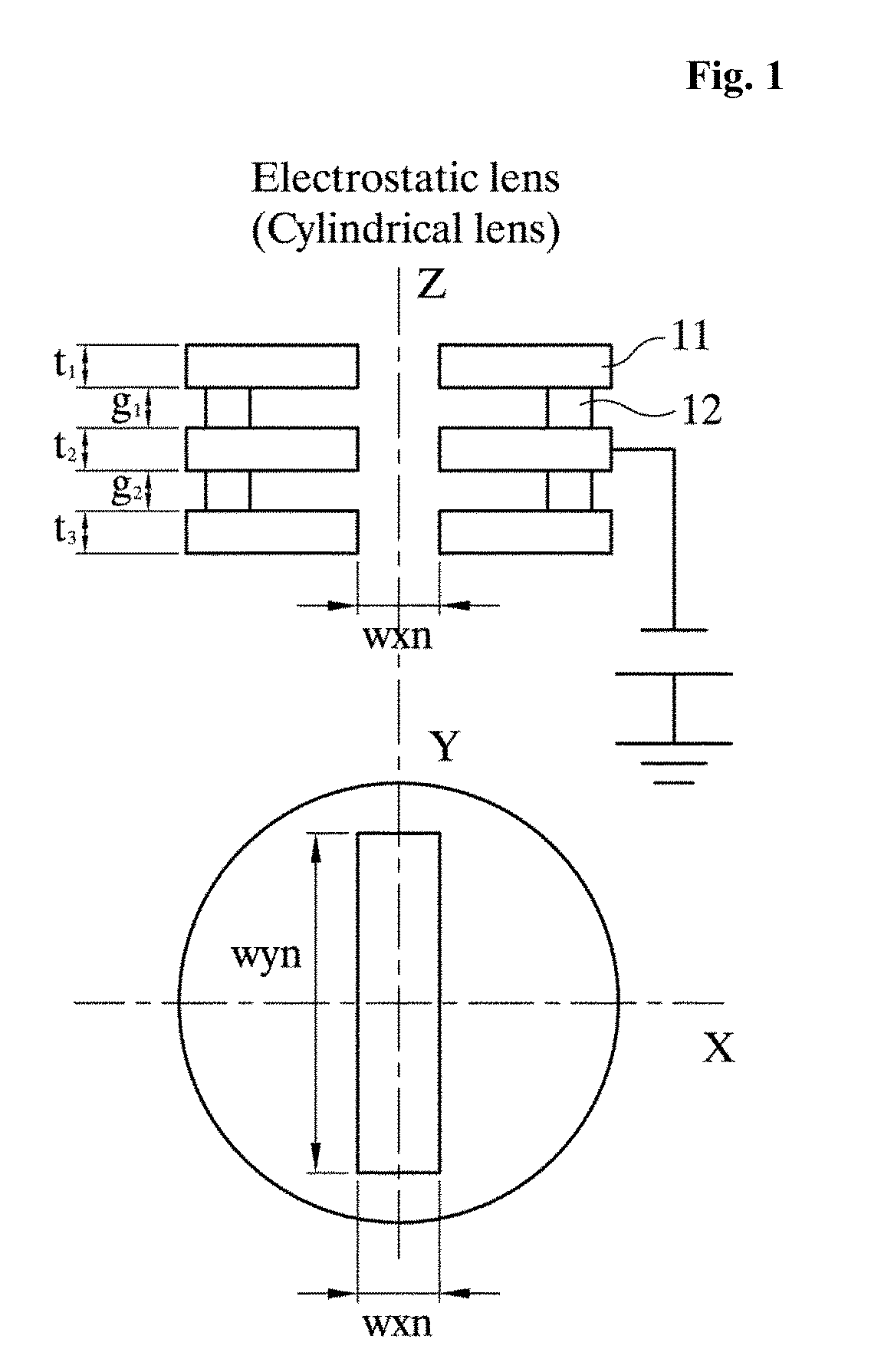
Monochromator and charged particle apparatus including the same
ActiveUS20150371811A1Enhance the imageStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMonochromatorMolecular physics
Disclosed herein are a monochromator and a charged particle beam apparatus including the same. The monochromator may include a first electrostatic lens configured to have a charged particle beam discharged by an emitter incident on the first electrostatic lens, refract a ray of the charged particle beam, and include a plurality of electrodes and a second electrostatic lens spaced apart from the first electrostatic lens at a specific interval and configured to have a central axis disposed identically with a central axis of the first electrostatic lens, have the charged particle beam output by the first electrostatic lens incident on the second electrostatic lens, refract the ray of the charged particle beam, and comprise a plurality of electrodes. Accordingly, there is an advantage in that a charged particle beam can have an excellent profile even after passing through the monochromator.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Systems and methods for detecting an image of an object by use of an x-ray beam having a polychromatic distribution
InactiveCN101405596AMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsAngle of incidenceMonochromator
Systems and methods for detecting an image of an object using an X-ray beam having a polychromatic energy distribution are disclosed. According to one aspect, a method can include detecting an image of an object. The method can include generating a first X-ray beam having a polychromatic energy distribution. Further, the method can include positioning a single monochromator crystal in a predetermined position to directly intercept the first X-ray beam such that a second X-ray beam having a predetermined energy level is produced. Further, an object can be positioned in the path of the second X-ray beam for transmission of the second X-ray beam through the object and emission from the object as a transmitted X-ray beam. The transmitted X-ray beam can be directed at an angle of incidence upon a crystal analyzer. Further, an image of the object can be detected from a beam diffracted from the analyzer crystal.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +2
Confocal spectrometer with astigmatic aperturing
A confocal spectrometer provides astigmatic optics which supply a monochromator or spectrograph with the image of a sample, with the astigmatic optics thereby providing separate first and second (tangential and sagittal) focal planes for the image. The monochromator / spectrograph has an entrance slit oriented along one of the focal planes, and this slit defines the spectral resolution of the monochromator / spectrograph and the field of view of the sample in one direction (in one focal plane). A supplemental slit is situated outside the monochromator / spectrograph adjacent the entrance slit, with the supplemental slit being oriented along the other focal plane. The supplemental slit therefore defines the field of view of the sample in a perpendicular direction (in the other focal plane). By varying the width of the supplemental and / or entrance slits, one may easily achieve the desired field of view.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRONICS SCI INSTR LLC
Photoelectric double-pulse laser induced breakdown spectrograph and spectral analysis method
InactiveCN101620183AHigh detection sensitivityHigh strengthAnalysis by material excitationOptical radiationCollection system
The invention discloses a photoelectric double-pulse laser induced breakdown spectrograph, comprising a pulse laser, a focusing lens, a movable platform, a discharge electrode, an optical diode, a pulse time-delay controller, a high-voltage pulse power supply, an optical collection system of optical radiation, a monochromator or a spectrograph, a photoelectric conversion element, a data collection unit and an electronic computer. The invention also discloses a spectral analysis method of the photoelectric double-pulse laser induced breakdown spectrograph. The photoelectric double-pulse laser induced breakdown spectrograph can greatly enhance the spectral analysis sensitivity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Membrane-Based Assay Devices that Utilize Time-Resolved Fluorescence
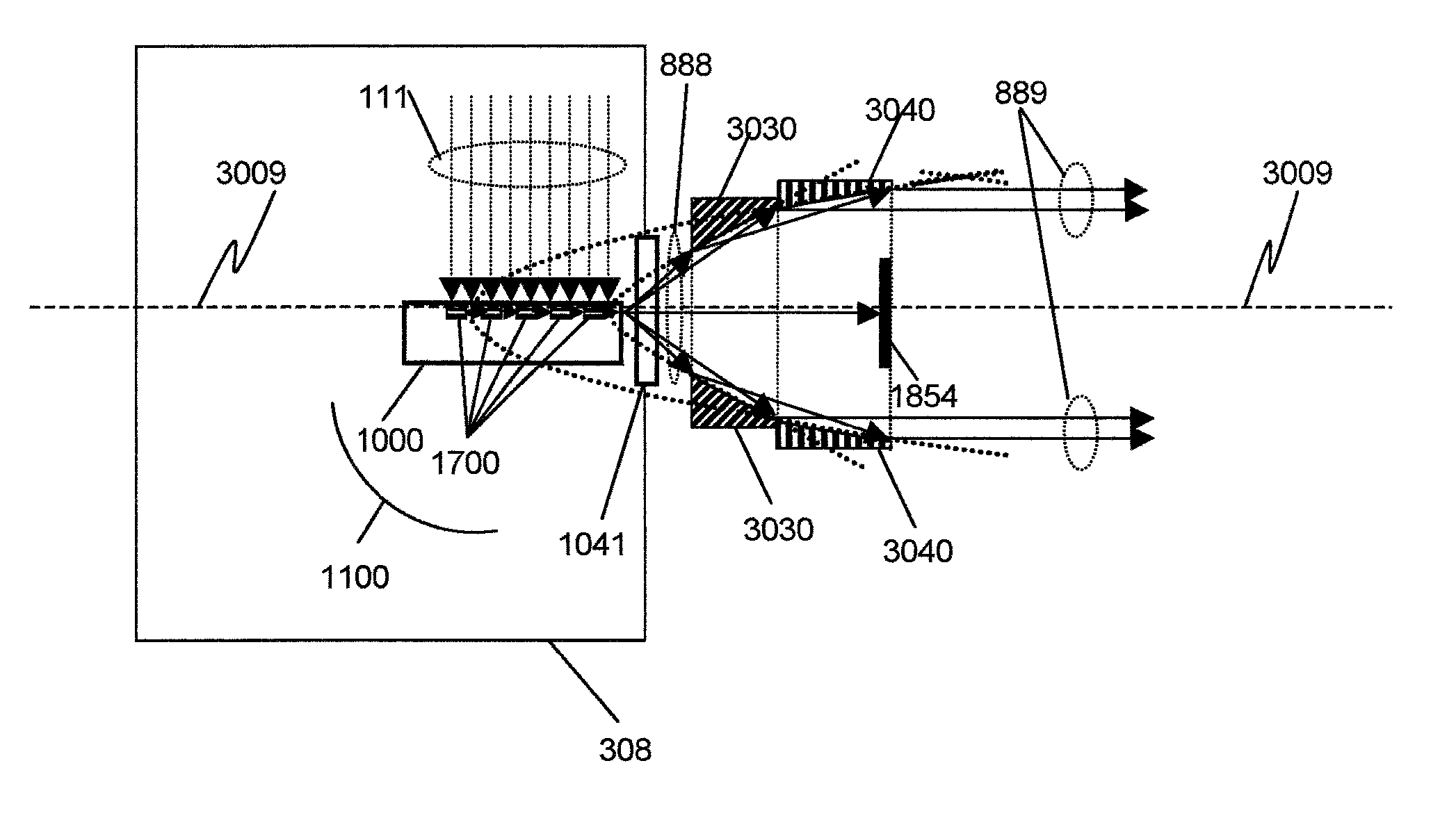
InactiveUS20090314946A1Accurately excite labels and detect fluorescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceRadiation intensity measurementAnalyteTest sample
A membrane-based assay device for detecting the presence or quantity of an analyte residing in a test sample is provided. The device utilizes time-resolved fluorescence to detect the signals generated by excited fluorescent labels. Because the labels can have relatively long emission lifetime, short-lived background interference can be practically eliminated through delayed fluorescence detection. In addition, the resulting fluorescent reader can have a simple and inexpensive design. For instance, in one embodiment, the reader can utilize a silicon photodiode and a pulsed light-emitting diode (LED) to accurately excite labels and detect fluorescence on a membrane-based assay device without requiring the use of expensive components, such as monochromators or narrow emission band width optical filters.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method and device for carrying out identification of bank notes based on spectrum analysis technique
InactiveCN102592347AUnique absorption propertiesUnique infrared absorption spectral characteristicsPaper-money testing devicesCorrelation analysisPrism
The invention discloses a method and a device for carrying out identification of bank notes based on a spectrum analysis technique. The device comprises a light source, a bank-note passing channel, a monochromator, a photosensitive sensor, a signal amplifier and a digital processing unit, wherein a chromatic dispersion element in the monochromator is a diffraction grating, a prism, or an optical filter with a spectral resolution. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out chromatic dispersion on reflected and transmitted light rays of a bank note by the monochromator; receiving the light intensity of each waveband by a receiving sensor so as to obtain reflected and transmitted spectral data of each waveband; carrying out relative analysis according to the data of a to-be-discriminated bank note and the data of a standard bank note, thereby obtaining relative coefficients; and discriminating whether the bank note is true and false according to the relative coefficients.
Owner:湖南丰汇银佳科技股份有限公司
Full-field spectral calibration device of push-broom type imaging spectrometer
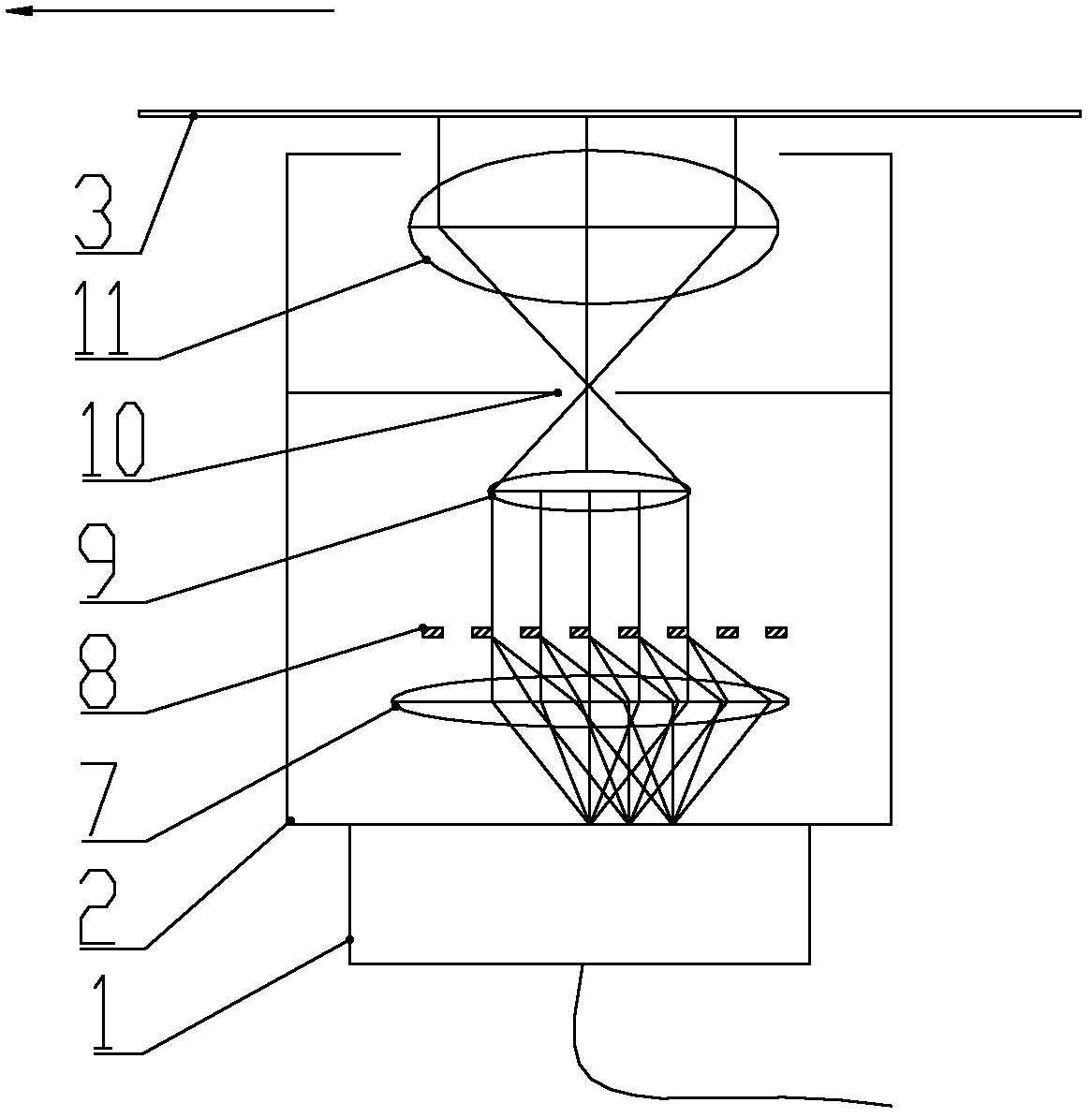
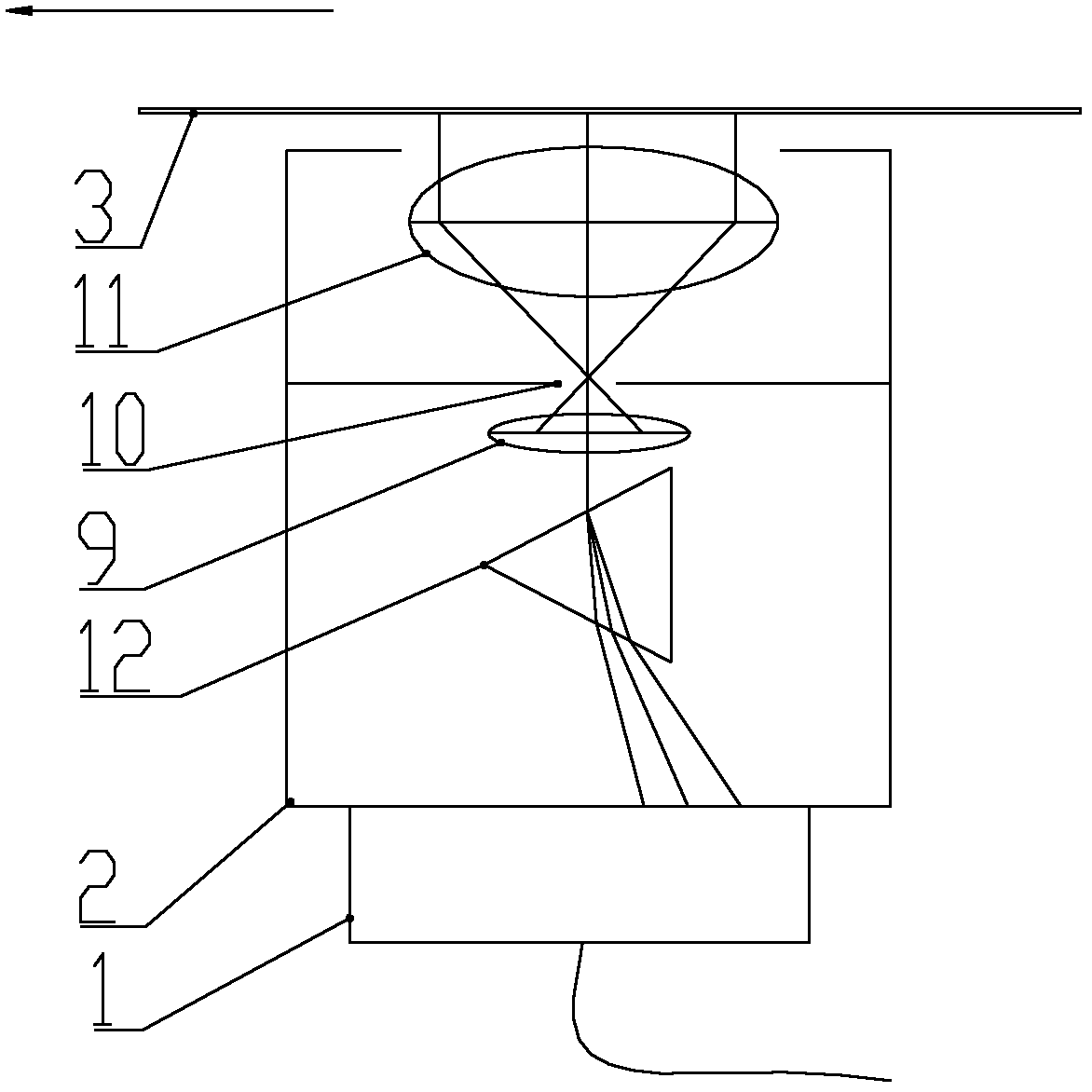
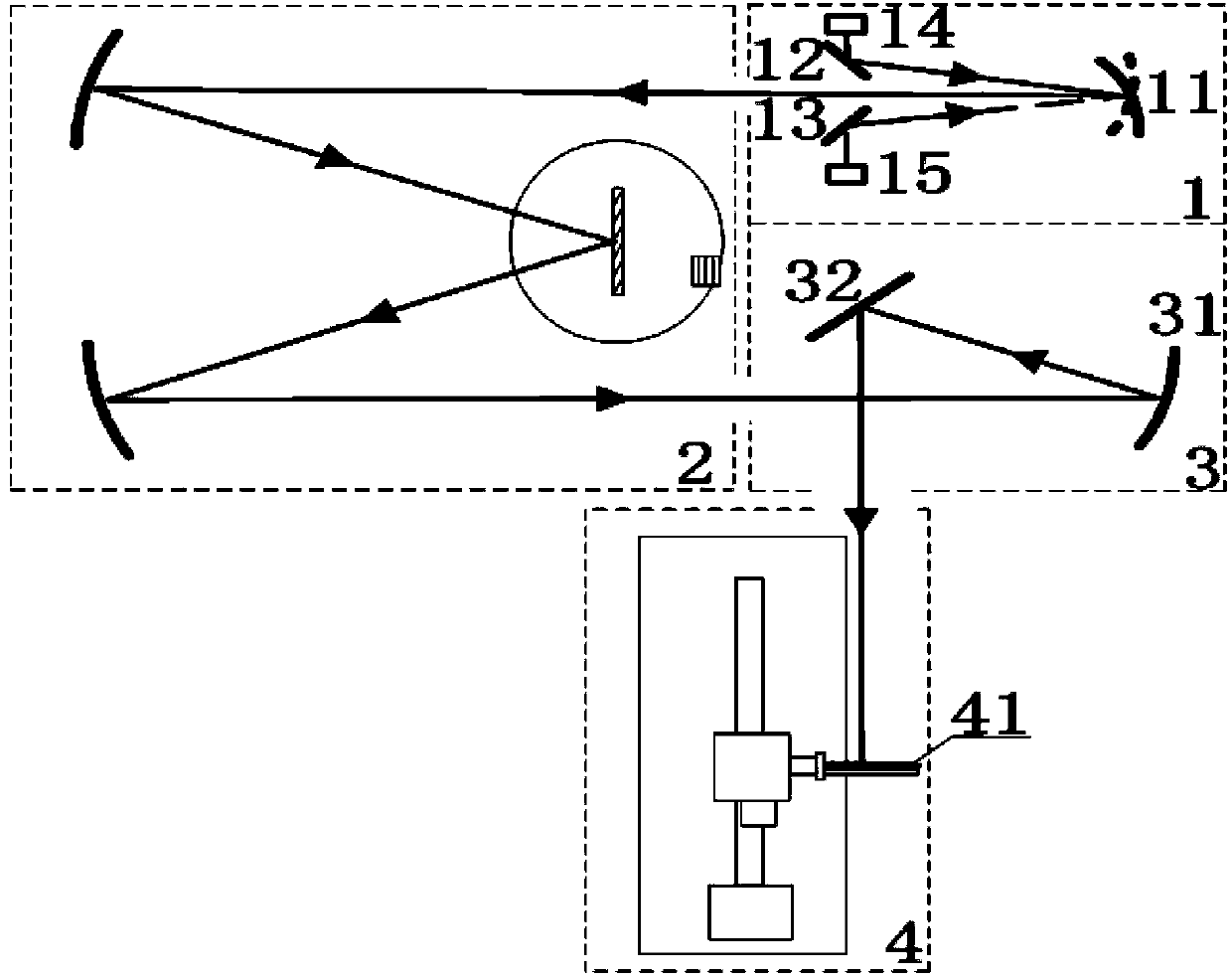
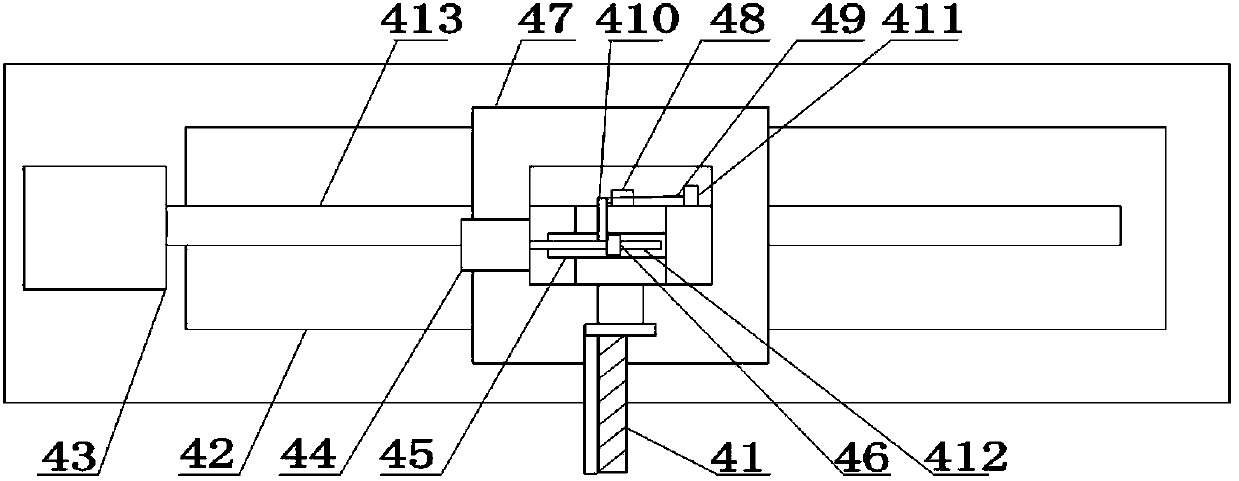
The invention provides a full-field spectral calibration device of a push-broom type imaging spectrometer. The device comprises a light source system (1), a monochromator (2), a collimation system (3) and a field scanning system (4), wherein light emitted by the light source system (1) is converted into monochromatic light through the monochromator (2), changed into parallel light through the collimation system (3) and revived by a to-be-calibrated imaging spectrometer after bent into different angles through the field scanning system (4). According to the full-field spectral calibration device, the parallel light with different field angles can be provided for the to-be-calibrated imaging spectrometer, so that full-field spectral calibration requirements of the push-broom type imaging spectrometer can be met. The full-field spectral calibration device is particularly suitable for full-field spectral calibration of a dispersion type imaging spectrometer in a visible light and infrared band.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A multi-purpose synchrotron radiation coherent X-ray diffraction microscopic imaging device and application
InactiveCN103134825ARealize free switchingRealize acquisitionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMicroscopic imageX-ray
The invention discloses a multi-purpose synchrotron radiation coherent X-ray diffraction microscopic imaging device. A synchrotron radiation X-ray light source, an undulator, a monochromator crystal, an X-ray shutter, a first lifting platform, a focusing device cavity, a vacuum piping, a second lifting platform, a multi-purpose sample room, a vacuum piping, a third lifting platform, a detector, and a computer which is used for collecting data and controlling an electric controlled translation platform are sequentially and coaxially arranged along the forward motion direction of light beam, wherein the monochromator crystal, the X-ray shutter and the first lifting platform are arranged on an electrical rotary platform, the focusing device cavity, the vacuum piping and the second lifting platform are arranged on the first lifting platform, the multi-purpose sample room, the vacuum piping and the third lifting platform are arranged on the second lifting platform, and the detector and the computer are arranged on the third lifting platform. According to the multi-purpose synchrotron radiation coherent X-ray diffraction microscopic imaging device, a low vacuum operating mode, a ventilation working mode, a freezing operating mode, X-ray focusing mode imaging or X-ray non-focusing mode imaging are achieved, the collection of three-dimension diffraction signals of samples are achieved by using a three-dimension rotating platform, a high quality three-dimension rebuilding result is obtained by using computer software, dying treatment and slicing treatment to the samples are needless, and train of thought is supplied to enrich a synchrotron radiation beam line imaging method.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Ultra-small angle x-ray scattering measuring apparatus
ActiveUS7646849B2Accurate captureSuppressing the smearing phenomenonRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsLattice planeSmall-angle X-ray scattering
An ultra-small angle X-ray scattering measuring apparatus includes a detector for detecting X-rays emitted from a sample, an X-ray collimating mirror arranged between the X-ray real focus and the sample, a monochromator arranged between the X-ray collimating mirror and the sample and an analyzer arranged between the sample and the detector. The X-ray collimating mirror includes a pair of X-ray mirrors that are arranged orthogonally relative to each other. The X-ray mirrors are multilayer film mirrors and their X-ray reflection surfaces are paraboloidal. The interplanar spacing of lattice planes of each of the multilayer films is continuously changed along the paraboloid so as to meet the Bragg's condition. The monochromator and the analyzer are formed by using a channel-cut crystal. The analyzer is driven to rotate for scanning around a 2θ-axial line and diffracted rays reduced to a spectrum by the analyzer are detected by the detector.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Novel system for detecting transmittance and reflectivity of lens of optical system
The invention discloses a novel system for detecting transmittance and reflectivity of a lens of an optical system and belongs to the field of test devices of optical systems. The system comprises a monochromator and the like, wherein a white-light source emits white light which enters the monochromator; a collecting mirror couples light beams modulated through a rotating reflecting mirror and then guides the coupled light beams into optical fibers; the optical fibers are connected with the collecting mirror; detectors are connected with a lock-in amplifier through data lines; integrating spheres are connected with the optical fibers; an electric motor is connected with the rotating reflecting mirror; the lock-in amplifier is connected with a computer through a data line; and a moving type reflecting mirror is located outside the monochromator, receives monochromatic spectrums emitted by the monochromator and reflects the monochromatic spectrums to a spherical reflecting mirror. When the system is used for measuring the transmittance of tested objects, the dual integrating spheres are adopted, so that the reflectivity can be measured simultaneously. Besides, a test sample chamber is placed outside the integrating spheres, and the tested objects are placed inside the integrating spheres.
Owner:长春市艾必利务科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com