Patents
Literature
87 results about "Undulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
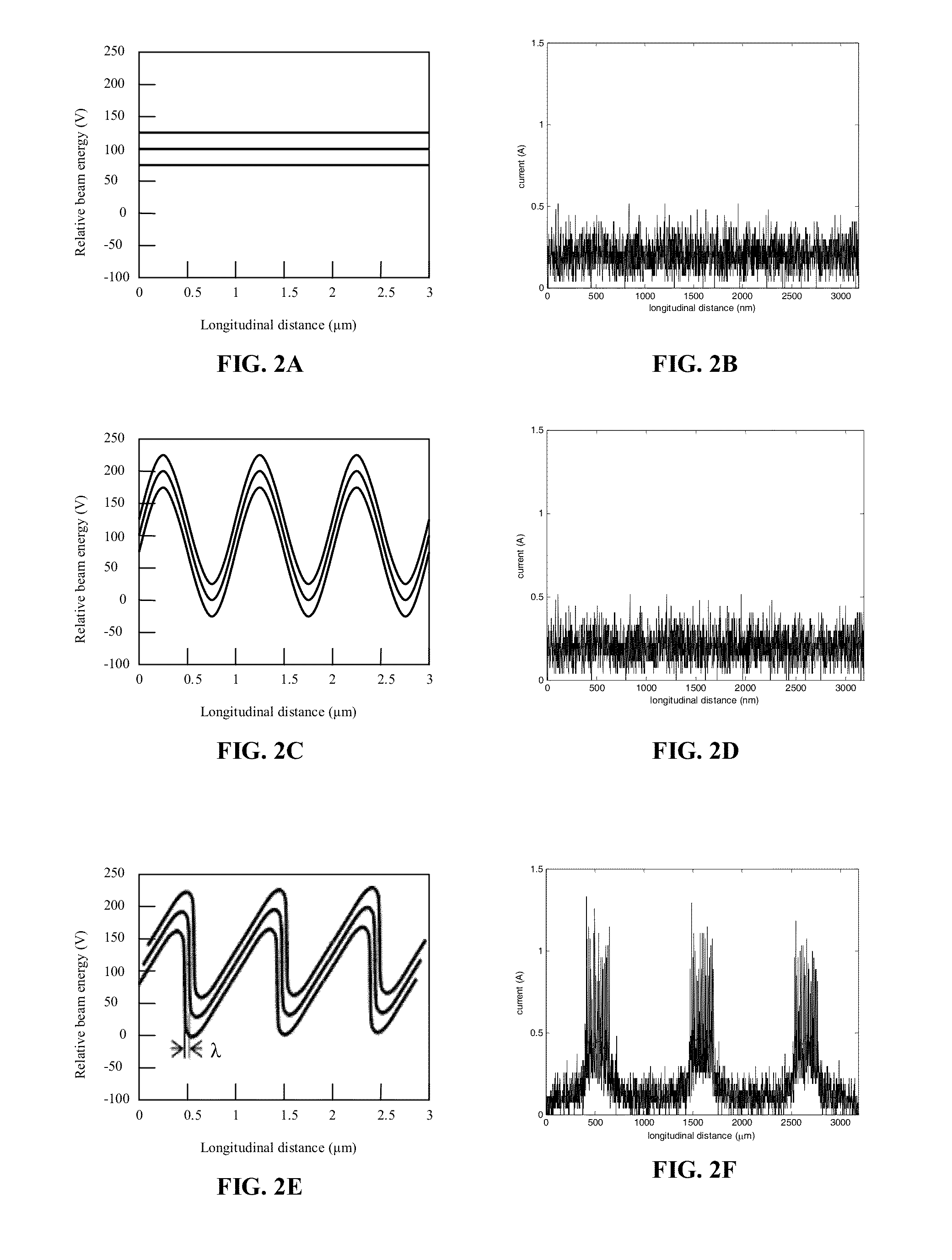
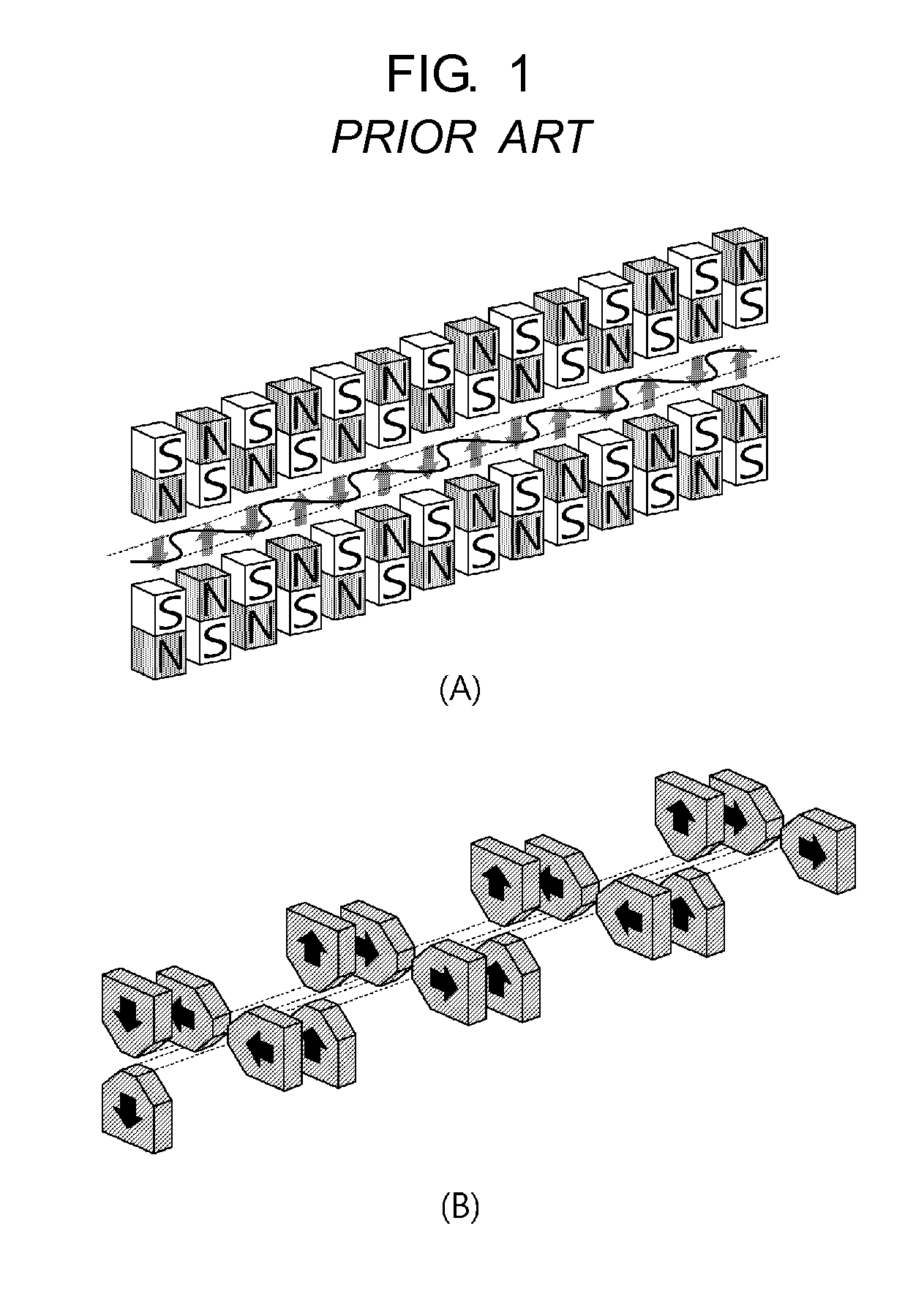
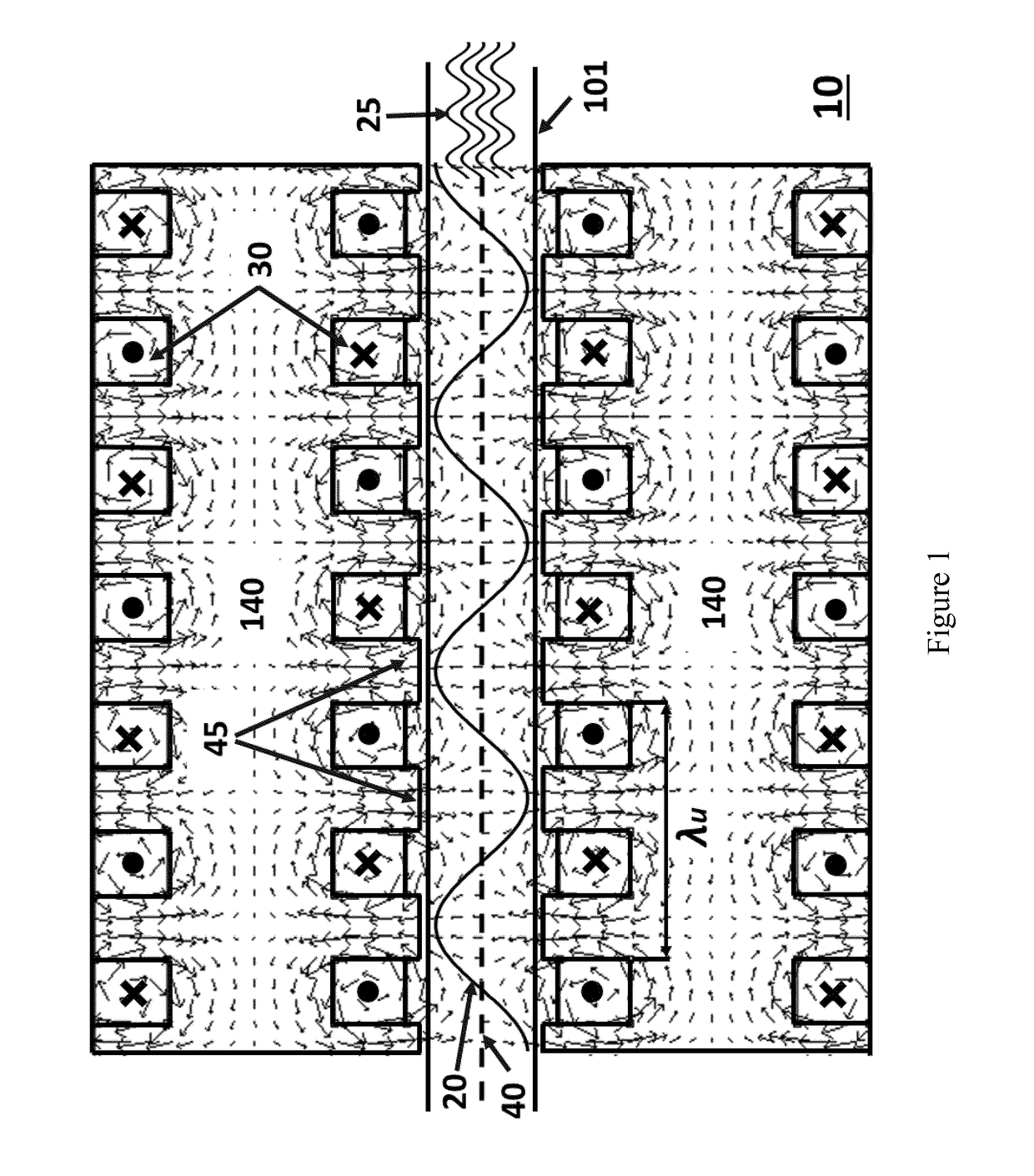
An undulator is an insertion device from high-energy physics and usually part of a larger installation, a synchrotron storage ring, or it may be a component of a free electron laser. It consists of a periodic structure of dipole magnets. These can be permanent magnets or superconducting magnets. The static magnetic field alternates along the length of the undulator with a wavelength λᵤ. Electrons traversing the periodic magnet structure are forced to undergo oscillations and thus to radiate energy.
A multi-purpose synchrotron radiation coherent X-ray diffraction microscopic imaging device and application
InactiveCN103134825ARealize free switchingRealize acquisitionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMicroscopic imageX-ray
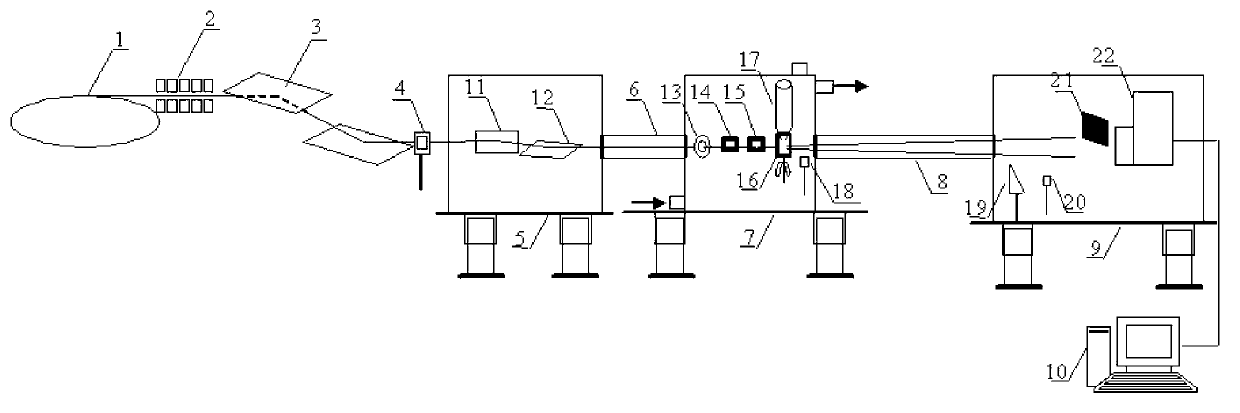
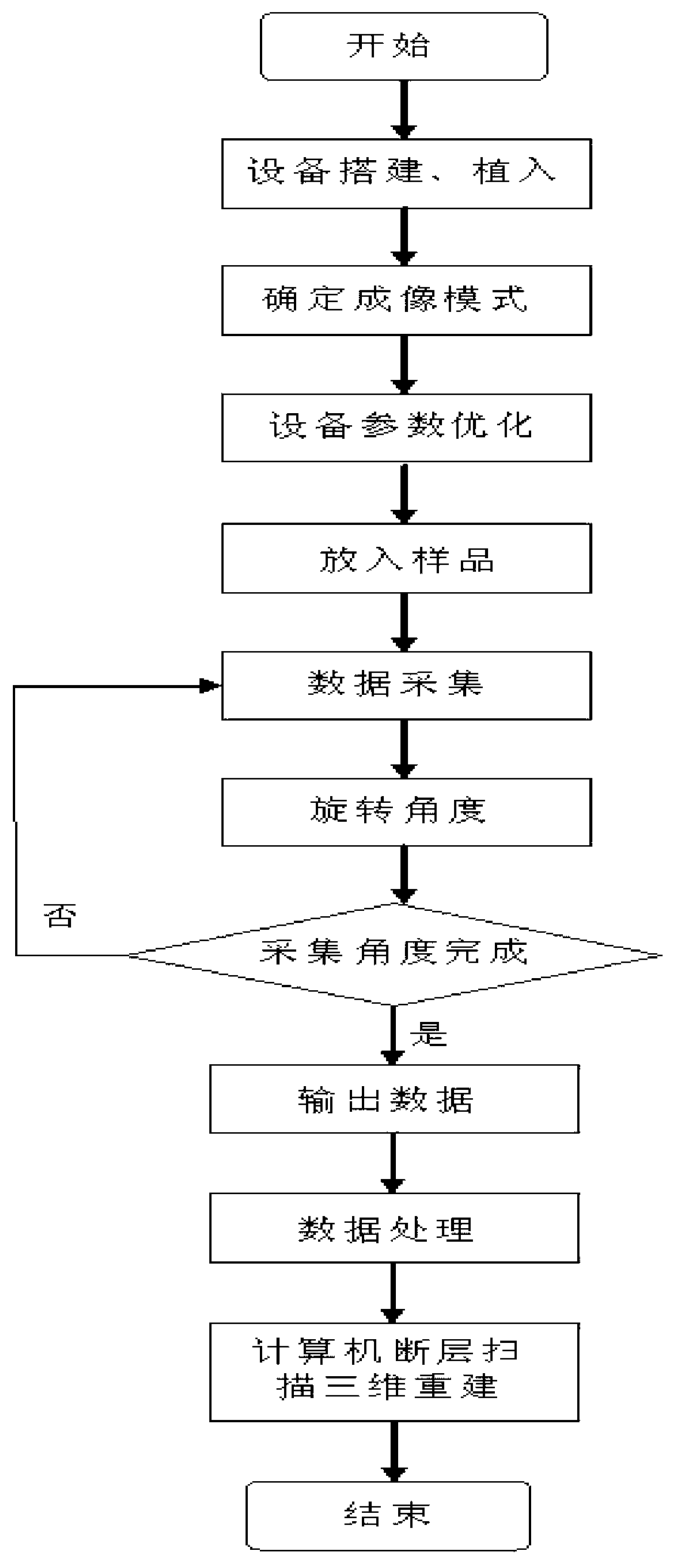
The invention discloses a multi-purpose synchrotron radiation coherent X-ray diffraction microscopic imaging device. A synchrotron radiation X-ray light source, an undulator, a monochromator crystal, an X-ray shutter, a first lifting platform, a focusing device cavity, a vacuum piping, a second lifting platform, a multi-purpose sample room, a vacuum piping, a third lifting platform, a detector, and a computer which is used for collecting data and controlling an electric controlled translation platform are sequentially and coaxially arranged along the forward motion direction of light beam, wherein the monochromator crystal, the X-ray shutter and the first lifting platform are arranged on an electrical rotary platform, the focusing device cavity, the vacuum piping and the second lifting platform are arranged on the first lifting platform, the multi-purpose sample room, the vacuum piping and the third lifting platform are arranged on the second lifting platform, and the detector and the computer are arranged on the third lifting platform. According to the multi-purpose synchrotron radiation coherent X-ray diffraction microscopic imaging device, a low vacuum operating mode, a ventilation working mode, a freezing operating mode, X-ray focusing mode imaging or X-ray non-focusing mode imaging are achieved, the collection of three-dimension diffraction signals of samples are achieved by using a three-dimension rotating platform, a high quality three-dimension rebuilding result is obtained by using computer software, dying treatment and slicing treatment to the samples are needless, and train of thought is supplied to enrich a synchrotron radiation beam line imaging method.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
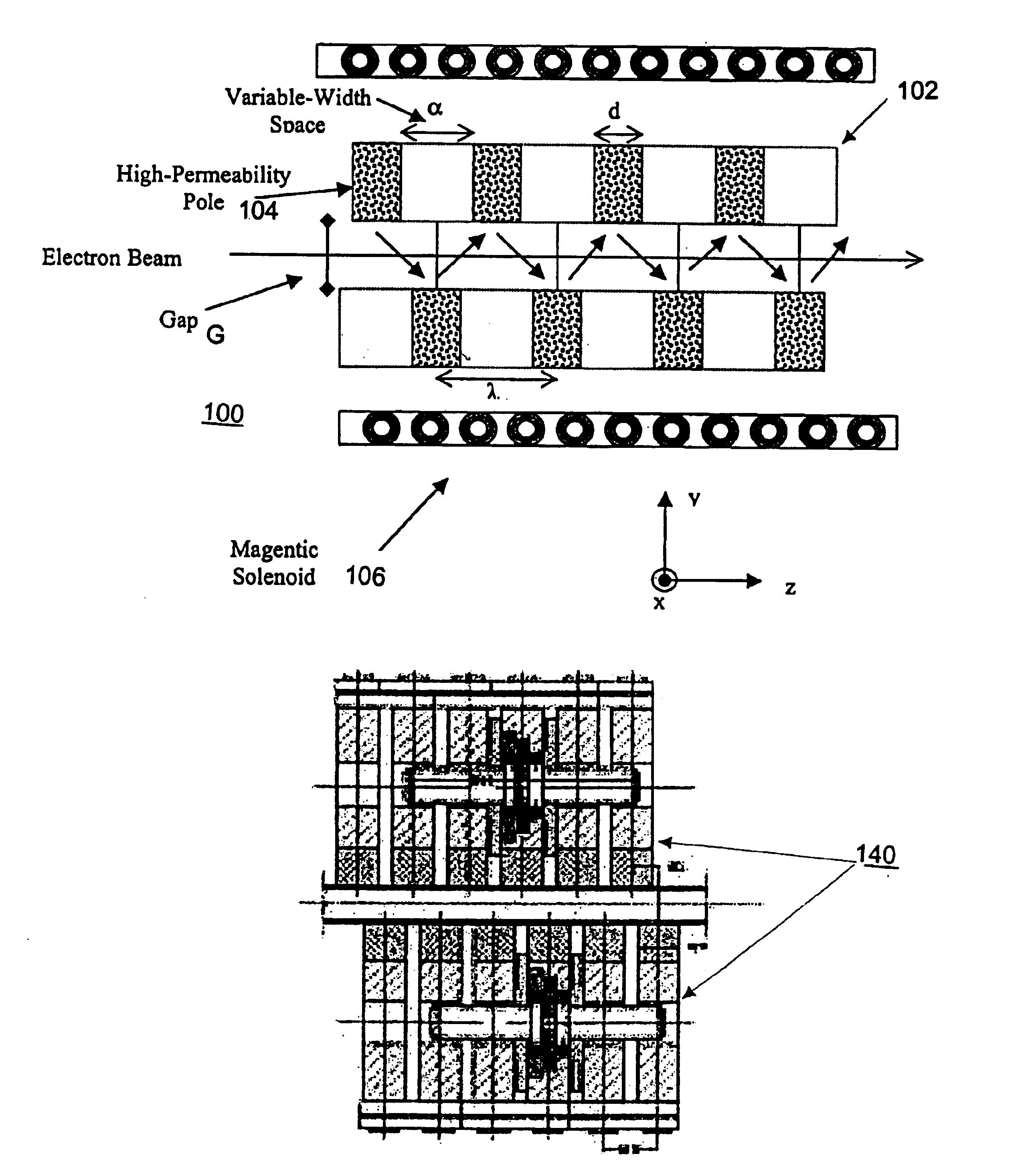
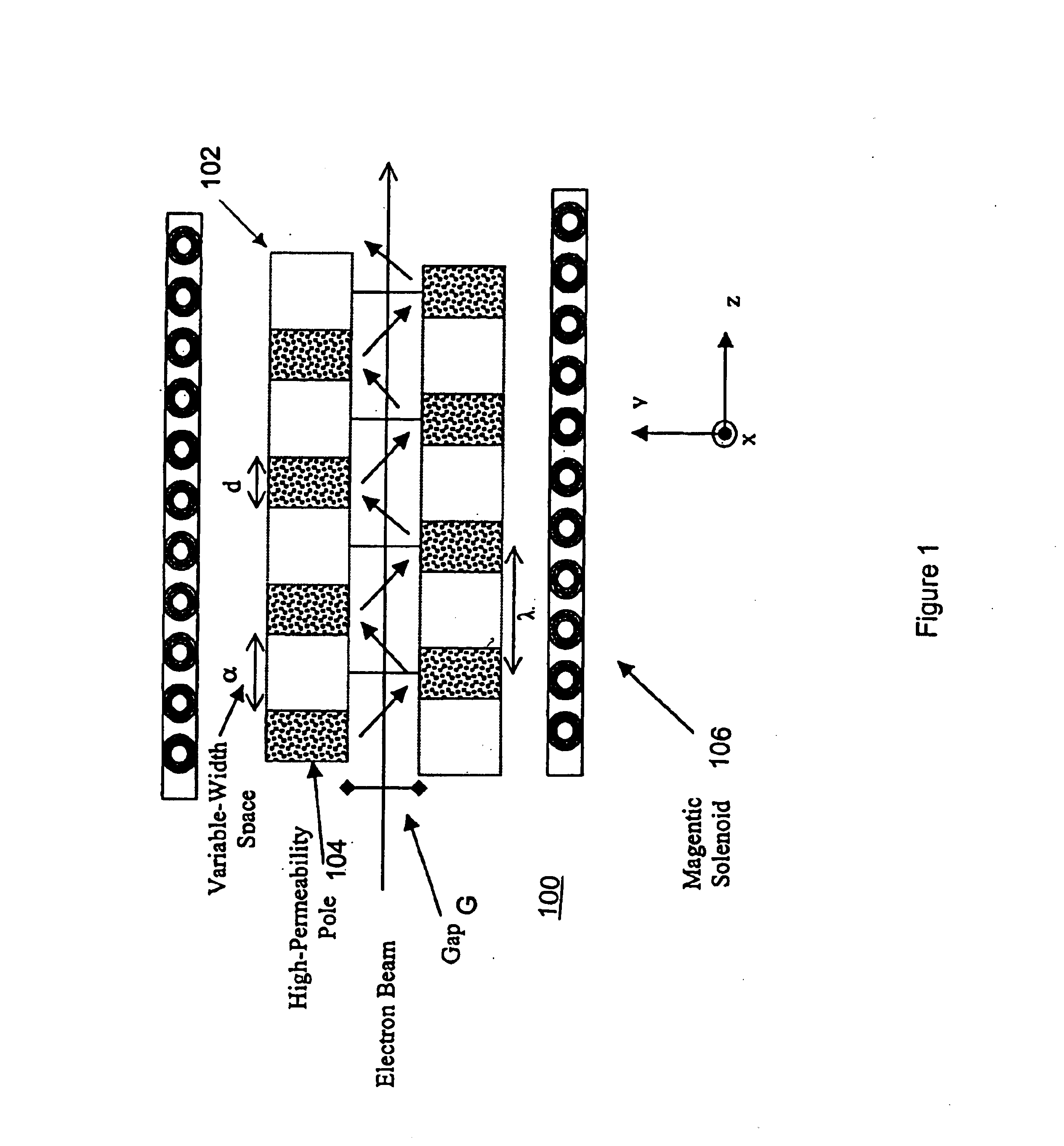
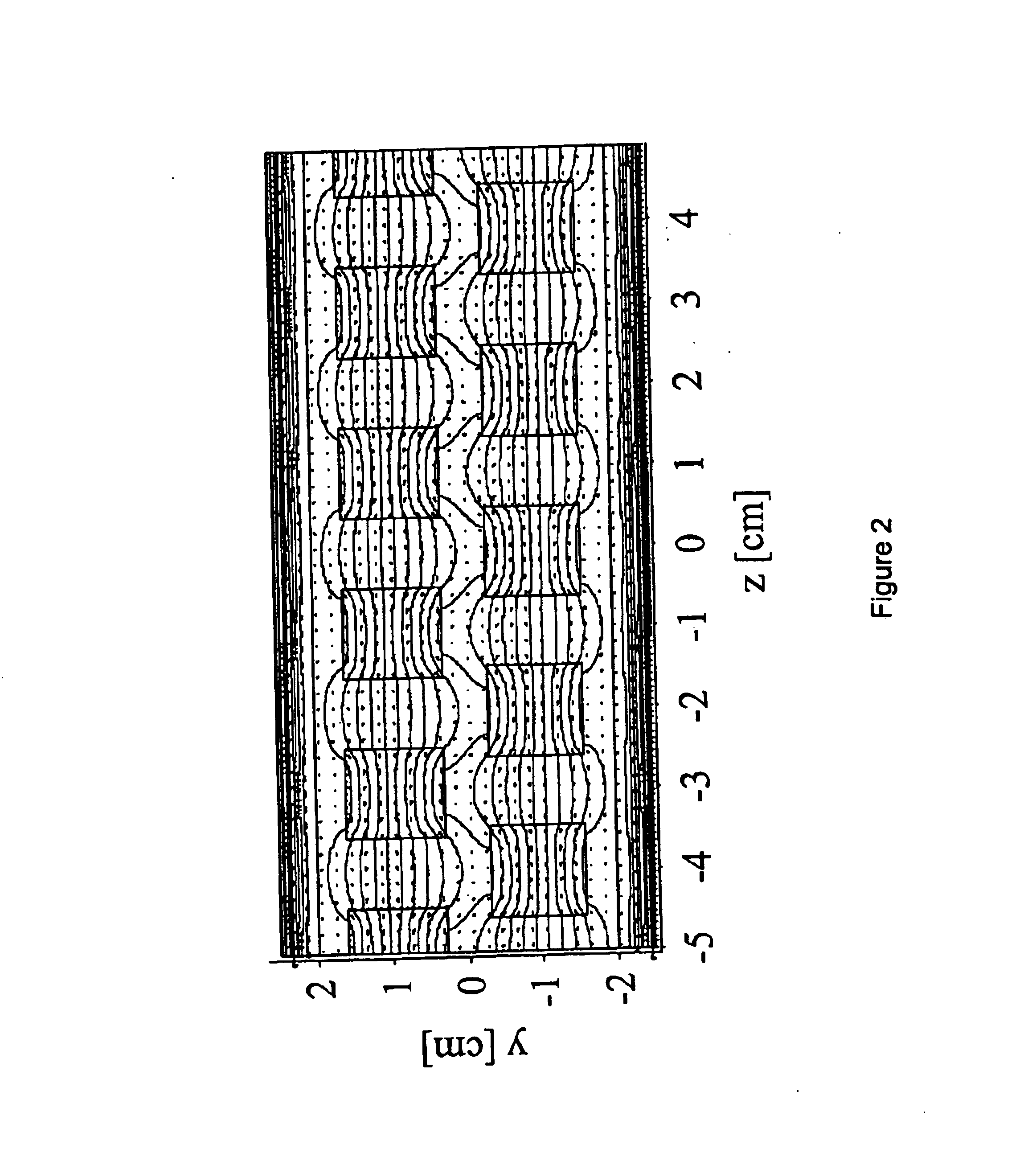
Variable-period undulators for synchrotron radiation
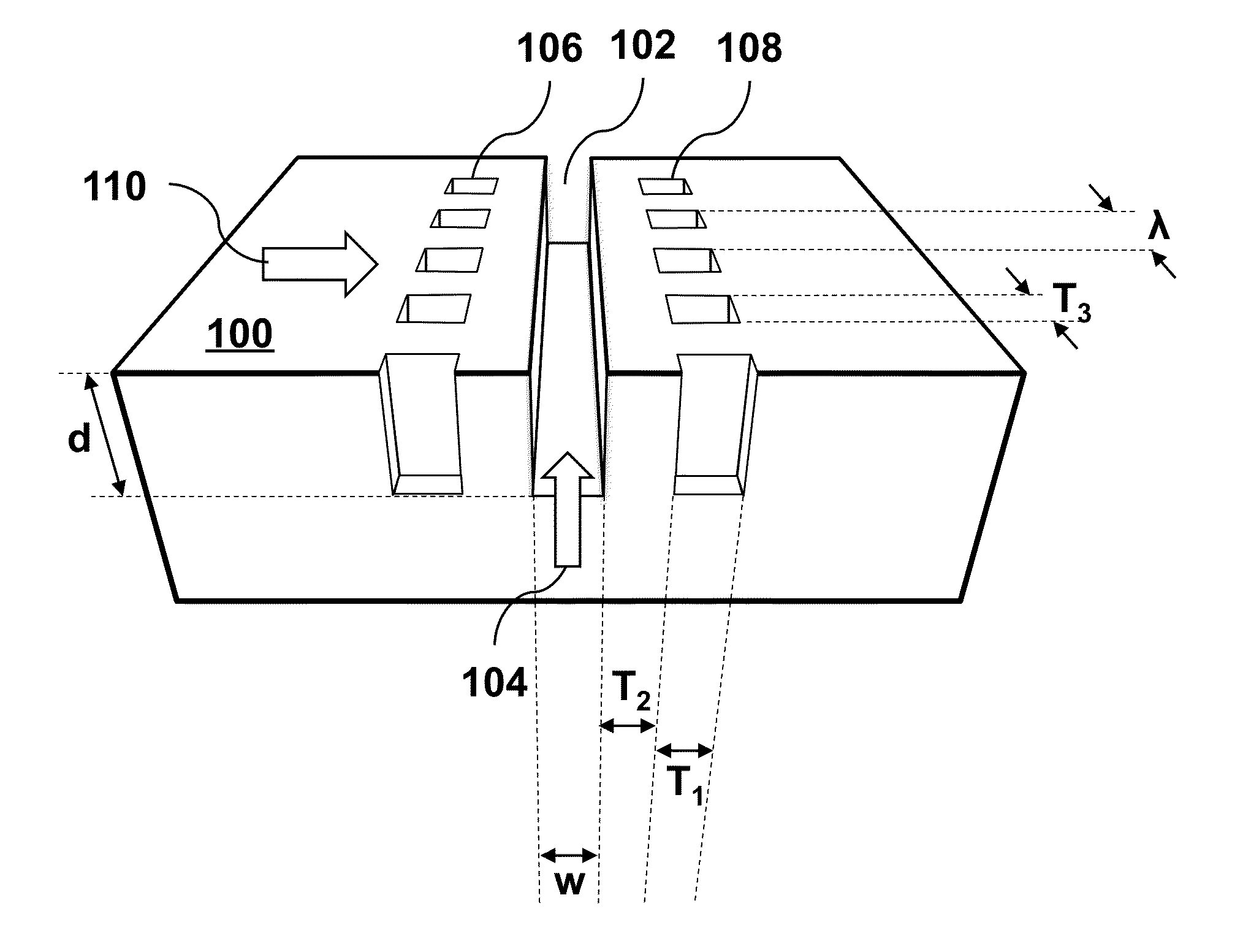
A new and improved undulator design is provided that enables a variable period length for the production of synchrotron radiation from both medium-energy and high-energy storage rings. The variable period length is achieved using a staggered array of pole pieces made up of high permeability material, permanent magnet material, or an electromagnetic structure. The pole pieces are separated by a variable width space. The sum of the variable width space and the pole width would therefore define the period of the undulator. Features and advantages of the invention include broad photon energy tunability, constant power operation and constant brilliance operation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
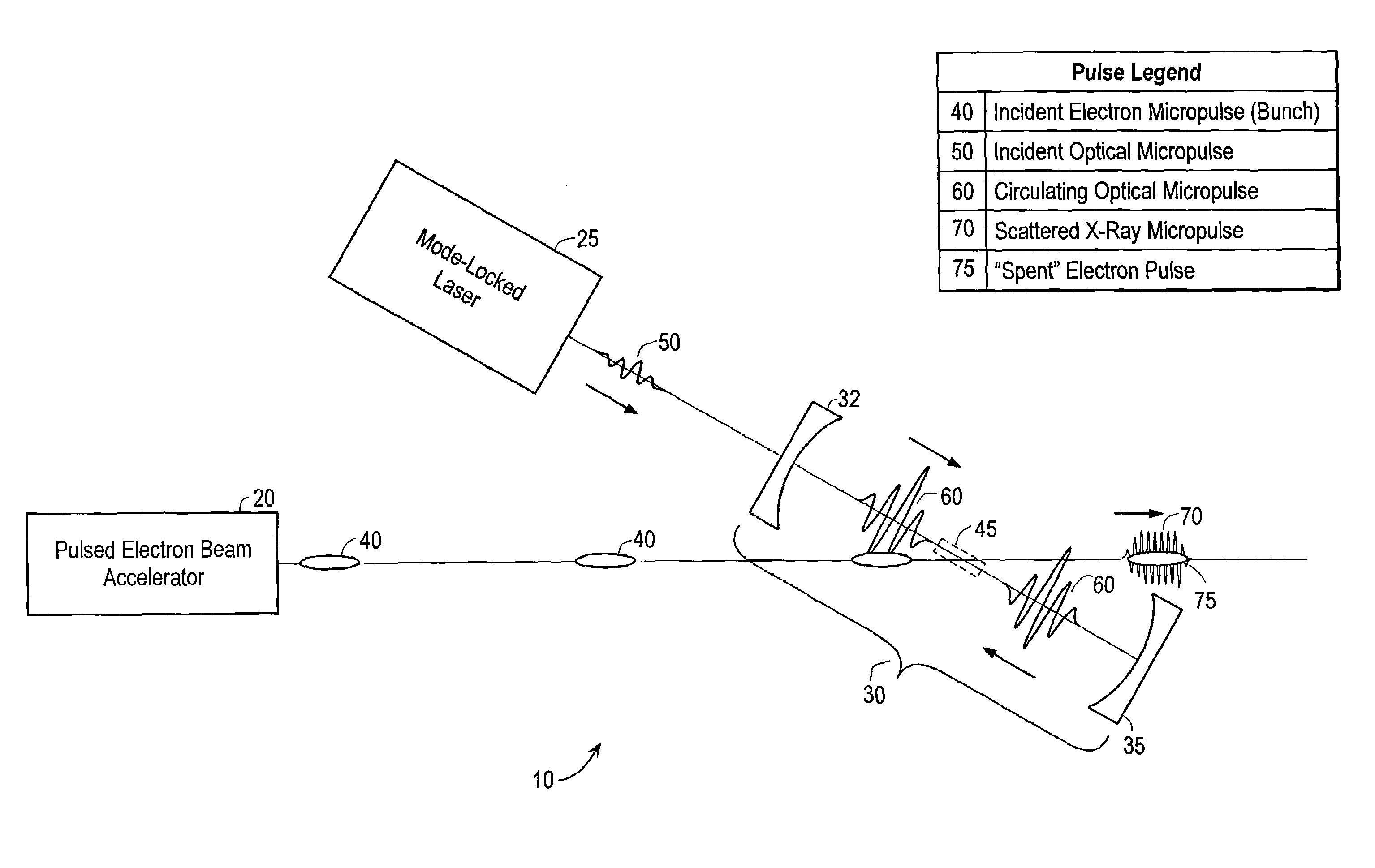
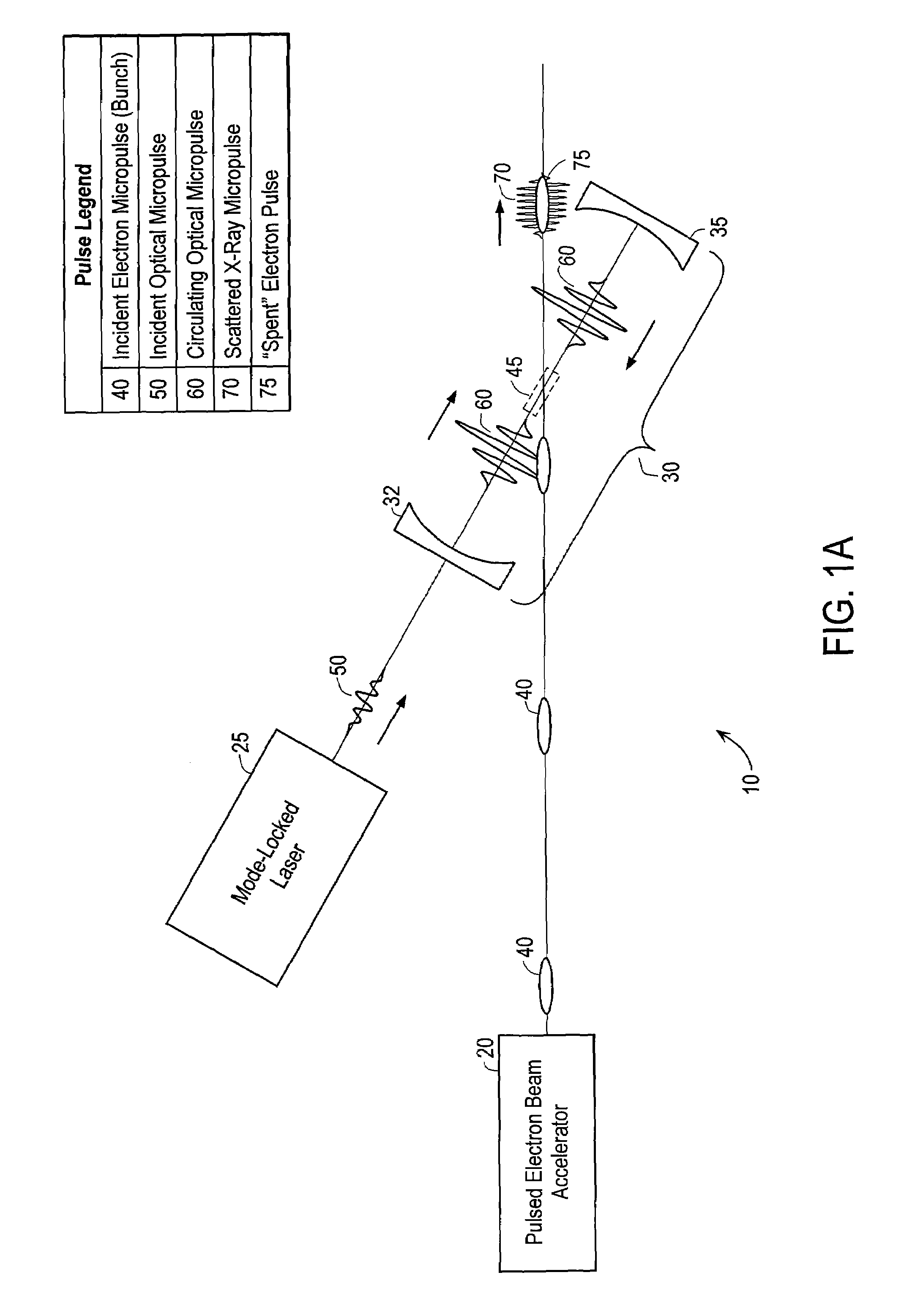
High efficiency monochromatic X-ray source using an optical undulator
InactiveUS7382861B2Level is generatedWeaken energyX-ray tube with very high currentX-ray apparatusOptical cavityX-ray
Owner:MADEY JOHN M J
Free electron laser based tunable narrow-band compact terahertz radiation source
ActiveCN105742943AImprove energy conversion efficiencyAdjustable frequencyMasersPhotocathodeElectromagnetic radiation
The invention discloses a free electron laser based tunable narrow-band compact terahertz radiation source. The free electron laser based tunable narrow-band compact terahertz radiation source comprises a laser source, a pulse accumulation light path, a reflecting mirror, a photocathode multi-cavity microwave electron gun, a solenoid coil and an undulator, wherein laser pulses emitted from the laser source are accumulated by n times through the pulse accumulation light path to generate a laser pulse string composed of 2n laser pulses, the laser pulse string irradiates on the surface of a negative electrode of the photocathode multi-cavity microwave electron gun by the reflecting mirror, and an electron bunch string is emitted from the surface of the negative electrode by a photoelectric effect, is accelerated by a microwave field generated by a microwave power source in a chamber of the photocathode multi-cavity microwave electron gun and enters the undulator after being transversely focused by a magnetic field of the solenoid coil so that electromagnetic radiation associated with THz waveband is stimulated. The technical scheme disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of compact structure, continuous and adjustable frequency and narrow bandwidth, and is easy to implement technically.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Temperature correction of wigglers and undulators
InactiveUS7196601B1Simple and inexpensiveLaser detailsTransit-tube focussing arrangementsCompensation effectUndulator
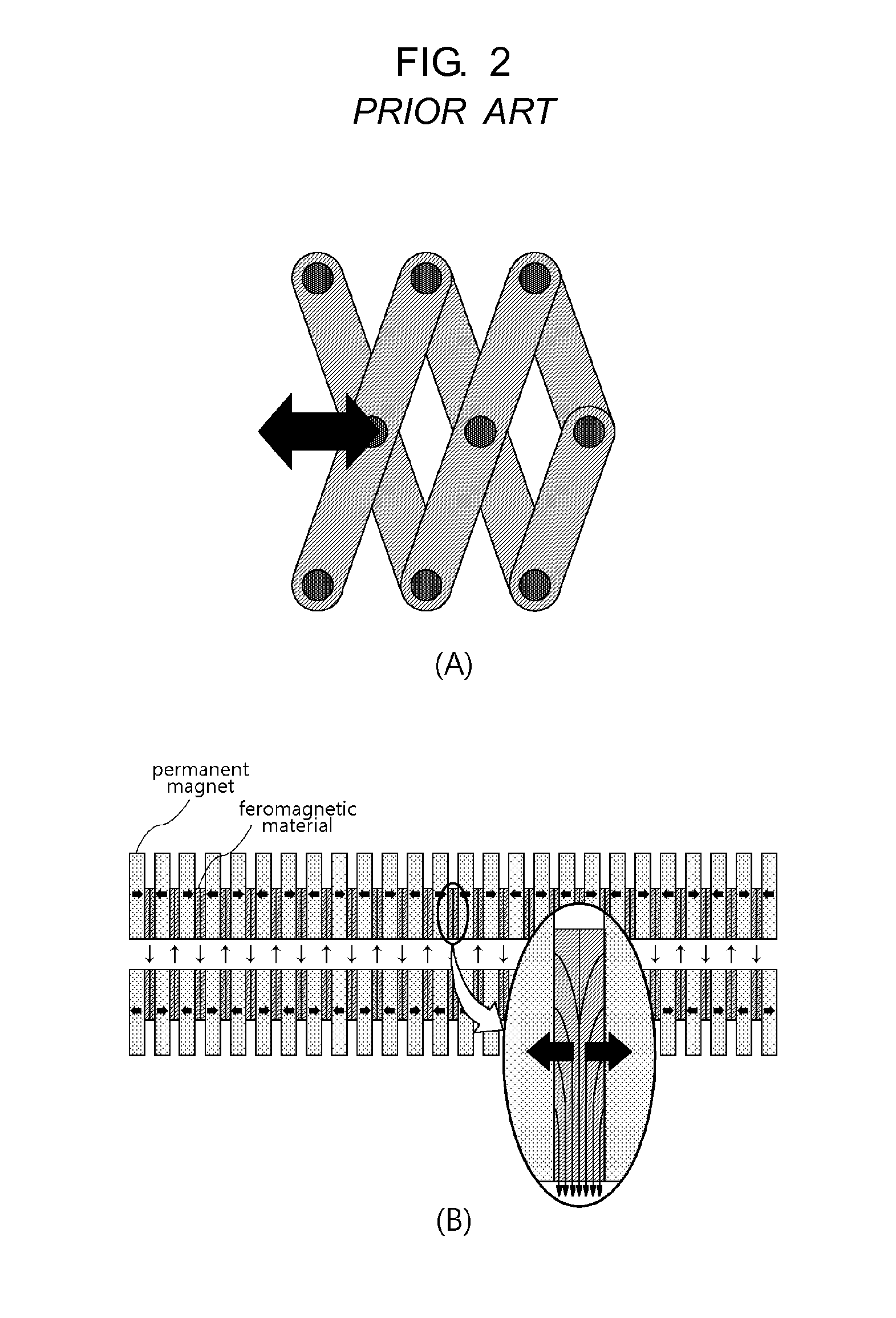
An undulator includes a periodic arrangement of magnets to produce a periodic spatial magnetic field distribution in a magnetic gap defined by the magnets. The undulator further includes a temperature-compensating material selectively arranged to compensate for a temperature-dependent change in the magnetic field of the undulator. The change may be in the strength of the magnetic field, or in the position of the magnetic field centerline. According to one aspect of the invention, the temperature-compensating material is movably arranged, so as to fine tune its compensation effect after it is initially arranged. Alternatively or additionally, the amount of temperature-compensating material may be adjusted to fine tune its compensation effect after it is initially arranged.
Owner:STI OPTRONICS
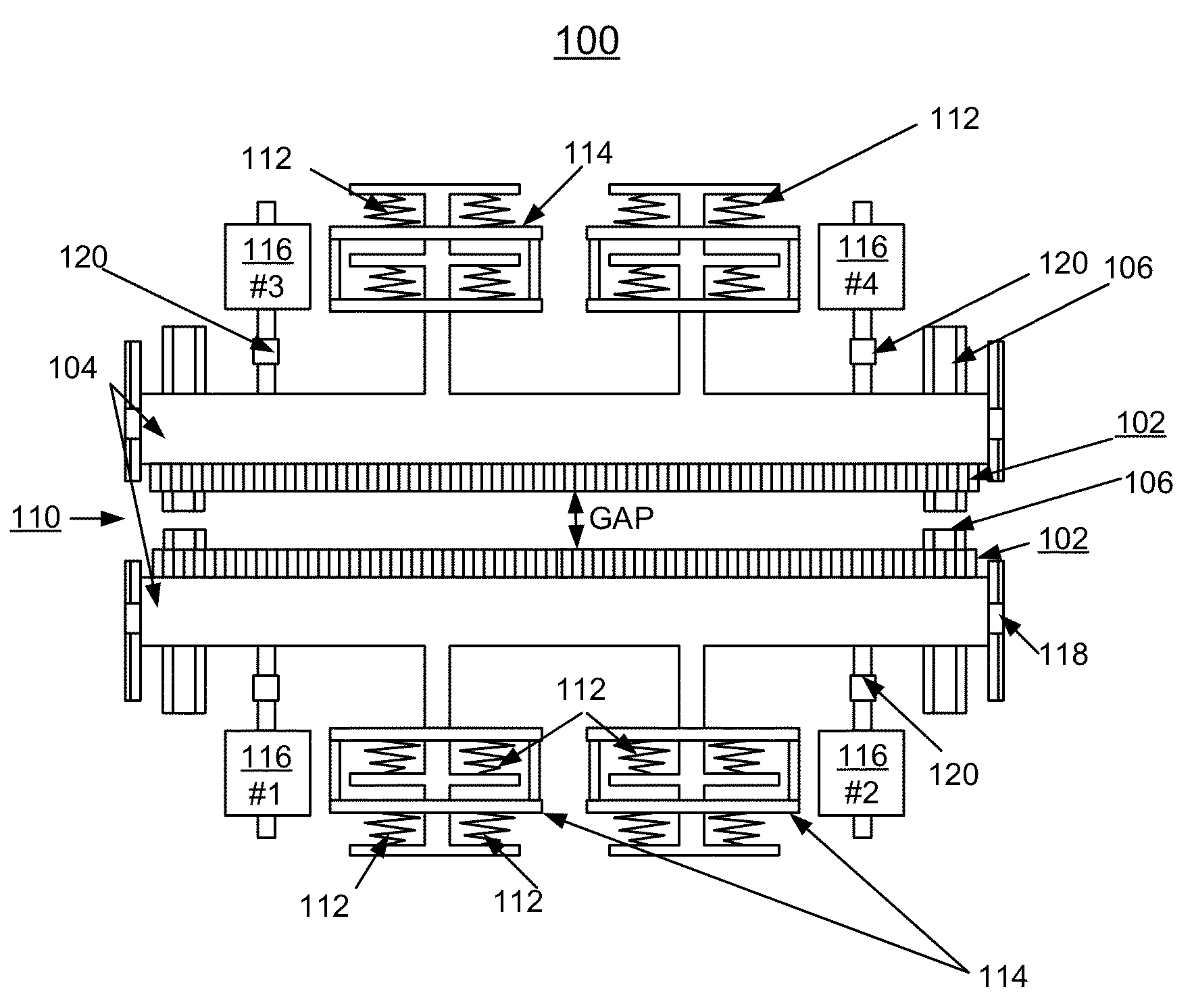
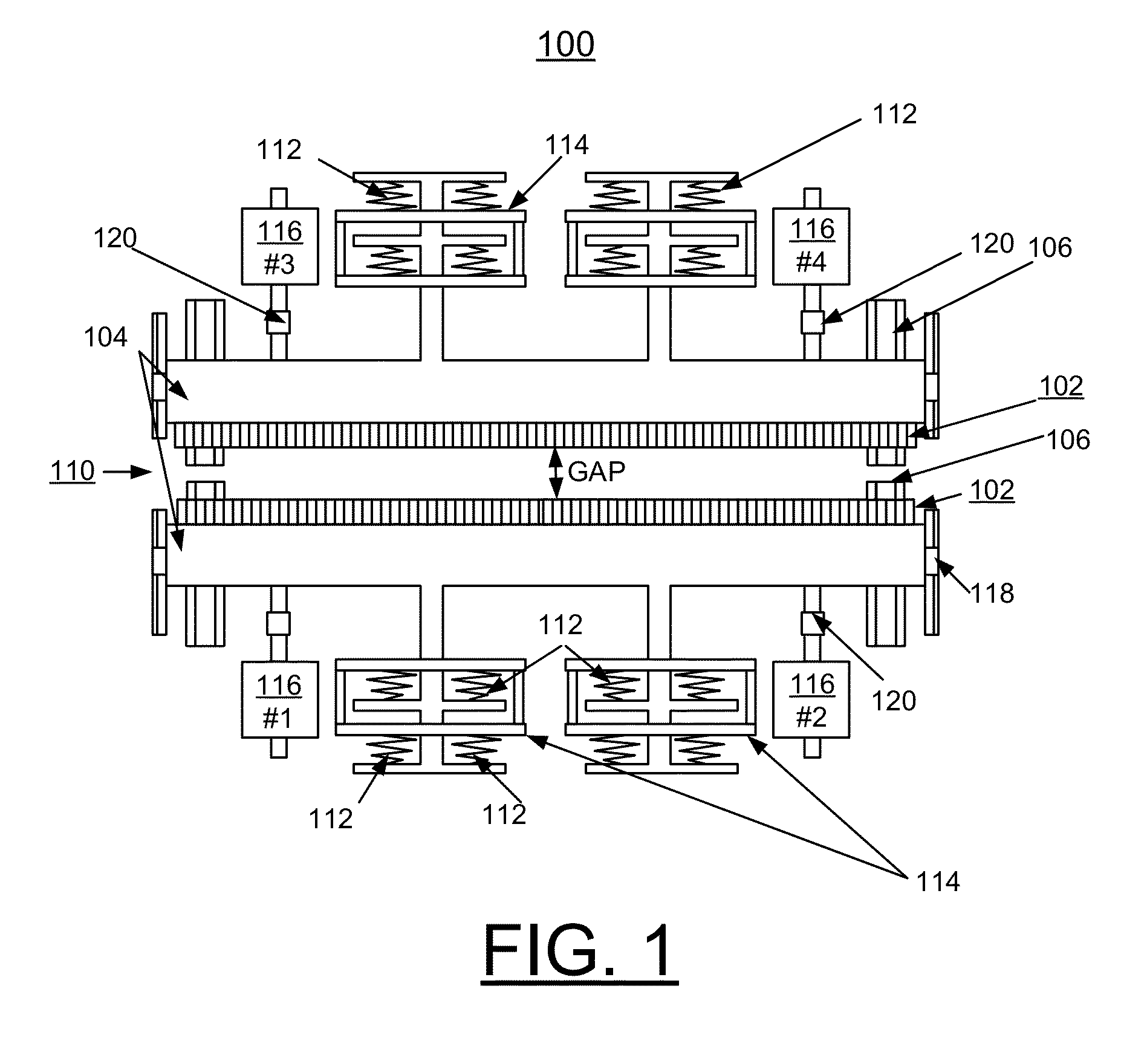
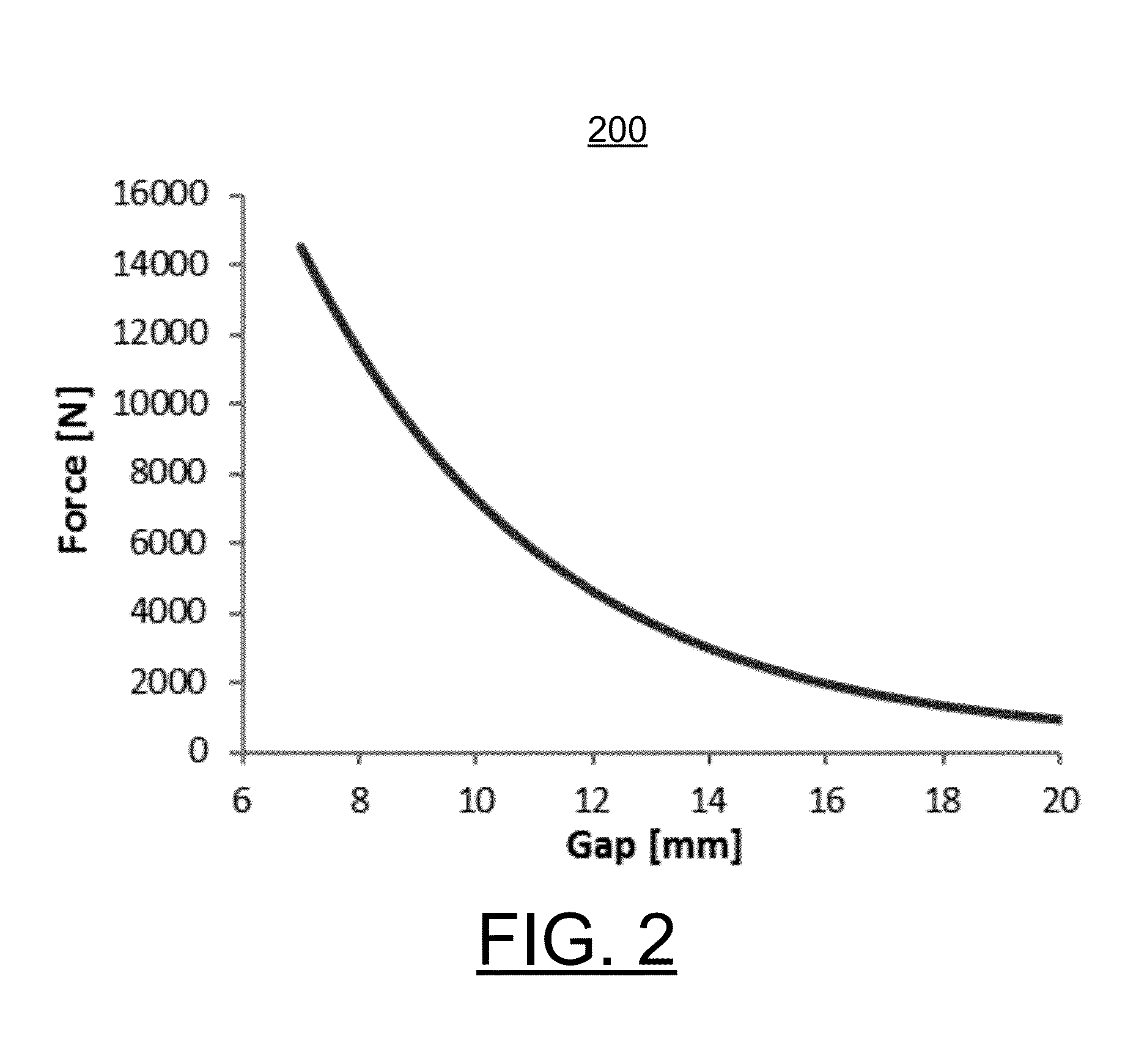
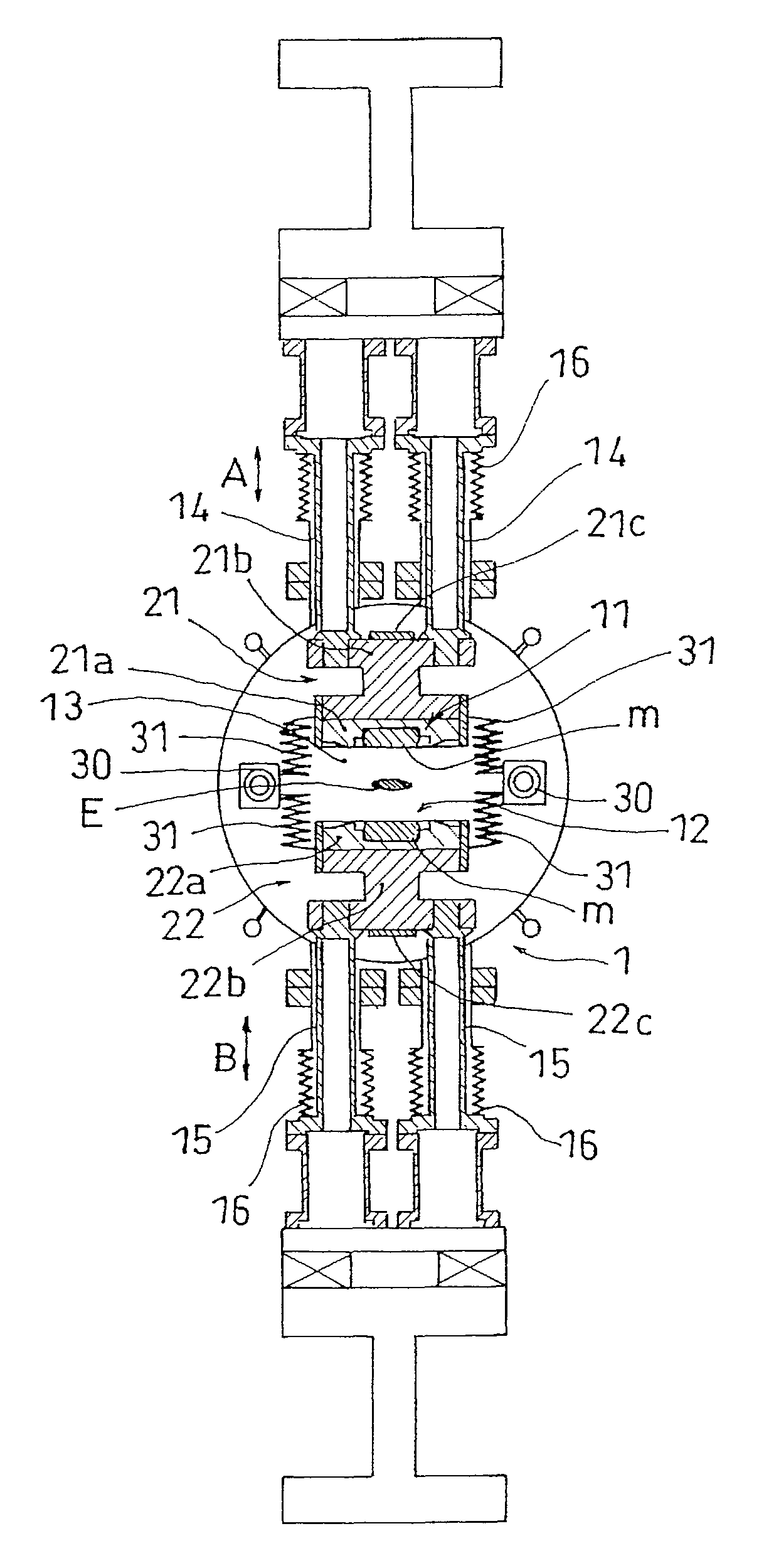
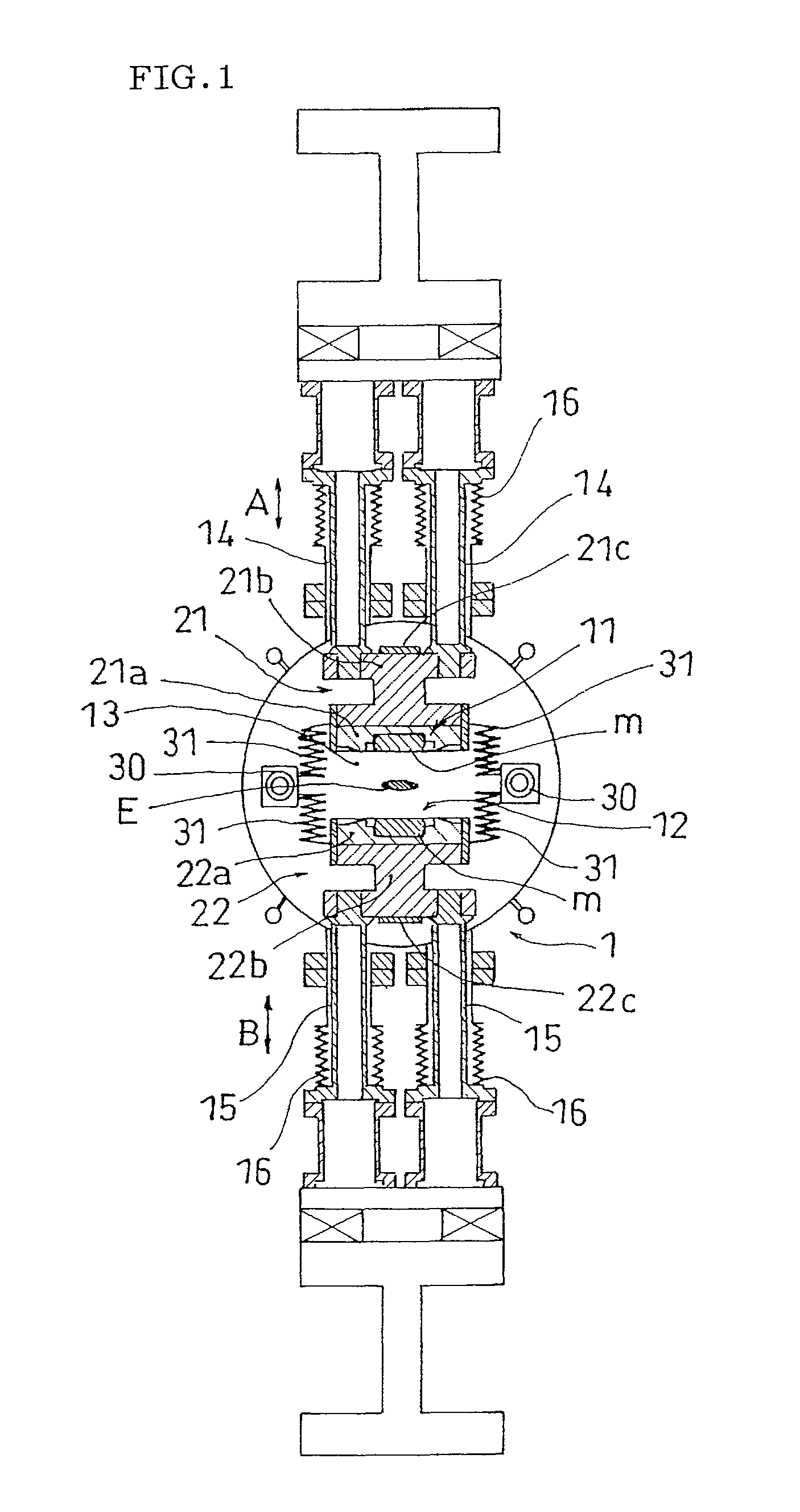
Undulator with dynamic compensation of magnetic forces
ActiveUS20160064129A1Overcome disadvantagesReliable and reproducible generationPermanent magnetsAcceleratorsMagnetic tension forceUndulator
A method and apparatus for implementing dynamic compensation of magnetic forces for undulators are provided. An undulator includes a respective set of magnet arrays, each attached to a strongback, and placed on horizontal slides and positioned parallel relative to each other with a predetermined gap. Magnetic forces are compensated by a set of compensation springs placed along the strongback. The compensation springs are conical springs having exponential-force characteristics that substantially match undulator magnetic forces independently of the predetermined gap. The conical springs are positioned along the length of the magnets.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
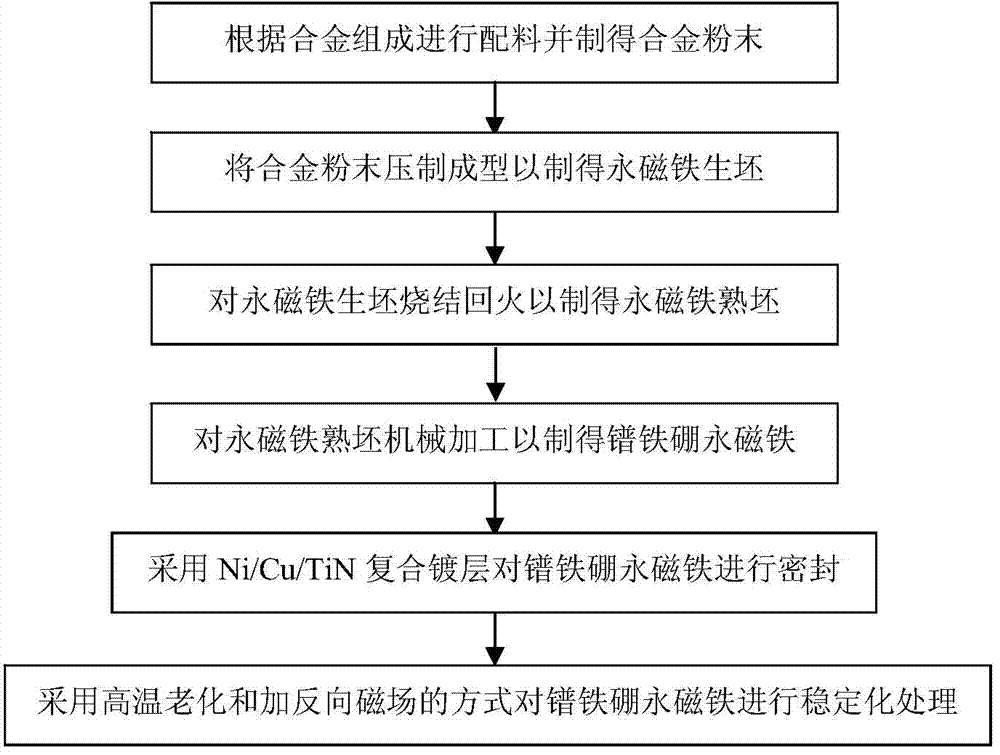
Praseodymium-Ferrum-Boron permanent magnet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103489620AStrong magnetismReduce manufacturing costInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsAlloyBoron
The invention provides a Praseodymium-Ferrum-Boron permanent magnet and a preparation method of the Praseodymium-Ferrum-Boron permanent magnet. The permanent magnet is made from an alloy with a mass percent represented by Pr<30.3+a+b>Fe<67.16-x-y-z>Cu<x>Nb<y>Al<z>B<1.04>, wherein a+b represents the lost mass percent of praseodymium in oxidization and melting processes; a+b is not larger than 1.5, x is not smaller than 0.15 and not larger than 0.20, y is not smaller than 0.14 and not larger than 0.5, and z is not smaller than 0.4 and not larger than 0.55. The Praseodymium-Ferrum-Boron permanent magnet can achieve high Br and high Hci simultaneously at normal temperature and is excellent in magnetic performance, low in preparation cost, and good in magnetic field stability, magnetic field homogeneity and plating airtightness; the Praseodymium-Ferrum-Boron permanent magnet can realize practical application in the engineering of high-precision low-temperature permanent magnet devices such as cryogenic permanent magnet undulators (CPMU) as well as in the fields of space instruments and meters.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Free-electron laser driven by fiber laser-based laser plasma accelerator
ActiveUS20160226212A1High repetition rateExtreme UltraVioletExcitation process/apparatusX-ray tube with very high currentPlasma accelerationLight beam
A Free Electron Laser source includes: a fiber-based laser having a plurality of amplifying fibres wherein an initial laser pulse is distributed and amplified, and element for grouping together the elementary pulses amplified in the fibre in order to form an a single amplified global laser pulse; a laser plasma accelerator wherein the global laser pulse generates relativistic electron beams, a beam focusing system transporting electron beams from the laser plasma accelerator, an undulator wherein relativistic electron beams generate an electromagnetic beam, and a beam separator system, wherein the electron beam and the electromagnetic beam are separated.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE
Method for enabling high-brightness, narrow-band orbital radiation to be utilized simultaneously on a plurality of beam lines
InactiveUS20050175042A1Radiation/particle handlingExcitation process/apparatusEnergy recovery linacElectron bunches
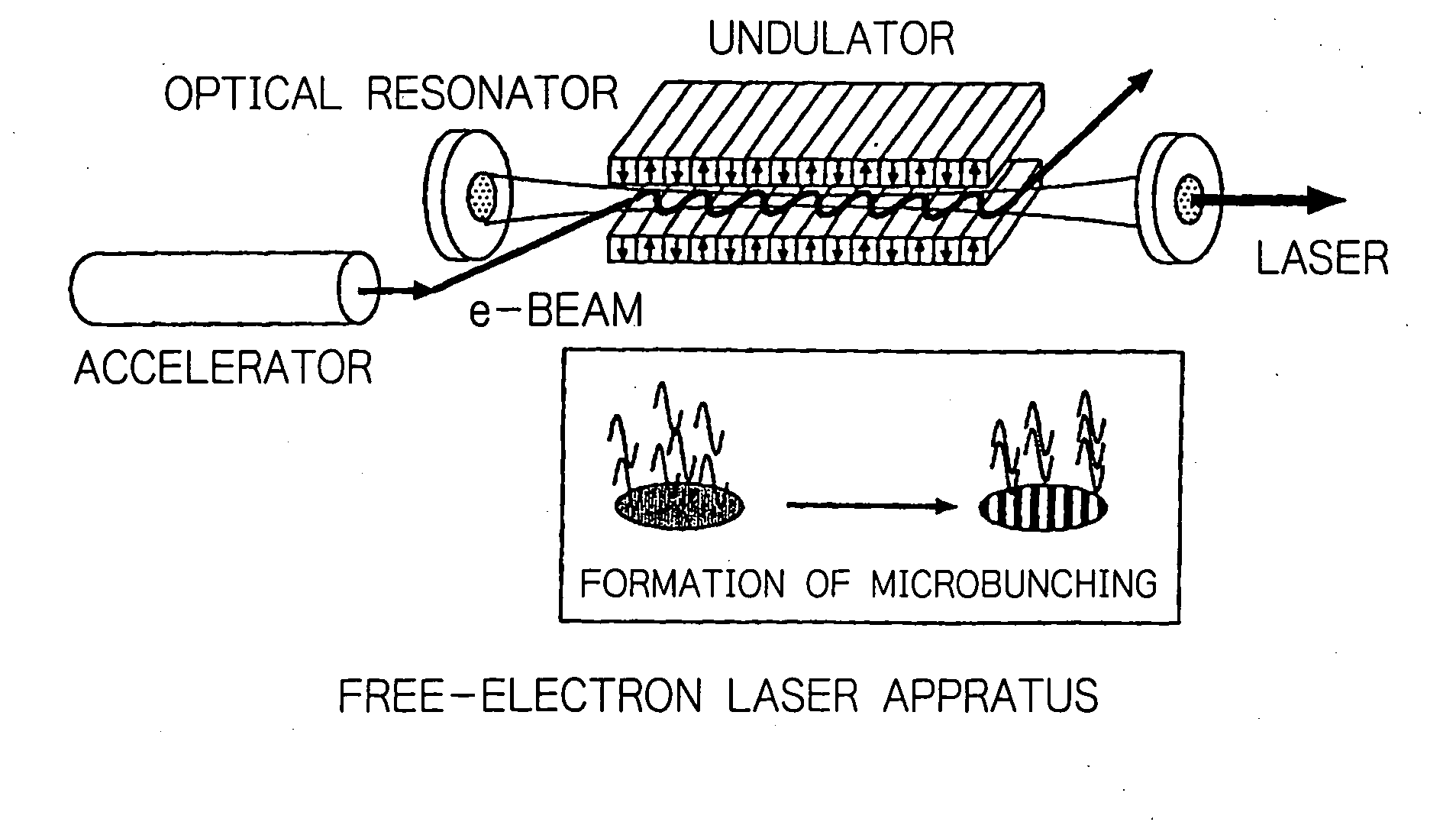
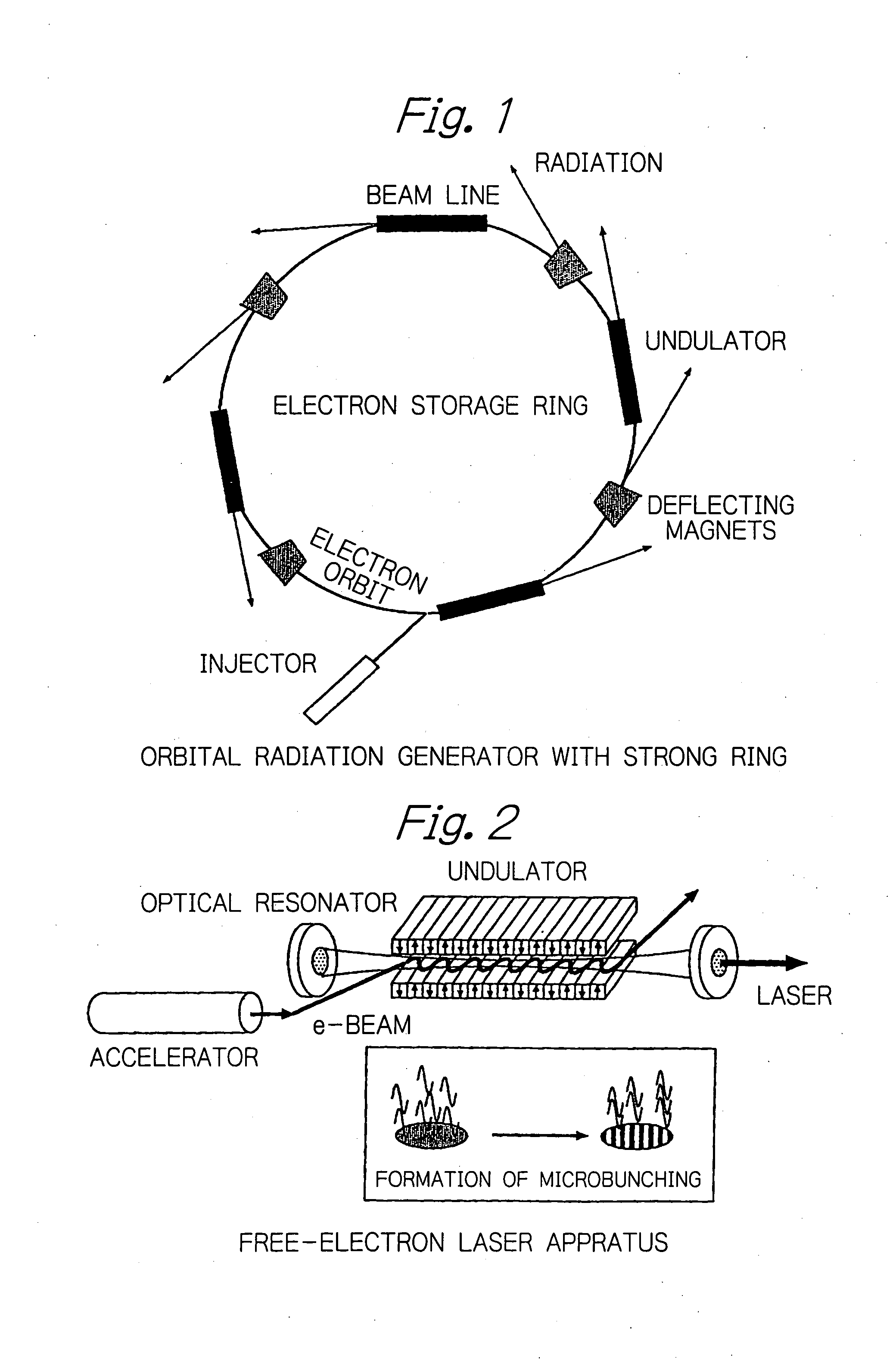
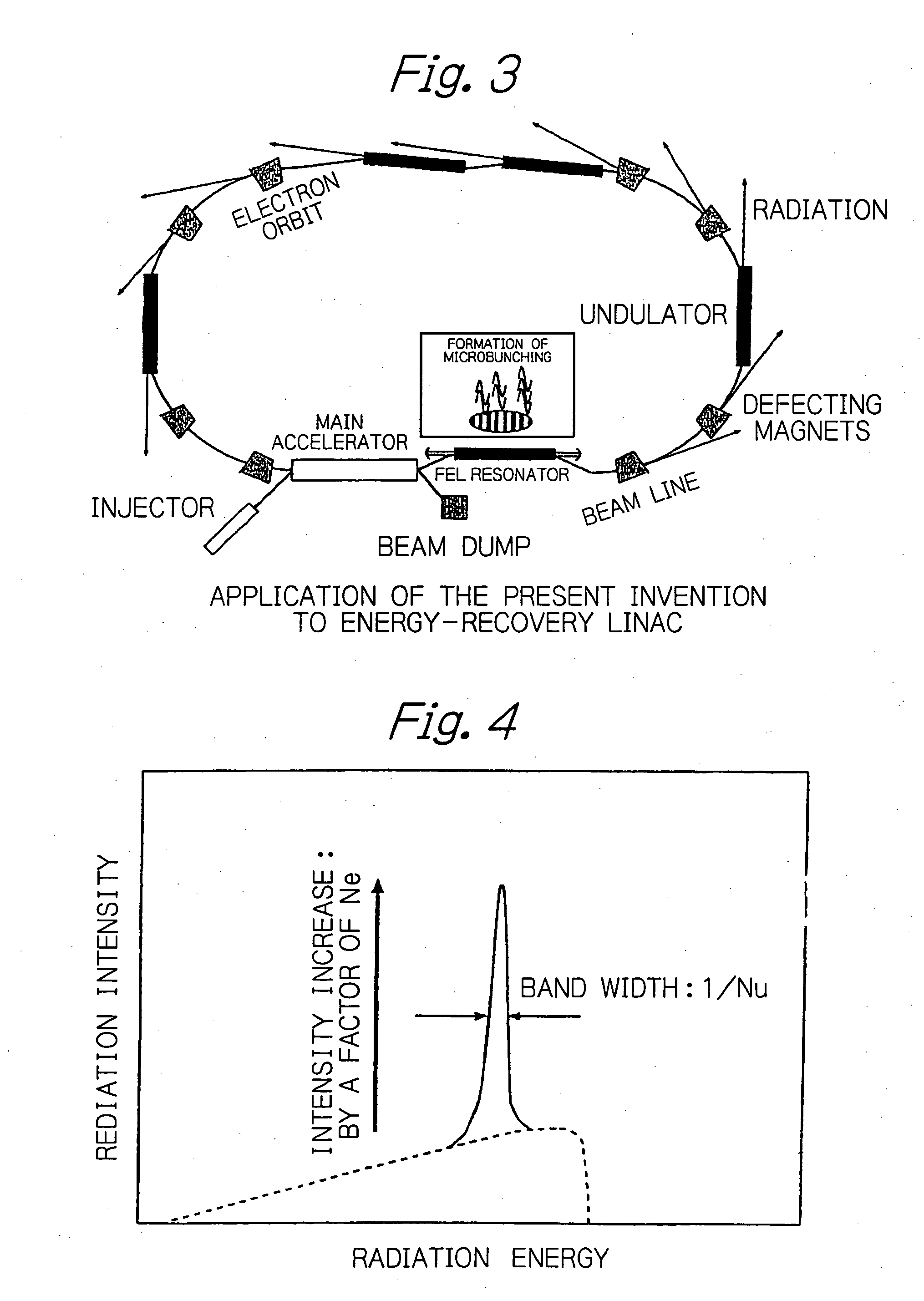
In an electron accelerator such as an electron storage ring, a linac or an energy-recovery linac, accelerated electron bunches are subjected to light-electron interaction to have a varying profile of electron density and the thus modulated electron bunches are passed between deflecting magnets or injected into an undulator to generate high-brightness, narrow-band orbital radiation, thereby enabling high-brightness, narrow-band orbital radiation to be utilized simultaneously on a plurality of beam lines.
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
Dielectric laser electron accelerators
ActiveUS20140070732A1Improved accelerator performanceSimplify the manufacturing processExcitation process/apparatusTransit-time tubesDielectricGrating
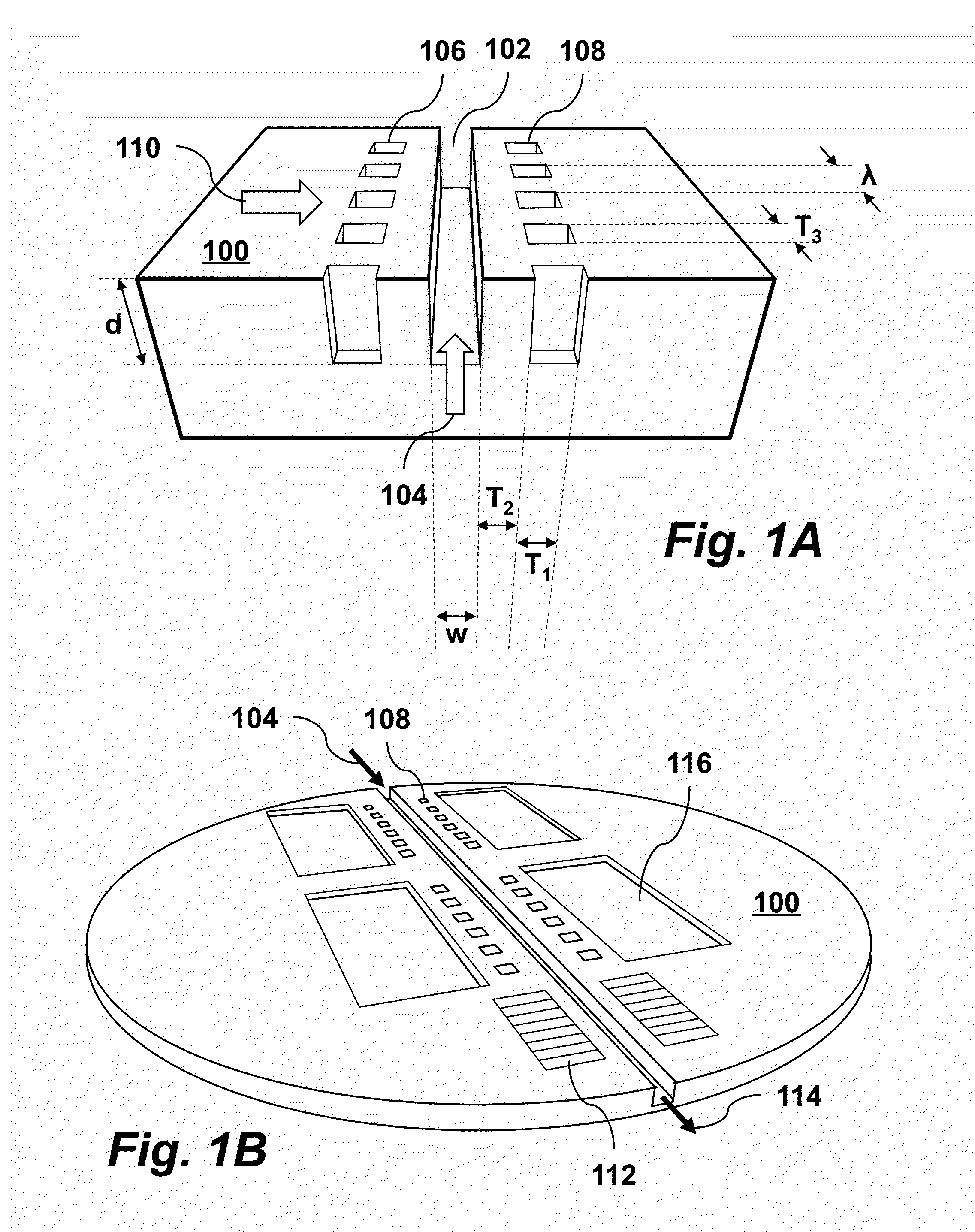
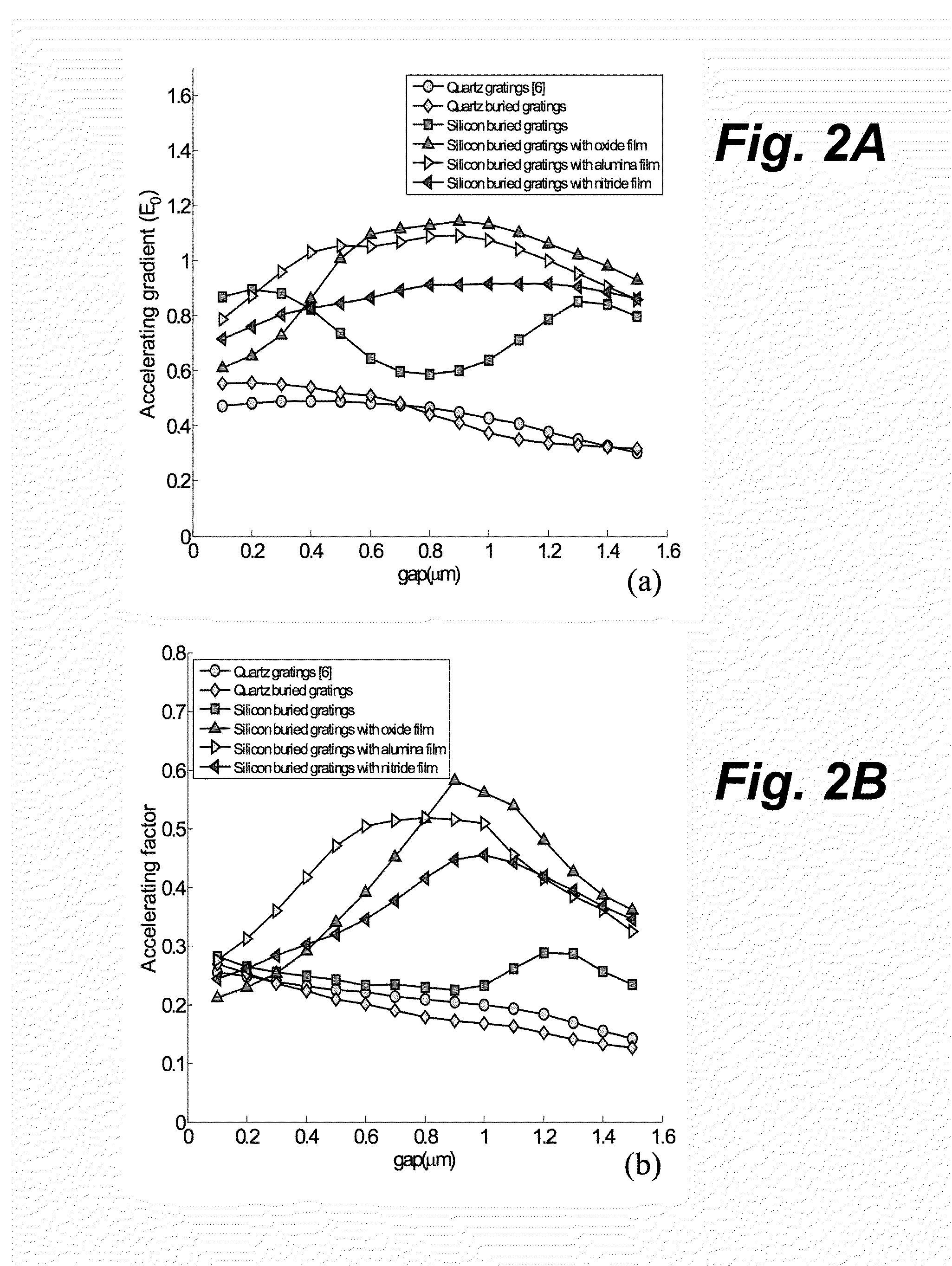
A laser-driven dielectric electron accelerator is composed of a dielectric photonic crystal accelerator structure having an electron beam channel and buried grating whose elements are arranged linearly parallel to the electron beam channel. The accelerator structure preferably has a thin film material coating. The grating may have an asymmetric structure. The accelerator and undulator structures may be integrated with on-chip optical and electronic devices such as waveguide devices and control circuits so that multiple devices can be fabricated on the same chip.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
DC high-voltage super-radiant free-electron based EUV source
InactiveUS20140239805A1Correction for dispersionLaser detailsDirect voltage acceleratorsPotential differenceSubject matter
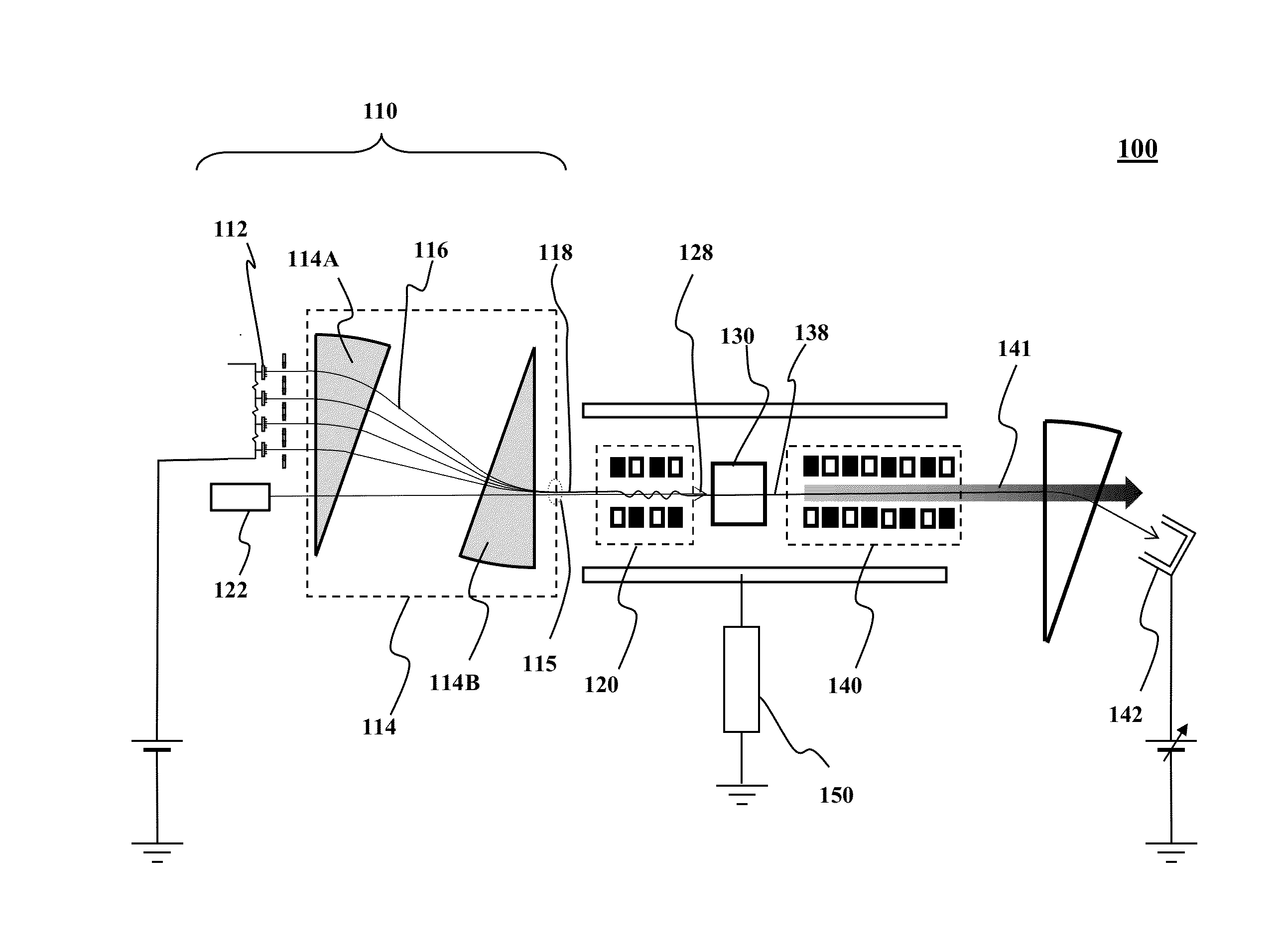
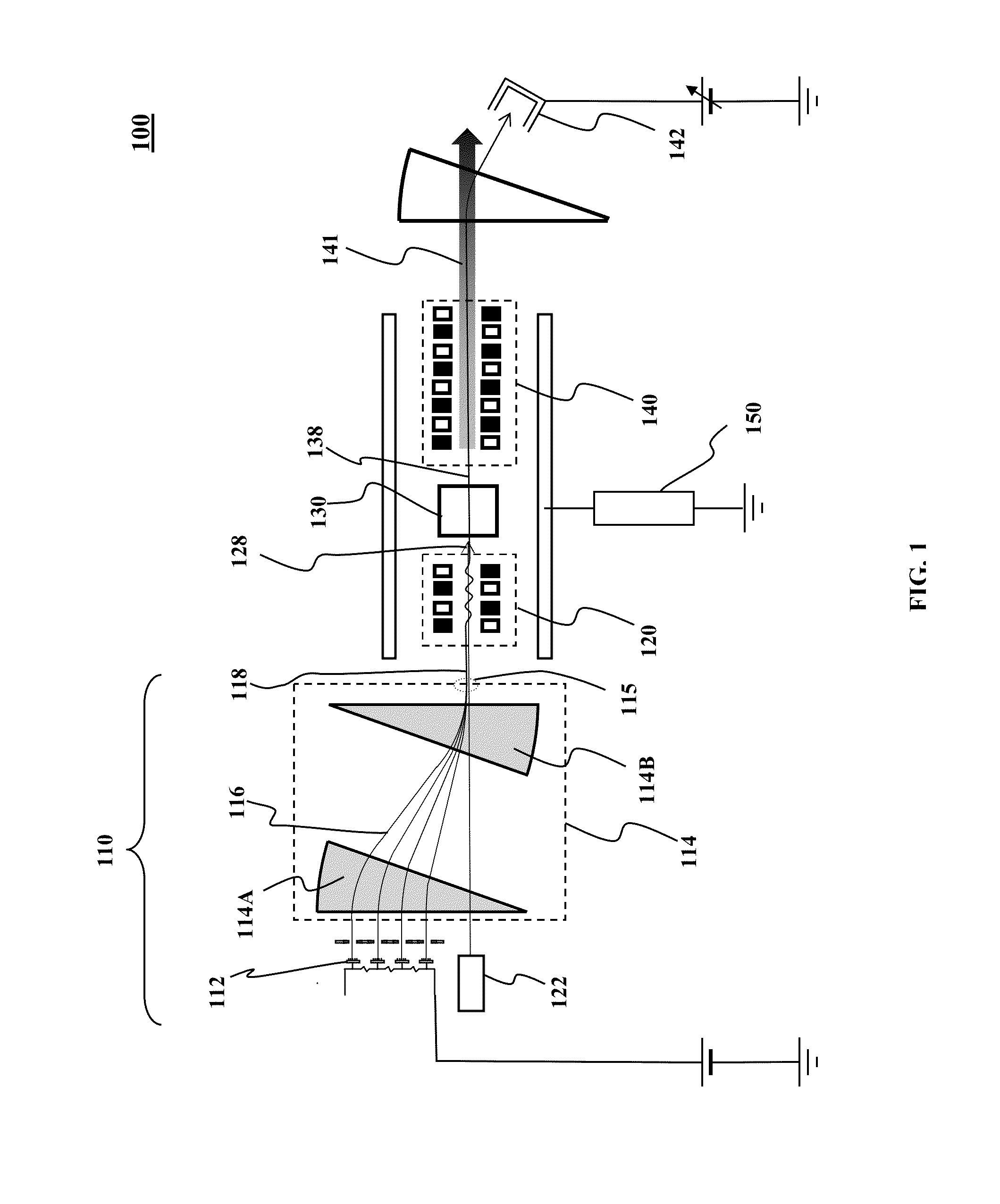
An array of spatially separated beamlets is produced by a corresponding array of charged particle emitters. Each emitter is at an electrostatic potential difference with respect to an immediately adjacent emitter in the array. The beamlets are converged laterally to form an charged particle beam. The beam is modulated longitudinally with infrared radiation to form a modulated beam. The charged particles in the modulated beam are bunched longitudinally to form a bunched beam. The bunched beam may be modulated with an undulator to generate a coherent radiation output. This abstract is provided to comply with rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
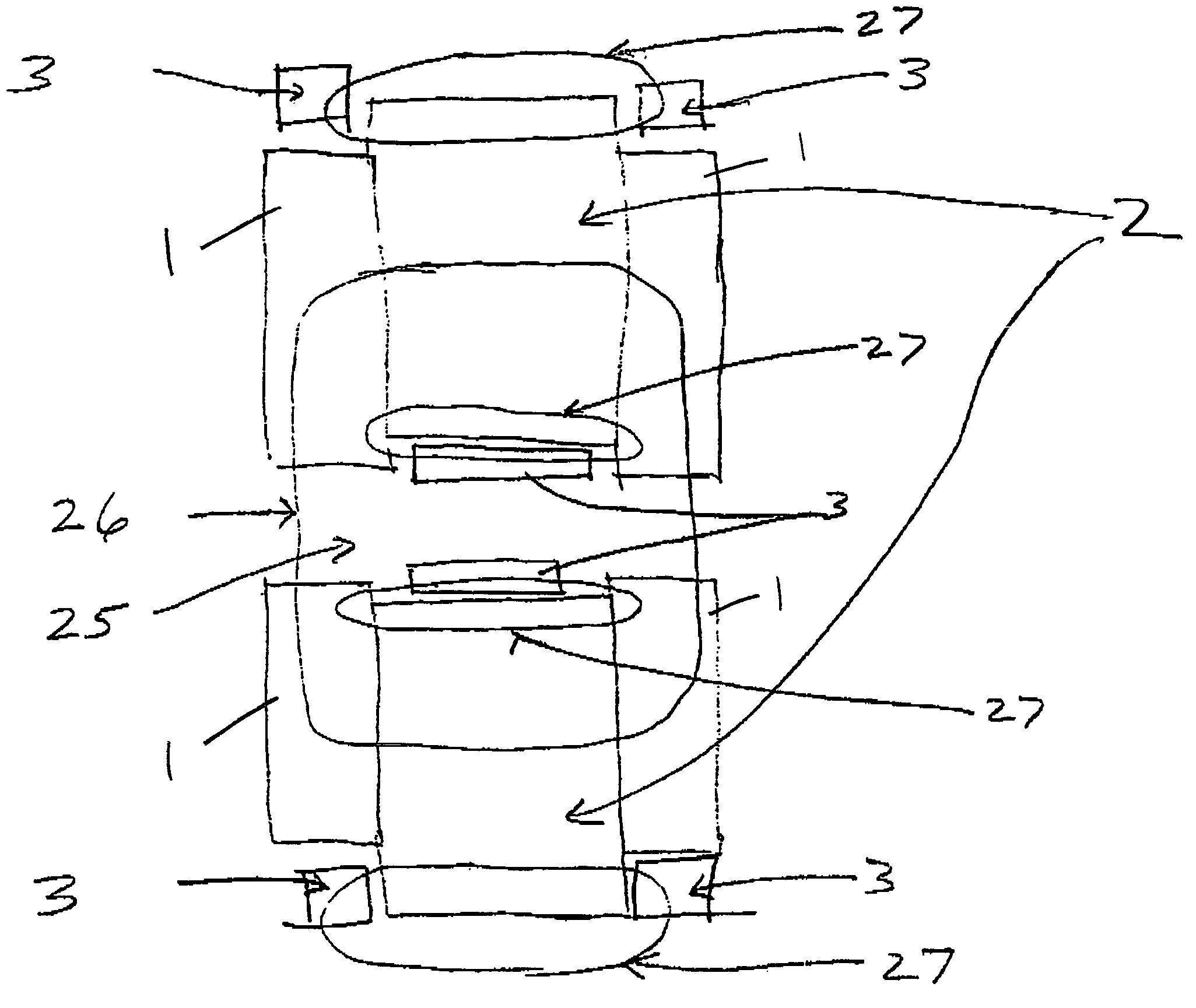
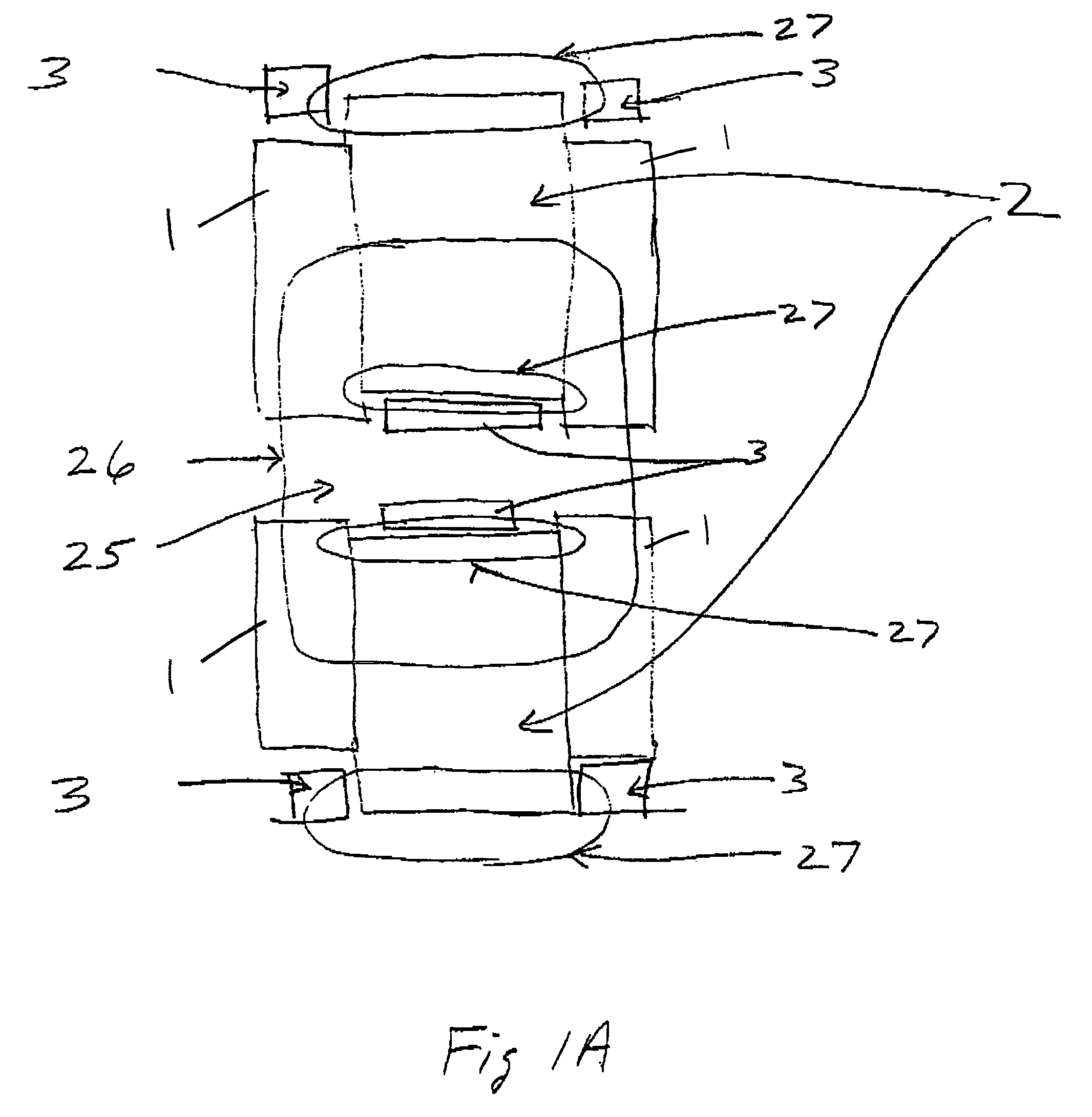
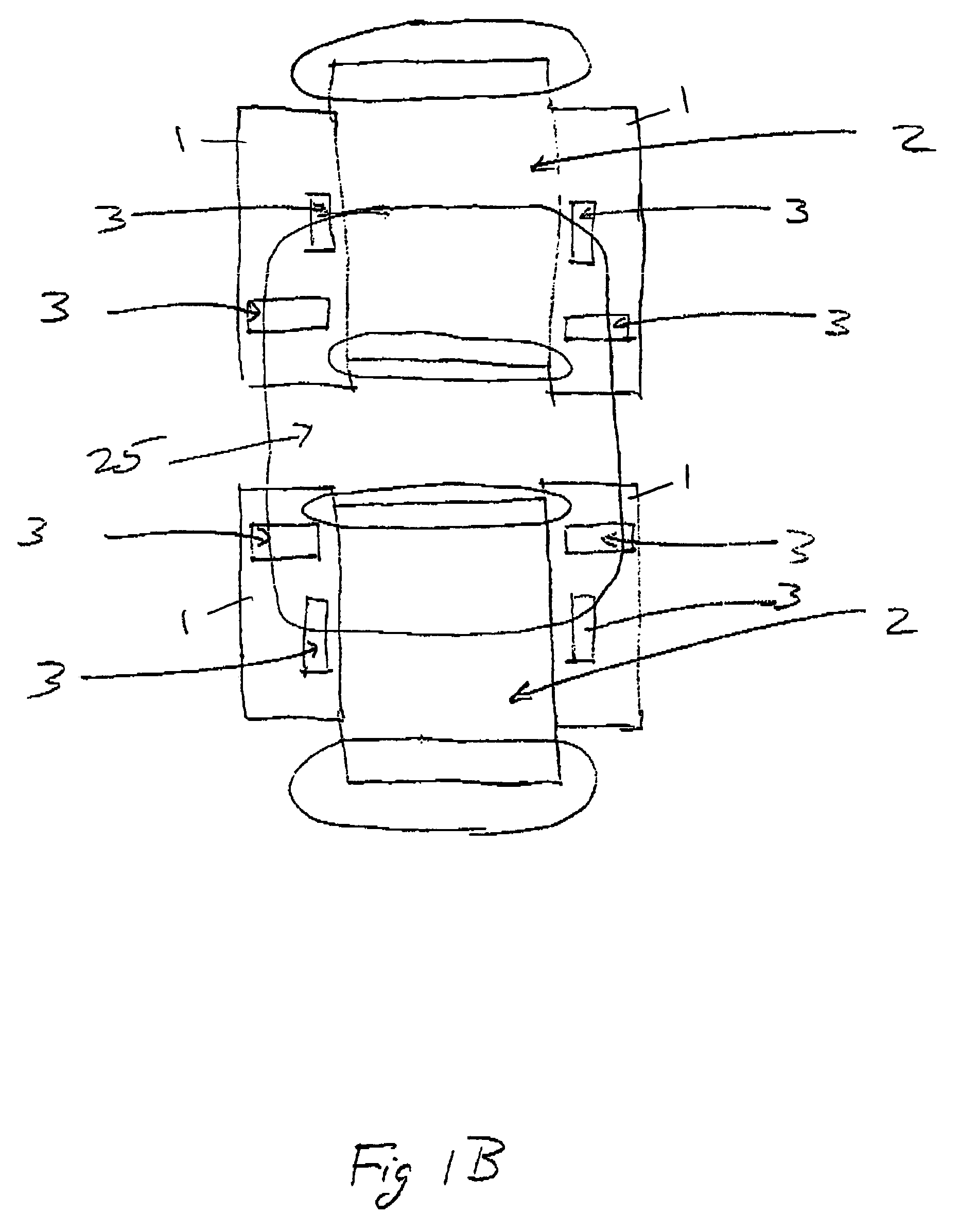
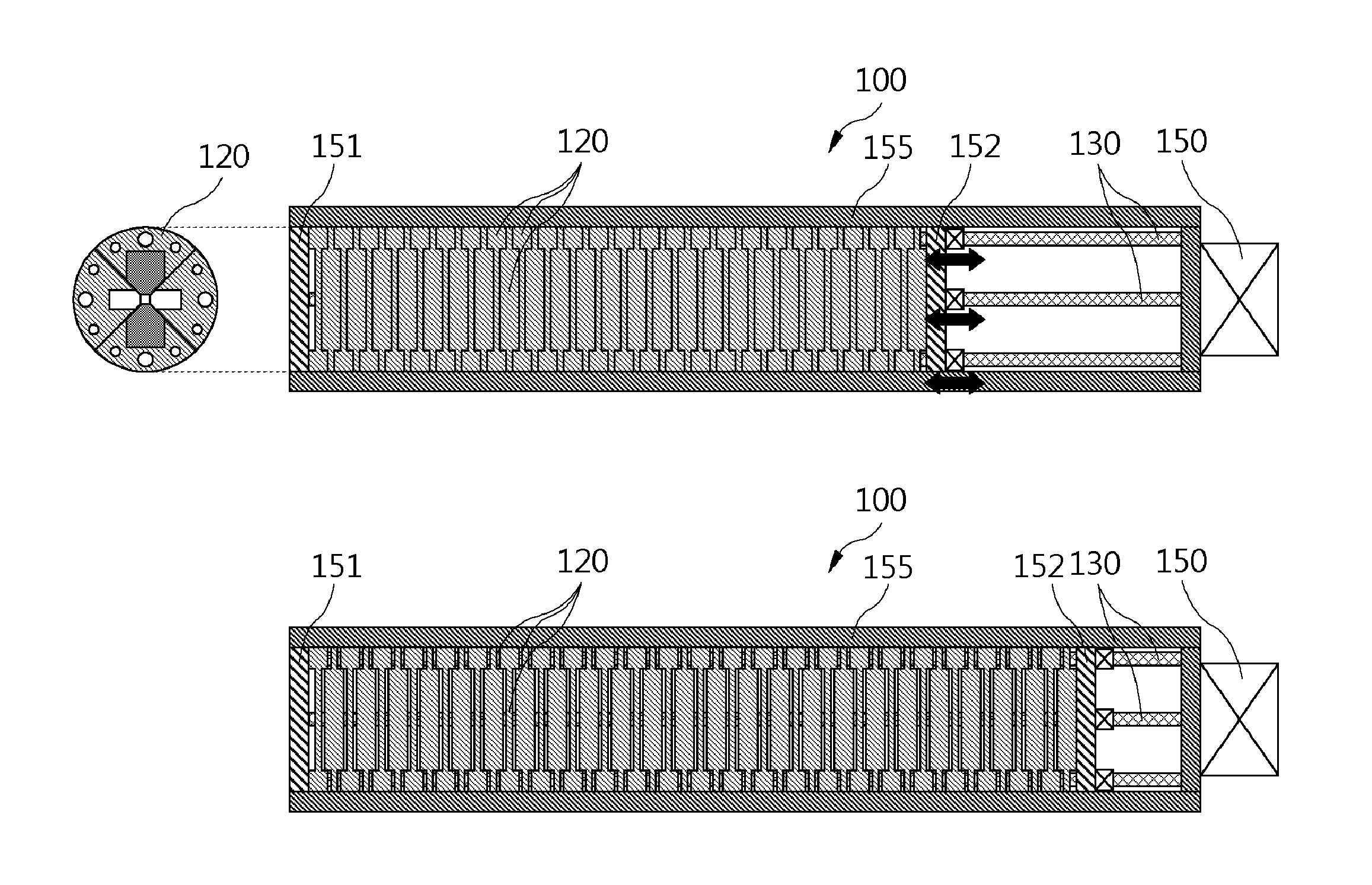
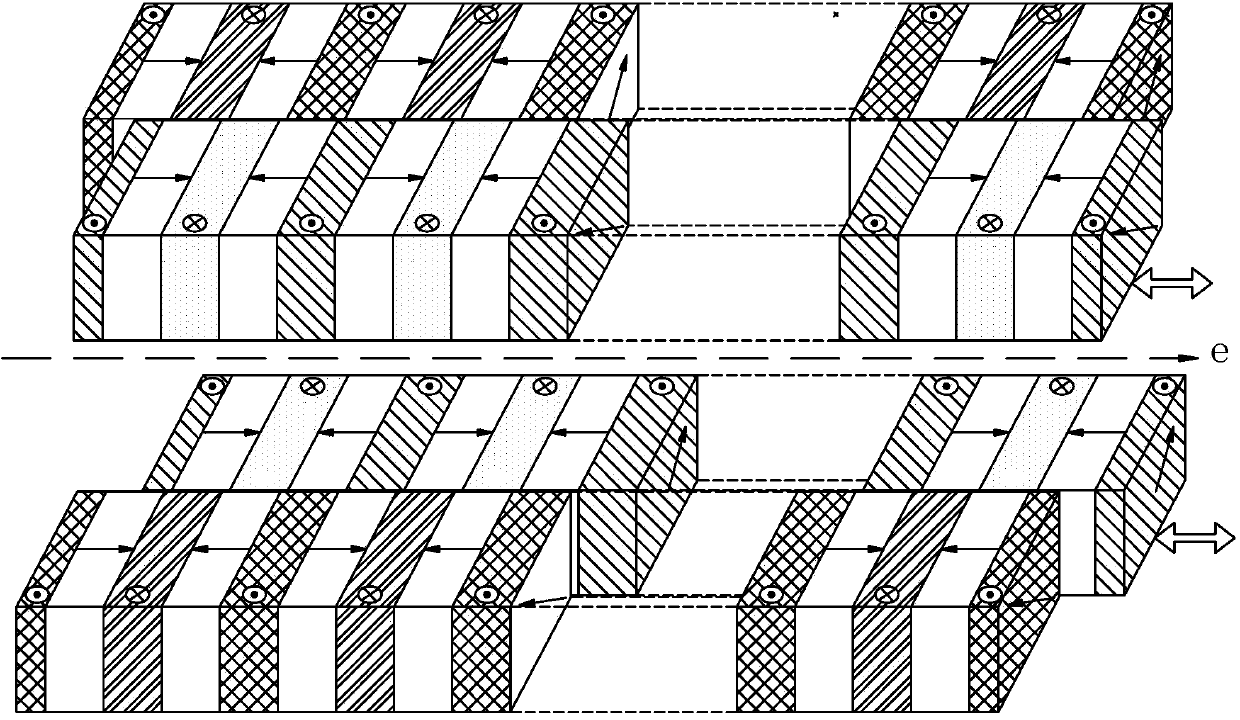
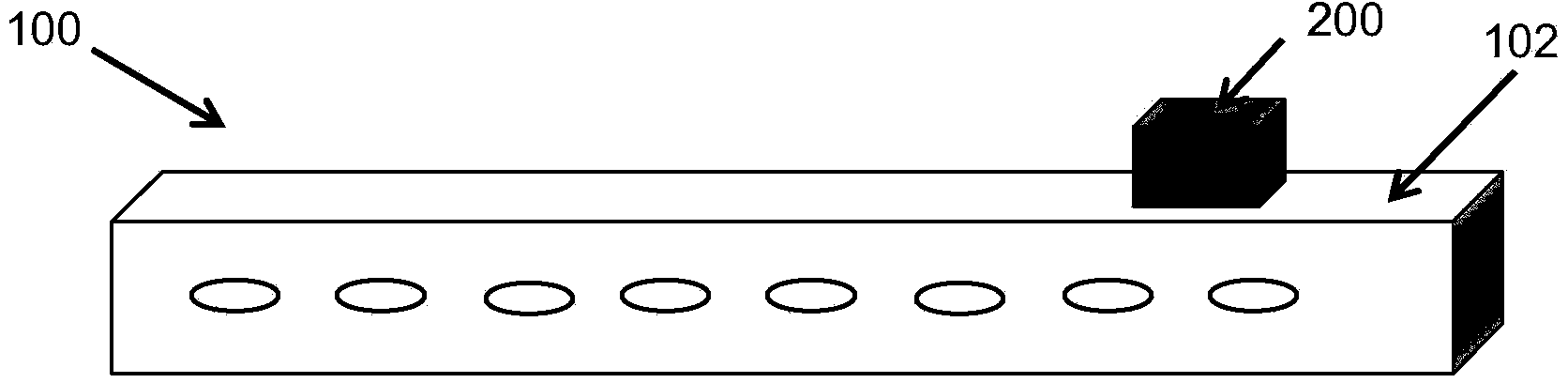
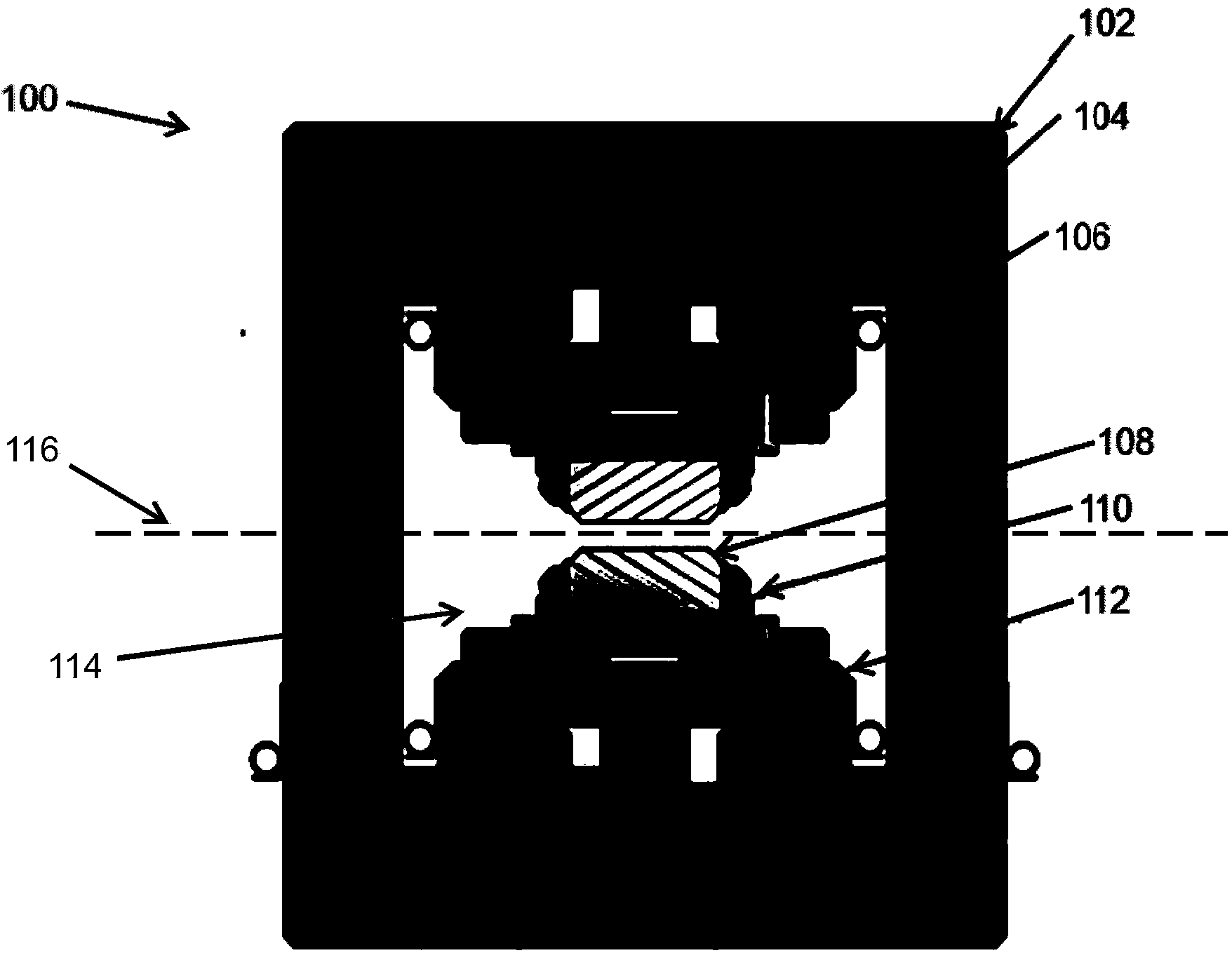
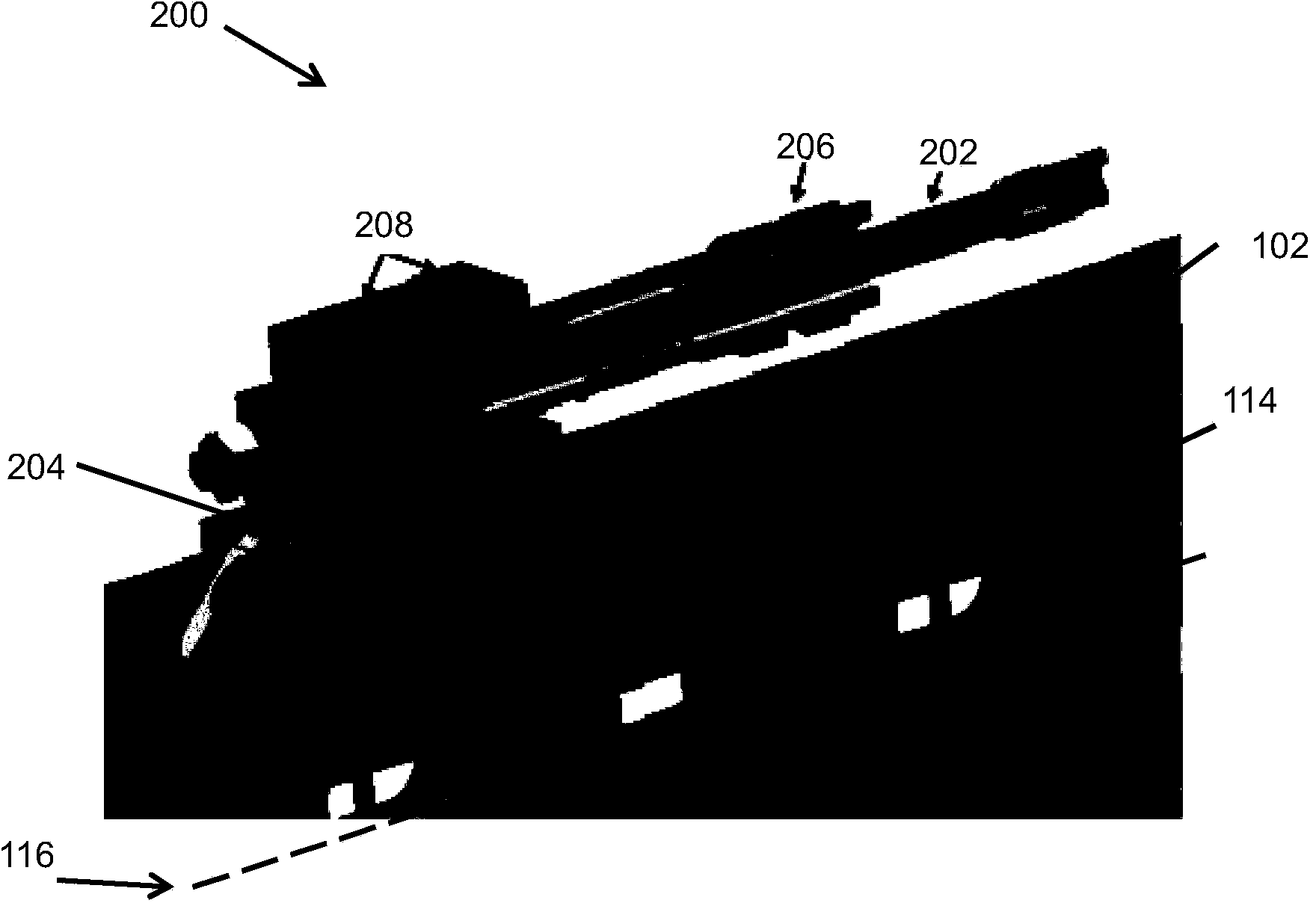
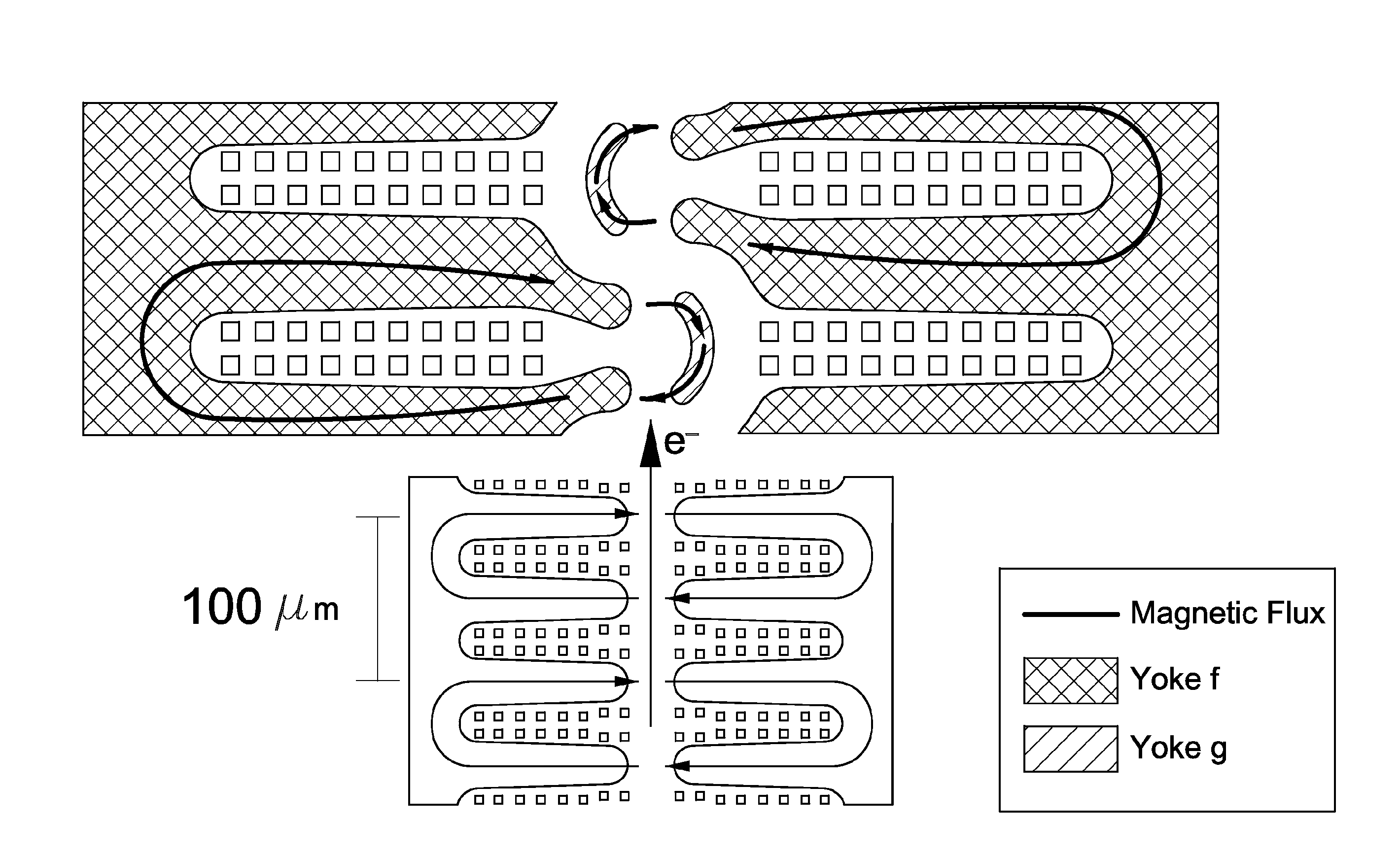
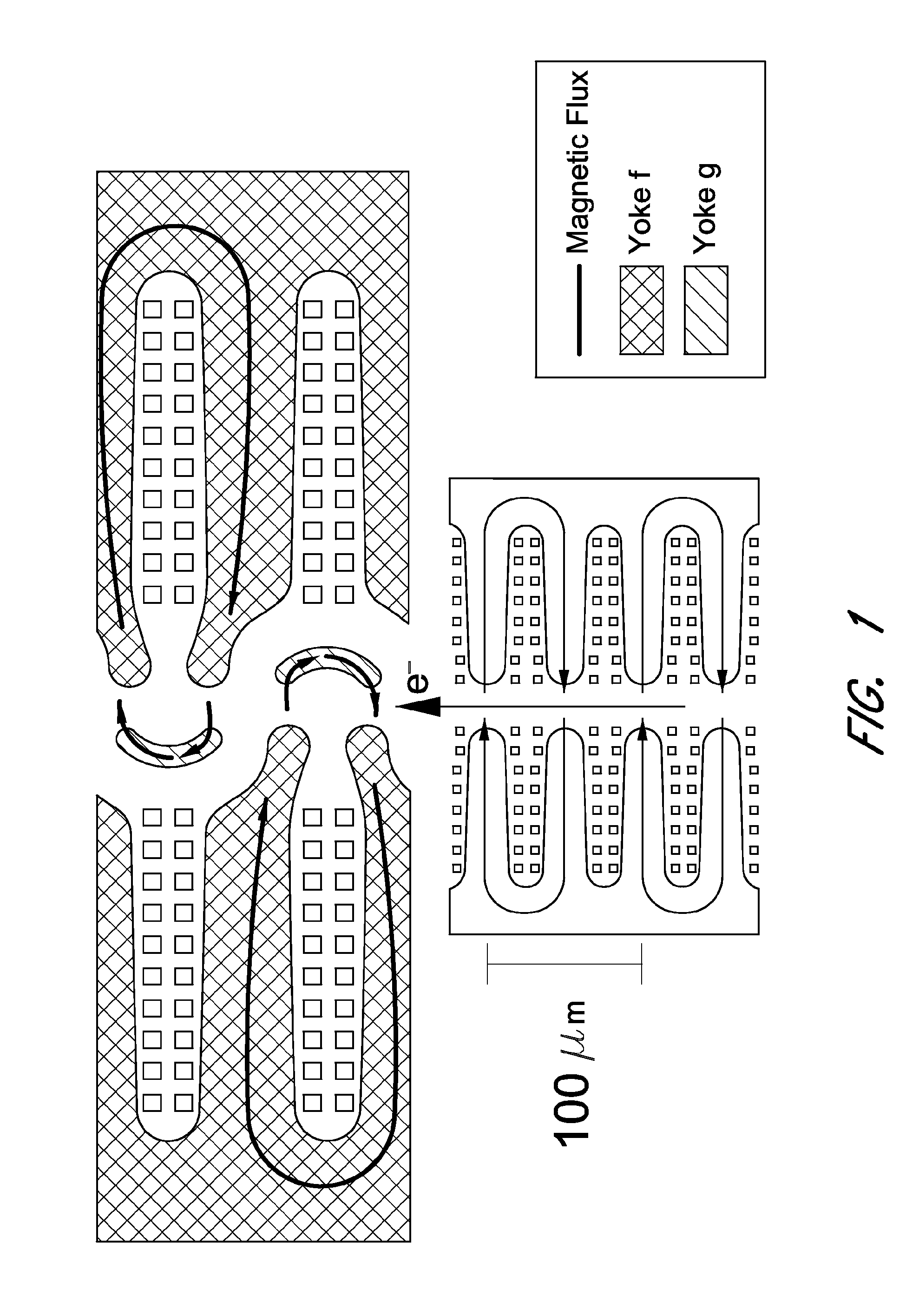
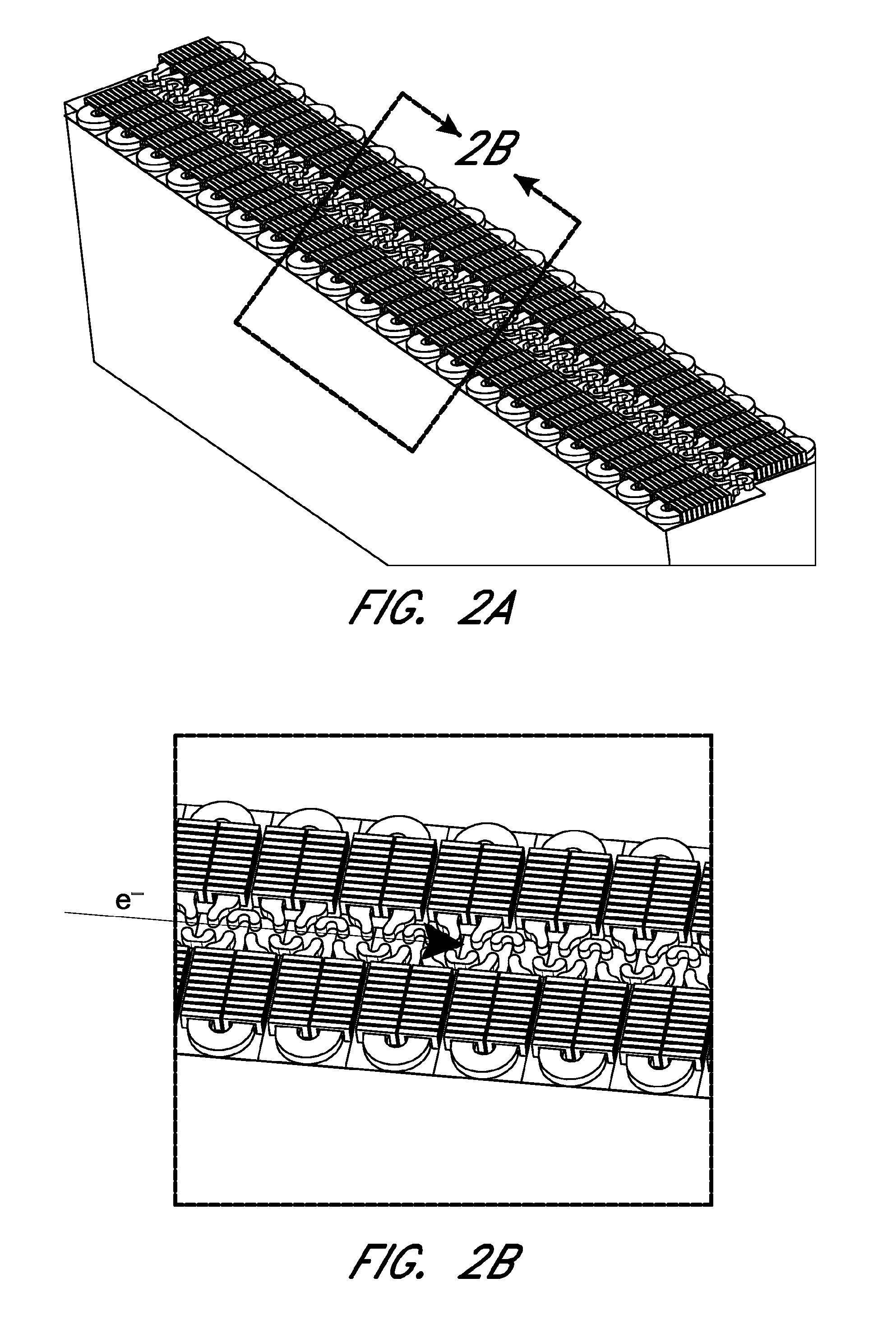
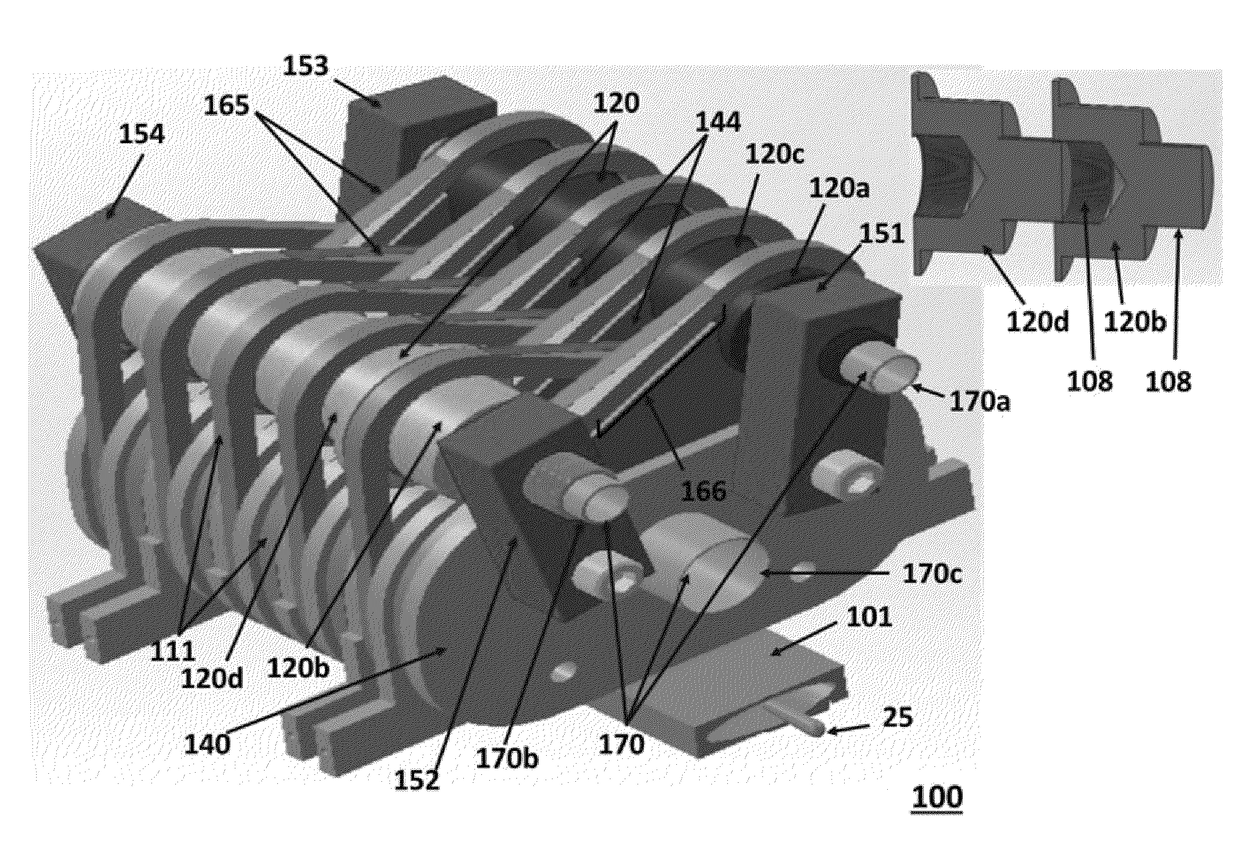
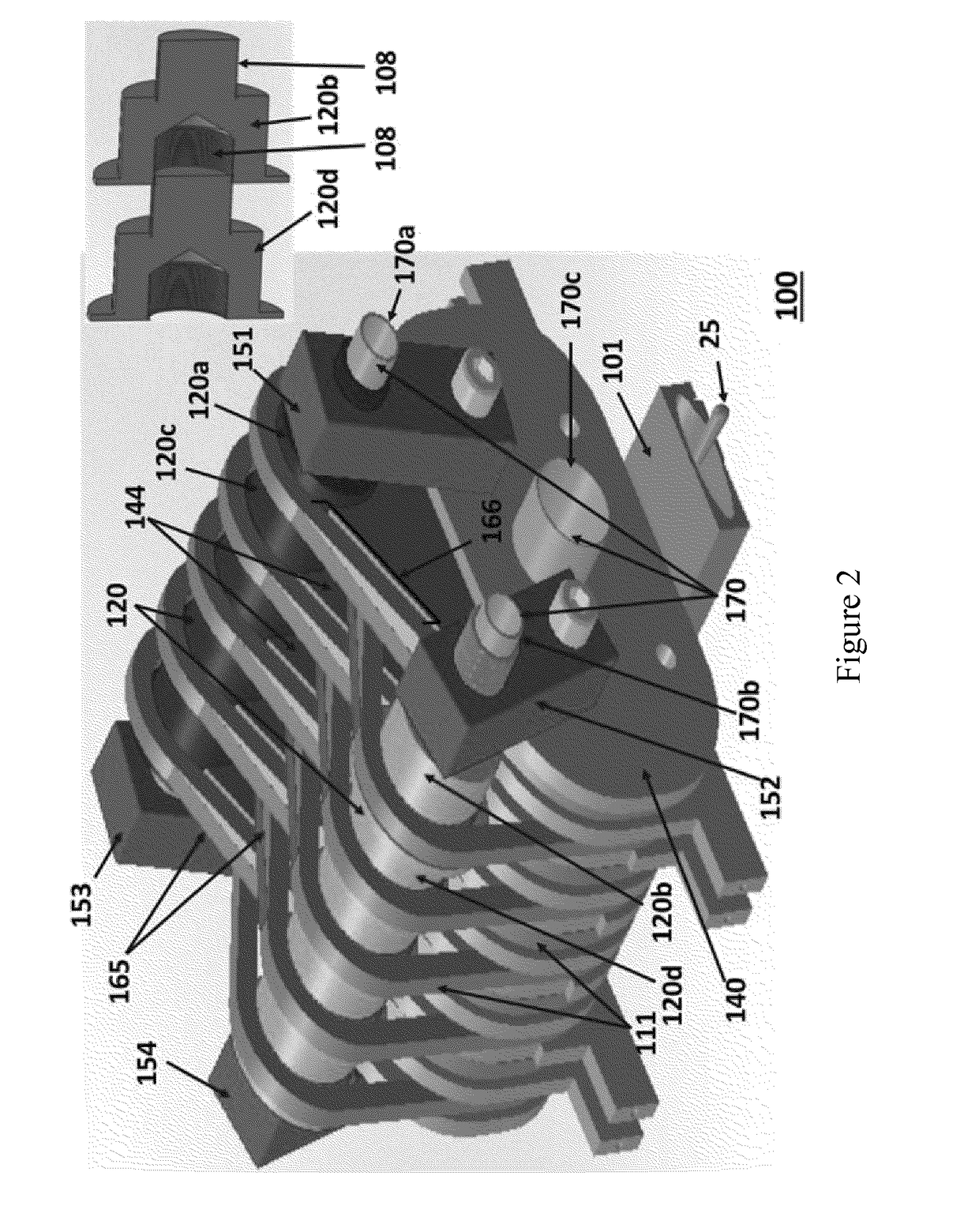
Undulator
ActiveUS7872555B2Improve featuresIntense magnetic fieldRadiation/particle handlingExcitation process/apparatusRoom temperatureVacuum chamber
Owner:RIKEN +1
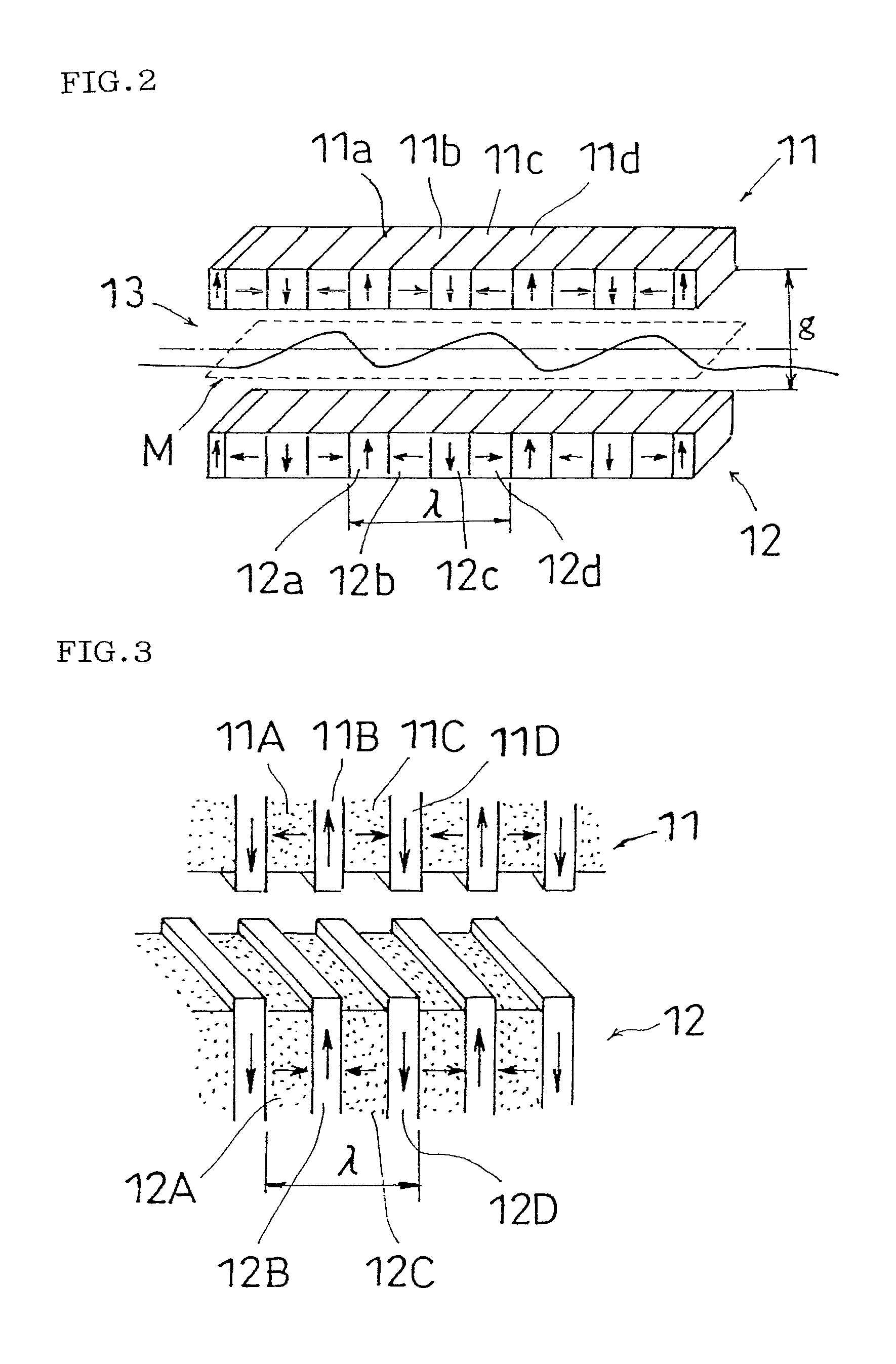
Variable-cycle permanent-magnet undulator
ActiveUS20150255201A1Wavelength stableSufficient strong magnetic fieldMagnetic resonance acceleratorsPermanent magnetsEngineeringUndulator
A variable-period permanent-magnet undulator which is applicable not only to a planar undulator but also to a helical undulator, in which permanent-magnets and ferromagnetic substances are alternately arranged, and the ferromagnetic substance interposed between the permanent-magnets is saturated to thus enable the magnets to be effectively spaced apart from each other by the repulsive force between the permanent-magnets, thereby adjusting the period of the magnetic field in an easy and precise manner.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Undulator
ActiveCN104409129AReduce heat loadReduce the number of rowsMagnetic resonance acceleratorsPermanent magnetsLight beamPairwise coupling
The invention provides an undulator. The undulator at least comprises M permanent magnet cycles which are sequentially arranged along the direction to which an electron beam transmits; each permanent magnet cycle is composed of four rows of permanent magnet structures, each row comprising N rows of permanent magnet sets, wherein each row of permanent magnet sets comprises K permanent magnet units; M, N and K are all the natural numbers more than and equal to 1; the permanent magnet structures in the four rows are pairwise coupled and then are oppositely arranged at two sides in the along to which the electron beam transmits and relatively displace to form at least one combined magnetic field through which the electron beam emits elliptically polarized light, circularly polarized light or linearly polarized light in any polarizing angle of 0 to 360 degrees, and the electron velocity direction is deviated from the direction of an axis of the undulator. The undulator has the advantages that either linearly polarized light or elliptically and circularly polarized lights can be produced, and the electron velocity direction is deviated from the direction of the axis of the undulator all the times, so that the thermal load of the synchronously-radiated beam lines can be greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
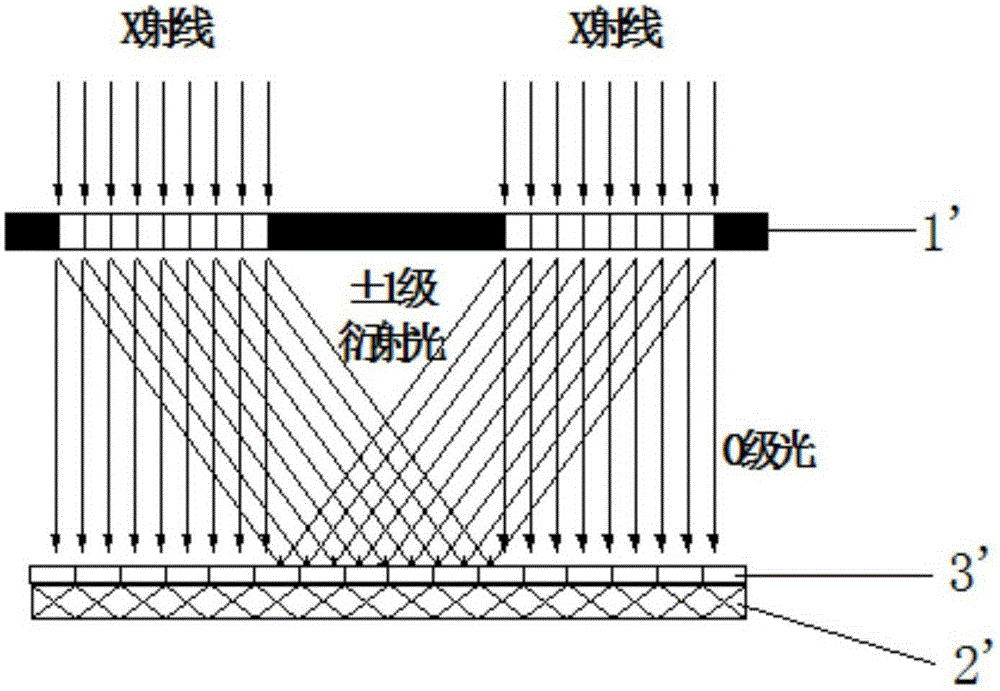
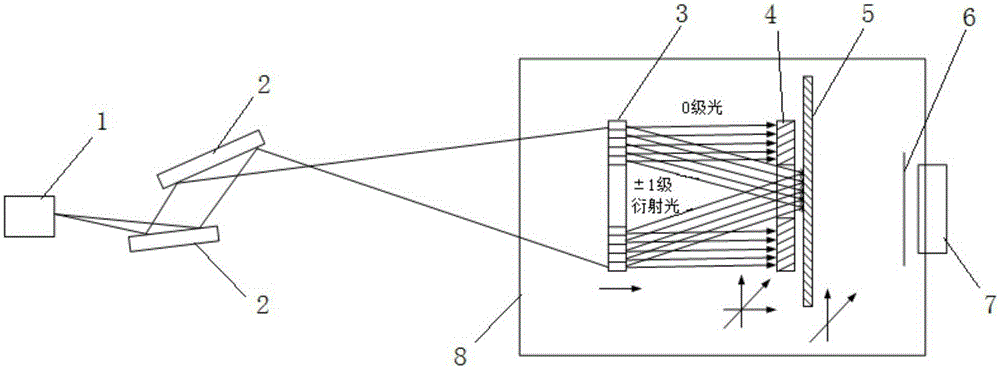
Synchrotron radiation X-ray large-area interference lithography system
ActiveCN105182701AAvoid exposureGuaranteed Alignment AccuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingBeam splitting
The invention relates to a synchrotron radiation X-ray large-area interference lithography system. The synchrotron radiation X-ray large-area interference lithography system comprises an undulator light source, multiple reflected focusing mirrors, a mask grating, a grading diaphragm with a diaphragm hole, a sample table with an observation hole, an aluminum film and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) detector which are arranged in sequence. According to the synchrotron radiation X-ray large-area interference lithography system disclosed by the invention, position alignment between the mask grating and the grading diaphragm is ensured by additionally arranging the grading diaphragm between the mask grating and a sample and by means of the CCD detector, so that the grading diaphragm has the capability of reliably sheltering 0-grade light generated by beam splitting passing the mask grating to prevent the 0-grade light from irradiating the sample, and therefore no 0-grade light region exists around a + / -1 grade diffracted light coherent region generated on the sample; accordingly, large-area splicing of an effective exposure area on the sample can be realized by moving the sample table. Meanwhile, X-ray is filtered by adopting the reflected focusing mirrors and the aluminum film, so that a relative position of the mask grating and the grading diaphragm can be observed clearly by using the CCD detector, and therefore the alignment precision therebetween can be ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
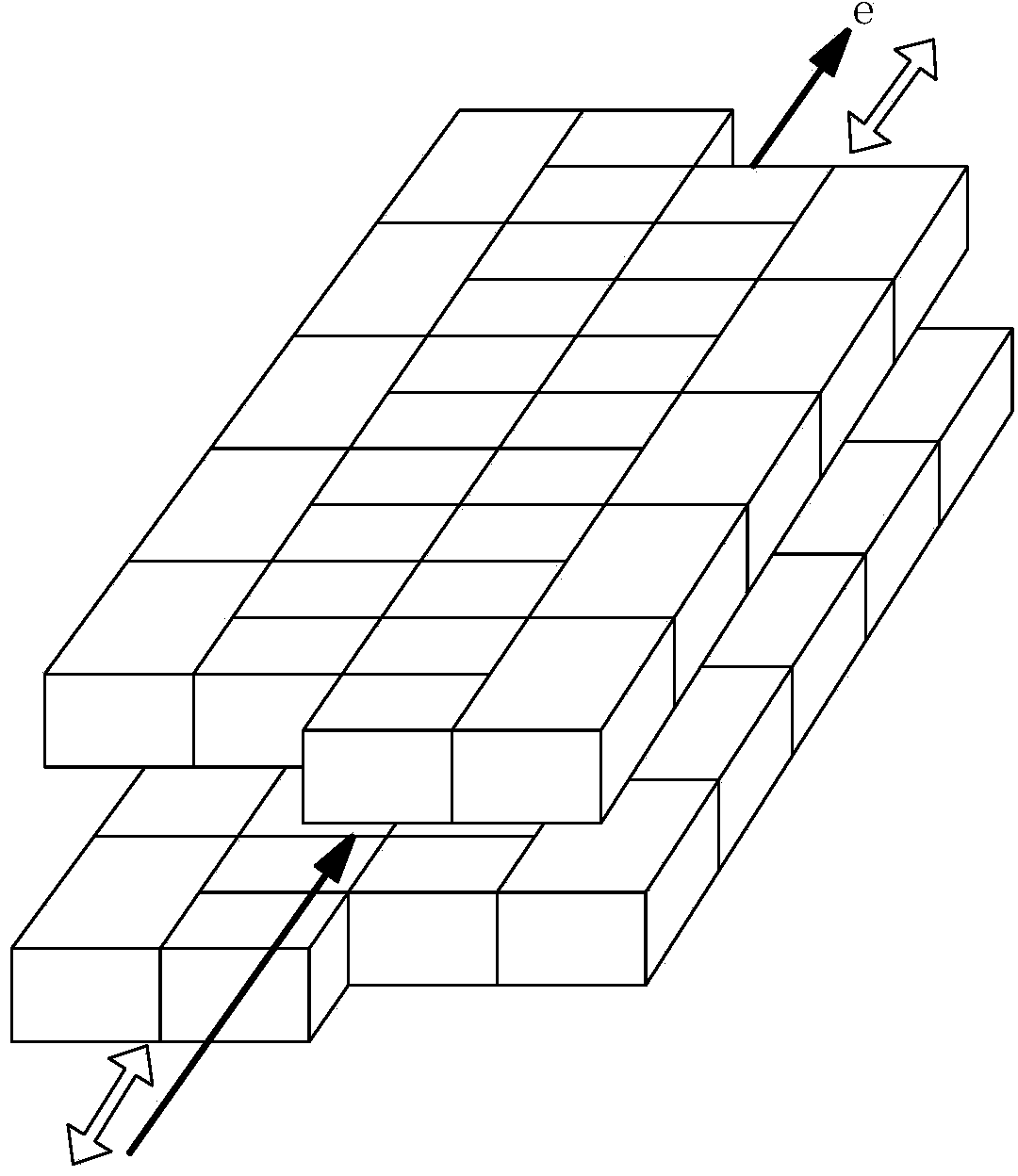
Compact undulator system and methods
ActiveCN103931061AReduce weightEasy to transportExcitation process/apparatusMagnetsMechanical integrityEngineering
An undulator with a compact construction is provided that reduces weight, complexity and cost. The compact undulator system and methods provides mechanical integrity without compromising magnetic field quality.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Superconducting undulator magnet
InactiveCN103440953AOvercome the disadvantage of inflexible adjustment of magnetic induction intensityReduce running resistanceSuperconducting magnets/coilsElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
The invention relates to a superconducting undulator magnet which comprises two columns of superconducting coil arrays longitudinally arranged at intervals and in parallel. Each column of superconducting coil arrays comprise a coil skeleton with high magnetic conductivity, n+1 magnetic poles which are axially arranged on the coil skeleton with the high magnetic conductivity at intervals, and n groups of coils which are formed by winding a single superconducting wire on the surface of the coil skeleton with the high magnetic conductivity and are positioned every two adjacent magnetic poles, and a direct-current power supply used for supplying the power to the coils, wherein the n represents a natural number; and the leading-in direction and the leading-out direction of the single superconducting wire during a winding process are arranged in a manner of enabling the directions of magnetic fields generated by the two adjacent coils to be opposite. The n groups of coils in each column of superconducting coil arrays are formed by winding the single superconducting wire, so that the running resistance of the n groups of coils is lowered. Thus, the cooling cost is effectively lowered while the running stability is improved at the same time. In addition, the magnetic induction intensity generated by the superconducting undulator magnet can be changed by regulating currents conducted into the coils.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
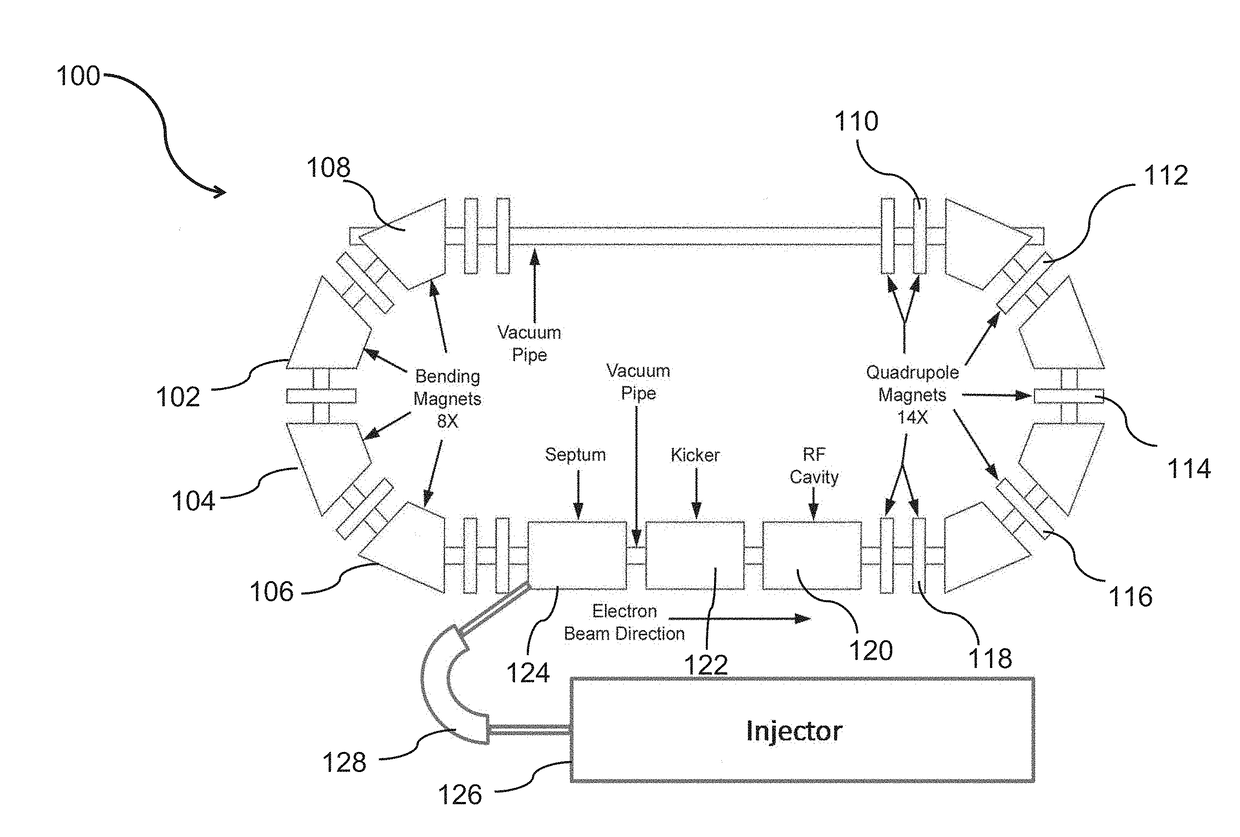
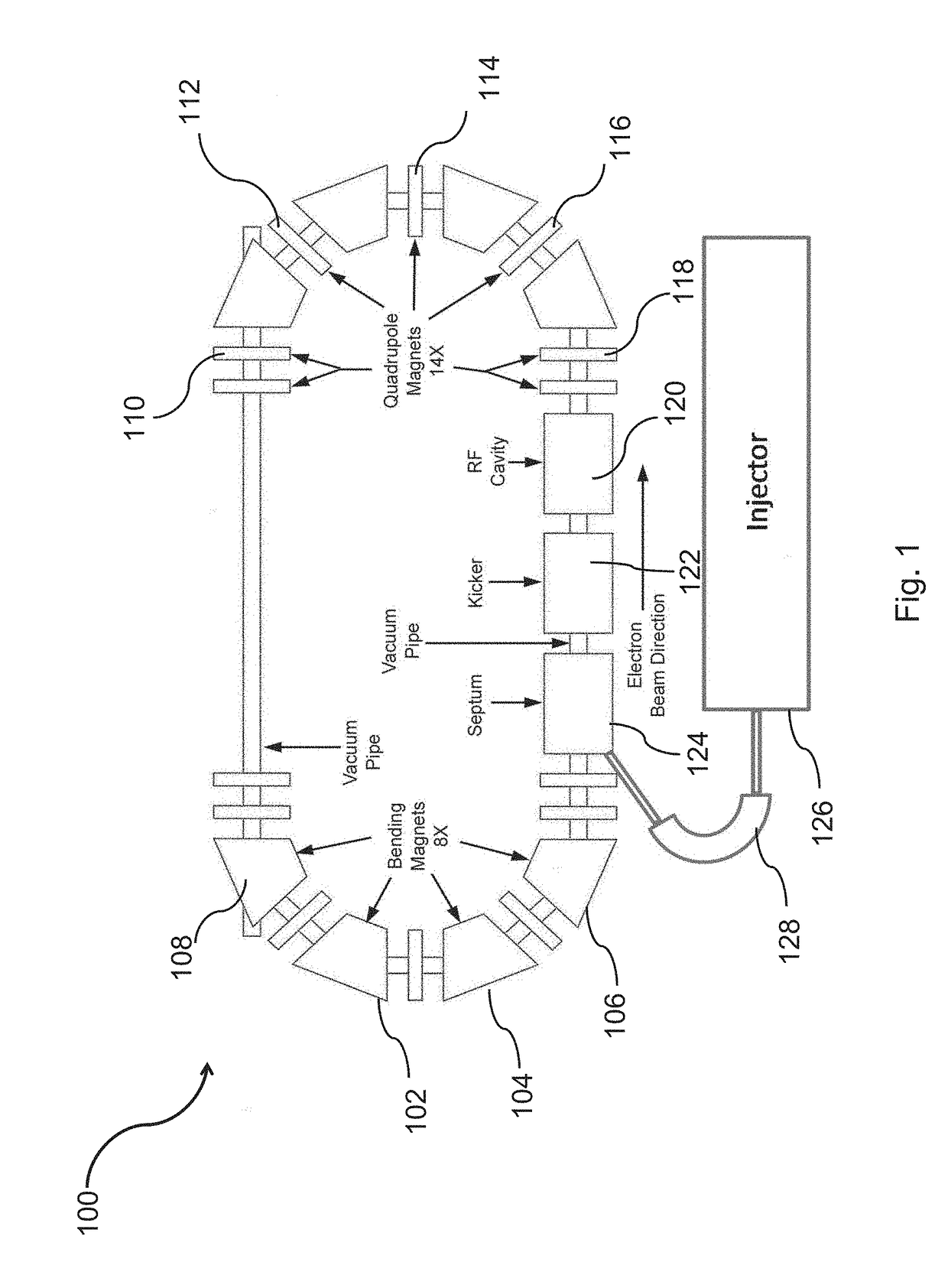
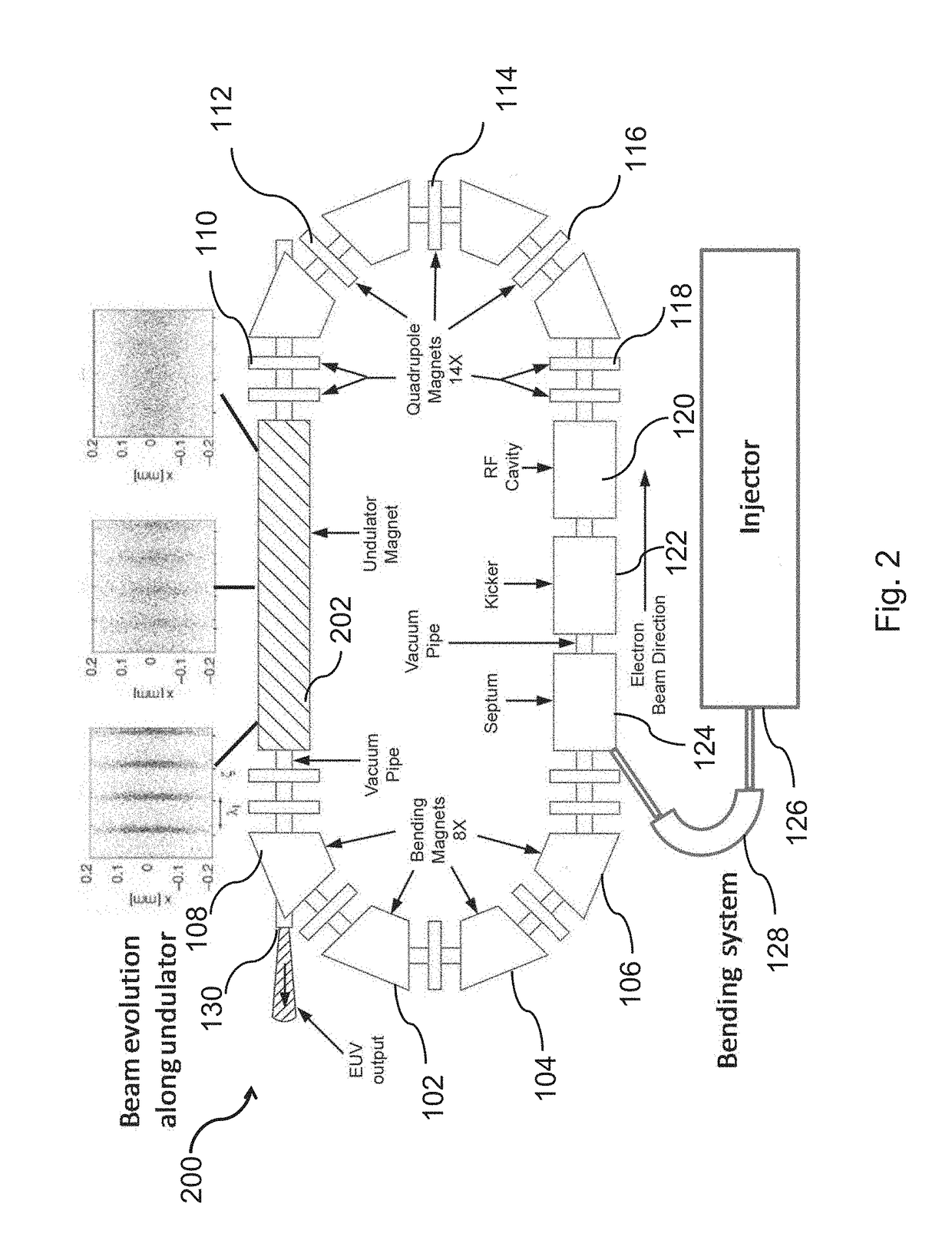
Compact storage ring extreme ultraviolet free electron laser
A high power extreme ultraviolet (EUV) beam is produced. An electron beam is injected in a compact electron storage ring configured for emission of free-electron laser (FEL) radiation. The electron beam is passed through a magnetic undulator on each of a plurality of successive revolutions of the electron beam around the compact electron storage ring. The electron beam is induced to microbunch and radiate coherently while passing through the magnetic undulator. A portion of the free-electron laser radiation at an extreme ultraviolet wavelength produced by an interaction of the electron beam through the magnetic undulator is outputted.
Owner:LYRA ACQUISITION HLDG LLC
Compac X-ray source for semiconductor metrology
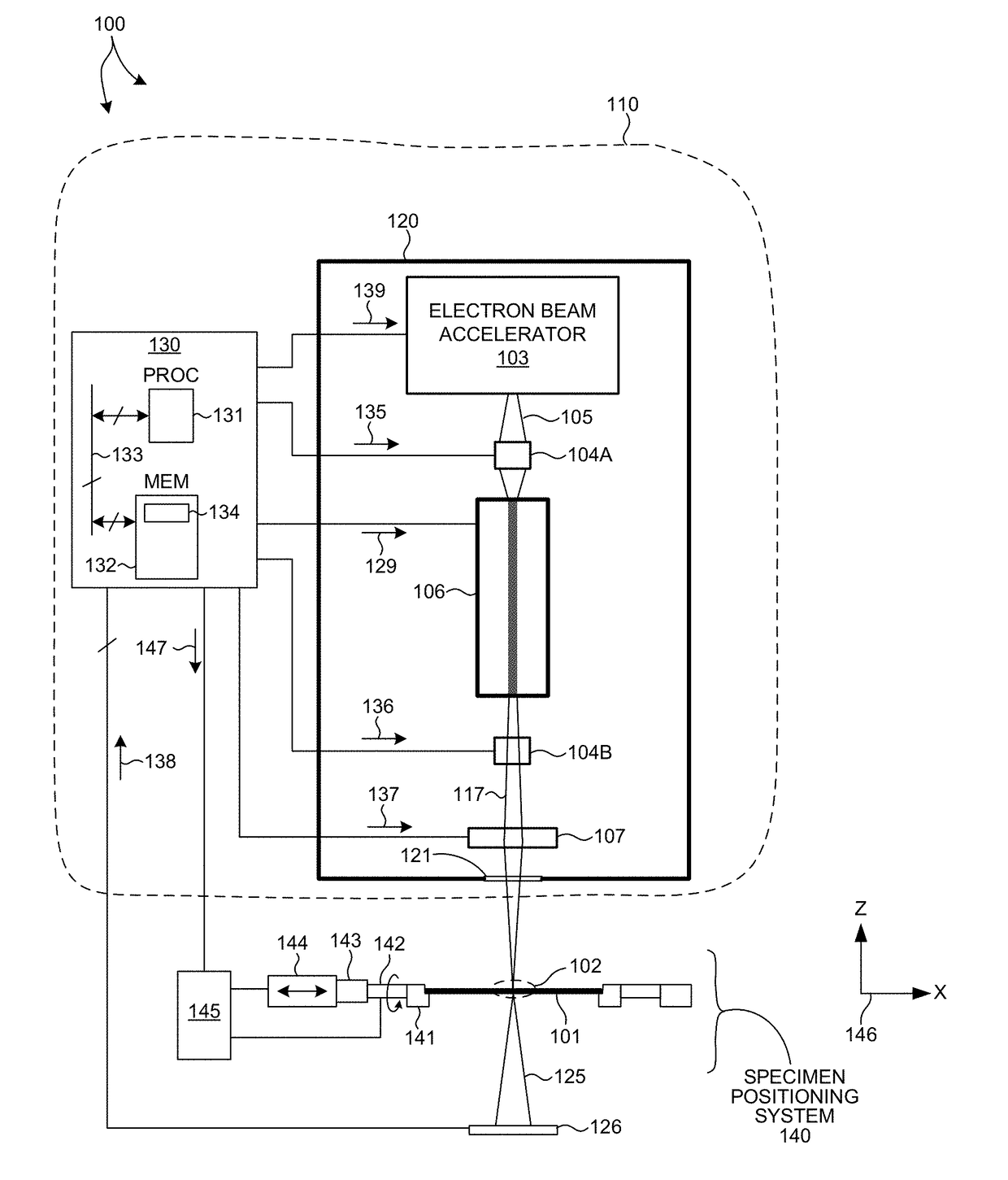
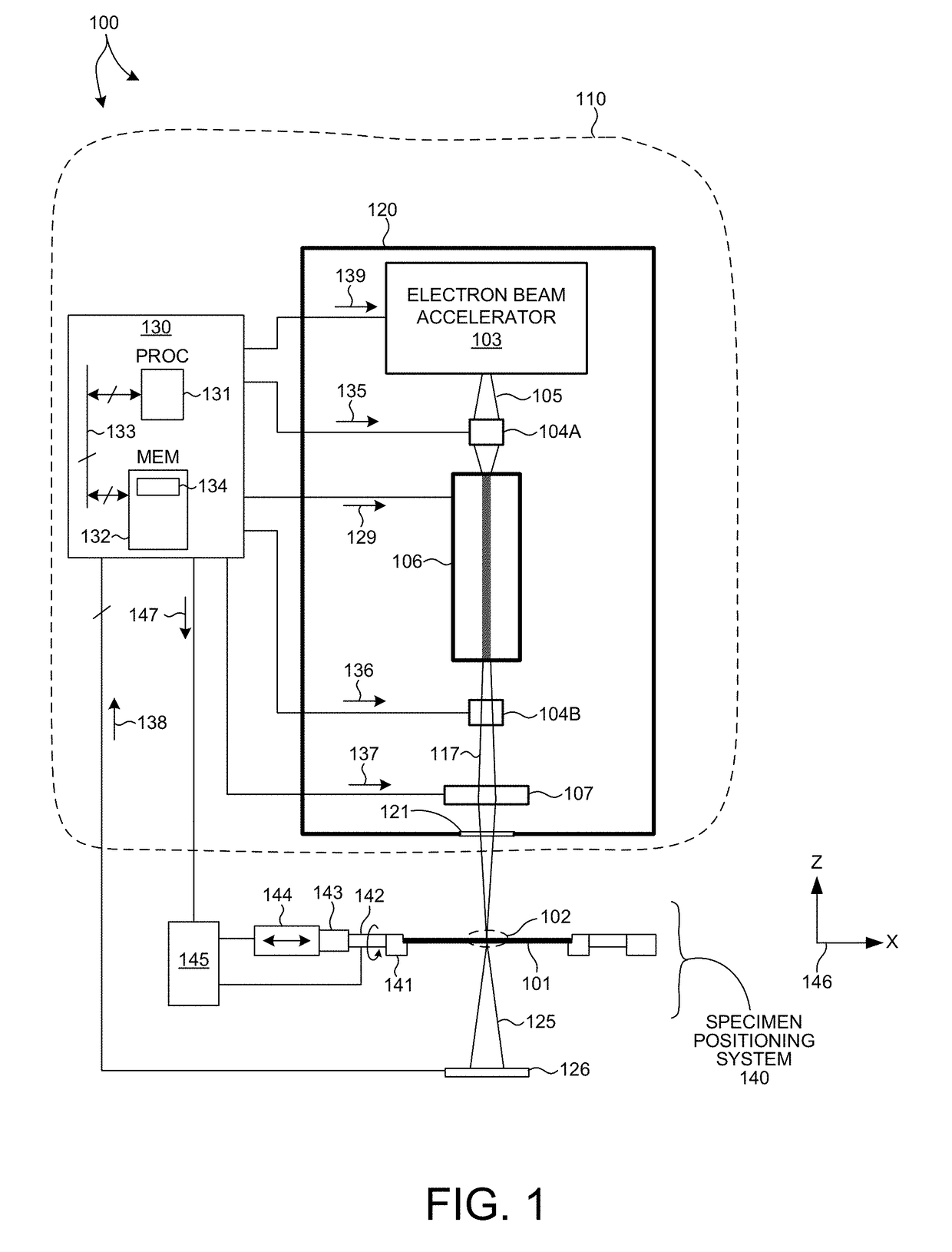
ActiveUS9826614B1Improve the measurement effectReduce noiseX-ray tube with very high currentX-ray apparatusPath lengthMetrology
Methods and systems for realizing a high brightness, compact x-ray source suitable for high throughput, in-line x-ray metrology are presented herein. A compact electron beam accelerator is coupled to a compact undulator to produce a high brightness, compact x-ray source capable of generating x-ray radiation with wavelengths of approximately one Angstrom or less with a flux of at least 1e10 photons / s*mm^2. In some embodiments, the electron path length through the electron beam accelerator is less than ten meters and the electron path length through the undulator is also less than 10 meters. The compact x-ray source is tunable, allowing for adjustments of both wavelength and flux of the generated x-ray radiation. The x-ray radiation generated by the compact x-ray source is delivered to the specimen over a small spot, thus enabling measurements of modern semiconductor structures.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Undulator
InactiveCN103337332ARandom combinationImprove performanceRadiation/particle handlingSuperconducting magnets/coilsRare earthMagnetic poles
The invention discloses an undulator which comprises a plurality of permanent magnet groups arranged sequentially, wherein each permanent magnet group comprises two groups of superconductive permanent magnets and two groups of rare-earth permanent magnets; the superconductive permanent magnets and the rare-earth permanent magnets are arranged on the two sides of a transmission path of an electron beam respectively; magnetic poles of the superconductive permanent magnets are opposite in direction; magnetic fields generated by the rare-earth permanent magnets strengthen magnetic fields generated by the superconductive permanent magnets on the transmission path of the electron beam; the temperature of the superconductive permanent magnets is lower than the superconductive critical temperature of the superconductive permanent magnets; and the magnetic induction intensity of magnetic fields generated by the permanent magnet groups on the transmission path of the electron beam has periodic variation in a direction of the transmission path of the electron beam. According to the undulator, a magnetic field with higher magnetic induction intensity is generated by the superconductive permanent magnets and the rare-earth permanent magnets in a magnetic field superposition manner, so that the performance of the undulator is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Surface-micromachined micro-magnetic undulator
ActiveUS20140301415A1Increase current densityReduce inductionCharged particle masersExcitation process/apparatusParticle acceleratorAccelerated particle
Various embodiments of undulators, methods of fabricating undulators, and systems incorporating undulators are described. Certain embodiments provide a compact, electromagnetic undulator. The undulator may comprise a substrate and one or more electromagnets, which may be formed on the substrate. Certain embodiments have a period not greater than about 5 mm. The undulator may be operatively coupled with a particle accelerator to provide a free electron laser system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Preparation method of high-performance permanent magnet and vacuum undulator magnetic structure with high-performance permanent magnet
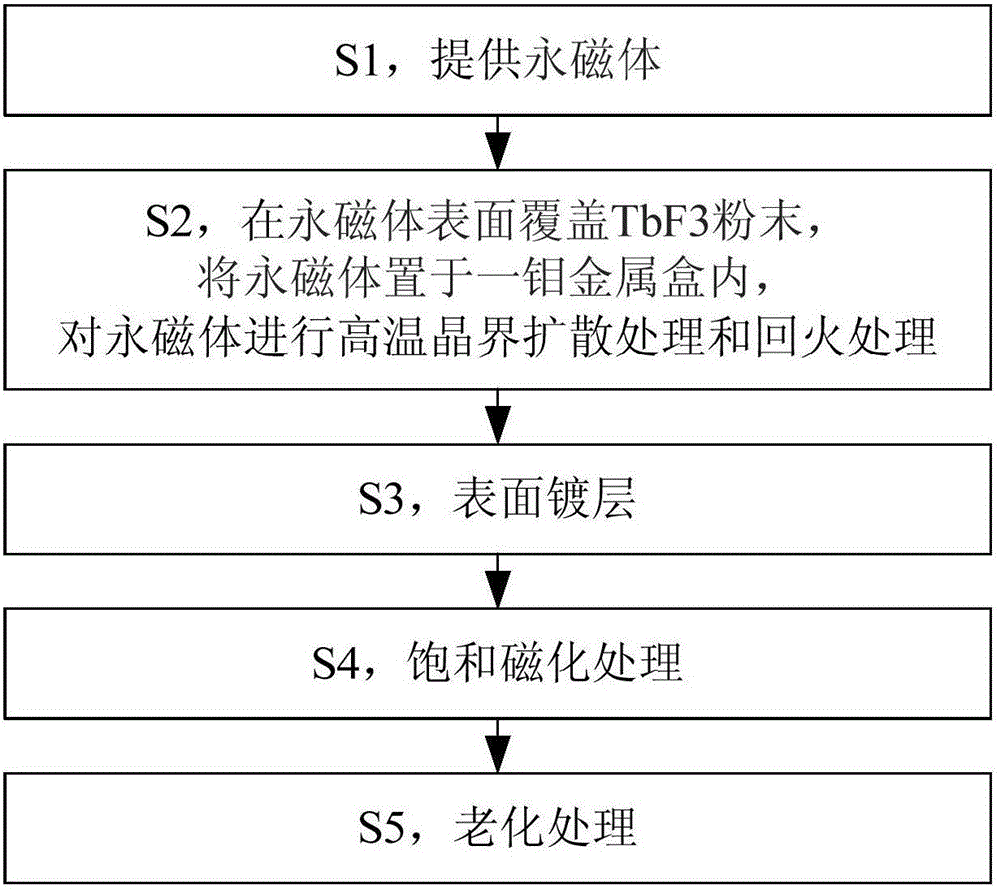
ActiveCN106847494AHcj consistency improvementReduce oxygen contentMagnetic materialsPermanent magnet manufactureState of artIntrinsics
The invention provides a preparation method of a high-performance permanent magnet and a vacuum undulator magnetic structure with the high-performance permanent magnet, wherein the preparation method comprises: S1, providing a permanent magnet 2.0-2.5 mm in magnetizing direction thickness; S2, covering the surface of the permanent magnet with TbF3 powder before placing the permanent magnet in a molybdenum box, subjecting the permanent box to high-temperature grain boundary diffusion, and annealing the permanent magnet; S3, coating the surface of the permanent magnet of step S3 with NiCuNi layer, TiN layer or NiCuTiN layer; S4, subjecting the permanent magnet of step 3 to saturation magnetization; S5, aging the permanent magnet of step S4. The problems of the prior art, such as poor uniformity of intrinsic coercive force in a permanent magnet and zero optimization on orienting thickens of the permanent magnet, are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DC high-voltage super-radiant free-electron based EUV source
An array of spatially separated beamlets is produced by a corresponding array of charged particle emitters. Each emitter is at an electrostatic potential difference with respect to an immediately adjacent emitter in the array. The beamlets are converged laterally to form an charged particle beam. The beam is modulated longitudinally with infrared radiation to form a modulated beam. The charged particles in the modulated beam are bunched longitudinally to form a bunched beam. The bunched beam may be modulated with an undulator to generate a coherent radiation output. This abstract is provided to comply with rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:KLA CORP
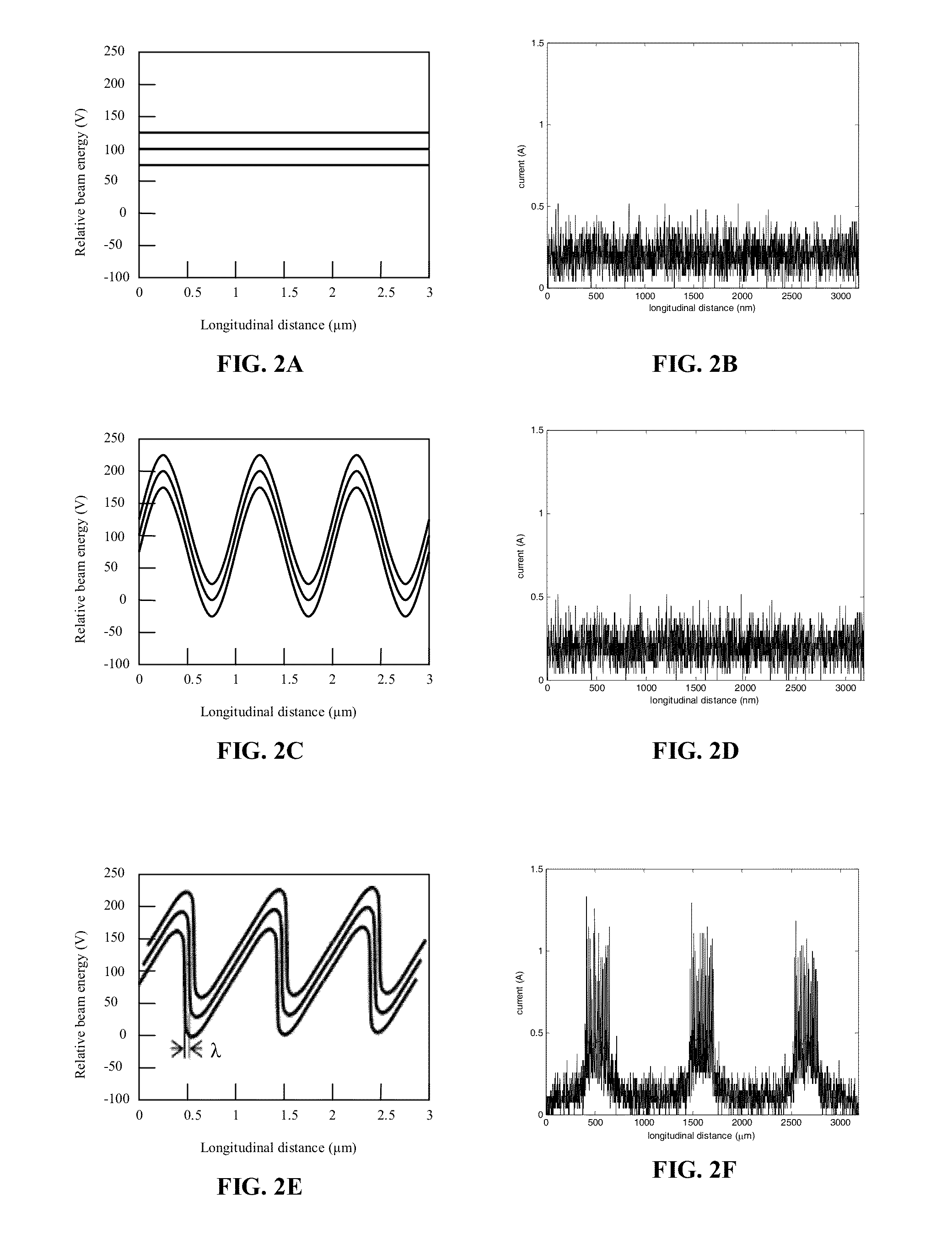
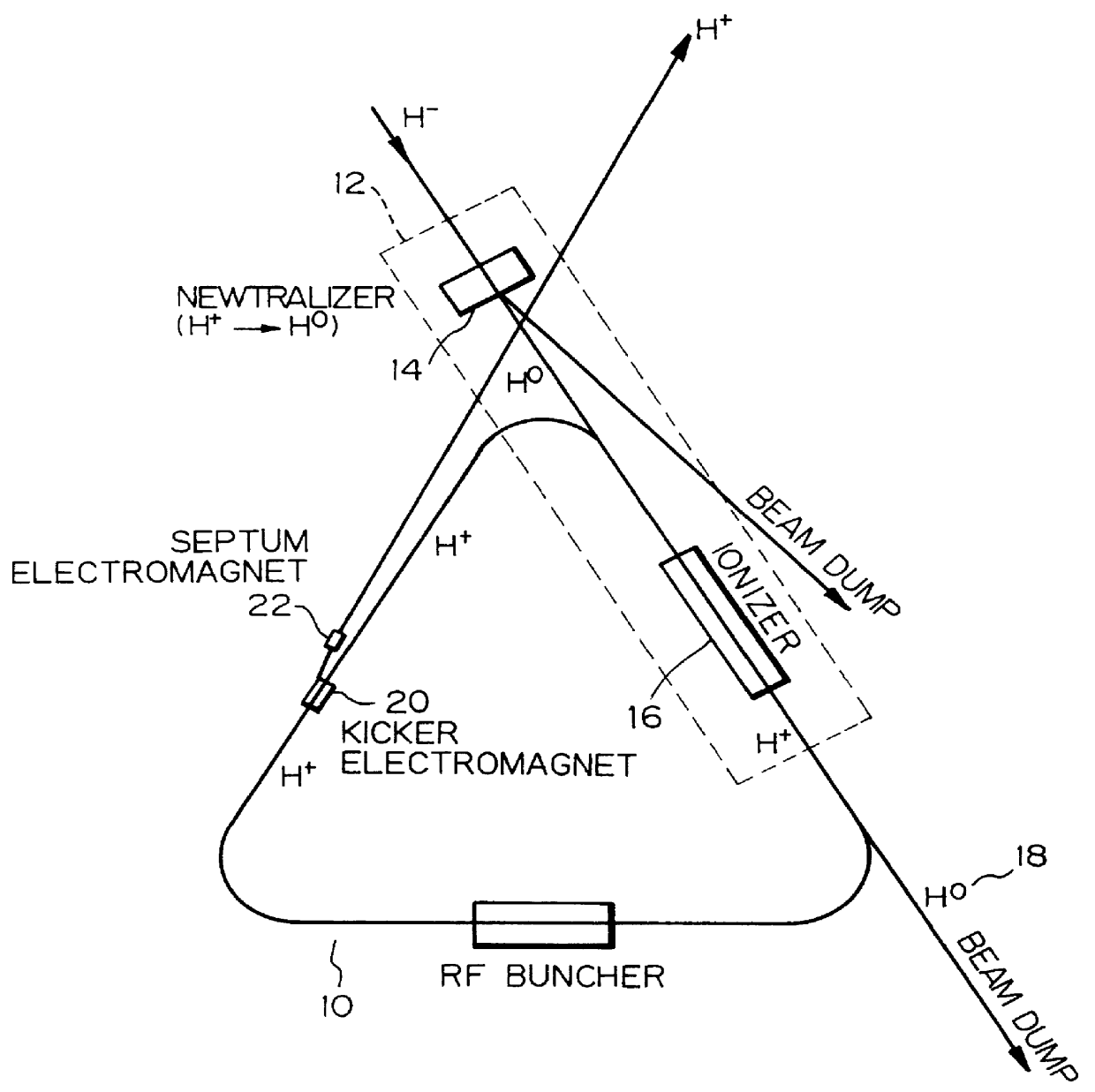
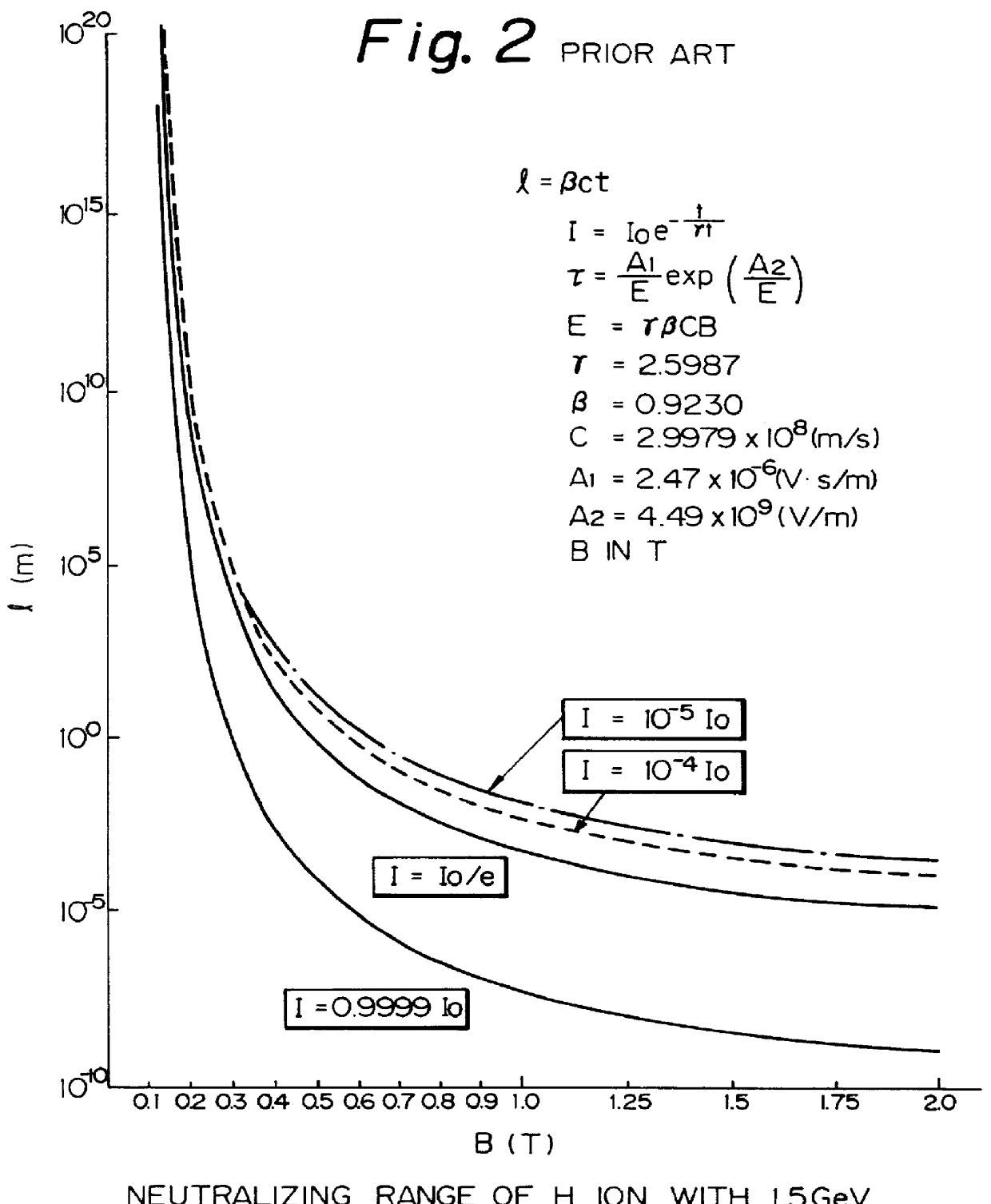
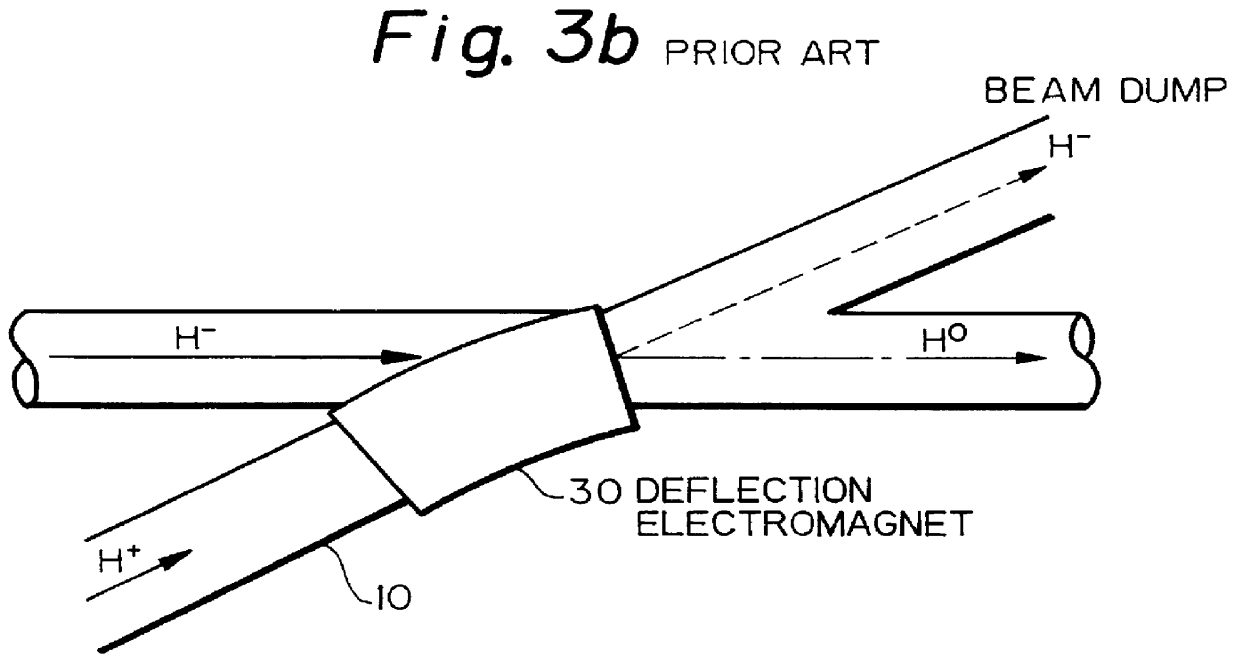
Charge-exchange device
InactiveUS6137246AReduce loadReduced the adverse affectParticle separator tubesConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRelativistic Doppler effectLaser beams
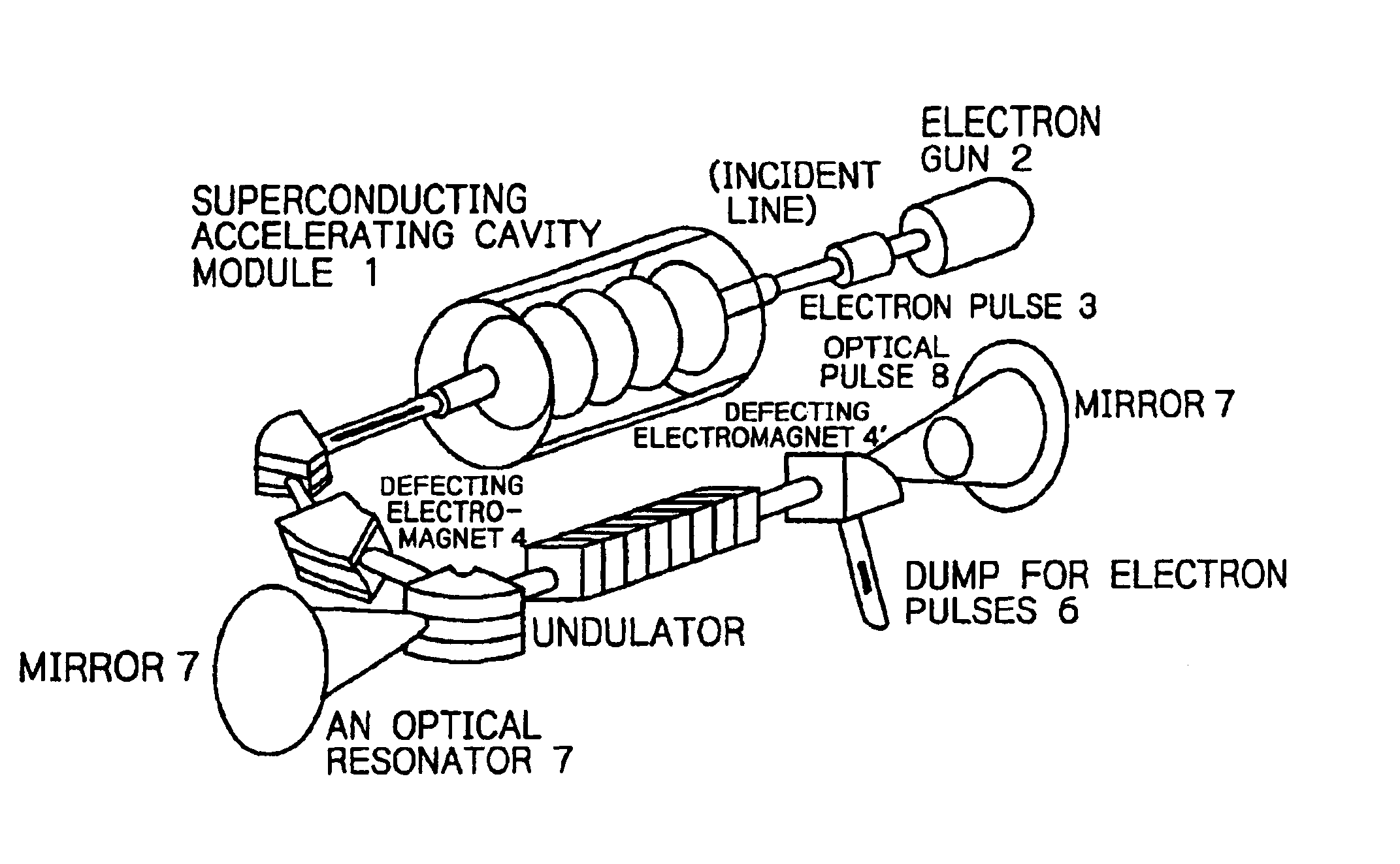
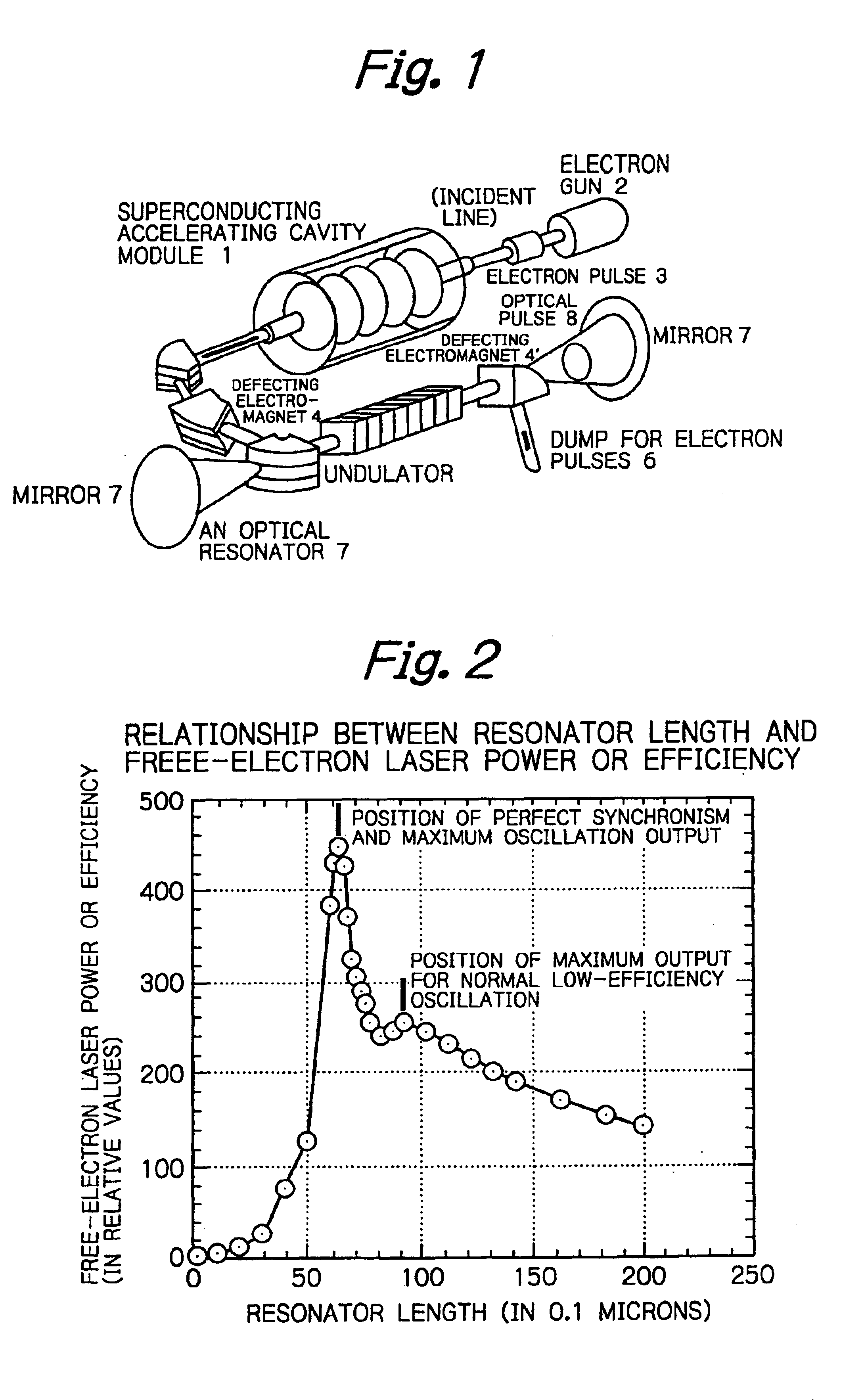
A charge-exchange device is disclosed which is able to considerably reduce, without the use of foils, radio activation caused by a beam deflection angle and, which also implements a further efficiency and reduction of a laser output. The charge-exchange device is provided with an undulator and an optical resonator. The undulator magnetic field which has been generated by the undulator generates the Lorentz electric field by interaction with the relativistic velocity of H0 neutral beam being injected. The optical resonator amplifies the photon density of the laser beam and causes it to collide against the injected H0 neutral beam, thereby resonantly exciting the H0 beam to the principal quantum number of 4. The H0 beam which has been resonantly excited or excited by the relativistic Doppler effect in the undulator magnetic field is ionized to H+ ion by the Lorentz electric field.
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
Continuous winding magnets using thin film conductors without resistive joints
ActiveUS20170162309A1Permanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
A continuous winding method produces a continuously wound electrical device, such an undulator. A continuous tape is wound about a series of turn around pins and in grooves in a magnetic core. A plurality of winding stacks are created, each transitioning to the next sequential stack by a transition tape portion extending from one turn around pin to the next turn around pin, which is position opposite with regard to the location of the pin on the magnetic core.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Permanent magnet undulator with adjustable polarization
InactiveCN109411109AReduced on-axis radiated power densityImprove inherent defectsRadiation/particle handlingPermanent magnetsHorizontal and verticalOptical polarization
The invention relates to a permanent magnet undulator with adjustable polarization, which belongs to the technical field of synchrotron radiation and conquers the defects caused by vacuum outer binarysymmetry inherent in APPLE-II structure. The undulator comprises M permanent magnet periodic units arranged sequentially along the electron beam axis direction, wherein each permanent magnet periodicunit comprises four rows of permanent magnet structures; M is a natural number greater than or equal to 1; the four rows of permanent magnet structures are uniformly distributed around the beam aperture and inclined at 45 degrees. The permanent magnet undulator in the invention fundamentally conquers the inherent defects of the APPLE-II undulator, ensures that the magnetic field components in thetwo orthogonal directions can achieve the optimal performance of the design. At the same time, it solves the problem of excessive axial radiation power of DELTA undulator in horizontal and vertical linear polarization mode.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Free electron laser radiation source for the EUV
Passage through LINACs of electron bunches in their acceleration phase is co-ordinated with passage through the LINACs of electron bunches in their deceleration phase. Each successive pair of electron bunches are spaced in time by a respective bunch spacing, in accordance with a repeating electron bunch sequence. The electron source provides clearing gaps in the electron bunch sequence to allow clearing of ions at the undulator. The electron source provides the clearing gaps in accordance with a clearing gap sequence such that, for each of the plurality of energy recovery LINACS, and for substantially all of the clearing gaps:- for each passage of the clearing gap through the LINAC in an acceleration phase or deceleration phase the clearing gap is co-ordinated with a further one of the clearing gaps passing through the LINAC in a deceleration phase or acceleration phase thereby to maintain energy recovery operation of the LINAC.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Tapering enhanced stimulated superradiant amplification
ActiveUS20170093113A1Enhanced stimulated superradiant amplification”Improve efficiencyExcitation process/apparatusAcceleratorsSaturation levelUndulator
A tapering enhanced stimulated superradiant amplification method and system which utilizes a strongly tapered undulator in reaching significant power outputs and conversion efficiencies. TESSA dramatically increases conversion / amplification efficiencies by violently (sharply) decelerating electrons and taking advantage of produced radiation to further drive interaction toward as it takes advantage of produced radiation to further drive interaction to increase overall radiation output. The system and method configures a strongly tapered undulator to operate in a new mode that is above normal input saturation levels to provide an amplified output with unexpectedly high efficiencies and power.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method and a device for realizing both high extraction efficiency of laser light from electron beams and femto-second ultra-short in free-electron lasers pulses
InactiveUS6970483B2Increase peak output powerImprove extraction efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusLaser lightPeak current
A method for realizing both high extraction efficiency of laser light from electron beams and femto-second ultra-short pulses in a free-electron laser, wherein the peak current of electron pulses from a superconducting or normal conducting linear accelerator serving as a driver for the free-electron laser is adjusted to be greater than a certain lower limit and electron beams are brought into perfect synchronism with light or the time of duration for which the electron pulses are repeated is made longer than the time to saturation of light oscillation (the time during which light is emitted due to the increase of optical output by an amount corresponding to the gain up to the point where the optical output does not increase any more), whereby the oscillation of light is facilitated, wherein the extraction efficiency of laser light from electron beams is increased to exceed the theoretical limit which is expressed by 1 / (2 Nw)˜1 / (4 Nw) (Nw=the number of undulator periods) of electron beam power or rendered proportional to the square of N, or the number of electrons in a micropulse, and wherein ultra-short pulses of the femto-second range are generated.
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
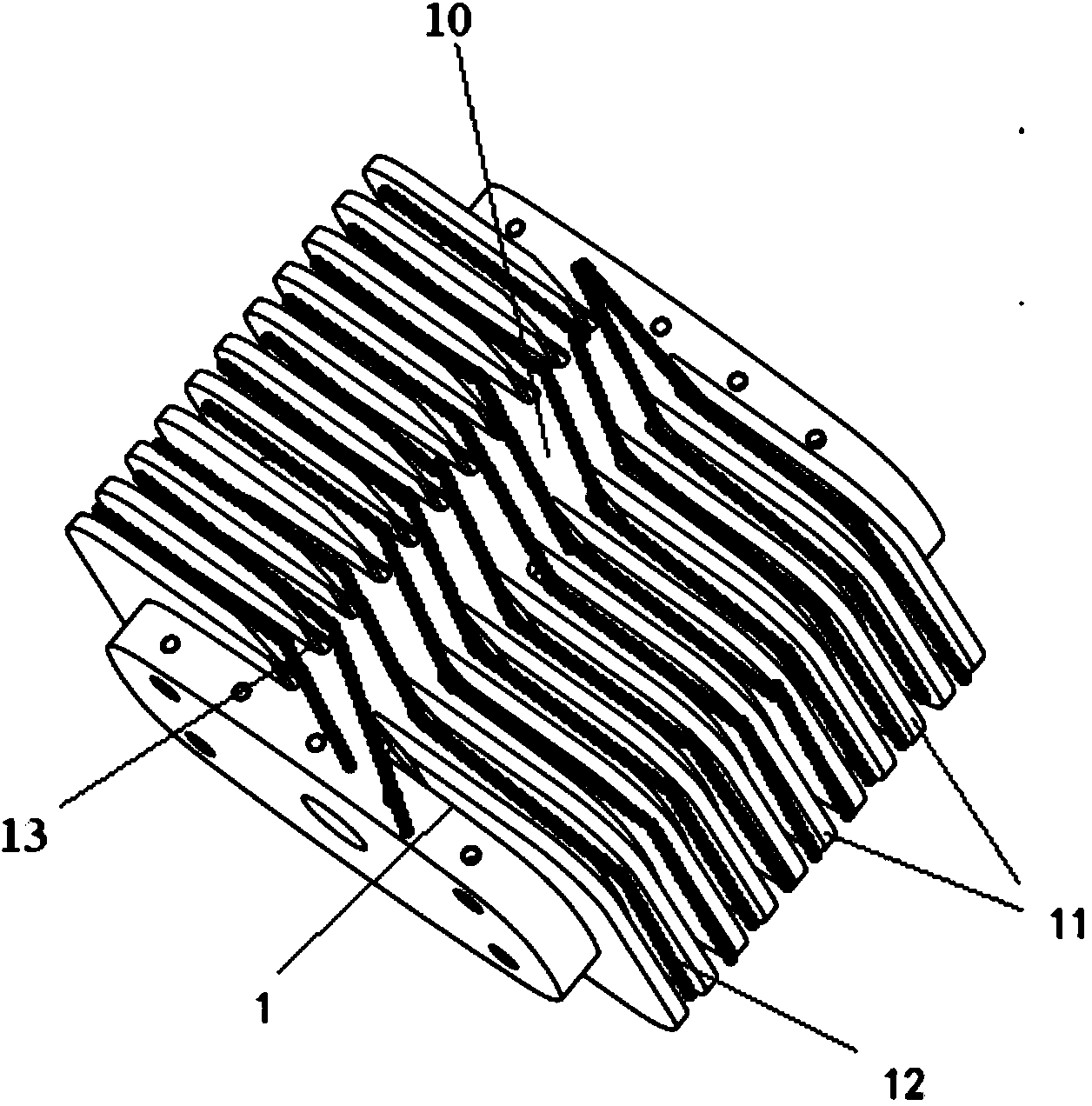
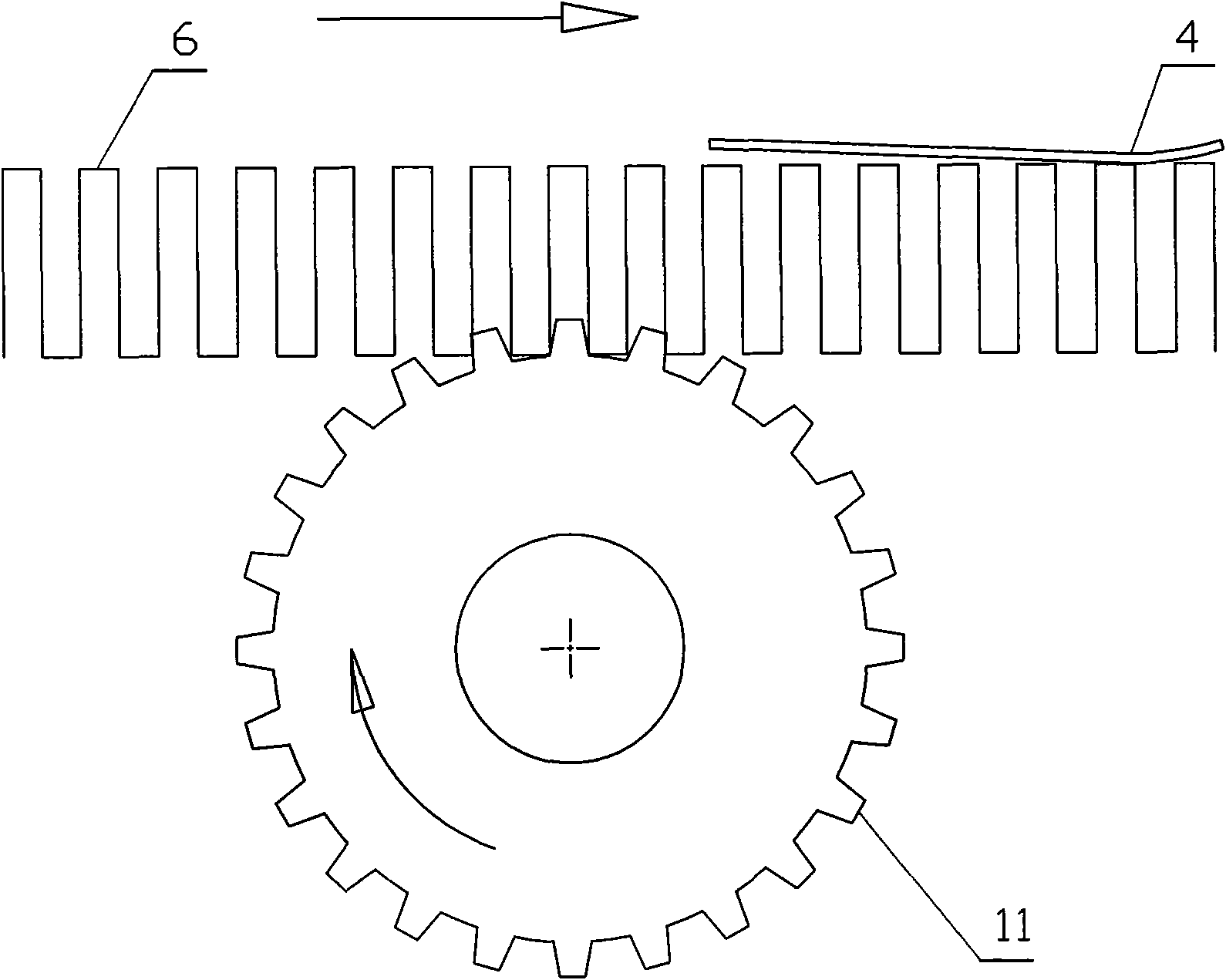
Small-sized automatic undulator and processing method
InactiveCN101607283AControllable degree of compressionEasy to operateShearing machine accessoriesShearing toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a small-sized automatic undulator and a processing method, which has the advantages of reasonableness and convenient use. A finished product can satisfy the requirements of use or drawing paper by only putting raw materials into the small-sized automatic undulator, thereby increasing production efficiency. A feeder is arranged on a ripple forming and punching charging device, the rear part of the ripple forming and punching charging device is connected with a ripple mesh gear propulsion device, and the rear part of the ripple mesh gear propulsion device is connected with a double-side four-edge cutter ripple strip intercepting device. The small-sized automatic undulator has three combination functions: the ripple impact molding, the ripple distance compression forming and the ripple strip are intercepted according to a set wave number, the efficiency is increased greatly, and the work which needs to be completed by three persons originally can be completed by one person.
Owner:DONGGUAN LONGKEY ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com