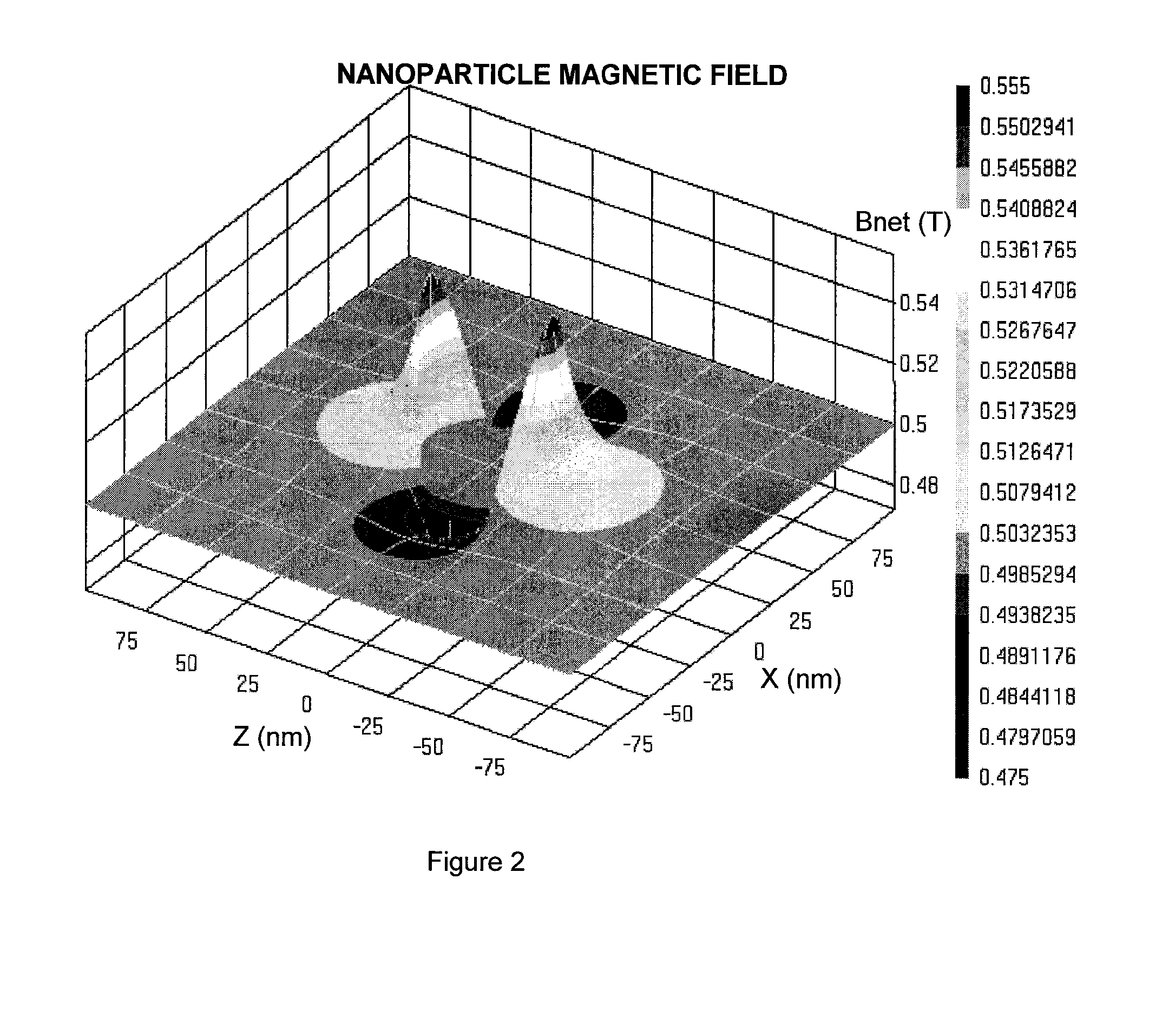
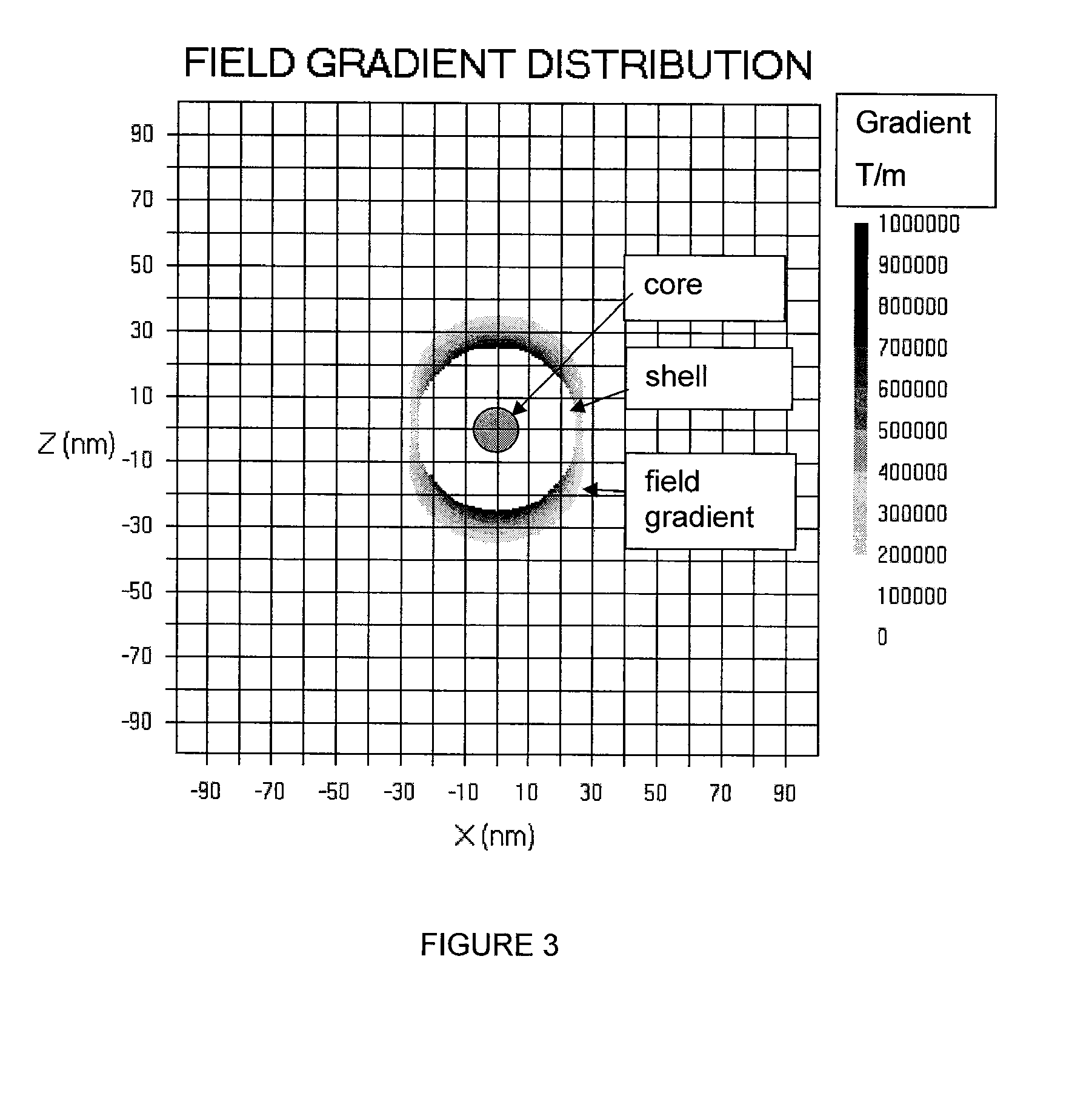
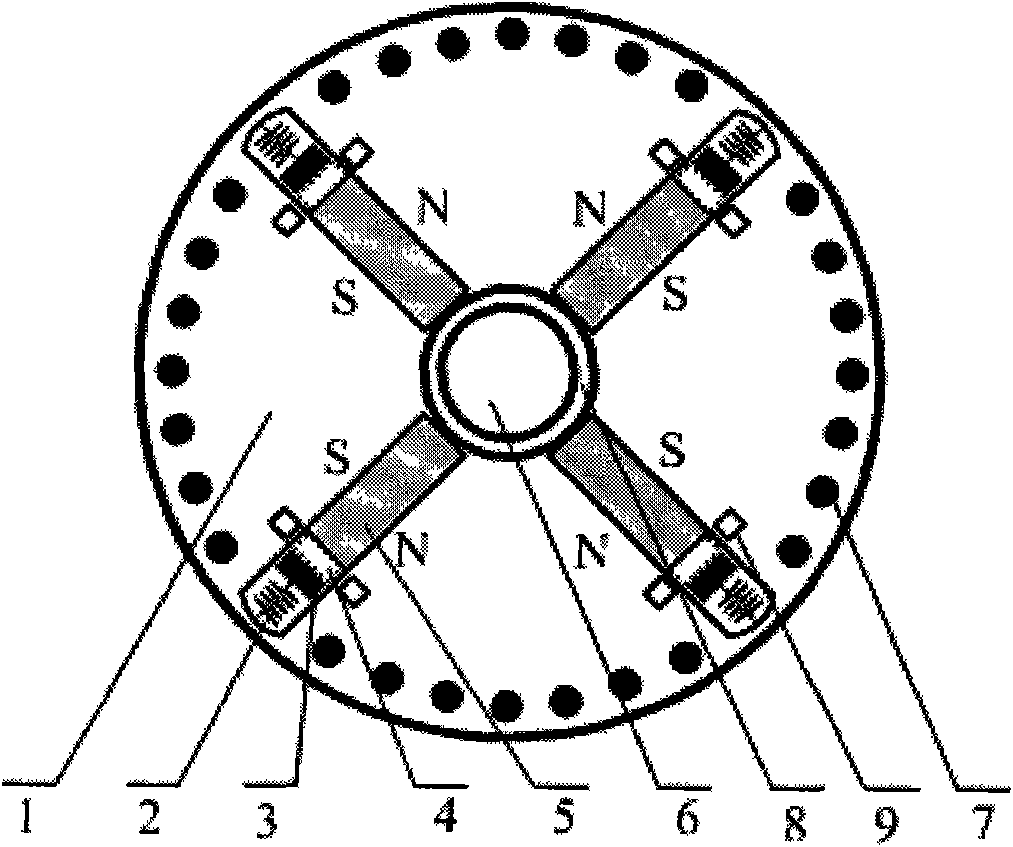
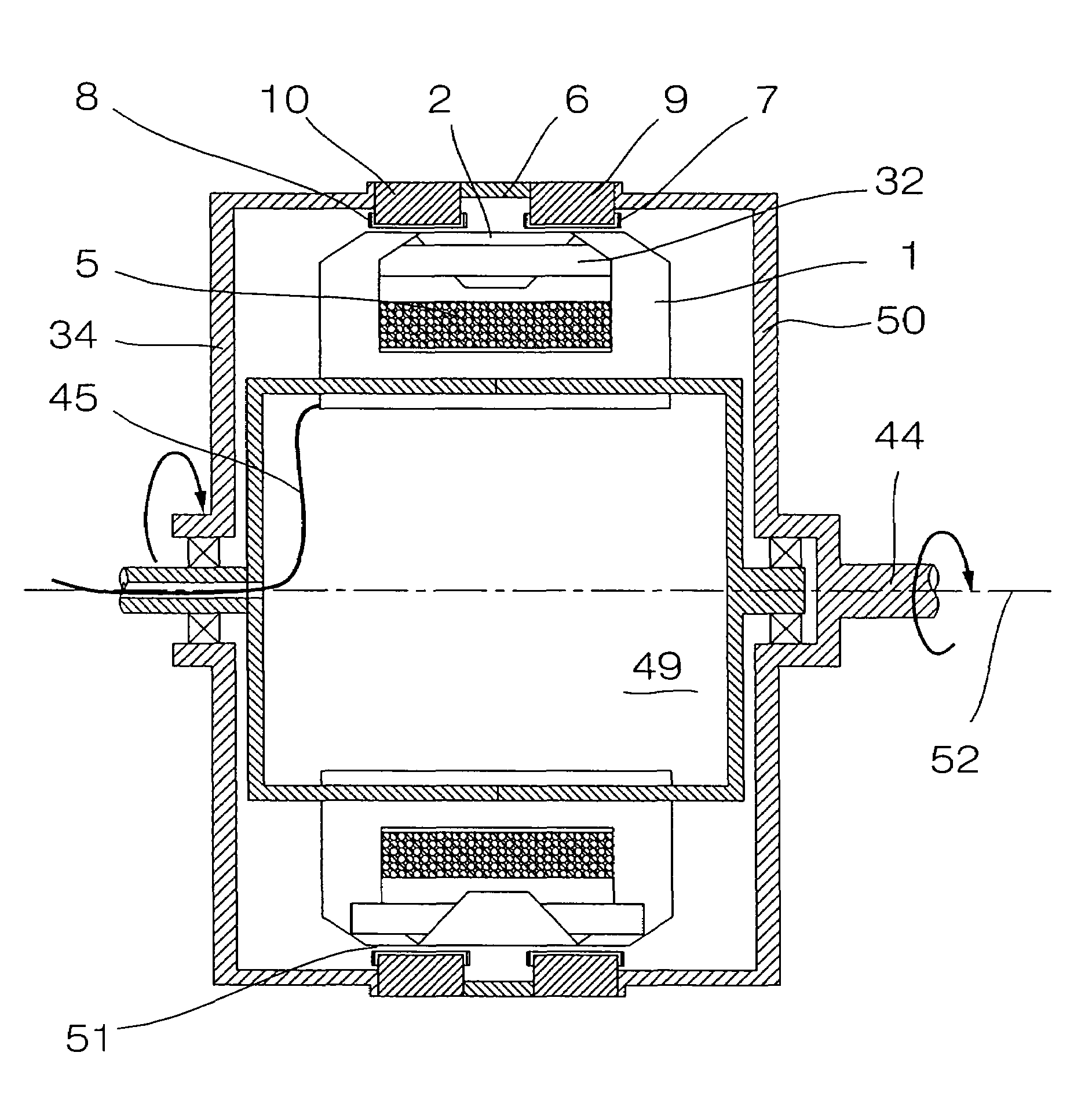
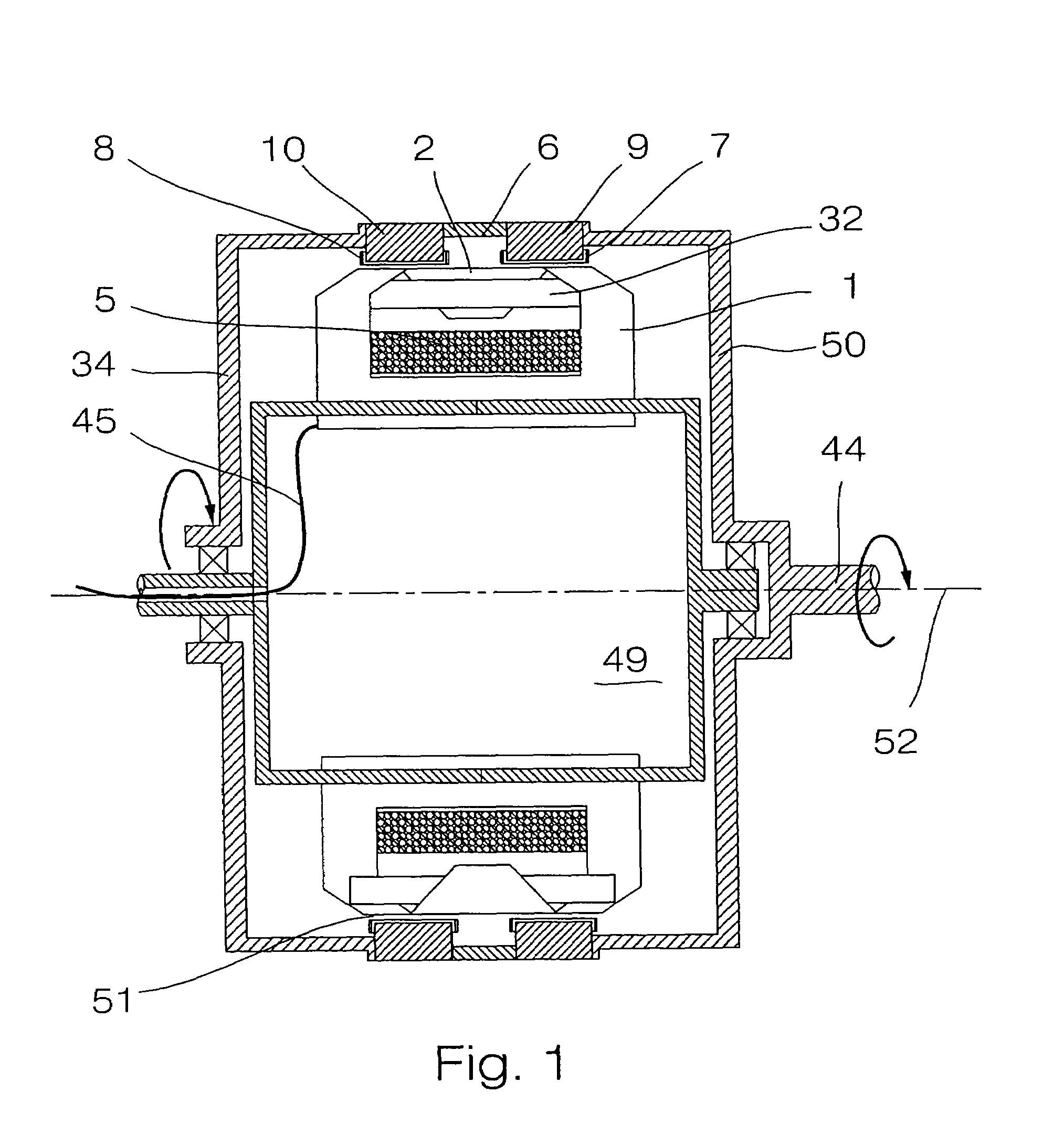
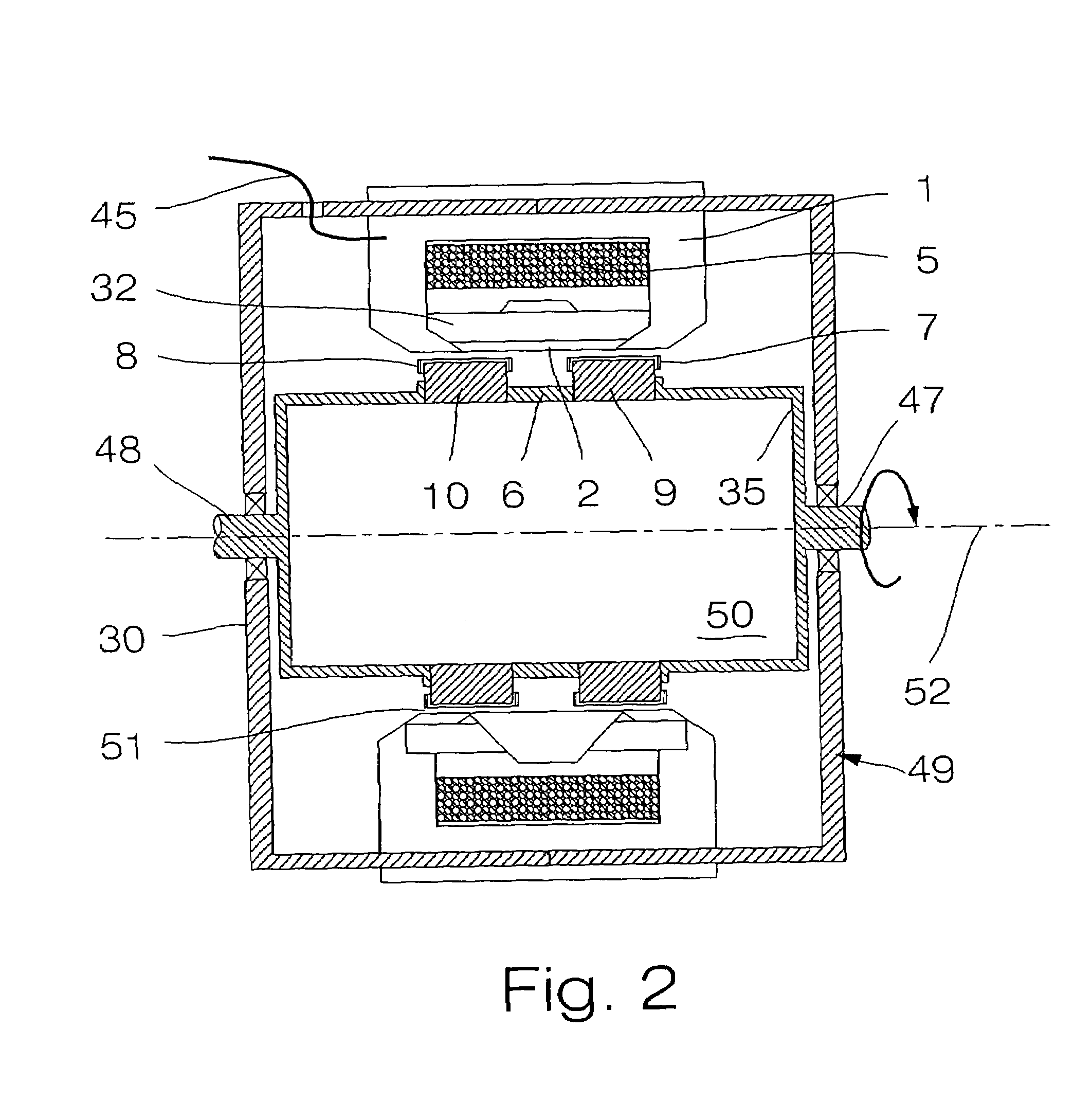
Patents
Literature
894 results about "Magnetic structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term magnetic structure of a material pertains to the ordered arrangement of magnetic spins, typically within an ordered crystallographic lattice. Its study is a branch of solid-state physics.
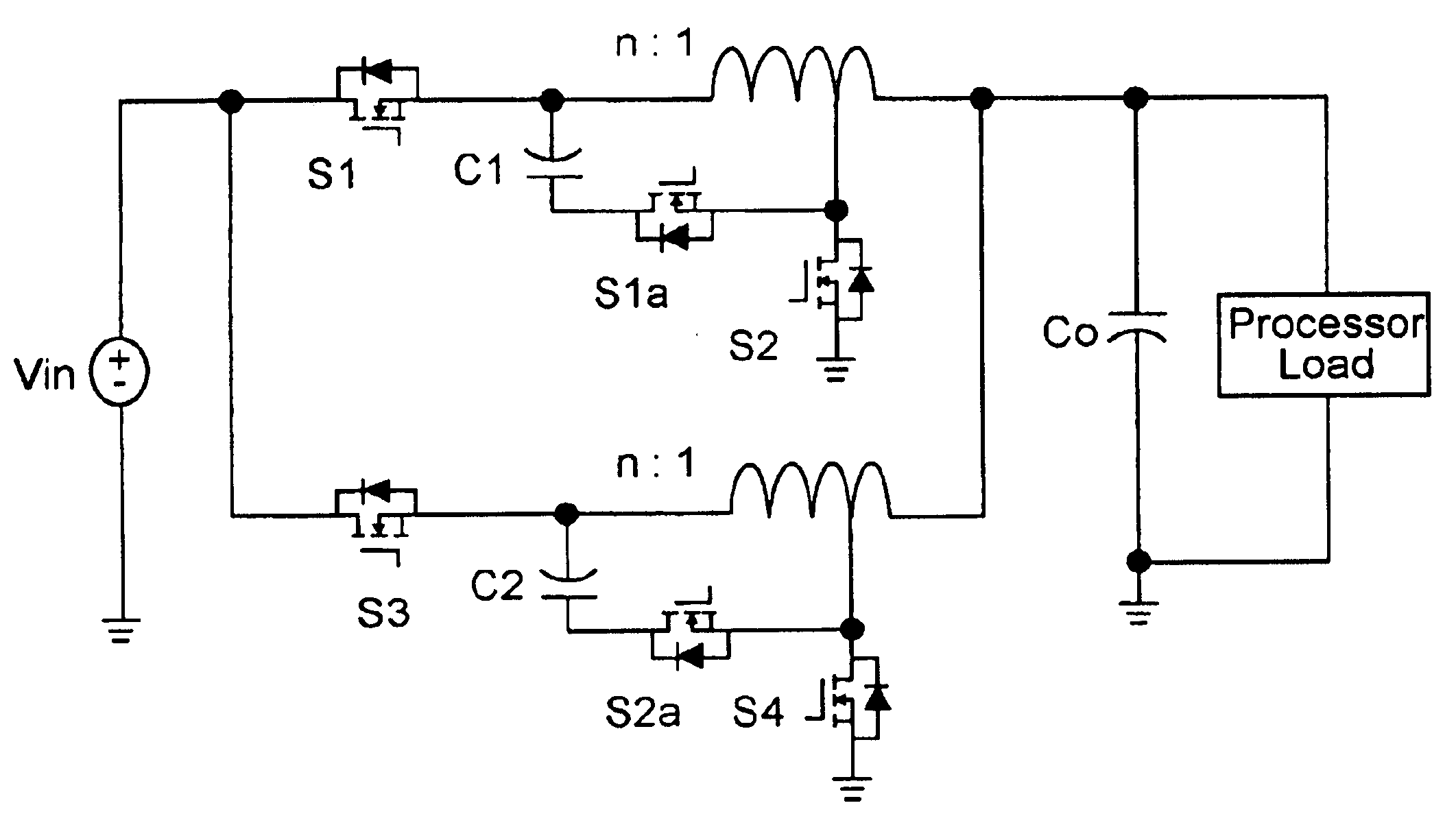
Multiphase clamp coupled-buck converter and magnetic integration
InactiveUS6784644B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage regulator modulePush pull
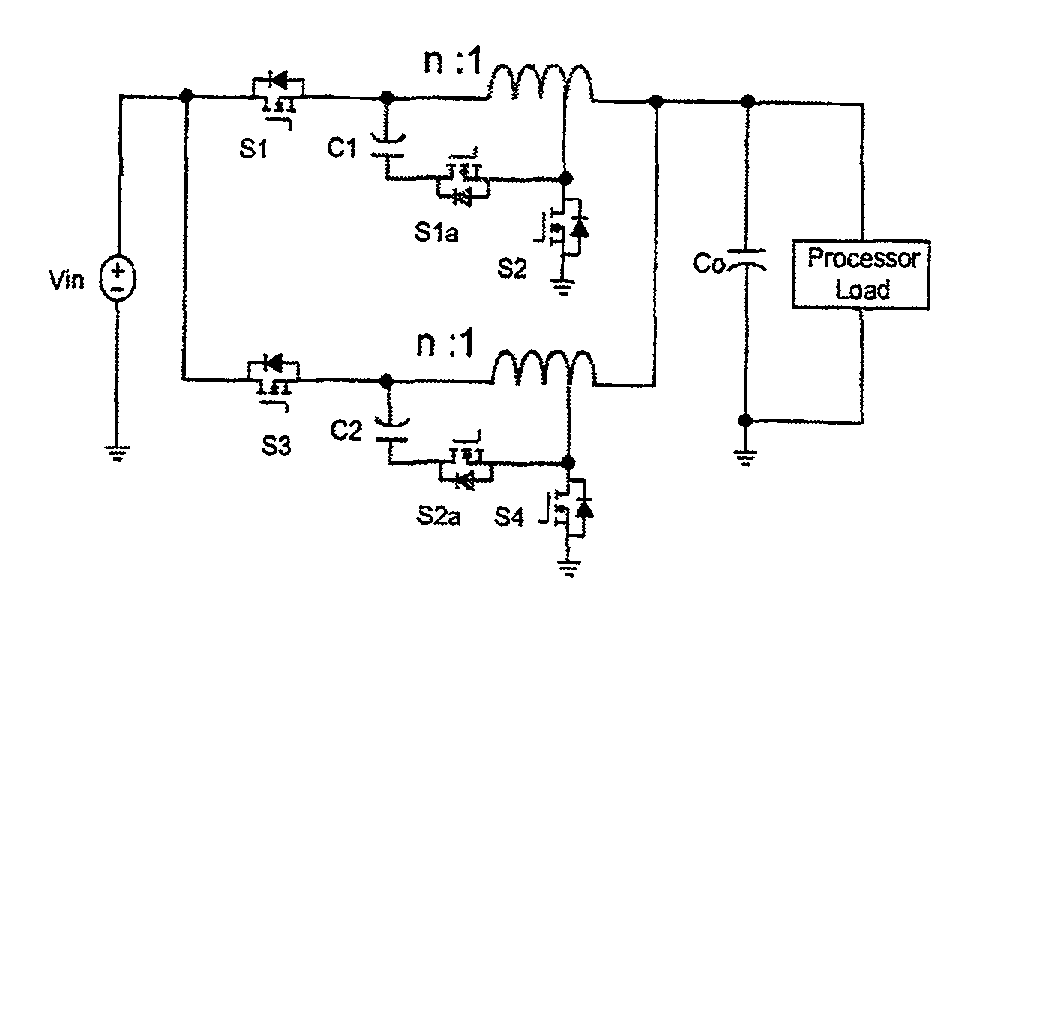
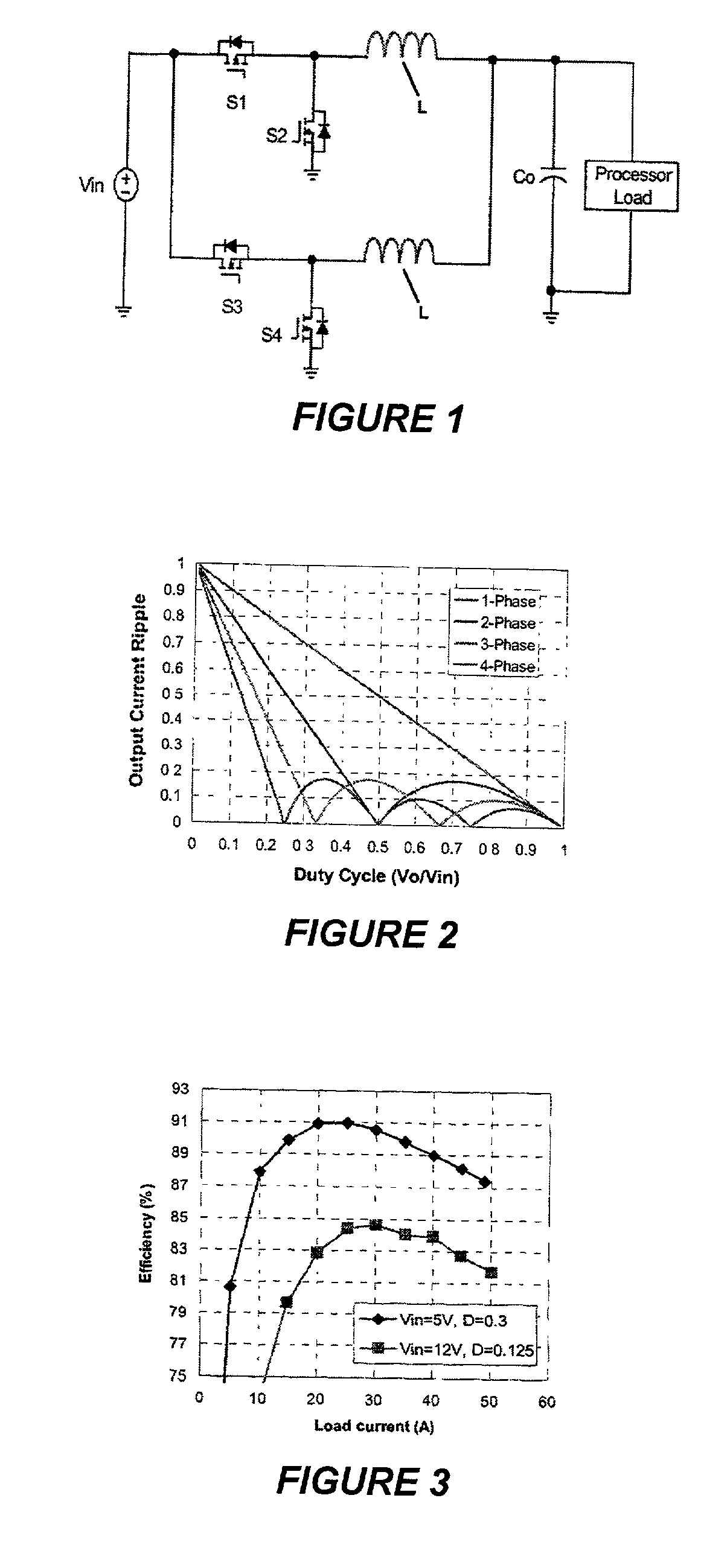
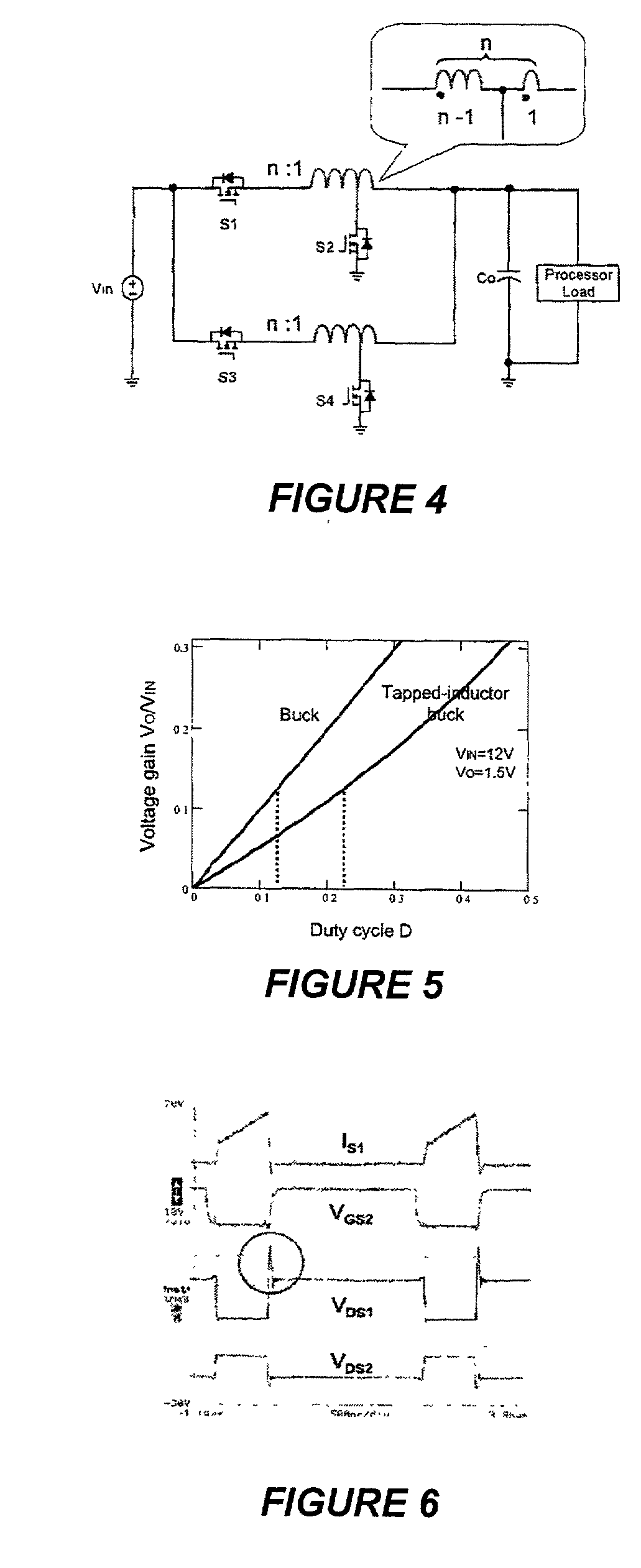
Voltage regulation, transient response and efficiency of a voltage regulator module (VRM) is improved where short duty cycles are necessitated by large differentials of input and output voltage by including at least one clamping of a tap of an inductance in series with an output of each of a plurality of parallel branches or phases which are switched in a complementary fashion or providing coupling between inductors of respective phases. Such coupling between inductors is achieved in a small module with an integrated magnetic structure. Reduced component counts are achieved while deriving built-in input and output filters. Principals of the invention can be extended to isolation applications and push-pull forward converts, in particular. A lossless clamping circuit is also provided allowing spike currents to be suppressed while returning power to the output of the VRM.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Inductive heating magnetic structure for removing condensates from electrical smoking device
ActiveUS7185659B2Enhance inductive heating techniqueReduce the required powerTobacco pipesTobacco devicesElectricityHeat power
Thermal cleaning of an electrically heated smoking device, and in particular the removal of condensates formed within the smoking device as a result of extended periods of use, is achieved with a cleaning system that utilizes inductive heating that provides efficient and intense localized heating in the cleaning process. The thermal power of the inductive heating process is increased or the power necessary to activate the inductive heating process is decreased by the addition of a magnetic shell by itself or in combination with a magnetic pin.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
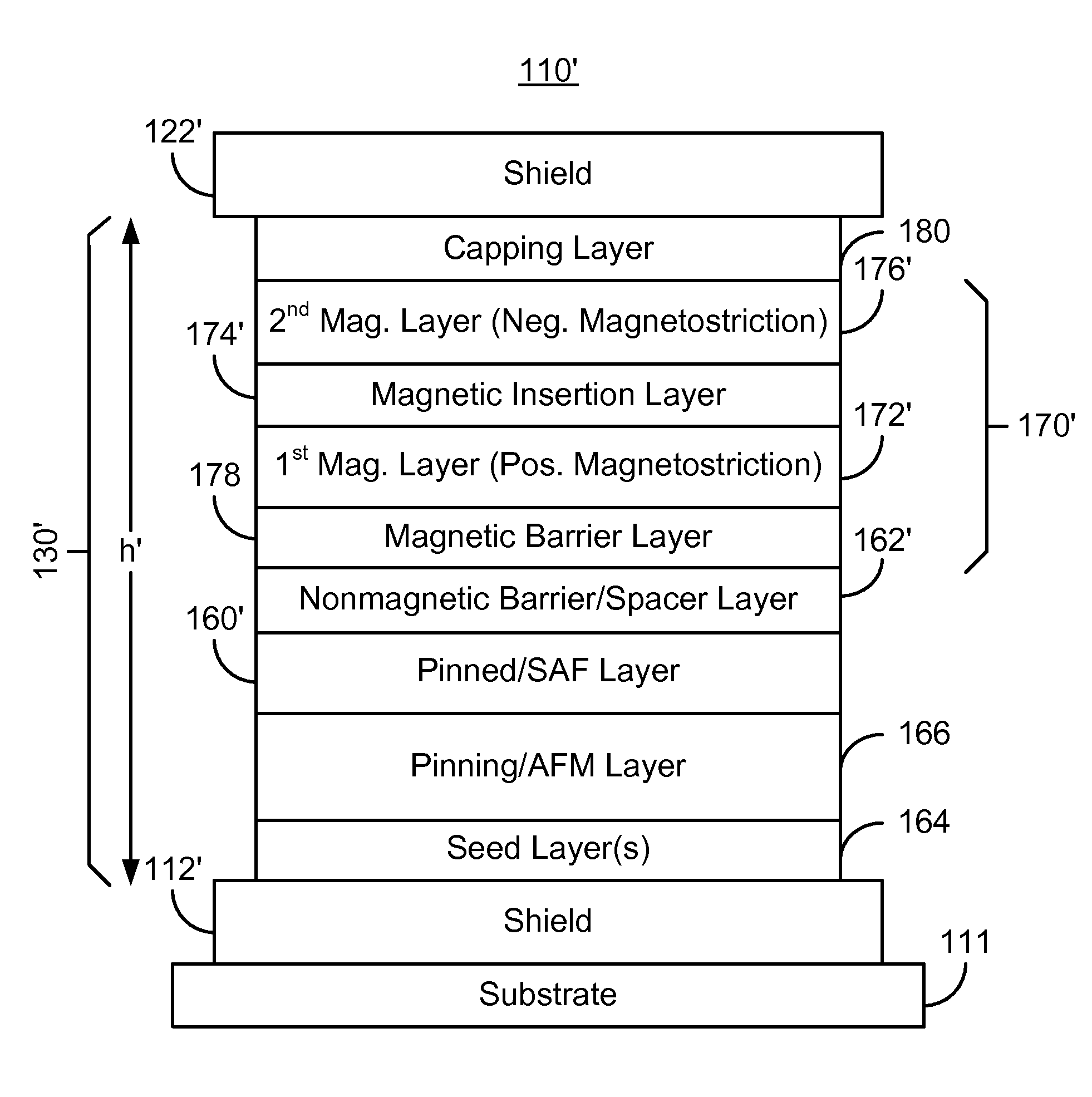
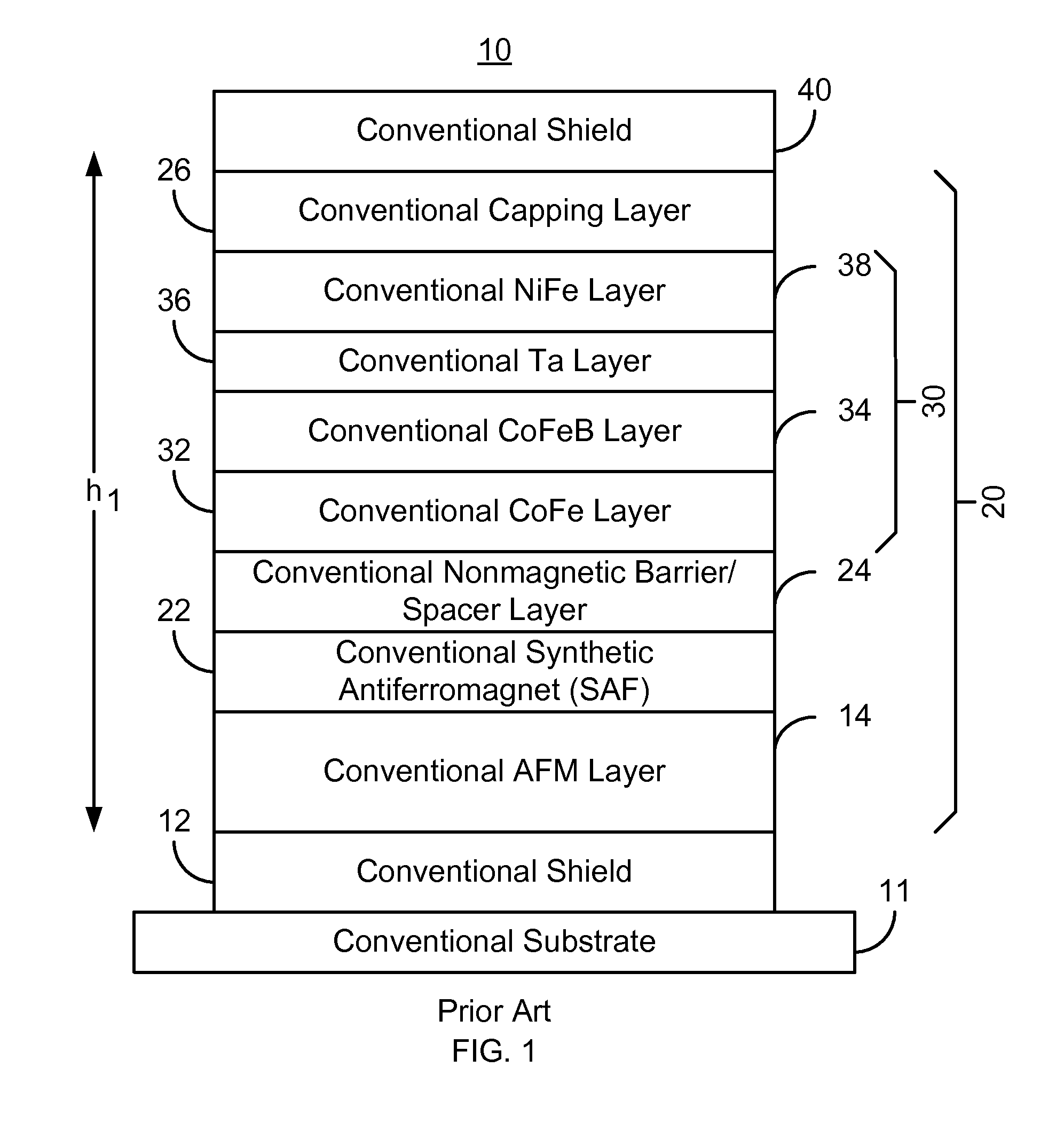
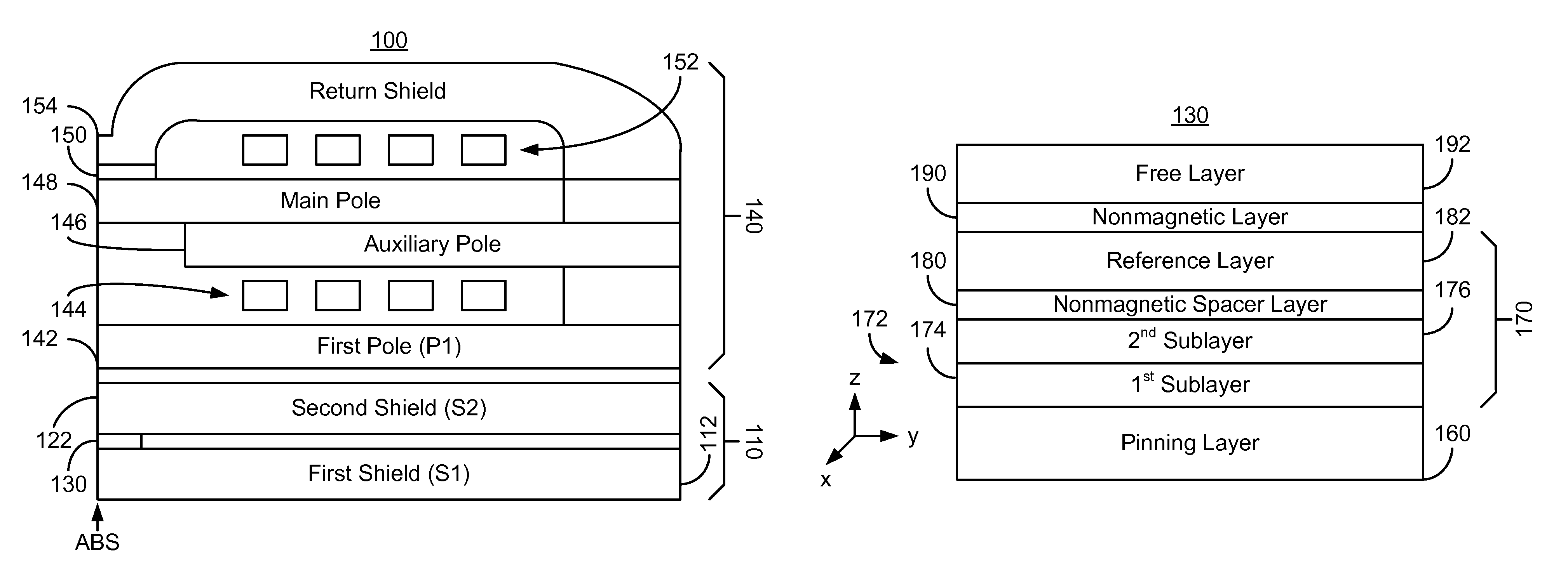
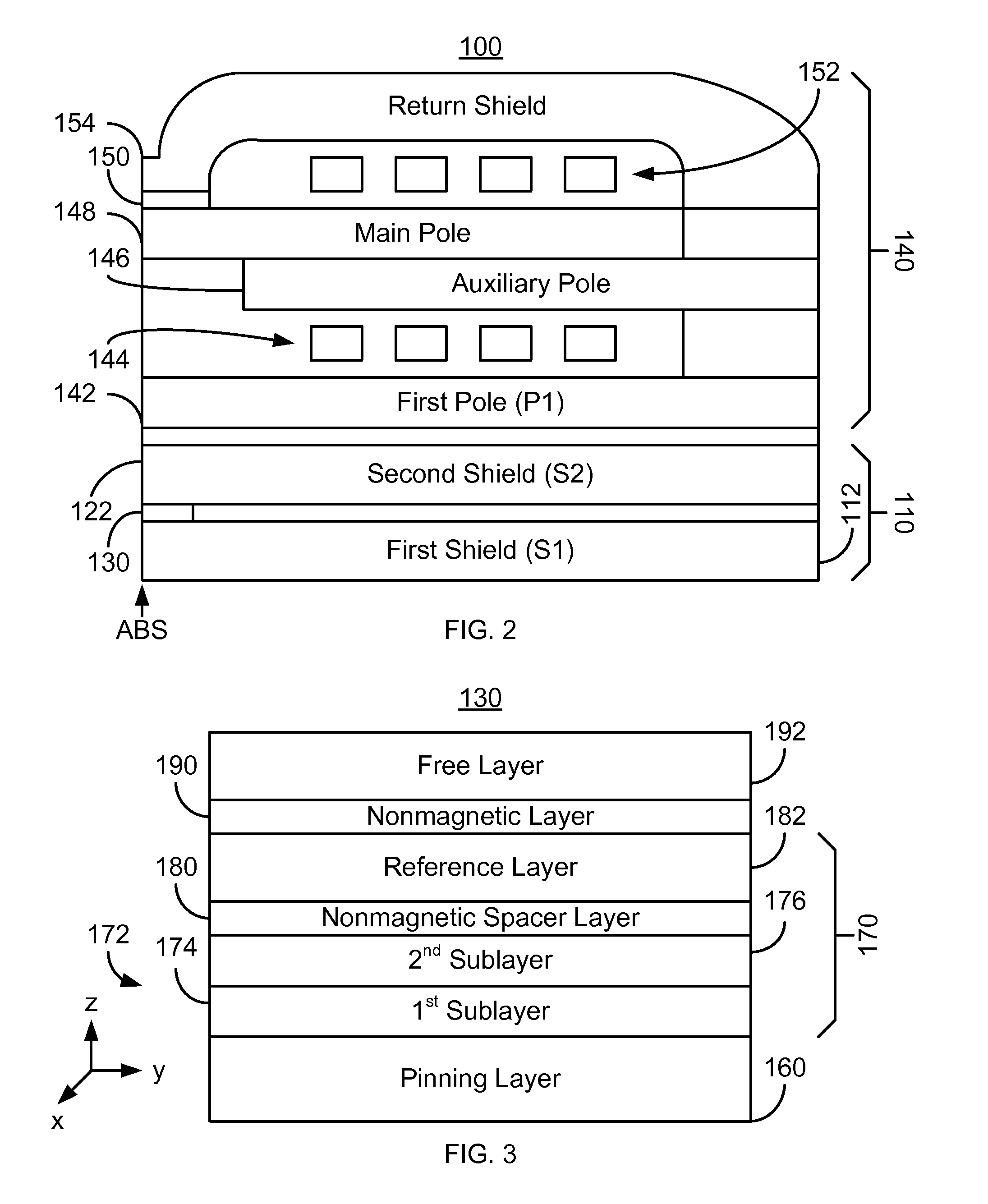
Method and system for providing a read sensor having a low magnetostriction free layer
ActiveUS8194365B1Magnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic transducersMagnetic layer
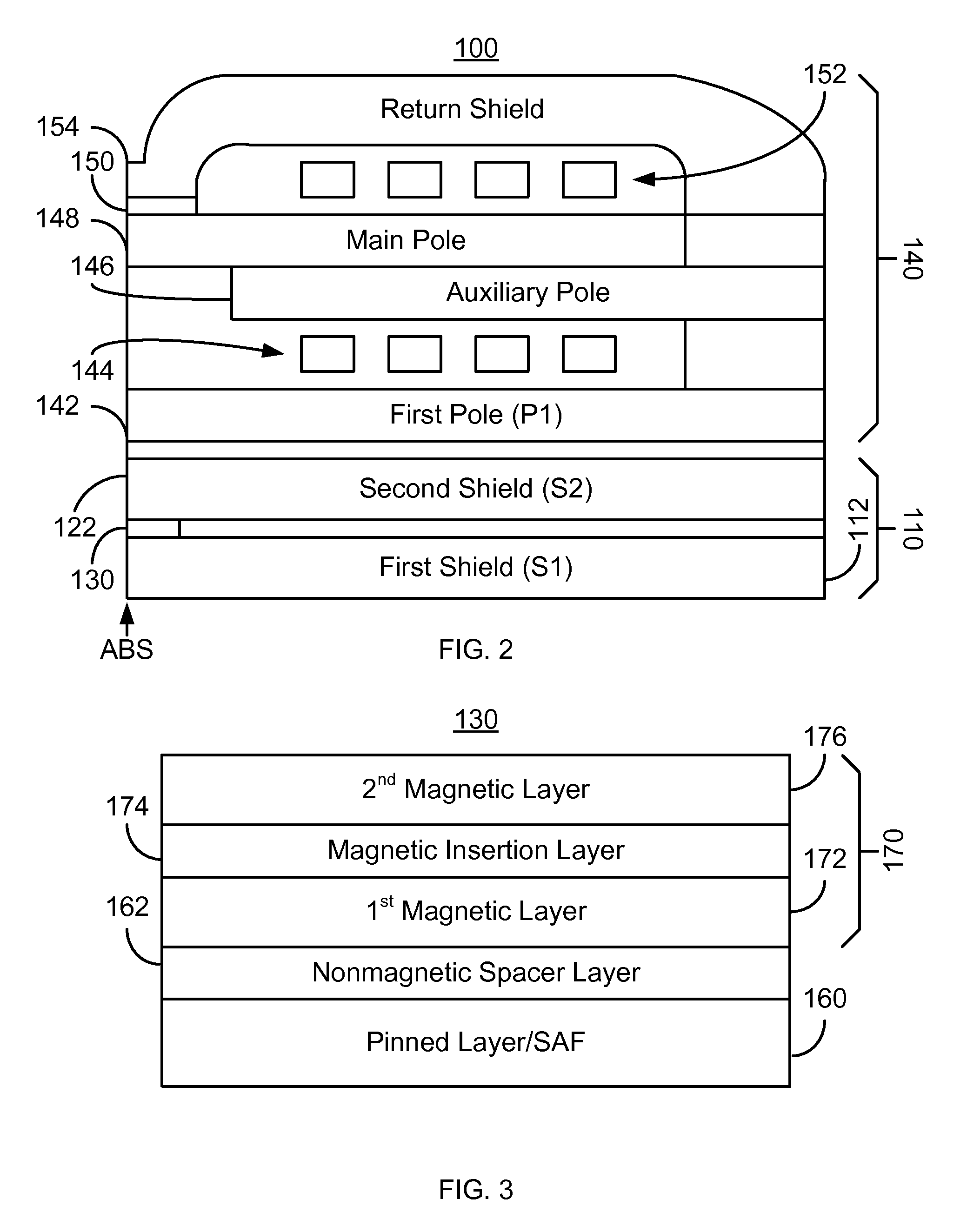
A method and system for providing a magnetic structure in magnetic transducer is described. The magnetic structure includes a pinned layer, a nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a free layer. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is between the pinned layer and the free layer. The free layer includes a first magnetic layer, a second magnetic layer, and a magnetic insertion layer between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The first magnetic layer has a first magnetostriction. The second magnetic layer has a second magnetostriction opposite to the first magnetostriction. The magnetic insertion layer provides a growth texture barrier between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
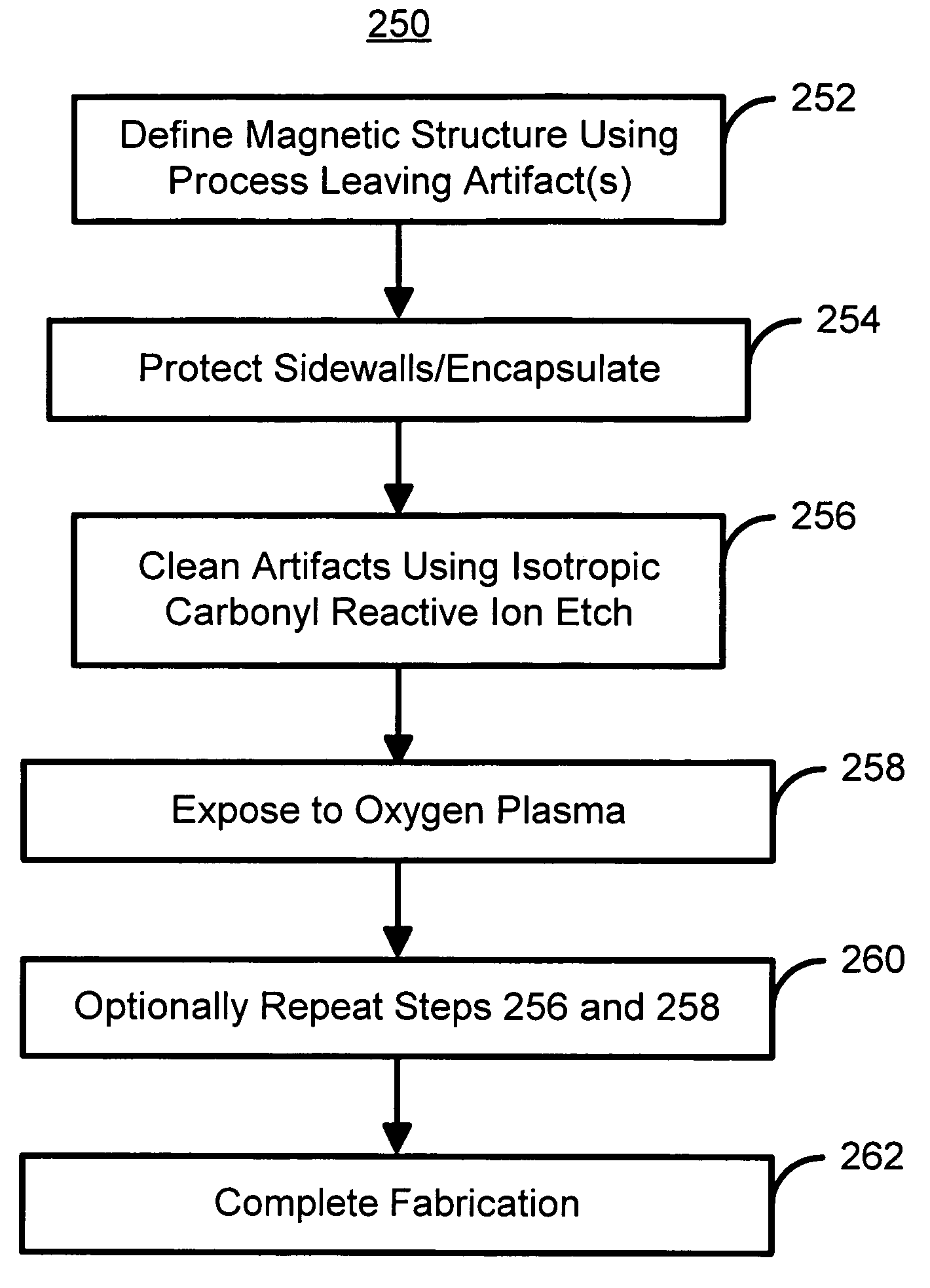
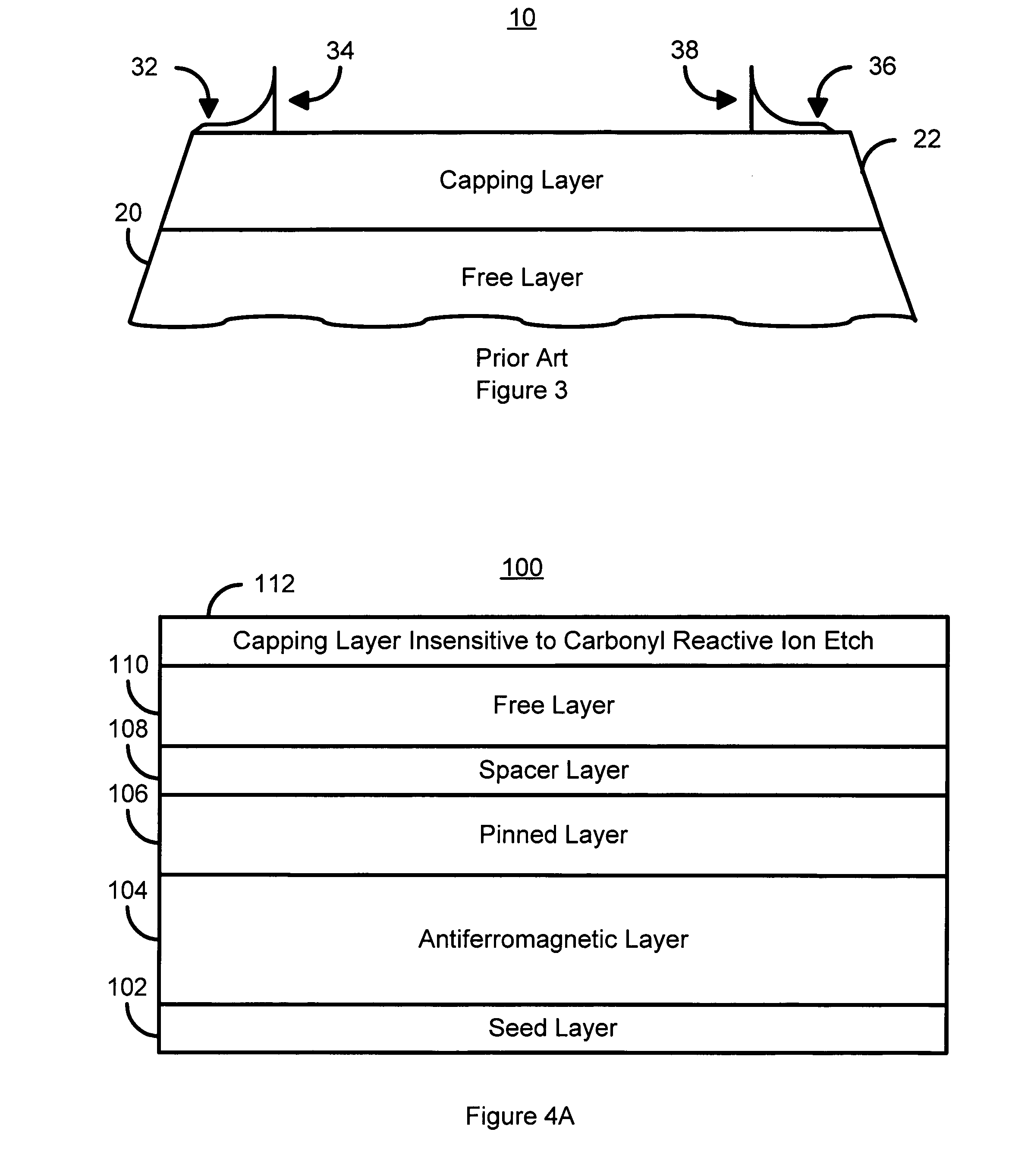
Method and system for cleaning magnetic artifacts using a carbonyl reactive ion etch
A method and system for providing a magnetic structure that includes at least one magnetic material is disclosed. The method and system include defining the magnetic structure. The magnetic structure also includes a top layer that is insensitive to an istroropic carbonyl reactive ion etch. The defining of the magnetic structure results in at least one artifact. The method and system further includes cleaning the at least one artifact using at least one isotropic carbonyl reactive ion etch.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and system for providing a magnetic transducer having an improved read sensor synthetic antiferromagnet
A method and system for providing a magnetic structure in magnetic transducer is described. The method and system include providing a pinning layer, a synthetic antiferromagnetic (SAF) adjacent to the pinning layer, a nonmagnetic layer, and a sensor layer. The SAF resides between the nonmagnetic and pinning layers. The nonmagnetic layer is between the SAF and the sensor layer. The SAF includes a pinned layer, a reference layer, and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between the pinned and reference layers. The pinned layer is magnetically coupled with the reference layer and includes sublayers. A first sublayer has a first blocking temperature distribution (TBD) and a first exchange energy. A second sublayer has a second TBD and a second exchange energy. The first sublayer is between the pinning layer and second sublayer. The first TBD is greater than the second TBD. The first exchange energy is less than the second exchange energy.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Flexible magnetic interconnects
ActiveUS20100197148A1Easy to customizeAllows in designIndoor gamesPoint-like light sourceFlexible circuitsEngineering
A flexible magnetic interconnect is disclosed. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a module having a recess therein. A magnetic structure is moveable within the recess and a flexible circuit cooperates with the module to retain the magnetic structure within the recess. Movement of the magnetic structure is caused by magnetic attraction between the magnetic structure and an external magnetic structure. The flexible circuit includes a compliant contact, which changes shape by movement of the magnetic structure.
Owner:APEX TECH INC
System and method for storing energy
InactiveUS20080074083A1Promote sportsCombination recordingPrimary cell to battery groupingEngineeringEnergy storage
A self-recharging battery comprising a generator and an energy storage device contained within the battery case. The generator comprises a magnetic structure configured to generate a compressed magnetic field and a coil configured to focus the compressed magnetic field in electrical conductive elements of the coil.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Modular lighting system and method employing loosely constrained magnetic structures
InactiveUS20130044501A1Present inventionPlanar light sourcesLighting support devicesMagnetic tension forceShortest distance
A lighting system including modules containing LEDs or other electroluminescent devices and loosely constrained magnetic structures at least partially contained within cavities in the module substrate that are connected to fixtures under magnetic force. The loosely constrained magnetic structures accommodate mechanical variations in the system and provide a method to connect modules mechanically, electrically and thermally to different fixtures or positions in fixtures without tools. The relatively short distance separating magnetic structures provides high connection forces with the use of relatively small magnets. Magnets and electrical contacts are not located directly between the LED subassembly and the fixture, which provides higher thermal conductivity pathways to remove heat from the LEDs. Biasing members may be used to increase thermal contact. Magnetic structures may, but are not required, to conduct electricity. Fixtures that attach to modules include rails, sockets, heat sinks and two-dimensional structures with recessed electrodes for improved electrical safety.
Owner:APEX TECH INC
Flexible magnetic interconnects
ActiveUS8187006B2Easy to customizeAllows in designIndoor gamesPoint-like light sourceFlexible circuitsEngineering
A flexible magnetic interconnect is disclosed. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a module having a recess therein. A magnetic structure is moveable within the recess and a flexible circuit cooperates with the module to retain the magnetic structure within the recess. Movement of the magnetic structure is caused by magnetic attraction between the magnetic structure and an external magnetic structure. The flexible circuit includes a compliant contact, which changes shape by movement of the magnetic structure.
Owner:APEX TECH INC
System and method for storing energy
InactiveUS7688036B2Promote sportsPrimary cell to battery groupingCombination recordingElectrical batteryEngineering
A self-recharging battery comprising a generator and an energy storage device contained within the battery case. The generator comprises a magnetic structure configured to generate a compressed magnetic field and a coil configured to focus the compressed magnetic field in electrical conductive elements of the coil.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Integrated magnetics for a DC-DC converter with flexible output inductor
InactiveUS7034647B2Simple designTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDc-dc conversionInductor windingsDc dc converter
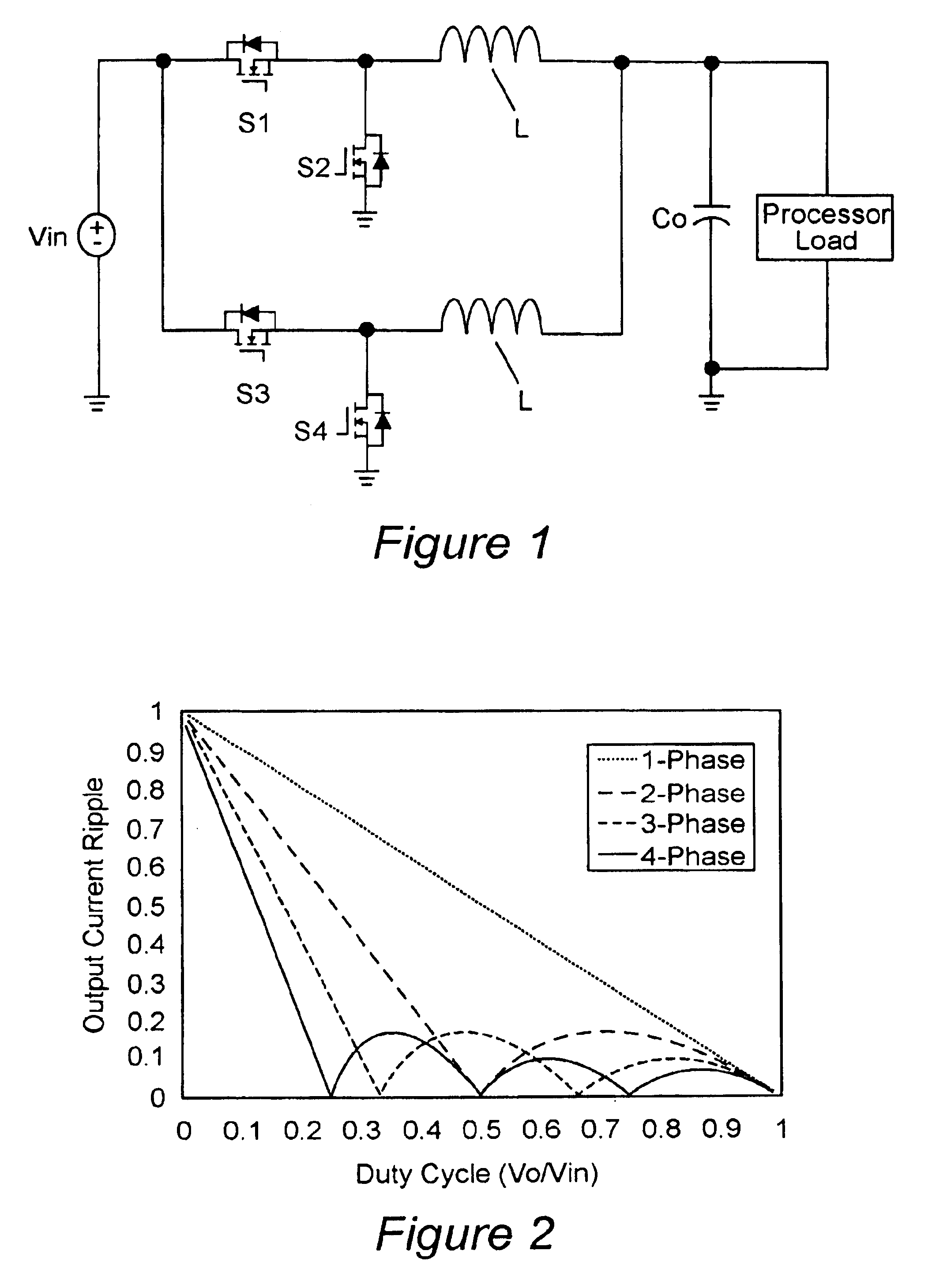
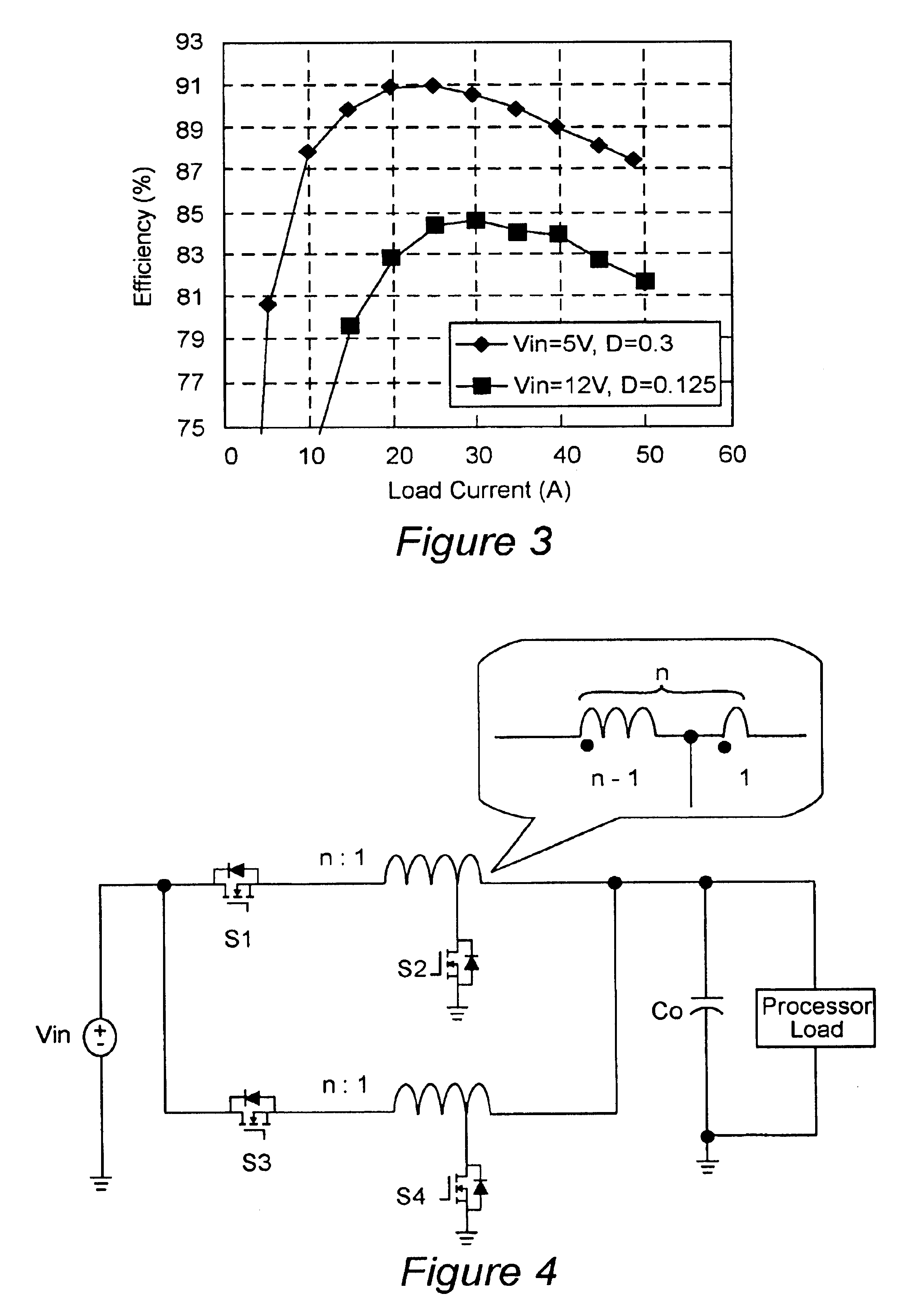
An integrated magnetic assembly that allows the primary and secondary windings of a transformer and a separate inductor winding to be integrated on a unitary magnetic structure is disclosed. The unitary magnetic structure includes first, second, and third legs that are physically connected and magnetically coupled. The primary and secondary windings of the transformer can be formed on the third leg of the unitary magnetic structure. Alternatively, the primary and secondary windings can be split between the first and second legs. Thus, the primary winding includes first and second primary windings disposed on the first and second legs and the secondary winding includes first and second secondary windings disposed on the first and second legs. The inductor winding may also be formed either on the third leg or it may split into first and second inductor windings and disposed on the first and second legs. In addition, one or more legs may include an energy storage component such as an air gap. This integration of the primary and secondary windings and the inductor winding on the unitary magnetic structure advantageously decouples the inductor function from the transformer function and allows the more optimal design of both the inductor and the transformer. The unitary magnetic structure may be coupled to a full bridge, a half bridge, or a push pull voltage input source to form a DC—DC converter.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Vertical winding structures for planar magnetic switched-mode power converters
ActiveUS7321283B2Total current dropMinimizes capacitive couplingTransformers/inductances casingsApparatus with intermediate ac conversionClose couplingCapacitance
A vertical winding structure for planar integrated magnetics used in switched-mode power converters maintains close coupling between the different windings but reduces the eddy current losses, lowers the DC winding resistance and reduces the number of layers of the PCB. Vertical and horizontal windings can be used together without sacrificing these performance advantages and further minimizing the capacitive coupling between the outer-leg windings and the center-leg winding. This winding structure can be used in a wide range of magnetic structures including isolated and non-isolated CDRs, interleaved CDRs, and buck and boost converters.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
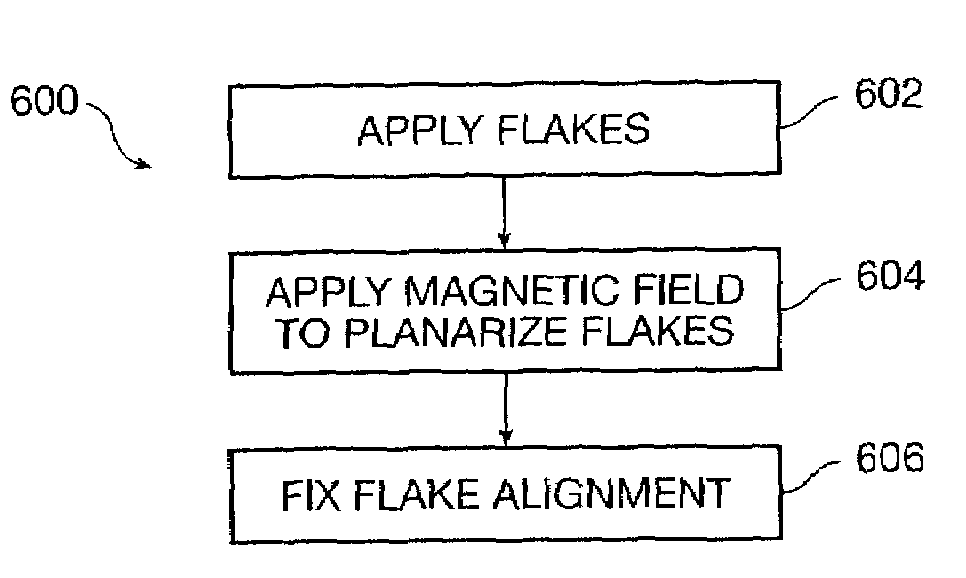
Magnetic planarization of pigment flakes
InactiveUS7258900B2Improve visual appearanceGood lookingPretreated surfacesPattern printingOut of planePigment
A magnetic field is applied to planarize magnetic pigment flakes relative to a surface. Pigment flakes, such as optically variable pigment flakes, are used in a variety of paints, inks, extrusions, powder coatings, and other forms for decorative and security applications. In many applications pigment flakes tend to align parallel to each other and to the surface to which they are applied. If the pigment flakes include a suitable magnetic structure, a magnetic field can be applied to subsequently align the flakes or enhance the alignment of the flakes in the plane of the substrate if the carrier that the flakes are dispersed in is still fluid. In some printing operations, pigment flakes that are applied parallel to the substrate are pulled out of plane when the print screen or printing die is lifted off the substrate. Application of a magnetic field can re-align pigment flakes to the plane of the substrate, enhancing the visual quality of the printed image, especially with optically variable pigments.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Modular lighting system and method employing loosely constrained magnetic structures
Owner:APEX TECH INC
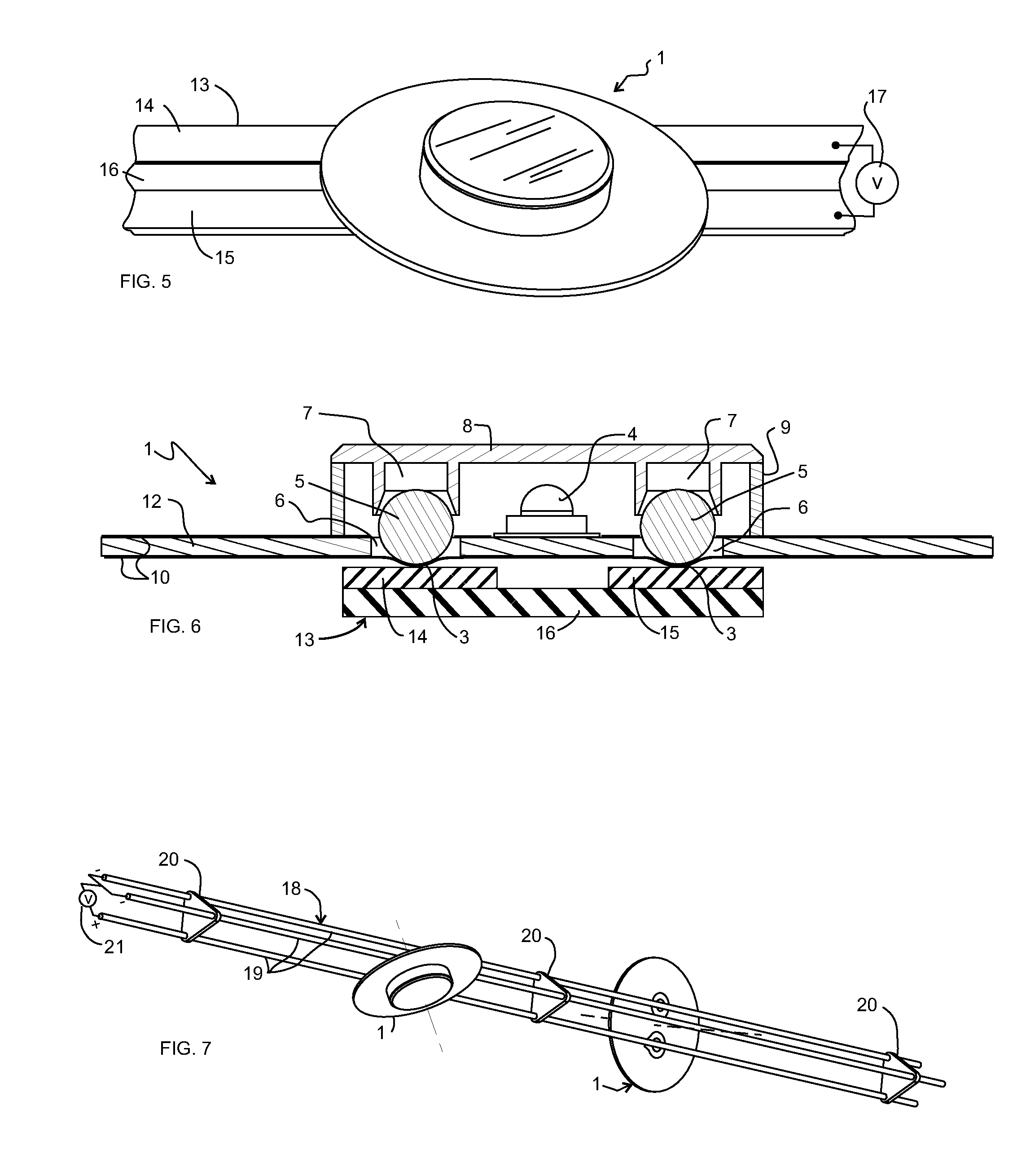
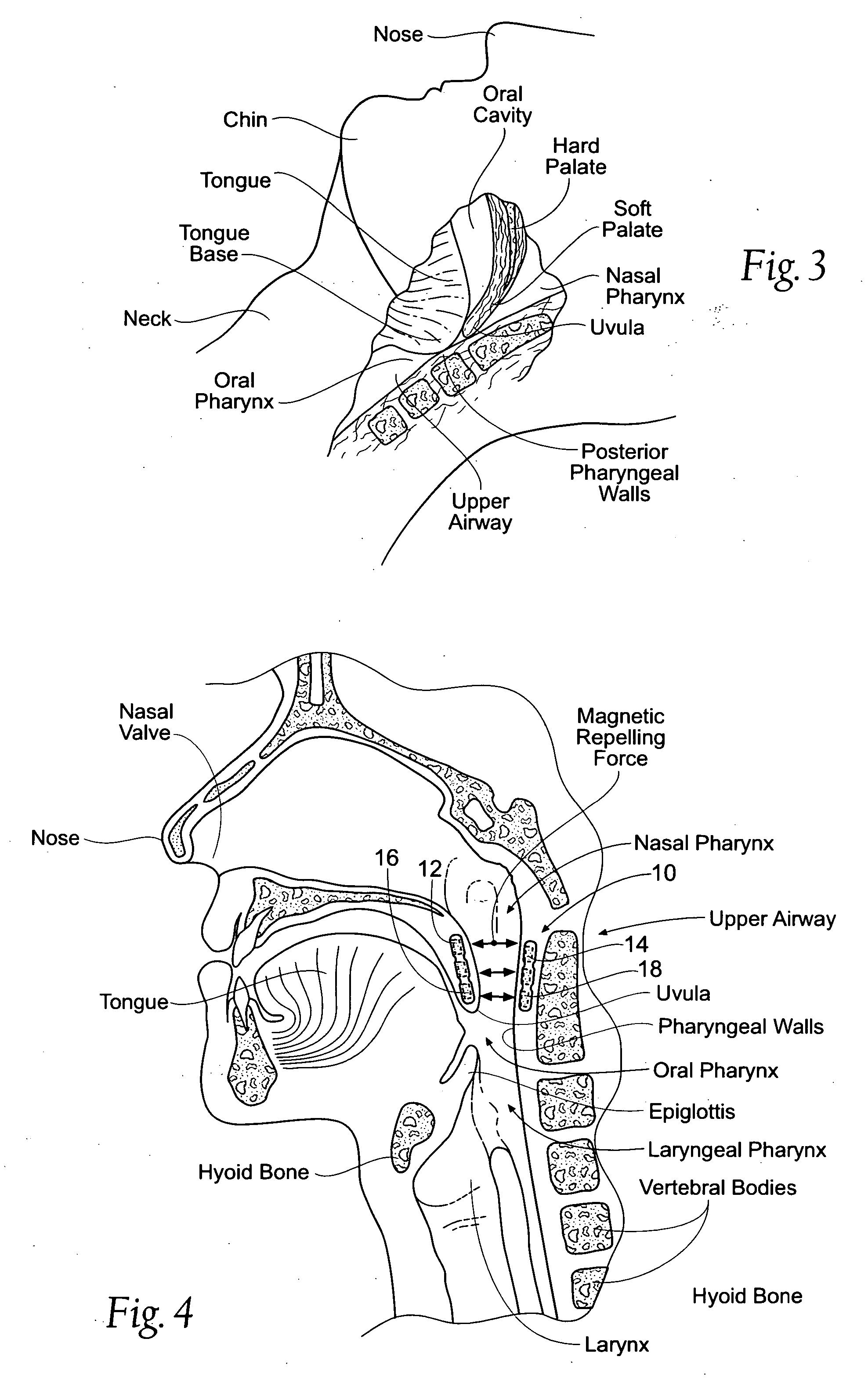
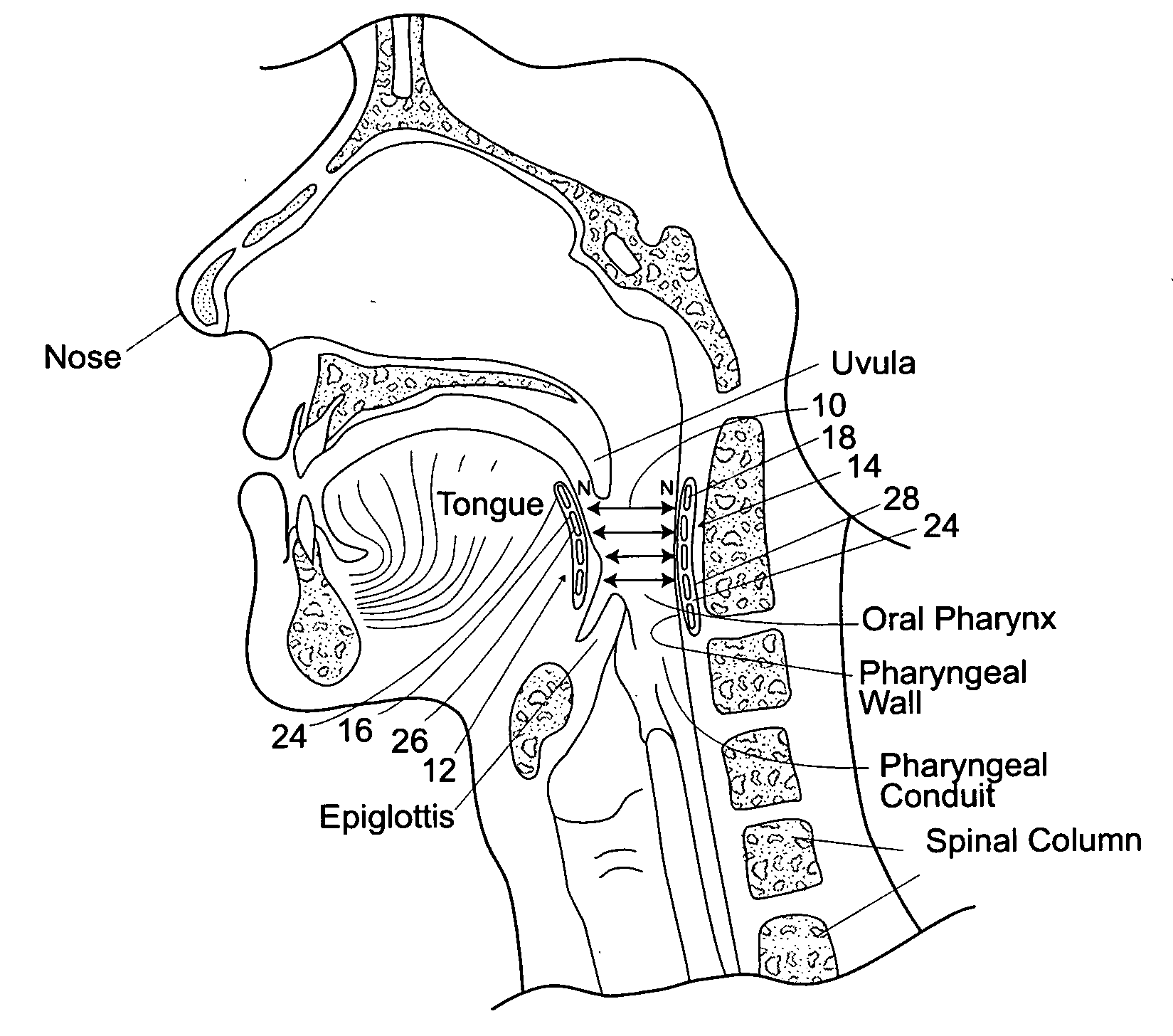
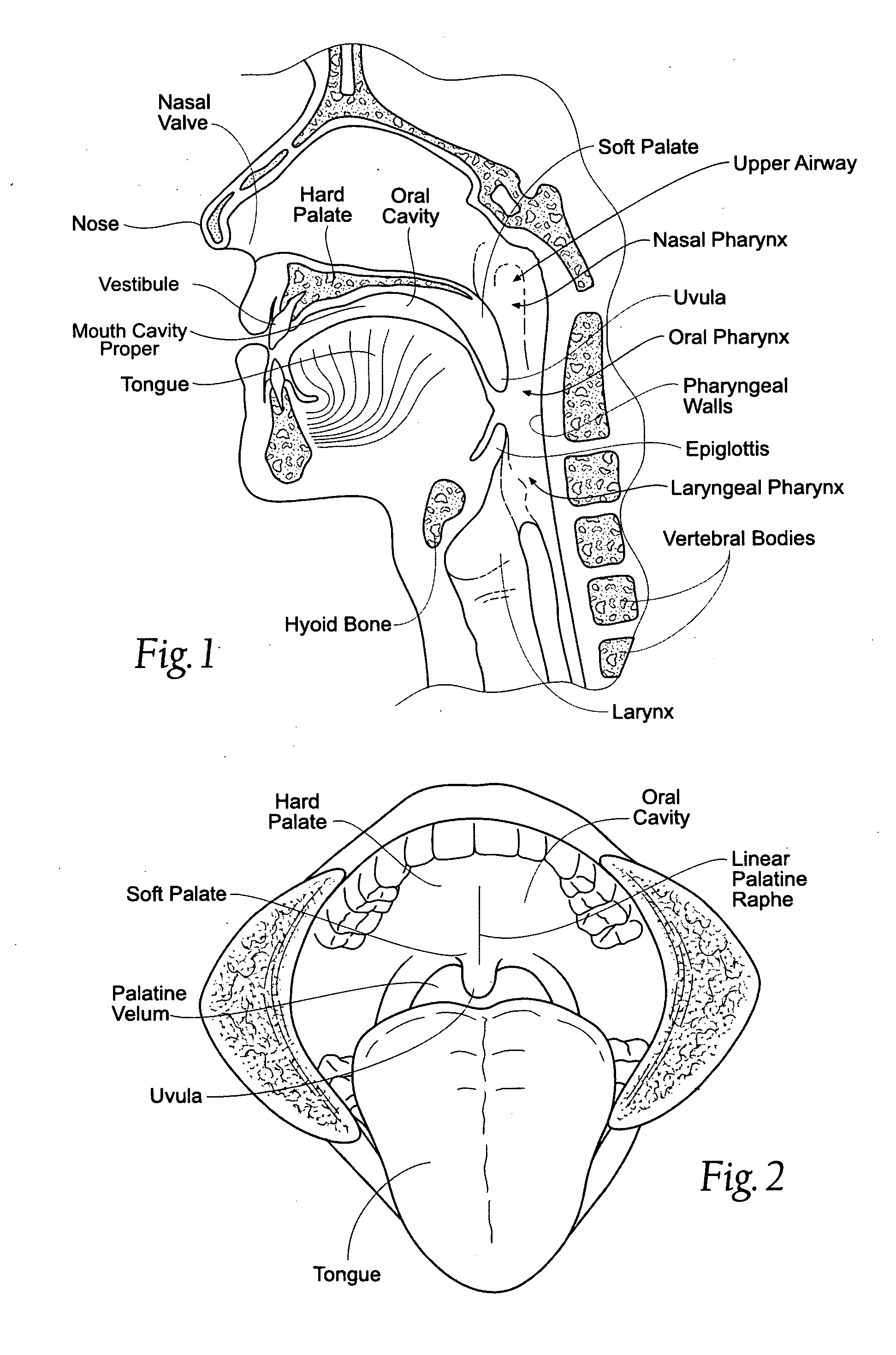
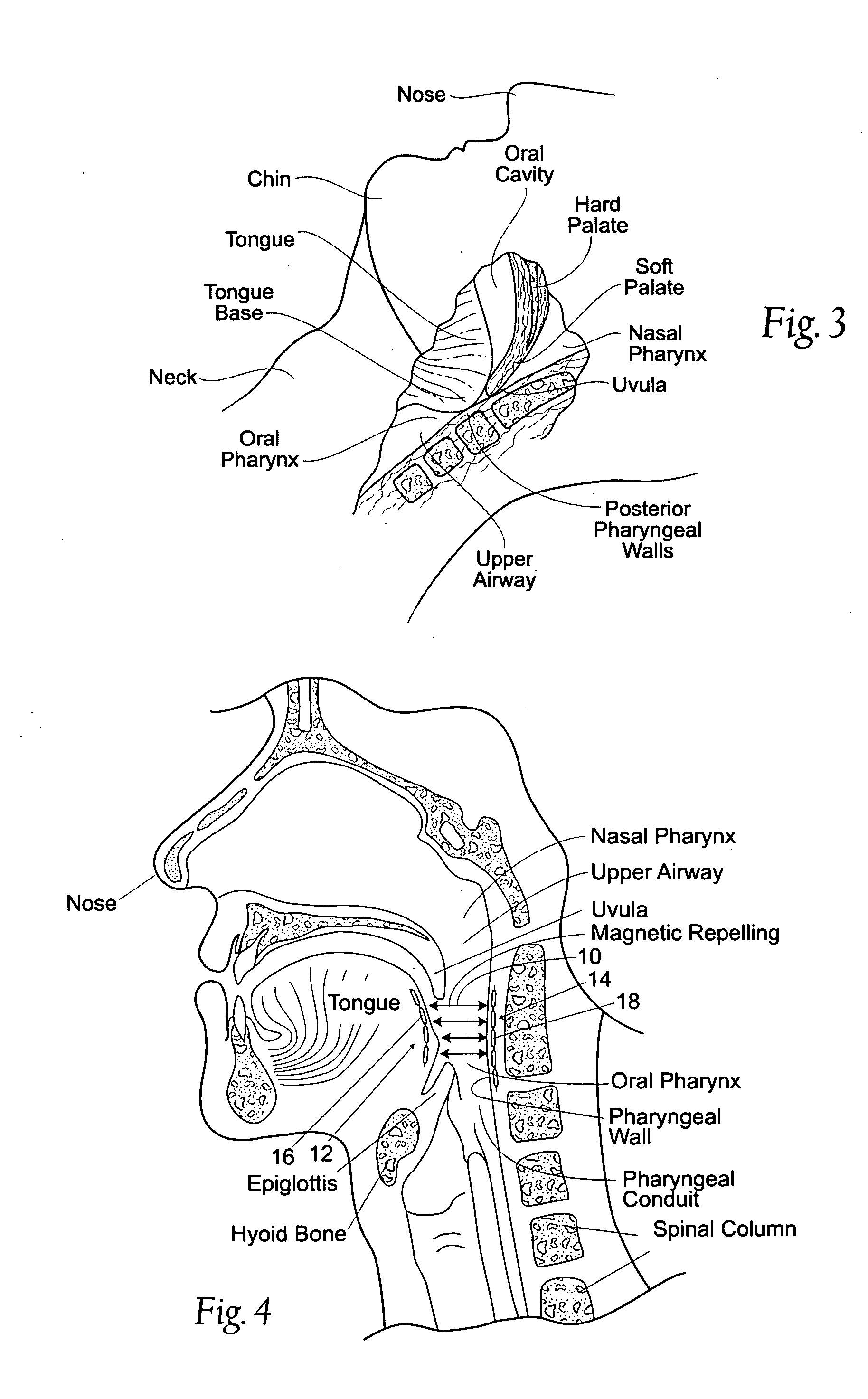
Devices, systems, and methods using magnetic force systems in or on soft palate tissue
InactiveUS20070256693A1Snoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesMagnetic tension forceMedicine
An implant system places magnetic structures in or on tissue that develop a magnetic repelling force between a soft palate a posterior pharyngeal wall. The magnetic repelling force has a magnitude F-mag, where F-mag=f (F-sep, F-nat), and where F-sep is a force required to separate soft palate tissue from pharyngeal wall tissue during sleep, and F-nat is a force exerted by native muscle on the soft palate during swallowing and / or drinking and / or speech. In another embodiment, a palate implant uses attractive magnetic force to keep the airway open.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Multiphase clamp coupled-buck converter and magnetic integration
InactiveUS20020118000A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionVoltage regulator modulePush pull
Voltage regulation, transient response and efficiency of a voltage regulator module (VRM) is improved where short duty cycles are necessitated by large differentials of input and output voltage by including at least one clamping of a tap of an inductance in series with an output of each of a plurality of parallel branches or phases which are switched in a complementary fashion or providing coupling between inductors of respective phases. Such coupling between inductors is achieved in a small module with an integrated magnetic structure. Reduced component counts are achieved while deriving built-in input and output filters. Principals of the invention can be extended to isolation applications and push-pull forward converts, in particular. A lossless clamping circuit is also provided allowing spike currents to be suppressed while returning power to the output of the VRM.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
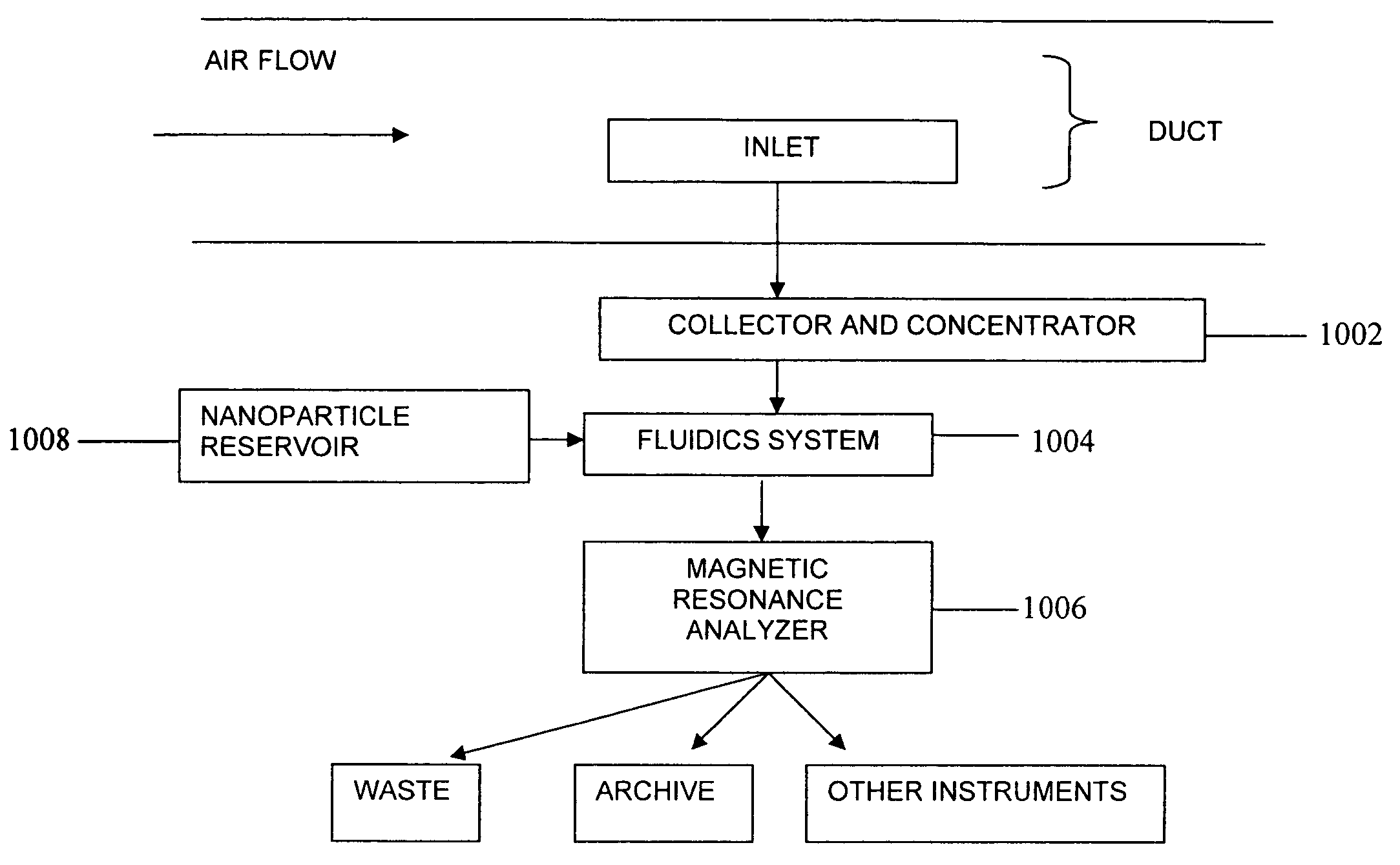
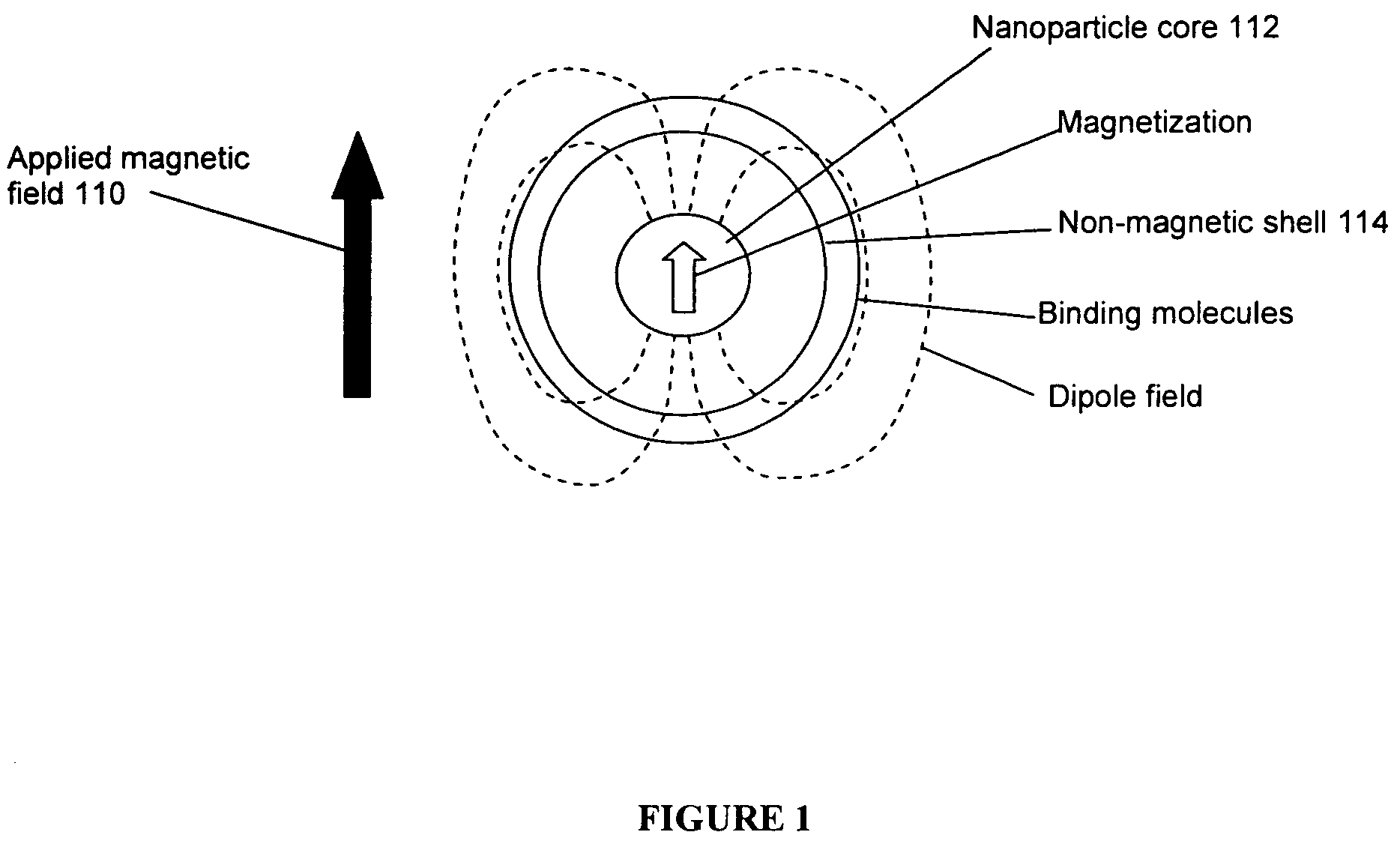
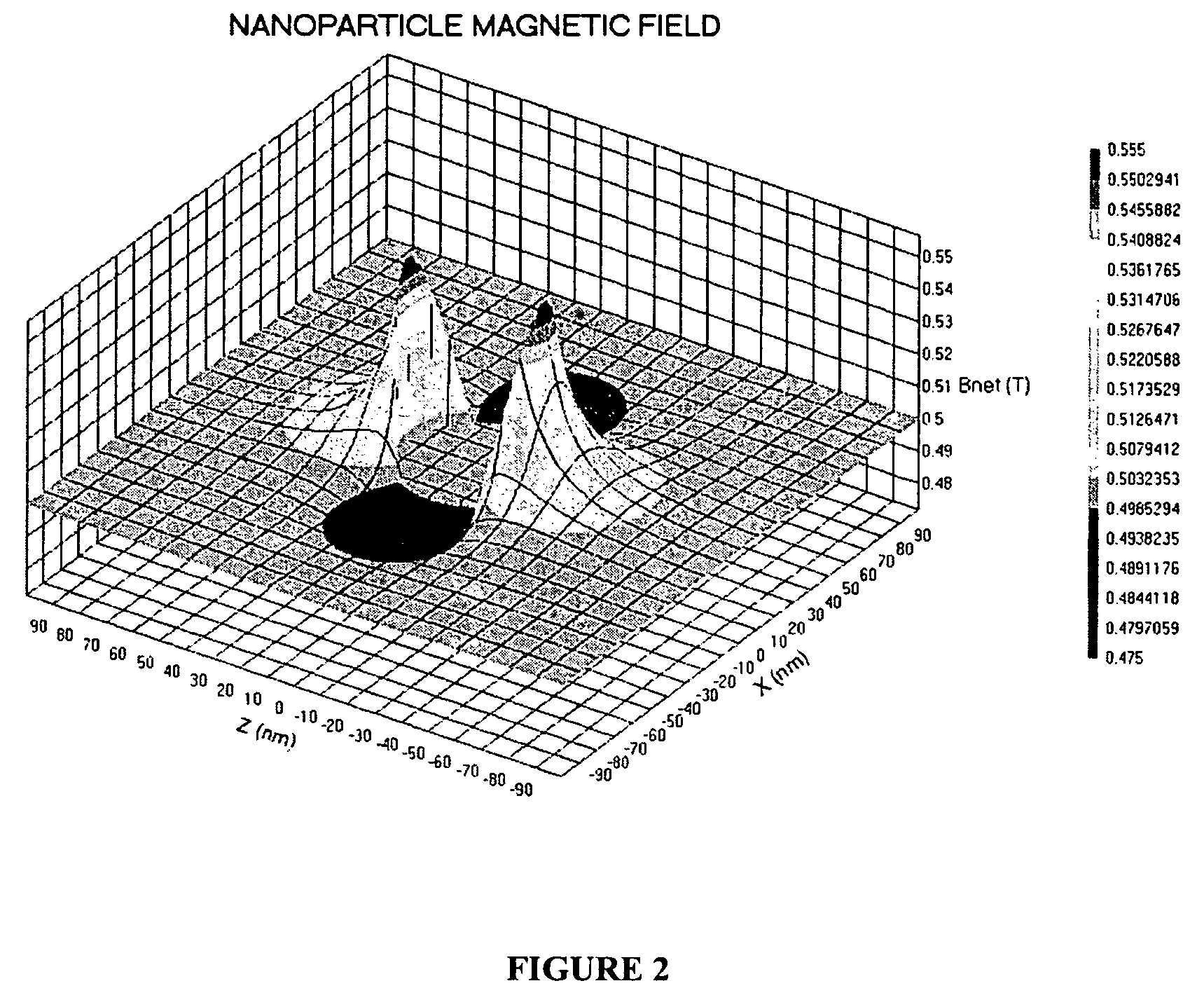
Magnetic resonance system and method to detect and confirm analytes
InactiveUS20070166730A1Easy to detectQuality improvementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismResonance measurementAnalyte
Owner:MENON INT
Position sensor, designed in particular for detecting a steering column torsion
InactiveUS7028545B2Better signal to noise ratioRaise the ratioWork measurementUsing electrical meansSteering columnEngineering
The invention concerns a position sensor, designed in particular for detecting a steering column torsion, consisting of a first magnetic structure including a plurality of magnets and a second magnetic structure including two ferromagnetic rings (6, 7) having a plurality of teeth (11, 12) and defining an air gap wherein is placed at least a magneto-sensitive element (15), the two magnetic structures being respectively integral with two parts in relative rotation. The invention is characterised in that the two ferromagnetic rings (6, 7) are nested and have each a substantially tubular part forming axially oriented teeth (11, 123) connected by a flux-closing zone (13, 14), the detecting air gap being delimited by said flux-closing zones.
Owner:MOVING MAGNET TECH
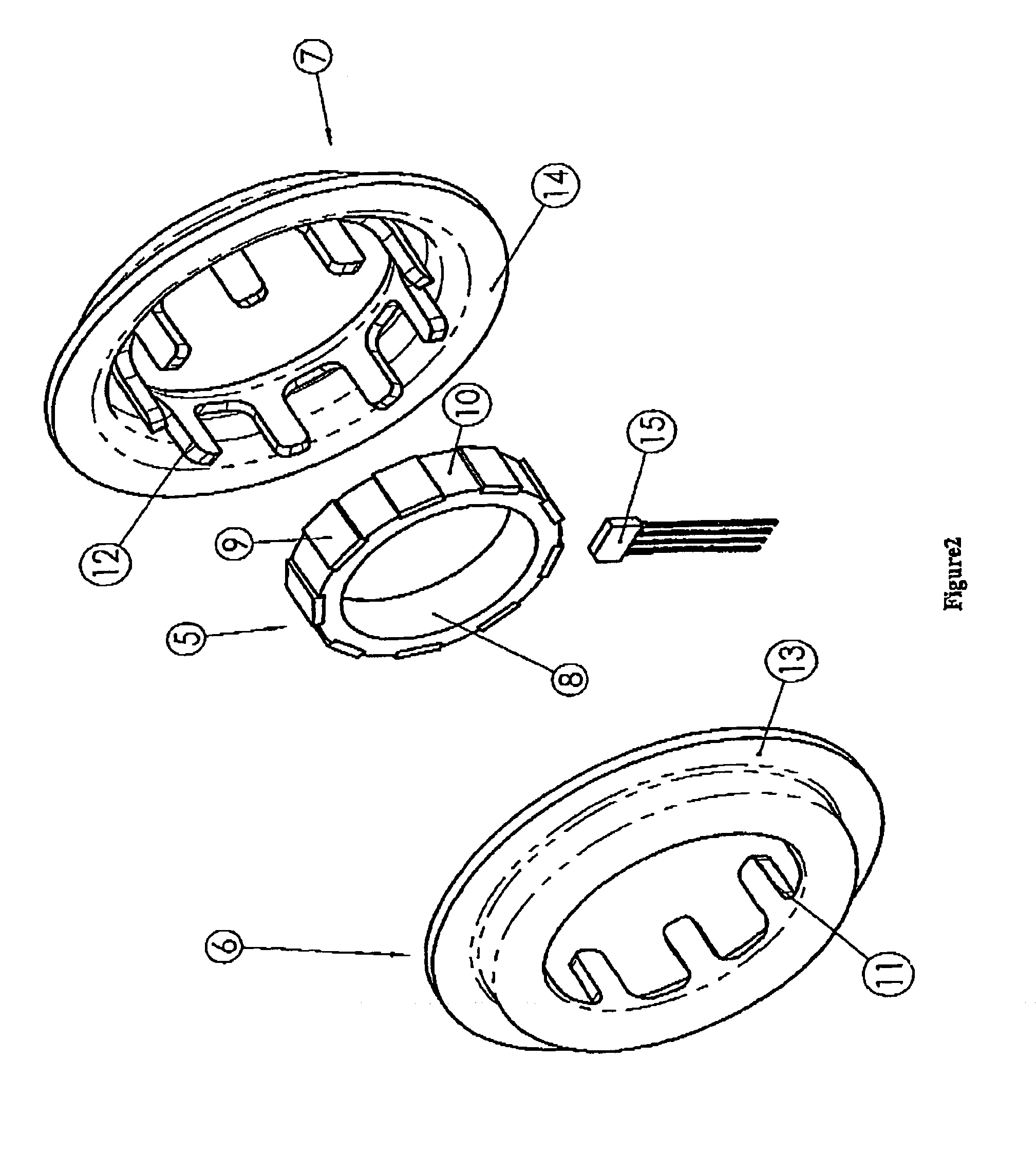
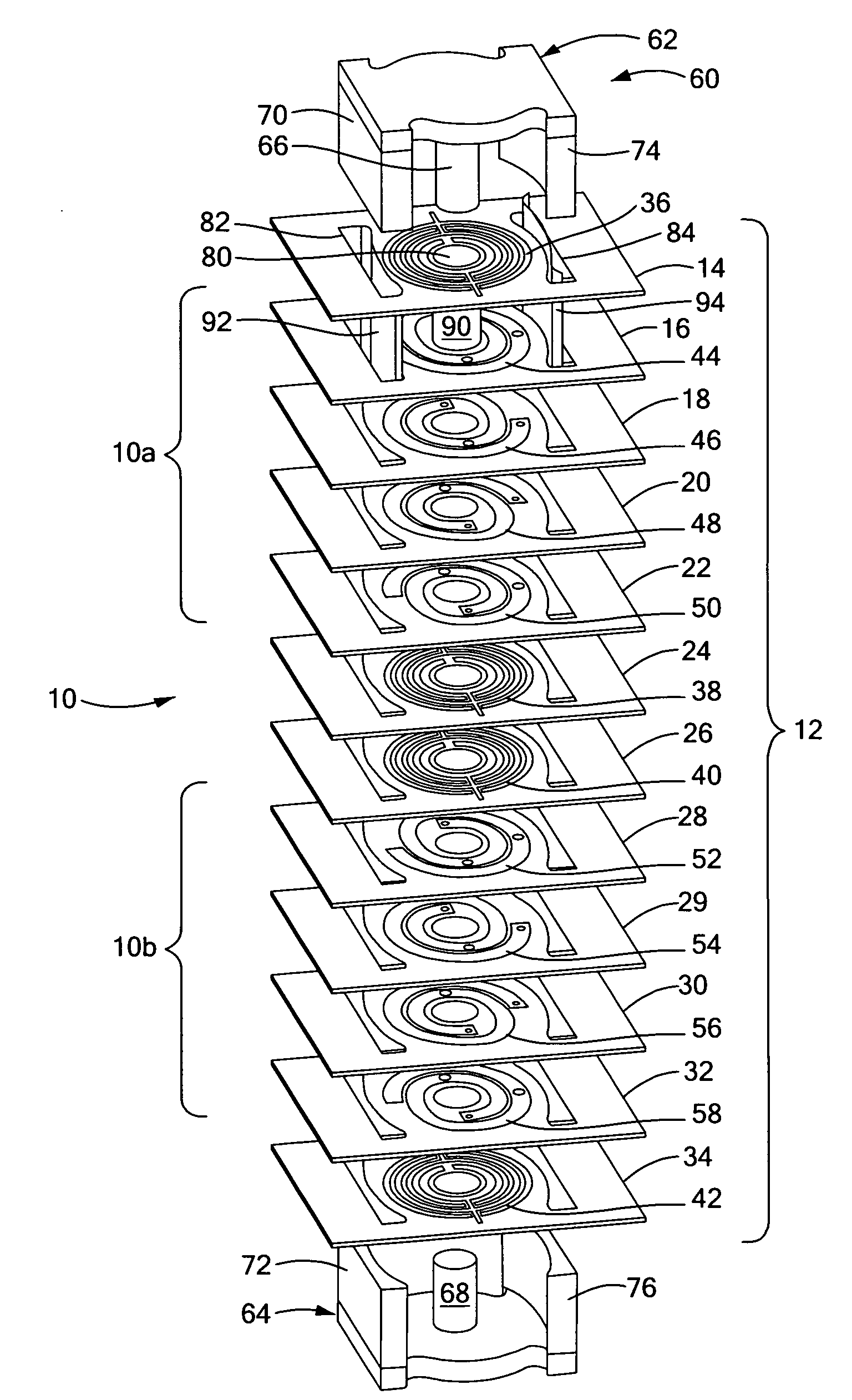
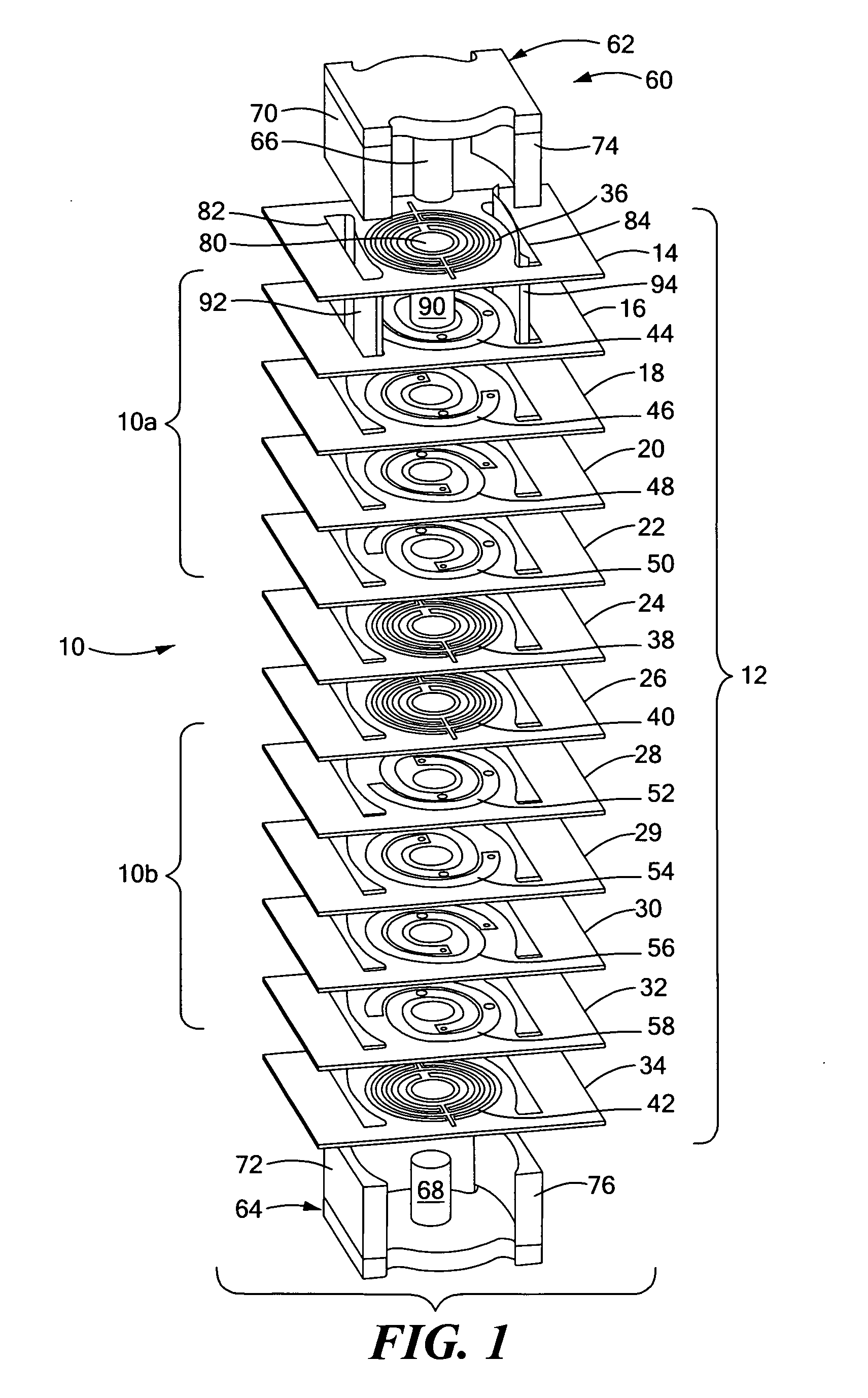
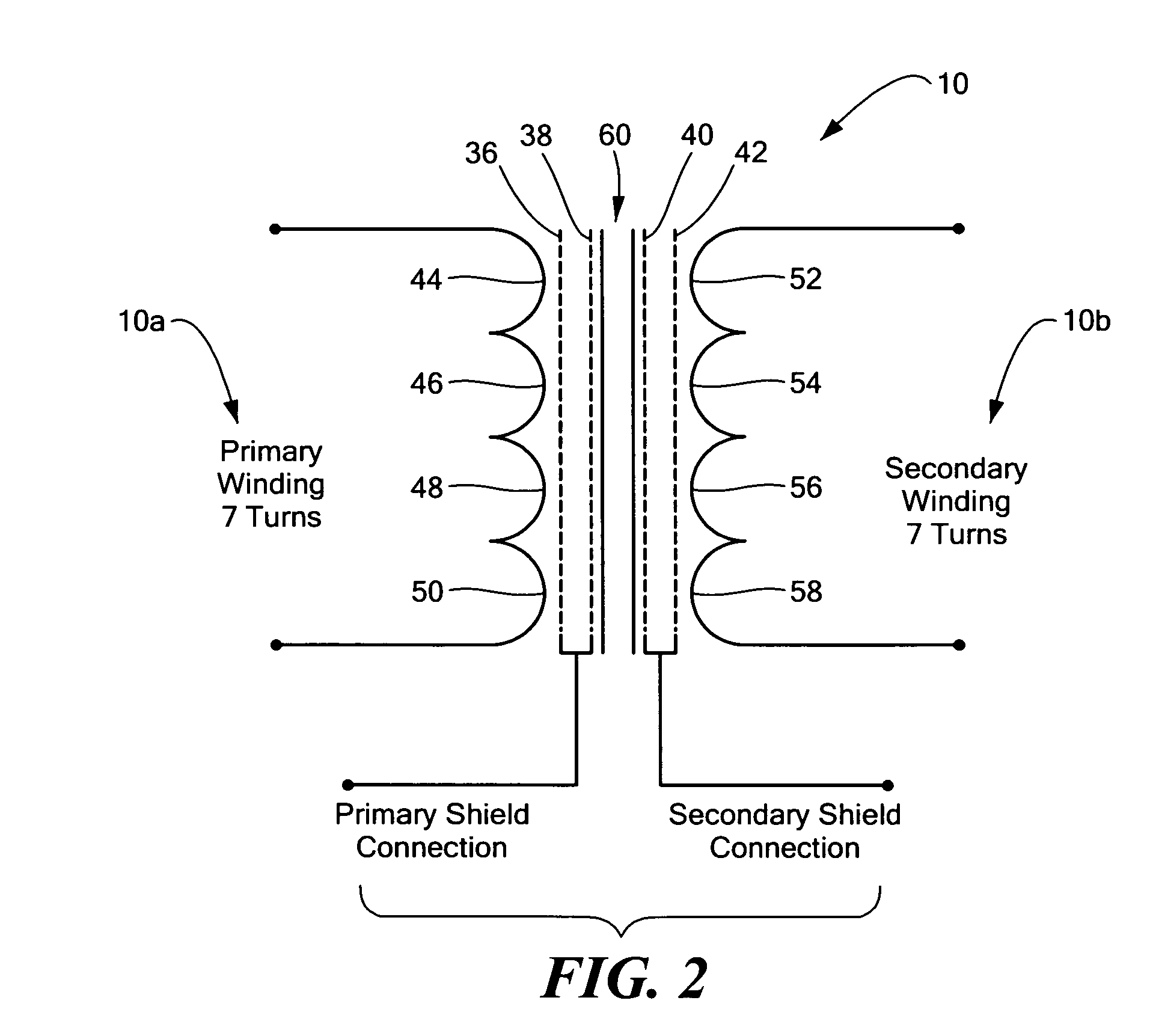
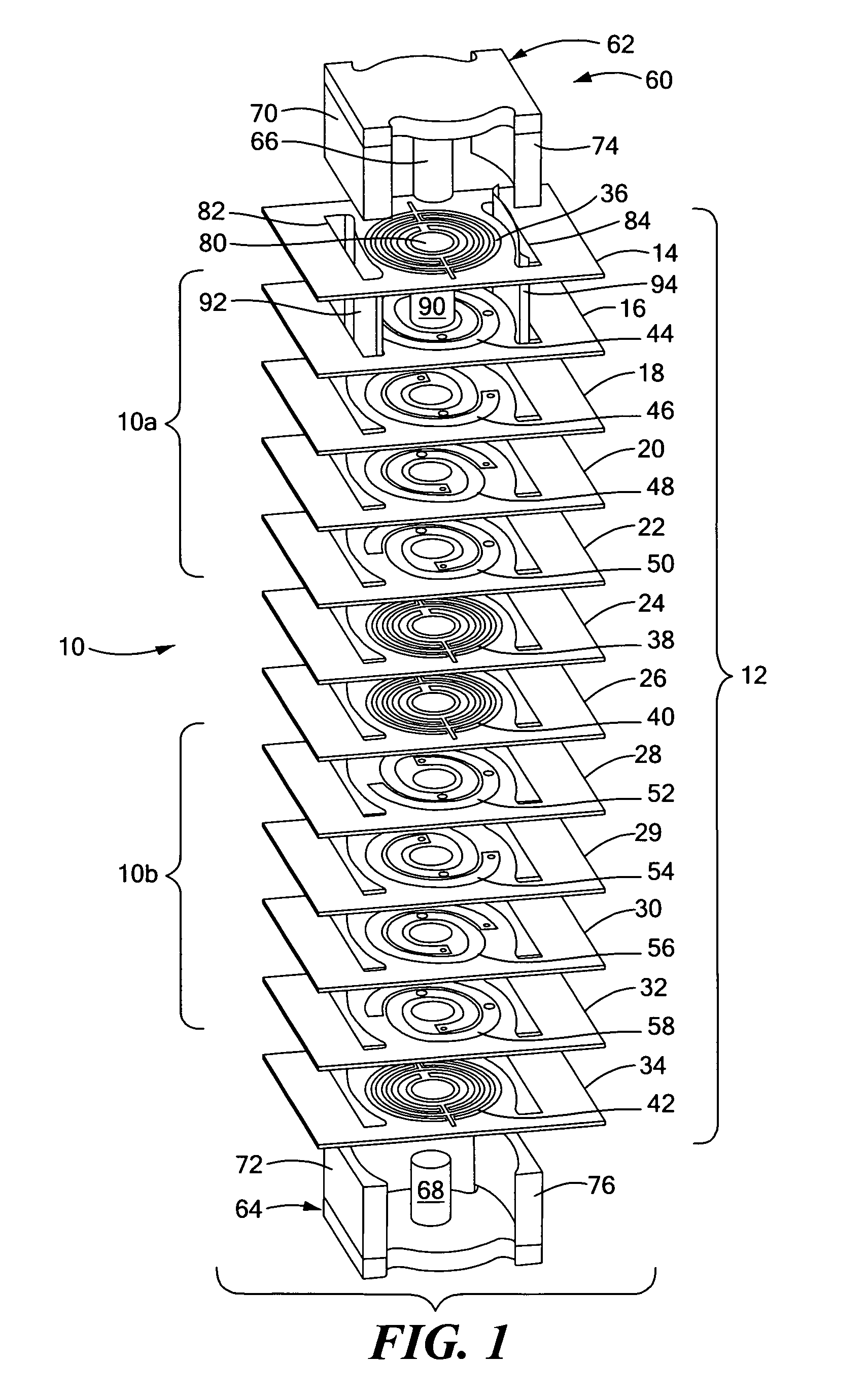
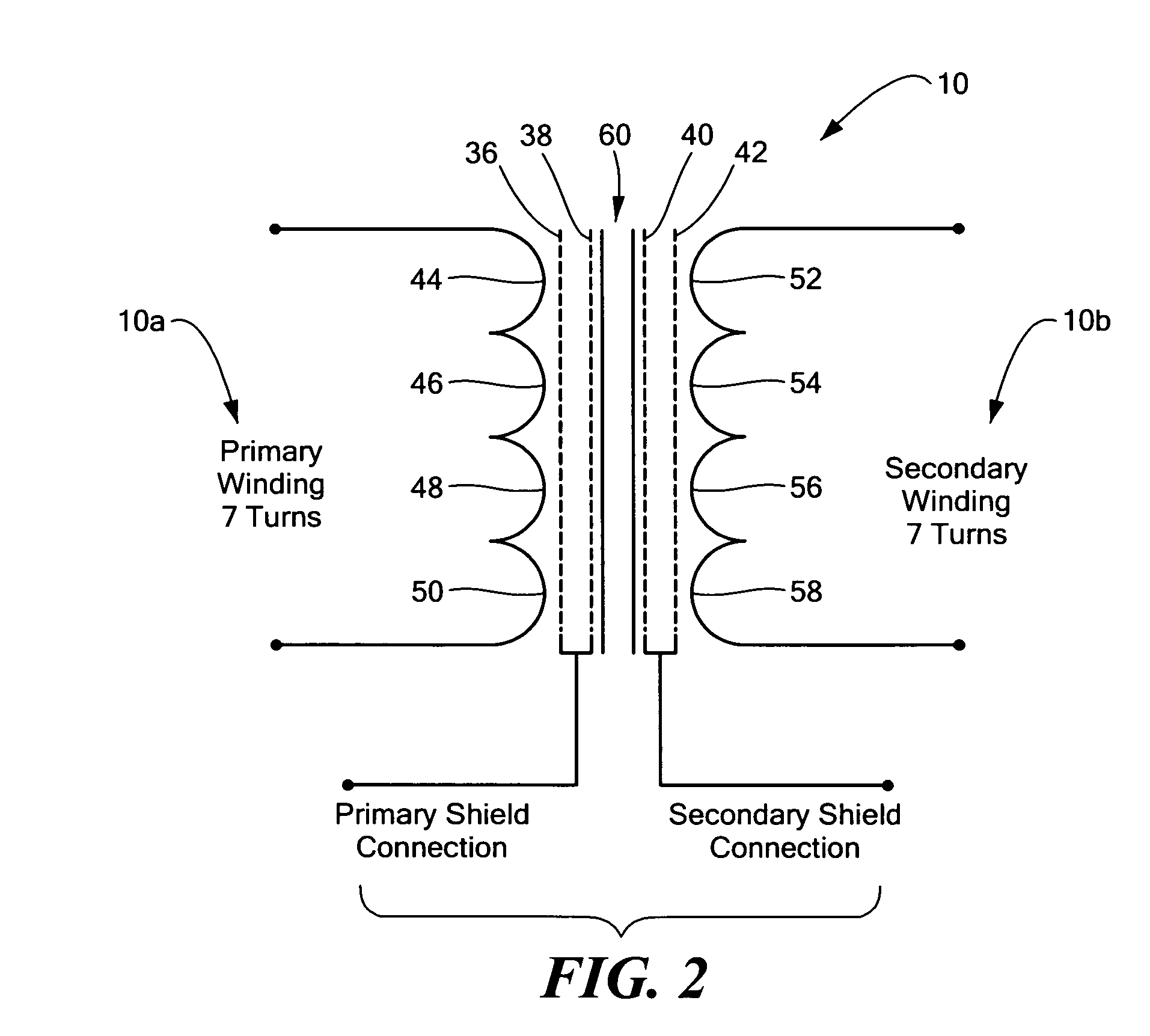
Planar magnetic structure
ActiveUS20100289610A1Reduce the voltage gradientTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsUnwanted magnetic/electric effect reduction/preventionElectrical conductorEddy current
An improved planar magnetic structure in which the voltage gradient between core and windings is reduced by shields disposed between the one or more legs of the core and the windings and extending through the PWB layers; vias are offset to permit them to be contained within the path of the winding; and the induced magnetic and eddy currents intrinsic to interstitial shield layers are reduced by configuring the shield conductors with pairs of courses with opposite and offsetting current propagation.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Matching a resonant frequency of a resonant cavity to a frequency of an input voltage
ActiveCN101933406APulse automatic controlMagnetic resonance acceleratorsResonant cavityPhase detector
A synchrocyclotron includes magnetic structures that define a resonant cavity, a source to provide particles to the resonant cavity, a voltage source to provide radio frequency (RF) voltage to the resonant cavity, a phase detector to detect a difference in phase between the RF voltage and a resonant frequency of the resonant cavity that changes over time, and a control circuit, responsive to the difference in phase, to control the voltage source so that a frequency of the RF voltage substantially matches the resonant frequency of the resonant cavity.
Owner:MEVION MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Planar magnetic structure
ActiveUS8089331B2Reduce the voltage gradientTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsUnwanted magnetic/electric effect reduction/preventionElectrical conductorEddy current
An improved planar magnetic structure in which the voltage gradient between core and windings is reduced by shields disposed between the one or more legs of the core and the windings and extending through the PWB layers; vias are offset to permit them to be contained within the path of the winding; and the induced magnetic and eddy currents intrinsic to interstitial shield layers are reduced by configuring the shield conductors with pairs of courses with opposite and offsetting current propagation.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
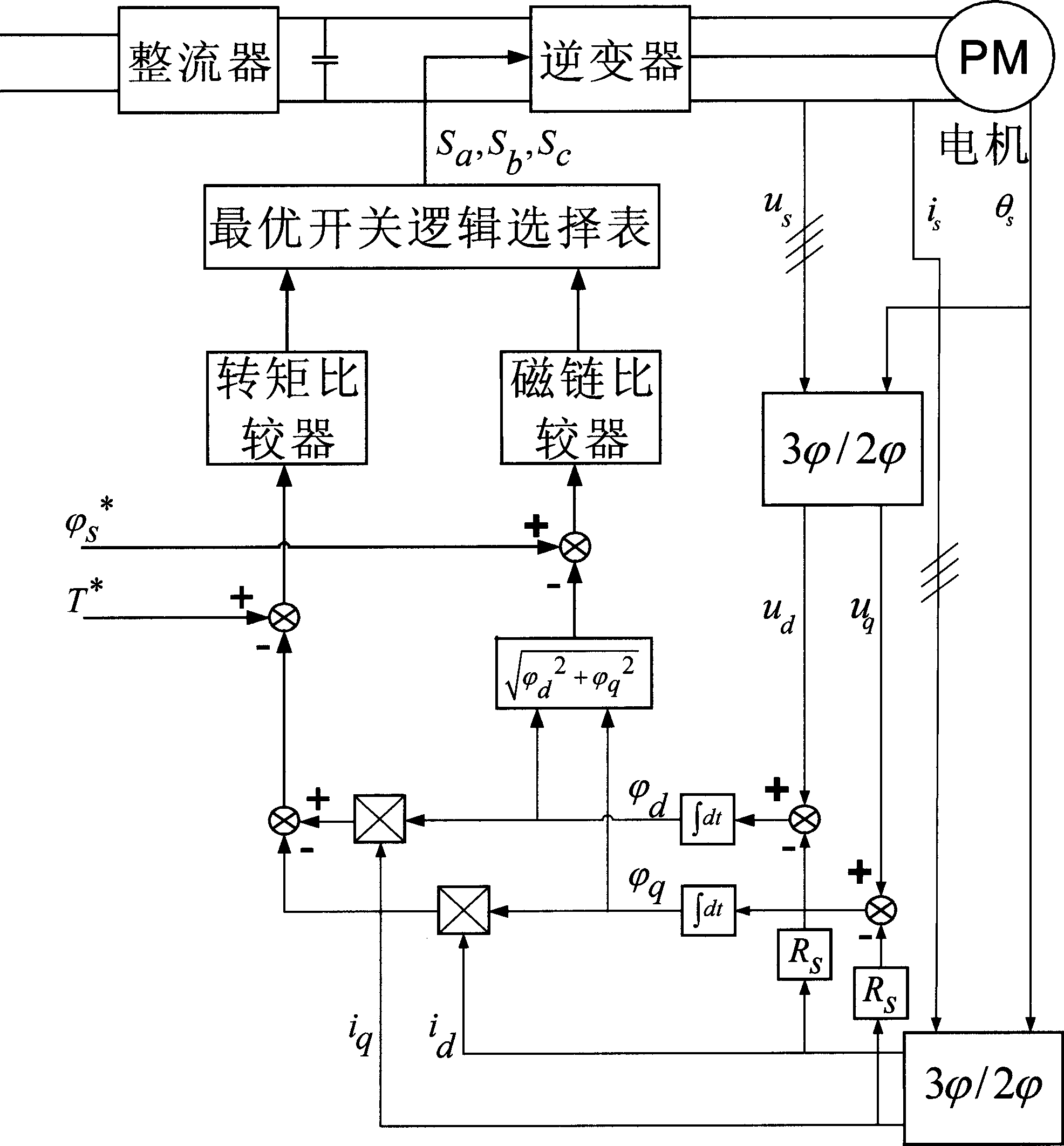
Automatic field-weakening method for built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN101783536AExtended pole-to-pole flux leakage pathsRealize automatic field weakening speed expansionMagnetic circuit rotating partsLow speedPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention relates to an automatic field-weakening method for a built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor, which solves the problem that field-weakening speed is difficult to widen due to the fixed rotor excitation and small reactance of armature reaction of a direct axis in the conventional permanent magnet synchronous motor in the market. In a rotor magnetic structure of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, a magnetic flux short-circuit block is arranged in a magnetic flux isolating layer in a quadrature axis direction with the help of an automatic adjustment action of a spring; when the rotary speed of the rotor is low, the short-circuit block is positioned at a low-speed position so that interelectrode magnet leakage through the isolating layer is small; when the rotary speed of the rotor is increased, the short-circuit block gradually deviates from the low-speed position to move towards the edge of the rotor under the action of rotating centrifugal force, which expands the interelectrode magnet leakage path; and the leakage magnet flux passing through the isolating layer is increased and the main magnet flux is reduced so that the aim of automatic filed-weakening widening speed is fulfilled in the motor body and a larger speed-adjusting range is reached. The method can be applied to the permanent magnet motors which have uncertain pole numbers and tangential or radial magnet structures.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
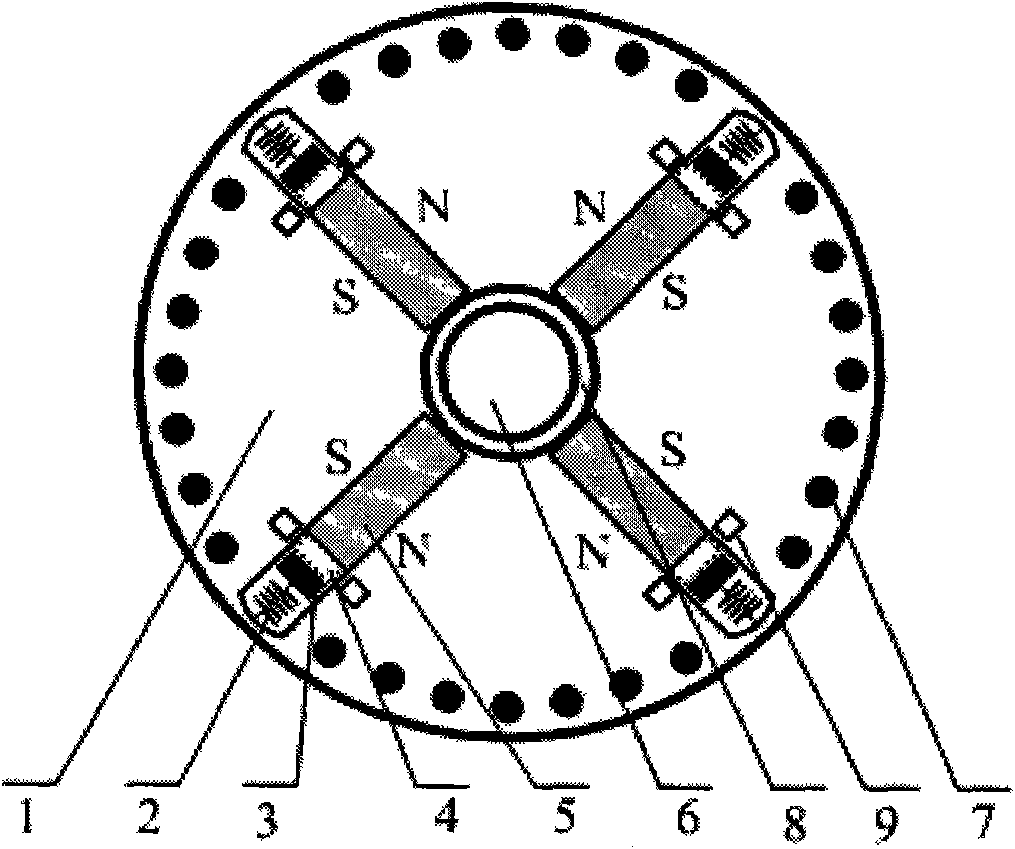
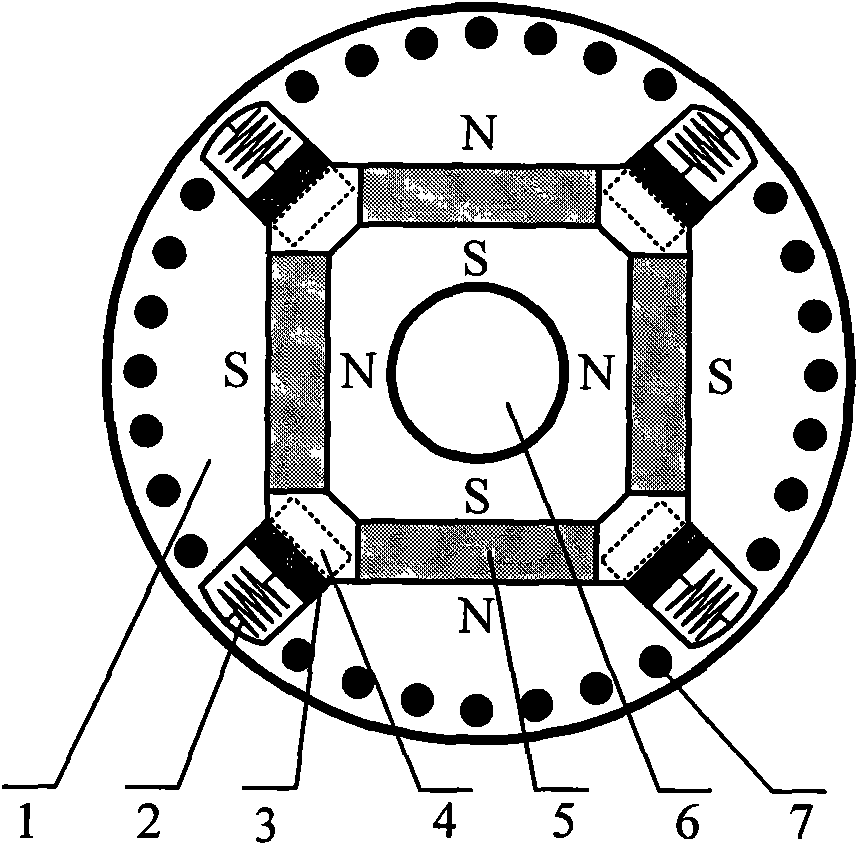
Transverse flux electrical machine with toothed rotor
InactiveUS6949855B2Easy to produceEasy to insertMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsTransverse fluxElectrical conductor
The invention concerns a transverse flux electrical machine operating with alternating current, having a first element having an alternate arrangement of excitation cores and of flux return cores and a winding of electrical conductors, the winding of electrical conductors being wound as a toroid, inside all said excitation cores; a second element having an exciter section comprising two toothed magnetic structures, each toothed magnetic structure comprising a number of slots equal in number to the total number of excitation cores and of flux return cores, the corresponding slots of each magnetic structure being toothed by being aligned; a magnetized sub-assembly is inserted inside each indentation so that an alternating arrangement of magnetic north poles and south poles is produced in each of these magnetic toothed structures of said exciter section; an air gap between the first element and the second element; at least one of the first element and of the second element being capable of rotating around a rotation axis that is common to the first element and to the second element.
Owner:EOCYCLE TECH
Magnetic resonance system and method to detect and confirm analytes
ActiveUS7781228B2Improve bindingReduce activity timeNanotechMagnetic measurementsResonance measurementProton magnetic resonance
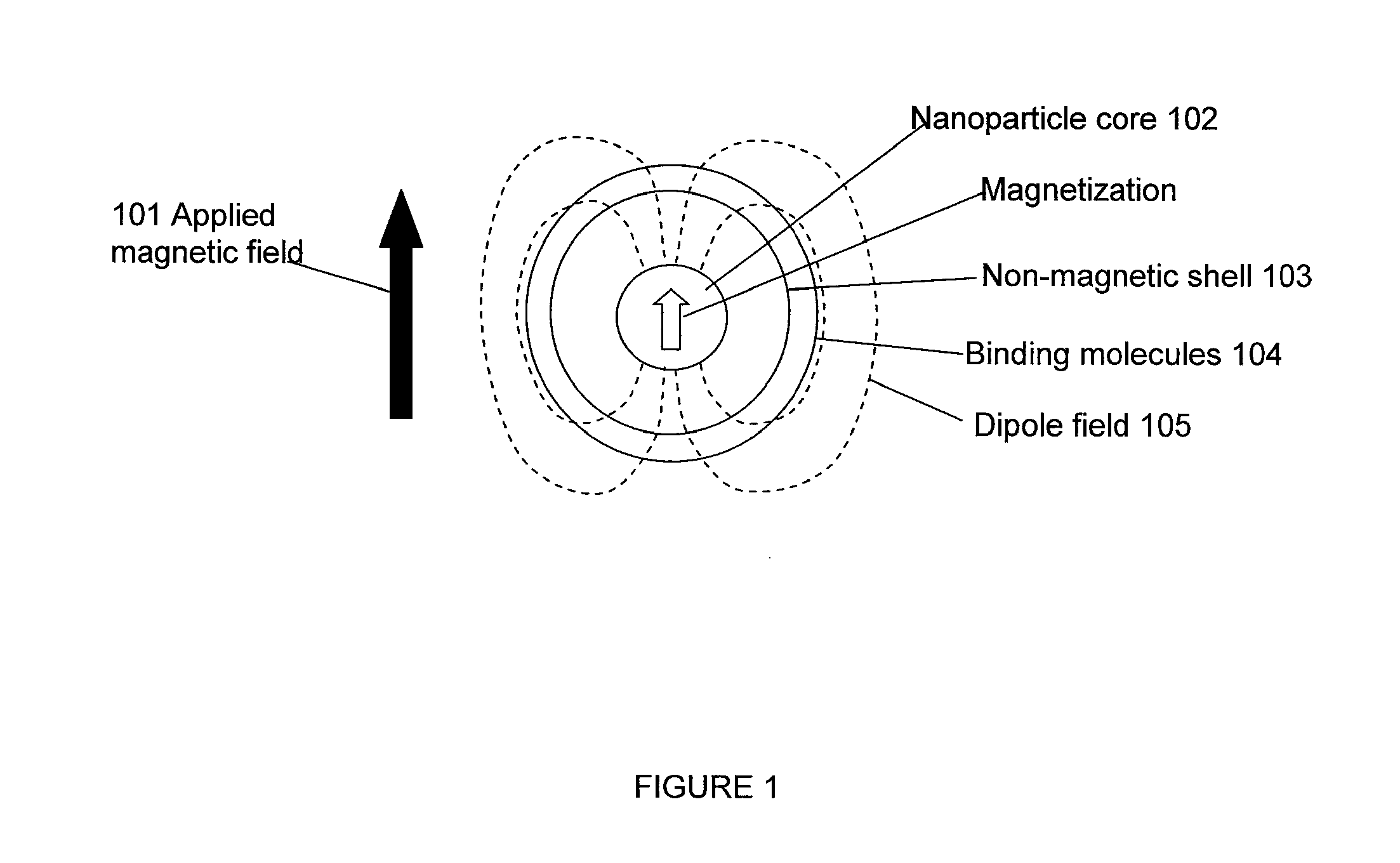
A system and method are provided to detect target analytes based on magnetic resonance measurements. Magnetic structures produce distinct magnetic field regions having a size comparable to the analyte. When the analyte is bound in those regions, magnetic resonance signals from the sample are changed, leading to detection of the analyte.
Owner:MENON BIOSENSORS
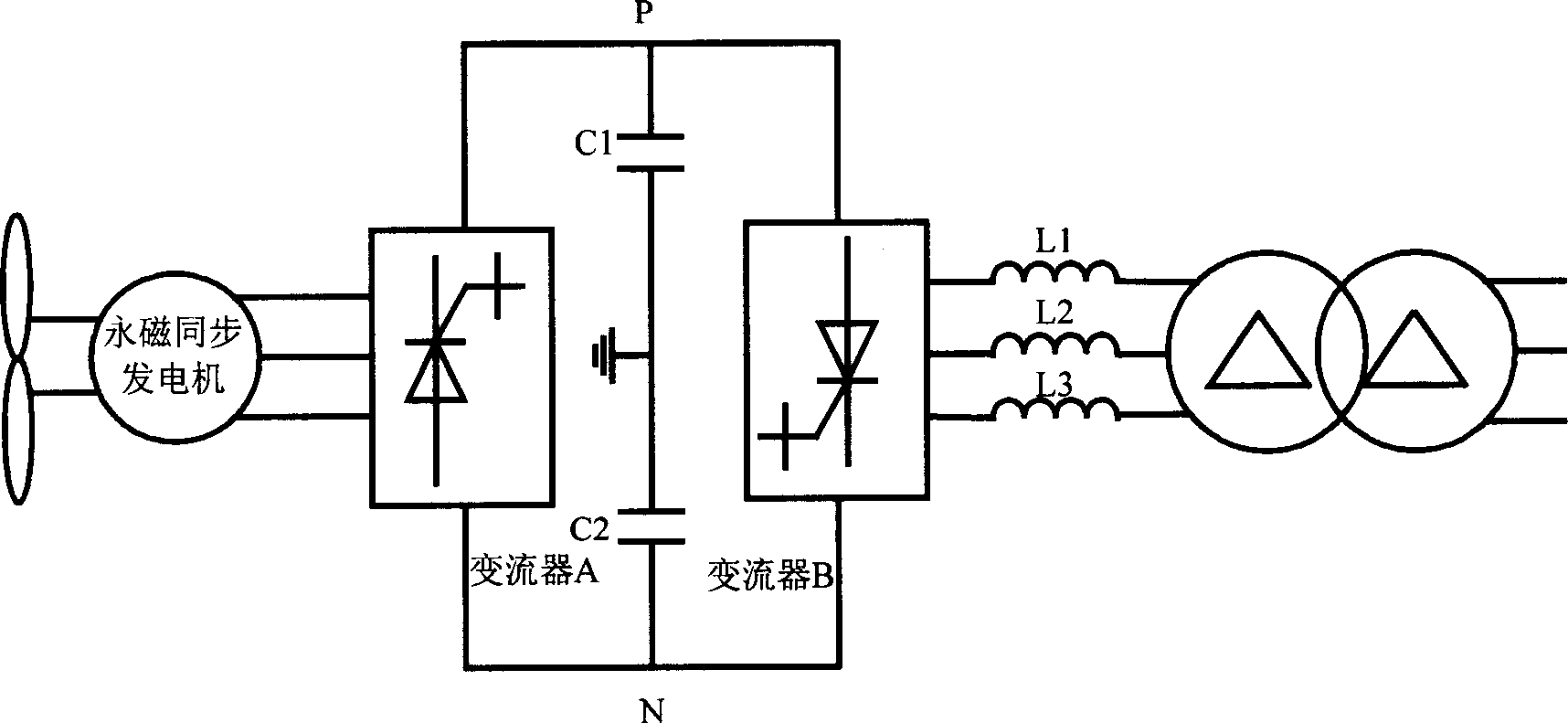
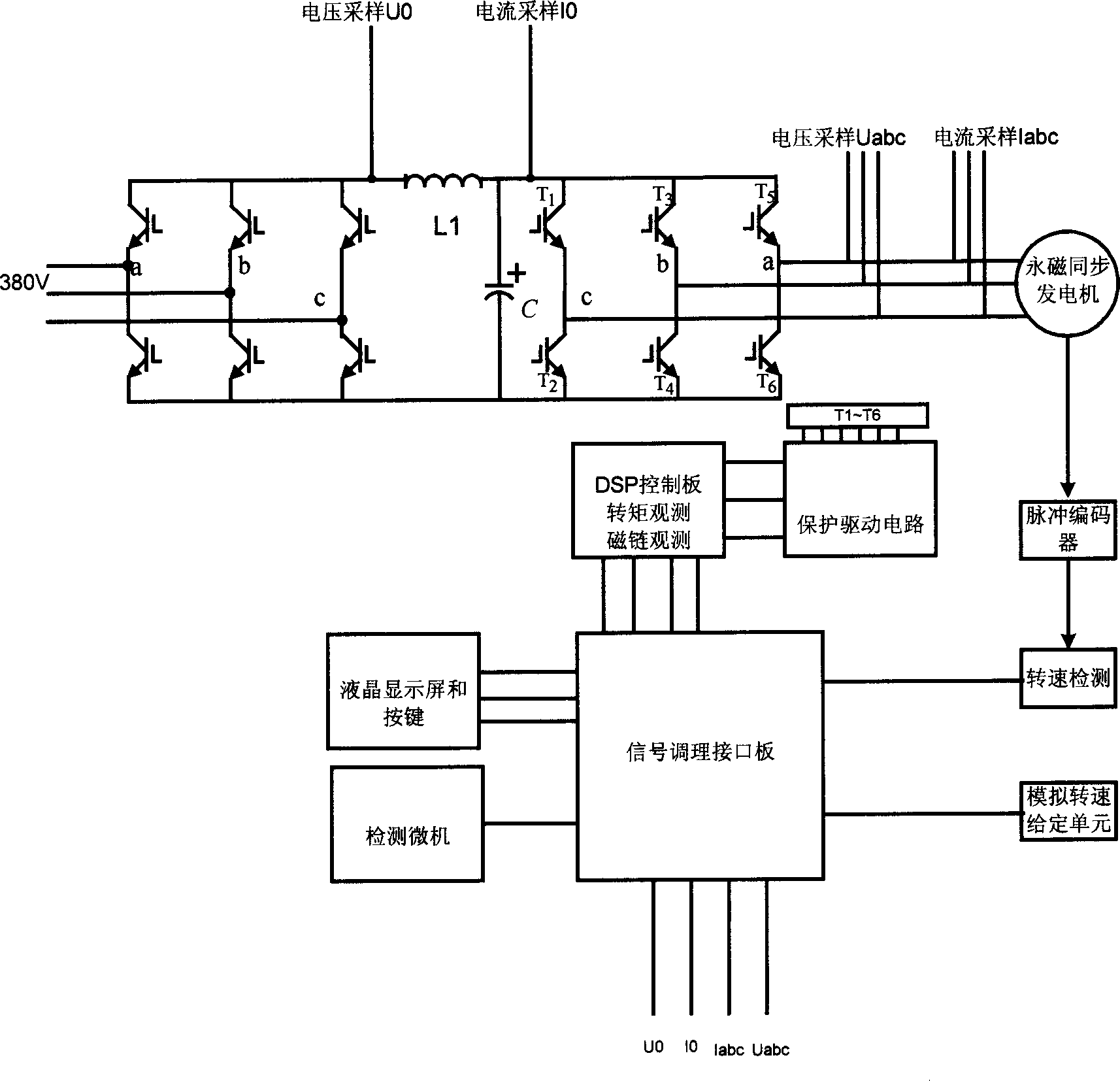
Control structure of full power type AC-DC-AC converter for wind power generation
ActiveCN1881767AReduce switching timesReduce switching lossesElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPower factorDc ac converter
The invention relates to a controller of full-power alternative-direct converter used in wind generation, wherein the alternative-direct converter is formed by network converter and the convert of generator; the used generator is a permanent-magnetic generator; the rotor is in permanent-magnetic structure, without external magnetic activate power supply; two convert loops both uses the PWM converters operating in four quadrants, based on full-control element, which can improve the dynamic response, reduce cost and impact, realize bidirectional transmission of electricity, and realize generating via power factor sine wave current parallel network; and the invention uses improved direct torque technique to control the converter, to confirm the sine wave change of input current at the stator, with quick response, low vibration, torque dynamic control and wide speed adjust range.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
Multi-layer structure and sensor and manufacturing process
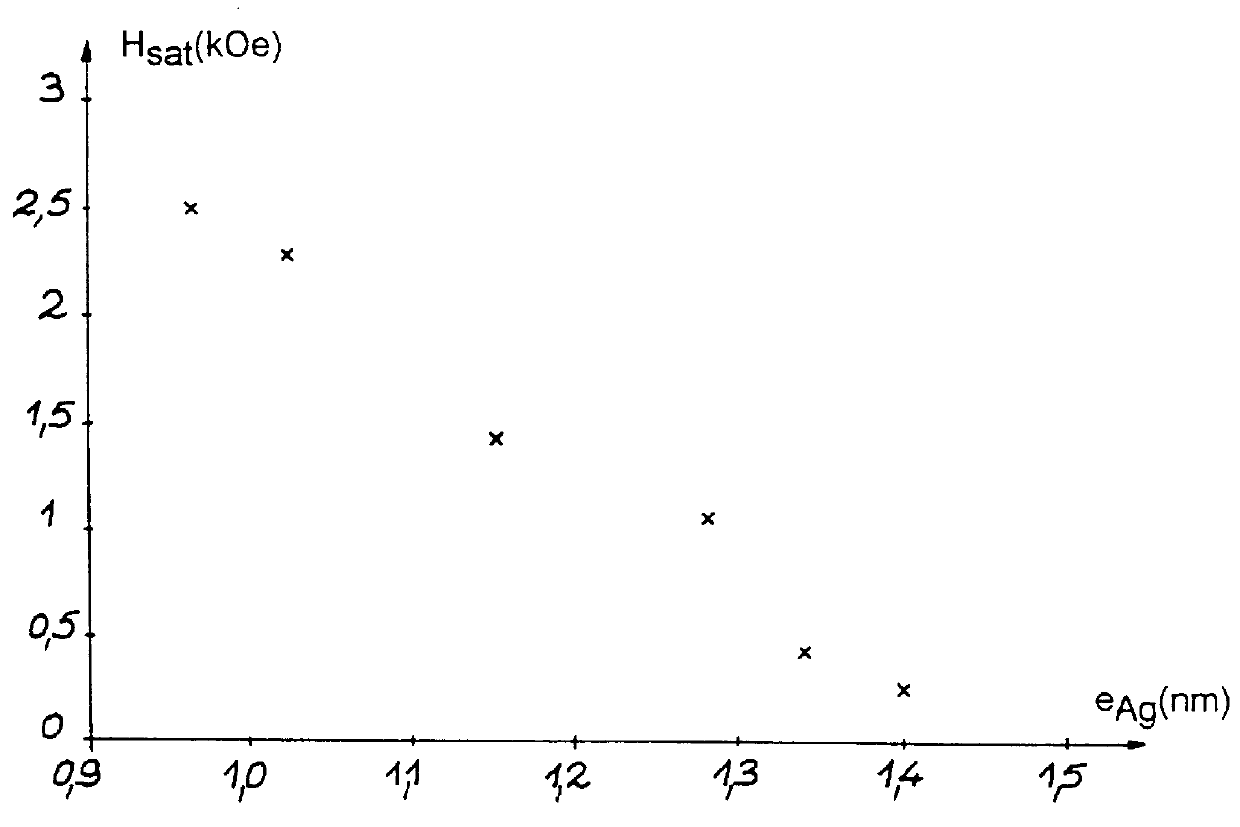
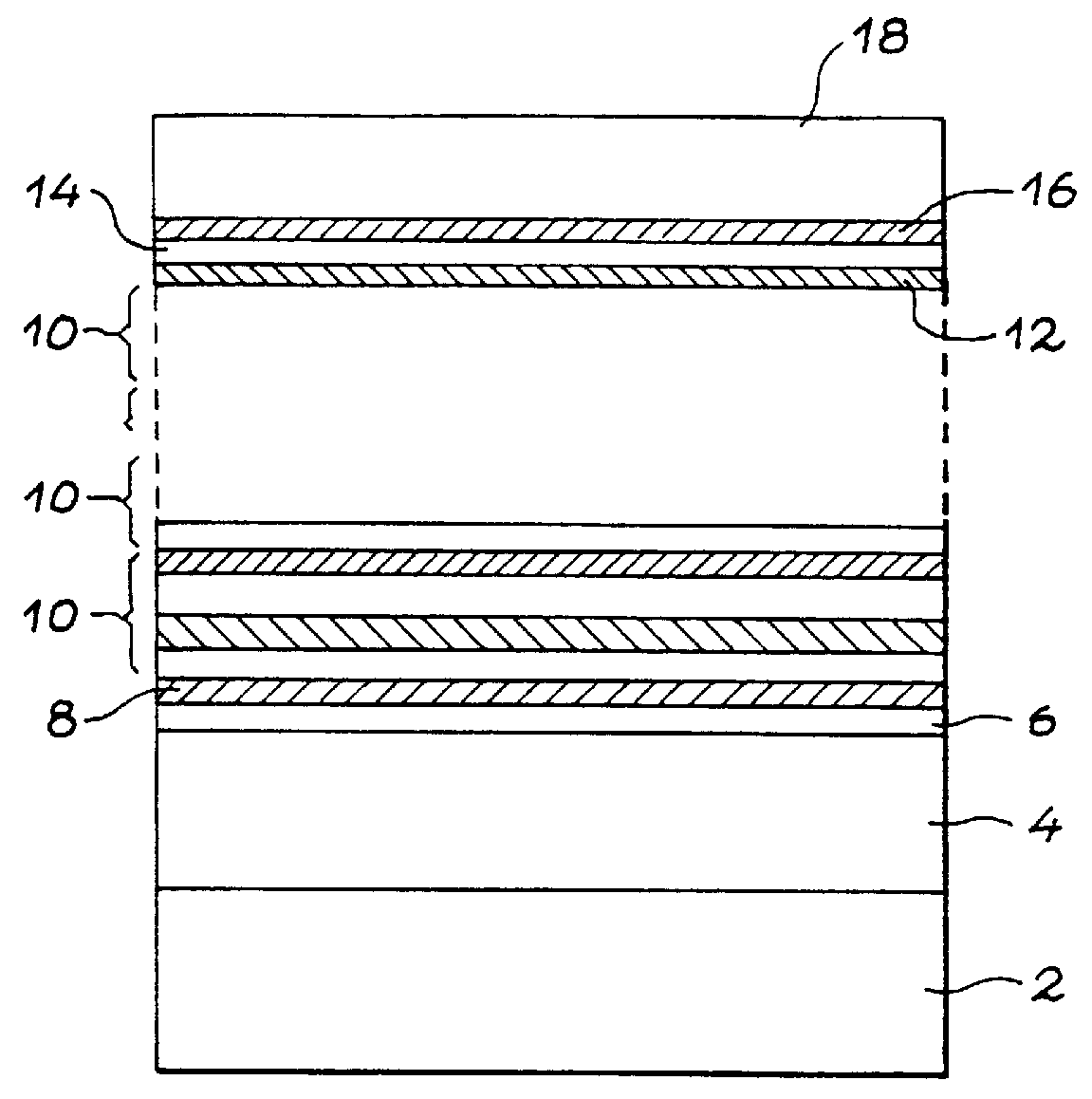
This invention relates to a multilayered magnetic structure comprising an alternate stack of: layers (6, 16) of a first type based on magnetic materials, layers (12) of a second type, made of Ag or an Ag rich alloy, a thin interface layer (8, 14) of Co or a Co rich alloy being located at the interface between layers of the first type and layers of the second type. The invention also relates to a process for making this type of structure. Applications to sensors based on magnetoresistive effects, such as current sensors or magnetic heads.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Bistable magnetic device using soft magnetic intermediary material
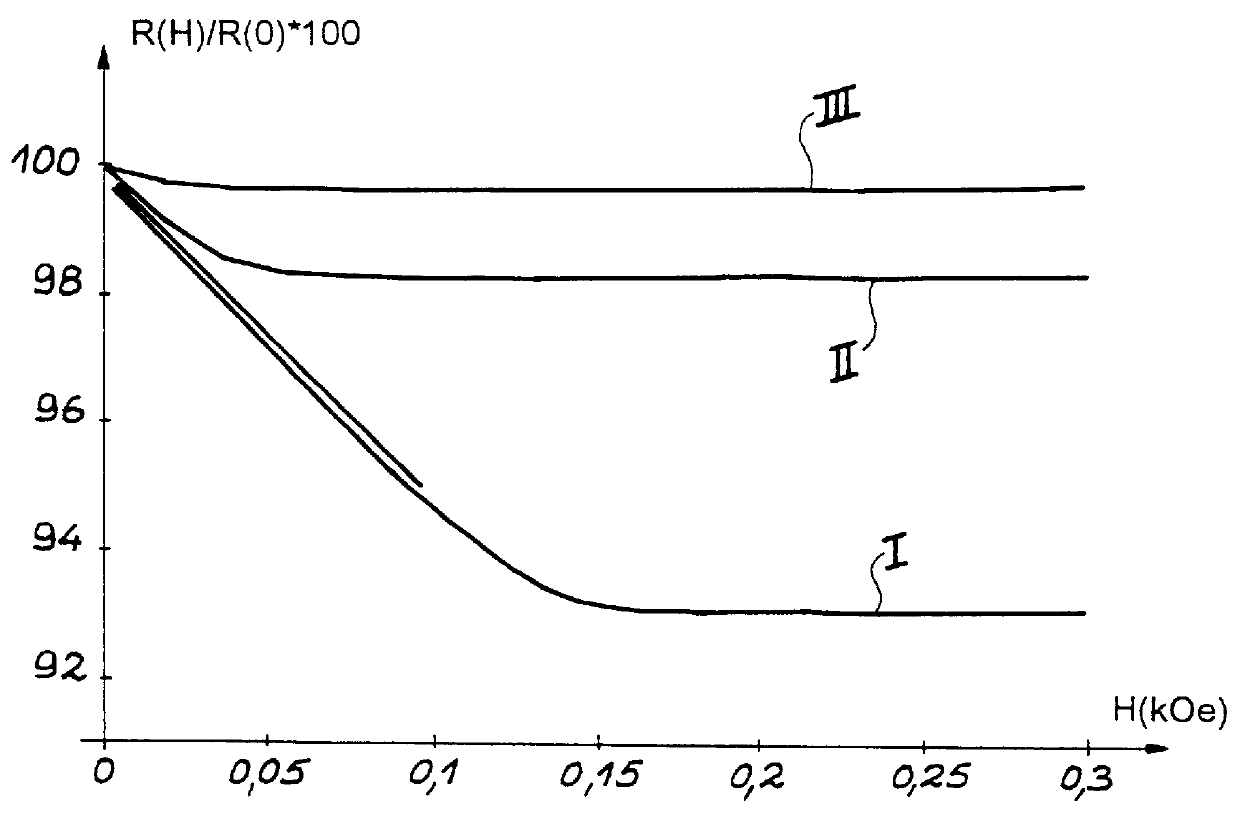
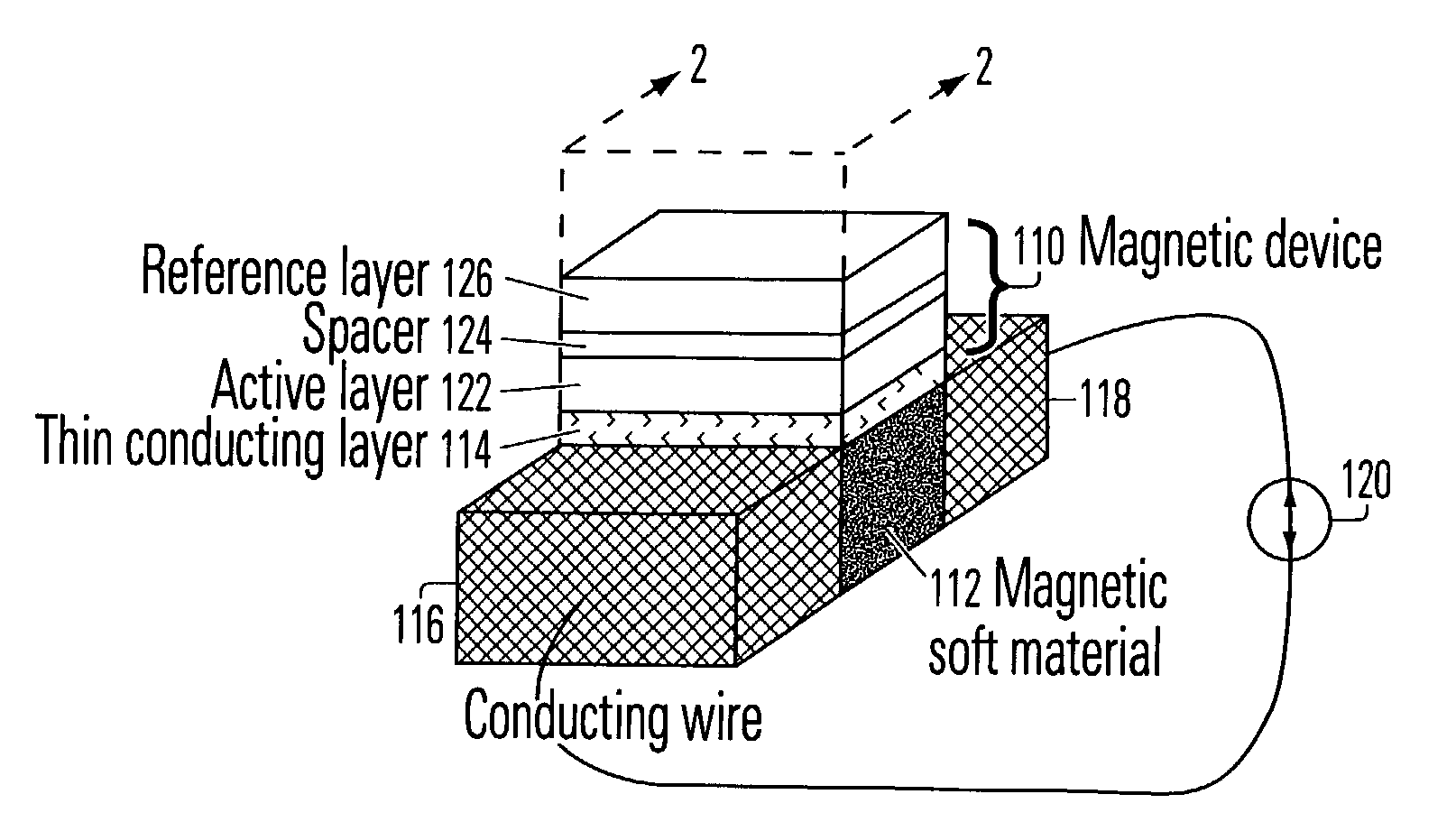
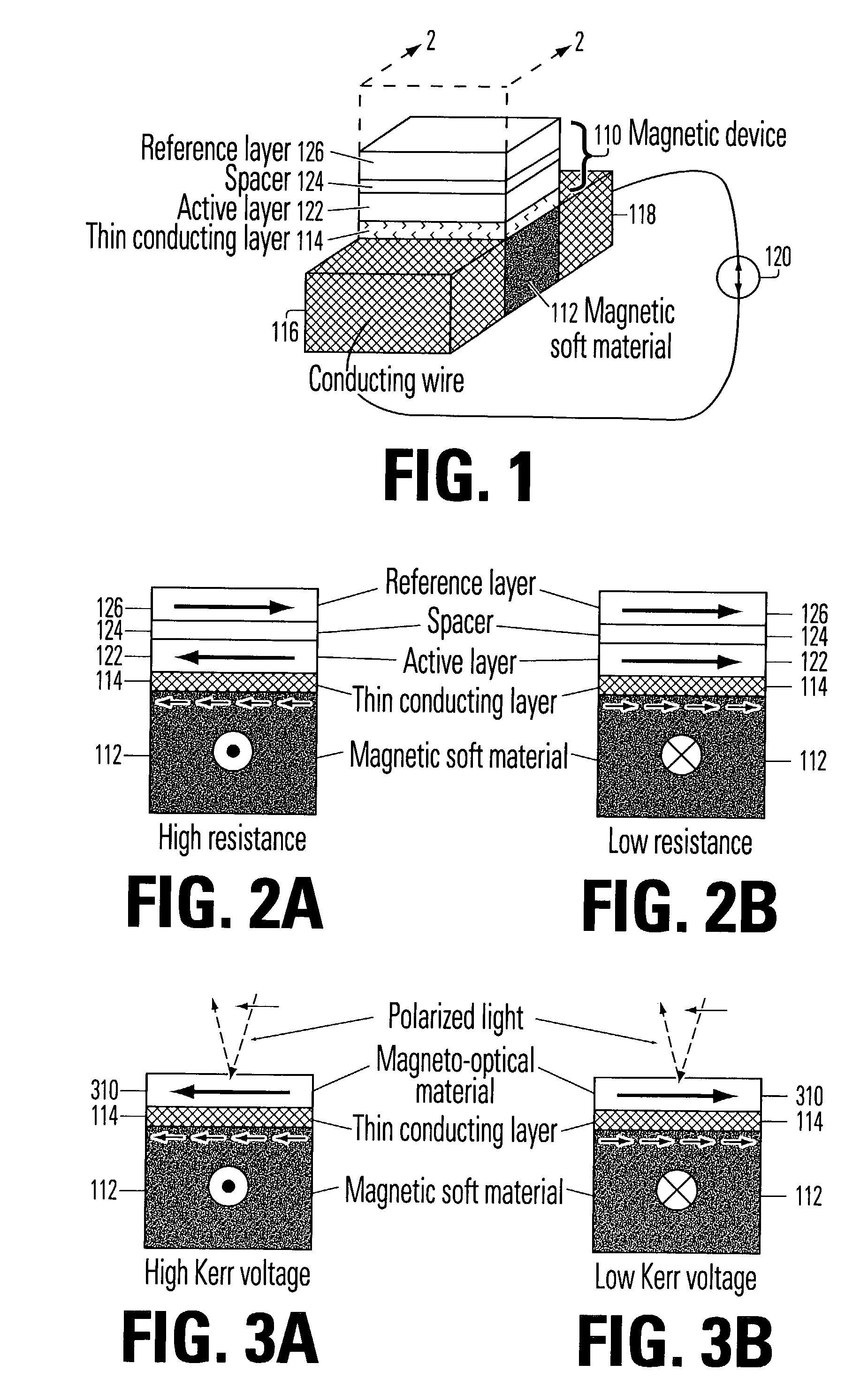
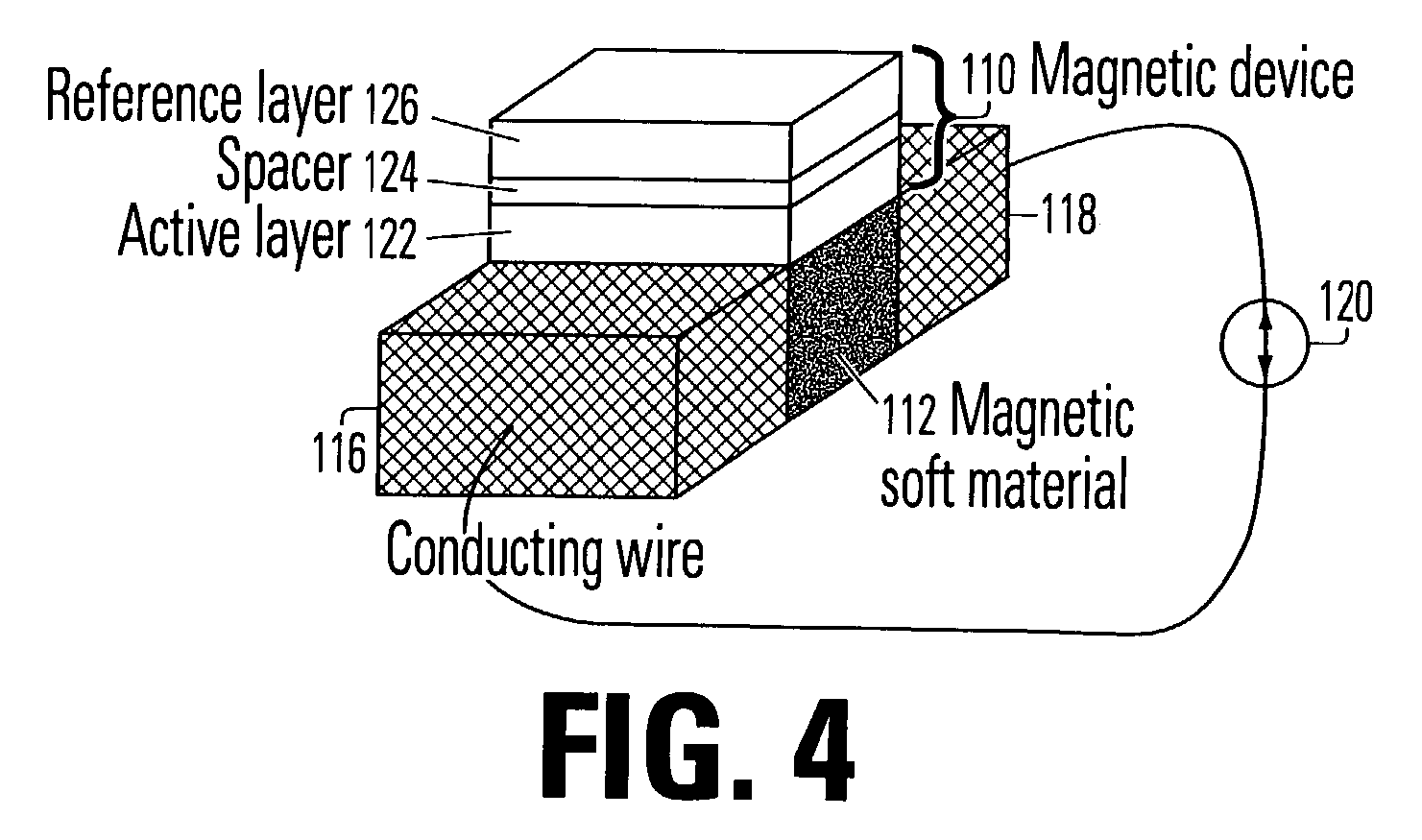
Roughly described, a magnetic structure includes an electrically conductive path for carrying current flow, a soft magnetic material with high permeability value in magnetic communication with the current flow so that it can be magnetized in either of two directions, and a magnetic device such as a magnetic random access memory cell, having an active layer that is quantum mechanically or magnetostatically coupled to the soft magnetic material. The soft magnetic material acts as an intermediary between the magnetic induction of the current flow and the magnetization of the active layer of the magnetic device to reduce the writing current.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
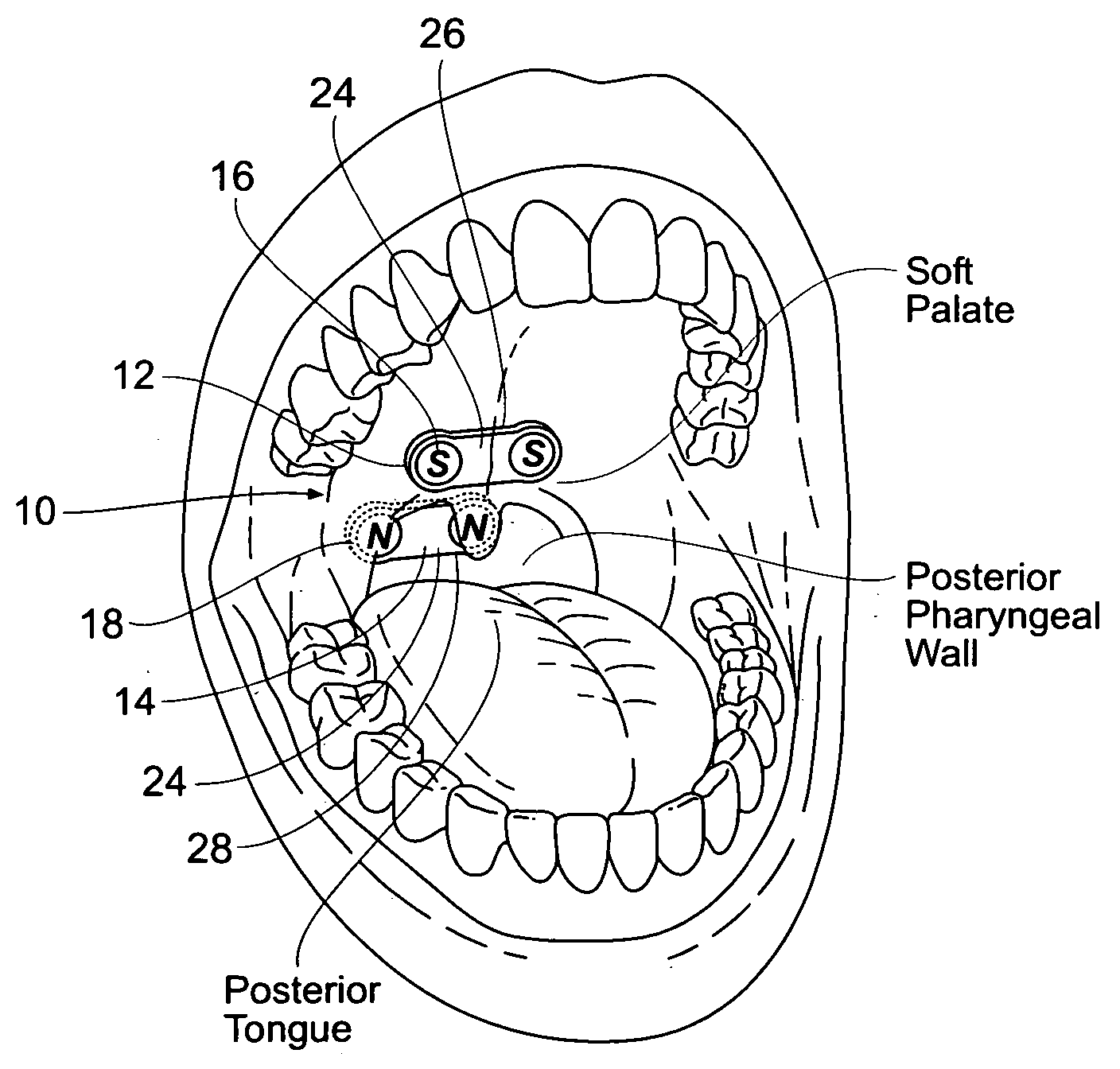
Magnetic devices, systems, and methods placed in or on a tongue
Magnetic structures develop a magnetic force between a tongue and a posterior pharyngeal wall to stabilize an orientation of the tongue. The magnetic structures include magnetic materials that are sized, configured, and arranged on at least one of the first and second magnetic structures, to maintain a substantially mutually repelling orientation between the first and second magnetic structures during a native range of movement of the tongue relative to the pharyngeal wall, i.e., during swallowing and / or drinking / and or speech.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Dual rotors mixed power composite magnetoelectric machine
InactiveCN1738163AEmission reductionImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsCooling/ventillation arrangementCooling effectInductor
The invention discloses a birotor combination power magneto inductor comprising inner and outer magneto inductors of radial magnetic structure, which comprise inner motor components formed by a input shaft, a inner rotor armature winding, a iron core of inner rotor, a iron core of outer rotor and a magnet steel of outer rotor; a outer motor components formed by a stator winding, a iron core of stator, a iron core of outer rotor, and a magnet steel of outer rotor. Wherein, the iron core of inner rotor is mounted and rotated on the input shaft; the iron core of stator is mounted on the housing; the iron core and magnet steel of outer rotor have rigid connection and rotate with the output shaft, while they are used by both inner and outer motor to via the coolant enter the cooling channel between the iron core of inner rotor and the input shaft, for cooling the iron core of inner rotor. The invention has lower cost, lower weight, tight structure, and better cooling effect.
Owner:CHINA AUTOMOTIVE TECH & RES CENT +2
Voice coil motor apparatus
InactiveUS20060214520A1Low costReduce frictionTelevision system detailsCarrier constructional parts dispositionEngineeringAutofocus
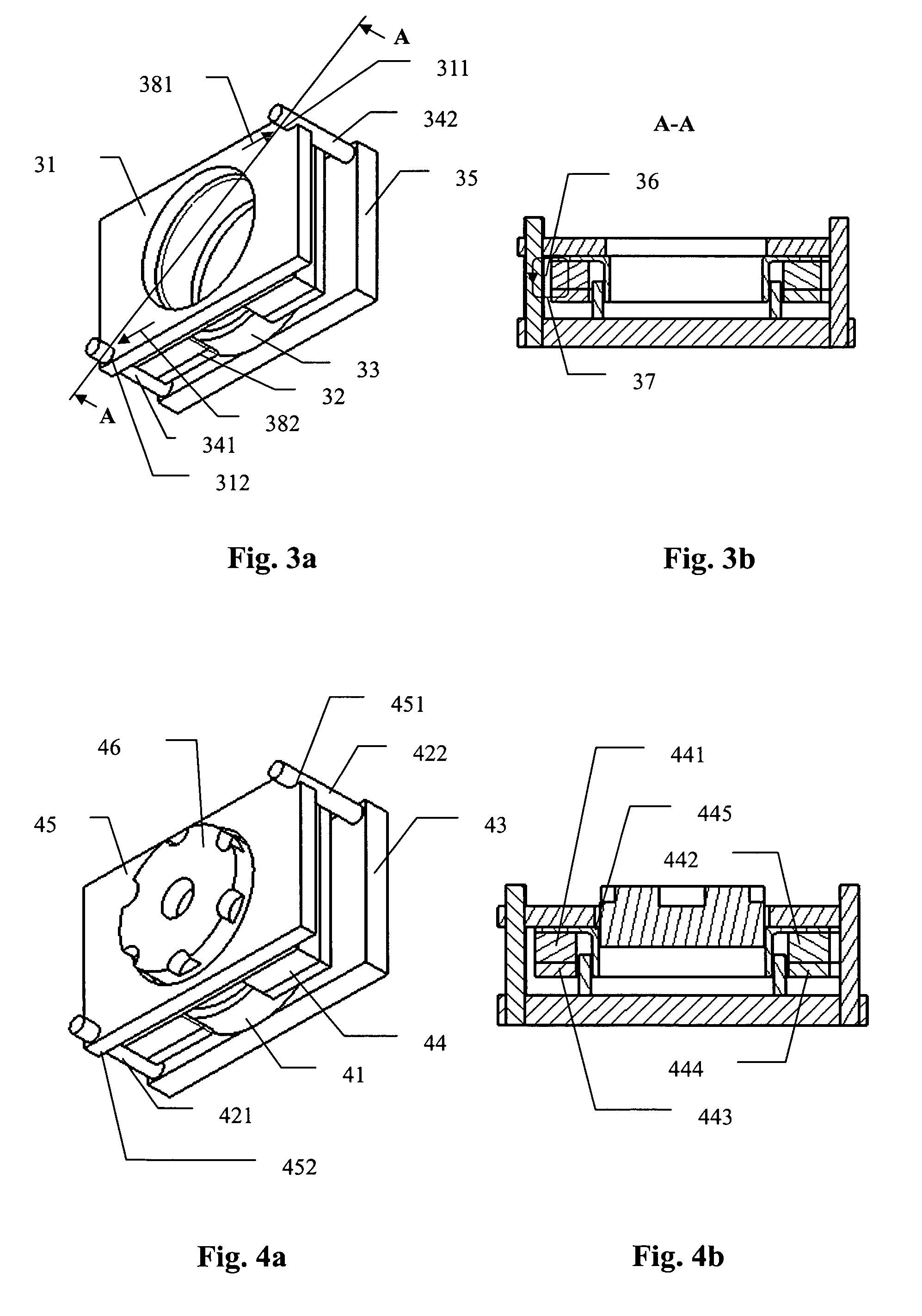
The present invention discloses a voice coil motor apparatus, especially one applied to an auto-focus or variable-focus lens module of a miniaturized camera. The voice coil motor apparatus of the present invention comprises: a voice coil motor, a plurality of steel guidance shafts, a lens holder, and a base. The voice coil motor includes a magnetic part, which further comprises magnets and yokes, and an electrical part, which further comprises a coil winding. The magnetic part is rigidly coupled to the lens holder to form the moving member of the apparatus. The electrical part and the steel guidance shafts are fixed on the base to form the non-moving member. The voice coil motor apparatus of the present invention is characterized in that the pre-loaded force due to the interaction between the leakage flux of the magnetic part and the steel guidance shafts eliminates the free-play resulting from the tolerance gap between the moving and the non-moving members in order to achieve a high repeatability of motion performance, and that the magnets and the yokes form a non-circular magnetic structure having a rectangular contour in order to minimize the overall dimension of the voice coil motor apparatus.
Owner:VASSTEK INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com