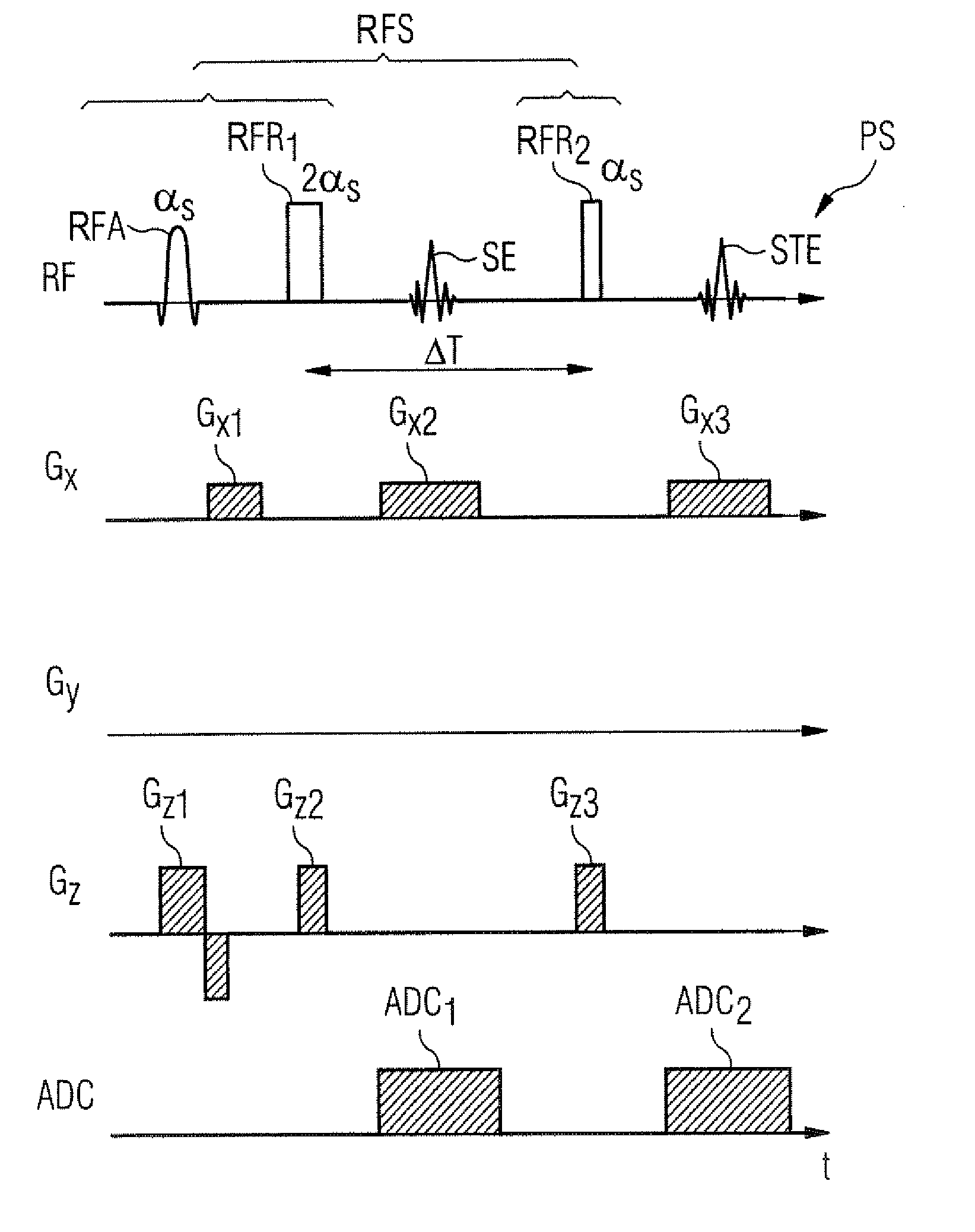
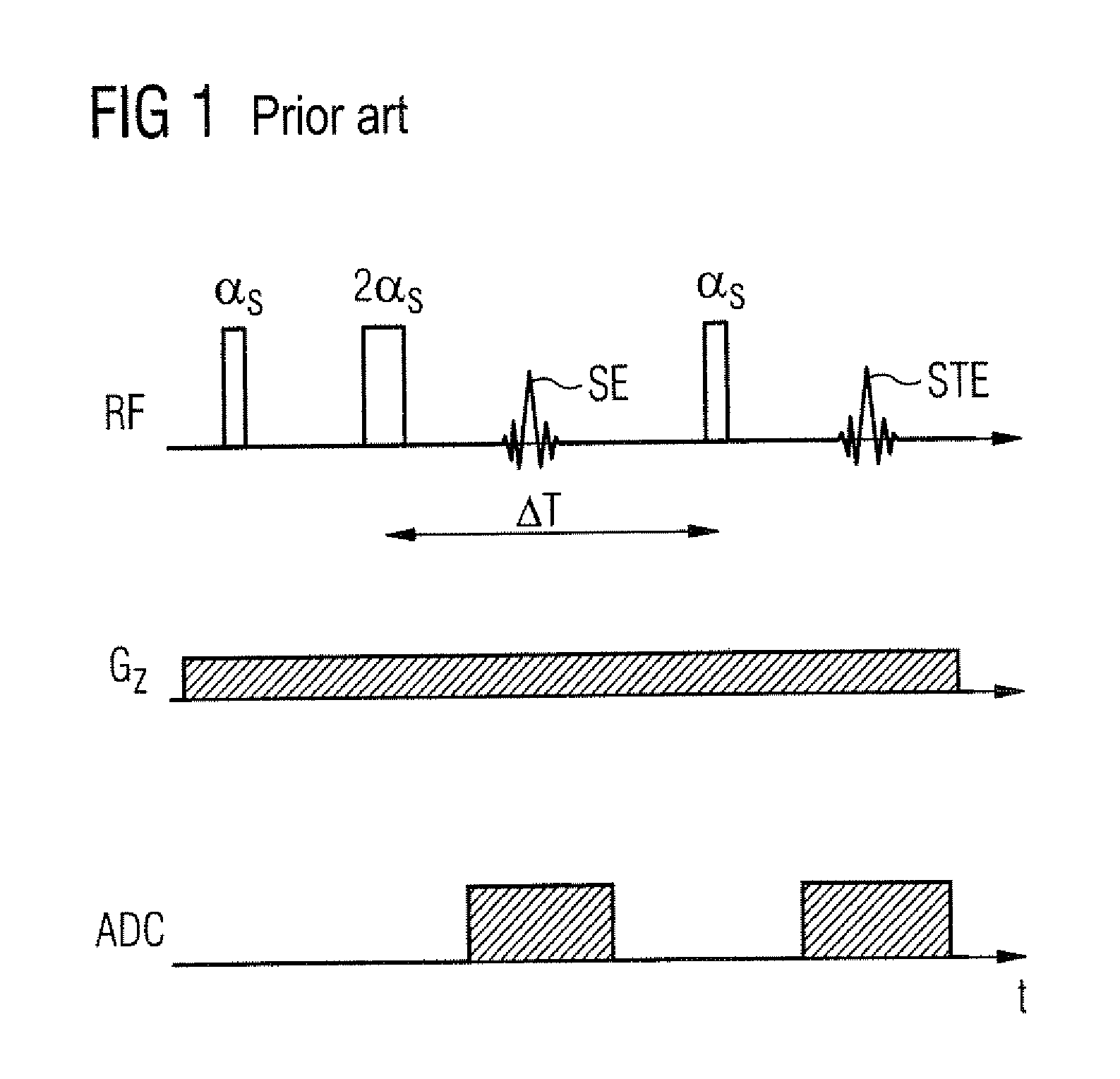
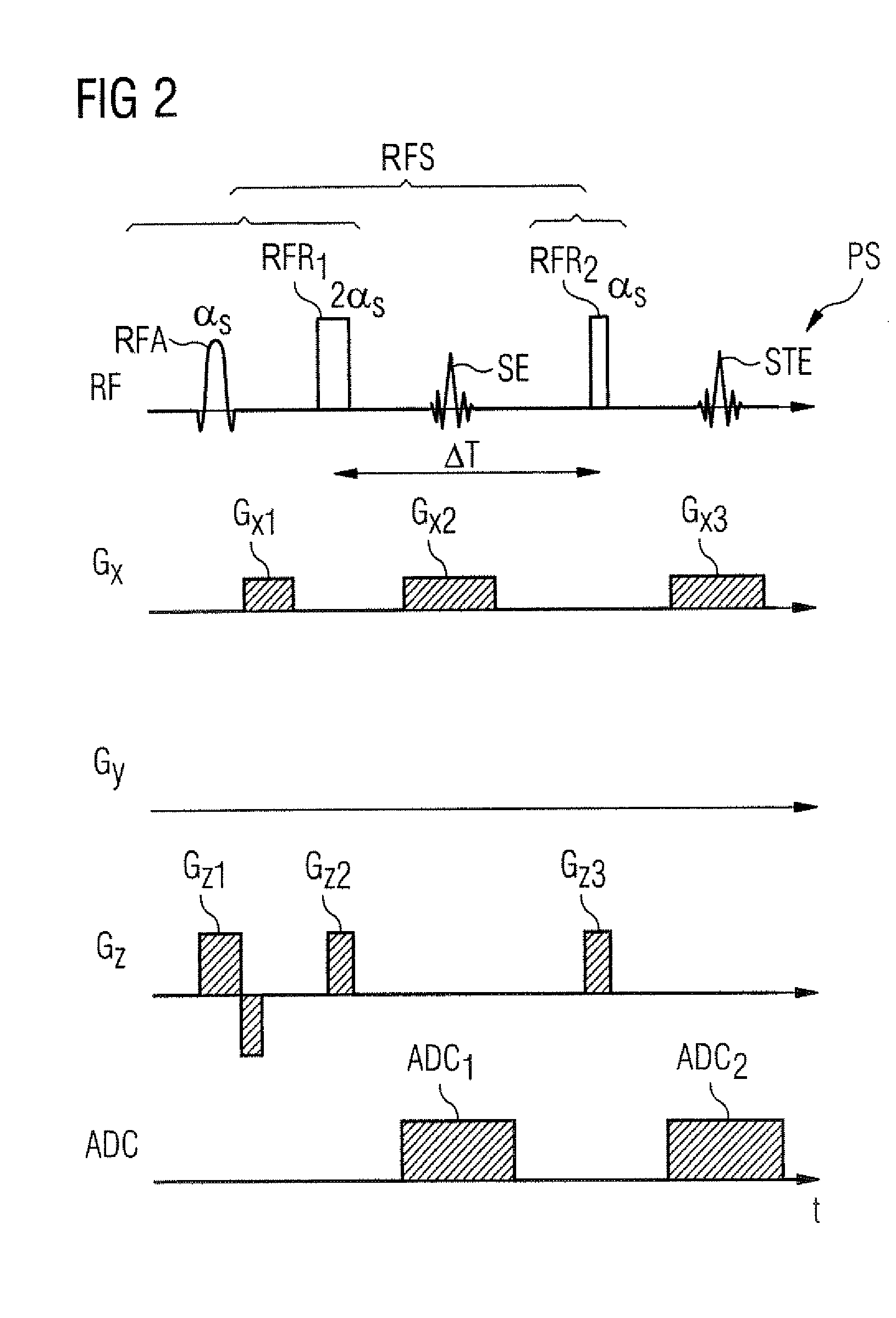
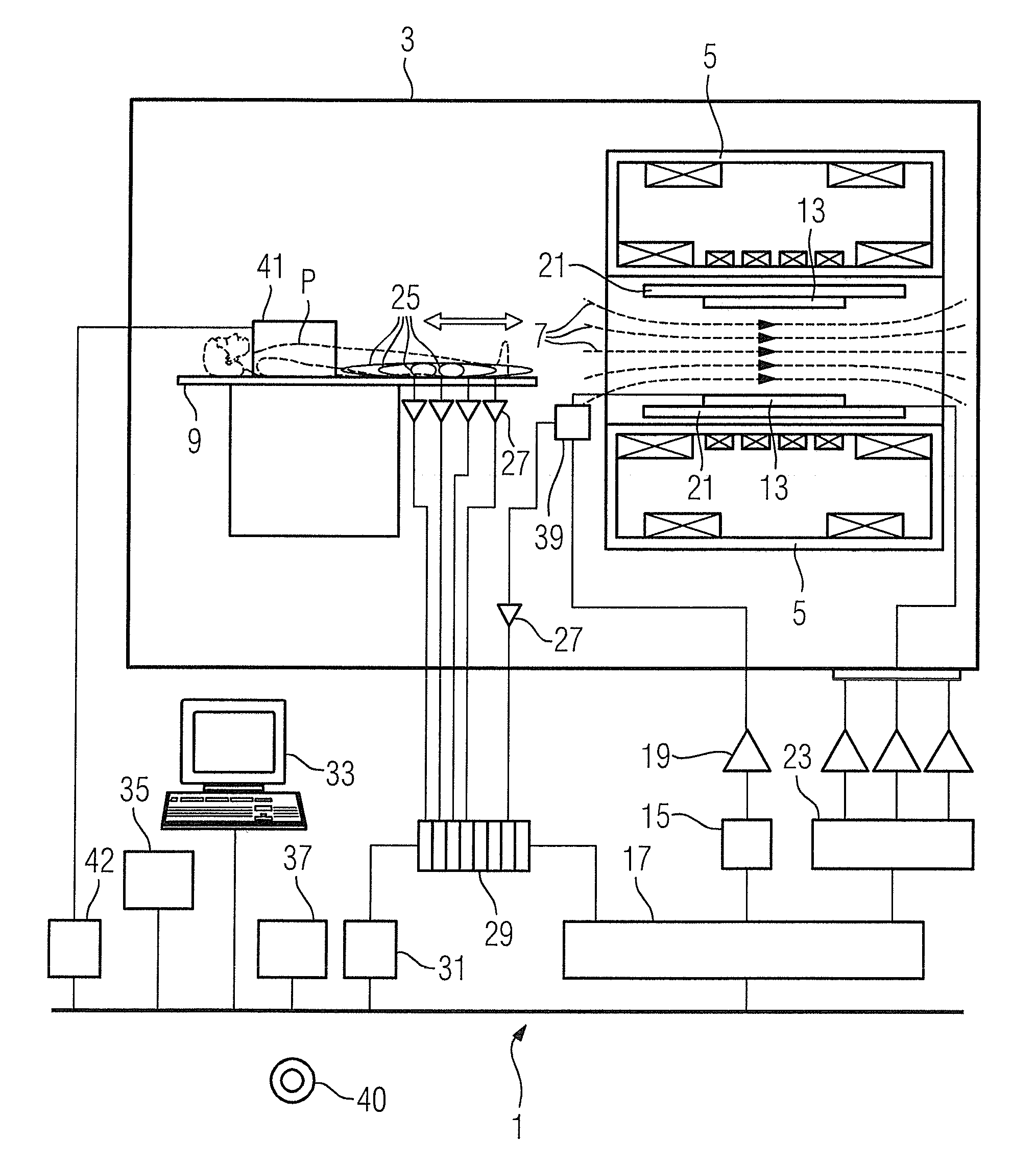
Patents
Literature
206 results about "Resonance measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
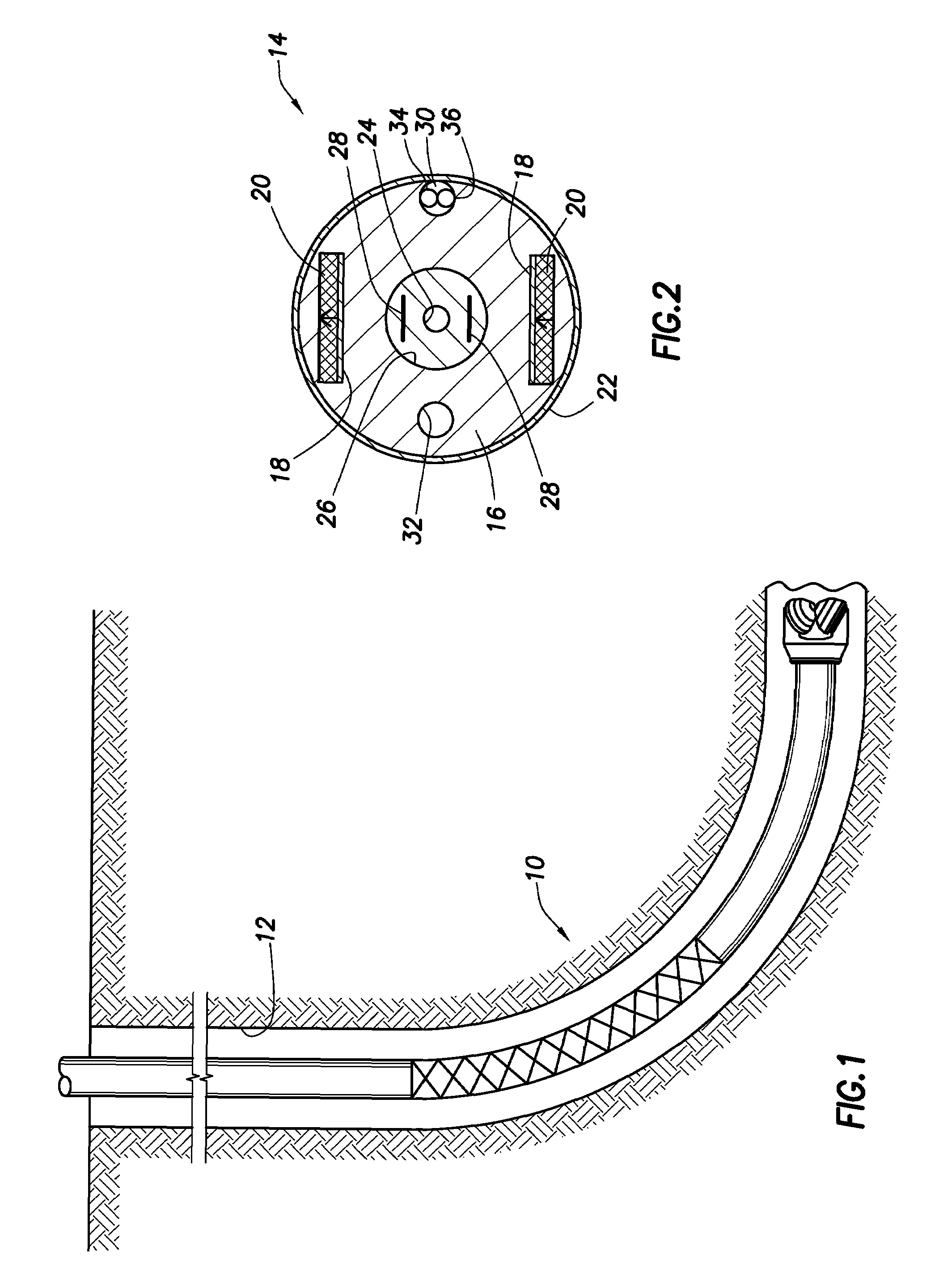
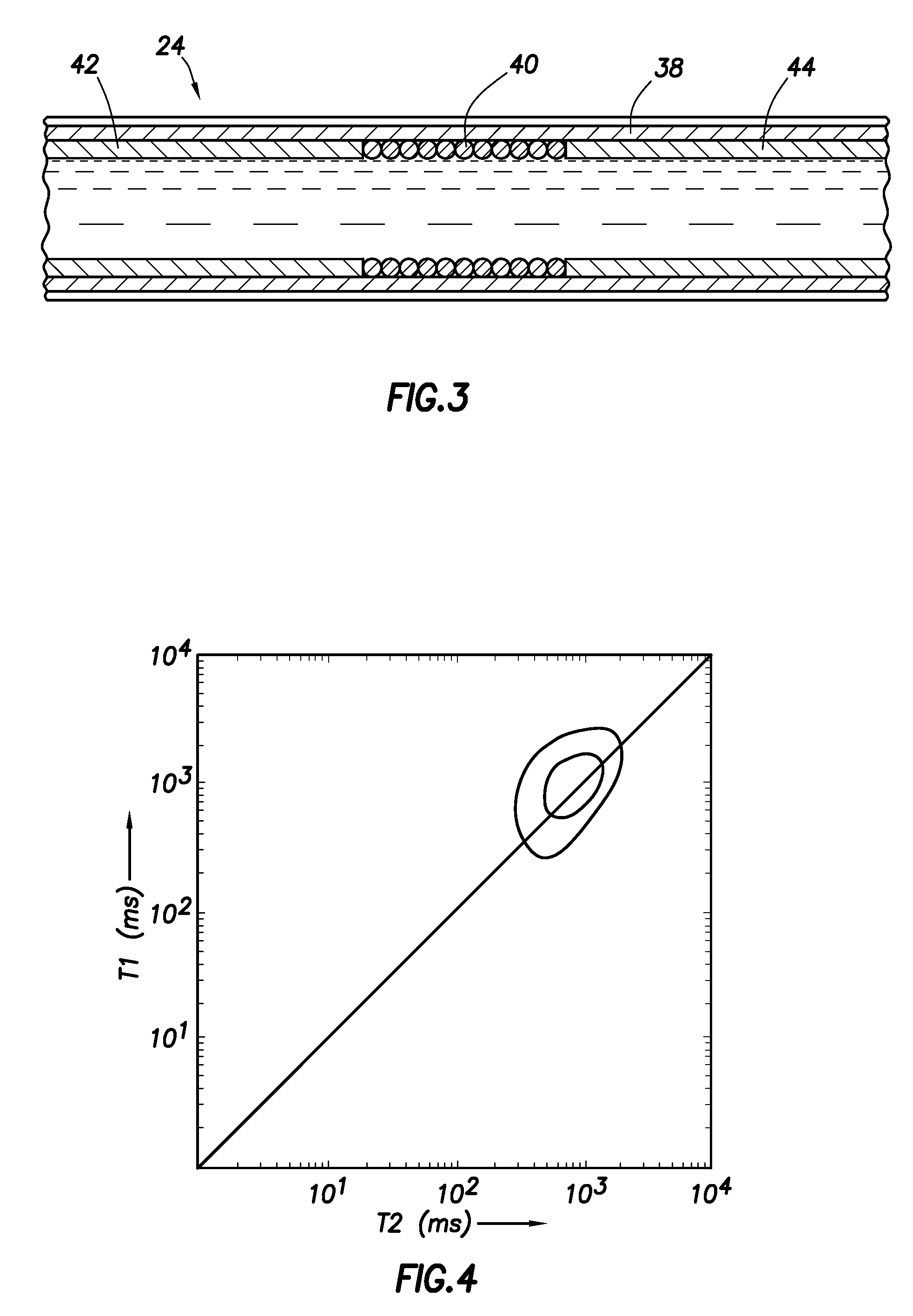
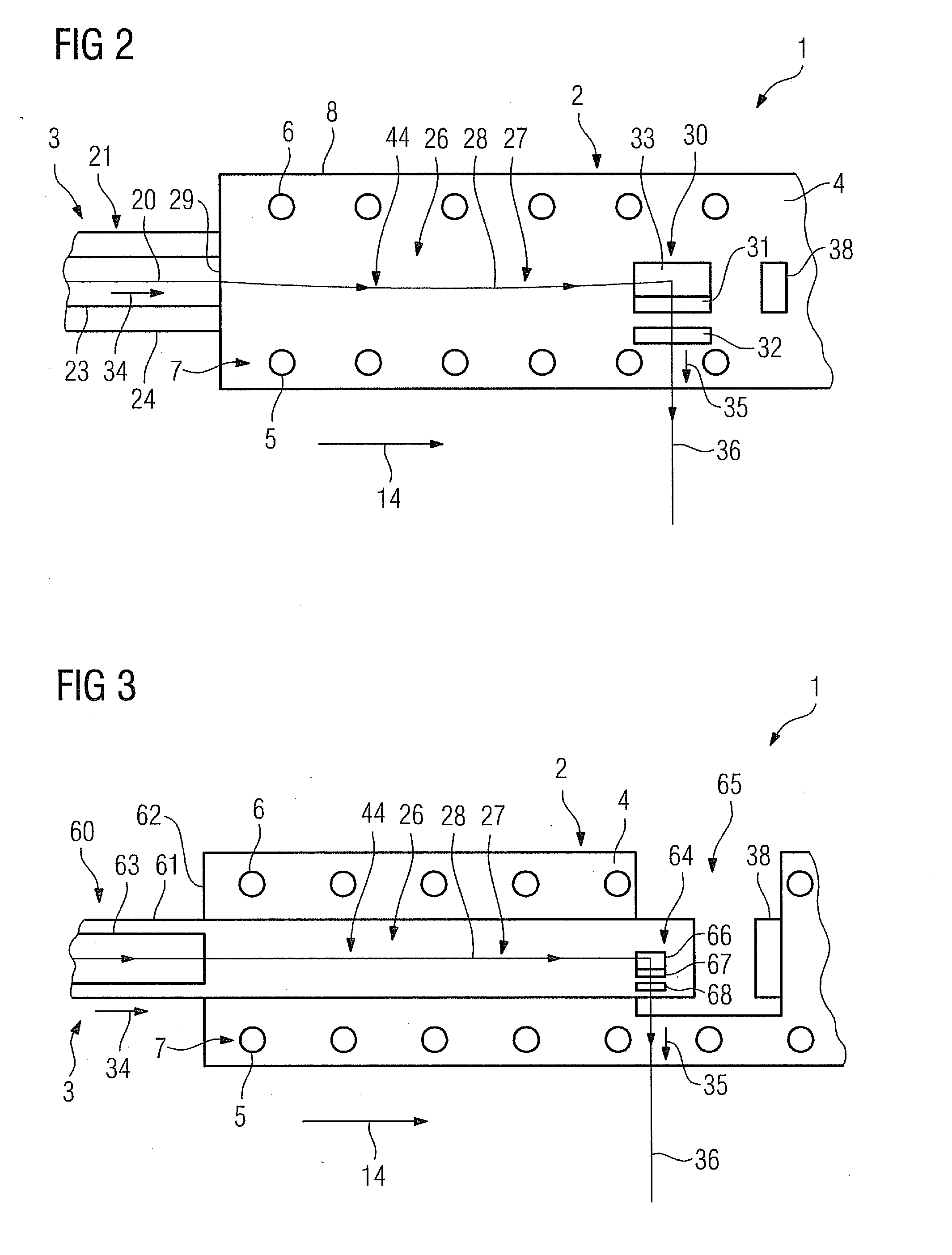
System and method for servo control of nonlinear electromagnetic actuators
InactiveUS20060171091A1Eliminate impactRemove noiseElectrical controlAC motor controlResonance measurementInstability
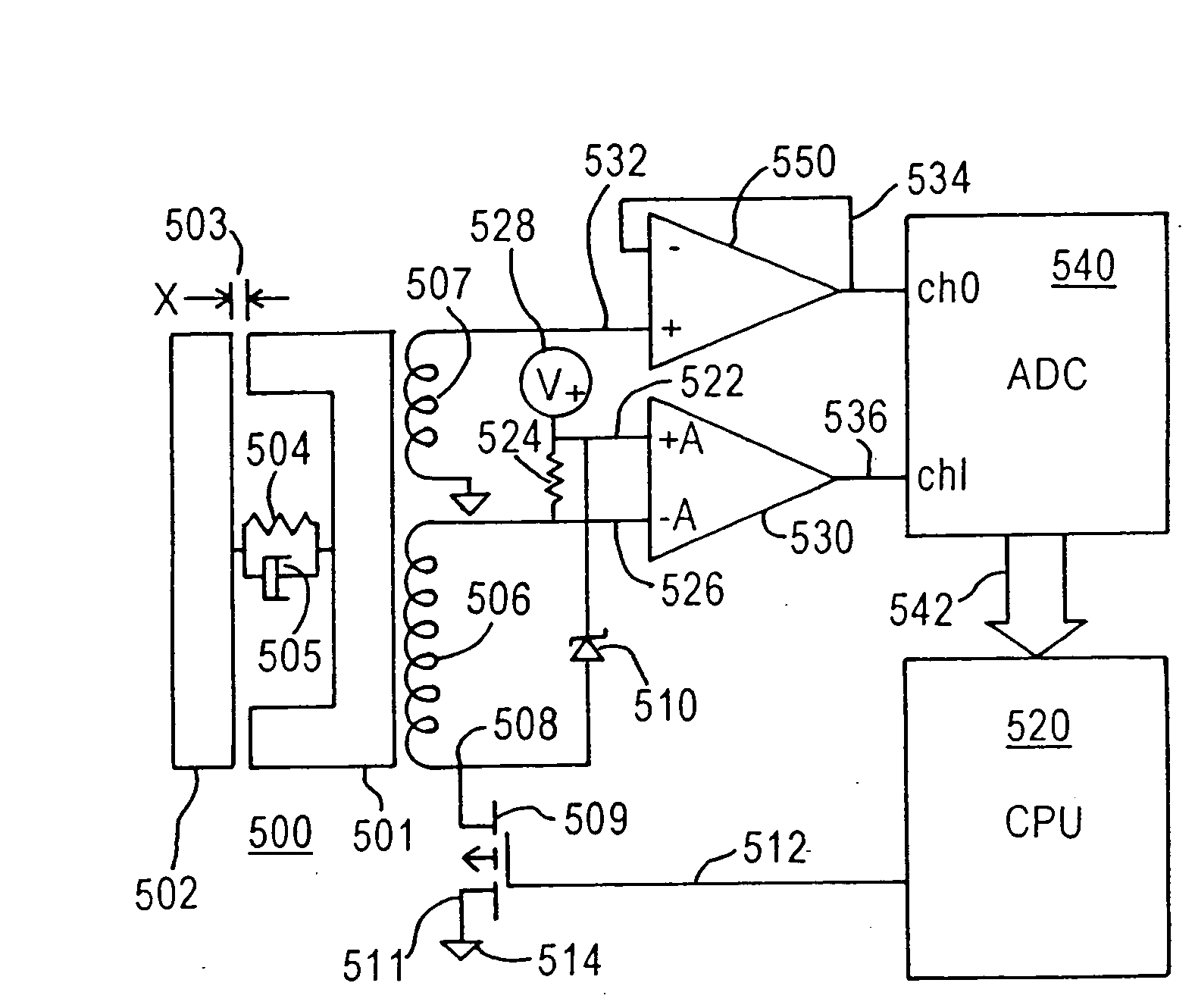
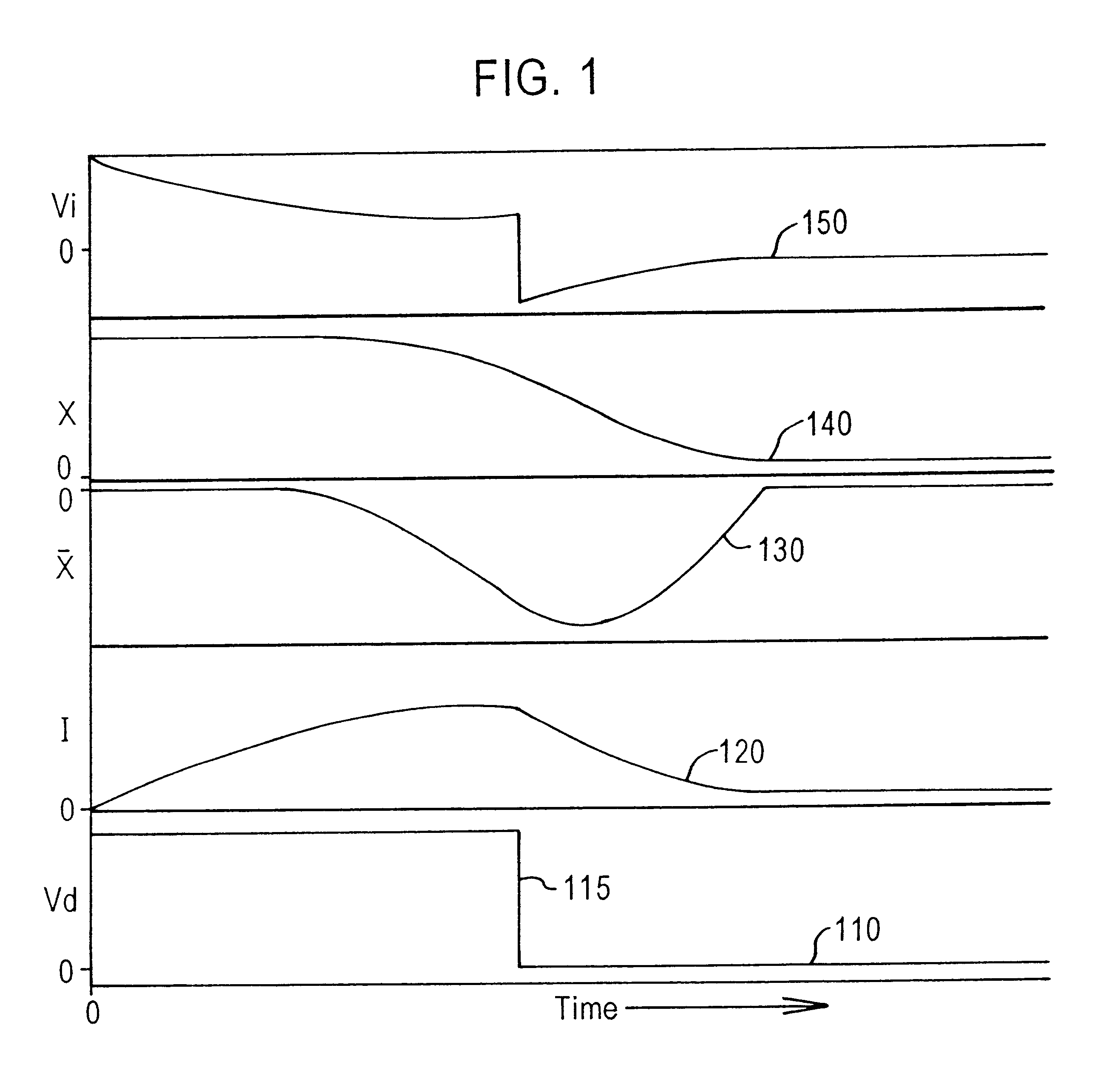
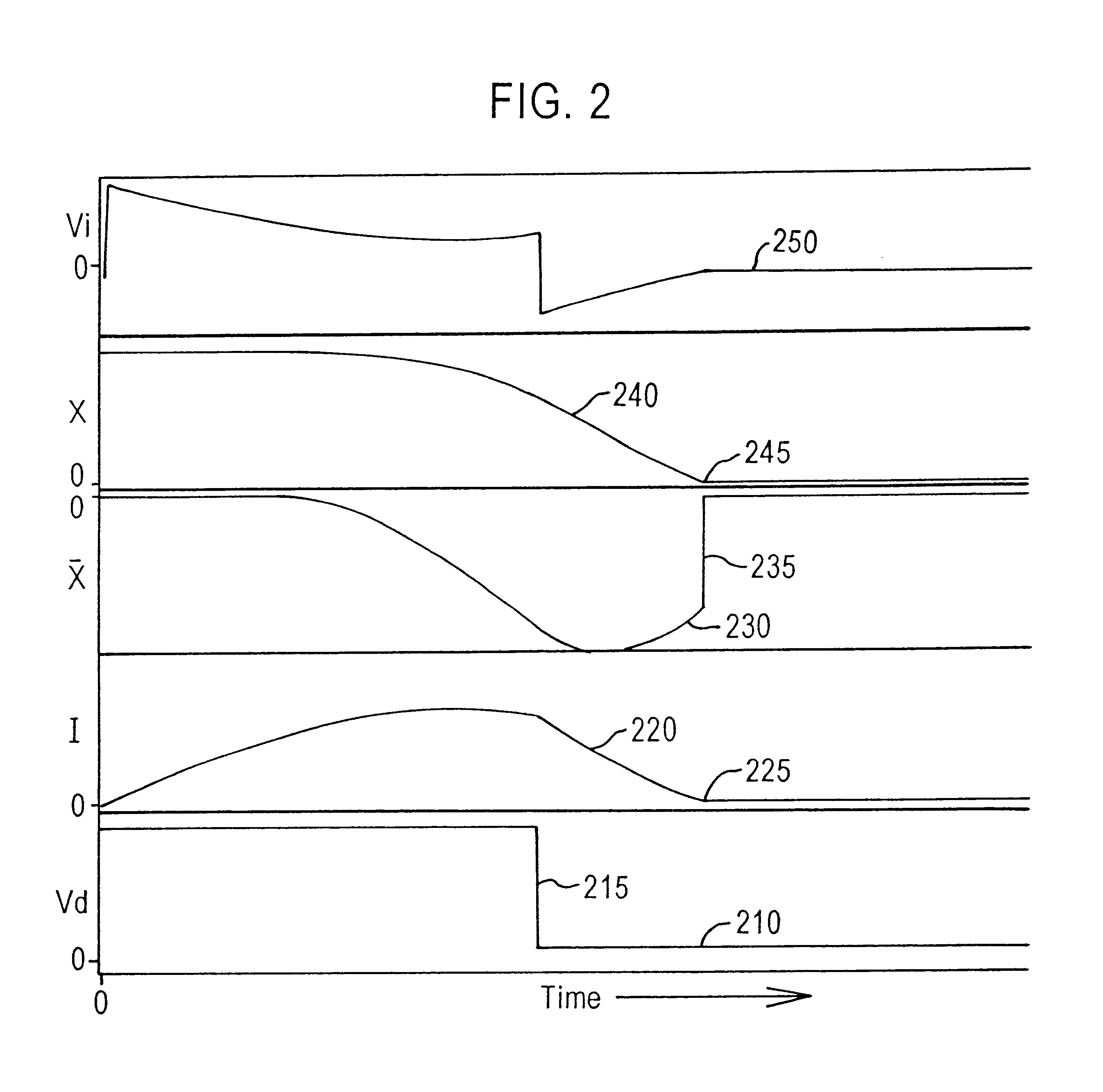
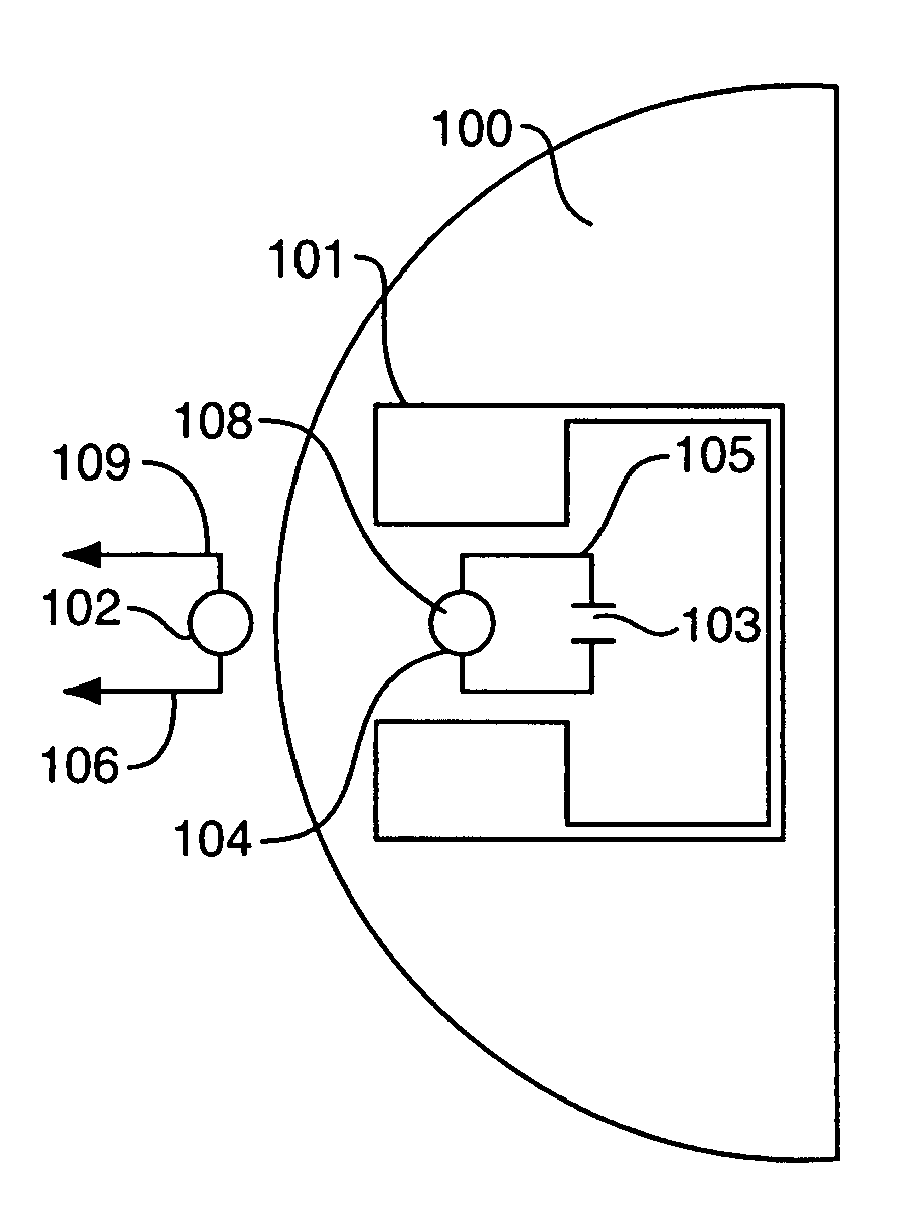
Servo control using ferromagnetic core material and electrical windings is based on monitoring of winding currents and voltages and inference of magnetic flux, a force indication; and magnetic gap, a position indication. Third order nonlinear servo control is split into nested control loops: a fast nonlinear first-order inner loop causing flux to track a target by varying a voltage output; and a slower almost linear second-order outer loop causing magnetic gap to track a target by controlling the flux target of the inner loop. The inner loop uses efficient switching regulation, preferably based on controlled feedback instabilities, to control voltage output. The outer loop achieves damping and accurate convergence using proportional, time-integral, and time-derivative gain terms. The time-integral feedback may be based on measured and target solenoid drive currents, adjusting the magnetic gap for force balance at the target current. Incorporation of permanent magnet material permits the target current to be zero, achieving levitation with low power, including for a monorail deriving propulsion from the levitation magnets. Linear magnetic approximations lead to the simplest controller, but nonlinear analog computation in the log domain yields a better controller with relatively few parts. When servo-controlled solenoids provide actuation of a pump piston and valves, electronic LC resonance measurements determine liquid volume and gas bubble volume.
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B +1
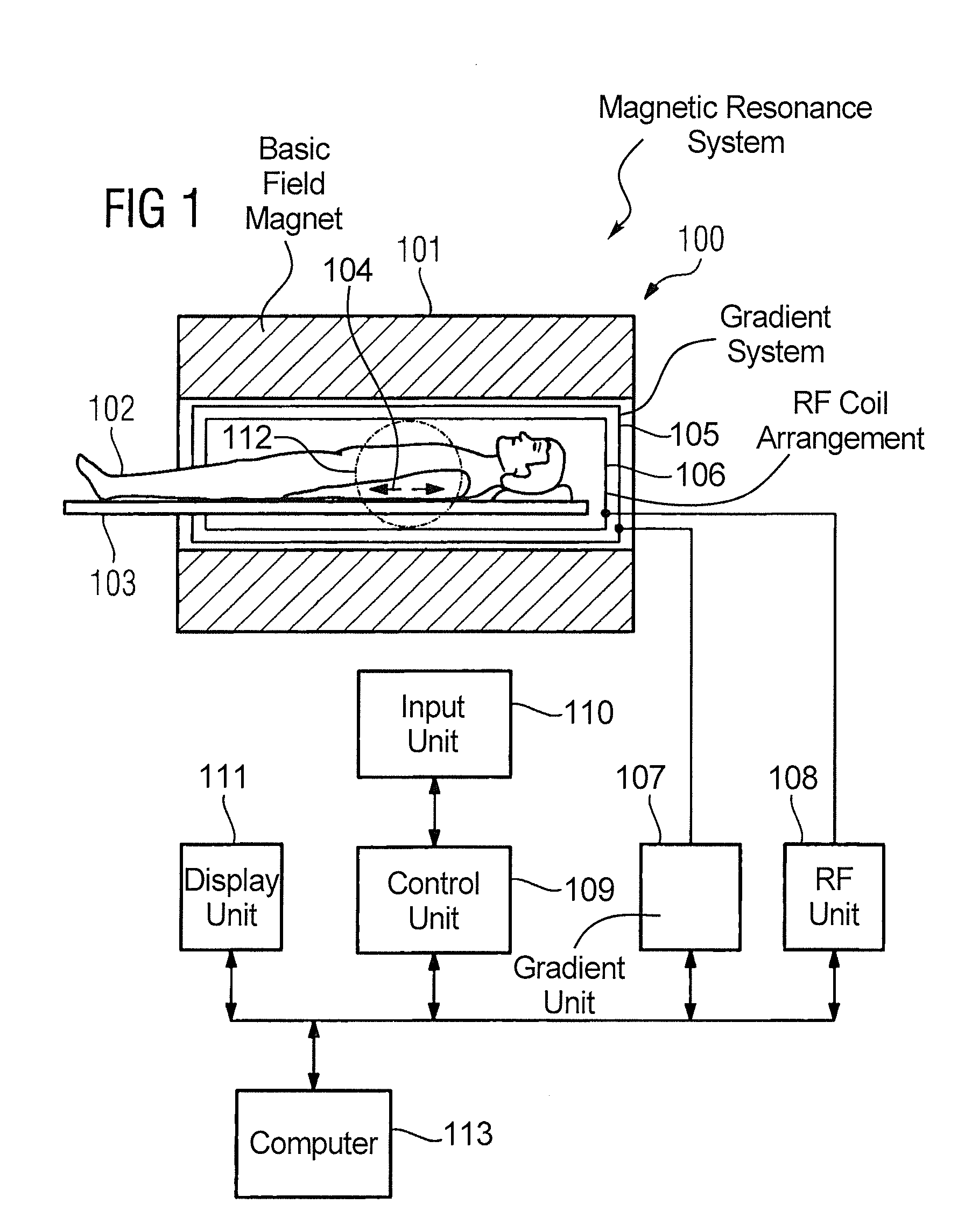
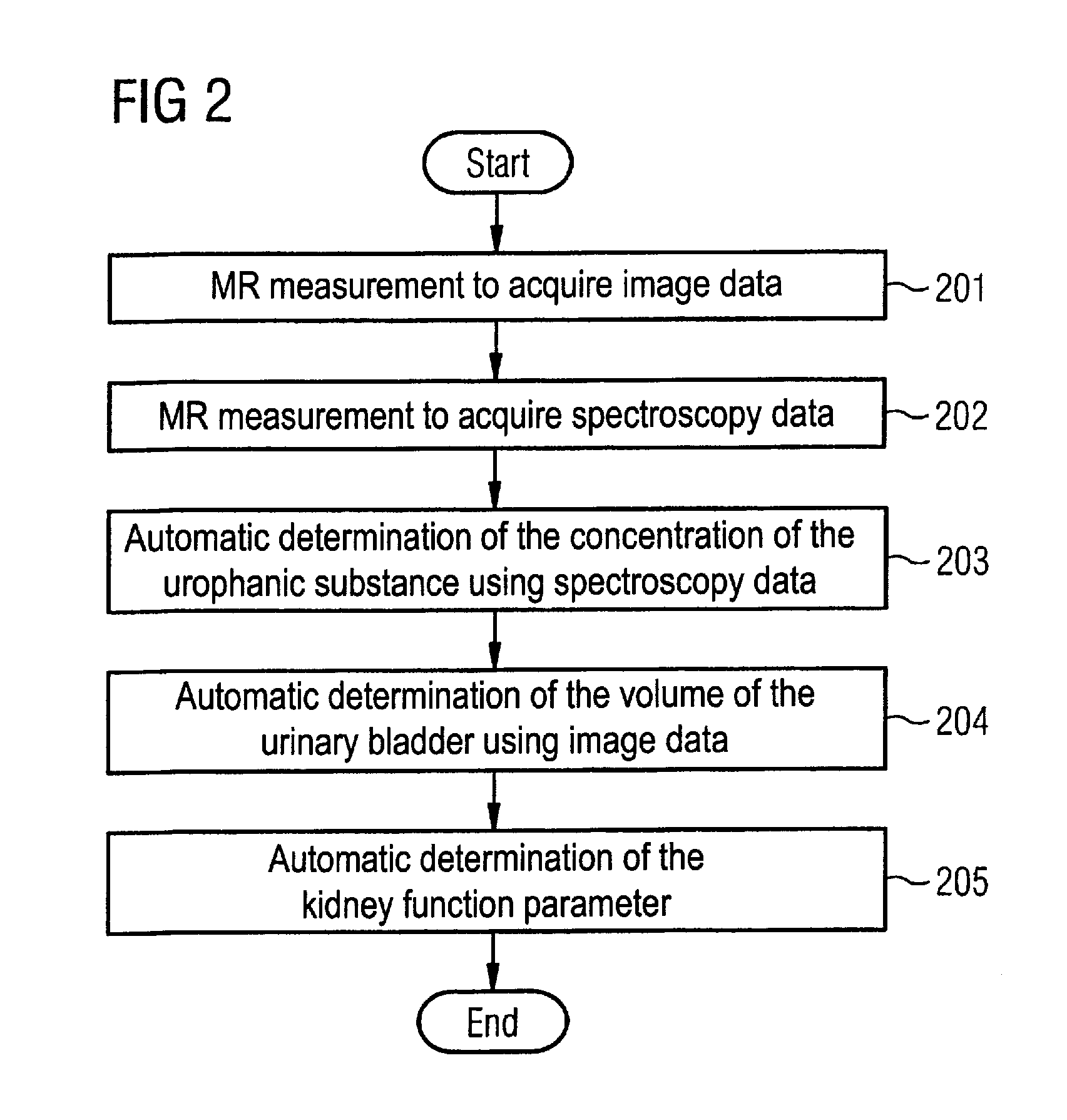
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for determining a kidney function parameter
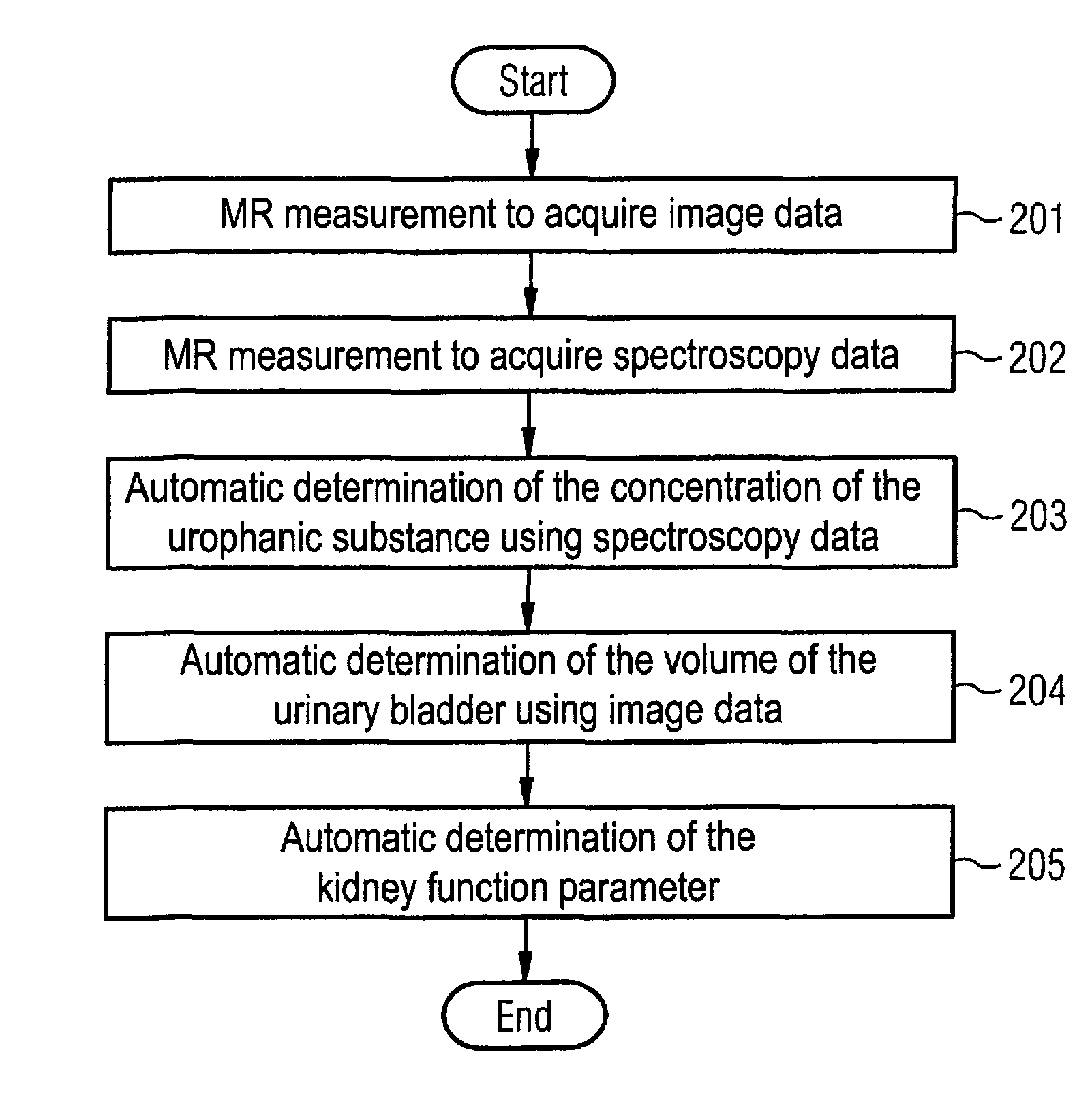
ActiveUS8260397B2Accurate measurementShort timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonance measurementRenal function
In a method to determine a kidney function parameter of kidneys of an examination person with the aid of magnetic resonance tomography, at least one magnetic resonance measurement is implemented for an examination region of the examination person that comprises a urinary bladder of the examination person, to acquire magnetic resonance data from the examination region that include at least image data. The concentration of a urophanic substance in the urinary bladder of the examination person is automatically determined based on the acquired magnetic resonance data. A volume of the urinary bladder is automatically determined based on the acquired image data. A kidney function parameter of the kidneys of the examination person is automatically determined on the basis of the determined concentration of the urophanic substance in the urinary bladder and of the specific volume of the urinary bladder.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
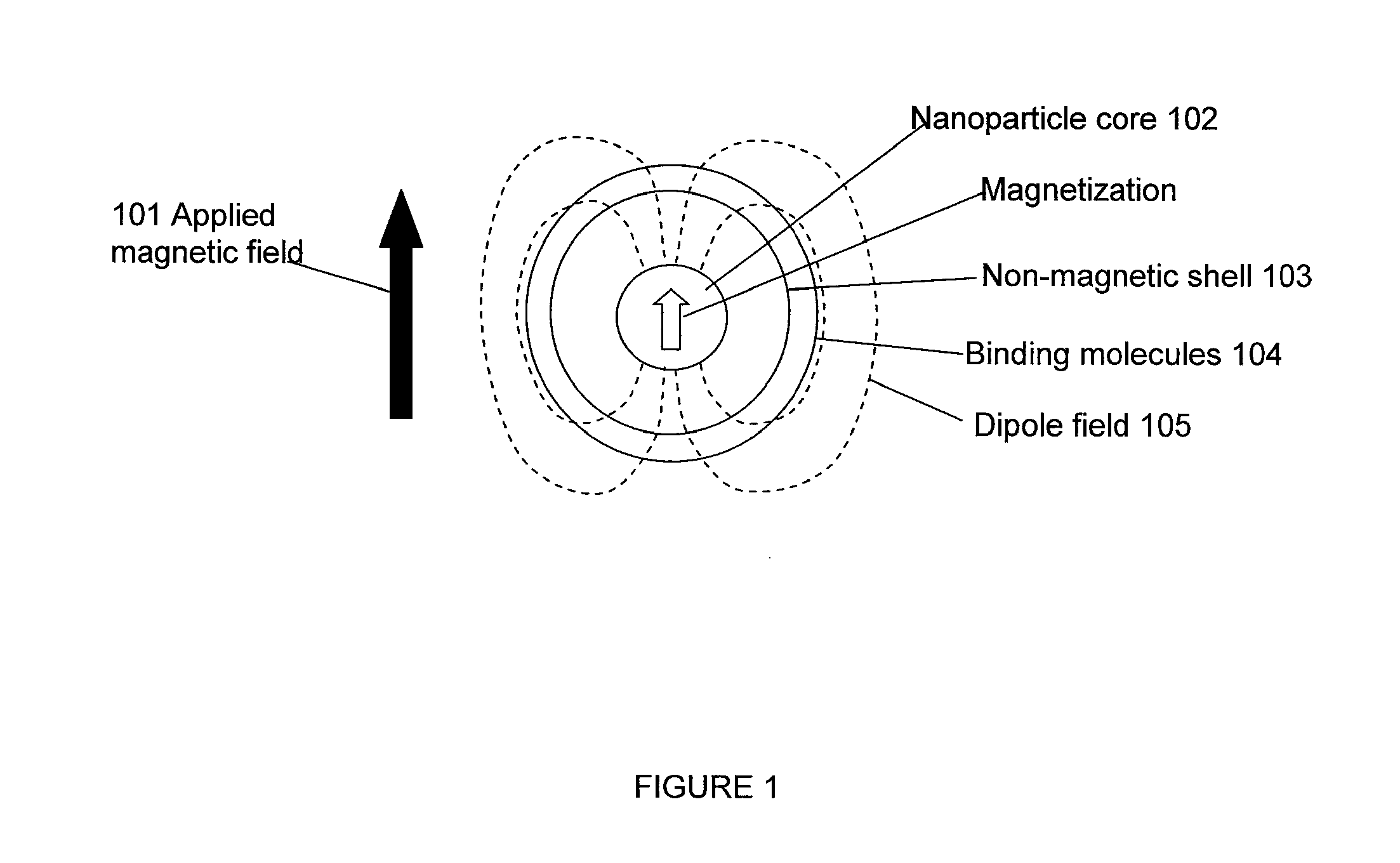
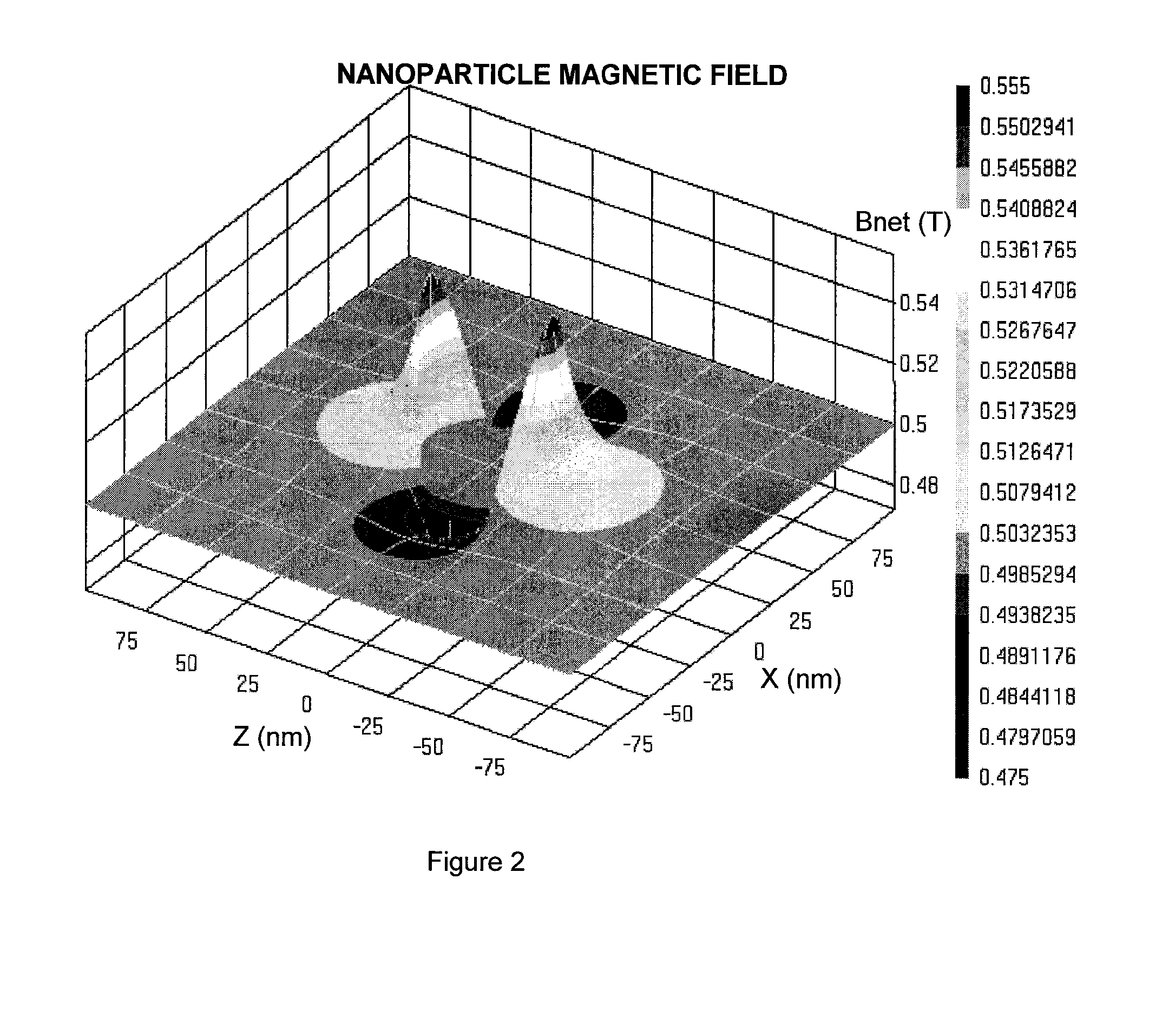
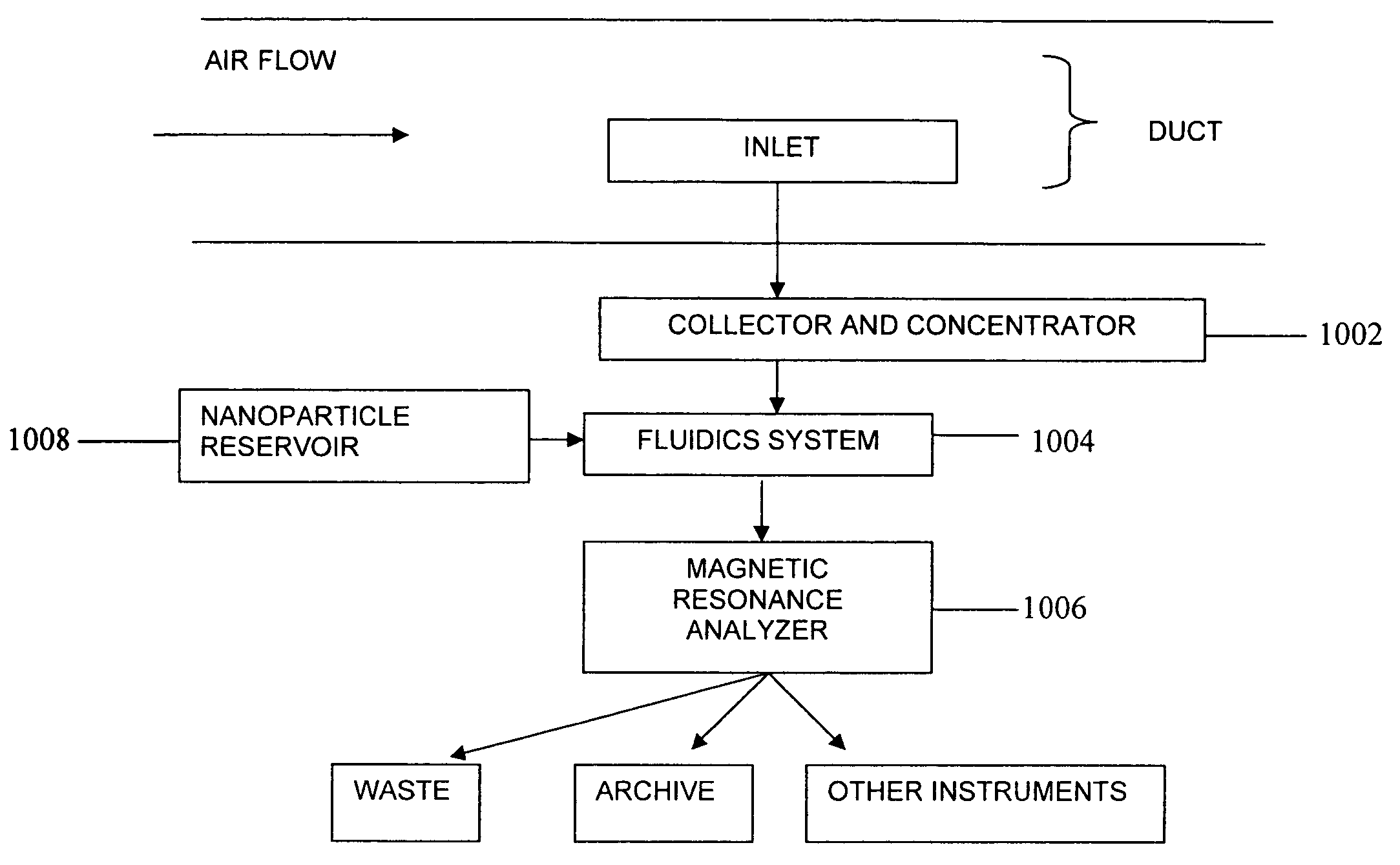
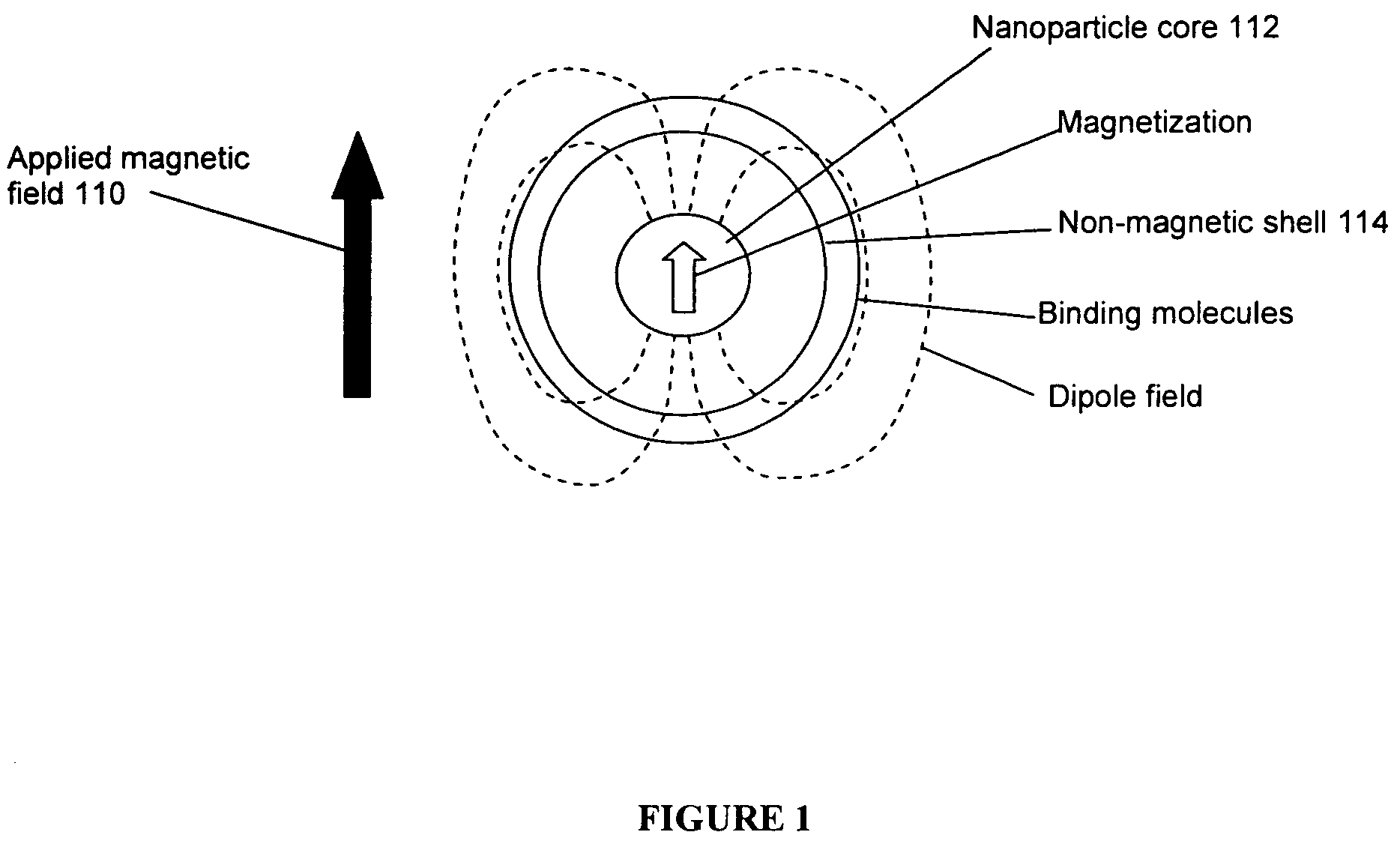
Magnetic resonance system and method to detect and confirm analytes
InactiveUS20070166730A1Easy to detectQuality improvementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismResonance measurementAnalyte
Owner:MENON INT
Dynamic hearing protection method and device
InactiveUS20130208909A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationHearing device active noise cancellationResonance measurementAudio frequency
A dynamic hearing protection method and device with which a hearing protection device specific differential head related transfer function corresponding to the difference between an open ear resonance measurement of the user's ear canal or an ear canal approximating the user's ear canal without the hearing protection device being worn in the ear canal and an open ear resonance measurement with the hearing protection device being worn in the ear canal as a function of the angle of sound incidence is determined and when using the hearing protection device, a frequency-dependent gain function to the captured audio signals selected according to the presently determined angle of sound incidence with each of the gain functions is determined by inverting the previously determined HPD specific differential HRTF for the respective sound incidence angle, to compensate for the effect of the presence of the hearing protection device on the open ear resonance.
Owner:PHONAK
Solenoid cassette pump with servo controlled volume detection
InactiveUS6942469B2Eliminate closure impactEliminate associated noiseAC motor controlElectrical controlResonance measurementDriving current
Servo controlled solenoids provide actuation of a pump piston and valves, and electronic LC resonance measurements to determine liquid volume and gas bubble volume. Third order nonlinear servo control is split into nested control loops: a fast nonlinear first-order inner loop causing flux to track a target by varying a voltage output, and a slower almost linear second-order outer loop causing magnetic gap to track a target by controlling the flux target or the inner loop. The inner loop uses efficient switching regulation, preferably based on controlled feedback instabilities, to control voltage output. The outer loop achieves damping and accurate convergence using proportional, time-integral, and time-derivative gain terms. The time-integral feedback may be based on measured and target solenoid drive currents, adjusting the magnetic gap for force balance at the target current.
Owner:THISTLE ADVISORS
Magnetic resonance system and method to detect and confirm analytes
ActiveUS7781228B2Improve bindingReduce activity timeNanotechMagnetic measurementsResonance measurementProton magnetic resonance
A system and method are provided to detect target analytes based on magnetic resonance measurements. Magnetic structures produce distinct magnetic field regions having a size comparable to the analyte. When the analyte is bound in those regions, magnetic resonance signals from the sample are changed, leading to detection of the analyte.
Owner:MENON BIOSENSORS
Method and magnetic resonance system for homogenizing the B1 field
ActiveUS7078901B2Promote homogenizationQuick searchElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceResonance measurementData acquisition
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Apparatus and method for varying magnetic field strength in magnetic resonance measurements
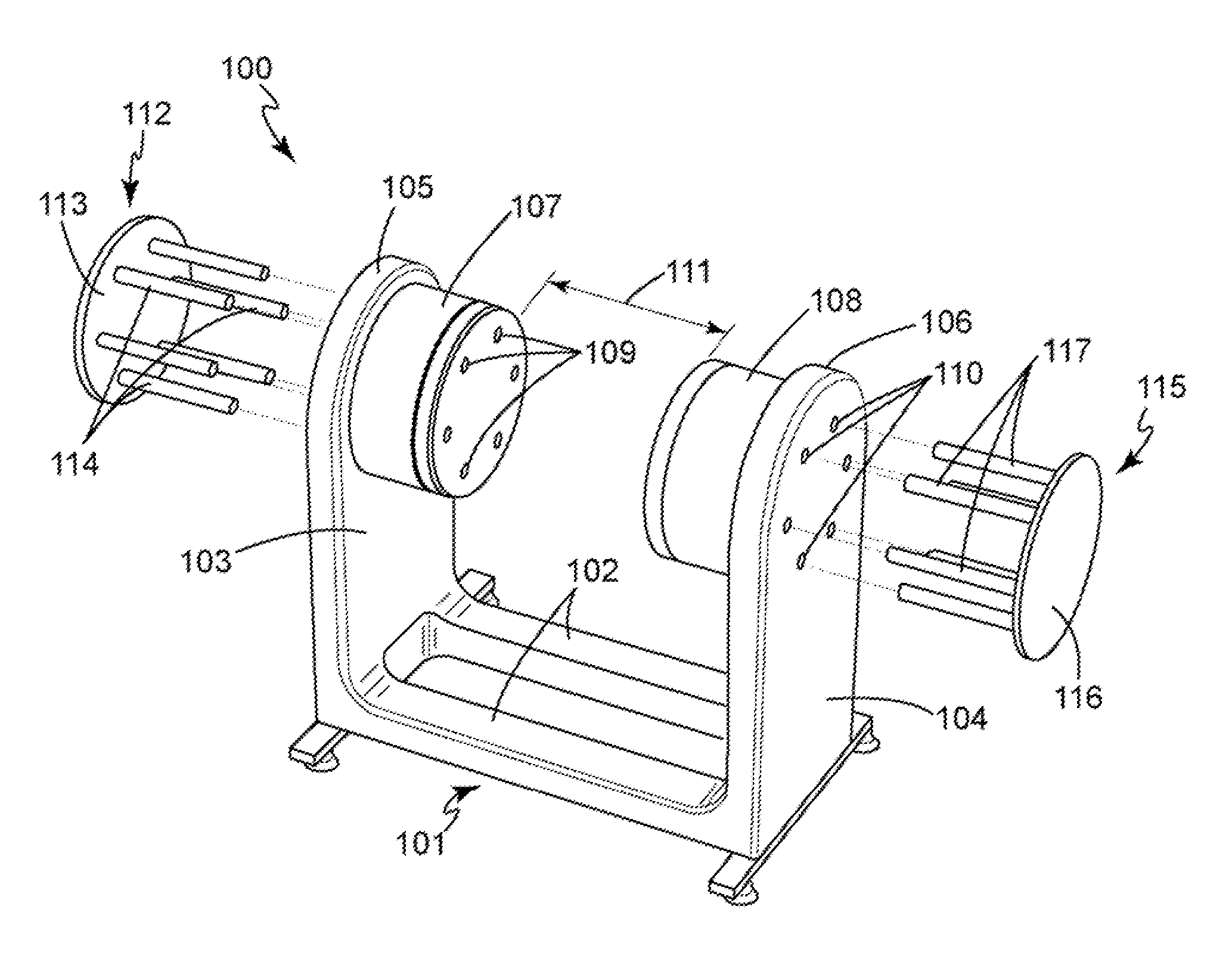
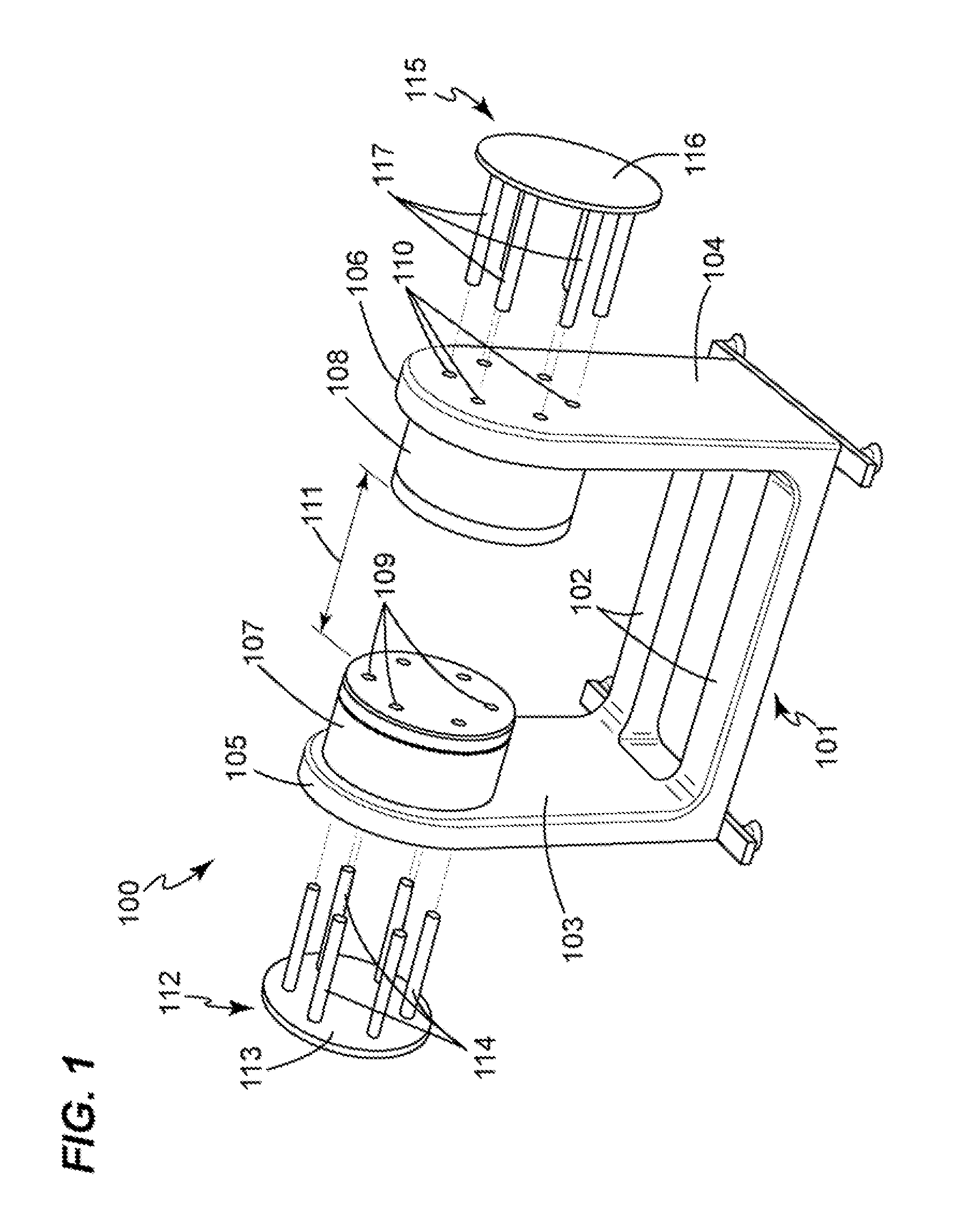
Apparatus and method for varying field strength in a magnetic resonance system while keeping a relatively uniform magnetic field distribution. In an embodiment, a two-pole, generally u-shaped magnet assembly generates a static and uniform magnetic field. The magnet assembly includes two facing magnet poles separated by an air gap. Holes may be formed with the magnet poles. The field control rods may be placed at a pre-determined distance into these holes and symmetrically or asymmetrically moved across each magnet poles in a controlled manner to change the magnetic field strength while keeping the uniform magnetic field distribution. Maximum magnetic field strength may occur when the rods are removed. Minimum magnetic field strength may occur when the rods are fully inserted.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
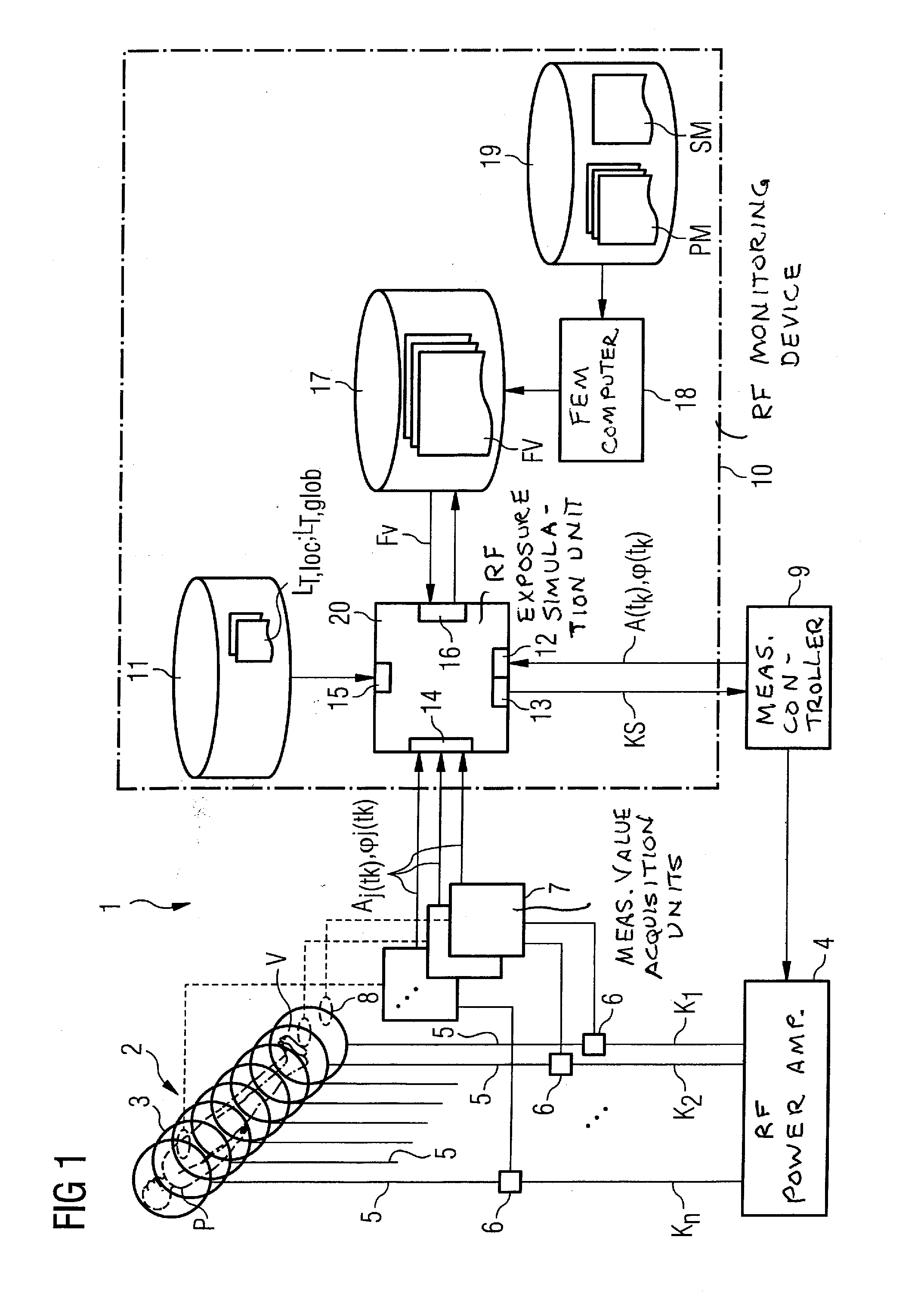
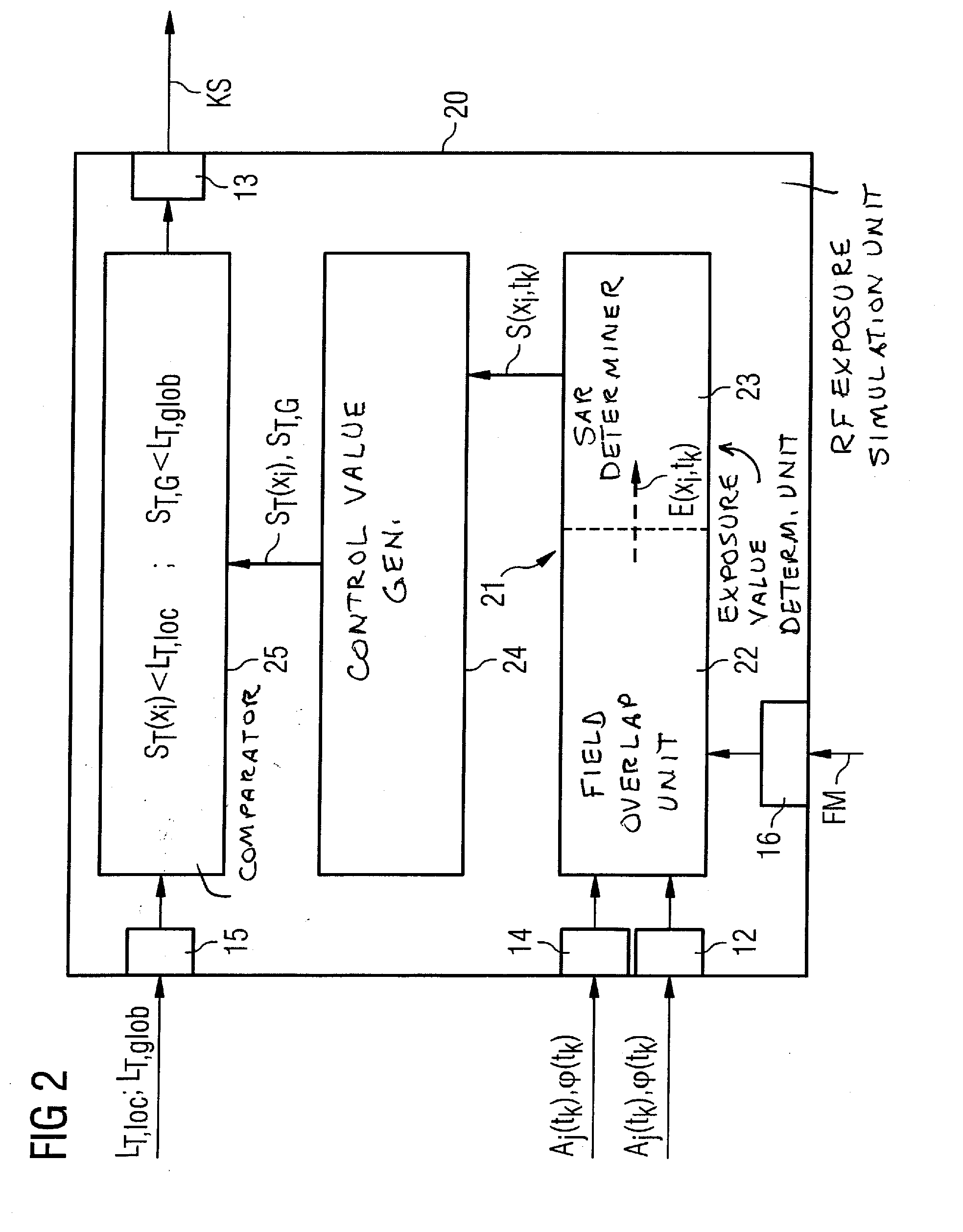
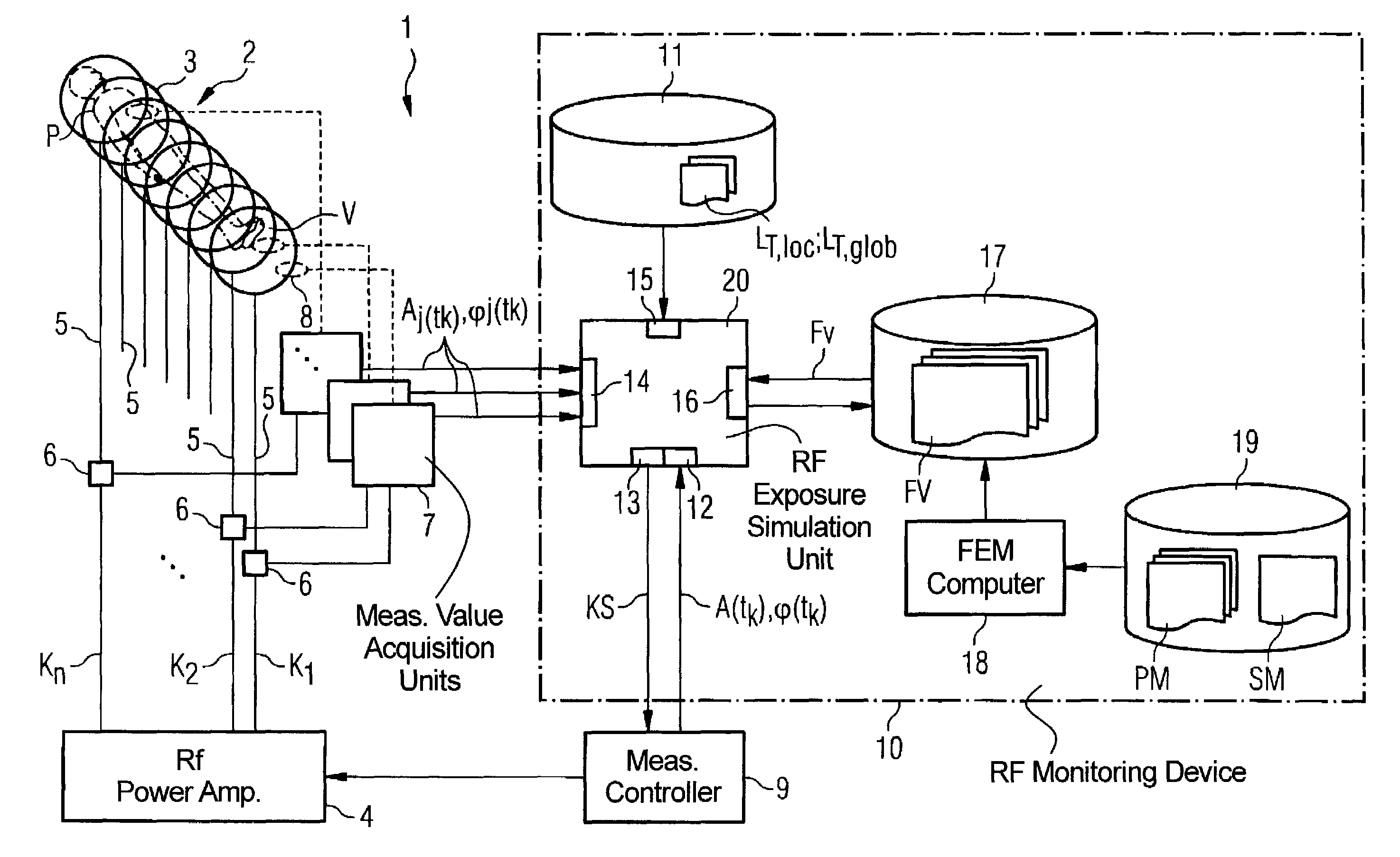
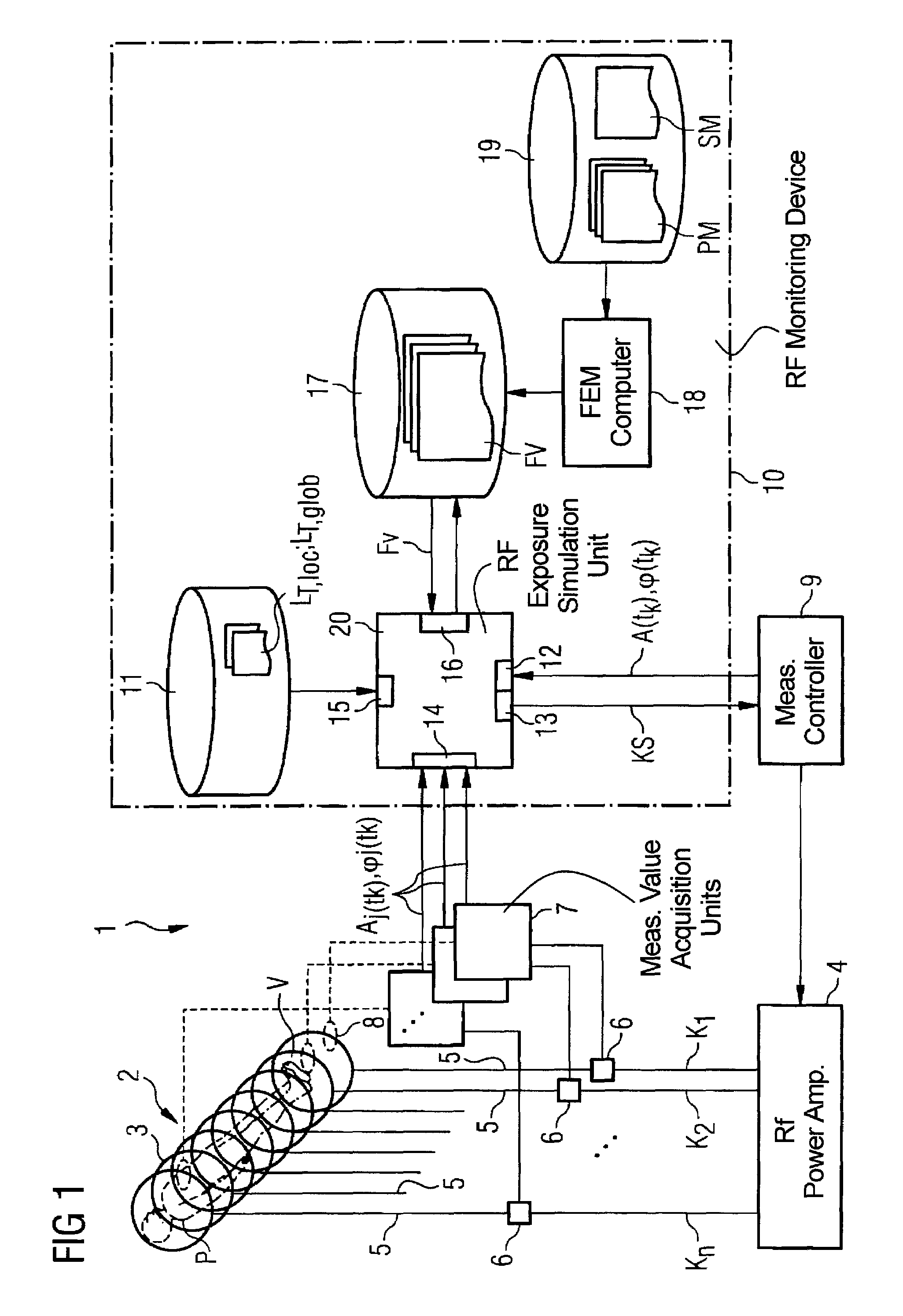
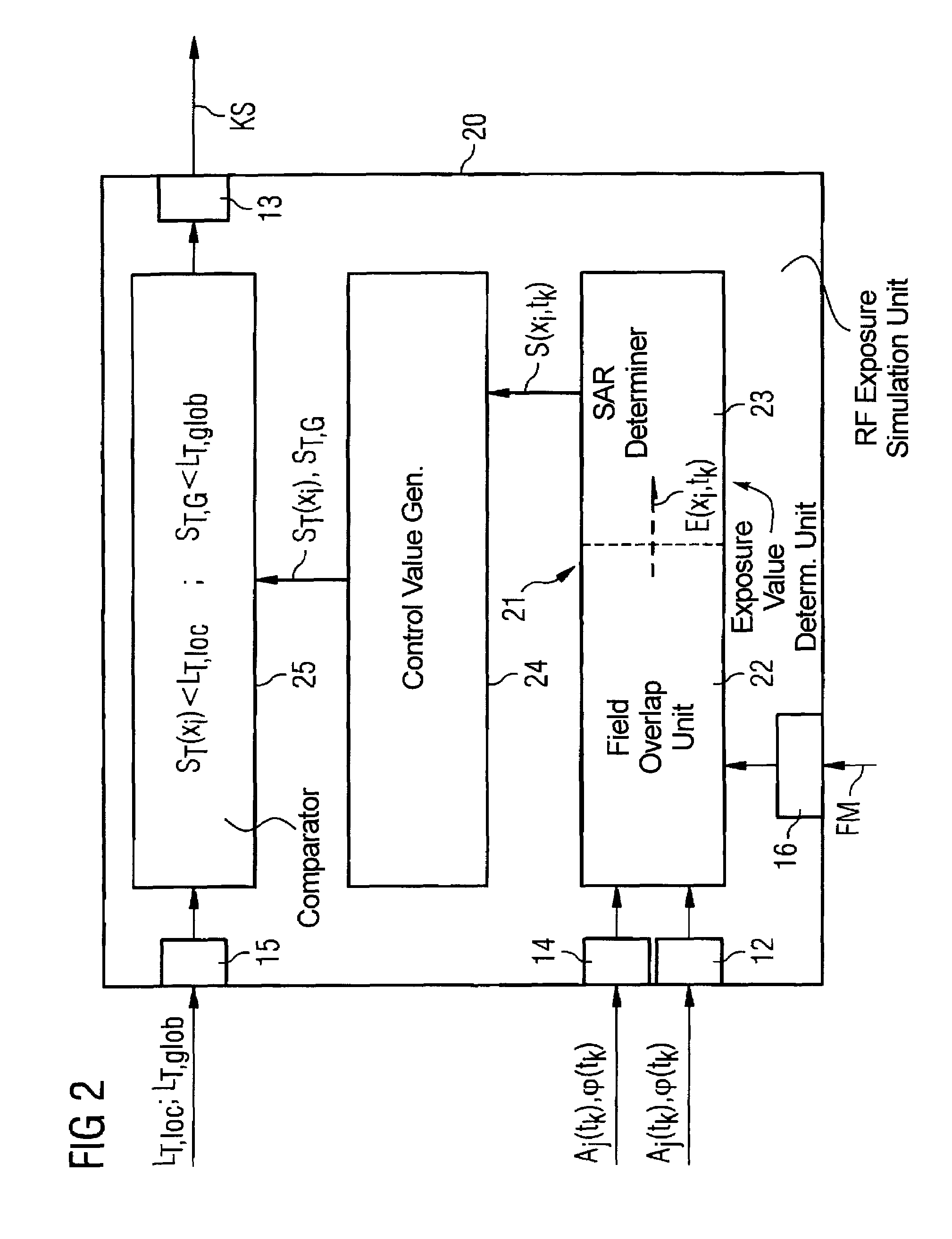
Method and device for monitoring radio-frequency exposure in a magnetic resonance measurement
InactiveUS20080157765A1Fast convergenceHigh transmission powerMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementControl signal
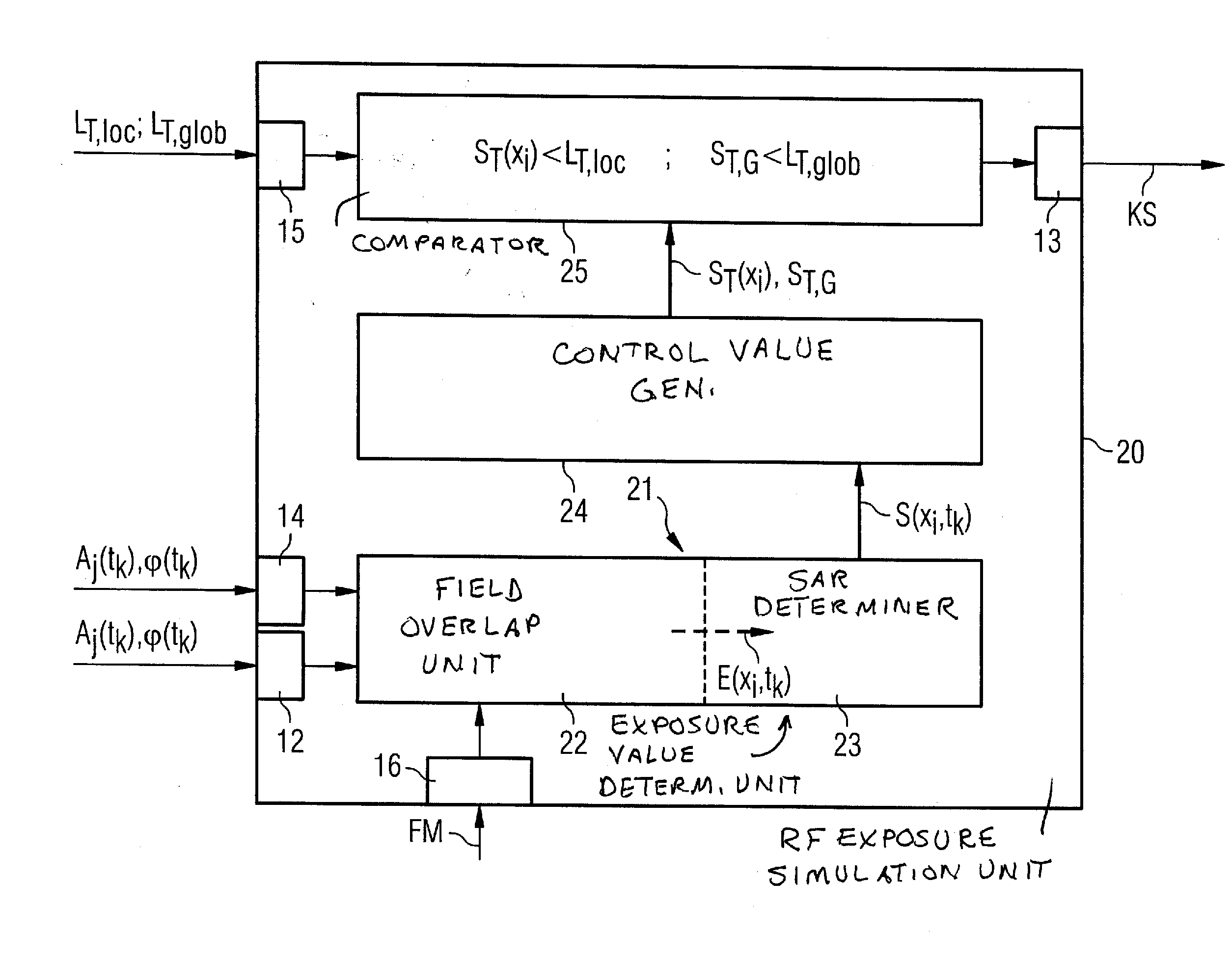
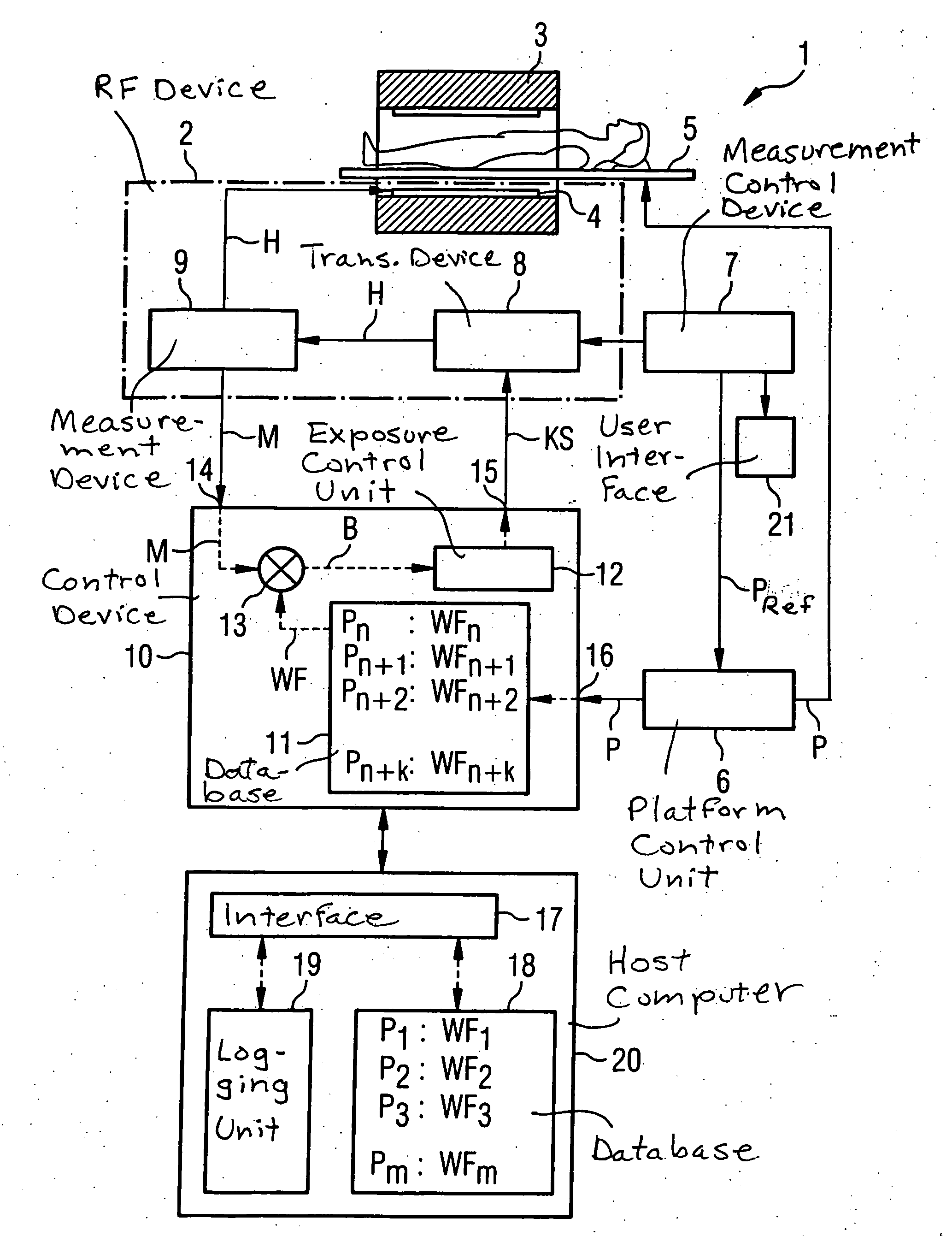
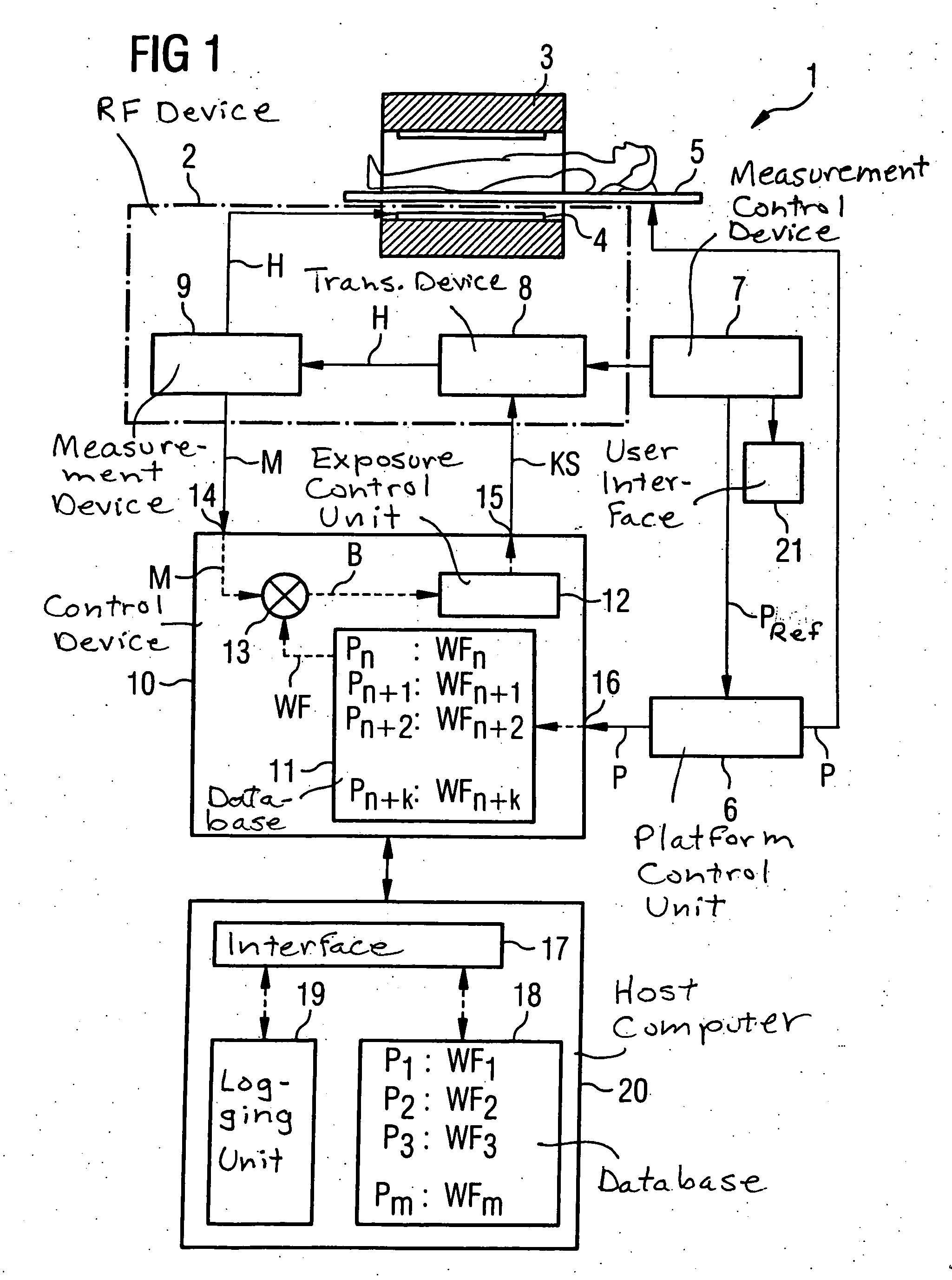
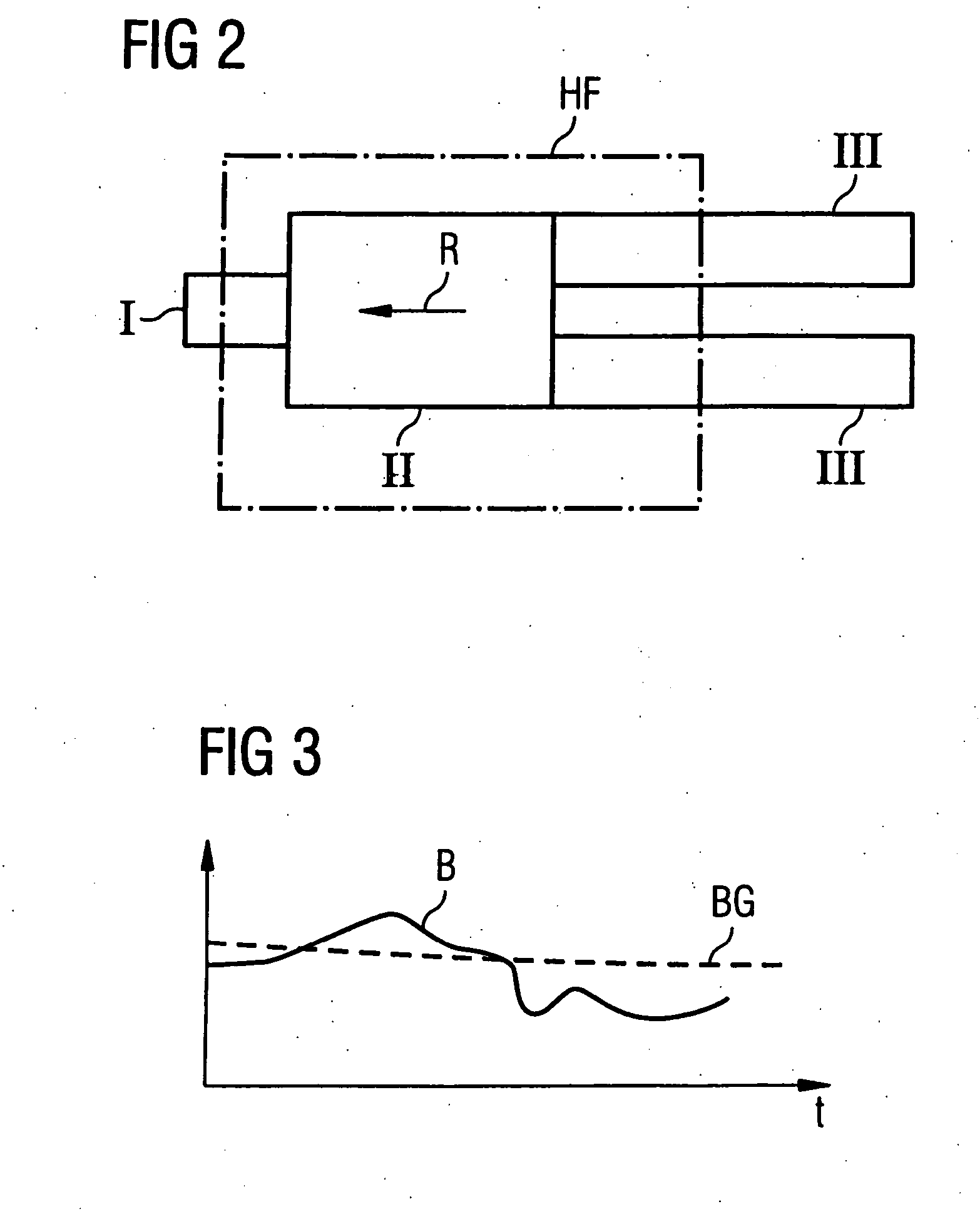
In a method and device for monitoring the physiologically effective radio-frequency exposure in at least one specific volume region of an examination subject in a magnetic resonance data acquisition scan in a magnetic resonance system, the magnetic resonance system having a radio-frequency antenna structure with a number of individually controllable radio-frequency signal channels for generation of radio-frequency field distributions in an examination volume including the examination subject, amplitude values are acquired that respectively represent, at specific acquisition points in time, a signal amplitude of the radio-frequency signals emitted or to be emitted via the radio-frequency signal channels in the course of the magnetic resonance measurement. Also, phase values are acquired that represent the phases of the appertaining radio-frequency signals at these points in time. Local exposure values are then determined on the basis of the amplitude values and phase values, these local exposure values respectively representing a physiological exposure that the radio-frequency pulses cause at the examination subject at a specific location at a specific time. Based on this, exposure control values are determined that are compared with predetermined exposure limit values. When an exposure limit values is reached or exceeded, a control signal is output.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and device for monitoring radio-frequency exposure in a magnetic resonance measurement
InactiveUS7622921B2Surpassing limit valueImprove image qualityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementControl signal
In a method and device for monitoring the physiologically effective radio-frequency exposure in at least one specific volume region of an examination subject in a magnetic resonance data acquisition scan in a magnetic resonance system, amplitude values are acquired that respectively represent, at specific acquisition points in time, a signal amplitude of the radio-frequency signals emitted or to be emitted via the radio-frequency signal channels. Also, phase values are acquired that represent the phases of the appertaining radio-frequency signals at these points in time. Local exposure values are then determined on the basis of the amplitude values and phase values, respectively representing a physiological exposure that the radio-frequency pulses cause at the examination subject at a specific location at a specific time. Based on this, exposure control values are determined that are compared with predetermined exposure limit values. When an exposure limit values is reached or exceeded, a control signal is output.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Apparatus and method for varying magnetic field strength in magnetic resonance measurements
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Method for quasi-continous dynamic motion correciton in magnetic resonance measurements
ActiveUS20120268124A1Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementDynamic motion
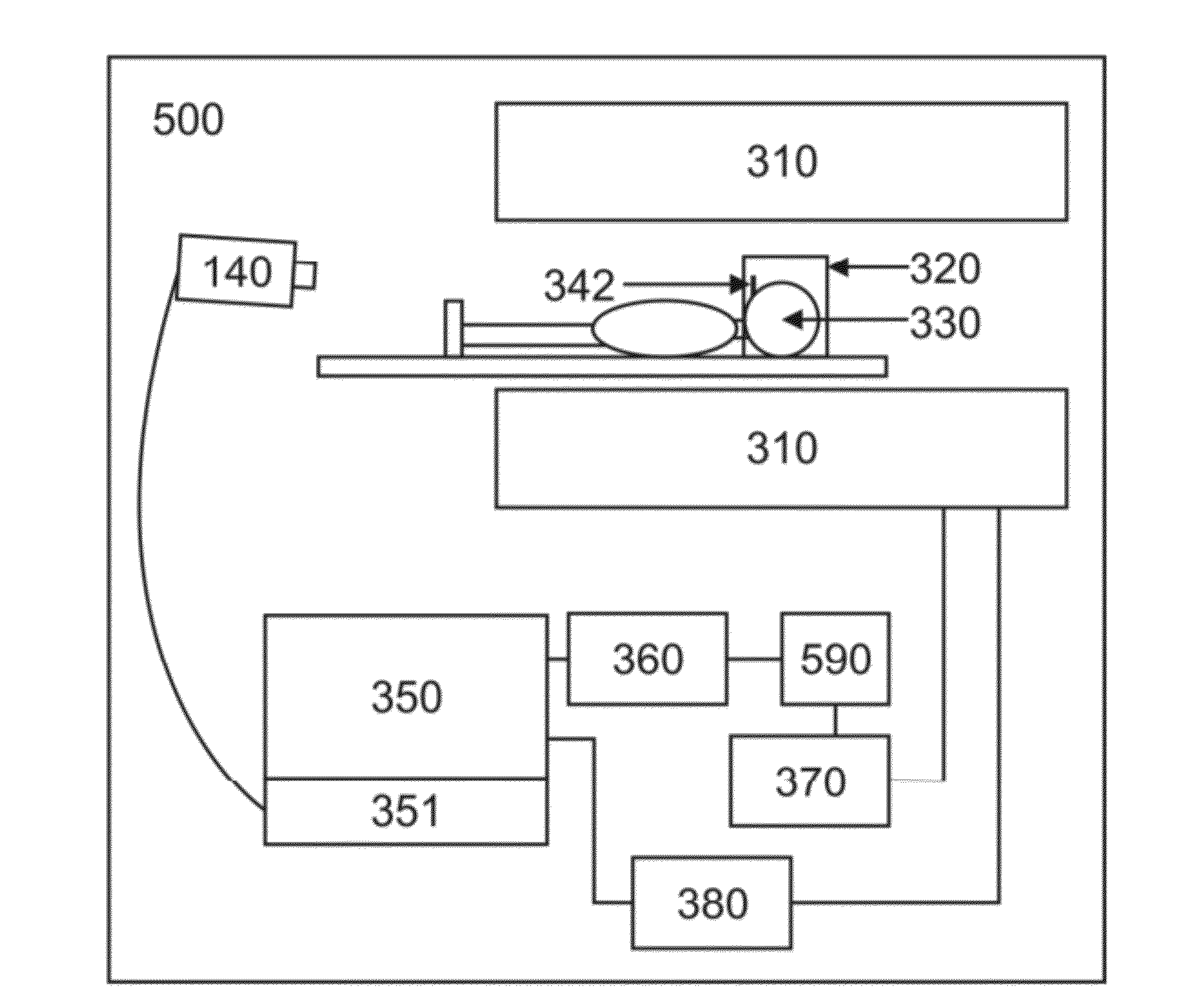
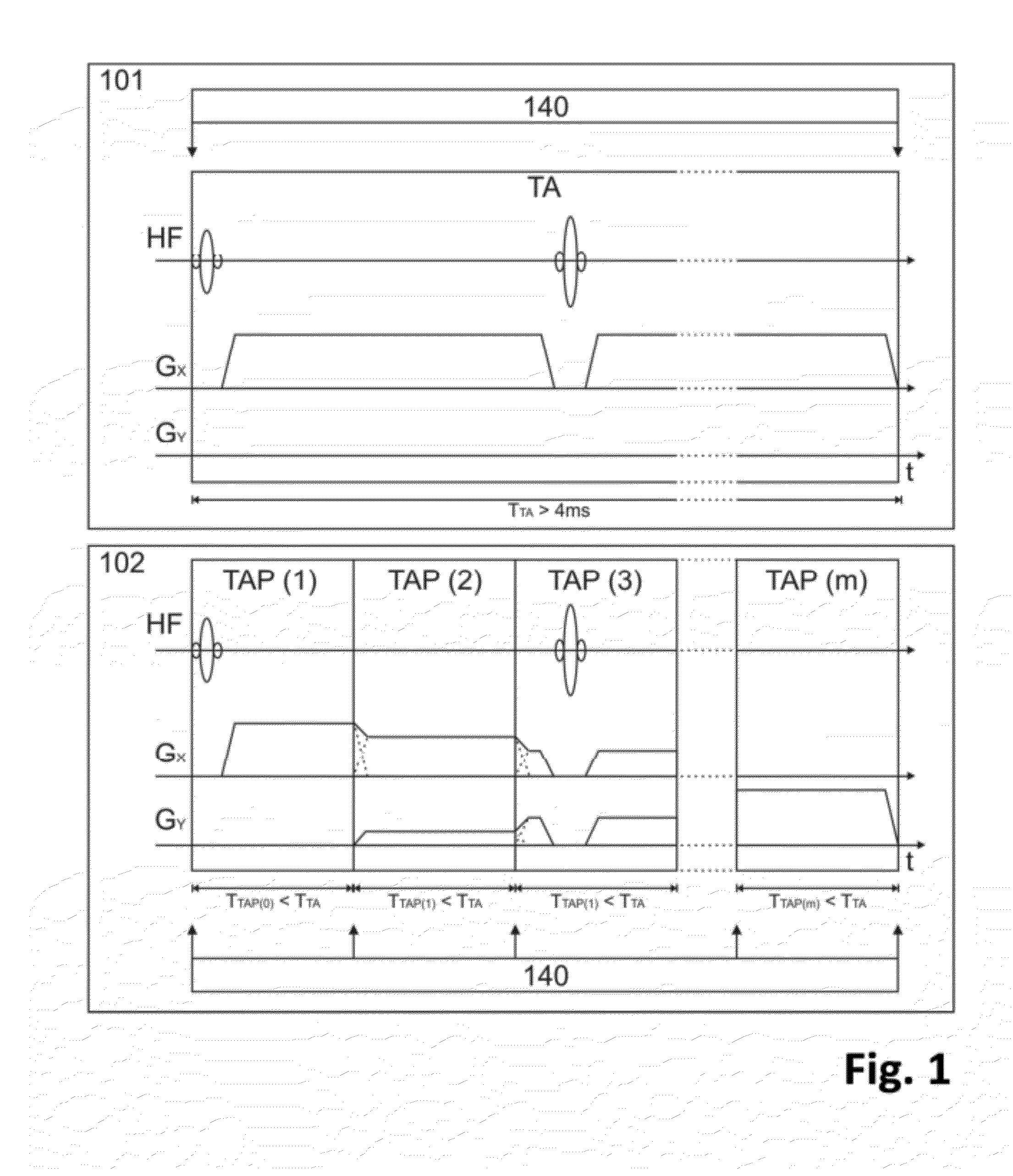
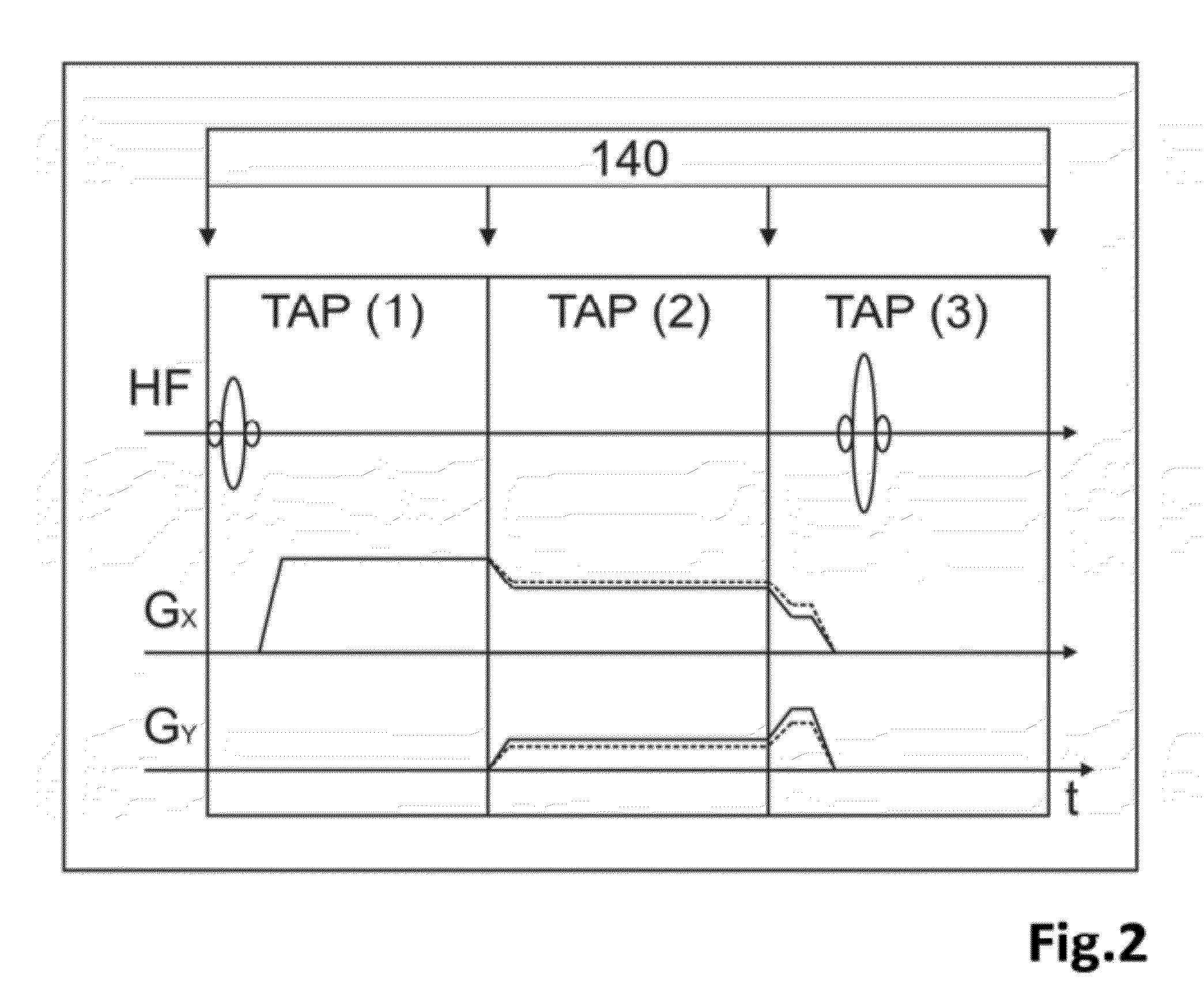
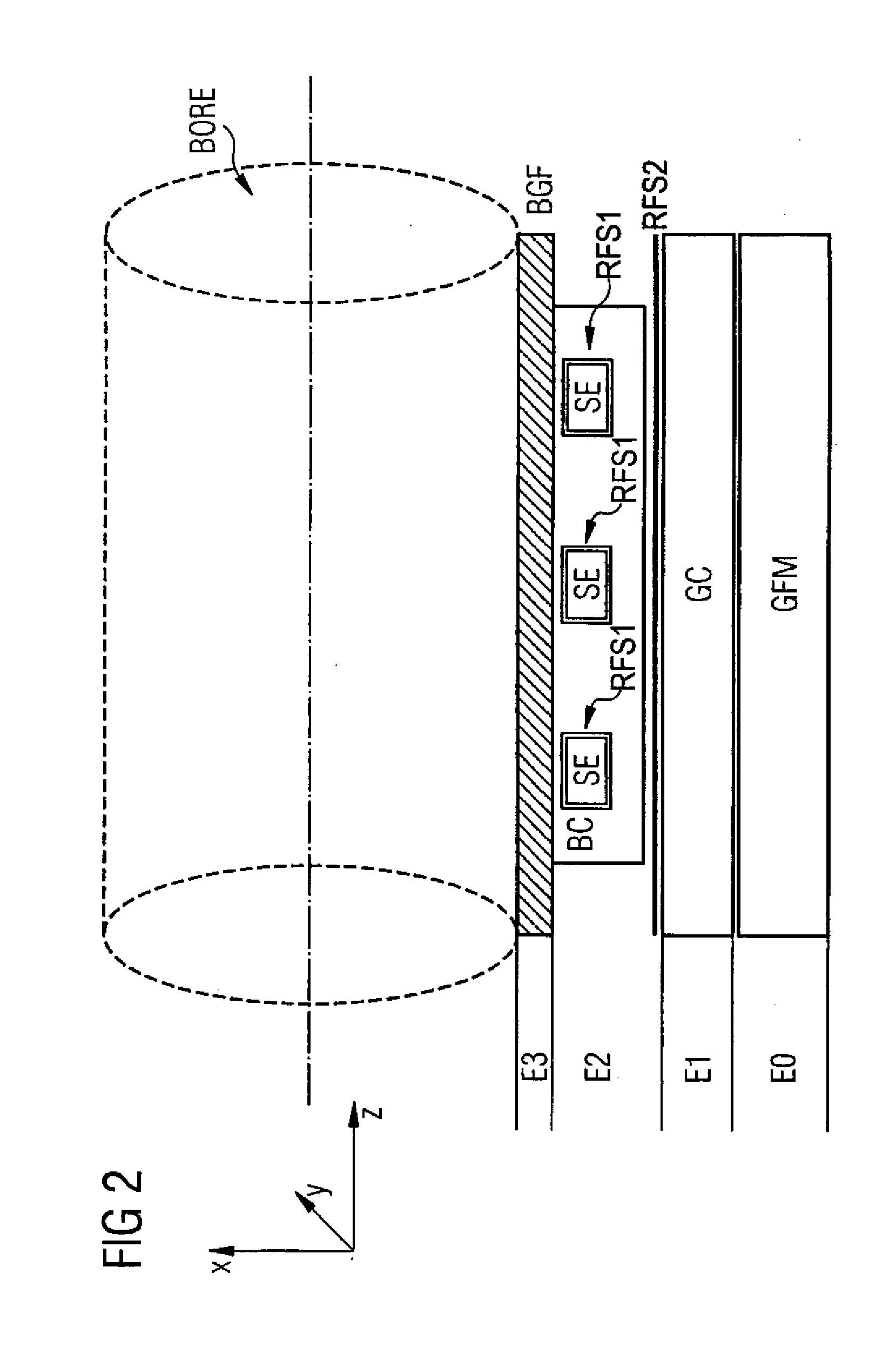
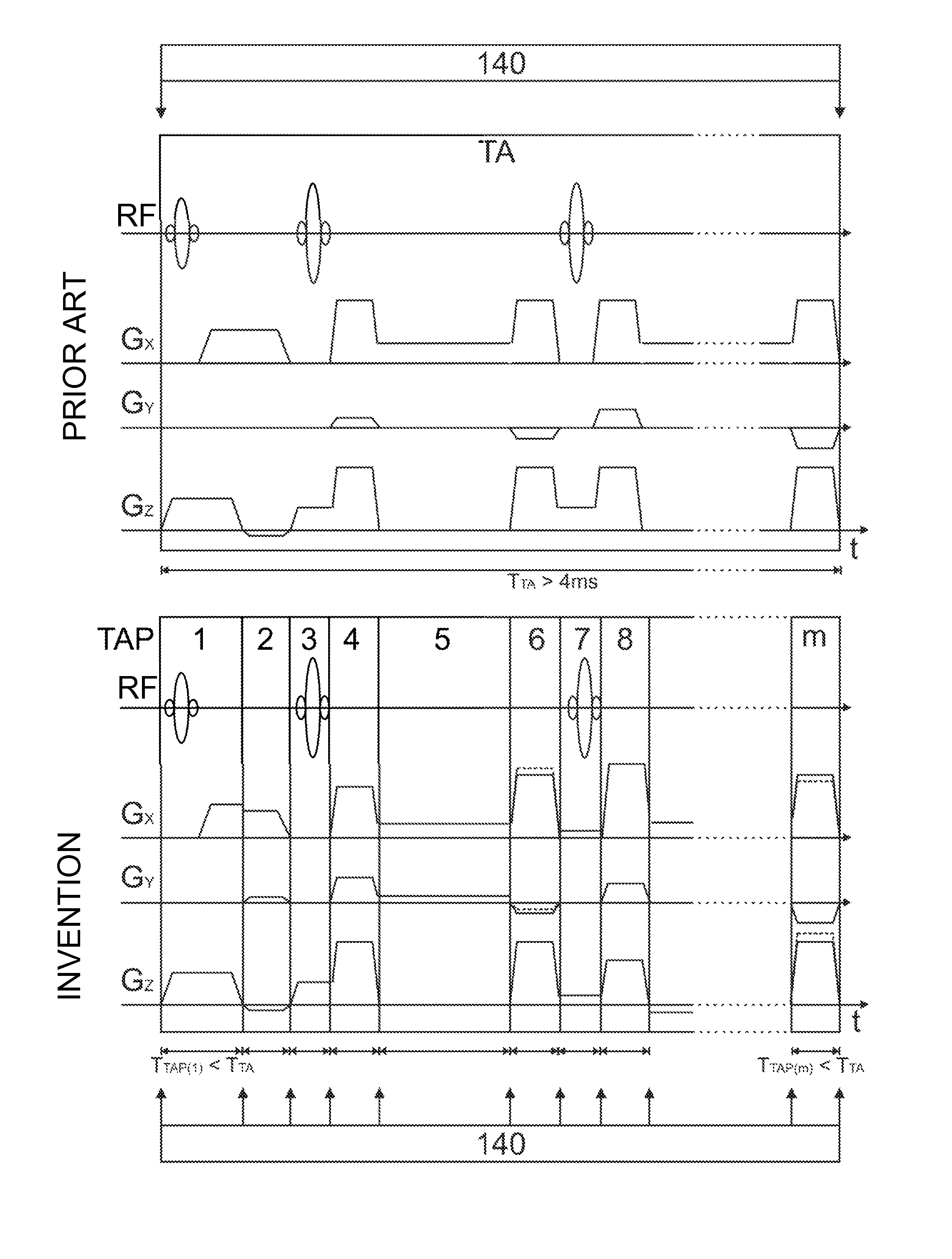
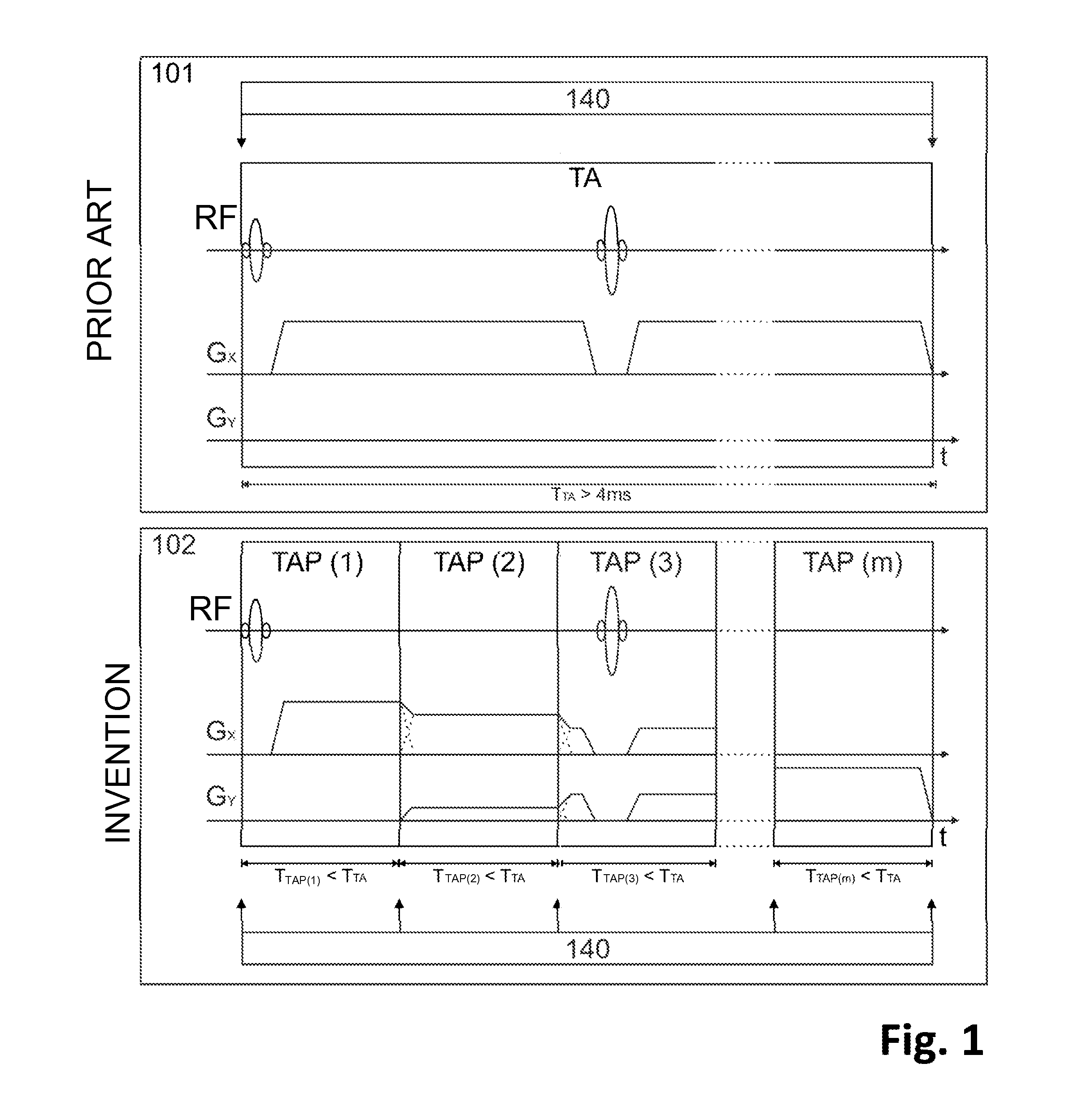
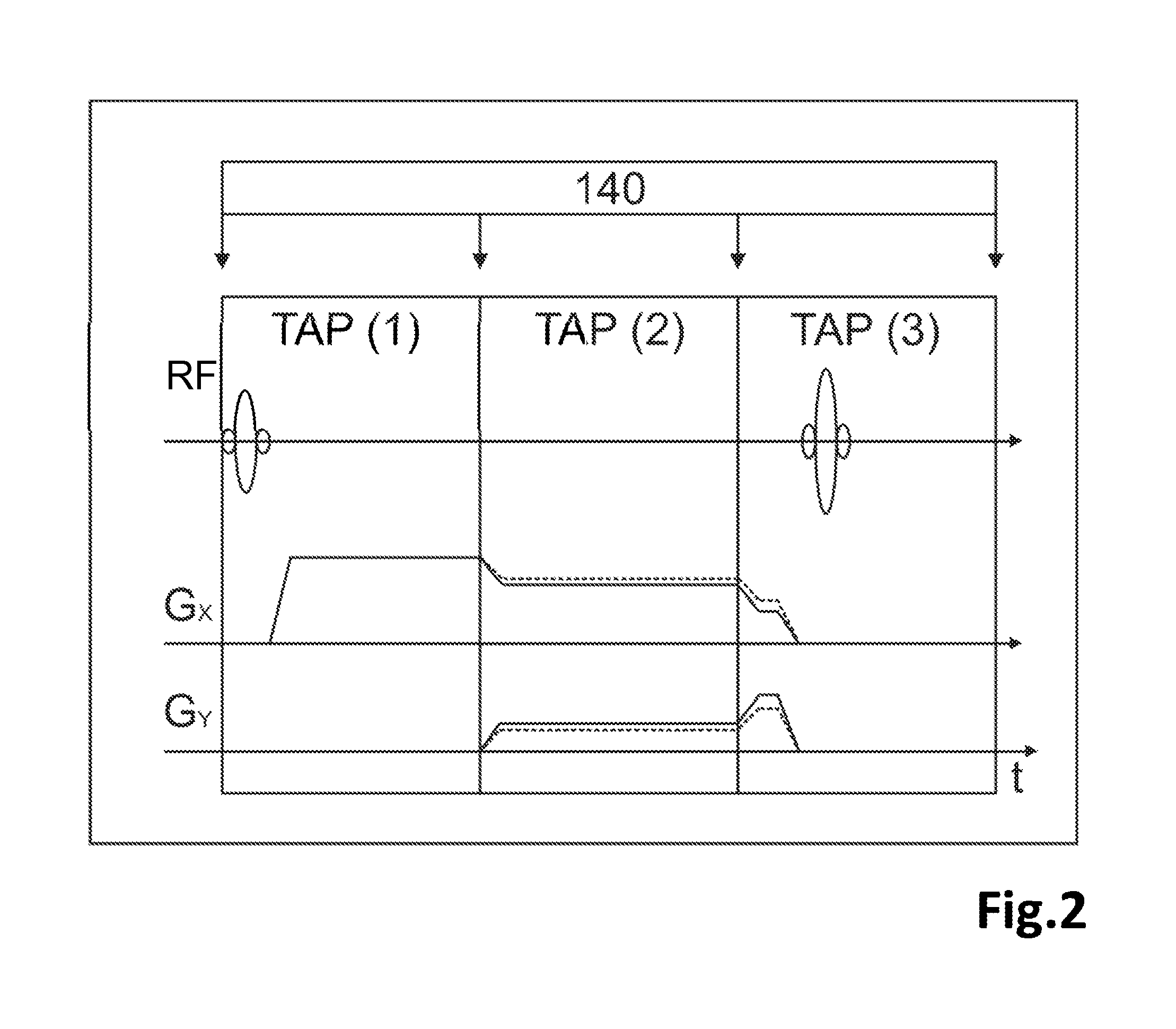
A method of MR imaging and spectroscopy reduces artifacts occurring due to the motion of an object to be represented, wherein the object position is determined quasi-continuously during the runtime of the MR acquisition, which includes one or more partial acquisitions (TA), and wherein motion correction is performed, which comprises dynamic adaptation of the frequency and phase settings of the RF system of the tomograph and of the orientation and amplitudes of the gradients during the runtime of the MR acquisition according to the current object position. The motion correction is thereby applied during a signal weighting period, during a signal read-out period, or between and / or during the two stated periods and the adaptations for motion correction are performed without interrupting or slowing the temporal progression of the MR acquisition. In this way, artifacts due to motion of the object to be represented can be further reduced.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Magnetic resonance system with implantable components and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20120223705A1Diagnostic recording/measuringAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance measurementProton magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance systems and methods of use thereof are provided. The systems employ implantable radiofrequency coils (105) and optionally implantable magnets (101). The systems can employ weak permanent magnets and / or permanent magnets that provide magnetic fields that are much less homogeneous than in conventional systems. This allows, for example, for inexpensive and simple probeheads for nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry with suitable biosensors. The methods of the present invention allow in-vivo magnetic resonance measurements and, in particular, monitoring of analytes and determination of medical diagnostic information, for example, based on determined magnetic resonance parameters.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
Method and device for monitoring a radio-frequency transmitter device in a magnetic resonance tomography system
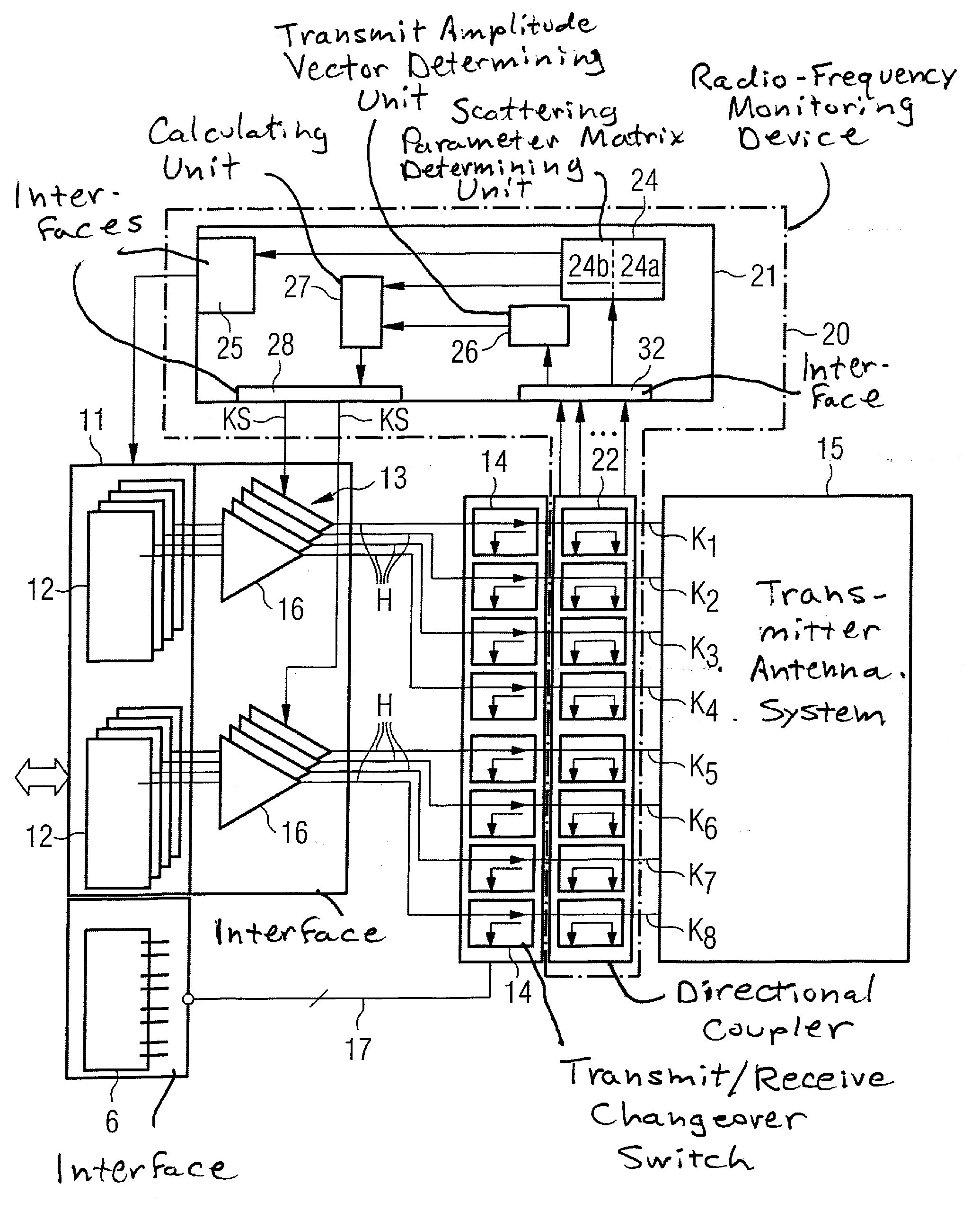
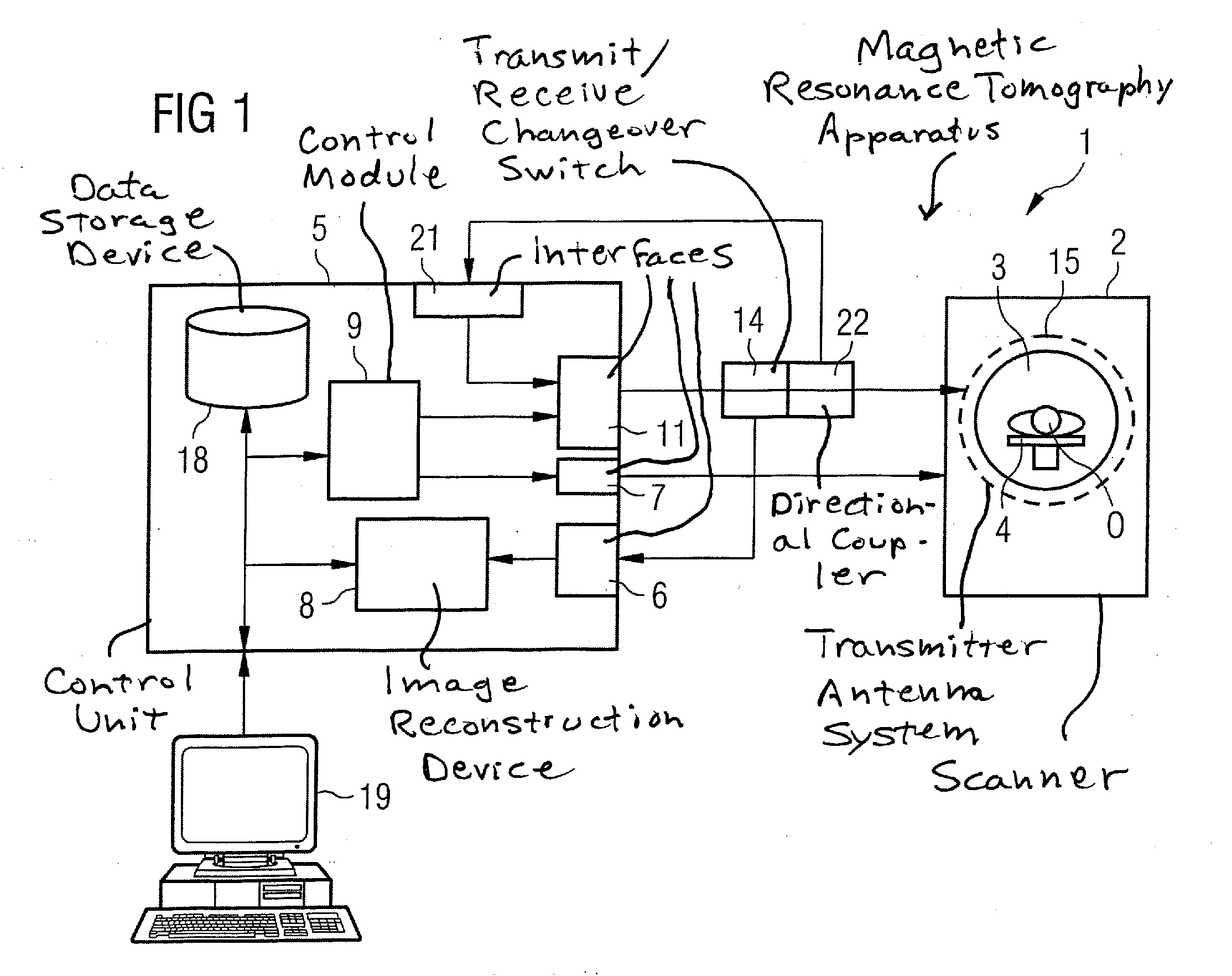
ActiveUS20100167668A1Peak loading is avoidedThreshold value is exceededModulation with suppressed carrierDiagnostic recording/measuringResonance measurementVoltage amplitude
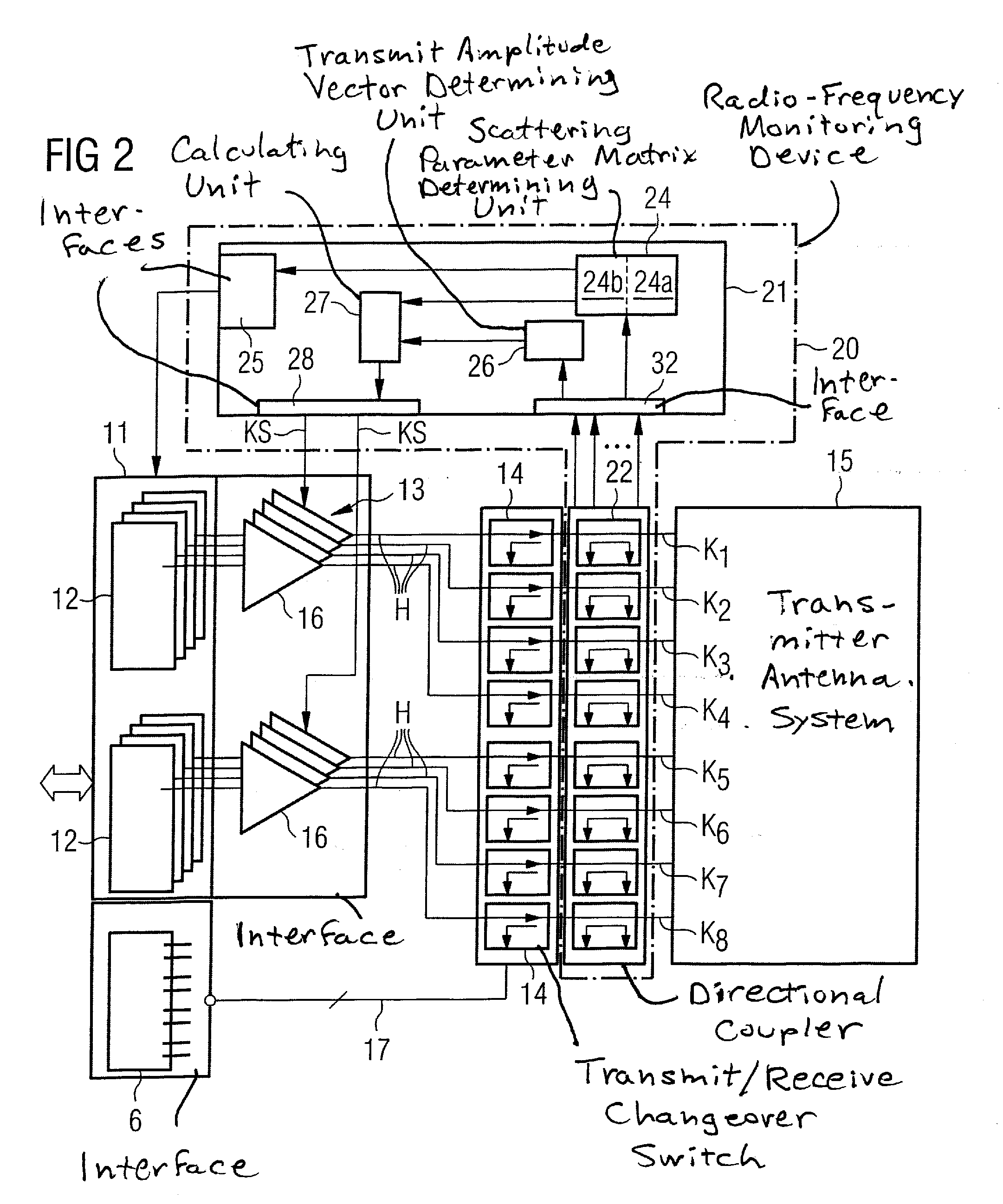
In a method and device for monitoring a radio-frequency transmit device of a magnetic resonance tomography system, having a transmitter antenna system that has a number of transmit channels, during a magnetic resonance measurement of an examination subject, a reference scattering parameter matrix of the transmitter antenna system is determined in the unloaded state, and a subject-specific scattering parameter matrix of the transmitter antenna system is determined in a state loaded with the subject of examination. Moreover, transmitter amplitude vectors are determined in time-dependent fashion that represent the radio-frequency voltage amplitudes on the individual transmit channels. On the basis of the subject-specific scattering parameter matrix, the reference scattering parameter matrix, and the transmit amplitude vectors, radio-frequency power values absorbed at particular transmit times in the subject are determined. Based on a large number of the determined radio-frequency power values, a number of monitoring values are formed. The radio-frequency transmit device is limited in its functioning when a monitoring value reaches or exceeds a prespecified boundary monitoring value.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
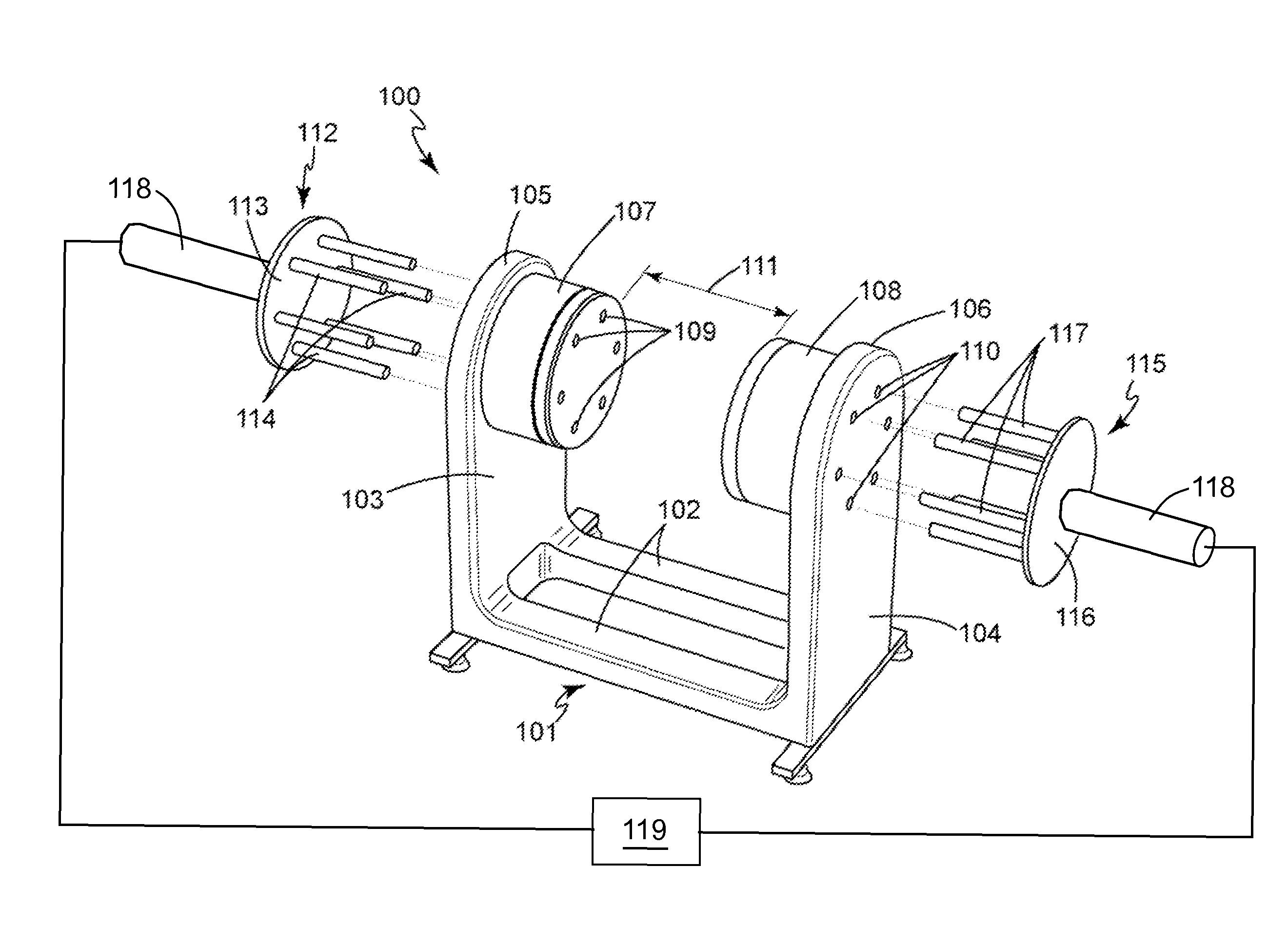
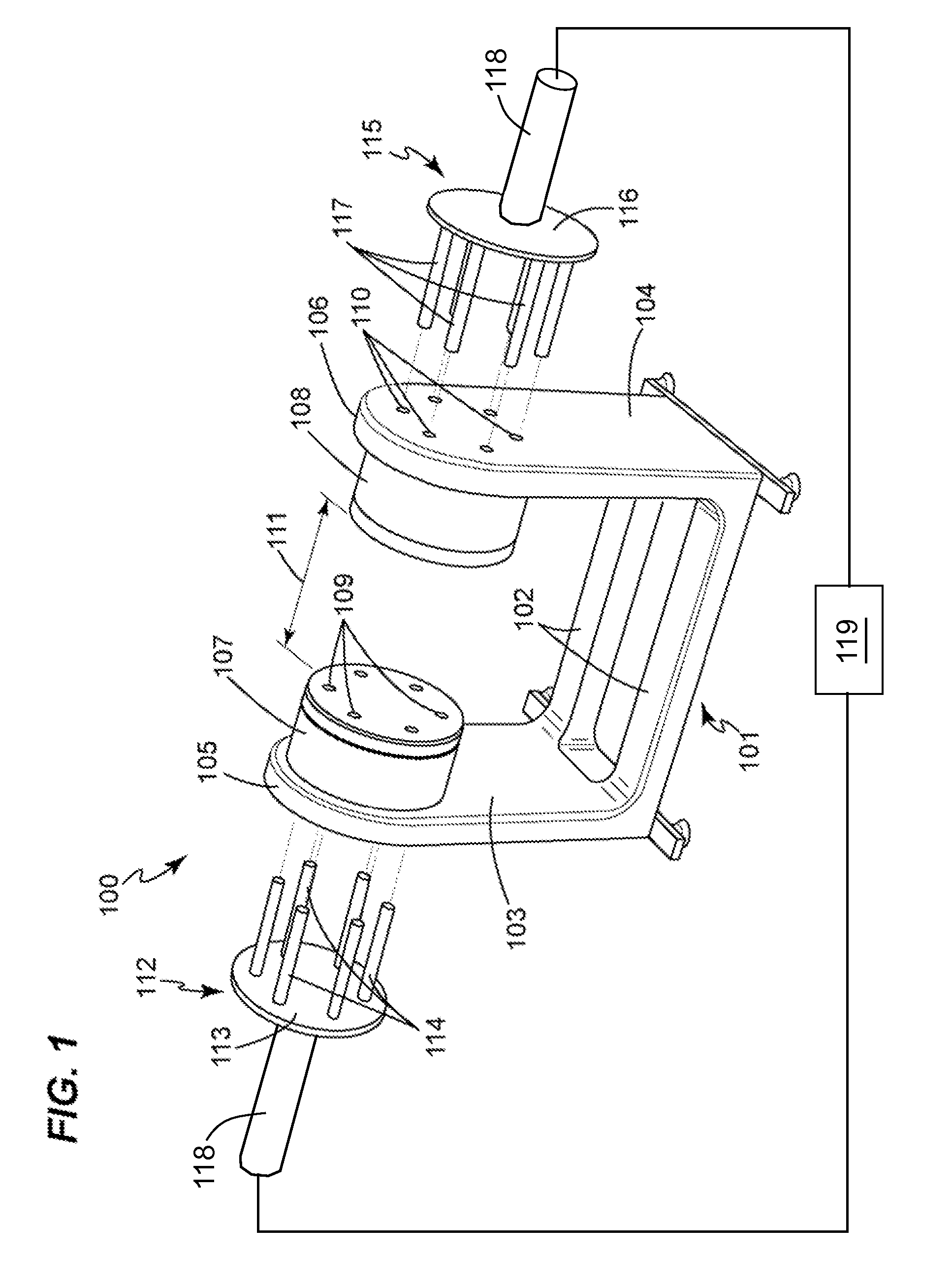
Apparatus and method for magnetic resonance measurements in an interior volume
InactiveUS6940378B2Desirable measurement flexibilityDesirable flexibilityPermanent magnetsMagnetic materialsResonance measurementMagnetization
A magnet assembly and a magnetic field configuration are disclosed for the generation of a magnetic field in a defined volume, with the field being homogeneous over a pre-determined portion of the volume and not homogeneous over the rest. The disclosed magnetic assembly has a plurality of spaced-apart magnets arranged in pairs. The magnets of each pair are be positioned diametrically opposite each other with respect to an enclosed volume. In different embodiments magnets may all be arranged such that their magnetization directions are substantially aligned, or could alternatively be arranged to have magnetizations pointing in different directions. The angular spacing between the magnets is selected in the range of approximately 13°-17° and could be as large as the size of the magnets. The assembly generates a homogeneous magnetic field within an inner portion of the defined volume, and a second magnetic field, substantially different from the homogeneous magnetic field throughout the remainder, i.e., in the periphery of the defined volume.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Self-fastening cage surrounding a magnetic resonance device and methods thereof
ActiveUS7400147B2High strengthPrevent leakageMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementHomogeneous magnetic field
The present invention discloses a novel self-fastening cage of a magnetic resonance device (MRD) (100) for providing a homogeneous, stable and uniform magnetic field therein, characterized by an outside shell comprising at least three flexi-jointed superimposed walls (1). In a technology of self-fastening cage, the invention teaches an effective multi-streamed MRD comprising a cage including a closed magnetic circuit constructed from strong permanent magnets; and an optional shimming mechanism selected from an array of active shim coils, passive shimming elements or any combination thereof; a contained cavity within which the magnetic field strength is approximately uniform; and a means, such as a plurality of conveyor belts, pipes or any other transportation means by which a plurality of samples are introduced into the region of uniform magnetic field; such that magnetic resonance measurements are made on a plurality of samples within the region of uniform magnetic field. The invention depicts a cost effective method for obtaining a self-fastening cage of a MRD (100) characterized by an outside shell comprising superimposing at least three flexi-jointed walls (1) so that a homogeneous, stable and uniform magnetic field is provided therein.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
High pressure/high temperature magnetic resonance tool
InactiveUS7683613B2Easy to useMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMaterial analysis by using resonanceResonance measurementHigh pressure
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus Having a Combined Magnetic Resonance Apparatus and Radiation Therapy Apparatus
InactiveUS20110196226A1High quality imagingUnwanted interferenceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonance measurementParticle beam
An apparatus having a combined magnetic resonance apparatus is proposed. The magnetic resonance apparatus features at least one main magnet for generating a main magnetic field in an examination space for a magnetic resonance measurement, and a radiation therapy apparatus, which is provided to generate a particle beam and which features a beam guide. The magnetic resonance apparatus features an essentially magnetic-field-free region and the beam guide for the particle beam runs along the essentially magnetic-field-free region.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
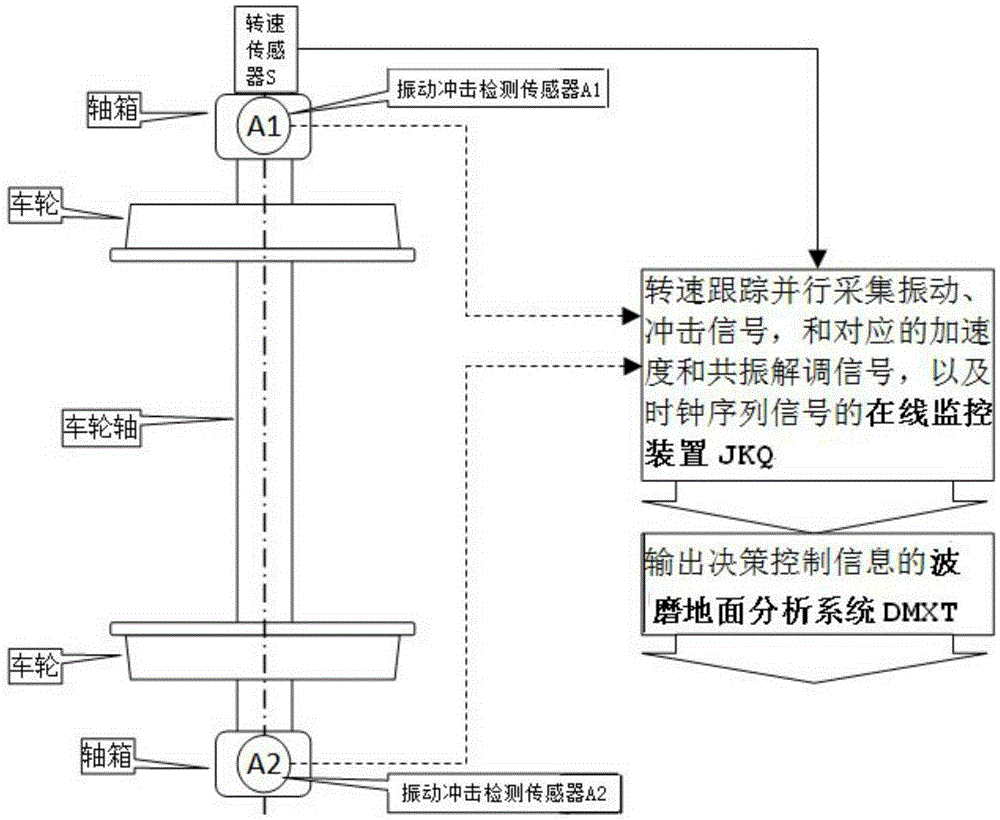
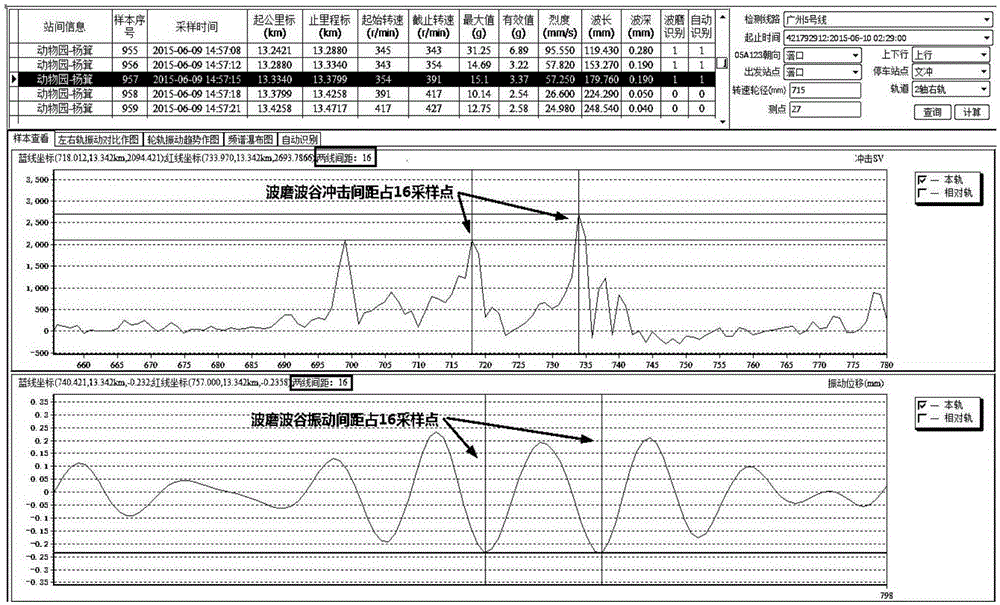
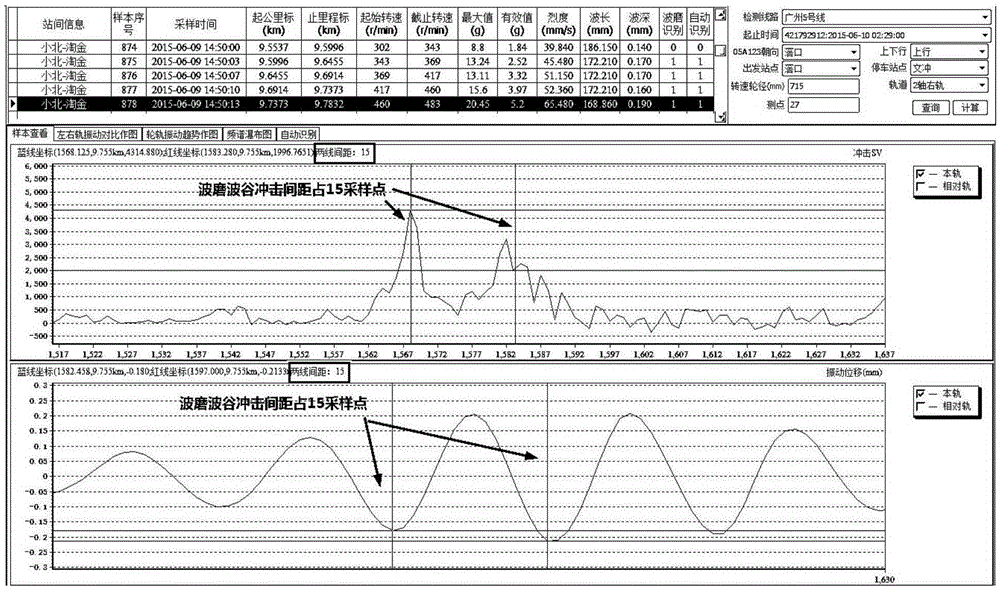
Method for measuring track corrugation by utilizing axle box vibration and impact information
ActiveCN105292177ANo need for night workReduce manual workloadRailway auxillary equipmentRailway profile gaugesResonance measurementEngineering
The invention provides a method for measuring track corrugation by utilizing axle box vibration and impact information. A vibration and impact information acquisition device contains a rotating speed sensor S arranged on a wheel set shaft of an operating vehicle, a vibration and impact detection sensor A1 and a vibration and impact detection sensor A2 which are arranged on an axle box bearing block at the two ends of a wheel set, an online monitoring device JKQ and a corrugation ground analysis system DMXT, wherein the rotating speed sensor S, the vibration and impact detection sensor A1 and the vibration and impact detection sensor A2 are connected with the online monitoring device JKQ, and detection, acquisition, diagnosis, analysis and decision of vehicular corrugation information of the operating vehicle are realized by virtue of the online monitoring device JKQ or by downloading data of the online monitoring device JKQ to the corrugation ground analysis system DMXT. The method for measuring the track corrugation by utilizing the axle box vibration and impact information has the advantages that the axle box vibration and impact information of the operating vehicle are acquired, based on a generalized resonance measurement principle, vehicular real-time track corrugation wave length and wave depth measurement and analysis or track corrugation wave length and wave depth measurement and analysis after downloading is completed are realized, and the manual workload is greatly reduced.
Owner:TANGZHI SCI & TECH HUNAN DEV CO LTD
Method and magnetic resonance system for adjustment of the field strength of RF pulses
InactiveUS20070145975A1Equal weightMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSpatially resolvedResonance measurement
In a method for adjustment of the field strength of radio-frequency pulses as well as a magnetic resonance measurement system, radio-frequency pulses are emitted by a radio-frequency antenna of a magnetic resonance measurement system in a magnetic resonance measurement A test volume slice is initially excited by emission of radio-frequency pulses with a defined pulse amplitude by the appertaining radio-frequency antenna and one-dimensional, spatially-resolved characteristic values are determined along an extent direction of the test volume slice. The one-dimensional, spatially-resolved characteristic values respectively represent a local field strength of the B1 field in strips of the test volume slice running perpendicular to the extent direction. An average value of the determined characteristic values is then formed over at least over one determined segment along the extent direction of the test volume slice. A pulse amplitude of the radio-frequency pulses that is to be set for the magnetic resonance measurement to be implemented is determined on the basis of the average value.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
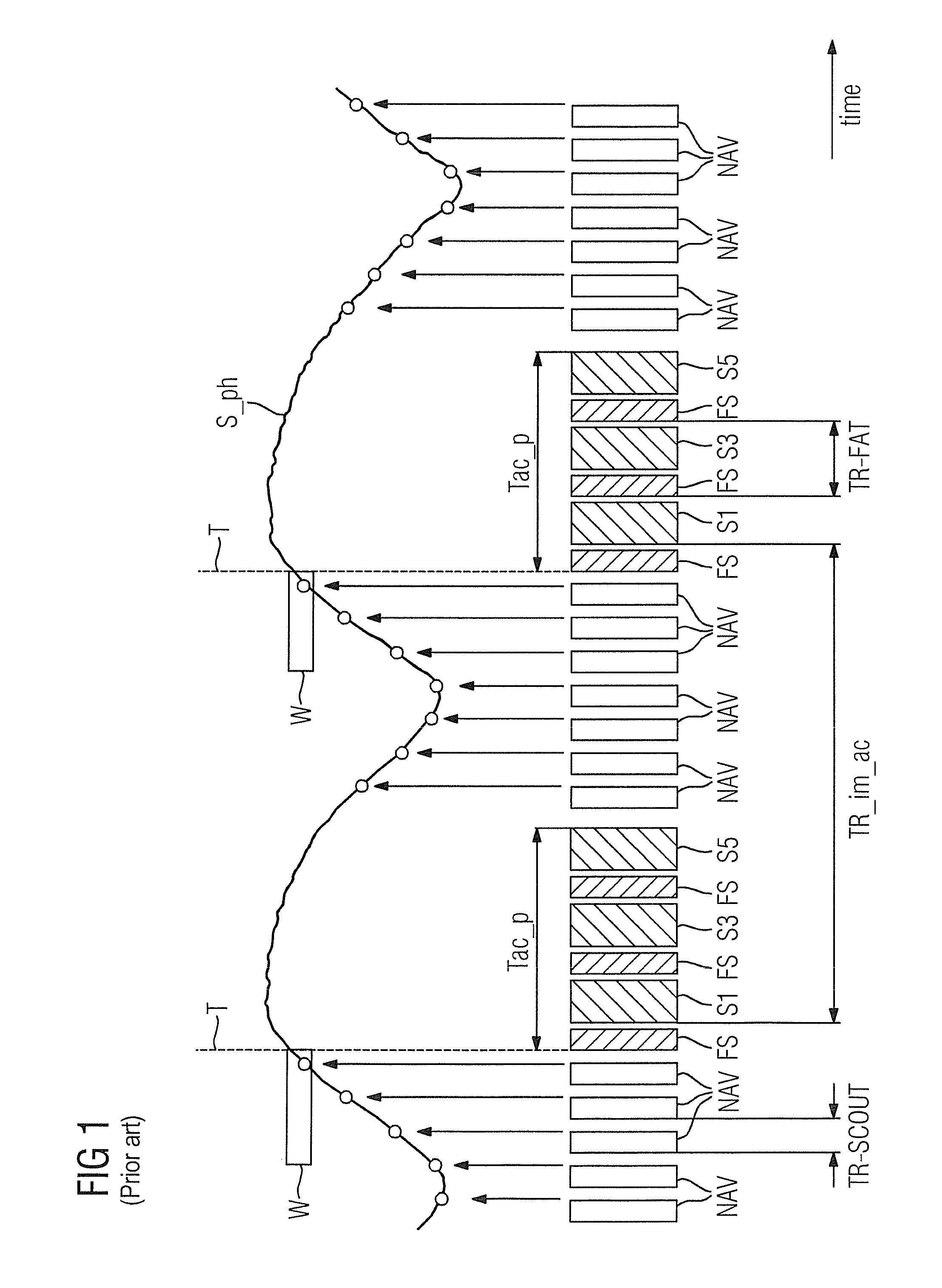
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for triggered acquisition of magnetic resonance measurement data
ActiveUS20120271155A1Long durationHigh absorption rateMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonance measurementEngineering
In a magnetic resonance method and apparatus, a) data points of a physiological signal are detected, b) a trigger condition is evaluated depending on the detected physiological data points, c) a preparation module is executed to suppress unwanted signals in the time period in which the trigger condition has not yet been satisfied, d) after satisfying the trigger condition, an acquisition phase of predetermined duration is started, that includes at least two similar preparation modules to suppress unwanted signals and a respective following acquisition module to acquire measurement data, and e) after the acquisition phase, a) through d) are repeated until all desired measurement data have been acquired, with a time interval between two successive preparation modules being the same after a first execution of a preparation module in c) until the end of the acquisition phase in a subsequent d).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
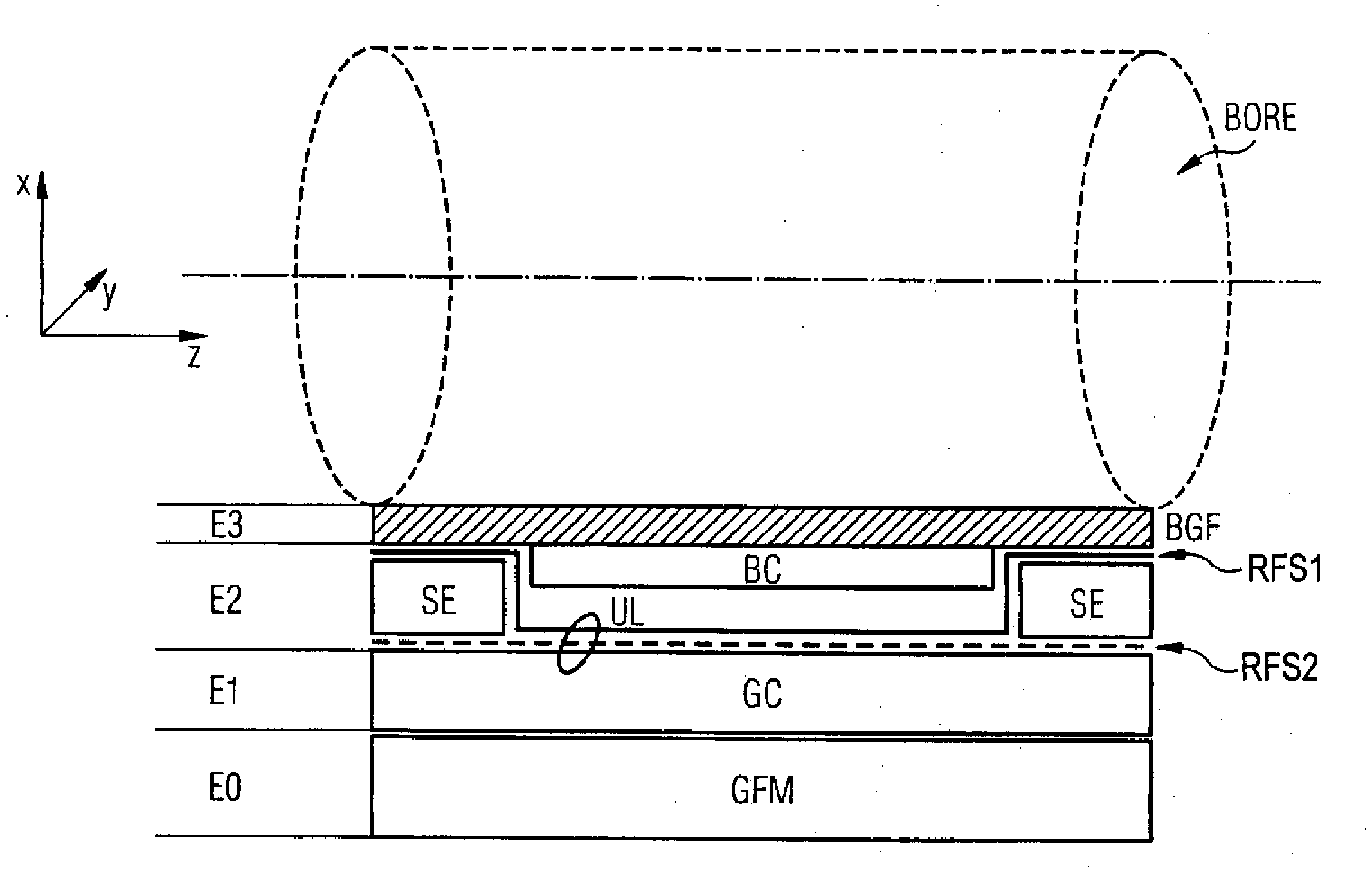
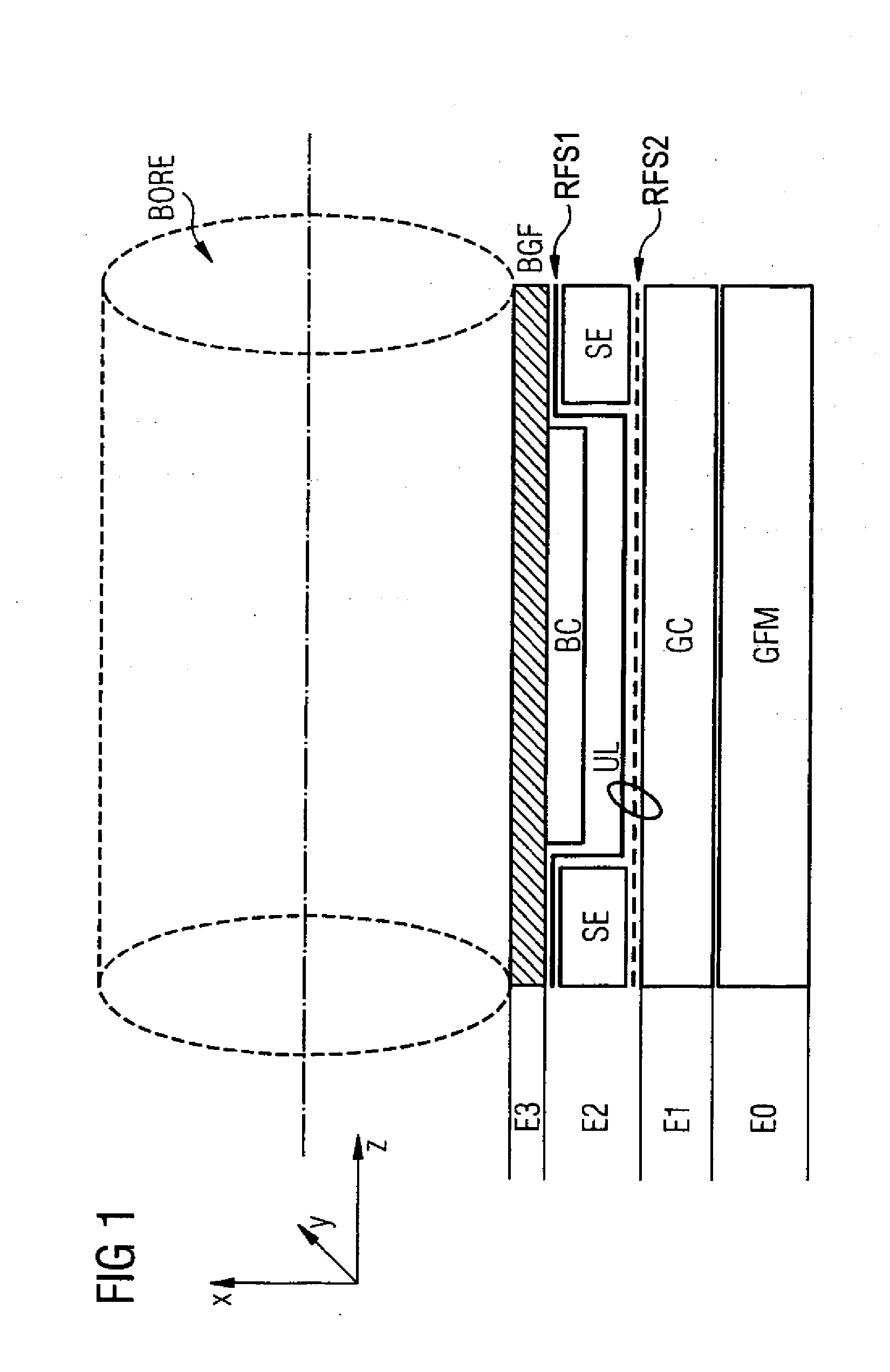
Magnetic resonance apparatus with shim arrangement
InactiveUS20090085567A1Reduced space requirementsLower the volumeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonance measurementAxis of symmetry
A magnetic resonance apparatus has an examination region to accommodate a patient to be examined, and a body coil that circumferentially encompasses the examination region and is designed for magnetic resonance examination of the patient. A gradient coil circumferentially encompasses the examination region and the body coil and is designed to detect the position of magnetic resonance measurement values. A basic field magnet is designed to form a basic magnetic field in the examination region for a patient examination to be conducted. The basic field magnet at least partially encompasses the examination region, the body coil and the gradient coil. A shim device is used that is designed to influence the basic magnetic field. Components of the shim device and components of the body coil are associated to exhibit a common distance relative to the longitudinal axis of symmetry of the examination region and thus encompass the examination region.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
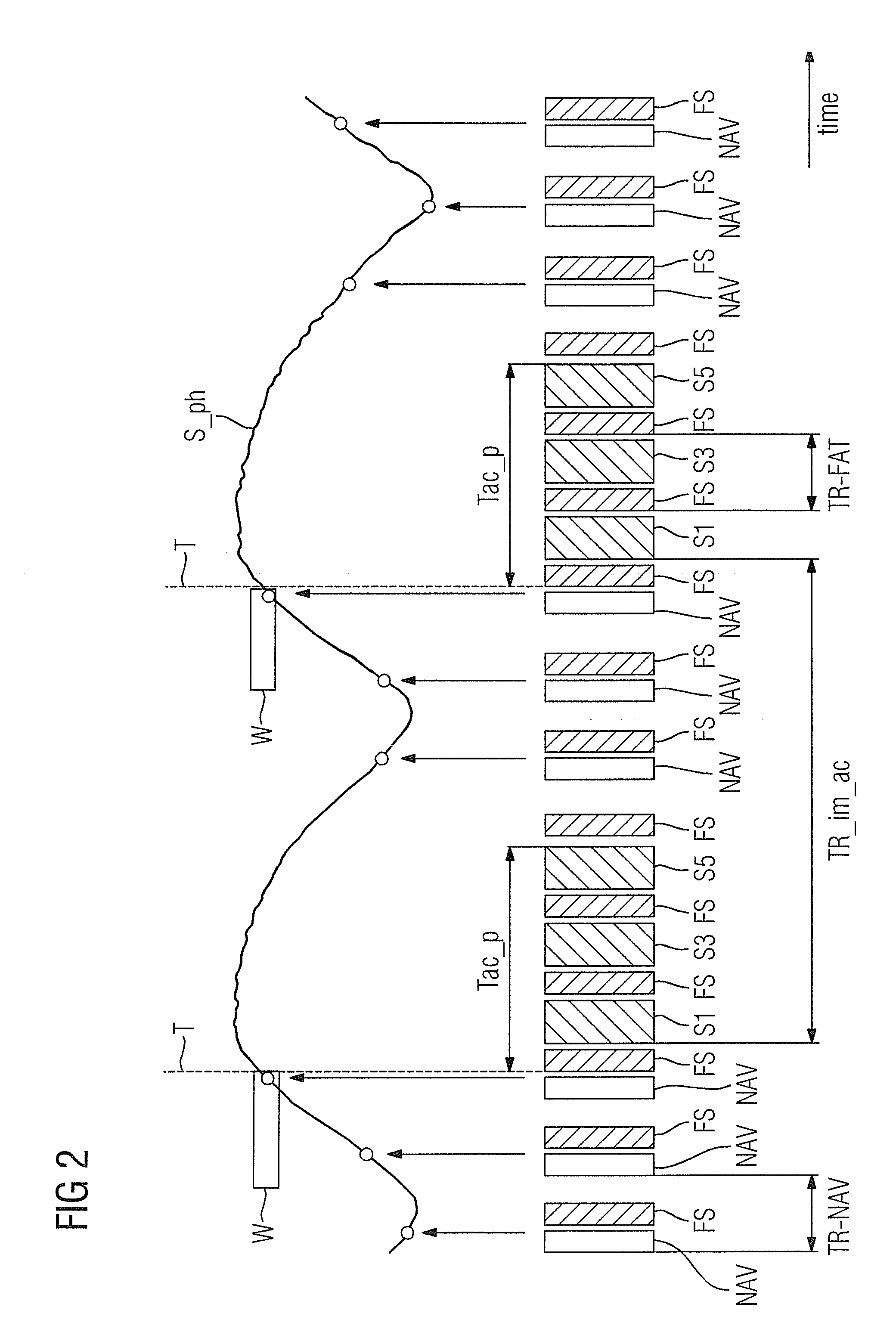
Method for quasi-continuous dynamic motion correction in magnetic resonance measurements
A method of MR imaging and spectroscopy to reduce artifacts occurring due to the motion of an object to be represented, wherein the object position is determined quasi-continuously during the runtime of the MR acquisition, which includes one or more partial acquisitions (TA), and wherein motion correction is performed, which comprises dynamic adaptation of the frequency and phase settings of the RF system of the tomograph and of the orientation and amplitudes of the gradients during the runtime of the MR acquisition according to the current object position. The motion correction is thereby applied during a signal weighting period, during a signal read-out period, or between and / or during the two stated periods and the adaptations for motion correction are performed without interrupting or slowing the temporal progression of the MR acquisition. In this way, artifacts due to motion of the object to be represented can be further reduced.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
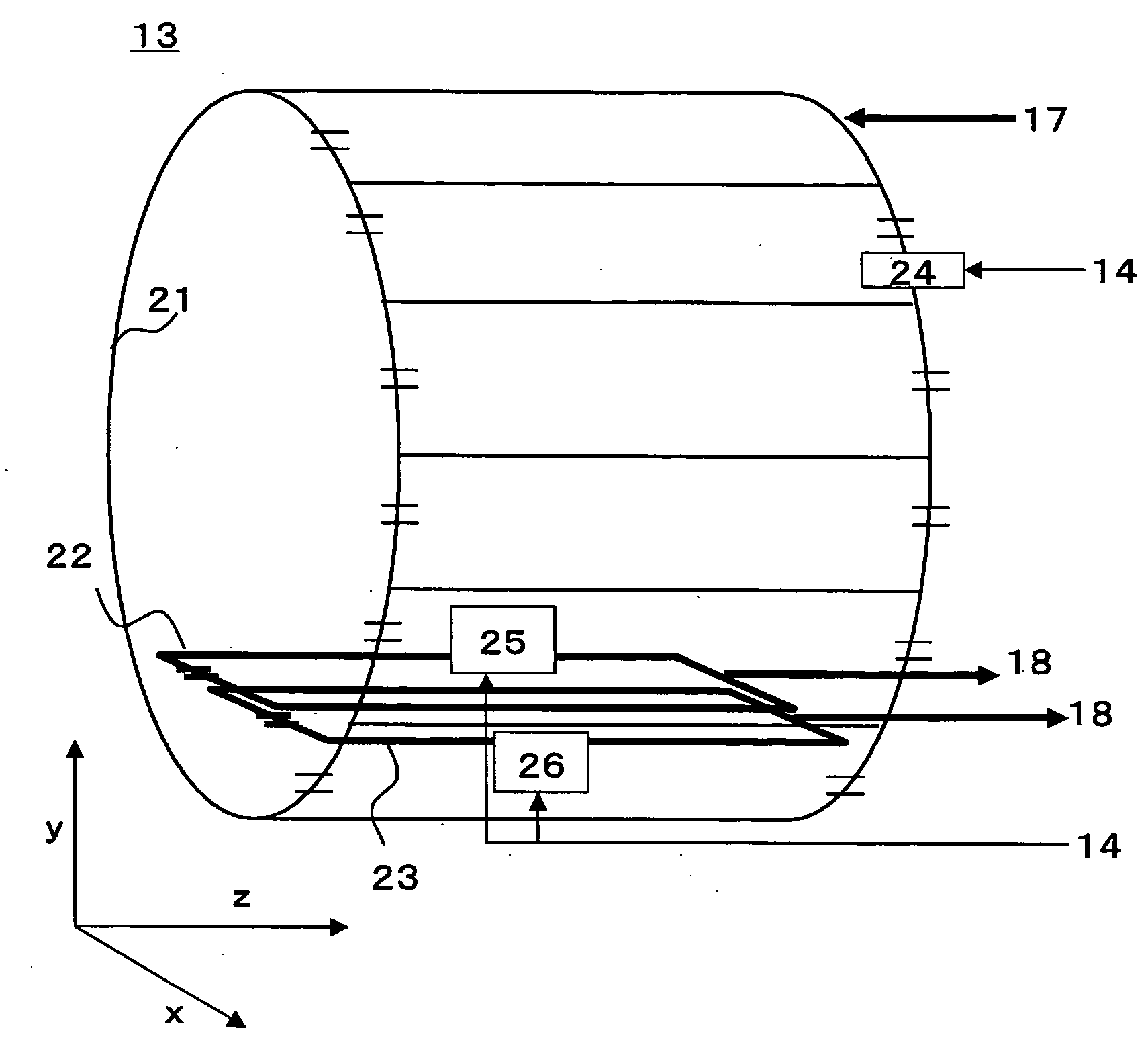
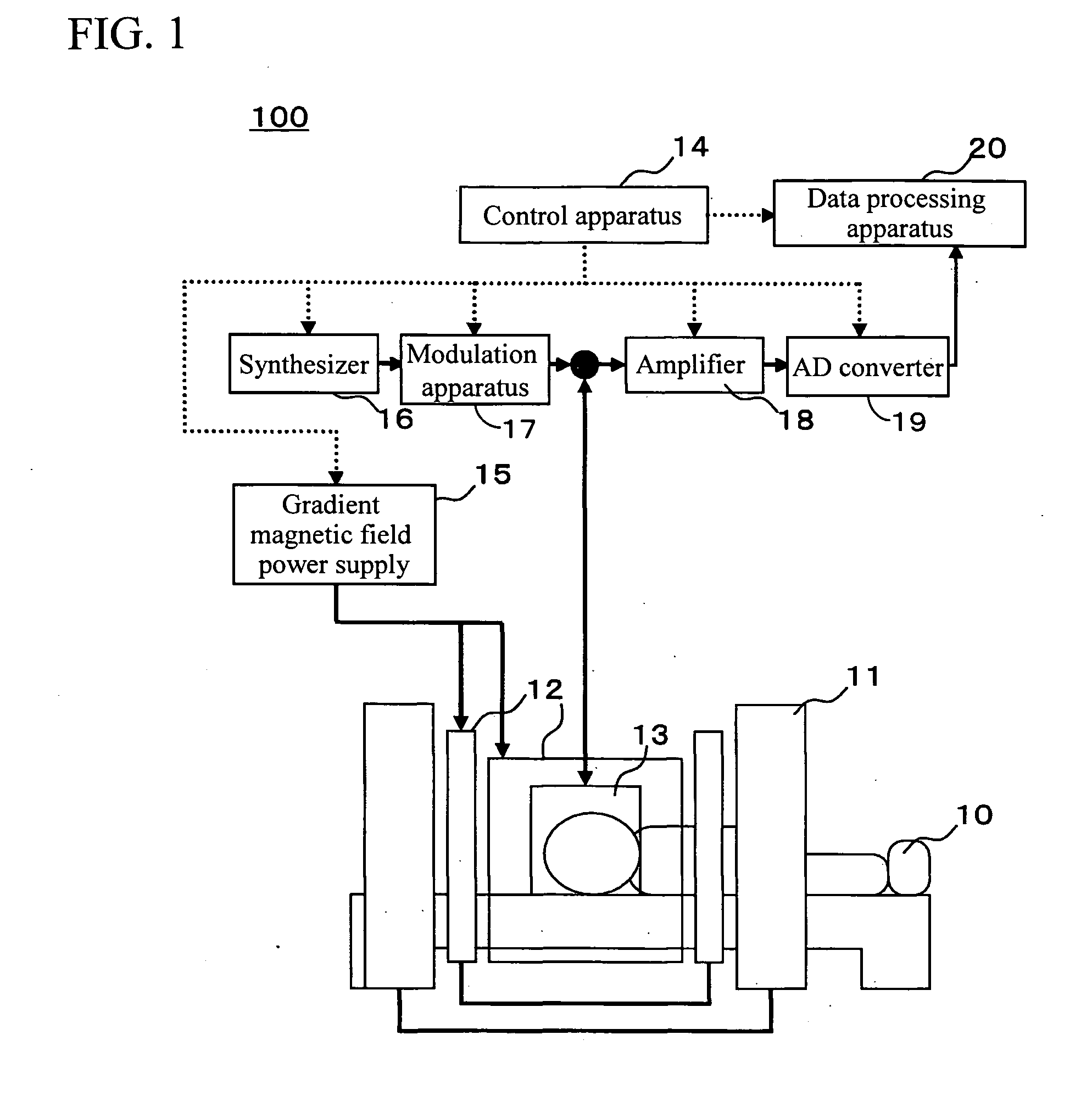
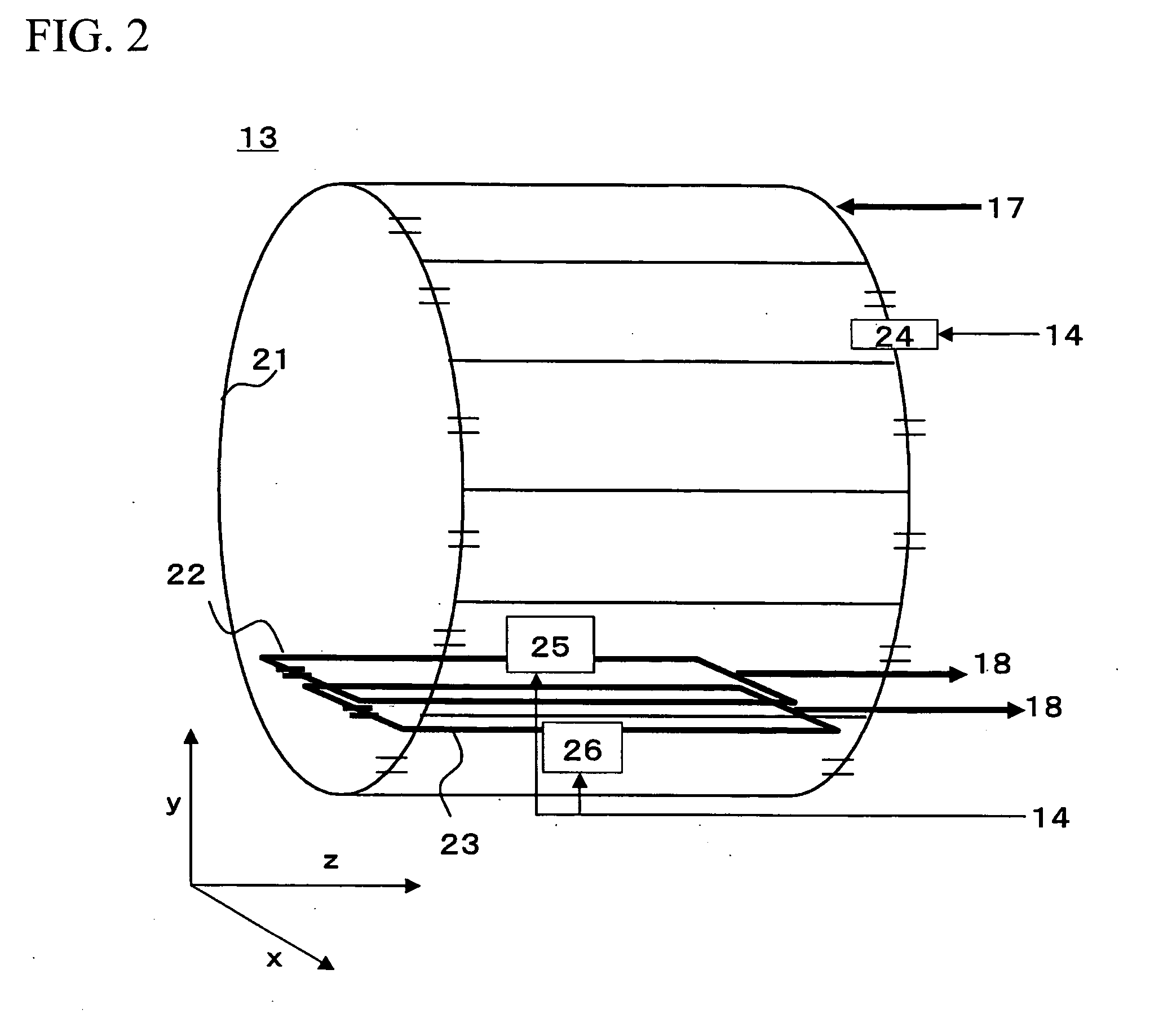
Magnetic resonance imaging system
InactiveUS20090085563A1Reduced measurement timeSuppress artifactsElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceResonance measurementBody movement
A magnetic resonance measurement technique is provided which shortens the measurement time while suppressing artifacts caused by body movement of a measuring object and enables high-speed imaging. An excitation pulse which excites a plurality of slice planes and an excitation pulse which excites slice planes perpendicular to the slice planes are applied and a plurality of substantially parallel linear crossing areas are simultaneously measured. Spatial information of a linear direction of the crossing areas is acquired by modulating a magnetic resonance signal from the crossing areas by a gradient magnetic field. A spatial information of a direction perpendicular to the linear direction is acquired by changing the position of the plane and an image is reconstructed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic resonance method using a phase-modulated pulse train with a constant small flip angle
InactiveUS20110241667A1Good signalReasonable ratioMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance measurementPulse sequence
A method for performing magnetic resonance measurements on a sample includes applying a first predetermined number of pulse trains for excitation, each pulse train having a constant amplitude and including a second predetermined number of pulses spaced by a predetermined time interval. The pulse trains are modulated by a bent function. After each pulse, data is sampled. Preferably a square number of pulses is generated being constant in power, and the Walsh transform of the sequence of their phases is constant in power, so that the power of the excitation in time and frequency domain is constant. The method can reduce power requirements and may permit undercutting specific absorption rate (SAR) limits due to the small excitation power necessary to create time signals with reasonable signal to noise ratio.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIV +1
Hydrocarbon polluted shallow groundwater magnetic resonance detection device and hydrocarbon polluted shallow groundwater magnetic resonance detection method
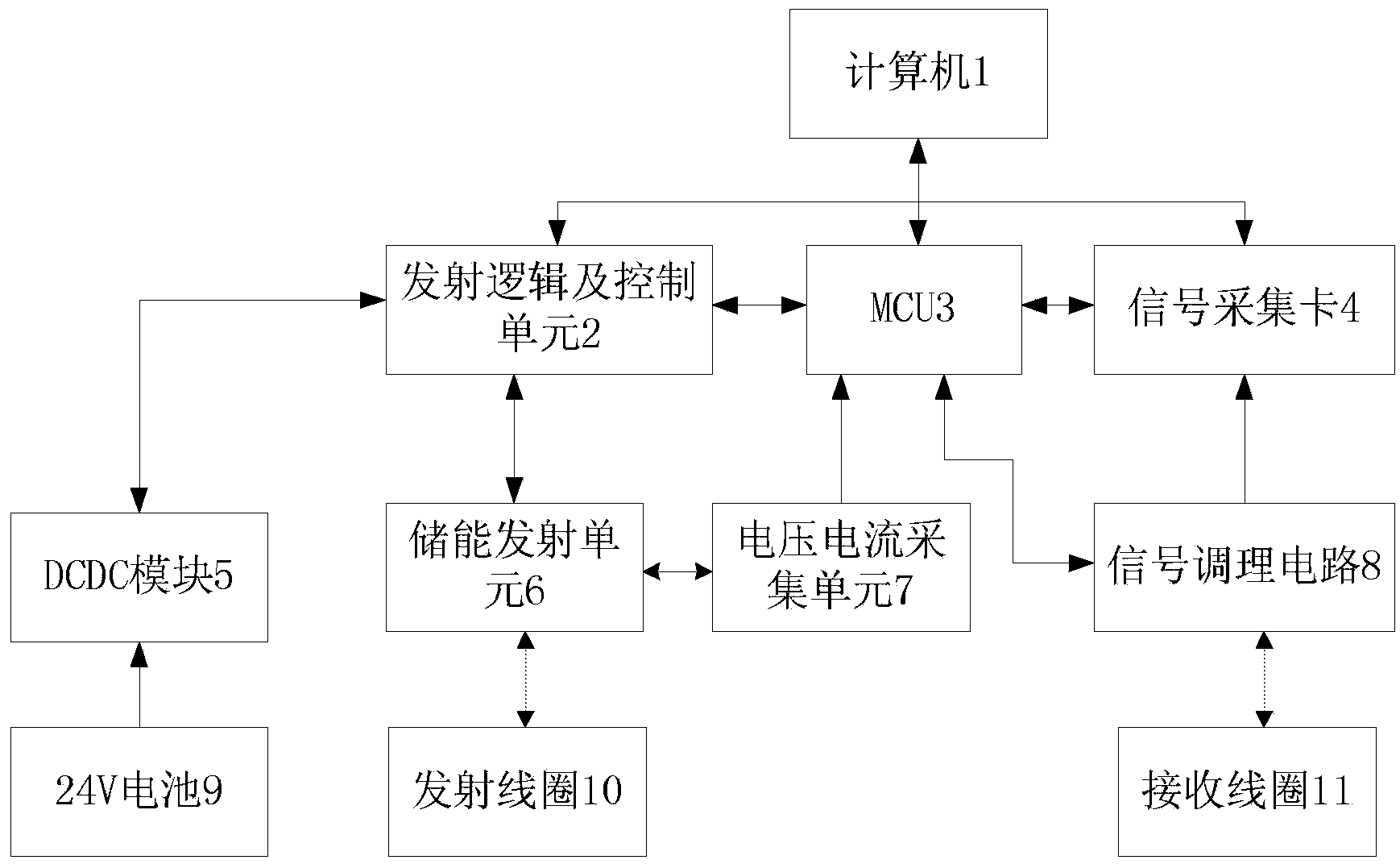
ActiveCN103852794AHigh strengthOvercome the shortcomings of inaccurate results caused by unevennessAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance measurementElectric power
The invention relates to a hydrocarbon polluted shallow groundwater magnetic resonance detection device and a hydrocarbon polluted shallow groundwater magnetic resonance detection method. According to the detection device, a computer is respectively connected with a transmission logic and control unit, an MCU (Microprogrammed Control Unit) and a signal acquisition card; a 24V battery is connected with a signal regulation circuit by virtue of a DCDC (Direct Current Direct Current) module, a transmission logic and control unit, the MCU and the signal acquisition card; an energy storage transmission unit is connected with the transmission logic and control unit; the energy storage transmission unit is connected with the signal regulation circuit by virtue of a voltage-current acquisition unit 7 and the MCU. By adopting the detection device, non-intrusive quantitative qualitative measurement is achieved, and testing result can be rapidly obtained on site. The intensity of a local magnetic field is improved by virtue of a permanent magnet, magnetic resonance measurement can be carried out at places with intensive electric power interference, the signal to noise ratio can be effectively improved, the constraint that the magnetic resonance exploration cannot be carried out because of intensive electric power interference is broken, and the defect that the result is not correct because of nonuniform magnetic field can be effectively overcome by use of spin echo pulse. Hydrocarbon pollution within 5m underground can be rapidly and accurately detected.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for controlling an RF transmission device, and MR apparatus and RF device for implementing the method
ActiveUS20060197528A1Prevents RF powerAvoid powerElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceResonance measurementTomography
In a method for controlling a radio-frequency device, and a magnetic resonance tomography system and a radio-frequency control device wherein the method is implemented, the RF device of a magnetic resonance tomography system is emitted during a magnetic resonance measurement of an examination subject that is moving relative to the transmission field of the RF device. The RF device emits RF pulses at chronological intervals, and measurement values are measured at chronological intervals. At chronological intervals, position values are determined that represent a current position of the examination subject relative to the transmission field. On the basis of the measurement values and the position values, exposure values are determined that represent a physiological degree of effectiveness that the RF pulses have on the subject exposed to the RF pulses. Based on a multiplicity of exposure values, exposure control values are respectively formed. The RF device is limited in its functioning if an exposure control value reaches or exceeds an exposure limit value.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for controlling t1 recovery process in magnetic resonance measurements
InactiveUS20100090693A1Quickly restores longitudinal magnetizationLimited durationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementTemporal resolution
Radiation damping (RD) is employed to hasten the recovery of longitudinal magnetization after RF excitation and signal readout in a magnetic resonance measurement cycle. A switch driven by the pulse sequence that performs the measurement cycle energizes a feedback RF coil driven by an amplified and phase shifted portion of the received MR signal. The recovery of longitudinal magnetization is thus under direct control of the MR system and enables the reduction of the otherwise inefficient waiting times that are required for natural T1 recovery of the excited spin magnetization. This enables shortened acquisition times, improved sensitivity, better spatial and temporal resolution, and reduction of motion artifacts that result from long acquisition times.
Owner:WALD LAWRENCE L +2
Method and magnetic resonance system for homogenizing the B1 field
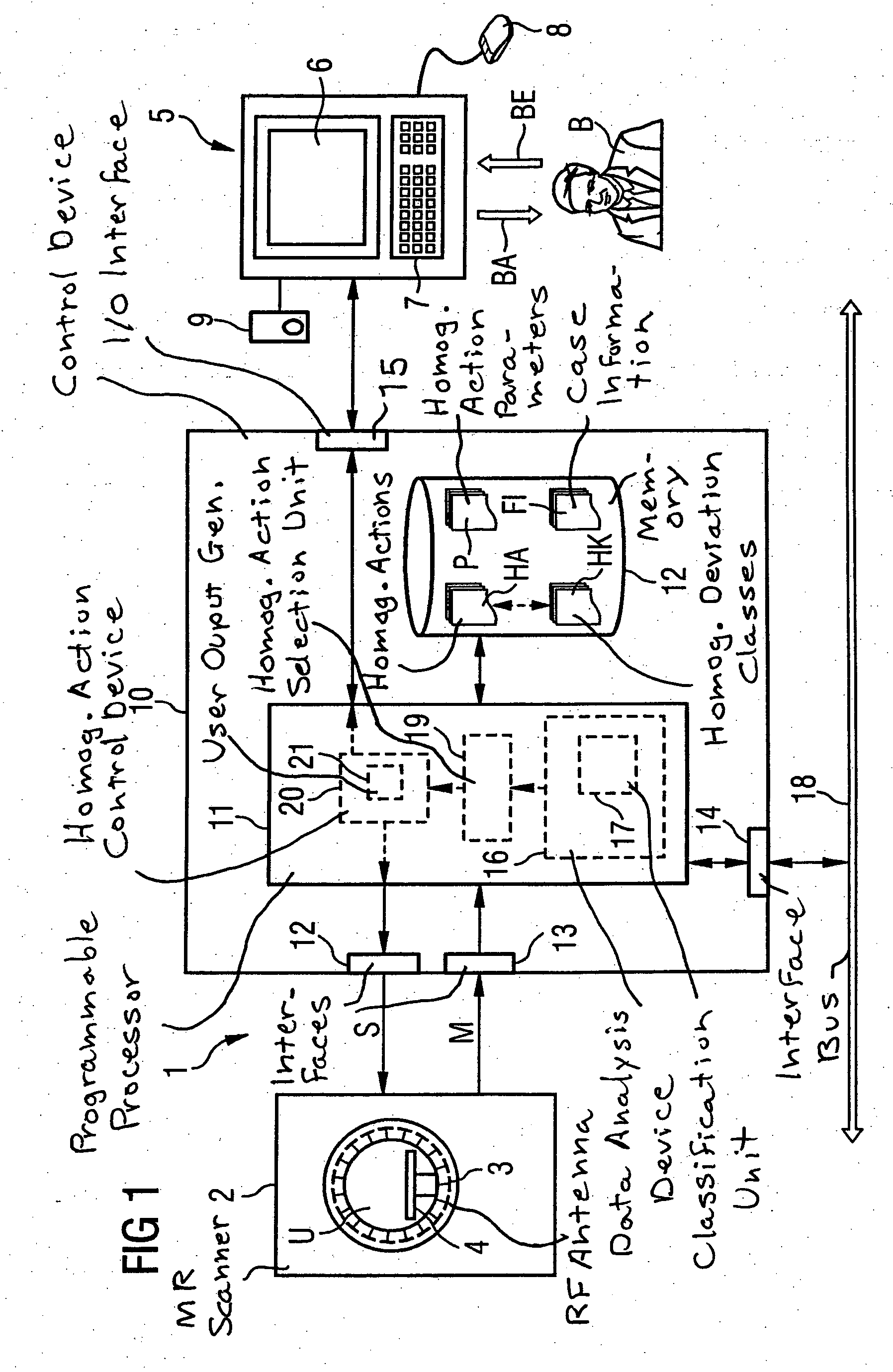
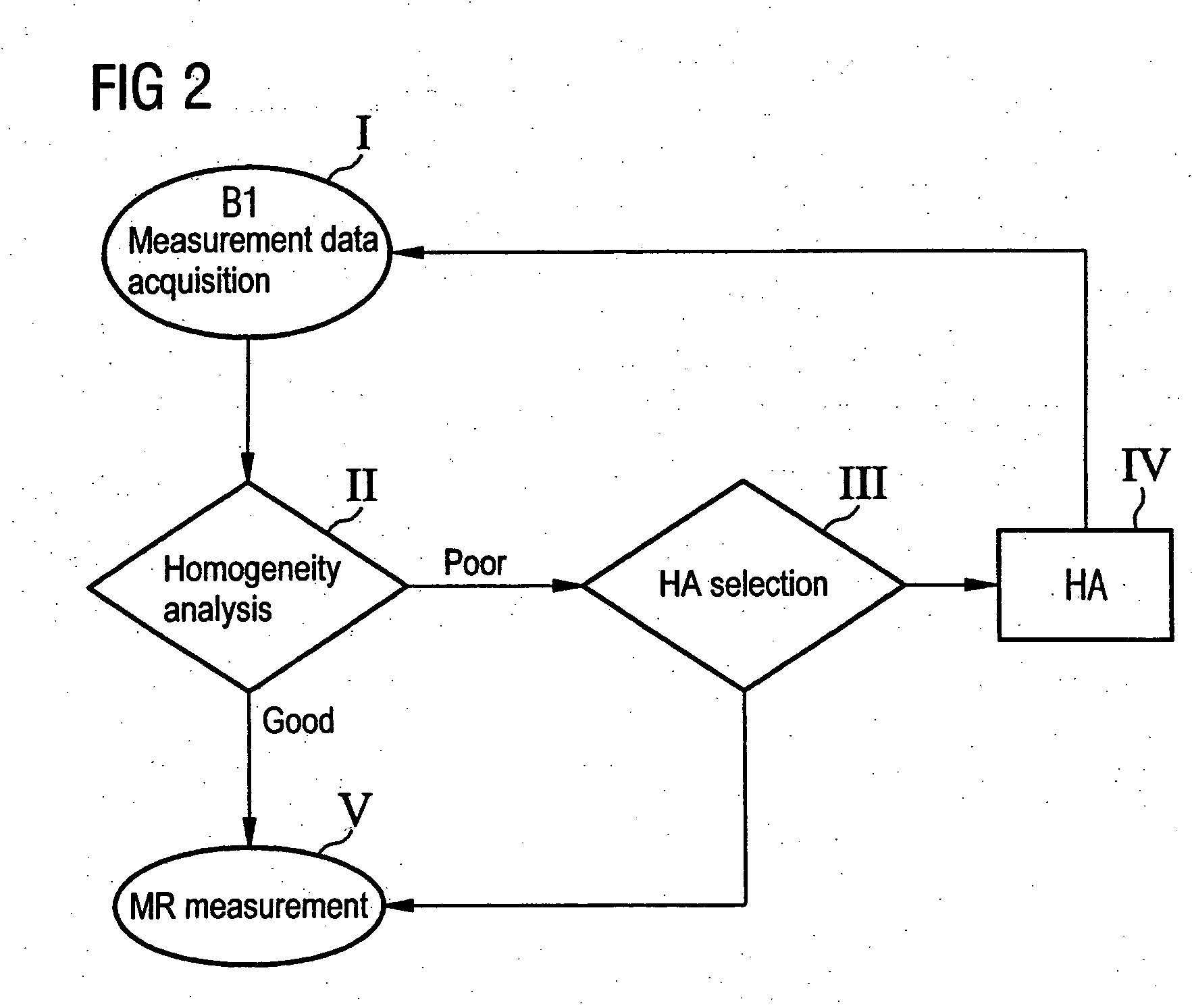
ActiveUS20050231203A1Promote homogenizationQuick searchElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceResonance measurementData acquisition
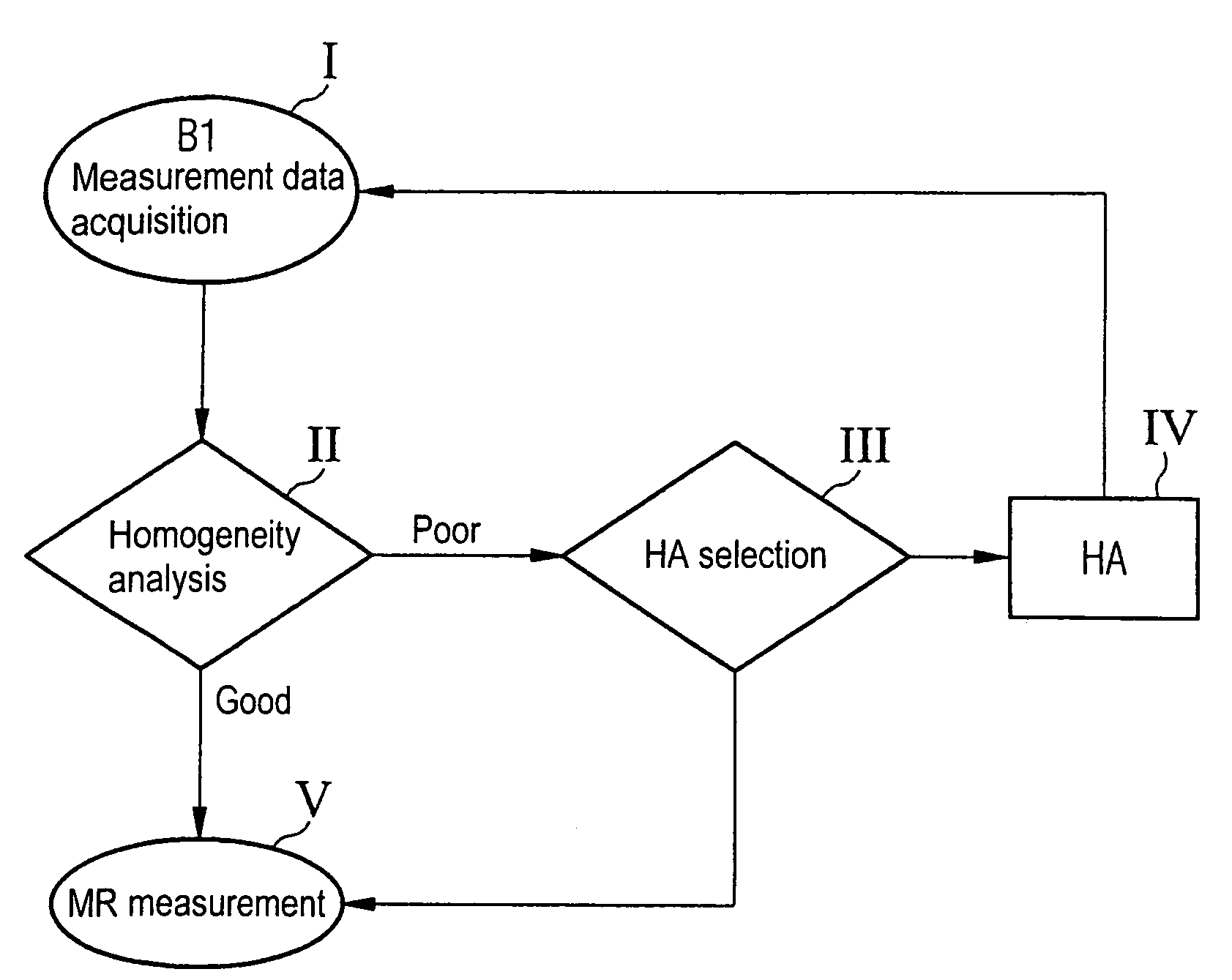
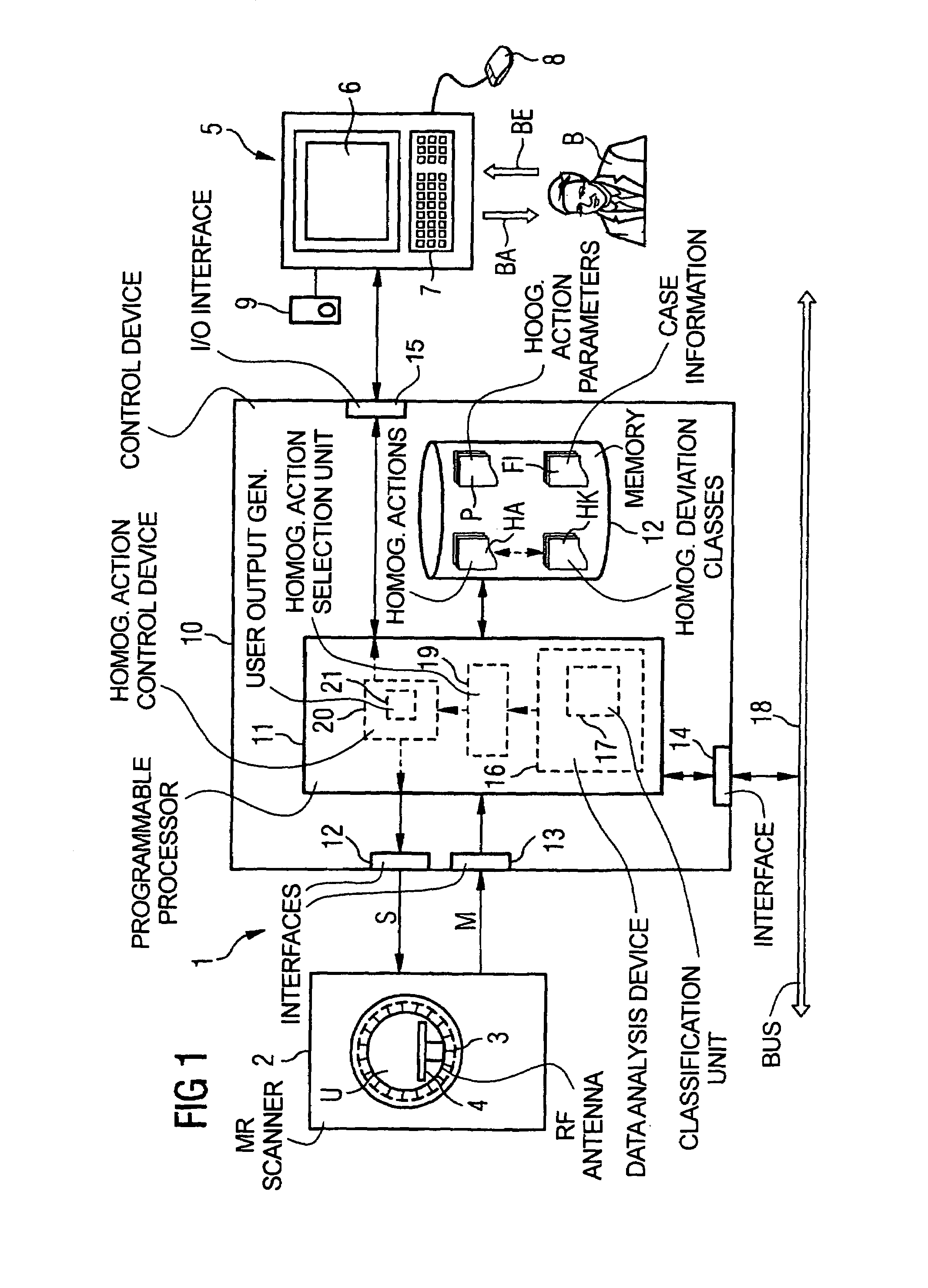
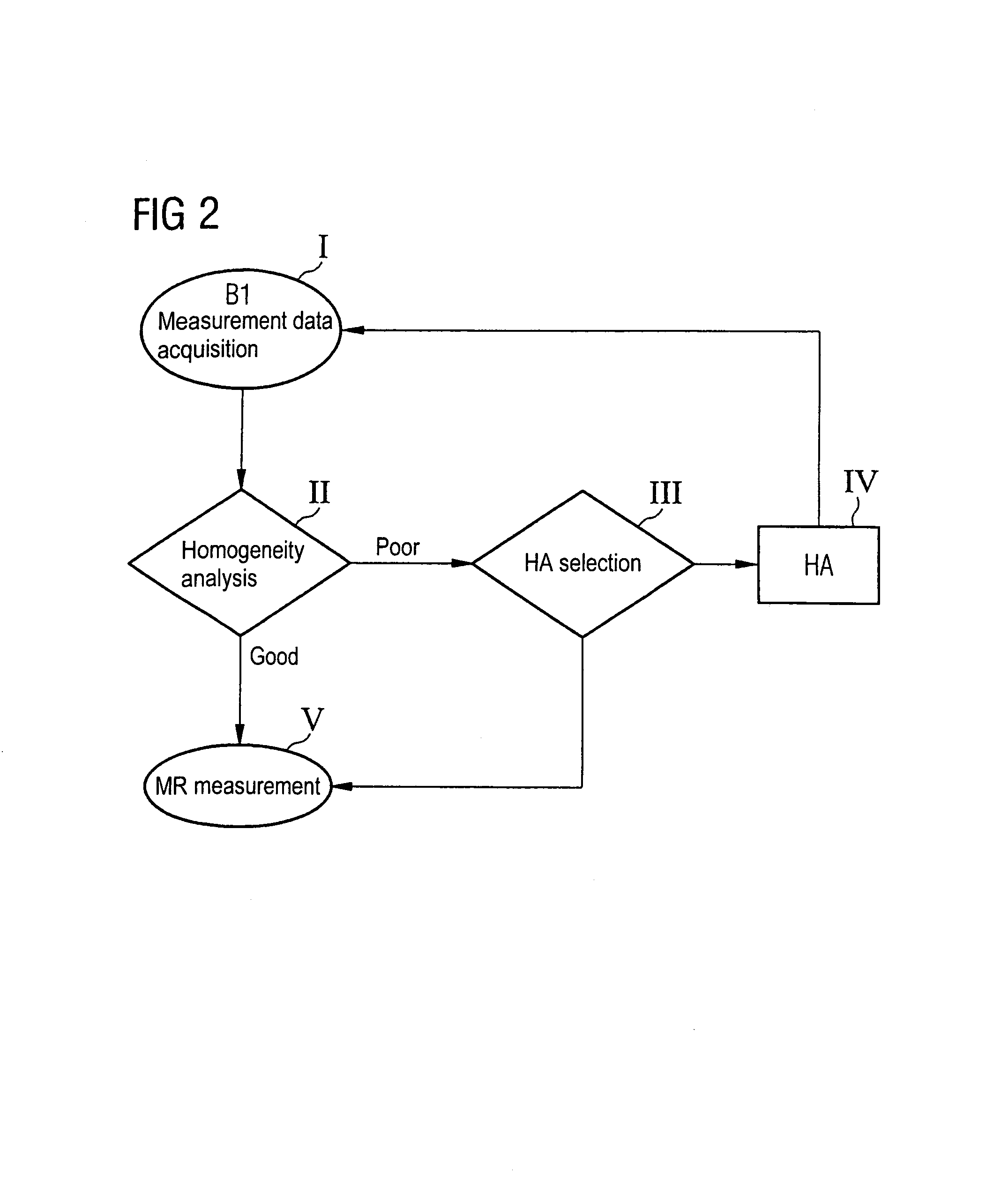
In a method and magnetic resonance system for homogenization of the B1 field for a magnetic resonance data acquisition with a number of iteration steps. An iteration step includes the following sub-steps: Measurement data are acquired that represent a B1 field distribution in at least one part of the examination volume of the magnetic resonance system. A B1 homogeneity analysis based on the acquired measurement data is automatically implemented. A specific homogenization action is automatically selected from among a number of possible homogenization actions based on the B1 homogeneity analysis, or the iterative homogenization method is ended if the diagnosed homogeneity is sufficient for an intended magnetic resonance measurement. The selected homogenization action is implemented.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and magnetic resonance system for determining the flip angle distribution in a volume of an examination subject
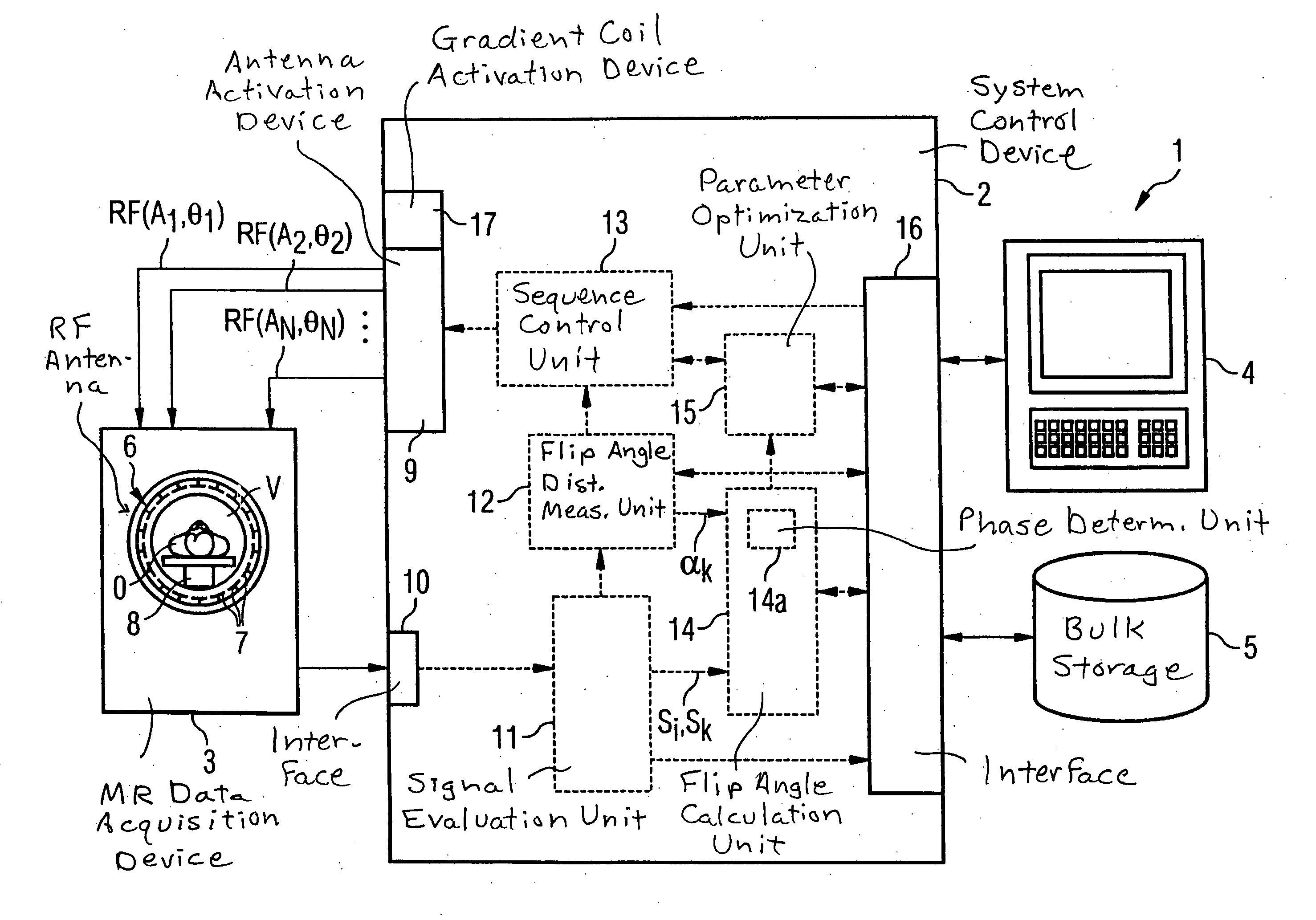
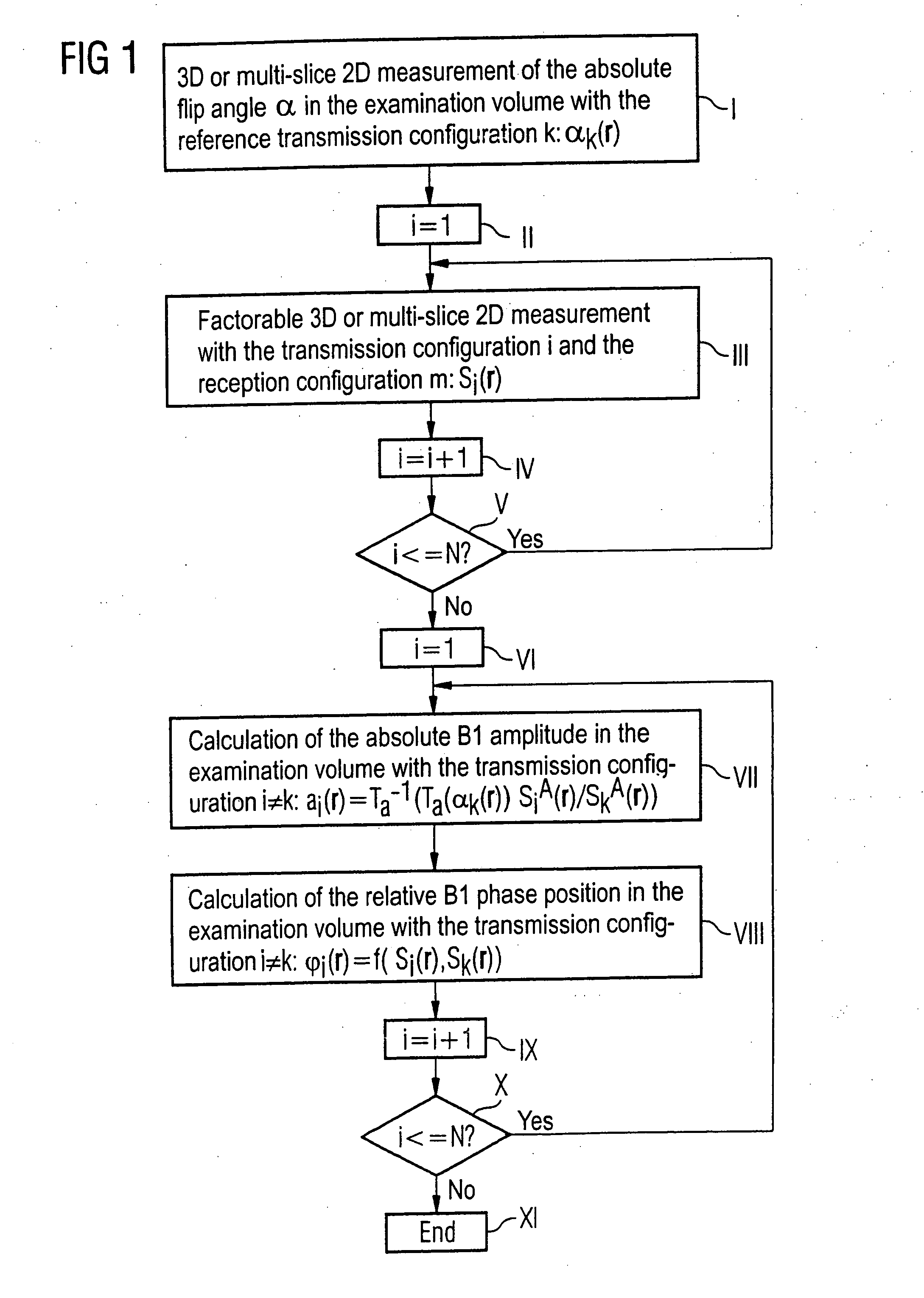
InactiveUS20070085537A1Quick fixSimple methodMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementSpatial correlation
In a method for determination of flip angle distributions for various antenna transmission configurations in a magnetic resonance system, magnetic resonance measurements are implemented with the various transmission configurations, with the reception configuration being identical for all implemented magnetic resonance measurements, and all magnetic resonance measurements for the various transmission configurations are implemented with a specific pulse sequence. This pulse sequence is selected such that the total function that describes the dependency of the image signal at a specific location on the flip angle achieved at this location with the radiated radio-frequency field, as well as on further MR-relevant parameters, can be factored into a first sub-function that describes the dependency of the image signal on the achieved flip angle and a second sub-function (Tb) that describes the dependency of the image signal on the further MR-relevant parameters, and such that the functional dependency of the image signal on the achieved flip angle is known. The absolute flip angle distribution is measured for a reference transmission configuration, and the flip angle distributions of the other transmission configurations are then respectively determined on the basis of the absolute flip angle distribution of the reference transmission configuration and on the basis of the ratio of the spatially-dependent image signals of the magnetic resonance measurements of the respective transmission configuration to the corresponding spatially-dependent image signals of the magnetic resonance measurement of the reference transmission configuration.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com