Patents
Literature
1032 results about "Force balance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
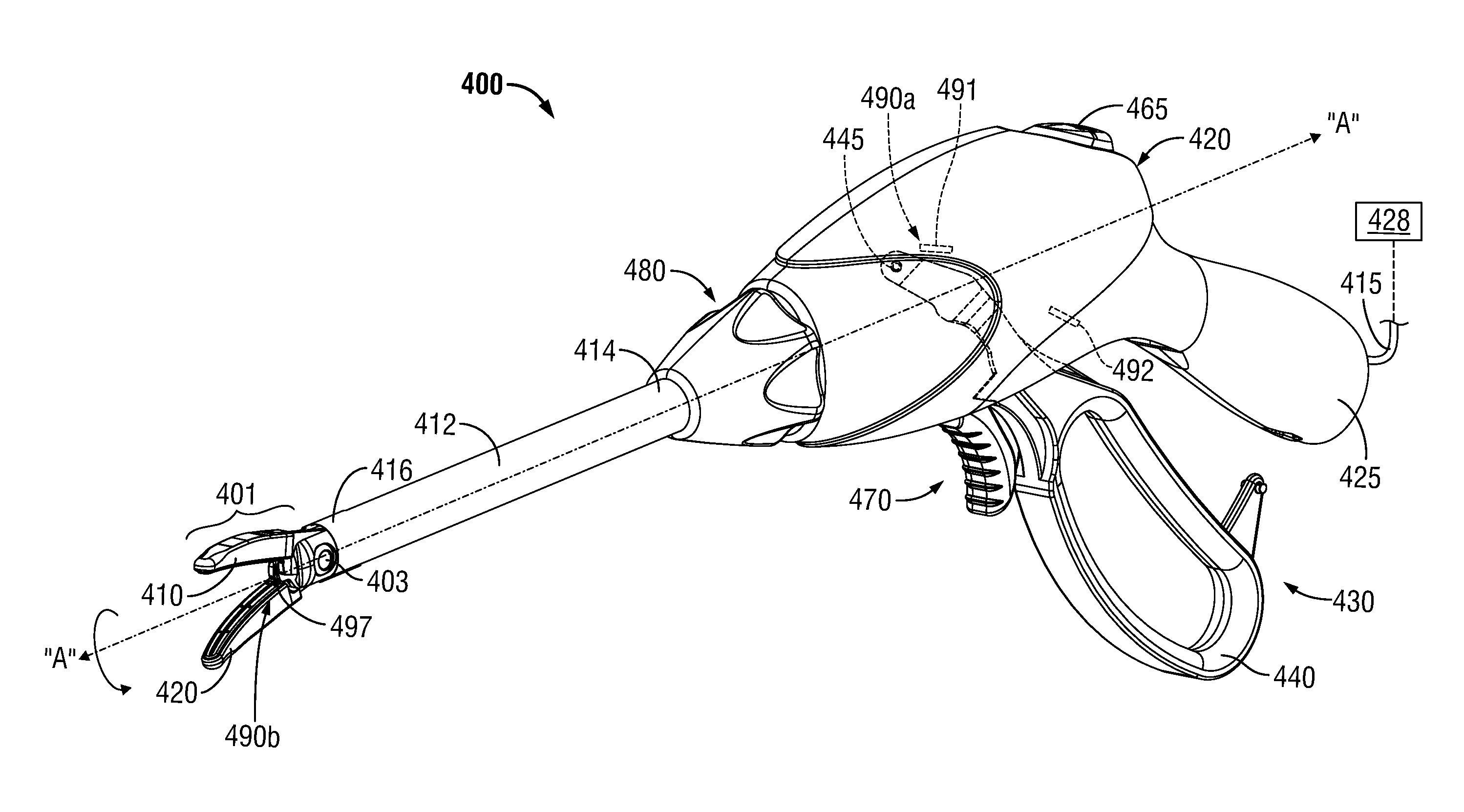
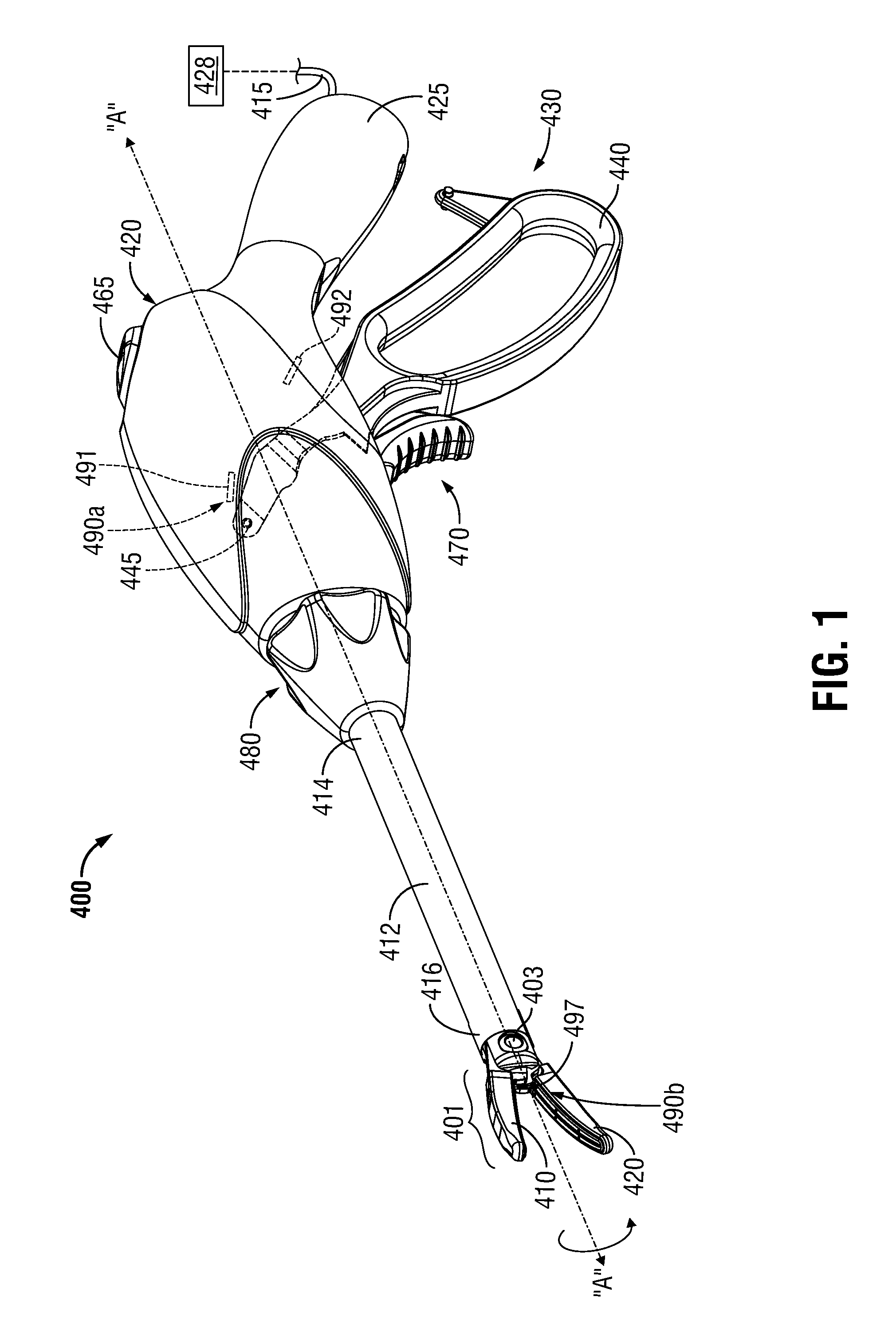
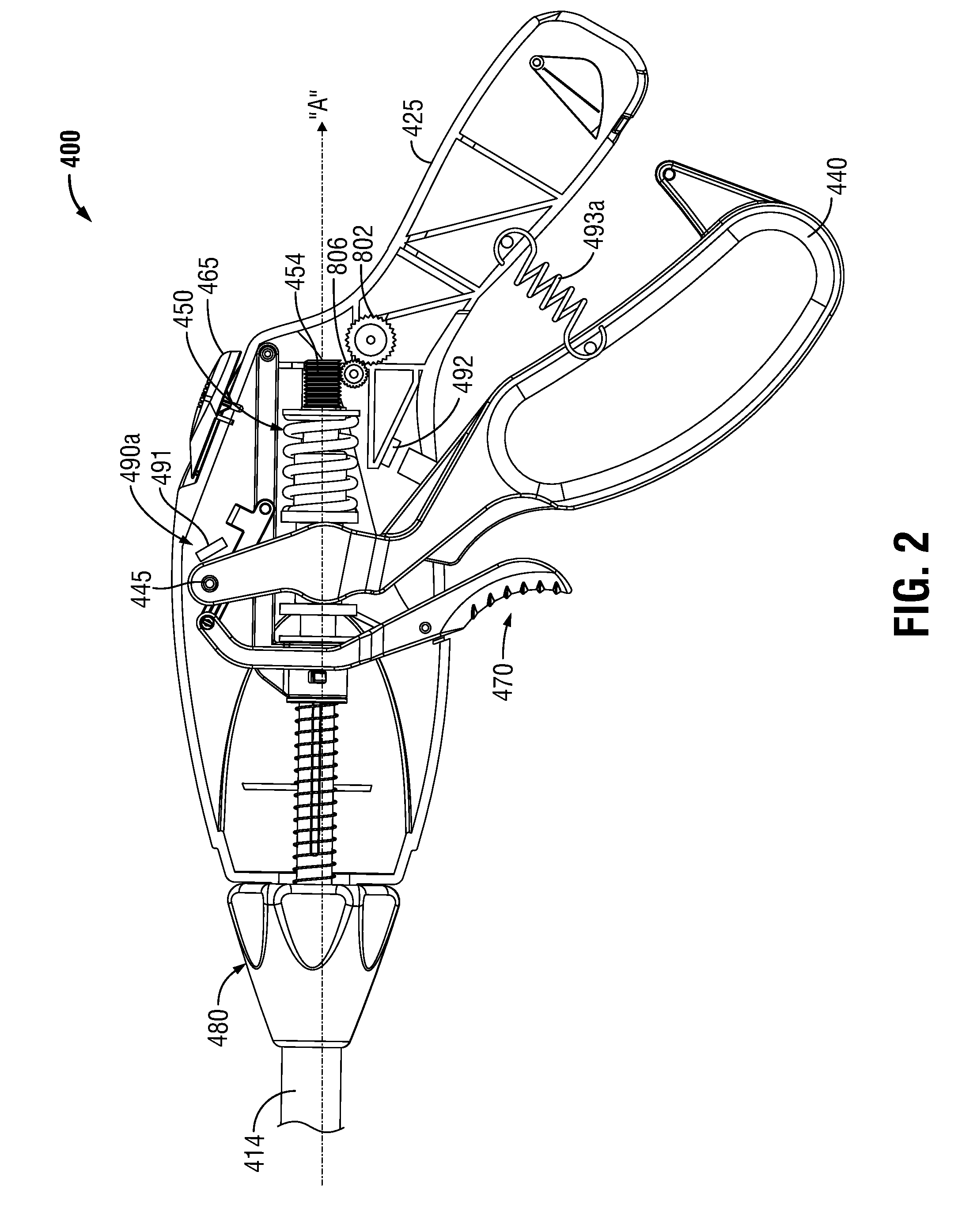
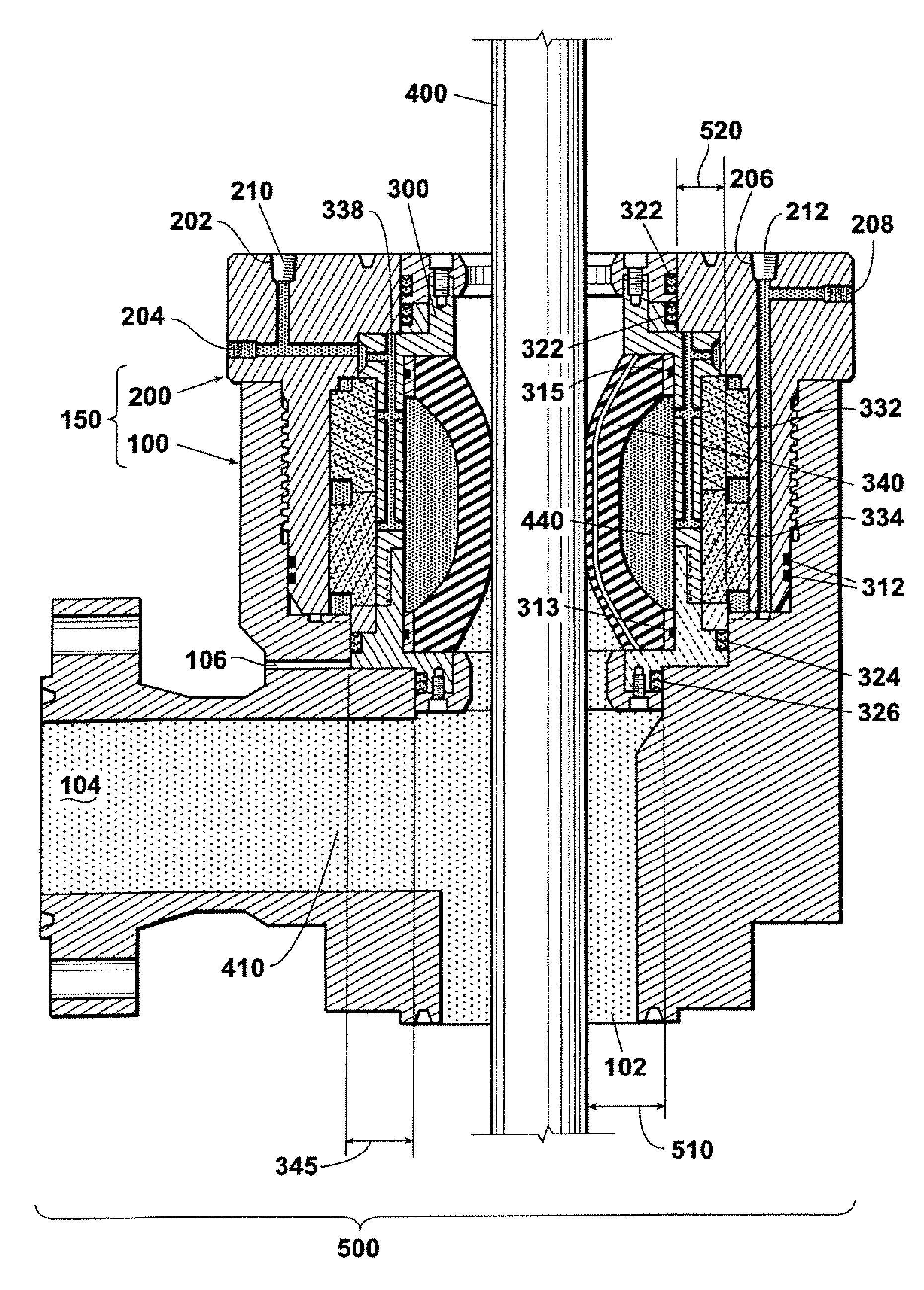
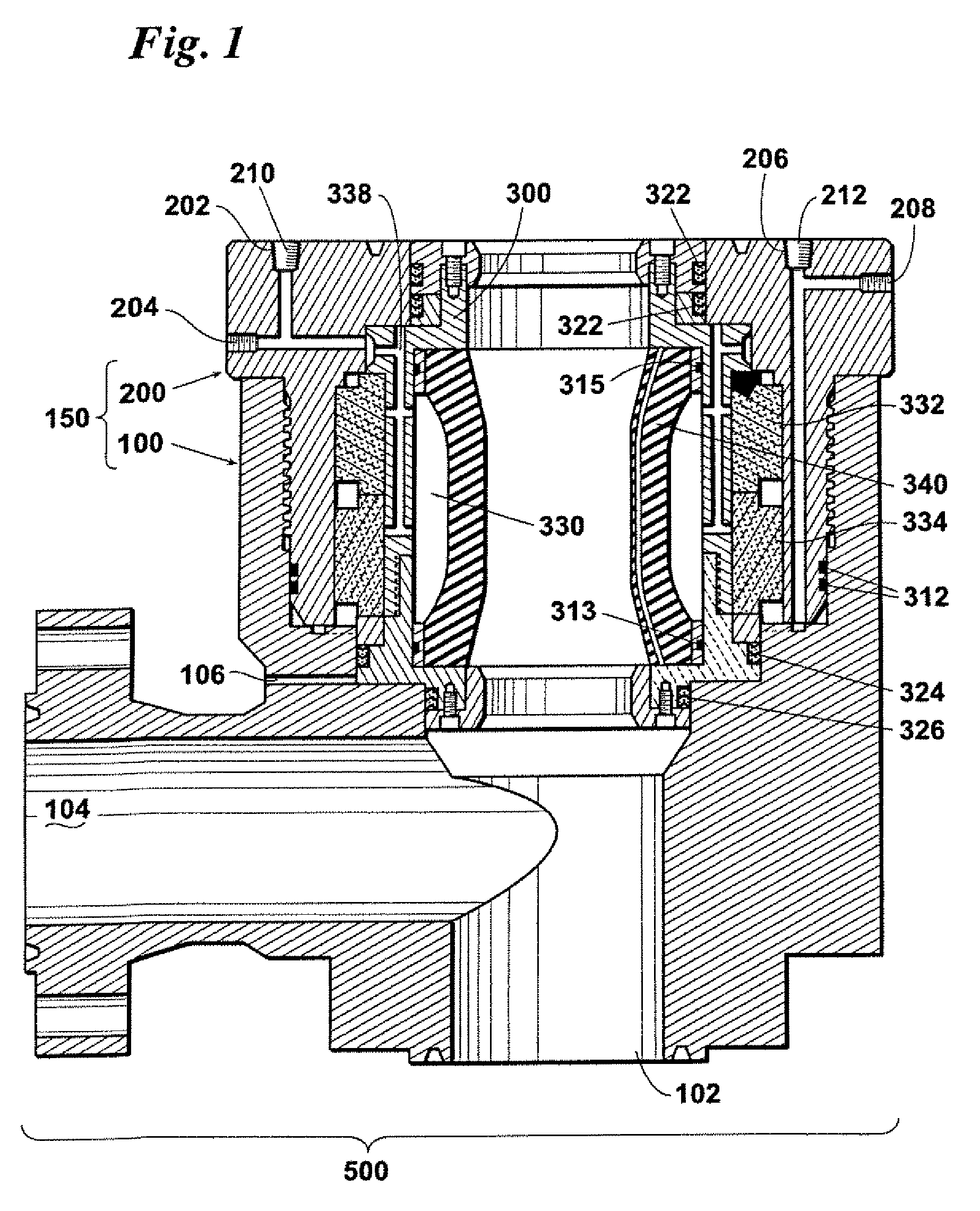
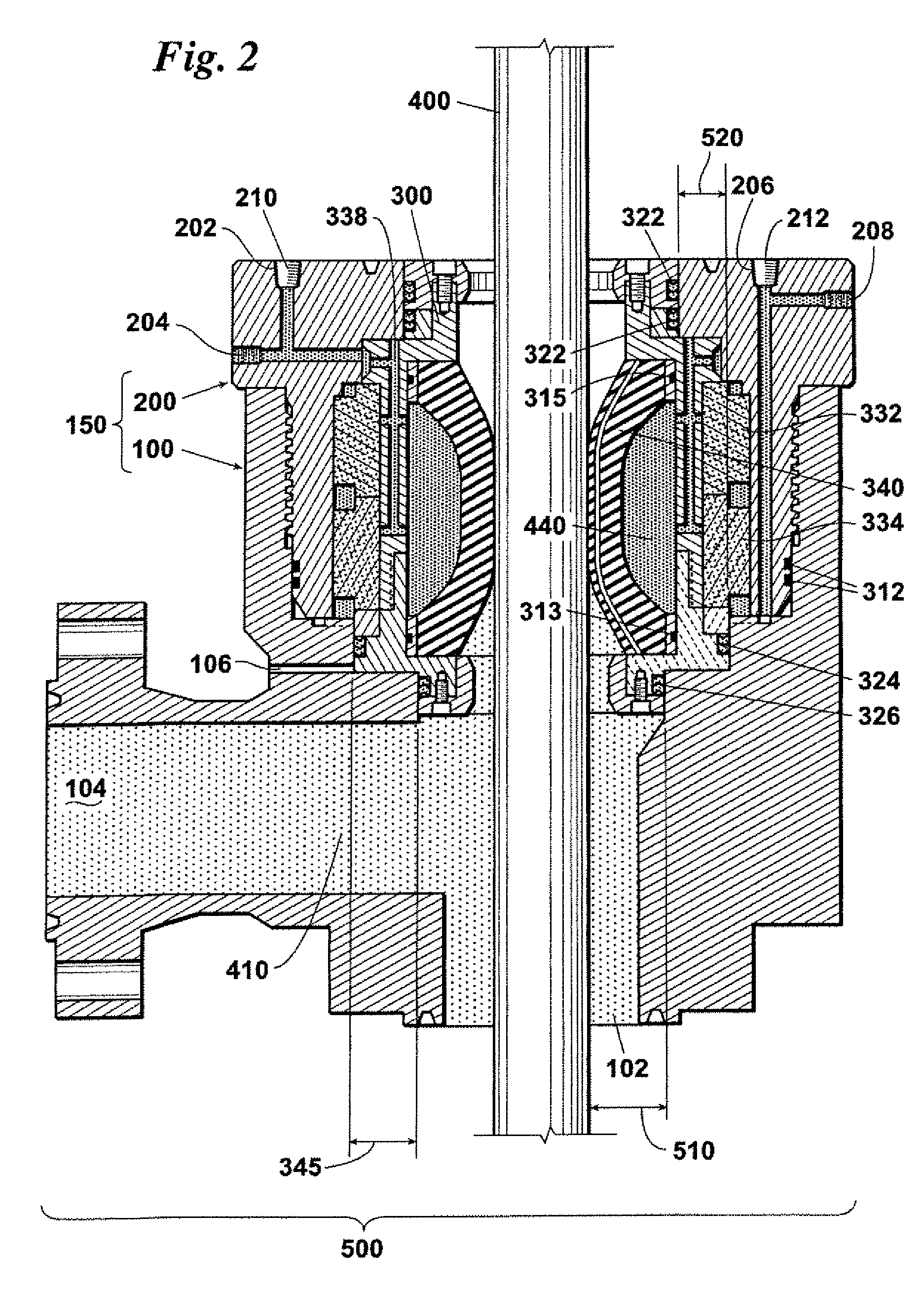
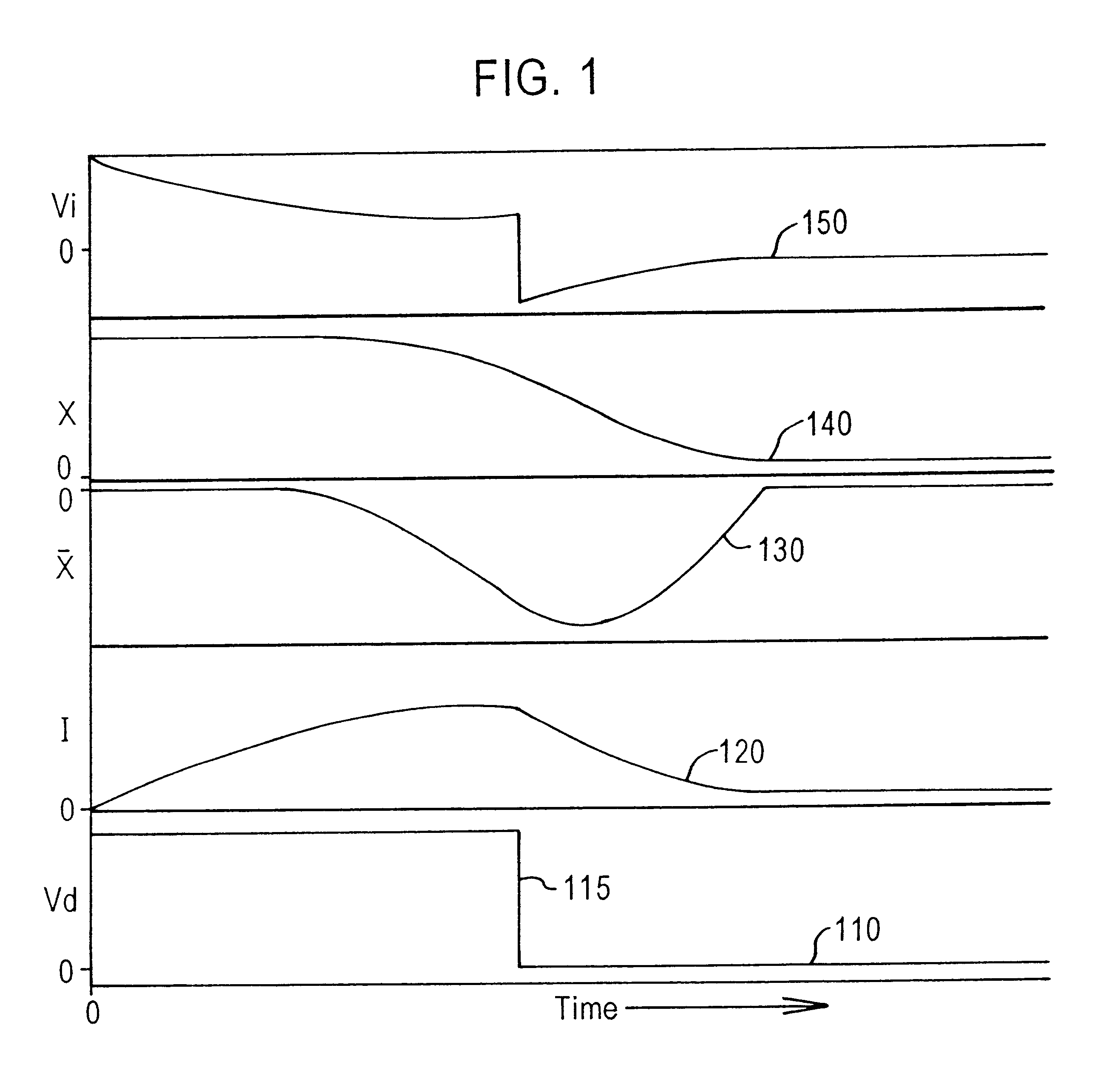
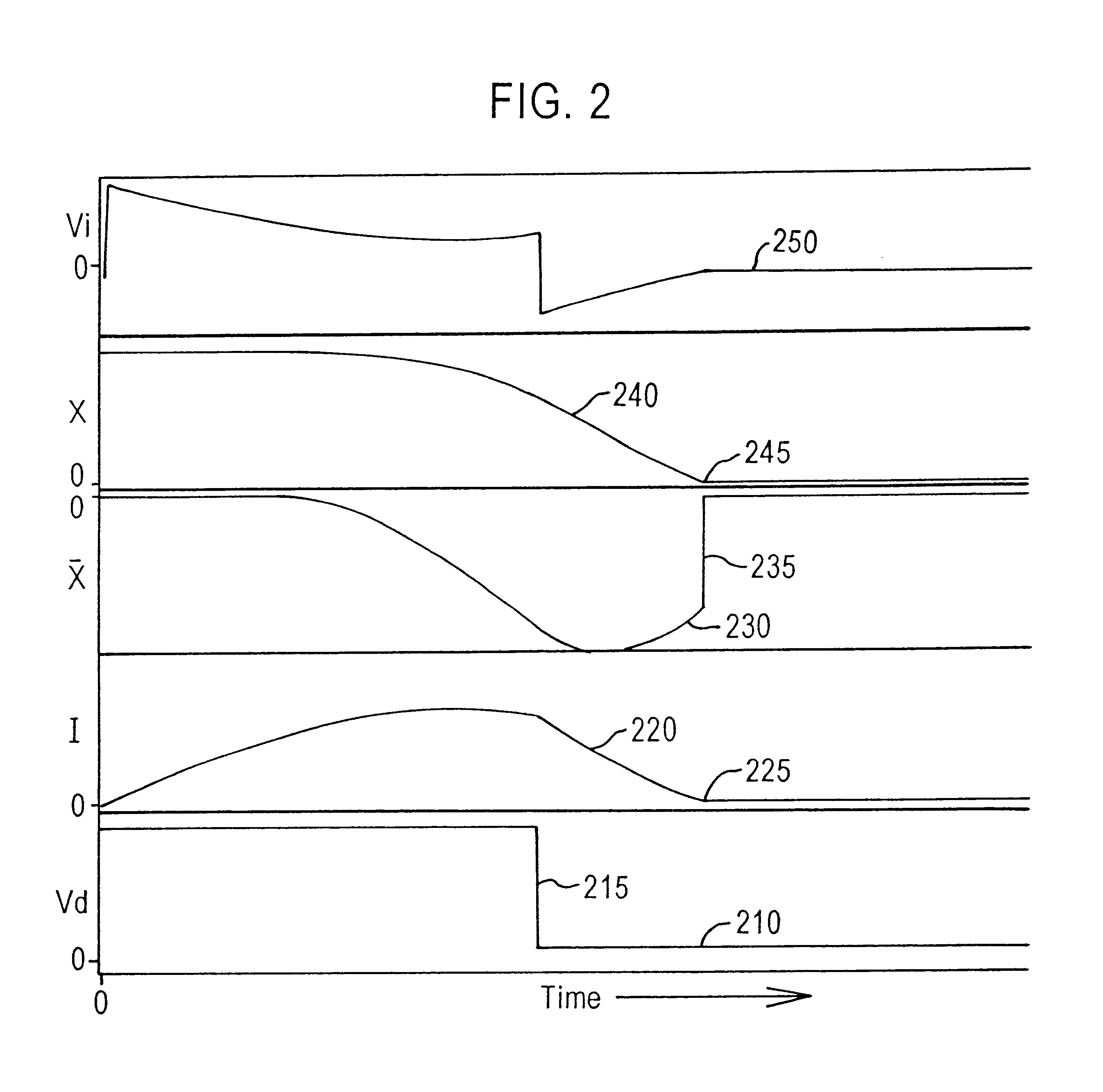
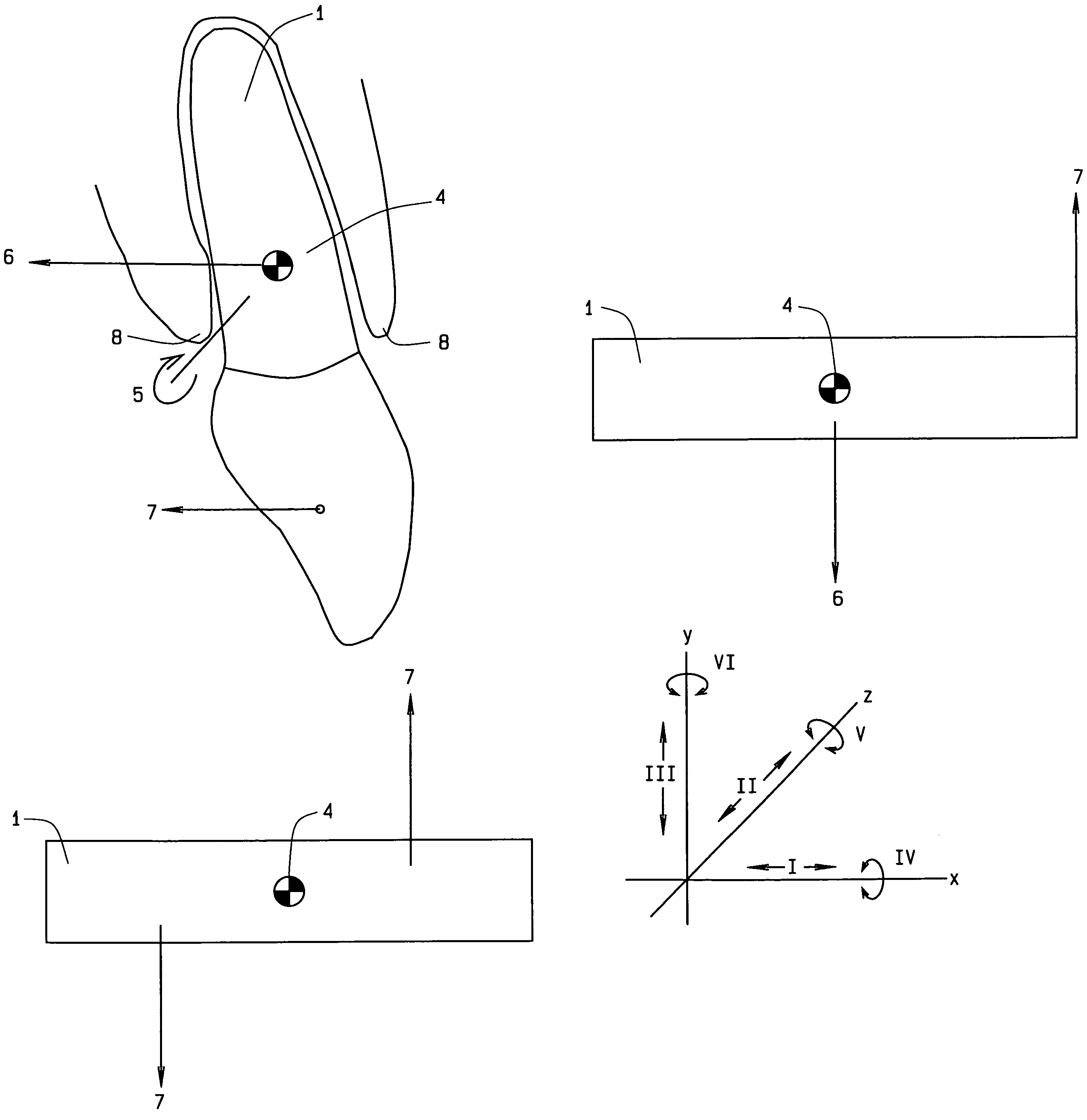
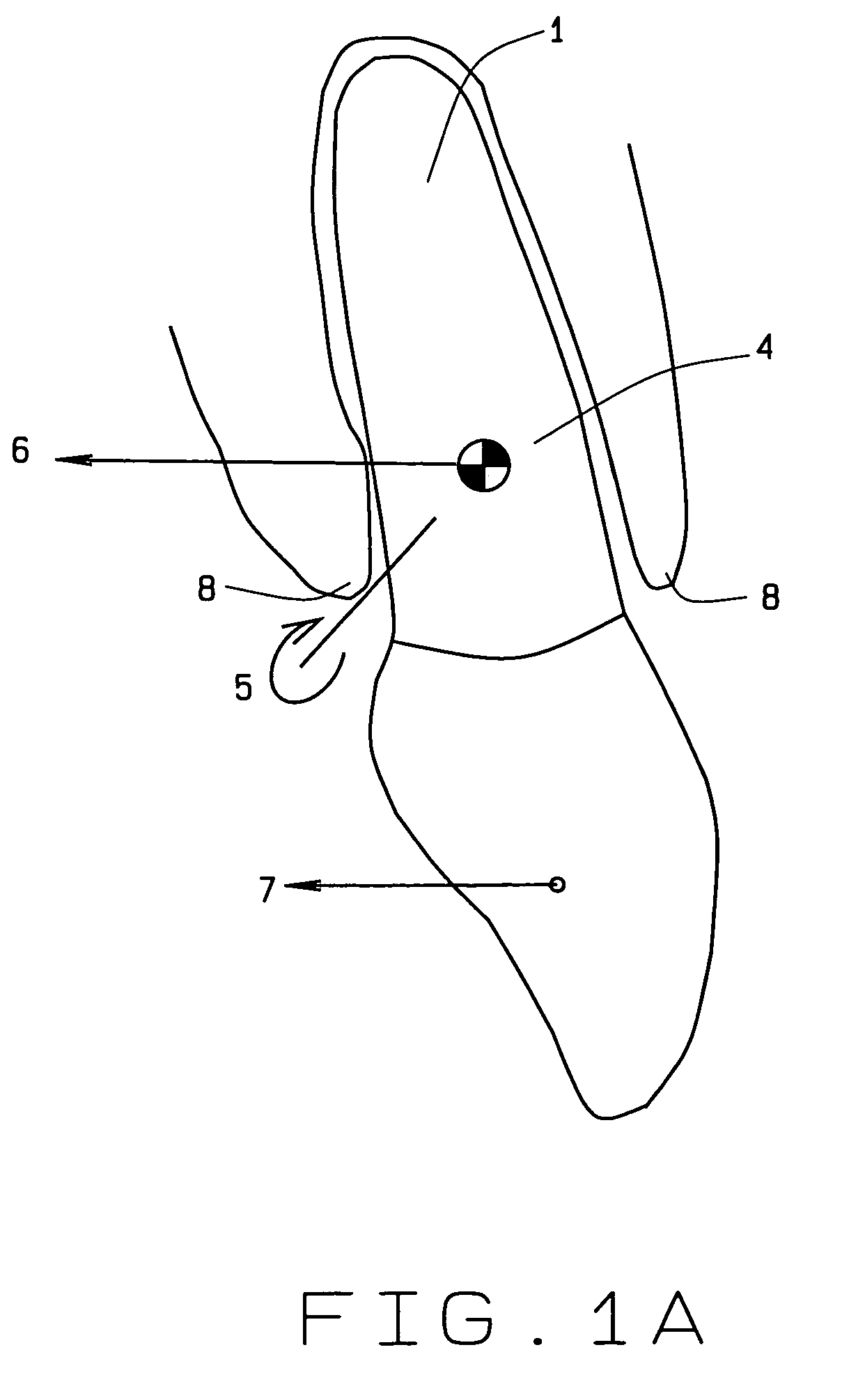
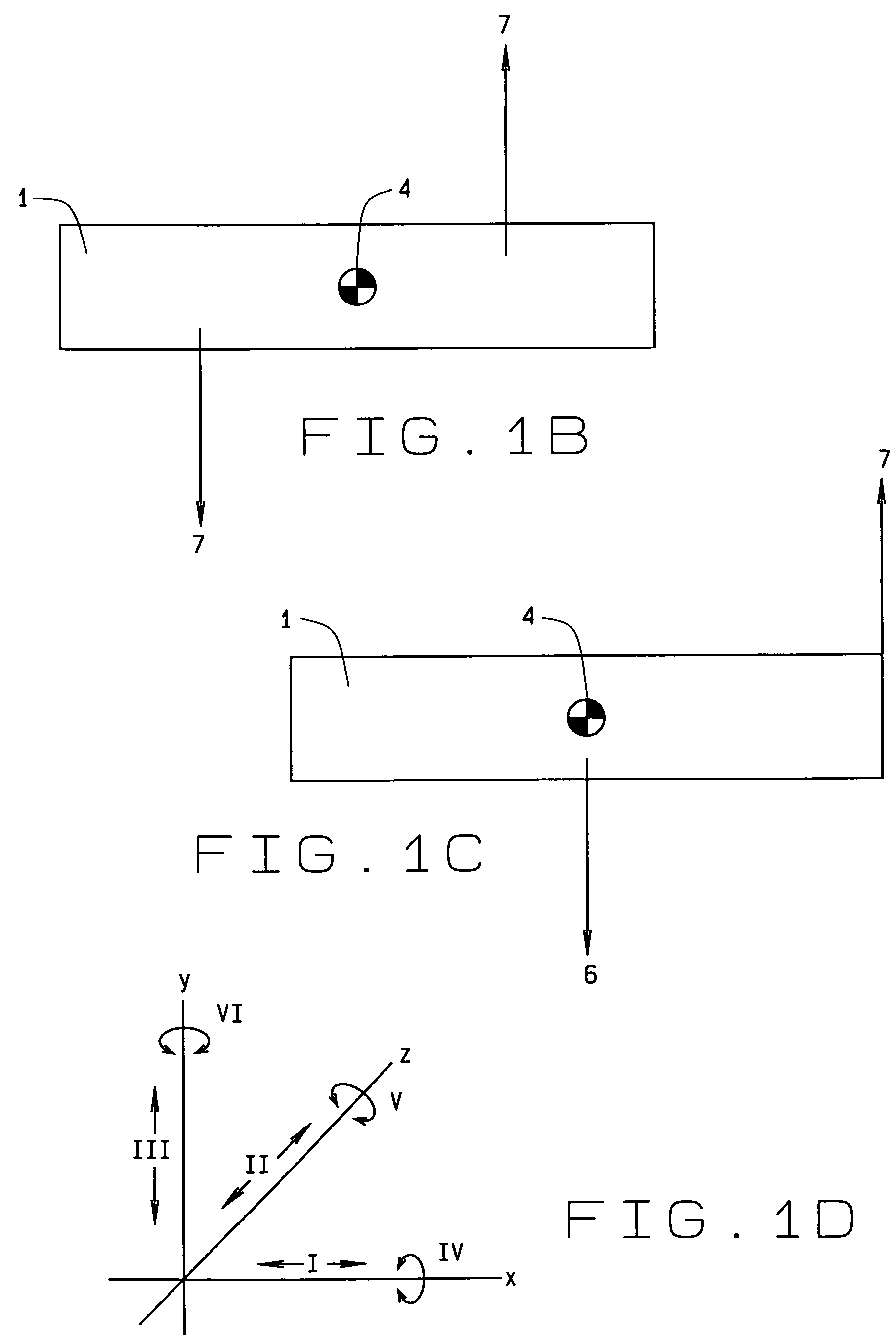
Vessel-sealing device including force-balance interface and electrosurgical system including same
ActiveUS20160074103A1Easily apply required forceImprove sealing functionDiagnosticsInstrument handpiecesVessel sealingReciprocating motion
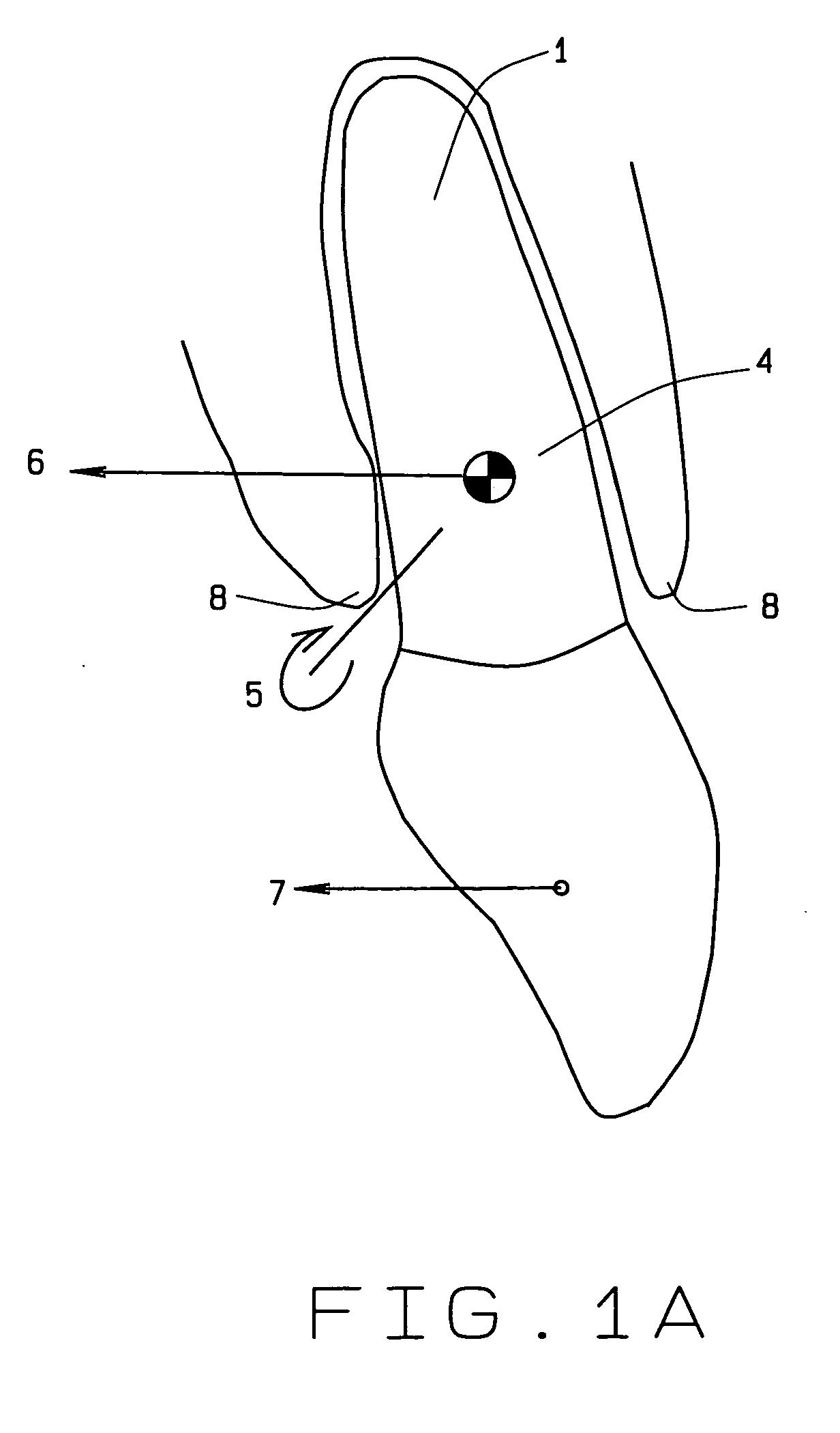
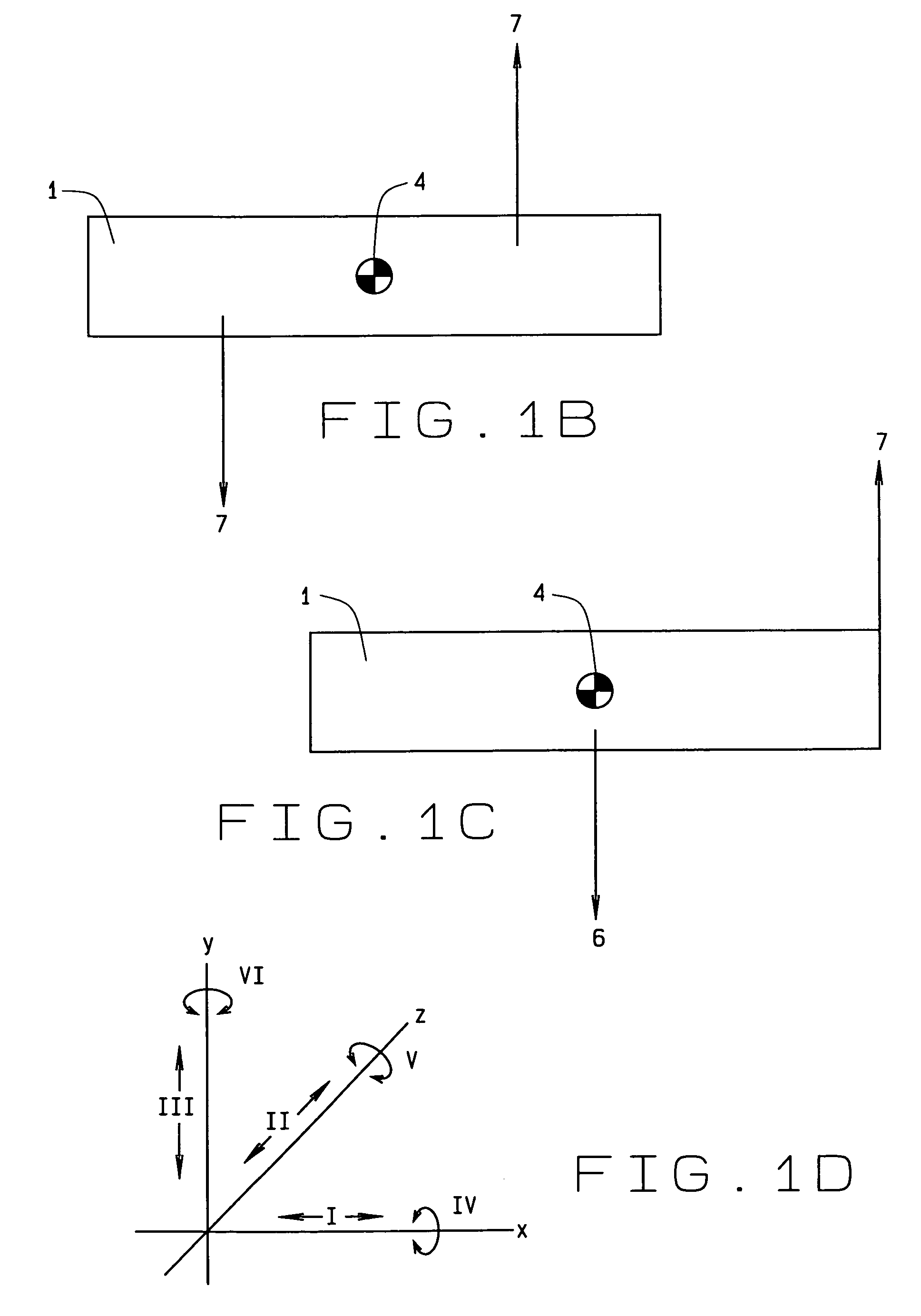
A surgical instrument includes a housing having a shaft affixed thereto, a reciprocatable drive rod slideably disposed at least partially within the shaft, and a force applicator coupled to the drive rod. The shaft includes first and second jaw members attached to a distal end thereof, at least one of which movable relative to the other from a first position wherein the jaw members are disposed in spaced relation relative to one another to at least a second position closer to one another wherein the jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue therebetween. The force applicator and the drive rod mechanically communicate to impart movement to at least one of the jaw members. The bipolar forceps includes a handle assembly and a force-balance interface. The force-balance interface configured to translate a multiple of the user-applied force exerted on the handle assembly into the jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
System and method for improved control of tooth movement with elastic repositioning appliances
InactiveUS20060223022A1Easy to controlGood tooth alignmentOthrodonticsDental toolsElectrical resistance and conductanceCoupling
Micro-regional force application improves the control of the orthodontic movement of teeth in all six degrees of freedom. Micro regional force application utilizes an elastic repositioning appliance, a tooth positioner, a polymeric shell, or preprogrammed series of polymeric shells. The key components of the invention are the envelope of freedom, the force applicators, force couplers, counterpart coupling, vector modifiers, seating guides, decouplers, and forced balance points. Further, computerized finite element analysis determines the center of resistance and the center of rotation for each tooth to be moved. The present invention gently rotates and translates one or more teeth to a desired straight position within a treatment plan.
Owner:SOLOMON FREDERICK
Hydraulically balanced reciprocating pulser valve for mud pulse telemetry
ActiveUS6898150B2Improve data transfer rateSurveyMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsDifferential pressureReciprocating motion
A reciprocating pulser system for generating pressure fluctuations in a flowing drilling fluid comprising a reciprocating poppet and a stationary valve assembly with axial flow passages. The poppet reciprocates in close proximity to the valve assembly, at least partially blocking the flow through the valve assembly and generating oscillating pressure pulses. The poppet passes through two zero speed positions during each cycle, enabling rapid changes in signal phase, frequency, and / or amplitude thereby facilitating enhanced data encoding. The poppet is driven by a linear electric motor disposed in a lubricant filled housing. In one embodiment, the housing to shaft seal is a flexible bellows. In one embodiment, a force balance spring is used to essentially offset the hydraulic flow forces on the poppet. In one embodiment, a bypass poppet is used to adjust the differential pressure across the valve assembly.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
System and method for servo control of nonlinear electromagnetic actuators
InactiveUS20060171091A1Eliminate impactRemove noiseElectrical controlAC motor controlResonance measurementInstability
Servo control using ferromagnetic core material and electrical windings is based on monitoring of winding currents and voltages and inference of magnetic flux, a force indication; and magnetic gap, a position indication. Third order nonlinear servo control is split into nested control loops: a fast nonlinear first-order inner loop causing flux to track a target by varying a voltage output; and a slower almost linear second-order outer loop causing magnetic gap to track a target by controlling the flux target of the inner loop. The inner loop uses efficient switching regulation, preferably based on controlled feedback instabilities, to control voltage output. The outer loop achieves damping and accurate convergence using proportional, time-integral, and time-derivative gain terms. The time-integral feedback may be based on measured and target solenoid drive currents, adjusting the magnetic gap for force balance at the target current. Incorporation of permanent magnet material permits the target current to be zero, achieving levitation with low power, including for a monorail deriving propulsion from the levitation magnets. Linear magnetic approximations lead to the simplest controller, but nonlinear analog computation in the log domain yields a better controller with relatively few parts. When servo-controlled solenoids provide actuation of a pump piston and valves, electronic LC resonance measurements determine liquid volume and gas bubble volume.
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B +1
Force Balanced Rotating Pressure Control Device
InactiveUS20080296016A1Extended service lifeLittle strengthSurveyDrilling rodsEngineeringHydraulic fluid
Force balancing adjusts hydraulic fluid pressure in an upper piston area of a Rotating Pressure Control Device (RPCD) that has an inner housing rotatably engaged within an outer housing by an upper bearing and a lower bearing. The hydraulic fluid pressure is adjusted to balance net force in a upper piston area and a lower piston area. The fluid pressure adjustment creates a force differential that balances the total load transmitted through the upper bearing and the lower bearing and thereby extends the life of the sealing element and bearings. Additionally, a wear indicator signals the end of the useful life of the drill pipe sealing element.
Owner:SUNSTONE TECH
Solenoid cassette pump with servo controlled volume detection
InactiveUS6942469B2Eliminate closure impactEliminate associated noiseAC motor controlElectrical controlResonance measurementDriving current
Servo controlled solenoids provide actuation of a pump piston and valves, and electronic LC resonance measurements to determine liquid volume and gas bubble volume. Third order nonlinear servo control is split into nested control loops: a fast nonlinear first-order inner loop causing flux to track a target by varying a voltage output, and a slower almost linear second-order outer loop causing magnetic gap to track a target by controlling the flux target or the inner loop. The inner loop uses efficient switching regulation, preferably based on controlled feedback instabilities, to control voltage output. The outer loop achieves damping and accurate convergence using proportional, time-integral, and time-derivative gain terms. The time-integral feedback may be based on measured and target solenoid drive currents, adjusting the magnetic gap for force balance at the target current.
Owner:THISTLE ADVISORS
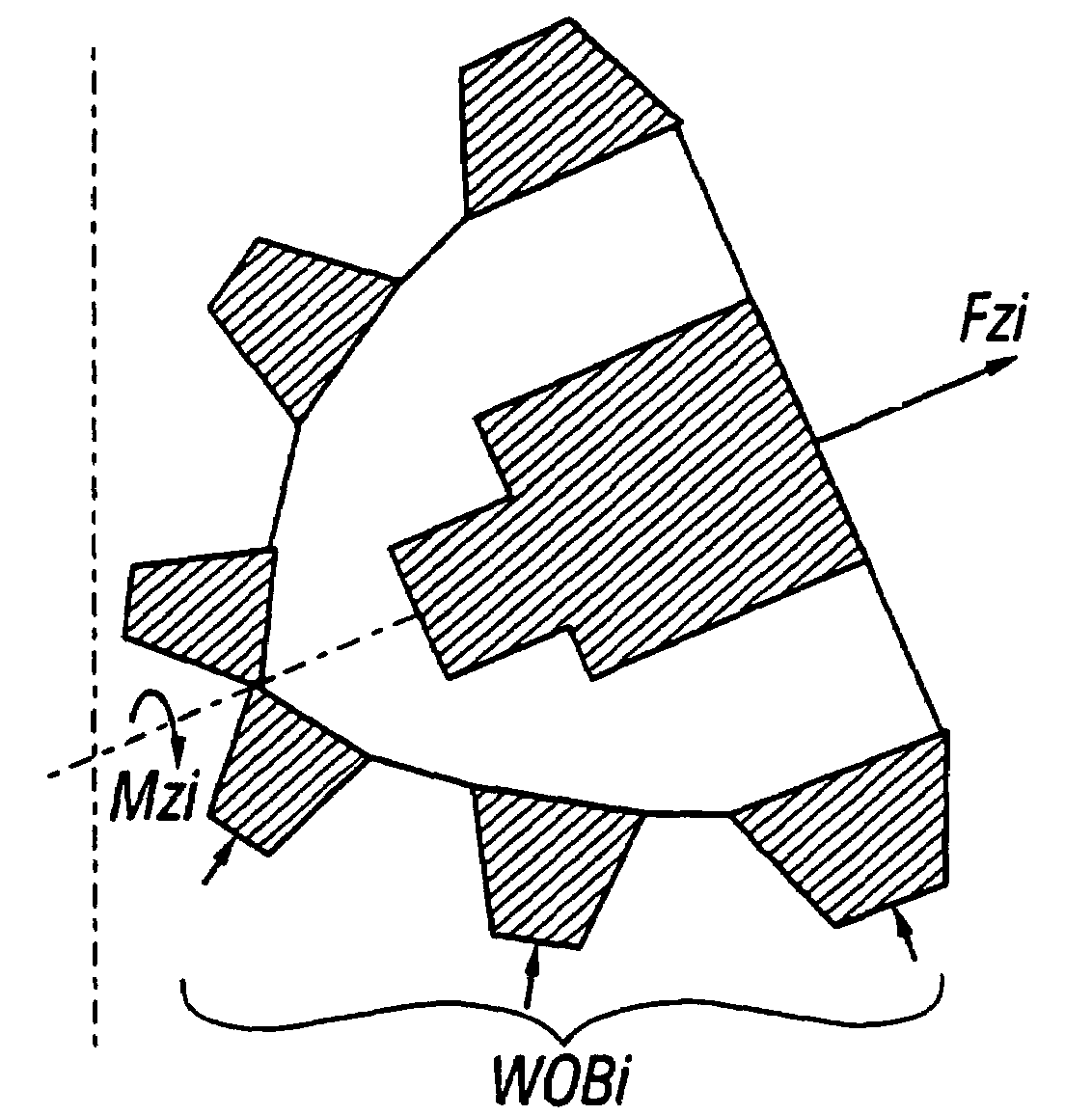
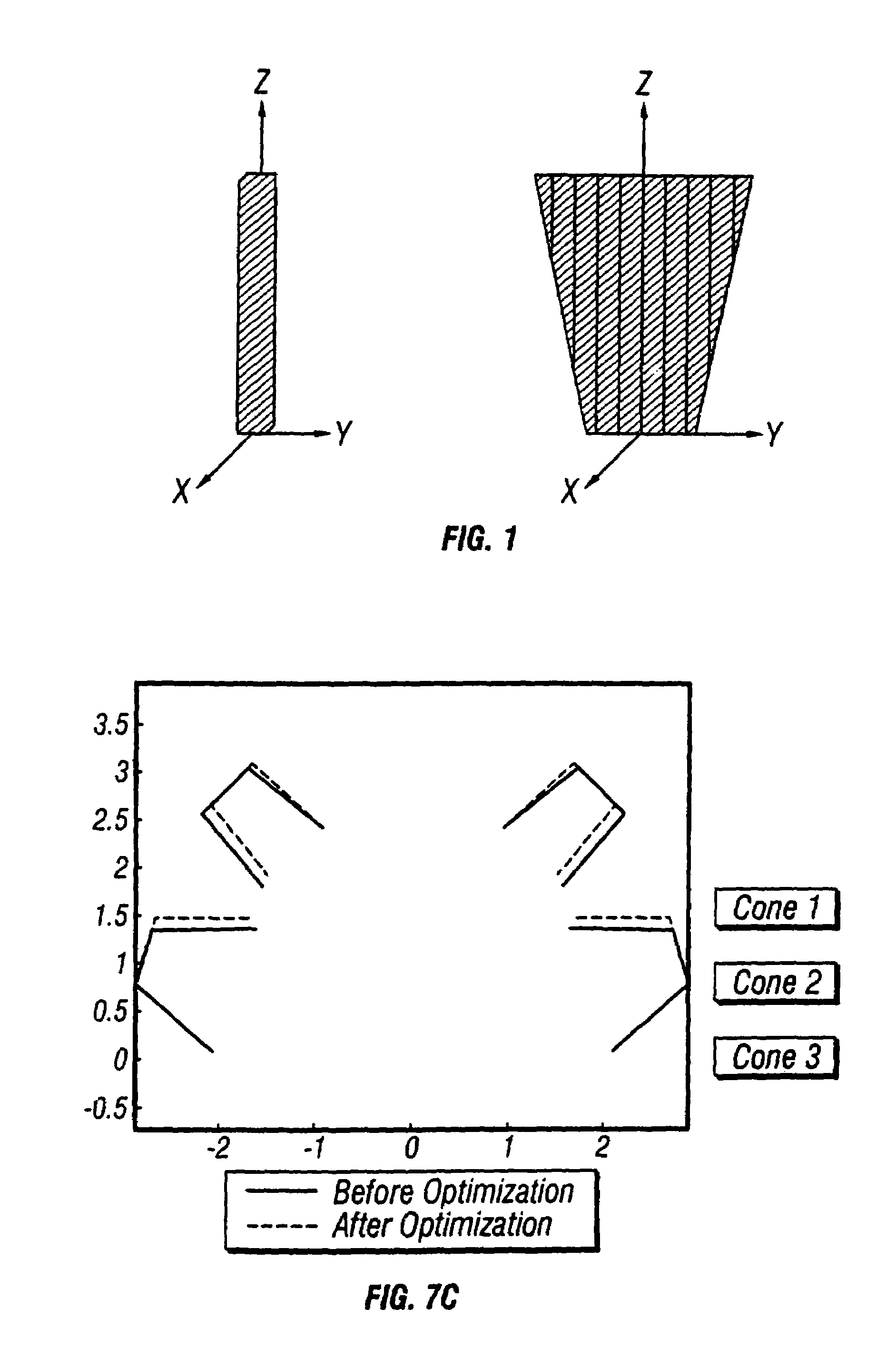
Force-balanced roller-cone bits, systems, drilling methods, and design methods
InactiveUS6986395B2Reduce rotationImprove drilling efficiencyEarth drilling toolsDrill bitsAxial forceEngineering
Roller cone drilling wherein the bit optimization process equalizes the downforce (axial force) for the cones (as nearly as possible, subject to other design constraints).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Force balanced asymmetric drilling reamer and methods for force balancing
A force balanced asymmetric drilling reamer comprising a plurality of blades, each blade having at least one cutter section and a gage section. The cutter section is designed to have a plurality of cutting devices for cutting through swelling formations and cutting free sloughing formations. The gage section has a full bore diameter with gage elements flushly coupled to gage section's outer surface. The blades may be curve / concave shaped or boomerang / chevron shaped, which thereby agitate the cutting beds. At least a portion of the drilling reamer's diameter is incrementally force balanced, starting from the outermost diameter, so that the net radial force is less than 10% of weight on bit with respect to the center of rotation. This balancing allows a greater cutter longevity and provides for a better wellbore condition. Optionally, at least a portion of the drilling reamer's surface may be treated by nitriding for repelling the cuttings.
Owner:VAREL INT IND
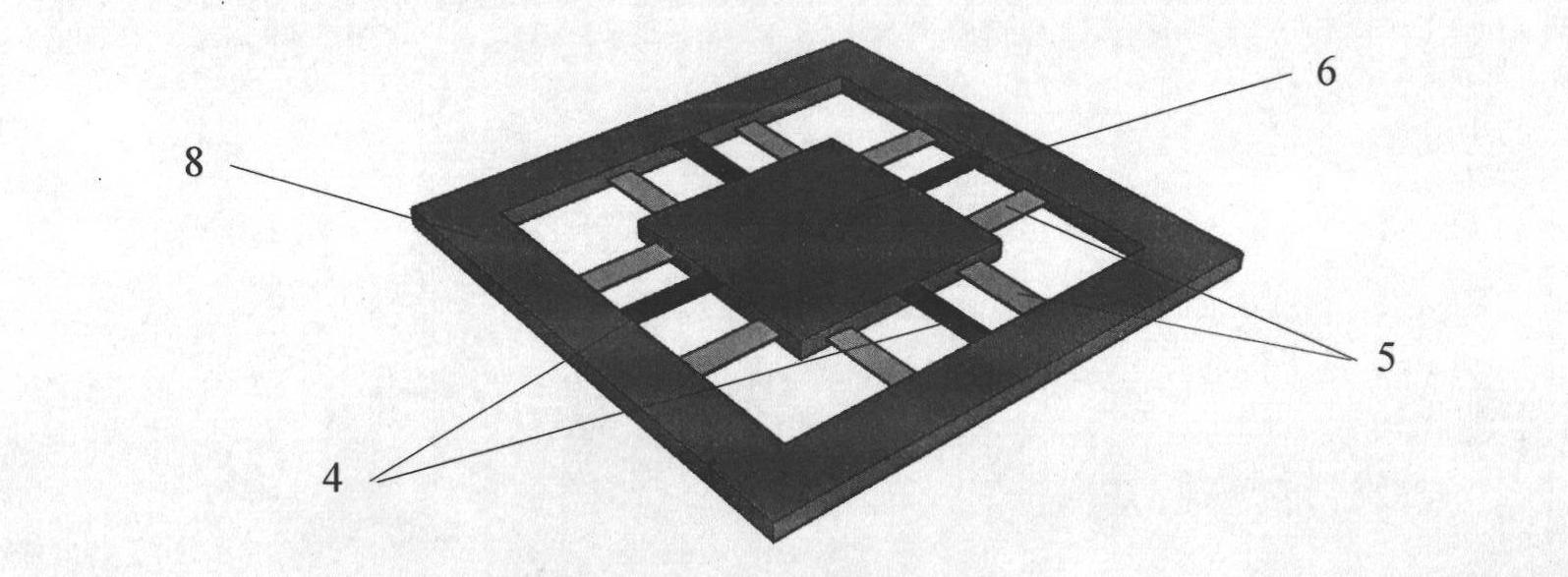
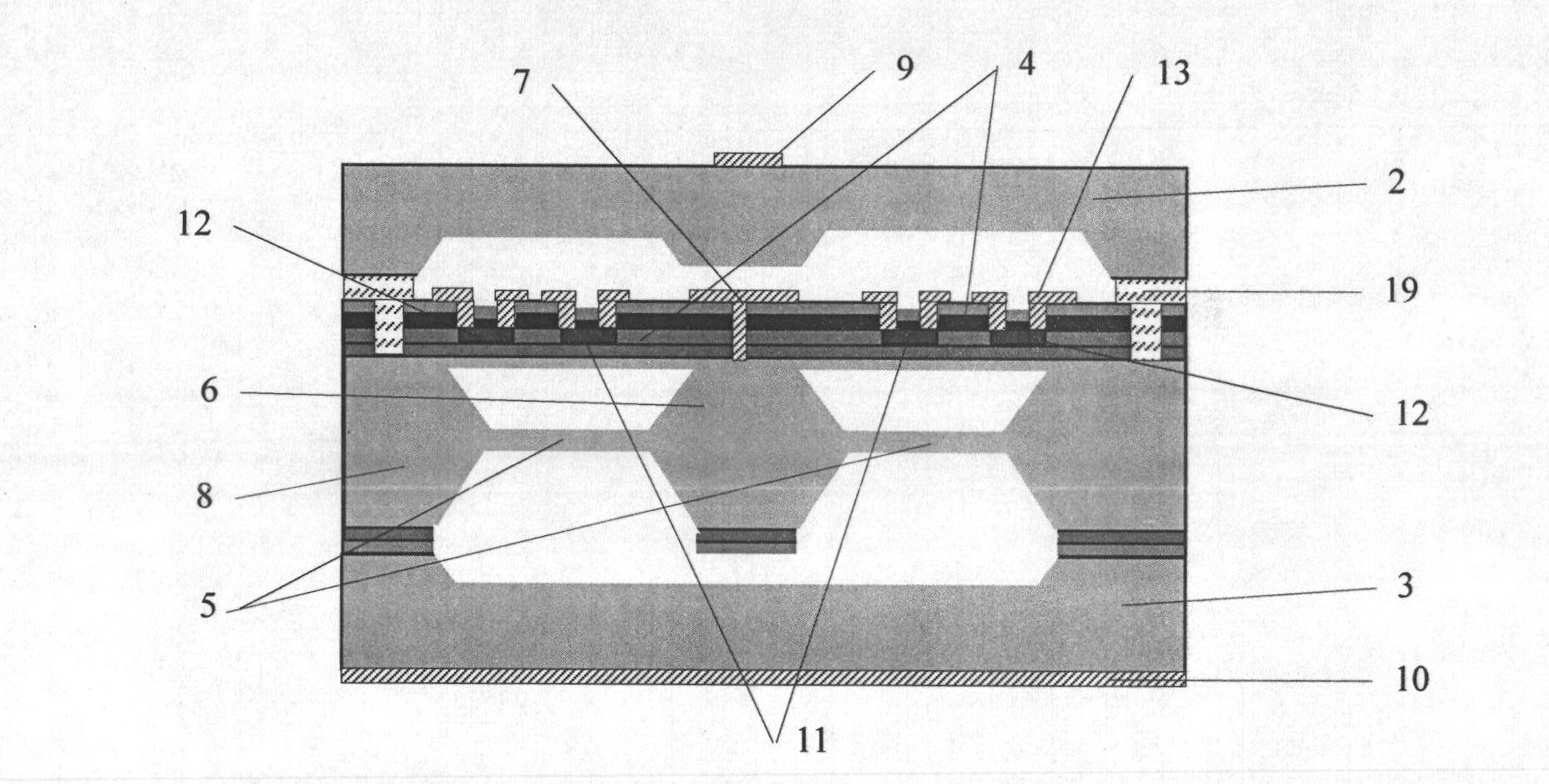
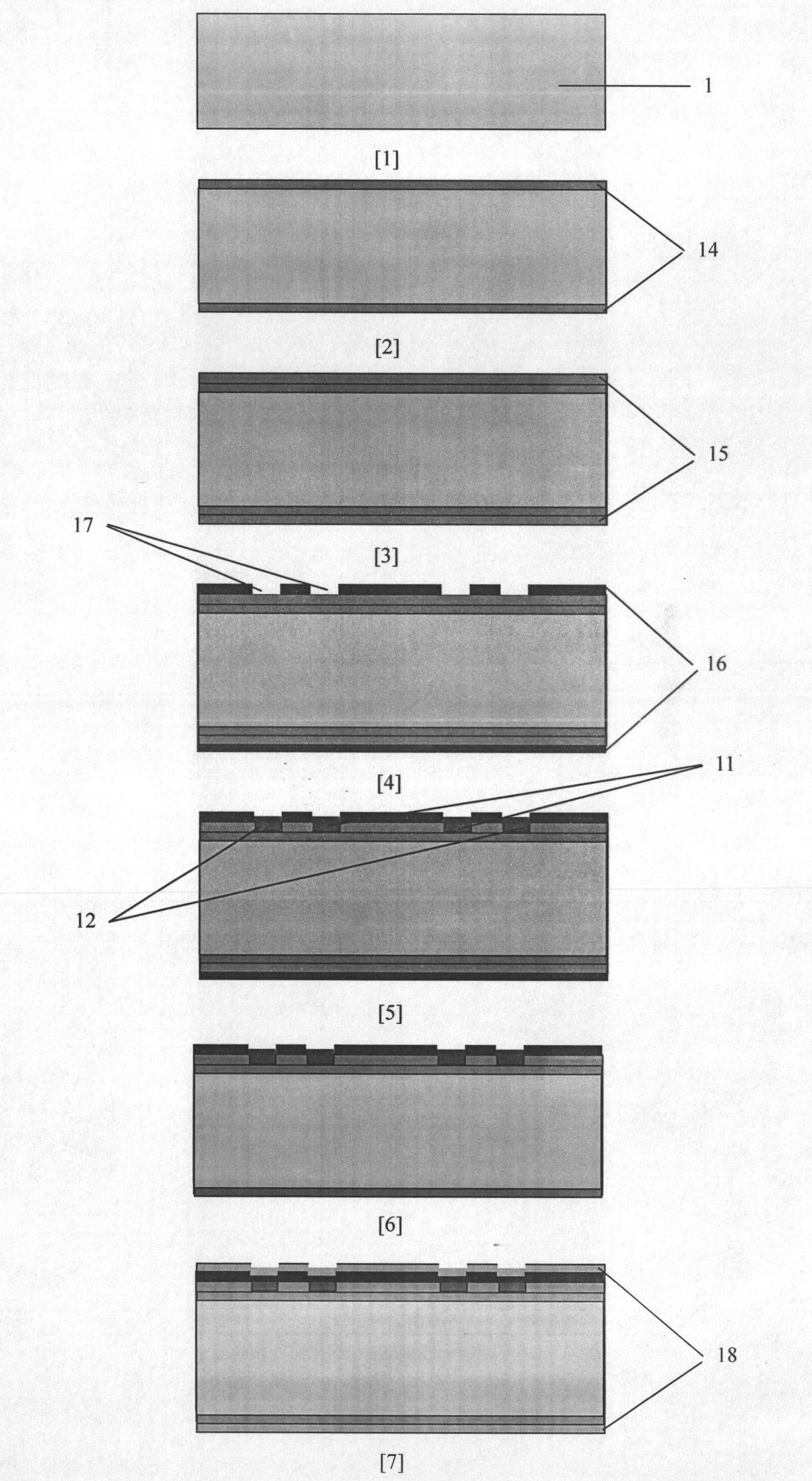
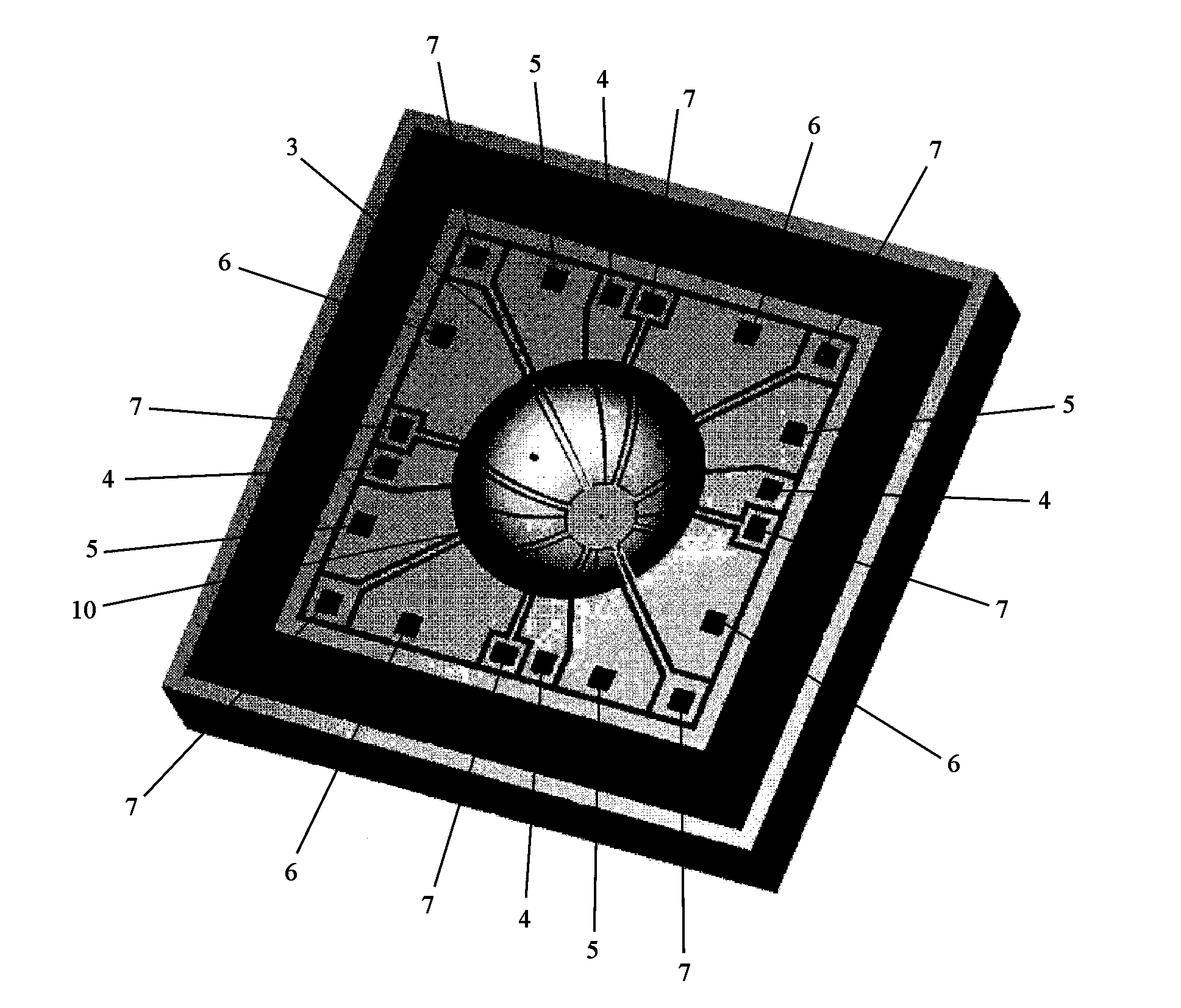
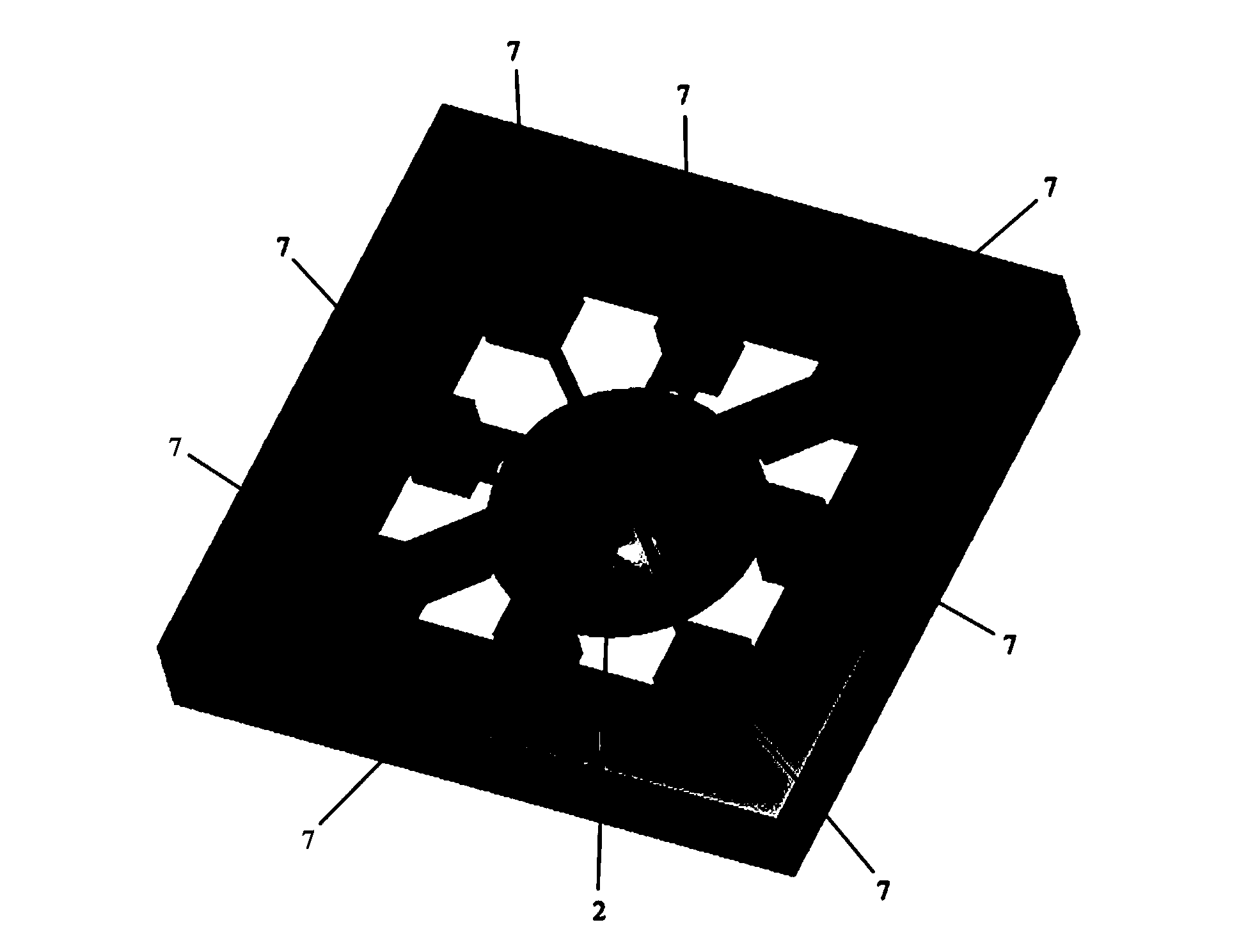
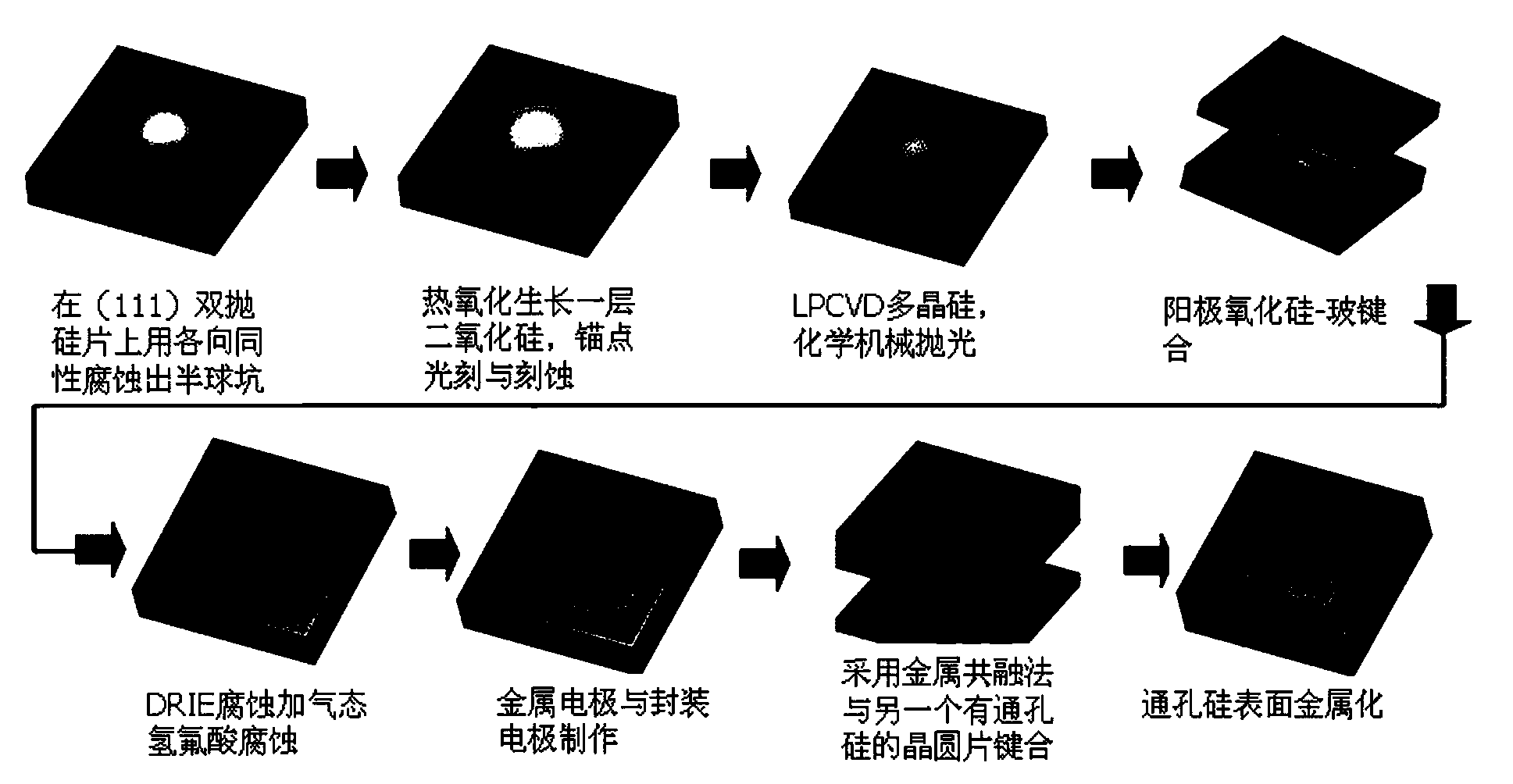
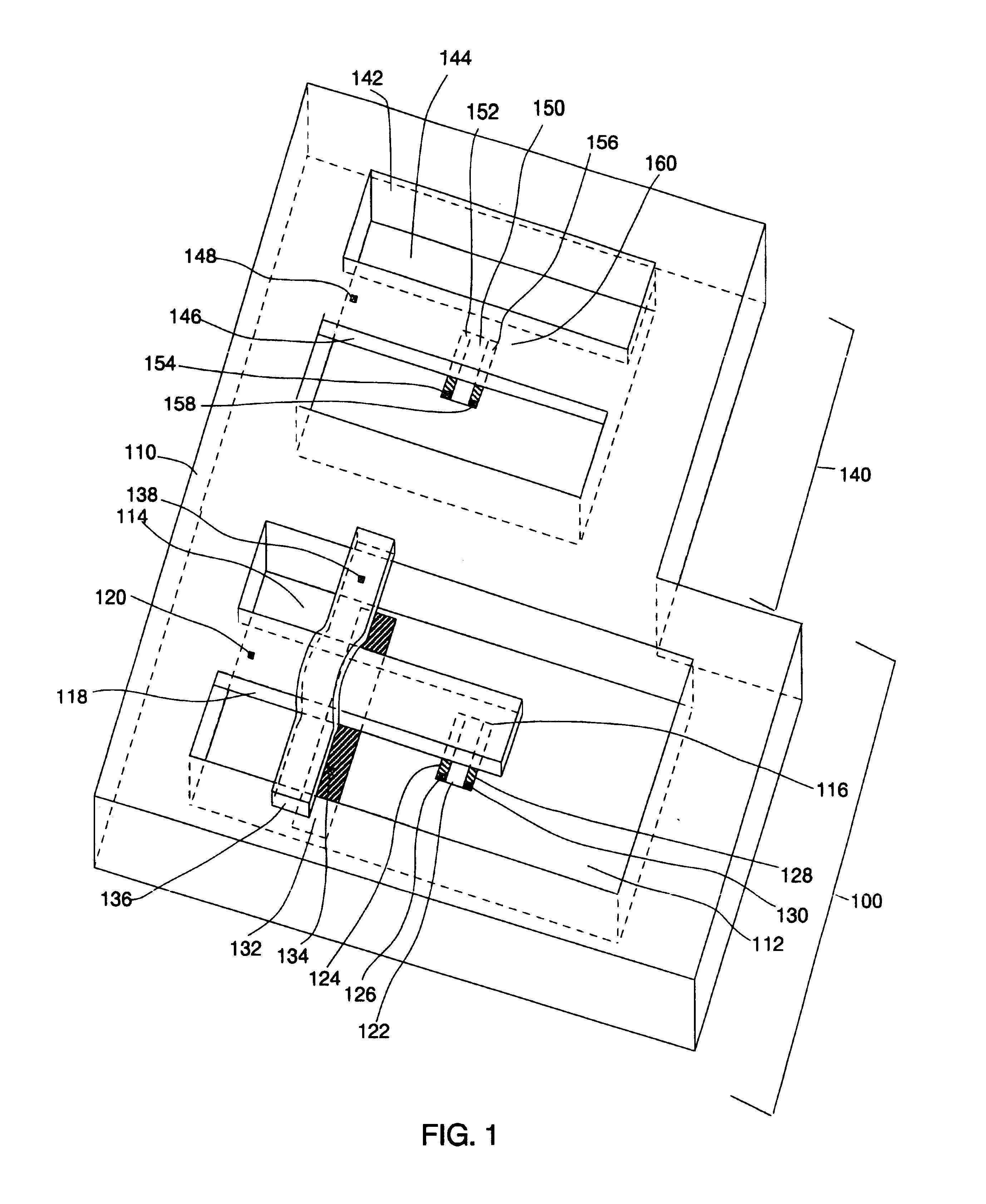
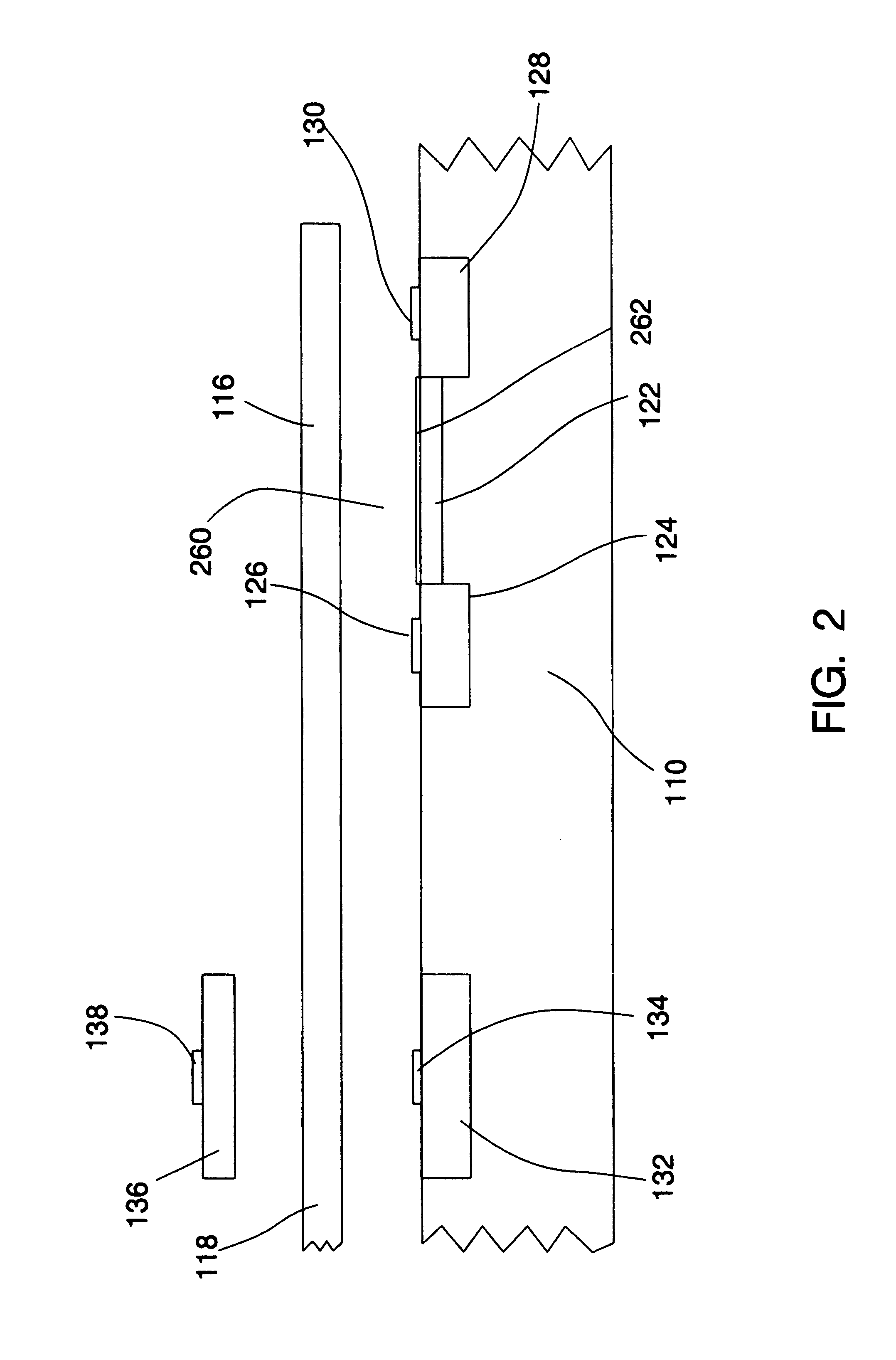
Resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer and manufacture method
InactiveCN102590555AMeet high performance requirementsImprove linearityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceResonance
The invention discloses a resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer and a manufacture method thereof, belonging to the field of microelectro mechanical systems. The resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer is structurally characterized by comprising an intermediate silicon sheet (1), an upper cover plate (2) and a lower bottom plate (3), wherein the intermediate silicon sheet (1) comprises a dual-end clamped beam resonators (4), a mass block (6), a support beam (5), a movable electrode (7) and a frame (8). The resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer is characterized in that an X axis and a Y axis acceleration signals in a chip plane are detected by adopting the dual-end clamped beam resonator (4) on the aspect of detection principle, the change of the resonance frequency of the dual-end clamped beam resonator (4) reflects the size and the direction of acceleration; and a Z axis acceleration signal in a vertical chip plane is detected by adopting a capacitance type sensitivity principle, and works in a closed loop force balance working mode. The mass block (6) has little motion displacement in the normal of a chip, and the Z axis input acceleration signal has little chiasma interference caused by detection of X axis and Y axis accelerations.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
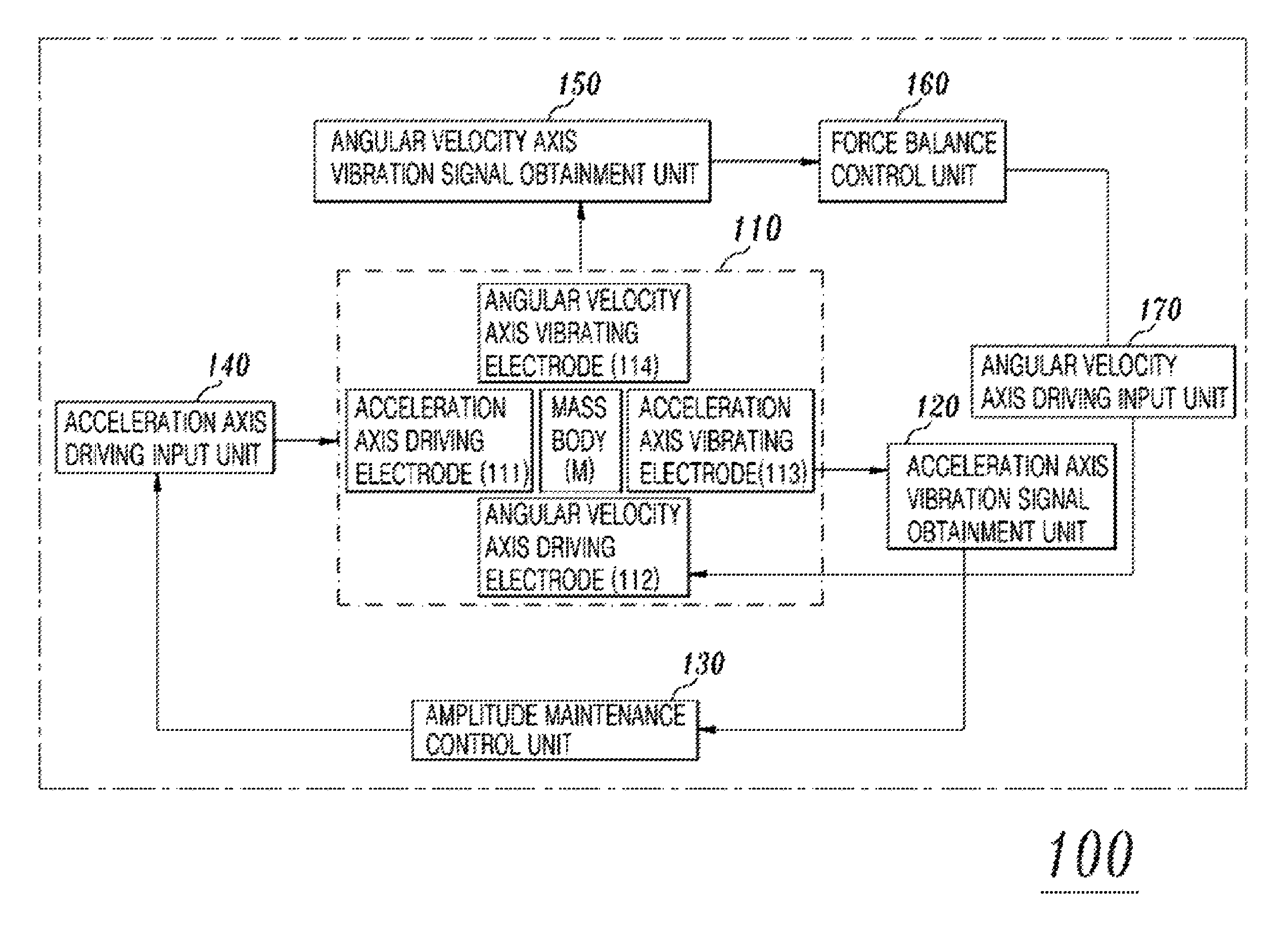
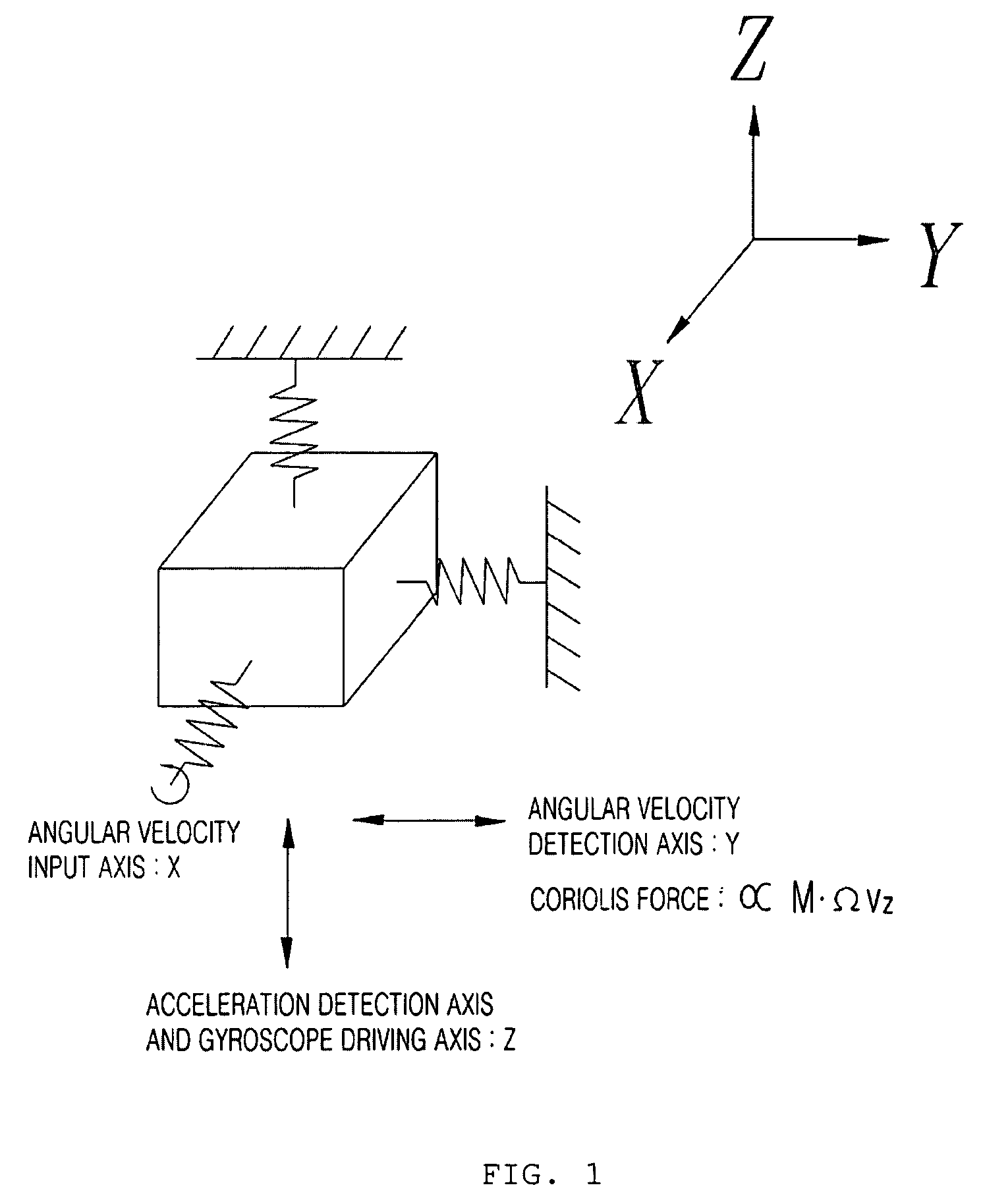
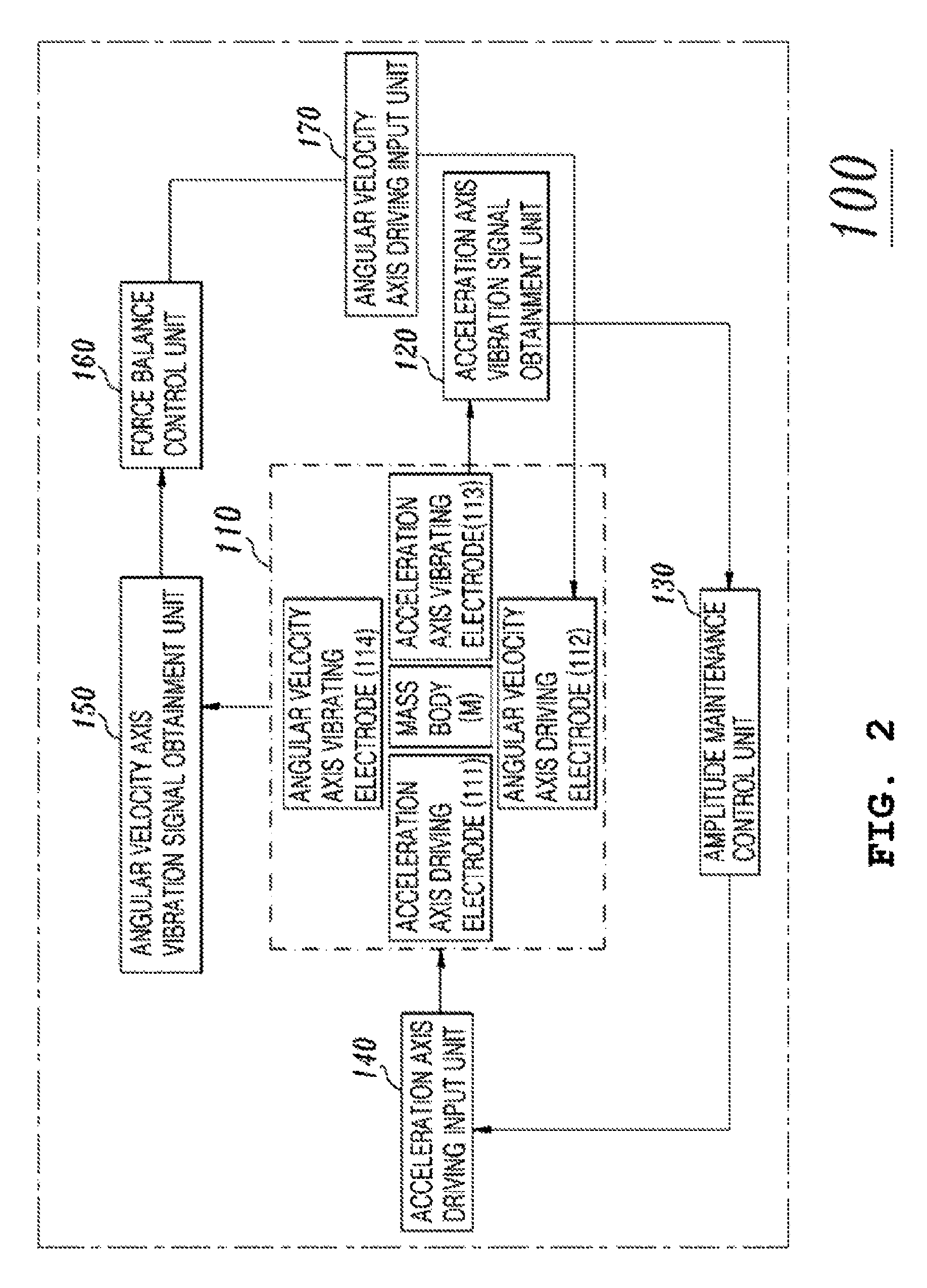
Combined accelerometer and gyroscope system
InactiveUS7765869B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsVibration amplitudeAccelerometer
An embodiment of the present invention relates to a combined accelerometer and gyroscope system. The combined accelerometer and gyroscope system includes a combined accelerometer and gyroscope for maintaining vibration of a mass body at a constant amplitude using an applied drive voltage, and detecting vibration signals in directions of an acceleration axis and an angular velocity axis. An acceleration axis vibration signal obtainment unit obtains the vibration signal in the direction of the acceleration axis. An amplitude maintenance control unit outputs an acceleration axis vibration maintenance control signal using the vibration signal. An acceleration axis driving input unit receives a voltage signal from the amplitude maintenance control unit and applies the voltage signal to the combined accelerometer and gyroscope. An angular velocity axis vibration signal obtainment unit obtains the vibration signal in the direction of the angular velocity axis. A force balance control unit outputs an angular velocity axis vibration maintenance control signal using the vibration signal received from the angular velocity axis vibration signal obtainment unit. An angular velocity axis driving input unit receives a voltage signal received from the force balance control unit and applies the voltage signal to the combined accelerometer and gyroscope.
Owner:KONKUK UNIV IND COOP CORP
Force balanced butterfly proportional hot gas valve
InactiveUS20080302991A1Cosmonautic vehiclesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesEngineeringVALVE PORT
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Assemblies comprising fastener with ergonomically balanced removal to insertion ratio
InactiveUS6868588B2Improve performanceLarge widthSnap fastenersSnap-action fastenersEngineeringForce balance
Assemblies comprising a fastener, which has engagement springs in opposite sides of the fastener. Each engagement spring has an engagement region comprising a hindrance portion, which increases considerably the removal to insertion force ratio as compared to such ratio in the absence of the hindrance portion, thus permitting very easy insertion with considerably more difficult removal of the fastener from the slot of a panel, which provides an efficient ergonomically balanced removal to insertion force ratio. The hindrance portion comprises ripples or other hindrance elements of unexpectedly minute dimensions for providing this efficient ergonomic force balance.
Owner:TERMAX CORP +1
Force balanced rotating pressure control device
InactiveUS7743823B2Extended service lifeLittle strengthSurveyDrilling rodsEngineeringHydraulic fluid
Owner:SUNSTONE TECH
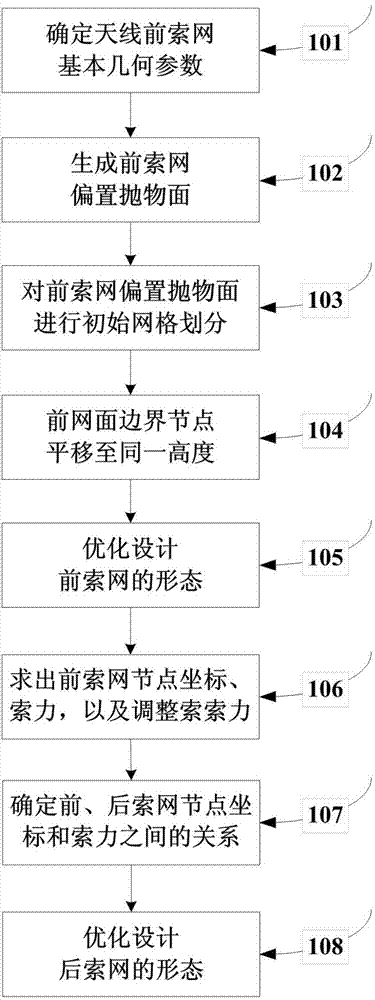
Initial form design method of deployable offset parabolic antenna cable net structure
InactiveCN103761369AImproves tension uniformityImprove applicabilitySpecial data processing applicationsCable netEngineering
The invention discloses an initial form design method of a deployable offset parabolic antenna cable set structure. In the method, the cable net structure initial form design includes front cable net design and rear cable net design. During the front cable net design, coordinates of front cable net nodes and cable force act together as design variables, and tensions of all internal cable sections of the front cable net are equal and the ratio of the maximum tension of the boundary cable to the maximum tension of the internal cable section is minimum on conditions that all boundary nodes are fixed and all the internal nodes are on the ideal paraboloid, in force-balance states and capable of covering effective optical aperture completely. During the rear cable net design, the minimization of the ratio of the tension level of the rear cable net to that of the front cable net is achieved on the condition that an adjusting cable keeps vertical and the relation among the total height of the antenna, the height of the front cable net and the minimum length of the adjusting cable is met. Therefore, node coordinates and cable force of the front cable net and the rear cable net are acquired to complete the initial form design.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Adaptive train model
An adaptive train model (ATM) for predicting train consist reactions to specific stimuli using a system including at least one measurement sensor located on the train consist, a data base, and a computer. The ATM collects sensor data as the consist is moving, determines a consist force balance utilizing the sensor data and the computer, determines a set of consist coefficients using the computer, and predicts train consist kinetic characteristic values using the consist force balance and the set of consist coefficients.
Owner:GE HARRIS RAILWAY ELECTRONICS L L C +1
Horizontal plane motion mechanism for towing tank test
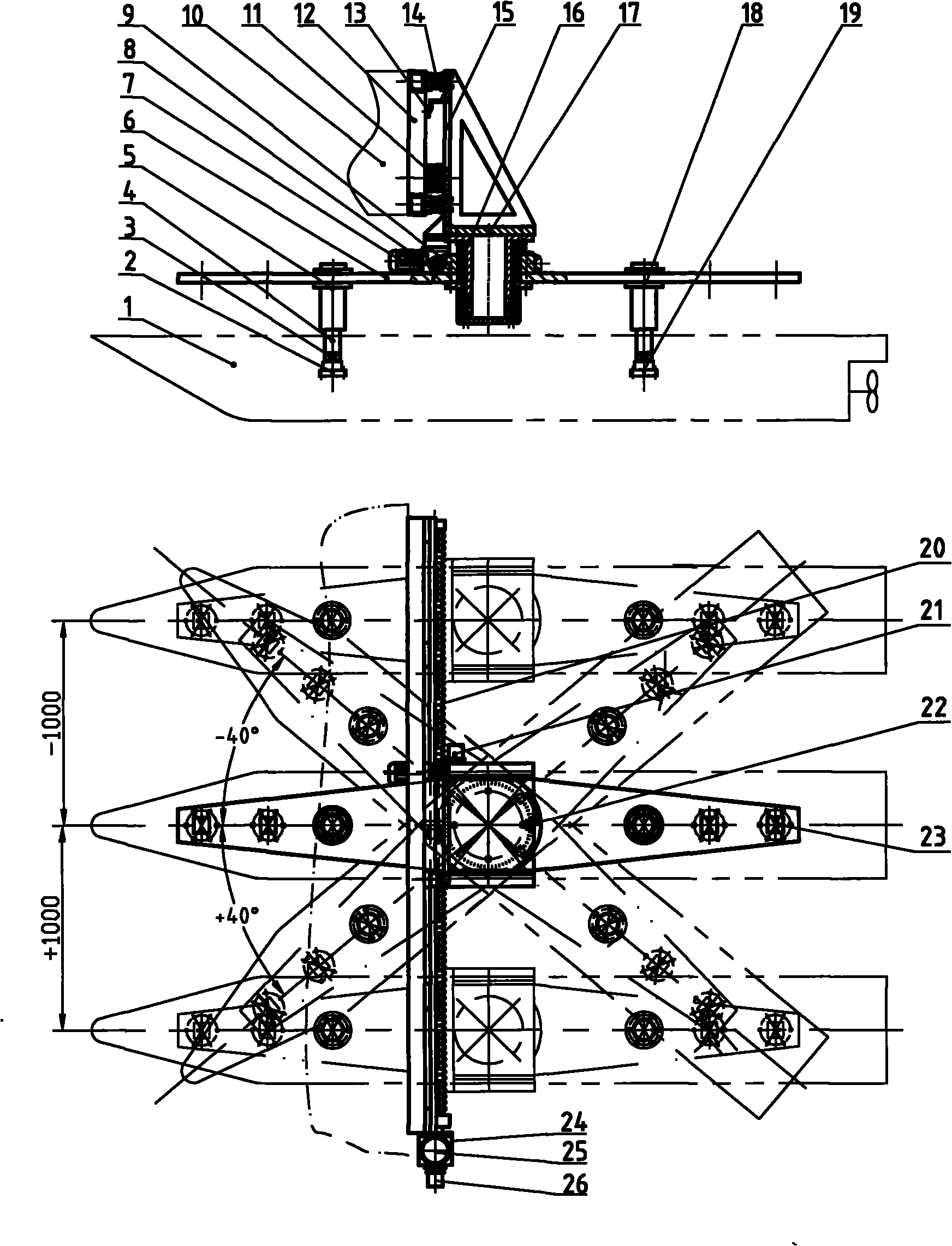
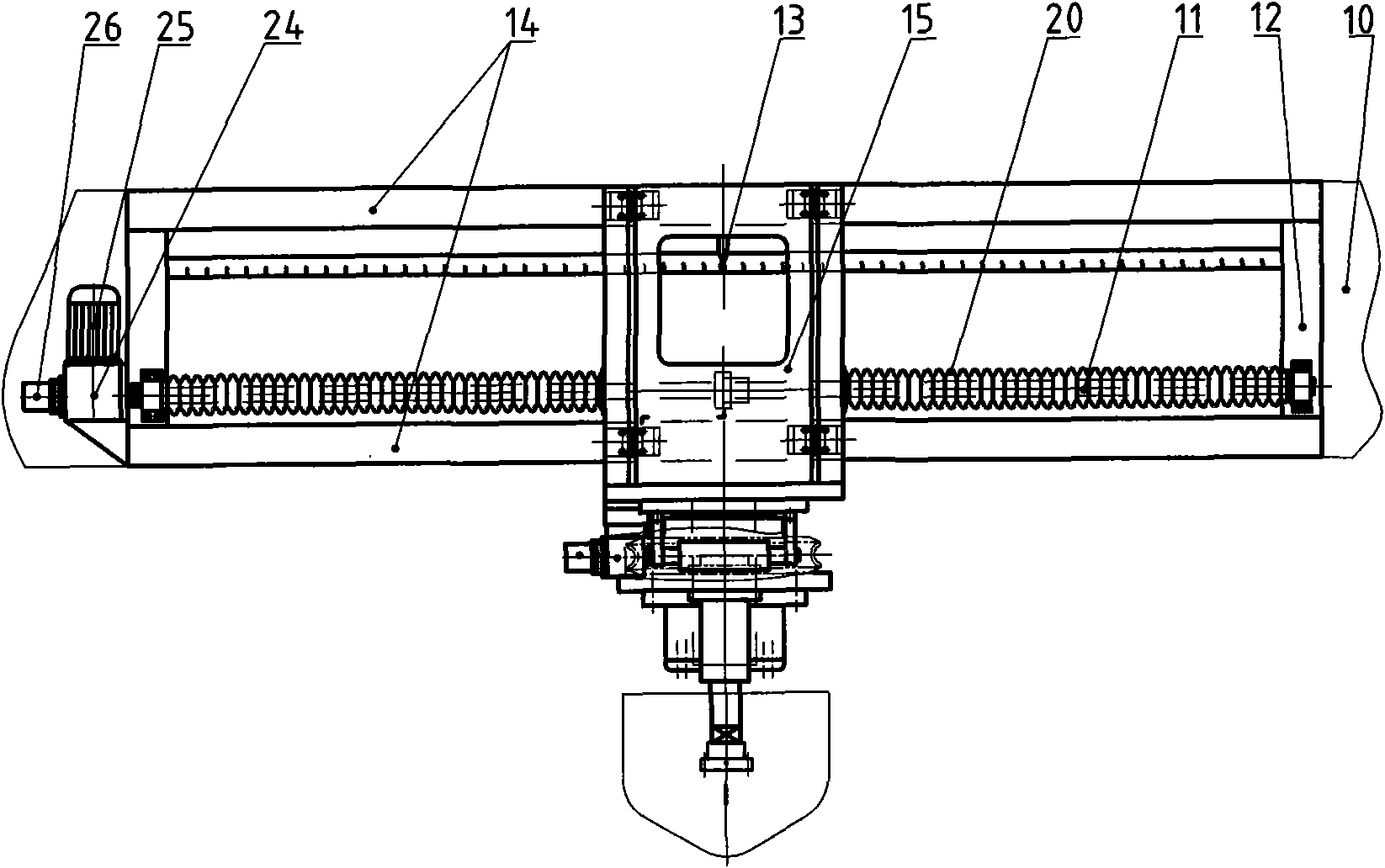
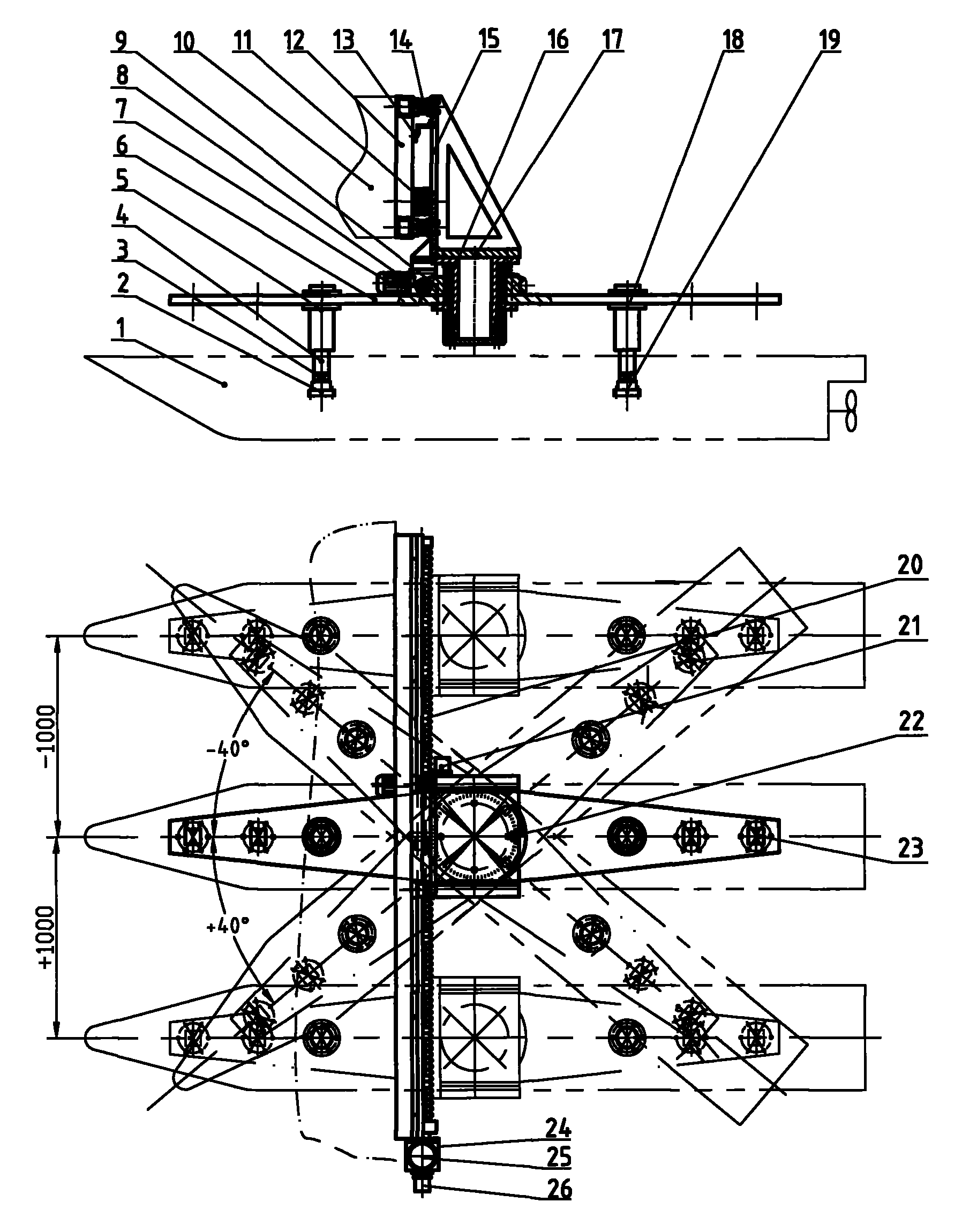
The invention discloses a horizontal plane motion mechanism for a towing tank test, which comprises a plane motion mechanism comprising a transverse oscillation frame 8, a transverse oscillation motion component 9, a yawing oscillation motion component 10, a transverse beam 6, a front connecting rod 5, a front connecting rod 11, adjusting rods 4 and 12, joints 3 and 13, force balances 2 and 14, and the like. The upper part of the horizontal plane motion mechanism is connected with a tank trailer 7 through the transverse oscillation frame 8, while the lower part is connected with a ship model 1 through the connecting rods 5 and 11 and force balances 2 and 14. By adopting a rolling guide rail, the transverse oscillation motion component has the characteristics of long service life, free maintenance for long-term work, high speed, low noise, high capacity of absorbing a mounting dimension error, and the like; and the transverse oscillation amplitude is over + / -1m, the ball screw precision is high and a transverse oscillation amplitude error is less than 0.2mm. Due to the adoption of a self-lubricating bearing and worm gear transmission, the yawing oscillation motion component has the advantages of wide rotation angle range, high torque, high self-locking property and high precision. A plurality of groups of connecting rod mounting holes are formed on the transverse beam and are suitable for different ship models. The connecting rod is provided with a linear bearing, and when the ship model is influenced by an external force to oscillate up and down, the connecting rod automatically adjusts the length, can remove a force in the vertical direction, and improves the accuracy of the maneuvering performance test. The control system is driven by a servo motor, a photoelectric encoder is used for sampling and feeding back, and a PLC programmable logic controller is used for controlling. The horizontal plane motion mechanism has the advantages of convenient control.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHUGUANG MACHINERY +1
Mass and mass center measuring device for guided missile in irregular shape
ActiveCN104075845AAvoid the problem of not being able to rotate at a large angleRealize clampingStatic/dynamic balance measurementEngineeringLoad cell
The invention relates to the technical field of measurement and control and particularly discloses a mass and mass center measuring device for a guided missile in an irregular shape. According to the measuring device, an inclined platform type measuring method is adopted, and an electric pushing rod below a bearing platform is adjusted, so that the platform is in the horizontal state or in the inclined state, pressure of each fulcrum in each state is measured through a weighing sensor, and the mass and the mass center positions of the measured guided missile can be obtained according to the force balance principle and the force moment balance principle. The measuring device comprises a lifting supporting unit, a sensor unit, a clamp unit and a joint measuring arm unit, wherein the clamp unit can be replaced with corresponding clamps and clamping rings according to clamping requirements of all kinds of section shapes of measured guided missiles; the joint measuring arm unit is used for measuring the position posture after the measured guided missiles are clamped and calibrating a system coordinate system. Compared with an existing measuring device, the measuring device is high in bearing capacity and reliability and can meet the requirements for mass and mass center measurement of the guided missiles in the irregular shape such as a non-circular special-shape section and large wingspan.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
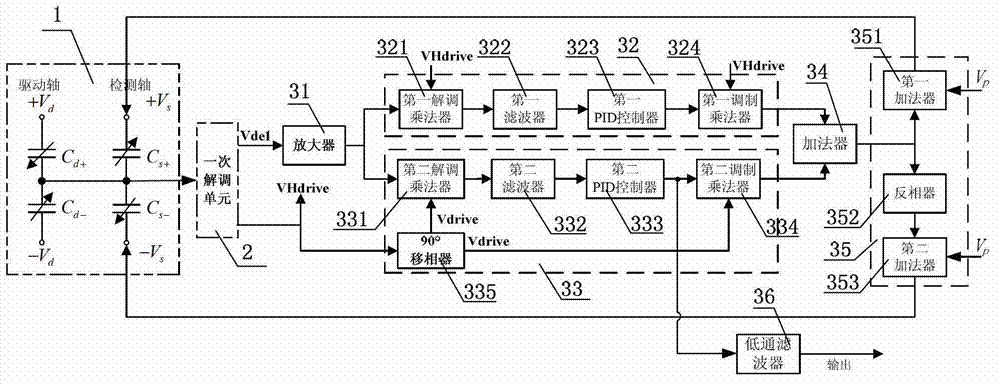
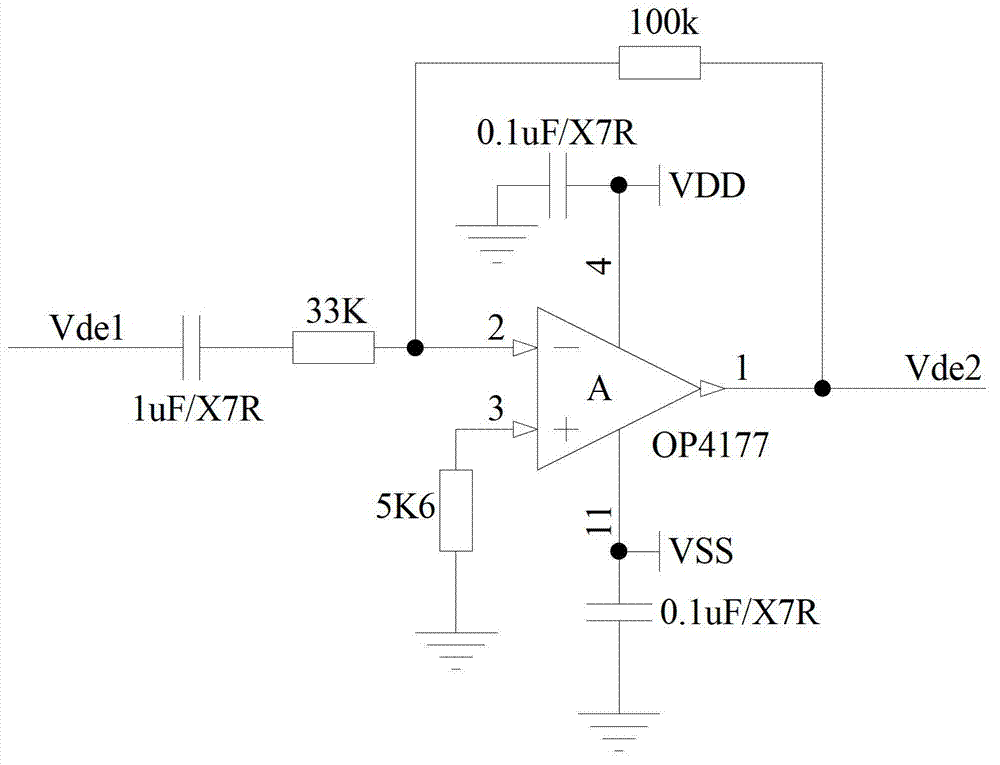
Silicon microgyroscope performance improving method and device based on force balance closed-loop control
ActiveCN103162680AImprove detection accuracyImprove sensitive output signal-to-noise ratioSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesLoop controlPhase difference
The invention discloses a silicon microgyroscope performance improving method and device based on force balance closed-loop control. The method comprises the following steps that: a detecting signal is modulated to a driving signal after being subjected to demodulation, filtering and PID control by the driving signal, thus acquiring a cross coupling error signal; a driving orthogonal signal which obtained by carrying out 90-degree phase shift on the detecting signal by the driving signal is subjected to demodulation, filtering and PID control so as to obtain a Coriolis signal; the cross coupling error signal and the Coriolis signal are overlapped and are loaded to the detecting electrode of a silicon microgyroscope together with a bias direct current. The device comprises an amplifier, a 90-degree phase shifter, a cross coupling error signal acquiring unit, a Coriolis signal acquiring unit, an adding device and a voltage output unit. According to the invention, force applied to detecting a quality block is counteracted so as to keep a detecting element at an original place, therefore, the influences of large cross coupling error, characteristic parameter drifting, phase difference in synchronous demodulation and the like on the performance of the silicon microgyroscope can be effectively avoided.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
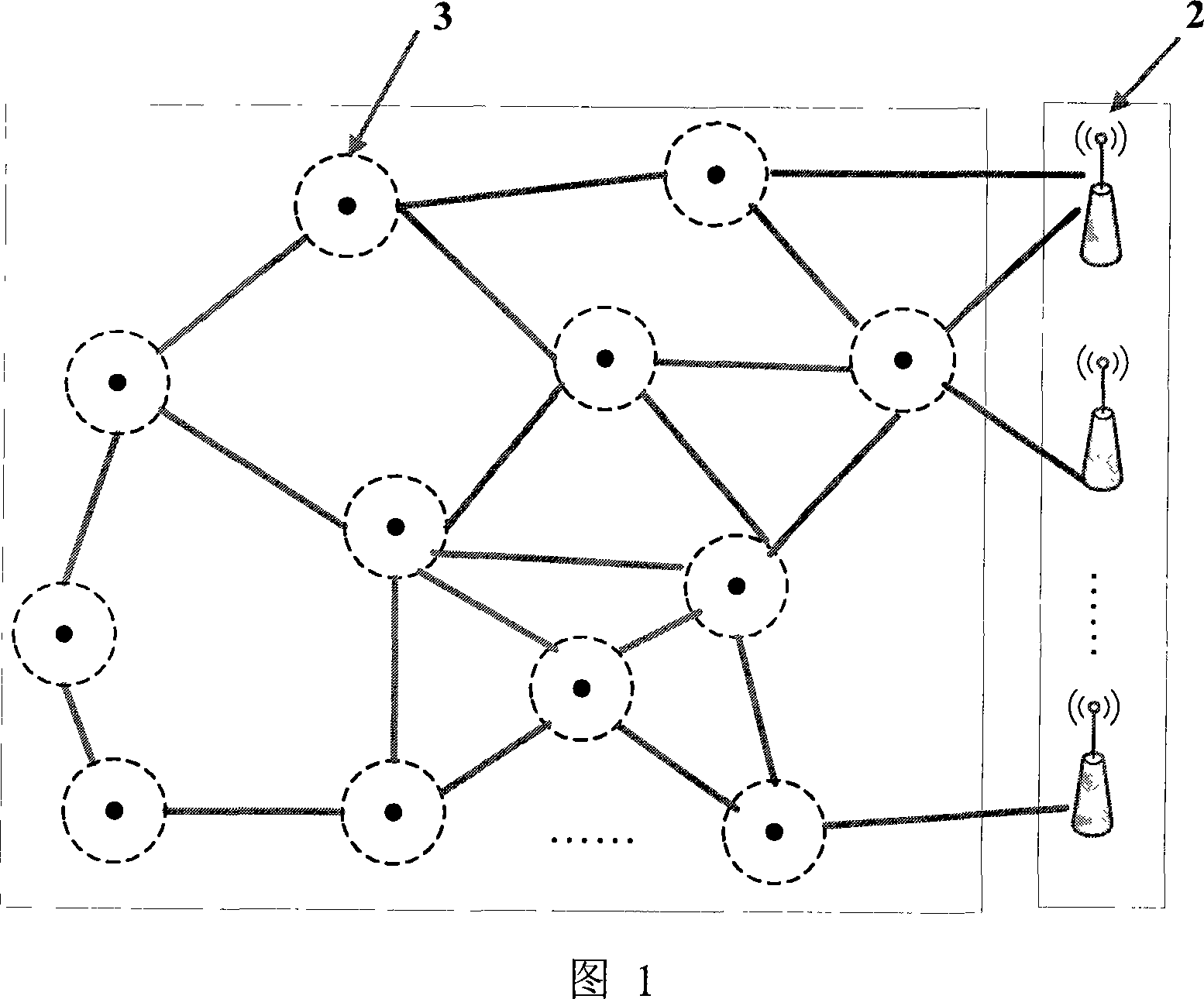
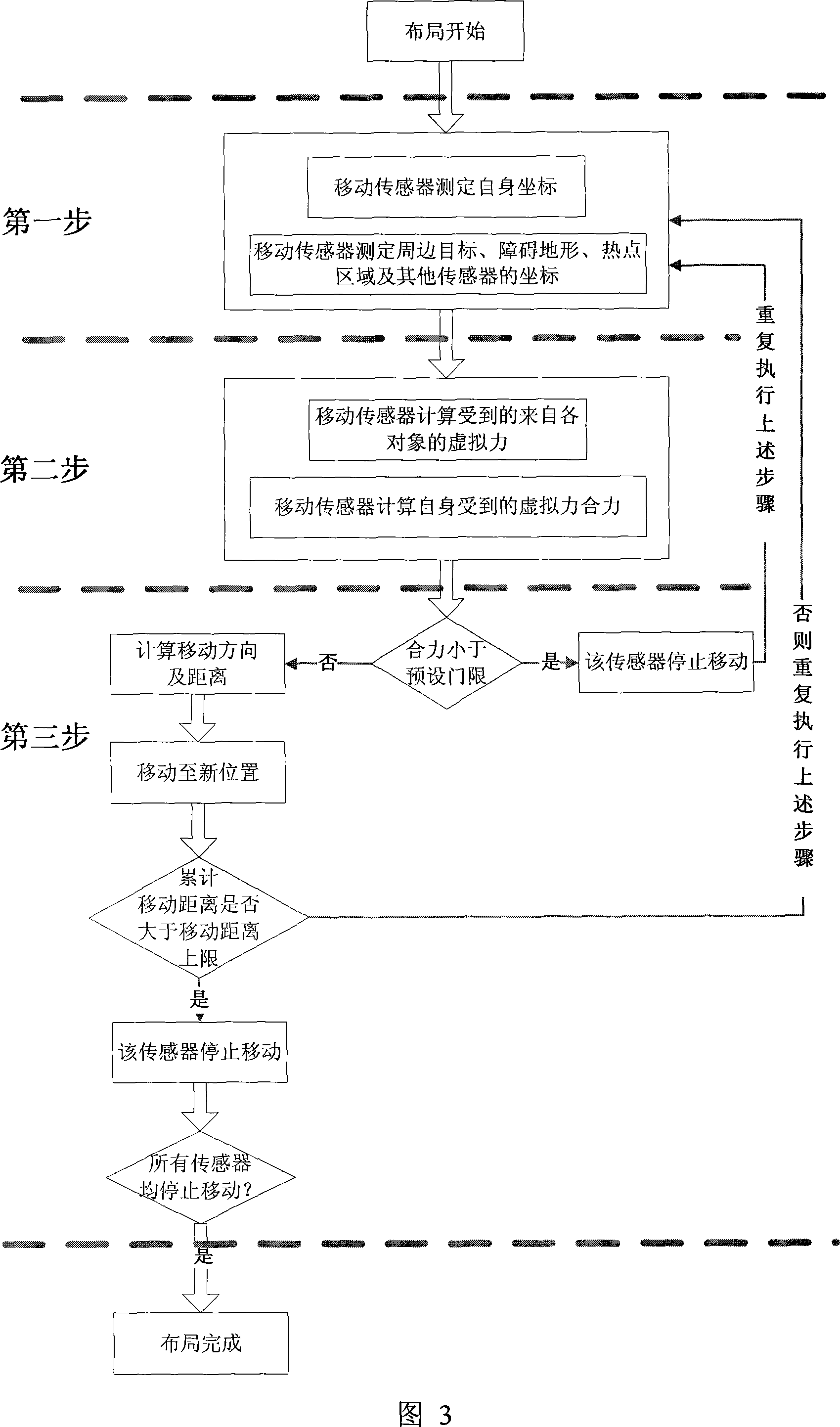
Method and device for layout mobile radio sensor network node based on virtual force
InactiveCN101051973ALayout Auto AdjustImprove observation effectData switching by path configurationMobile wireless sensor networkWireless sensor networking
The method comprises: estimating the direction and distance that the sensor node should be moved by calculating the size and direction of virtual force loaded by each sensor node; driving the sensor node to make relevant movement until reaching a force-balanced point-namely realizing a distribution of sensor network node. By the invention, the sensor nodes can automatically move according to its located geographical environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hemispherical resonance micro mechanical gyroscope and processing technology thereof
ActiveCN103528576AReduce the driving voltageReduce output noiseDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesGyroscopeSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to a hemispherical resonance micro mechanical gyroscope. The hemispherical resonance micro mechanical gyroscope comprises a resonance layer, wherein the resonance layer comprises a hemispherical shell which has a concave inner surface and an outer surface opposite to the inner surface, the peak of the hemispherical shell is an anchor point, a plurality of silicon spherical surface electrodes are arranged around the hemispherical shell, the silicon spherical surface electrodes comprise drive electrodes, force balance electrodes, signal detection electrodes and shield electrodes, the drive electrodes, the force balance electrodes and the signal detection electrodes are separated by the shield electrodes, the hemispherical shell and the plurality of silicon spherical surface electrodes surrounding the hemispherical shell form a plurality of capacitors, and the resonance layer is made of polycrystalline silicon or silicon dioxide or silicon nitride or diamond. The hemispherical resonance micro mechanical gyroscope adopts the technology based on silicon micro machining, has small size and low production cost, has batch production capacity and has the sensitivity not depending on the amplitude, has low drive voltage, can greatly lower the output noise, and has higher accuracy compared with the existing gyroscope.
Owner:NORTH ELECTRON RES INST ANHUI CO LTD
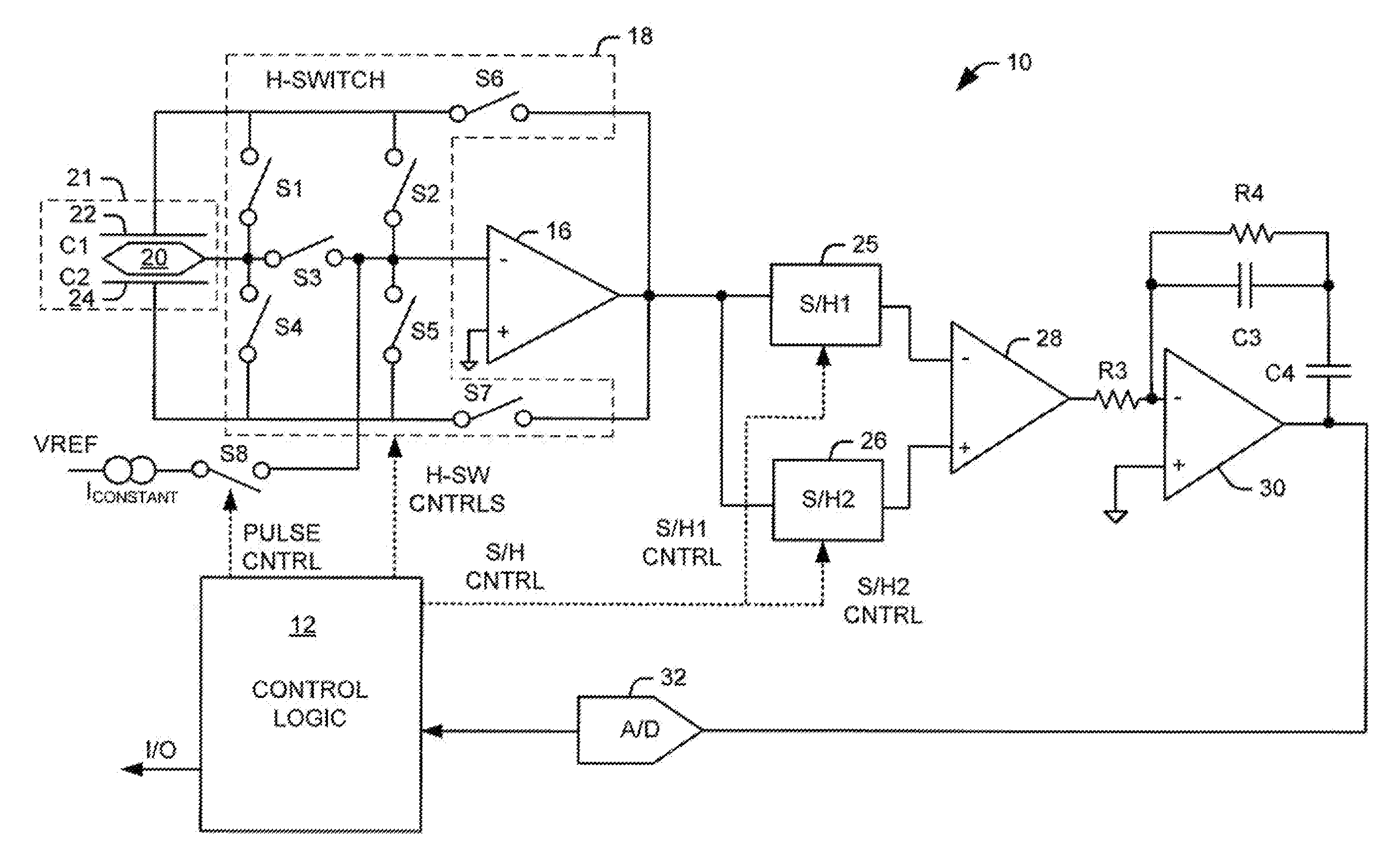
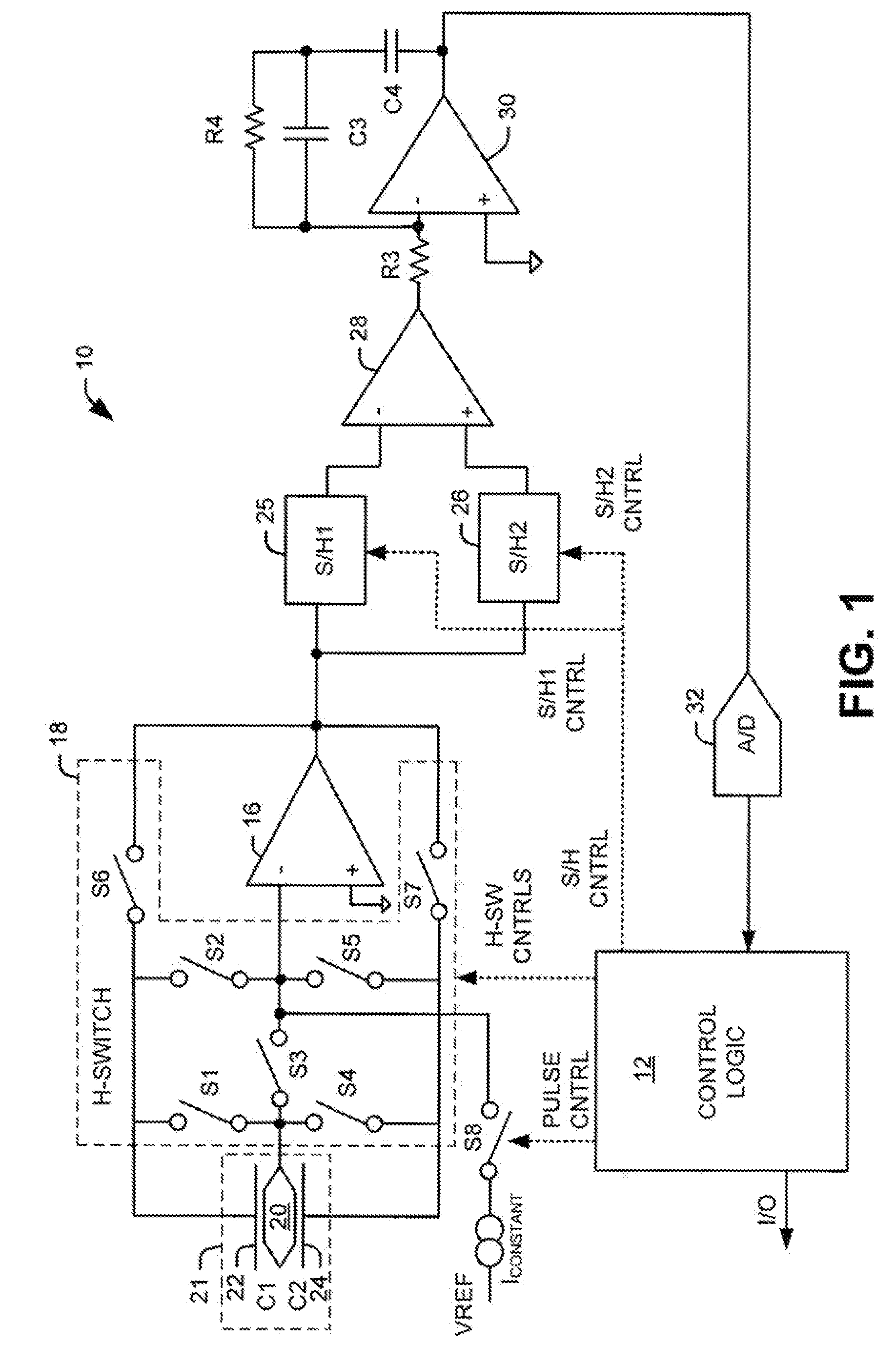
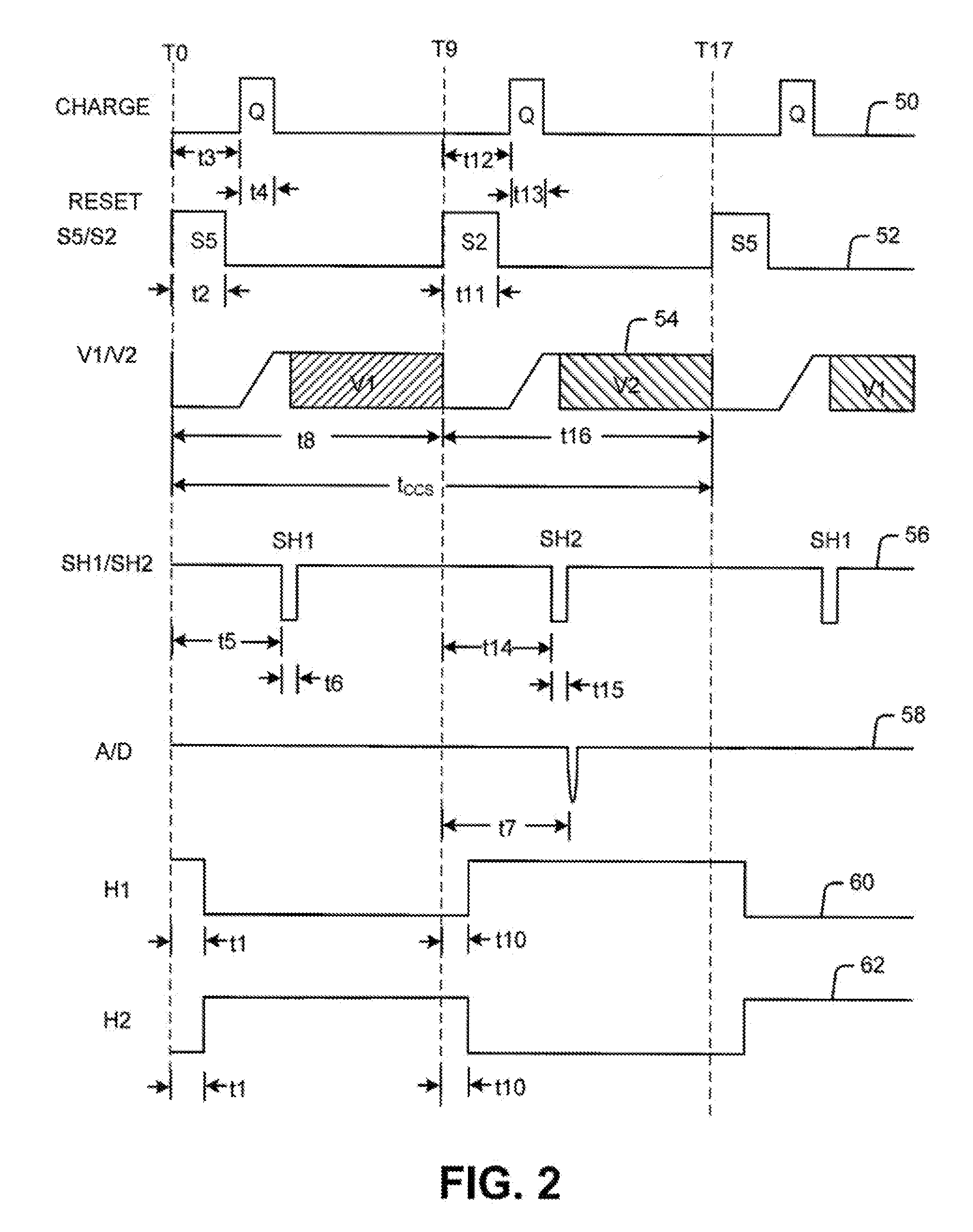
System and Method for Mitigating Errors in Electrostatic Force Balanced Instrument
ActiveUS20080295597A1Reduce errorsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesWeighing apparatus testing/calibrationElectrical polarityEngineering
System and method for mitigating errors in electrostatic force balanced instrument is provided. The system and method mitigate errors in measurement readings caused by charge buildup in force balanced instruments that employ charge pulses to generate an electrostatic force to null an inertial proof mass disposed between opposing electrodes. The system and method mitigate charge buildup by applying charge pulses to each opposing electrode of a sensing element for a given charge cycle time period in a normal polarity configuration followed by charge pulses to each opposing electrode of the sensing element for a second given charge cycle time period in a reverse polarity conjuration.
Owner:LITTON SYST INC
Buoyancy force and attitude balancing device used for long-voyage AUV and control method
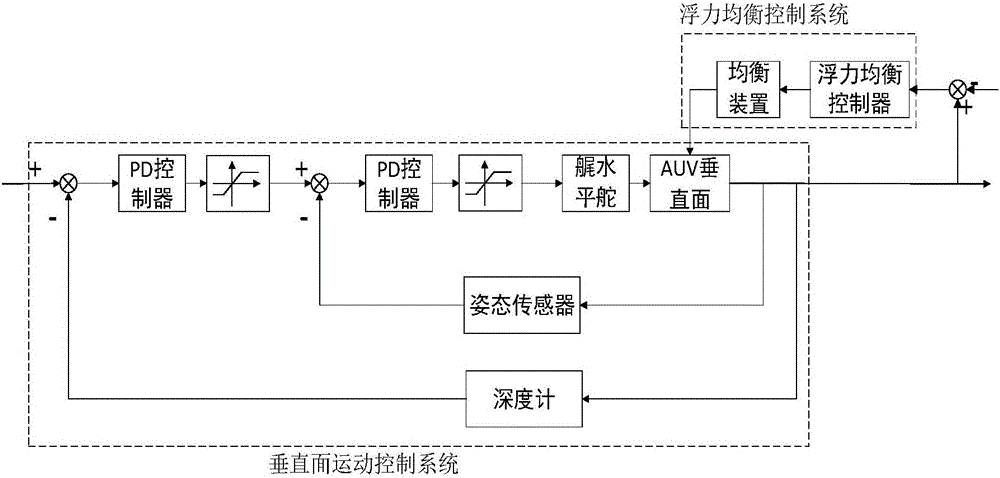
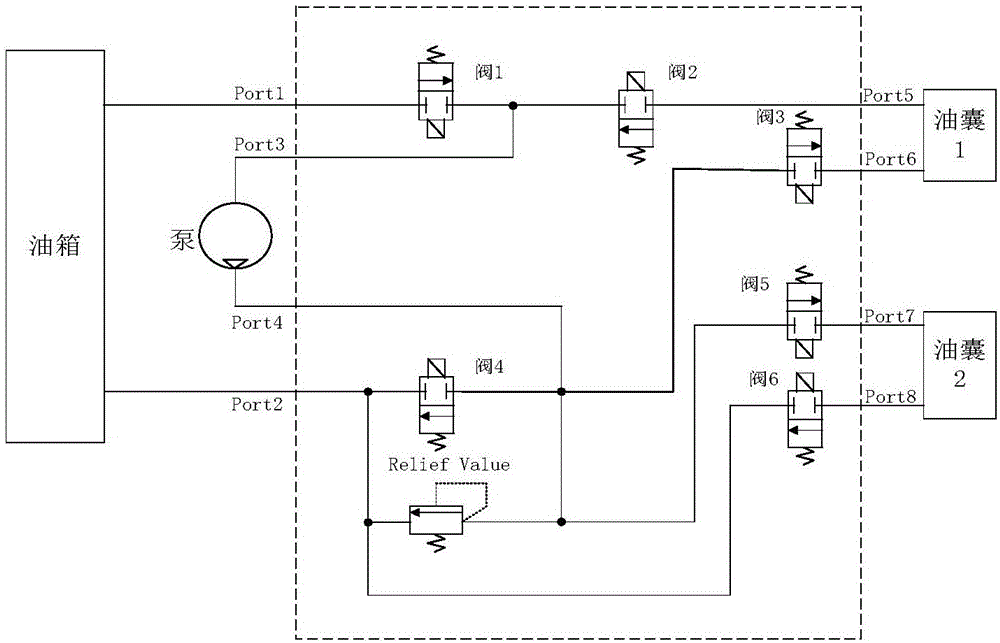
ActiveCN106542071AVoyage savingIncrease the voyageUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentVertical planeUnderwater navigation
The invention provides a buoyancy force and attitude balancing device used for long-voyage AUV and a control method. The buoyancy force and attitude balancing device comprises a buoyancy force balancing device, a buoyancy force balancing controller, a vertical plane motion controller, an attitude sensor and a depth sensor, wherein the attitude sensor is used for detecting an attitude, during underwater navigation, of the AUV; the depth sensor is used for detecting depth, during underwater navigation, of the AUV; the vertical plane motion controller is used for controlling the AUV to move at definite depth on the vertical plane; the buoyancy force balancing controller is used for controlling speed that an oil pump pumps oil into oil bags or sucks oil from the oil bags in the buoyancy force balancing device; the buoyancy force balancing device is used for regulating buoyancy force and a longitudinal inclination attitude, during underwater navigation, of the AUV; the buoyancy force balancing device consists of a pressure-resistant oil tank and two oil bags; the pressure-resistant oil tank is on the gravity center of the AUV; and the two oil bags are separately arranged at the bow and the stern of the AUV. The buoyancy force and attitude balancing device provided by the invention can be used for effectively regulating buoyancy force and gravity force balancing, in water, of the AUV, and eliminating longitudinal inclination angle errors of the AUV, so that resistance when the AUV navigates at definite depth is reduced, and AUV voyage is increased under the condition of carrying same energy sources.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Towing device for ship model test in ice zone
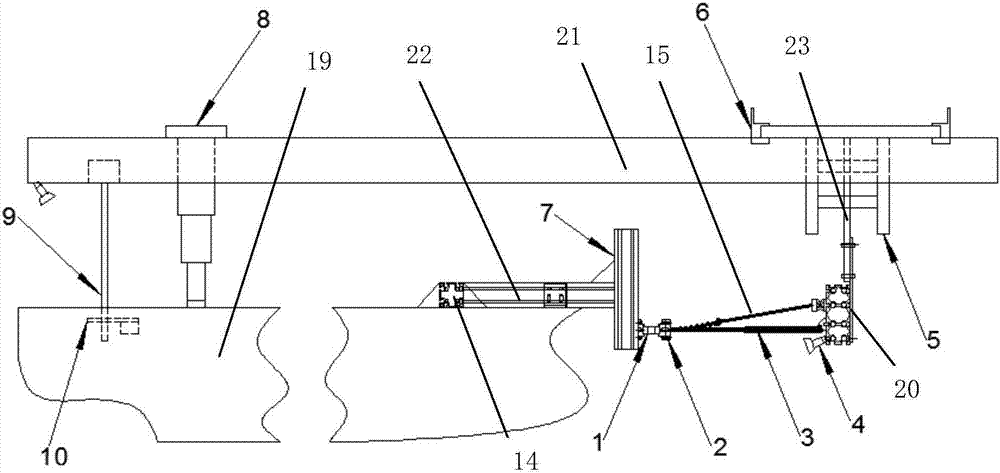
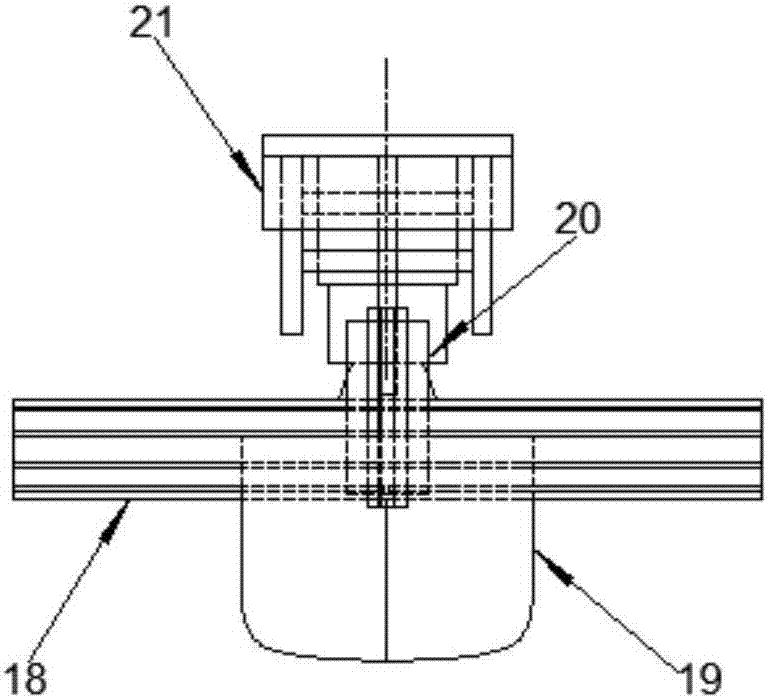
ActiveCN107097901AAvoiding Negative Values in Resistance MeasurementsExact courseHydrodynamic testingVessel designingMarine engineeringModel test
The invention provides a towing device for a ship model test in an ice zone. The towing device comprises a fixing device used for being mounted on a ship model, a balance fixing device, a traction device and a towing platform, wherein the balance fixing device is used for fixing a force balance in the process of test; one end of the traction device is connected with the balance fixing device through a damping rod buffer and two tension springs, and the other end of the traction device is connected with a fixing mold frame of the towing platform through plastic-coating steel wires, the damping buffer and aluminum profiles; the fixing mold frame is fixed on a side axle of a laboratory trailer; besides, a guide rod and a fastening and lifting device control cabinet are mounted. The towing device disclosed by the invention is suitable for the towing test research for the ship model during the sailing of the ship model in the ice zone, and has stable course stability, so that hydrodynamic performance of the ship model during the sailing of the ship model in the ice zone can be more reliably measured, and the accuracy of the test is effectively improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
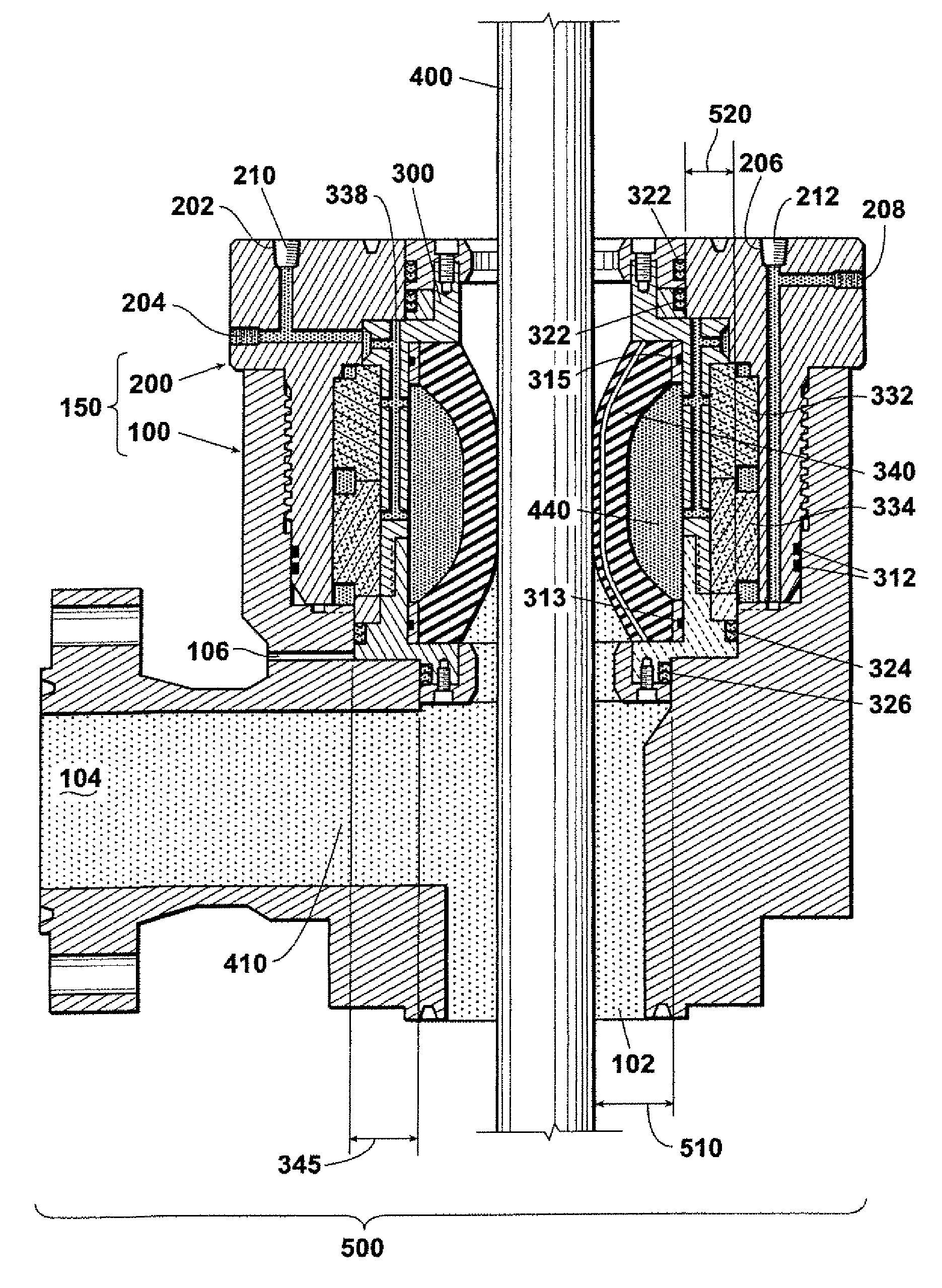
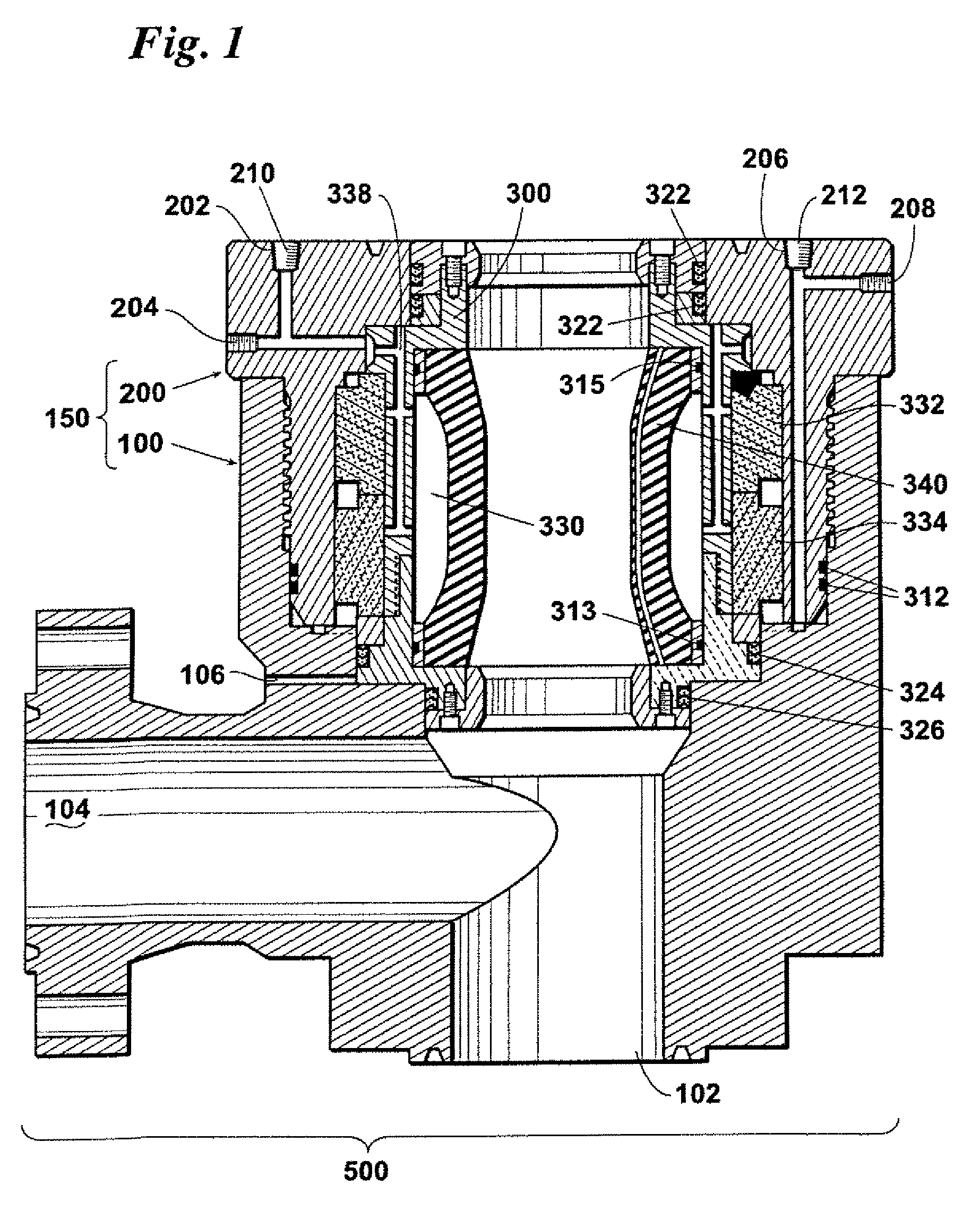
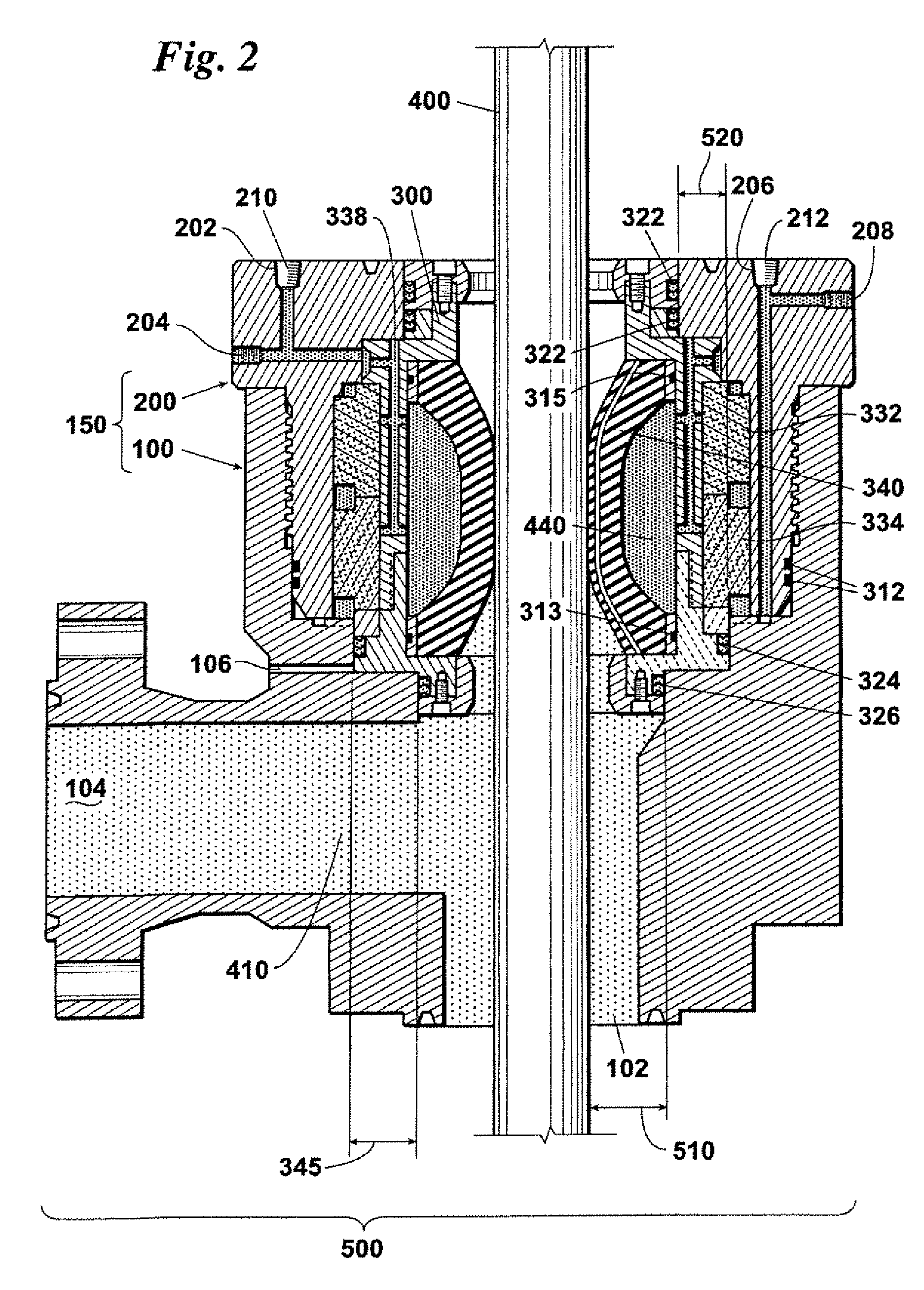
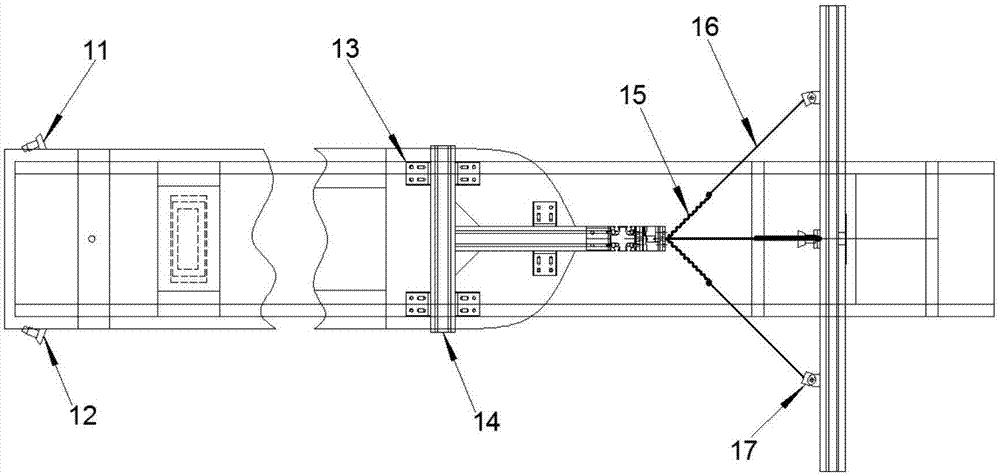
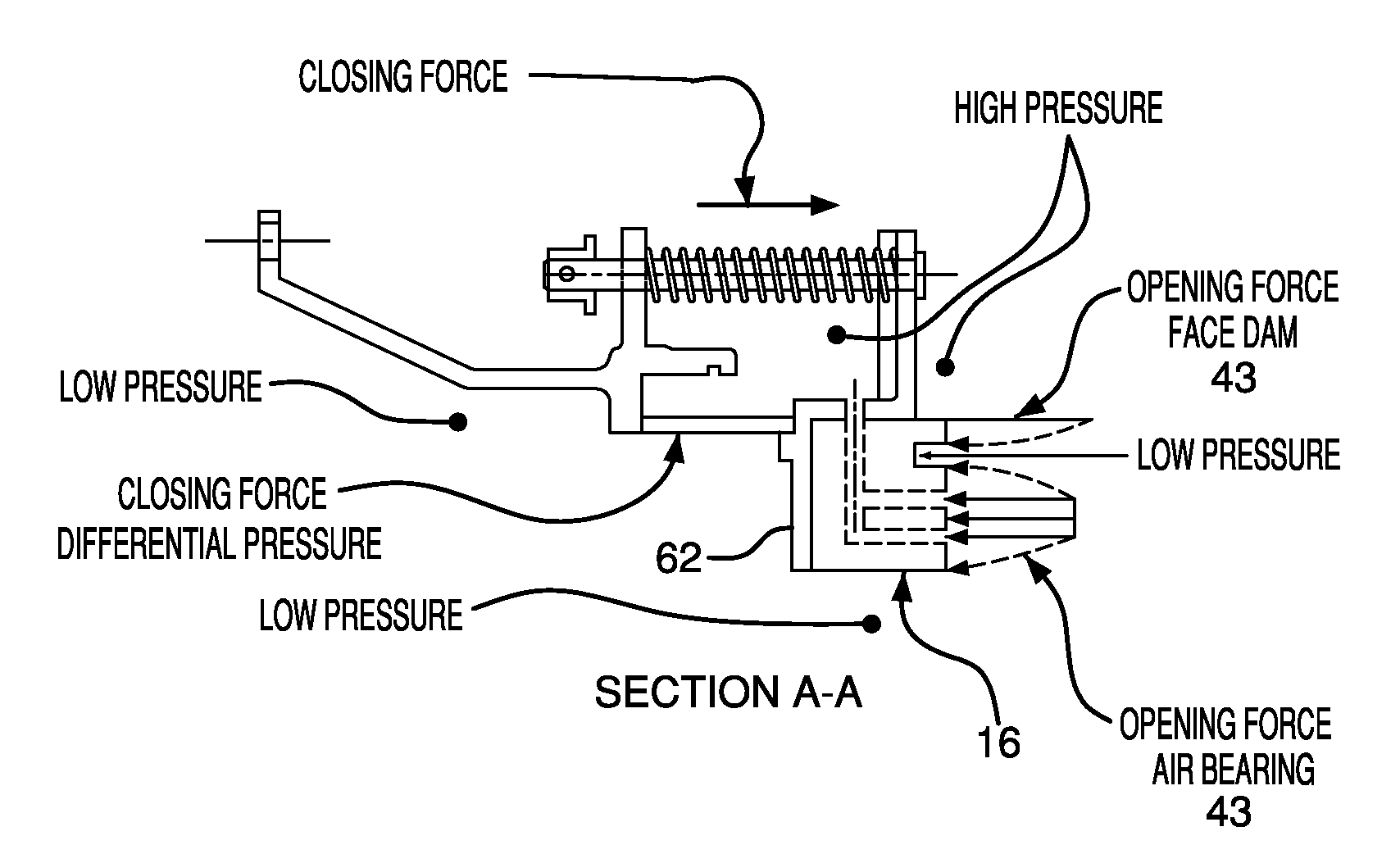
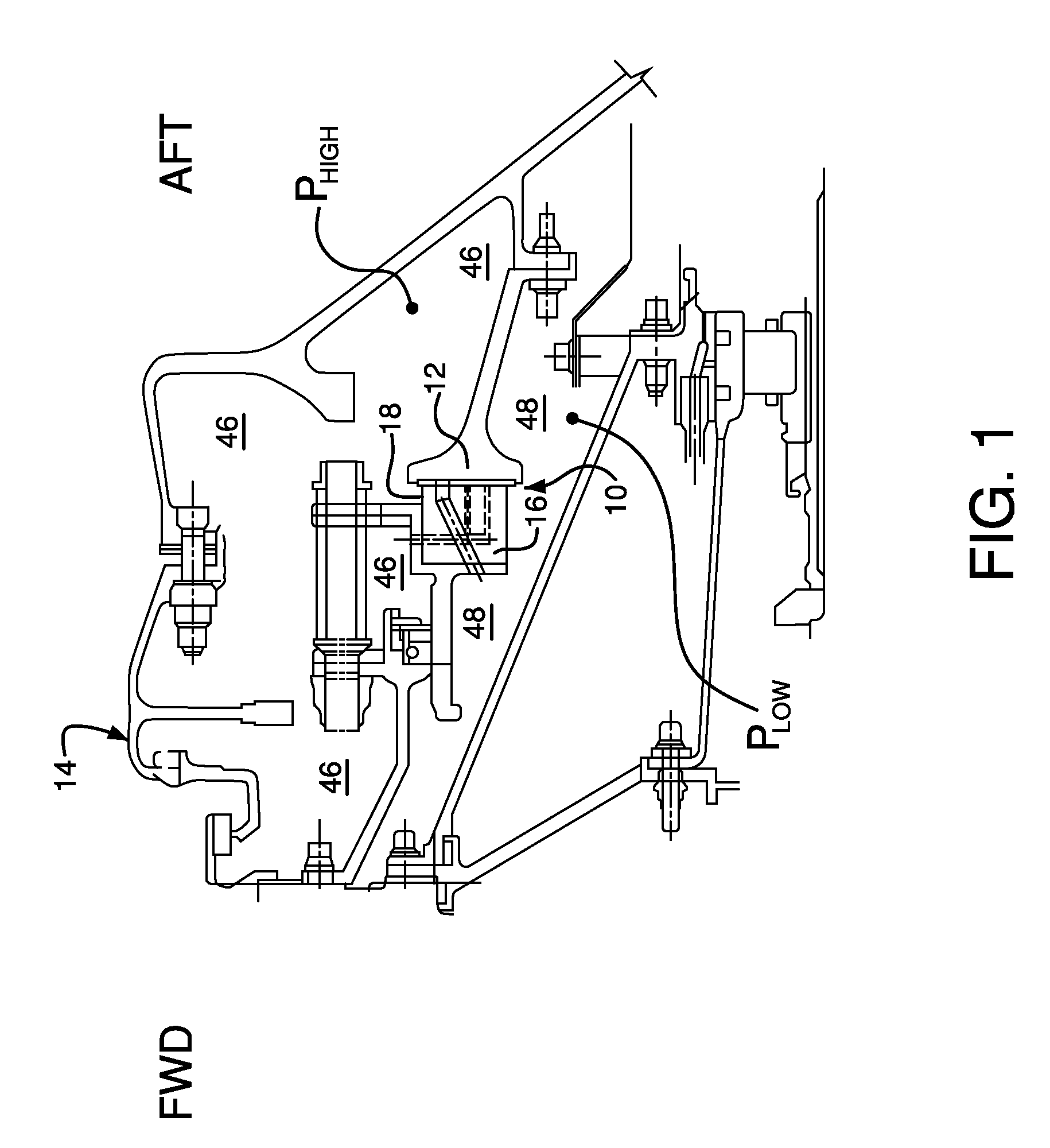
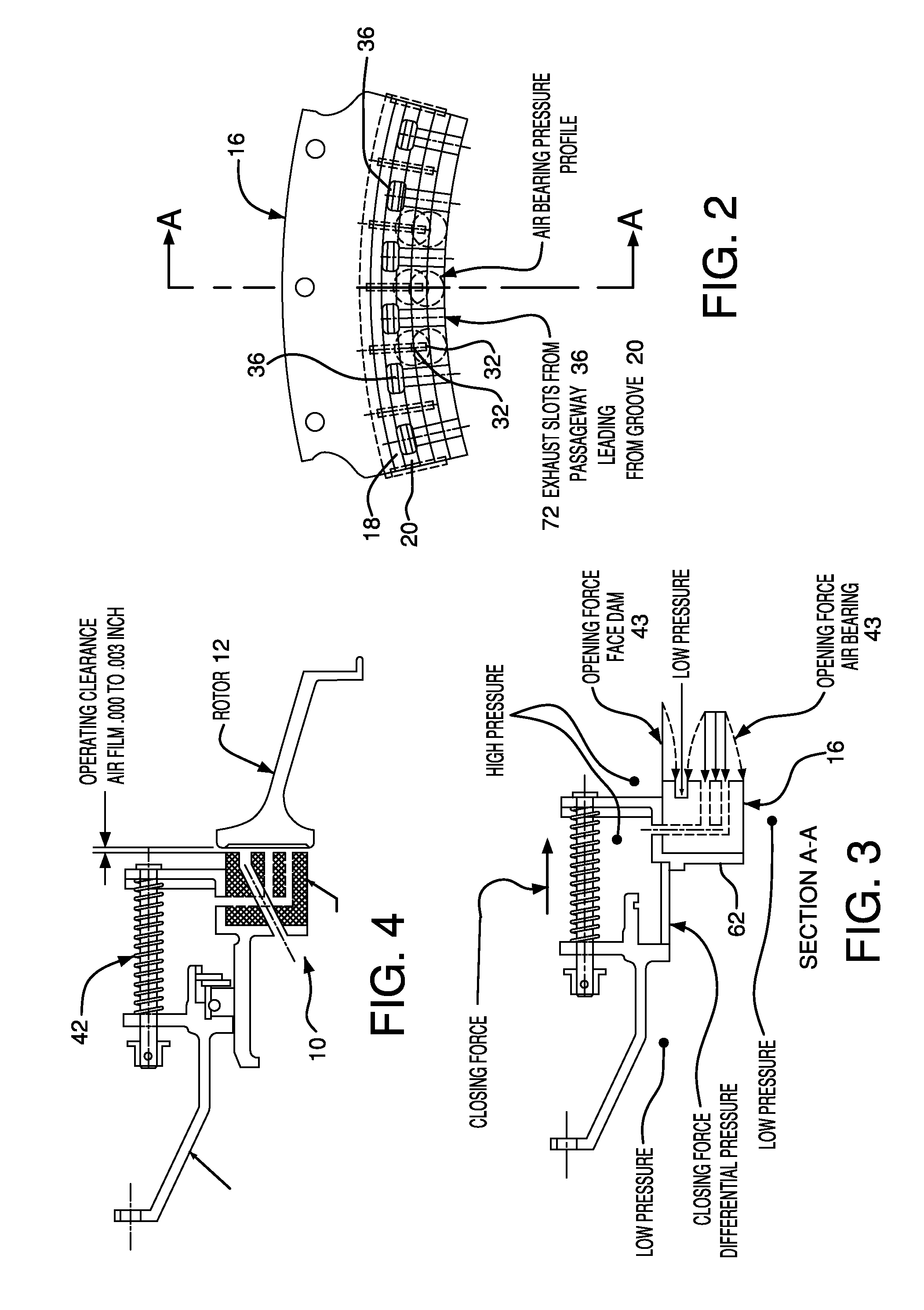
Carbon hydrostatic face seal
A force balanced seal for use with a rotor in the turbomachine has a member in opposed facing disposition to the rotor with a face dam portion of the member having a surface parallel with the sealing surface of the rotor, a groove in the member facing the rotor and bounding the face dam surface, an air bearing surface in the member facing the sealing surface of the rotor, a second passageway through the member from the air bearing surface to a radially outwardly facing surface of the member and a first passageway through the member from the groove to a member surface facing oppositely from the air bearing surface. An operating clearance between the seal and rotor is maintained by a closing force, exerted through a plurality of springs, and an opposing opening force created by pressurized air venting through the second passageway to the first passageway.
Owner:STEIN SEAL
System and method for improved control of tooth movement with elastic repositioning appliances
InactiveUS7374421B2Quality improvementControl over tooth movementOthrodonticsDental toolsCouplingElement analysis
Micro-regional force application improves the control of the orthodontic movement of teeth in all six degrees of freedom. Micro regional force application utilizes an elastic repositioning appliance, a tooth positioner, a polymeric shell, or preprogrammed series of polymeric shells. The key components of the invention are the envelope of freedom, the force applicators, force couplers, counterpart coupling, vector modifiers, seating guides, decouplers, and forced balance points. Further, computerized finite element analysis determines the center of resistance and the center of rotation for each tooth to be moved. The present invention gently rotates and translates one or more teeth to a desired straight position within a treatment plan.
Owner:SOLOMON FREDERICK
Differential wideband vibration sensor
InactiveUS6220096B1Eliminates costly precision tuningIncrease capacitanceVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringField-effect transistor
This invention relates to an apparatus for making highly sensitive differential measurements of acceleration. The vibration sensor includes the use of moveable gate field effect transistors to sense the motion of a cantilever beam relative to the motion sensed by a reference structure, it also includes an actuator element formed by a pair of electrodes actuating electrostatically on the beam. A feedback control loop is also included for force balance operation resulting in a very wide dynamic range for the sensor.
Owner:INTERSCI
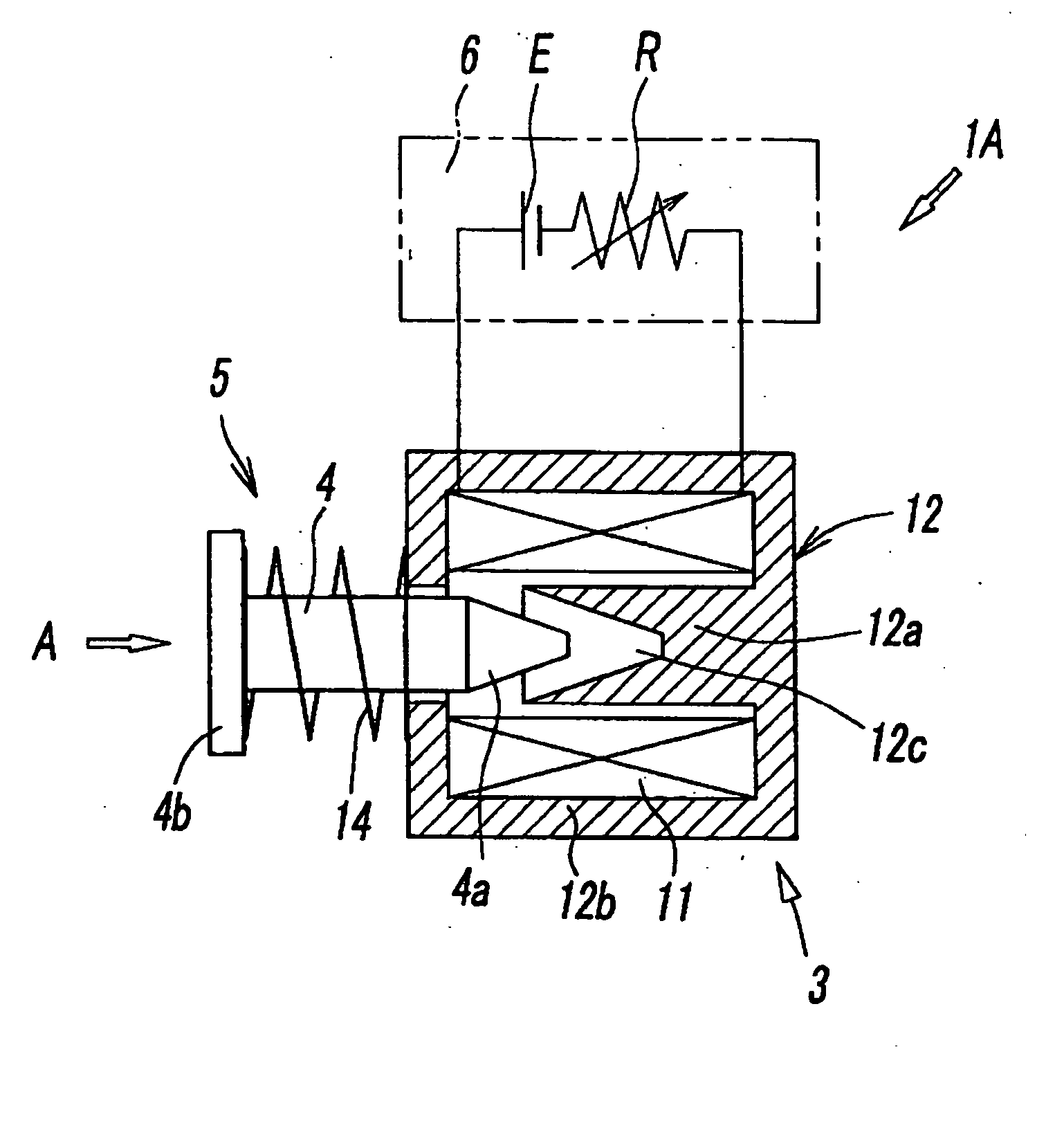
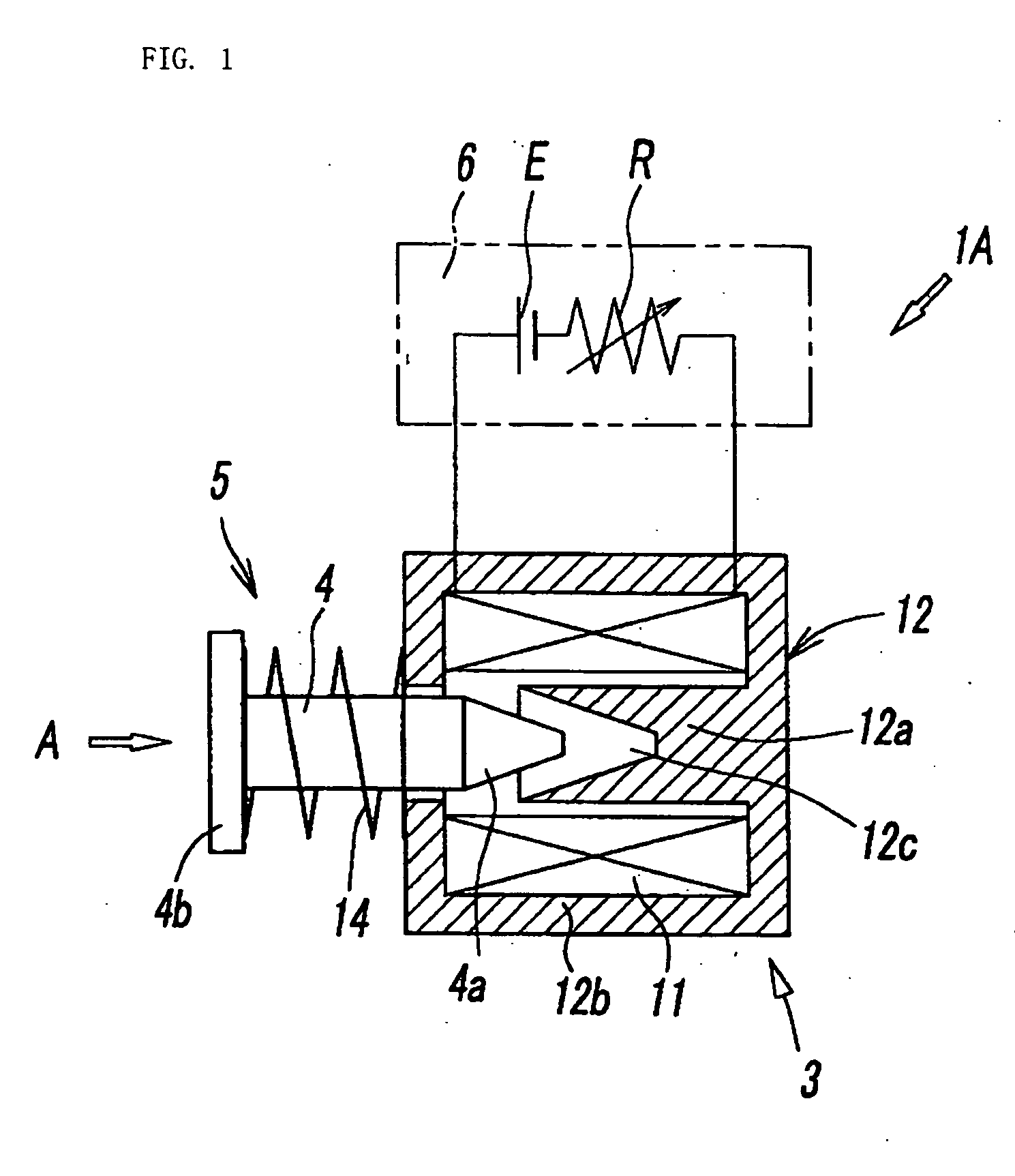
Linear actuator capable of low-speed driving
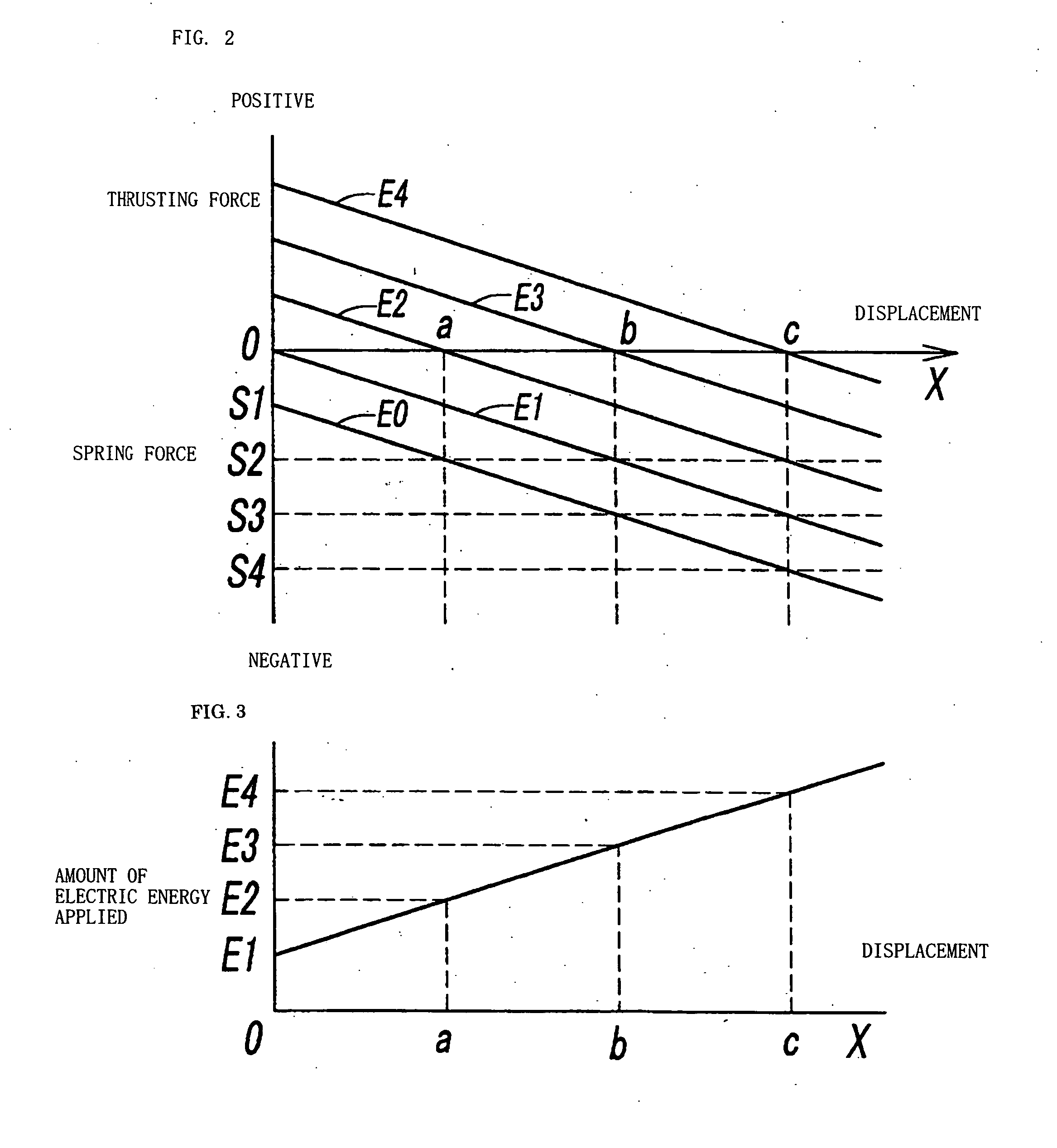
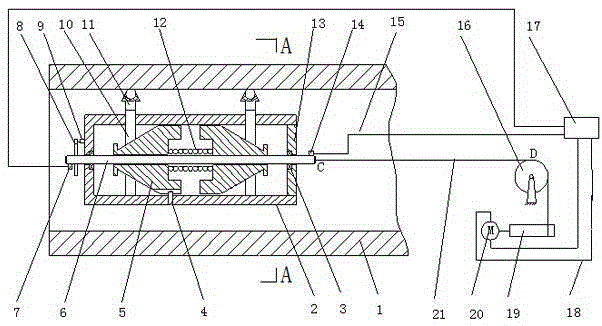
ActiveUS20050012405A1Simple and inexpensiveMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlLow speedSpring force
Disclosed herein is a simple, inexpensive linear actuator which is capable of controlling the displacement of the movable body by regulating the amount of electric energy applied without the necessity of detecting the displacement of the movable body with a displacement sensor or controlling the displacement of the movable body by feedback control in response to the detected value. The linear actuator comprises an electromagnetic unit which generates magnetic force in response to the amount of electric energy applied, a movable body which is displaced linearly by magnetic force as thrust force which is supplied from the electromagnetic unit, a spring means which applies a spring force to the movable body in the direction opposite to the direction of said thrust force, and a control apparatus which controls the amount of electric energy to be applied to said electromagnetic unit, wherein said control apparatus is so constructed as to control the rate of displacement of said movable body in response to the amount of electric energy applied, with voltage or current applied to said electromagnetic unit varying from that which generates a thrust force balancing with said spring force.
Owner:SMC CORP
Self-centering depth hole parameter measurement device
InactiveCN105371775AAccurate measurementTo achieve the purpose of fixing the shaft in the deep holeUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceEngineering
The invention discloses a self-centering depth hole parameter measurement device, comprising a centering device, a measurement recording device and a processing device. The centering device is arranged in a depth center of the workpiece and comprises a sleeve, a centering shaft, three conical bodies, six measurement rods and a spring. The recording device comprises two distance measurement sensors which are fixed on two ends of the centering shaft; the two distance measurement sensors are electrically connected to the control terminal; the processing device comprises a second motor, a reel and a flexible rope; one end of the flexible rope is connected to one end of the centering shaft; the other end of the flexible rope is wound on the reel; the rotation shaft of the reel is connected to the output shaft of the second motor; the two conical bodies move toward the two sides under the resetting force of the spring and a measurement rod slides inside a sliding groove, which causes the measurement rod to radially move outwardly until the measurement head of the measurement rod is abutted against the inner wall of the workpiece depth hole, and thus the two conical bodies are under a force balance state; and, at this time, the centering shaft is positioned on the axis of the depth hole, which achieves the goal of depth hole shaft centering and guarantees the precise measurement of the related parameters of the workpiece depth hole.
Owner:南京上环宇精密检测技术有限公司
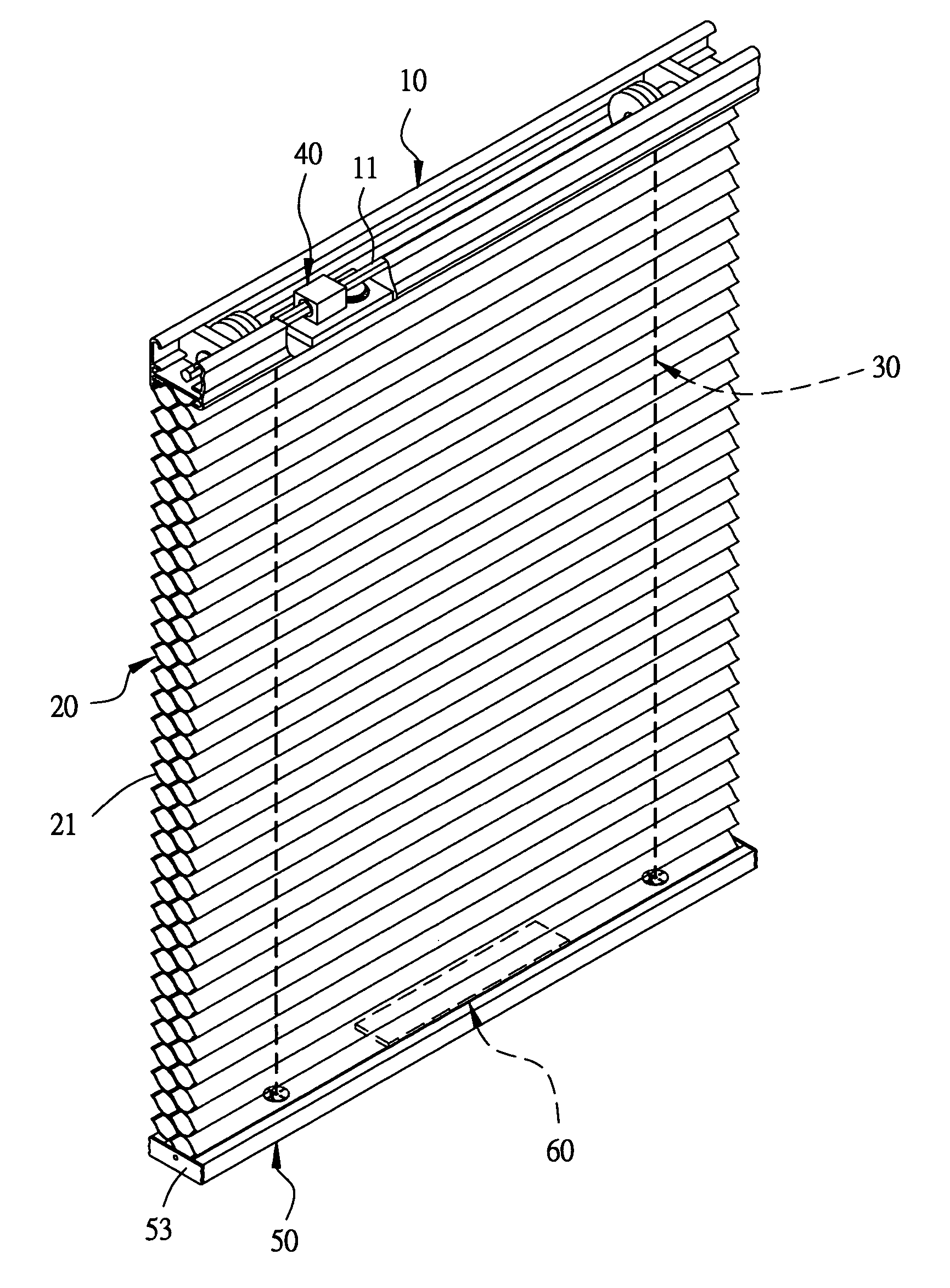
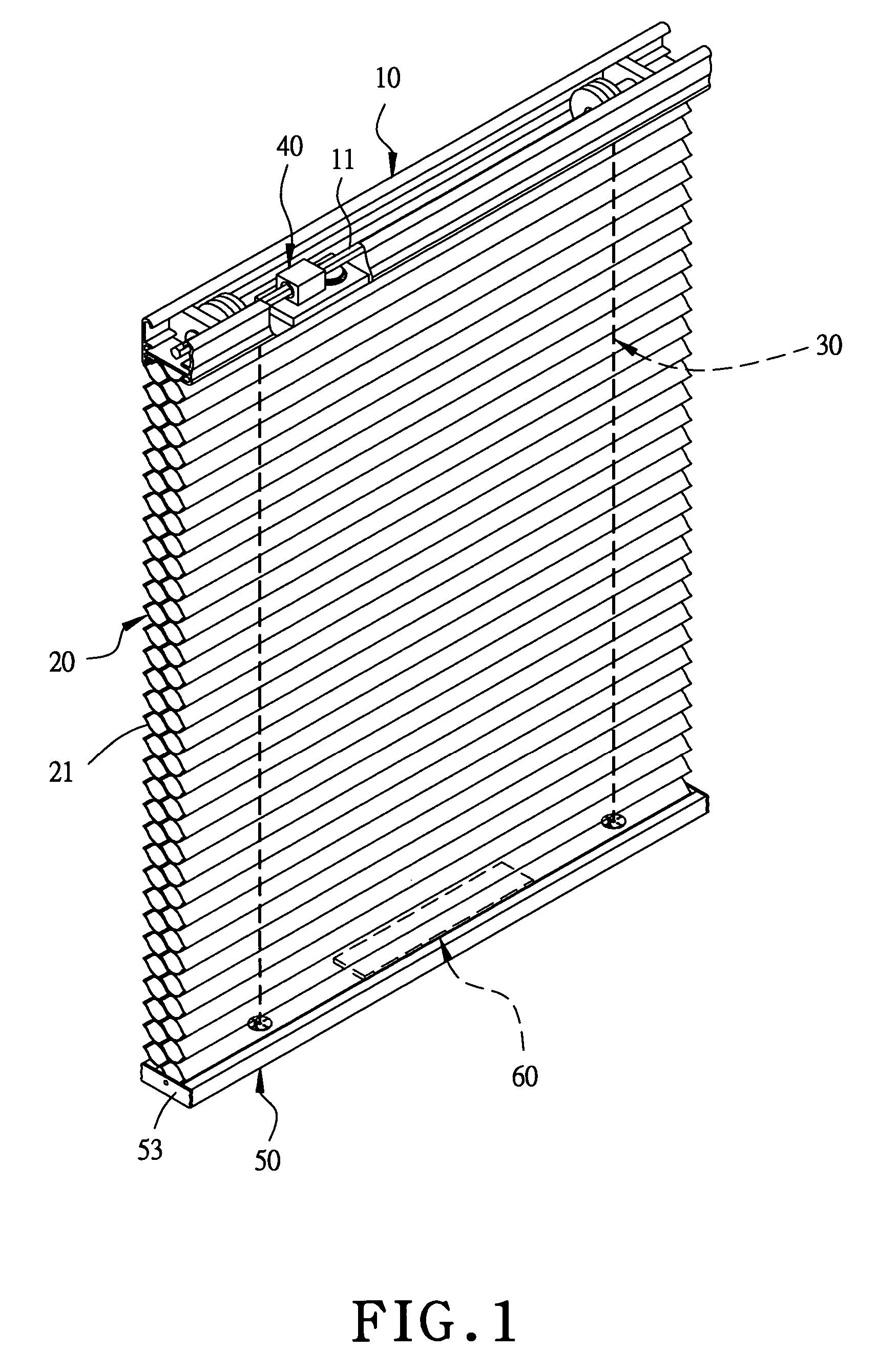
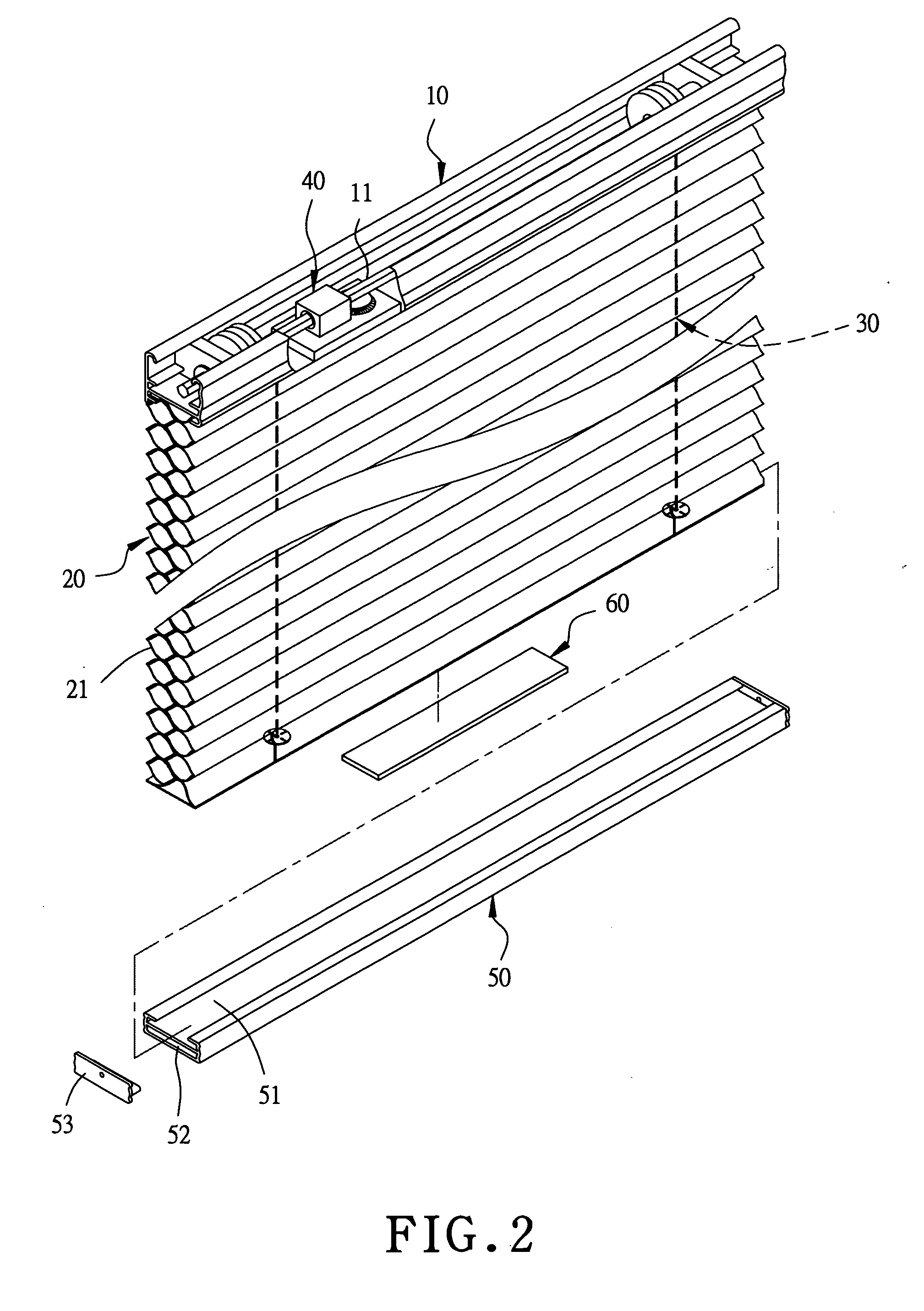
Equilibrium device for a blind without pull cords
An equilibrium device for a blind without pull cords includes at least one movable weight-balancing member installed at a proper location in the interior of the lower rod of a blind. The weight-balancing member is provided for increasing and adjusting the weight of the blind so as to keep the weight of the blind and the elastic force produced by an elastic force mechanism in a force balanced condition after the blind is cut in width and lightened, enabling the blind to be collapsed upward and stretched downward normally.
Owner:NIEN MADE ENTERPRISE CO LTD
Self-force balancing thrust bearing test board
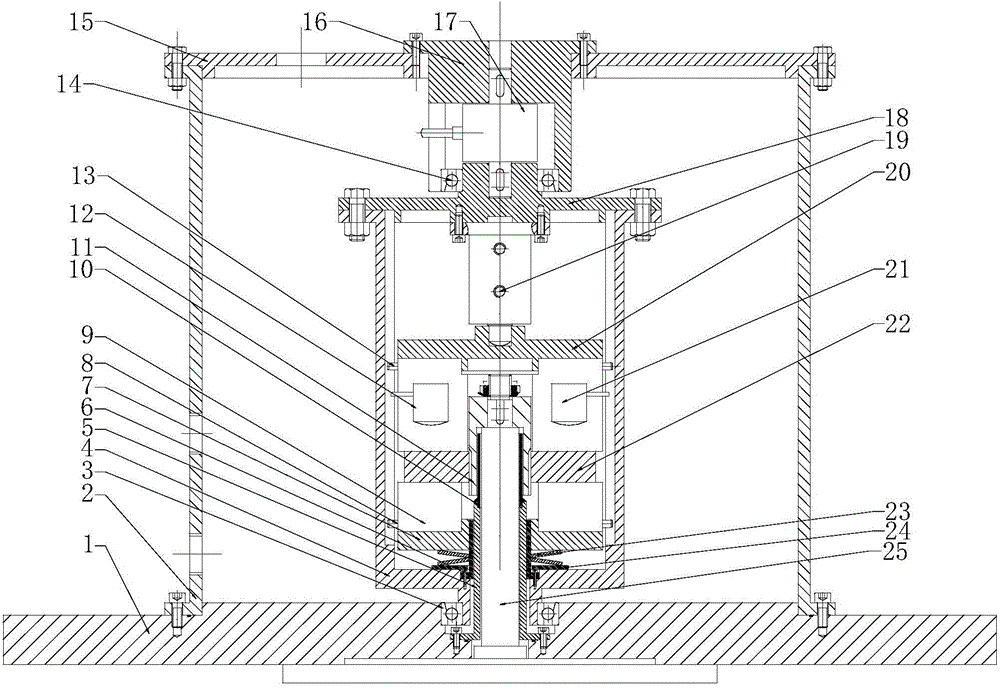
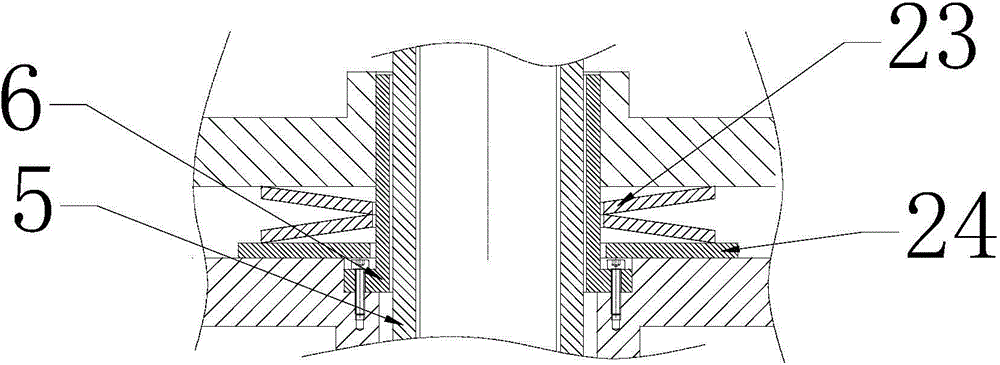
ActiveCN104807641AReduce measurement error of secondary friction characteristicsPrevent leakageMachine bearings testingHydraulic cylinderFriction torque
The invention discloses a self-force balancing thrust bearing test board, which comprises a base; a medium container is connected onto the base; a lubrication medium inlet and a lubrication medium outlet are formed in the medium container; a load-bearing frame is arranged in the medium container; the upper end of the load-bearing frame is connected with an load-bearing frame end cover; a projecting shaft of a torque sensor is respectively connected with a medium container cover bearing seat and the load-bearing frame end cover; the load-bearing frame end cover is connected with a hydraulic cylinder; a piston rod of the hydraulic cylinder is connected with a balancing thrust bearing assembly through an upper load-bearing disc; the balancing thrust bearing assembly and a test thrust bearing assembly are arranged in the load-bearing frame in a back-to-back manner, and share the upper end face and the lower end face of a thrust disc; a lower load-bearing plate is connected with a belleville spring assembly; torque generated by friction between the end face of the thrust disc and the face of a bearing bush and friction torque for supporting an antifriction bearing are measured through the torque sensor; the friction characteristic of a thrust bearing is analyzed through a pressure sensor in the balancing thrust bearing assembly; the service condition of the thrust bearing of a lubricating agent can be simulated. The measurement accuracy of a friction performance coefficient is increased by the self-force balancing thrust bearing test board disclosed by the invention.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com