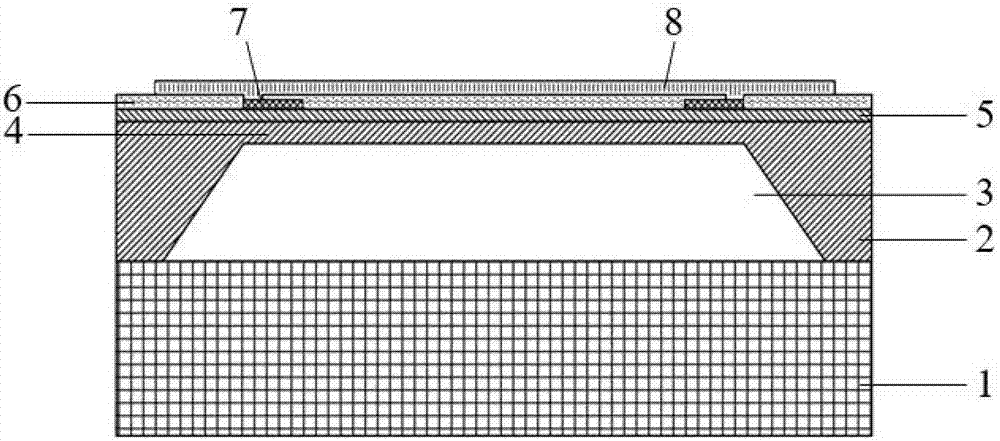
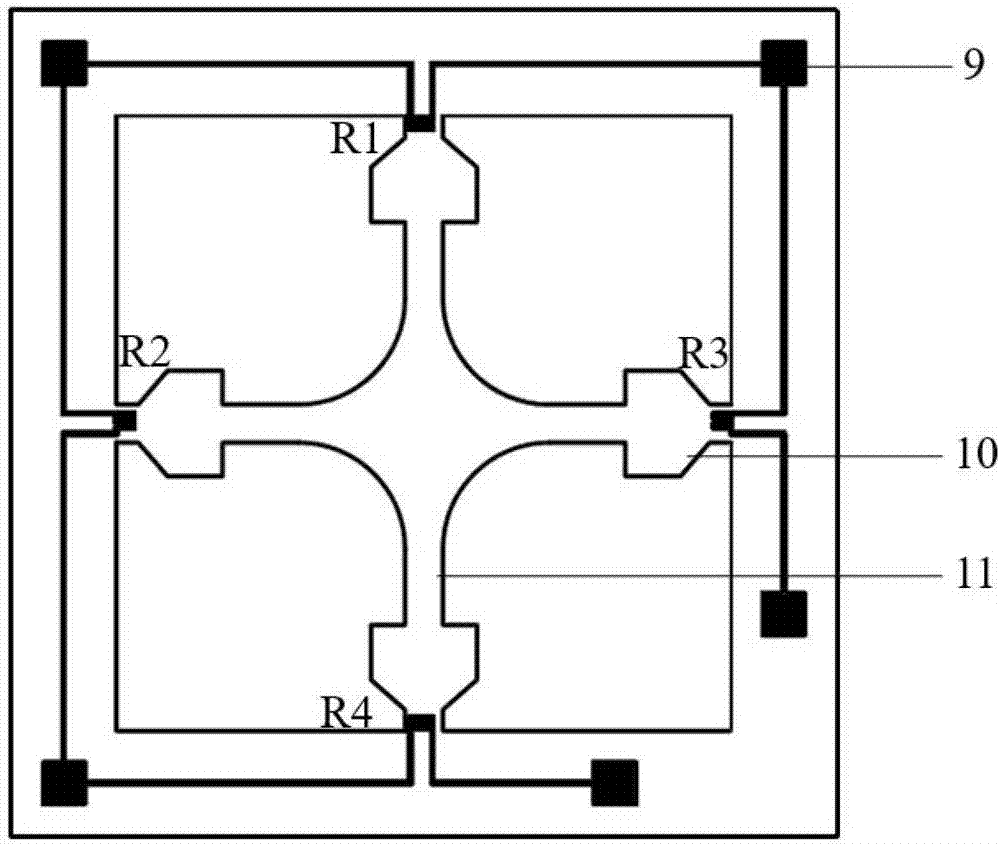
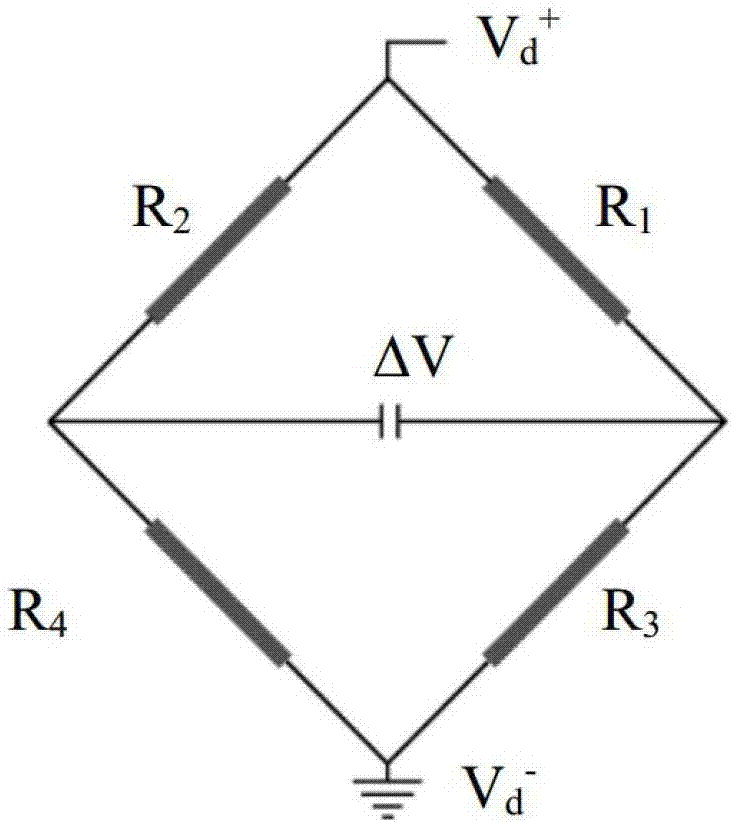
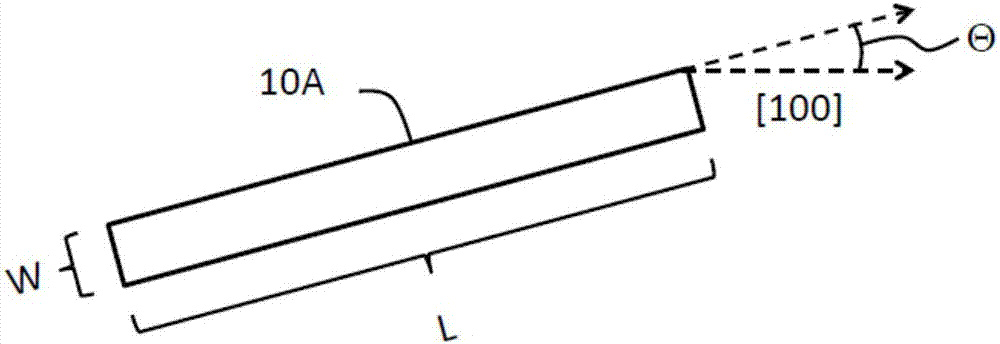
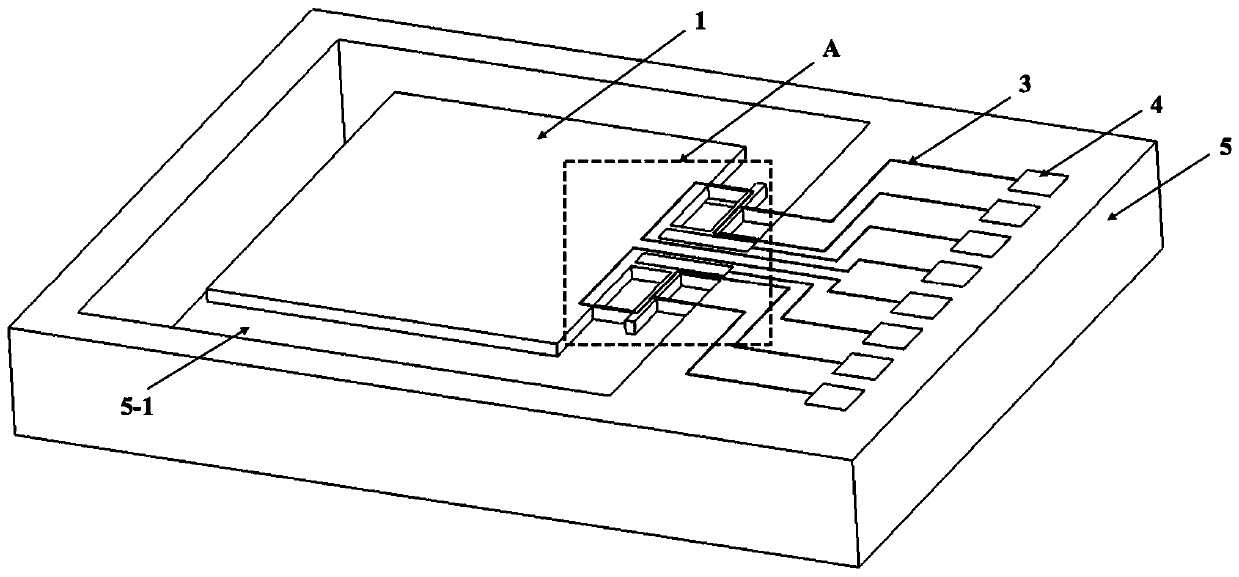
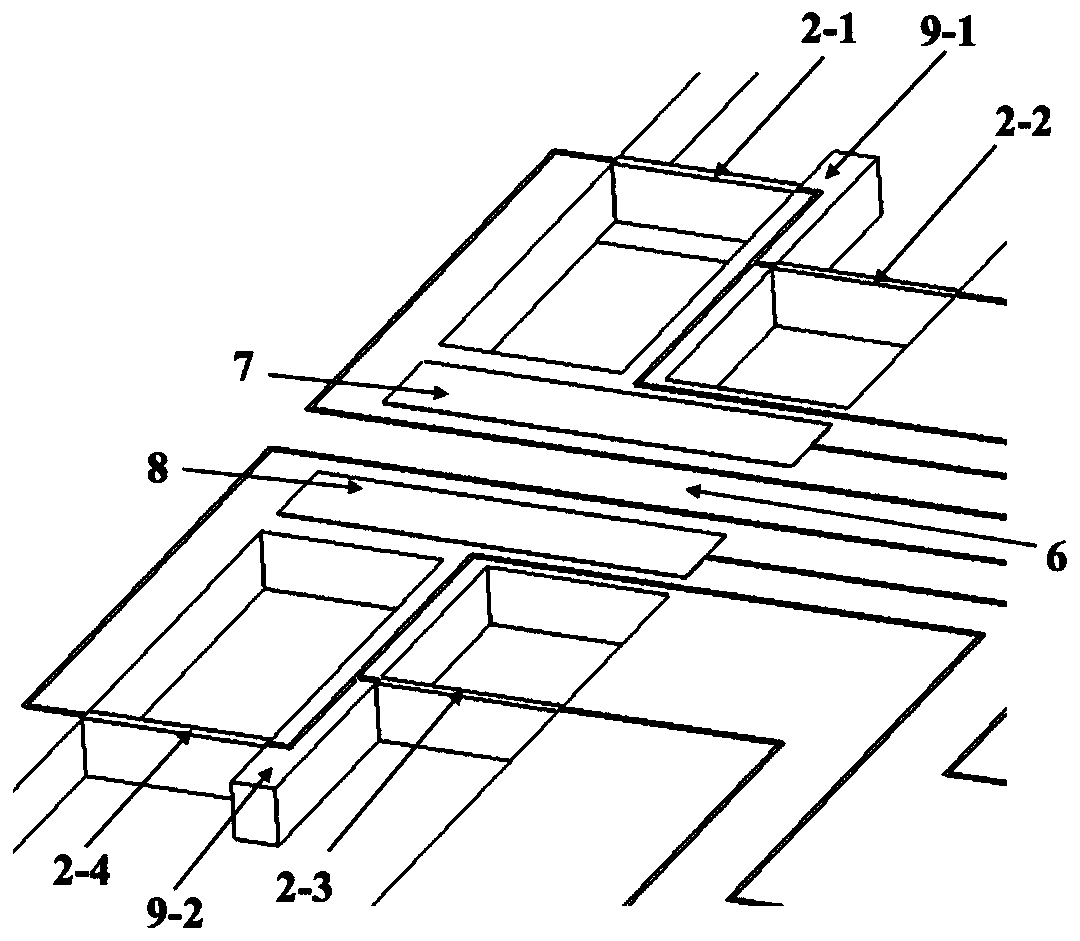
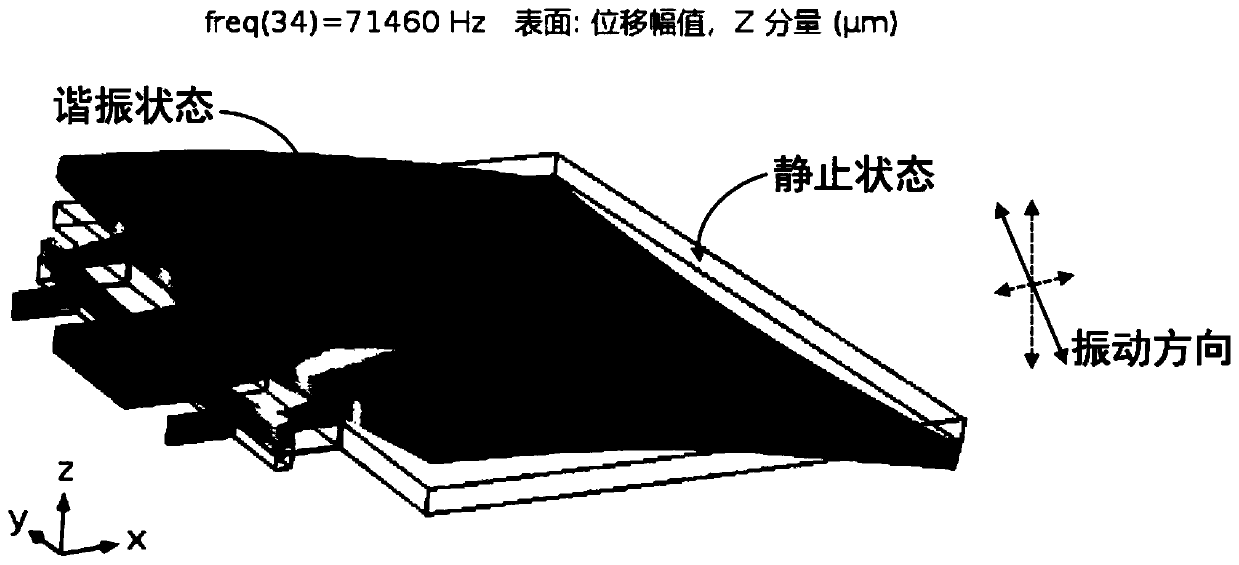
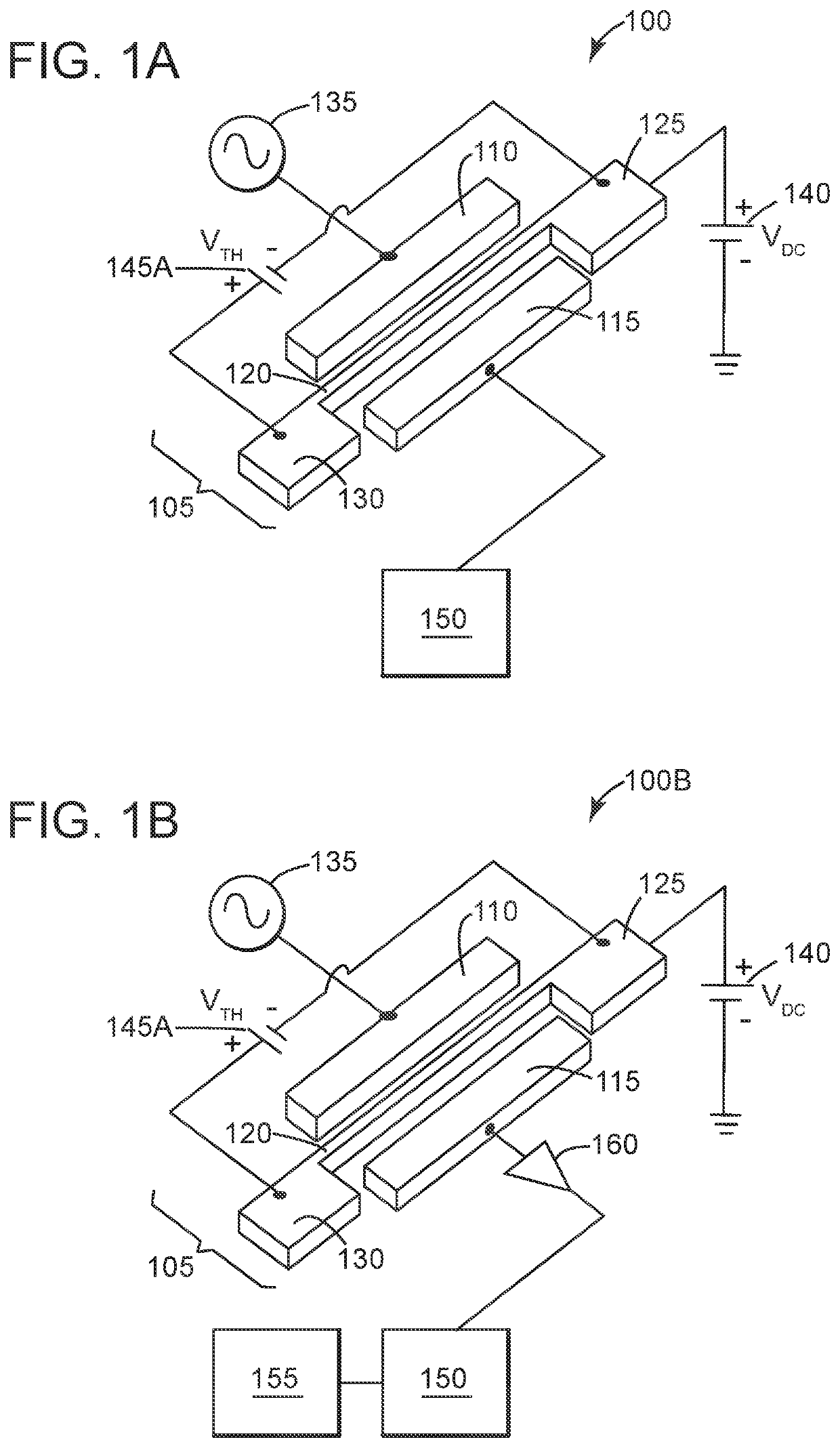
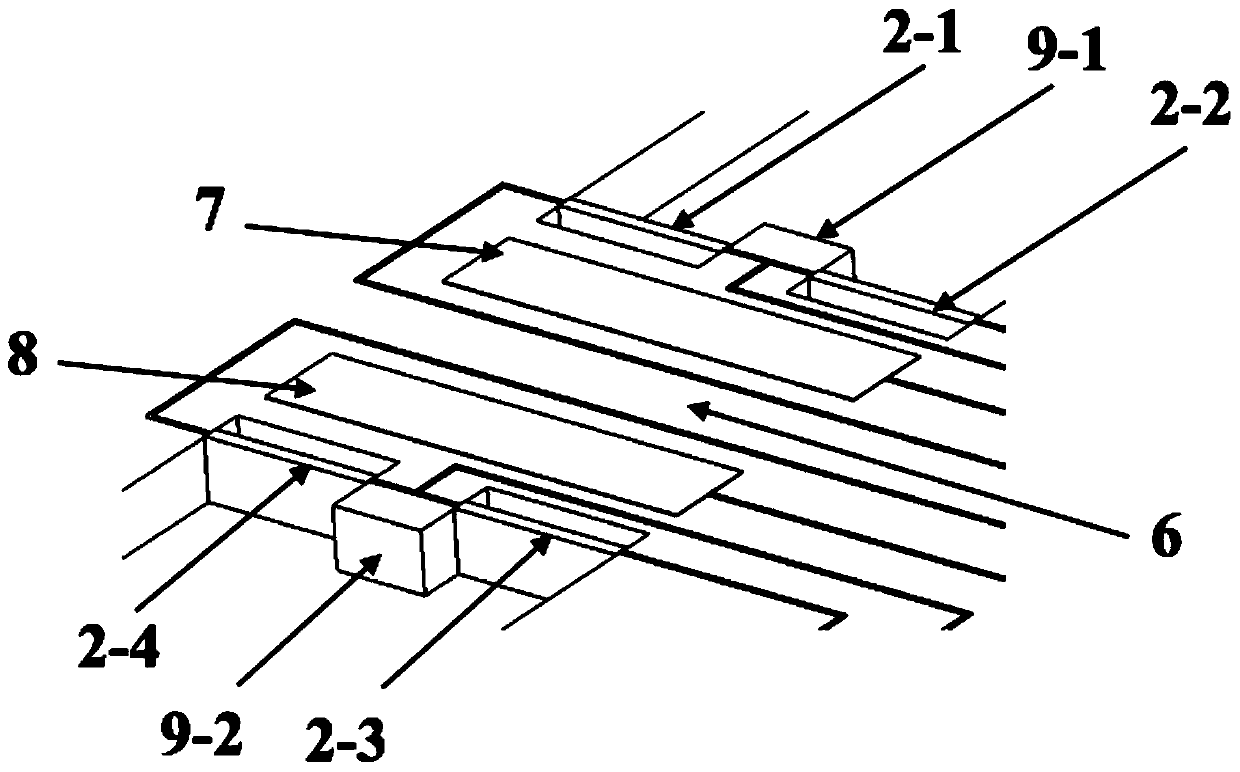
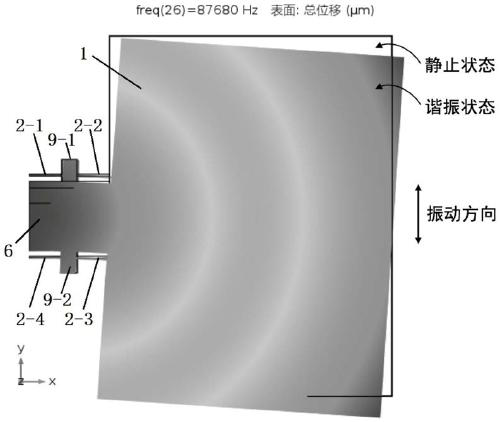
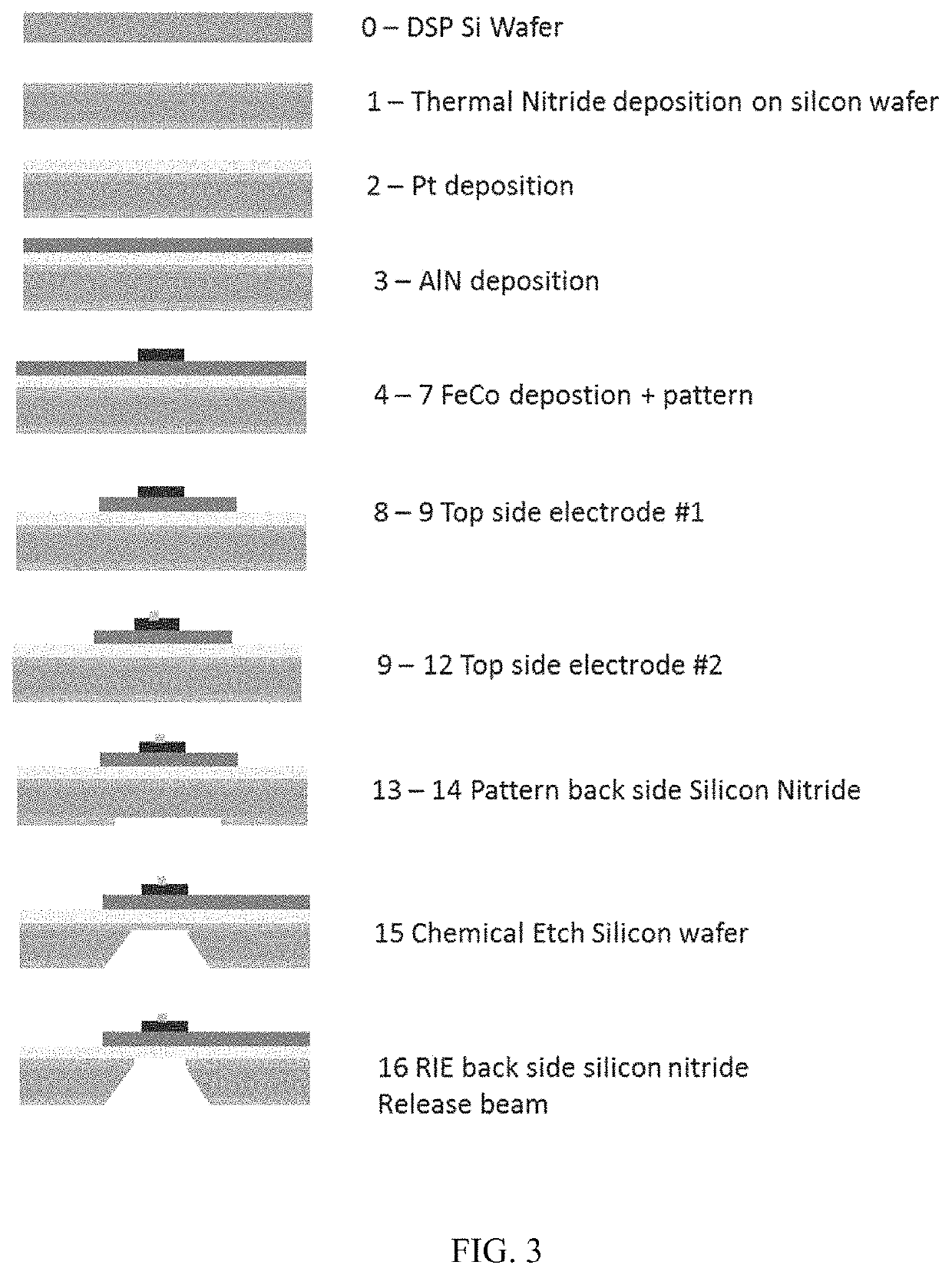
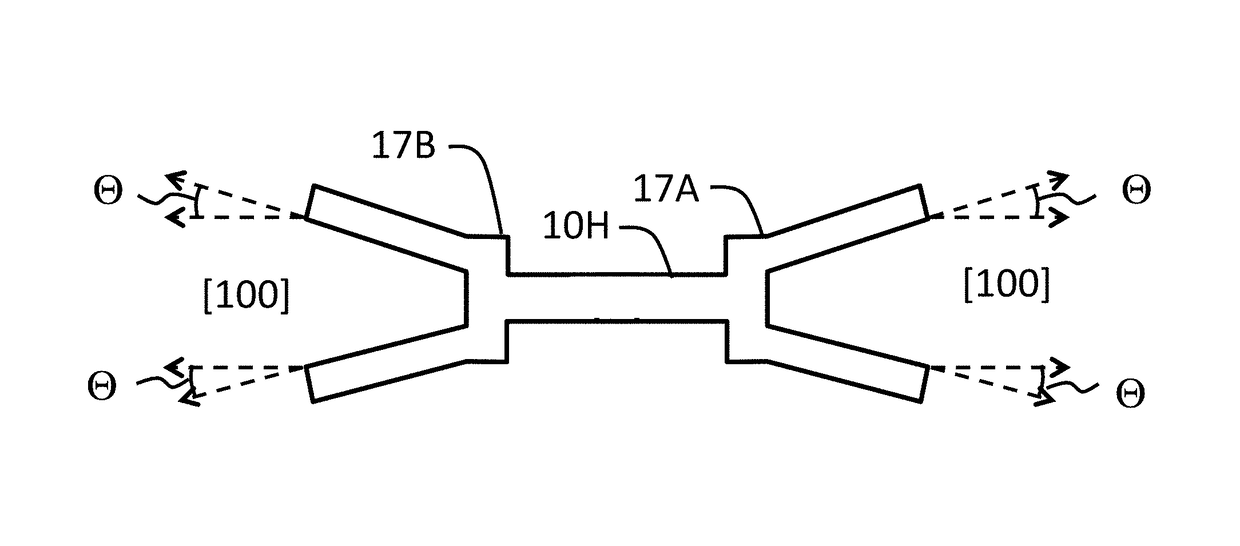
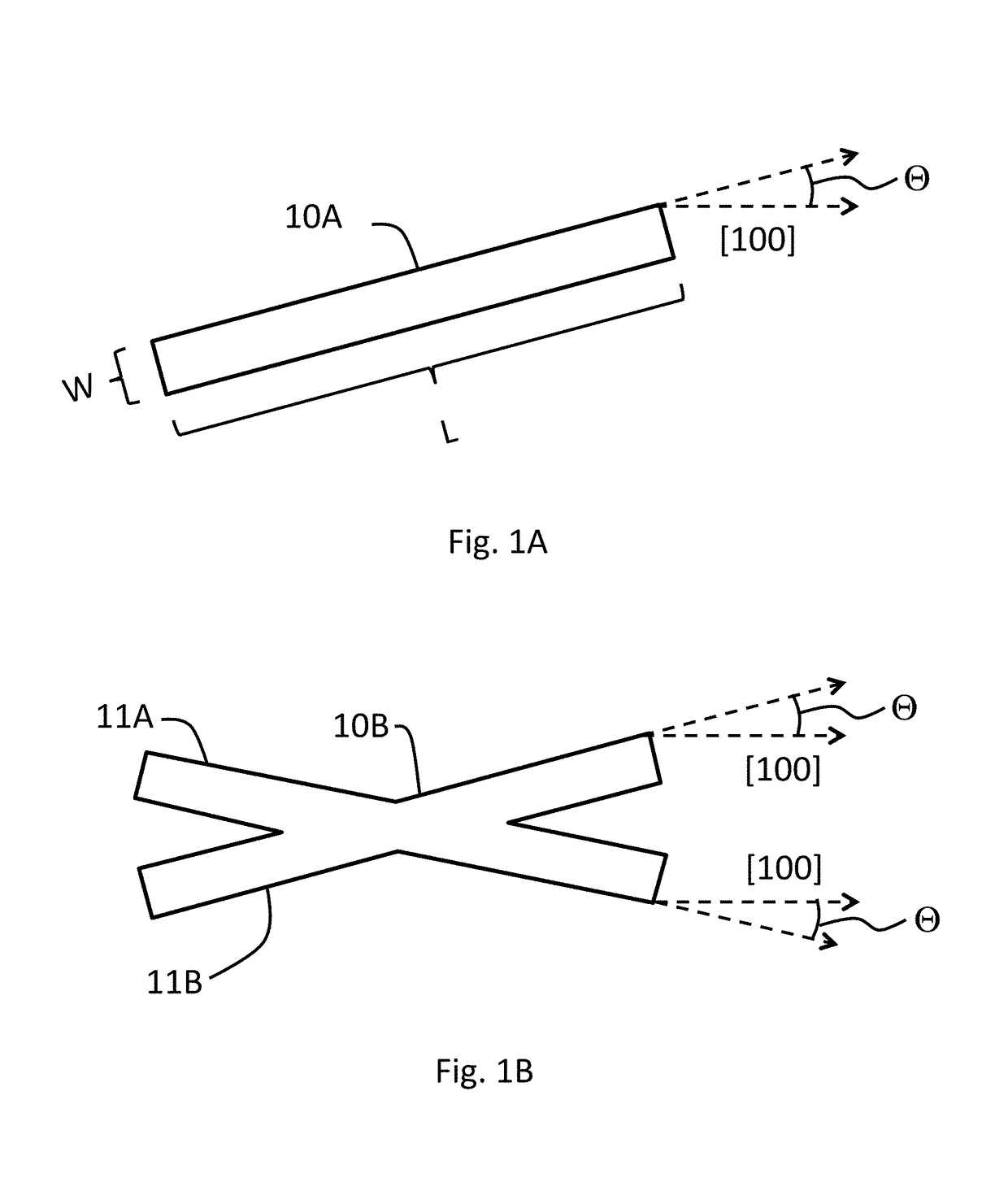
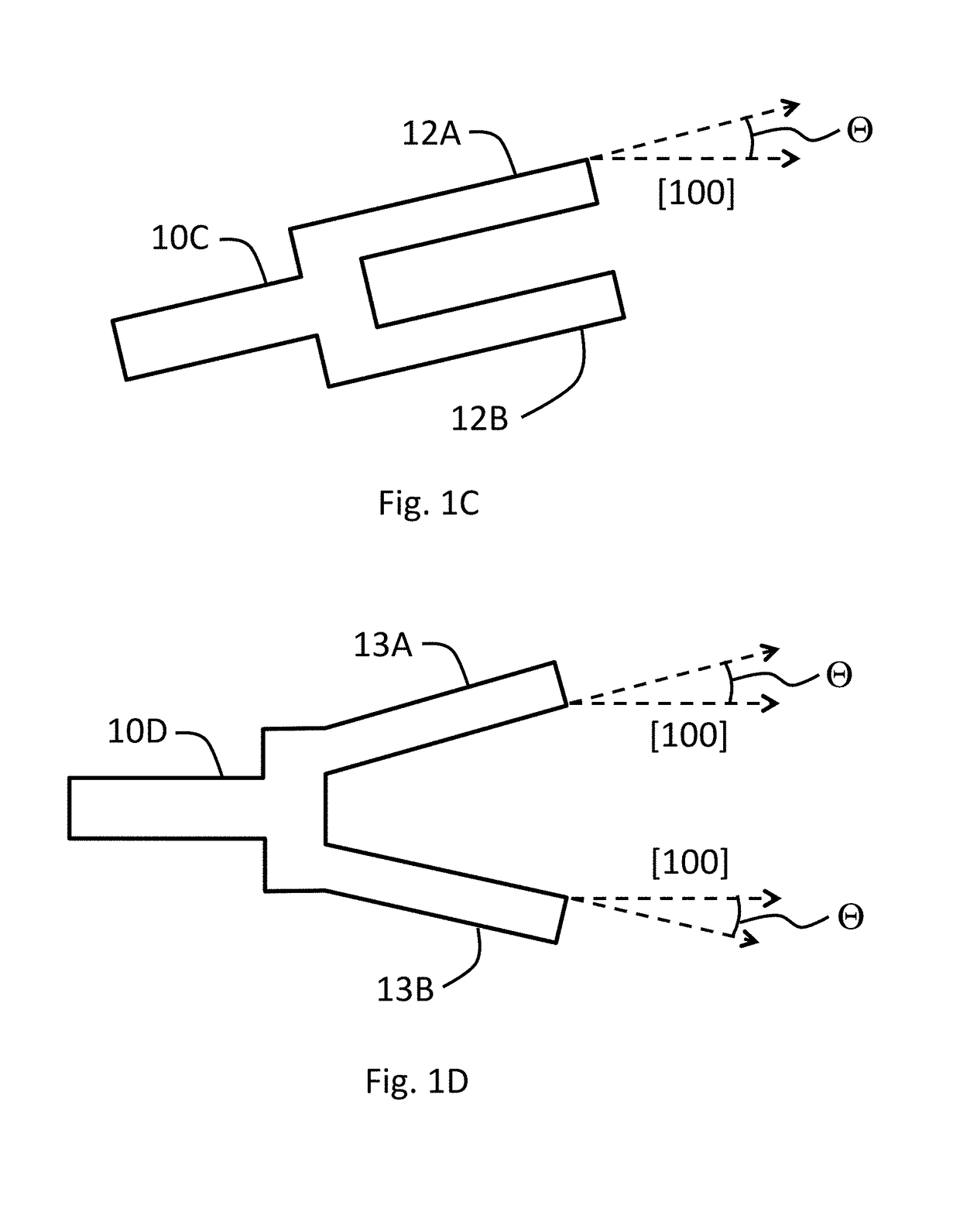
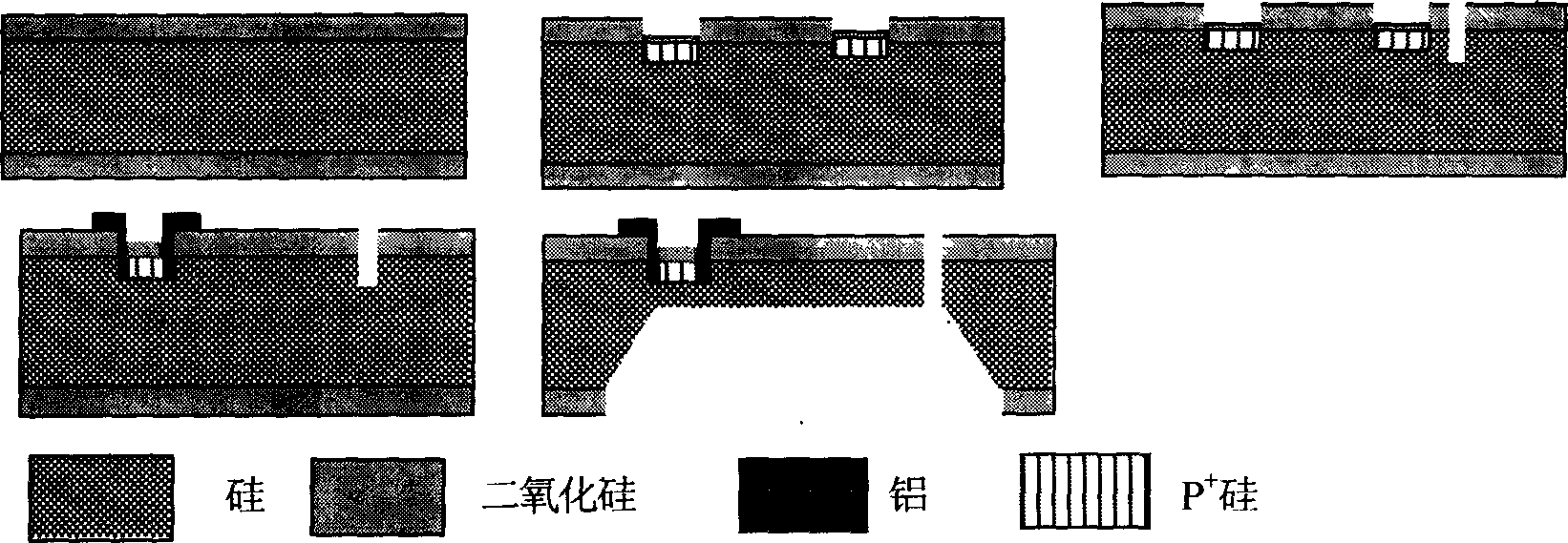
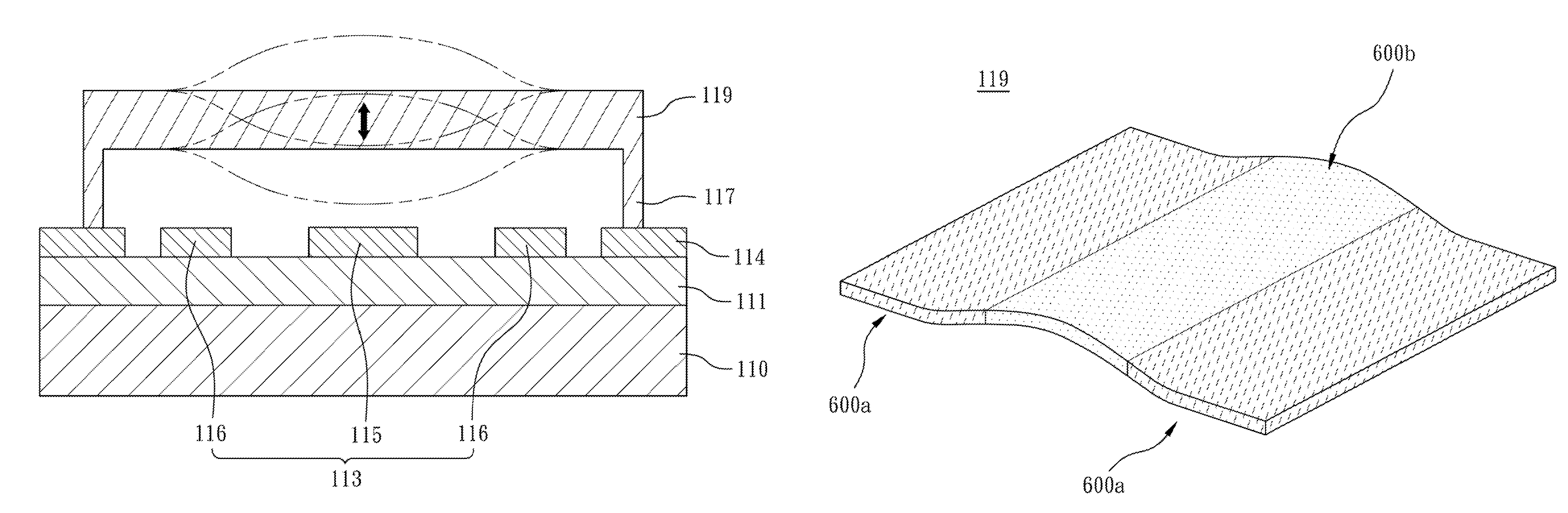
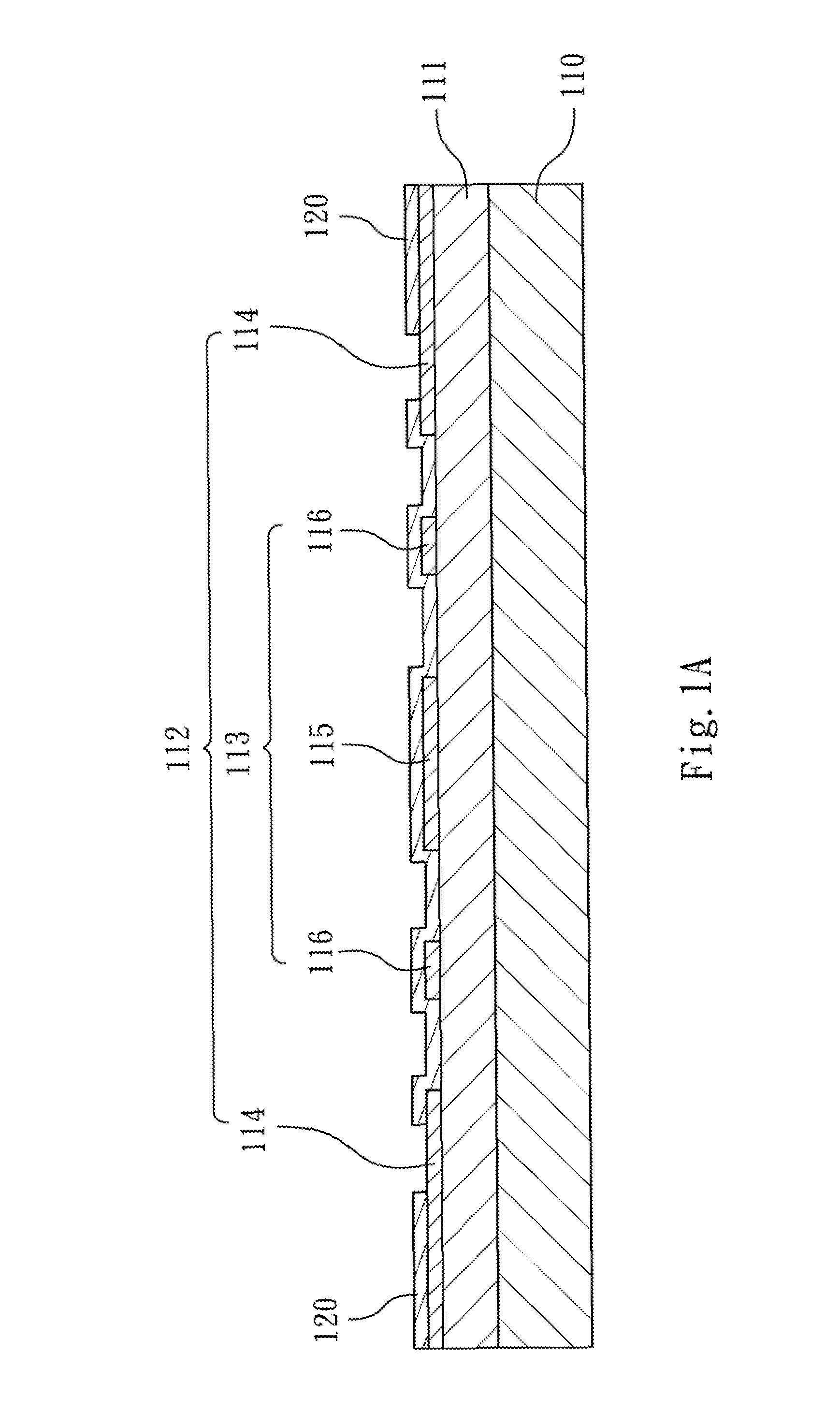
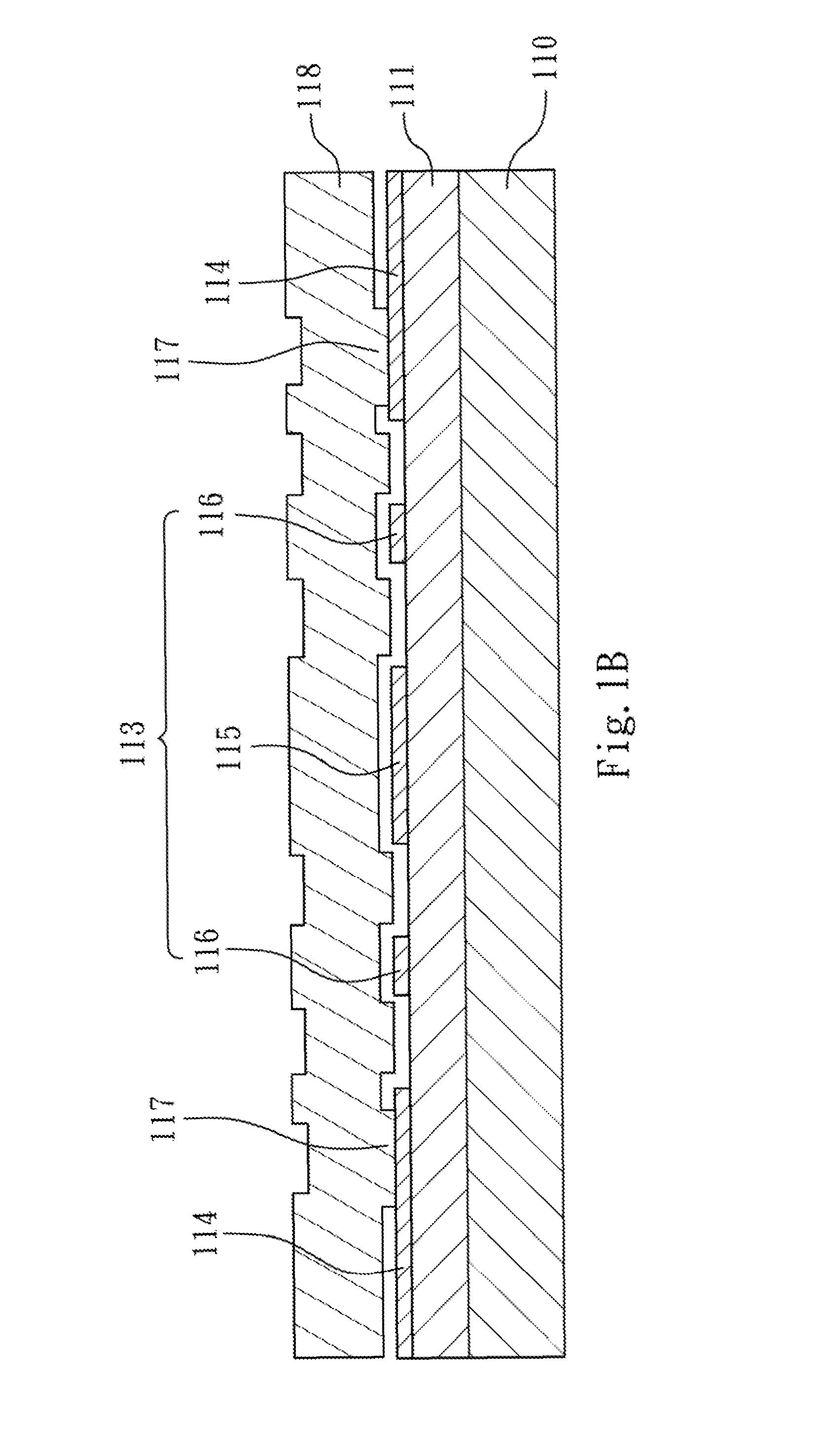
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Beam resonator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
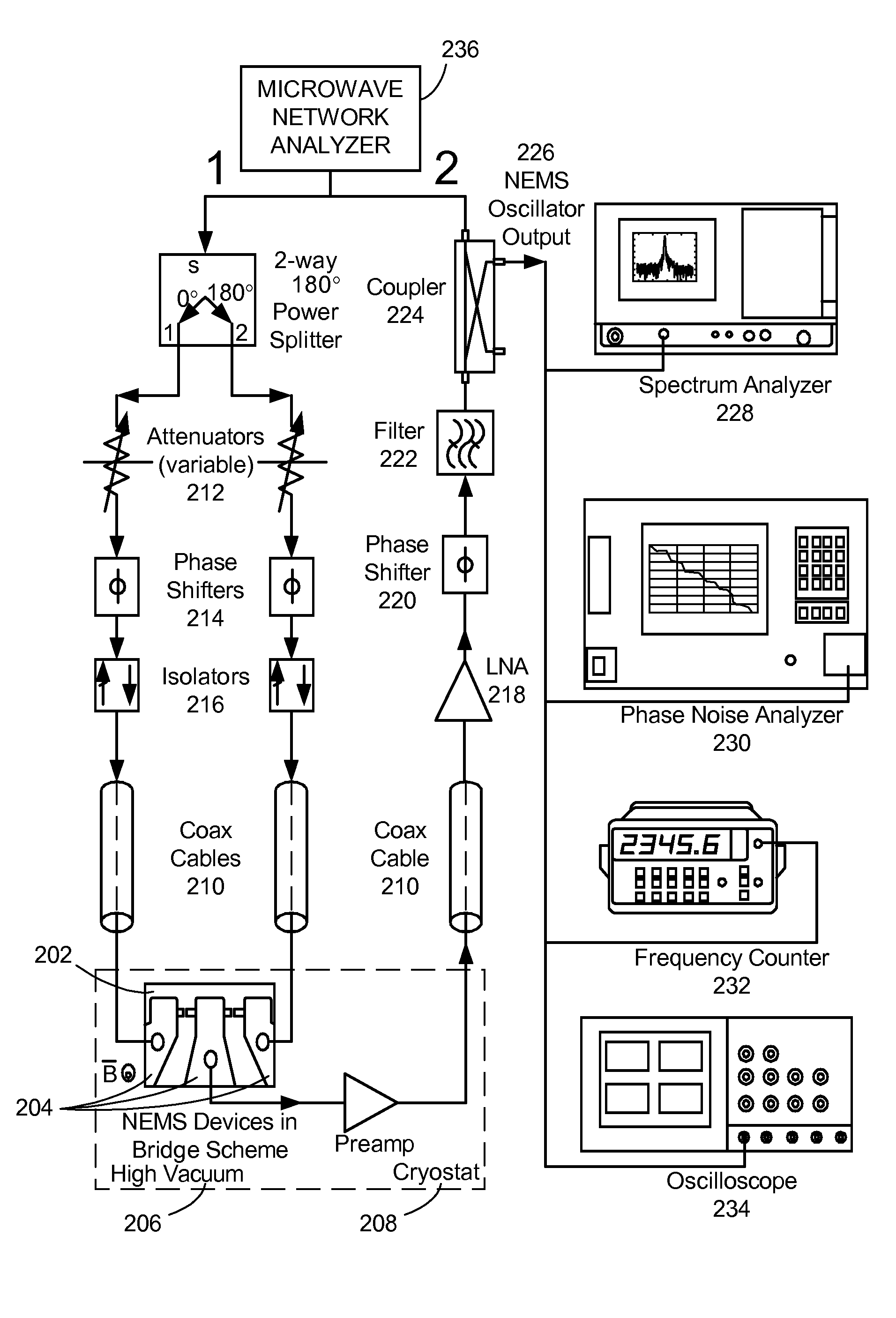
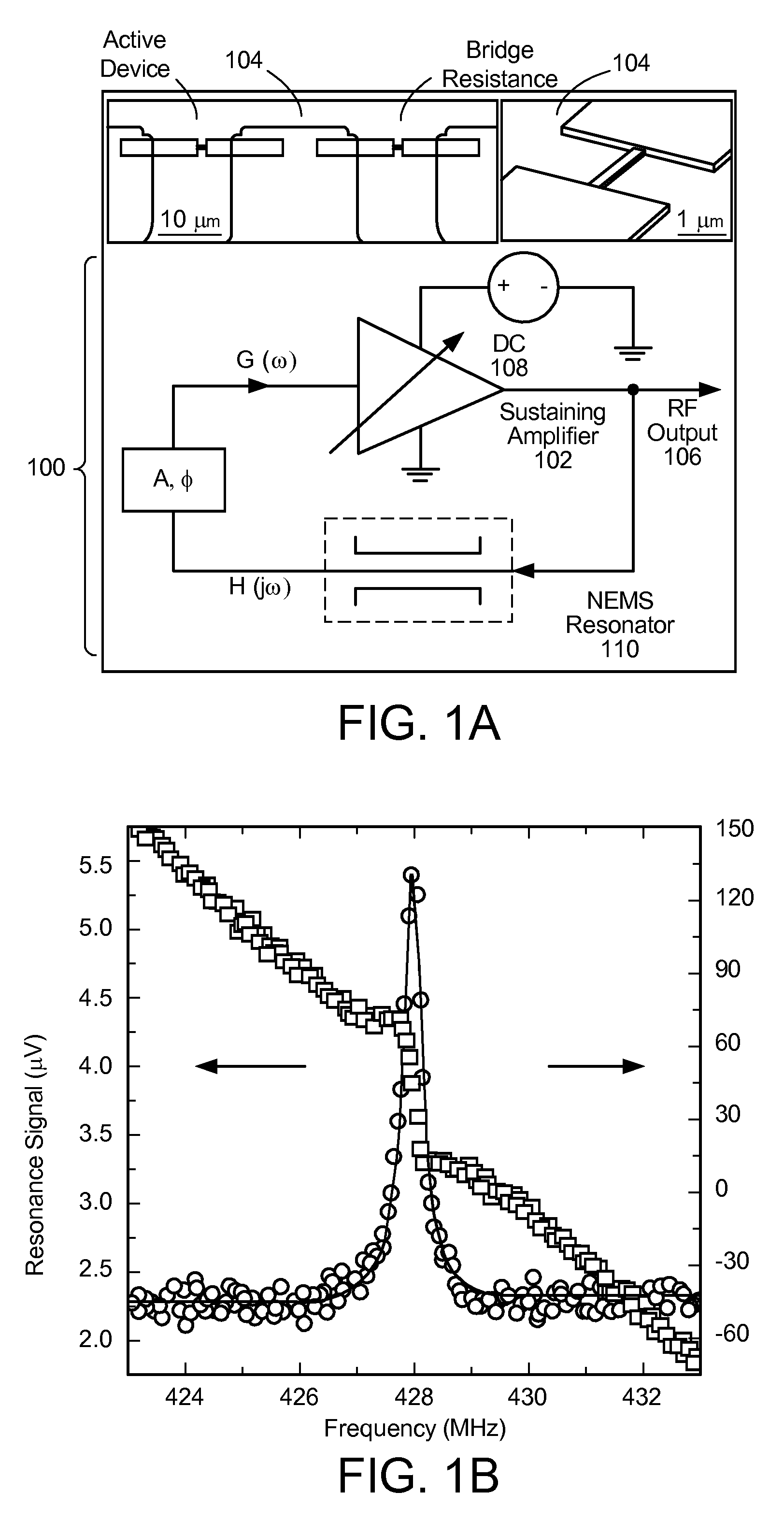
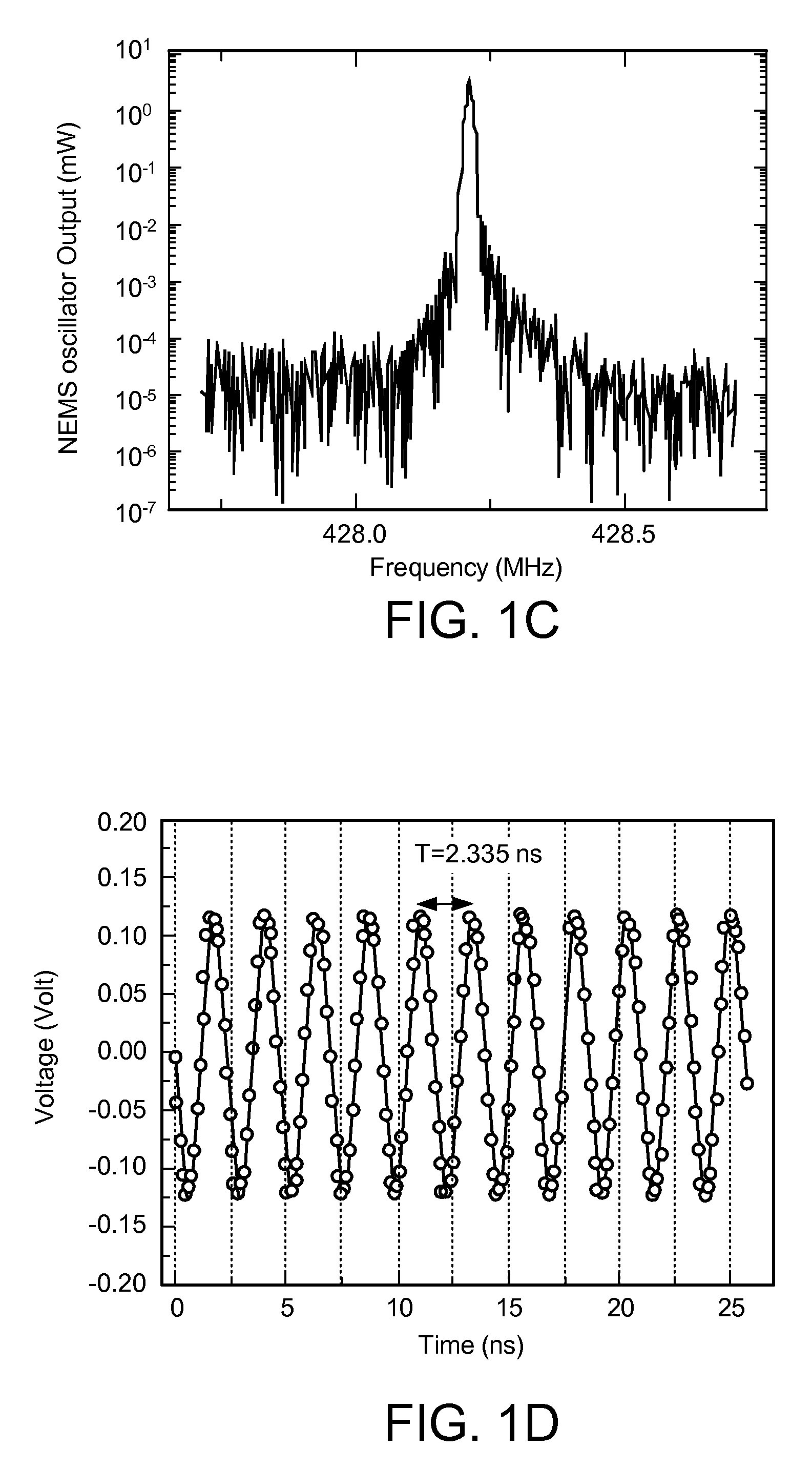
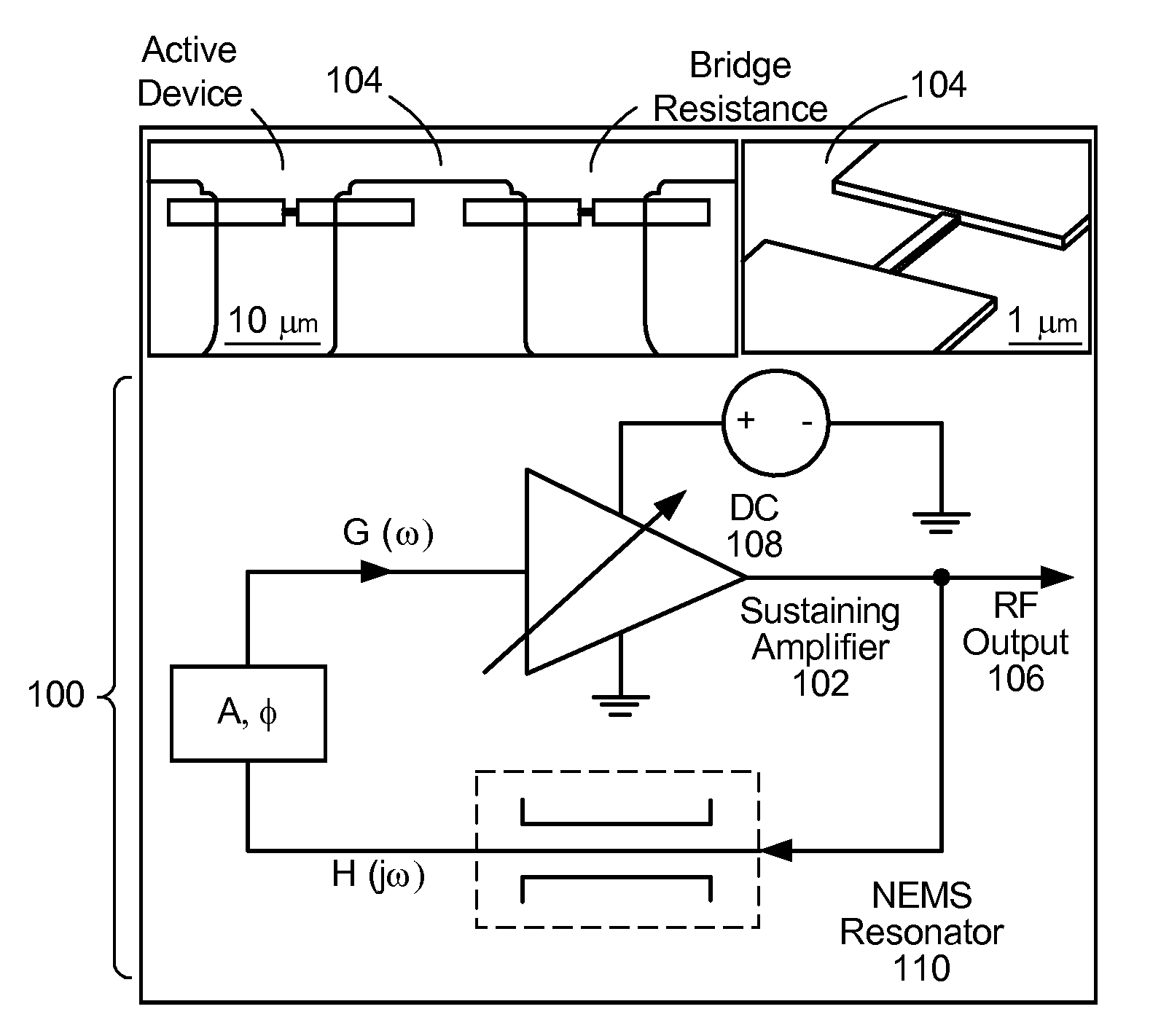
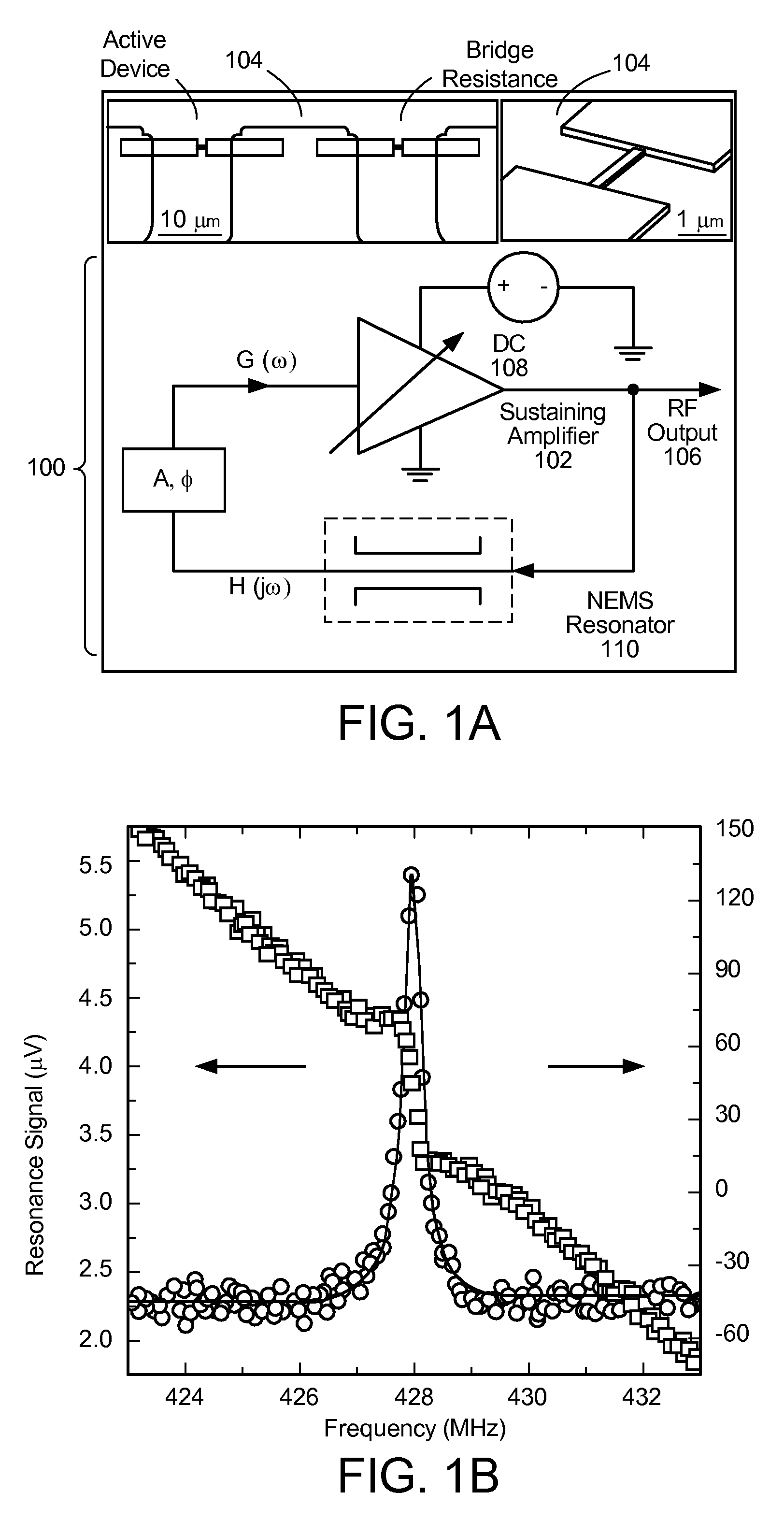
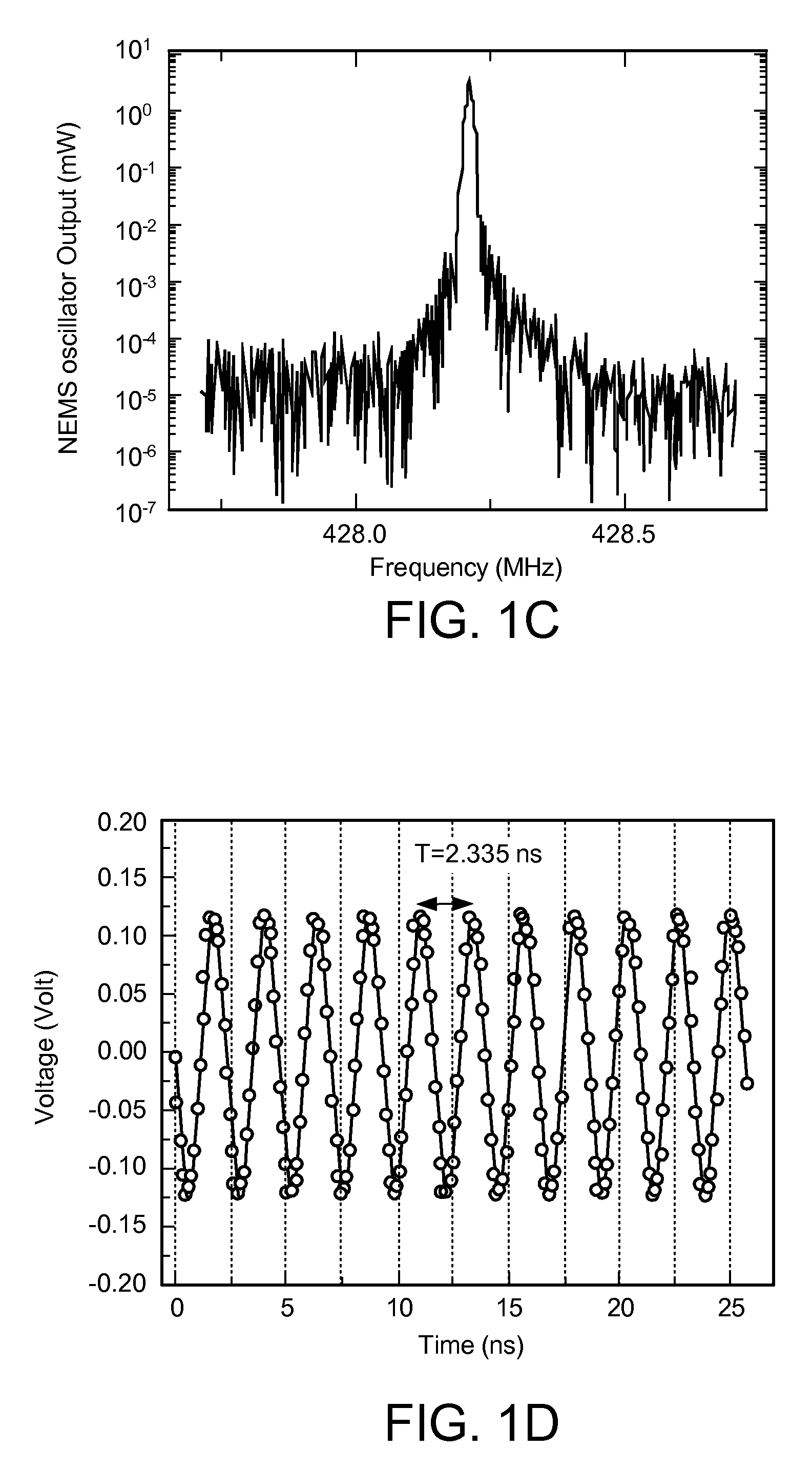
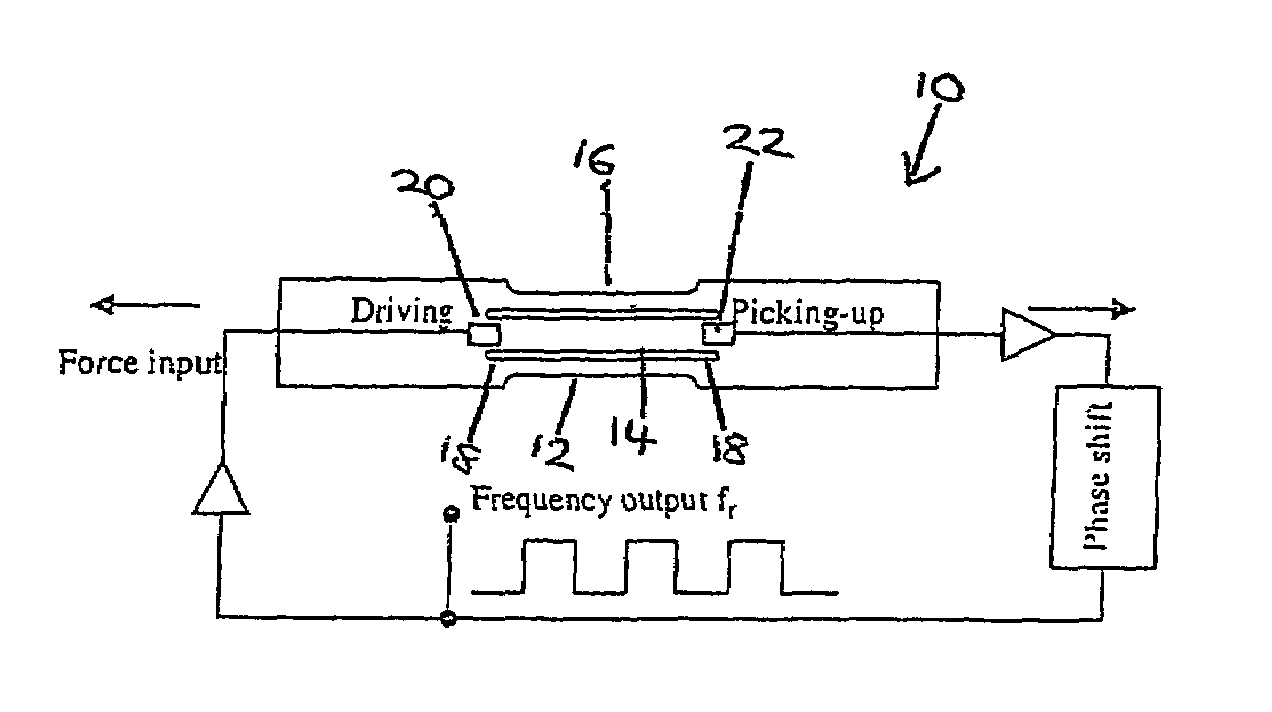
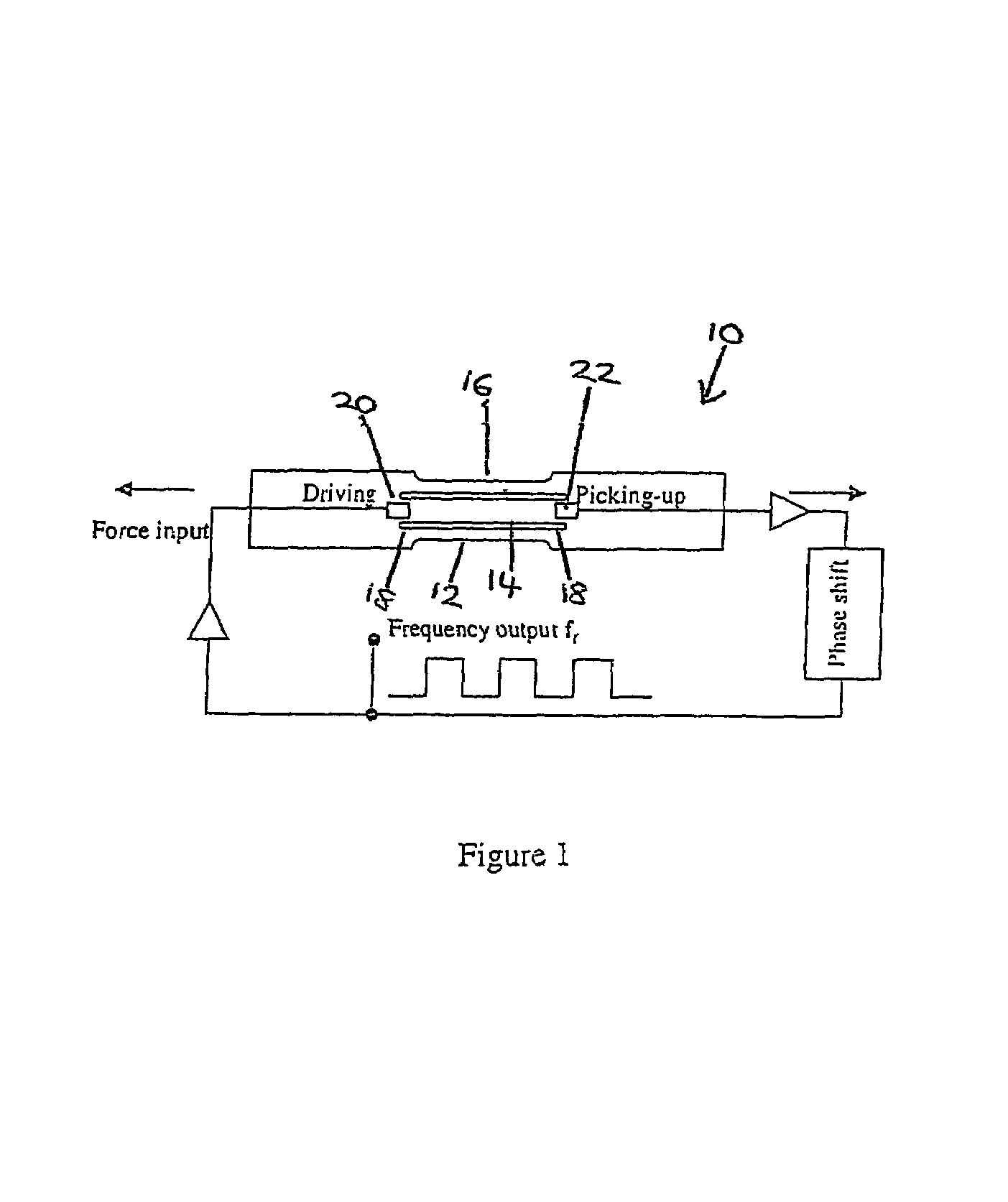
Ultra-high frequency self-sustaining oscillators, coupled oscillators, voltage-controlled oscillators, and oscillator arrays based on vibrating nanoelectromechanical resonators
ActiveUS7724103B2Noteworthy performanceNoteworthy stabilityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersBeam resonatorVIT signals
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
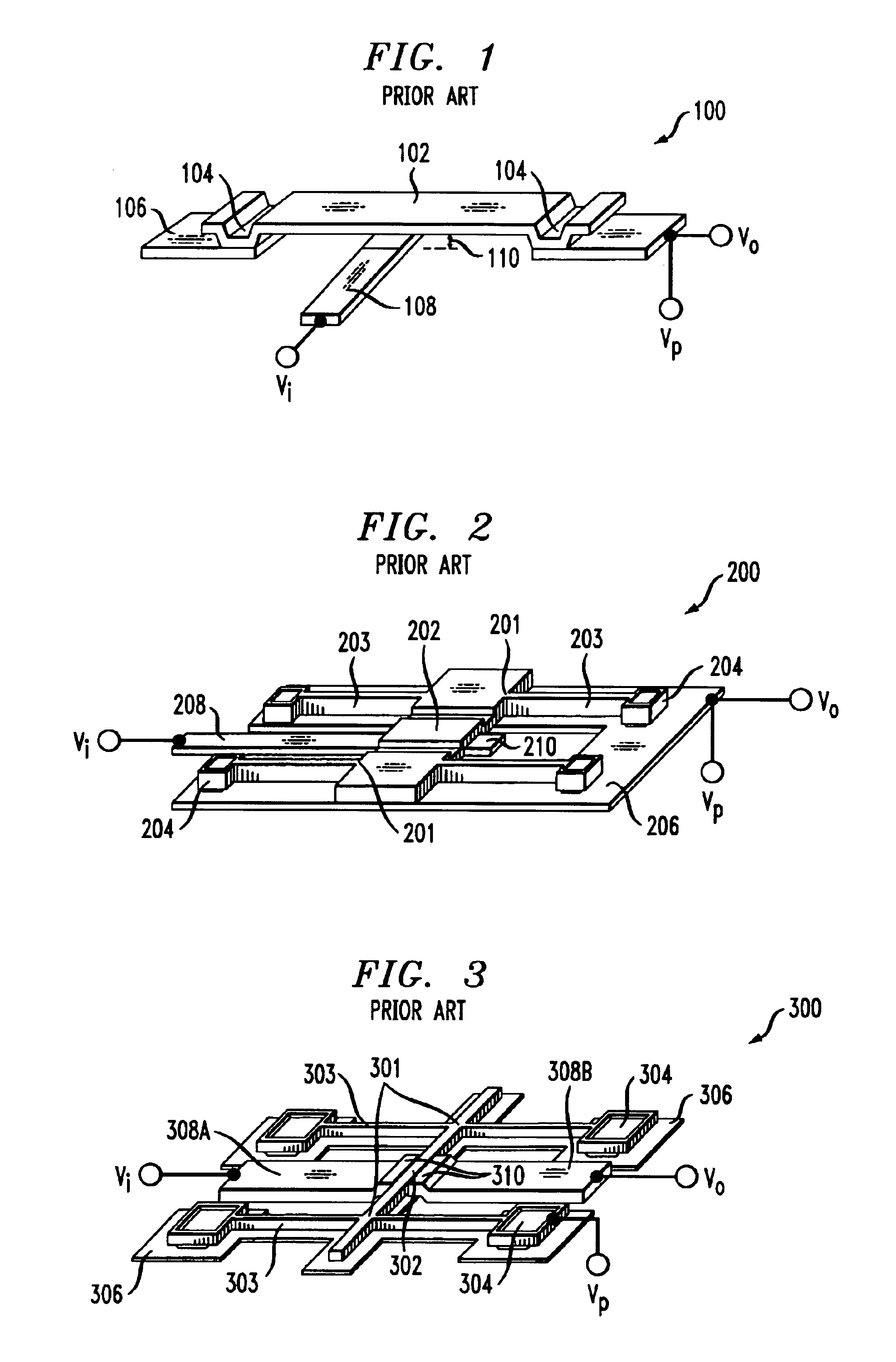
Micromechanical resonator having short support beams
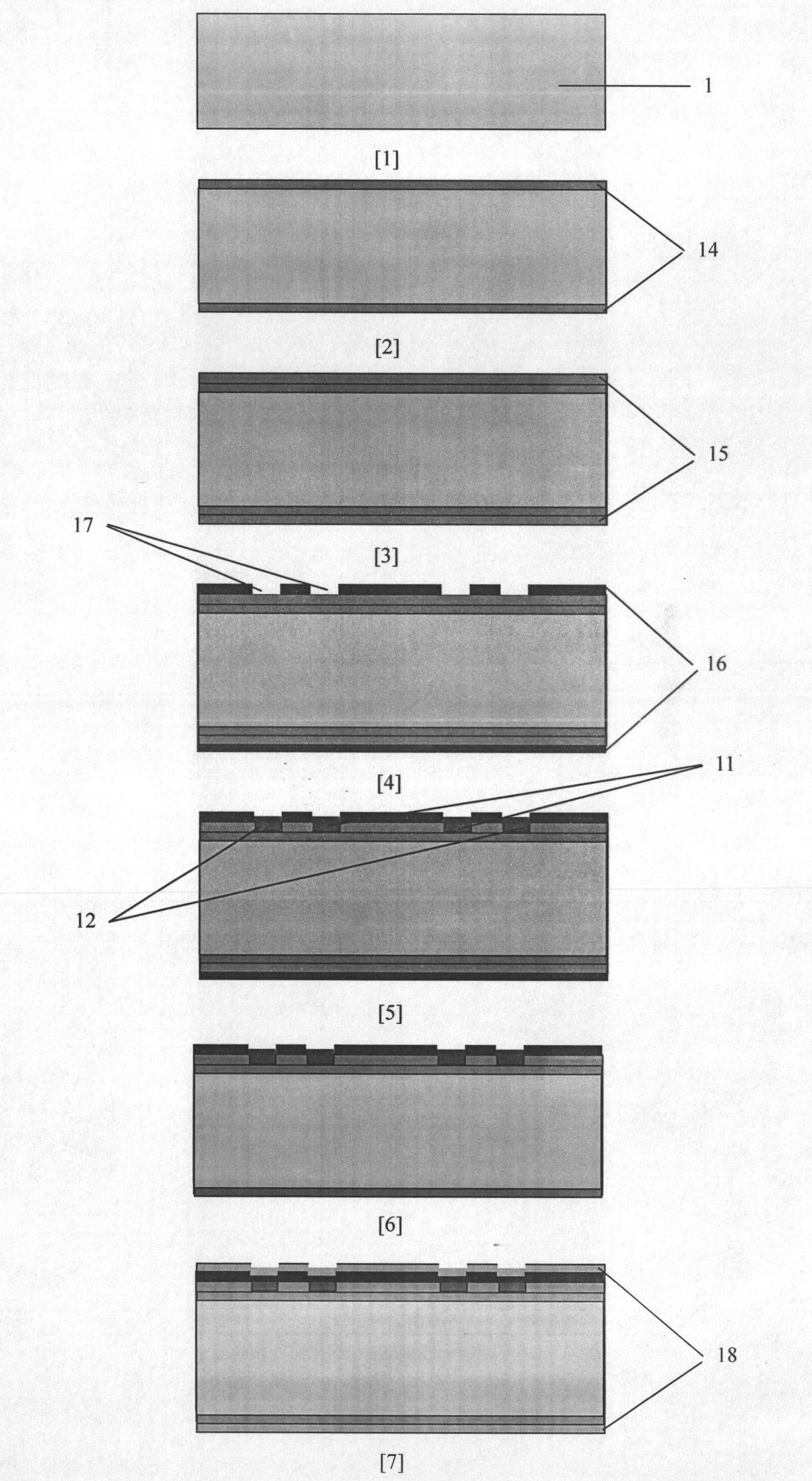
InactiveUS6930569B2Reduce the possibilitySmall sizePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksLength waveBeam resonator
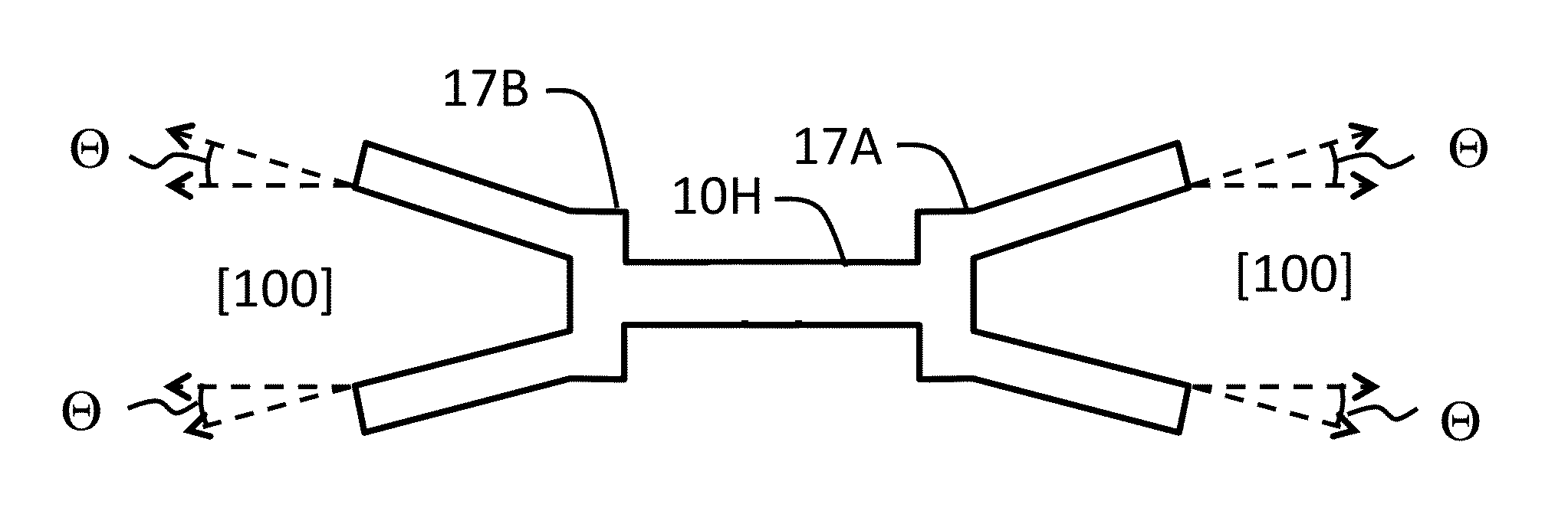
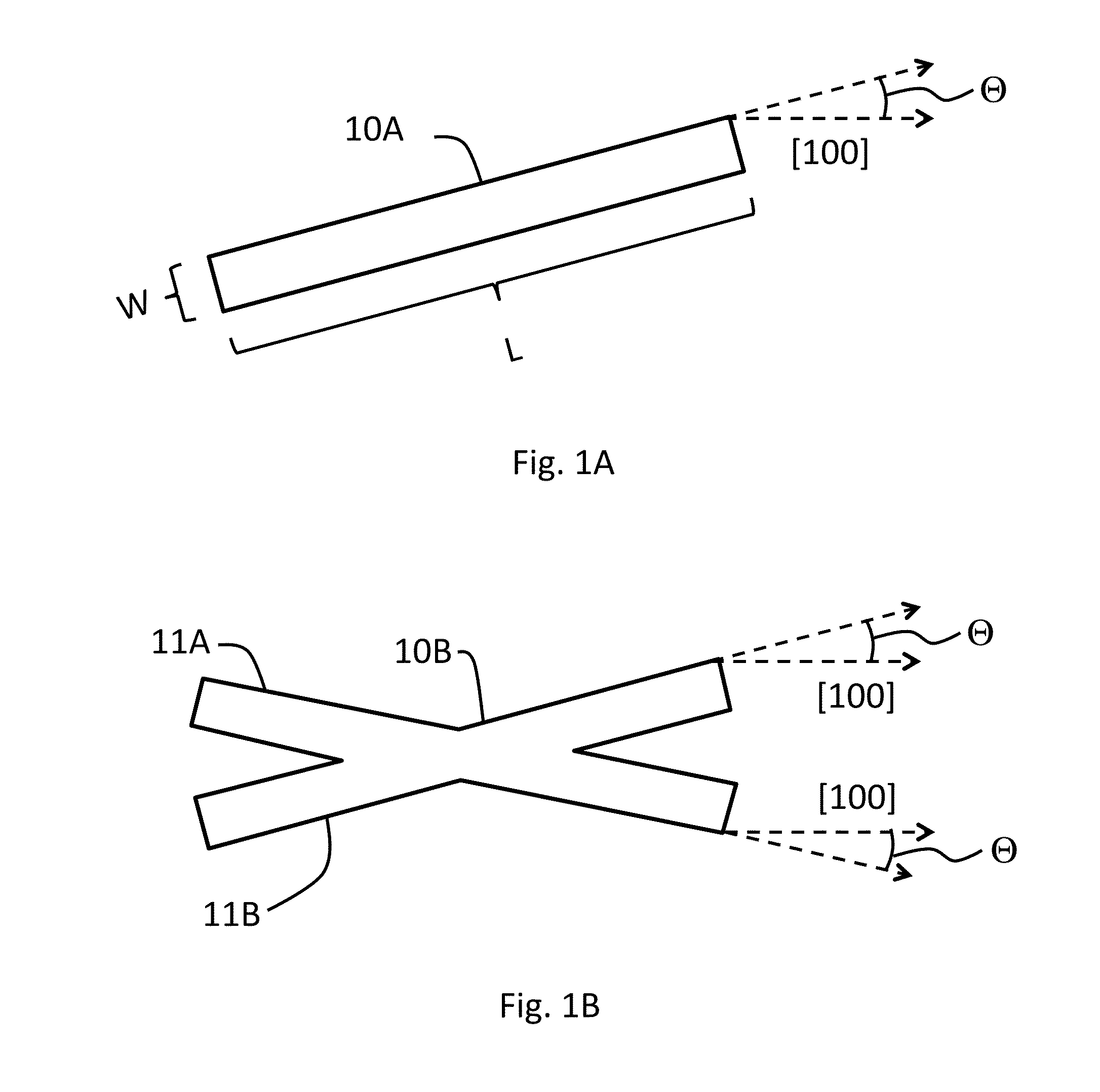
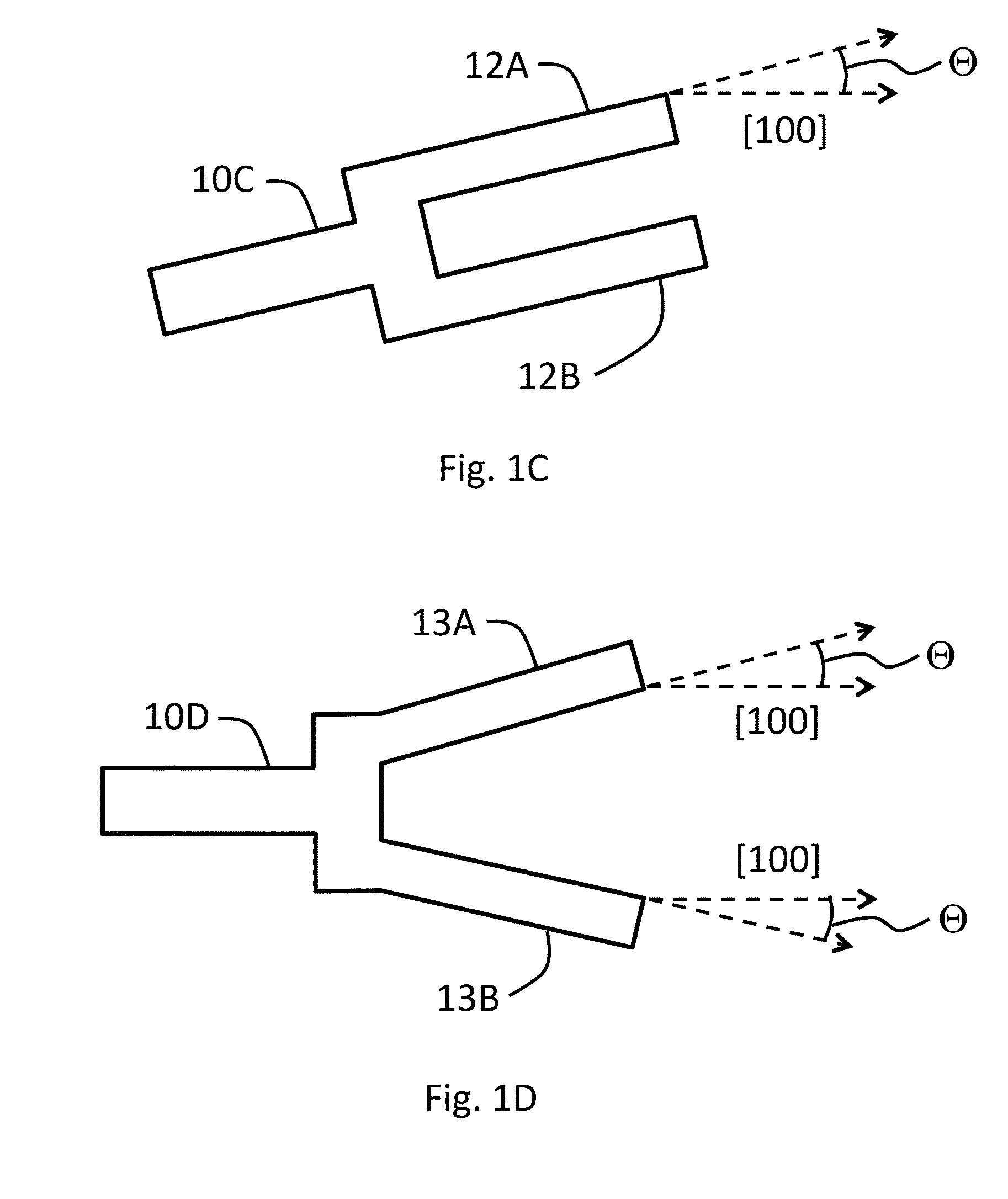
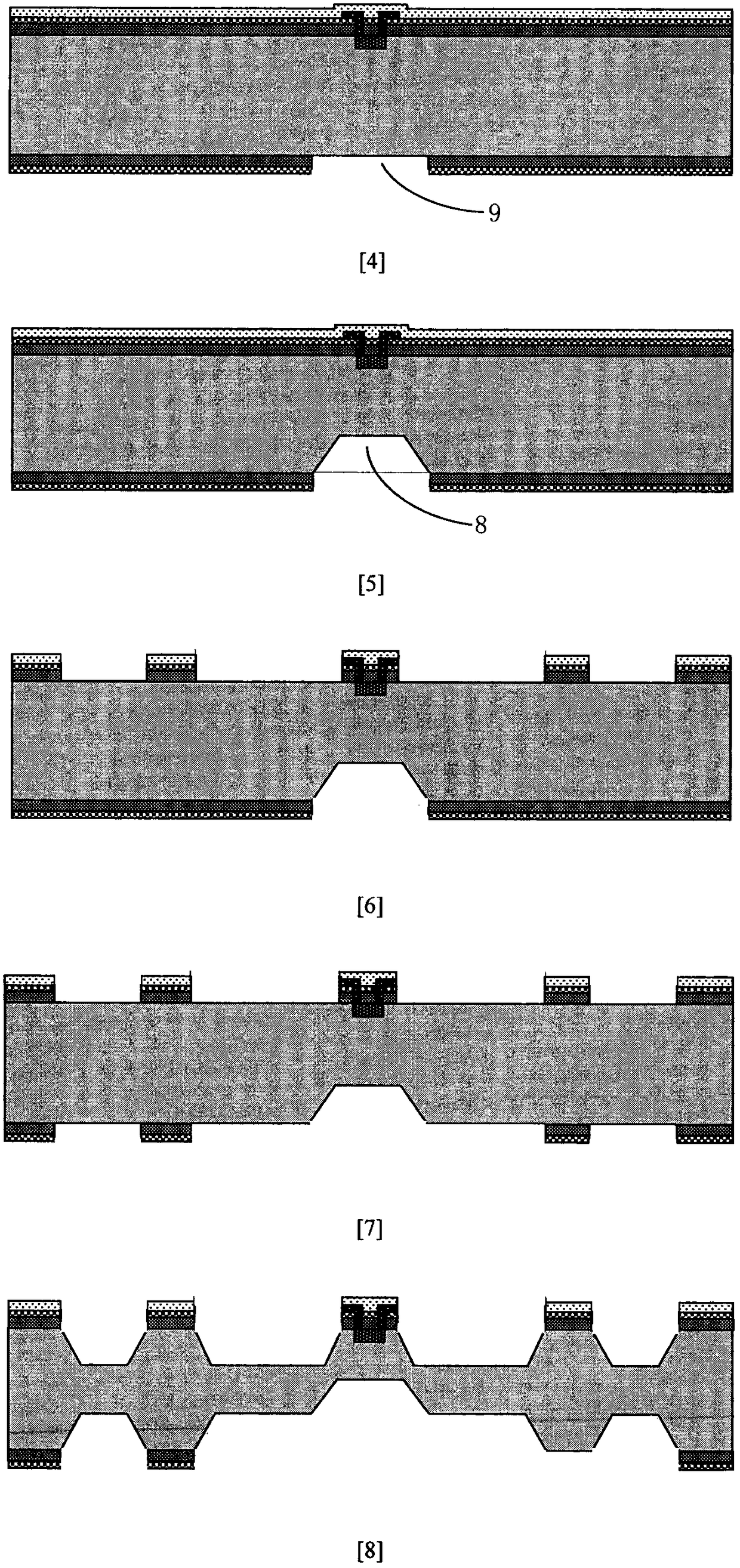
The illustrative embodiment of the present invention is a vertical-mode, free-free beam resonator, and micromechanical circuits that include one or more such resonators. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment, the resonator comprises a movable beam that overlies a drive electrode. The movable beam is supported by a plurality of supports, the length of which is substantially less than one-quarter of a wavelength of the resonant frequency of the resonator.
Owner:MICREL
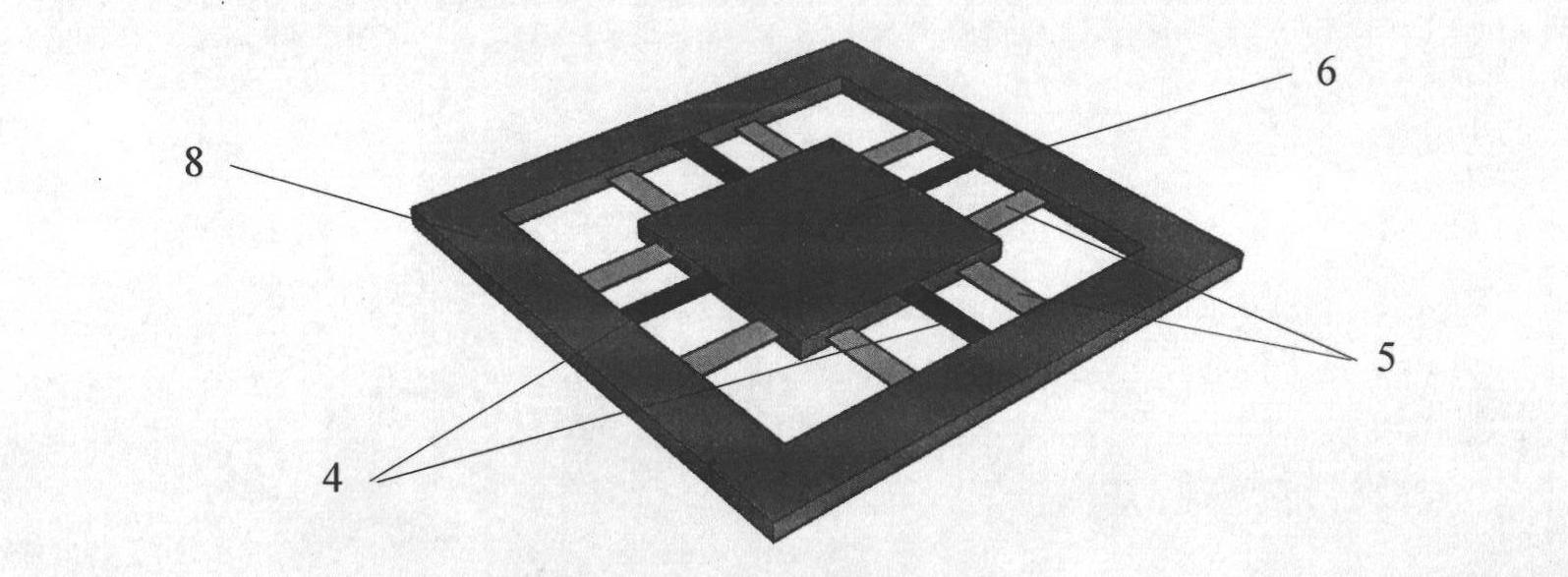
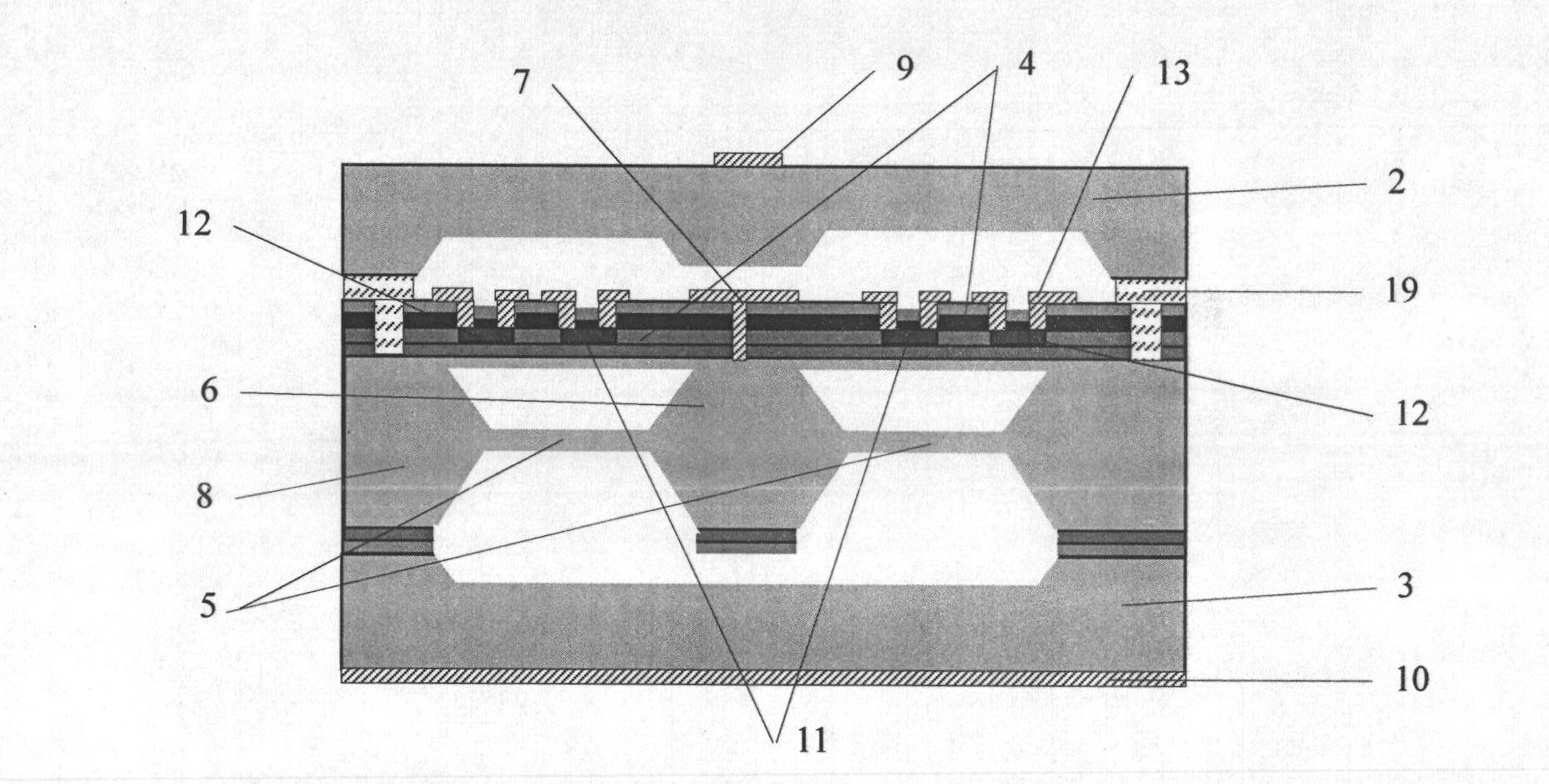
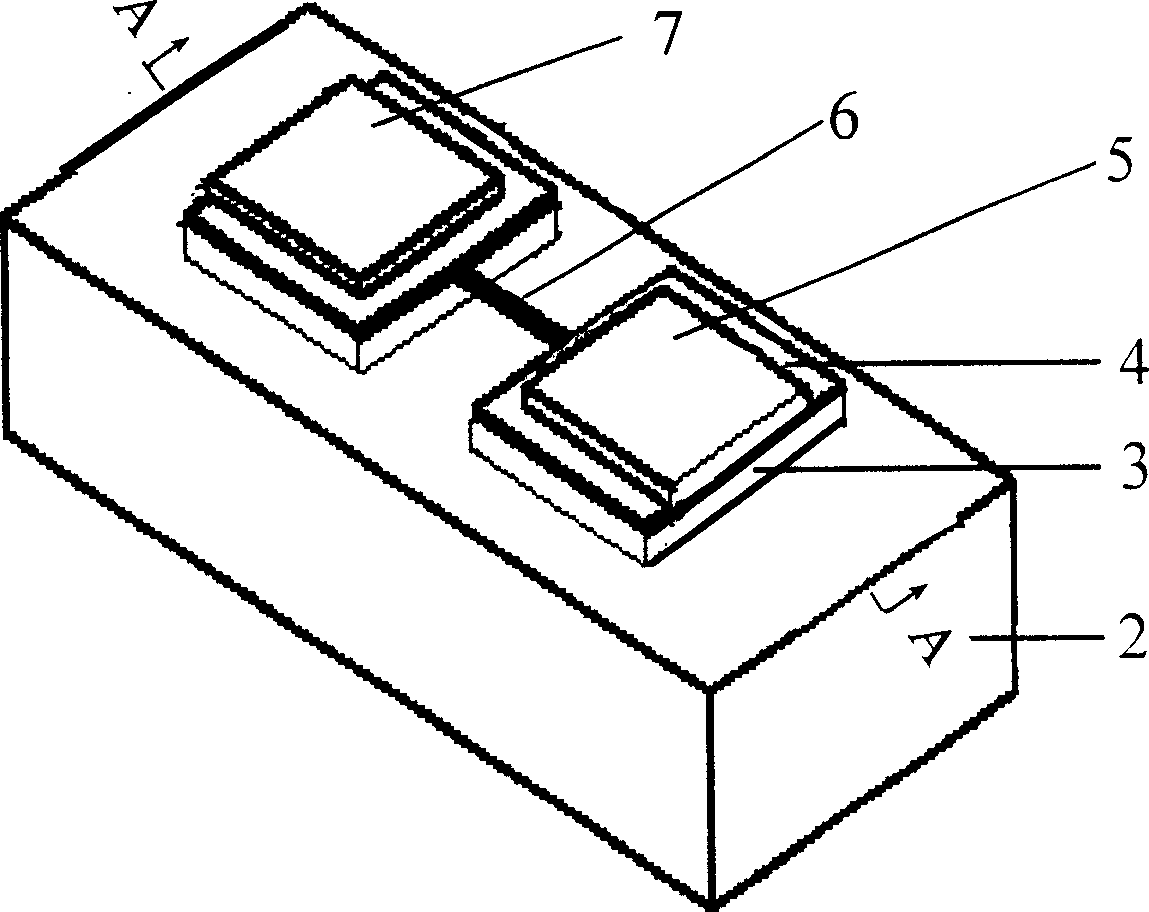
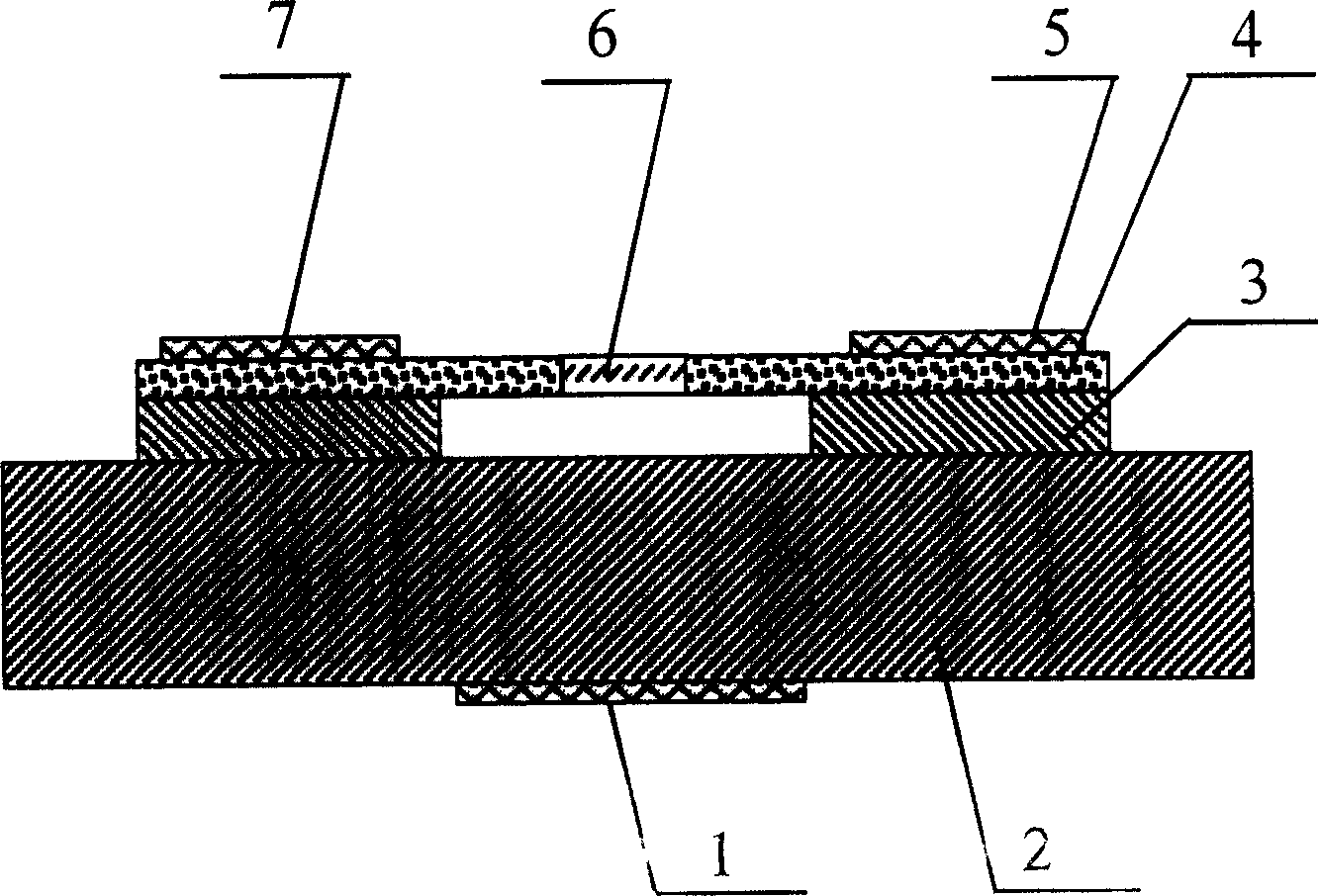
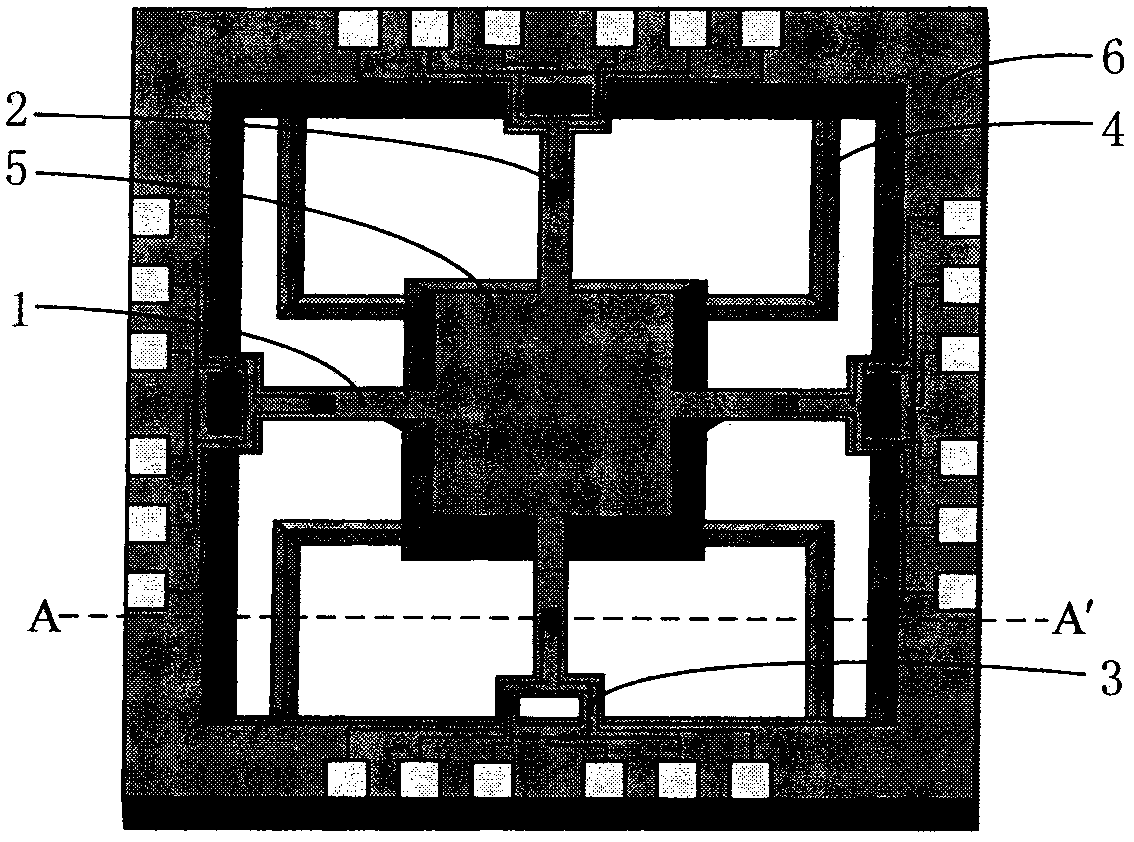
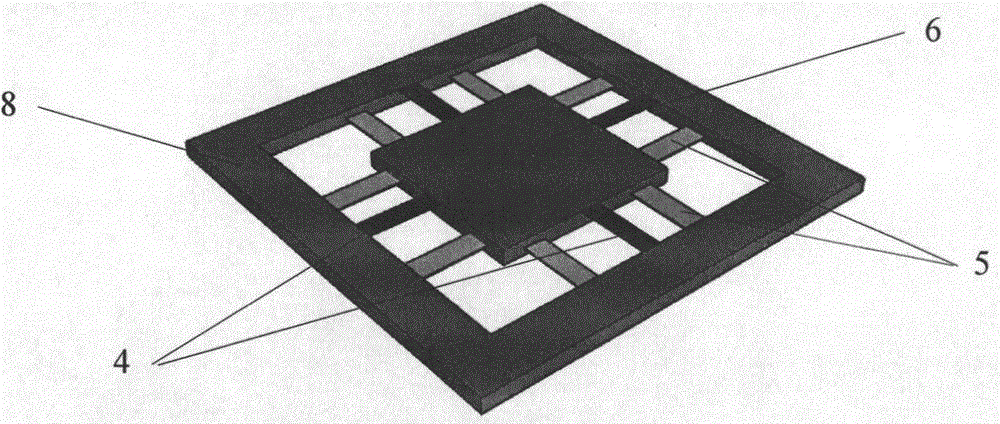
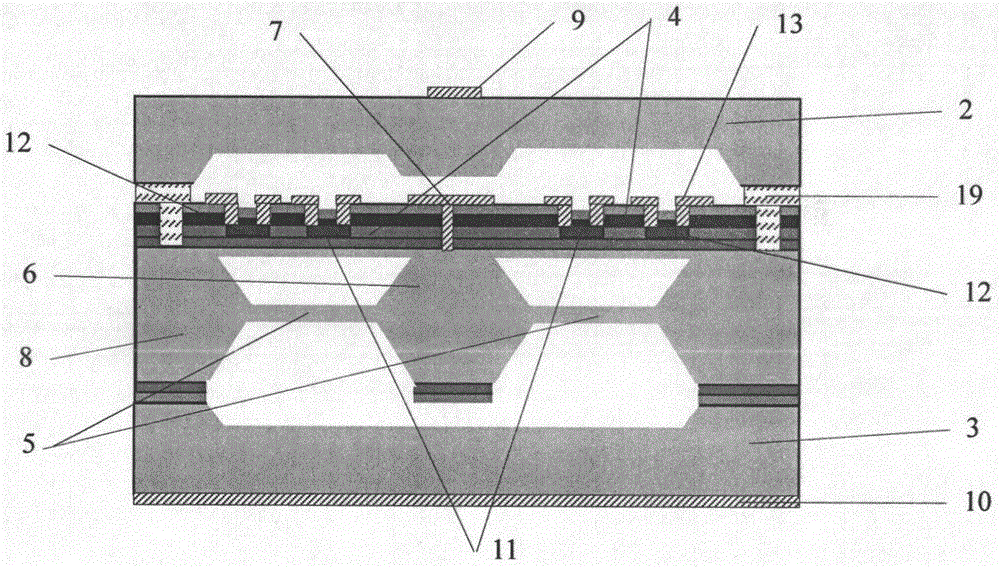
Resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer and manufacture method
InactiveCN102590555AMeet high performance requirementsImprove linearityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceResonance
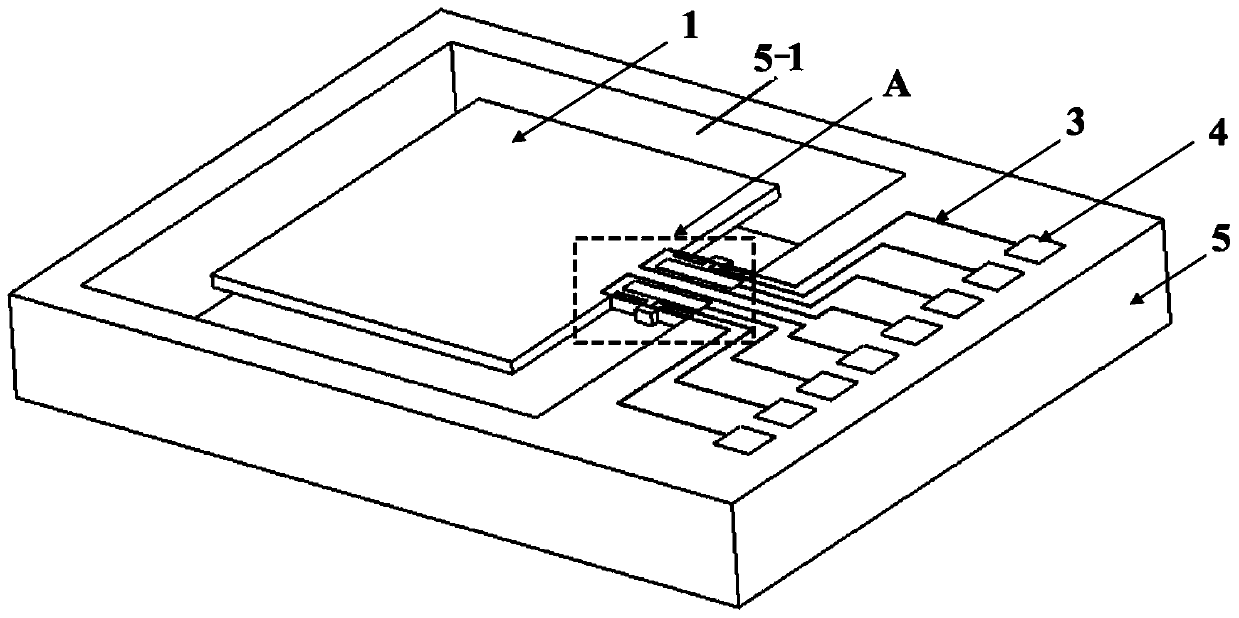
The invention discloses a resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer and a manufacture method thereof, belonging to the field of microelectro mechanical systems. The resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer is structurally characterized by comprising an intermediate silicon sheet (1), an upper cover plate (2) and a lower bottom plate (3), wherein the intermediate silicon sheet (1) comprises a dual-end clamped beam resonators (4), a mass block (6), a support beam (5), a movable electrode (7) and a frame (8). The resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer is characterized in that an X axis and a Y axis acceleration signals in a chip plane are detected by adopting the dual-end clamped beam resonator (4) on the aspect of detection principle, the change of the resonance frequency of the dual-end clamped beam resonator (4) reflects the size and the direction of acceleration; and a Z axis acceleration signal in a vertical chip plane is detected by adopting a capacitance type sensitivity principle, and works in a closed loop force balance working mode. The mass block (6) has little motion displacement in the normal of a chip, and the Z axis input acceleration signal has little chiasma interference caused by detection of X axis and Y axis accelerations.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
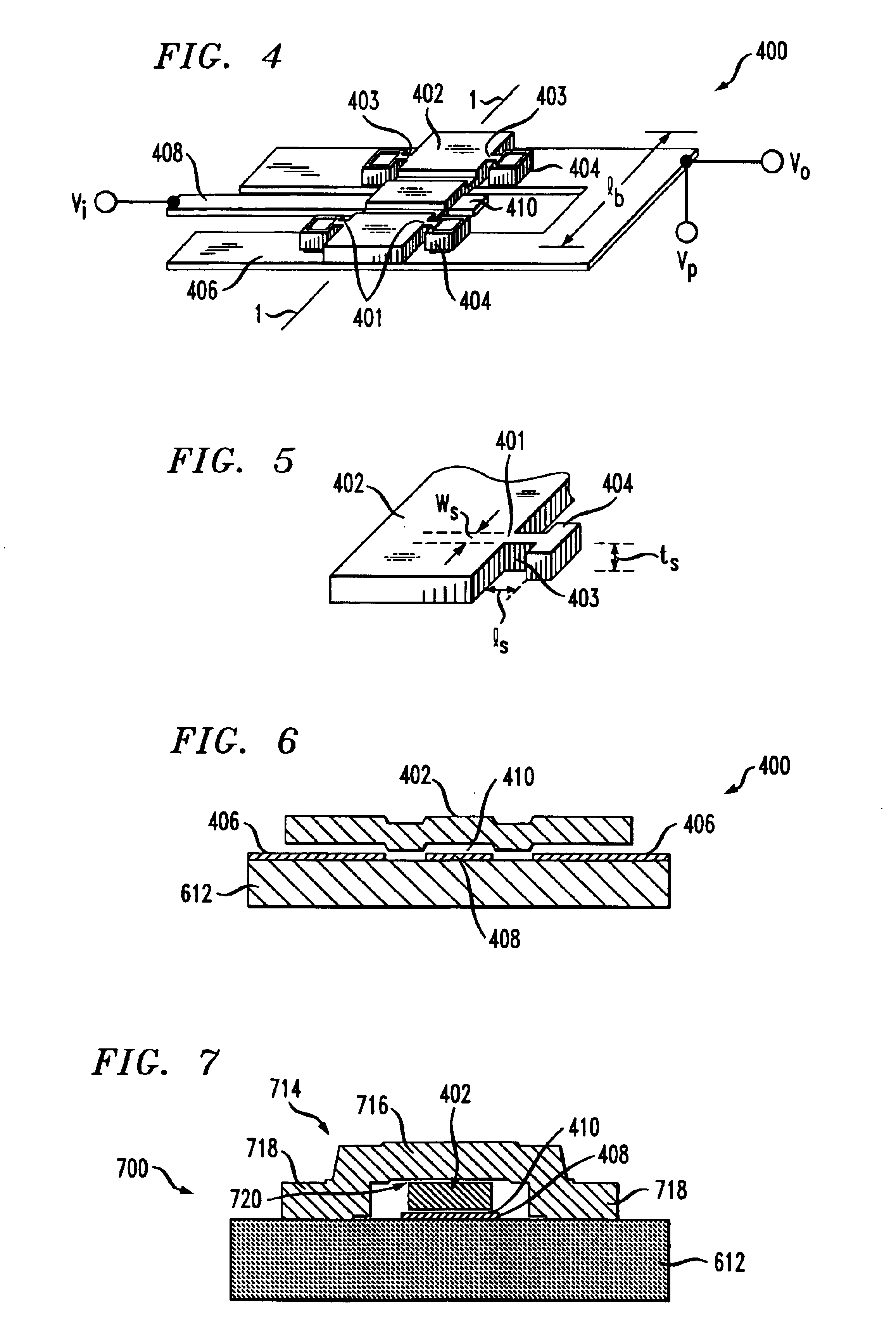
Apparatus comprising a micromechanical resonator
ActiveUS20050024165A1Decrease in electrical stiffnessIncrease temperaturePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksLight beamLength wave
The illustrative embodiment of the present invention is a vertical-mode, free-free beam resonator, and micromechanical circuits that include one or more such resonators. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment, the resonator comprises a movable beam that overlies a drive electrode. The movable beam is supported by a plurality of supports, the length of which is substantially less than one-quarter of a wavelength of the resonant frequency of the resonator.
Owner:MICREL
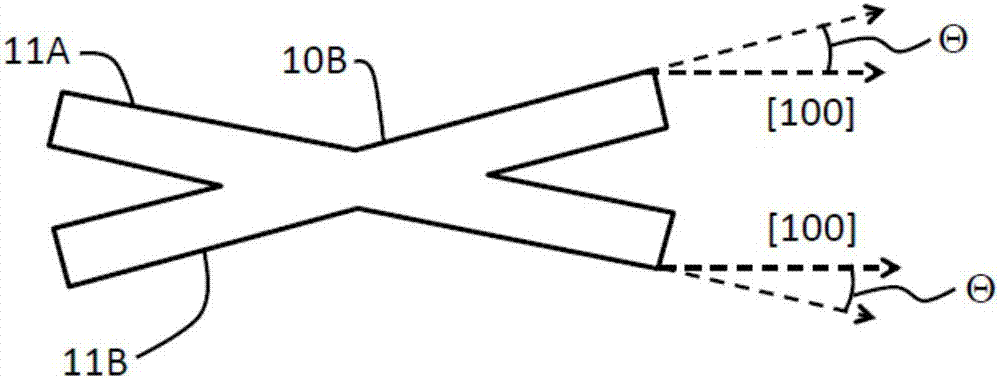
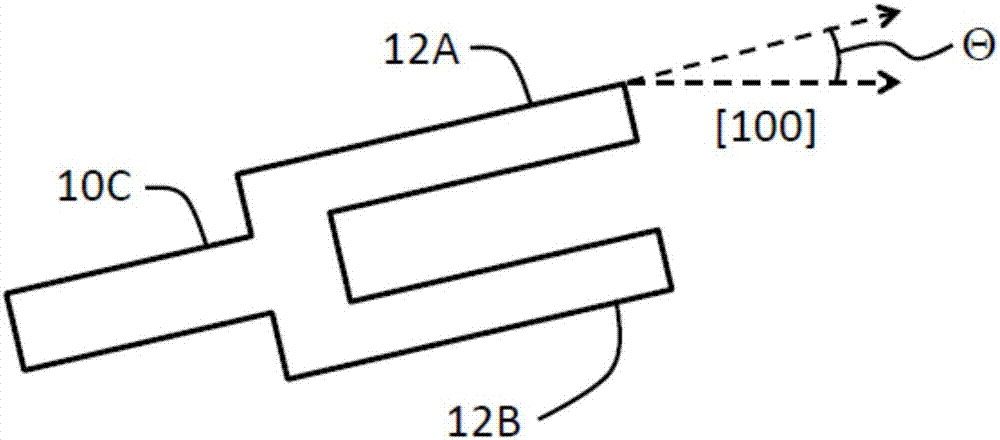
Temperature compensated beam resonator
ActiveUS20160099703A1Improve stabilityEasy to manufactureImpedence networksGenerators/motorsResonanceLight beam
The invention provides a microelectromechanical resonator device comprising a support structure and a resonator manufactured on a (100) or (110) semiconductor wafer, wherein the resonator is suspended to the support structure and comprises at least one beam being doped to a doping concentration of 1.1*1020 cm−3 or more with an n-type doping agent and is being capable of resonating in a length-extensional, flexural resonance or torsional mode upon suitable actuation. In particular, the doping concentration and angle of the beam are chosen so as to simultaneously produce zero or close to zero second order TCF, and even more preferably zero or close to zero first and second order TCFs, for the resonator in said resonance mode, thus providing a temperature stable resonator.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
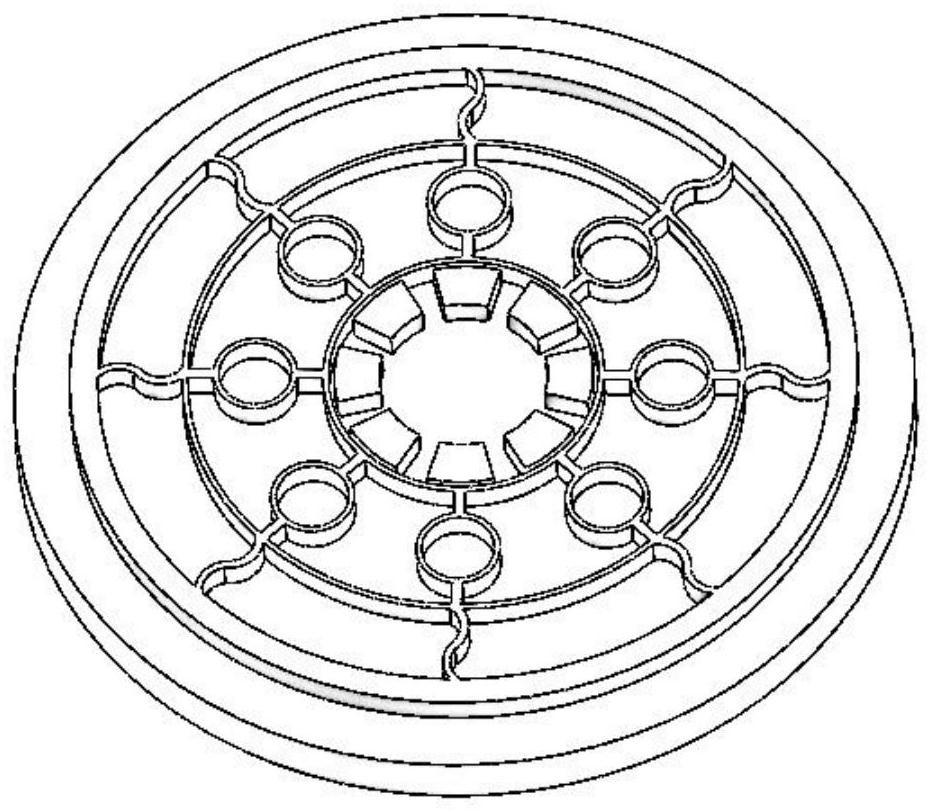
Disc multi-ring outer S-shaped flexible beam resonator gyro and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105371833ASimple processing stepsEase of mass productionSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesEngineeringBeam resonator
The invention provides a disc multi-ring outer S-shaped flexible beam resonator gyro and a preparation method thereof. The resonator gyro comprises: a substrate; a disc multi-ring outer S shaped flexible beam resonator, which includes a most peripheral ring, a plurality of concentric rings, a plurality of S-shaped flexible beams and multiple groups of spokes, wherein the most peripheral ring is connected to the substrate, the concentric rings are connected through the multiple spokes, and both ends of the plurality of S-shaped flexible beams are all connected to the inside of the most peripheral ring and the outside of the concentric rings' largest ring; and a group of electrodes that are distributed on the inside edge of the disc multi-ring outer S-shaped flexible beam resonator, with each electrode being connected to the substrate respectively. The disc multi-ring outer S-shaped flexible beam resonator gyro provided by the invention has the advantages of small volume, stable structure, and sensitive response, etc., and has good symmetry, thus being able to achieve high performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Ultra-high frequency self-sustaining oscillators, coupled oscillators, voltage-controlled oscillators, and oscillator arrays based on vibrating nanoelectromechanical resonators
ActiveUS20080204152A1Noteworthy frequency stabilityNoteworthy noise performanceMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersBeam resonatorUhf oscillators
A self-sustaining ultra-high frequency oscillator and method enable the ability to oscillate and output a signal. A balanced bridge circuit is utilized to null an embedding background response. A first vibrating nanoelectromechanical (NEMS) beam resonator is part of one of the branches of the balanced bridge circuit and determines the frequency of the oscillator's output signal. A feedback loop establishes and sets oscillation conditions of the oscillator's signal. Further, the feedback loop connects an output of the first resonator to an input of the balanced bridge circuit.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Nano-beam resonator with field effect pipe manufactured using sacrifice layer corrosion technology
InactiveCN1618727ASimple preparation processLow costImpedence networksIndividual molecule manipulationMetallic electrodeField-effect transistor
A nanobeam resonator with FET is prepared by sacrifice layer etching process, and is composed of nanobeam resonator and its metallic electrodes. Said etching process includes such steps as preparing the nanobeam on the silicon layer on the insulating material (SOI), doping B or P to both ends of nanobeam to form P-i-P or N-i-N channel structure used as the channel of FET, and using the bottom electrode as the grid of FET.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
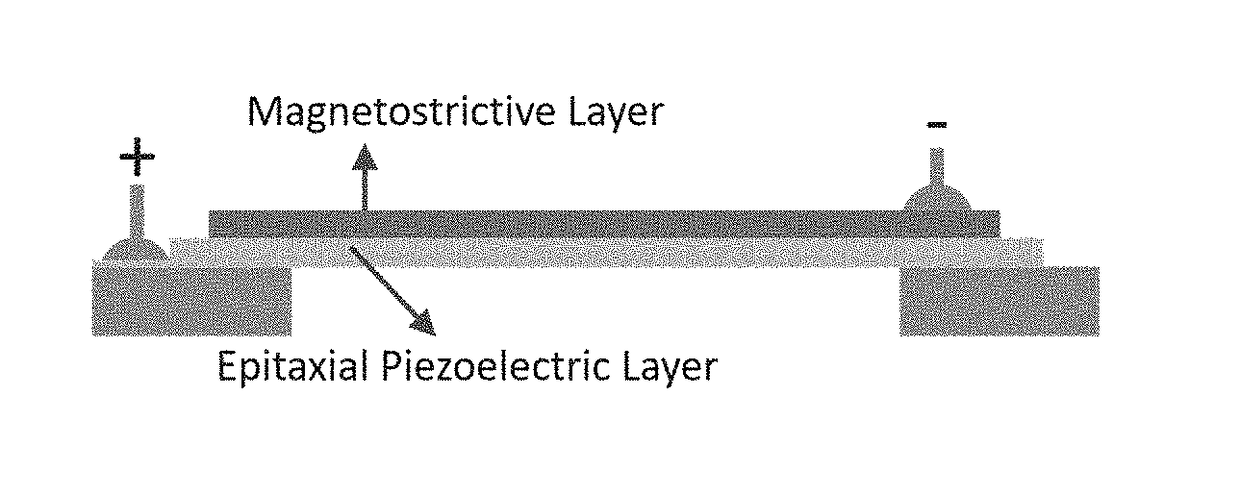
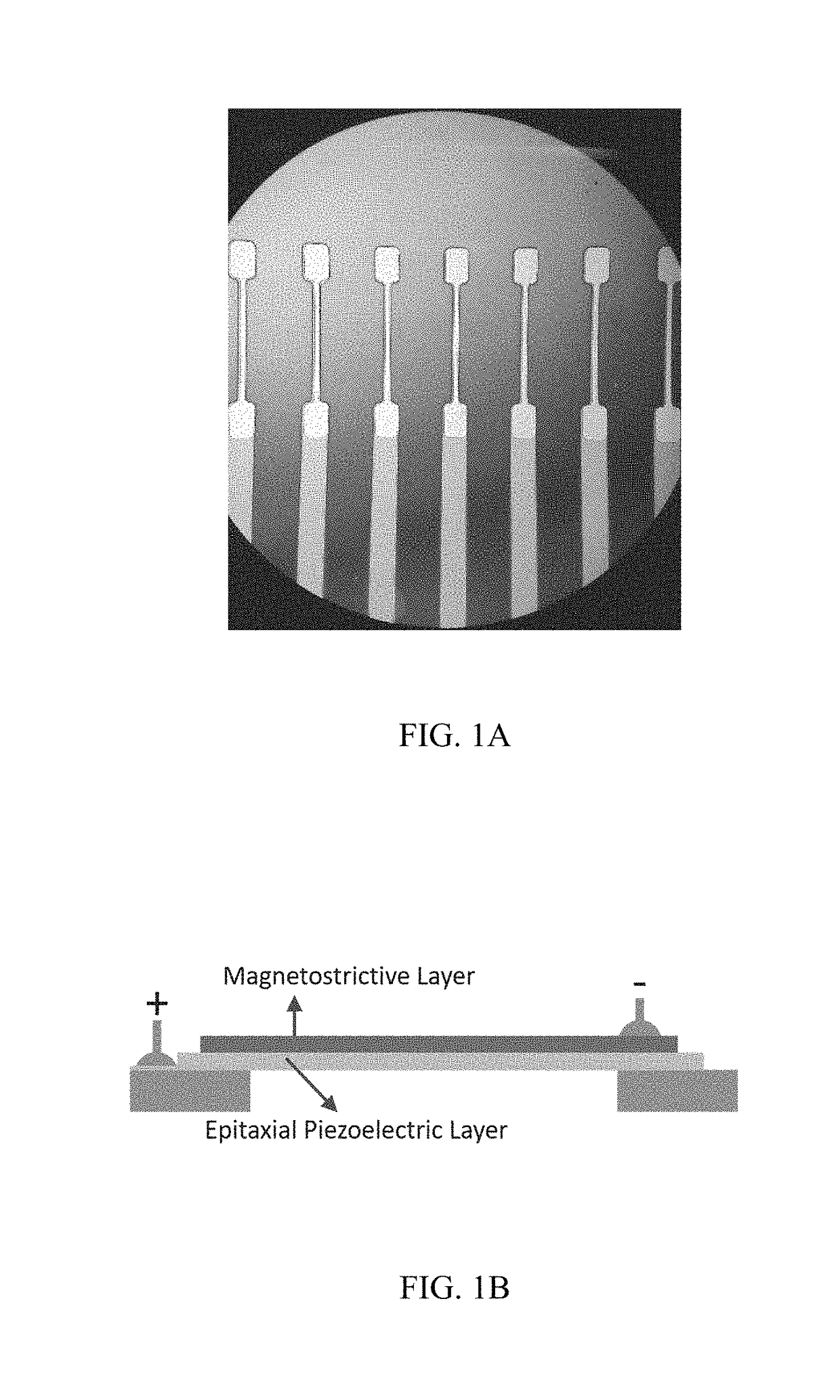
Ultra-low power magnetoelectric magnetic field sensor
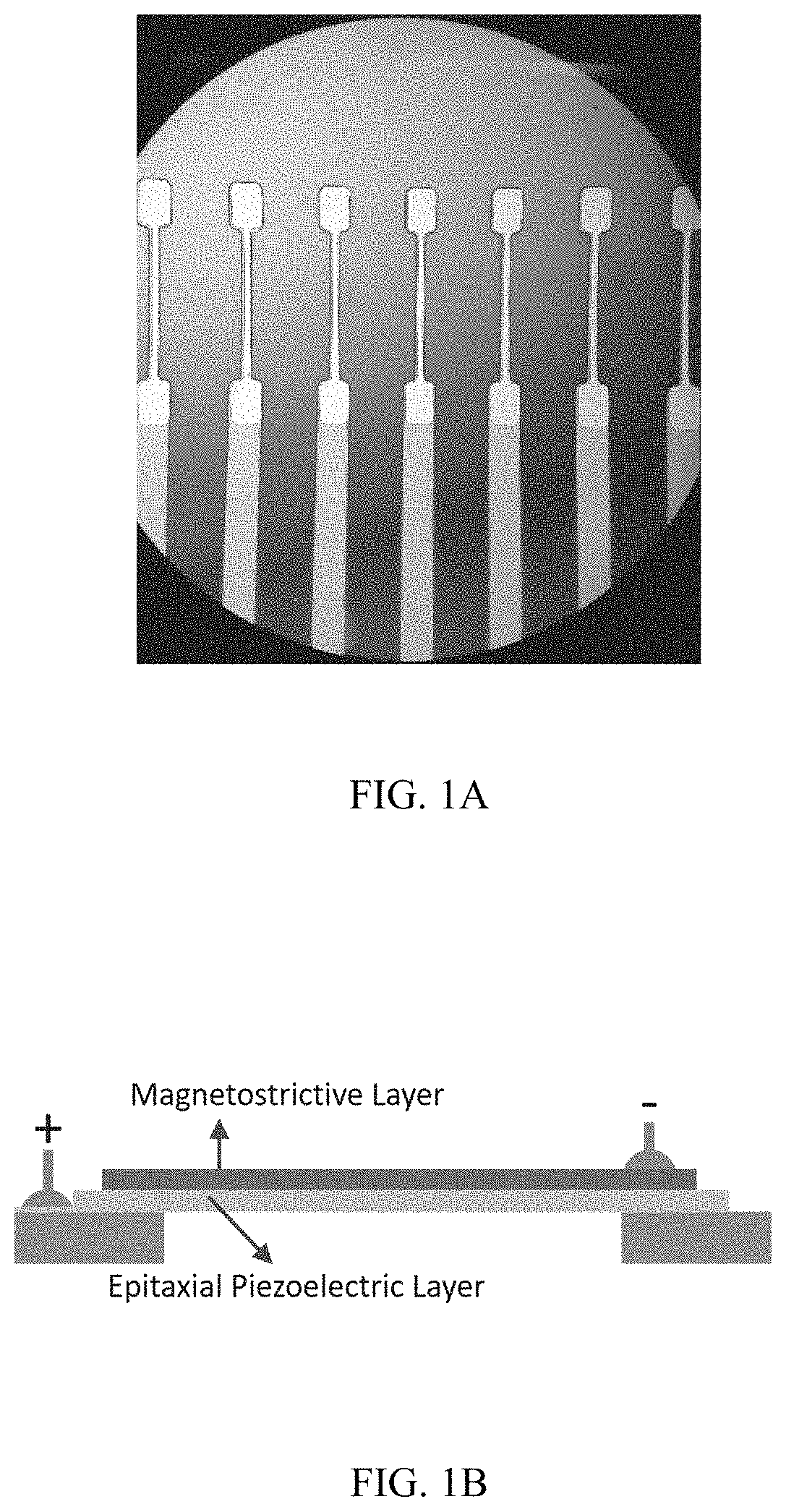
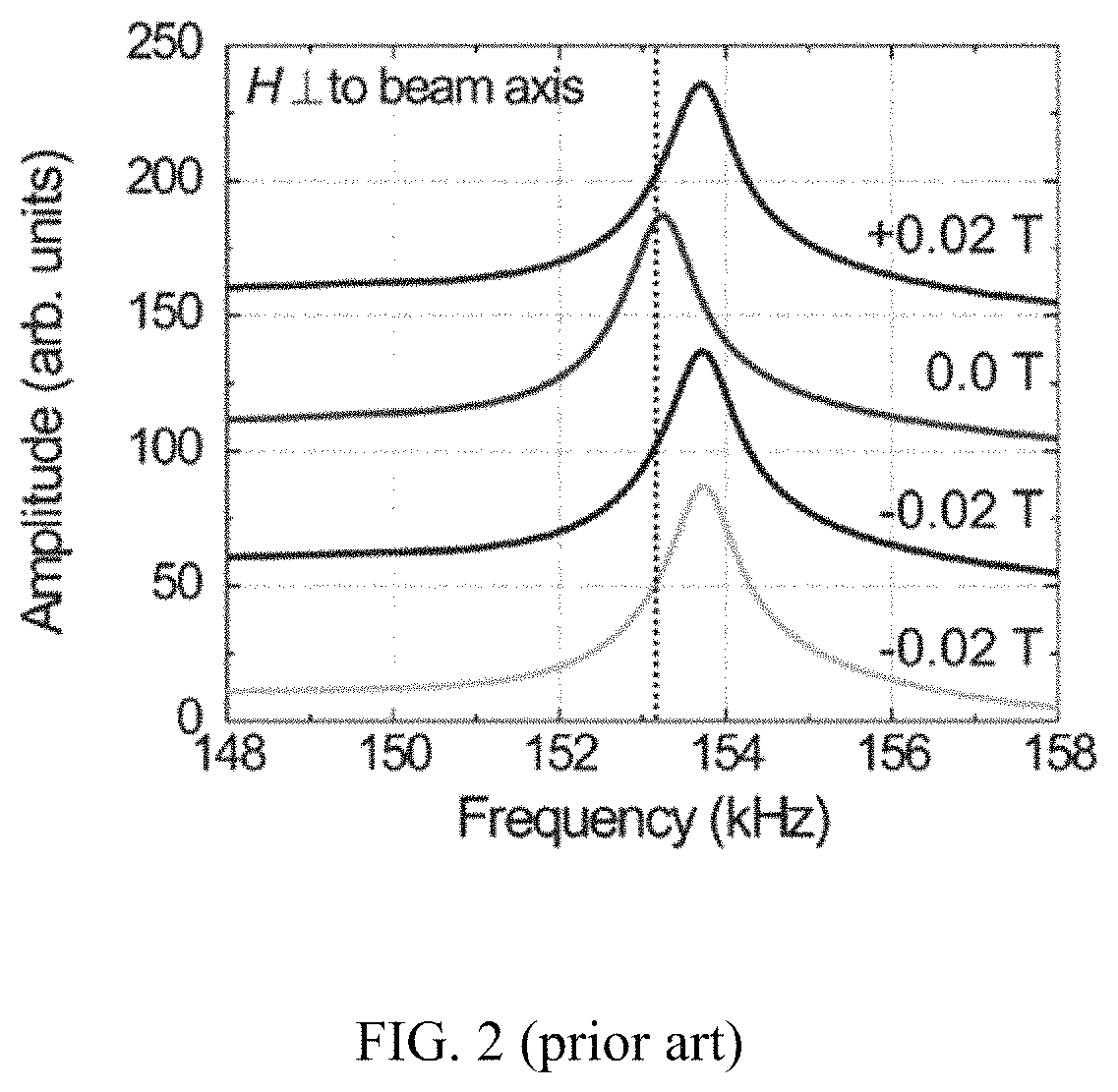
ActiveUS20180259599A1Average power consumptionEnhances strain couplingNanomagnetismMagnetostrictive device manufacture/assemblyElectromagnetic fieldBeam resonator
A high-sensitivity and ultra-low power consumption magnetic sensor using a magnetoelectric (ME) composite comprising of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric layers. This sensor exploits the magnetically driven resonance shift of a free-standing magnetoelectric micro-beam resonator. Also disclosed is the related method for making the magnetic sensor.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Low-thermoelastic damping cantilever micro beam resonator having through hole structures
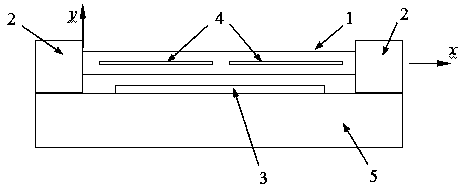
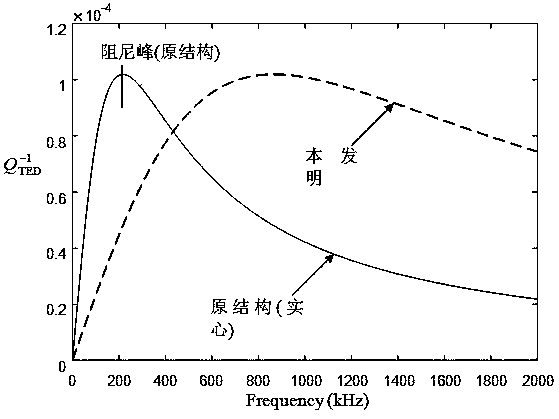
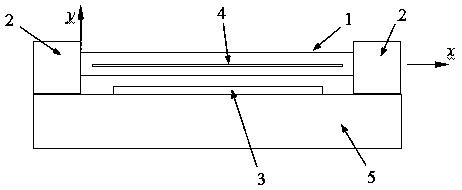
ActiveCN107592089AReduce thicknessIncrease the frequency bandImpedence networksThermoelastic dampingCantilever
The present invention belongs to the micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) field and relates to a low-thermoelastic damping cantilever micro beam resonator having through hole structures. The low-thermoelastic damping cantilever micro beam resonator comprises a base, a driving electrode, a cantilever supporting portion and a suspension micro beam; the driving electrode is arranged on the upper surface of the base; the cantilever supporting portion is arranged at one end of the upper surface of the base; one end of the suspension micro beam is fixed on the cantilever supporting portion, and atthe same time, the suspension micro beam is located above the driving electrode; the long sides of the suspension micro beam are parallel to the base; rectangular through holes are formed in a side surface where the sides of the suspension micro beam at the length direction and the sides of the suspension micro beam at the thickness direction; the rectangular through holes are located at the center of the side surface; the length of the rectangular through holes is not smaller than a length of 0.8 times of the length of the side surface; and the width of the rectangular through holes is not larger than a width of 0.1 times of the width of the side surface. The damping peak of the resonator is in high frequencies, and is not within operating frequencies.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Micro electronmechanical system pressure sensor chip of beam film mechanism and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106946211AImprove linearityHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsImpedence networksDiaphragm structureSystem pressure
The invention discloses a microelectromechanical system pressure sensor chip of a beam-membrane mechanism and a preparation method thereof. It includes a glass substrate, an n-type monocrystalline silicon element body, an isolation layer, and a protective layer; the outer edge of the n-type monocrystalline silicon element body is supported above the glass substrate, and the middle part of the n-type monocrystalline silicon element body is a hollow structure. A closed cavity is formed between the two; the top wall of the closed cavity is provided with a diaphragm pressure-sensitive structure; the diaphragm pressure-sensitive structure is divided into a flat die layer and a beam-membrane mechanism layer; Composed of beams, the beam-membrane mechanism has the advantages of good linearity and high sensitivity. The varistor is made of single crystal silicon, and an isolation layer is provided between the pressure-sensitive film and the varistor, which further improves the sensitivity and temperature characteristics, and overcomes the defects in the prior art such as sensor failure caused by excessive temperature. The preparation process of the sensor is simple and easy, the cost is low, and the sensor is easy to be integrated and miniaturized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Temperature compensated beam resonator
The invention provides a microelectromechanical resonator device comprising a support structure and a resonator manufactured on a (100) or (110) semiconductor wafer, wherein the resonator is suspended to the support structure and comprises at least one beam being doped to a doping concentration of 1.1*1020 cm-3 or more with an n-type doping agent and is being capable of resonating in a length-extensional, flexural resonance or torsional mode upon suitable actuation. In particular, the doping concentration and angle of the beam are chosen so as to simultaneously produce zero or close to zero second order TCF, and even more preferably zero or close to zero first and second order TCFs, for the resonator in said resonance mode, thus providing a temperature stable resonator.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
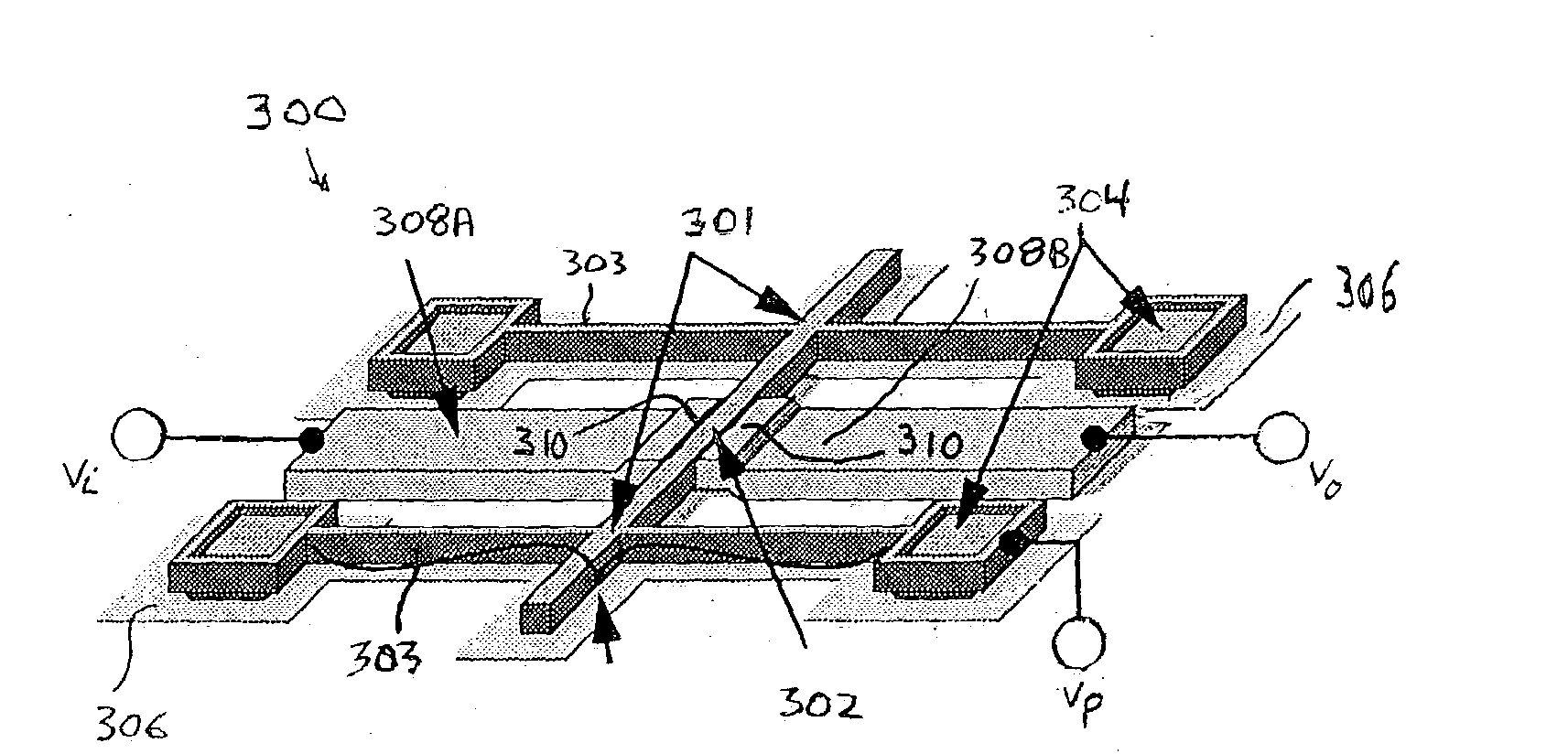
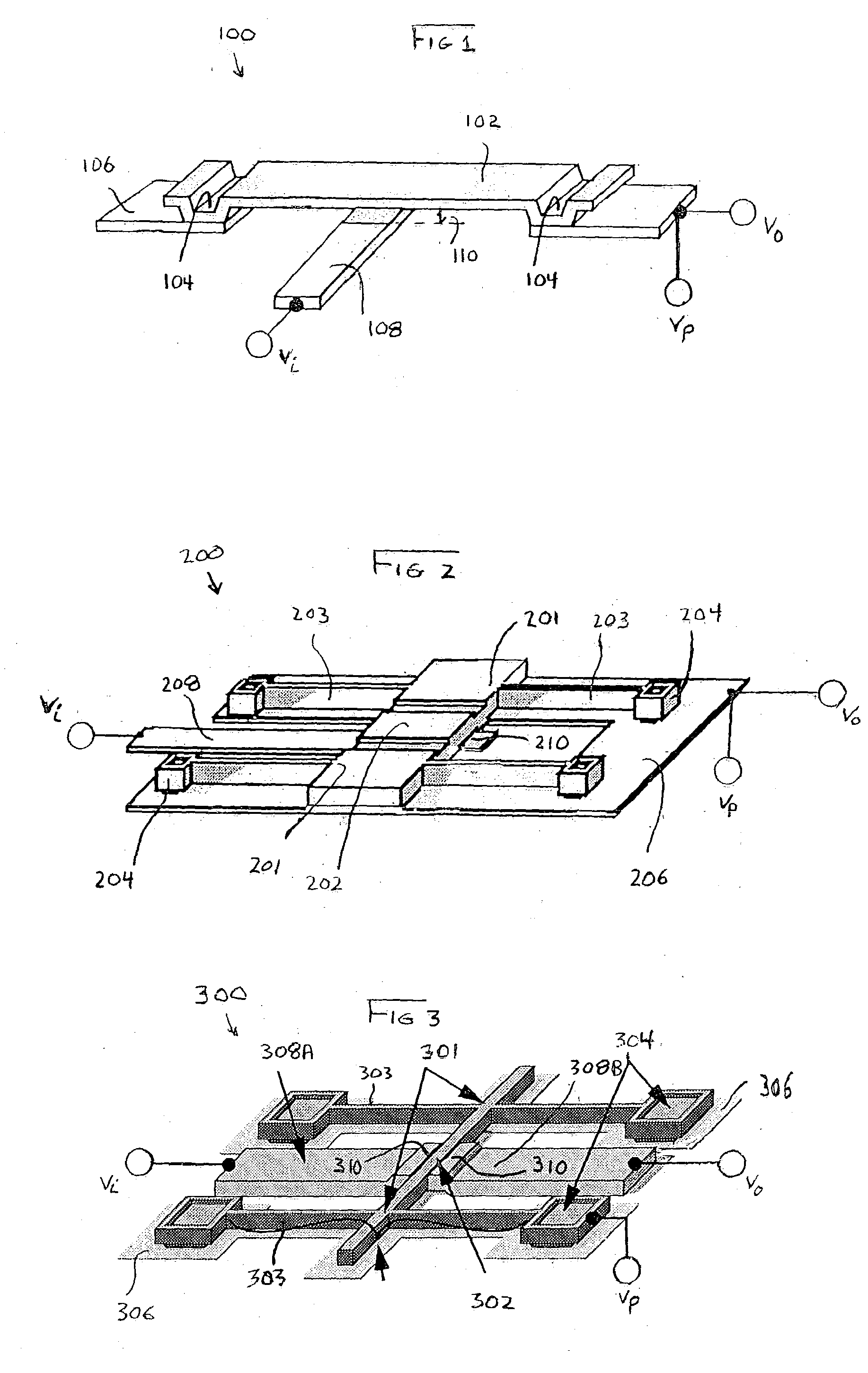
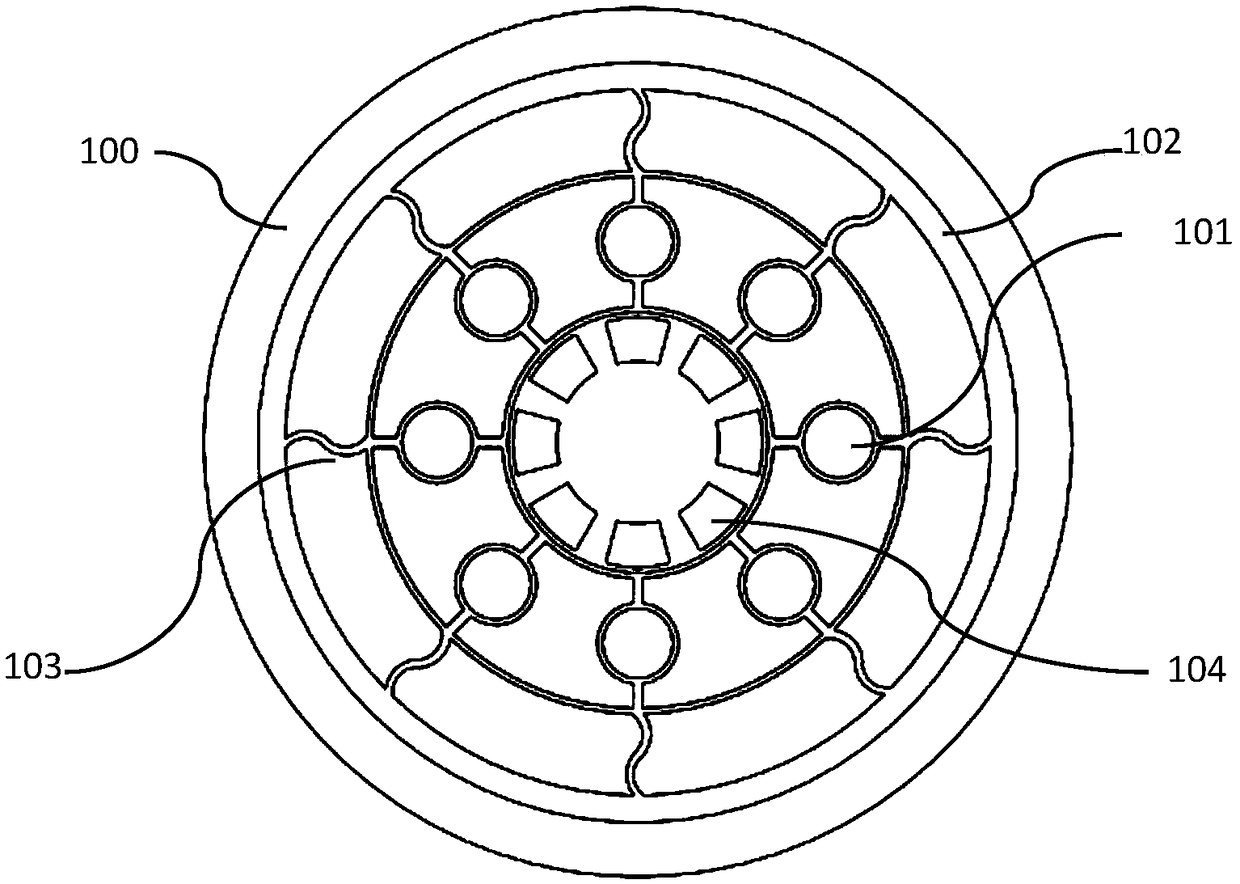
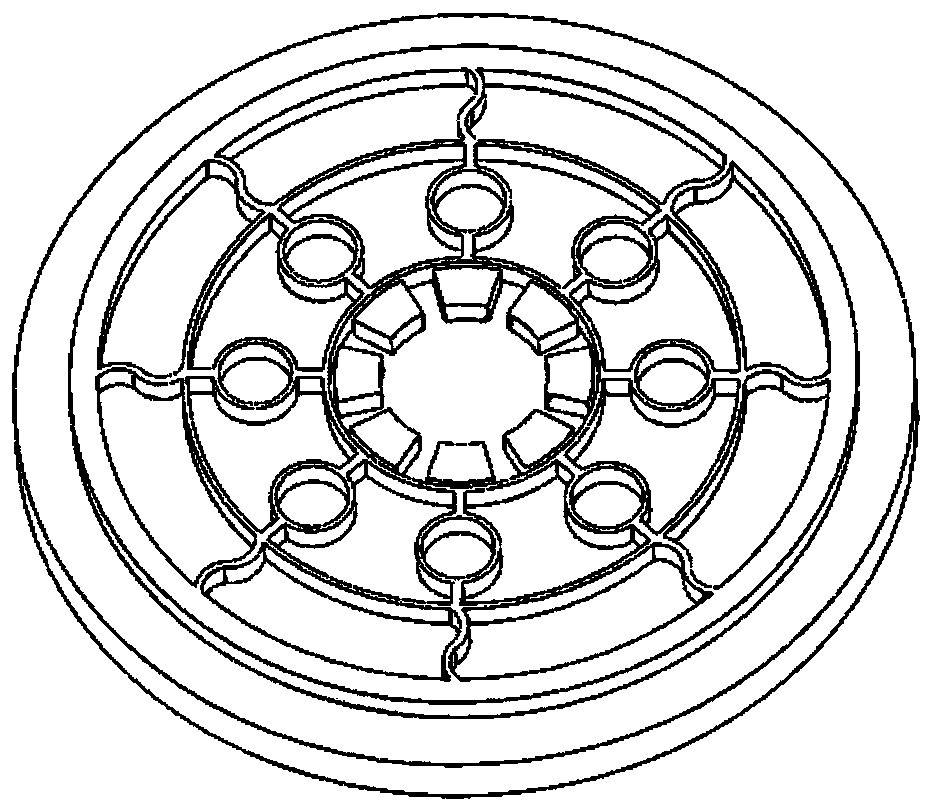
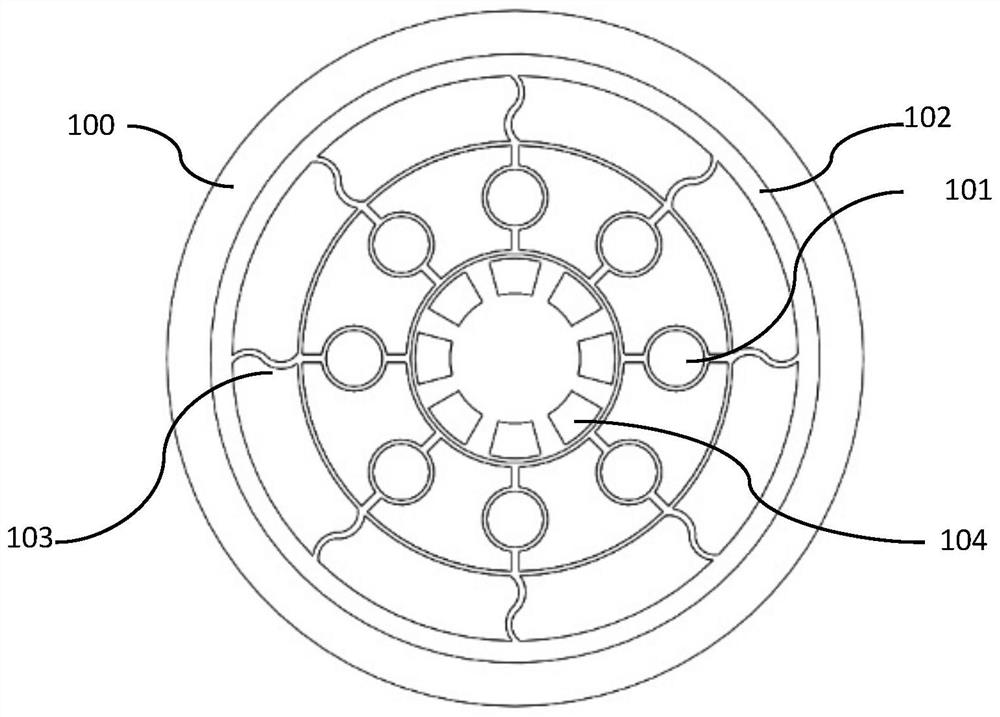
Internally-driven circular beam resonance micro-gyroscope of nickel electrode
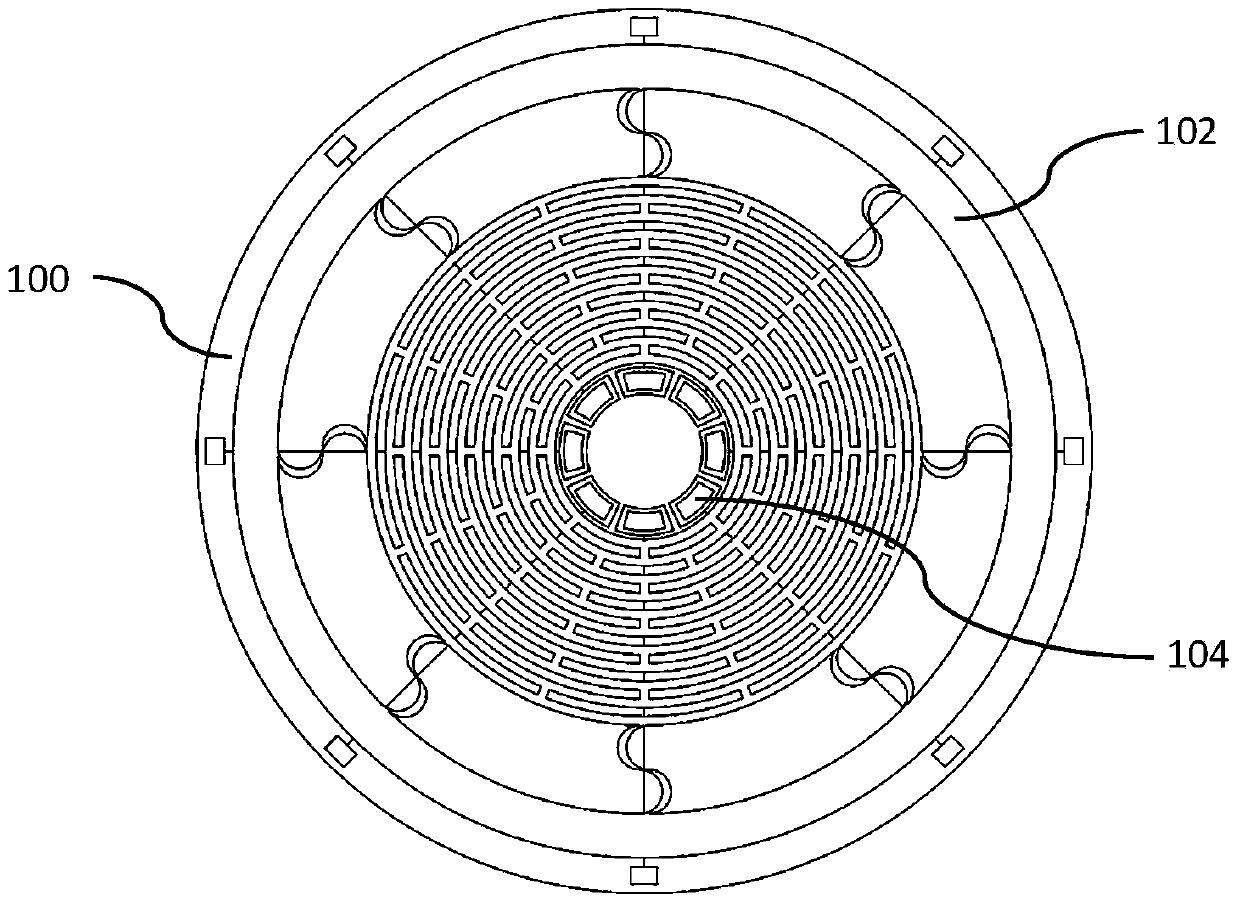
ActiveCN108871304AStable structureImprove performanceSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeResonance
The invention provides an internally-driven circular beam resonance micro-gyroscope of a nickel electrode mechanism. The internally-driven circular beam resonance micro-gyroscope of the nickel electrode mechanism comprises a substrate (100), a resonator (102) and an electrode mechanism (104). The substrate (100) is provided with a bulge 108. The resonator (102) is installed in the bulge 108. The electrode mechanism (104) is uniformly distributed on the substrate (100) along a circumferential direction. The electrode mechanism (104) is fan-shaped, and the electrode mechanism (104) is made of nickel. The internally-driven circular beam resonance micro-gyroscope of the nickel electrode adopts a circular beam resonance structure, and has high symmetry. The internally-driven circular beam resonance micro-gyroscope of the nickel electrode adopts an S-type flexible fixed beam, is relatively stable in structure, and shock-resistant, and has good performance. Relative to electrodes distributedon the outer circle of the circular beam resonator, the nickel electrode distributed on the inner edge of the circular beam resonator is capable of improving a Q value of the internally-driven circular beam resonance micro-gyroscope of the nickel electrode, thereby response is more sensitive.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Low-heat elastic damping two-end-fixed micro-beam resonator with through hole structure
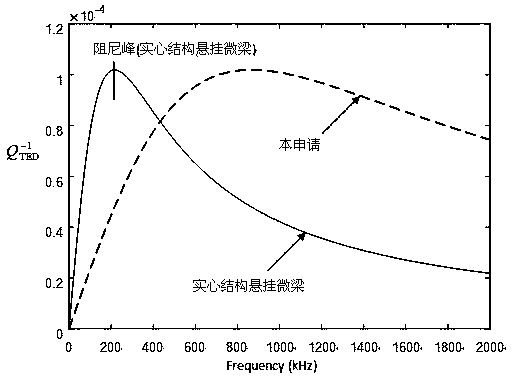
InactiveCN108471297ALow thermoelastic energy lossReduced thermoelastic dampingImpedence networksSolid structureThermoelastic damping
The invention relates to a low-heat elastic damping two-end-fixed micro-beam resonator with a through hole structure. The through hole structure can be an elongated rectangular through hole or a circular through hole. The device comprises a low-heat elastic damping micro beam with a through hole structure, two end fixing supports and an electrode for electrostatic excitation. The previous two end-fixing micro-beam (rectangular cross section) is of a solid structure, the thermal elastic damping peak of the solid structure is at a low frequency section, the damping peak corresponds to the maximum thermal elastic energy loss, which is completely detrimental to the micro-beam device operating in a low-frequency section. The physical principle of the low-heat elastic damping two-end-fixed micro-beam adopting a long and narrow rectangular through hole scheme provided by the invention is as follows: long and narrow rectangular holes are formed along the length direction; the number of the rectangular holes is at least two; due to hole opening, the thickness of the beam is thinned, and the thermal elastic damping peak is moved to a high-frequency section, so that the thermal elastic energyloss of the micro-beam is greatly lower than that of the original solid micro-beam device under the situation that the operation (vibration) frequency is not changed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High-quality-factor piezoelectric cantilever beam density sensor chip and working method and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111579426AImprove reliabilityHigh sensitivityDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingCantilevered beamPiezoelectric cantilever
The invention discloses a high-quality-factor piezoelectric cantilever beam density sensor chip and a working method and a preparation method thereof. The high-quality-factor piezoelectric cantileverbeam density sensor chip comprises a silicon substrate and a silicon micro-cantilever beam resonator, wherein the silicon micro-cantilever beam resonator comprises a micro-cantilever beam suspension structure, a clamped beam structure, a piezoresistive beam structure and a piezoresistive connection beam structure. The silicon micro-resonance cantilever beam structure is covered with a low-stress aluminum nitride piezoelectric film through an MEMS process, double piezoelectric electrodes are used for introducing alternating voltage with a certain frequency and generating piezoelectric driving force based on an inverse piezoelectric effect, four sensitive resistor strips on four piezoresistive beams are connected through metal leads on piezoresistive connecting beams to form a Wheatstone full bridge,and are used for detecting resonance stress and converting the resonance stress into voltage signals to be output by arranging the Wheatstone bridge, and a cantilever beam out-of-plane vibration mode can be obtained in a piezoelectric excitation mode. The density sensor chip has high sensitivity and high-quality factors in fluid, an application range of fluid density measurement can be remarkably widened, and measurement precision and sensitivity are high.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
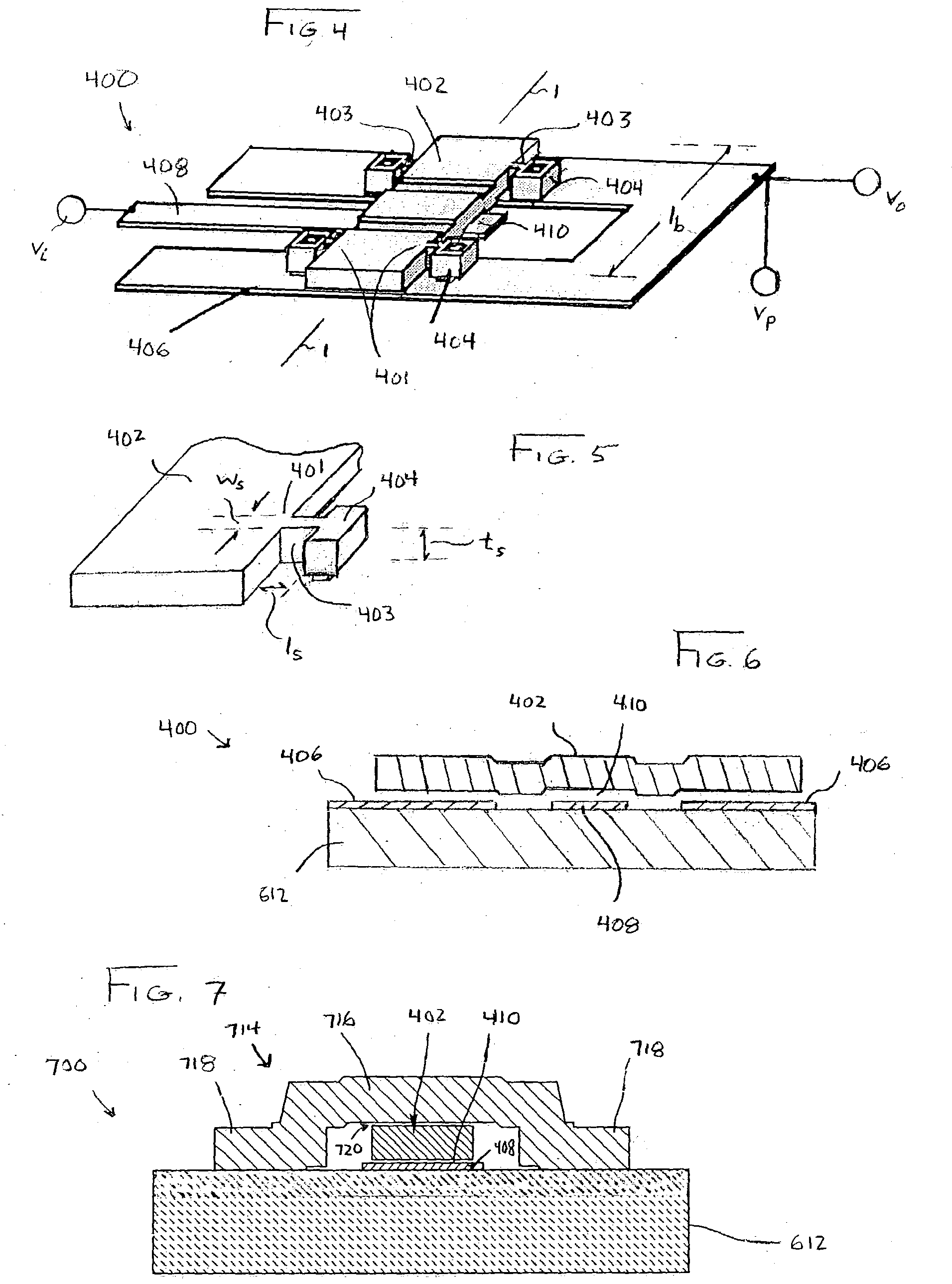
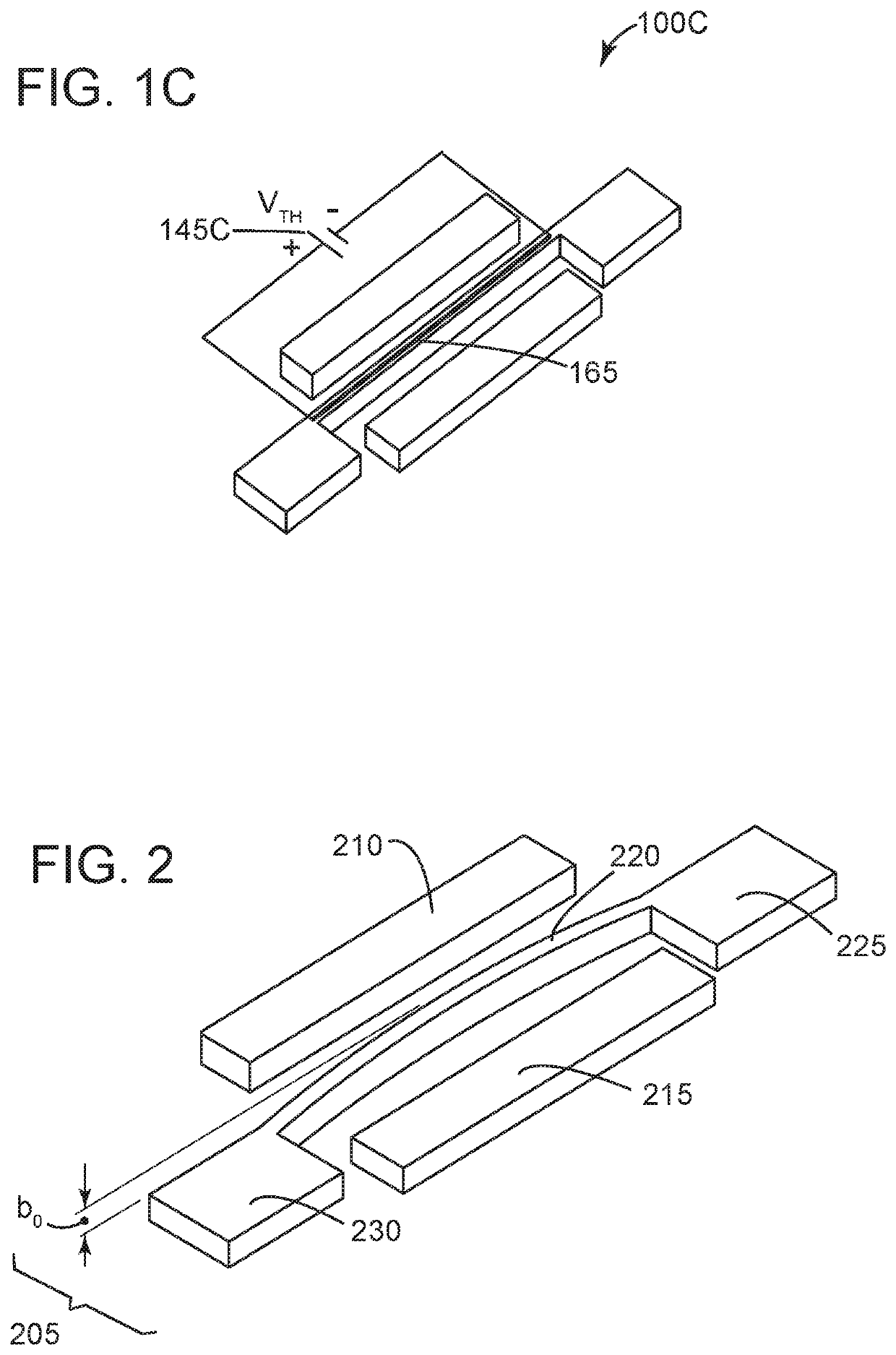
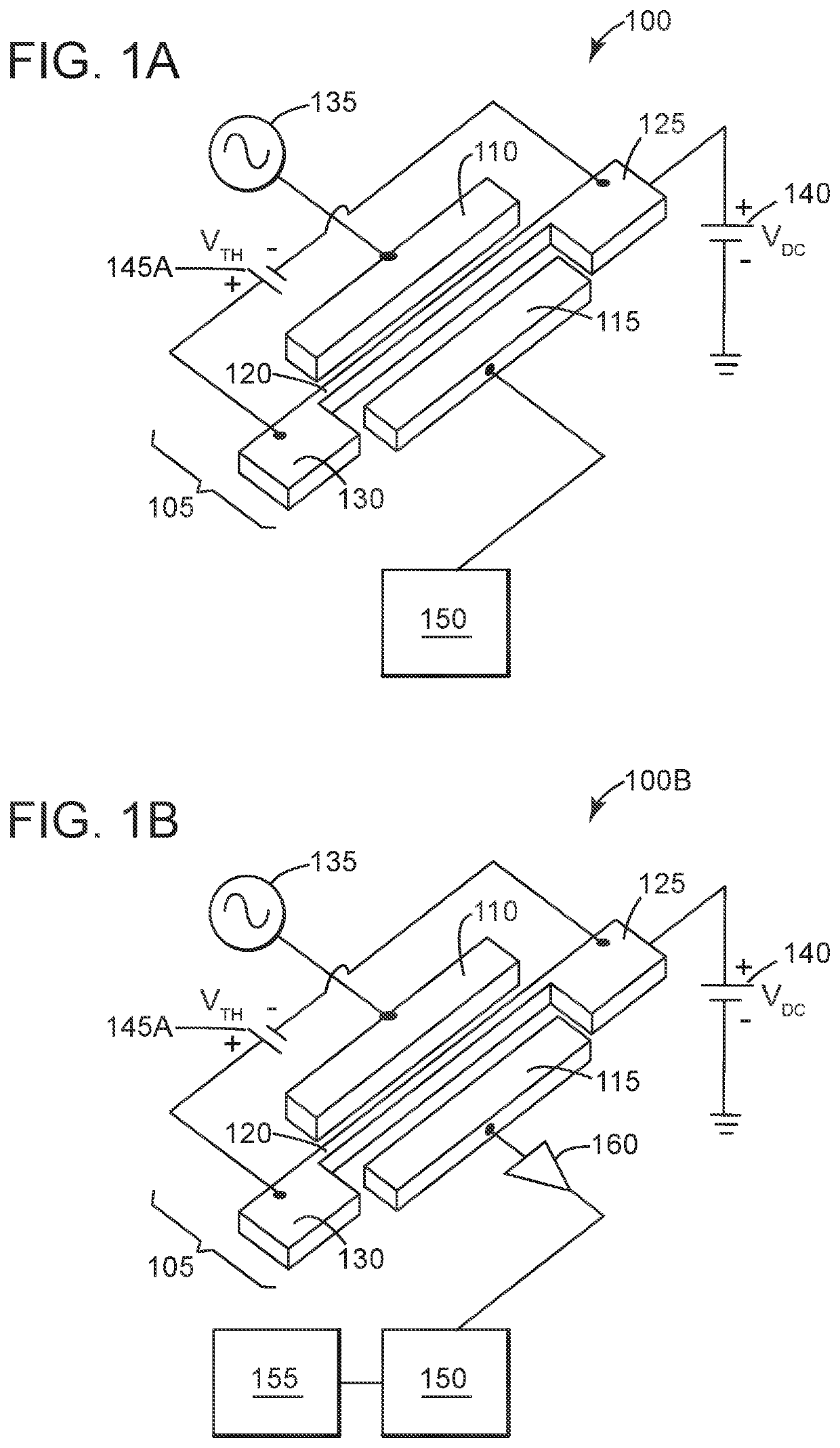
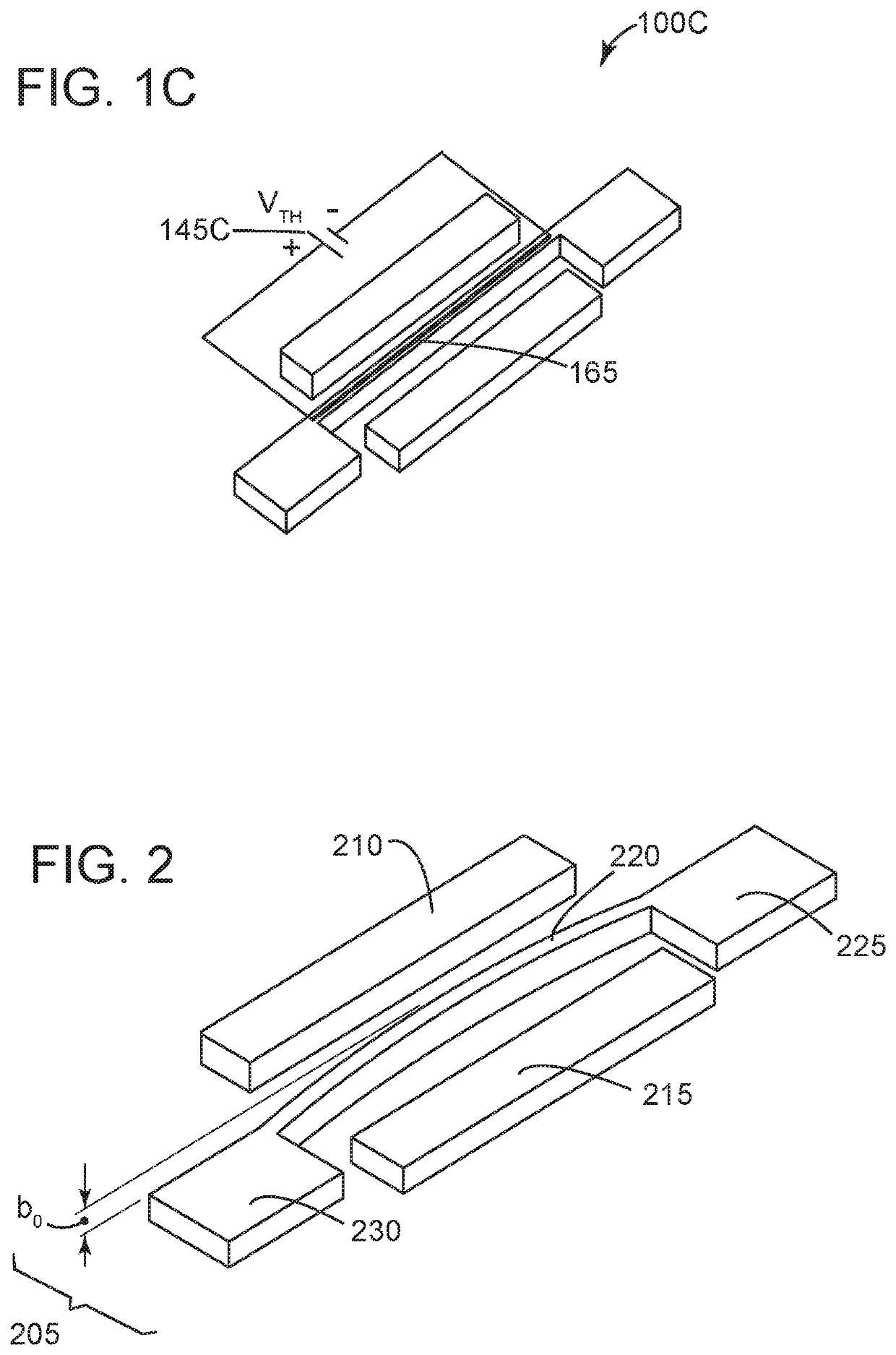
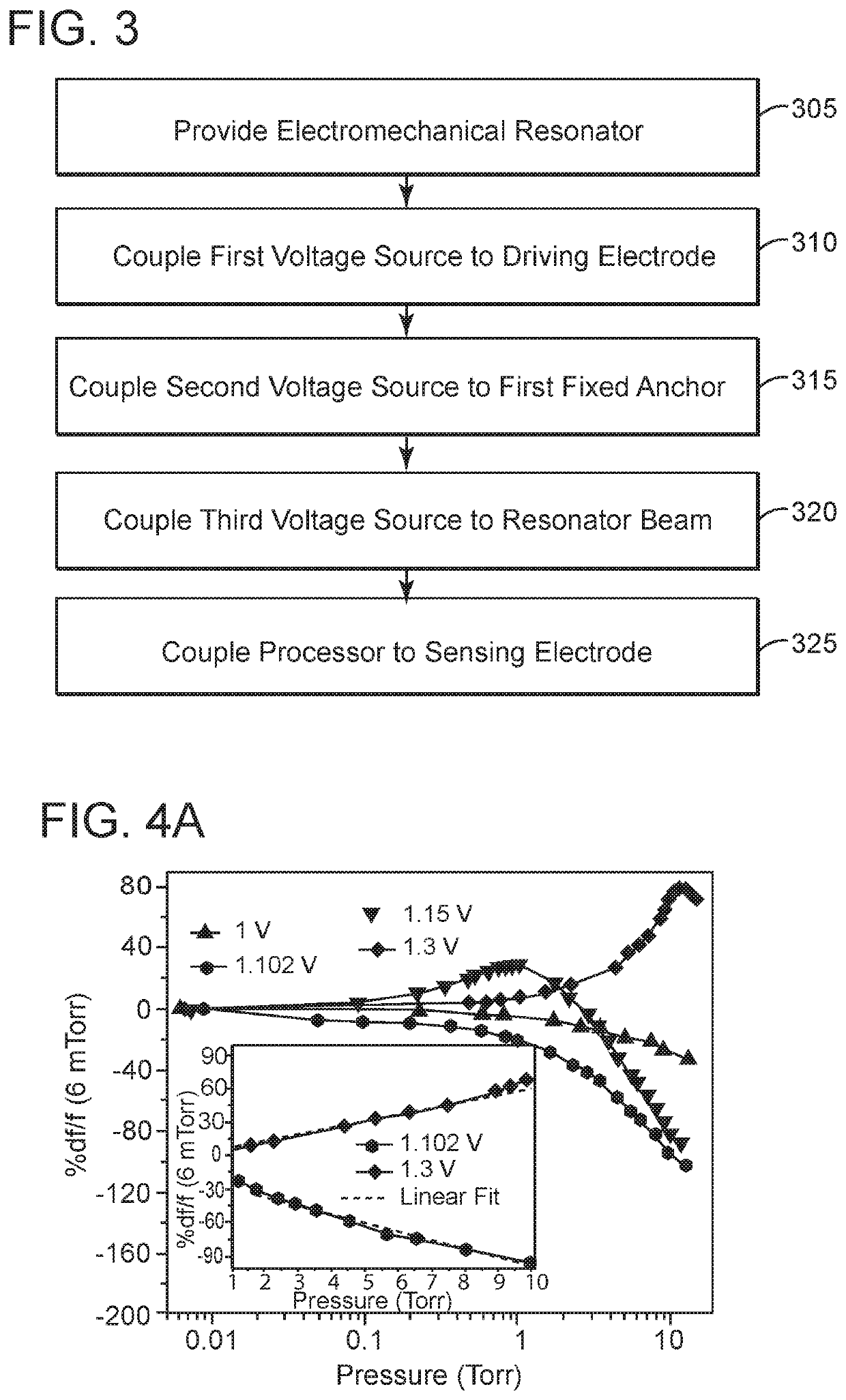
Electromechanical pressure sensor
ActiveUS11274983B2Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsVacuum gauge using gaseous frictional resistance variationAC - Alternating currentVoltage source
An electromechanical pressure sensor includes an electromechanical resonator having a driving electrode, a sensing electrode, and a beam resonator arranged between the driving and sensing electrodes. The beam resonator includes a resonator beam coupled on a first end to a first fixed anchor and coupled on a second end to a fixed second fixed anchor. The electromechanical resonator also includes a first voltage source coupled to the driving electrode and configured to provide an alternating current to the driving electrode and a second voltage source coupled to the first fixed anchor. The second voltage source provides a DC bias to the resonator beam. The electromechanical resonator further includes a third voltage source coupled to the resonator beam via the first and second fixed anchors. The third voltage source is configured to supply a voltage to the resonator beam that results in a temperature differential between the resonator beam and the first and second fixed anchors. The electromechanical resonator also includes a processor coupled to the sensing electrode and configured to correlate a voltage on the sensing electrode with a pressure value.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Resonant accelerometer based on bident type resonant beam
The invention discloses a structure, a manufacturing method and a working principle of a resonant accelerometer based on a bident type resonant beam, and belongs to the field of the micro-electro mechanical system. The structure disclosed by the invention is that the resonant accelerometer is composed of a bident resonant beam (1), an excitation resistor (2), a piezoresistor (3), a crab leg type support beam (4), a mass block (5), a frame (6), and a metal internal lead (7); a center of gravity of the mass block (5) is located in a neutral surface of the crab leg type support beam (4). On the aspect of the detection principle, the sensor is characterized in that the axial stress of the bident type resonant beam (1) is changed under the acceleration effect parallel to a chip surface, therebychanging the resonance frequency thereof; and the size and the direction of the acceleration can be obtained by detecting the resonance frequency change; compared with the dual-end clamped straight beam resonator, the resonant accelerometer based on the bident resonant beam has greater detection sensitivity.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Resonant sensor assembly
InactiveCN1802557AHigh quality factorFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesStress distributionElement analysis
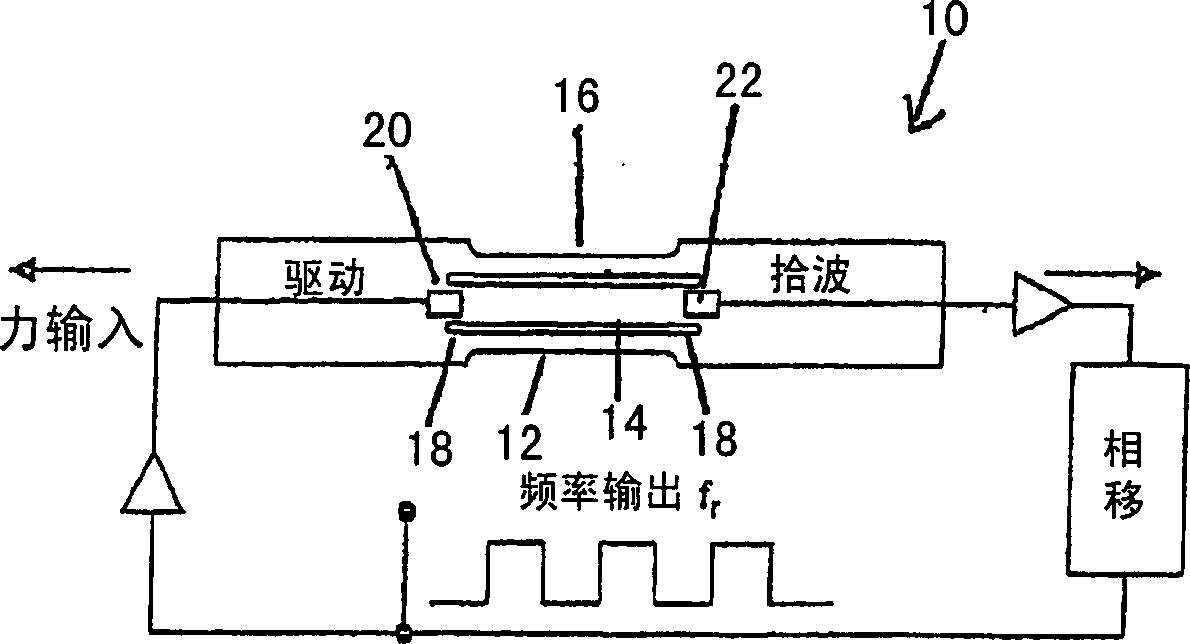
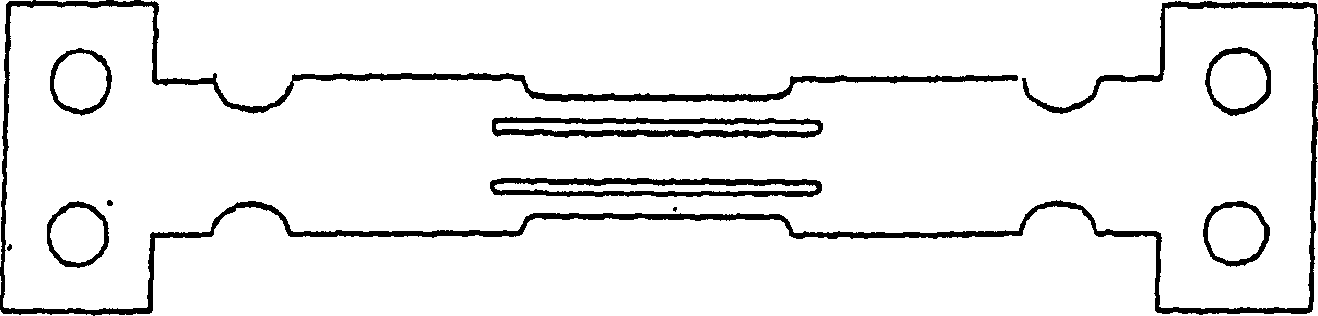
A triple beam resonator (10) is provided with three beams or tines (12, 14, 16) aligned in parallel alongside each other and joined at a decoupling zone (18) at each end, which is in turn connected to the surrounding material. The central beam (14) is twice the width of the two outer beams (12, 16). The resonating element has a length of 15.5 mm, a thickness of 0.25 mm and beam widths of 2 mm and 1 mm. The distance between the beams is 0.5 mm. Finite element analysis predicts the modal behaviour with stress distribution and eigenfrequencies of the resonator (10). Thick-film PZT elements (20, 22) were printed on separate regions at each end of the central beam (14), where maximum stresses exist as the resonator (10) operates in its favoured mode of vibration. The PZT element (20) at one end drives the vibrations, while the PZT element (22) at the other end detects them. Positioning the PZT driving and sensing elements (20, 22) on the regions of maximum stresses maximises the degree of mechanical coupling between the active piezoelectric layer and the resonator for generation of both driving forces and sensing signals. Very high quality factors of 3100 and higher have been experienced. Furthermore, the resonator can be manufactures by batch production techniques while maintaining high reliability and reproducibility.
Owner:BRUNEL UNIVERSITY
Multi-operation-mode piezoelectric viscosity sensor chip and working method and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111537396AExpand the measurement rangeHigh precisionFlow propertiesDecorative surface effectsCantilevered beamFluid viscosity
The invention discloses a multi-operation-mode piezoelectric viscosity sensor chip and a working method and a preparation method thereof. The multi-operation-mode piezoelectric viscosity sensor chip comprises a silicon substrate and a silicon micro-cantilever resonator. The silicon micro-resonance cantilever beam structure is covered with a low-stress aluminum nitride piezoelectric film through anMEMS process. The double piezoelectric electrodes can be used for introducing alternating voltages with a certain frequency and generating a piezoelectric driving force by utilizing an inverse piezoelectric effect; a vibration signal of the silicon micro-cantilever resonator can also be converted into a detectable voltage signal through a piezoelectric effect; four sensitive piezoresistive stripson four piezoresistive beams form a Wheatstone full bridge through metal leads on piezoresistive connecting beams so as to detect resonance stresses and convert the resonance stresses into voltage signals for output. An in-plane vibration mode of the cantilever beam resonator can be obtained through a piezoelectric excitation mode, a piezoelectric and piezoresistive double-detection mode is adopted for output of vibration electric signals. The viscosity sensor chip has high-quality factors in fluid, and the application range and the measurement precision of fluid viscosity can be remarkably improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ultra-low power magnetoelectric magnetic field sensor
ActiveUS10877110B2Enhances strain couplingHigh sensitivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyNanomagnetismBeam resonatorResonance shift
A high-sensitivity and ultra-low power consumption magnetic sensor using a magnetoelectric (ME) composite comprising of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric layers. This sensor exploits the magnetically driven resonance shift of a free-standing magnetoelectric micro-beam resonator. Also disclosed is the related method for making the magnetic sensor.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Temperature compensated beam resonator
The invention provides a microelectromechanical resonator device comprising a support structure and a resonator manufactured on a (100) or (110) semiconductor wafer, wherein the resonator is suspended to the support structure and comprises at least one beam being doped to a doping concentration of 1.1*1020 cm−3 or more with an n-type doping agent and is being capable of resonating in a length-extensional, flexural resonance or torsional mode upon suitable actuation. In particular, the doping concentration and angle of the beam are chosen so as to simultaneously produce zero or close to zero second order TCF, and even more preferably zero or close to zero first and second order TCFs, for the resonator in said resonance mode, thus providing a temperature stable resonator.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Resonant sensor assembly
InactiveUS7498721B2Quality factorImprove automationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsStress distributionElement analysis
A triple beam resonator (10) is provided with three beams or tines (12, 14, 16) aligned in parallel alongside each other and joined at a decoupling zone (18) at each end, which is in turn connected to the surrounding material. The central beam (14) is twice the width of the two outer beams (12, 16). The resonating element has a length of 15.5 mm, a thickness of 0.25 mm and beam widths of 2 mm and 1 mm. The distance between the beams is 0.5 mm. Finite element analysis predicts the modal behavior with stress distribution and eigenfrequencies of the resonator (10). Thick-film PZT elements (20, 22) were printed on separate regions at each end of the central beam (14), where maximum stresses exist as the resonator (10) operates in its favored mode of vibration. The PZT element (20) at one end drives the vibrations, while the PZT element (22) at the other end detects them. Positioning the PZT driving and sensing elements (20,22) on the regions of maximum stresses maximizes the degree of mechanical coupling between the active piezoelectric layer and the resonator for generation of both driving forces and sensing signals. Very high quality factors of 3100 and higher have been experienced. Furthermore, the resonator can be manufactures by batch production techniques while maintaining high reliability and reproducibility.
Owner:BRUNEL UNIVERSITY
Electromechanical pressure sensor
ActiveUS20210140841A1Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsVacuum gauge using gaseous frictional resistance variationAC - Alternating currentEngineering
An electromechanical pressure sensor includes an electromechanical resonator having a driving electrode, a sensing electrode, and a beam resonator arranged between the driving and sensing electrodes. The beam resonator includes a resonator beam coupled on a first end to a first fixed anchor and coupled on a second end to a fixed second fixed anchor. The electromechanical resonator also includes a first voltage source coupled to the driving electrode and configured to provide an alternating current to the driving electrode and a second voltage source coupled to the first fixed anchor. The second voltage source provides a DC bias to the resonator beam. The electromechanical resonator further includes a third voltage source coupled to the resonator beam via the first and second fixed anchors. The third voltage source is configured to supply a voltage to the resonator beam that results in a temperature differential between the resonator beam and the first and second fixed anchors. The electromechanical resonator also includes a processor coupled to the sensing electrode and configured to correlate a voltage on the sensing electrode with a pressure value.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Micro bridge resonator temp ecompensation structure
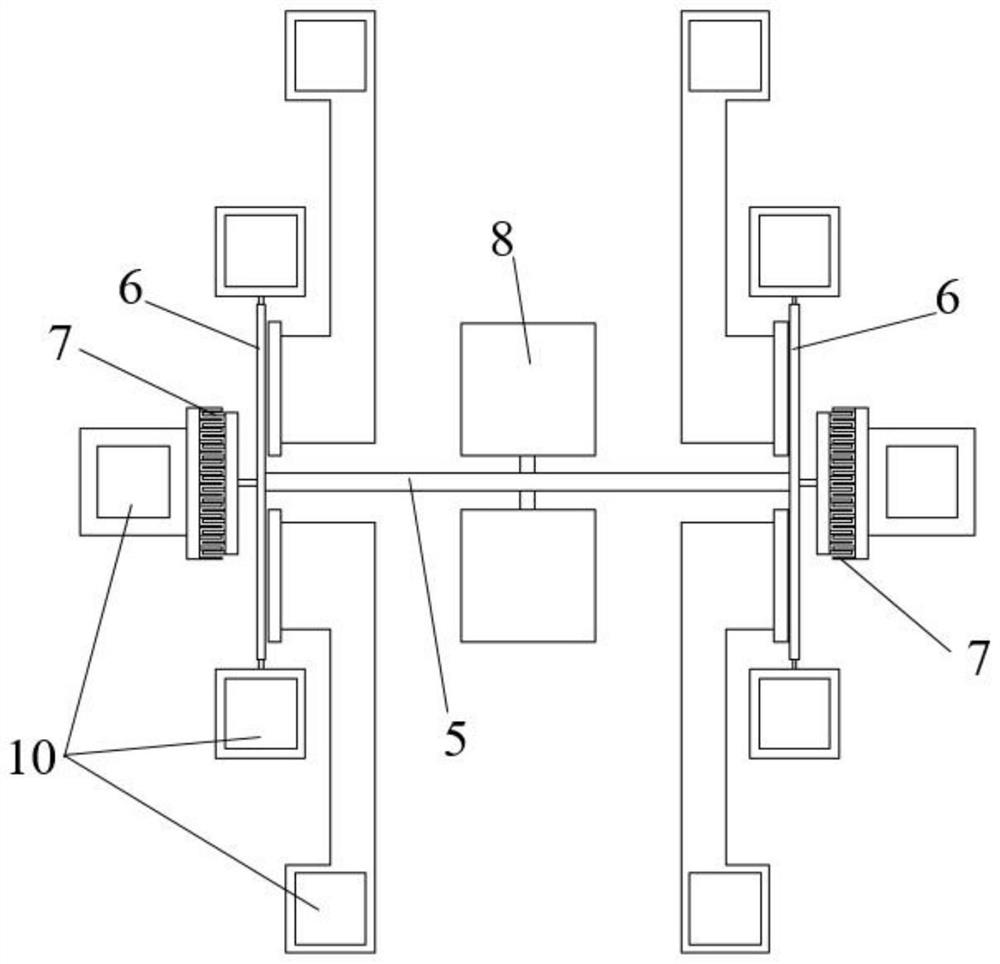
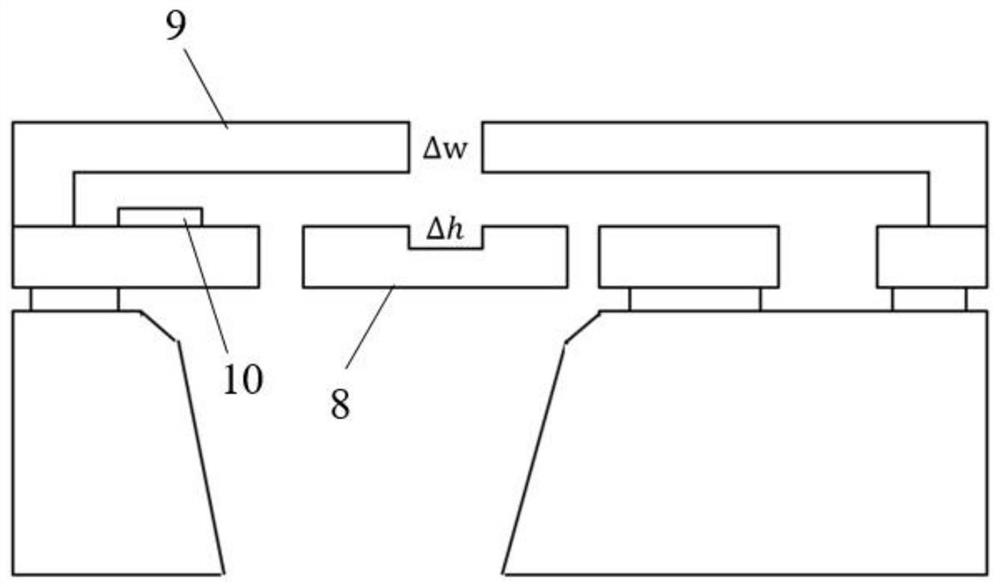
The invention discloses a frequency output composite micro-beam resonator with temperature self-compensation function. The resonator is composed of a micro-bridge resonator and a micro-cantilever beam resonator fabricated on the same chip. The beam resonators have the same material, equal or similar thickness, and the same manufacturing process and are manufactured at the same time, so they can respond to temperature changes synchronously; the distance between the micro-bridge resonator and the micro-cantilever beam resonator is on the order of microns, so the temperature-sensitive element can be accurately Reflects the temperature of the microbridge resonator. Through data fusion technology, the resonant frequency of the micro-cantilever beam resonator as a temperature-sensitive element can compensate the cross-sensitivity of the temperature change to the resonant frequency of the micro-bridge resonator in real time, thereby reducing the temperature coefficient of the resonant frequency of the micro-bridge resonator and improving the resonator. range of working temperature.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Micromechanical resonator oscillator structure and driving method thereof
This invention provides a micromechanical resonator oscillator structure and a driving method thereof. As power handling ability of a resonator is proportional to its equivalent stiffness, a better power handling capability is obtained by driving a micromechanical resonator oscillator at its high equivalent stiffness area. One of the embodiments of this invention is demonstrated by using a beam resonator. A 9.7-MHZ beam resonator via the high-equivalent stiffness area driven method shows better power handling capability and having lower phase noise.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
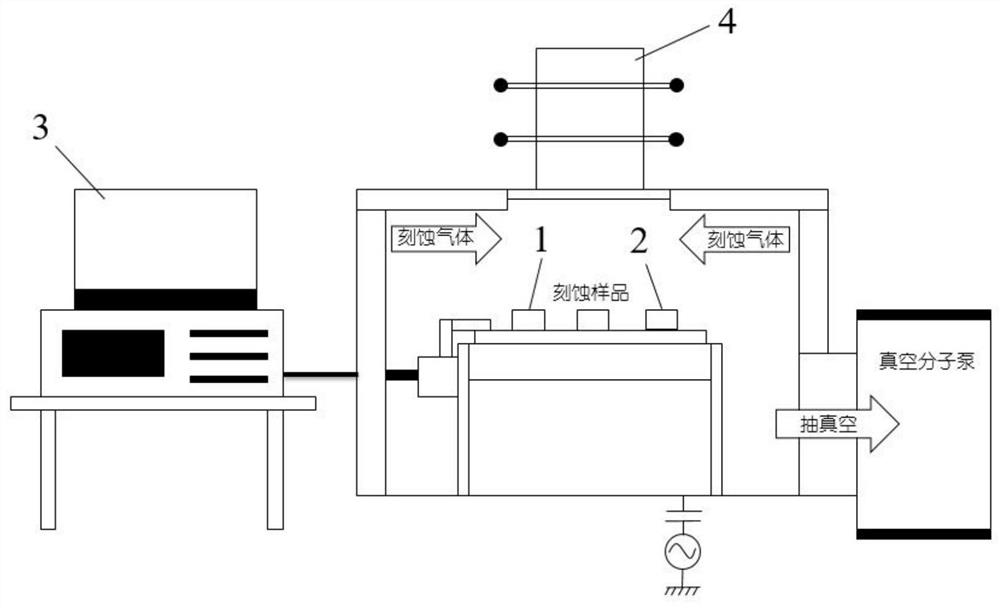
A Resonator-Based Etching Endpoint Detection System and Method
ActiveCN111653467BGuaranteed accuracyLow costElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsData acquisitionSilicon oxide
A resonator-based etching endpoint detection system and method, including a coupled beam resonator and a temperature compensation sensor placed in the etching chamber of an etching machine at the same time, and the etching signal of the coupled beam resonator and the temperature compensation sensor The data acquisition is completed through a closed-loop oscillator circuit respectively, and the two closed-loop oscillator circuits send the etching signal data to the host computer for data processing, and display it graphically through the host computer, and the etching signal data of the host computer and the etching machine are shared The coupled beam resonator includes a connecting rod. The two ends of the connecting rod are respectively connected to the inner side of the middle part of the resonant beam. The upper and lower ends of the resonant beam are fixedly supported by anchor points. The outer end of the device is fixed by anchor points; there are etched square plates hanging on both sides of the middle of the connecting rod, and the etched square plates are used as etching areas; the detection system of the present invention has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, high detection accuracy, and can accurately control Silicon, silicon oxide and other etching depth and other advantages.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Nickel Electrode Driven Circular Beam Resonant Microgyroscope
ActiveCN108871304BStable structureImprove performanceSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesEngineeringNickel electrode
The present invention provides a resonant micro-gyroscope with a circular beam internally driven by a nickel electrode mechanism, comprising a base (100), a resonator (102) and an electrode mechanism (104); the base (100) is provided with a protruding portion 108; The resonator (102) is arranged in the protruding part 108; the electrode mechanism (104) is evenly distributed on the base (100) along the circumferential direction. The electrode mechanism (104) is fan-shaped; the material of the electrode mechanism (104) is nickel. The nickel electrode internal drive circular beam resonant micro gyro adopts a circular beam resonant structure, which has a high degree of symmetry; the nickel electrode internal drive circular beam resonant micro gyro adopts an S-shaped flexible fixed beam, which has a relatively stable structure, impact resistance, and excellent performance . Compared with the electrodes distributed on the outer circle of the circular beam resonator, the nickel electrodes distributed on the inner edge of the circular beam resonator can improve the Q value of the circular beam resonant micro-gyroscope driven by the nickel electrode, so the response is more sensitive.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Resonance-force balance capacitive three-axis acceleration sensor and manufacturing method
InactiveCN102590555BMeet high performance requirementsImprove linearityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceResonance
The invention discloses a resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer and a manufacture method thereof, belonging to the field of microelectro mechanical systems. The resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer is structurally characterized by comprising an intermediate silicon sheet (1), an upper cover plate (2) and a lower bottom plate (3), wherein the intermediate silicon sheet (1) comprises a dual-end clamped beam resonators (4), a mass block (6), a support beam (5), a movable electrode (7) and a frame (8). The resonance-force balance capacitance type three-axis acceleration transducer is characterized in that an X axis and a Y axis acceleration signals in a chip plane are detected by adopting the dual-end clamped beam resonator (4) on the aspect of detection principle, the change of the resonance frequency of the dual-end clamped beam resonator (4) reflects the size and the direction of acceleration; and a Z axis acceleration signal in a vertical chip plane is detected by adopting a capacitance type sensitivity principle, and works in a closed loop force balance working mode. The mass block (6) has little motion displacement in the normal of a chip, and the Z axis input acceleration signal has little chiasma interference caused by detection of X axis and Y axis accelerations.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
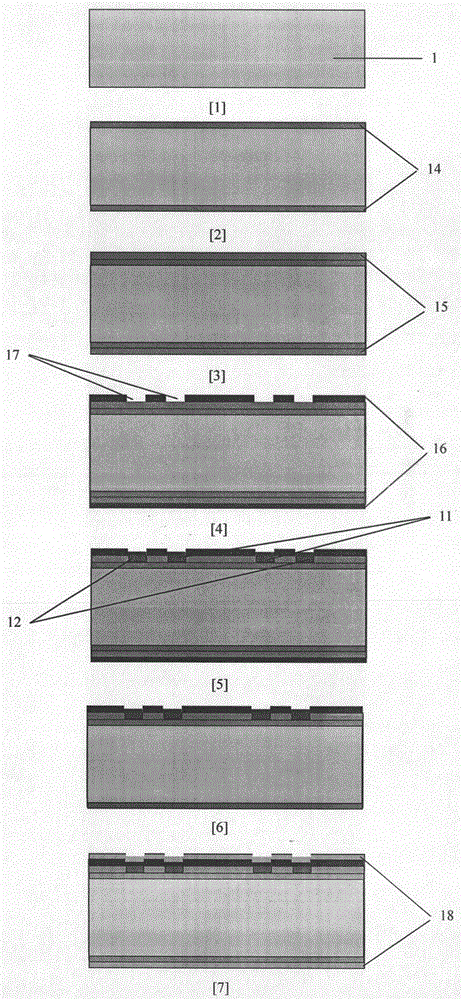
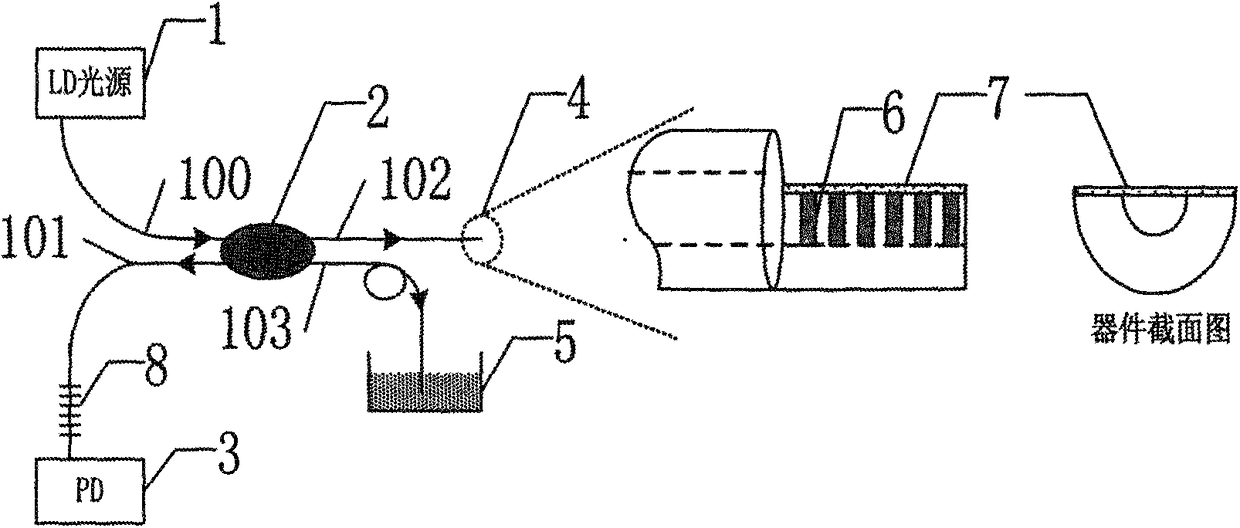
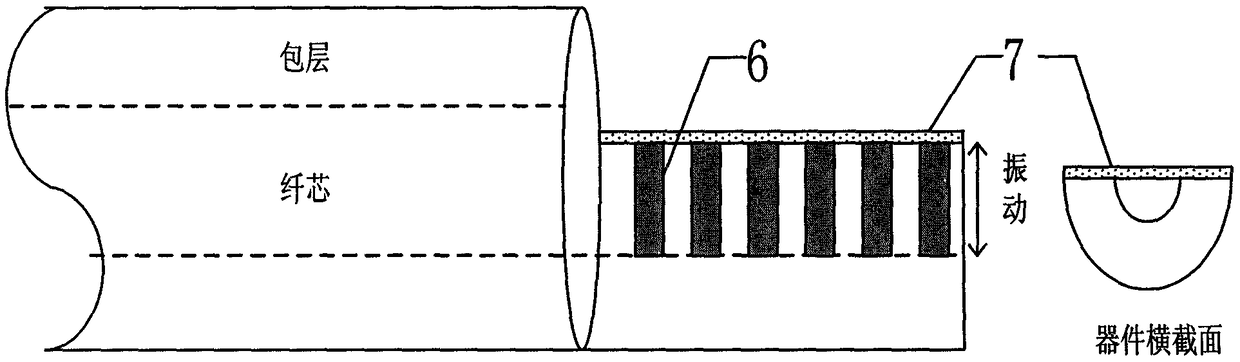
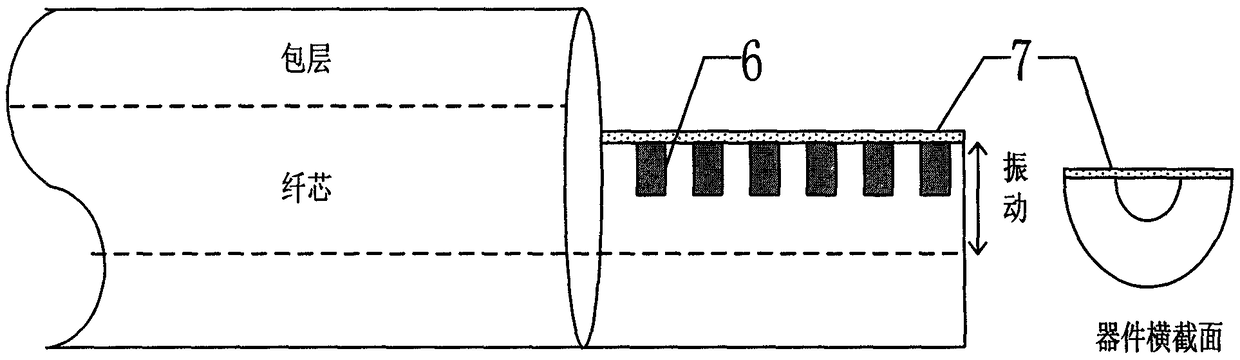
An Optically Excited Fiber Bragg Grating Cantilever Beam Resonator Vacuum Sensor
The invention relates to an optically-excited fiber grating cantilever beam harmonic oscillator vacuum degree sensor, and belongs to the technical field of fiber sensors. The optically-excited fiber grating cantilever beam harmonic oscillator vacuum degree sensor comprises an LD light source, a directional fiber coupler, a photoelectric detector, a sensing probe, coupling liquid, a micro-machined fiber grating, a metal plated film, and a coupling filtering FBG. The quality factors of the fiber grating cantilever beam harmonic oscillator sensor are influenced by air damping so as to influence the resonance amplitude of a fiber grating cantilever beam and finally change the wavelength of the reflection signal center of the FBG cantilever beam harmonic oscillator sensor, and thus the vacuum degree can be measured. The optically-excited fiber grating cantilever beam harmonic oscillator vacuum degree sensor has the advantages of simple structure and strong anti-electromagnetic interference performance, and can satisfy the requirement of micro, real-time on-line distributed and multi-point monitoring.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
A high quality factor piezoelectric cantilever beam density sensor chip and its working method and preparation method
ActiveCN111579426BImprove reliabilityHigh sensitivityDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingCantilevered beamPiezoelectric cantilever
The invention discloses a high-quality factor piezoelectric cantilever beam density sensor chip and its working method and preparation method, including a silicon substrate and a silicon micro-cantilever resonator, wherein the silicon micro-cantilever resonator includes a micro-cantilever suspension structure, a solid Support beam structure, piezoresistive beam structure and piezoresistive connecting beam structure. The silicon microresonant cantilever beam structure is covered with a low-stress aluminum nitride piezoelectric film through the MEMS process. The double piezoelectric electrodes are used to pass through a certain frequency of alternating voltage and generate piezoelectric driving force based on the inverse piezoelectric effect. Four piezoelectric electrodes The four sensitive resistance strips on the resistance beam are connected by the metal leads on the piezoresistive beam to form a Wheatstone full bridge, which is used to detect the resonant stress and convert it into a voltage signal output by arranging the Wheatstone bridge. The method can obtain the out-of-plane vibration mode of the cantilever beam. The density sensor chip has high sensitivity and high quality factor in the fluid, which can significantly improve the application range of fluid density measurement, and has high measurement accuracy and sensitivity.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com