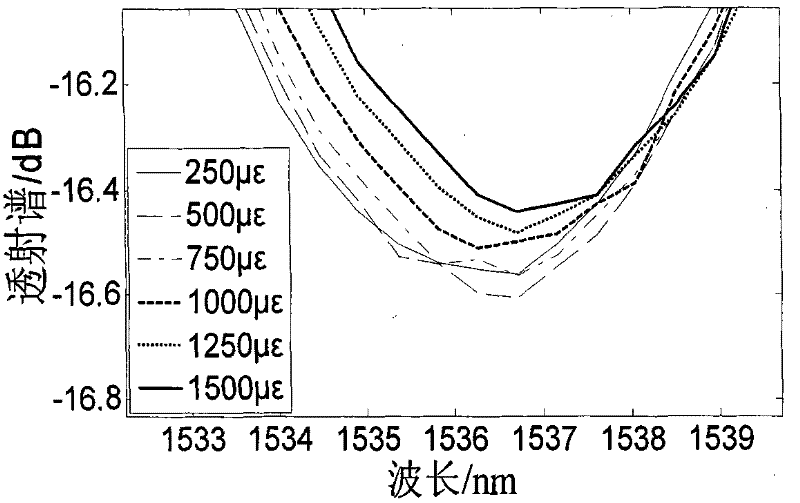
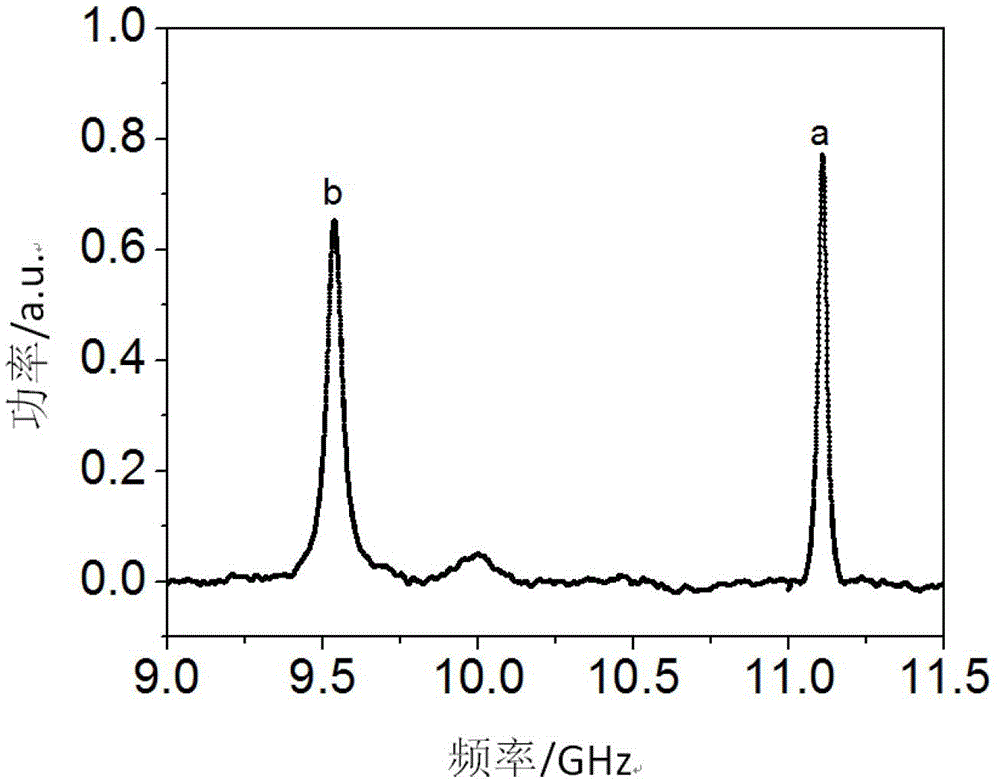
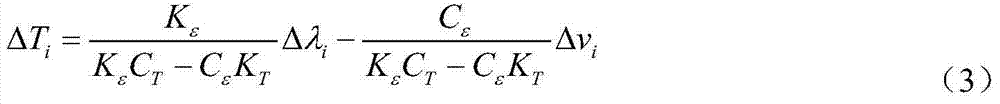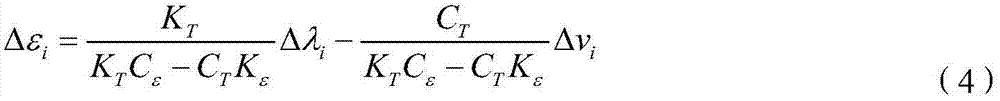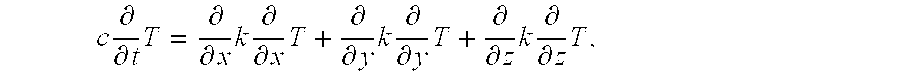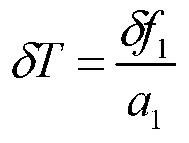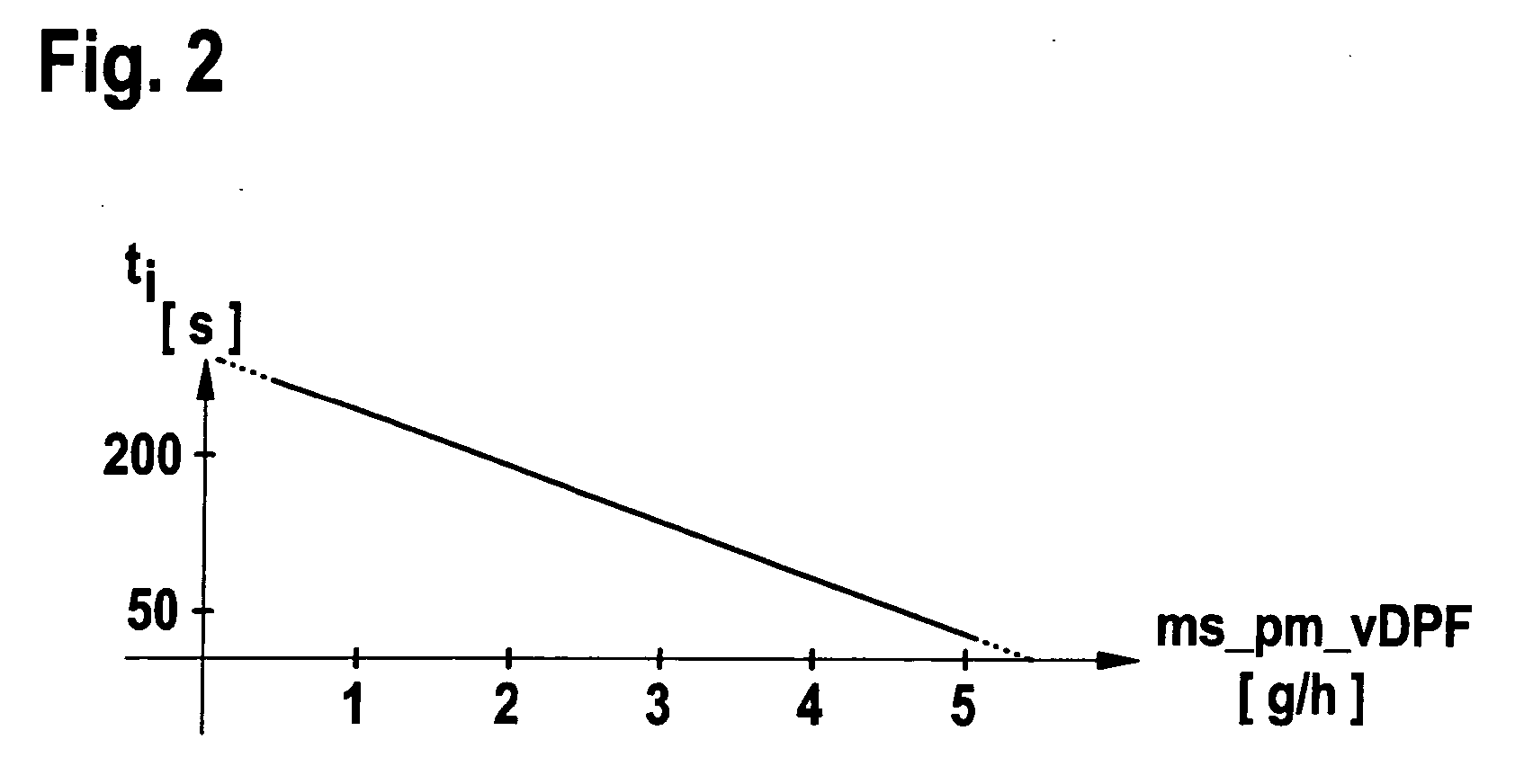Patents
Literature
201 results about "Cross sensitivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cross Sensitivity A sensitivity reaction to a drug that predisposes a person to react similarly to a different, but related, drug. For example, a person who has an allergic reaction to penicillin may also have an allergic reaction to amoxicillin, a related antibiotic.
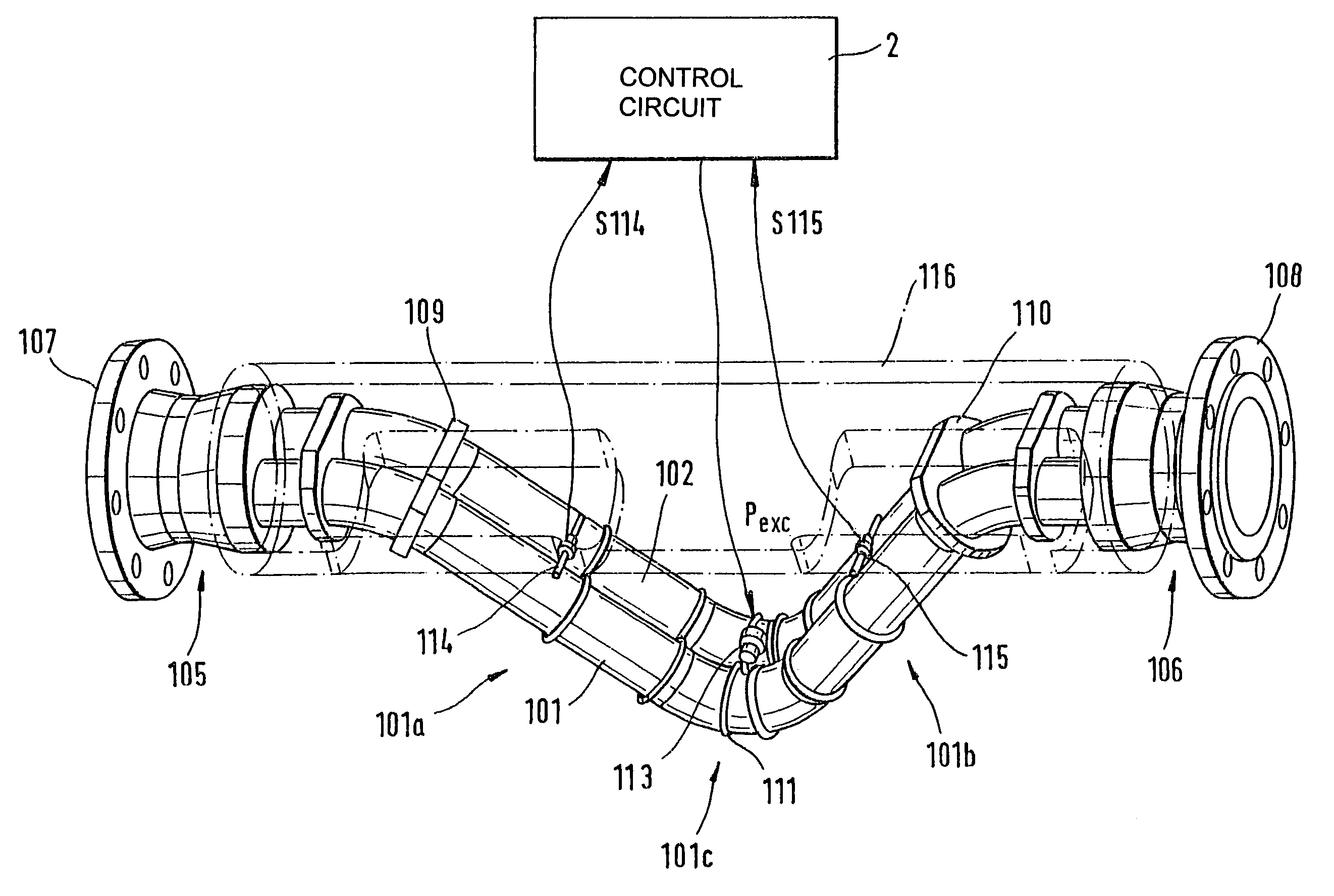
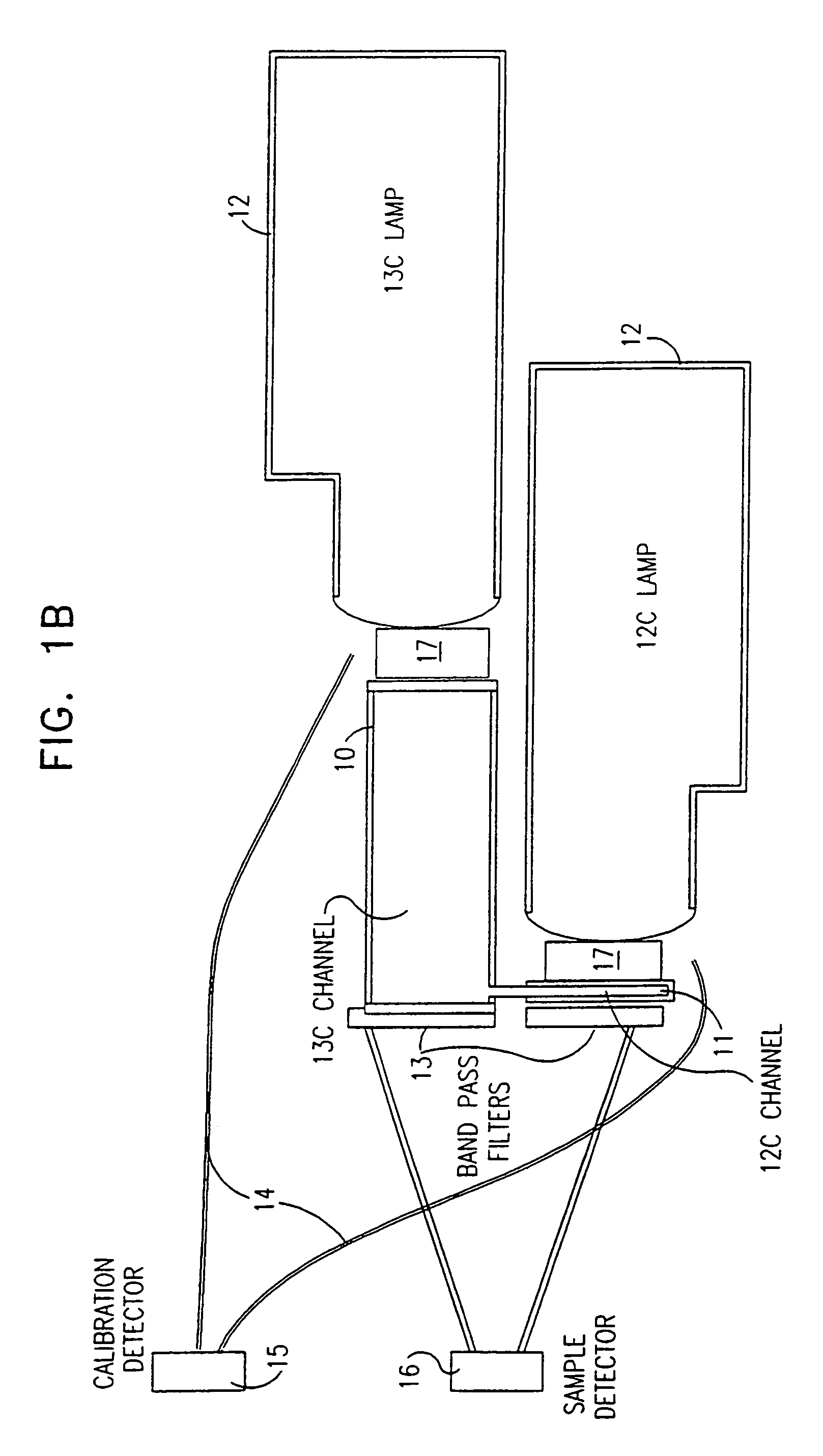
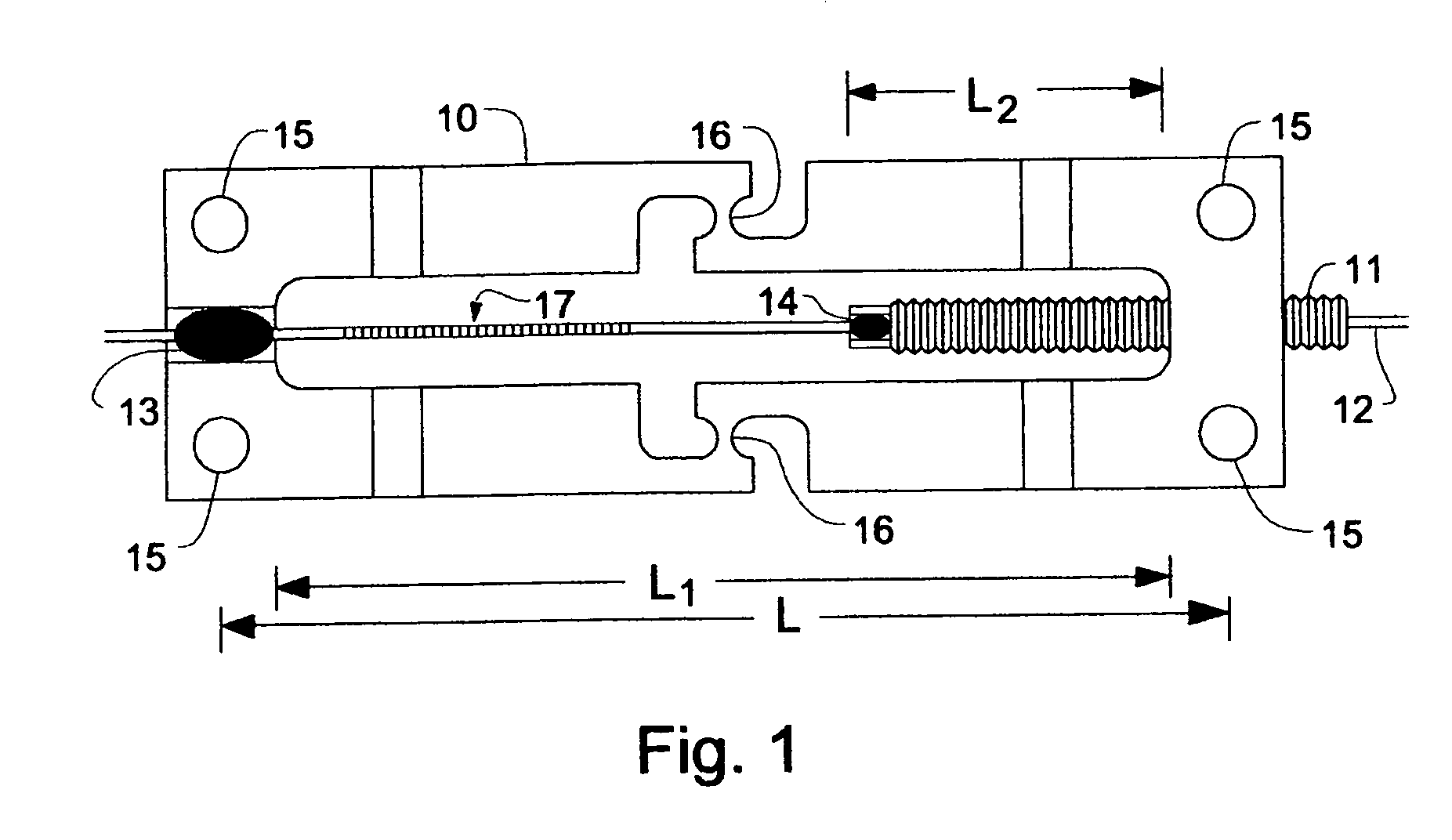
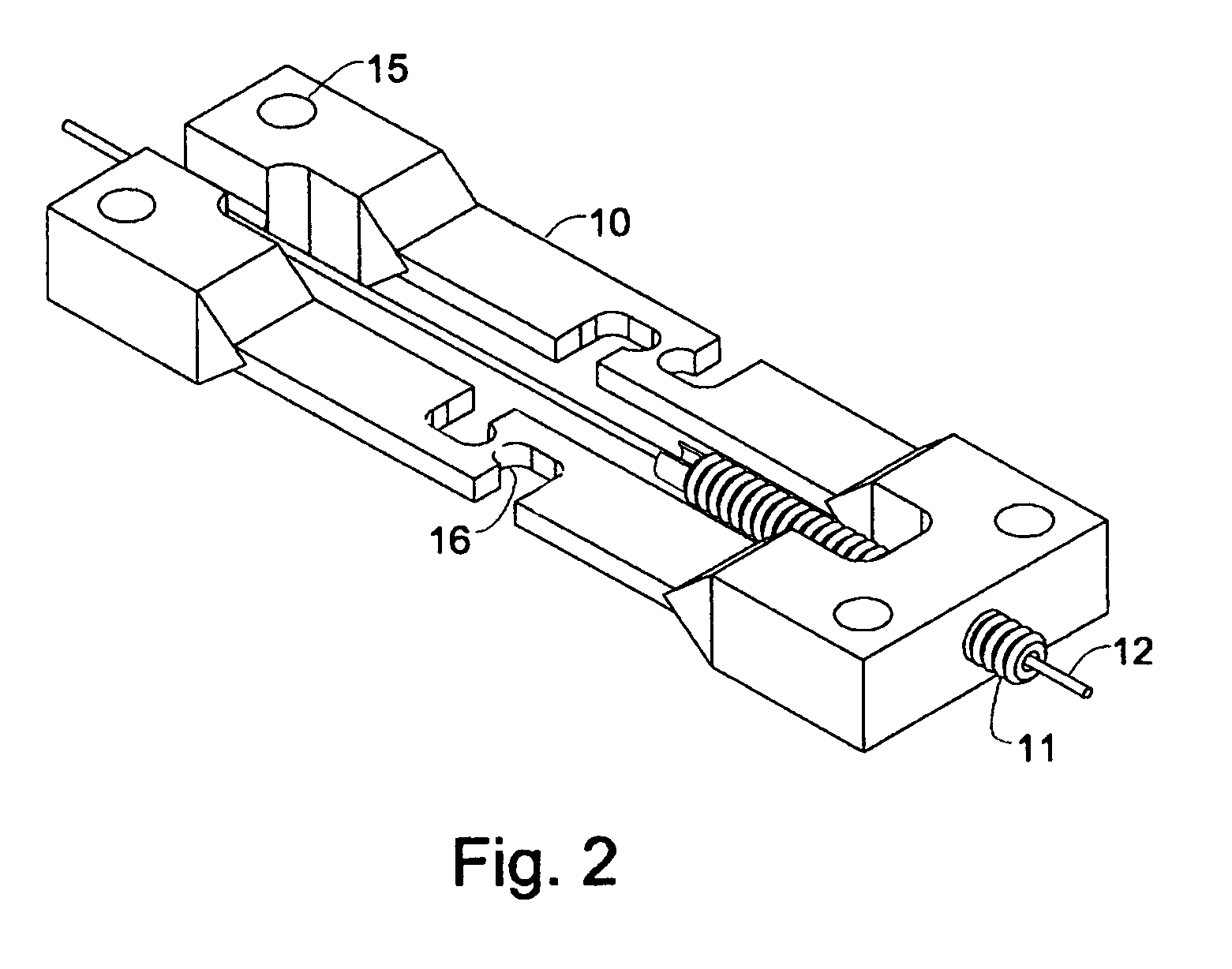
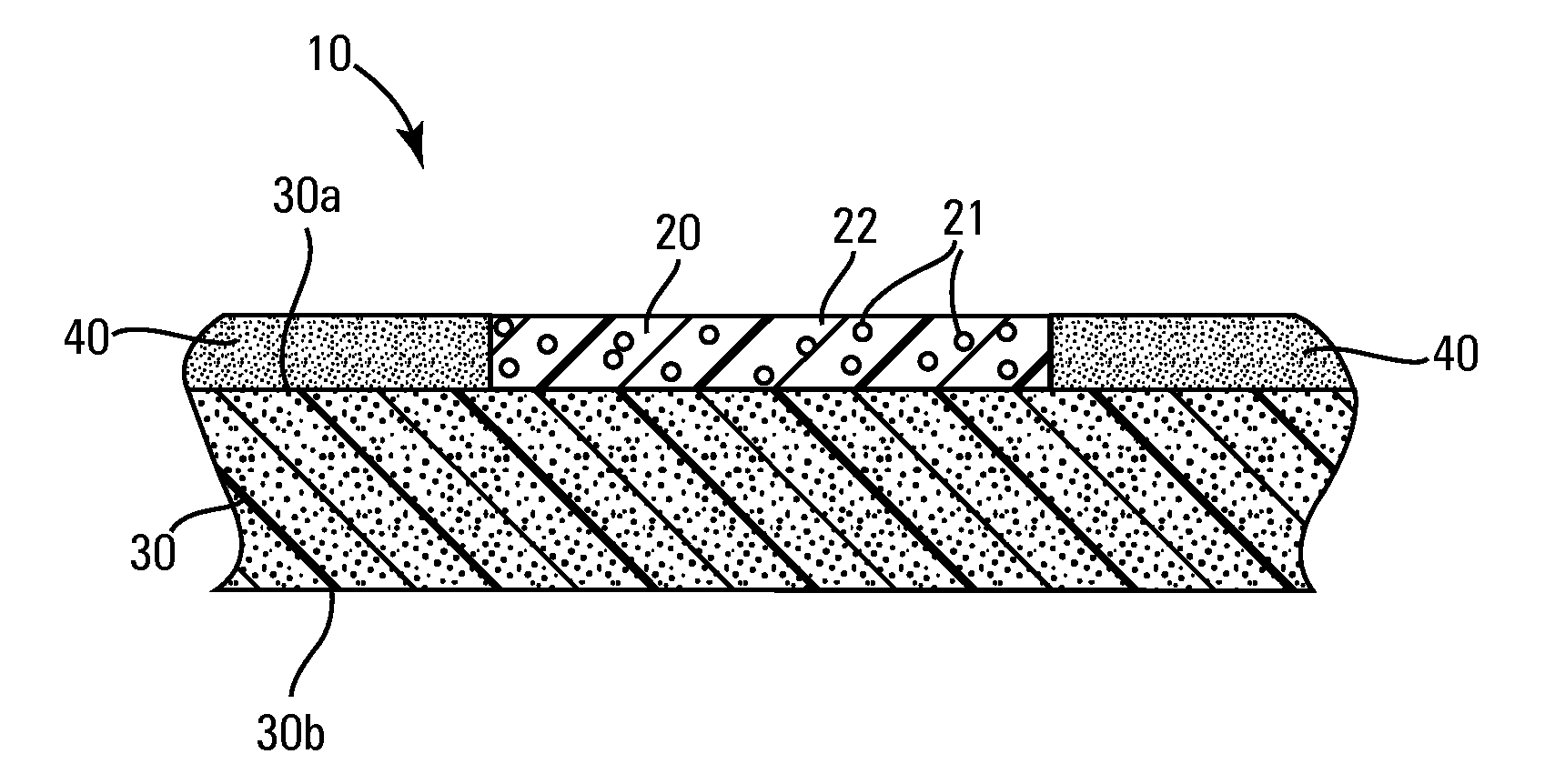
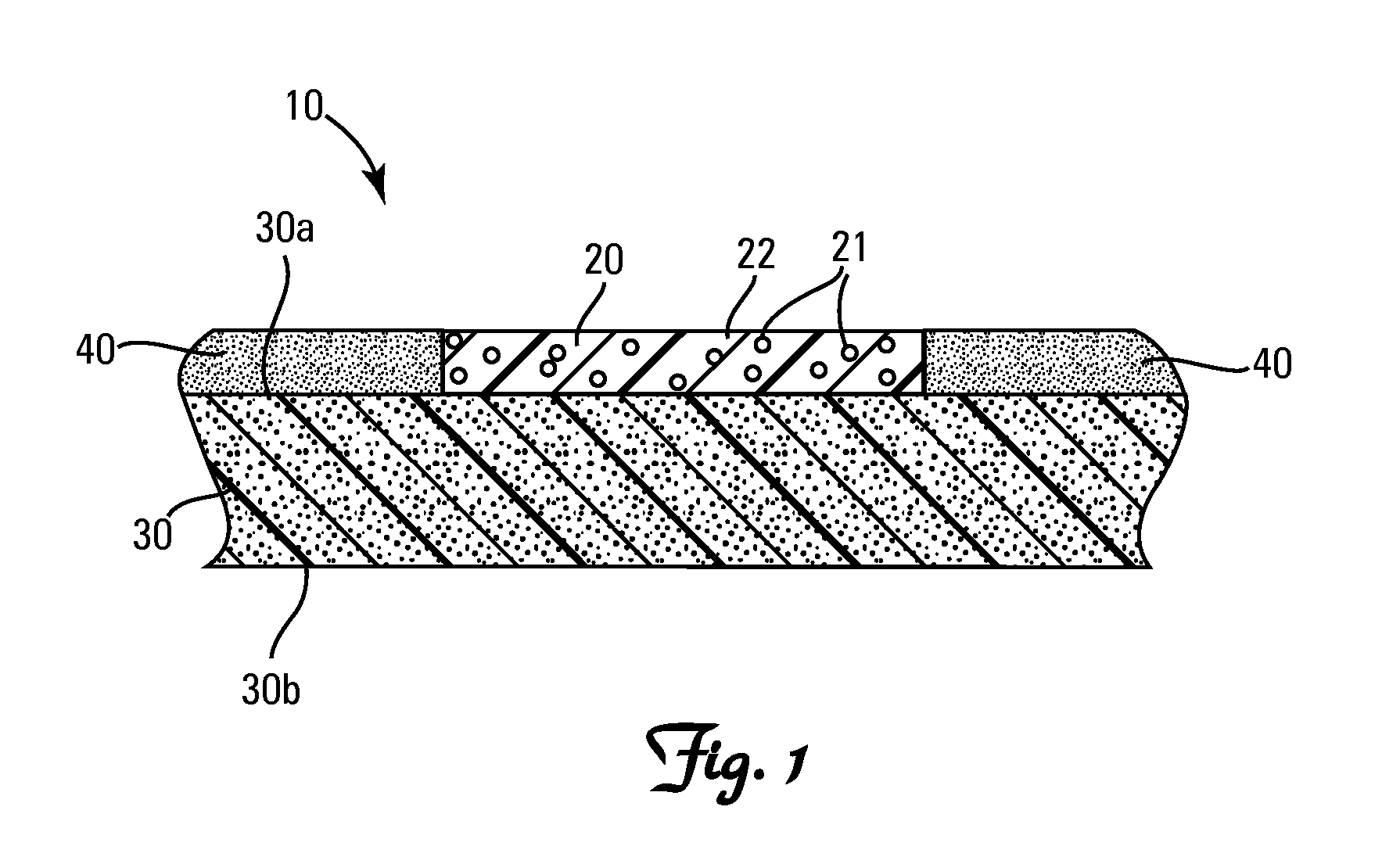
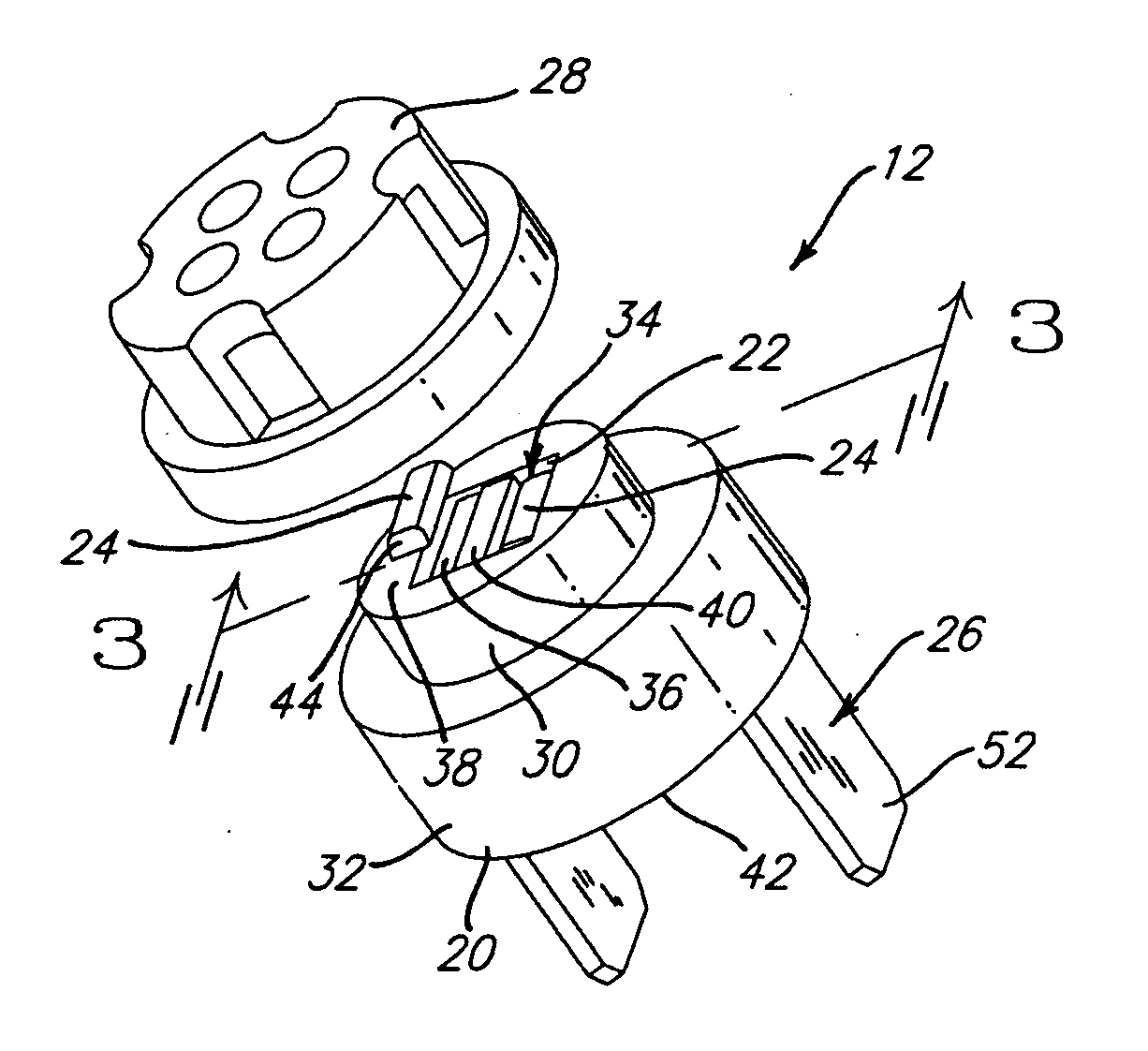
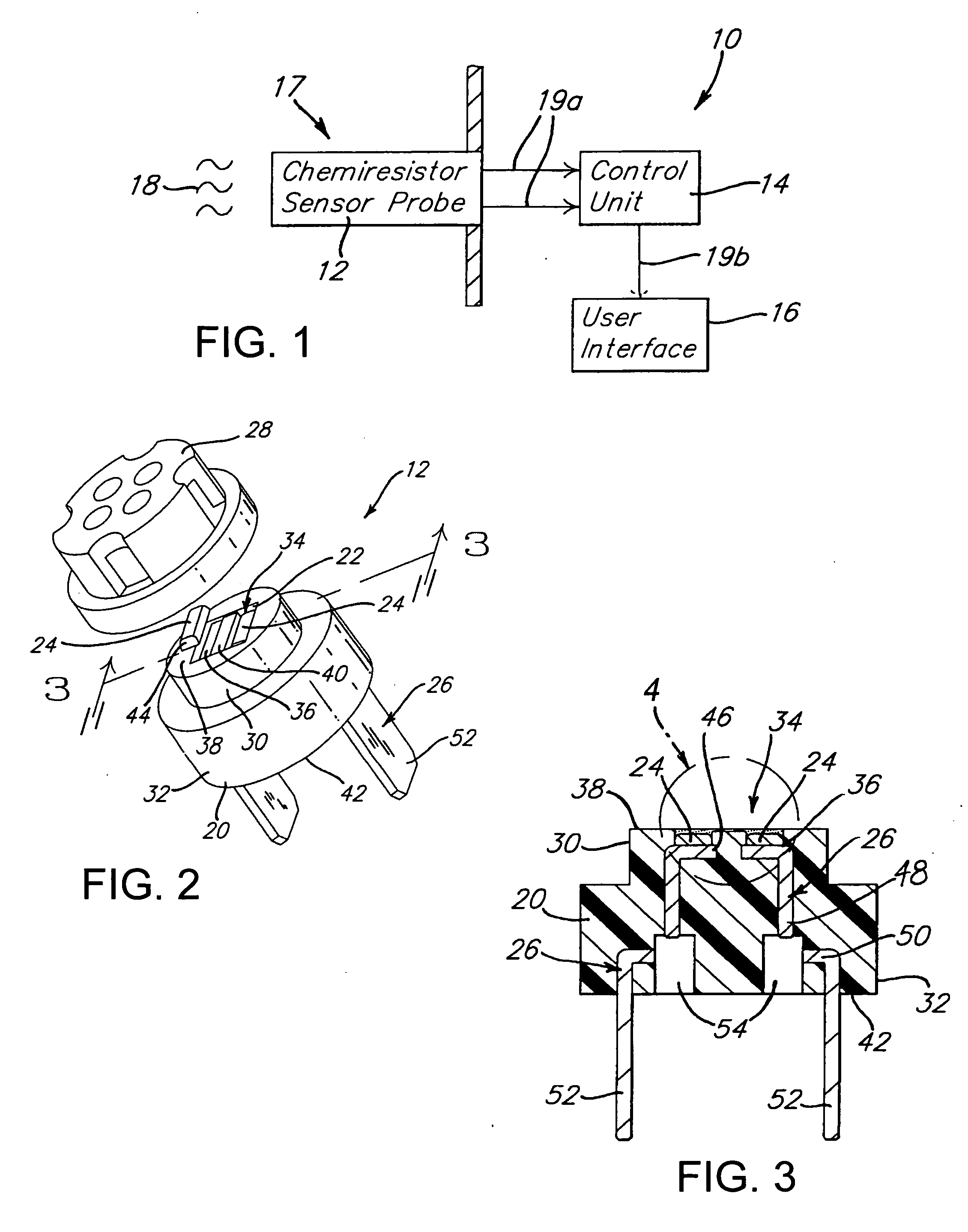
Vibratory transducer
InactiveUS6920798B2Easy to manufactureEasy to bendMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCross sensitivityStraight tube
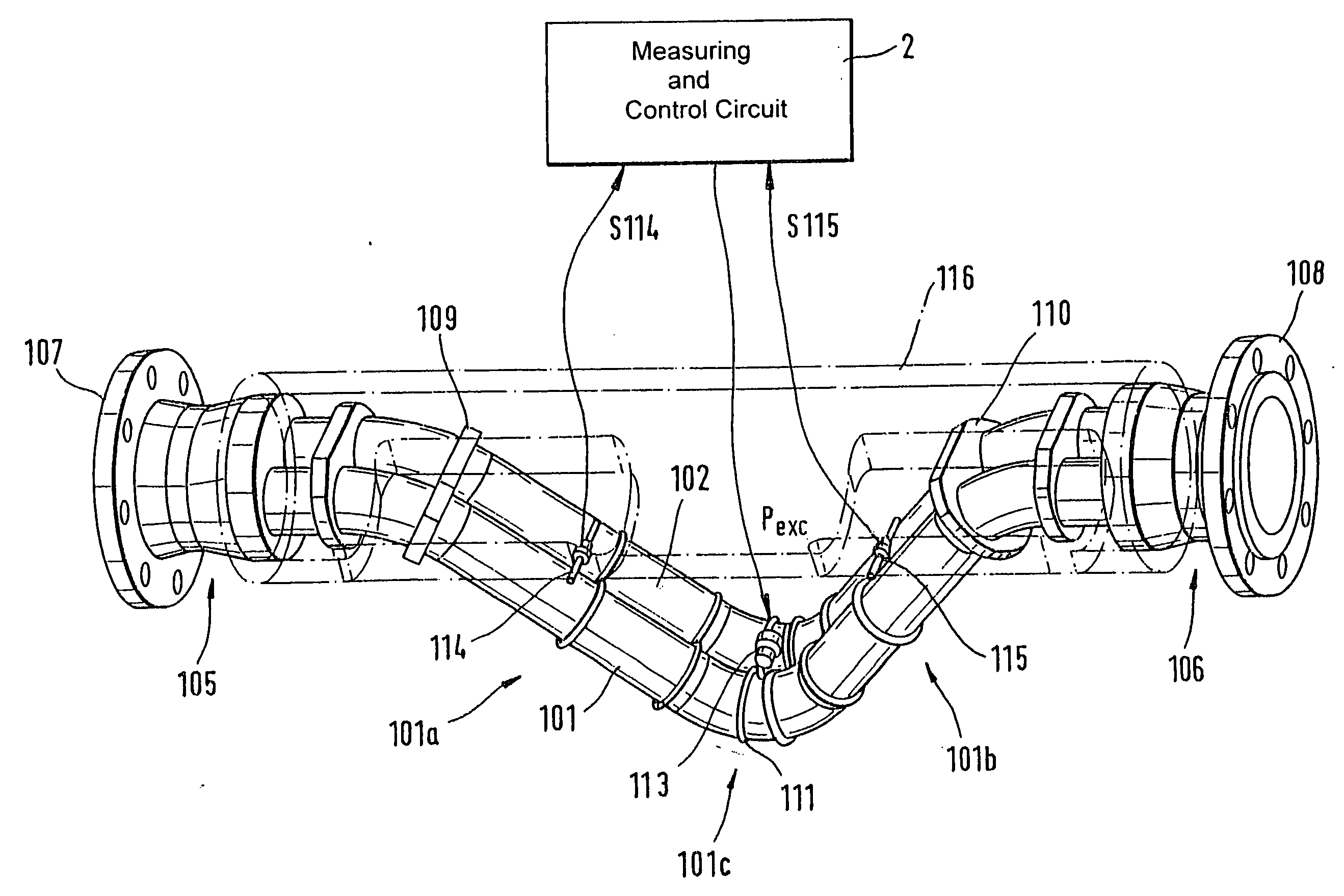
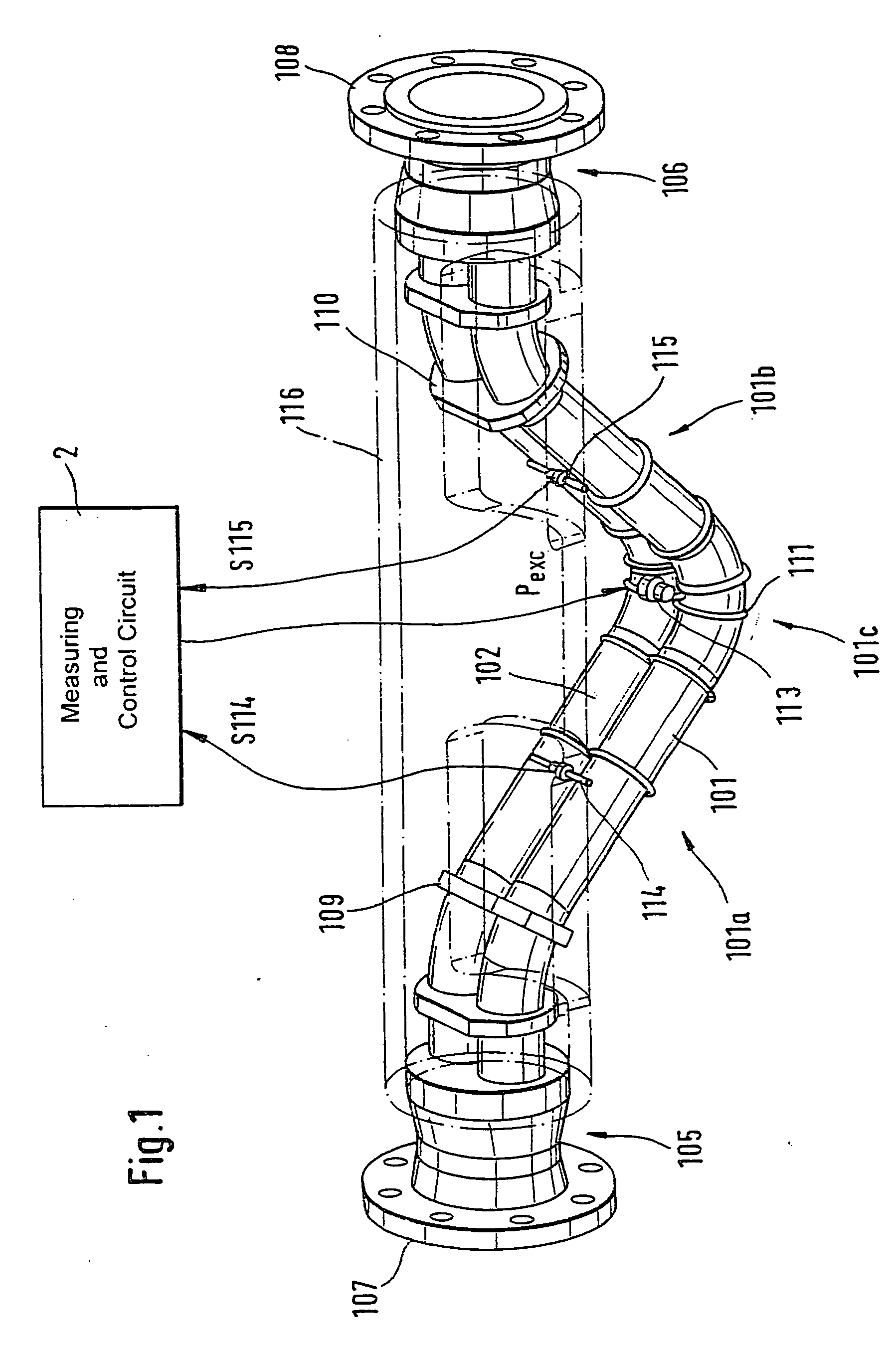
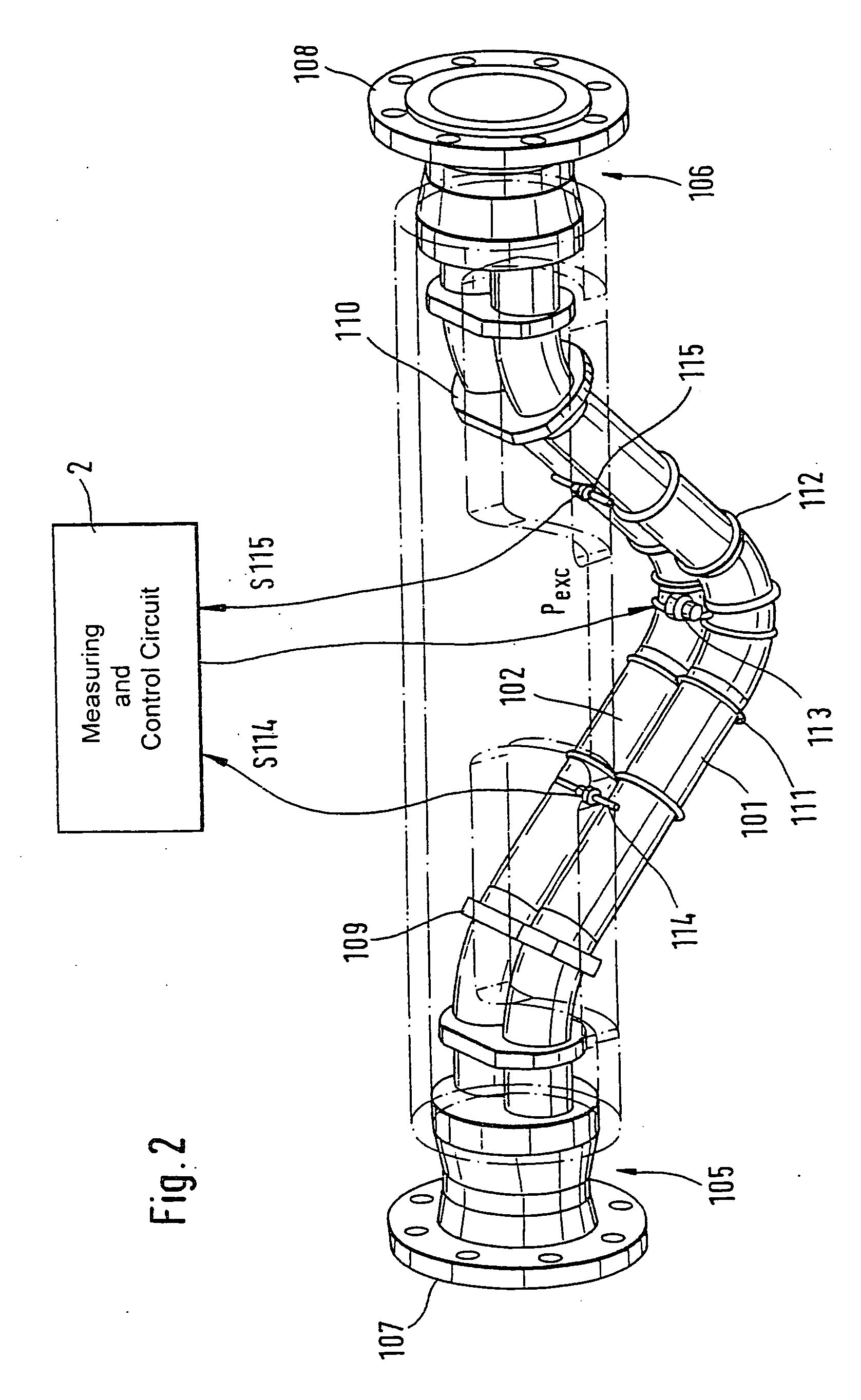
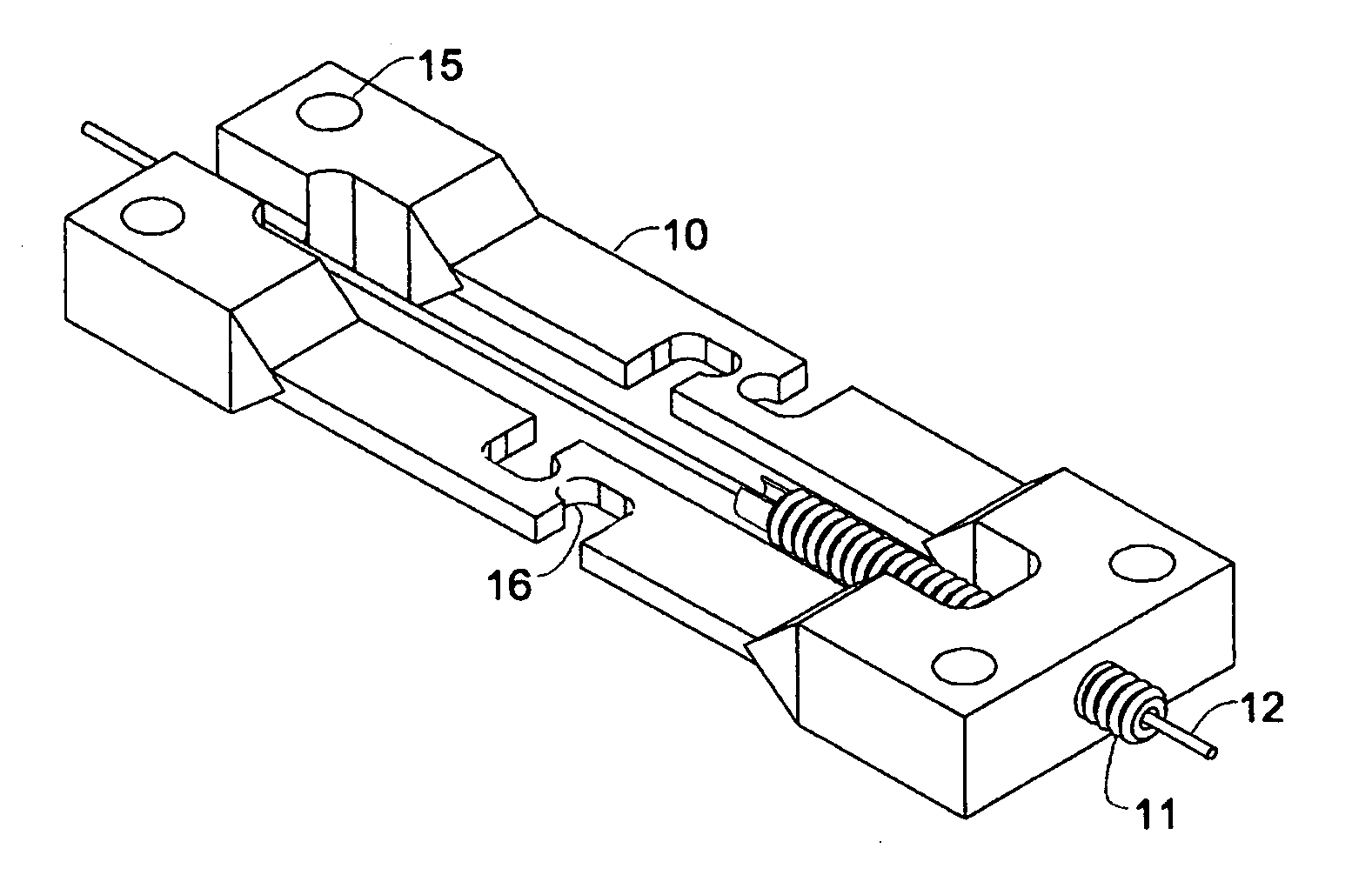
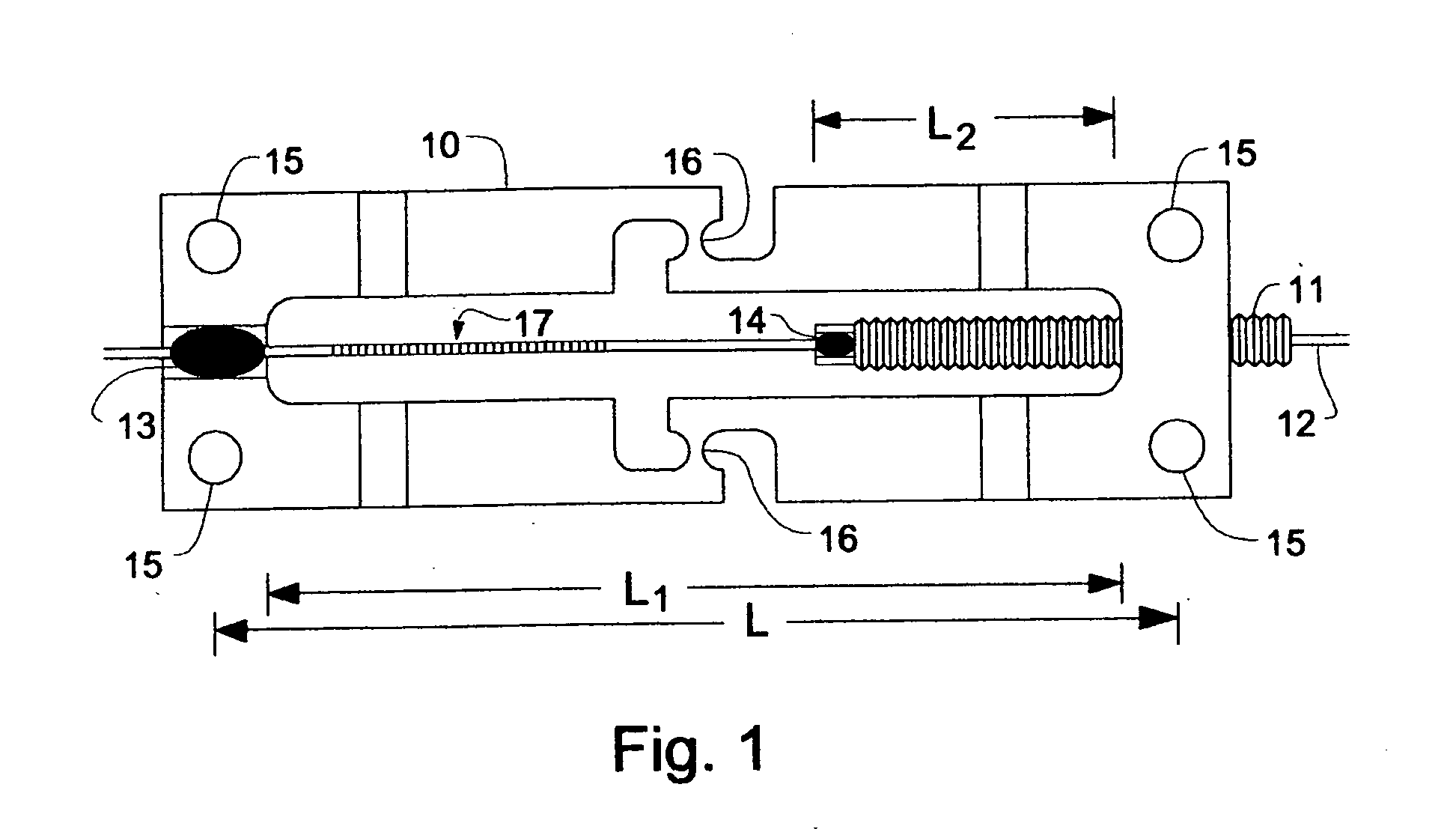
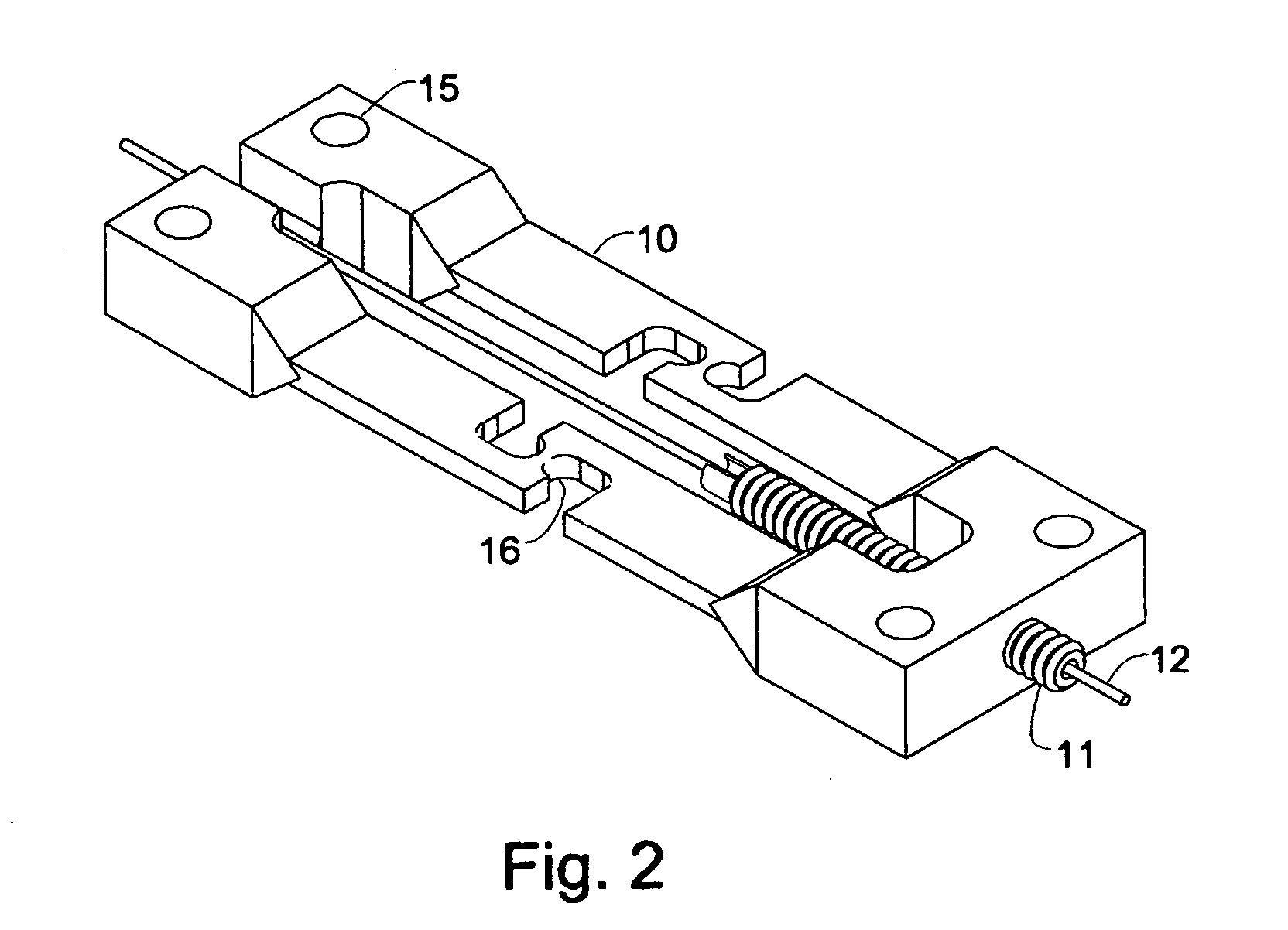
The transducer (1) has at least one at least temporarily vibrating flow tube (101) of predeterminable lumen for conducting a fluid. The flow tube (101) communicates with a connected pipe via an inlet tube section (103), ending in an inlet end, and an outlet tube section (104), ending in an outlet end, and in operation performs flexural vibrations about an axis of vibration joining the inlet and outlet ends. The flow tube (101) has at least one arcuate tube section (101c) of predeterminable three-dimensional shape which adjoins a straight tube segment (101a) on the inlet side and a straight tube segment (101b) on the outlet side. At least one stiffening element (111, 112) is fixed directly on or in close proximity to the arcuate tube segment (101c) to stabilize the three-dimensional shape. By means of the at least one stiffening element (111, 112), the cross sensitivity of the transducer (1) is greatly reduced, so that cross talks from pressure to mass flow signals are minimized and the accuracy of the transducer is improved.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
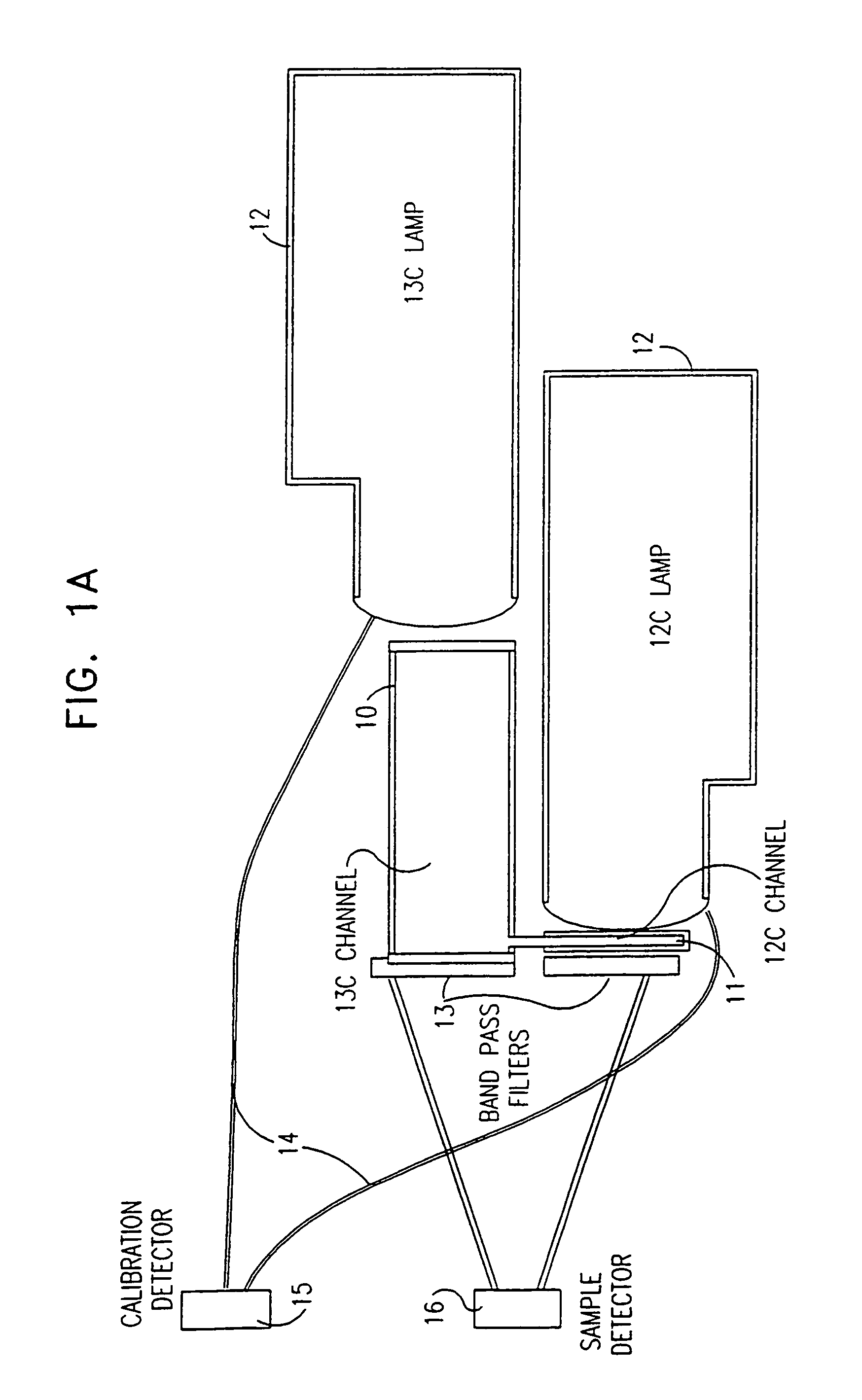
Isotopic gas analyzer
InactiveUS7063667B1Low costShort path lengthWithdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationCross sensitivityAbsorption cell
An NDIR spectrometer based on the use of wavelength specific lamp sources, whose emission spectrum consists of discrete, narrow lines characteristic of the isotope present in the lamp, and which it is desired to measure with the spectrometer. This allows very high intrinsic sensitivity, enabling the use of an extremely compact absorption cell with a very short path length. In addition, the source can be self-modulated, such that problems associated with external choppers are avoided. Furthermore, there is insignificant cross sensitivity between the isotopes themselves and between the isotopes and other ambient gases in the operating environment.
Owner:BREATHID 2006
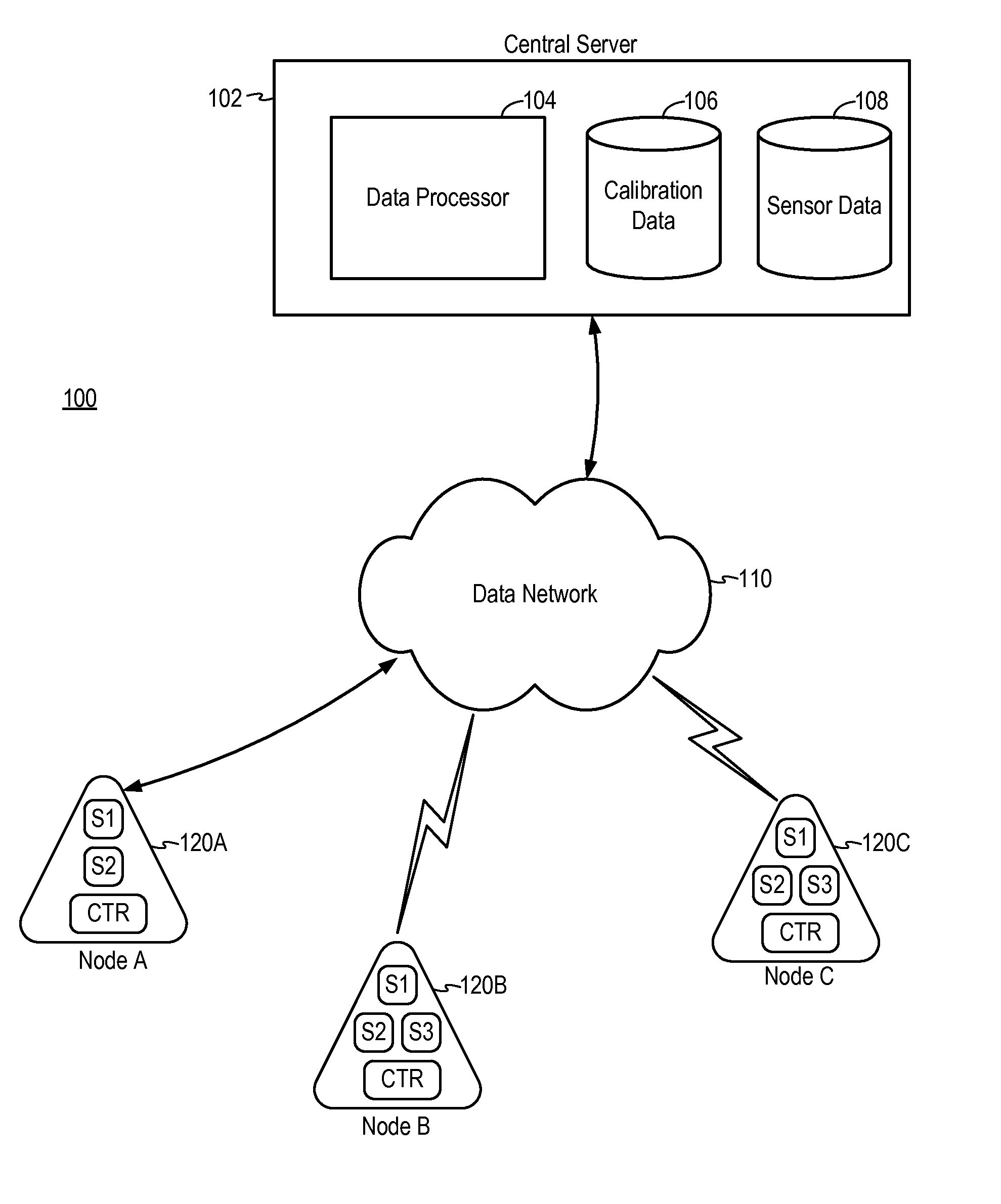
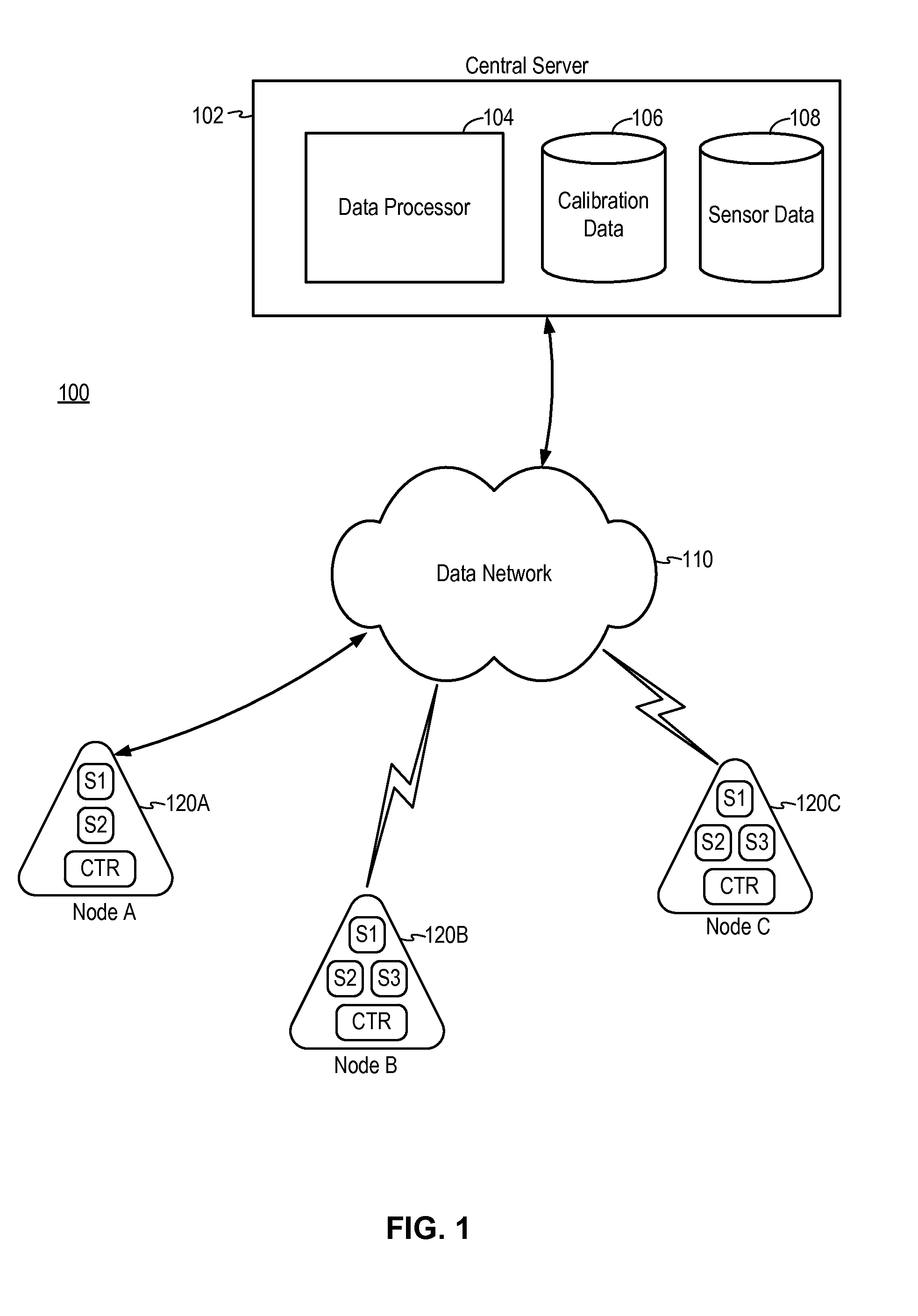
Calibration method for distributed sensor system
ActiveUS20140278186A1Testing/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsCross sensitivityCrowd sourcing
Methods of calibrating sensors in a distributed sensor system including a set of spatially distributed base units in communication with a central server over a data network include using a reference sensor, using a reference base unit, using crowd-sourced calibration, using sensor data collected in the same base unit, using sensor cross-sensitivity, or using sensor data from known environmental conditions.
Owner:ACLIMA
Capacitive micro-acceleration sensor with symmetrically combined elastic beam structure and production method thereof
ActiveCN101858929AReduce sensitivityGreat lateral sensitivityPrecision positioning equipmentPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCross sensitivityShaped beam
The invention relates to a capacitive micro-acceleration sensor with a symmetrically combined elastic beam structure and a production method thereof. The acceleration sensor comprises a symmetric center mass block, an external support frame, eight symmetric straight beams, two symmetric frame beams, a combined elastic beam structure, an upper cover plate and a lower cover plate, wherein the eight symmetric straight beams are used for connecting the center mass block with the external support frame, and the combined elastic beam structure is formed by connecting eight symmetric L-shaped beams together; and the other end of each straight elastic beam connected with the frame beams is connected to the middle or a vertex angle at the top end and the bottom end of the lateral face of the center mass block, and the other end of each L-shaped beam connected with the frame beams is connected to the inner side face of the external support frame. The acceleration sensor adopts the combined elastic beam structure which is formed by connecting the symmetric straight beams, the frame beams and the L-shaped beams together, has high symmetry and can remarkably reduce the cross-sensitivity of the sensor; and the sensor is produced by adopting a microelectronic mechanical system technology and is the capacitive micro-acceleration sensor with high sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-temperature Fabry-Perot (FP) composite micro/nano fiber temperature and pressure sensor
ActiveCN105043588AHigh temperature limitSmall structure sizeThermometers using physical/chemical changesFluid pressure measurement by optical meansCross sensitivityEngineering
The invention relates to a high-temperature Fabry-Perot composite micro / nano fiber temperature and pressure sensor, and belongs to the technical field of fiber sensors. The sensor comprises a fiber access segment, a pressure sensor segment and a temperature sensor segment, wherein the fiber access segment includes a solid fiber, the pressure sensor includes a hollow thin-wall fiber, and the temperature sensor includes another solid fiber. Cylindrical holes are formed in the end portions of the two solid fibers respectively in a femtosecond second processing method, and then welded to form an FP interference type pressure cavity, one fiber serves as the fiber access segment, the other fiber is cut and ground to the solid fiber of certain thickness, a temperature sensor is thus formed, and the difference between the cavities lengths of the temperature sensor and the pressure sensor is controlled to decouple double-parameter measurement. Compared with the prior art, the sensor of the invention is small in structural size, resistant to high temperature, capable of measure the temperature and pressure at the same time, and free of cross sensitivity of the two parameters.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Passive athermal fiber bragg grating strain gage
ActiveUS7068869B1Enhanced positive temperature sensitivityReduced positive temperature sensitivityForce measurementCoupling light guidesFiberCross sensitivity
Fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) are particular suitable for measuring strain. However, a single parameter measurement is difficult to implement, since cross-sensitivity to temperature compels the use of an additional temperature reference, e.g. a strain-inactive FBG. The development of a passive athermal fiber Bragg grating strain gage is thus of particular interest since it renders optional the measurement of temperature, benefiting large scale system design and performance. In view of this need, a package for fiber Bragg gratings that enables strain measurements to be performed while canceling temperature sensitivity is disclosed. The proposed design is based on a structure composed of two parts, which can be made of the same material, having a defined length ratio that allows the adjustment of the temperature sensitivity to zero, providing athermal operation of the strain gage. Moreover, the disclosed passive athermal scheme is adjustable to further compensate for structural thermal expansion, enabling the load-induced strain component to be decoupled from the temperature-induced strain component.
Owner:ARAUJO FRANCISCO MANUEL MOITA +1
Optical fiber vibrative sensor based on optical fiber raster
InactiveCN1587946ASolve the problem of cross-sensitivitySolving Vibration Measurement ProblemsVibration testingVibration amplitudeCross sensitivity
A optical fiber microvibration sensor based on optical fiber raster, uses resonance of suspended Prague optical fiber raster and subject to be measured to magnify vibration amplitude of the object to be measured, and it can do wavelength type modulation or intensity type modulation measurement of light. Two contacts on one end of 2x2 coupler are separately linked to wide - band light source, spectrum analyzer or, and two contacts on another end to matching fluid and transmission optical fiber which crosses contacts to enter insulating cylinder and with one end charactered suspended Prague optical fiber raster in the wavelength type modulation its fixed in the center by union joint. In the structure of using spectrum analyzer for wavelength type modulation measurement, suspended Prague optical fiber raster for calibrating reflected light central wavelength of vibration equilibrium position is charactered on transmission optical fiber near inlet of the connector. The invention has solved the problem of optical fiber raster cross sensitivity, measuring microvibration of large instrument in circumstance of strong electromagnetic field and high voltage.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and device for measuring temperature and strain of isotactic ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber gratings simultaneously based on Brillouin scattering
InactiveCN103674086AOptimize layoutLower deployment costsThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFiberCross sensitivity
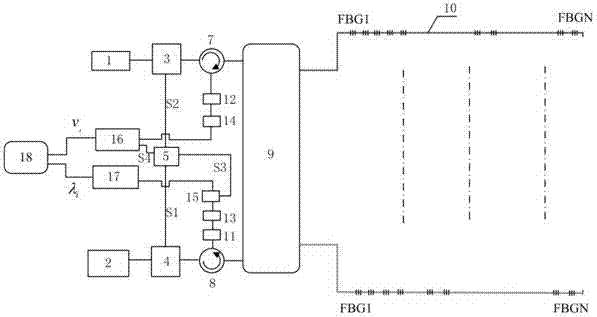
The invention discloses a method and device for measuring the temperature and strain of isotactic ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber gratings simultaneously based on Brillouin scattering. The method includes the steps that the ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber gratings are continuously and dynamically etched through monopulse laser energy based on the drawing tower technology to obtain high-capacity optical fiber grating array sensing fibers, wherein m optical fibers and 2*m optical switches are connected to serve as a sensing probe; the reflection center wavelength lambda[i] and Brillouin frequency shift v[i] of each optical fiber grating are obtained through a high-speed CCD wavelength demodulation module and a Brillouin frequency shift heterodyne demodulation module; solving is carried out according to the Brillouin frequency shift and temperature and strain parameters of the optical fiber gratings to obtain the temperature and strain of the optical fiber gratings at each position. The method and device overcome the defects that the Brillouin sensing technology is low in precision and low in speed, simplify high-capacity ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber grating array optical fiber cabling complexity, improve high-capacity ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber grating array optical fiber cabling operability, overcome the cross sensitivity of the temperature and strain of the optical fiber gratings and improve distributed sensing detection precision.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Sensor structure for simultaneously measuring temperature and strain of long period fiber gratings (LPFGs)
ActiveCN102162753ARealize measurementResolving temperature-strain cross-sensitivityThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansCross sensitivityLong-period fiber grating
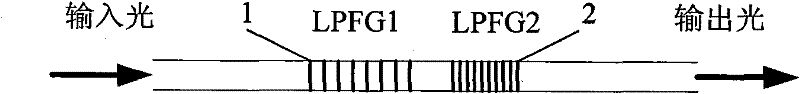
The invention provides a sensor structure for simultaneously measuring the temperature and strain of long period fiber gratings (LPFGs). The sensor structure is characterized in that a pair of LPFGs which are written by high-frequency CO2 laser pulse in a fiber and have different periods are selected, namely an LPFG only sensitive to temperature variation and an LPFG sensitive to both temperaturevariation and strain variation; and the respective variation of the temperature and the strain can be accurately measured by cascading the two LPFGs. The sensor structure has the following prominent advantages: the temperature variation is measured by using the LPFG which has a specific period and is only sensitive to temperature variation, and the variation of the temperature and the strain is measured by using the other LPFG, thus realizing measurement of the two parameters (the temperature and the strain), and providing a scheme for solving the problem of cross sensitivity of the temperature and the strain; and meanwhile, the sensor has the capability of normally working at the high temperature of 750 DEG C and is unnecessary to be specially packaged.
Owner:饶云江
Graphene oxide based capacitive temperature sensor and production method thereof
InactiveCN104390720AHigh sensitivityResolve cross-sensitivityThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansCapacitanceCross sensitivity
The invention discloses a graphene oxide based capacitive temperature sensor and a production method thereof. The capacitive temperature sensor comprises a substrate, lower electrodes, an insulation layer, a graphene oxide layer and a graphene layer from the bottom to the top successively. The lower electrodes are divided into two parts which are not in contact, that is, a left lower electrode and a right lower electrode. The left lower electrode and the insulation layer, the graphene oxide layer and the graphene layer form a left plate capacitor structure. The right lower electrode and the insulation layer, the graphene oxide layer and the graphene layer form a right plate capacitor structure. The left plate capacitor structure and the right plate capacitor structure are connected in series to be output. According to the temperature sensor and the production method thereof, a sandwich structure is used as the sensitive capacitor, so that the sensor sensitivity is high; the electrodes on the sensitive capacitor are formed by the graphene oxide layer, and accordingly, during electric conduction, moisture is separated, and temperature and humidity cross sensitivity is prevented; the graphene oxide layer is produced through chemical reduction of the graphene oxide upper surface, therefore, the process is simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
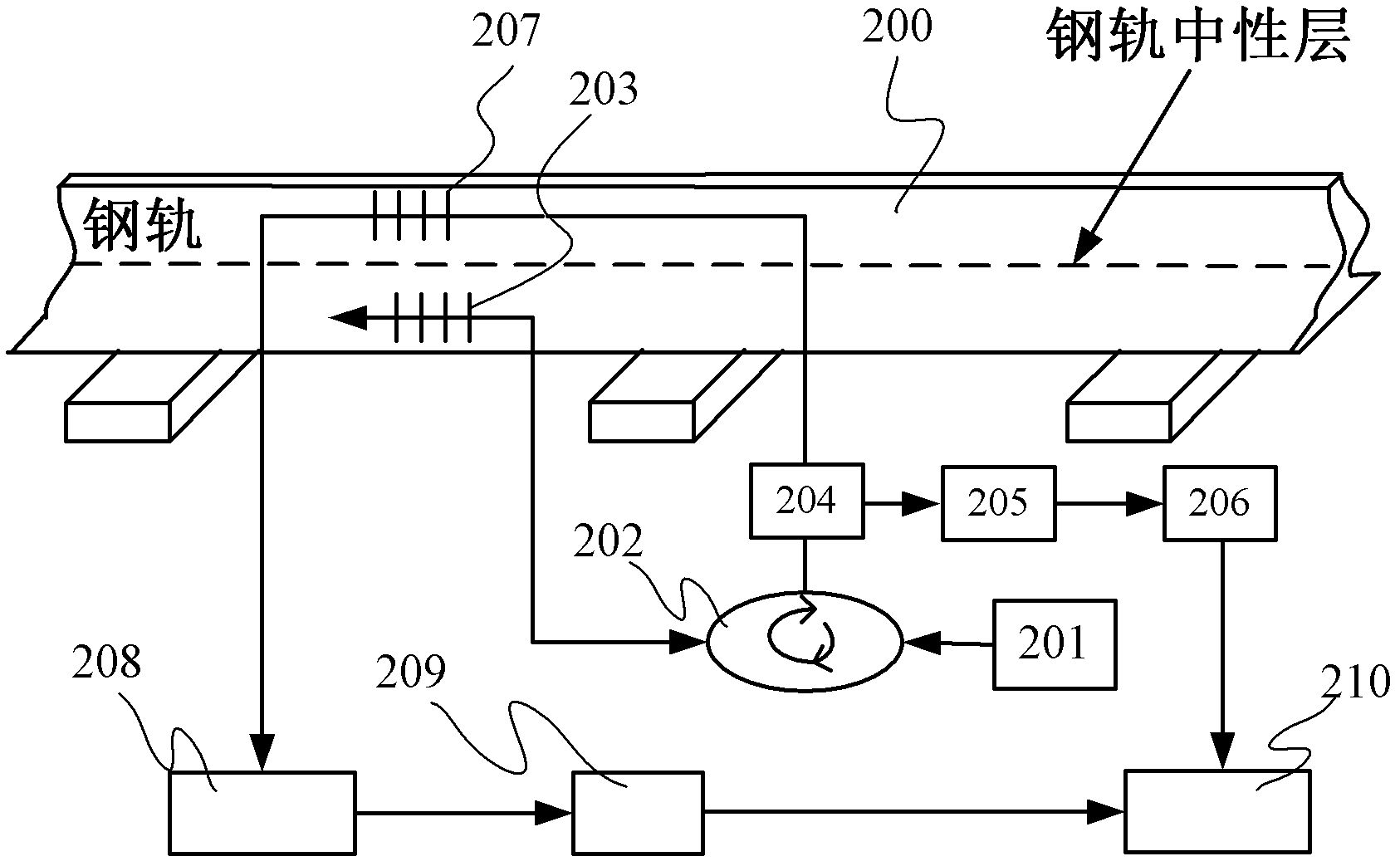
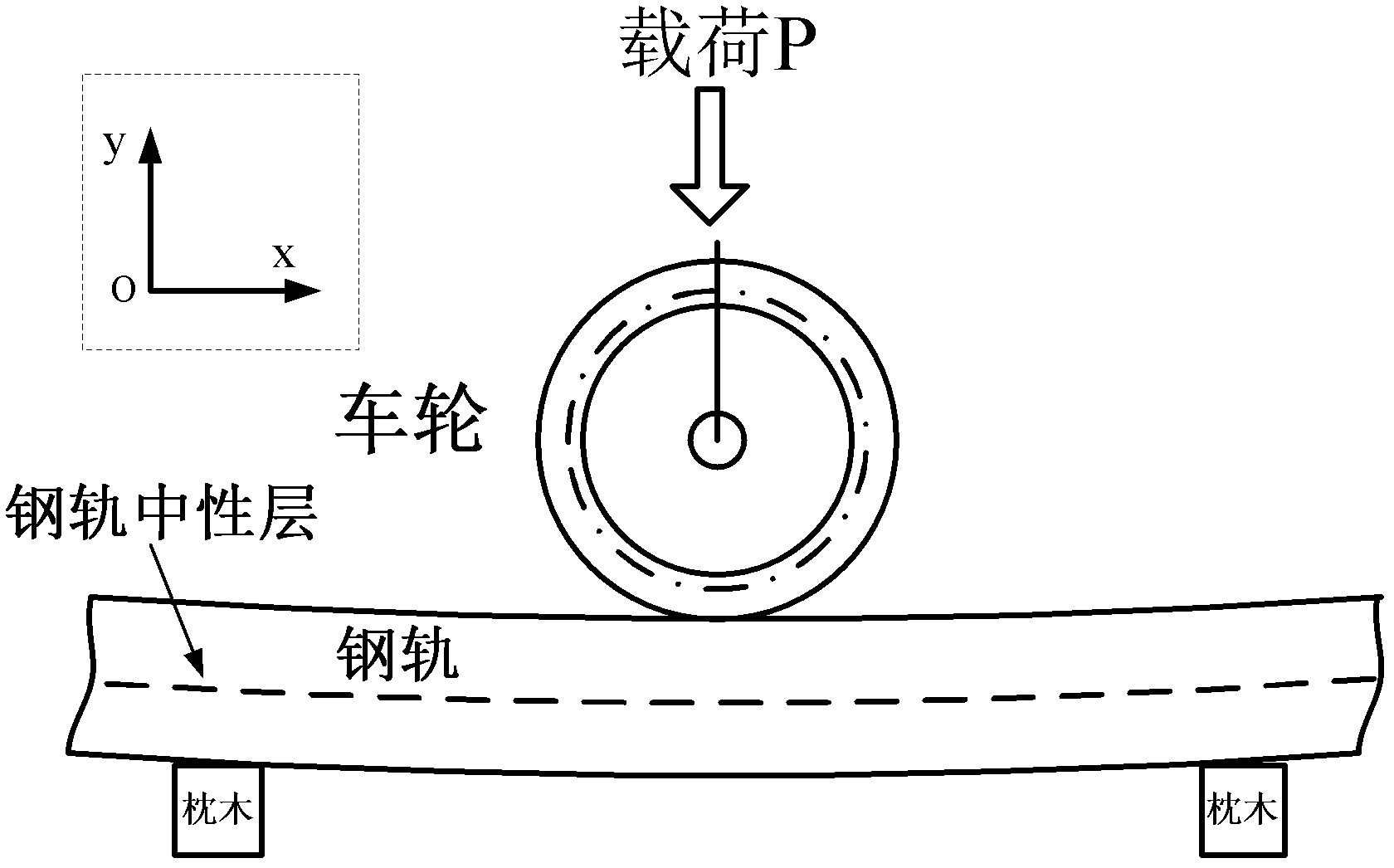
Rail straining and sensing method based on bidirectional strain matching fiber grating demodulating technique
InactiveCN102589460ASuitable for dynamic strain monitoringSolve the problem of temperature-strain cross-sensitivityUsing optical meansCross sensitivityFiber
The invention discloses a rail straining and sensing method based on bidirectional strain matching fiber grating demodulating technique. The method can be used for monitoring the quantity of shafts, the weight of the wheels or the positions of trains in running as well as the single-point or multi-point strain distributing conditions of the track. Compared with the traditional matching fiber grating demodulating technique, the method is different in that two matching gratings are respectively arranged on the side surfaces which are close to the top and the bottom of a rail in the system; according to the bidirectional strain (pulling strain and pressing strain) acted on the two gratings, the monitoring sensitivity can be improved, and the problem of the cross sensitivity of the strain temperature of the fiber grating during measuring the rail strain can be effectively solved. The method is simple in structure and fast to sample. The method is also be suited to monitor the dynamic strain of the rail.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
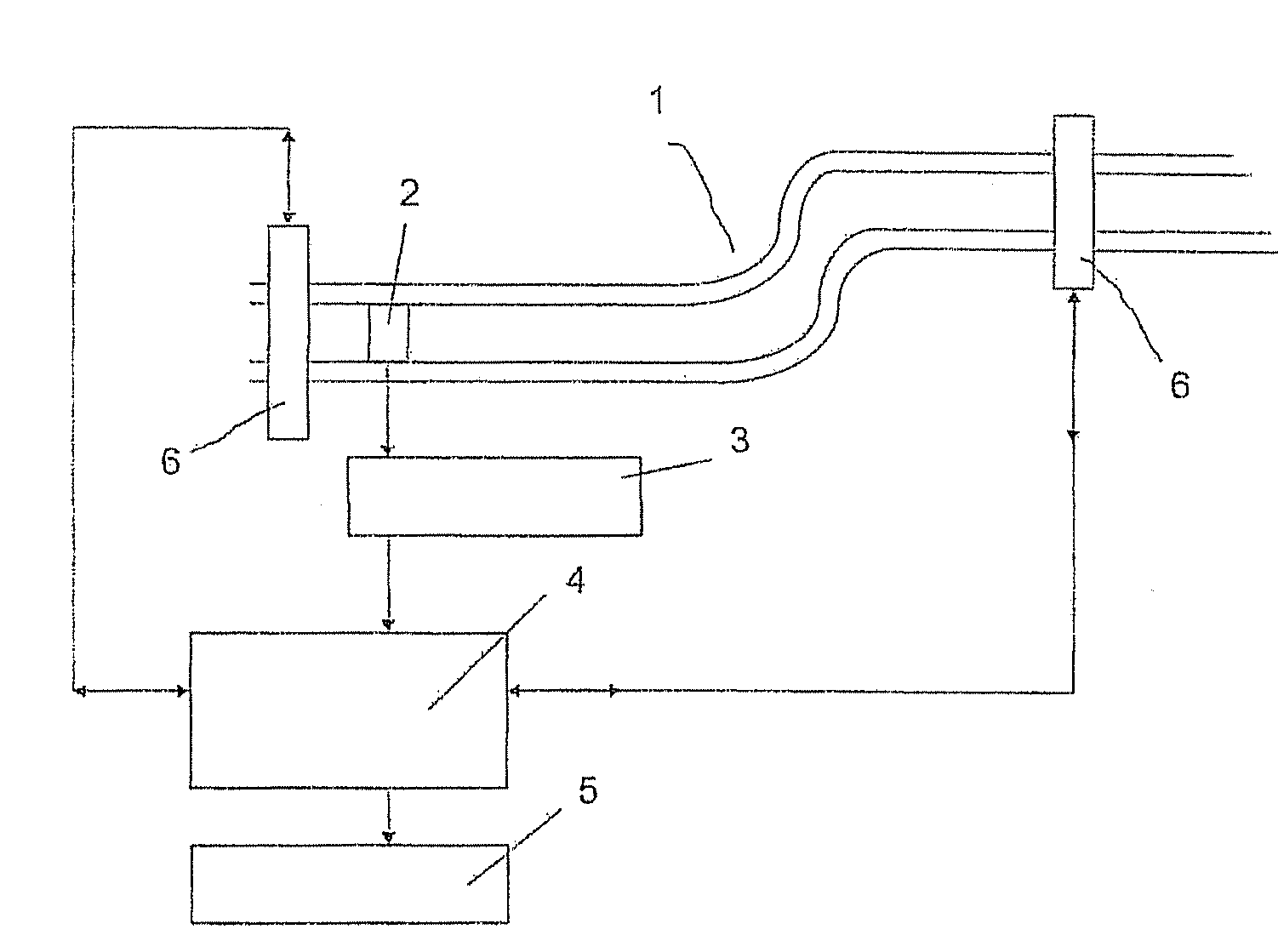
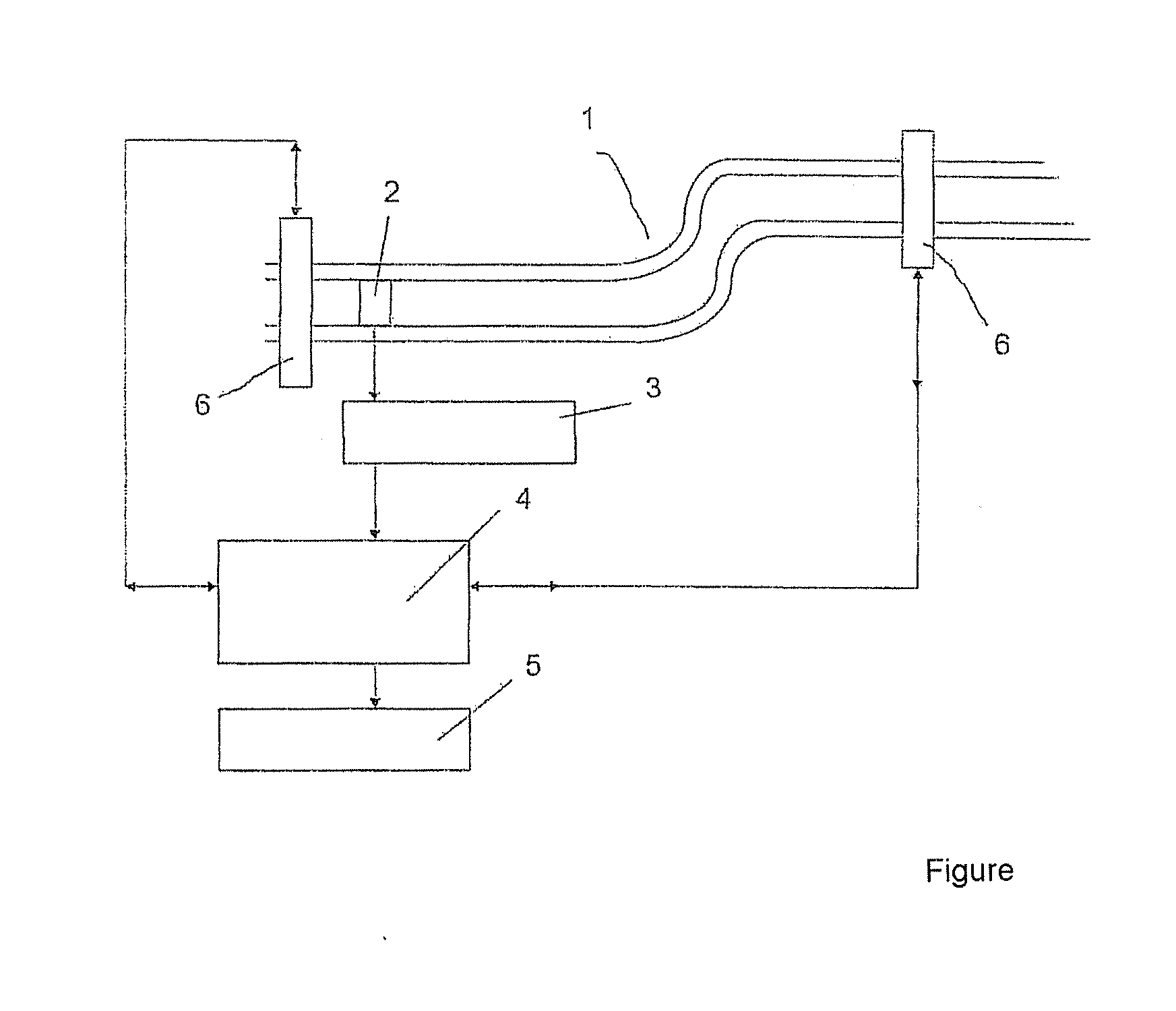
Vibration-type measuring device and method for operating such a measuring device
InactiveUS20080127745A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionCross sensitivityMeasurement device
The disclosure relates to a vibration-type measuring device for measuring at least one process variable, in particular a mass flow rate, a density, a viscosity, a pressure or the like, in particular in a process line through which a medium can flow, which device comprises at least one measurement sensor which provides a measurement signal that can be influenced by the process variable, the measured value determined for the process variable by the measuring device being able to be determined from a functional relationship in conjunction with measurement parameters from the measurement signal, and the measurement parameters having a temperature-dependent cross-sensitivity with respect to the temperature distribution in the measuring device. The measuring device comprises at least one temperature sensor, by means of which the local temperature can be measured, and a temperature distribution field can then be calculated with electronic means using a temperature distribution theorem, and correction values for compensating for the temperature-dependent cross-sensitivities of the measurement parameters can be determined from the temperature field data.
Owner:ABB PATENT GMBH
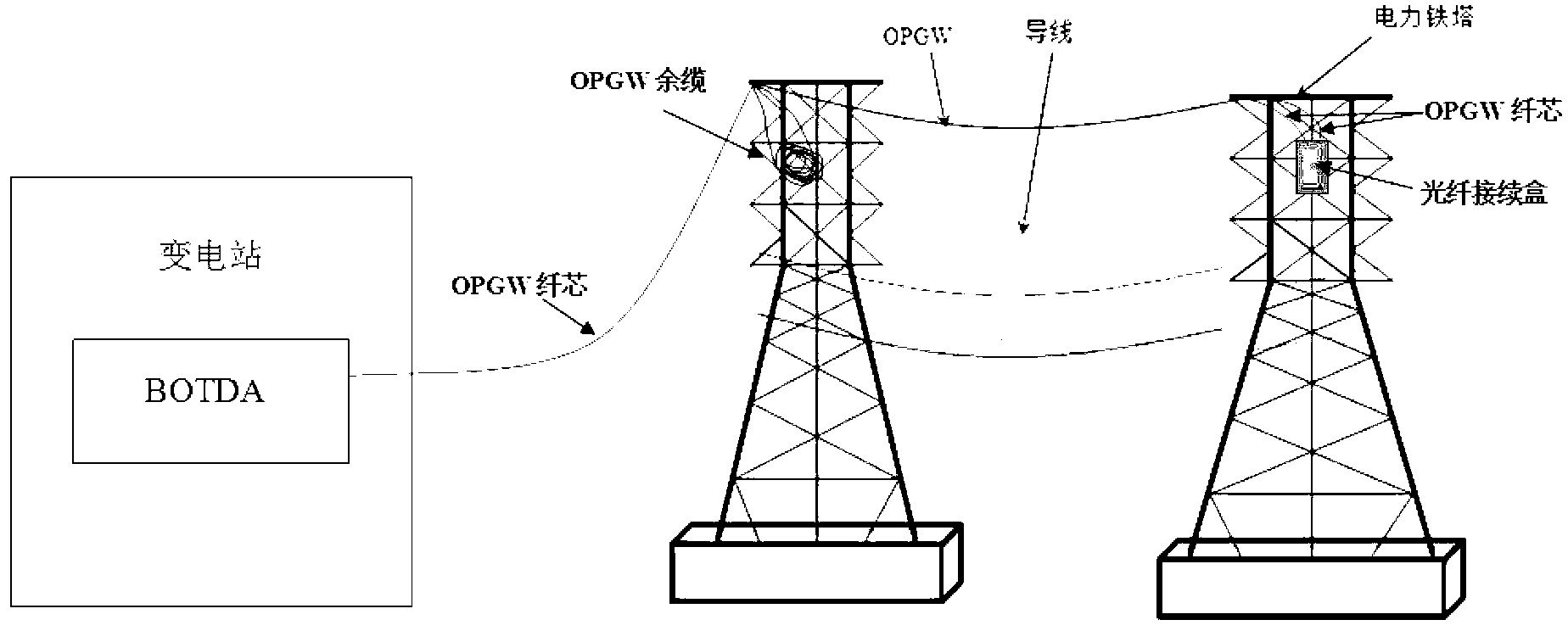
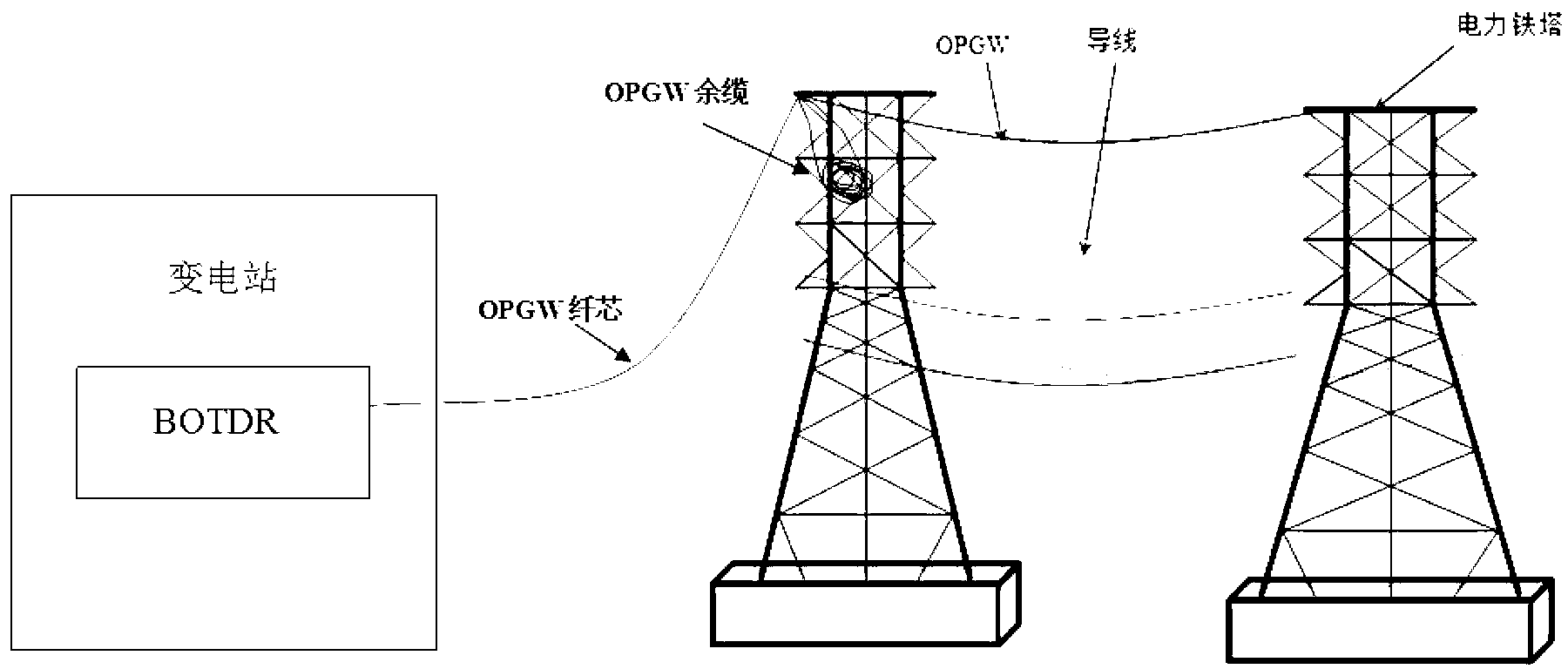
Method utilizing optical fiber composite overhead ground wire redundant cable to solve cross sensitivity existing in optical fiber Brillouin scattering monitoring
InactiveCN103323140ASimultaneously monitor temperatureSimultaneous monitoring of strainThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansCross sensitivityStress factor
The invention provides a method utilizing an OPGW redundant cable to solve cross sensitivity existing in optical fiber Brillouin scattering monitoring, and belongs to the technical field of photoelectronic measurement. An optical fiber Brillouin scattering demodulation analyzer is connected with the optical fiber core of an OPGW. Only temperature changes can cause the Brillouin scattering frequency shift of the OPGW redundant cable on an electric power iron tower, and ice accretion, wind blowing and other external stress factors cannot cause the Brillouin scattering frequency shift. Temperature compensation is carried out on a Brillouin scattering monitor technology through the OPGW redundant cable, the temperature and strain information of the overhead OPGW is demodulated out, the running state of the OPGW is reflected through the temperature and strain information of the OPGW, and the failure point of the OPGW is located through a Brillouin scattering sensor technology. The temperature complementation is carried out by utilizing the OPGW redundant cable on the electric power iron tower, the temperature and the strain along the OPGW are monitored, and the on-line monitor of the running state of the OPGW can be achieved.
Owner:YUN NAN ELECTRIC TEST & RES INST GRP CO LTD ELECTRIC INST +1
Photoluminescent oxygen probe with reduced cross-sensitivity to humidity
InactiveUS20110136247A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAnalysis by electrical excitationCross sensitivityPolyolefin
An oxygen-sensitive probe having reduced cross-sensitivity to humidity and methods of manufacturing and using such probes to measure oxygen concentrations within an enclosed space. The probe includes a thin film of an oxygen-sensitive photoluminescent dye on a first major surface of a microporous wettable polyolefin support layer. The dye is preferably a solid state composition comprising the oxygen-sensitive photoluminescent dye embedded within an oxygen-permeable hydrophobic polymer matrix.
Owner:MODERN CONTROLS +1
Distributed strain and temperature optical fiber sensor based on brillouin scattering
ActiveCN102980681AHigh resolutionStrong temperatureThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansCross sensitivityLong-period fiber grating
The invention discloses a distributed strain and temperature optical fiber sensor based on brillouin scattering. The sensor comprises a light source, an electro-optical modulator, a pulse signal source, a first erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, a second erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, a circulator, a first optical coupler, a second optical coupler, double balance detectors, a signal processing system and a sensing optical fiber. The sensing optical fiber comprises a long period optical fiber grating and is an all-solid photonic crystal band gap optical fiber. Output light of the light source is divided into two paths, wherein one path of the output light is modulated to be detection pulse light by means of the electro-optical modulator, is amplified through the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifiers and is input into the sensing optical fiber through the circulator. The sensor can simultaneously obtain temperature and strain with high resolution through a single measurement, and can well solve the problem of cross sensitivity existing in measurement of a brillouin sensor.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for simultaneously measuring temperature and stress of fiber bragg gratings (obtained by corrosion) with different diameters
InactiveCN102829893AAddress cross-sensitivity issuesLow costForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesCross sensitivityFiber
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously measuring temperature and stress of fiber bragg gratings (obtained by corrosion) with different diameters. The method comprises a fiber bragg grating demodulation instrument or a device which has functions similar to those of the fiber bragg grating demodulation instrument, and the fiber bragg gratings (obtained by the corrosion) with the different diameters, wherein the fiber bragg grating demodulation instrument can be used for fast scanning lasers with different wavelengths; when the lasers with a certain length can meet reflection conditions of the central wavelengths of the fiber bragg gratings, the lasers with the certain wavelength can be sent back to the fiber bragg grating demodulation instrument and are recorded; and the fiber bragg gratings with the different diameters have different stress sensitivities and same temperature senstivity, so that two different fiber bragg gratings can generate different central wavelength drifts under a same environmental influence, two wavelength drift equations obtained by using the two fiber bragg gratings are simultaneous, namely the change conditions of the environment temperature and the stress can be respectively obtained by solving the simultaneous equations. According to the scheme, the characteristic that fiber bragg gratings with the different diameters have the different stress sensitivities is utilized, and the method is easy and feasible, is low in cost and can effectively overcome the cross sensitivity problem of the fiber bragg gratings.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Raman-scattering-based method and device for simultaneously measuring temperature and strain of identical weak fiber gratings
The invention discloses a Raman-scattering-based method and device for simultaneously measuring the temperature and the strain of identical weak fiber gratings. According to the method and device, by the utilization of the wire-drawer-tower technology, ultralow-reflectivity identical weak fiber gratings are dynamically and continuously inscribed through single pulse energy to serve as a sensing probe; after modulation of pulse signals is performed, Bragg reflection signals and backward Raman scattering signals of the sensing probe are sent to a high-speed CCD wavelength demodulation module and a Raman temperature demodulation module respectively; temperature distribution T[i] at all the fiber gratings and reflection center wavelength lambda[i] of the fiber gratings are obtained respectively; temperature measurement of the Raman temperature demodulation module serves as temperature compensation data of strain measurement, and measurement data of the high-speed CCD wavelength demodulation module serve as correction for temperature measurement. The method and device can overcome the defects that the Raman sensing technology is low in accuracy and speed, and strain can not be measured, meanwhile, large capacity weak optical grating array fiber cabling complexity and operability can also be simplified, and cross sensitivity of the temperature and the strain of the gratings is avoided.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH +1
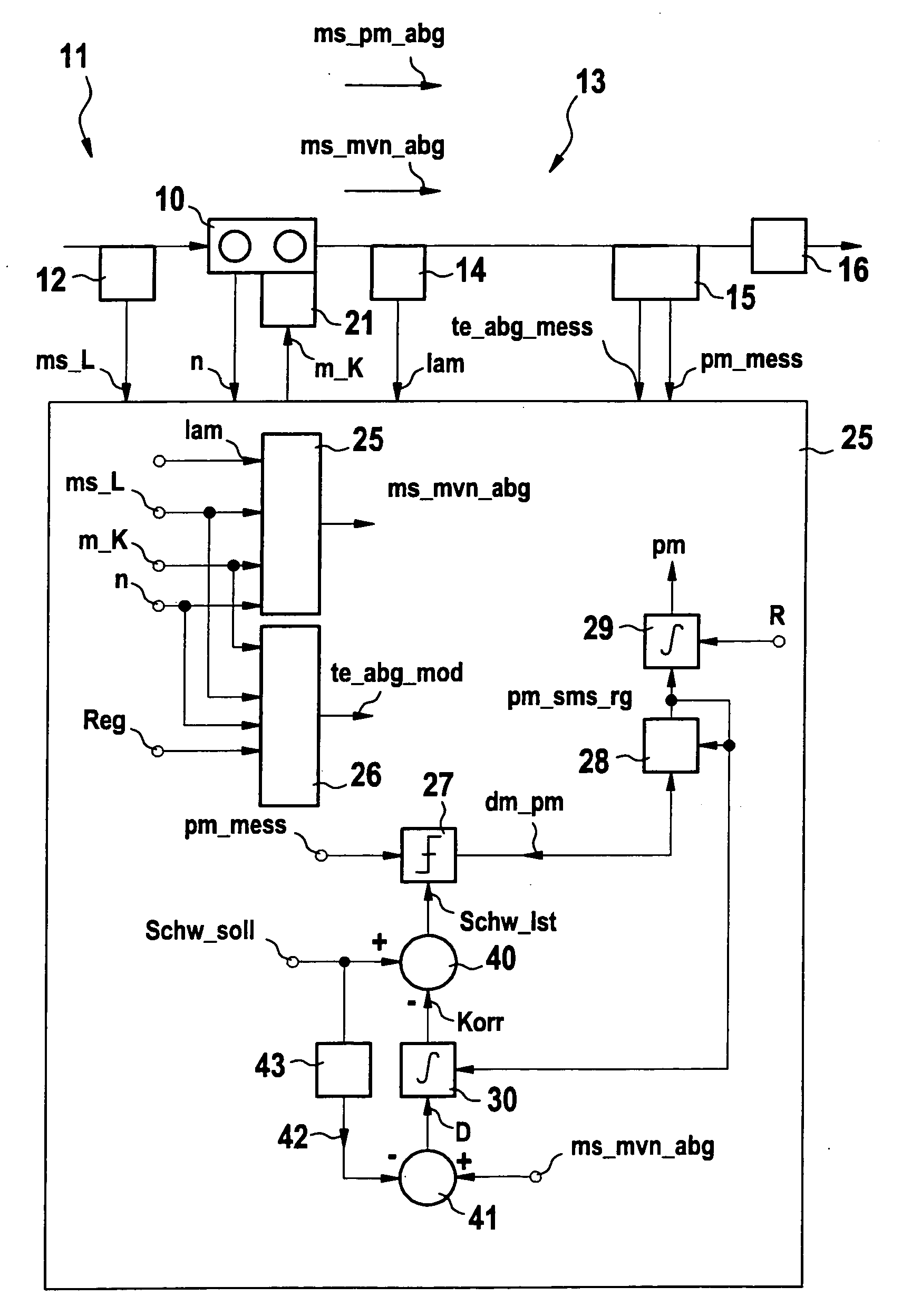
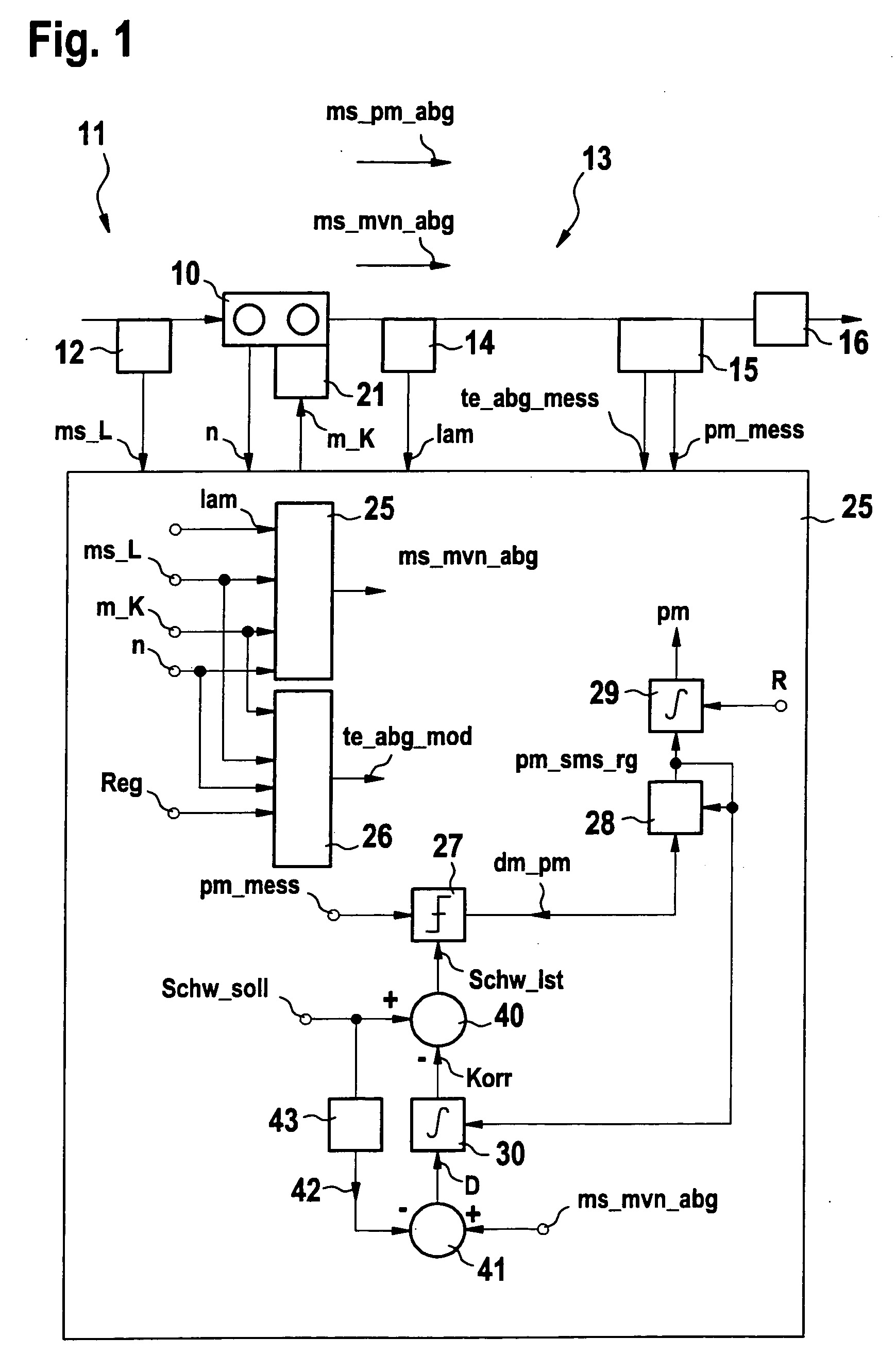
Method for operating a sensor for recording particles in a gas stream and device for implementing the method
ActiveUS20070089478A1High measurement accuracyElectrical controlTesting/calibration apparatusCross sensitivityEngineering
A method for operating a sensor for recording particles in an exhaust gas flow and a device for carrying out the method are provided, in which at least one measure of the exhaust gas flow is ascertained and in which the measure of the exhaust gas flow is taken into consideration in the valuation of the particle sensor signal made available by the particle sensor. The procedure is based on the knowledge that the exhaust gas flow, for instance, the exhaust gas volume flow, has an influence on the particle sensor signal made available by the particle sensor, especially when the measuring effect is based on the depositing of particles on a sensor surface. Using the procedure, a possibly present cross sensitivity of the particle sensor with respect to different exhaust gas flows is taken into consideration, so that the measuring accuracy is increased.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
An optical fiber sensing system temperature compensating method
The invention provides an optical fiber sensing system temperature compensating method comprising the following steps: 1, temperature calibrating is carried out on an optical sensor to obtain a temperature sensitivity coefficient K[T1]; 2, temperature calibrating is carried out the optical sensor attached in an adhesive mode to the surface of a test piece, of which the materials is same with a to-be-measured piece so as to obtain a material uniform thermal expansion coefficient K[T2]; 3, strain calibrating is carried out on the optical sensor to obtain a strain sensitivity coefficient K [Epsilon]; and 4, in strain and deformation measurement carried out on the to-be-measured piece, strain applied to the to-be-measured piece is measured by an optical fiber strain sensor, and an optical fiber temperature sensor is used to make temperature compensating for the strain sensor; and influences by uniform thermal expansion are rejected to obtain effective deformation strain data. The invention is mainly used for occasions such as strain and deformation caused by fore bearing and non-uniform thermal expansion in optical fiber sensing network measurement, and difficulties in measuring by the optical fiber sensor with regard to deformation and uniform thermal expansion of the measured piece and strain and temperature cross sensitivity are overcome.
Owner:山东双测安全信息技术产业研究院有限公司
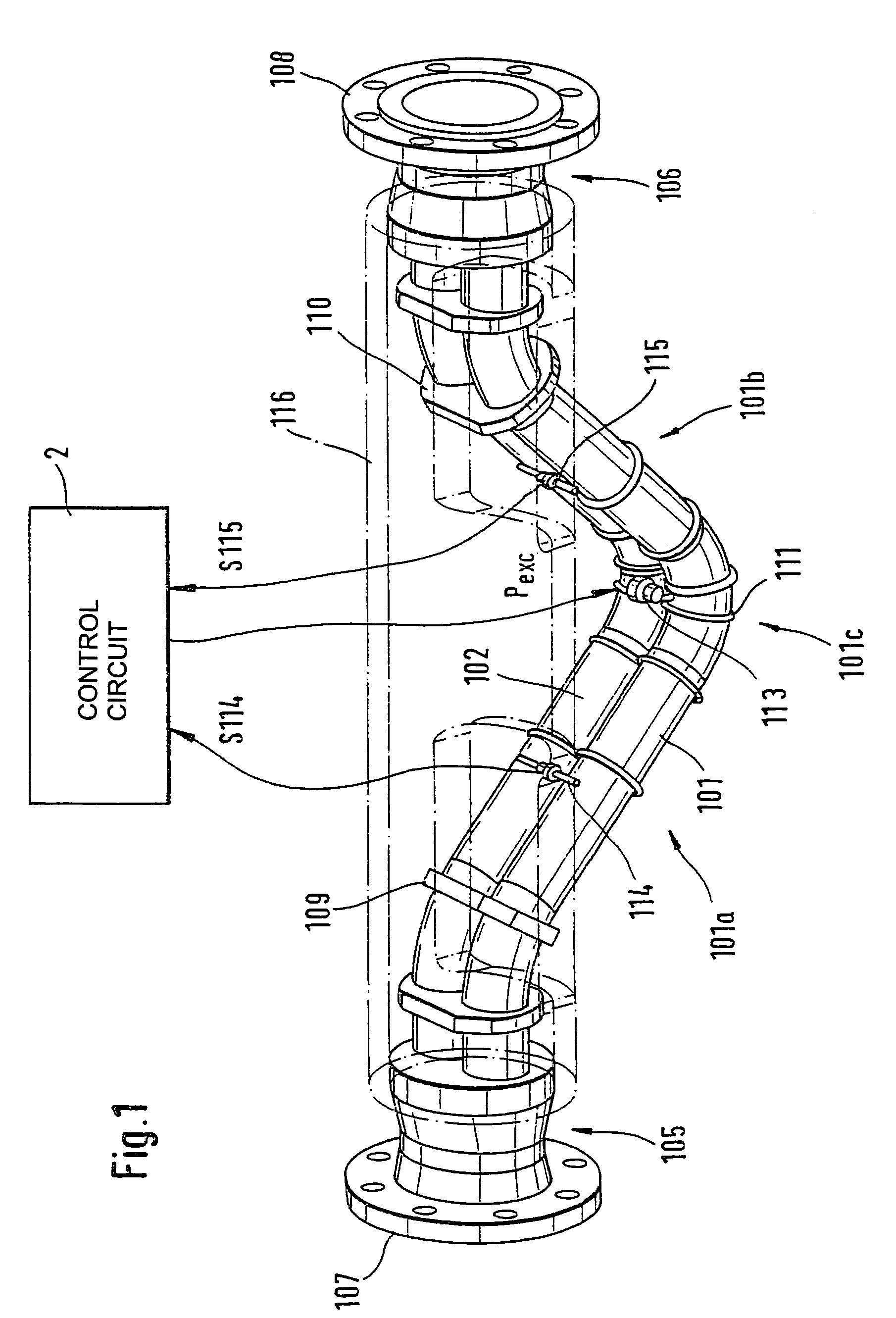
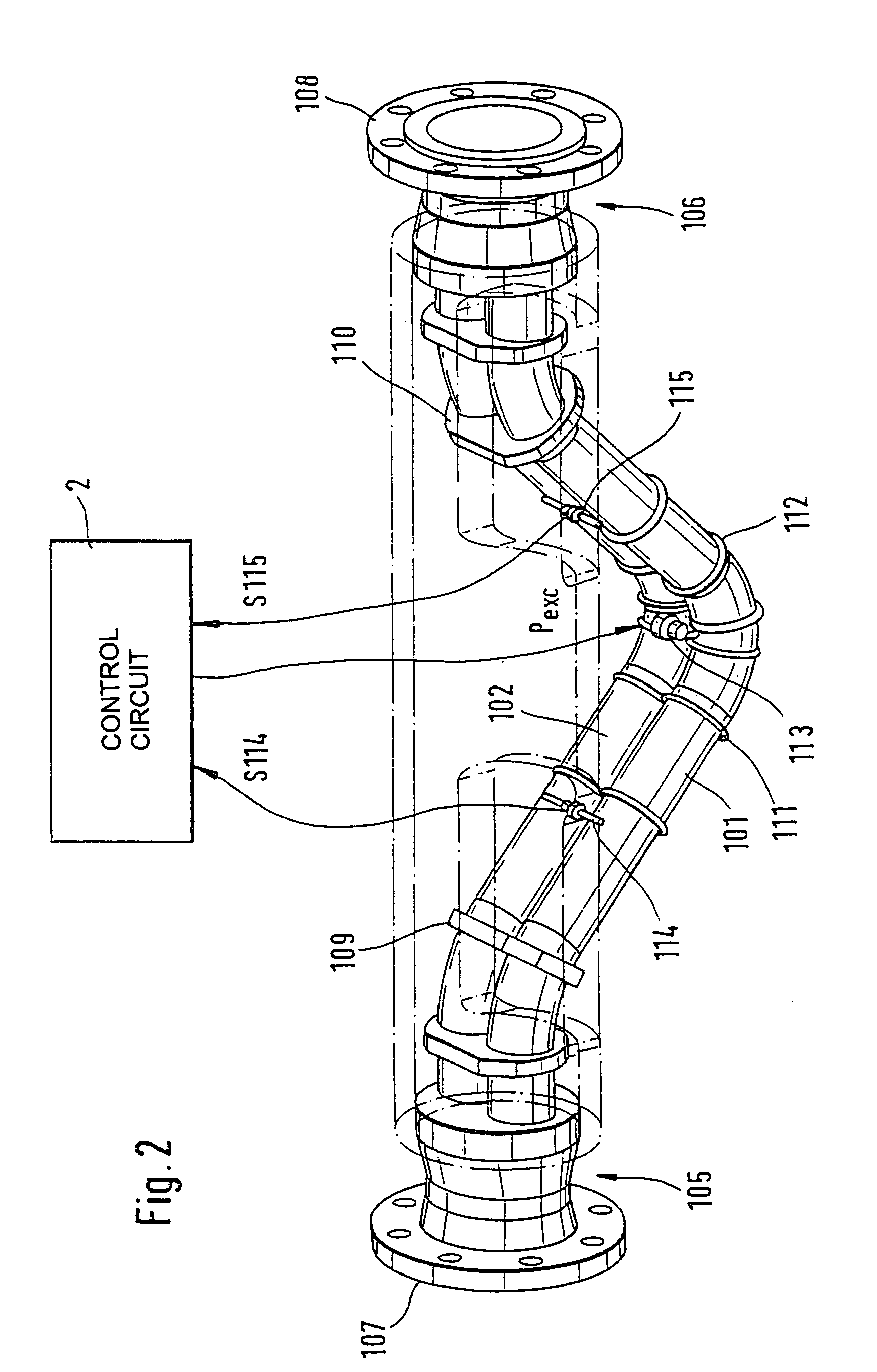
Vibratory transducer
InactiveUS20050072238A1Reduce quality problemsHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCross sensitivityStraight tube
The transducer (1) has at least one at least temporarily vibrating flow tube (101) of predeterminable lumen for conducting a fluid. The flow tube (101) communicates with a connected pipe via an inlet tube section (103), ending in an inlet end, and an outlet tube section (104), ending in an outlet end, and in operation performs flexural vibrations about an axis of vibration joining the inlet and outlet ends. The flow tube (101) has at least one arcuate tube section (101c) of predeterminable three-dimensional shape which adjoins a straight tube segment (101a) on the inlet side and a straight tube segment (101b) on the outlet side. At least one stiffening element (111, 112) is fixed directly on or in close proximity to the arcuate tube segment (101c) to stabilize the three-dimensional shape. By means of the at least one stiffening element (111, 112), the cross sensitivity of the transducer (1) is greatly reduced, so that cross talks from pressure to mass flow signals are minimized and the accuracy of the transducer is improved.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Polarization maintaining optical fiber interferometer capable of simultaneously measuring strain and temperature
ActiveCN107894245AAddress cross-sensitivity issuesSimple structureForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesCross sensitivityRayleigh scattering
The invention provides a polarization maintaining optical fiber interferometer capable of simultaneously measuring strain and temperature. The system comprises a narrow-band light source, a total polarization-maintaining Mach-Zehnder interferometer, an interference signal detection unit, a differential circuit and a demodulation system. A polarization-maintaining optical fiber device is adopted toconstruct a full-polarization-maintaining interferometer, and the optical signals are simultaneously transmitted in the fast axis and the slow axis of the polarization maintaining optical fiber, andtwo sensing systems are formed. The two sensing systems have different responses to the temperature and the strain respectively, so that simultaneous measurement of the two can be realized. The Mach-Zehnder interference structure does not have back-reflection transmission, and rayleigh scattering noise in the light transmission process is effectively inhibited. Light in the polarization maintaining optical fiber is separated from the fast and slow axes, the differential circuit is used for carrying out differential processing on the coaxial signals, the noise is reduced, and the measurement precision is improved. The polarization maintaining optical fiber interferometer is simple to manufacture, convenient to measure, high in precision and capable of effectively overcoming the problem of cross sensitivity. The polarization maintaining optical fiber interferometer can be applied to the fields of oil exploration, and seismic observation.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
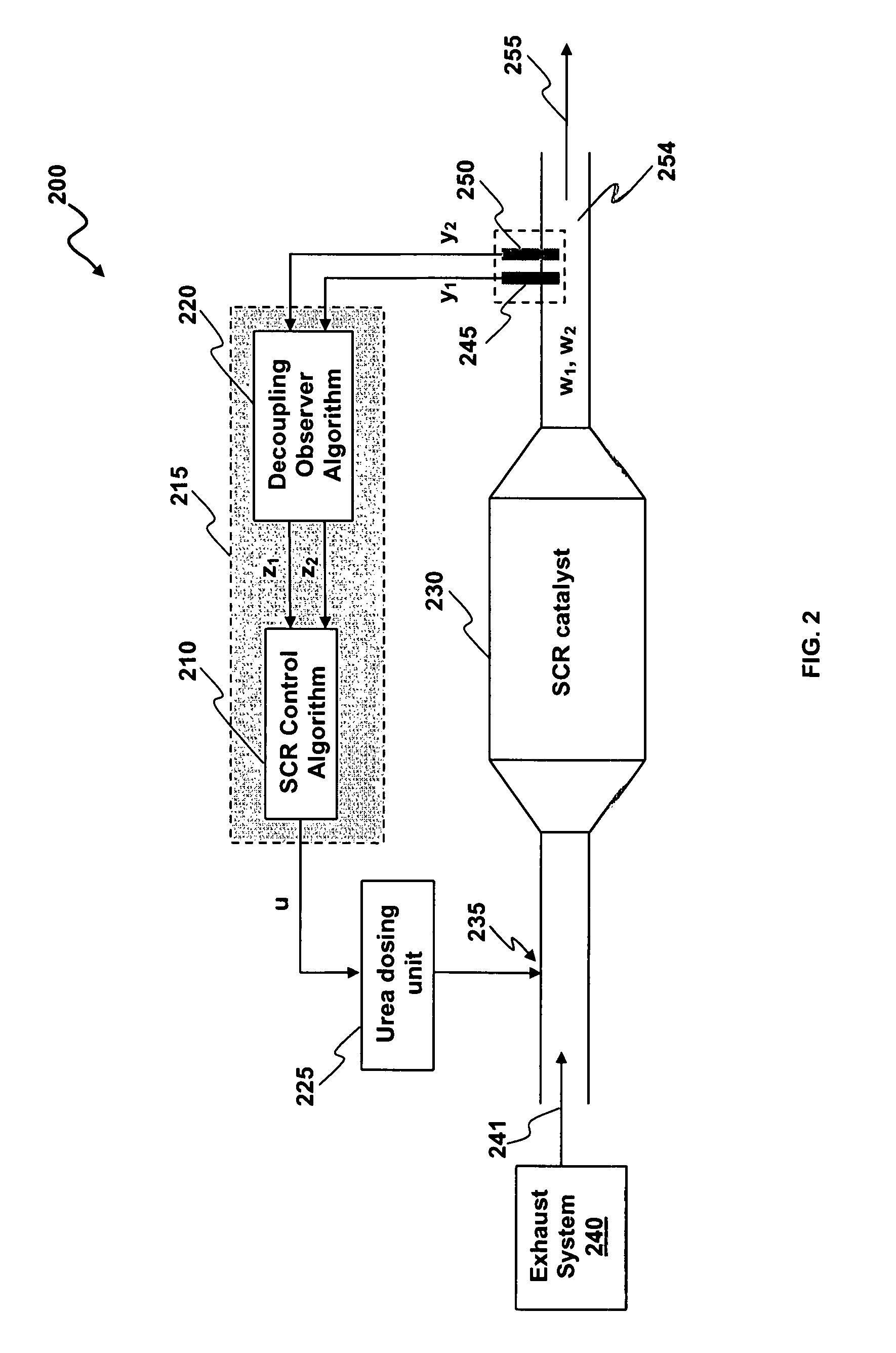
Method and system for the simultaneous measurement of a plurality of properties associated with an exhaust gas mixture
A method for simultaneously measuring one or more properties (e.g. temperature, concentration of NOx and ammonia, etc) in an exhaust gas mixture. Signals from one or more sensors that are cross-sensitive to one or more gases can be combined. A decoupling observer algorithm can be applied, such that these cross-sensitivities are decoupled. The sensors simultaneously obtain an estimate of one or more gases in the diesel exhaust. A decoupling observer algorithm can be structured and arranged to be operable among a plurality of positions corresponding to several internal configurations.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
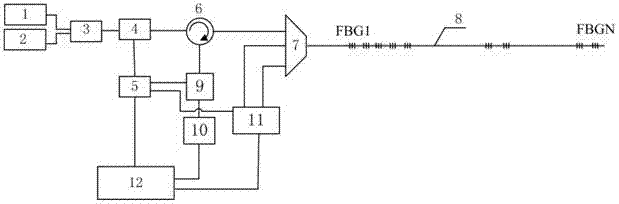
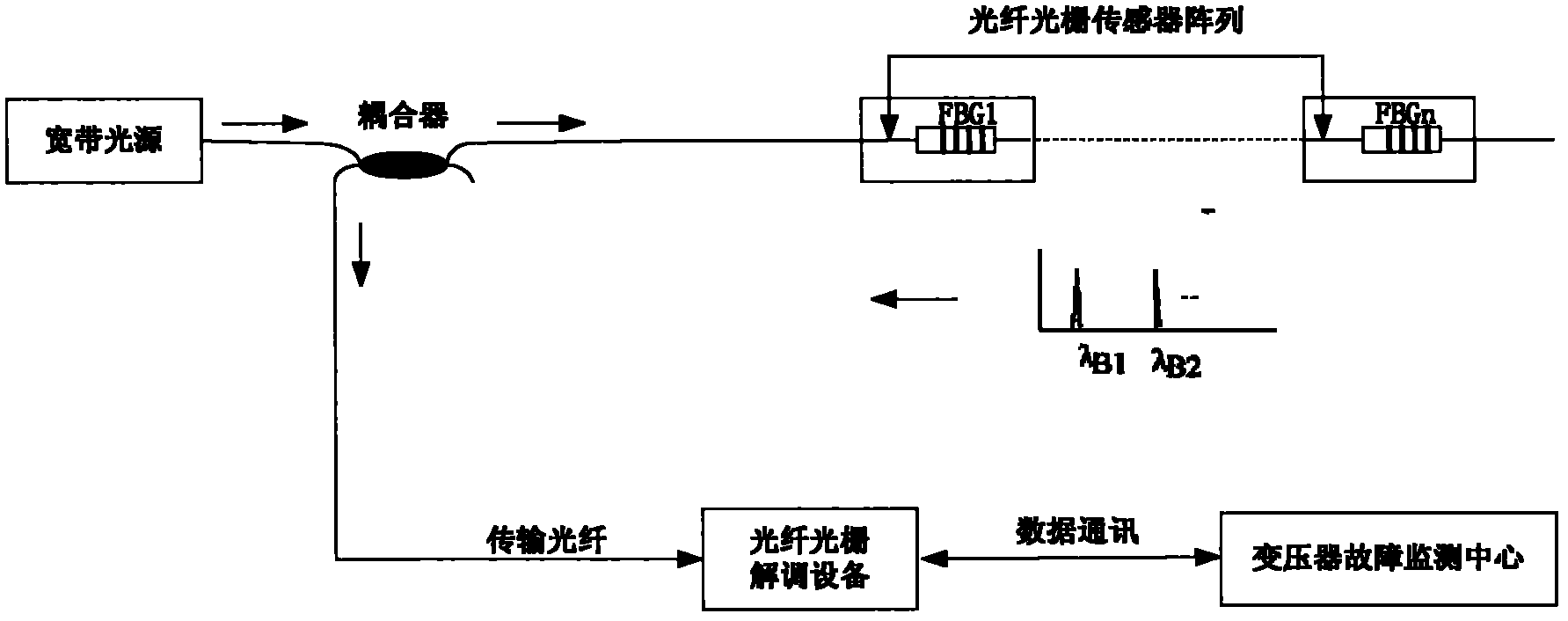
Fiber bragg grating (FBG) sensor based transformer fault gas monitoring system
ActiveCN102033041AHigh selectivityAddress cross-sensitivity issuesPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansSensor arrayCross sensitivity
The invention discloses a fiber bragg grating (FBG) sensor based transformer fault gas monitoring system in the technical field of on-line monitoring system. The system comprises a gas sensor array, FGG demodulation equipment, a transformer fault monitoring center and the like. In the system, an FBG sensor is adopted, and the FBG sensor has strong anti-electromagnetic interference and is beneficial to application to environment with extremely severe electromagnetic environment; the sensor has high sensitivity and high resolution and can be used for simultaneously detecting all parts of the transformer on line, thereby the system maintenance cost is greatly reduced; and the system solves a series of problems of cross sensitivity among gases, slow oil-gas separation and balancing, short breathable film service life, and the like in the traditional fault monitoring method.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Dotted groove type optical fiber cladding surface Bragg raster
InactiveCN105334566APronounced birefringenceUnique structureOptical waveguide light guideFibre with gratingsCross sensitivityLong-period fiber grating
The invention discloses a dotted groove type optical fiber cladding surface Bragg raster, which is characterized in that the optical fiber cladding surface Bragg raster is arranged on the outer surface of the optical fiber cladding of the single mode fiber; the optical fiber cladding surface Bragg raster consists of a plurality of dotted grooves which cause the structural damage to the optical fiber cladding and have periodicity; and the center points of all dotted grooves are in the same line which is parallel with a center axis of the optical fiber. The dotted groove type optical fiber cladding surface Bragg raster is unique in structure, simple in manufacture method, miniaturized and fiber-optical. The invention has a characteristic sensitive to the outside medium, which is similar to the long period optical fiber bragg gating, has a high Q value factor and has a cross sensitivity effect which is much lower than the long period optical fiber bragg gating; the temperature, pressure and the strain sensitivity are higher than that of the traditional optical fiber Bragg raster; the raster zone of the optical fiber cladding has obvious double refraction effect and can be widely applicable to the fields like the biology, chemical engineering, medical science, the bioscience, etc.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Fine core microstructure optical fiber interferometer sensor and temperature and strain detection method therefor
InactiveCN106568466ASimple structureImprove accuracyThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansCross sensitivityHigh humidity
The invention discloses a fine core microstructure optical fiber interferometer sensor and a temperature and strain detection method therefor. The fine core microstructure optical fiber interferometer sensor comprises a broadband light source, a sensing head and a spectrograph, wherein the sensing head is a fine core microstructure optical fiber having an air dome layer, and two ends of the fine core microstructure optical fiber are respectively connected with the broadband light source and the spectrograph via single mode optical fibers. Light emitted from the broadband light source enters the fine core microstructure optical fiber via the single mode optical fibers; because the single mode optical fibers and the fine core microstructure optical fiber are mismatched in mode field, the spectrograph outputs spectrums which include interference fringe spectrums, and temperature change or strain can cause wavelength shift of an interference fringe wave trough; when the wavelength shift of the interference fringe wave trough is known, temperature change or strain can be calculated correspondingly. Due to the air dome layer in the fine core microstructure optical fiber, a technical problem of refraction index cross sensitivity of external environment can be prevented; temperature and strain detection accuracy of the sensor is improved, and the sensor disclosed in the invention can be effectively applied to high humidity or liquid environment.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Micro-socle girder resonator with low temperature cross sensitivity
InactiveCN101064197AThe temperature compensation method is simple and easySimple structureSolid-state devicesInstrumental componentsCross sensitivityResonance
This invention discloses one micro hanging arm resonance device with low frequency temperature parameters, wherein it adopts dioxide silicon or silicon or silicon nitride double structure to realize temperature self-compensation; through theory computation and experiment it expresses optimum thickness proportion as 1. 1-1. 7 and the other proportion as 0. 9-1. 2; the diode silicon is grown by thermal oxidation method by low gas phase deposition method process.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for real-time measurement of fuel gas compositions and heating values
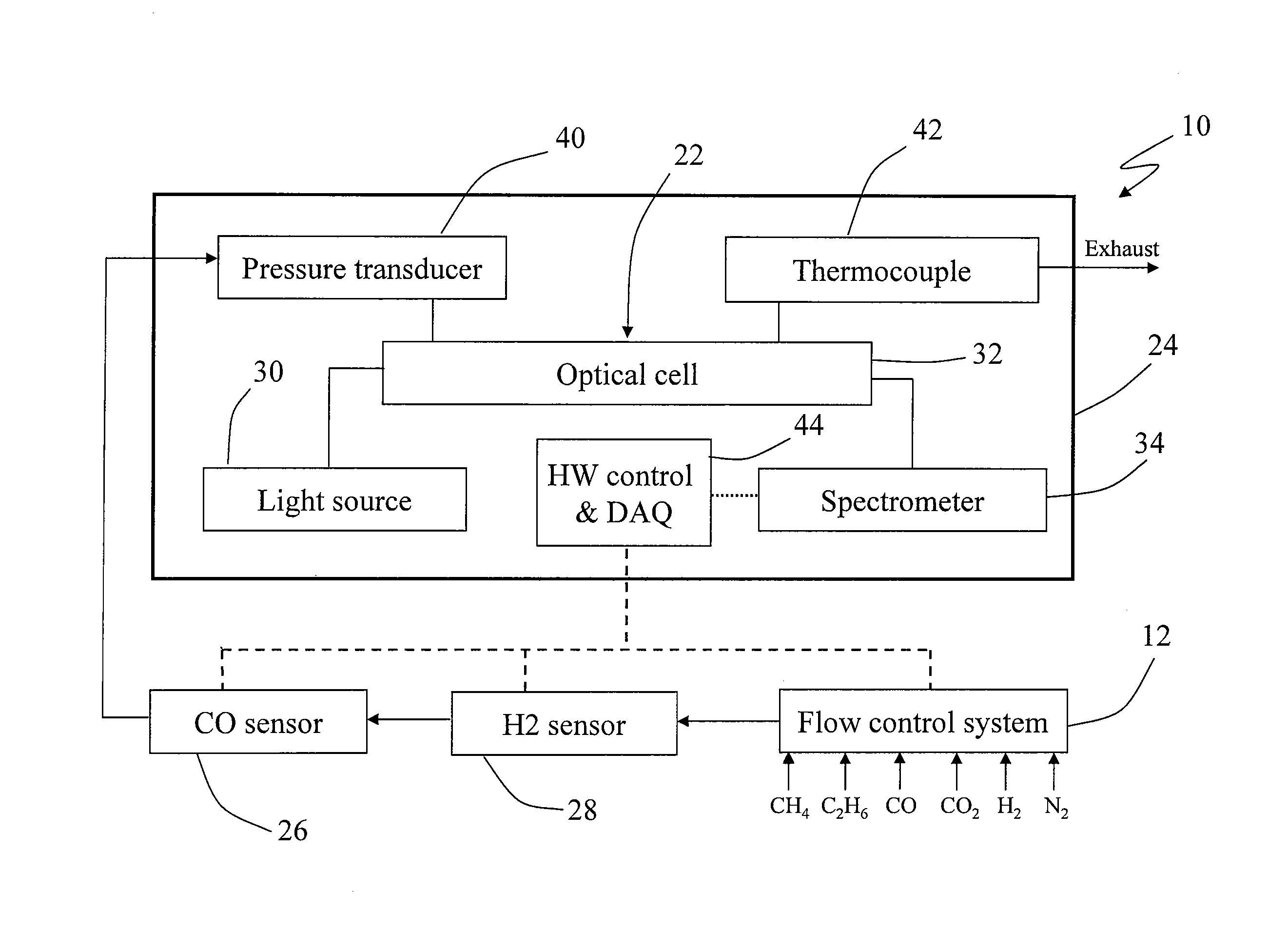
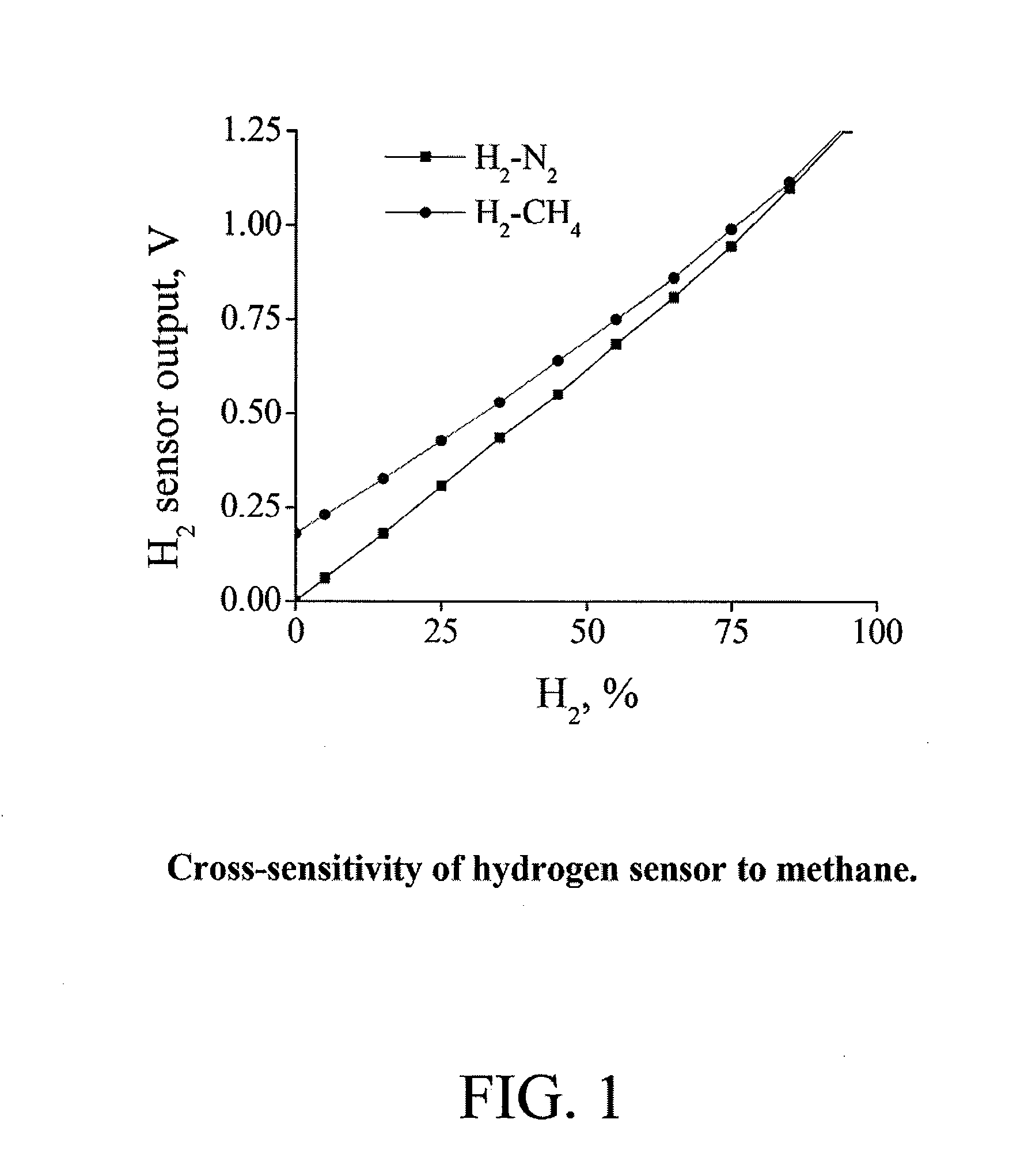
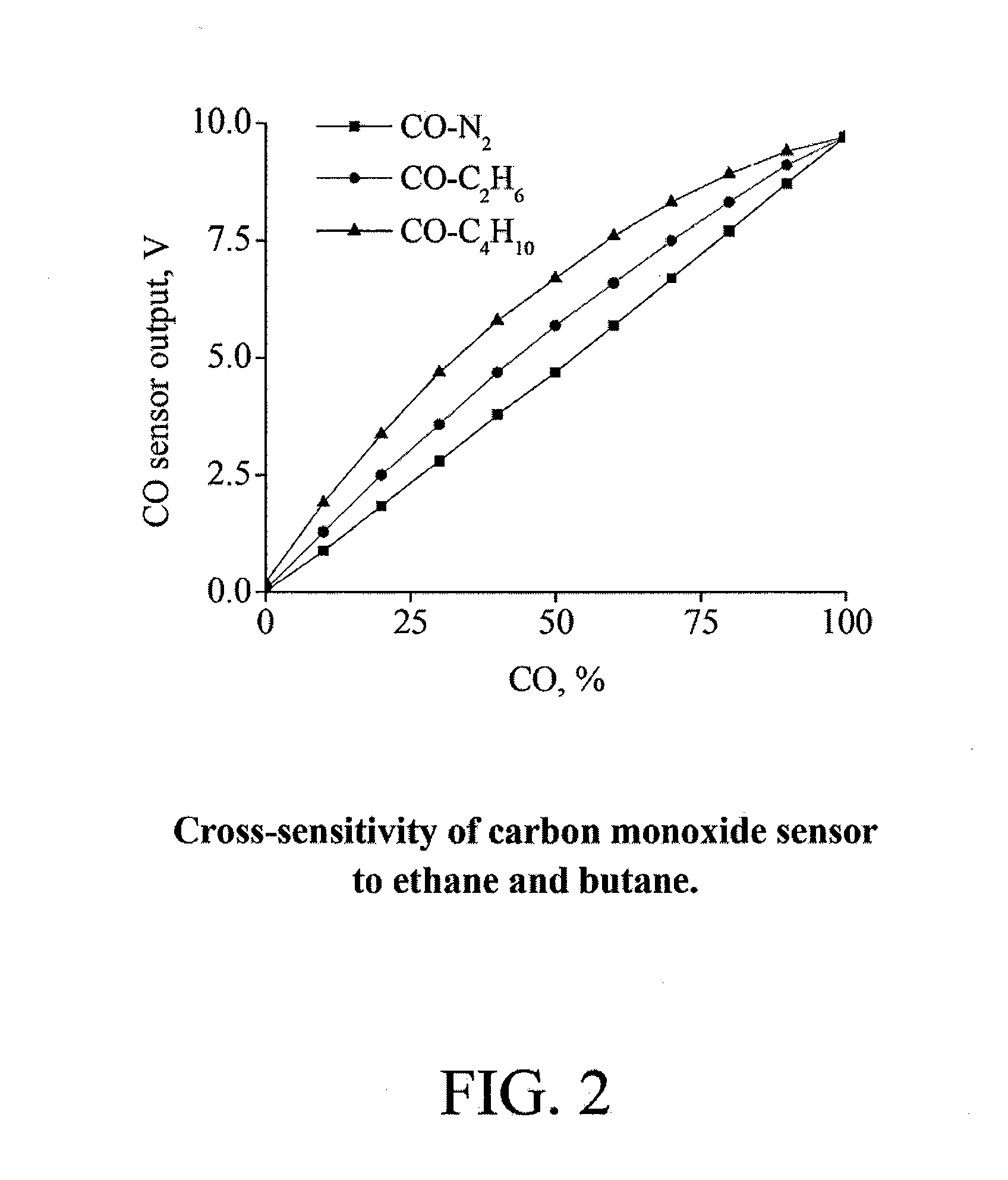
ActiveUS20140326049A1Reduce the impactEfficiency optimizationFuel testingInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsCross sensitivityGas composition
An exemplary embodiment can be an apparatus for real-time, in situ measurement of gas compositions and heating values. The apparatus includes a near infrared sensor for measuring concentrations of hydrocarbons and carbon dioxide, a mid infrared sensor for measuring concentrations of carbon monoxide and a semiconductor based sensor for measuring concentrations of hydrogen gas. A data processor having a computer program for reducing the effects of cross-sensitivities of the sensors to components other than target components of the sensors is also included. Also provided are corresponding or associated methods for real-time, in situ determination of a composition and heating value of a fuel gas.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Passive athermal fiber bragg grating strain gage
Fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) are particular suitable for measuring strain. However, a single parameter measurement is difficult to implement, since cross-sensitivity to temperature compels the use of an additional temperature reference, e.g. a strain-inactive FBG. The development of a passive athermal fiber Bragg grating strain gage is thus of particular interest since it renders optional the measurement of temperature, benefiting large scale system design and performance. In view of this need, a package for fiber Bragg gratings that enables strain measurements to be performed while canceling temperature sensitivity is disclosed. The proposed design is based on a structure composed of two parts, which can be made of the same material, having a defined length ratio that allows the adjustment of the temperature sensitivity to zero, providing athermal operation of the strain gage. Moreover, the disclosed passive athermal scheme is adjustable to further compensate for structural thermal expansion, enabling the load-induced strain component to be decoupled from the temperature-induced strain component.
Owner:ARAUJO FRANCISCO MANUEL MOITA +1
Method for detecting temperature and magnetic field simultaneously based on magnetofluid-filled crystal fiber loop mirror
InactiveCN103616046AImprove stabilityHigh measurement sensitivityMeasurement devicesCross sensitivityMatrix method
The invention relates to a method for detecting micro photoelectrons, in particular to a method for detecting temperature and a magnetic field simultaneously based on a magnetofluid-filled crystal fiber loop mirror. According to the method, magnetofluid is selectively filled into air holes of a structurally-symmetrical photonic crystal fiber along the center line in the horizontal direction; the birefringence characteristic of the photonic crystal fiber is changed accordingly, and a temperature / magnetic field-adjustable birefringent photonic crystal fiber is formed; a traditional birefringent fiber in a Sagnac fiber loop mirror is replaced by the temperature / magnetic field-adjustable birefringent photonic crystal fiber, the distance between two adjacent resonance valleys and the drift distance of the resonance valleys are changed along with the changes of the temperature and the magnetic field with different change sensibilities, and accordingly the temperature and the magnetic field can be simultaneously detected through the two-parameter matrix method. The method improves the stability performance and measuring sensitivity of a sensor, solves the problem of cross sensitivity of the temperature and the magnetic field of the optical fiber sensor and achieves the purpose of measuring the temperature and the magnetic filed simultaneously through one optical fiber.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF ENG
Methods of minimizing temperature cross-sensitivity in vapor sensors and compositions therefor
ActiveUS20070095678A1Improve responsivenessMinimize changesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementCross sensitivityElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention relates to methods of making compositions for sensor films used for detecting chemical analytes within sensors, such as polymer-absorption chemiresistors (i.e., conductometric sensors). The sensor films have reduced cross-sensitivity to temperature, while maintaining sensitivity to the chemical analytes. The sensor matrix includes components that are associated with a first temperature coefficient of resistance, such as a polymer resin and / or a first conductive particle. The sensor matrix further comprises a second species, preferably a conductive particle, which has a second temperature coefficient of resistance that is opposite to the first temperature coefficient of resistance. The second species has an opposite influence on a resistance response of the sensor from the first species. In this manner, the sensor matrix exhibits a minimized response in resistance to any changes in temperature.
Owner:THERM O DISC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com