Patents
Literature
4474 results about "Circular segment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In geometry, a circular segment (symbol: ⌓) is a region of a circle which is "cut off" from the rest of the circle by a secant or a chord. More formally, a circular segment is a region of two-dimensional space that is bounded by an arc (of less than 180°) of a circle and by the chord connecting the endpoints of the arc.
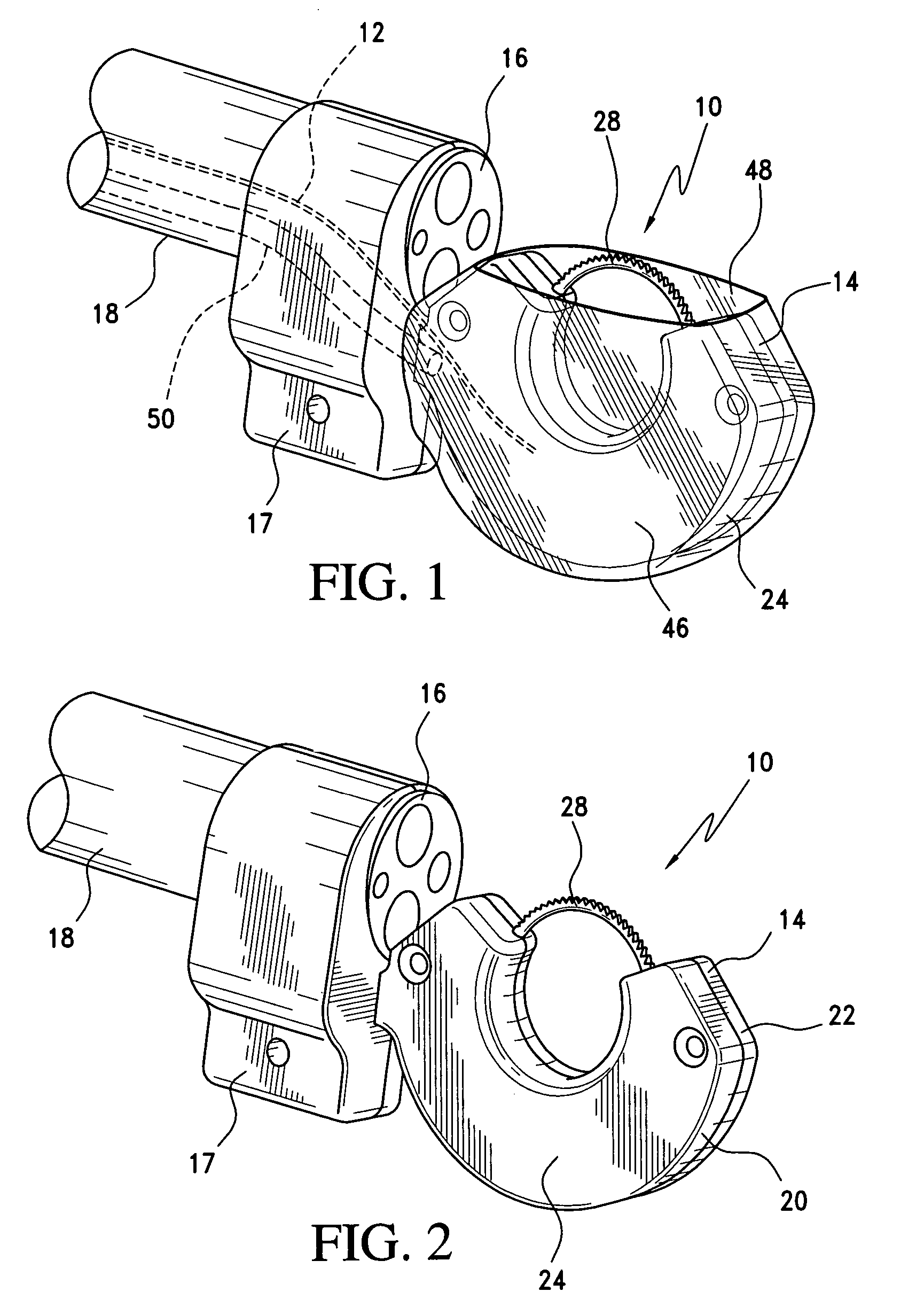
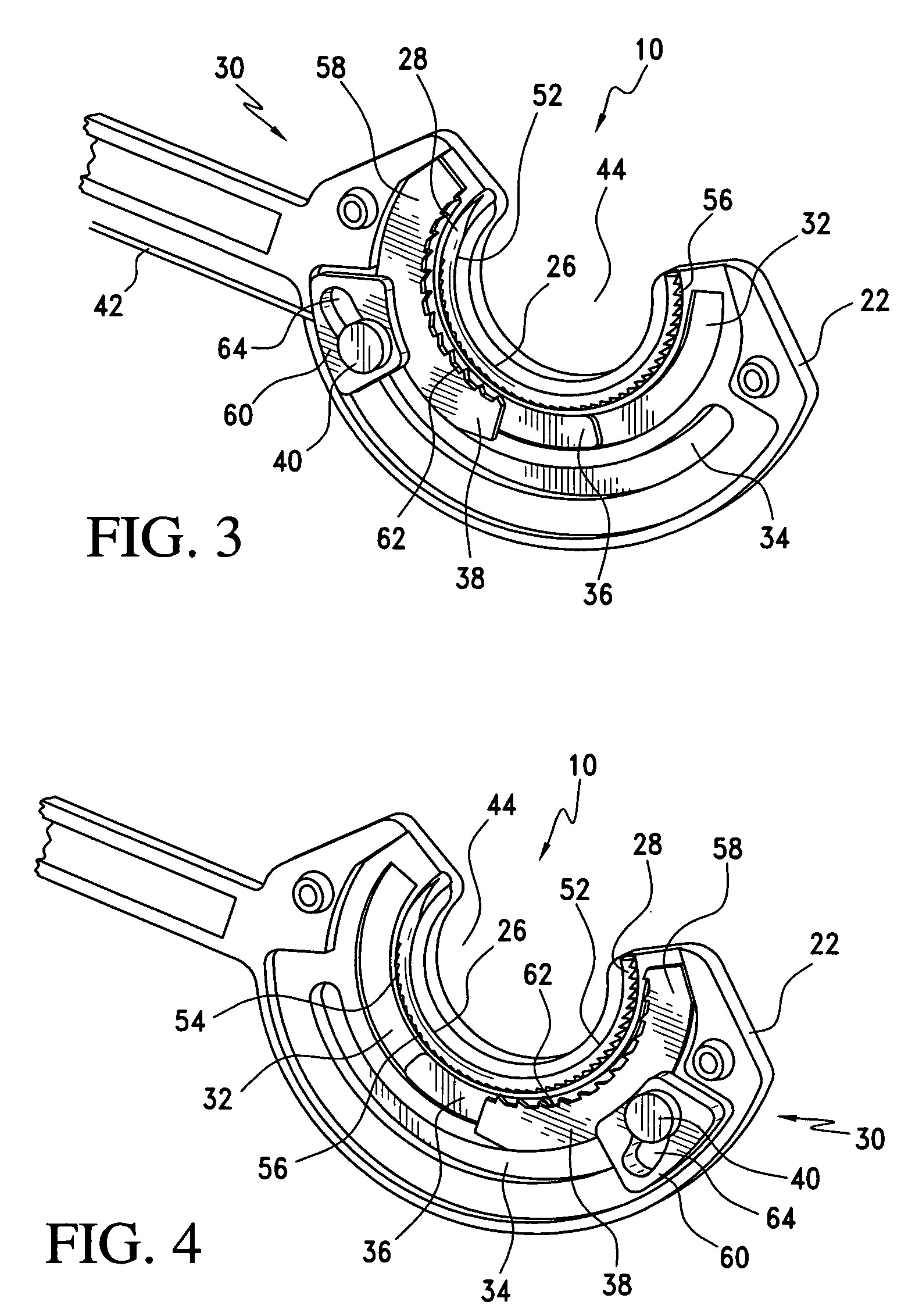
Surgical fastening device with initiator impregnation of a matrix or buttress to improve adhesive application
A material comprising a matrix or a buttress is impregnated with an adhesive initiator and is used with a surgical stapling device and an adhesive. The tissue and material are stapled together, and a knife in the surgical stapling device cuts the tissue and the material. The adhesive is applied across the cut and sets up or polymerizes to seals the cut when the adhesive contacts the adhesive initiator. The surgical stapling device can place the staples in a linear, arcuate, or circular array, and can anastomose luminal tissue. The methods of use can include stapling luminal tissue end to end, stapling two portions of material onto ether side of tissue, and stapling two portions of tissue onto a portion of material. Additionally, a portion of adhesive filed material can be stapled onto one side of portion of tissue and the adhesive initiator impregnated material can be stapled onto the other. Cutting the material and tissue provides a path for the adhesive across the cut, and catalyzes the adhesive from contact with the adhesive initiator.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
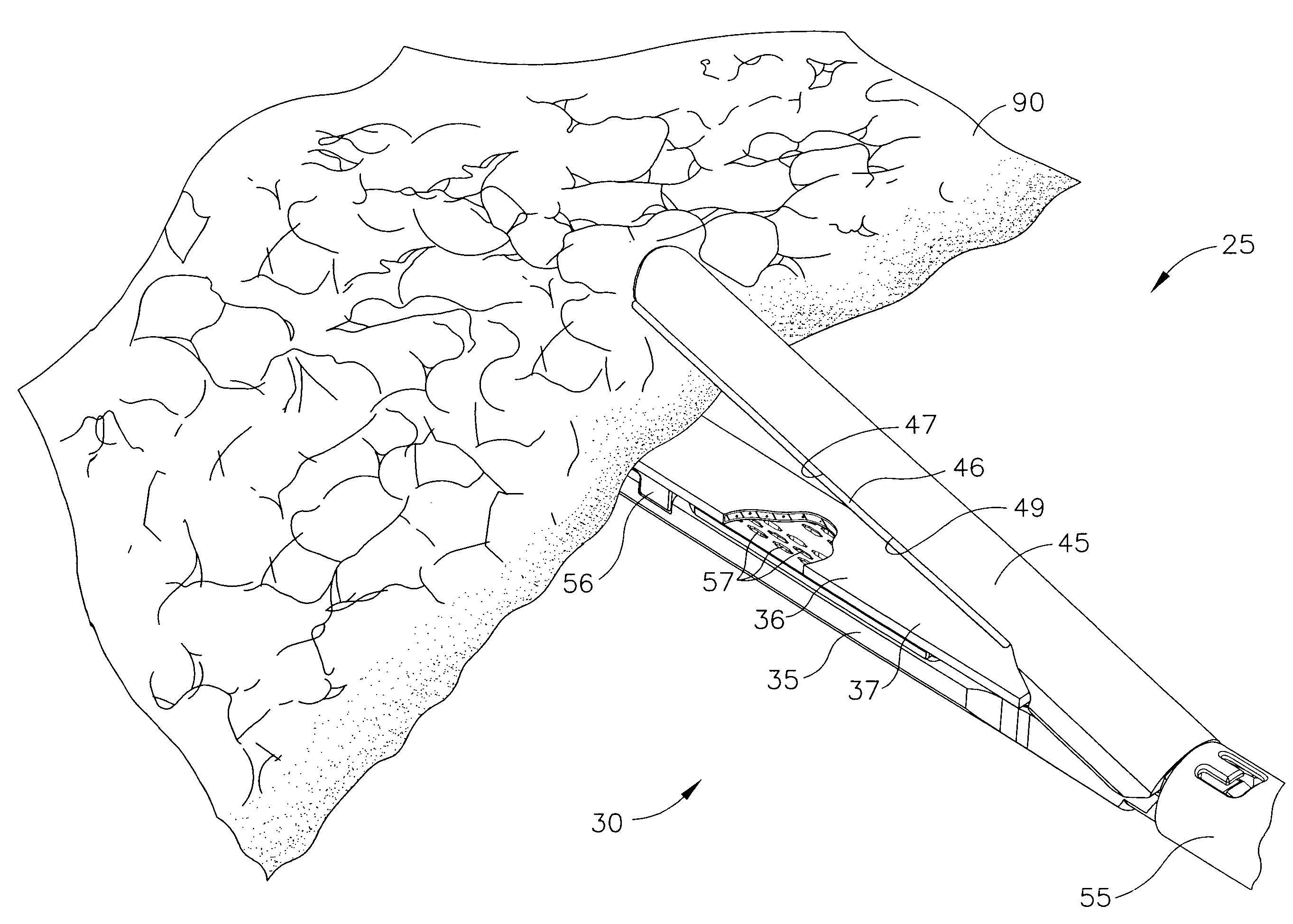
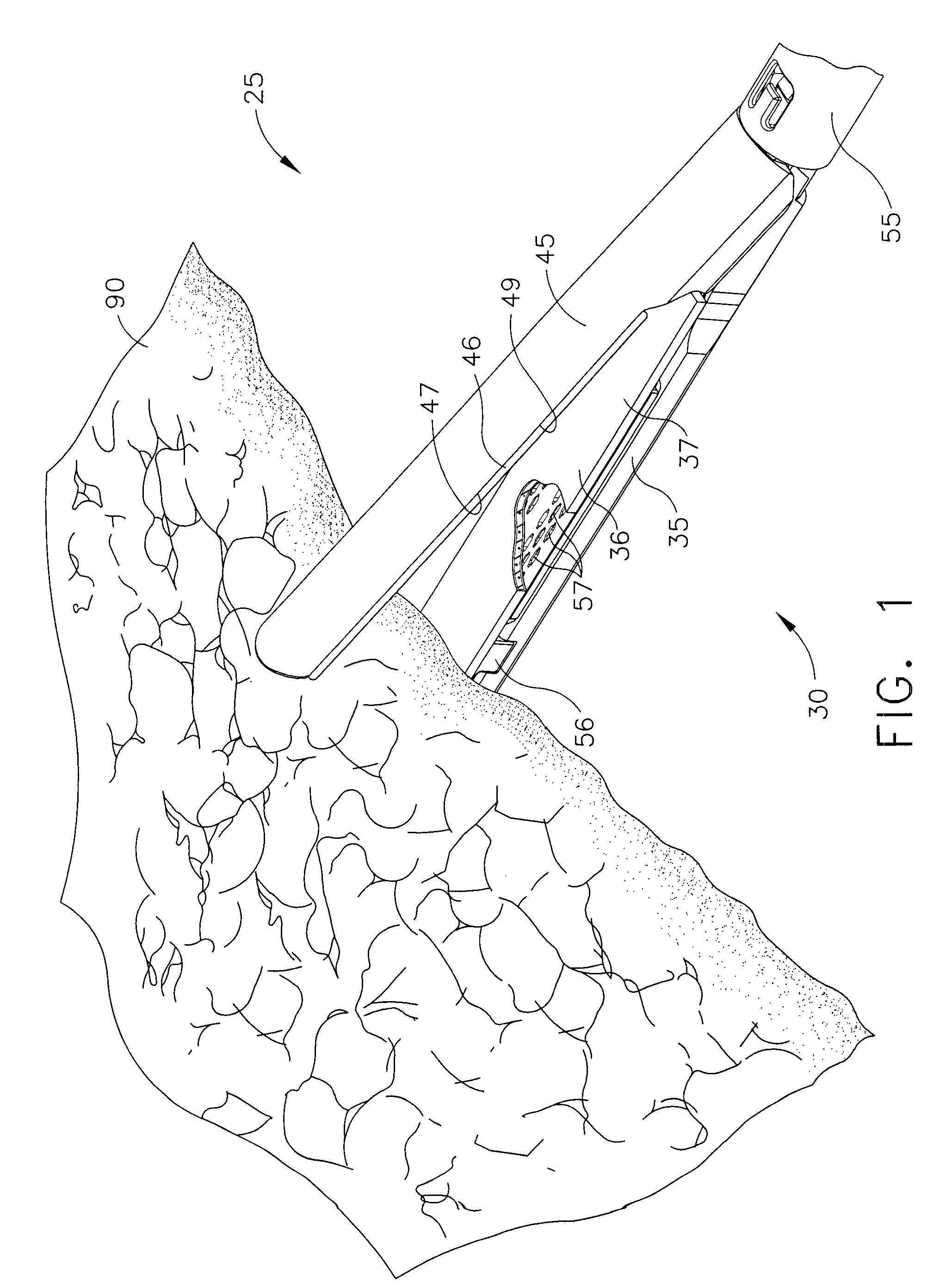
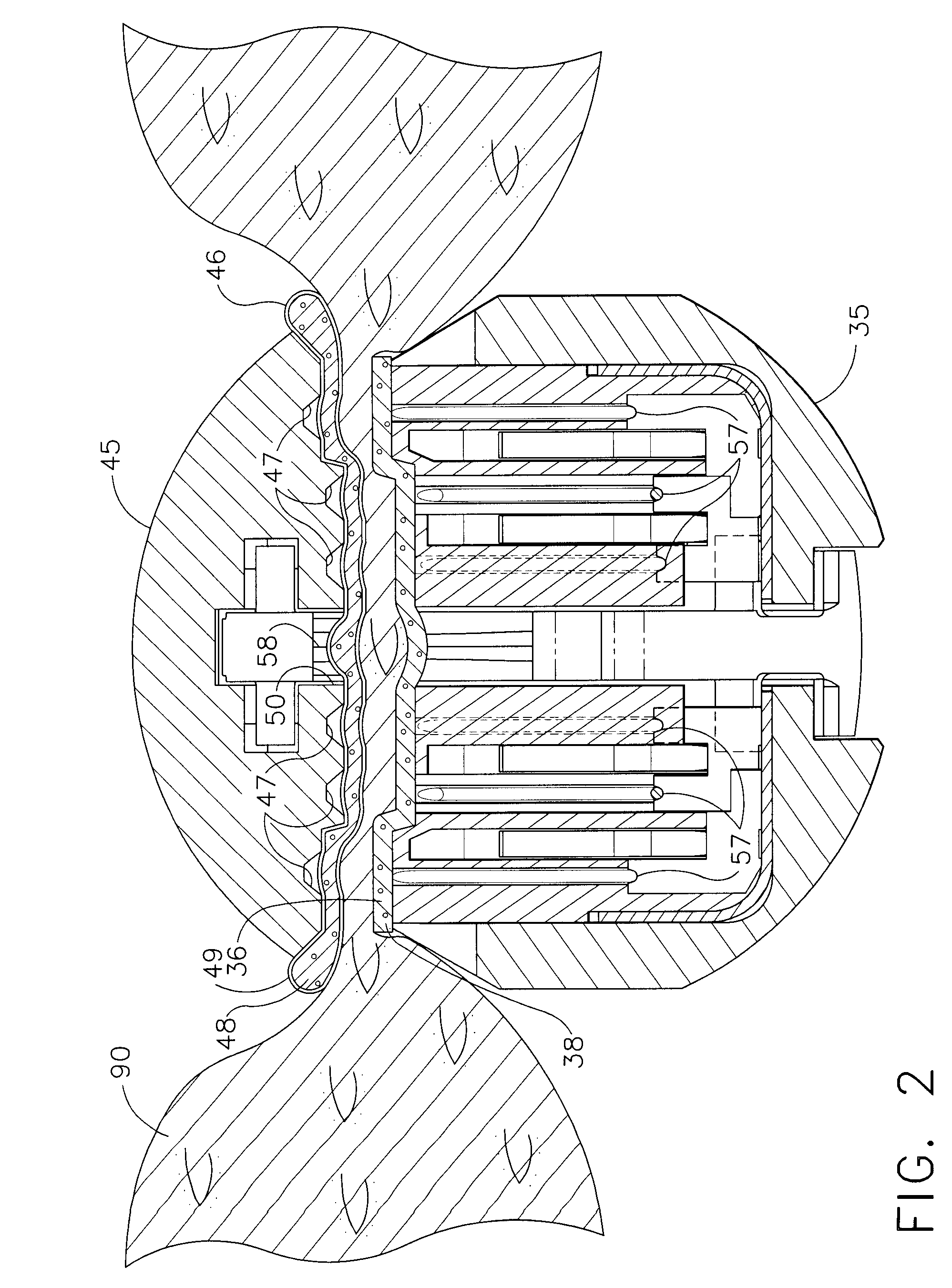
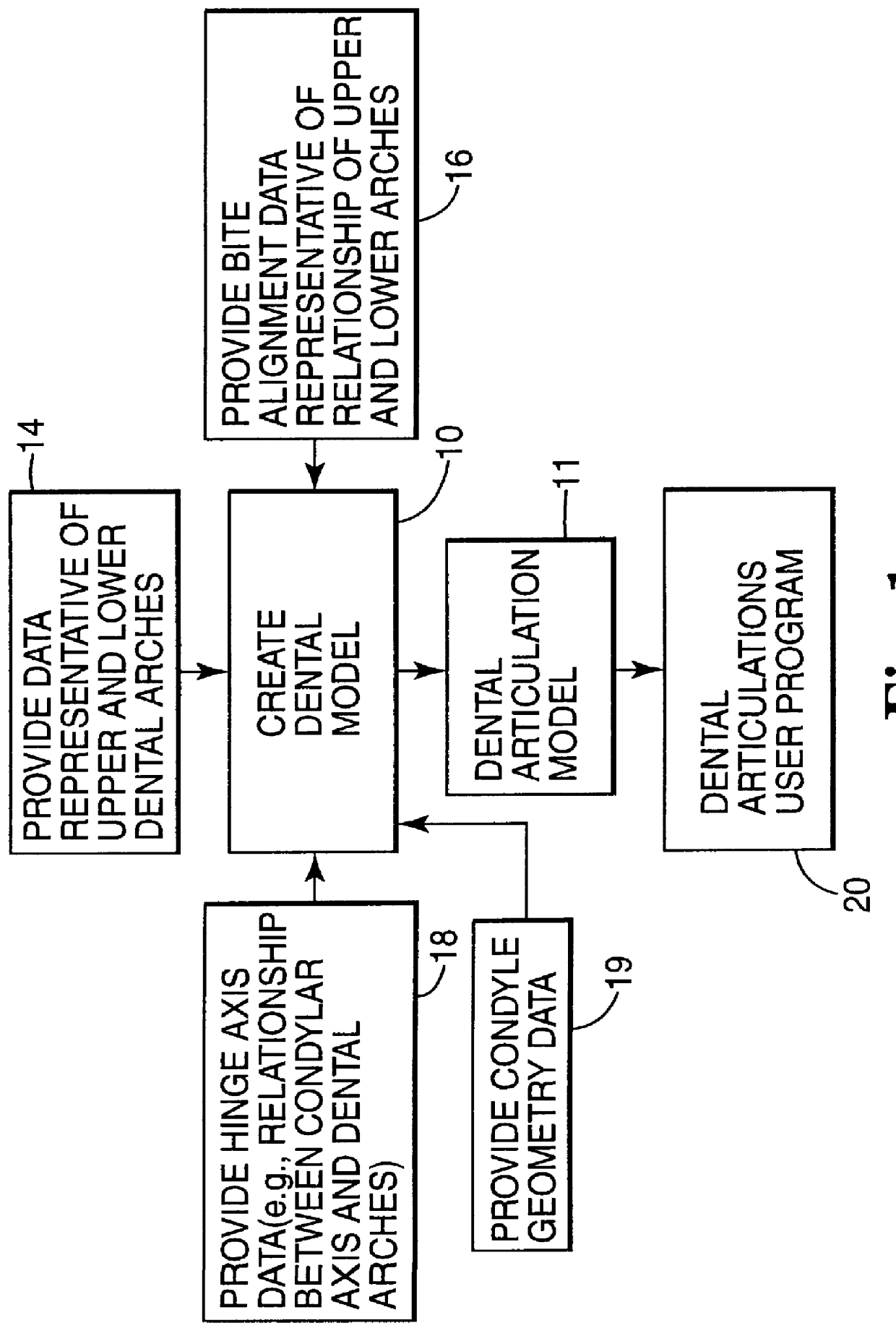
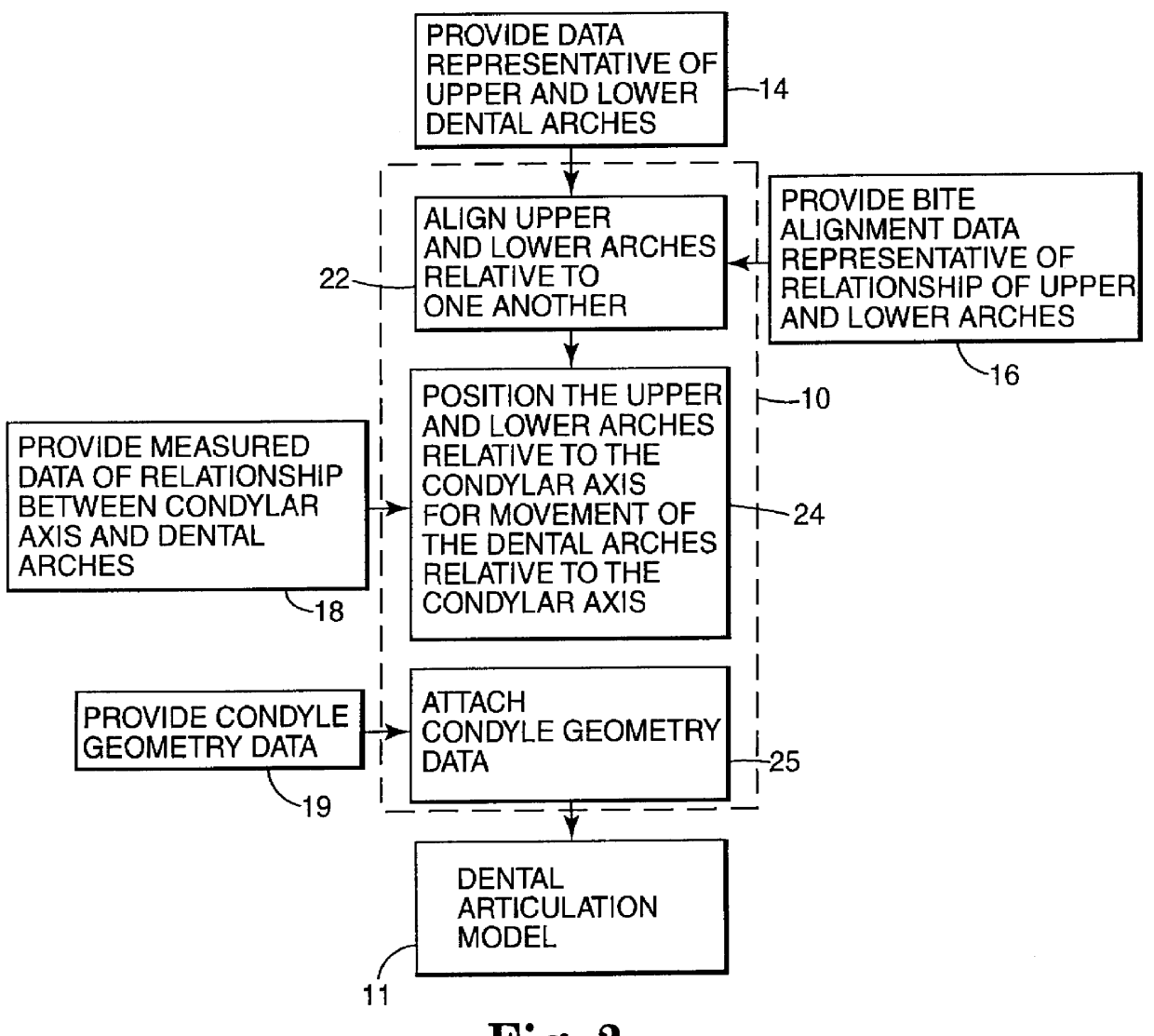
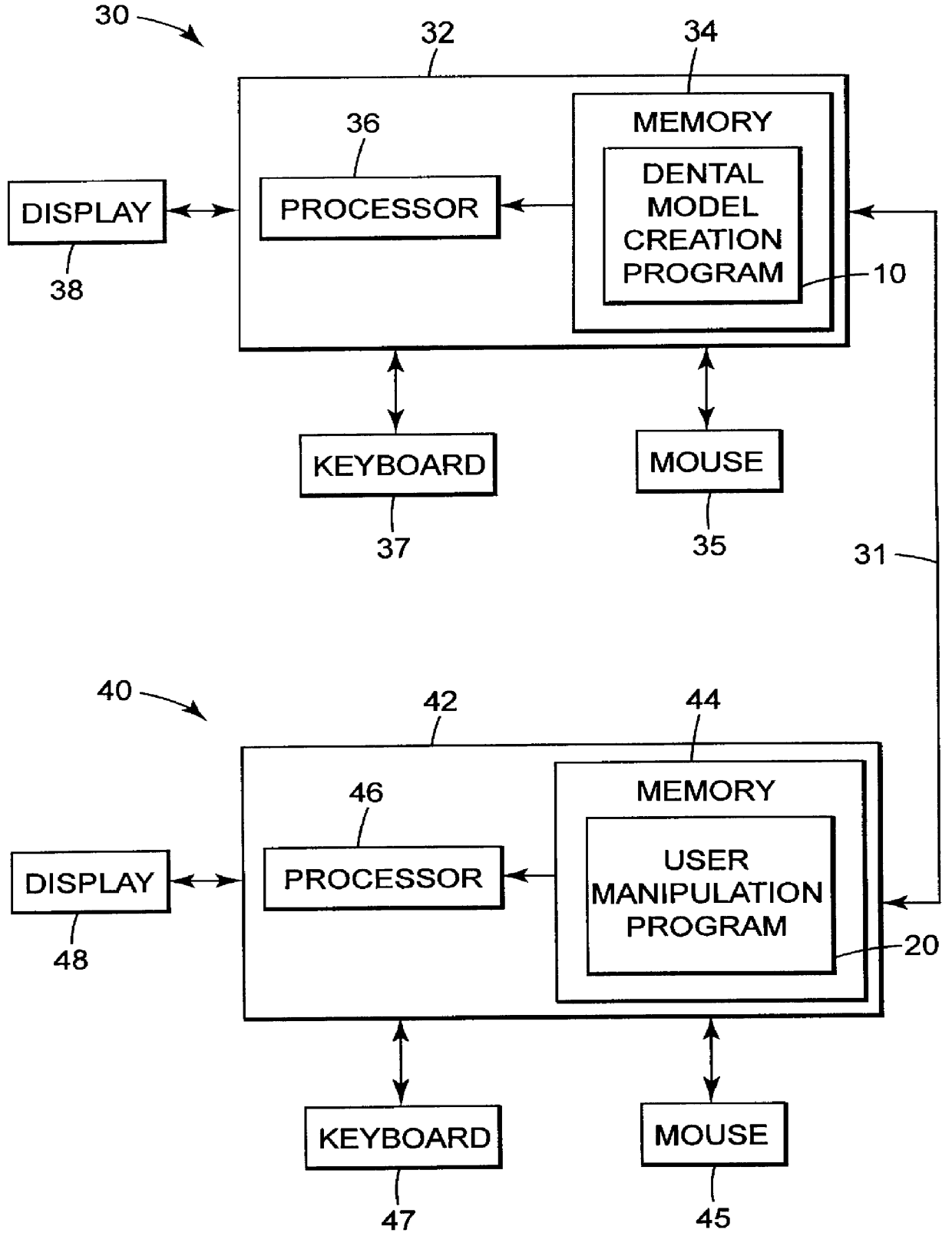
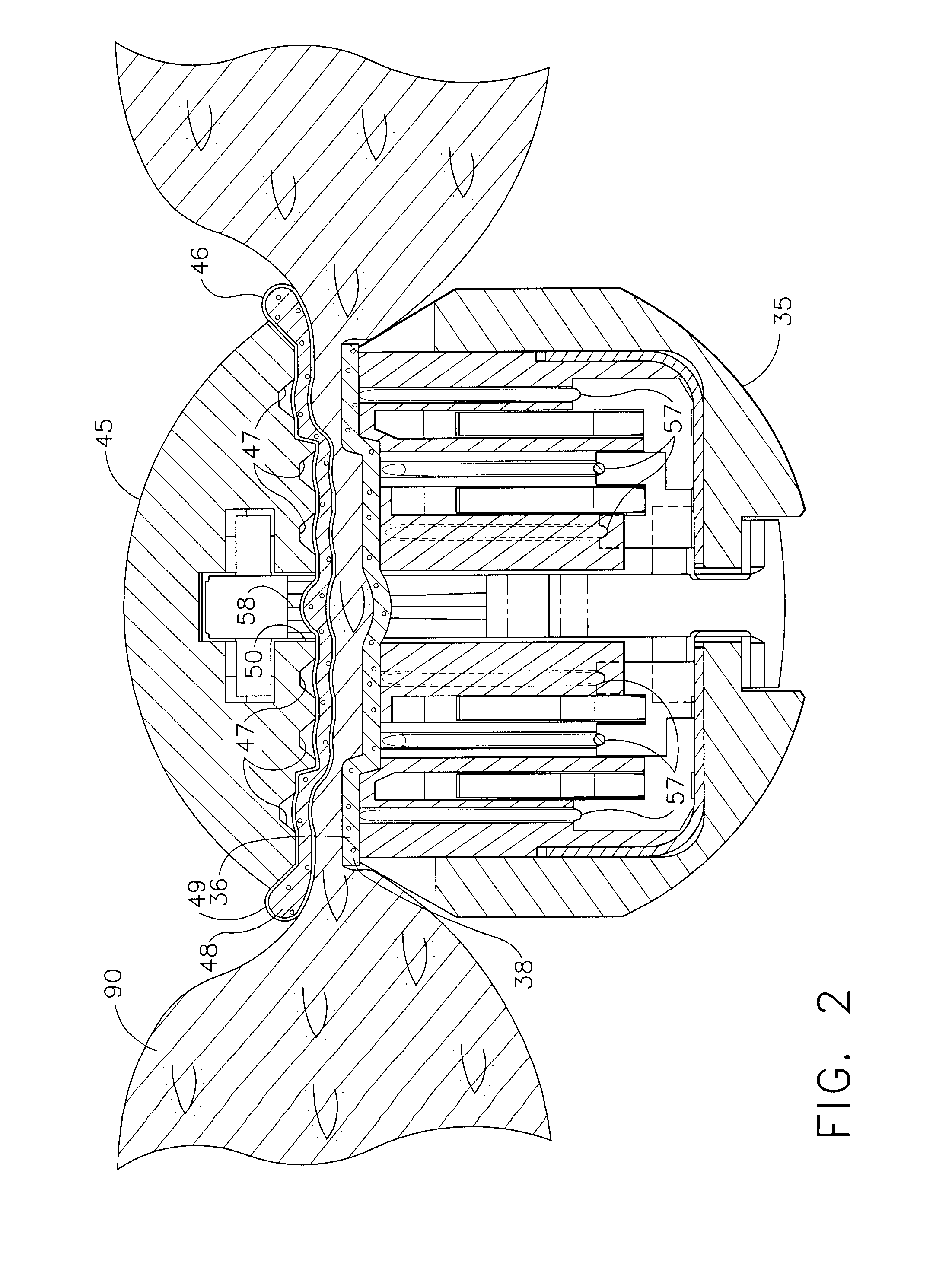
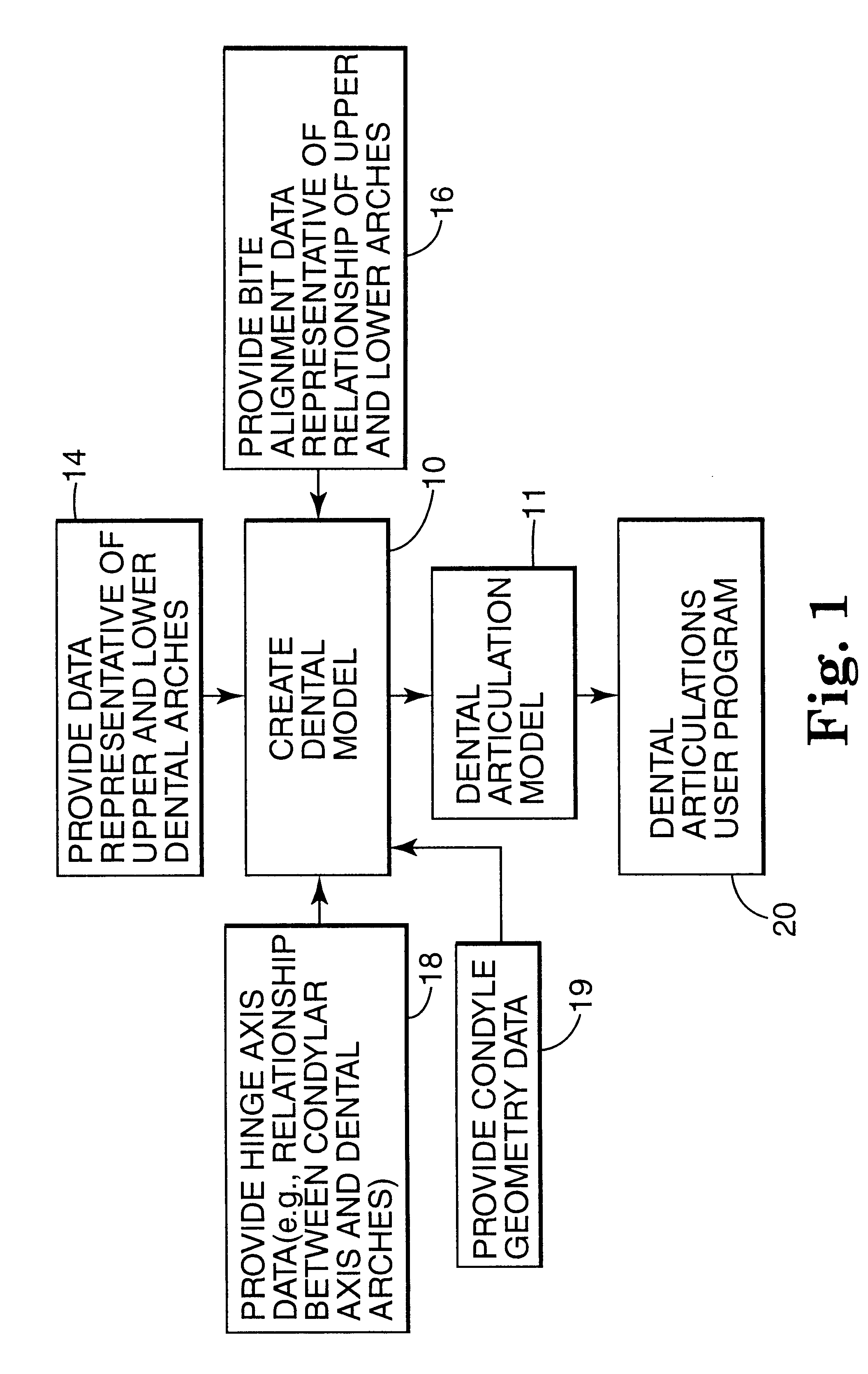
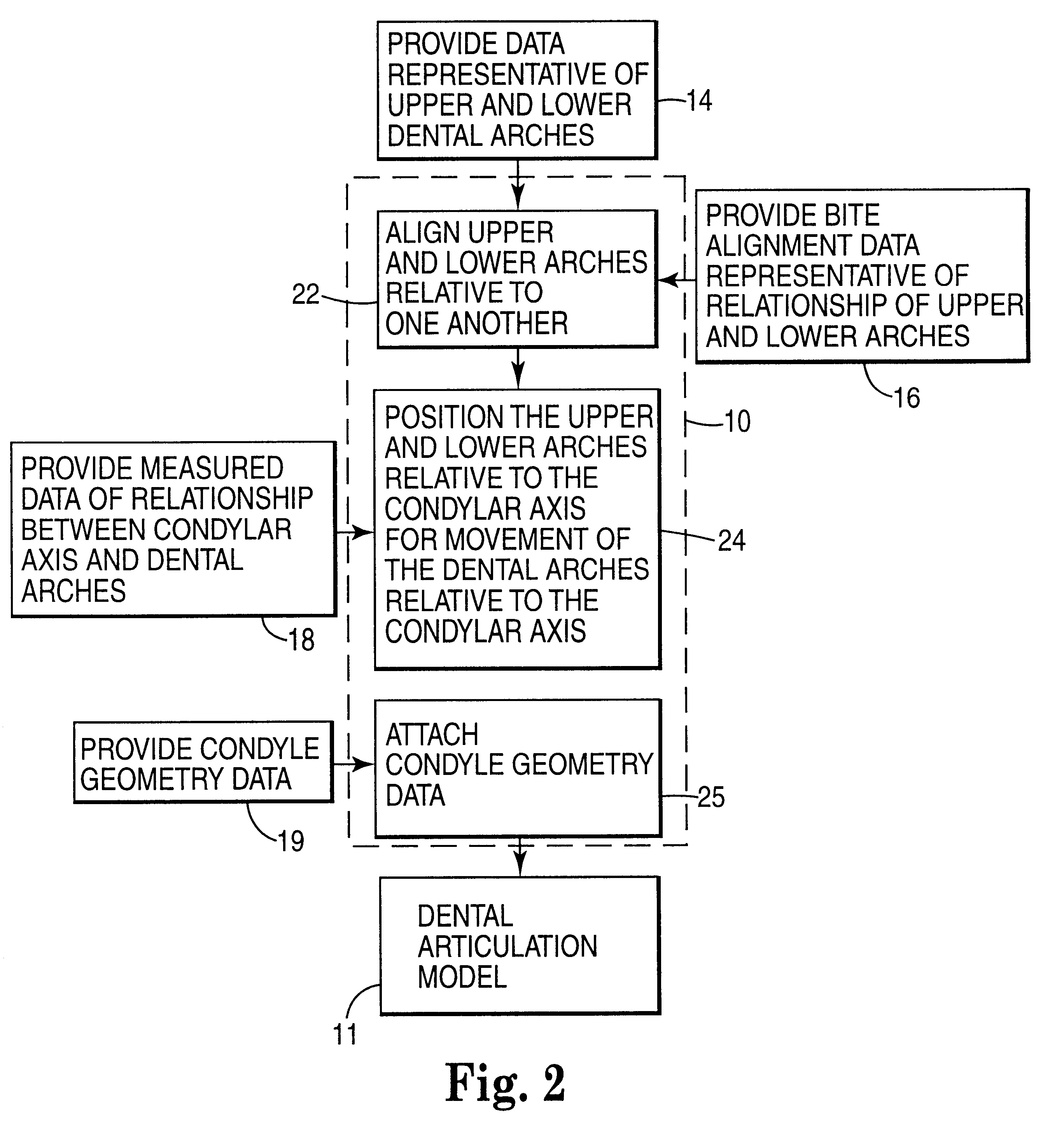
Methods for use in dental articulation
A computer implemented method of creating a dental model for use in dental articulation includes providing a first set of digital data corresponding to an upper arch image of at least a portion of an upper dental arch of a patient, providing a second set of digital data corresponding to a lower arch image of at least a portion of a lower dental arch of the patient, and providing hinge axis data representative of the spatial orientation of at least one of the upper and lower dental arches relative to a condylar axis of the patient. A reference hinge axis is created relative to the upper and lower arch images based on the hinge axis data. Further, the method may include bite alignment data for use in aligning the lower and upper arch images. Yet further, the method may include providing data associated with condyle geometry of the patient, so as to provide limitations on the movement of at least the lower arch image when the arch images are displayed. Further, a wobbling technique may be used to determine an occlusal position of the lower and upper dental arches. Various computer implemented methods of dental articulation are also described. For example, such dental articulation methods may include moving at least one of the upper and lower arch images to simulate relative movement of one of the upper and lower dental arches of the patient, may include displaying another image with the upper and lower dental arches of the dental articulation model, and / or may include playing back recorded motion of a patient's mandible using the dental articulation model.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO +1
Surgical Fastening Device With Initiator Impregnation of a Matrix or Buttress to Improve Adhesive Application
A material comprising a matrix or a buttress is impregnated with an adhesive initiator and is used with a surgical stapling device and an adhesive. The tissue and material are stapled together, and a knife in the surgical stapling device cuts the tissue and the material. The adhesive is applied across the cut and sets up or polymerizes to seals the cut when the adhesive contacts the adhesive initiator. The surgical stapling device can place the staples in a linear, arcuate, or circular array, and can anastomose luminal tissue. The methods of use can include stapling luminal tissue end to end, stapling two portions of material onto ether side of tissue, and stapling two portions of tissue onto a portion of material. Additionally, a portion of adhesive filed material can be stapled onto one side of portion of tissue and the adhesive initiator impregnated material can be stapled onto the other. Cutting the material and tissue provides a path for the adhesive across the cut, and catalyzes the adhesive from contact with the adhesive initiator.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Methods for use in dental articulation
A computer implemented method of creating a dental model for use in dental articulation includes providing a first set of digital data corresponding to an upper arch image of at least a portion of an upper dental arch of a patient, providing a second set of digital data corresponding to a lower arch image of at least a portion of a lower dental arch of the patient, and providing hinge axis data representative of the spatial orientation of at least one of the upper and lower dental arches relative to a condylar axis of the patient. A reference hinge axis is created relative to the upper and lower arch images based on the hinge axis data. Further, the method may include bite alignment data for use in aligning the lower and upper arch images. Yet further, the method may include providing data associated with condyle geometry of the patient, so as to provide limitations on the movement of at least the lower arch image when the arch images are displayed. Further, a wobbling technique may be used to determine an occlusal position of the lower and upper dental arches. Various computer implemented methods of dental articulation are also described. For example, such dental articulation methods may include moving at least one of the upper and lower arch images to simulate relative movement of one of the upper and lower dental arches of the patient, may include displaying another image with the upper and lower dental arches of the dental articulation model, and / or may include playing back recorded motion of a patient's mandible using the dental articulation model.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
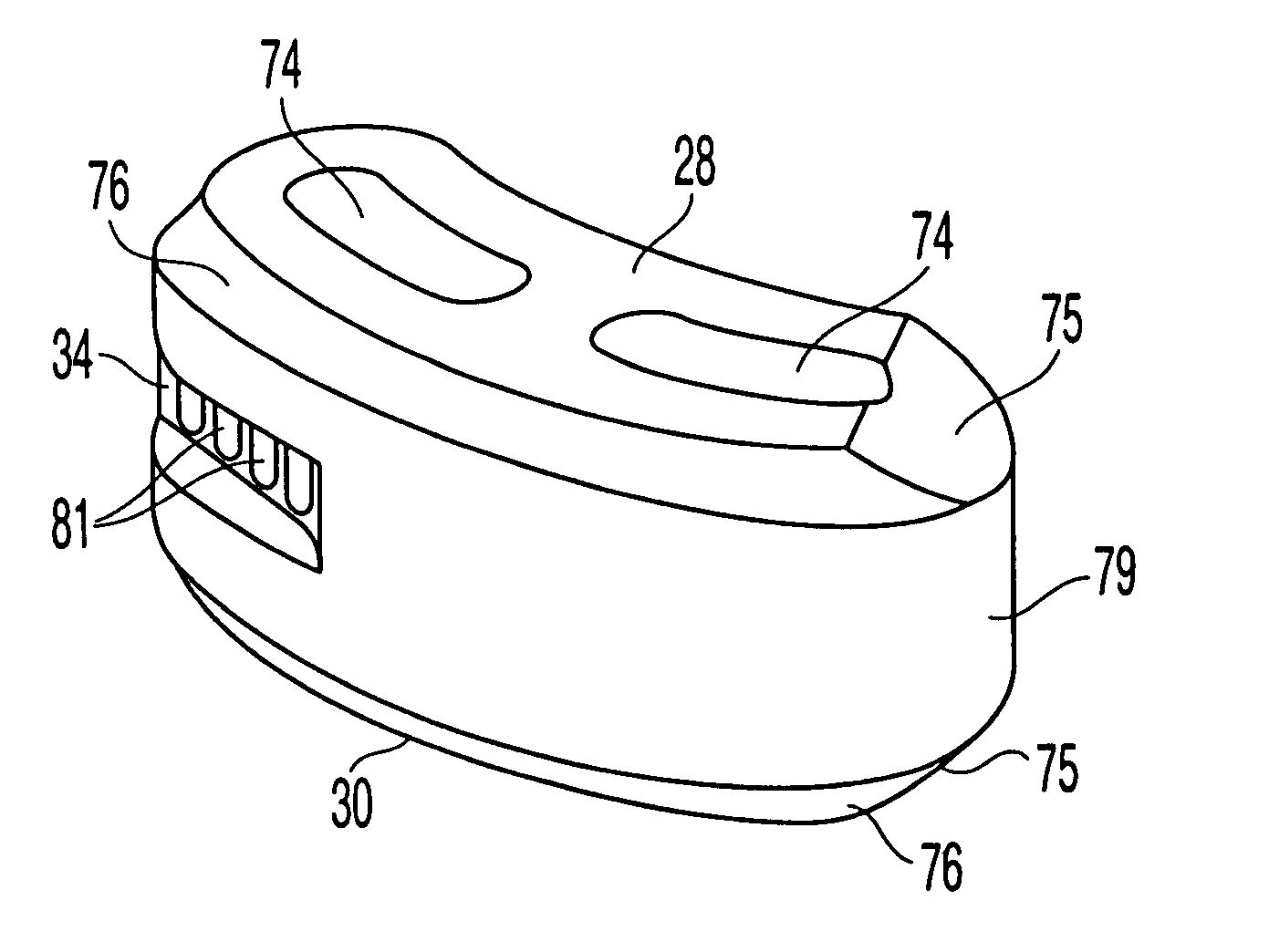
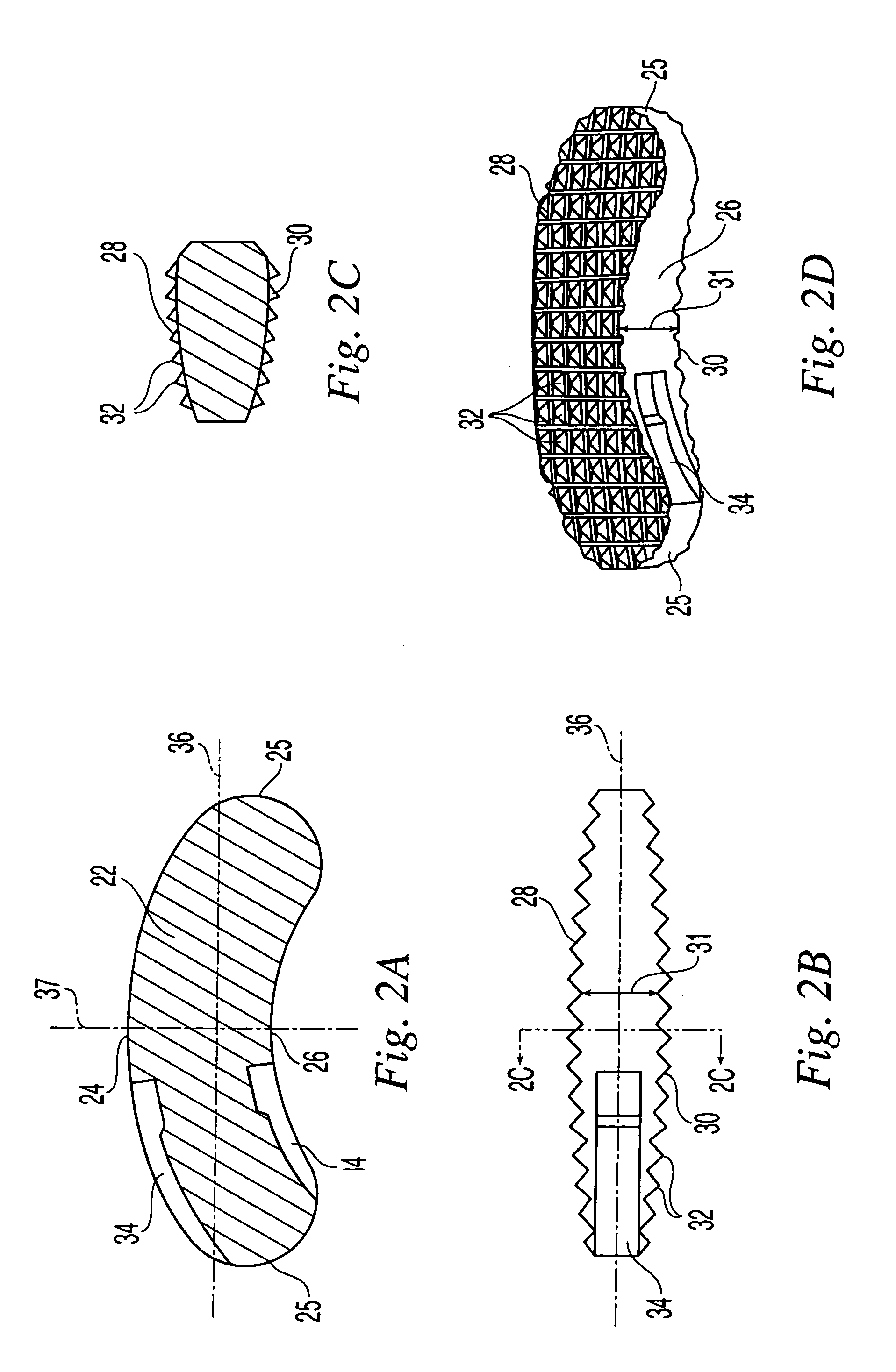
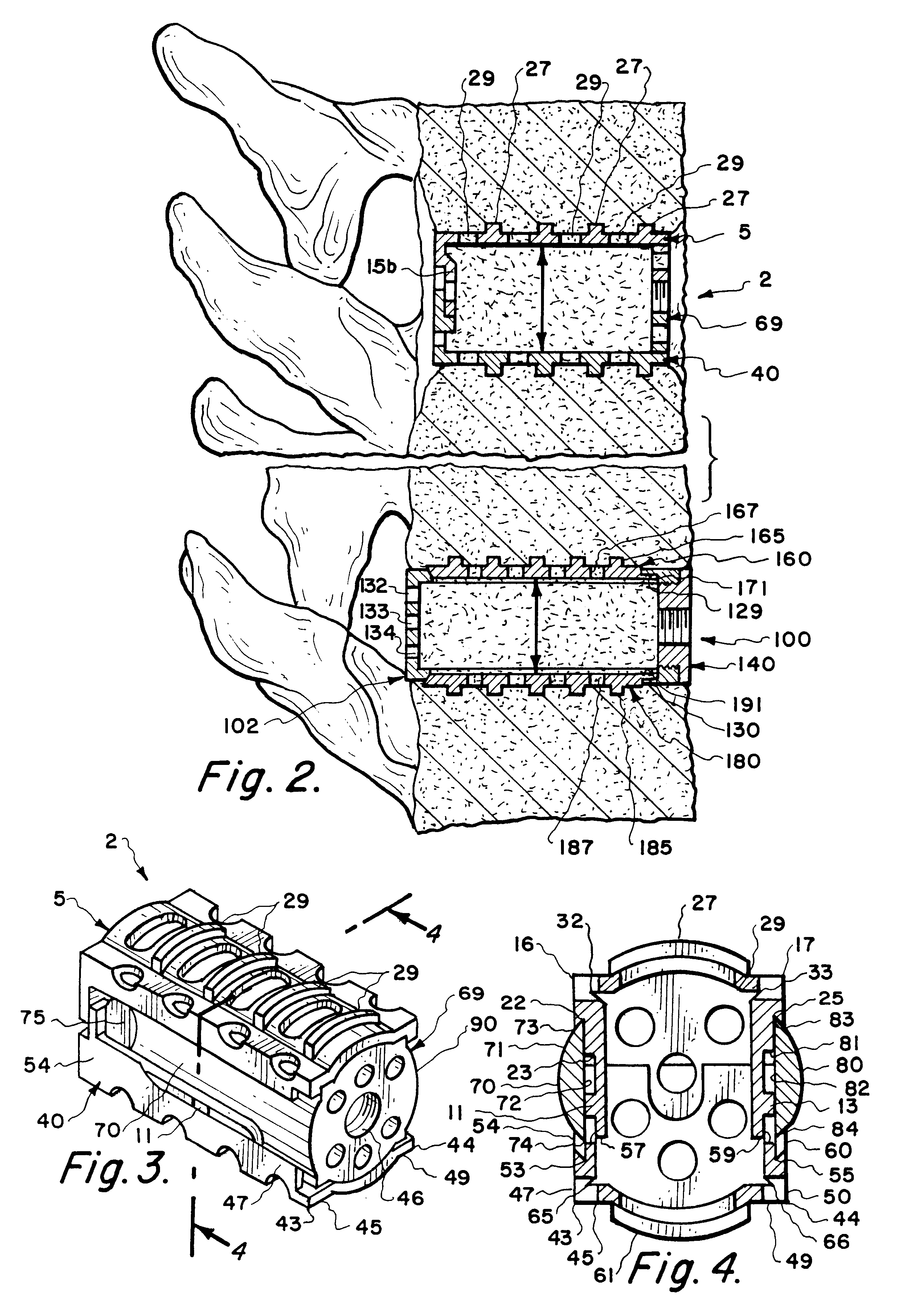
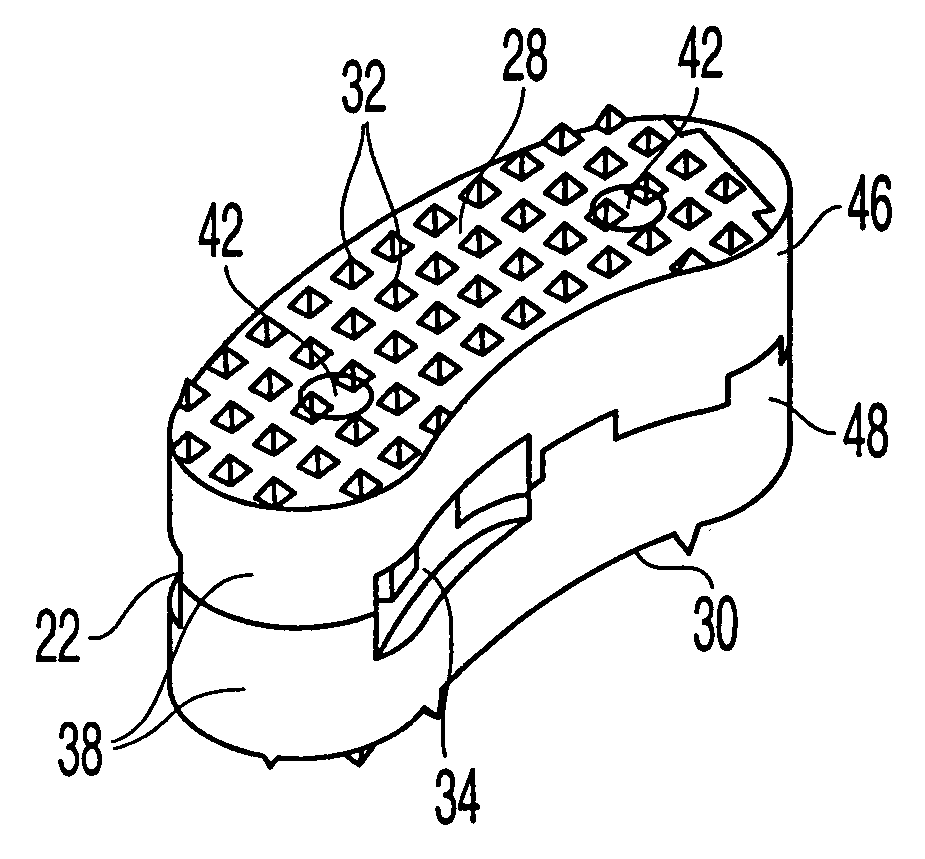
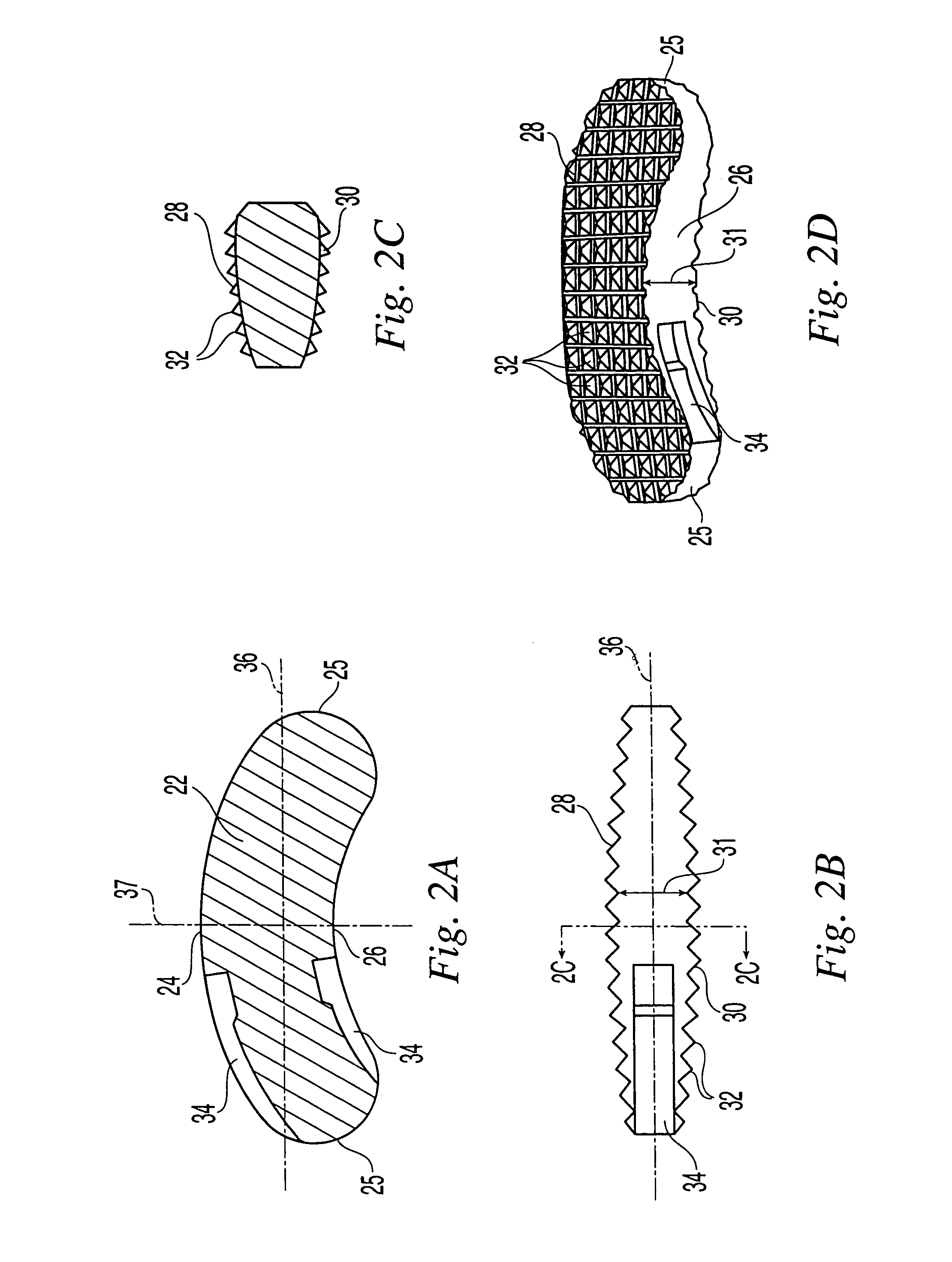
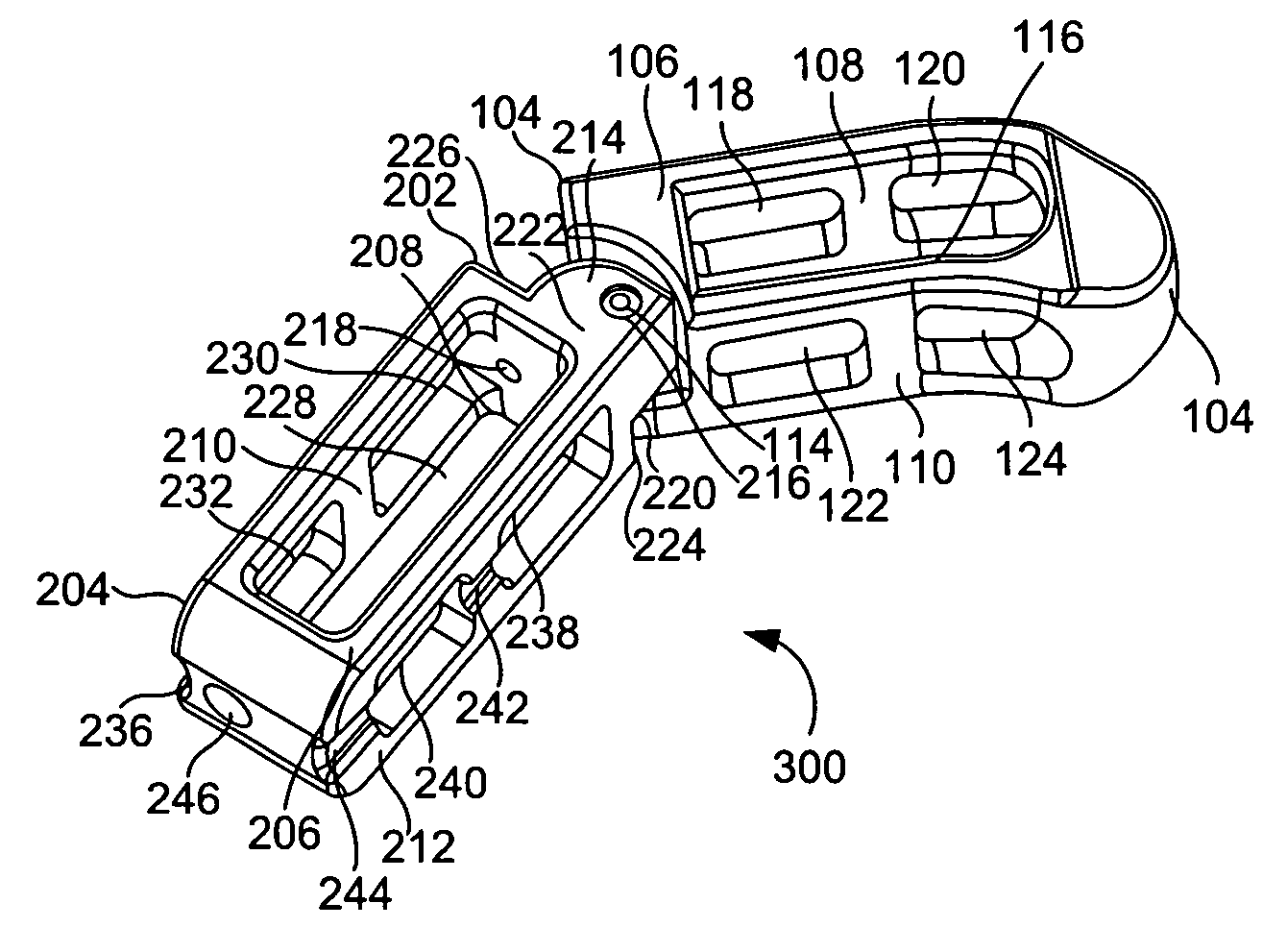
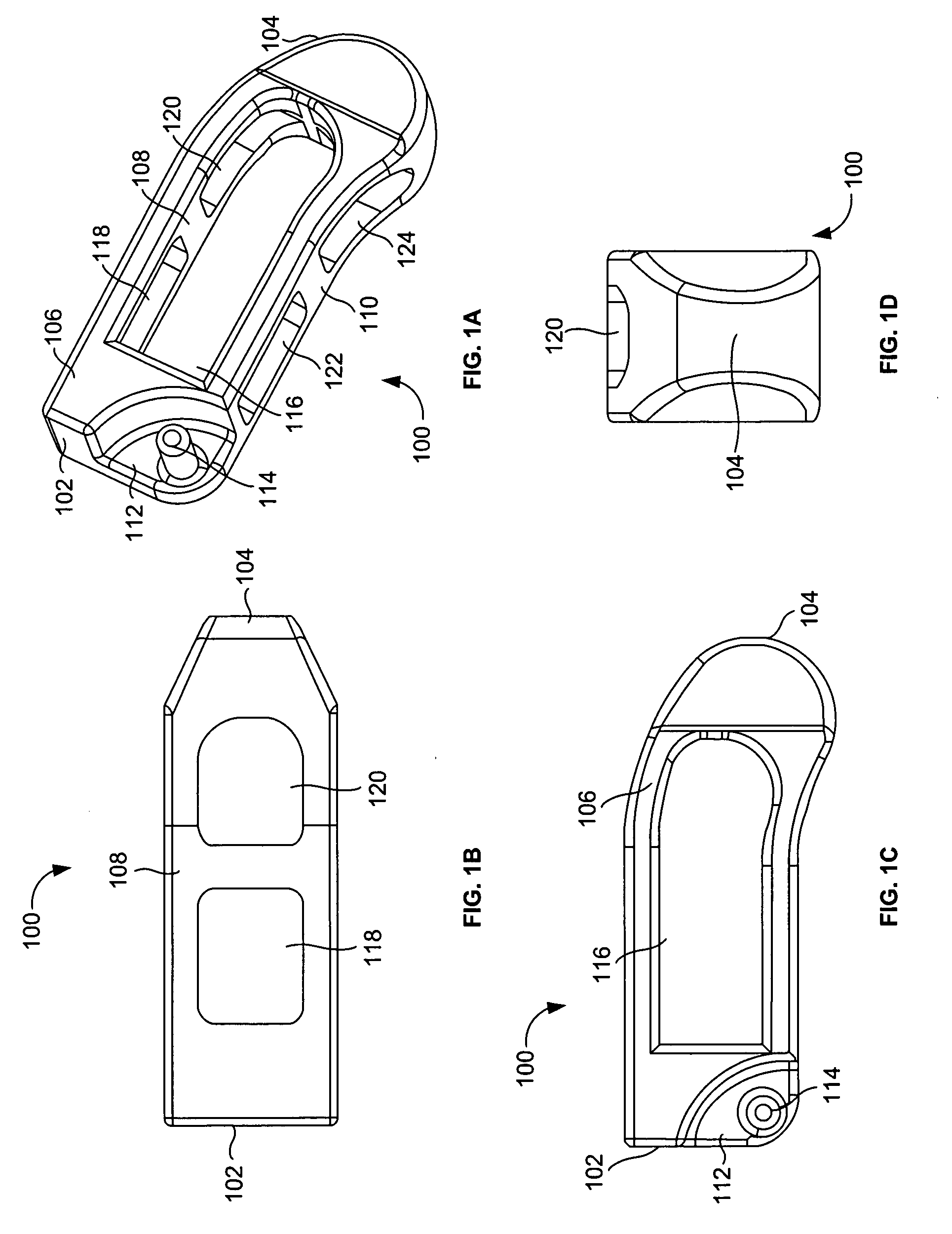
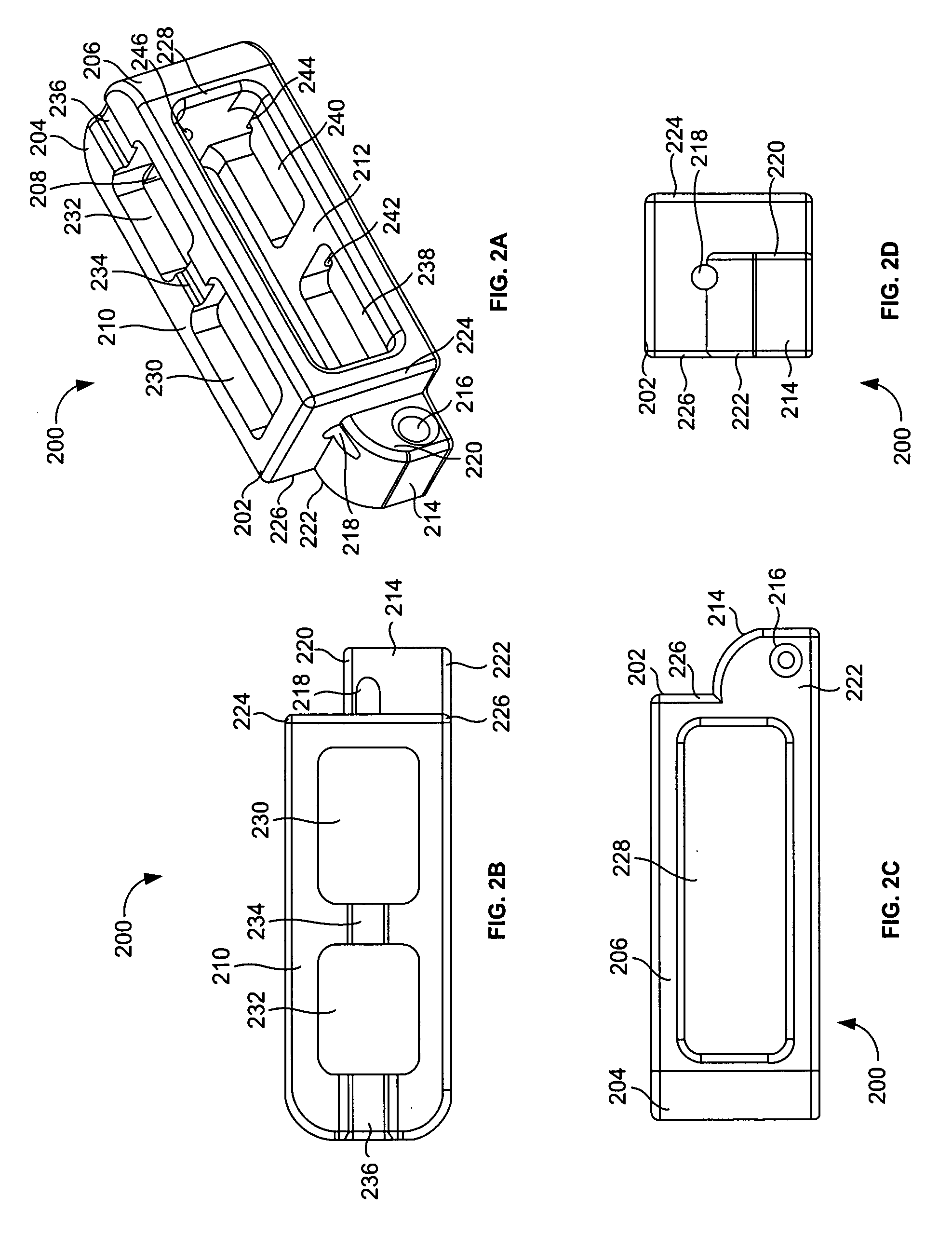
Intervertebral implant for transforaminal posterior lumbar interbody fusion procedure
InactiveUS6974480B2Easy to insertPrevent slippingBone implantSurgeryTransforaminal approachSpinal column
An intervertebral implant for fusing vertebrae is disclosed. The implant has a body with curved, substantially parallel posterior and anterior faces separated by two narrow implant ends, superior and inferior faces having a plurality of undulating surfaces for contacting upper and lower vertebral endplates, and at least one depression in the anterior or posterior face for engagement by an insertion tool, at least two vertical through-channels extending through the implant from the superior face to the inferior face, a chamfer on the superior and inferior surfaces at one of the narrow implant ends, and a beveled edge along a perimeter of the superior and inferior faces. The arcuate implant configuration and the chamfers on the superior and inferior faces at the narrow end facilitate insertion of the implant from a transforaminal approach into a symmetric position about the midline of the spine so that a single implant provides balanced support to the spinal column. The implant may include radiopaque markers extending through the thickness of the implant to indicate the location and size of the implant. The implant may be formed of a plurality of interconnecting bodies assembled to form a single unit. An implantation kit and method are also disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC +1
Bone fastener and instrument for insertion thereof
InactiveUS6258091B1Quickly and efficientlyEasy to disassembleSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisArcuate shapeScrew thread
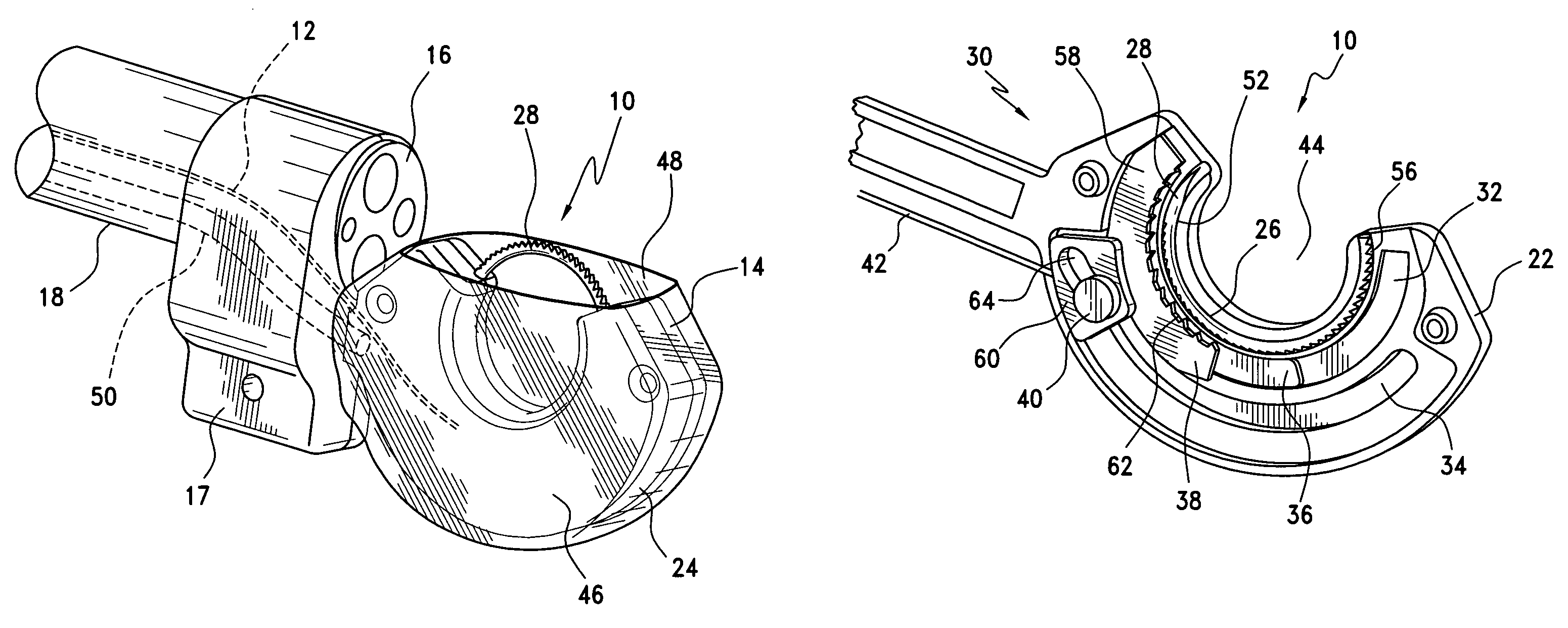
A bone member fastener for closing a craniotomy includes a cap and a base interconnected by a narrow cylindrical collar. The cap has an externally threaded stud that screws into an internally threaded bore of the collar, thereby allowing the cap and base to be brought into clamping engagement against the internal and external faces of a bone plate and surrounding bone. In a particularly disclosed embodiment, the base of the fastener is placed below a craniotomy hole with the collar projecting into the hole, and the stud of the cap is screwed into the bore of the base from above the hole to clamp a bone flap against the surrounding cranium. This device provides a method of quickly and securely replacing a bone cover into a craniotomy. The distance between the cap and base can be selected by how far the threaded stud of the cap is advanced into the internally threaded collar. The fastener is therefore adaptable for use in several regions of the skull having various thicknesses. An insertion tool with a long handle permits safe and convenient placement of the base between the brain and the internal face of the bone plate. Some disclosed embodiments of the fastener have a cap and base that conform to the curved surface of the skull, for example by having an arcuate shape or flexible members that conform to the curvature of the bone plate and surrounding cranial bone as the fastener is tightened.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET CMF & THORACIC
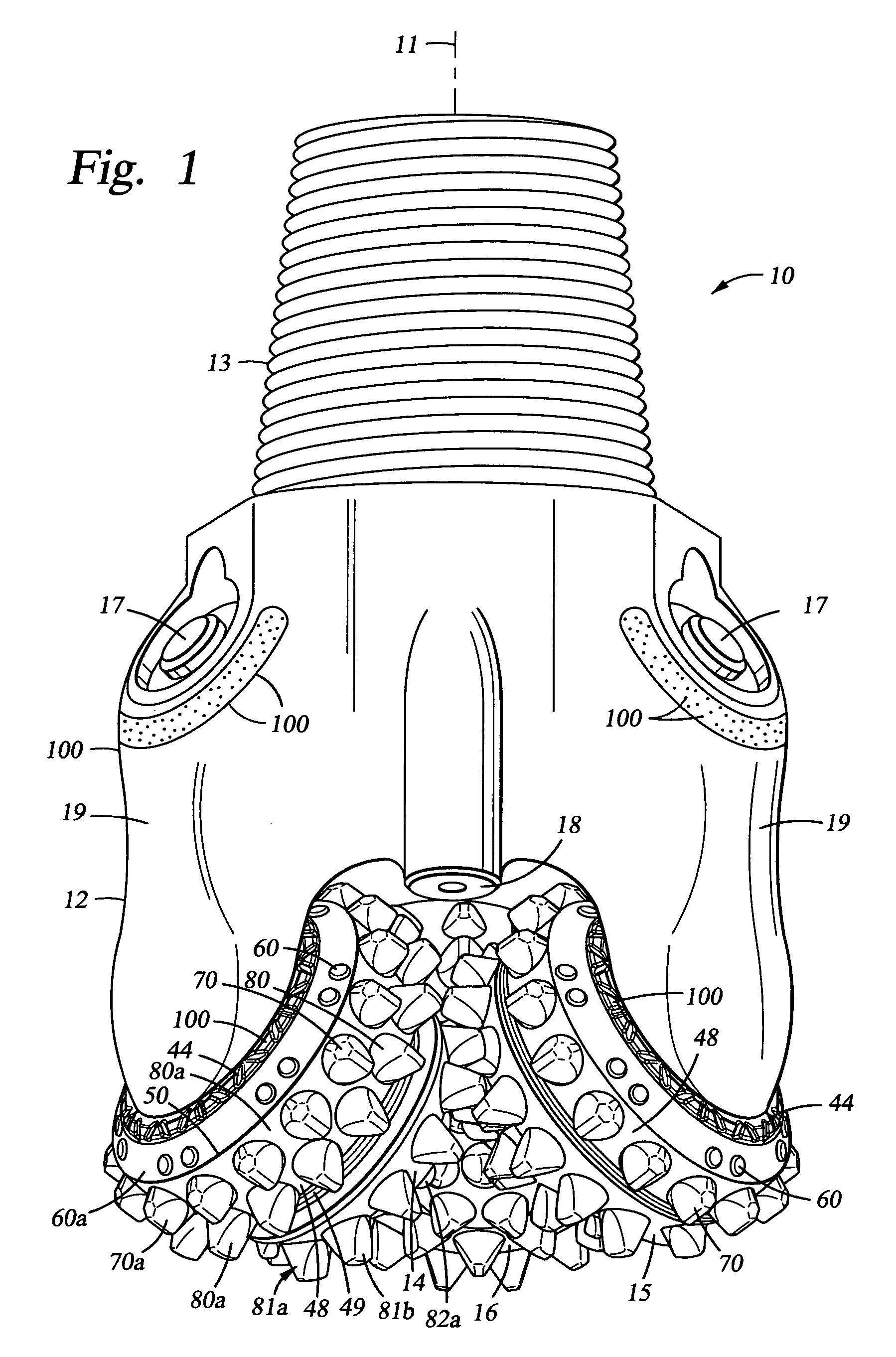
Drill bit arcuate-shaped inserts with cutting edges and method of manufacture
InactiveUS7331410B2Extended bit lifeImprove abilitiesDrill bitsMetal-working drilling toolsStress relievingEngineering
Disclosed are a variety of arcuate-shaped inserts for drill bits, and in particular, for placement in rolling cone cutters of drill bits. The arcuate inserts include 360° or ring-shaped inserts, as well as inserts of smaller arcuate length. The arcuate inserts are suitable for use in all surfaces of the rolling cone cutter, and in other locations in drill bits, and may have specialized cutting surfaces and material enhancements to enhance their cutting duty performance. Certain arcuate inserts may include stress relieving discontinuities such that, upon assembly into the cone or during drilling, the arcuate inserts may fragment in a controlled and predicted manner into shorter arcuate lengths.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
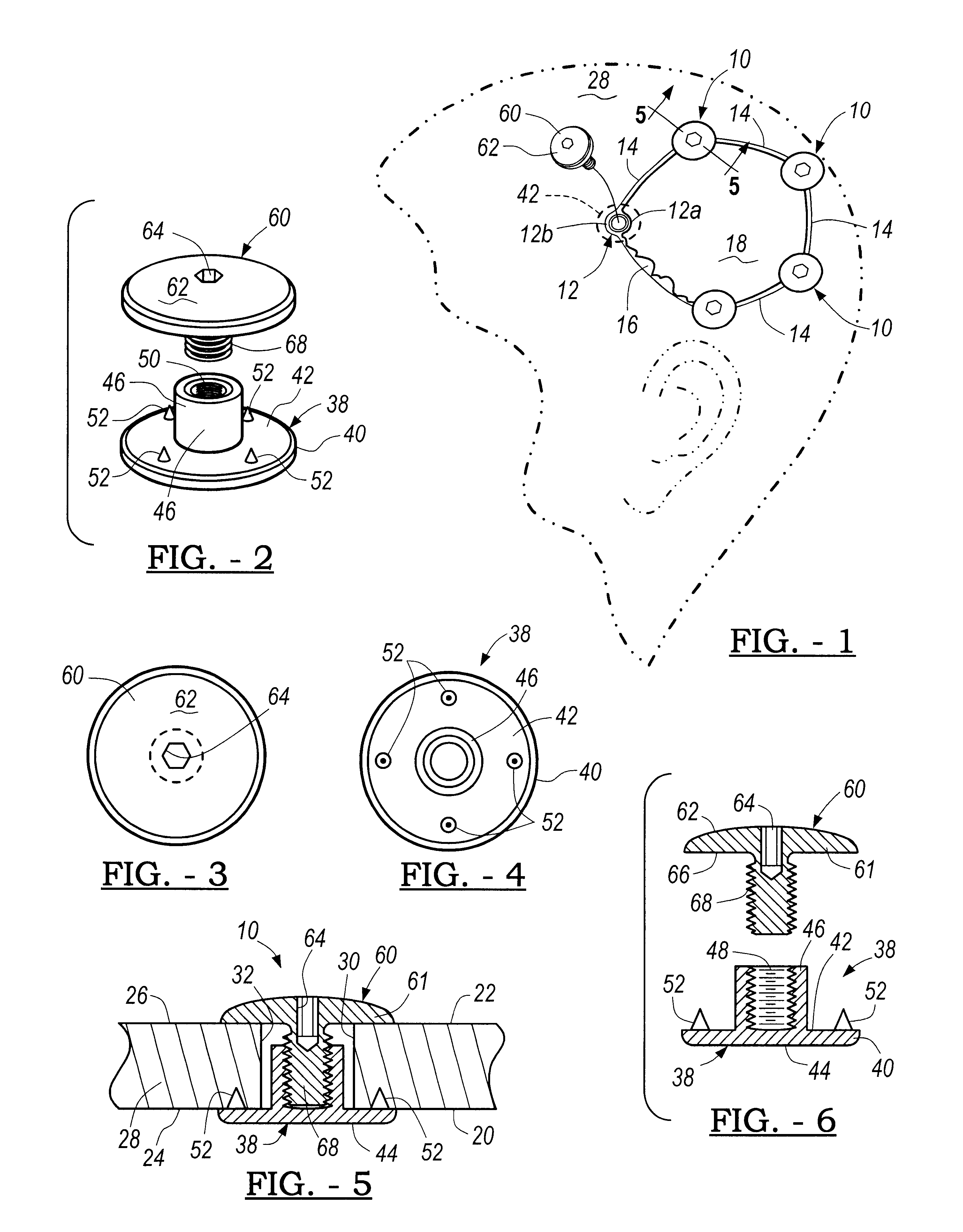
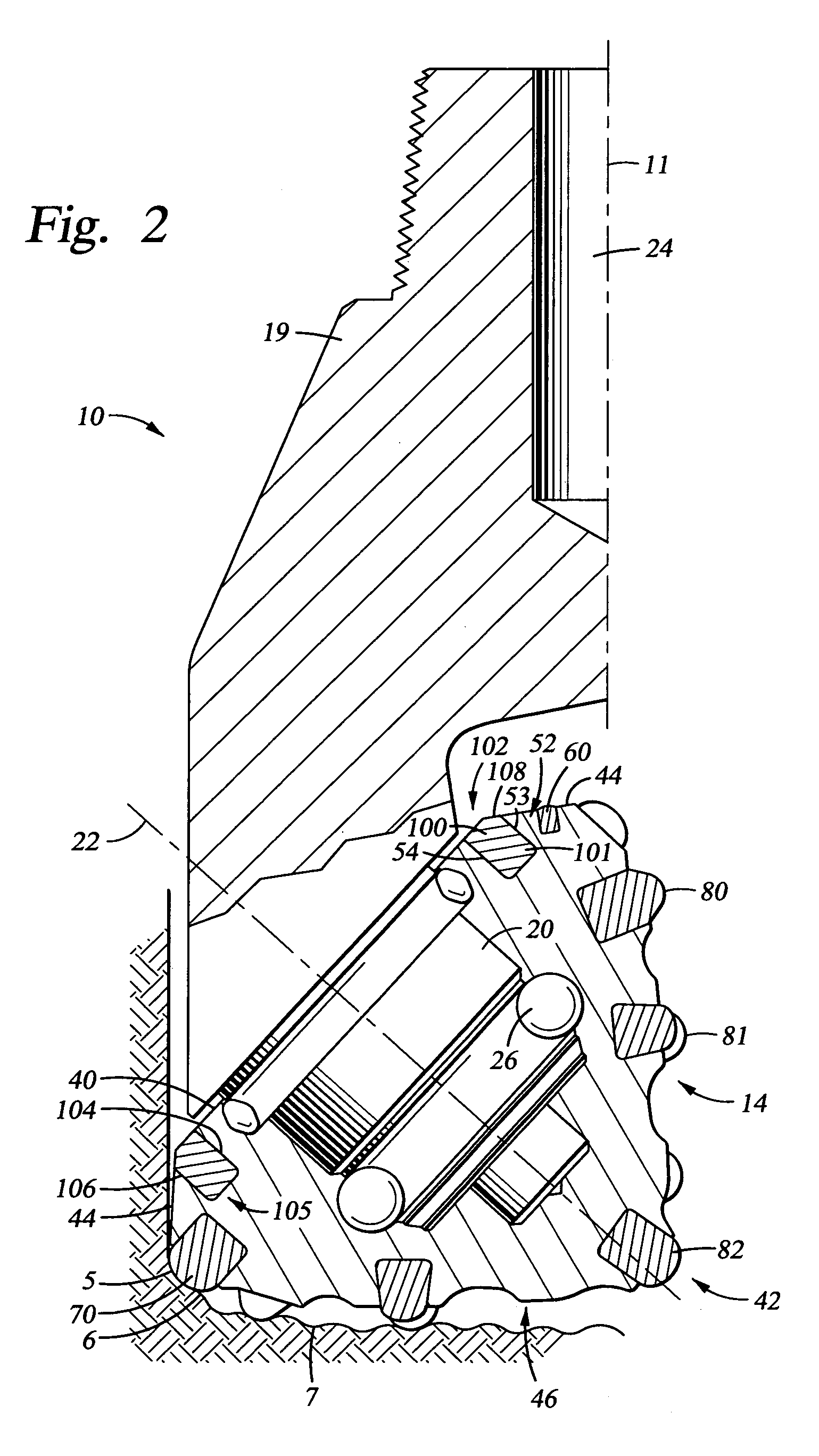
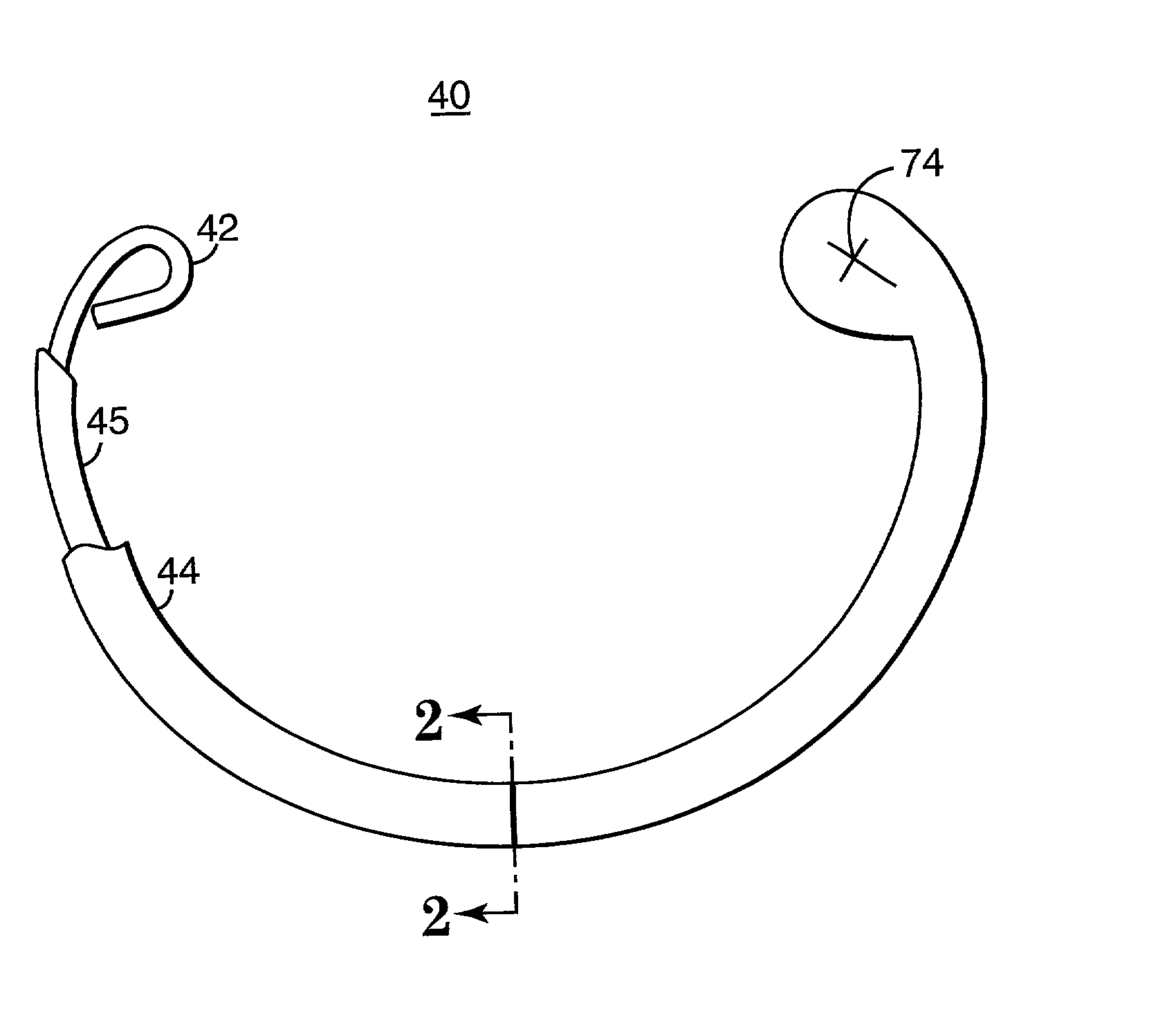
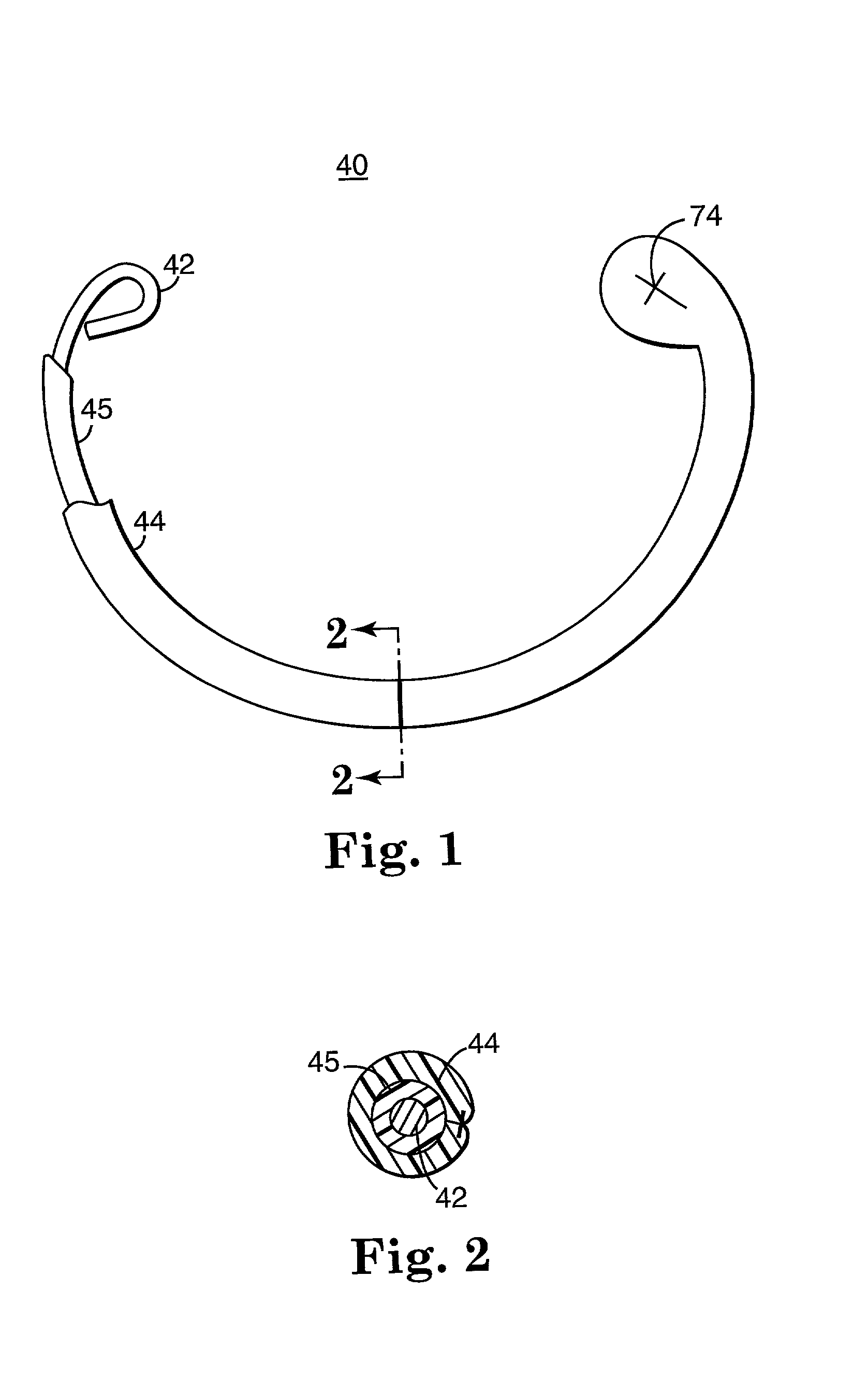
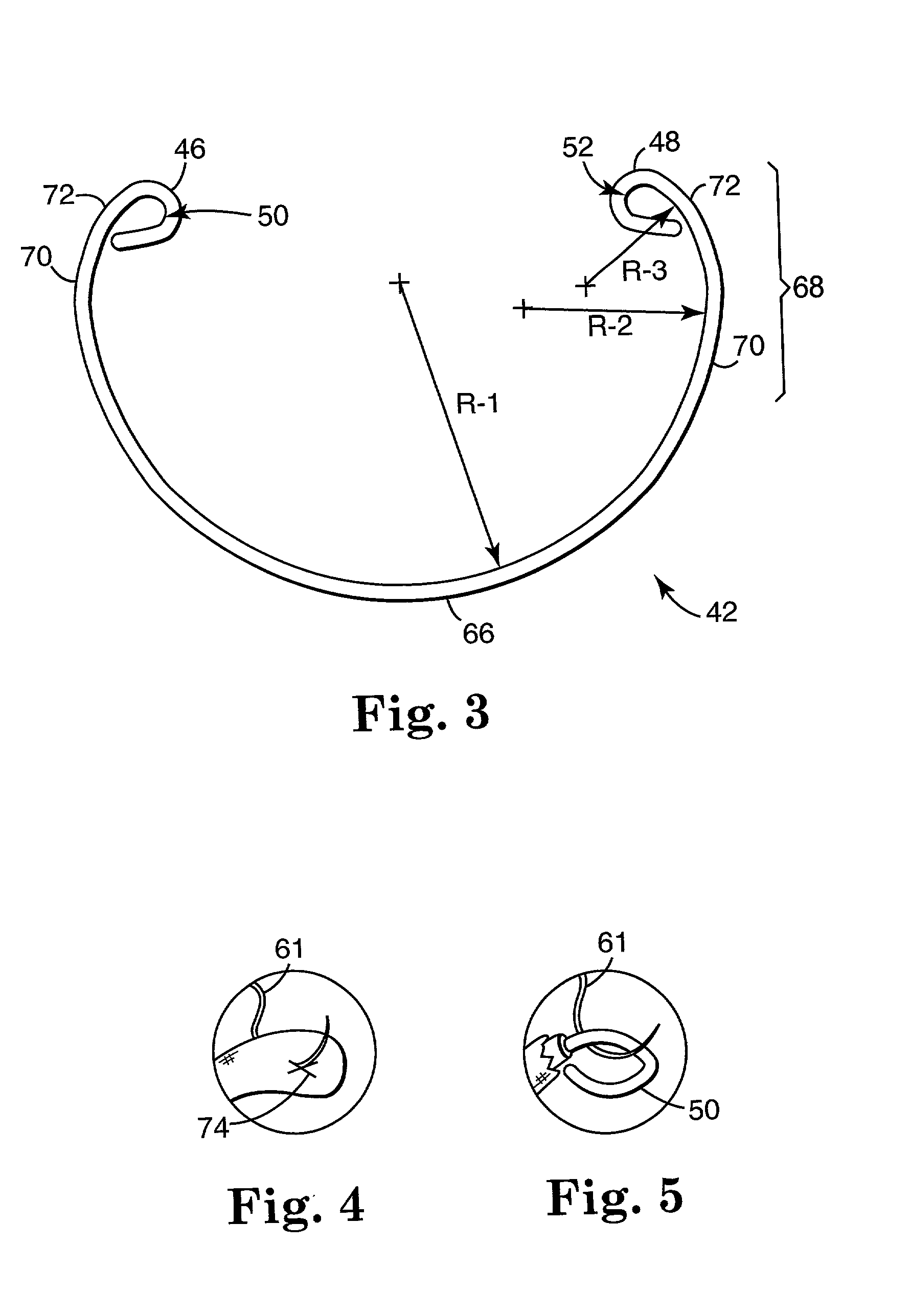
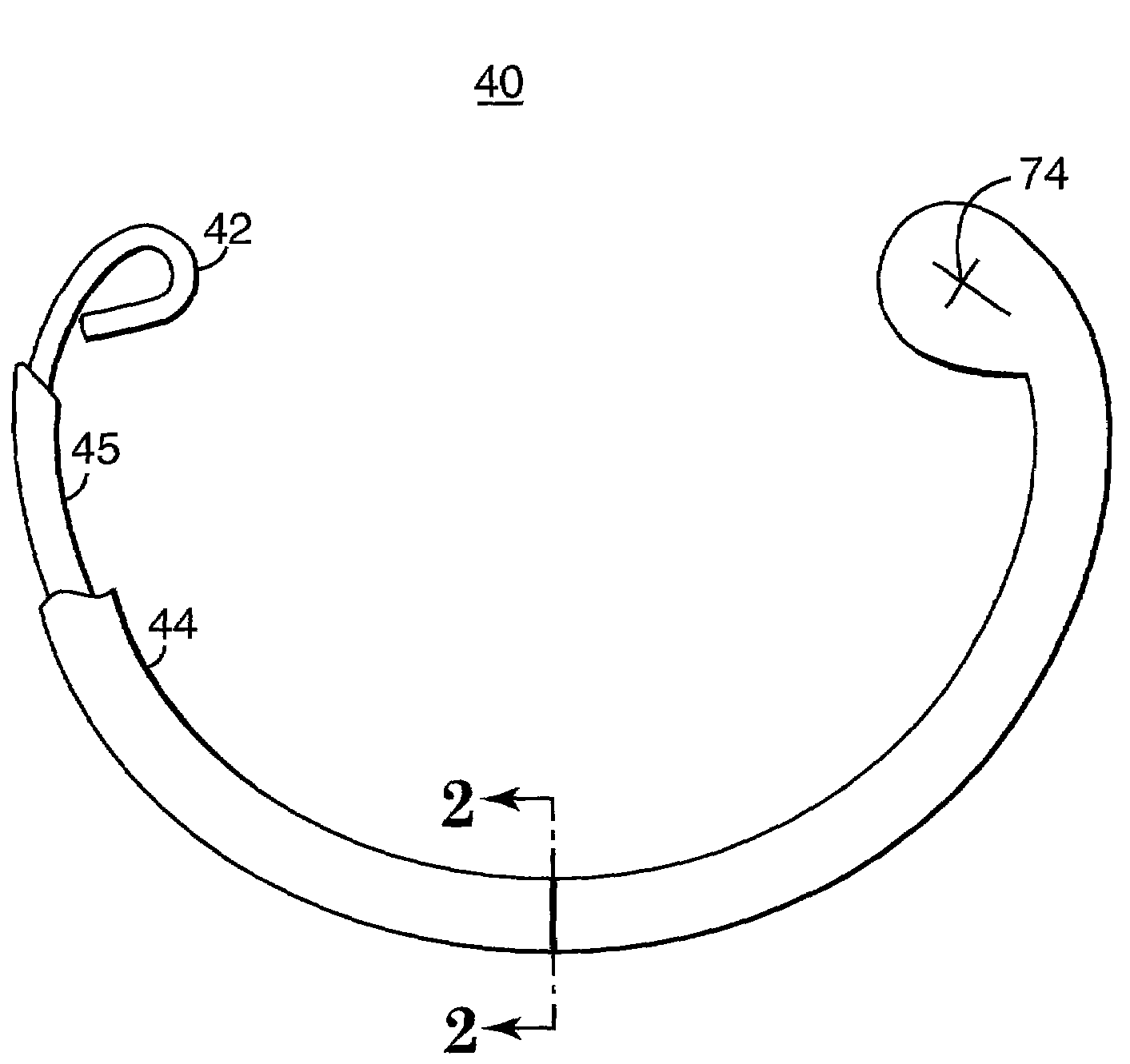
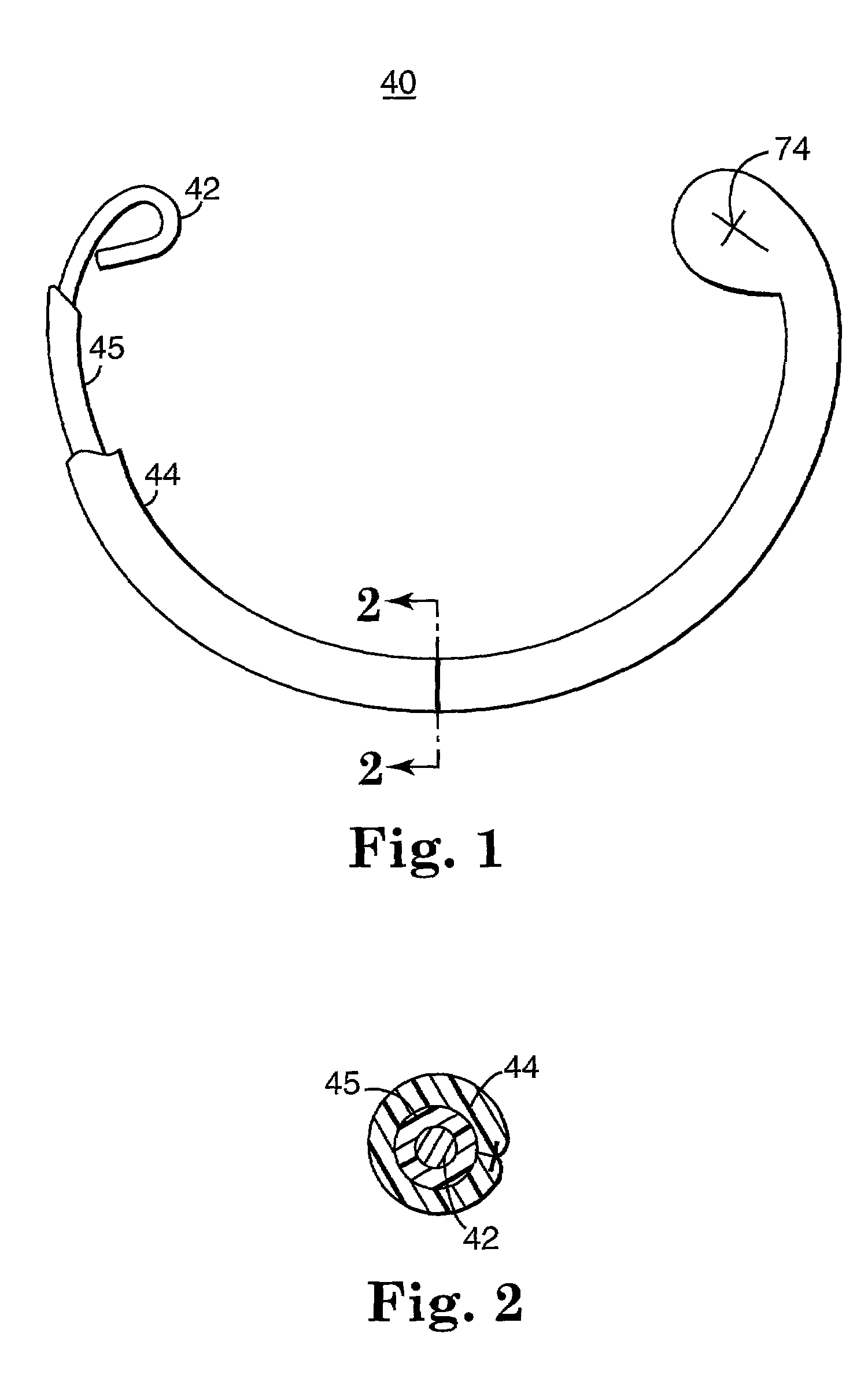
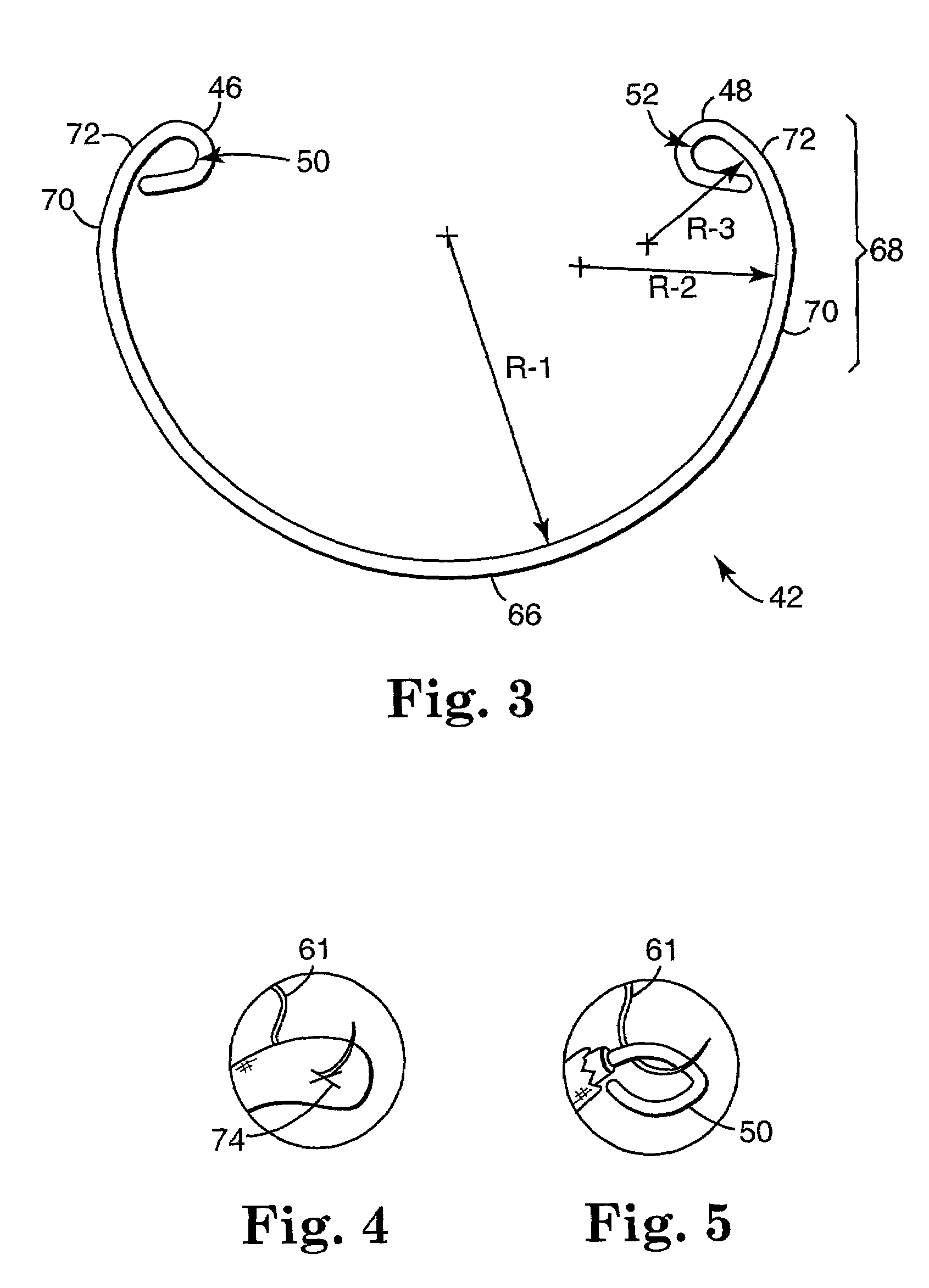
Annuloplasty band and method
InactiveUS20020129820A1Easy to implantEasy accessSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsEngineeringMitral valve operation
An annuloplasty band comprising a sheath, and a generally arcuate stiffening element disposed within the sheath. The stiffening element extends from a first end to a second end, and preferably includes eyelets at its first and second ends adapted to receive sutures to secure the annuloplasty band to a valve annulus. The annuloplasty band preferably has a low profile (e.g., a thickness less than 3 mm). In embodiments intended for mitral valve repair, the eyelets are particularly adapted to receive sutures to secure the annuloplasty band to the antero-lateral trigone and postero-medial trigone. A holder and sizer device useful with the annuloplasty band are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Bipolar electrosurgical instrument for sealing vessels
InactiveUS7179258B2Shorten the timeExpand accessSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsBipolar electrosurgeryVascular tissue
A bipolar electrosurgical instrument has opposable seal surfaces on its jaws for grasping and sealing vessels and vascular tissue. Inner and outer instrument members allow arcuate motion of the seal surfaces. An open lockbox provides a pivot with lateral support to maintain alignment of the lateral surfaces. Ratchets on the instrument members hold a constant closure force on the tissue during the seal process. A shank portion on each member is tuned to provide an appropriate spring force to hold the seal surfaces together. During surgery, the instrument can be used to grasp and clamp vascular tissue and apply bipolar electrosurgical current through the clamped tissue. In one embodiment, the seal surfaces are partially insulated to prevent a short circuit when the instrument jaws are closed together. In another embodiment, the seal surfaces are removably mounted on the jaws.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
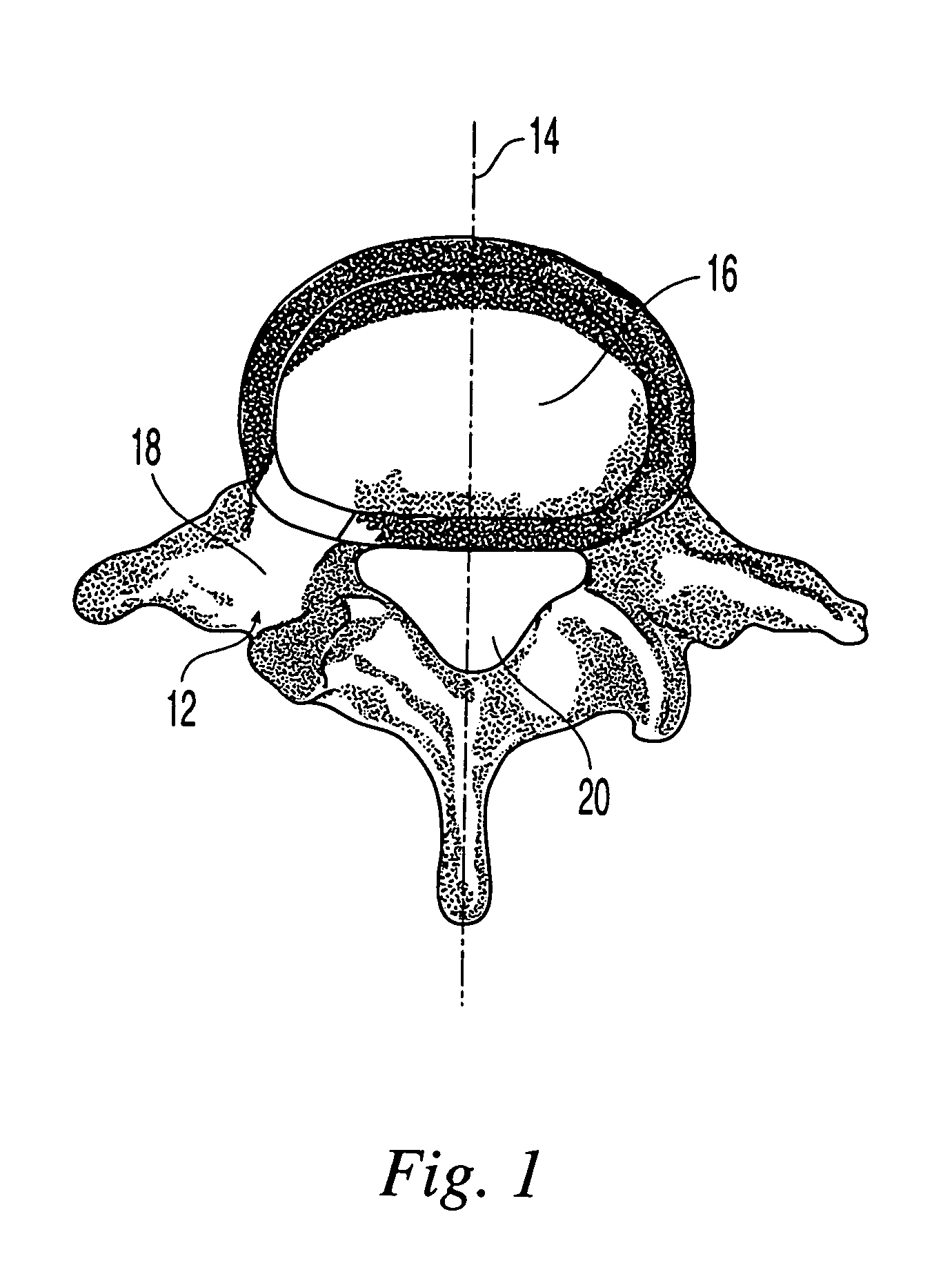
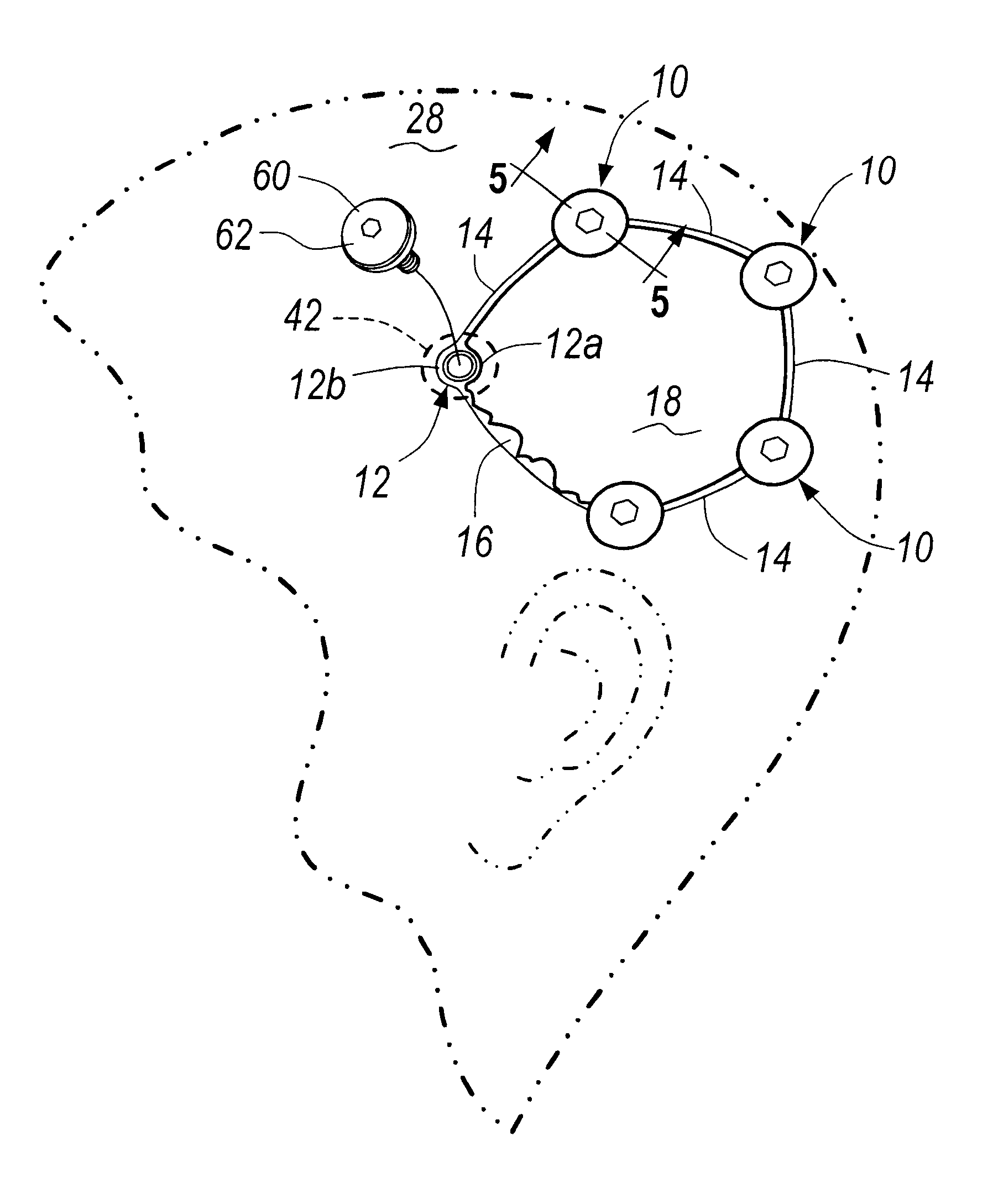
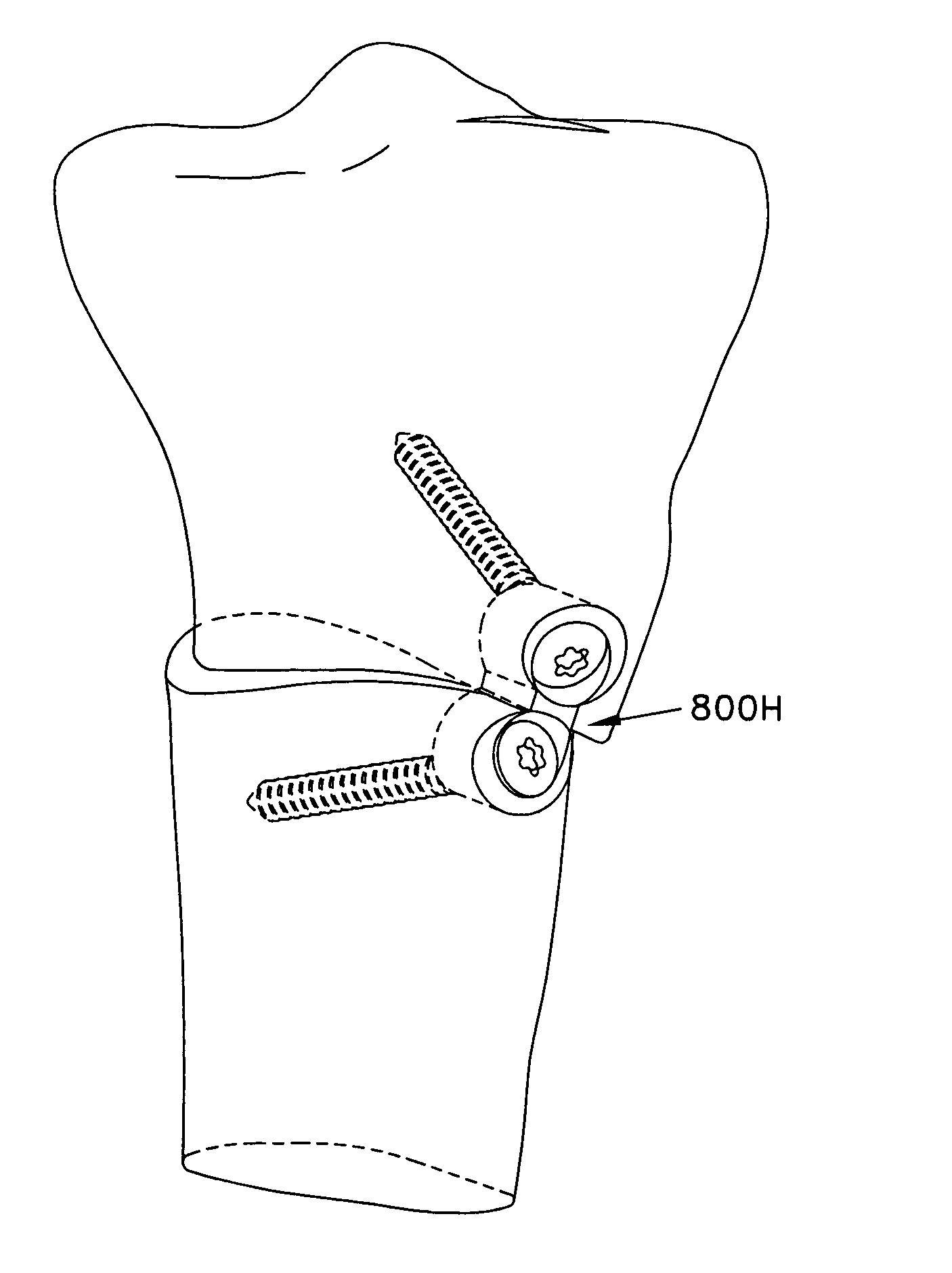
Systems and methods for spinal fixation
InactiveUS6923811B1Maintain alignmentProvide protectionInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsScrew systemIntervertebral space
Featured are a method and apparatus for fixing adjacent vertebrate of a spine that avoids the need and associated problems with prior cage or straight rod and screw systems. Methods and apparatus of the invention utilize a new implant member, which preferably is arcuate. Preferred methods of the invention for stabilizing adjacent vertebrae of the spine, include steps of providing a positioning apparatus including two guide sleeves, each guide sleeve having a long axis and locating the two guide sleeves with respect to the adjacent vertebrae such that a vertex formed by the long axis of each guide sleeve is located in the intervertebral space for the adjacent vertebrae. The method further includes forming an aperture in each of the adjacent vertebrae using the guide sleeves and inserting an implant into the apertures formed in each of the adjacent vertebrae so that the implant extends between the adjacent vertebrae and through the intervertebral space. In an alternative method a cutting fixture including a pivot arm is secured to the adjacent vertebrae and a cutting device is secured to the pivot arm. The pivot arm and cutting device are configured and arranged so that rotation of the pivot arm about a particularly located pivot point allows the cutting device to form the aperture in each of the adjacent vertebrae. Another alternative method for fixing adjacent vertebrate of a spine includes the step of forming a common channel in and between the adjacent vertebrae and inserting a biscuit implant in the common so as to bridge between the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:K2M
Expandable spinal implants
A cylinder-shaped expandable spinal implant is disclosed. The implant is a hollow housing having a cylinder-shaped wall, with a circular sealed distal end, and an opposite proximal circular open end. The open end of the housing has internal threads for securing a cap to it. A removable cap is threaded on the open end of the housing. The housing has two opposite large rectangular openings located longitudinally in the wall of the housing for receiving two arcuate sections. Each arcuate section is positioned in the rectangular opening in the wall of the implant. A locking means for locking the arcuate section in the rectangular opening in the wall is provided. A plurality of small ports are drilled in the wall for allowing bone growth after implantation of said implant in a patient. The arcuate sections have transverse ribs for locking the implant in position are implantation. Openings between the ribs are provided for allowing bone growth.
Owner:KOROS TIBOR
Bipolar electrosurgical instrument for sealing vessels
InactiveUS7241296B2Fast fusionShorten the timeSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsPower flowBipolar electrosurgery
A bipolar electrosurgical instrument has opposable seal surfaces on its jaws for grasping and sealing vessels and vascular tissue. Inner and outer instrument members allow arcuate motion of the seal surfaces. An open lockbox provides a pivot with lateral support to maintain alignment of the lateral surfaces. Ratchets on the instrument members hold a constant closure force on the tissue during the seal process. A shank portion on each member is tuned to provide an appropriate spring force to hold the seal surfaces together. During surgery, the instrument can be used to grasp and clamp vascular tissue and apply bipolar electrosurgical current through the clamped tissue. In one embodiment, the seal surfaces are partially insulated to prevent a short circuit when the instrument jaws are closed together. In another embodiment, the seal surfaces are removably mounted on the jaws.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Flooring products and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20060032175A1Improve moisture resistanceStrutsSynthetic resin layered productsThick plateNatural fiber
A plank is described wherein the plank comprises a core, and optionally, a print layer, and optionally an overlay. The core includes from about 30 wt % to about 95 wt % at least one polymeric material, by weight of the core, and from about 5 wt % to about 70 wt % of least one natural fiber or flour, by weight of the core, wherein the core includes a top surface and a bottom surface, and opposing sides, wherein said plank is substantially moisture resistant, having a swelling property of from about 0.5% to about 5% by NALFA Thickness Test Section 3.2 LF 01-2003 standard, and wherein said plank includes a bow of from about 0.5% to about 4%. In addition, a method of making the plank is further described.
Owner:MANNINGTON MILLS
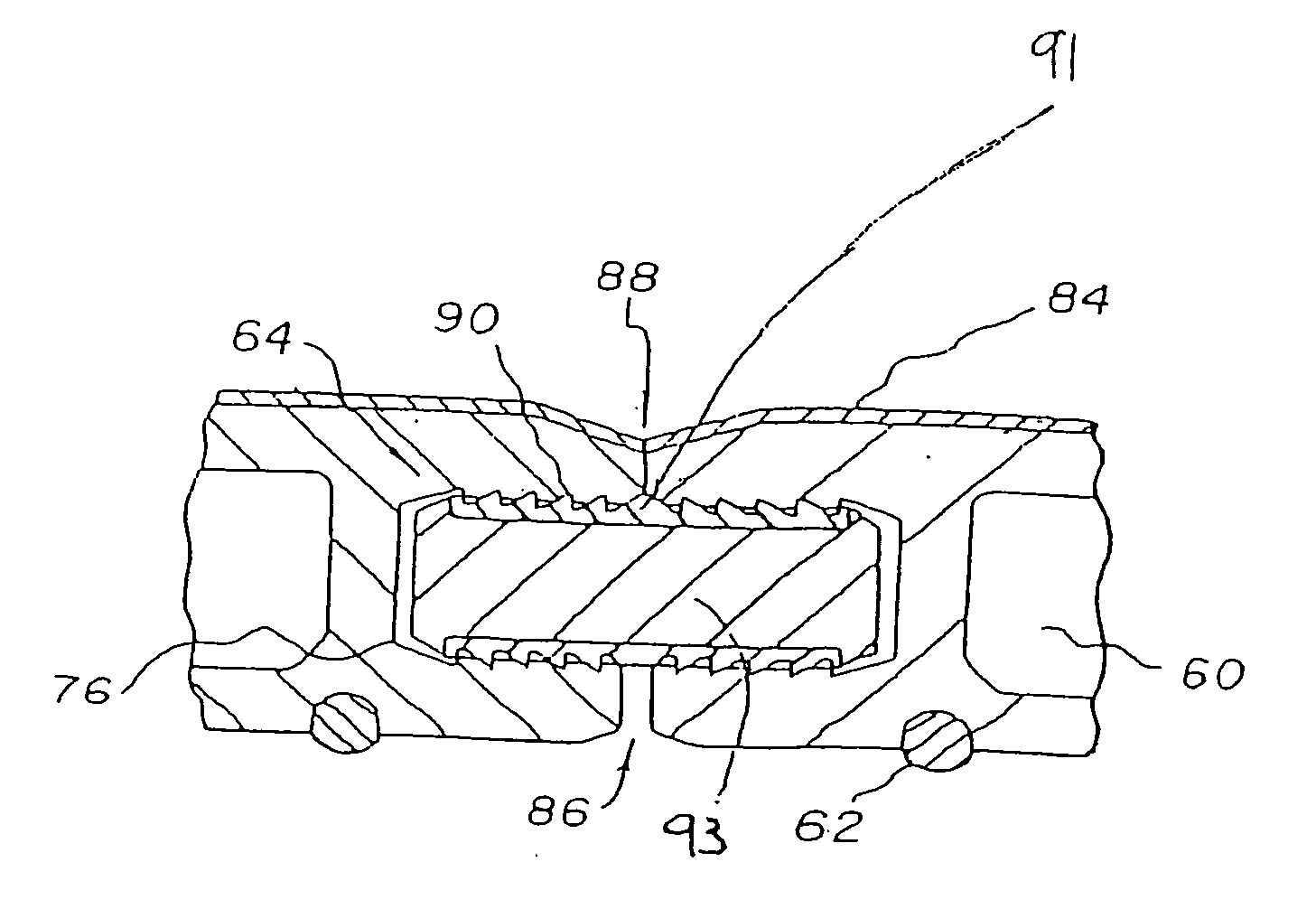
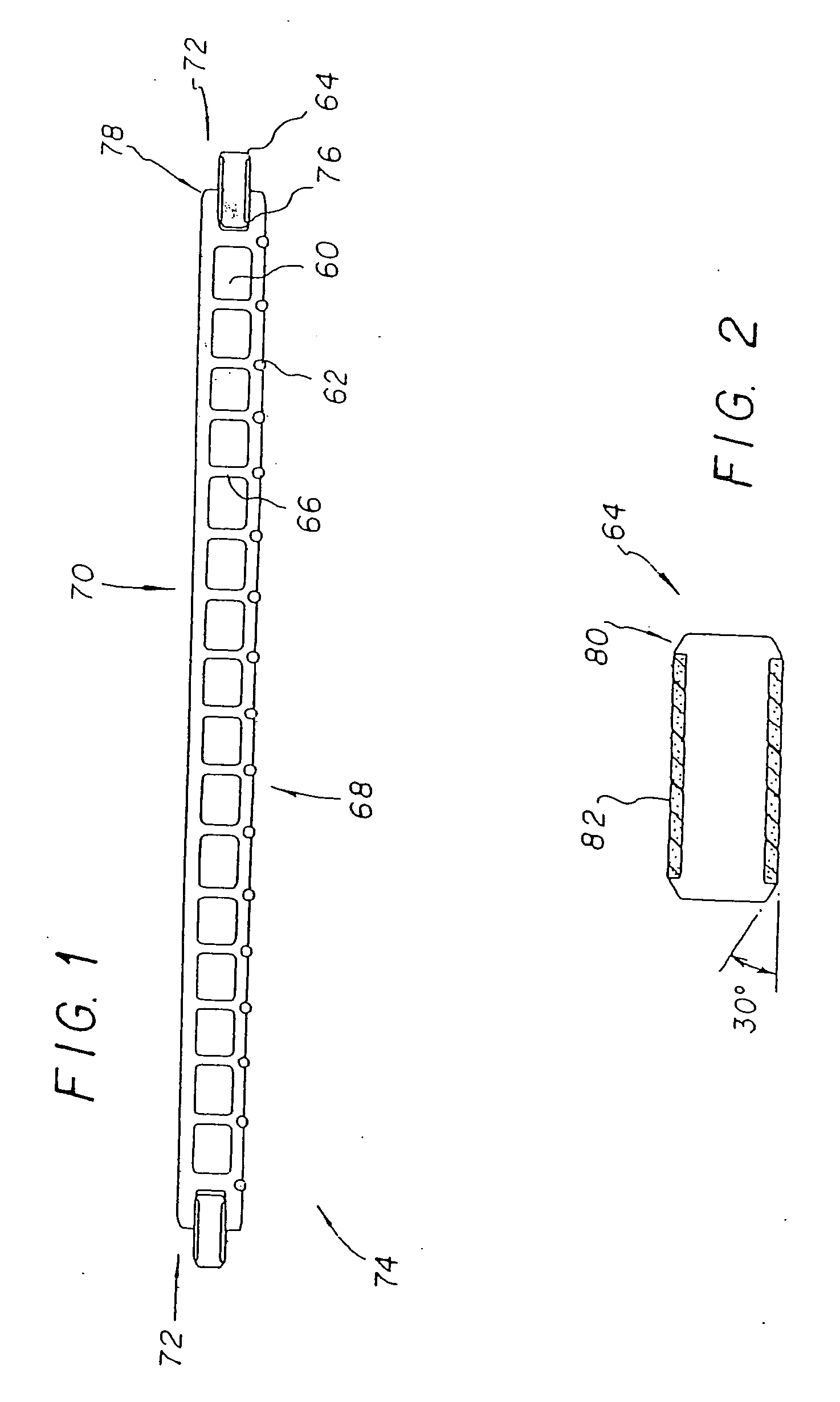
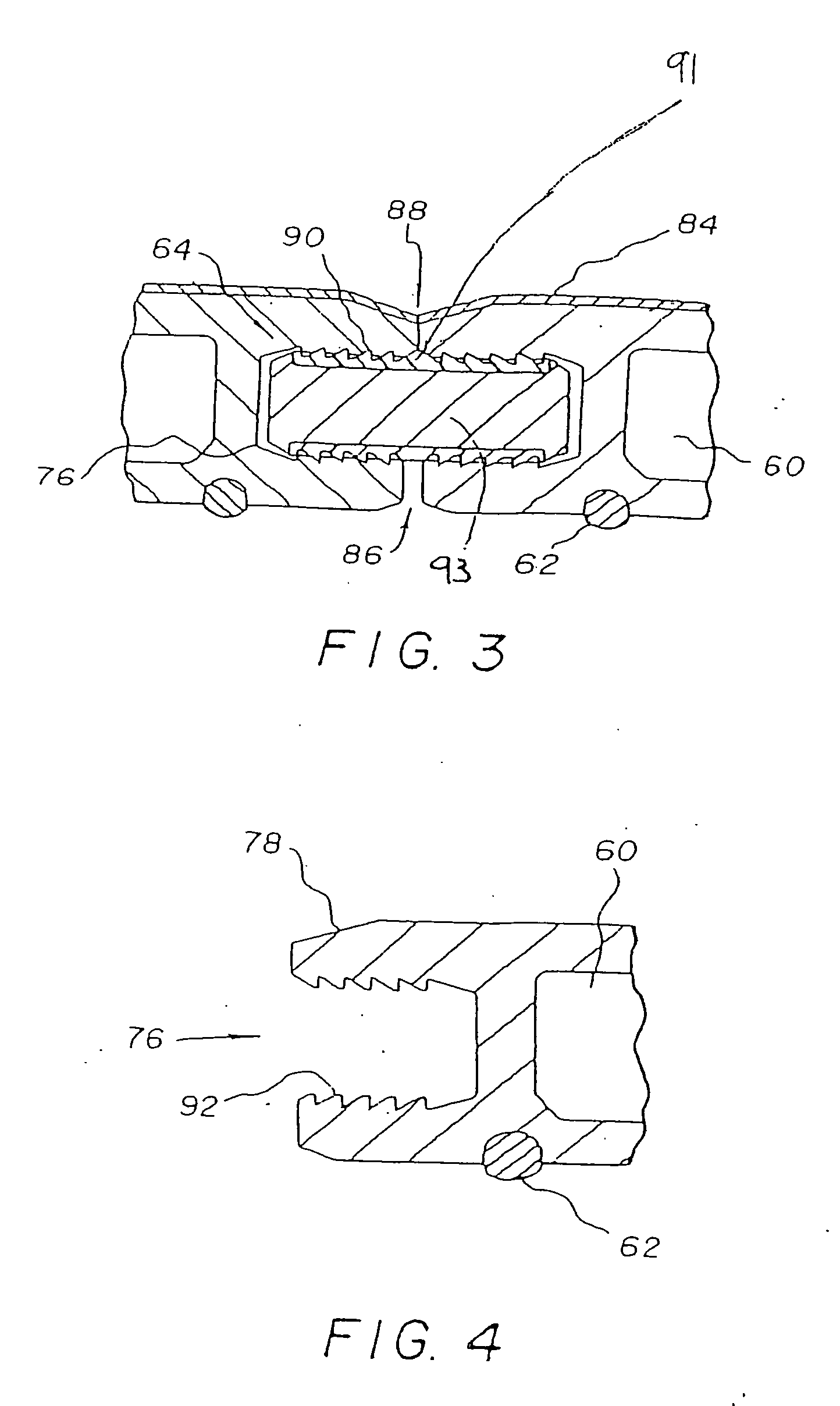
Arcuate fixation member
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
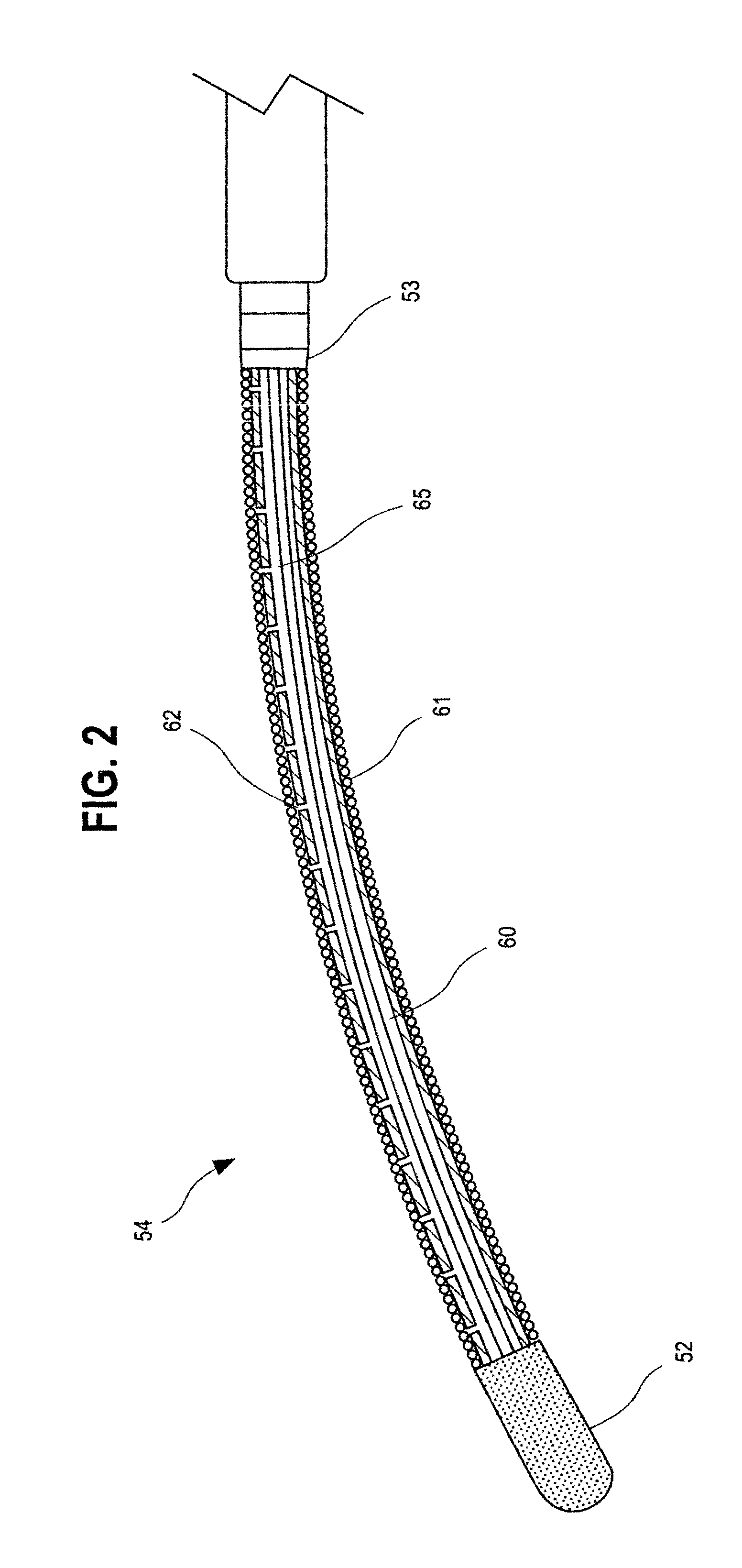
Medical Fastening Device
A tissue fastening device is provided. The tissue fastening device may include an elongate member having fastener guides extending between a working end and a control end and a firing aperture disposed on the working end, an arcuate needle disposed within the firing aperture of the working end and rotatable between a retracted position and an extended position, the arcuate needle including an antegrade recess configured to engagably receive an end of a fastener during advancement of the arcuate needle, and a drive mechanism operatively coupled to the arcuate needle and configured to, upon actuation, advance the arcuate needle in a forward rotation to engage the end of the fastener to be installed and push the end of the fastener through one of a tissue and a prosthetic material into a helical configuration.
Owner:SURGIMATIX
Disposable medical fluid unit having rigid frame
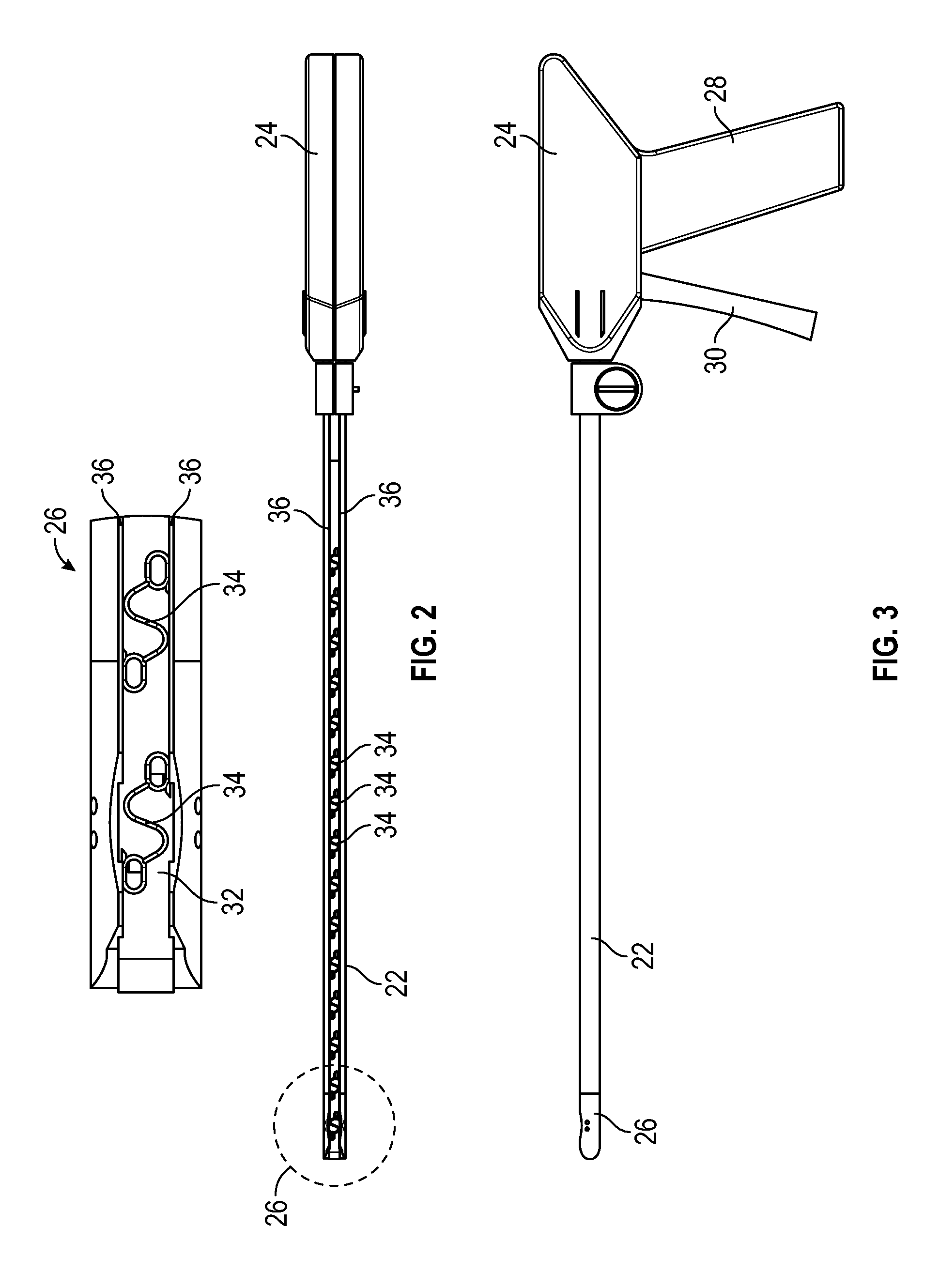
ActiveUS7175606B2Strengthen the systemImprove methodMedical devicesPressure infusionPeritoneal dialysisBiomedical engineering
A method, system and apparatus for performing peritoneal dialysis are provided. To this end, in part, a frame of a disposable unit for a medical fluid system is provided. The frame includes a body having a pair of opposing sides and defining a space between the sides, and a number of membranes sealed to the body along the opposing sides. The body and the membranes form at least one medical fluid pathway in the space between the opposing sides, and the opposing sides are bowed.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
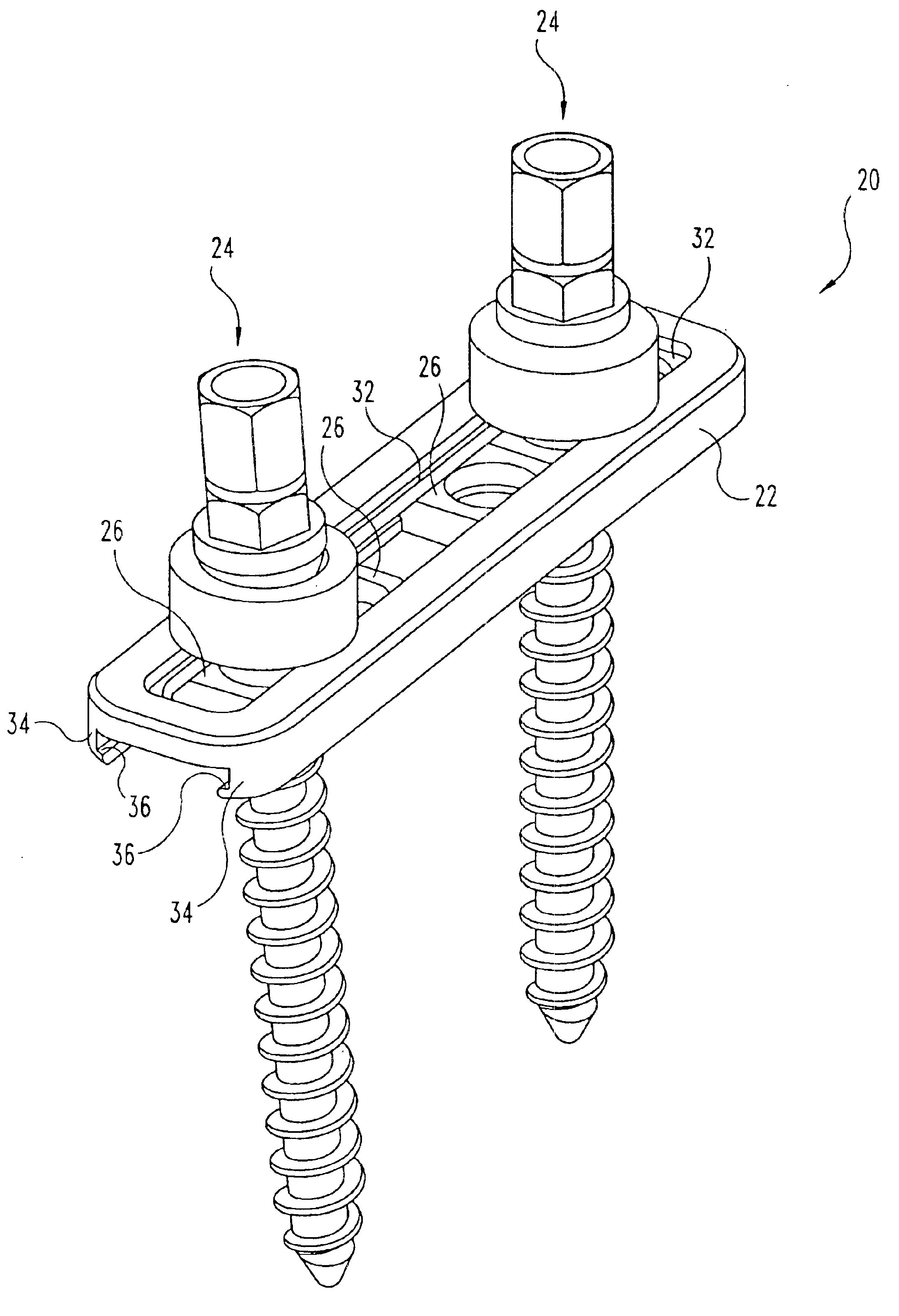
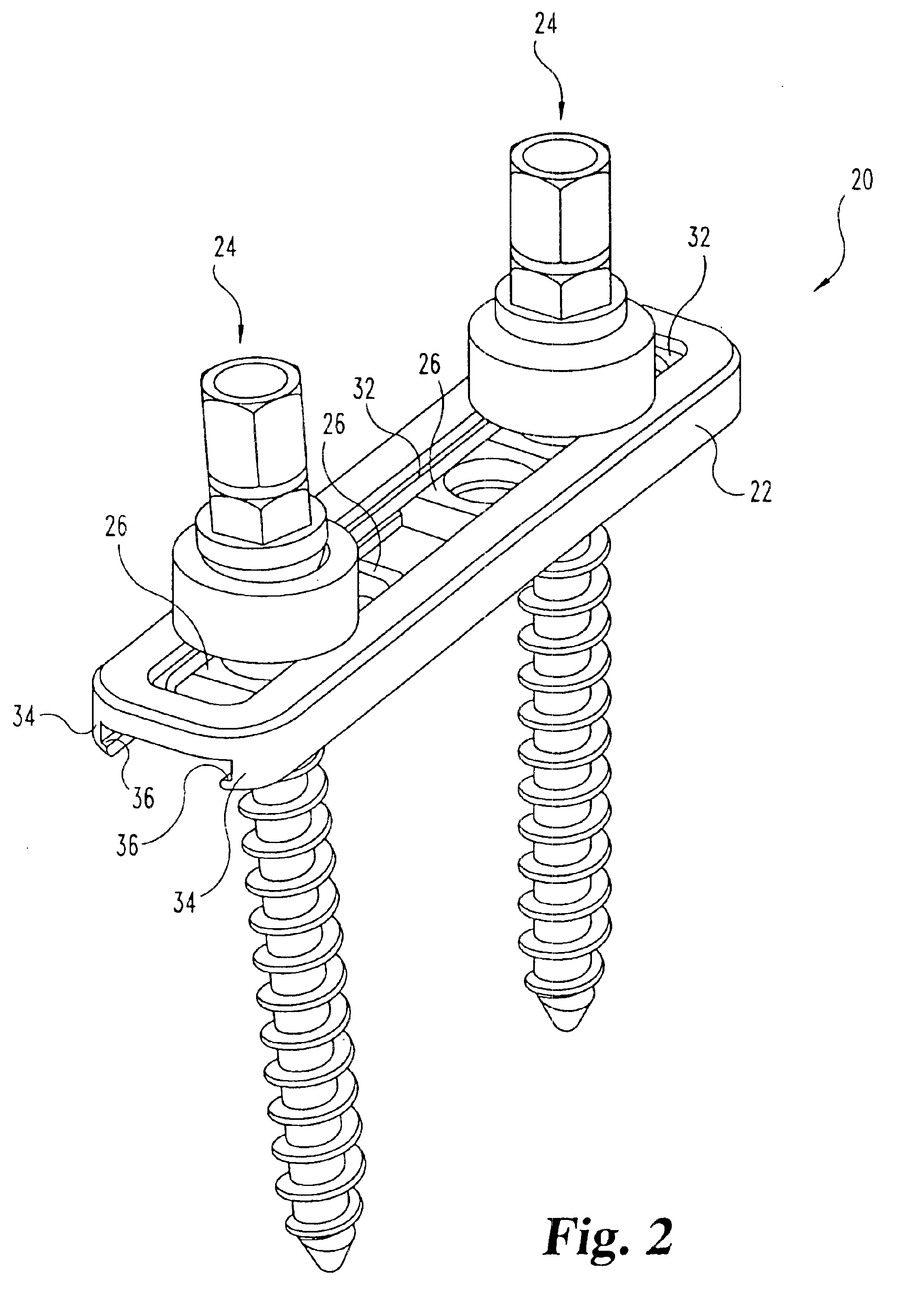
Multi-axial bone anchor system
InactiveUS6858031B2Improved multi-axial capabilityEase of use and stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantBiomedical engineering
A spinal implant system is disclosed for the fixation of bone segments in the spine. The system includes an elongated member, one or more bone anchor assemblies, and stabilizer members which are fitted within the elongated member. A bone anchor is attached to a bone, and the elongated member and stabilizer are fitted over the bone anchor. A rounded washer and nut having a corresponding rounded underside surface are fitted on to the bone anchor over the elongated member, and tightened. The configuration of the bone anchor assembly, including an intermediate portion of the bone anchor, the arcuate washer, and the nut, along with the configuration of the sliding support, allows multi-axial positioning of the bone anchor with respect to the elongated member at a plurality of locations along a slotted member.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
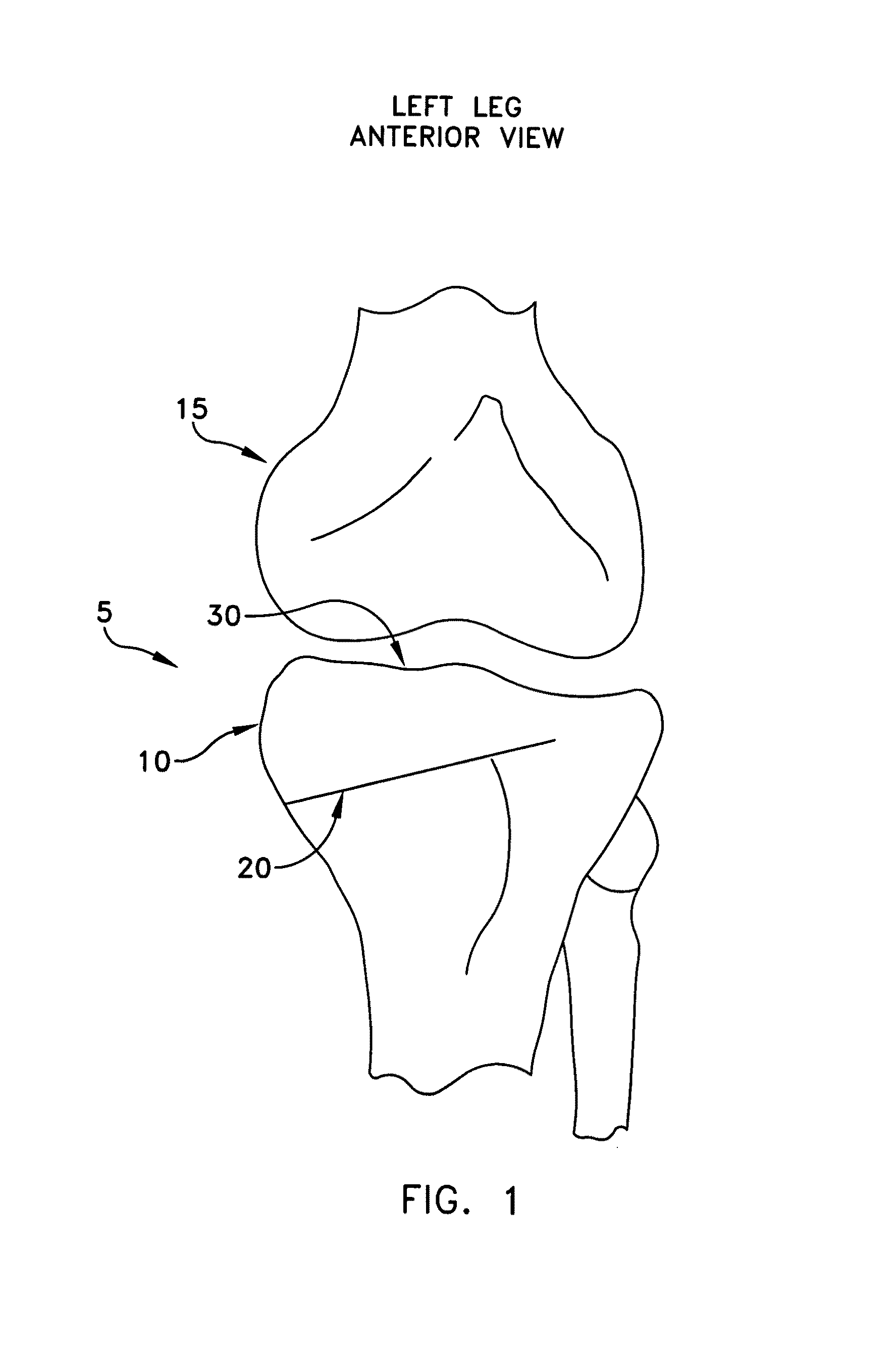
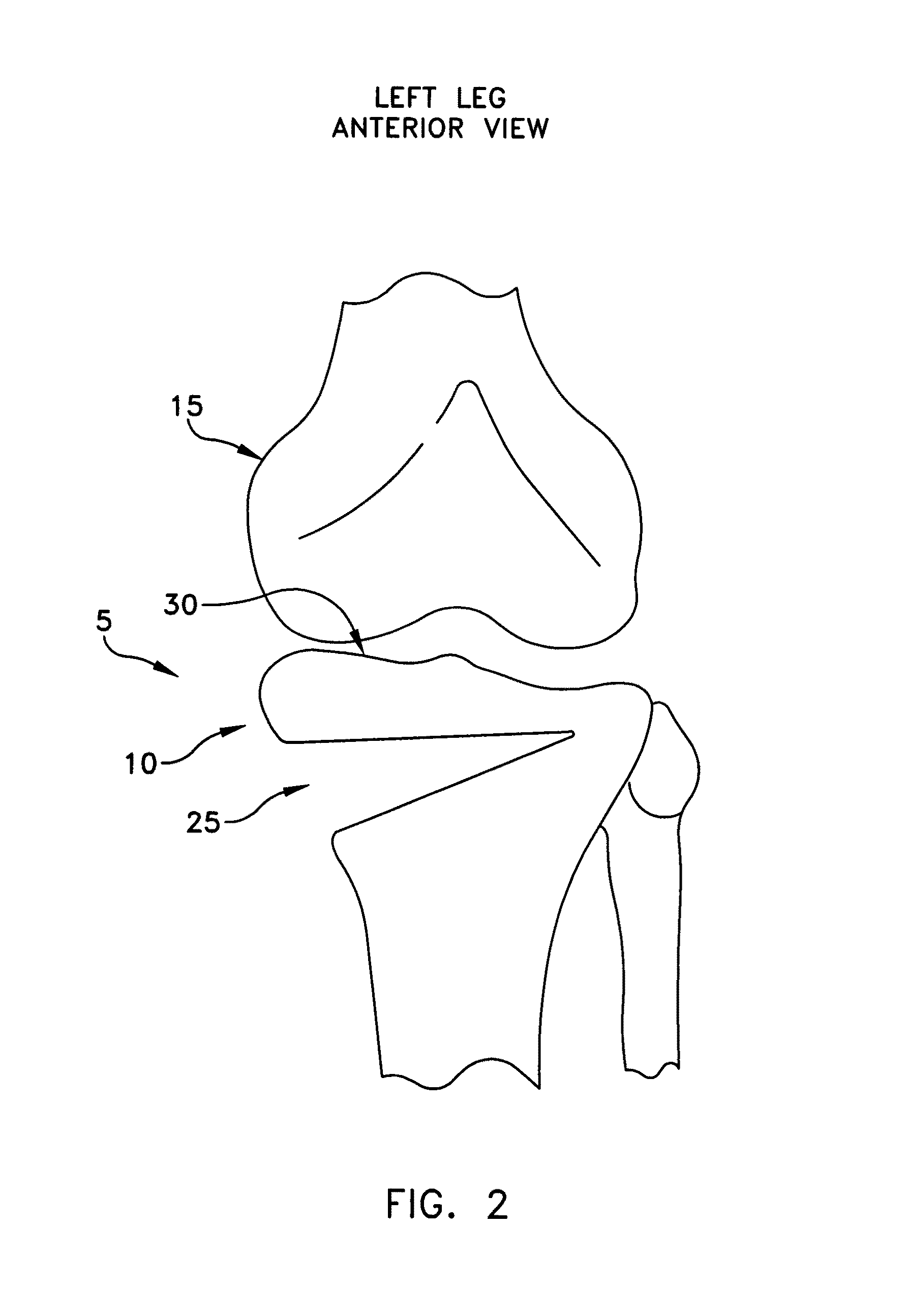
Method and apparatus for performing a high tibial, dome osteotomy
A method for performing a high tibial, dome osteotomy to adjust the lateral and / or angular disposition of the tibial plateau relative to the lower portion of the tibia, the method comprising: forming an arcuate osteotomy cut in the tibia to subdivide it into upper and lower portions; manipulating the upper and lower portions to adjust their lateral and / or angular dispositions relative to one another; forming a pair of keyholes along the osteotomy cut; forming a keyhole slot to connect the two keyholes; forming a fixation hole in the tibia for each keyhole; providing an implant comprising a pair of keys connected by a bridge, each key comprising a bore for receiving a fixation screw therein; inserting the implant so that the keys are disposed in the keyholes, and so that the bores of the keys are aligned with the fixation holes; and inserting fixation screws through the bores of the keys and into the fixation holes of the keyholes so as to stabilize the upper and lower portions of the tibia.
Owner:ARTHREX
Annuloplasty band and method
InactiveUS6955689B2Easy accessConvenient and accurate evaluationSuture equipmentsBone implantEngineeringMitral valve operation
An annuloplasty band comprising a sheath, and a generally arcuate stiffening element disposed within the sheath. The stiffening element extends from a first end to a second end, and preferably includes eyelets at its first and second ends adapted to receive sutures to secure the annuloplasty band to a valve annulus. The annuloplasty band preferably has a low profile (e.g., a thickness less than 3 mm). In embodiments intended for mitral valve repair, the eyelets are particularly adapted to receive sutures to secure the annuloplasty band to the antero-lateral trigone and postero-medial trigone. A holder and sizer device useful with the annuloplasty band are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
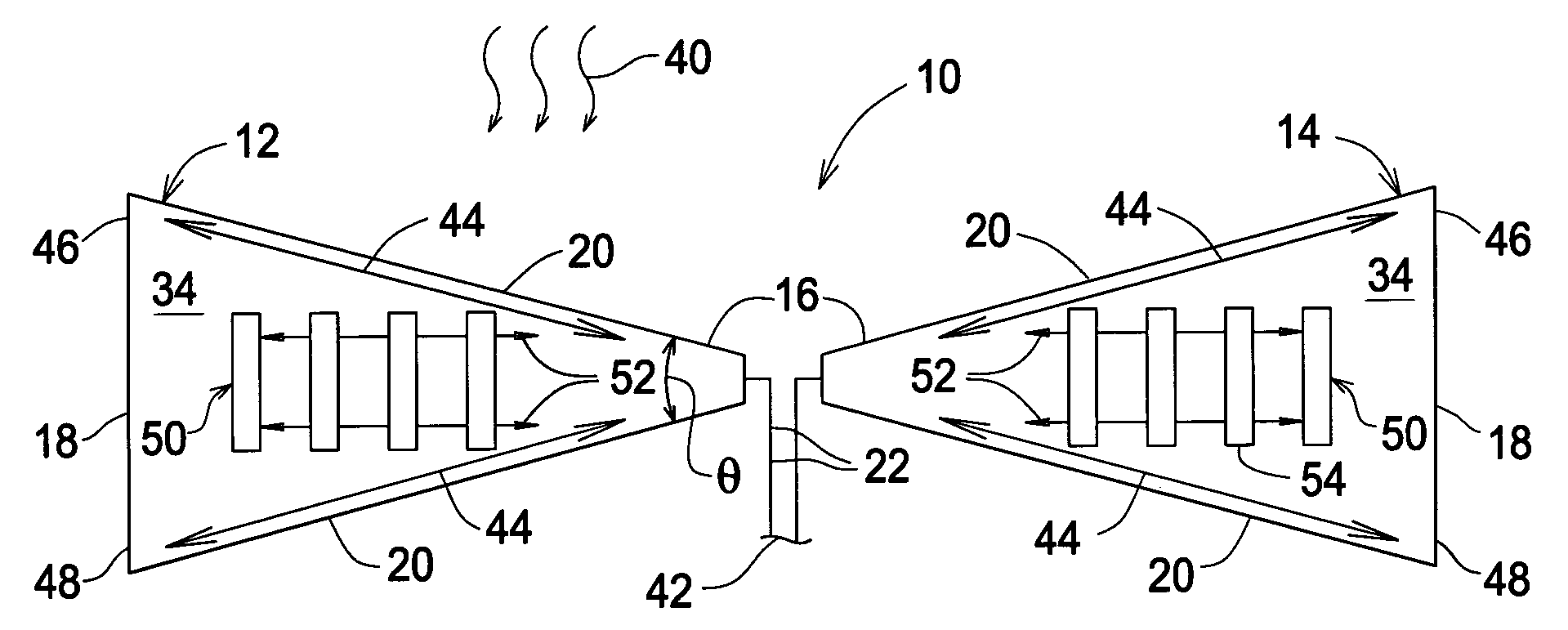
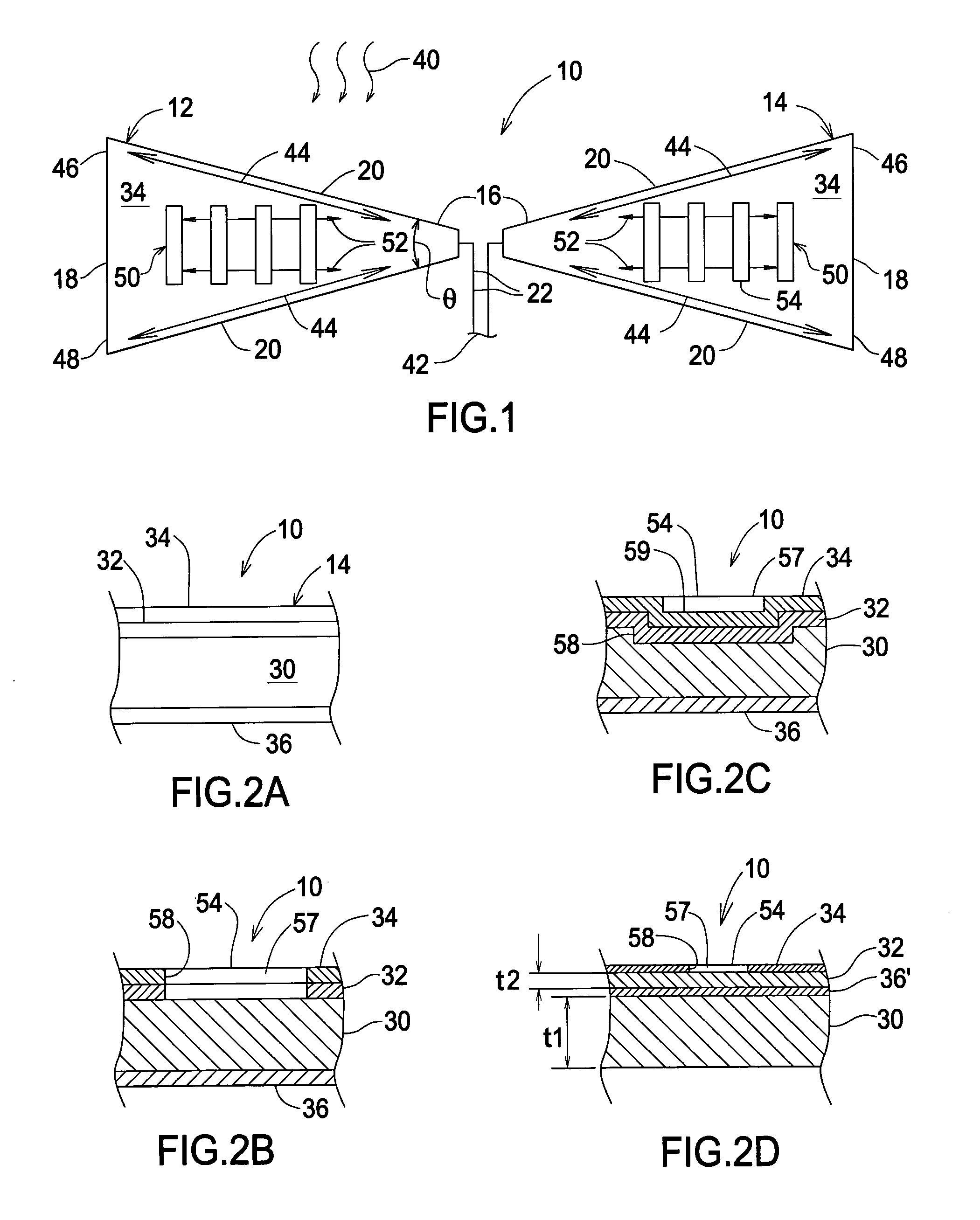
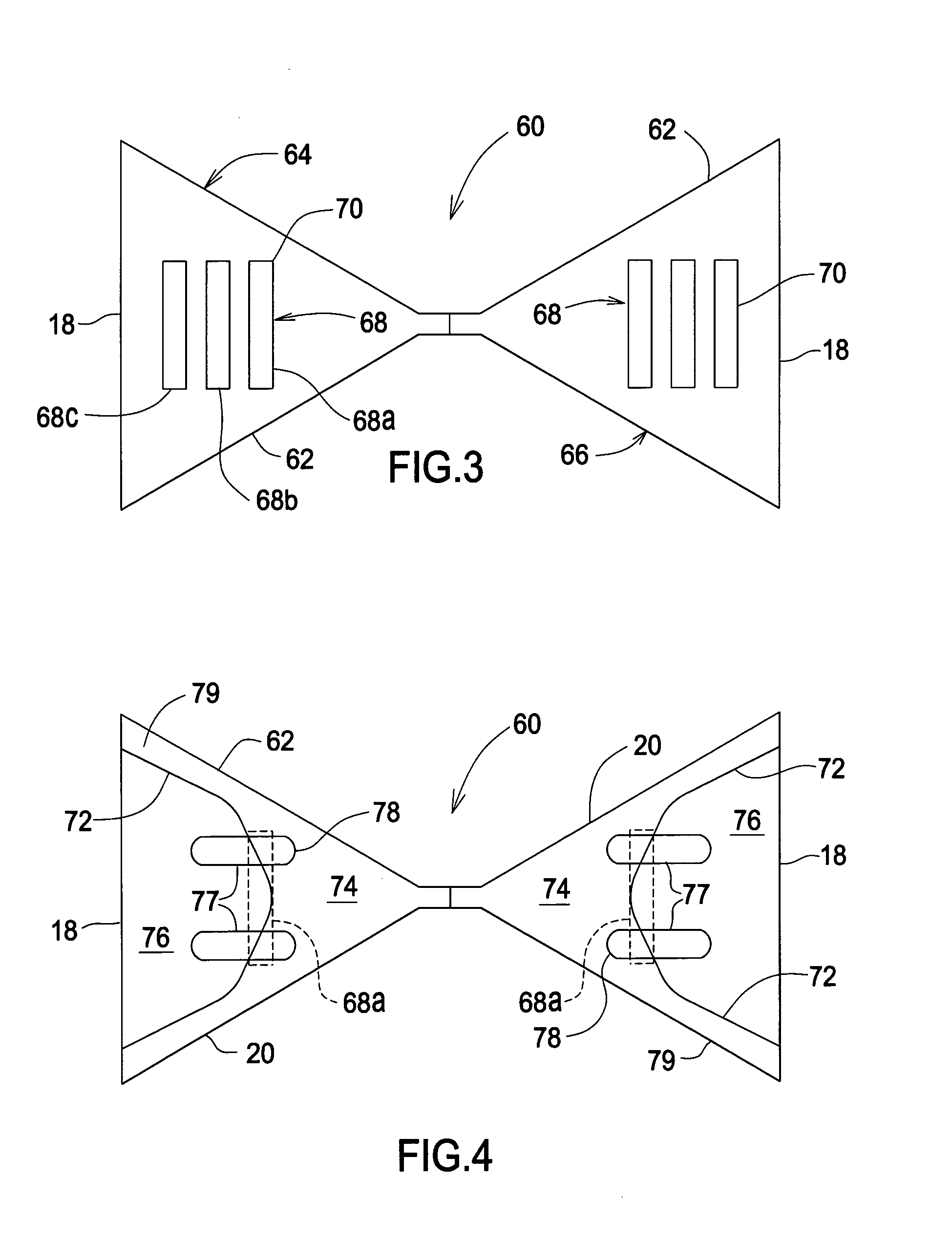
Planar antenna with supplemental antenna current configuration arranged between dominant current paths
InactiveUS7019704B2Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCircular segmentElectric current
An antenna arrangement is described in which a pair of at least generally planar opposing antenna arms each support a first high frequency antenna current responsive to an input. Each arm includes a peripheral outline for confining the first high frequency current to a pair of first and second dominant paths, that are defined by the peripheral outline, in a spaced apart relationship across each of the opposing antenna arms so as to define an isolated area between the first and second paths. A configuration is located in this area of at least one of the antenna arms for producing an additional high frequency current responsive to the input. The additional high frequency current cooperates with the first high frequency antenna current to produce an overall antenna response. In one feature, the opposing antenna arms are bow arms which cooperate to define an overall bow-tie configuration as the peripheral outline.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Ball seat having segmented arcuate ball support member
ActiveUS20090159289A1Increase pressureReduce the possibilityFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Anastomosis instrument and method for performing same
InactiveUS7169158B2Reduce the possibilityReduce slippageSuture equipmentsStaplesVascular anastomosisSurgical department
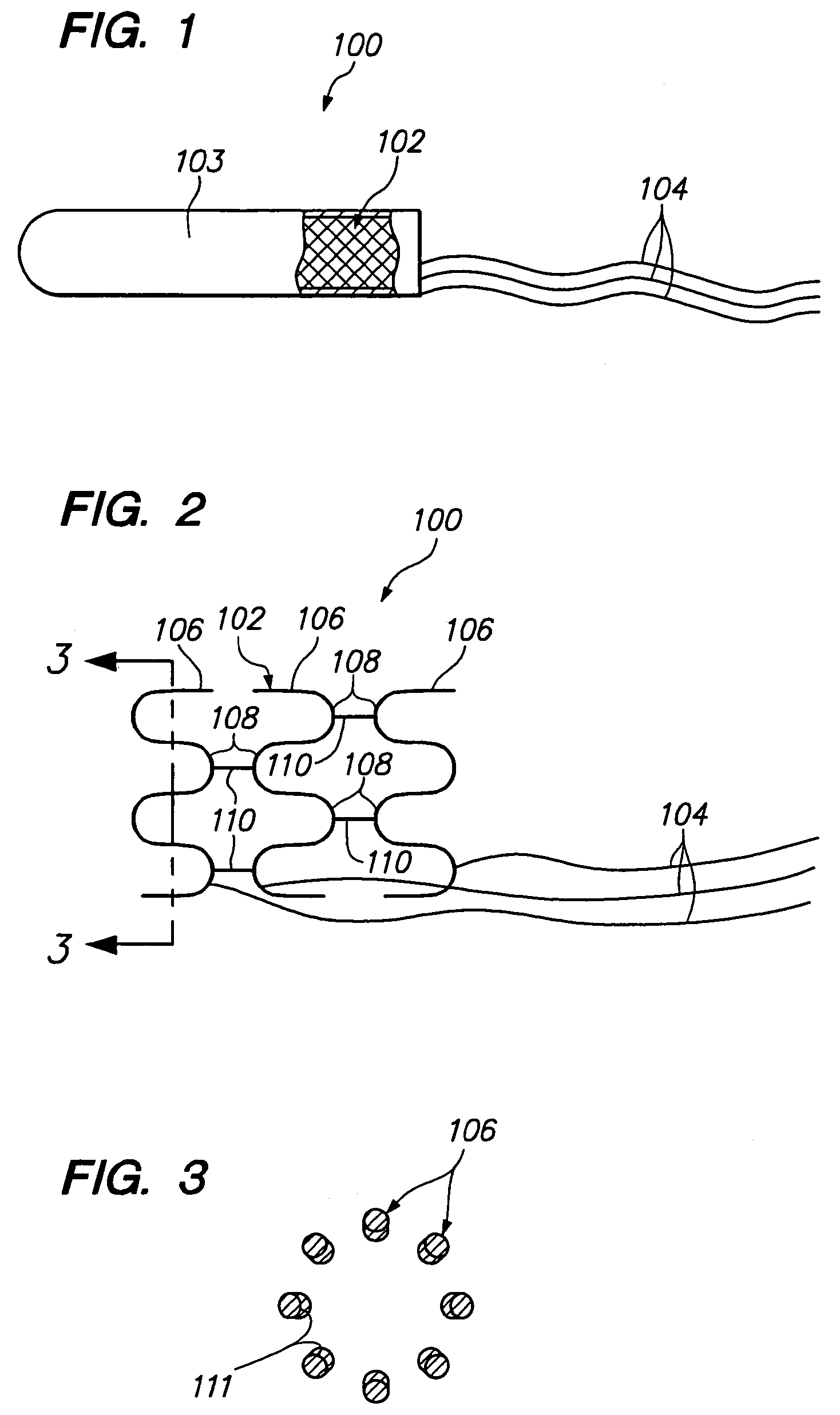
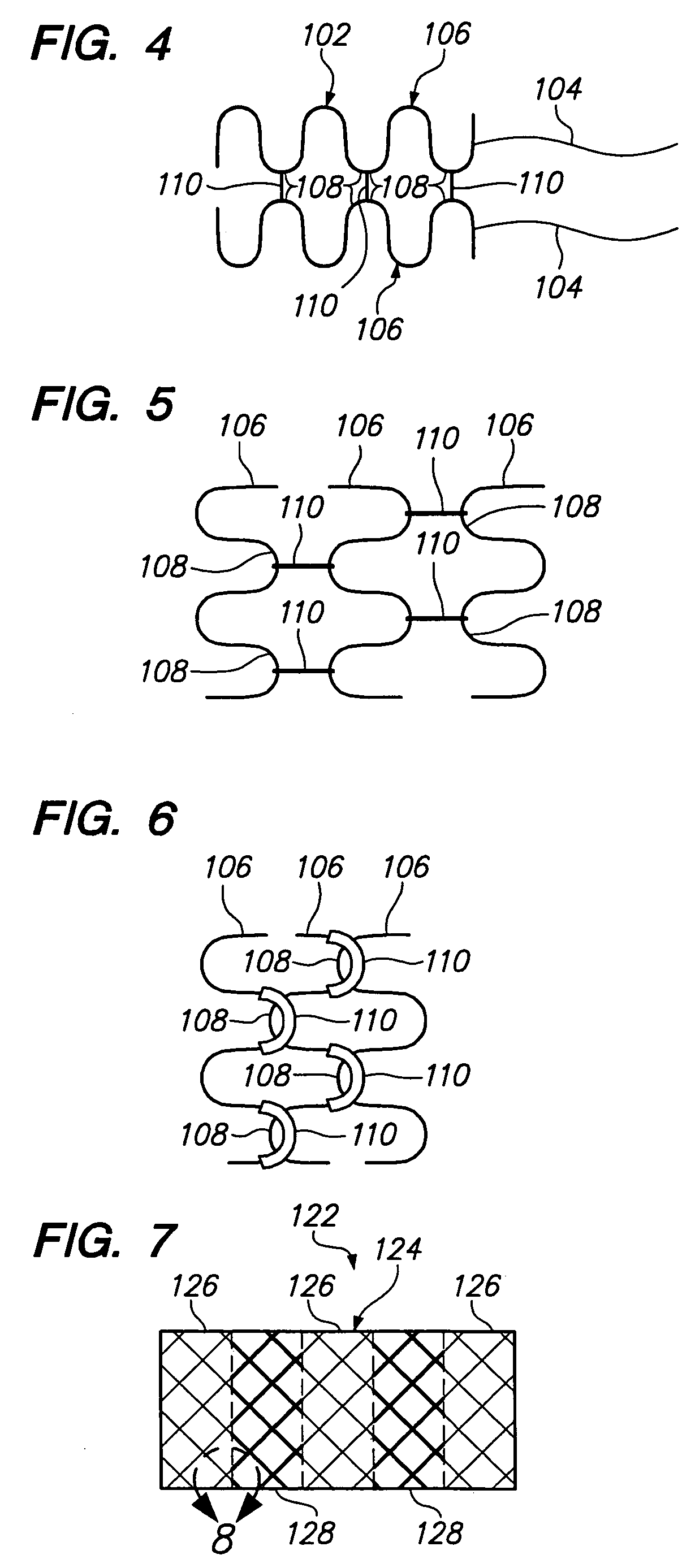
A tissue retaining ring for use with a plurality of surgical fasteners mounted within a disposable loading unit utilized during a vascular anastomosis inlcudes a genrally circular, semi-pliable material having a series of alternating loops and arcuate portions. Each of the loops defines an aperture therein which is dimensioned to receive a distal end of one of the plurality of surgical fasteners. When the instrument is fired, the surgical fasteners are simultaneously deformed through the tissue ring and through the tissue. The tissue retaining ring holds the tissue in place along the surgical fastener and reduces the chances of tissue slippage after deformation.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Ablation catheter with cooled linear electrode
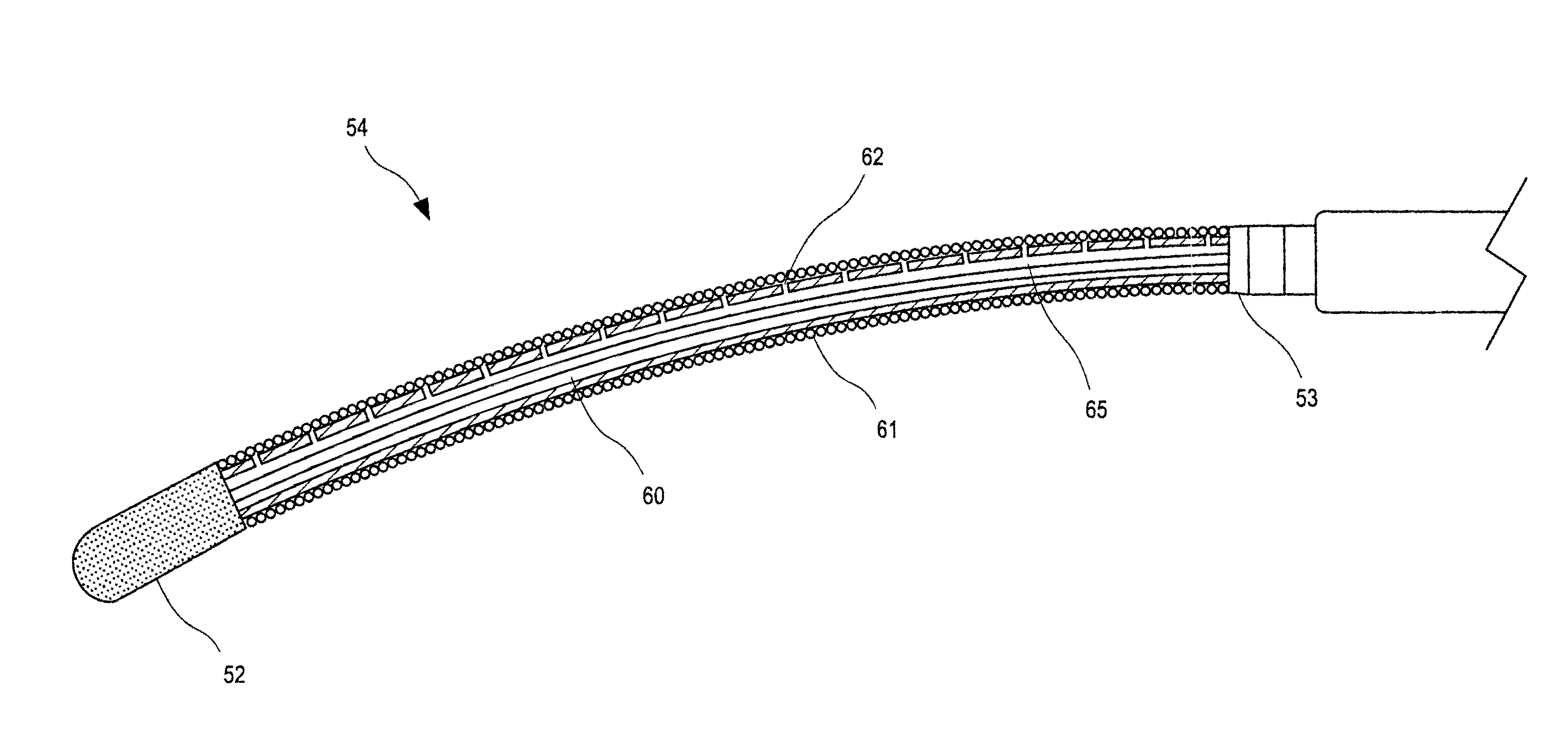
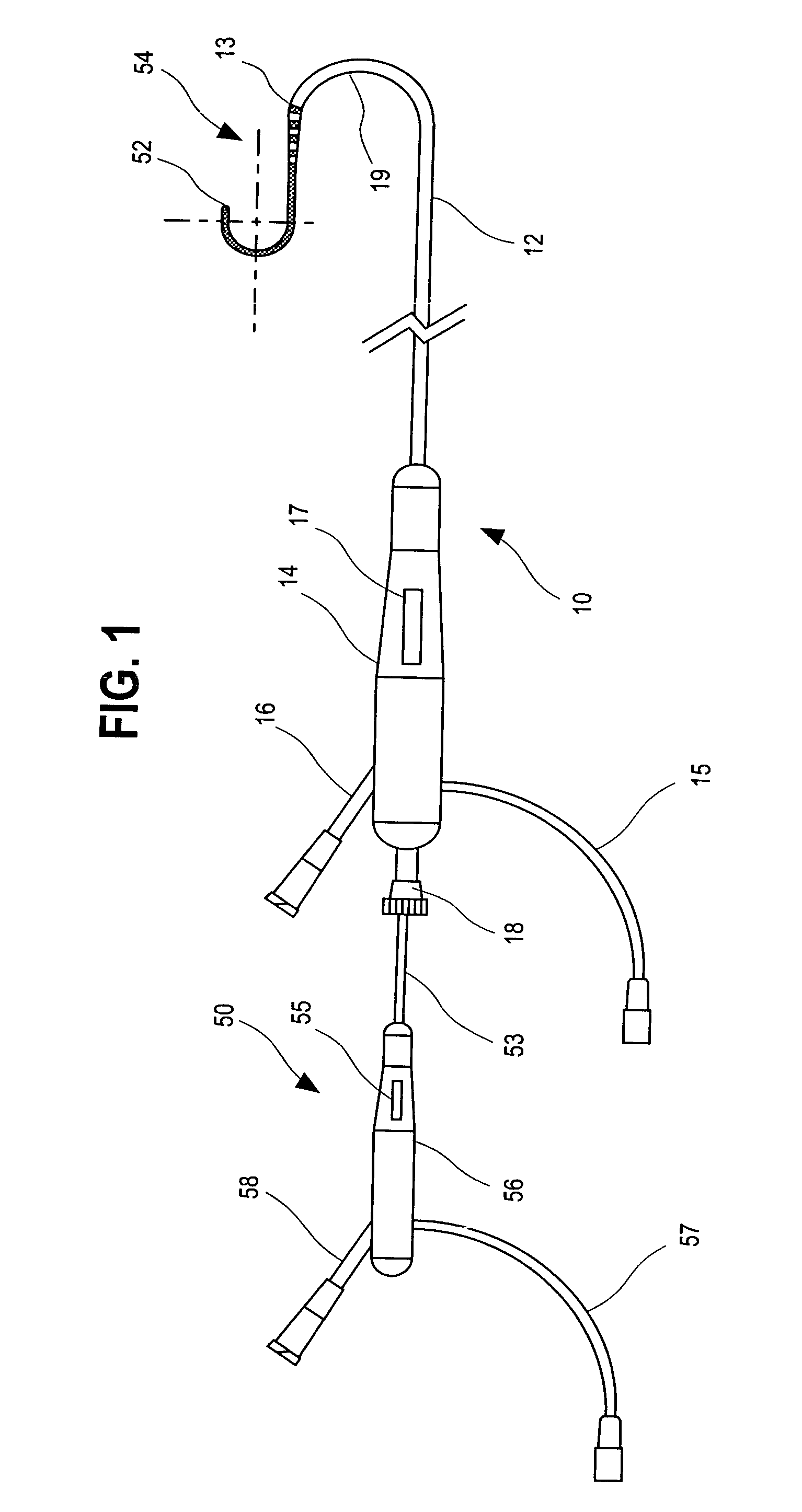
InactiveUS6986769B2Precise positioningDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingArcuate shapeCircular segment
The ablation catheter is comprised of a guiding catheter and an inner catheter. The guiding catheter is comprised of a shaft section which is attached to an articulating section at its distal end and a first handle at its proximal end. The inner catheter is comprised of an elongated central shaft, an electrode assembly attached to the distal end of the central shaft, and a second handle attached to the proximal end of the central shaft. The electrode assembly is comprised of a flexible plastic catheter tube having an outer surface, a porous tip electrode, and at least one linear electrode carried on the outer surface of the catheter tube. The electrode assembly is articulated to better align the electrode assembly to the generally arcuate shape of the inner chambers of the heart.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Method of performing a transforaminal posterior lumber interbody fusion procedure
InactiveUS7226483B2Easy to insertPrecise positioningBone implantDiagnosticsSpinal columnTransforaminal approach
An intervertebral implant for fusing vertebrae is disclosed. The implant has a body with curved, substantially parallel posterior and anterior faces separated by two narrow implant ends, superior and inferior faces having a plurality of undulating surfaces for contacting upper and lower vertebral endplates, and at least one depression at a first end for engagement by an insertion tool. The arcuate implant configuration facilitates insertion of the implant from a transforaminal approach into a symmetric position about the midline of the spine so that a single implant provides balanced support to the spinal column. The implant may be formed of a plurality of interconnecting bodies assembled to form a single unit. An implantation kit and method are also disclosed.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Vibratory transducer
InactiveUS6920798B2Easy to manufactureEasy to bendMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCross sensitivityStraight tube
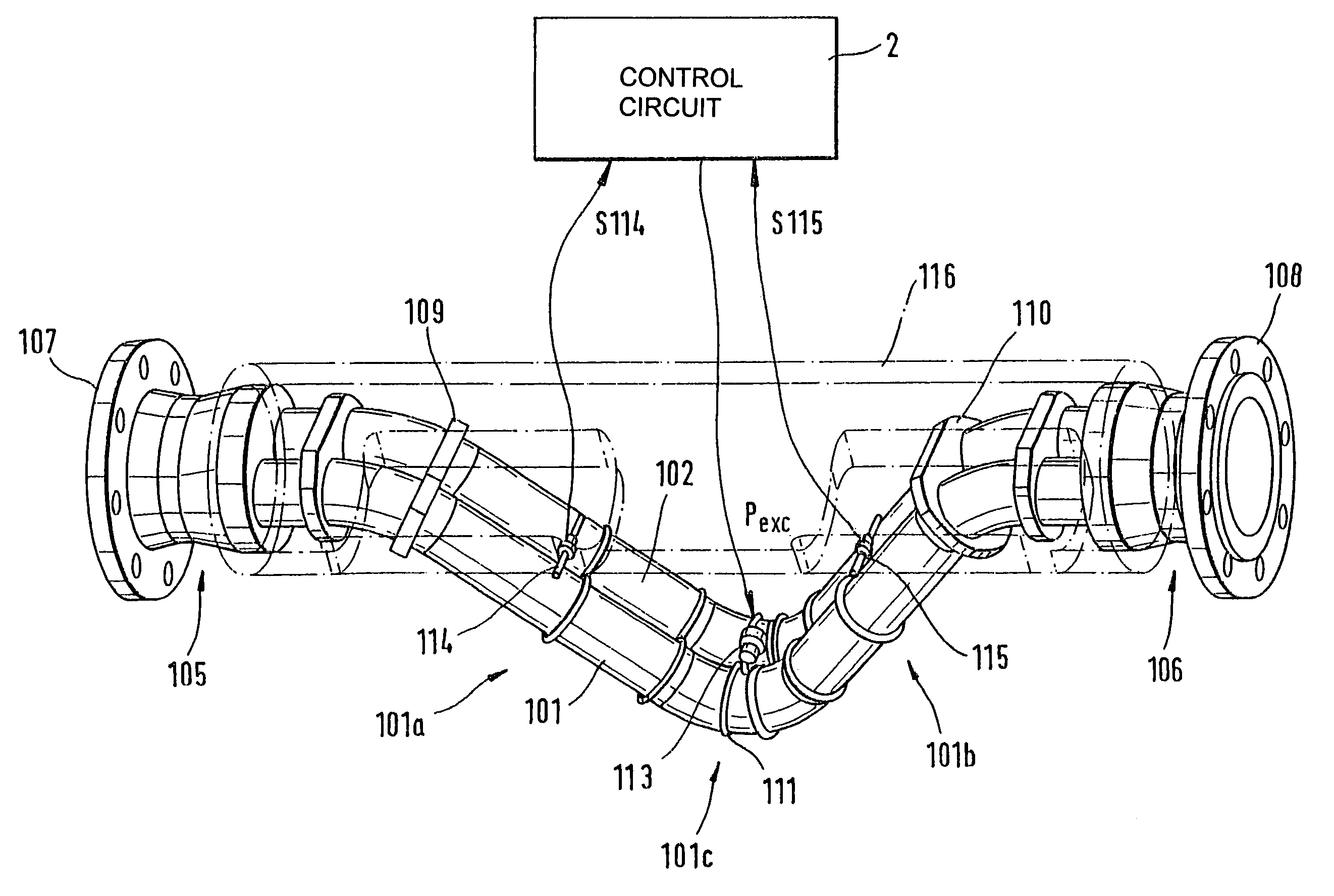
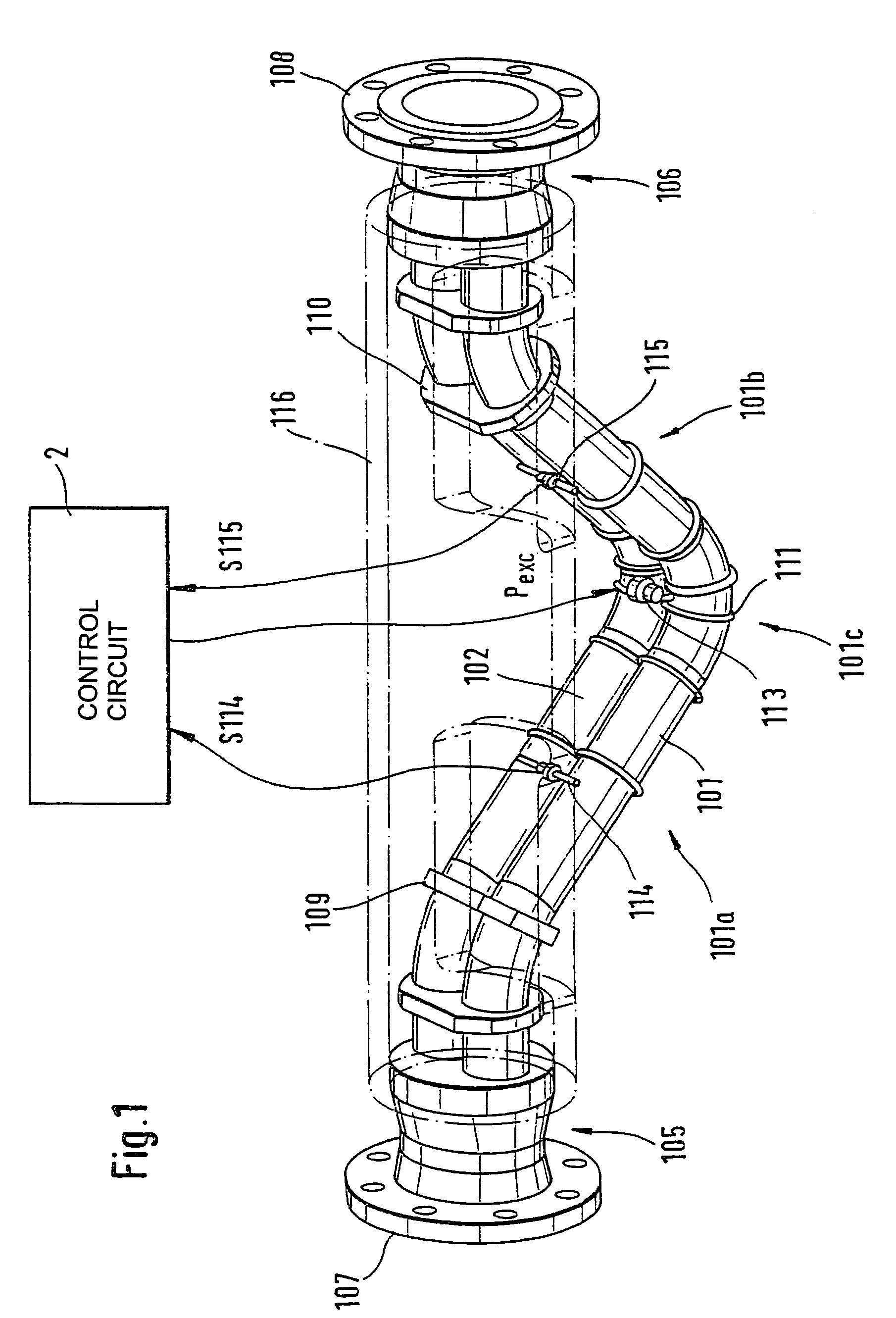
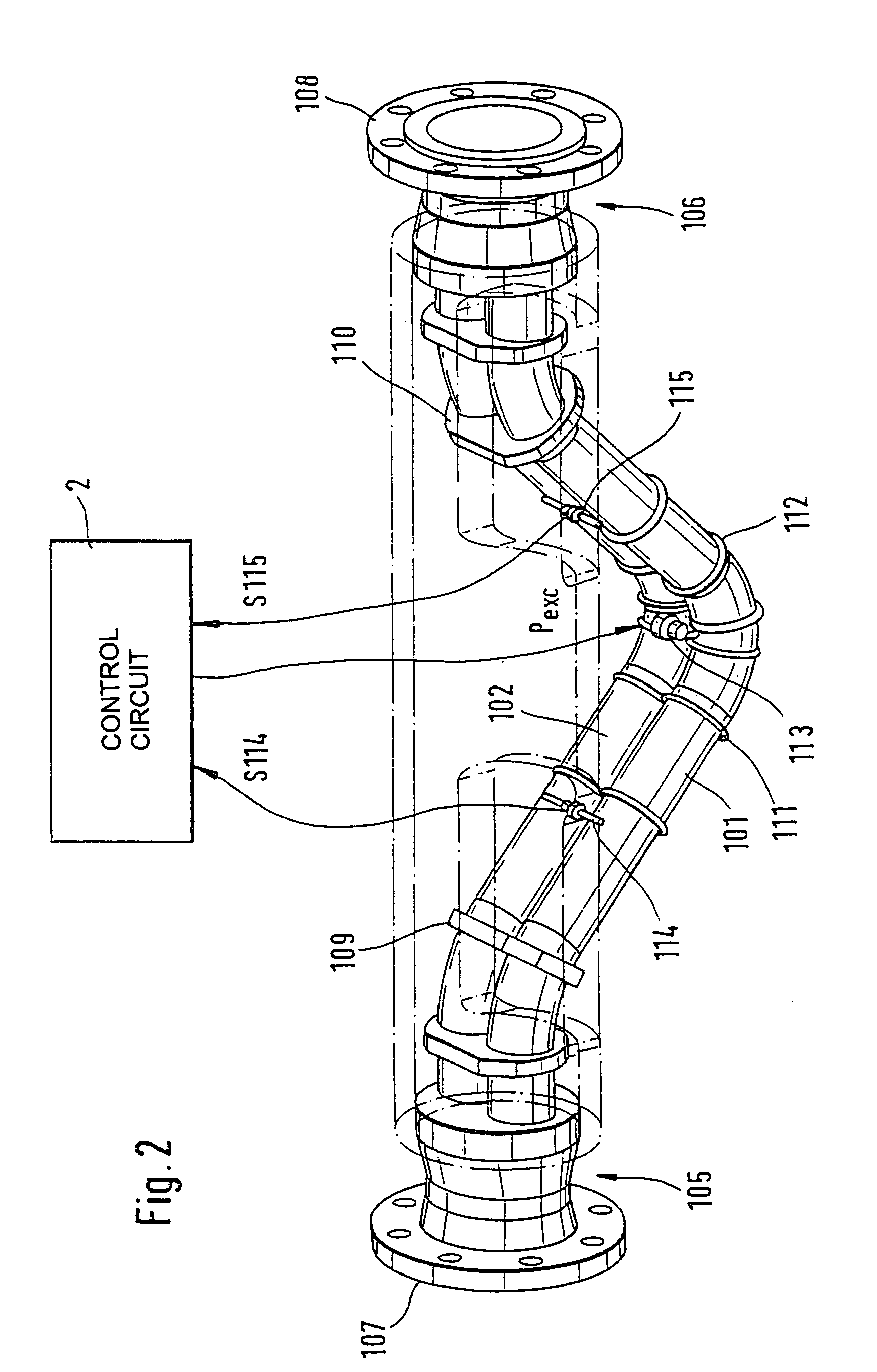
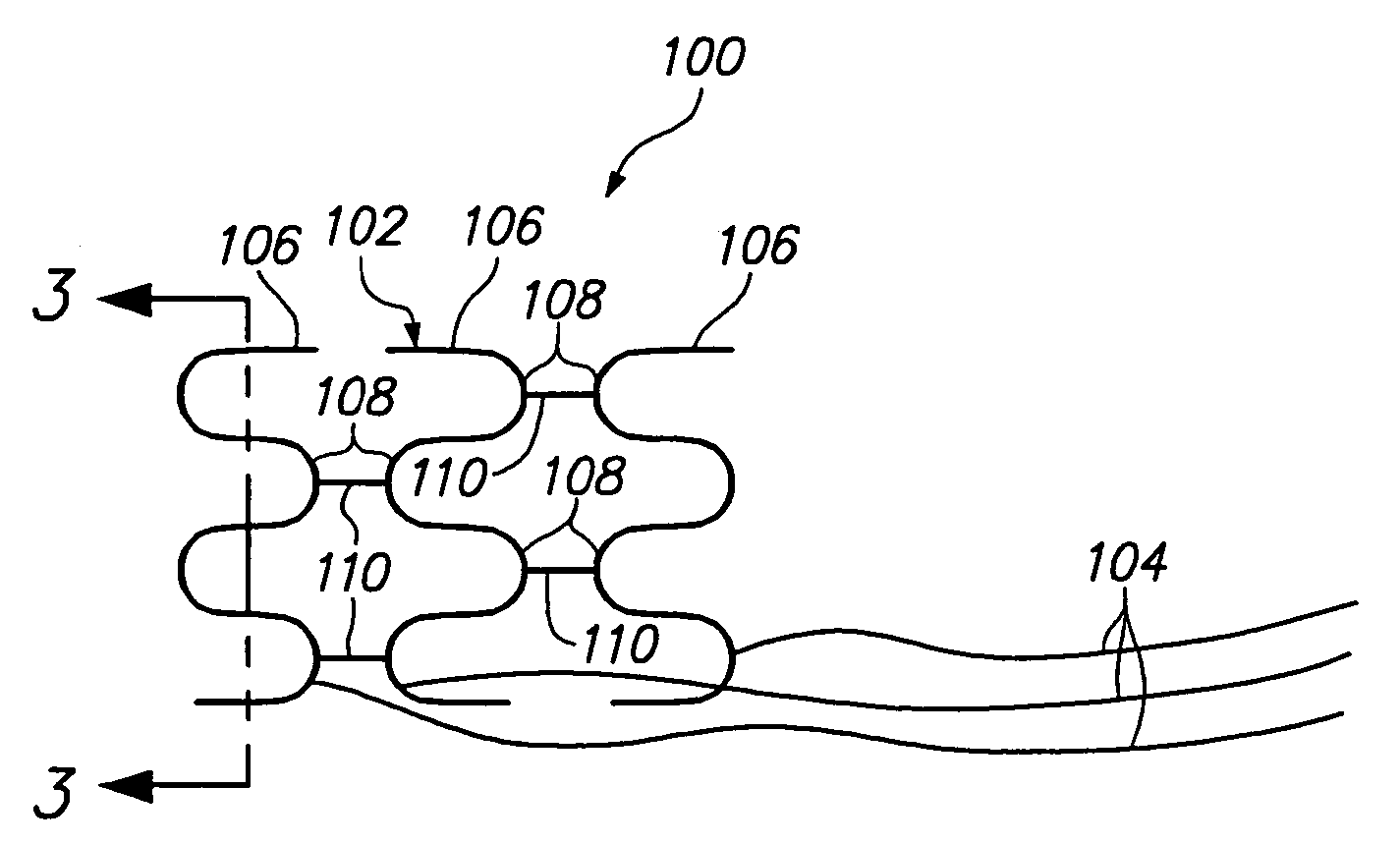
The transducer (1) has at least one at least temporarily vibrating flow tube (101) of predeterminable lumen for conducting a fluid. The flow tube (101) communicates with a connected pipe via an inlet tube section (103), ending in an inlet end, and an outlet tube section (104), ending in an outlet end, and in operation performs flexural vibrations about an axis of vibration joining the inlet and outlet ends. The flow tube (101) has at least one arcuate tube section (101c) of predeterminable three-dimensional shape which adjoins a straight tube segment (101a) on the inlet side and a straight tube segment (101b) on the outlet side. At least one stiffening element (111, 112) is fixed directly on or in close proximity to the arcuate tube segment (101c) to stabilize the three-dimensional shape. By means of the at least one stiffening element (111, 112), the cross sensitivity of the transducer (1) is greatly reduced, so that cross talks from pressure to mass flow signals are minimized and the accuracy of the transducer is improved.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
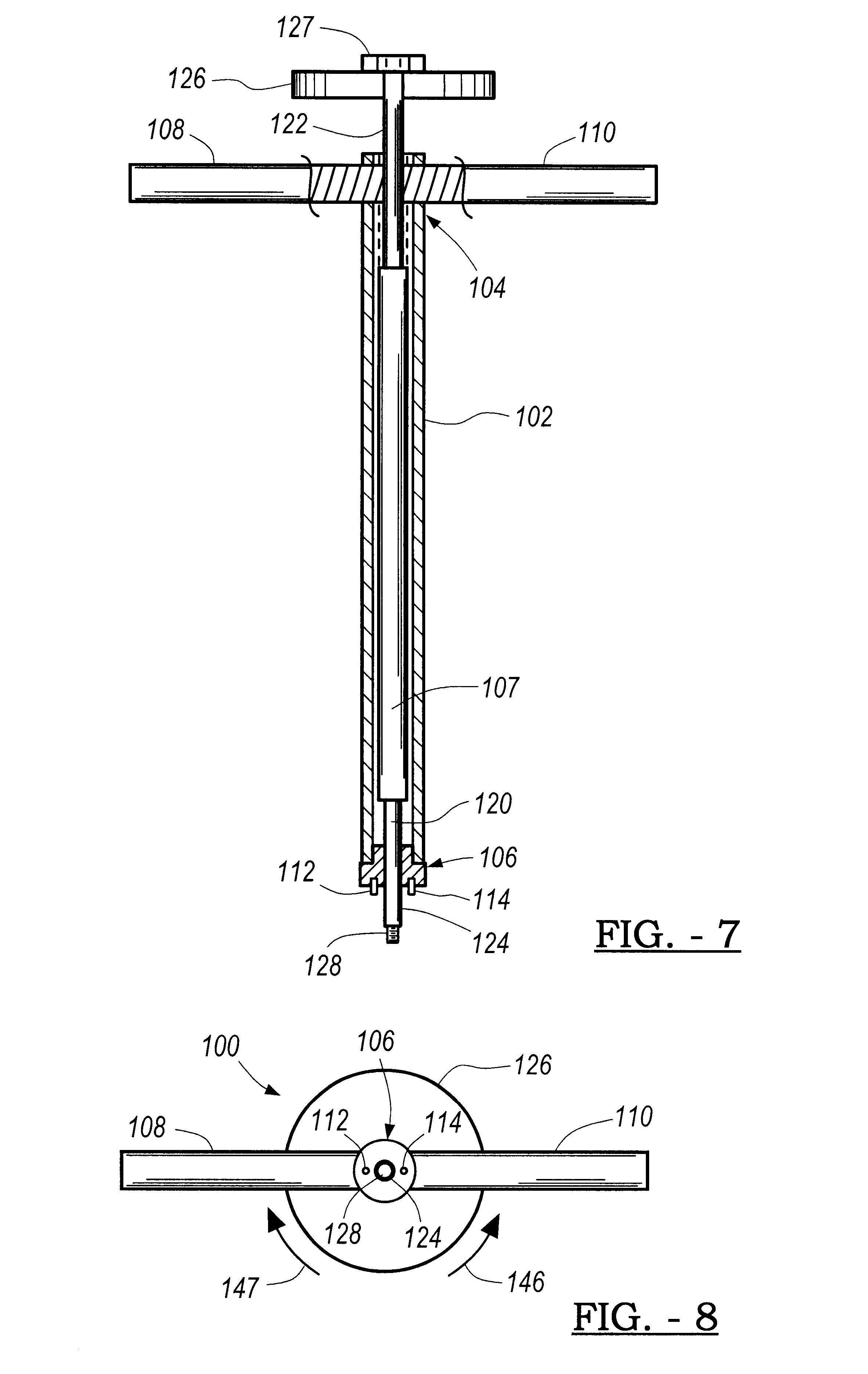
Intravascular self-anchoring electrode body with arcuate springs, spring loops, or arms
InactiveUS7231260B2Efficient receptionGuaranteed normal transmissionStentsTransvascular endocardial electrodesMedicineMedical device
An expandable intravascular medical device comprises an arcuate spring configured to be expanded into contact with the inner surface of a blood vessel. Another medical device comprises an electrode support structure, e.g., a non-tubular arcuate structure or a cylindrical member, and a plurality of resilient spring loops laterally extending from the support structure. The contact created between the loops and a blood vessel is sufficient to anchor the medical device within the blood vessel. In another embodiment, the medical device comprises an elongated member and two resilient spring arms extending distally from the elongated member. The arms are configured to be laterally moved towards each other to place the medical device in a collapsed geometry, and configured to be laterally moved away from each into contact with an inner surface of a blood vessel to place the medical device an expanded geometry.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
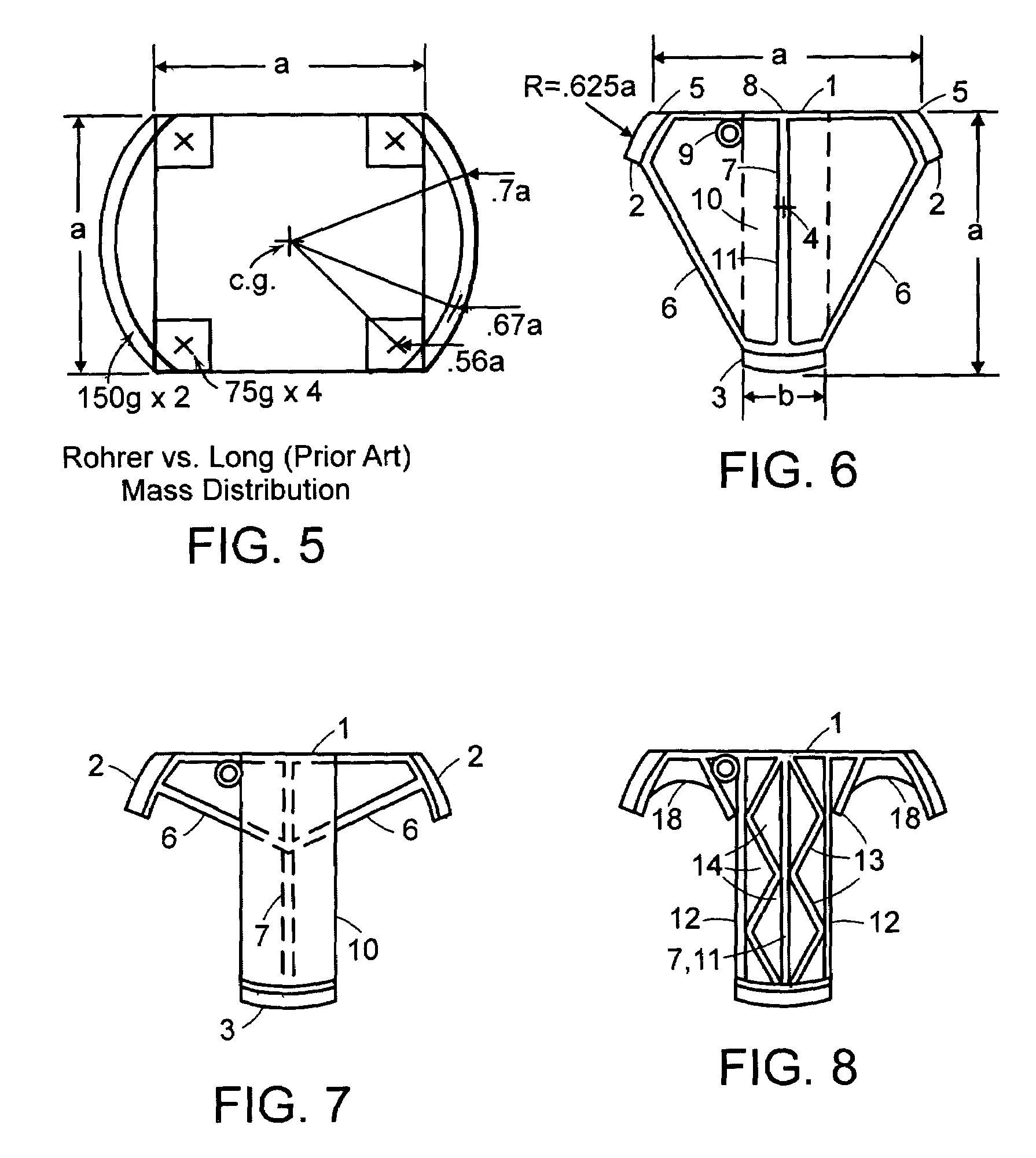
Golf putter with improved moment of inertia, aim and feel
InactiveUS7077758B2Maximizes clubhead planar moment of inertia (MOICH)Undesirable torsional vibrationGolf clubsRacket sportsVisibilityEngineering
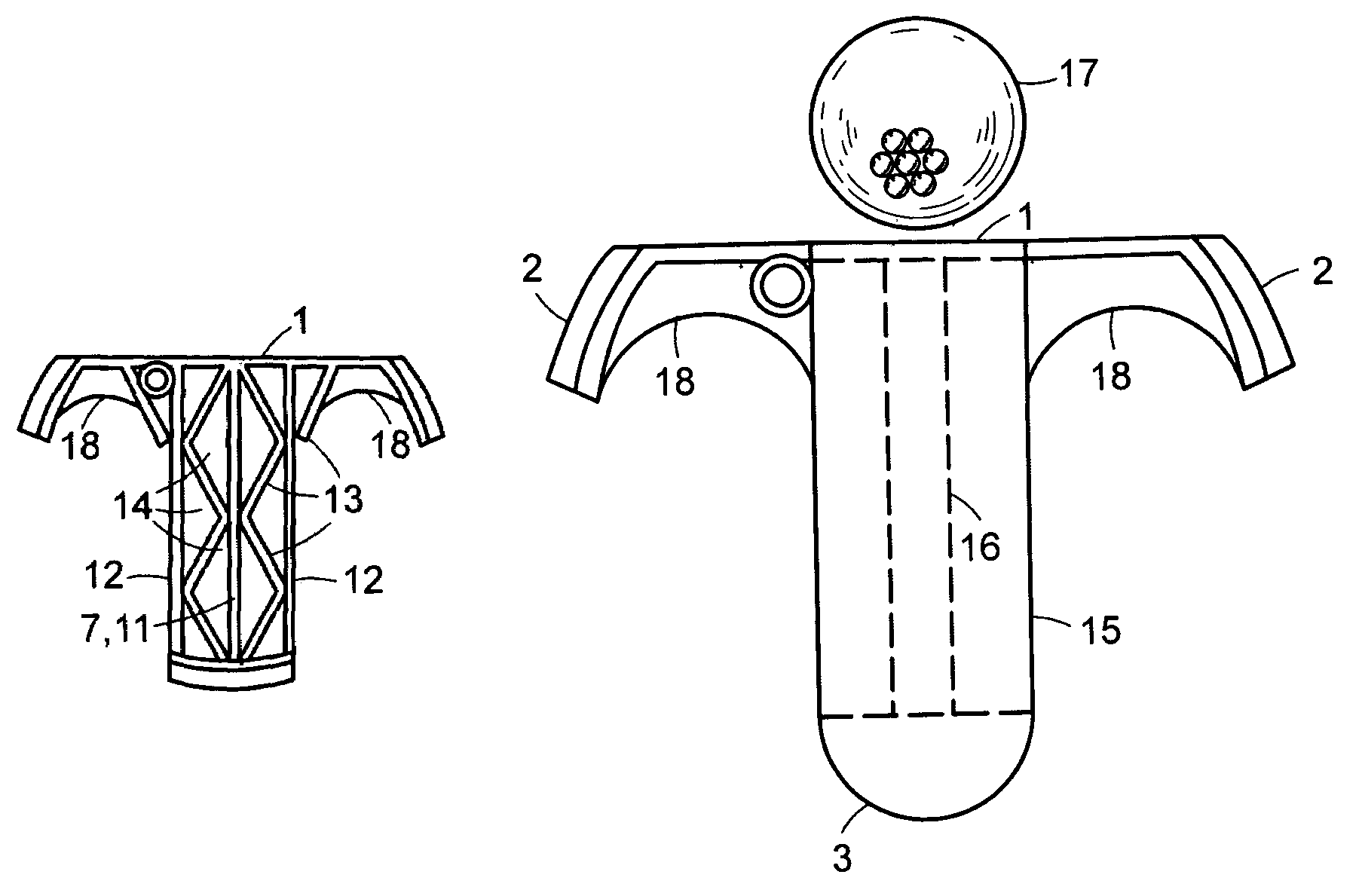
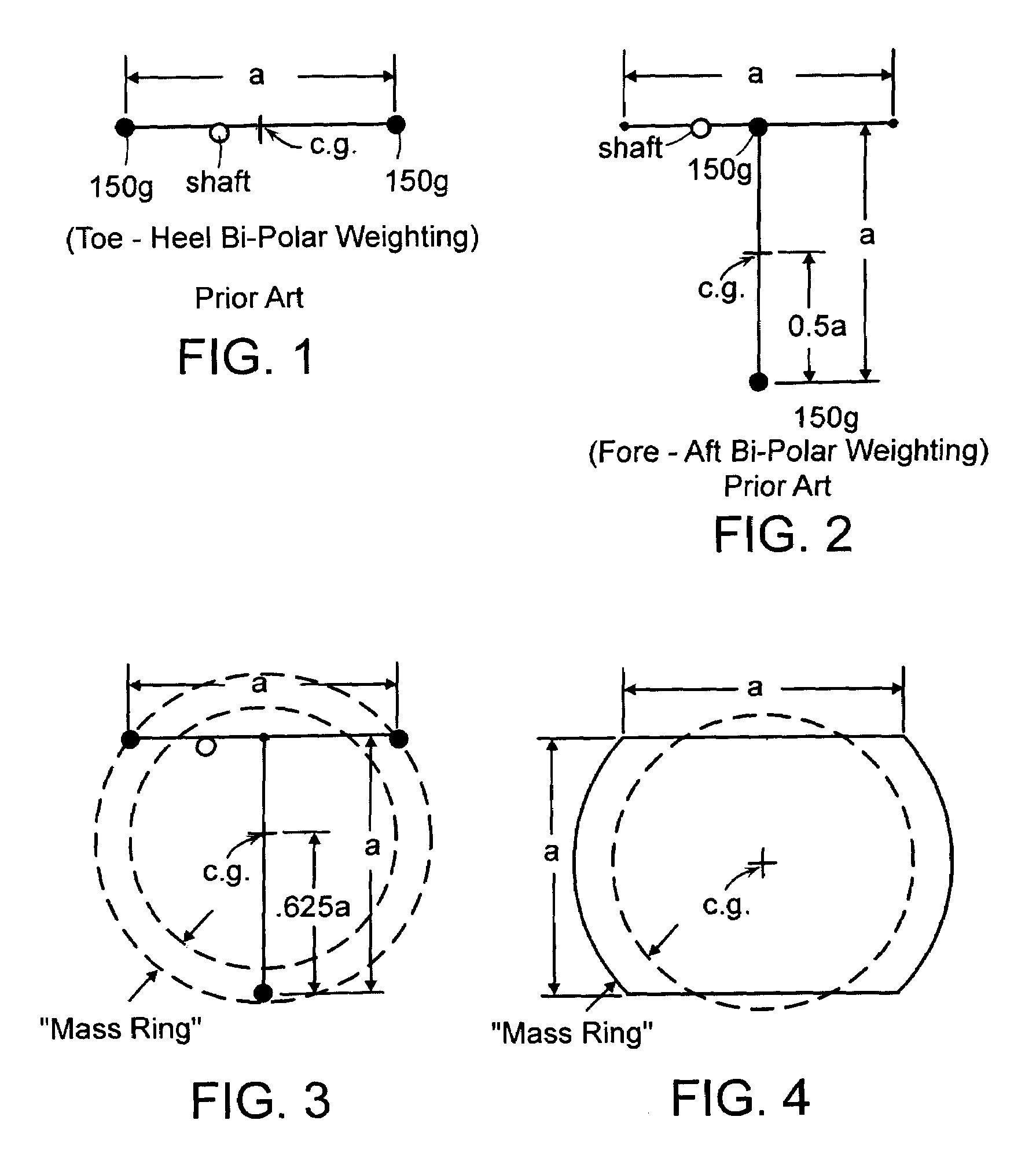
A golf putter in which most of the clubhead mass is distributed at three or more individual or one or more arcuate locations within a “Mass Ring” approximately equidistant from, and as remote as possible from, the clubhead planar center of mass with the clubshaft axis preferably forward of the clubhead center of mass thus maximizing both putter and clubhead planar moment of inertia for improved putter performance during mis-hits. Maximum remote mass is achieved by interconnecting the remote high mass areas (Mass Ring) with the putterface striking area and the putter shaft connection point with a light weight rigid open (see thru) truss system so arranged to enhance the visibility of the Sighting Field and / or aim or Sight Line on the putterhead while preventing undesirable vibration of individual clubhead members.
Owner:ROHRER TECH
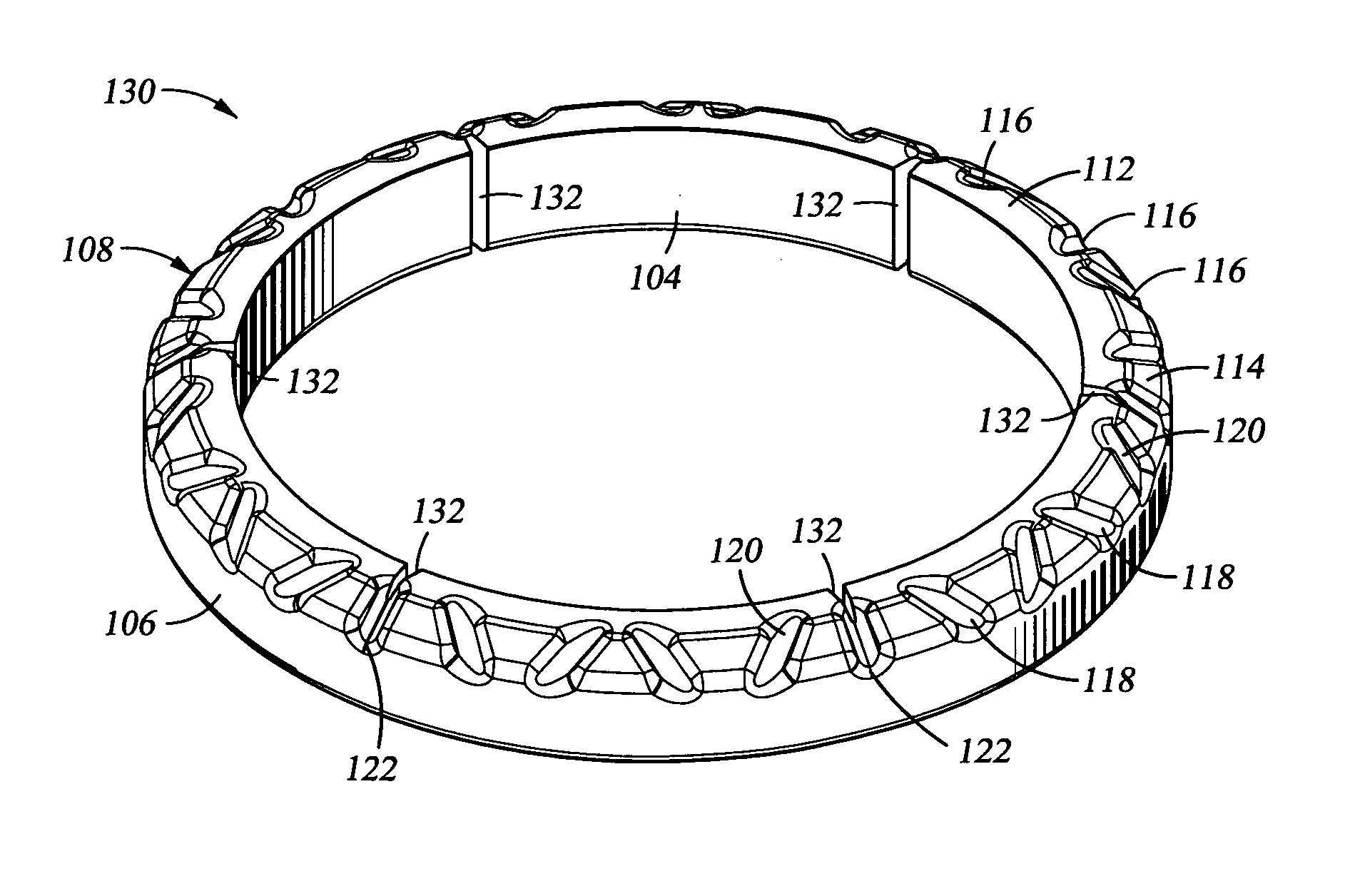
Catheter with variable arcuate distal section
ActiveUS20130006238A1Enhanced surface contactGood and more controlled distribution of loadElectrocardiographyCatheterCircular segmentHelix
A catheter includes an elongated body, a distal assembly with a shape-memory member defining a generally circular form, and a control handle adapted to actuate a deflection puller wire for deflecting a portion of the elongated body, and a contraction wire for contracting the generally circular form. The generally circular form which carries at least one ring electrode has an off-edge configuration relative to the elongated body such that a longitudinal axis of the elongated body does not intersect the circumference of the circular form and the generally circular form spirals about the longitudinal axis of the elongated body. Moreover, the circular form can have an on-axis configuration such that the longitudinal axis of the elongated body is axially aligned with a central longitudinal axis of the circular form, or an off-axis configuration such that these axes are axially offset from each other. In a more detailed embodiment, the catheter has a distal assembly with a helical form or a crescent form carrying a plurality of irrigated ablation ring electrodes and a plurality of smaller ring electrodes adapted for impedance recording or PV potential recording. A support member with shape memory extends through the distal assembly to provide the helical or crescent form. The support member has a varying stiffness along its length, for example, a decreasing stiffness toward a distal end of the support member. The support member can also be hollow so that it can receive a mandrel whose stiffness is greater than that of the support member.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Maximum support tlif implant
A transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) implant to be placed in an intervertebral space includes a front member and a back member. The front member includes a first end having a hinge, a second end, a pair of lateral portions, a top wall and a bottom wall, an opening configured through the pair of lateral portions and a plurality of openings in each of the top wall and the bottom wall. The back member includes a first end having an arcuately-shaped attachment head comprising a receptor dimensioned and configured to accommodate the hinge of the front member, a second end, a pair of lateral portions, a top wall, a bottom wall and an opening configured through the pair of lateral portions. The top wall and the bottom wall of the back member further comprise a plurality of openings.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
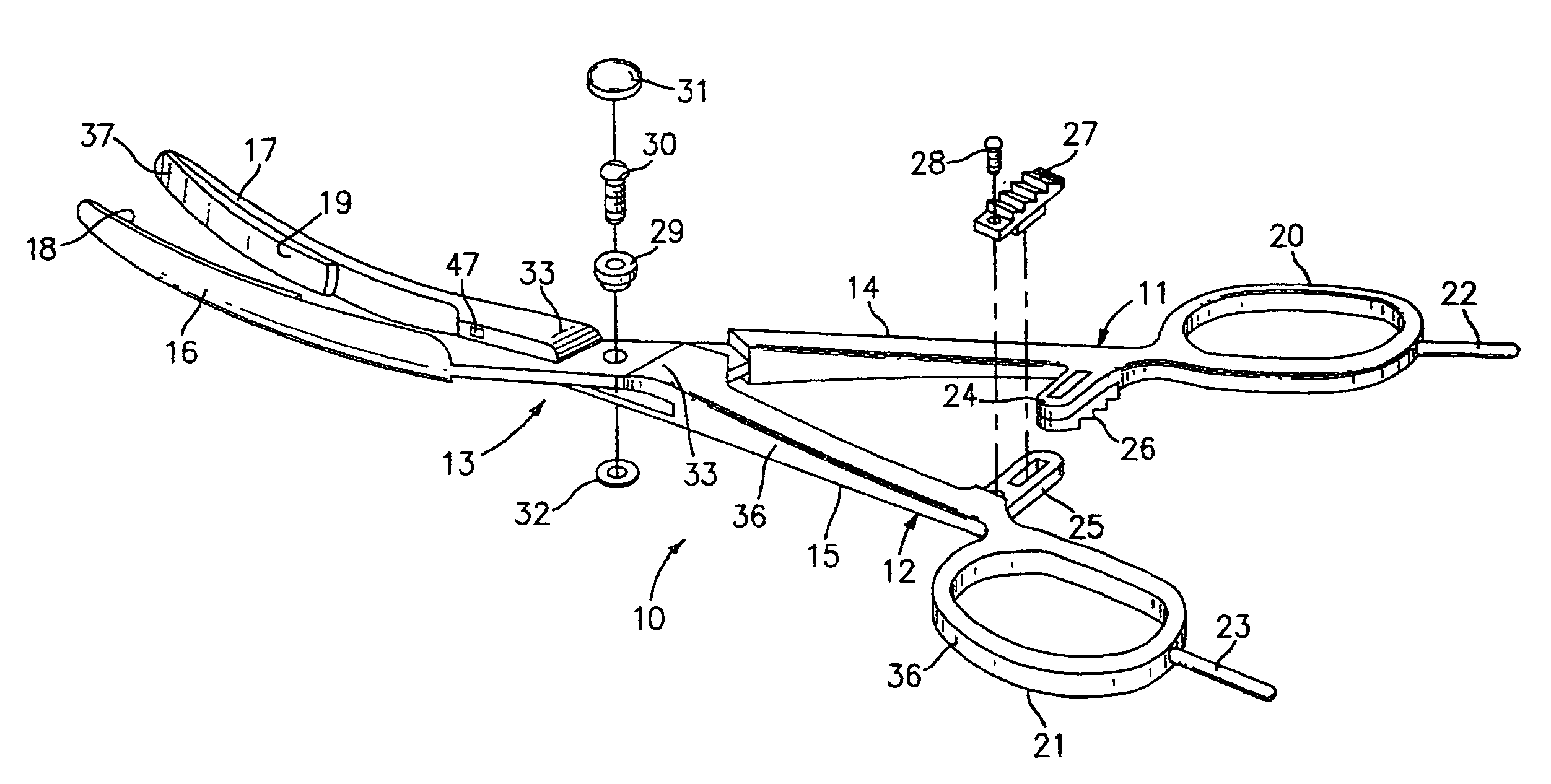
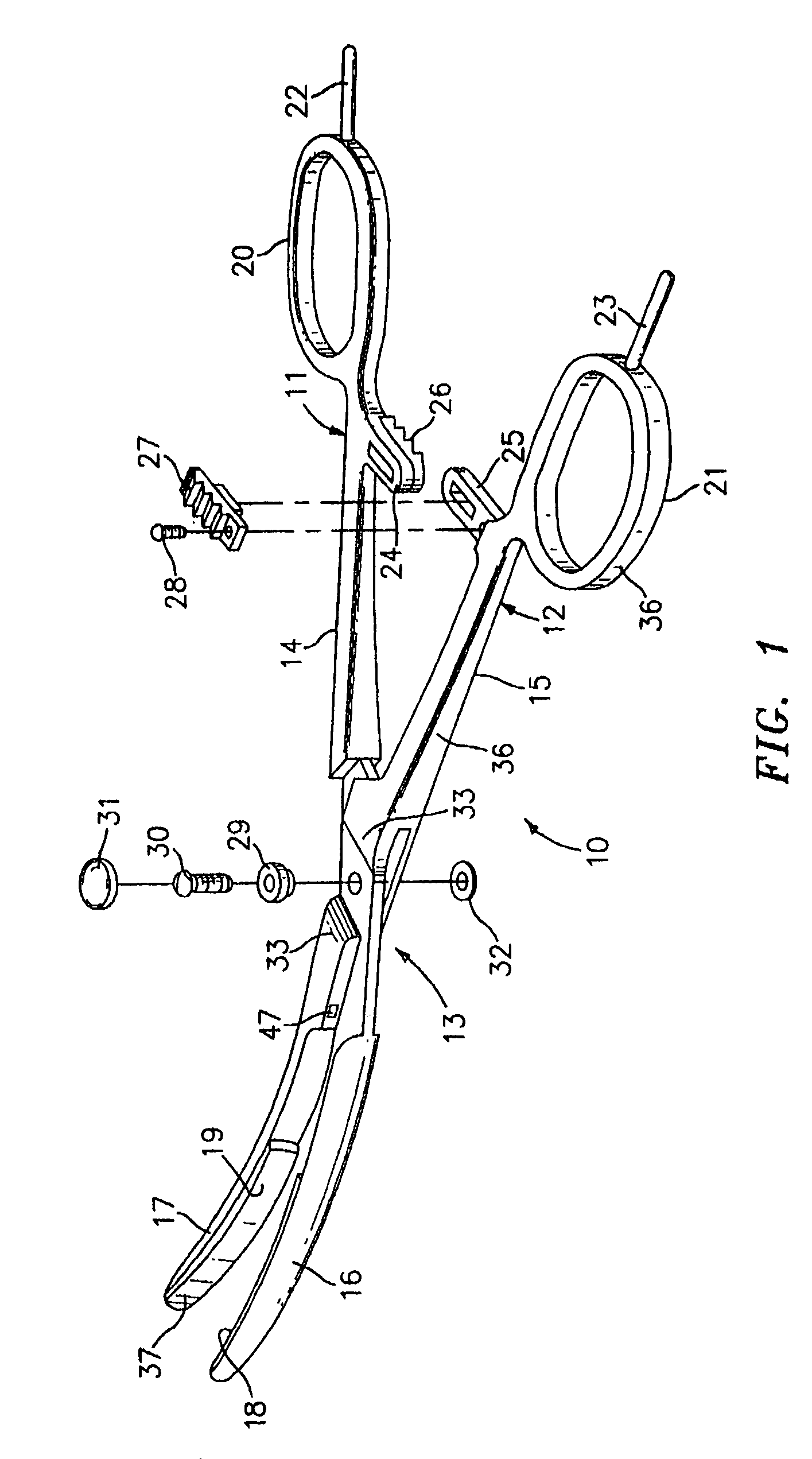
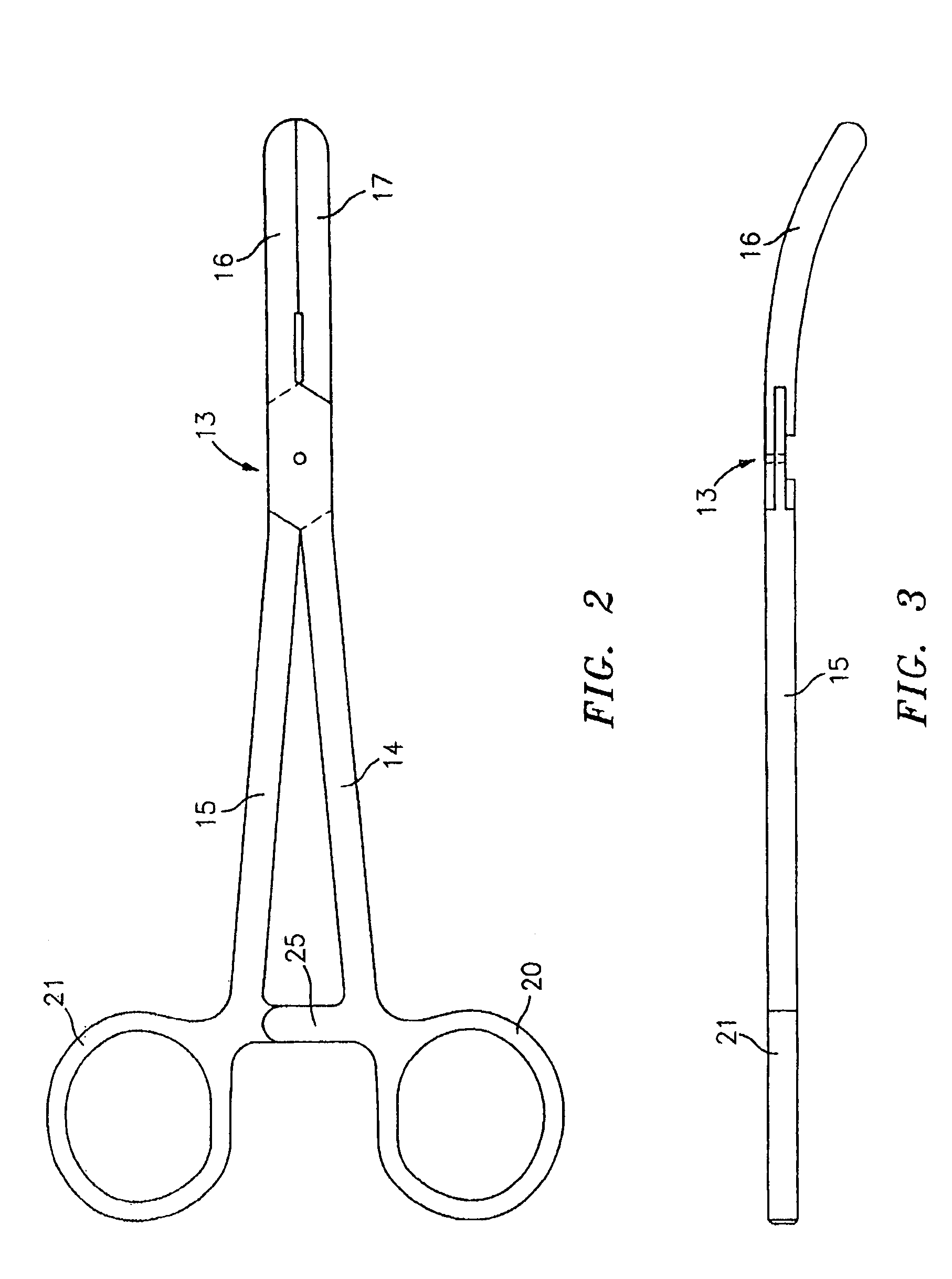
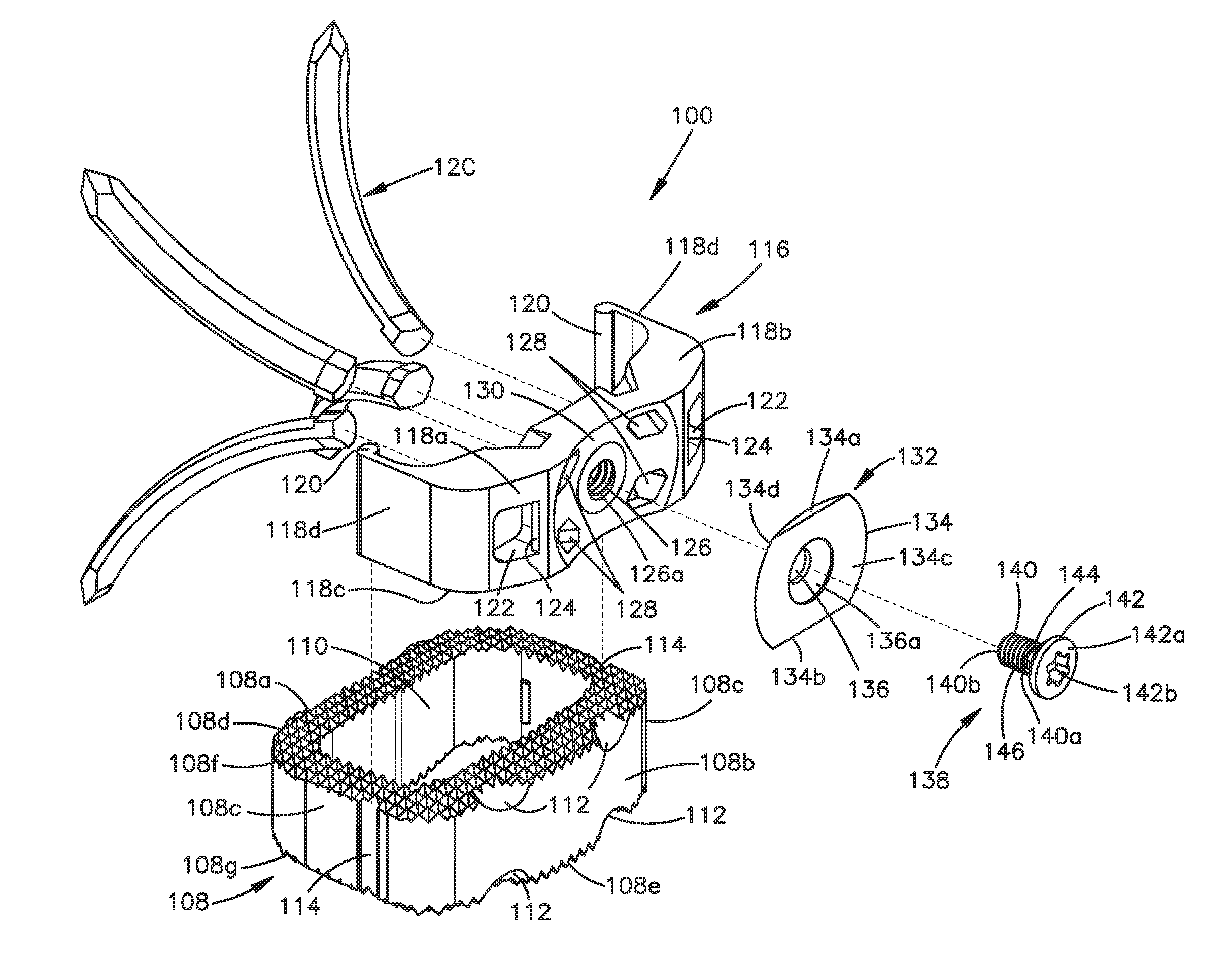
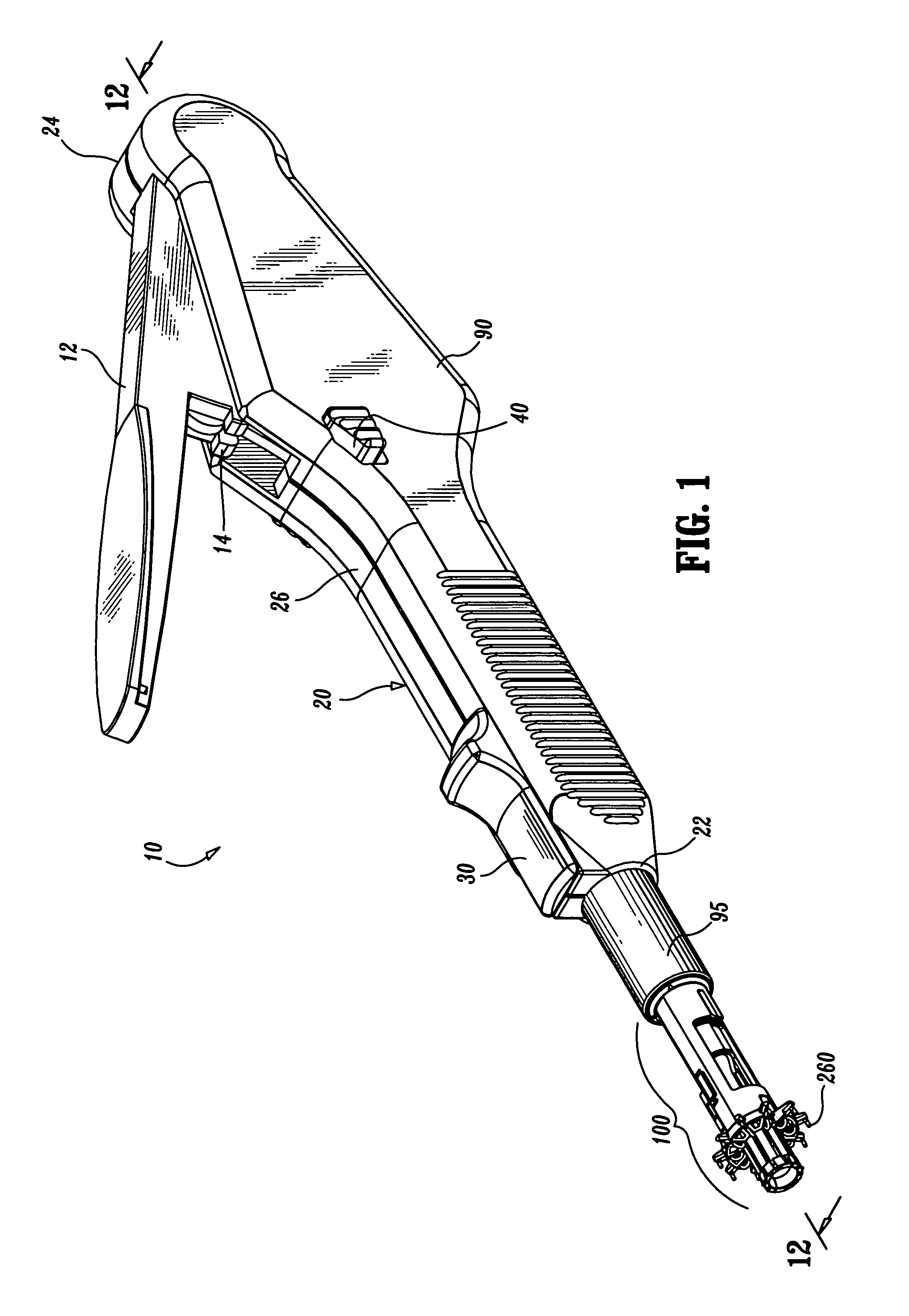
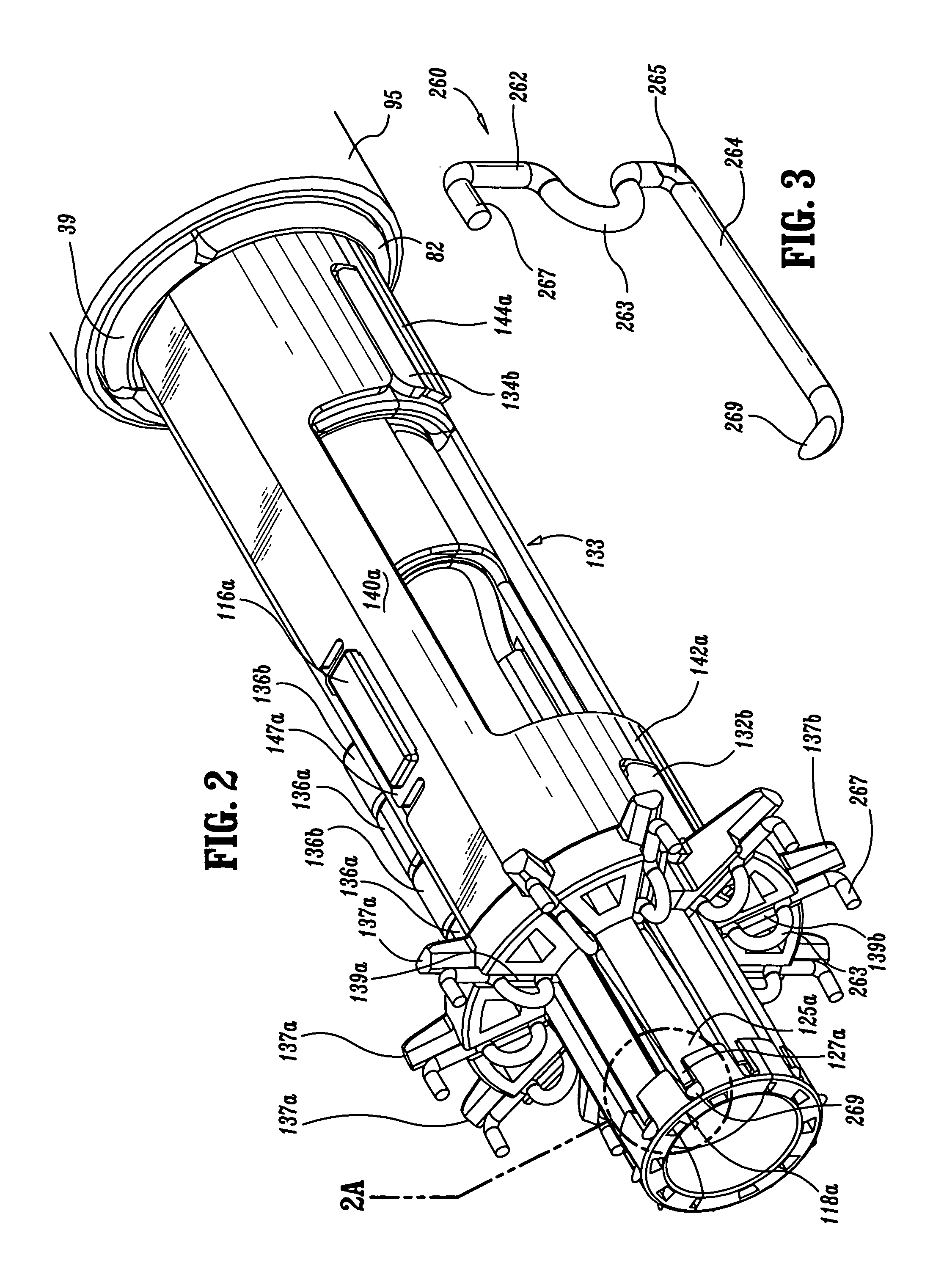
Surgical suturing apparatus
A surgical suturing apparatus includes a suture housing, a needle mounted within the suture housing for movement about an arcuate path, and a drive assembly operably associated with the needle for controlling movement of the needle with a suture secured thereto about the arcuate path in a manner facilitating application of the suture to tissue. The drive assembly includes a friction camming member that moves along the suture housing under the control of the drive mechanism, wherein actuation of the drive mechanism causes the friction camming member to selectively engage and disengage the needle causing the needle to move about the arcuate path.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com