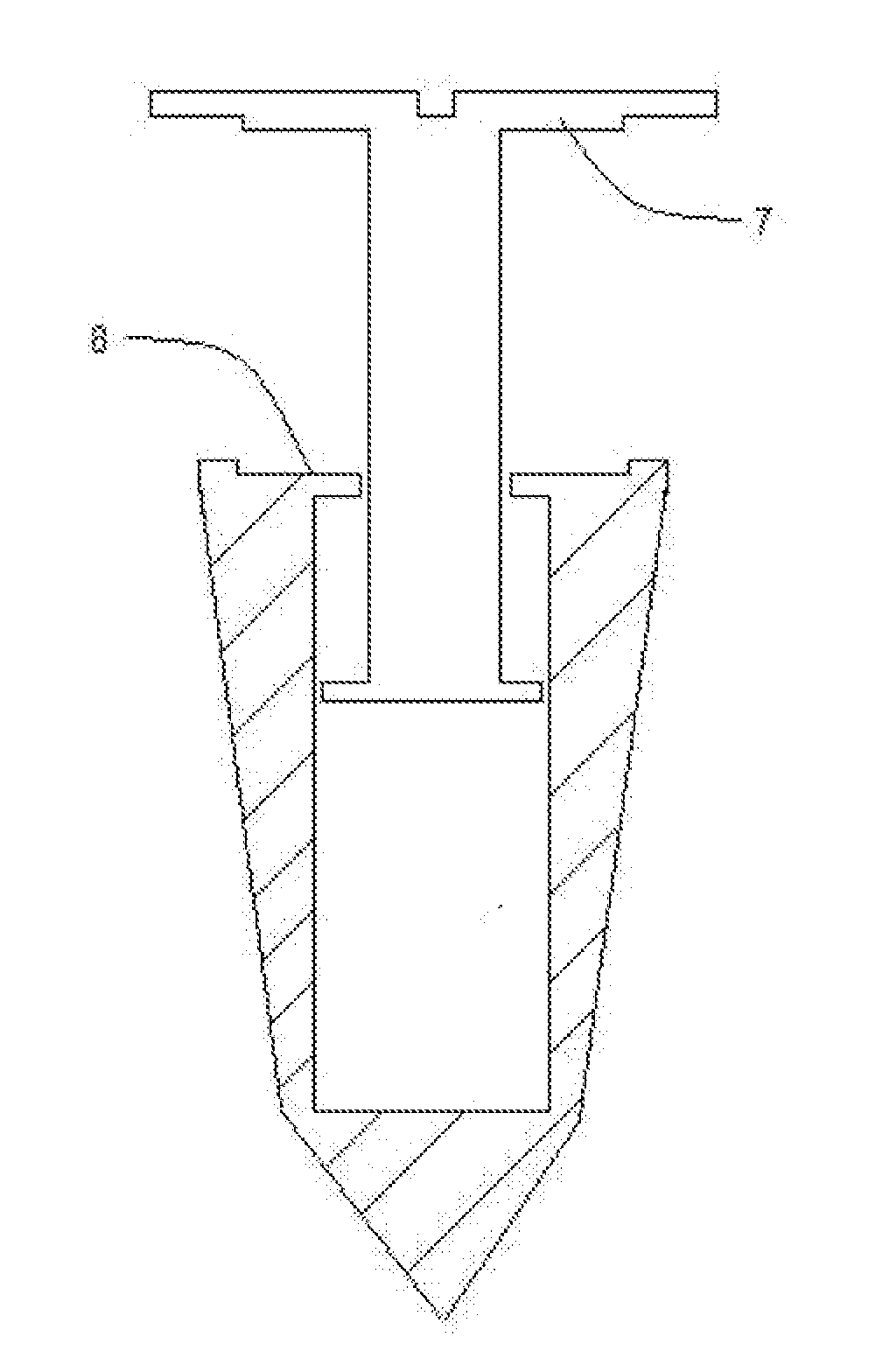
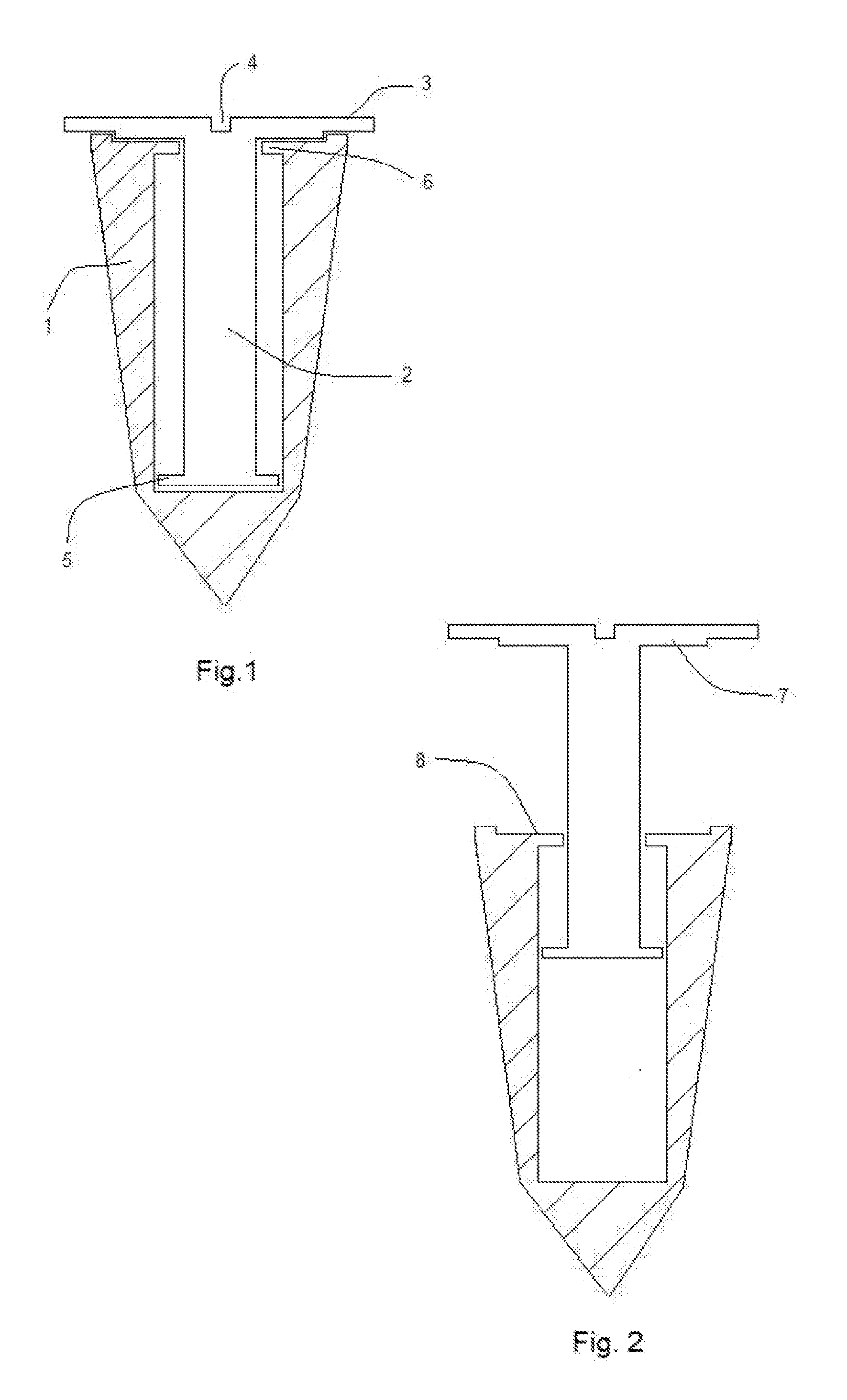
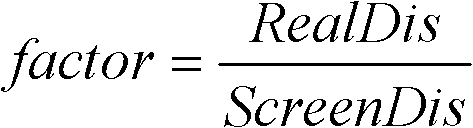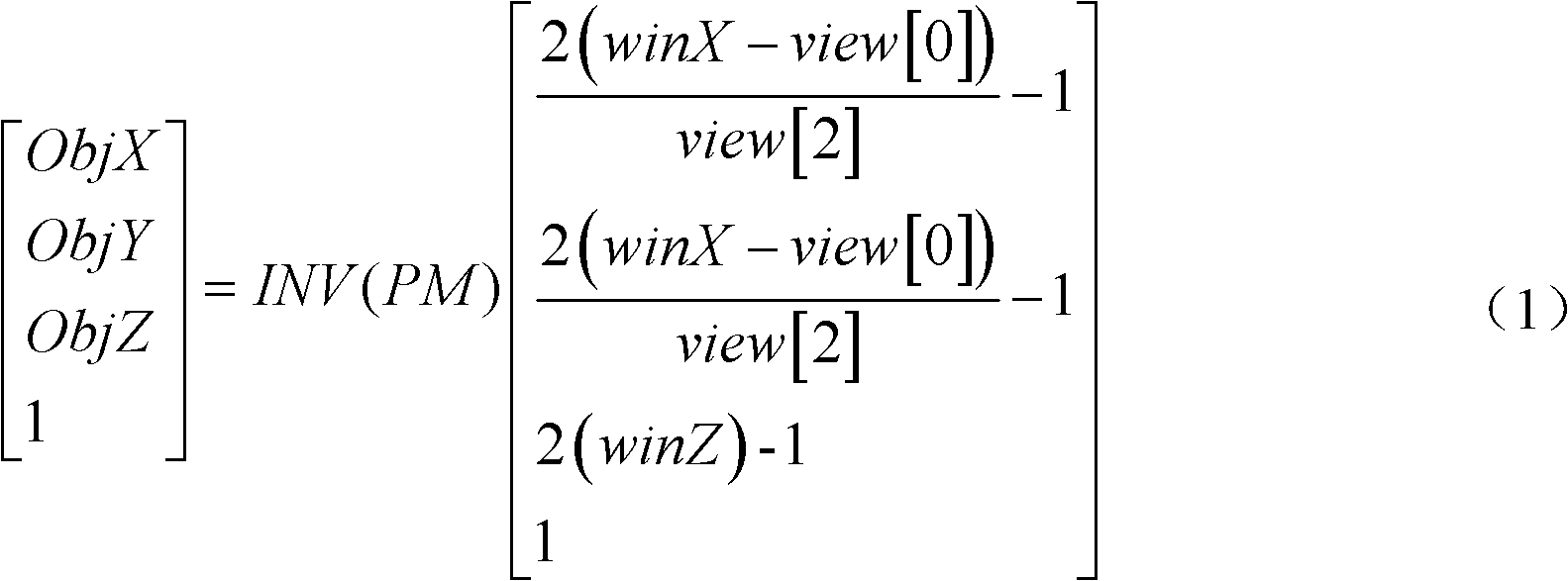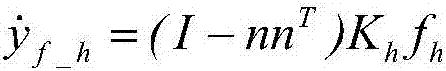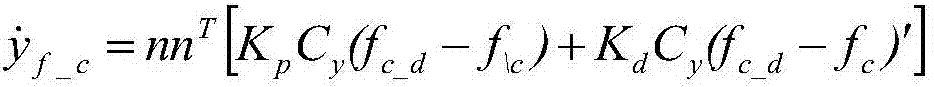Patents
Literature
268 results about "Craniotomy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
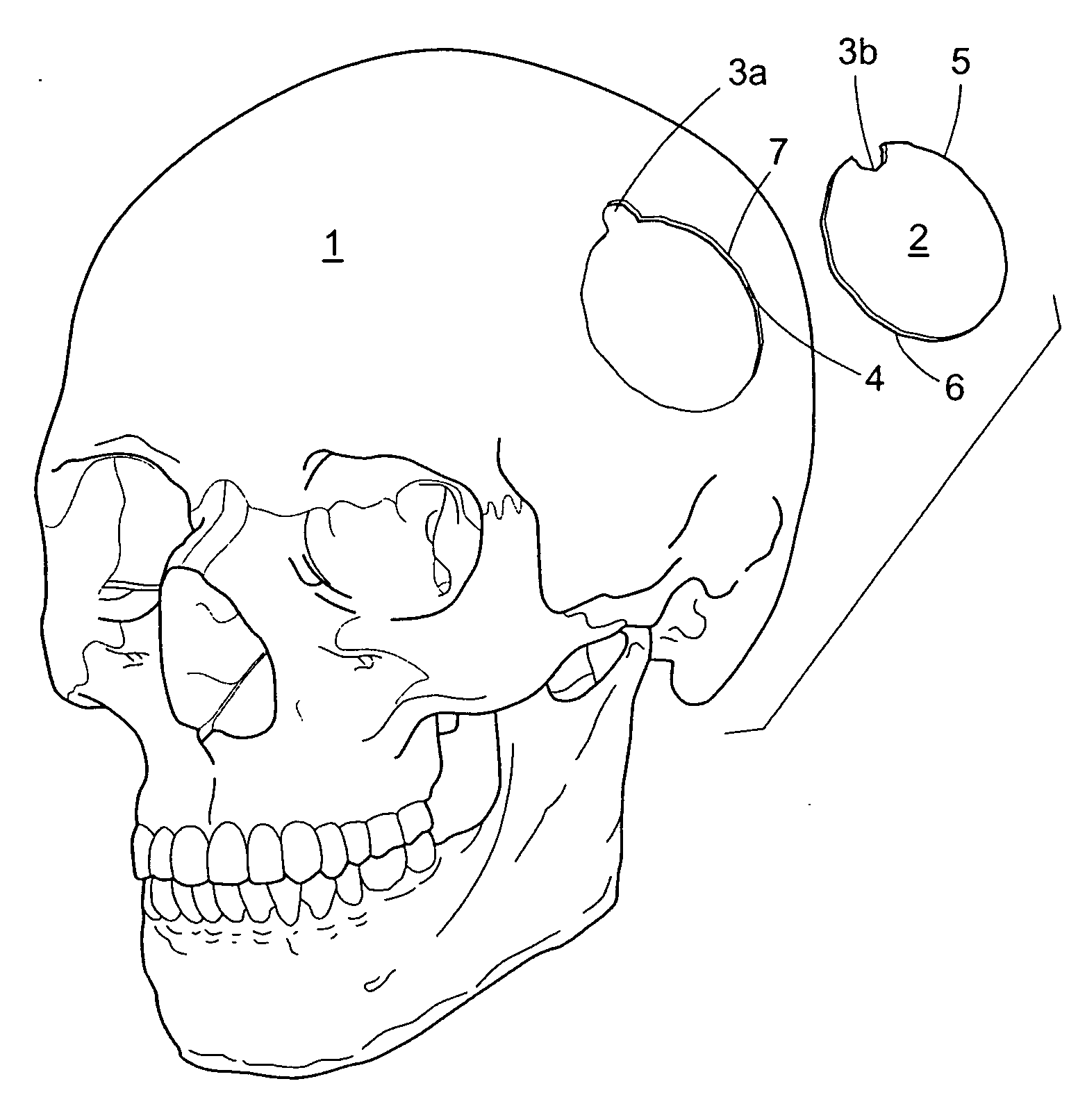
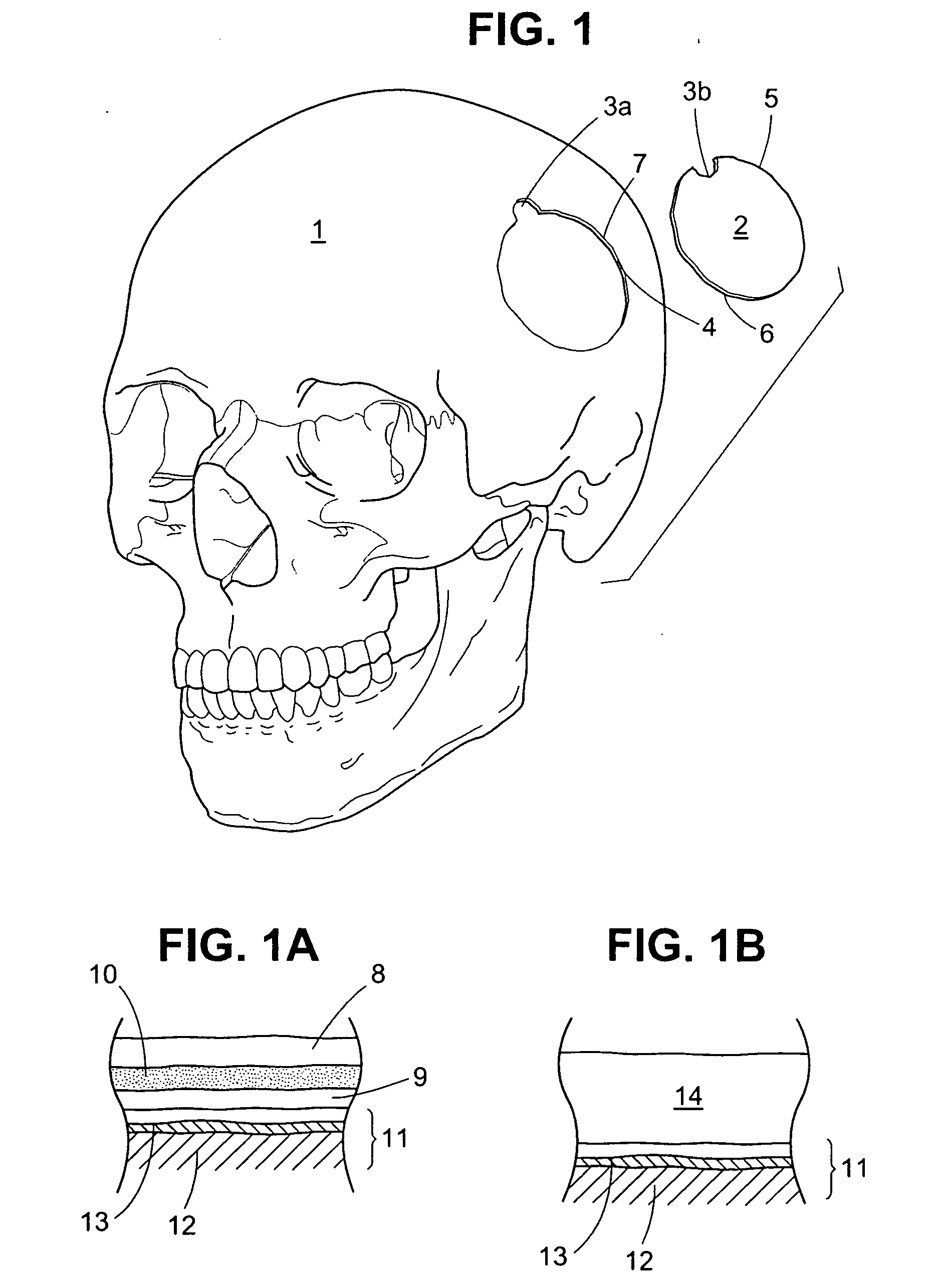
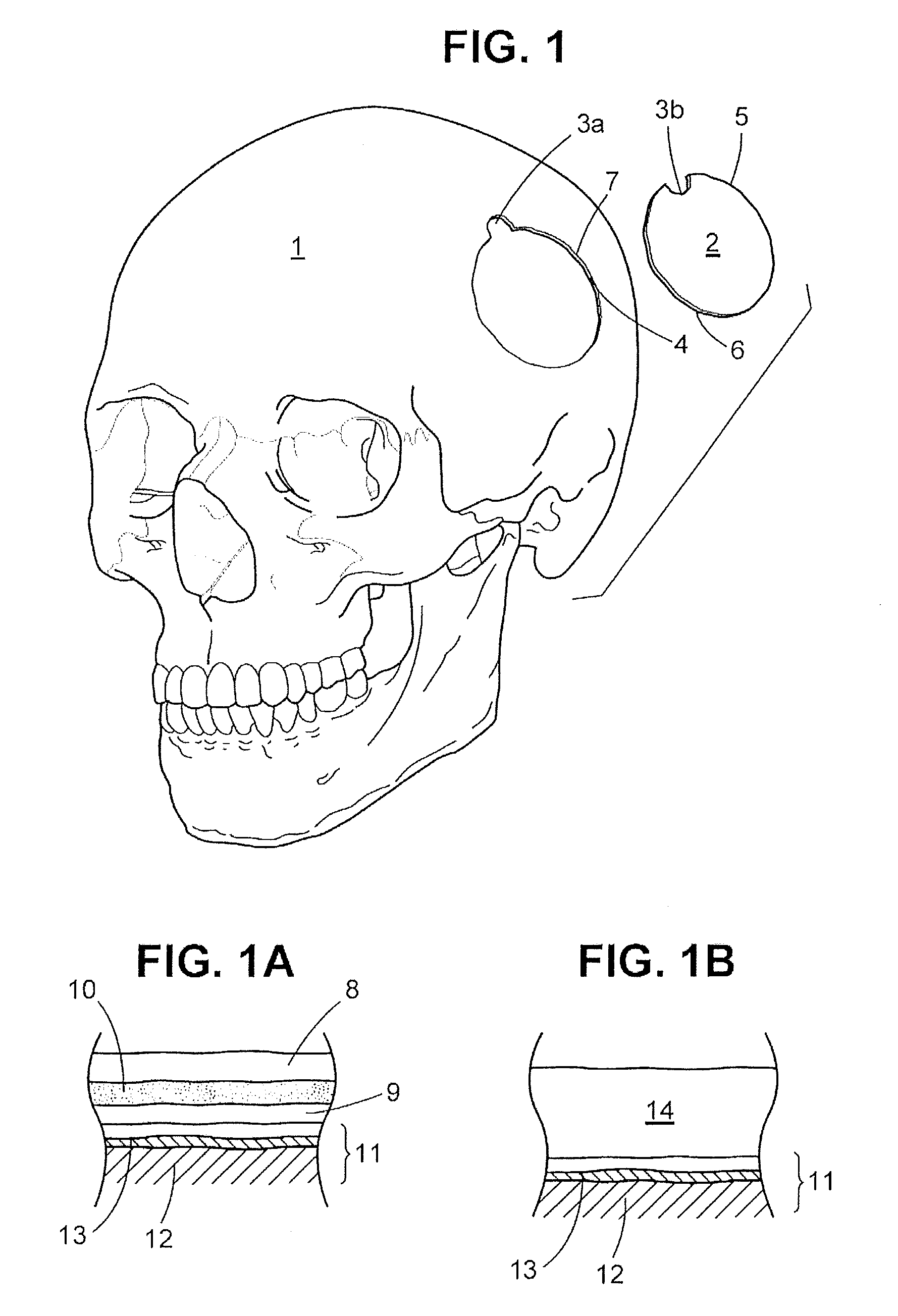
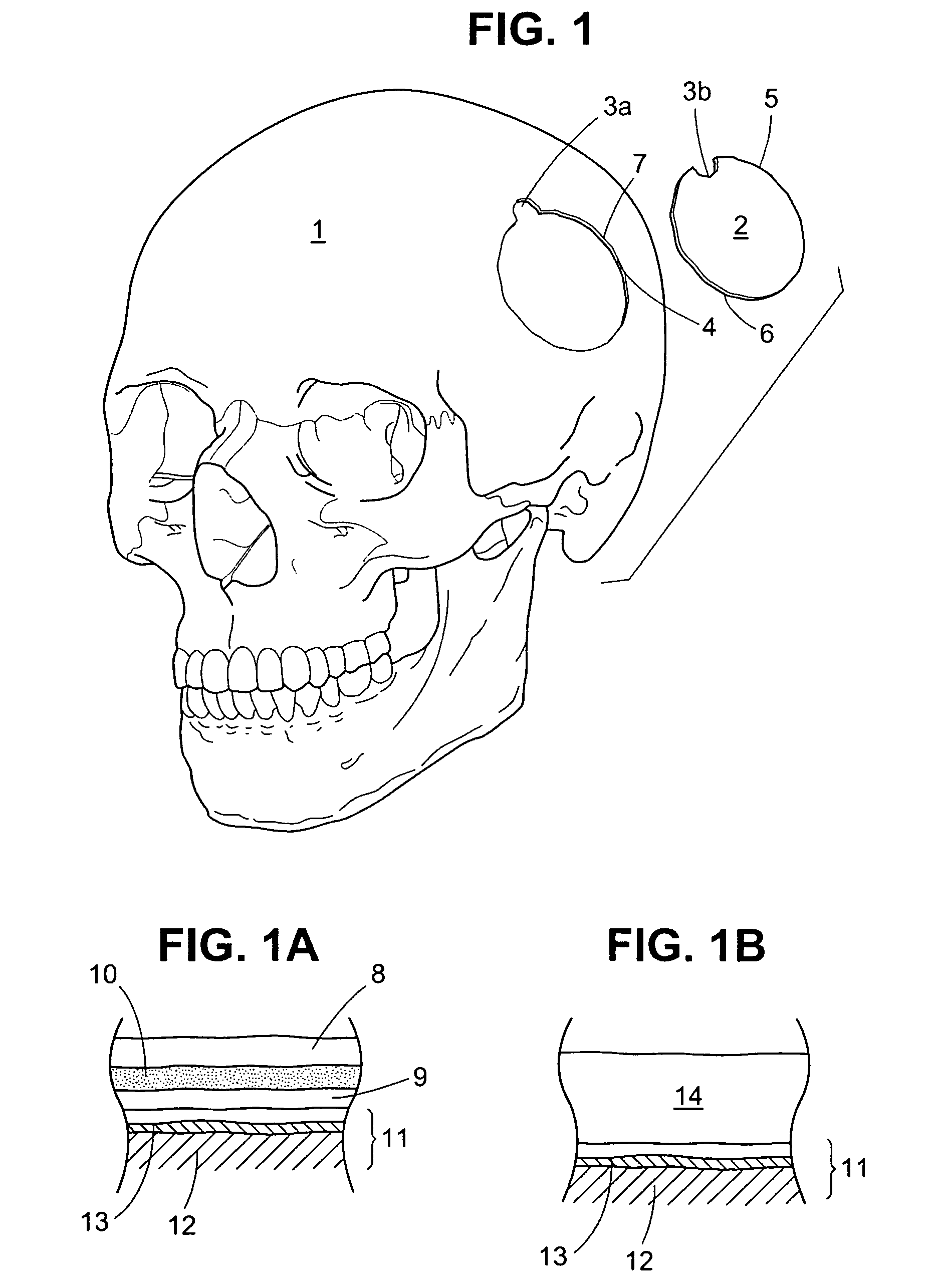
A craniotomy is a surgical operation in which a bone flap is temporarily removed from the skull to access the brain. Craniotomies are often critical operations, performed on patients who are suffering from brain lesions or traumatic brain injury (TBI), and can also allow doctors to surgically implant deep brain stimulators for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and cerebellar tremor.
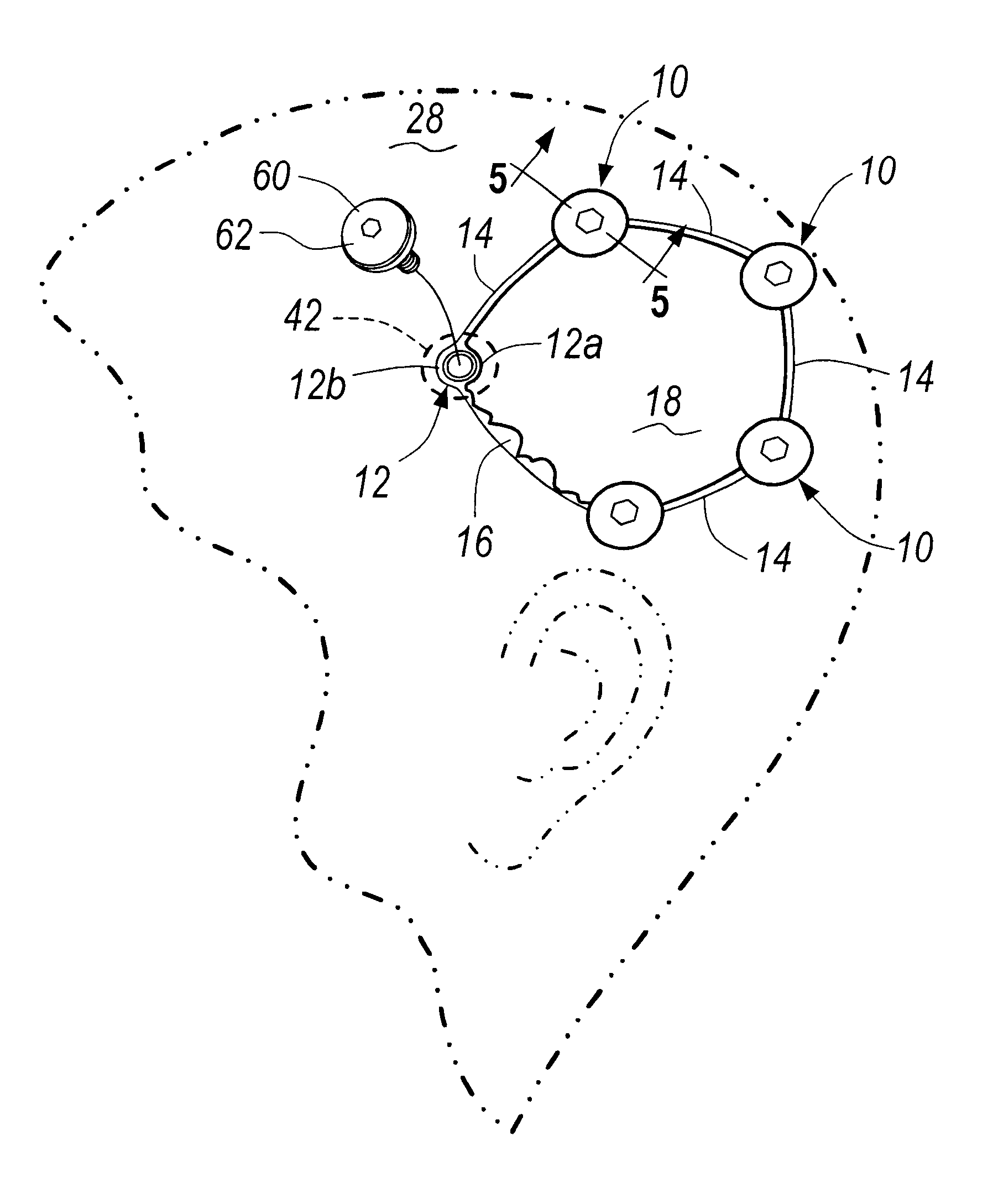
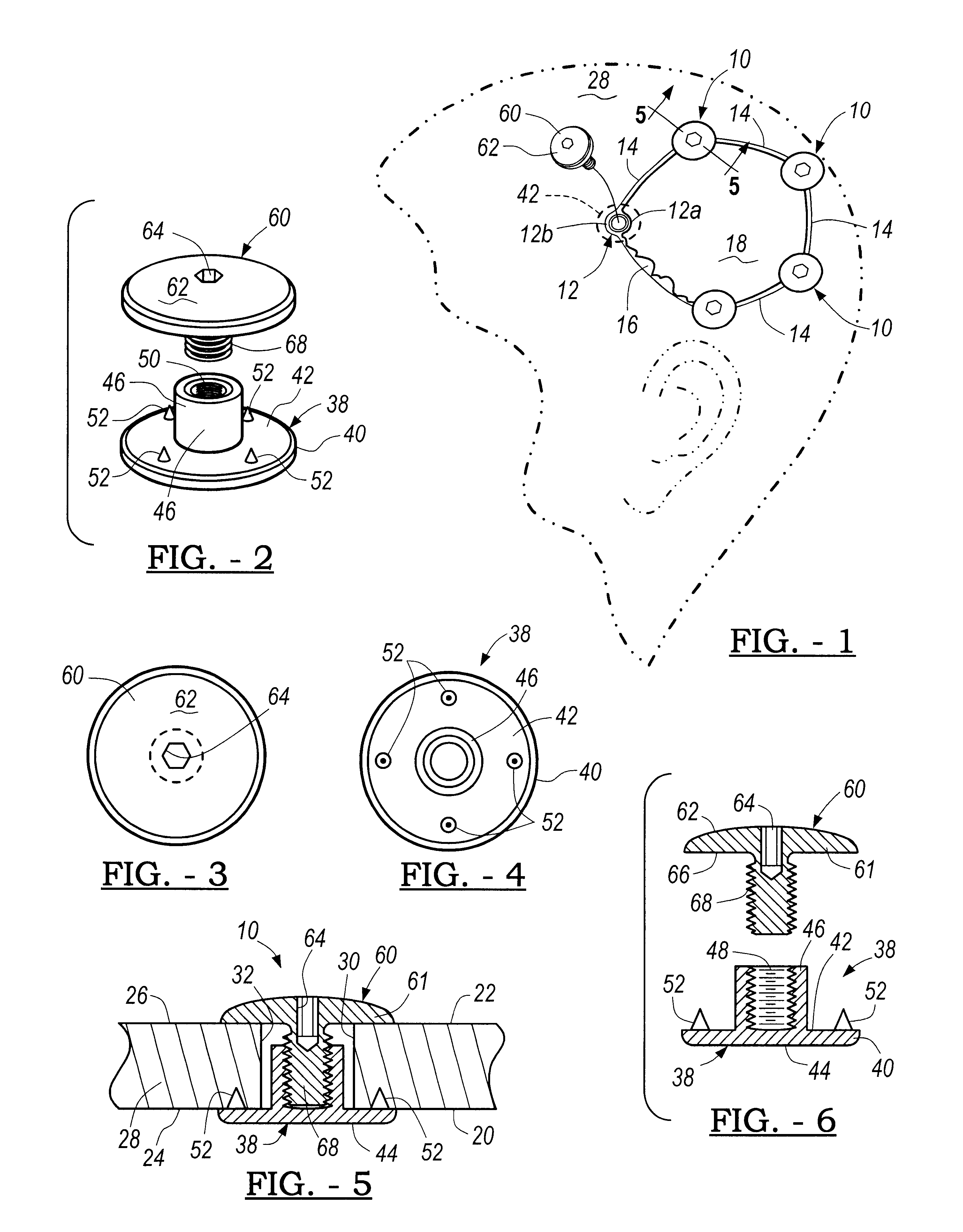
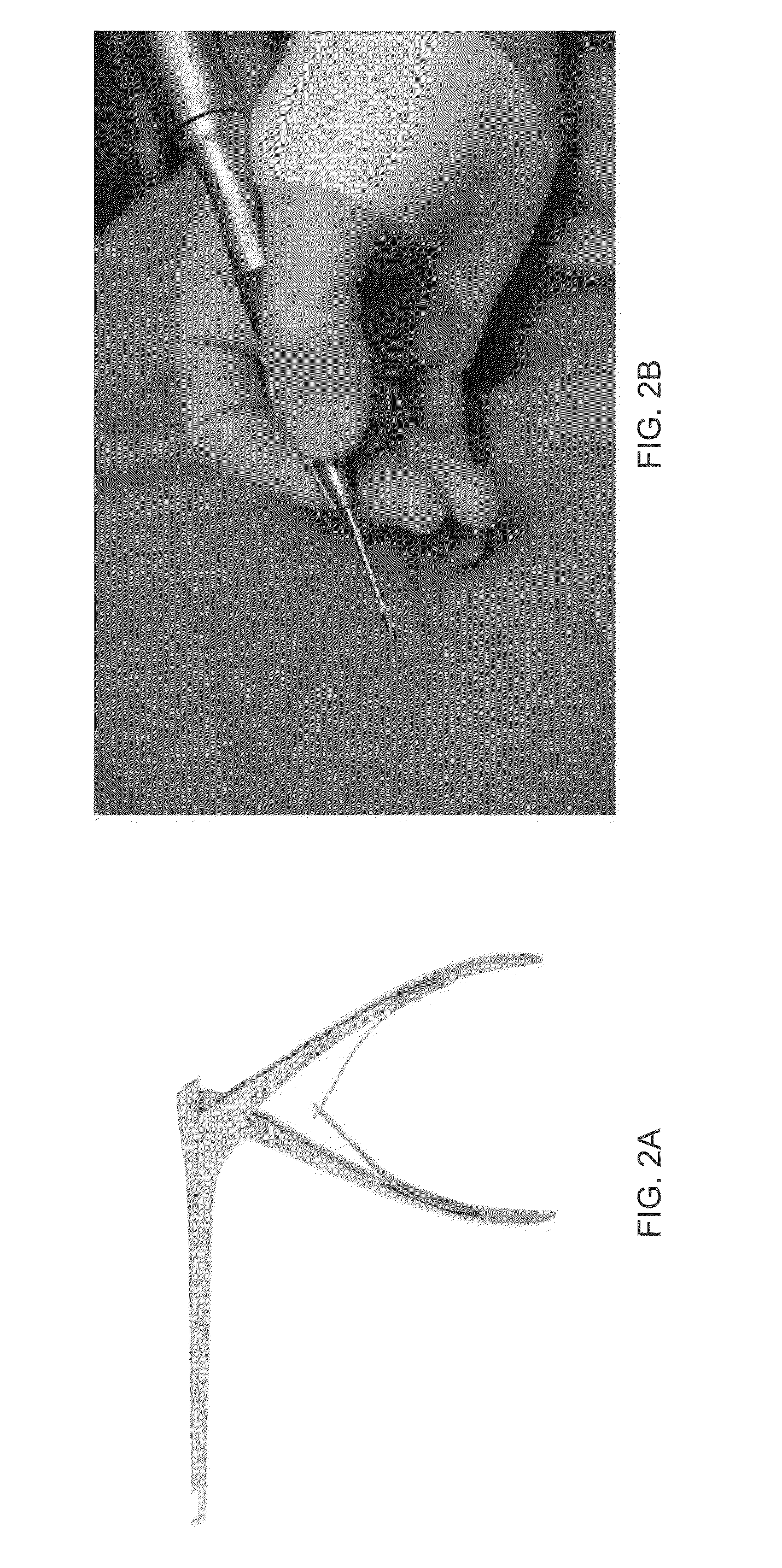
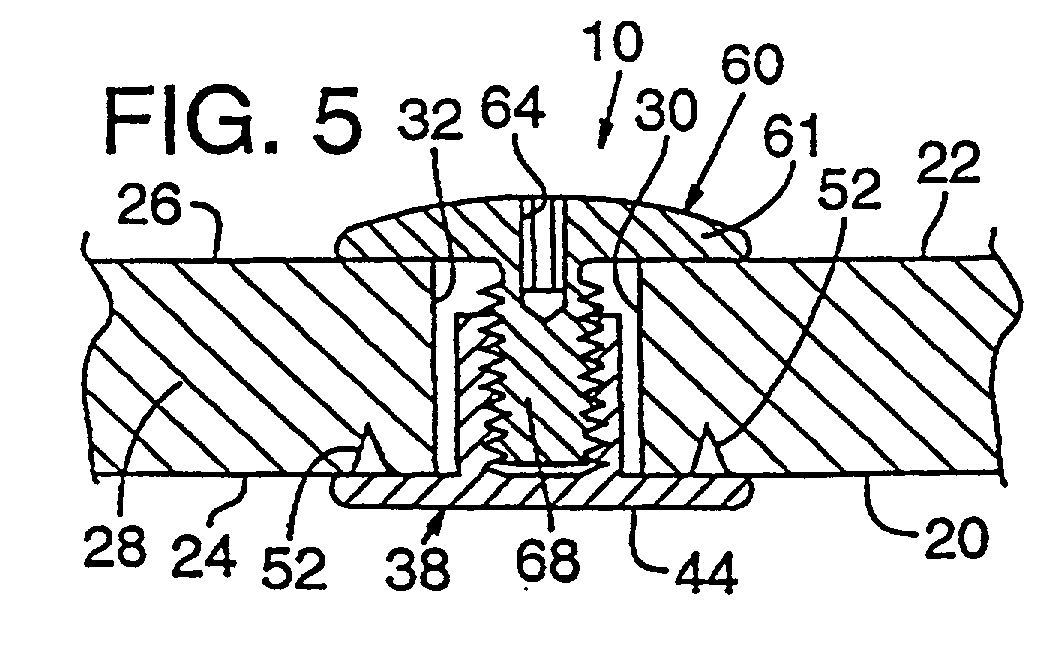
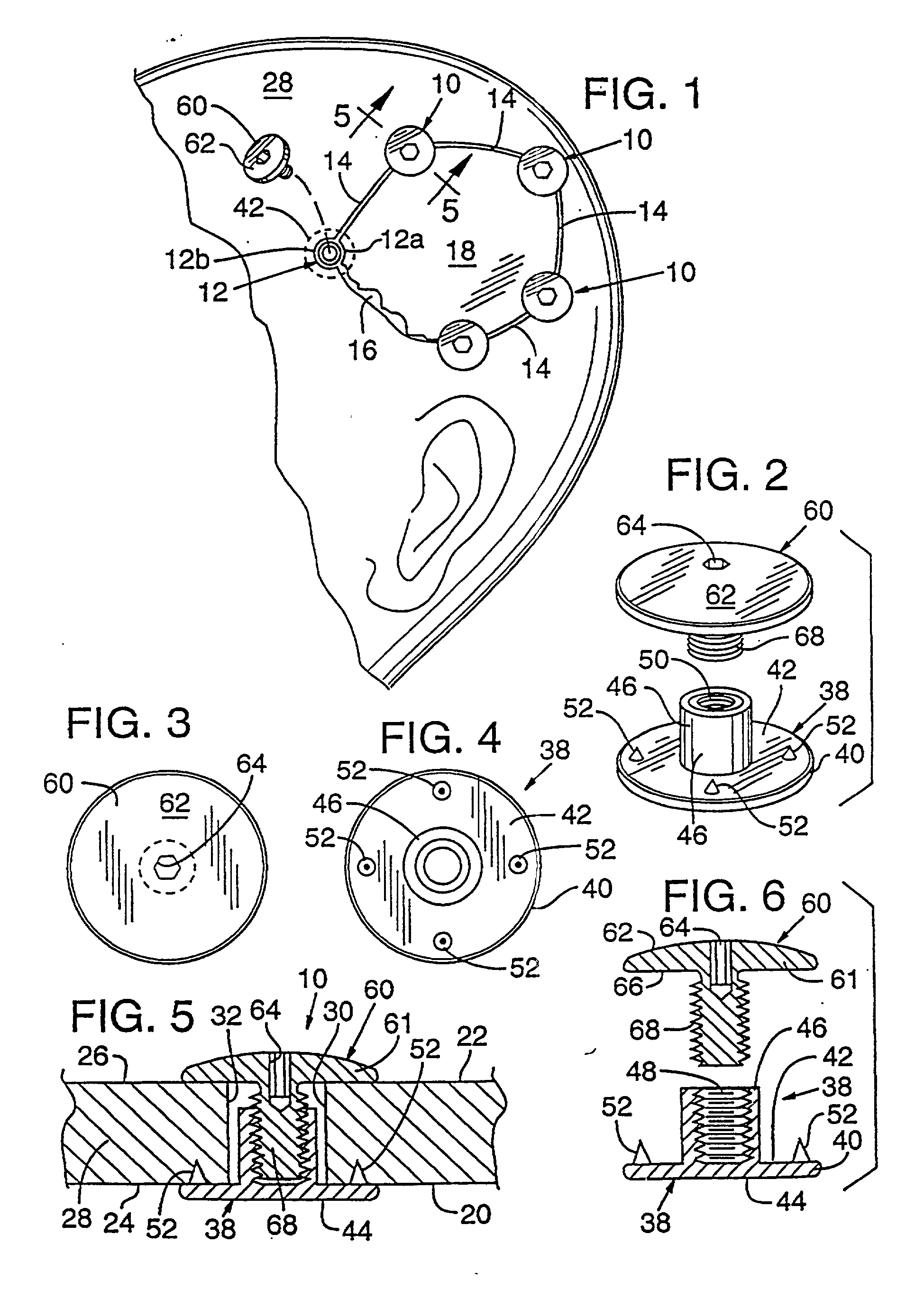
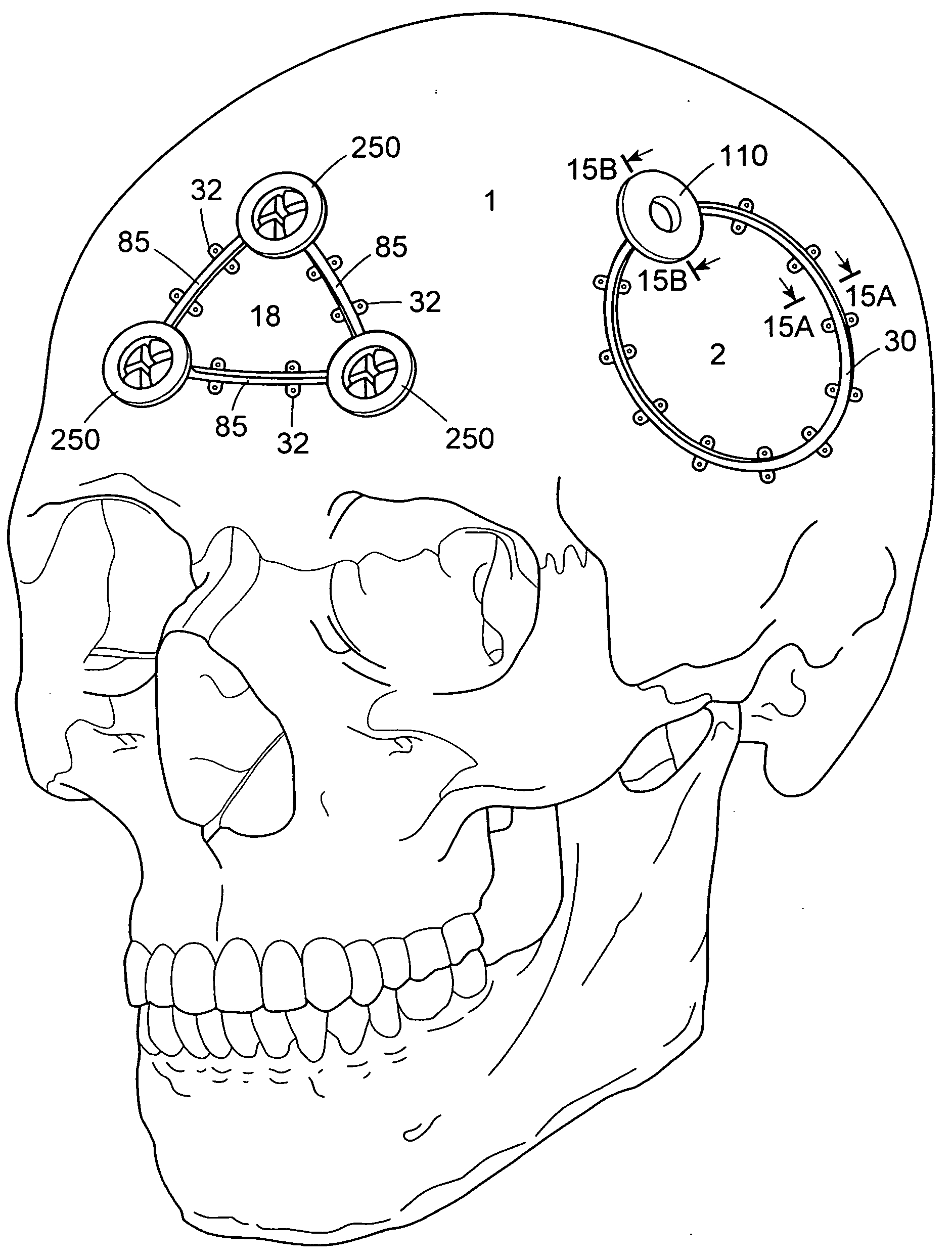
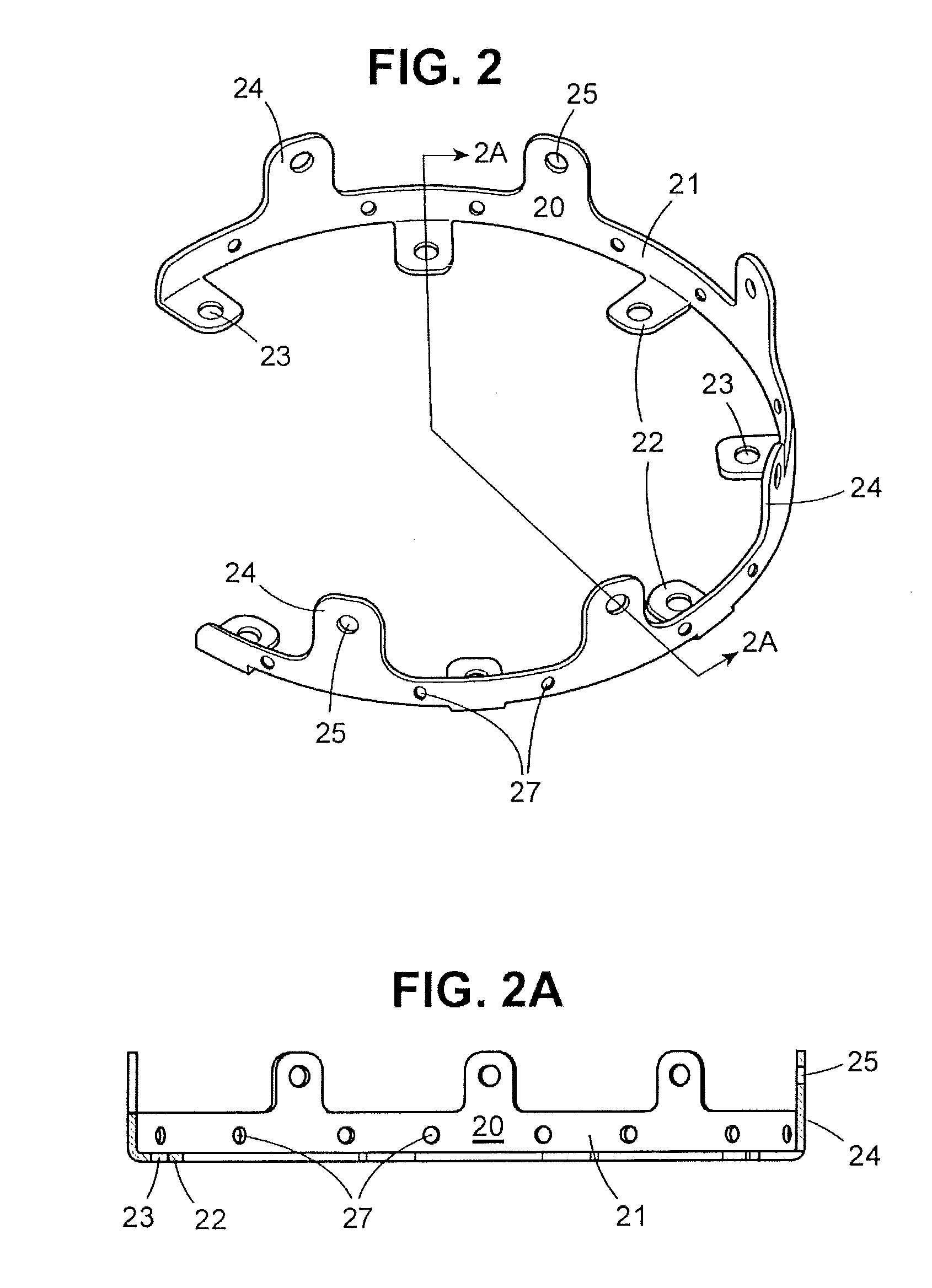
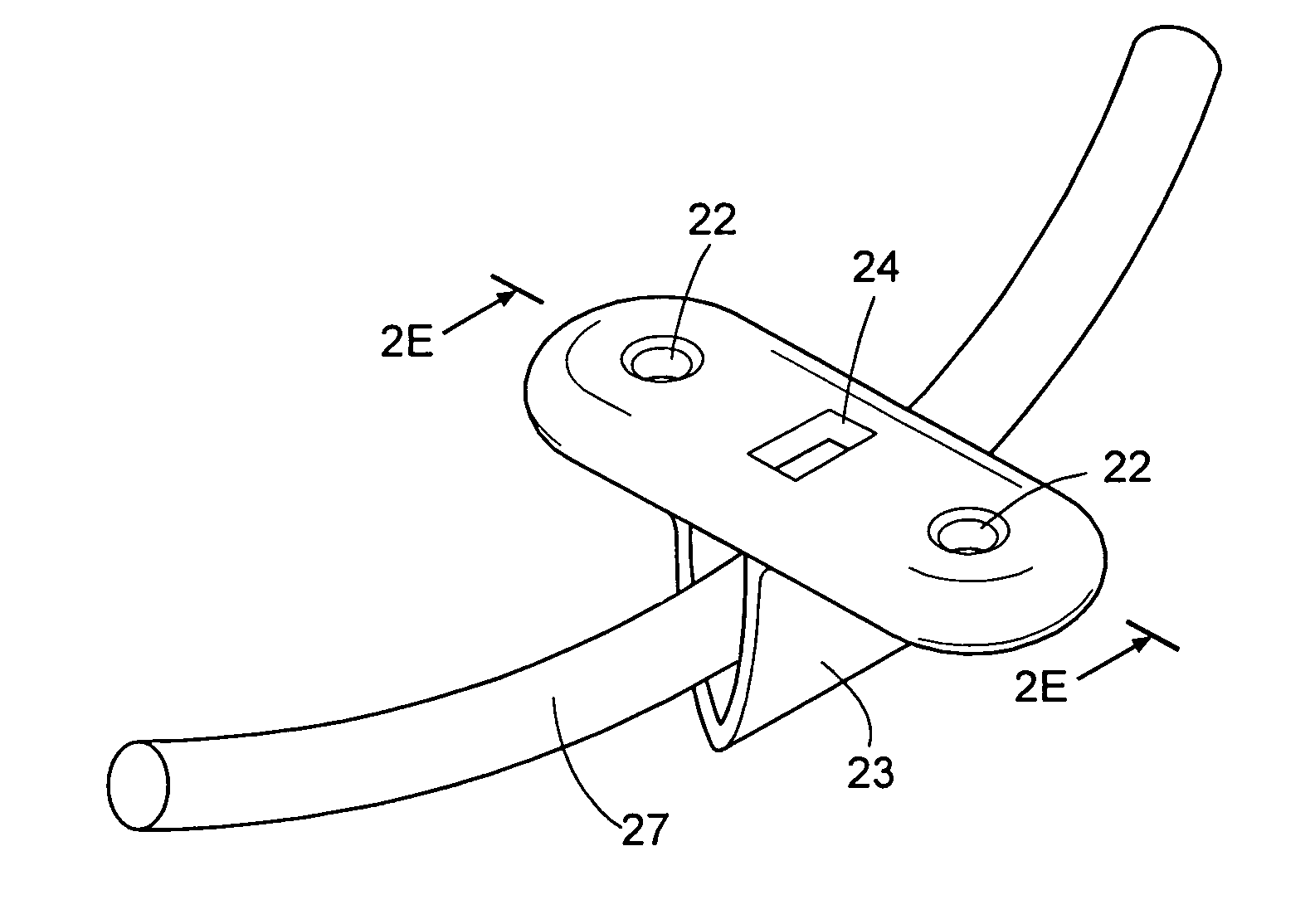
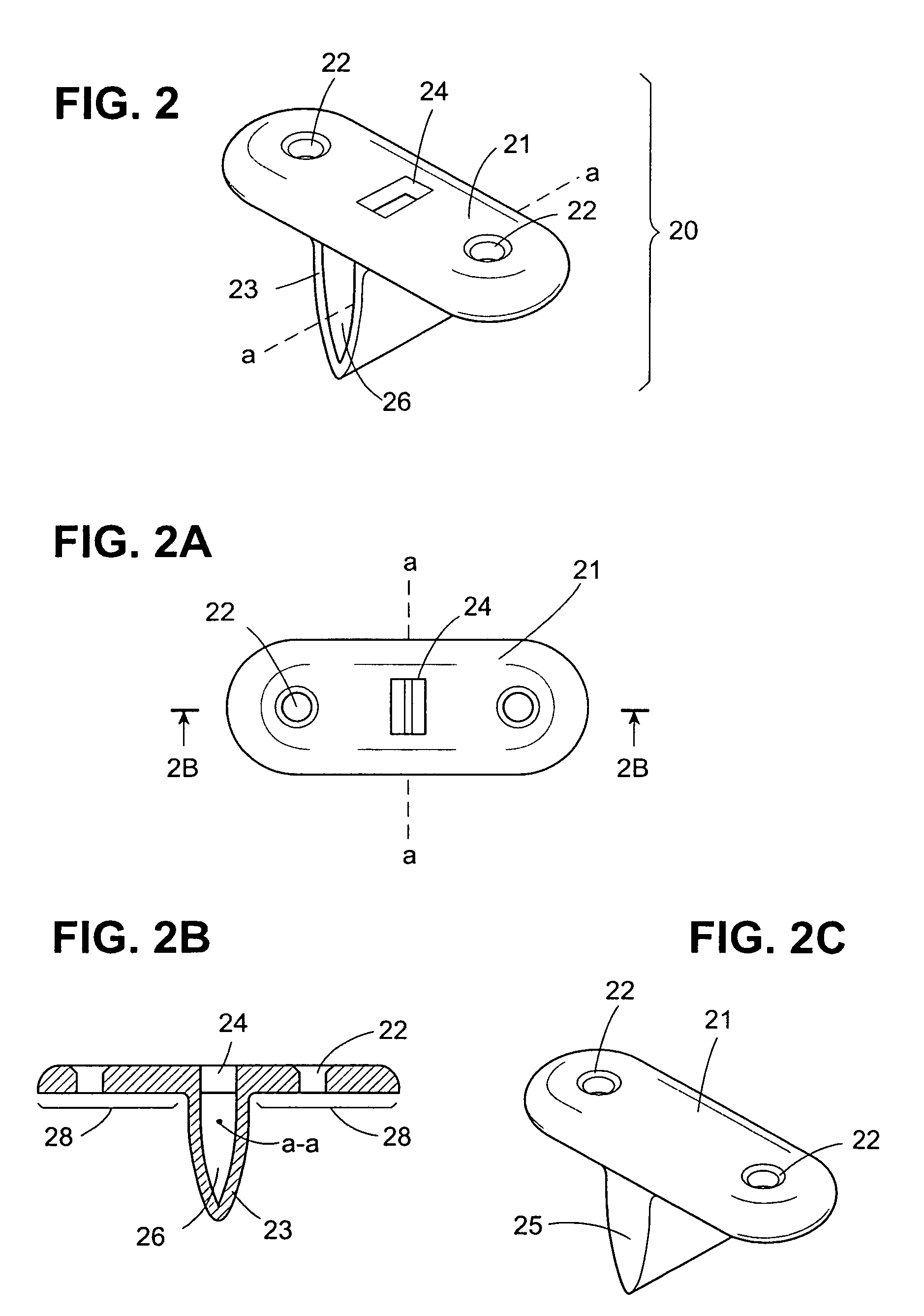
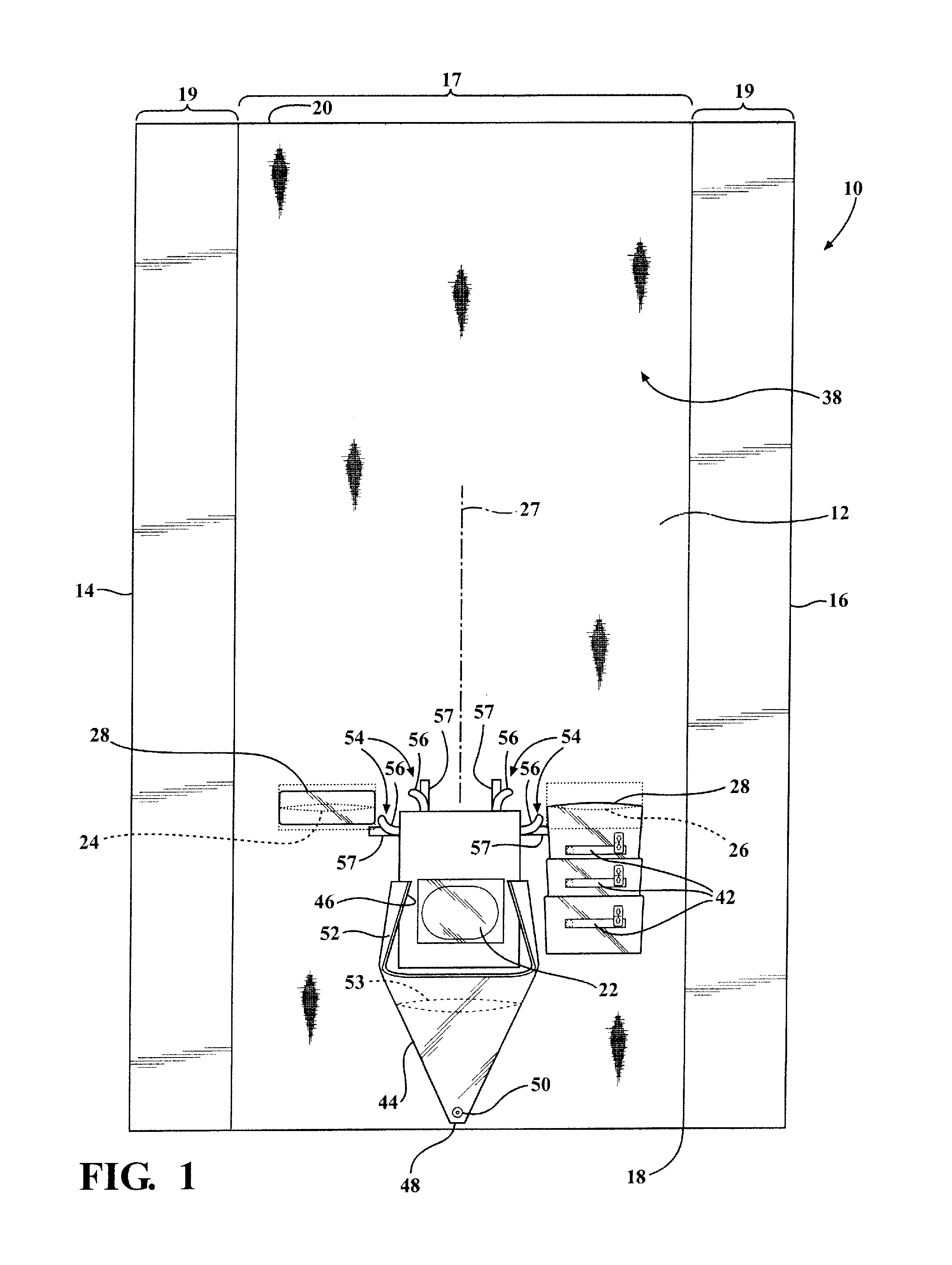
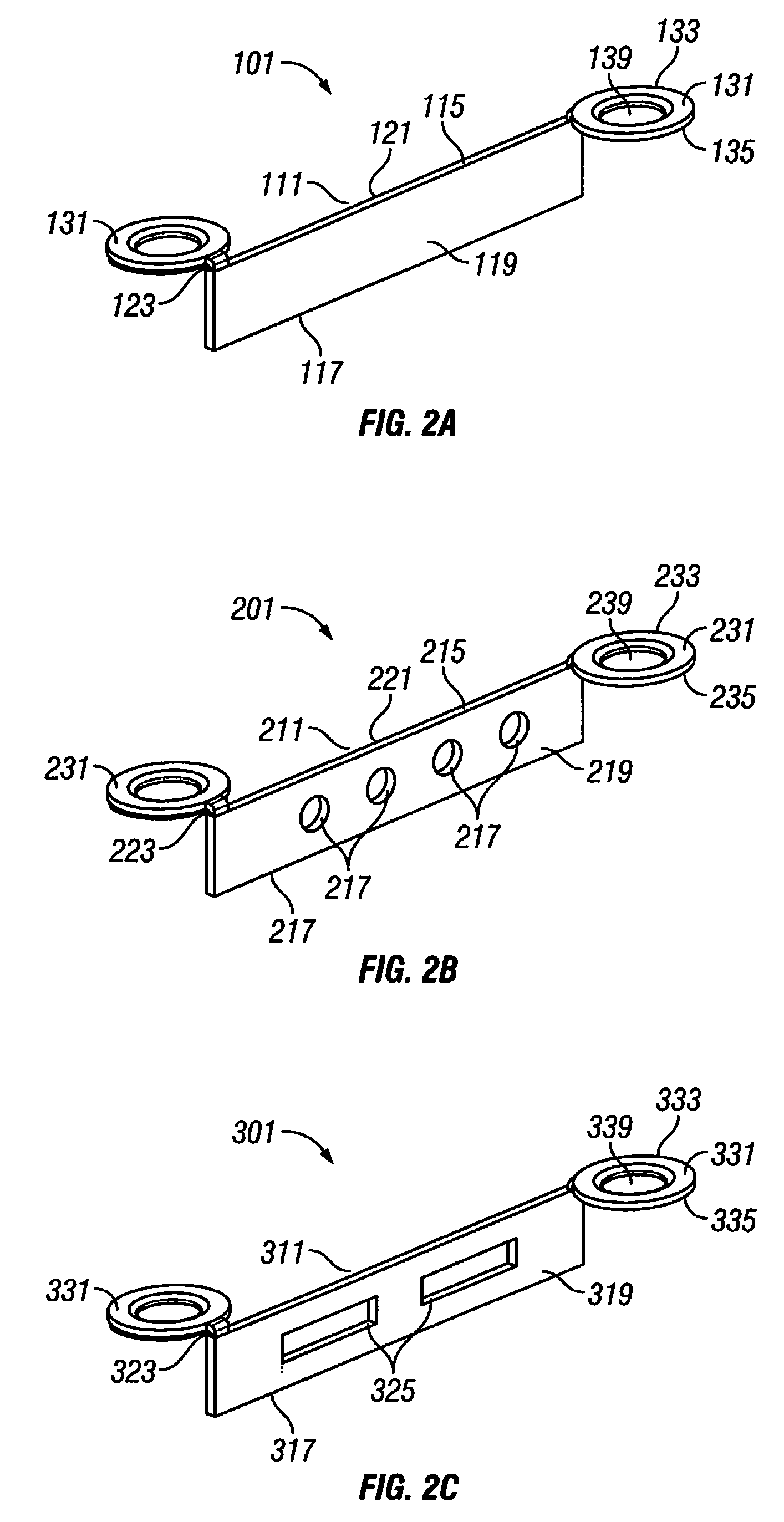
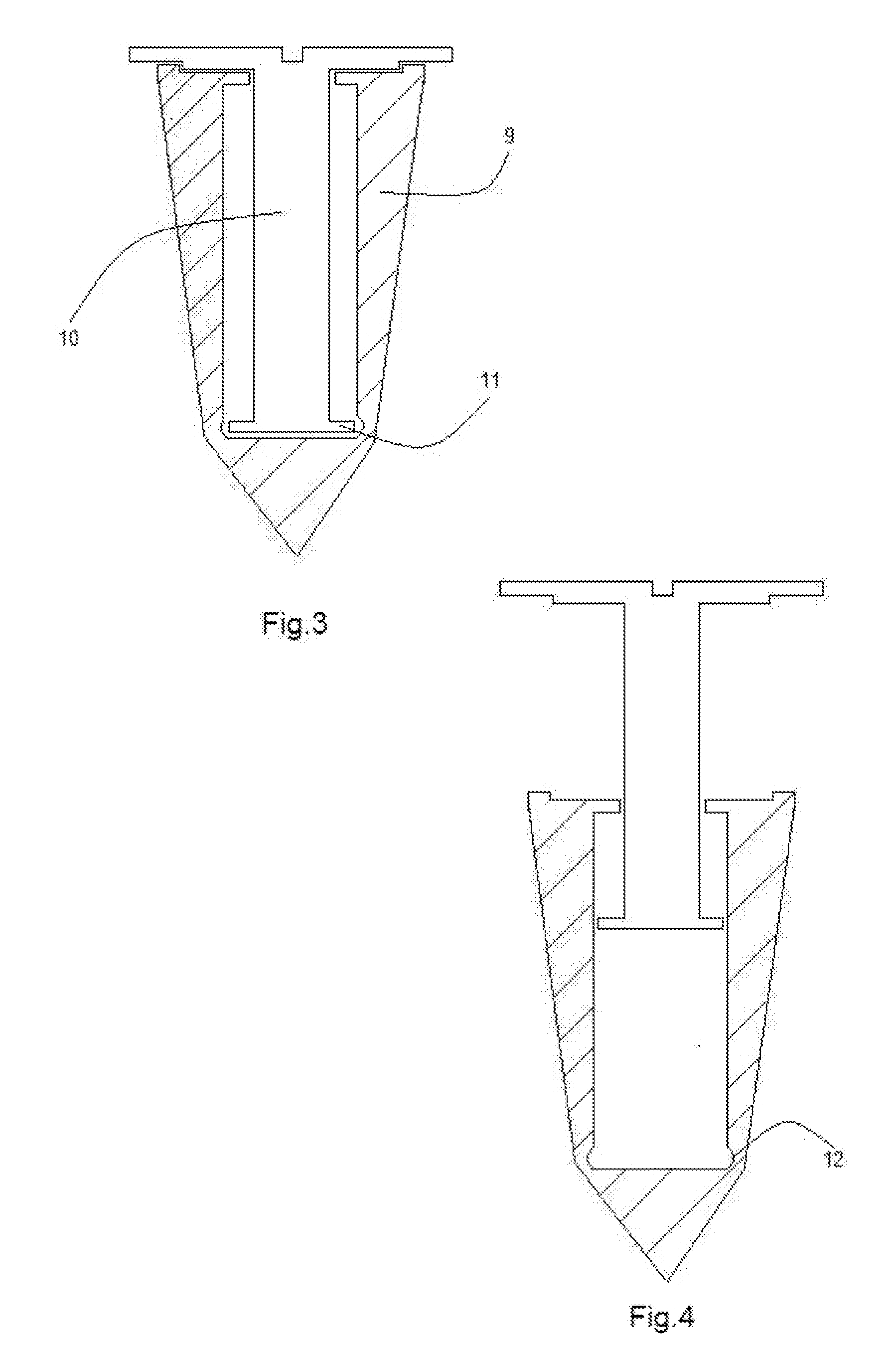
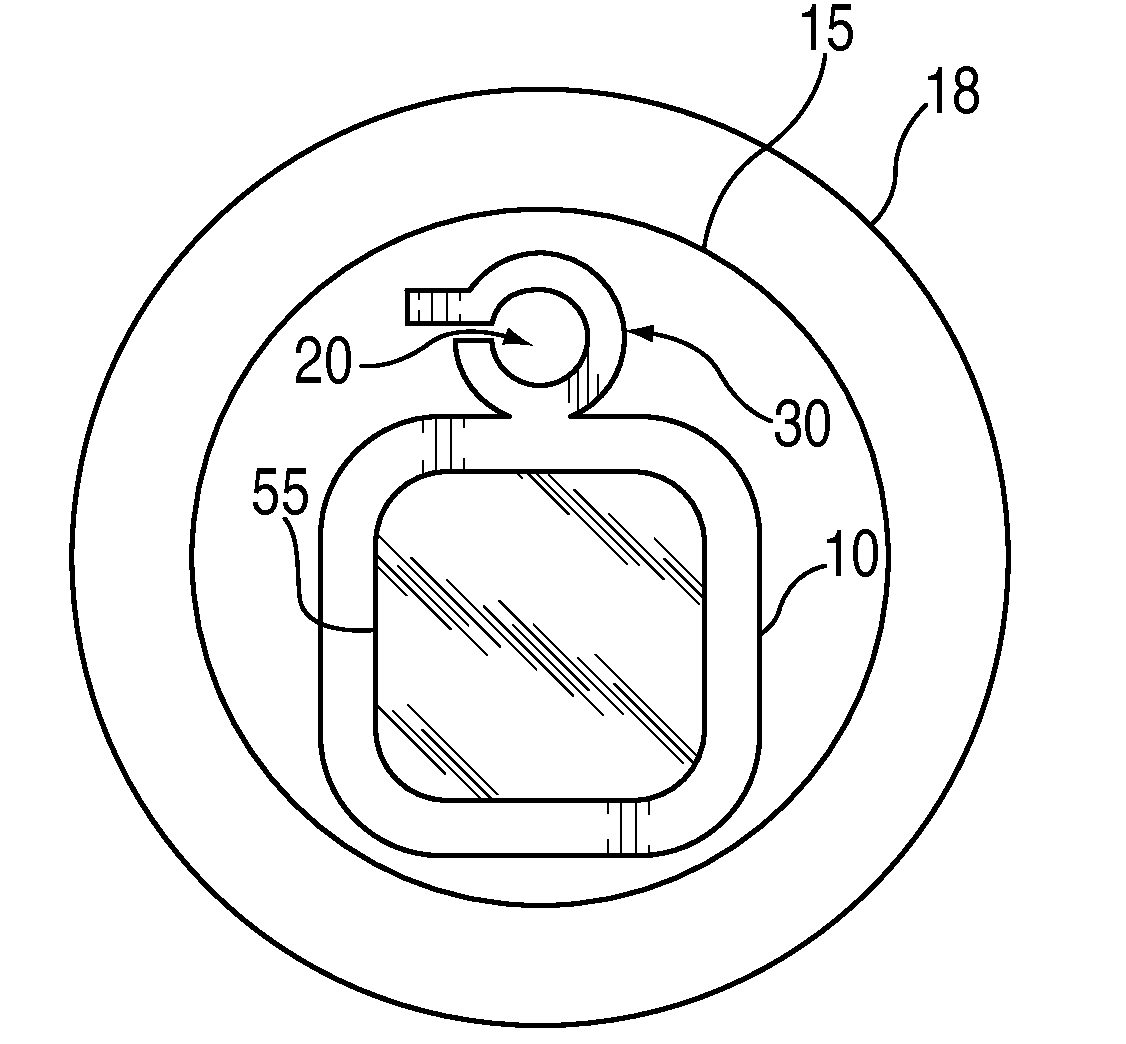
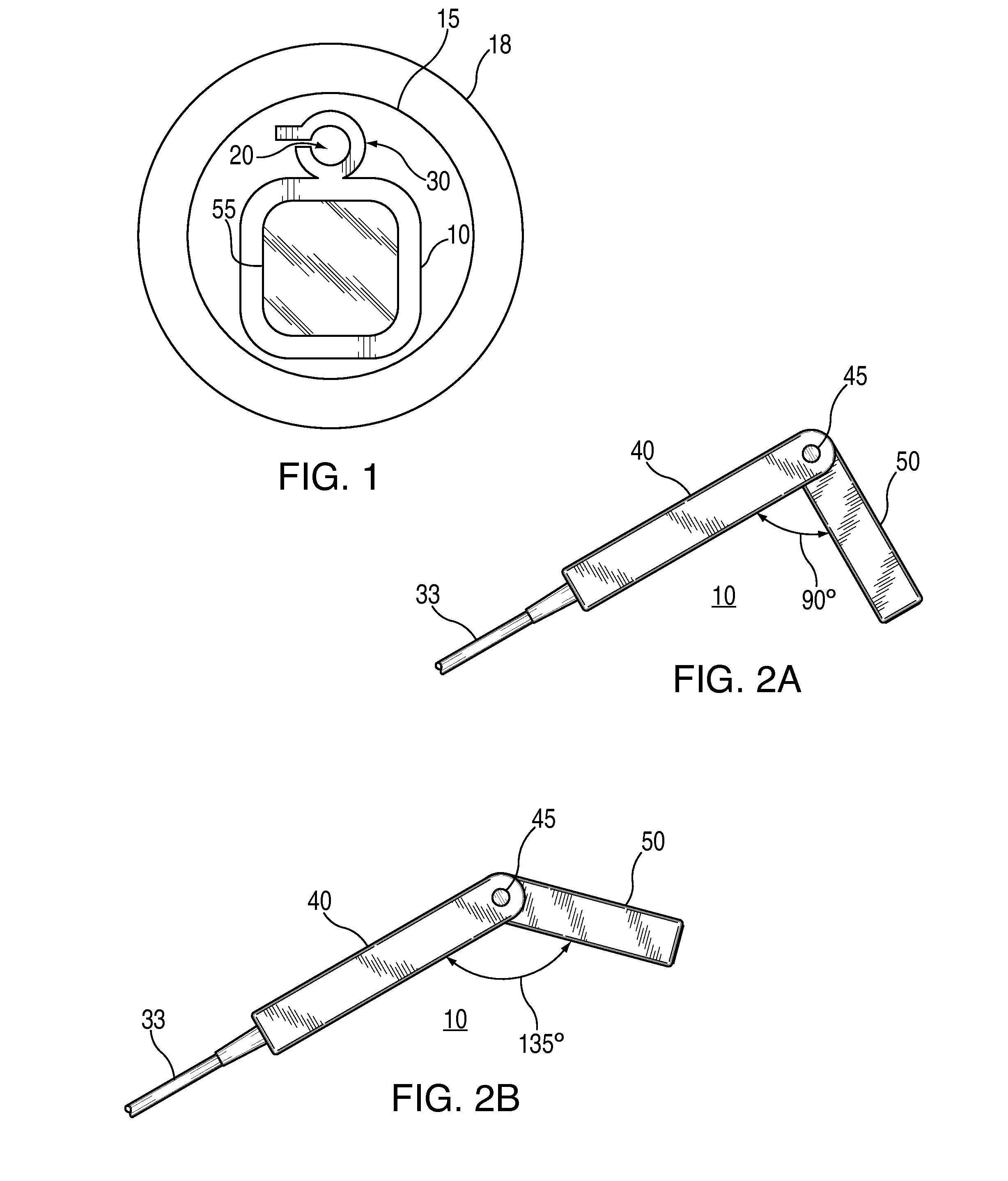
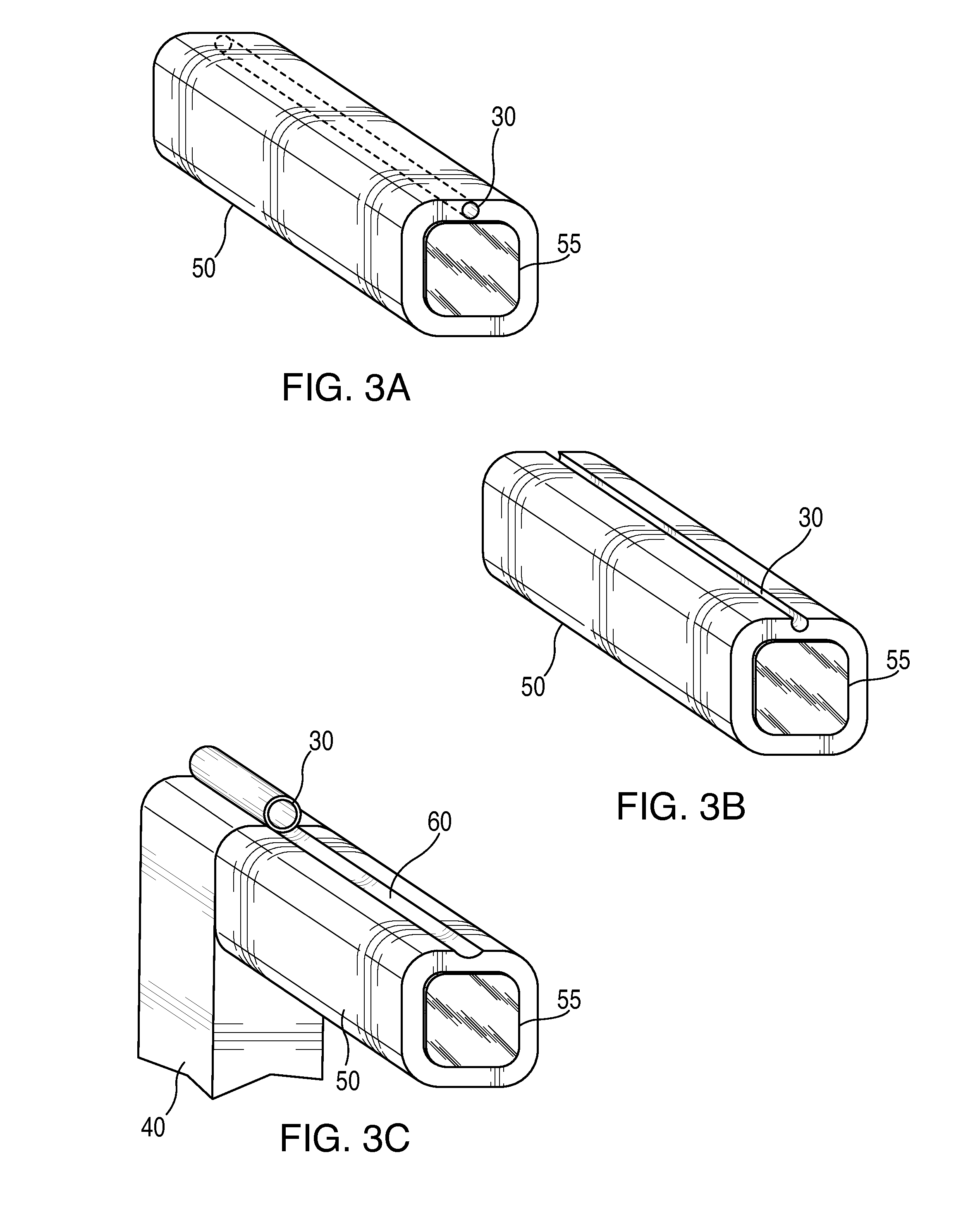
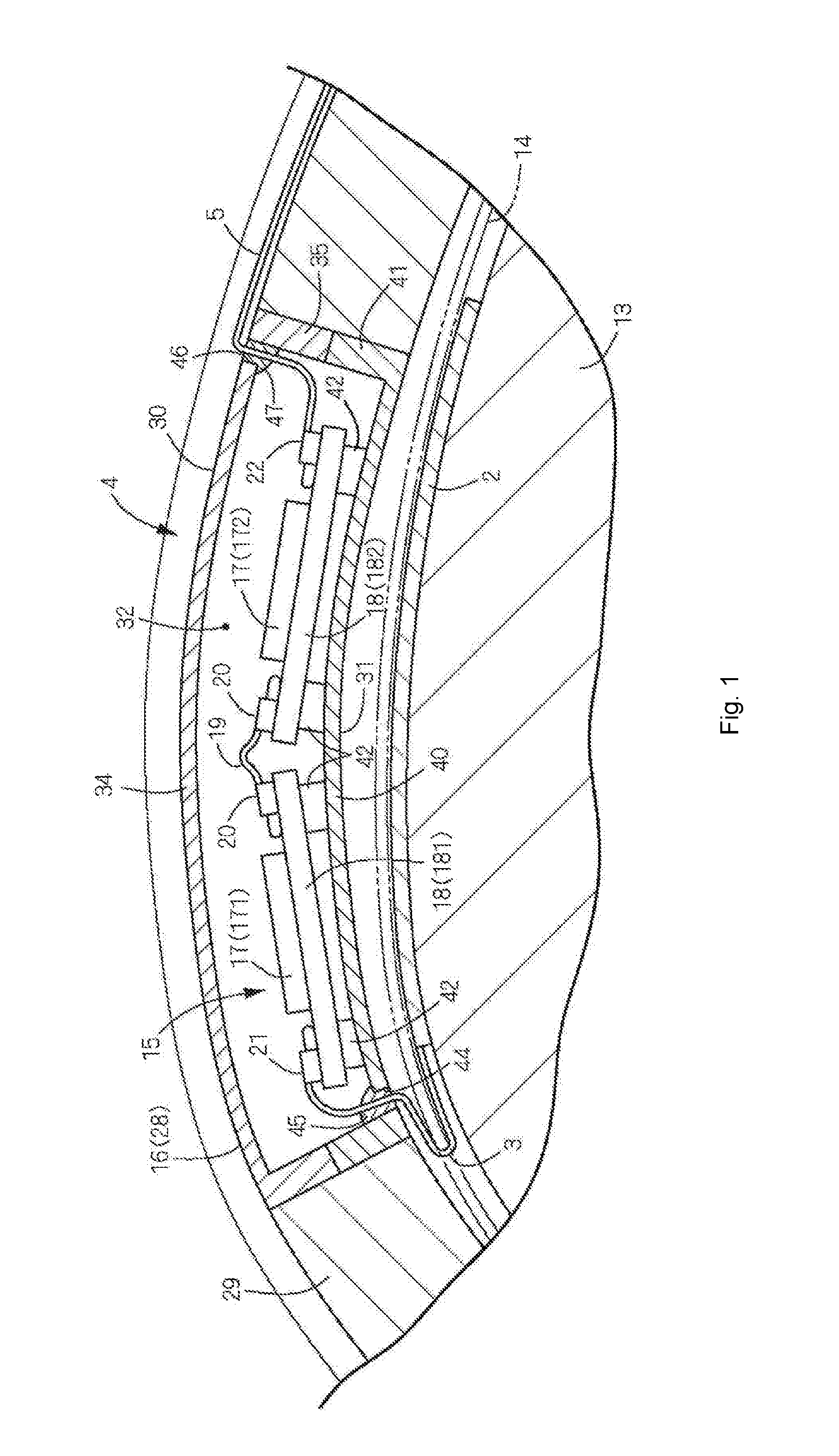
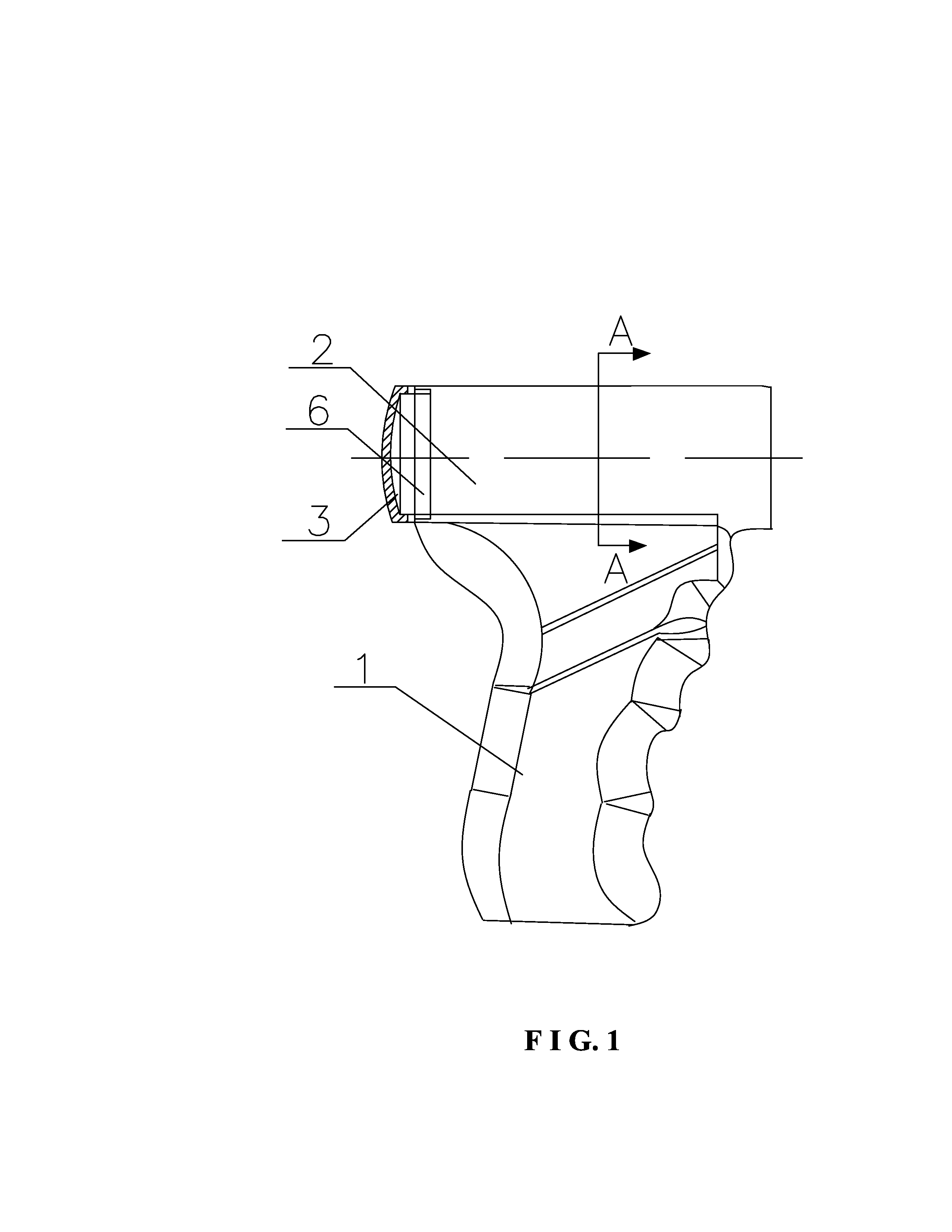
Bone fastener and instrument for insertion thereof
InactiveUS6258091B1Quickly and efficientlyEasy to disassembleSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisArcuate shapeScrew thread
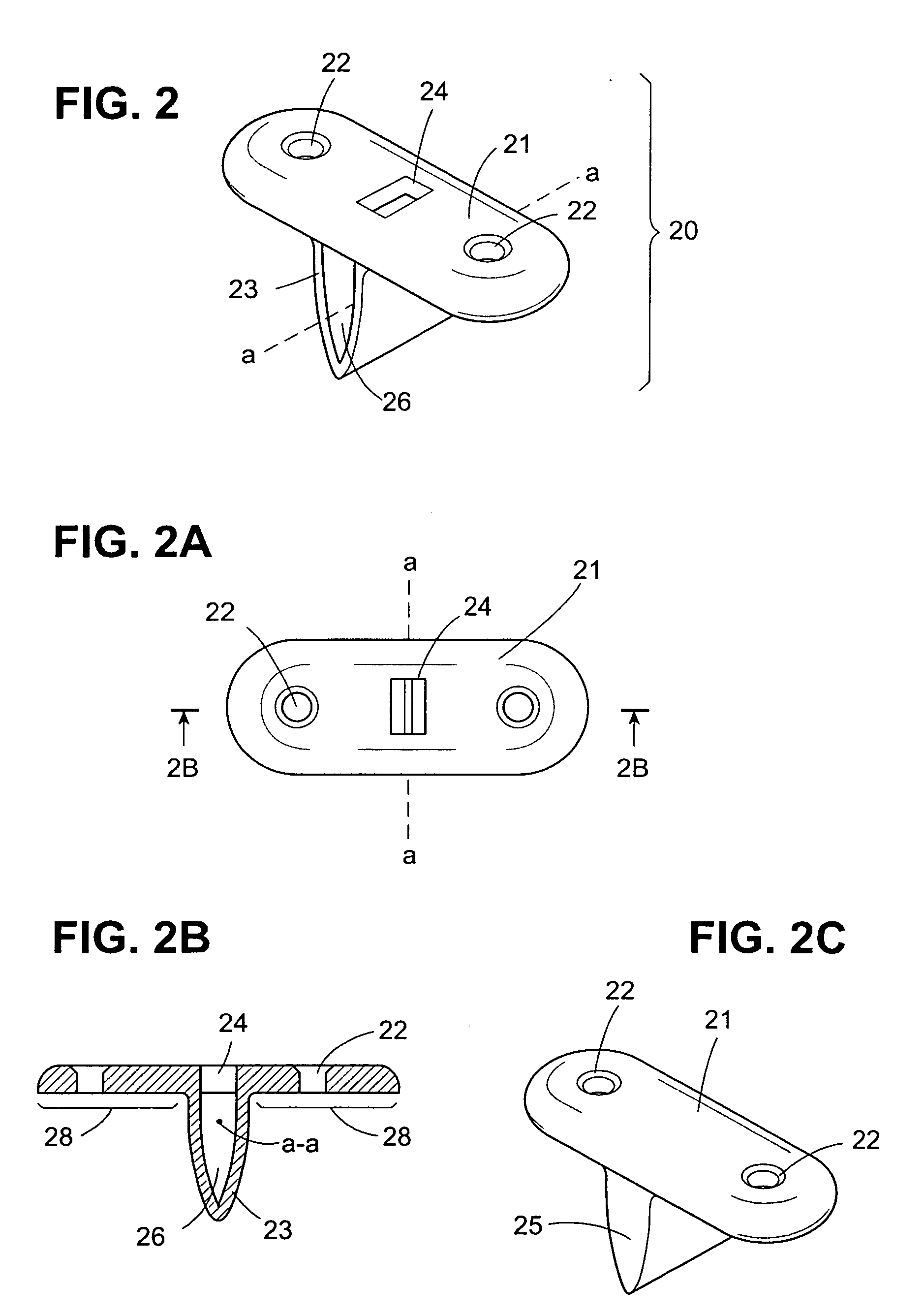
A bone member fastener for closing a craniotomy includes a cap and a base interconnected by a narrow cylindrical collar. The cap has an externally threaded stud that screws into an internally threaded bore of the collar, thereby allowing the cap and base to be brought into clamping engagement against the internal and external faces of a bone plate and surrounding bone. In a particularly disclosed embodiment, the base of the fastener is placed below a craniotomy hole with the collar projecting into the hole, and the stud of the cap is screwed into the bore of the base from above the hole to clamp a bone flap against the surrounding cranium. This device provides a method of quickly and securely replacing a bone cover into a craniotomy. The distance between the cap and base can be selected by how far the threaded stud of the cap is advanced into the internally threaded collar. The fastener is therefore adaptable for use in several regions of the skull having various thicknesses. An insertion tool with a long handle permits safe and convenient placement of the base between the brain and the internal face of the bone plate. Some disclosed embodiments of the fastener have a cap and base that conform to the curved surface of the skull, for example by having an arcuate shape or flexible members that conform to the curvature of the bone plate and surrounding cranial bone as the fastener is tightened.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET CMF & THORACIC
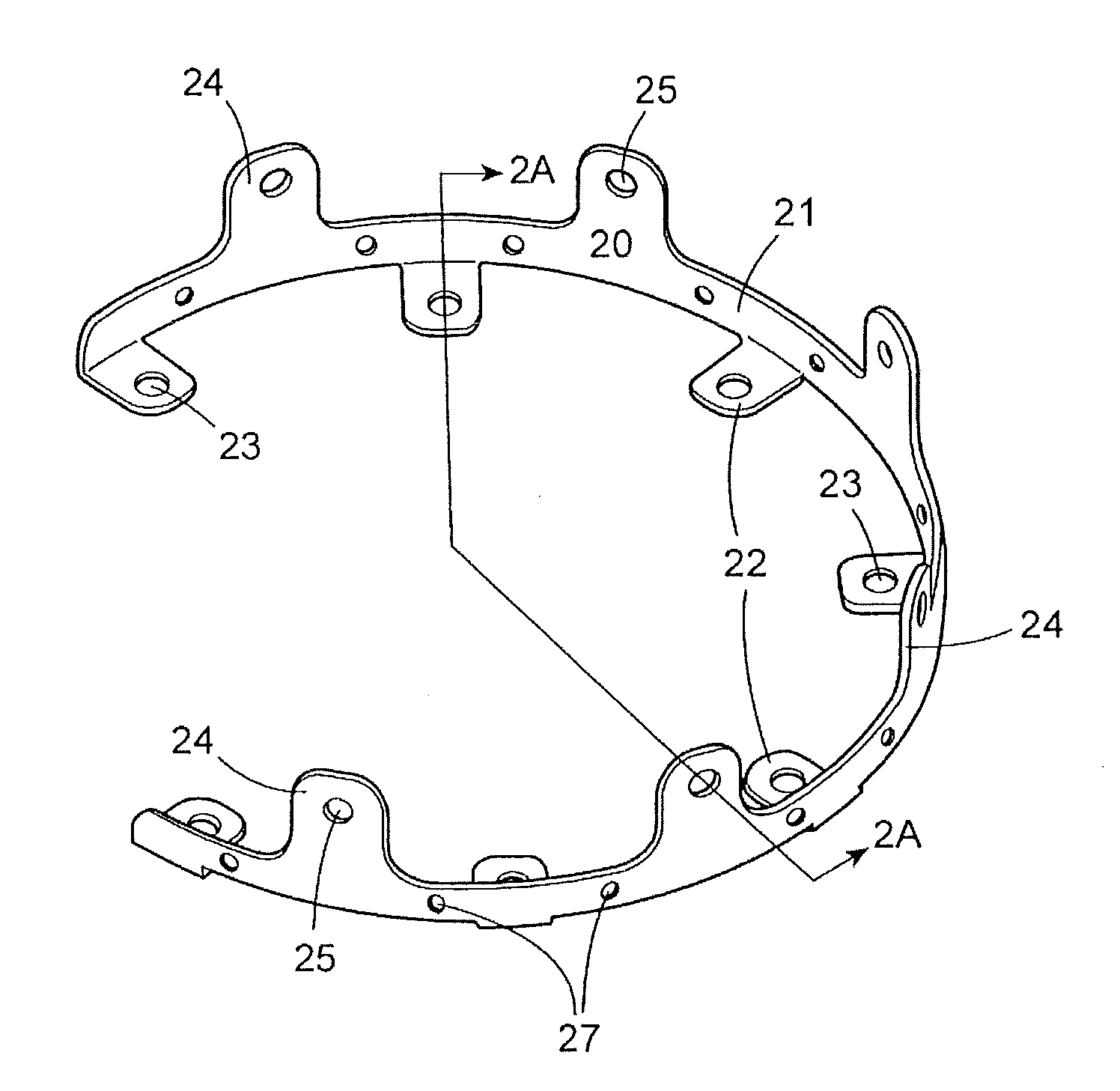
Craniotomy Closures
ActiveUS20090076617A1Maintaining contourReduced flexibilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSurgical siteBone growth
Craniotomy closures comprising surgical fasteners are described for use in reattaching a skull flap removed from the skull of a patient during brain surgery. Methods of using the same are also described. Surgical strips used in combination with the fasteners are shaped to follow the perimeter contour of the skull flap. The craniotomy closures are designed to encourage bone growth and healing of the skull flap and they can be used to deliver medication and bone growth enhancement materials to the surgical site.
Owner:NEW AMSTERDAM LLC
Robot Assisted Volume Removal During Surgery
ActiveUS20160151120A1Efficient removalShorten operation timeMedical imagingDiagnosticsSurgical operationRobotic arm
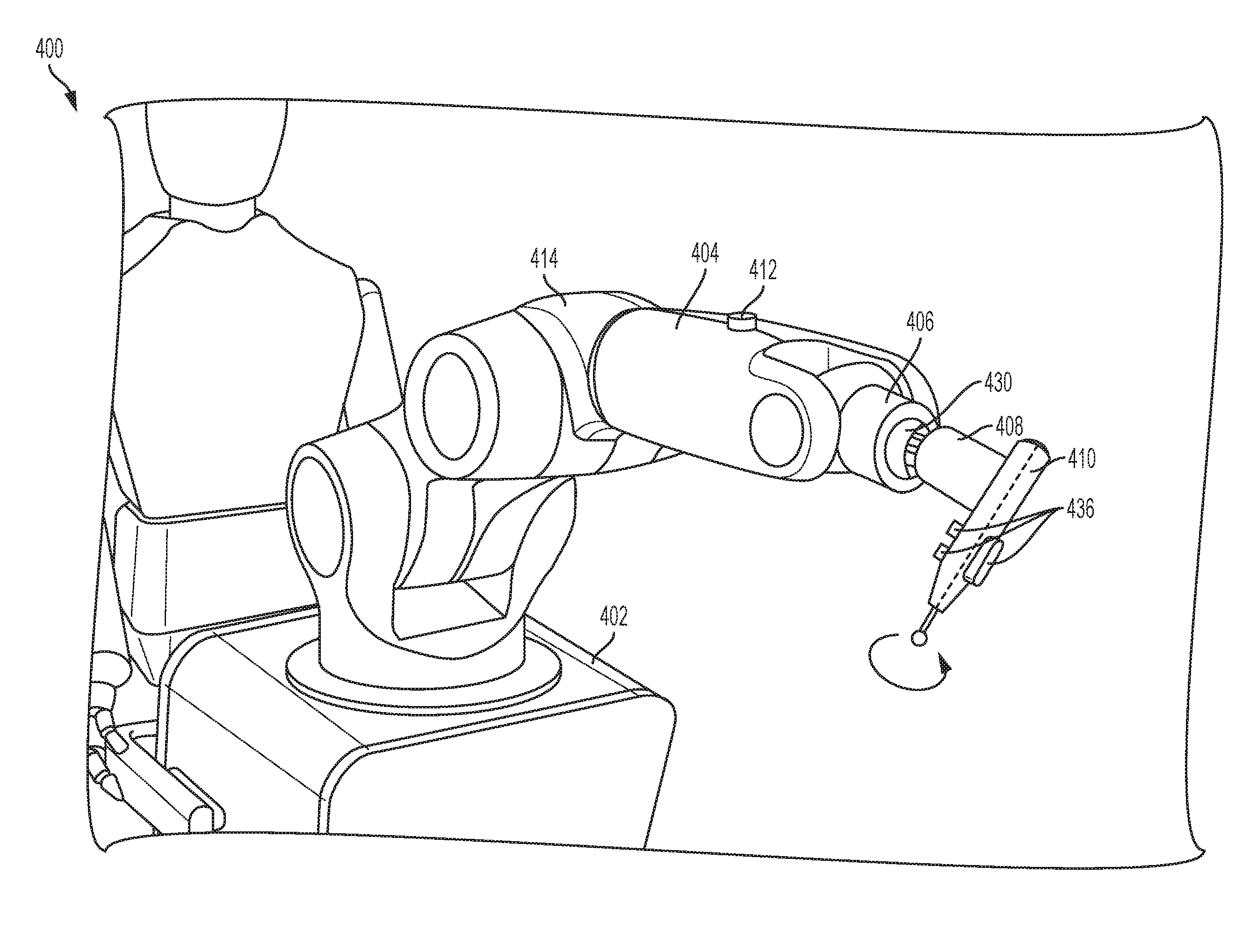
Described herein is a device and method used to effectively remove volume inside a patient in various types of surgeries, such as spinal surgeries (e.g. laminotomy), neurosurgeries (various types of craniotomy), ENT surgeries (e.g. tumor removal), and orthopedic surgeries (bone removal). Robotic assistance linked with a navigation system and medical imaging it can shorten surgery time, make the surgery safer and free surgeon from doing repetitive and laborious tasks. In certain embodiments, the disclosed technology includes a surgical instrument holder for use with a robotic surgical system. In certain embodiments, the surgical instrument holder is attached to or is part of an end effector of a robotic arm, and provides a rigid structure that allows for precise removal of a target volume in a patient.
Owner:KB MEDICAL SA
Bone fastener and instrument for insertion thereof
InactiveUS20020004661A1Quickly and efficientlyEasy to disassembleSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisArcuate shapeCranial bone
A bone member fastener for closing a craniotomy includes a cap and a base interconnected by a narrow cylindrical collar. The cap has an externally threaded stud that screws into an internally threaded bore of the collar, thereby allowing the cap and base to be brought into clamping engagement against the internal and external faces of a bone plate and surrounding bone. In a particularly disclosed embodiment, the base of the fastener is placed below a craniotomy hole with the collar projecting into the hole, and the stud of the cap is screwed into the bore of the base from above the hole to clamp a bone flap against the surrounding cranium. This device provides a method of quickly and securely replacing a bone cover into a craniotomy. The distance between the cap and base can be selected by how far the threaded stud of the cap is advanced into the internally threaded collar. The fastener is therefore adaptable for use in several regions of the skull having various thicknesses. An insertion tool with a long handle permits safe and convenient placement of the base between the brain and the internal face of the bone plate. Some disclosed embodiments of the fastener have a cap and base that conform to the curved surface of the skull, for example by having an arcuate shape or flexible members that conform to the curvature of the bone plate and surrounding cranial bone as the fastener is tightened.
Owner:BIOMET MICROFIXATION
Craniotomy closures and plugs
ActiveUS20070173844A1Maintaining contourIncrease flexibilityDental implantsSnap-action fastenersSurgical siteBrain section
Strip fasteners and cranial plugs for use in reattaching a skull flap removed during brain surgery and methods of using the same. The strip fasteners are flexible and can be shaped to follow the perimeter contour of the skull flap. The cranial plugs can be used to reattach the skull flap or they can be installed after the skull flap is reattached using the strip fasteners. In some embodiments, the cranial plug(s) and strip fasteners can be installed at the same time. The strip fasteners and cranial plugs are designed to encourage bone growth and healing of the skull flap and they can be used to deliver medication and bone growth enhancement compositions to the surgical site.
Owner:NEW AMSTERDAM LLC
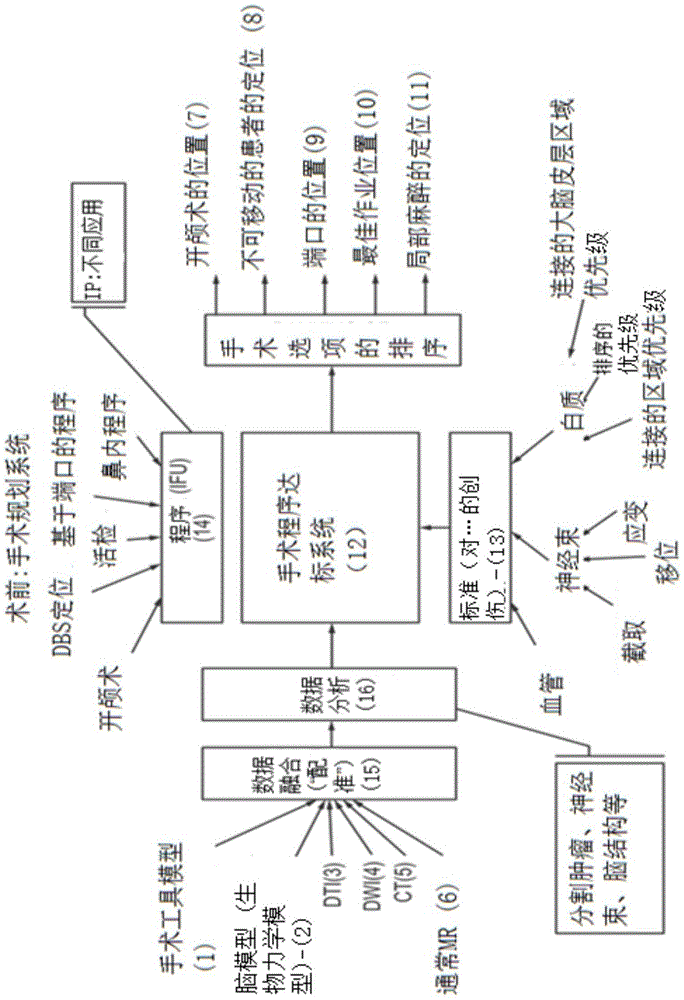
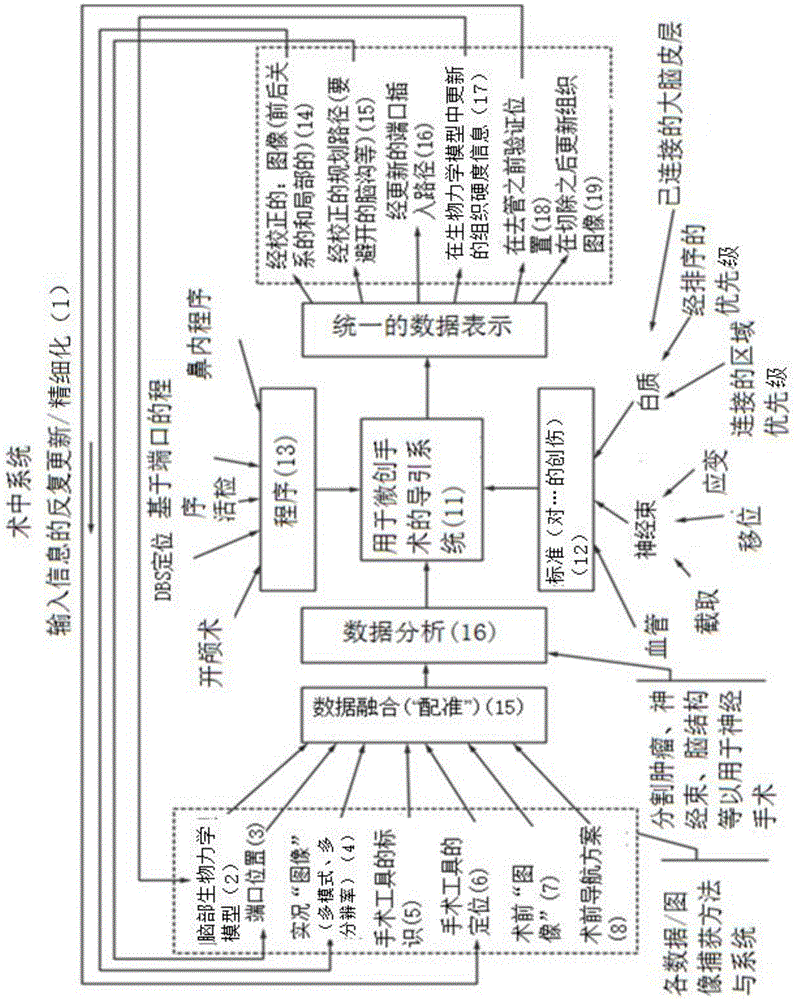
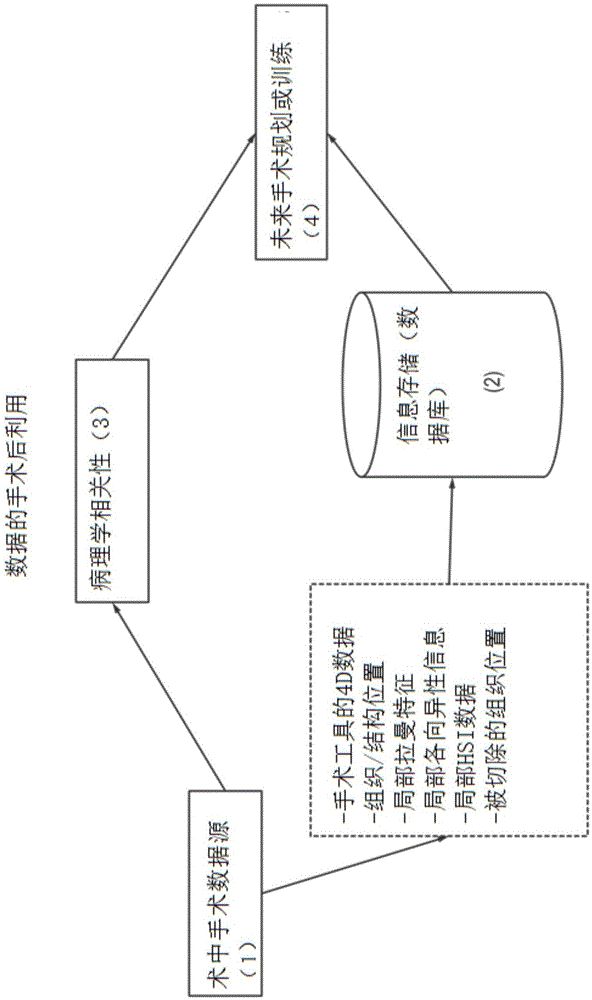
Planning, navigation and simulation systems and methods for minimally invasive therapy
Disclosed herein are planning, navigation and simulation systems and methods for minimally invasive therapy in which the planning method and system uses patient specific pre-operative images. The planning system allows for multiple paths to be developed from the pre-operative images, and scores the paths depending on desired surgical outcome of the surgery and the navigation systems allow for minimally invasive port based surgical procedures, as well as craniotomies in the particular case of brain surgery.
Owner:SYNAPTIVE MEDICAL (BARBADOS) INC
Craniotomy Closures and Plugs
InactiveUS20100179553A1Maintaining contourIncrease flexibilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical siteEngineering
Strip fasteners and cranial plugs for use in reattaching a skull flap removed during brain surgery and methods of using the same. The strip fasteners are flexible and can be shaped to follow the perimeter contour of the skull flap. The cranial plugs can be used to reattach the skull flap or they can be installed after the skull flap is reattached using the strip fasteners. In some embodiments, the cranial plug(s) and strip fasteners can be installed at the same time. The strip fasteners and cranial plugs are designed to encourage bone growth and healing of the skull flap and they can be used to deliver medication and bone growth enhancement compositions to the surgical site.
Owner:FIRST COMMERCE BANK
Craniotomy closures
ActiveUS8460346B2Maintaining contourReduced flexibilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSurgical siteBone growth
Craniotomy closures comprising surgical fasteners are described for use in reattaching a skull flap removed from the skull of a patient during brain surgery. Methods of using the same are also described. Surgical strips used in combination with the fasteners are shaped to follow the perimeter contour of the skull flap. The craniotomy closures are designed to encourage bone growth and healing of the skull flap and they can be used to deliver medication and bone growth enhancement materials to the surgical site.
Owner:NEW AMSTERDAM LLC
Wireless Recording and Stimulation of Brain Activity
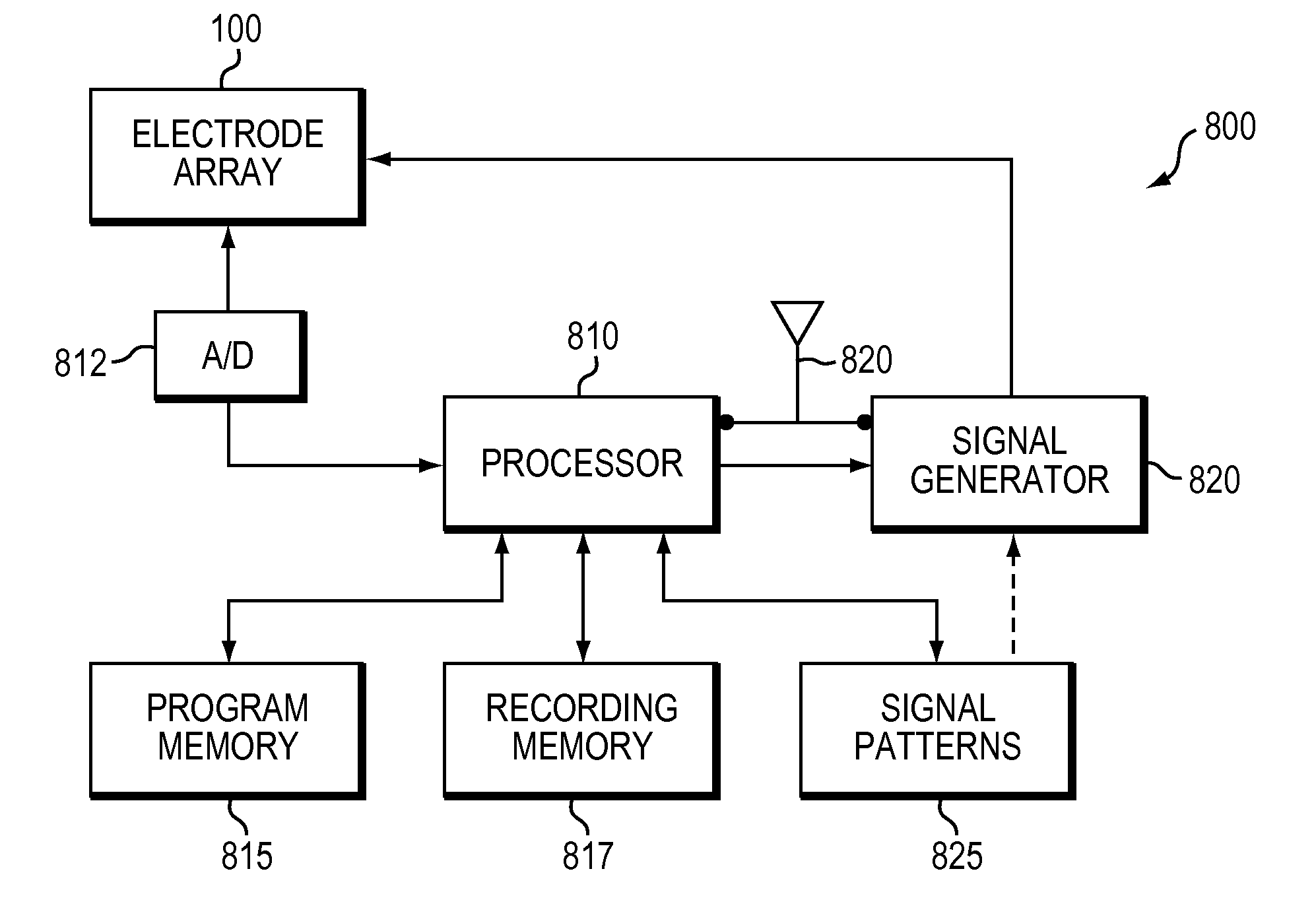
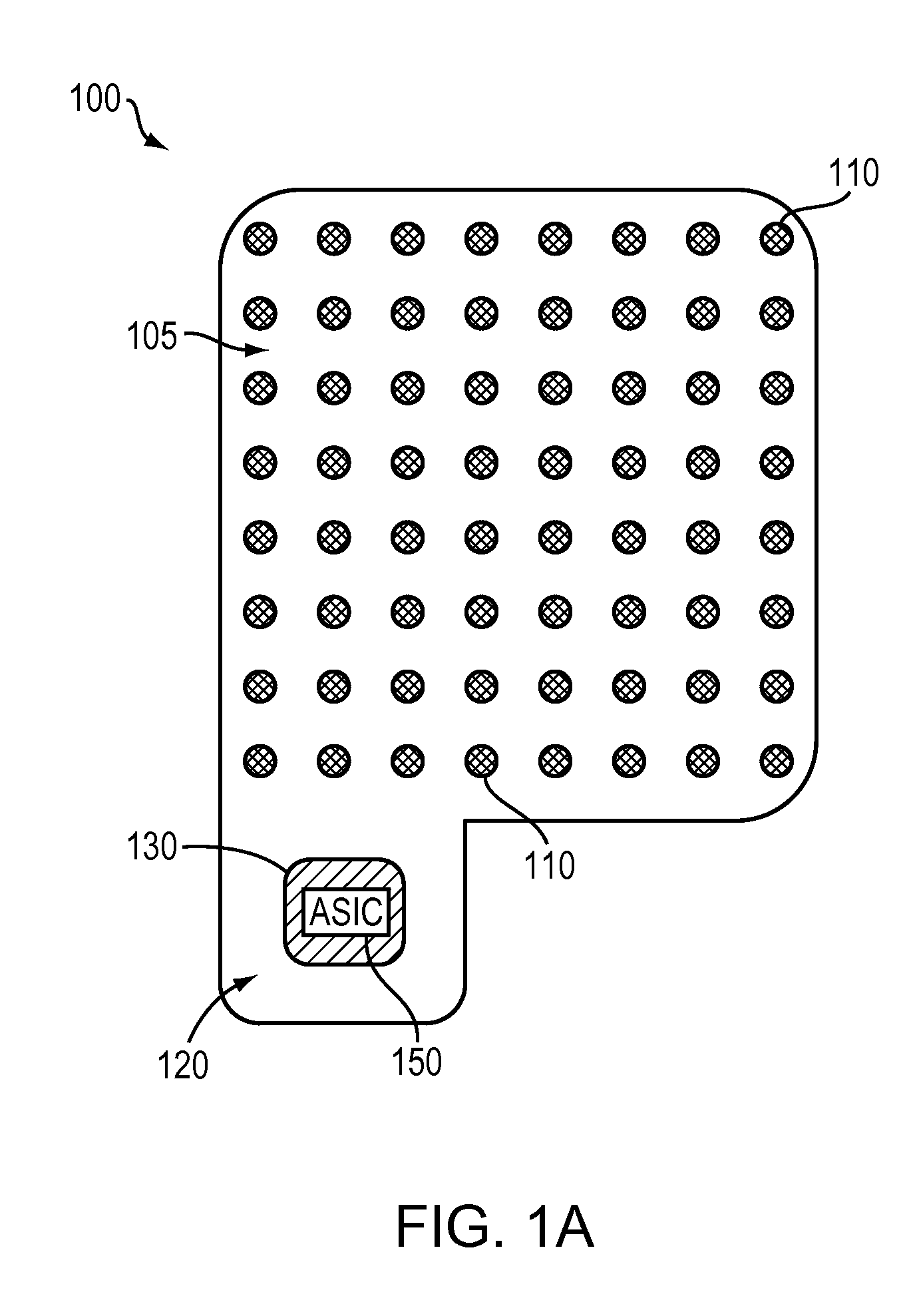
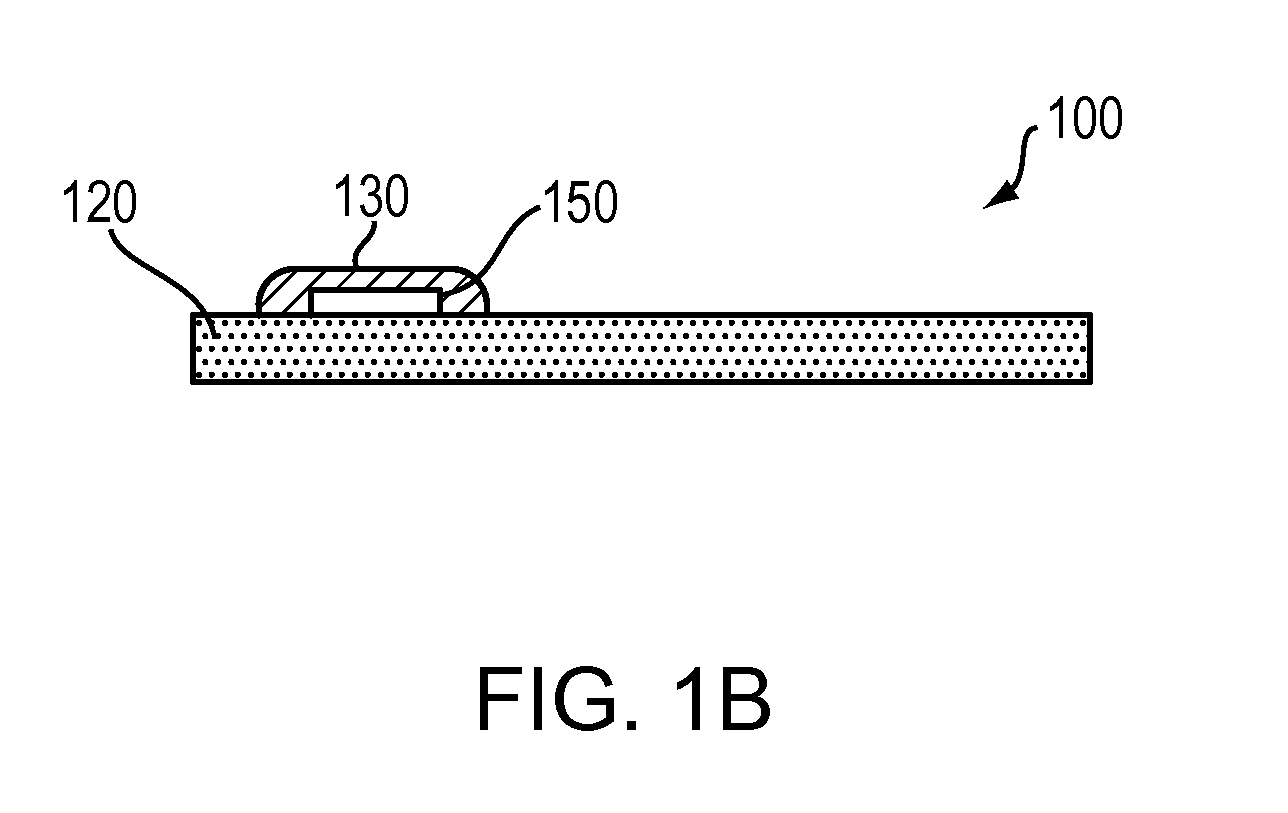
InactiveUS20100198297A1Avoid lengthAvoiding costly hospitalizationElectroencephalographyHead electrodesMedicineElectroencephalography
Subdural arrays transmit electrocorticogram recordings wirelessly, across the patient's skull, allowing the craniotomy used for surgical placement of the arrays to be completely closed. In various embodiments, the arrays also respond to commands, applying signal patterns to the patient's brain for diagnostic and treatment purposes.
Owner:SIGENICS +2
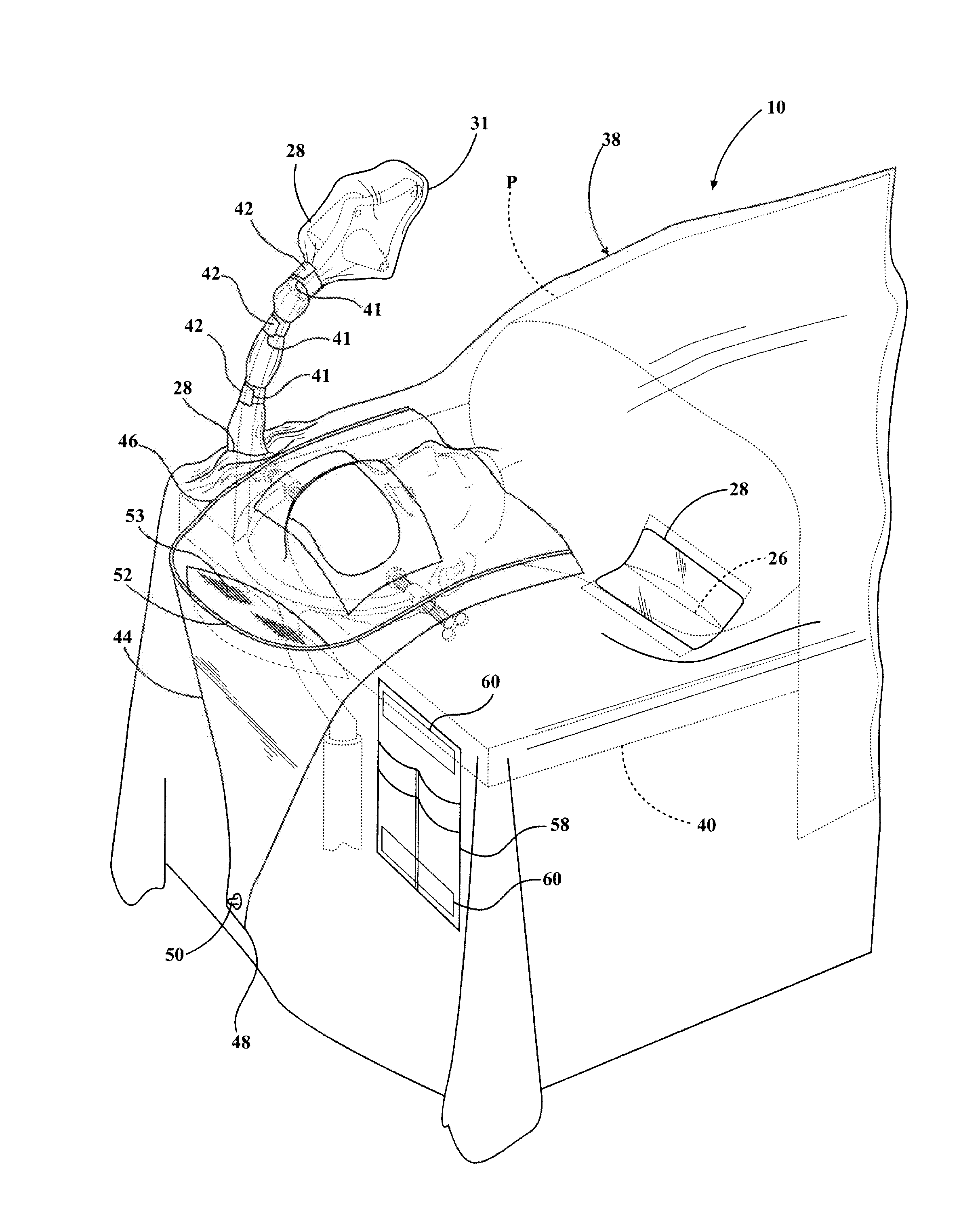
Craniotomy Drape and Method of Simultaneously Draping a Sterile Barrier Over a Patient and Navigation Tracker
A sterile craniotomy drape and method of simultaneously draping a sterile barrier over a patient and a navigation tracker prior to performing a craniotomy procedure are provided. The sterile craniotomy drape has a flexible, sterile wall with opposite edges extending lengthwise between opposite ends. The wall is sized to substantially cover a patient lying on a patient support surface of an operating table. The wall has a cranial region adapted to be attached to the patients head and at least one opening adjacent the cranial region. A flexible, tubular sterile sleeve has an open end attached to the wall about the at least one opening. The sleeve extends away from the wall to a free end for receipt of a navigation tracker therein.
Owner:TIDI PROD LLC
Cranial plating and bur hole cover system and methods of use
InactiveUS20120289964A1Reduce protrusionAddress bad outcomesInternal osteosythesisBone platesCovering systemCranial surface
The present disclosure is for a device, tooling, methods of use and kits containing the cranial plates and bur hole covers used for resecuring a cranial flap after a craniotomy. The cranial repair system is meant to reduce the profile of cranial plates or bur hole covers on the external surface of the cranium after a craniotomy is performed. The embodied devices of present disclosure are designed to reside substantially within the kerf or bur holes and thus minimize the surface area of devices resides on the external surface of the cranium. Additional embodiments include kits, tooling and methods to further reduce and / or eliminate the external profile of the cranial plate on the external cranial surface.
Owner:OSTEOMED
Wireless recording and stimulation of brain activity
InactiveUS8849369B2Lengthy and costly hospitalizationReduce morbidityElectroencephalographyHead electrodesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationCerebral activity
Owner:SIGENICS +2
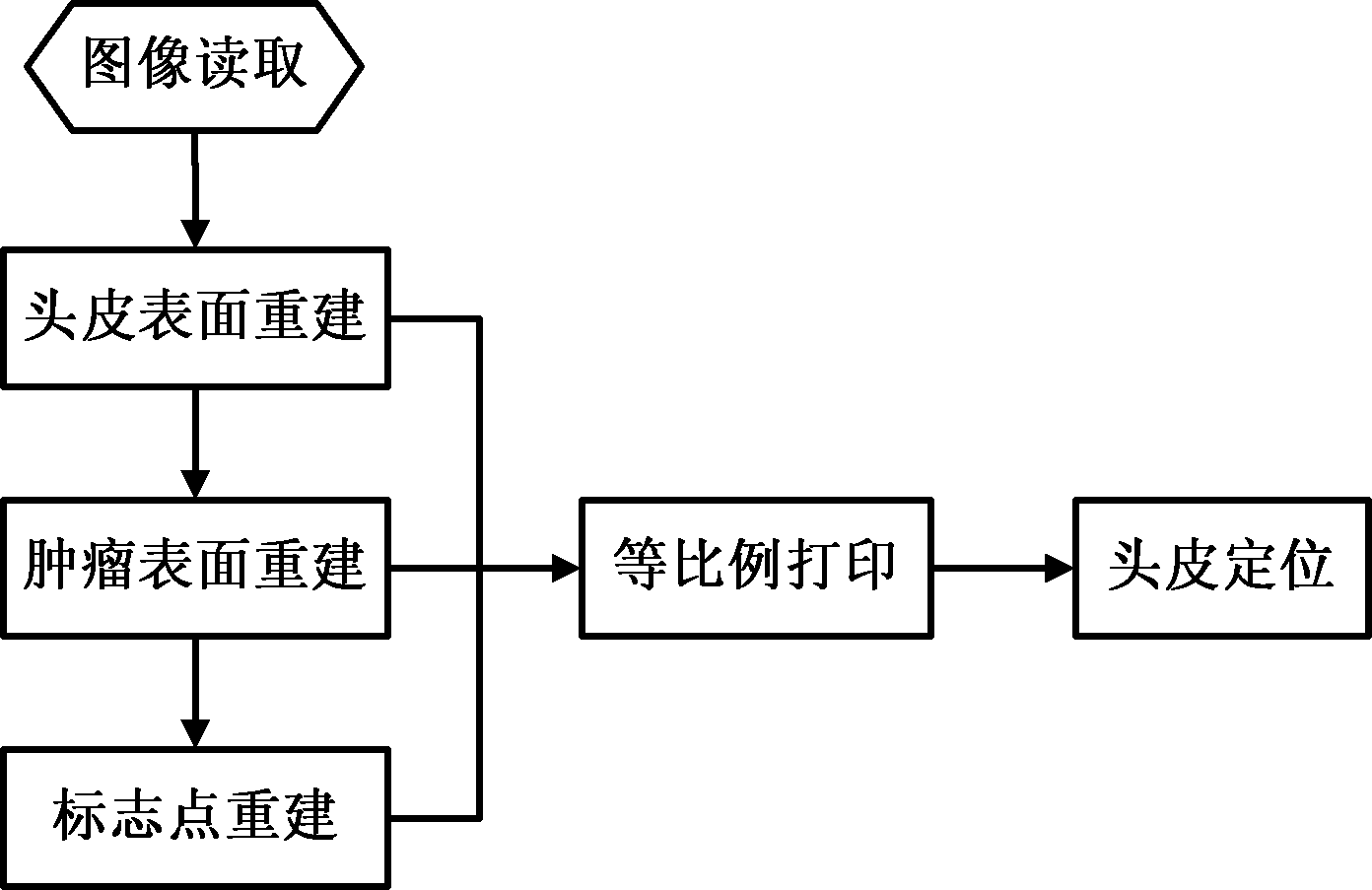
Method for processing scalp positioning images of brain tumors
ActiveCN102592283AEasy to implementShorten operation timeImage analysis3D modellingImaging equipmentImage Reslicing
The invention discloses a method for processing scalp positioning images of brain tumors, which comprises the following steps of: (1) preliminarily estimating a scalp projected area of a brain tumor of a patient, adhering two mark points which can be identified by an imaging device in the area, obtaining a two-dimensional medical image slice set from the imaging device, and reconstructing a three-dimensional profile of a scalp layer; (2) manually drawing a profile line of the tumor on a two-dimensional image, and reconstructing the surface of the tumor; (3) determining the positions of the two mark points on the two-dimensional image, and reconstructing the mark points; and (4) rotating a profile image of the reconstructed three-dimensional profile image to an appropriate position, and then printing the image in an equal proportion. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention is implemented simply; and when the method is applied to the positioning of a brain tumor, the positioning precision meets the demands of tumor resection through a craniotomy, the shortening of operation time and the reduction of surgical traumas are facilitated, and the incision length can be minimized under the premise of guaranteeing good exposures.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
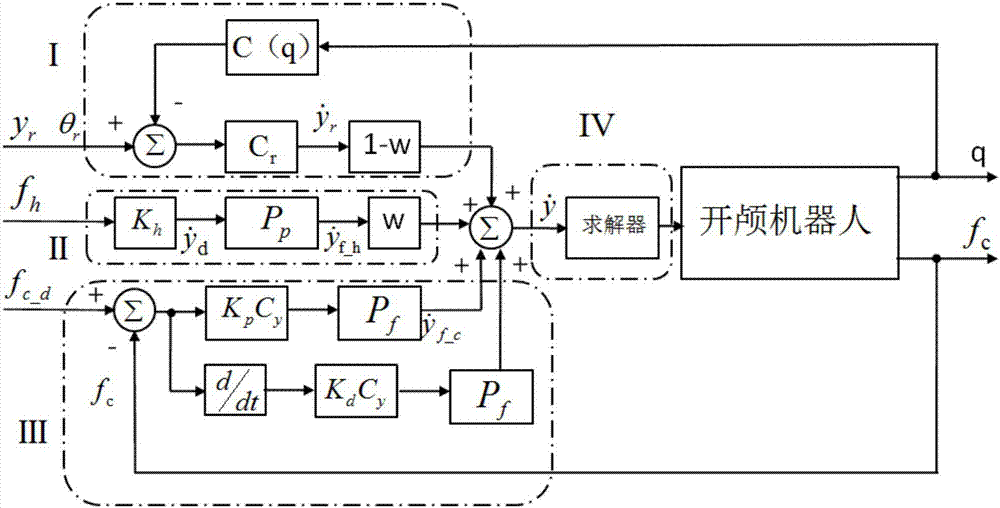
Cooperative interaction control system for craniotomy robot
ActiveCN106965175ASolve the problem of controlling positionEnhanced interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical robotsMilling cutterSimulation
The invention discloses a cooperative interaction control system for a craniotomy robot. The cooperative interaction control system comprises a motion limiting module, a doctor-robot interaction module, a robot-patient interaction module and a solver. The motion limiting module is used for tracking the position of the robot in real time and is compared with a limited area, so that the robot is limited within a certain area for movement. The doctor-robot interaction module is used for completing real-time speed control over the robot by doctors. In the skull milling process, the robot-patient interaction module is used for keeping a certain contact force between the tail end of a milling cutter and the bottom face of a skull and further keeping a certain drilling force in the skull drilling process. The solver is used for completing inverse kinematics resolving of the robot and further used for inputting and outputting robot motion and joint motion speeds separately so as to drive the robot to move. According to the cooperative interaction control system, the advantages that the flexibility of the doctors is high and the precision of the robot is high are integrated, operation efficiency and quality can be improved while operation safety is improved, and the craniotomy fatigue degree of the doctors is lowered.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
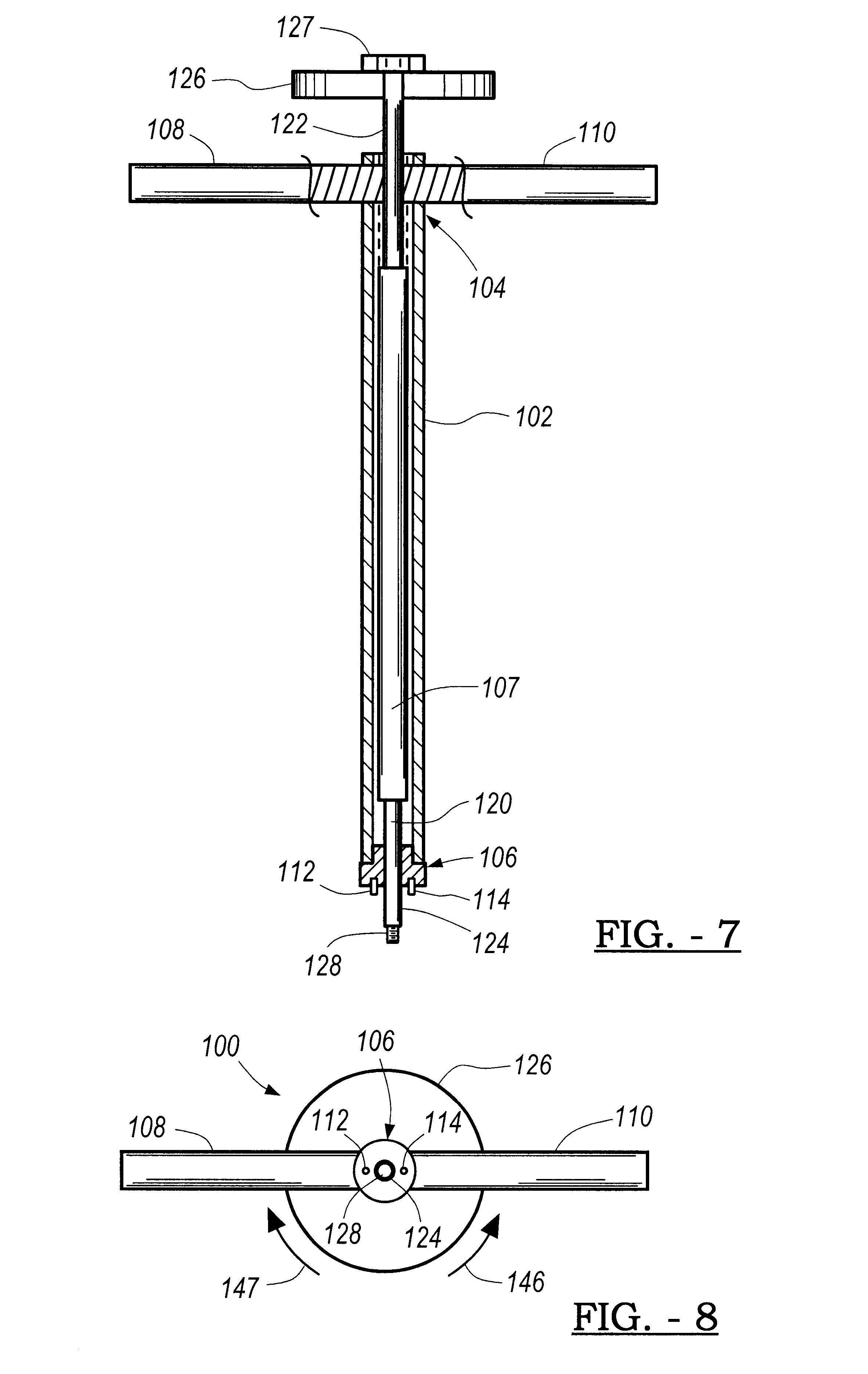
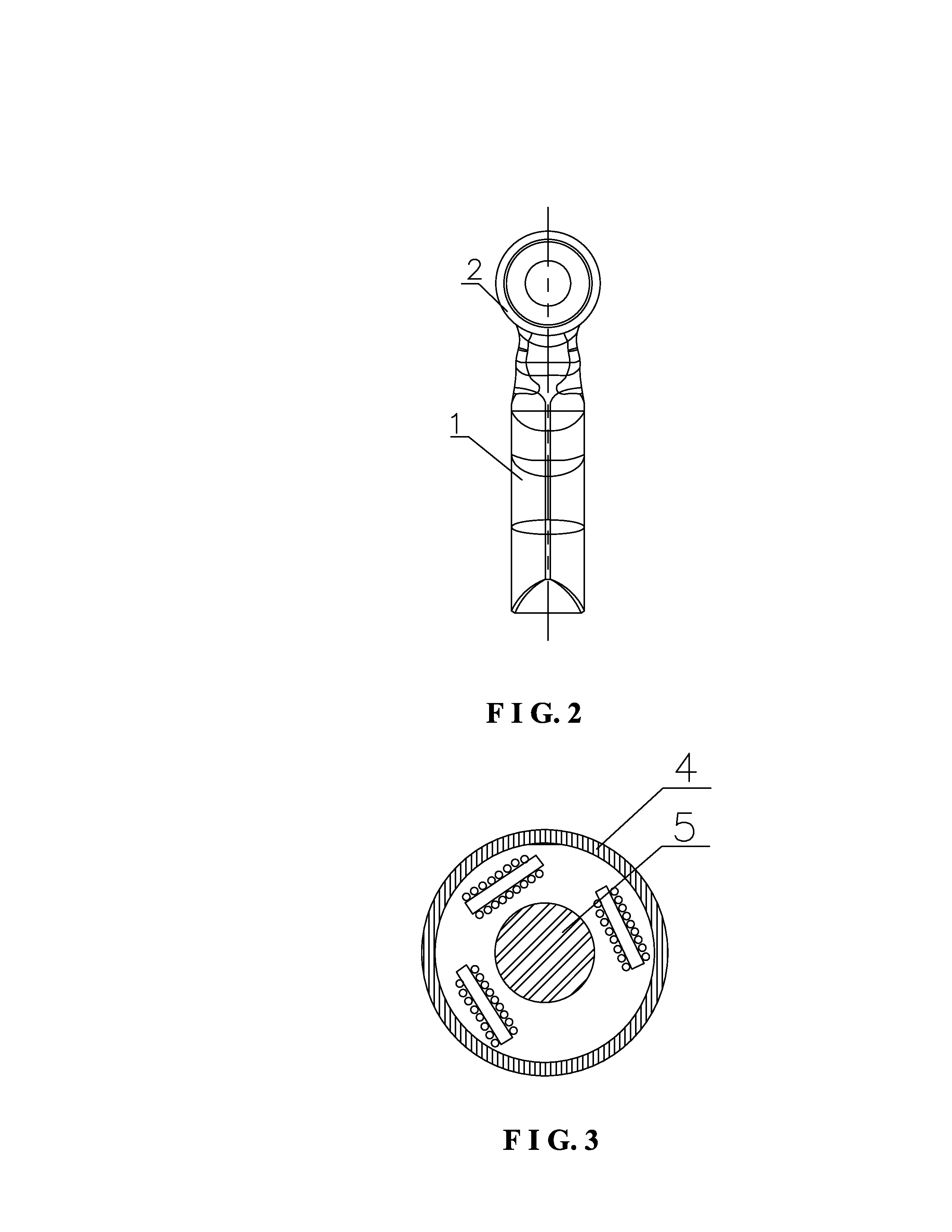
Telescopic cranial bone screw
The invention provides a method and apparatus for cranial fixation following a craniotomy and treatment for increased intracranial pressure. The cranial fixation device comprises of plates attached to the skull with a telescopic screw. The telescopic screw provides constrained movement of the bone flap relative to the skull to accommodate an increase in the intracranial pressure.
Owner:KHANNA ROHIT
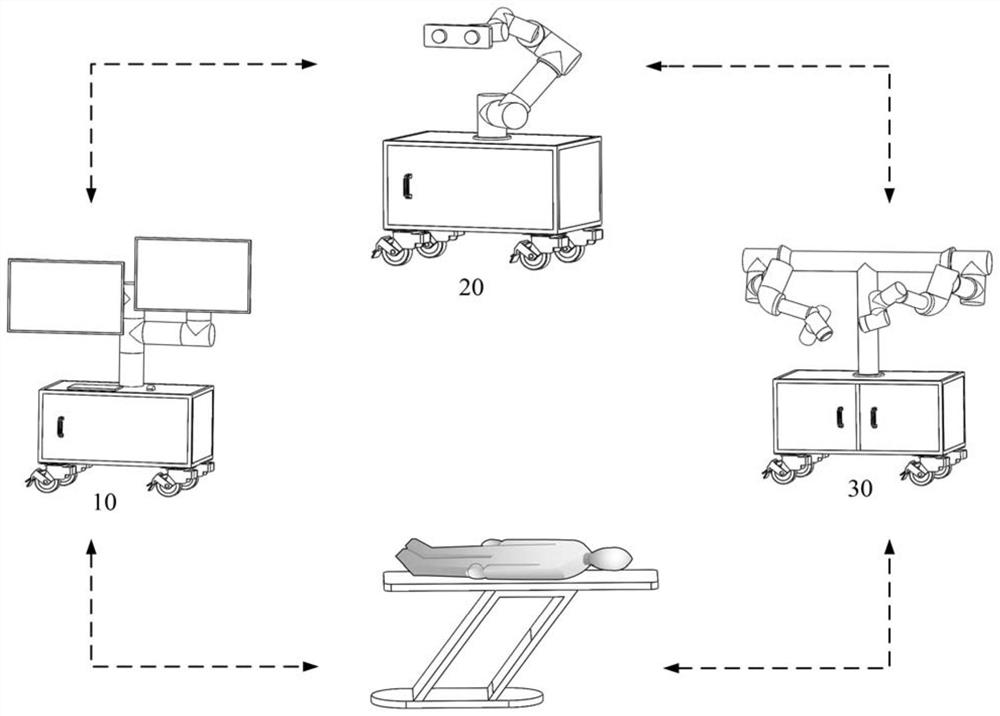
Craniotomy robot system and craniotomy method thereof
PendingCN111728696ARealize window openingSolve the blocked viewSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationImaging processing
The invention discloses a craniotomy robot system and a craniotomy method thereof. The system comprises a data processing mechanism, a collaborative optical navigation mechanism and a double-arm surgical robot mechanism. The data processing mechanism comprises a main control trolley, and a first image processing workstation and a second image processing workstation which are fixedly mounted on themain control trolley; the collaborative optical navigation mechanism comprises a navigation trolley, a six-degree-of-freedom navigation mechanical arm fixedly installed on the navigation trolley andan optical position indicator fixedly installed on a flange at the tail end of the navigation mechanical arm ;and the double-arm surgical robot mechanism comprises a surgical cart, a first six-degree-of-freedom surgical mechanical arm and a second six-degree-of-freedom surgical mechanical arm, wherein the first six-degree-of-freedom surgical mechanical arm and the second six-degree-of-freedom surgical mechanical arm are fixed onto the surgical trolley. According to the craniotomy method, skull drilling, milling and intracranial micromanipulation can be achieved accurately and quickly under theguidance of the collaborative optical navigation mechanism, operation precision can be effectively improved, the exposure time of craniotomy can be shortened, and the working intensity of doctors canbe relieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Medical bone wound hemostatic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106215225ADelicate feelImprove plasticitySurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismWound healingBiopolymer
The invention discloses a medical bone wound hemostatic material. The bone wound hemostatic material is composed of the following raw materials by mass percent: 5-80% of sterilized biopolymer and 20-95% of medical calcium salt. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the medical bone wound hemostatic material. The medical bone wound hemostatic material prepared according to the method provided by the invention has the advantages of high plasticity, moderate plasticity, fine hand feeling, no local stimulation, excellent plasticity, performance safety, convenience in use and long-term storage. The medical bone wound hemostatic material provided by the invention can quickly stop bleeding in a practical application, has a function of promoting curing, is capable of increasing the wound healing effect and can prevent inflammation, edema and necrosis from happening. The medical bone wound hemostatic material can be widely used for stopping bleeding for the cavum medullare section and the bone section in craniotomy, thoracotomy and orthopedic surgery.
Owner:杭州中科理化生物医药技术有限公司
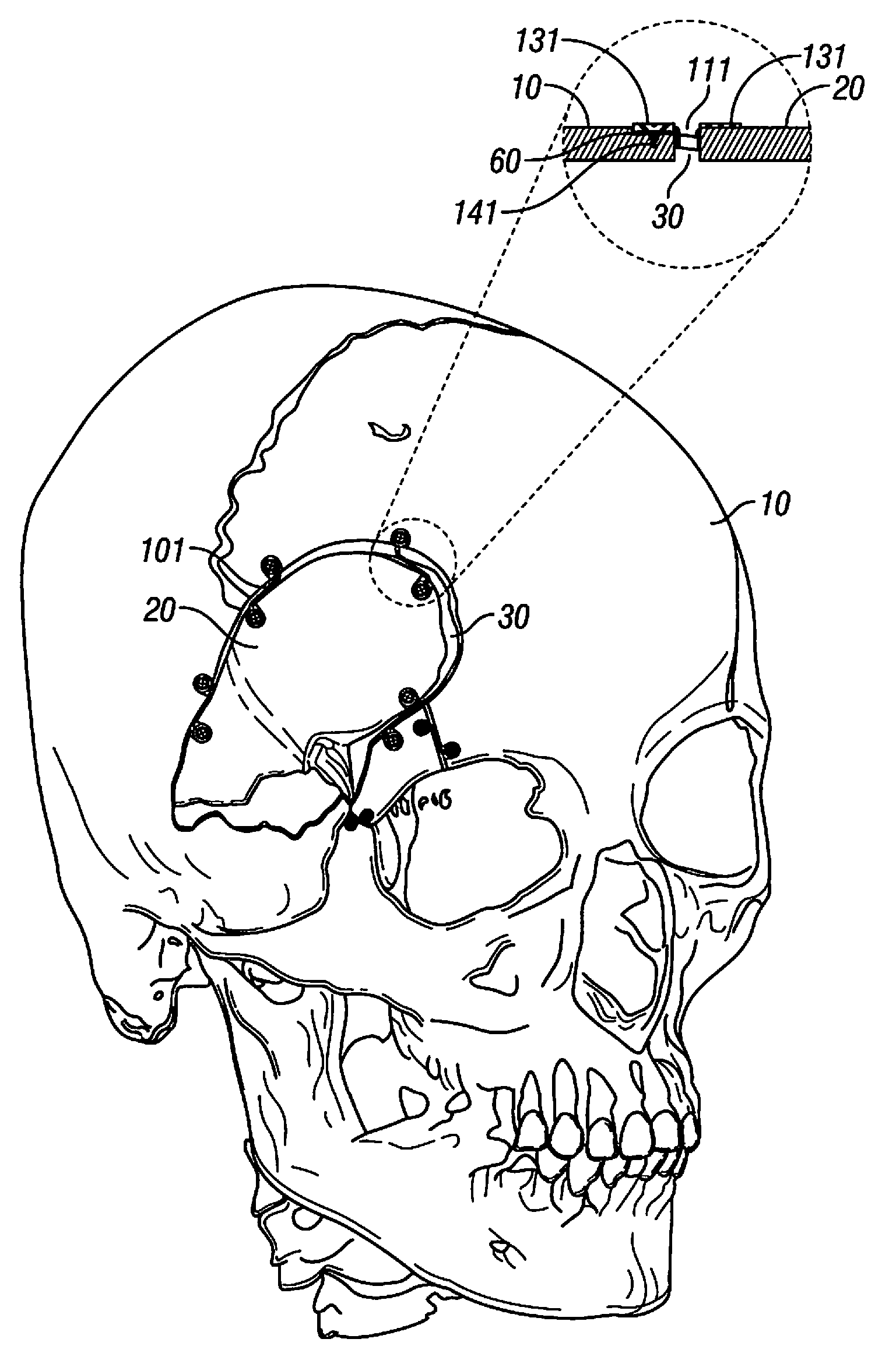
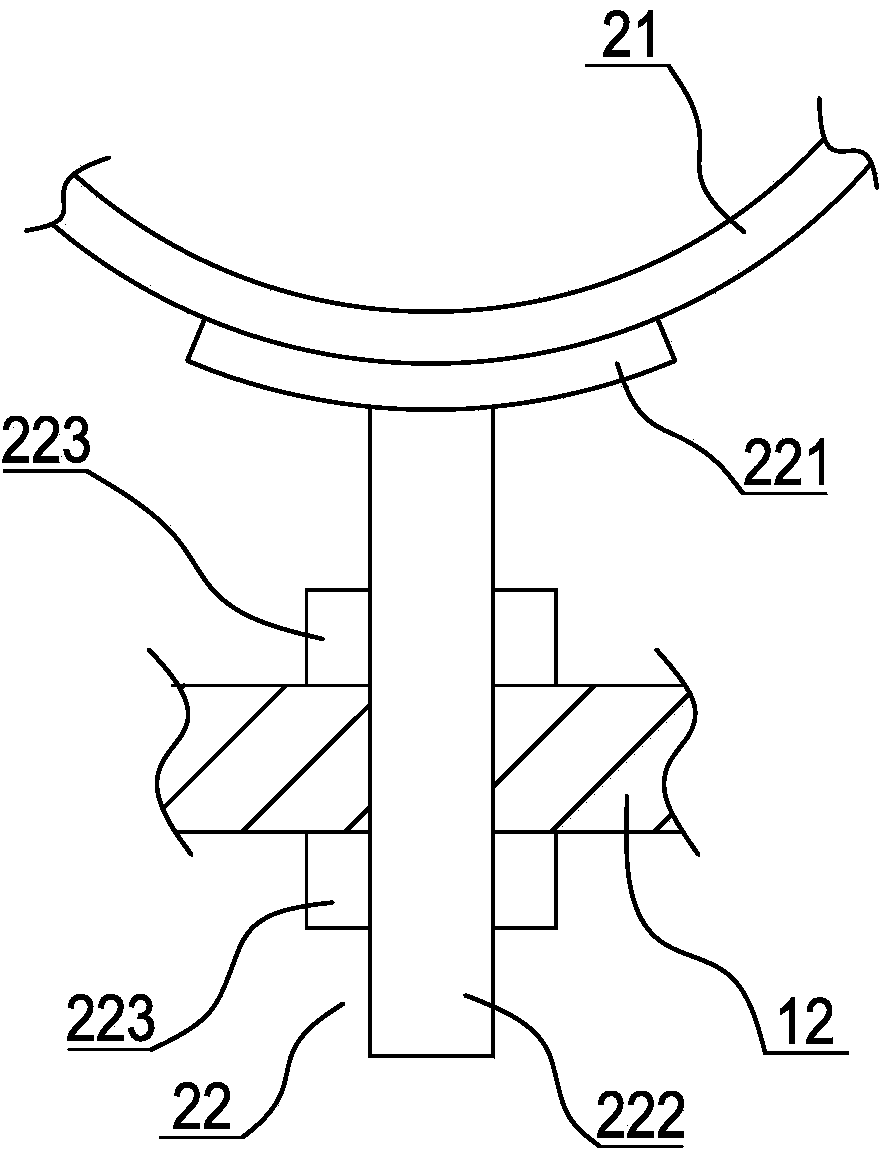
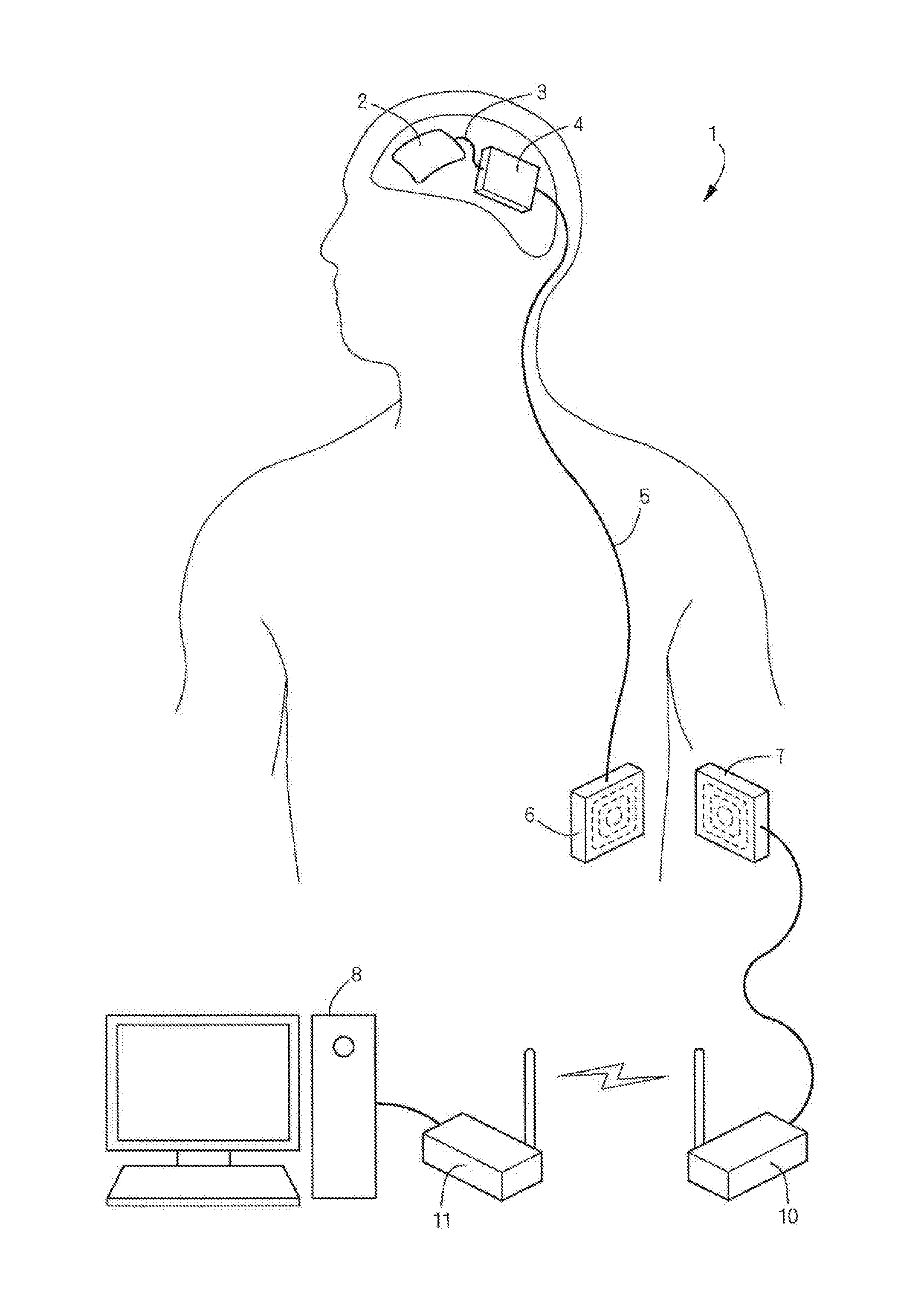
Casing for in vivo implantation device, in vivo implantation device, production method for casing for in vivo implantation device, and treatment support method using in vivo implantation device
InactiveUS20150289980A1High strengthImprove securityProgramme controlHead electrodesImplanted deviceIn vivo
To allow an implantable device including an electronic circuit to be implanted in the head in a more preferable manner in terms of appearance and safely. This implantable device is used for a brain-machine interface or the like.A casing 16 of an implantable device 4 configured to be implanted in a human head has an outer convexity surface 30 matching an external shape of a resected skull 27 related to at least a craniotomy site 26 of the artificial bone 28 designed in accordance with a skull shape of each person in order to fill the craniotomy site 26. That is, the outer convexity surface 30 of the artificial bone 28 is provided with two functions: the original function of filling the craniotomy site 26 as the artificial bone 28 and a function of serving as the casing 16 of the implantable device 4.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Transcranial ultrasound transducer with stereotactic conduit for placement of ventricular catheter
InactiveUS20110009739A1Overcome problemsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsCraniotomyUltrasonic transmission
An apparatus, system and method for performing a ventriculostomy using an ultrasound probe is disclosed. A head portion of the probe is connected to a handle portion at a proximal end of the head portion. A transducer is mounted in a distal end of the head portion to transmit ultrasound waves into the patient. The head portion includes a conduit portion arranged to accept and to accurately direct a catheter into the body of the patient in a direction parallel to the direction of the ultrasound waves. The head portion is sized to fit into a conventionally-sized craniotomy. An adjustment mechanism connects the head portion to the handle portion for selectively adjusting the angle between the handle portion and the head portion. A sterile sheath having an integral conduit assembly for mounting to the head is optionally provided. An illuminator is optionally provided on the probe.
Owner:PHILLIPS SCOTT B +1
Adjustable and controllable cerebrovascular thrombectomy stent and delivery control system
The invention relates to an adjustable and controller cerebrovascular thrombectomy stent and a delivery control system. The thrombectomy stent is formed by braiding a plurality of nickle-titanium memory alloy wires; the delivery control system is composed of a delivery guide wire, a delivery pipe, a delivery handle, a regulating and control button, a locking button and a developing marker; the proximal end of the delivery guide wire is fixed to the regulating and control button; the distal end of the thrombectomy stent is fixed to the delivery guide wire; the proximal end of the thrombectomy stent is fixed to the distal end of the delivery pipe; and the proximal end of the delivery pipe is fixed to the delivery handle. A minimally invasive surgery can be conducted under a circumstance of not implementing craniotomy; by pushing the delivery pipe, the thrombectomy device can reach a thrombus site, and radial dimensions of the thrombectomy device can be controlled by virtue of the regulating and control handle, so that a first bump and a second bump can be formed; and by locking the locking button on the handle, the maximum grabbing force and safety of drawing thrombus can be guaranteed.
Owner:上海微密医疗科技有限公司
Craniotomy device for anatomy
InactiveCN103622724AAvoid swingingReduce the burden onVivisection diagnosticsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a craniotomy device for anatomy. The craniotomy device comprises a stretchy support which is provided with an adjustable head fixing device. The edge of the upper portion of the stretchy support is provided with a plurality of oil cylinders, the two ends of piston rods of the oil cylinders stretch out of cylinder bodies, one end of each piston rod is fixedly connected to the stretchy support, the other ends of the piston rods are fixedly connected into a whole through a connecting support, rail plates fixedly connected with the cylinder bodies of the oil cylinders are vertically arranged among the oil cylinders, the rail plates are concentrically provided with at least two circles of cutting rail ring grooves which are internally provided with a plurality of partition blocks, the partition blocks are integrated with the rail plates so that the cutting rail ring grooves can be divided into a plurality of saw web guiding grooves, the saw web guiding grooves are internally and transversely provided with movable saw web fixing rods, one end of each saw web fixing rod is provided with a saw web shaft, one end of each saw web shaft is fixedly connected with a saw web, and the other end of each saw web shaft is connected with a power source through a transmission flexible shaft. According to the craniotomy device, working efficiency is high, operation is convenient, and the meninx tissues in the skull can be effectively prevented from being injured.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
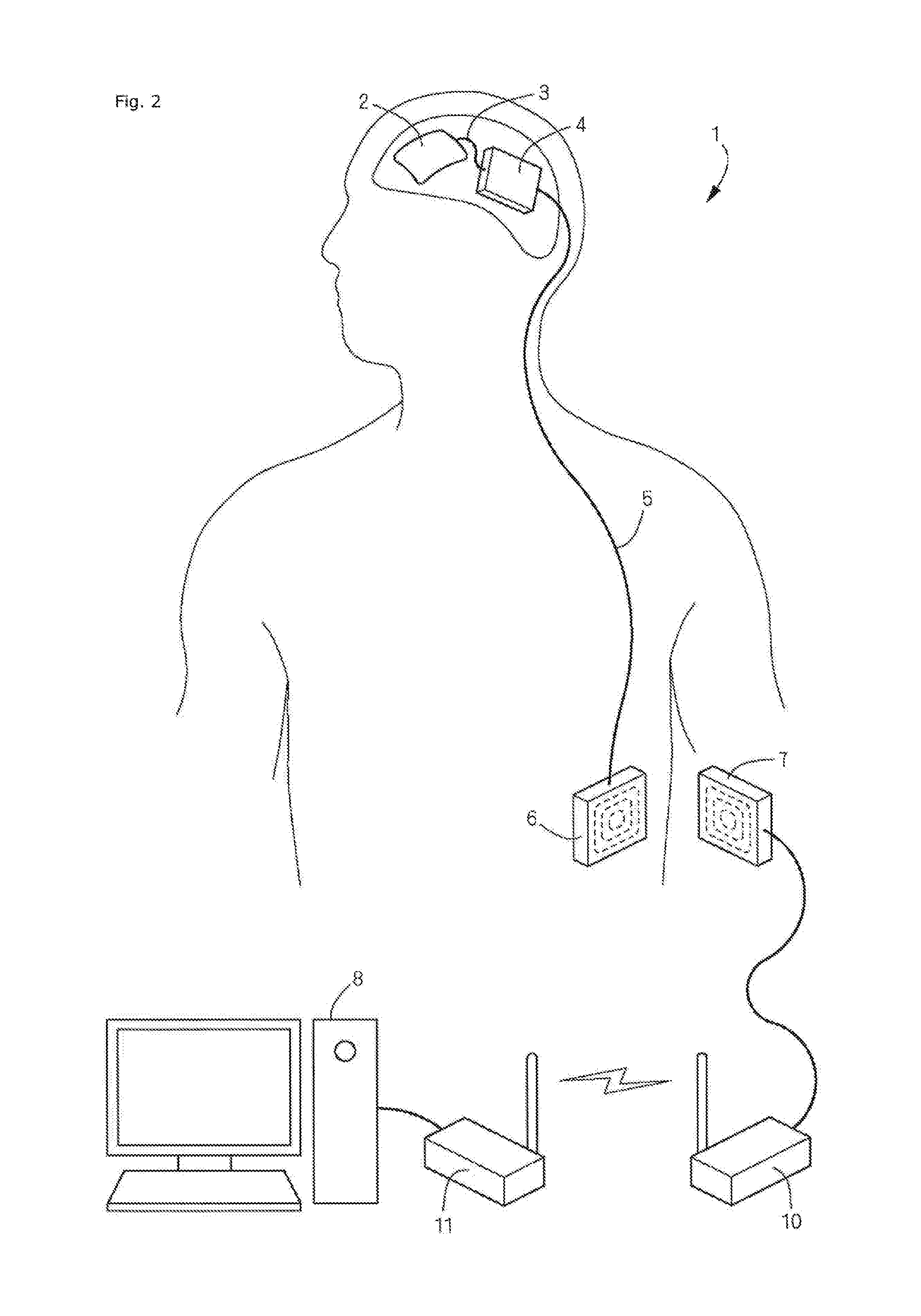
Casing of implantable device and implantable device, method for manufacturing casing of implantable device, and method for supporting treatment using implantable device
ActiveUS20170049398A1High strengthImprove securityElectroencephalographyInput/output for user-computer interactionSurgical siteImplanted device
To allow an implantable device including an electronic circuit to be implanted in the head in a more preferable manner in terms of appearance and safely. This implantable device is used for a brain-machine interface or the like. A casing of an implantable device configured to be implanted in a human head has an outer convexity surface matching an external shape of a resected skull related to at least a craniotomy site of the artificial bone designed in accordance with a skull shape of each person in order to fill the craniotomy site. That is, the outer convexity surface of the artificial bone is provided with two functions: the original function of filling the craniotomy site as the artificial bone and a function of serving as the casing of the implantable device.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Trephine having limiting sleeve
The invention relates to a trephine having a limiting sleeve, wherein the trephine is used for a medical surgery purpose in skull defect and skull puncture surgeries. The trephine with the limiting sleeve comprises a motor, an internal trephine, and at least one trephine sleeve. The internal trephine is nested in the trephine sleeve by means of at least two bearings and is driven, by means of themotor, to rotate. The external trephine sleeve defines and adjusts the cutting depth of the internal trephine, while protecting a surgery operator and the tissue around a surgical site from being injured by a trephine rotating at a high speed; moreover, by drilling using the trephine having a limiting sleeve, a bone flap can be completely removed and retrieved from a trephined bone. The present invention realizes standardization and repetition of cranial defect and drilling surgery, and makes the surgery simple, easy to operate, safe and reliable, efficient, and is less traumatic. In a commonmedical researching laboratory condition, the trephine supplies a surgery technological insurance for a skull defect model and a clinical medical craniotomy and skull puncture of mice to large animals.
Owner:王力平
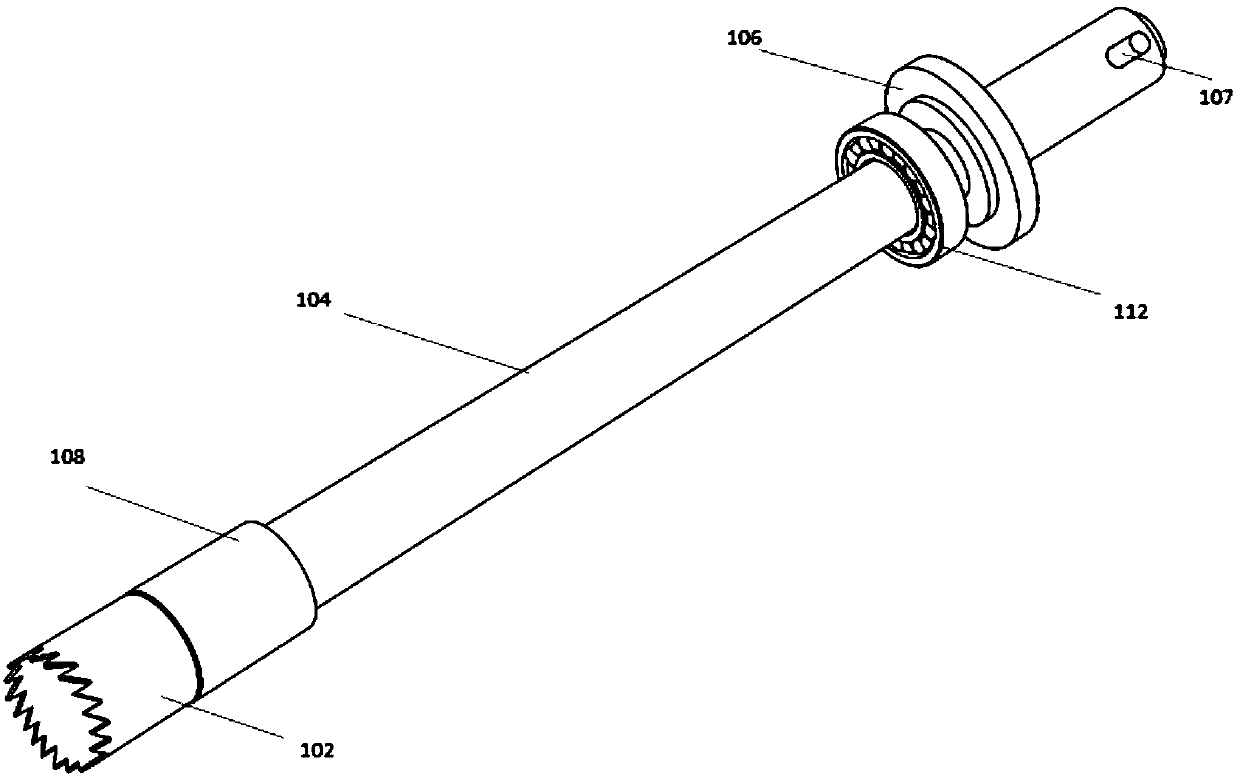
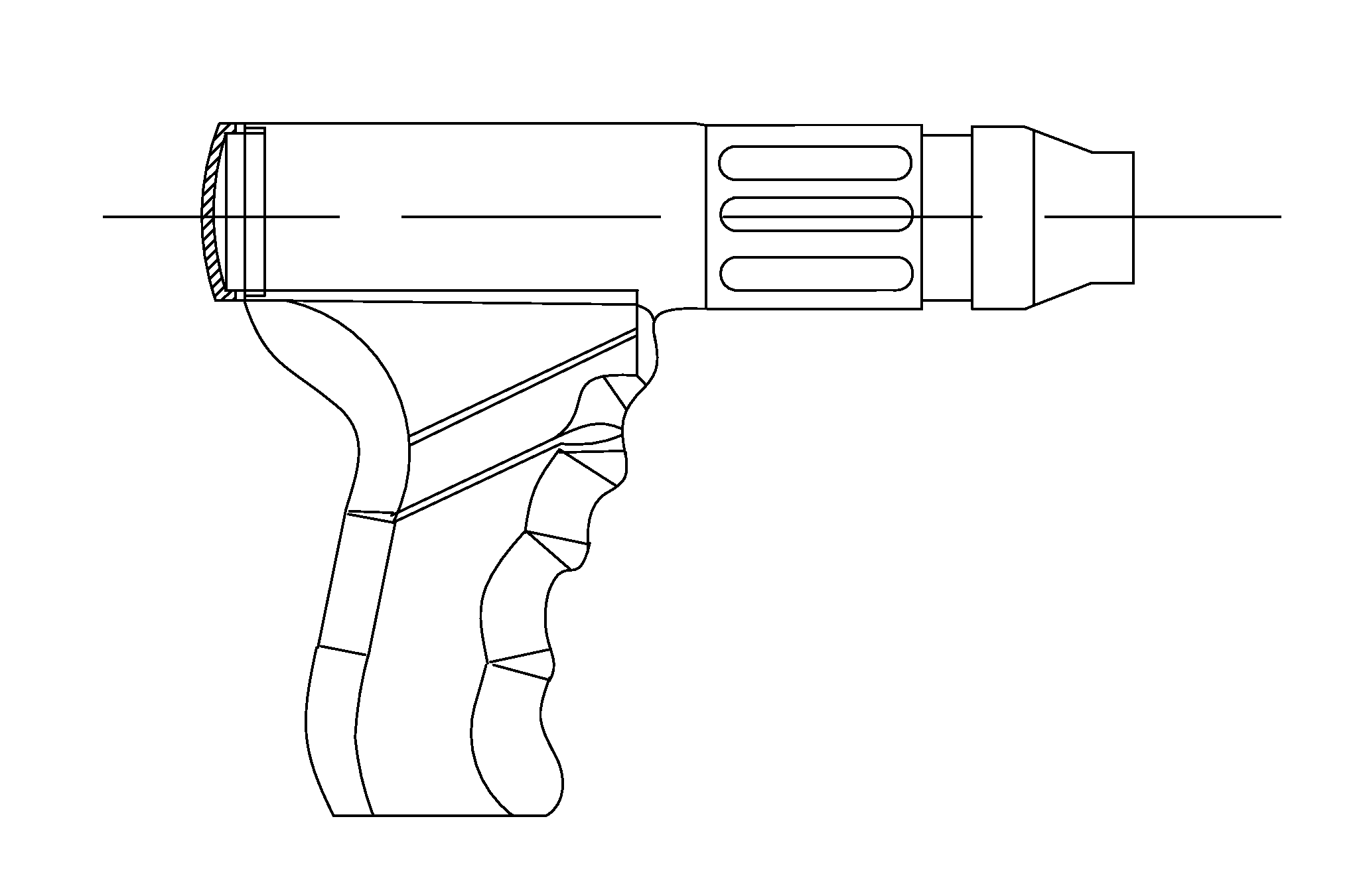
Craniotomy drill
ActiveUS20130178856A1Improve waterproof performanceEasy and convenient to operateSurgeryReduction driveEngineering
A craniotomy drill includes a main machine, a retarder and a locking seat. A drill transmission rod connected to the output shaft of the retarder is inserted in the locking seat. The main machine comprises a handle at the lower portion and an accommodating part at the upper portion, with a stator and a rotor of a DC electric motor being provided inside the accommodating part and a wall of the accommodating part being the stator housing of the DC electric motor. This craniotomy drill has a simple structure with the wall of the accommodating part as the stator housing of the electric motor, such that the volume and the weight are reduced. It is safe in use without the risk of the electric motor sliding out. By utilizing materials and processes of water resistant technology and an integrative design, a relatively good water resistant performance is achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING RUNZE PHARM CO LTD
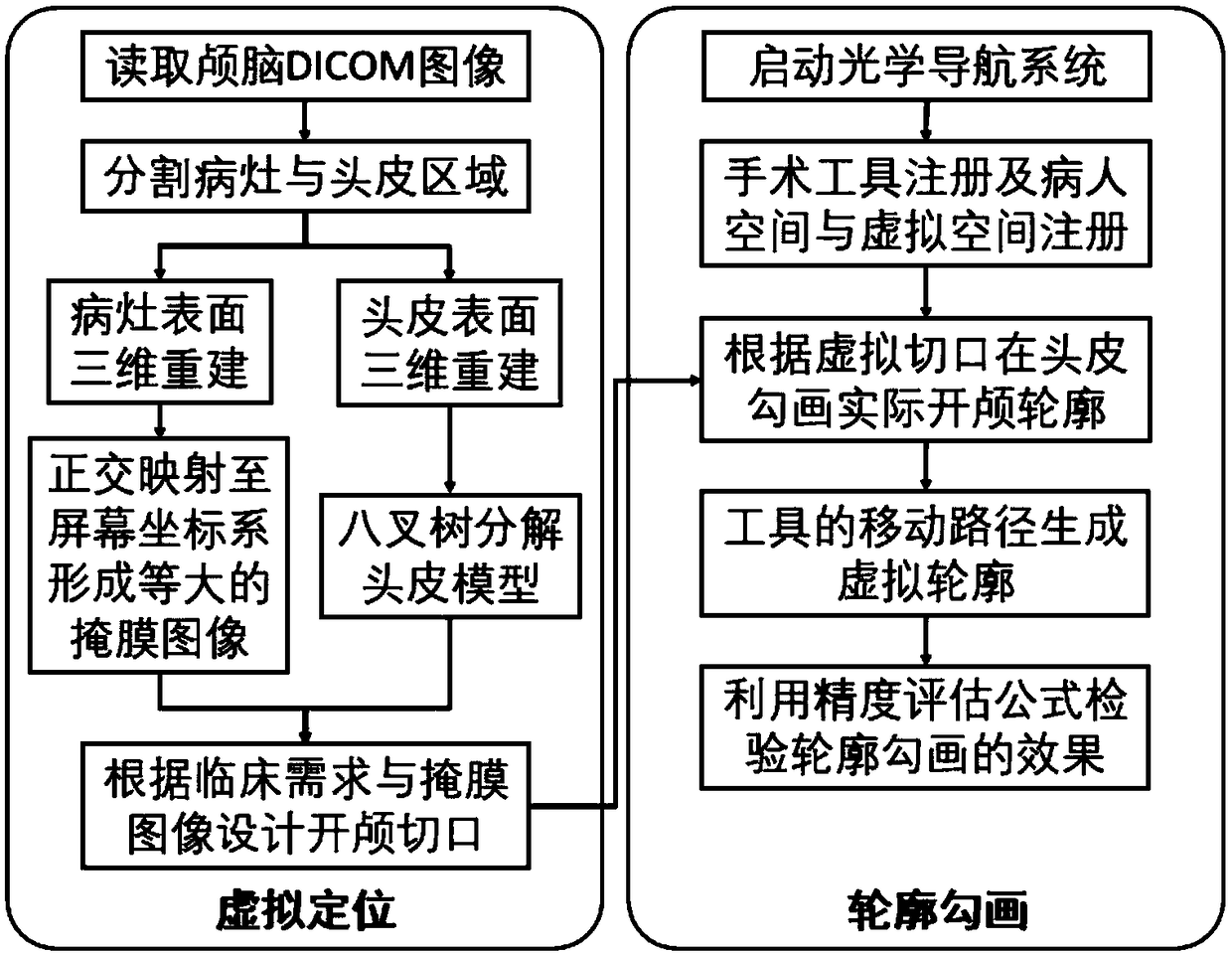
Three-dimensional visualized scalp craniotomy positioning method combined with optical surgery navigation
ActiveCN109493943ABreak through the disadvantages of designing craniotomy contoursRealize tracking and positioningImage enhancementImage analysisVirtual spaceImaging data
The invention discloses a three-dimensional visualized scalp craniotomy positioning method combined with optical surgery navigation, and the positioning method comprises the steps: 1), introducing a CT image sequence of a patient's brain to perform segmentation, obtaining two-dimensional image data of an intracranial lesion and the scalp; 2), performing three-dimensional reconstruction according to the two-dimensional images of the lesion and the scalp, and performing rendering into a three-dimensional model in a virtual space, and performing the orthogonal mapping of the lesion model to the scalp to design an adaptive craniotomy contour; 3), combining an optical surgical navigator to complete the registration of a surgical tool and the patient's space and the virtual space, tracking the surgical tool in real time, and drawing the actual craniotomy contour on a real skull scalp along the virtual craniotomy contour; 4) recording and displaying a movement path of the tip of the surgicaltool through employing a virtualization method; 5), solving the distance between the actual contour and the designed contour in the virtual space to assess the accuracy of craniotomy. The method provides a reference for a doctor to draw a contour, and breaks through the shortcomings of the traditional method that the naked eye is closely focused on the lesion to design the craniotomy contour.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
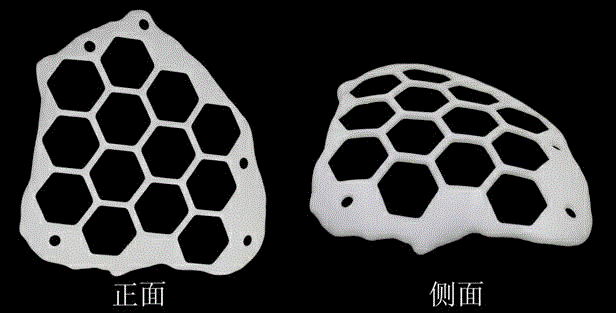
Ex-scalp skull deletion repairing technique
The invention provides an ex-scalp skull deletion repairing technique, and relates to the technical field of skull repairing, in particular to an early ex-scalp skull deletion repairing technique performed through a 3D printed photosensitive reticular lamina. Skull deletion usually causes multiple complications, skull repairing is a preferred method for preventing the complications from occurring, but it is generally acknowledged that skull repairing is advisably performed after craniotomy is performed for 3-6 months, and occurrence of the complications is difficult to avoid due to the fact that a patient is not protected by the skull before skull repairing is performed. The complications caused by skull deletion of the patient can be decreased by performing the ex-scalp skull deletion repairing technique through the 3D printed photosensitive reticular lamina. The technique can be operated under local infiltration anesthesia, the process is simple, and pain brought to the patient is little. According to the technique, a 3D printing technique and a skull CT three-dimensional reconstruction technique are combined, the reticular lamina which has the thickness of 2-4 mm and is internally hollowed into a hexagonal lattice shape is made by taking photosensitive resin as a material, and therefore the reticular lamina not only has the certain strength but also has a breathable effect.
Owner:姚安会 +2
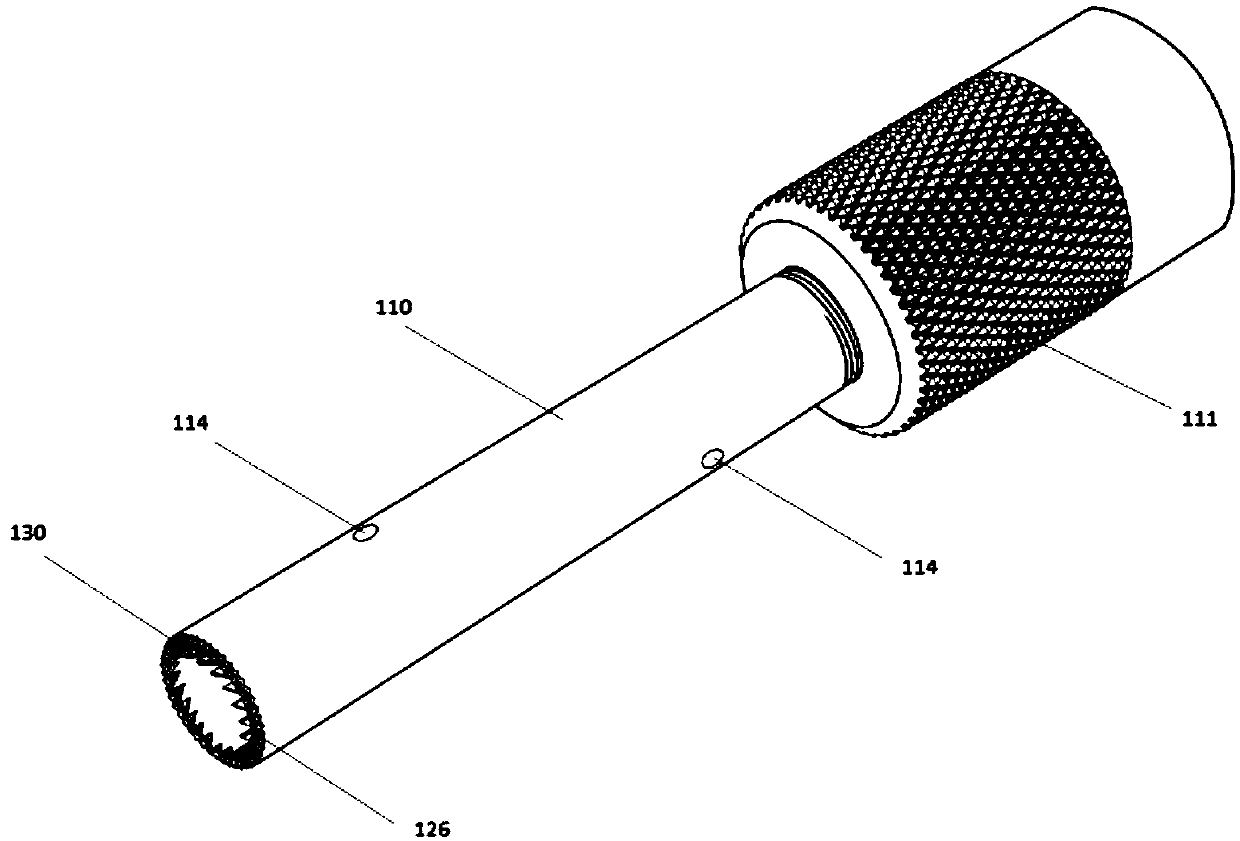
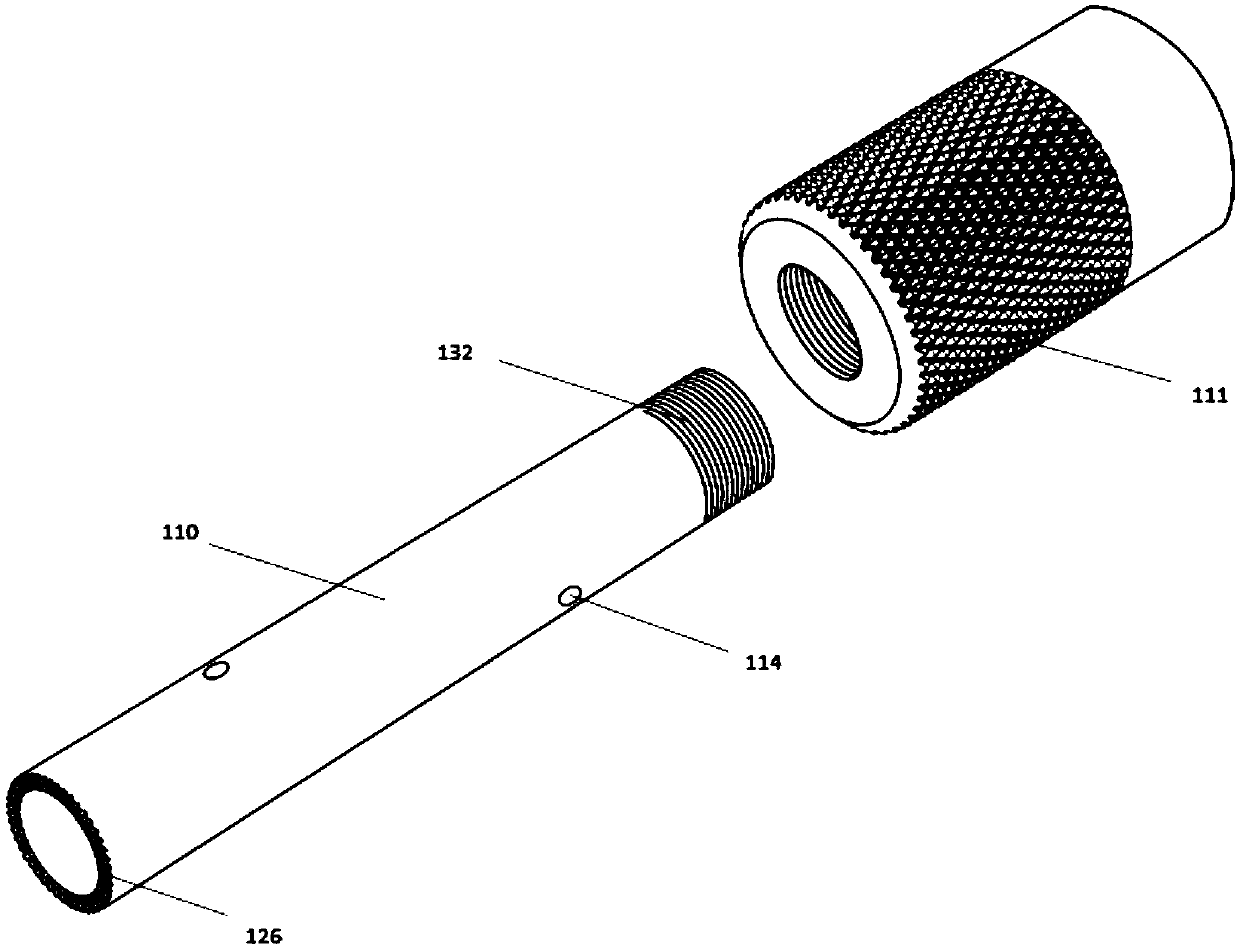
Craniotomy drill
The invention discloses a craniotomy drill, comprising a host machine, a speed reducer and a locking base which are in threaded connection in turn; a drill transmission rod connected with the output shaft of the speed reducer is inserted in the locking base; the craniotomy drill is characterized in that the host machine comprises a handle (1) at the lower side and a containing part (2) at the upper side; containing part (2) is internally provided with a stator having a DC motor and a rotor (5); and the wall (4) of the containing part (2) is the outer housing of the DC motor stator. The craniotomy drill has simple structure, and the wall of the containing part is directly used as the outer housing of the motor stator, thereby reducing the volume and reducing the entire weight. The craniotomy drill can prevent the motor from being slid off and can have comparatively high safety performance. Simultaneously, the craniotomy drill has integrated design and comparatively excellent waterproofperformance because of waterproof material and technique.
Owner:CHONGQING RUNZE PHARM CO LTD
Method for fixing fish brain tissue specimen through systemic heart perfusion
InactiveCN104568542AFix fixityTissue AutolysisPreparing sample for investigationSurgical veterinaryIntubationCommon cardinal veins
The invention discloses a method for fixing a fish brain tissue specimen through systemic heart perfusion. The method is mainly characterized in that after fish anesthesia, thoracotomy is performed on the periphery of a heart surface projection area of the fish, ventral aorta intubation is performed through the ventricle, common cardinal vein intubation is performed through the atrium, ligation with an operation thread is used for fixing, and an out flow tube is connected with a graduated vessel for measuring liquid out-flowing quantity; a constant-speed perfusion pump is used for perfusing normal saline through a perfusion tube, and a 10% formalin solution is adopted for reperfusion; when perfusion is started, a line is marked on the skull instantly and craniotomy is performed, and the perfusion time is then decided through combination of the perfusion quantity and the out-flowing quantity when the color of the brain tissue changes white; the brain is picked and placed in the 10% formalin solution to be fixed for 48 h after perfusion is stopped, and the brain tissue specimen with complete structure, normal form and good state is obtained. By means of the method, the problems of insufficient fixing, non-comprehensive fixing area, tissue autolysis, cell deformation and the like of the fish brain tissue can be solved effectively, the brain tissue specimen with more complete structure and more ideal state is obtained easily, and the natural form is retained better.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
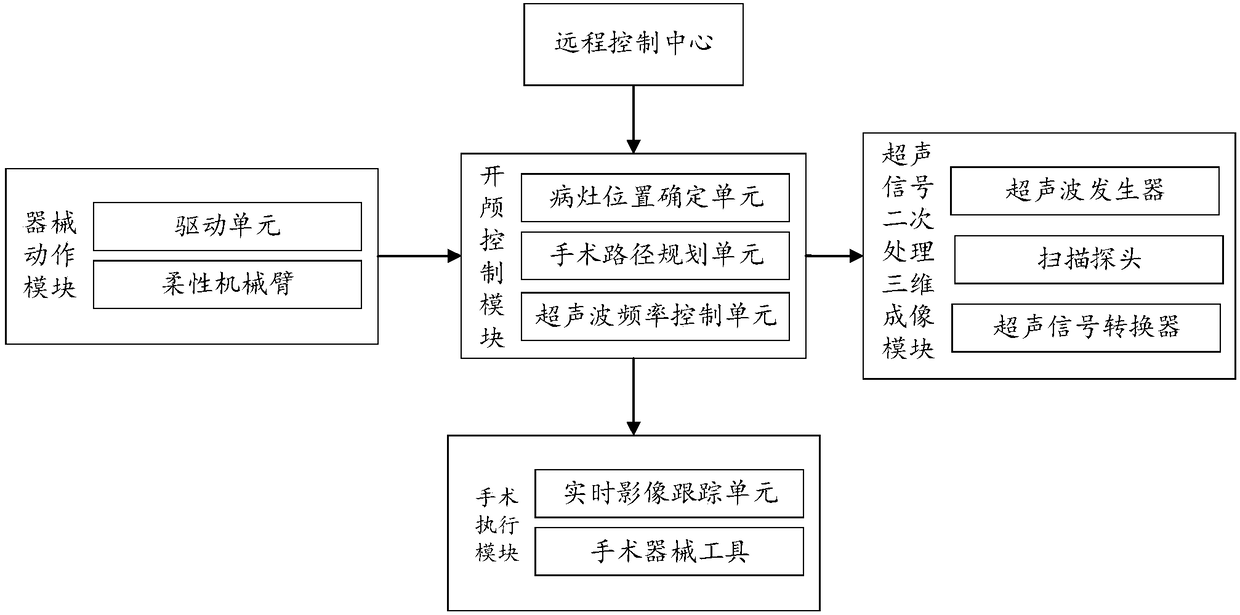
Ultrasonic-based craniotomy robot system
InactiveCN108577968AHigh precisionShorten the recovery periodDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSurgical operationEngineering
The invention provides an ultrasonic-based craniotomy robot system. The system comprises a remote control center, a craniotomy control module, an ultrasonic signal secondary processing three-dimensional imaging module, a surgical execution module and an instrument working module. The remote control center is used for receiving image data, determining the location of a brain lesion, and initially planning a surgical path. The craniotomy control module is used for planning a secondary surgical path. The ultrasonic signal secondary processing three-dimensional imaging module is used for utilizingultrasonic waves to carry out three-dimensional imaging, and performing an ultrasonic surgical operation according to the secondary surgical path. The surgical execution module is used for performingsurgical operation according to a real-time image. The ultrasonic-based craniotomy robot system solves the problem of low surgical success rate or even inability to perform an operation due to lack of a professional neurosurgeon in a remote area, the surgical success rate is improved, guidance of the lesion position is automatically carried out, the recovery period of a patient is greatly shortened, and risk of a surgery failure is reduced.
Owner:刘伟民
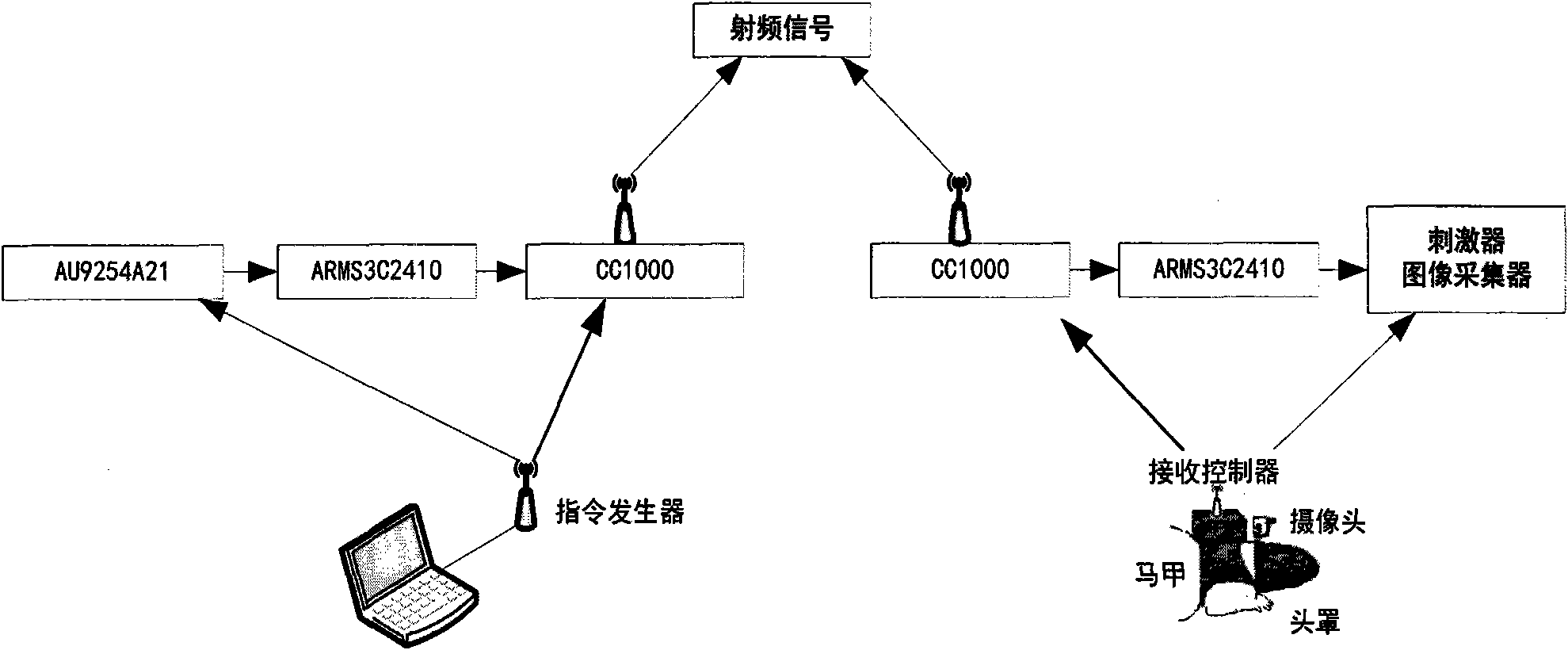
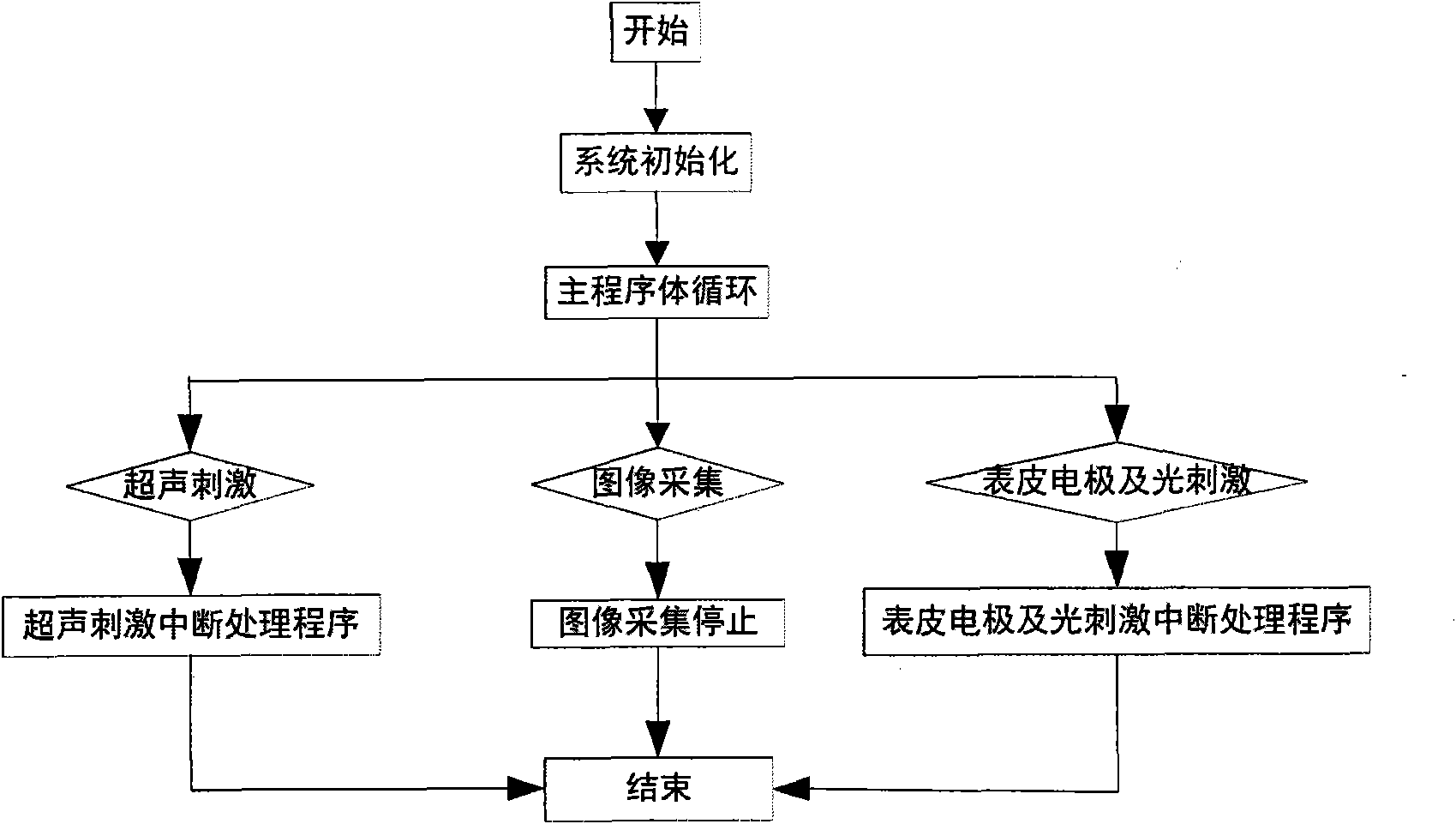
Method for controlling movement of woundless rat robot
InactiveCN101861836AEasy to operateIncrease success rateTaming and training devicesBiological bodyNeurolysis
The invention discloses a method for controlling movement of a woundless rat robot. The conventional animal robot has the defects of difficult development process and low success rate by adopting a creative movement control mode. The invention adopts a mode of integrating ultrasonic stimulation with epidermal electrode stimulation and LED light auxiliary stimulation, wherein the ultrasonic stimulation is used for stimulating sense of hearing; the epidermal electrode stimulation is used for stimulating sense of pain; and the LED light auxiliary stimulation is used for stimulating sense of vision to make the rat robot have active escape behavior so as to control the movement of the rat robot. The method for controlling movement by adopting a woundless rat movement control mode has the advantages of solving the problems of neurolysis, difficult operation and the like in creative stimulation control, accelerating practical process, along with no need of craniotomy on the rat, short development cycle, and wide development potential in aspects of personnel search and rescue, military activities, and acquisition of physiological parameters of organisms in the future.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com