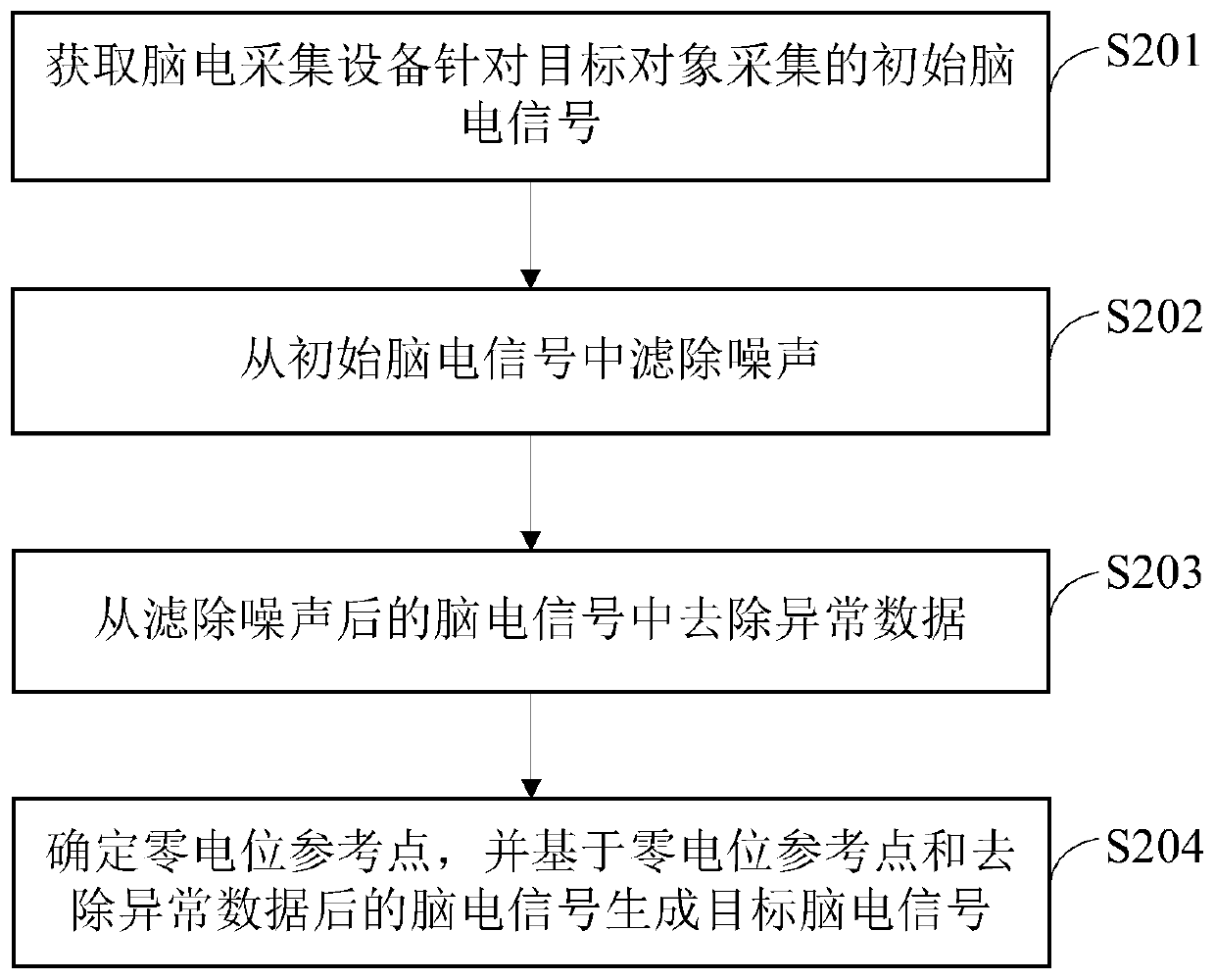
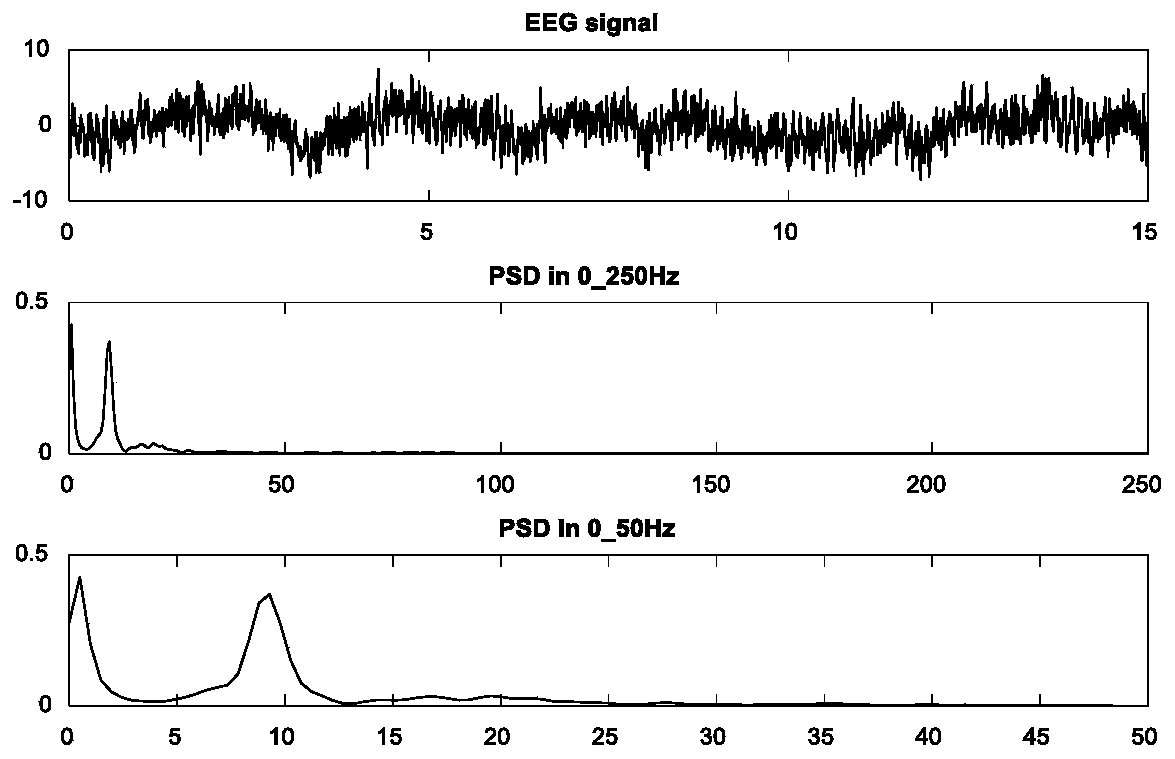
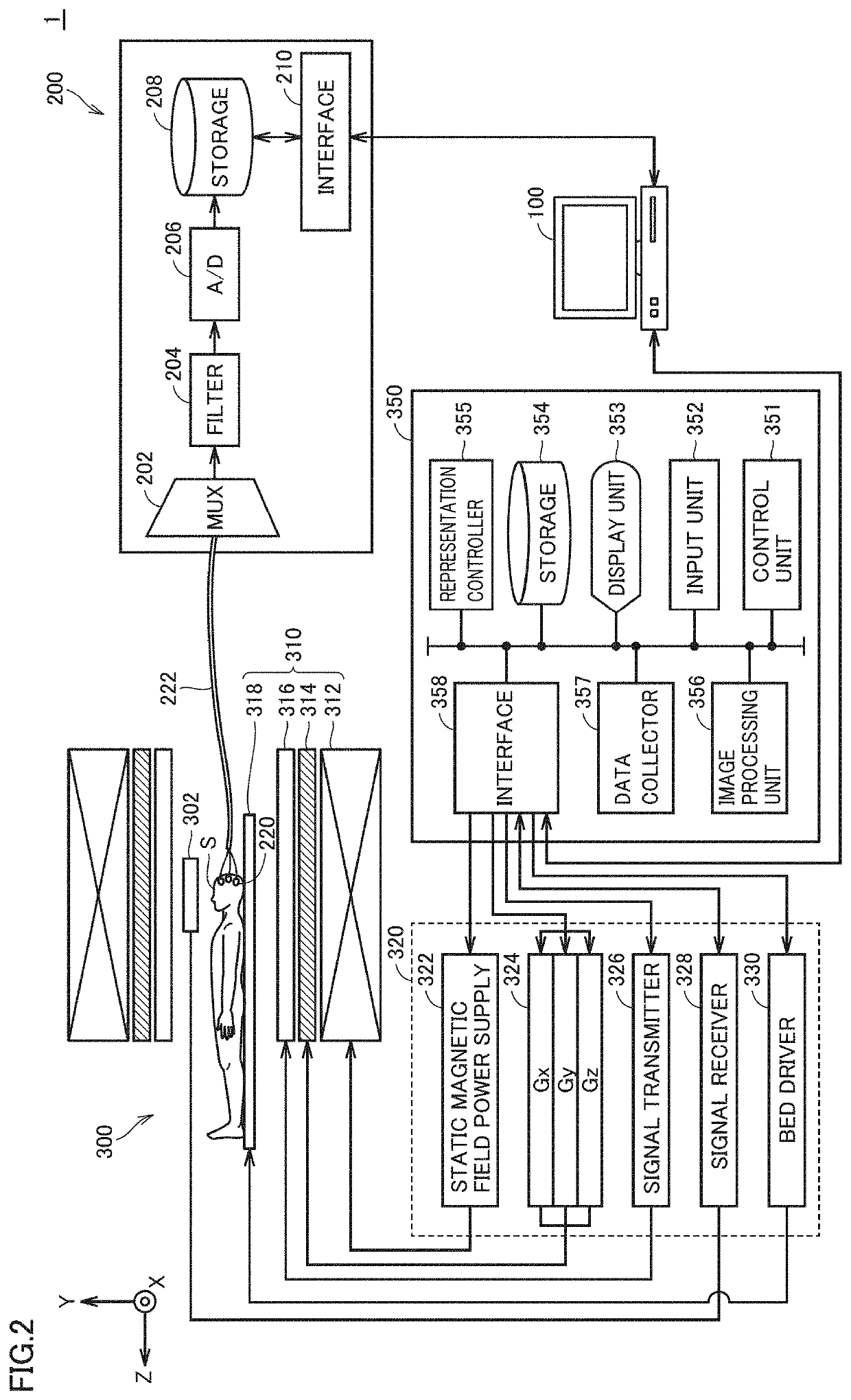
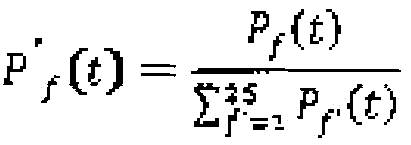Patents
Literature
131 results about "Cerebral activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A method of examining brain activity in animals and humans by recording the total bioelectric activity of the various zones, regions, and lobes of the brain. The procedure is used in modern neurophysiology, neuropathology, and psychiatry.
Method and apparatus for electromagnetic modification of brain activity
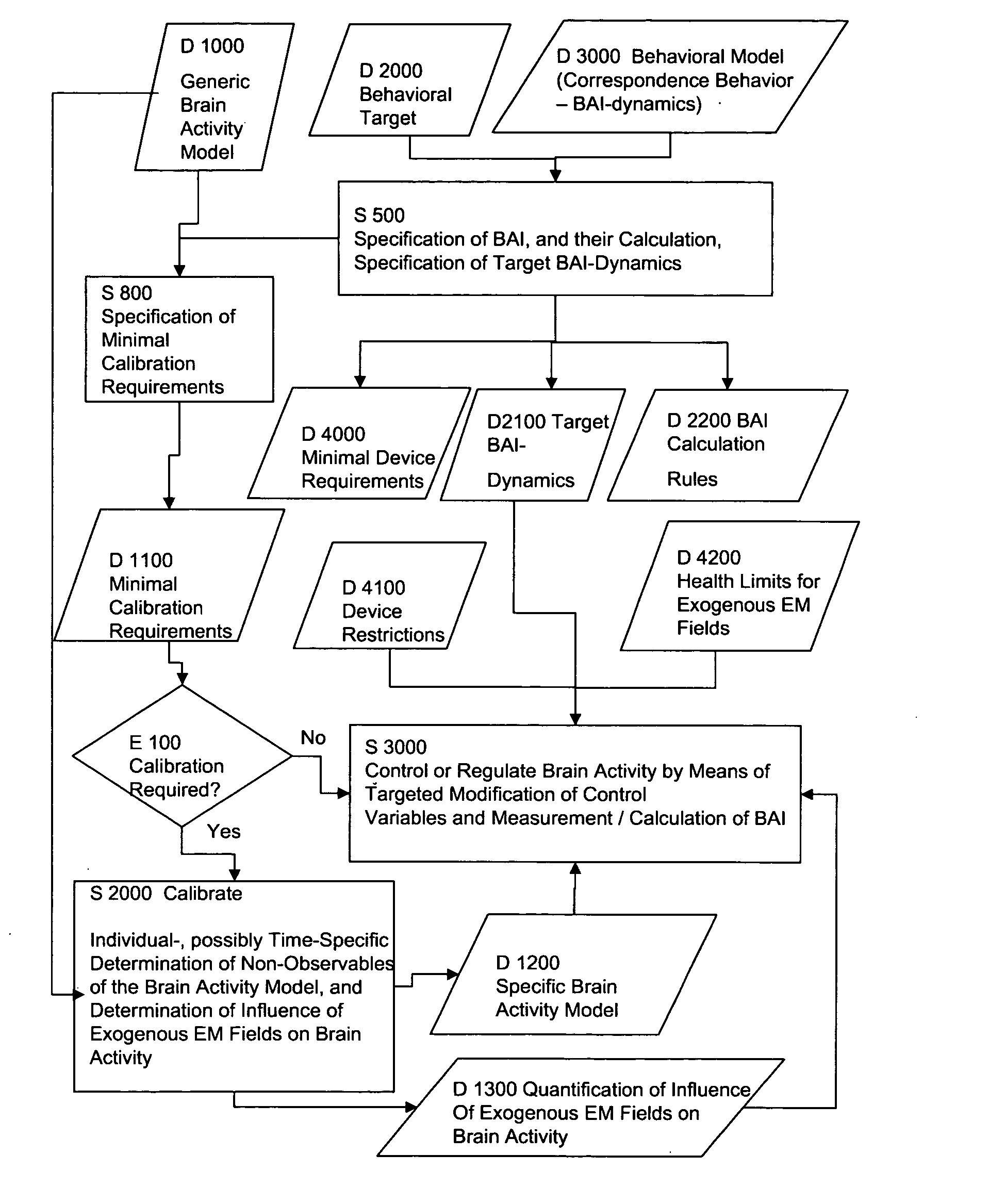
A method and an apparatus for the electromagnetic modification of brain activity, in particular for the model-based controlled or regulated, respectively, electromagnetic modification of brain activity in vivo, as well as to the resulting modification of behavior is disclosed. A brain activity model (which describes the influence of exogenous electric and / or magnetic fields on a brain activity) is used, and a behavioral model (which describes the correspondence between brain activity and behavior) is used. Thereby it becomes possible, for the first time ever, to influence the behavior of a person by means of exogenous input in a controlled way. Intra-individual and / or time-dependent non-observables, as well as to determining individual, is provided, if necessary intra-individual and / or time-dependent translation operators from extracranial signal to control force, whereby a secure and controlled intervention as part of a open or closed control loop is created, which in turn results in achieving a brain activity target in a reliable way. Using a behavioral model ensures that achieving a brain activity target corresponds to achieving the individual behavioral target of the user.
Owner:JOUAN
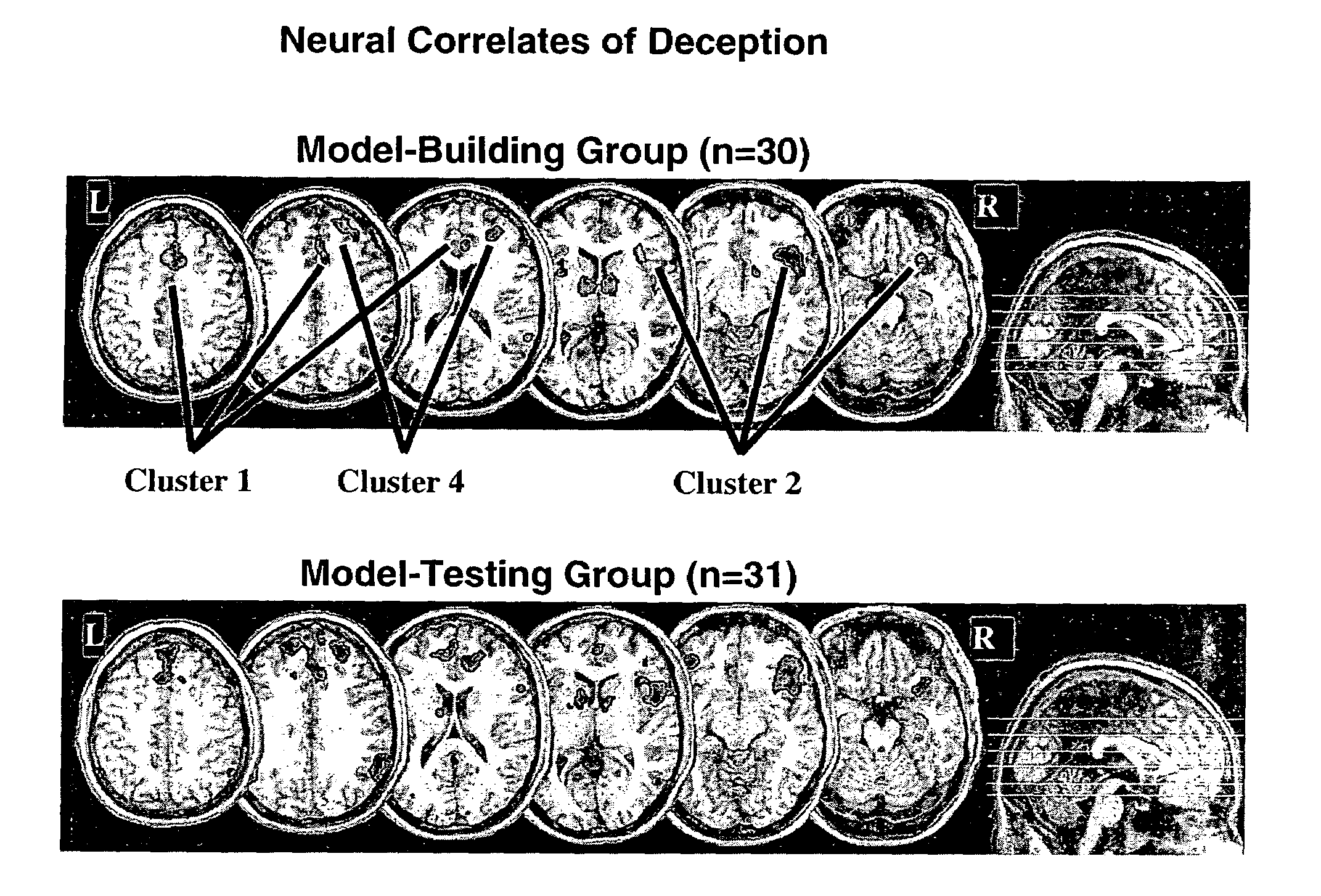
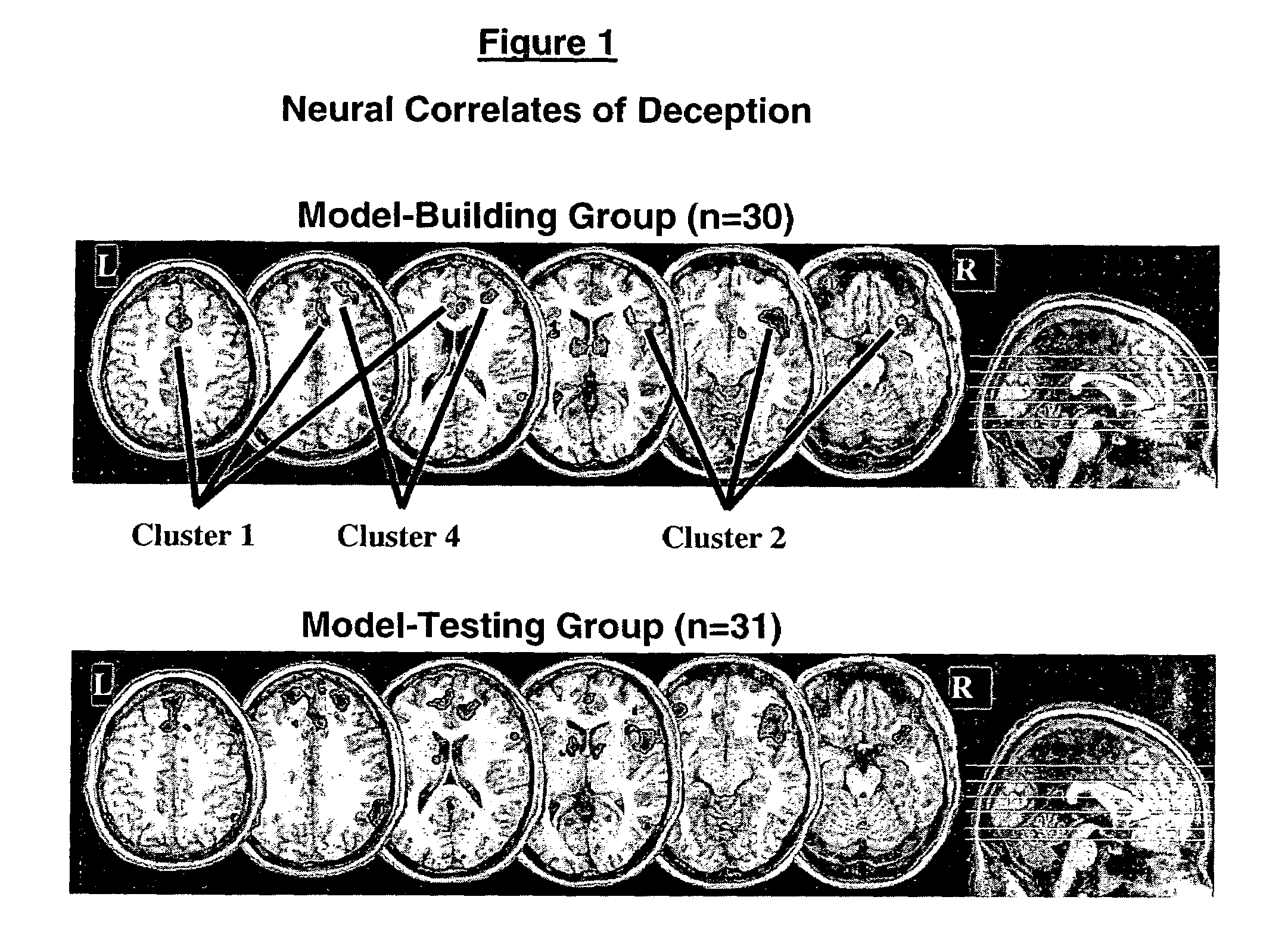
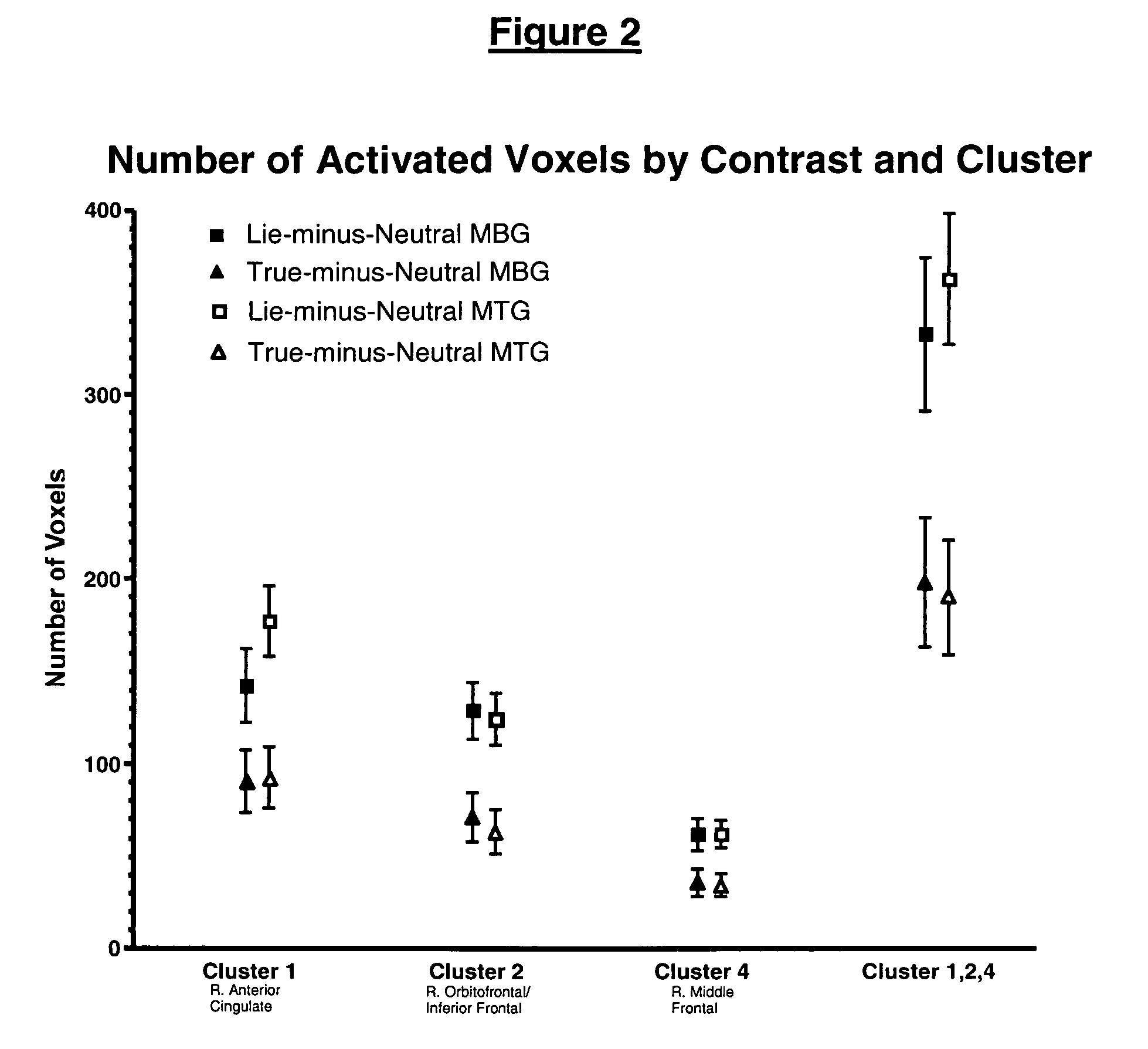
Systems and methods for detecting deception by measuring brain activity
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Method and apparatus for objectively measuring pain, pain treatment and other related techniques
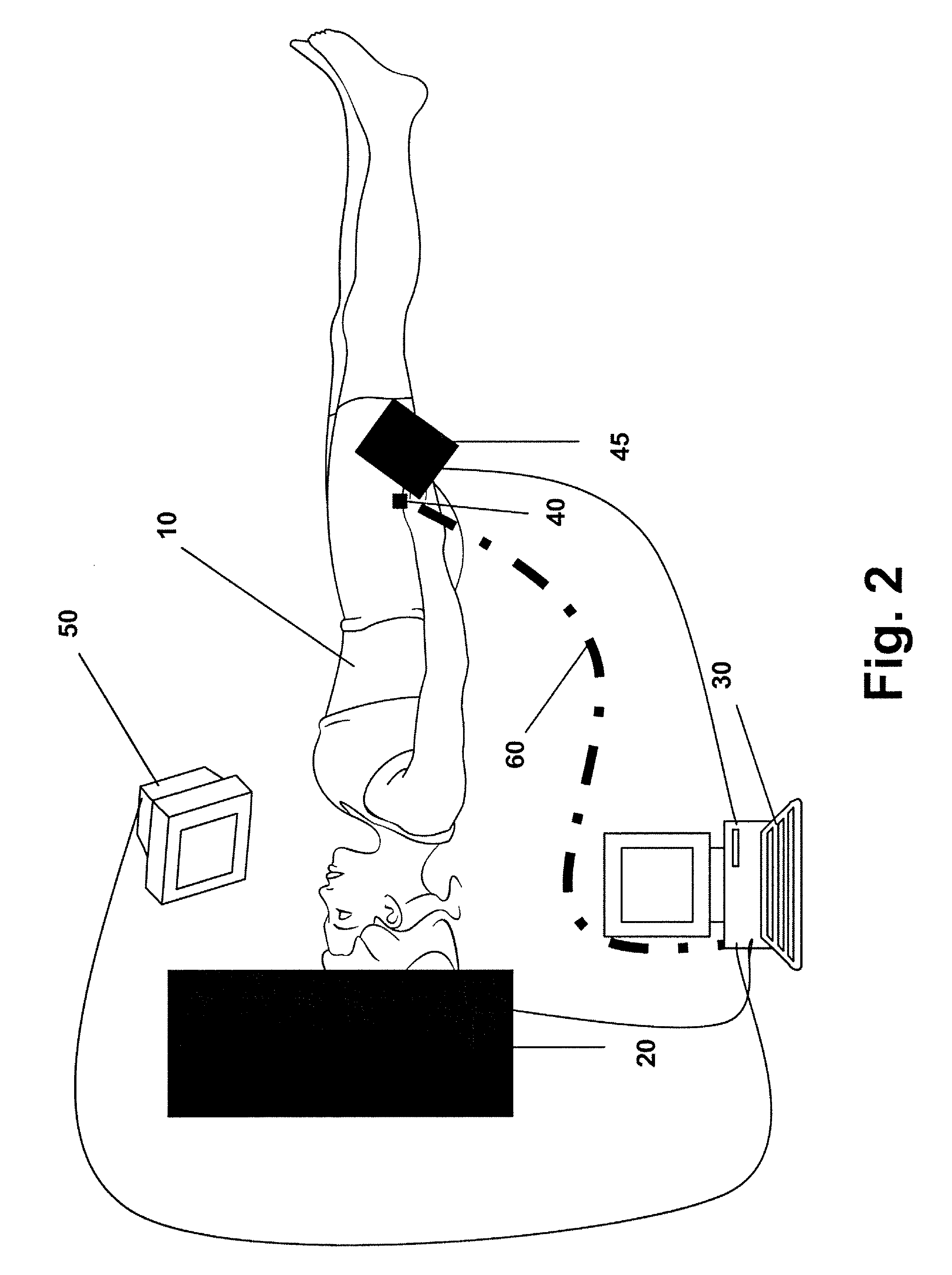
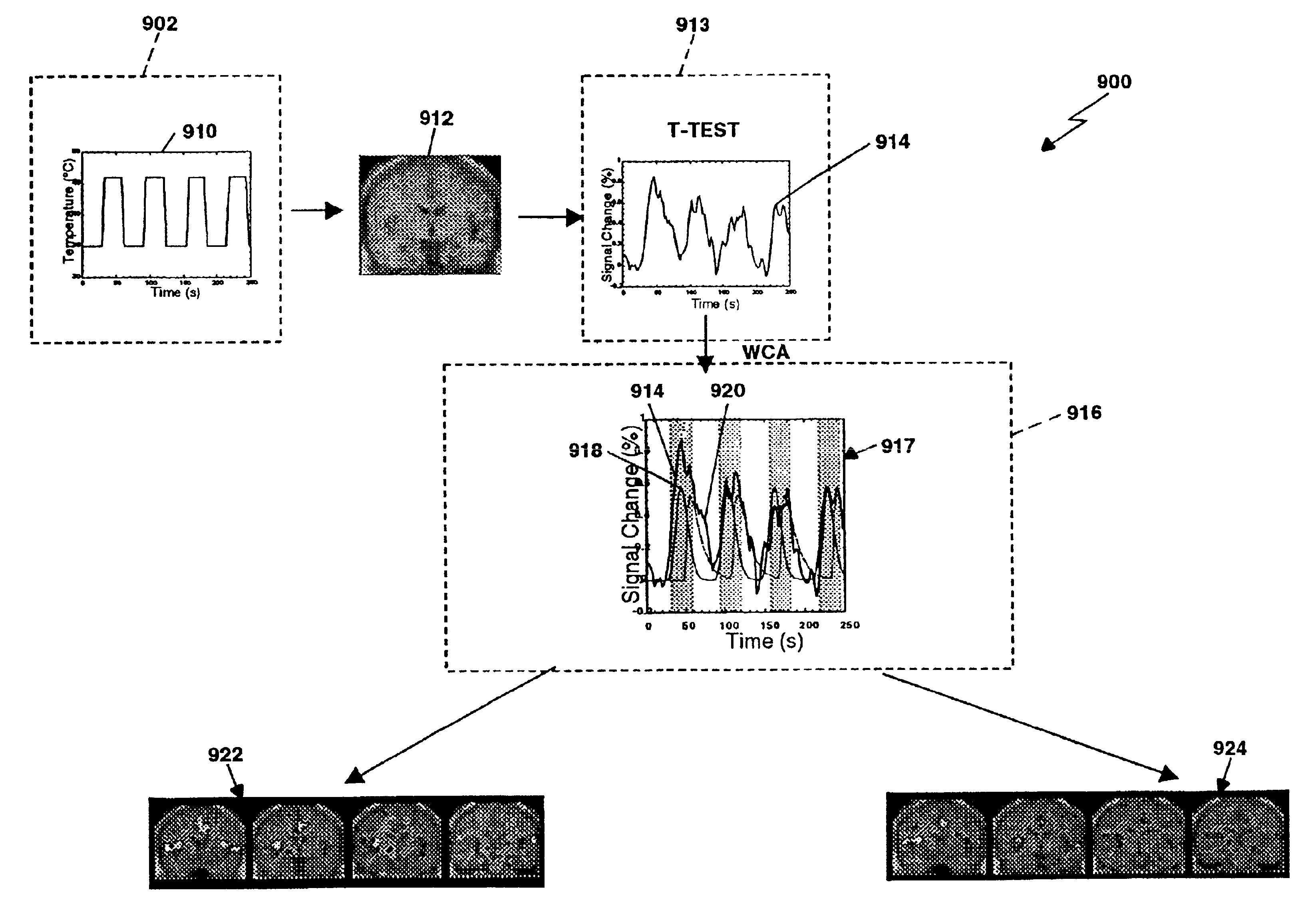
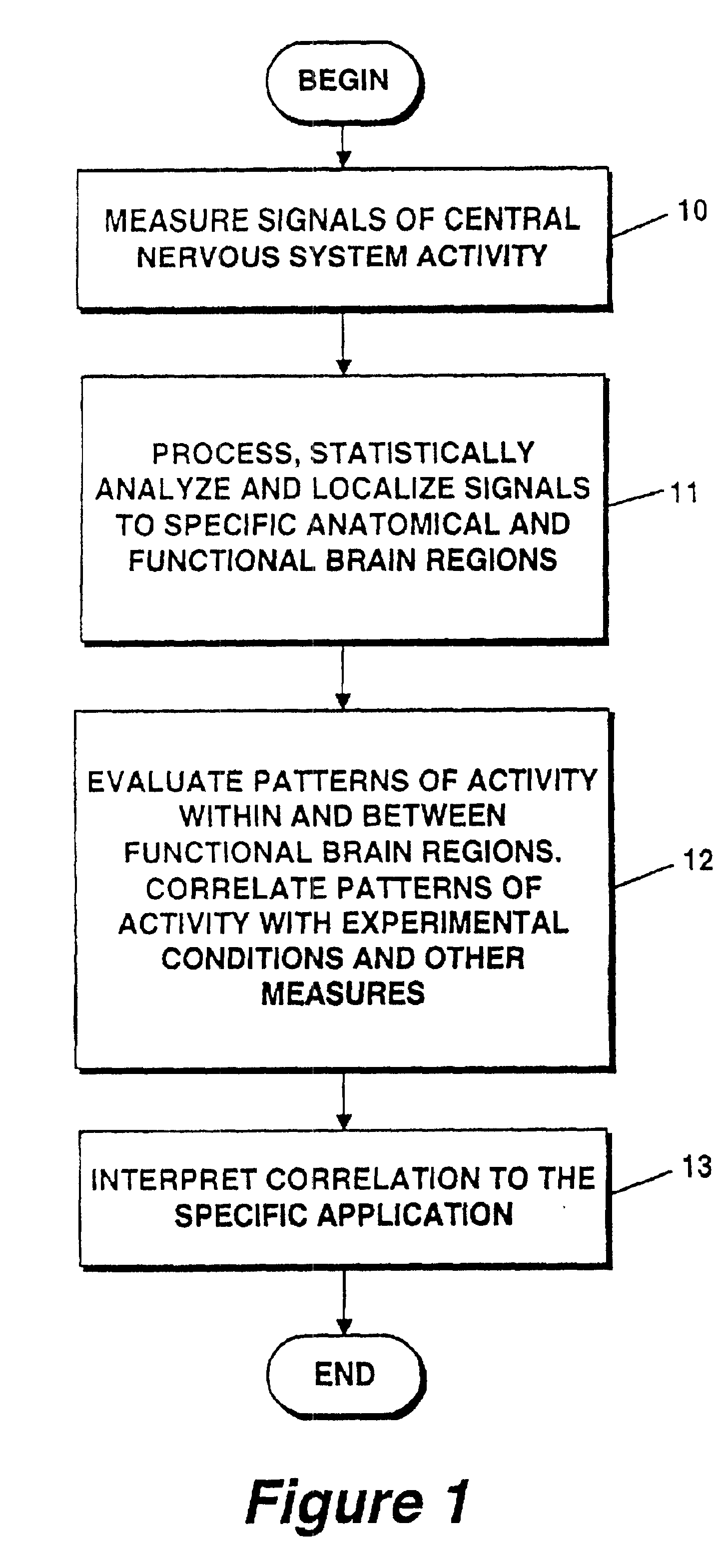
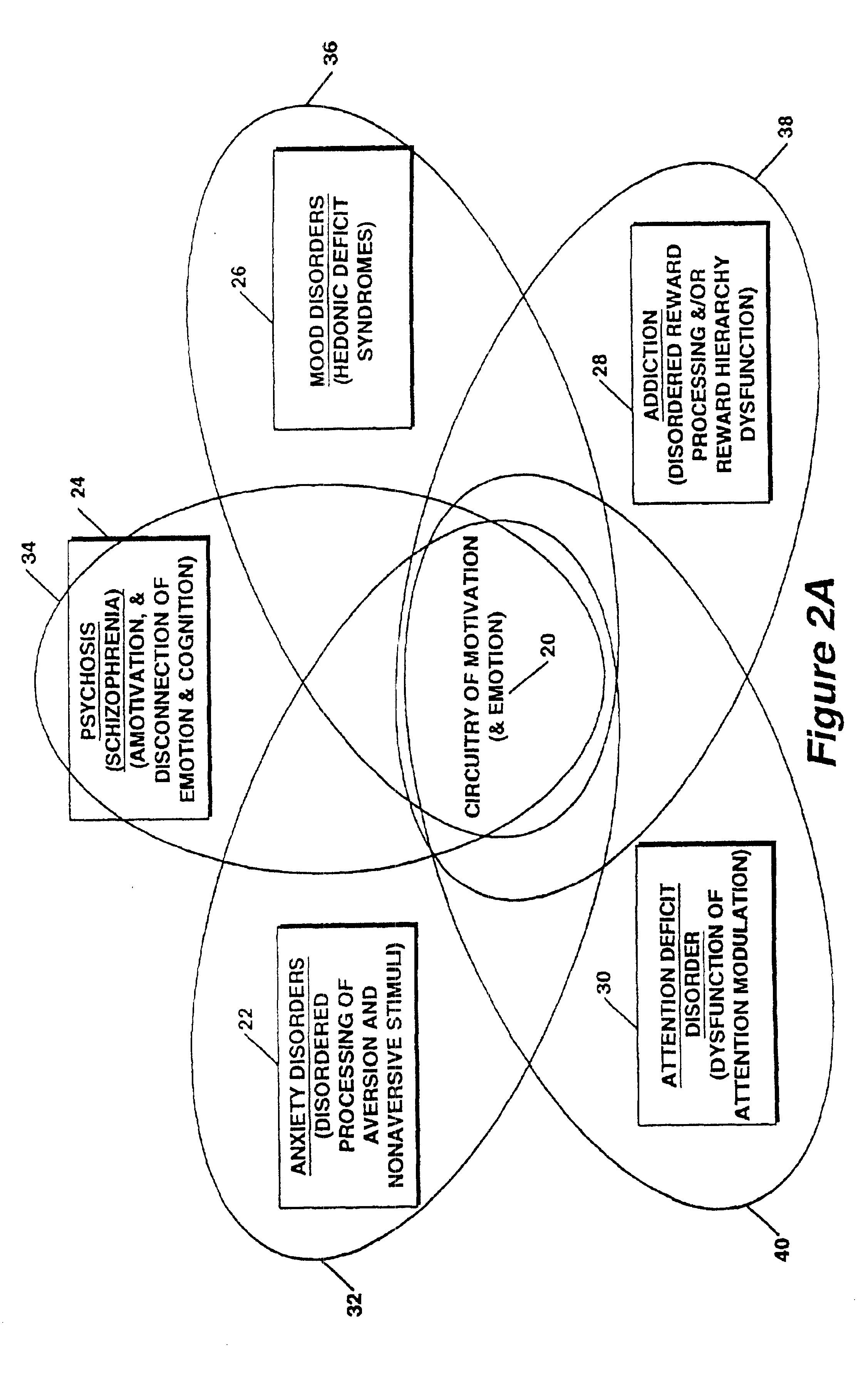
A method for measuring indices of brain activity includes non-invasively obtaining signals of central nervous system (CNS) activity, localizing signals to specific anatomical and functional CNS regions, correlating the signals from pain and reward brain regions, and interpreting the correlation results. The results of interpreting the correlation results can be used for objectively measuring, in individual humans or animals, their responses to motivationally salient stimuli including but not limited to stimuli which are internal or external, conscious or non-conscious, pharmacological or non-pharmacological therapies, and diseased based processes. This method for measuring brain activity in reward / aversive central nervous system regions, can further be used to determine the efficacy of compounds.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
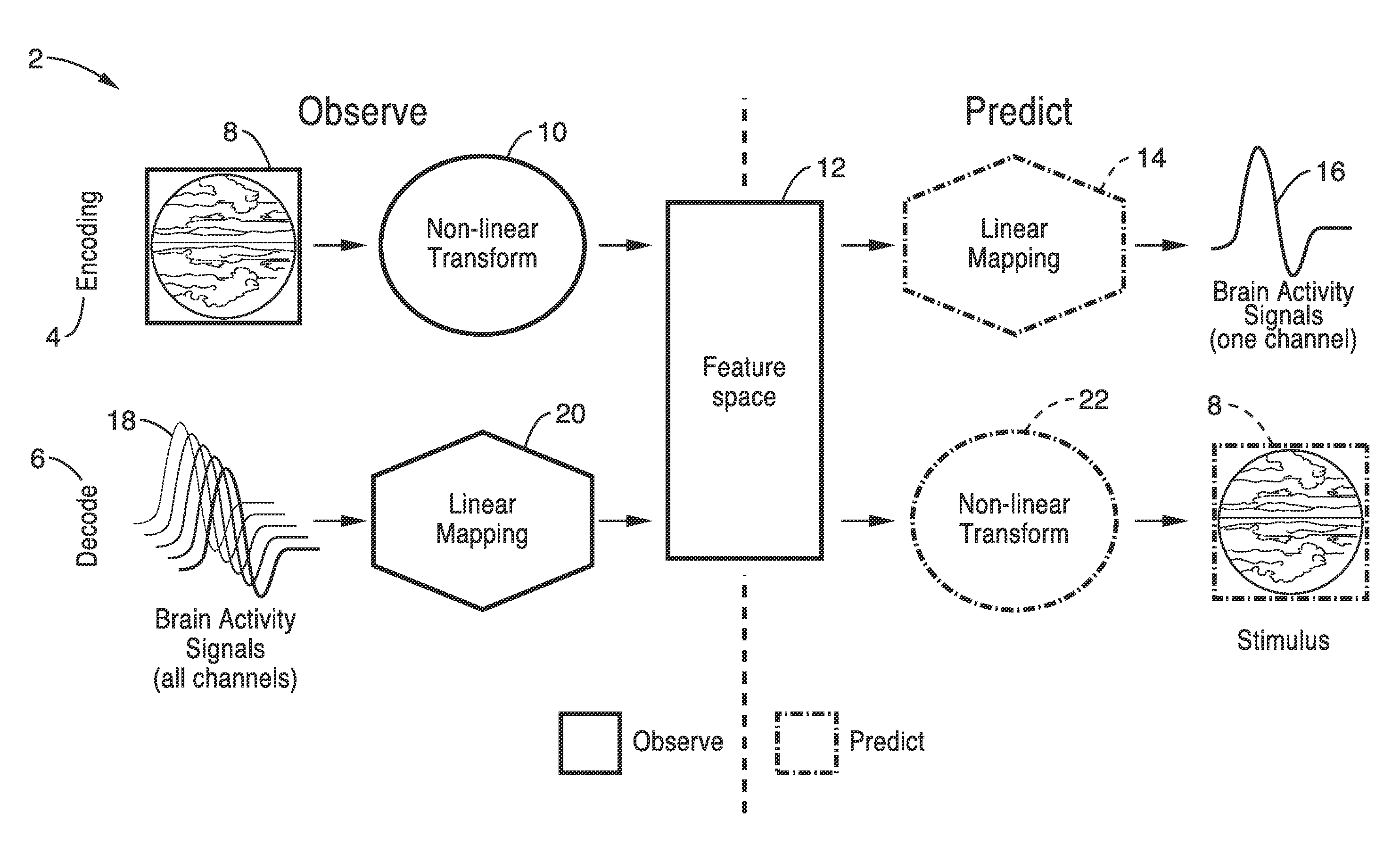
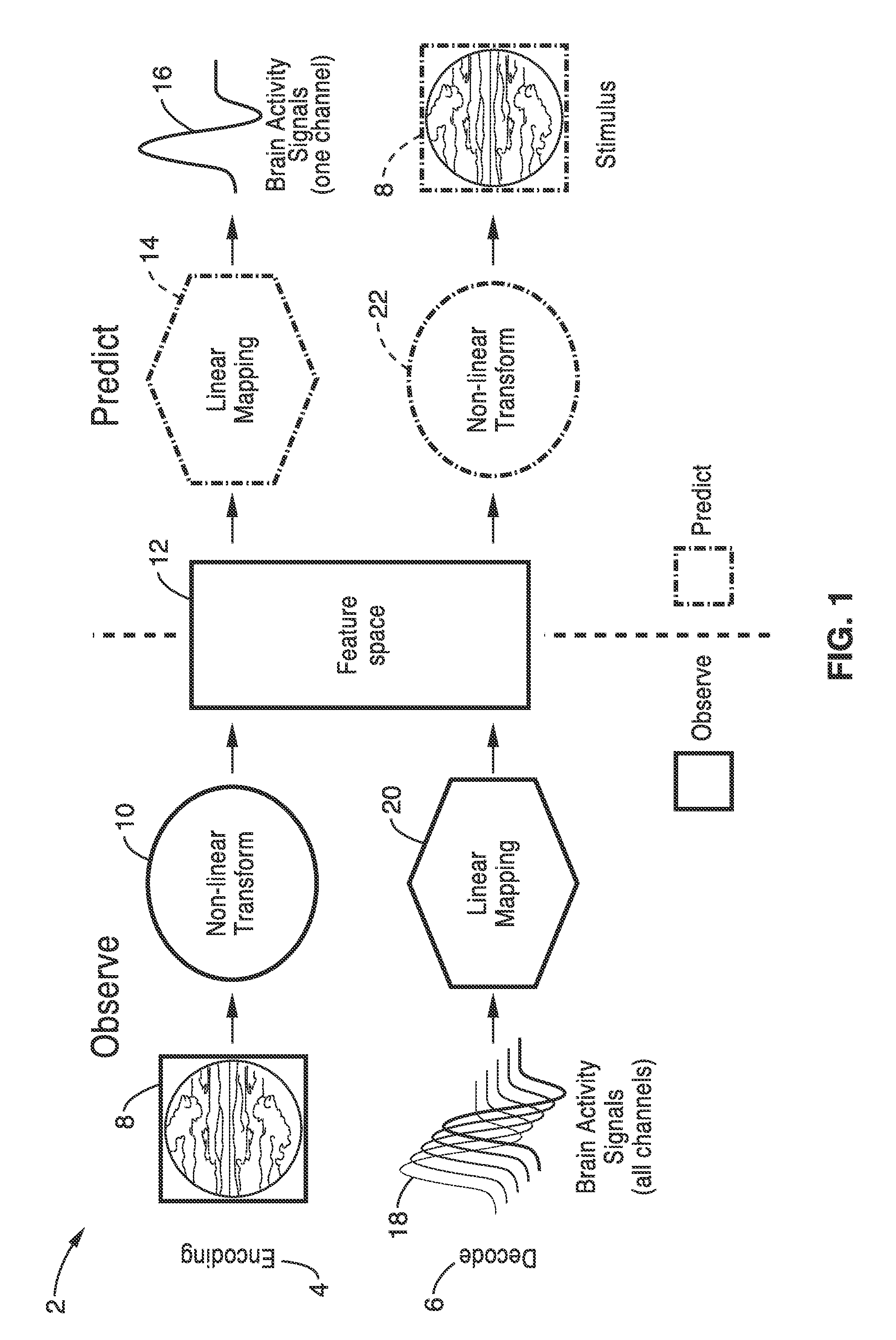
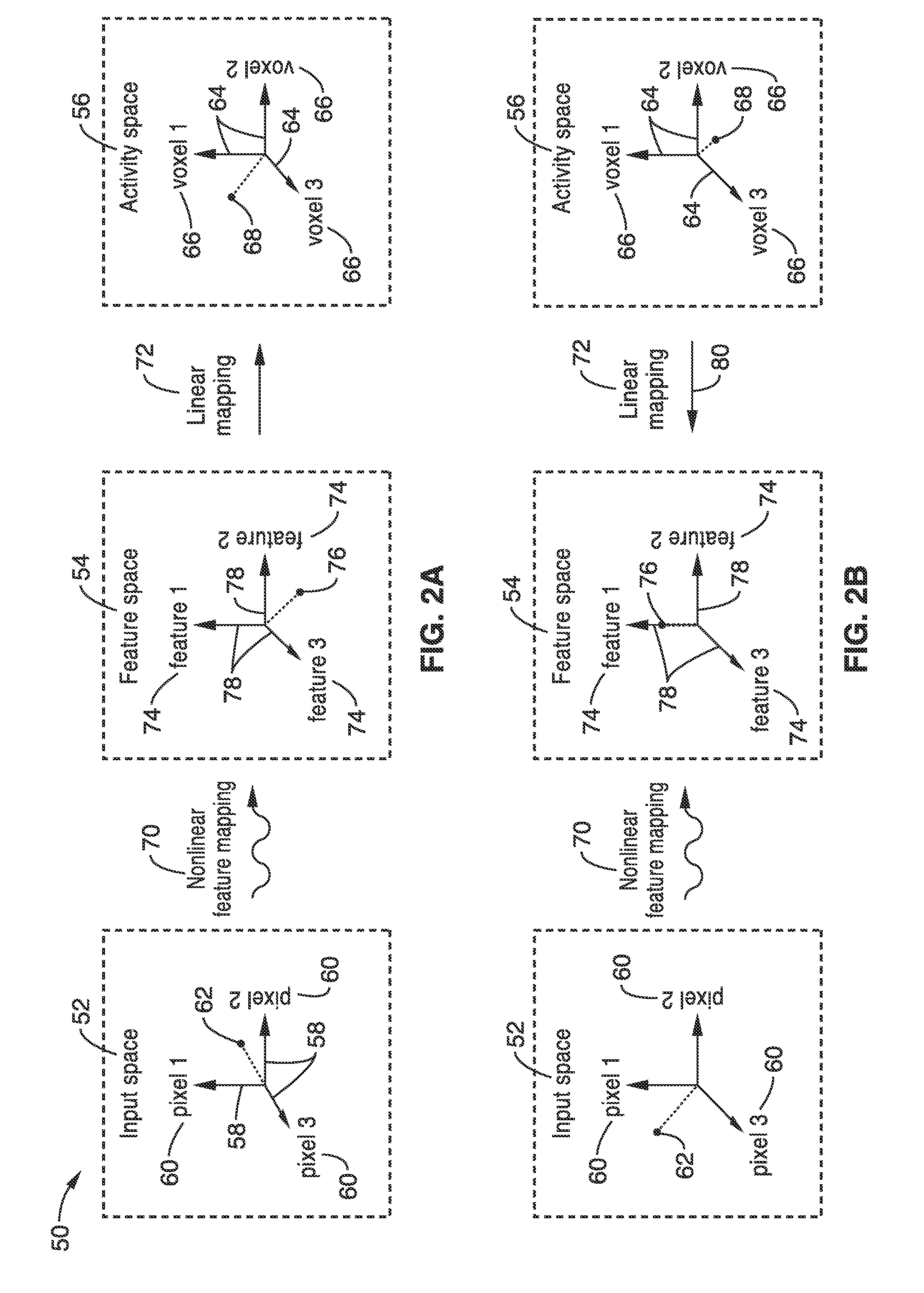
Apparatus and method for decoding sensory and cognitive information from brain activity
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
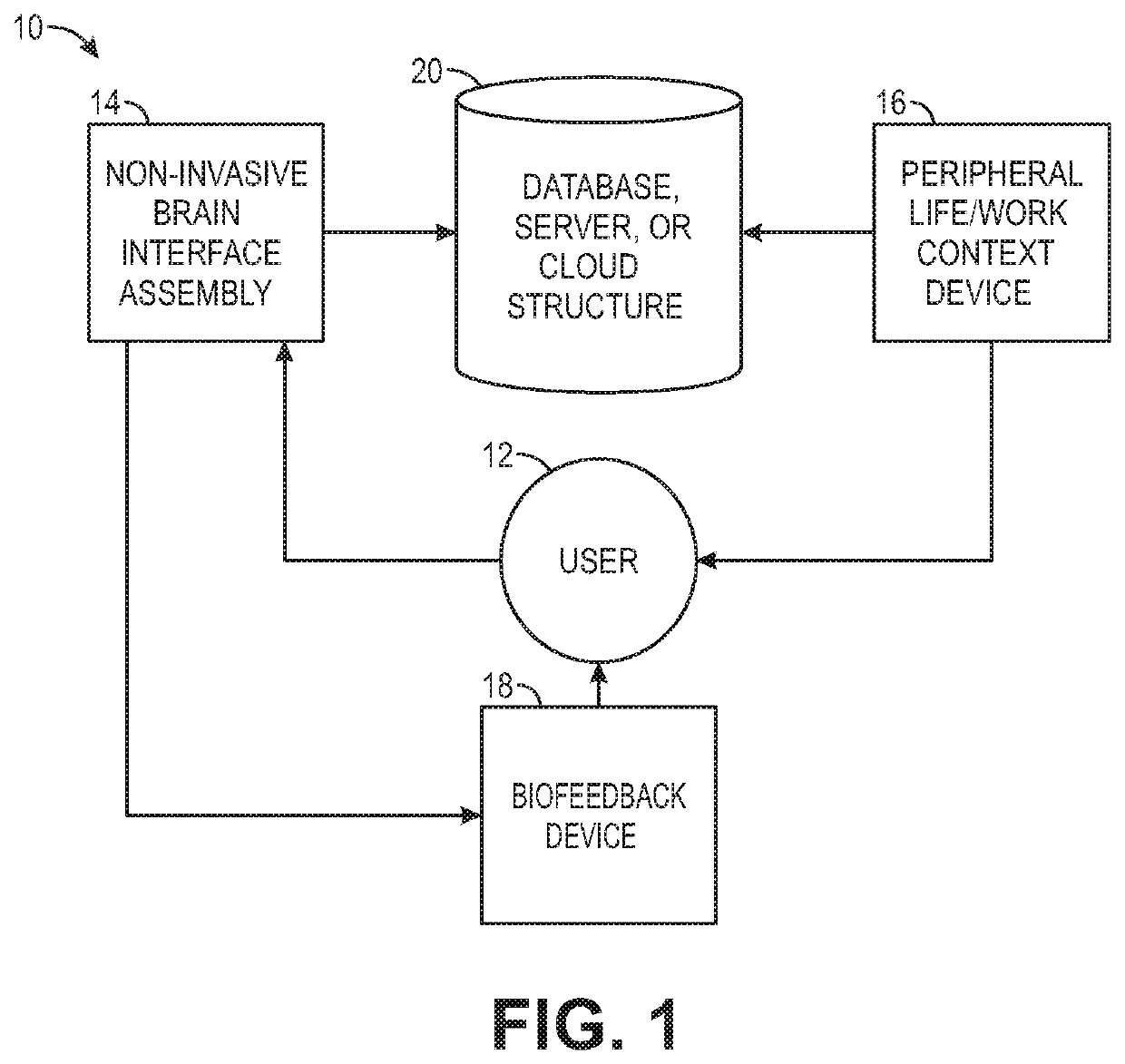
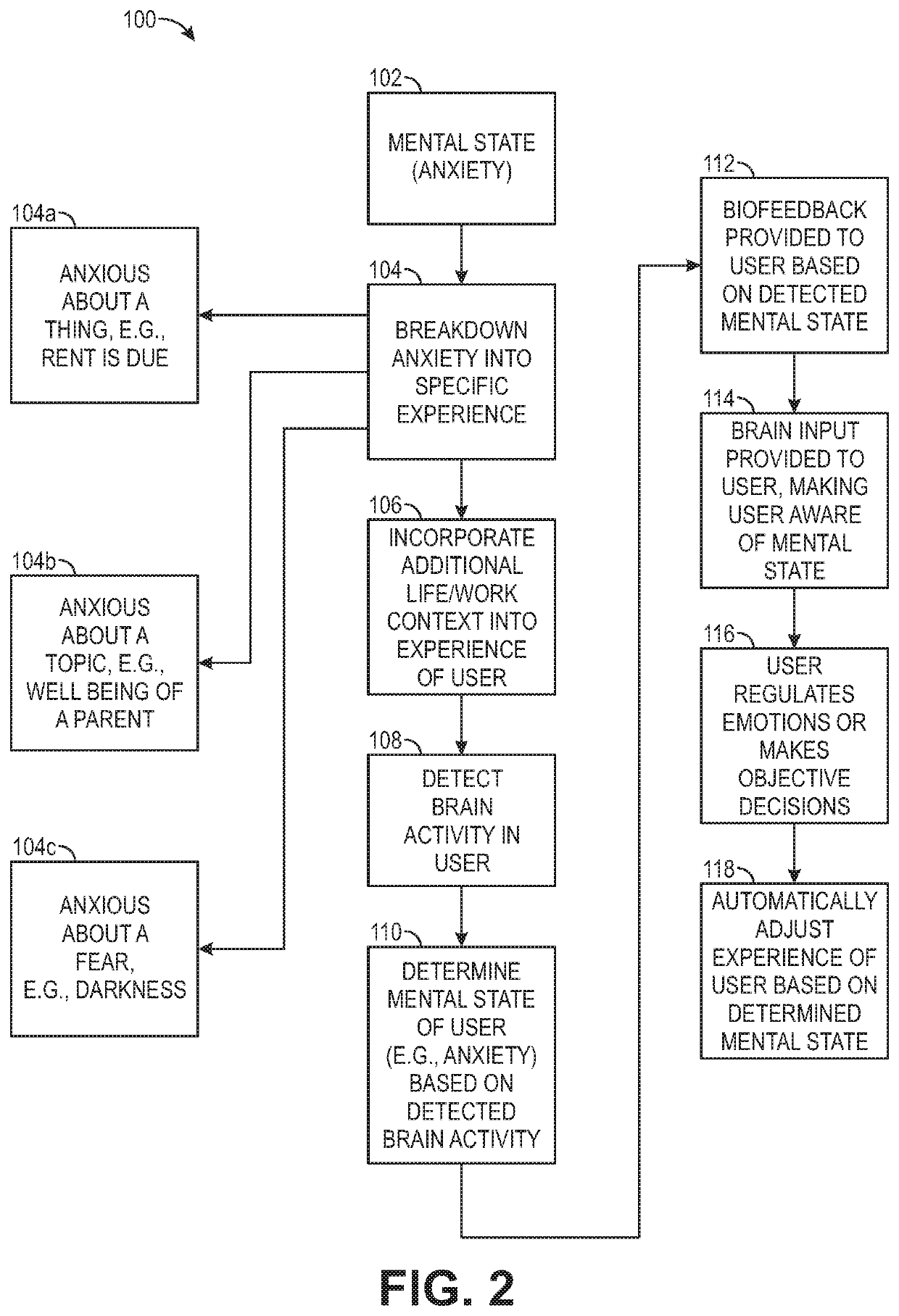
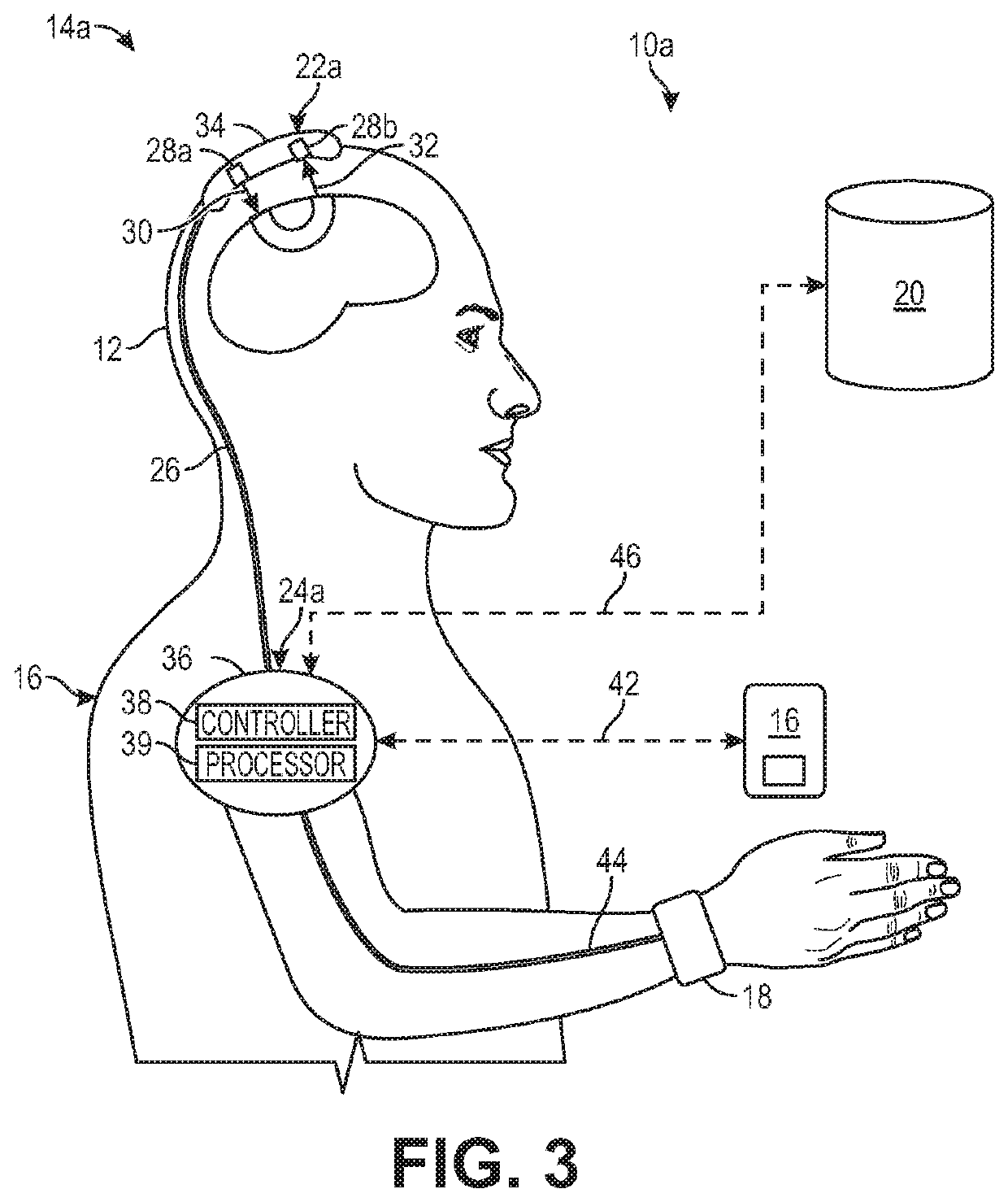
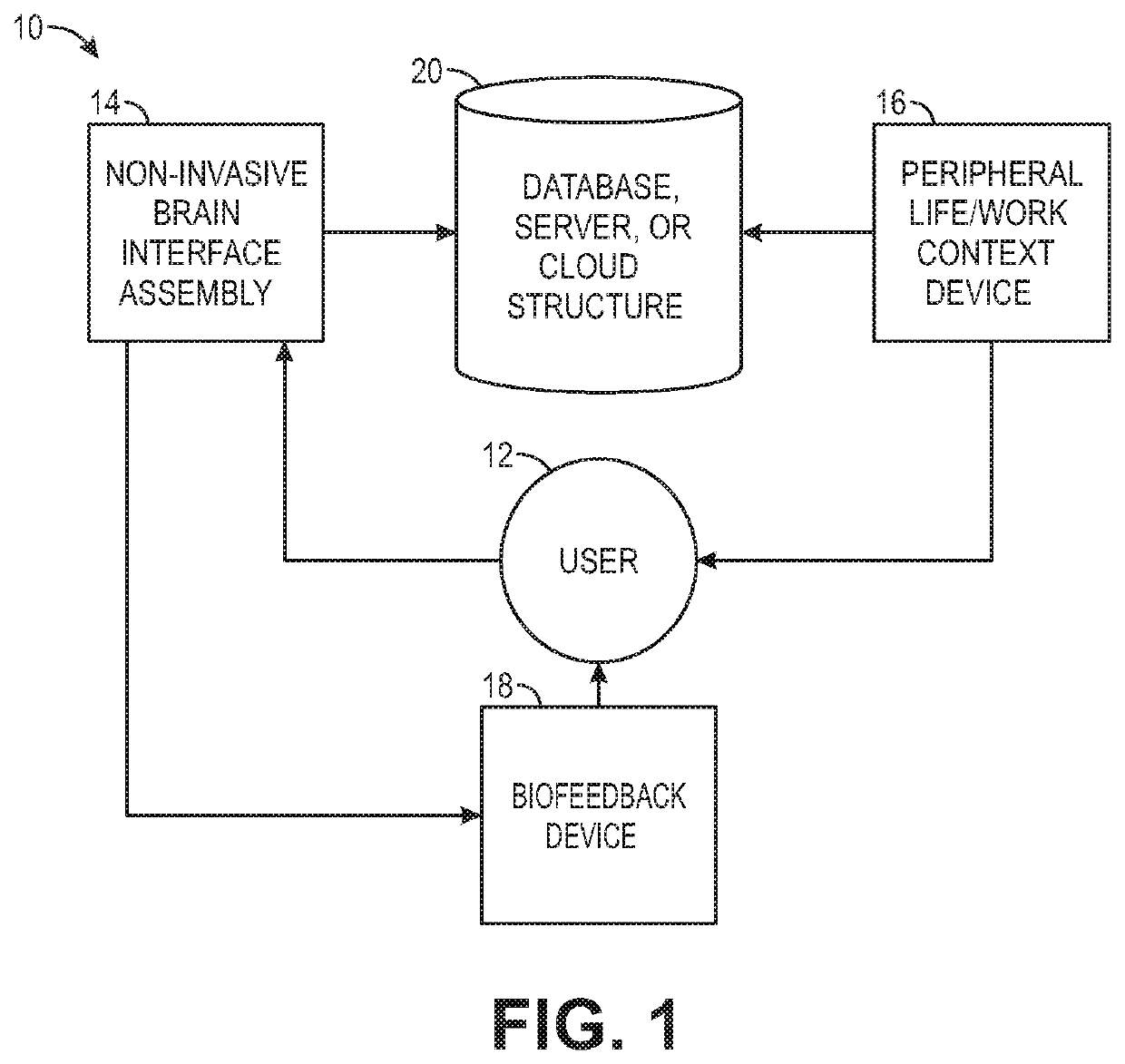
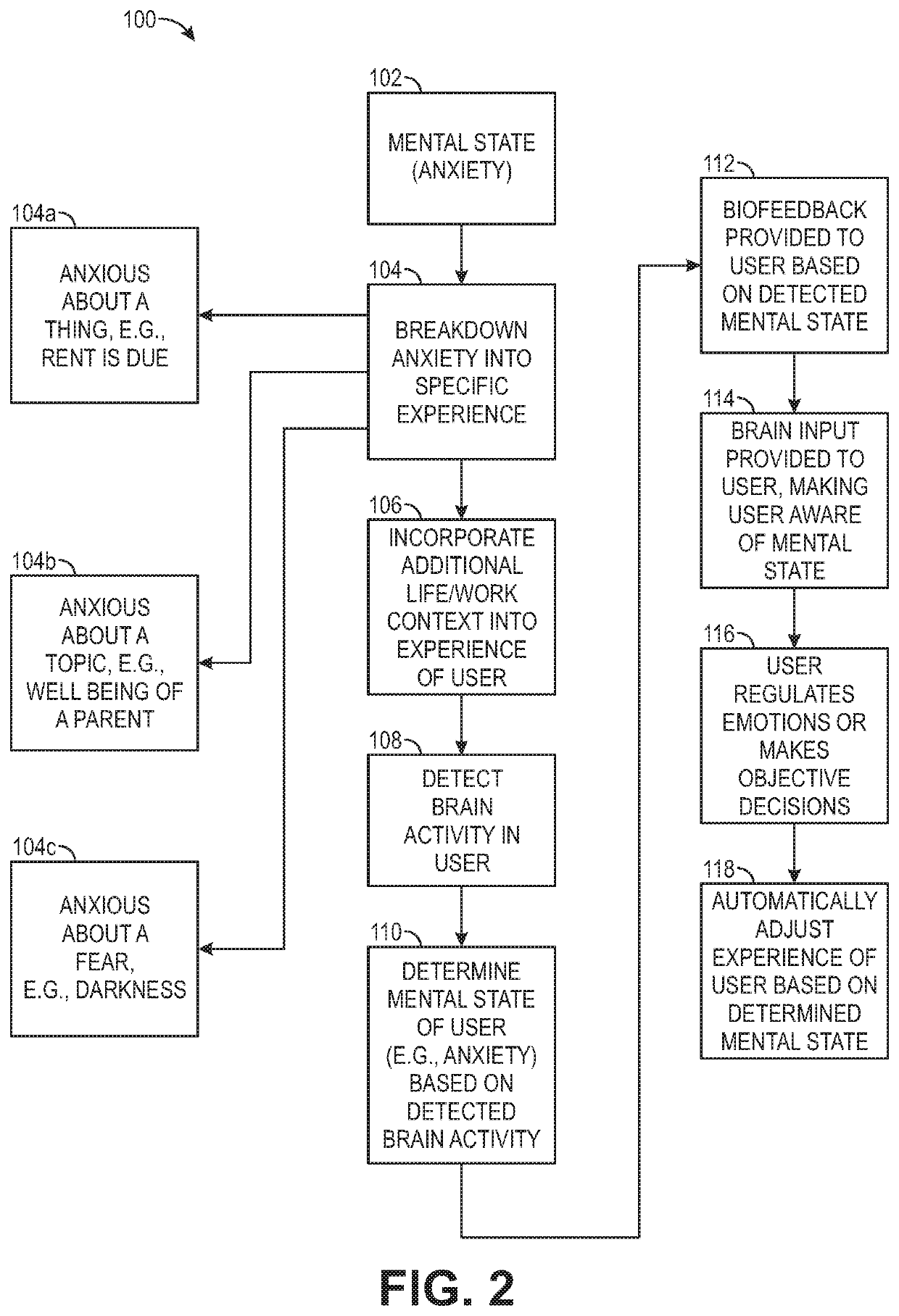
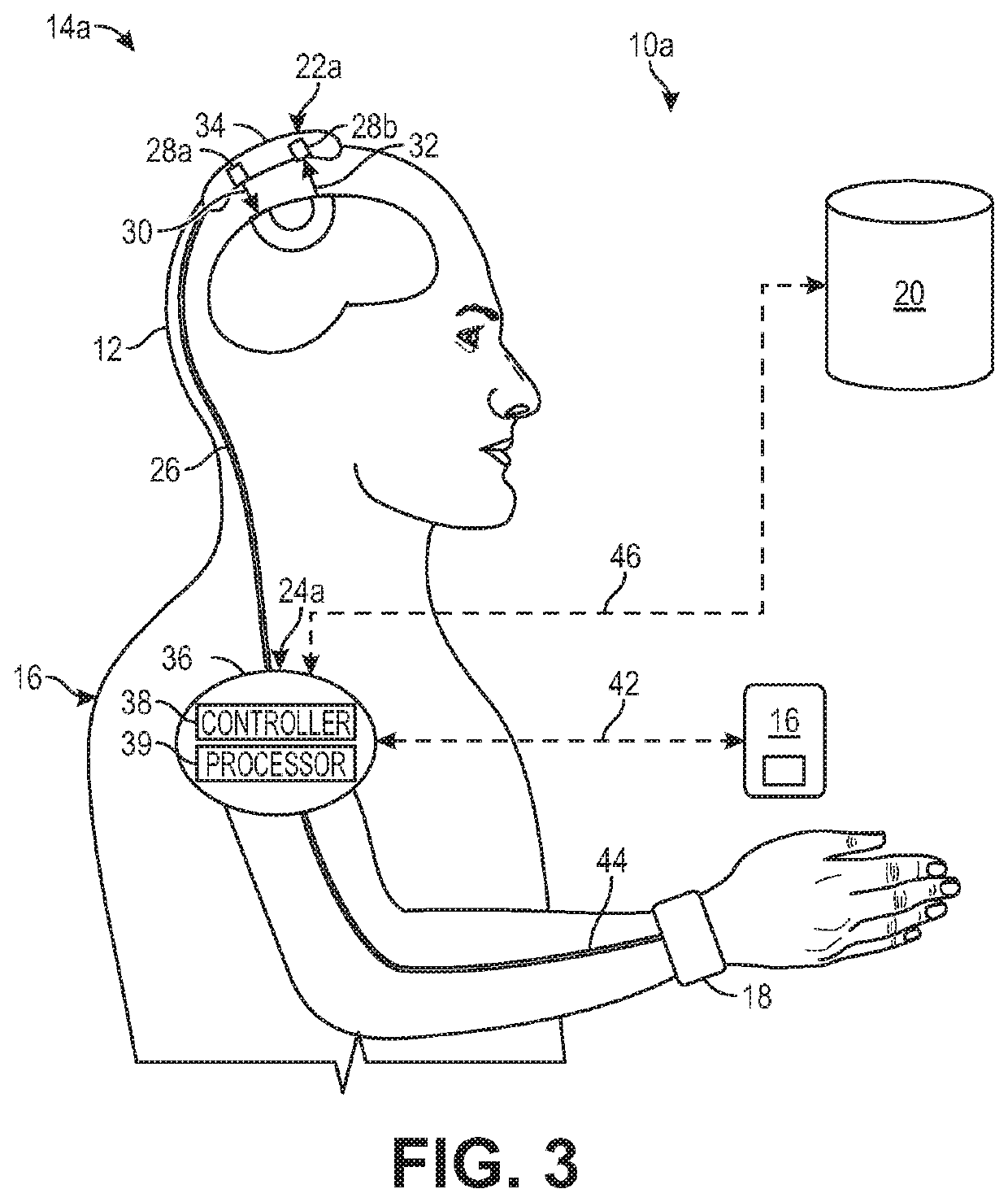
Biofeedback for awareness and modulation of mental state using a non-invasive brain interface system and method
A mental state awareness system comprises a non-invasive brain interface assembly configured for detecting brain activity of a user, a processor configured for determining a mental state of a user based on the detected brain activity, and a biofeedback device configured for automatically providing biofeedback to the user indicative of the determined mental state of the user.
Owner:HI LLC
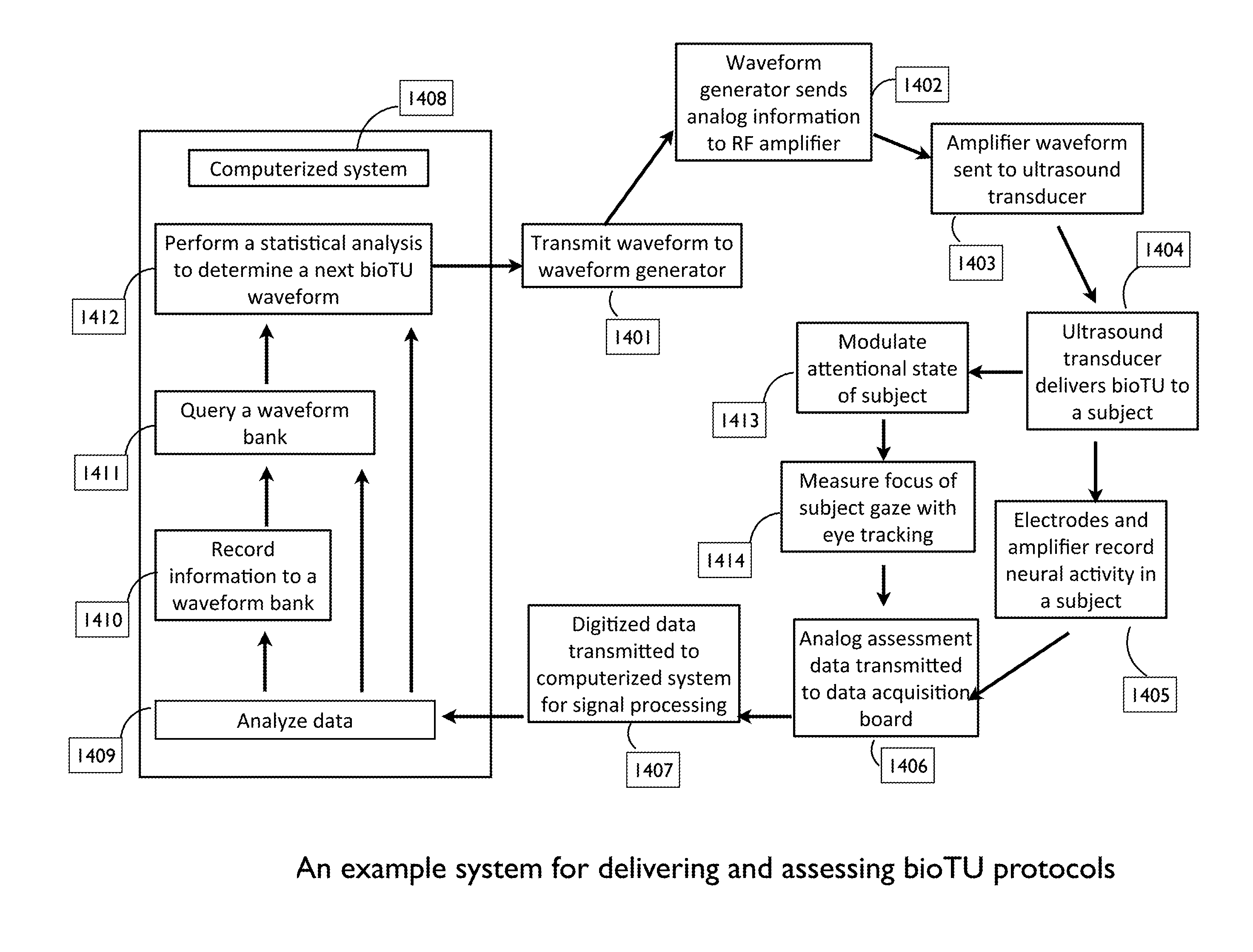
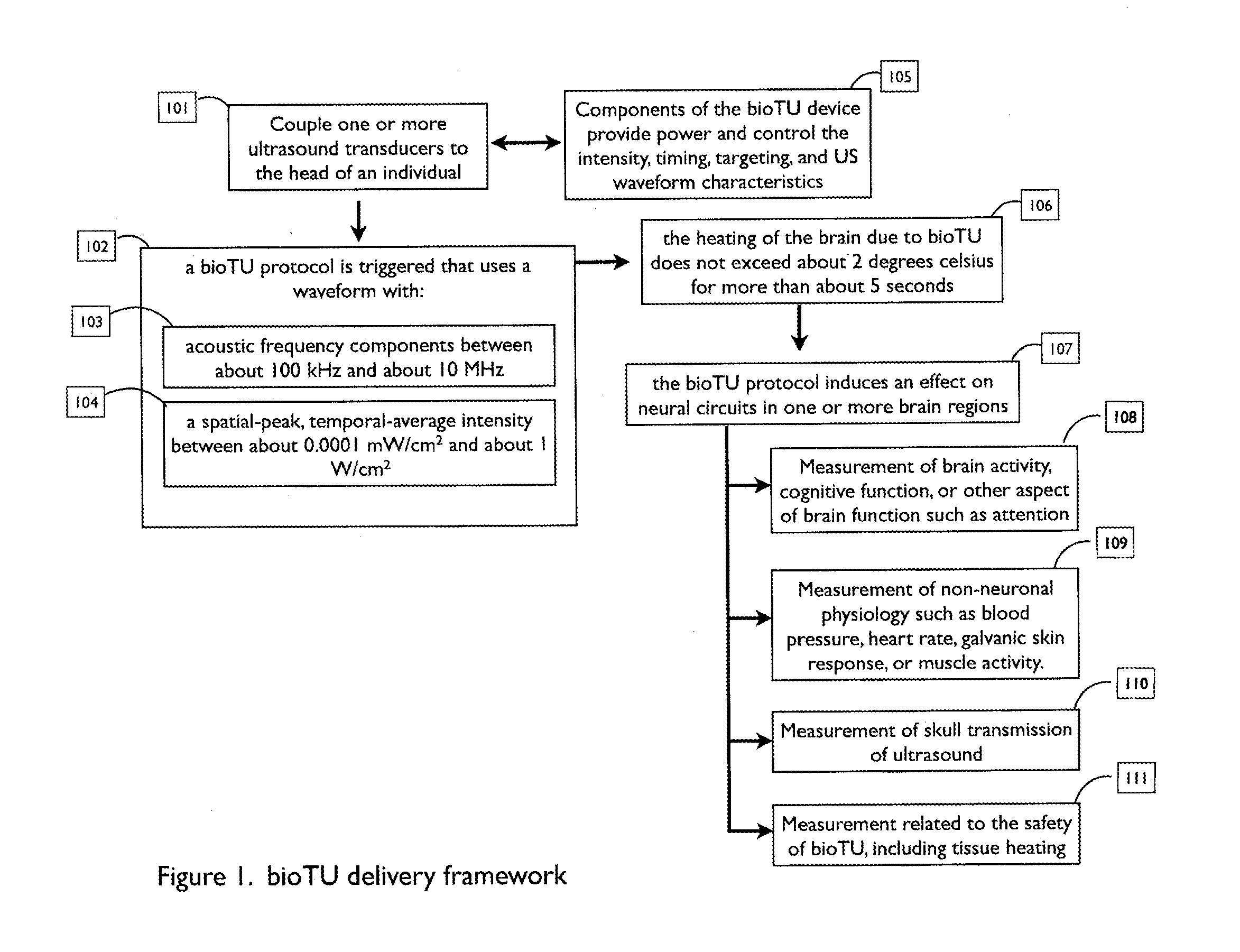
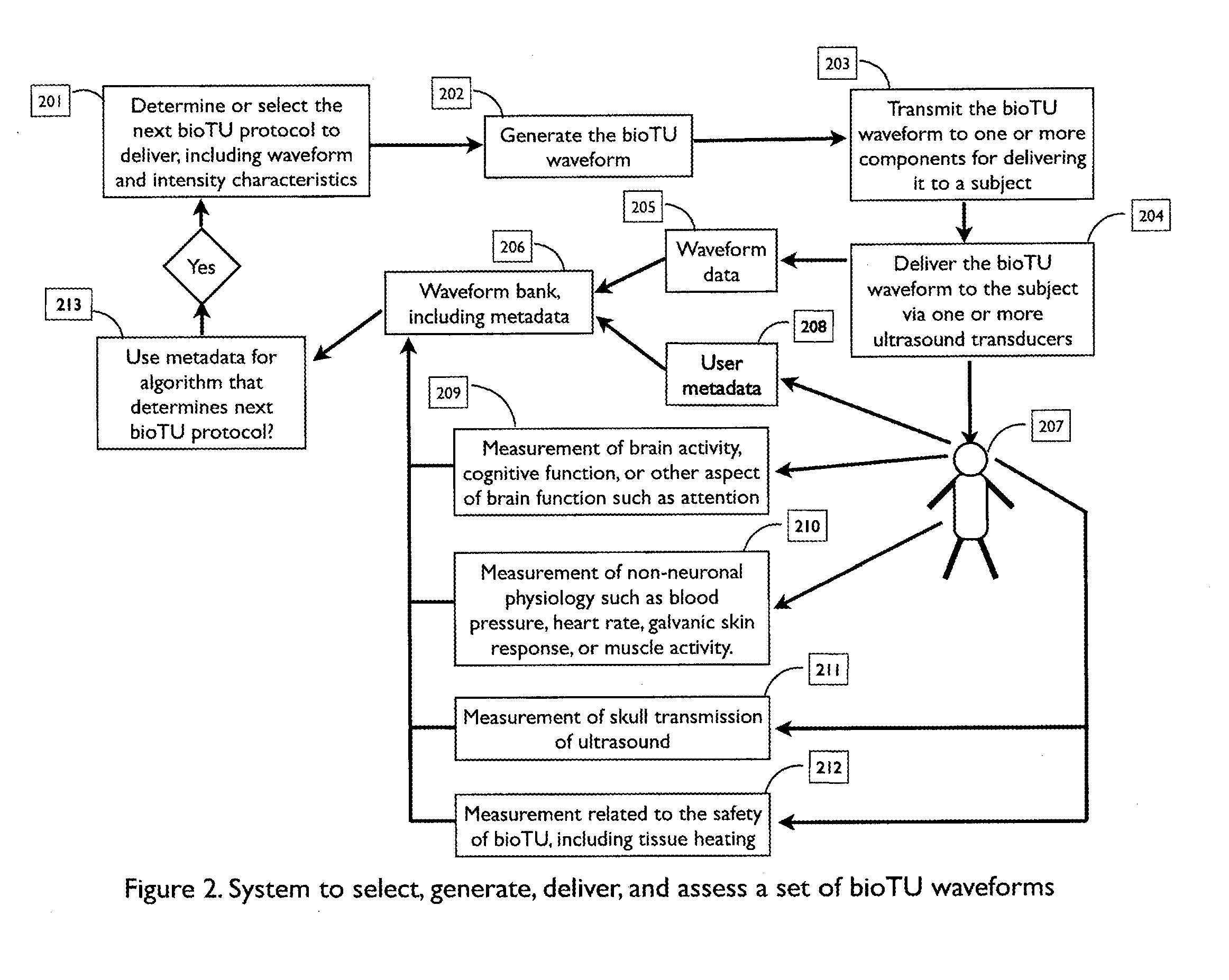
Optimization of ultrasound waveform characteristics for transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation
InactiveUS20130197401A1Increase choiceEfficient identificationUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesNeuromodulationBrain function
The present invention relates to methods and systems for achieving effective neuromodulation by transcranial ultrasound (bioTU). Embodiments of the invention include methods and systems for selecting, generating, and delivering transcranial ultrasound to the brain of a living subject. Methods and systems are described for determining the effect of bioTU on brain function. Certain embodiments of the present invention include methods and systems for measuring at least one quantifiable metric of brain activity, cognitive function, or physiology in order to optimize the ultrasound waveforms delivered. In an embodiment, the invention uses a closed-loop design to iteratively improve the effectiveness of bioTU waveforms delivered.
Owner:THYNC
Systems and methods for analyzing brain activity and applications thereof
In some embodiments, the present invention provides an exemplary inventive system that includes: an apparatus to record: individual's brain electrical activity, a physiological parameter of the individual, and iii) an environmental parameter; a computer processor configured to perform: obtaining a recording of the electrical signal data; projecting the obtained recording of electrical signal data onto a pre-determined ordering of a denoised optimal set wavelet packet atoms to obtain a set of projections; normalizing the particular set of projections of the individual using a pre-determined set of normalization factors to form a set of normalized projections; determining a personalized mental state of the individual by assigning a brain state; determining a relationship between: the physiological parameter, the environmental parameter, and the personalized mental state; generating an output, including: a visual indication, representative of the personalized mental state, and) a feedback output configured to affect the personalized mental state of the individual.
Owner:NEUROSTEER INC
Questions and control paradigms for detecting deception by measuring brain activity
InactiveUS7565193B2High measurement sensitivityElectroencephalographyElectromyographyCerebral activityPhysical therapy
Owner:CEPHOS
Biofeedback for awareness and modulation of mental state using a non-invasive brain interface system and method
A mental state awareness system comprises a non-invasive brain interface assembly configured for detecting brain activity of a user, a processor configured for determining a mental state of a user based on the detected brain activity, and a biofeedback device configured for automatically providing biofeedback to the user indicative of the determined mental state of the user.
Owner:HI LLC
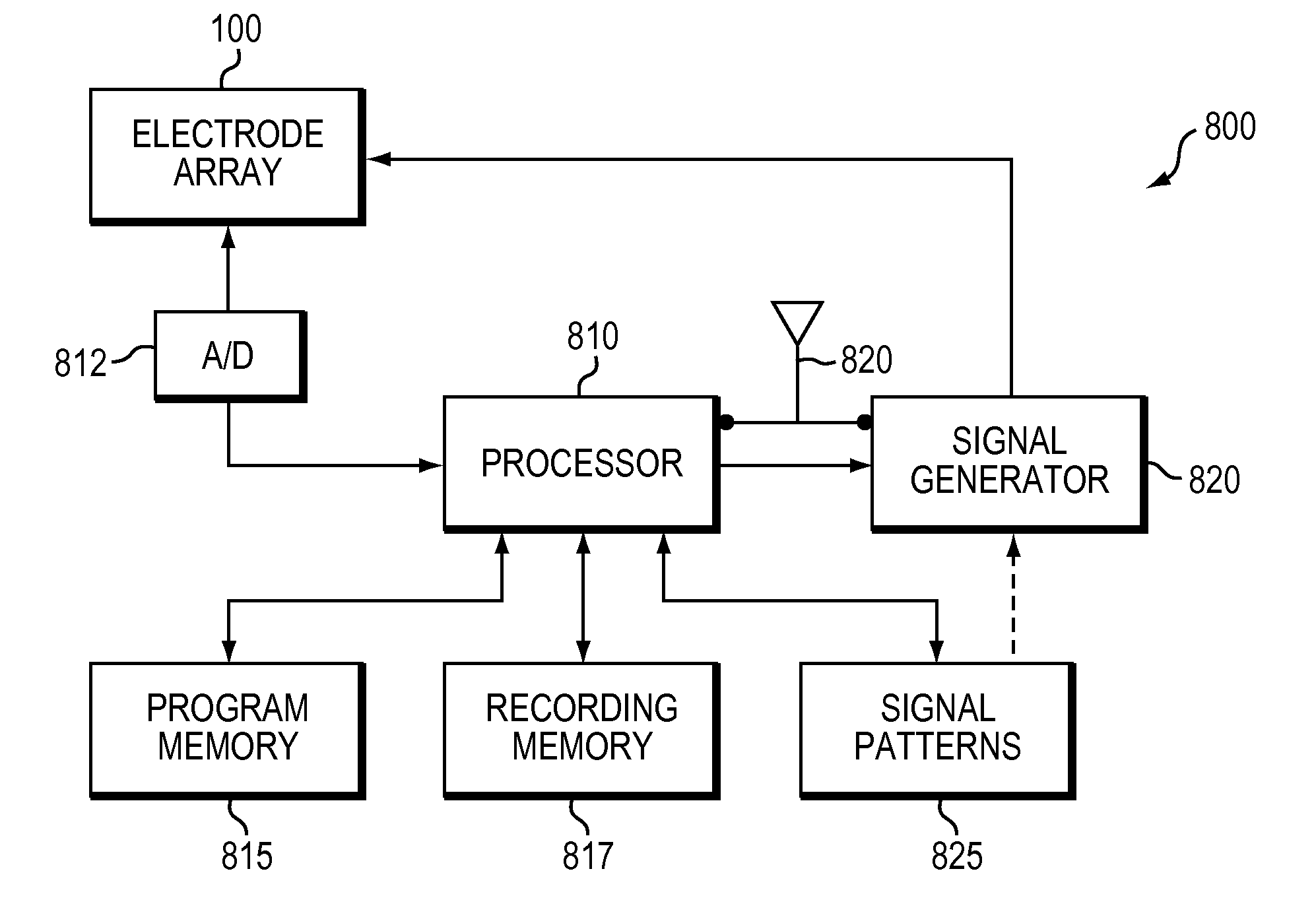
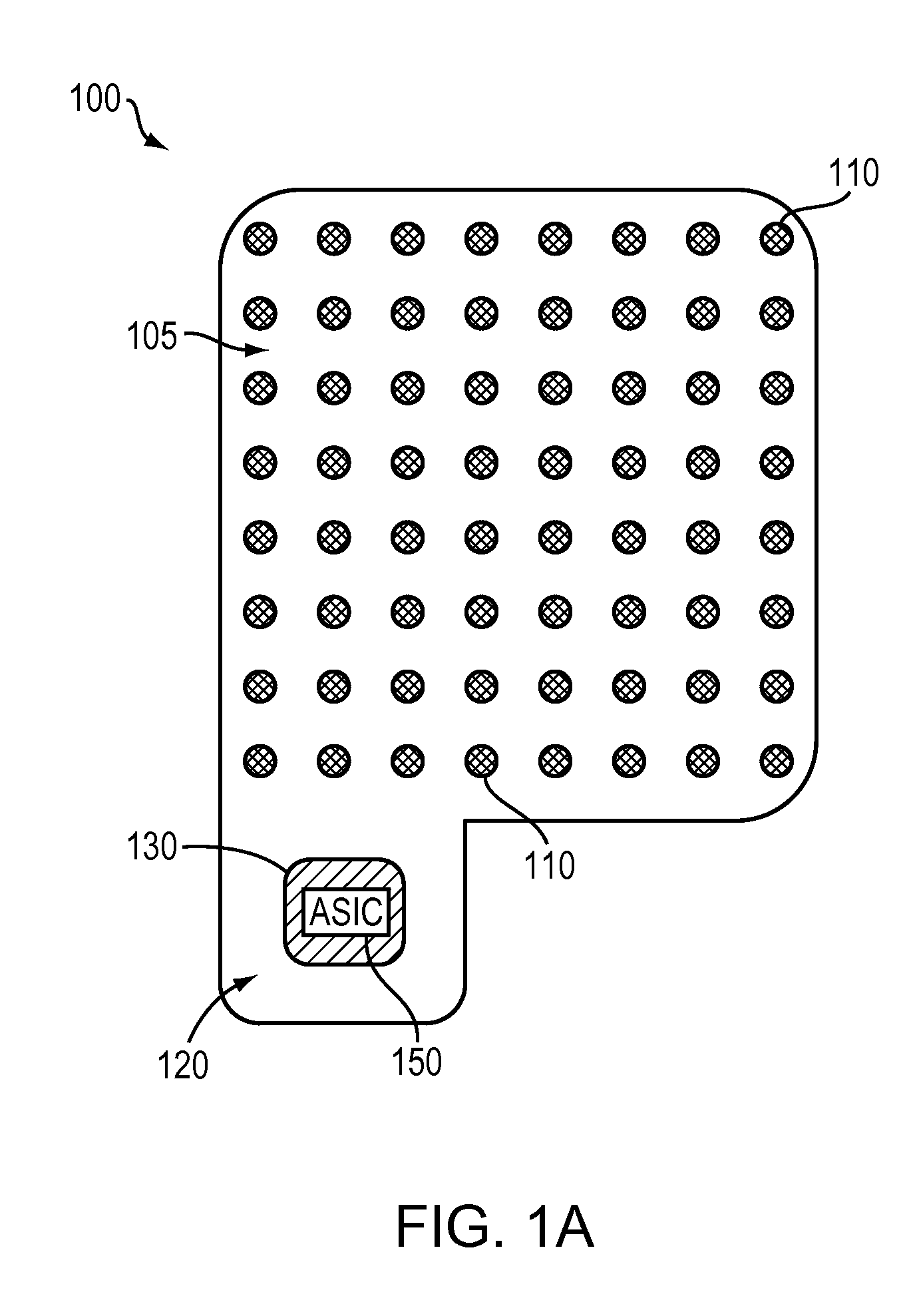
Wireless Recording and Stimulation of Brain Activity
InactiveUS20100198297A1Avoid lengthAvoiding costly hospitalizationElectroencephalographyHead electrodesMedicineElectroencephalography
Subdural arrays transmit electrocorticogram recordings wirelessly, across the patient's skull, allowing the craniotomy used for surgical placement of the arrays to be completely closed. In various embodiments, the arrays also respond to commands, applying signal patterns to the patient's brain for diagnostic and treatment purposes.
Owner:SIGENICS +2
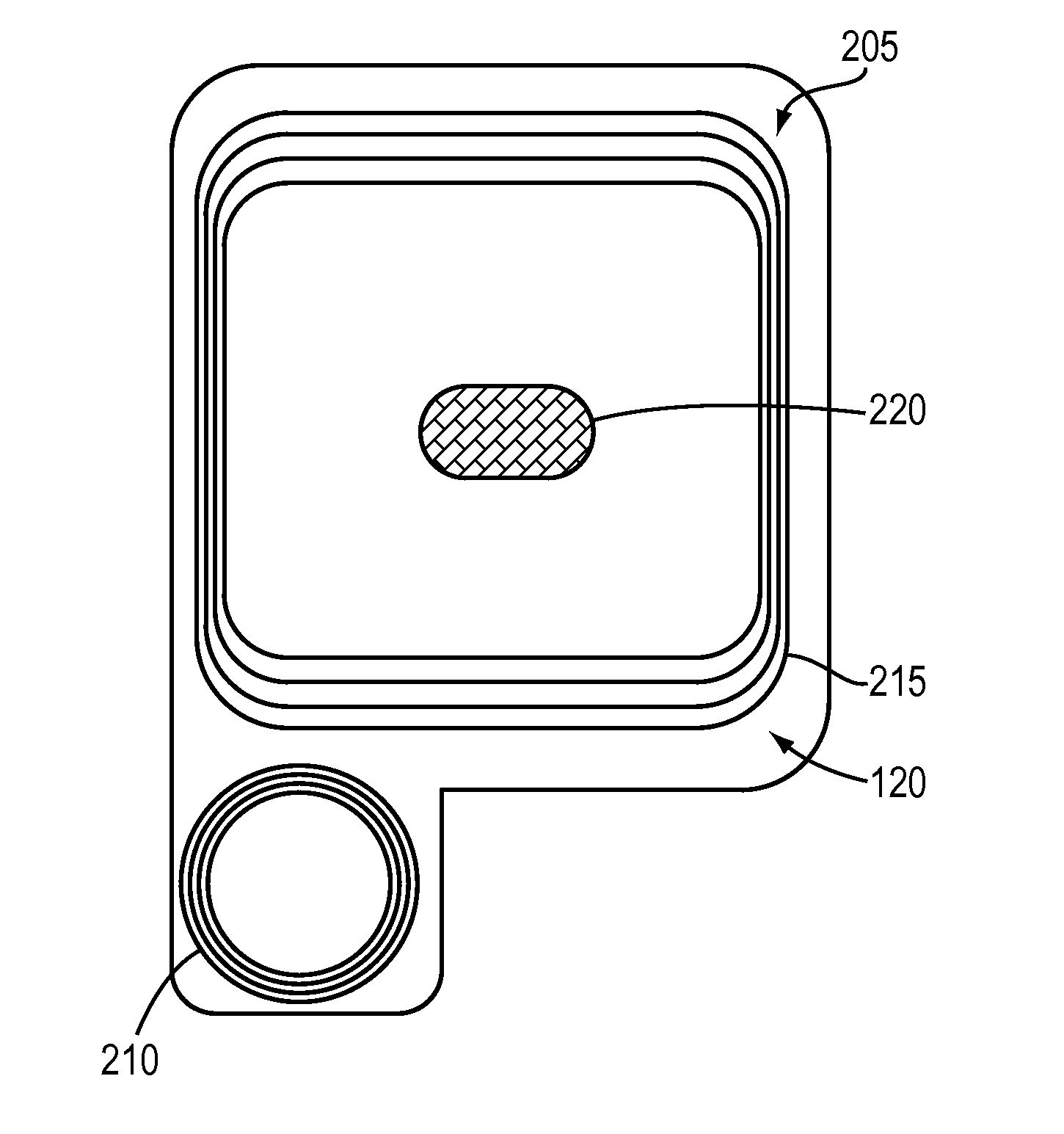
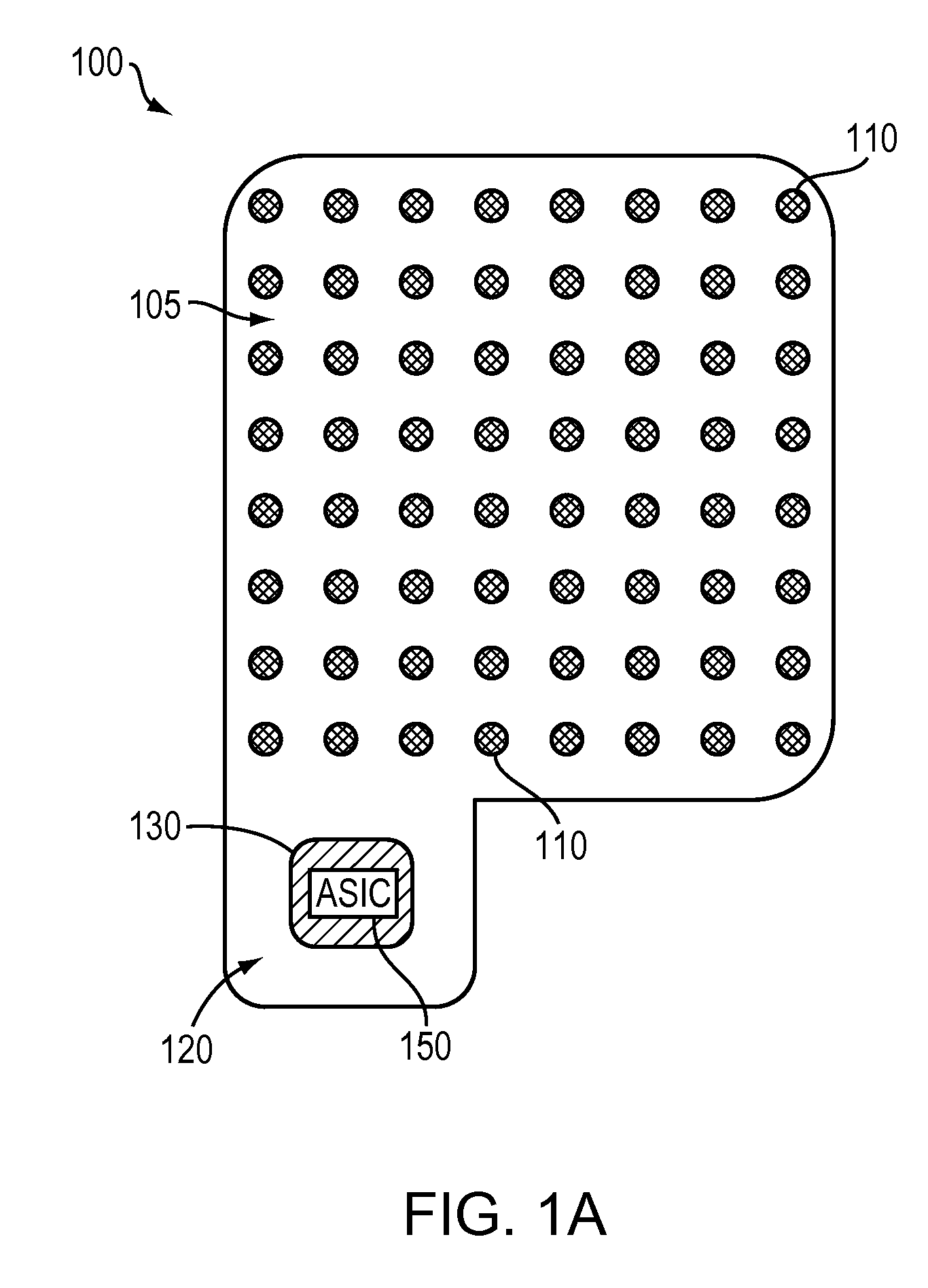
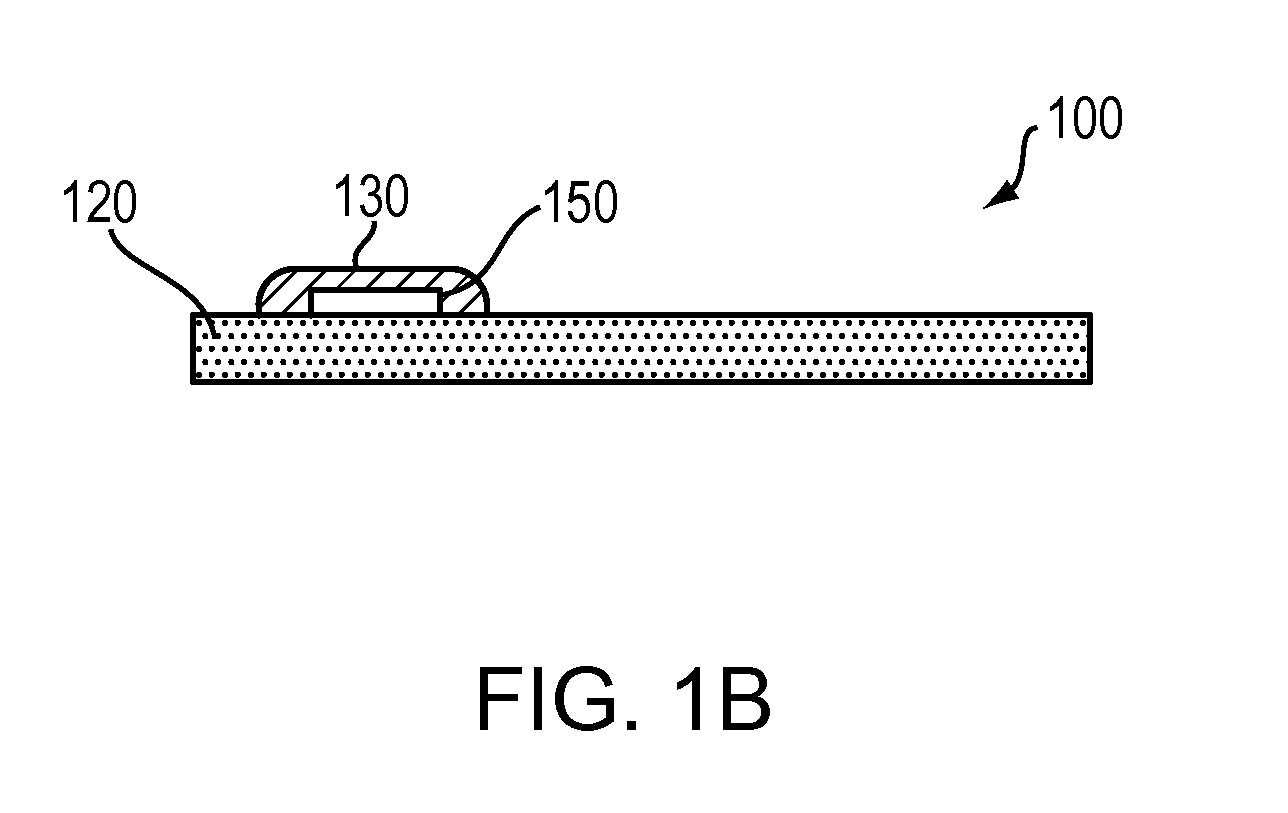
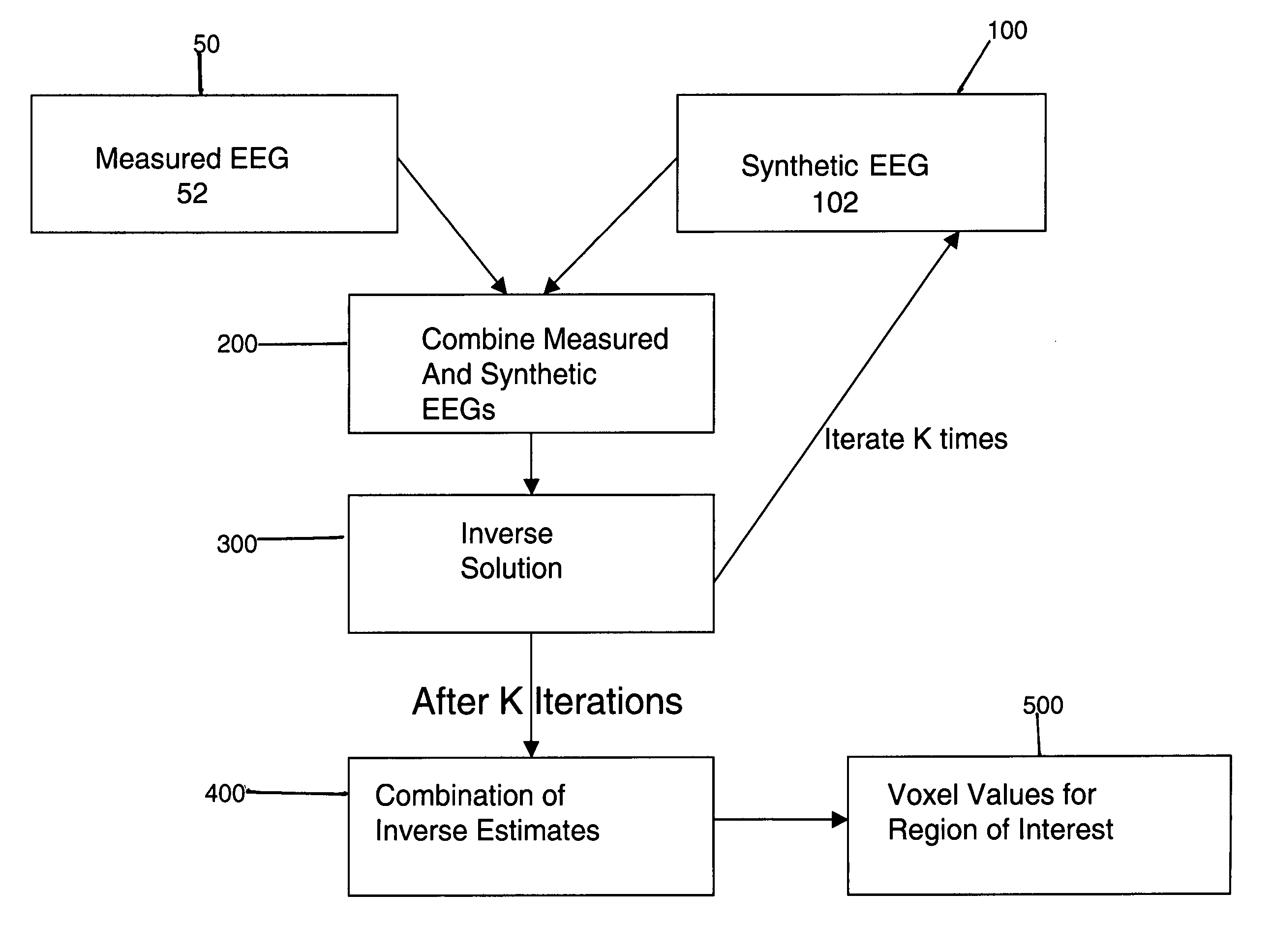
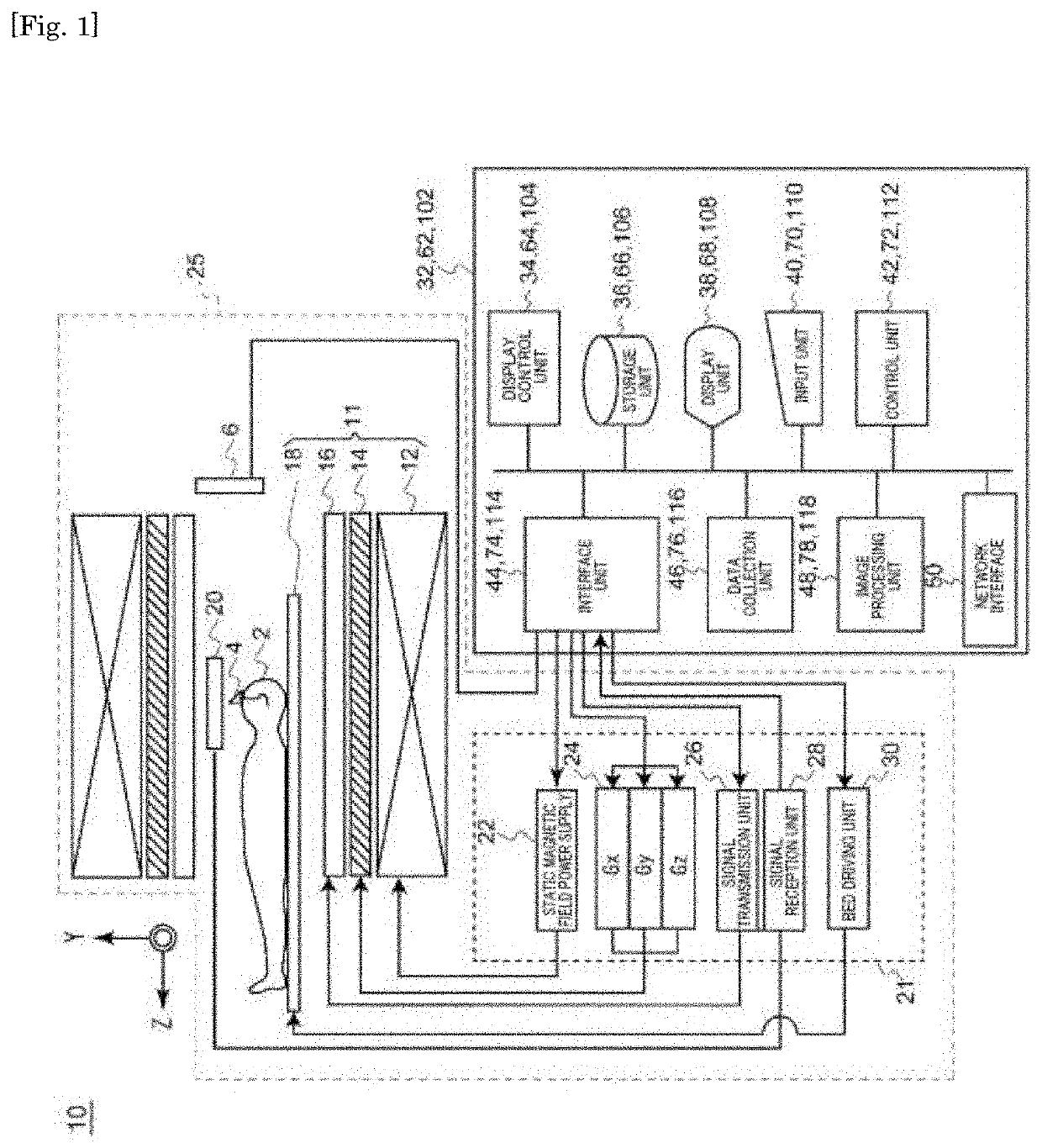
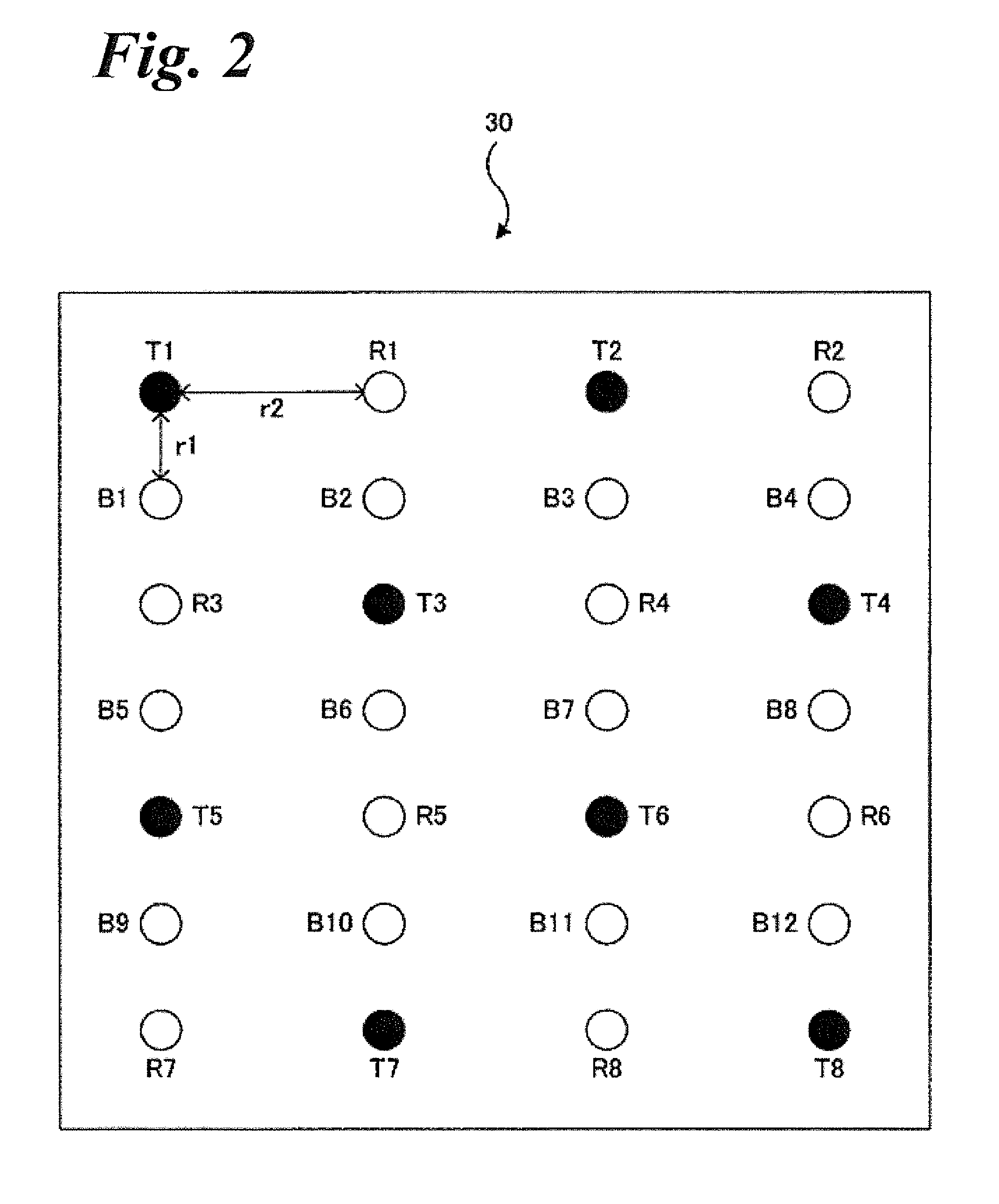
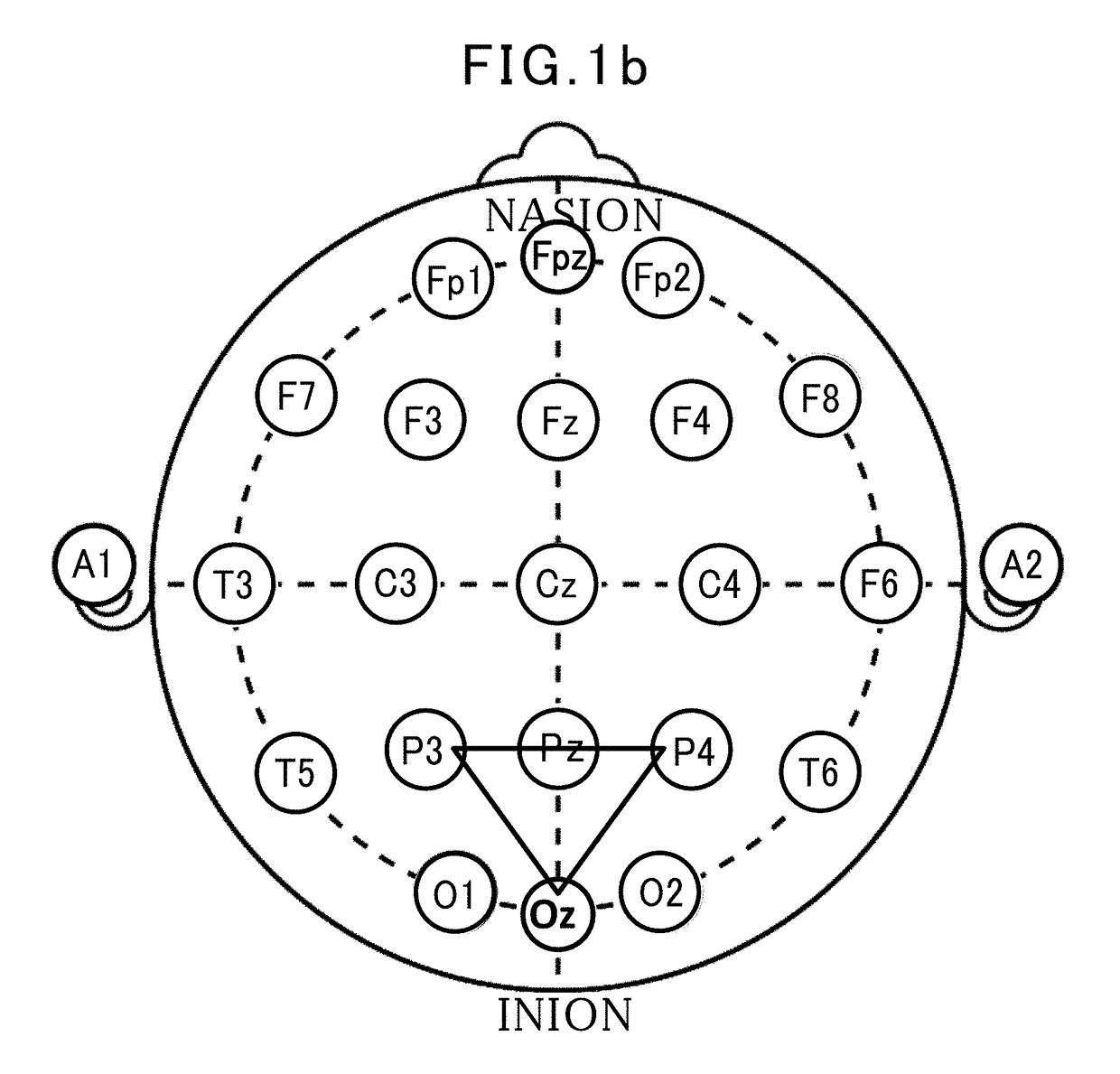
System and method for EEG imaging of cerebral activity using small electrode sets
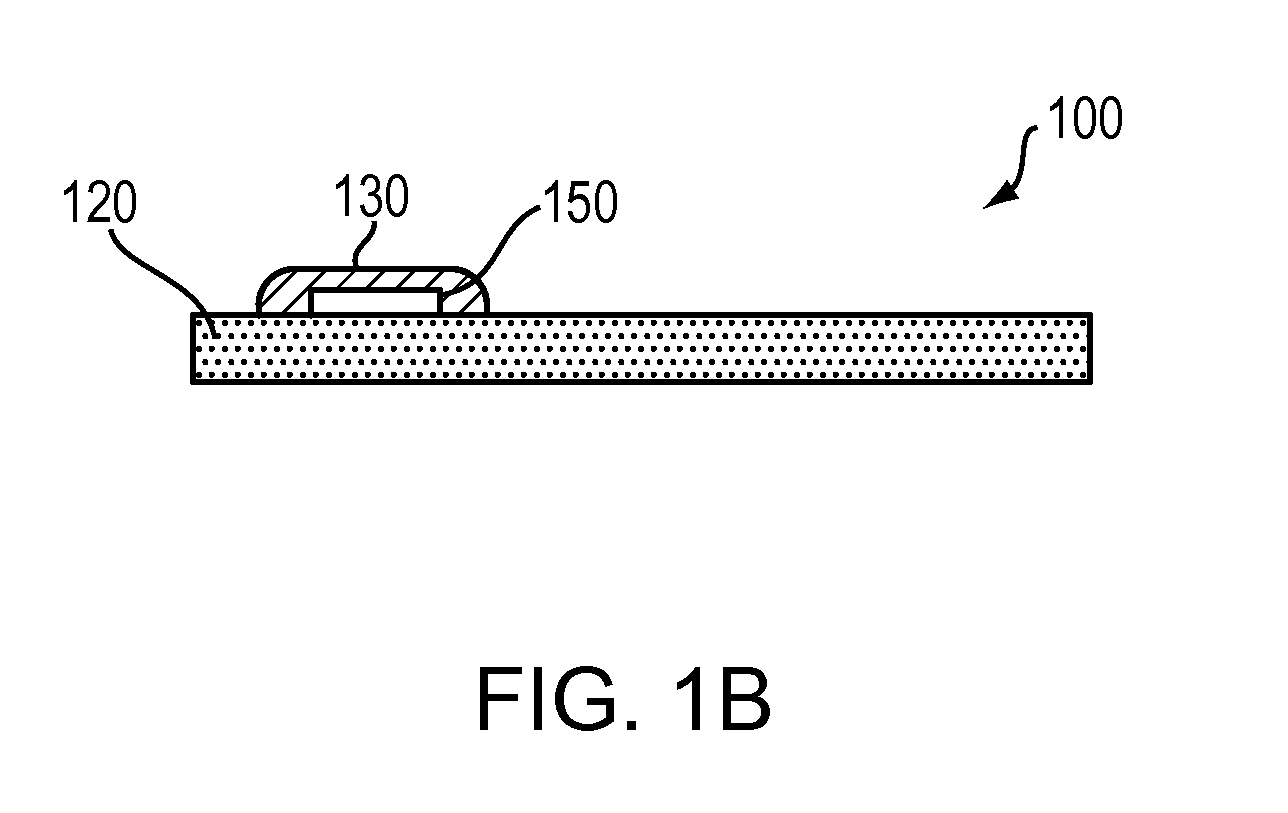
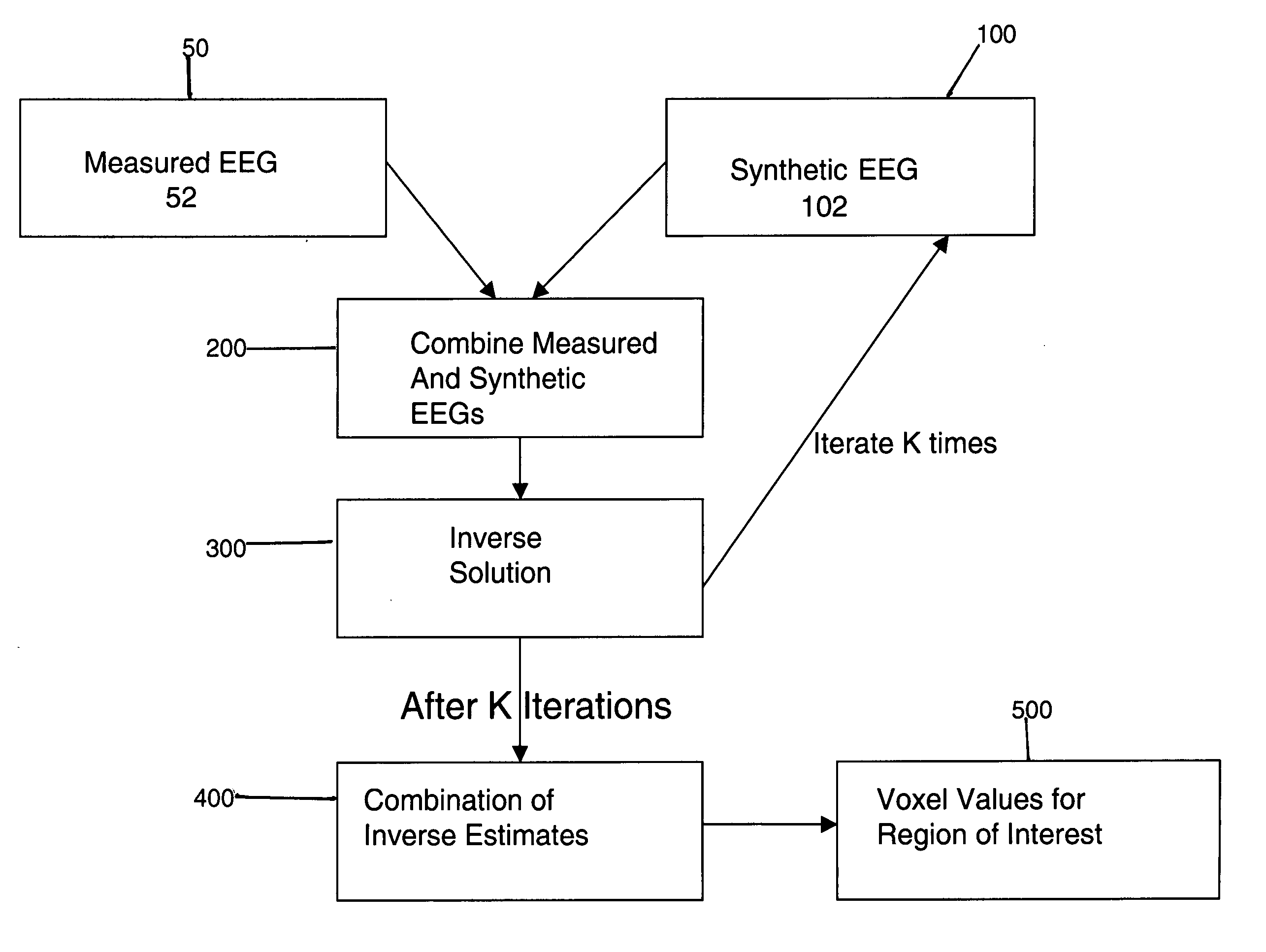
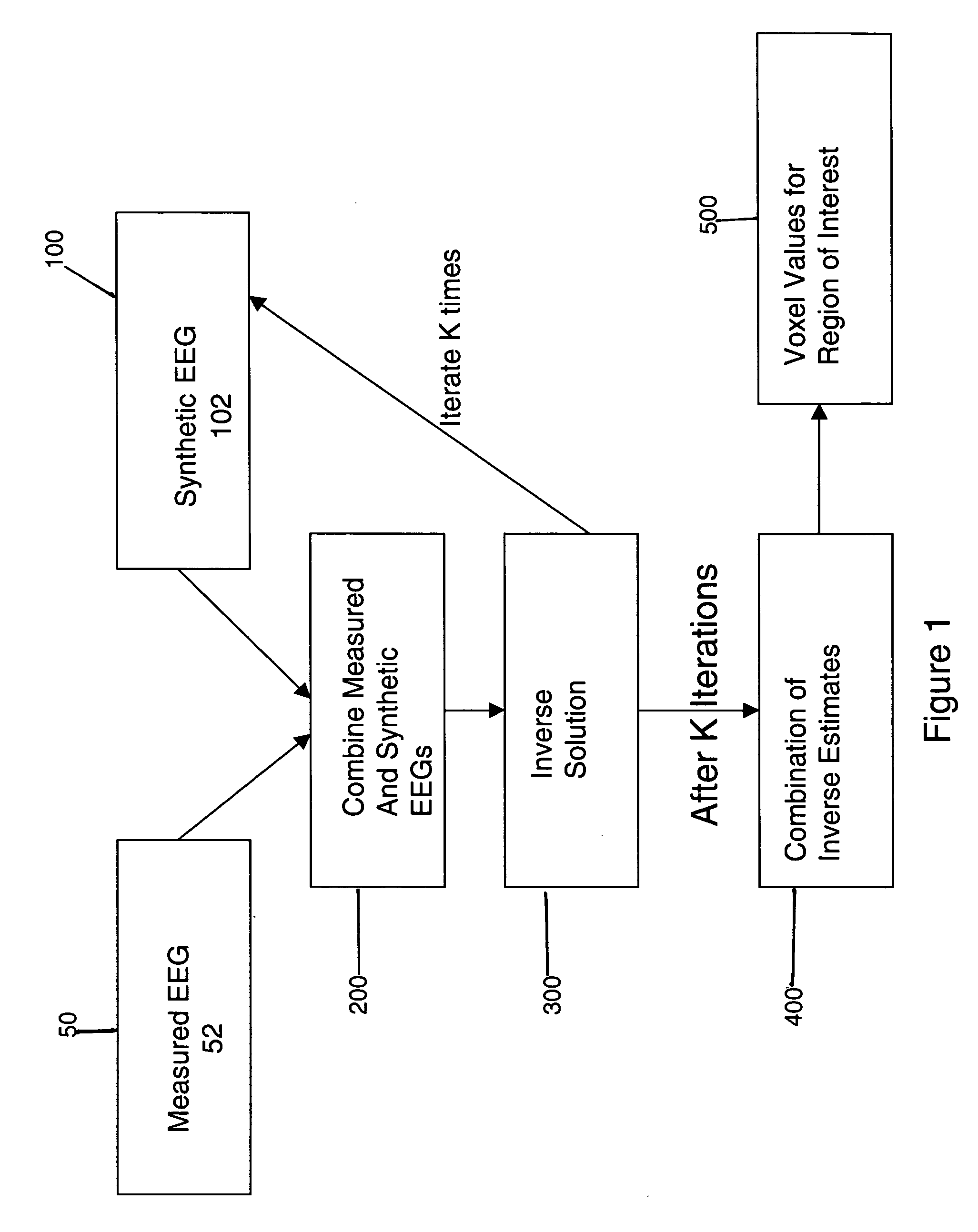
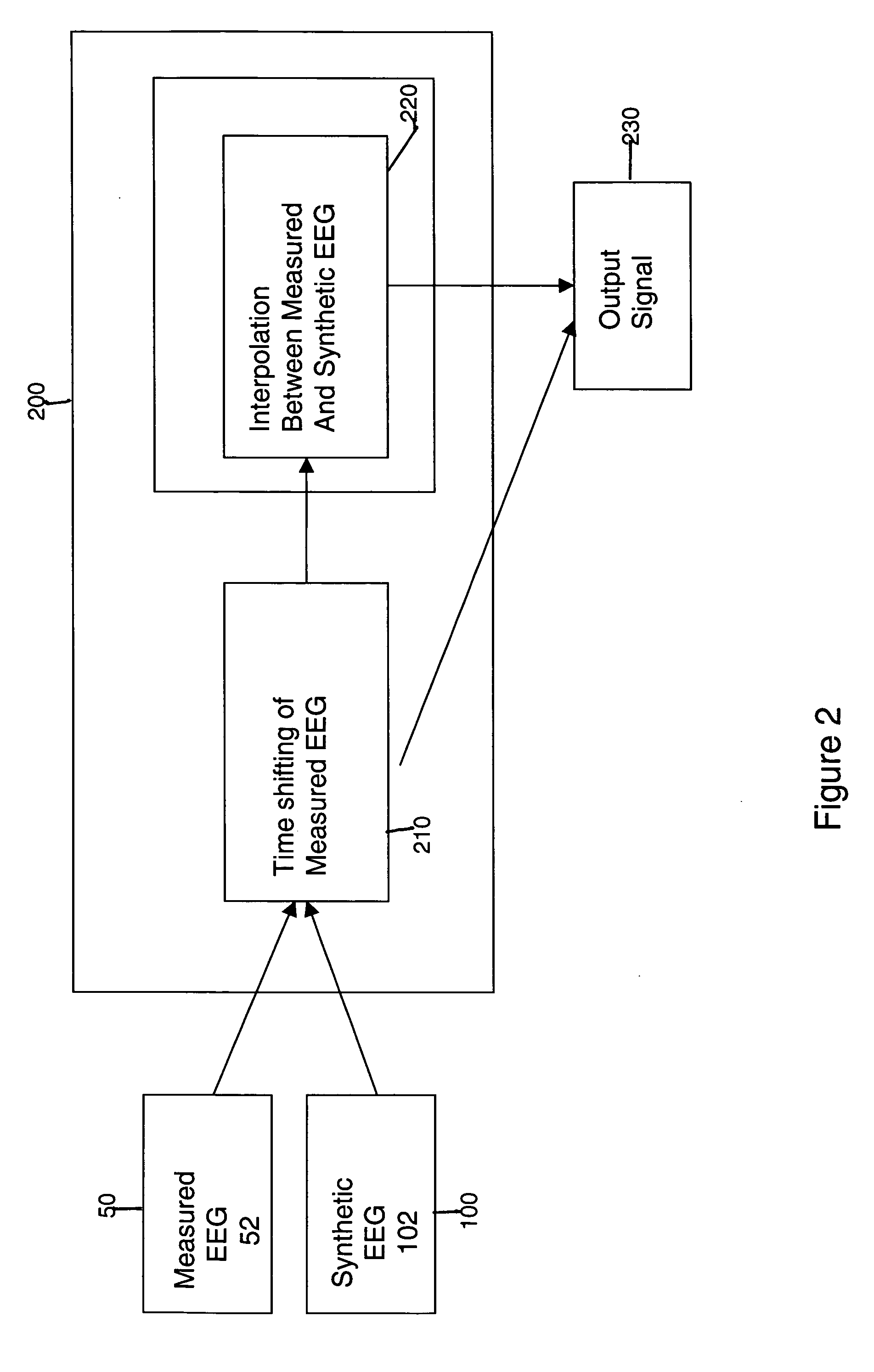
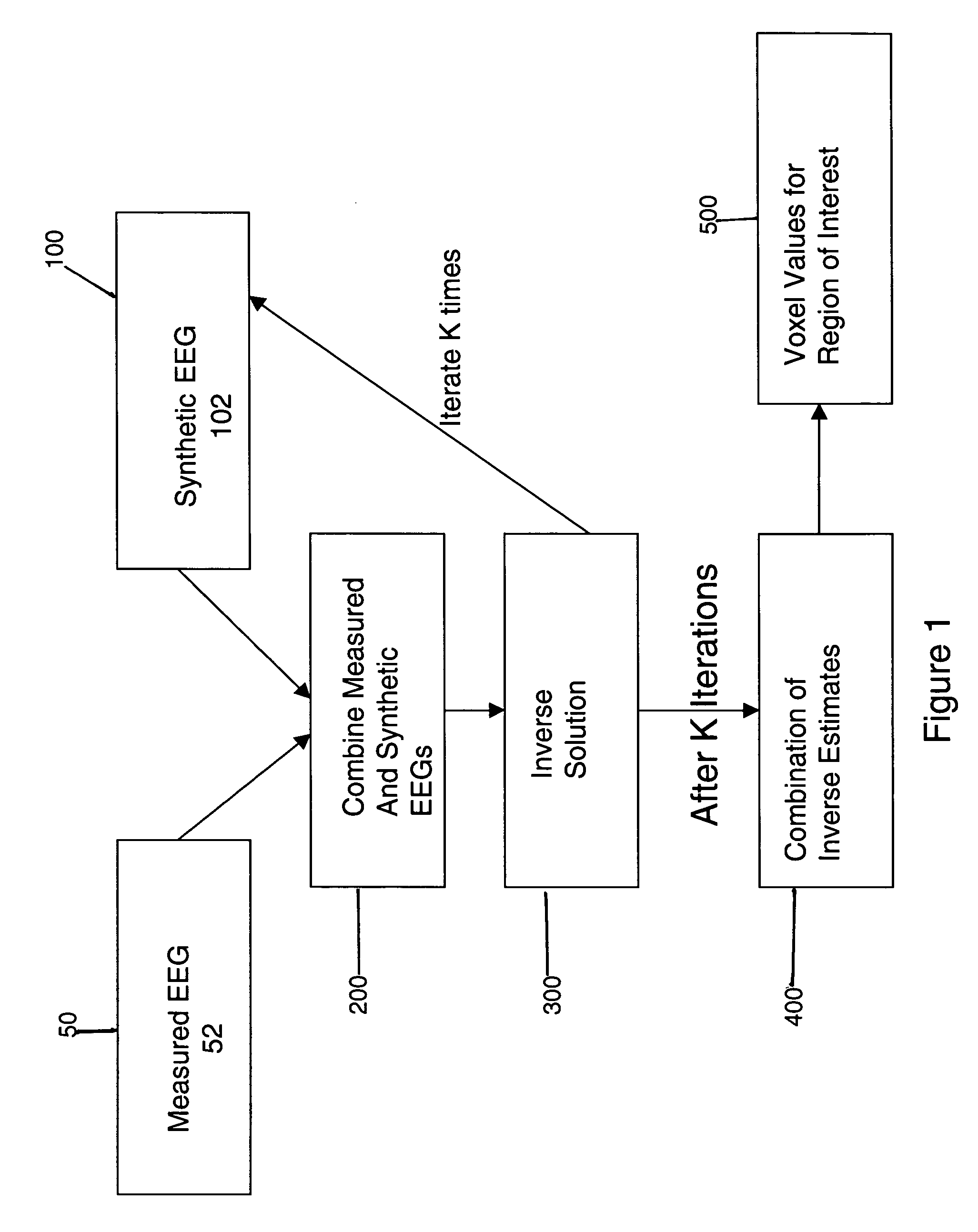
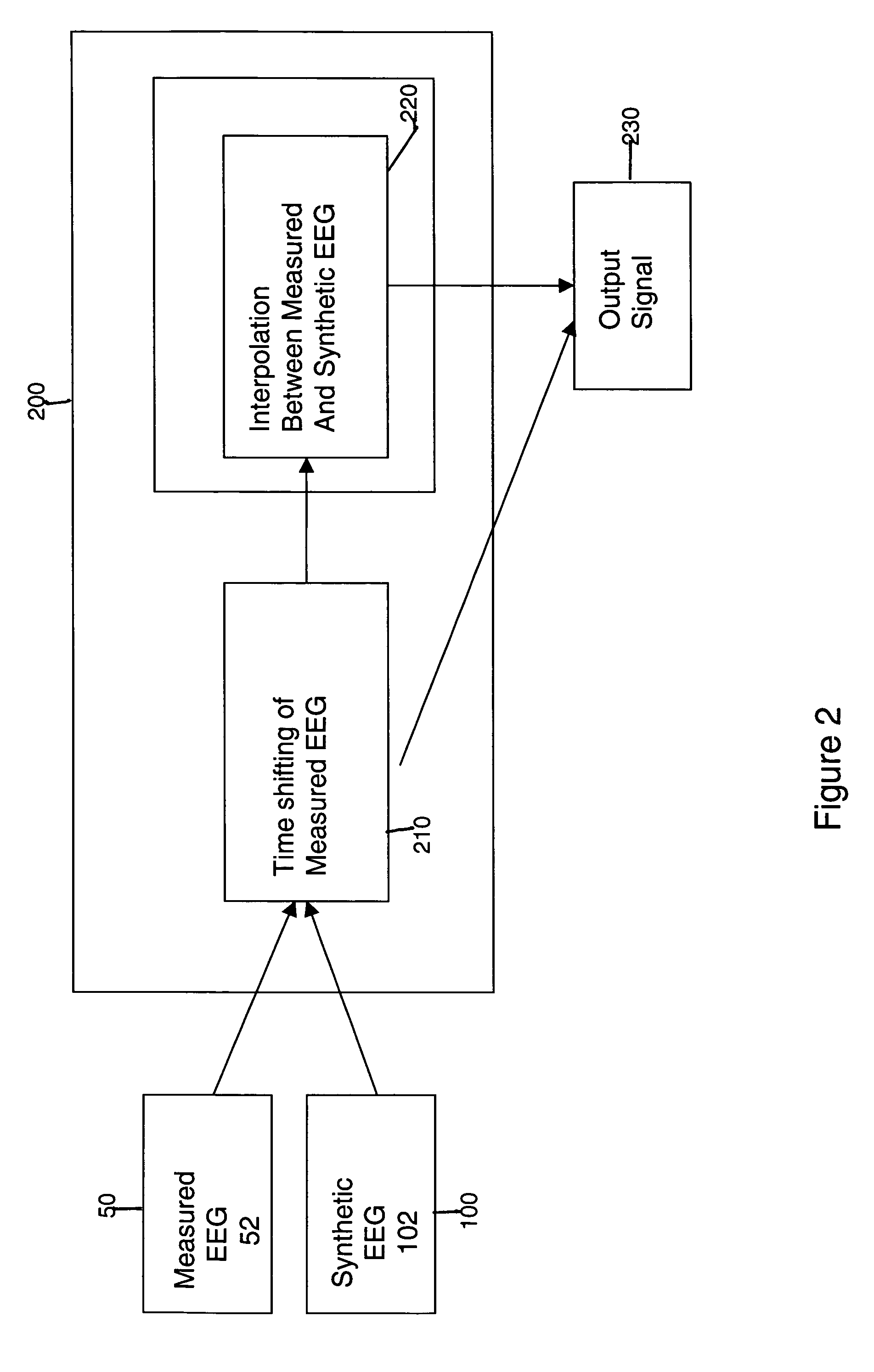
The invention provides a method of estimating cerebral sources of electrical activity from a small subset of EEG channels utilizing existing methods to provide a 3-dimensional, discrete, distributed, linear solution to the inverse problem using inputs consisting of a small number of EEG channels (e.g., 4 channels) augmented with synthetic EEG data for the other channels. The resultant image of cerebral electrical activity in the region of the EEG channels from which data is recorded is of comparable spatial resolution in the corresponding region to images of cerebral electrical activity obtained using a complete set of EEG channels (e.g., using 24 channels).
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Wireless recording and stimulation of brain activity
InactiveUS8849369B2Lengthy and costly hospitalizationReduce morbidityElectroencephalographyHead electrodesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationCerebral activity
Owner:SIGENICS +2
System and method for EEG imaging of cerebral activity using small electrode sets
The invention provides a method of estimating cerebral sources of electrical activity from a small subset of EEG channels utilizing existing methods to provide a 3-dimensional, discrete, distributed, linear solution to the inverse problem using inputs consisting of a small number of EEG channels (e.g., 4 channels) augmented with synthetic EEG data for the other channels. The resultant image of cerebral electrical activity in the region of the EEG channels from which data is recorded is of comparable spatial resolution in the corresponding region to images of cerebral electrical activity obtained using a complete set of EEG channels (e.g., using 24 channels).
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
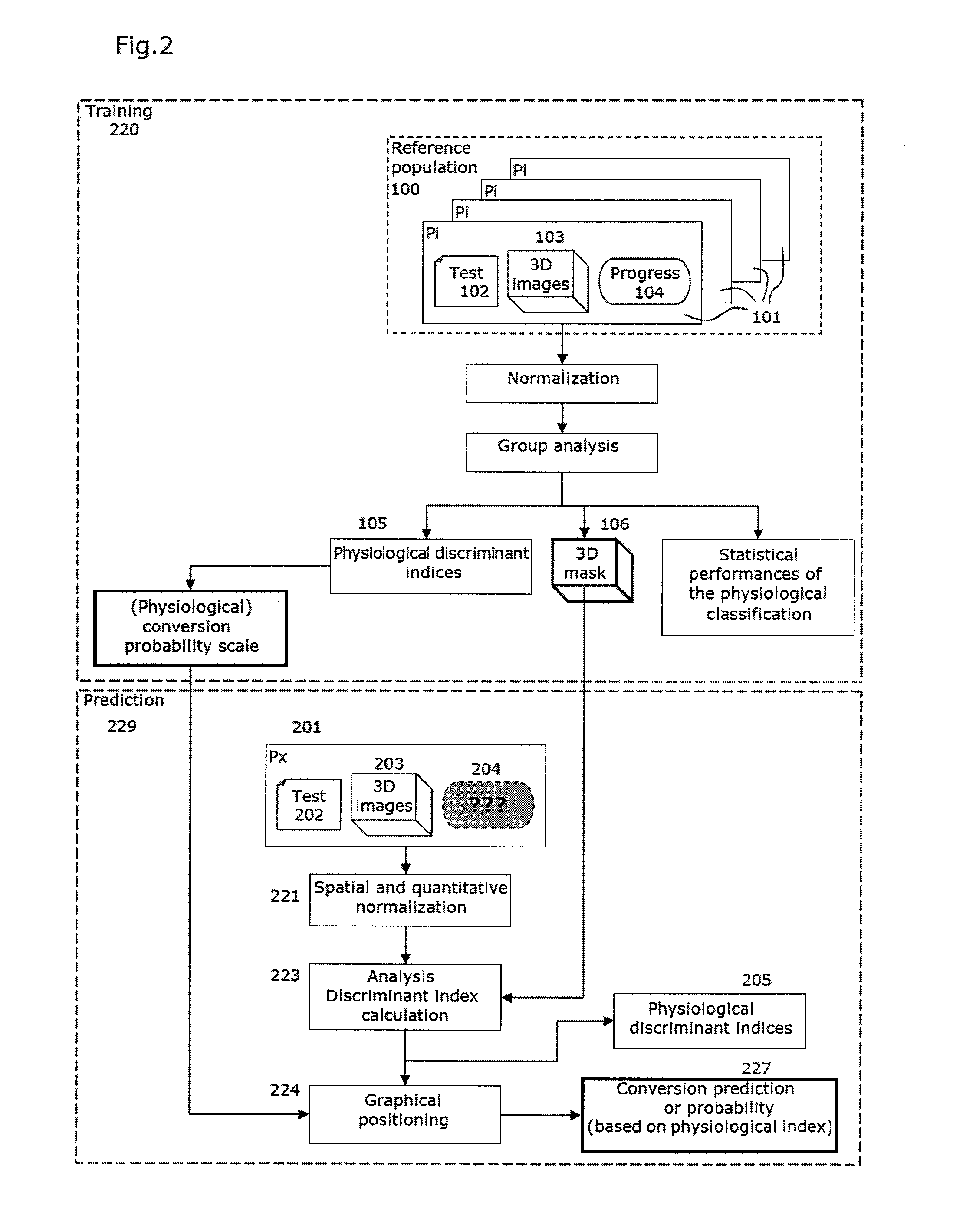
Method and automated system for assisting in the prognosis of alzheimer's disease, and method for training such a system
InactiveUS20110046451A1Easy to distinguishImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelCerebral activity
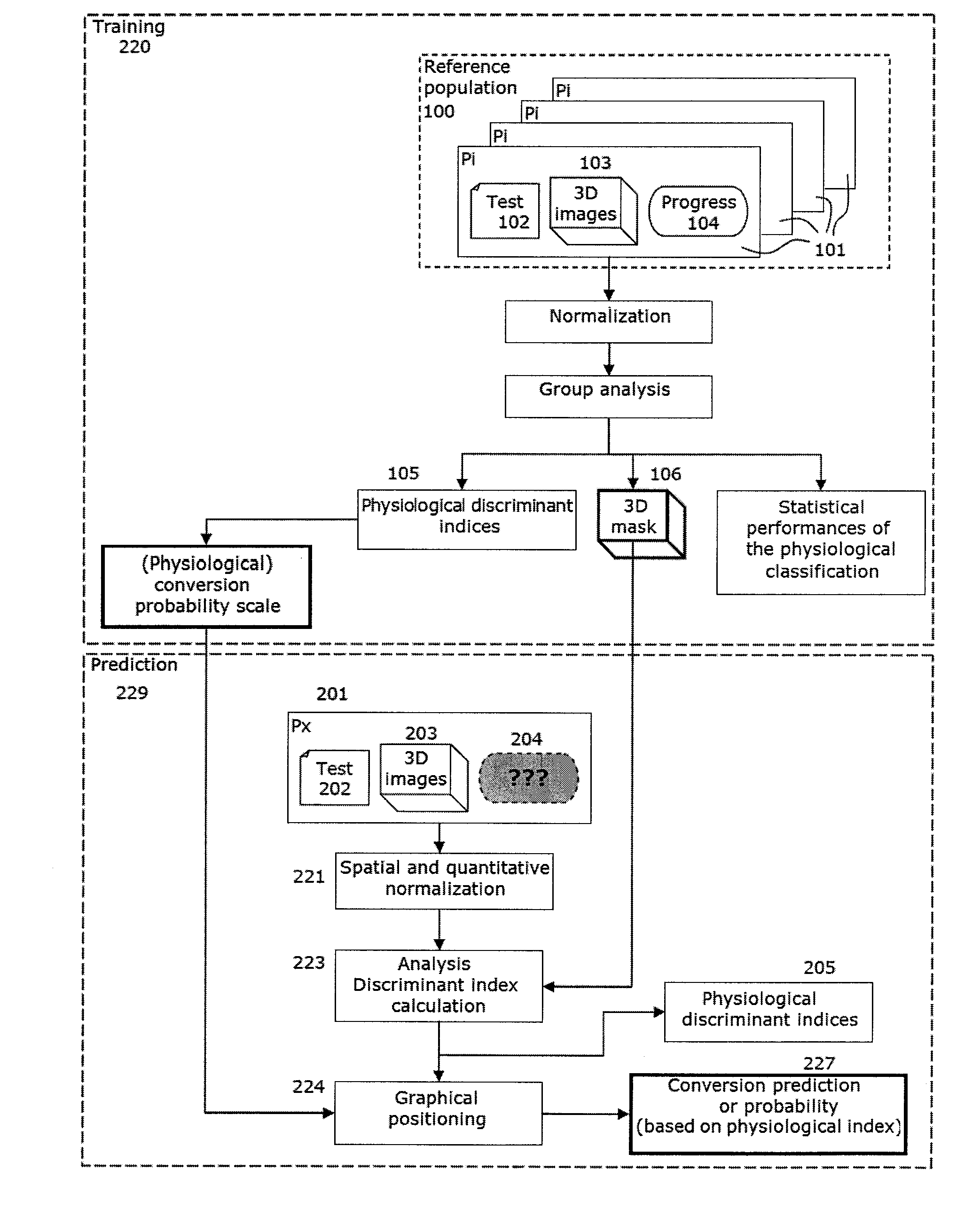
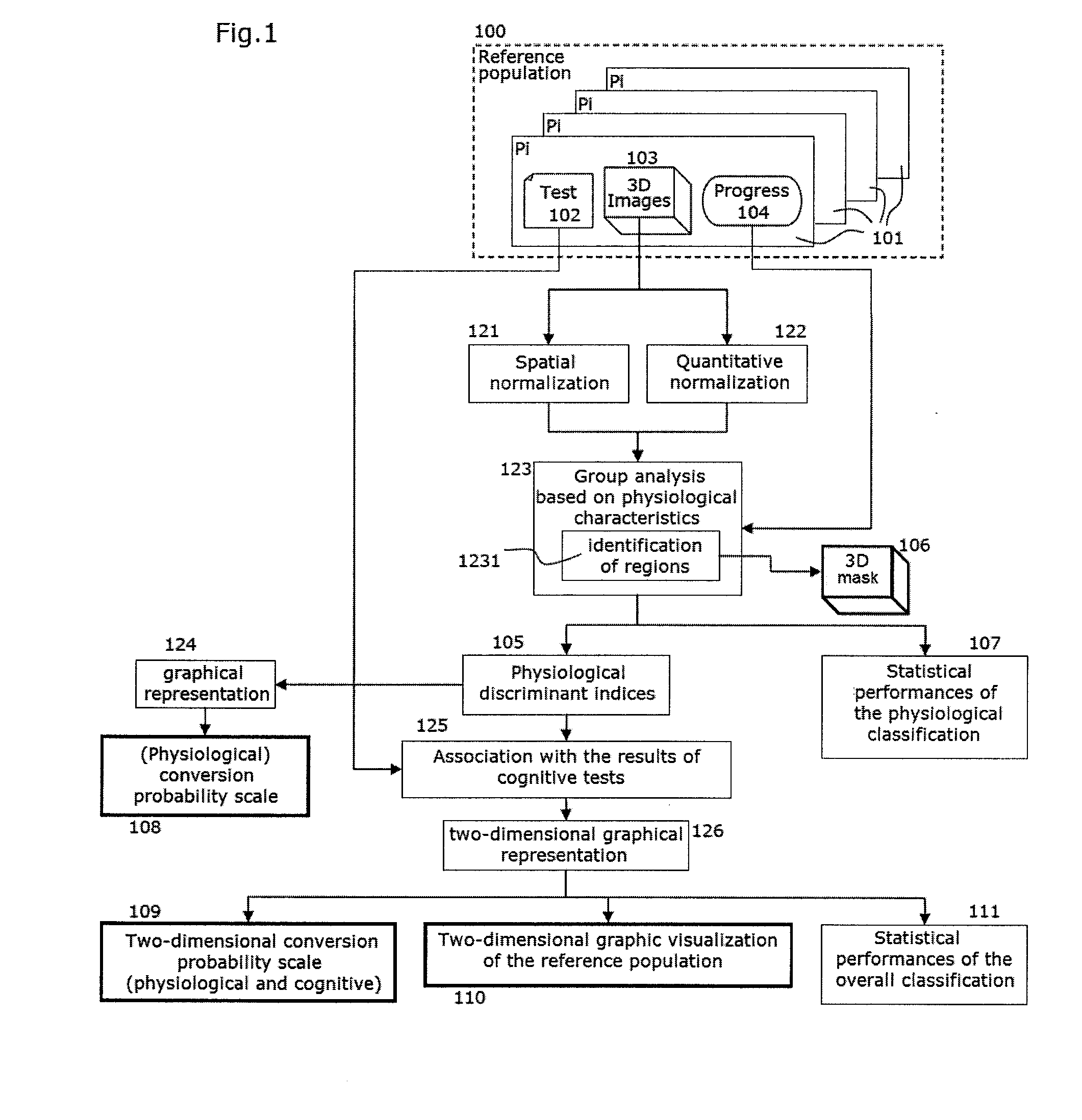
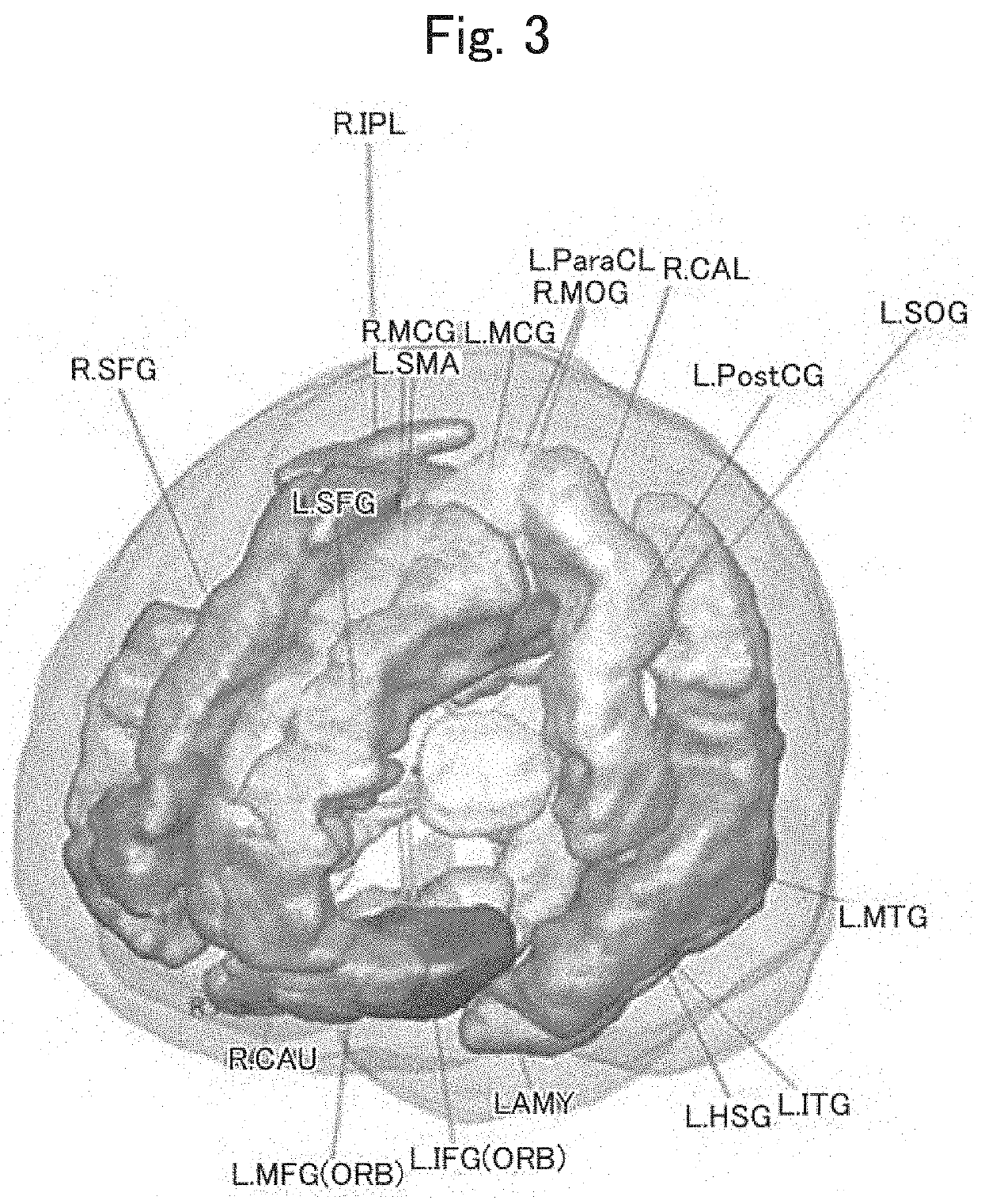
A method and automated system for assisting in the prognosis of the progress and for assisting in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease in patients suffering from mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Also provided is a method for training such a system related to identifying discriminant regions of the brain and using these regions to fine tune the assistance method, based on new known cases.Imaging data (PET or SPECT) is used, representing the cerebral activity in a plurality of spatial zones (voxels). The method then includes a normalization processing of the image data, and analysis of the cerebral activity values read in a selection of voxels forming at least one predetermined discriminant region, defined by its coordinates within a spatial reference system.
Owner:UNIV PIERRE & MARIE CURIE +1
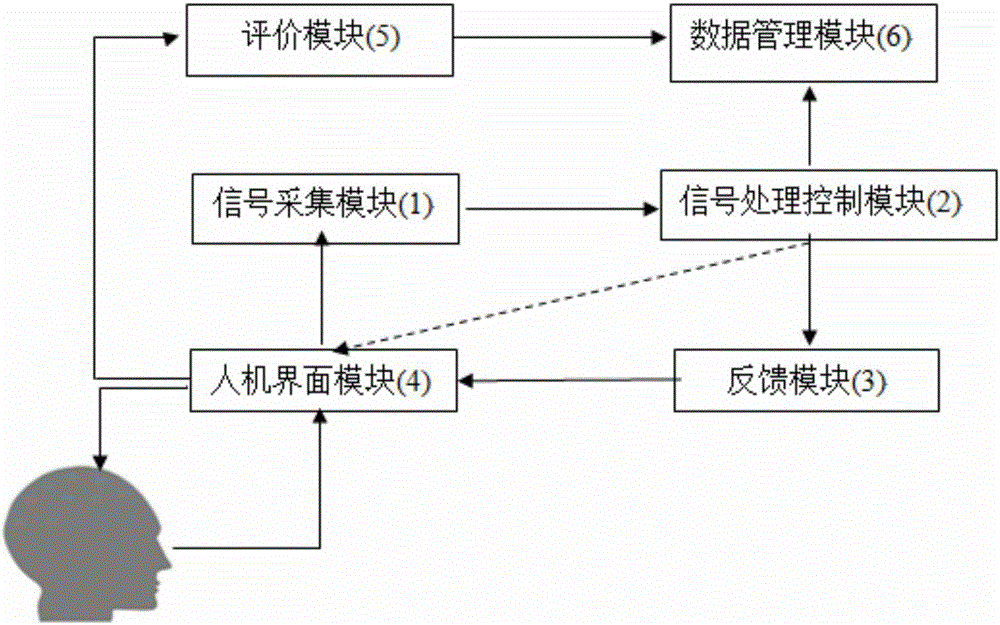
Emotional control system based on electroencephalogram feedback
ActiveCN106267514ALow costImprove time resolutionMedical devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman–machine interfaceCerebral activity
The invention discloses an emotional control system based on electroencephalogram feedback, comprising an information acquisition module, a signal processing control module, a feedback module, a human-machine interface module, an evaluation module and a data management module. The invention relates to the field of emotional control and electrophysiology, and the ability to control emotions is trained by using electroencephalogram biofeedback technology; since the brain is plastic, electroencephalograms may reflect transient changes in cerebral activity; the ability of the brain to control emotions is trained through biofeedback technology, it is possible to improve the ability of a subject to control emotions, and by using an electroencephalogram biofeedback system herein, it is possible to effectively improve the ability of personnel to adjust negative emotions.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
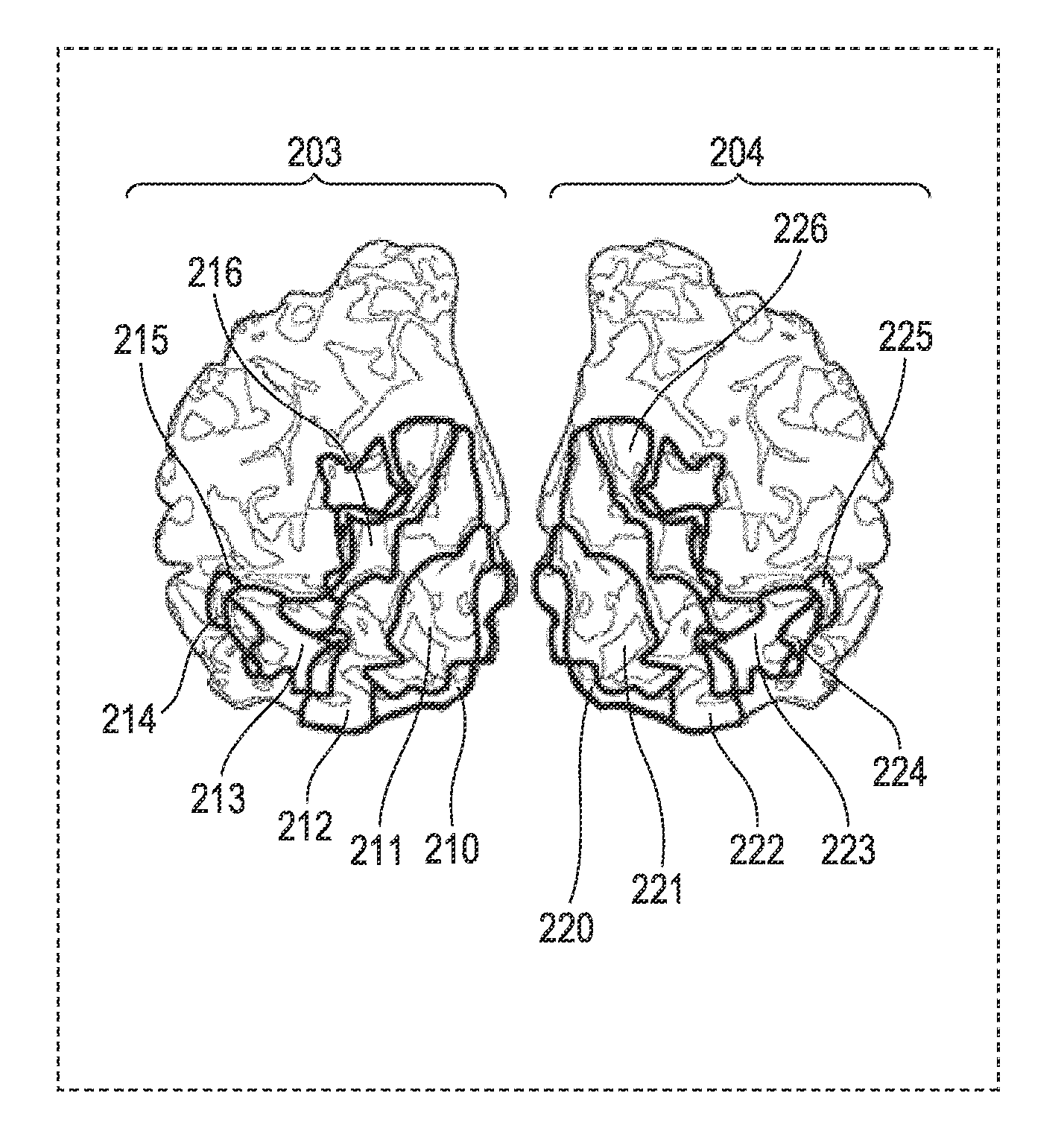
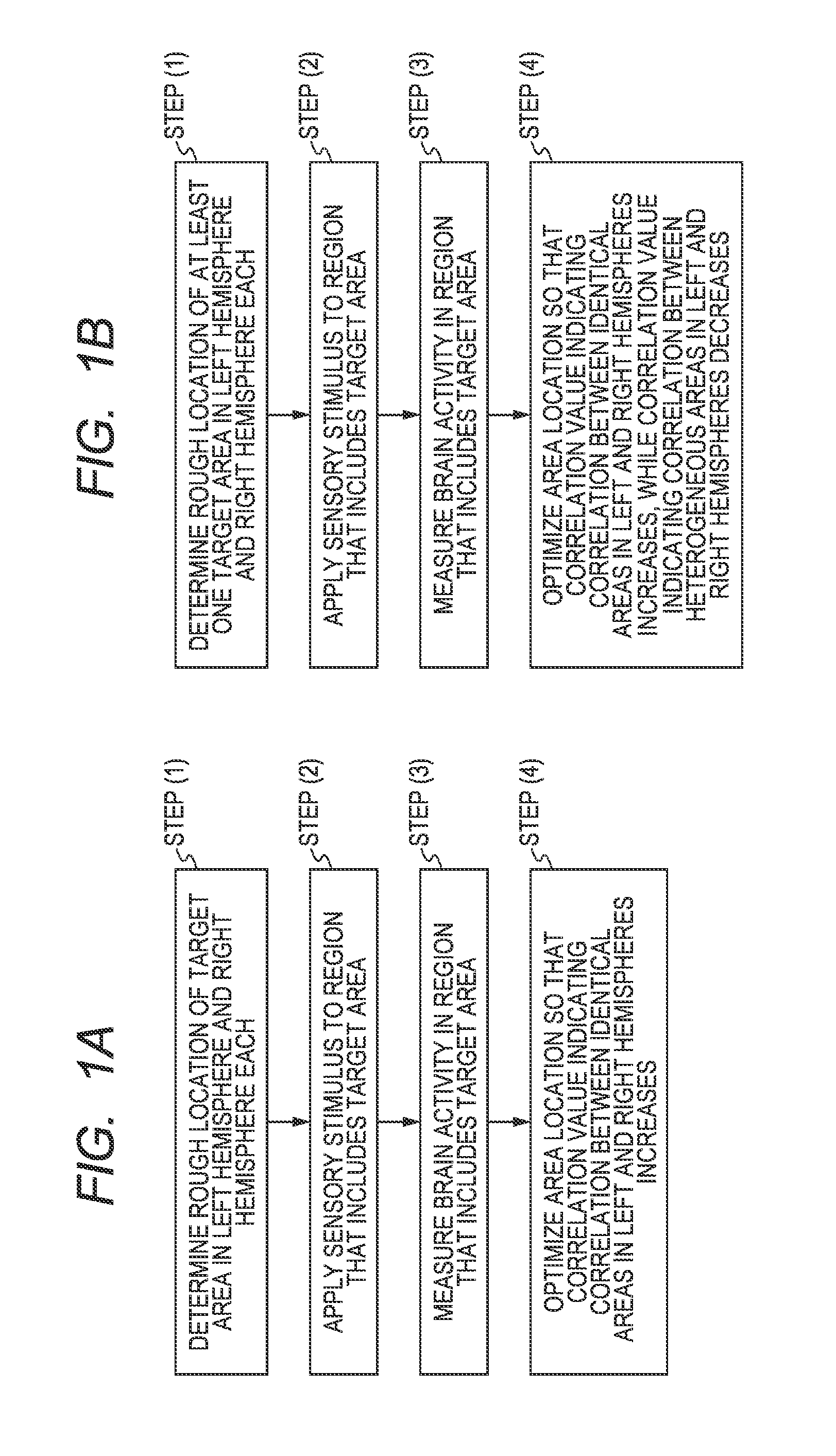
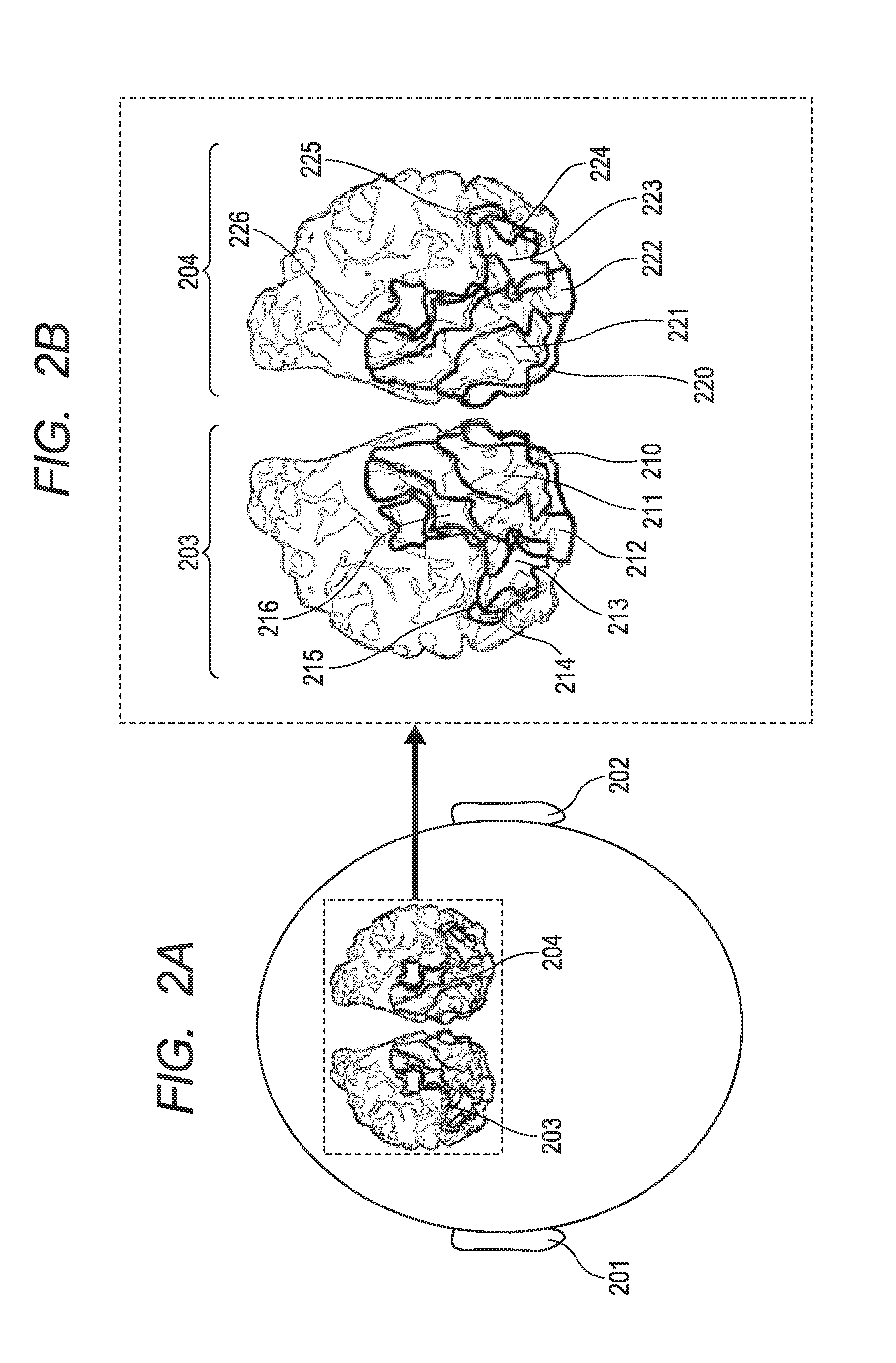
Method of identifying the spatial distribution of areas in a sensory area of brain, program, and recording medium therefor
InactiveUS20140371573A1ElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using spectroscopyRight hemisphereComputer science
A method of identifying a spatial distribution of areas includes: a first step of determining a rough spatial distribution of at least one area in a sensory area of cerebral cortex in each of a left hemisphere and right hemisphere of the brain that is a target area of the identification; a second step of applying a sensory stimulus to the identification target area; a third step of obtaining brain activity information; and a fourth step of using the brain activity information to calculate one of a coefficient of cross-correlation, and coherence, between brain activity information of areas, assessing synchrony between the left and right hemispheres, and changing the spatial distribution determined in the first step.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for desynchronization of neural brain activity
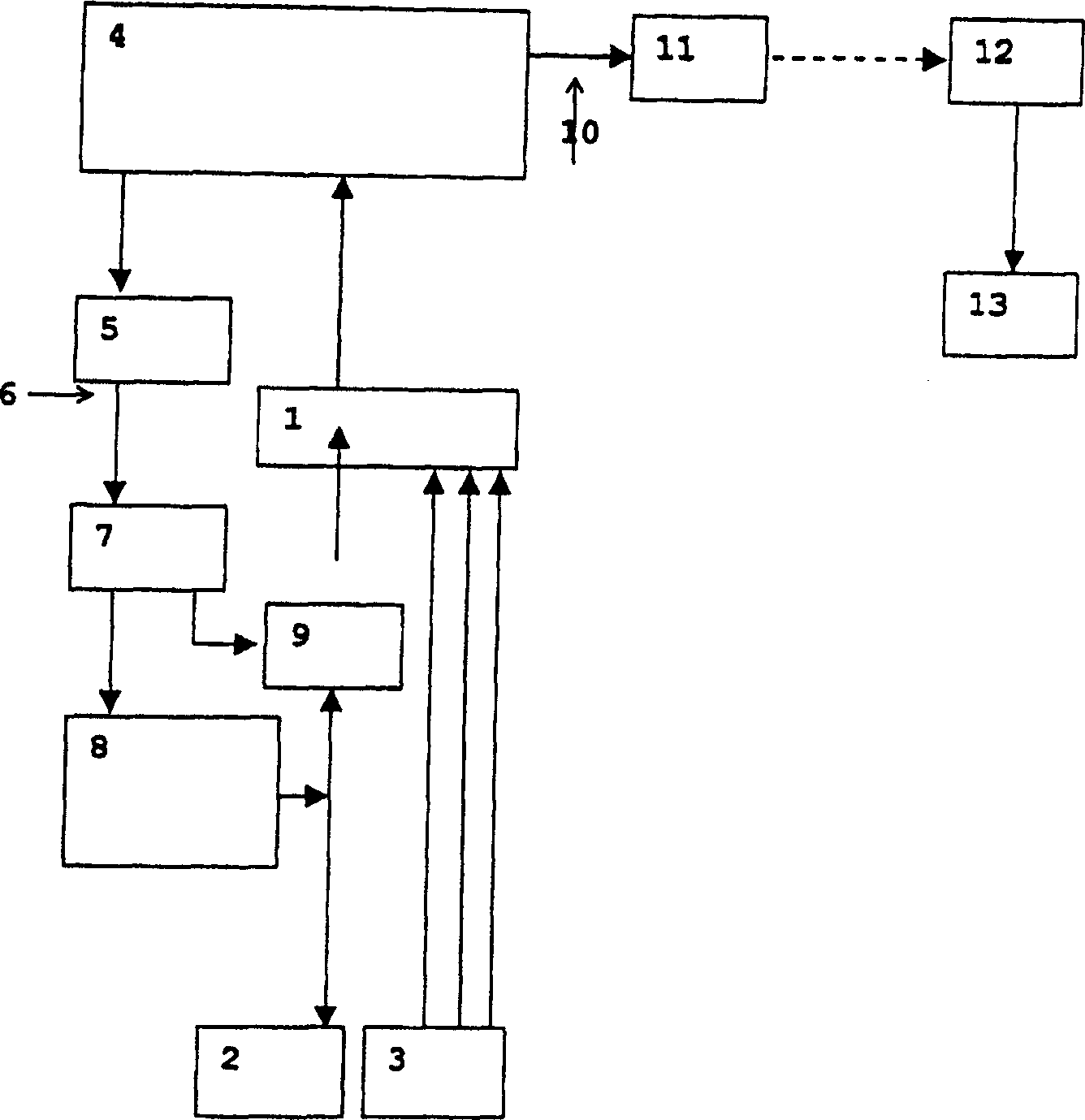
The invention relates to a device for desynchronising neuronal, morbidly synchronous cerebral activity. According to the invention, the activity in at least two sub-sections of a cerebral area or at least two functionally allied cerebral areas is stimulated with the aid of at least two electrodes, which surprisingly causes a desyncronisation in the affected neurone population of an afflicted person, thus suppressing the symptoms. The stimulation feedback signal, i.e. the measured, time-delayed and processed neuronal activity is used as the individual stimulus. The invention thus permits a self-regulating demand control of the amplitude of the stimulation signal, whereby the intensity of the stimulation pulses are automatically minimised after successful desynchronisation. To operate successfully, the device requires neither complex calibration nor regulation of the stimulation parameters, the latter however can be advantageously adapted and optimised by the additional controller. Said device comprises at least two stimulating electrodes (2) and at least one sensor (3), which are controlled by a controller in such a way that they cause localised desynchronisation.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
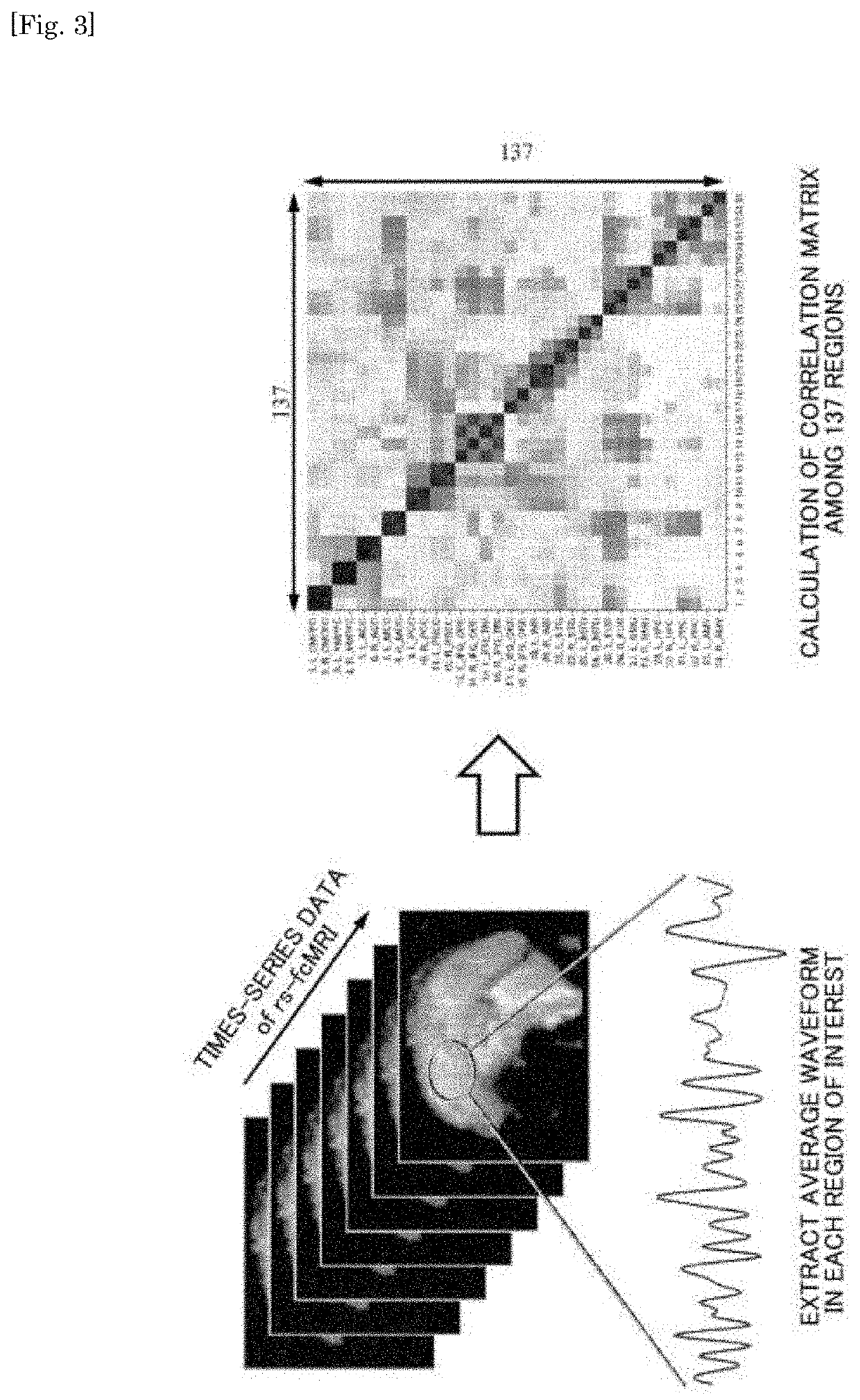
Data processing method based on rfMRI (resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging) of idiopathic epilepsy
InactiveCN105708462AAvoid Brain Activity DifferencesImprove matchDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseData acquisition
The invention discloses a resting-state functional magnetic resonance data processing method based on primary epilepsy, which belongs to the technical field of data processing for disease detection, and comprises the following steps: S1. data collection; S2. data preprocessing; S3 .Data analysis: including ReHo data analysis, ALFF data analysis and FC data analysis, all ReHo, ALFF, FC maps are analyzed separately, and then aggregated to determine the changed brain regions. The data processing method of the present invention is extremely valuable for the exploration of multifocal epileptic lesions, avoids the difference in brain activity caused by complex task stimuli, and basically controls the experimental conditions of different subjects at the same level, and is easy to cooperate and more It is easy to draw reliable conclusions. It understands the pathogenesis of certain clinical symptoms of epileptic patients from the perspective of brain function, can help locate epileptic foci and surrounding functional areas, and guide epilepsy surgery and the resection range of epileptic foci.
Owner:内蒙古医科大学附属医院
Differentiation device, differentiation method for depression symptoms, determination method for level of depression symptoms, stratification method for depression patients, determination method for effects of treatment of depression symptoms, and brain activity training device
PendingUS20210034912A1Discriminate the level of the depressive symptomImage enhancementMedical data miningFunctional connectivityCerebral activity
Objective discrimination of a disease label of a depressive symptom with respect to an active state of a brain is achieved. One means for solving the problems of the present invention is to provide a discriminating device for assisting in determination of whether a subject has a depressive symptom. The discriminating device includes a storage device for storing information for identifying a classifier generated by classifier generation processing based on a signal obtained by using a brain activity detecting apparatus to measure, in advance and time-sequentially, a signal indicating a brain activity of a plurality of predetermined regions of each brain of a plurality of participants in a resting state, the plurality of participants including healthy individuals and patients with depression. The classifier is generated so as to discriminate a disease label of a depressive symptom based on a weighted sum of a plurality of functional connectivities selected by feature selection as being relevant to the disease label of the depressive symptom through machine learning from among functional connectivities of the plurality of predetermined regions. The discriminating device further includes a processor configured to execute discriminating processing of generating a classification result for the depressive symptom of the subject by using the classifier.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT +1
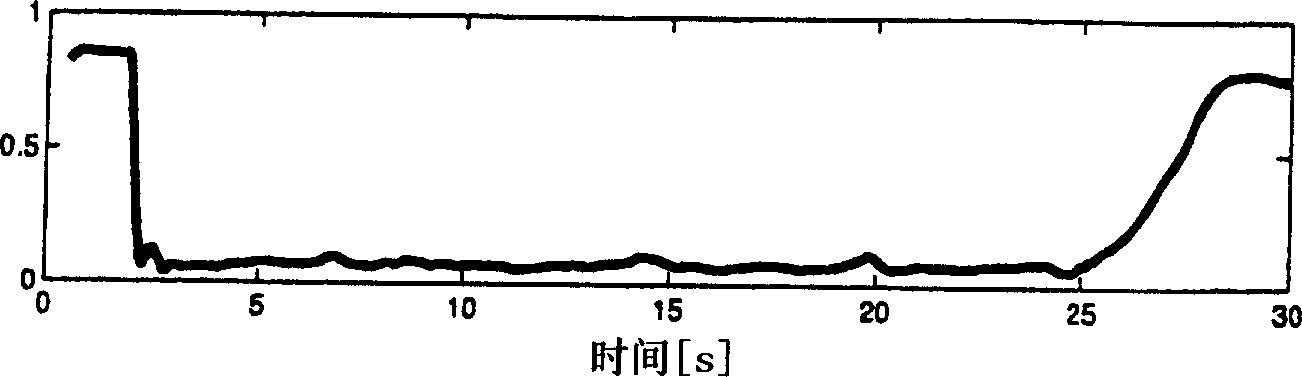
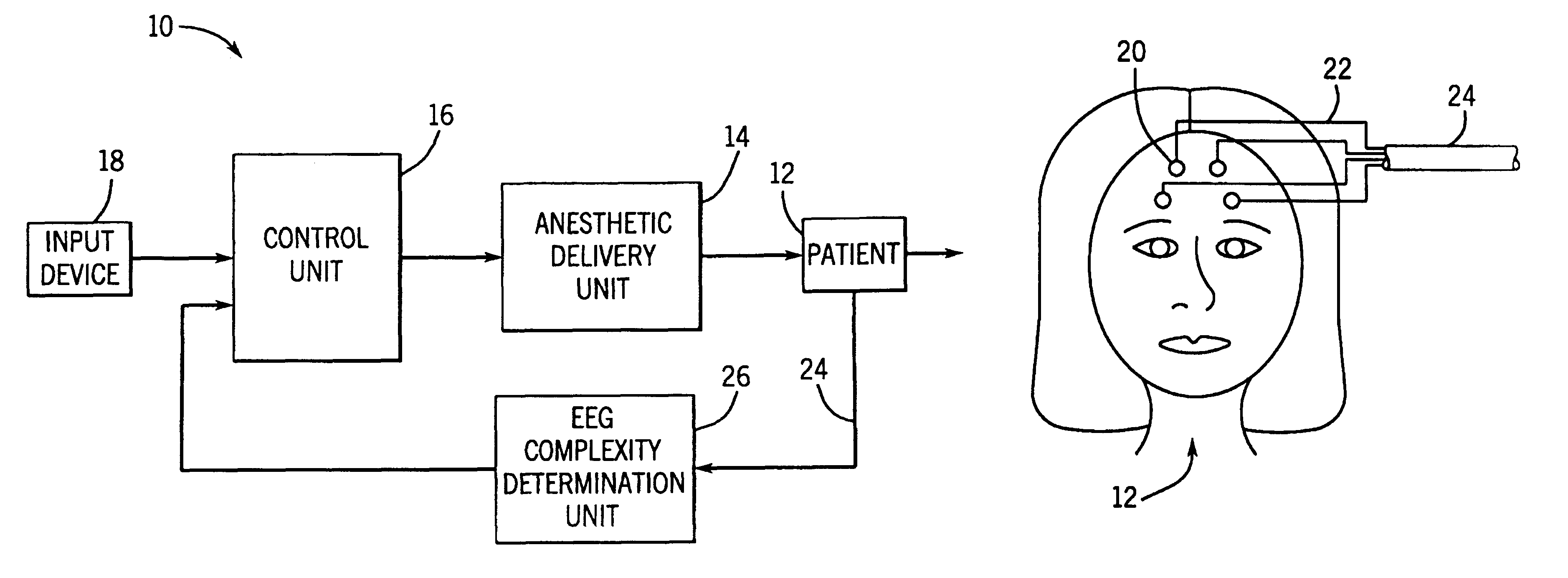
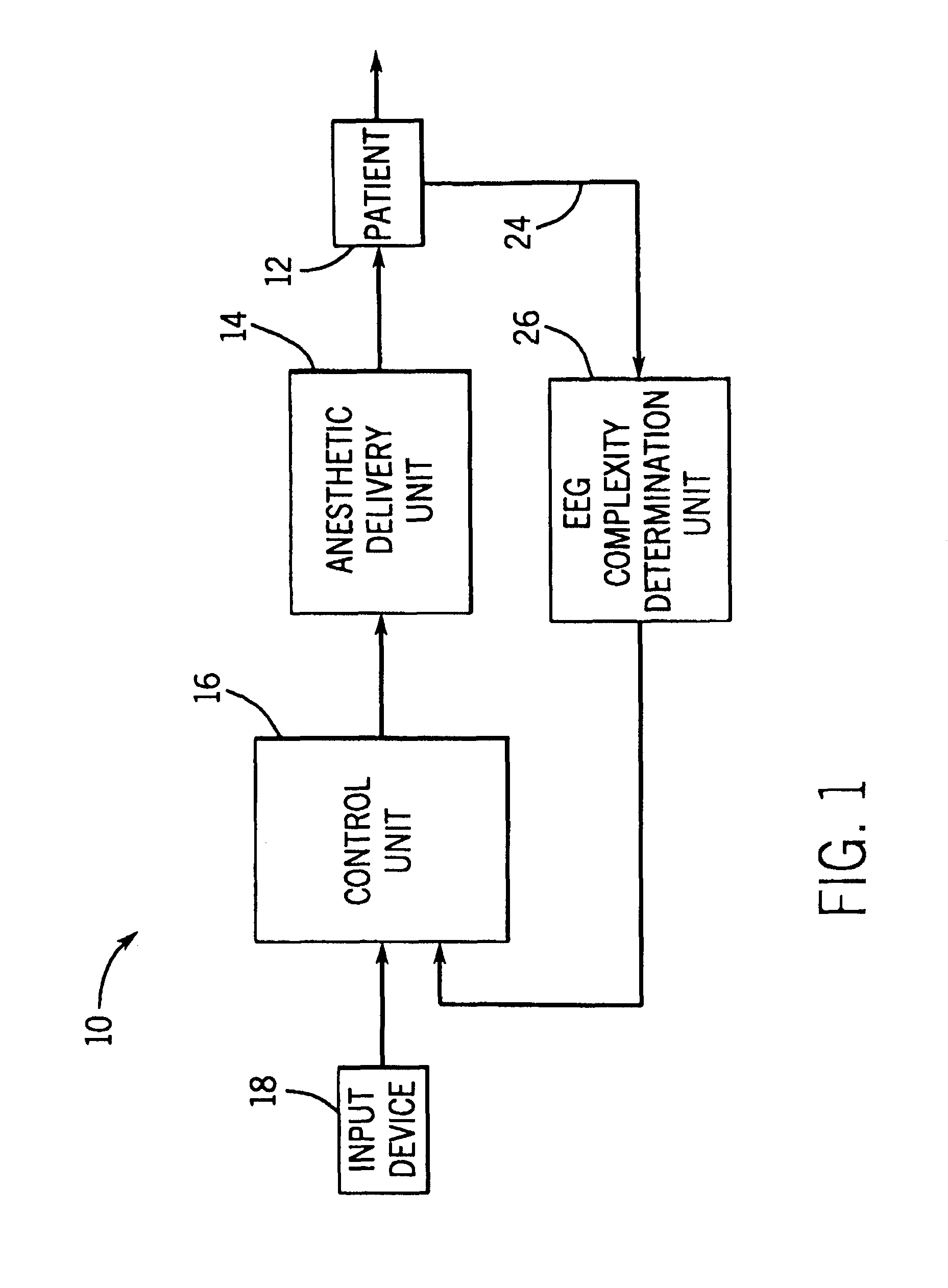
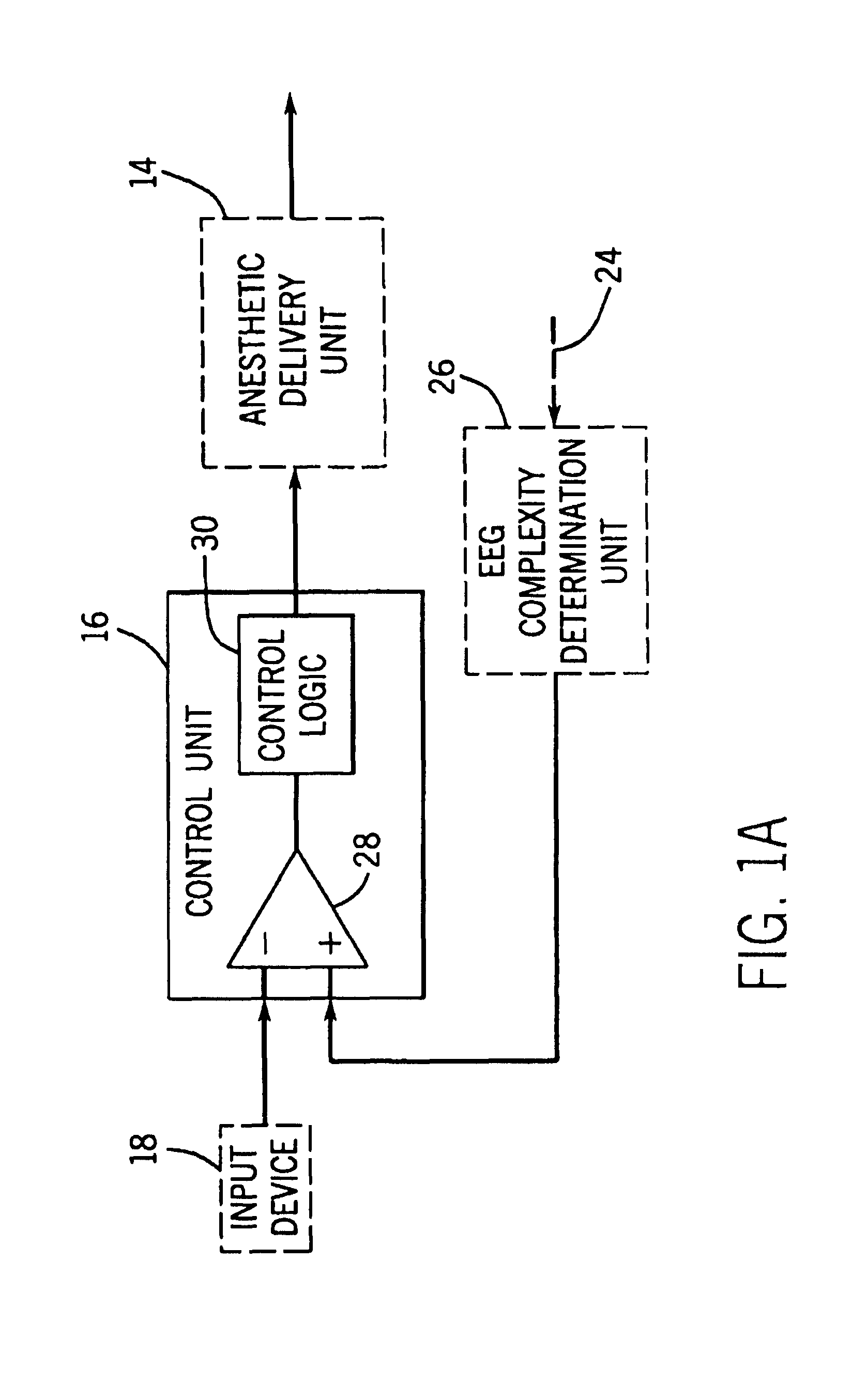
Closed loop drug administration method and apparatus using EEG complexity for control purposes
InactiveUSRE41291E1Prolonged administration of drugImprovement in administrationRespiratorsElectrocardiographyCerebral activityClosed loop
A closed loop method and apparatus for controlling the administration of an hypnotic drug to a patient. Electroencephalographic (EEG) signal data is obtained from the patient. At least one measure of the complexity of the EEG signal data is derived from the data. The complexity measure may comprise the entropy of the EEG signal data. The EEG signal data complexity measure is used as the feedback signal in a control loop for an anesthetic delivery unit to control hypnotic drug administration to the patient in a manner that provides the desired hypnotic level in the patient. An EEG signal complexity measure obtained from the cerebral activity of the patient can be advantageously used in conjunction with a measure of patient electromyographic (EMG) activity to improve the response time of hypnotic level determination and of the feedback control of drug administration. A pharmacological transfer function may be used, along with pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic models.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE FINLAND
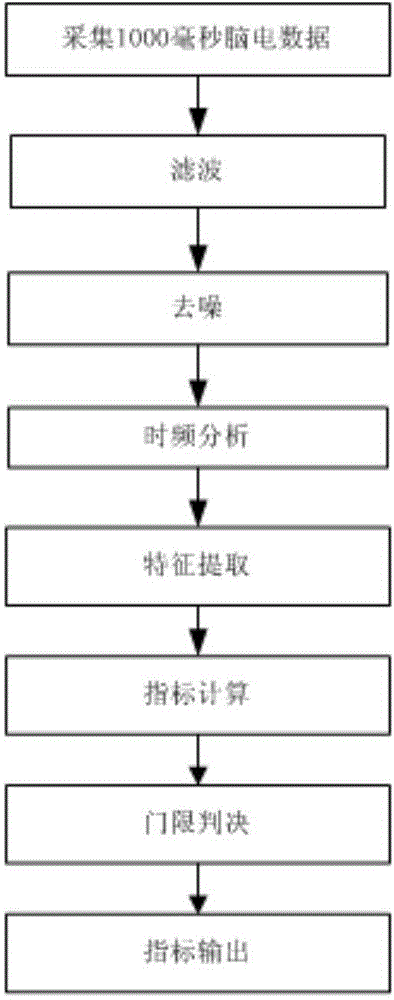
Frequency domain feature extracting algorithm applied to single-lead portable brainwave equipment
ActiveCN103815901AJudging mental stateImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionAlgorithm
The invention relates to the field of brainwave signal processing, in particular to a frequency domain feature extracting algorithm applied to single-lead portable brainwave equipment. The algorithm is applicable feature extraction of the single-lead portable brainwave equipment and capable of reflecting cognition states. The algorithm includes: preprocessing, and feature expressing, extracting and indexation indicating. The algorithm outputs an alertness level index and a nervousness level index. The alertness level index: S1(t)=c(t) / a(t), wherein t refers to time, and a and c respectively refer to the energy of alpha and theta; the nervousness level index: S2(t)=b()t*c(t), wherein t refers to time, and b and c respectively refer to the energy of beta and theta. Compared with judgments totally depending on experiences and subjectivity in the prior art, the algorithm has the advantages that the mental state of a testee can be judged scientifically and objectively, the multi-index synergy degree indexes reflecting the optimal working states can be further extracted, and whether brain activity states is suitable for work or not can be comprehensively expressed.
Owner:广州爱生科技发展有限公司
Differentiation device, differentiation method for depression symptoms, determination method for level of depression symptoms, stratification method for depression patients, determination method for effects of treatment of depression symptoms, and brain activity training device
The present invention differentiates objective disease labels for depression symptoms relative to brain activity states. As one means to address the problem to be addressed thereby, the present invention provides a differentiation device that is for helping to determine whether a subject has depression symptoms. The differentiation device comprises a storage device that is for storing informationthat specifies a classifier that has been generated by classifier generation processing from signals obtained by using a brain activity detection device to chronologically premeasure signals that indicate brain activity in a plurality of prescribed regions of the resting brains of each of a plurality of participants that include healthy and depressive patients. The classifier: is generated on thebasis of a weighted sum of a plurality of functional connectivities that, from among functional connectivities between the plurality of prescribed regions, have, by means of machine learning, been selected by feature selection as being related to disease labels for depression symptoms; and is generated to differentiate the disease labels for depression symptoms. The differentiation device also comprises a computing device. Using the classifier, the computing device executes differentiation processing that generates classification results for the depression symptoms of the subject.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT +1
Brain functional connectivity correlation value adjustment method, brain functional connectivity correlation value adjustment system, brain activity classifier harmonization method, brain activity classifier harmonization system, and brain activity biomarker system
A harmonization system for a brain activity classifier harmonizing brain measurement data obtained at a plurality of sites to realize a discrimination process based on brain functional imaging: obtains data, for a plurality of traveling subjects as common objects of measurements at each of the plurality of measurement sites, resulting from measurements of brain activities of a predetermined plurality of brain regions of each of the traveling subjects; calculates, for each of the traveling subjects, prescribed elements of a brain functional connectivity matrix representing the temporal correlation of brain activities of a set of the plurality of brain regions; using a generalized linear mixed model, calculates measurement bias data 3108 for each element of the brain functional connectivity matrix, as a fixed effect at each measurement site with respect to an average of the corresponding element across the plurality of measurement sites and across the plurality of traveling subjects; and thereby executes a harmonizing process.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
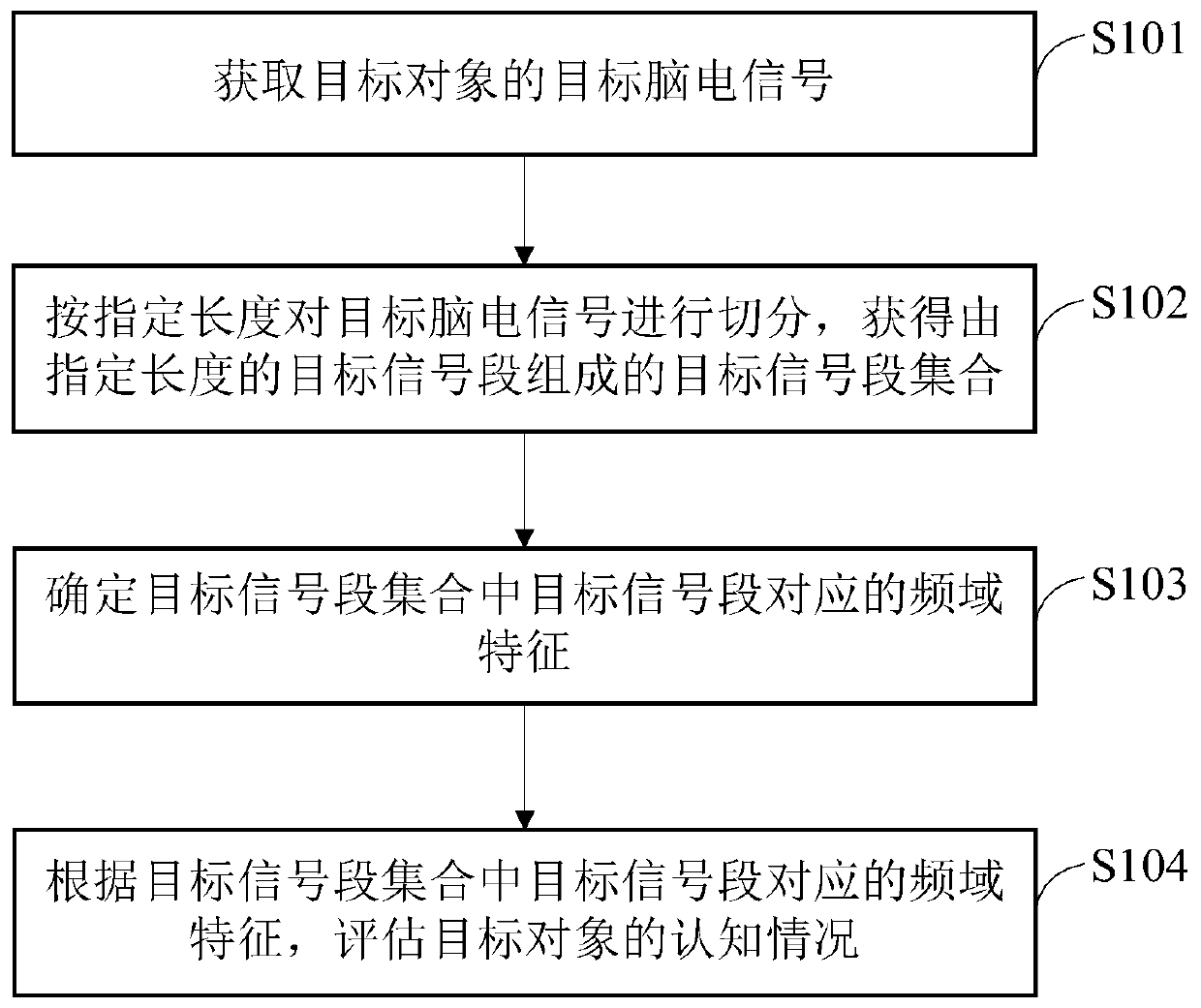
Object cognitive evaluation method, device, equipment and readable storage medium
InactiveCN110859616AImprove evaluation efficiencyReduce labor costsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEvaluation resultMedicine
The invention provides an object cognitive evaluation method, a device, equipment and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a target electroencephalogram signal of a target object; secondly, segmenting the target electroencephalogram signal according to specified lengths to obtain a target signal segment set consisting of target signal segments with the specified lengths; thirdly, determining frequency domain characteristics corresponding to the target signal segments in the target signal segment set; and finally, evaluating a cognitive condition of the target object according to the frequency domain characteristics corresponding to the target signal segments in the target signal segment set. According to the cognitive evaluation method ofthe object, a cognitive condition of the target object can be automatically evaluated by using the electroencephalogram signal; an evaluation basis is the electroencephalogram signal which can reflectan activity state of a human brain, so that an evaluation result is not influenced by an education degree of the target object; and in addition, the evaluation method provided by the invention is high in efficiency and low in cost, is convenient and fast, and has strong universality.
Owner:IFLYTEK CO LTD
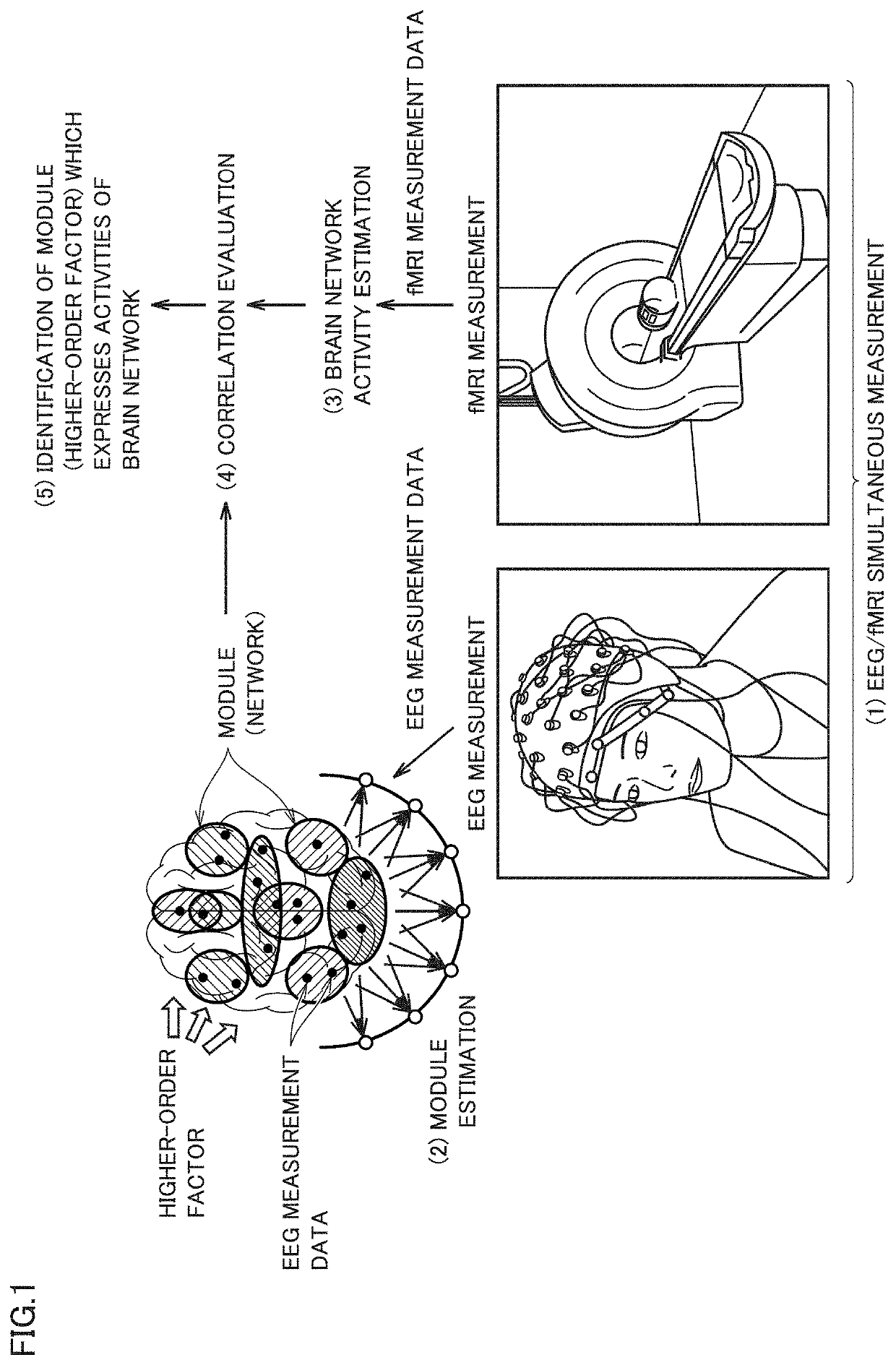
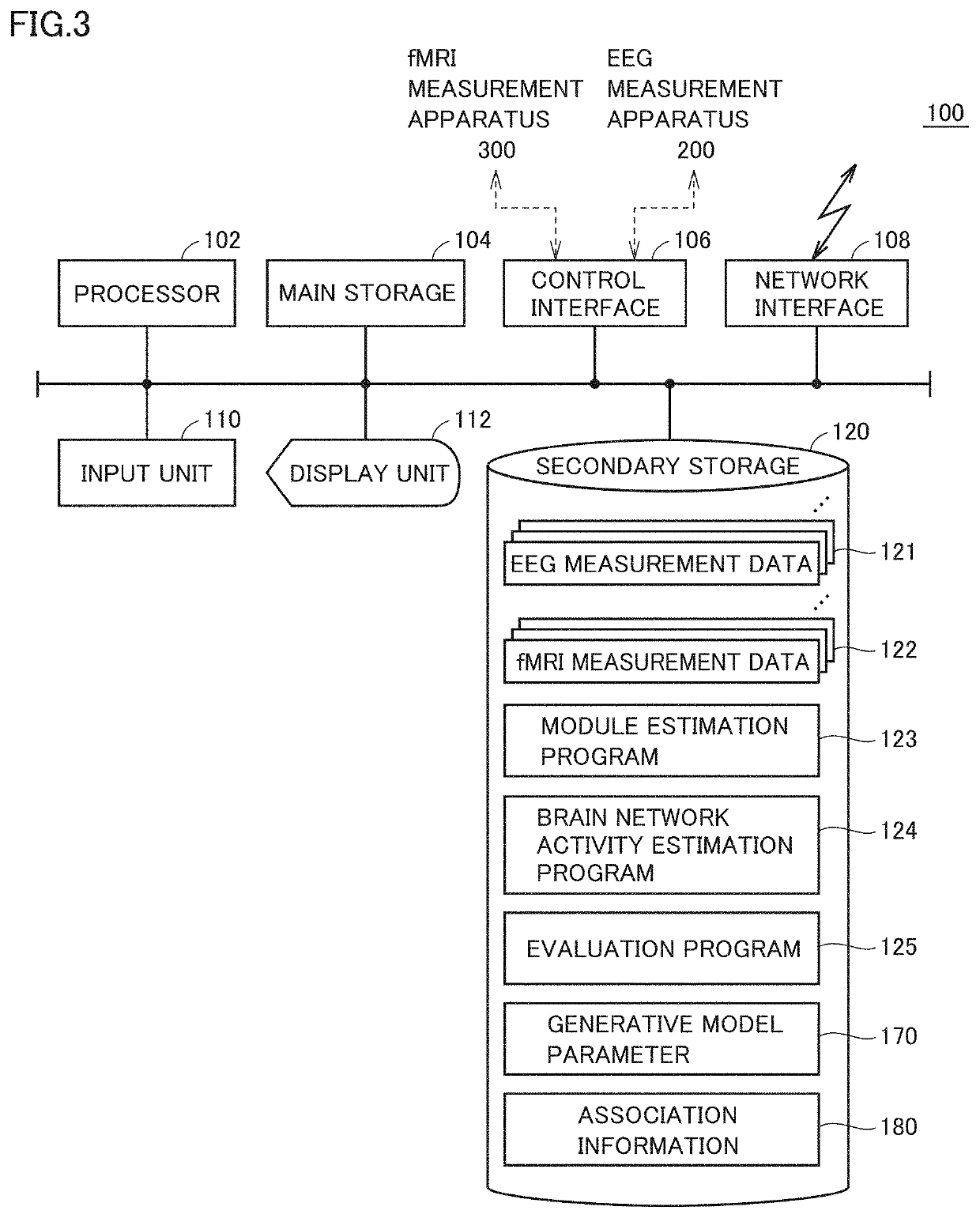
Brain network activity estimation system, method of estimating activities of brain network, brain network activity estimation program, and trained brain activity estimation model
PendingUS20210035665A1High activityElectroencephalographySensorsPattern recognitionFeature estimation
A brain network activity estimation system includes means for obtaining brain wave measurement data and functional magnetic resonance imaging measurement data simultaneously measured from a subject, means for constructing a feature estimation model which receives the brain wave measurement data as input data and determining a parameter which defines the feature estimation model, means for calculating a feature value for each module based on an output value from each module that is calculated when the brain wave measurement data is provided as the input data, means for calculating an image feature value for each brain network based on the functional magnetic resonance imaging measurement data, and means for determining one or more modules which express activities of a specific brain network among a plurality of modules by evaluating correlation between the feature value for each module and the image feature value for each brain network.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
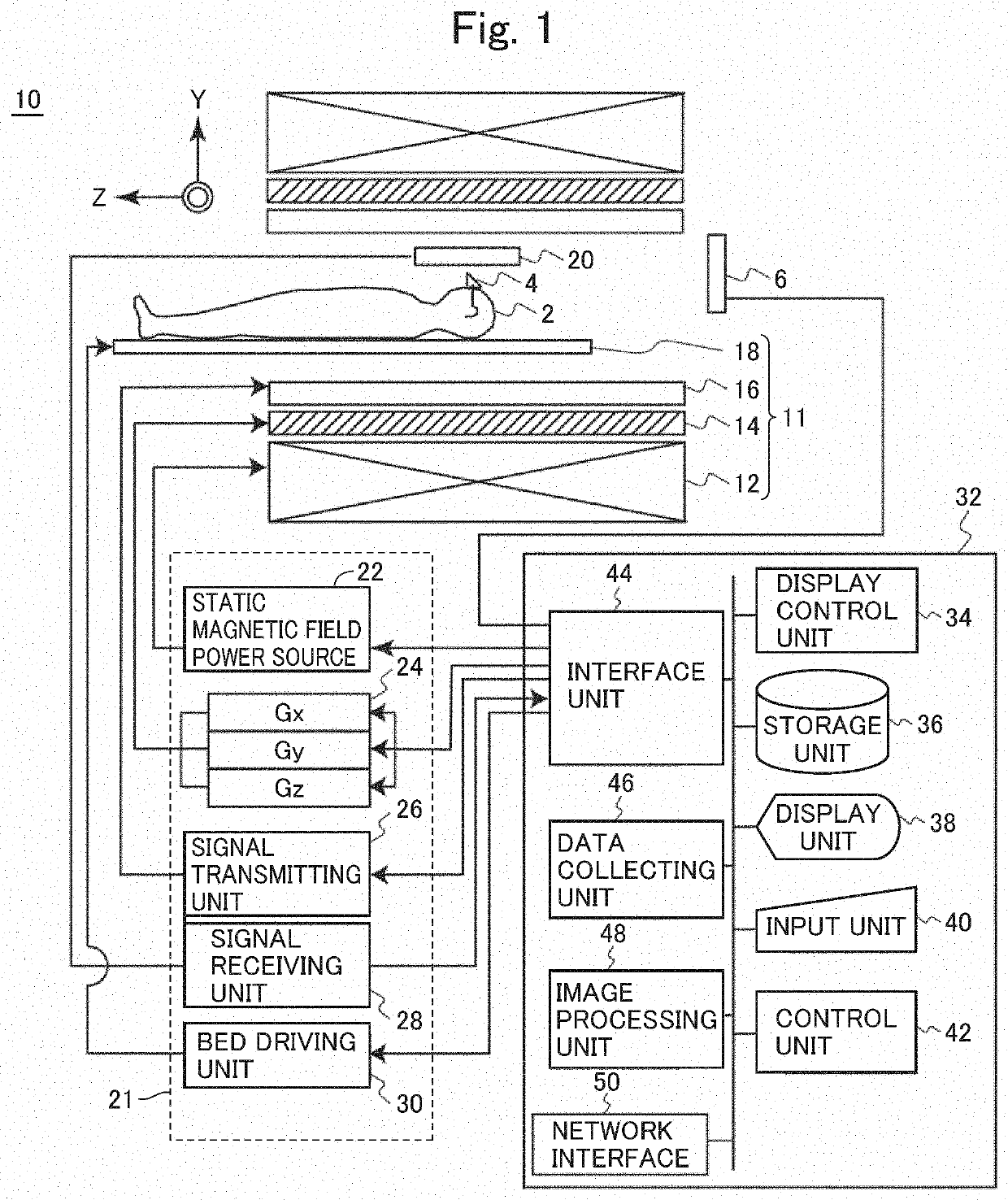
Device for measuring and/or stimulating brain activity
ActiveUS20200060571A1High activityShorten operation timeElectroencephalographySensorsEEG deviceCerebral activity
A device for measuring and / or stimulating a brain activity, preferably an EEG device, comprising means for transmitting and / or detecting physiological signals produced by the brain of an individual, and a support for the transmission and / or detection means, wherein the support is configured to extend over the top of the individual's head, the support comprising means for removably attaching to an accessory intended to be worn by the individual, on his or her head, such as an audio headset, the support being configured such that, when the device is worn by the individual, the means for transmitting and / or detecting physiological signals are held in substantially close contact with the individual's head by the accessory.
Owner:CONSCIOUS LABS SAS
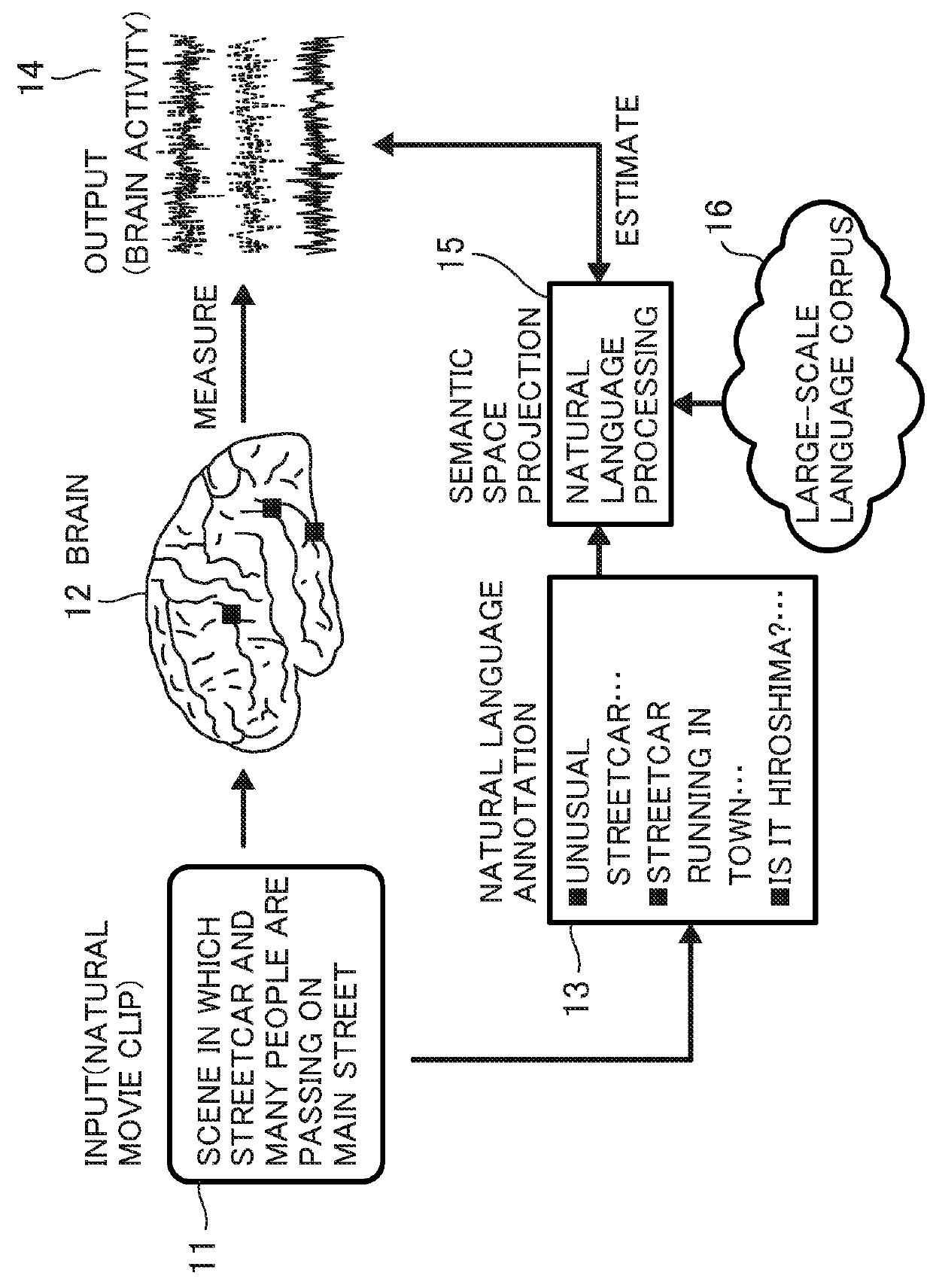
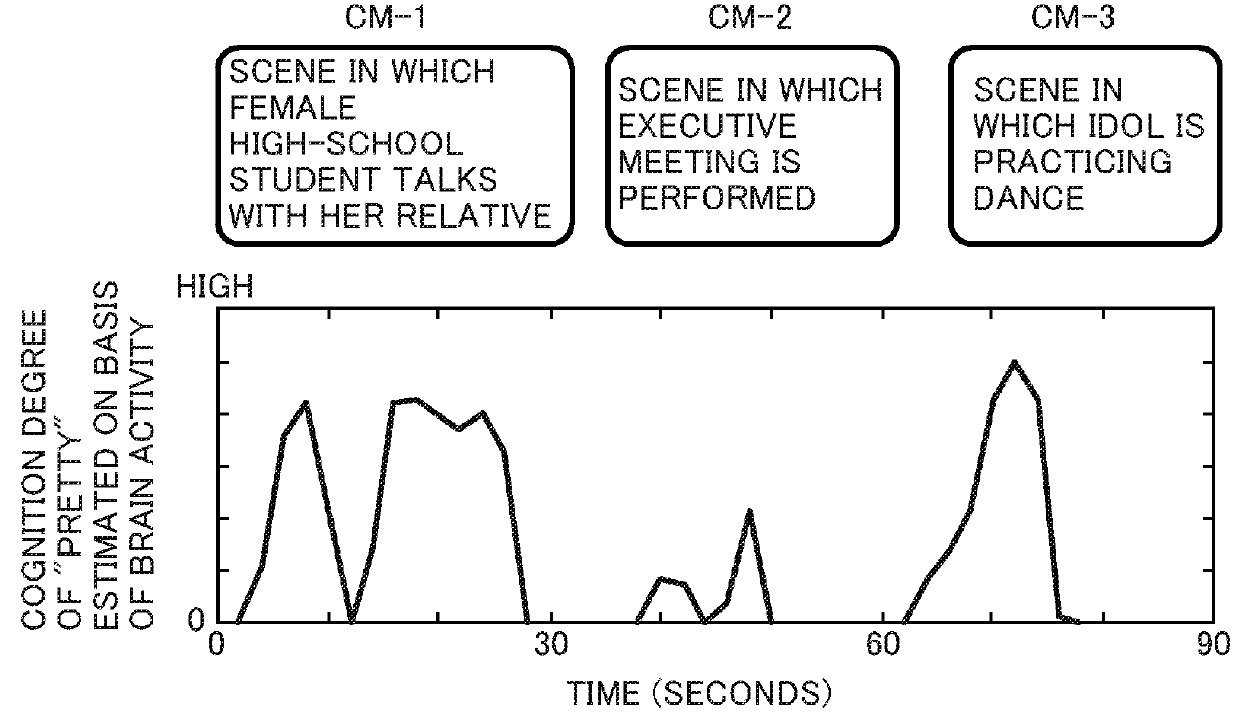
Method for estimating perceptual semantic content by analysis of brain activity
InactiveUS20180092567A1ElectroencephalographyInput/output for user-computer interactionEstimation methodsSemantic space
A perceptual semantic content estimation method includes: (A) inputting, to data processing means, brain activity induced in a subject by a training stimulation and detected as an output of a brain activity detection means and an annotation of a perceptual content; (B) associating a sematic space representation of the training stimulation and the output of the brain activity detection means in a stored semantic space and storing the association in a training result information storage means; (C) inputting, to the data processing means, an output when the brain activity detection means detects brain activity induced by a novel stimulation, and obtaining a probability distribution in the semantic space which represents perceptual semantic contents for the output of the novel stimulation-induced brain activity by the brain activity detection means on the basis of the association; and (D) estimating a highly probable perceptual semantic content on the basis of the probability distribution.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
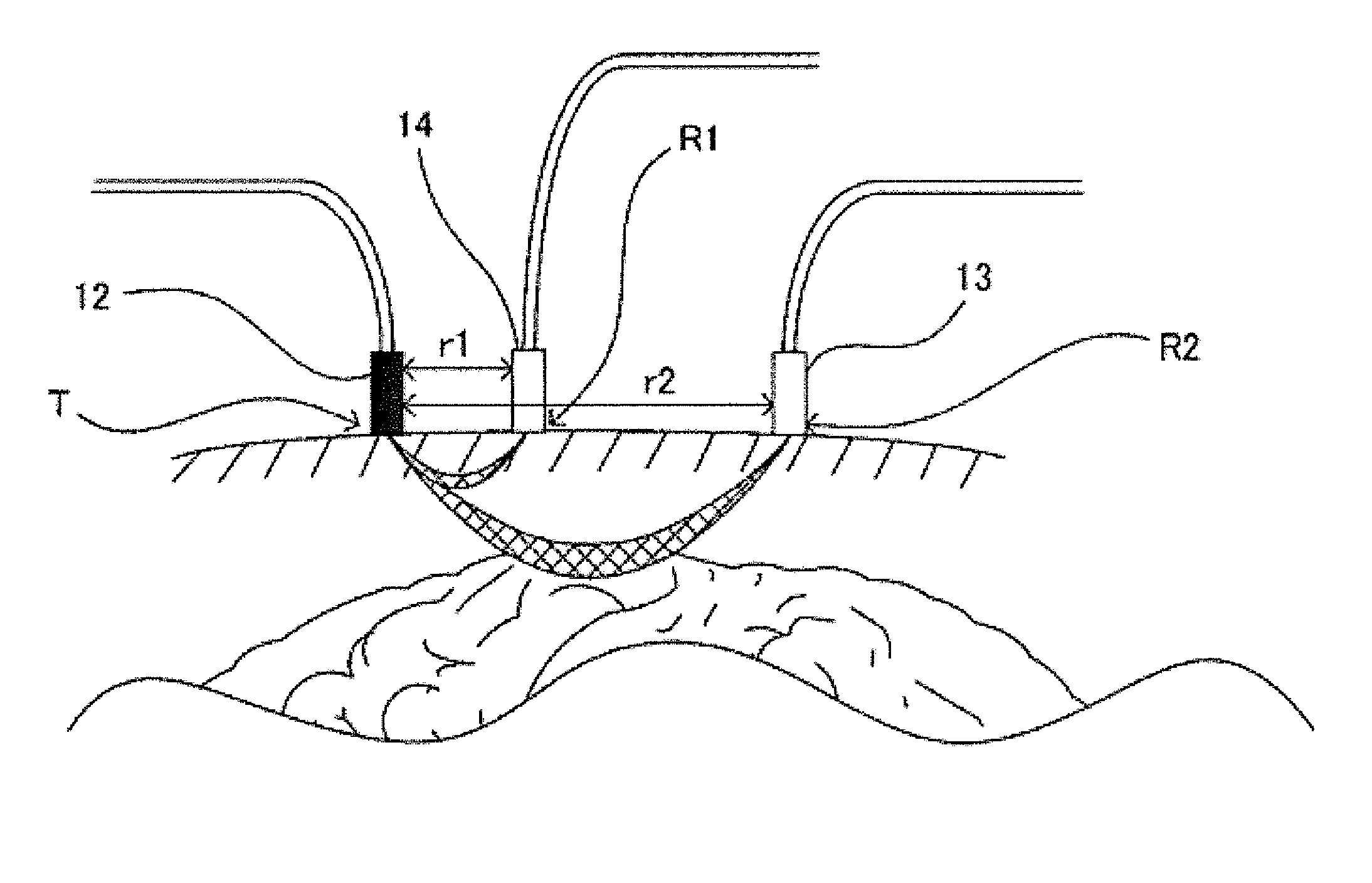
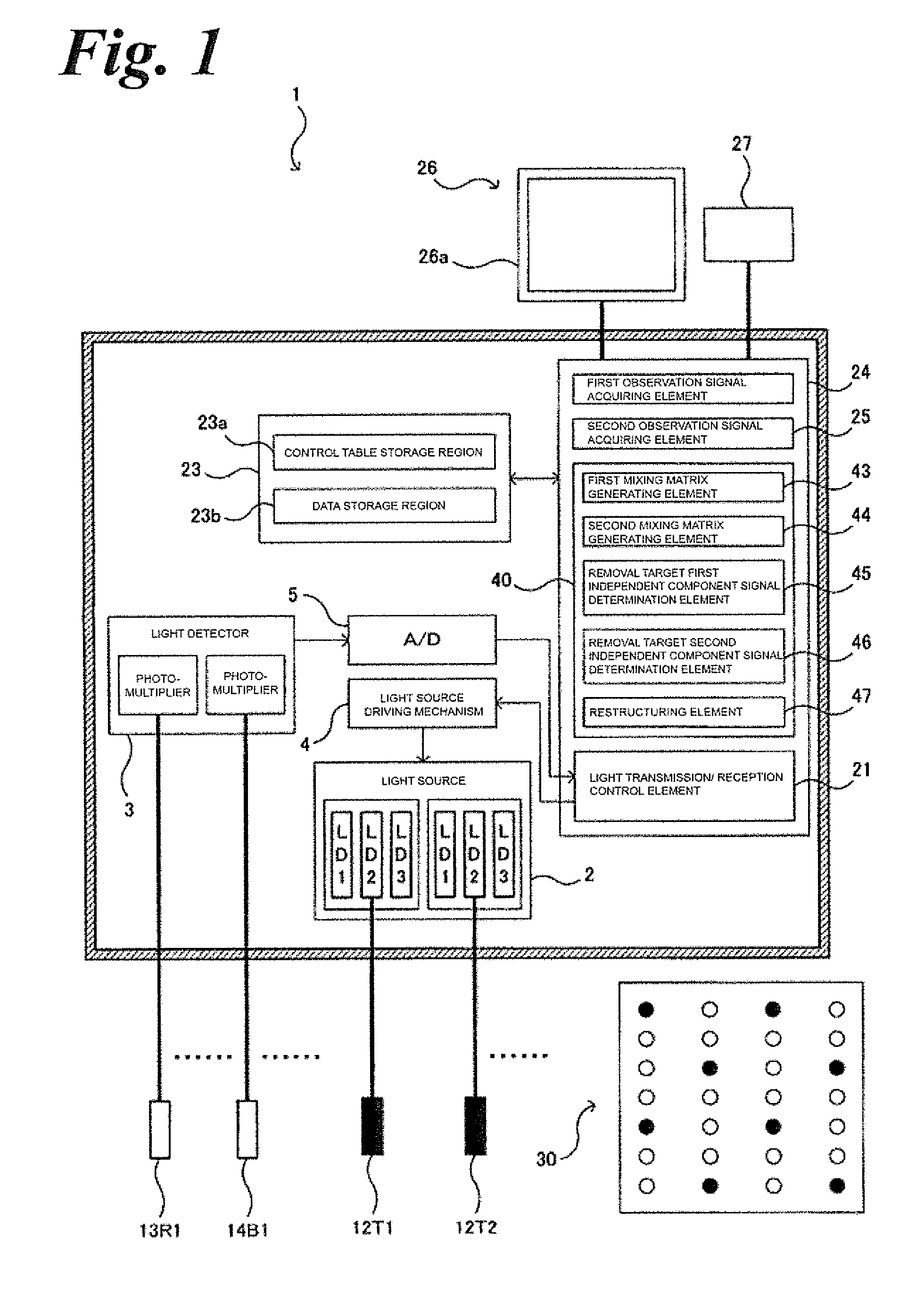
Optical biological measurement device and analysis method using the same
ActiveUS20150201841A1Accurate diagnosisDetectable lightDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTime courseMeasurement device
An optical biological measuring device includes a light transmission / reception element 30 having a plurality of light transmission probes 12, light reception probes 13 and reference probes 14; a second observation signal acquiring element 25 for acquiring a second observation signal indicating a time-course variation relating to a cerebral activity; a first observation signal acquiring element 24 for acquiring a first observation signal indicating a time-course variation relating to the blood flow in the skin; and an analysis control element 40 for generating a removal target component removal observation signal based on the first and second observation signals.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Brain activity training apparatus, brain activity training method and brain activity training program
PendingUS20200410890A1ElectroencephalographyArtificial lifeFunctional connectivityPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Neurofeedback training executed by a brain activity training apparatus for performing a training to change the correlation of connectivity between brain areas utilizing correlation of measured connectivity between brain areas involves repetition of a plurality of trials. Each trial includes a resting period Trest, a self-regulation period TNF and a presenting period TScore presenting feedback information. The brain activity training apparatus calculates, from signals detected from a trainee in the resting period by a brain activity detecting device, a baseline level of degrees of activity of prescribed regions corresponding to the functional connectivity as the object of training, calculates, from signals detected in the self-regulation period and from the baseline level, time correlation of degrees of activity of the prescribed regions corresponding to the functional connectivity as the object of training, and calculates information to be fedback.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
Brain activity measurement device, program, and method
ActiveUS20170245804A1Reduce the amount of calculationHigh precisionMedical simulationElectroencephalographyBrain sectionActivity measurement
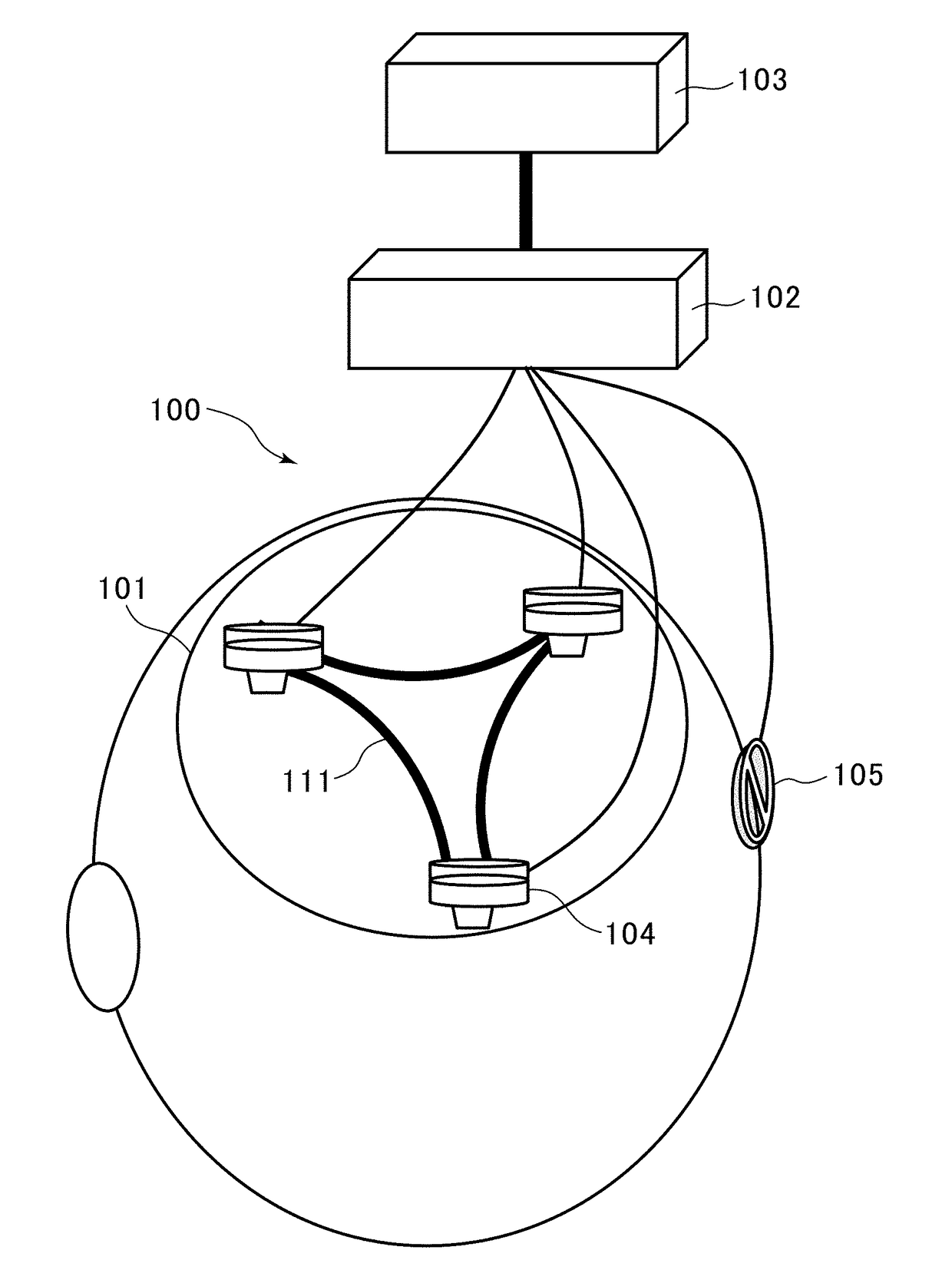
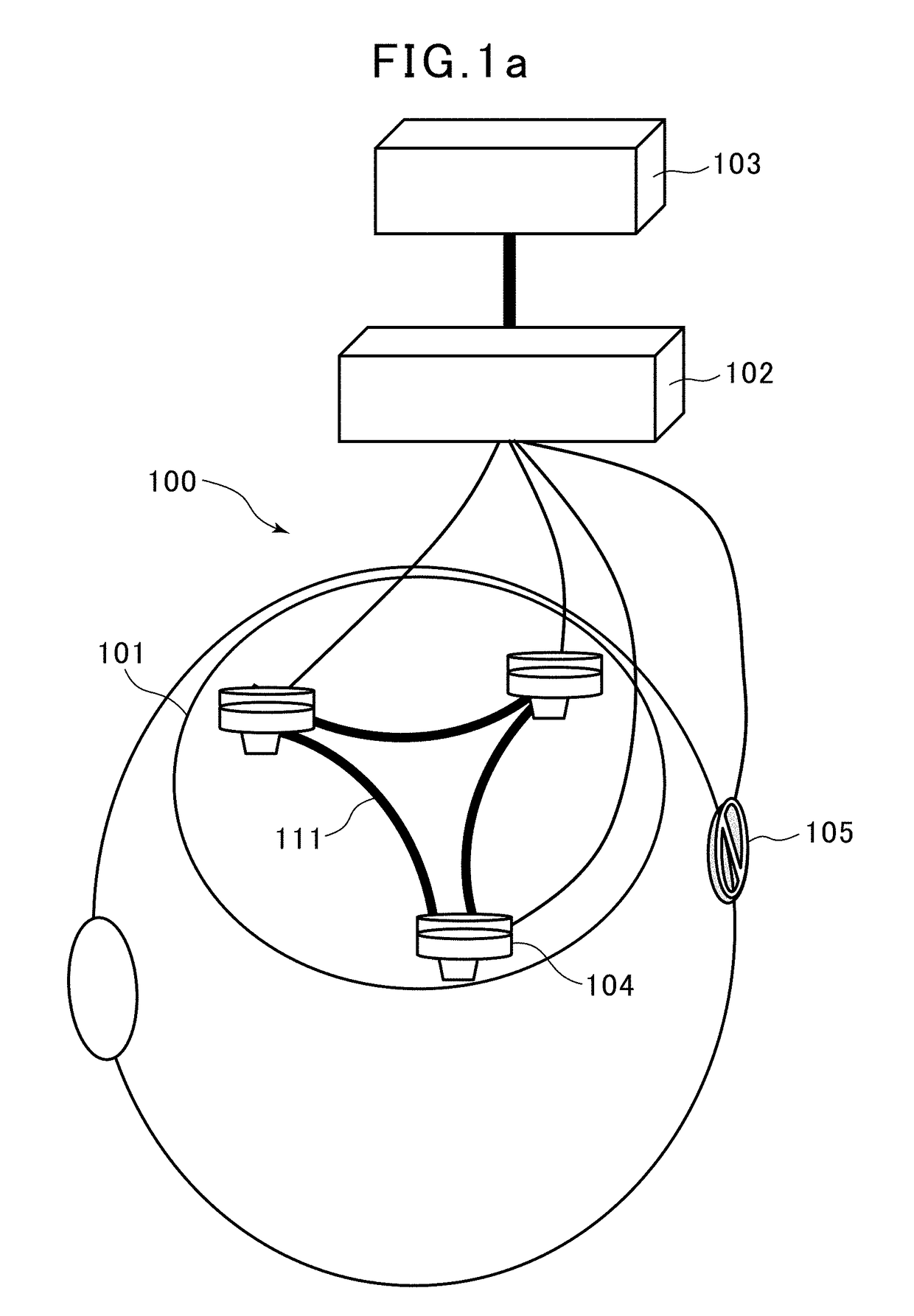
[Problem]It is intended to quantitatively evaluate deterioration in brain function associated with a disease such as dementia, with a high degree of accuracy by a simplified method using signals acquired from a few sensors arranged on the scalp.[Solution]The present invention relates to a brain activity measurement device comprising: a signal acquisition part configured to acquire a signal from a brain of the subject, using three sensors attached to different locations on the surface of the head of a subject; a data extraction part configured to extract, from each of the three signals acquired from respective ones of the sensors, a deep-brain potential signal having a specific frequency band arising from an activity of a deep brain region, and acquire data from the extracted deep-brain potential signal with a sampling period; a correlation value calculation part configured to calculate a correlation value indicative of a correlative relationship among the deep-brain potential signals acquired from each respective sensors, based on a phase relationship among three pieces of time-series data each extracted from the respective sensors by the data extraction part; and an index value calculation part configured to analyze the deep-brain potential signals from the deep brain region, based on the calculated correlation value, to calculate an index value for determining a brain function.
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com