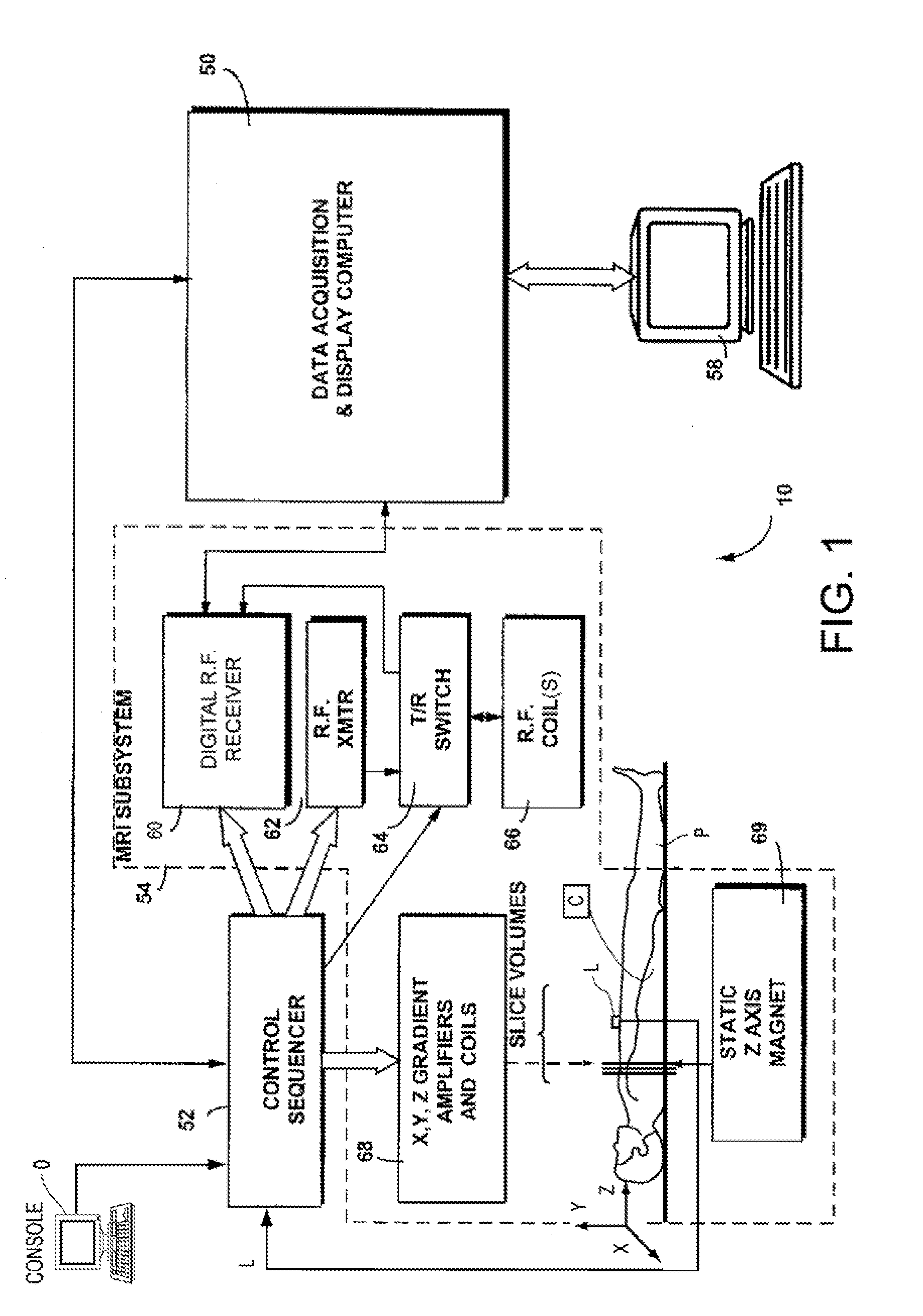
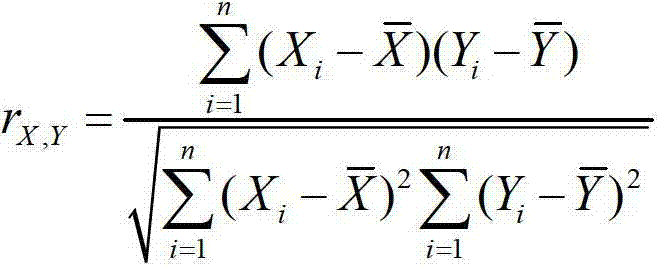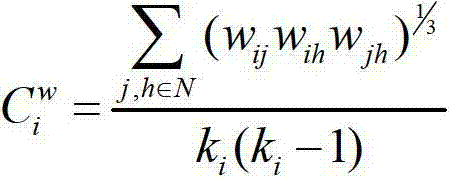Patents
Literature
256 results about "Functional magnetic resonance imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
<ul><li>fMRI is largely used in research but their clinical use is limited. It helps to learn how the diseased or injured brain is functioning. It is also used to assess effects of stroke, traumatic brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders.</li><li>The test is usually safe but should be avoided in pregnant women.</li><li>It is not performed in patients with certain metal implants such as ear implants, cardiac defibrillators, and pacemakers.</li></ul>
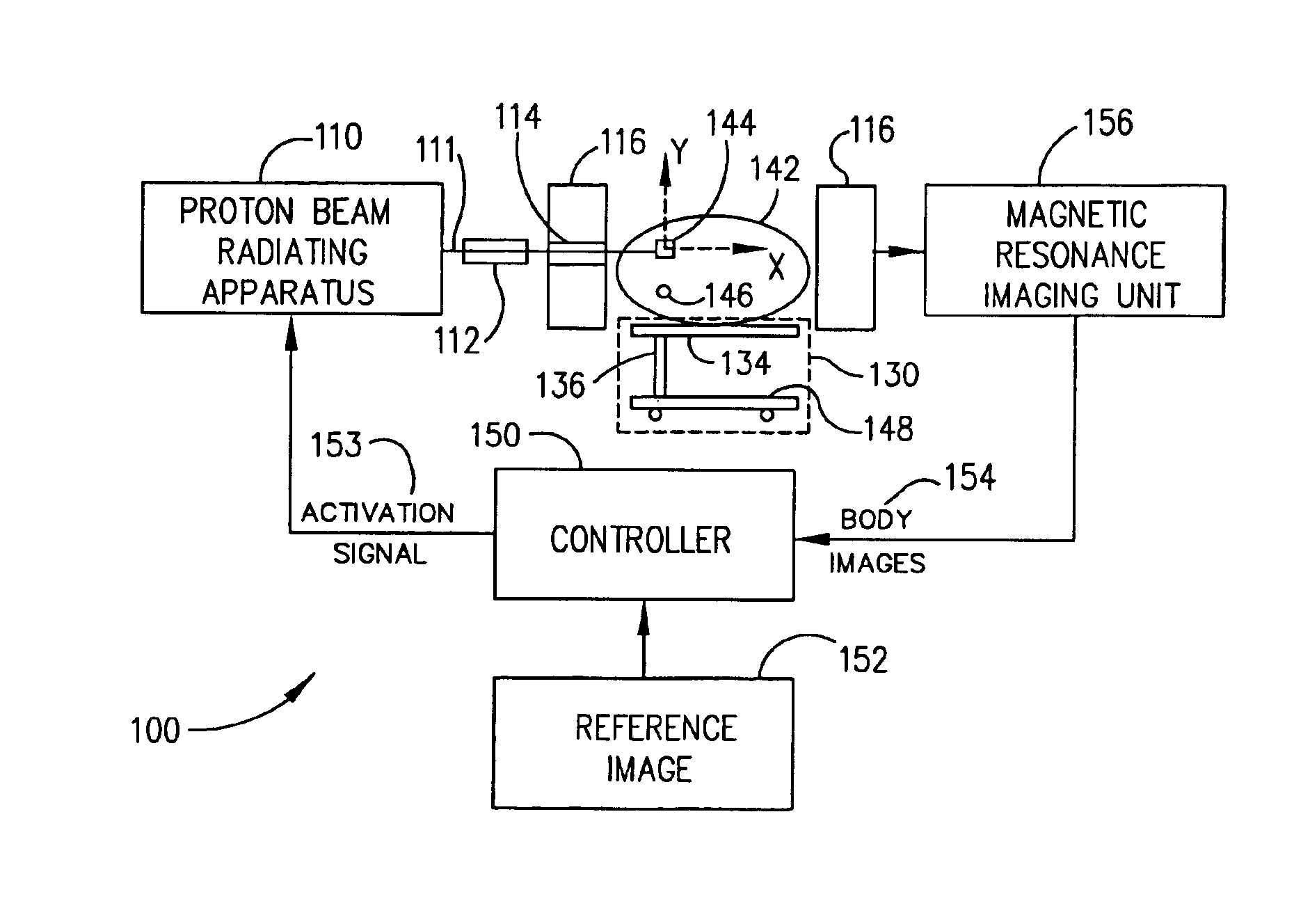
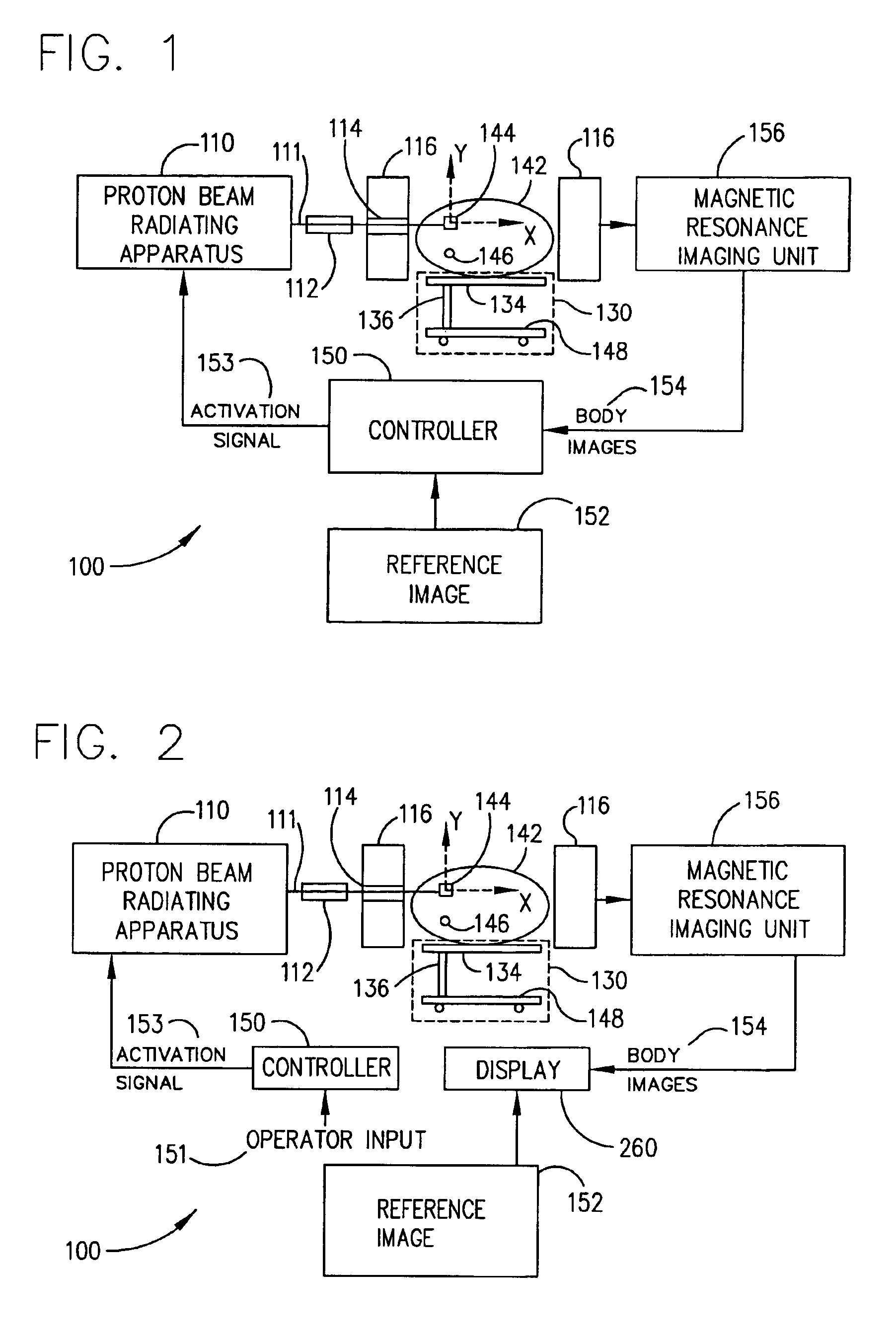
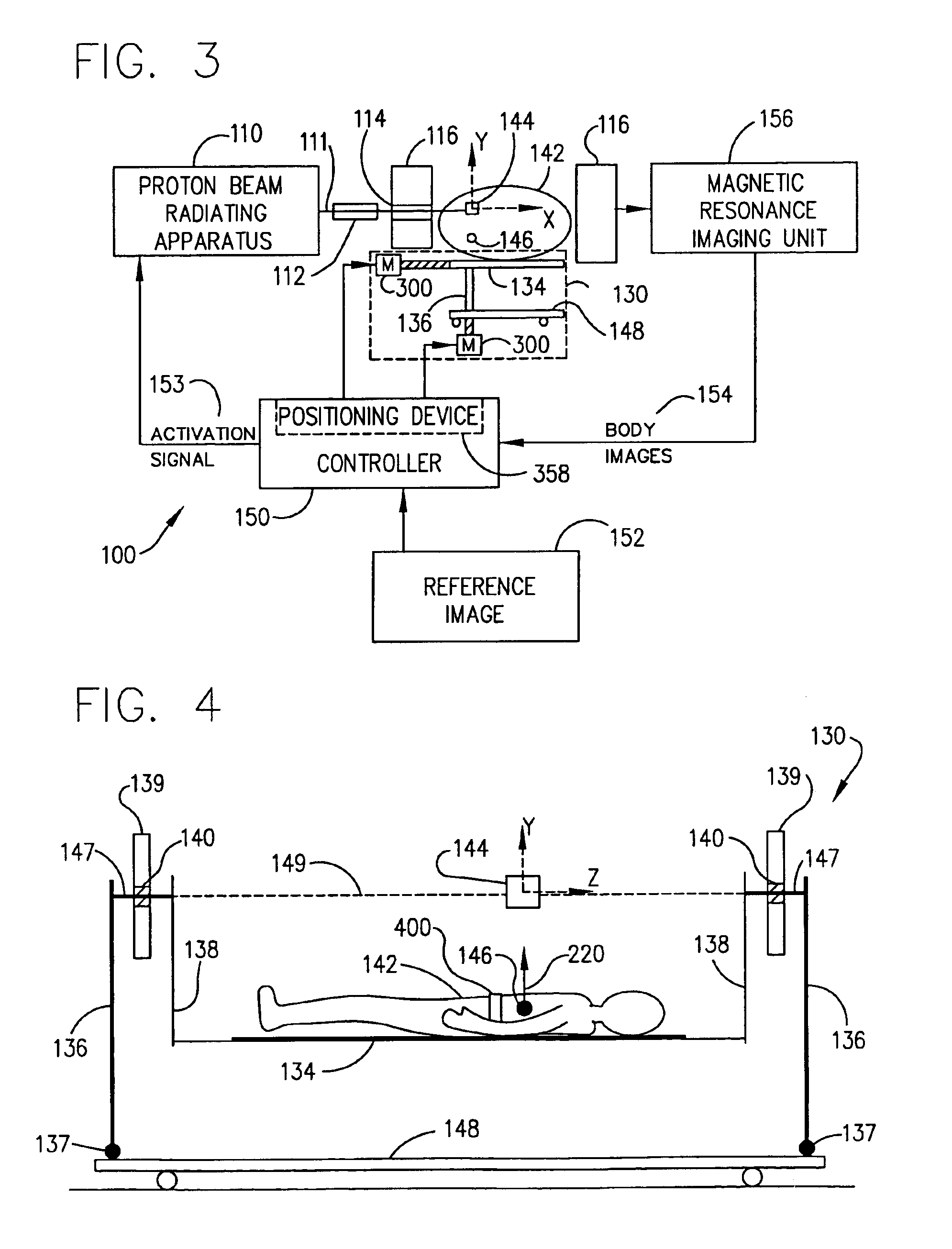
Method for combining proton beam irradiation and magnetic resonance imaging
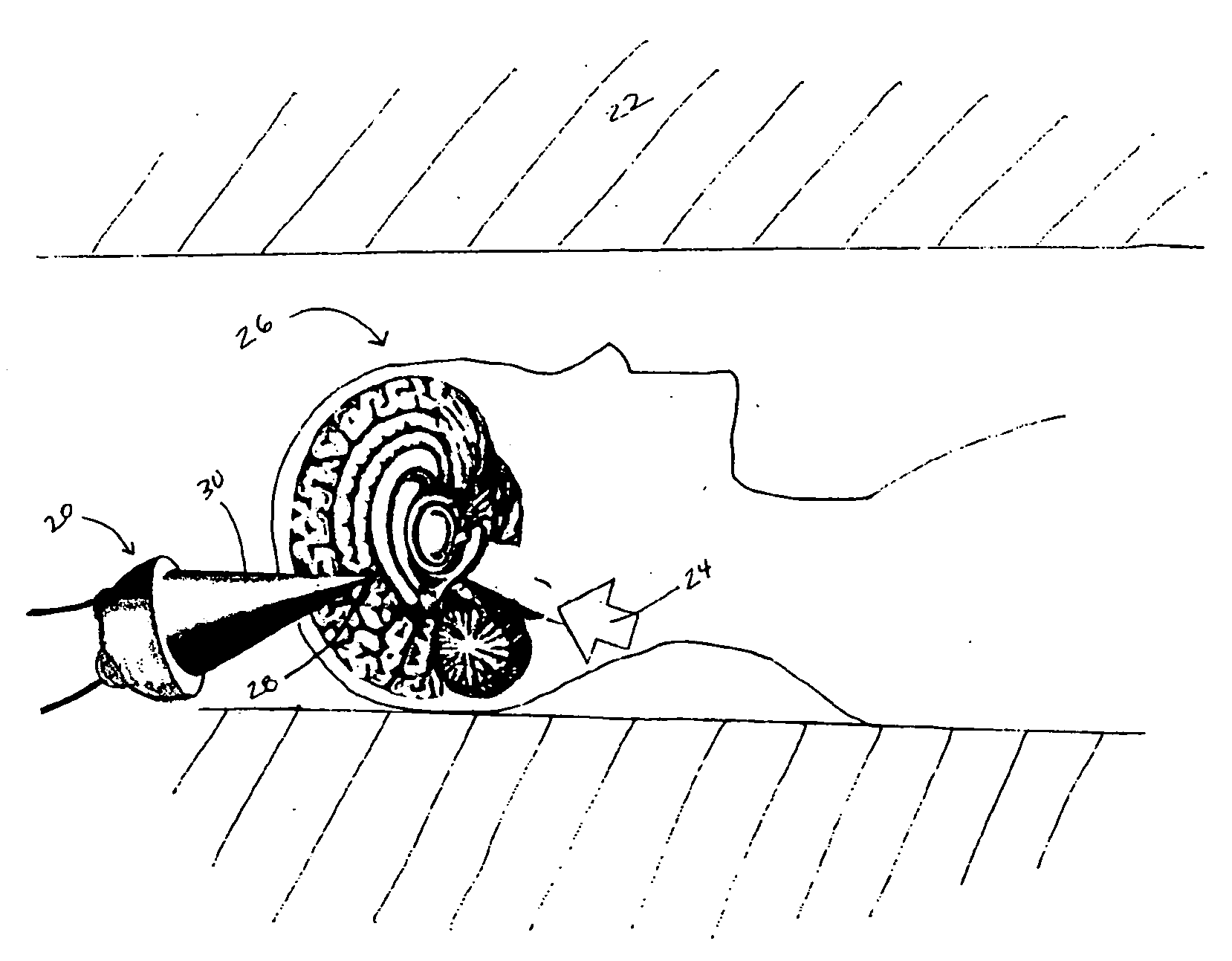
A method which coordinates proton beam irradiation with an open magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) unit to achieve near-simultaneous, noninvasive localization and radiotherapy of various cell lines in various anatomic locations. A reference image of the target aids in determining a treatment plan and repositioning the patient within the MRI unit for later treatments. The patient is located within the MRI unit so that the target and the proton beam are coincident. MRI monitors the location of the target. Target irradiation occurs when the target and the proton beam are coincident as indicated by the MRI monitoring. The patient rotates relative to the radiation source. The target again undergoes monitoring and selective irradiation. The rotation and selective irradiation during MRI monitoring repeats according to the treatment plan.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
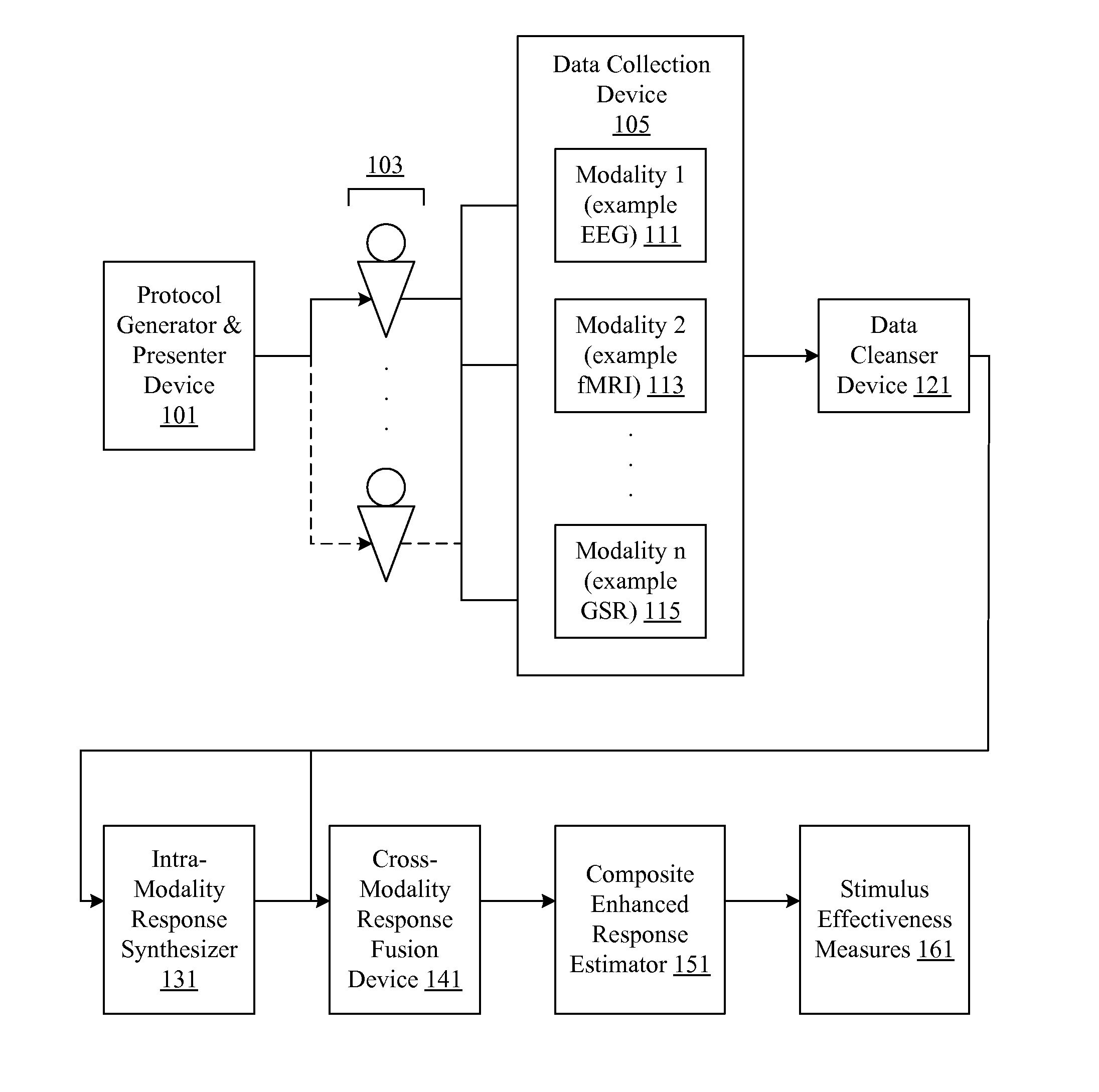
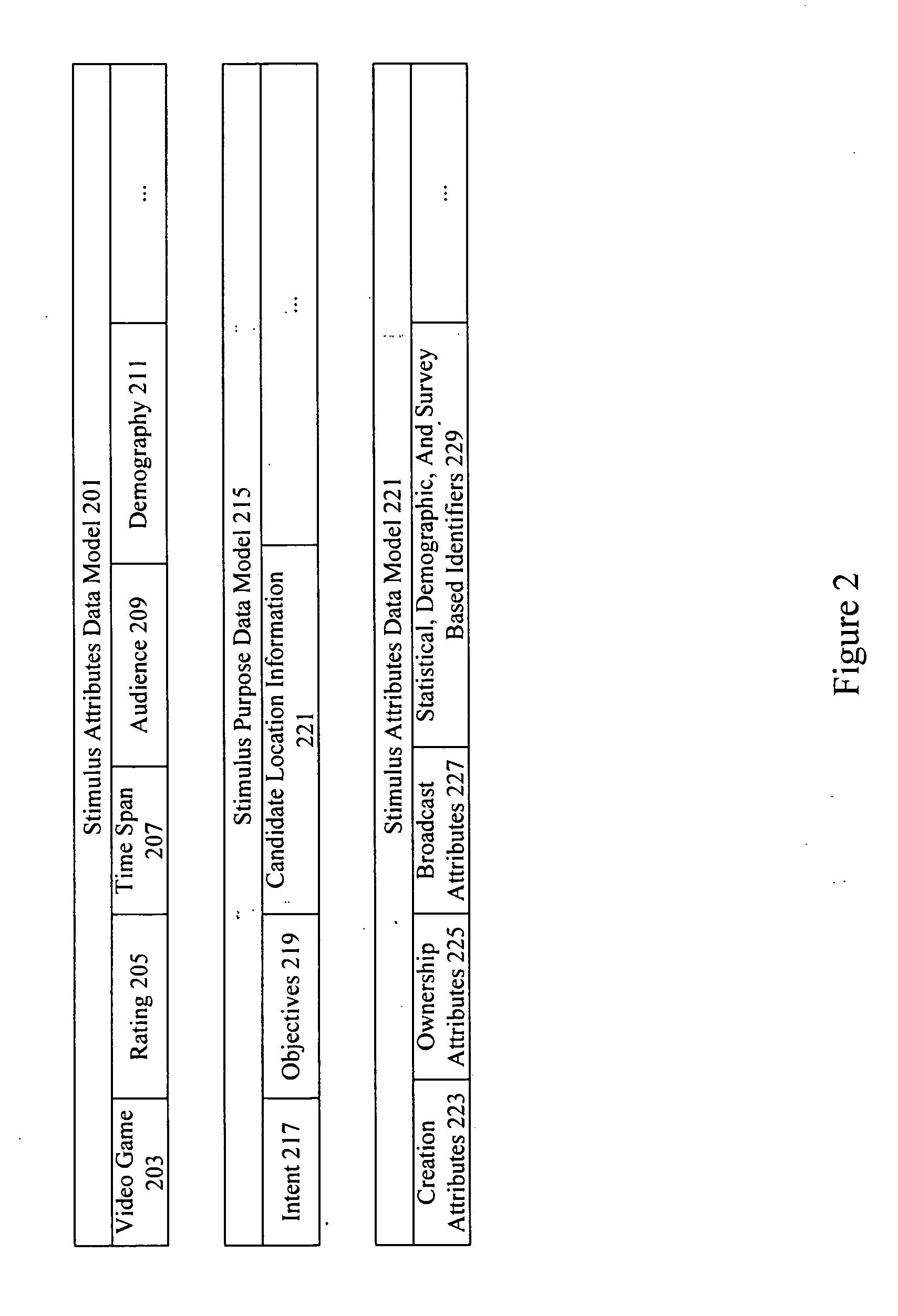
Audience response analysis using simultaneous electroencephalography (EEG) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (FMRI)
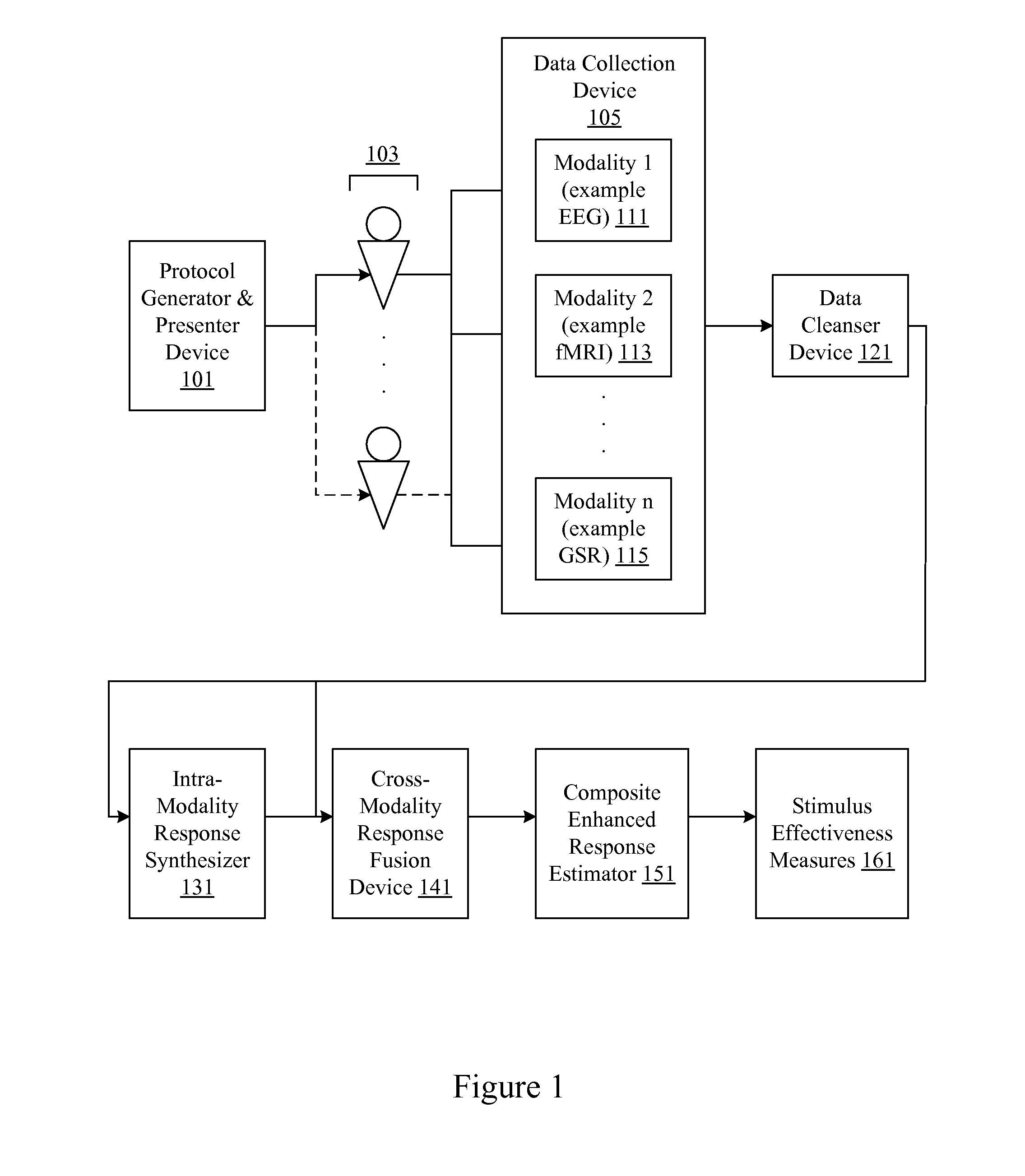
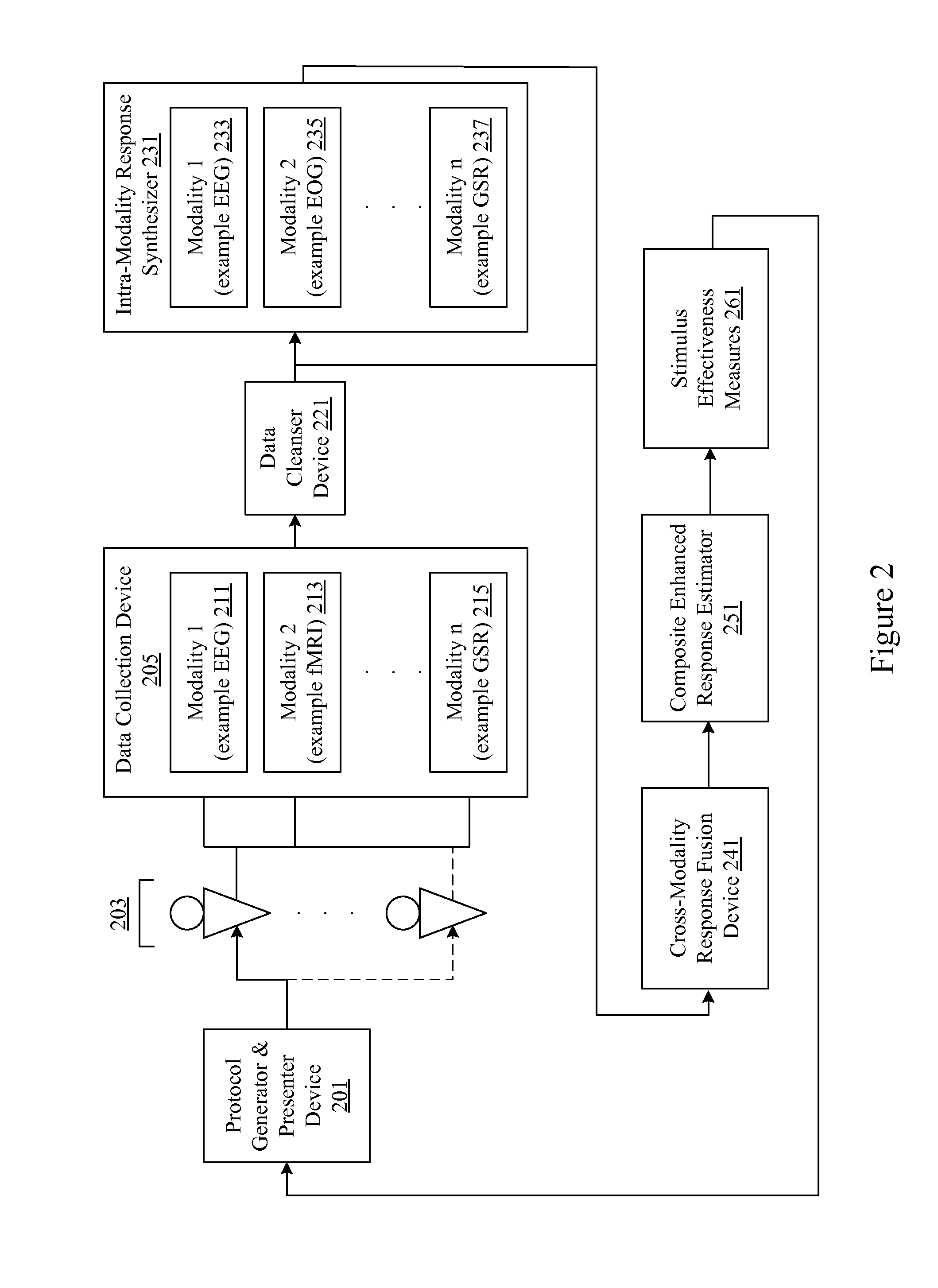
Neuro-response data including Electroencephalography (EEG), Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is filtered, analyzed, and combined to evaluate the effectiveness of stimulus materials such as marketing and entertainment materials. A data collection mechanism including multiple modalities such as, Electroencephalography (EEG), Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), Electrooculography (EOG), Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), etc., collects response data from subjects exposed to marketing and entertainment stimuli. A data cleanser mechanism filters the response data and removes cross-modality interference.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
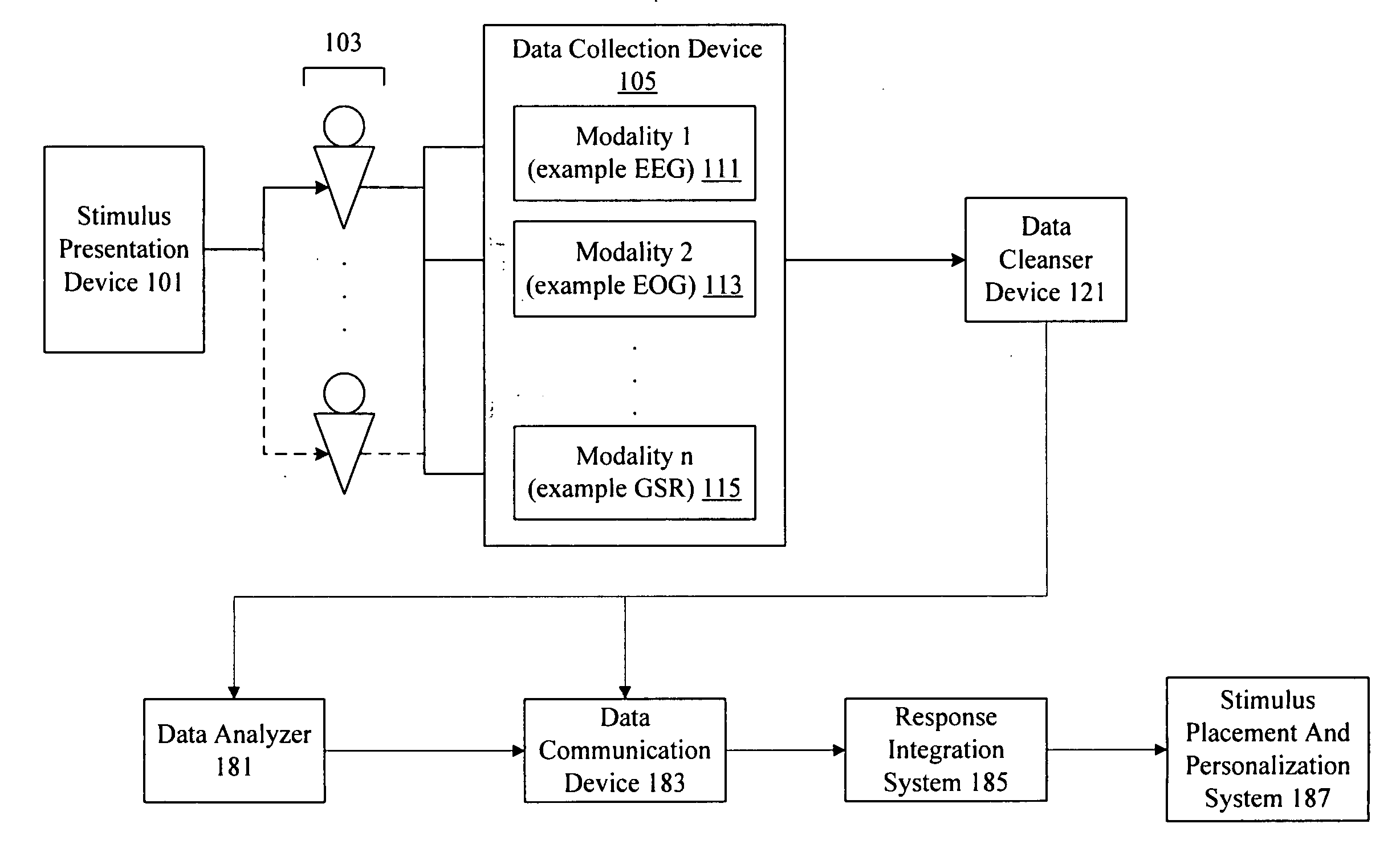
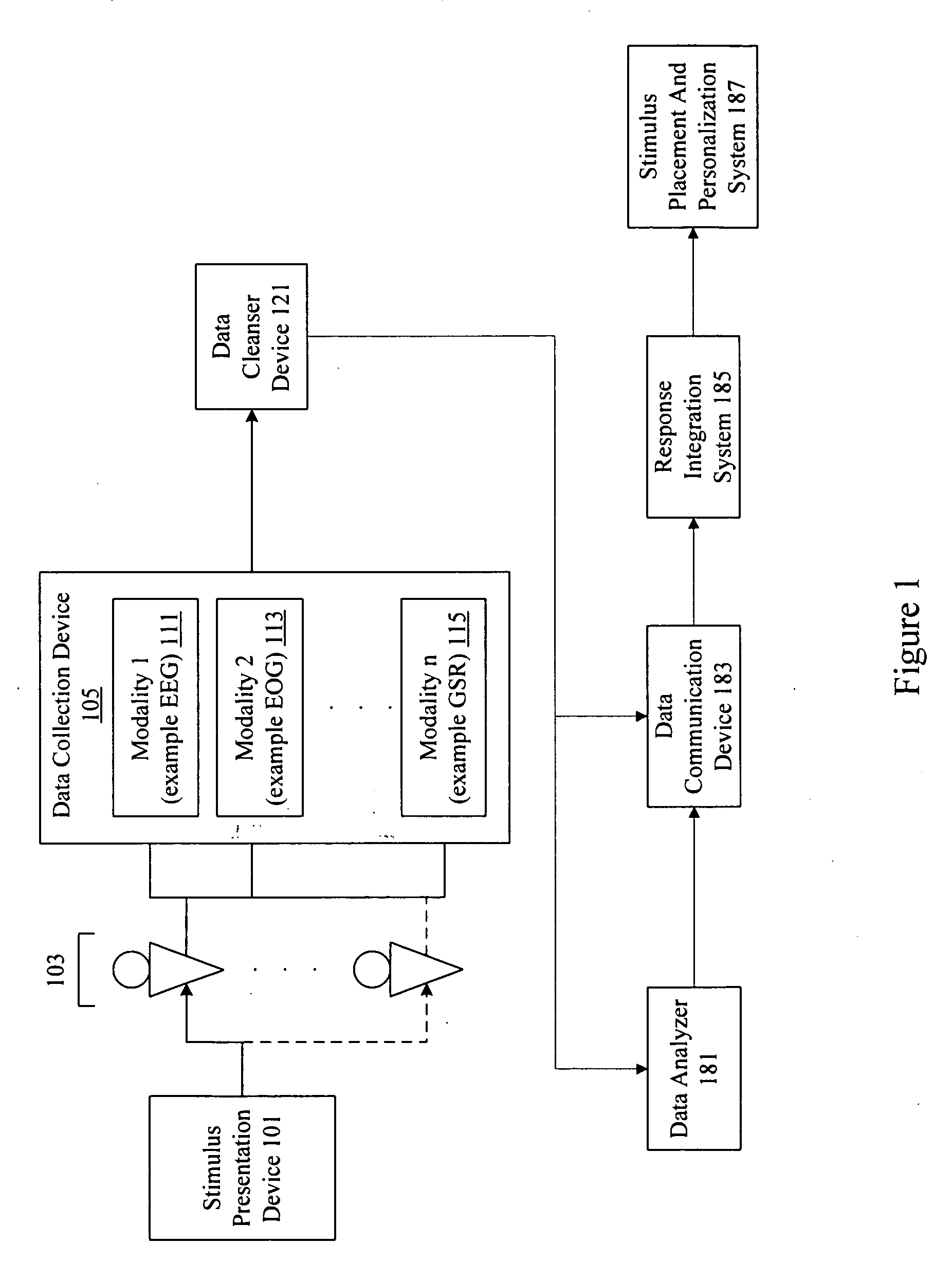
Personalized stimulus placement in video games
A system analyzes neuro-response measurements from subjects exposed to video games to identify neurologically salient locations for inclusion of stimulus material and personalized stimulus material such as video streams, advertisements, messages, product offers, purchase offers, etc. Examples of neuro-response measurements include Electroencephalography (EEG), optical imaging, and functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), eye tracking, and facial emotion encoding measurements.
Owner:THE NIELSEN CO (US) LLC
Methods for modifying electrical currents in neuronal circuits
InactiveUS20070299370A1Change propertiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyBrain circuitNeuronal circuits
Disclosed herein are methods for modifying electrical currents in brain circuits through the simultaneous use of focused ultrasound pulse (FUP) and an existing brain-imaging system, such as a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) system. The methods are used for research, treatment and diagnosis of psychiatric, neurological, and neuroendocrine disorders whose biological mechanisms include brain circuits. The methods include the simultaneous steps of applying FUP to a live neuronal circuit within a brain and monitoring a brain image produced by a brain imaging system during the application of FUP.
Owner:BRAINSONIX CORP
Rapid magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography of multiple anatomical territories
InactiveUS6493571B1Reduce osmotic pressureHigh resolutionBedsDiagnostic recording/measuringIodinated Contrast AgentSingle injection
A procedure and apparatus are provided which allow rapid positional change in the patient centering in order to facilitate the imaging of blood vessels in a series of different views. This procedure and apparatus can also facilitate the imaging of other tissues of the body at different spatial locations as well. The procedure and apparatus reduce the time required for obtaining the necessary images for a medical imaging examination using a single injection of an MRI or iodinated contrast agent.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
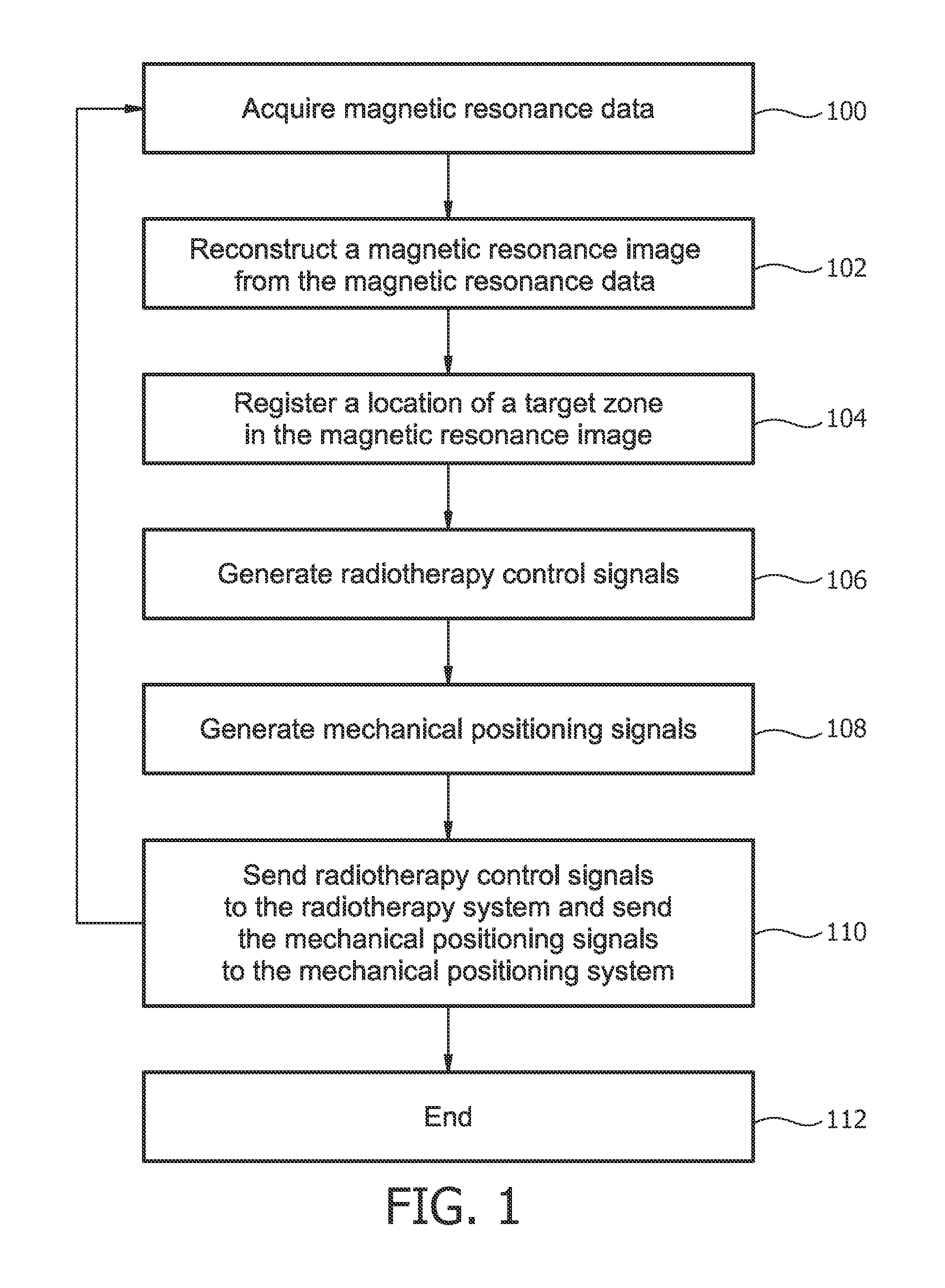
Therapeutic apparatus comprising a radiotherapy apparatus, a mechanical positioning system, and a magnetic resonance imaging system
ActiveUS20130261430A1Accurate directionHigh resolutionSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringControl signalResonance
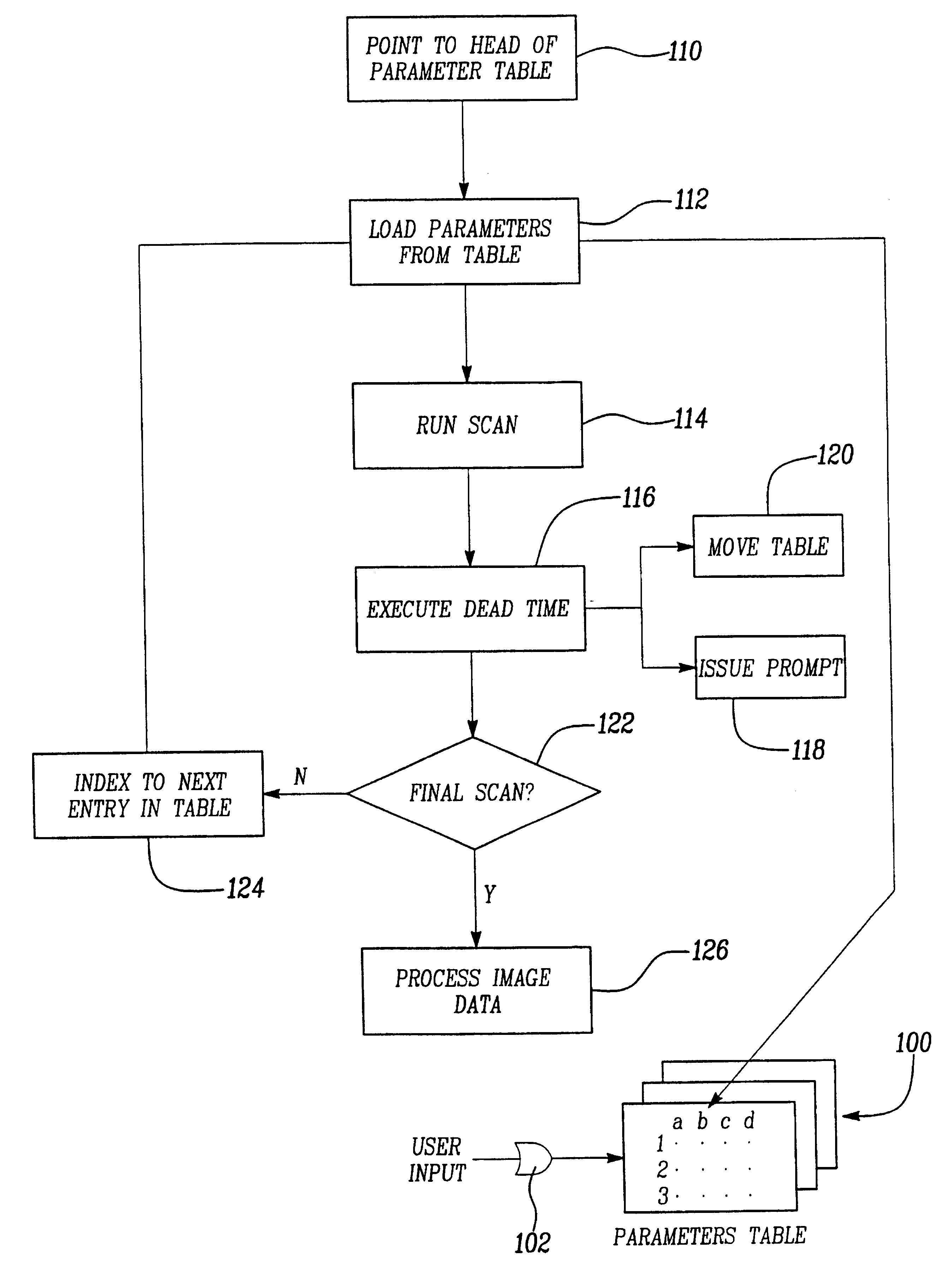
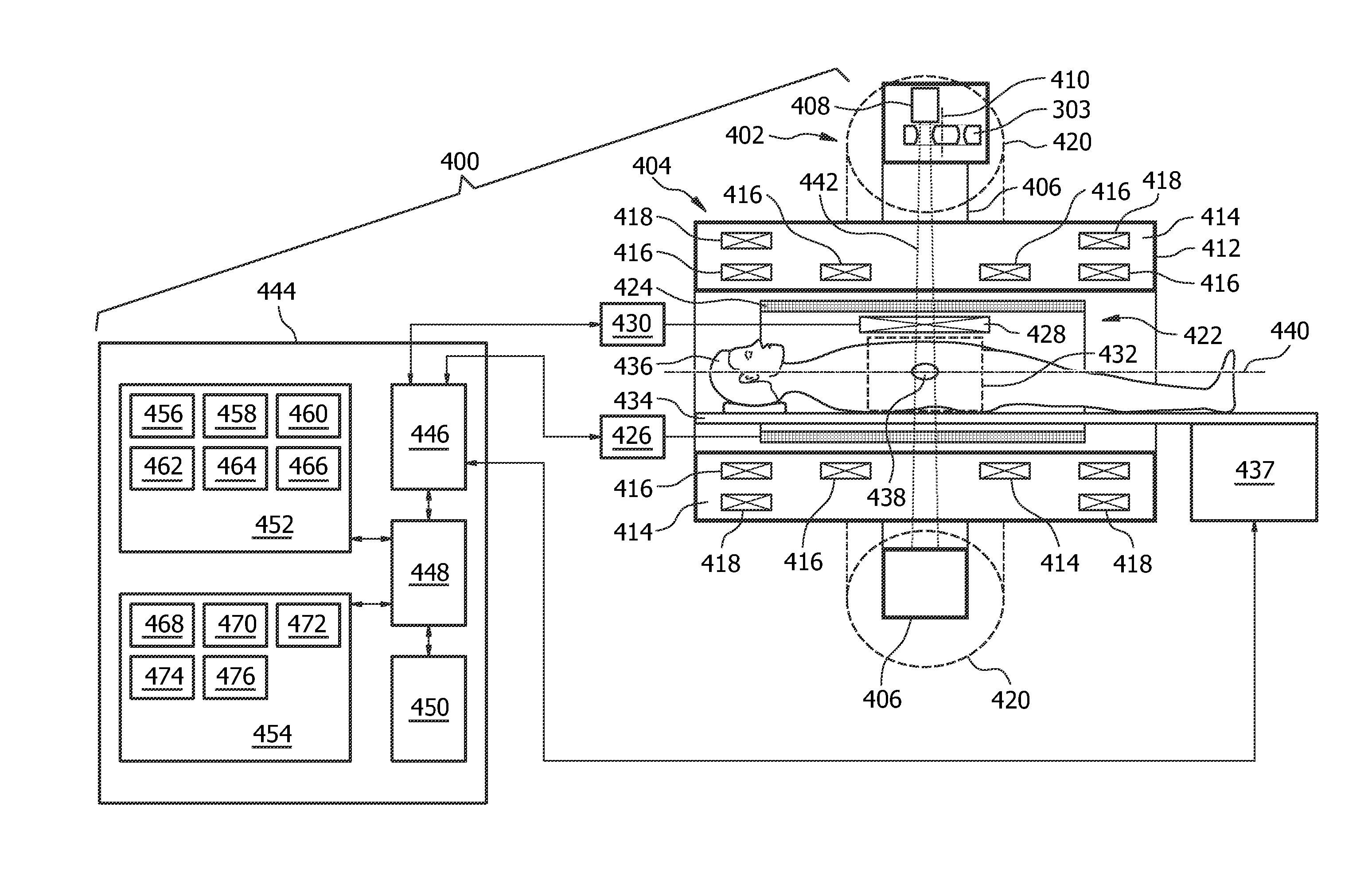
A therapeutic apparatus (400, 500) comprising a radiotherapy apparatus (402), a mechanical positioning system, and a magnetic resonance imaging system (404). The radiotherapy apparatus comprises a radiotherapy source (408). The radiotherapy apparatus is adapted for rotating the radiotherapy source at least partially around a subject support. The therapeutic apparatus further comprises a memory containing machine executable instructions (468, 470, 472, 474, 476). Execution of the instructions causes a processor to repeatedly: acquire (100) the magnetic resonance data using the magnetic resonance imaging system; reconstruct (102) a magnetic resonance image (460) from the magnetic resonance data; register (104) a location (462) of the target zone in the magnetic resonance image; generate (106) radiotherapy control signals (464) in accordance with the location of the registered target zone; generate (108) mechanical positioning control signals (466) in accordance with the registered target zone and the radiotherapy control signals; and send (110) the radiotherapy control signals to the radiotherapy system and send (110) the mechanical positioning control signals to the mechanical positioning system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
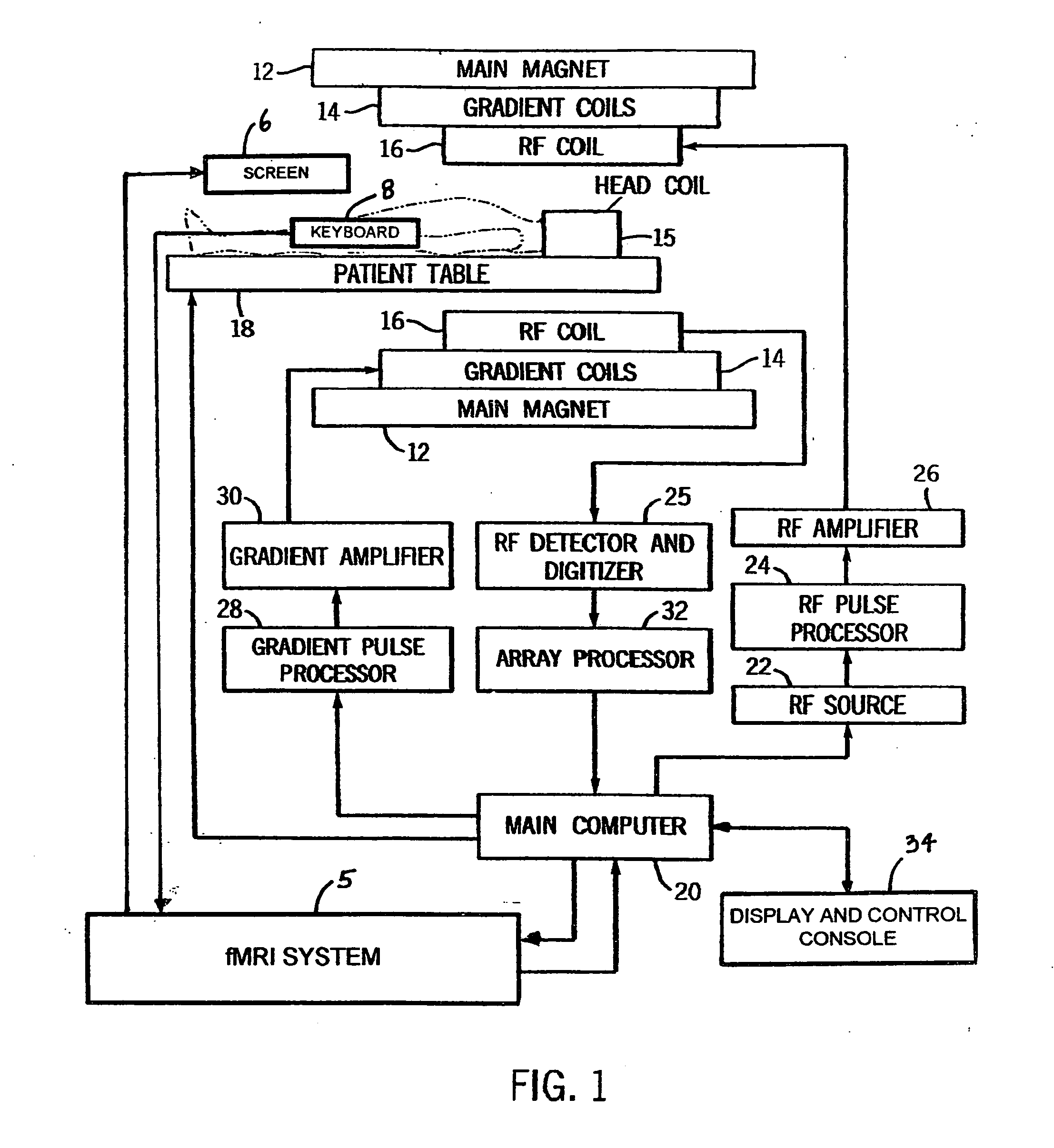
fMRI system for use in assessing the efficacy of therapies in treating CNS disorders
InactiveUS20050107682A1High level of sensitivityStrong specificityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseMedicine
A system for assessing the medical effectiveness of therapies such as pharmaceutical medications for use in treating central nervous system disorders. Functional magnetic resonance imaging techniques are utilized in measuring neural activity induced by specific activation tasks in specific regions of the brain that are known to be affected by a central nervous system disorder. The levels of neural activity induced in patients subject to the disorder when on and off of the therapy are compared and then compared with normative data generated with respect to healthy individuals under comparable conditions. These comparisons quantify and assess the efficacy of the therapy.
Owner:RAO STEPHEN M +1
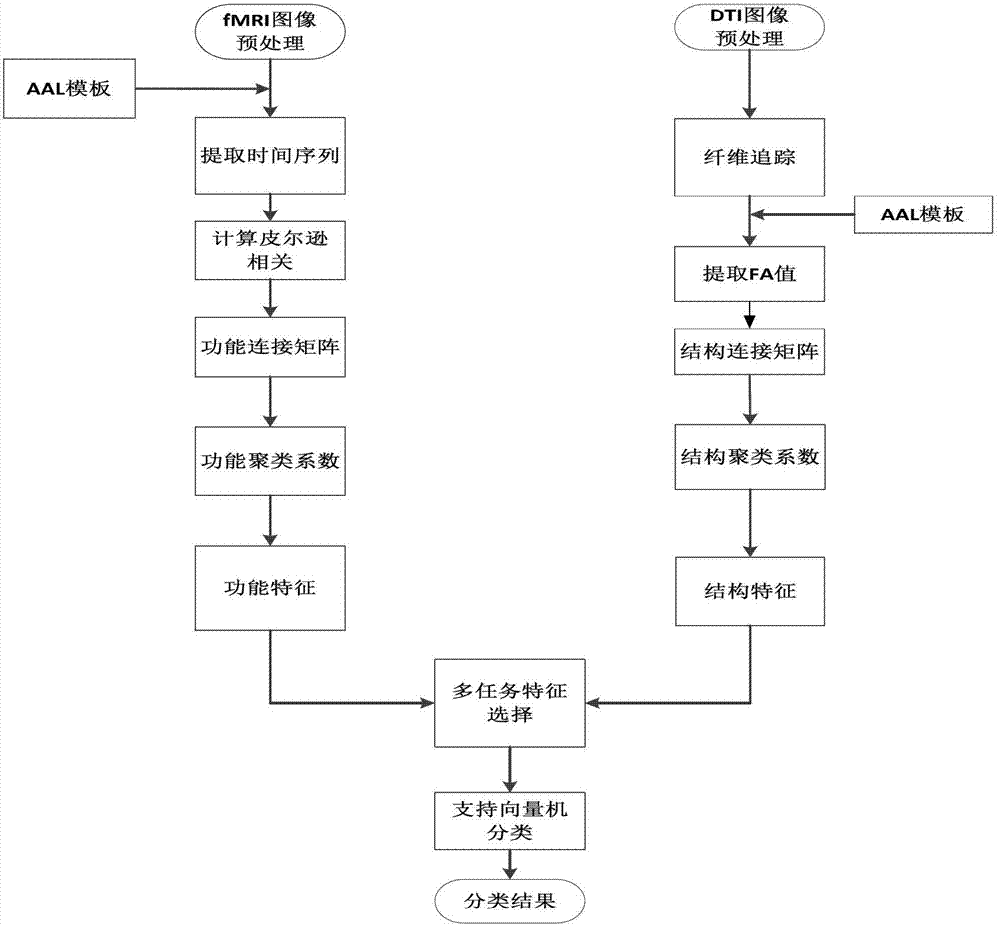
Multimodal brain network feature fusion method based on multi-task learning
InactiveCN103093087ACustomer Service RelevanceImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsFiberDiagnostic Radiology Modality
The invention discloses a multimodal brain network feature fusion method based on multi-task learning, and the multimodal brain network feature fusion method based on the multi-task learning includes the steps of preprocessing the obtained functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) images and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) images, registrating the preprocessed fMRI image to the standard AAL template, carrying out a fiber tracking for preprocessed DTI images, calculating fiber anisotropy (FA) value, and constructing structure connection matrix through the AAL template. Clustering coefficient of each brain area in a function connection matrix and the structure connection matrix is calculated to be regarded as function features and structure features. As two different tasks, the function features and the structure features assess an optimal feature set by solving the problem of multi-task learning optimization. The method uses information with multiple modalities complementing each other to learn simultaneously and to classify, improves the classification accuracy, solves the problems that a single task feature does not consider the correlation between features, and the fact that only one modality feature is used for pattern classification can bring to insufficient amount of information.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Evaluation of Alzheimer's disease using an independent component analysis of an individual's resting-state functional MRI
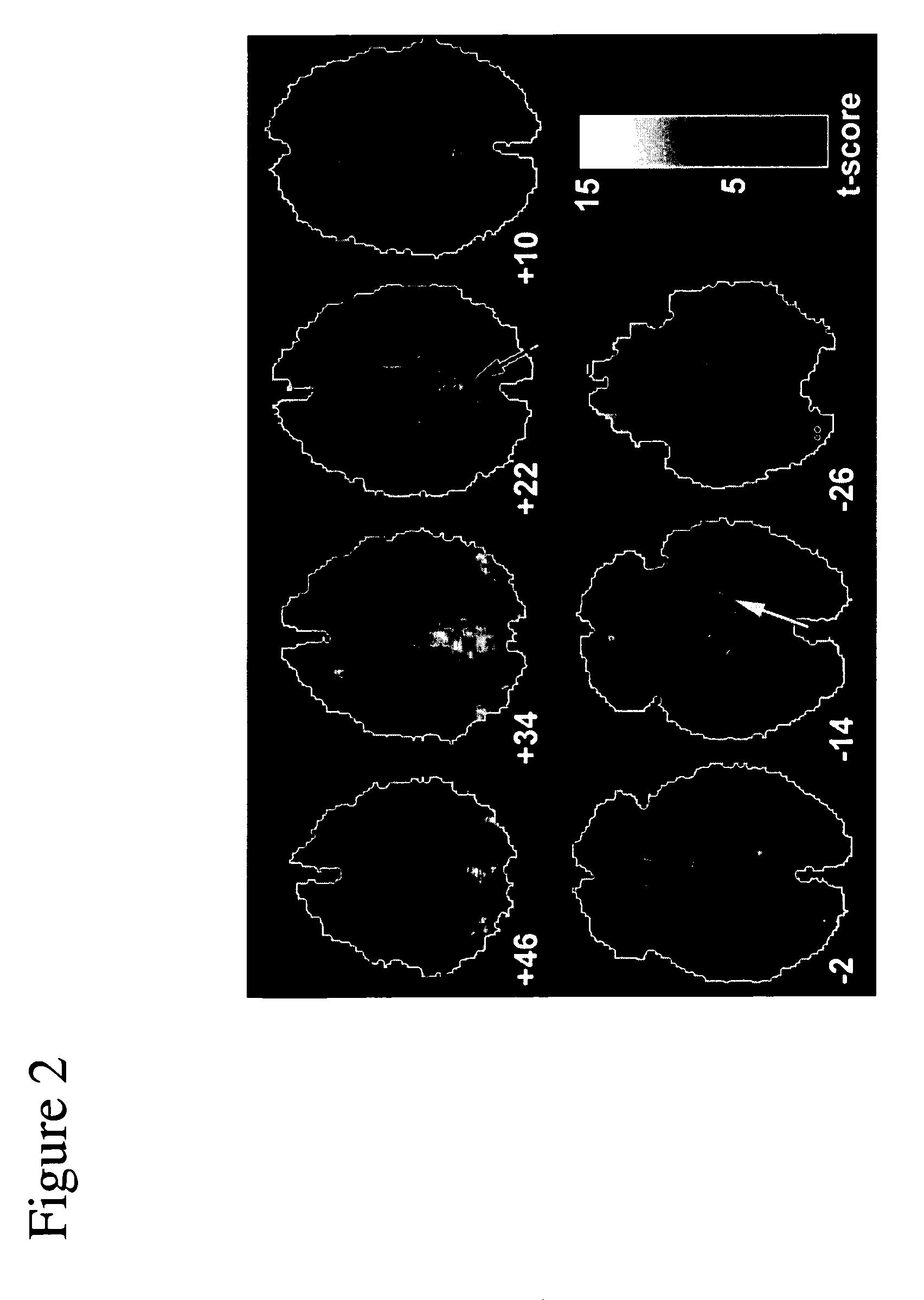
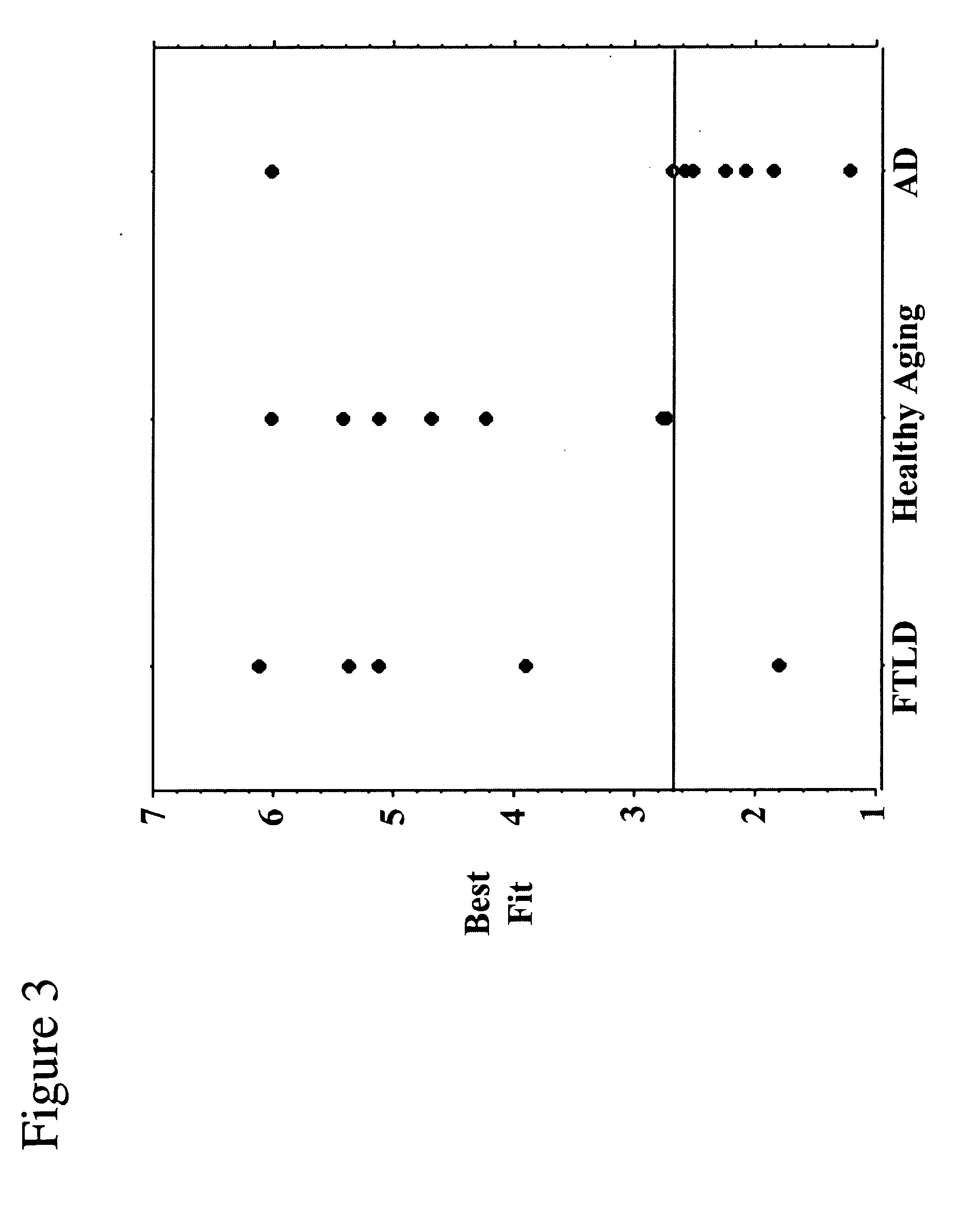
InactiveUS20050215884A1More automatedMore objectiveDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseFunctional methods
A clinically valuable method is provided for evaluating the onset or progression of Alzheimer's disease using a non-invasive biomarker obtained from an independent component analysis (ICA) of an individual's resting state functional MRI. The method is relatively more automated and objective than previous methods and exploits dysfunctional connectivity across an entire network of brain regions in Alzheimer's disease. It eliminates the need for investigator's intervention as much as possible and is more robust than structural and functional methods targeting the hippocampus.
Owner:GREICIUS MICHAEL D +2
Catheter electrode that can simultaneously emit electrical energy and facilitate visualization by magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20090171187A1Reduce in quantityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEngineeringConductive materials
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Multi-modal imaging of blood flow
ActiveUS20130144140A1Improved and non-invasive measurement of blood flow and blood volumeLow costDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterData setImaging data
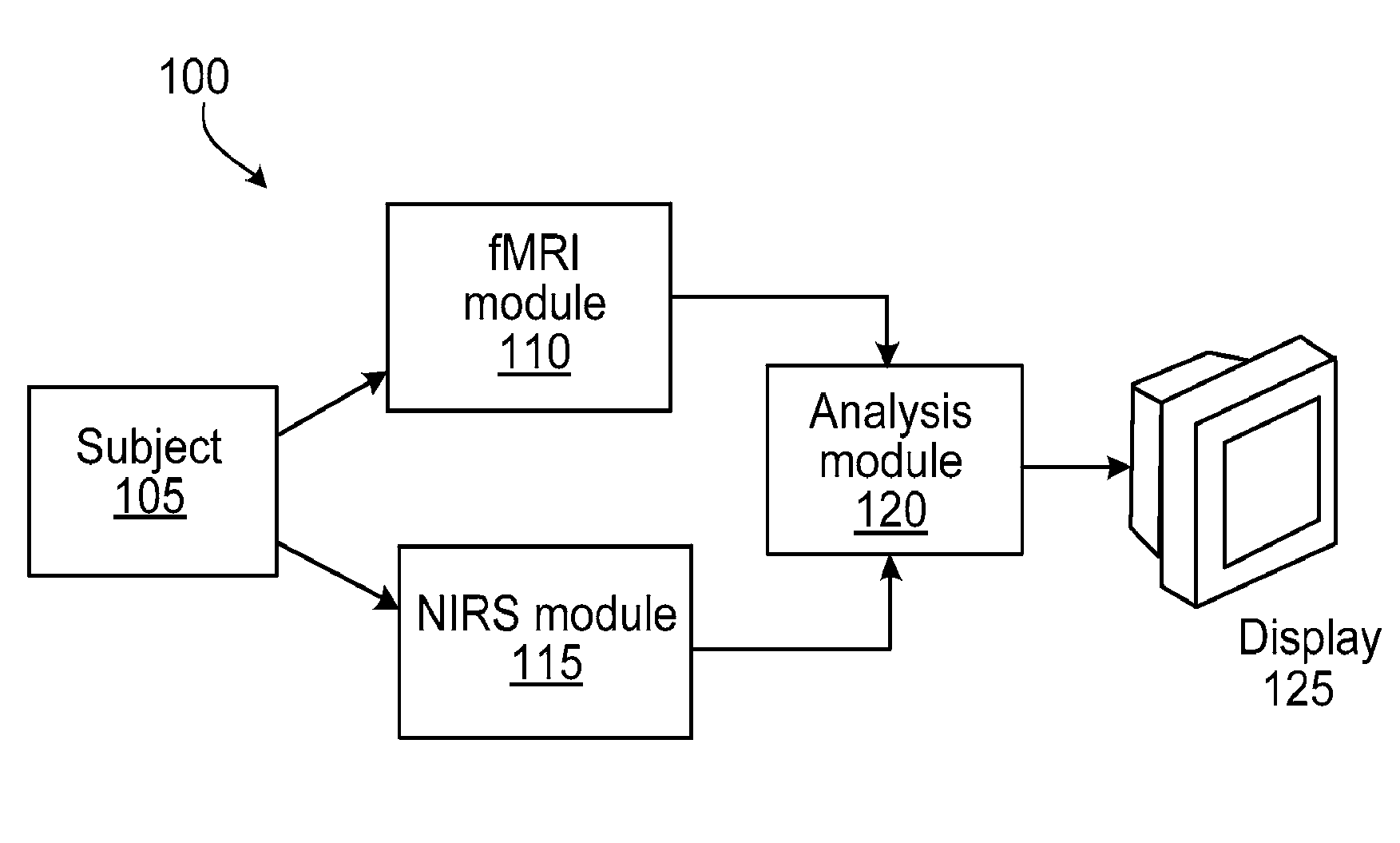
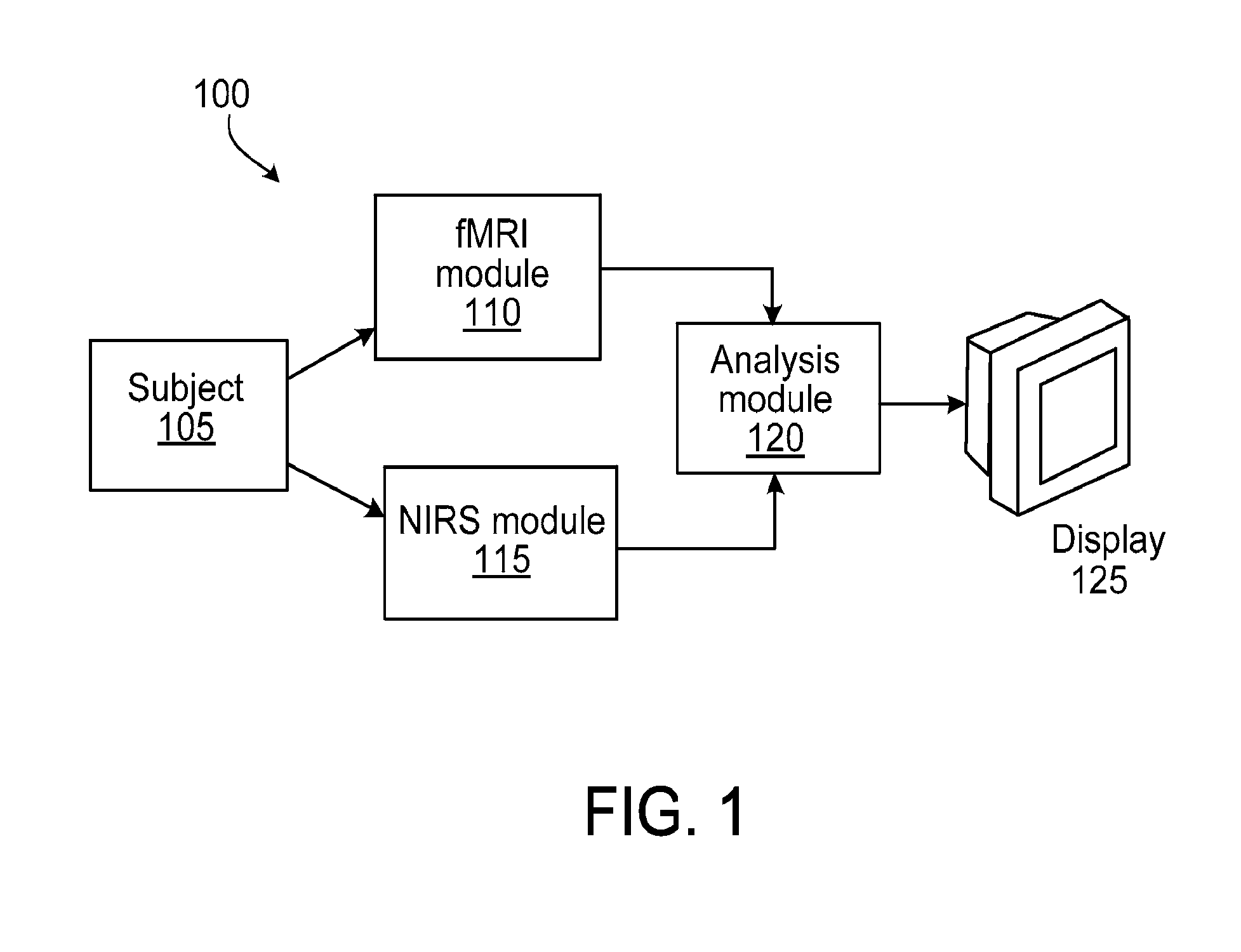
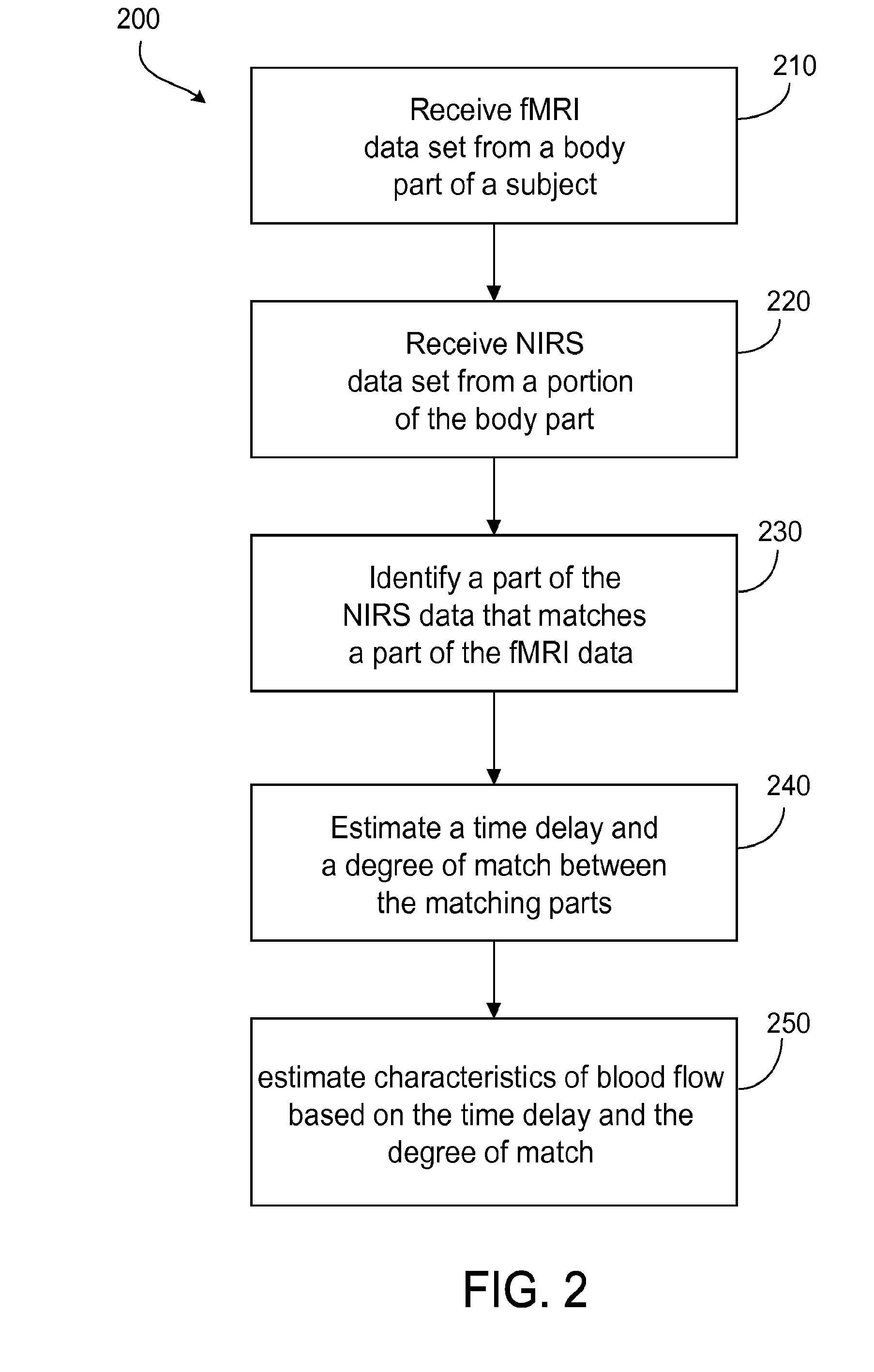
The application features methods, devices, and systems for measuring blood flow in a subject. The computer-implemented methods include receiving functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data that provides information on at least one of volume or oxygenation of blood at one or more locations in a body over a first predetermined length of time. The methods also include receiving near-infrared spectroscopic (NIRS) imaging or measurement data representing at least one of blood concentration or oxygenation at a first portion of the body over a second predetermined length of time. The methods further include deriving, from the fMRI data corresponding to a second portion of the body, a time varying data set representing changes in blood oxygenation or volume or both blood oxygenation and volume at the second portion over the first predetermined length of time and determining, by a computing device, a time delay and a value of a similarity metric corresponding to a part of the spectroscopic imaging data that most closely matches the time varying data set. The time delay represents a difference between a first time in which blood flows from a third portion in the body to the first portion and a second time in which blood flows to the second portion from the third portion. The value of the similarity metric represents an amount of blood at the second portion. An estimate of a characteristic of at least one of blood flow or blood volume in the second portion at a given time is determined based on the time delay and the value of the similarity metric.
Owner:THE MCLEAN HOSPITAL CORP
System and method to analyze blood parameters using magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20100030062A1Accurate measurementClear attributionMagnetic measurementsSensorsVascular compartmentCerebral metabolic rate
A system and method for accurately producing MR images of selected vascular compartments includes employing a control scan and a tag scan, each including velocity selective modules that suppress signal from blood flowing faster than a given cutoff velocity, to acquire control and tag sets of NMR data that may be subtracted to produce a compartment-specific MR image that is substantially free of information from stationary tissues and blood outside the selective vascular compartments. Accordingly, physiological parameters, such as oxygen saturation (SaO2), oxygen extraction fraction (OEF), and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2), can be generated from the compartment-specific images. Further still, kinetic curves of oxygen exchange can be created, thus providing detailed insight into oxygen exchange dynamics.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for preparing brain tissue and vascular entity composite model based on MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CTA (CT angiography)
InactiveCN108210072AHigh degree of simulationReduce the risk of surgeryAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputerised tomographsHead and neckImaging data
The invention discloses a method for preparing brain tissue and vascular entity composite model based on MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CTA (CT angiography). The method includes: 1), acquiring image data of head and neck skull, brain tissue, vessel and arterial aneurysm; 2), leading acquired MRI and CTA original image data into three-dimensional reconstruction software, structuring a 3D composite virtual model containing the skull, brain tissue, vessel and arterial aneurysm and outputting to a 3D printer for 3D model printing in a format that the 3D printer can print to acquire the three-dimensional entity composite model containing the skull, brain tissue, vessel and arterial aneurysm. The model is quite high in simulation degree, so that doctors can perform preoperative discussionof surgical planning, preoperative risk assessment and design of operative route or even simulate operation in combination with the model; the brain tissue model is of fluid silicone brain tissue thatcan be pulled apart and can be pulled apart as in actual operation, so that the doctors are more confident, and operation risks are lowered.
Owner:扈玉华
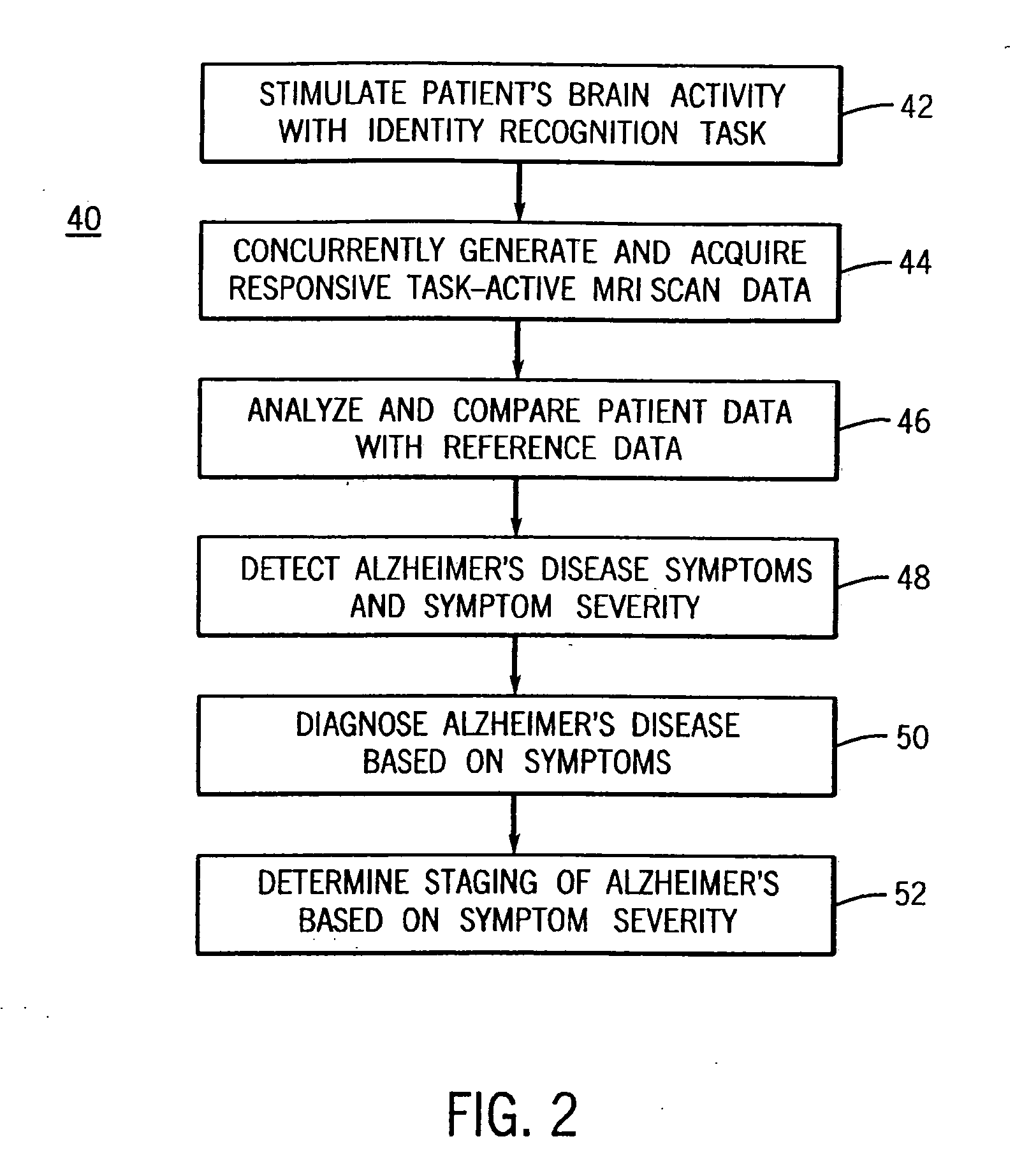
System for detecting symptoms, determining staging and gauging drug efficacy in cases of Alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20050197560A1Accurate diagnosisEfficient and consistent and reliable mannerMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringIdentity recognitionPatients symptoms
A system for using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) for detecting symptoms indicative of Alzheimer's disease, diagnosing Alzheimer's disease and gauging the efficacy of medications used in treating Alzheimer's disease. The system includes steps involving activating a selected region of the brain which may be affected by Alzheimer's disease using an identity recognition type task, concurrently acquiring task-active MRI data responsive to the task, comparing the patient's task-active MRI data to reference data derived from a database of task-active data from healthy individuals and detecting whether the patient has symptoms related to Alzheimer's disease. The severity of the patient's symptoms and the staging of the disease may also be determined. Also, a medication may be administered to the patient and the efficacy of the medication may be gauged based on the severity of the patient's symptoms.
Owner:RAO STEPHEN M +1
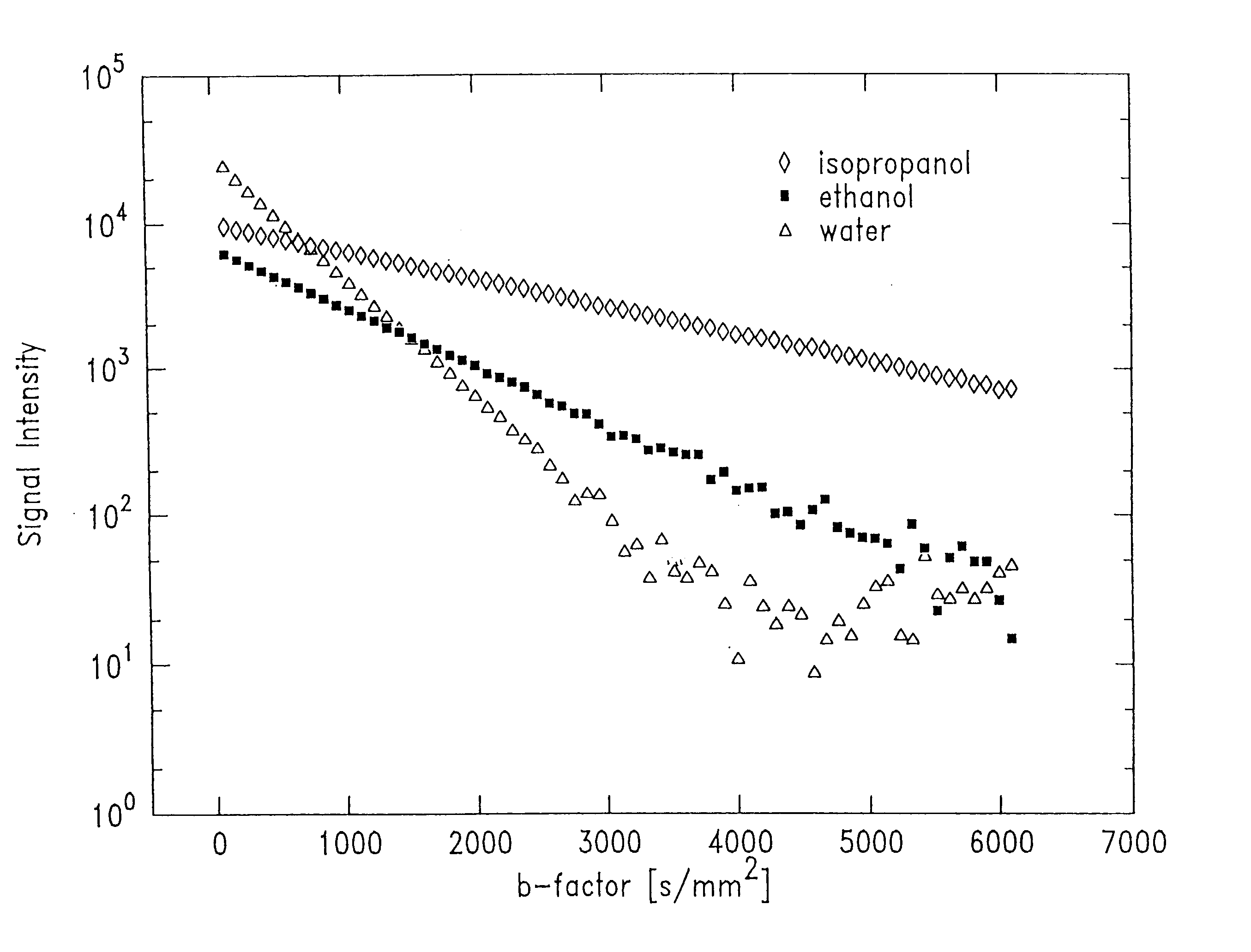
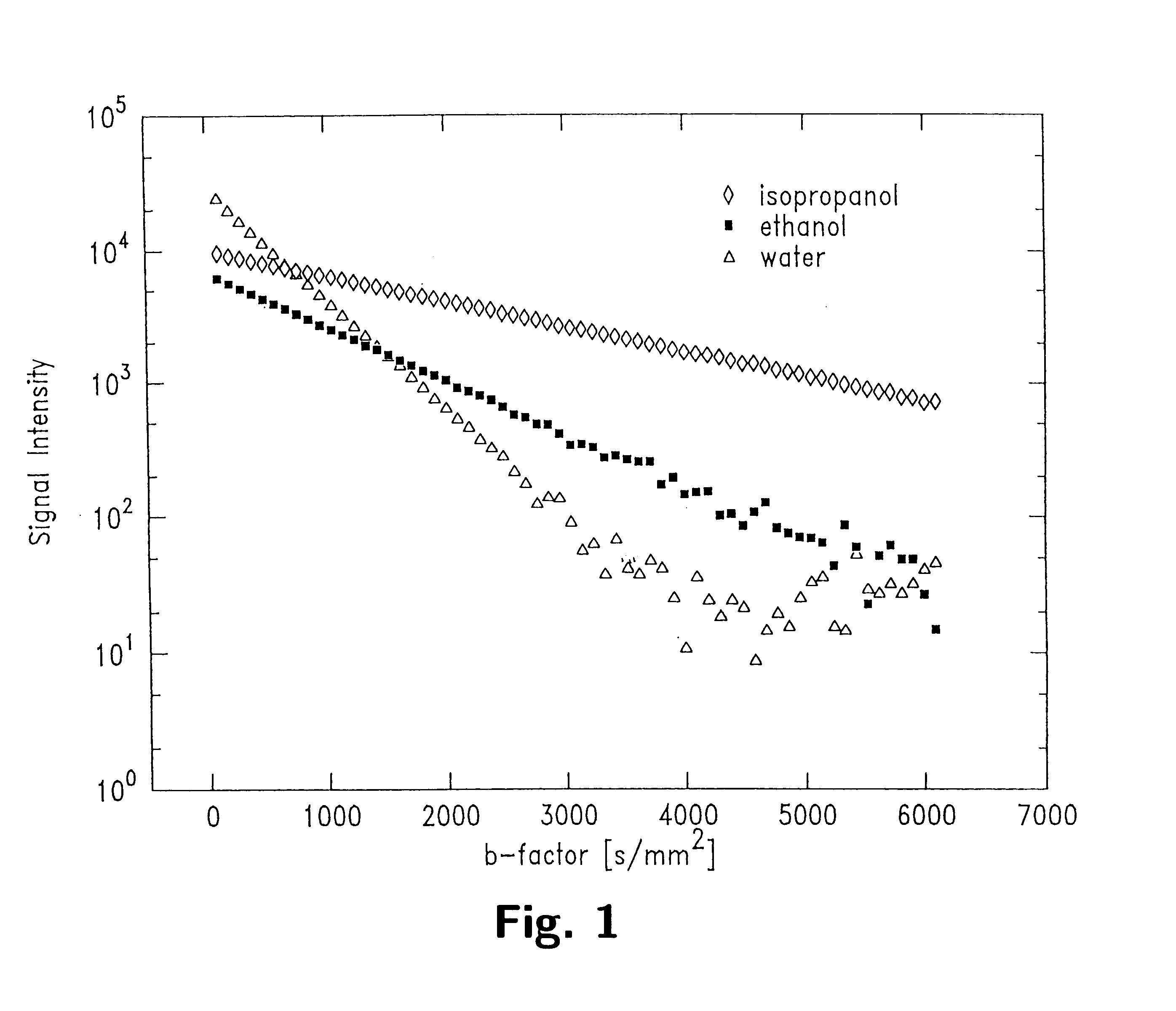
Method of fast and reliable tissue differentiation using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6751495B2Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsB factorTissues types
Quantified differences, such as chi<2 >error parameters, between a mono-exponential, logarithmic best fit of a series of line scan diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance signals taken over a range of b-factors between about 100 and about 5000 sec / mm<2 >are obtained. The quantified differences so generated are displayed as an image wherein the brightness of each pixel depends upon the size of its associated quantified difference. The resulting image is characterized by high signal to noise ratio and distinctness between varying tissue types.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
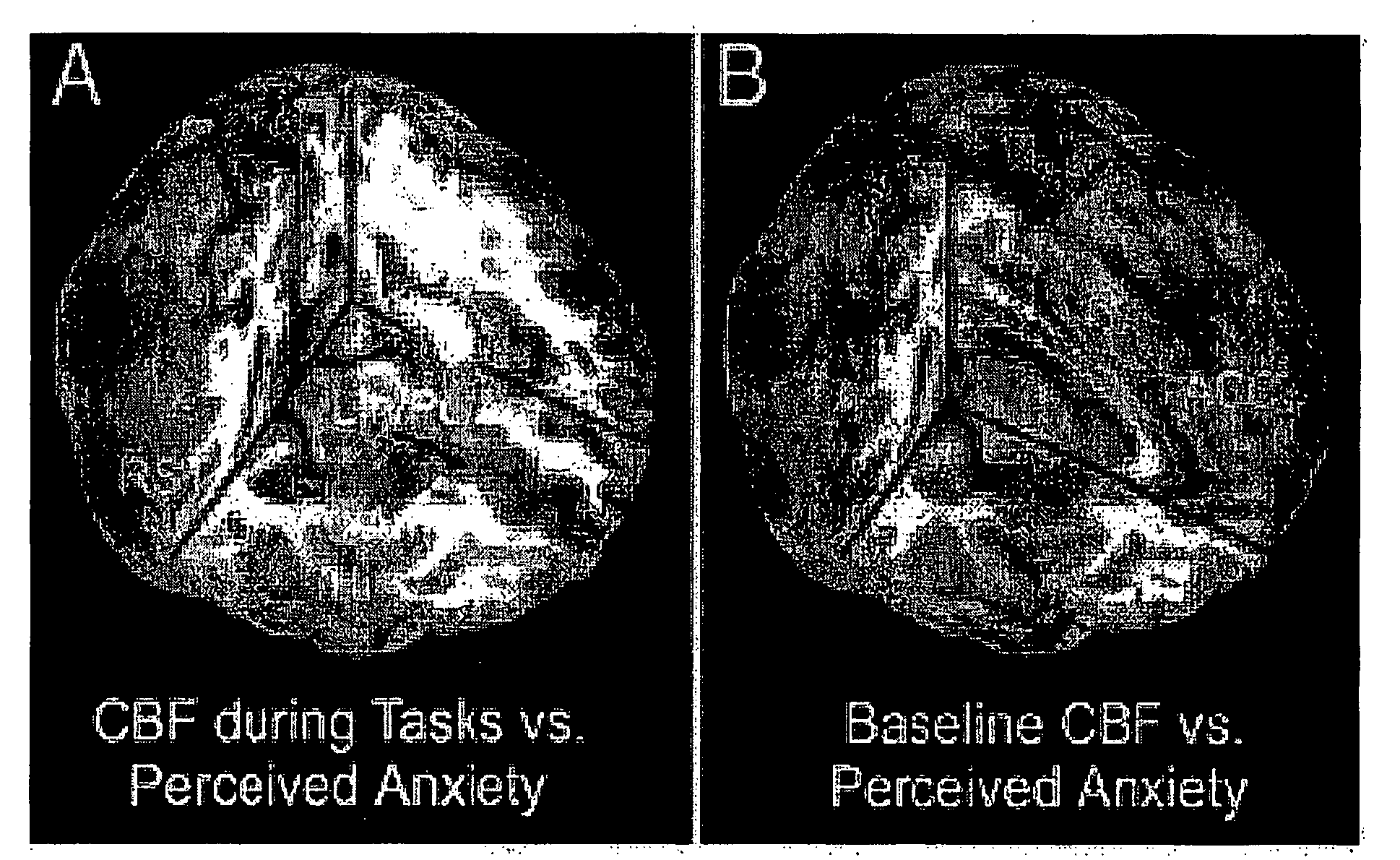
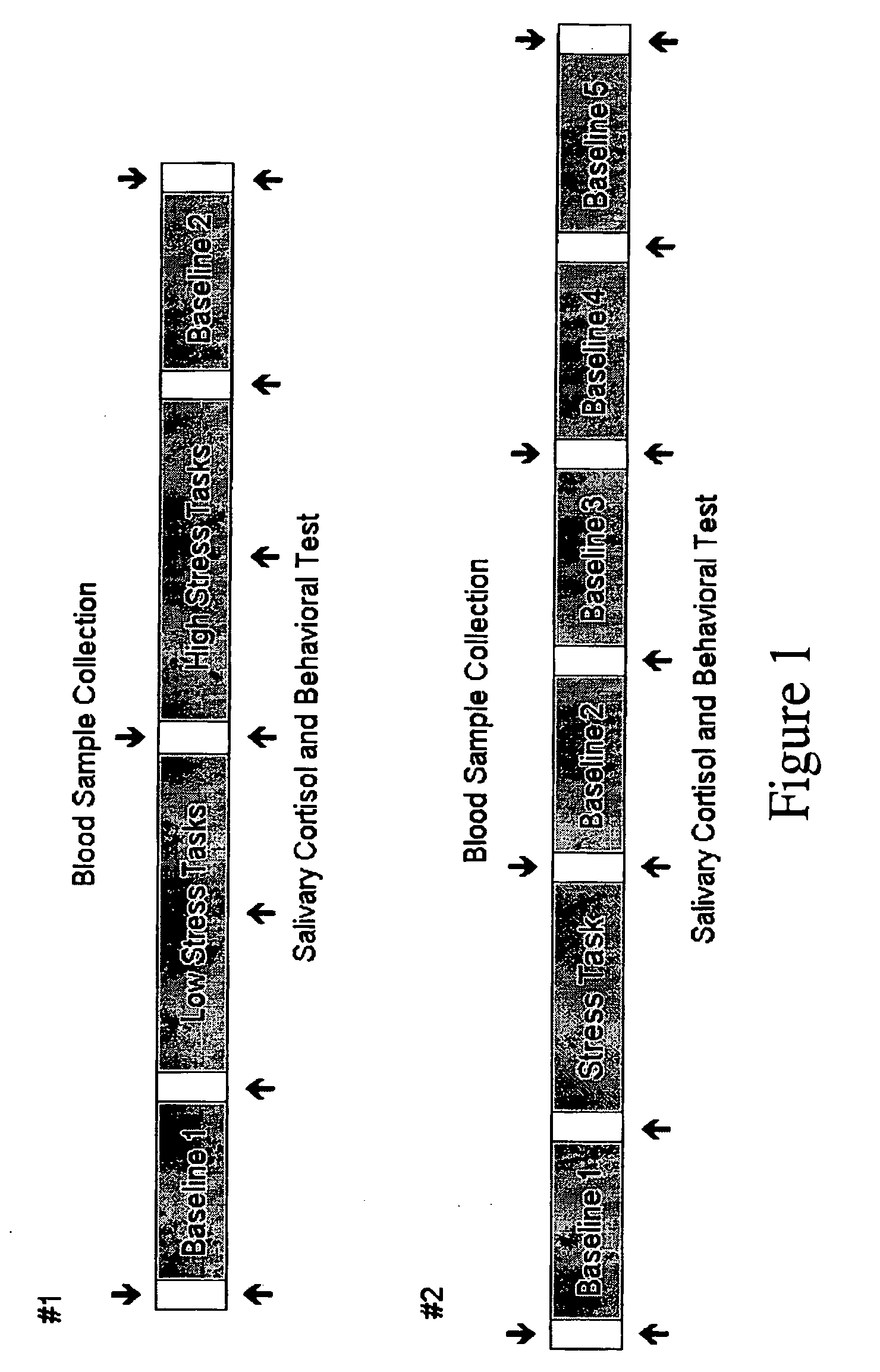
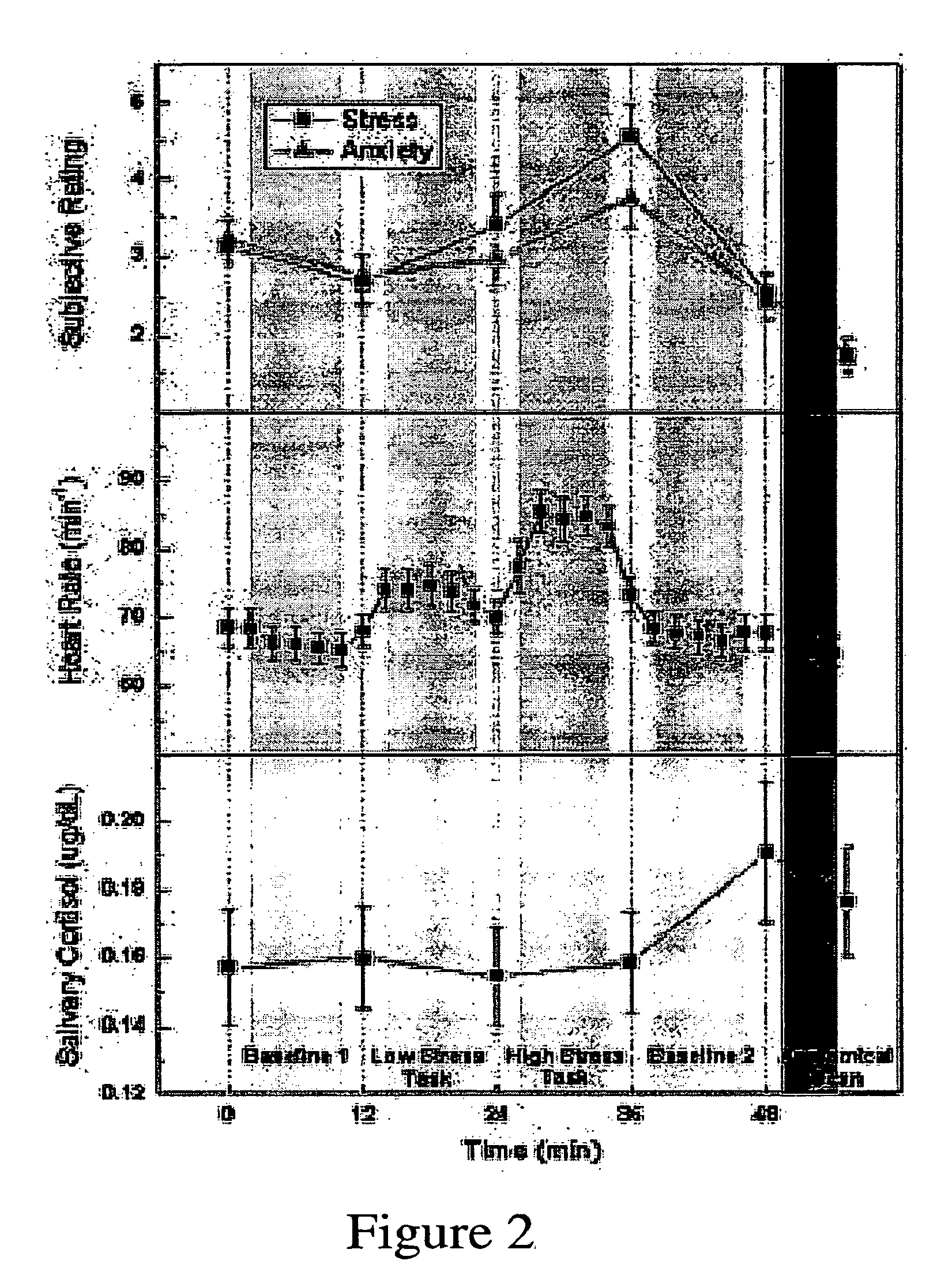
Assessing subject's reactivity to psychological stress using fmri
This invention relates to the use of a quantitative functional MRI (fMRI)—arterial spin-labeling perfusion MRI or absolute T2 mapping MRI or a combination thereof in the non-invasive neuroimaging of a subject's brain in response to stress-inducing psychological stimuli, which can be utilized to predict individual stress reactivity as well as to be used as a human model for testing or optimizing psychopharmacological agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
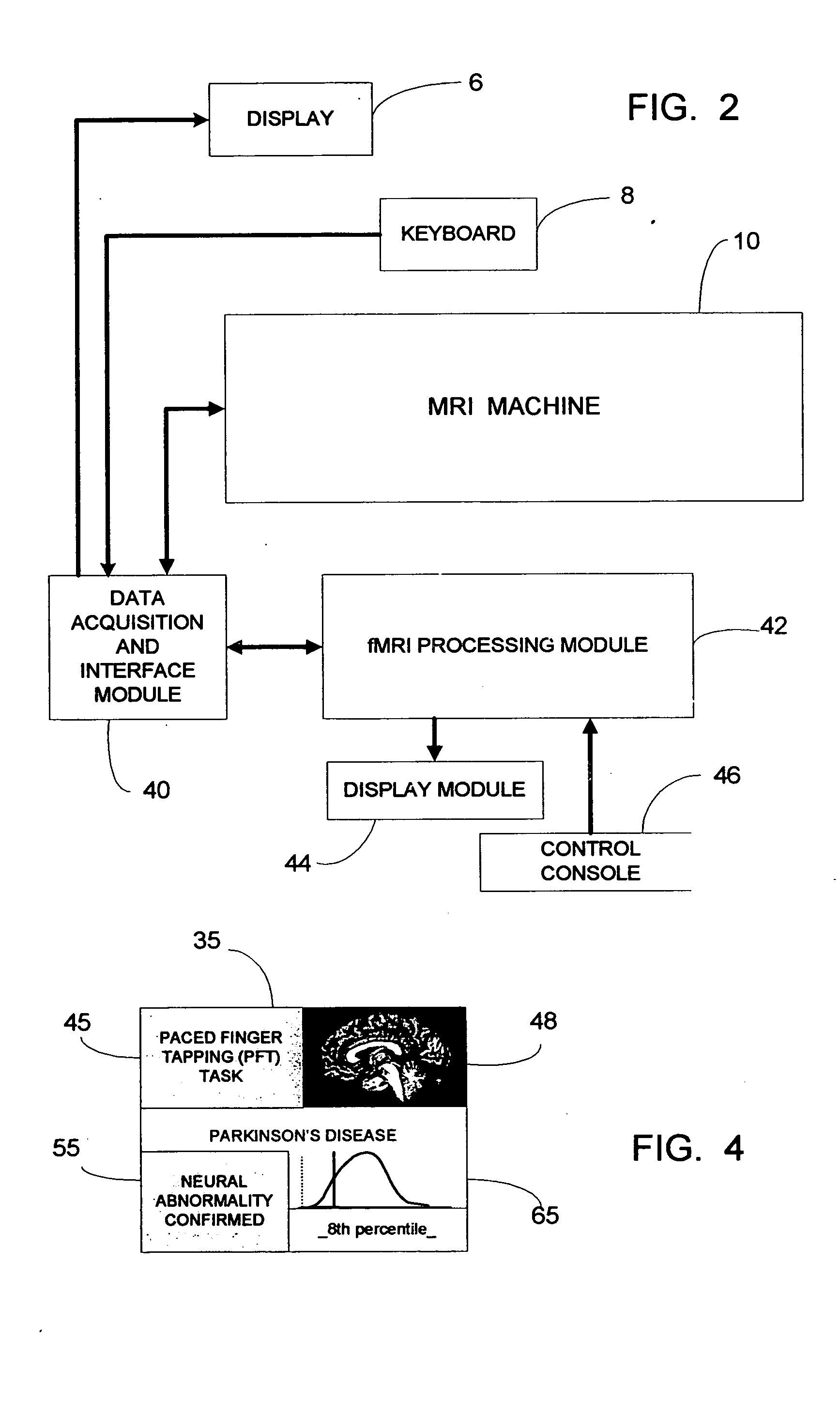
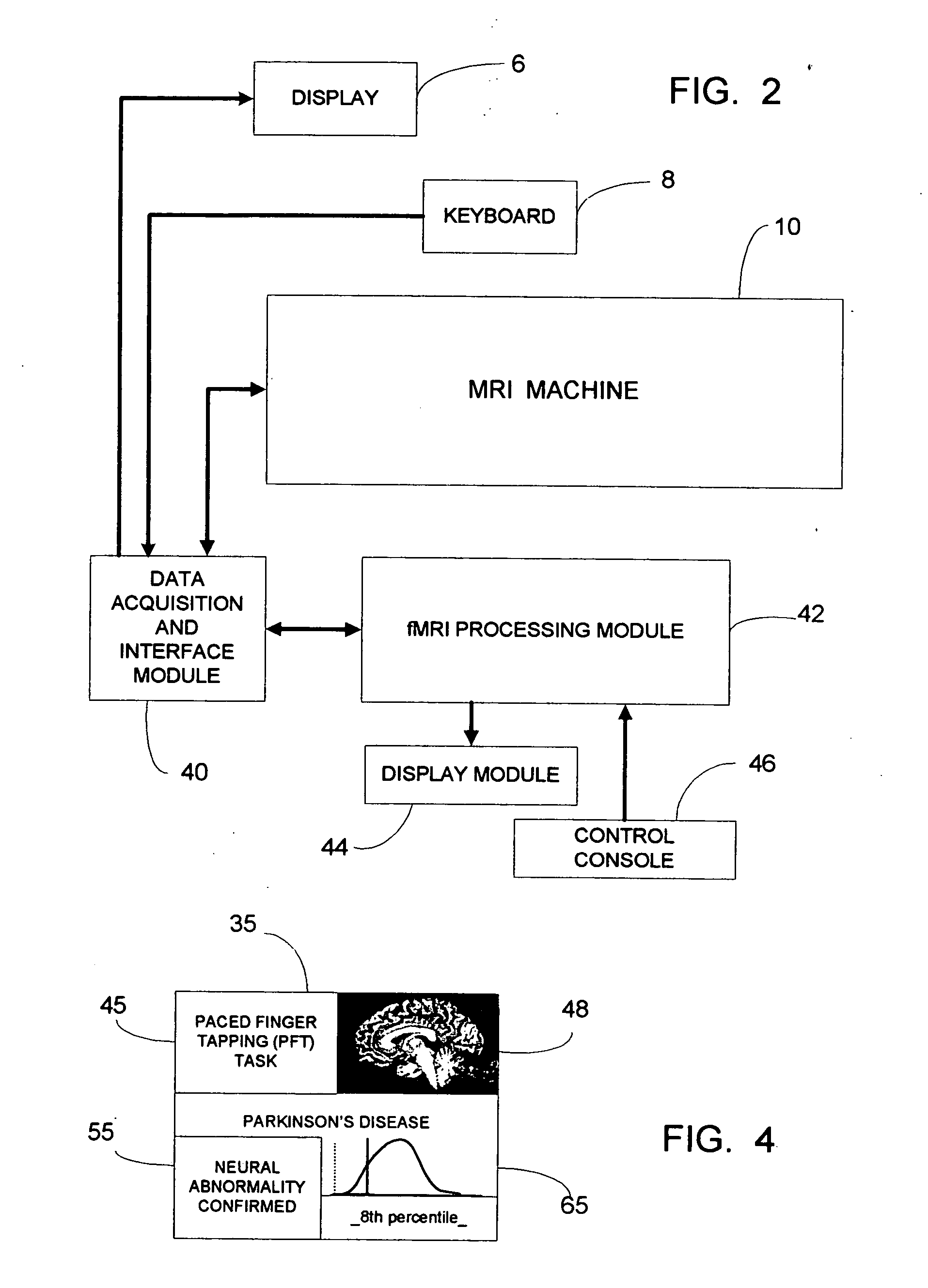
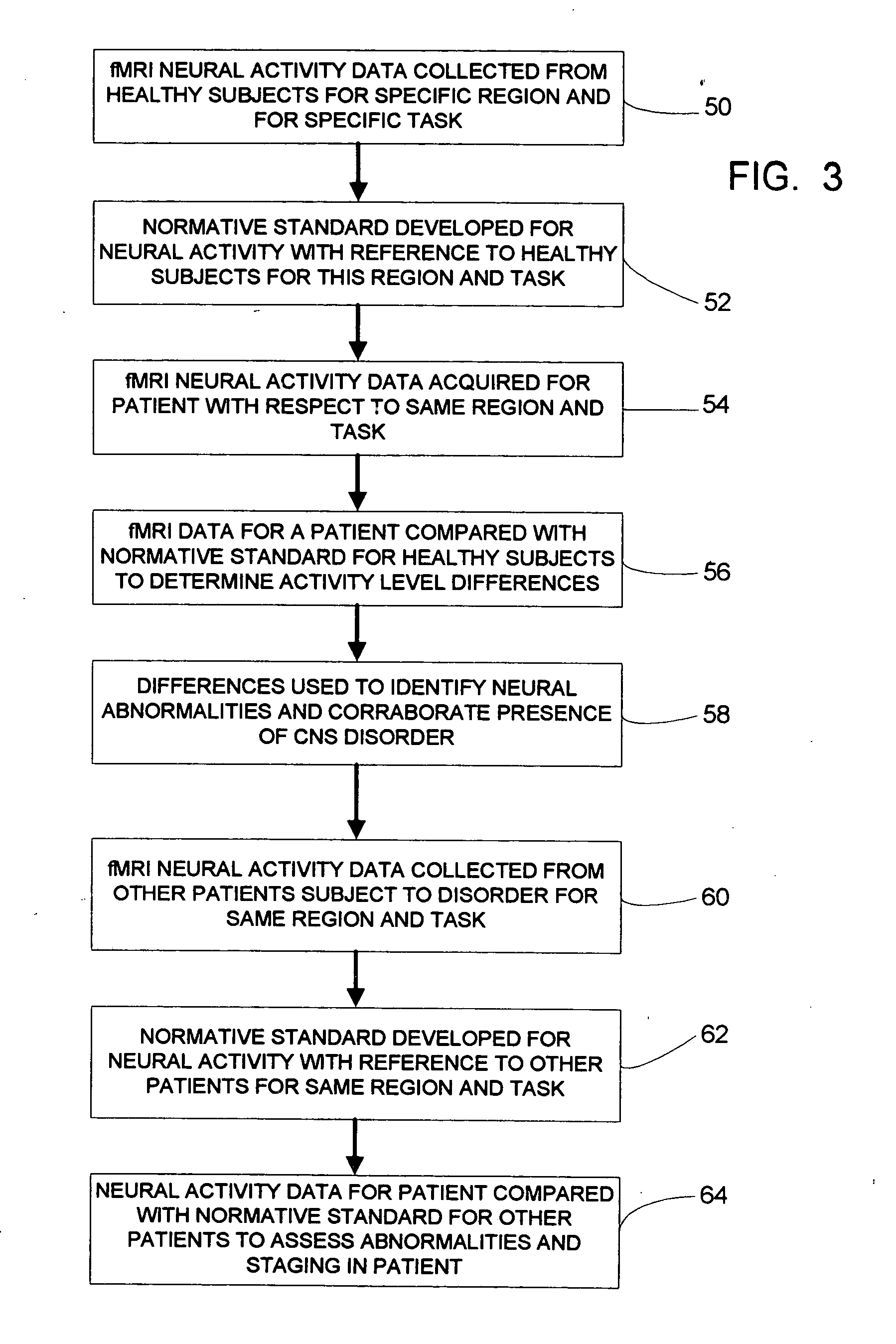
fMRI system for use in detecting neural abnormalities associated with CNS disorders and assessing the staging of such disorders
InactiveUS20050085705A1High level of sensitivityStrong specificityComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseClinical psychology
A system for detecting neural abnormalities associated with specific central nervous system disorders in patients suspected of suffering from said disorders and for assisting in assessing the staging of said disorders in patients suffering from said disorders. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) techniques are used to generate fMRI time series image data with respect to a selected regions of interest in the brain known to be affected by given disorders in response to activation tasks known to induce neural activity specifically in these regions. The fMRI data is used in generating statistically based standards and profiles by which abnormalities can be identified and the staging of disorders can be assessed. The results are diagrammatically or graphically displayed so that the data, standards and profiles can be usefully compared.
Owner:RAO STEPHEN M +1
Method for acquiring nerve navigation system imaging data
The invention discloses a method for acquiring the imaging data of a neuro navigation system, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring scanned images in a functional magnetic resonance imaging mode, wherein the functional magnetic resonance imaging mode comprises BOLD scan cortex functional imaging and DTI scan alba functional imaging; transmitting the scanned images according to DICOM and classifying and converting the scanned images; and according to category, and carrying out the registration and fusion of the neuro navigation structural images and the converted scanned images, wherein the registration and fusion comprises the registration mapping of BOLD activation maps and the fusion of DTI maps. Therefore, the neuro functional images are registered and fused in neuro navigation, cerebral white matter fiber tracks is carried out and used as image data of the neuro navigation system so as to provide a powerful tool for making surgical plan before a surgery and protecting normal brain functions in the surgery and to provide a platform for brain function research.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH TECH CO LTD
Methods for modifying electrical currents in neuronal circuits
Disclosed herein are methods for modifying electrical currents in brain circuits through the simultaneous use of focused ultrasound pulse (FUP) and an existing brain-imaging system, such as a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) system. The methods are used for research, treatment and diagnosis of psychiatric, neurological, and neuroendocrine disorders whose biological mechanisms include brain circuits. The methods include the simultaneous steps of applying FUP to a live neuronal circuit within a brain and monitoring a brain image produced by a brain imaging system during the application of FUP.
Owner:BRAINSONIX CORP
Method for improving magnetic resonance imaging of the breast
InactiveUS20080214930A1Enhancing magnetic resonance (MR) imageCut skinDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAir interfaceMedicine
The present invention provides a fat saturation device to be used in conjunction with a magnetice resonance imaging (MRI) breast coil, which provides padding for the comfort of the patient being imaged while eliminating the skin-air interface, thereby reducing the level of artefacts in the image. The device comprises a coil surface pad that contacts the surface of the coil, the pad having apertures therein through which the patients breasts extend when the patient is positioned on the coil for imaging. Aperture sleeves that are removable or retractable extend from the bottom surface of the coil surface into the apertures of the breast coil. The device comprises a fat saturation material.
Owner:ORGAMEND
NMR imaging equipment stability and method for measuring image-forming index
InactiveCN101322648AObjective analysisAvoid subjectivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDICOMNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
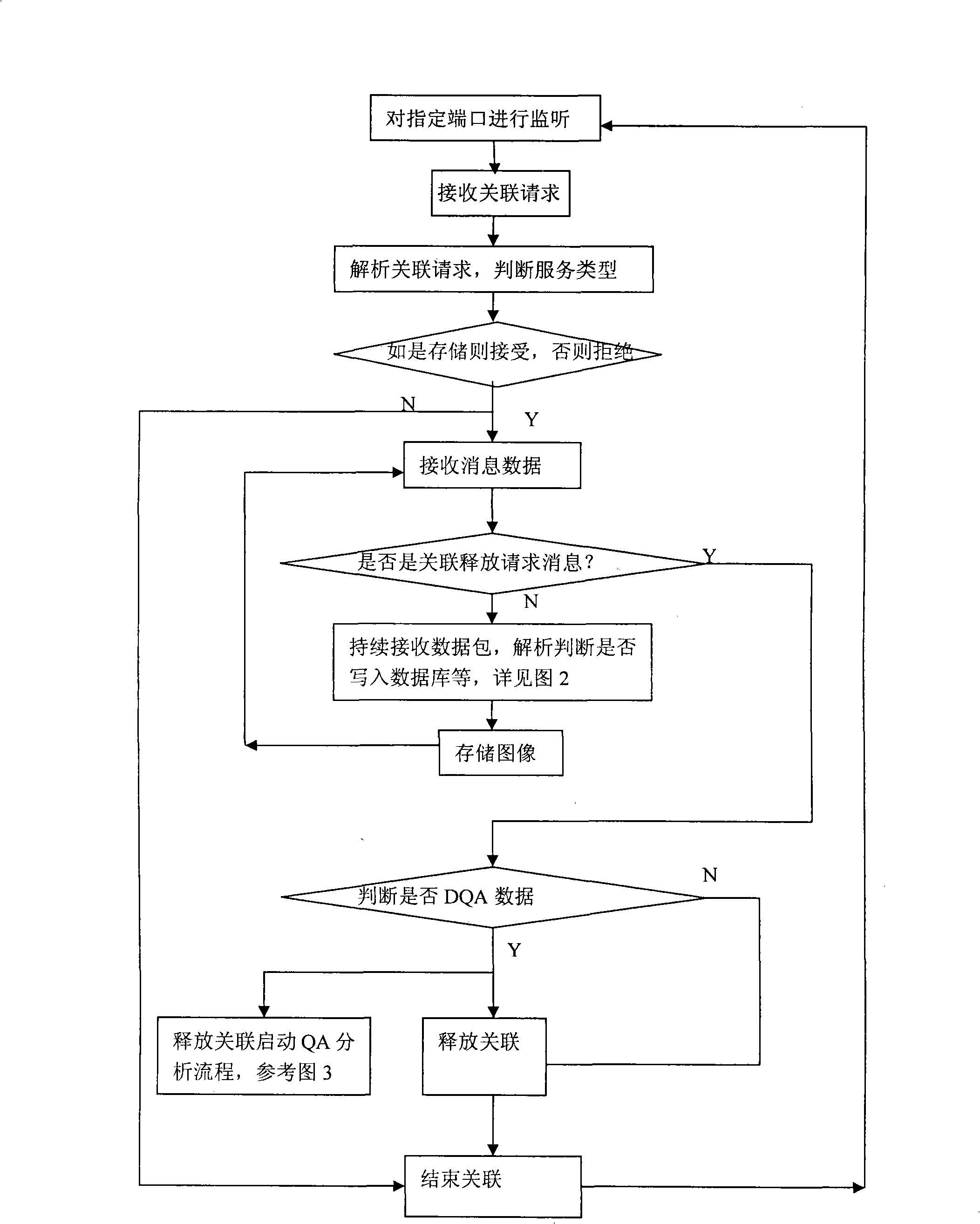
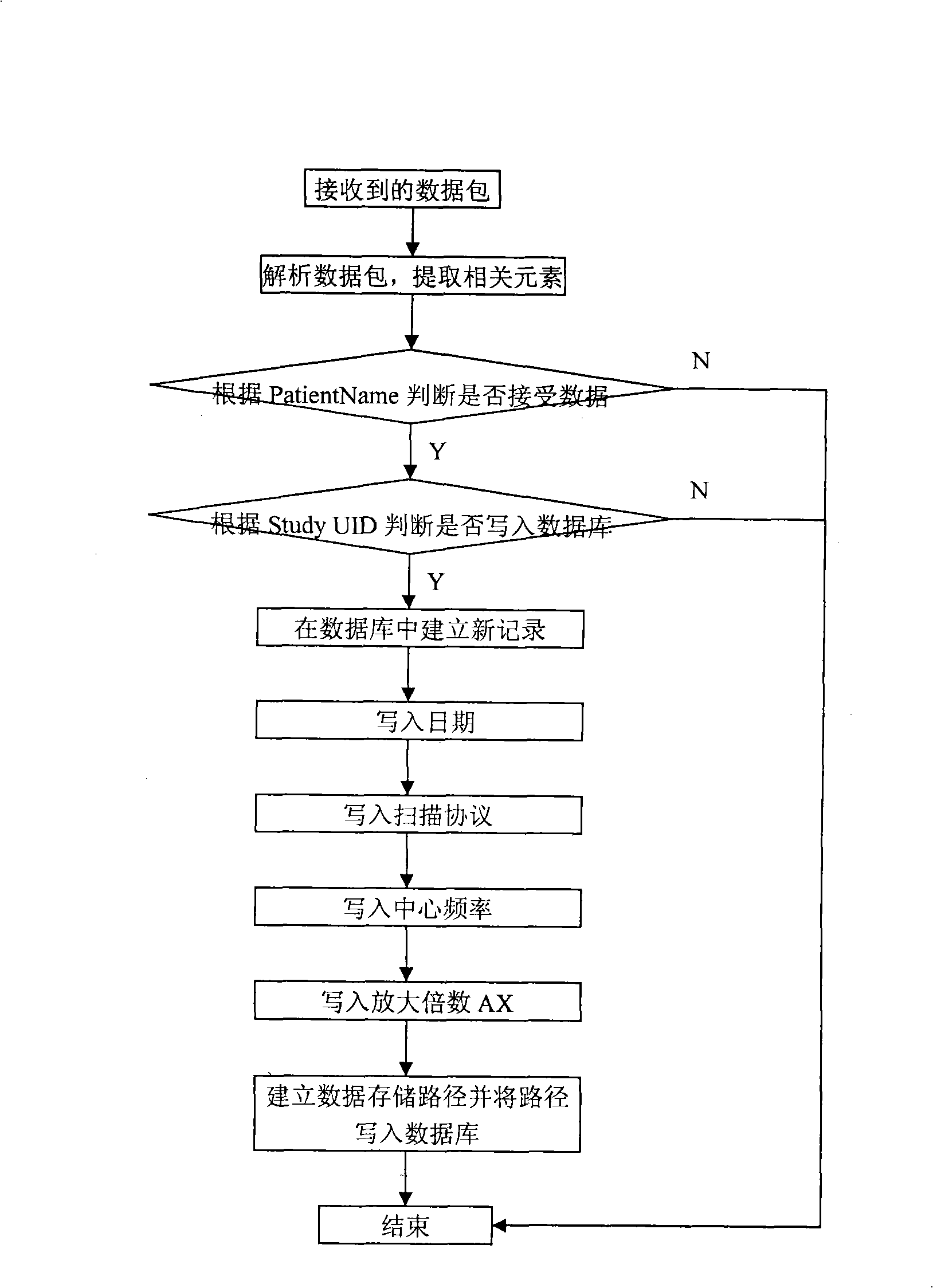
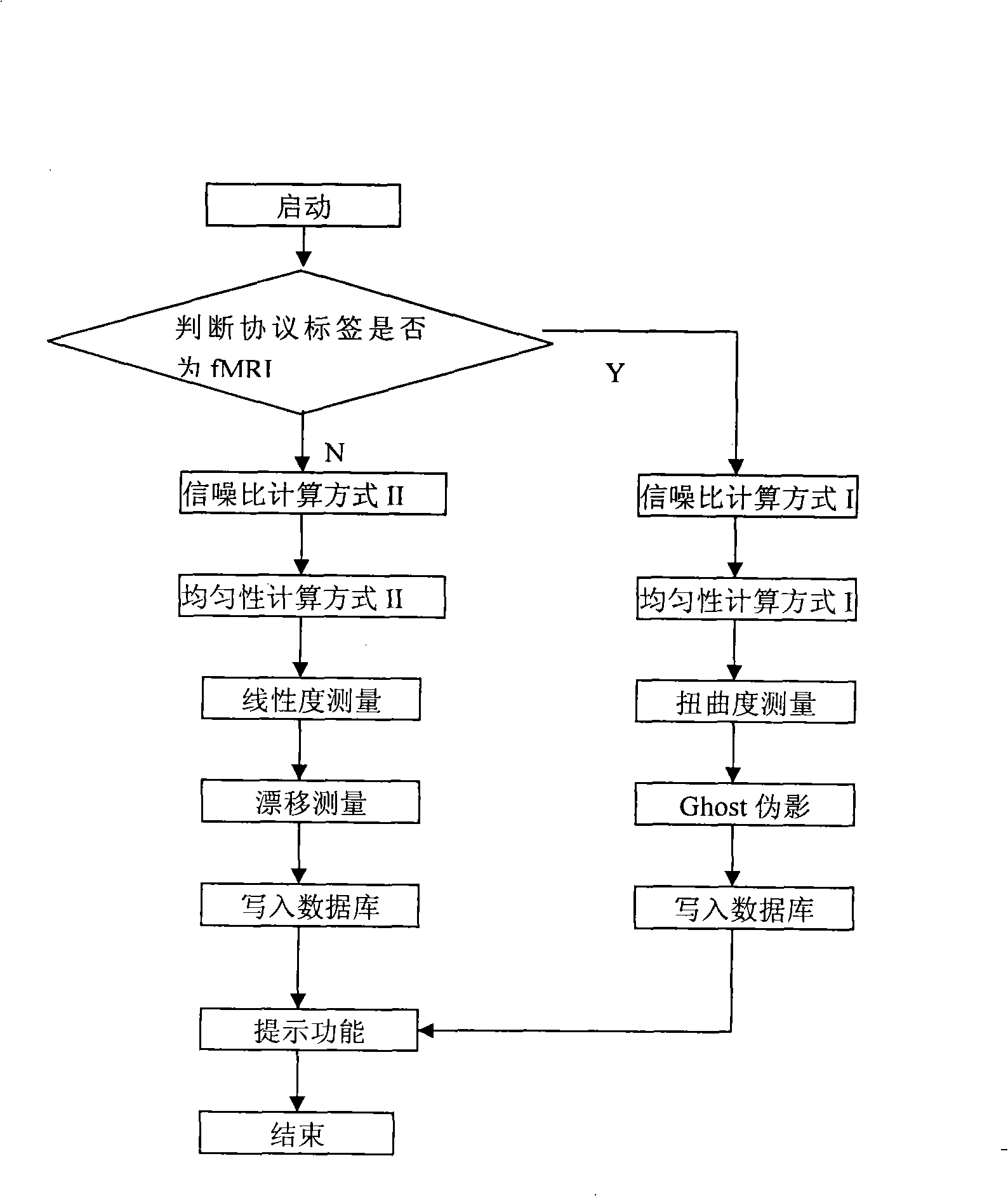
The invention discloses a method for measuring the stability and imaging indexes of a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging device and is characterized in that: the images of a water phantom are obtained by adopting the nuclear magnetic resonance imaging device to scan the water phantom, the images are transmitted to a specific nuclear magnetic resonance imaging quality assurance and analysis work station by a DICOM protocol, and then the quality assurance and analysis work station is self started and enters a corresponding measurement process (referring to the figure 1 in the abstract of the process) according to DICOM control elements so as to process and calculate the images of the water phantom; the measuring content includes common nuclear magnetic resonance imaging quality assurance indexes, the shifting indexes which have important significance to Functional MRI, and other indexes; meanwhile, an automatic early warning mechanism is established for auto prompting when an abnormal condition occurs and gives the possible reason, and all measured results are sent into a database for long-term analysis of data and evaluation of running state of the device, so as to offer guidance to relevant technicians to master device state and carry out equipment testing.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
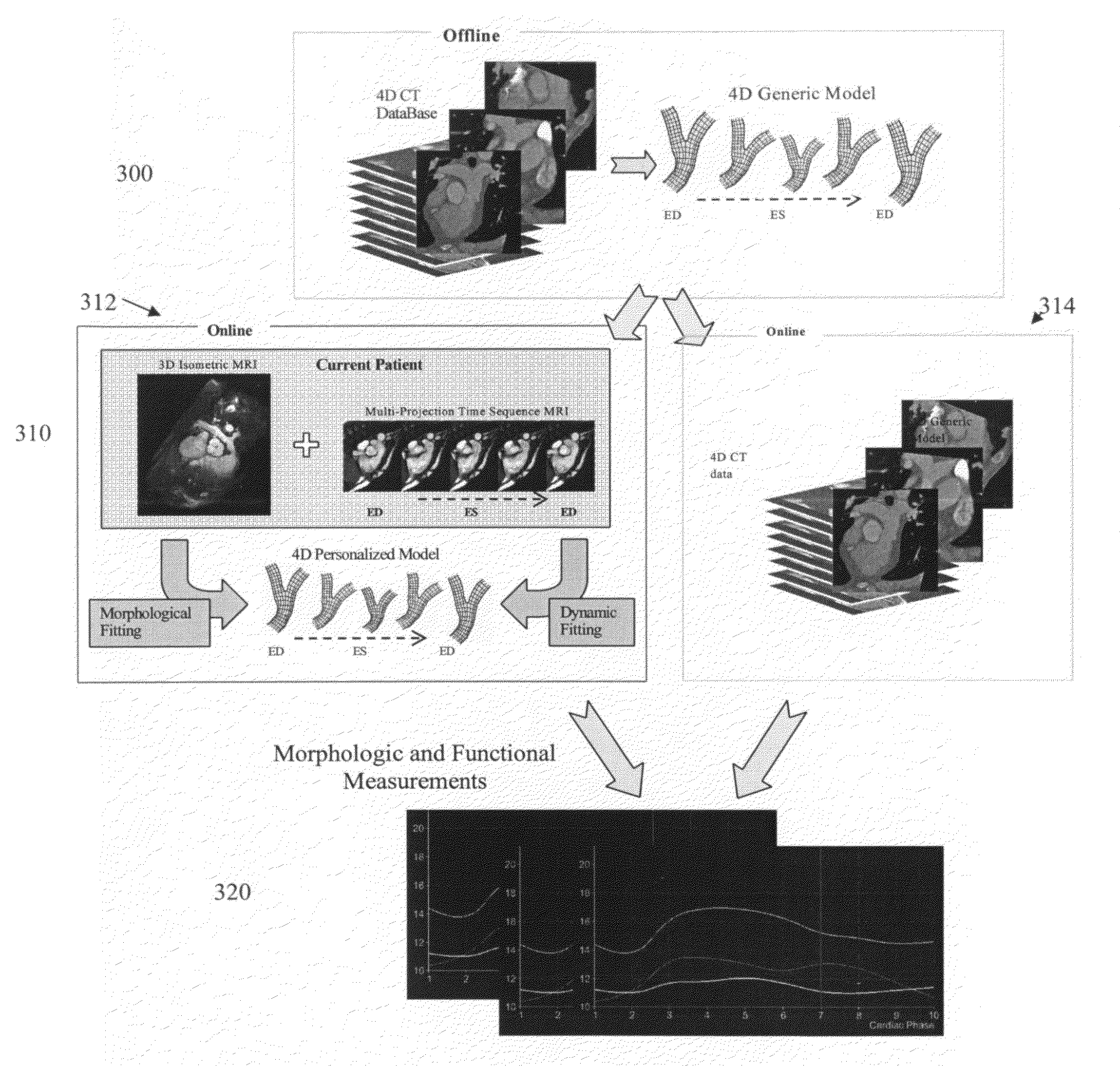
Method and system for dynamic pulmonary trunk modeling in computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging
A method and system for modeling the pulmonary trunk in 4D image data, such as 4D CT and MRI data, is disclosed. Bounding boxes are detected in frames of the 4D image data. Anatomic landmarks are detected in the frames of the 4D image data based on the bounding boxes. Ribs or centerlines of the pulmonary artery are detected in the frames of the 4D image data based on the anatomic landmarks, and a physiological pulmonary trunk model is fit the frames of the 4D image data based on the detected ribs and anatomic landmarks. The boundary of the pulmonary trunk is detected in order to refine the boundary of the pulmonary trunk model in the frames of the 4D image data, resulting in a dynamic model of the pulmonary trunk. The pulmonary trunk can be quantitatively evaluated using the dynamic model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Scanning focal point apparatus
ActiveUS20070029491A1Maximizing spatial resolutionMaximizing sensitivitySolid-state devicesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPhoton emission
A collimator, and in particular a method for making a collimator for use with a small high resolution single-photon emission computed tomographic (SPECT) imaging tool for small animal research. The collimator is sized, both functionally and structurally, particularly smaller than known collimators and appropriately scaled to achieve a highly sensitive collimator which facilitates desired reconstruction resolutions for small animals, as well as compliments other functional imaging modalities such as positron emission tomography (PET), functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), electroencephalography (EEG), and event-related potential (ERP), magneto-encephalography (MEG), and near-infrared optical imaging.
Owner:NEUROLOGICA CORP
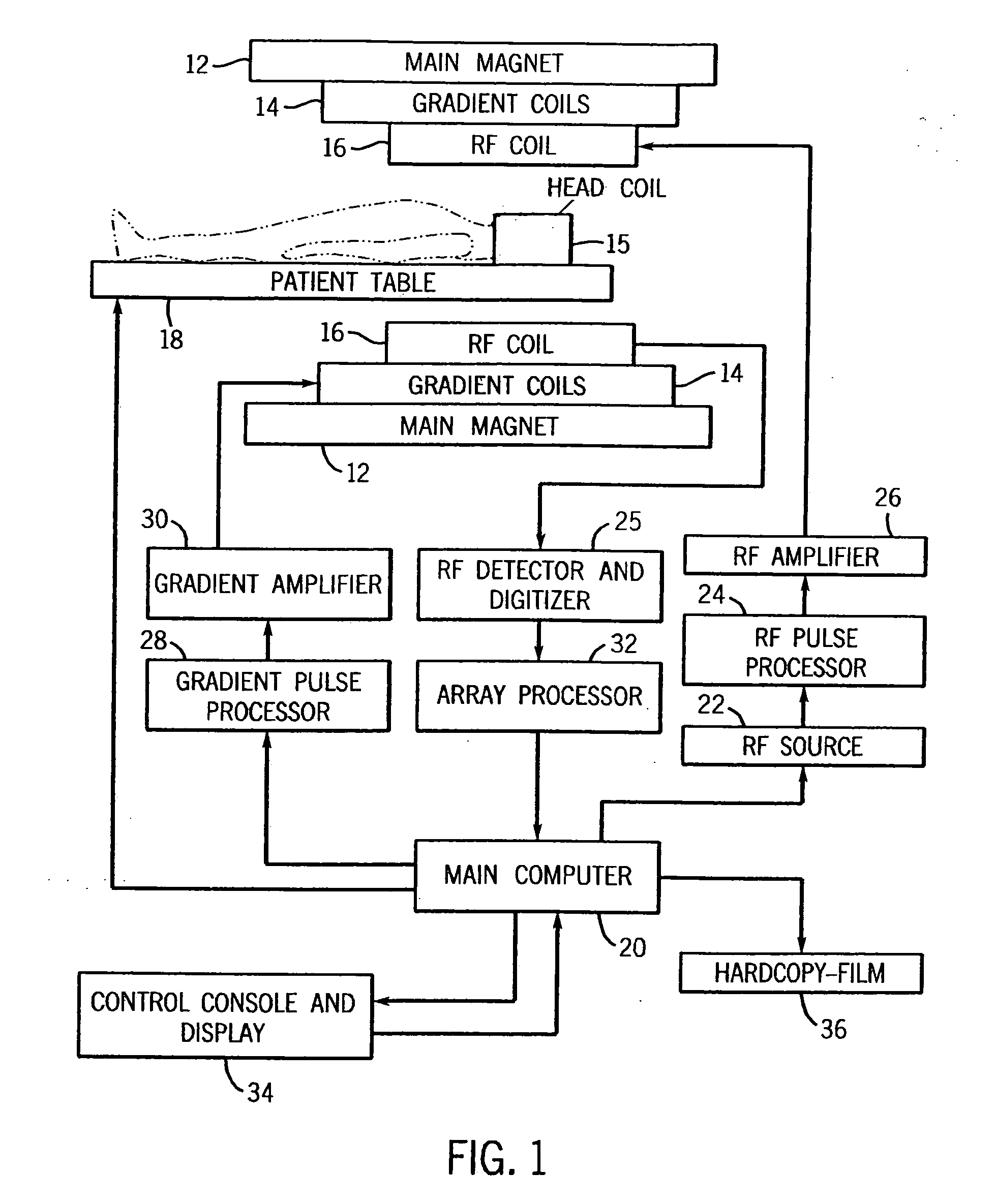
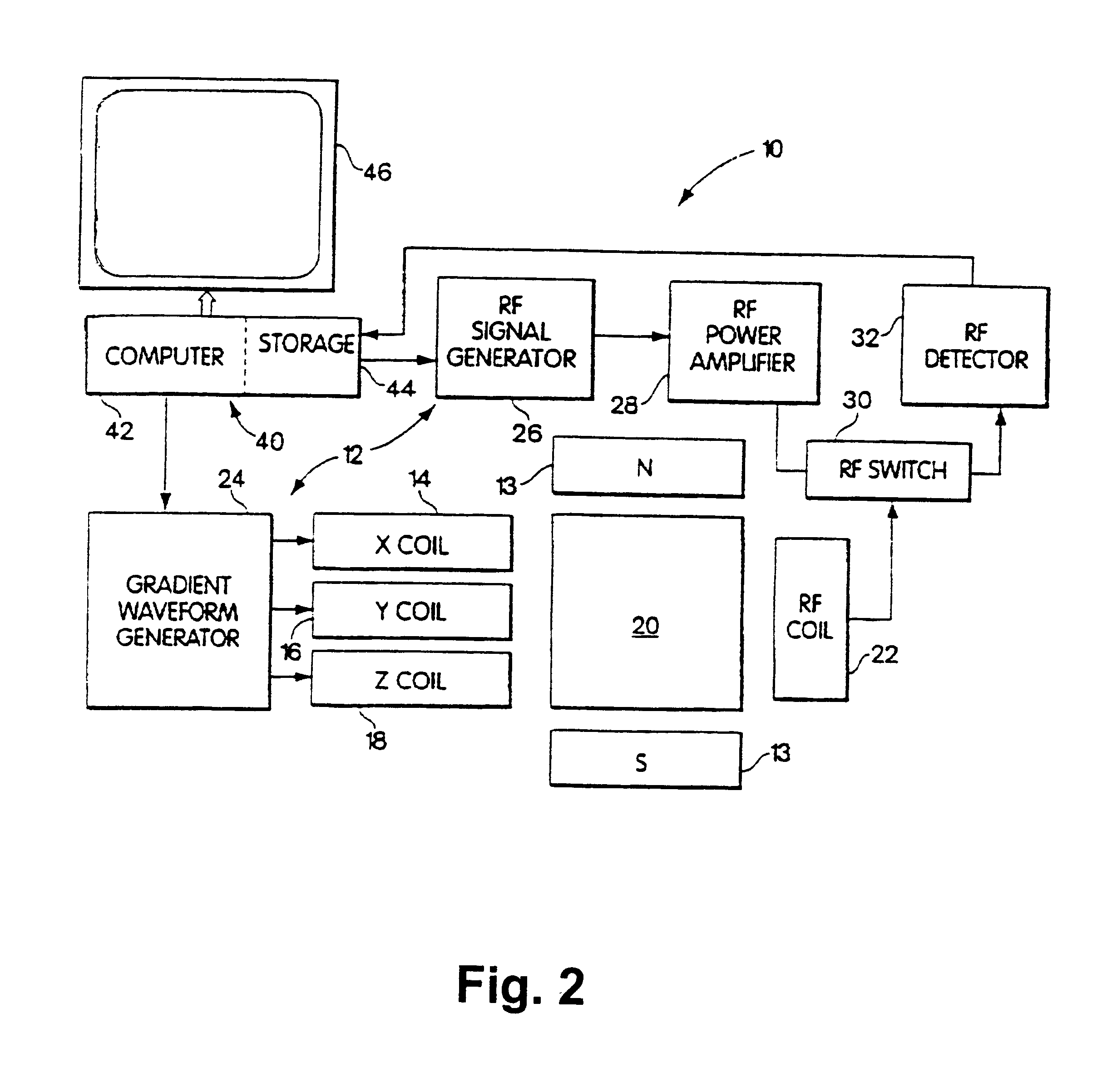
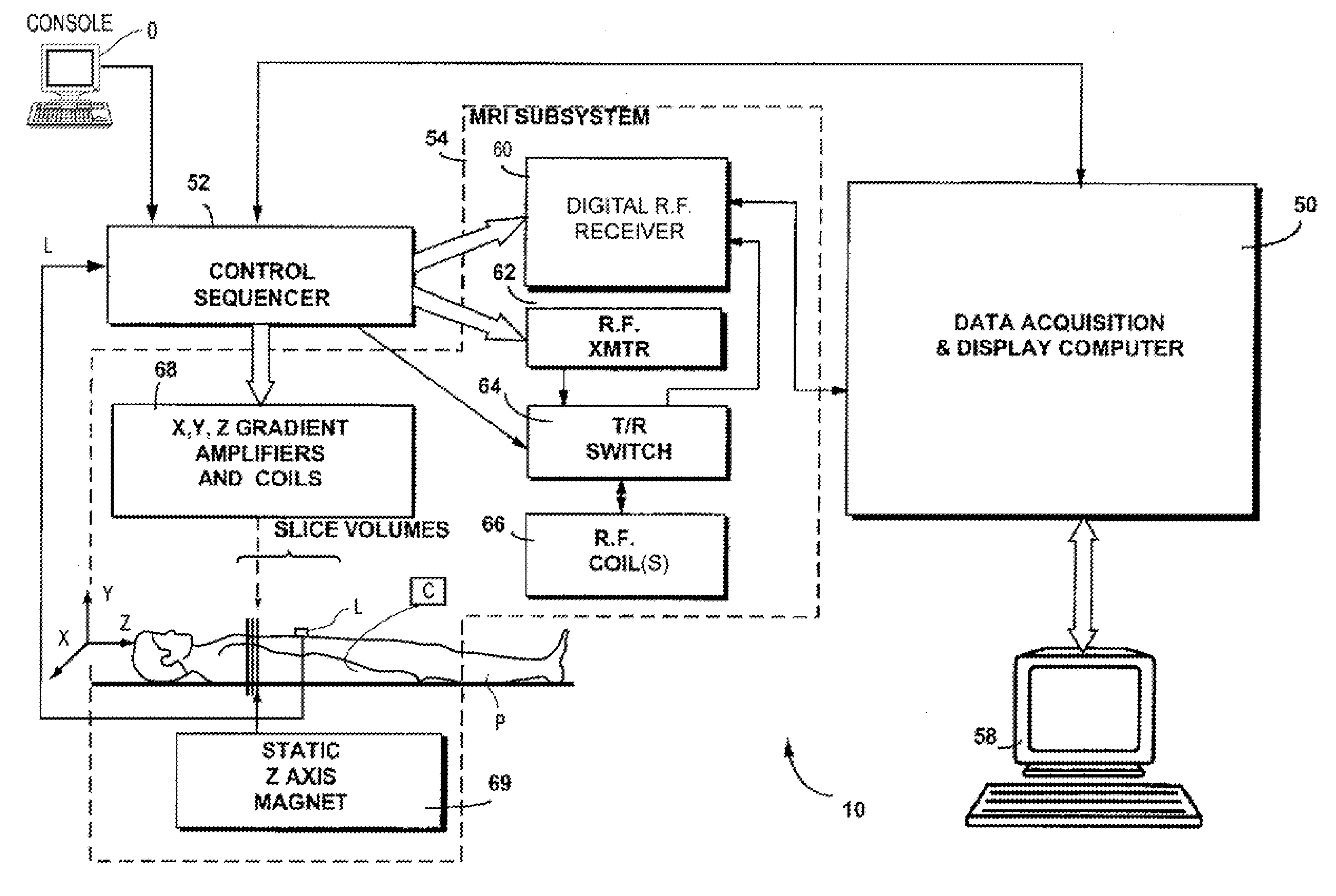
System and method for acquiring magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data
ActiveUS8744154B2Easy to useEasy retrievalMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer scienceImaging data
A method for acquiring image data from a patient with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. The proposed method comprises the steps of: a) predefining a number of scan geometries for acquiring the image data from at least one region of interest (ROI) relative to the patient, b) performing at least one scan for acquiring the image data in accordance with at least one of the predefined scan geometries, c) analysing in the image data a position of the region of interest to detect a deviation from the at least one predefined scan geometry, d) changing the at least one predefined scan geometry if said deviation exceeds a predetermined threshold value, and e) repeating steps b) to d) until a predetermined number of scans has been performed. Thus, by means of the proposed method the utility of such predefined scan geometries is greatly enhanced.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
fMRI data acquisition system
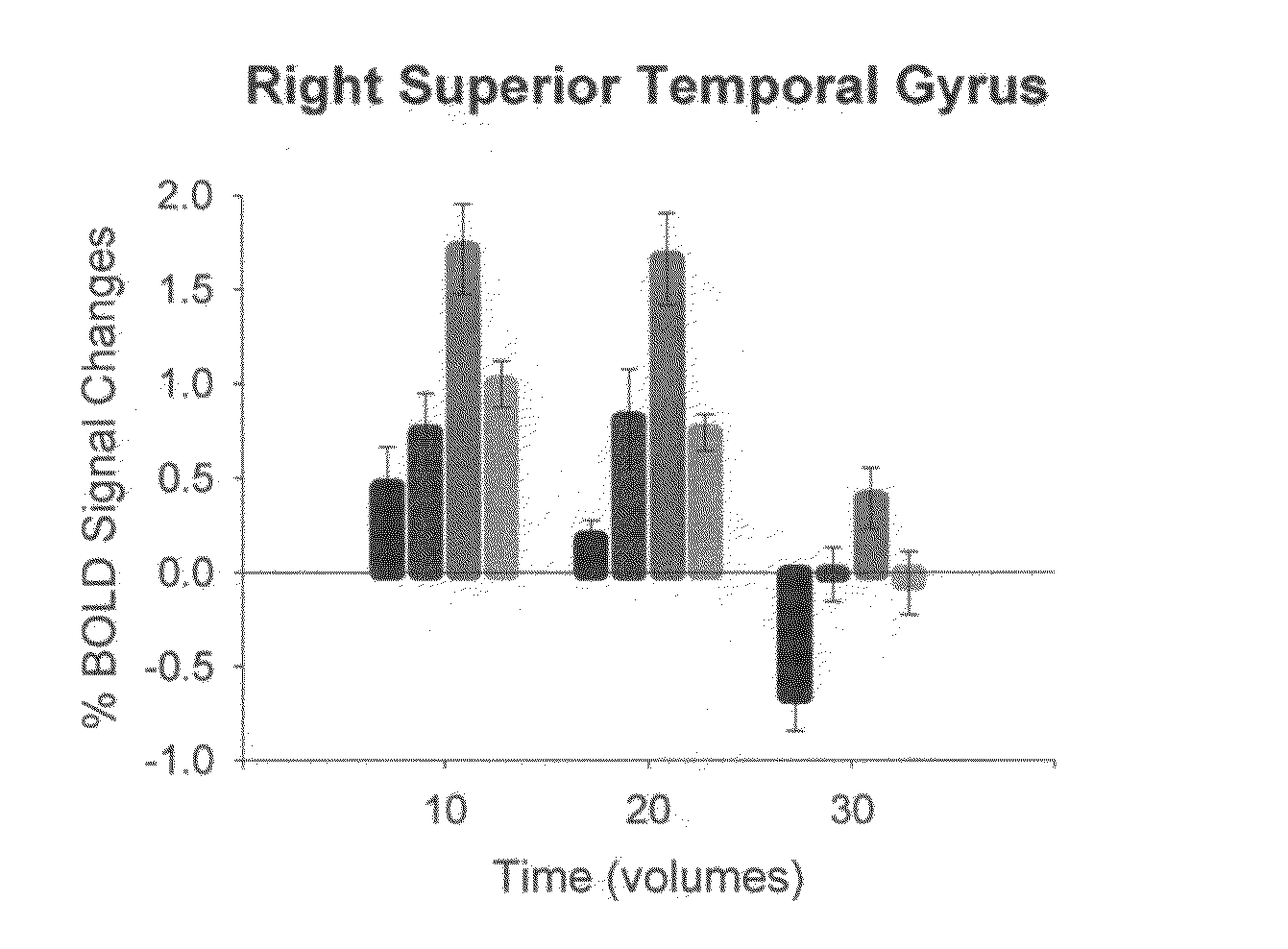
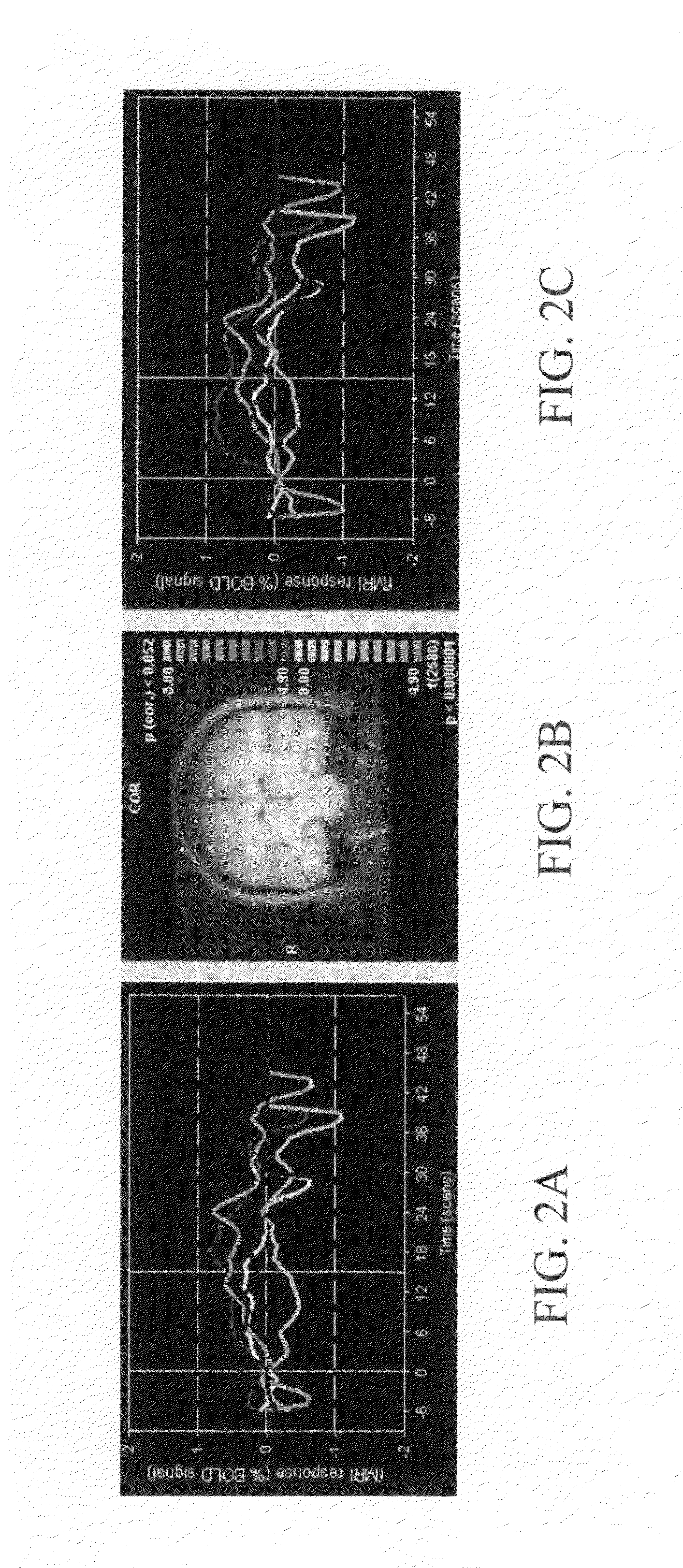
InactiveUS20070167724A1Easy to manageMinimize and correct head movementMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringBehavioral responseNeural biology
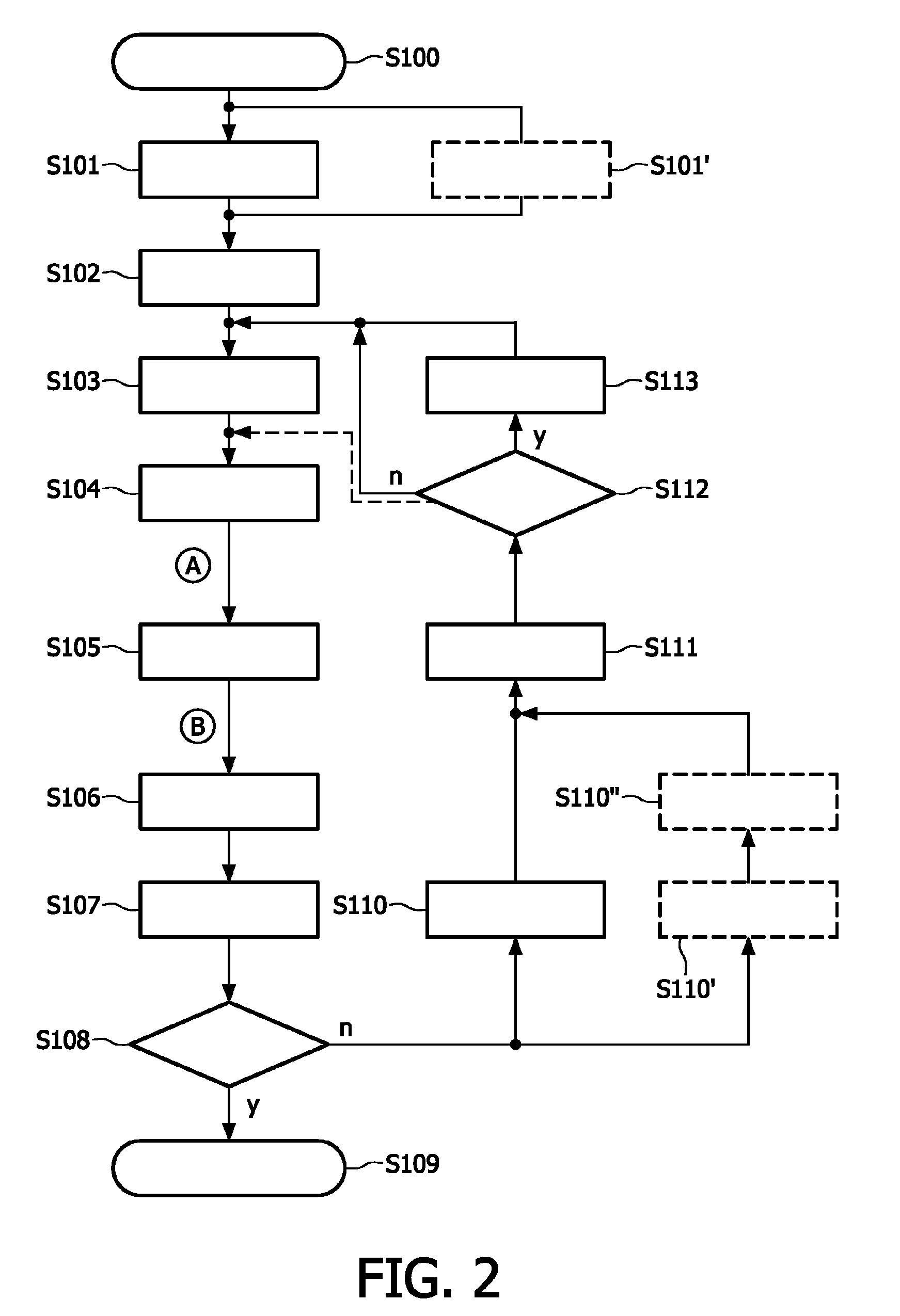
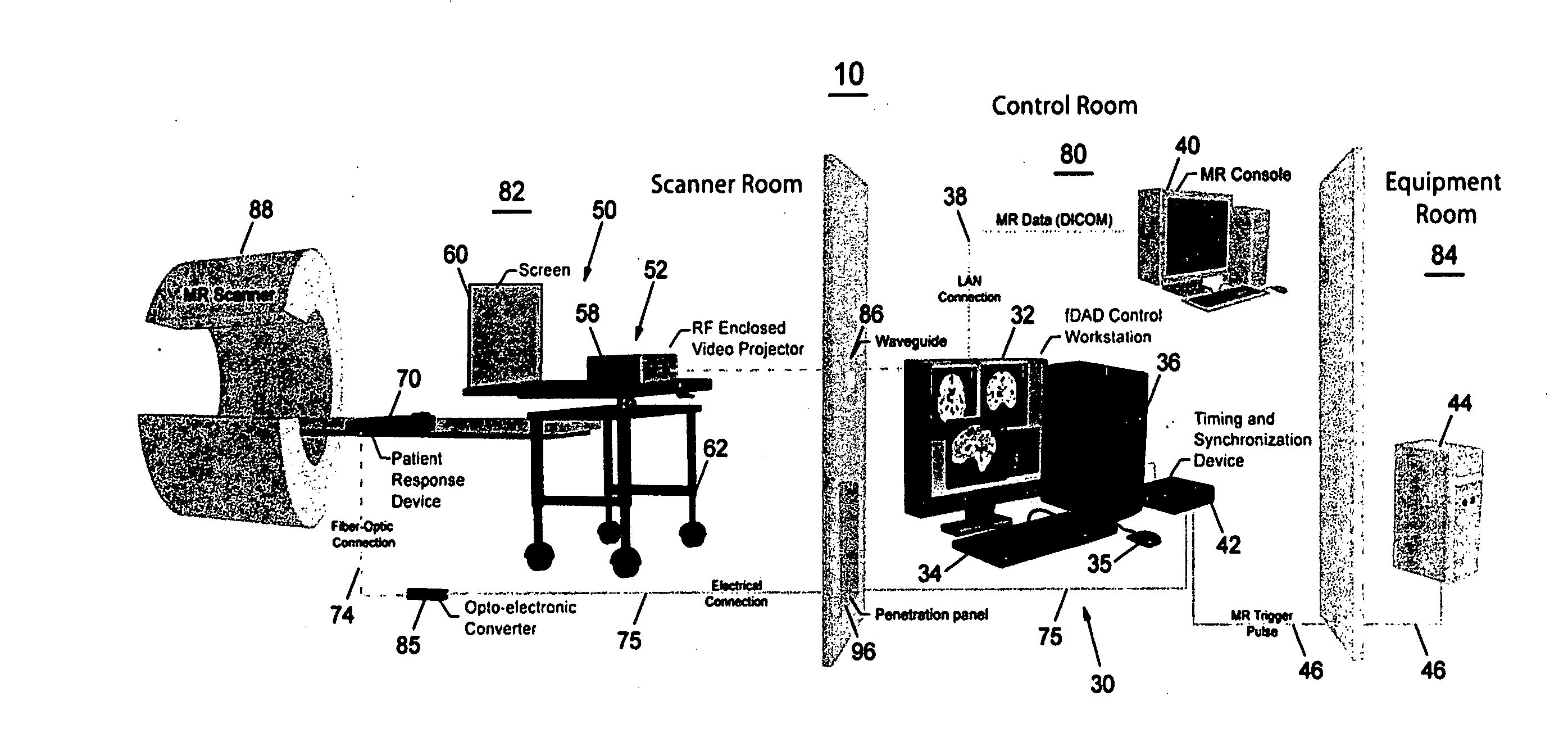
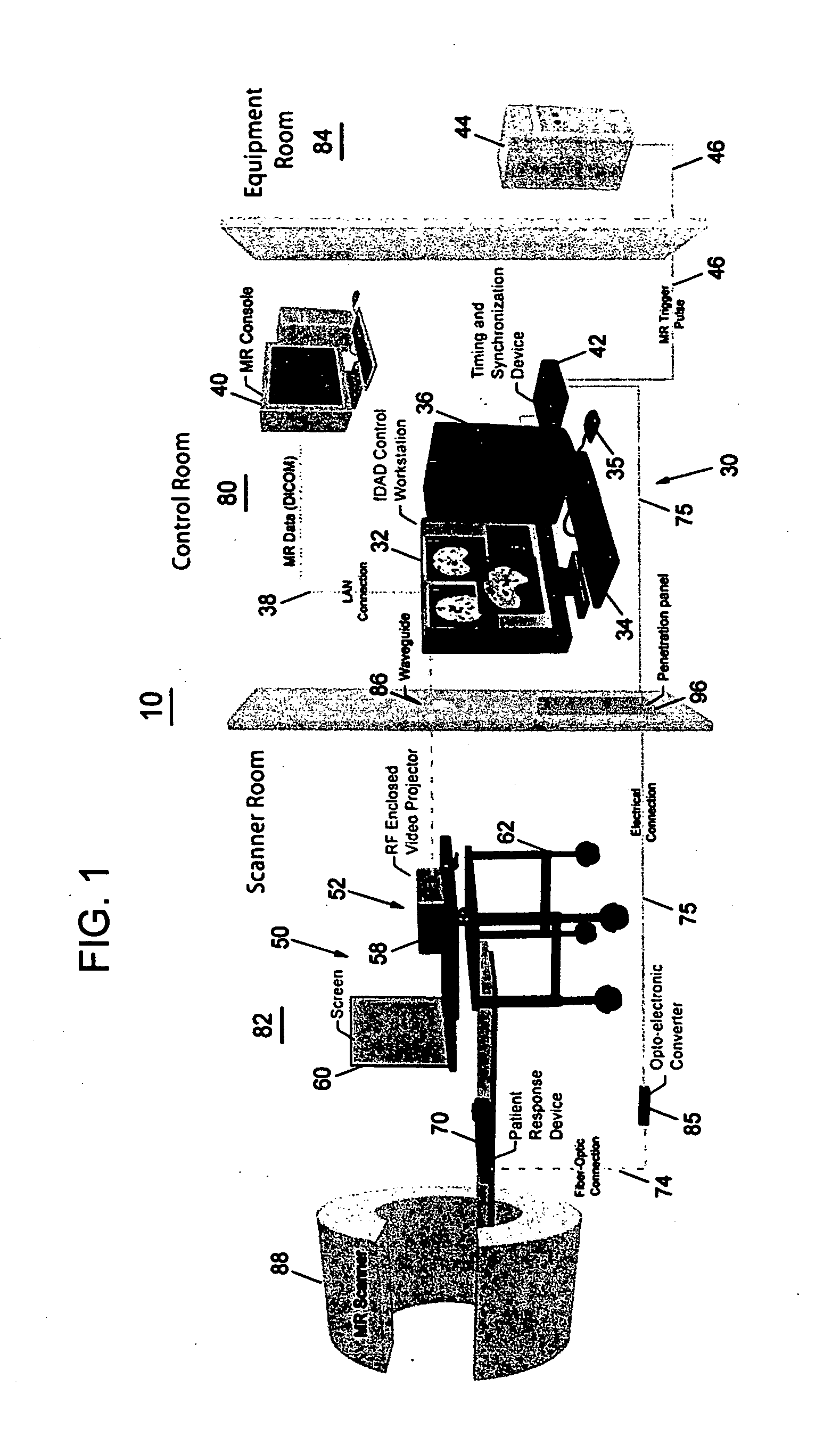
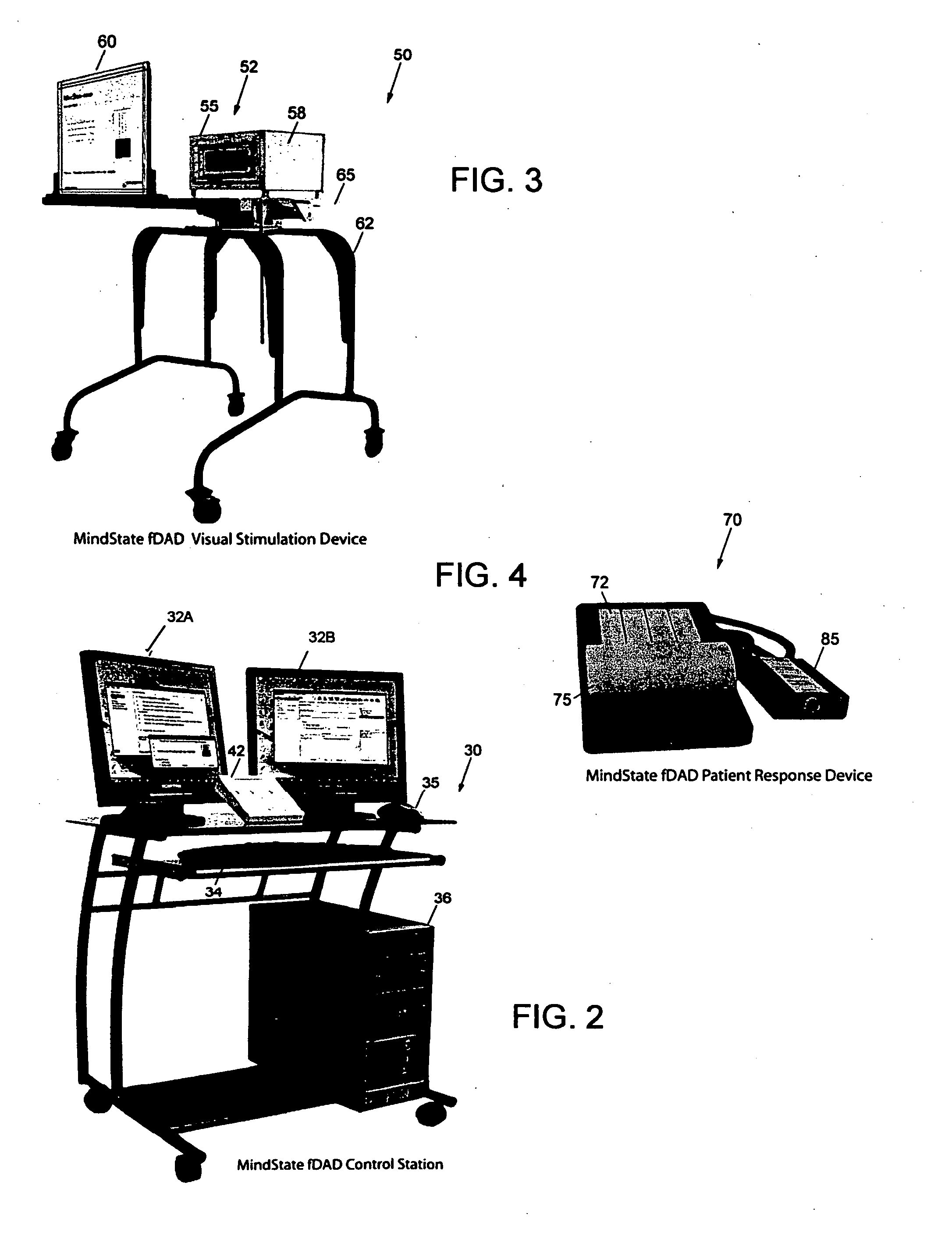
A data acquisition system for use in conducting functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. fMRI studies can provide clues to the neurobiological basis of CNS disorders and reliable and quantifiable data relating to their symptoms. The data acquisition system includes a control station, a patient stimulus and response system and fMRI data acquisition software for controlling the operation of the system in response to operator input and acquiring fMRI data comprising MR images and associated behavioral response data. The stimulus and response system presents visual or auditory or other stimuli to the patient under direction of the control station while functional MRI scanning takes place. The MRI image data is collected from the MRI scanner and combined with the behavioral data generated as the patient responds to the stimuli and archived for later analysis and use. The system includes quality control measures for properly setting up the equipment and preparing and training the patient and for verifying data quality during the different steps in the process.
Owner:GADAGKAR HRISHIKESH P +3
Three-dimensional graphical lamina positioning method in magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance imaging system
ActiveCN102908142AReduce complexityReduce difficultyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGraphicsReference image
The invention belongs to the field of magnetic resonance imaging, and particularly relates to a three-dimensional graphical lamina positioning method in magnetic resonance imaging. The three-dimensional graphical lamina positioning method comprises the following steps of: loading a two-dimensional reference image to a two-dimensional positioning view and visualizing the two-dimensional reference image in a three-dimensional positioning view; then displaying a lamina graphical object on the two-dimensional and three-dimensional positioning views; and timely updating adjustment in the two-dimensional or three-dimensional positioning view to the three-dimensional or two-dimensional positioning view, wherein positioning reference variation caused by the adjustment is also timely reflected on a parameter editor. The invention also provides a magnetic resonance imaging system. According to the three-dimensional graphical lamina positioning method in the magnetic resonance imaging and the magnetic resonance imaging system thereof, the position and the direction of the three-dimensional graphical object can be intuitively displayed and operated, what you see is what you get, the lamina positioning step is simplified, the operation difficulty is reduced, and the study period is shortened.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE CO LTD
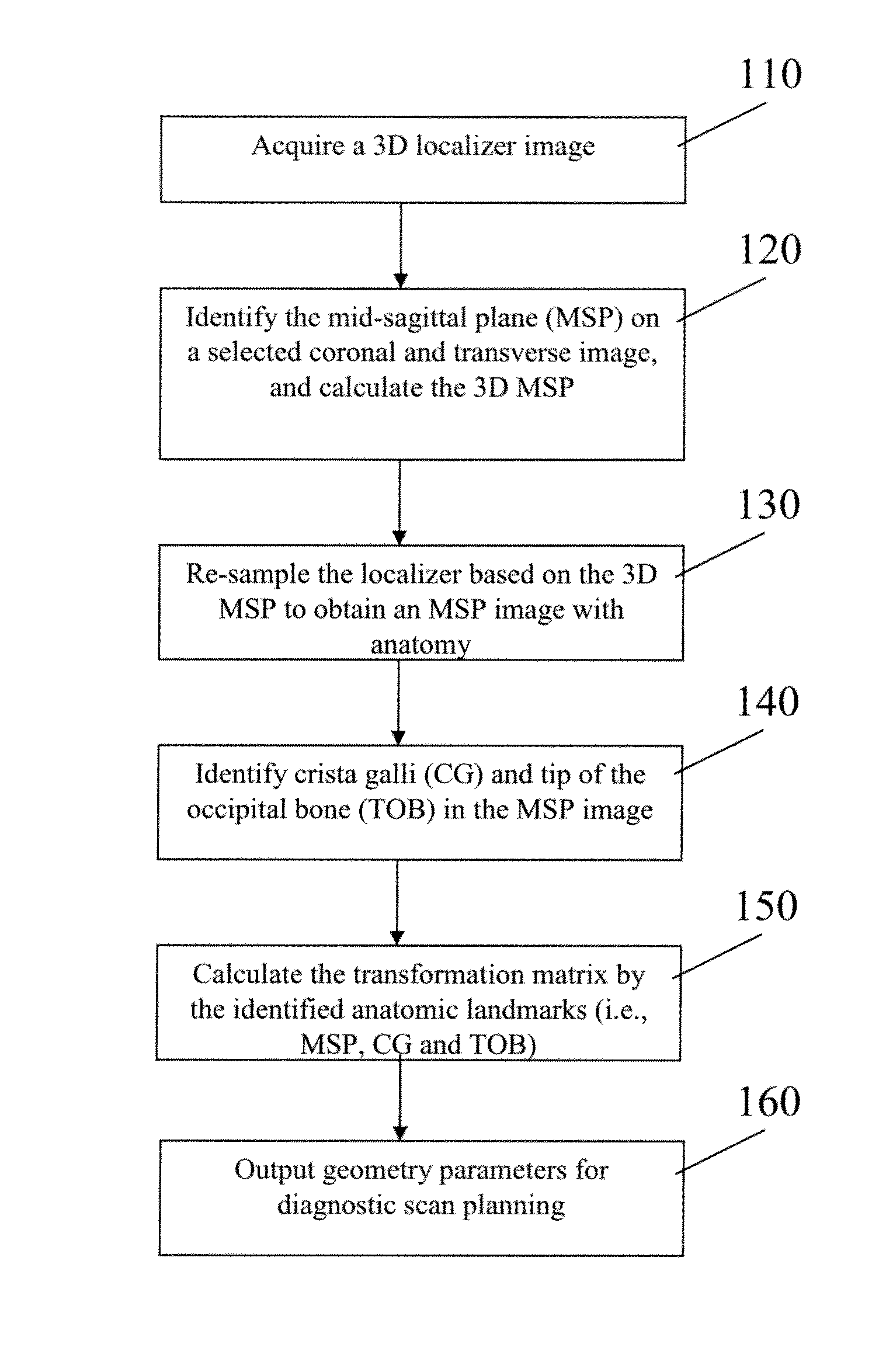
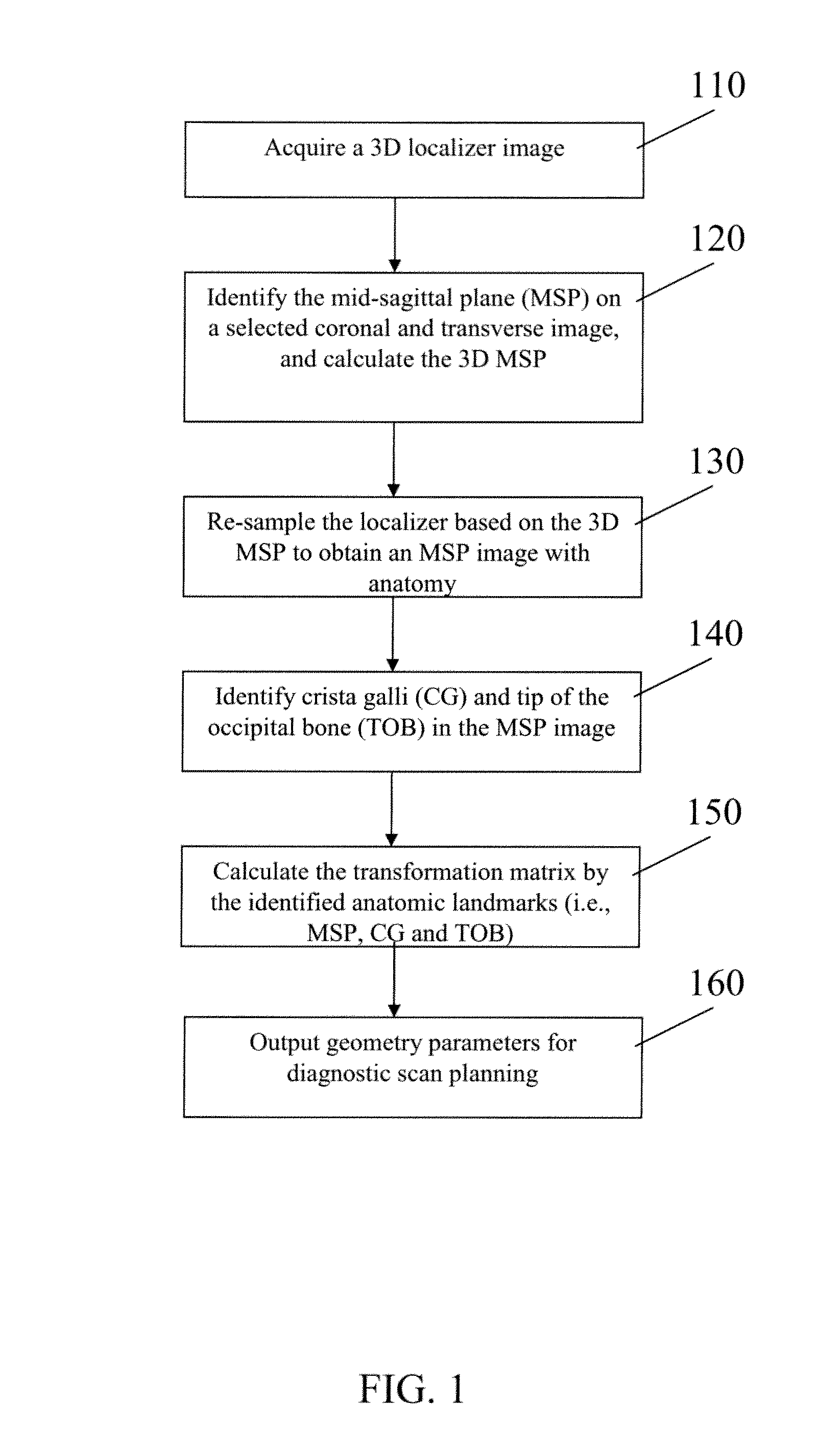
Automatic alignment of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain scan by anatomic landmarks
InactiveUS8190232B2Maximize magnitudeMinimize the differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringBrain sectionLandmark
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Dimensional approach to identifying emotional responses using functional brain imaging
ActiveUS8239000B1Large populationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityStaff satisfaction
The present invention concerns methods for evaluating the emotional response to stimuli, such as marketing communications. The present invention includes a method for correlating an emotional response to brain imaging data, a method identifying an emotional response to a stimulus, and a system for identifying an emotional response to a stimulus. The present invention can incorporate a psychological non-verbal measure, such as AdSAM®, and a neural-physiological measure, functional brain imaging, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), positron emission tomography (PET), or other functional brain imaging modality. For example, in marketing communication research, the emotional response data can be determined for such things as product concepts, advertising (concept and / or finished ads), product attributes, product benefits, brands, logos, tag lines, packaging, music, etc. The method of the invention can also be used to assess emotional response to different purchase options (e.g., retail vs. online), lifestyle issues, product usage situations, and other scenarios. In personnel management studies, the method of the invention can be used to measure employee satisfaction or employee morale.
Owner:MORRIS JON D +1
Method for mapping image reference points to facilitate biopsy using magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20090143672A1Improve image qualityQuickly assess accuracy of targetingVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionCystTissue characterization
In NMR / MRI imaging, a location is noted for a point in the imaged space, and referred to a reference location so that the point in imaged space is known thereafter, without the need to locate the point again in further imaging steps. For breast cancer diagnosis and biopsy, a breast holding fixture immobilizes the breast. A volumetric image is taken encompassing a portion of the breast. In the same or a subsequent image, a fiducial mark is detected to determine the position of a holder for a biopsy tool or other modality. The tissue feature can be a tumor, cyst or tubal lesion, made temporarily visible in the image by perfusion with a contrast agent. After the contrast agent dissipates, the location of the tissue feature can still be determined by reference to the position of the fiducial marker, which is optional adjustable by post-imaging metered displacement.
Owner:AURORA HEALTHCARE US CORP
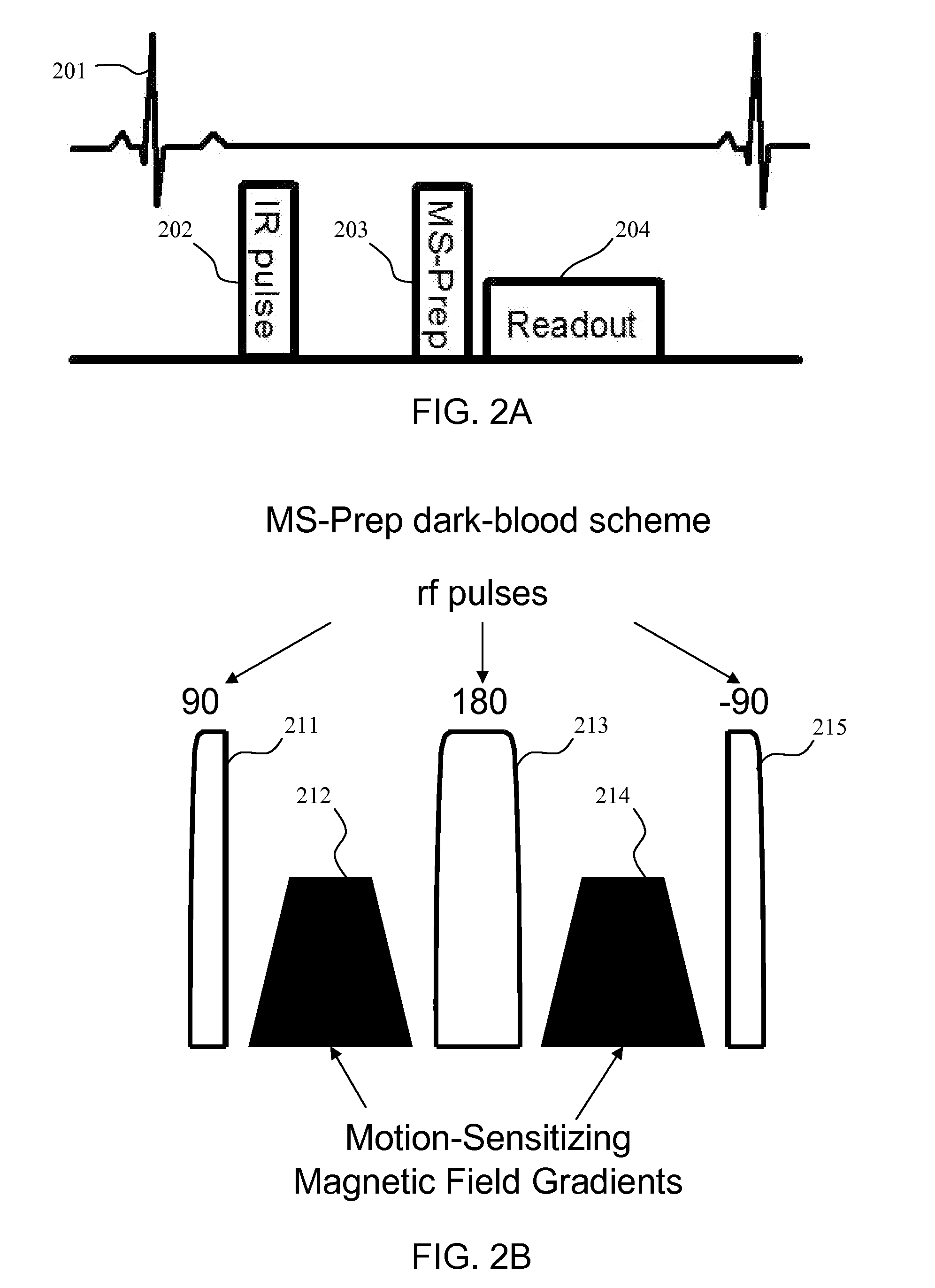
Motion-attenuated contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and related method thereof
ActiveUS20100191099A1Improve visualizationReduce signalingElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsContrast levelVentricular cavity
A system and method for providing a dark-blood technique for contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance, improving visualization of subendocardial infarcts or perfusion abnormalities that may otherwise be difficult to distinguish from the bright blood pool. In one technique the dark-blood preparation is performed using a driven-equilibrium fourier transform (DEFT) preparation with motion sensitizing gradients which attenuate the signal in the ventricular cavities related to incoherent phase losses resulting from non-steady flow within the heart. This dark-blood preparation preserves the underlying contrast characteristics of the pulse sequence causing a myocardial infarction to be bright while rendering the blood pool dark. When applied to perfusion imaging, this dark-blood preparation will help eliminate artifacts resulting from the juxtaposition of a bright ventricular cavity and relatively dark myocardium.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com