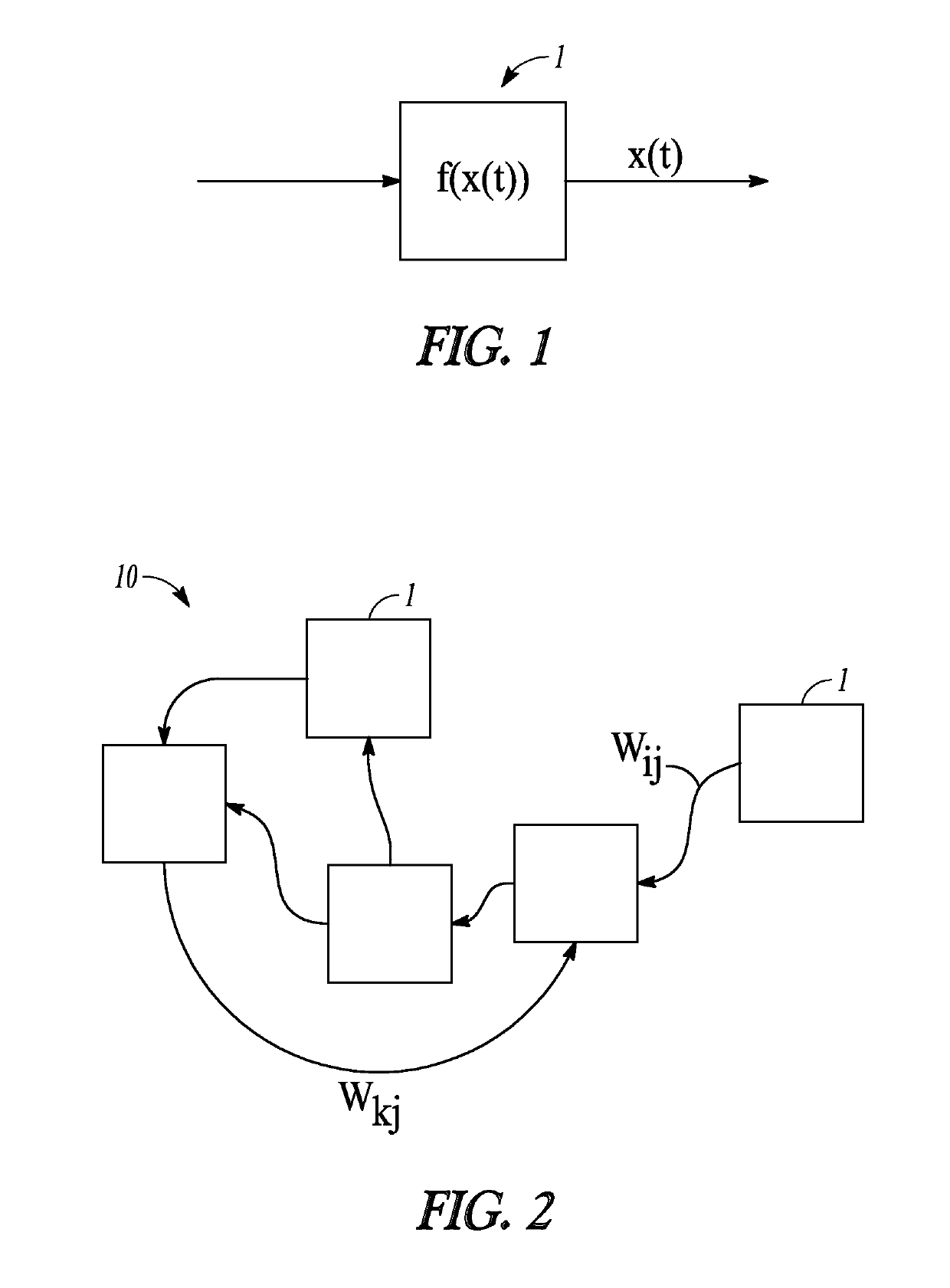
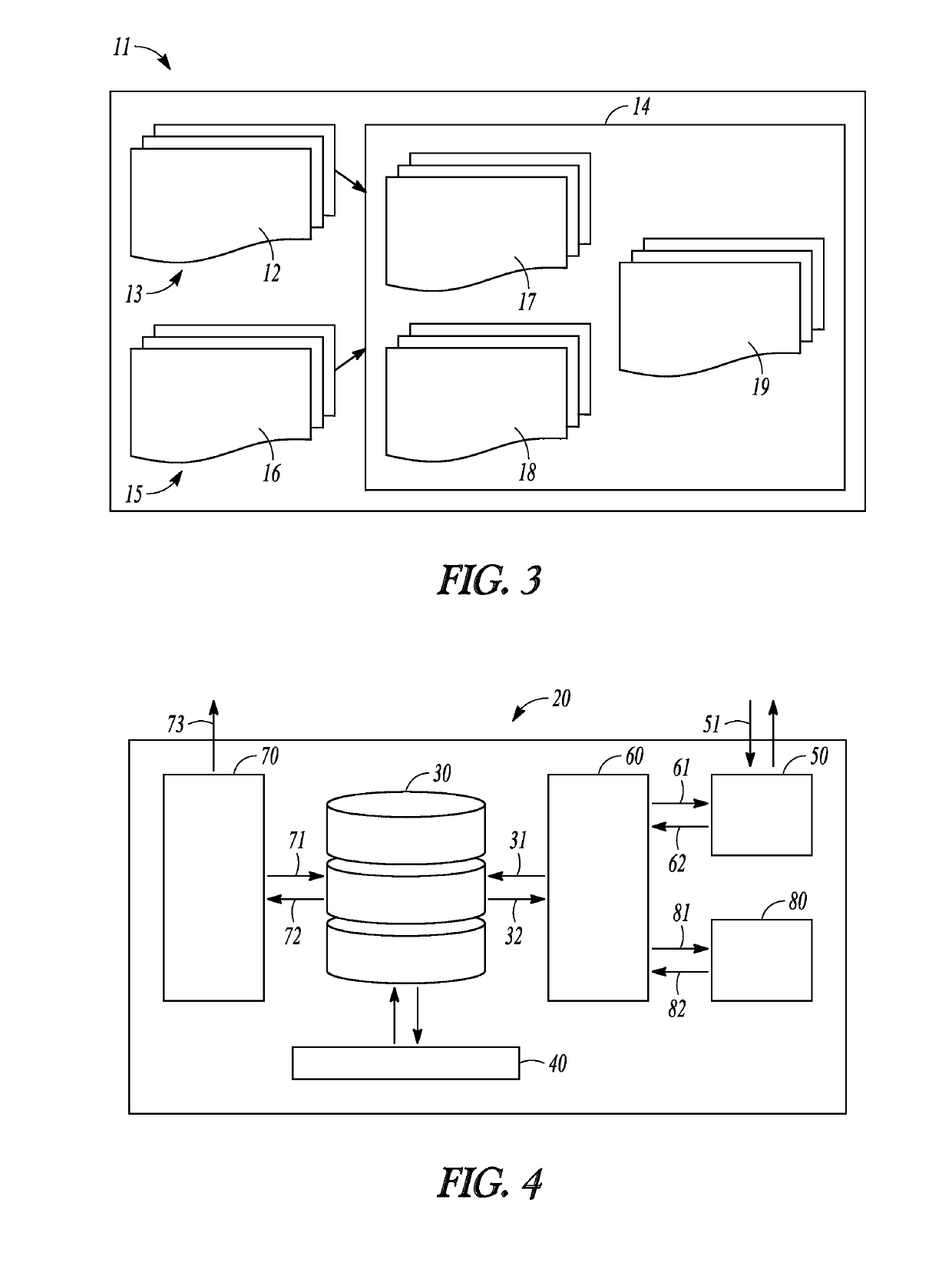
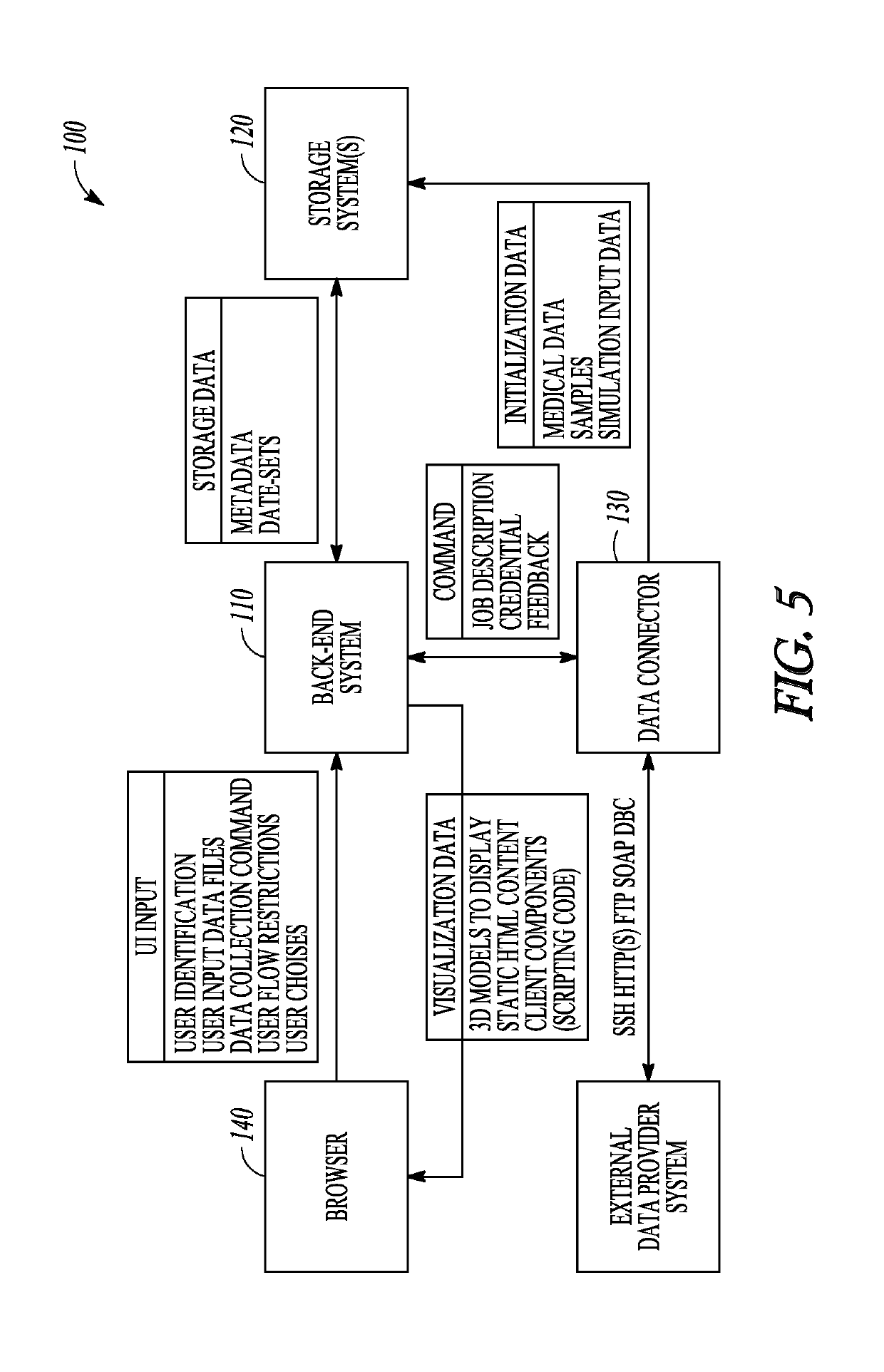
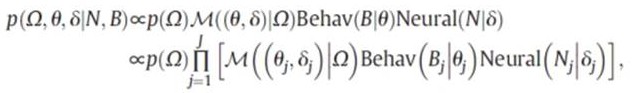Patents
Literature
55 results about "Neuroimaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neuroimaging or brain imaging is the use of various techniques to either directly or indirectly image the structure, function, or pharmacology of the nervous system. It is a relatively new discipline within medicine, neuroscience, and psychology. Physicians who specialize in the performance and interpretation of neuroimaging in the clinical setting are neuroradiologists.
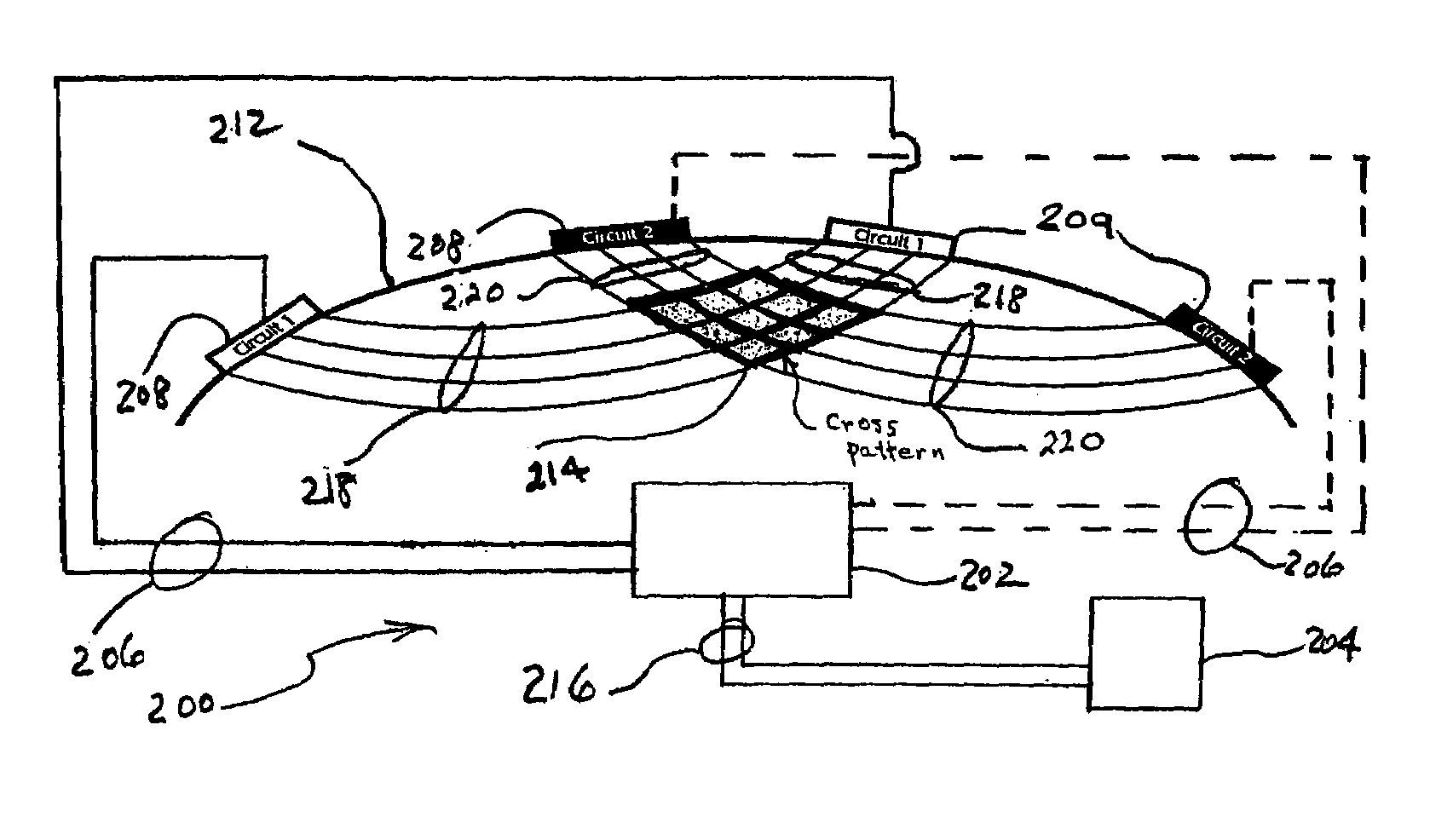
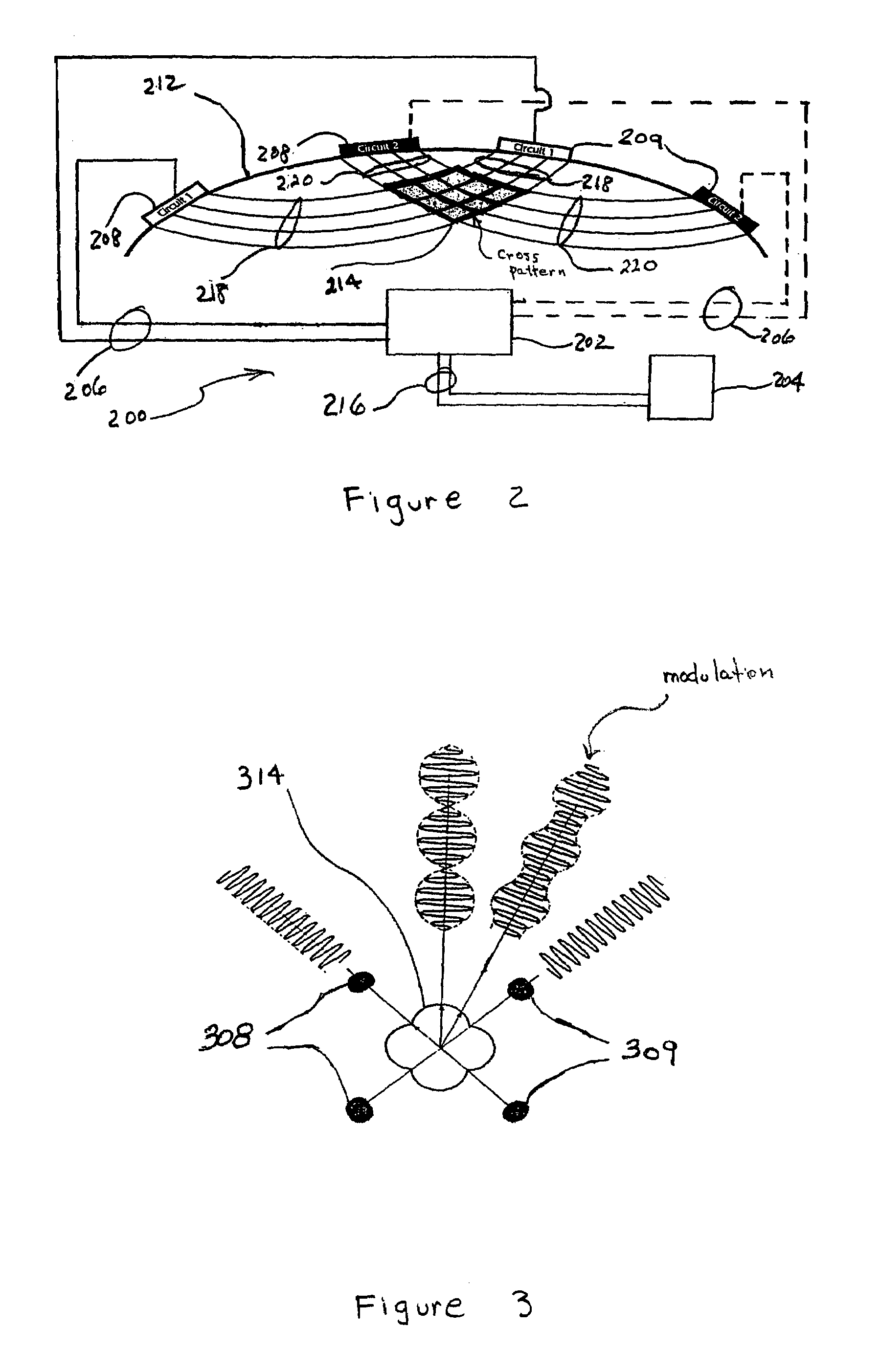
Surface stimulation for tremor control
InactiveUS7228178B2Improve accuracy and reliabilityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationNervous systemMedicine
Apparatus and methods for non-invasive electrical stimulation of the brain through skin surface stimulation of the peripheral nervous system as a treatment for movement disorders. Skin surface electrodes are positioned at predetermined peripheral surface stimulation sites on the skin surface using a variety of neural imaging techniques. A pulsatile electrical current is generated at the stimulation sites through a variety of standard electrical stimulation devices. Stimulation of the peripheral surface stimulation sites translates to electrical stimulation of a specific area of the brain.
Owner:MEAGAN MEDICAL
Real-time multimode neurobiophysiology probe
Apparatus and methods in which very small volumes of material may be extracted, delivered, interrogated or stimulated via optical, electromagnetic or mechanical means, in vivo or in vitro, for site-specific detection, characterization, stimulation, diagnostics or therapy, comprising optical, fluidic, chemical, electromagnetic and biological techniques applied via a microprobe in a single intra-parenchymal tissue perforation procedure in the brain. The primary use of the device is in neuroscience research, clinical diagnostics and therapeutics applications in the brain, however, the device may also be beneficially applied to other organs and biological systems. Human clinical applications may include neurosurgical intra-operative monitoring, extra-operative chronic monitoring of devices introduced in an operation, and diagnostic monitoring combined with simultaneous neuroimaging.
Owner:BLUMENFELD WALTER +2
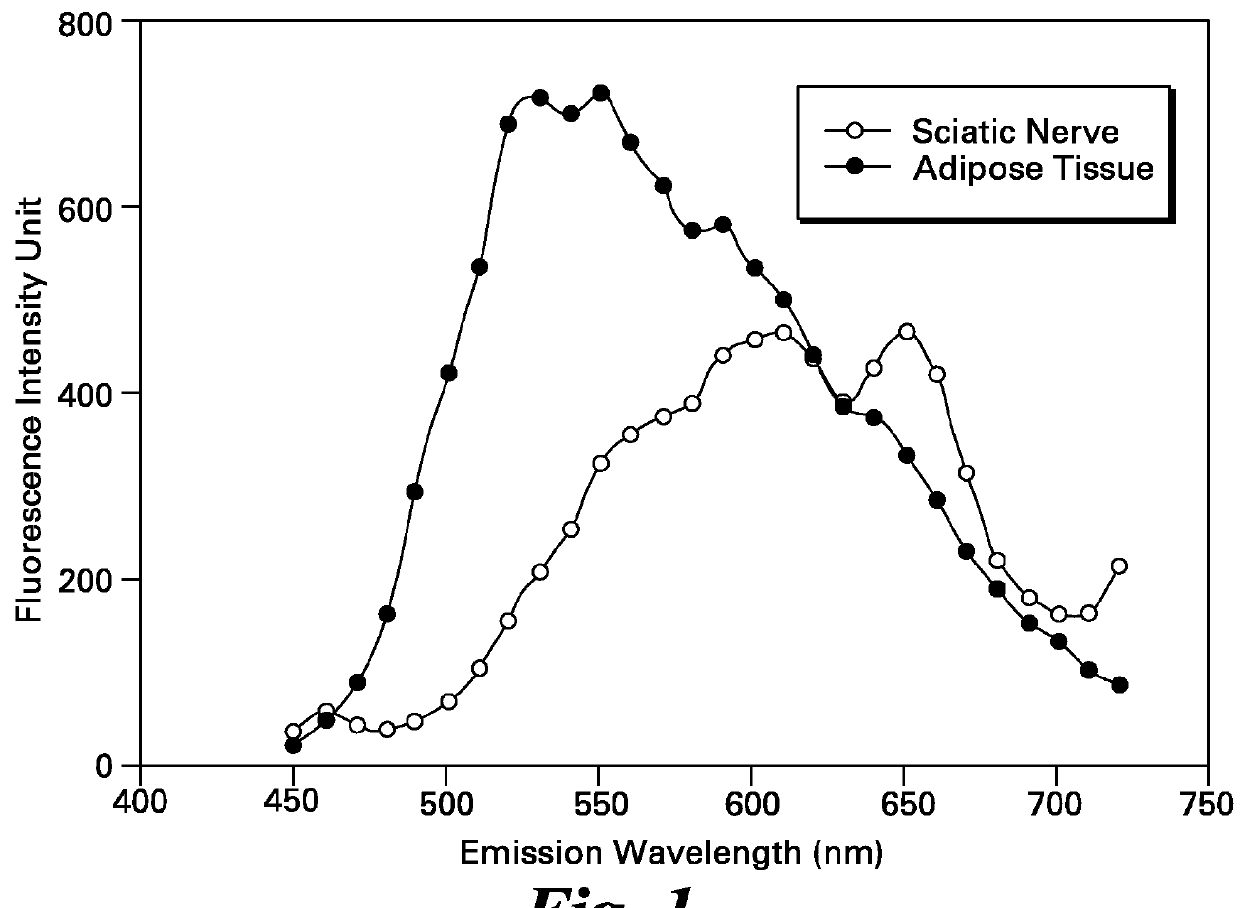
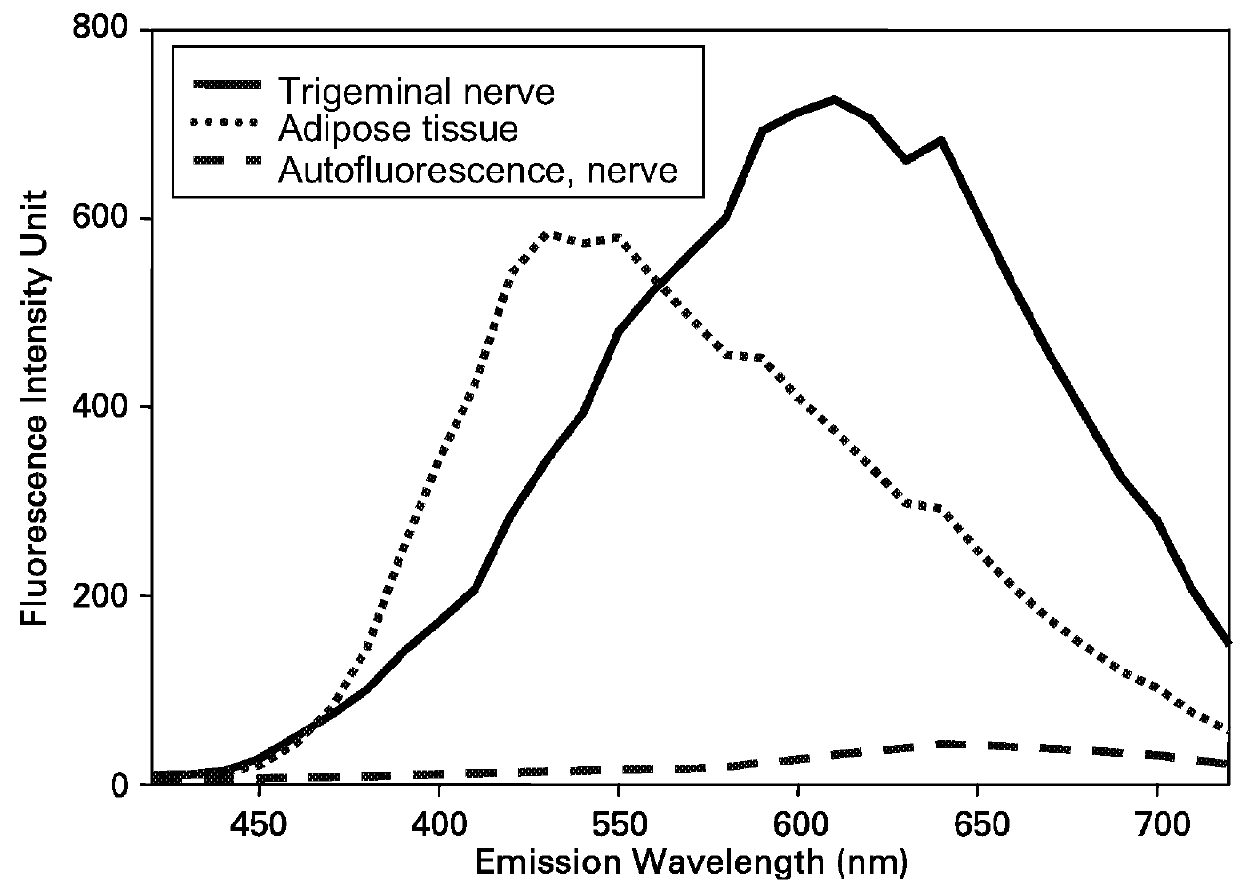
Imaging methods and compositions comprising fluorescent dyes associated with viral components for nerve imaging
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for imaging nerve cells. The composition comprises a fluorescent dye; and a viral component selected from a neurotropic, replication-defective virus, a viral protein of a neurotropic virus, and a capsid of a neurotropic virus. Although the fluorescent dye in itself cannot penetrate nerve cells, the fluorescent dye is bound to the viral component to form a dye / viral component complex that is capable of penetrating nerve cells.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
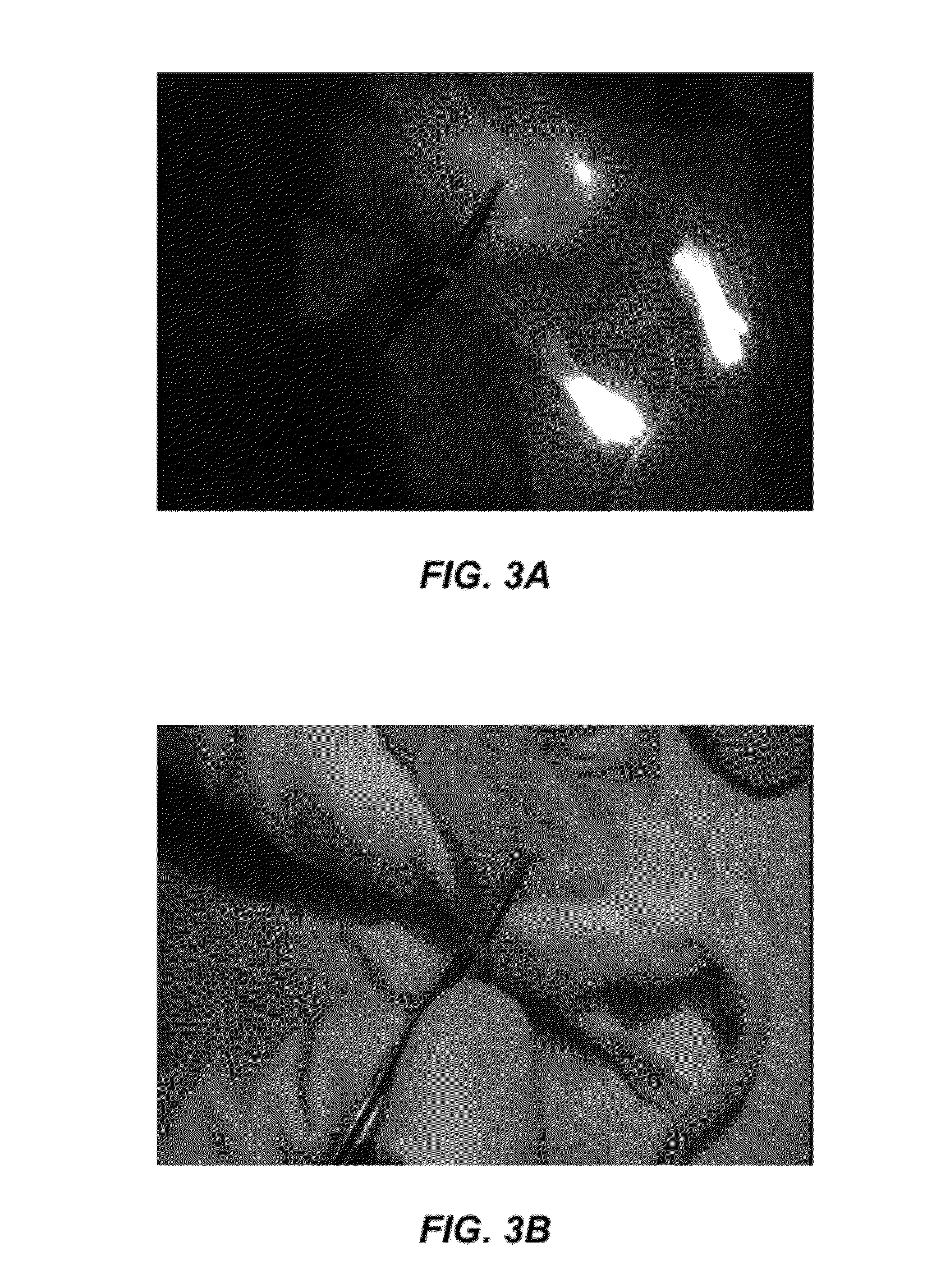
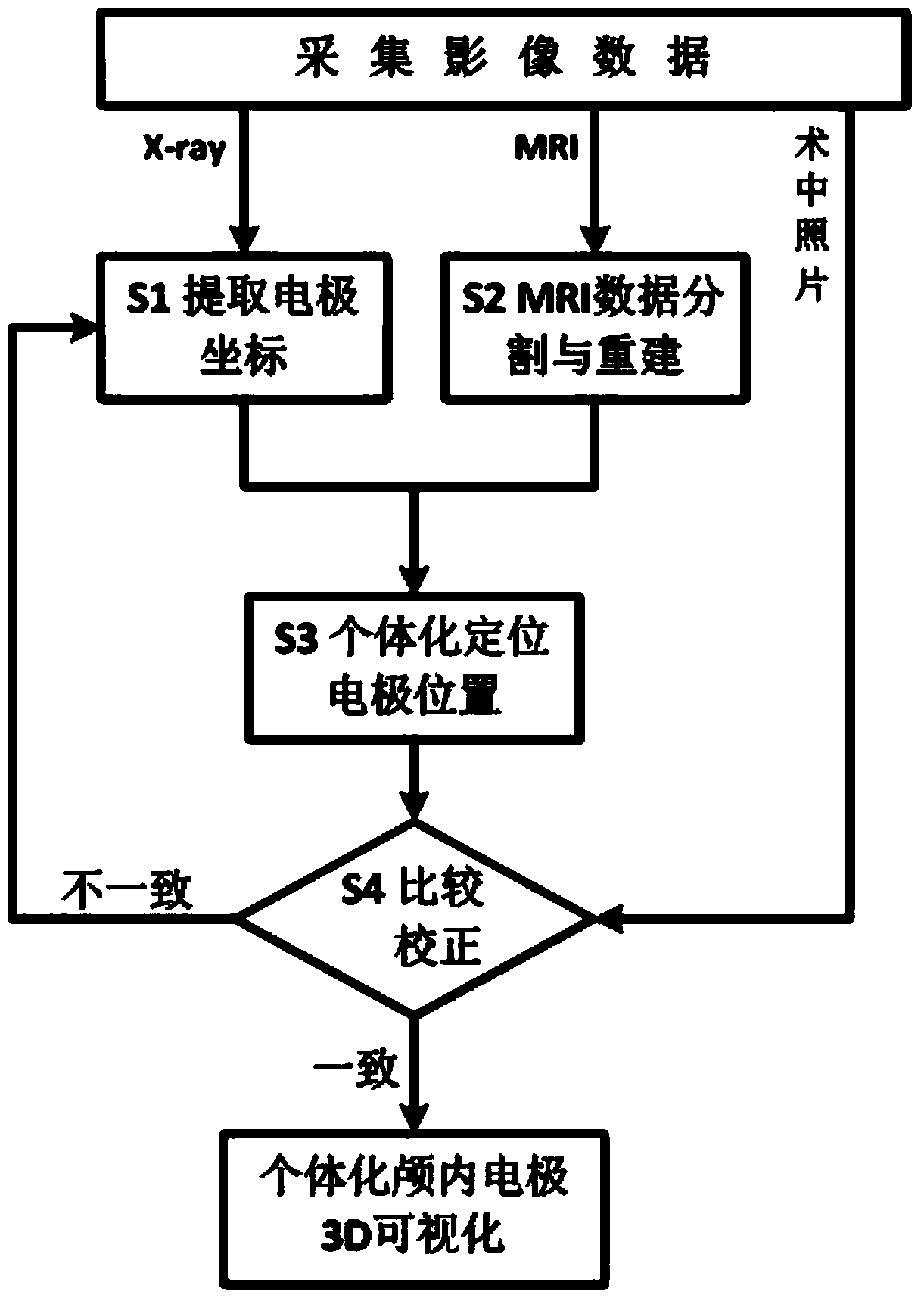
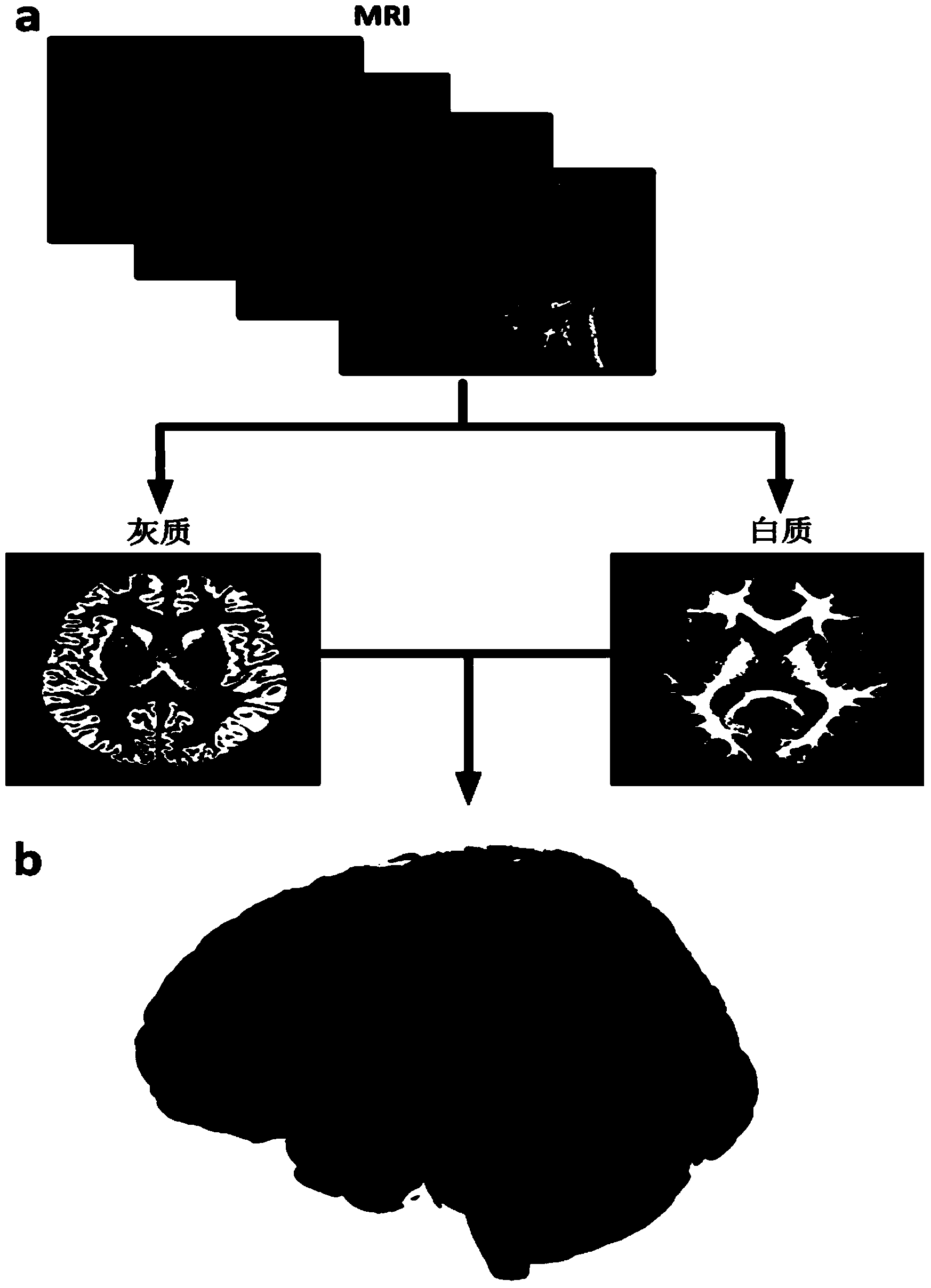
Encephalic electrode individualization locating method based on multimode medical image data fusion
InactiveCN103932796ARealize high-precision individual positioningPrecise positioningDiagnosticsSurgeryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityAnatomical structures
An encephalic electrode individualization locating method based on multimode medical image data fusion relates to the fields of medical instruments and medical image processing and neuroimaging. By means of multimode medical image data including magnetic resonance images, X-ray images and intranperative optical photos, the space position relation of an encephalic electrode and a brain tissue structure is comprehensively measured, a relation between the position of the encephalic electrode and a brain anatomical structure is established, and accurate and fast individualization locating of the encephalic electrode is achieved. The encephalic electrode individualization locating method based on multimode medical image data fusion can be used in the fields of cognitive neuroscience basic research, clinic neurosciences and the like, provide accurate brain space position information for an encephalic electroencephalogram signal, and enhance application value in the aspect of electrophysiological basis research.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
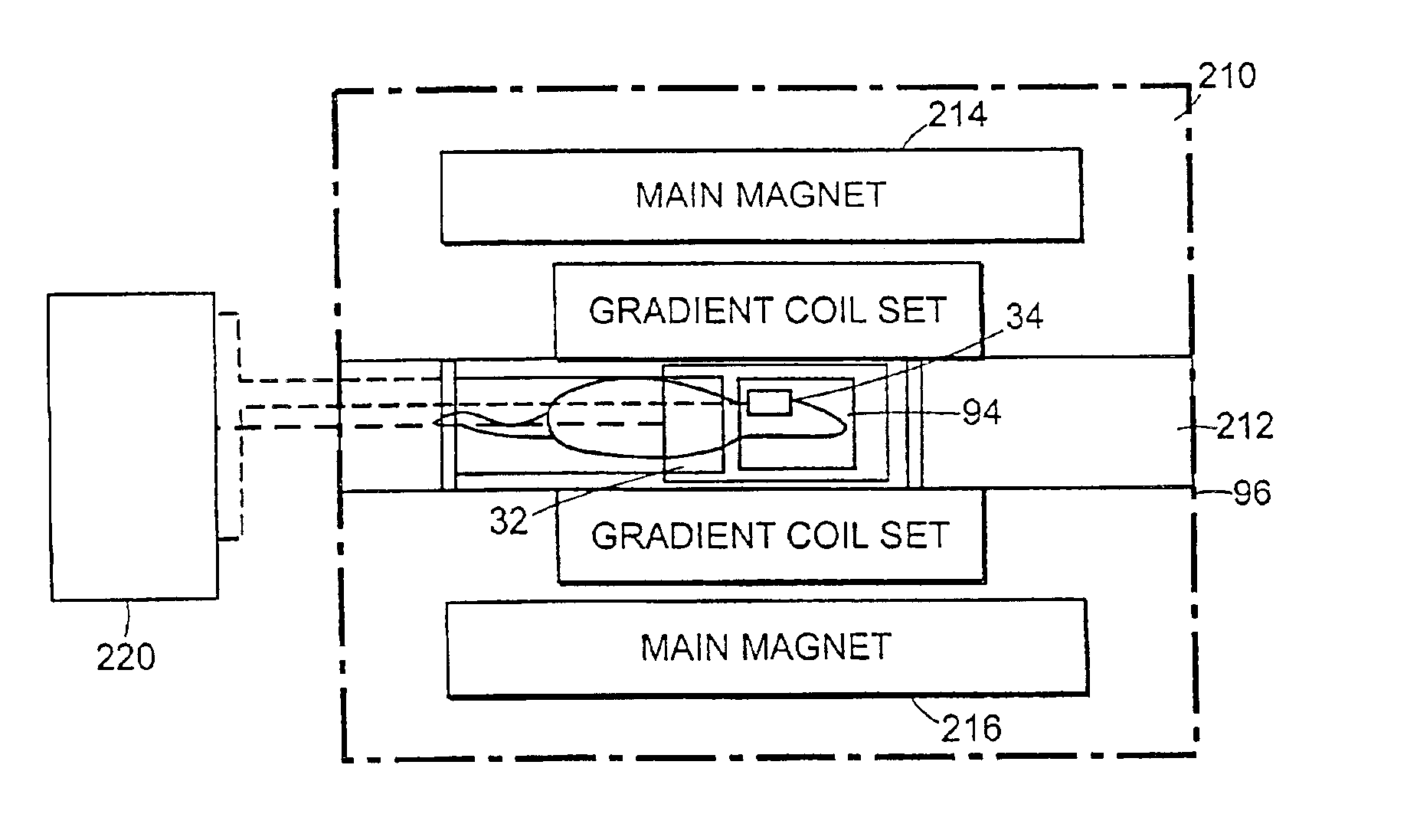
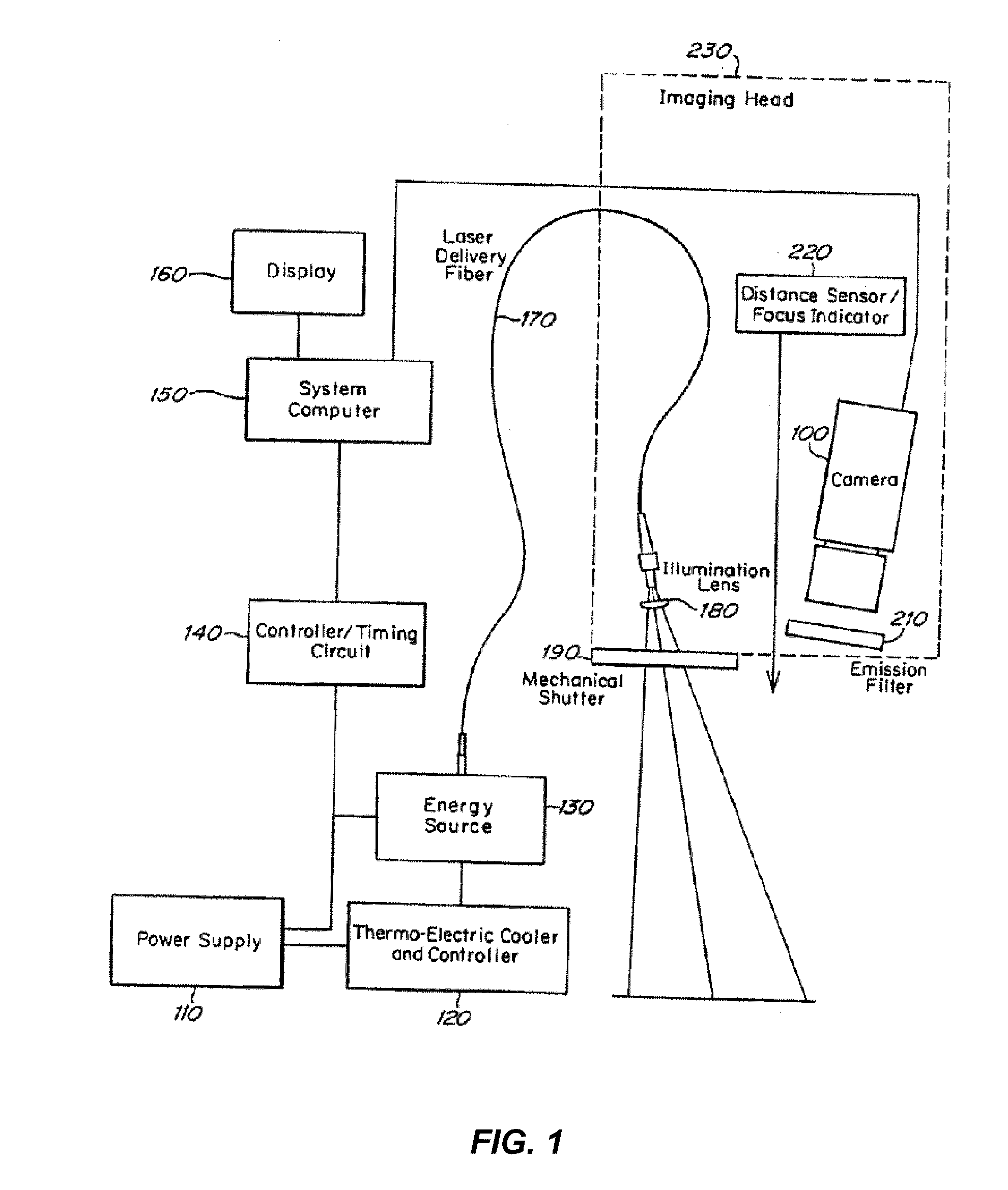
Method and apparatus for performing neuroimaging
InactiveUS6873156B2Remove Motion ArtifactsEnhanced signalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDual coilHigh field magnetic resonance imaging
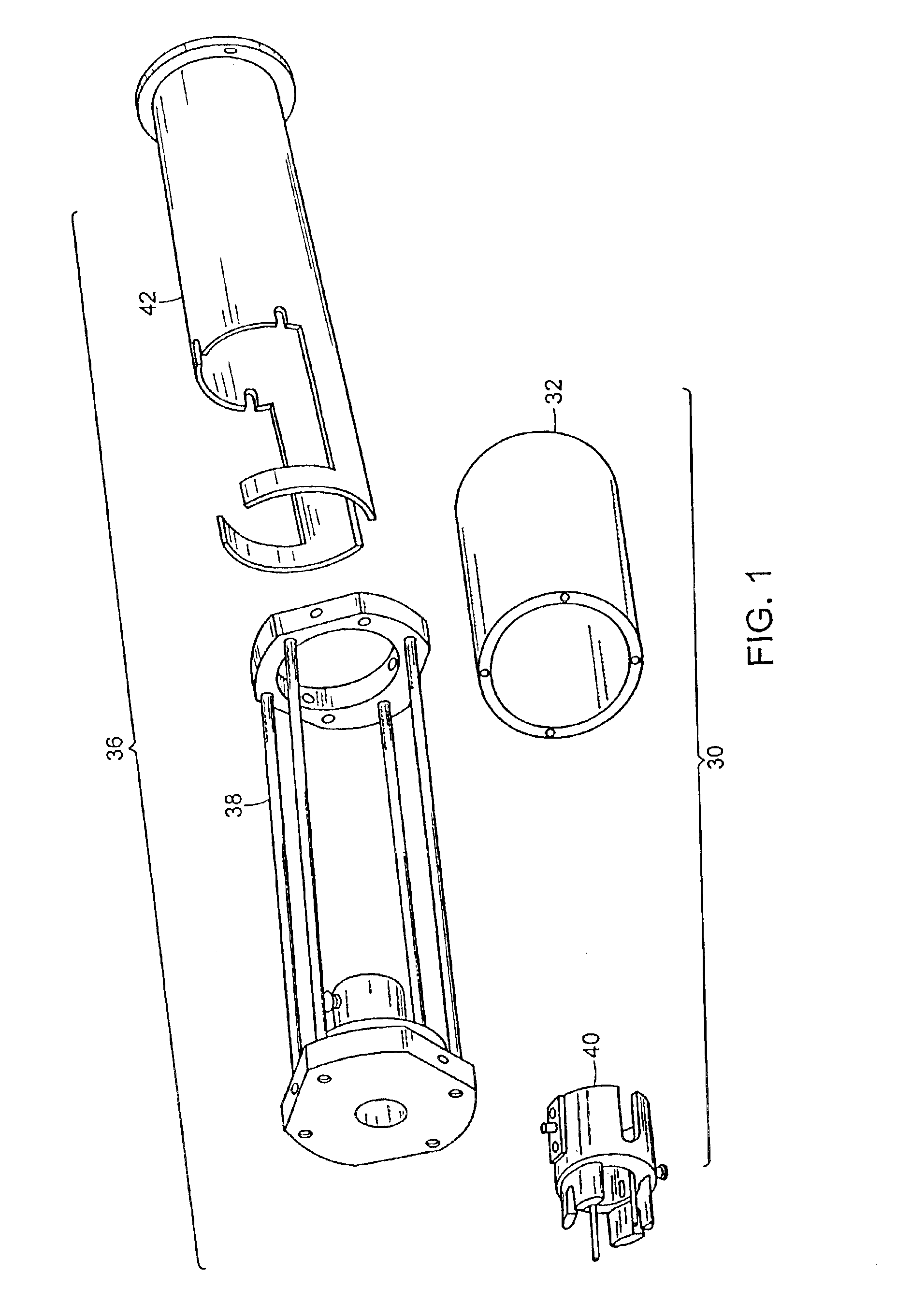
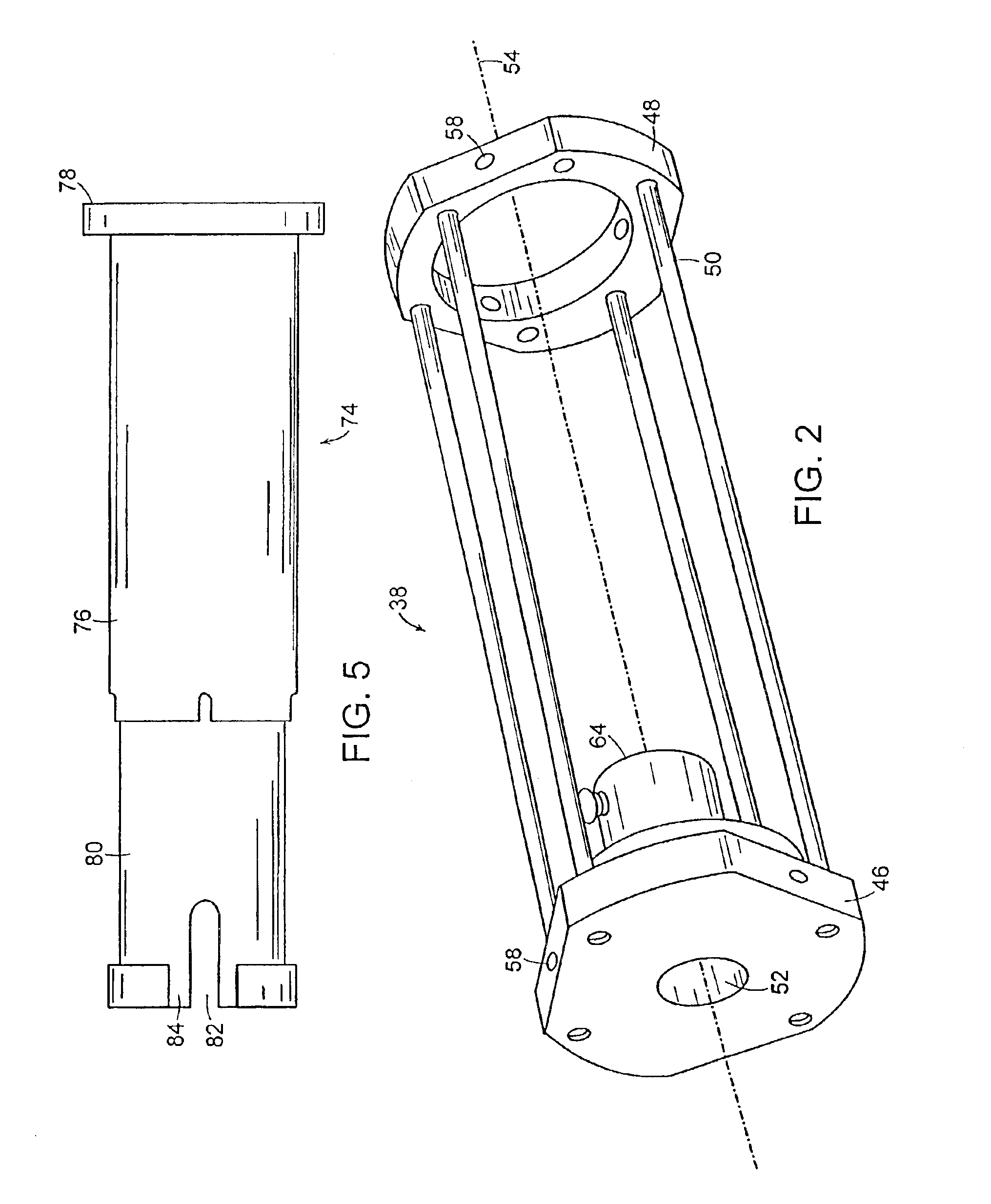
The present invention relates to systems and methods of performing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in awake animals. The invention utilizes head and body restrainers to position an awake animal relative to a radio frequency dual coil system operating in a high field magnetic resonance imaging system to provide images of high resolution without motion artifact.
Owner:EKAM IMAGING
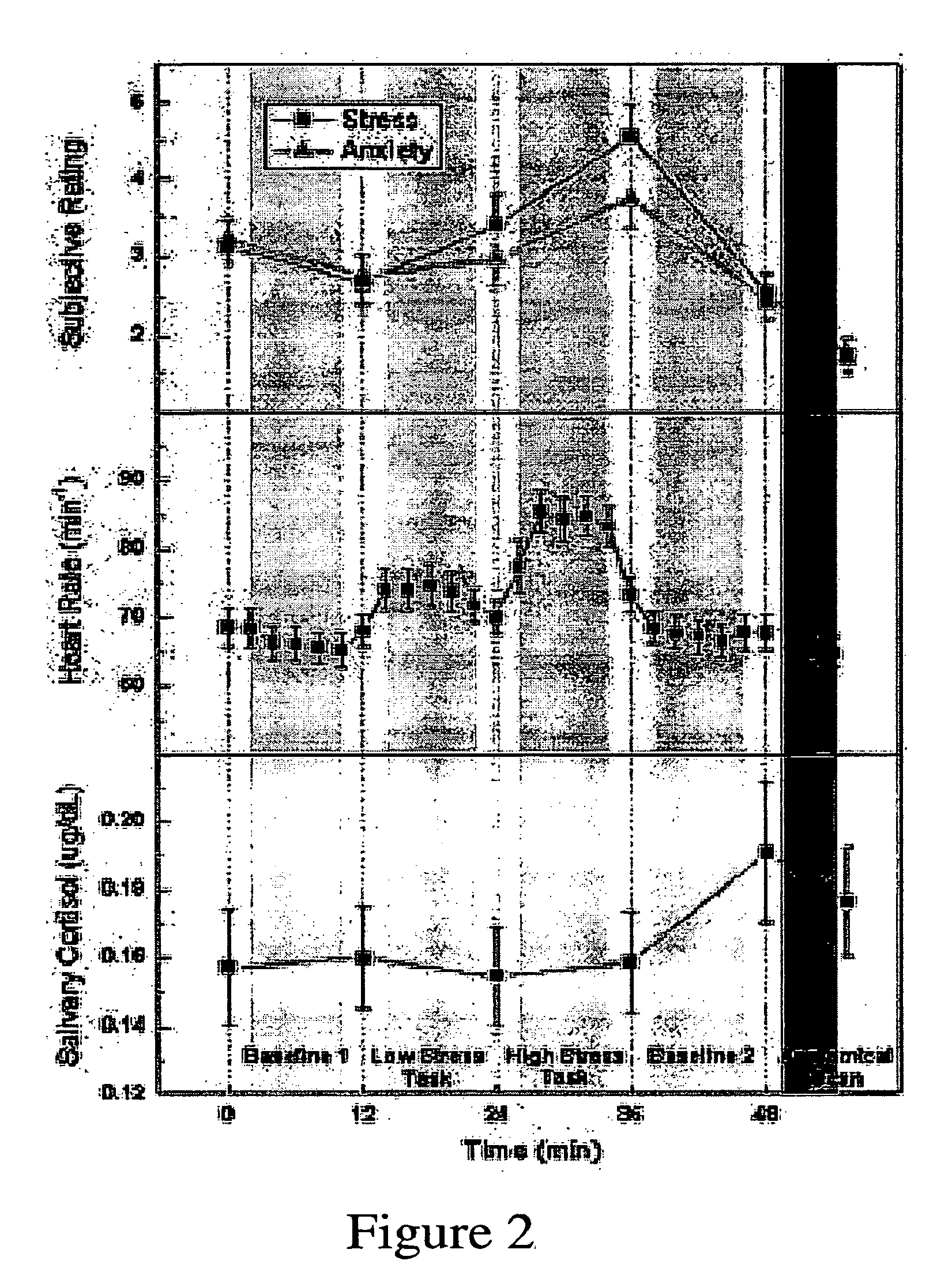
Assessing subject's reactivity to psychological stress using fmri
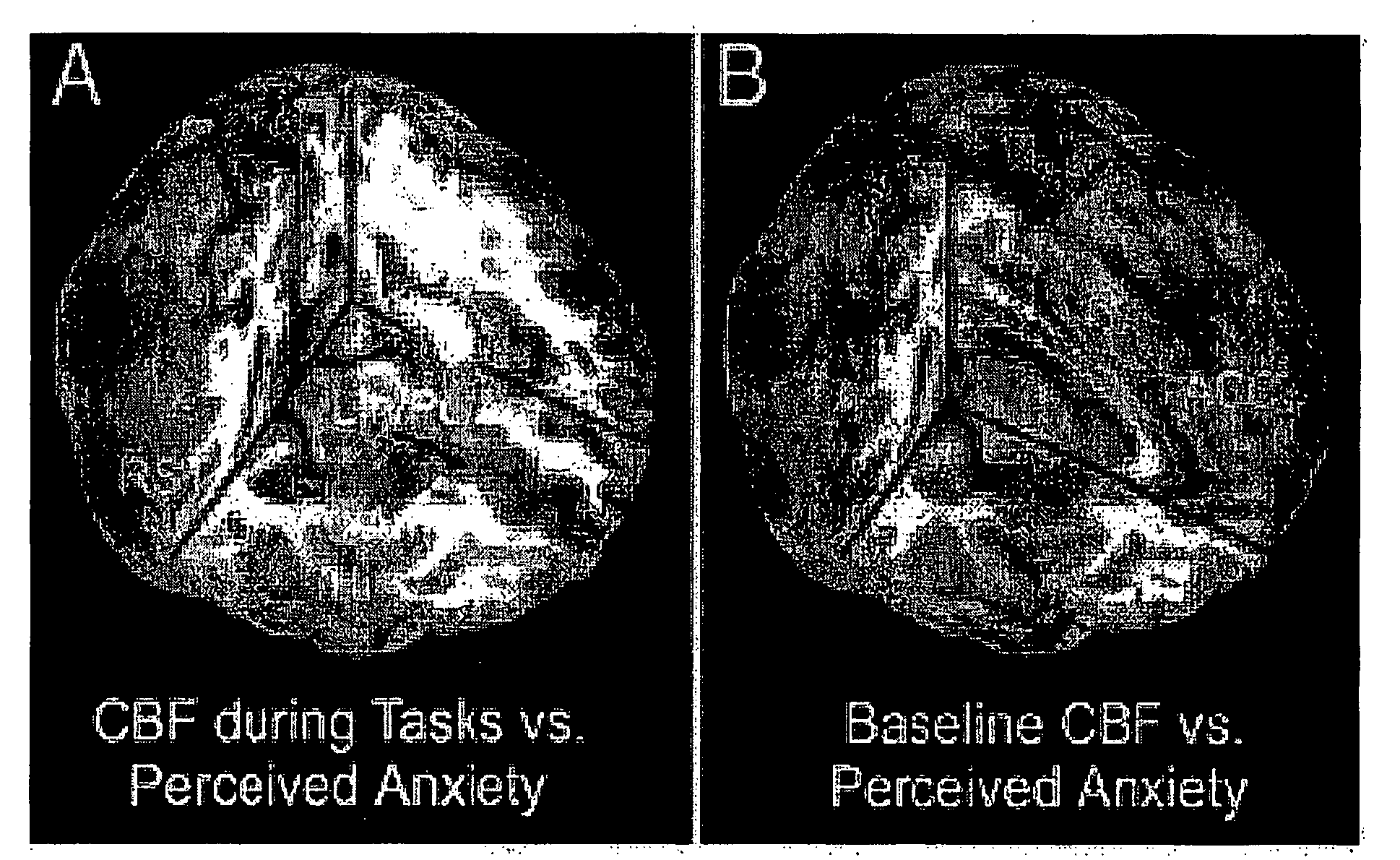
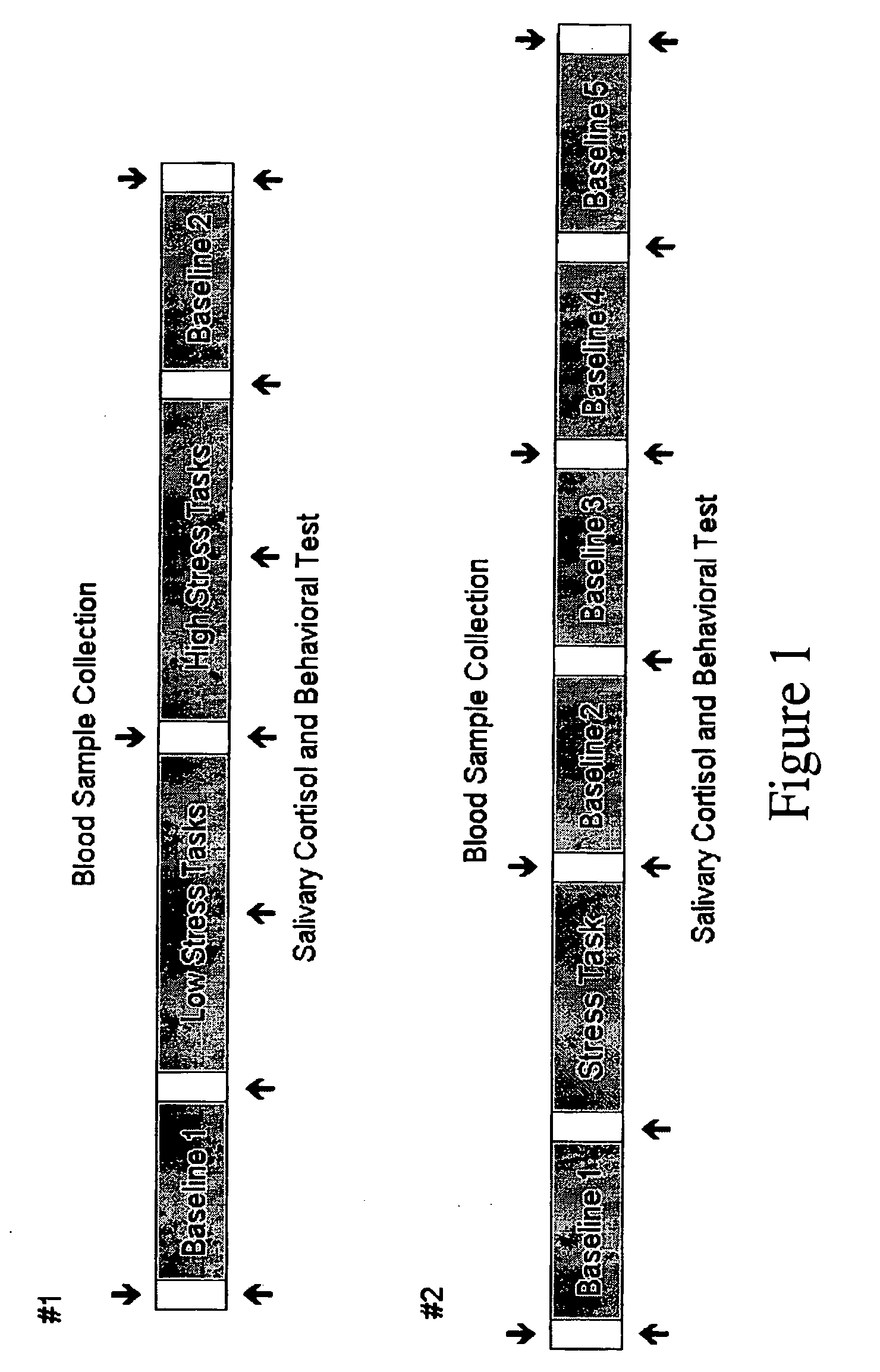
This invention relates to the use of a quantitative functional MRI (fMRI)—arterial spin-labeling perfusion MRI or absolute T2 mapping MRI or a combination thereof in the non-invasive neuroimaging of a subject's brain in response to stress-inducing psychological stimuli, which can be utilized to predict individual stress reactivity as well as to be used as a human model for testing or optimizing psychopharmacological agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Imaging methods and compositions comprising fluorescent dyes associated with viral components for nerve imaging
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for imaging nerve cells. The composition comprises a fluorescent dye; and a viral component selected from a neurotropic, replication-defective virus, a viral protein of a neurotropic virus, and a capsid of a neurotropic virus. Although the fluorescent dye in itself cannot penetrate nerve cells, the fluorescent dye is bound to the viral component to form a dye / viral component complex that is capable of penetrating nerve cells.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Method and computing system for modelling a primate brain
In one aspect the application relates to a computing system for providing data for modelling a human brain comprises a database including a plurality of datasets (or allow access to a plurality of datasets), each dataset including at least a dynamical model of the brain including at least one node and a neurodataset of a neuroimaging modality input. The at least one node include a representation of a local dynamic model and a parameter set of the local dynamic model.
Owner:CODEBOX COMPDIENSTE +5
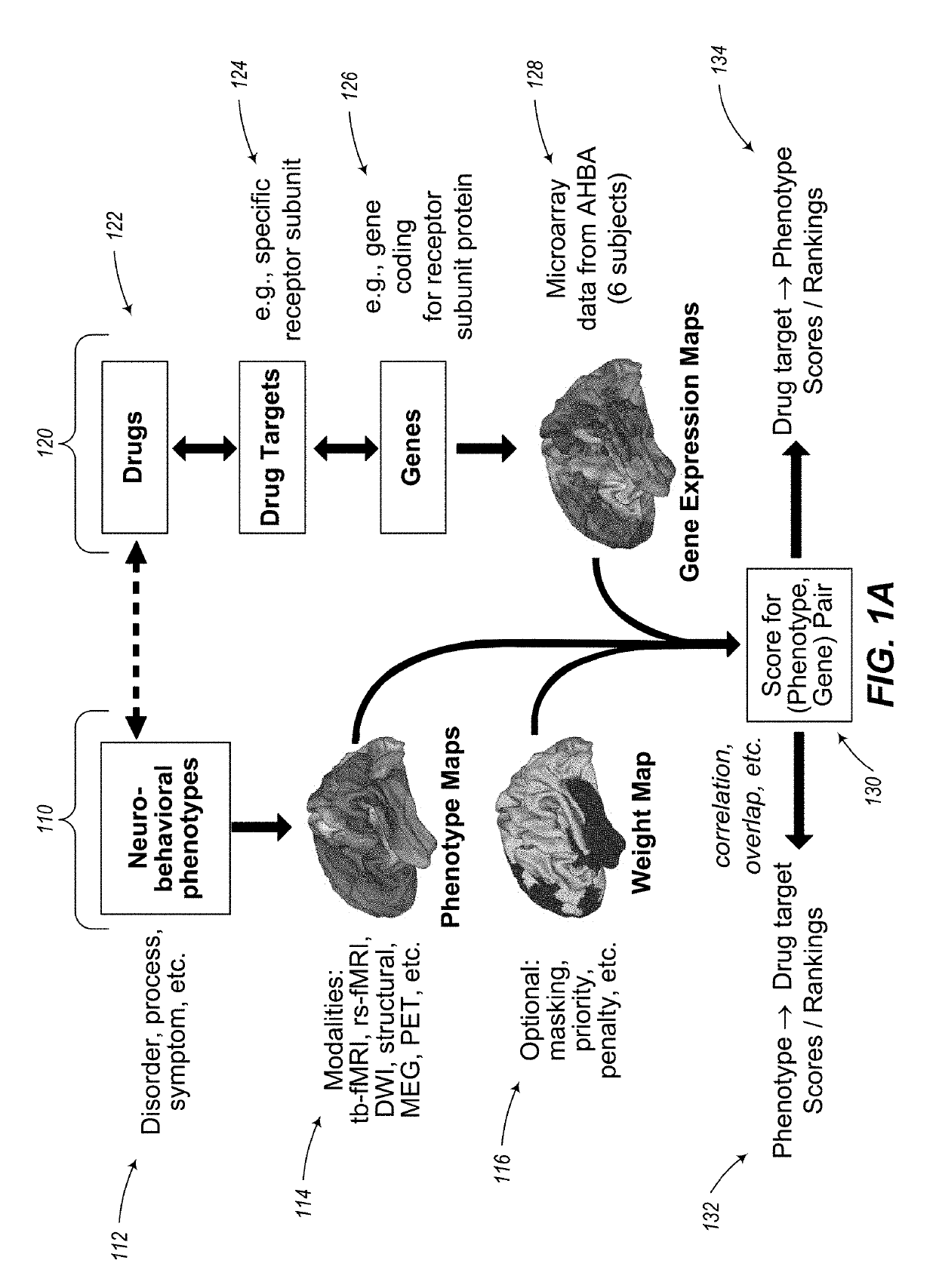
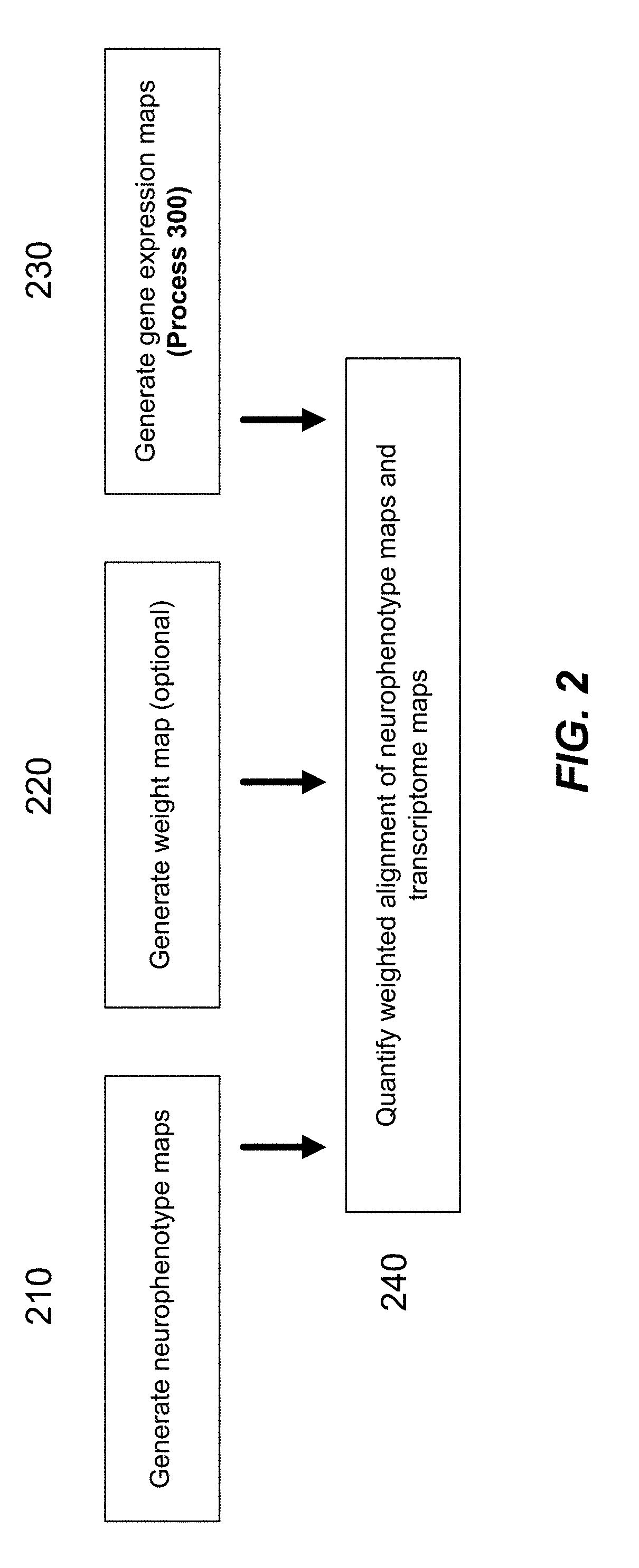
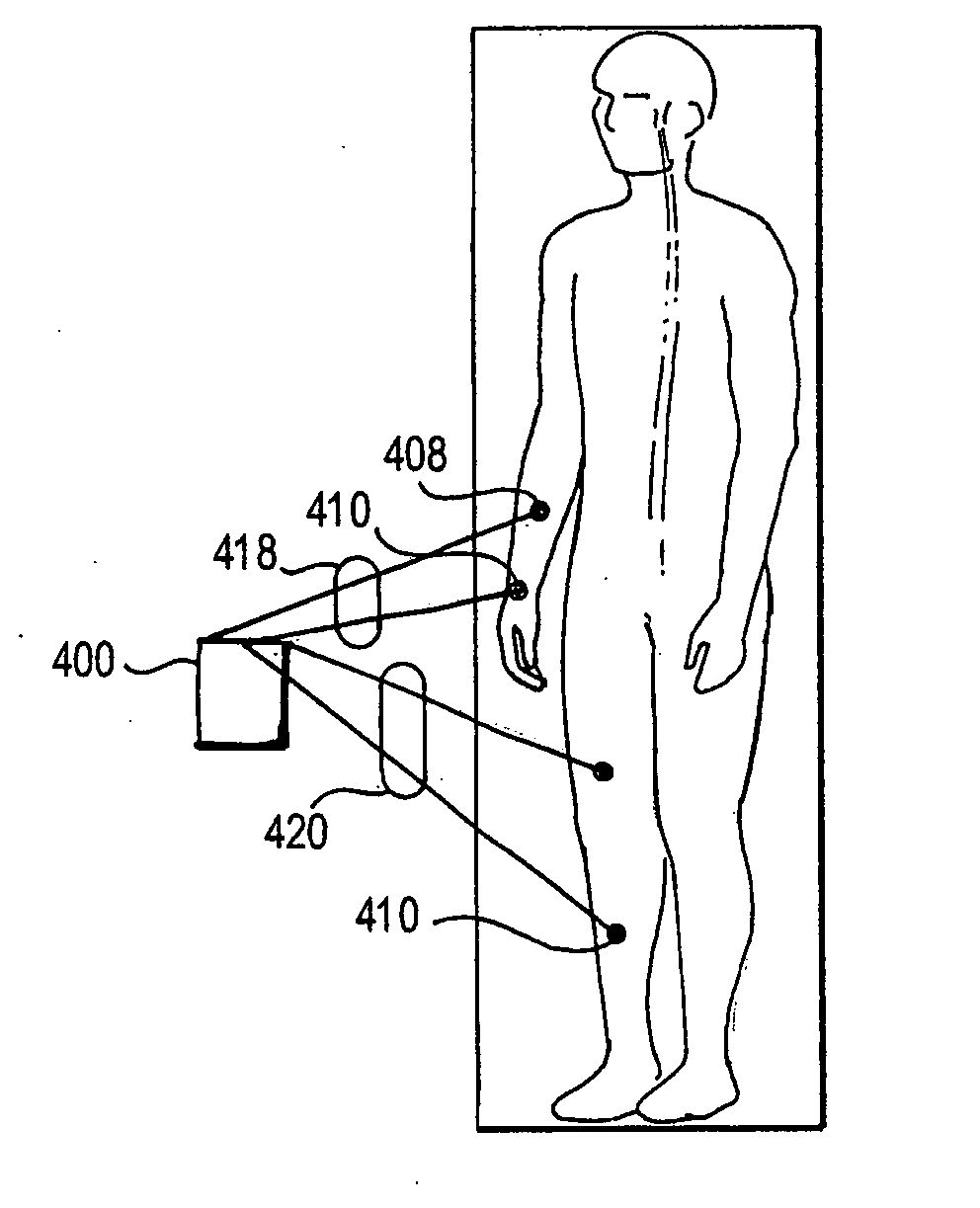
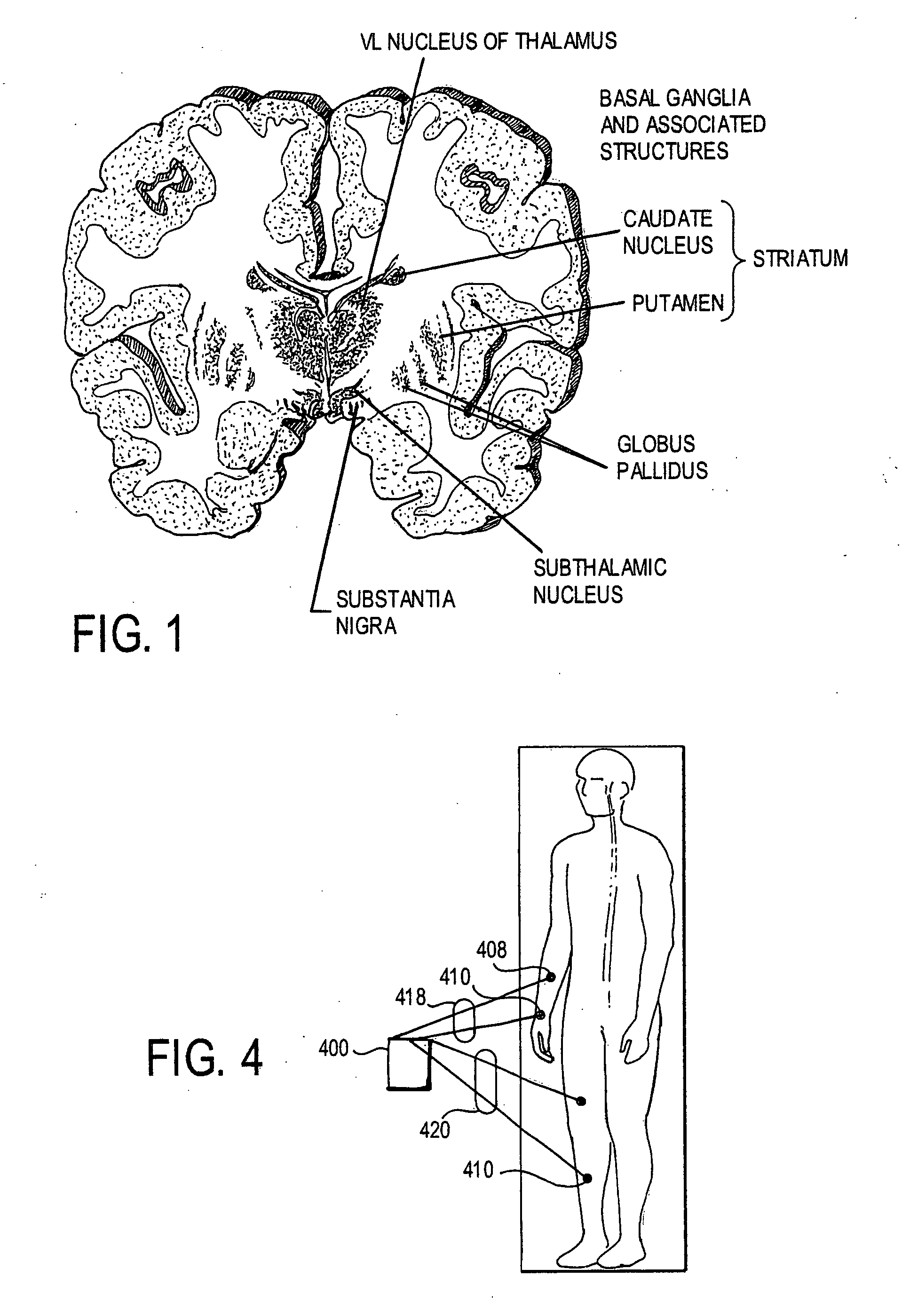
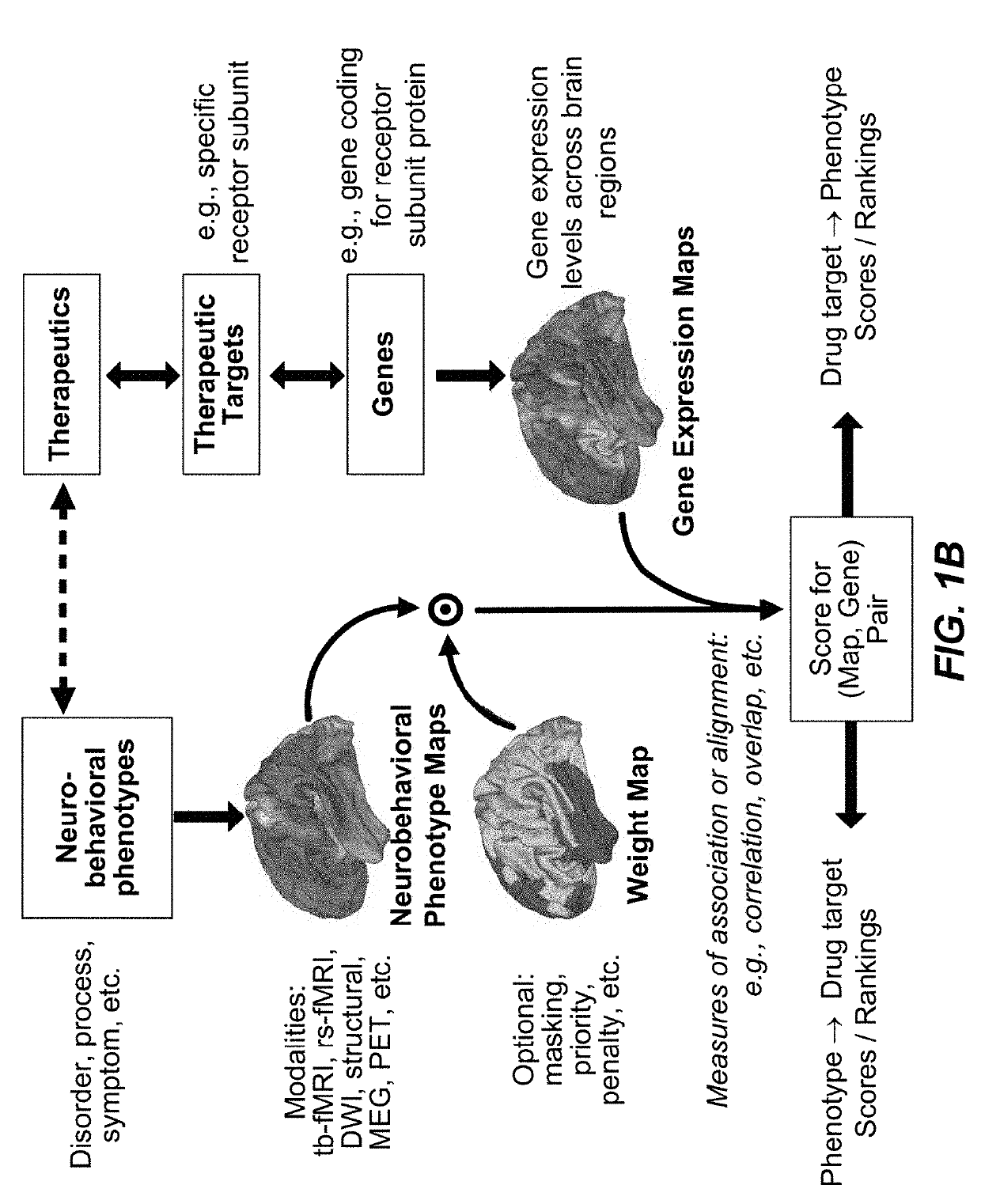
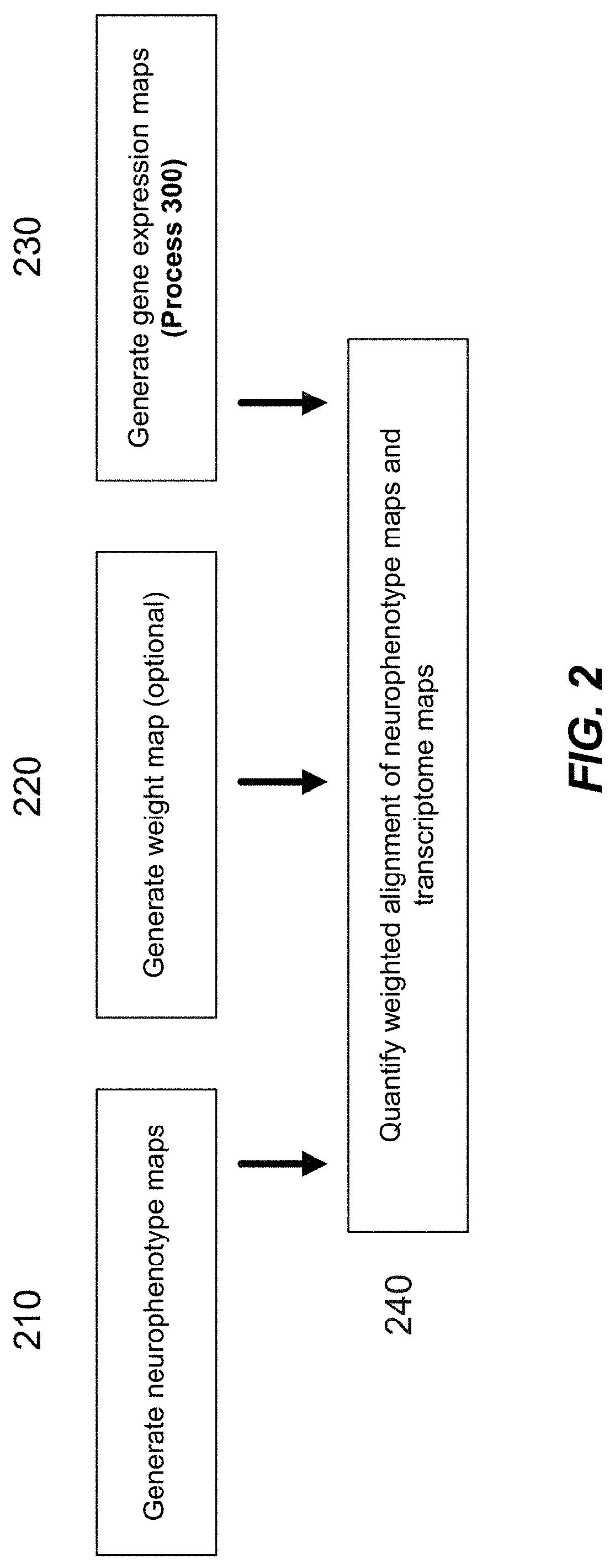
Methods and tools for detecting, diagnosing, predicting, prognosticating, or treating a neurobehavioral phenotype in a subject
InactiveUS20190102511A1Efficient designPrecise positioningDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsPharmacometricsGenotype
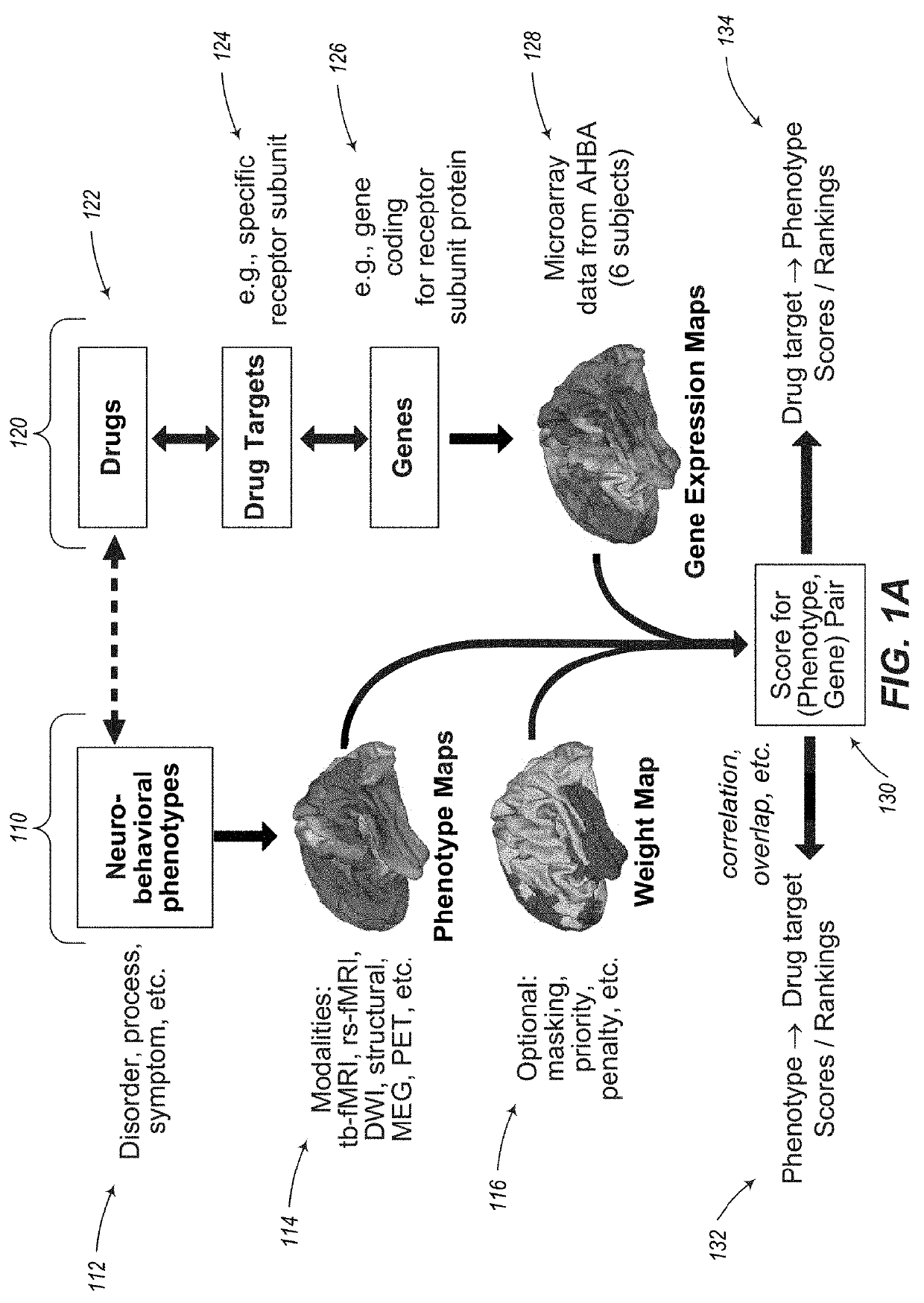
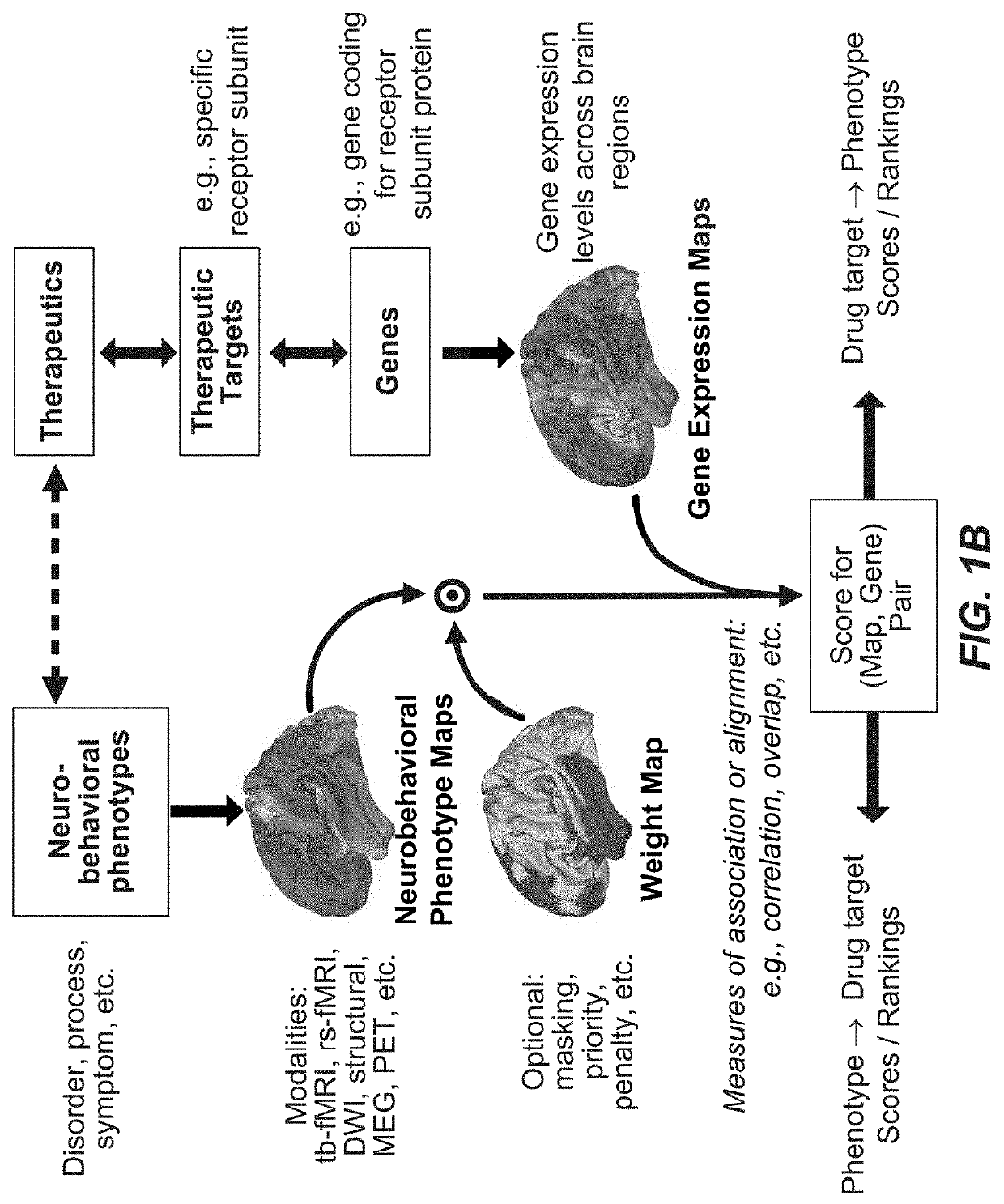
The present tools and methods for detecting, diagnosing, predicting, prognosticating, or treating a neurobehavioral phenotype in a subject. These tools and methods relates to a genotype and neurophenotype topography-based approach for analyzing brain neuroimaging and gene expression maps to identify drug targets associated with neurobehavioral phenotypes and, conversely, neurobehavioral phenotypes associated with potential drug targets, to develop rational design and application of pharmacological therapeutics for brain disorders, and to provide methods and tools for treatment of subjects in need of neurological therapy.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
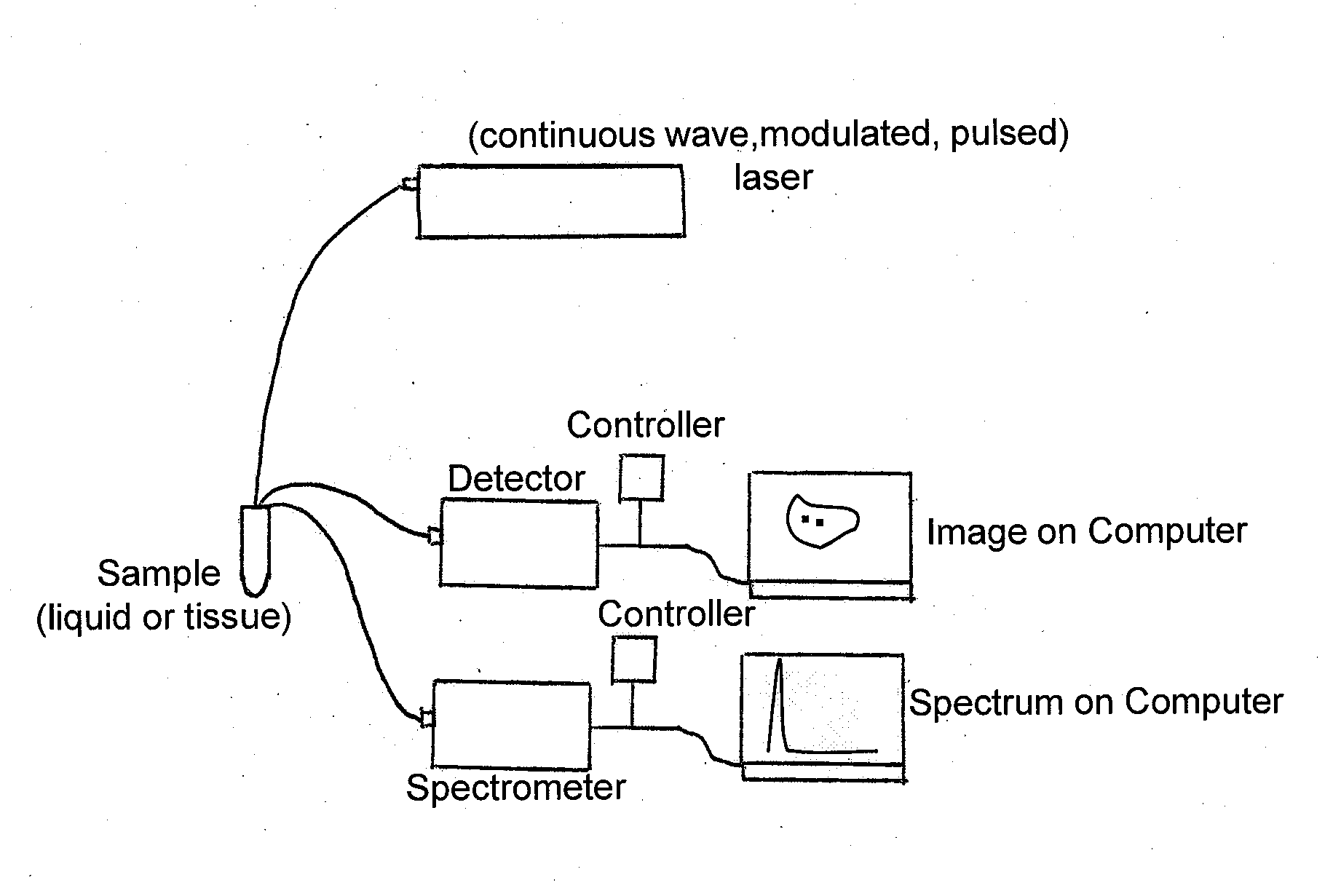
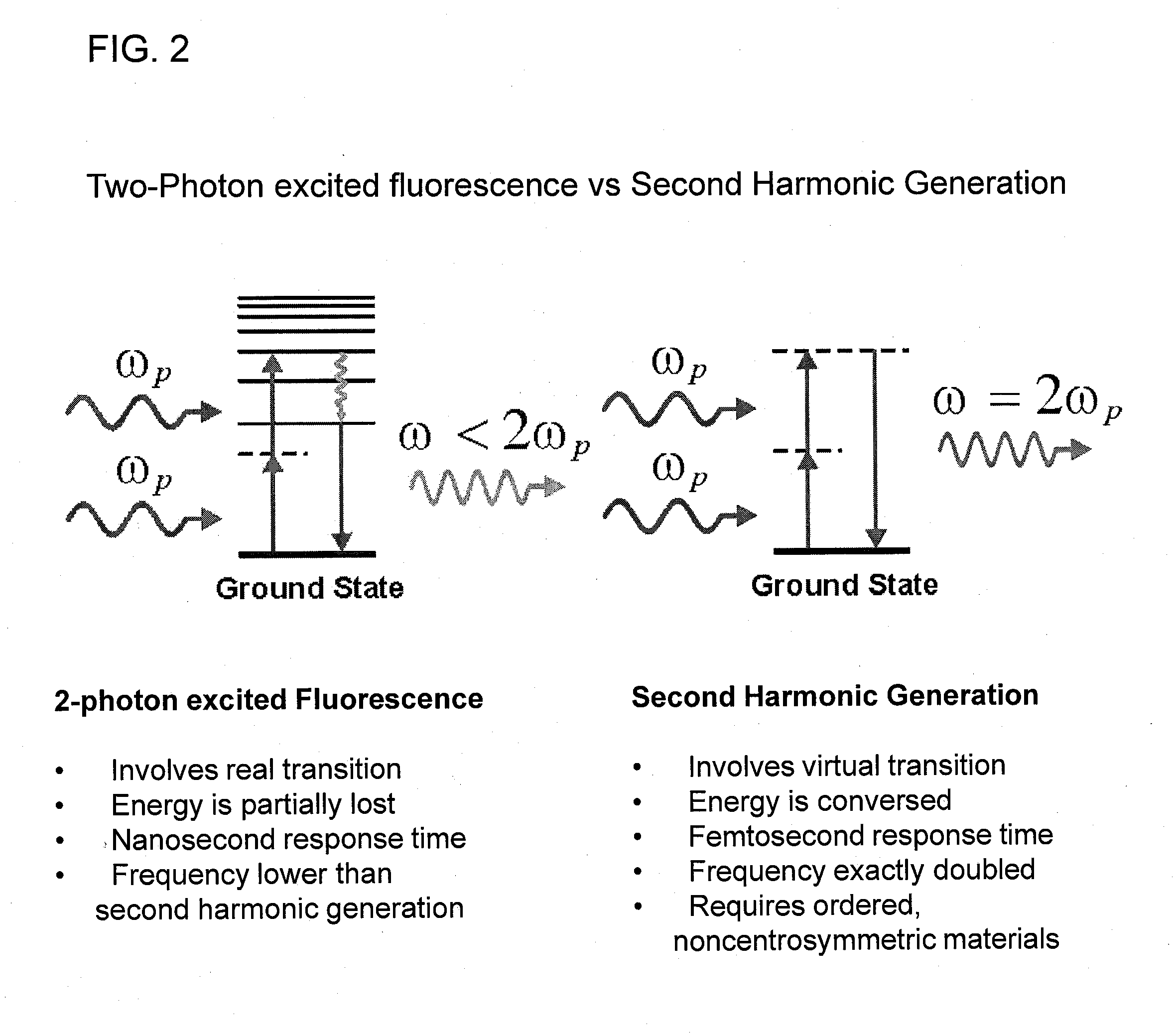
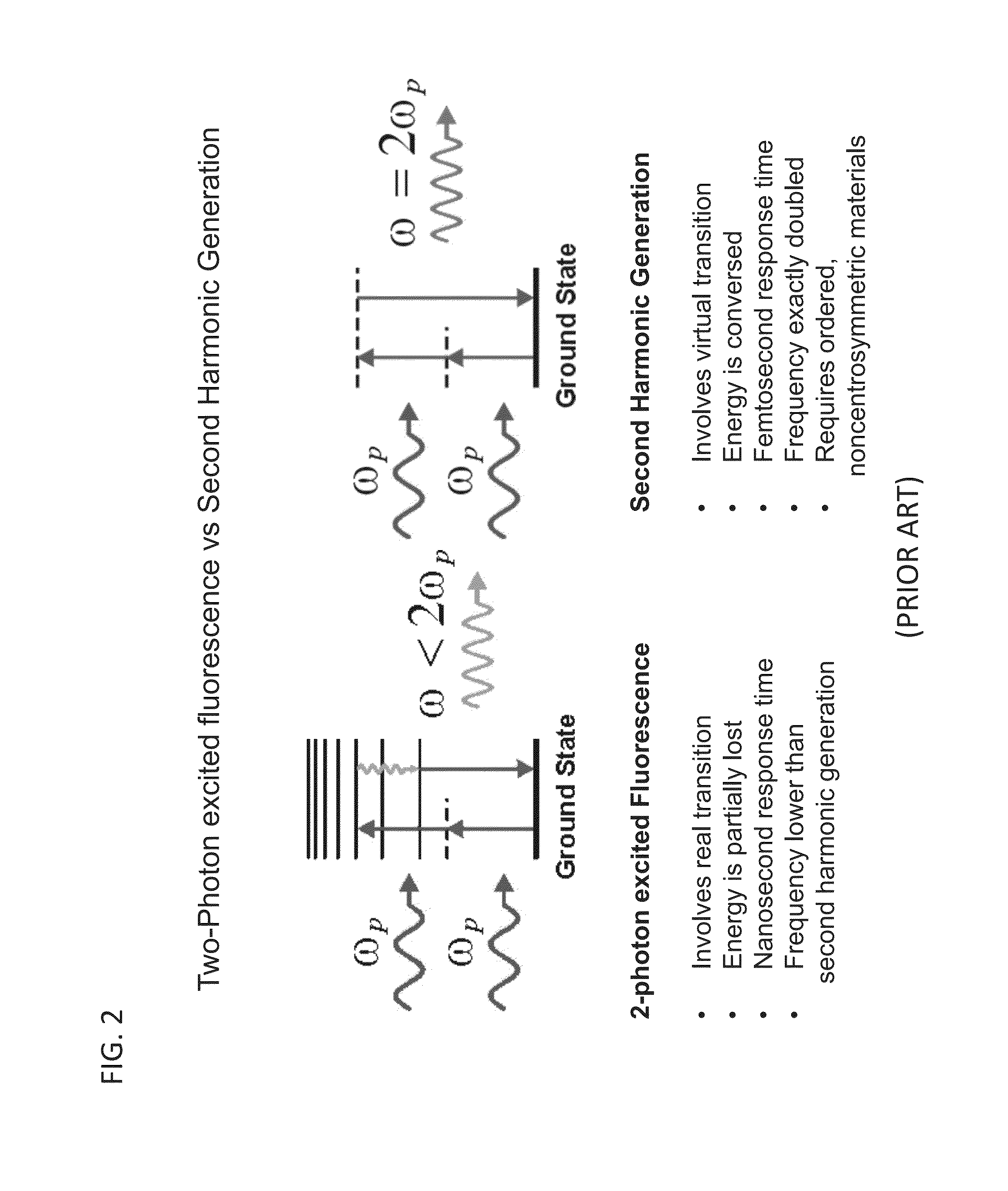
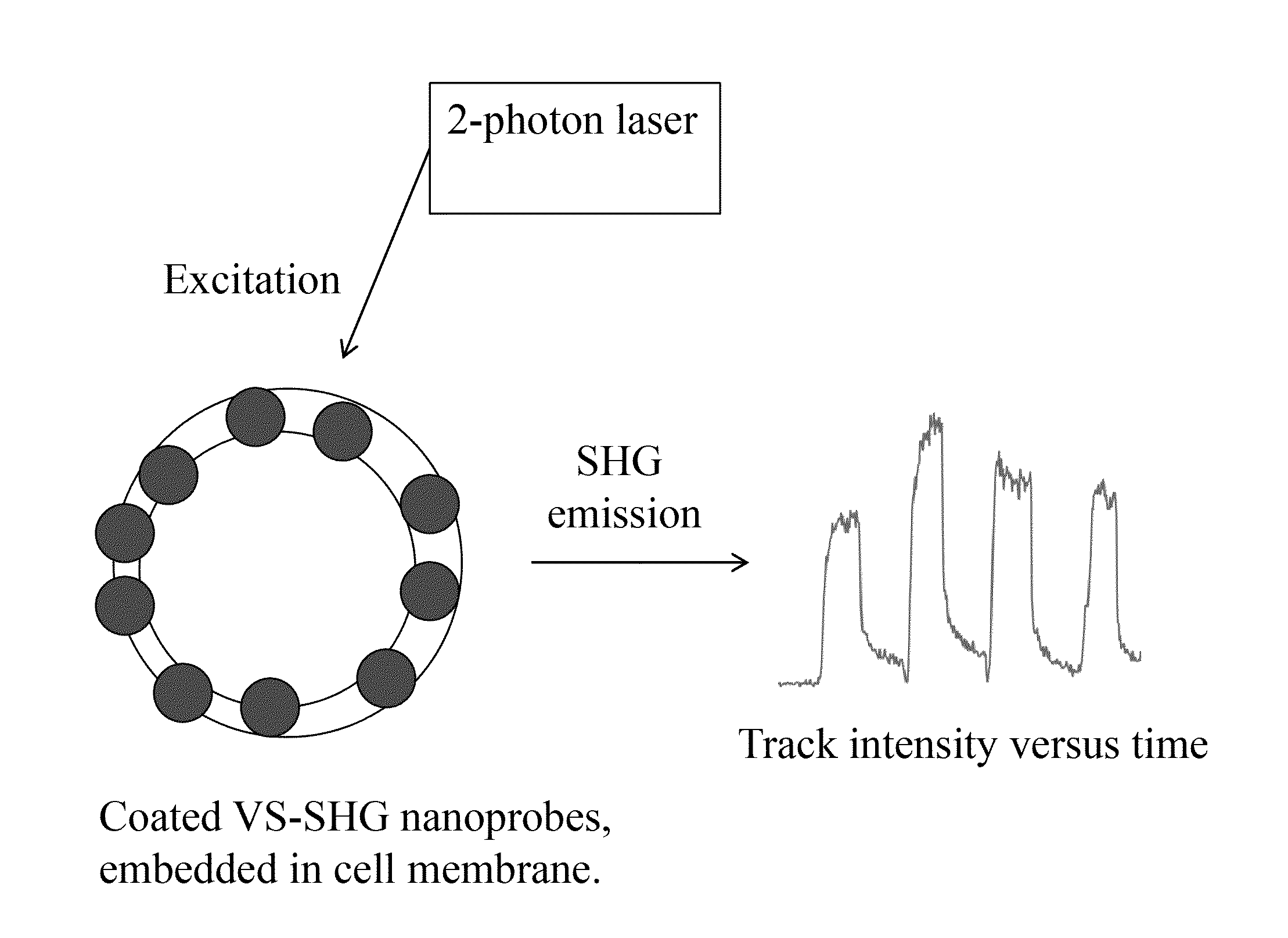
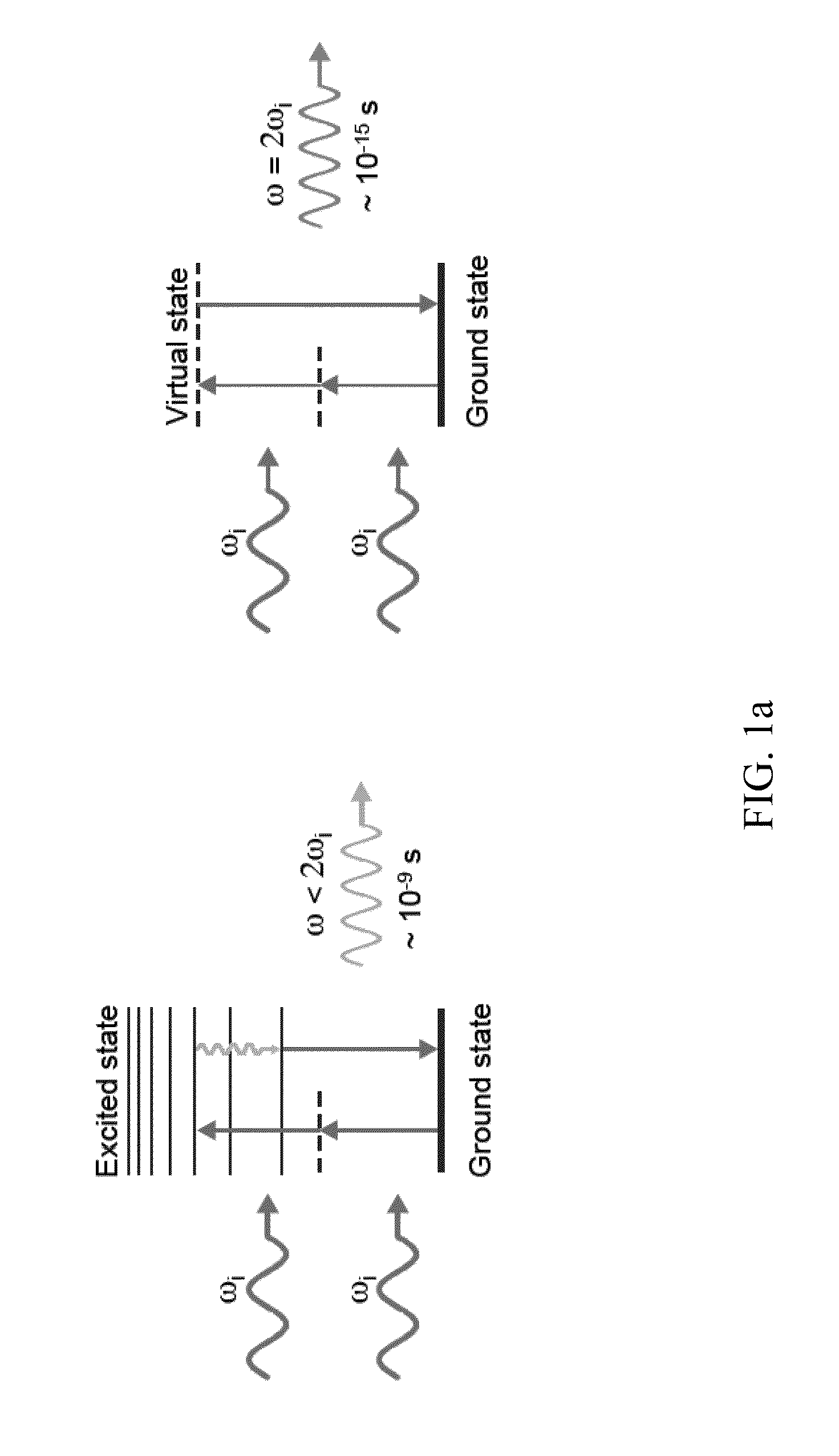
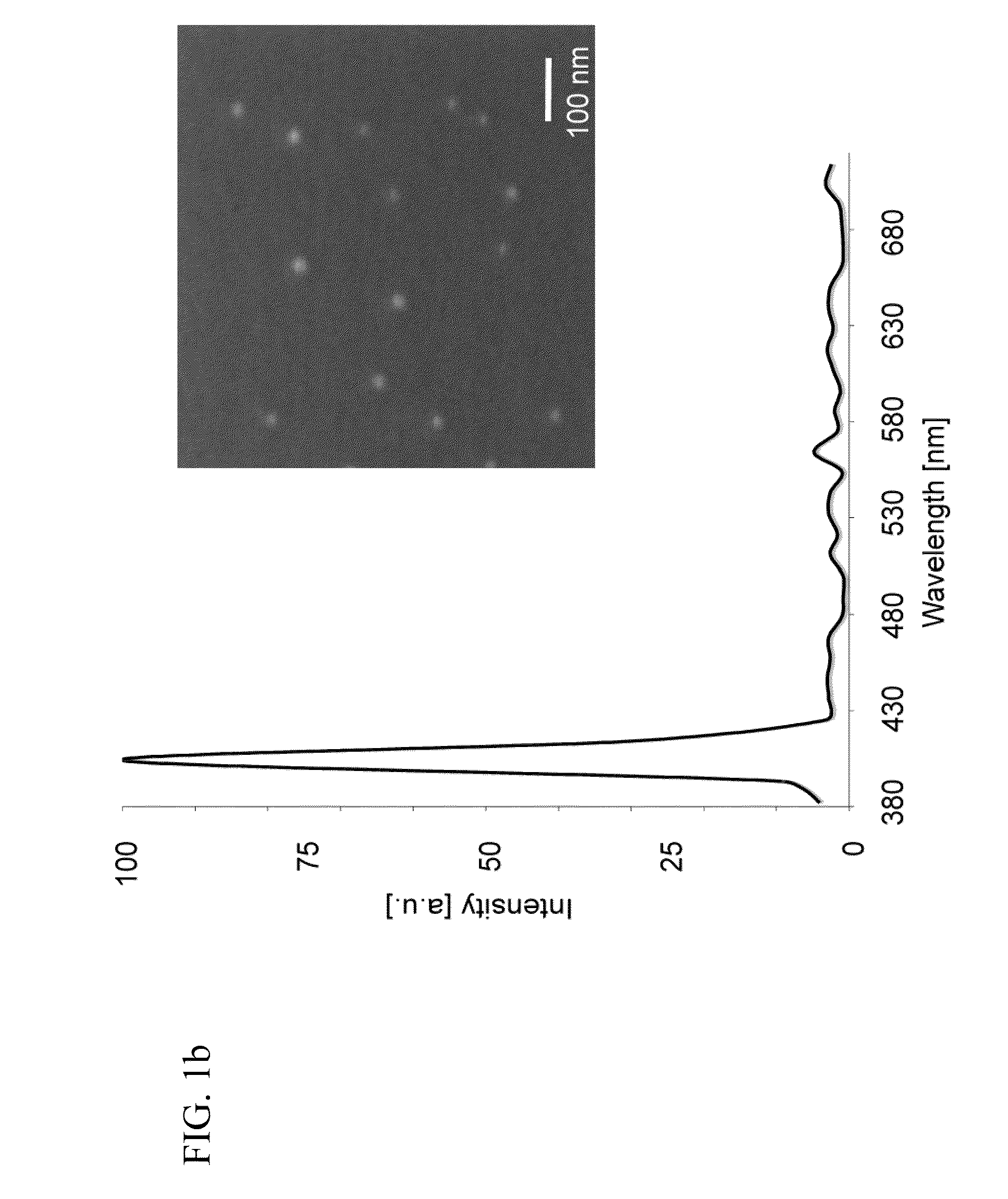
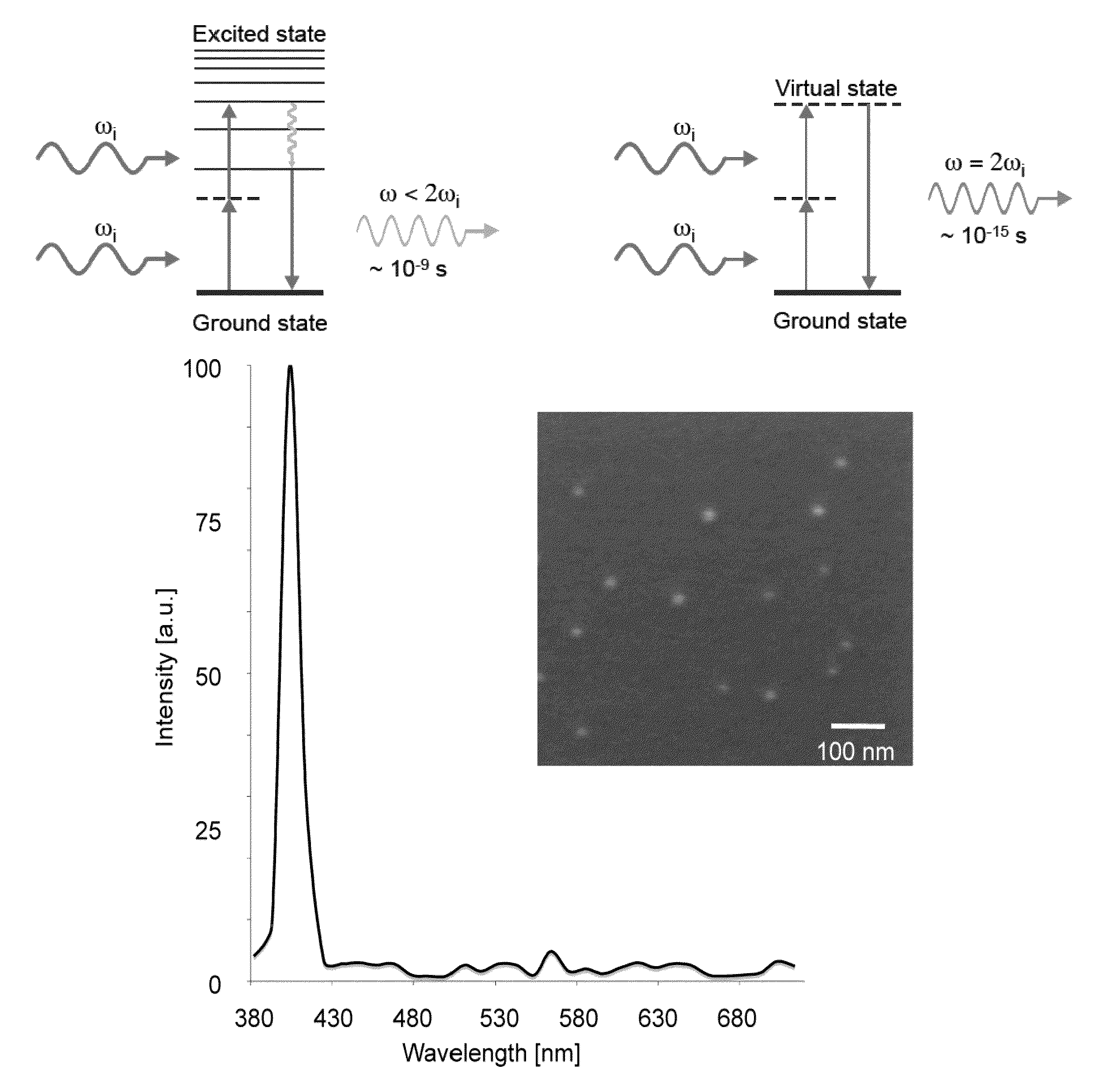
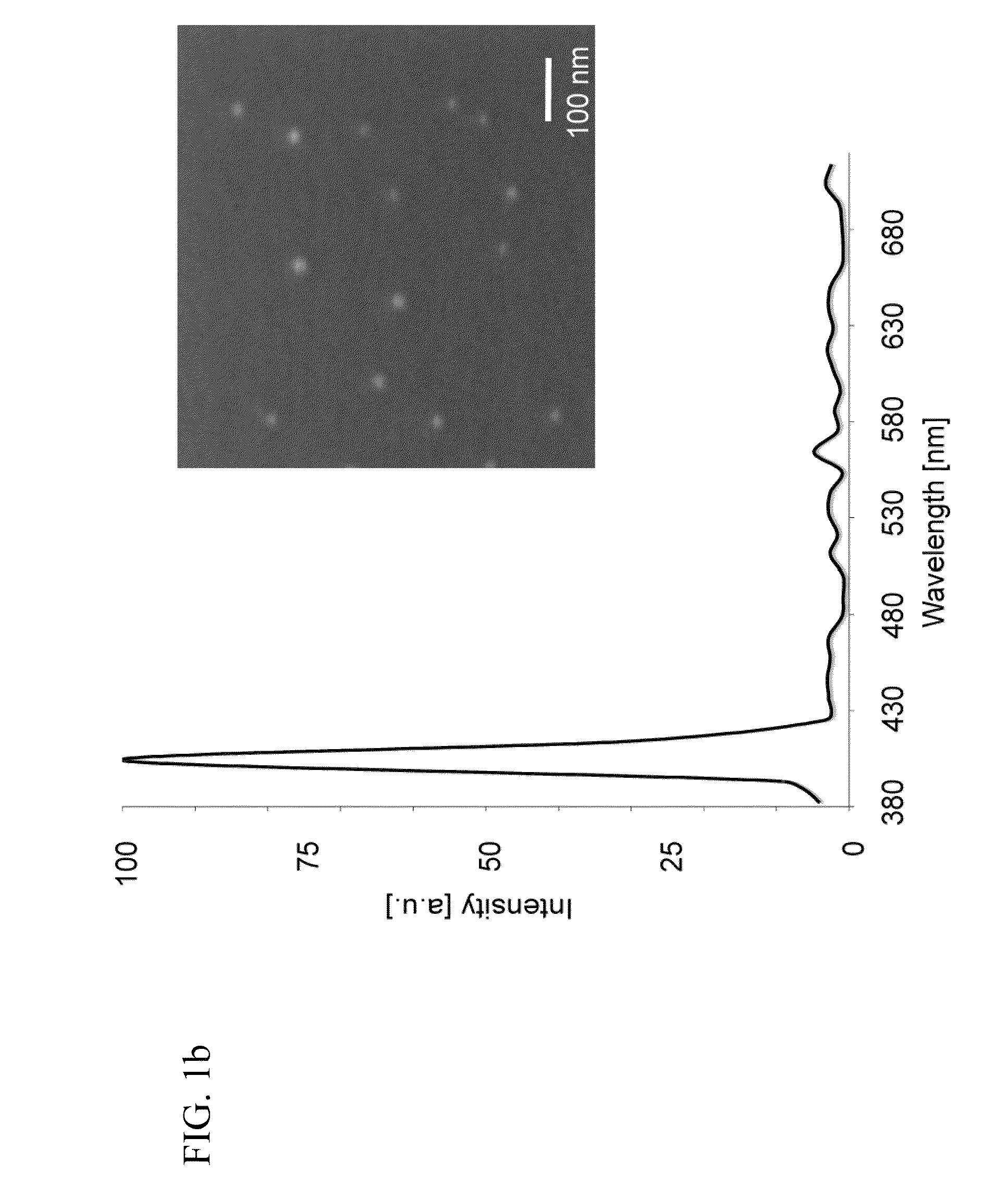
Second harmonic imaging nanoprobes and techniques for use thereof
ActiveUS20120141981A1Enhances electric fieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell signalingPhoton
Second harmonic nanoprobes for imaging biological samples and a method of using such probes to monitor the dynamics of biological process using a field resonance enhanced second harmonic (FRESH) technique are provided. The second harmonic generating (SHG) nanoprobes are comprised of various kinds of nanocrystals that do not possess an inversion symmetry and therefore are capable of generating second harmonic signals that can then be detected by conventional two-photon microscopy for in vivo imaging of biological processes and structures such as cell signaling, neuroimaging, protein conformation probing, DNA conformation probing, gene transcription, virus infection and replication in cells, protein dynamics, tumor imaging and cancer therapy evaluation and diagnosis as well as quantification in optical imaging.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
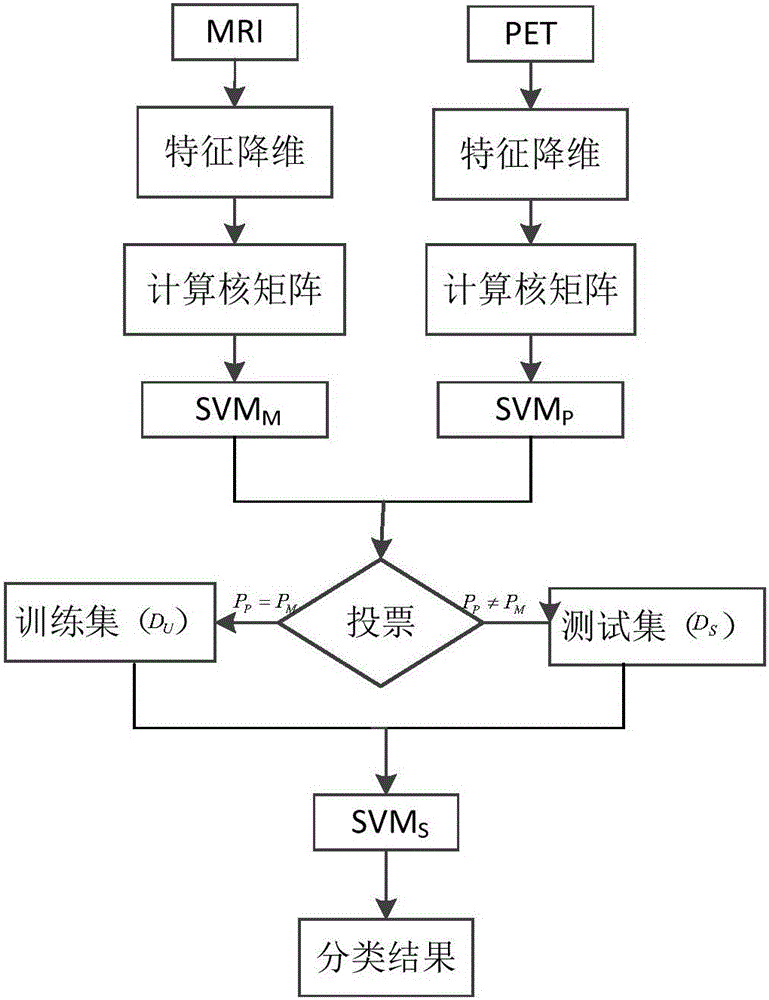
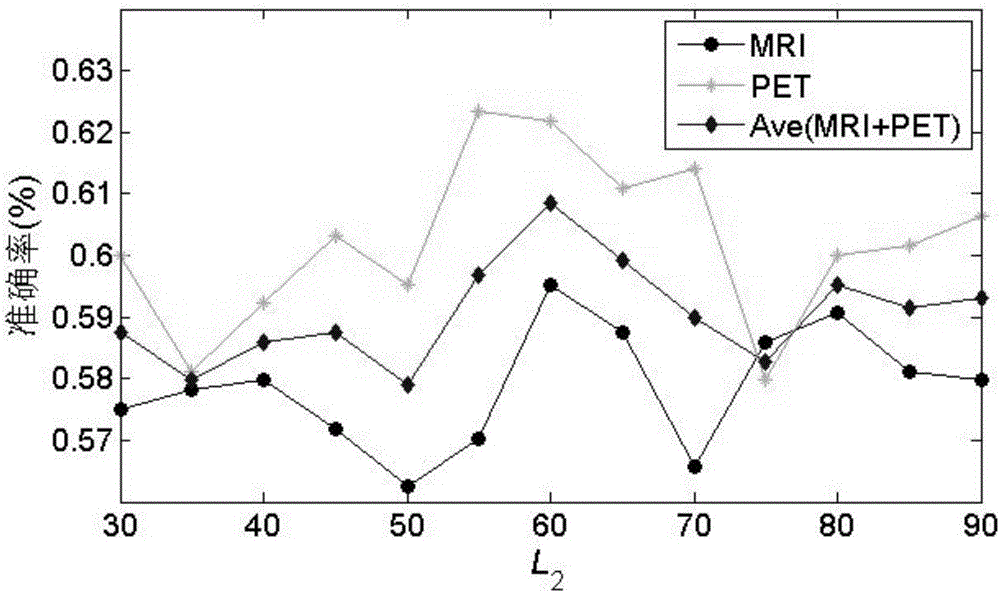
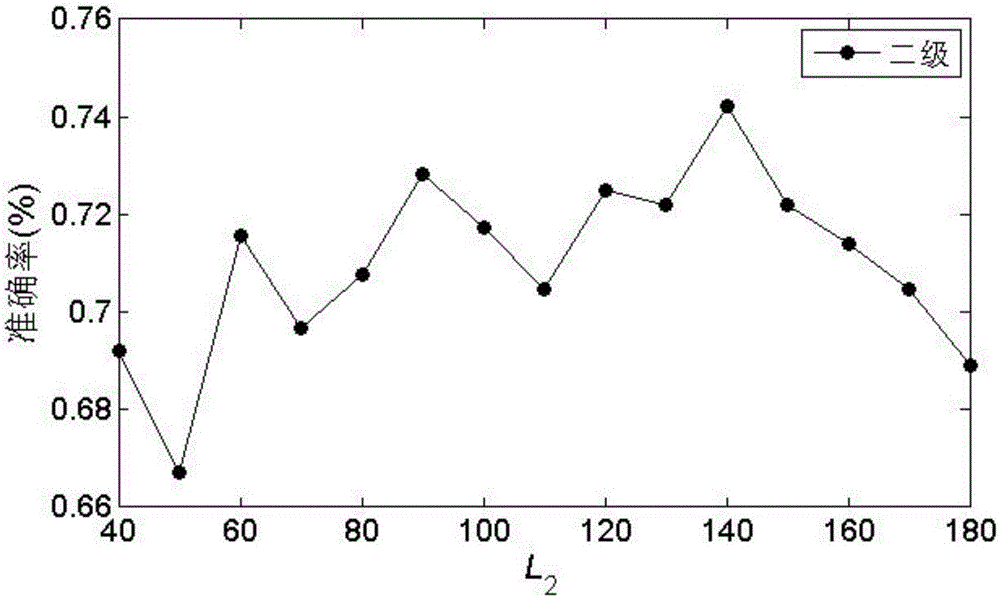
Progressive type mild cognitive impairment identification method based on neuroimaging
InactiveCN106096636AImprove classification performanceImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsFeature DimensionVoxel
The invention discloses a progressive type mild cognitive impairment identification method based on neuroimaging, and belongs to the technical field of computer image processing. The MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) graph and the PET (Positron Emission Tomography) graph of a test sample are downloaded from an ADNI (Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative) database and are subjected to preprocessing and sample screening to obtain N groups of sample images; the AAL (Anatomical Automatic Labeling) template of the human is selected to independently manufacture 90 cerebral region templates for the sample images, and the grey matter voxel value of a corresponding cerebral region is obtained to obtain N*180-dimensional data; and finally, a second level integration classifier is constructed, feature dimension reduction is carried out on the obtained data, a reduced dimension is subjected to optimization, and the data is applied to the second level integration classifier to carry out classification identification on progressive type MCI (Mild Cognitive Impairment) patients and non-progressive type MCI patients. The data is subjected to the dimension reduction processing by a random projection method, then, the data is applied to the second level integration classifier, classification accuracy is 74.22%, sensitivity is 66.25%, specificity is 82.19%, operation speed is improved, and the classification accuracy is improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
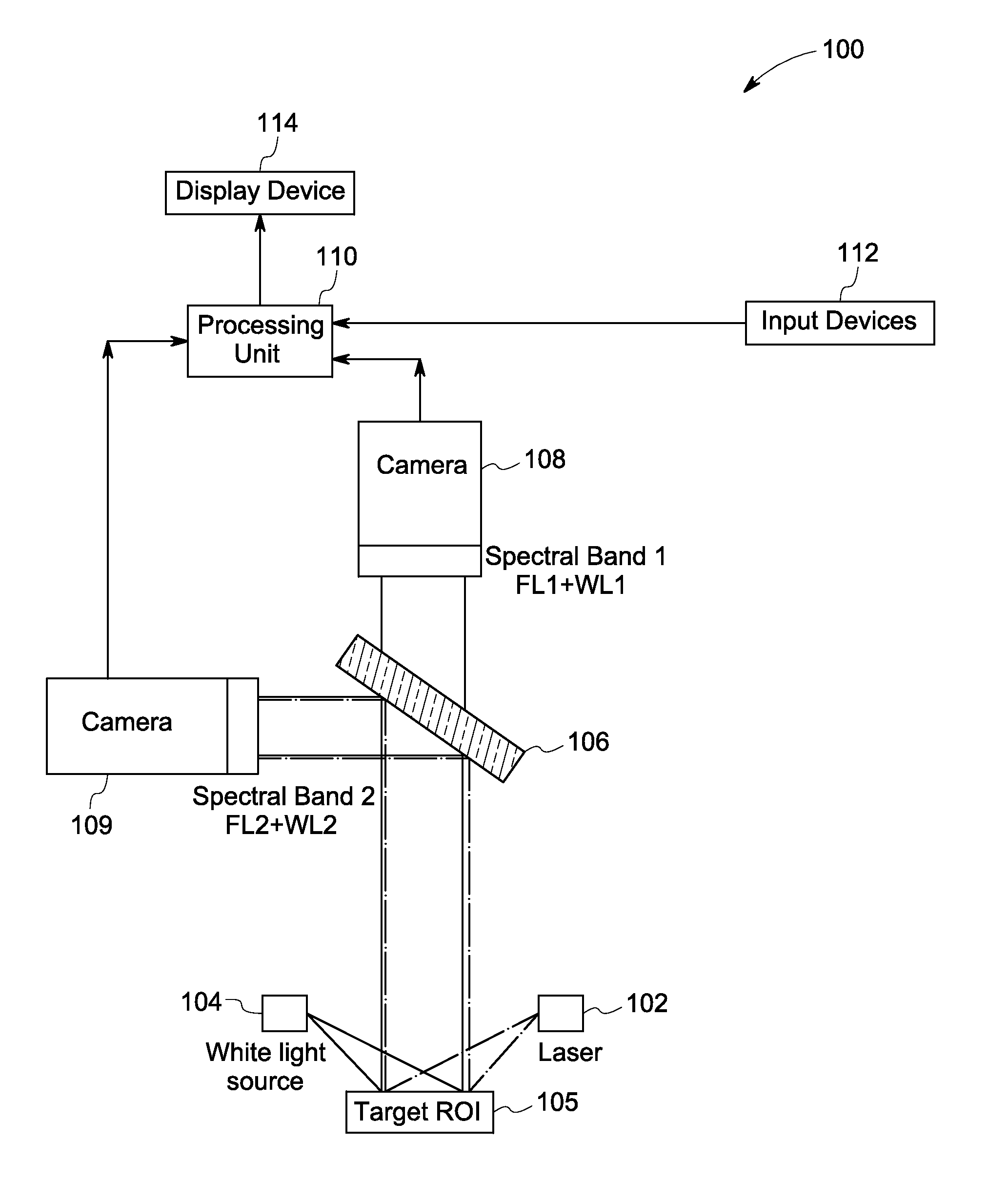
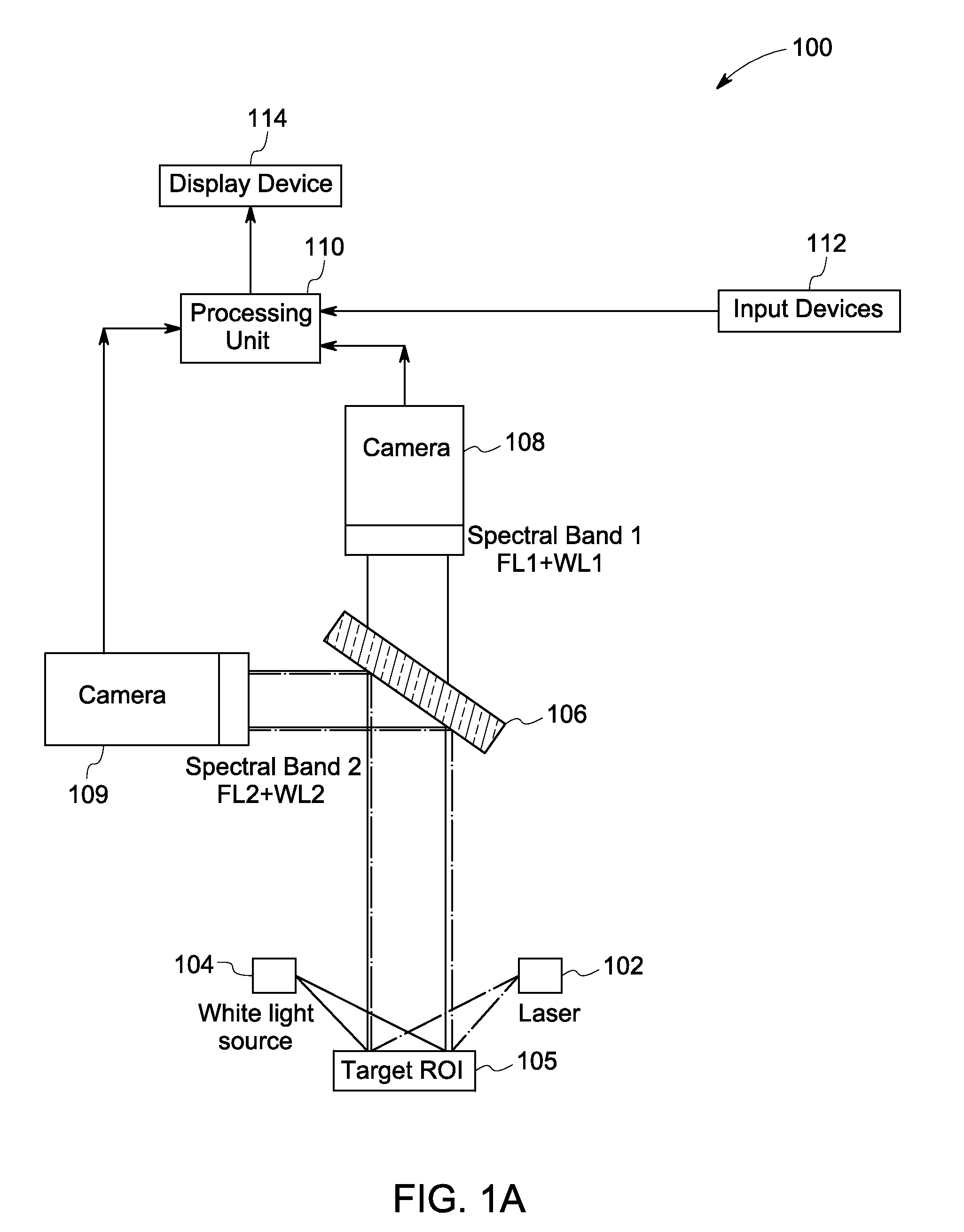
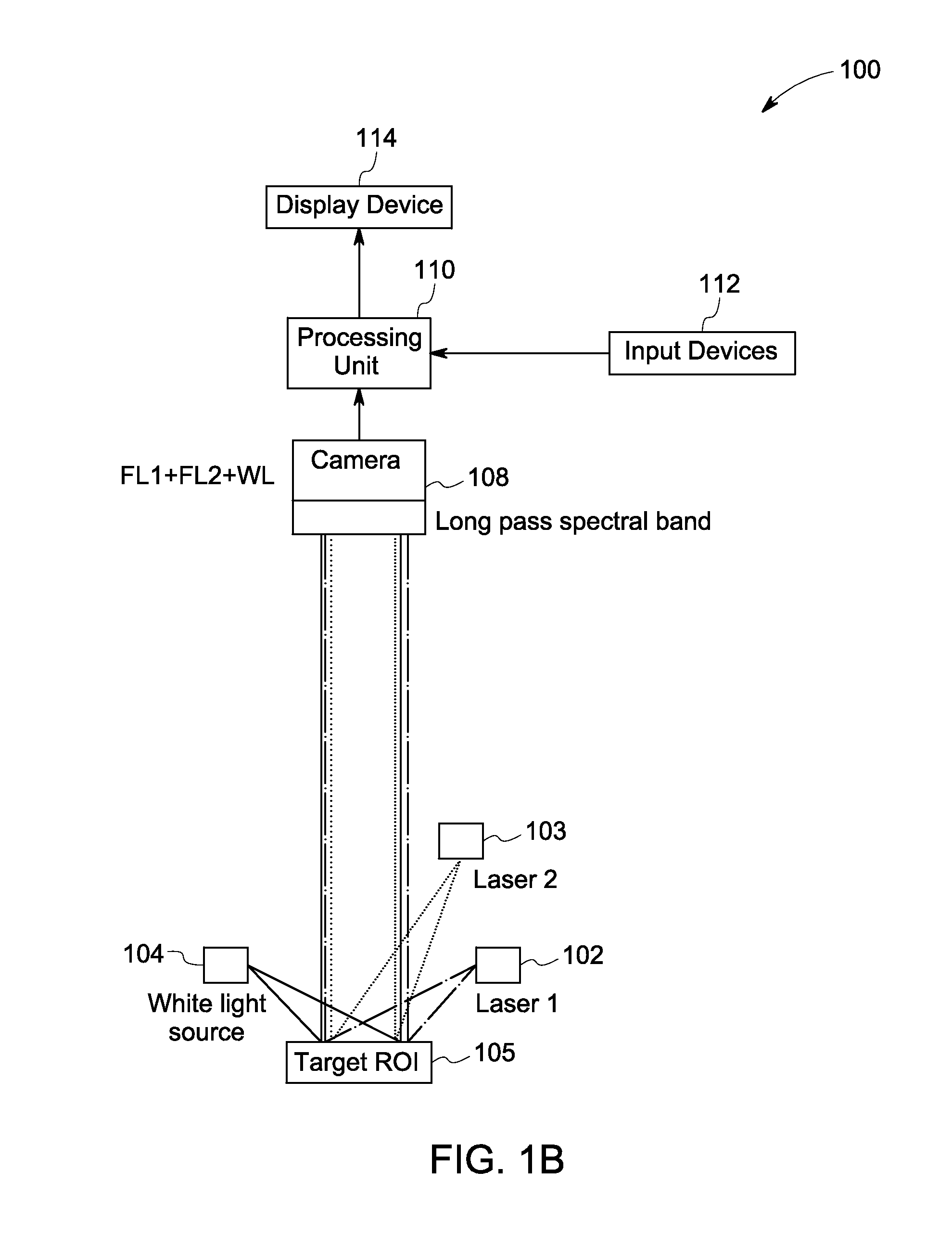
Systems and methods for nerve imaging
Systems and methods for imaging are presented. The method includes producing excitation light configured to induce fluorescence in an imaging agent that selectively binds to a target species in a region of interest (ROI) of a subject that also includes a background species. A first and a second spectral region are selected such that a determined difference between fluorescence corresponding to the target and the background species in the first spectral region differs from a corresponding difference in the second spectral region. First and second fluorescence images are generated from the fluorescence corresponding to the first and second spectral regions. Additionally, a fluorescence ratio for the background species in the first and second fluorescence image is determined. The first fluorescence image is then multiplied or divided with the determined ratio to generate an intermediate image that is subtracted from the second fluorescent image to reconstruct a background-subtracted image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Functionalization of and use of functionalized second harmonic generating nanoprobes
Functionalized second harmonic nanoprobes for imaging samples and a method of using such probes to monitor the dynamics different processeses using a variety of imaging techniques are provided. The functionalized second harmonic generating (SHG) nanoprobes are comprised of various kinds of nanocrystalline materials that do not possess an inversion symmetry and therefore are capable of generating second harmonic signals that can then be detected by conventional two-photon microscopy, and are provided with functional surface modifications that allow for targeted imaging of a variety of biological and non-biological processes and structures such as cell signaling, neuroimaging, protein conformation probing, DNA conformation probing, gene transcription, virus infection and replication in cells, protein dynamics, tumor imaging and cancer therapy evaluation and diagnosis as well as quantification in optical imaging.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Imaging methods and compositions comprising fluorescent dyes associated with viral components for nerve imaging
InactiveUS20120078093A1Reduce riskViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesMedicineFluorescence
Owner:NOVADAQ TECH ULC
Surface stimulation for tremor control
InactiveUS20070208385A1Improve accuracy and reliabilityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationNervous systemMedicine
Apparatus and methods for non-invasive electrical stimulation of the brain through skin surface stimulation of the peripheral nervous system as a treatment for movement disorders. Skin surface electrodes are positioned at predetermined peripheral surface stimulation sites on the skin surface using a variety of neural imaging techniques. A pulsatile electrical current is generated at the stimulation sites through a variety of standard electrical stimulation devices. Stimulation of the peripheral surface stimulation sites translates to electrical stimulation of a specific area of the brain.
Owner:MEAGAN MEDICAL
Methods and tools for detecting, diagnosing, predicting, prognosticating, or treating a neurobehavioral phenotype in a subject
ActiveUS20190272889A1Efficient designPrecise positioningDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsDiseasePharmacometrics
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Multipurpose analysis using second harmonic generating nanoprobes
ActiveUS20100233820A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCell signaling
Second harmonic nanoprobes for multipurpose imaging of samples and a method of using such probes to monitor nucleotide sequencing in a Multi-SHG Detection Imaging (MSDI) modality and to monitor external electric field using voltage sensitive second harmonic generating (SHG) nanoprobes are provided. The SHG nanoprobes are comprised of various kinds of nanocrystals that do not possess an inversion symmetry and therefore are capable of generating second harmonic signals that can then be detected by conventional two-photon microscopy for in vivo imaging of biological processes and structures such as cell signaling, neuroimaging, protein conformation probing, DNA conformation probing, gene transcription, virus infection and replication in cells, protein dynamics, tumor imaging and cancer therapy evaluation and diagnosis as well as quantification in optical imaging for a wide-range of biological and non-biological processes and devices.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
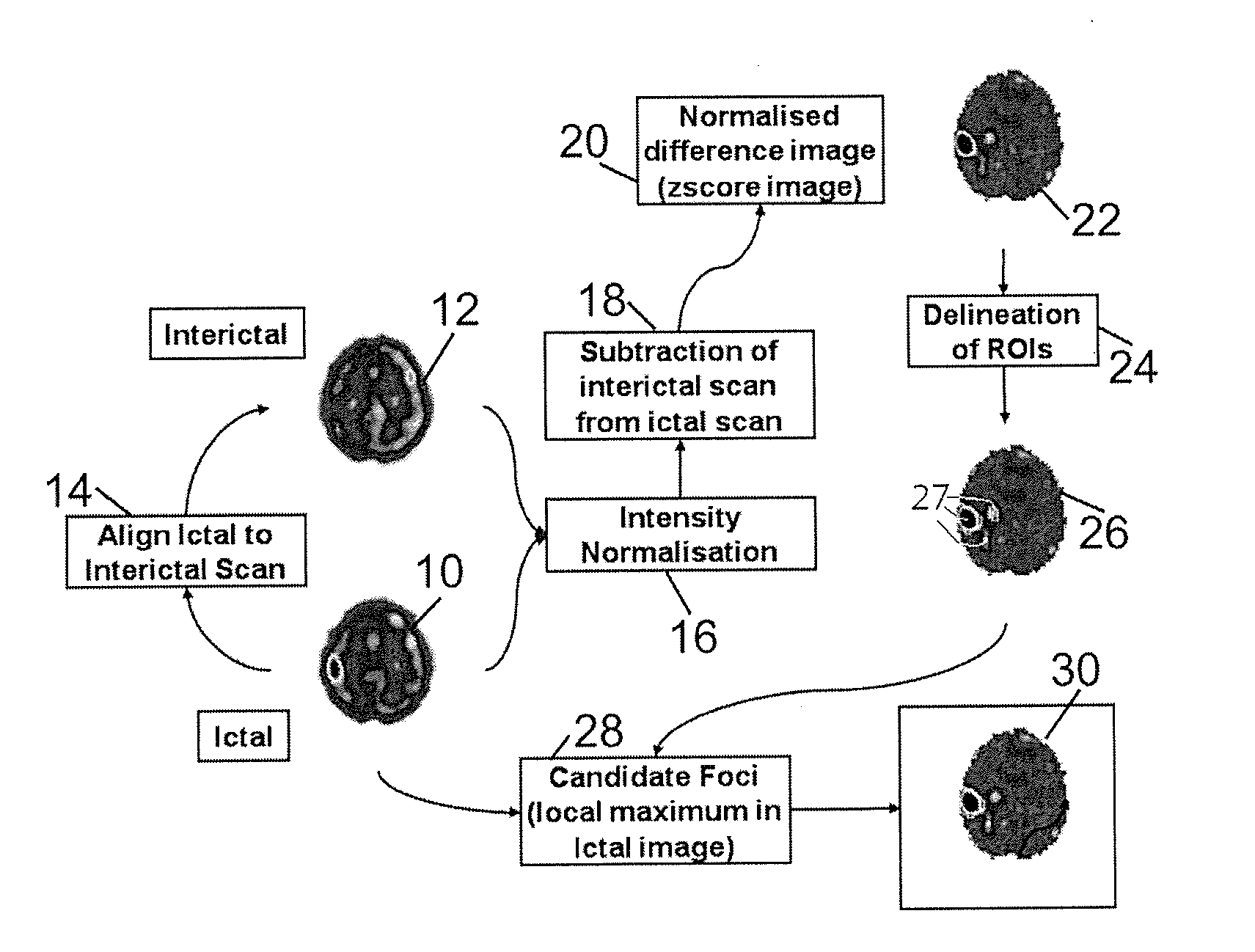
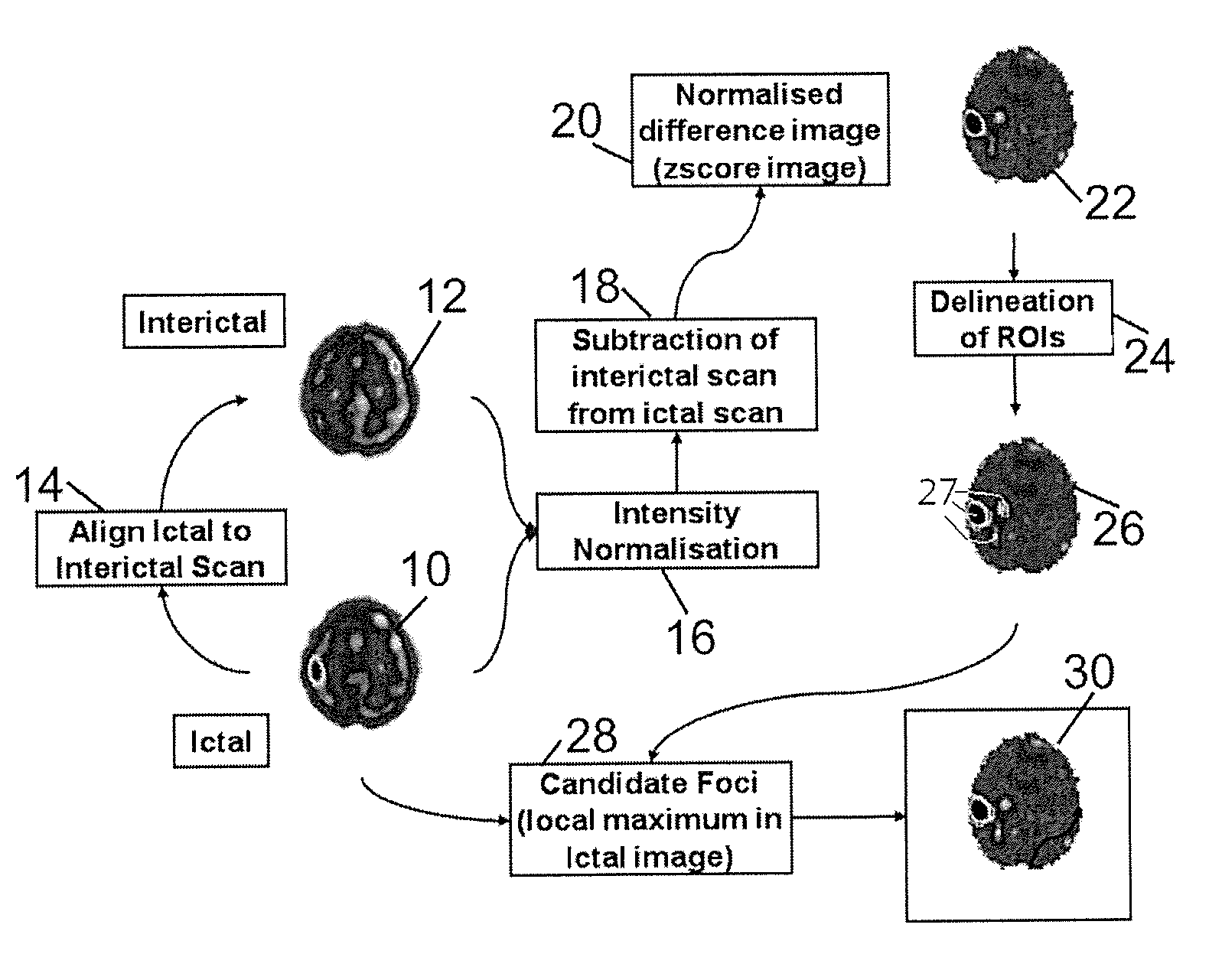
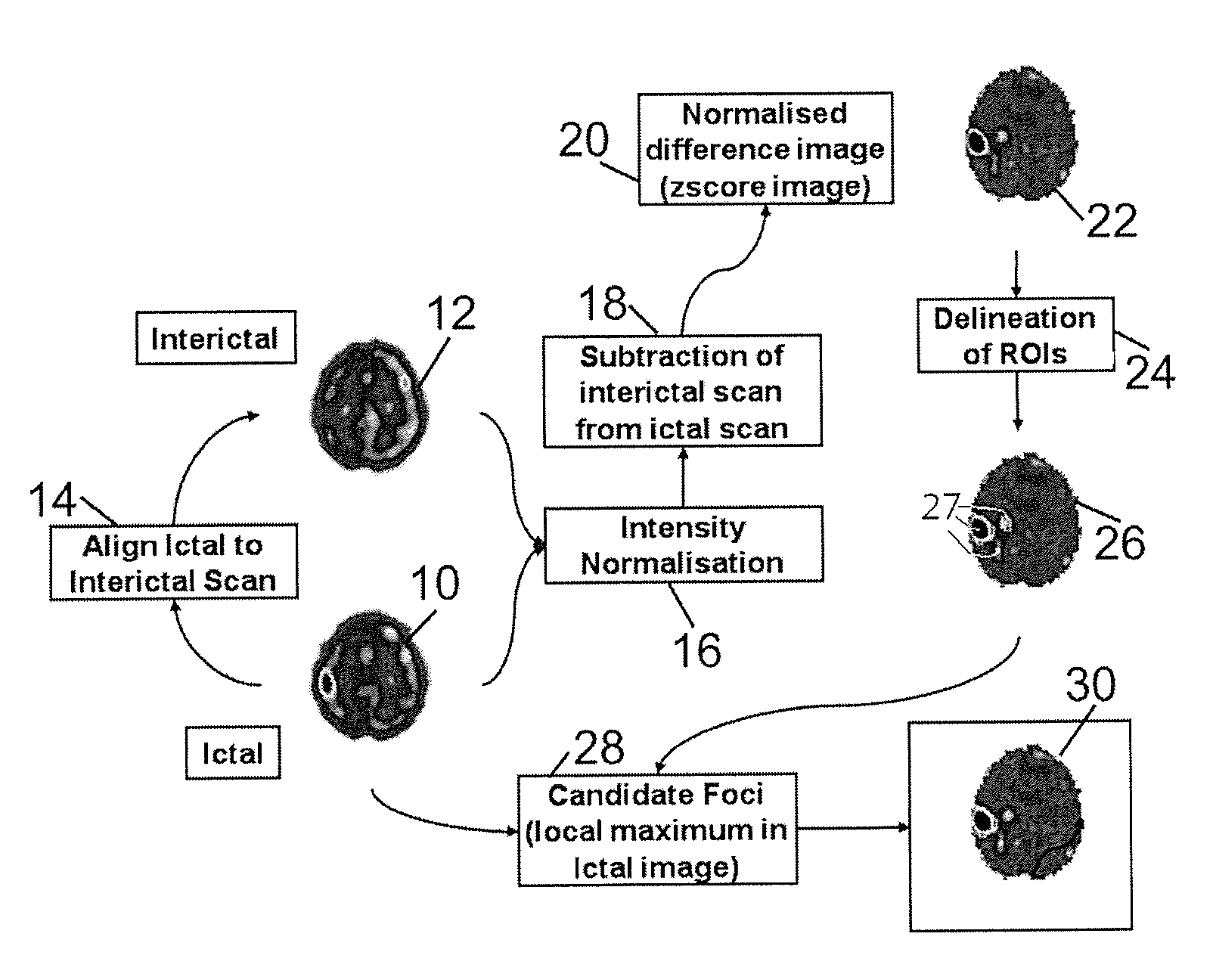
Method for localization of an epileptic focus in neuroimaging
ActiveUS20140270438A1Reduce the amount requiredEasy to explainImage enhancementImage analysisNeuroimagingRegion of interest
In a method for localizing a candidate foci in neuroimaging, two images are acquired, one being a baseline (interictal) image and another being an intervention (ictal) image. The two images are aligned and the intensities of the images are normalized. A difference image is calculated by subtracting the baseline (interictal) image from the intervention (ictal) image. The difference image is normalized and regions of interest are selected as candidate foci.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
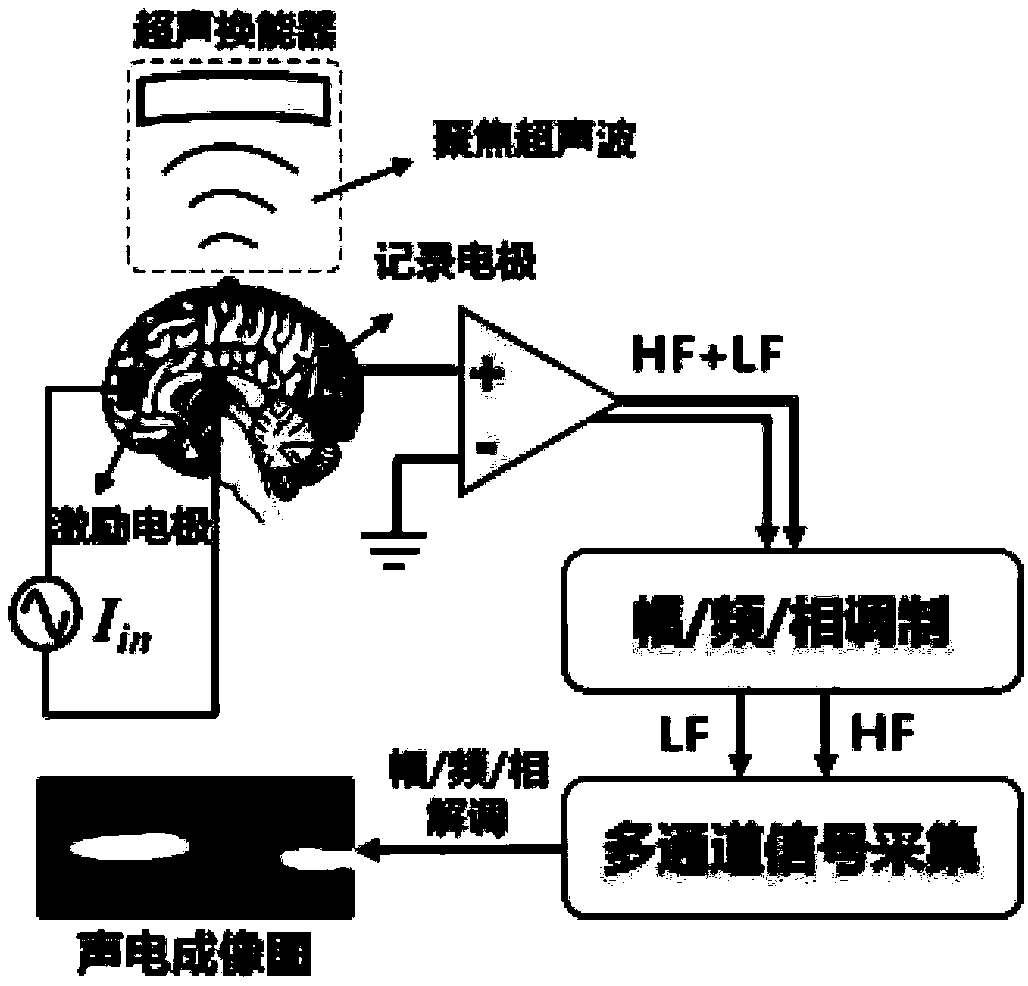
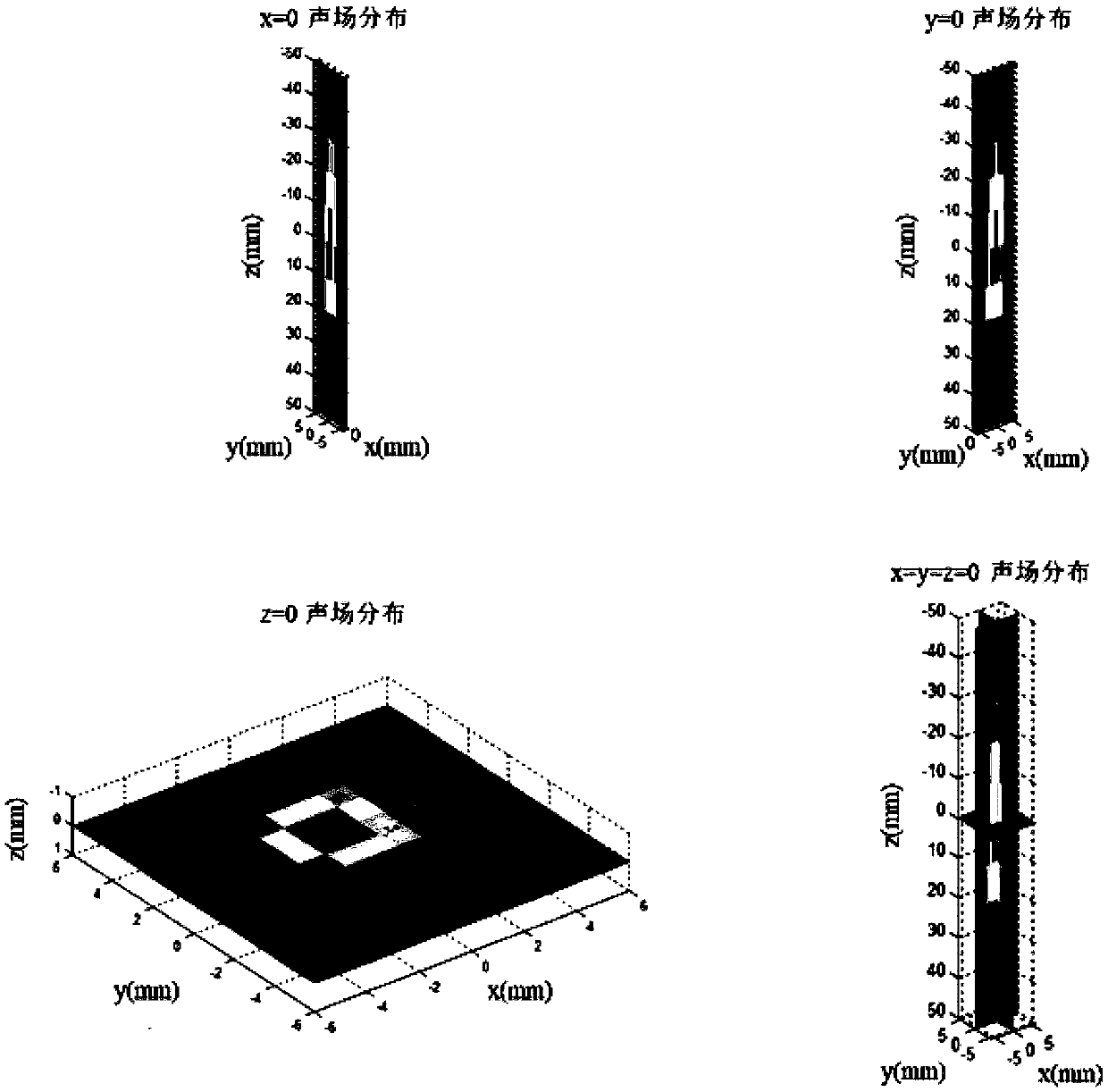
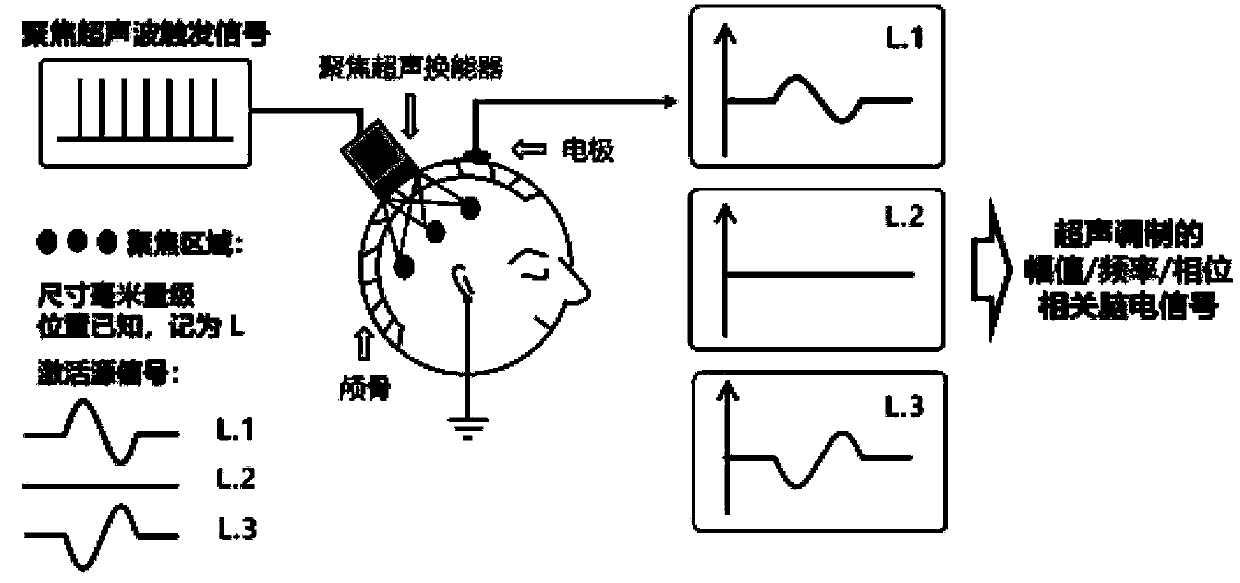
4D transcranial focused ultrasonic neuroimaging method based on acoustoelectric effect
ActiveCN109645999AImprove time resolutionImprove spatial resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correlationSonification
The invention discloses a 4D transcranial focused ultrasonic neuroimaging method based on an acoustoelectric effect. The method includes the steps that a focused ultrasonic signal generator and an energy converter are adopted to achieve generation and emission of focused ultrasonic signals, and focused ultrasonic characteristics under different parameters are determined; an electroneurographic signal collecting device composed of an electroencephalogram collecting system provided with an electroencephalogram electrode, an electroencephalogram amplifier and an electroencephalogram filter and anelectroneurographic-signal measuring system based on ultrasonic modulation is installed and connected; ultrasonic waves are spread through the cranium and focused on a certain position, and based onthe acoustoelectric effect principle, scalp electroencephalogram signals after ultrasonic modulation, namely, acoustoelectric signals are collected; through the amplitude values, the frequency and thephase position relevance of the acoustoelectric signals and activation source signals, the electroencephalogram signals are subjected to spatial encoding and demodulation, 4D neuroimaging of high space-time resolution is achieved, and multiple requirements in practical application are met.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
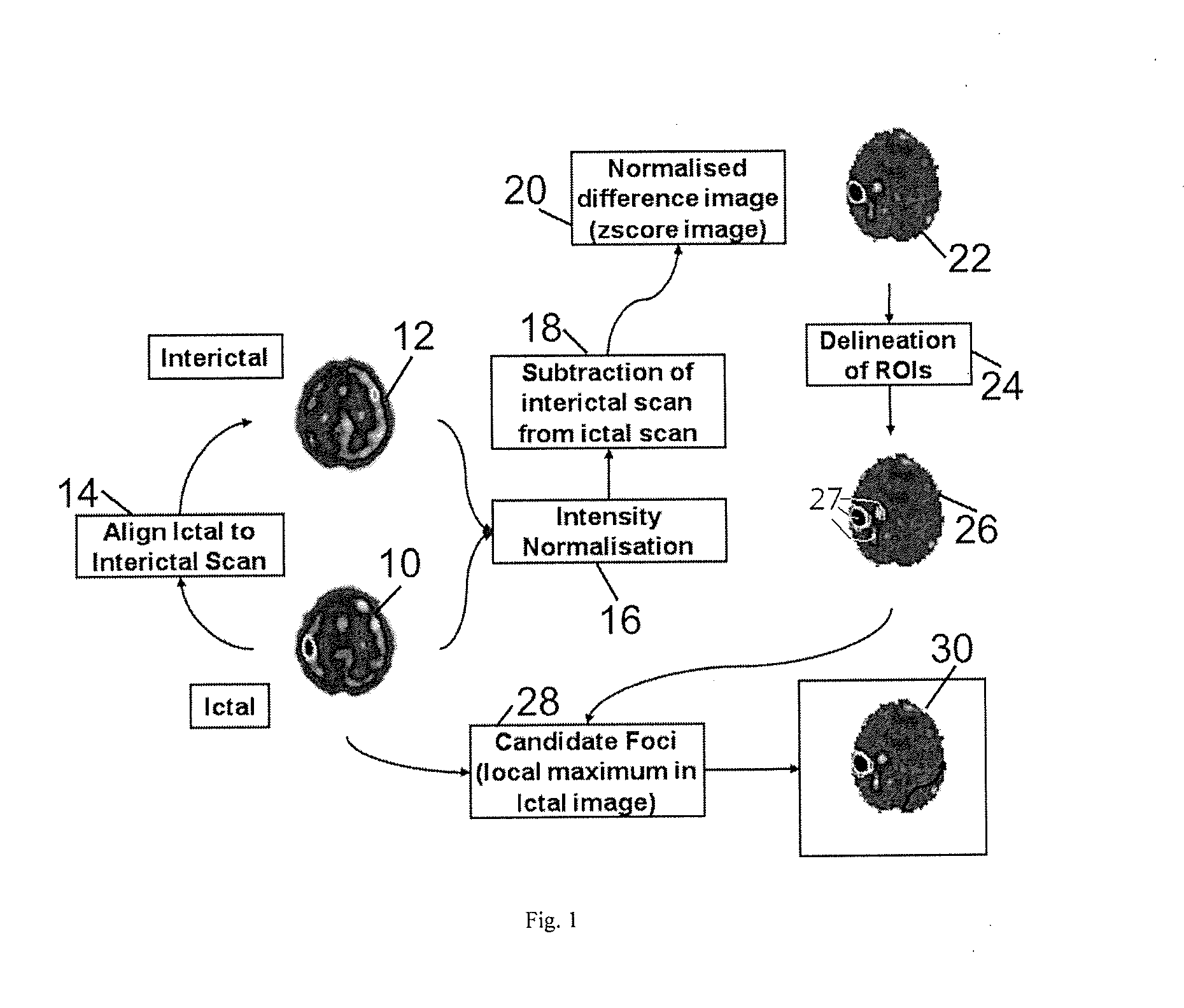
Method for localization of an epileptic focus in neuroimaging
ActiveUS9171366B2Reduce the amount requiredEasy to explainImage enhancementImage analysisNeuroimagingRegion of interest
In a method for localizing a candidate foci in neuroimaging, two images are acquired, one being a baseline (interictal) image and another being an intervention (ictal) image. The two images are aligned and the intensities of the images are normalized. A difference image is calculated by subtracting the baseline (interictal) image from the intervention (ictal) image. The difference image is normalized and regions of interest are selected as candidate foci.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Multipurpose analysis using second harmonic generating nanoprobes
ActiveUS8945471B2Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCell signaling
Second harmonic nanoprobes for multipurpose imaging of samples and a method of using such probes to monitor nucleotide sequencing in a Multi-SHG Detection Imaging (MSDI) modality and to monitor external electric field using voltage sensitive second harmonic generating (SHG) nanoprobes are provided. The SHG nanoprobes are comprised of various kinds of nanocrystals that do not possess an inversion symmetry and therefore are capable of generating second harmonic signals that can then be detected by conventional two-photon microscopy for in vivo imaging of biological processes and structures such as cell signaling, neuroimaging, protein conformation probing, DNA conformation probing, gene transcription, virus infection and replication in cells, protein dynamics, tumor imaging and cancer therapy evaluation and diagnosis as well as quantification in optical imaging for a wide-range of biological and non-biological processes and devices.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Composition and processes for crossing the blood-brain barrier with polypeptides for in vivo neuroimaging
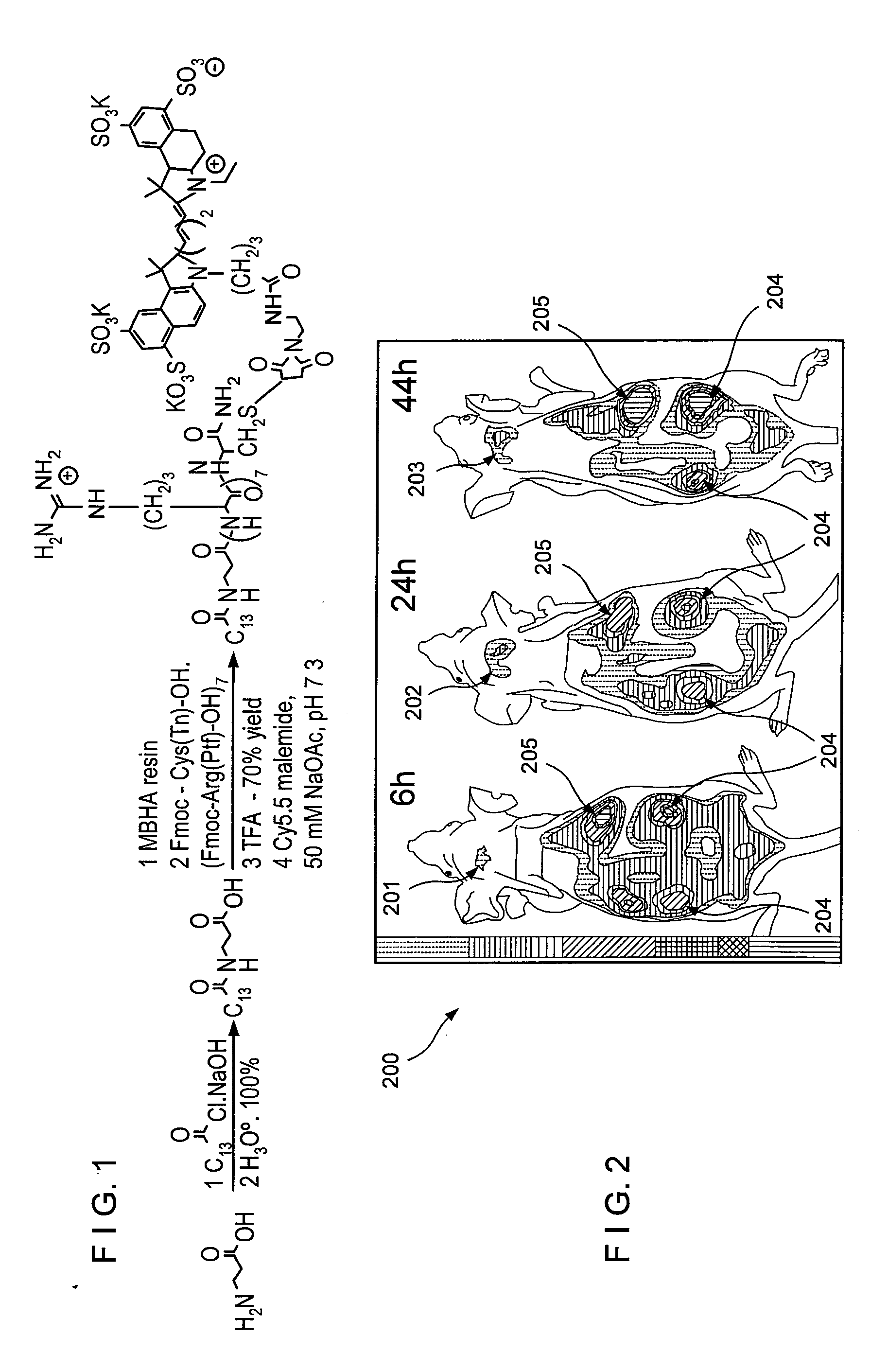
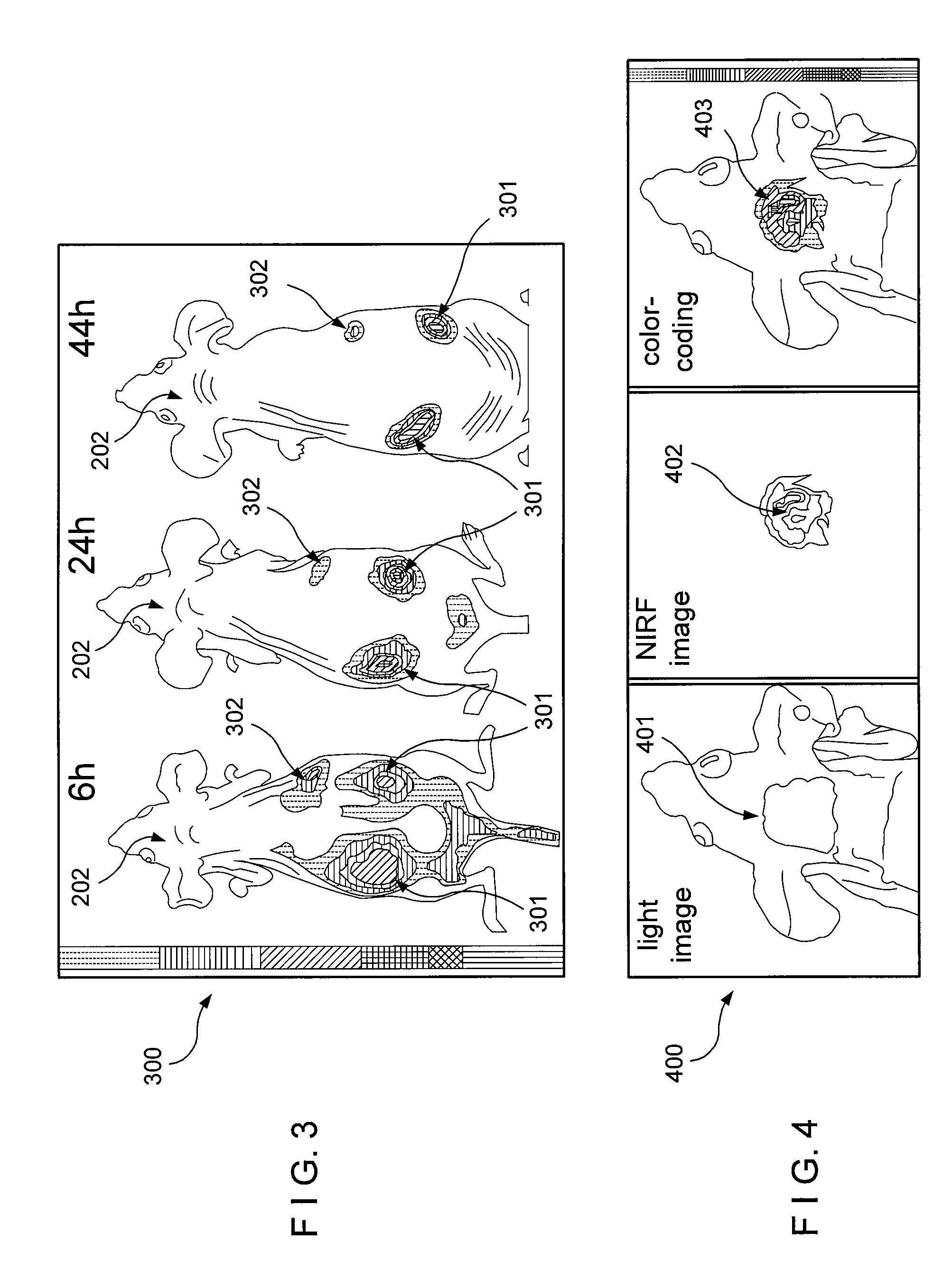
According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a versatile delivery module based on a myristoylated polyarginine backbone can be provided to cross a blood-brain barrier (“BBB”). An incorporation of a fatty acid group can be achieved using a Schotten-Bauman reaction with quantitative yield, and a peptide can be further synthesized by conventional solid phase peptide synthesis (“SPPS”). An in vivo distribution of the delivery module into a brain over time using near-infrared (“NIR”) fluorescence imaging can be obtained. A fluorescent cargo can be detected in vivo after an intravenous injection and can be further characterized in perfused brains. A staining of an excised brain can show that the delivery module can primarily accumulate in neurons with occasional localization in astrocytes and endothelial cells. This exemplary approach can be used for the delivery of imaging probes and targeted therapeutics across the BBB.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
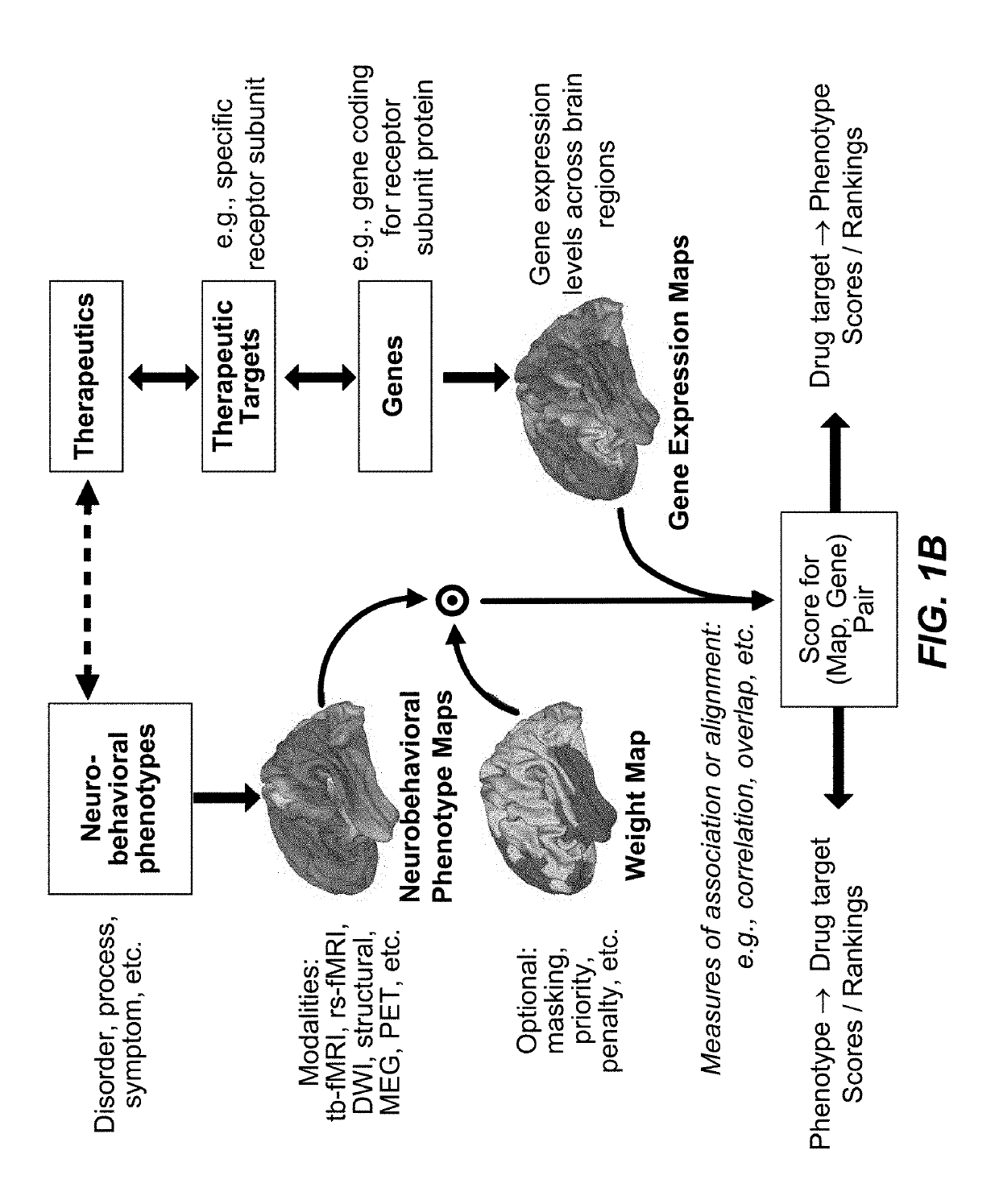
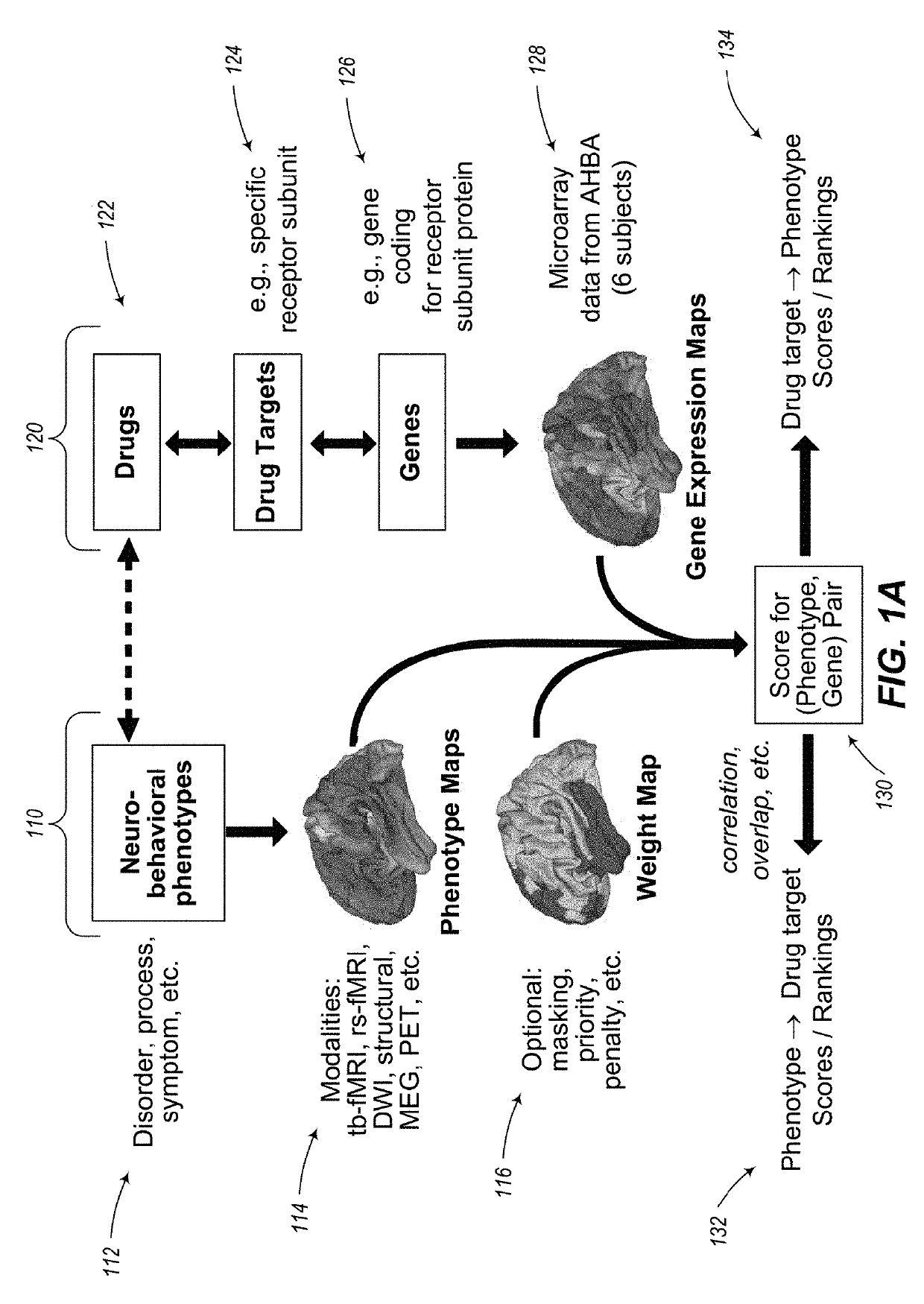
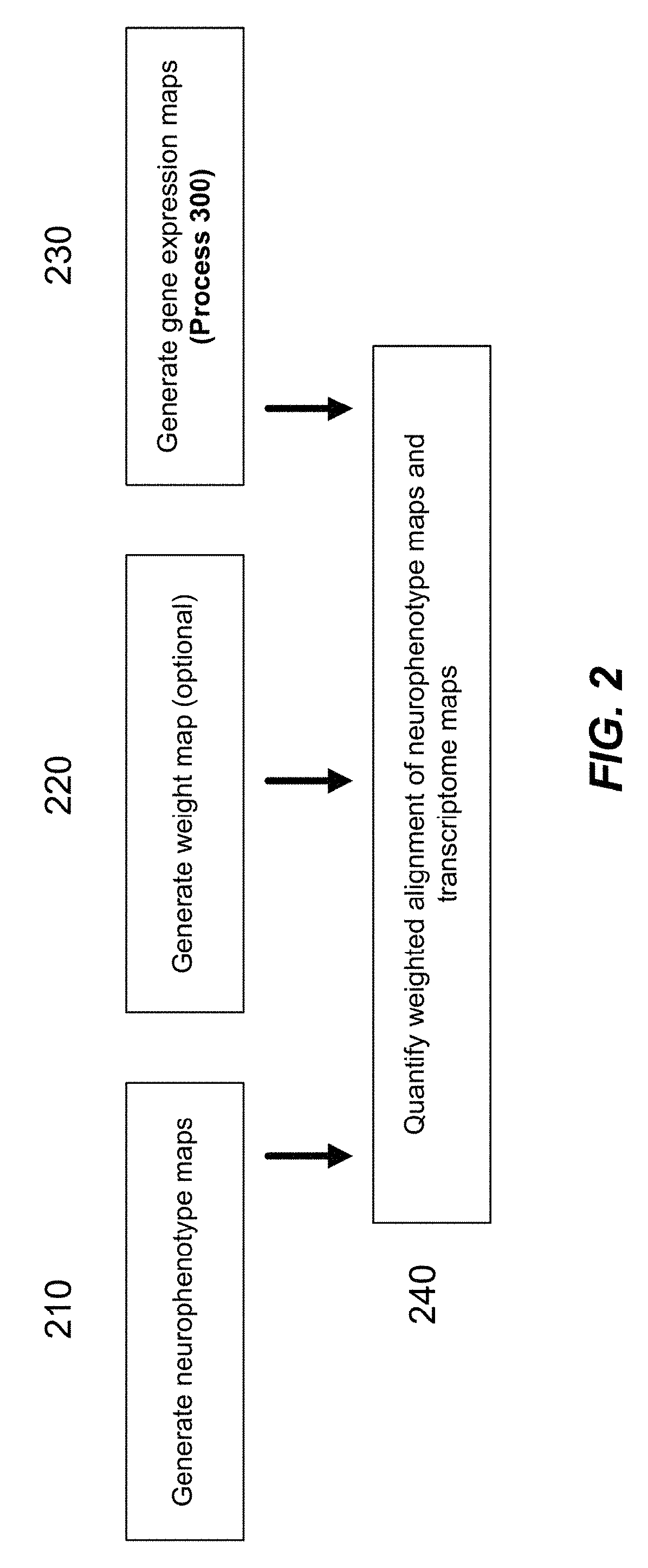
Methods and systems for computer-generated predictive application of neuroimaging and gene expression mapping data
ActiveUS20190355439A1Efficient designPrecise positioningDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsImaging brainTopography
The present disclosure relates to computer generated topographies from computer correlations of neurobehavioral phenotype mapping data and gene expression mapping data. Neurobehavioral phenotype mapping data is obtained for a selected phenotype and correlated with gene expression mapping data for one or more genes to define a phenotype-gene pair topography for each phenotype-gene pair. A score for each phenotype-gene pair is determined based on the correlation. The scores are used to identify genes, or drug targets, associated with the respective gene of the respective phenotype-gene pair. Conversely, gene expression mapping data is obtained for a selected gene and correlated with neurobehavioral phenotype mapping data for one or more phenotypes to define a gene-phenotype topography for each gene-phenotype pair. A score for each gene-phenotype pair is determined based on the correlation. The scores are used to identify a phenotype associated with the respective phenotype-gene pair.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
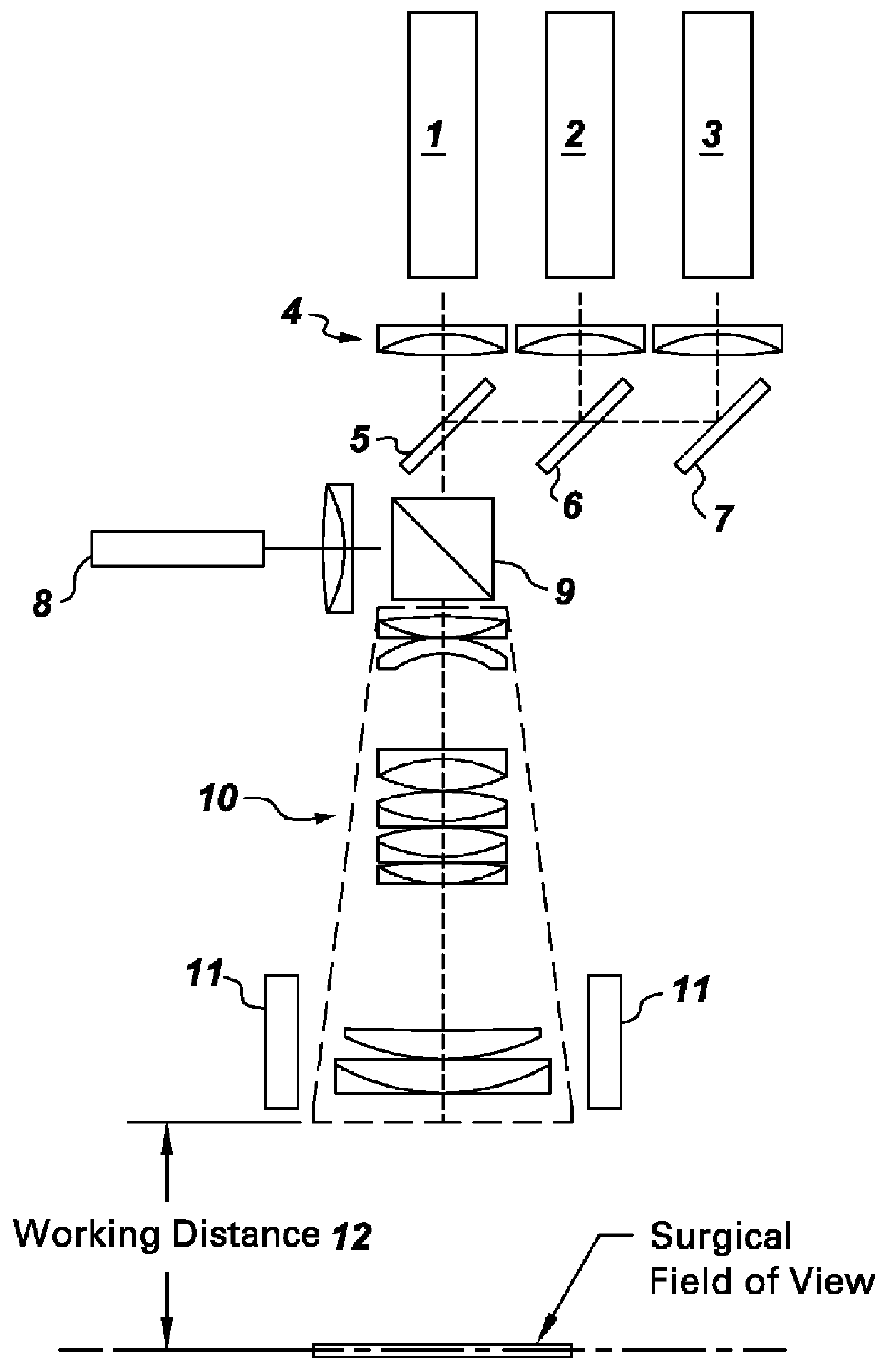
Systems for intraoperative nerve imaging
Disclosed are systems for intraoperative nerve imaging using compact high collection power imaging devices for fluorescence and white light imaging of myelin basic protein (MBP) nerve imaging agents during open and minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
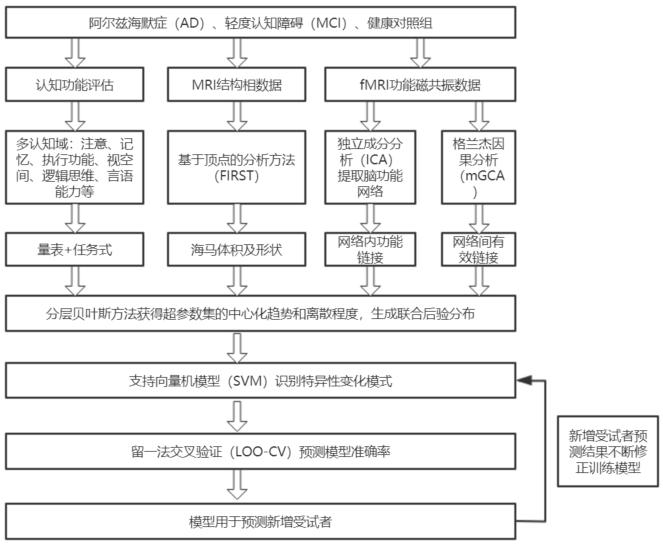
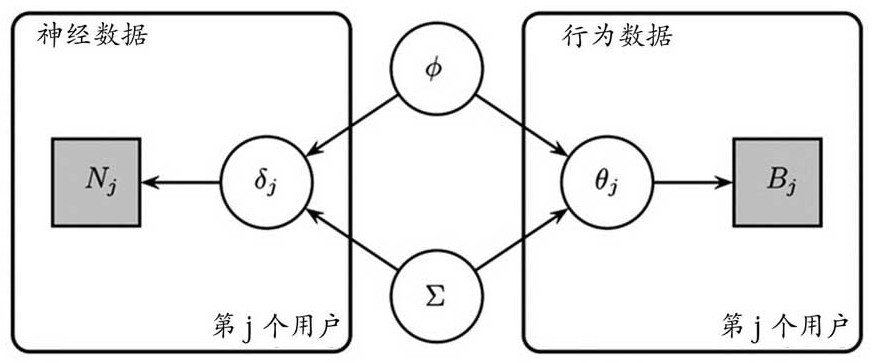
Cognition and brain image data integration evaluation method for Alzheimer's disease
PendingCN114188013ACombine accuratelyMedical data miningKernel methodsFunctional connectivitySupervised learning
The invention relates to the field of online auxiliary evaluation, in particular to a cognitive and brain image data integration evaluation method for Alzheimer's disease. According to the method, firstly, multi-field screening and evaluation of the cognitive function are carried out, the purposes of rapid screening and detailed evaluation of the cognitive function are achieved, then multi-mode magnetic resonance imaging data analysis is carried out, and the multi-mode magnetic resonance imaging data analysis comprises the steps of extracting hippocampus volume and shape analysis, calculating a function connection value of a cognitive-related brain function network, and calculating the cognitive-related brain function network. As an index in the aspect of neuroimaging, the brain function is evaluated. Carrying out cognitive and neural Bayesian joint modeling; and finally, classifying and identifying the specific change mode of the Alzheimer's disease by using supervised learning.
Owner:BEIJING WISPIRIT TECH CO LTD
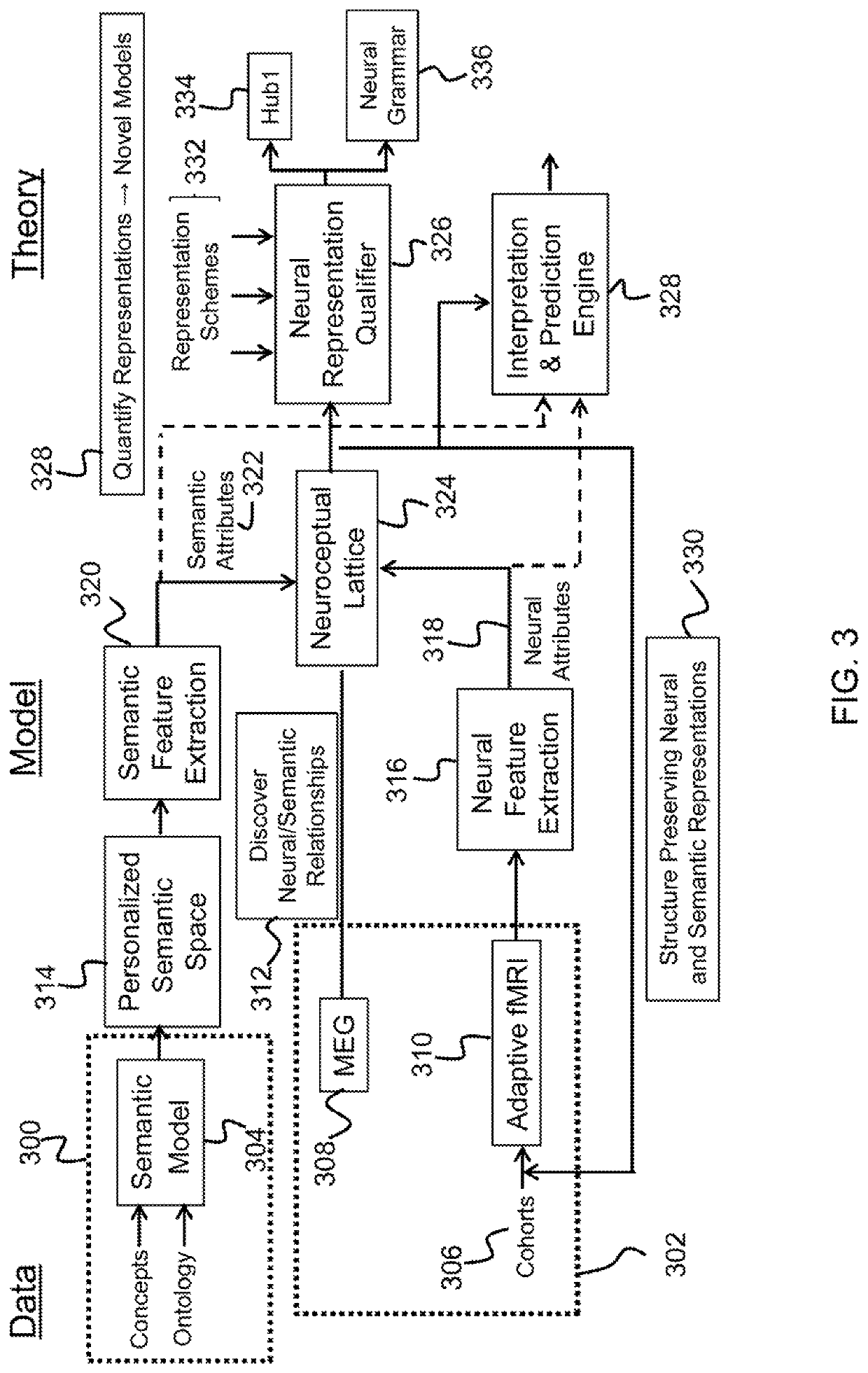
Method and system to predict and interpret conceptual knowledge in the brain
Described is a system for explaining how the human brain represents conceptual knowledge. A semantic model is developed, and a behavioral exam is performed to assess a calibration subject into a cohort and reveal semantic relationships to modify a personalized semantic space developed by the semantic model. Semantic features are extracted from the personalized semantic space. Neural features are extracted from neuroimaging of the human subject. A neuroceptual lattice is created having nodes representing attributes by aligning the semantic features and the neural features. Structures in the neuroceptual lattice are identified to quantify an extent to which the set of neural features represents a target concept. The identified structures are used to interpret conceptual knowledge in the brain of a test subject.
Owner:HRL LAB
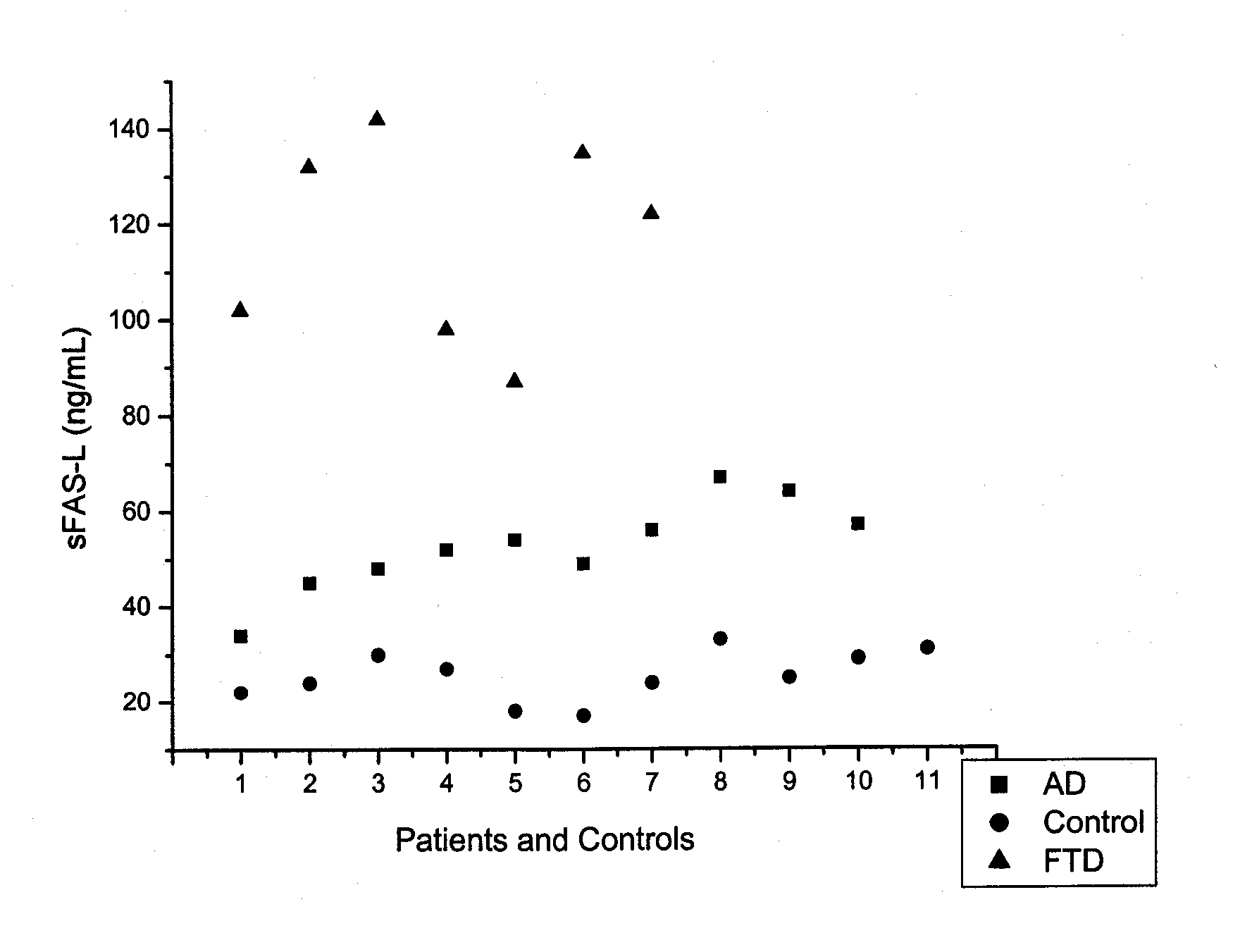
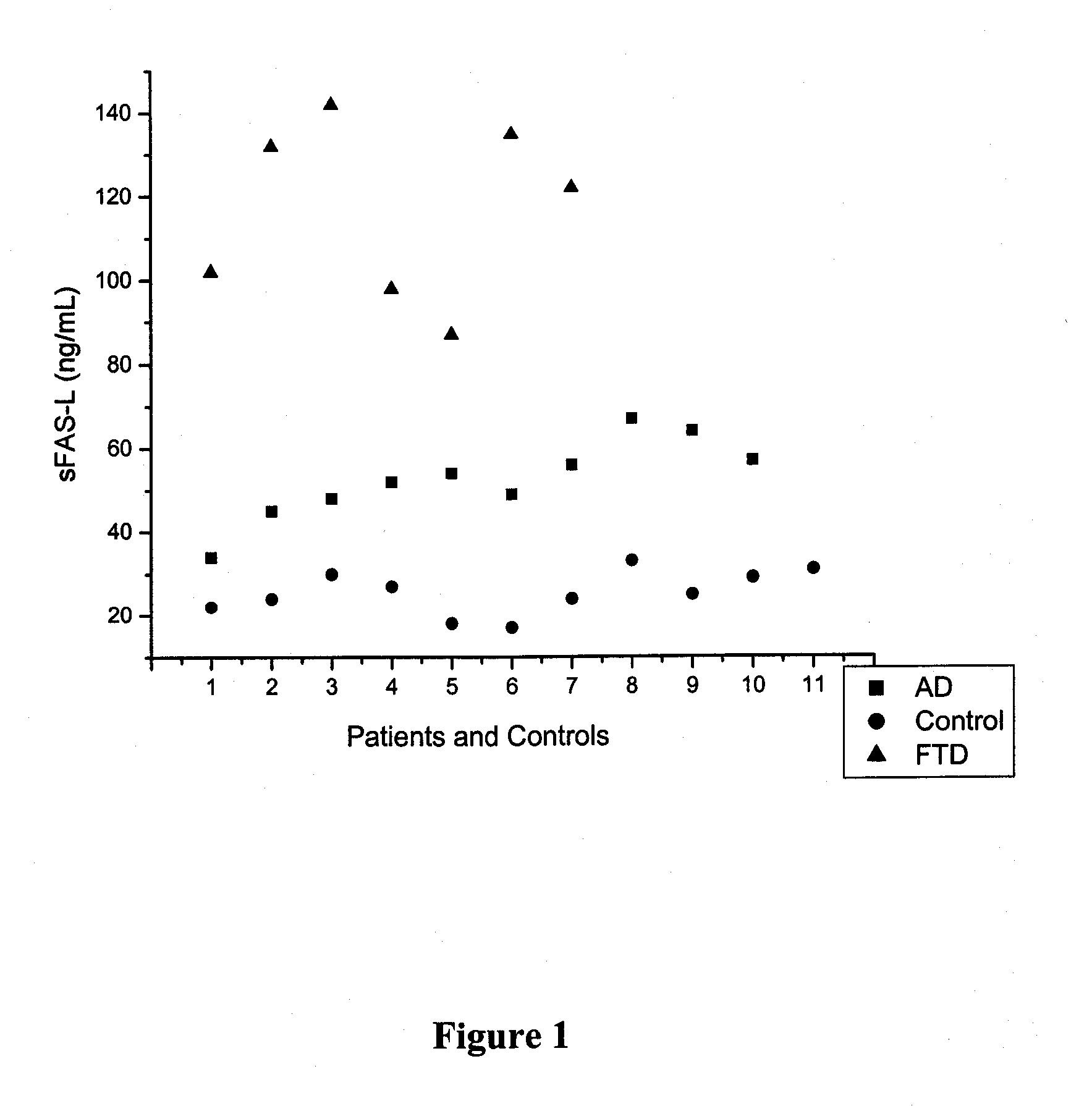
Methods and kits for the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease versus frontotemporal dementia and for the diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia, comprising FAS-L and CK 18 as biomarkers
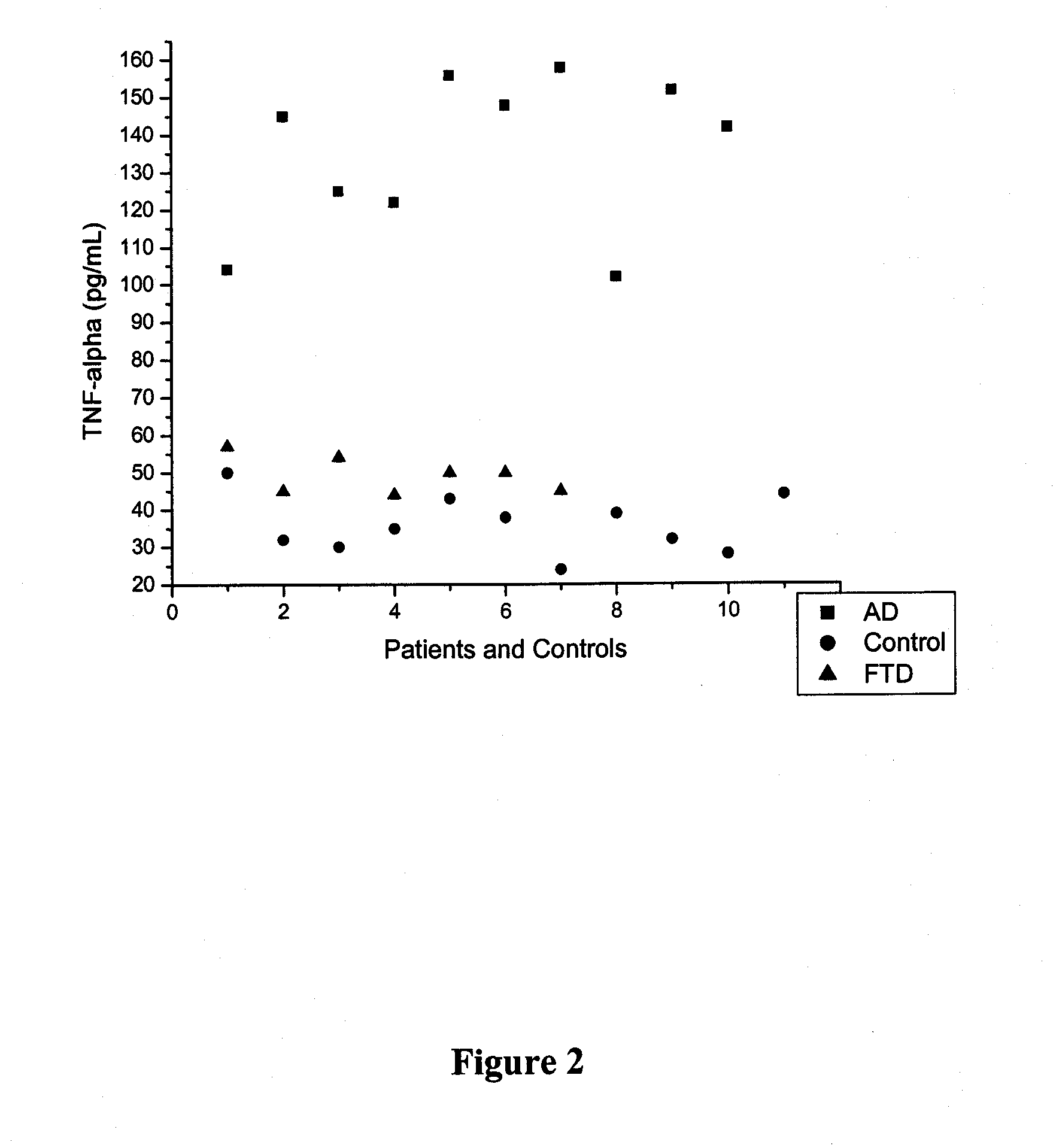
The invention relates to methods and kits for the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) versus frontotemporal dementia (FTD), using biomarkers TNF-α, FAS-L and CK18, taken from a biological sample. Differences in biomarker levels can be used to distinguish between AD and FTD The invention is based on a discovered correlation between FTD and markers FAS-L and CK18. Therefore the invention also relates to the diagnosis of FTD using FAS-L and CK18. The serum concentrations of these biomarkers can further be used as an index of the severity of disease, and may occur in conjunction with clinical-based diagnostic testing and neuro-imaging assessment.
Owner:NEUMAN MANUELA G
Method for neurostimulation enhanced team performance
ActiveUS9878155B1Eliminate artifactsImprove task performanceElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyPerformance enhancementMedicine
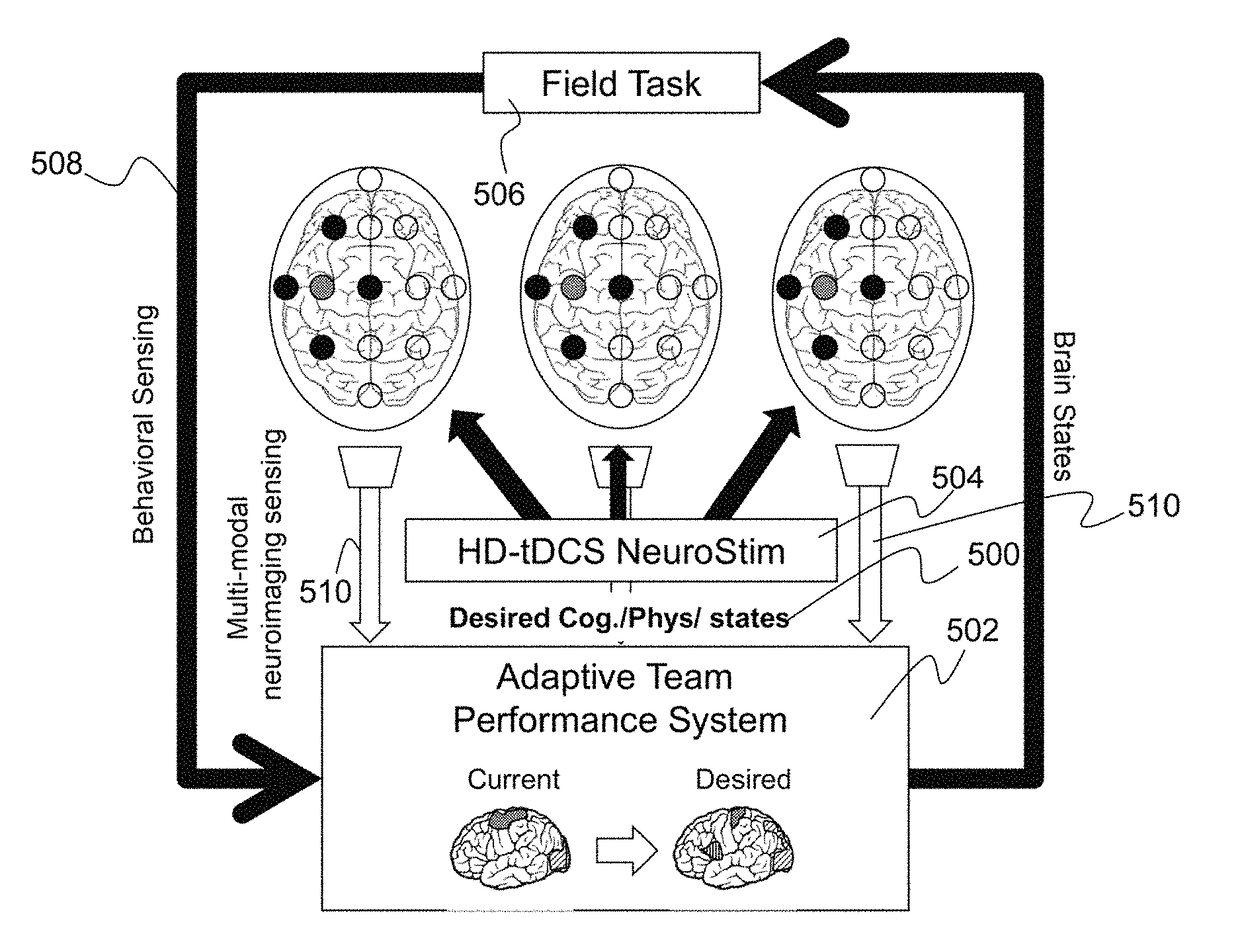
Described is a system for augmenting team performance via individual neurostimulation. An assessment is generated for each team member of a team while the team member is performing a behavioral task using neuroimaging data. A target brain state is selected in team members for team performance enhancement. The target brain state is associated with specific brain regions, and the system determines a HD-tCS neurostimulation needed to reach the specific brain regions to induce the target brain state in the team members. The determined HD-tCS neurostimulation is applied to the team members while simultaneously sensing, via real-time neuroimaging, neural activity in each team member while the team member performs a behavioral task. Team performance is enhanced by adjusting the HD-tCS neurostimulation of each team member, based on the sensed neural activity, to direct each team member toward the target brain state.
Owner:HRL LAB
Method and computing system for modelling a primate brain
In one aspect the application relates to a computing system for providing data for modelling a human brain comprises a database including a plurality of datasets (or allow access to a plurality of datasets), each dataset including at least a dynamical model of the brain including at least one node and a neurodataset of a neuroimaging modality input. The at least one node include a representation of a local dynamic model and a parameter set of the local dynamic model.
Owner:CODEBOX COMPDIENSTE +5
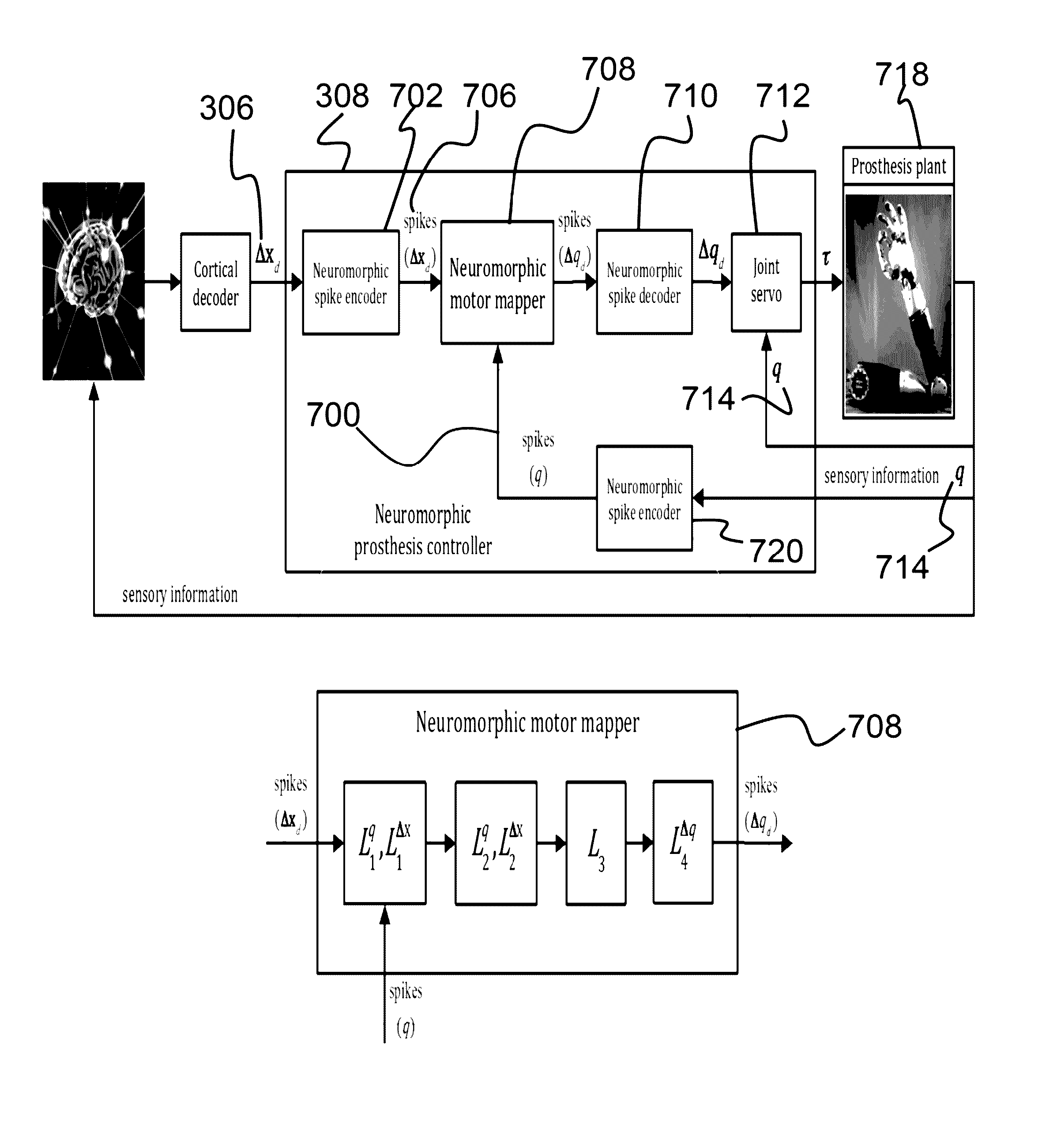
System for controlling brain machine interfaces and neural prosthetic systems
ActiveUS9566174B1Low costMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman–machine interfaceProsthesis
Described is a system for controlling a torque controlled prosthetic device given motor intent inferred from neuroimaging data. The system includes at least one torque controlled prosthetic device operably connected with one or more processors. Further, the system is configured to receive neuroimaging data of a user from a neuroimaging device and decode the neuroimaging data to infer spatial motion intent of the user, where the spatial motion intent includes desired motion commands of the torque controlled prosthetic device represented in a coordinate system. The system thereafter executes, with a prosthesis controller, the motion commands as torque commands to cause the torque controlled prosthetic device to move according to the spatial motion intent of the user.
Owner:HRL LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com