Patents
Literature
352 results about "Spatial encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
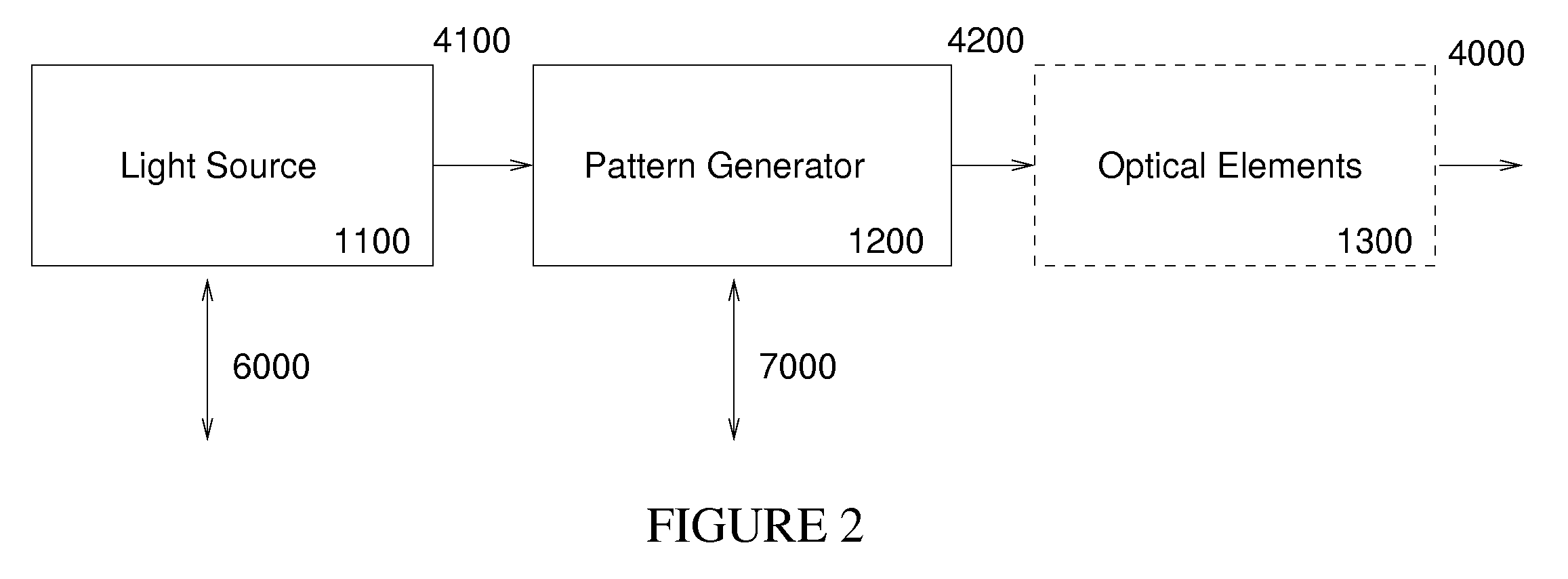
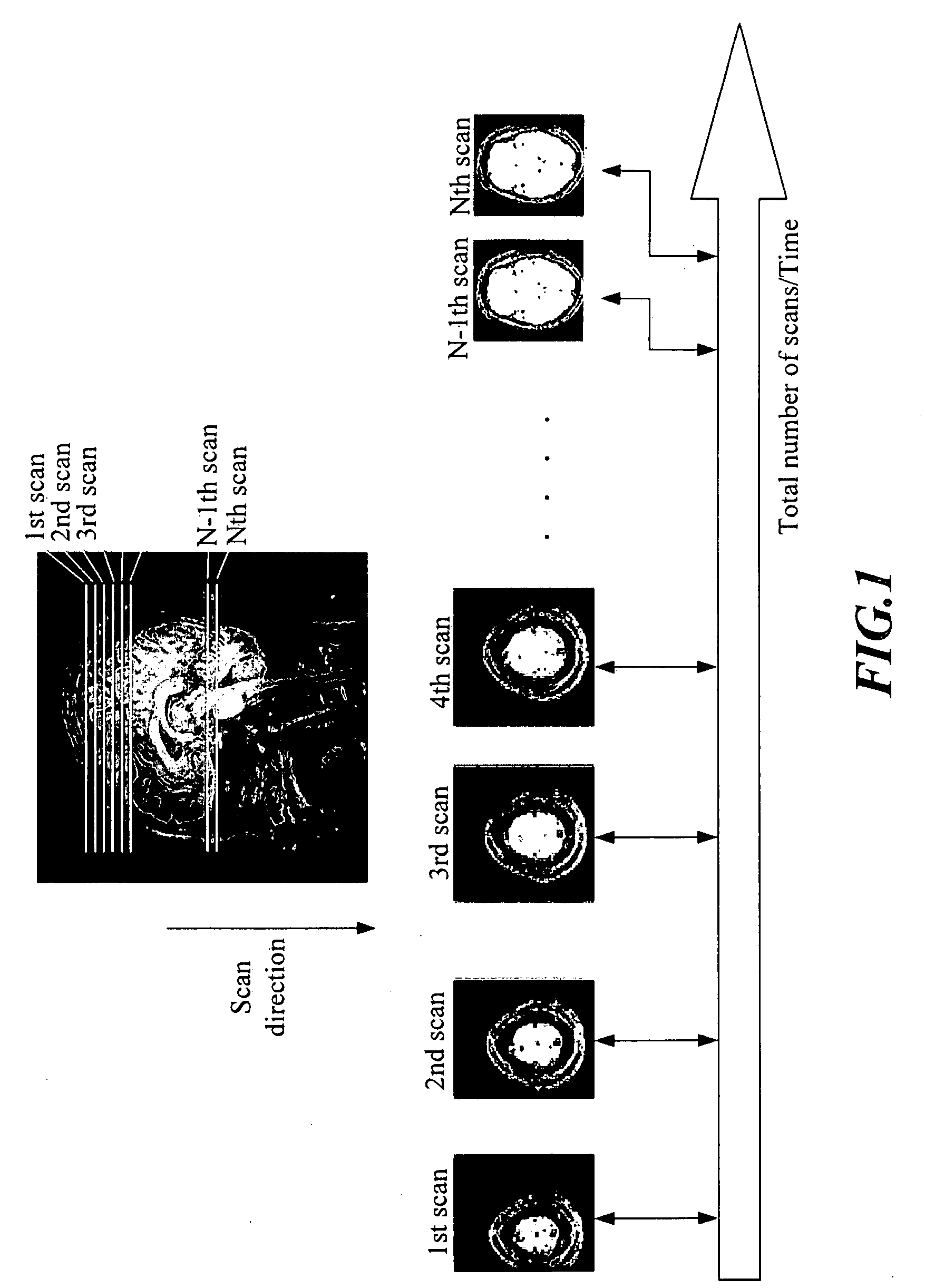
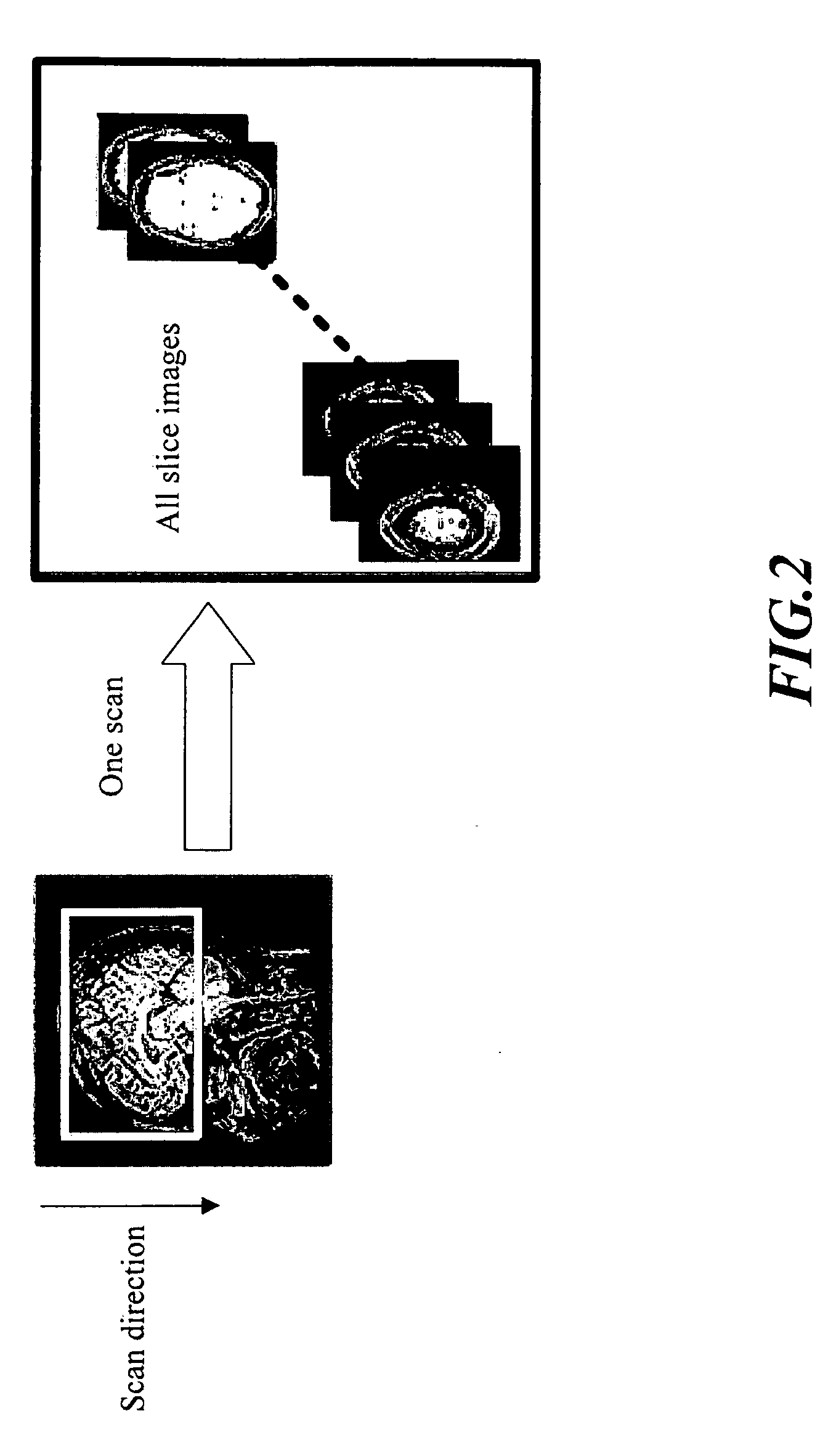
Spatial Encoding. Spatial encoding is probably the most well known and the most intuitive coding method. When spatially encoding, the power (amplitude) of a sample at a particular point in time or space is recorded. ie. over time for audio waves and over space for images.
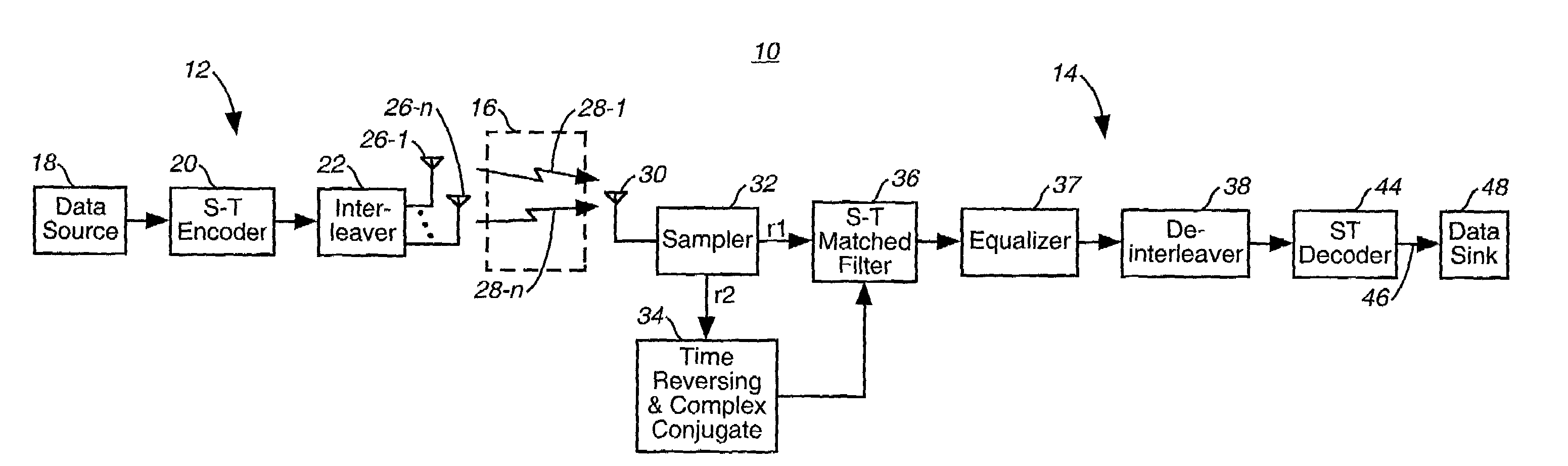
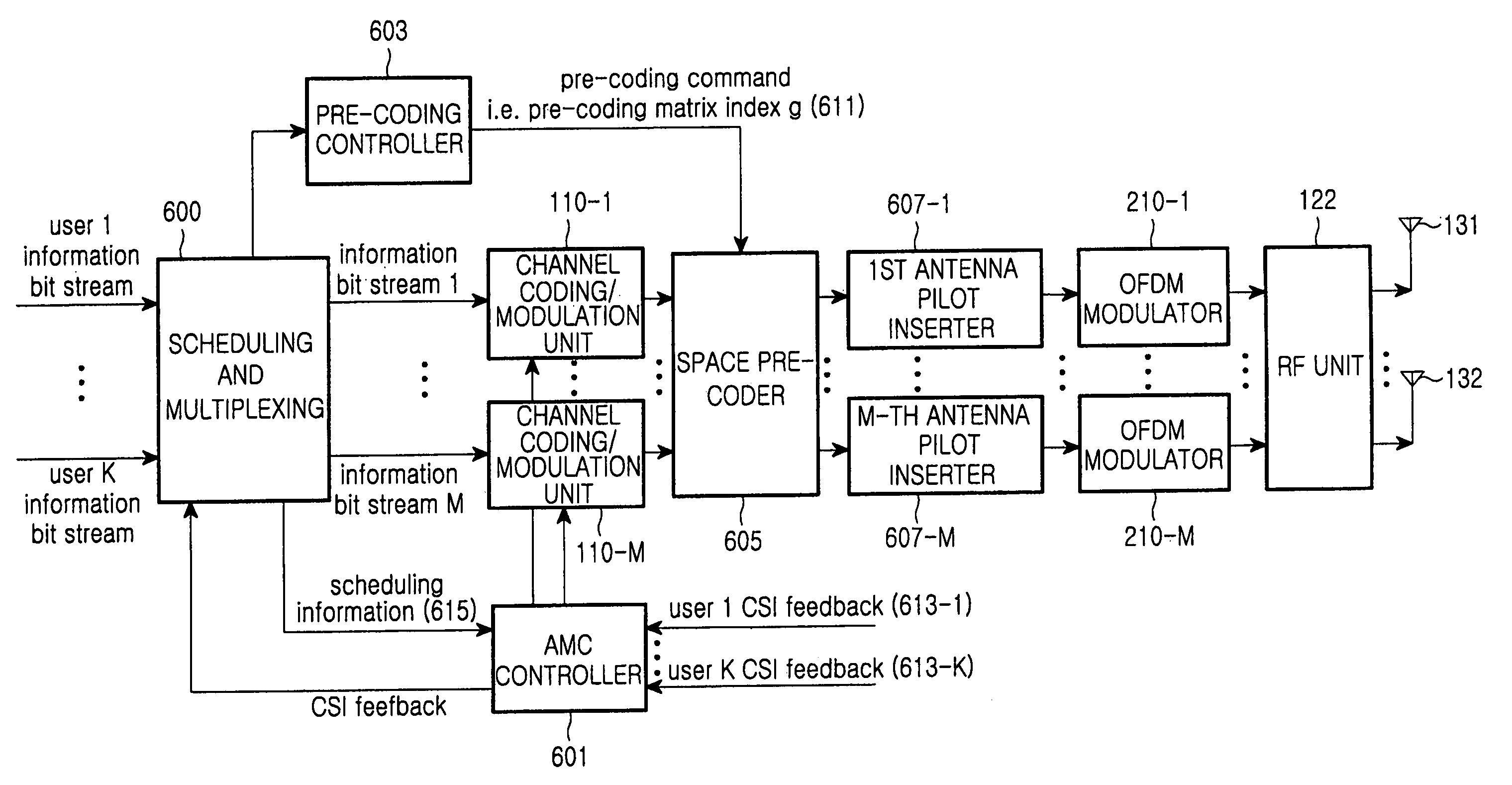
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving data in a multi-antenna communication system
ActiveUS20070104283A1Increase system capacityData augmentationSpatial transmit diversitySecret communicationChannel state informationMultiplexing
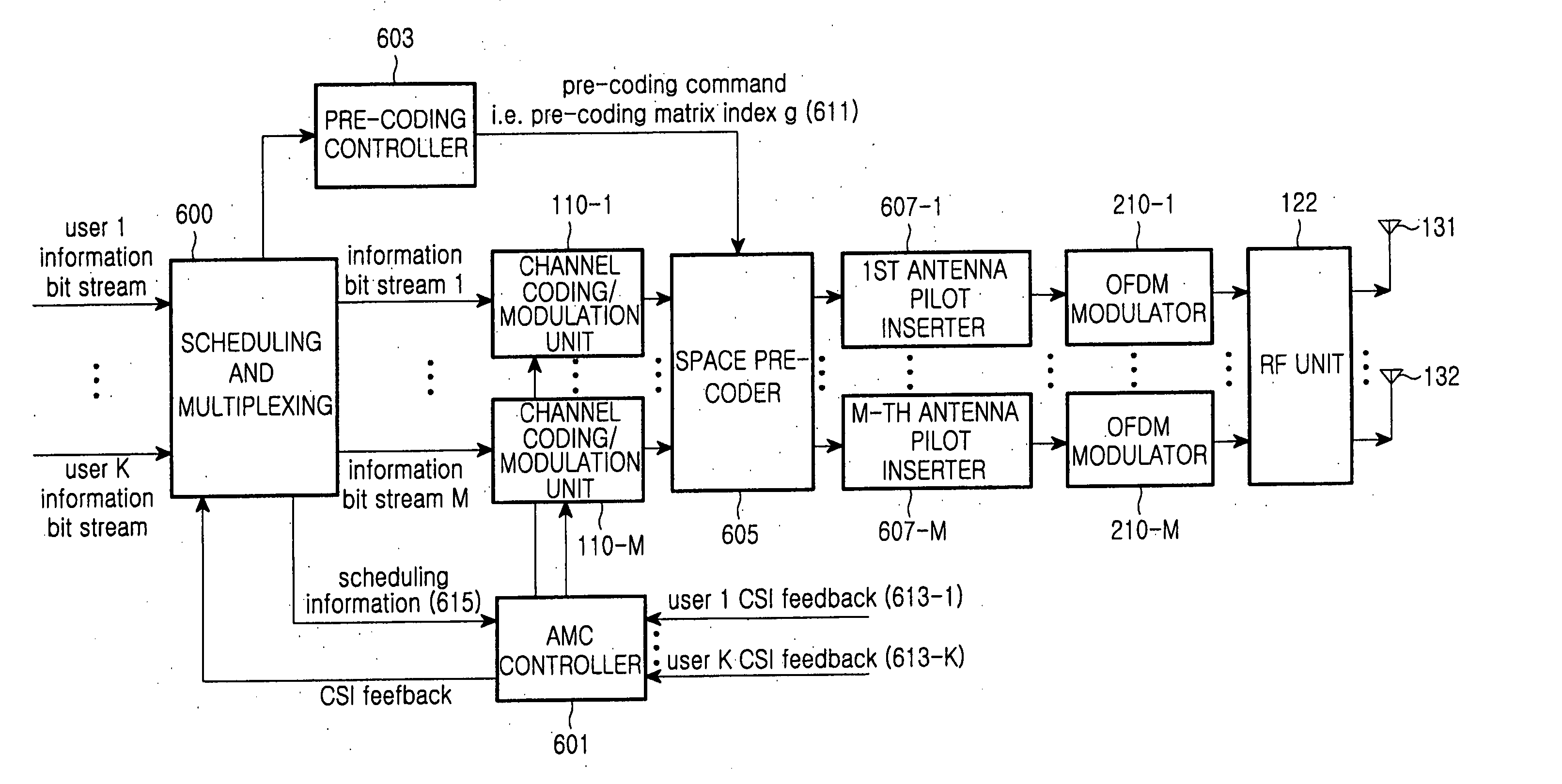
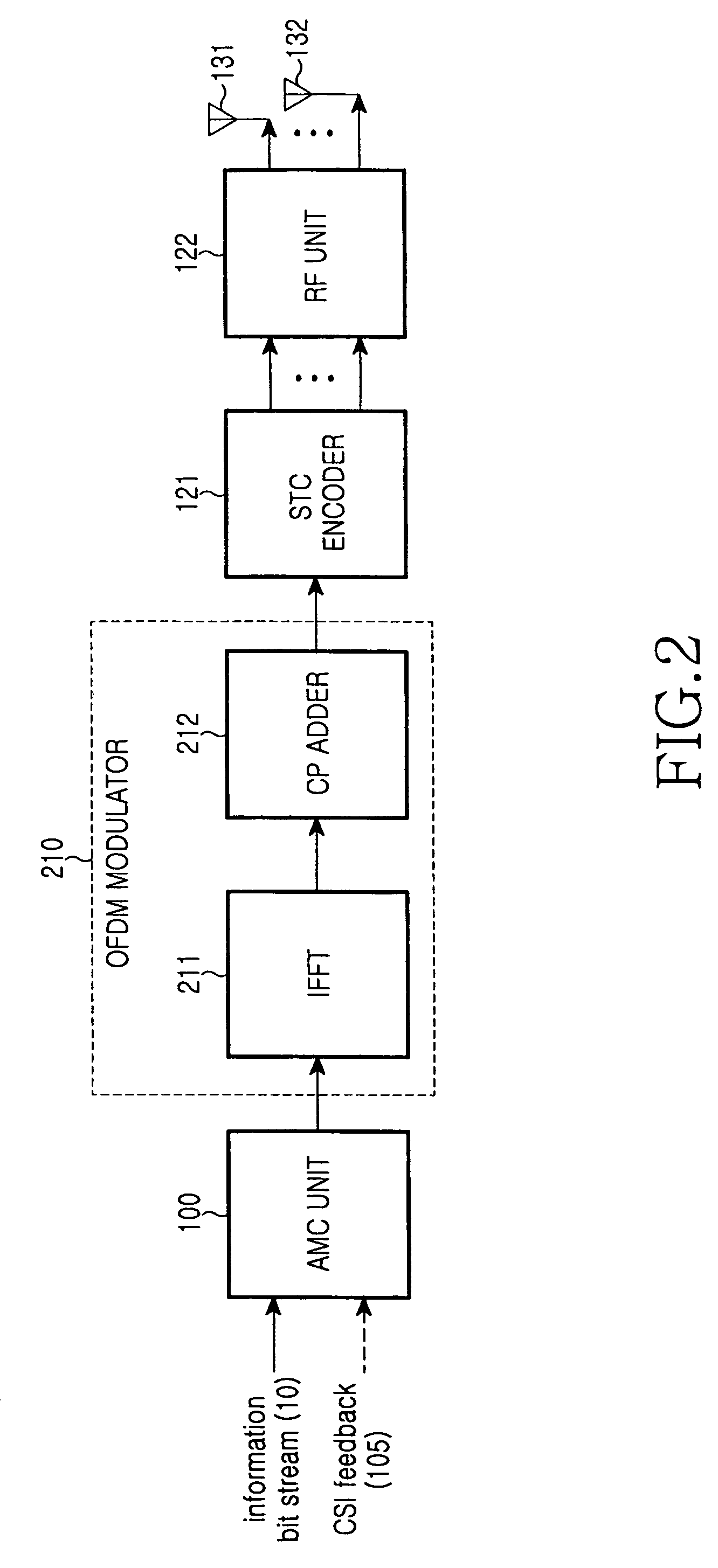
An apparatus for transmitting data in a base station of a wireless communication system that transmits data depending on channel status information fed back from terminals and uses a plurality of antennas. Based on the channel status information, a scheduler determines a terminal to which the base station will transmit data, determines antennas via which the base station will transmit data among the plurality of antennas, and determines a space pre-coding method. A multiplexer multiplexes transmission data into a plurality of data streams according to the number of the determined antennas. A modulation and coding unit performs modulation and coding on each of the data streams. A pre-coding controller outputs a matrix select signal for selecting one of a plurality of space pre-coding matrixes according to the space pre-coding method. A space pre-coder spatial-codes each of the coded streams with the matrix selected based on the matrix select signal. An OFDM modulator performs OFDM modulation on each of the spatial-coded streams. An RF unit transmits each of the OFDM-modulated streams via an associated antenna.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
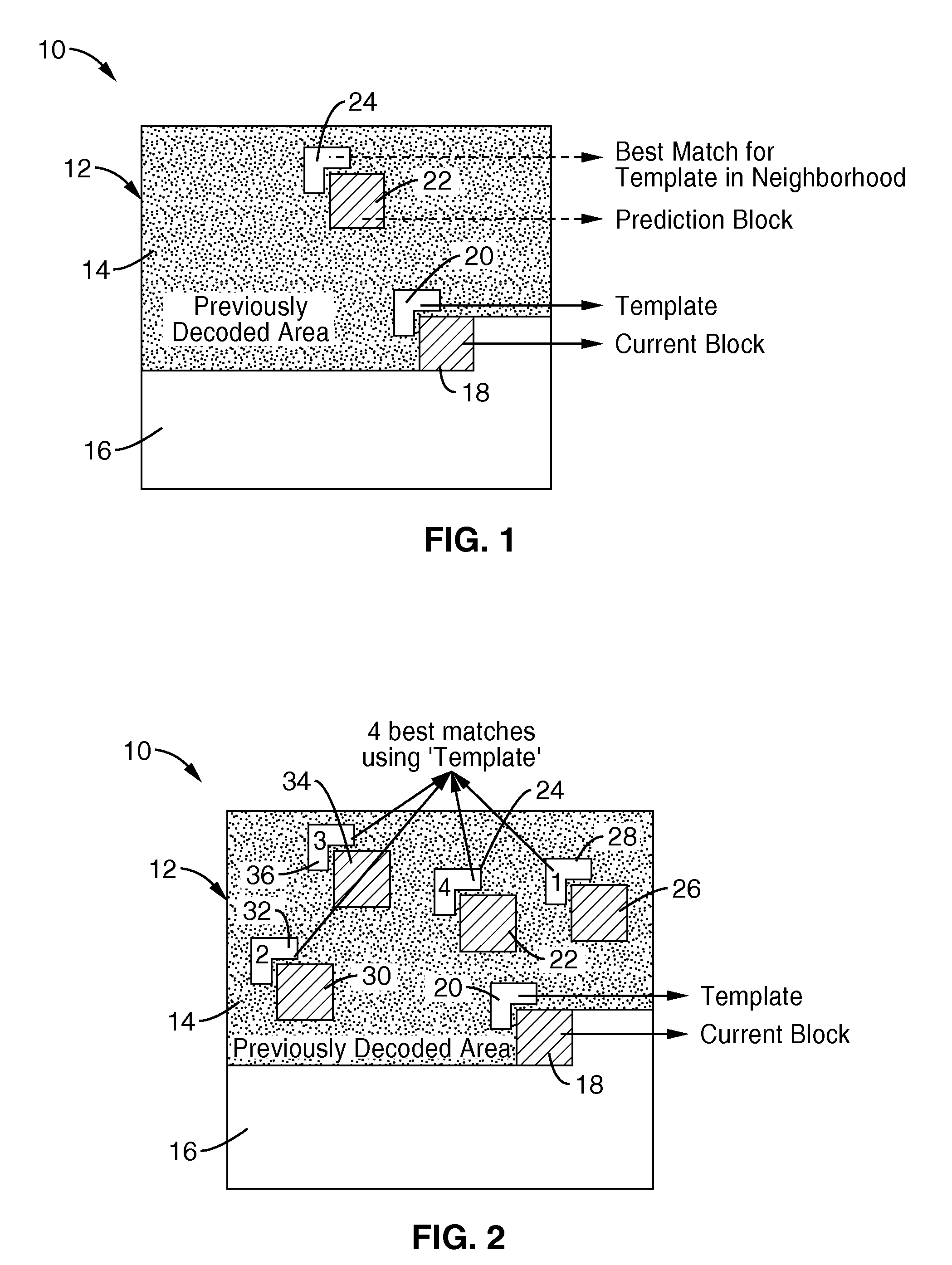
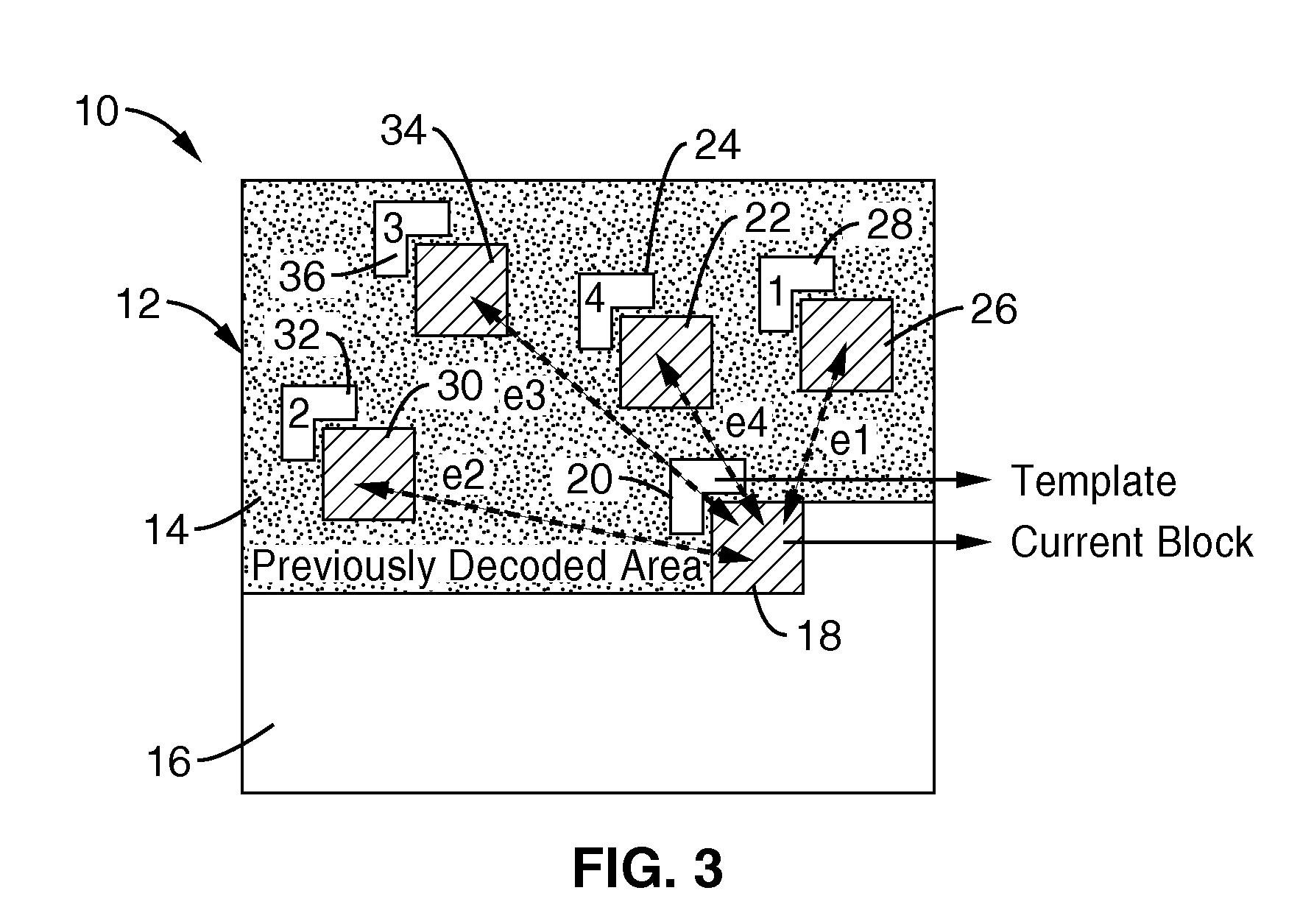
Template matching scheme using multiple predictors as candidates for intra-prediction
InactiveUS20090180538A1Improve compression efficiencyEliminate spaceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTemplate matchingVideo sequence
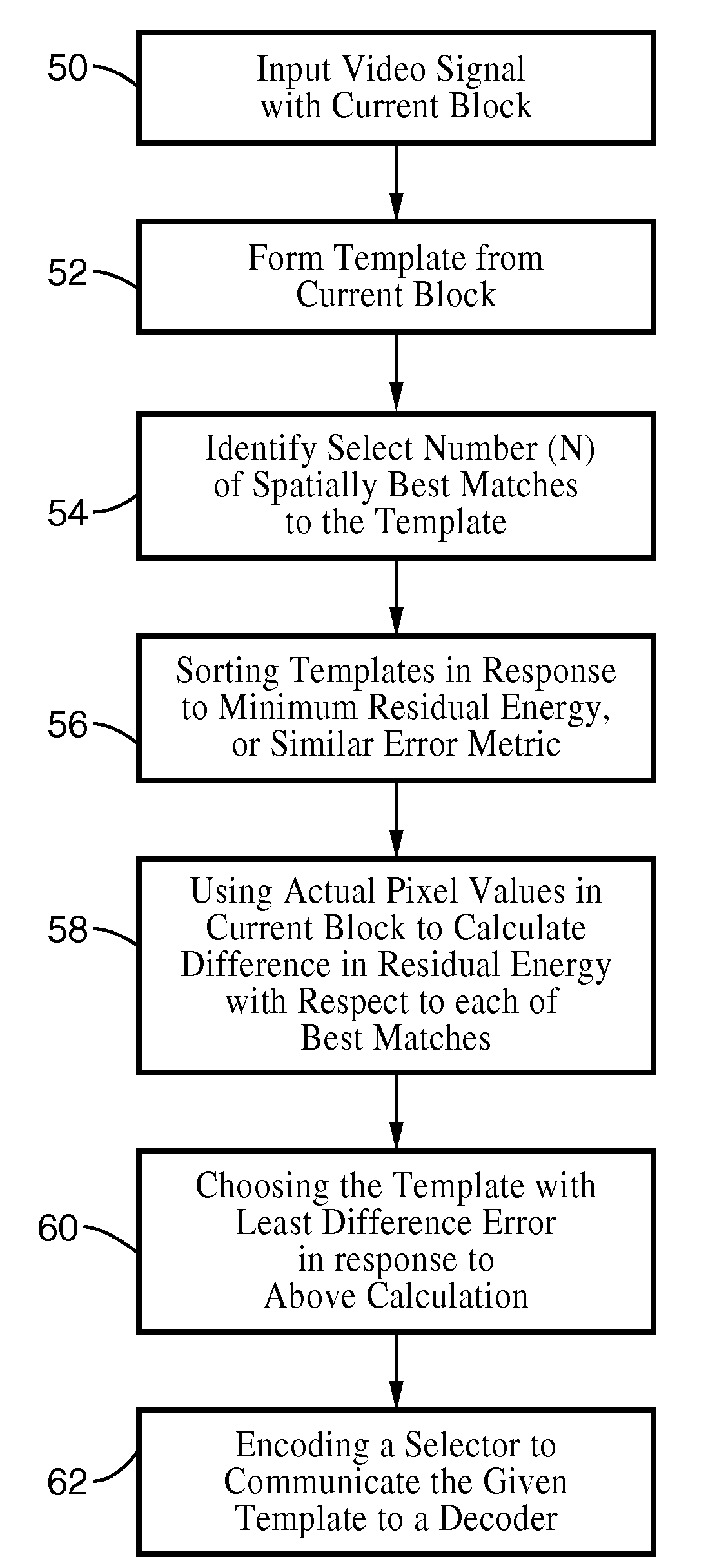
An apparatus and method for spatial encoding of intra-predictions for a current block of a video sequence without the need to average across a number of best template matches. The encoder identifies and sorts the best template matches for the current block within previously coded and reconstructed blocks which neighbor the current block of video. In response to determining actual predictive error for the sorted list of matches, a selector is generated identifying which of the sorted templates is optimal. The selector is then communicated for receipt by the decoder, which is adapted for performing the same template matching and sorting, which is followed by selection of the optimum candidate in response to using the selector. In response to the selector information the decoder can provide optimum template matching without the compromise or overhead of taking averages across the best template candidates.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
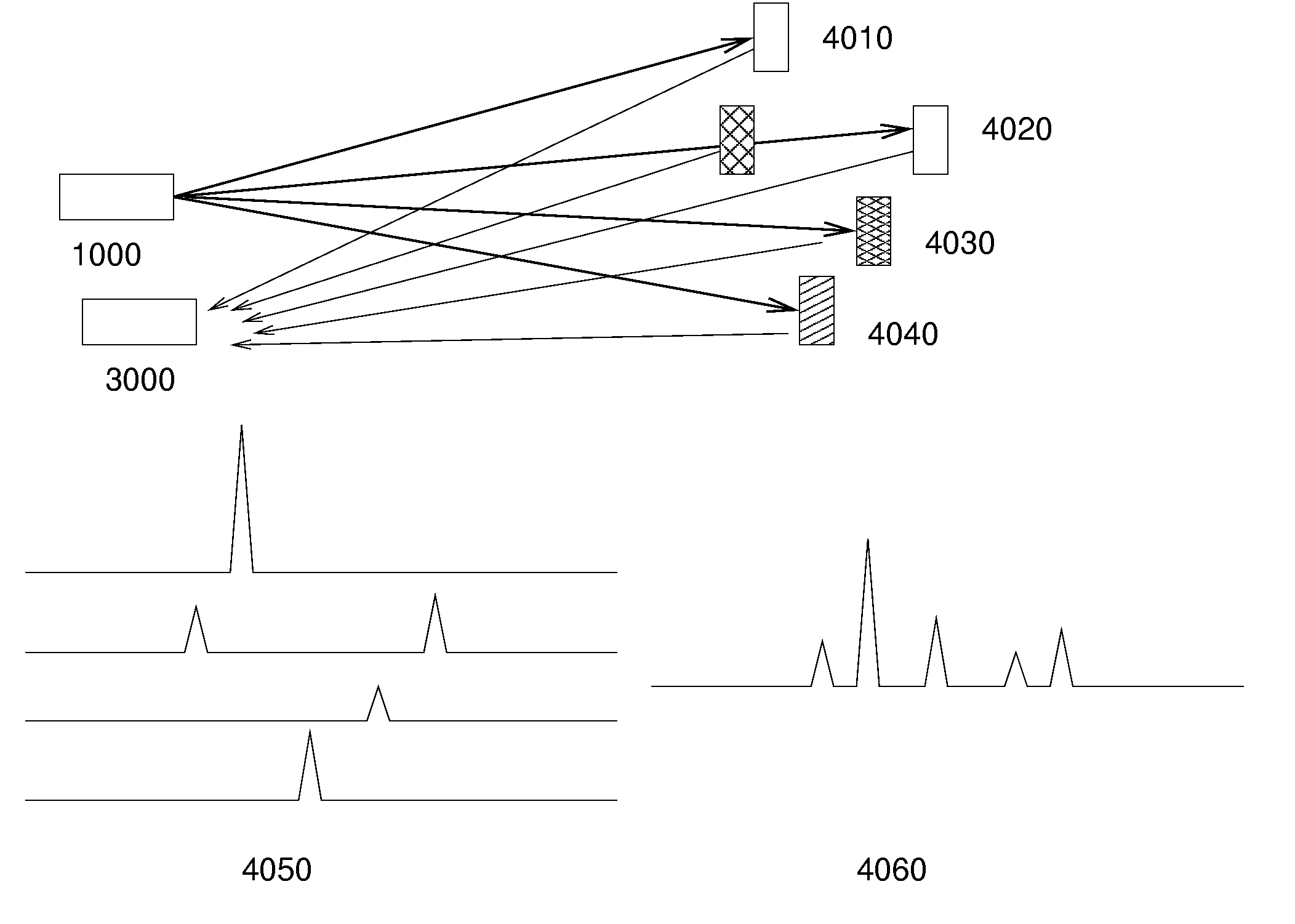
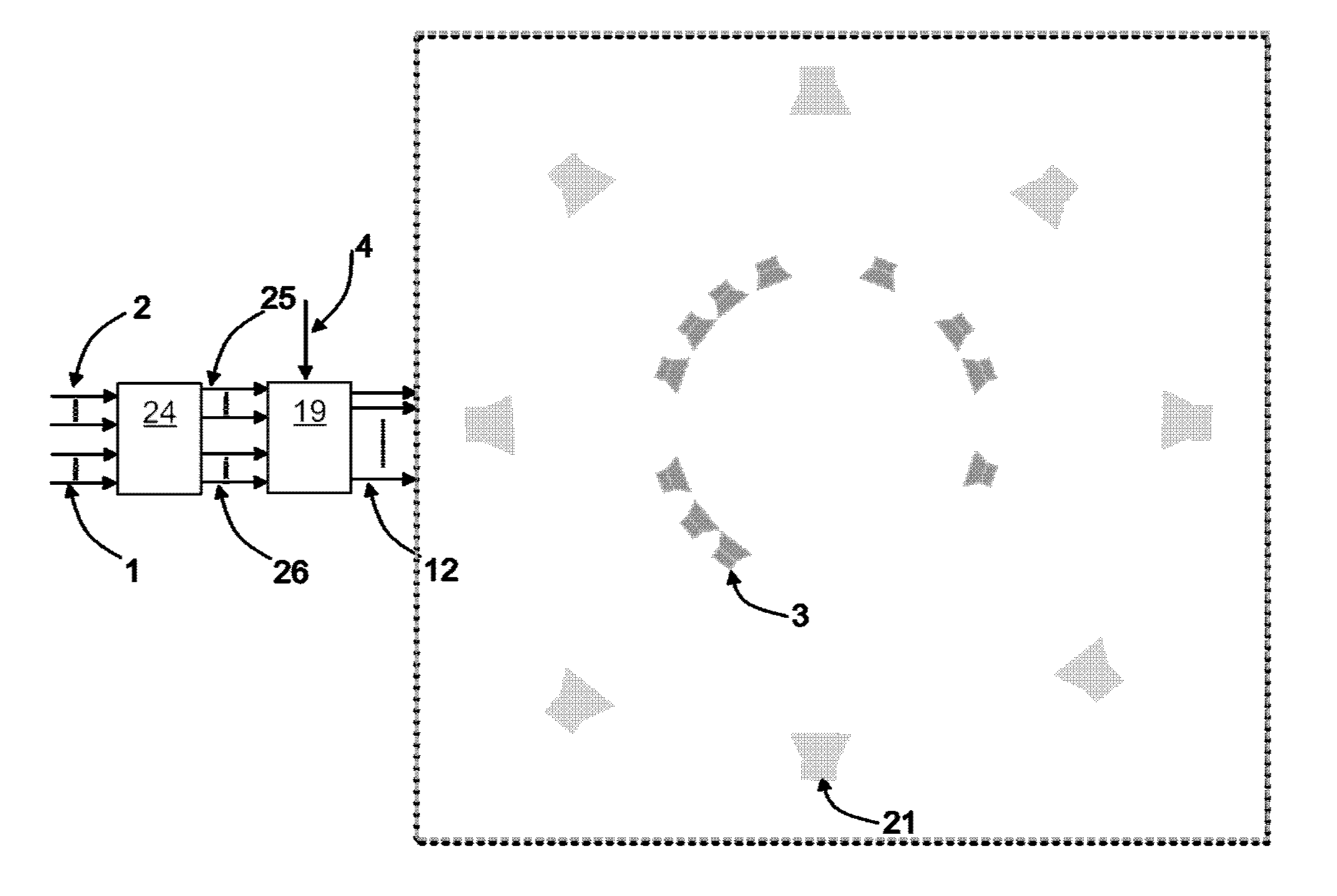
Multiplexed, spatially encoded illumination system for determining imaging and range estimation
InactiveUS20040213463A1Increased complexityIncrease diversityCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansLight equipmentOphthalmology
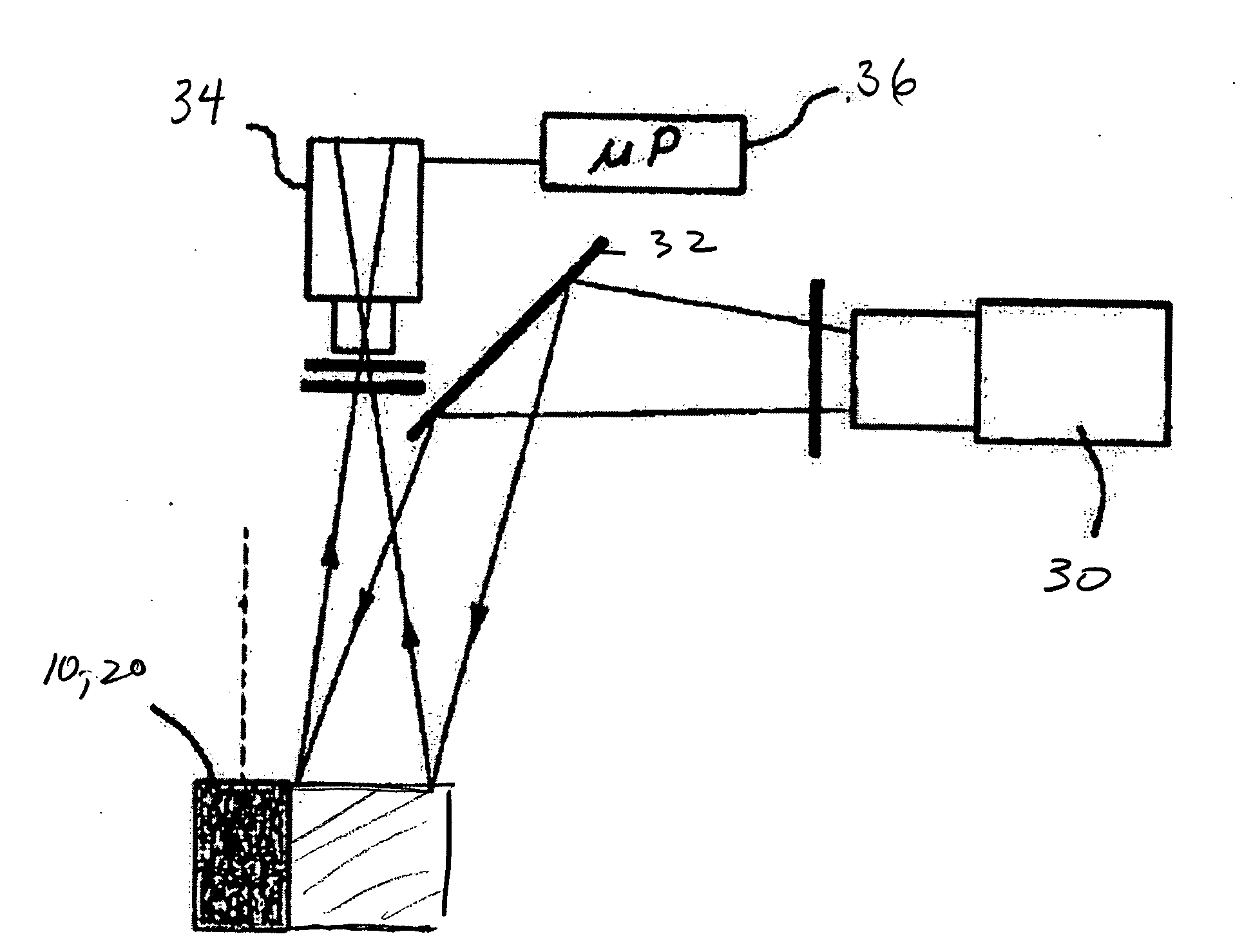
A illumination device sequentially projects a selective set of spatially encoded intensity light pulses toward a scene. The spatially encoded patterns are generated by an array of diffractive optical or holographic elements on a substrate that is rapidly translated in the path of the light beam. Alternatively, addressable micromirror arrays or similar technology are used to manipulate the beam wavefront. Reflected light is collected onto an individual photosensor or a very small set of high performance photodetectors. A data processor collects a complete set of signals associated with the encoded pattern set. The sampled signals are combined by a data processing unit in a prescribed manner to calculate range estimates and imaging features for elements in the scene. The invention may also be used to generate three dimensional reconstructions.
Owner:MORRISON RICK LEE
Method and device for enhanced sound field reproduction of spatially encoded audio input signals
ActiveUS20130148812A1Stereophonic circuit arrangementsStereophonic systemsSpatial analysisSpatial encoding
A method for sound field reproduction into a listening area of spatially encoded first audio input signals according to sound field description data using an ensemble of physical loudspeakers. The method includes computing reproduction subspace description data from loudspeaker positioning data describing the subspace in which virtual sources can be reproduced with the physically available setup. Then, second and third audio input signals with associated sound field description data, in which second audio input signals include spatial components of the first audio input signals located within the reproducible subspace and third audio input signals include spatial components of the first audio input signals located outside of the reproducible subspace. A spatial analysis is performed on second audio input signals to extract fourth audio input signals corresponding to localizable sources within the reproducible subspace with associated source positioning data. Components of second audio input signals after spatial analysis are merged with third audio input signals into fifth audio input signals with associated sound field description data for reproduction within the reproducible subspace. Loudspeaker alimentation signals are computed from fourth and fifth audio input signals.
Owner:SENNHEISER ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
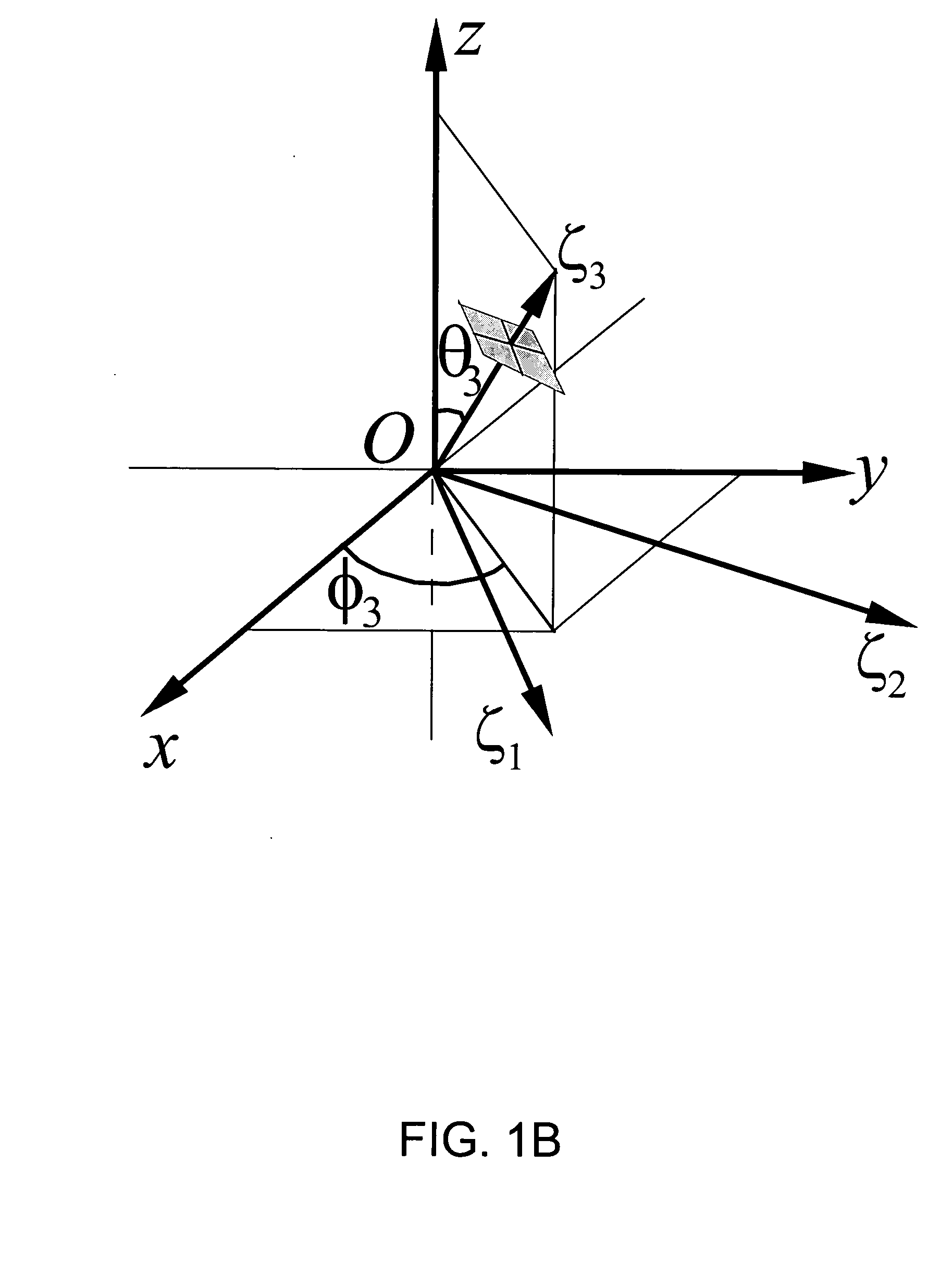
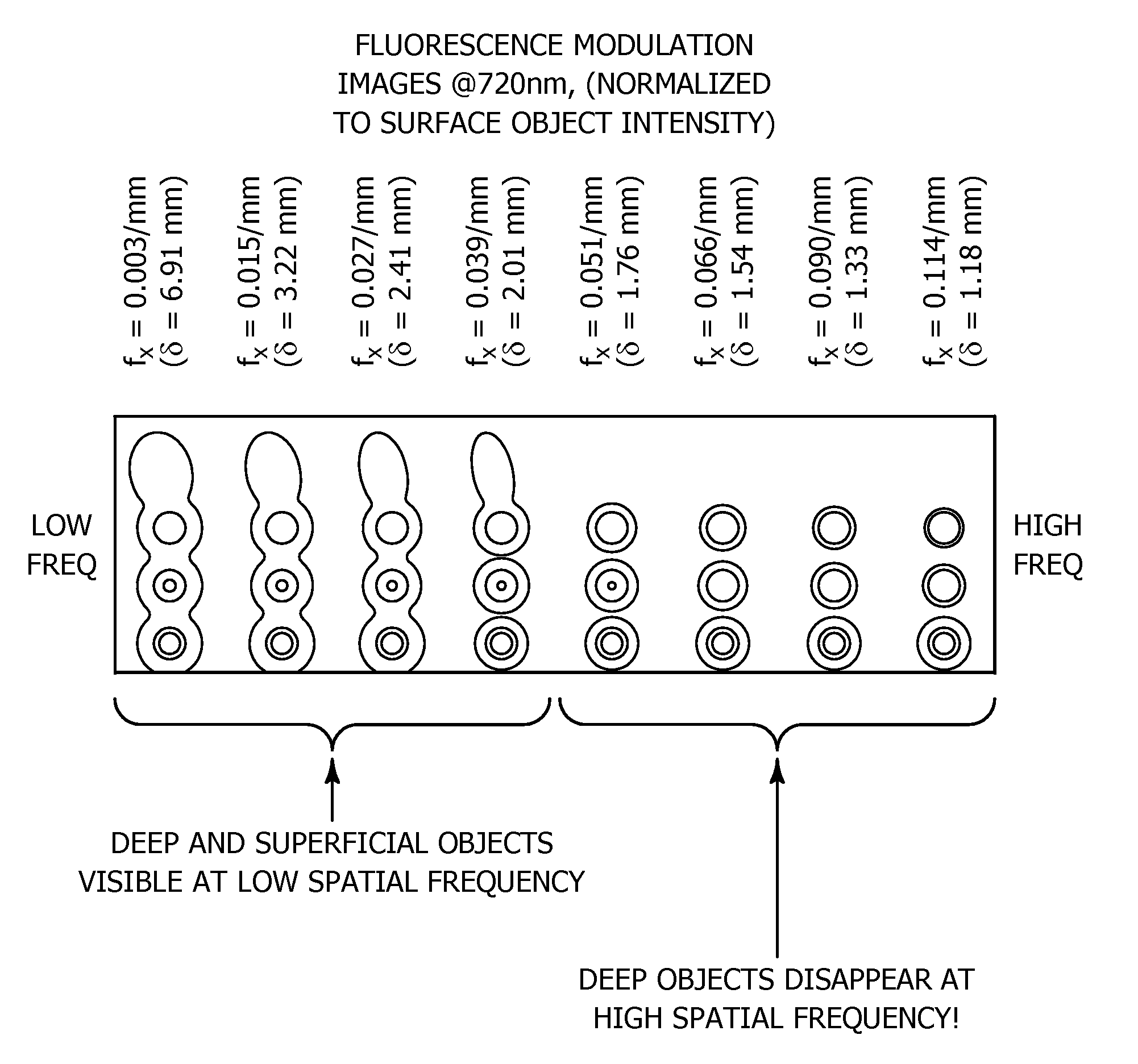
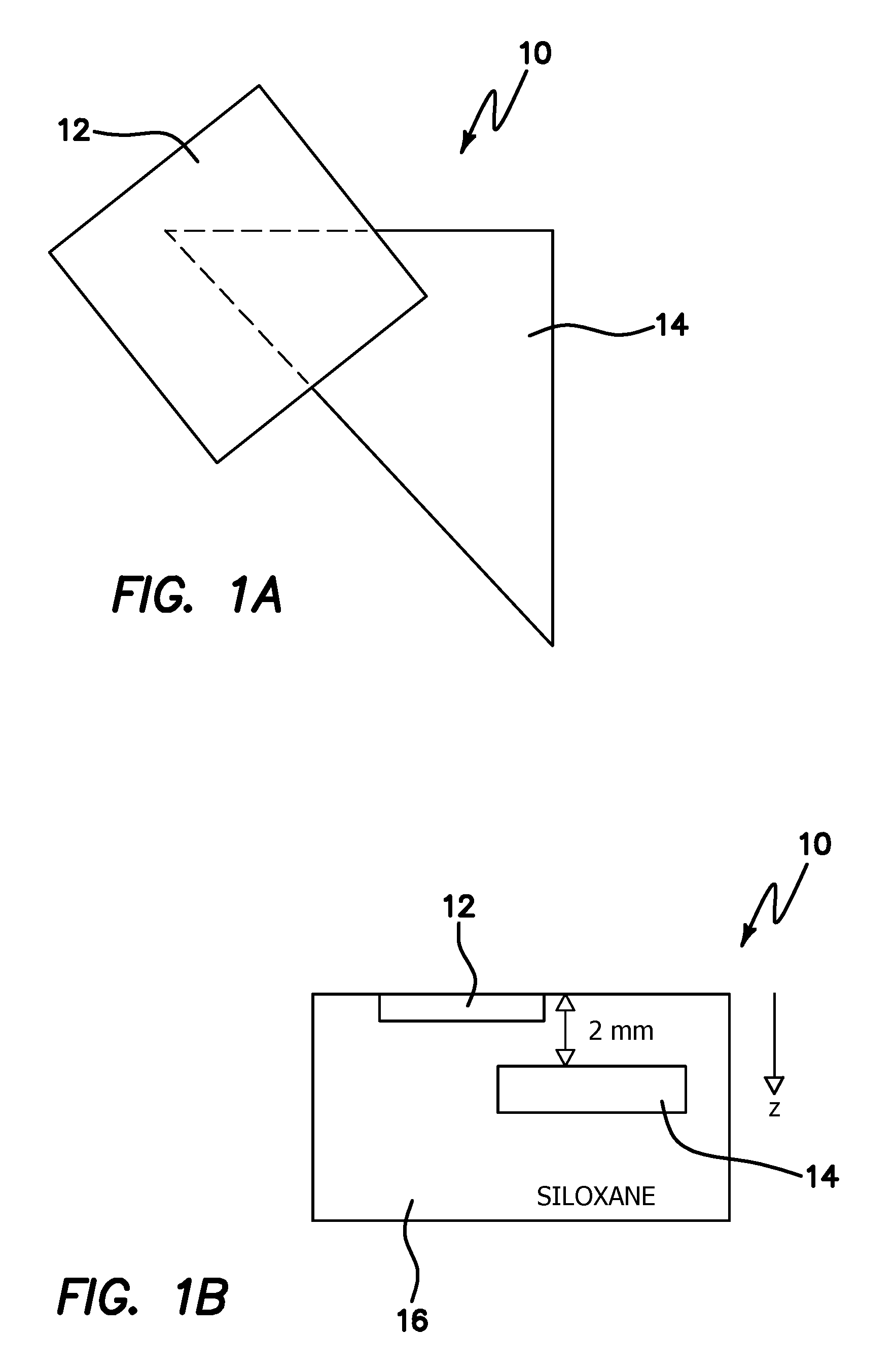
Method and apparatus for high resolution spatially modulated fluorescence imaging and tomography
An improvement in a method for quantitative modulated imaging to perform depth sectioned reflectance or transmission imaging in a turbid medium, such as human or animal tissue is directed to the steps of encoding periodic pattern of illumination preferably with a fluorescent excitation wavelength when exposing a turbid medium to the periodic pattern to provide depth-resolved discrimination of structures within the turbid medium; and reconstructing a non-contact three dimensional image of the structure within a turbid medium. As a result, wide field imaging, separation of the average background optical properties from the heterogeneity components from a single image, separation of superficial features from deep features based on selection of spatial frequency of illumination, or qualitative and quantitative structure, function and composition information is extracted from spatially encoded data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
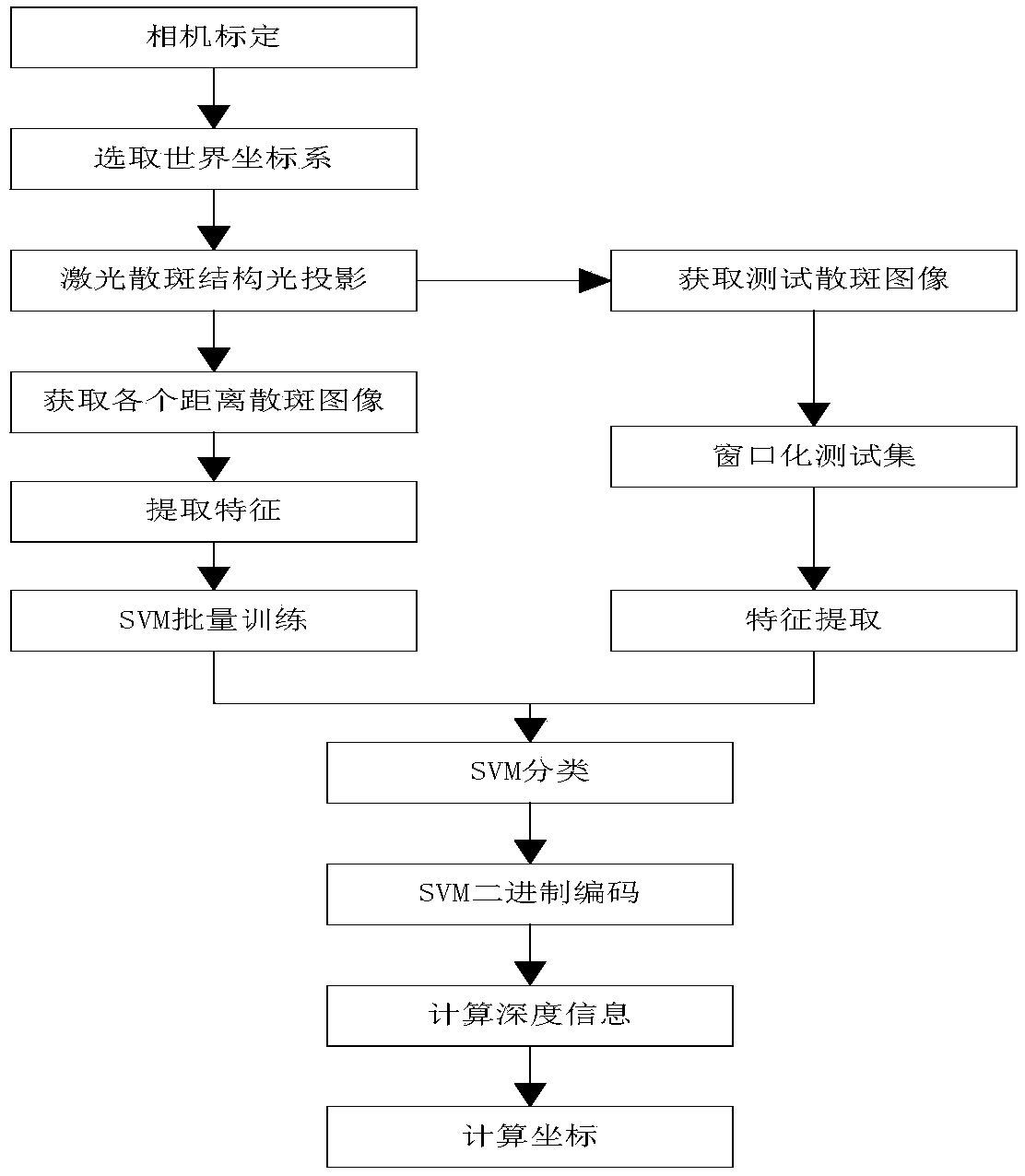
Method for three-dimensional reconstruction of laser speckle structured light and depth information
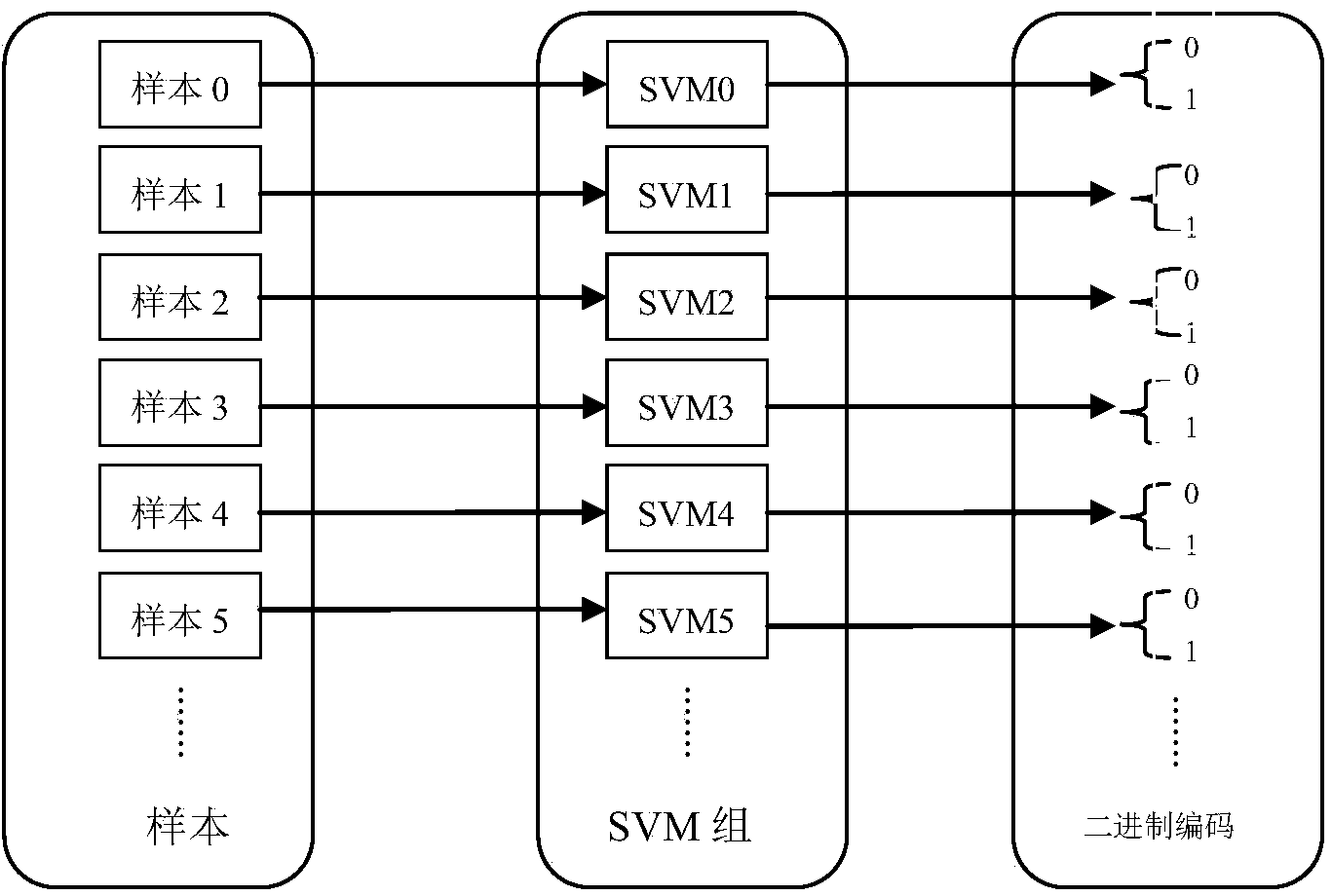
The invention provides a method for three-dimensional reconstruction of laser speckle structured light and depth information. The three-dimensional reconstruction technology is an important subject for machine vision research and refers to the content that a three-dimensional space geometrical shape of a three-dimensional body is restored through images of the three-dimensional body. Generally, three-dimensional reconstruction is conducted through the binocular parallax principle of a binocular camera or through a triangulation method or space codes are obtained through the structured light and the depth information is obtained through the triangulation method. The method aims at obtaining the depth information through the laser speckle structured light, a similar invention such as the kinect of the Microsoft Corporation also obtains the depth information (namely different depths are matched through a cross-correlation function of laser speckles) of an object through the method, and the difference is an algorithm for obtaining the depth information through the speckles. According to the method, parallel code number sorting is conducted on each pixel block one by one by a thinning window through multiple support vector machines, so that the depth of each pixel window is obtained, coordinates under a world coordinate system of the object are obtained by inversely solving a camera model through the depth information, and therefore the depth information with the higher accuracy can be obtained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
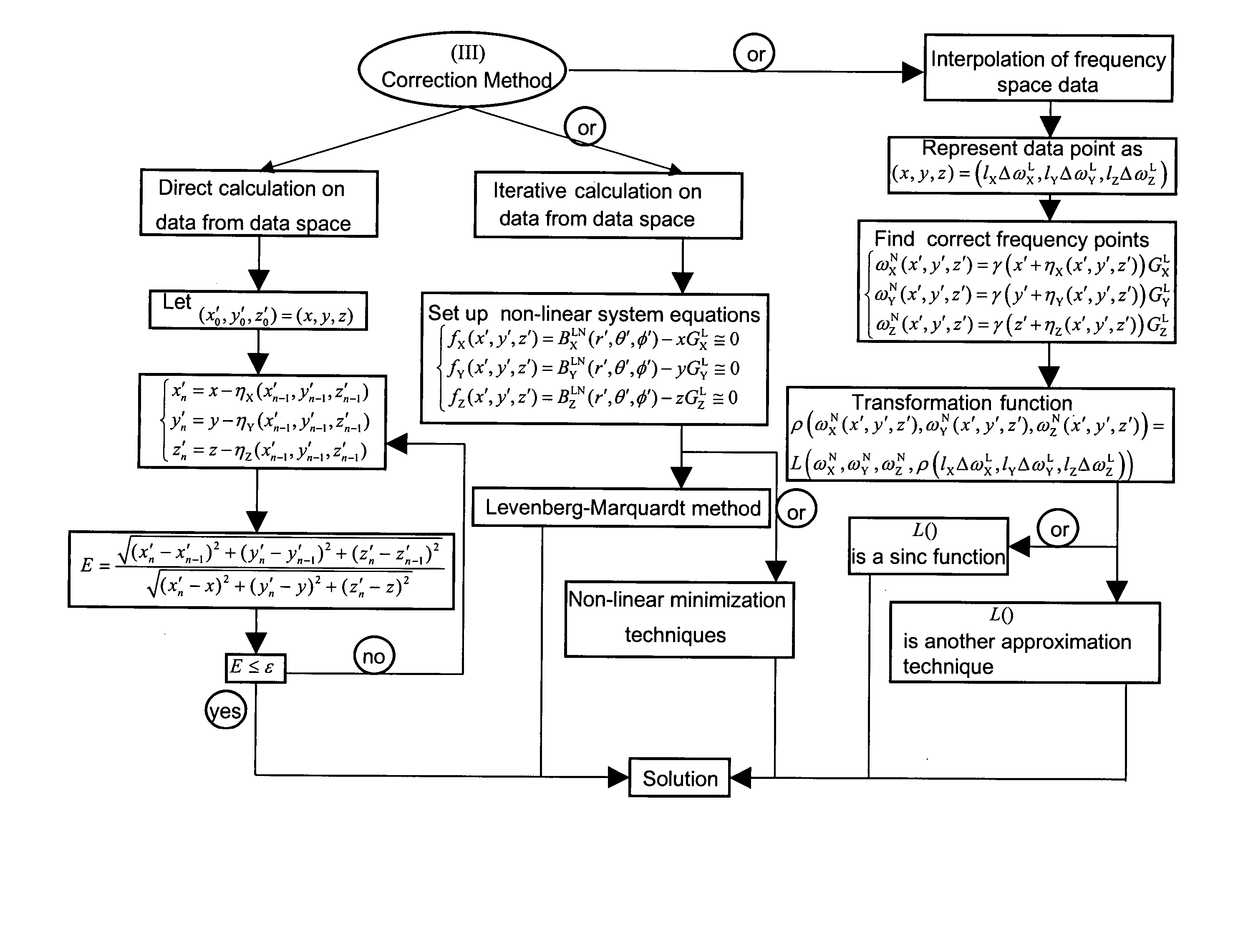
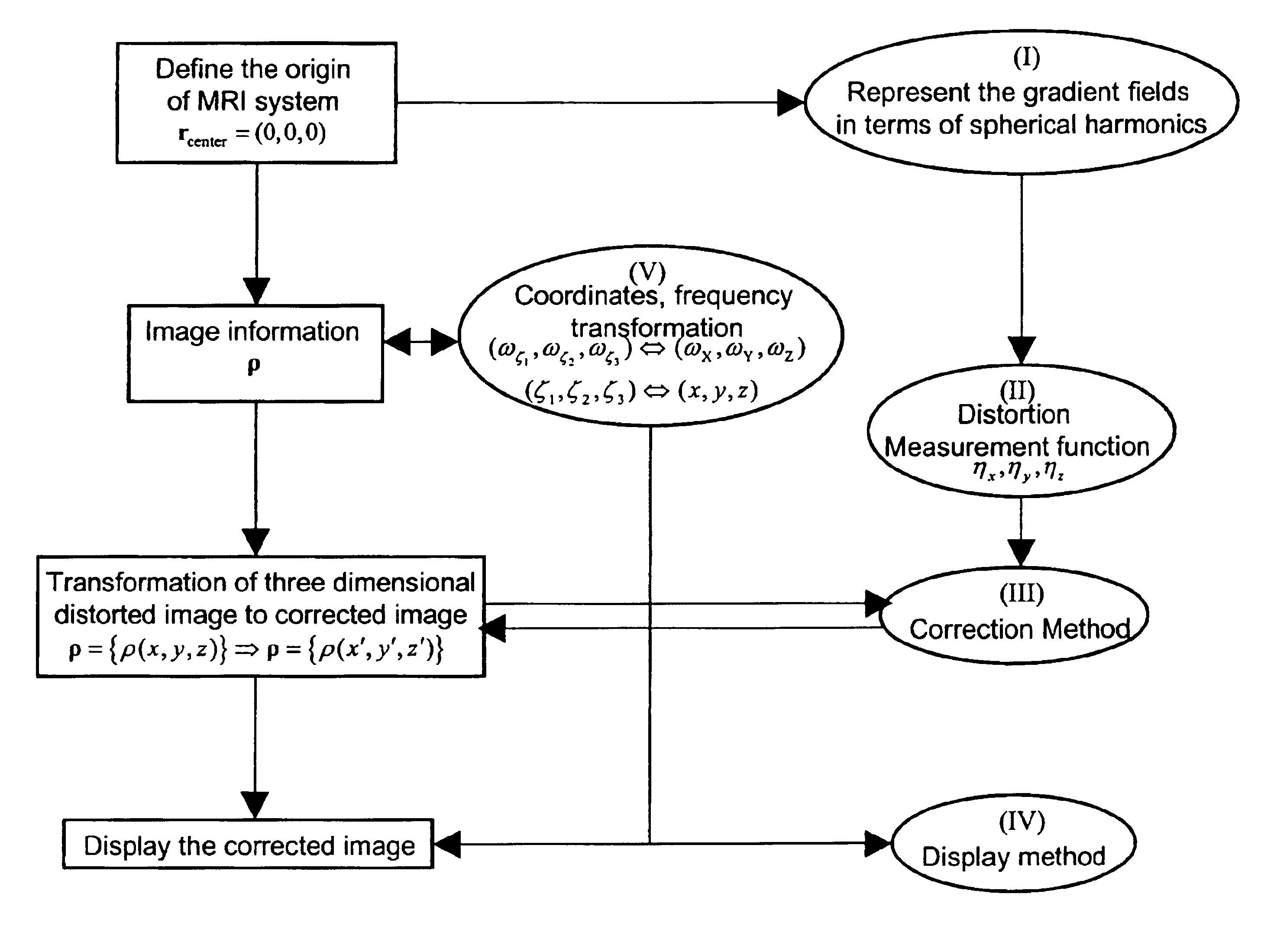
Correction of magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS20050024051A1Avoid artifactsAccurate imagingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientFourier transform on finite groups
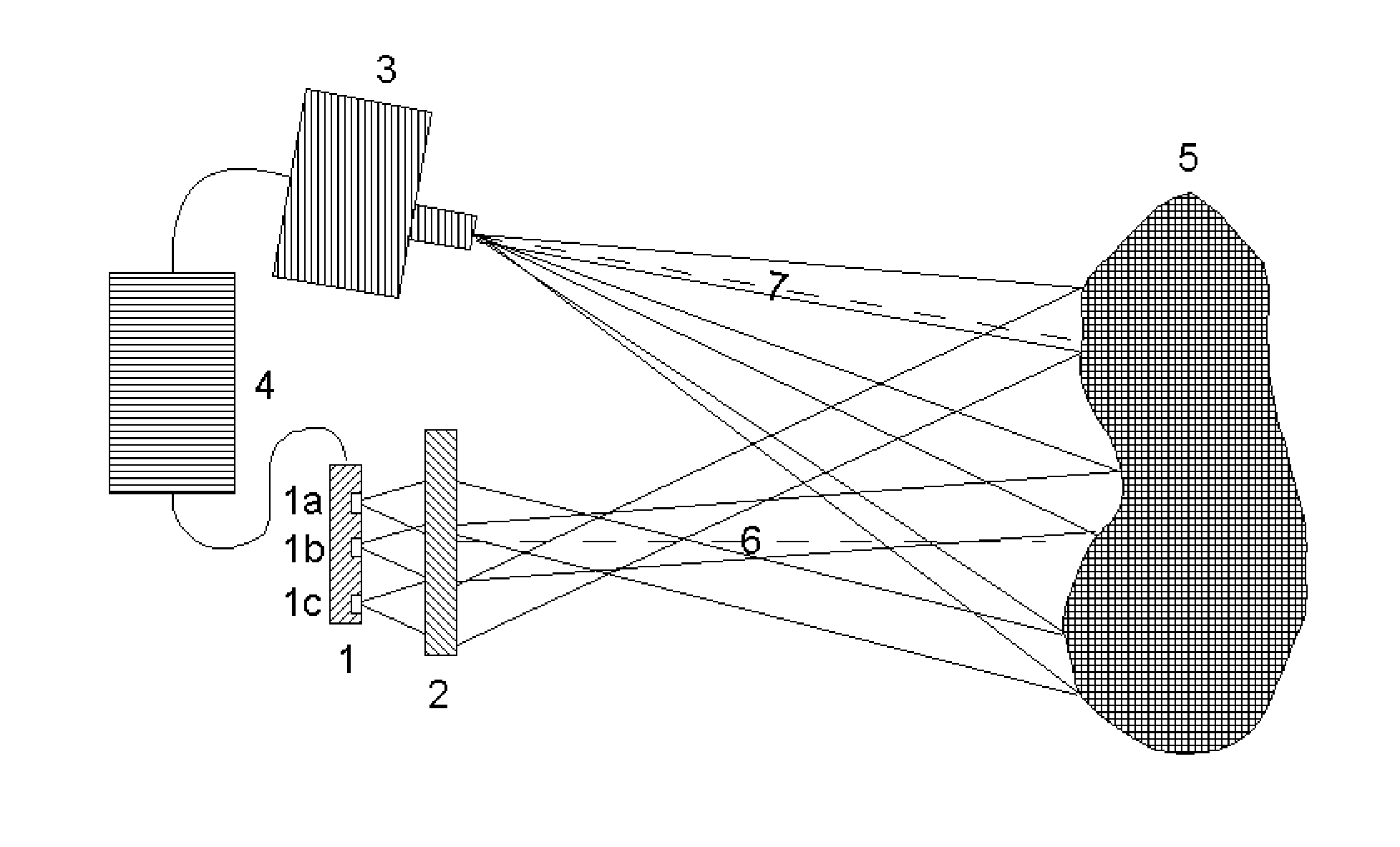
Spatial encoding in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques is achieved by sampling the signal as a function of time in the presence of magnetic field gradients, e.g., X, Y, and Z gradients. The gradient magnets have in the past been assumed to generate a linear gradient, and typical image reconstruction techniques have relied upon this assumption. However, to achieve high speed performance, gradient magnets often sacrifice linearity for speed. This non-linearity, in turn, results in distorted images, the distortion often being sufficiently large to compromise the usefulness of MRI images for stereotaxy or longitudinal studies, where precise volumetric information is required. The disclosure provides practical methods for correcting distorted images resulting from such non-linearity in the gradient fields, as well as distortions resulting from translational, rotational, and / or winding / design errors in the field generating devices. The methods employ spherical harmonic expansions of the gradient fields and fast Fourier transform techniques to provide well-corrected images without undue computational burdens.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Method and apparatus for high resolution spatially modulated fluorescence imaging and tomography
An improvement in a method for quantitative modulated imaging to perform depth sectioned reflectance or transmission imaging in a turbid medium, such as human or animal tissue is directed to the steps of encoding periodic pattern of illumination preferably with a fluorescent excitation wavelength when exposing a turbid medium to the periodic pattern to provide depth-resolved discrimination of structures within the turbid medium; and reconstructing a non-contact three dimensional image of the structure within a turbid medium. As a result, wide field imaging, separation of the average background optical properties from the heterogeneity components from a single image, separation of superficial features from deep features based on selection of spatial frequency of illumination, or qualitative and quantitative structure, function and composition information is extracted from spatially encoded data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
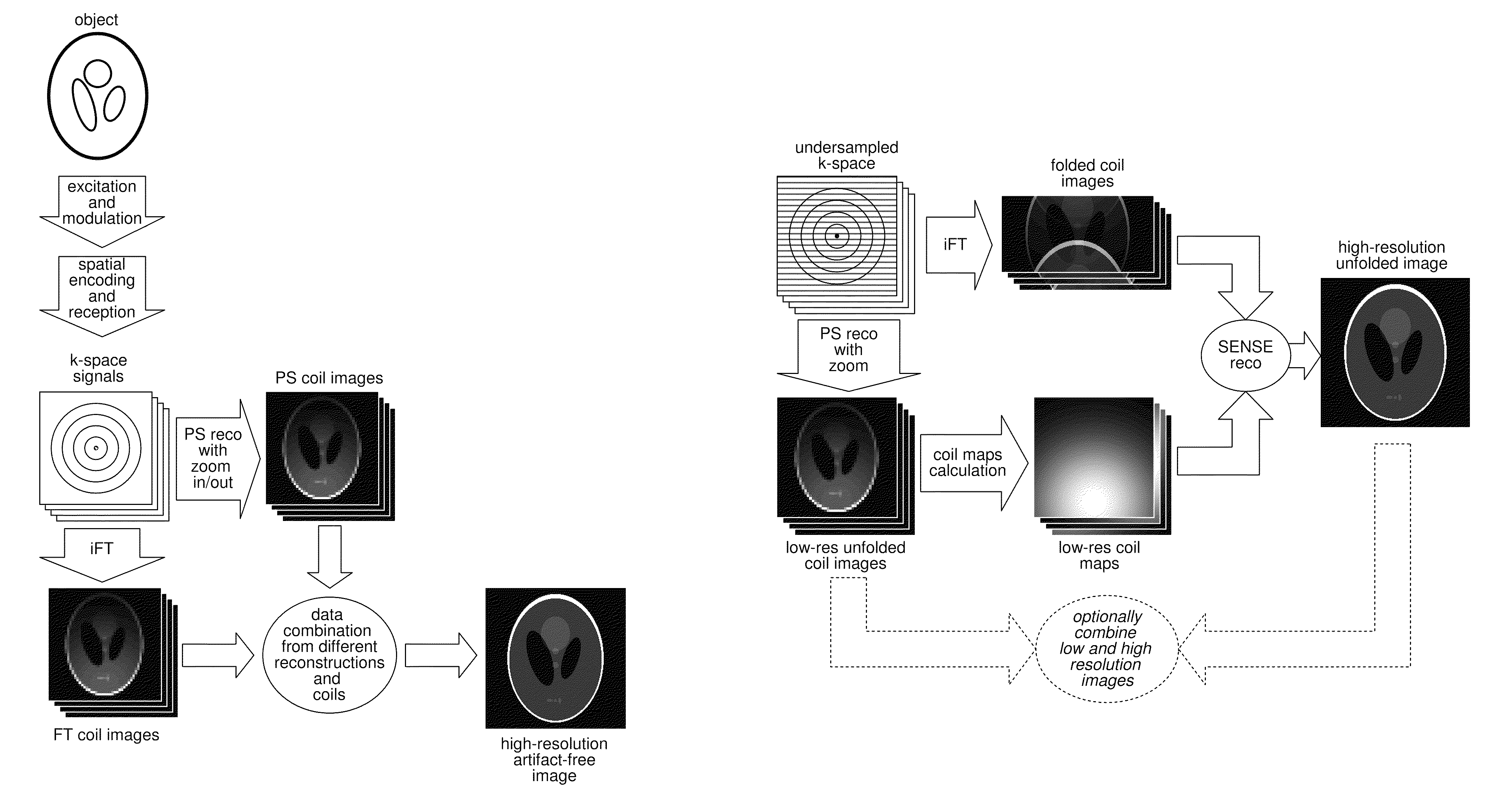
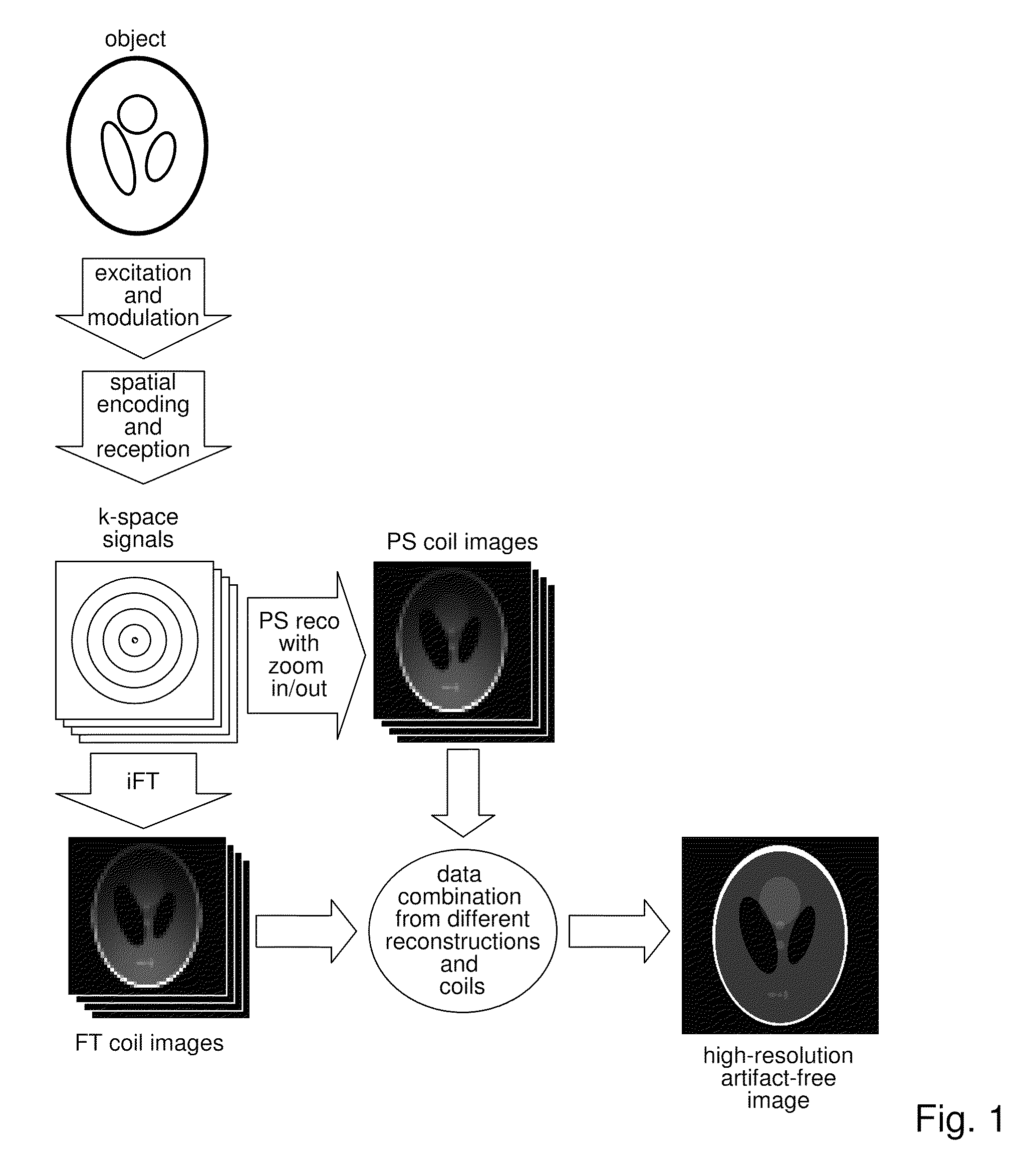
Method for data acquisition acceleration in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using receiver coil arrays and non-linear phase distributions
InactiveUS20110148410A1Specifically designedIncrease freedomElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRTransverse magnetizationData acquisition
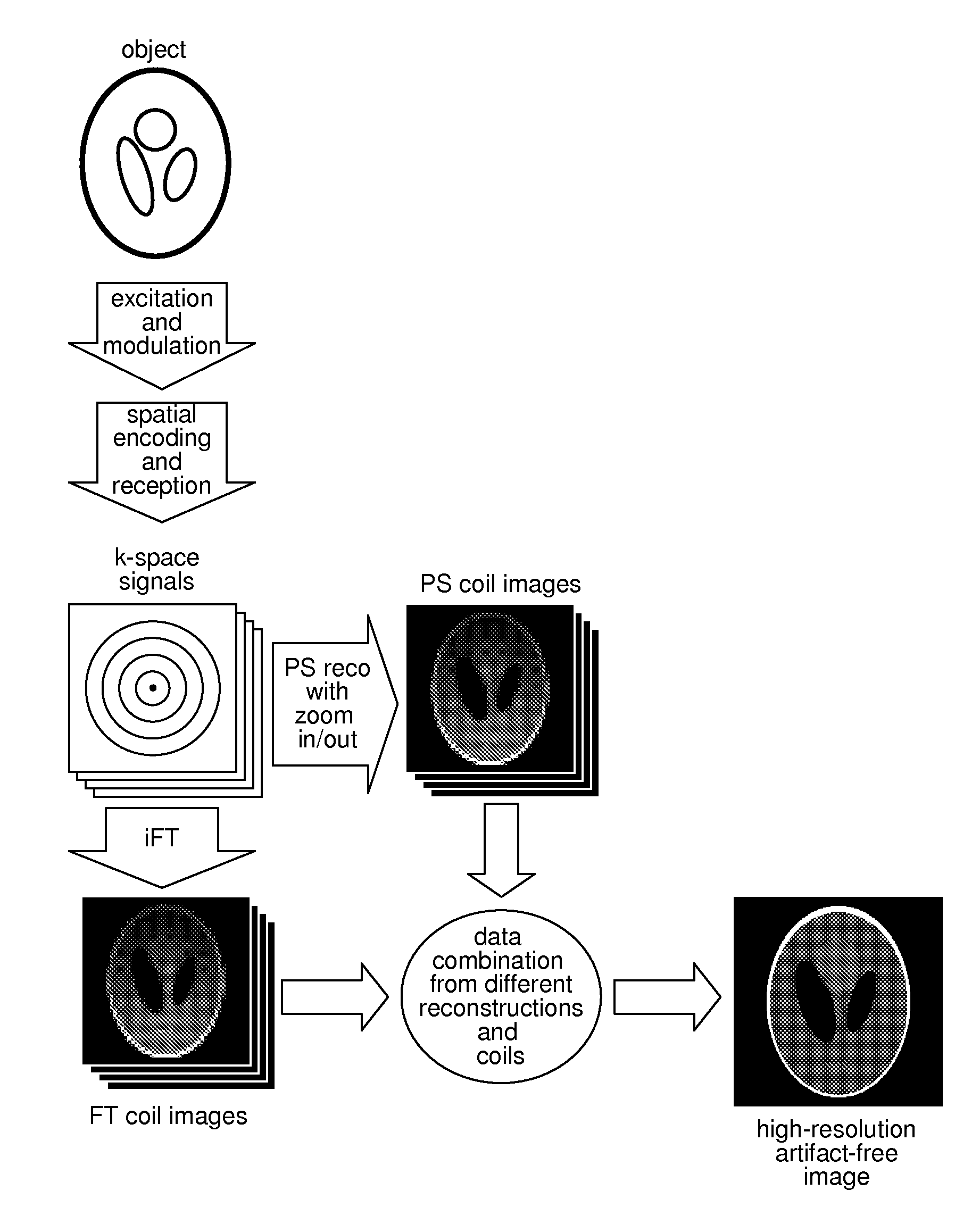
A method for accelerating data acquisition in MRI with N-dimensional spatial encoding has a first method step in which a transverse magnetization within an imaged object volume is prepared having a non-linear phase distribution. Primary spatial encoding is thereby effected through application of switched magnetic fields. Two or more RF receivers are used to simultaneously record MR signals originating from the imaged object volume, wherein, for each RF receiver, an N-dimensional data matrix is recorded which is undersampled by a factor Ri per selected k-space direction. Data points belonging to a k-space matrix which were not recoded by a selected acquisition schema are reconstructed using a parallel imaging method, wherein reference information concerning receiver coil sensitivities is extracted from a phase-scrambled reconstruction of the undersampled data matrix. The method generates a high-resolution image free of artifacts in a time-efficient manner by improving data sampling efficiency and thereby reducing overall data acquisition time.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
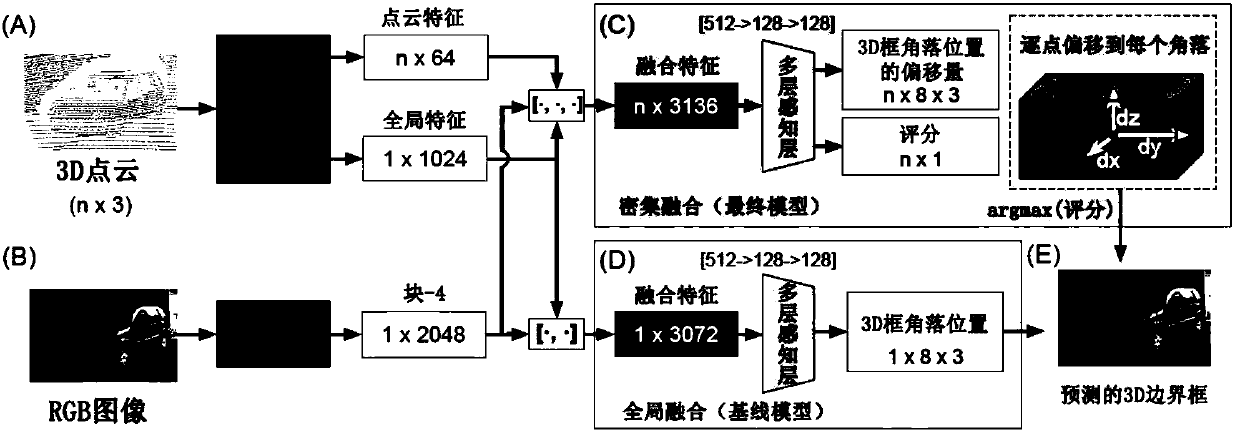
Method for detecting three-dimensional object based on point fusion network
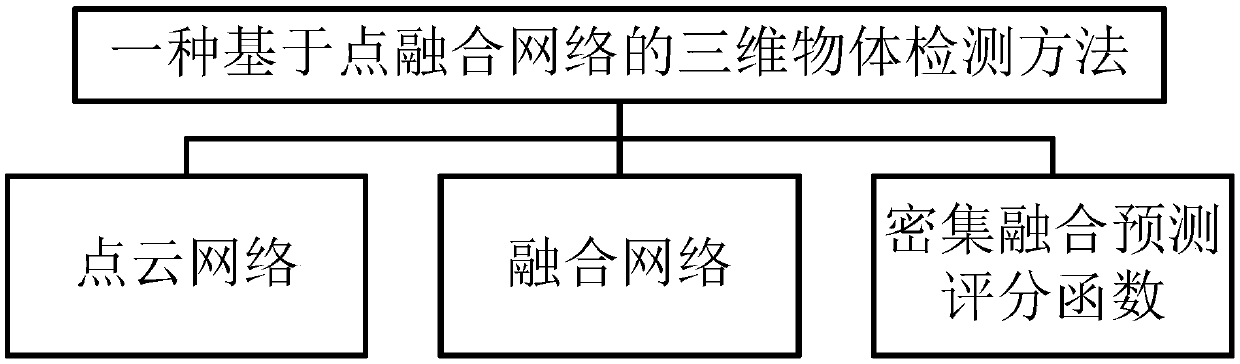
The invention puts forward a method for detecting a three-dimensional object based on a point fusion network. The method comprises a point cloud network, a fusion network, and dense fusion predictionscoring functions. The method comprises the following steps: a point cloud network model is used for taking in original point cloud, learning spatial coding of each point and aggregating global pointcloud features; the features are used for classification and semantic segmentation; in the fusion network, image features extracted via a convolutional neural network and corresponding point cloud features generated via a sub-network of the point fusion network are used as input; these functions are combined, a three-dimensional bounding box is output for a target object, a supervisory scoring function is used to directly train the network to predict whether points are within the target bounding box, and an unsupervised scoring function can help the network select a best prediction point. Viathe method, how to combine images and depth information optimally can be directly learned; lossy input preprocessing such as quantization or projection or the like can be prevented; the method can begenerally applicable, and accuracy thereof is greatly improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
Systems and methods for spatially adaptive video encoding
ActiveUS20170237983A1Lower latencyIncrease contentDigital video signal modificationSelective content distributionVideo encodingSpatial encoding
Systems and methods for providing video content using spatially adaptive video encoding. Panoramic and / or virtual reality content may be viewed by a client device using a viewport with viewing dimension(s) configured smaller than available dimension(s) of the content. Client device may include a portable media device characterized by given energy and / or computational resources. Video content may be encoded using spatially varying encoding. For image playback, portions of panoramic image may be pre-encoded using multiple quality bands. Pre-encoded image portions, matching the viewport, may be provided and reduce computational and / or energy load on the client device during consumption of panoramic content. Quality distribution may include gradual quality transition area allowing for small movements of the viewport without triggering image re-encoding. Larger movements of the viewport may automatically trigger transition to another spatial encoding distribution.
Owner:GOPRO
Apparatus and method for spatial encoding of a search space
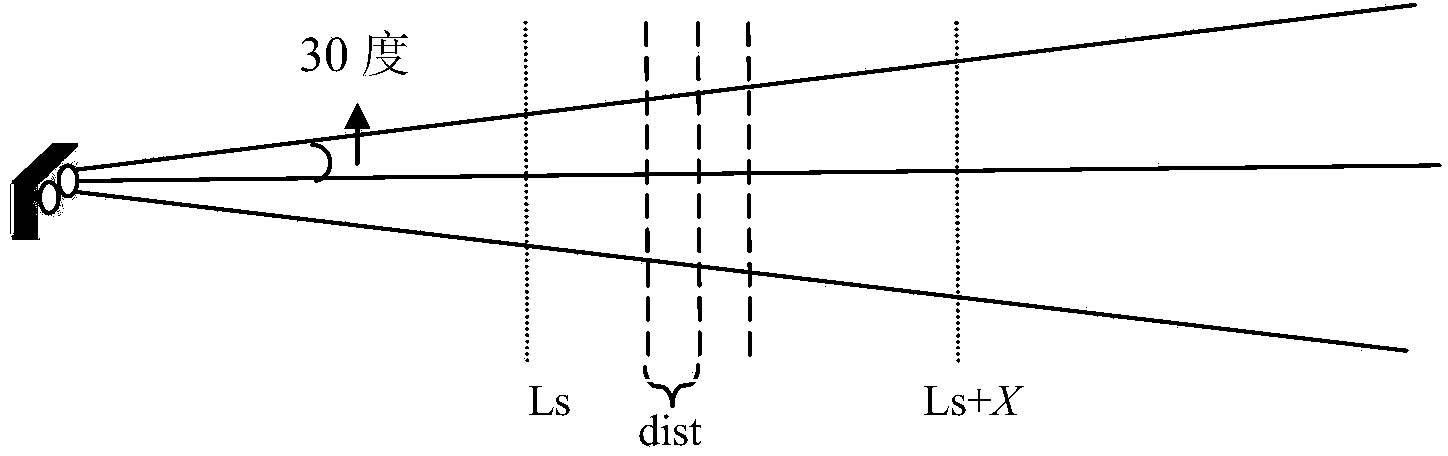
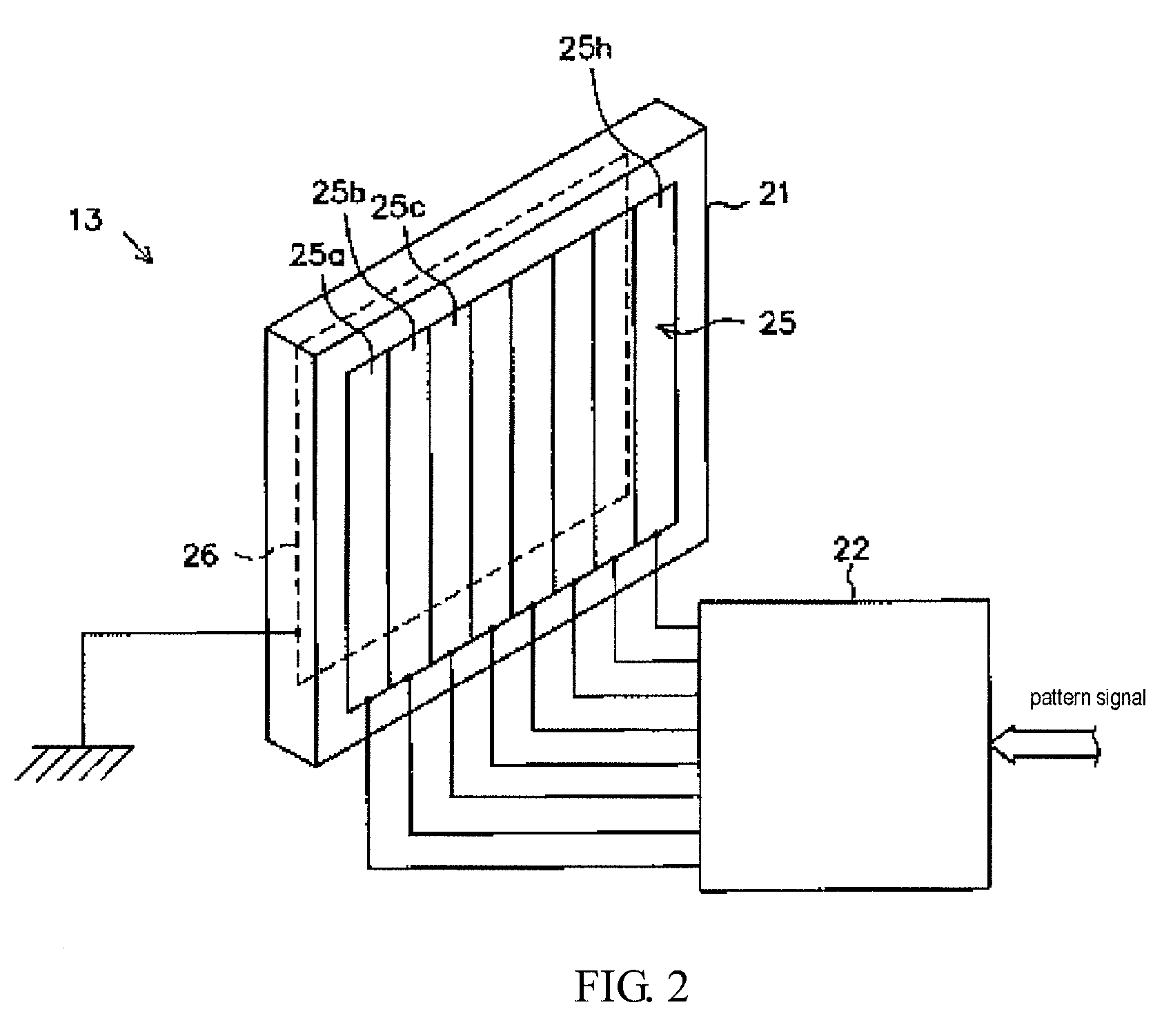
Spatial encoding of a search space is achieved by an array of radiation or acoustic energy detectors receiving data from at least one radiation or energy source. At least one radiation source capable of providing a predetermined type of radiation is used. The radiation may be in the form of a plurality of beams arrayed along at least one directional axis, and arranged in successive alignment to exhibit a directional component. The directional component is characterized by a frequency variance between successive beams in accordance with direction and disposed so radiation therefrom propagates within the search space. At least one radiation detector capable of detecting the radiation is provided, and is disposed to detect at least that type of radiation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Apparatus, and associated method, for space-time encoding, and decoding, data at a selected code rate
InactiveUS6999472B2Facilitate decodingSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsComputer hardwareSpatial encoding
Apparatus, and an associated method, for space-time encoding data to be communicated upon a communication channel susceptible to fading. Multi-rate data services can be effectuated through appropriate selection of the code rate by which data is encoded. And, the coding of space-time encoded data is facilitated as different permutations of coded data symbols are separate transmitted upon separate communication paths.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
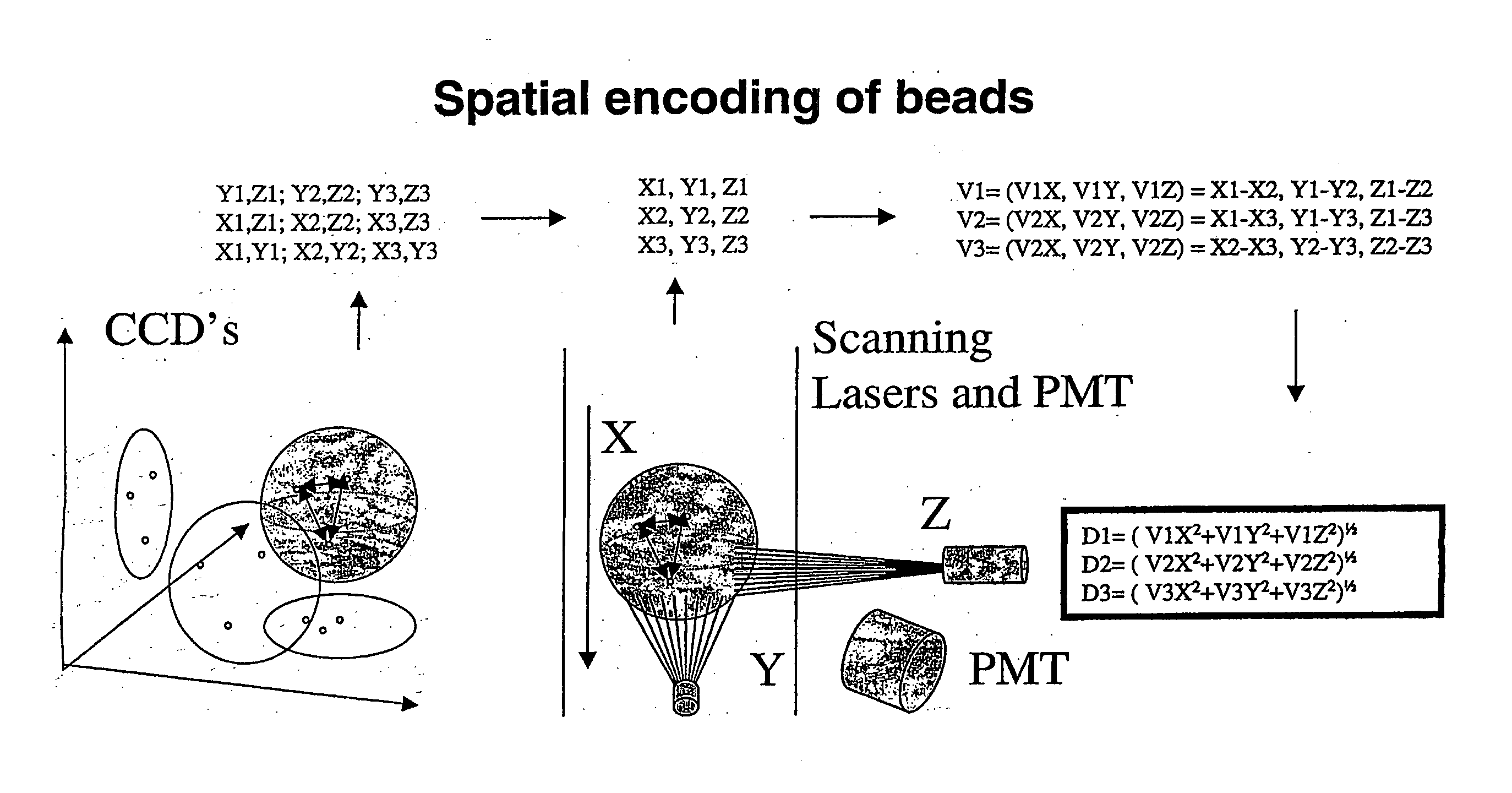
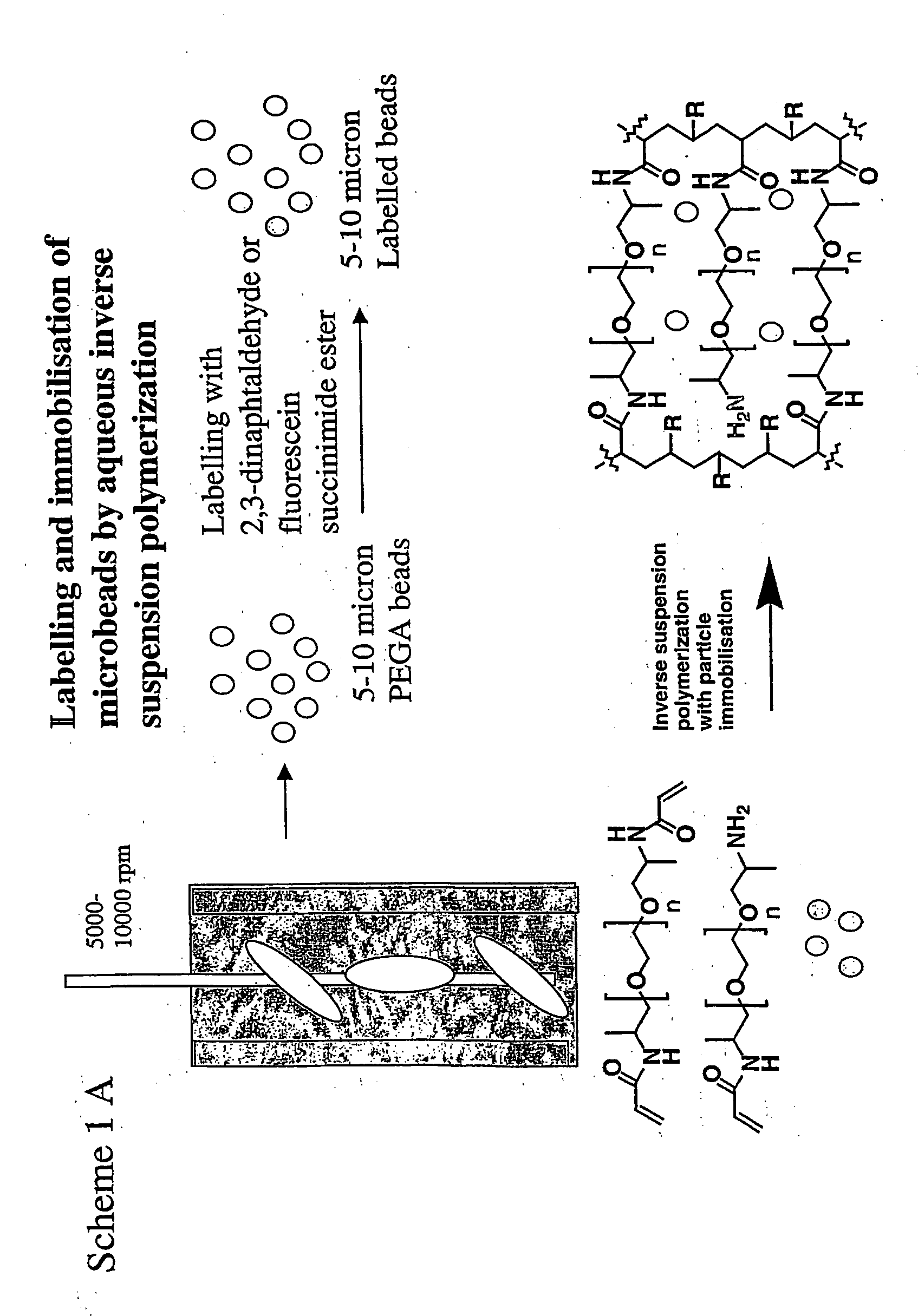
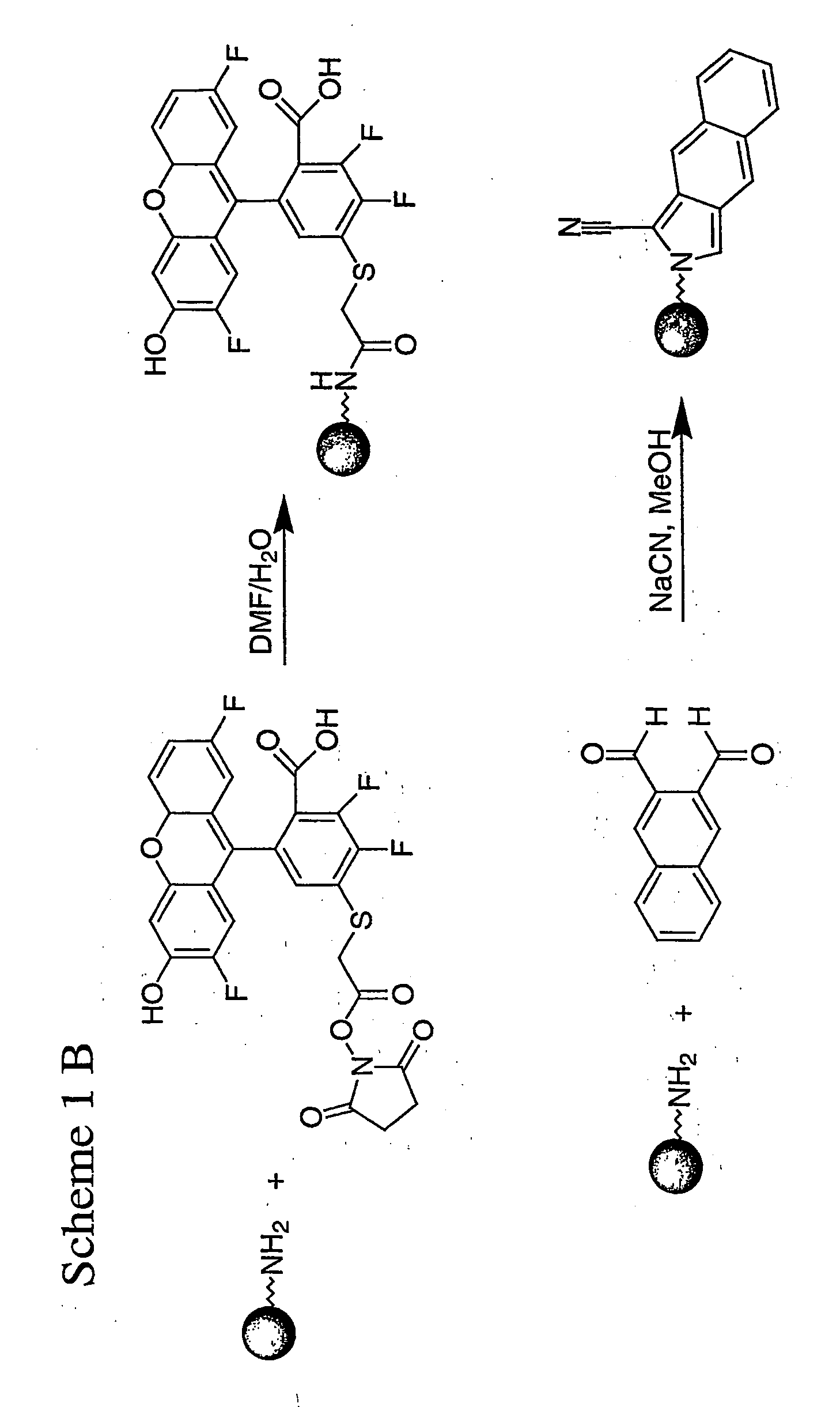
Spatially encoded polymer matrix
ActiveUS20060127369A1Increase diversityIncrease in sizeBiocideSequential/parallel process reactionsSolid phasesChemistry
The invention relates to a spatially encoded polymer matrix in the form of a bead or a granule for combinatorial solid phase synthesis, assaying, functional proteomics and diagnostic use. Compositions of such beads or granules are also provided. Each beaded polymer matrix of the composition comprises a plurality of spatially immobilised particles. The spatial immobilisation of the particles confers on each beaded polymer matrix a “fingerprint” which enables identification of unique beads in a population of beads. The unique identification of individual beads makes it possible to perform combinatorial chemistry strategies while logging individual chemical transformation. Also provided are methods for detection of relative positions in space of particles, methods for generating matrices, methods for distance matrix determination, methods for identifying individual matrices and devices for recording and storing images of matrices.
Owner:MPM HLDG APS
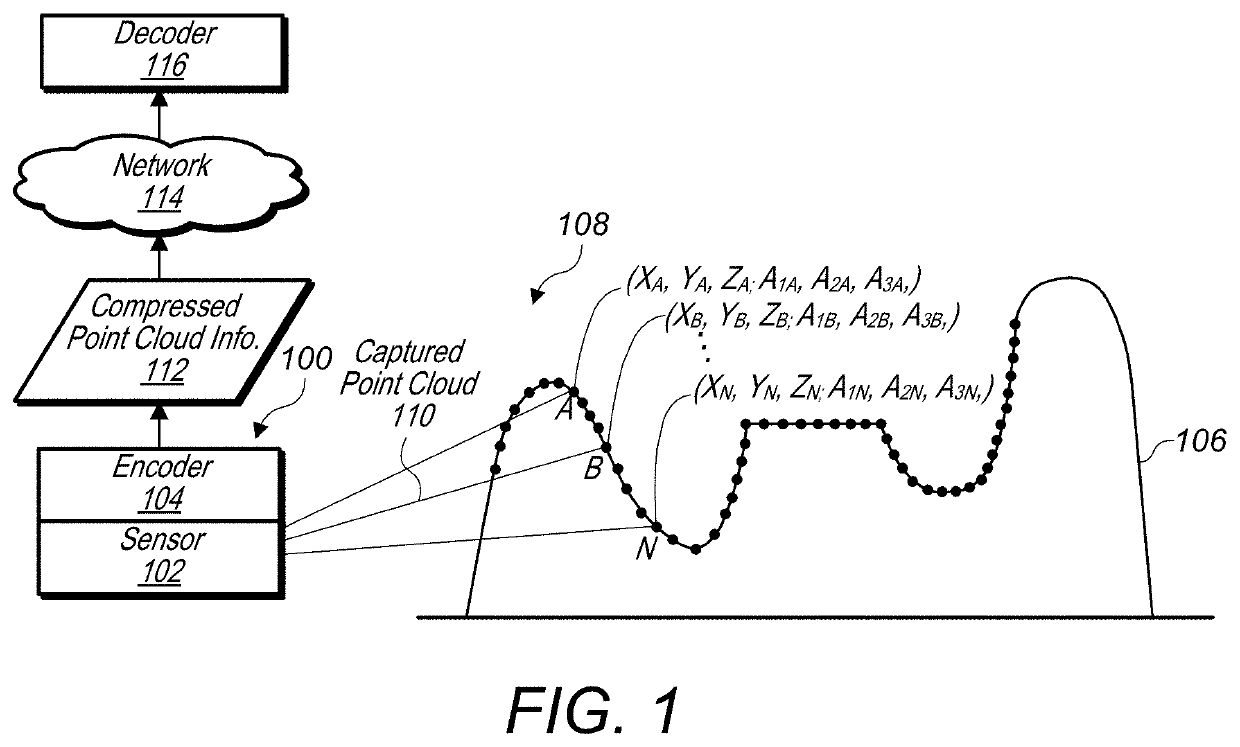
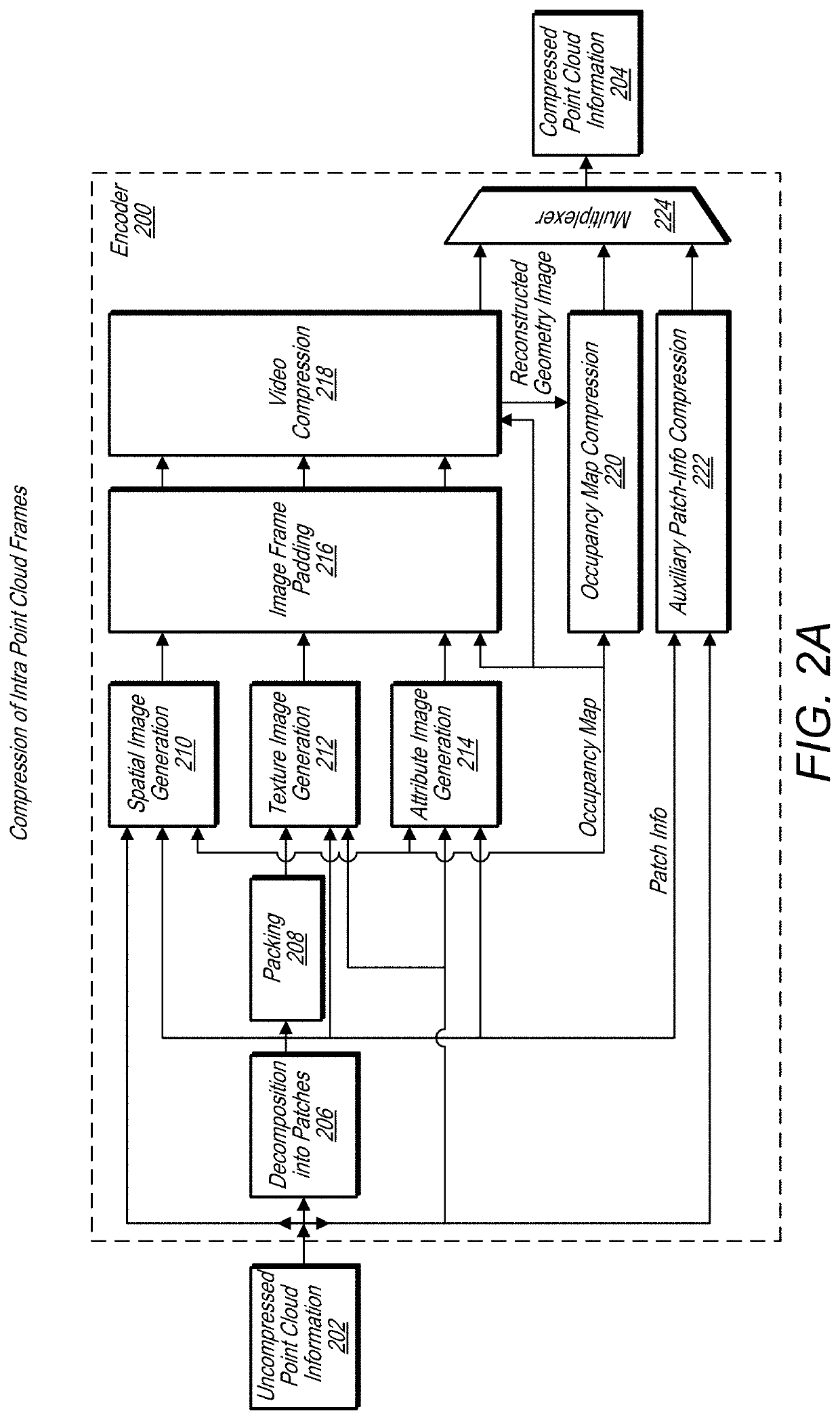
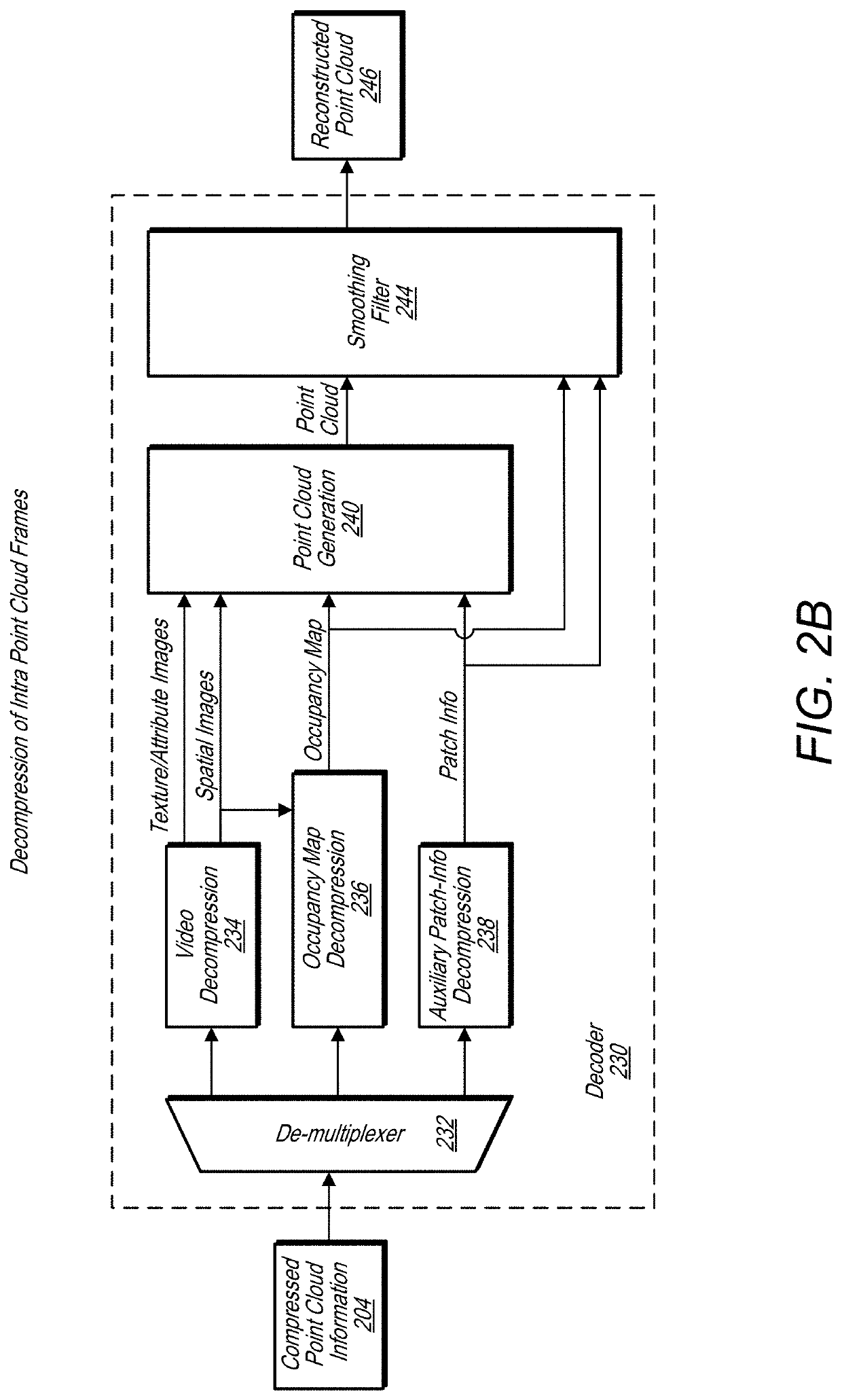
Quantized depths for projection point cloud compression
A system comprises an encoder configured to compress attribute information and / or spatial information for a point cloud and / or a decoder configured to decompress compressed attribute and / or spatial information for the point cloud. The encoder is configured to convert a point cloud into an image based representation. The encoder packs patch images into an image frame and fills empty spaces in the image frame with a padding. The encoder is also configured to determine quantized minimum depths and / or maximum depths patch images in the image frames, wherein depth information is signaled relative to the quantized minimum depth.
Owner:APPLE INC
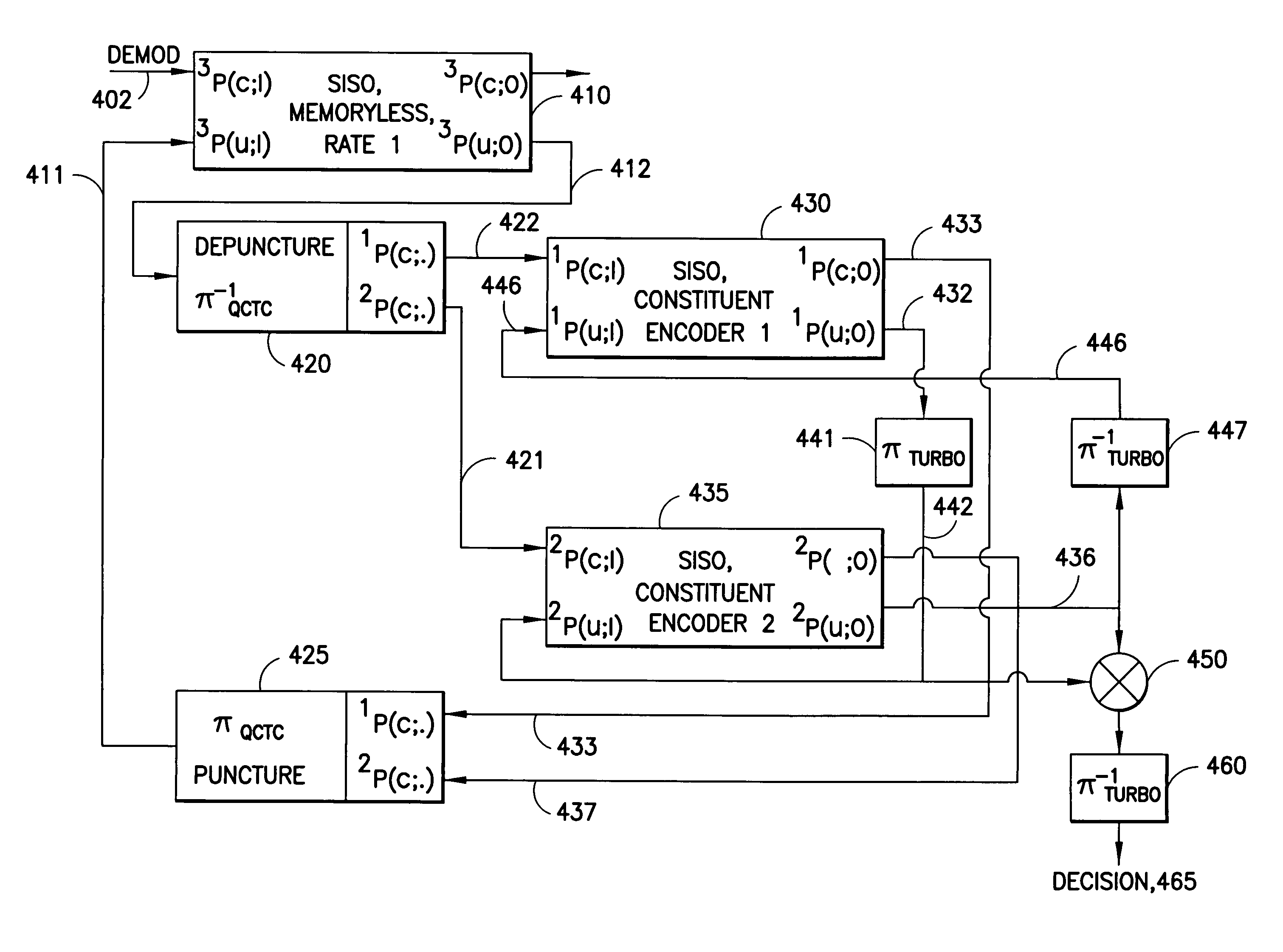
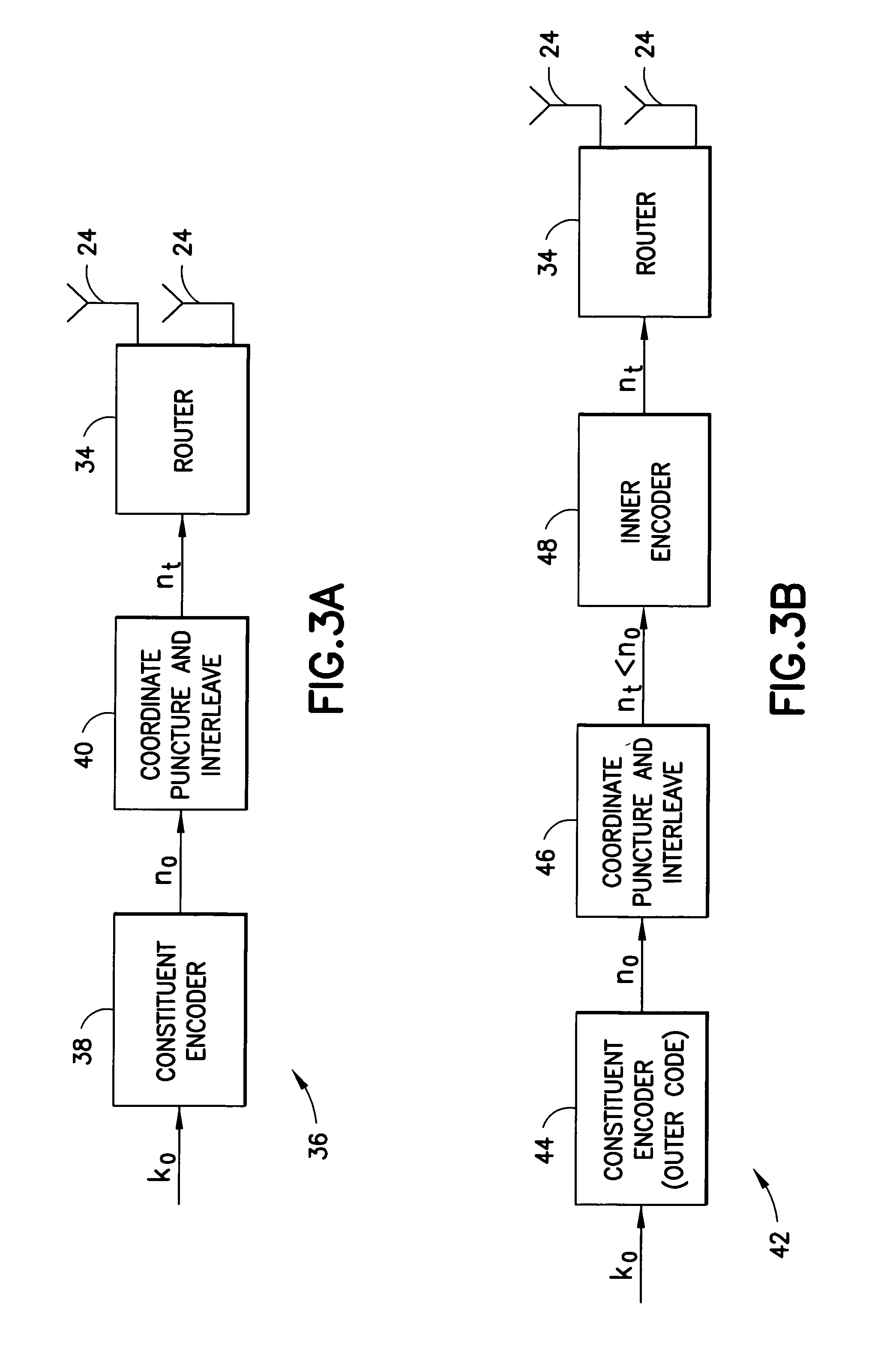
Apparatus using concatenations of signal-space codes for jointly encoding across multiple transmit antennas, and employing coordinate interleaving
InactiveUS8031793B2Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresSymbol of a differential operatorSpatial encoding
A system for transmitting data over a MIMO channel has a transmitter and a receiver. In the transmitter, the input data is encoded over at least two pipes by a concatenation of at least two constituent signal-space encoders. Each constituent encoder is used to generate, in response to the input data, a sequence of symbols from a channel alphabet having at least one dimension. Each symbol of the channel alphabet includes at least one complex symbol having real and imaginary coordinates. The transmitter interleaves the coordinates of the sequence of channel alphabet symbols, and transmits (from at least two transmit antennas) the interleaved coordinates. Preferably, each constituent encoder maximizes a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance between members of all valid pairs of symbol sequences, maximizes a minimum Euclidean distance between members of all valid pairs of different codewords, and obeys an equal eigenvalue criterion.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Spatially coded structured light generator
ActiveUS20150301181A1Overcome limitationsOptical rangefindersSemiconductor laser optical deviceEngineeringSpatial encoding
A spatially coded structured light is generated by an array of laser diodes (1) in order to perform structured light triangulation. The laser diodes (1a-c) are VCSEL, where the light is emitted in the direction perpendicular to the semiconductor wafer surface. Plural such laser diodes (1a-c) are integrated monolithically to form an array (1). The position of the individual laser diodes in the array is coded spatially to form a non-regular unique pattern. The light output by the lasers is projected by a refractive or diffractive optical system (2) into the space to be monitored to form the structured light pattern. An object (5) to be investigated may be illuminated by the VCSEL array (1) and a camera (3) captures the frames. A processing unit (4) controls the power of VCSEL (1a-c) and processes the data from the camera (3).
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
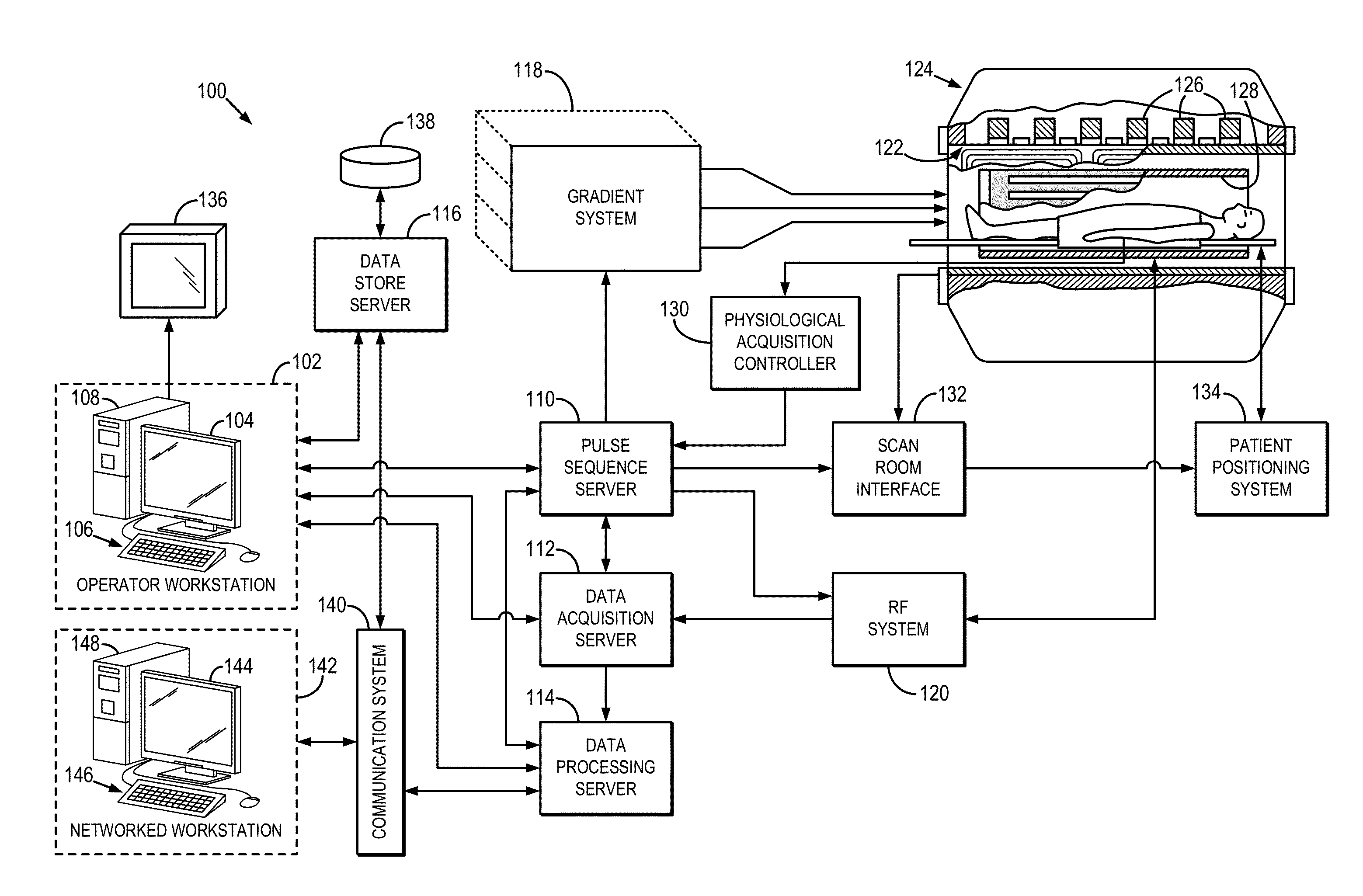
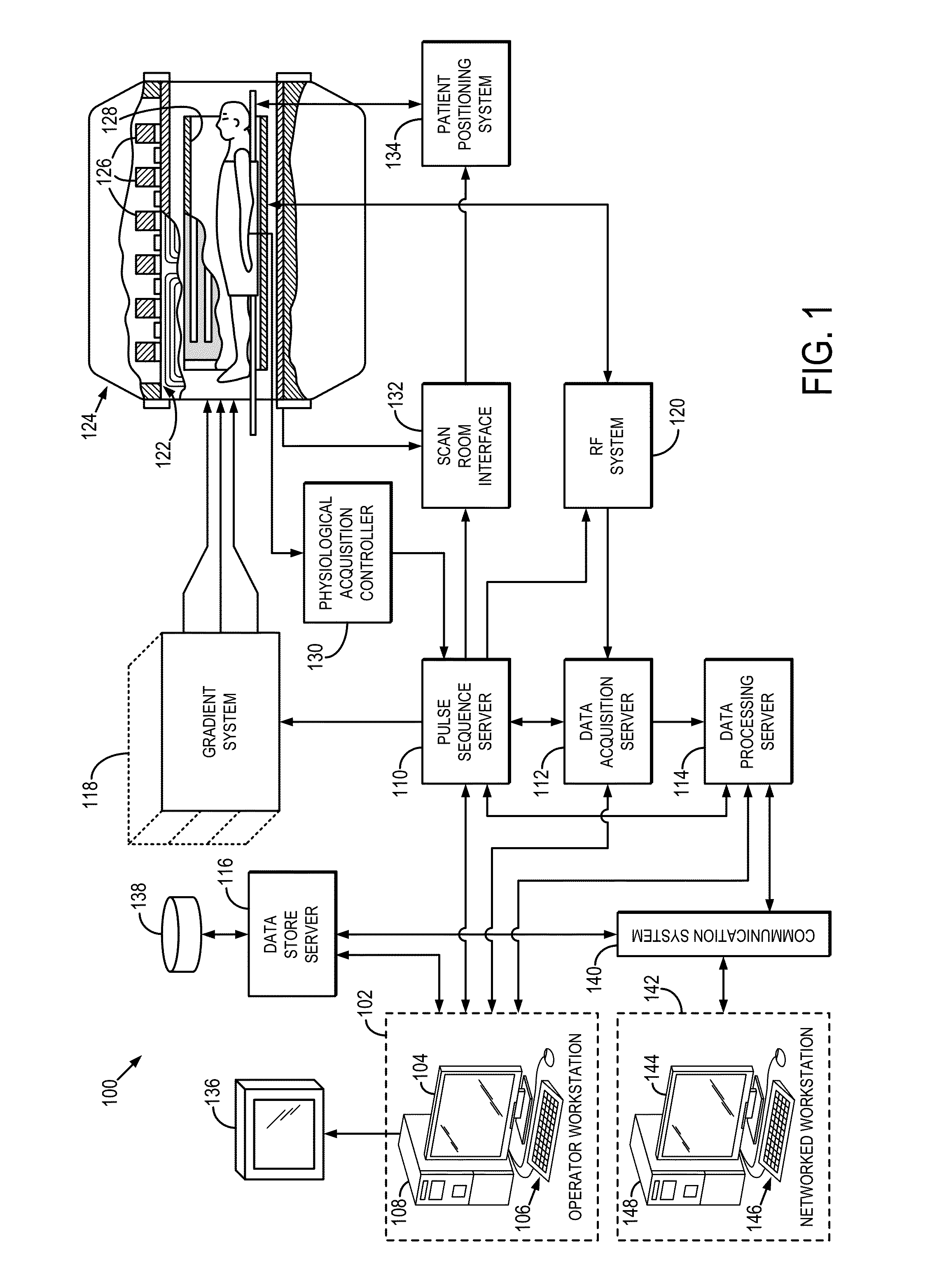
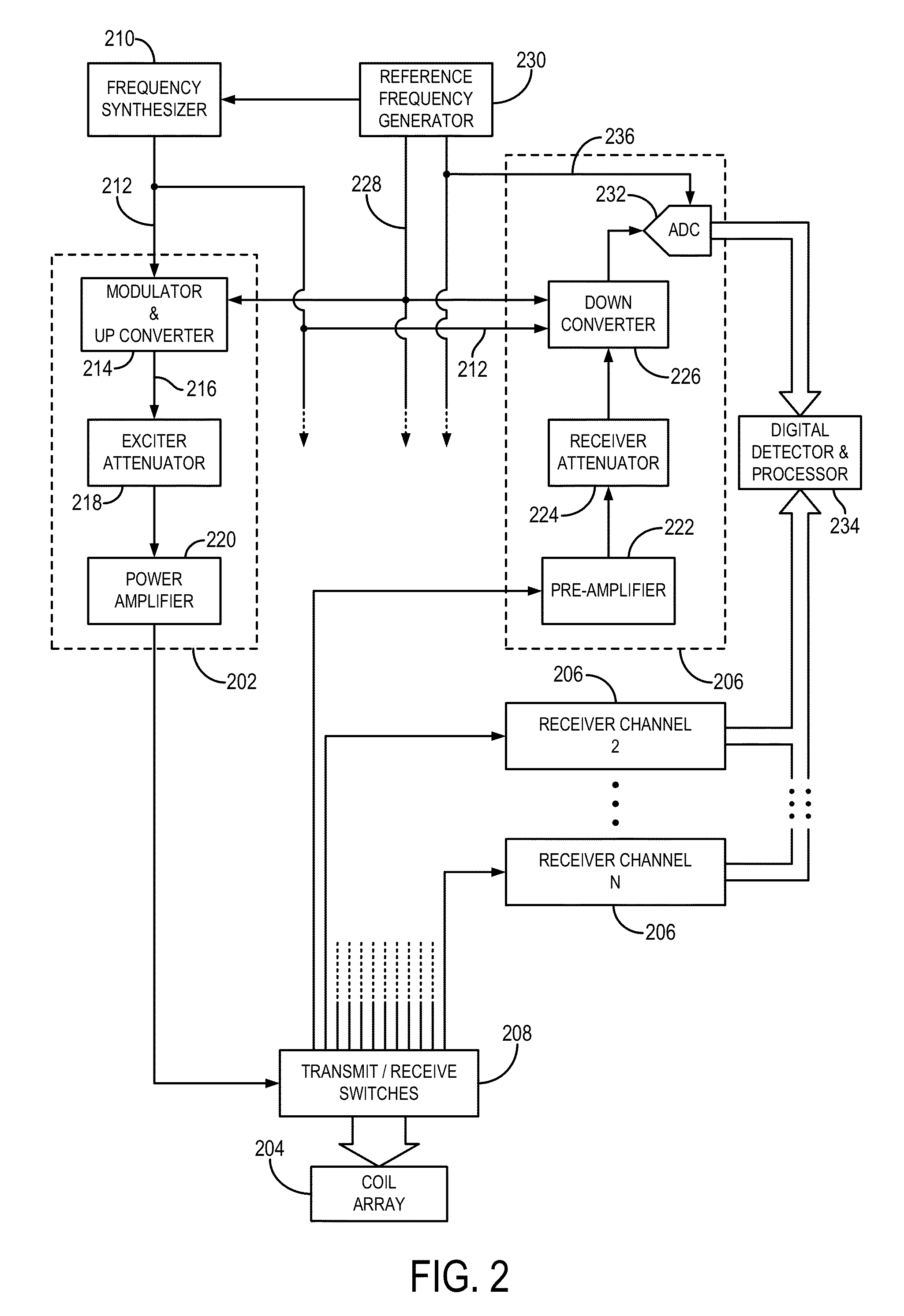
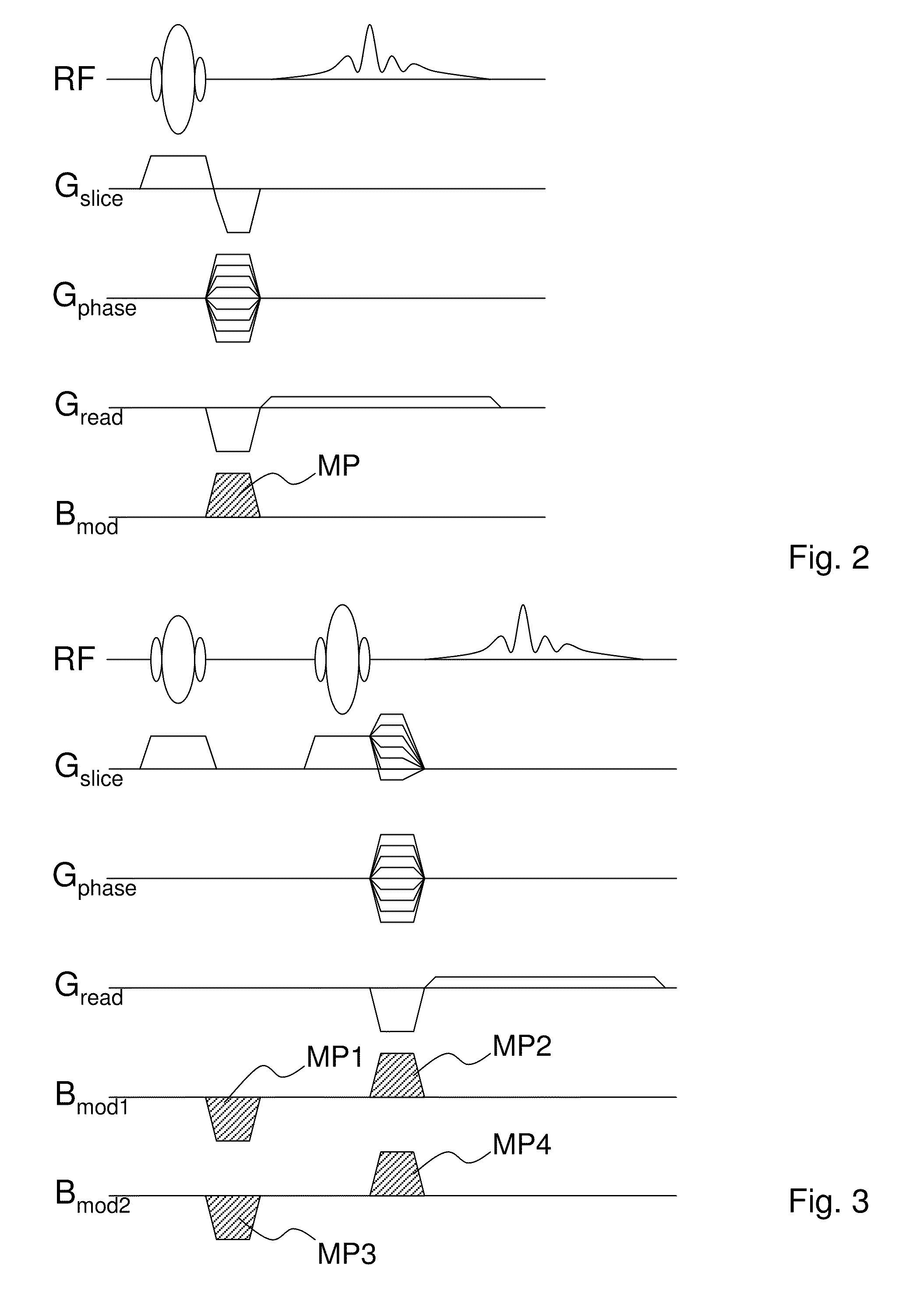
Method and apparatus for simultaneously acquiring multiple slices/slabs in magnetic resonance system
ActiveUS20090278538A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsMagnetic field gradientResonance
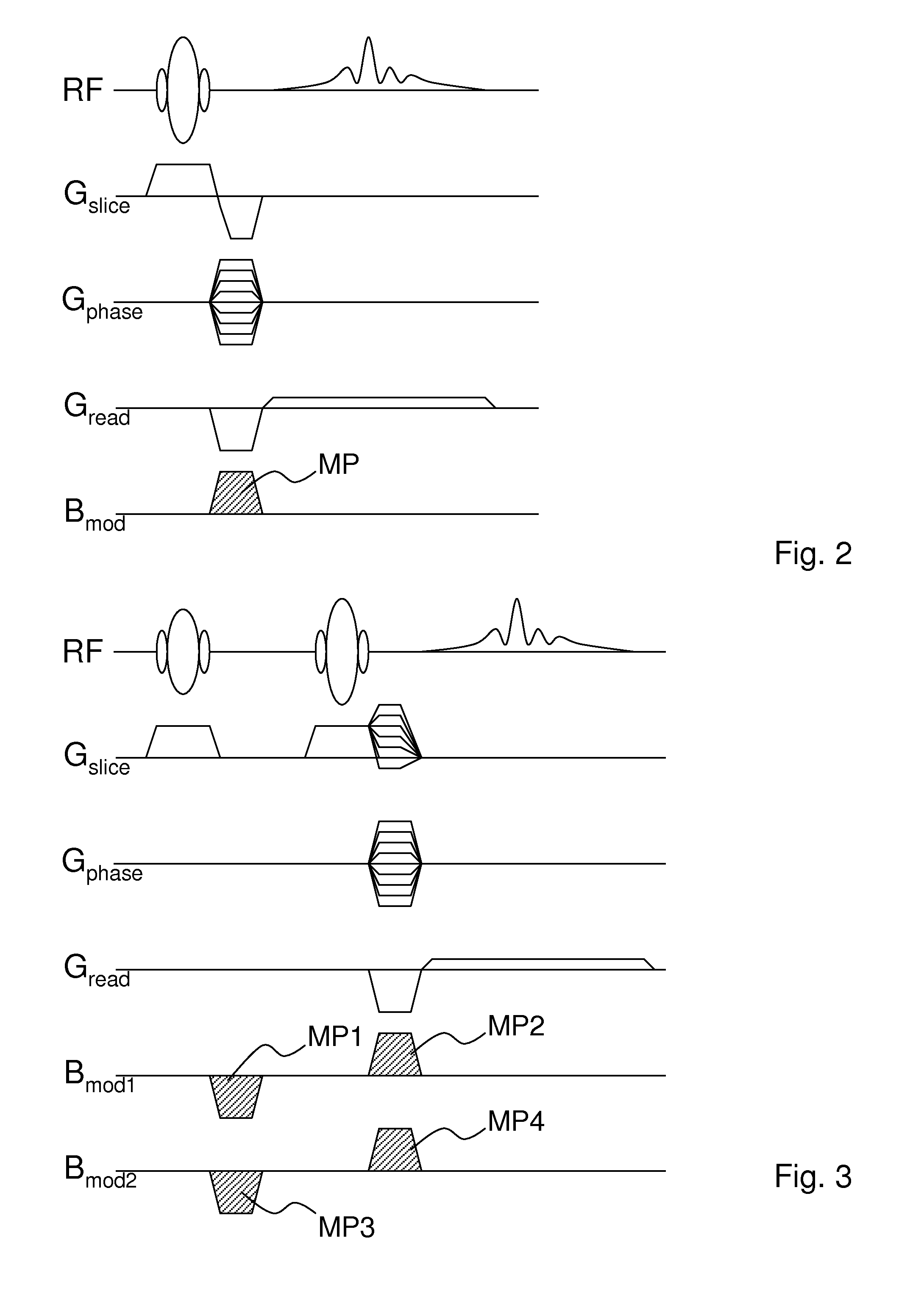
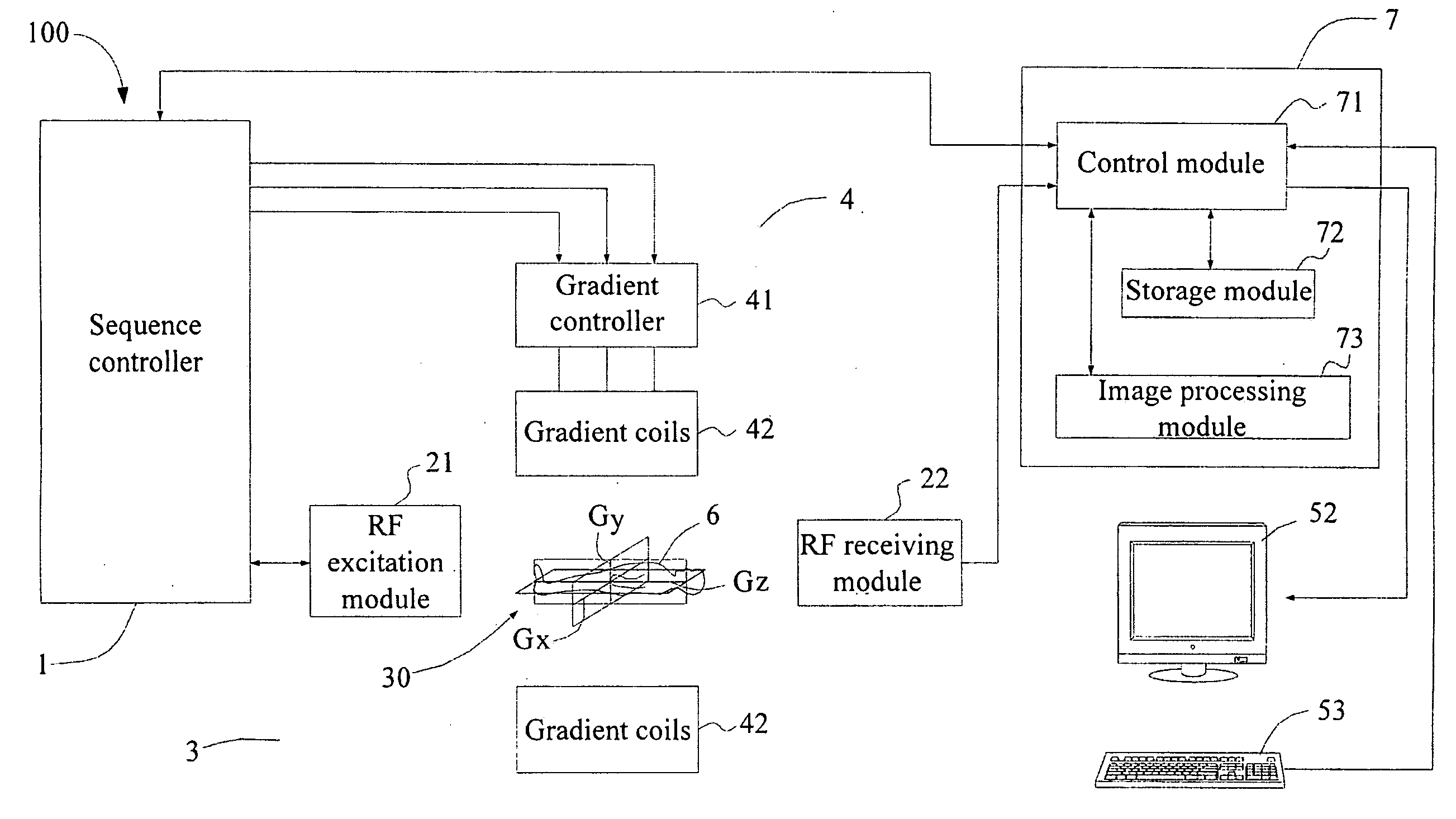
Provided is a method for simultaneously acquiring magnetic resonance slices / slabs of a subject. The method comprises steps as follows. First, apply one or more than one RF pulse, which carries at least two frequency components, and a slice / slab selection magnetic field gradient so that at least two slices / slabs of the subject respectively corresponding to the at least two frequency components are excited simultaneously. Second, apply a spatial encoding magnetic field gradient. Third, apply a slice / slab separation magnetic field gradient so as to separate the at least two slices / slabs. The method according to the present invention can be used to acquire data for simultaneously reconstructing multiple slices / slabs. The method is compatible with existing MRI systems.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving data in a multi-antenna communication system
ActiveUS7697622B2Data augmentationReduce the amount requiredSpatial transmit diversitySecret communicationChannel state informationCommunications system
An apparatus for transmitting data in a base station of a wireless communication system that transmits data depending on channel status information fed back from terminals and uses a plurality of antennas. Based on the channel status information, a scheduler determines a terminal to which the base station will transmit data, determines antennas via which the base station will transmit data among the plurality of antennas, and determines a space pre-coding method. A multiplexer multiplexes transmission data into a plurality of data streams according to the number of the determined antennas. A modulation and coding unit performs modulation and coding on each of the data streams. A pre-coding controller outputs a matrix select signal for selecting one of a plurality of space pre-coding matrixes according to the space pre-coding method. A space pre-coder spatial-codes each of the coded streams with the matrix selected based on the matrix select signal. An OFDM modulator performs OFDM modulation on each of the spatial-coded streams. An RF unit transmits each of the OFDM-modulated streams via an associated antenna.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for encoding cellular spatial position information
A system, methods, and apparatus are described to collect and prepare single cells and groups of cells from microsamples of specimens and encode spatial information of the physical position of the cells in the specimen. In some embodiment, beads or surfaces with oligonucleotides containing spatial barcodes are used to analyze DNA or RNA. The spatial barcodes allow the position of the cell to be defined and the nucleic acid sequencing information, such as target sequencing, whole genome, gene expression, used to analyze the cells in a microsample for cell type, expression pattern, DNA sequence, and other information, in the context of the cell's physical position in the specimen. In other embodiment, markers such as isotopes are added to a microsample to encode spatial position with mass spectoscopy or other analysis. The spatial encoded information is then readout by analysis such as DNA sequencing, mass spectrometry, fluorescence, or other methods.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY SCI
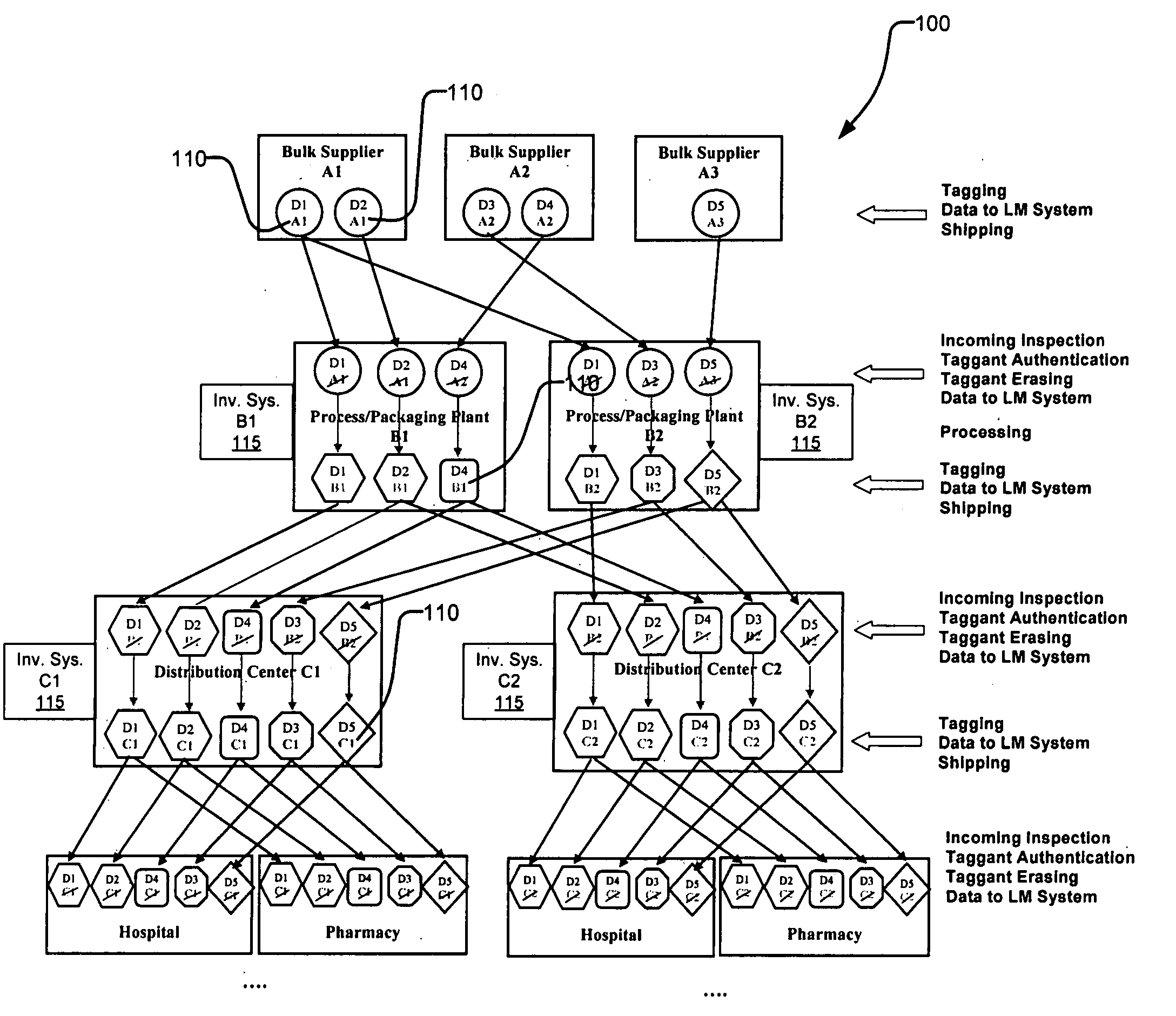
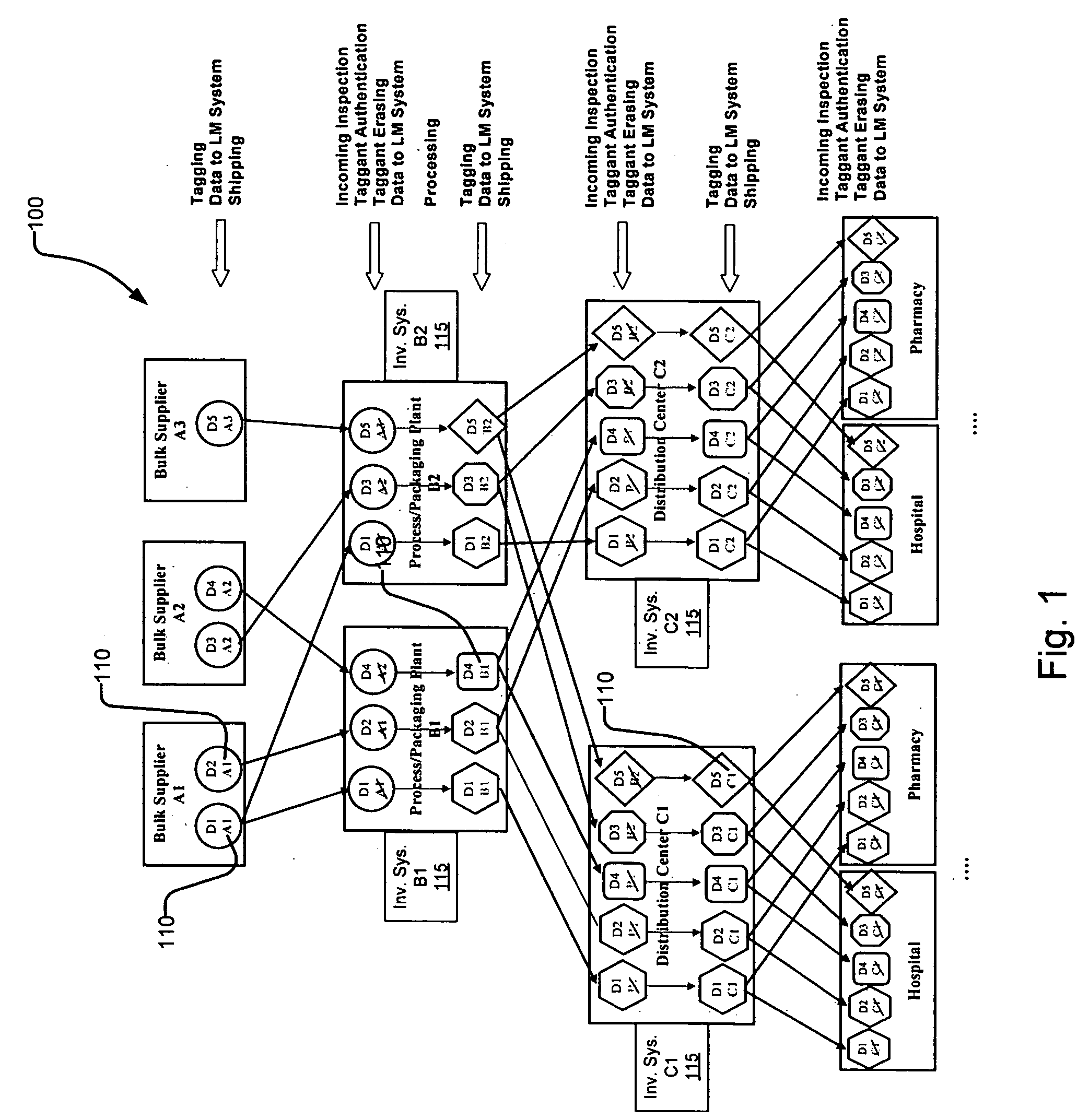
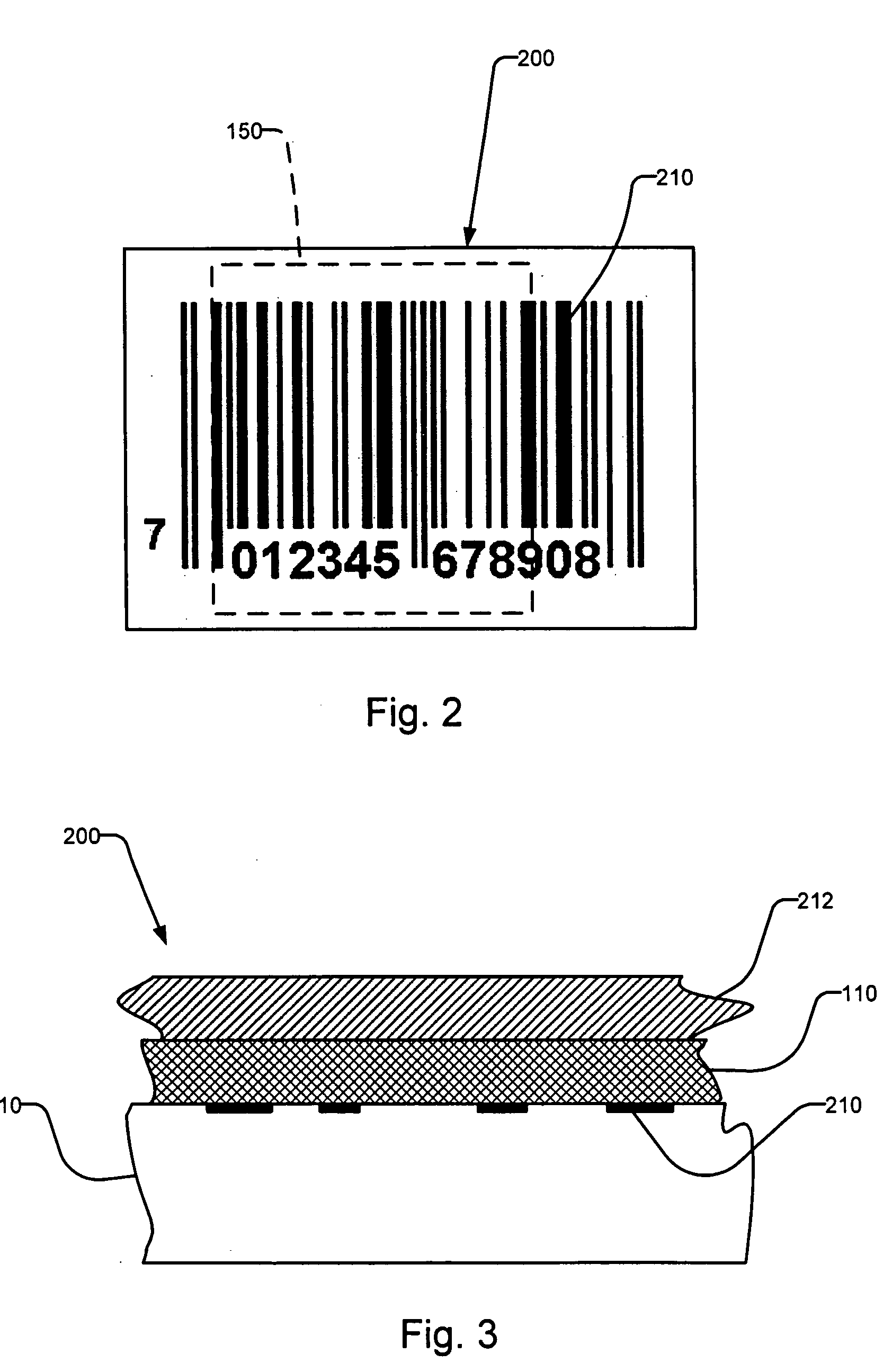
Erasable taggant distribution channel validation method and system
InactiveUS20050255599A1Cost-effectiveOther printing matterPaper-money testing devicesCost effectivenessValidation methods
To address counterfeit problems, for example, we propose a secure, flexible, and cost-effective authentication solution that can be integrated into conventional distribution logistic systems. The proposed solution for product authentication and distribution channel validation comprises three major components: 1) machine-readable Raman-active chemical taggant; 2) a taggant reader; and 3) a taggant eraser. The proposed solution is to control and validate the distribution channel by authenticating the origin of products. Authentication is accomplished by verification of distinct taggants associated with the articles, such as on its label, along with other product distribution information in optical, spatial-encoding indicia, such as a barcode. The taggant information is used to identify, validate, and distinguish the origin of the source of the articles, such as goods or products. The taggant material is thereafter rendered unreadable by modifying the taggants to make obtaining the information unfeasible, thereby controlling the taggants' lifecycle.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Correction of magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS7088099B2Reduce computing timeExtension of timeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientSpatial encoding
Spatial encoding in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques is achieved by sampling the signal as a function of time in the presence of magnetic field gradients, e.g., X, Y, and Z gradients. The gradient magnets have in the past been assumed to generate a linear gradient, and typical image reconstruction techniques have relied upon this assumption. However, to achieve high speed performance, gradient magnets often sacrifice linearity for speed. This non-linearity, in turn, results in distorted images, the distortion often being sufficiently large to compromise the usefulness of MRI images for stereotaxy or longitudinal studies, where precise volumetric information is required. The disclosure provides practical methods for correcting distorted images resulting from such non-linearity in the gradient fields, as well as distortions resulting from translational, rotational, and / or winding / design errors in the field generating devices. The methods employ spherical harmonic expansions of the gradient fields and fast Fourier transform techniques to provide well-corrected images without undue computational burdens.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
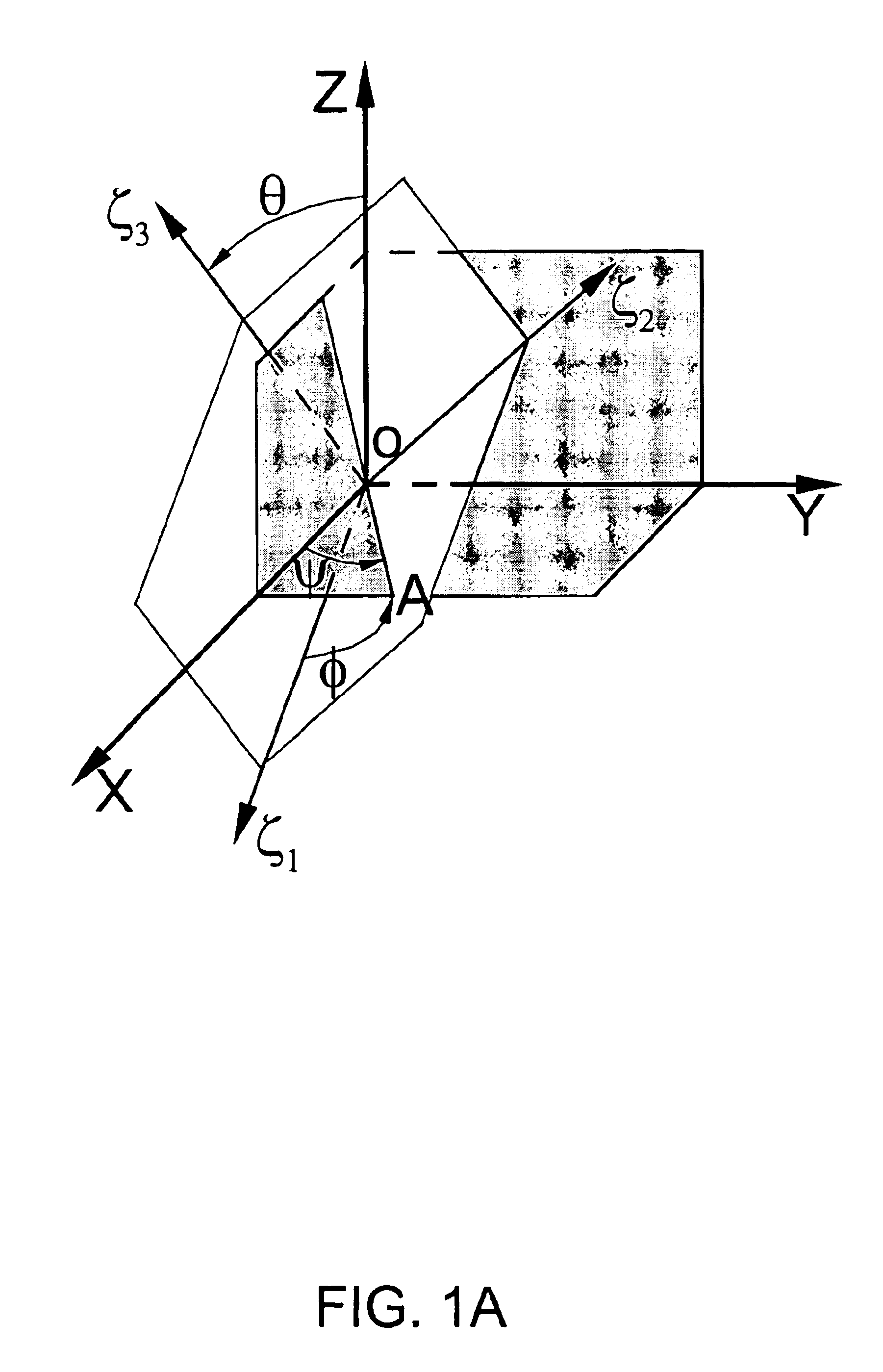
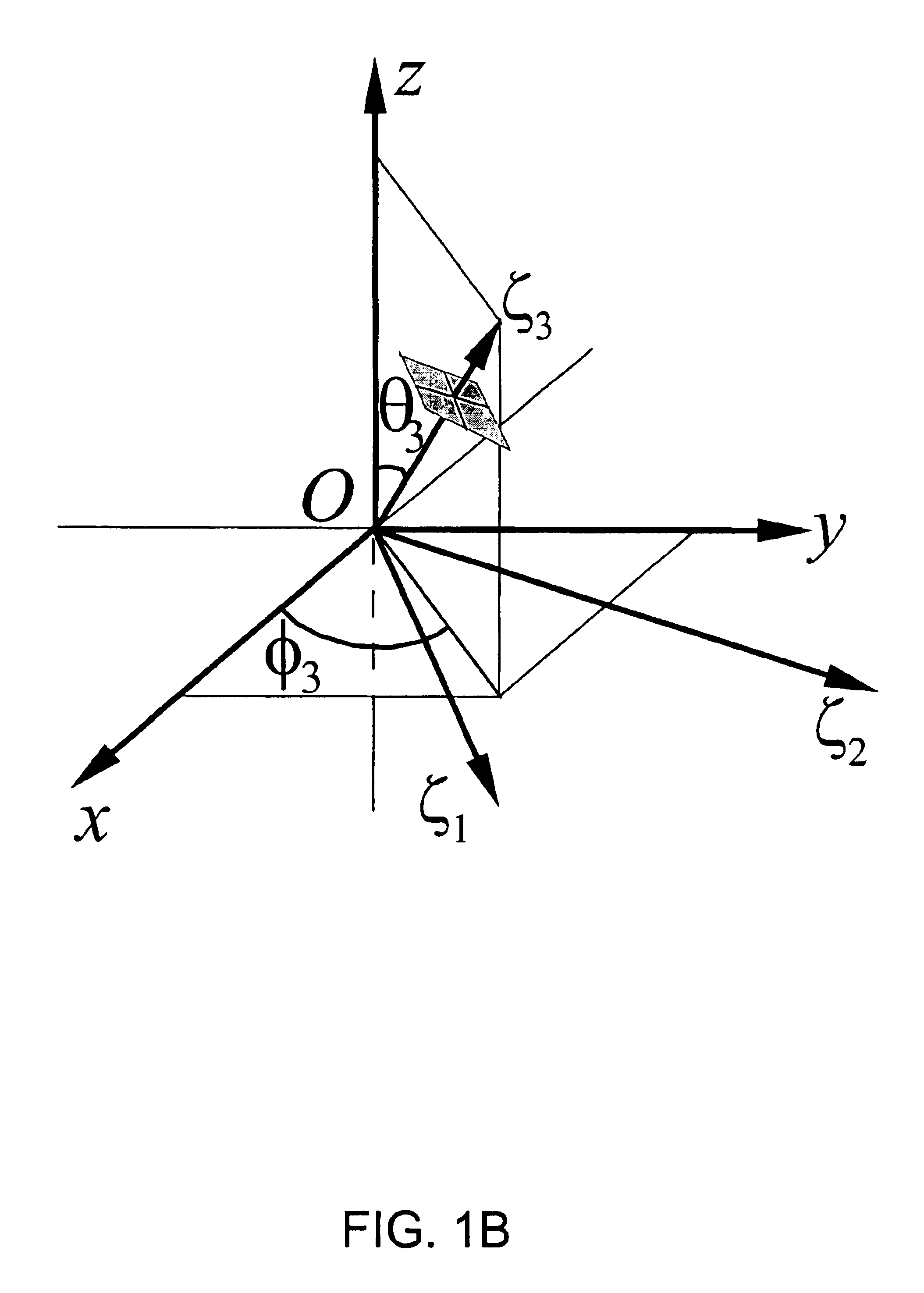
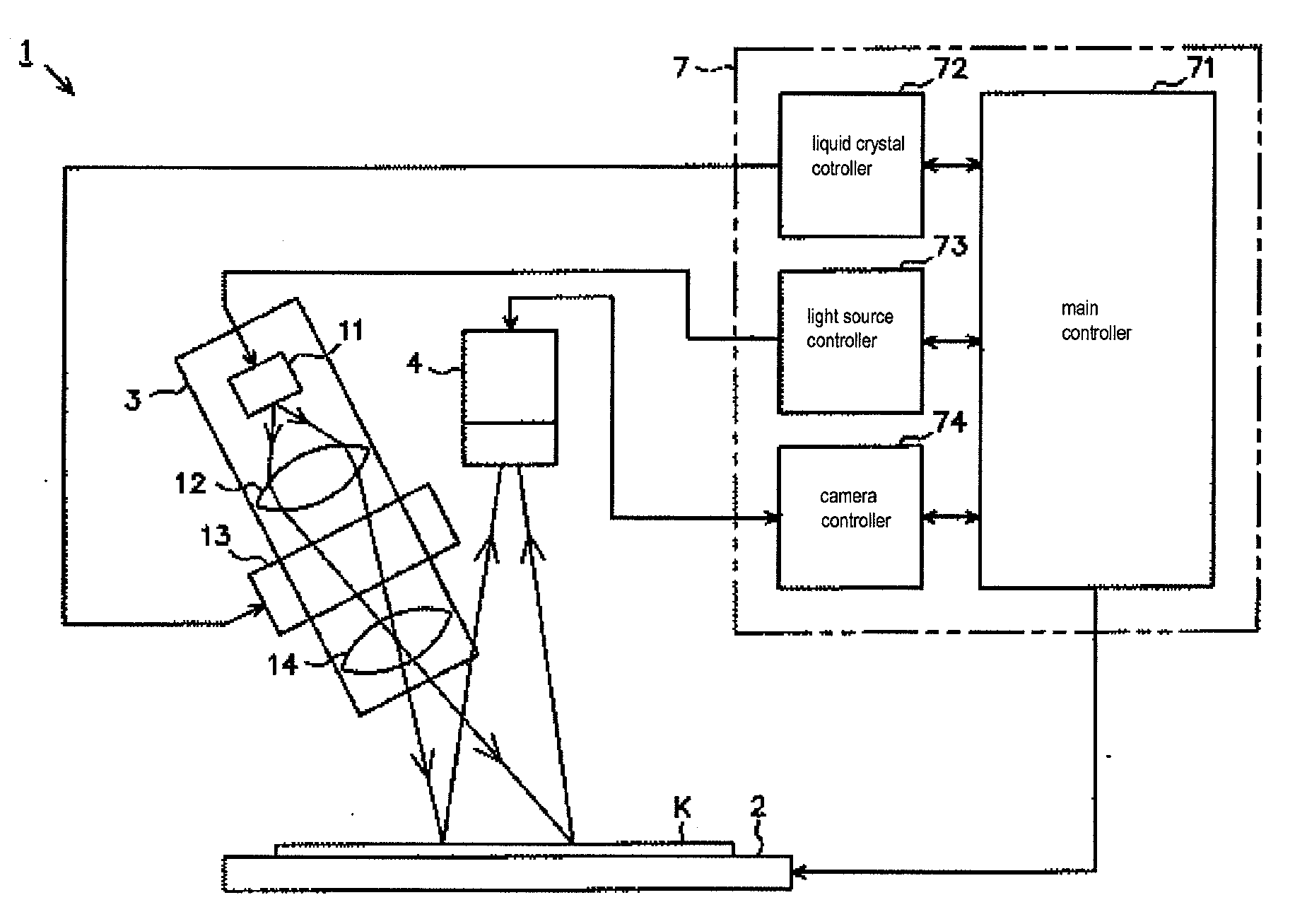
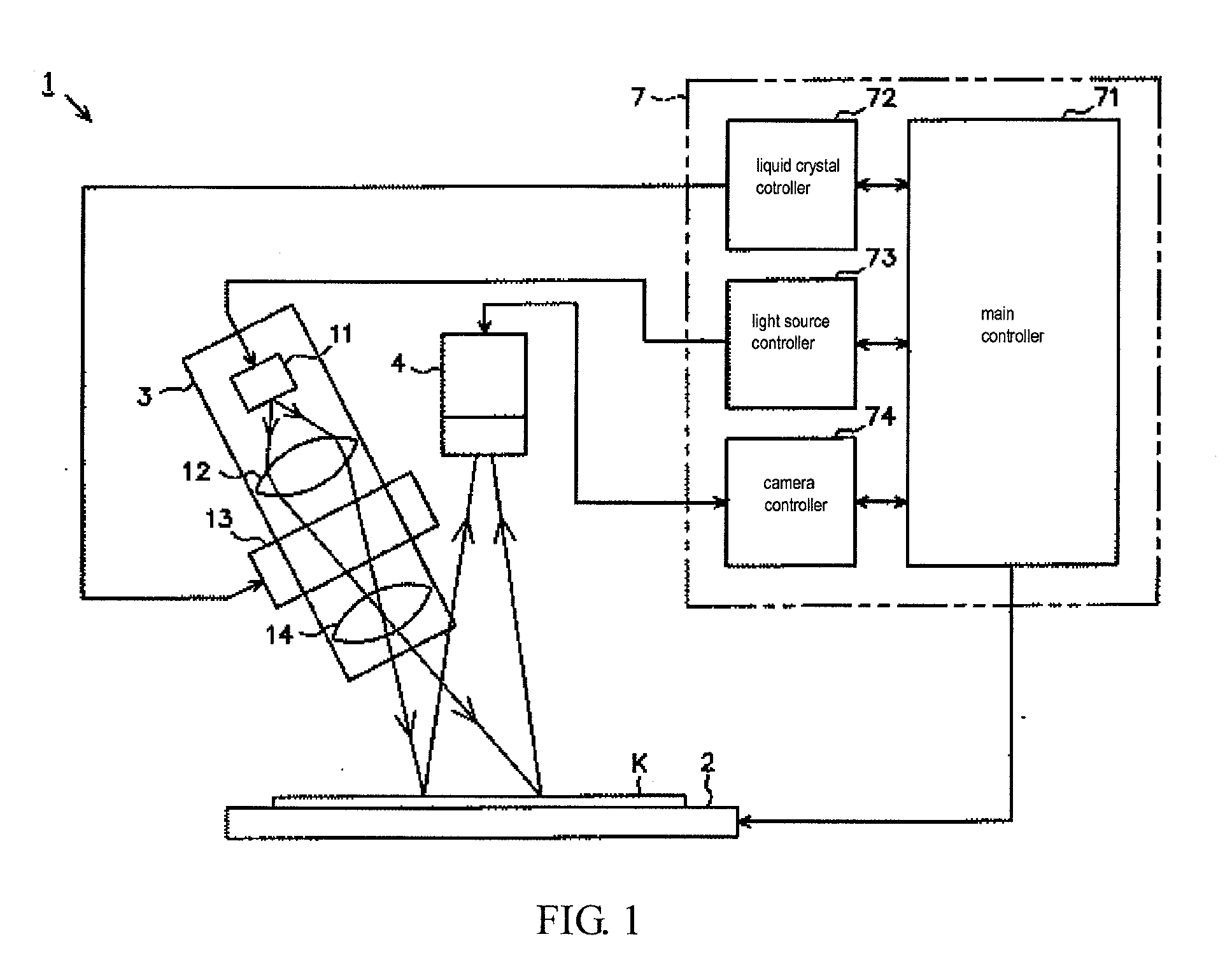
Three-dimensional measuring device and board inspection device
ActiveUS20100194855A1Increase heightHigh precision measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionPhase shiftedThree dimensional measurement
A three-dimensional measuring device includes an irradiation means capable of irradiating a striped light pattern used for a spatial encoding method and a striped light pattern used for a phase shift method on a measurement object part on a board main body, an imaging means capable of imaging a measurement object part irradiated by the light pattern, an image control means for controlling imaging by the imaging means, a first calculation means for calculating a height of the measurement object part according to the phase shift method based on a multiplicity of image data imaged by the imaging means, and a second calculation means capable of using the spatial encoding method to identify a line corresponding to the measurement object part from among the image data at a time of calculation by the first calculation means by the phase shift method based on the image data.
Owner:CKD
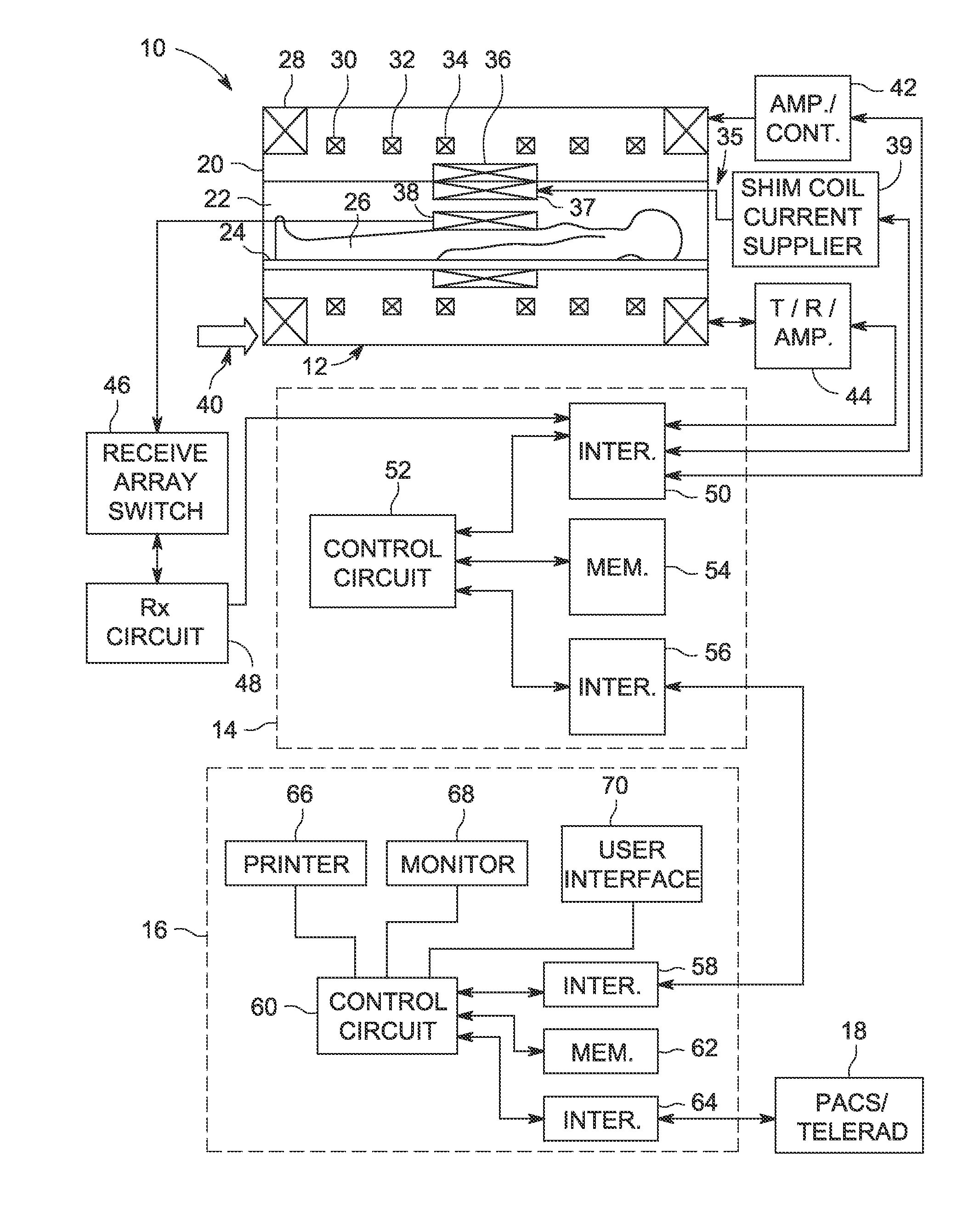
System and method for externally calibrated parallel imaging in the presence of an inhomogeneous magnetic field
ActiveUS20160154080A1Efficient measurementReduce acquisition timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceParallel imaging
A system and method for accelerated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) includes controlling an RF system of an MRI system to acquire coil calibration data from a subject including a material causing inhomogeneities in a static magnetic field of the MRI system when arranged in the bore of the MRI system. After acquiring the coil calibration data, the RF system is controlled to acquire imaging data from the subject at multiple different resonance frequency offsets. The spectral bin images relate specific resonance frequencies to distinct spatial locations in the static magnetic field of the MRI system. An image of the subject is reconstructed from the imaging data using coil calibration data and the spectral bin data to provide spatial encoding of the image.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for data acquisition acceleration in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with N-dimensional spatial encoding using two or more receiver coil arrays and non-linear phase distributions
InactiveUS8354844B2Improve applicabilityEasy access to dataMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationData acquisition
A method for accelerating data acquisition in MRI with N-dimensional spatial encoding has a first method step in which a transverse magnetization within an imaged object volume is prepared having a non-linear phase distribution. Primary spatial encoding is thereby effected through application of switched magnetic fields. Two or more RF receivers are used to simultaneously record MR signals originating from the imaged object volume, wherein, for each RF receiver, an N-dimensional data matrix is recorded which is undersampled by a factor Ri per selected k-space direction. Data points belonging to a k-space matrix which were not recoded by a selected acquisition schema are reconstructed using a parallel imaging method, wherein reference information concerning receiver coil sensitivities is extracted from a phase-scrambled reconstruction of the undersampled data matrix. The method generates a high-resolution image free of artifacts in a time-efficient manner by improving data sampling efficiency and thereby reducing overall data acquisition time.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
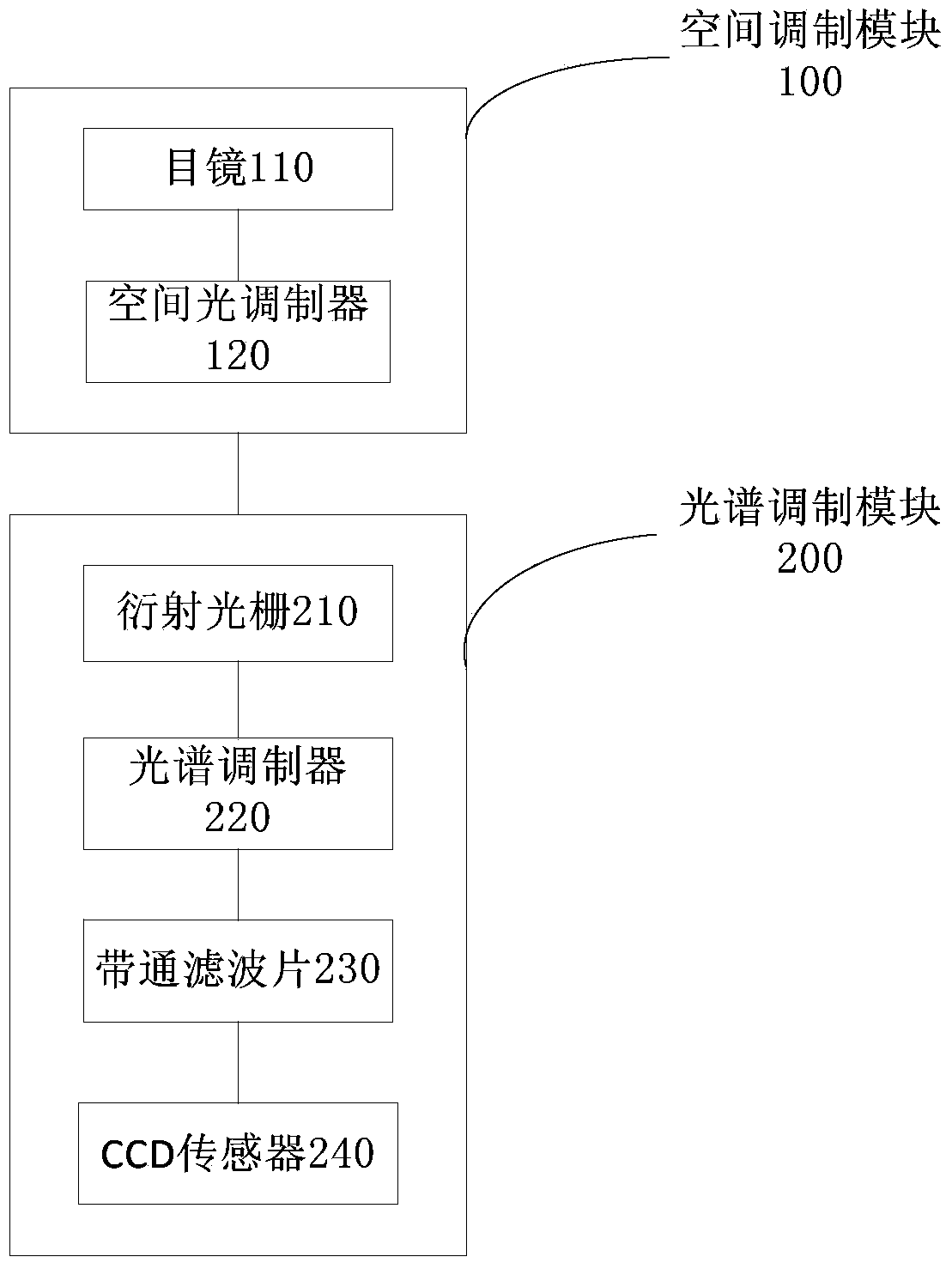
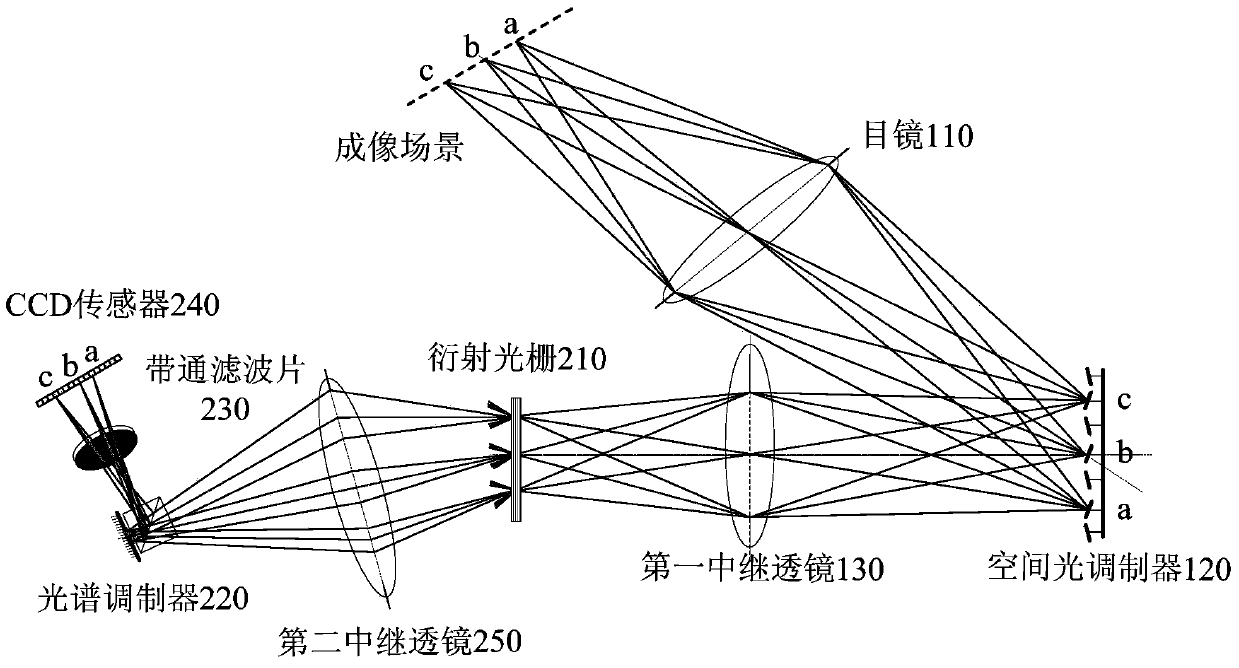
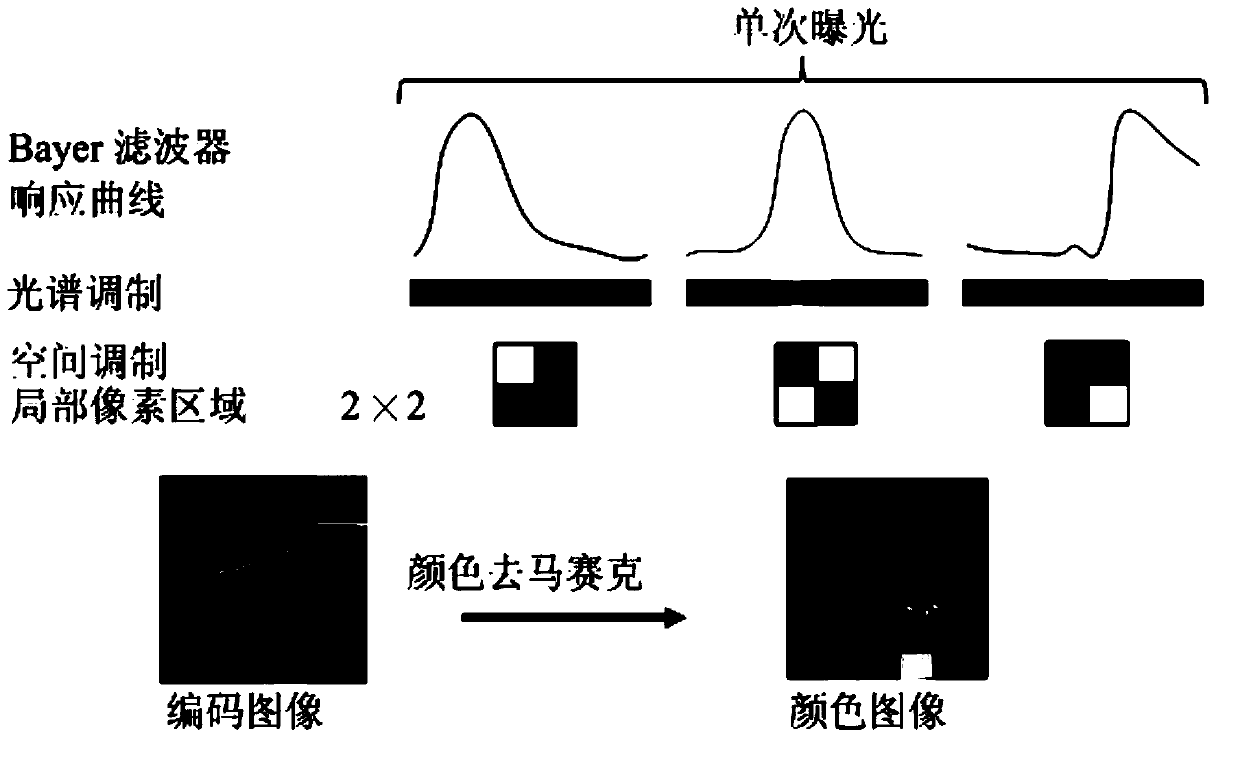
Pairs coding compression hyperspectral imaging device
The invention provides a pairs coding compression hyperspectral imaging device. The pairs coding compression hyperspectral imaging device comprises an eye lens for converging and imaging a scene hyperspectral signal, a spatial light modulator for performing spatial modulation on the hyperspectral signal, a diffraction grating for dispersing the modulated hyperspectral signal to obtain a dispersion spectrum of spatial coding, a spectrum modulator for realizing spectrum modulation on the hyperspectral signal, a the band-pass filter for filtering spectrums of unneeded spectrum segments, and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) sensor for recording and storing images. According to the device in the embodiment, pairs coding three-dimensional hyperspectral data are coded into images acquired by a two-dimensional sensor by using patterns of the spatial light modulator and the spectrum modulator varying in a synergic manner within single exposure time. By designing different light modulation functions and applying corresponding reconstruction algorithms, a plurality of different acquisition modes, comprising programmable space variant filters, multipath multiplex hyperspectral imaging and high-resolution compression hyperspectral imaging are realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Systems and methods for shim current calculation
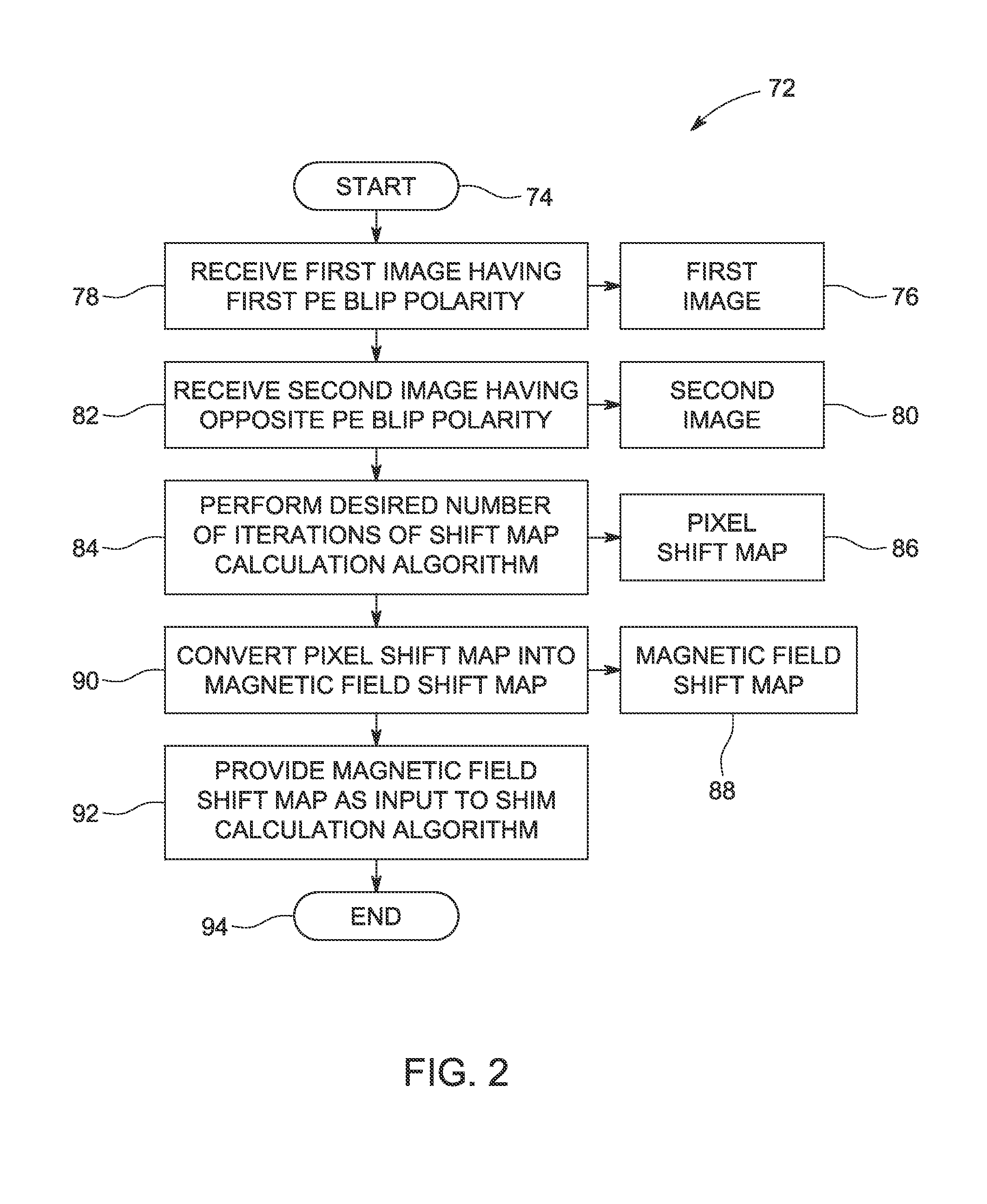
ActiveUS20140062475A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientResonance
A method includes receiving a forward spatial encoding polarity magnetic resonance (MR) coil image and a reverse spatial encoding polarity MR coil image generated from data obtained with a magnetic field gradient that is reversed with respect to the magnetic field gradient with which the forward spatial encoding polarity MR coil image is acquired. The method also includes performing an iterative shift map calculation algorithm to determine a pixel shift map corresponding to a minimized difference between the forward and reverse spatial encoding polarity MR coil images, converting the pixel shift map into a magnetic field shift map by determining a magnetic field value corresponding to each pixel in the pixel shift map, and providing the magnetic field shift map as an input to a shim calculation process that includes determining a level of at least one shim current.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for acquiring two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy of magnetic resonance by single sweeping
InactiveCN104237820AShorten the timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyChemical reactionMetabolite
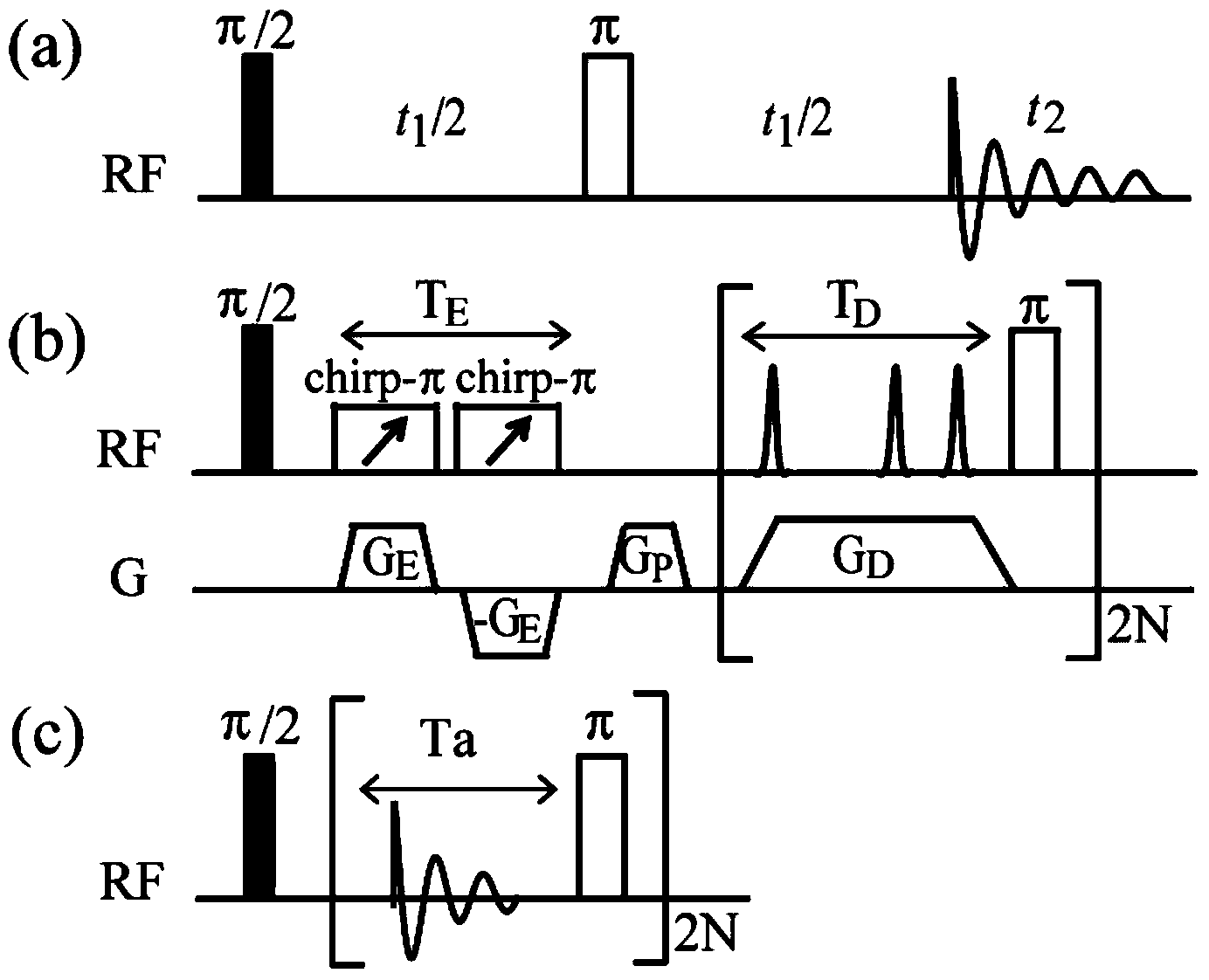
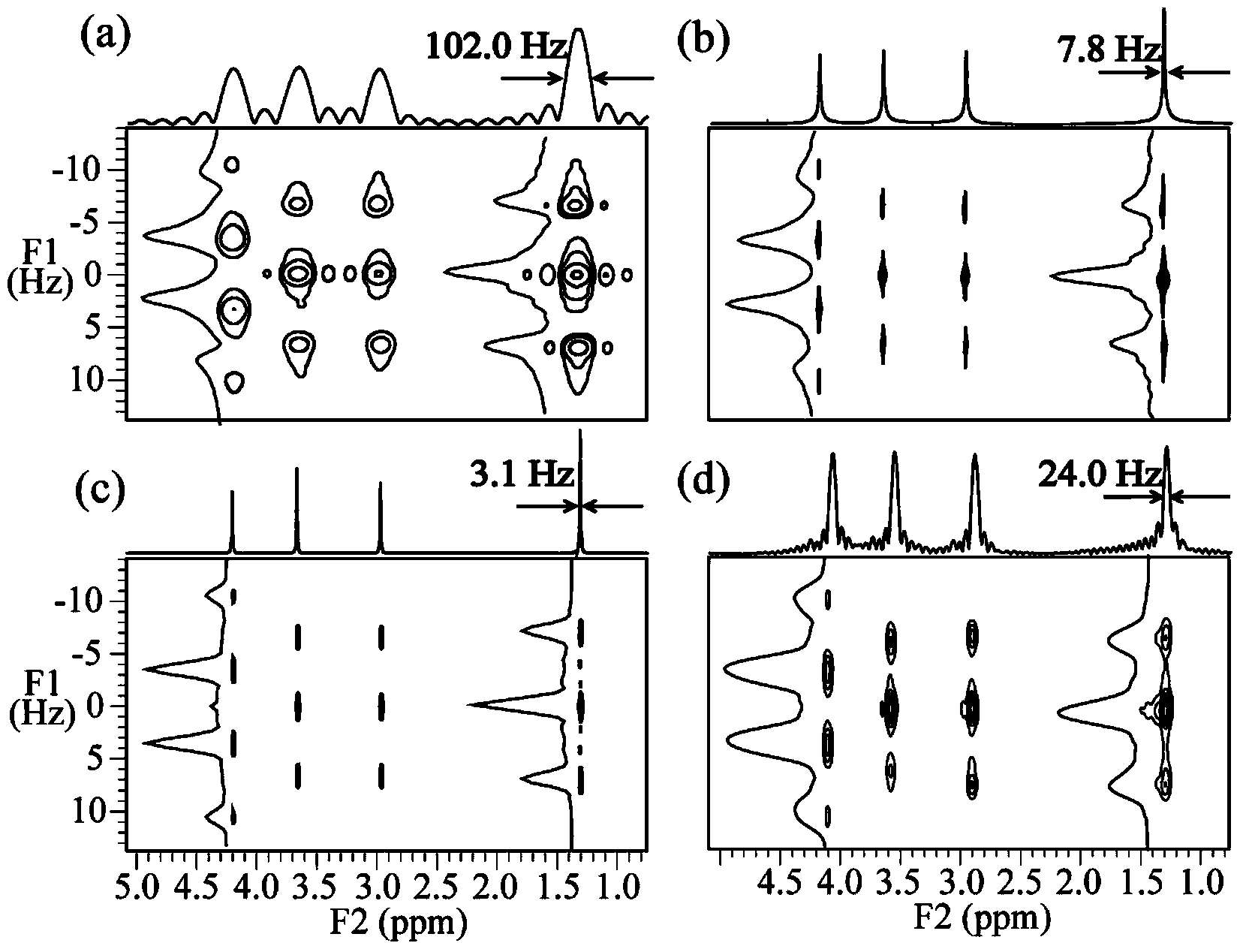
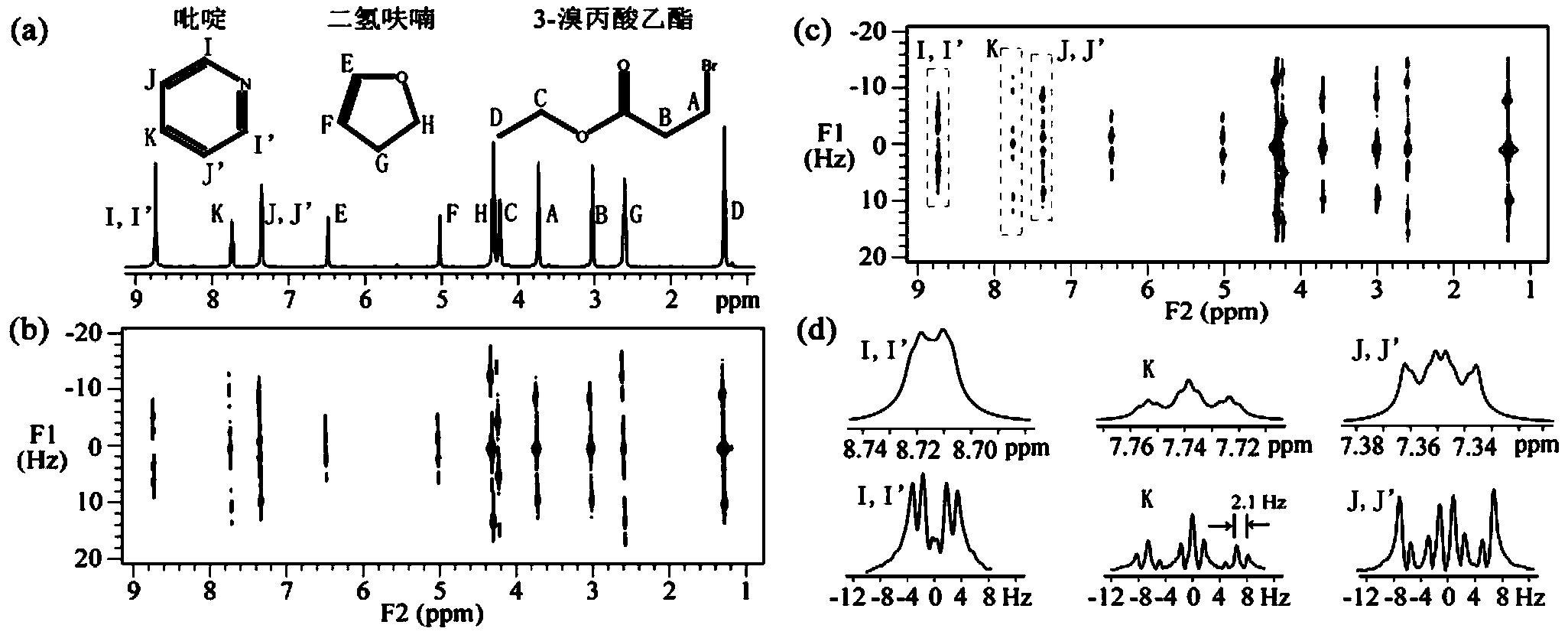
The invention provides a method for acquiring two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy of magnetic resonance by single sweeping. Through a module executing 'sampling and 180-degree pulsing' repeatedly after exciting a magnetization vector to an XY plane, data needed for two-dimensional J- resolved spectroscopy can be acquired by only one-time excitation. In order to acquire better resolution on a direct dimension F2 of a spectrogram, raw data are predicted along the direct dimension F2, and signals are attenuated completely. Compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantage that time of experiment is shortened greatly; compared with a previous spatial encoding method, the method is equivalent to the previous method in experimental time, can provide higher signal to noise ratio and resolution, and is simple in sequence and convenient to operate; compared with a one-dimensional spectroscopy method, the method is equivalent to the method in experimental time, but can provide finer J-coupling split peak information. The simple and efficient method plays an important role in metabolite batch testing, organic chemistry reaction and bioassay.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
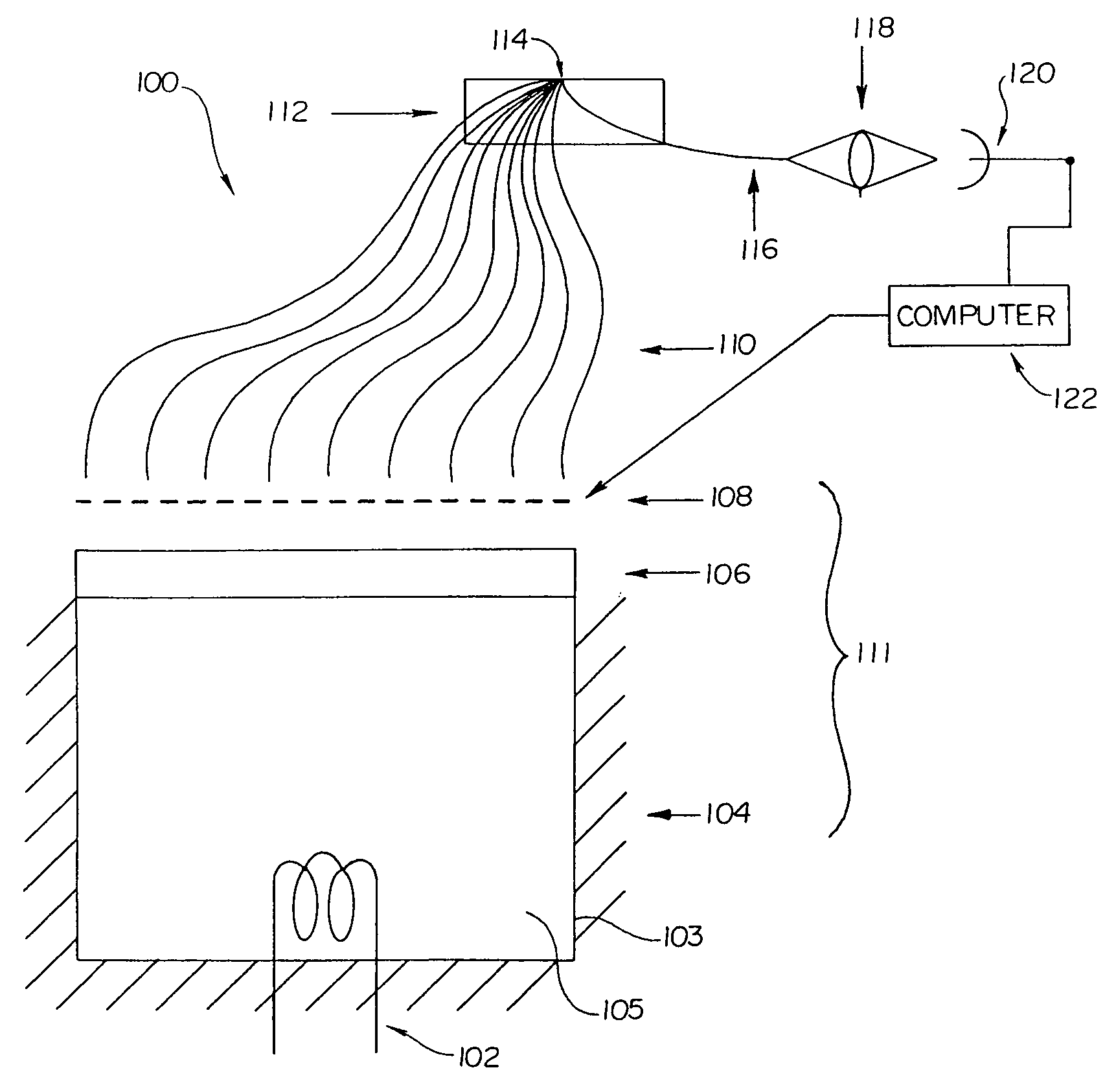
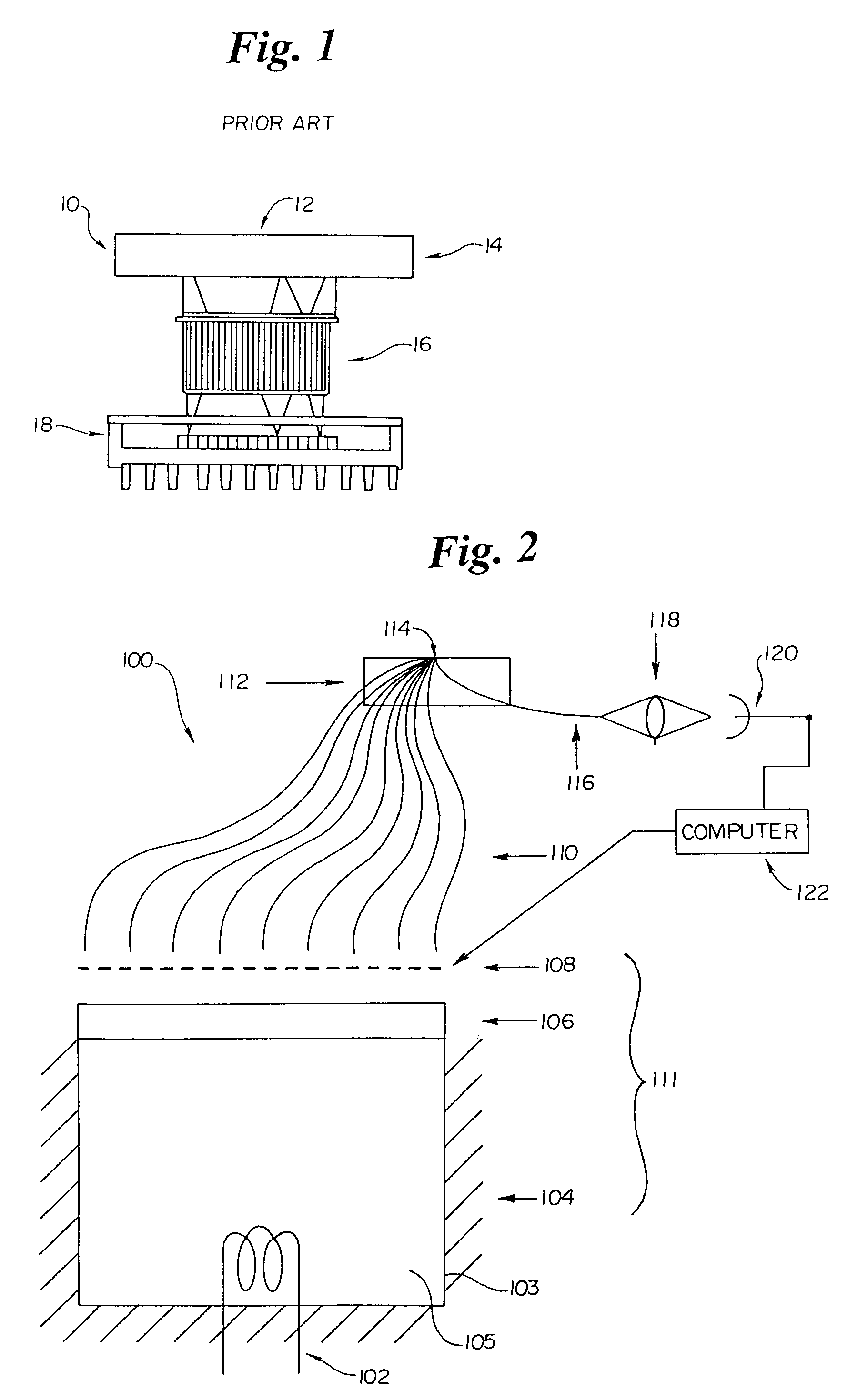
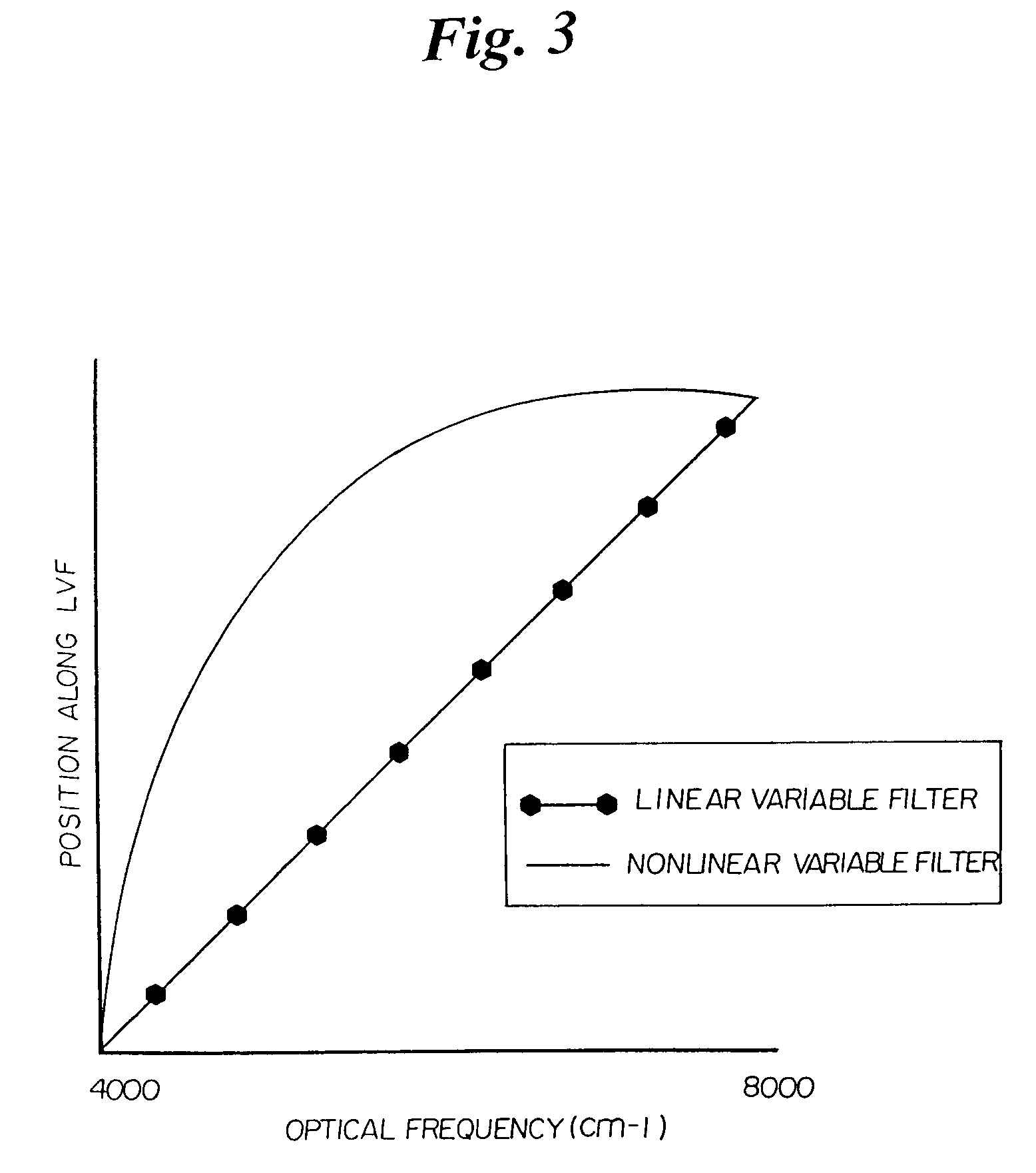
Encoded variable filter spectrometer
InactiveUS7126682B2Optimizes optical throughputImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBandpass filteringOptical power
Spectroscopic system and spectrometers including an optical bandpass filter unit having a plurality of bandpass regions and a spatial encoding unit for encoding discrete frequencies of light passing through the optical filter. The incorporation of the encoding unit allows the spectrometer system to use a detector having one or a small number of elements, rather than using a more expensive detector array typically used with filter-based spectrometers. The system can also include an integrating chamber that collects the light that is not transmitted through the bandpass filter unit, and redirects this light to strike the filter unit again, resulting in a significant increase in the optical power passing through the filter. The integrating chamber maximizes the return of the reflected light to the filter assembly and minimizes optical losses. The integrating chamber may be an orthogonal design to preserve the optical geometric characteristics of the light entering the chamber.
Owner:RIO GRANDE MEDICAL TECH
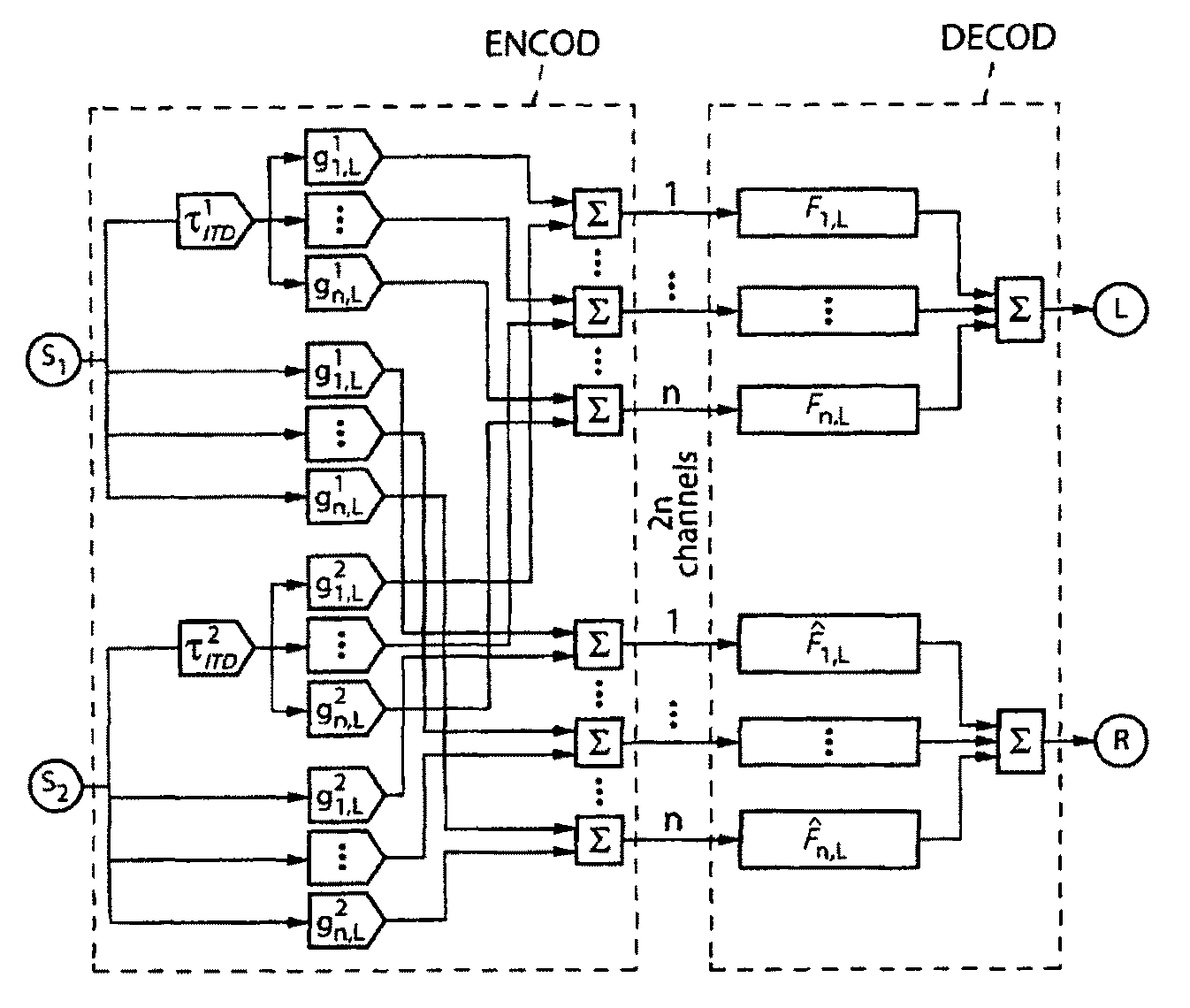
Optimization of binaural sound spatialization based on multichannel encoding
ActiveUS9215544B2Promote reconstructionIncrease amplitudePseudo-stereo systemsTwo-channel systemsArray data structureAcoustic transfer function
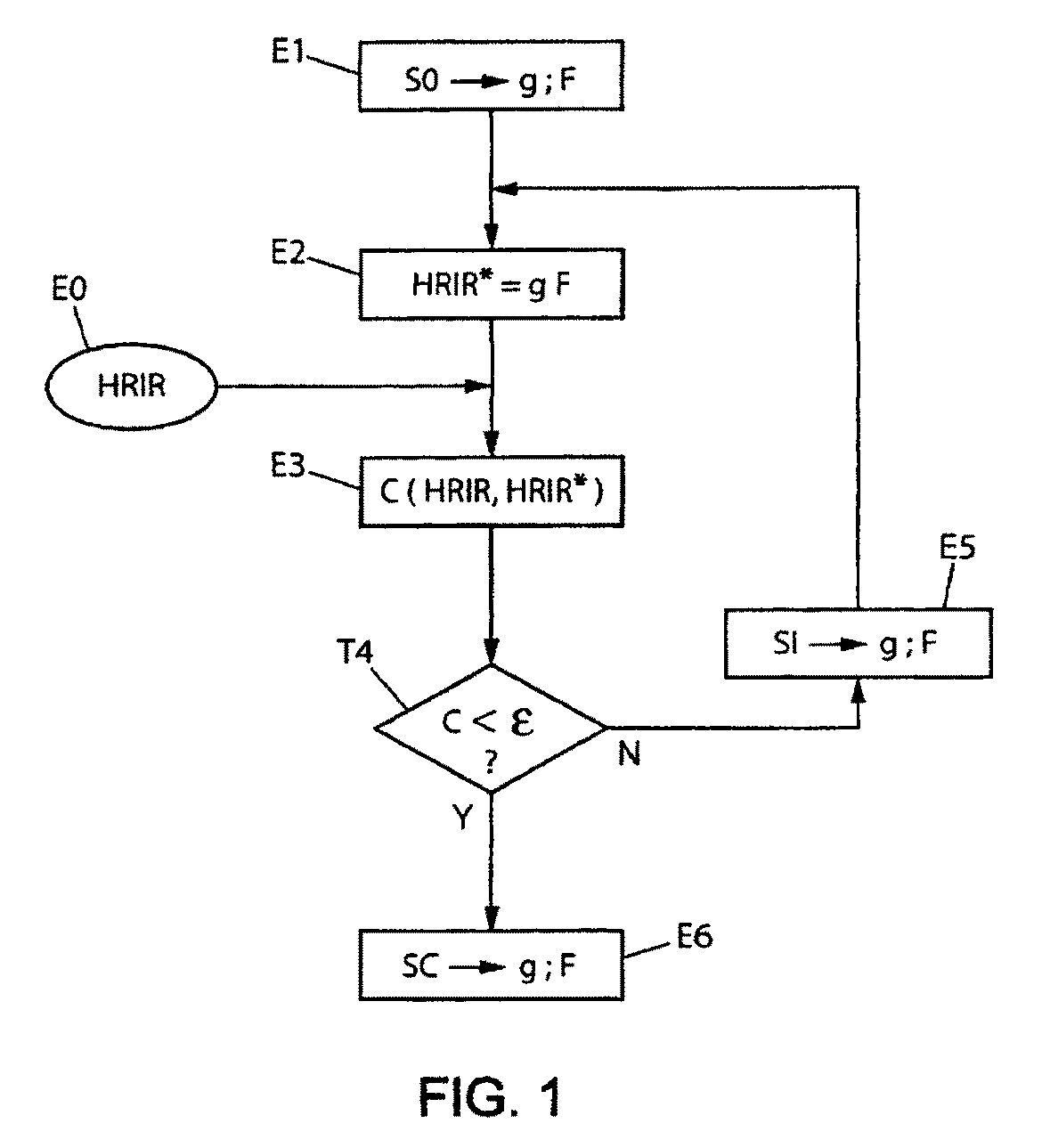
The invention concerns sound spatialization with multichannel encoding for binaural reproduction on two loudspeakers, the spatial encoding being defined by encoding functions associated with multiple encoding channels and the decoding by applying filters for binaural reproduction. The invention provides for an optimization as follows: a) obtaining a original set of acoustic transfer functions particular to an individual's morphology (HRIR;HRTF), b) selecting spatial encoding functions (g(θ,φ,n)) and / or decoding filters (F(t,n)), and c) through successive iterations, optimizing the filters associated with the selected encoding functions or the encoding functions associated with the selected filters, or jointly the selected filters and encoding functions, by minimizing an error (c(HRIR,HRIR*)) calculated based on a comparison between: the original set of transfer functions (HRIR), and a set of reconstructed transfer functions (HRIR*) from encoding functions and decoding filters, whether optimized and / or selected.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com