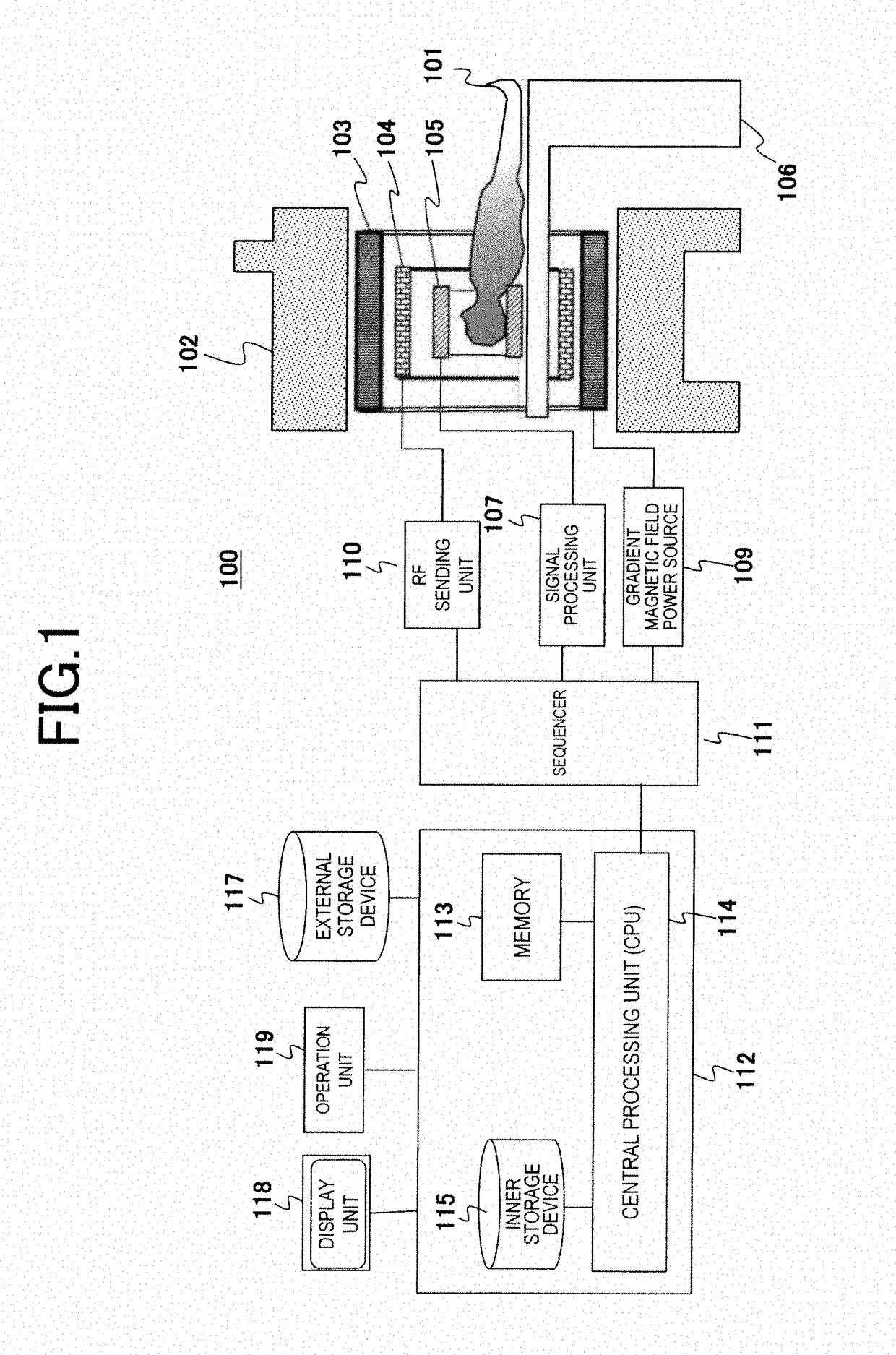
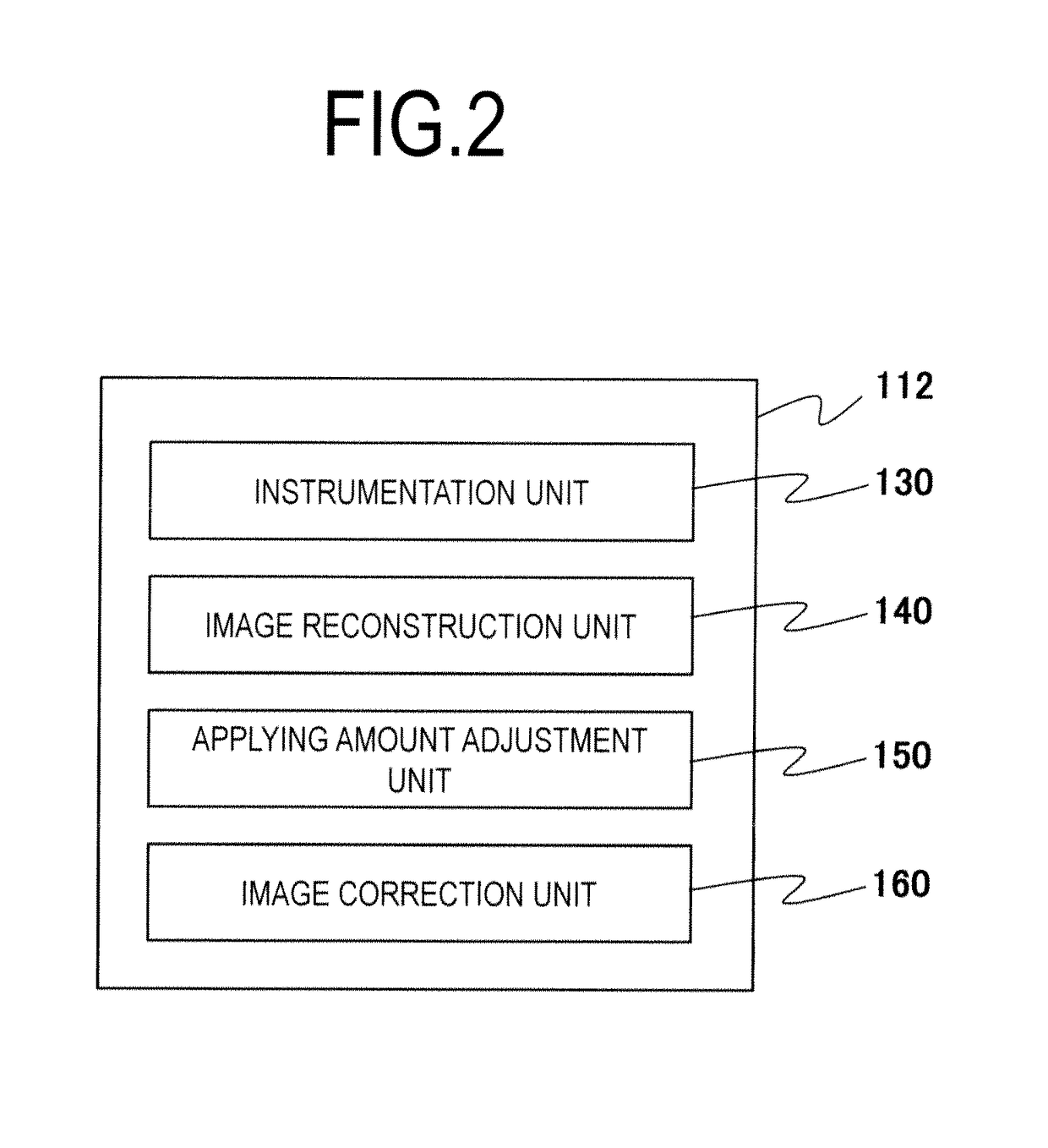
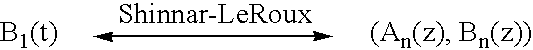Patents
Literature
88 results about "Transverse magnetization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
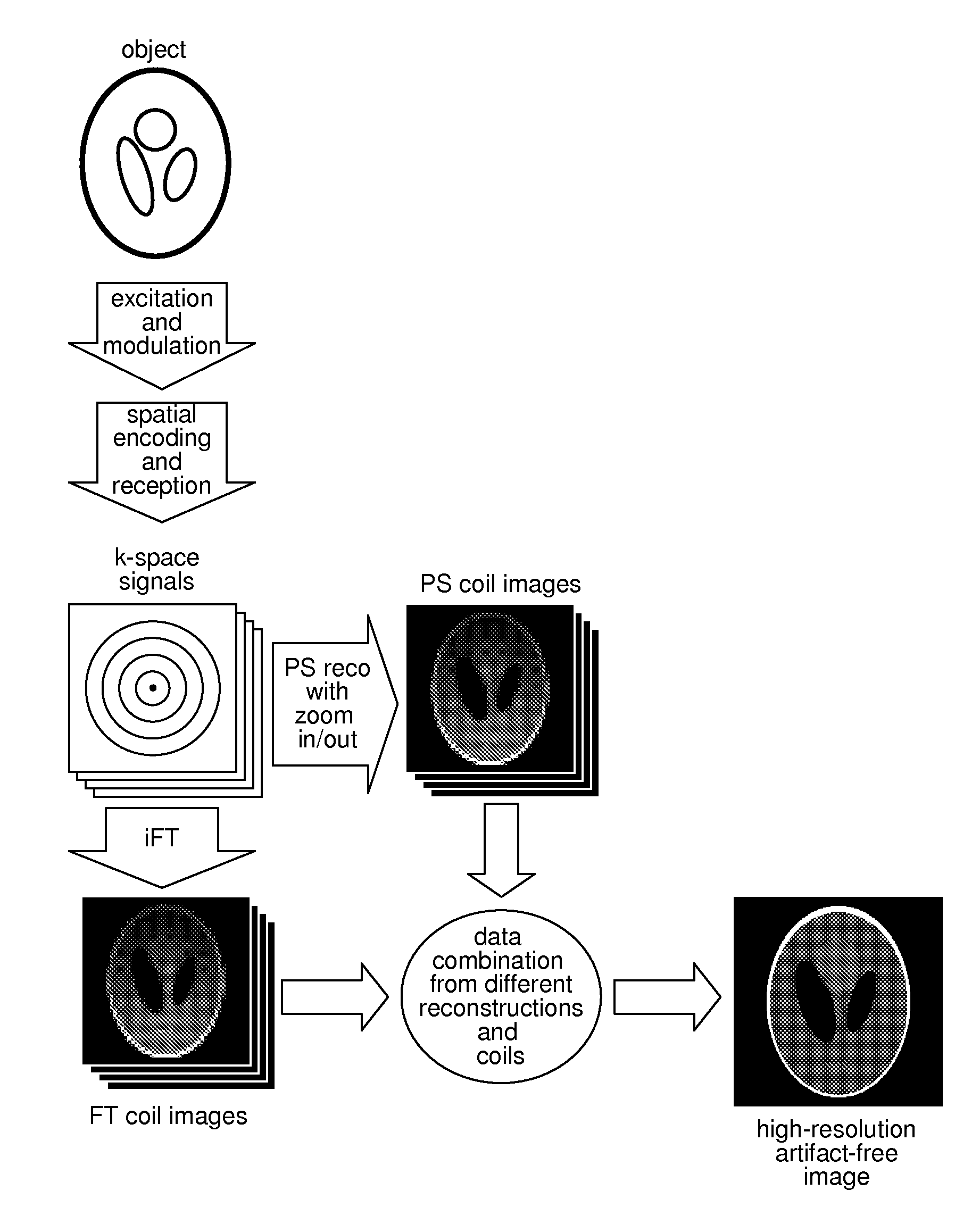
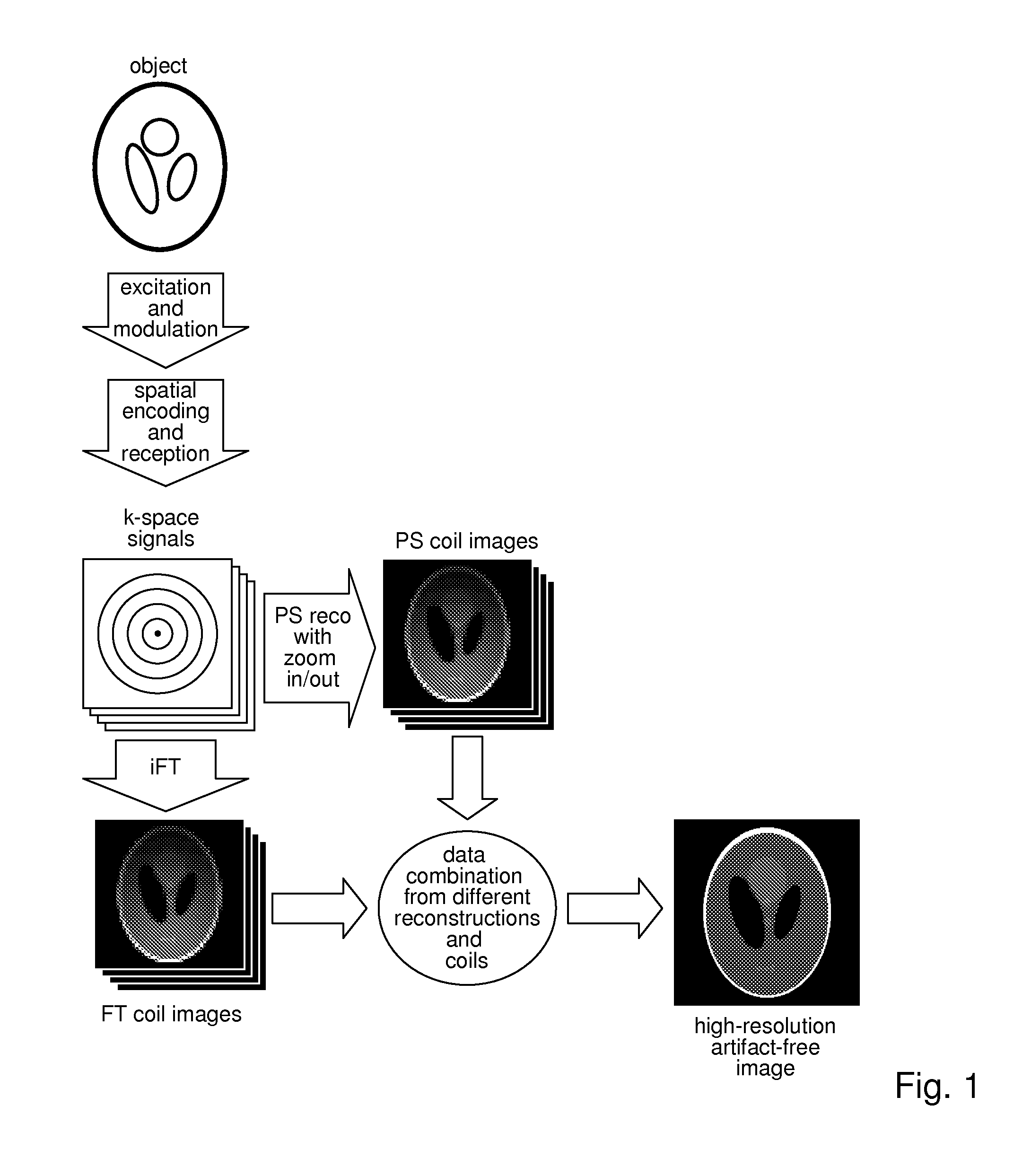
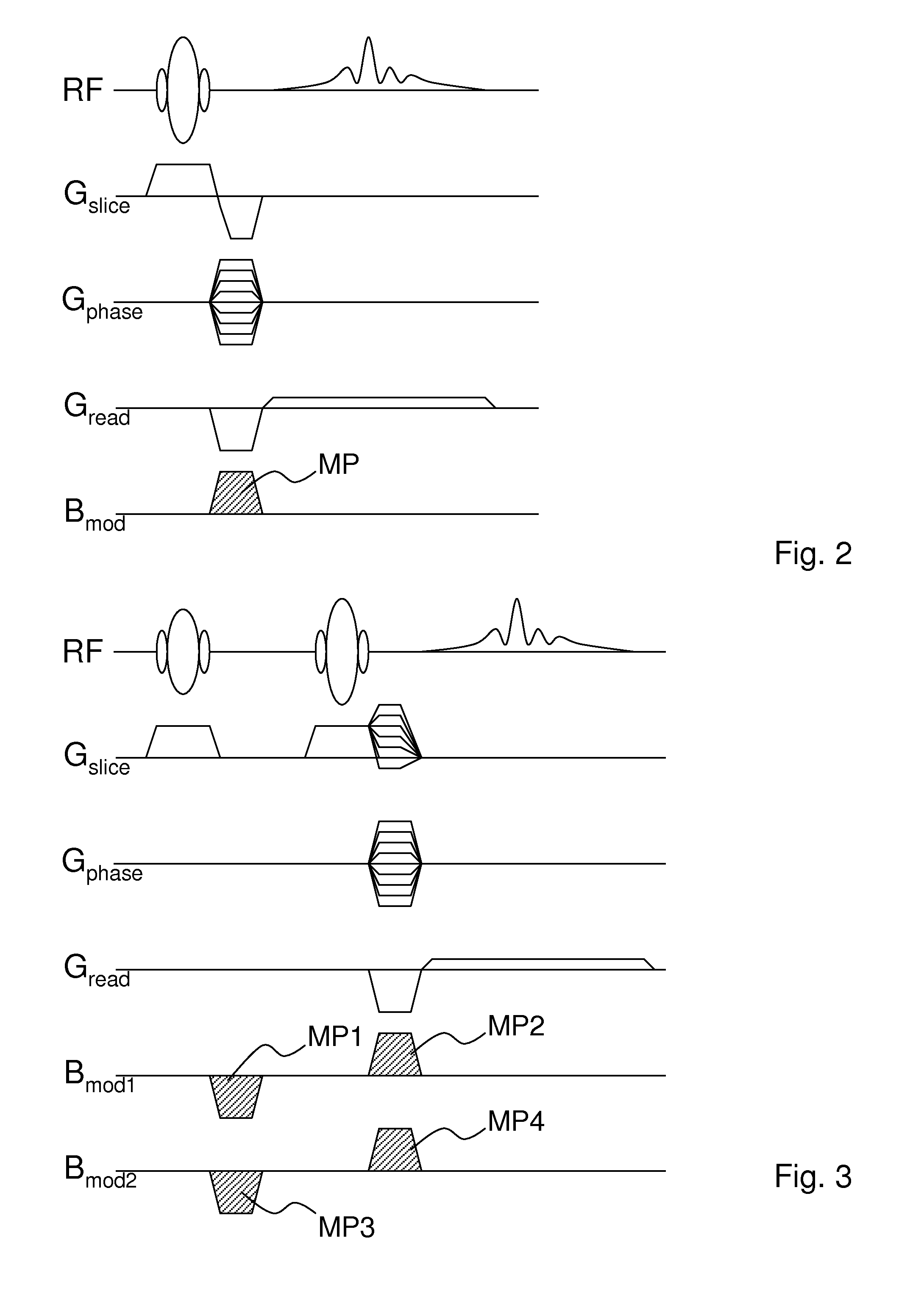
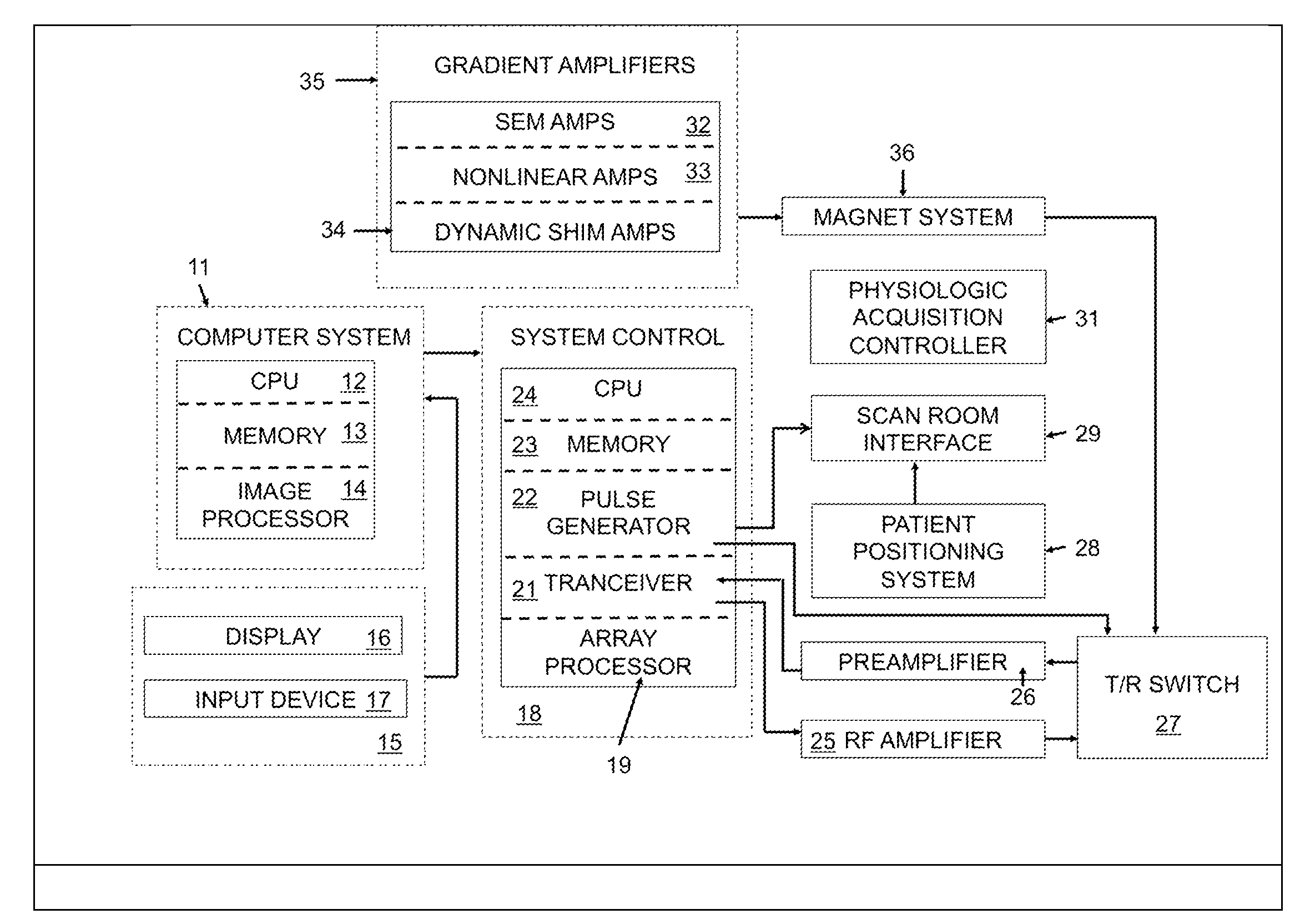
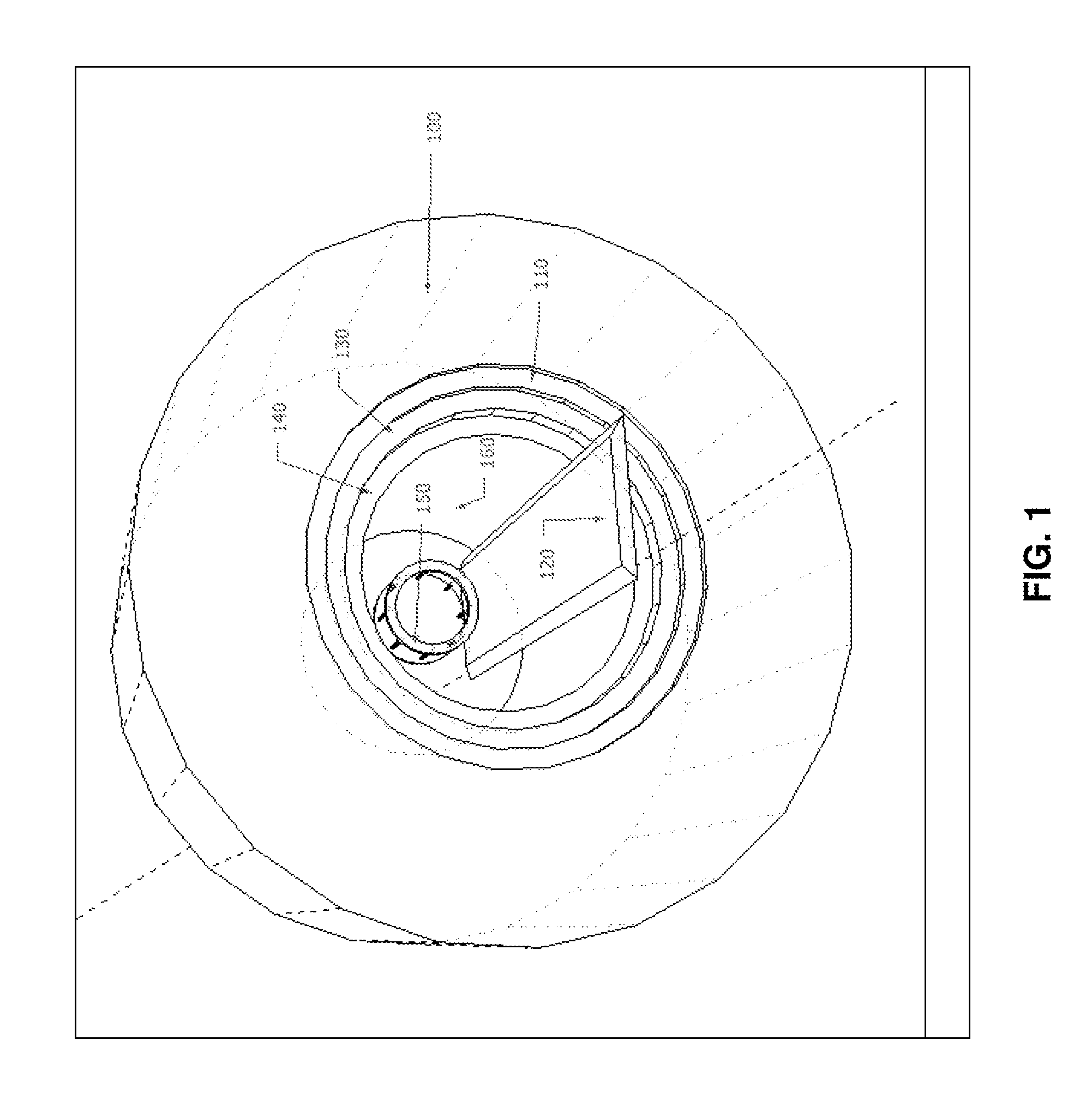
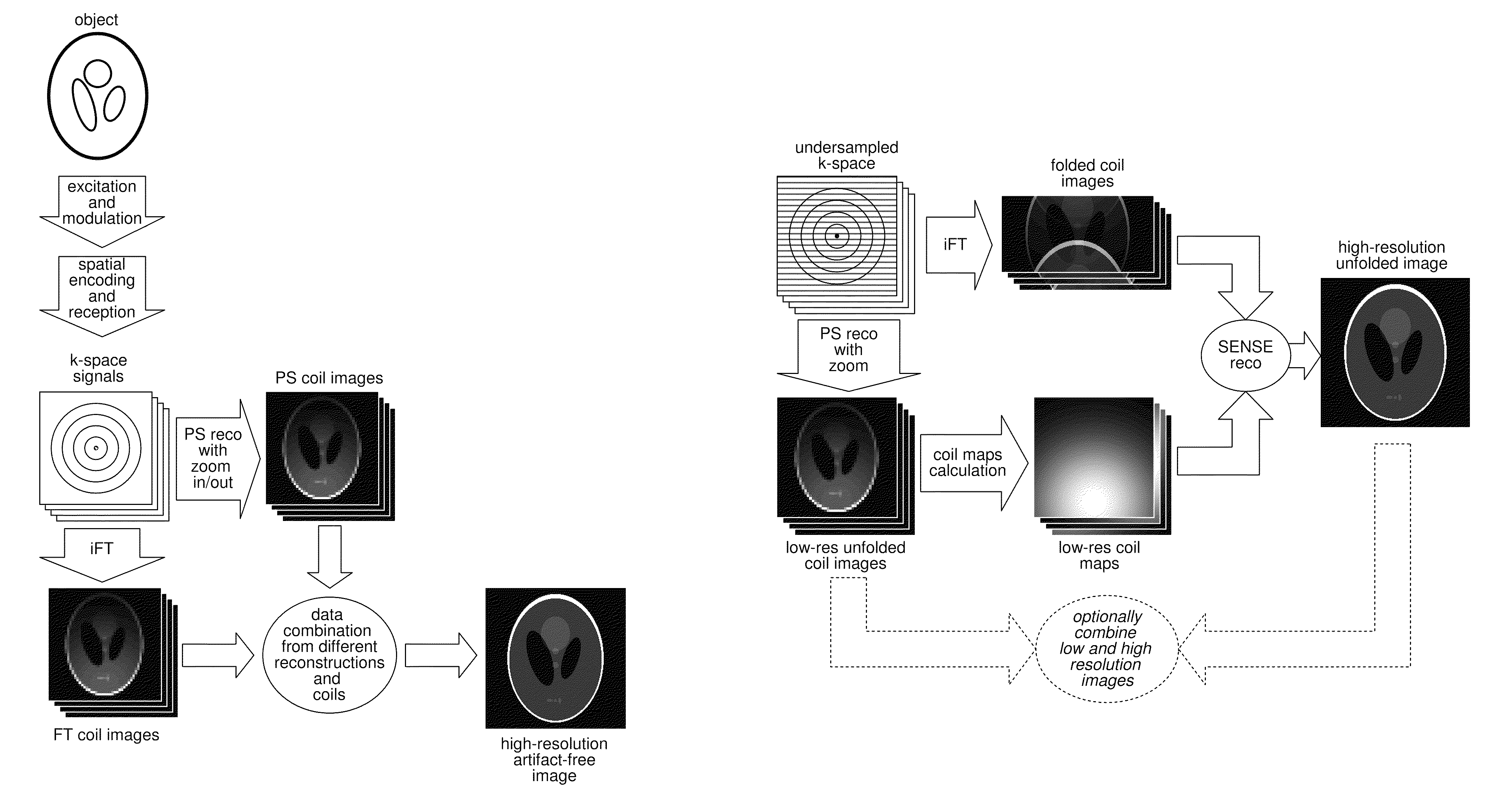
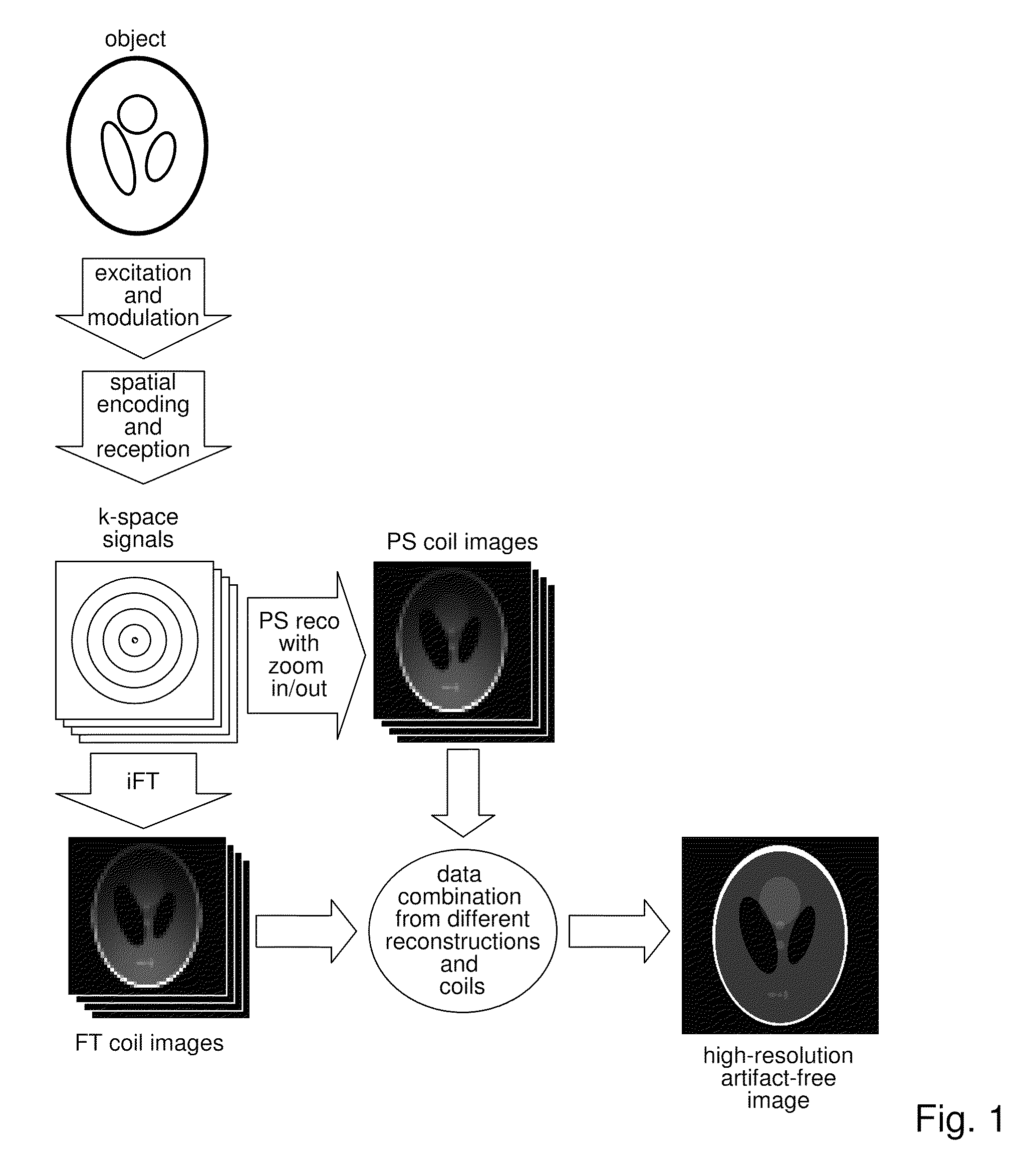
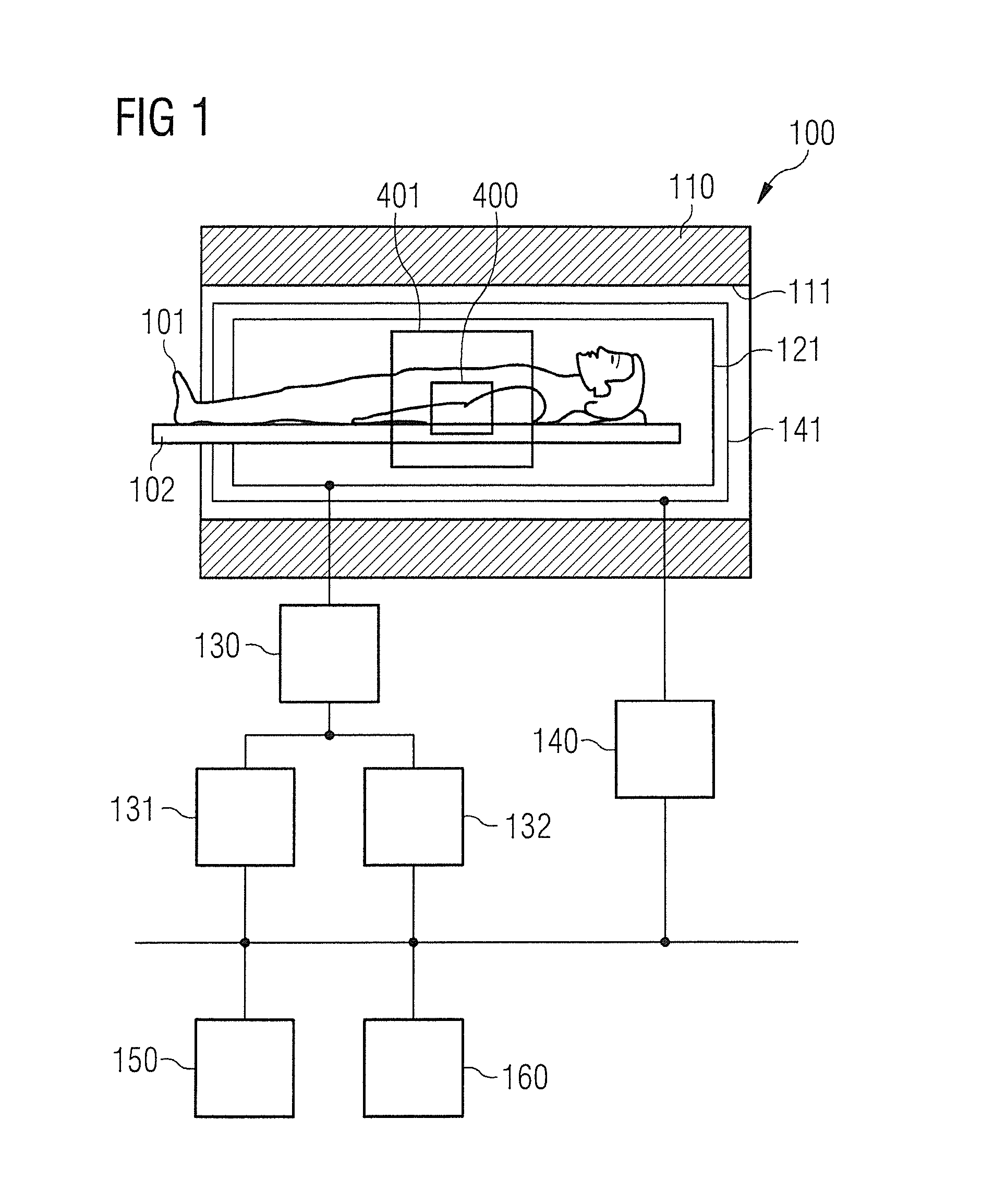
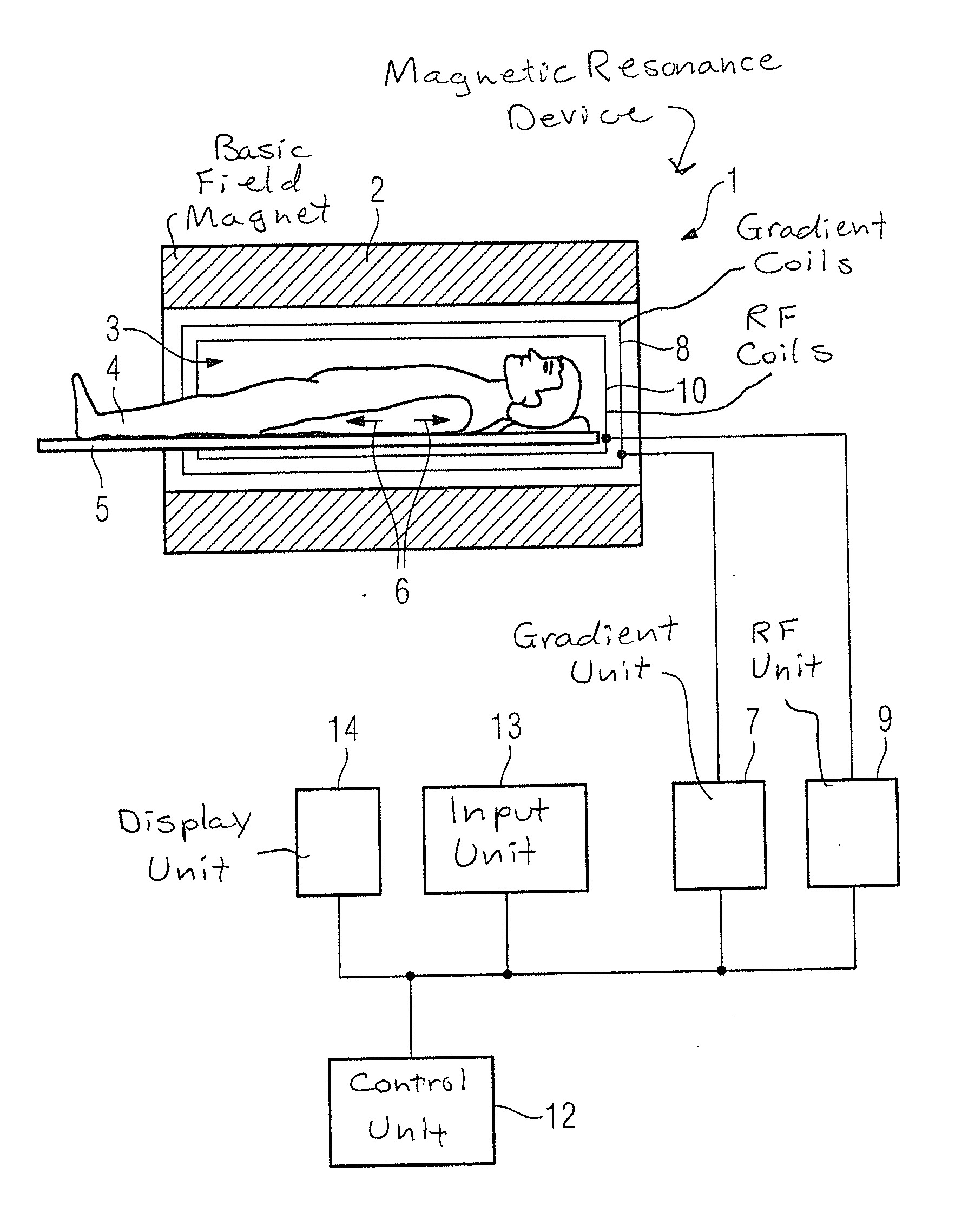
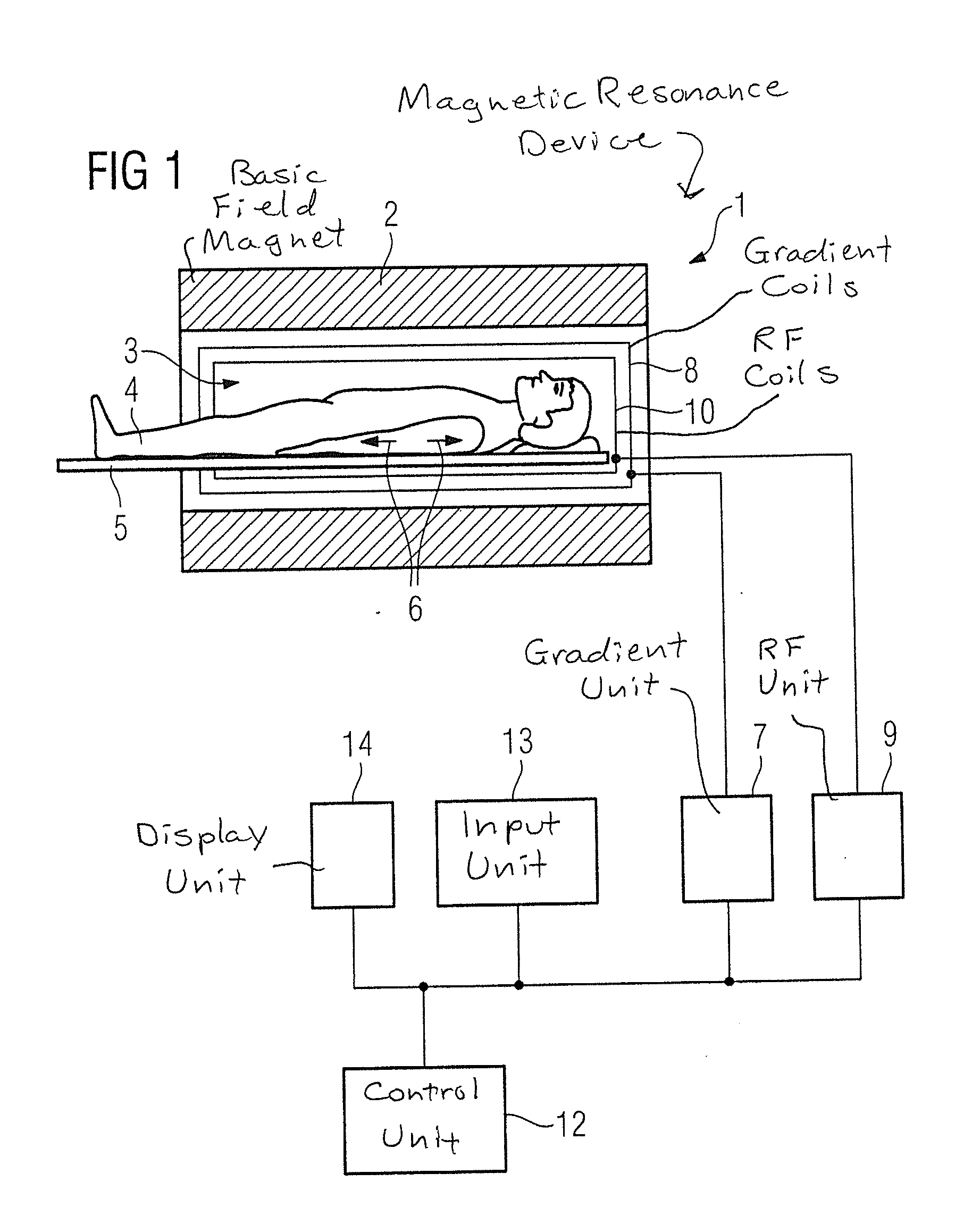
Method for data acquisition acceleration in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using receiver coil arrays and non-linear phase distributions
InactiveUS20110148410A1Specifically designedIncrease freedomElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRTransverse magnetizationData acquisition
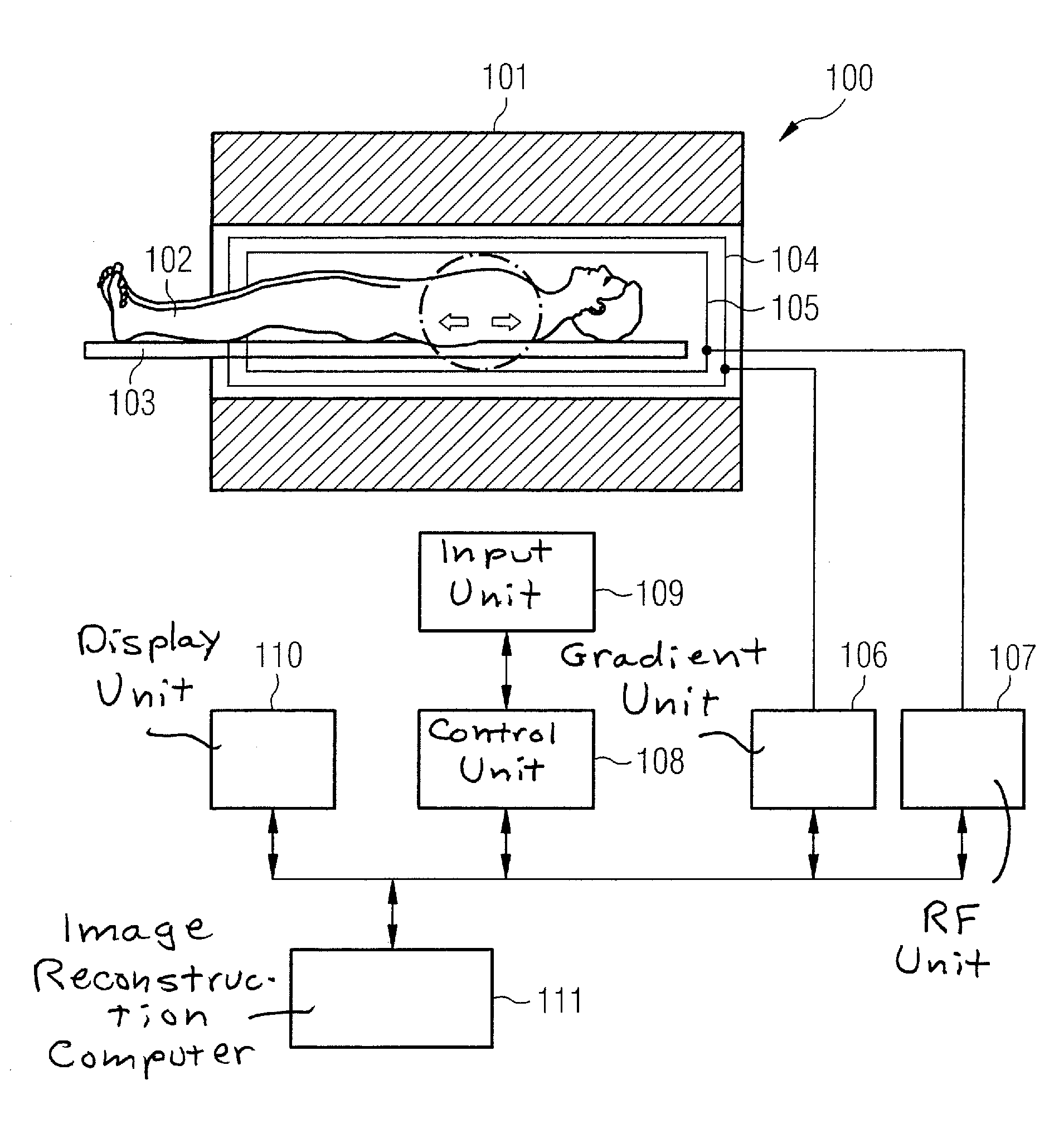
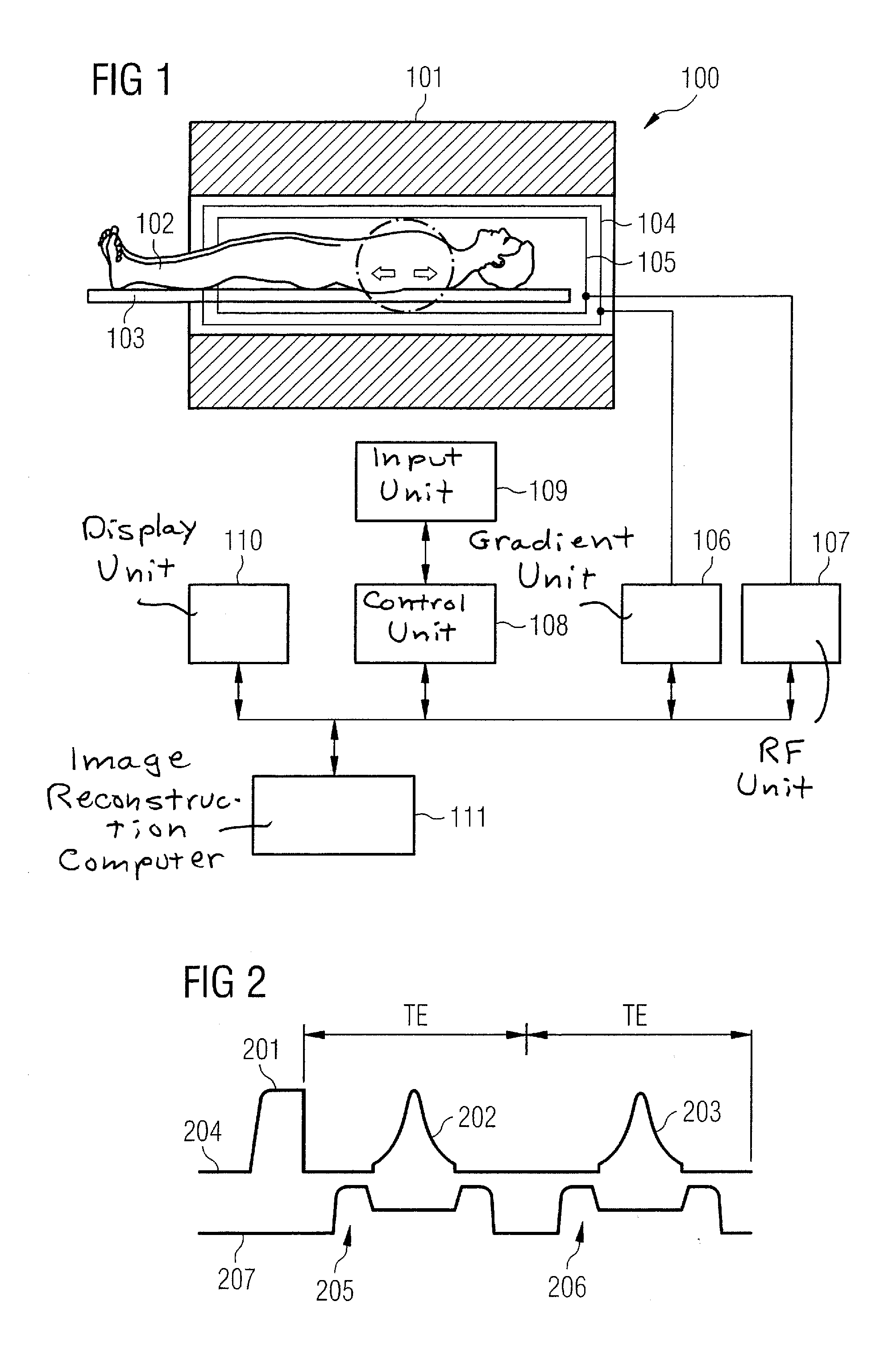
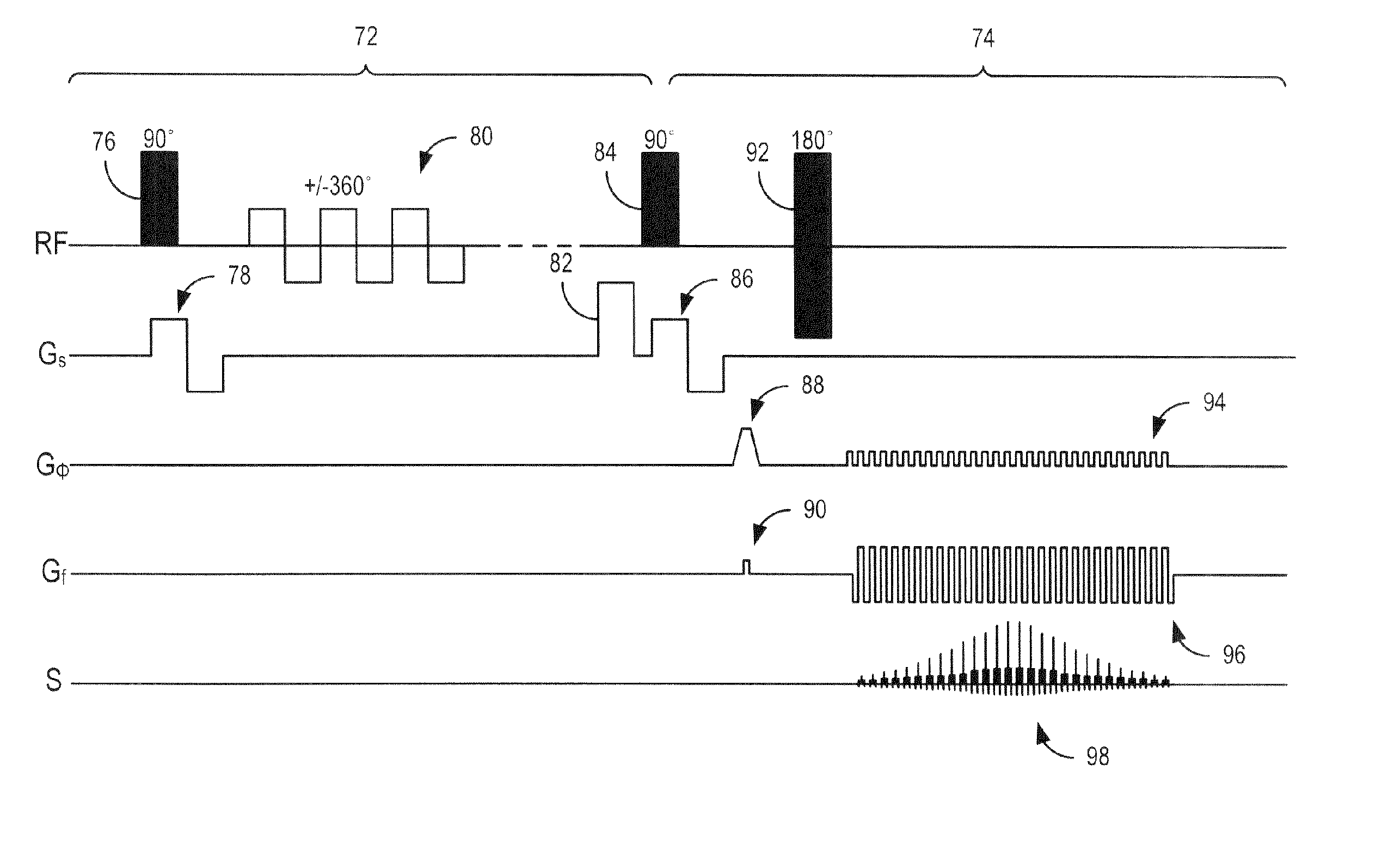
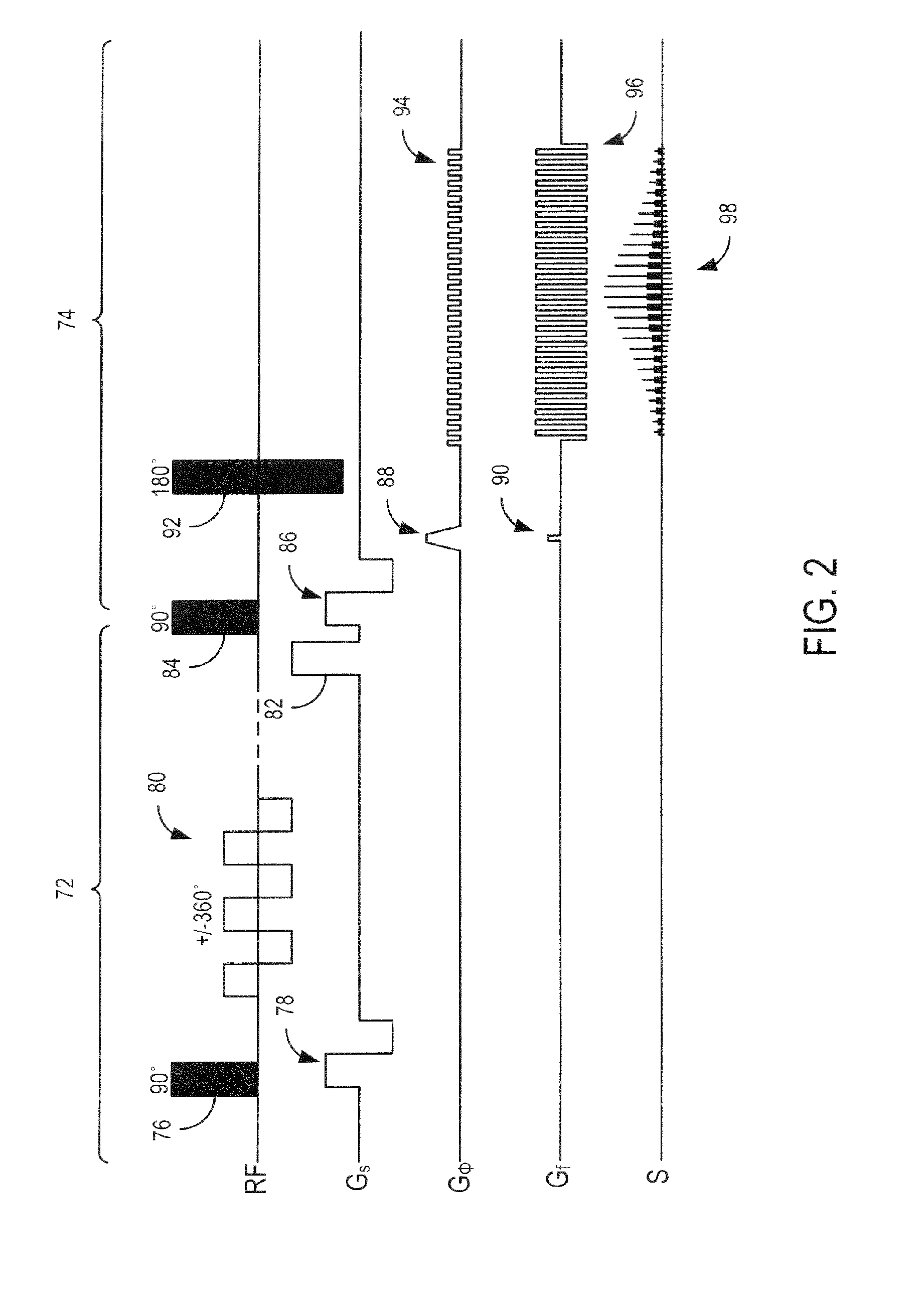
A method for accelerating data acquisition in MRI with N-dimensional spatial encoding has a first method step in which a transverse magnetization within an imaged object volume is prepared having a non-linear phase distribution. Primary spatial encoding is thereby effected through application of switched magnetic fields. Two or more RF receivers are used to simultaneously record MR signals originating from the imaged object volume, wherein, for each RF receiver, an N-dimensional data matrix is recorded which is undersampled by a factor Ri per selected k-space direction. Data points belonging to a k-space matrix which were not recoded by a selected acquisition schema are reconstructed using a parallel imaging method, wherein reference information concerning receiver coil sensitivities is extracted from a phase-scrambled reconstruction of the undersampled data matrix. The method generates a high-resolution image free of artifacts in a time-efficient manner by improving data sampling efficiency and thereby reducing overall data acquisition time.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
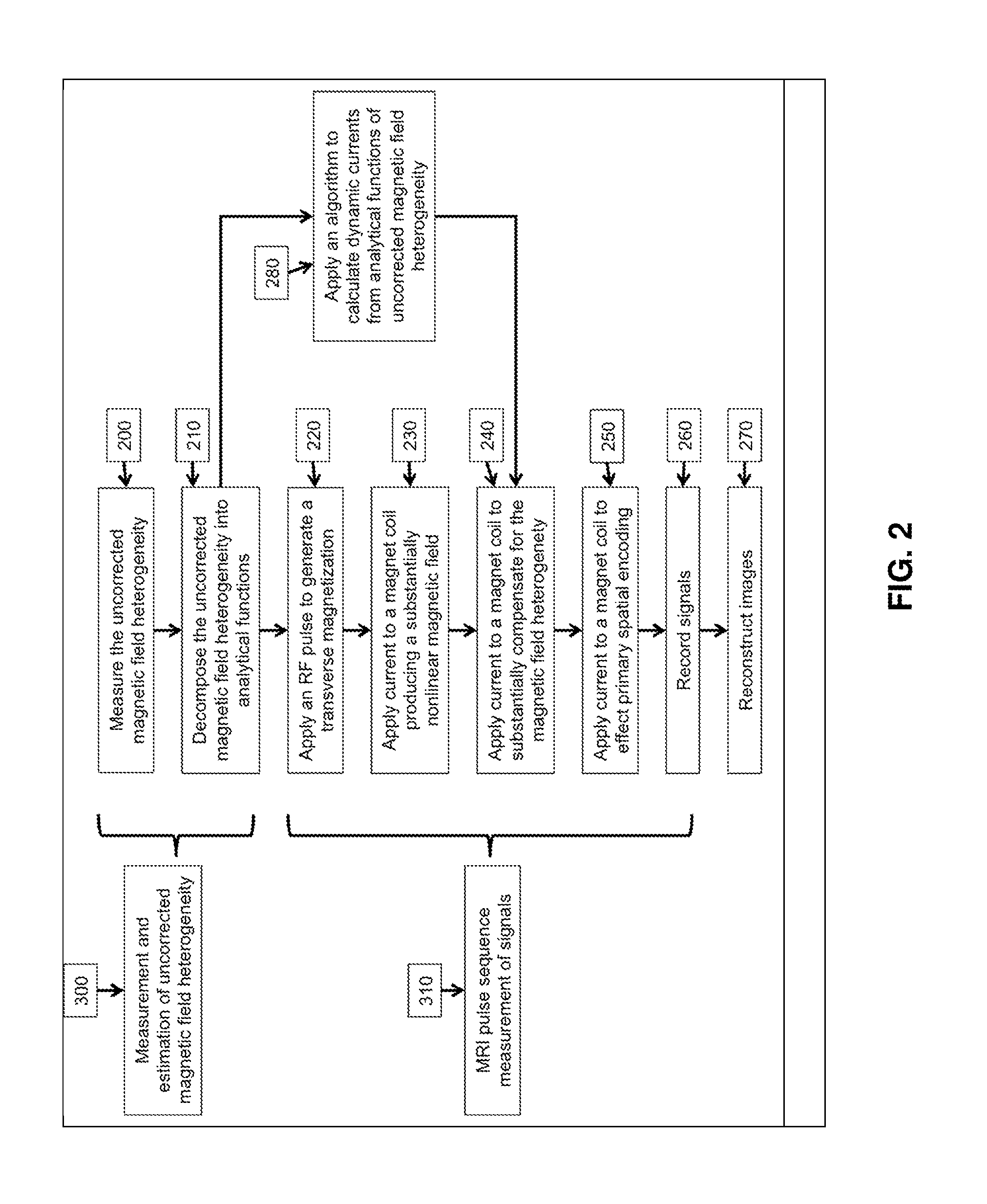
Method of dynamically compensating for magnetic field heterogeneity in magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20120249137A1Lower requirementMinimize homogeneityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationMR - Magnetic resonance
A method to compensate for the magnetic field heterogeneity inside an object of investigation in a MR device obtains an uncorrected magnetic field distribution of the object and executes an MR sequence with a desired k-space coverage by applying RF pulses to generate a transverse magnetization within the object. MR signal data is recorded, magnetic field shimming parameters are dynamically updated and MR signal data are reconstructed to produce images or localized spectroscopic data. Artifacts in a reconstructed image resulting from an uncorrected magnetic field distribution are suppressed by temporally separating MR signals originating from at least two different sub-volumes within a volume of transverse magnetization by generating a nonlinear phase distribution within the object and by dynamically updating shimming parameters to compensate for the field inhomogeneity distributions within the different sub-volumes in the volume of transverse magnetization.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
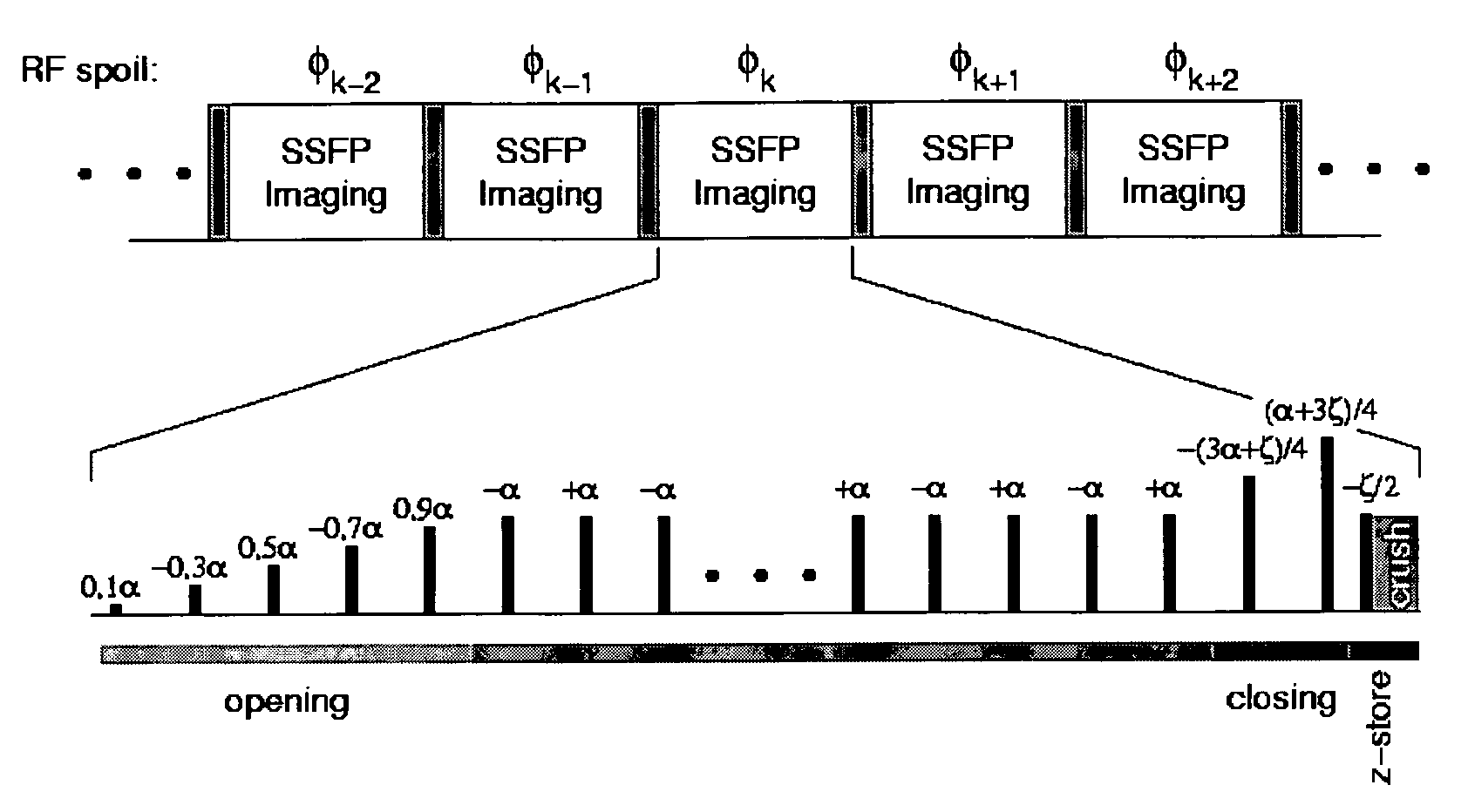
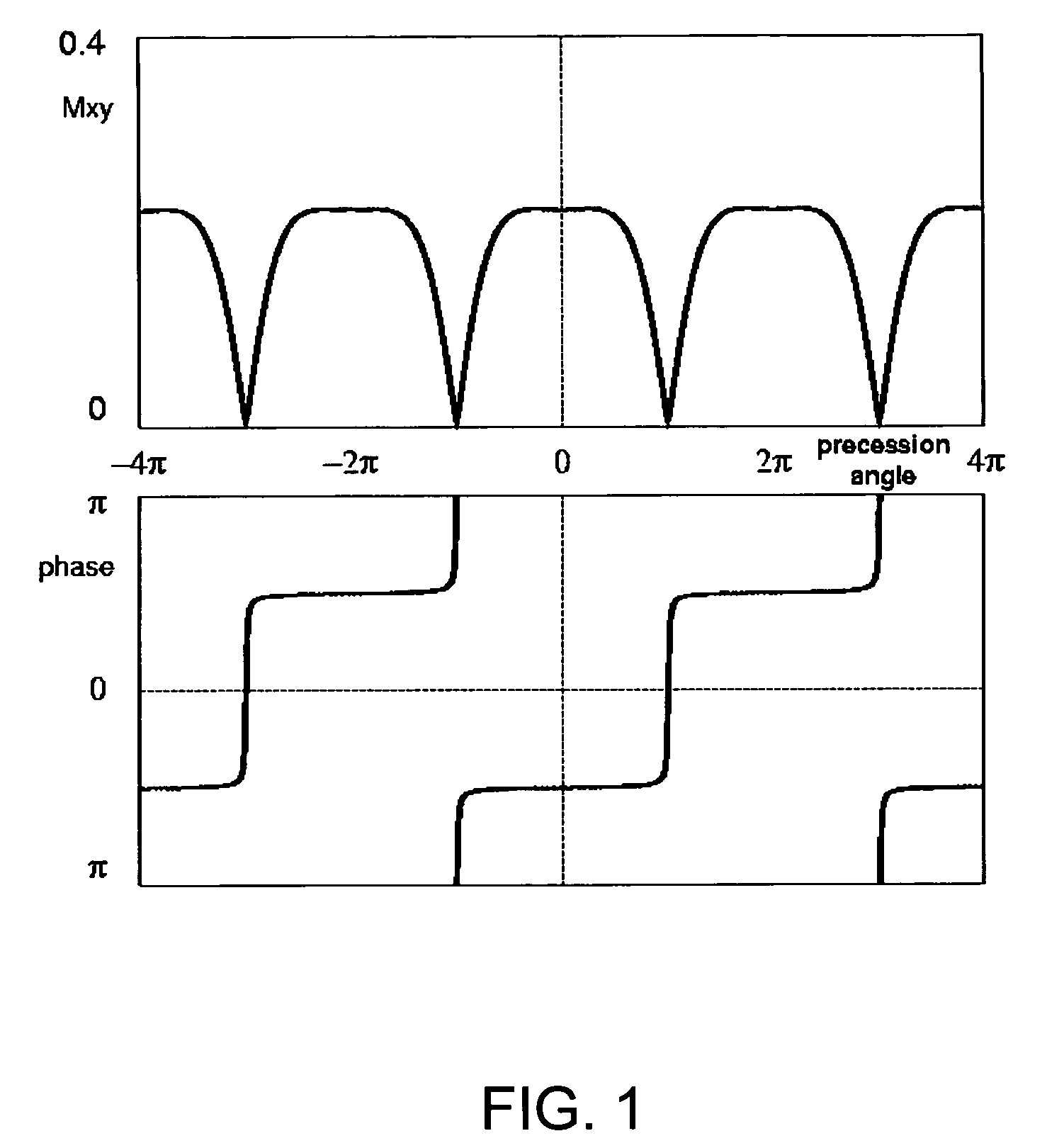
Spectrally selective suppression with steady-state free precession
ActiveUS7253620B1Little disturbanceEnhanced inhibitory effectMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationCine imaging
A method that exploits the intrinsic selectivity of steady-state free precession (SSFP) to perform spectral suppression is disclosed. Such a method avoids the need to incorporate additional spectrally selective pulse sequence elements. The scheme is based on breaking the FISP imaging sequence into short trains having, for example, 8–64 RF pulses. At the moment of echo formation (i.e., TE=TR / 2) after the last full RF pulse of the train, water signal is z-stored. Residual transverse magnetization, which include isochromats phase-opposed to the on-resonance water, is gradient crushed and RF spoiled. The stored magnetization is subsequently re-excited with little disturbance to the on-resonance steady-state water signal. The additional time required to perform the steady-state interruption is typically as little as a single TR, minimally affecting the efficiency of the imaging process. The sequence can be employed repetitively, greatly reducing the amplitude of fat signals throughout a real-time or cine imaging process.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method and apparatus for acquiring free-breathing MR images using navigator echo with saturation RF pulse
ActiveUS7689263B1Uniform recoveryOvercomes drawbackMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTransverse magnetizationSpins
A system and method of free-breathing MR imaging saturates an entire navigator profile at the end of an imaging segment of physiological motion cycle, e.g., heart cycle, thereby providing a uniform recovery of longitudinal magnetization for the next imaging cycle. Through use of at least one dephaser gradient following the image acquisition segment and a navigator RF saturation pulse, residual transverse magnetization is dephased and spins within a navigator tracker are saturated to ensure a uniform recovery of longitudinal magnetization for the next imaging period.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus of background suppression in MR imaging using spin locking
ActiveUS7064545B2Efficient magnetizationLongitudinal magnetization regrowth is minimizedMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionBlood flowTransverse magnetization
The present invention is directed to a method and system of tissue or background suppression for the acquisition of image data from blood flow or tissue perfusion. Background suppression with minimal effects upon inflowing spins is achieved through a series of spin locking low level RF pulses that cause adiabatic demagnetization of tissue with a relaxation time T1-rho that is intermediate between T1 and T2 relaxation times. In this regard, the effective transverse magnetization of static tissue resulting from the application of a series of low level RF pulses is reduced and, with the spin locking, longitudinal magnetization regrowth is minimized. As such, inflowing spins to an imaging volume may be directly imaged with significant background tissue suppression. The present invention is particularly applicable to time-of-flight MRA and MR perfusion imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
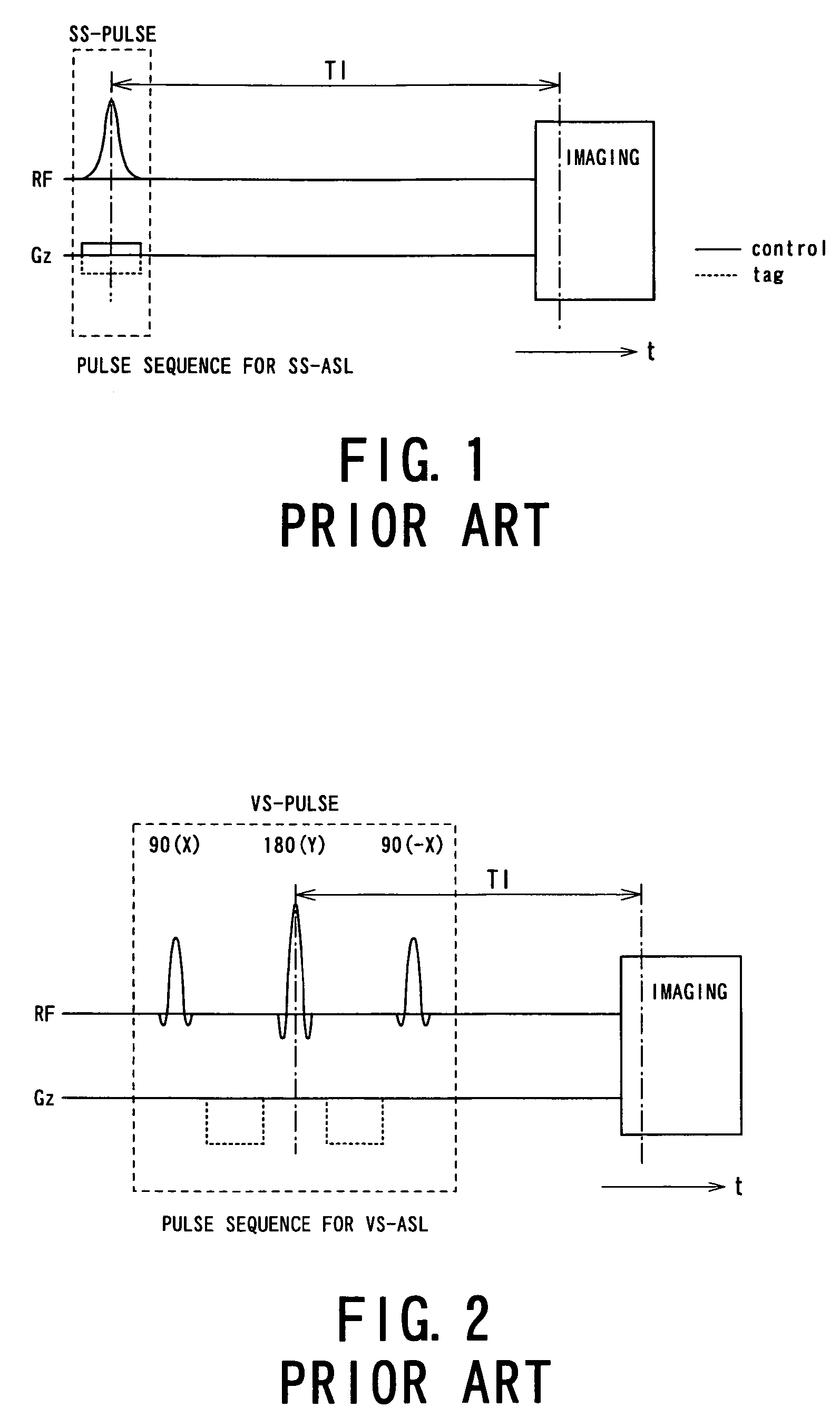
MRI apparatus and ASL imaging technique
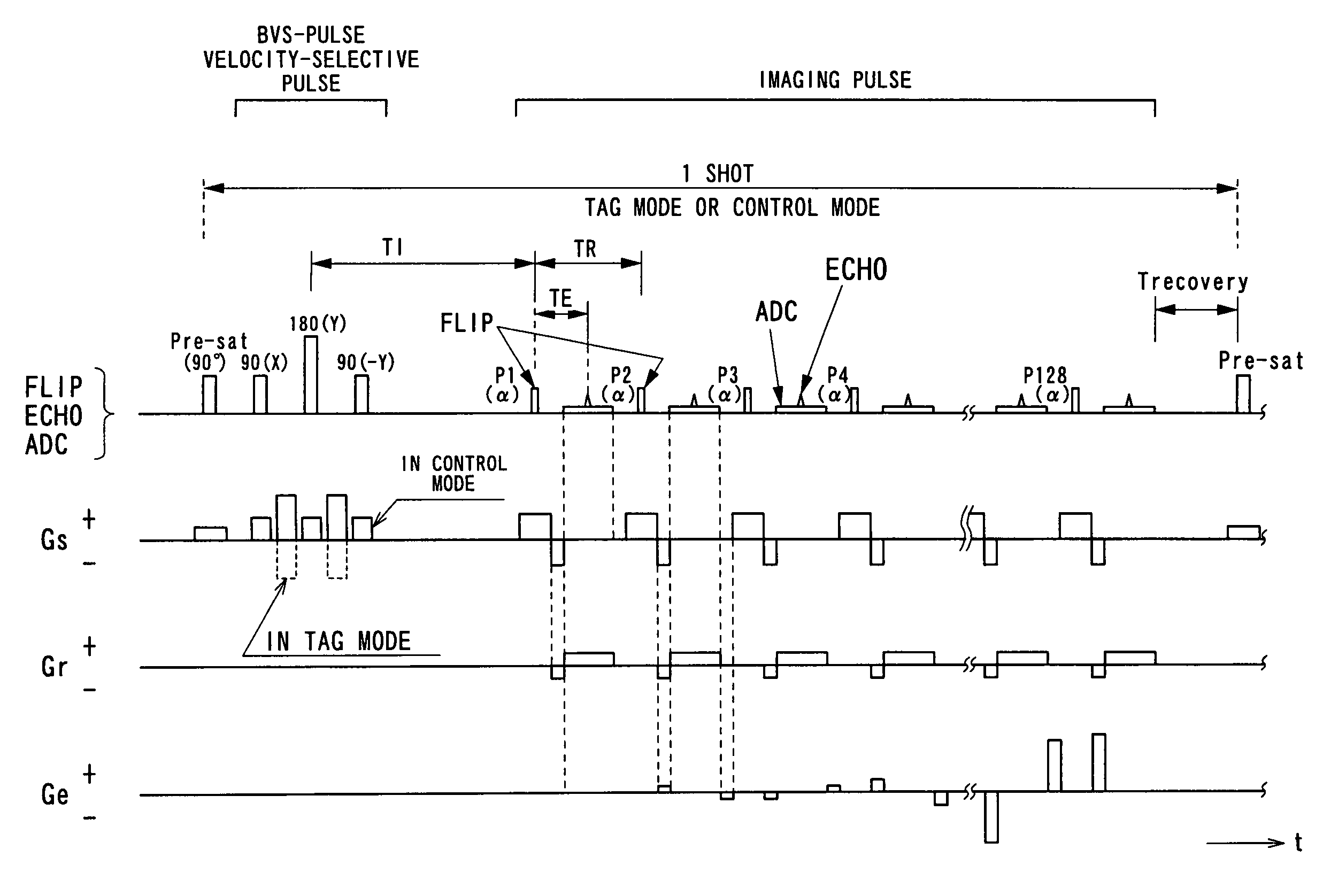
ActiveUS7545141B2Reducing Td time-induced errorHigh sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase shiftedSelective excitation
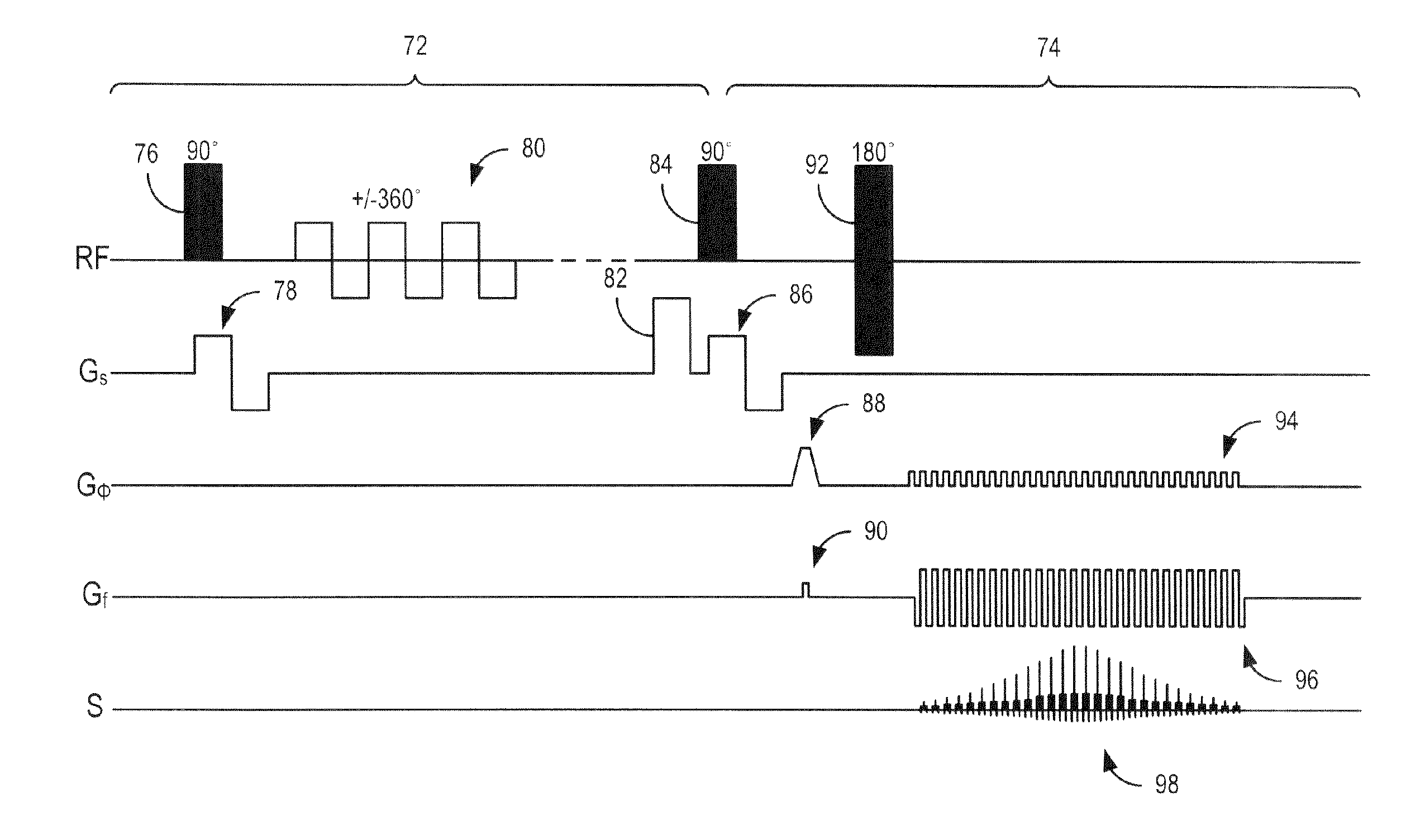
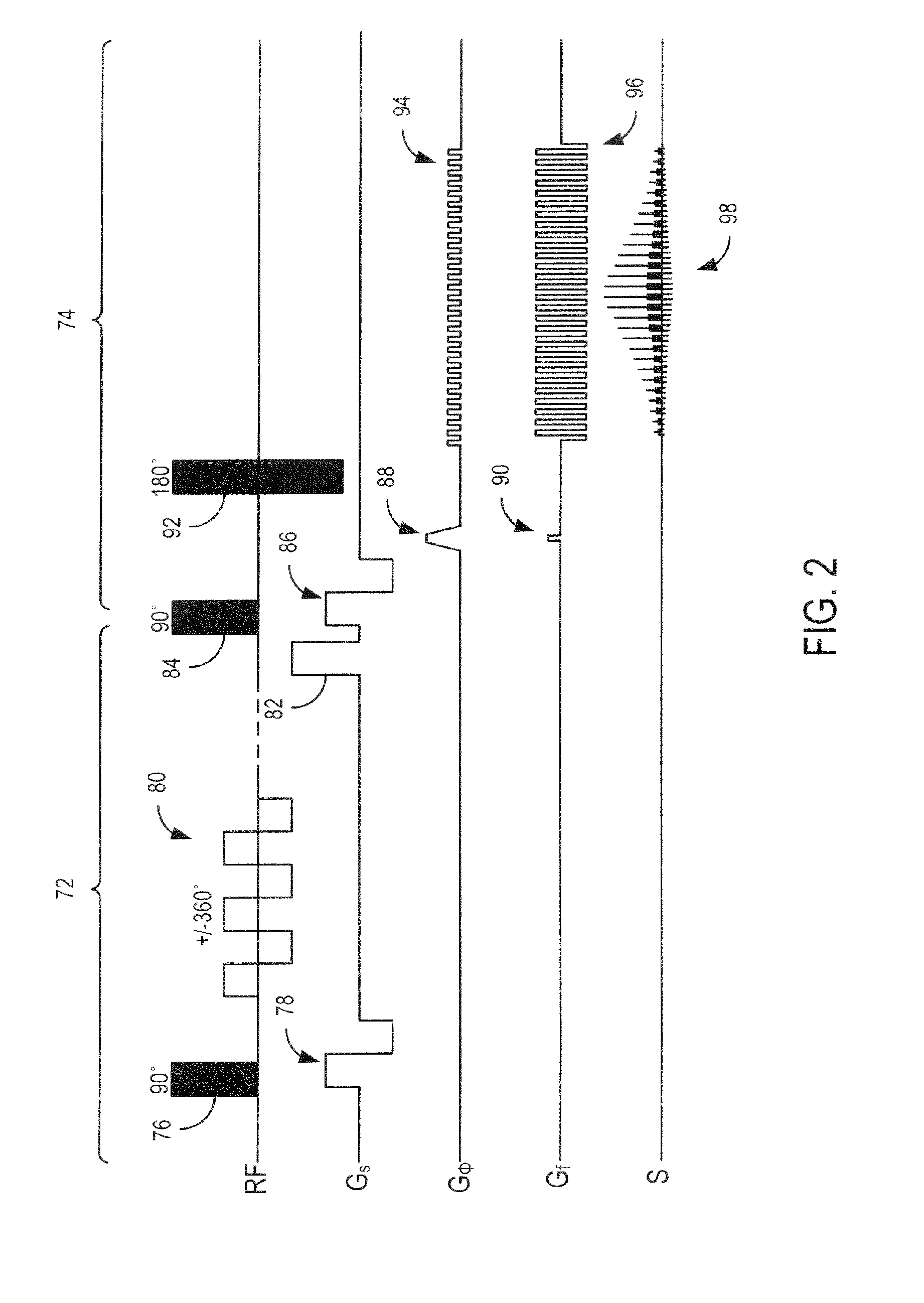
An MRI apparatus obtains an ASL (Arterial Spin Labeling) image of a region to be imaged in a subject by performing a scan to the region to be imaged independently in a control mode and in a tag mode according to a pulse sequence based on an ASL technique. The pulse sequence includes a velocity-selective pulse, BVS (Band-limited Velocity-Selective)-pulse, that selectively excites magnetization spins in a blood flow passing through the region to be imaged and having a constant velocity range for the spins to undergo transition to transverse magnetization, and then performs excitation to cause the transverse magnetization to flip back to longitudinal magnetization. The velocity-selective pulse is formed in such a manner that the transverse magnetization excited in each of the control mode and the tag mode gives rise to a phase shift in an opposite polarity upon velocity-selective excitation.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
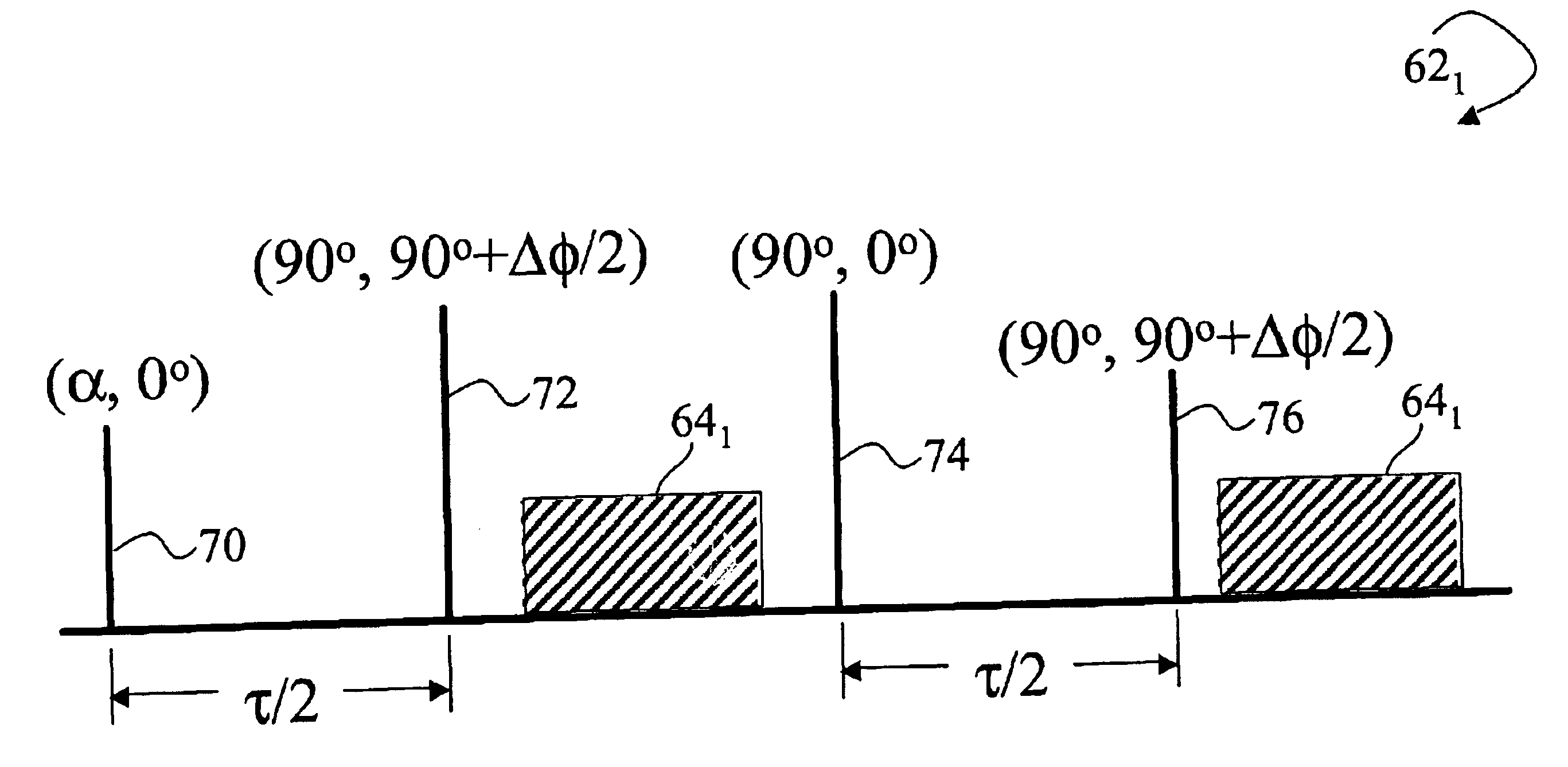
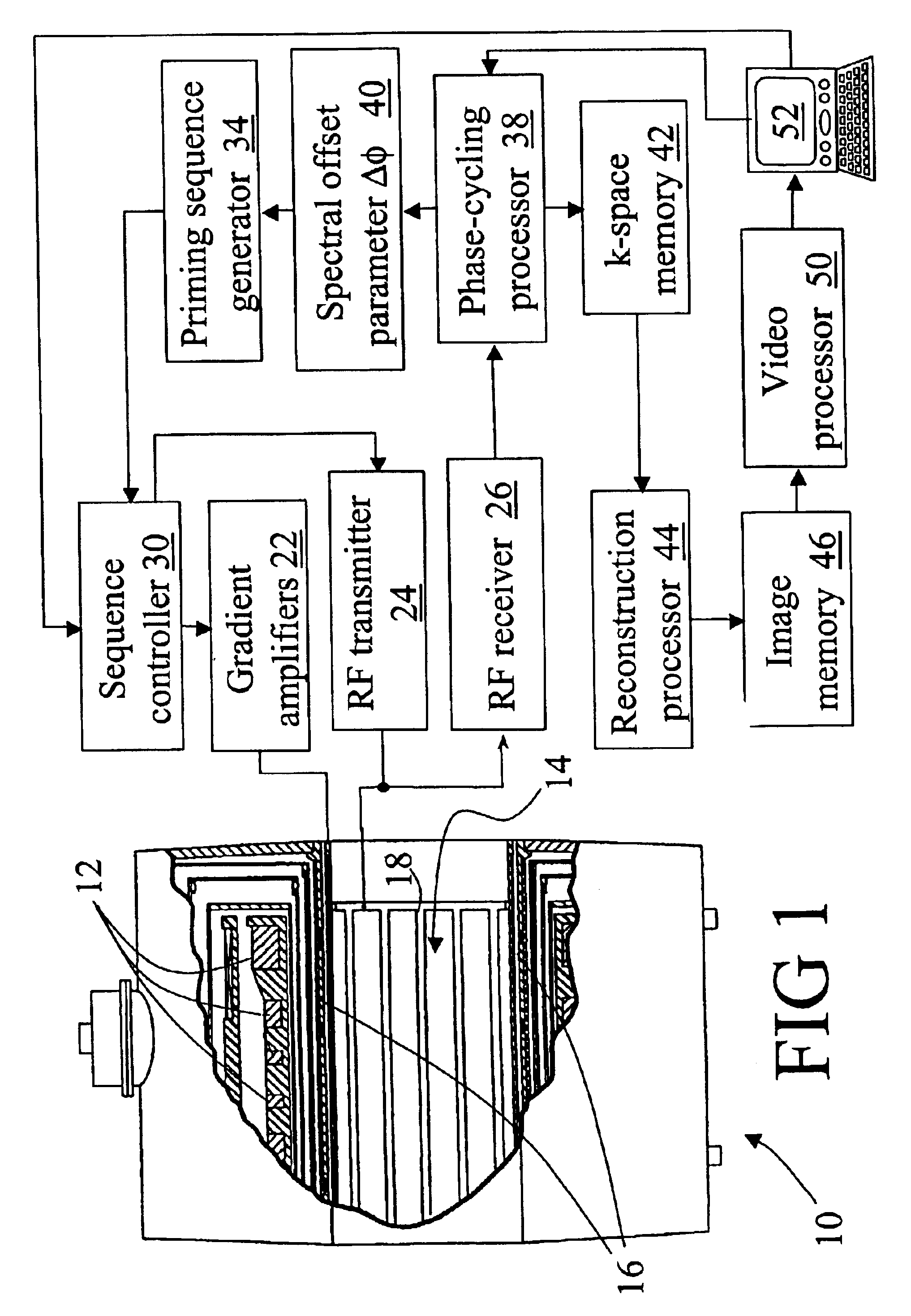
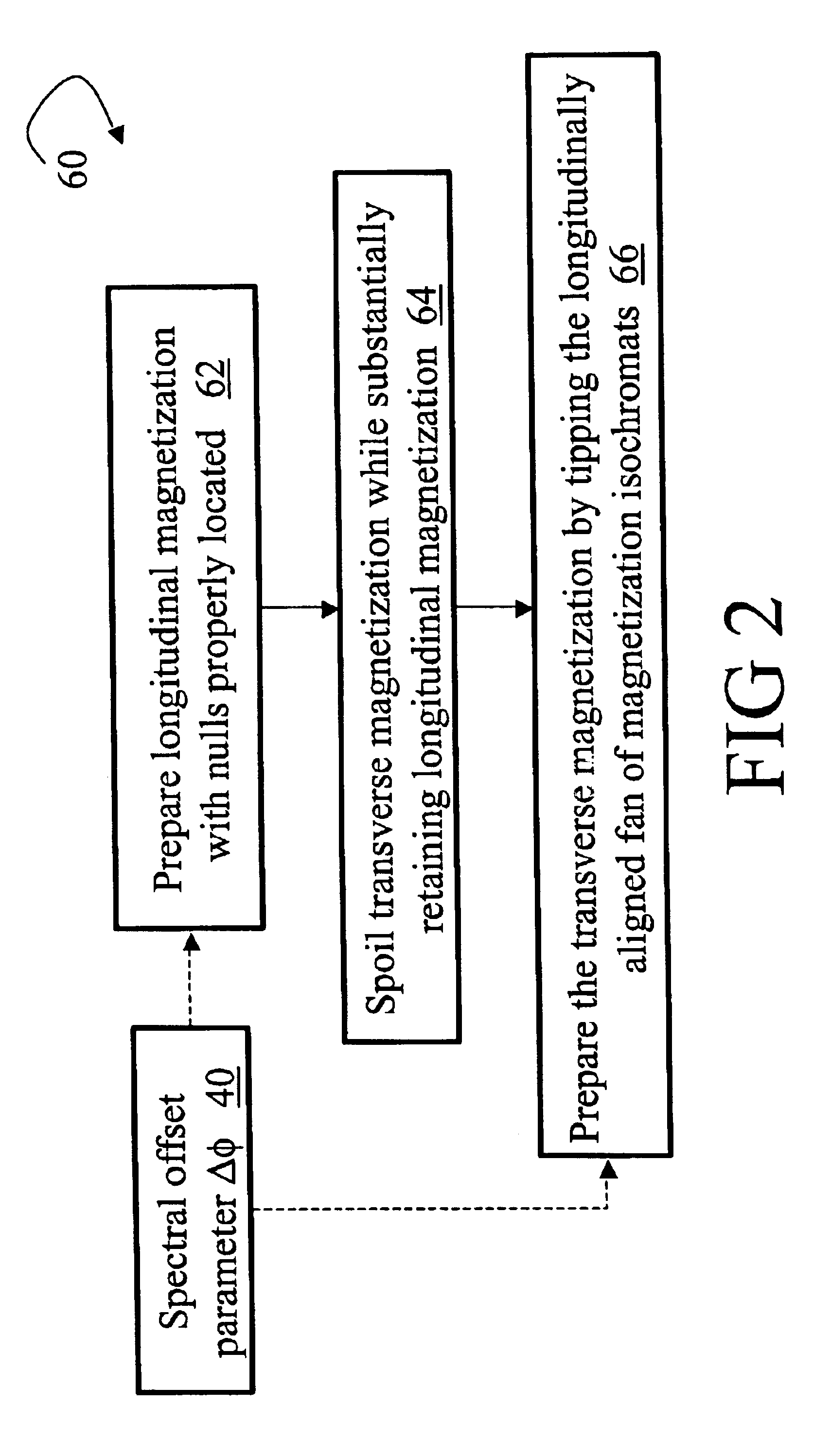
Magnetization primer sequence for balanced steady state free precision imaging
InactiveUS6885193B2Reduce Image ArtifactsReduced image scanning timeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsTransverse magnetizationResonance
To prepare magnetization for steady state magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance is primed using a parameterized priming sequence (60). The parameterized priming sequence (60) has a spectral offset parameter value (40) corresponding to a spectral offset of the steady state imaging. Subsequent to the priming, steady state magnetic resonance imaging data at the first spectral offset is acquired using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner (10). A reconstruction processor (44) reconstructs the imaging data to generate an image representation. Preferably, the parameterized priming sequence (60) includes a longitudinal priming sequence (62) that prepares longitudinal magnetization in a state approximating a steady state longitudinal magnetization. A spoiler sequence (64) spoils transverse magnetization while retaining longitudinal magnetization. A transverse priming sequence (66) prepares traverse magnetization in a state approximating a steady state transverse magnetization.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for data acquisition acceleration in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with N-dimensional spatial encoding using two or more receiver coil arrays and non-linear phase distributions
InactiveUS8354844B2Improve applicabilityEasy access to dataMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationData acquisition
A method for accelerating data acquisition in MRI with N-dimensional spatial encoding has a first method step in which a transverse magnetization within an imaged object volume is prepared having a non-linear phase distribution. Primary spatial encoding is thereby effected through application of switched magnetic fields. Two or more RF receivers are used to simultaneously record MR signals originating from the imaged object volume, wherein, for each RF receiver, an N-dimensional data matrix is recorded which is undersampled by a factor Ri per selected k-space direction. Data points belonging to a k-space matrix which were not recoded by a selected acquisition schema are reconstructed using a parallel imaging method, wherein reference information concerning receiver coil sensitivities is extracted from a phase-scrambled reconstruction of the undersampled data matrix. The method generates a high-resolution image free of artifacts in a time-efficient manner by improving data sampling efficiency and thereby reducing overall data acquisition time.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
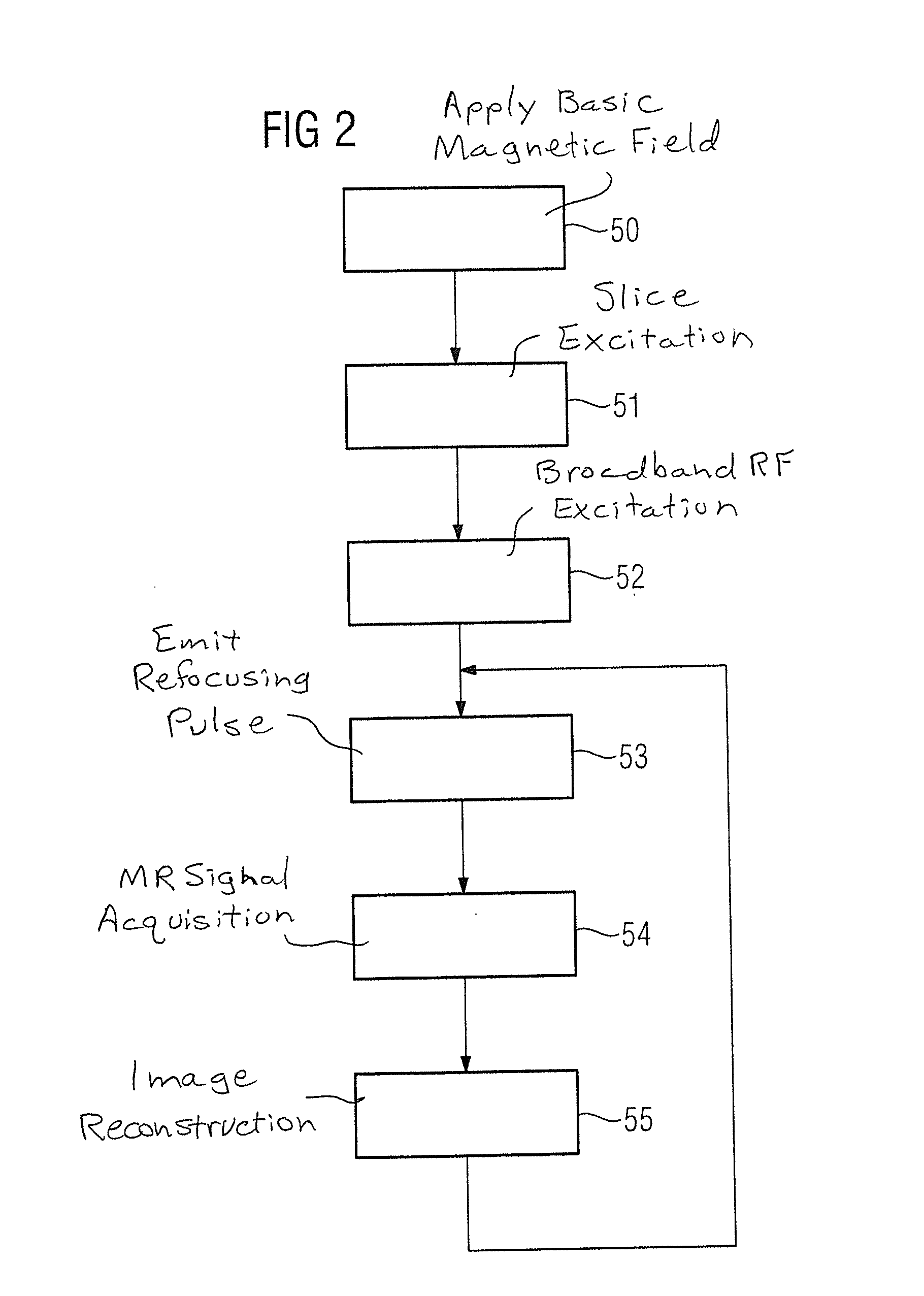
Method and magnetic resonance system to excite nuclear spins in a subject
InactiveUS20100013479A1Reduce background signalReduce the impactMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationSpins
In a method and system to generate an excitation in an examination subject to acquire magnetic resonance signals from a region of the examination subject, basic magnetic field is generated, an adiabatic half-passage (AHP) pulse is radiated to generate a transverse magnetization in the subject, and at least one first and one second adiabatic full-passage (AFP) pulse is radiated to generate a slice-selective rephasing of the transverse magnetization. The time interval between the first adiabatic half-passage pulse and the first adiabatic full-passage pulse is at least 37 ms, and the time interval between the first adiabatic full-passage pulse and the second adiabatic full-passage pulse is at least 75 ms.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
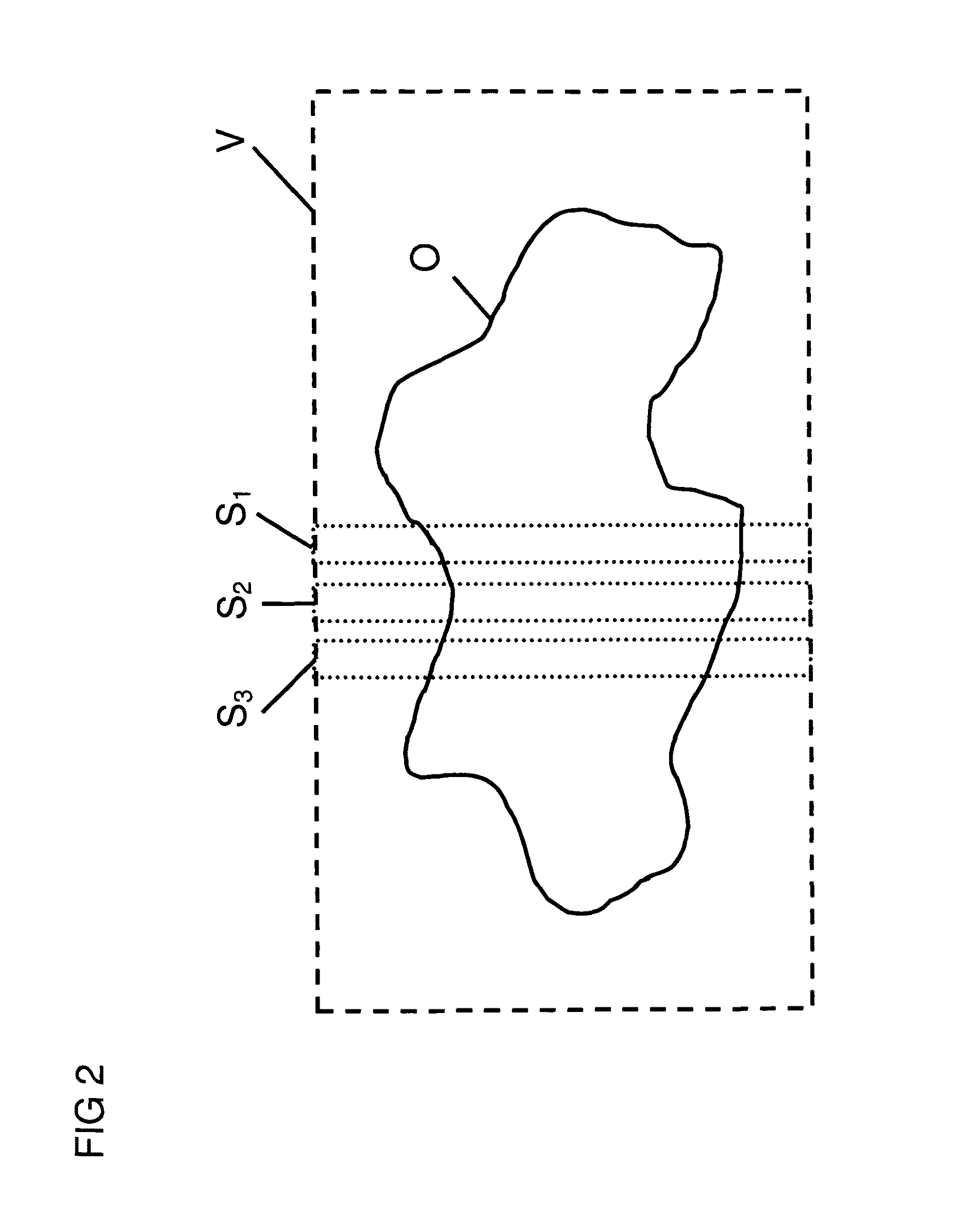
Method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals with use of local spatially encoding magnetic fields
InactiveUS7843195B2Reduce field of viewReduced measurement timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationExcitation pattern
A method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance (MR) signals from an imaging region has a preparatory step in which an encoding scheme with I phase encoding steps is defined, for each phase encoding step according to the phase encoding scheme, an excitation pattern of the transverse magnetization is defined and RF pulses to be irradiated to implement this pattern are calculated, wherein the same phase is defined at all spatial locations of the imaging region within an MSEM region and, in the execution step, according to the spatial encoding scheme each encoding step is performed I times according to the phase encoding scheme, wherein selection of the imaging region, amplitude modulation, and phase encoding are performed with the calculated RF pulses during excitation of the nuclear spin. This results in unique determination of the spatial distribution of the magnetic resonance signals with a simple RF receiver configuration using local gradient systems.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus with simultaneous image acquisition of multiple sub-volumes with synchronous acquisition of navigators
ActiveUS20170146631A1Improved movement correctionReduce decreaseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceTransverse magnetization
In a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and a method for generating magnetic resonance image data of a field of view of an examination object, magnetic resonance raw data are acquired by preferably different transverse magnetizations being excited in at least one sub-volume of a navigator volume and at least one sub-volume of an image volume, and are used for position determination and for imaging. These preferably different transverse magnetizations are simultaneously present in at least one period of the scan.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20130088228A1Efficient gradientSmall gradientMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationResonance
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, a magnetization of nuclear spins in a subject is prepared in multiple preparation modules of an acquisition sequence. MR signals are acquired with at least one imaging module of the sequence. Spoiler gradient fields are generated in the multiple preparation modules in order to affect a transverse magnetization of the spins. The spoiler gradient fields that are applied in at least two different preparation modules are spatially varied along different directions. Spoiler gradient moments of the spoiler gradient fields are selected so that, for at least one of three orthogonal spatial directions, a weighted sum of the spoiler gradient moments that are applied along this spatial direction satisfies a threshold condition.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
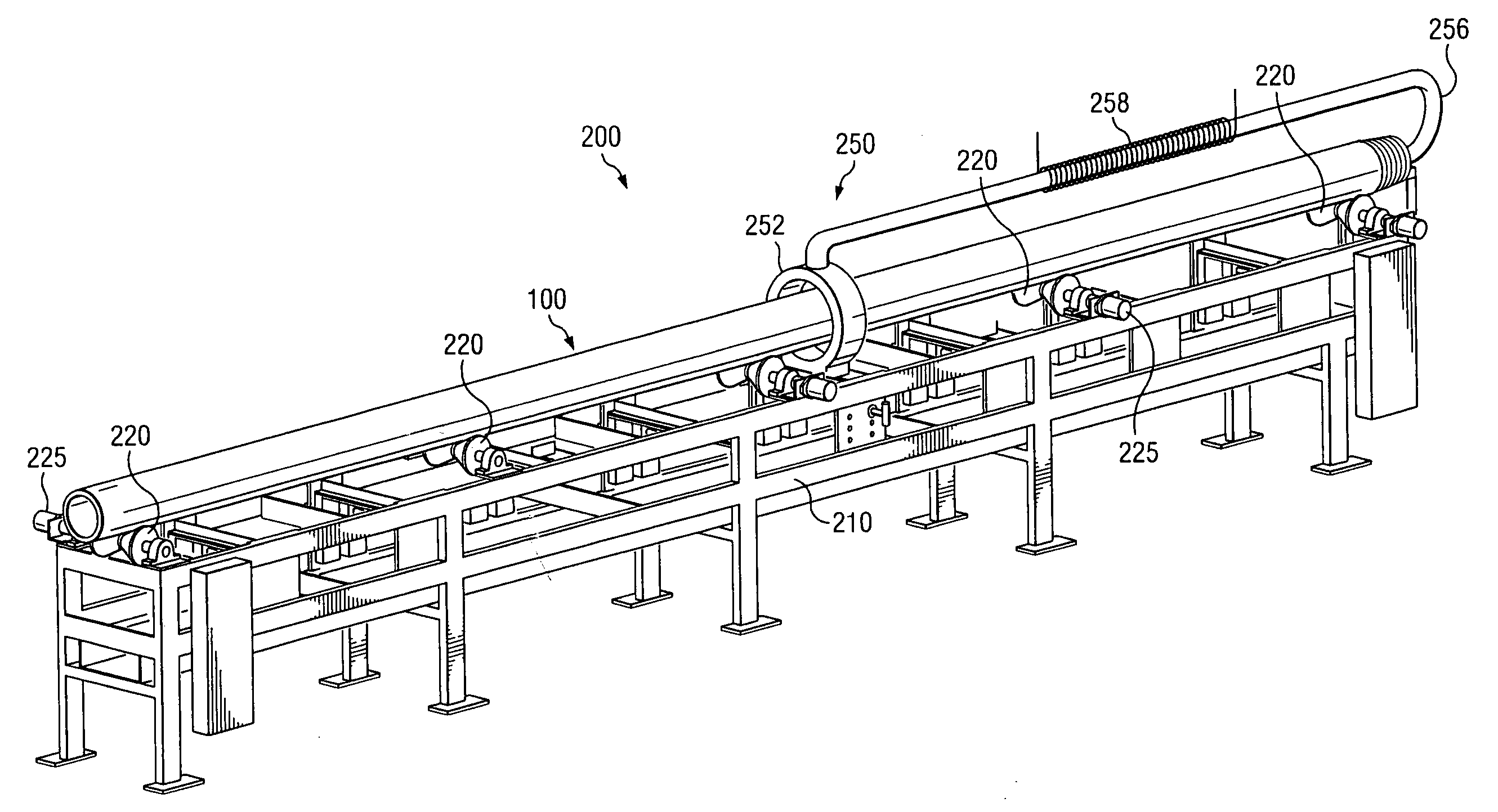
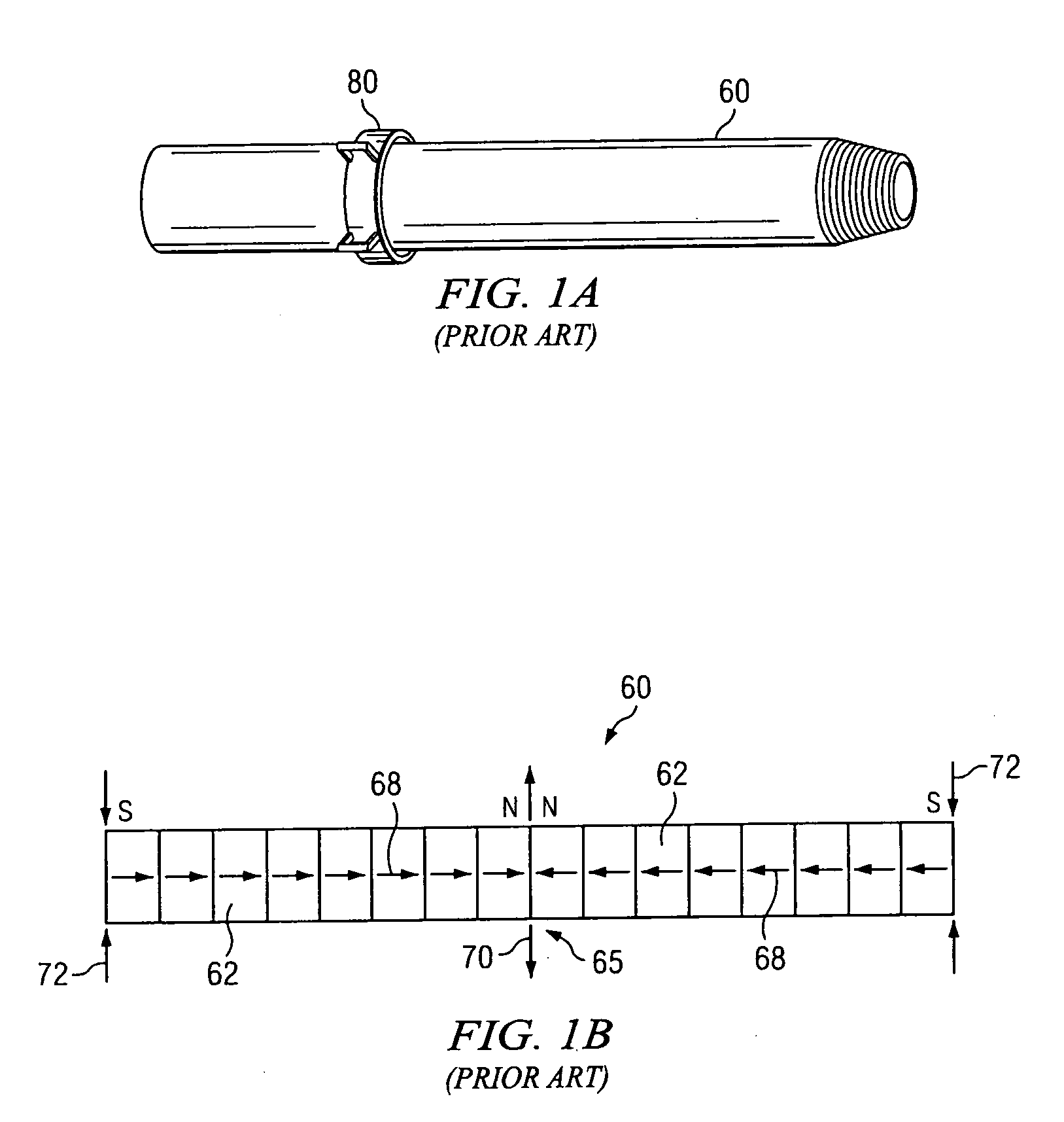
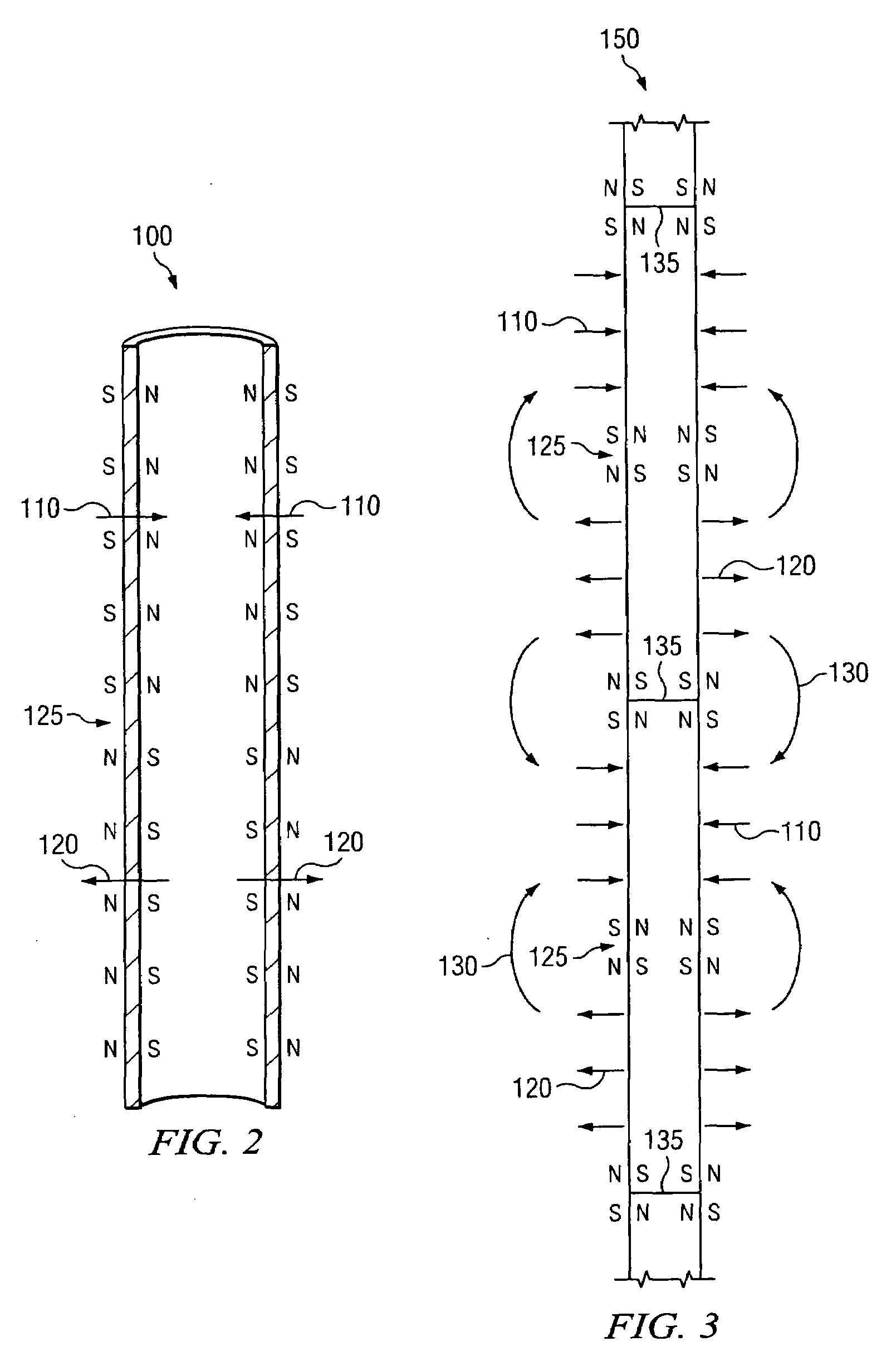
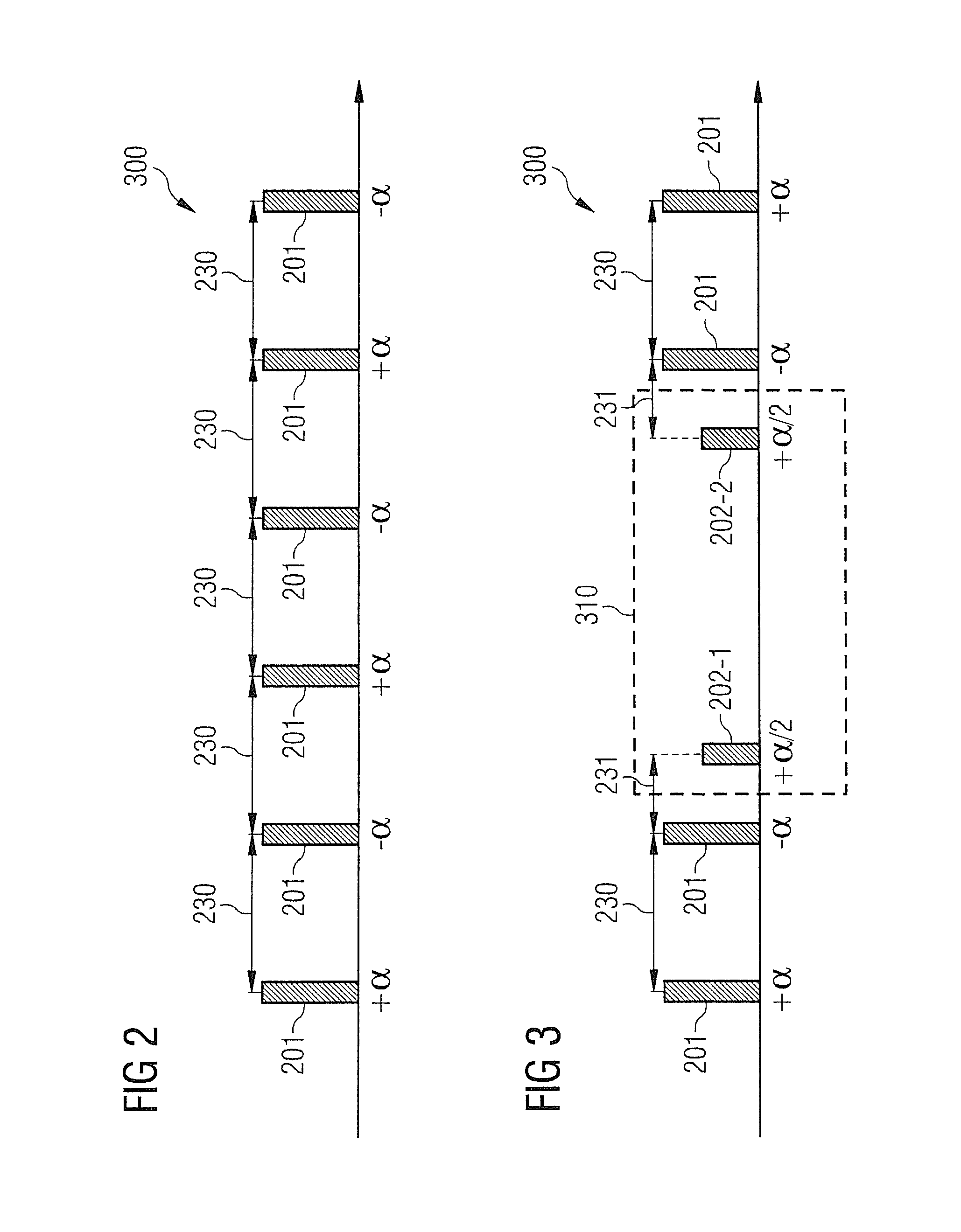
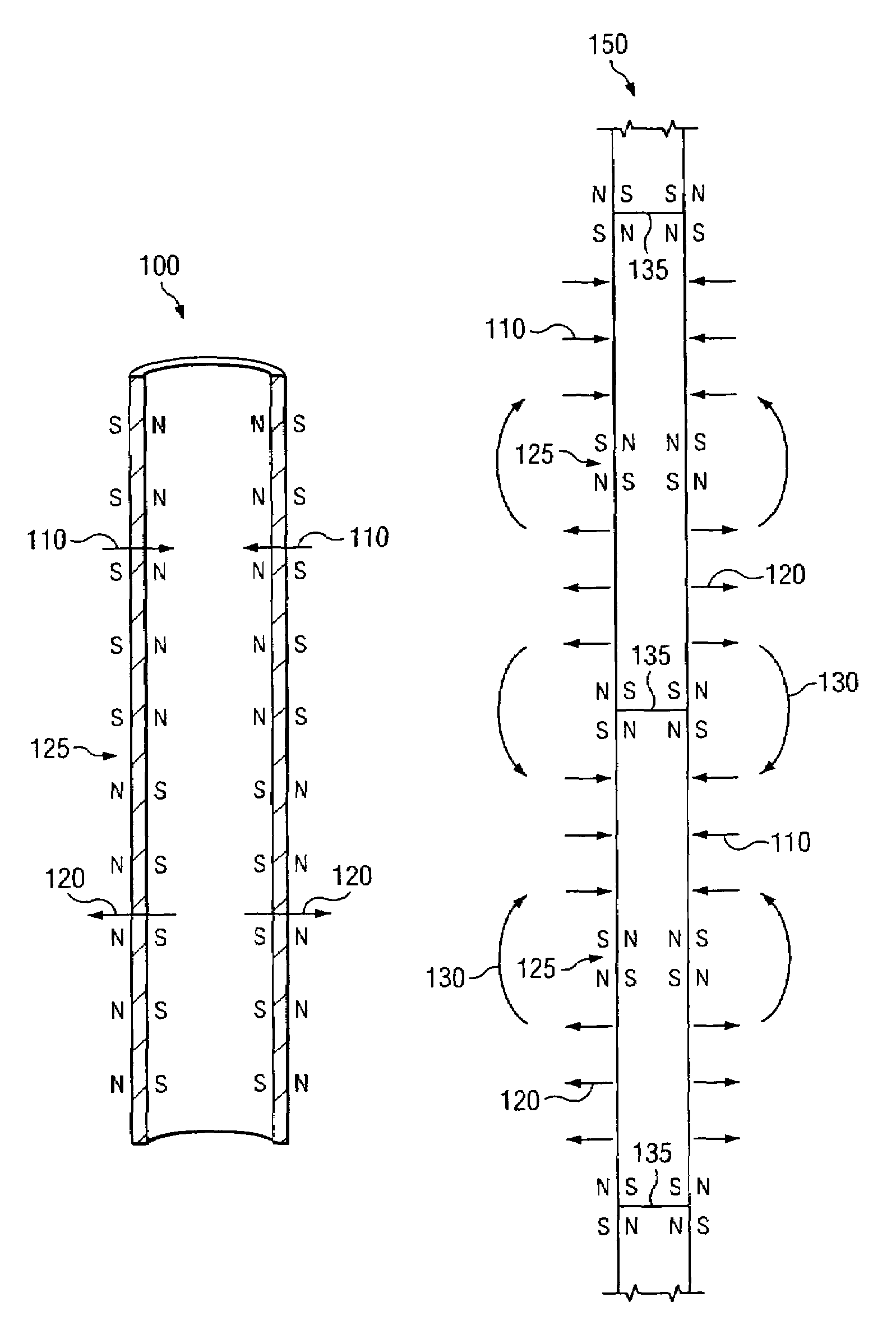
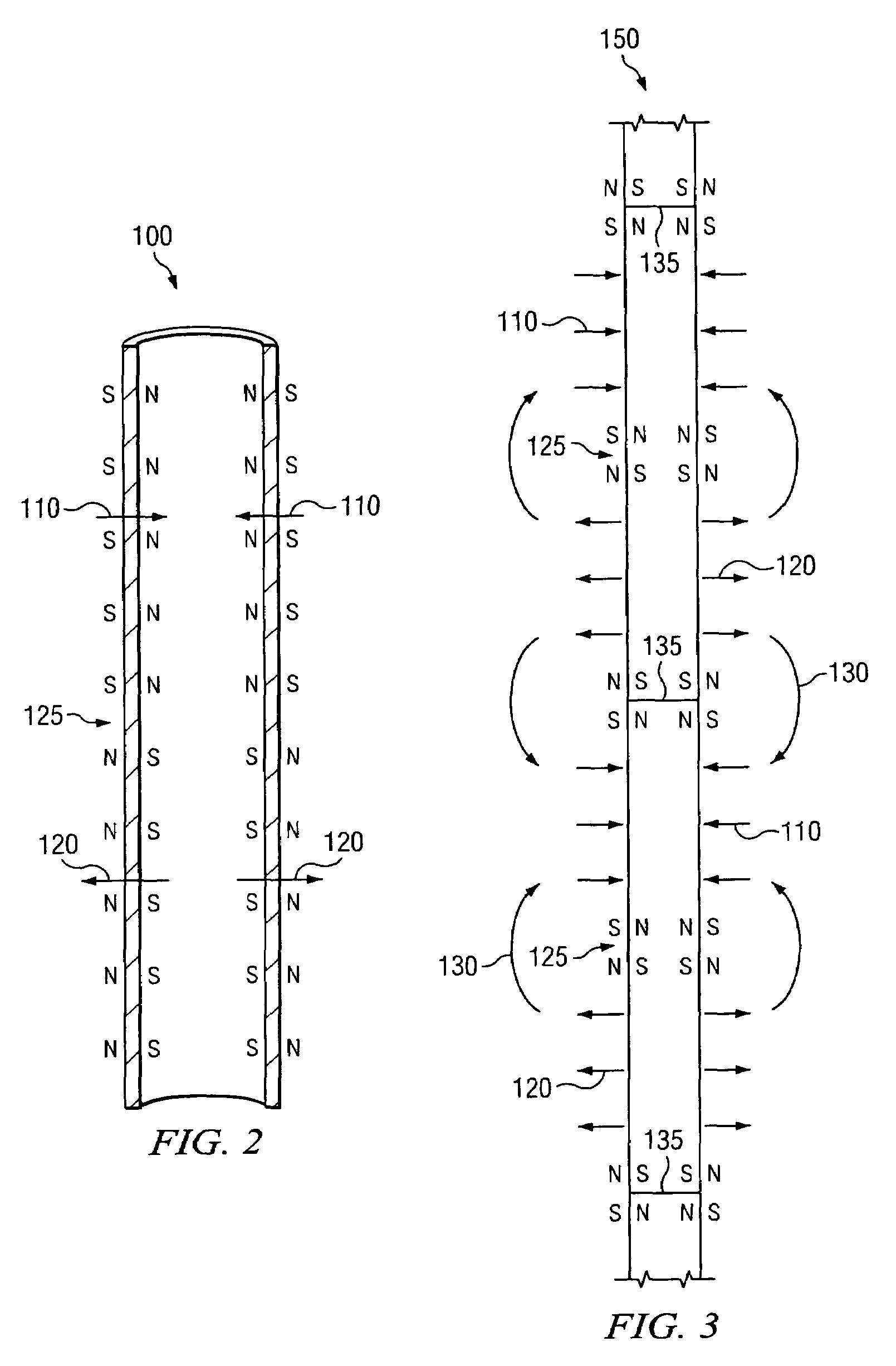
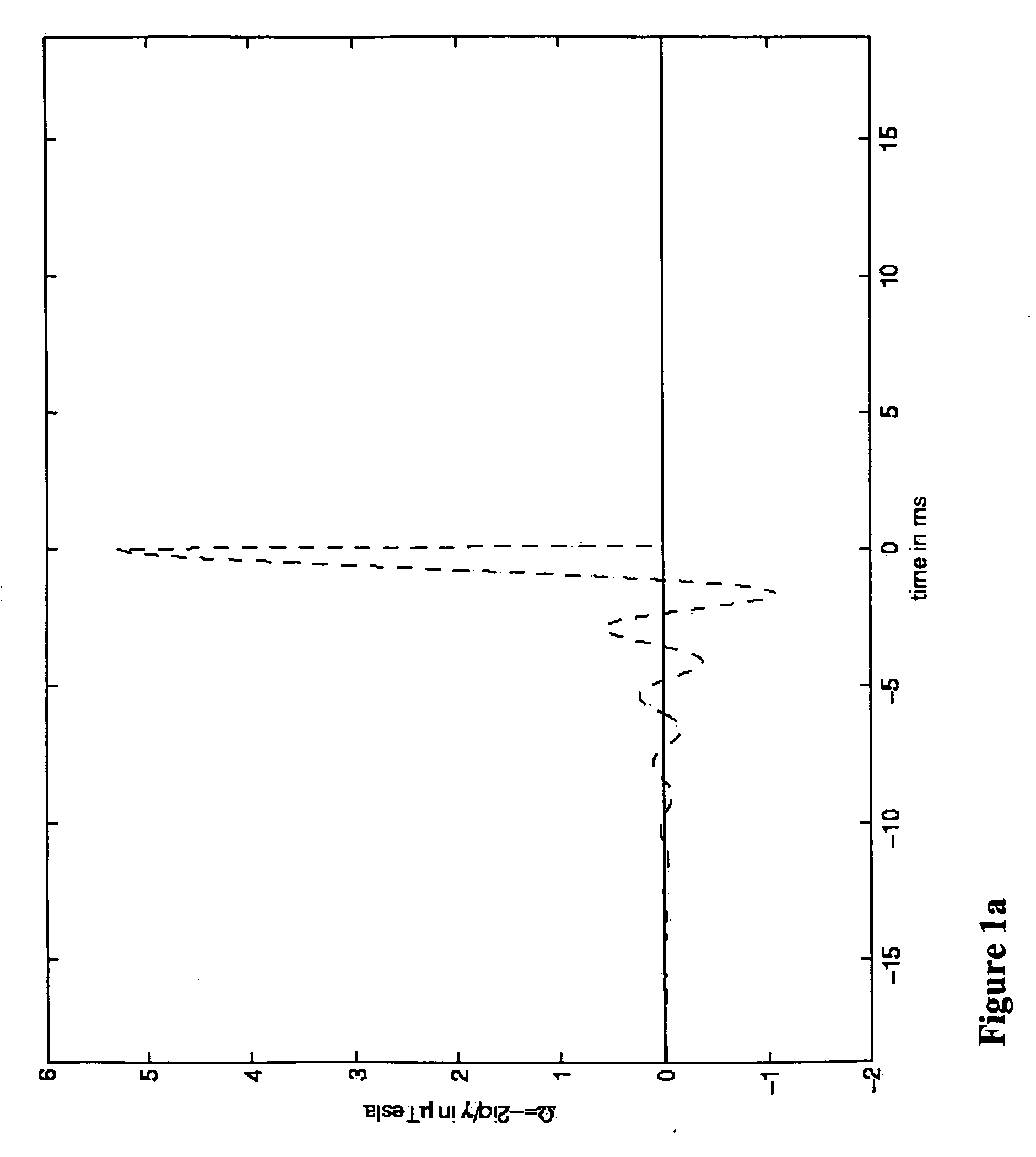
Transverse magnetization of casing string tubulars
InactiveUS20090173504A1Strong, highly uniform magnetic fieldAccurate distance measurementElectromagnets without armaturesDrilling rodsTransverse magnetizationCasing string
A method and apparatus for imparting a transverse magnetization to a wellbore tubular is disclosed. In certain exemplary embodiments, tubulars are magnetized to include at least one flux reversal (e.g., at the center of the tubular) at which the direction of the transverse field changes (i.e., from pointing radially inward to pointing radially outward). A plurality of such magnetized wellbore tubulars may be coupled together and lowered into a target well to form a magnetized section of a casing string. Exemplary embodiments of the invention may be utilized to impart a strong, highly uniform magnetic field about a string of wellbore tubulars, thereby providing for improved passive ranging and wellbore twinning.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
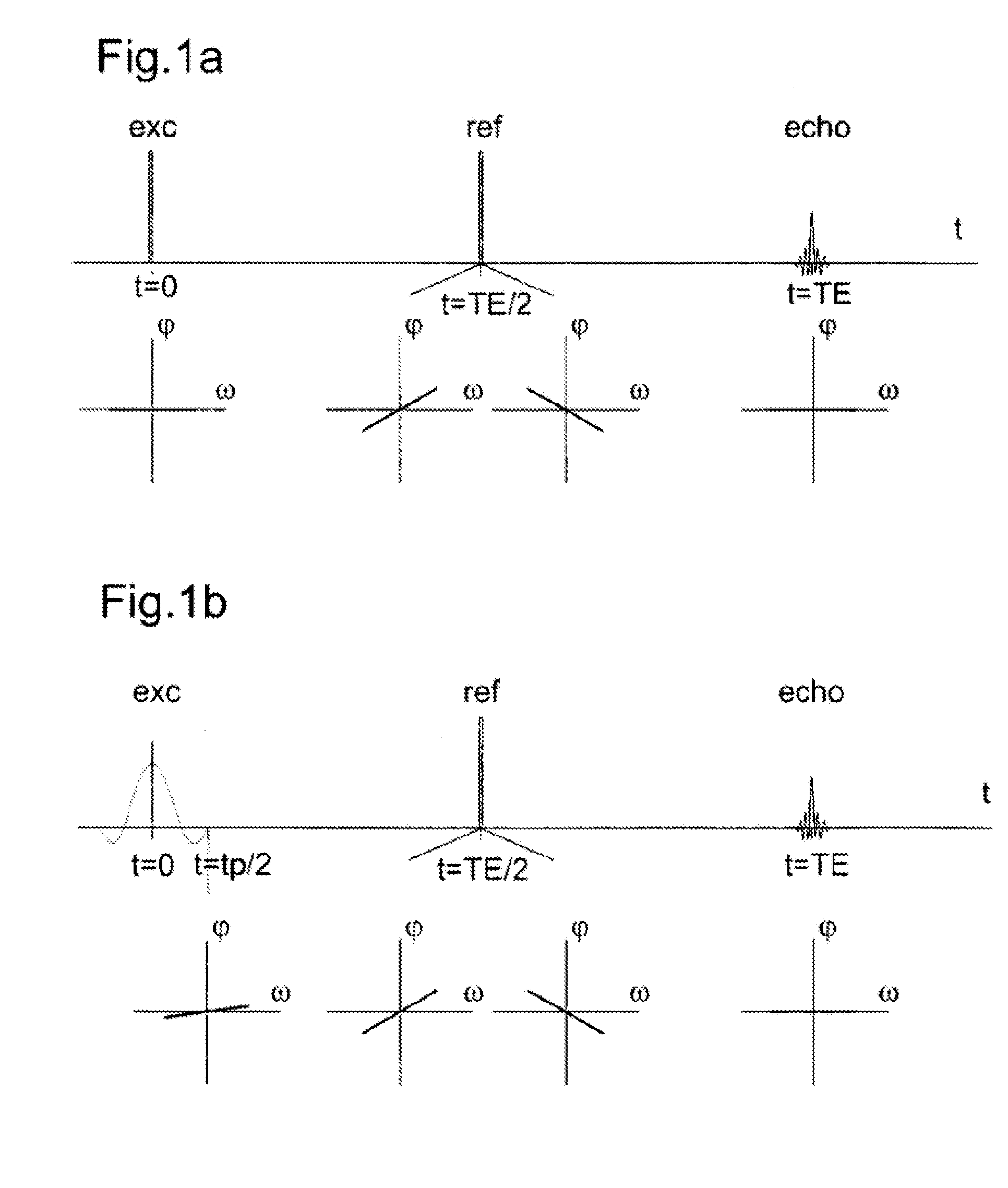
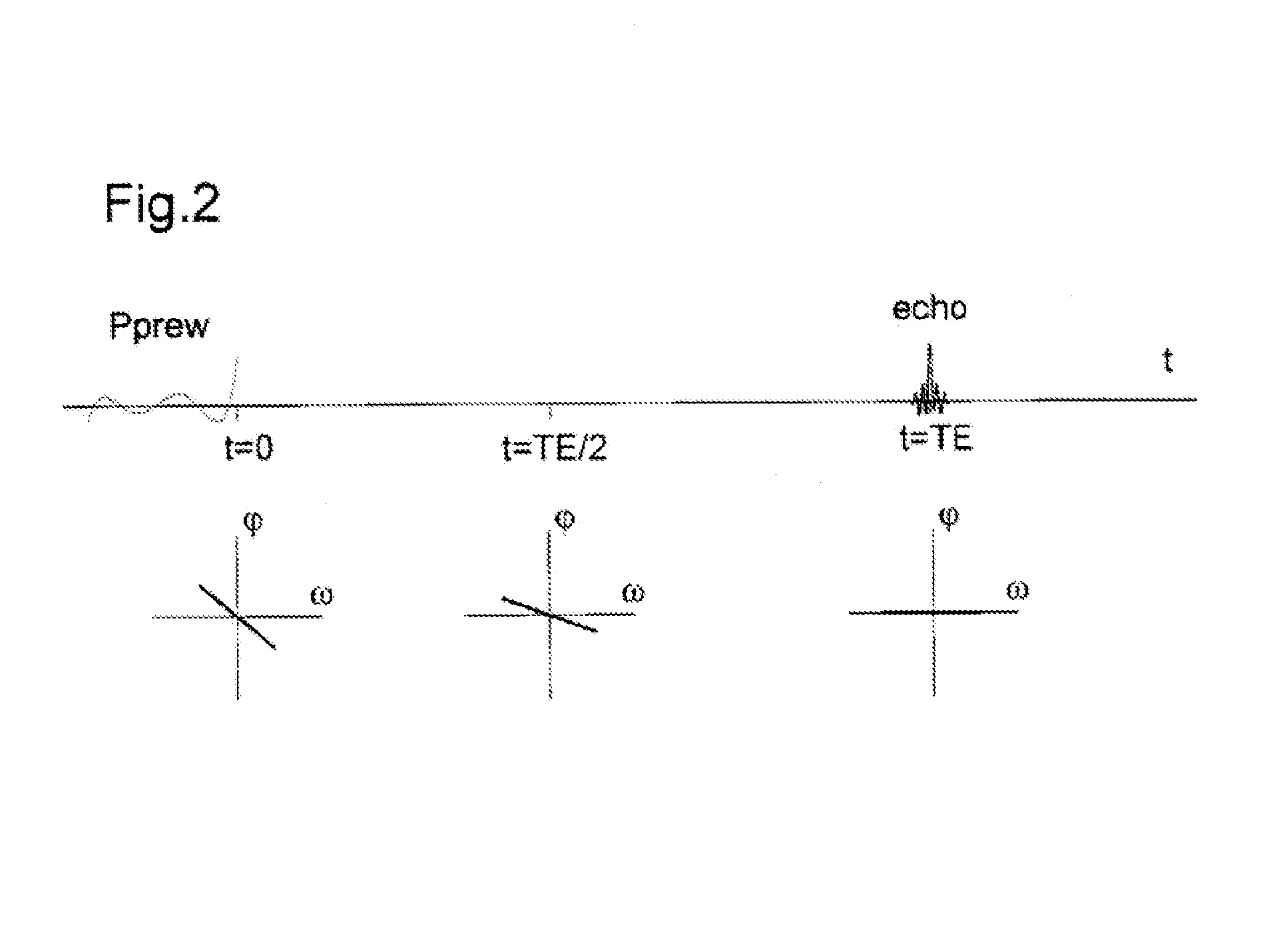
Method of magnetic resonance with excitation by a prewinding pulse
InactiveUS20150323631A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceTransverse magnetization
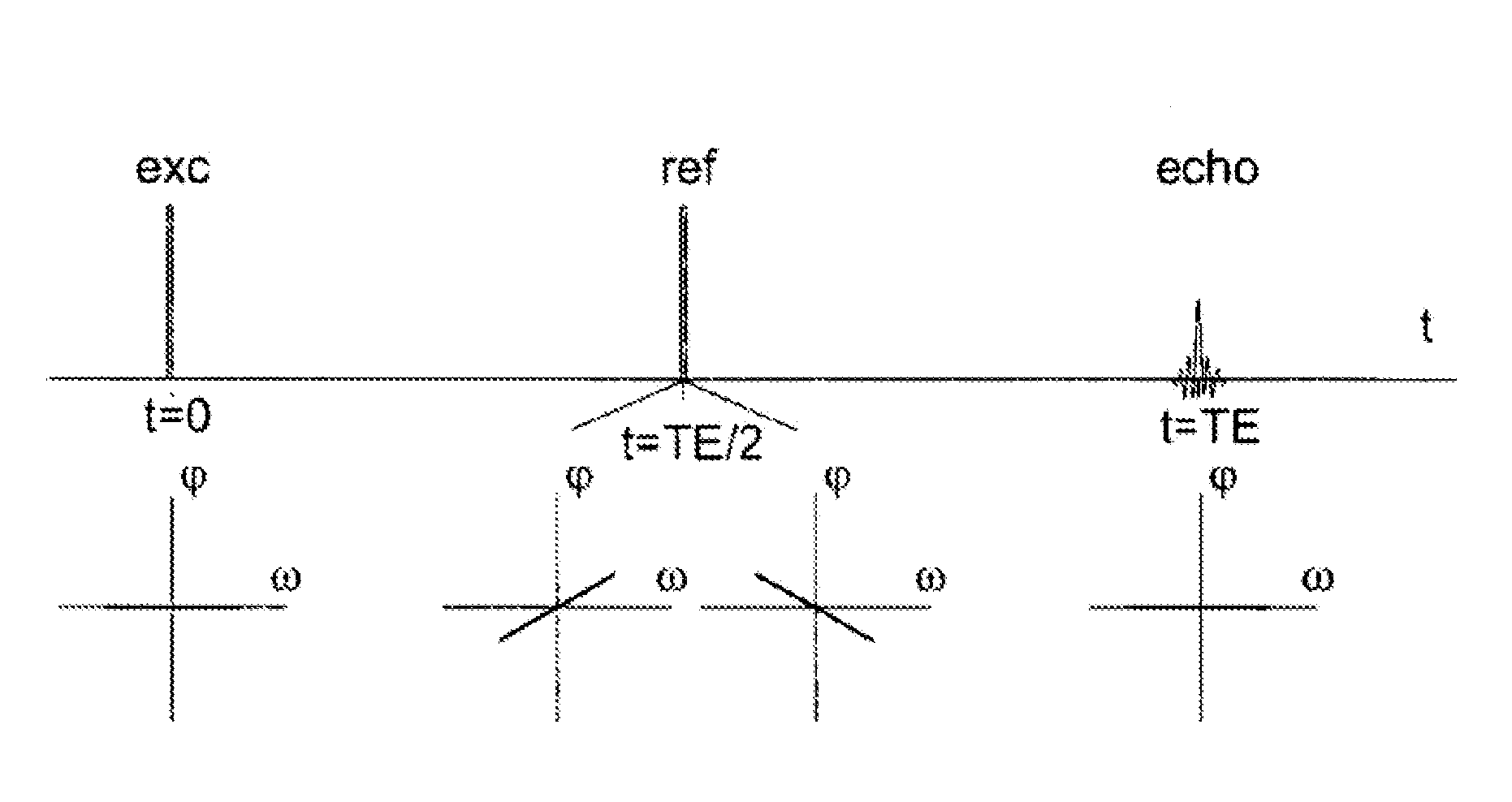
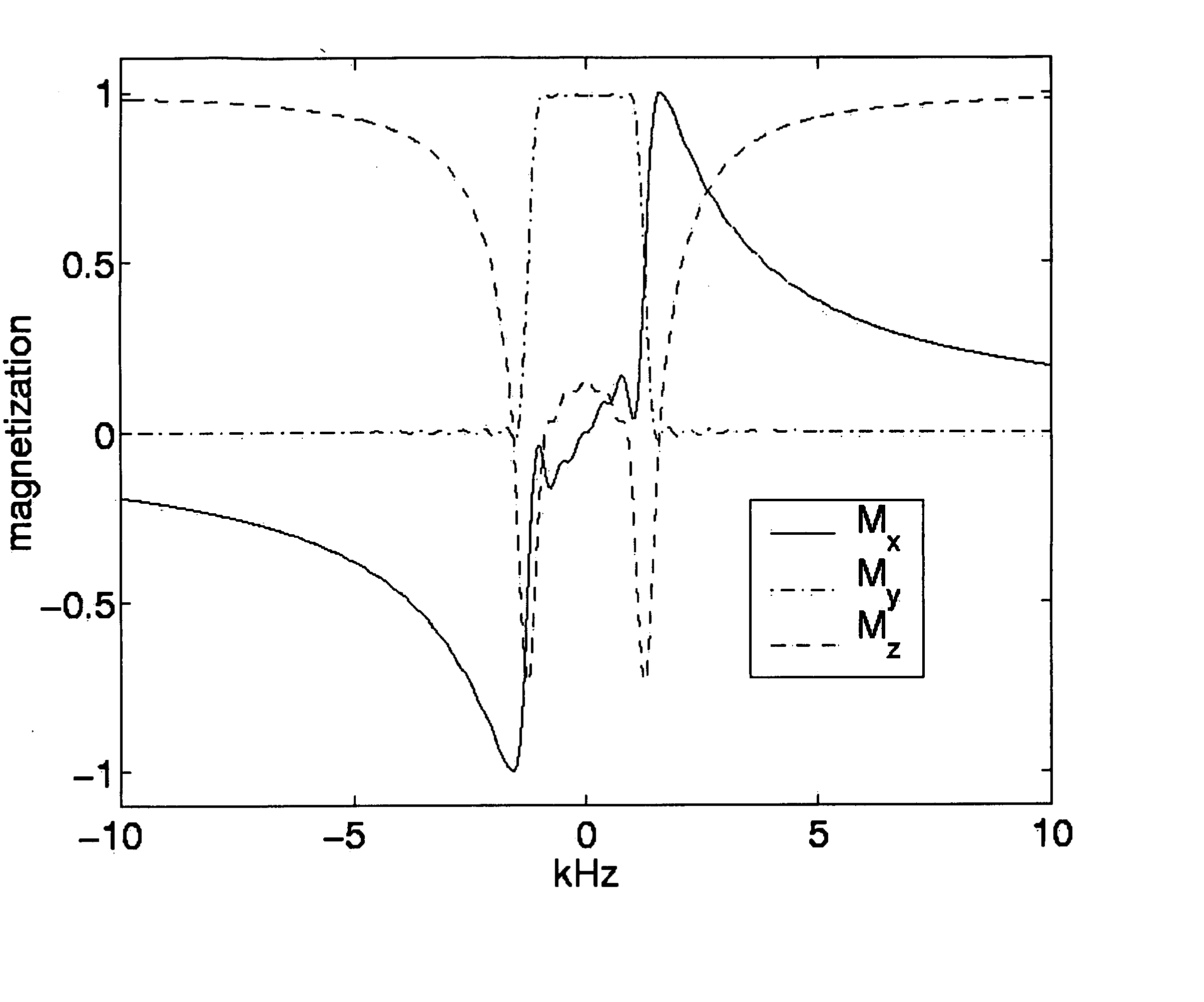
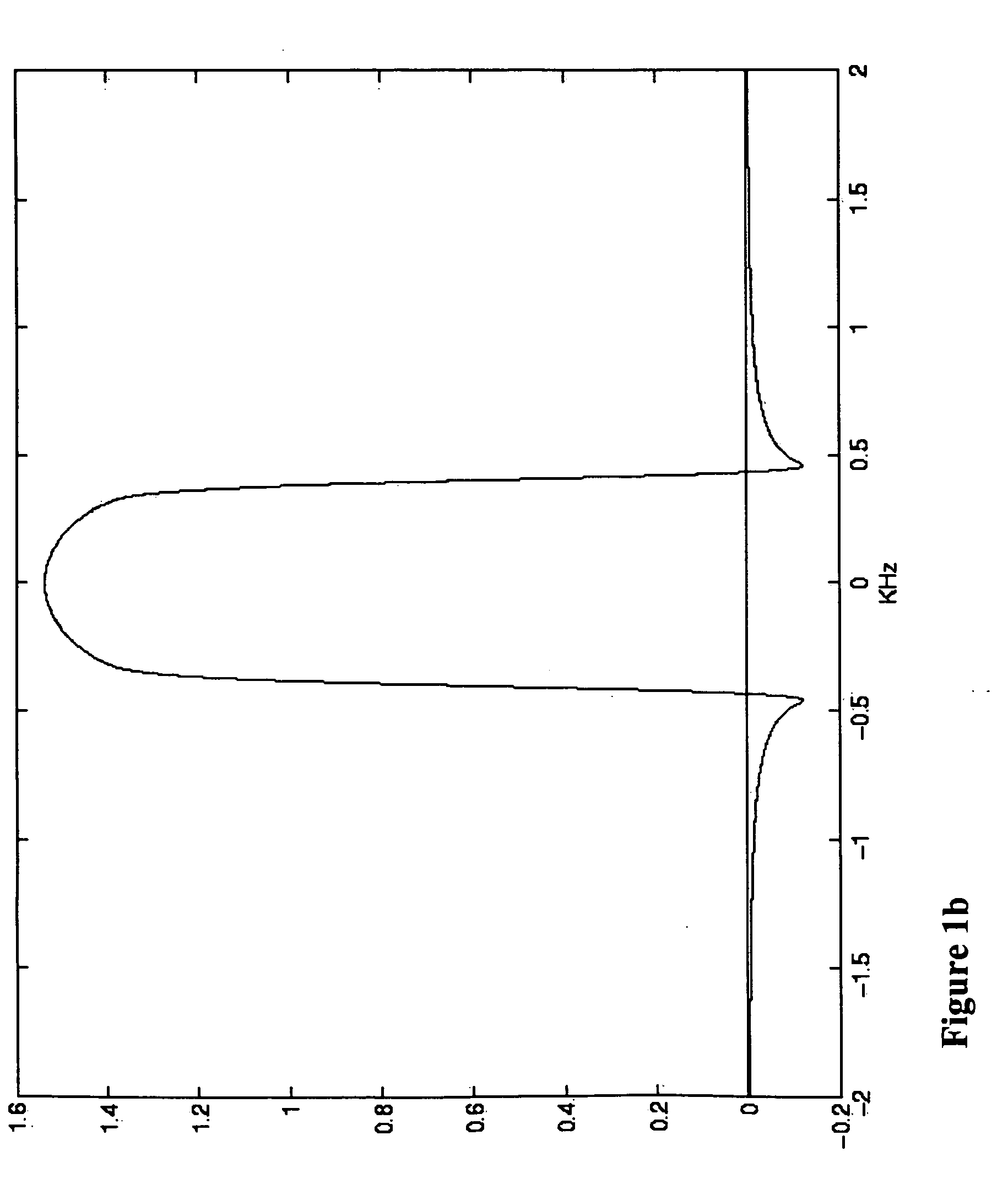
A method of magnetic resonance, in which a sample introduced in a measurement volume in an external magnetic field is excited by an excitation pulse and the signal formed by the transverse magnetization thus produced is read out by a receiving coil. The method is characterized in that a prewinding pulse is used as the excitation pulse, which prewinding pulse is characterized in that the formed transverse magnetization M⊥(ω) of spins of different Larmor frequency ω after the pulse has a phase φ0(ω), wherein φ0(ω) as a function of ω within a predefined frequency range Δω has an approximately linear course having negative slope, such that the spins refocus after an echo time defined by the pulse without an additional refocusing pulse being necessary.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
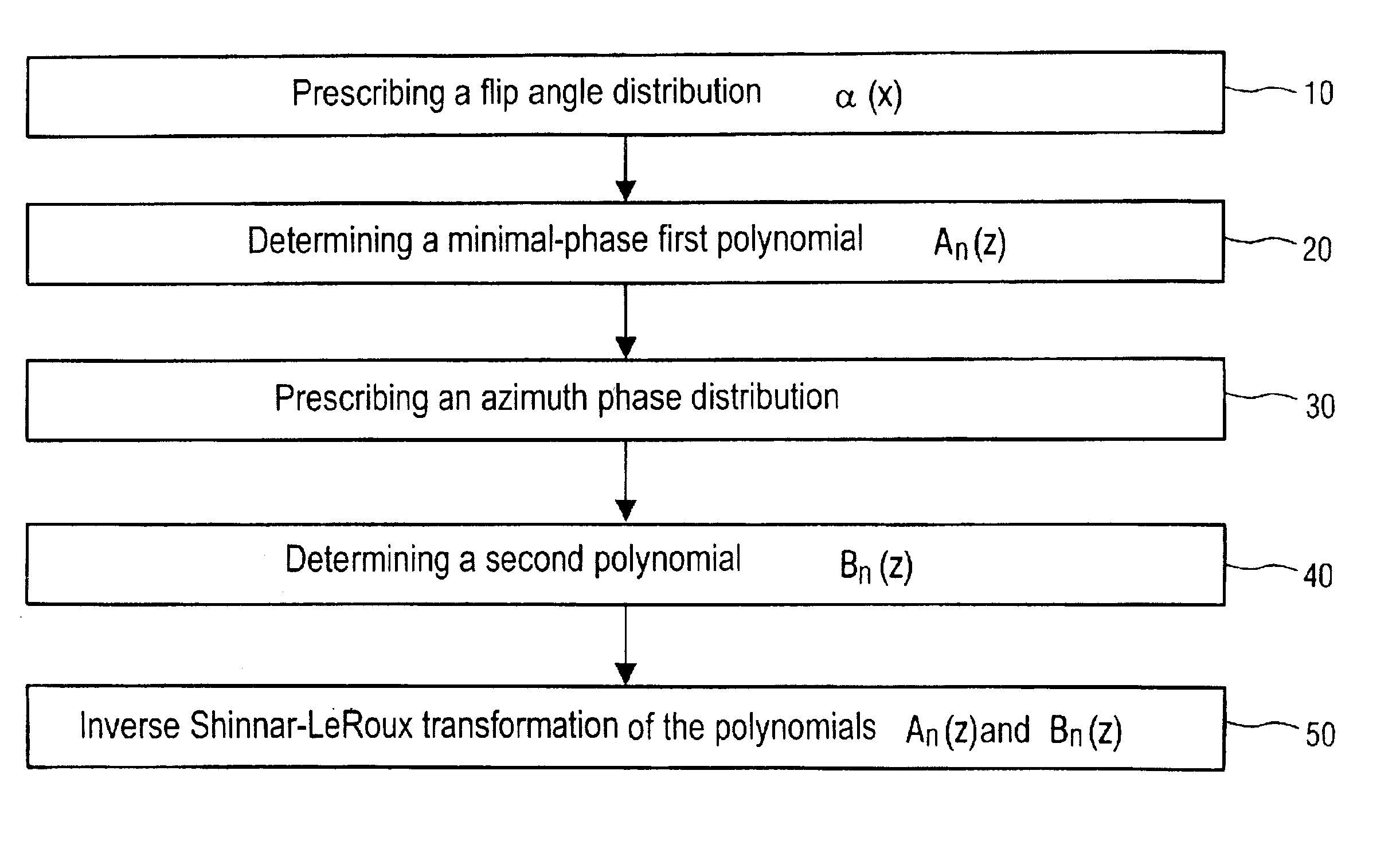
Method for designing a selective RF pulse for use in a magnetic resonance apparatus
InactiveUS6853192B2Reduced dynamic rangeMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceTransverse magnetization
In a method for designing a selective RF pulse for a magnetic resonance apparatus, based on a determination of a first polynomial (An(z)) and a second polynomial (Bn(z)) that are Shinnar-LeRoux transforms of the RF pulse, a flip angle distribution (α(x)) to be achieved with the RF pulse is prescribed, the first polynomial (An(z)) is determined proceeding from the flip angle distribution (α(x)), the phase distribution of the transverse magnetization to be achieved with the RF pulse is prescribed, and the second polynomial (Bn(z)) is determined such that the magnitude is determined by the flip angle distribution (α(x)) and the phase thereof corresponds to a sum of the prescribed phase distribution and the phase of the, first polynomial (An(z)).
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
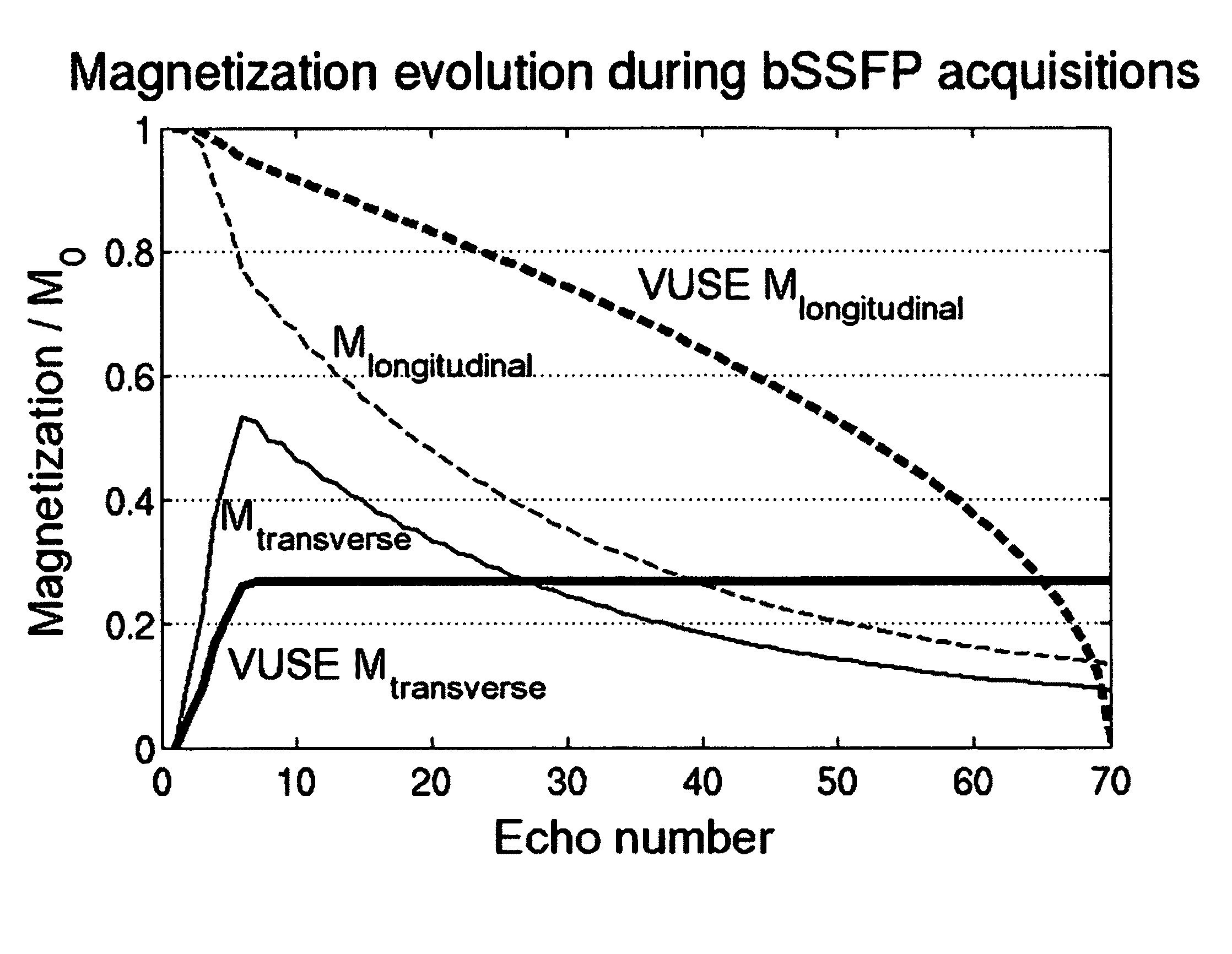
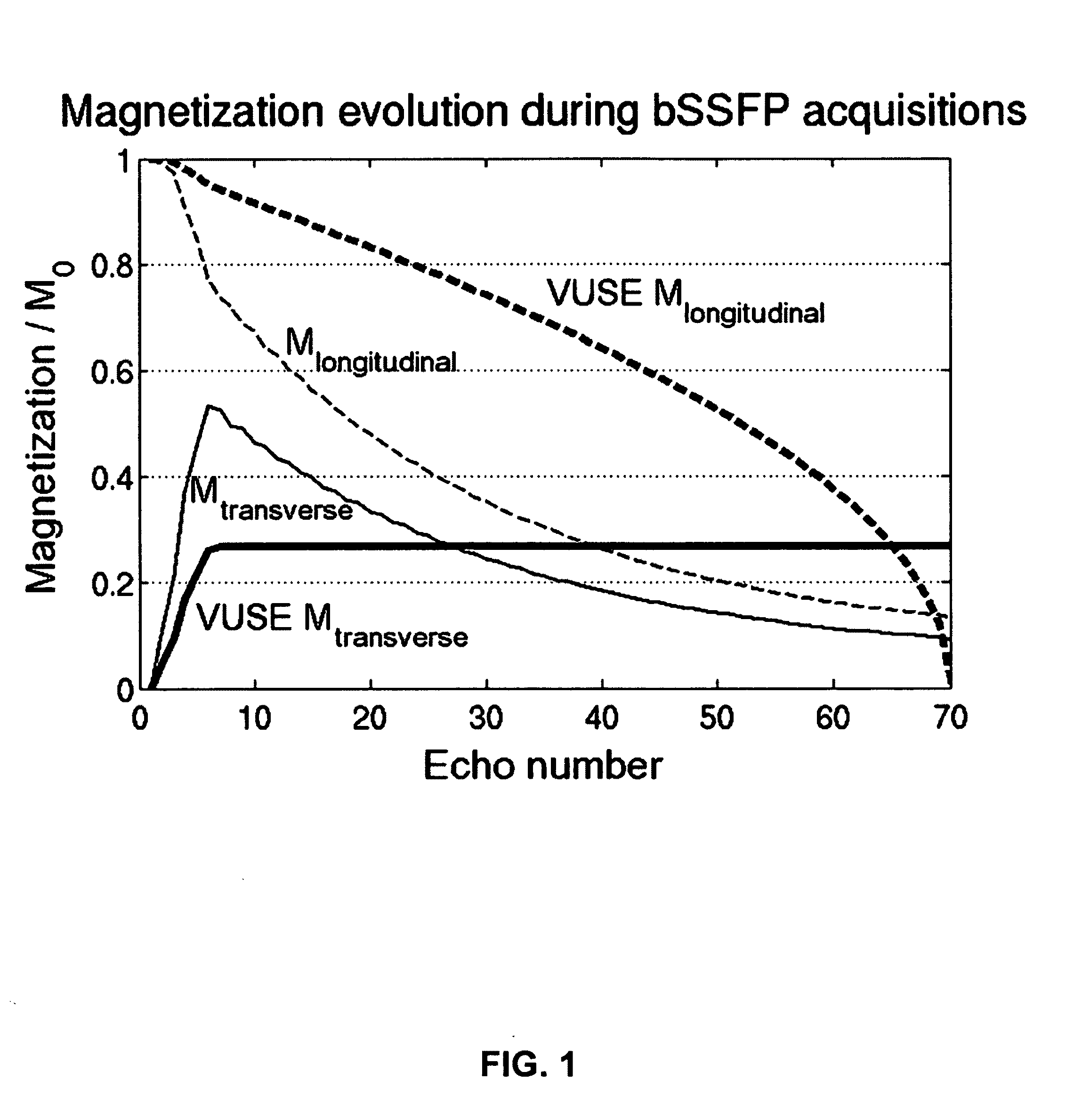
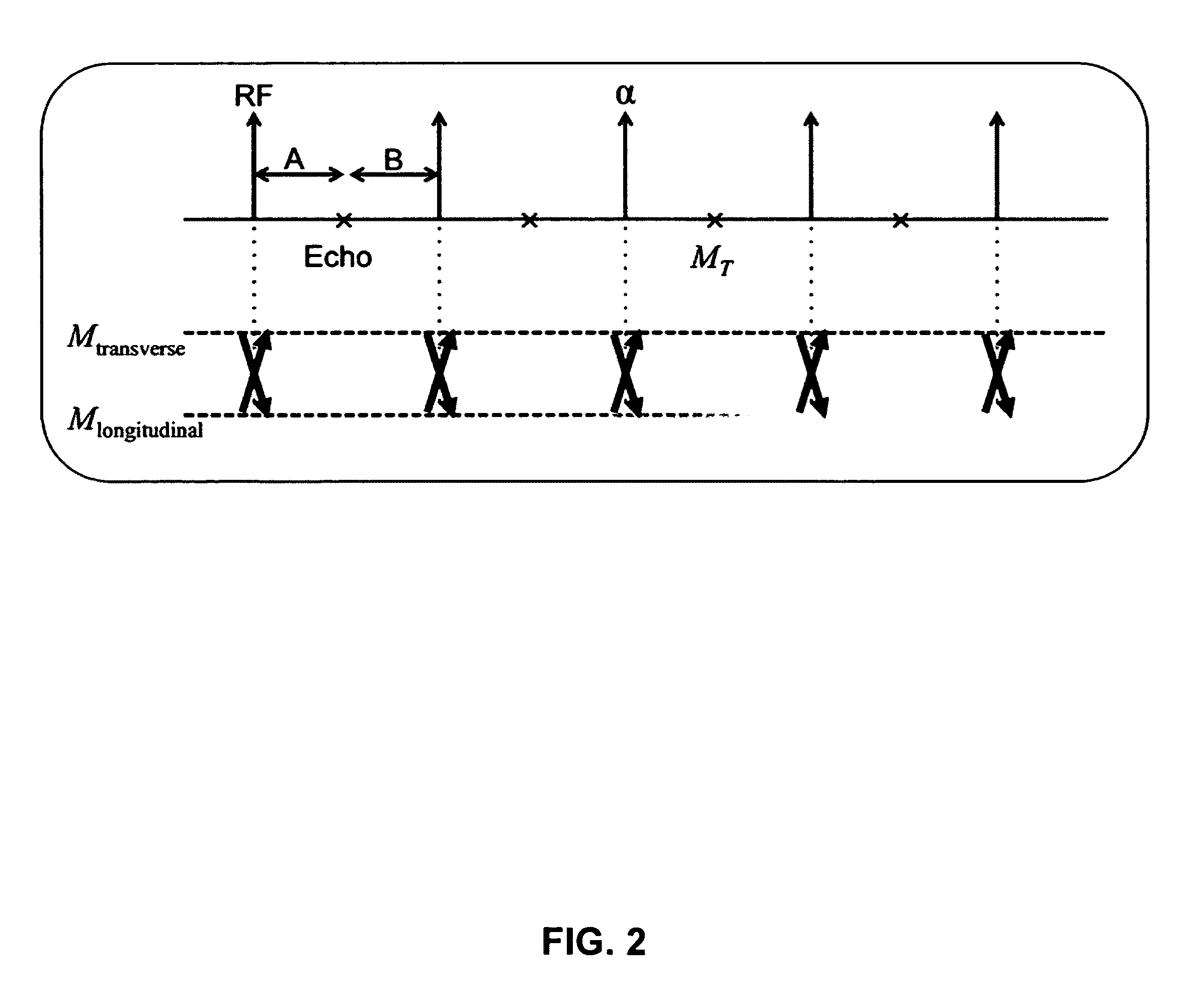
Balanced steady-state free-precession transient imaging using variable flip angles for a predefined signal profile
ActiveUS20110210732A1Enhanced signalImprove overall utilizationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationBloch equations
A magnetic resonance imaging system or method is provided including a balanced steady-state free-precession transient imaging (transient bSSFP) device capable of increasing the overall signal during transient bSSFP acquisition by fully or better utilization of the magnetization through variable RF flip angles. The transient bSSFP device is capable of generating a series of echoes with a desired transverse magnetization profile MT. It is further capable of generating RF pulses each having a distinct RF flip angle for each of the echoes in the series of echoes. The transient bSSFP device is coupled to a computer capable of calculating the distinct RF flip angle for the nth echo in the series of echoes. The computer calculation utilizes a program encoding an analytical inversion of the Bloch equation. Once the RF flip angle is calculated, it is used by the transient bSSFP device in the generation of the nth echo.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
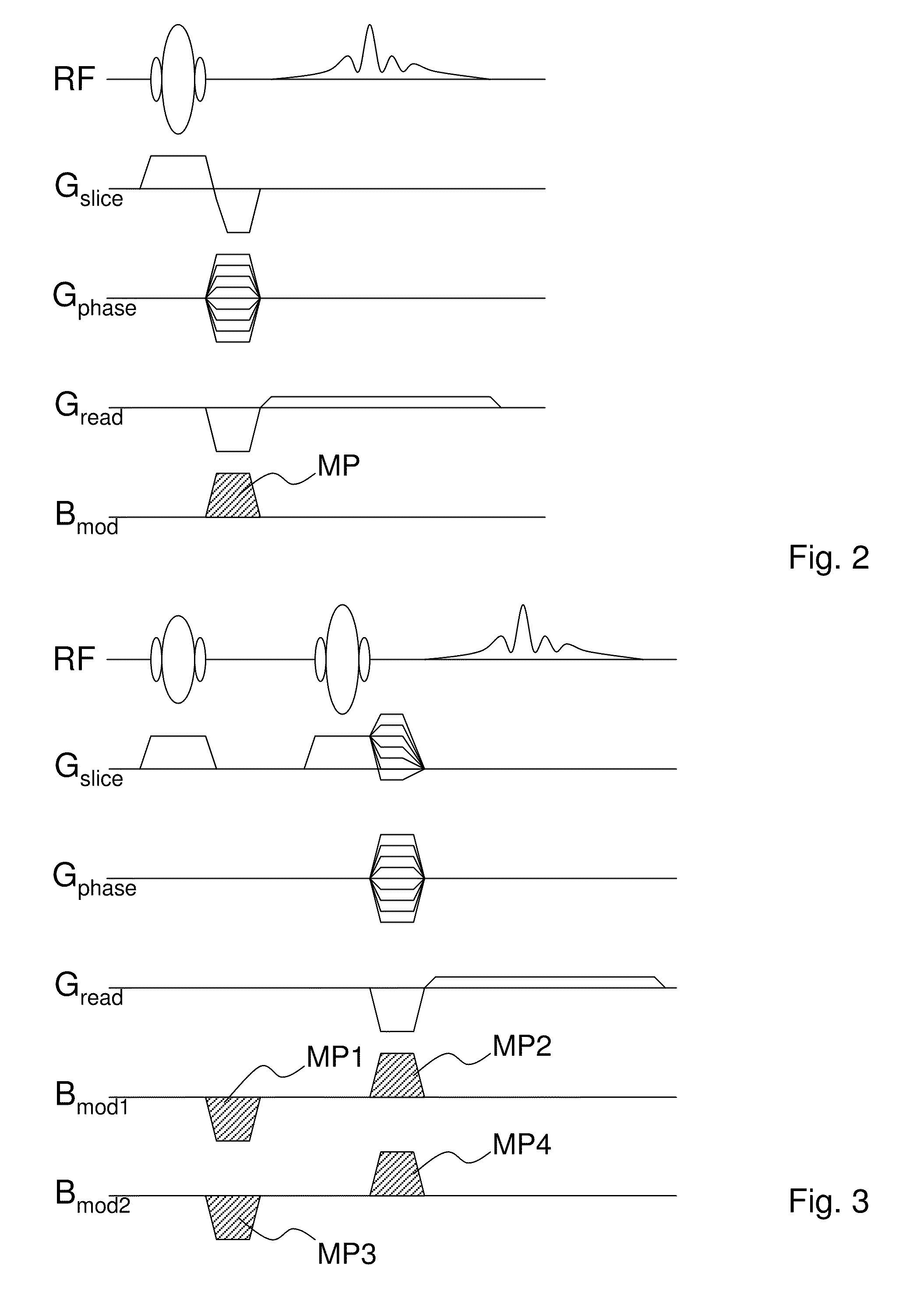
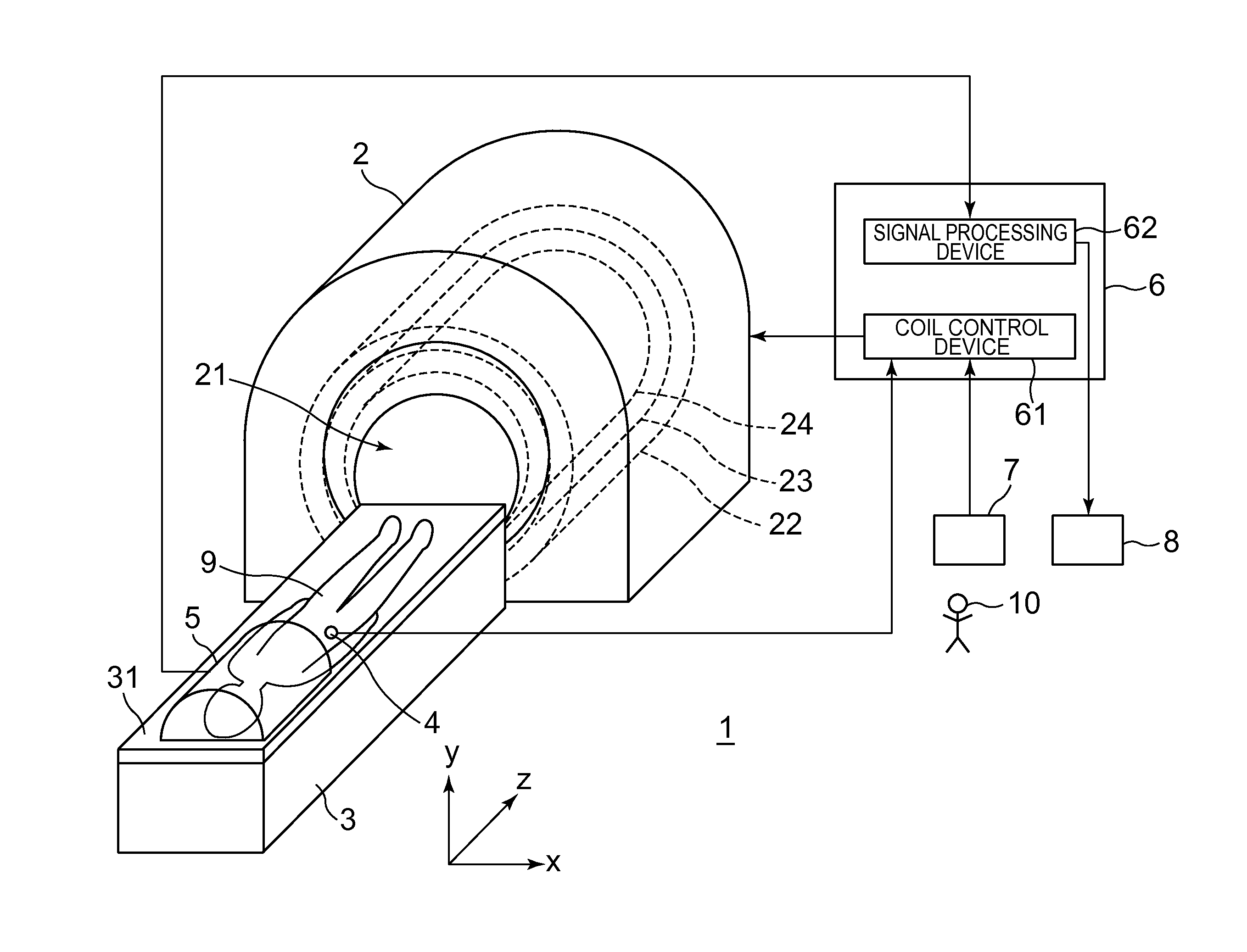
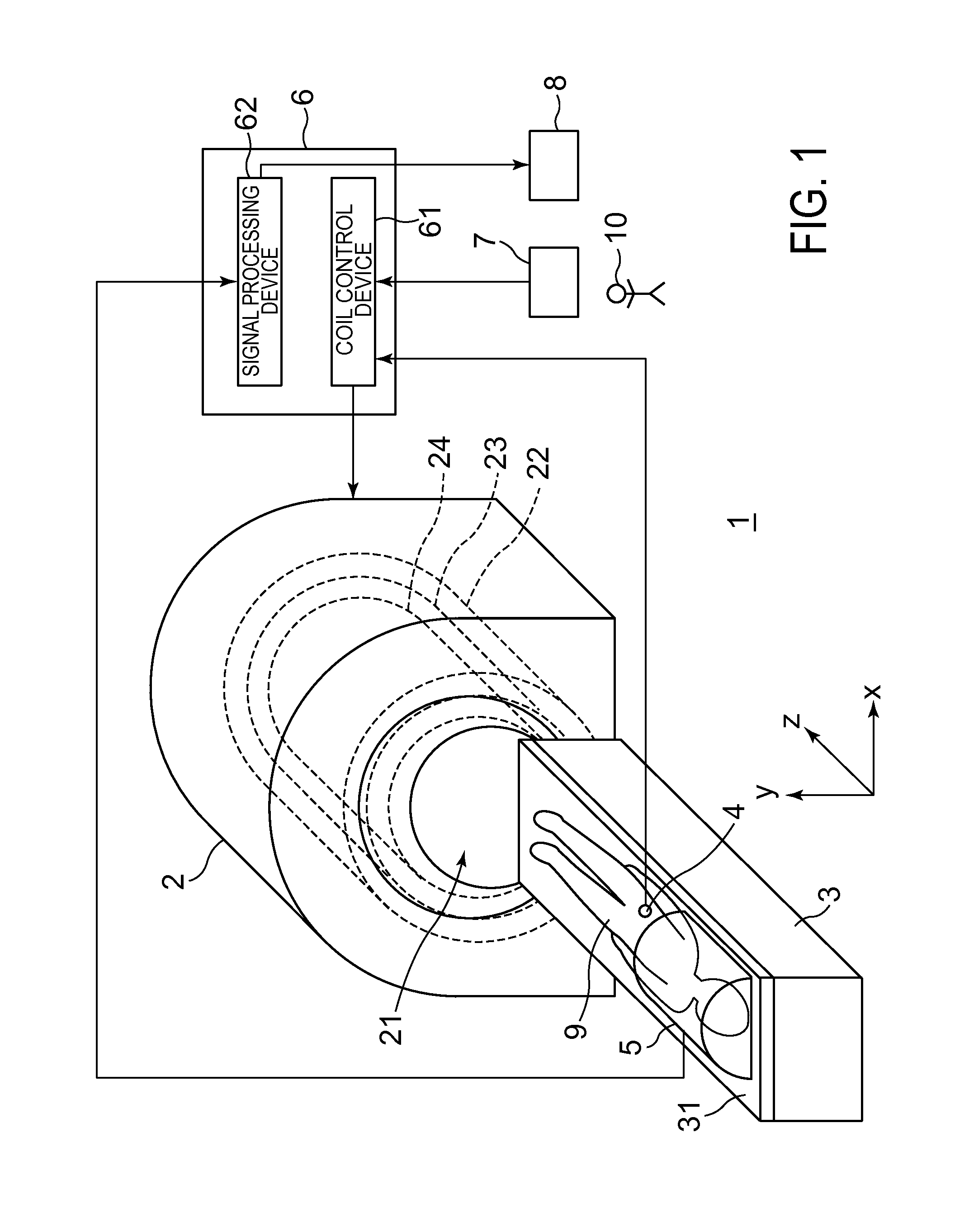
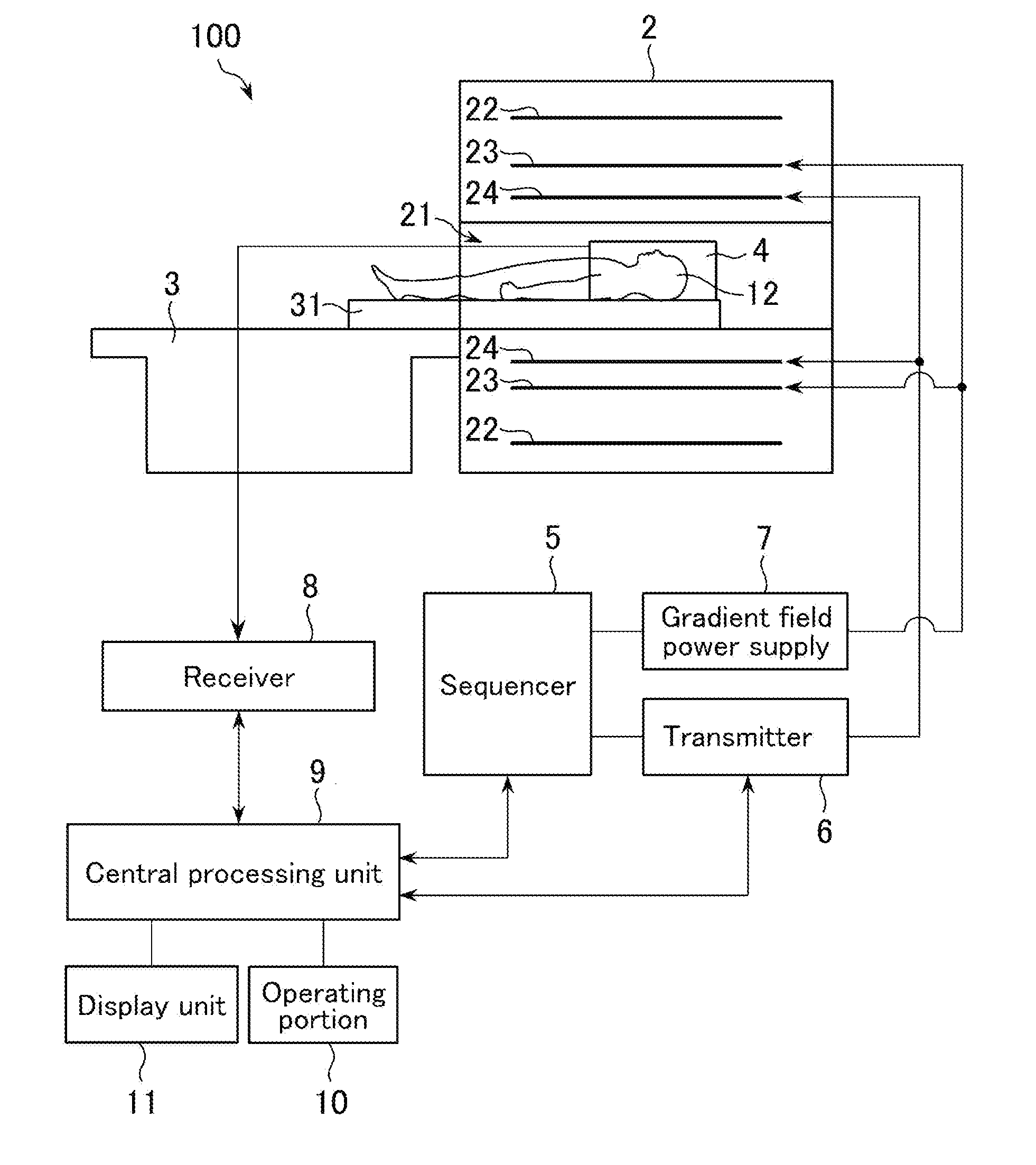
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
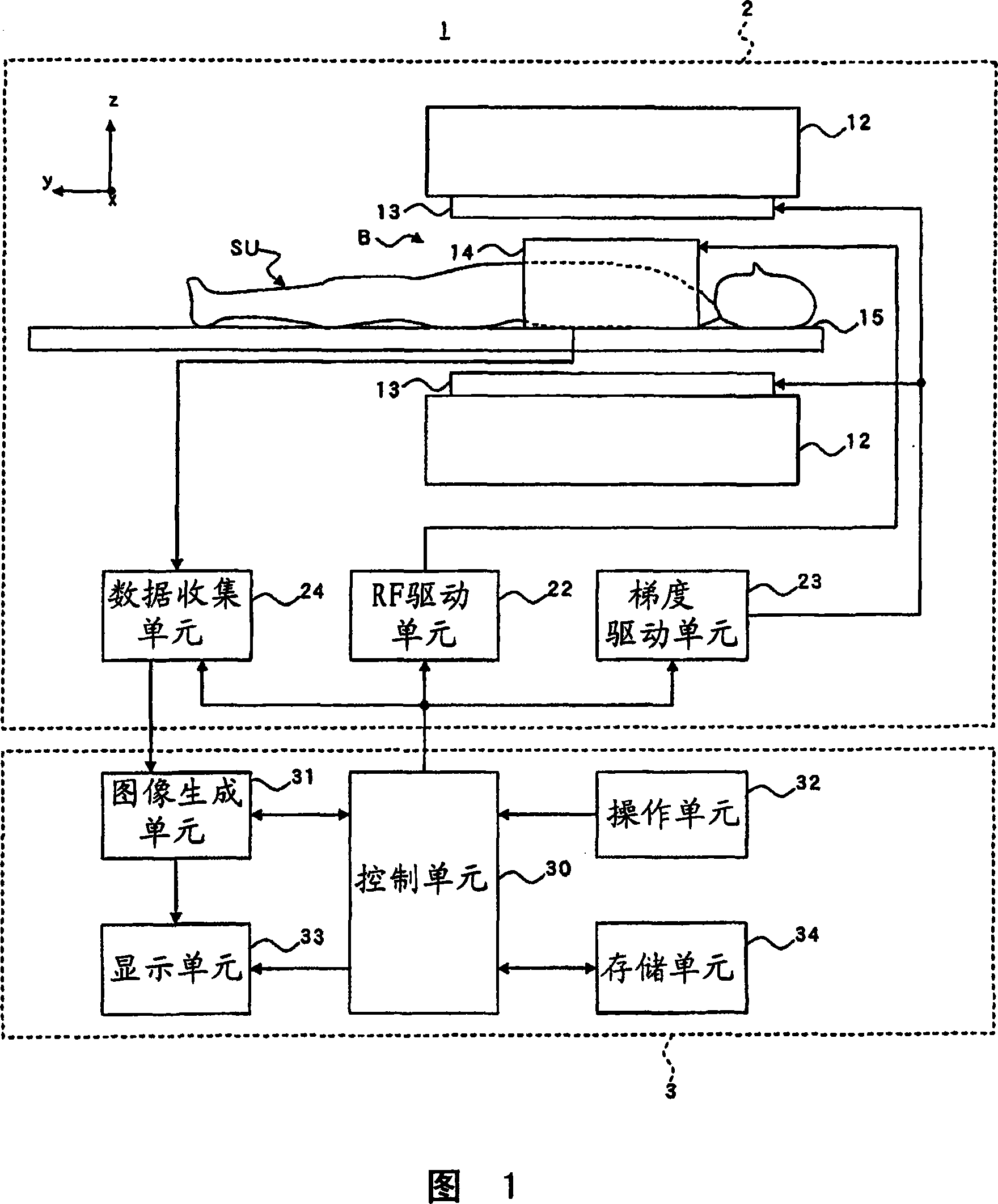
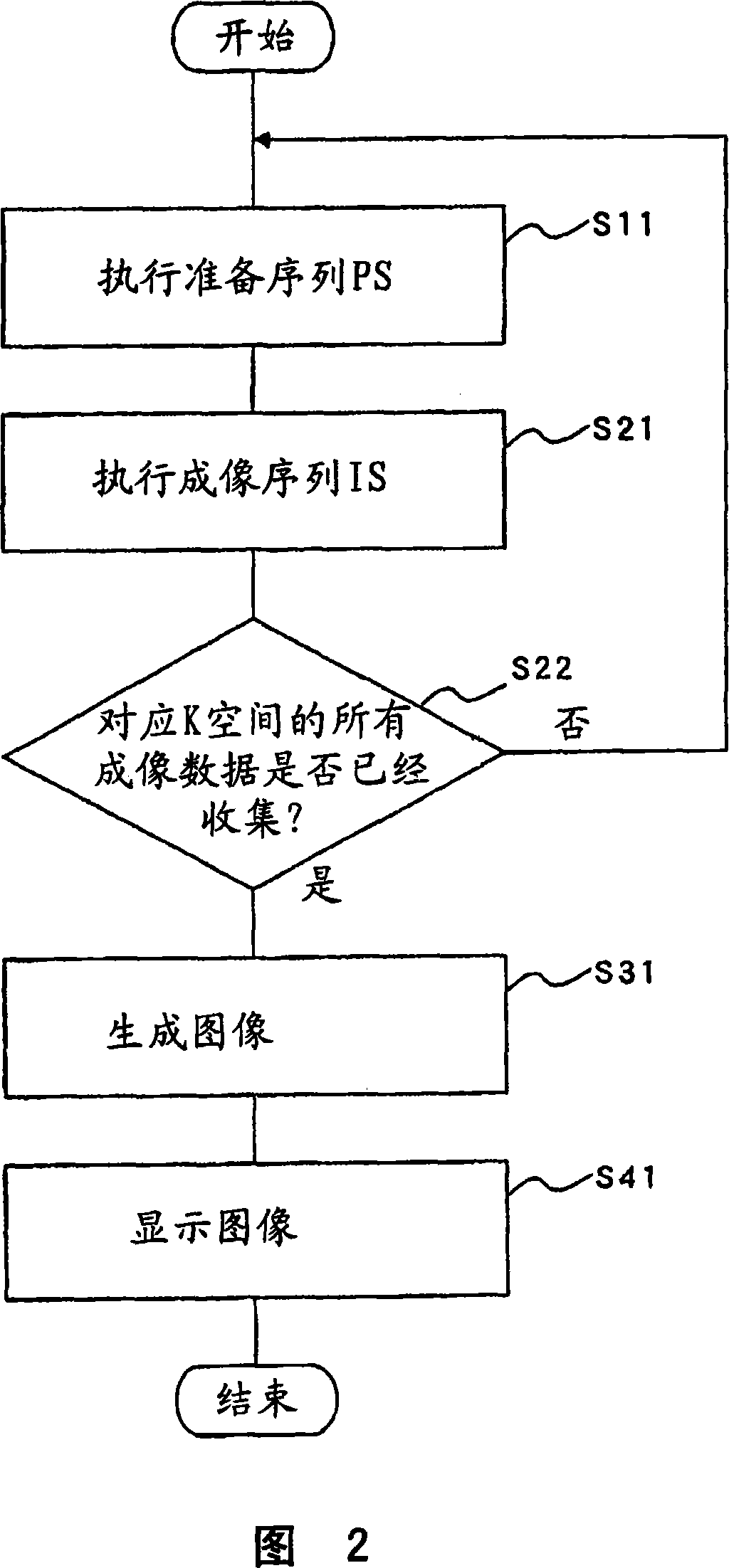
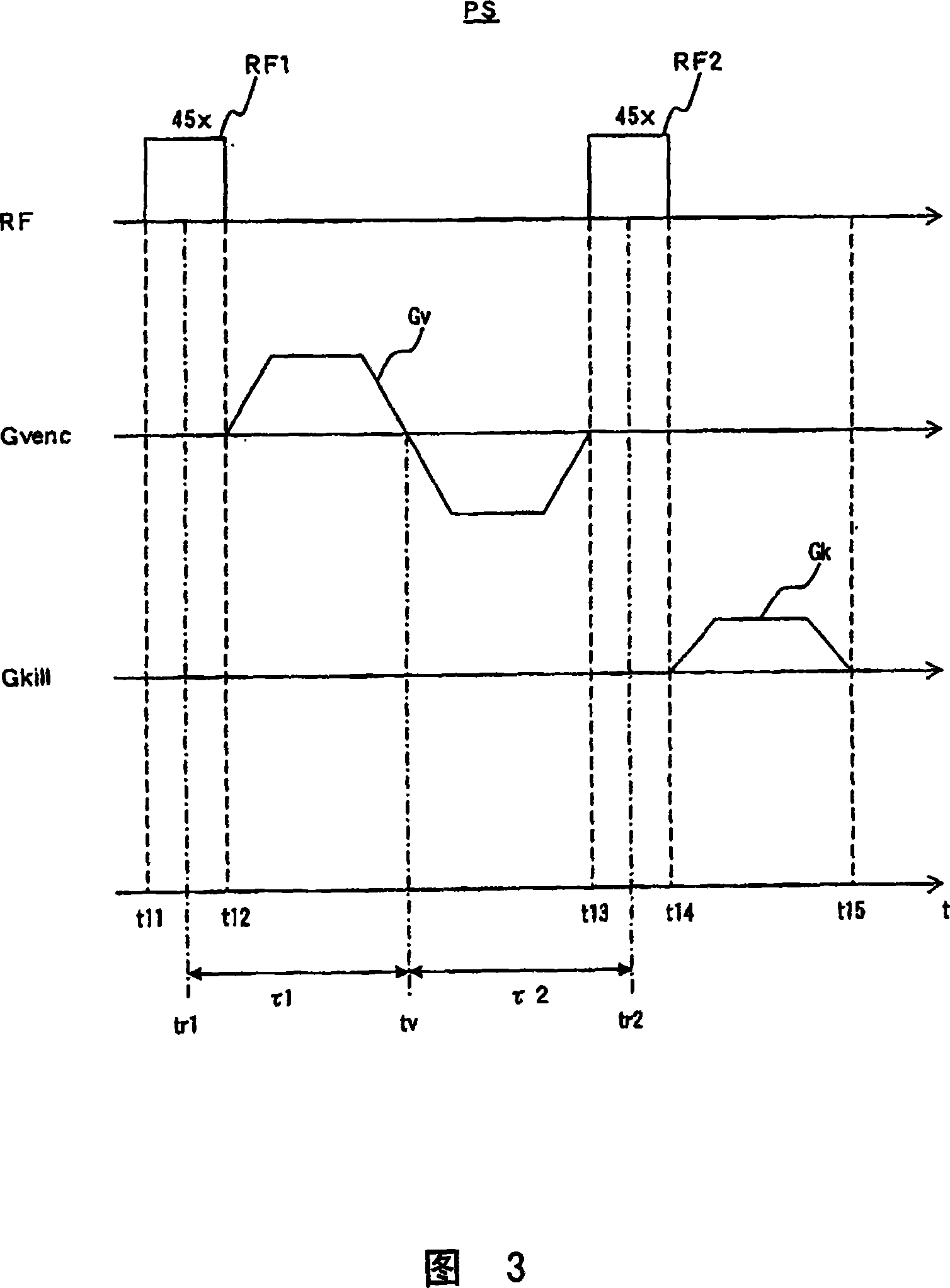
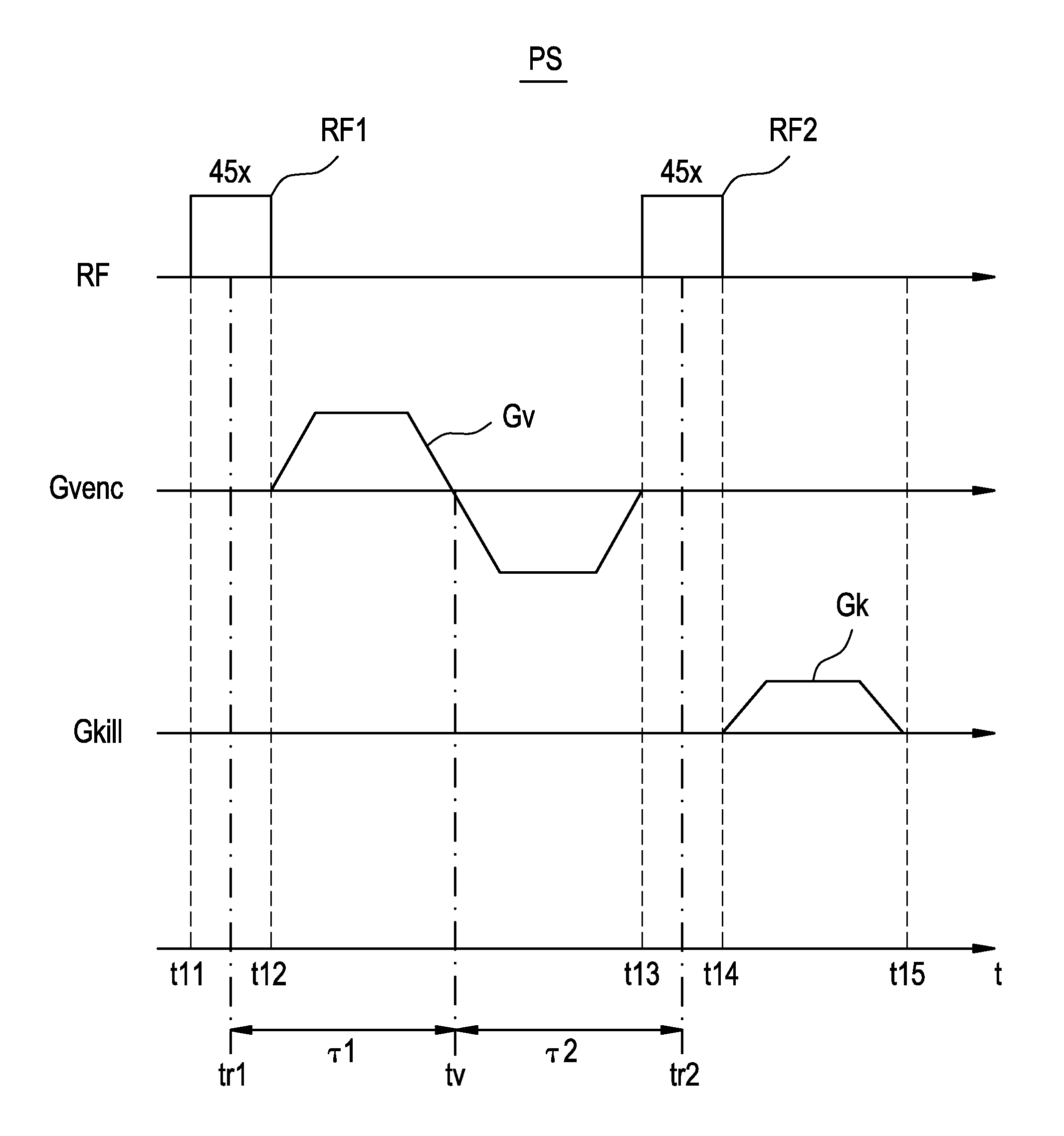
ActiveCN101023866AImprove image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSpin-flipTransverse magnetization
Versatility and the quality of images are to be improved. As preparation pulses, a first RF pulse to flip along the yz plane spins oriented in a magnetostatic field direction in a subject; a velocity encoding gradient pulse which, in spins flipped by that first RF pulse, mutually shifts the phase of spins in a static state and the phase of spins in a moving state; and a second RF pulse to flip along the yz plane spins whose phase has been shifted by the velocity encoding gradient pulse are successively transmitted. After that, a killer pulse is transmitted to extinguish the transverse magnetizations of the spins flipped by the second RF pulse.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Method and magnetic resonance system to excite nuclear spins in a subject
InactiveUS7847551B2Reduce impactReduce background signalMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationSpins
In a method and system to generate an excitation in an examination subject to acquire magnetic resonance signals from a region of the examination subject, basic magnetic field is generated, an adiabatic half-passage (AHP) pulse is radiated to generate a transverse magnetization in the subject, and at least one first and one second adiabatic full-passage (AFP) pulse is radiated to generate a slice-selective rephasing of the transverse magnetization. The time interval between the first adiabatic half-passage pulse and the first adiabatic full-passage pulse is at least 37 ms, and the time interval between the first adiabatic full-passage pulse and the second adiabatic full-passage pulse is at least 75 ms.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and magnetic resonance system for imaging particles
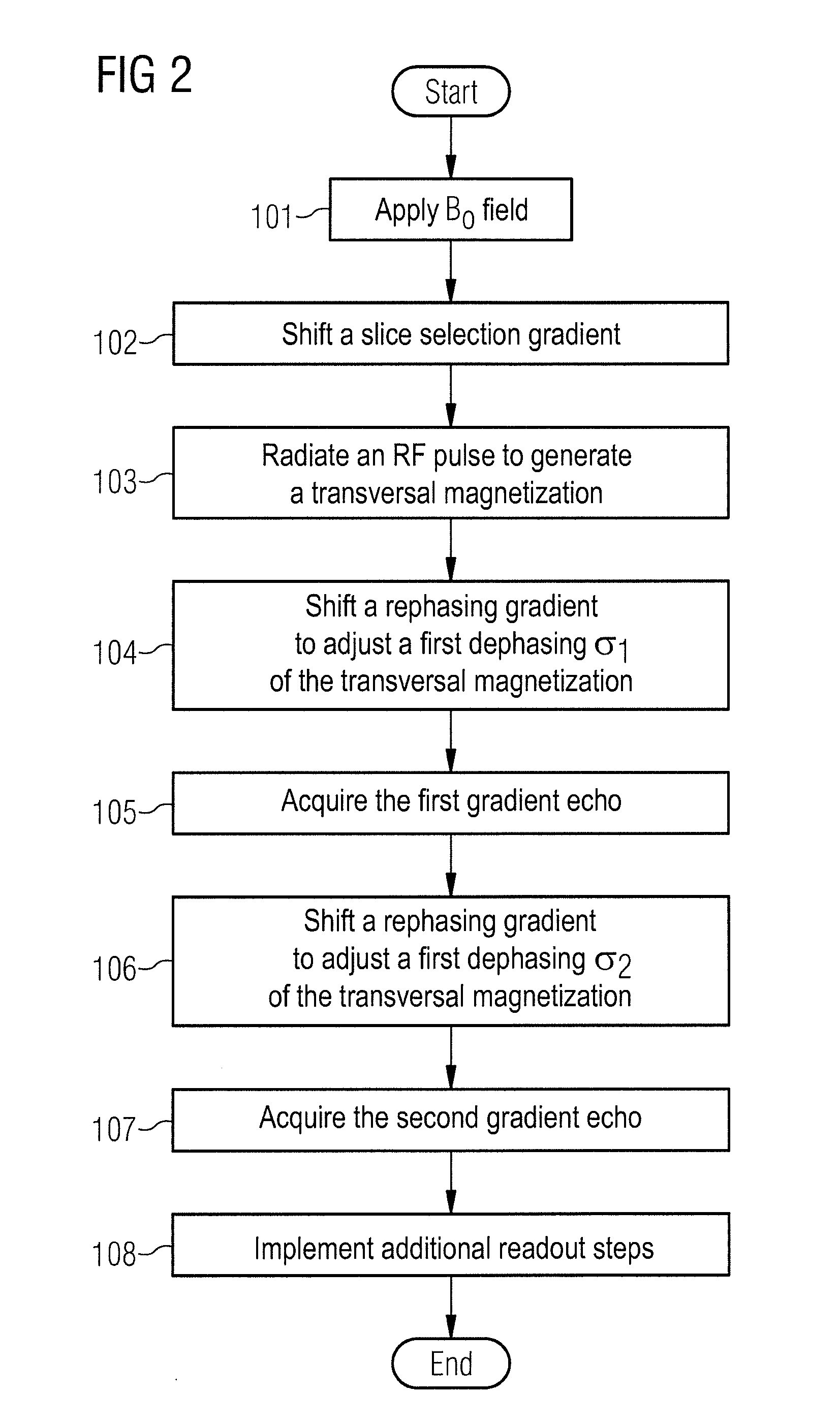
InactiveUS20110115487A1Enhance the imageAvoid disadvantagesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonance measurementTransverse magnetization
A method and magnetic resonance system for imaging a particle that is located in an examination subject with an imaging magnetic resonance measurement execute a gradient echo sequence in which at least two gradient echoes are acquired following a single excitation pulse, wherein the particle in an applied basic magnetic field causes a magnetic interference field. An RF pulse is radiated to generate a transverse magnetization from a magnetization appearing in the basic magnetic field. A first dephasing gradient is shifted to adjust a first dephasing of the transverse magnetization, and the first gradient echo is acquired. A second dephasing gradient is shifted to adjust a second dephasing of the transverse magnetization that is different than the first dephasing, and the second gradient echo is acquired. The two dephasing gradients are shifted such that a dephasing of the transverse magnetization caused by the interference field of the particle is at least partially compensated in a region around the particle or within the particle given the acquisition of at least one of the echoes.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and program
ActiveUS20100198046A1Image degradationElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsProton magnetic resonanceTransverse magnetization
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes a gradient coil for applying a gradient pulse, a transmitting coil for transmitting an RF pulse, and a coil control device for controlling the gradient coil and the transmitting coil in such a manner that a pulse sequence for (A) making an absolute value of longitudinal magnetization of a first background tissue and an absolute value of longitudinal magnetization of a second background tissue longer in T1 value than the first background tissue smaller than an absolute value of longitudinal magnetization of body fluid of a subject, (B) acquiring magnetic resonance signals from the subject, and (C) flipping transverse magnetization of the second background tissue to longitudinal magnetization is repeatedly executed.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
ActiveUS9014782B2Quality improvementHighly versatileDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSpin-flipTransverse magnetization
Versatility and the quality of images are to be improved. As preparation pulses, a first RF pulse to flip along the yz plane spins oriented in a magnetostatic field direction in a subject; a velocity encoding gradient pulse which, in spins flipped by that first RF pulse, mutually shifts the phase of spins in a static state and the phase of spins in a moving state; and a second RF pulse to flip along the yz plane spins whose phase has been shifted by the velocity encoding gradient pulse are successively transmitted. After that, a killer pulse is transmitted to extinguish the transverse magnetizations of the spins flipped by the second RF pulse.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Method for magnetic resonance imaging, and magnetic resonance system
ActiveUS20140218027A1Reduced measurement timeReduce signalingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPrecessionTransverse magnetization
In magnetic resonance imaging using a measurement sequence of the “free precession of transverse magnetization in the steady state”-type i.e., an SSFP measurement sequence, during the SSFP measurement sequence, the implementation of a preparation sequence takes place to reduce a signal contribution of the transverse magnetization in an outer region surrounding a measurement region in the MR imaging. The implementation of the preparation sequence includes the radiation of a multidimensional, spatially selective RF pulse that acts in a spatially selective manner on the transverse magnetization in the outer region. Saturation of the transverse magnetization and / or dephasing of the transverse magnetization in the outer region can be achieved by the multidimensional, spatially selective RF pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
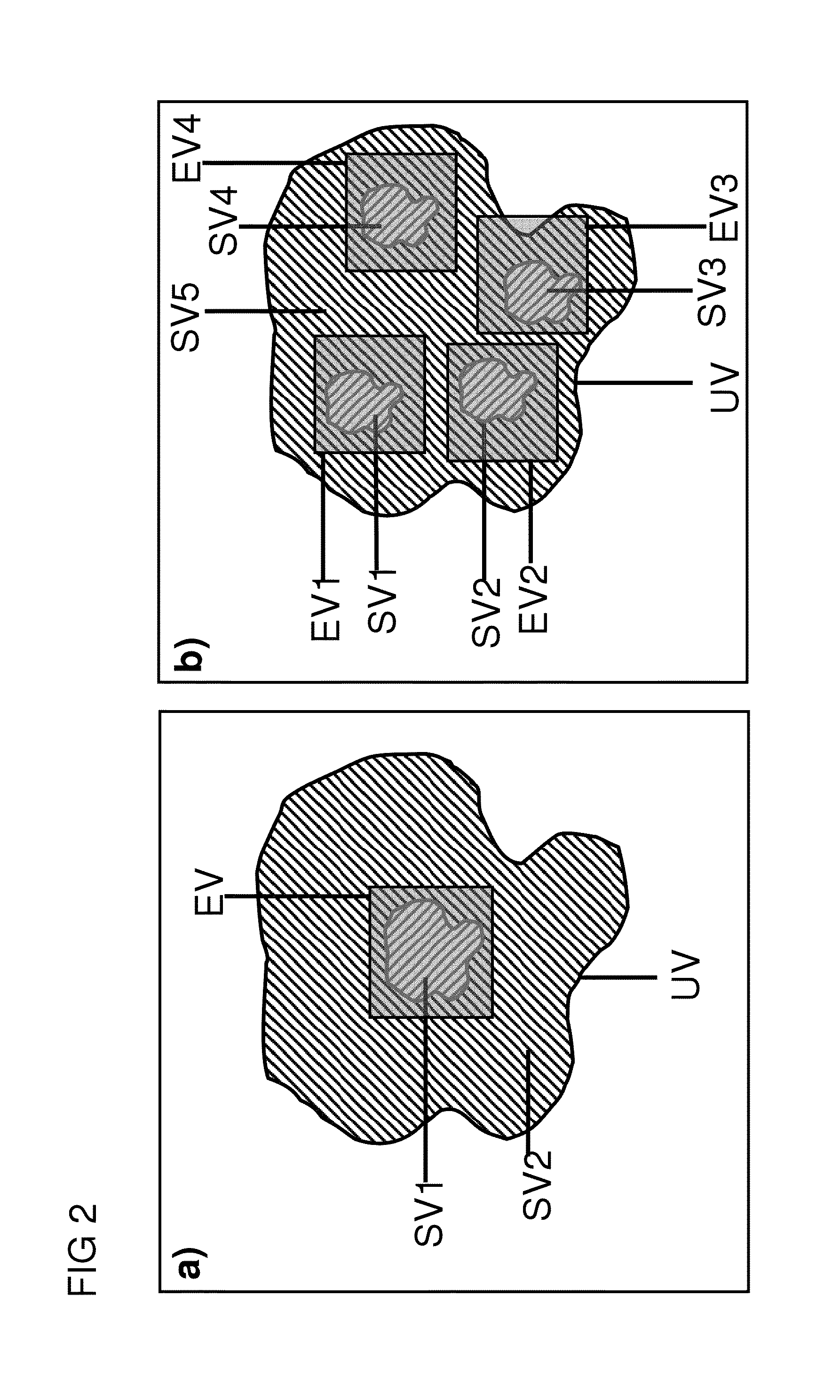
Method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals in subvolumes of an object under examination
ActiveUS20150084627A1Permit separationShorten the lengthDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSpatially resolvedImaging quality
A method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals from at least one of N subvolumes predefines a reception encoding scheme and determines unique spatial encoding for at least one of the subvolumes but not for the entire volume under examination (UV). A transmission encoding scheme is also defined, wherein encoding is effected via the amplitude and / or phase of the transverse magnetization. The temporal amplitude and phase profile of the RF pulses is then calculated and each reception encoding step is carried out I times with variations according to the I transmission encoding steps in the transmission encoding scheme. The method makes it possible to largely restrict the spatially resolving MR signal encoding and image reconstruction to subvolumes of the object under examination without the achievable image quality sensitively depending on imperfections in the MR apparatus.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Transverse magnetization of casing string tubulars
InactiveUS7712519B2Strong, highly uniform magnetic fieldAccurate distance measurementElectromagnets without armaturesDrilling rodsTransverse magnetizationCasing string
A method and apparatus for imparting a transverse magnetization to a wellbore tubular is disclosed. In certain exemplary embodiments, tubulars are magnetized to include at least one flux reversal (e.g., at the center of the tubular) at which the direction of the transverse field changes (i.e., from pointing radially inward to pointing radially outward). A plurality of such magnetized wellbore tubulars may be coupled together and lowered into a target well to form a magnetized section of a casing string. Exemplary embodiments of the invention may be utilized to impart a strong, highly uniform magnetic field about a string of wellbore tubulars, thereby providing for improved passive ranging and wellbore twinning.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and magnetic resonance device for imaging of particles
InactiveUS20110187366A1Large contrast rangeEasy to detectElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRResonance measurementParticle imaging
In a magnetic resonance method and apparatus for imaging a particle that is located in an examination subject, a pulse sequence is emitted that includes an excitation pulse that generates a transverse magnetization of the examination subject from a magnetization appearing in a basic magnetic field, so the particle causes a magnetic interference field in the applied basic magnetic field in a magnetic resonance measurement. After the excitation pulse, at least one spectrally selective refocusing pulse is generated in a non-resonant frequency range at the generation of a spin echo.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20120274322A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRTransverse magnetizationSpins
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus that carries out a pulse sequence for making a signal of a first substance within an object smaller than a signal of a second substance within the object. The pulse sequence includes an α°-pulse for exciting the object, a refocus pulse for refocusing a phase of spin within a region excited by the α°-pulse, and a readout gradient field for acquiring a magnetic resonance signal from the region. The α°-pulse has a spectral selectivity such that a transverse magnetization of the first substance is made smaller than a transverse magnetization of the second substance. The refocus pulse has a spectral selectivity such that a phase of spin of the second substance is refocused and refocusing of a phase of spin of the first substance is suppressed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for obtaining amplitude and phase profiles of RF pulses for spatially selective excitation
ActiveUS7999545B2Reduce field of viewReduced measurement timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSelective excitationTransverse magnetization
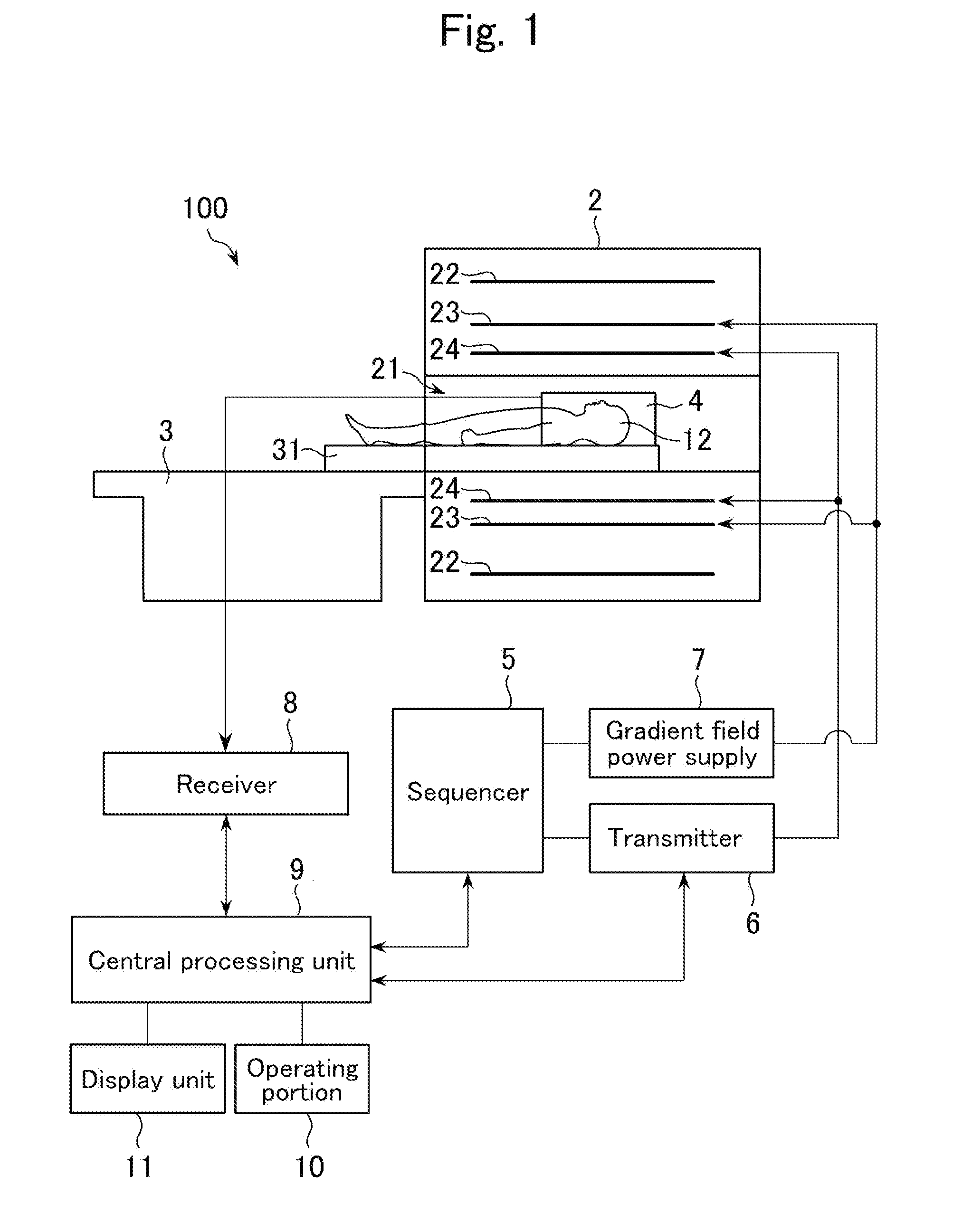
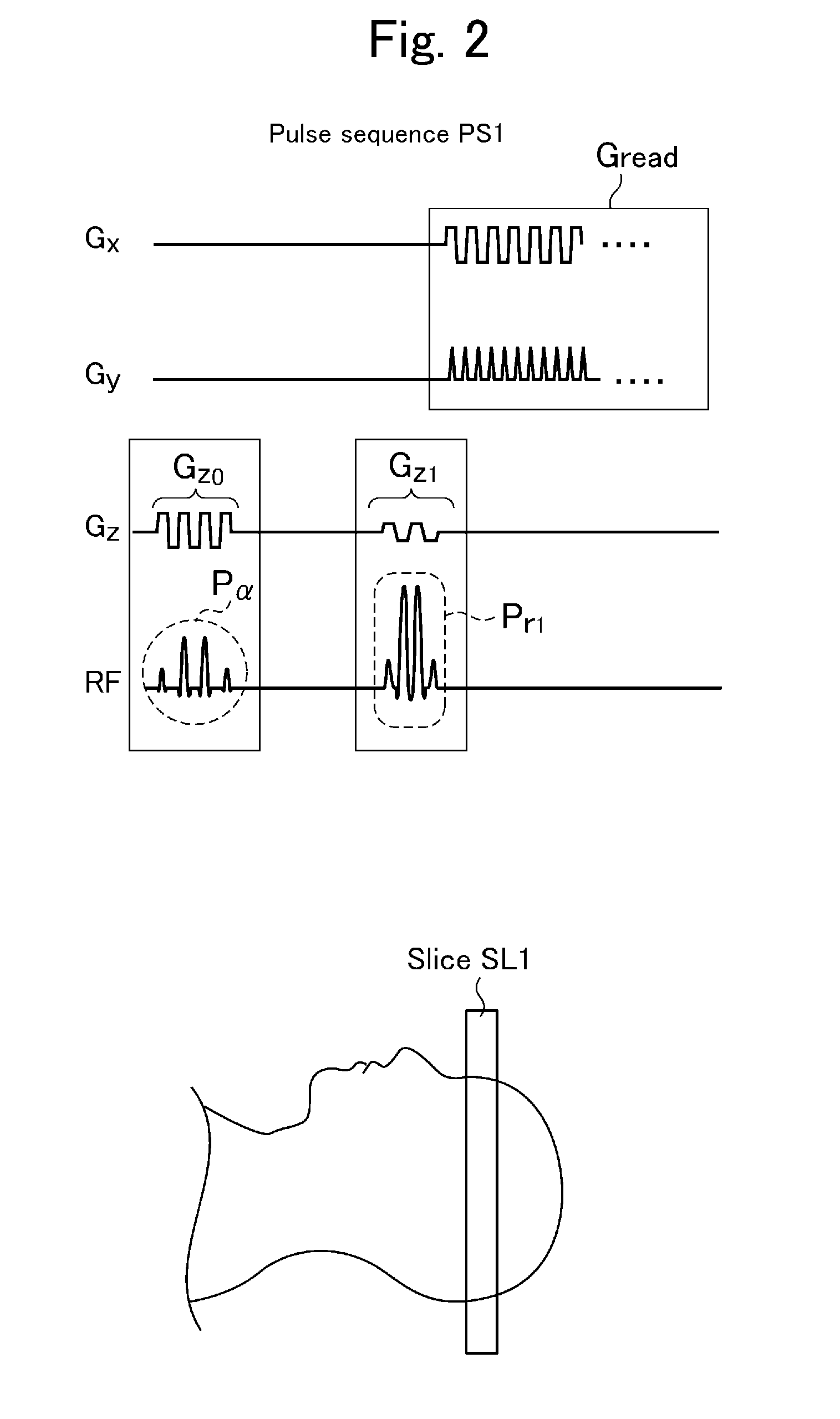
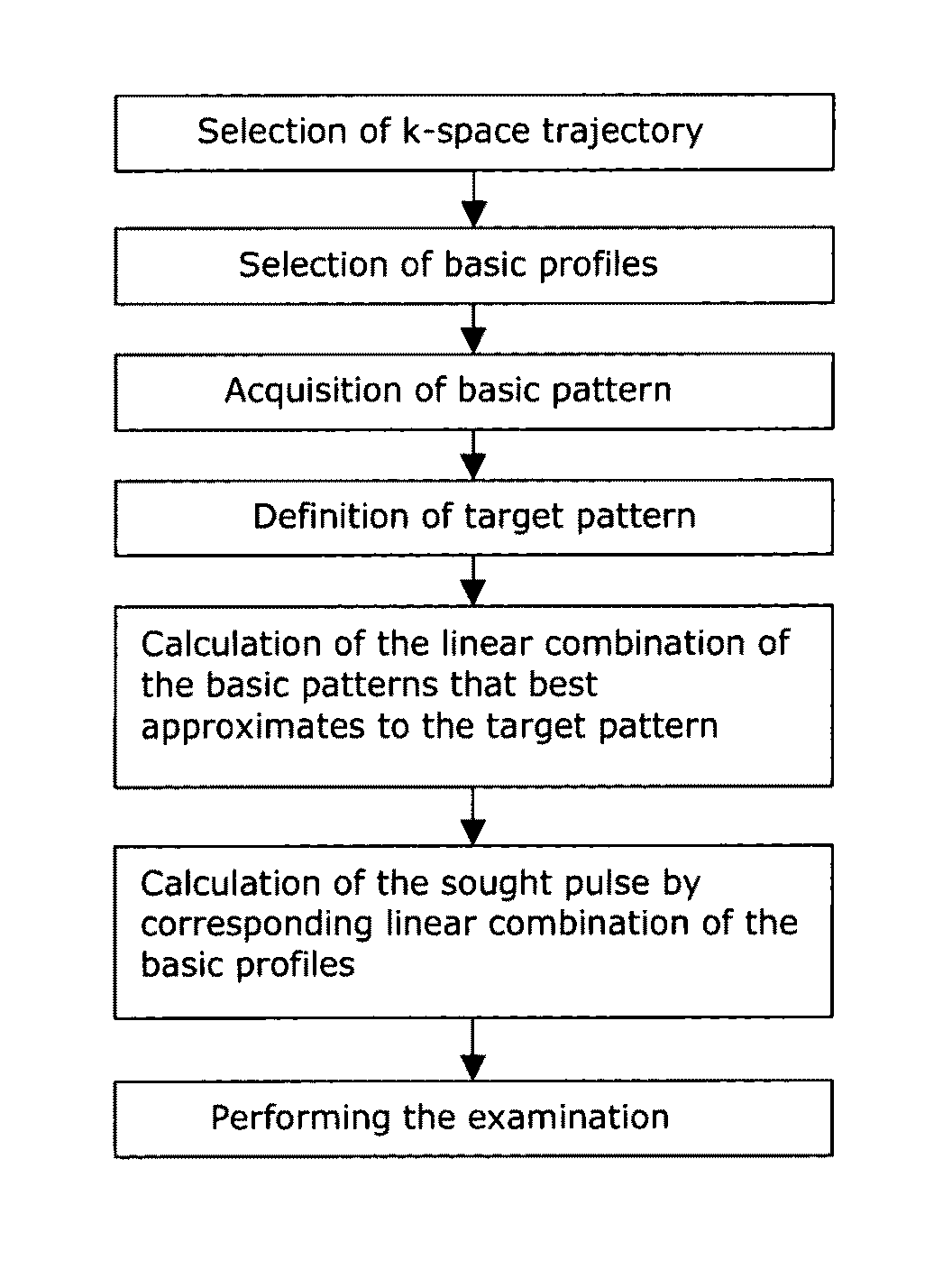
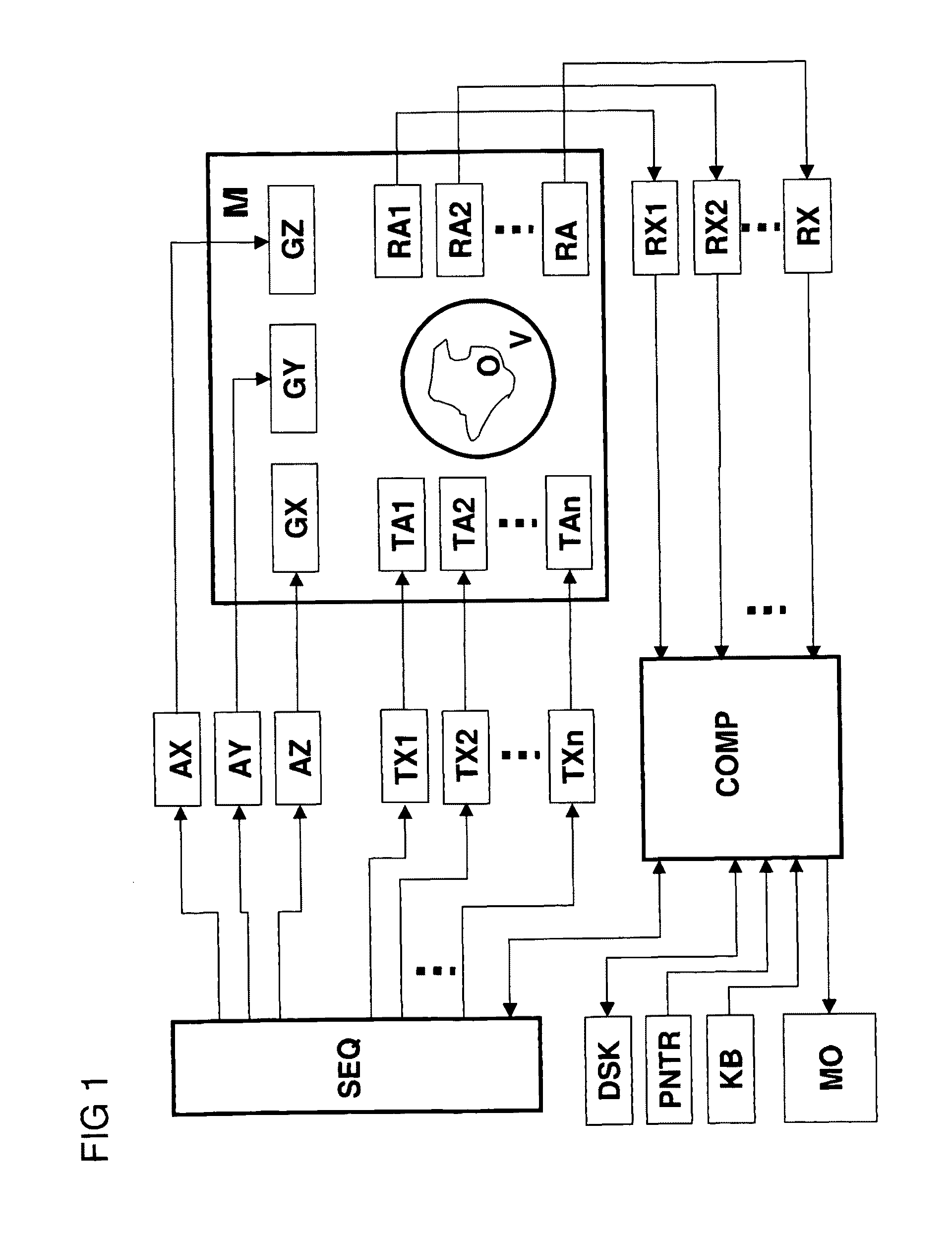
A method for determining amplitude and phase dependencies of radio frequency pulses that are irradiated during traversal of a defined k-space trajectory to produce a spatial pattern of the transverse magnetization in an MR experiment using at least one RF transmission antenna, is characterized in that, in a calibration step, a set of basic pulses is defined, each basic pulse is irradiated individually, the specified k-space trajectory is traversed and at least one set of basic patterns is produced by detection of the MR signals thus excited, which in a range to be examined of the object, are proportional to the complex transverse magnetization produced, wherein the k-space trajectory is traversed fully identically every time at least from the beginning of the irradiation of each basic pulse, and, in a calculation step, a defined target pattern is approximated with a linear combination of the basic patterns of a set or with a mathematical association of linear combinations, with which, within each set, the basic patterns are identically combined, and the amplitude and phase dependencies to be determined are obtained as the corresponding linear combination of the basic pulses. Experimental imperfections can be intrinsically compensated for in this way.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI +1
Exact half pulse synthesis via the inverse scattering transform
ActiveUS20050127911A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioNoise is uncorrelatedMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringTransverse magnetizationInverse scattering transform
A method of obtaining an arbitrary, admissible transverse magnetization profile as the summed response of two, self refocused selective “half pulse” excitations for use in, e.g., magnetic resonance imaging pulse generation. The problem of finding the pair of half pulses is rephrased in the inverse scattering formalism and a simple closed form algorithm for the solution is given, provided the target transverse profile has constant phase (modulo 180°). The problem has a unique low energy solution for sufficiently small, complex valued data, and an algorithm for finding the solution is provided. This solution is used to generate pairs of half pulses for given target transverse profiles.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method and apparatus of background suppression in mr imaging using spin locking
ActiveUS20060043970A1Overcomes drawbackMinimal effectMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationBlood flow
The present invention is directed to a method and system of tissue or background suppression for the acquisition of image data from blood flow or tissue perfusion. Background suppression with minimal effects upon inflowing spins is achieved through a series of spin locking low level RF pulses that cause adiabatic demagnetization of tissue with a relaxation time T1-rho that is intermediate between T1 and T2 relaxation times. In this regard, the effective transverse magnetization of static tissue resulting from the application of a series of low level RF pulses is reduced and, with the spin locking, longitudinal magnetization regrowth is minimized. As such, inflowing spins to an imaging volume may be directly imaged with significant background tissue suppression. The present invention is particularly applicable to time-of-flight MRA and MR perfusion imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20170227621A1Suppress artifactsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSlice thicknessImaging condition
In a sequence of emitting a plurality of refocus RF pulses after one excitation RF pulse, in order to suppress a cusp artifact at a known magnetic field distortion generation position regardless of an imaging condition, such as a slice thickness or an FOV, between an excitation RF pulse and an initial refocus RF pulse, by generating a phase shift to transverse magnetization at the position, and by applying an extremely small dephase gradient magnetic field in the phase encoding direction and / or in the slice encoding direction, a signal value of an NMR signal (echo signal) is suppressed at the position, and the cusp artifact is deteriorated.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com