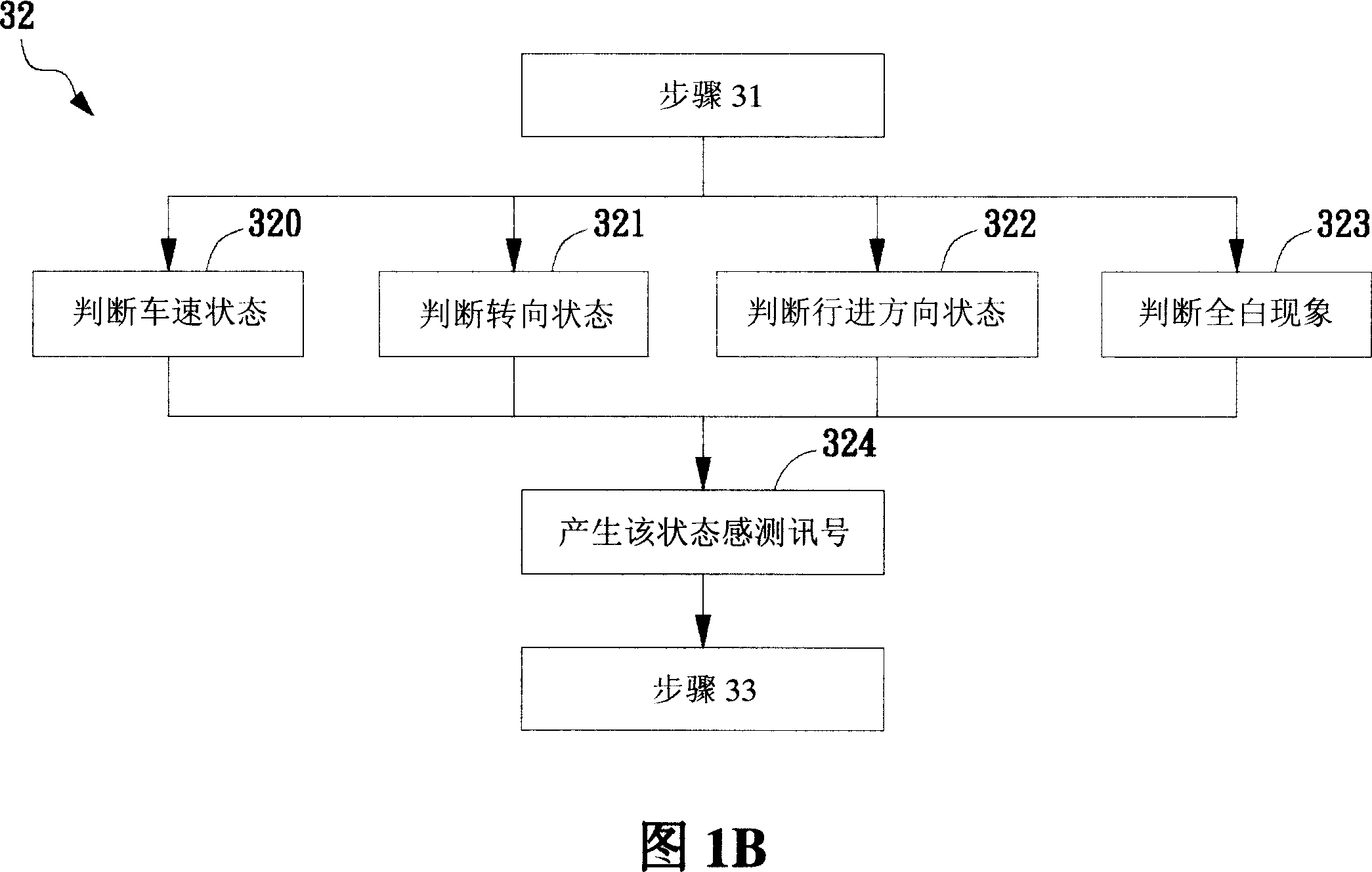
Patents
Literature
68results about How to "Reduce field of view" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
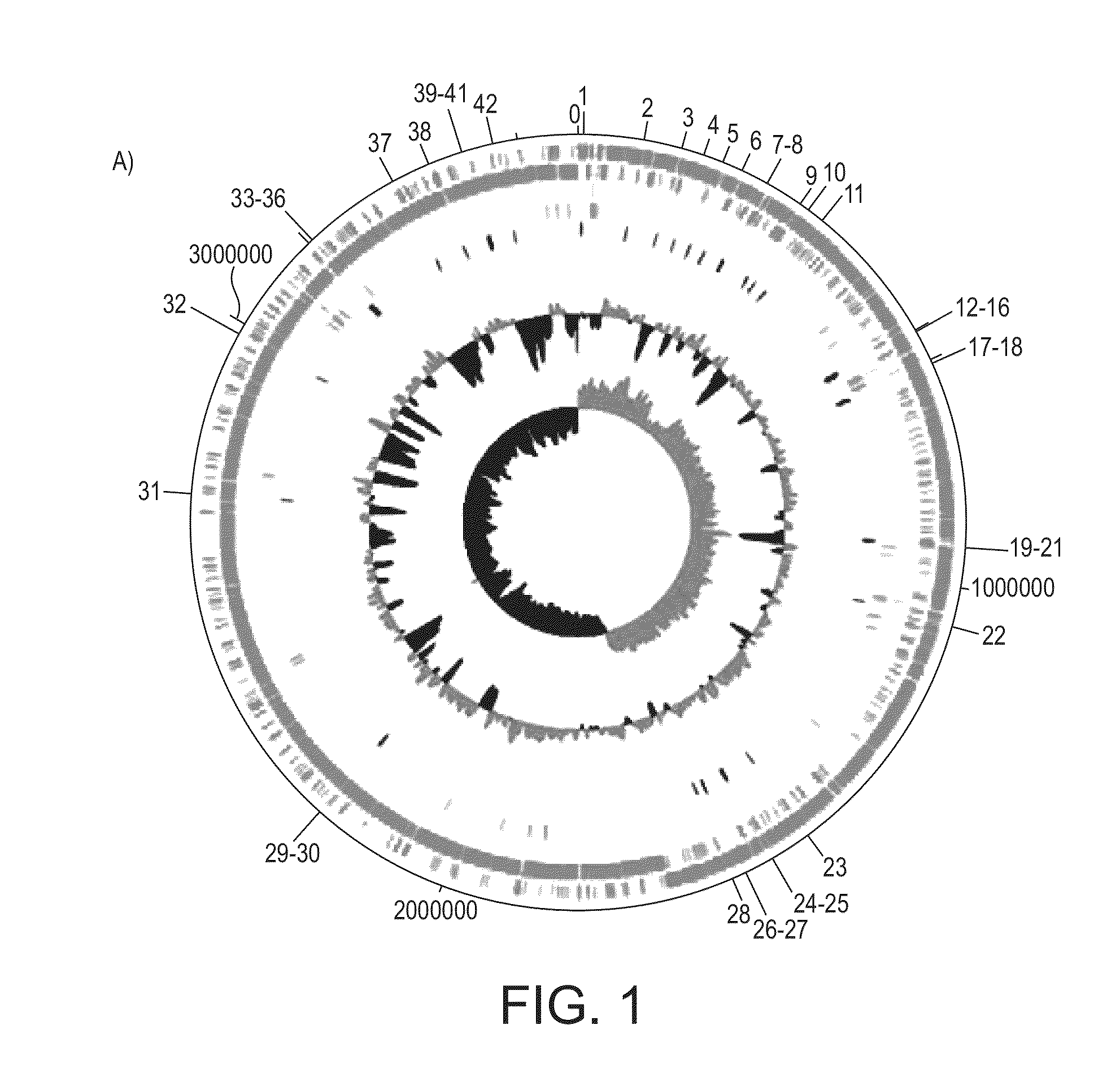
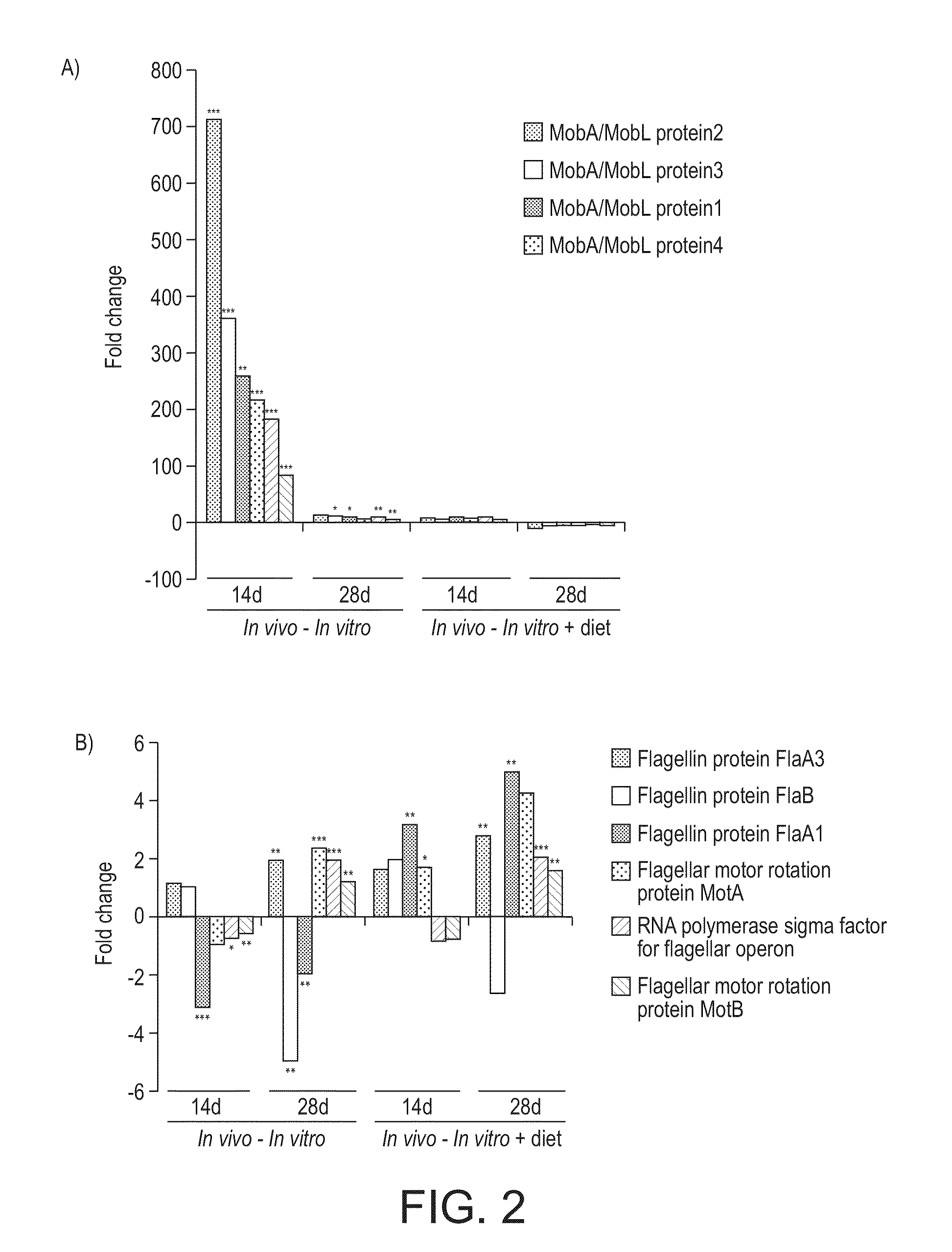
Polypeptide and immune modulation
ActiveUS20150071957A1Strong elevationReduced gene expressionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideRoseburia
The present invention relates to Roseburia flagellin, and / or a polynucleotide sequence encoding said Roseburia flagellin, and / or a vector comprising said polynucleotide sequence, and / or a host cell, including bacteria, comprising said vector, and / or a host cell, including bacteria, comprising said polynucleotide sequence, for use in modulating the inflammation of a tissue or an organ in a subject.
Owner:4D PHARMA RES LTD +1
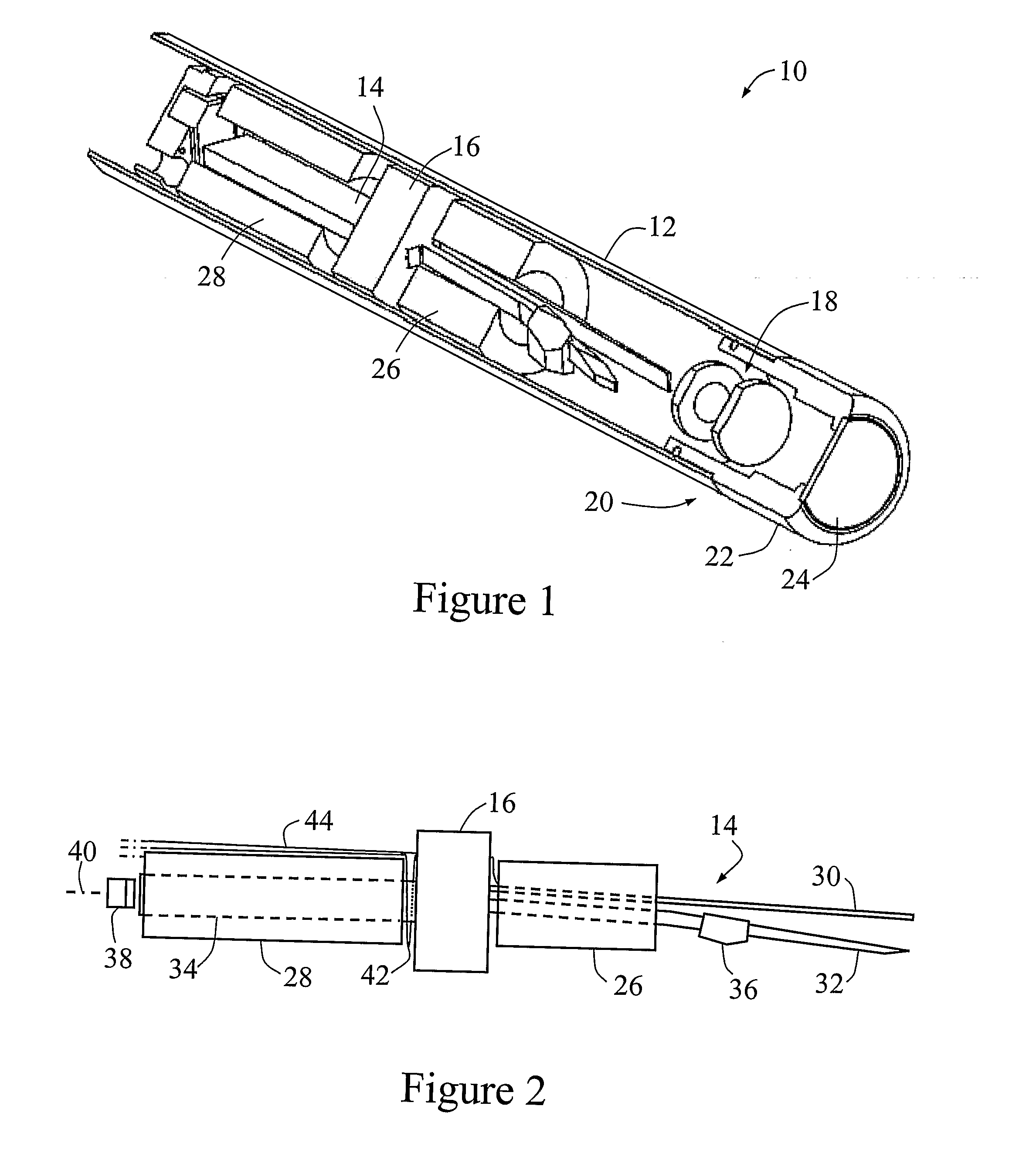
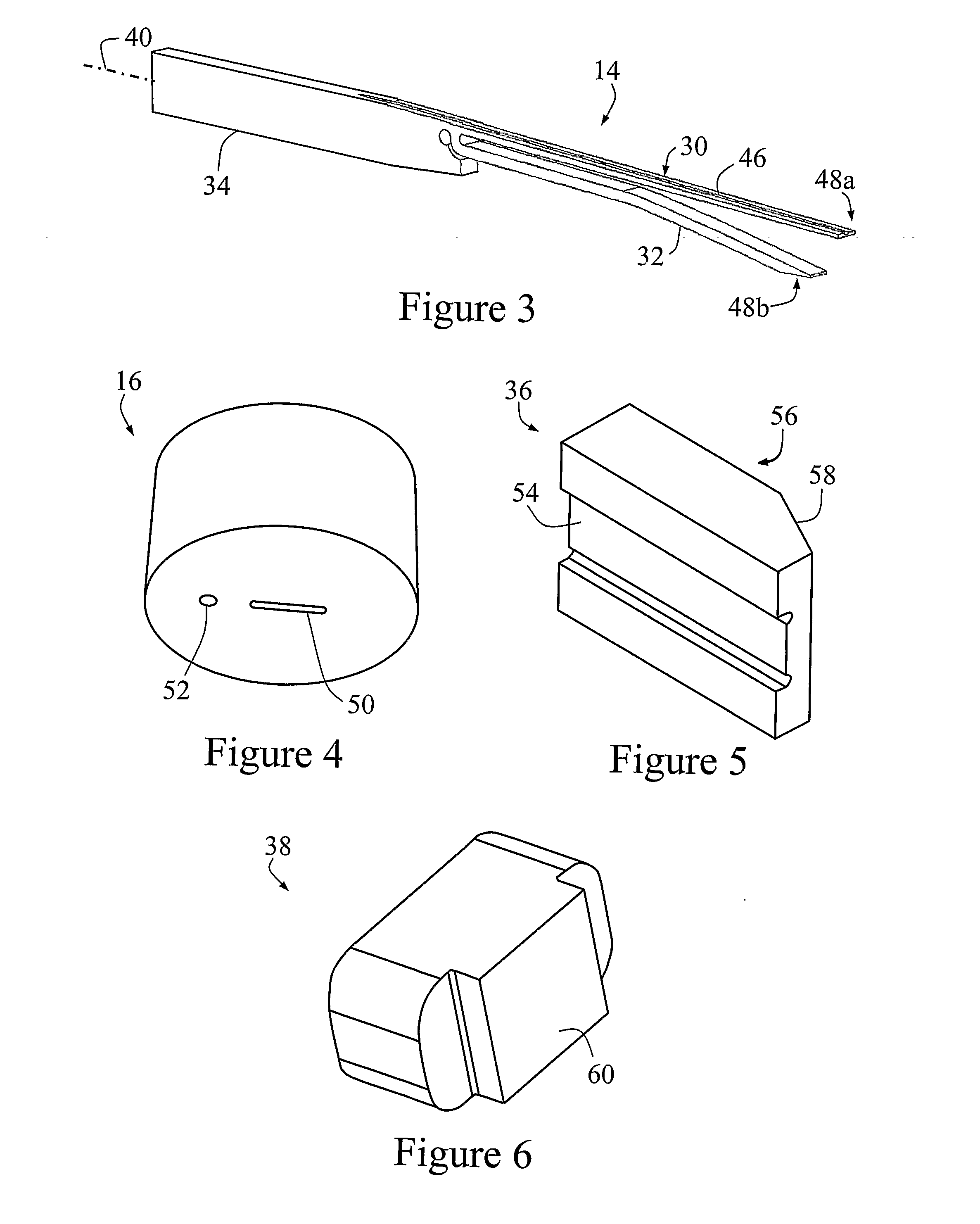
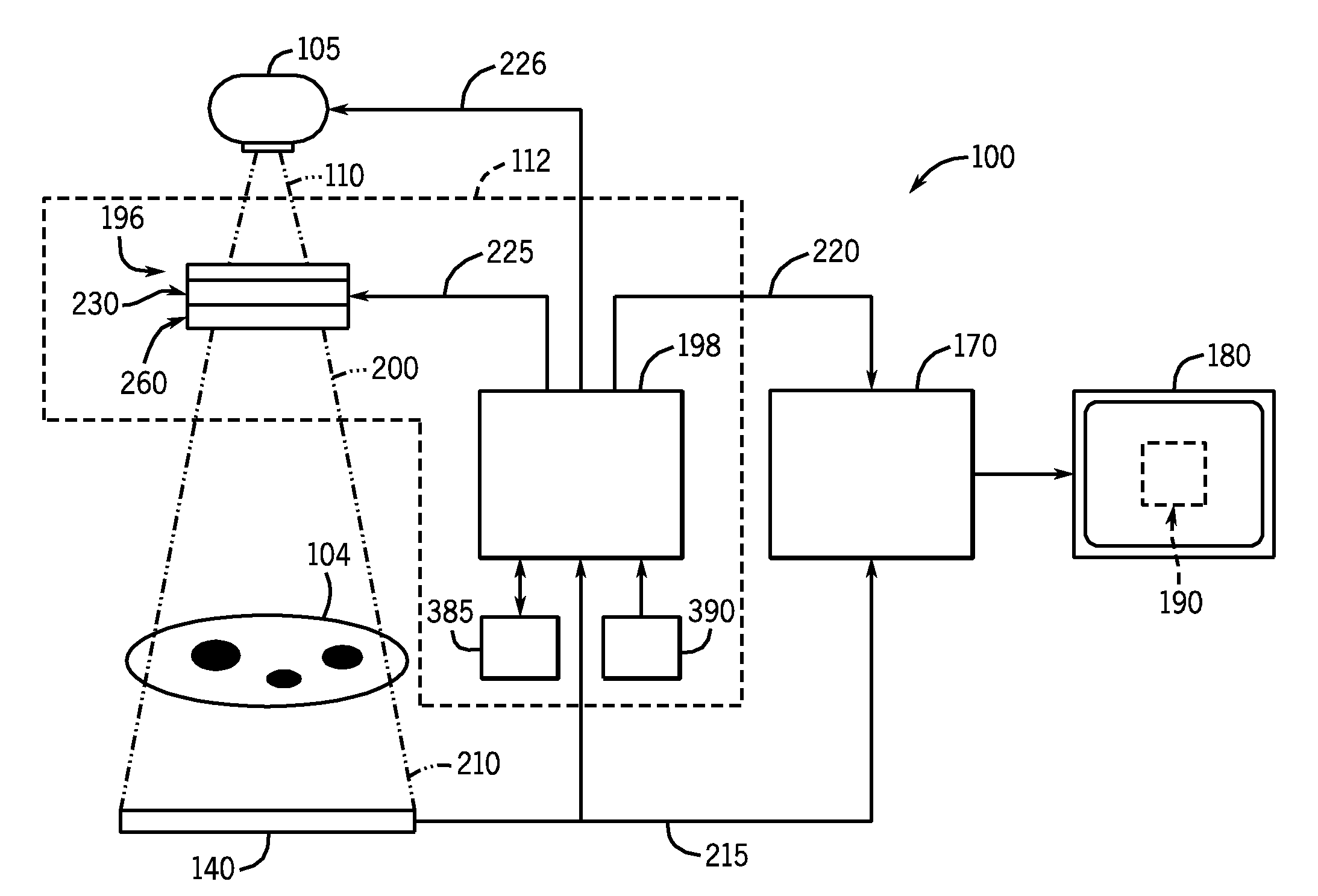
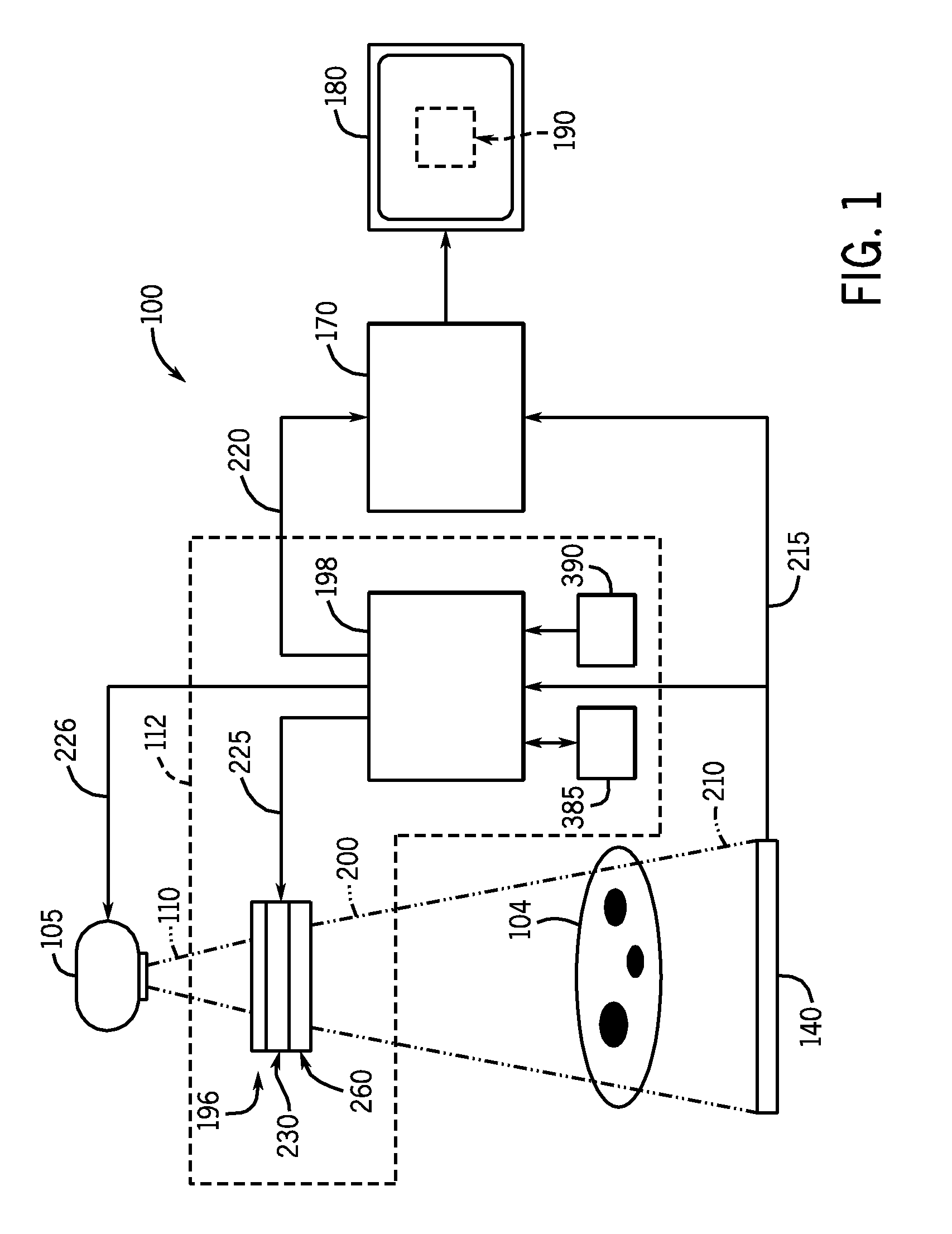
Tuning-Fork-Type Scanning Apparatus with a Counterweight
ActiveUS20070242330A1Compensation-greater lengthReduce the overall diameterBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsEndoscopesTuning forkEngineering
A scanning method and apparatus, the apparatus comprising a fork with first and second forwardly extending tines and a rearwardly extending counterweight member, a mount for supporting the fork at a point between the tines and the counterweight member, and a drive for effecting relative vibration between the tines to provide a fast scan and for driving the fork to provide a slow scan transverse to the fast scan.
Owner:OPTISCAN +1
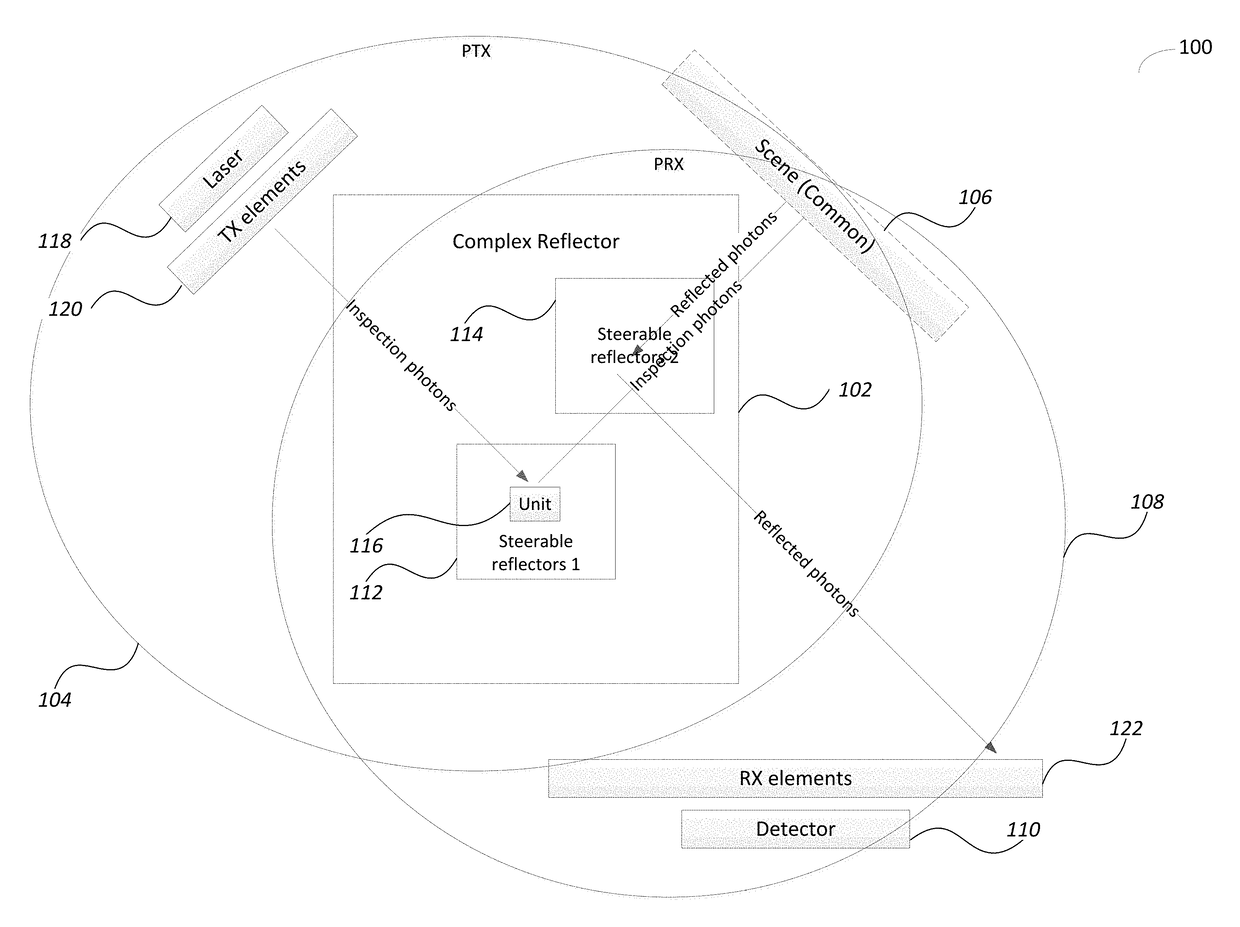
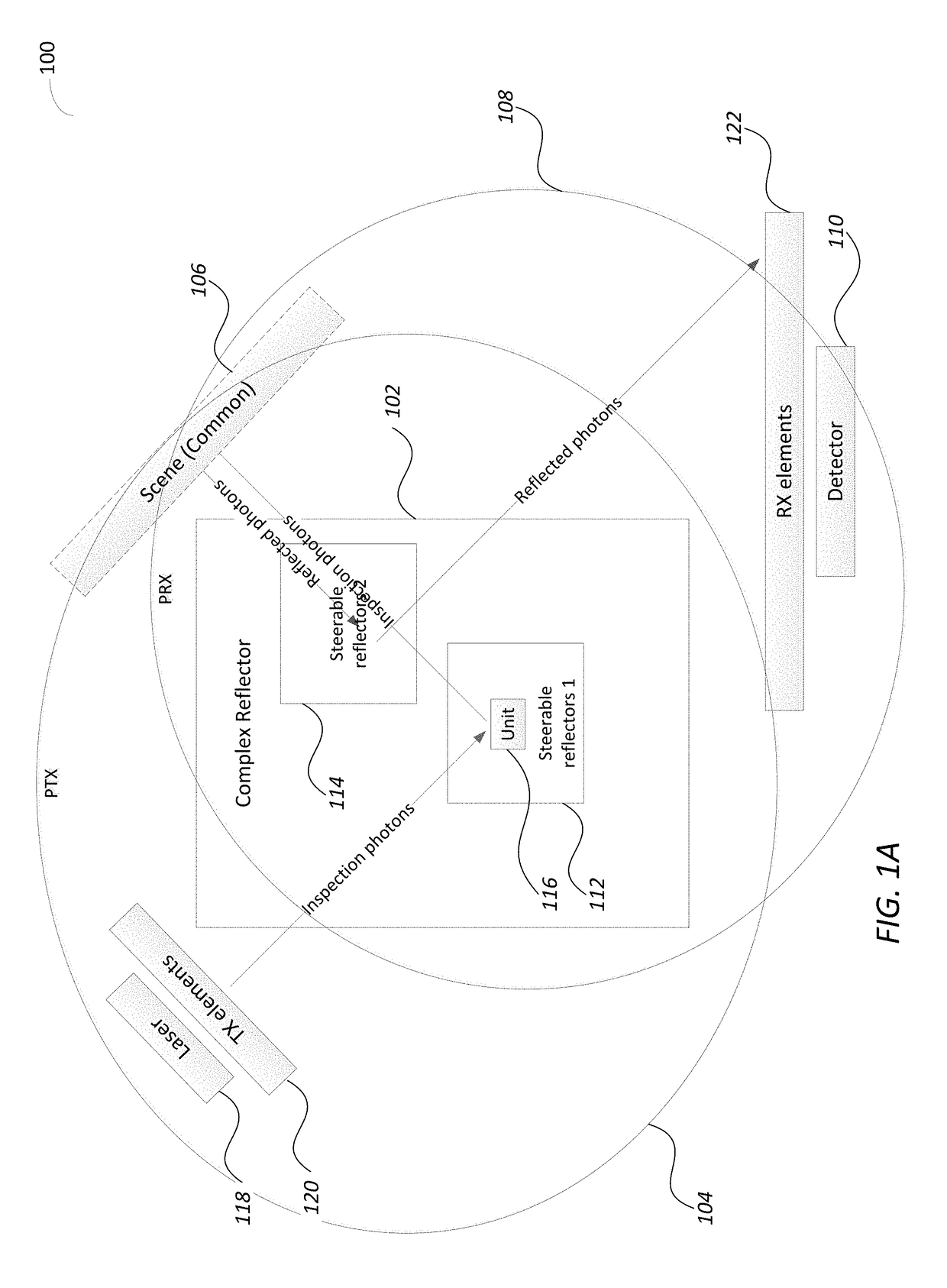
Methods Circuits Devices Assemblies Systems and Functionally Associated Machine Executable Code for Light Detection and Ranging Based Scanning
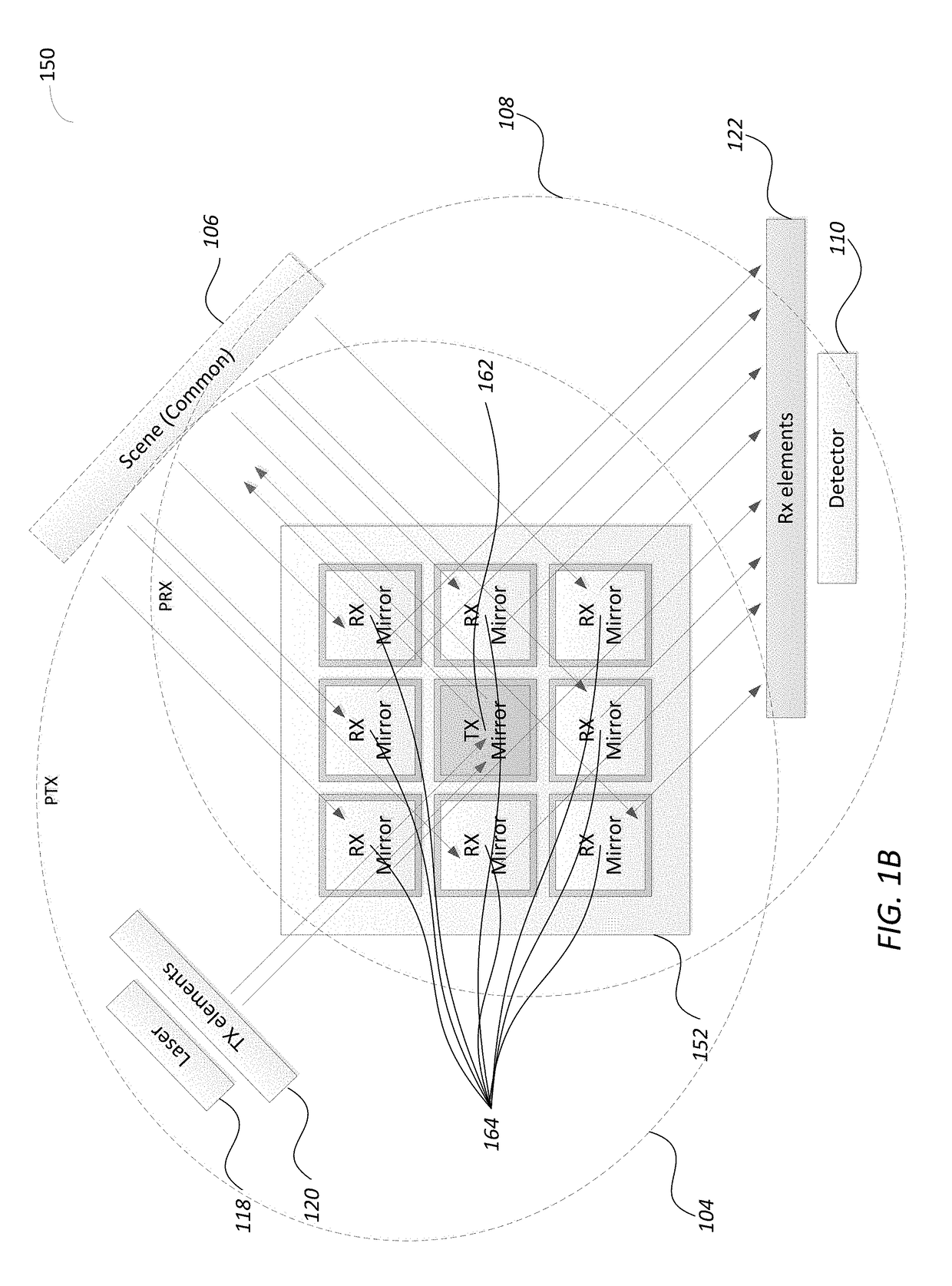
InactiveUS20180081038A1Reduce field of viewIncreases beam spreadElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhoton emissionPhotonics
Disclosed is a light detection and ranging (Lidar) device including a photonic pulse emitter assembly including one or more photonic emitters to generate and focus a photonic inspection pulse towards a photonic transmission (TX) path of the Lidar device, a photonic detection assembly including one or more photo sensors to receive and sense photons of a reflected photonic inspection pulses received through a receive (RX) path of the device, a photonic steering assembly located along both the TX and the RX paths and including a Complex Reflector (CR) made of an array of steerable reflectors, where a first set of steerable reflectors are part of the TX path and a second set of steerable reflectors are part of the RX path.
Owner:INNOVIZ TECH LTD
Optical communication system with cats-eye modulating retro-reflector (MRR) assembly, the cats-eye mrr assembly thereof, and the method of optical communication
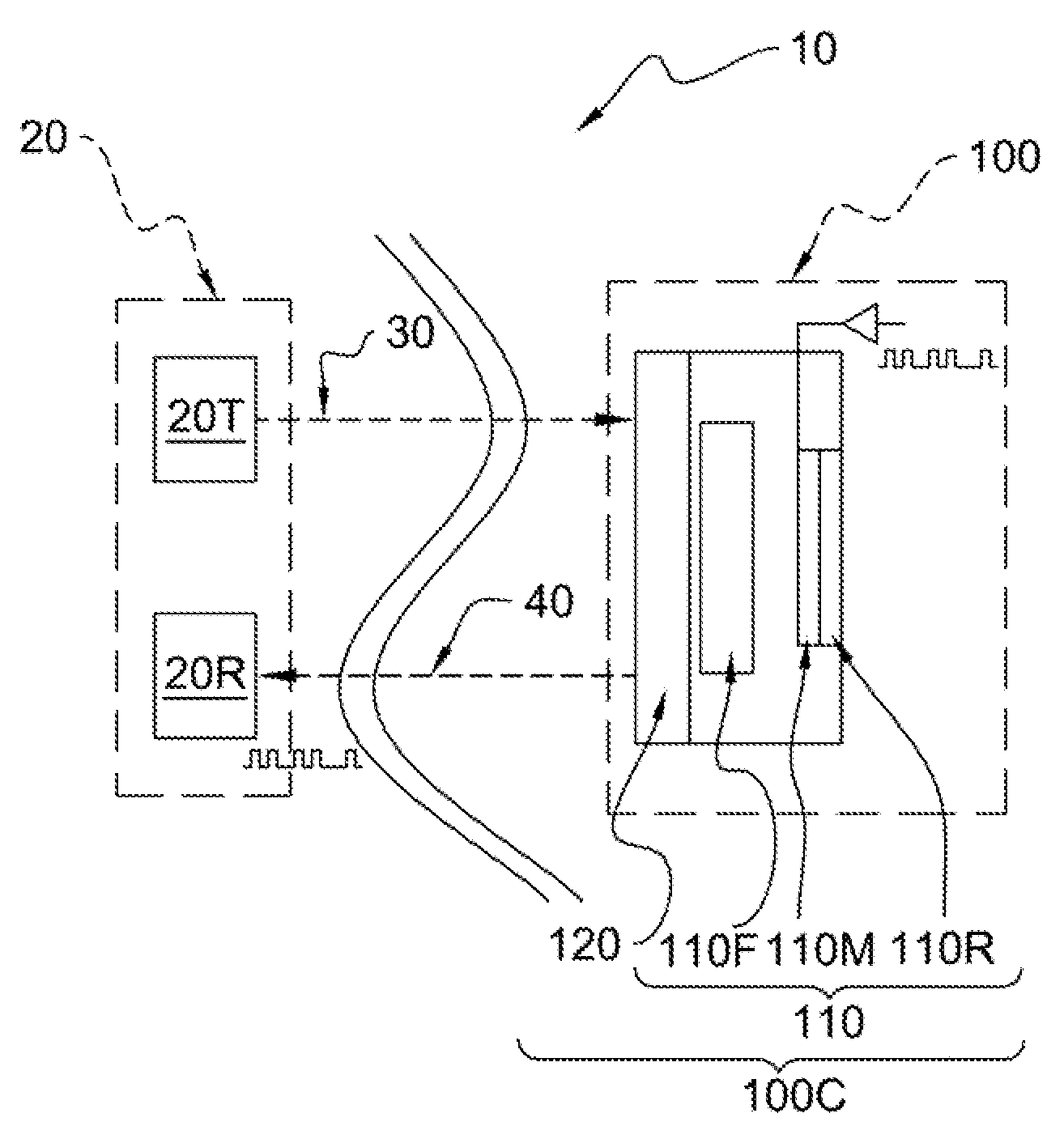
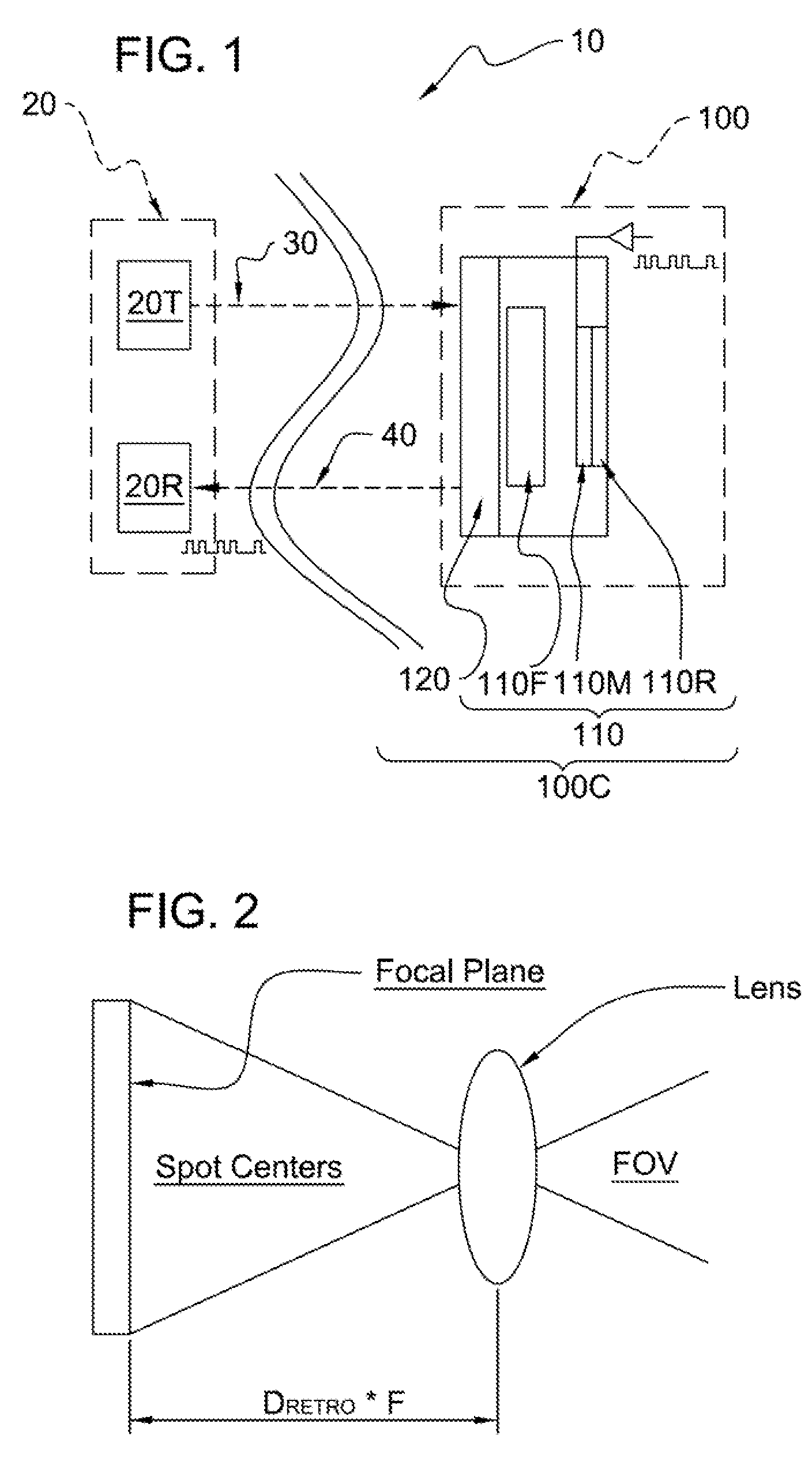
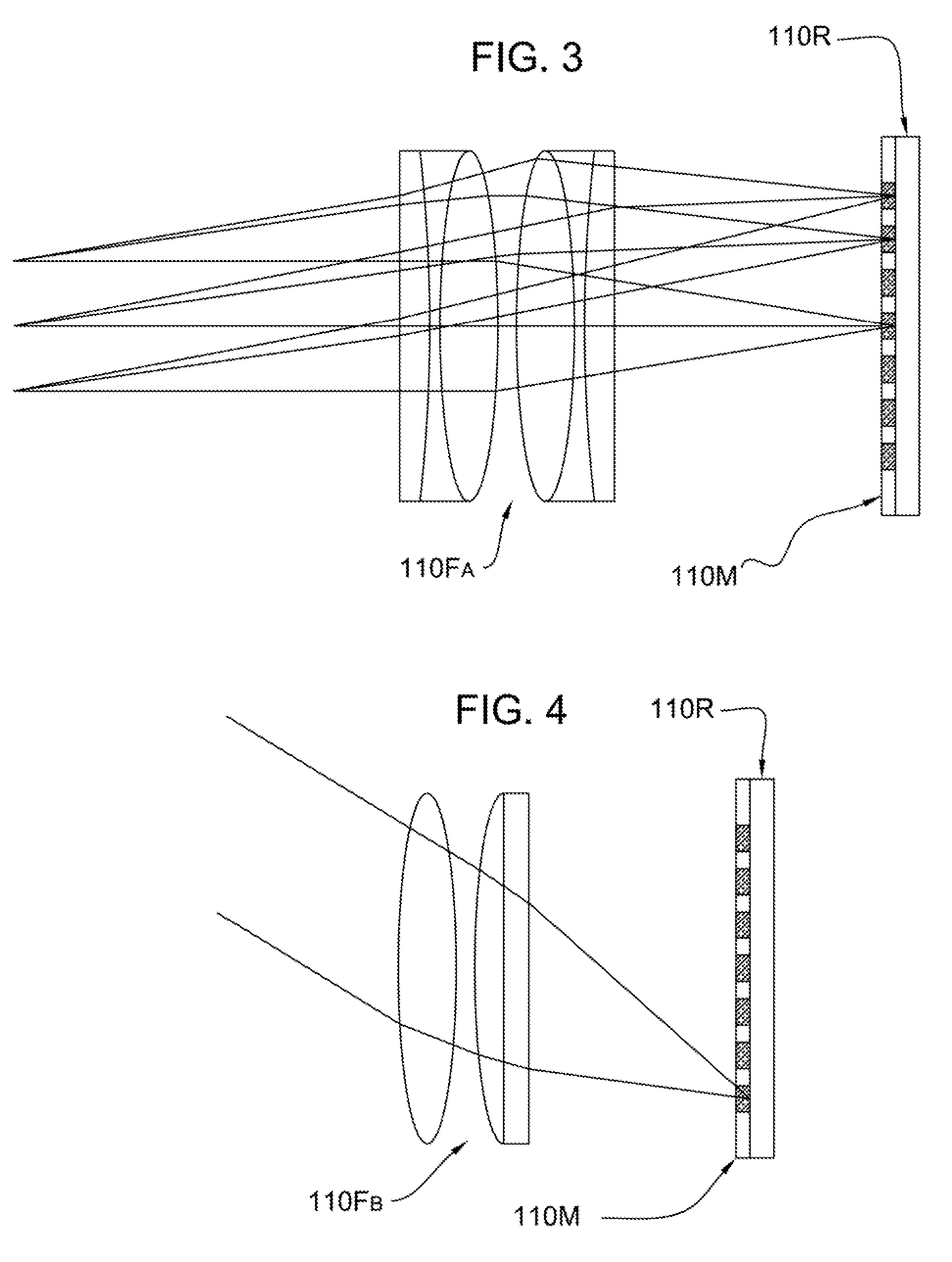
InactiveUS20070297805A1Reduce field of viewMultiple station single light sourceCommunications systemModulating retro-reflector
An optical communicating system and method thereof includes first and second terminals. The first terminal has a transmitter for transmitting an interrogating light beam and a receiver for receiving the interrogating light beam. The second terminal has a cats-eye modulating retroreflector (MRR), which includes a modulator for modulating the interrogating light beam received from the transmitter an optical focusing device for focusing the interrogating light beam from the transmitter to the modulator, and a reflector for reflecting the modulated light beam to the receive. It can include a beam deflector positioned at the aperture of the optical focusing device of the catseye MRR to reduce the field of view of the cats-eye MRR, It can also include an angle of arrival sensor for sensing the angle of arrival of the interrogating beam at the second terminal. One or more pixels of the modulator can be activated to permit the activated pixel(s) to modulate the interrogating beam, which is reflected back to the receiver, and the beam deflector both can be controlled based on the angle of arrival detected
Owner:RABINOVICH WILLIAM +1
Methods, apparatus, and computer-program products for increasing accuracy in cone-beam computed tomography
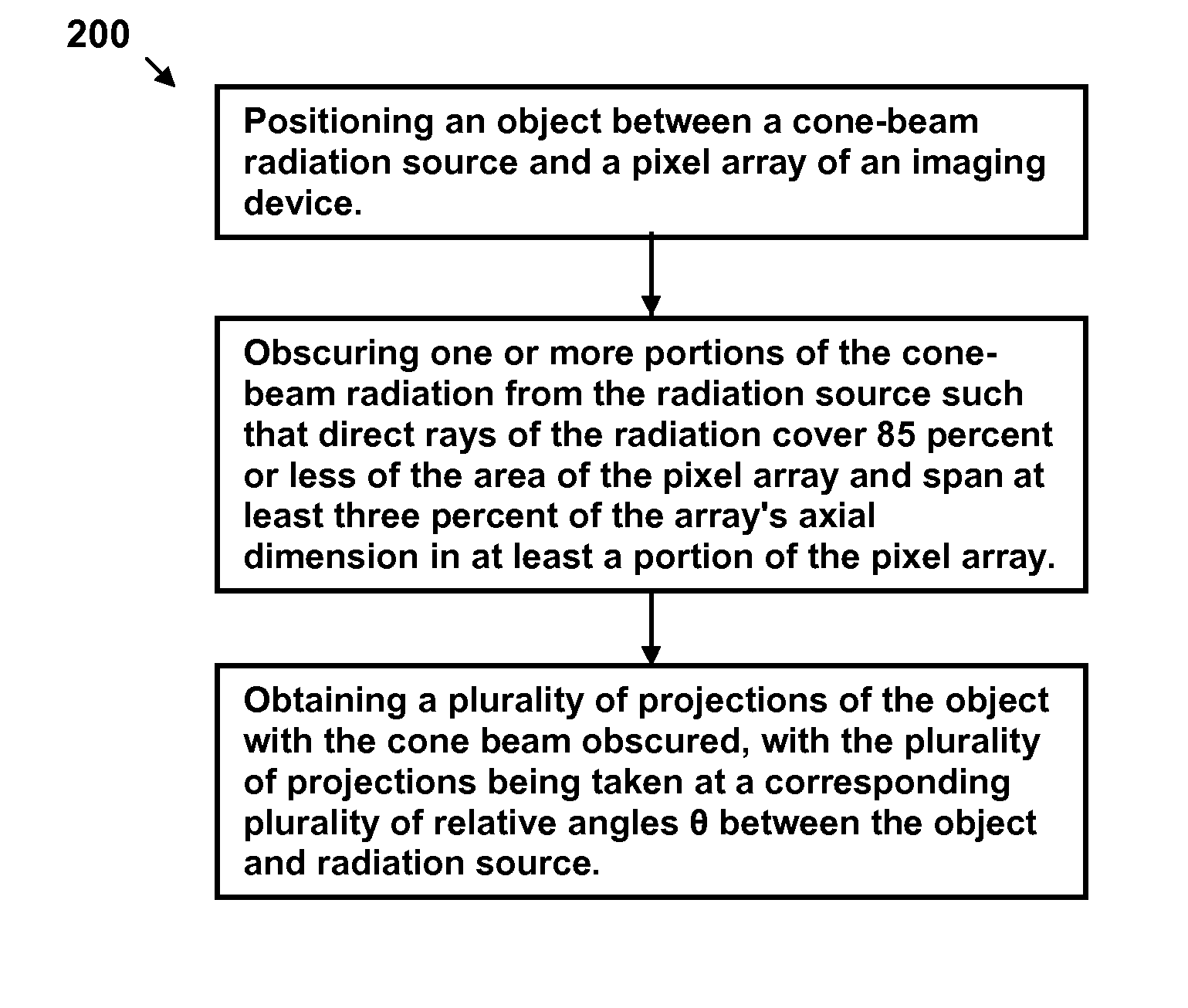
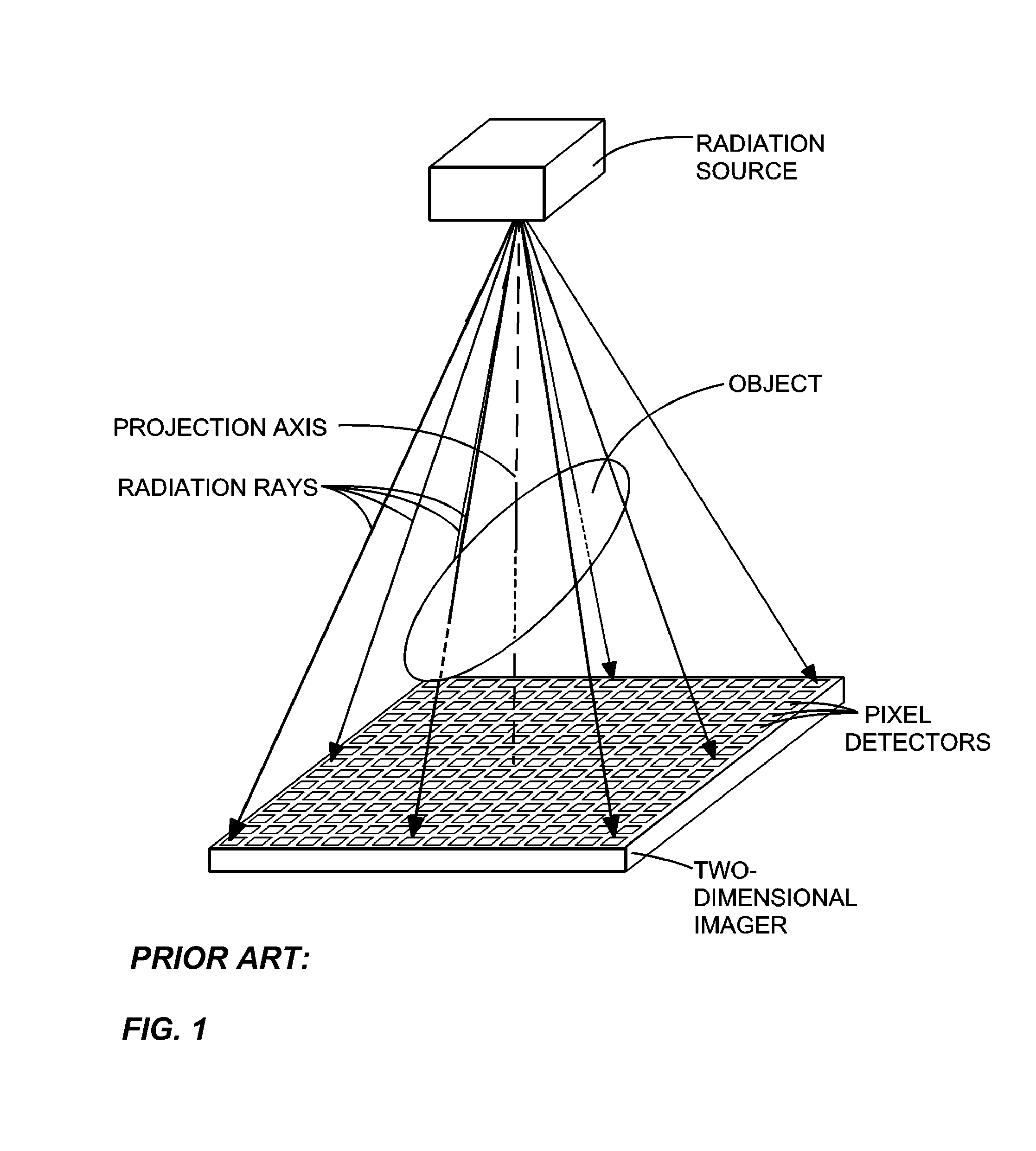
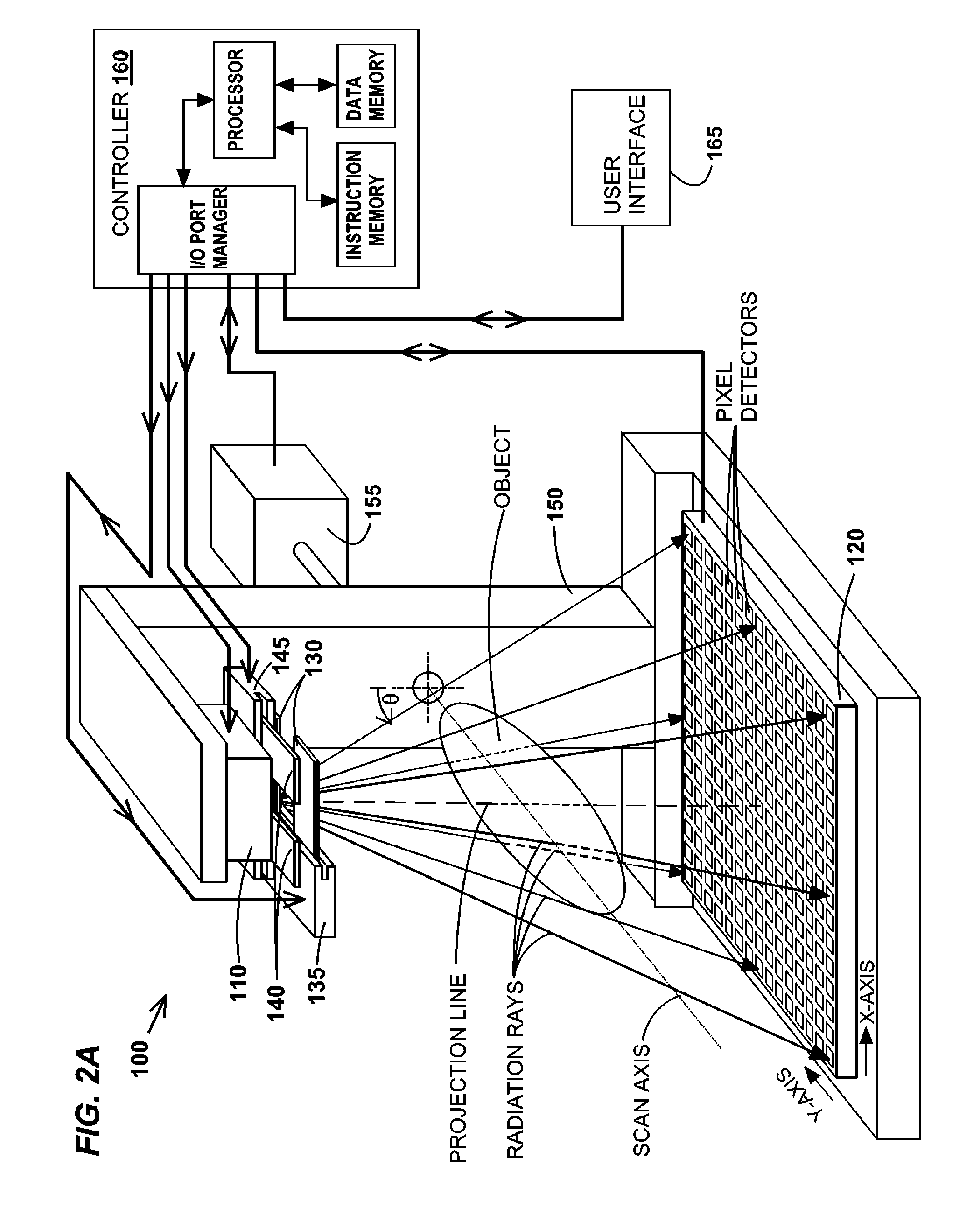
ActiveUS8009794B2Reduce errorsImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSources of errorTomography
Disclosed are methods, systems, and computer-product programs for increasing accuracy in cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) by obscuring portions of the radiation source so that the radiation only passes through the specific areas of the patient related to the regions-of-interest to the doctor. The obscuring action causes less radiation scattering to occur in the patient's body, thereby reducing a major source of error in the image accuracy caused by scattered radiation. Scattered radiation received by detector pixels that are obscured by direct-line of sight radiation may be used to estimate the scattered radiation in the un-obscured portion, which can be used to further increase the accuracy of the image.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Method for obtaining amplitude and phase dependencies of RF pulses for spatially selective excitation
ActiveUS20100253336A1Reduce lengthSpectral selectivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRRadio frequencyNuclear magnetic resonance
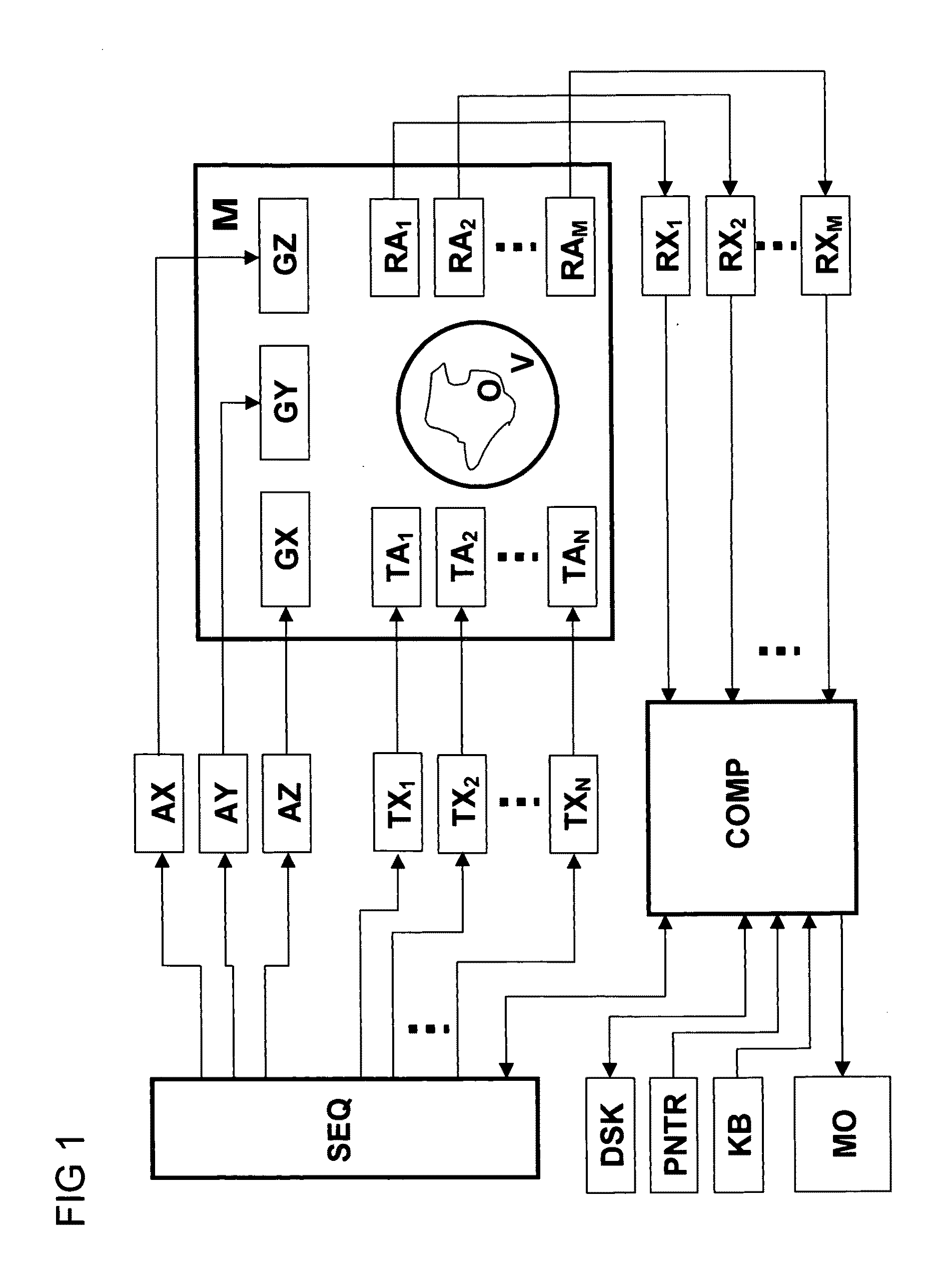
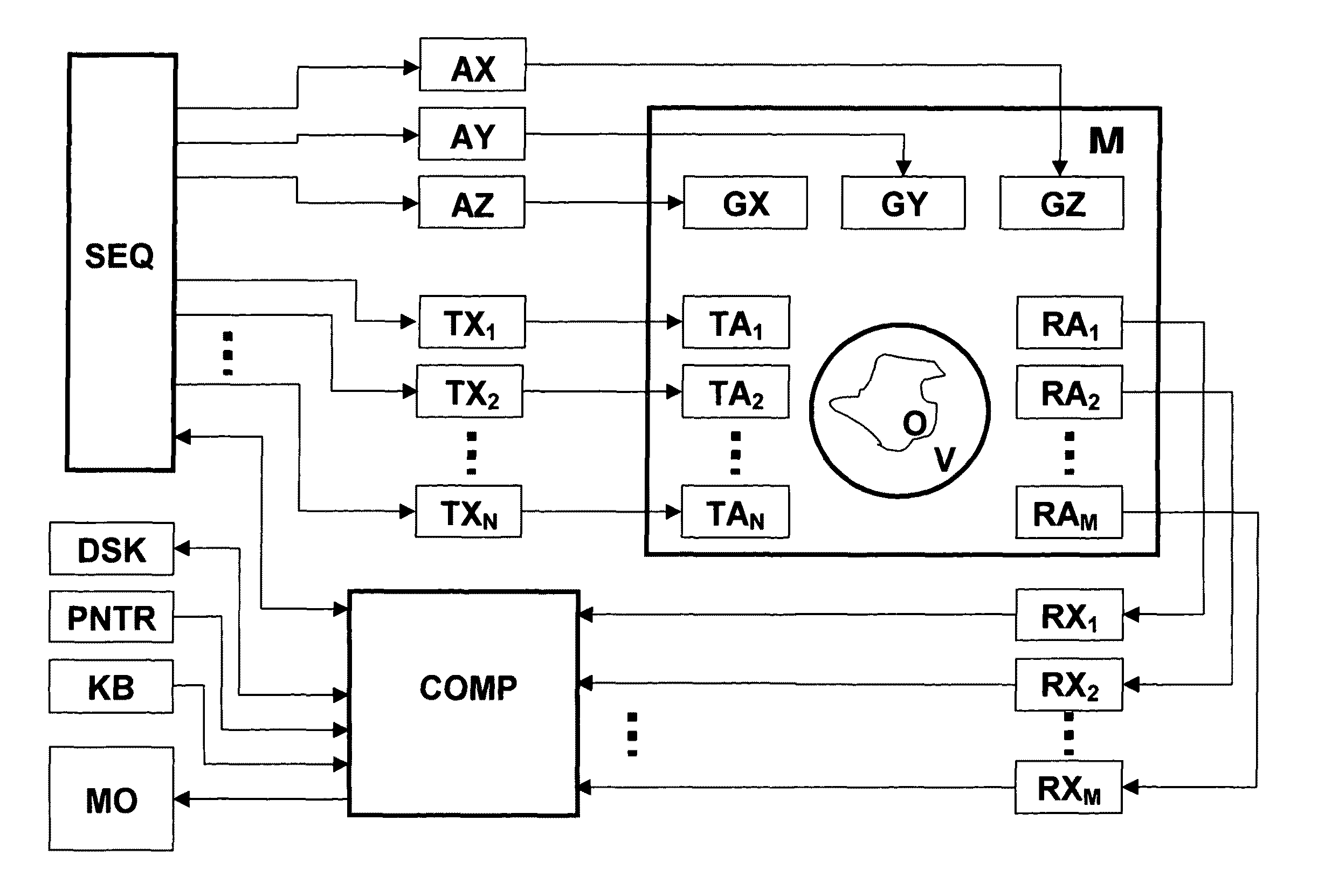
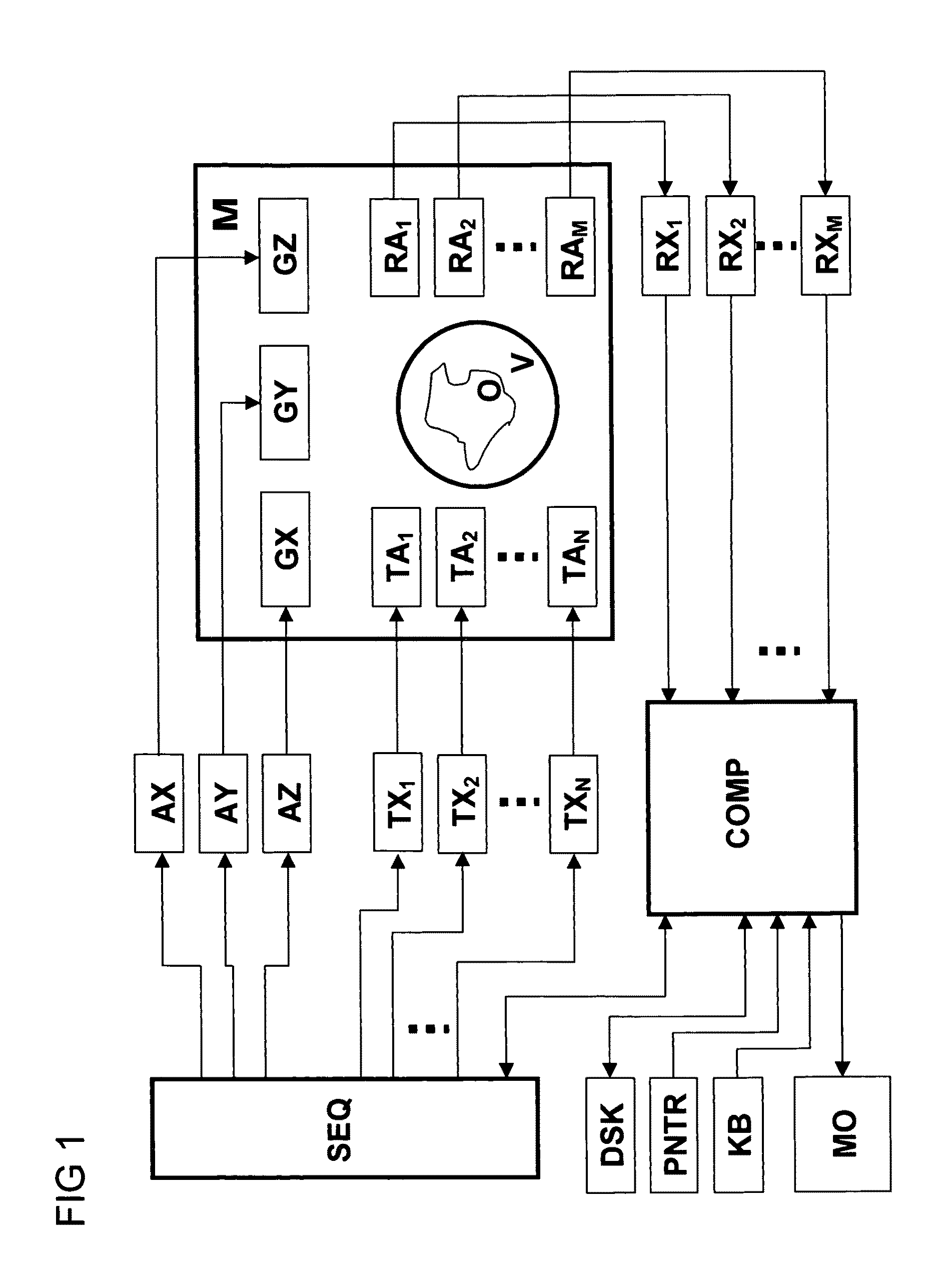
A method for obtaining amplitude and phase dependencies of radio frequency pulses, which are irradiated within the scope of a main magnetic resonance experiment for generating a predetermined n-dimensional spatial distribution (n>=1) of transverse magnetization in an object by means of at least one radio frequency transmitting antenna of a magnetic resonance measuring system in combination with spatially and temporally varying additional magnetic fields which are superimposed on the static and homogeneous base field of the magnetic resonance measuring system and change the transverse magnetization phase in the object in dependence on location and time is characterized in that, prior to performance of the main experiment, a preparational measurement is performed in which the change with time of the transverse magnetization phase in the object under the action of the additional magnetic fields is measured in a position-resolved fashion and the amplitude and phase dependencies of the radio frequency pulses for the main experiment are calculated on the basis of this change with time of the transverse magnetization phase, which is measured in a position-resolved fashion. In this fashion, experimental imperfections in the form of unintentional additional magnetic fields can be measured, taken into consideration and compensated for.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Tomosynthesis mammography system with enlarged field of view
InactiveUS20120224664A1High image resolutionLarge field of viewMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisX-ray
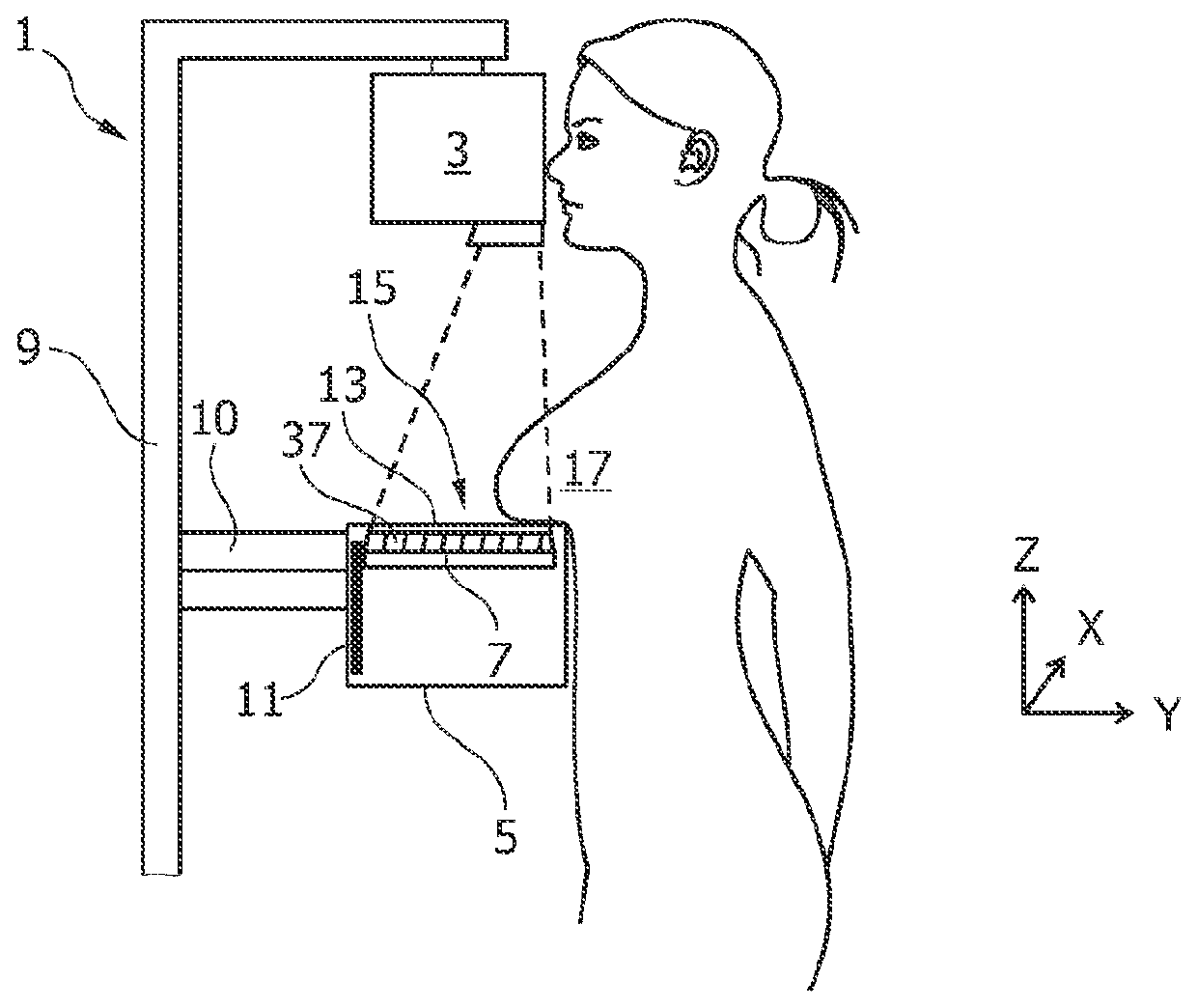
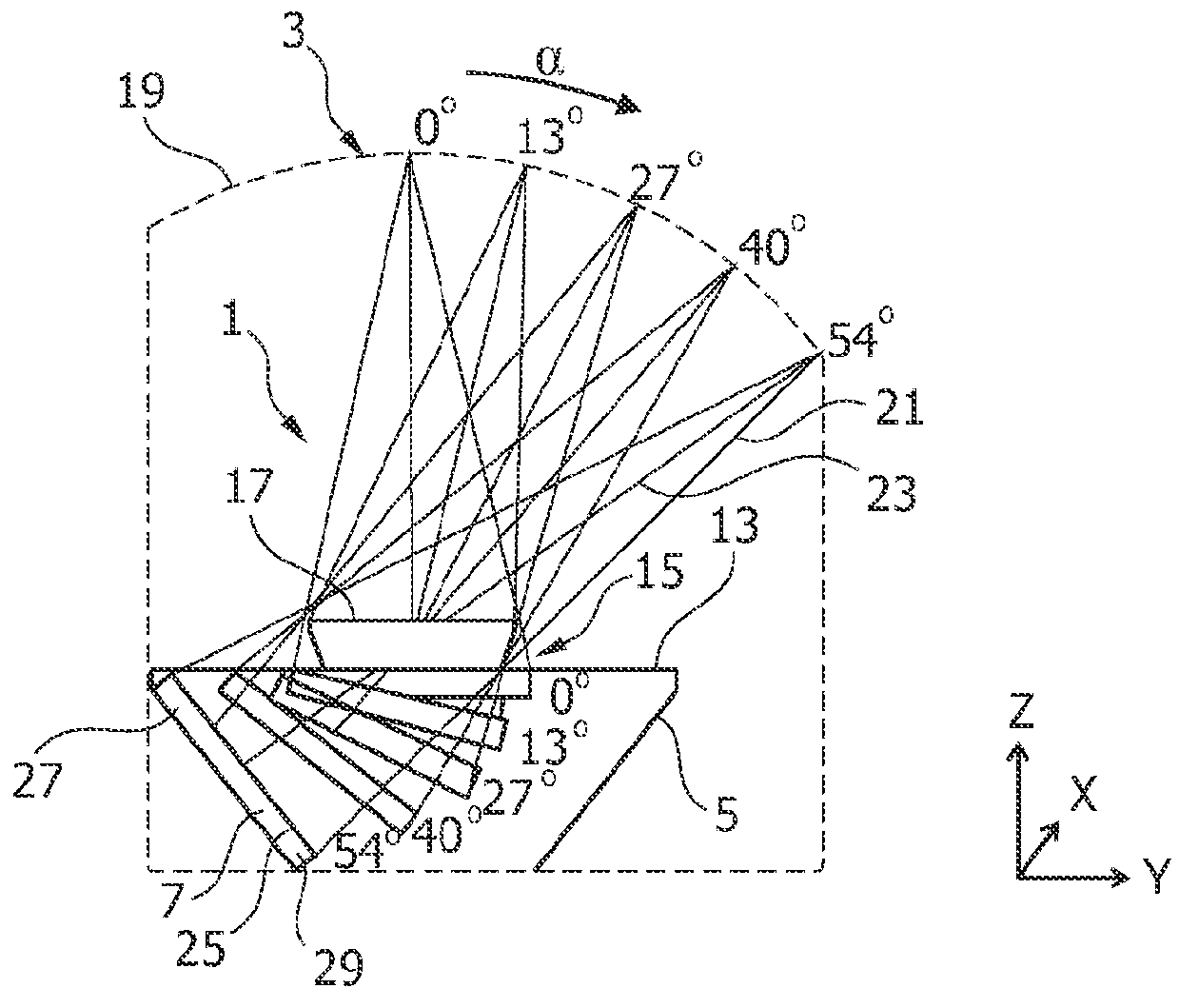
A tomosynthesis system for acquiring a three-dimensional image of an object such as a mammography image of a female breast is proposed. The tomosynthesis system (1) comprises an X-ray source (3), an X-ray detector (7), a support arrangement (15) and a moving mechanism (11). The X-ray source (3) and the X-ray detector (7) are adapted for acquiring a plurality of X-ray images while irradiating the object (17) with an X-ray beam (21) from a plurality of tomographic angles α. The moving mechanism (11) is adapted to pivot the X-ray detector (7) in positions such that for each tomographic angle α a detection surface (25) of the X-ray detector (7) is oriented to be substantially perpendicular to the X-ray beam (21). The moving mechanism (11) is adapted to move the X-ray detector (7) in positions such that a distance between the X-ray source (3) and the detector (7) is increased with increasing tomographic angle a thereby enabling that the X-ray detector (7) remains within an enlarged housing (5) during an entire tomographic image acquisition procedure.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Methods, Apparatus, and Computer-Program Products for Increasing Accuracy in Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
ActiveUS20090190714A1Reduce errorsImproving Imaging AccuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersComputer scienceCone beam computed tomography
Disclosed are methods, systems, and computer-product programs for increasing accuracy in cone-beam computed tomography.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Method and system for controlling radiation intensity of an imaging system
ActiveUS20080037709A1Minimize distortionMinimum delayRadiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationUltimate tensile strengthRadiation beam
A system for and a method of controlling a spatial distribution of radiation intensity in a beam of radiation is provided. The system includes a control device located to receive the initial beam of radiation from the radiation source. The control device includes a first radiation absorbing structure located at a position in generally superposing alignment relative a position of a second radiation absorbing structure. Each first and second radiation absorbing structure is operable to independently articulate. The modulator configuration signal is operable to cause adjustment of the position of at least one of the first and second radiation absorbing structures relative to the other so as to selectively adjust a spatial distribution of radiation intensity of a modulated beam.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals with use of local spatially encoding magnetic fields
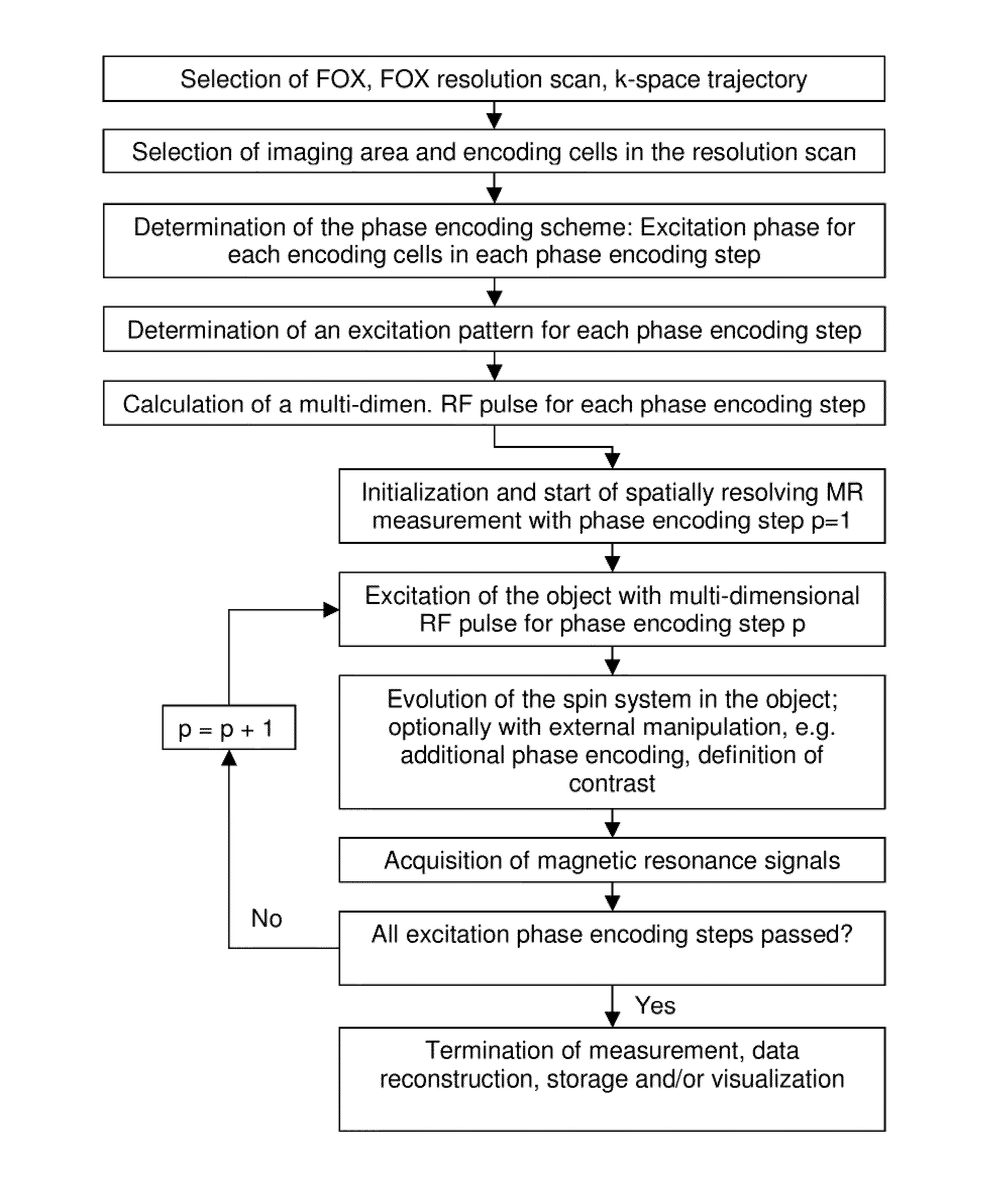
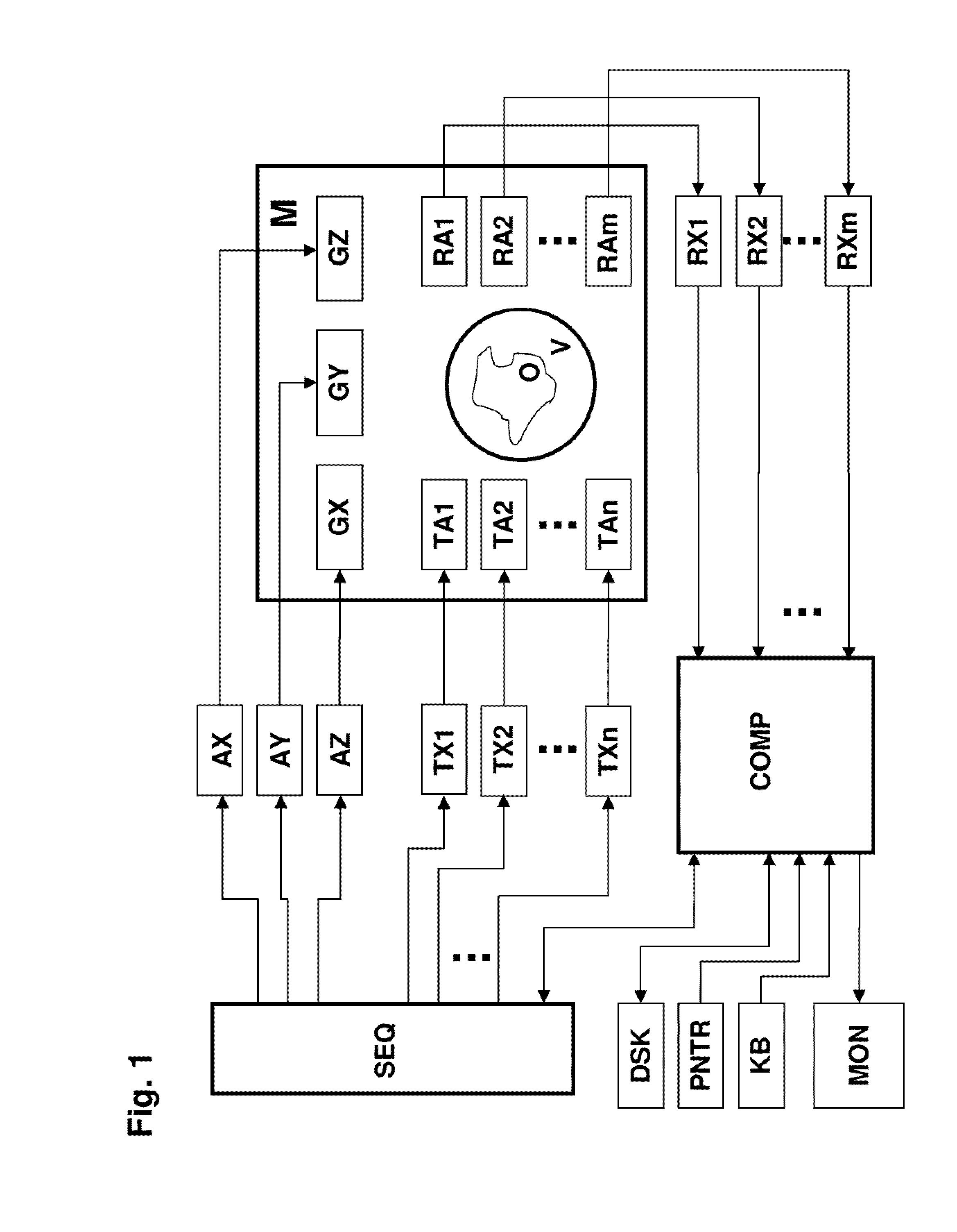
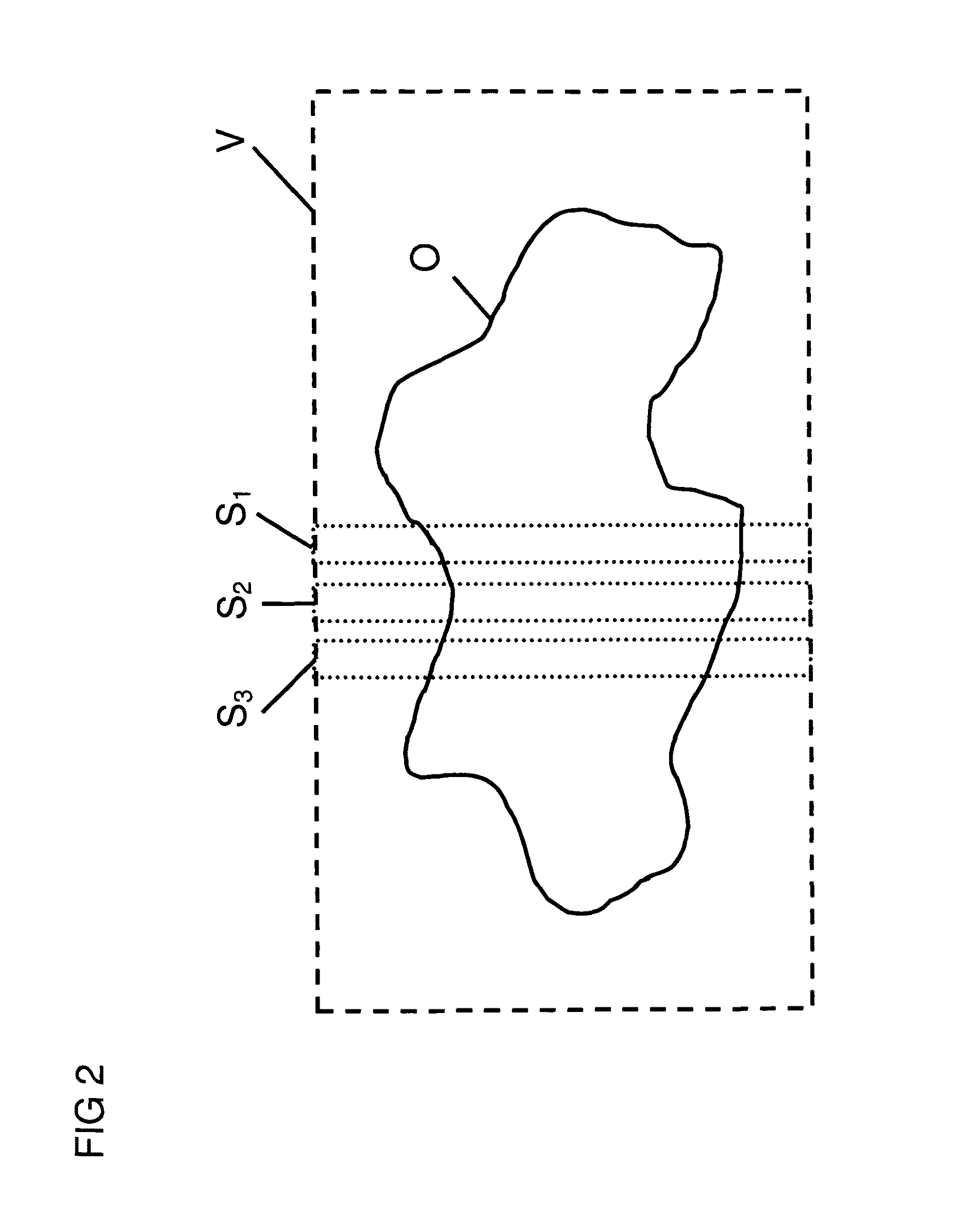
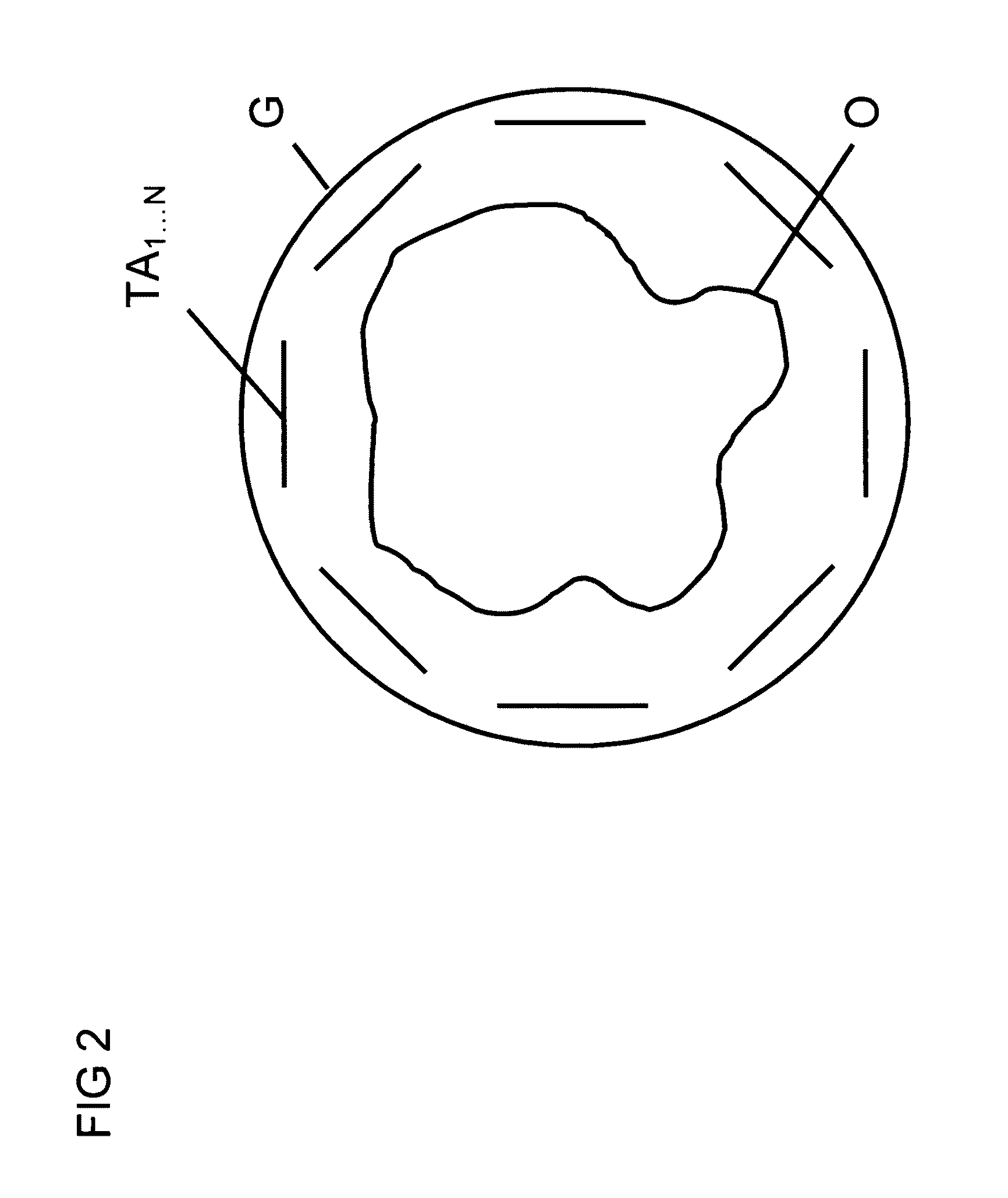
InactiveUS7843195B2Reduce field of viewReduced measurement timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationExcitation pattern
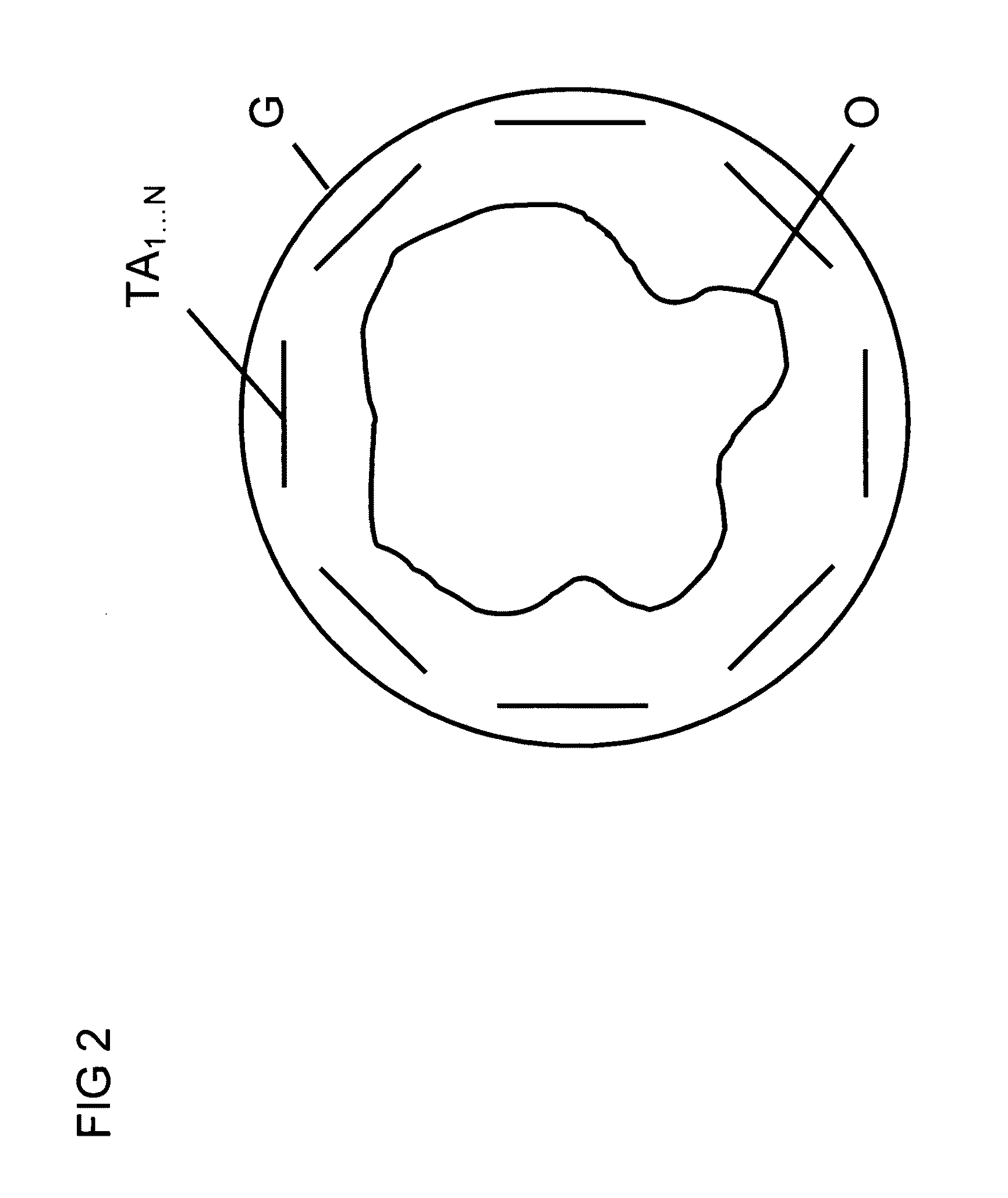
A method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance (MR) signals from an imaging region has a preparatory step in which an encoding scheme with I phase encoding steps is defined, for each phase encoding step according to the phase encoding scheme, an excitation pattern of the transverse magnetization is defined and RF pulses to be irradiated to implement this pattern are calculated, wherein the same phase is defined at all spatial locations of the imaging region within an MSEM region and, in the execution step, according to the spatial encoding scheme each encoding step is performed I times according to the phase encoding scheme, wherein selection of the imaging region, amplitude modulation, and phase encoding are performed with the calculated RF pulses during excitation of the nuclear spin. This results in unique determination of the spatial distribution of the magnetic resonance signals with a simple RF receiver configuration using local gradient systems.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Machine vision based LED detection device and detection method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of machine vision, in particular to a machine vision based LED detection device and a detection method thereof. The LED detection device comprises a carrier plate clamp, a camera obscura and an industrial personal computer, an industrial camera connected with the industrial personal computer is arranged in the camera obscura, a prime lens is arranged on the industrial camera, a condensation plate disposed at the front end of the prime lens is further arranged in the camera obscura, at least two positioning lamps are arranged on a plane of the condensation plate, through holes are formed in a coordinate system plane formed by the positioning plates, and the carrier plate clamp is connected with the through holes through a conduction fiber. The machine vision based LED detection device can detect LEDs quickly, efficiently and stably with low cost, and is applicable to any application environment needing to detect a large quantity of printed circuit board LEDs; the detection method can quickly and efficiently complete detection of dozens of LEDs, and is simple, convenient and rapid to operate.
Owner:华高科技(苏州)有限公司
Method for presenting content based on checking of passenger equipment and distraction
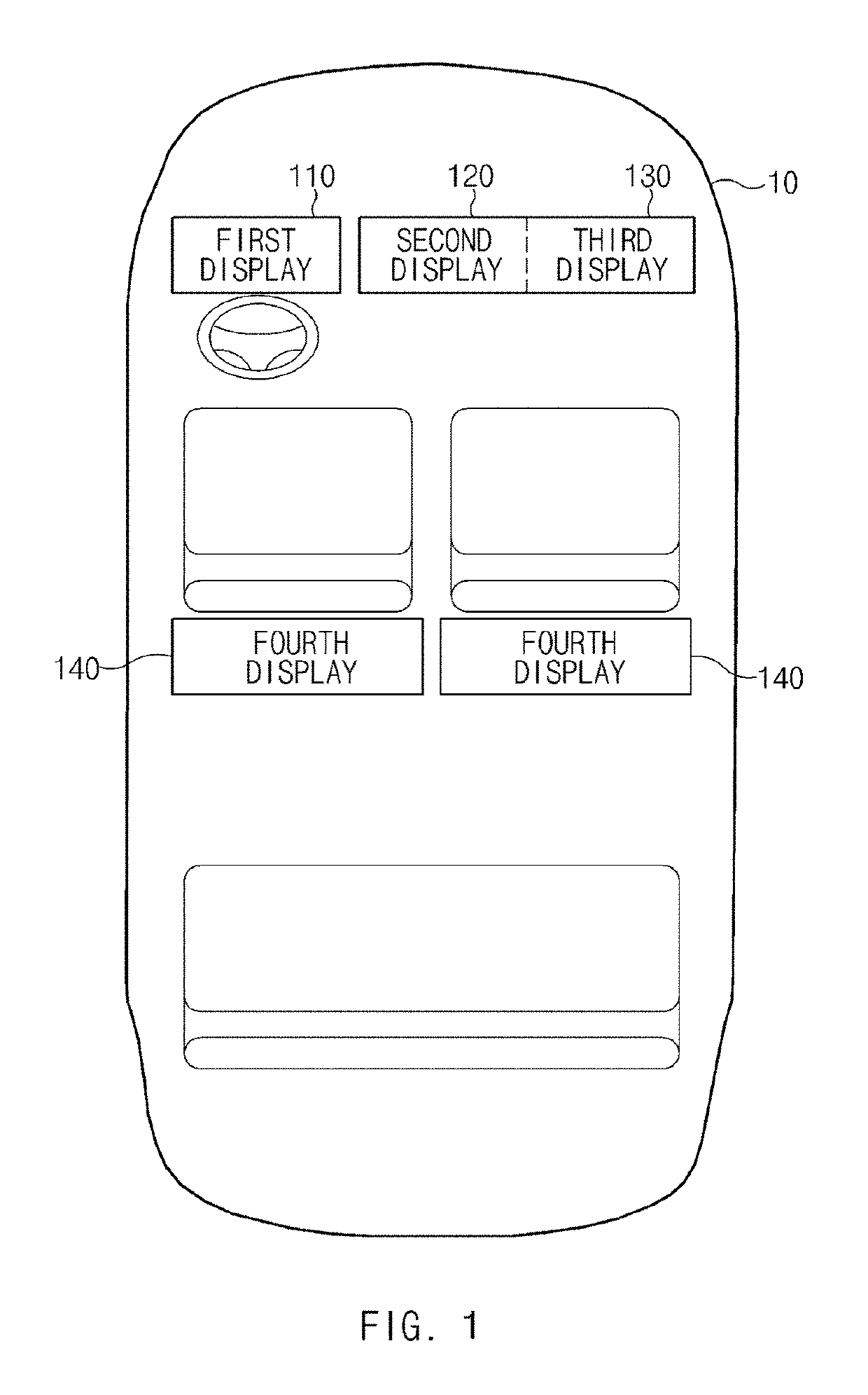
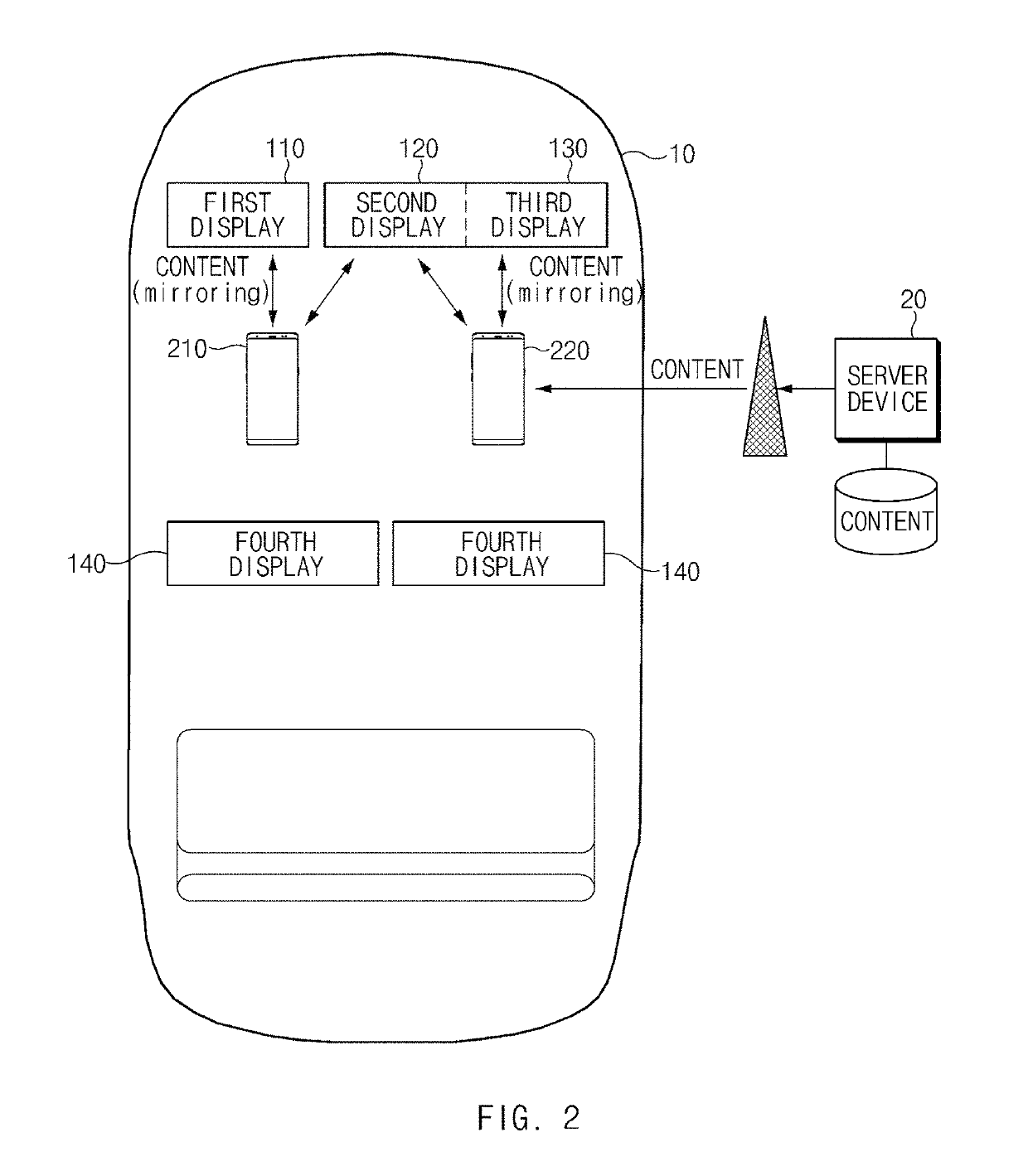
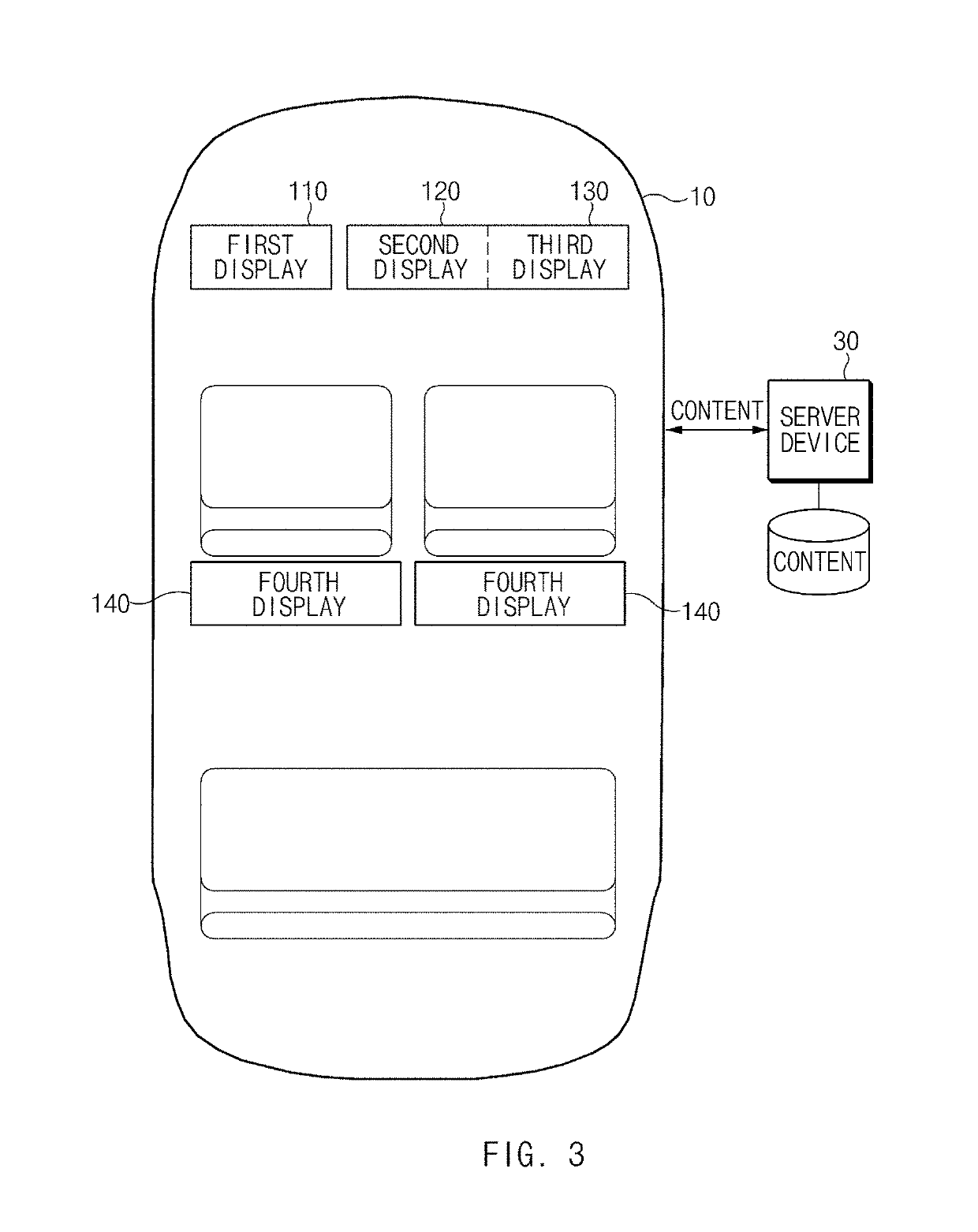
ActiveUS20190196679A1Reduce field of viewNarrow downDashboard fitting arrangementsStatic indicating devicesDistractionComputer science
A vehicular electronic device includes a first communication circuit; a second communication circuit, a first display corresponding to a driver-seat and a second display corresponding to a non-driver seat, and a processor, wherein the processor is configured, upon receiving content via the first communication circuit, to determine a display to present the received content among the first display or the second display, upon determination that the first display is to present the received content, to determine, based on vehicle information received from the second communication circuit, whether a user is in a driving mode, upon determination that the user is in the driving mode, to identify a type of the received content, when the received content is of a first type, to present the received content on the first display, and when the received content is of a second type, not to present the received content on the first display.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device for visually confirming forward direction
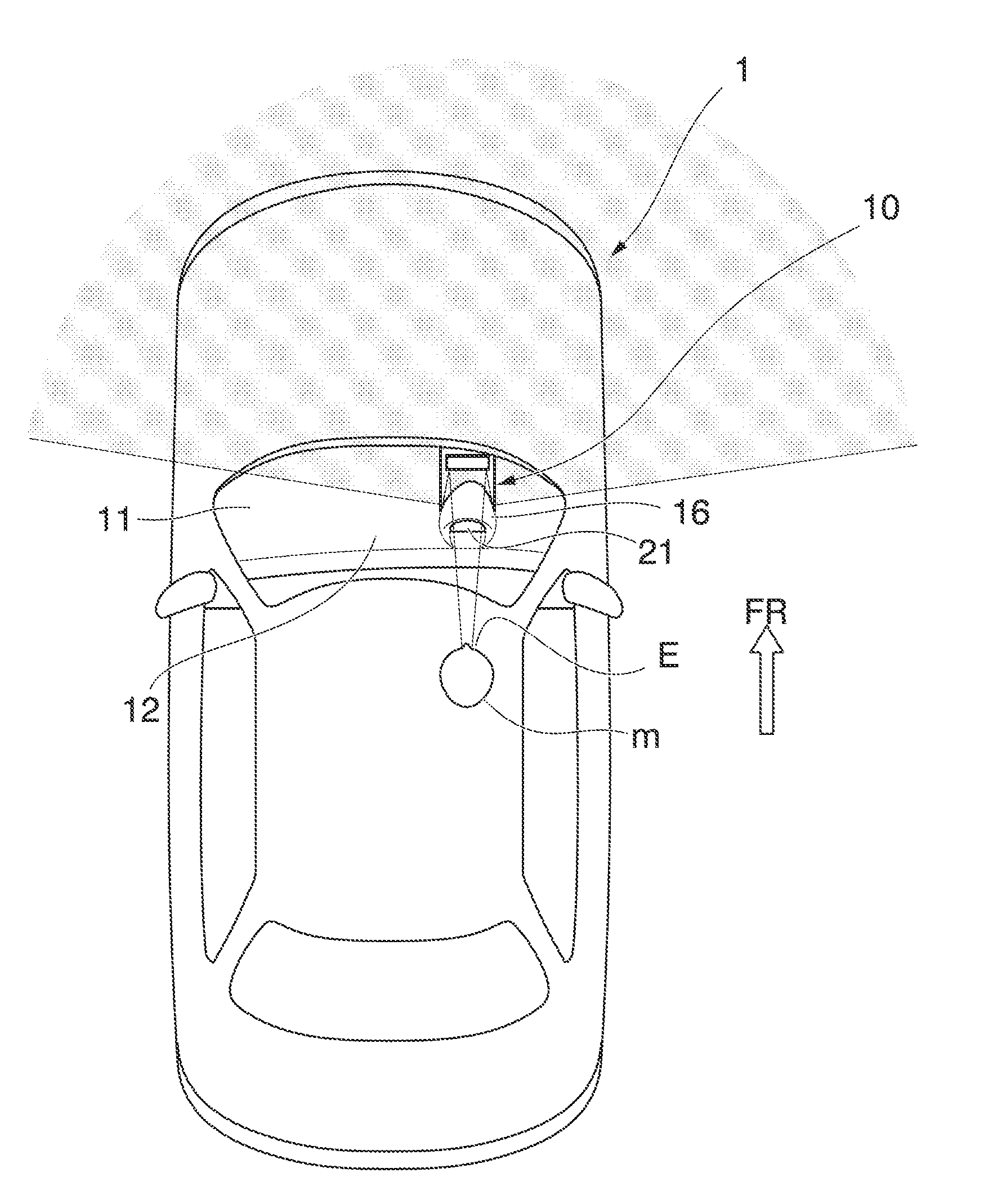
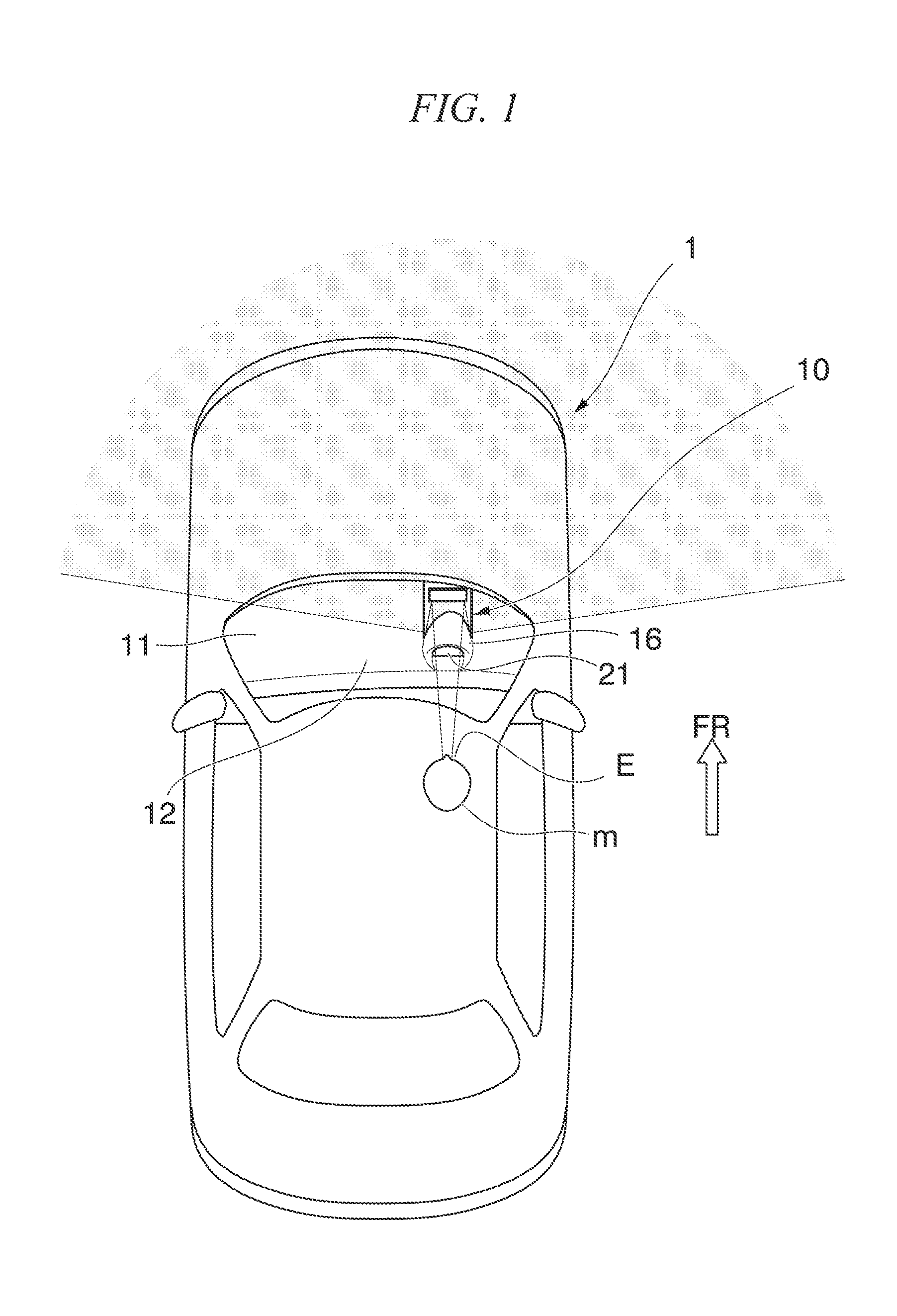
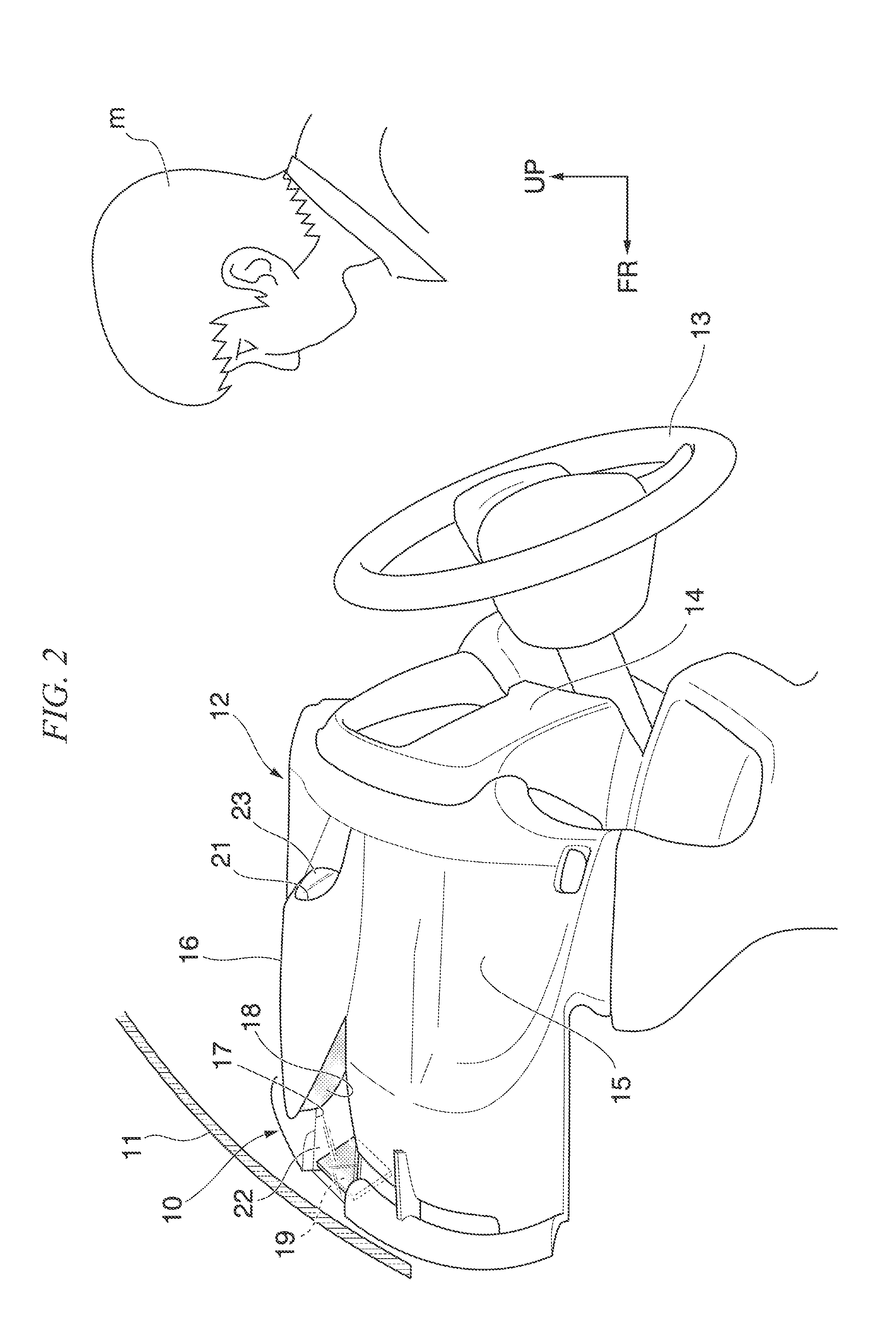
A device for visually confirming a forward direction that allows a crew member to visually confirm a desired range on the forward side of a vehicle includes a first reflecting mirror that reflects the desired range and a second reflecting mirror that reflects a reflected image reflected on the first reflecting mirror toward the crew member, the first reflecting mirror is arranged on a dashboard that is located inside the vehicle, and the second reflecting mirror is arranged on a lower side of the dashboard, and a first light transmitting part and a second light transmitting part are disposed in an area that connects the first reflecting mirror and the second reflecting mirror and an area that connects the second reflecting mirror and an eye-point of the crew member.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
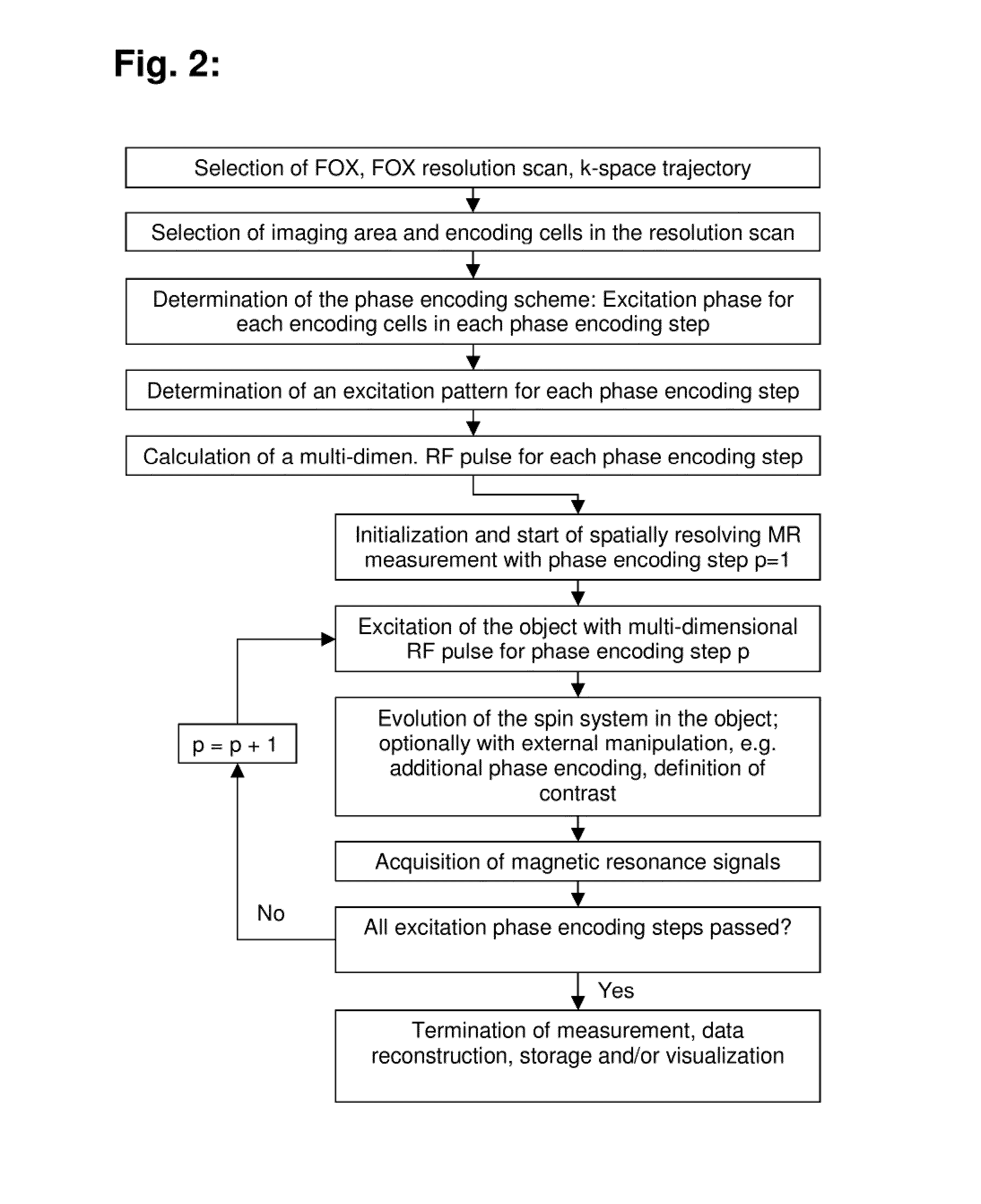
Method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals through multi-dimensional RF excitation pulses
ActiveUS8082127B2Short relaxation timeEliminate delaysUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpatial encodingMulti dimensional
A method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals from an imaging area, wherein nuclear spins are excited in a spatially encoded fashion through multi-dimensional RF pulses, is characterized in that in a definition step, a resolution grid with resolution grid cells is predetermined, and in accordance with a predetermined phase encoding scheme, an excitation pattern is defined for each phase encoding step, in which the amplitudes within the imaging area are set in accordance with a predetermined distribution identically for each phase encoding step. In a preparatory step, the amplitude and phase behavior of the RF pulses to be irradiated is calculated in accordance with a predetermined k-space trajectory for each defined complex excitation pattern.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
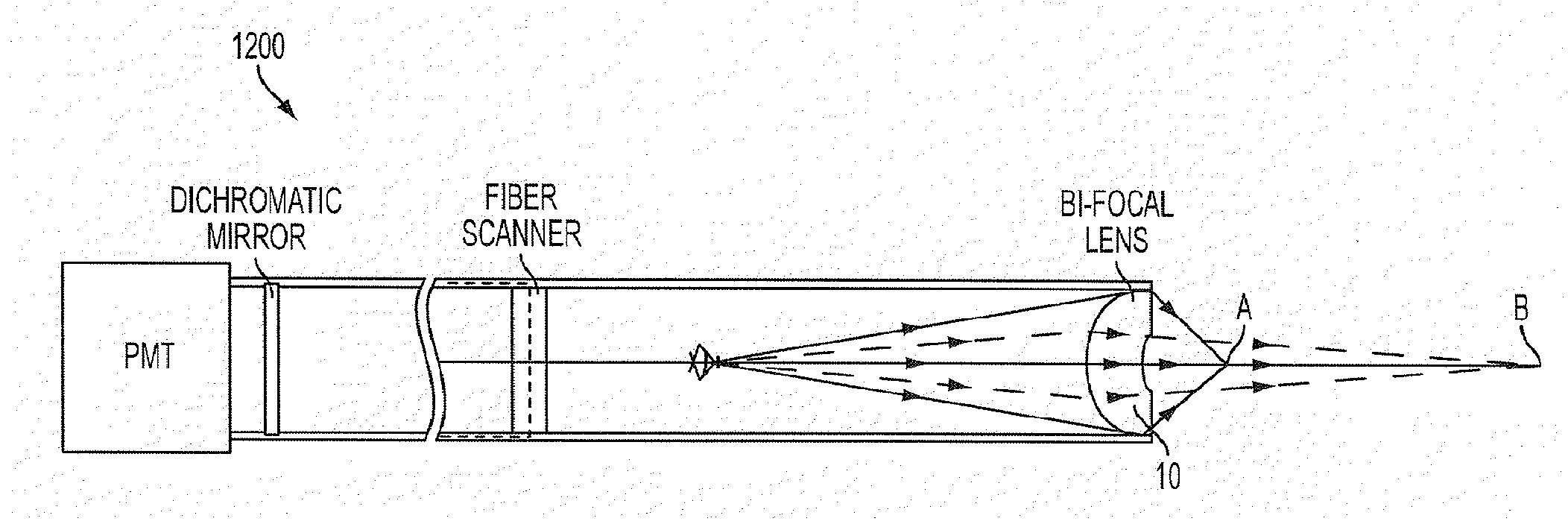
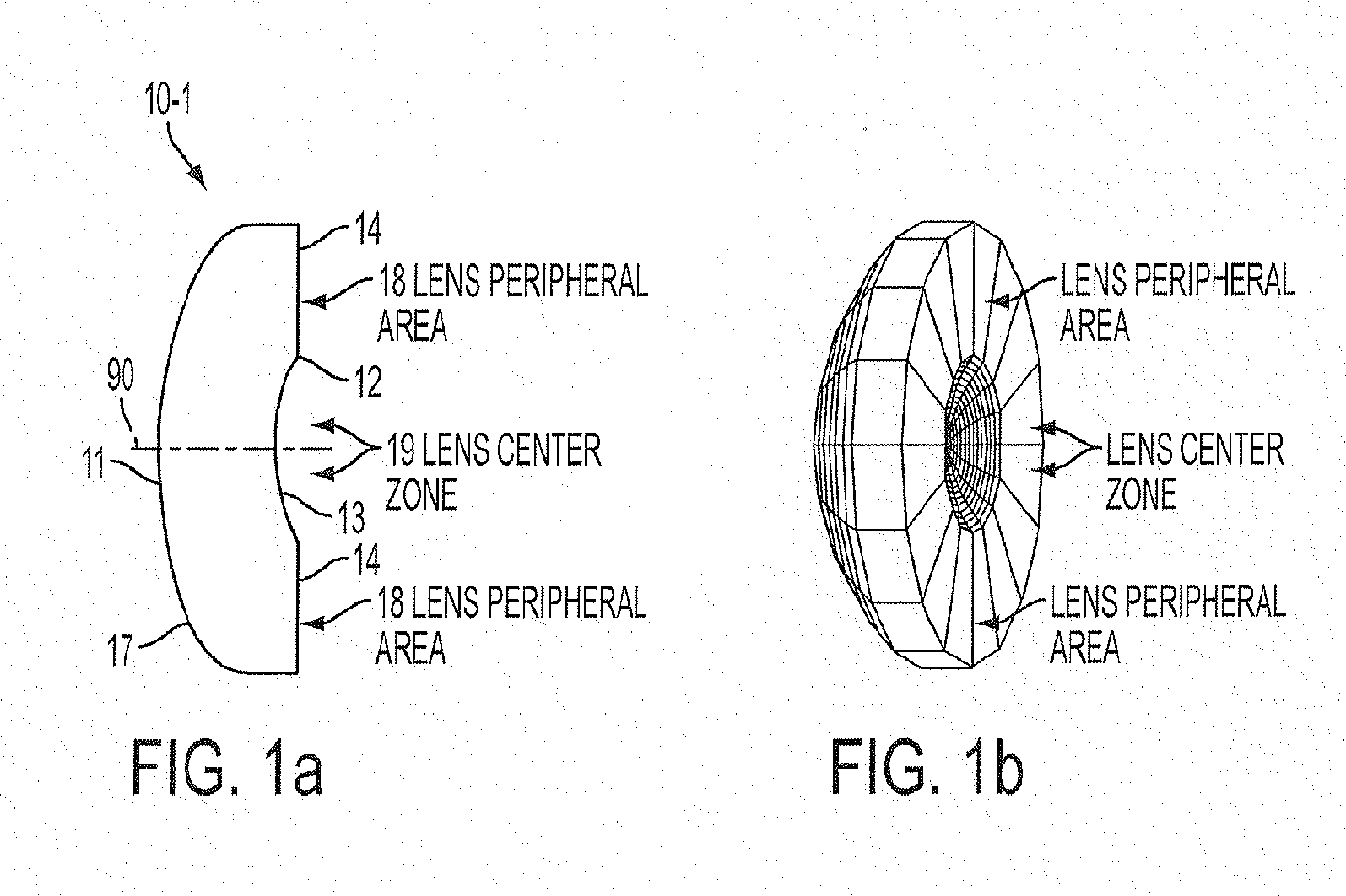
Multi-focal optical component, optical system, and imaging method
ActiveUS20130006056A1High resolutionReduce field of viewSurgeryEndoscopesCamera lensAnterior surface
An optical lens comprising a lens body that transmits light in an optical path there through, wherein the lens body consists of an anterior surface, a posterior surface, and a medium there between, further wherein one of the anterior surface and the posterior surface has a single curvature and the other of the anterior surface and the posterior surface has at, least two optical zones each having a different curvature. An optical system, comprising a multi-photon endoscope having a distal end, and the optical lens disposed in the distal end. A method for obtaining an image of an object comprising providing the multi-photon endoscope, propagating light from the endoscope scanner one optical zone of the lens to focus the light at a focus location, and propagating light from the scanner through a different optical zones of the lens to focus the light at a different focus location.
Owner:CORNELL UNIV - CORNELL CENT FOR TECH ENTERPRISE & COMMERICIALIZATION CCTEC
Component mounting machine
A rotary head is configured of at least two types of rotary heads, such as a first rotary head in which four suction nozzles are respectively held to be rotatable on the circumference, and a second rotary head in which the suction nozzles of which the number is more than four are respectively held to be rotatable on a pitch circle diameter which is the same as that of the suction nozzle of the first rotary head, the first rotary head is attached to the drive unit, and a control device which controls an angular position of the first rotary head and an angular position of the components suctioned to the suction nozzles, to be respectively controlled to be changed by 45 degrees when the components held by the suction nozzles are imaged by a component camera is provided.
Owner:FUJI MASCH MFG CO LTD
Apparatus and method for simultaneously acquiring multiple images with a given camera
InactiveUS20090102939A1Firmly connectedReduce field of viewTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSingle imageMultiple image
An apparatus and method for acquiring multiple images of a given scene. The apparatus allows a standard video imaging camera to simultaneously detect multiple images through the use of reflective surfaces. In at least one embodiment, the multiple images allow for a single image to be created having a high dynamic range. In another embodiment, method for efficiently determining an infrared image is provided.
Owner:VISION TECH INC
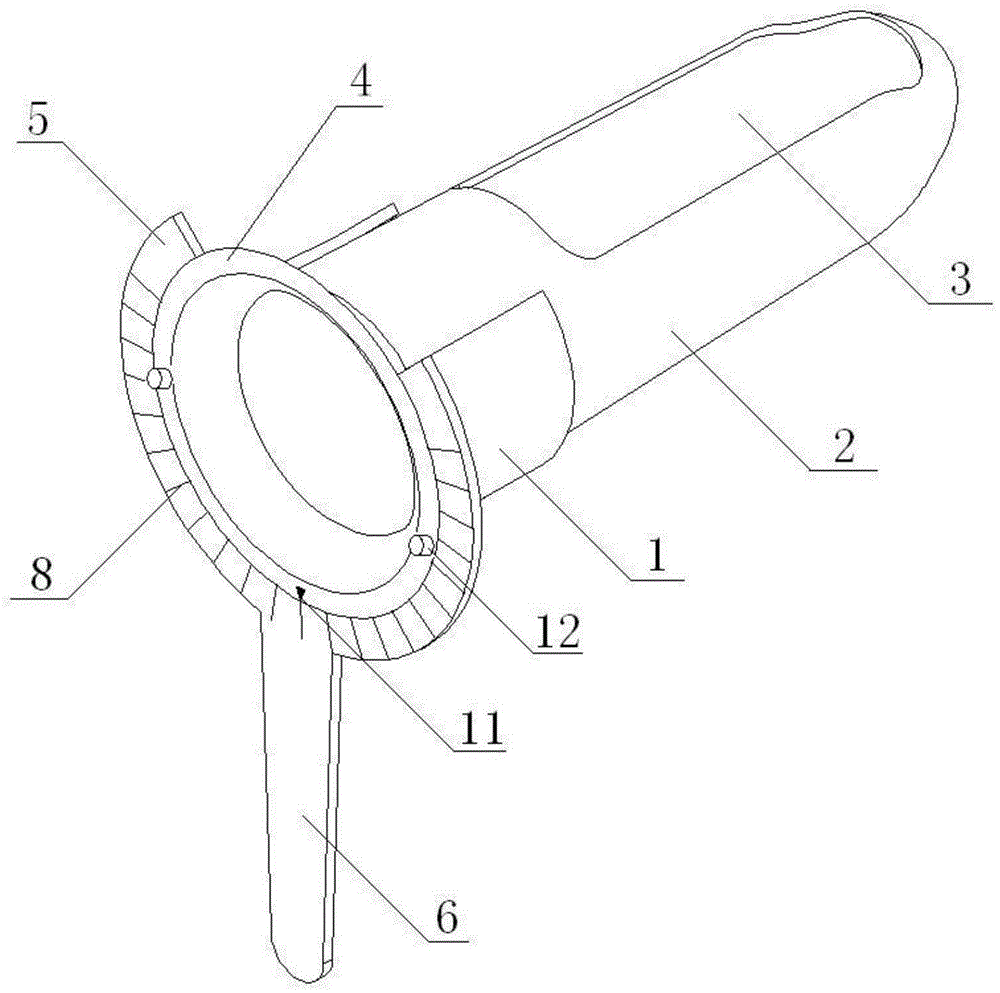
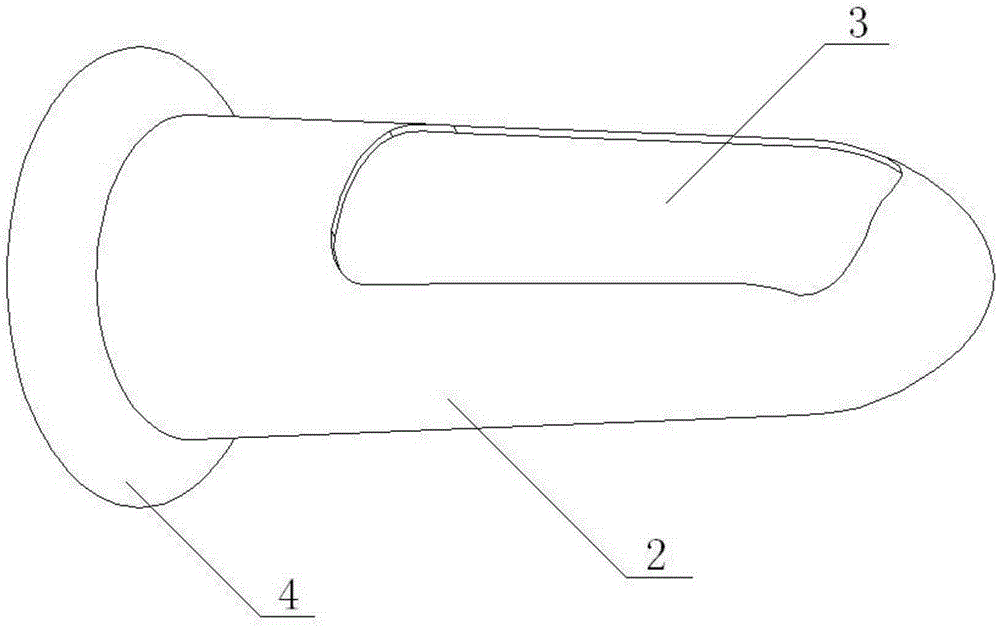
Rectum dilator
The invention belongs to the field of medical instruments and discloses a rectum dilator. The rectum dilator comprises an anus expansion ring and a movable casing, wherein the movable casing can be inserted into the anus expansion ring; the movable casing and the anus expansion ring can carry out opposite advancing and retreating and rotational motion; the near end of the movable casing is open and the far end is closed; a window region is formed in the side wall, close to the far end, of the casing; and a labial margin is arranged at the near end of the casing. The rectum dilator is simple in structure, diverse in function, easy to operate and low in cost, and can be operated by a single person; and medical workers for walking equipment are liberated.
Owner:丁永斌
Method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals in subvolumes of an object under examination
ActiveUS20150084627A1Permit separationShorten the lengthDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSpatially resolvedImaging quality
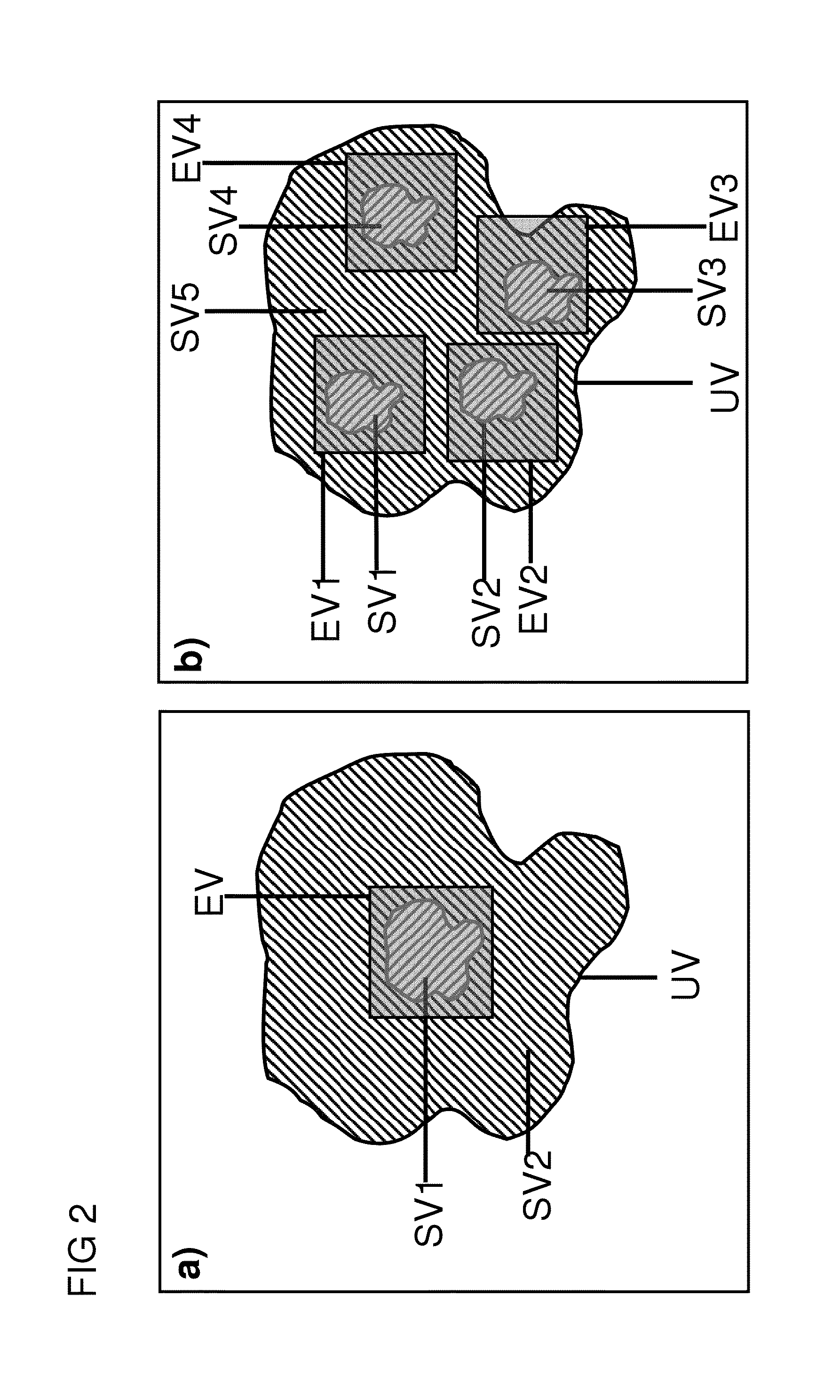
A method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals from at least one of N subvolumes predefines a reception encoding scheme and determines unique spatial encoding for at least one of the subvolumes but not for the entire volume under examination (UV). A transmission encoding scheme is also defined, wherein encoding is effected via the amplitude and / or phase of the transverse magnetization. The temporal amplitude and phase profile of the RF pulses is then calculated and each reception encoding step is carried out I times with variations according to the I transmission encoding steps in the transmission encoding scheme. The method makes it possible to largely restrict the spatially resolving MR signal encoding and image reconstruction to subvolumes of the object under examination without the achievable image quality sensitively depending on imperfections in the MR apparatus.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Device for viewing a digital image
InactiveUS20140368633A1Improve concentrationReduce field of viewColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsDigital imageVisual perception
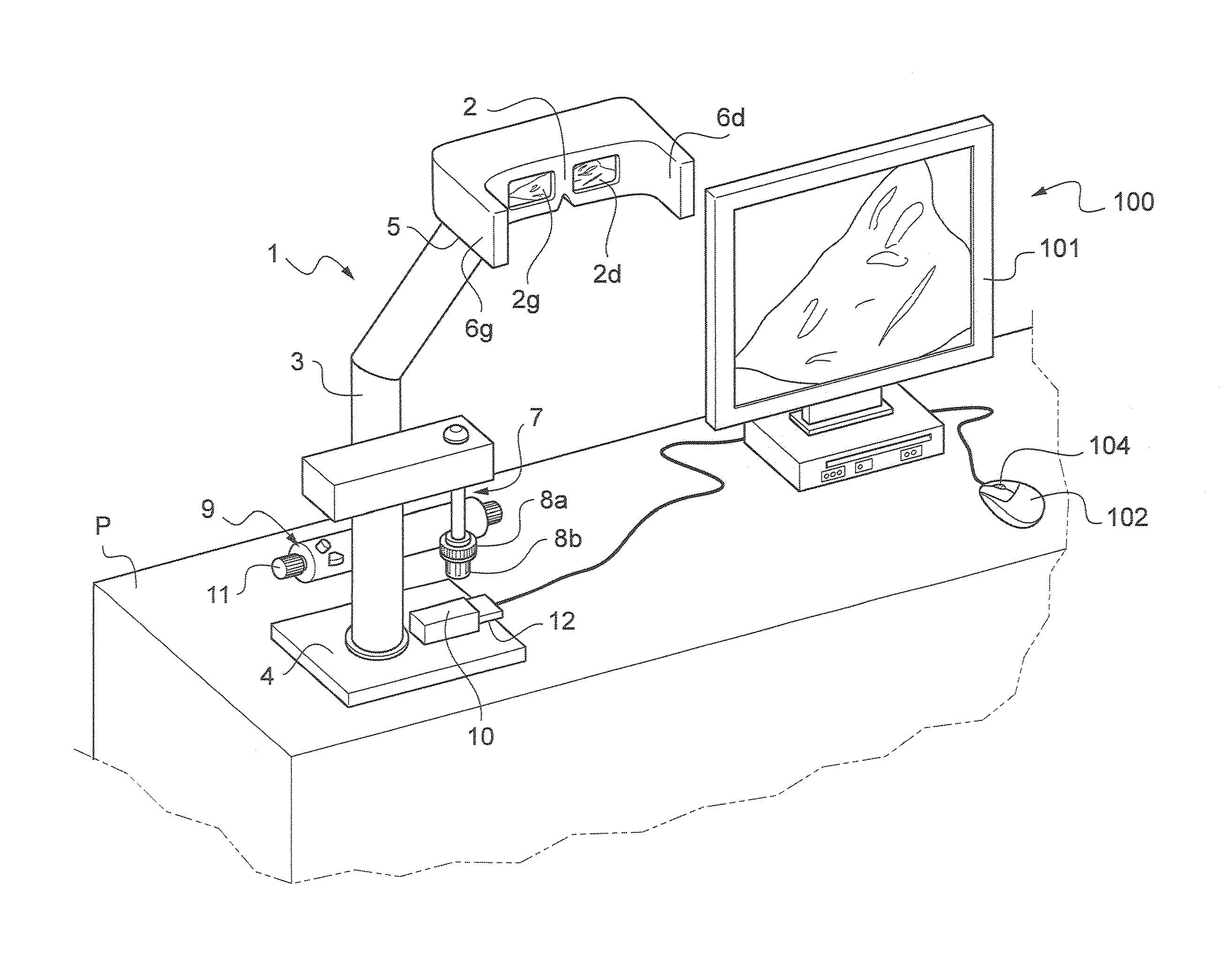
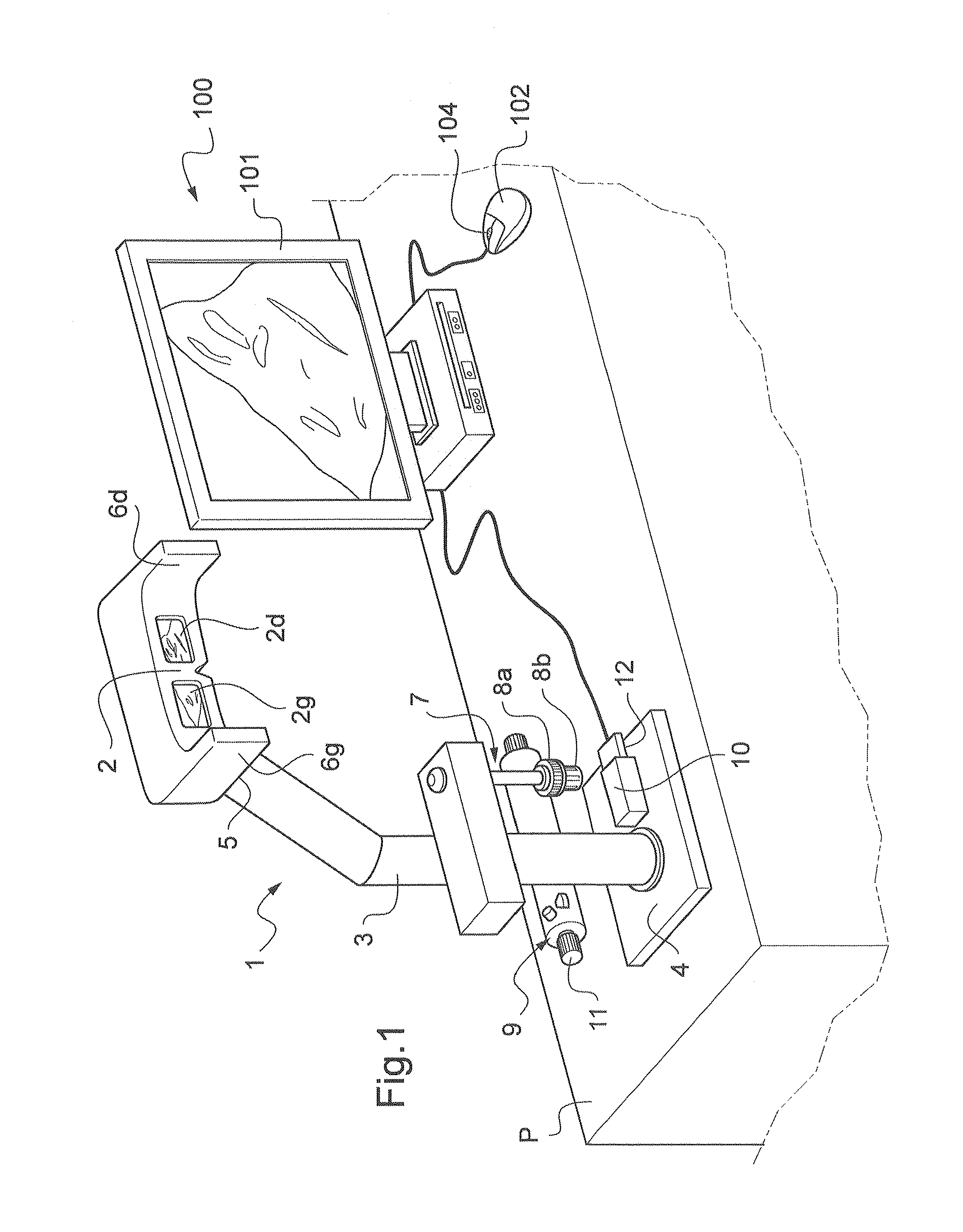
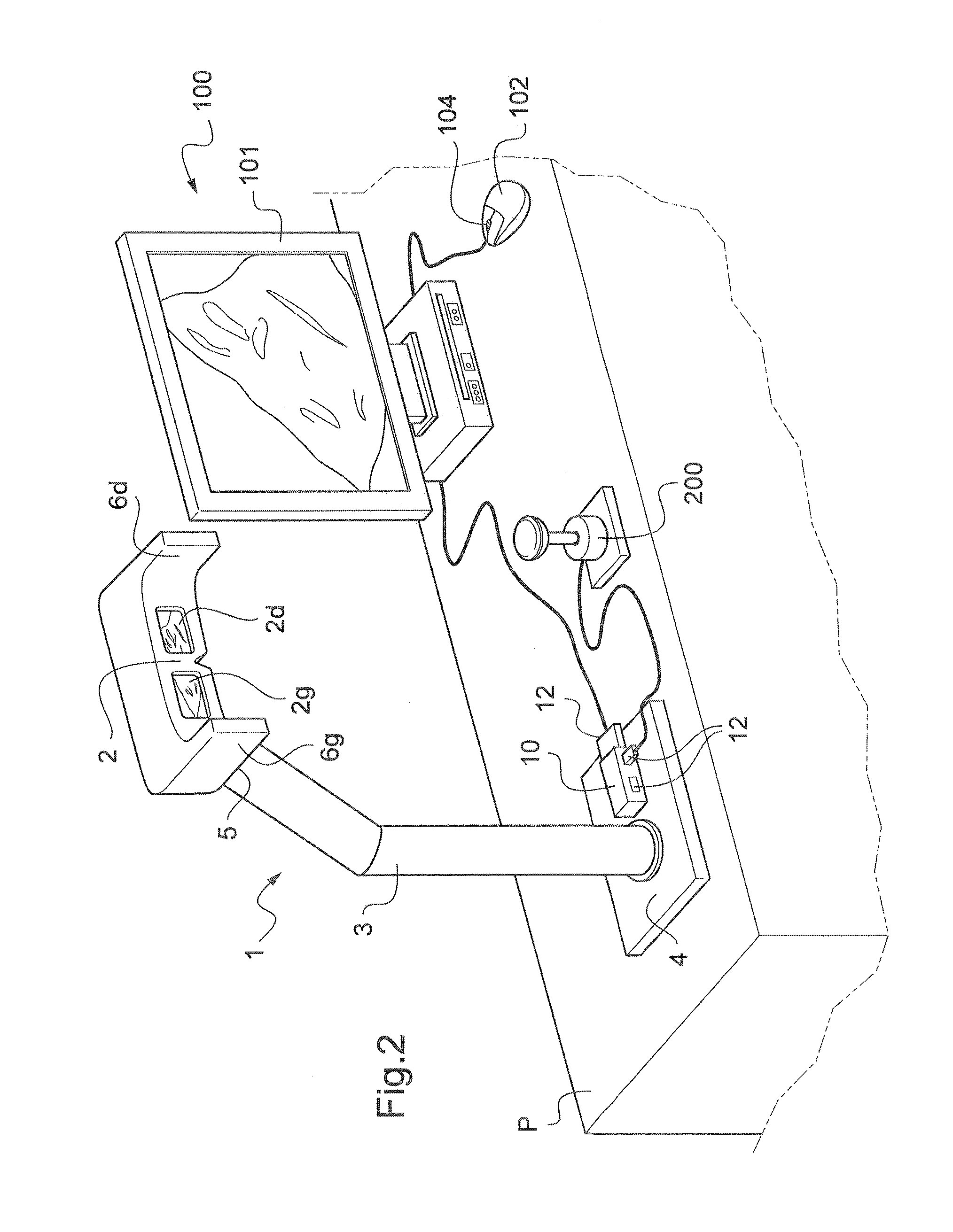
The invention relates to a device for viewing a digital image comprising means (2) for viewing at least one portion of the digital image. According to the invention, the viewing means include a viewing mask (2) held by a stand (3) such that the viewing mask (2) is used at the eye level of a user such that same can bring his / her eyes closer to the viewing mask in order to examine the portion of the digital image displayed, the viewing mask comprising side extensions (6g, 6d) for protecting the user from outer visual interferences, and in that the viewing device further includes at least one movement handling device (7, 200) that can be controlled by the user in order to control virtual movement of the digital image such that the user is able to view another portion of the digital image.
Owner:UNIV PIERRE & MARIE CURIE +1
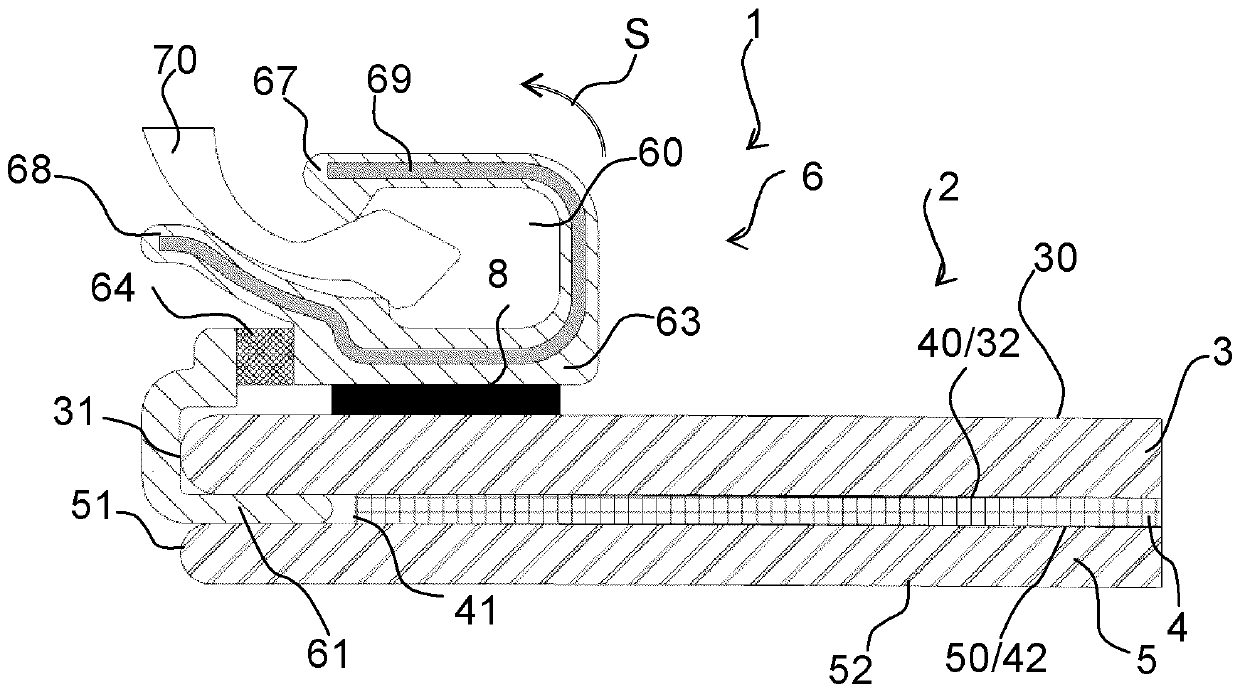
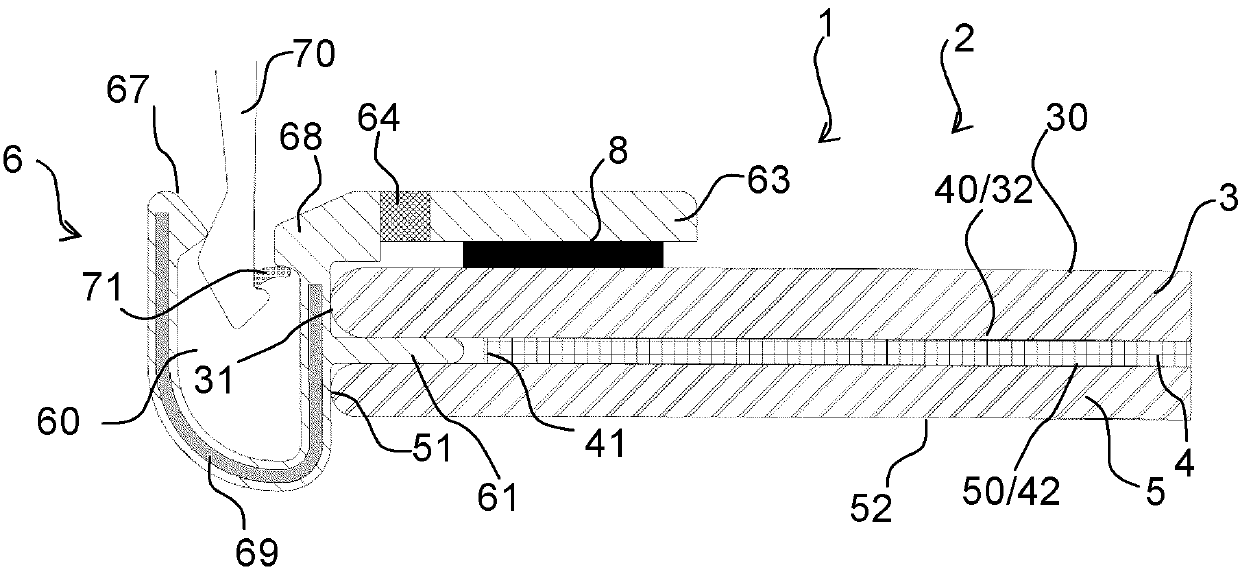
Laminated glazing comprising a profiled clipping bead
The invention relates to glazing (1), especially glazing for a vehicle, comprising a laminated glazed element (2) comprising an outer pane of glass (3), an inner pane of glass (5) and an interlayer pane made of a plastic material (4) arranged between said two panes of glass, characterised in that said profiled bead (6) comprises, as seen in the cross-section, an interlayer wing (61) arranged between the interlayer face of said outer pane of glass (3) and the interlayer face (50) of said inner pane of glass (5).
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
Vehicle assisted monitoring apparatus and method
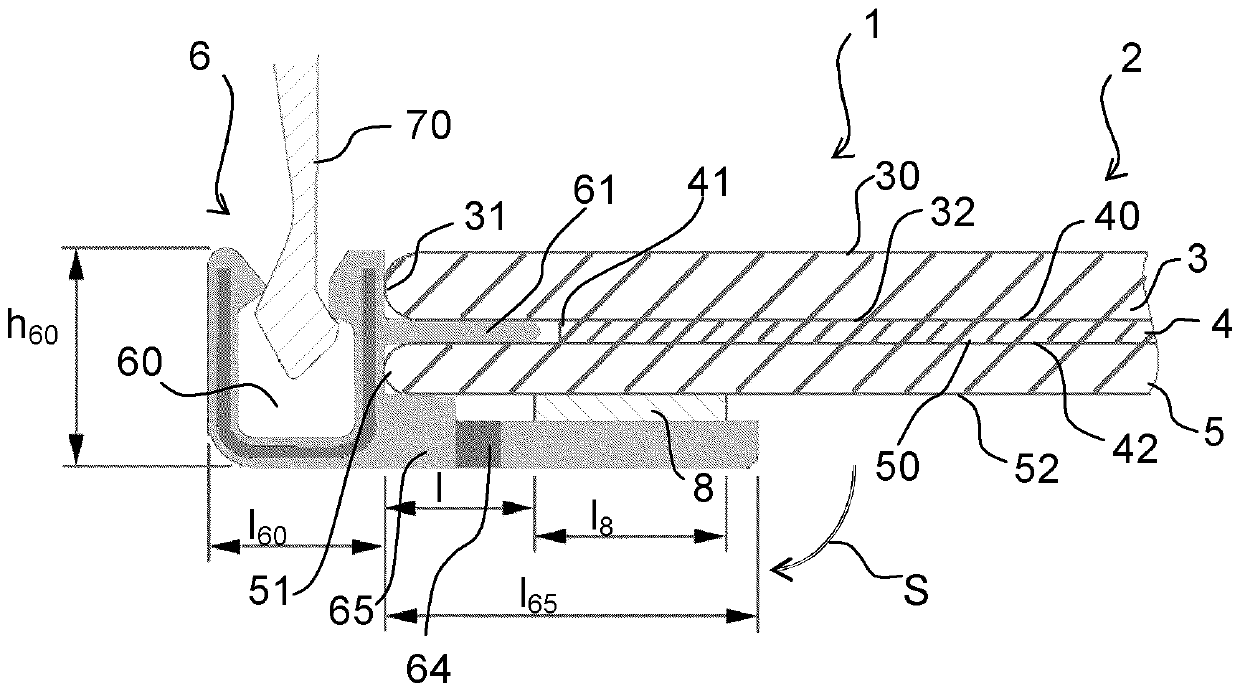
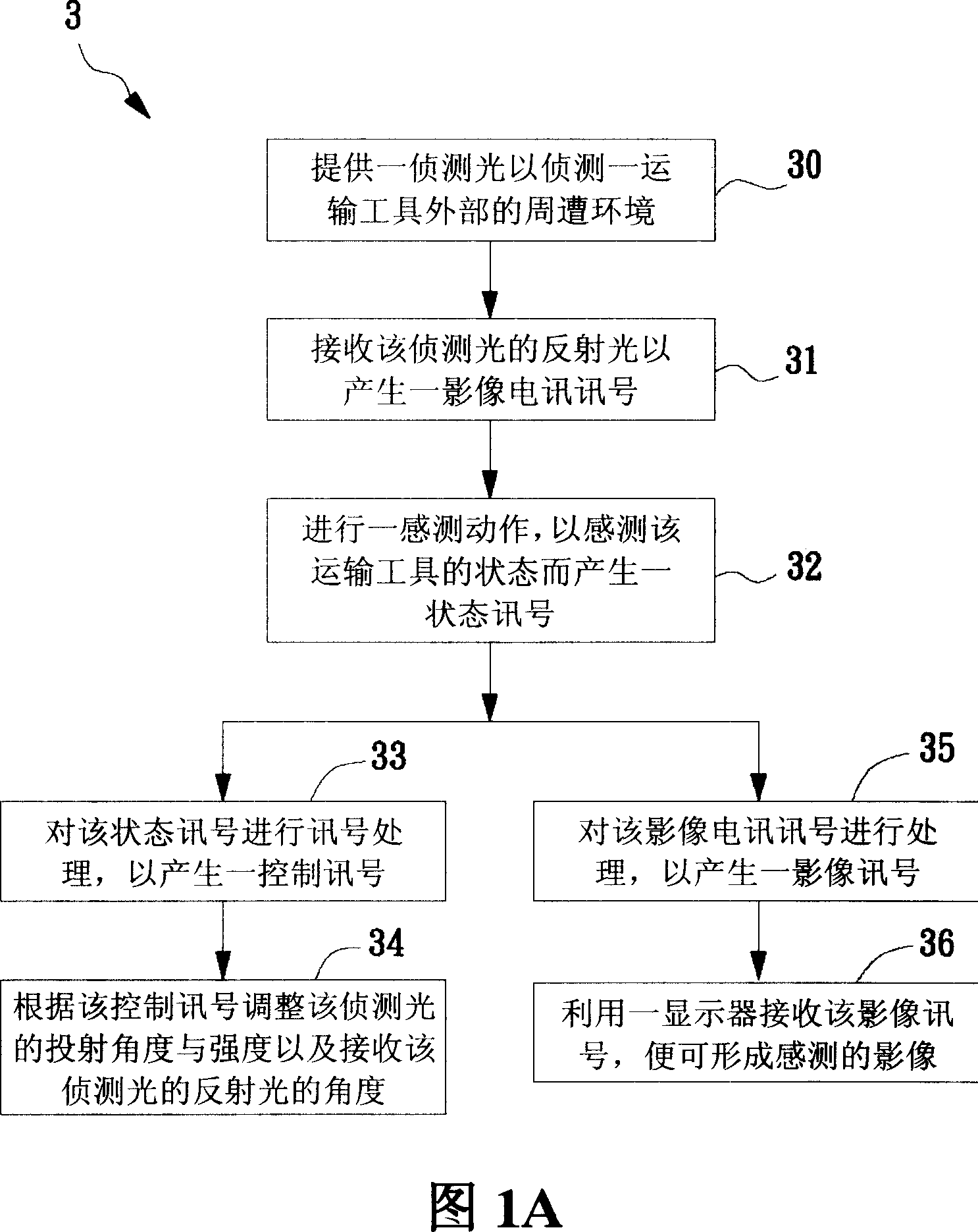
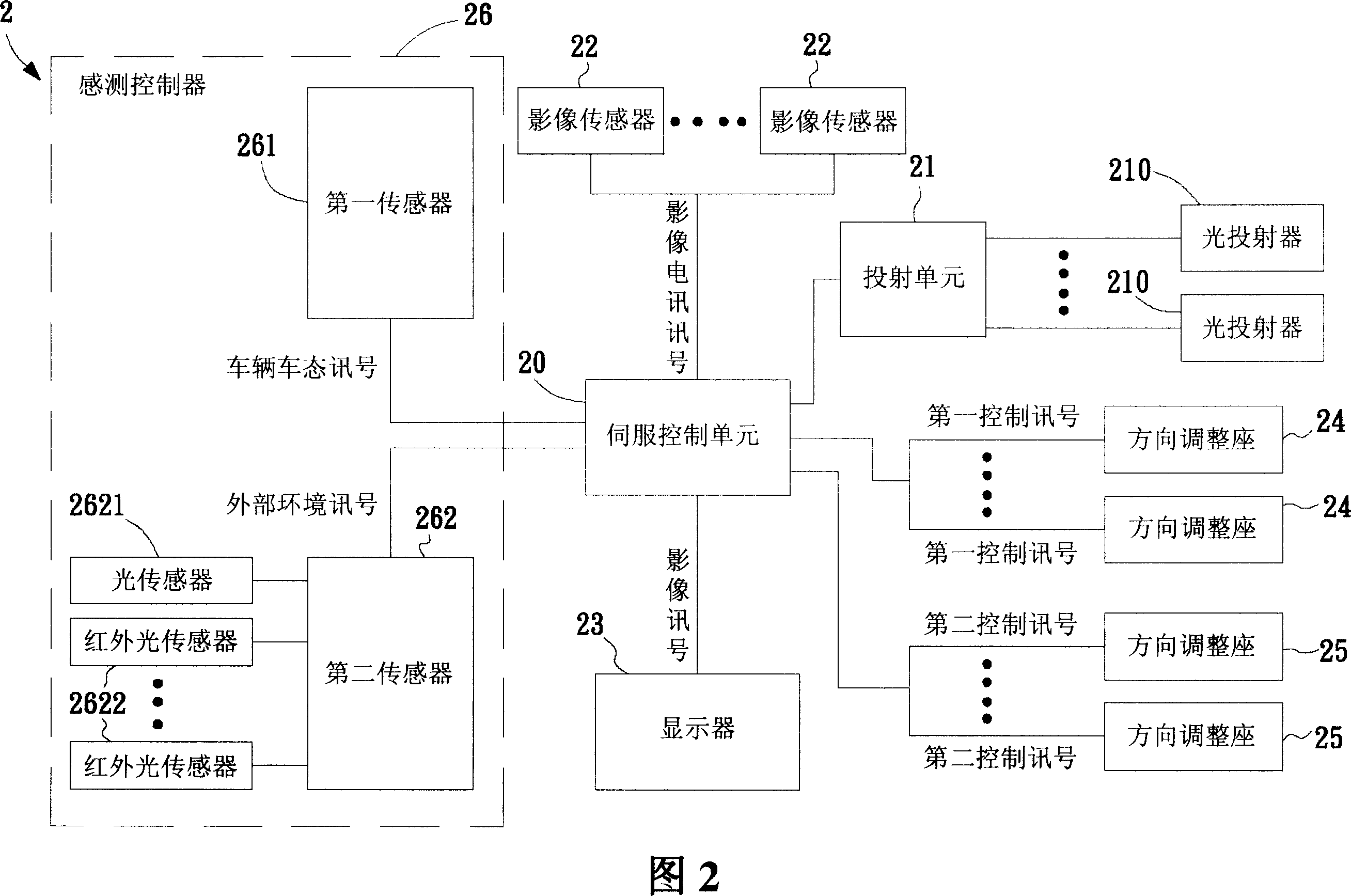
InactiveCN101014119AReach recognitionTo achieve the purpose of identifying surrounding obstaclesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDriver/operatorControl signal
The invention relates to one car aid monitor method, which comprises the following steps: providing one detection light for one commission tool outer environment; receiving the detection light reflection light to generate one image signal; processing one sensor operation for the tool to generate one status signal; processing status signals to generate one control signals; according to control signal to adjust projection angle and to receive the reflection angle. The invention also provides one car aid monitor device.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for obtaining amplitude and phase profiles of RF pulses for spatially selective excitation
ActiveUS7999545B2Reduce field of viewReduced measurement timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSelective excitationTransverse magnetization
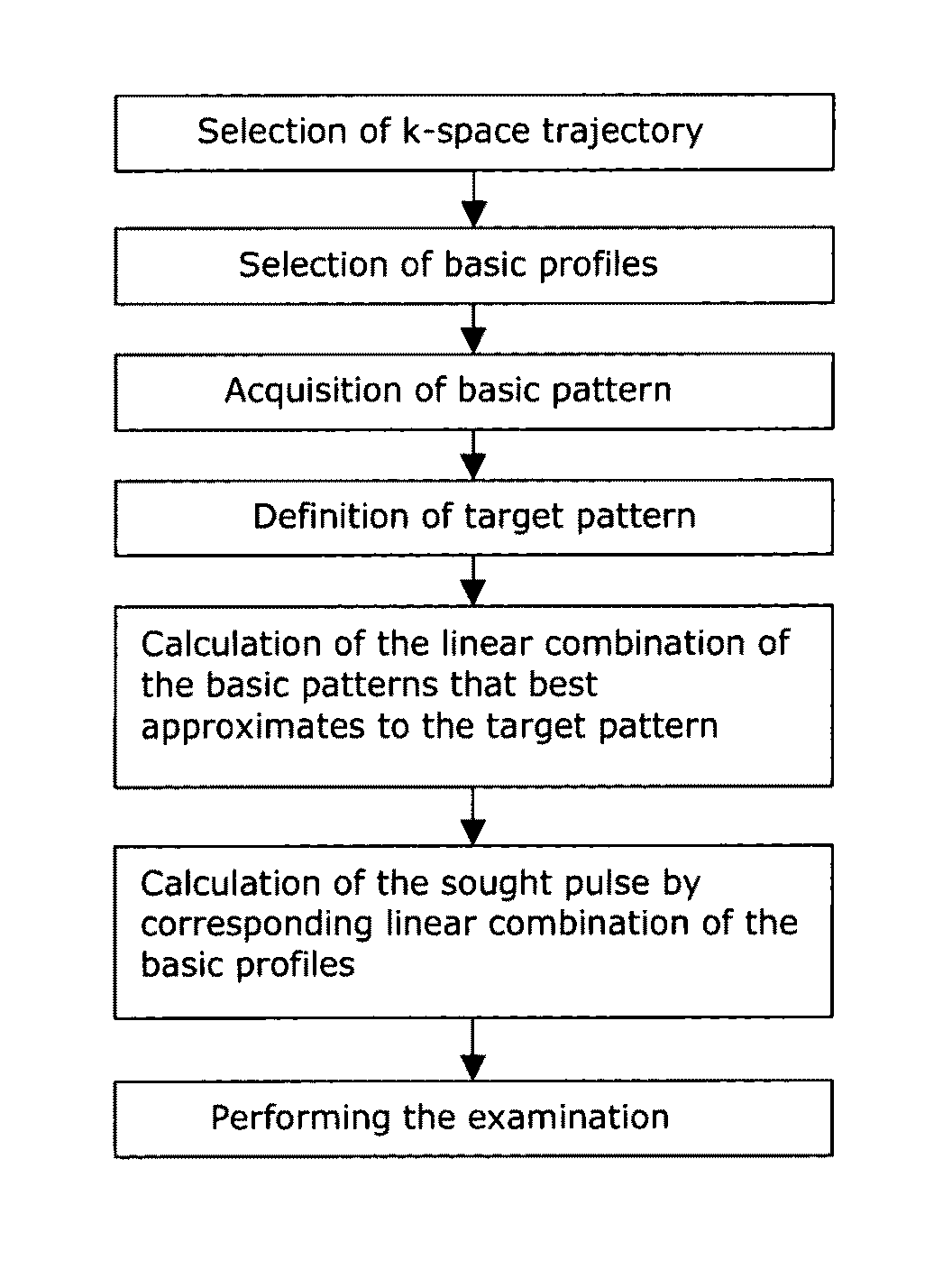
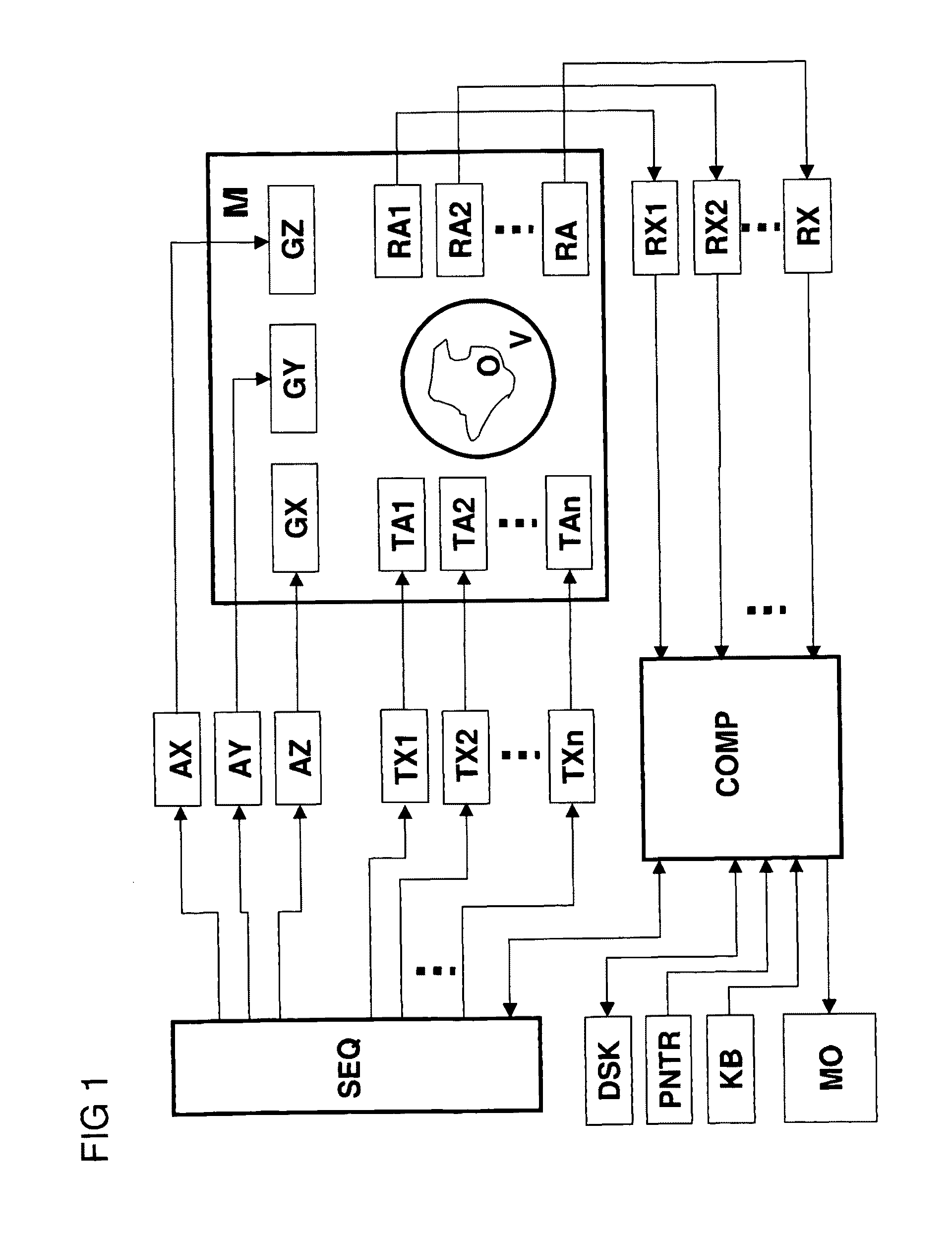
A method for determining amplitude and phase dependencies of radio frequency pulses that are irradiated during traversal of a defined k-space trajectory to produce a spatial pattern of the transverse magnetization in an MR experiment using at least one RF transmission antenna, is characterized in that, in a calibration step, a set of basic pulses is defined, each basic pulse is irradiated individually, the specified k-space trajectory is traversed and at least one set of basic patterns is produced by detection of the MR signals thus excited, which in a range to be examined of the object, are proportional to the complex transverse magnetization produced, wherein the k-space trajectory is traversed fully identically every time at least from the beginning of the irradiation of each basic pulse, and, in a calculation step, a defined target pattern is approximated with a linear combination of the basic patterns of a set or with a mathematical association of linear combinations, with which, within each set, the basic patterns are identically combined, and the amplitude and phase dependencies to be determined are obtained as the corresponding linear combination of the basic pulses. Experimental imperfections can be intrinsically compensated for in this way.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI +1
Method for obtaining amplitude and phase dependencies of RF pulses for spatially selective excitation
ActiveUS8508224B2Reduce field of viewReduced measurement timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceSelective excitation
A method for obtaining amplitude and phase dependencies of radio frequency pulses, which are irradiated within the scope of a main magnetic resonance experiment for generating a predetermined n-dimensional spatial distribution (n>=1) of transverse magnetization in an object by means of at least one radio frequency transmitting antenna of a magnetic resonance measuring system in combination with spatially and temporally varying additional magnetic fields which are superimposed on the static and homogeneous base field of the magnetic resonance measuring system and change the transverse magnetization phase in the object in dependence on location and time is characterized in that, prior to performance of the main experiment, a preparational measurement is performed in which the change with time of the transverse magnetization phase in the object under the action of the additional magnetic fields is measured in a position-resolved fashion and the amplitude and phase dependencies of the radio frequency pulses for the main experiment are calculated on the basis of this change with time of the transverse magnetization phase, which is measured in a position-resolved fashion. In this fashion, experimental imperfections in the form of unintentional additional magnetic fields can be measured, taken into consideration and compensated for.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
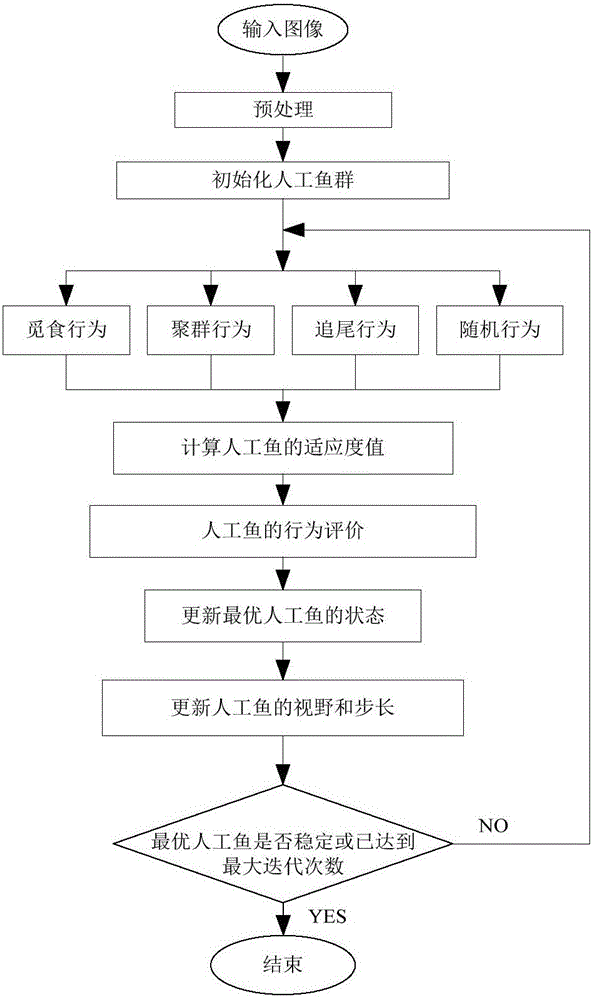
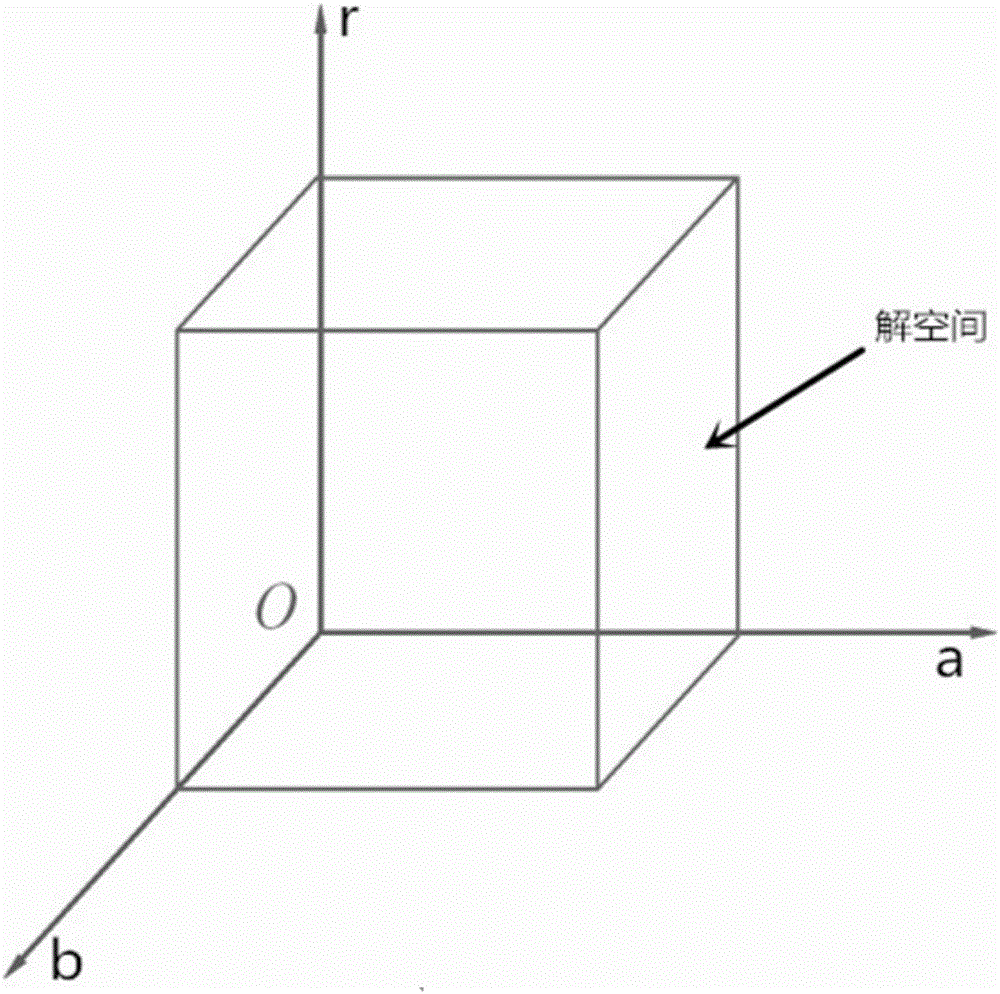
Artificial fish swarm algorithm-based circular workpiece detection method
ActiveCN106097307AEliminate the effects ofEliminate distractionsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionHough transform
The invention discloses an artificial fish swarm algorithm-based circular workpiece detection method, and belongs to the technical field of computer information image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly pre-processing a to-be-detected image to obtain edge information of a circular workpiece; determining a three-dimensional solution space according to the size of a to-be-detected workpiece image and initiating an artificial fish swarm to ensure that each artificial fish is randomly distributed in the solution space; and finally carrying out continuous interaction and coordination behaviors on the artificial fish swarm by adopting a self-adaptive field of view and a step size, so as to carry out heuristic search on a circle passing through most edge points in the solution space to obtain a circle center and a radius of the workpiece. Compared with the traditional method for detecting circles through Hough Transform, the method disclosed by the invention can realize parallel search in a parameter space without traversing the whole space, so that the space overhead and time overhead are greatly decreased and the detection precision is improved; and the method has the characteristics of being rapid, correct and robust.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
System of receive coils and pads for use with magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20120133365A1Improve imaging resolutionReduce field of viewElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRReceiver coilEngineering
There is described embodiments of a coil and pad system for use with an MRI machine. The coil and pad system includes a plurality of coils sized to accommodate a plurality of patient ranges of various heights and body weights. There is also a plurality of pads designed to work in conjunction with the plurality of coils to accommodate patient ranges of various heights and body weights.
Owner:MENTIS
Distributed optical resonator with thin receiver unit
ActiveUS20180034557A1Most efficientReduce input powerOptical resonator shape and constructionElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsElectricityLight beam
A receiver for receiving an incident beam of optical power from a remote transmitter over a predefined field of view, comprising an input lens having a high durability coating that can withstand domestic handling and contamination. Such a high durability coating may reflect a non-insignificant part of the light incident thereon. Behind the lens, there is fitted a retroreflector disposed such that it reflects that part of the incident beam traversing the lens, back through the lens to the transmitter. Reflections from the front surface of the lens impinge on one or more transparent beam catchers appropriately located, and equipped with energy conversion devices, such as photovoltaic cells, to convert light from the reflections of the incident beam into electricity. Additional energy conversion devices may be located inward of the lens, to collect and convert reflections from the inner surface of the lens, of light returning from the retroreflector.
Owner:WI CHARGE
Extender lens and laser processing optical system
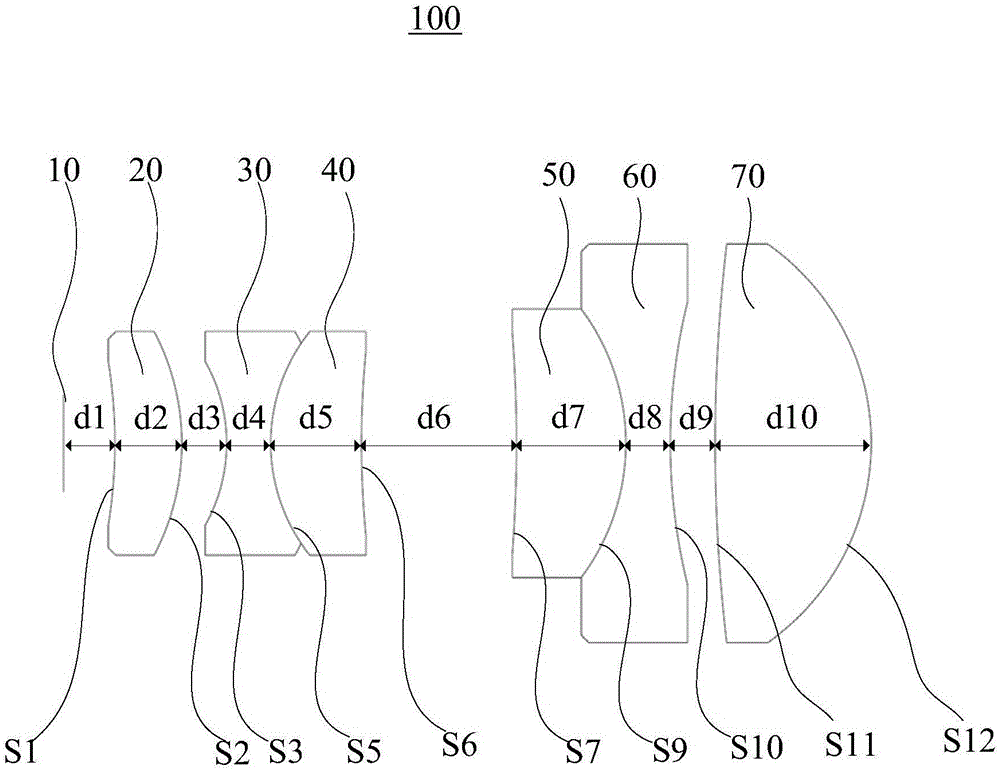
ActiveCN105044881AImprove clarityReduce field of viewOptical elementsLaser processingImage resolution
The invention relates to an extender lens and a laser processing optical system. The extender lens includes a diaphragm, a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens and a sixth lens which are successively arranged along the progressing direction of an incident light, wherein the first lens is a meniscus lens and has a meniscus direction opposite to the progressing direction of the incident light. The second lens is a double-concave negative lens. The third lens is meniscus lens and has a meniscus direction in line with the progressing direction of the incident light. The second lens and the third lens glue together; the fourth lens is a meniscus lens and has a meniscus direction opposite to the progressing direction of the incident light. The fifth lens is a double-concave negative lens. The fourth lens and the fifth lens glue together. The sixth lens is a double-convex positive lens. The extender lens has a focal length of -14.4367 mm and an entrance pupil diameter of 3.16875 mm. The extender lens can increase image resolution and has small aberration.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
Method and device for insulating the face of person from the external environment including harmful gas
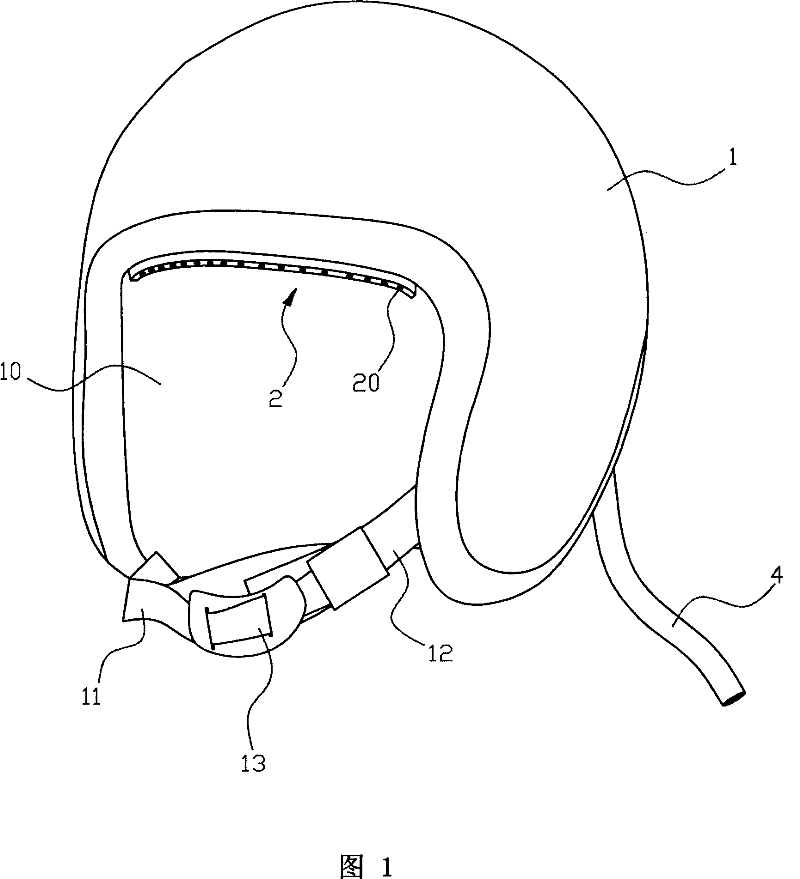
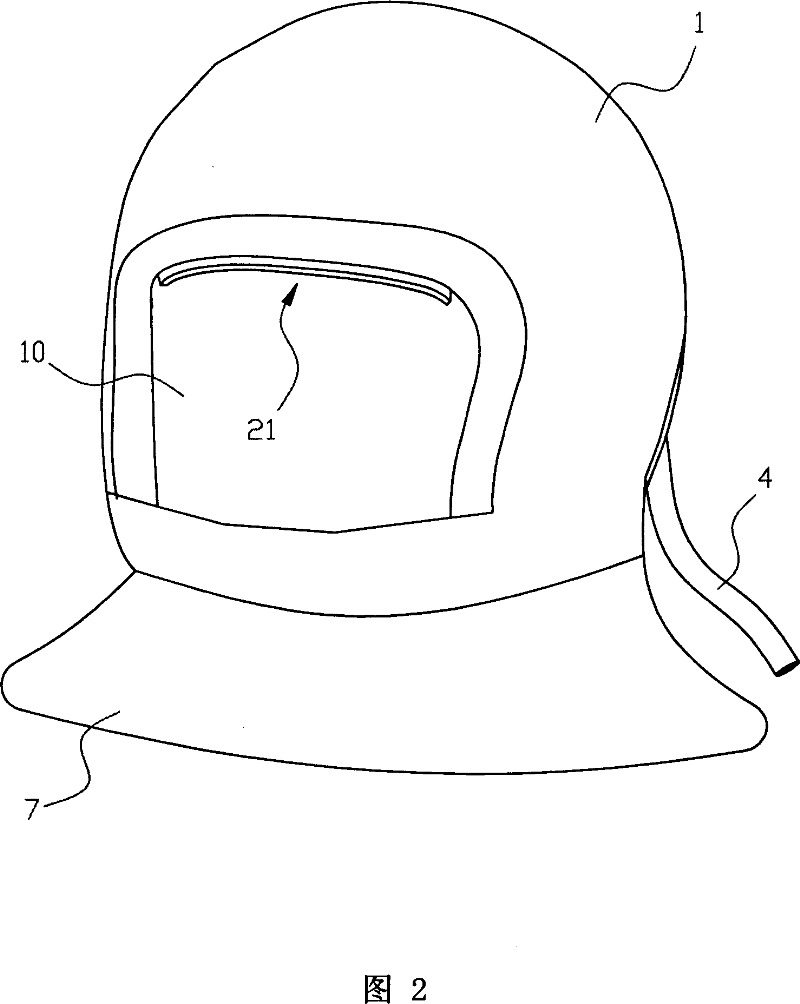
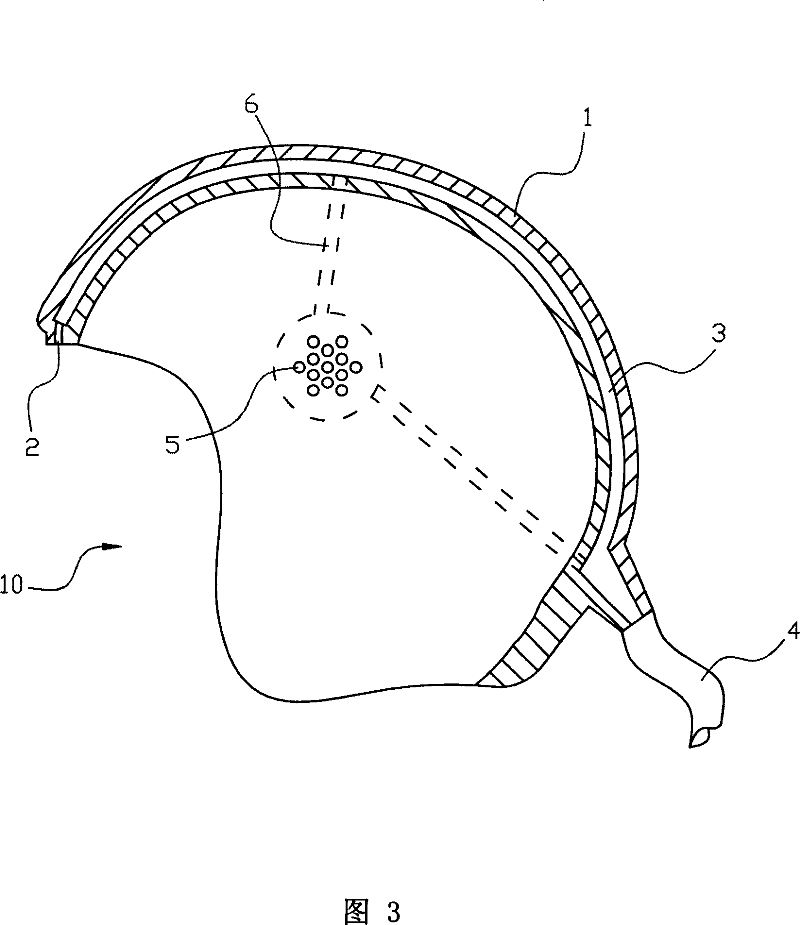
InactiveCN101041104APrevent intrusionEffectively block intrusionBreathing masksEngineeringField of view
A method for separating face from outer harmful gas comprises that (1), setting a separating space at the face, (2) forming a wind curtain at the separating space to insulate outer harmful gas from face. And the device comprises a helm covering the head with an opening at the front of the face, a bar wind outlet downward at the top side of the opening, and a wind channel in the interlayer of the helm and communicated with the wind outlet, while the wind channel via a tube is communicated with a pressure source outside the helm. The invention uses the wind curtain to insulate face from harmful gas outside, to insulate harmful gas from breath system, without affecting vision and view sight.
Owner:颜迪忠
System of receive coils and pads for use with magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS8952695B2Reduce field of viewImprove imaging resolutionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceEngineeringReceiver coil
There is described embodiments of a coil and pad system for use with an MRI machine. The coil and pad system includes a plurality of coils sized to accommodate a plurality of patient ranges of various heights and body weights. There is also a plurality of pads designed to work in conjunction with the plurality of coils to accommodate patient ranges of various heights and body weights.
Owner:DAVIS ALBERT MICHAEL +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com