Patents
Literature
494results about How to "High image resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method, system and apparatus for dark-field reflection-mode photoacoustic tomography
InactiveUS20060184042A1Enhance the imageMinimize interferenceCatheterDiagnostics using tomographyUltrasonic sensorAcoustic wave
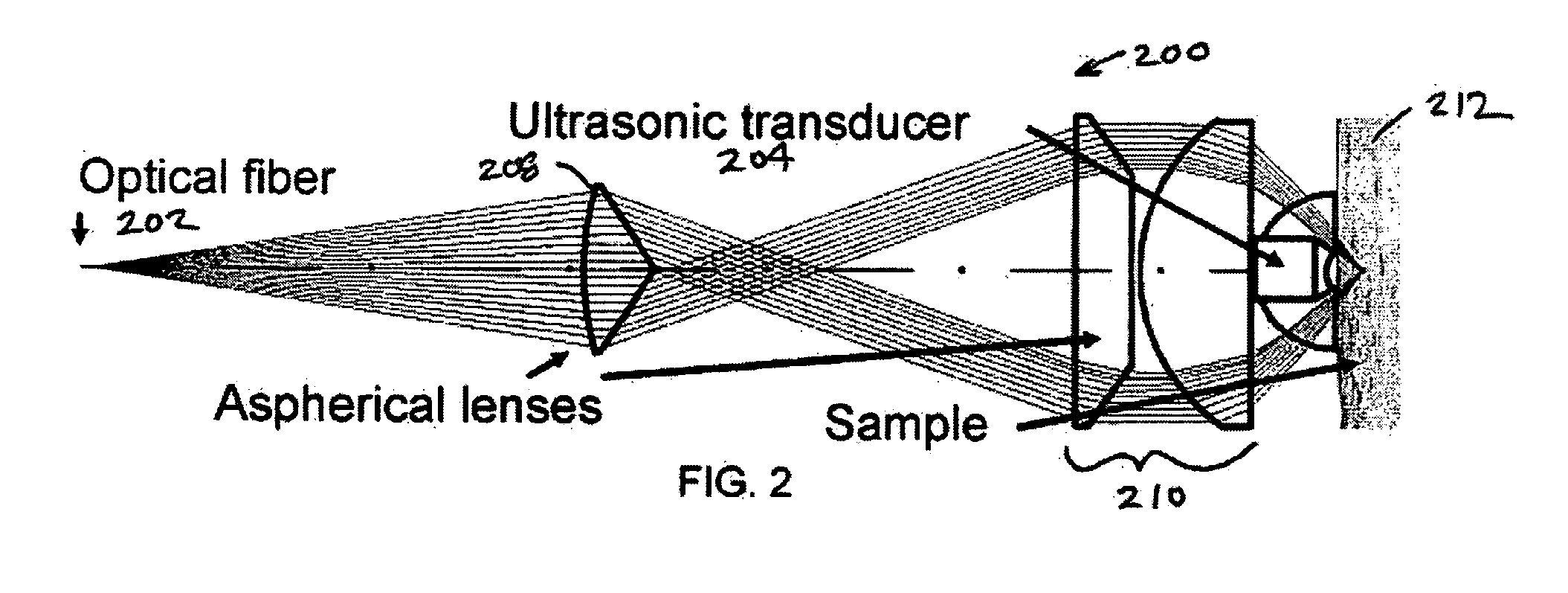
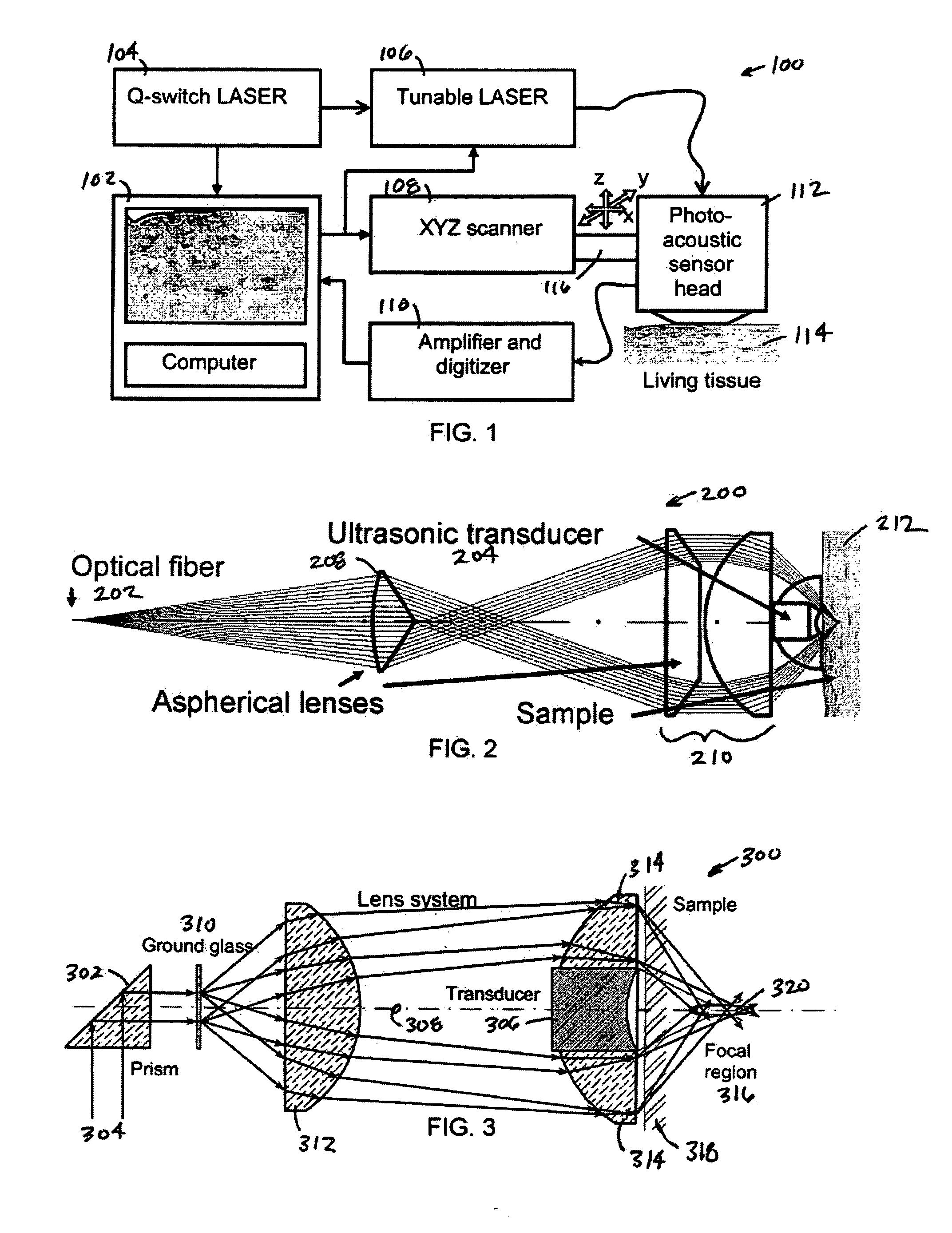
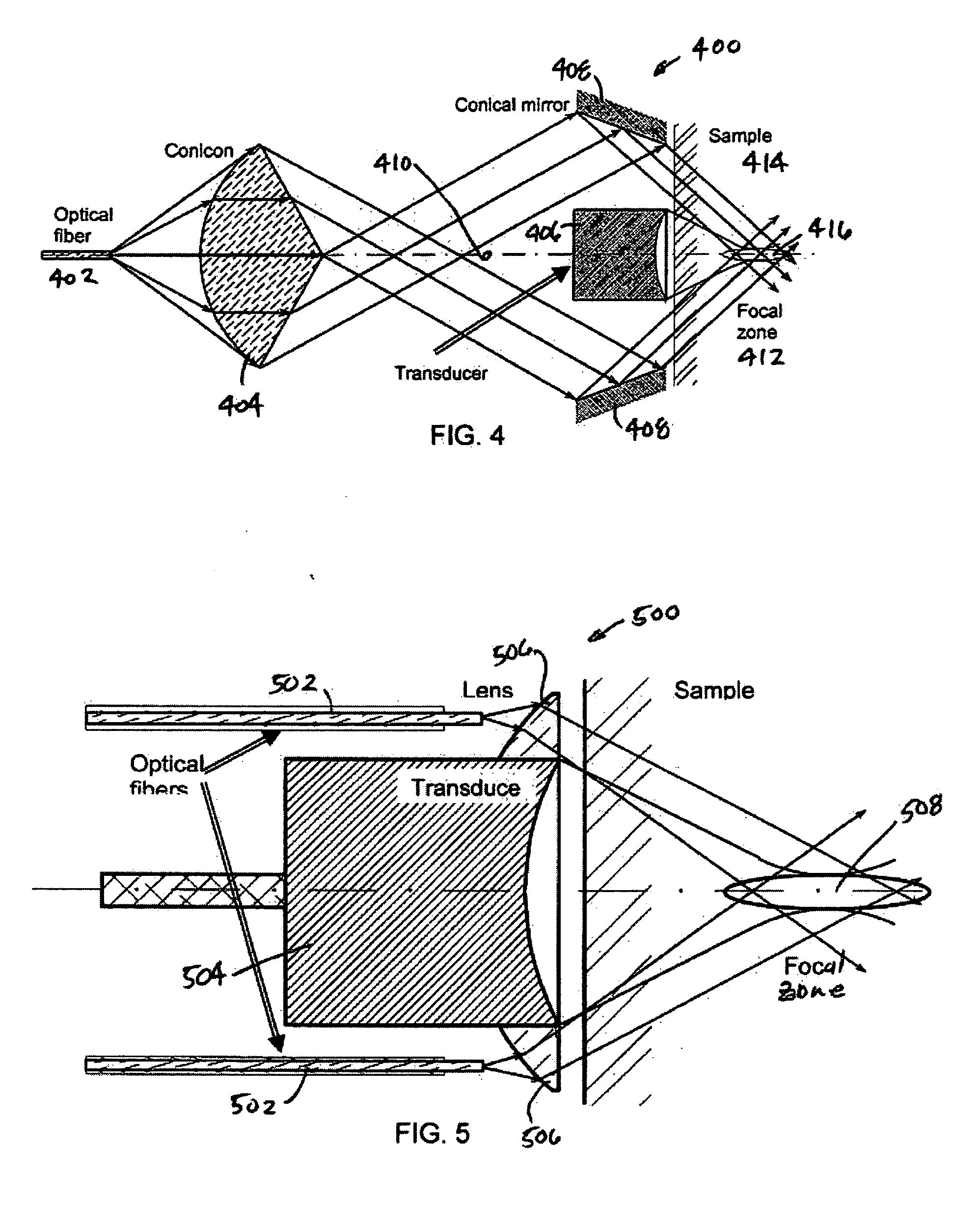
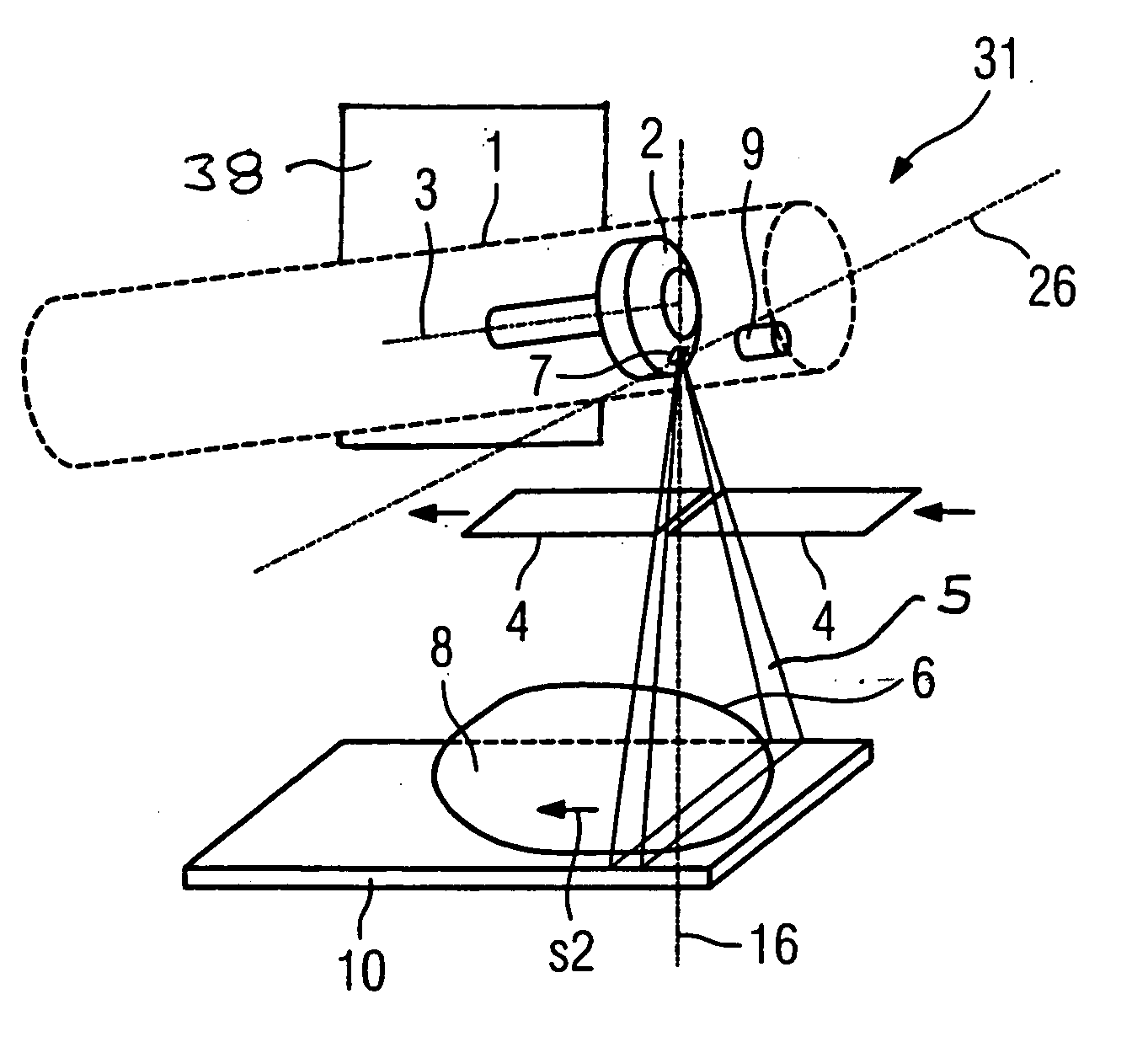
The present invention provides a method, system and apparatus for reflection-mode microscopic photoacoustic imaging using dark-field illumination that can be used to characterize a target within a tissue by focusing one or more laser pulses onto a surface of the tissue so as to penetrate the tissue and illuminate the target, receiving acoustic or pressure waves induced in the target by the one or more laser pulses using one or more ultrasonic transducers that are focused on the target and recording the received acoustic or pressure waves so that a characterization of the target can be obtained. The target characterization may include an image, a composition or a structure of the target. The one or more laser pulses are focused with an optical assembly of lenses and / or mirrors that expands and then converges the one or more laser pulses towards the focal point of the ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
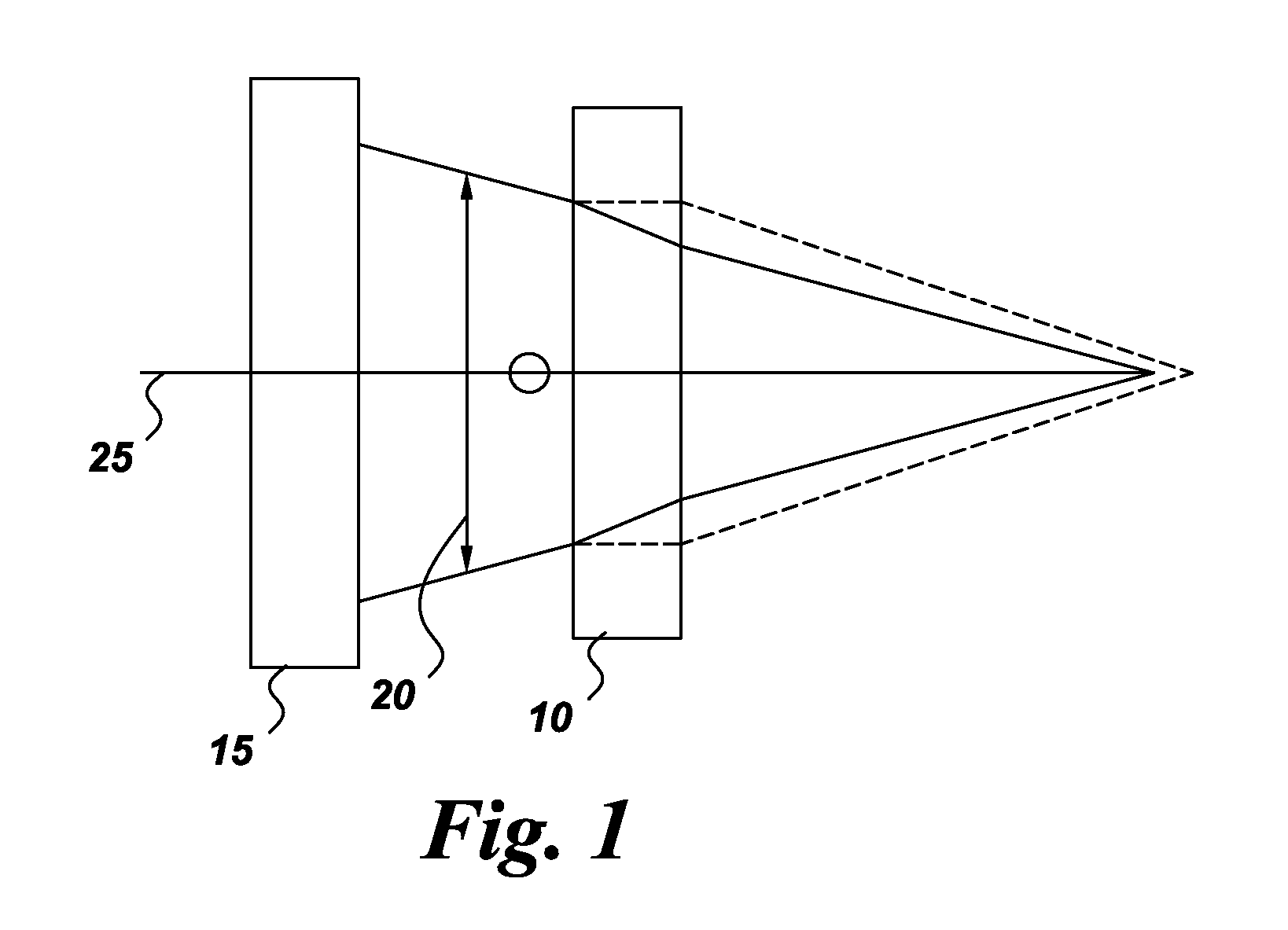
Optical lens system
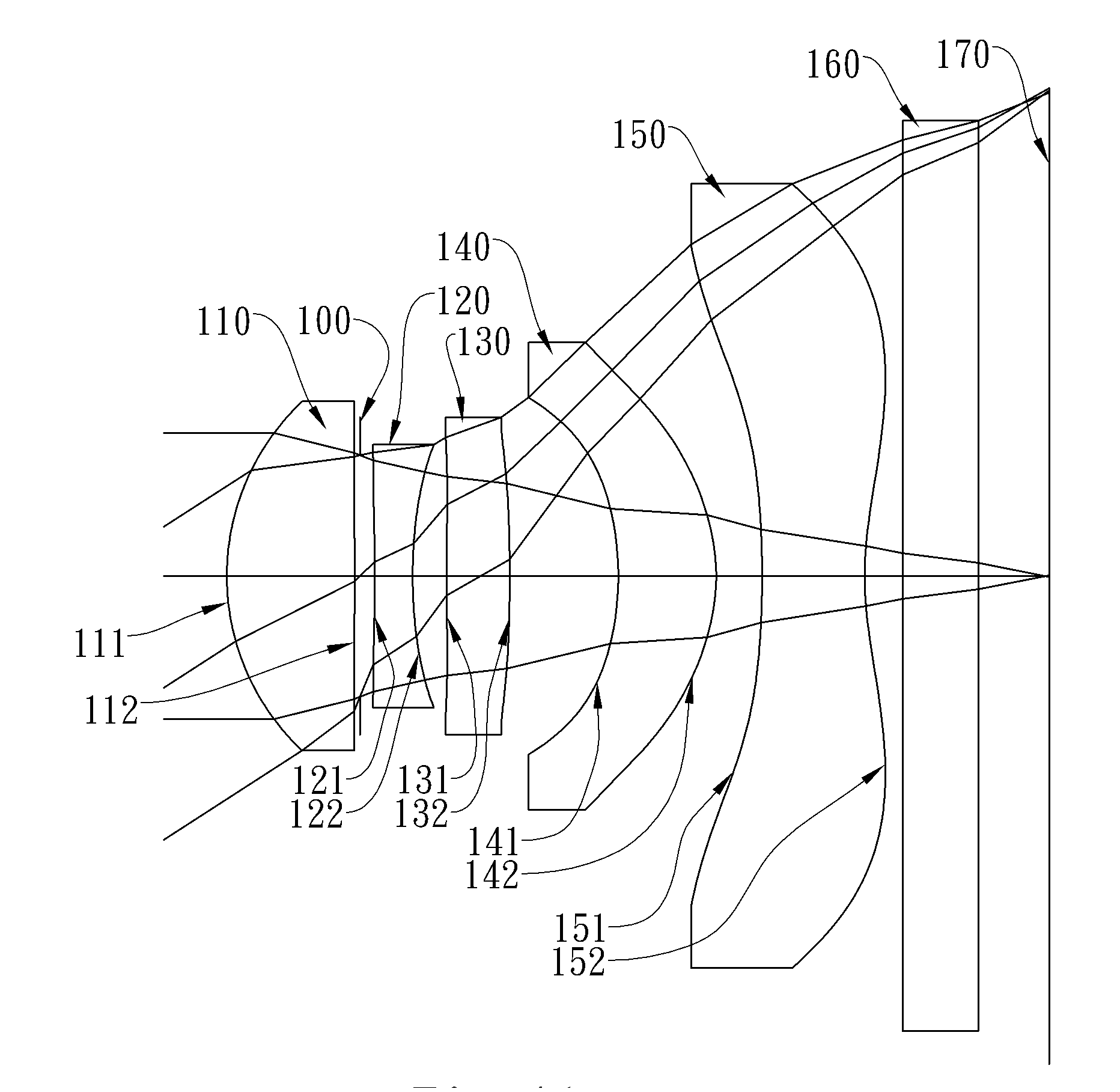
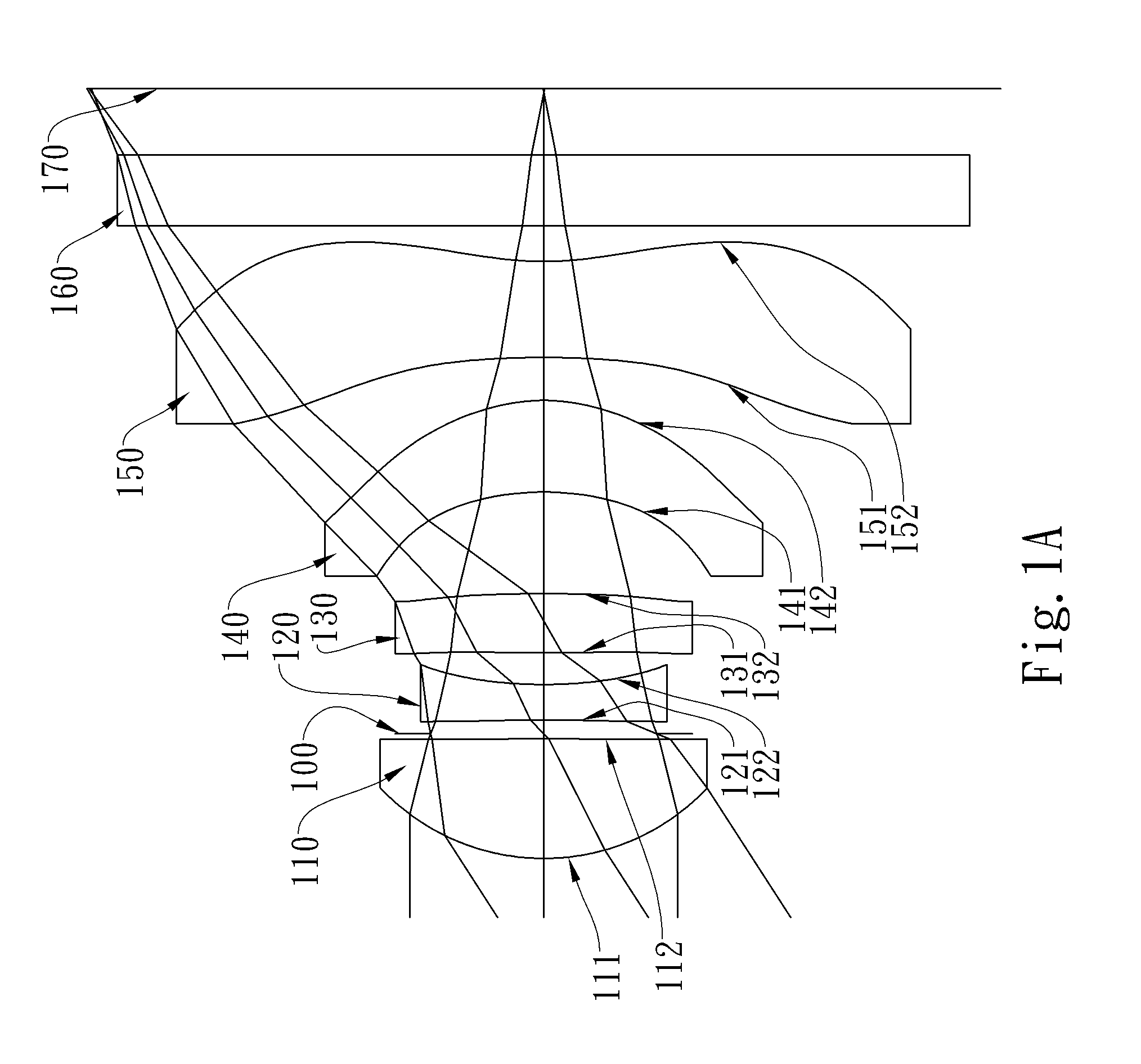
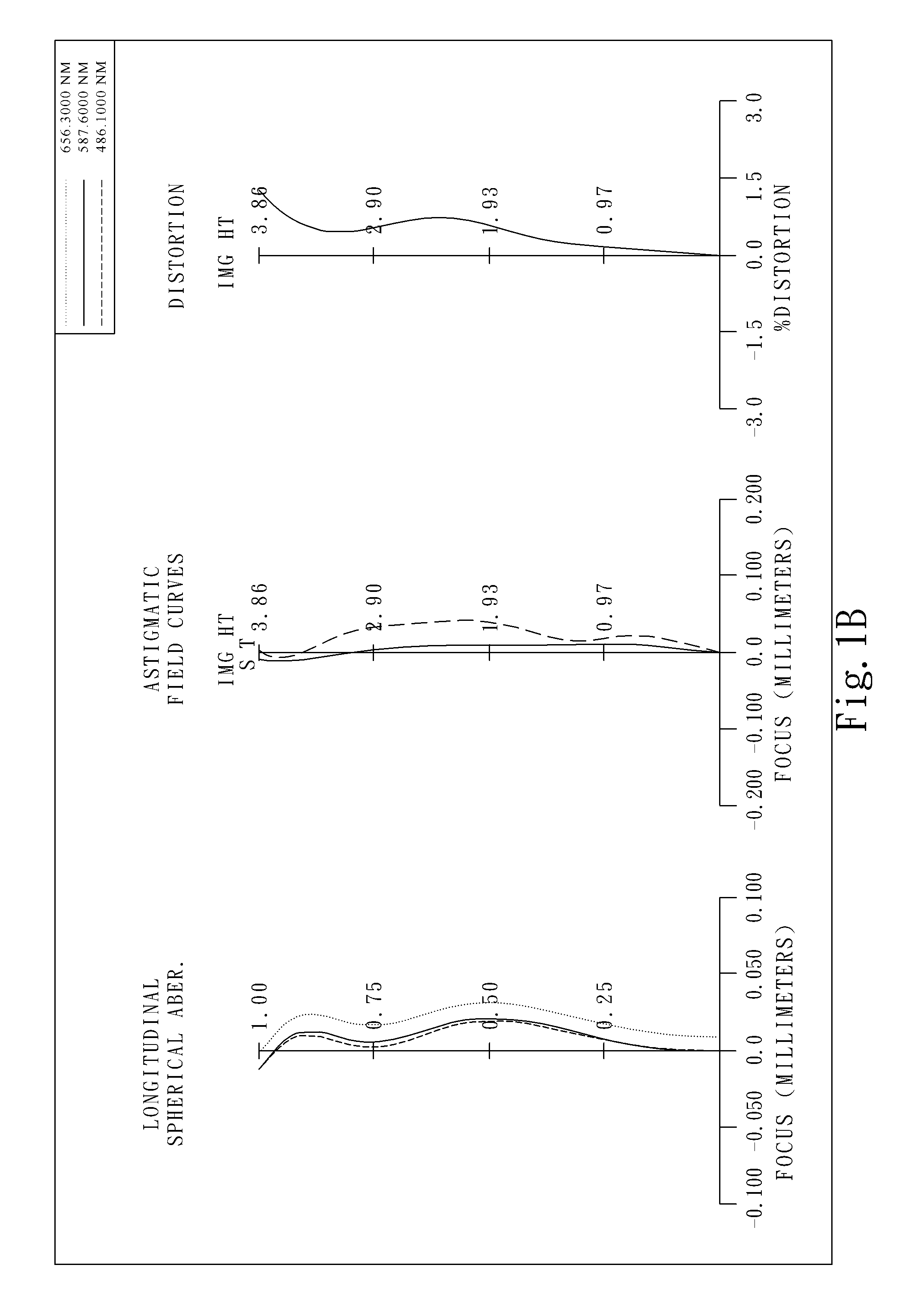
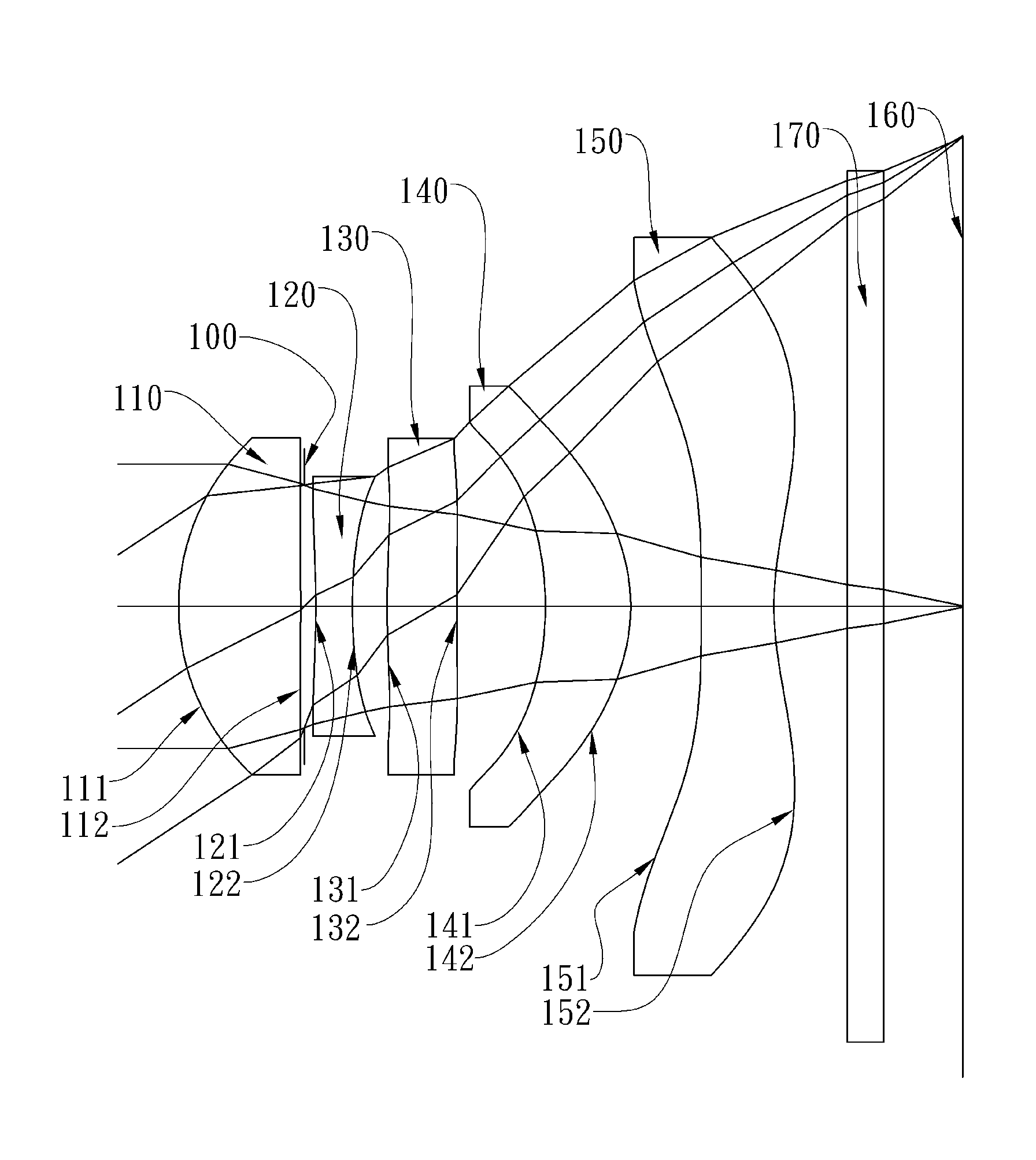
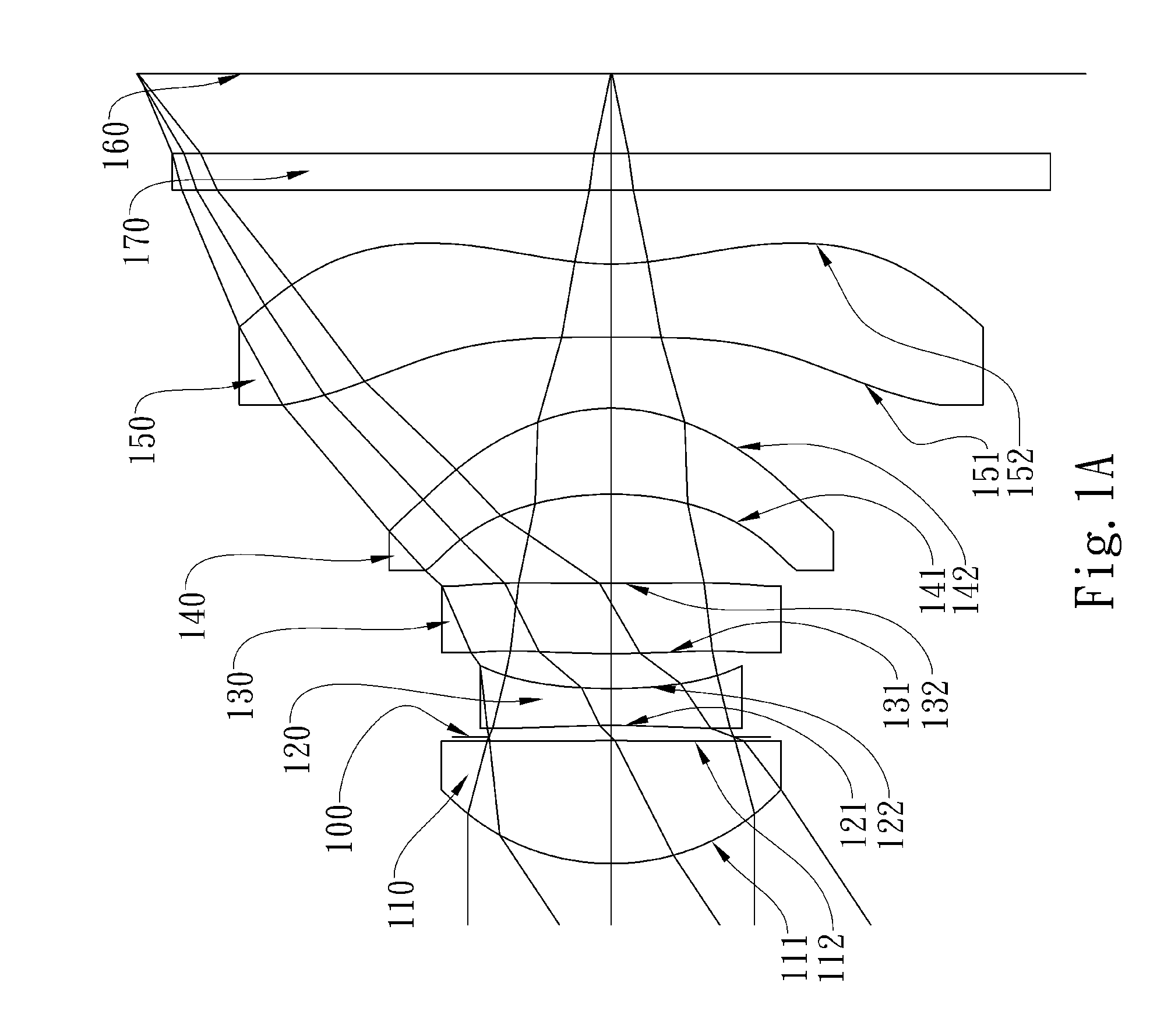
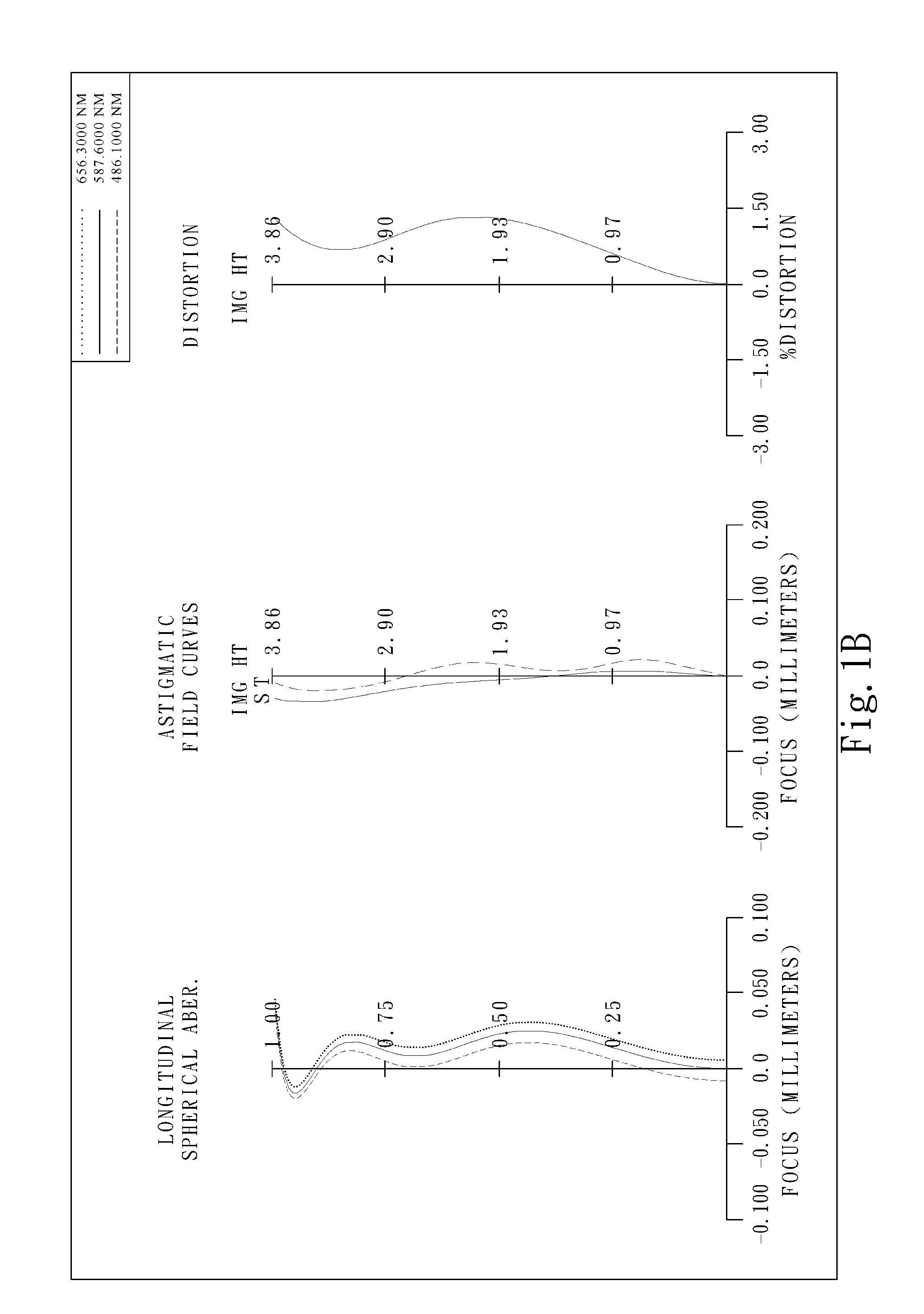
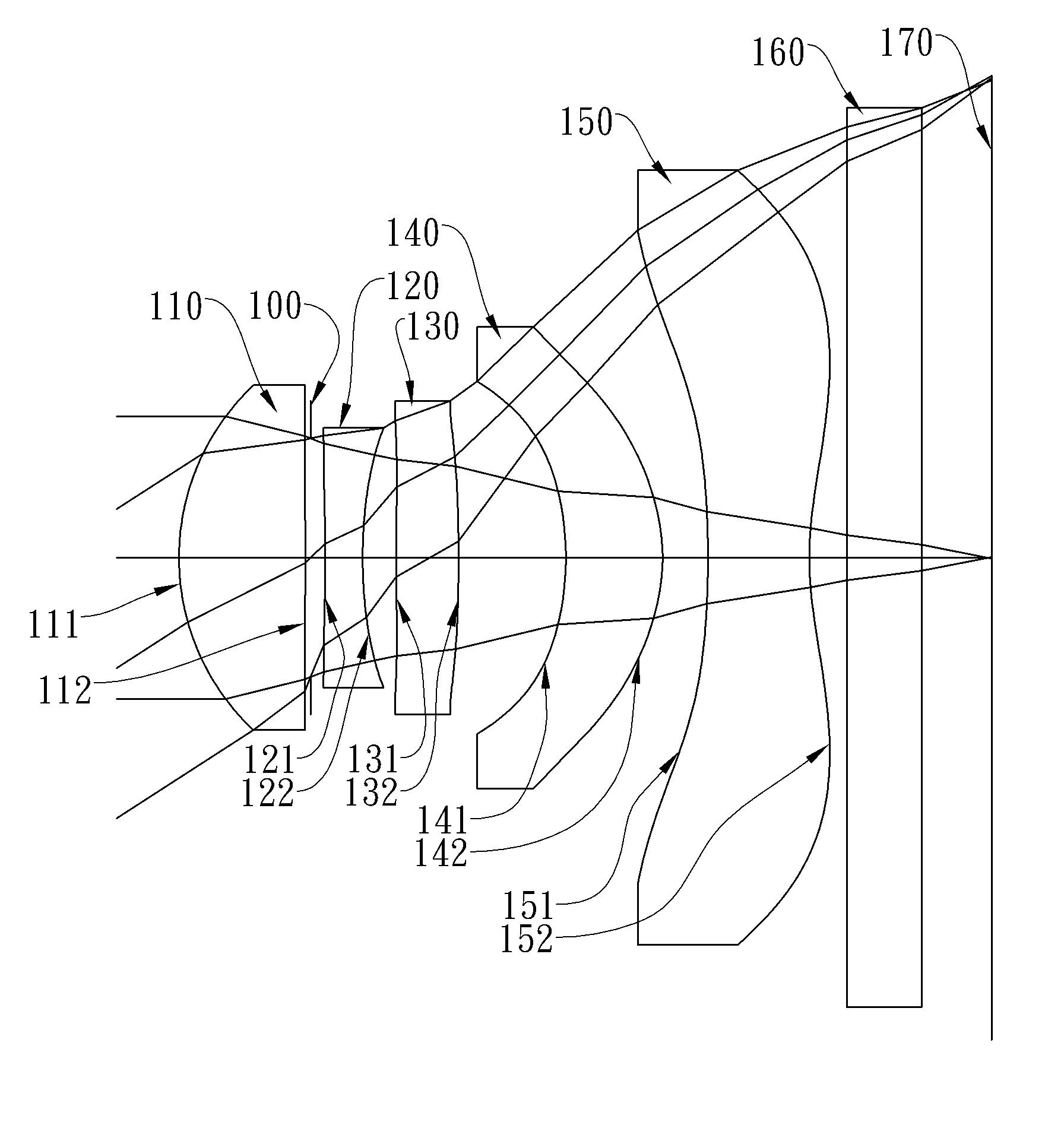
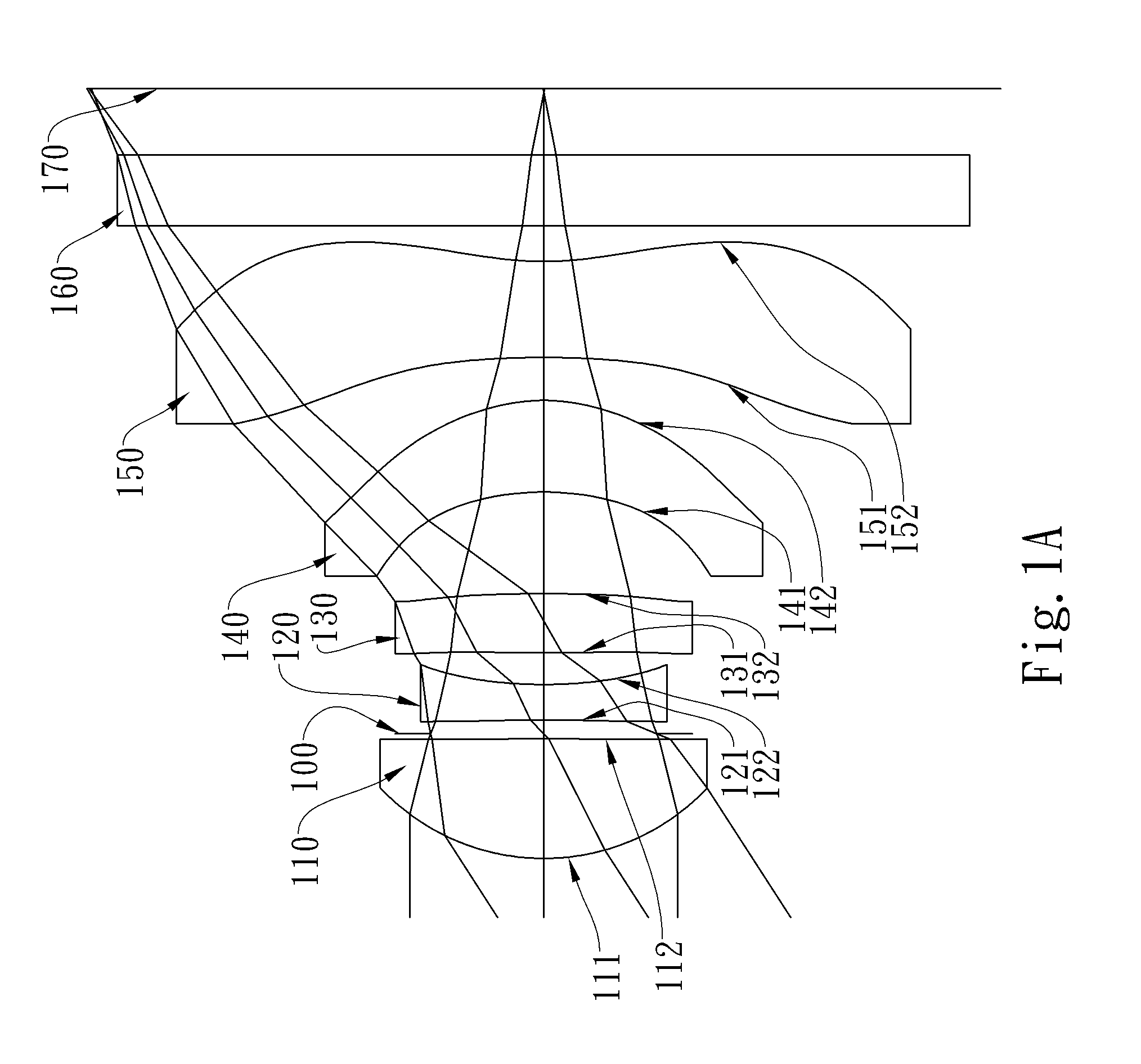
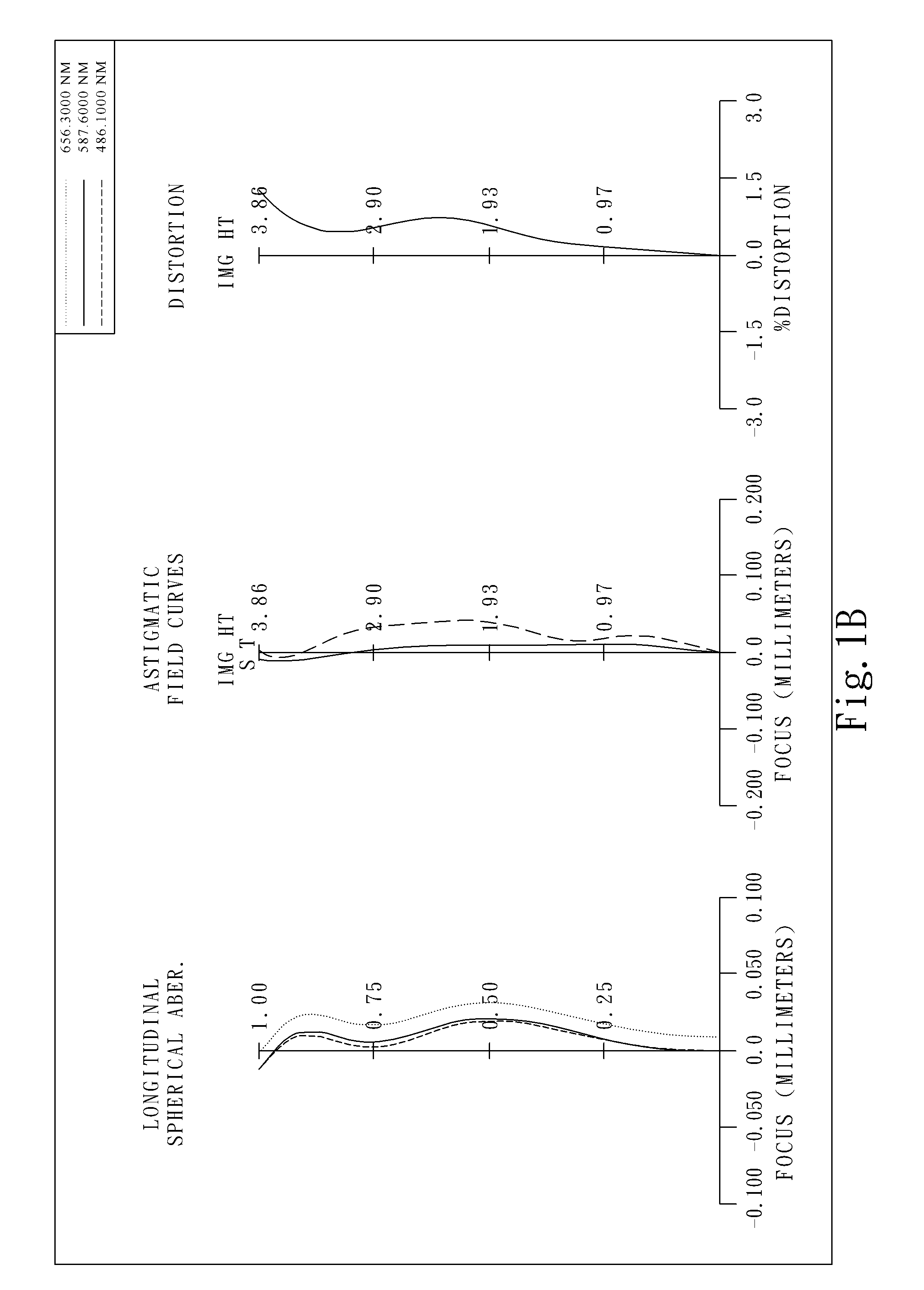
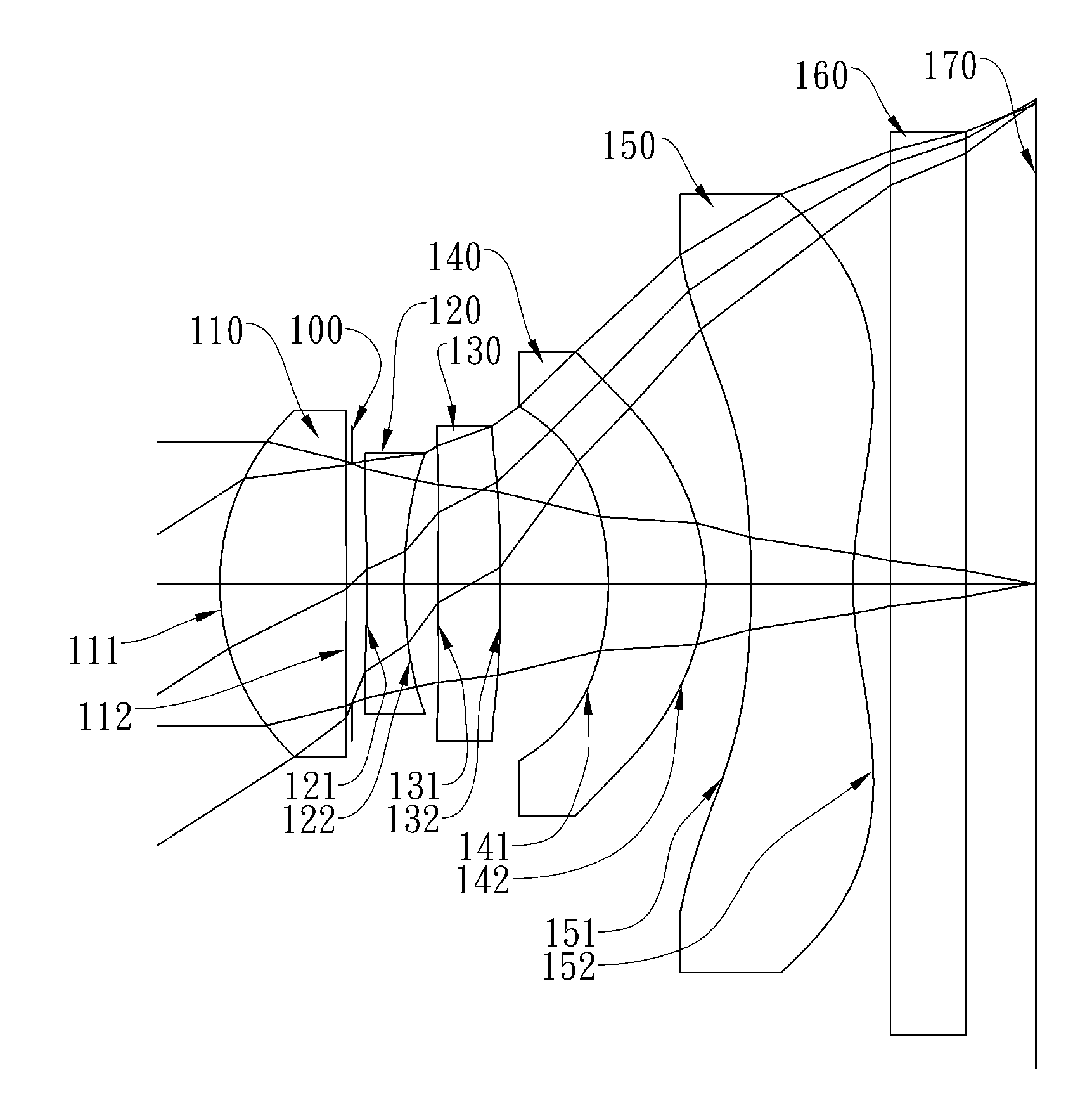
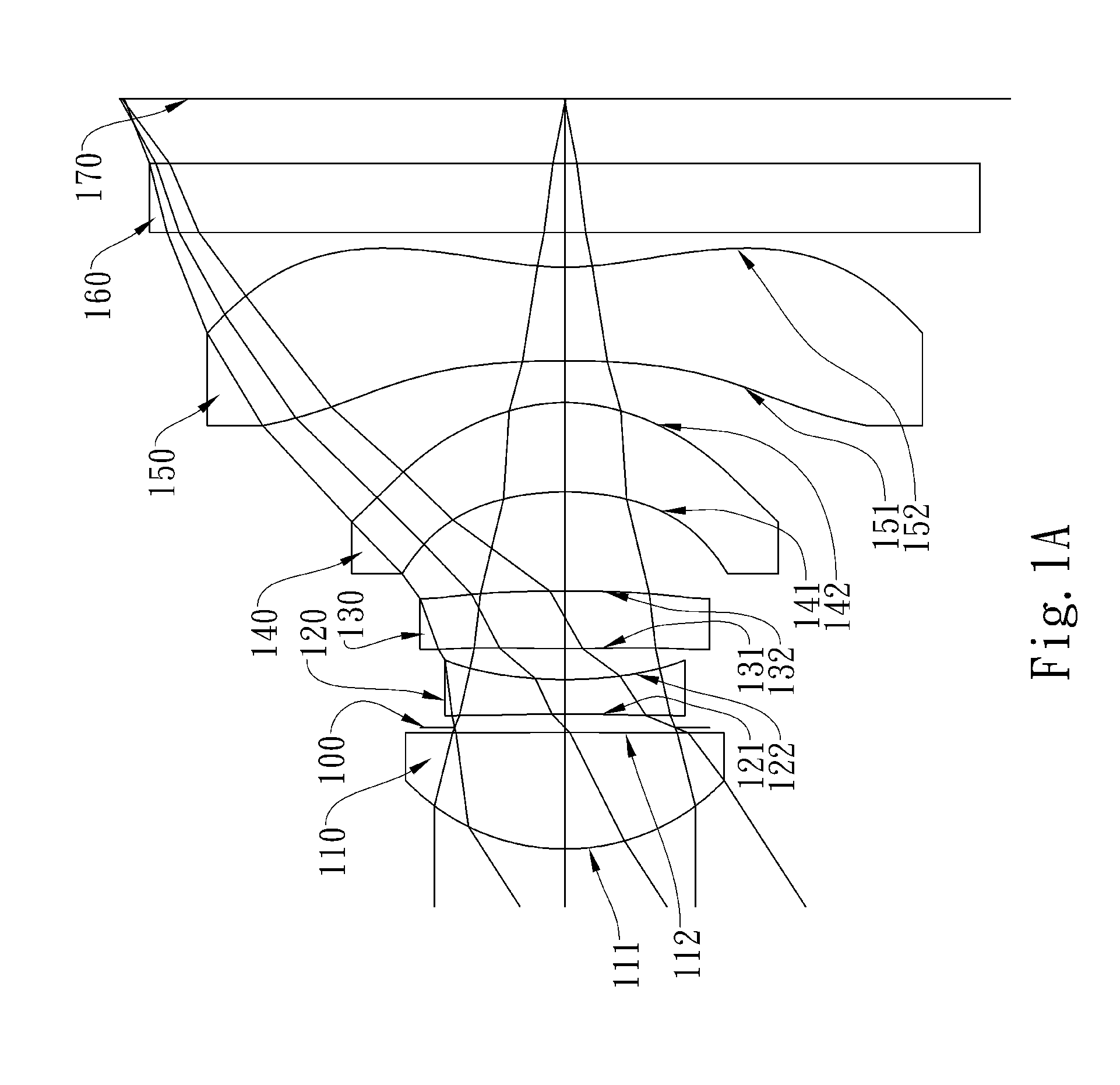
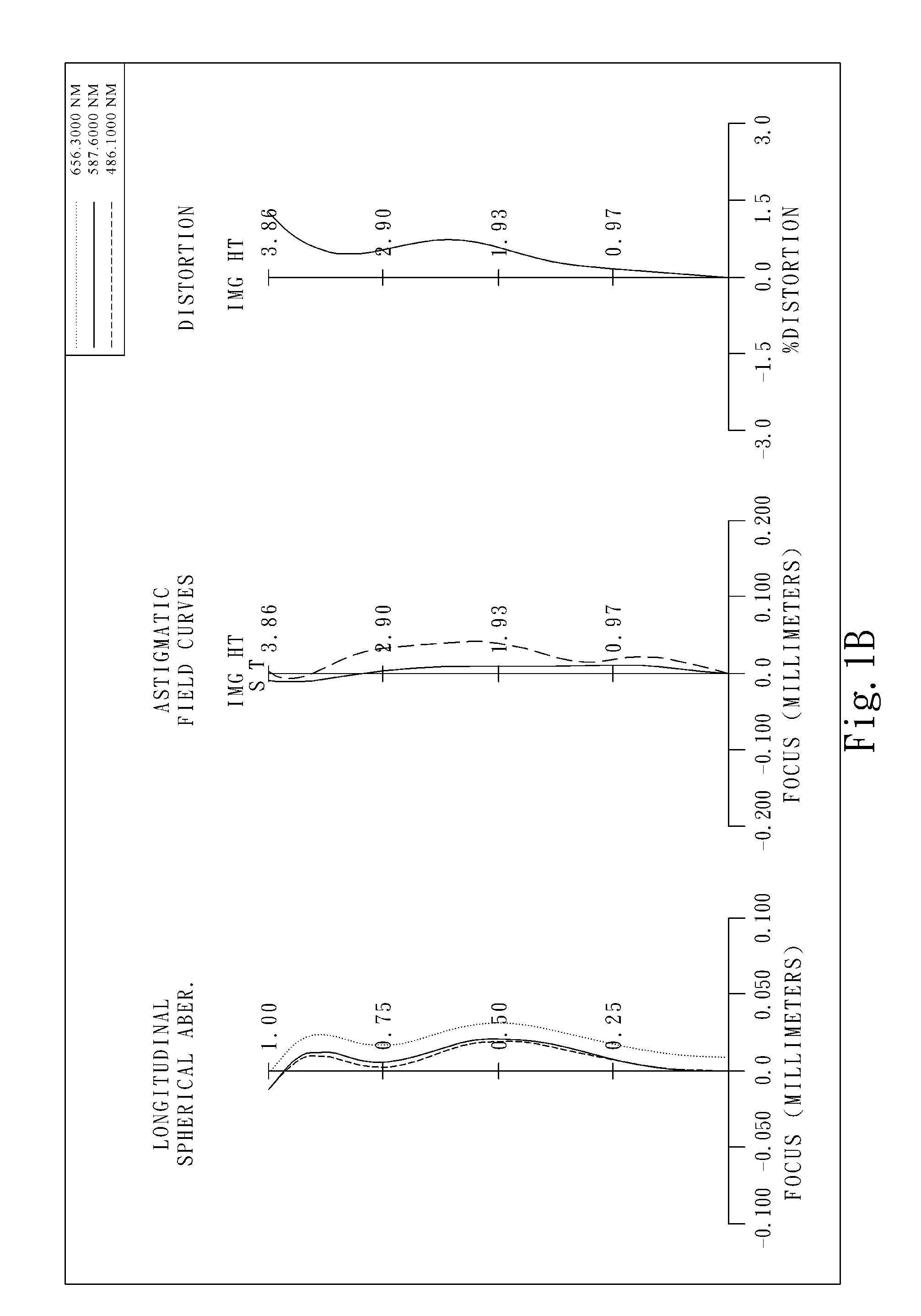
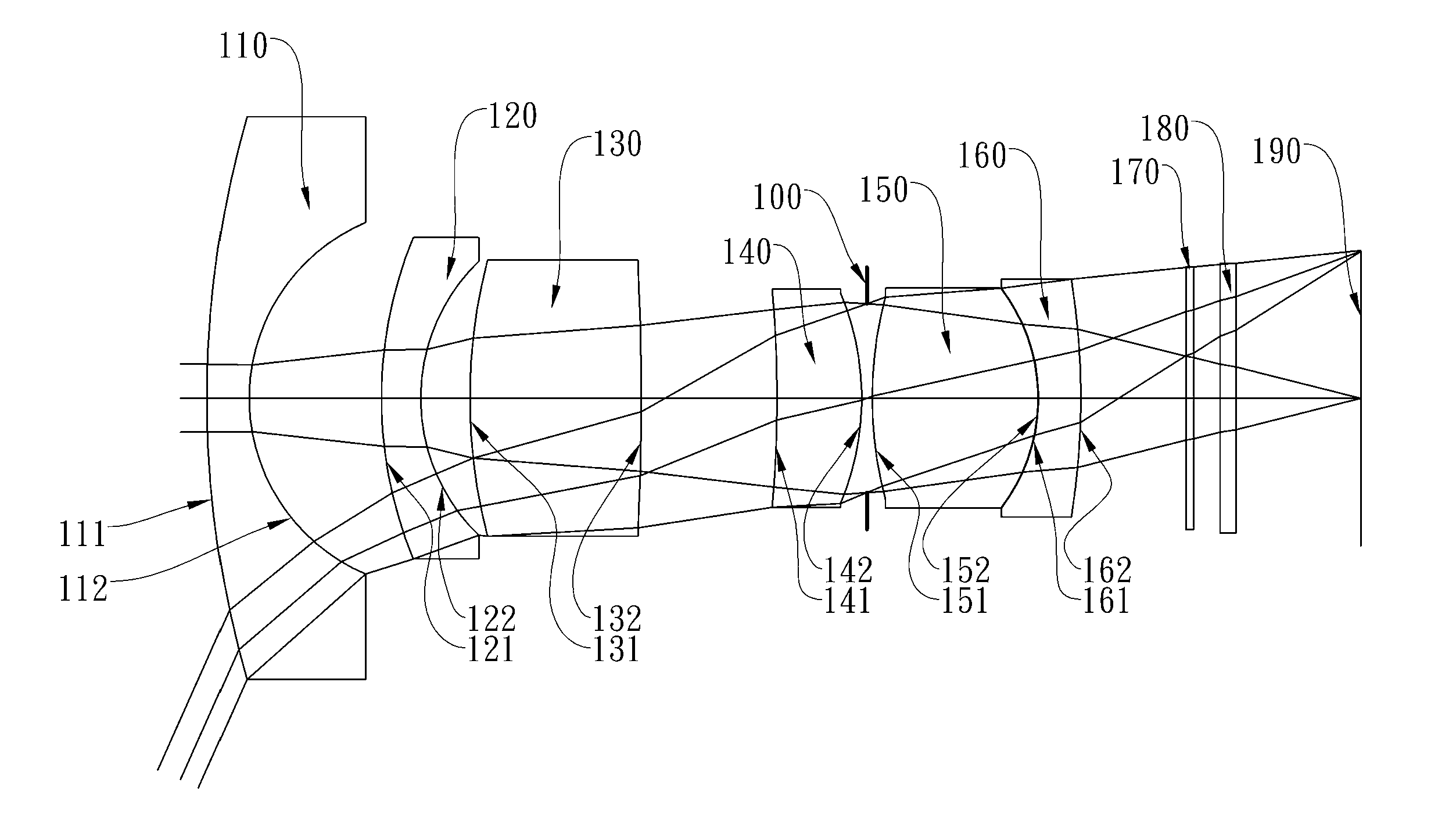
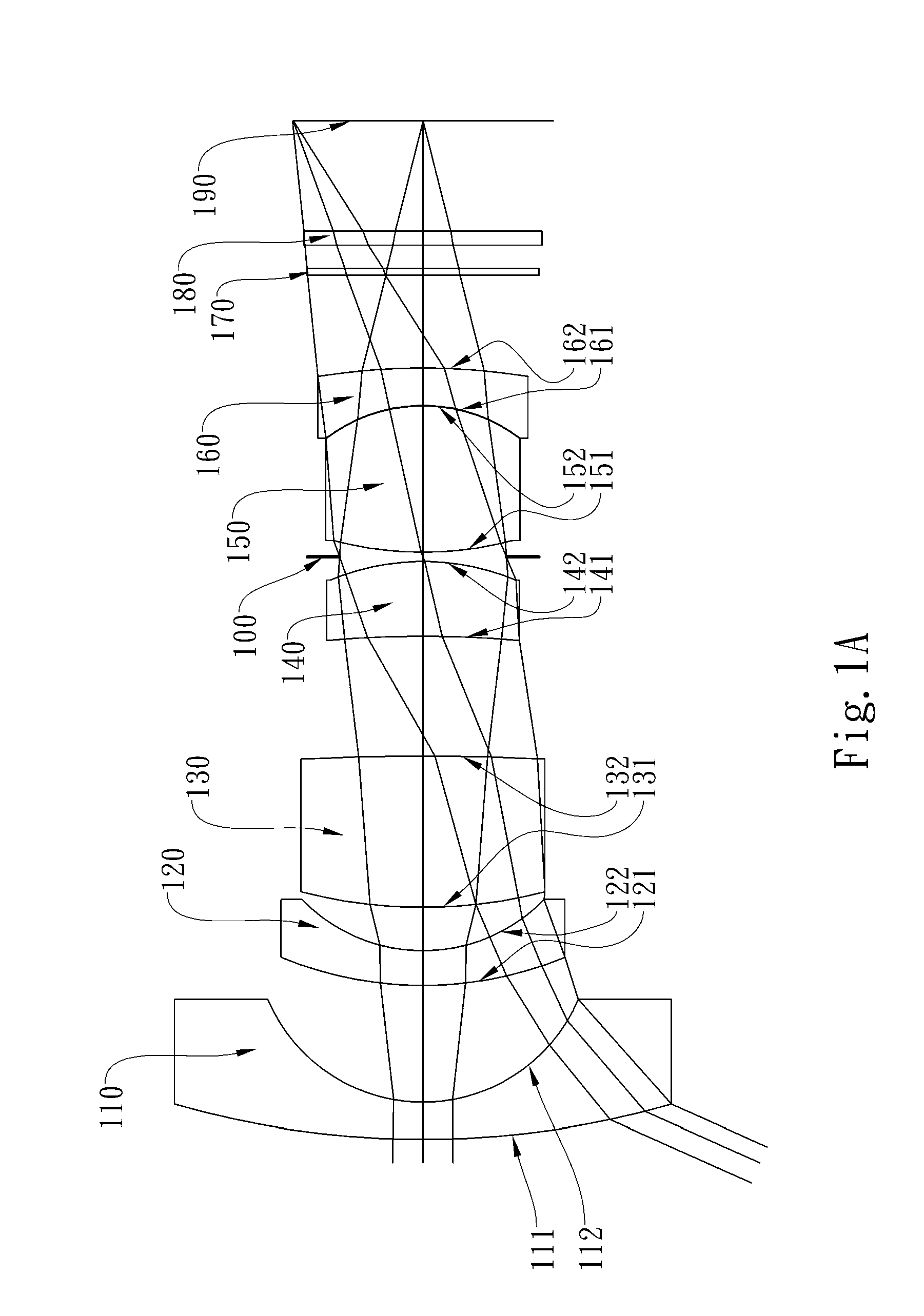
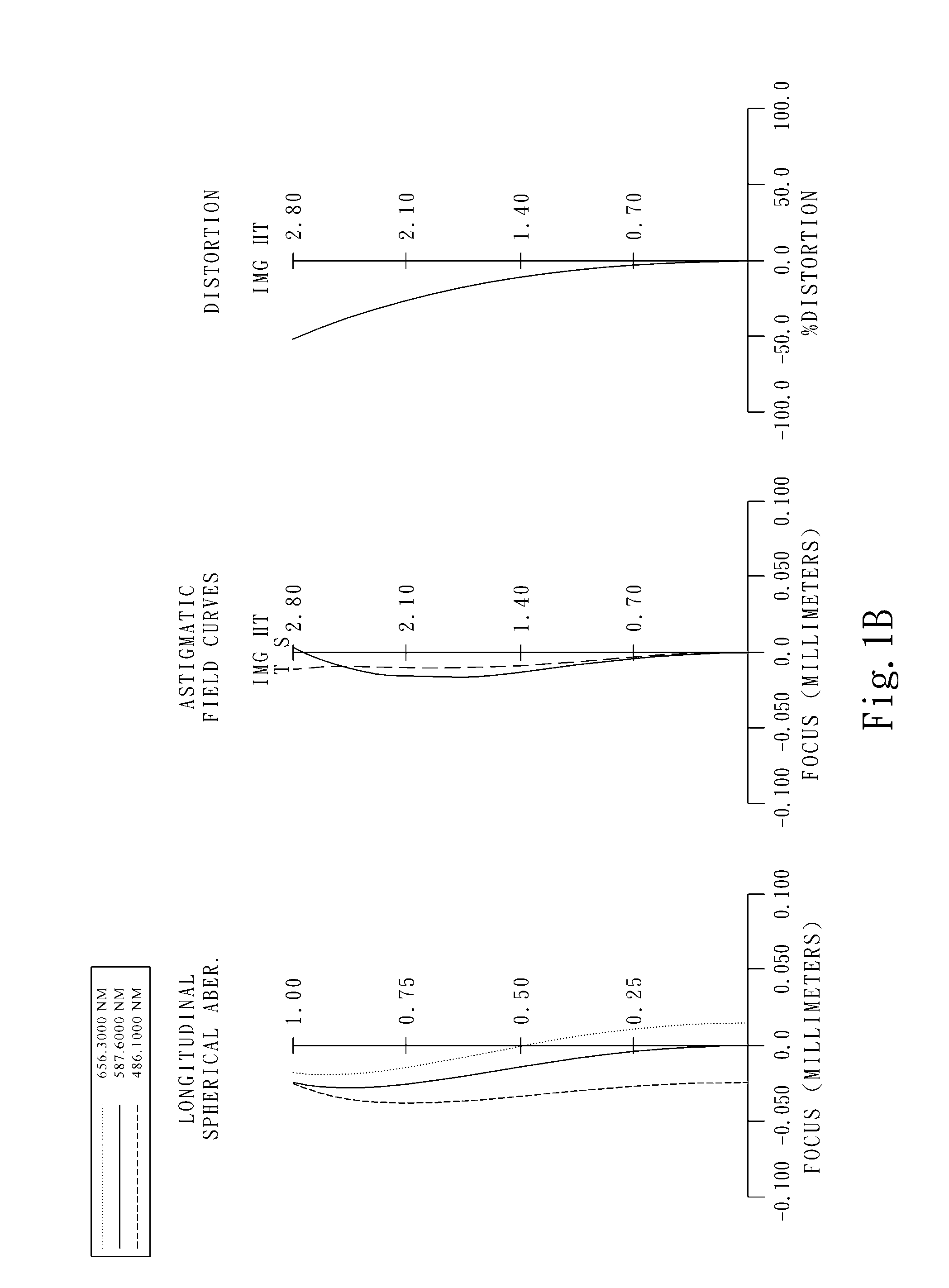
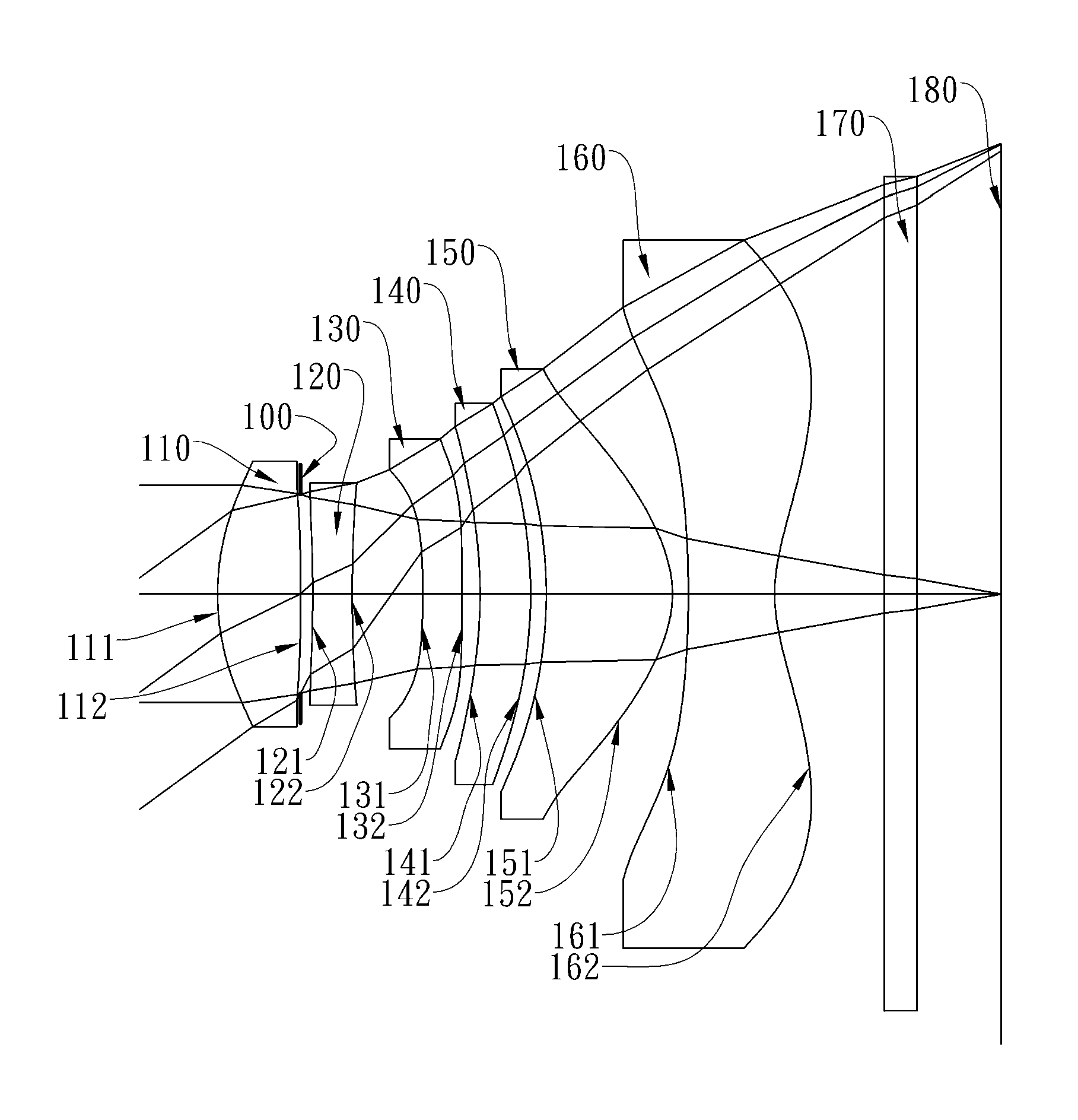
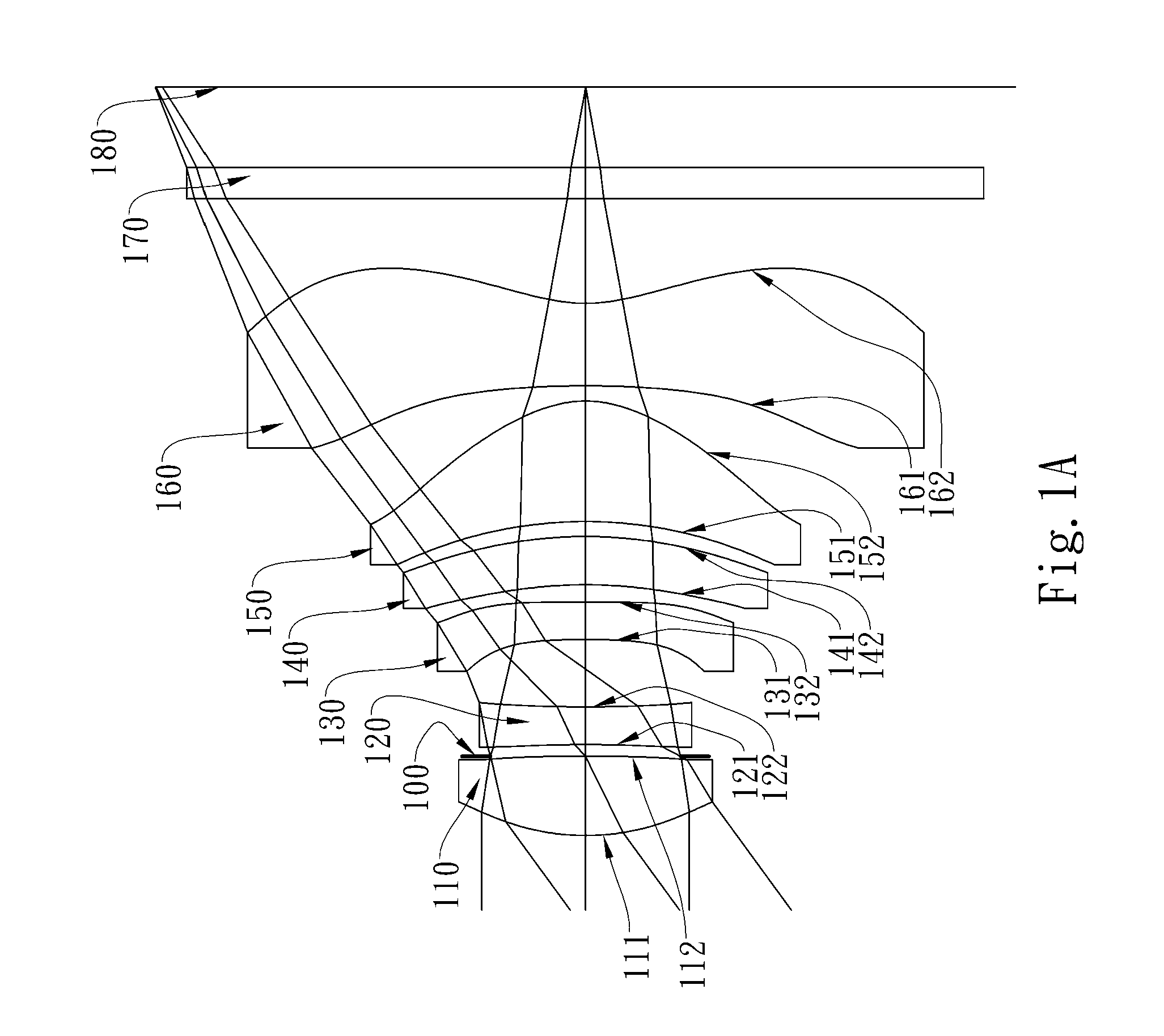
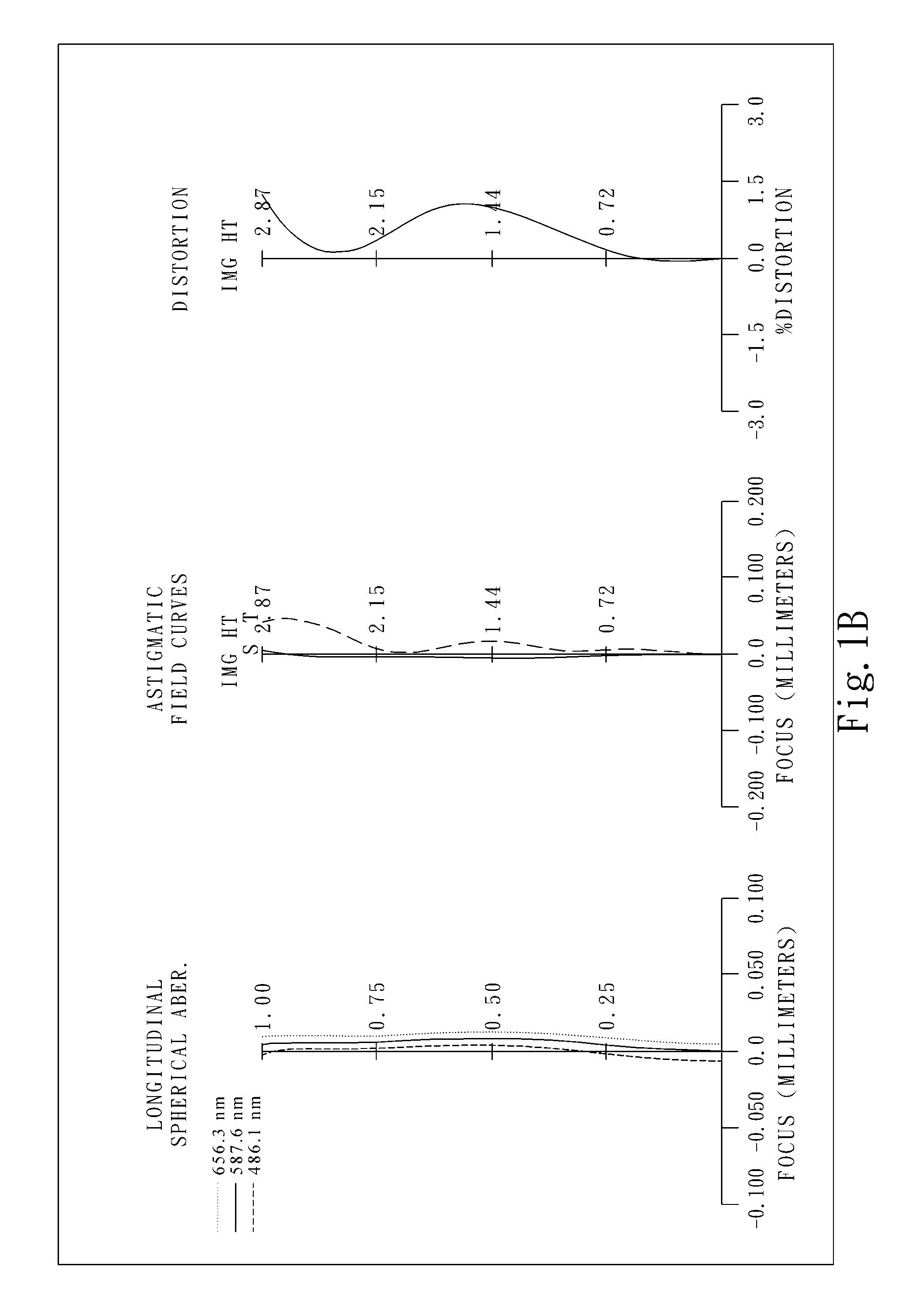
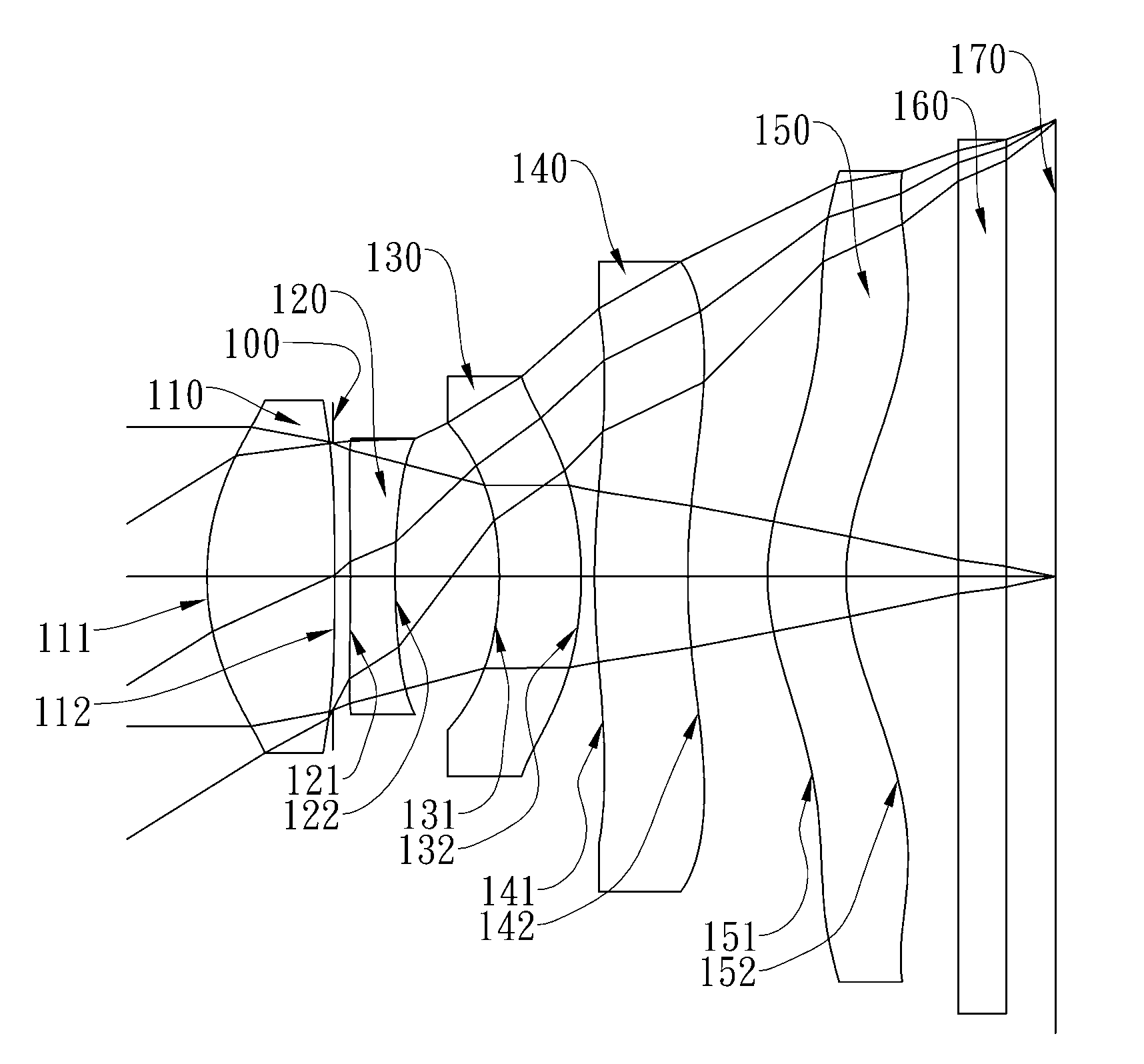
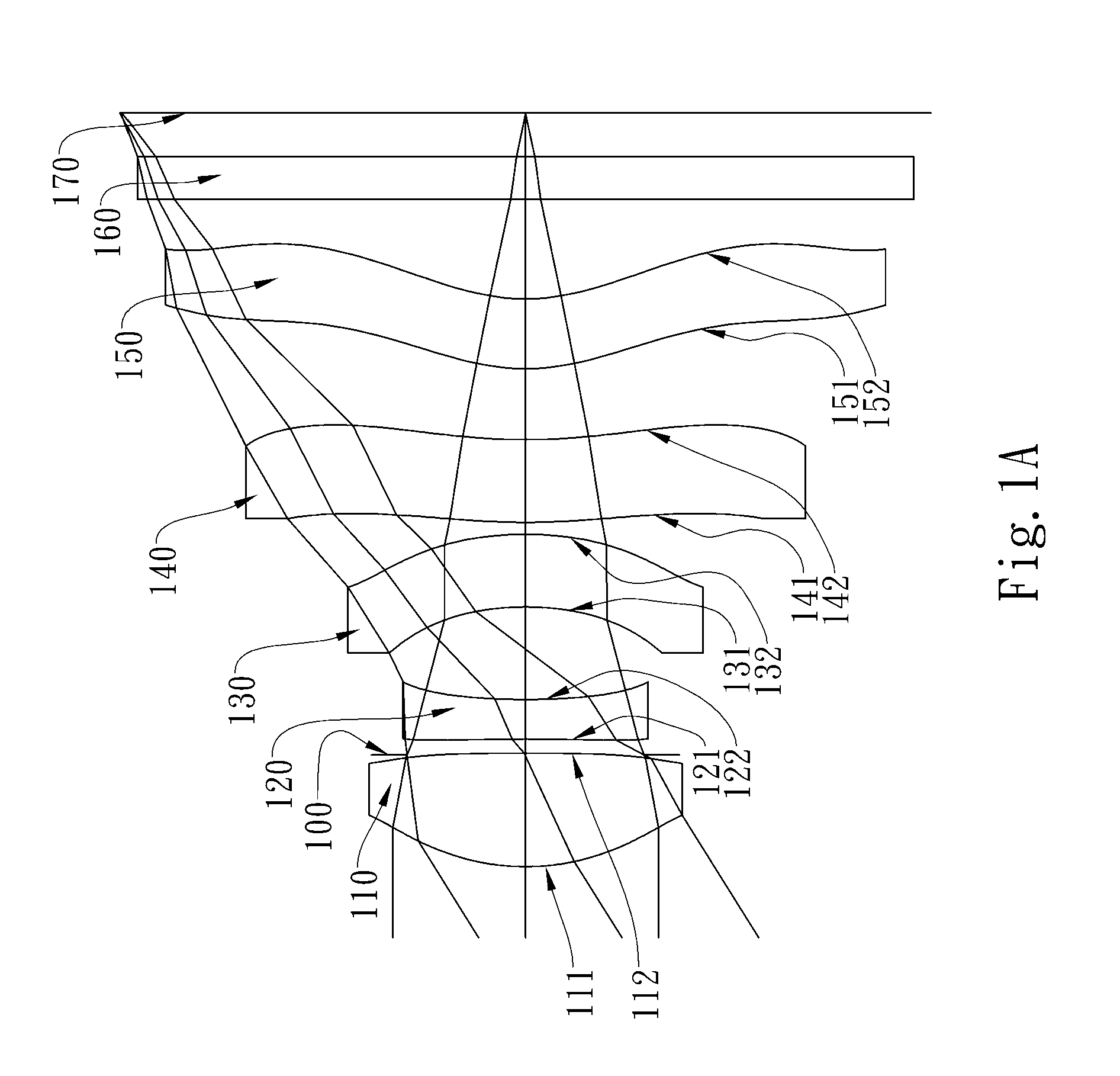
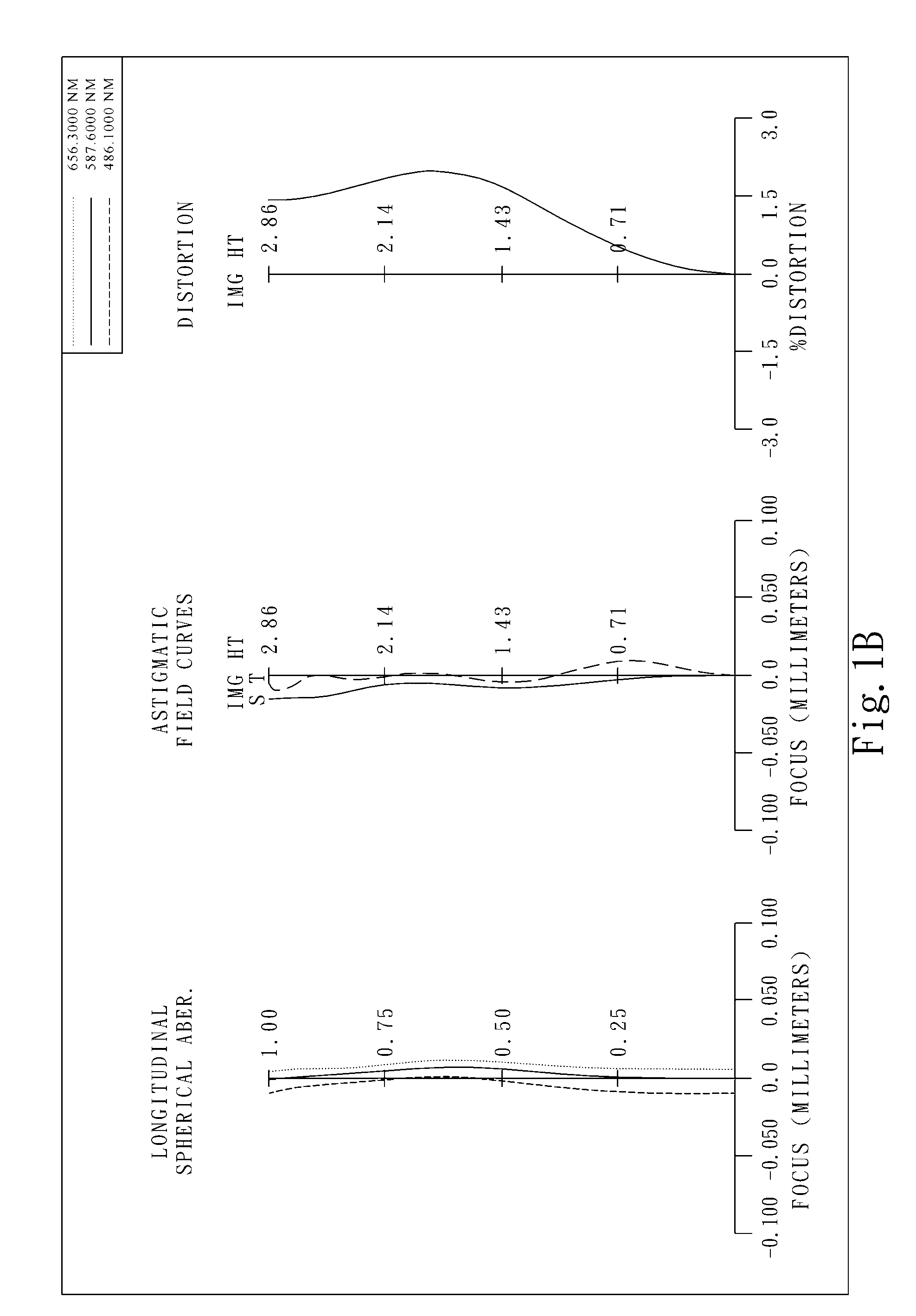
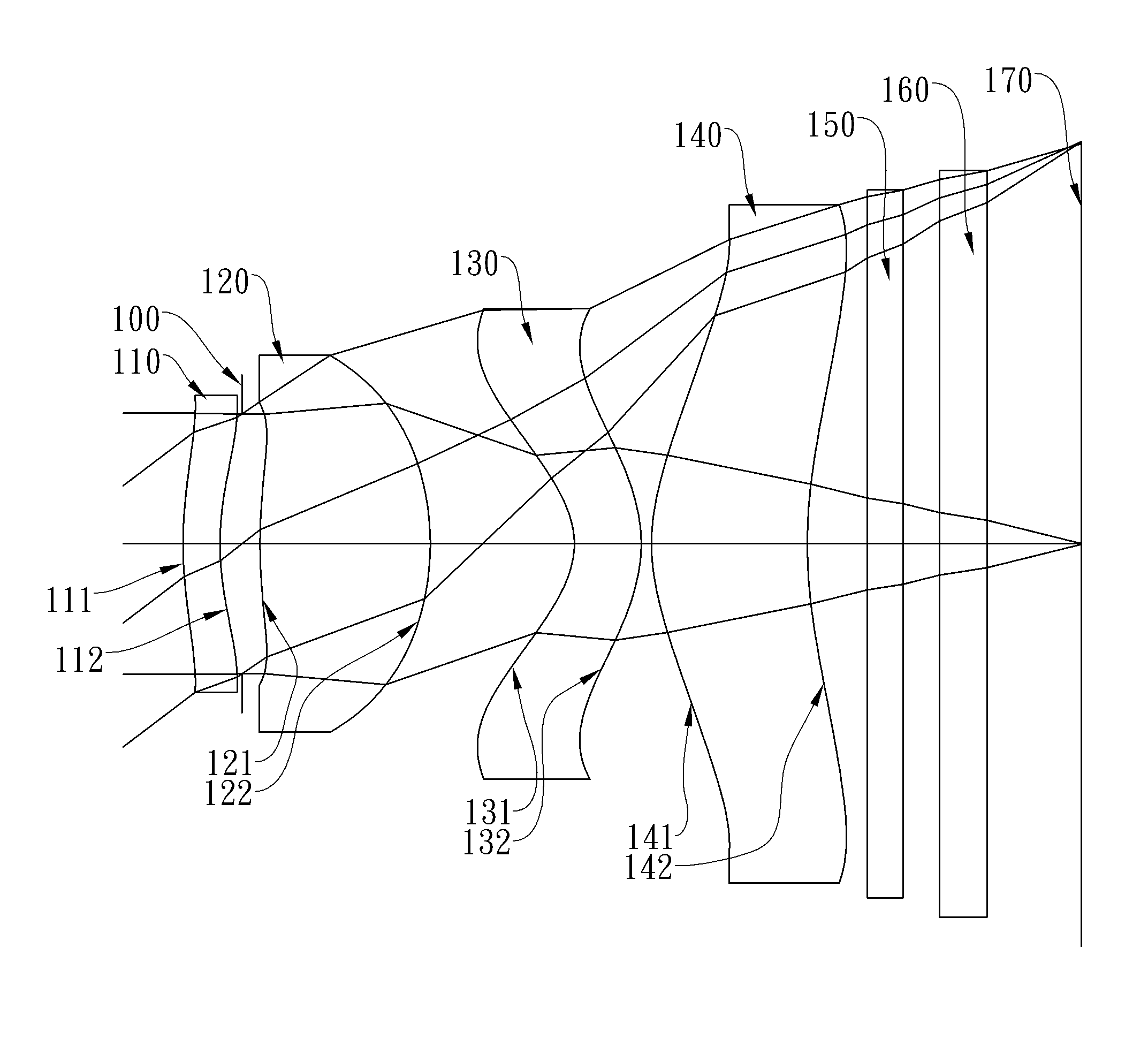
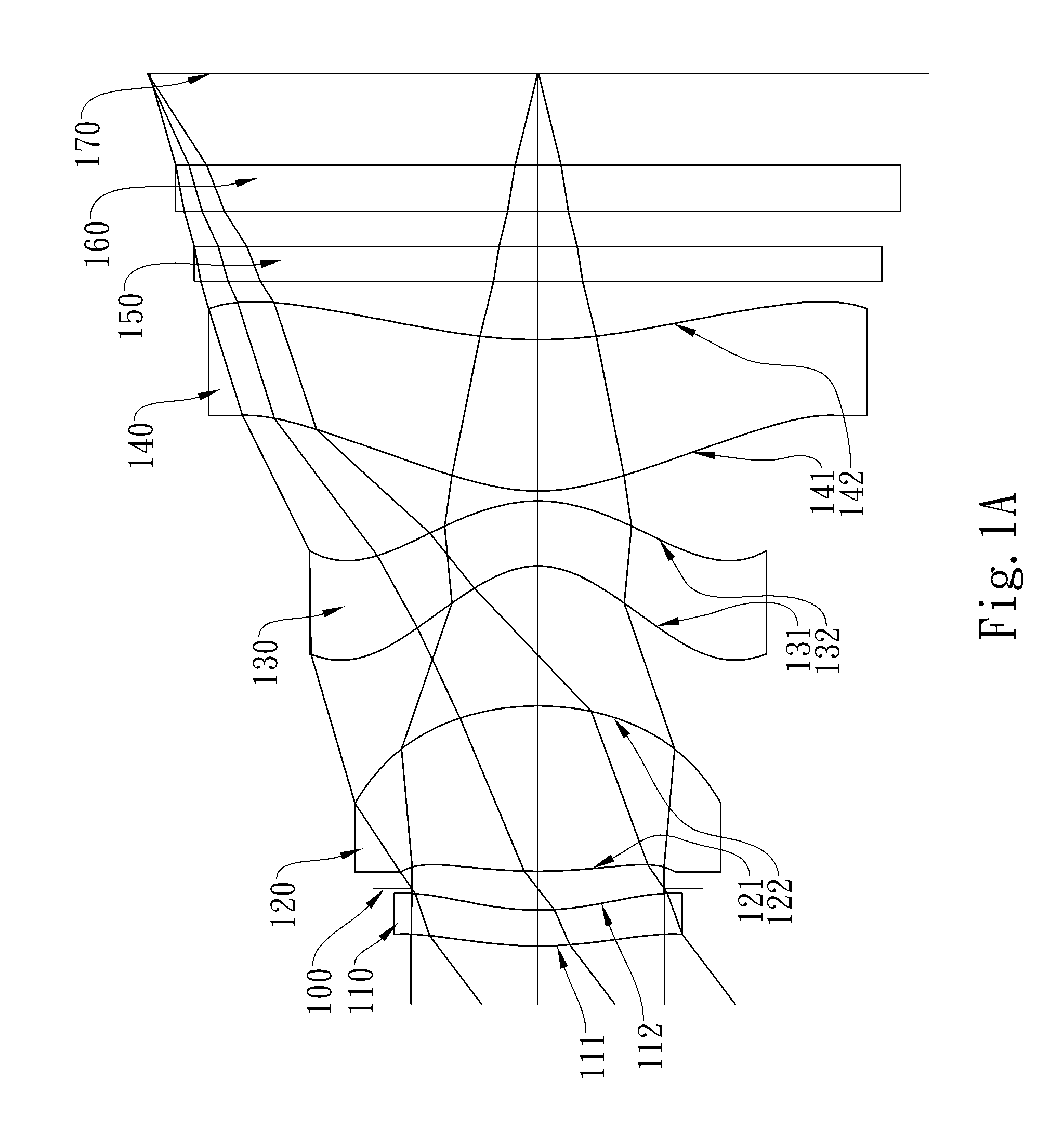
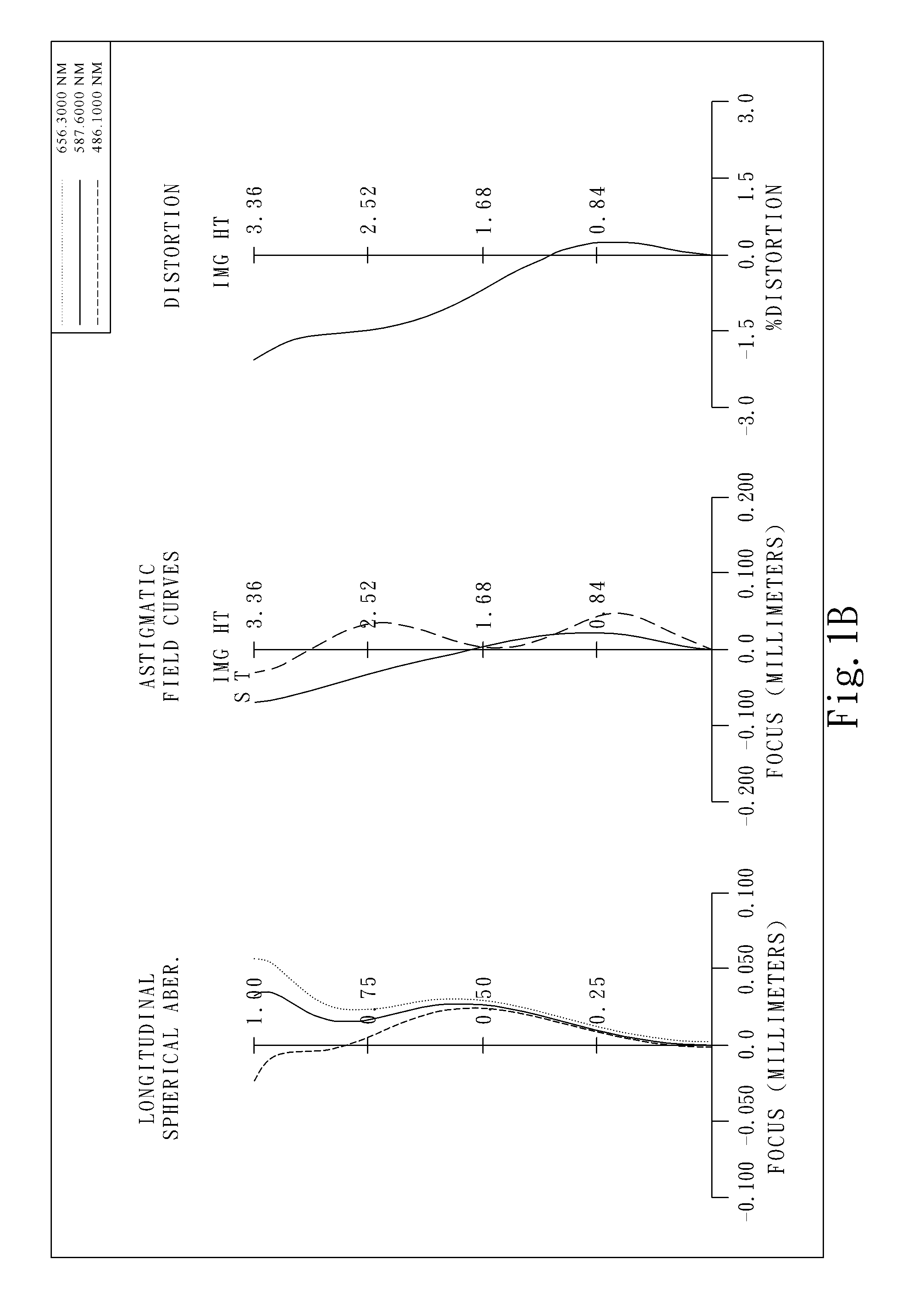
The present invention provides an optical lens system comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a fourth lens element; and a fifth lens element having a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric and at least one inflection point being formed on the image-side surface. Such arrangement of optical elements can effectively minimize the size of the optical lens system, lower the sensitivity of the optical system, and obtain higher image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical imaging lens system
This invention provides an optical imaging lens system including five lens elements with refractive power, in order from an object side toward an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface, a second lens element with negative refractive power, a third lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, a fourth lens element having both surfaces being aspheric, a fifth lens element having a concave image-side surface with at least one inflection point formed thereon. By such arrangement, the total track length and the sensitivity of the optical imaging lens system can be reduced while achieving high image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical lens system
The present invention provides an optical lens system comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a fourth lens element; and a fifth lens element having a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric and at least one inflection point being formed on the image-side surface. Such arrangement of optical elements can effectively minimize the size of the optical lens system, lower the sensitivity of the optical system, and obtain higher image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical lens system
The present invention provides an optical lens system comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a fourth lens element; and a fifth lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric and at least one inflection point being formed on the image-side surface. Such arrangement of optical elements can effectively minimize the size of the optical lens system, lower the sensitivity of the optical system, and obtain higher image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Confocal microscope
InactiveUS7339148B2Increase speedHigh image resolutionRadiation pyrometryOptical rangefindersCamera lensLight beam
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Apparatus and method for non-contact electrical impedance imaging
ActiveUS8295921B2Reliable imagingHigh image resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A method of electrical impedance imaging using multiple electrodes in which each of the multiple electrodes does not contact the object to be imaged but is electrically coupled to the object via electrically conductive fluid in which the object is at least partially immersed.
Owner:WANG WEI DR
Imaging optical lens assembly
ActiveUS20120170142A1High image resolutionAberration correctionTelevision system detailsOptical elementsPhysicsImage resolution
This invention provides an imaging optical lens assembly, in order from an object side to an image side comprising: a front lens group, an aperture stop and a rear lens group; wherein the front lens group comprises, in order from the object side to the image side: a first lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with positive refractive power and a fourth lens element with positive refractive power; wherein the rear lens group comprises, in order from the object side to the image side: a fifth lens element with positive refractive power; and a sixth lens element with negative refractive power; wherein the fifth lens element and the sixth lens element are connected to form a doublet. By such arrangement, sufficient field of view is provided, and the aberration of the lens assembly is corrected for obtaining high image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Adjustment method of printing positions, a printing apparatus and a printing system
InactiveUS6960036B1High quality imagingPreventing Image Quality DeteriorationSpacing mechanismsGratingImage resolution
By using an ink jet head, which has for each color two parallel columns of nozzles arranged side by side in the main scan direction and shifted from each other by one-half the pitch at which the nozzles are arranged in each column, odd-numbered rasters and even-numbered rasters making up an image are printed by the two nozzle columns. The registration between the odd- and even-numbered rasters is secured during the printing to produce an image with high print quality. For that purpose, the ink ejection timing between the two raster groups is shifted by a predetermined interval to form a plurality of adjustment patterns; the adjustment patterns printed are checked and, according to the check result, an adjustment value for the ink ejection timing between the two ink nozzle columns is entered; and the entered adjustment value is stored to be reflected on the actual printing operation. To facilitate the adjustment pattern check, the plurality of adjustment patterns have a dot distribution with a blue noise characteristic at a resolution at which the printing apparatus can print.
Owner:CANON KK
Positive-working radiation-sensitive imageable elements
InactiveUS20110059399A1High sensitivityHigh image resolutionPlaten pressesPhotosensitive materialsImideAryl
Positive-working imageable elements having improved sensitivity, high resolution, and solvent resistance are prepared using a water-insoluble polymeric binder comprising vinyl acetal recurring units that have pendant hydroxyaryl groups, and recurring units comprising carboxylic acid aryl ester groups that are substituted with a cyclic imide group. These imageable elements can be imaged and developed to provide various types of elements including lithographic printing plates.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method and system for generating fully-textured 3D
InactiveUS6999073B1Easy to set upView effectivelyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionGeneration processField of view
A 3D modeling system for automatically generating fully-textured 3D models of objects from a sequence of images taken around the objects is disclosed. There are several processes developed to facilitate the operation of the 3D modeling system by an ordinary skilled person. One of the processes is the automatic calibration of a camera using only a portion of a calibration disc to essentially provide a larger effective field of view of the camera. Another process is a space carving process that subdivides volumetric cells recursively to fit to a 3D object using a tree structure that encodes the entire process. Still another process is a 3D mesh model generation process that begins with the tree structure and generates self-constraint and interconnected triangles, in a sense that all triangles intersect with each other either not at all or at common boundary faces, to represent the shape of the 3D object. Yet still another process is a textured patch process that provides a useful mechanism for a user to edit and modify a fully-textured 3D model in a desired manner by the user.
Owner:GEOMETRIX
Imaging device including a plurality of lens elements and a imaging sensor
InactiveUS7880794B2High image resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionOptical power
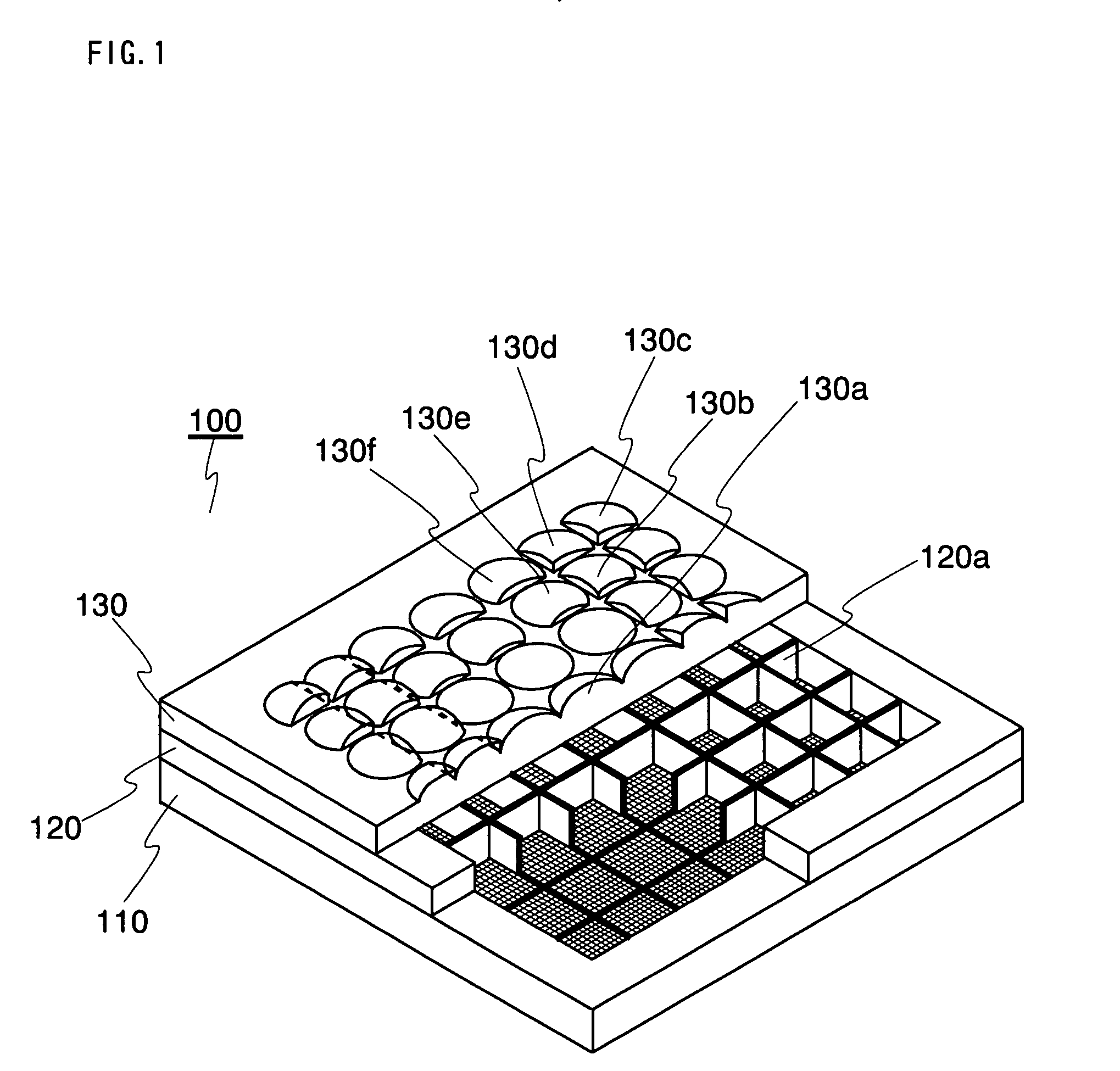
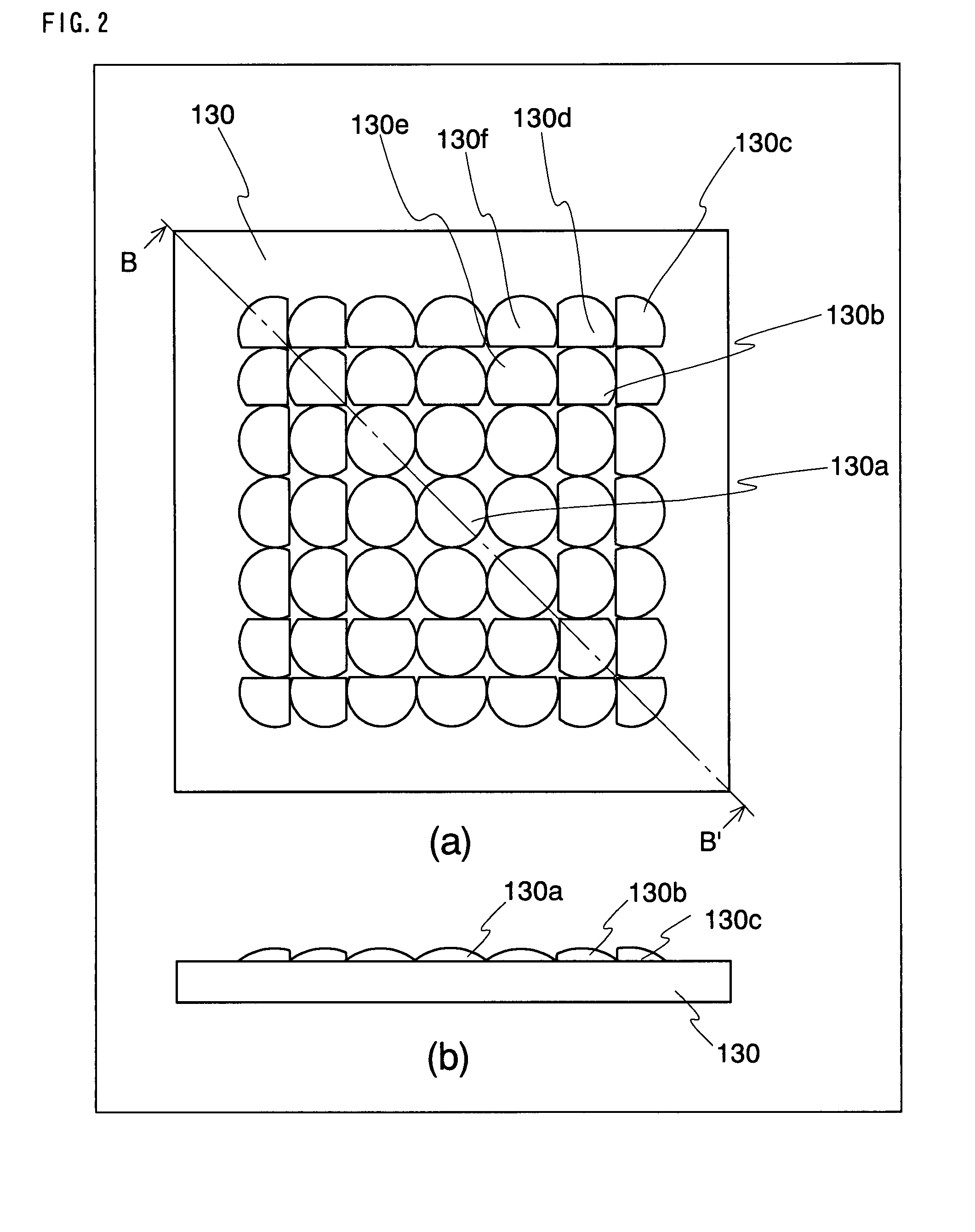
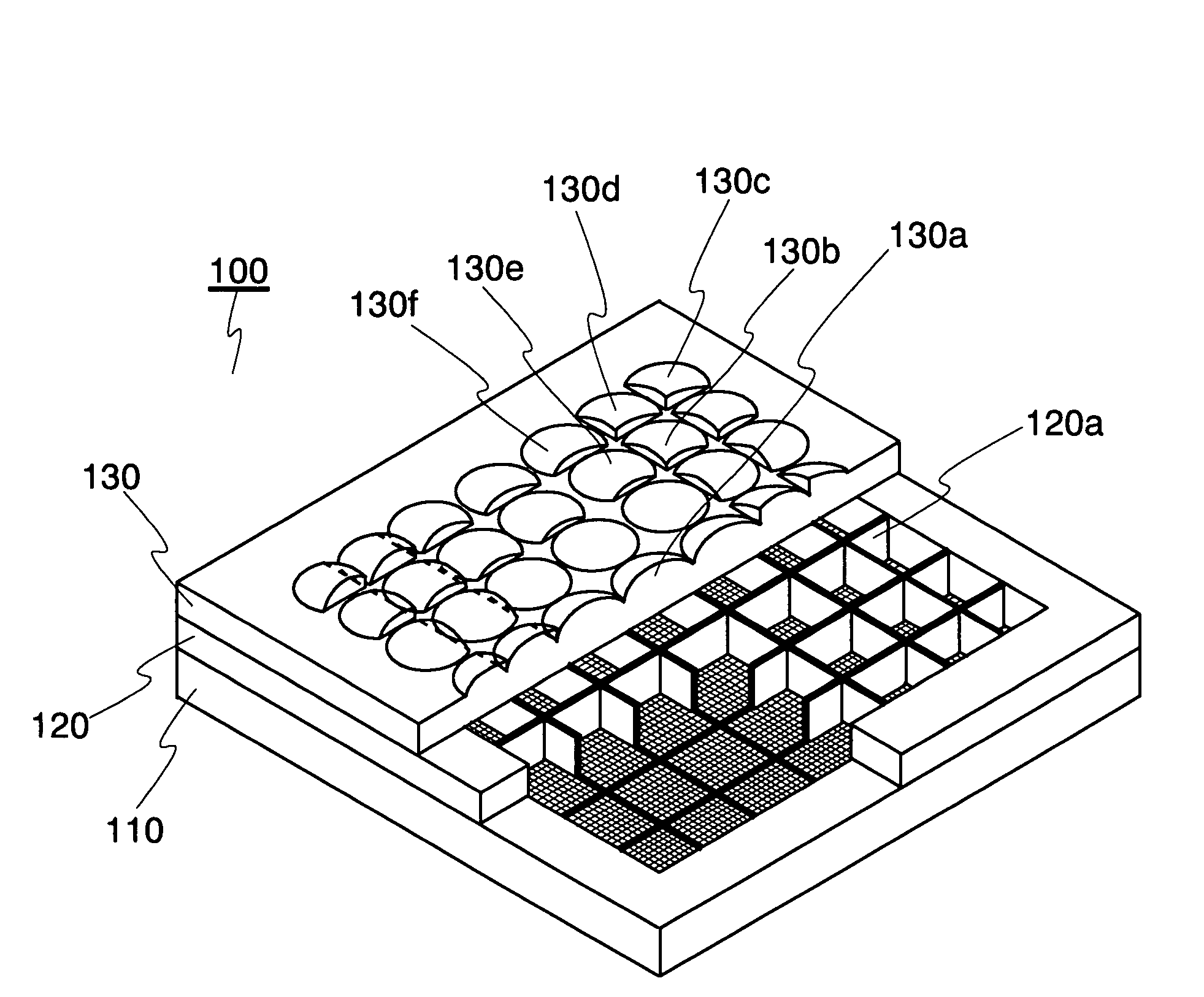
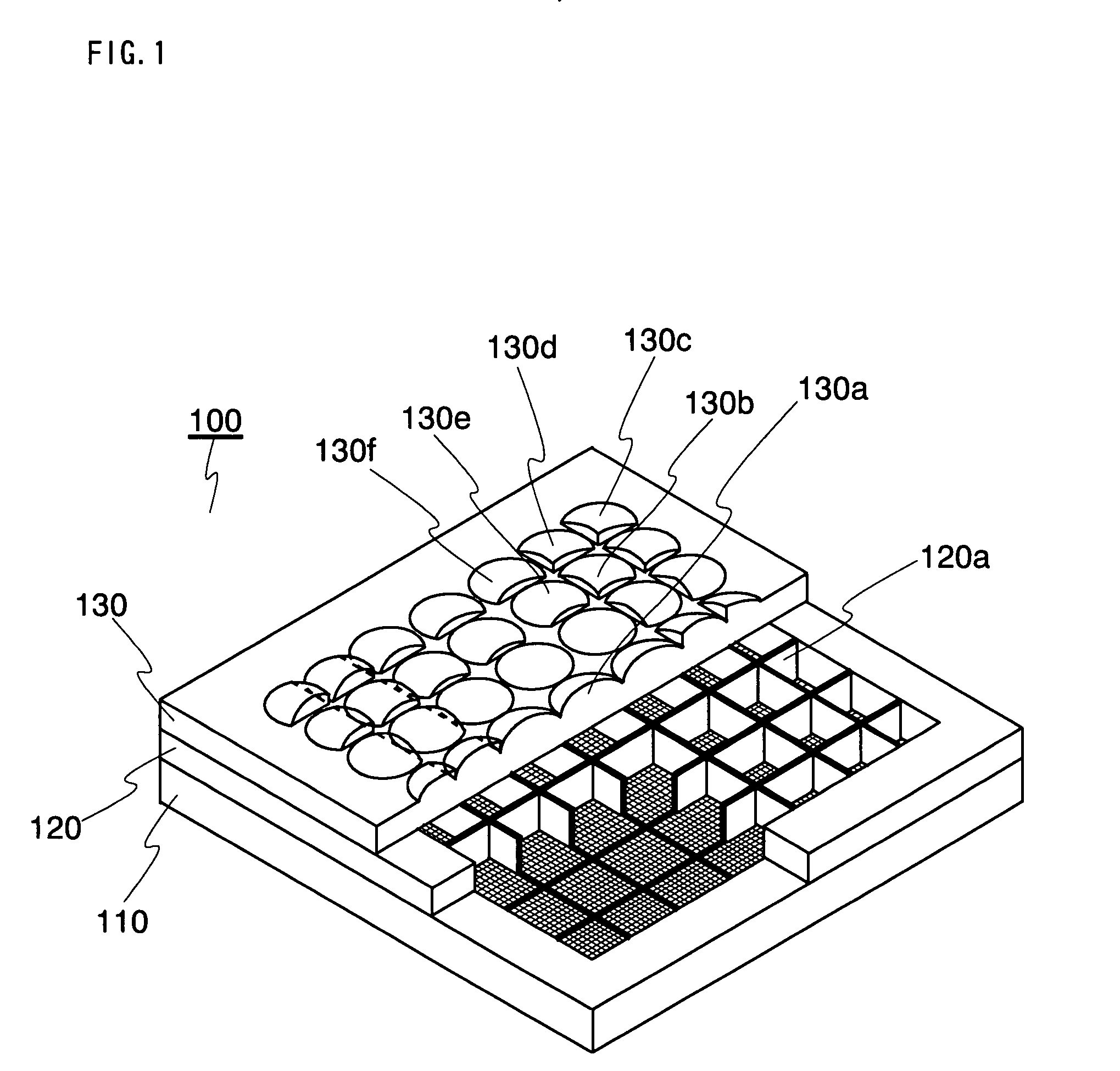
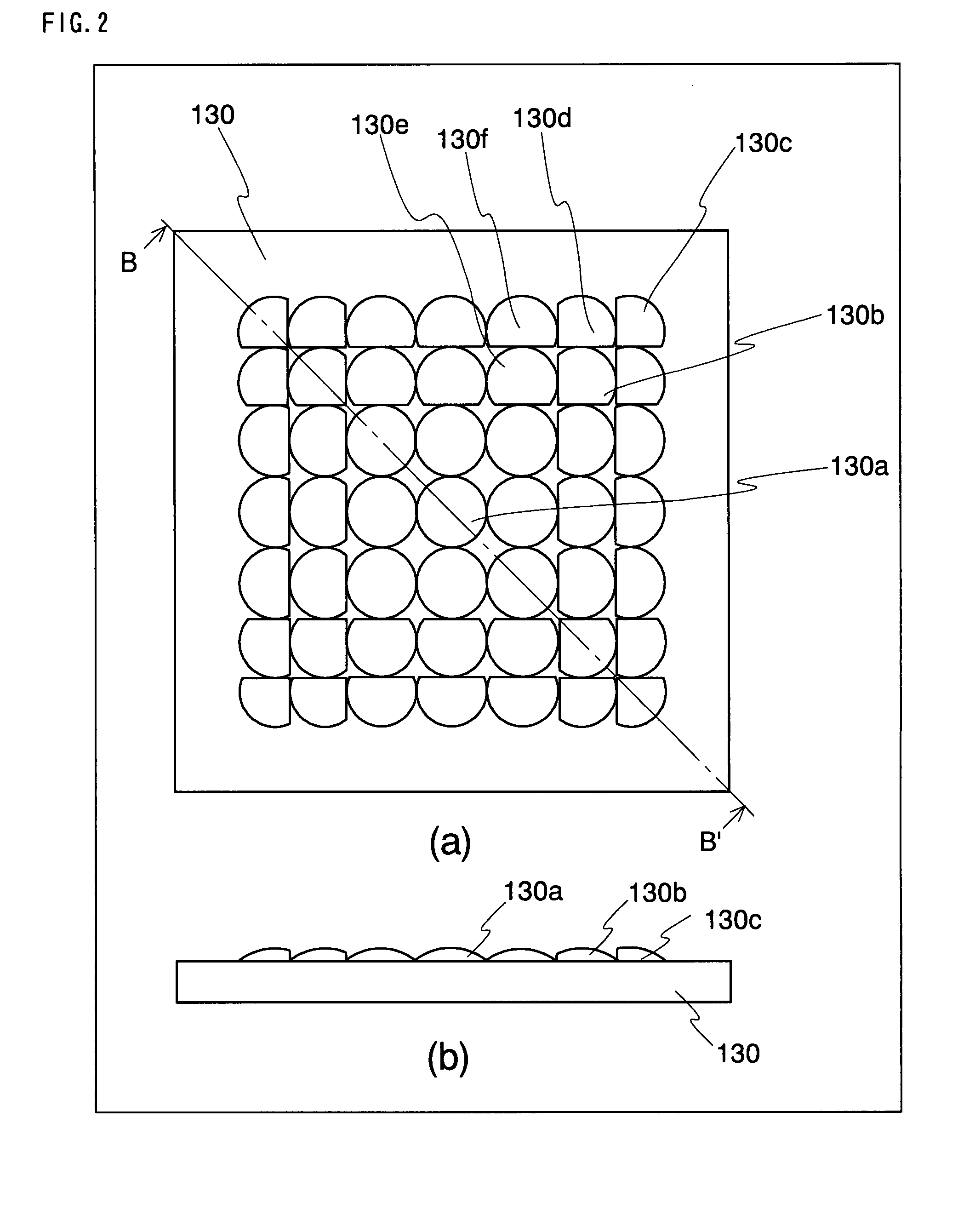
An object of the present invention is to provide: a thin imaging device in which a high image resolution is obtained and in which the resolution does not uniformly vary even when the shooting distance is changed; and a lens array used therein. The present invention relates to an imaging device comprising: a lens array 130 constructed by arranging in parallel a plurality of lens elements having optical power in at least one surface; and an image sensor 110 in which an optical image formed by an optical system having each of the lens elements is received by each of mutually different imaging regions each having a plurality of photoelectric conversion sections so that the optical image is converted into an electric image signal, wherein each lens element and the imaging region corresponding to the lens element constitute an imaging unit, while the imaging units have diverse imaging region areas. The present invention relates also to a lens array used therein.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image capturing lens assembly
This invention provides an image capturing lens assembly, in order from an object side to an image side comprising: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element; a third lens element; a fourth lens element having at least one of an object-side surface and an image-side surface thereof being aspheric; a fifth lens element with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface, at least one of an object-side surface and the image-side surface thereof being aspheric, and the fifth lens element is made of plastic; and a sixth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface, at least one of an object-side surface and the image-side surface thereof being aspheric, and the sixth lens element is made of plastic. By such arrangement, the photo-sensitivity and the total track length of the image capturing lens assembly can be reduced. Furthermore, the aberration and astigmatism of the assembly can be effectively corrected for obtaining higher image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Stereoscopic three-dimensional display based on multi-screen splicing
InactiveCN102231044ATo achieve the suspension effectStrong expandabilityProjectorsStereoscopic photographyCamera lensParallax
The invention discloses a stereoscopic three-dimensional display based on multi-screen splicing. The stereoscopic three-dimensional display comprises a two-dimensional display array, a projection lens array, an aperture array and a directional scattering screen. By utilizing a two-dimensional display pixel region segmentation mode and ensuring each display region of the display array to form a projector together with an aperture and a projection lens which is directly in front of the region, all projectors are staggered in vertical direction and project the images corresponding to the display regions to a same position on the directional scattering screen so as to form an image in front of an arc-shaped screen; and the images displayed in each display region are spliced by the images of a three-dimensional object from different visual angles according to a specific segmentation and recombination method. The stereoscopic three-dimensional display provided by the invention has the advantages of achieving high image resolution and high visual angle resolution and realizing observation of an exquisite three-dimensional image with a horizontal parallax. Compared with the single naked-eye display, stereoscopic three-dimensional display provided by the invention has the advantages that the multi-screen splicing settings ensures that the extension of visual angles is realized, and the spatial scale and viewing range of the three-dimensional images are increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Imaging device and lens array used therein
InactiveUS20090122175A1High image resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionOptical power
An object of the present invention is to provide: a thin imaging device in which a high image resolution is obtained and in which the resolution does not uniformly vary even when the shooting distance is changed; and a lens array used therein. The present invention relates to an imaging device comprising: a lens array 130 constructed by arranging in parallel a plurality of lens elements having optical power in at least one surface; and an image sensor 110 in which an optical image formed by an optical system having each of the lens elements is received by each of mutually different imaging regions each having a plurality of photoelectric conversion sections so that the optical image is converted into an electric image signal, wherein each lens element and the imaging region corresponding to the lens element constitute an imaging unit, while the imaging units have diverse imaging region areas. The present invention relates also to a lens array used therein.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
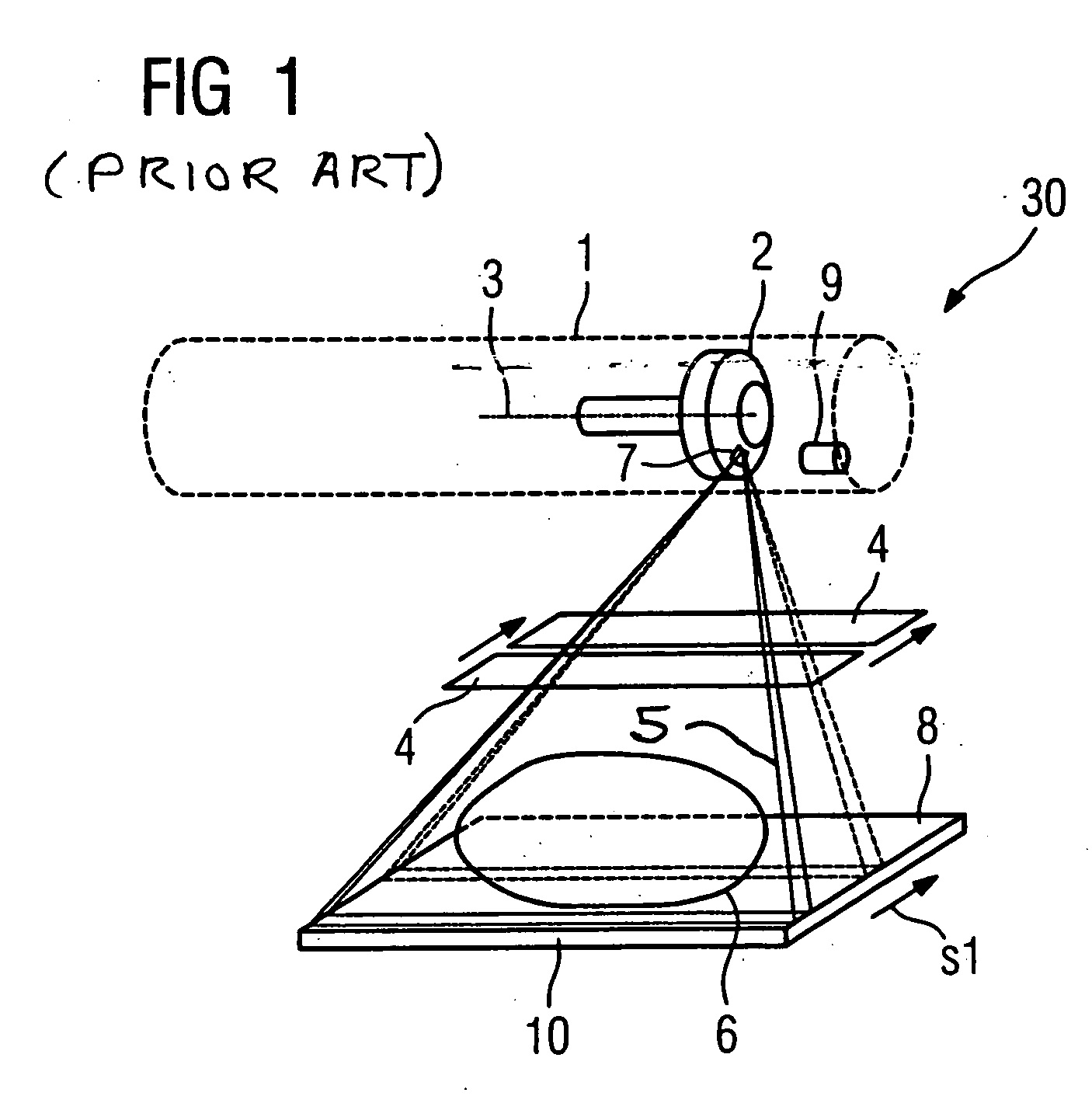
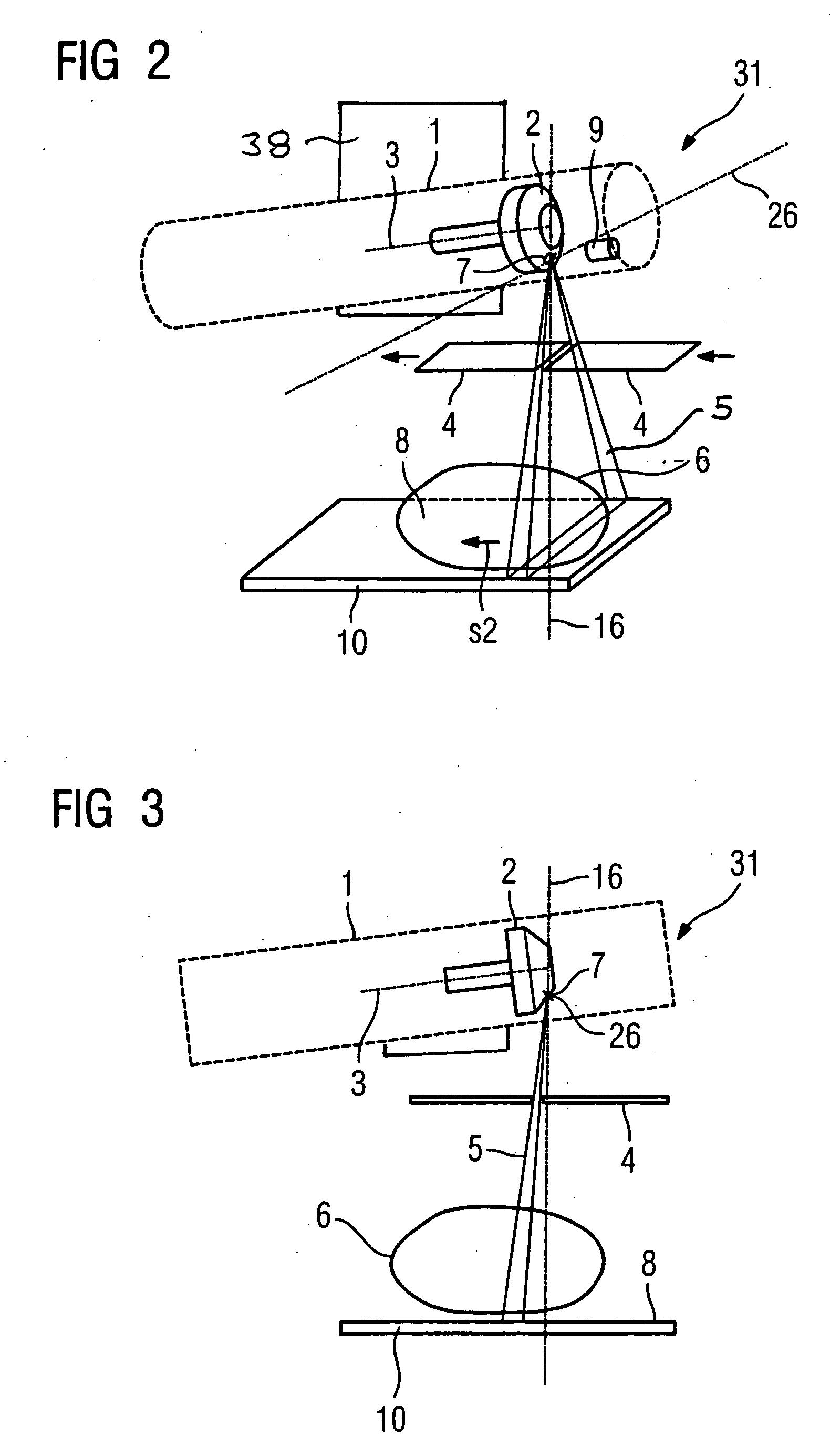
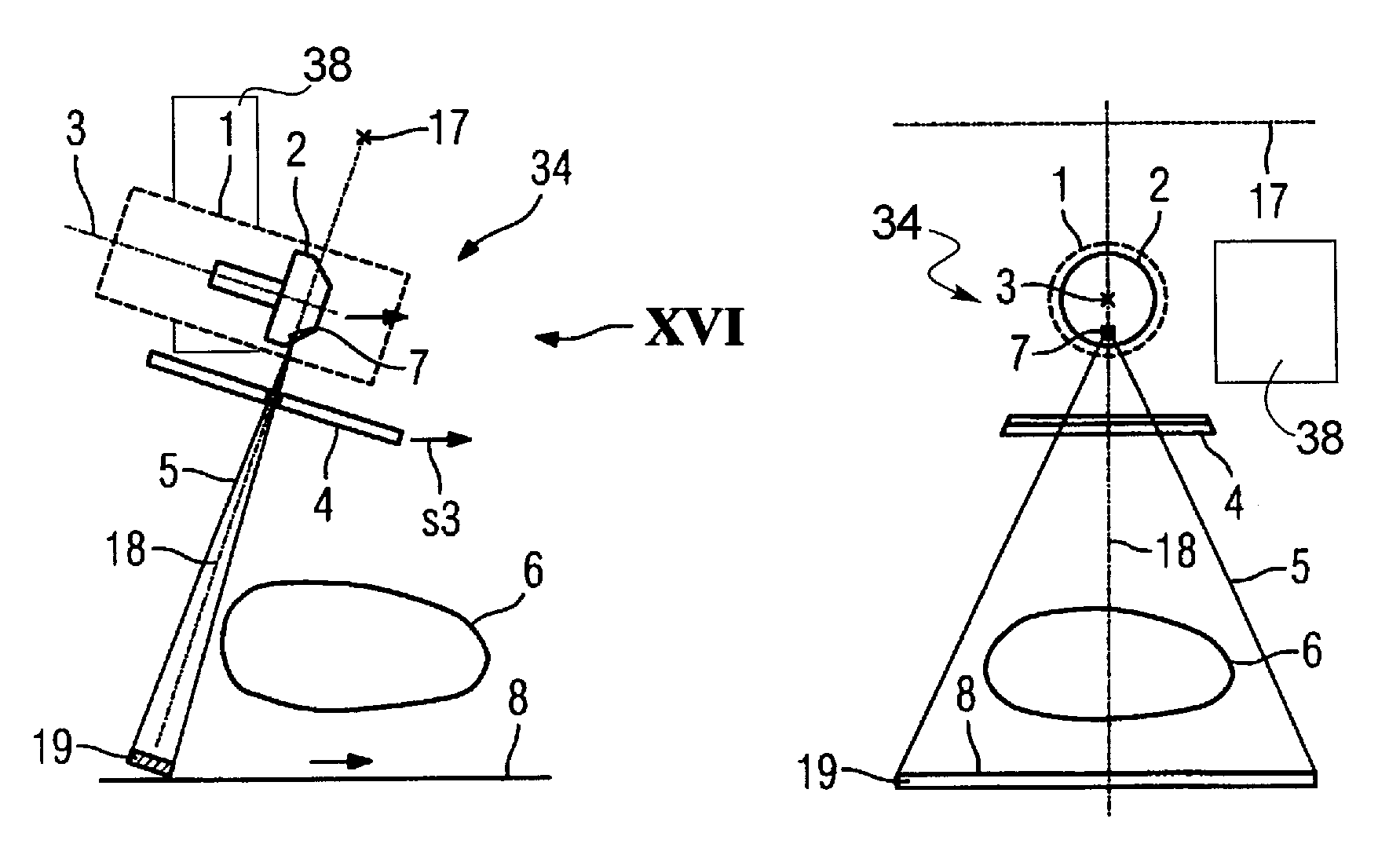
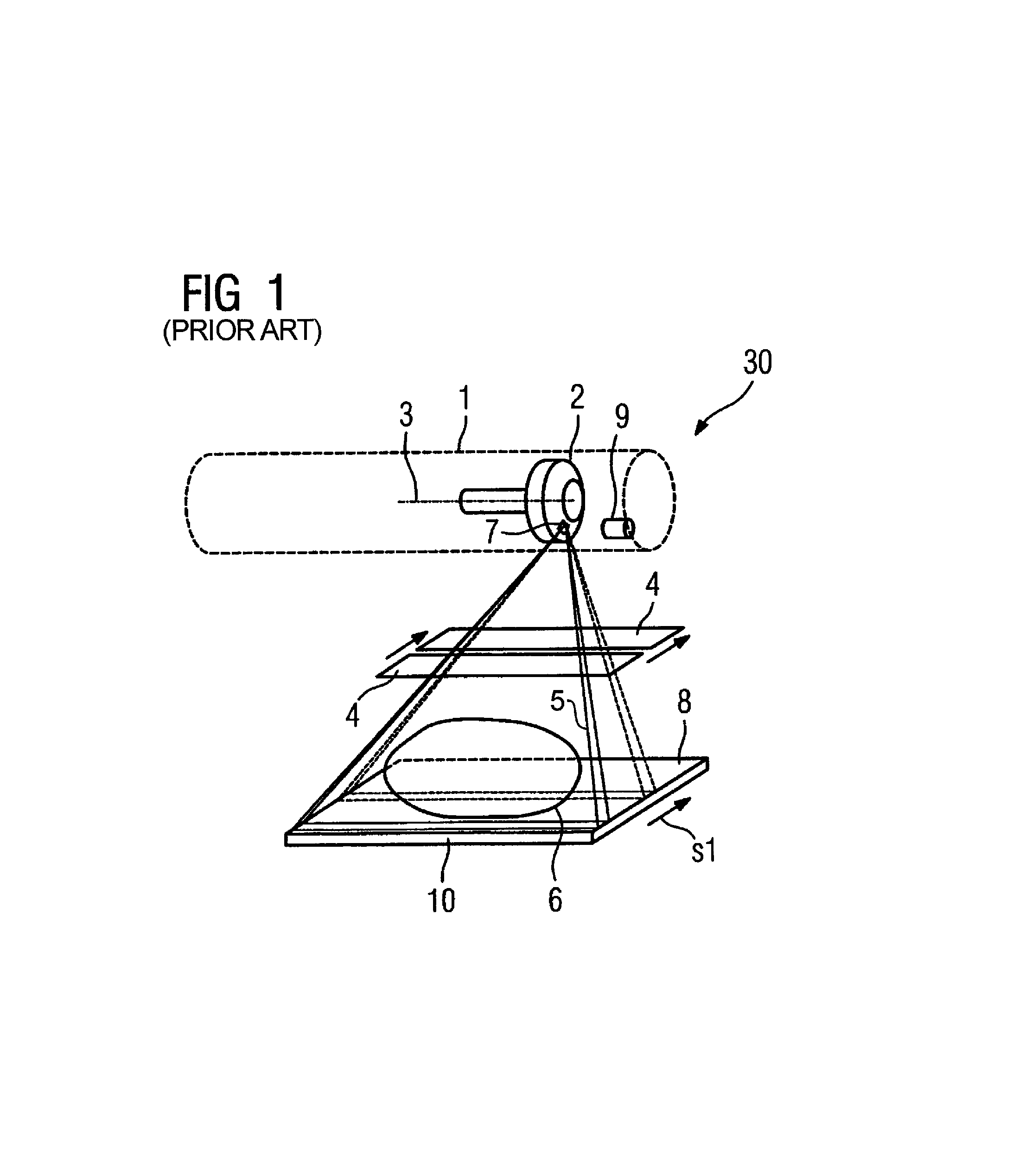
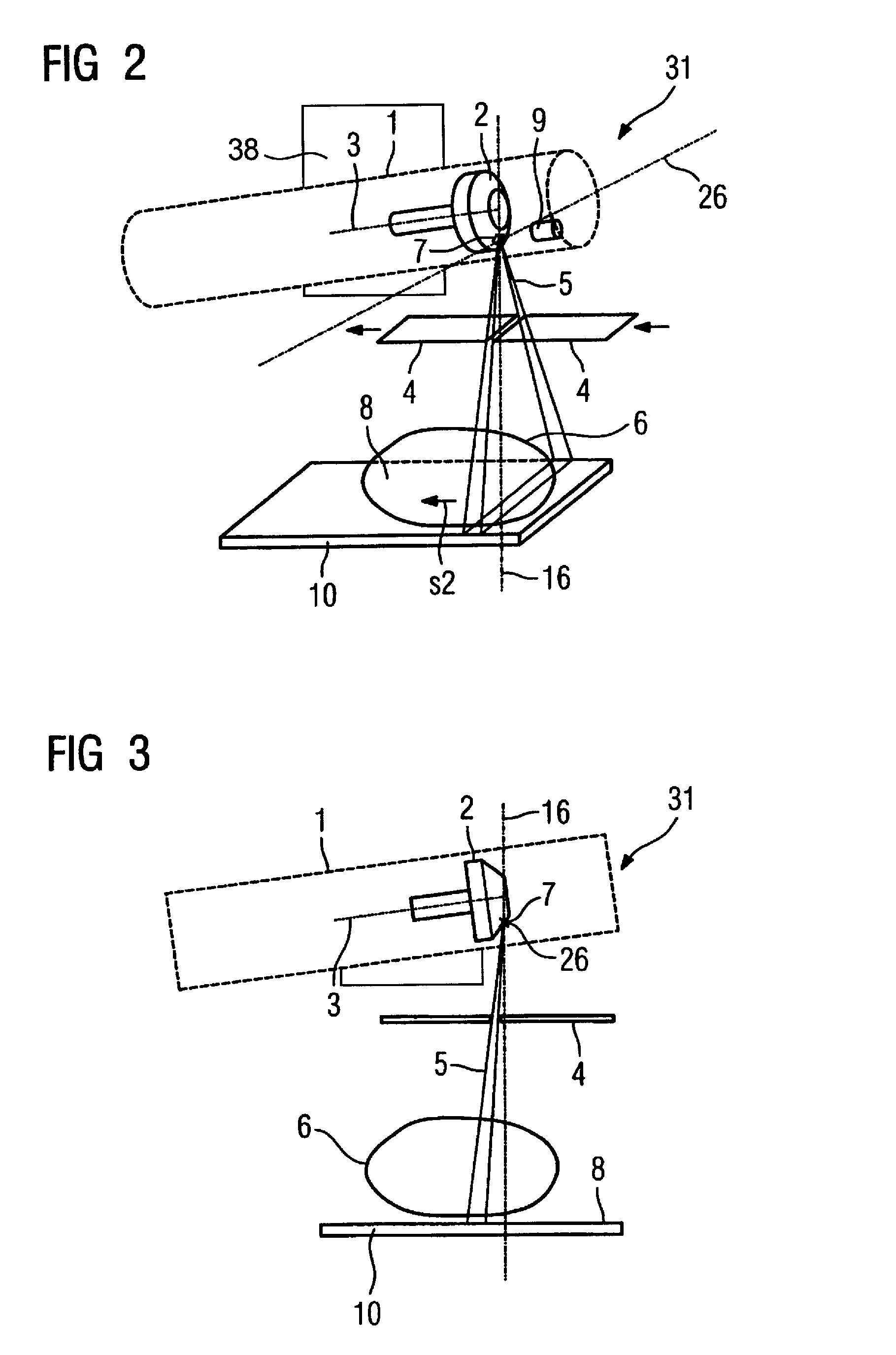
X-ray device that emits an x-ray beam with a scanning-like movement
InactiveUS20060034426A1Quality improvementLow-cost mannerX-ray tube electrodesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRotational axisImage resolution
An x-ray device includes an x-ray tube for generation of an x-ray emanating from a focal spot of a rotary anode rotatable around a rotation axis and a slit-shaped diaphragm for generation of a fan-shaped x-ray beam that is gated from the x-ray and emission is moved through an examination region in the manner of a scan. To improve the image resolution, the fan-shaped x-ray beam can be moved over the examination region essentially in the direction of the rotational axis of the rotary anode by tilting the x-ray tube on the focal spot, with the x-ray tube being tilted on the focal spot so that the fan-shaped x-ray beam is always gated from the region of the overall emitted x-ray beam having the highest-image resolution or the highest image definition in the movement through the examination region.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and system for contactless fingerprint detection and verification
ActiveUS20110064282A1High image resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisFingerprintFingerprint detection
This invention provides a method for contactless fingerprint detection and verification comprising illuminating a fingerprint and directing a reflected light through an imaging system using liquid crystal panels and birefringent elements to polarize the light. A plurality of polarized images are captured and used to calculate the depth of structural features on the fingertip. A means to generate a two-dimensional rolled equivalent image of the fingerprint is also provided which may then be used for verification and authentication. The invention also provides an imaging system for carrying out the method.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and System for Random Steerable Sar Using Compressive Sensing
ActiveUS20140266869A1Improve imaging resolutionFlexible steeringRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsImage resolution
A synthetic aperture radar image is generated by directing randomly a beam of transmitted pulses at an area using a steerable array of antennas, wherein the area is uniformly by the transmitted pulses while the array of antennas moves along a path. A sparse reconstruction procedure is applied to received signals from the area due to reflecting the transmitted pulses to generate the image corresponding to the area. The radar system can operate in either sliding spotlight mode, or scan mode. The area can be of an arbitrary shape, and a resolution of the image can be increased.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Semiconductor photosensitization device, production method and application thereof
ActiveCN101707202AReduce manufacturing costHigh image resolutionTelevision system detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing cost reductionPixel density
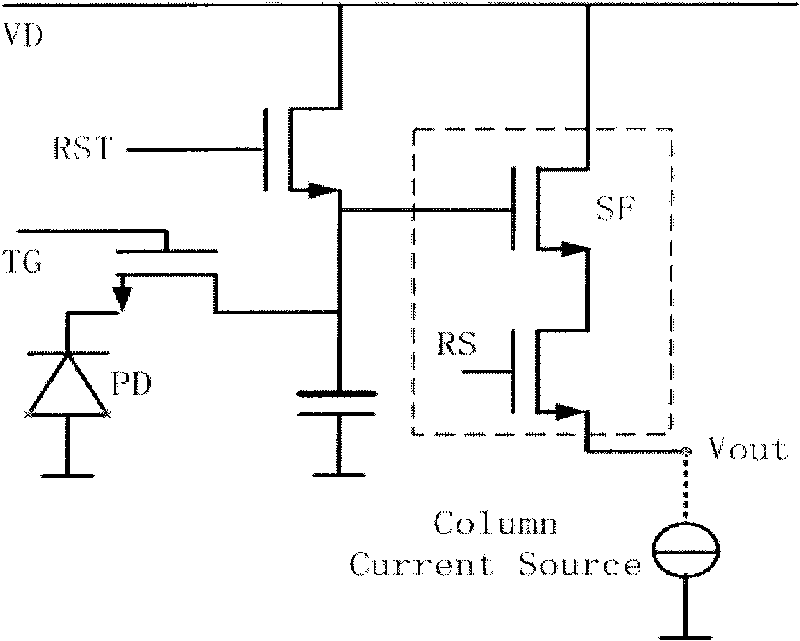
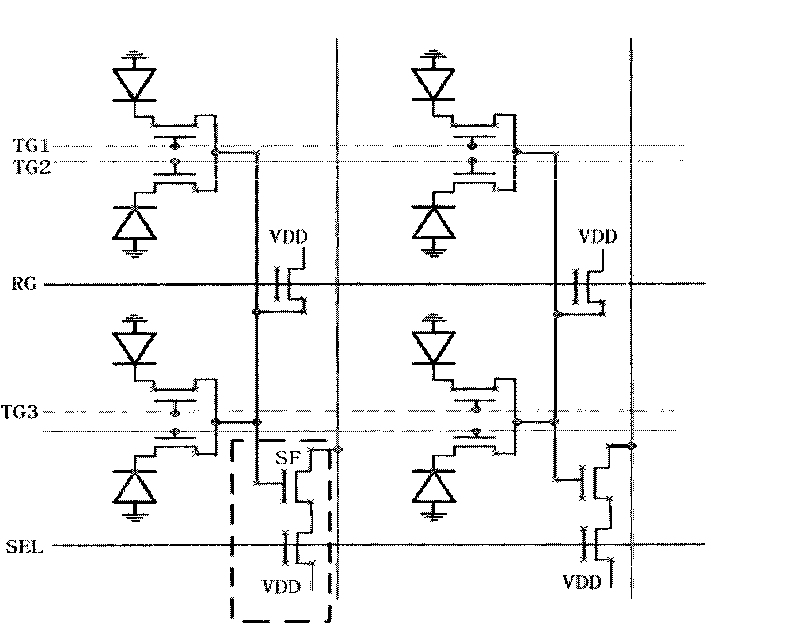
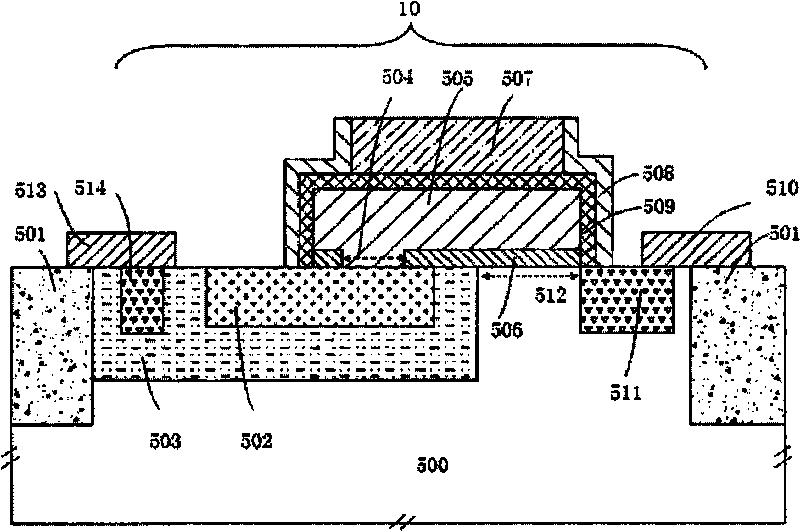
The invention discloses a semiconductor photosensitization device which comprises a source electrode, a drain electrode, a control grid, a floating grate region, a substrate, and a p-n node diode for connecting a floating gate region and a drain electrode. The floating grate region of the semiconductor photosensitization device is used for storing charges, and the floating grate potential of the semiconductor photosensitization device is related to light exposure intensity and time, thus, the invention can be used as a semiconductor photosensitization device. The invention also discloses production methods of the semiconductor photosensitization device and an image sensor, as well as an image sensor formed by arrays formed by the semiconductor photosensitization device. The semiconductor photosensitization device can simplify the design of a single pixel unit in a traditional image sensor and reduce the area occupied by the single pixel unit, thereby improving the pixel density of the image sensor, increasing the resolution of the image sensor and reducing the production cost of the image sensor.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIENTAL SEMICONDUCTOR CO LTD
Optical imaging lens assembly
This invention provides an optical imaging lens assembly comprising five lens elements with refractive power, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with negative refractive power; a fourth lens element with negative refractive power having at least one of the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; and a fifth lens element having a concave image-side surface, at least one of the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric, and made of plastic. By such arrangement, photosensitivity and total track length of the optical imaging lens assembly can be reduced, and the aberration and astigmatism of the assembly can be effectively corrected. Moreover, high image resolution can be obtained.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical photographing system
ActiveUS8014080B1Reduce track lengthIncrease photosensitivityLensMagnifying glassesImage resolutionView angle
This invention provides an optical photographing system comprising four lens elements with refractive power, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element; a second lens element with positive refractive power, and at least one of the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; a third lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, and both of the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; a fourth lens element with positive refractive power, and both of the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; wherein the optical photographing system further comprises an aperture stop positioned between an object and the second lens element. By such arrangement, total track length of the optical photographing system can be effectively reduced. Wide view-angle and high image resolution are also obtained.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
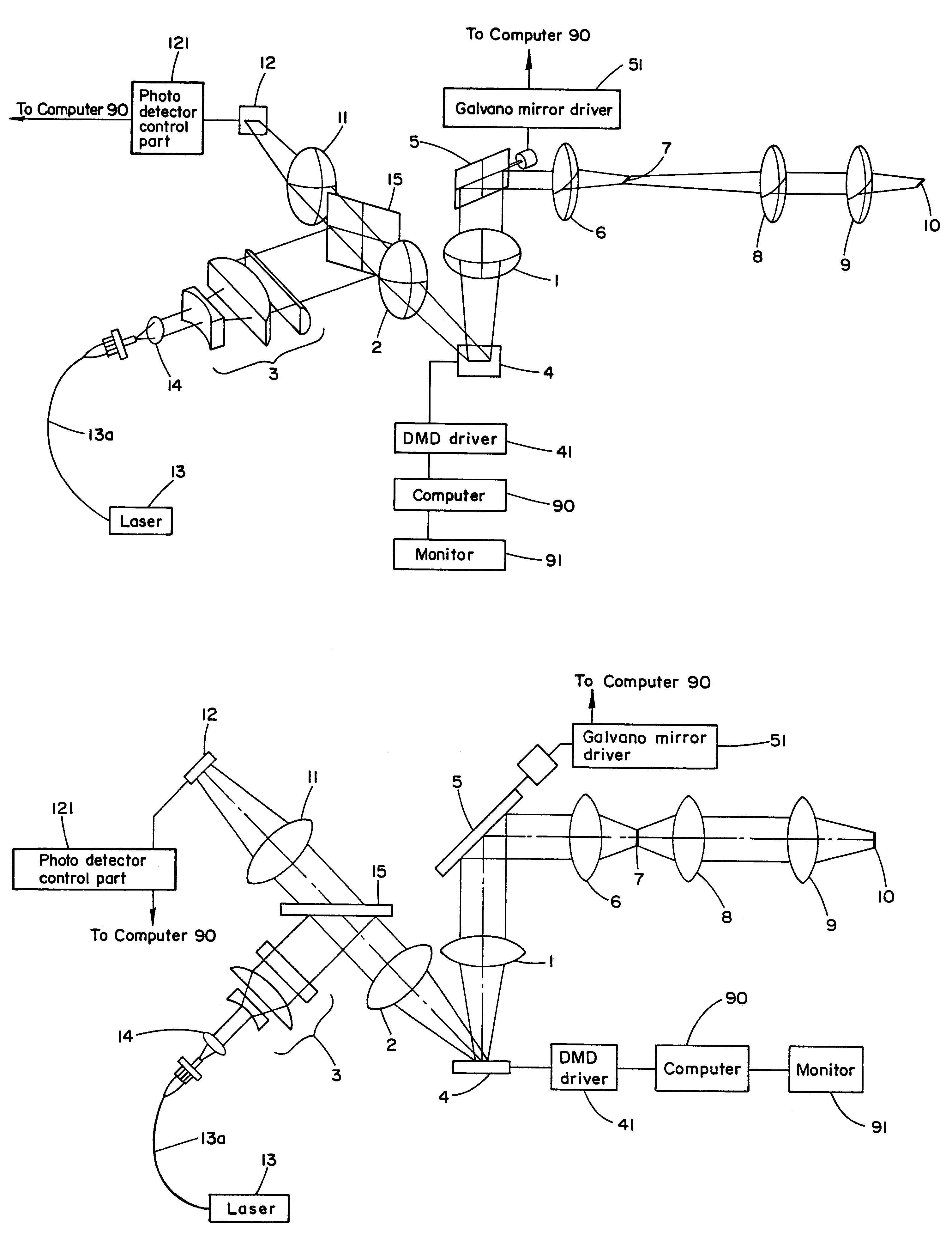
Method and apparatus for enhanced spatial bandwidth wavefronts reconstructed from digital interferograms or holograms
InactiveUS20120116703A1Improve efficiencyIncrease of spatial bandwidthNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementDigital variable/waveform displayWavefrontImage resolution
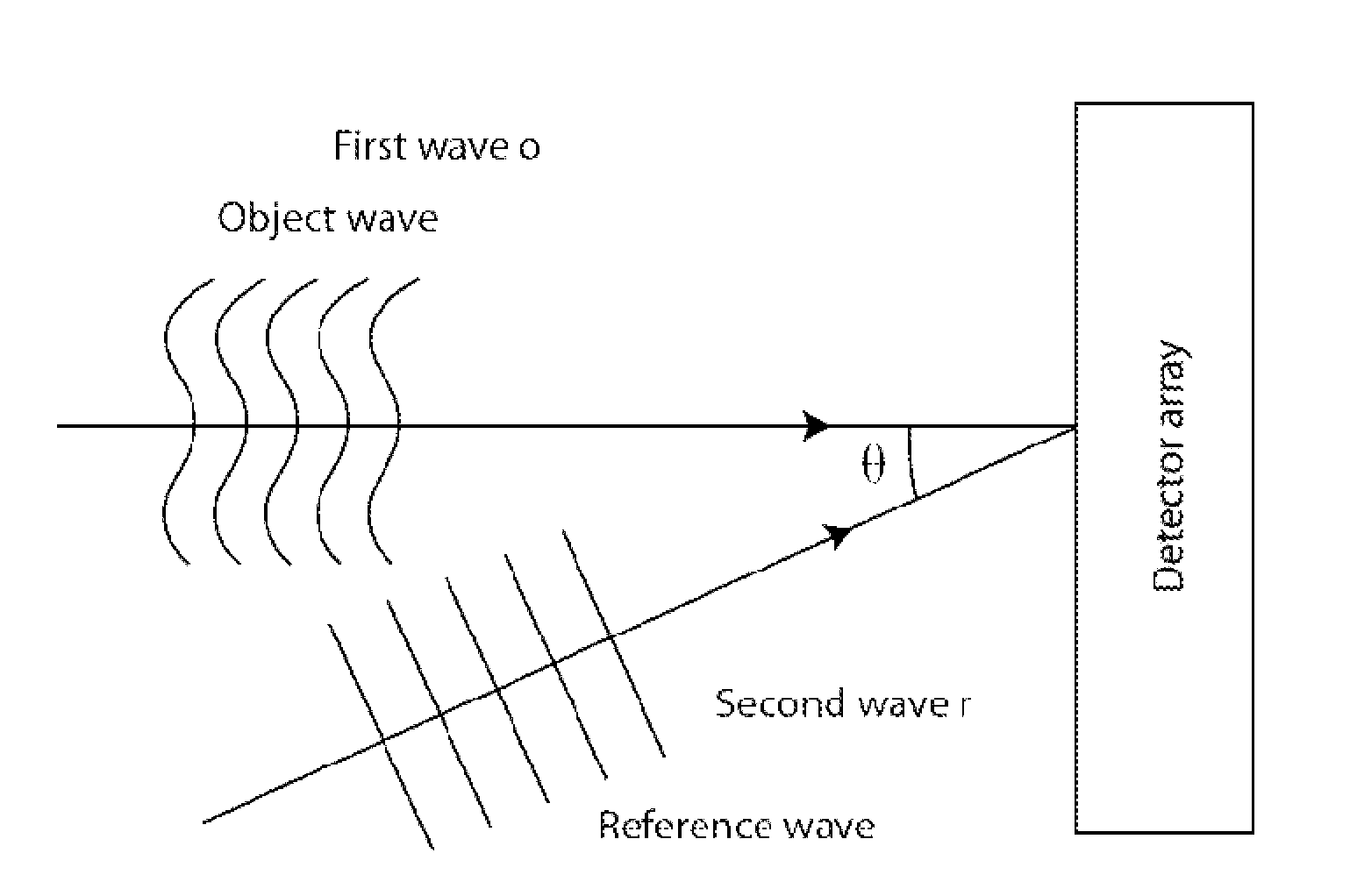
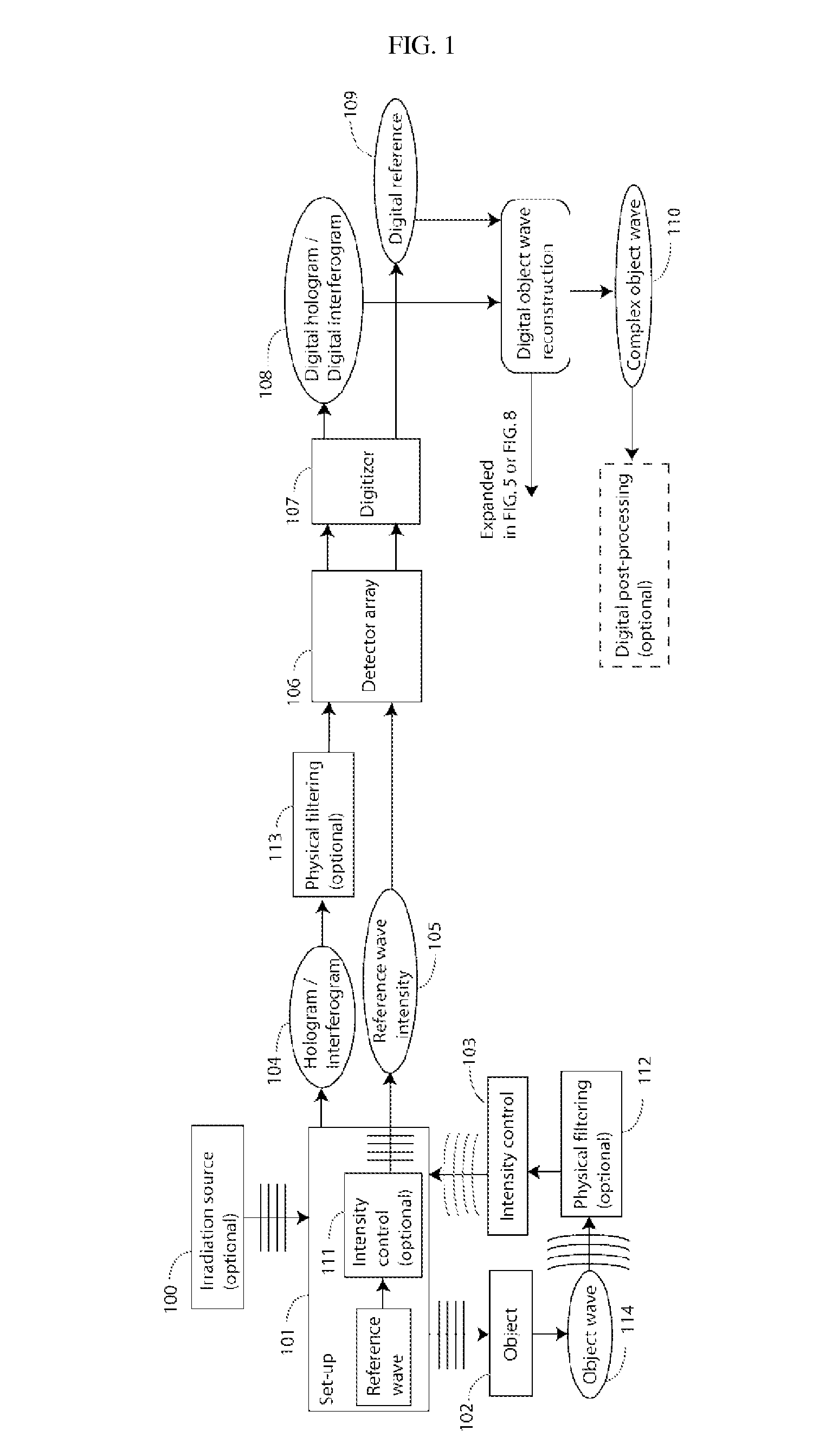
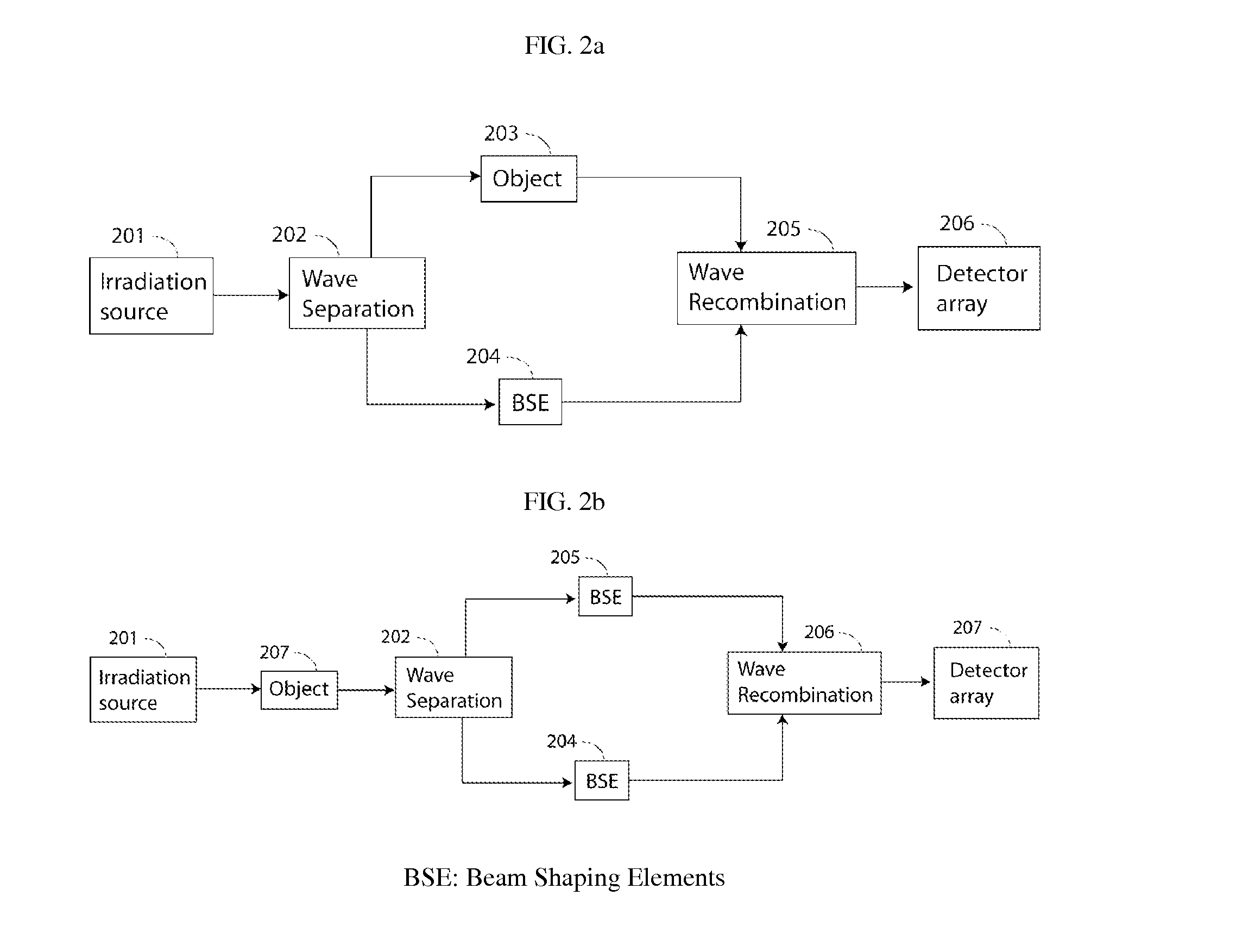
The present invention discloses a method and an apparatus to compute a complex wavefield, referred to as the object wave o, by means of measuring the intensity signal resulting from the interference of the said object wave with a second wave termed the reference wave. The second wave r is assumed to have some non-vanishing mutual coherence with the said object wave o. The reference wave can be obtained from a source or from the object wave itself. The wave may be emitted from sources of variable degree of coherence and can be scattered waves, but also light-emitting molecules, matter waves such as electron beams or acoustical sources. The disclosed method relates to the said “non-linear method” (NLM). The innovation resides in the fact that the NLM improves considerably the bandwidth of the wavefront reconstructed from off-axis interferograms and holograms obtained in a single shot. The advantage is the significant improvement of the resolution of the images obtained from the reconstructed wavefront, i.e. amplitude and phase images. The said method also suppresses the artifacts resulting from the intensity recording of interferograms and holograms. The method is general in the sense that it can be used for any interferometric measurement, provided that it satisfies the simple requirement that the intensity of the reference wave is larger than the intensity of the object wave, and that the object wave modulated by the reference is confined to at least a quadrant of the spectrum. The disclosed method applies to interferometry, holography in optics, electron waves and acoustics. In particular, it can be implemented in phase, fluorescence, luminescence, electron and acoustic microscopy.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Light Profile Microscopy Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20080218850A1High image resolutionWide image fieldMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesImage resolutionEllipse
An apparatus and method allowing an optimized illumination in a light profile microscope by excitation of a sample with an elliptically collimated beam. The beam, which is typically supplied by a laser is collimated with unequal beam waist radii (and Rayleigh ranges) along major and minor axes orthogonal to a propagation direction, and approximates a plane sheet of illumination. The plane sheet of illumination is aligned with a thinnest width dimension thereof along the optic axis of the microscope objective, and with a center thereof at the object plane of the objective. Excitation light in a test sample is thereby confined to within a narrow thickness of the object plane of the objective lens, which minimizes out-of focus light in the image. The major axis width of the plane illumination sheet is typically a factor of ten or more greater than the minimum width, allowing a large area of the test sample to be illuminated and imaged. This excitation arrangement optically emulates the operation of micro-toming a thin cross section of a material for analysis, and provides optimum resolution and field in a light profile microscope.
Owner:POWER JOAN F
Adjustment method of printing positions, a printing apparatus and a printing system
InactiveUS20060044334A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationQuality improvementSpacing mechanismsOther printing apparatusGratingImage resolution
By using an ink jet head, which has for each color two parallel columns of nozzles arranged side by side in the main scan direction and shifted from each other by one-half the pitch at which the nozzles are arranged in each column, odd-numbered rasters and even-numbered rasters making up an image are printed by the two nozzle columns. The registration between the odd- and even-numbered rasters is secured during the printing to produce an image with high print quality. For that purpose, the ink ejection timing between the two raster groups is shifted by a predetermined interval to form a plurality of adjustment patterns; the adjustment patterns printed are checked and, according to the check result, an adjustment value for the ink ejection timing between the two ink nozzle columns is entered, and the entered adjustment value is stored to be reflected on the actual printing operation. To facilitate the adjustment pattern check, the plurality of adjustment patterns have a dot distribution with a blue noise characteristic at a resolution at which the printing apparatus can print.
Owner:CANON KK
Petoscope based on bionic oculus and method thereof
InactiveCN1932841ARealize the collection functionRealize Stereo MeasurementCharacter and pattern recognitionState parameterGray level
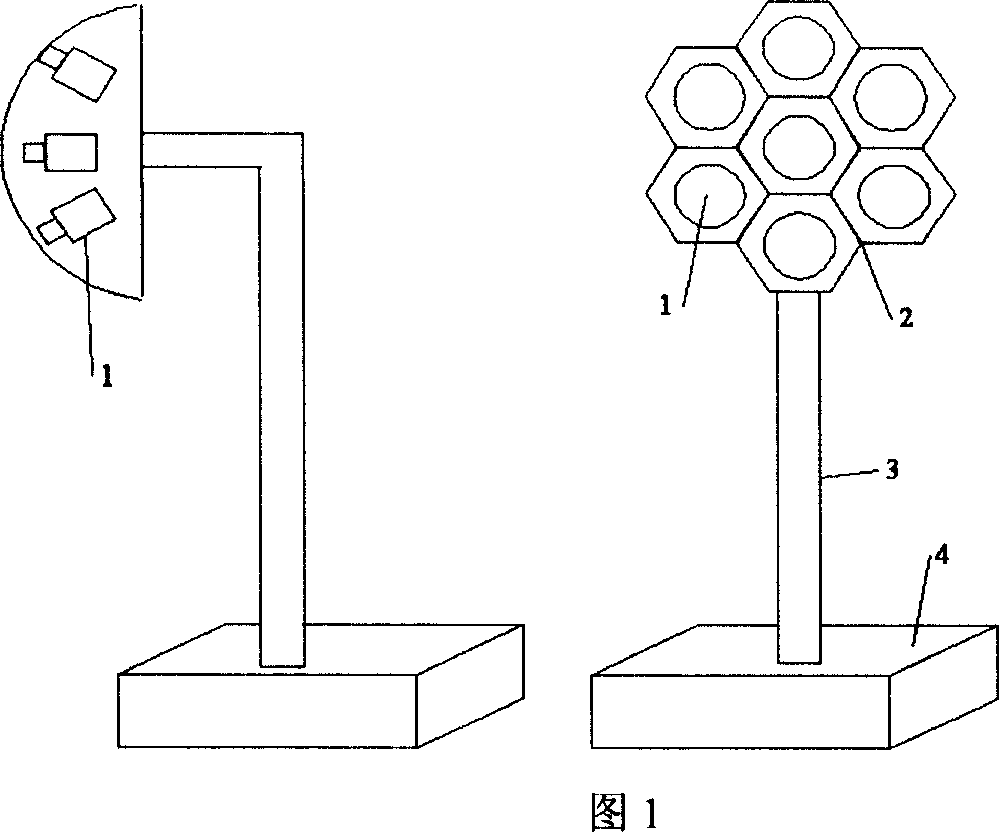
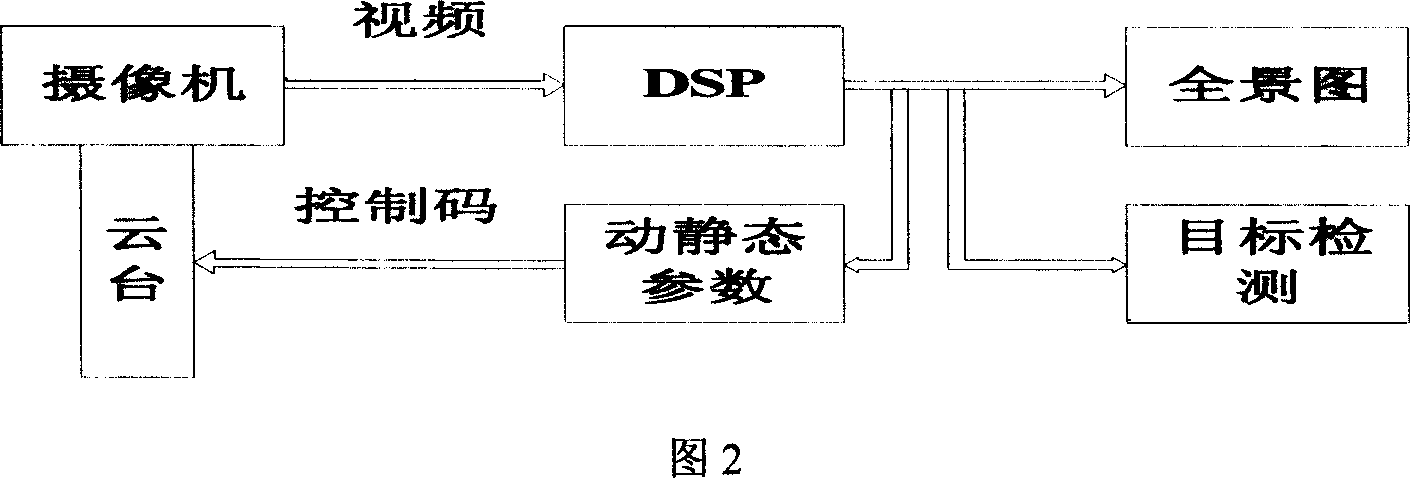
One moveable goal detecting equipment and method based on artificial compound belongs to artificial compound moveable goal detecting system. It relates to camera, outline border, standing pole, Yunnan and DSP processor. The moveable goal detecting method uses moveable goal division arithmetic to pick up and identify moveable goal form the video frequency picture having moveable goal. The dynamic and static state parameter testing method uses some cameras to screen the moveable goal to calculate the coordinate under the appointed world coordinate system and draw the movement track and speed. The moveable goal tracking method is about dividing up the dynamic and static state parameter of moveable goal to judge its movement trend, and run Yunnan to follow moveable goal by serial port. The panorama creating method takes the method gray-level relativity method and put multi-way overlap pictures together one large-scale seamless picture. It owns large watch field, high distinguish rate and delicacy rate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Attribute face image generate method, device, system and readable storage medium
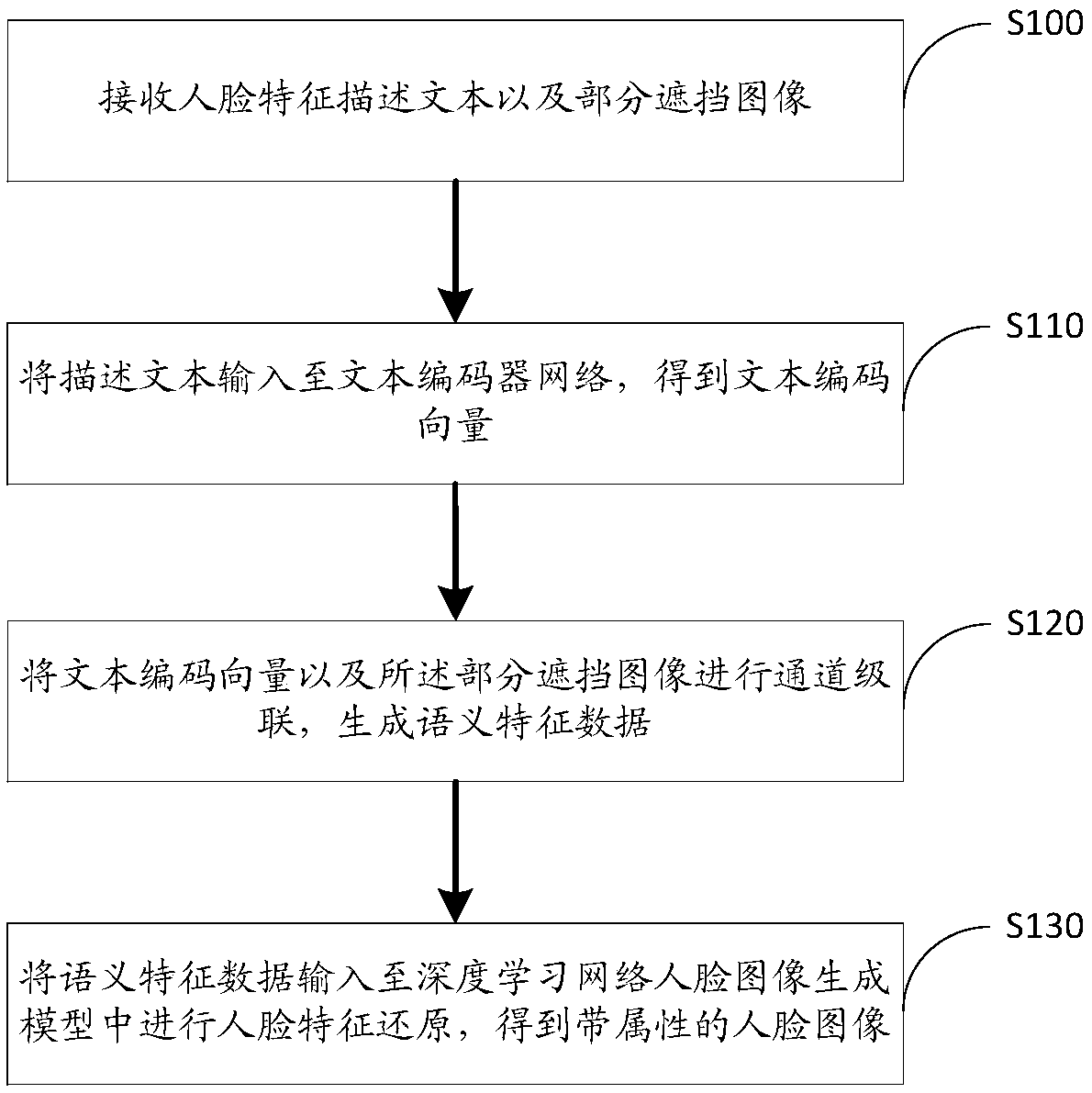
ActiveCN109147010AIncrease authenticityHigh image resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisData setFeature description
The invention discloses a method for generating a face image with attributes, including receiving face feature description text and partial occlusion image; the description text being inputted to a text encoder network to obtain a text encoding vector; text coding vector and partially occluded image being cascaded to generate semantic feature data; the semantic feature data being input into the face image generation model to restore the face feature, and the face image with attributes being obtained. Among them, the face image generation model is a depth learning network which is optimized according to the text data set and the training set image training. The image generation method can generate a face image which conforms to the attributes described in the text according to the detail description of the text. The invention also discloses a face image generation device with attributes, a system and a computer-readable storage medium, which have the beneficial effects.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
X-ray device that emits an x-ray beam with a scanning-like movement
InactiveUS7286645B2Quality improvementHigh image definitionX-ray tube electrodesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRotational axisSoft x ray
An x-ray device includes an x-ray tube for generation of an x-ray emanating from a focal spot of a rotary anode rotatable around a rotation axis and a slit-shaped diaphragm for generation of a fan-shaped x-ray beam that is gated from the x-ray and emission is moved through an examination region in the manner of a scan. To improve the image resolution, the fan-shaped x-ray beam can be moved over the examination region essentially in the direction of the rotational axis of the rotary anode by tilting the x-ray tube on the focal spot, with the x-ray tube being tilted on the focal spot so that the fan-shaped x-ray beam is always gated from the region of the overall emitted x-ray beam having the highest image resolution or the highest image definition in the movement through the examination region.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
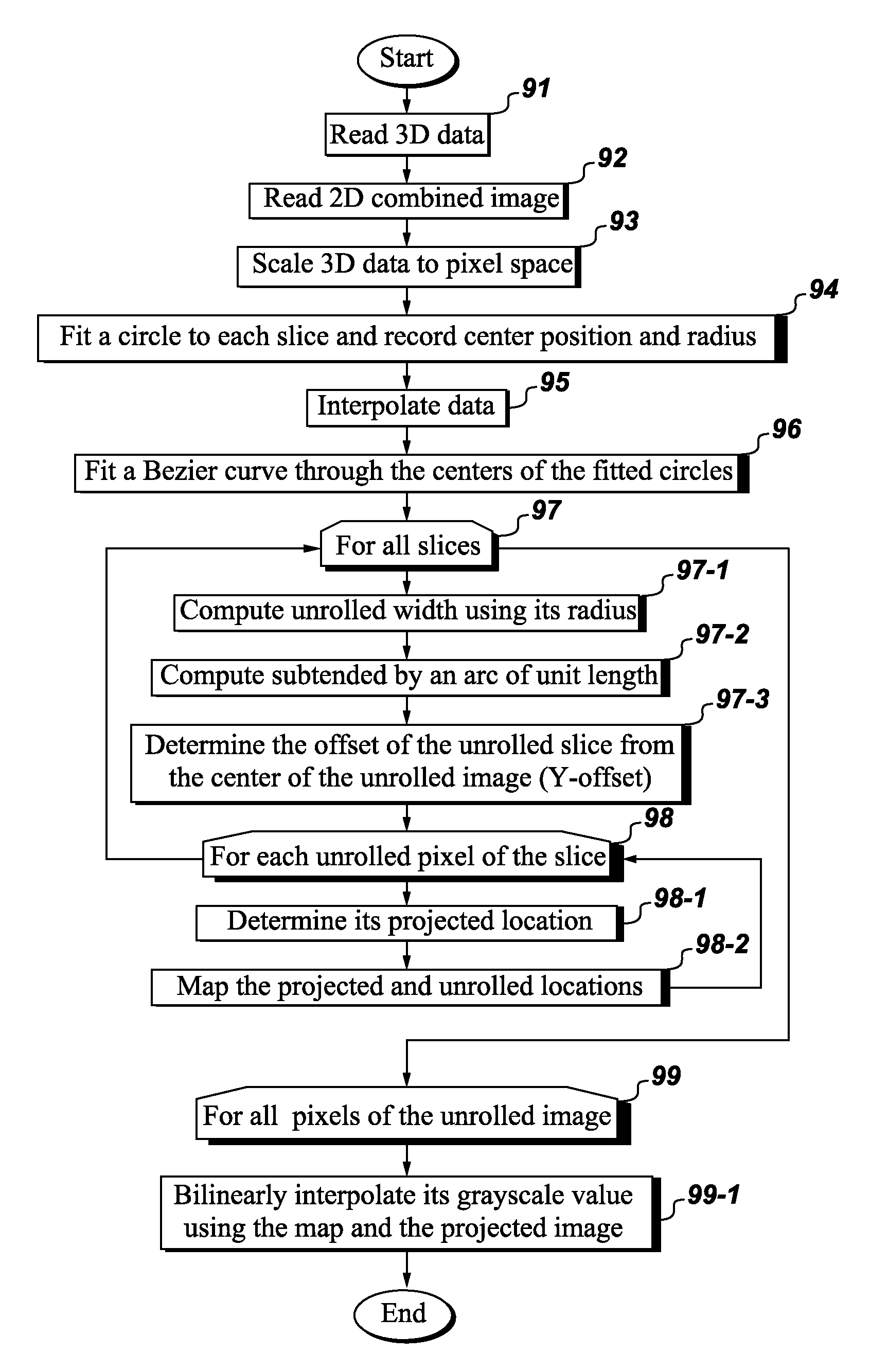
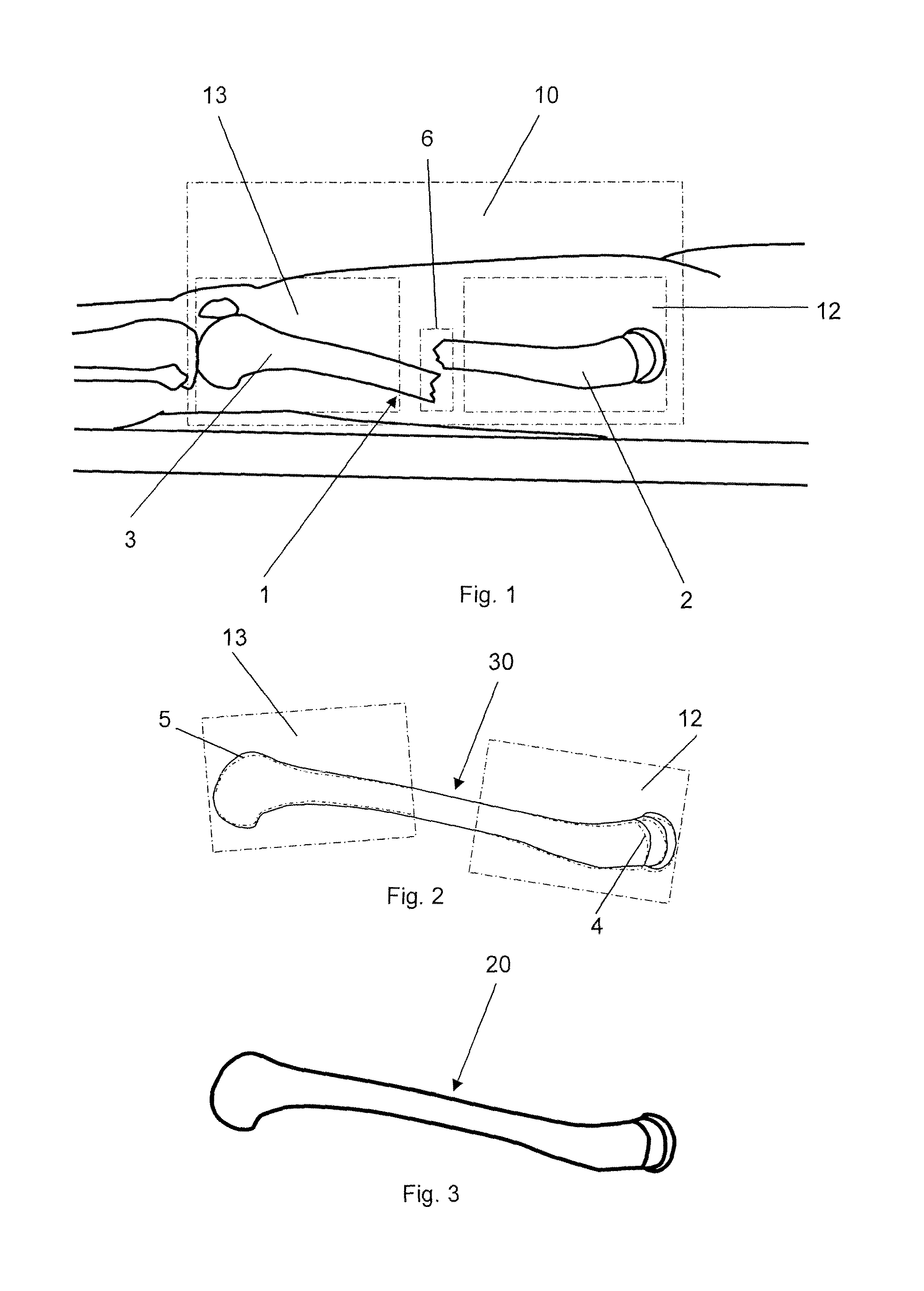
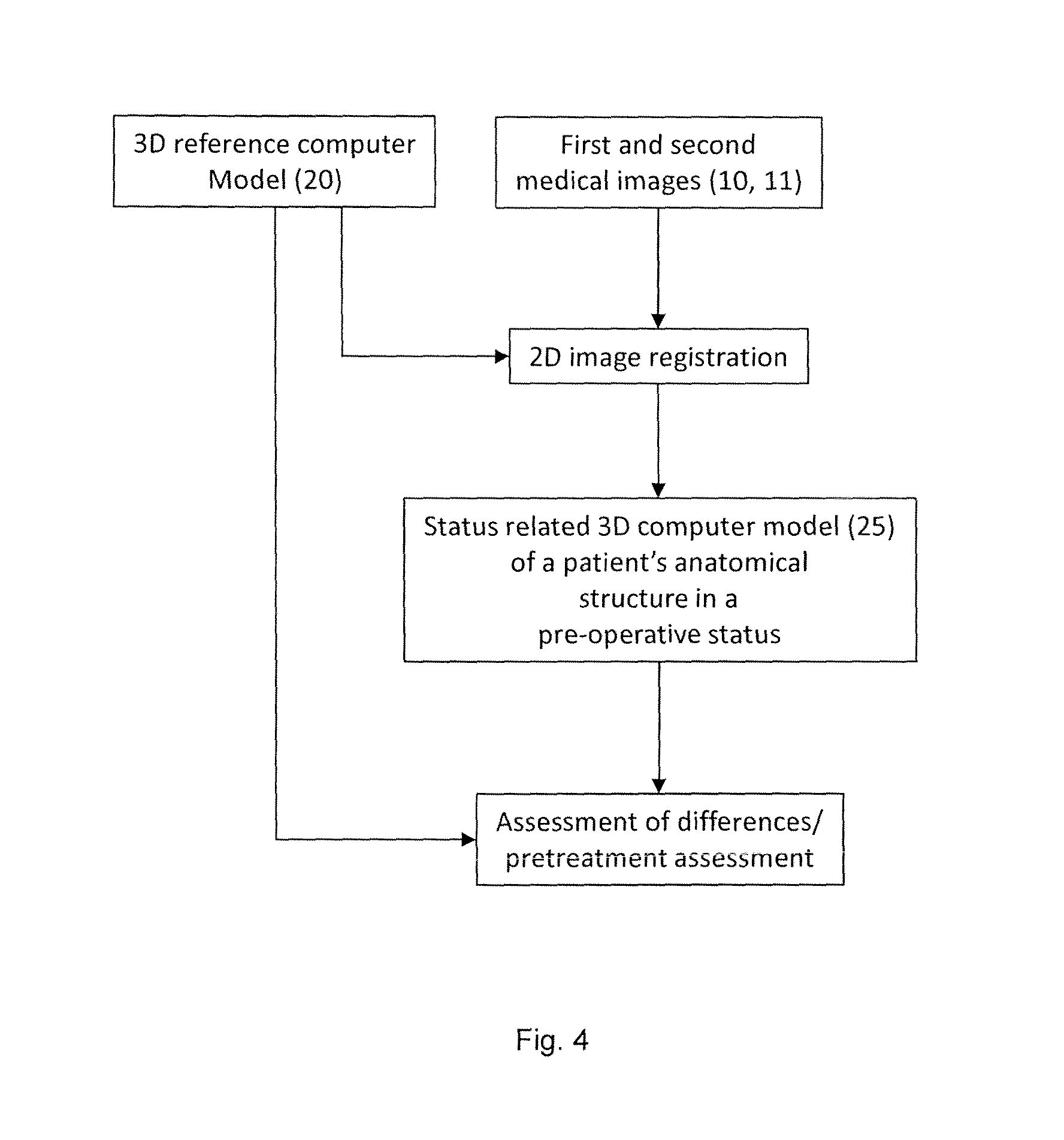
Method for generating a 3D reference computer model of at least one anatomical structure
InactiveUS20160331463A1Time availableHigh image resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisMedical imagingComputer-aided
A method for generating a 3D reference computer model of at least one anatomical structure for comparison with a selectable pre-, intra- or postoperative set of medical images of at least one anatomical structure, the method including: acquiring at least a first and a second medical image of at least one anatomical structure in a preoperative status from different perspectives using a computer assisted medical imaging device, wherein the first and second medical images are represented by a respective first and second set of digital 2D image data; and generating a 3D reference computer model of an anatomical structure by selecting and extracting a 3D atlas model of an anatomical structure to be treated from a generic anatomical atlas provided in the form of a digital data source, and registering at least a section of each of the first and second medical images to the selected 3D atlas model.
Owner:AO TECH AG
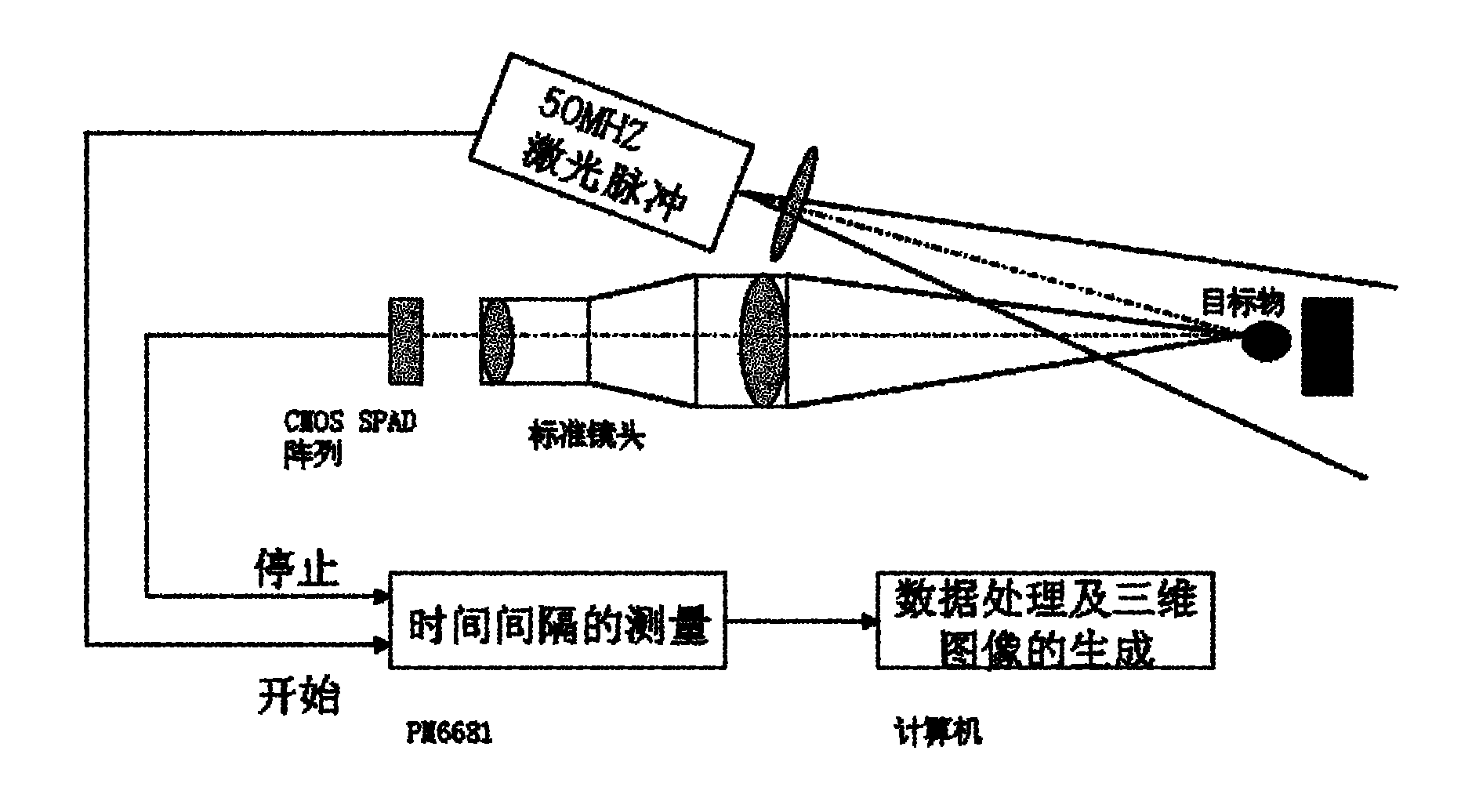
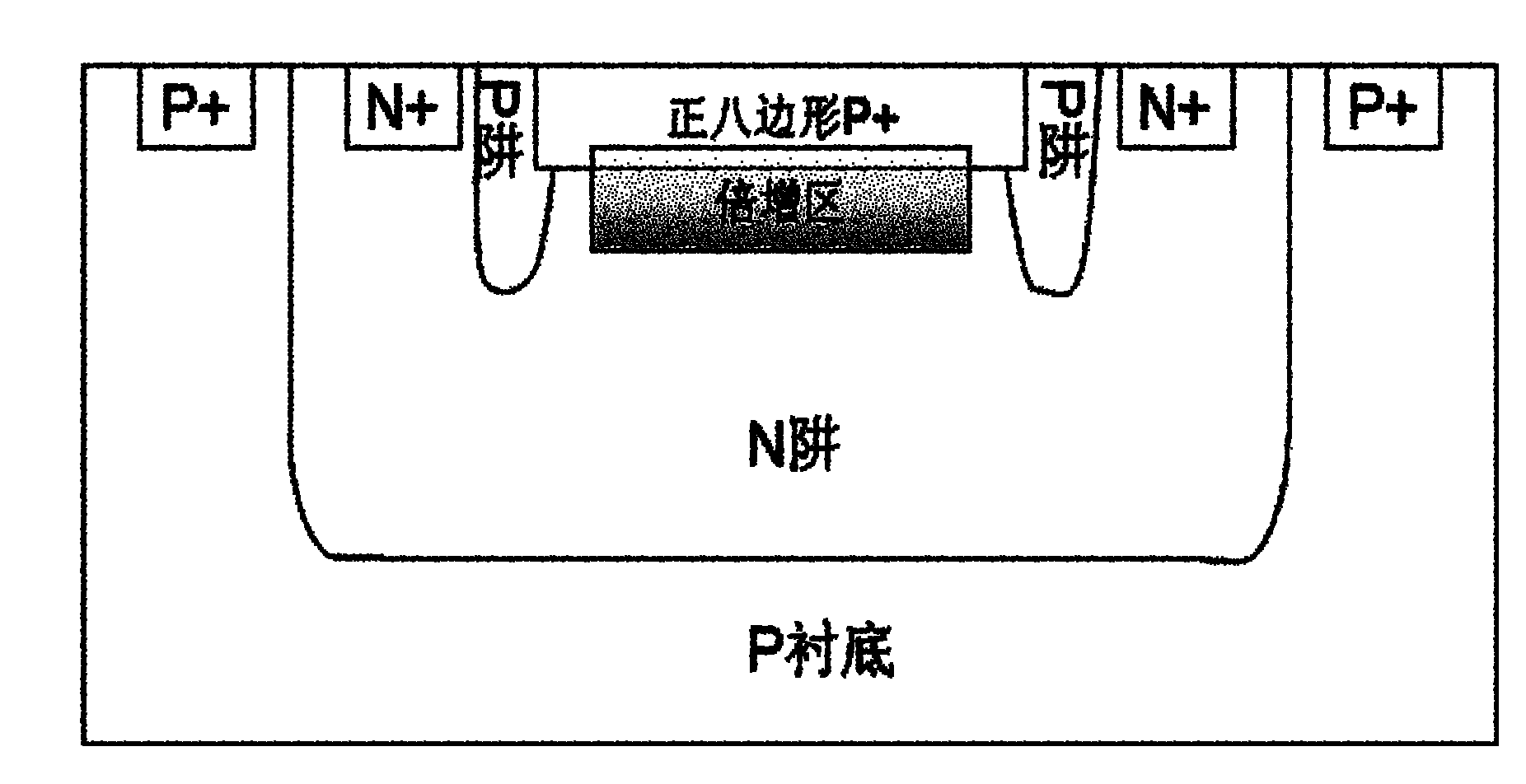
Single-photon avalanche diode and three-dimensional CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) image sensor based on same
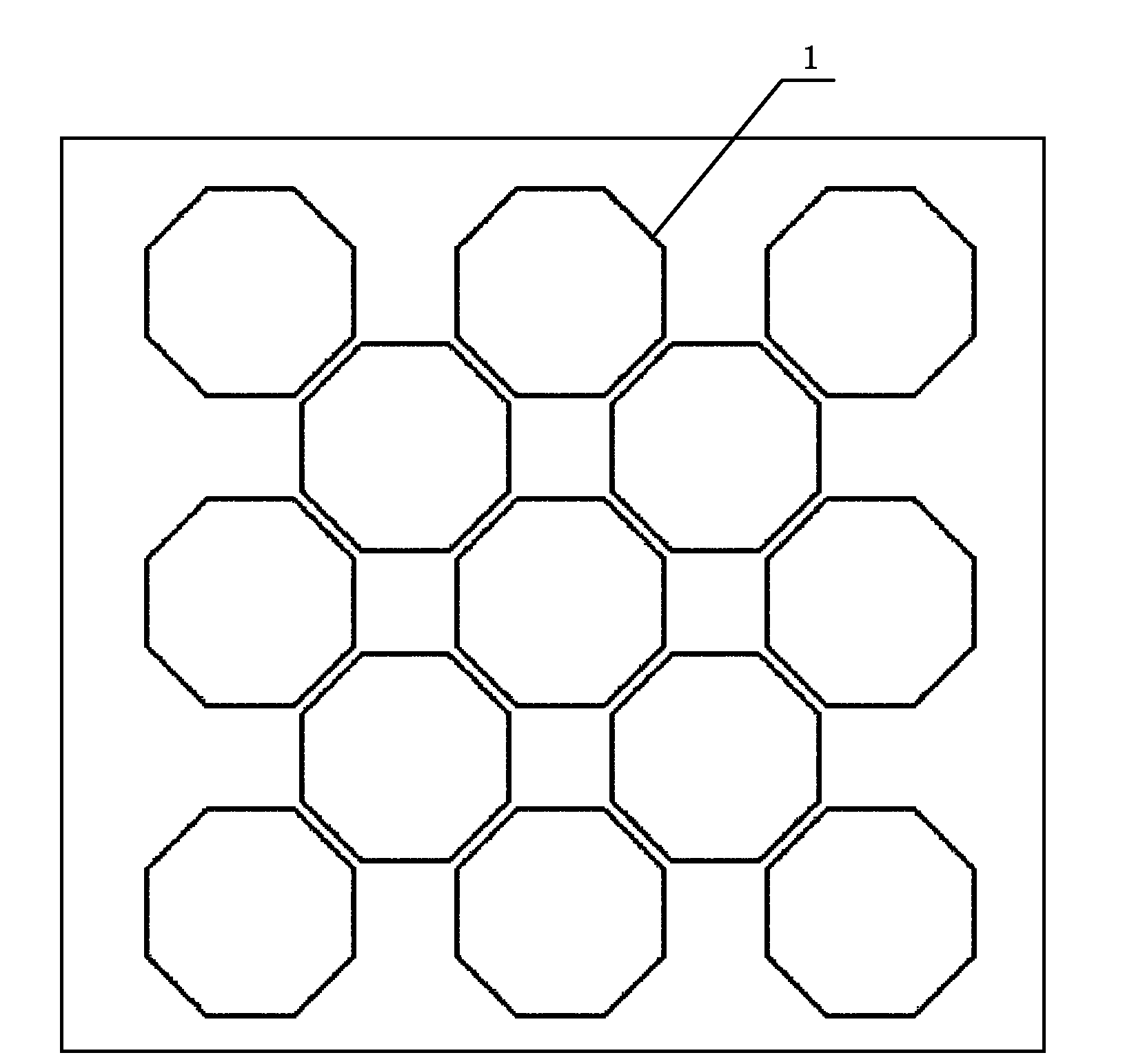
InactiveCN101931021AImprove uniformityFully magnifiedTelevision system detailsFinal product manufactureHorizontal and verticalElectron
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic technologies and photoelectronic imaging technologies, in particular relates to a single-photon avalanche diode and a three-dimensional CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) image sensor based on the diode. The single-photon avalanche diode of the invention improves the traditional rectangular photosensitive PN junction into a regular octagon and can conveniently and simply weaken edge breakdown and improve gain uniformity. A two-dimensional pixel array of the three-dimensional CMOS image sensor based on the diode comprises unit pixels of the regular octagon-shaped single-photon avalanche diode and is arrayed in a honeycomb-shape, thereby being convenient for interpolation and improving resolution in horizontal and vertical direction.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Light profile microscopy apparatus and method
InactiveUS7538879B2High image resolutionWide image fieldMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesImage resolutionEllipse
An apparatus and method allowing an optimized illumination in a light profile microscope by excitation of a sample with an elliptically collimated beam. The beam, which is typically supplied by a laser is collimated with unequal beam waist radii (and Rayleigh ranges) along major and minor axes orthogonal to a propagation direction, and approximates a plane sheet of illumination. The plane sheet of illumination is aligned with a thinnest width dimension thereof along the optic axis of the microscope objective, and with a center thereof at the object plane of the objective. Excitation light in a test sample is thereby confined to within a narrow thickness of the object plane of the objective lens, which minimizes out-of focus light in the image. The major axis width of the plane illumination sheet is typically a factor of ten or more greater than the minimum width, allowing a large area of the test sample to be illuminated and imaged. This excitation arrangement optically emulates the operation of micro-toming a thin cross section of a material for analysis, and provides optimum resolution and field in a light profile microscope.
Owner:POWER JOAN F
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com