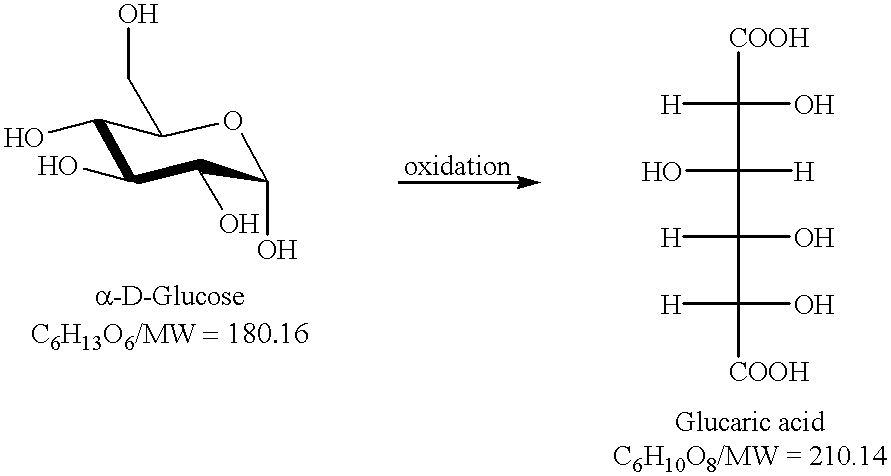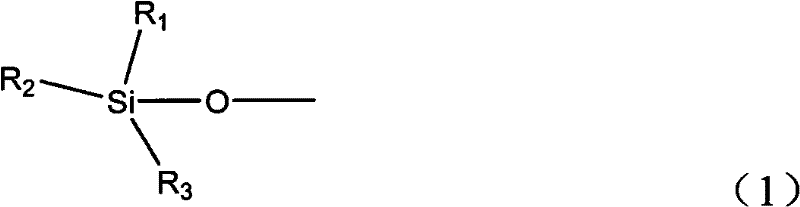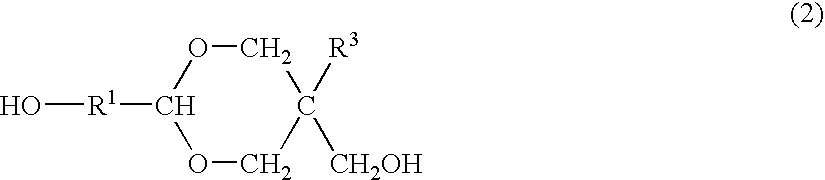Patents
Literature
2228 results about "Acetal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
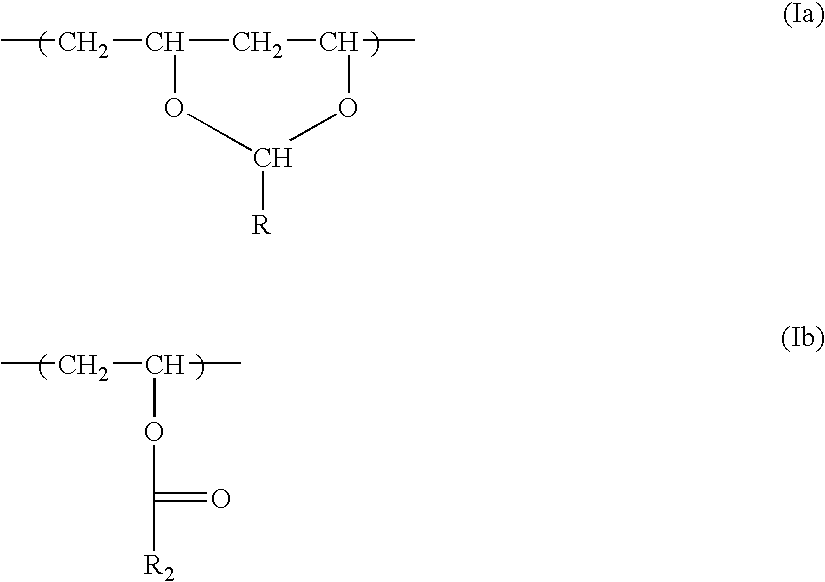
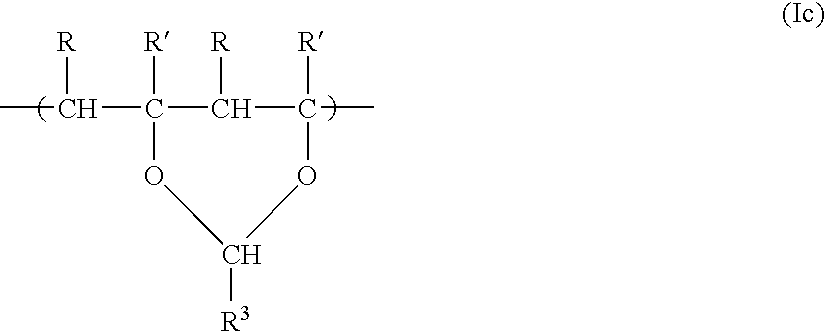
An acetal is a functional group with the connectivity R₂C(OR')₂). Here, the R groups can organic fragments (a carbon atom, with arbitrary other atoms attached to that) or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments not hydrogen. The two R' groups can be equivalent to each other (a "symmetric acetal") or not (a "mixed acetal"). Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon, but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it, and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry.
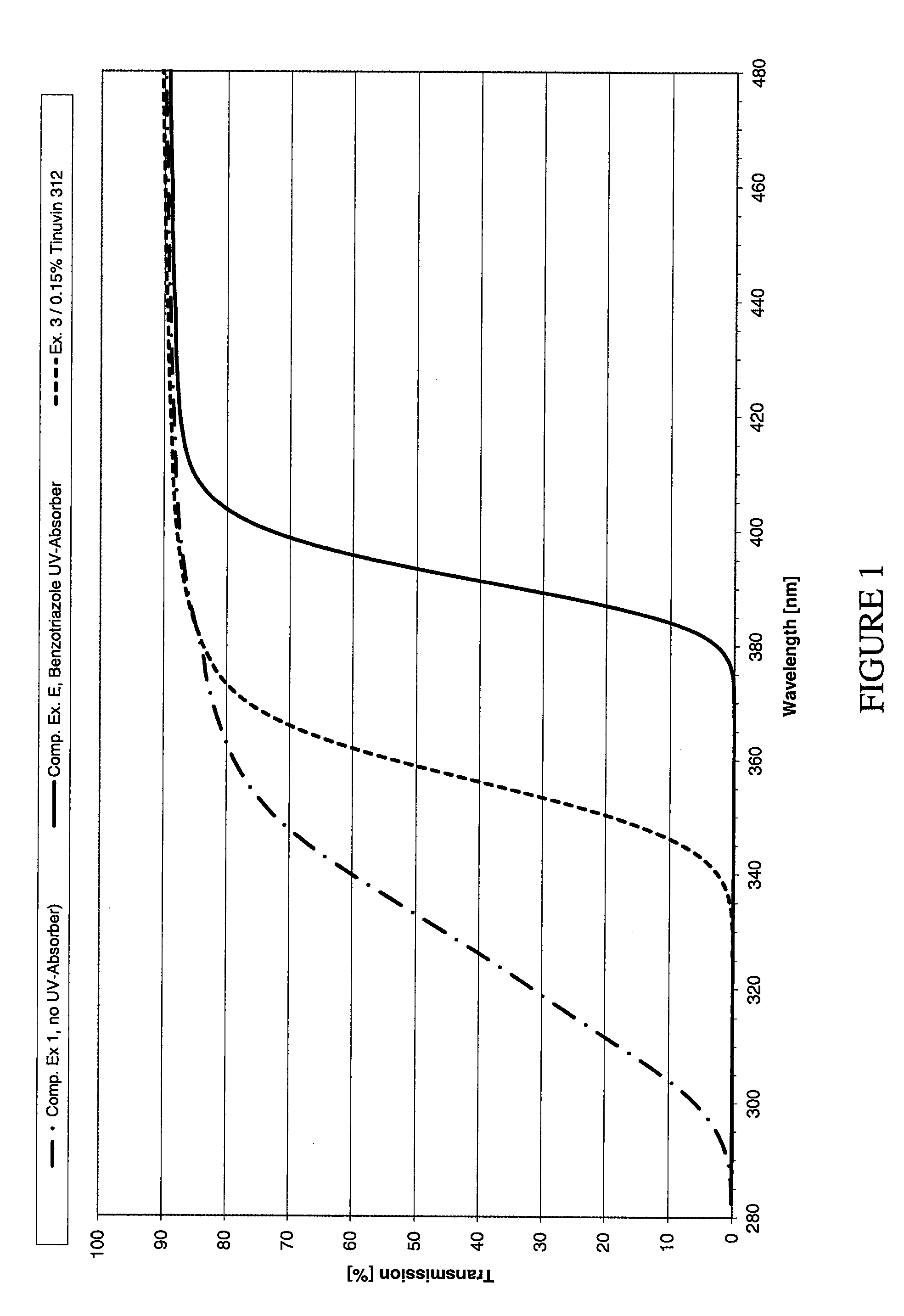
Plasticizer-Containing Films Based On Polyvinyl Acetal Having Selective Permeability For UV Radiation
InactiveUS20120052310A1Climate change adaptationSynthetic resin layered productsPlasticizerUltraviolet
Plasticizer-containing films based on polyvinyl acetal containing a UV absorbers of the oxanilide type of formula (1)exhibit high UVA transmission while also exhibiting low UVB transmission, with reduced tendency to yellow.
Owner:KURARAY EURO GMBH
Multilayer Films Or Plasticizer-Containing Polyvinyl Acetal With Sound-Absorbing Properties
ActiveUS20100028642A1Improve sound absorptionLow costSynthetic resin layered productsConstructions elementsPolyvinyl acetatePolyvinyl alcohol
An interlayer film for laminated glass with sound-absorbing properties contains at least two individual films, wherein the first individual film comprises a polyvinyl acetal with a portion of polyvinyl acetate groups of 0.1 to 11 mol % and a second individual film comprises a polyvinyl acetal with a portion of polyvinyl acetate groups of between 5 and 8 mol %.
Owner:KURARAY EURO GMBH
Method for the oxidation of aldehydes, hemiacetals and primary alcohols
InactiveUS6498269B1Economical and effectiveGuaranteed economic efficiencySugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationHalogenBromine
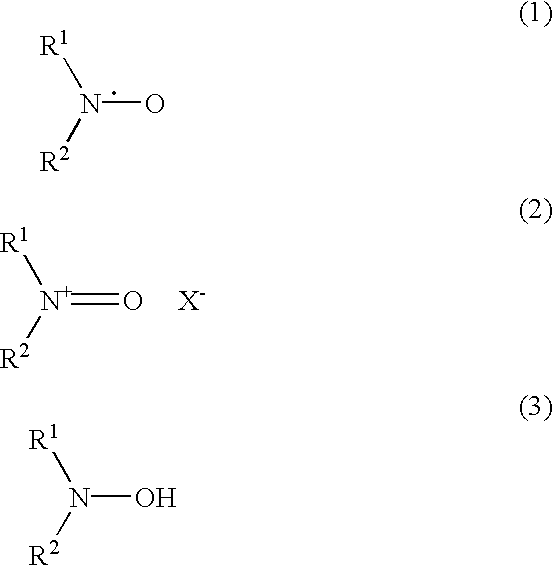
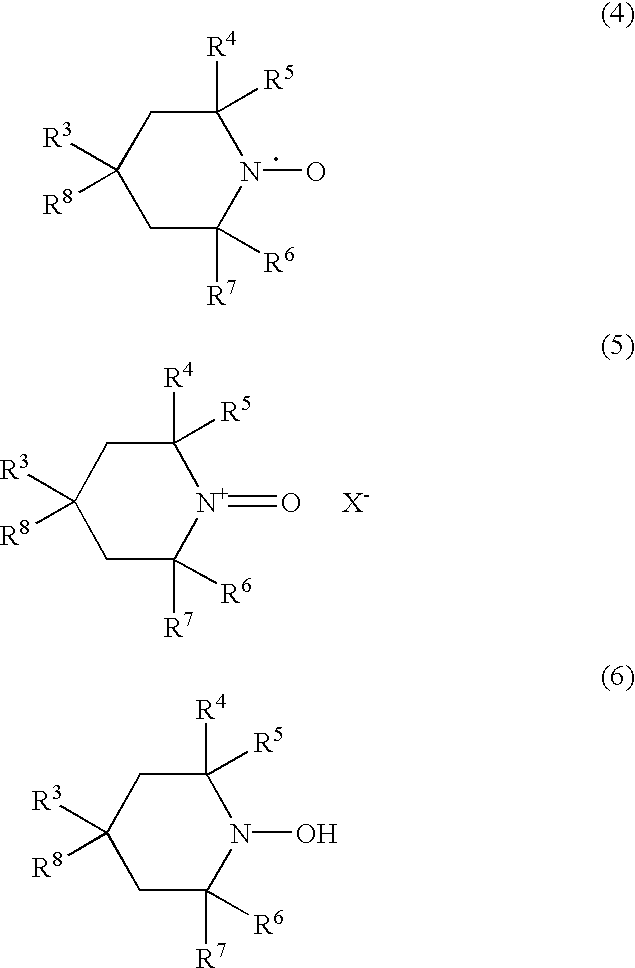
A method for the oxidation of substrates comprising treating an aqueous, basic solution of a substrate having an oxidizable functionality using an elemental halogen as terminal oxidant in the presence of an oxoammonium catalyst / halide co-catalyst system. Use of elemental halogen, preferably chlorine gas or elemental bromine, unexpectedly allows oxidation without significant degradation of the substrate. The substrate is preferably a monosaccharide, oligosaccharide, or polysaccharide, and the oxidizable functionality is preferably an aldehyde, hemiacetal, or a primary alcohol. An effective source of the oxoammonium catalyst is 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyl-1-oxy (TEMPO) and a particularly economical and effective catalyst is 4-acetylamino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyl-1-oxy.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Liquid dispersion comprising dibenzylidene sorbital acetals and ethoxylated nonionic surfactants
InactiveUS6102999ALow viscosityInexpensive fluid dispersionOrganic chemistryTransportation and packagingPeristaltic pumpPolyolefin
This invention relates to a fluid dispersion of at least one dibenzylidene sorbitol acetal derivative. The sorbitol acetal derivative is useful as a clarifying agent for polyolefins and the inventive fluid dispersion permits improvements in the handling and processing of and mixing within the polyolefin composition. The inventive dispersion must be shelf stable, retain its nucleating effects, be compatible with polypropylene (and other polyolefins), and possess both short-term and long-term viscosities which permit acceptable transport through a standard polyolefin-manufacturing peristaltic pump. The preferred inventive dispersion thus comprises 3,4-DMDBS and at least one ethoxylated nonionic surfactant having an HLB of greater than about 8.5. Preferred surfactants include those selected from the group consisting essentially of ethoxylated sorbitan (C8-C22) monoesters and ethoxylated nonyl-phenol ethers. The inventive dispersion may be introduced within any polyolefin composition, preferably polypropylene, which may then be molded into any shape or form. A method of producing a polyolefin plastic utilizing the inventive dispersion is also provided.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Method for producing hydrocarbons and oxygen-containing compounds from biomass
InactiveUS20050112739A1Improve direct utilizationImprove utilizationOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationChemical industryChemical reaction
The present invention generally relates to biochemical and chemical industry, and more particularly to a method which can be used in fermenting carbohydrate substrates of plant origin for producing C1-C5 alcohols, and for synthesis of higher alcohols, other oxygen-containing compounds and hydrocarbons as well as for the production of motor fuel components from biomass. Since C6 and higher alcohols, ethers, acetals, and higher hydrocarbons are not obtainable by a direct biochemical route, it is proposed to synthesize these using known chemical reactions, wherein by-products of fermentation are as raw materials for said synthesis.
Owner:SWEDISH BIOFUELS AB
High-Strength Film Laminates Having Layers Of Plasticizer-Containing Polyvinyl (N)Acetal and Plasticizer-Containing Polyvinyl (Iso)Acetal
ActiveUS20130022824A1Improve mechanical propertiesHigh plasticizer compatibilitySynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsArchitectural glassGlass composites
The invention relates to film laminates, formed from at least three layers A, B and C, each layer containing at least one plasticizer and at least one polyvinyl acetal, wherein, at least one of the layers A, B or C contains at least one polyvinyl (iso)acetal having a mean degree of polymerisation of less than 3000, 10 to 25% by weight of polyvinyl alcohol groups and a proportion 50 to 80% by weight of polyvinyl (iso)acetal groups, and wherein layer B has a plasticizer content of less than 32% by weight. The film laminates can be used for the production of glass / film laminate / glass composites for motor vehicles, aircraft, ships, architectural glazings, façade components, or for the production of photovoltaic modules.
Owner:KURARAY EURO GMBH
Method of nucleating a polyolefin composition with acetal-based compounds
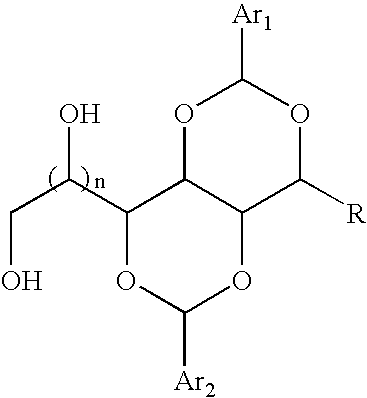
An acetal-based composition useful as a nucleating, gelling, thickening or clarifying agent is disclosed. The composition may be synthesized or provided in many different forms, including multicarbon diacetals formed from carbohydrates. Once synthesized, the compound may be employed as an additive in a plastic composition, such as (for example) a polypropylene copolymer. Co-additives may also be employed. Several aryl structures may reside upon the hydrocarbon chain backbone. One structure of such an acetal-based composition which happens to have two aryl-containing groups is shown:wherein:n is 0, 1 or 2;Ar1 and Ar2 are independently selected from substituted or unsubstituted aryl-containing groups; andR is selected from the group consisting of: alkenyls, alkyls, alkoxy, hydroxyl alkyls, and alkyl-halides.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO +1
Decorative safety glass
An image-bearing article comprising an interlayer bearing an image wherein the interlayer is an acoustic poly(vinyl acetal) interlayer having a Tg 23° C. or less. The acoustic poly(vinyl acetal) interlayer is preferably laminated to a film layer, a white layer, a second interlayer sheet or a rigid layer. The image-bearing article can preferably be coated on the image-bearing side and over the image with an adhesion promoter.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Manufacture of alcohols
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Positive-working radiation-sensitive imageable elements
InactiveUS20110059399A1High sensitivityHigh image resolutionPlaten pressesPhotosensitive materialsImideAryl
Positive-working imageable elements having improved sensitivity, high resolution, and solvent resistance are prepared using a water-insoluble polymeric binder comprising vinyl acetal recurring units that have pendant hydroxyaryl groups, and recurring units comprising carboxylic acid aryl ester groups that are substituted with a cyclic imide group. These imageable elements can be imaged and developed to provide various types of elements including lithographic printing plates.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Hybrid contact lenses prepared with expansion controlled polymeric materials
A hybrid contact lens includes a substantially rigid center portion and a substantially flexible skirt portion connected to the center portion. The skirt portion is formed using xerogels compatible with diluents comprising at least one selected from polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, lactide, glycolide, a polyacetal, a cyclic acetal, a polyketal, a cyclic ketal, a polyorthoester, a cyclic orthoester, di-t-butyl-dicarbonate, tris(trimethylsilyl)amine, and 2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide. These diluents are formulated to function as a stand-in for water in the xerogel polymer, allowing the xerogel to form and bond to the rigid center portion in its fully expanded state. Upon hydration of the hybrid lens, substantially little dimensional change, and thus substantially little distortion, is obtained in the skirt portion. The diluents of the present invention further preserve the mechanical integrity of the xerogel, allowing the xerogel to be machined to final shape, improving the dimensional tolerances which can be achieved in the hybrid lens.
Owner:SYNERGEYES
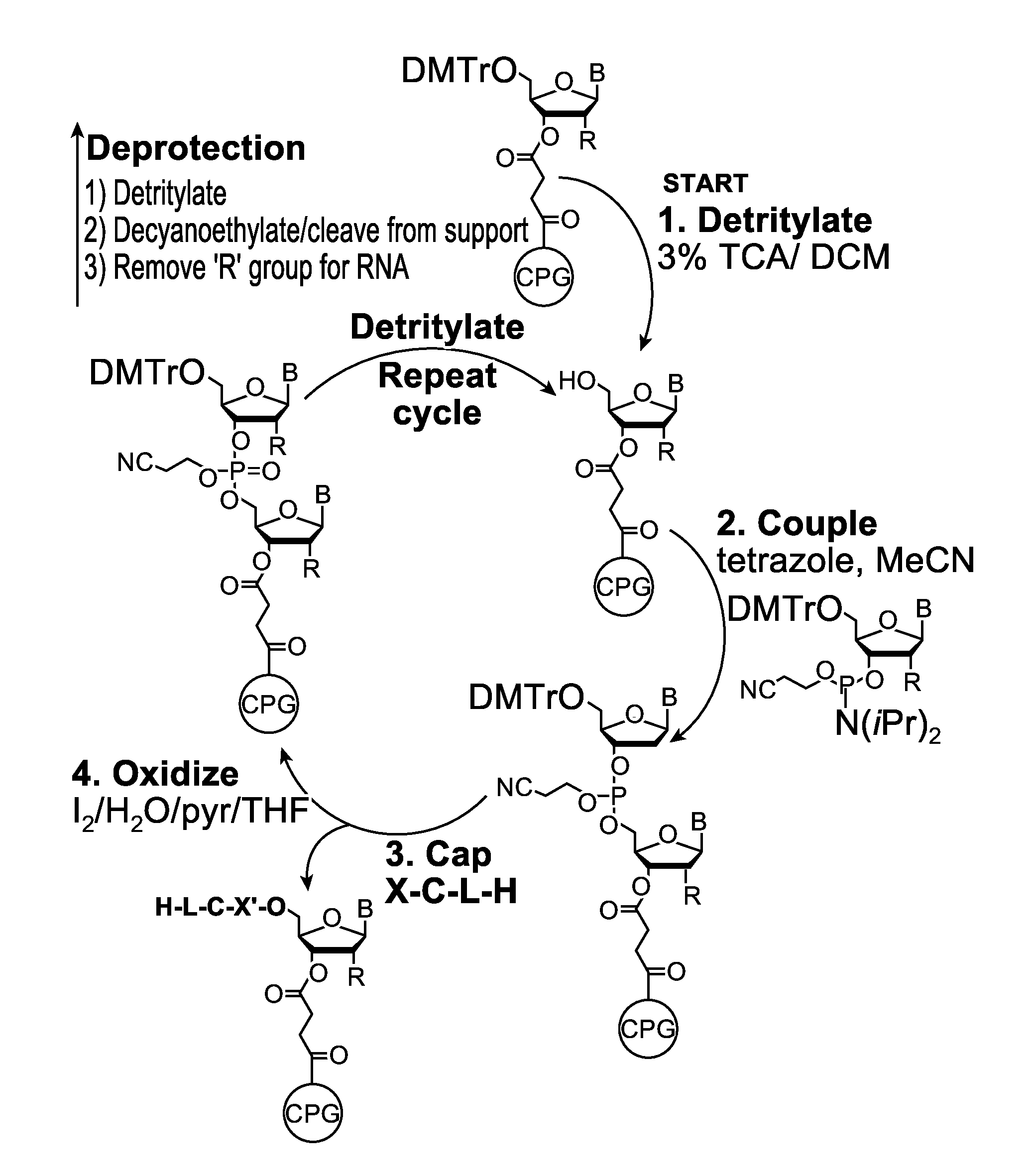
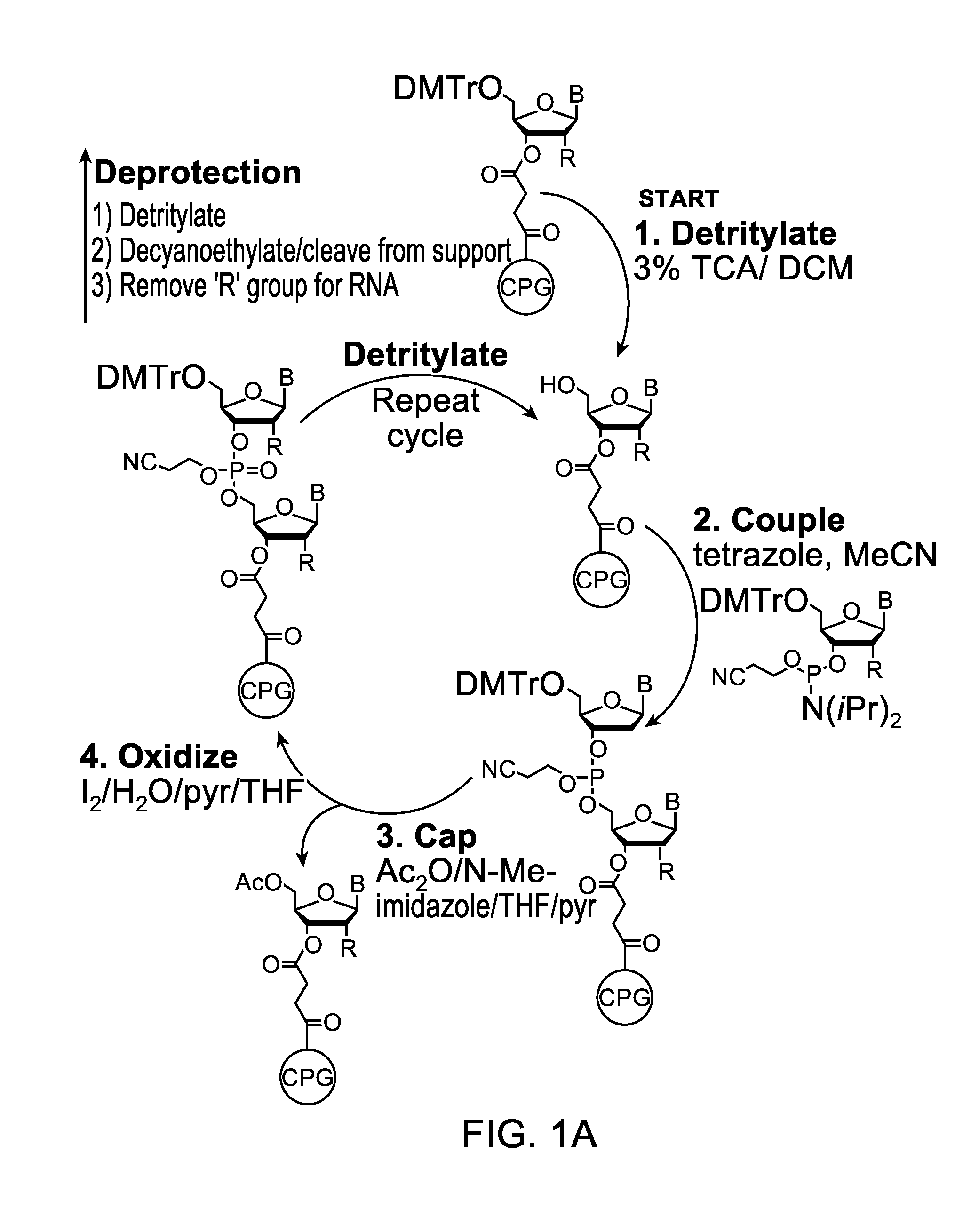
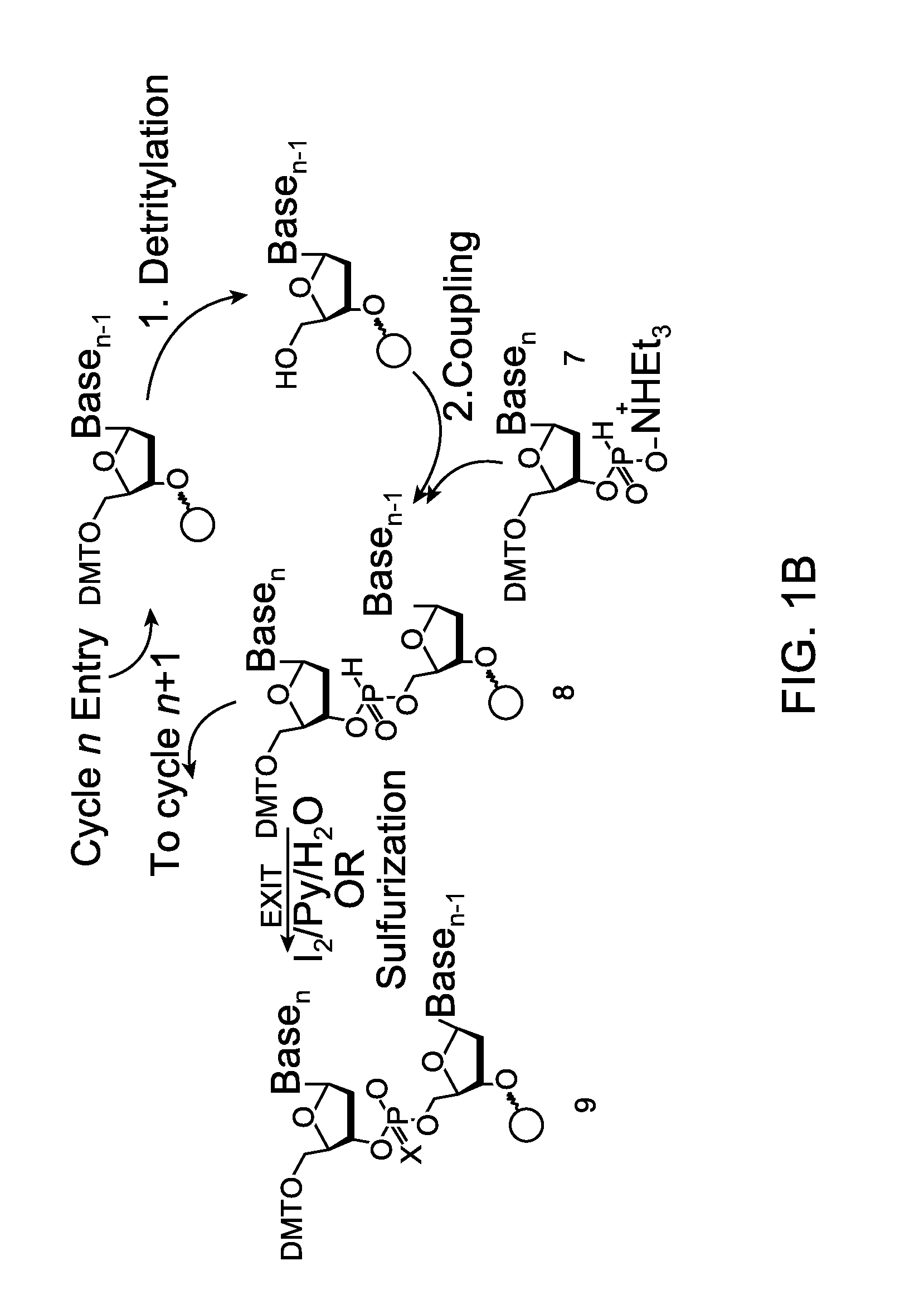
Novel methods for the synthesis and purification of oligomers
InactiveUS20130137861A1Carbamic acid derivatives preparationSugar derivativesOligomerOligonucleotide synthesis
A reagent for oligonucleotide synthesis or purification, wherein the reagent has a structure of:X—C-L-H (Formula A)wherein X is a phosphoramidite group, an H-phosphonate group, an acetal group, or an isocyanate; C is a direct bond or a cleavable adaptor represented by —Ca-Cb—; L is a hydrocarbyl chain; and H is a terminal alkyne or an activated cyclooctyne. The reagent of Formula (A) can be used in the synthesis and purification of oligonucleotides.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
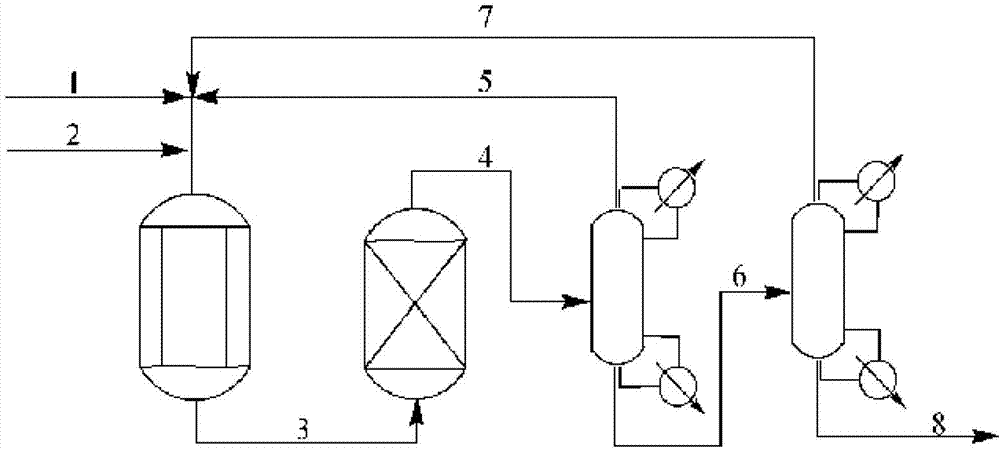
Method for continuous production of polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether
InactiveCN102786397ARealize industrial productionImprove stabilityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystDistillation
The invention provides a method for continuous production of polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: a) feeding dimethoxymethane and hot-melted paraformaldehyde into a fixed bed reactor and adopting an acidic resin catalyst, so as to prepare polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether (DMM3-8), wherein the reaction temperature is 120-180 DEG C and the pressure is 0.1-10 MPa; b) cooling the reaction product, and then performing adsorptive separation through a dehydrating tower, so as to obtain polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether of which most water, cytidine glycol and hemiacetal are desorbed; c) feeding the polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether subjected to desorption into a distillation tower for separation, wherein most of a low-boiling component (dimethoxymethane (DMM)), poly-di-formaldehyde dimethyl ether (DMM2), a by-product (methanol) and triformol are extracted first, and then the materials in a tower kettle are fed into a rectifying tower in the next step, so as to extract the rest of the DMM2 and the triformol; and d) returning the low-boiling component (dimethoxymethane (DMM)), the methanol, the DMM2 and the triformol, which are evaporated out by the distillation tower and the rectifying tower in the last step, into the fixed bed reactor to continue to react to prepare polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
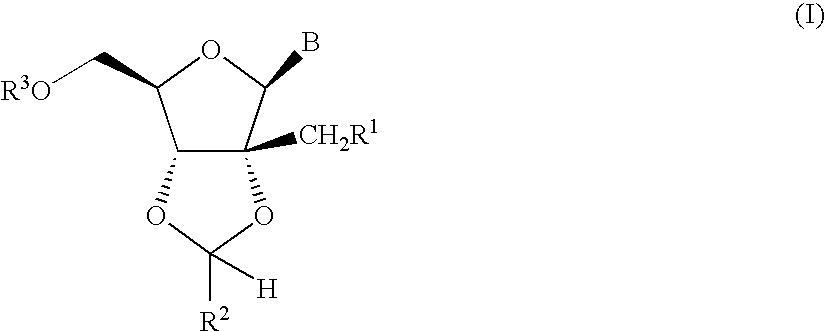
Ribonucleoside cyclic acetal derivatives for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection
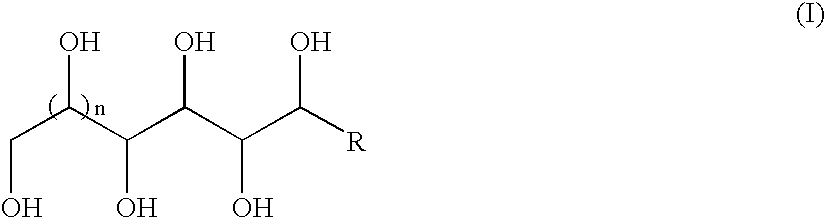
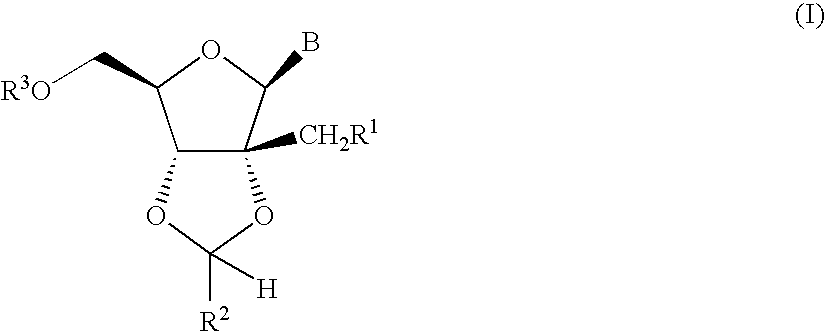
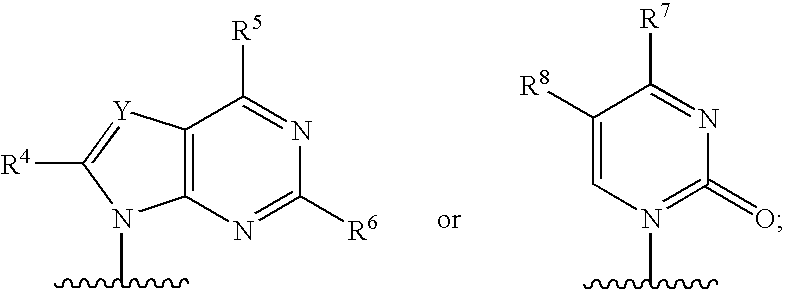
The present invention provides ribonucleoside 2′,3′-cyclic acetals of structural formula I which are precursors or prodrugs of inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral polymerase. These compounds are precursors of inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral replication and are useful for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection. They are particularly useful as precursors or prodrugs of inhibitors of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase, as precursors or prodrugs of inhibitors of HCV replication, and / or for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. The invention also describes pharmaceutical compositions containing such ribonucleoside 2′,3′-cyclic acetals alone or in combination with other agents active against RNA-dependent RNA viral infection, in particular HCV infection. Also disclosed are methods of inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA viral replication, and / or treating RNA-dependent RNA viral infection with the ribonucleoside 2′,3′-cyclic acetals of the present invention.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Polyvinyl acetal laminate and use thereof
InactiveUS20120204940A1Improve interlayer adhesionSimilar polaritySynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
It is an object of the present invention to provide a laminate of a layer that contains a polyvinyl acetal and a layer that contains a polyolefin (hydrocarbon polymer), which exhibits excellent adhesion between the layers. The present invention relates to a laminate obtained by laminating a layer A that includes a composition A containing a polyvinyl acetal and a layer B that includes a composition B containing a polyolefin and / or an adhesive functional group-containing olefinic polymer, wherein a mass ratio of (the polyolefin) / (the adhesive functional group-containing olefinic polymer) is 0 / 100 to 99.95 / 0.05.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Processing of positive-working lithographic printing plate precursor
InactiveUS20100047723A1Simplify image processingDevelopment and “ gummingDuplicating/marking methodsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBoiling pointChemical compound
Positive-working imageable elements can be imaged and processed using a processing solution that comprises at least 0.03 N of an organic amine or a mixture thereof, whose conjugated acids have a pKa greater than 9 and a boiling point greater than 150° C. The imageable element is a single-layer, infrared radiation-sensitive positive-working imageable element comprising a substrate and an infrared radiation absorbing compound. It also has an imageable layer that comprises a developability-enhancing compound and a poly(vinyl acetal) in which at least 25 mol % of its recurring units comprise pendant phenol, naphthol, or anthracenol groups that are substituted with one or more electron-withdrawing groups.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
High-strength film laminates having layers of plasticizer-containing polyvinyl (N)acetal and plasticizer-containing polyvinyl (ISO)acetal
ActiveUS8597792B2Improve mechanical propertiesGood compatibilitySynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsArchitectural glassGlass composites
The invention relates to film laminates, formed from at least three layers A, B and C, each layer containing at least one plasticizer and at least one polyvinyl acetal, wherein, at least one of the layers A, B or C contains at least one polyvinyl (iso)acetal having a mean degree of polymerization of less than 3000, 10 to 25% by weight of polyvinyl alcohol groups and a proportion 50 to 80% by weight of polyvinyl (iso)acetal groups, and wherein layer B has a plasticizer content of less than 32% by weight. The film laminates can be used for the production of glass / film laminate / glass composites for motor vehicles, aircraft, ships, architectural glazings, façade components, or for the production of photovoltaic modules.
Owner:KURARAY EURO GMBH
Process for production of a composition useful as a fuel
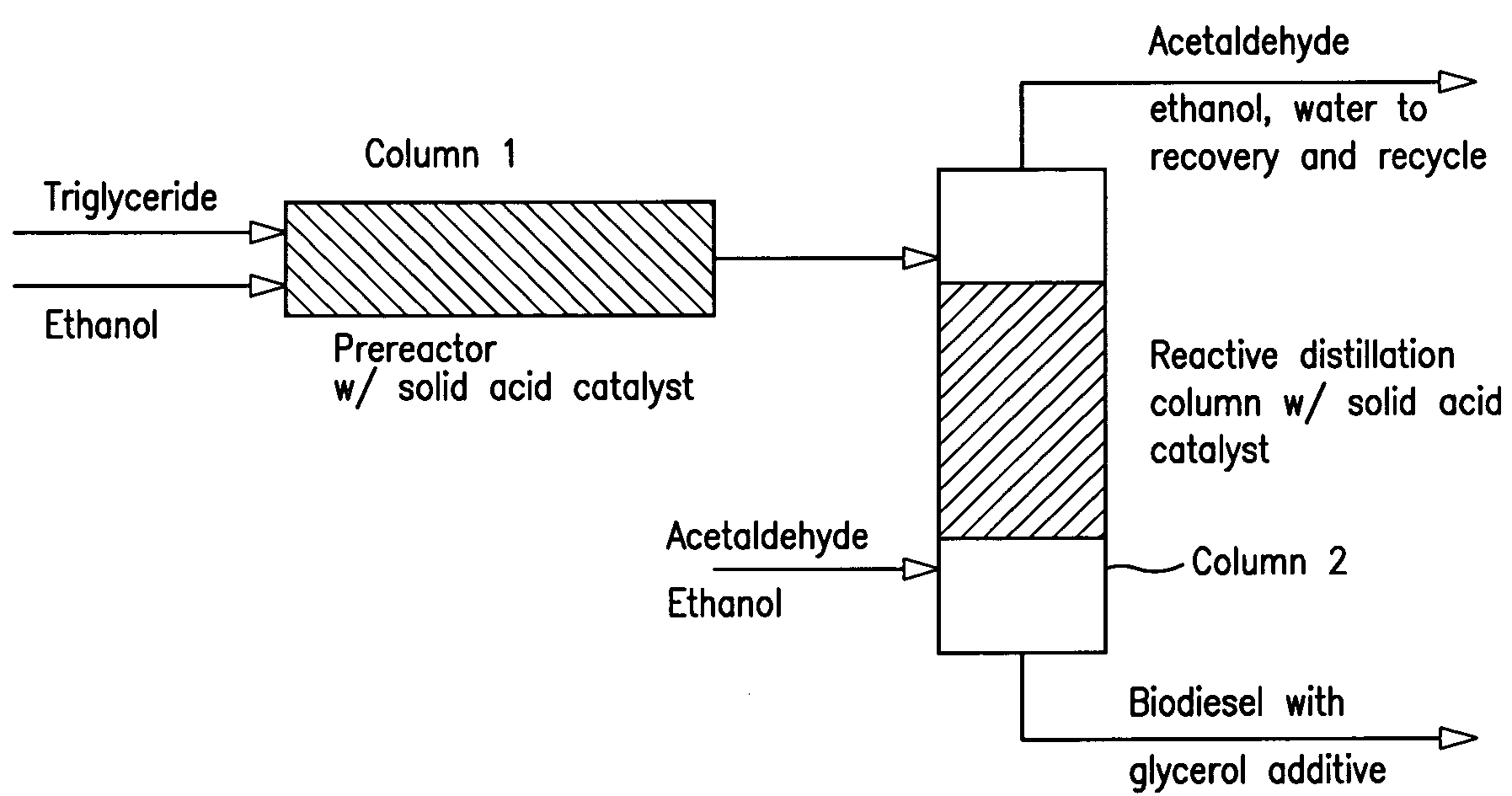
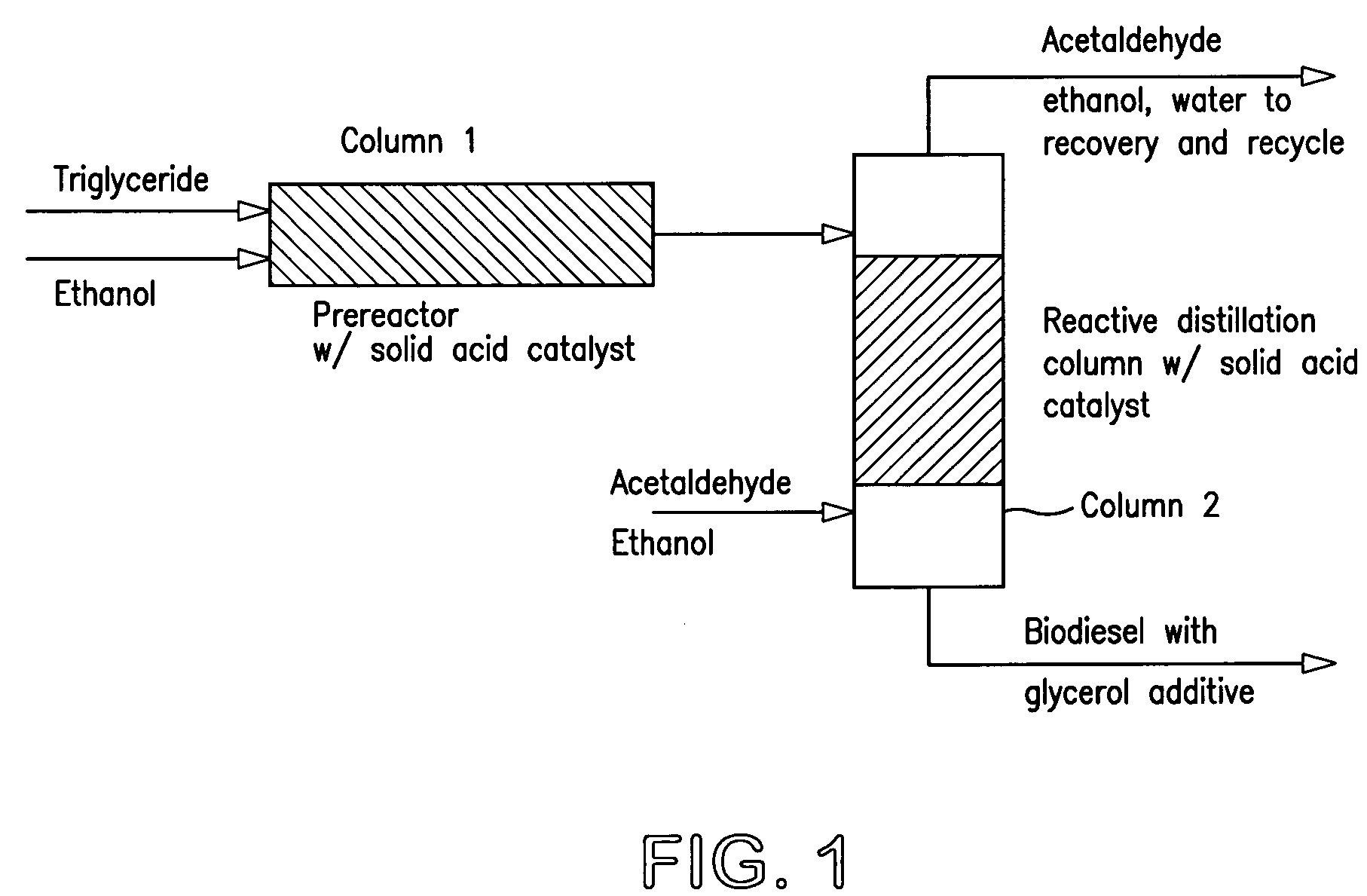
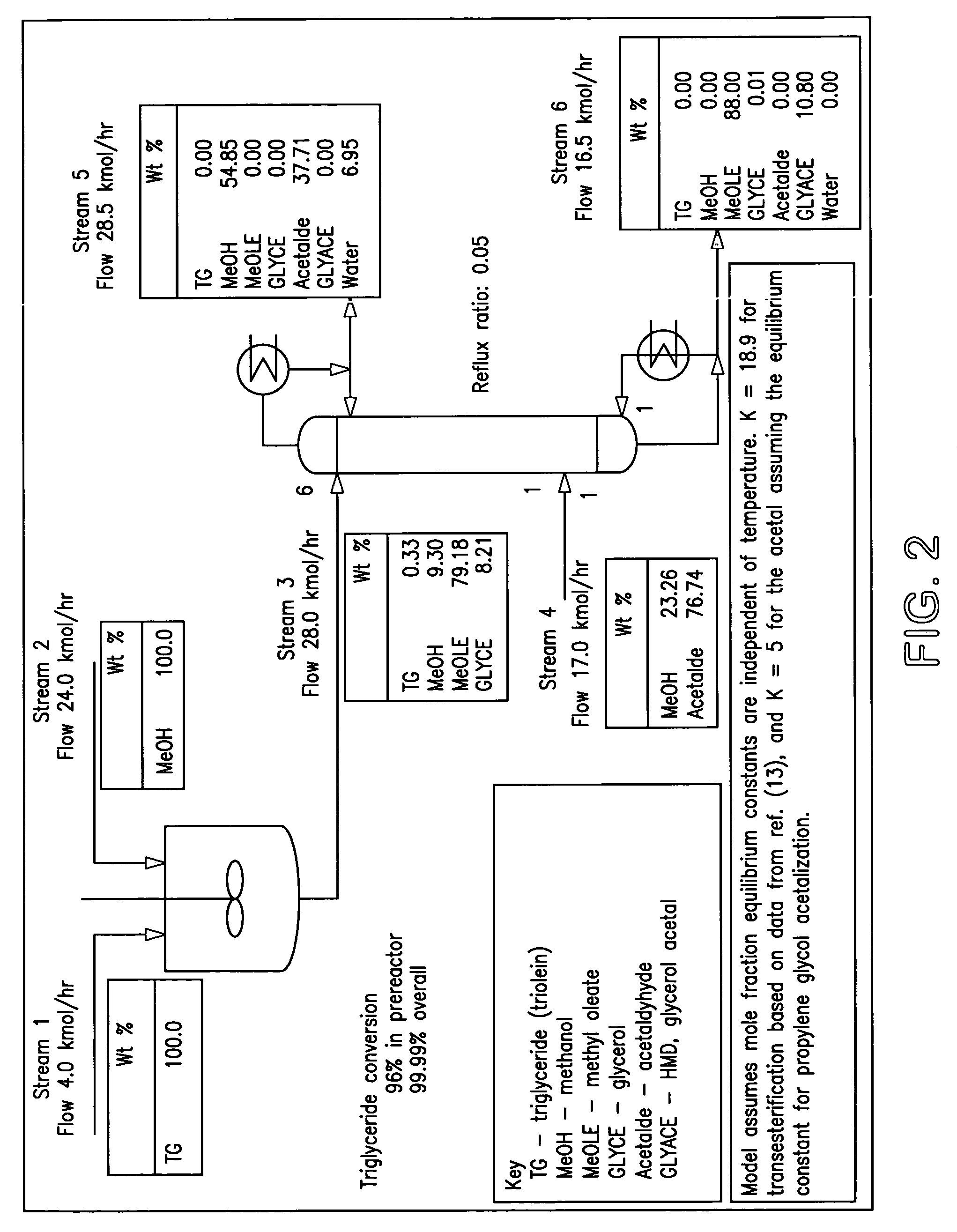
InactiveUS7321052B2Easy to operateFuel propertyFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationHeating oilTG - Triglyceride
A process for the preparation of a fuel oil (diesel fuel or heating oil) composition which is a mixture of an alkanol tranesterified fatty acid ester triglyceride and an acetal of glycerol is described. The process preferably provides a prestep of the formation of at least some of the alkanol transesterified triglyceride containing the glycerol for use in the formation of the acetal of glycerol. The composition can also be formed from a reaction of 1,1-dimethoxy- or 1,1-diethoxyethane and glycerol to form the acetal in the alkanol transesterified triglyceride.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Thermoplastic resin sheet and laminate
ActiveUS20070014976A1Improve impact resistanceReduced in surface densitySynthetic resin layered productsVehicle componentsAcetic acidPVA - Polyvinyl alcohol
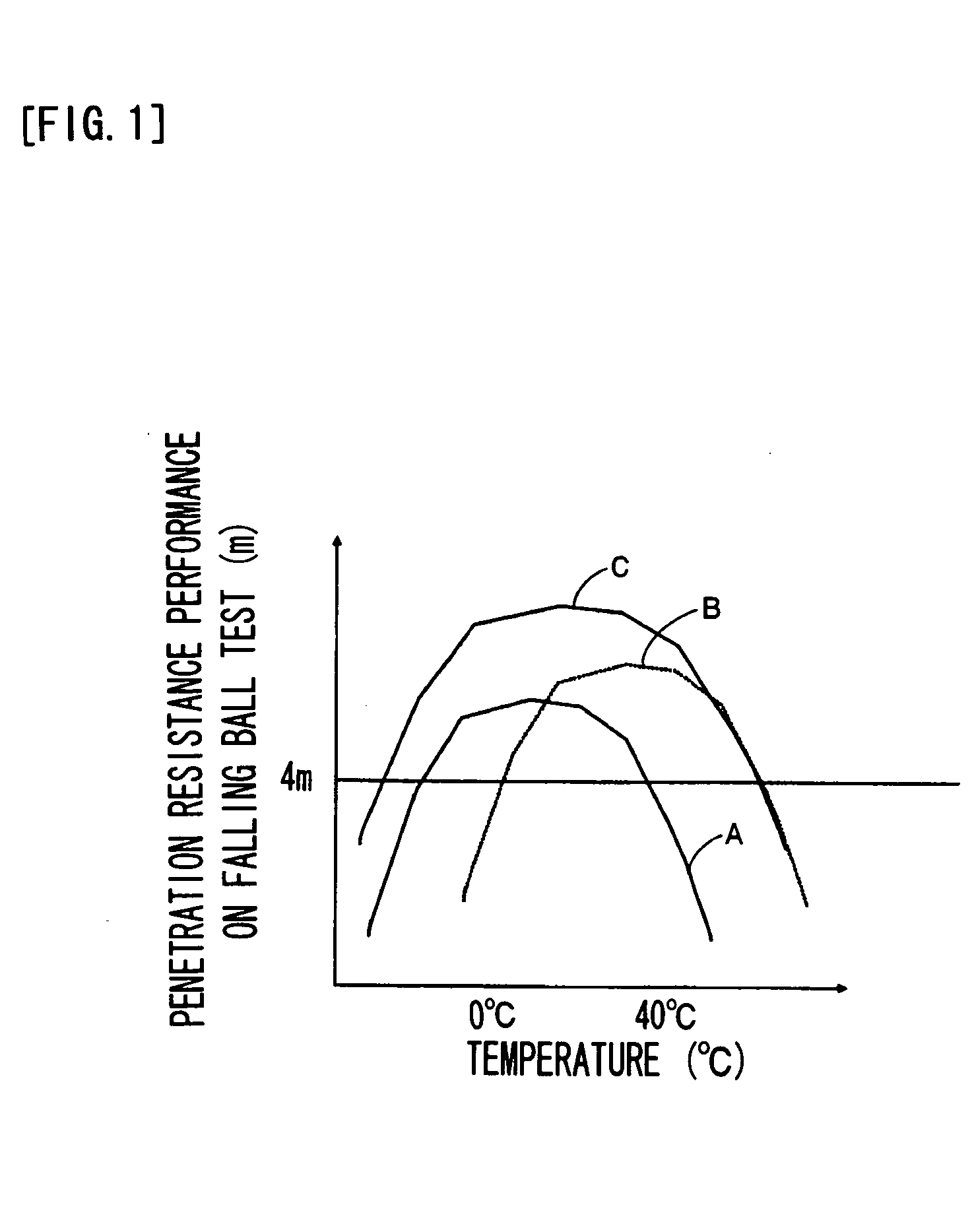
A thermoplastic resin sheet is provided which has good penetration resistance over a range from low to high temperature region and can be used as an intermediate film of a laminated glass. The thermoplastic resin sheet has such a layered structure that a first polyvinyl acetal resin layer (A) is provided on each side of a second polyvinyl acetal resin layer (B). The first polyvinyl acetal resin layer (A) is comprised mainly of an acetalized product of polyvinyl alcohol with aldehyde (a) having 4-6 carbon atoms. The second polyvinyl acetal resin layer (B) is comprised mainly of a coacetalized product of polyvinyl alcohol with aldehyde (a) having 4-6 carbon atoms and aldehyde (b) having 1-3 carbon atoms. A polymer unit (X) derived from the aldehyde (a) and a polymer unit (Y) derived from the aldehyde (b), in total, account for at least 55% by mole while the first polymer unit (X) alone accounts for 0.5-80% by mole of the total of the coacetalized product.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Composition having excellent transparency
ActiveUS20160046783A1High transparencyPoor transparencyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPolyvinyl alcoholCLARITY
To provide a laminated product of a layer including a polyvinyl acetal and a layer including a hydrocarbon-based polymer, having excellent adhesion between the layers.A composition including, with respect to 100 parts by mass of a polyvinyl acetal satisfying definition 1 and / or definition 2, 30 to 70 parts by mass of a plasticizer including 0.5 to 100% by mass of a plasticizer containing a polar group and 0 to 99.5% of a plasticizer containing no polar group.Definition 1: When 1 g of a polyvinyl acetal is dissolved in 100 g of methanol, an undissolved content is 2.5 to 90% by mass.Definition 2: When 1 g of a polyvinyl acetal is dissolved in 100 g of chloroform, an undissolved content is 5 to 70% by mass.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Preparation method of butanediol secondary hydrogenation catalyst by butynediol two-step hydrogenation
ActiveCN101306368AUniform depositionGood dispersionPreparation by hydrogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNickel saltSURFACTANT BLEND
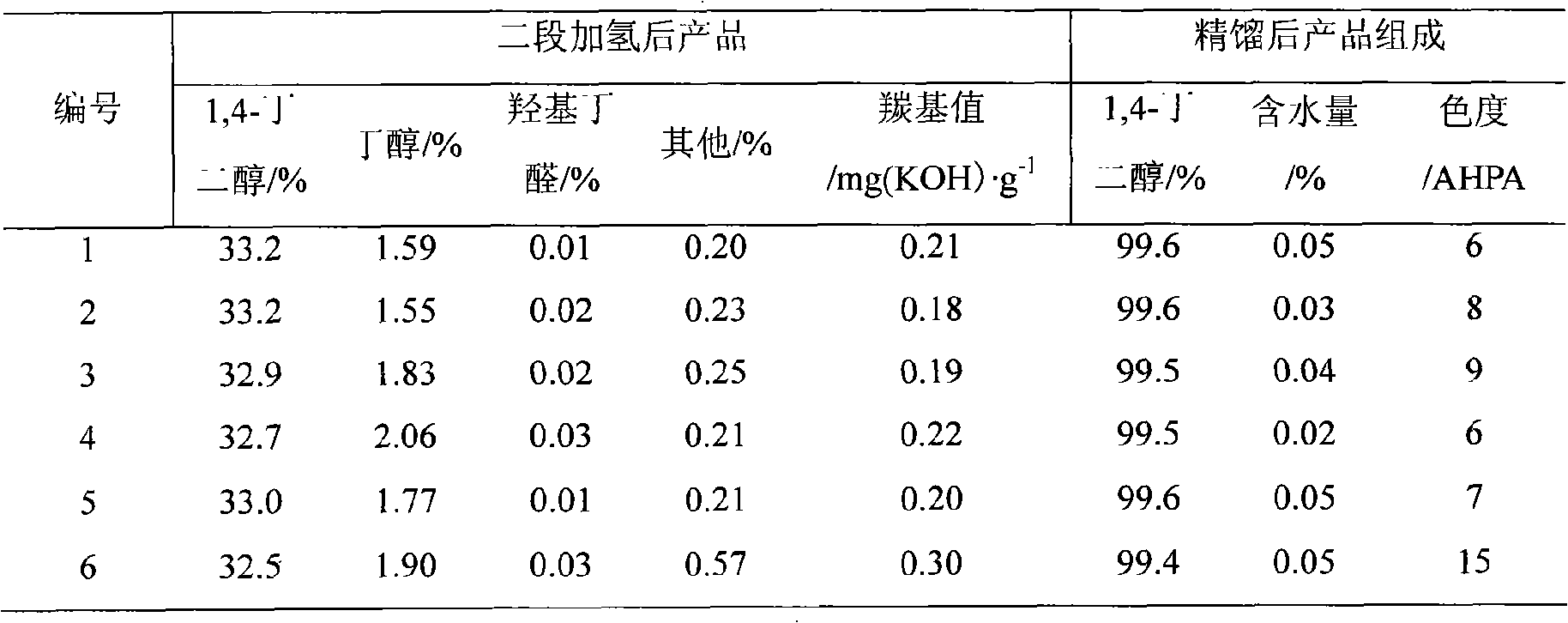
The invention provides a method for preparing a butanediol secondary hydrogenation catalyst through adopting the butynediol two-step hydrotreation, and the method comprises the following steps: an accelerant is introduced into an alumina carrier; the carrier is heated; mixed nickel complex solution containing organic nickel salt, inorganic nickel salt and surfactant is prepared; the mixed nickel salt solution is dipped on the heated carrier, and the catalyst product with the nickel content of 5-25 w% and the accelerant content of 0.001-6 w% can be obtained by drying, baking, deoxidizing and passivating. The catalyst can be used in the process of preparing the butanediol secondary hydrogenation by adopting the butynediol two-step hydrotreation, the carbonyl can be reduced to be lower than 0.2 mg (KOH)*g<-1>, and the contents of acetal and butylene glycol are enabled to be reduced to the lowest level. Through the subsequent rectification, the butylene glycol product with the purity more than or equal to 99.5 percent and the chromaticity lower than or equal to 10 AHPA can be produced.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Radiation-sensitive compositions and elements with solvent resistant poly(vinyl acetal)s
InactiveUS20090004599A1Improve the immunityIncrease the lengthPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsRadiation sensitivityCompound (substance)
A radiation-sensitive composition can be used to prepare positive-working imageable elements having improved solvent resistance and is useful for making lithographic printing plates. The composition includes an alkaline soluble polymeric binder that is a specific poly(vinyl acetal) that exhibits improved resistance to press chemicals, and a radiation absorbing compound.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
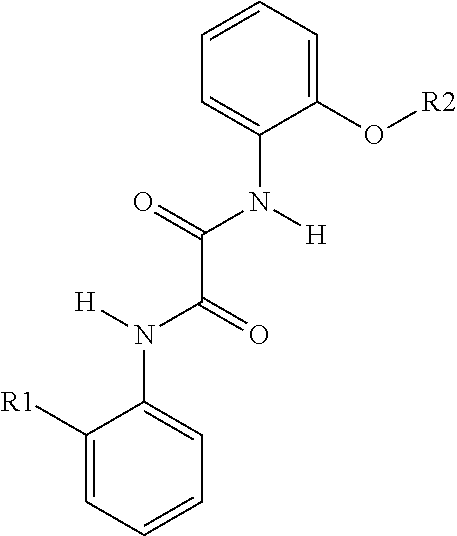
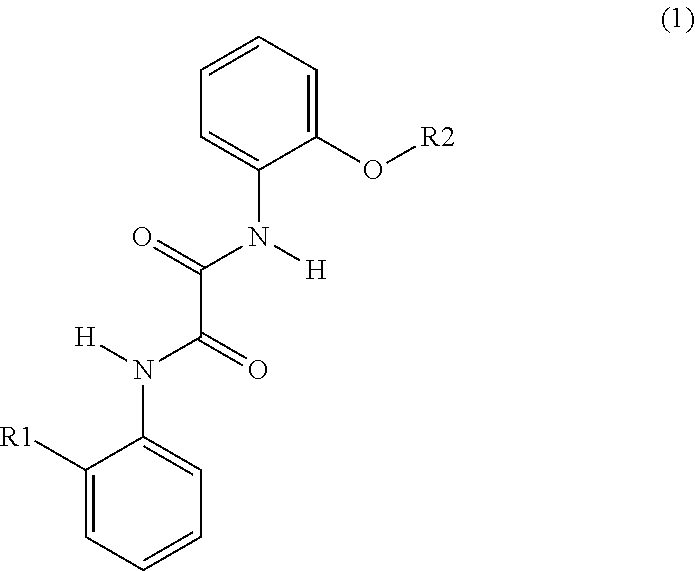
Polymer interlayers comprising UV absorbers
InactiveUS20150158276A1Synthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsPlasticizerUltraviolet
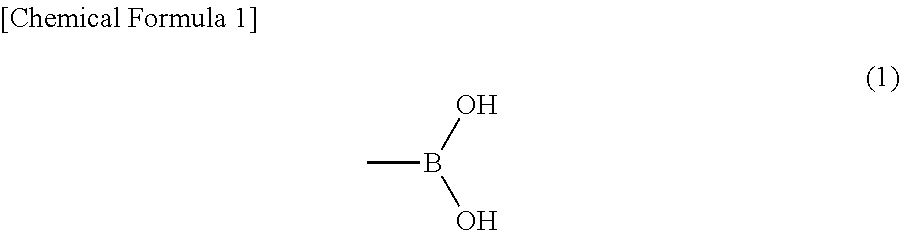
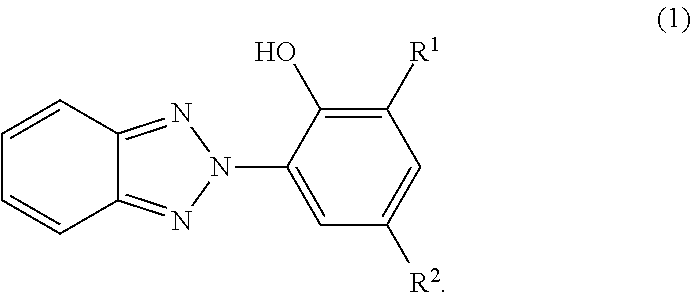
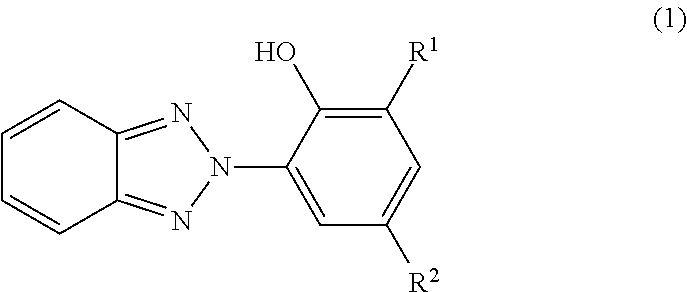
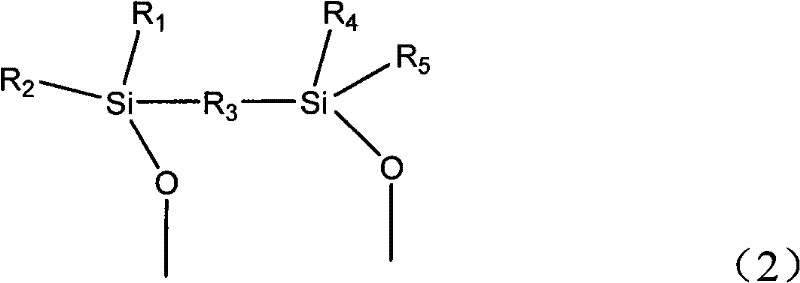
A UV stable polymer composition comprising a poly(vinyl acetal) resin, a plasticizer and at least one UV absorber, wherein the ultraviolet absorber comprises structure (1)
Owner:SOLUTIA INC
Method for preparing alcohols by selectively hydrogenating aldehydes
ActiveCN102408304AHigh selectivityHydrophobicOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSilanesReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing alcohols by selectively hydrogenating aldehydes, belonging to hydrogenation technologies. In order to meet the requirements of people on two aspects, i.e. the improving of the selectivity on preparing the alcohols by hydrogenating the aldehydes and the prolonging of the service life of a catalyst currently, the method proposes that: the aldehydes are taken as raw materials; the reaction temperature is 20-300 DEG C; the reaction pressure is 0.1-7.0 MPa; the weight space velocity of the aldehydes is 0.02-20 h<-1>; the aldehydes and hydrogen gas are in contact with a hydrogenation catalyst; and the aldehydes are produced into corresponding alcohols through selectively hydrogenating. In the method, the hydrogenation catalyst comprises a carrier, a metal active component and silane groups; the silane groups are grafted through a silylanizing treatment; and the content of the silane groups in the total weight of the catalyst is 0.05 wt% to 25 wt%. Compared with the existing method, with the adoption of the catalyst in the method provided by the invention, the selectivity is high, the amount of byproducts, such as ethers, esters and acetals is greatly lowered; and meanwhile, the generation amount of carbon deposit is little, so that the catalyst has longer service life.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Degradable superabsorbent polymers
InactiveUS20130065765A1Increase demandSufficient amountBiocideGlass/slag layered productsGlyoxylic acidFiber
The present disclosure relates to degradable superabsorbent materials based on acetals of glyoxylic acid and derivatives thereof with polyvinyl alcohol, and methods of making the polymers. The polymers are used to make superabsorbent particles, coatings, sheets, and fibers. Formulations and articles including the superabsorbent polymers, particles, coatings, sheets, and fibers are also disclosed.
Owner:RELUCEO
Process for producing polyester resins
The process of the present invention for producing a polyester resin comprising a dicarboxylic acid constitutional unit and a diol constitutional unit having a cyclic acetal skeleton comprises a step (1) of subjecting a diol (A) having a cyclic acetal skeleton and an ester (D) to transesterification reaction and a step (2) of mainly converting the resultant oligomer into a high polymer. The step (1) simultaneously satisfies the requirements (i) to (iv) as described in the specification. In the process of the present invention, the polyester resins having excellent moldability and mechanical properties are stably produced by a transesterification method which is less detrimental to environments.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Liquid dispersion comprising dibenzylidene sorbitol acetals ethoxylated nonionic surfactants
InactiveUS6127470ALow viscosityInexpensive fluid dispersionTransportation and packagingMixingPeristaltic pumpPolyolefin
This invention relates to a fluid dispersion of at least one dibenzylidene sorbitol acetal derivative. The sorbitol acetal derivative is useful as a clarifying agent for polyolefins and the inventive fluid dispersion permits improvements in the handling and processing of and mixing within the polyolefin composition. The inventive dispersion must be shelf stable, retain its nucleating effects, be compatible with polypropylene (and other polyolefins), and possess both short-term and long-term viscosities which permit acceptable transport through a standard polyolefin-manufacturing peristaltic pump. The preferred inventive dispersion thus comprises 3,4-DMDBS and at least one ethoxylated nonionic surfactant having an HLB of greater than about 8.5. Preferred surfactants include those selected from the group consisting essentially of ethoxylated sorbitan (C8-C22) monoesters and ethoxylated nonyl-phenol ethers. The inventive dispersion may be introduced within any polyolefin composition, preferably polypropylene, which may then be molded into any shape or form. A method of producing a polyolefin plastic utilizing the inventive dispersion is also provided.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Glass laminates comprising acoustic interlayers and solar control films
ActiveUS20090011230A1Synthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageInter layerEngineering
An acoustic solar control laminate comprising a multi-layer interlayer formed of a solar control film bonded between two polymeric sheets with at least one being an acoustic poly(vinyl acetal) sheet is provided.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
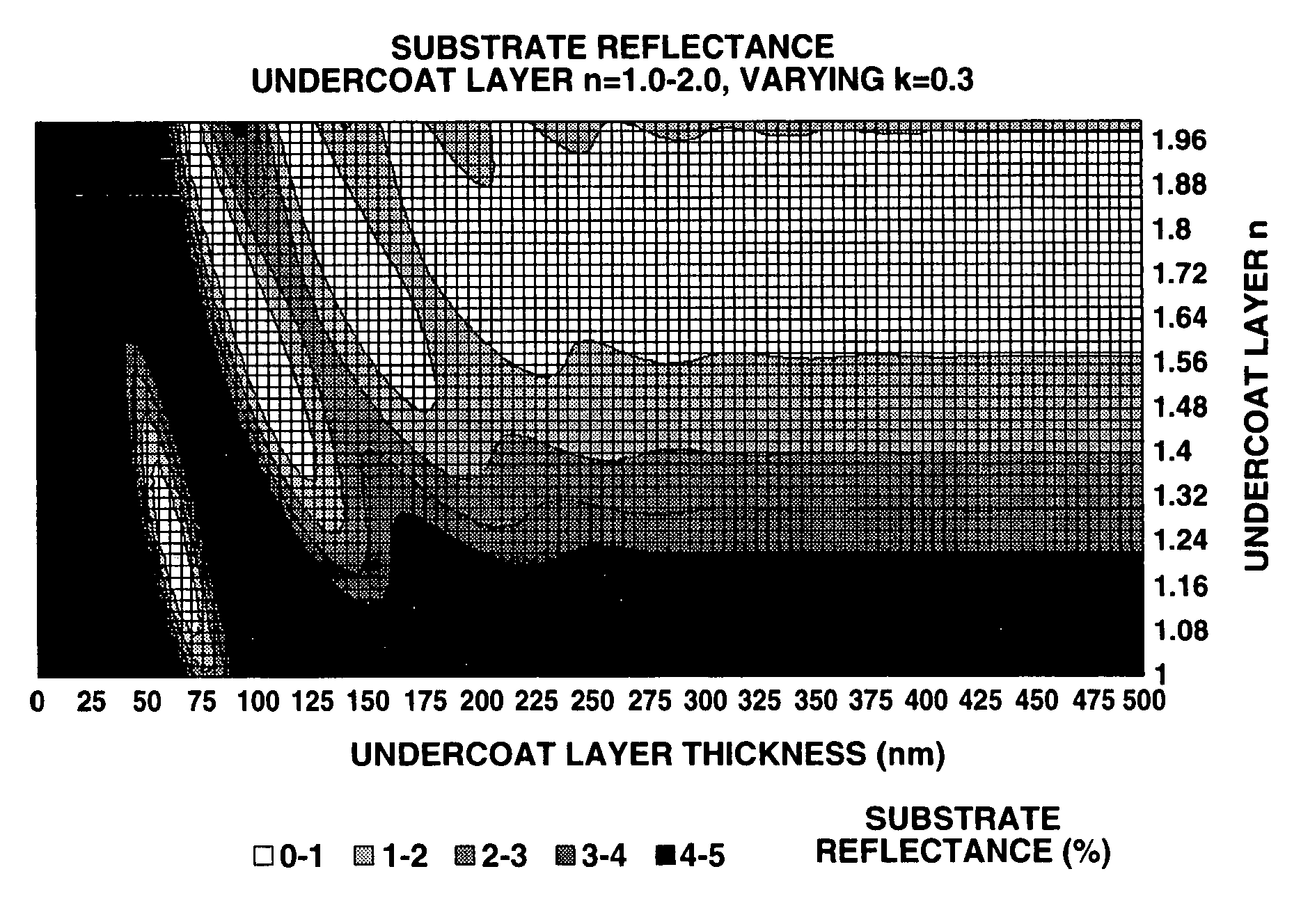
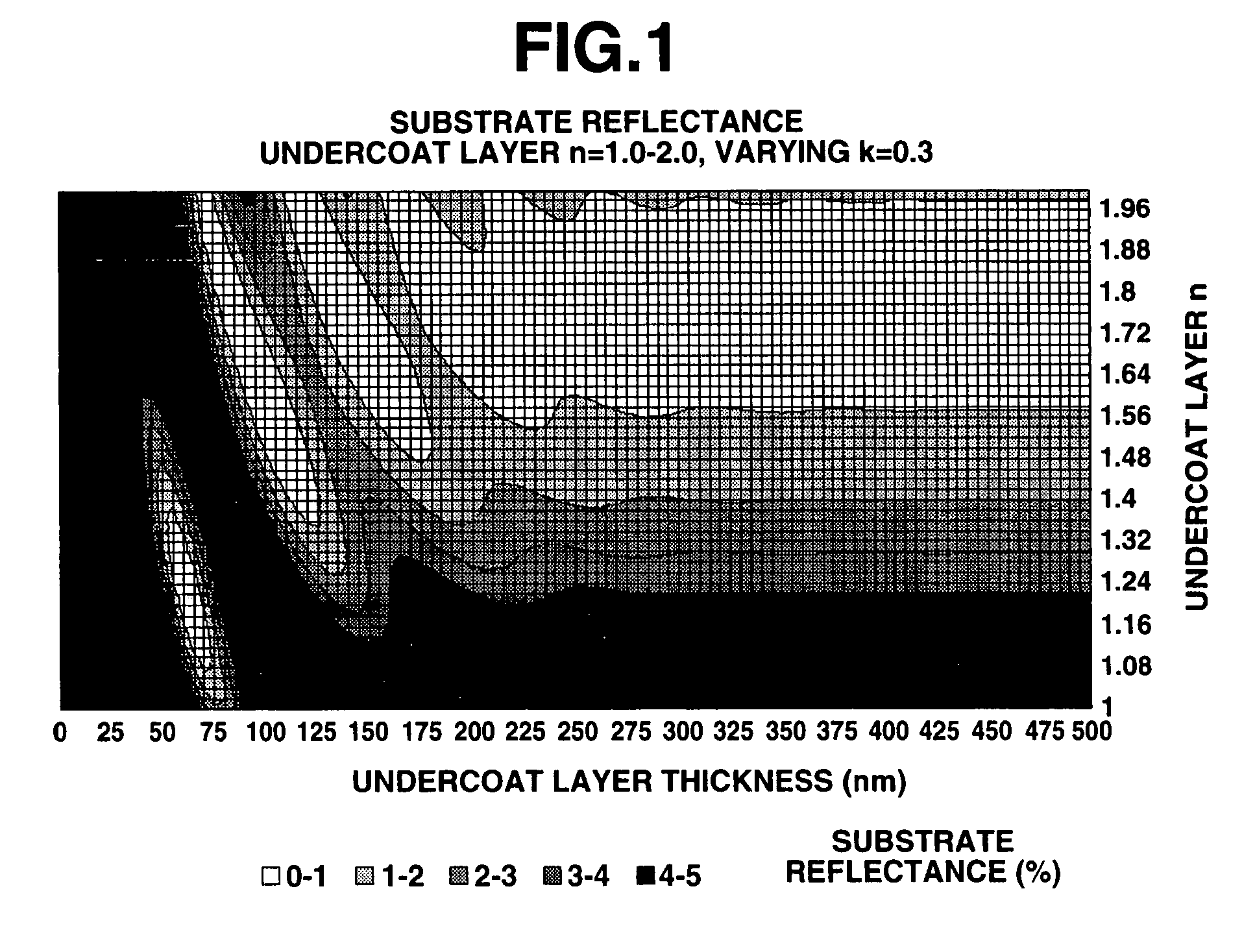
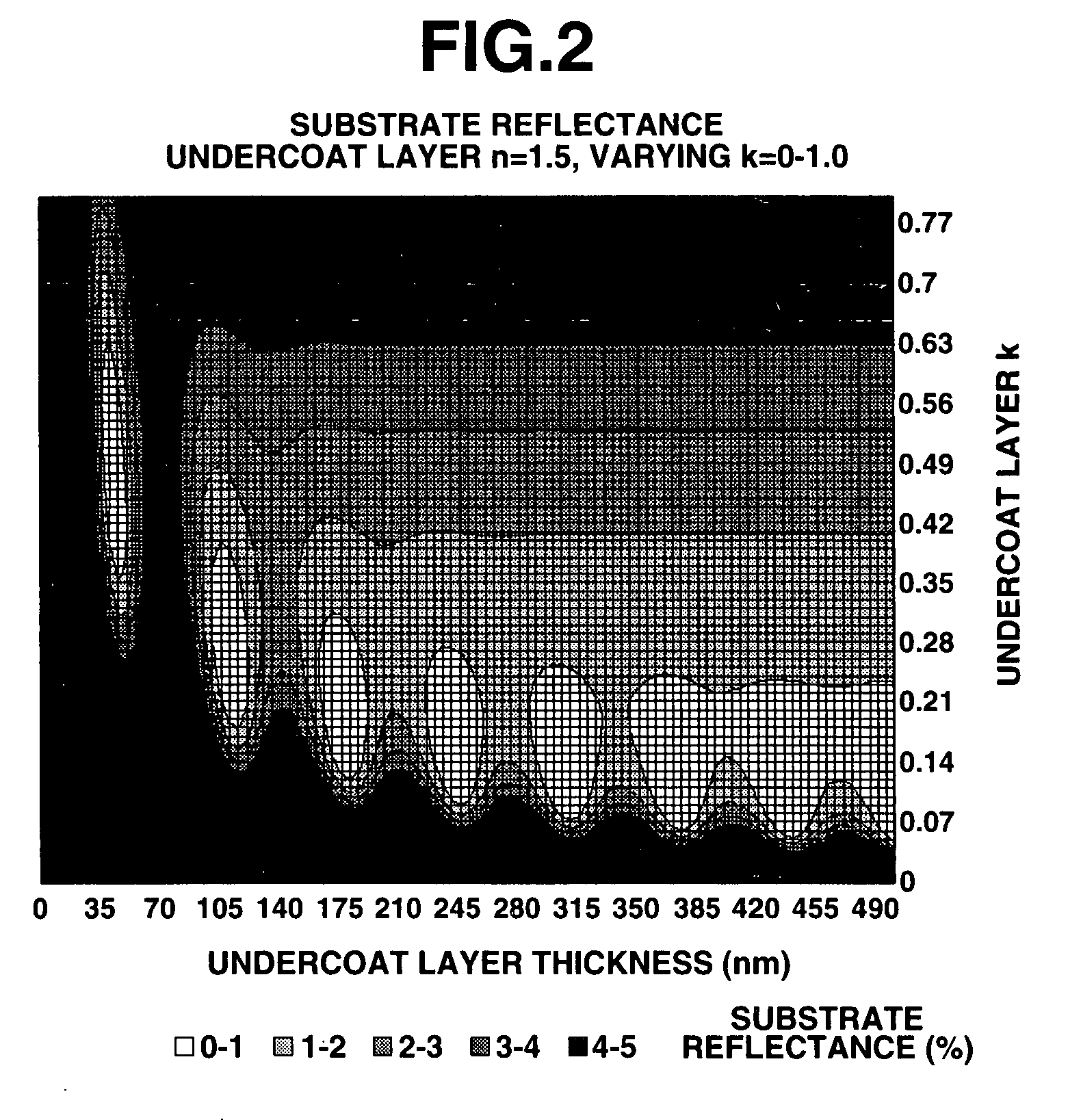
Photoresist undercoat-forming material and patterning process
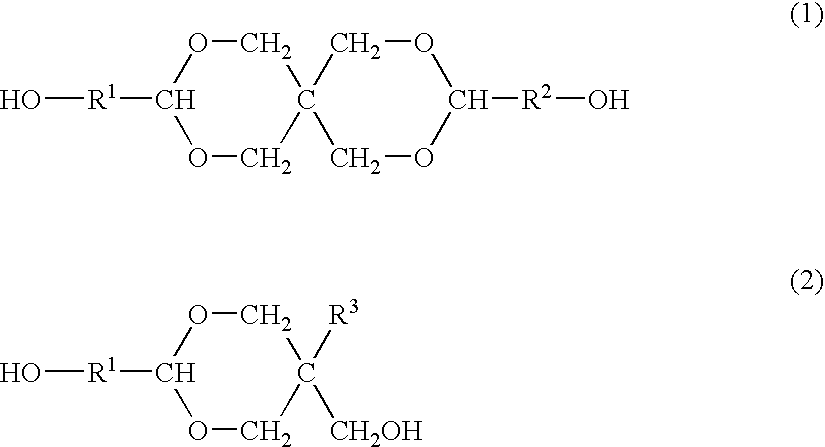
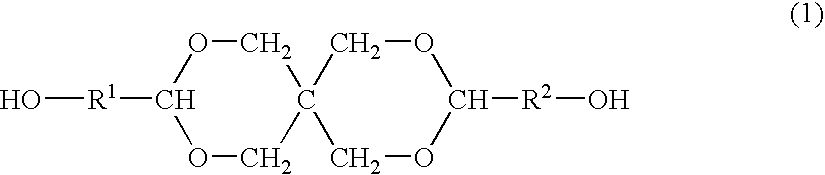
ActiveUS20070275325A1Satisfactory antireflective effectImprove corrosion resistancePhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive material processingResistGlycylxylidide
A material comprising a specific bisphenol compound of formula (1) is useful in forming a photoresist undercoat wherein R1 and R2 are H, alkyl, aryl or alkenyl, R3 and R4 are H, alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, acetal, acyl or glycidyl, R5 and R6 are alkyl having a ring structure, or R5 and R6 bond together to form a ring. The undercoat-forming material has an extinction coefficient sufficient to provide an antireflective effect at a thickness of at least 200 nm, and a high etching resistance as demonstrated by slow etching rates with CF4 / CHF3 and Cl2 / BCl3 gases for substrate processing.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com