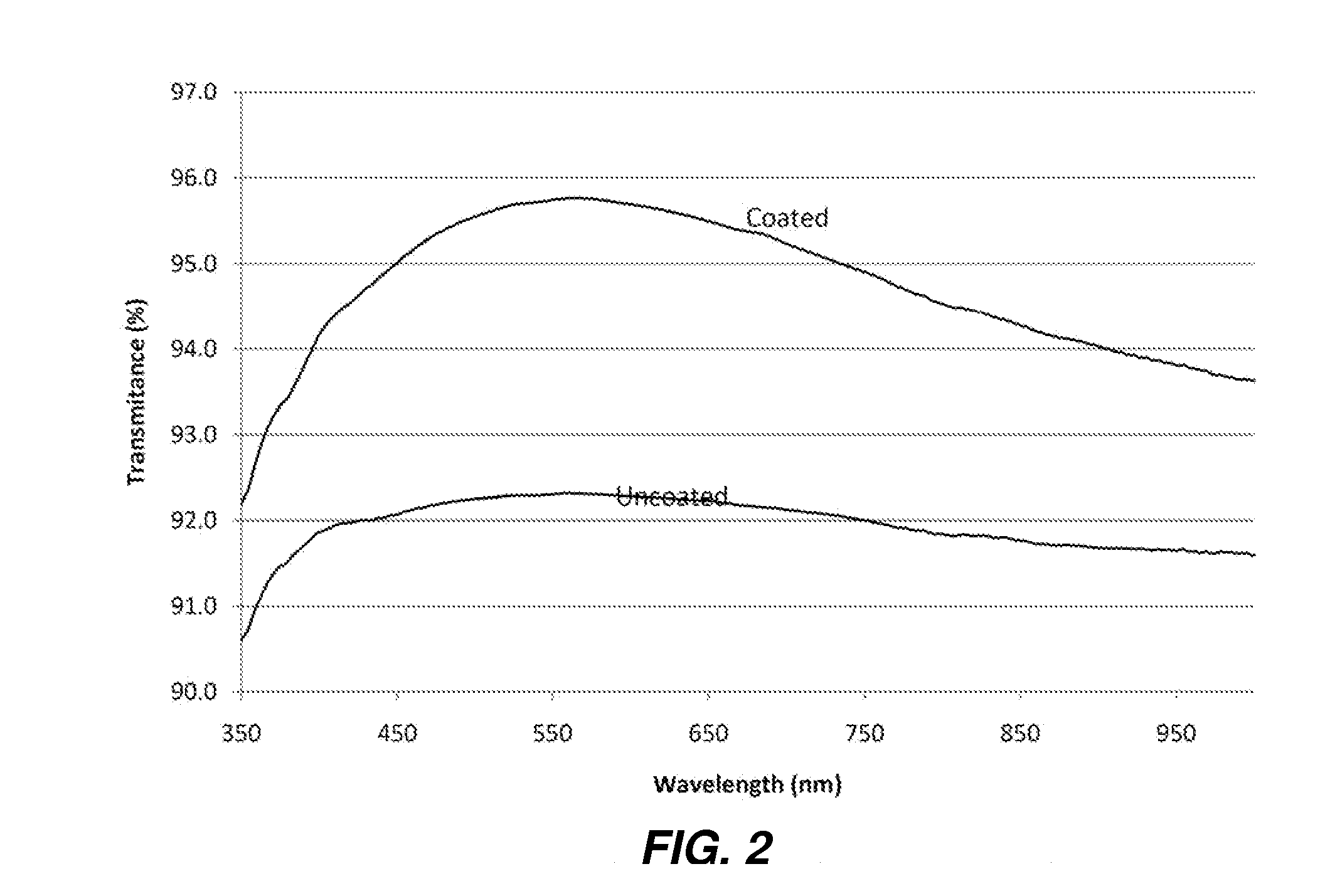
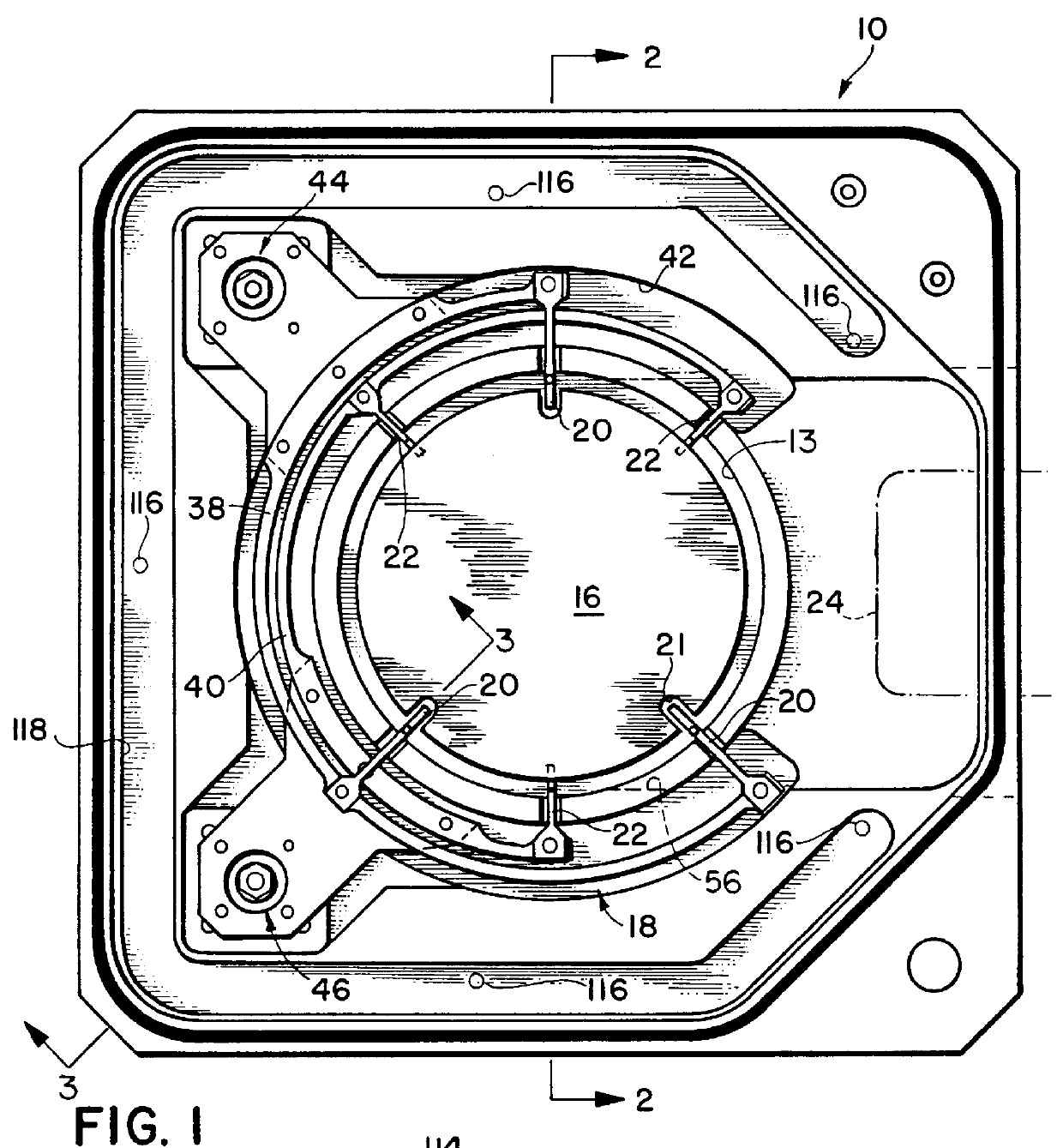
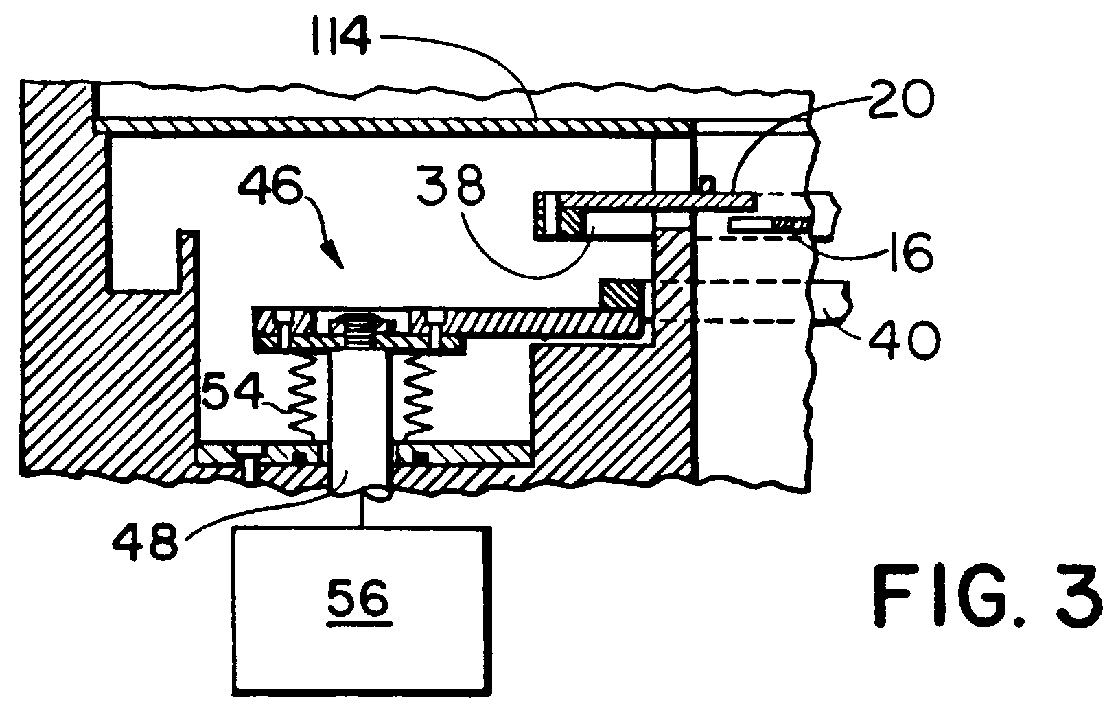
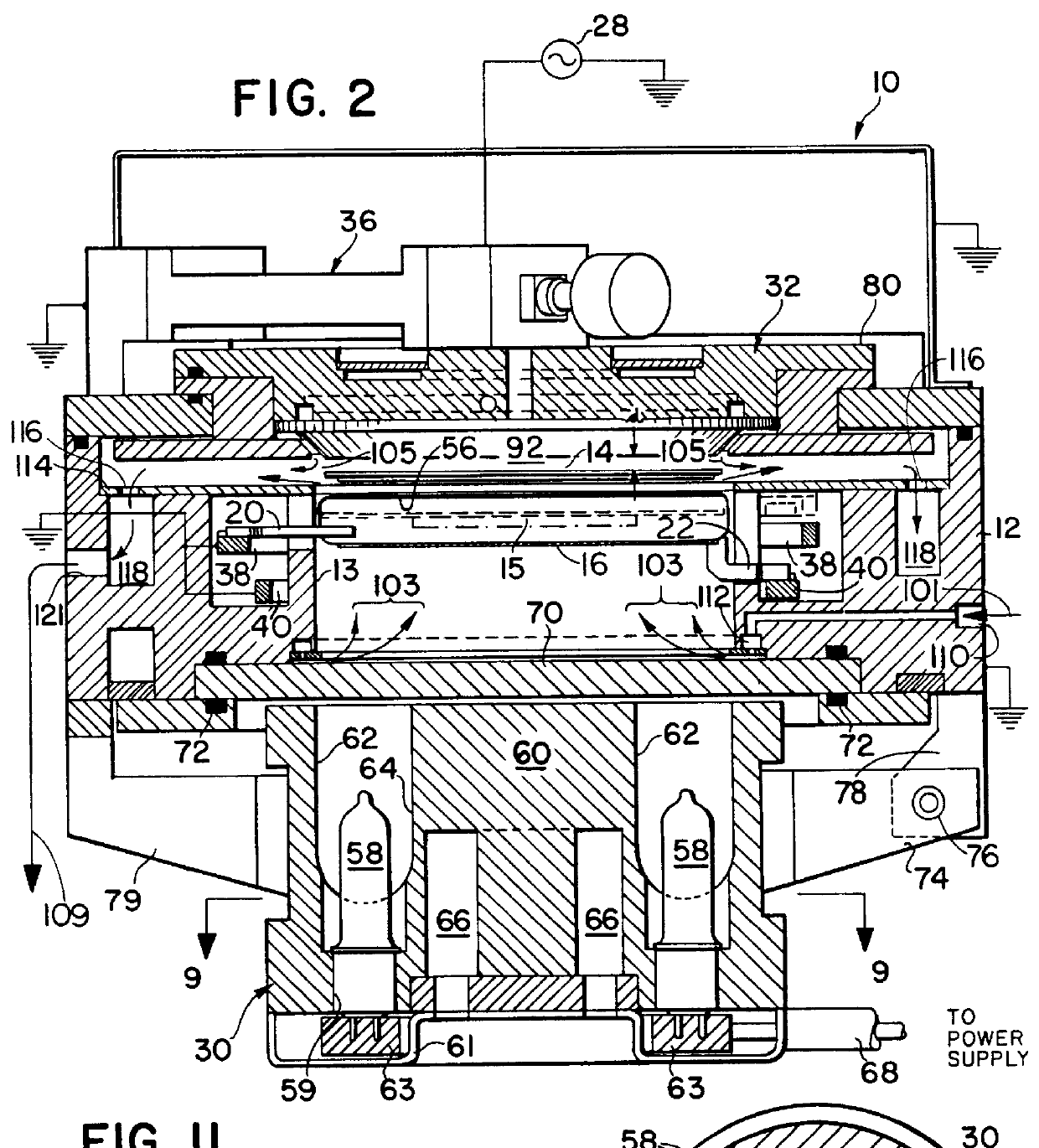
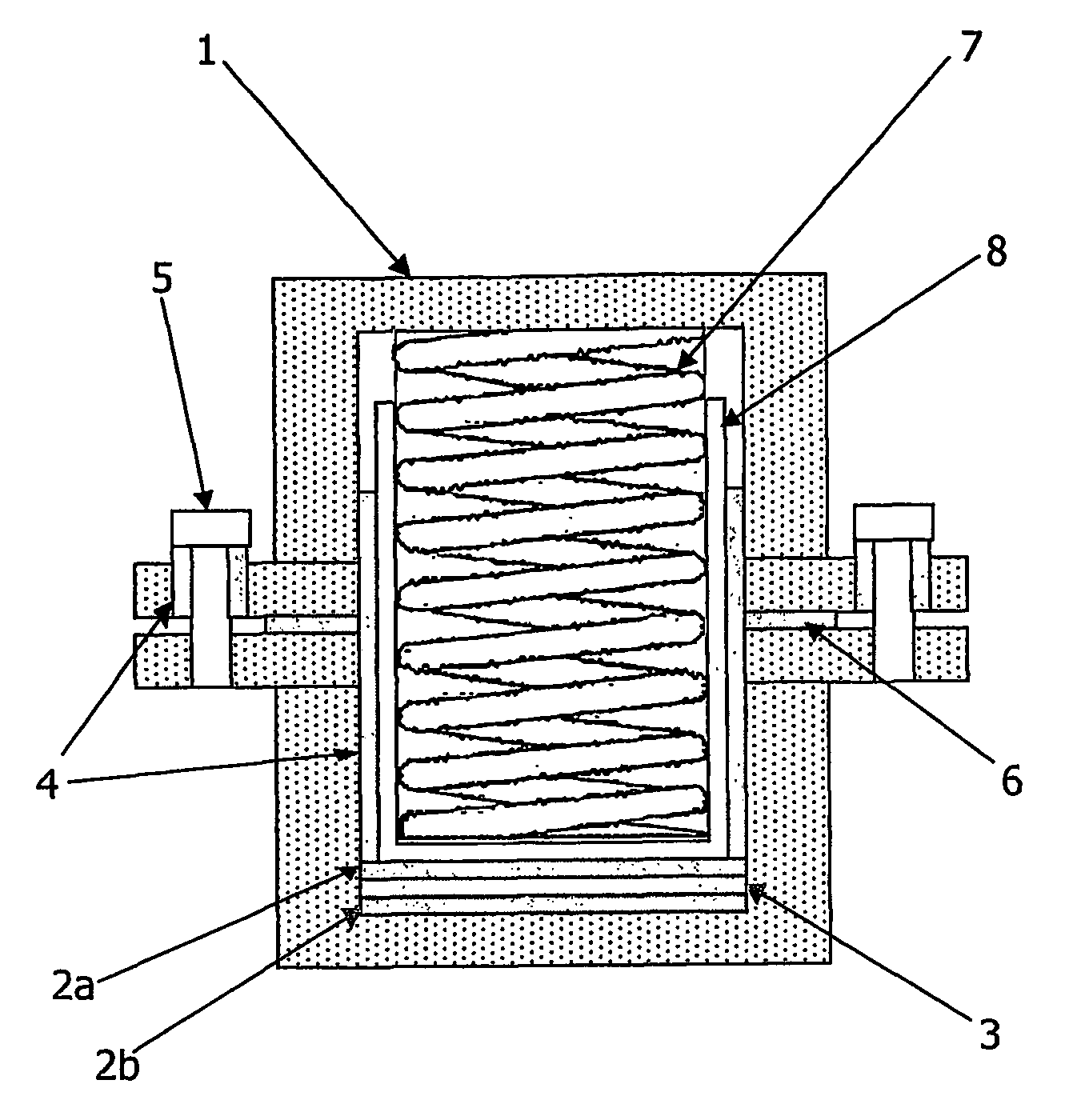
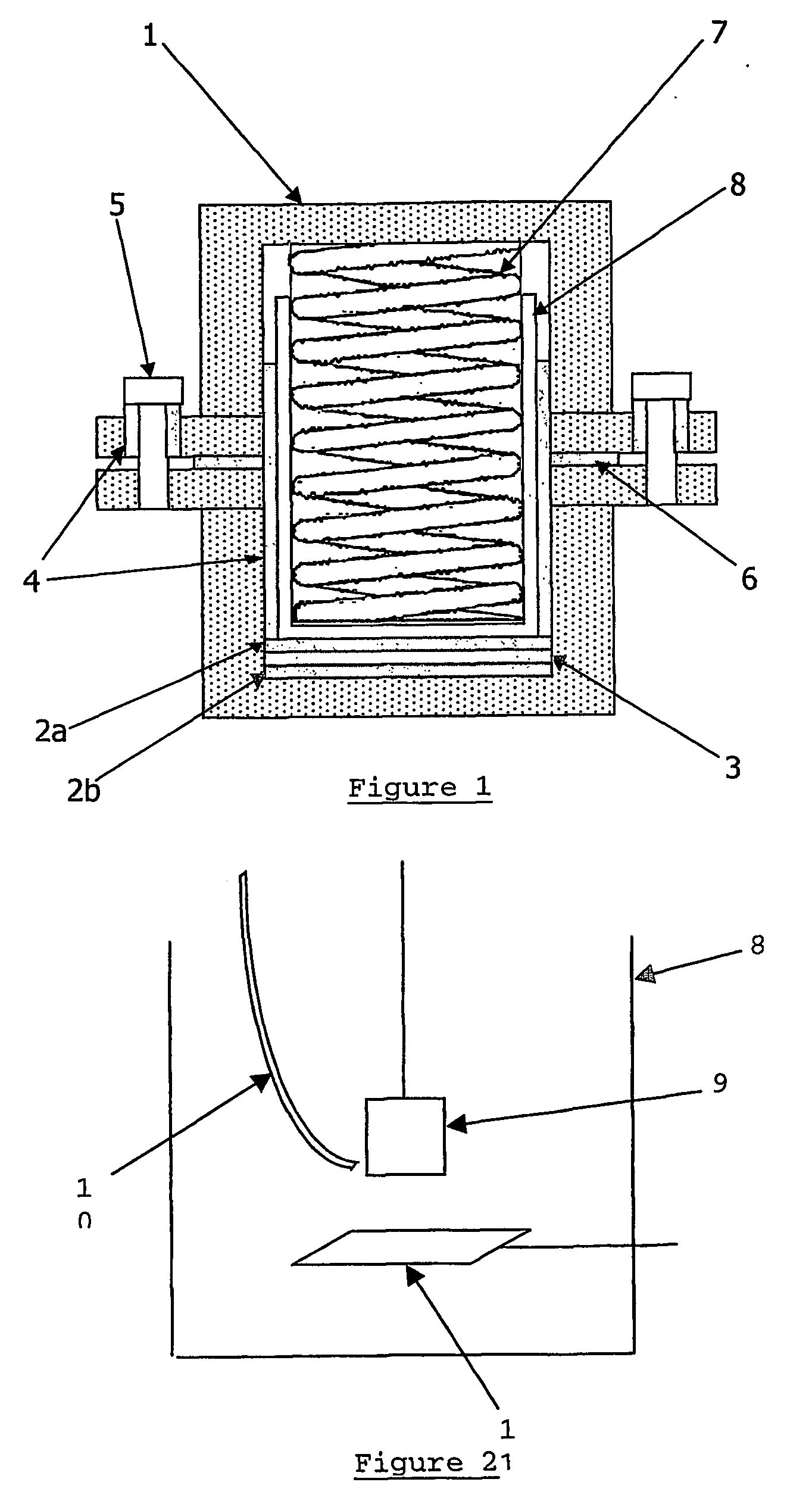
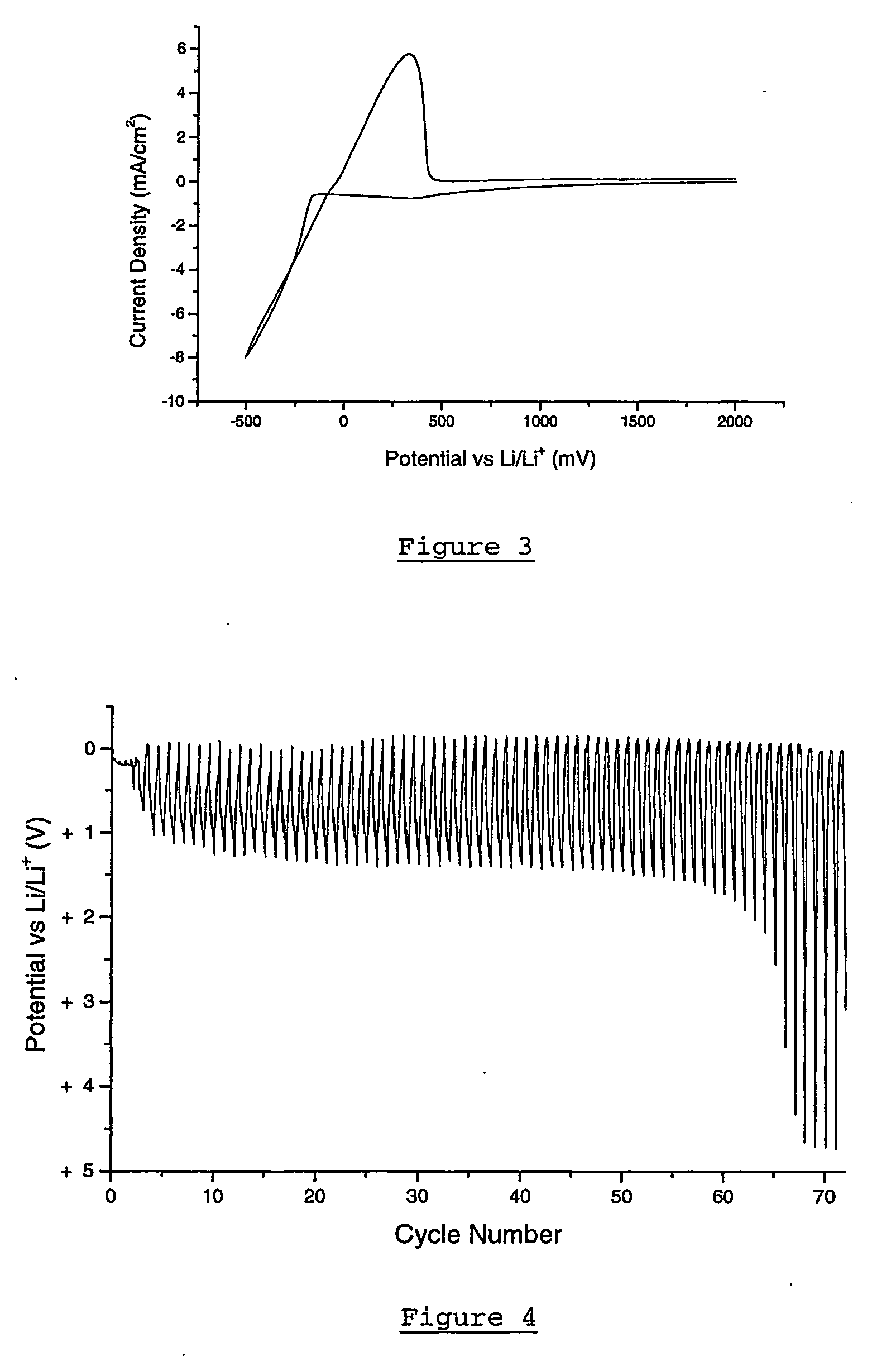
Patents
Literature
1086results about How to "Uniform deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
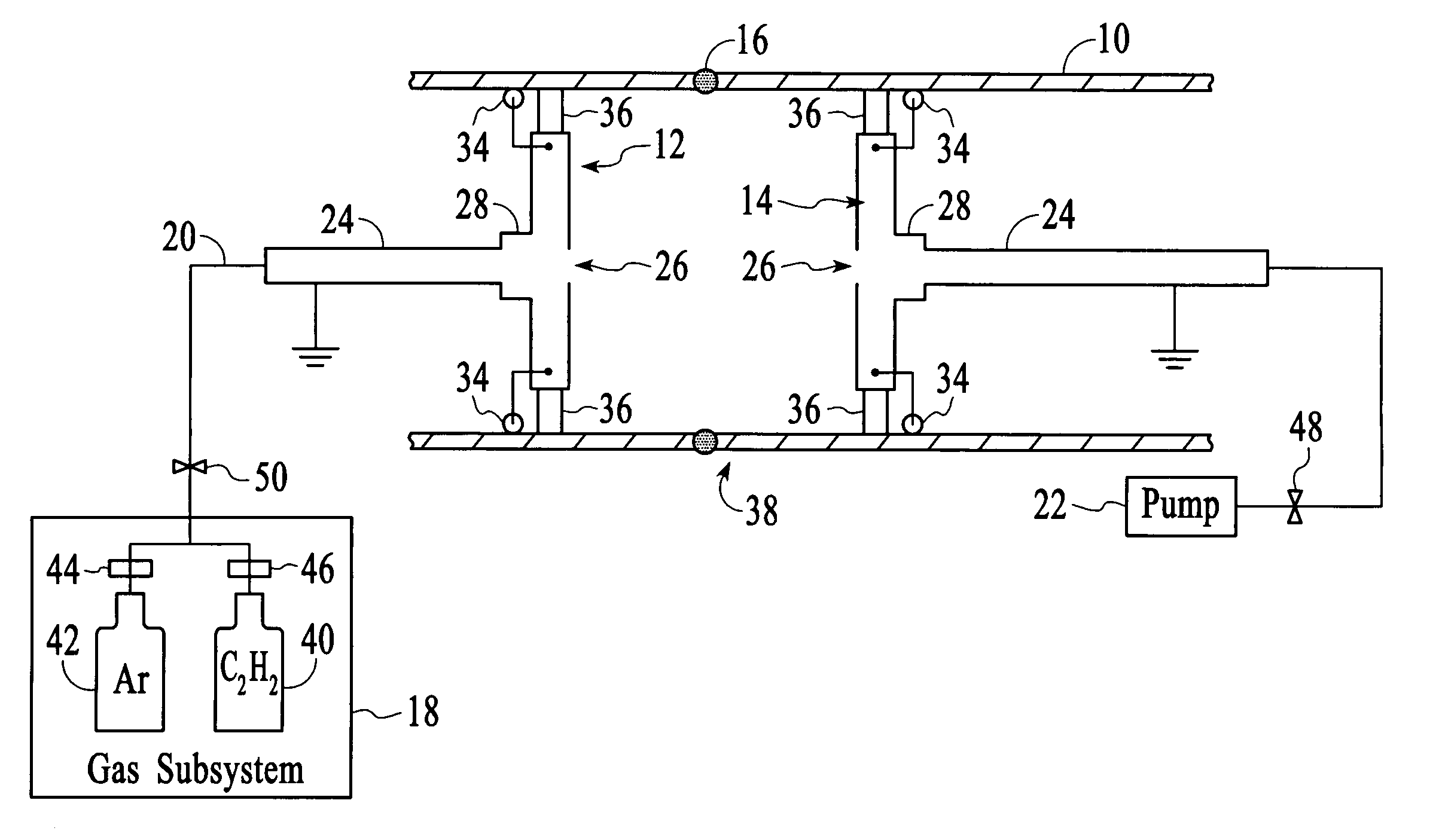
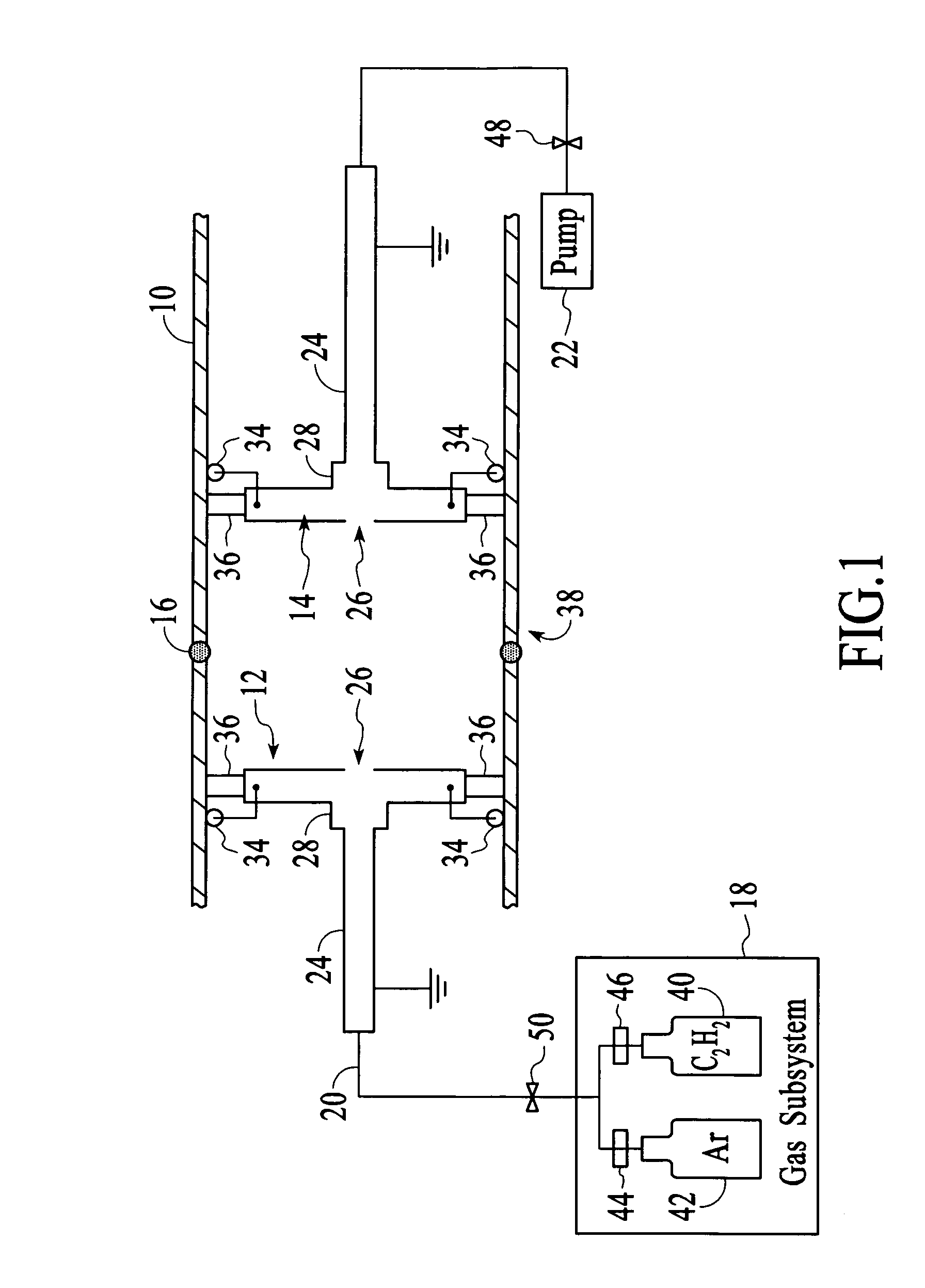
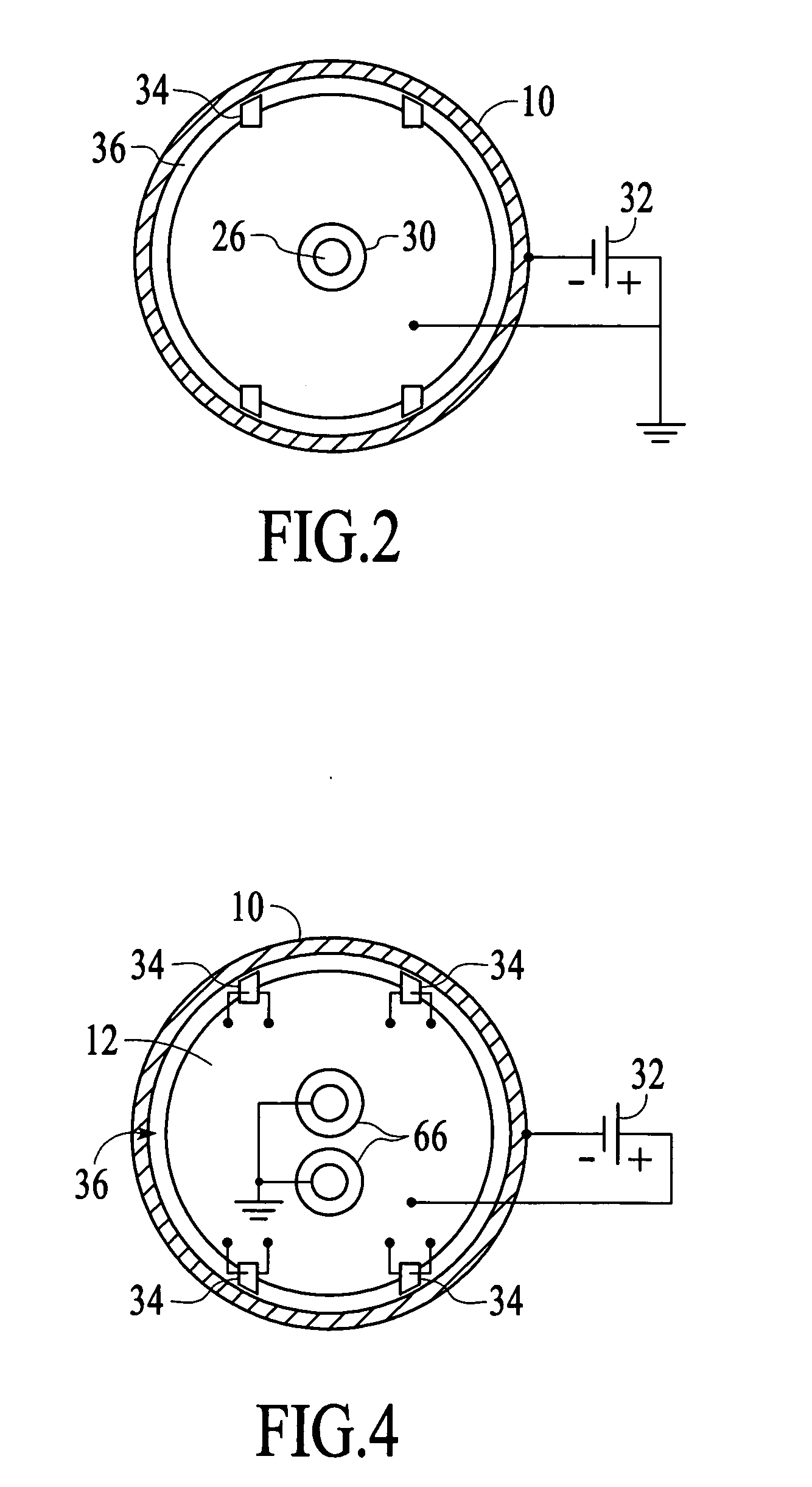
Substrate transfer apparatus and thin film deposition apparatus having the same
InactiveUS20150122180A1Accurately and sequentially transferringEfficient transferVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEngineering
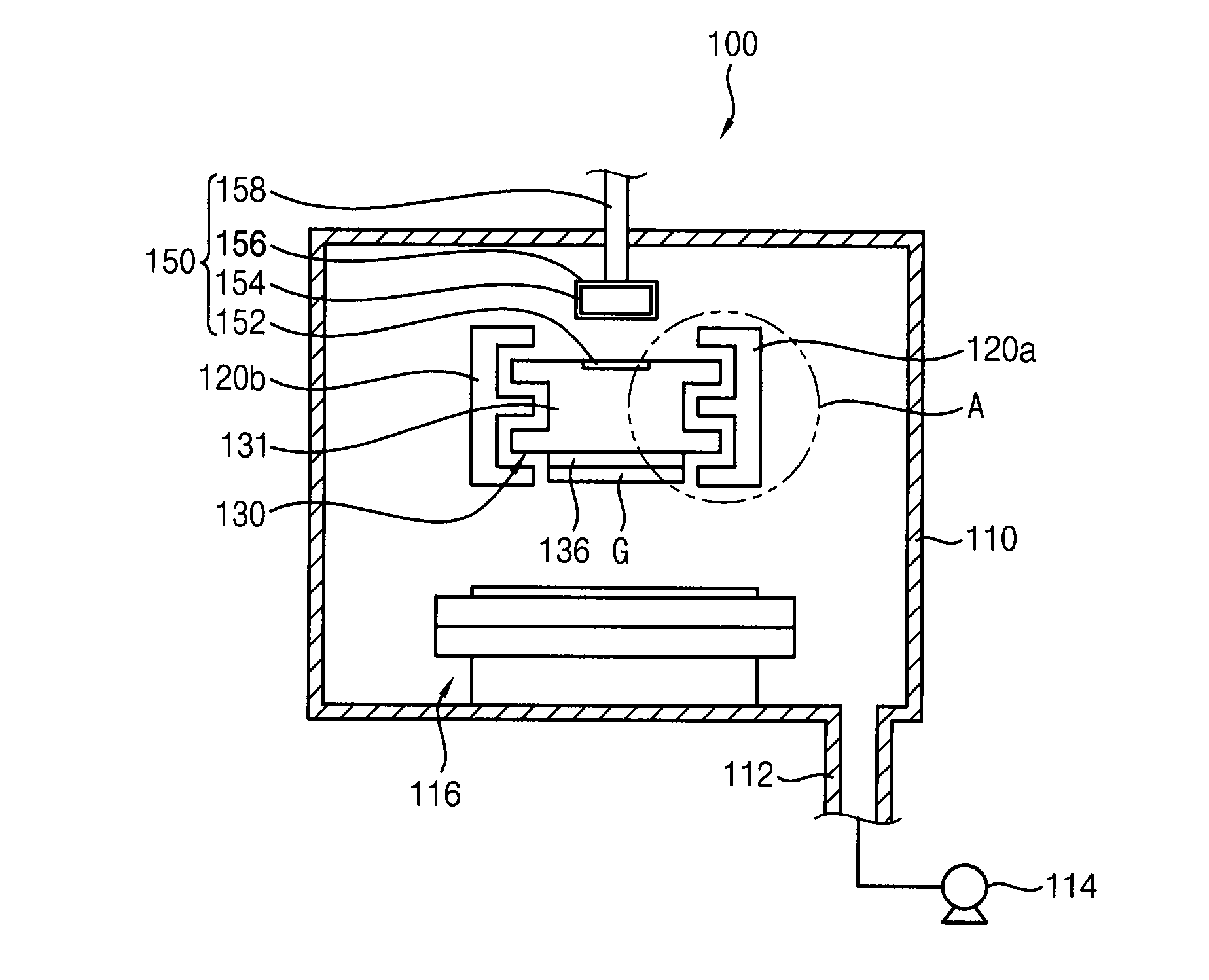
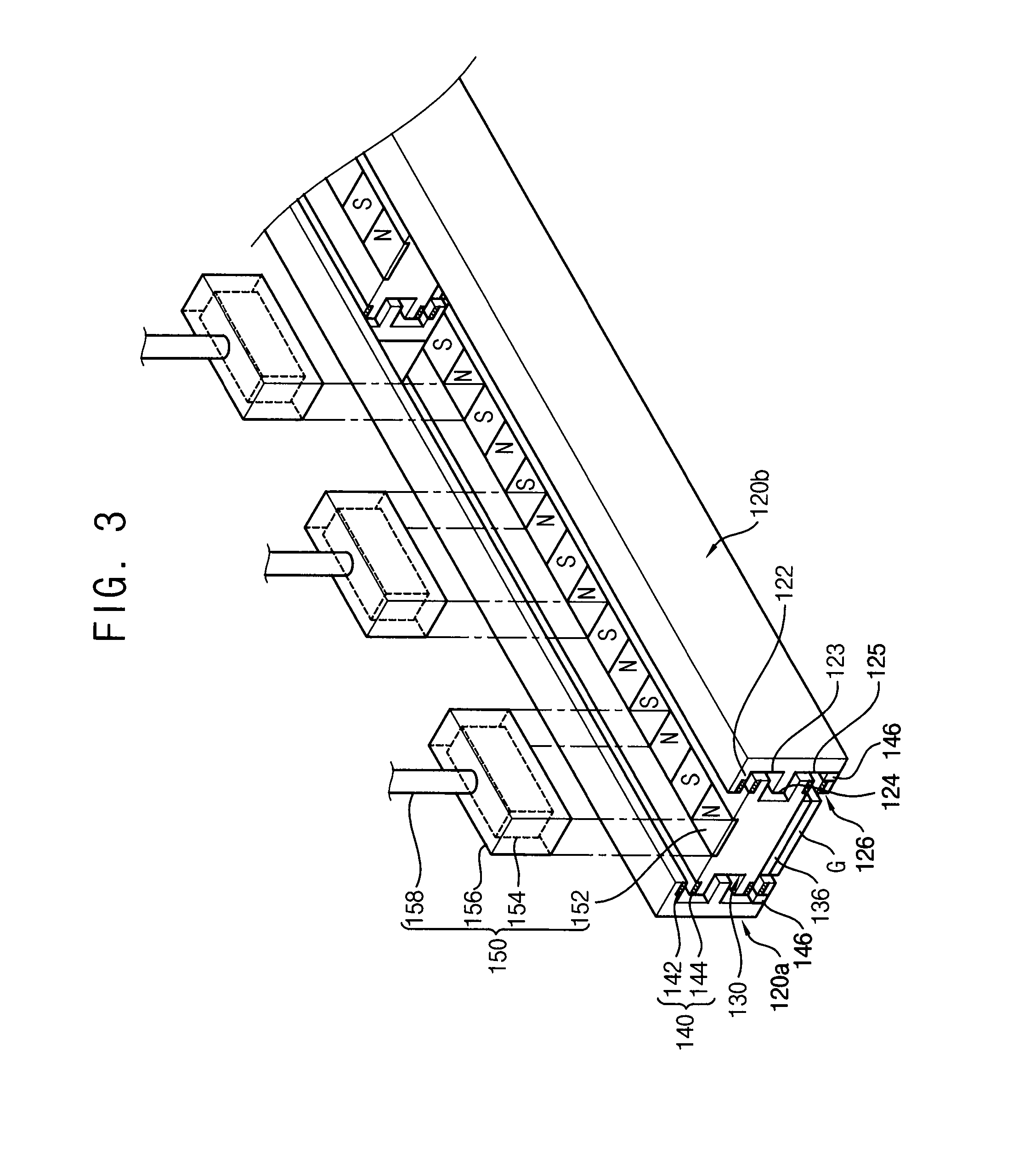
A substrate transfer apparatus includes a guide rail, a carrier, a magnetic levitation unit, and a transferring unit. The guide rail is in a vacuum evacuable chamber. The carrier may carry a substrate and may be linearly movable along the guide rail. The magnetic levitation unit is configured to generate a magnetic levitation force between the guide rail and the carrier. The transferring unit is configured to generate a momentum for linearly transferring the carrier and includes a plurality of first transferring magnetic material members on an upper surface of the carrier, a plurality of second transferring magnetic material members over the carrier and spaced apart from the first transferring magnetic material members, and a plurality of containers in which the plurality of second transferring magnetic material members is respectively disposed.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Co-evaporation system comprising vapor pre-mixer
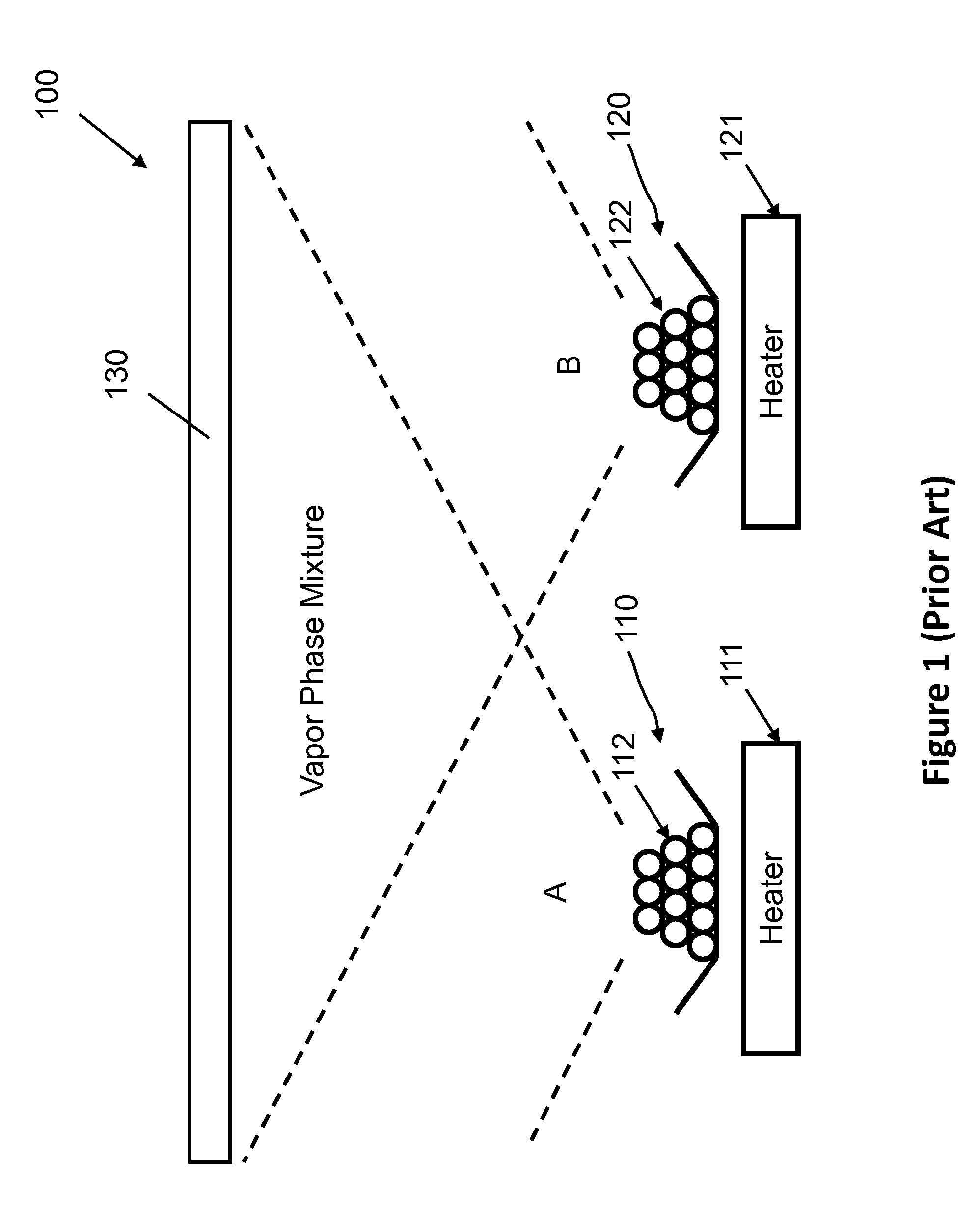
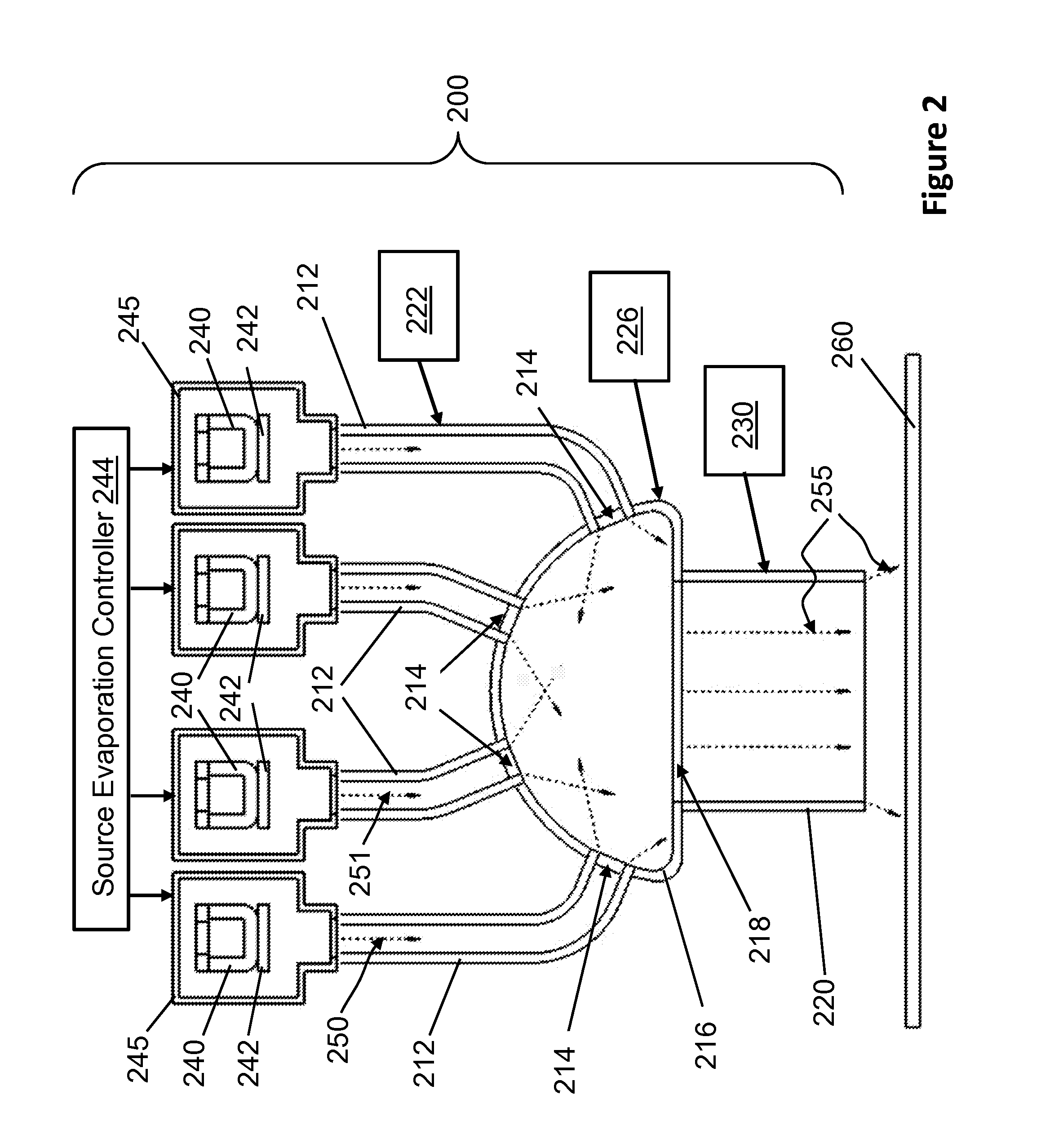
InactiveUS20130302520A1Uniform depositionUniform composition ratioVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSource materialEvaporation
A processing system for depositing a plurality of source materials on a substrate, includes a first thermal evaporation source that can evaporate a first source material to produce a first vapor, a second thermal evaporation source that can evaporate a second source material to produce a second vapor, a vapor mixing chamber that allows the first vapor and the second vapor to be mixed to produce a mixed vapor, and conduits that can separately transport the first vapor and the second vapor to the vapor mixing chamber. The mixed vapor can be directed toward a substrate to deposit a mixture of the first source material and the second source material on the substrate. The processing system can also include vapor filters configured to regulate flows of the first vapor and the second vapor, and a mixed vapor filter to regulate flow of the mixed vapor.
Owner:WANG KAI AN +4
Method of forming a silicon nitride layer
ActiveUS7229502B2Uniform thicknessReduce internal stressVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNitrogenEngineering
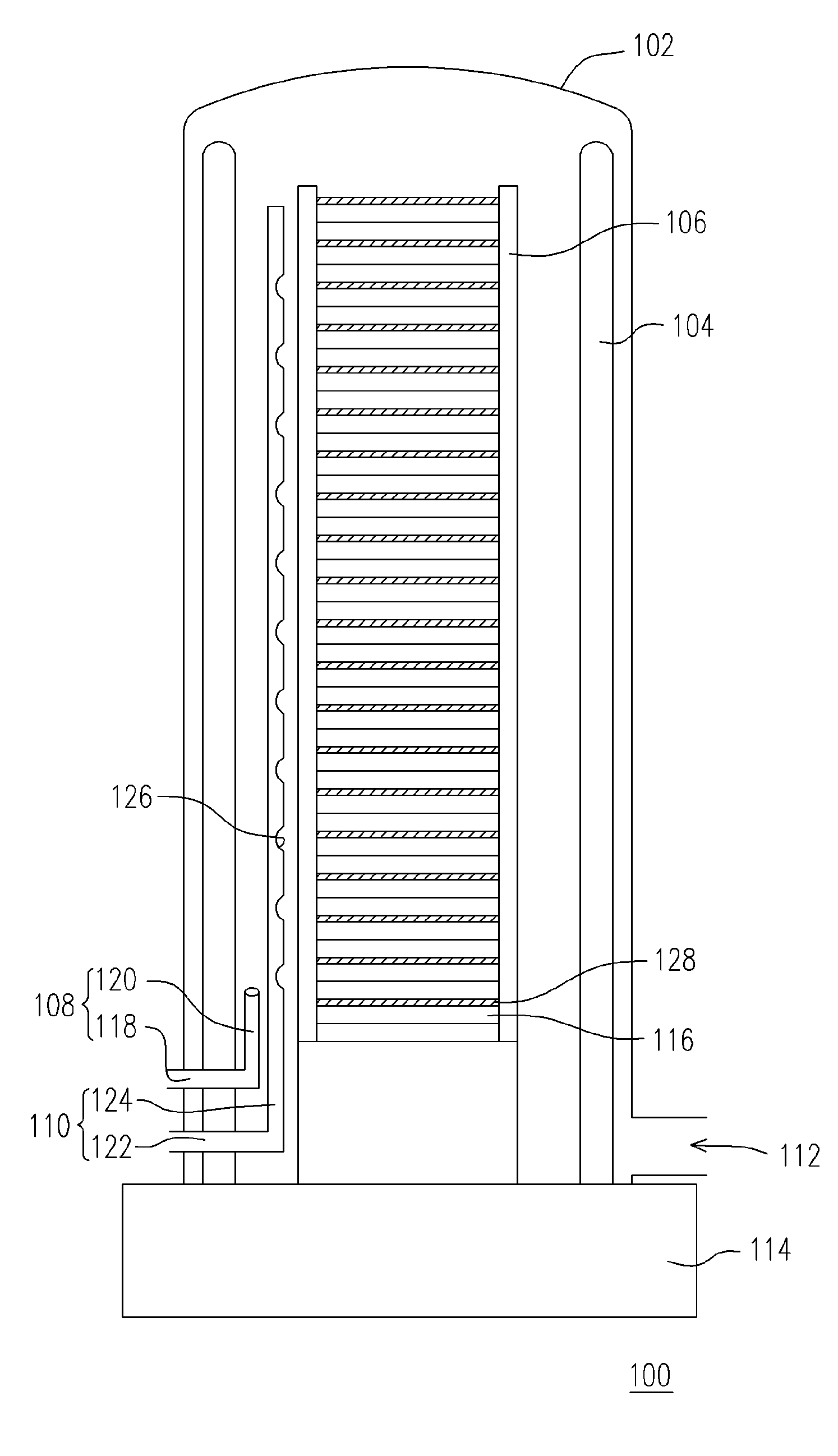
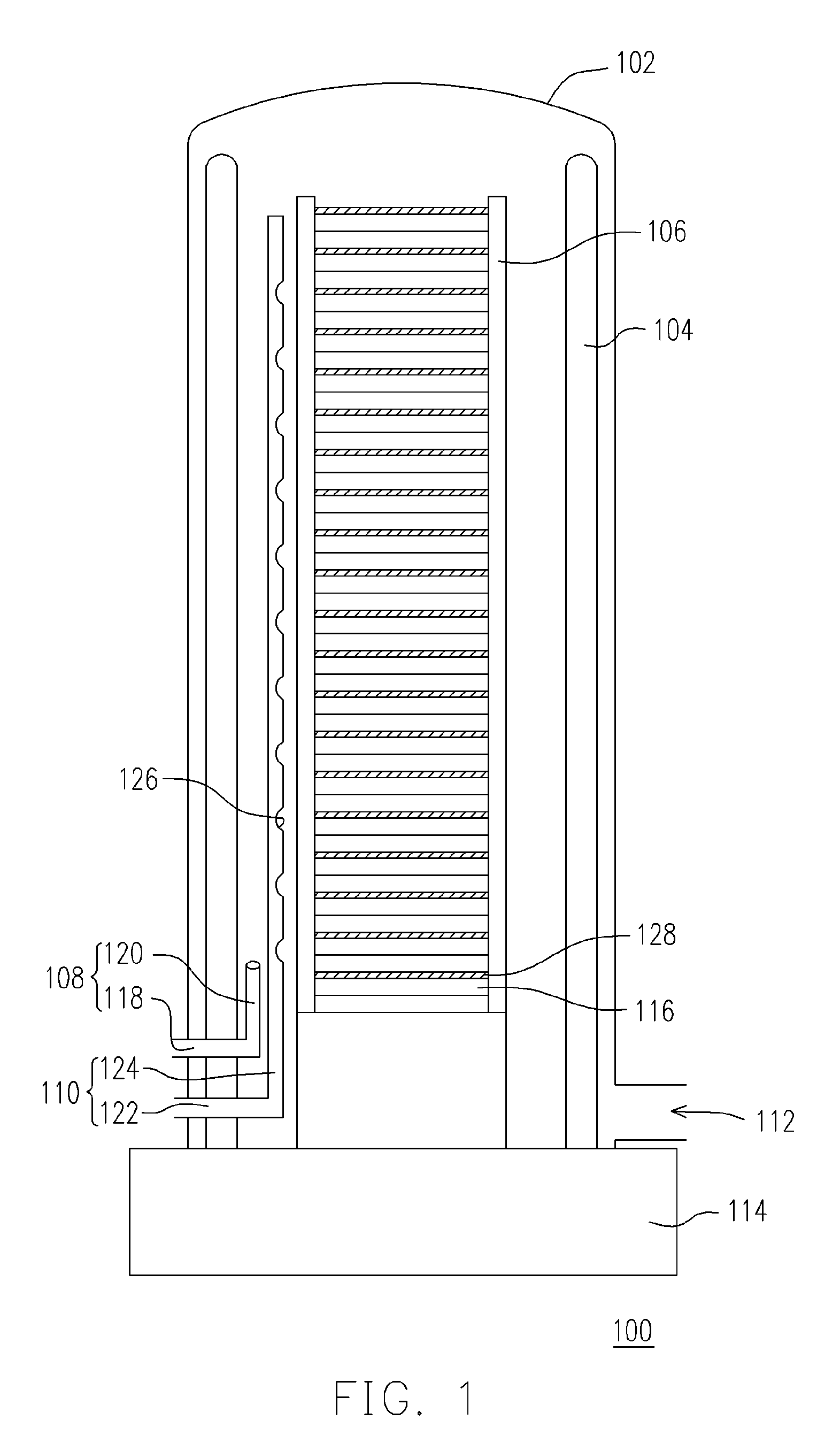
A method of forming a silicon nitride layer is provided. A deposition furnace having an outer tube, a wafer boat, a gas injector and a uniform gas injection apparatus is provided. The wafer boat is positioned within the outer tube for carrying a plurality of wafers. The gas injector is positioned between the outer tube and the wafer boat. Similarly, the uniform gas injection apparatus is positioned between the outer tube and the wafer boat. Gas injected into the uniform gas injection apparatus is uniformly distributed throughout the entire deposition furnace. To form a silicon nitride layer on each wafer, a silicon-containing gas is passed into the deposition furnace via the gas injector and a nitrogen-mixed carrier gas is passed into the deposition furnace via the uniform gas injection apparatus.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
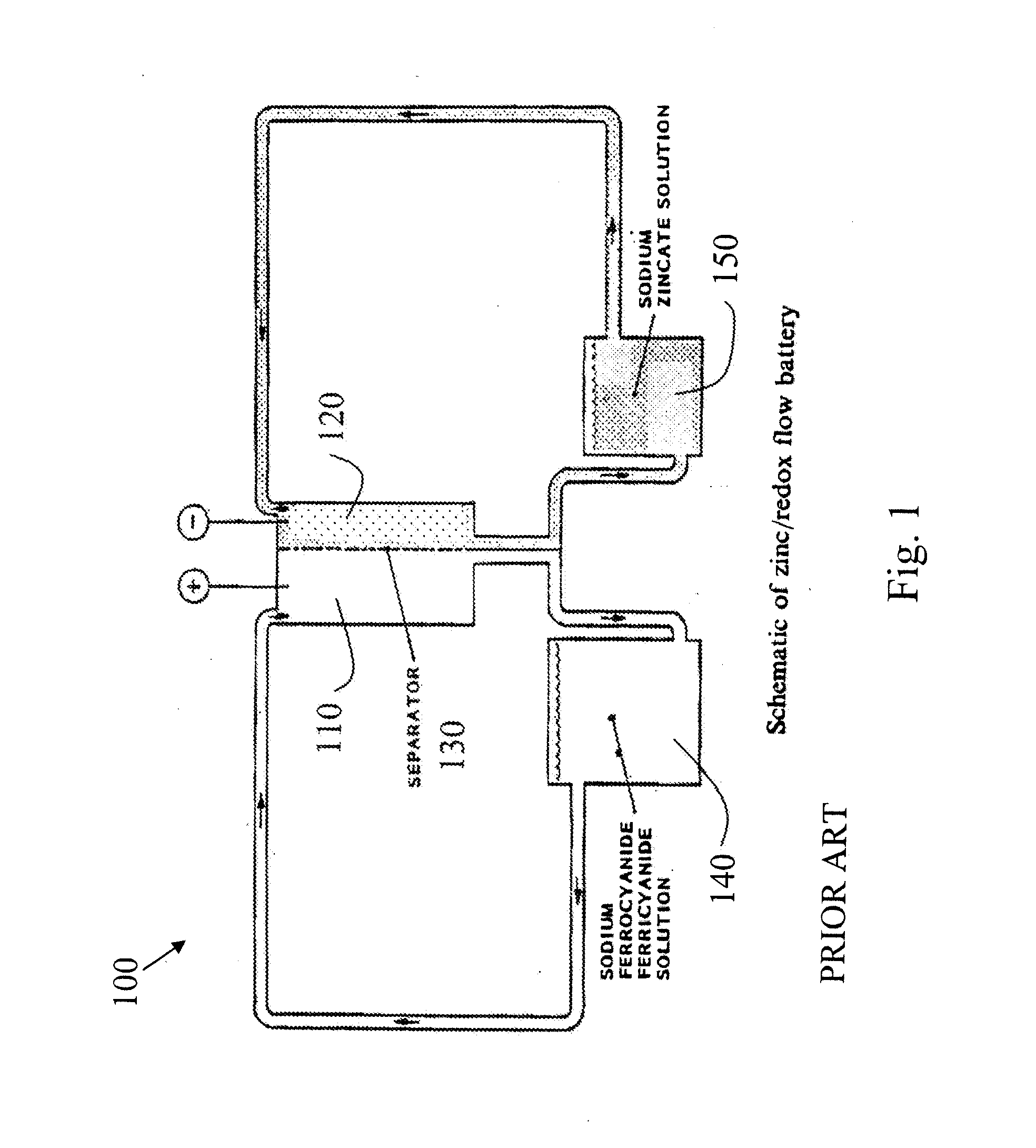
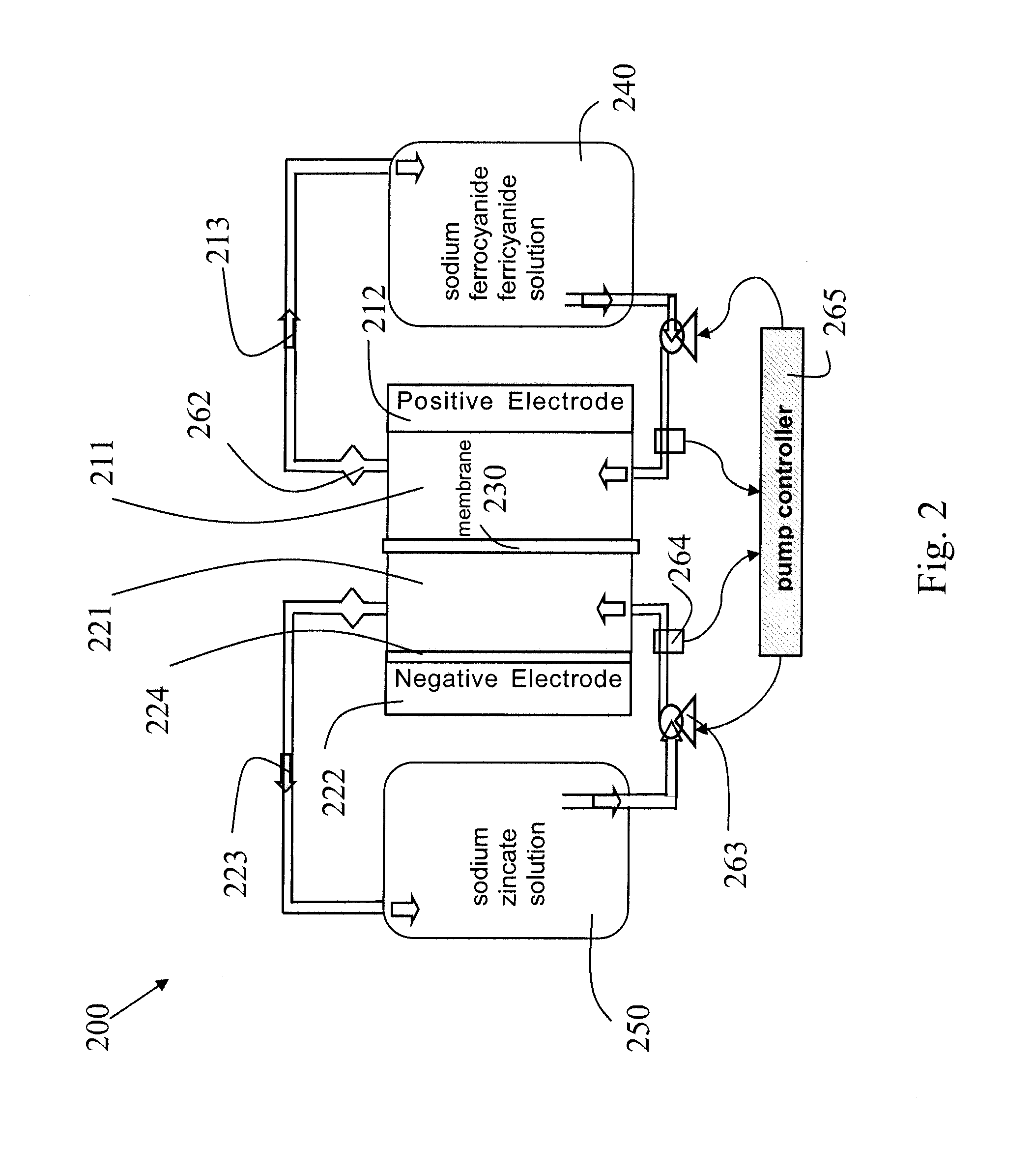
High performance flow battery
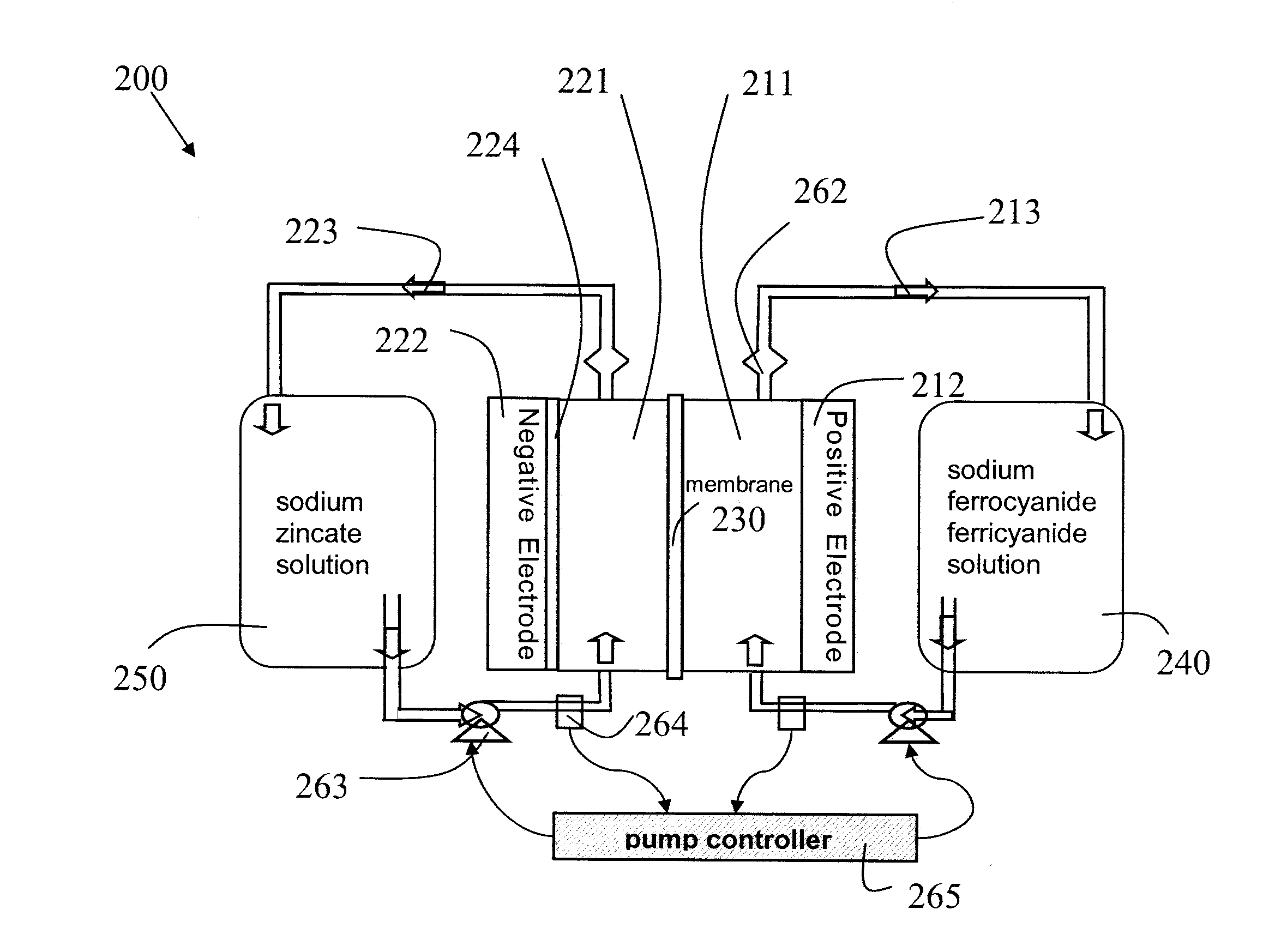
InactiveUS20110244277A1High performanceImprove the level ofElectrolyte moving arrangementsIndirect fuel cellsFerricyanideIon
High performance flow batteries, based on alkaline zinc / ferro-ferricyanide rechargeable (“ZnFe”) and similar flow batteries, may include one or more of the following improvements. First, the battery design has a cell stack comprising a low resistance positive electrode in at least one positive half cell and a low resistance negative electrode in at least one negative half cell, where the positive electrode and negative electrode resistances are selected for uniform high current density across a region of the cell stack. Second, a flow of electrolyte, such as zinc species in the ZnFe battery, with a high level of mixing through at least one negative half cell in a Zn deposition region proximate a deposition surface where the electrolyte close to the deposition surface has sufficiently high zinc concentration for deposition rates on the deposition surface that sustain the uniform high current density. The mixing in the flow may be induced by structures such as: conductive and non-conductive meshes; screens; ribbons; foam structures; arrays of cones, cylinders, or pyramids; and other arrangements of wires or tubes used solely or in combination with a planar electrode surface. Third, the zinc electrolyte has a high concentration and in some embodiments has a concentration greater than the equilibrium saturation concentration—the zinc electrolyte is super-saturated with Zn ions.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Assembly and method for delivering a reactant material onto a substrate
InactiveUS20070166459A1Facilitate depositionFacilitate chemical reactionsChemical vapor deposition coatingBiomedical engineering
An assembly and method for delivering a reactant material onto a substrate is described and which includes a delivery member which has a first surface, and an opposite second surface, and wherein the second surface is positioned adjacent to a substrate, and wherein an elongated substantially continuous channel is formed in the second surface of the delivery member, and which is coupled in fluid flowing relation relative to a source of reactant material, and wherein the elongated substantially continuous channel delivers the reactant material onto the substrate.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO-FABRICATION EQUIP INC ASIA
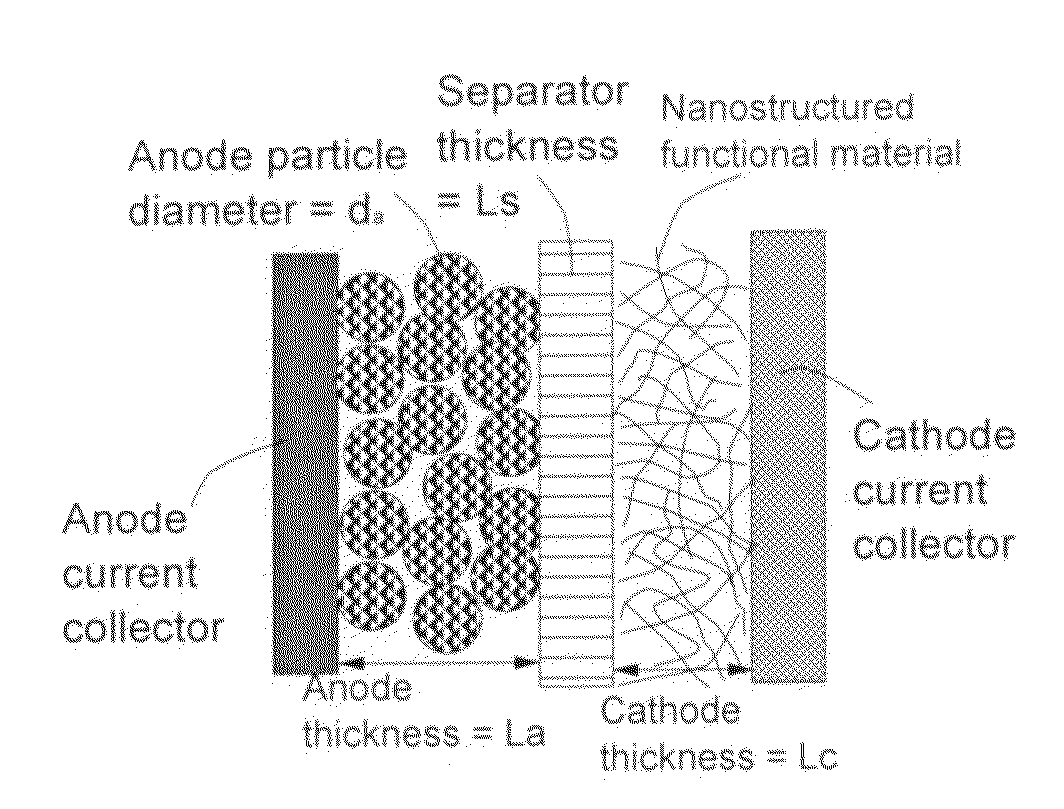
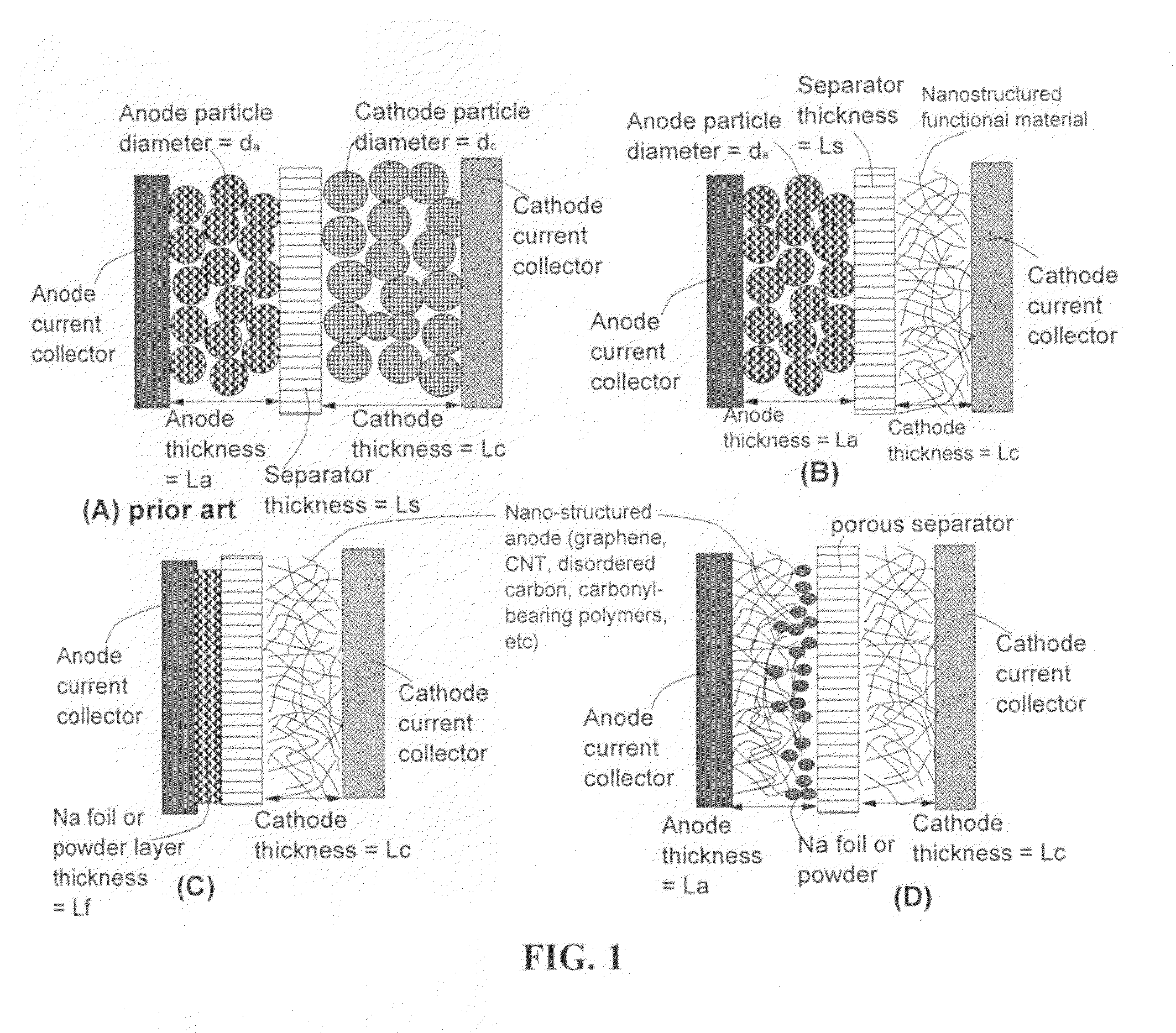
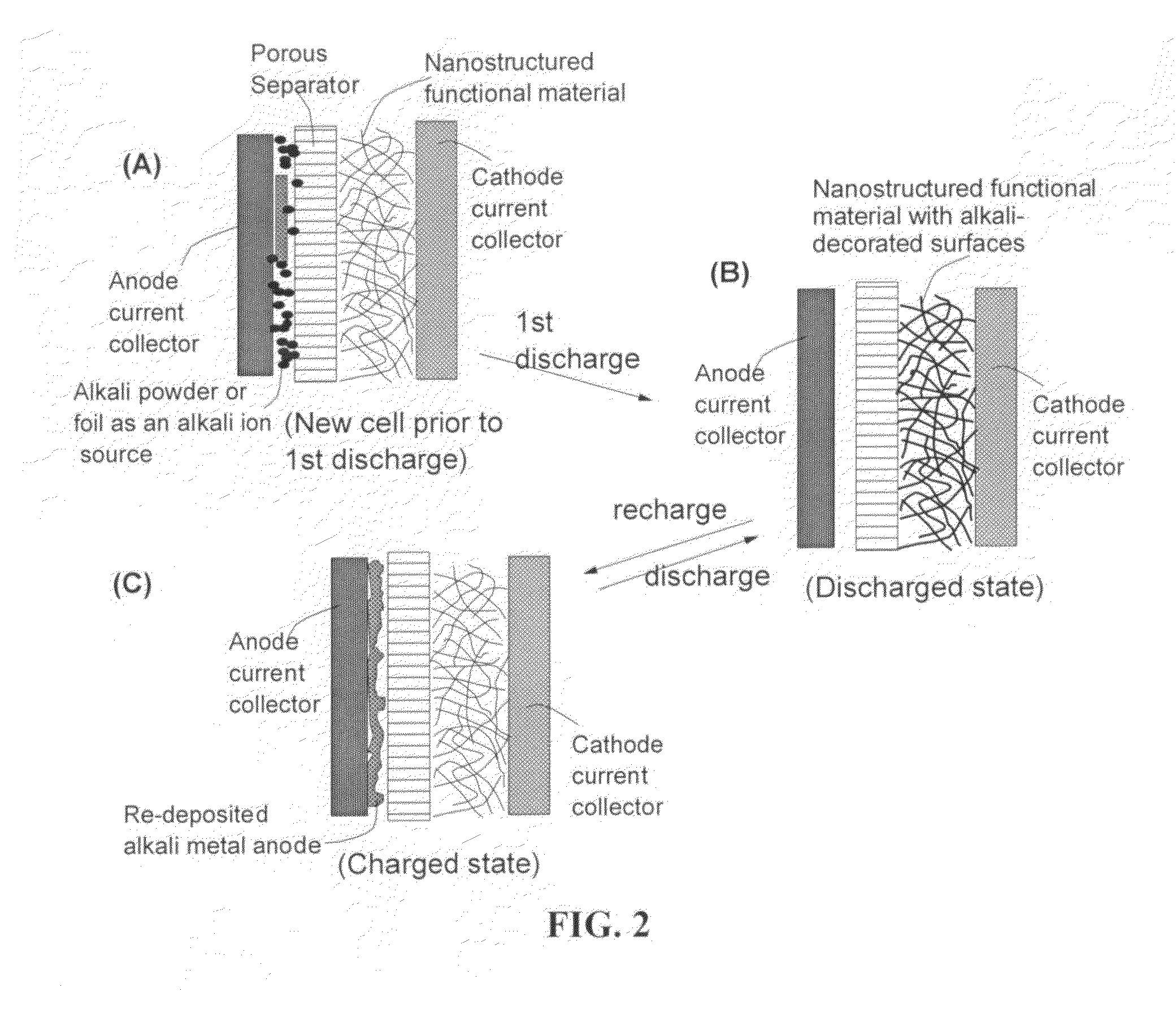
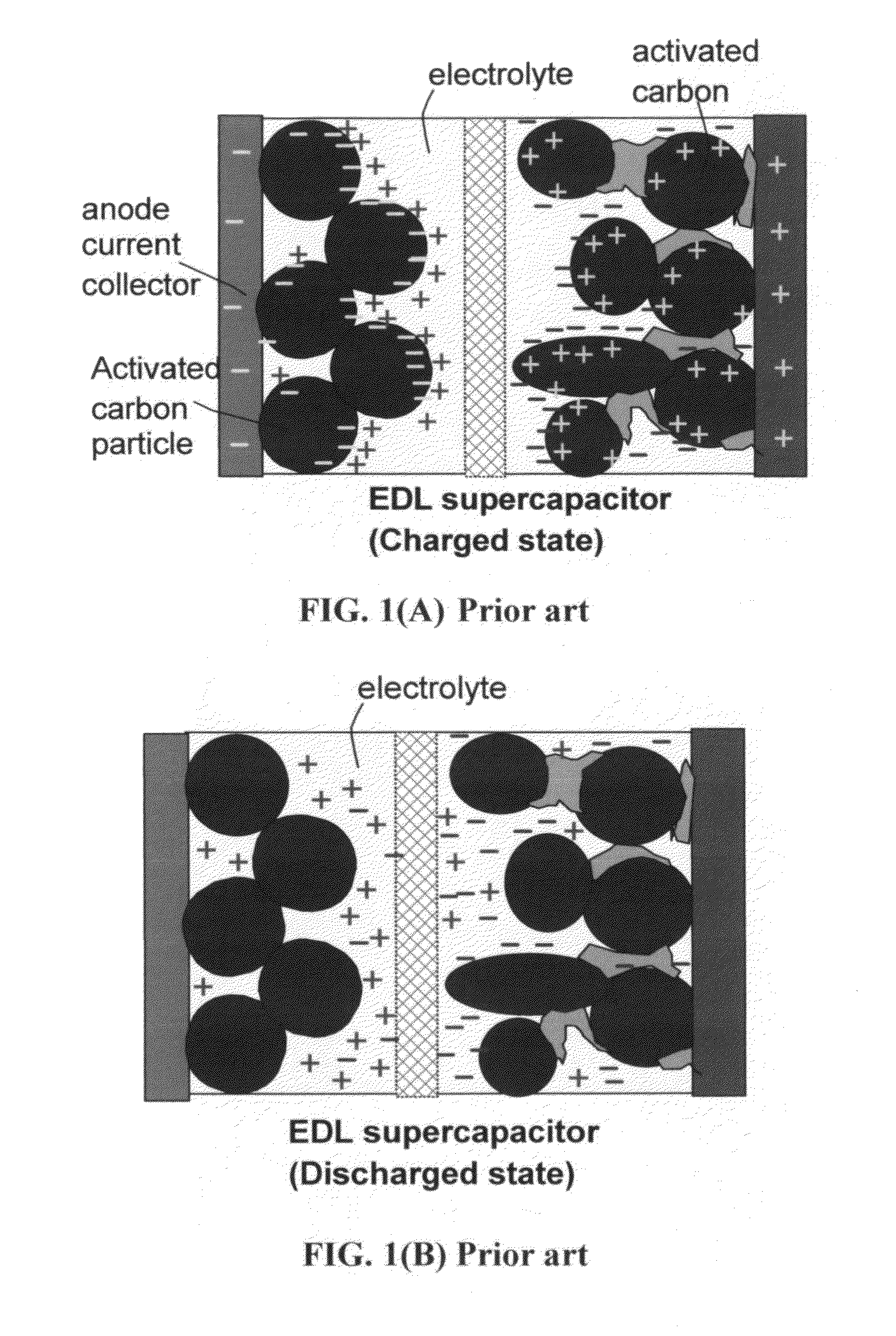
Partially and fully surface-enabled metal ion-exchanging energy storage devices
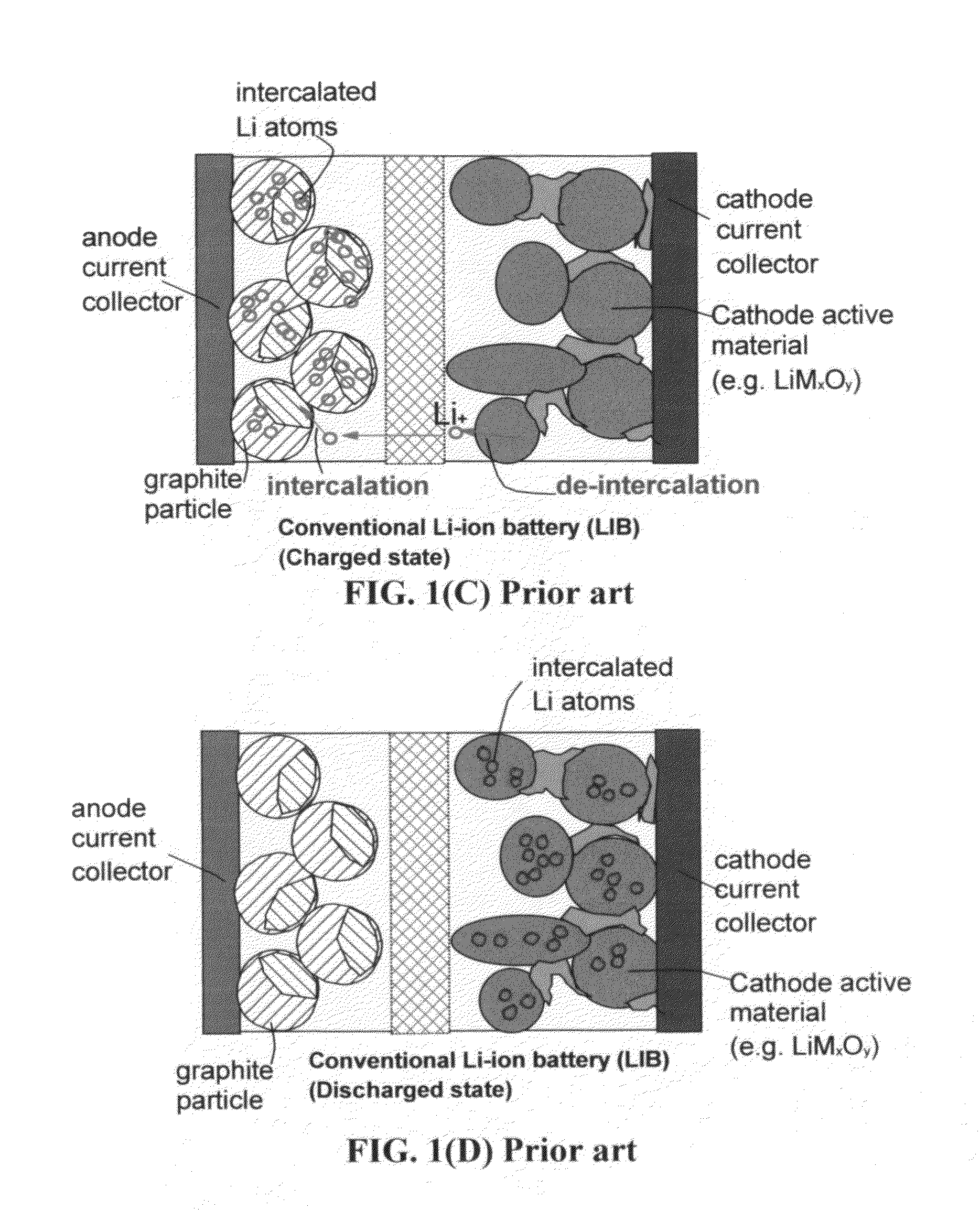
ActiveUS20120171574A1Eliminates potential formation of dendriteUniform depositionMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrolytesIon exchangeLithium electrode
A surface-enabled, metal ion-exchanging battery device comprising a cathode, an anode, a porous separator, and a metal ion-containing electrolyte, wherein the metal ion is selected from (A) non-Li alkali metals; (B) alkaline-earth metals; (C) transition metals; (D) other metals such as aluminum (Al); or (E) a combination thereof; and wherein at least one of the electrodes contains therein a metal ion source prior to the first charge or discharge cycle of the device and at least the cathode comprises a functional material or nano-structured material having a metal ion-capturing functional group or metal ion-storing surface in direct contact with said electrolyte, and wherein the operation of the battery device does not involve the introduction of oxygen from outside the device and does not involve the formation of a metal oxide, metal sulfide, metal selenide, metal telluride, metal hydroxide, or metal-halogen compound. This energy storage device has a power density significantly higher than that of a lithium-ion battery and an energy density dramatically higher than that of a supercapacitor.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Method and system for coating internal surfaces using reverse-flow cycling
InactiveUS20060198965A1Provide uniformity in coatingEfficiently coat workpieceSolid state diffusion coatingChemical vapor deposition coatingControl systemMechanical engineering
A method and system for coating the internal surfaces of a workpiece is presented. A bias voltage is connected to a workpiece, which functions as a cathode. A gas source and a vacuum source are coupled to each opening through a flow control system. The flow control system is capable of a first mode which enables a first opening to function as a gas inlet and a second opening to function as a vacuum exhaust. The flow control system also has a second mode which enables a first opening to function as a vacuum exhaust and a second opening to function as a gas inlet. The cycling may also be used to coat internal surfaces of a workpiece with a single opening. Cycling the flow control system between the first mode and second mode is performed until a uniform coating along the internal surfaces of the workpiece is achieved.
Owner:SUB ONE TECH
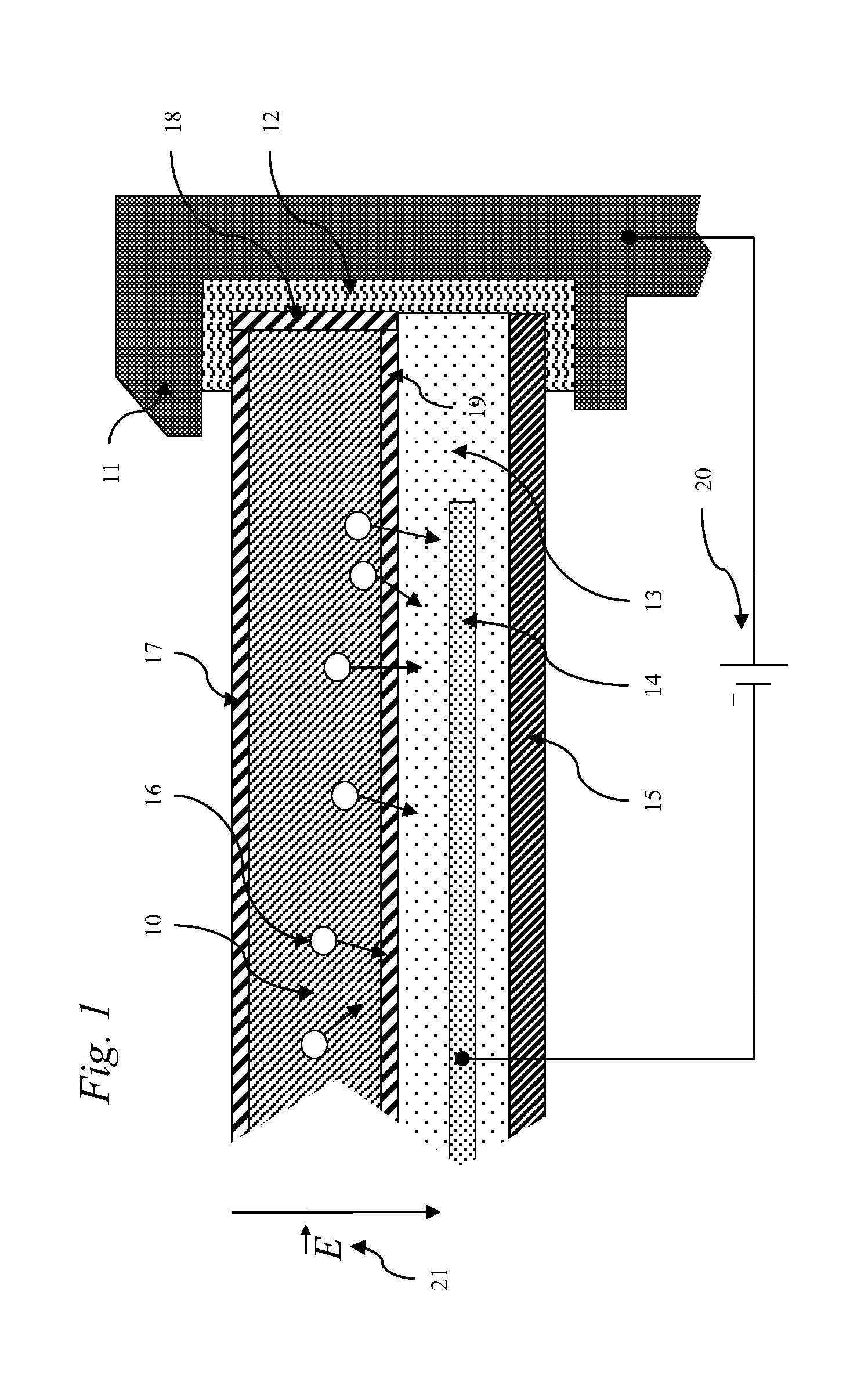
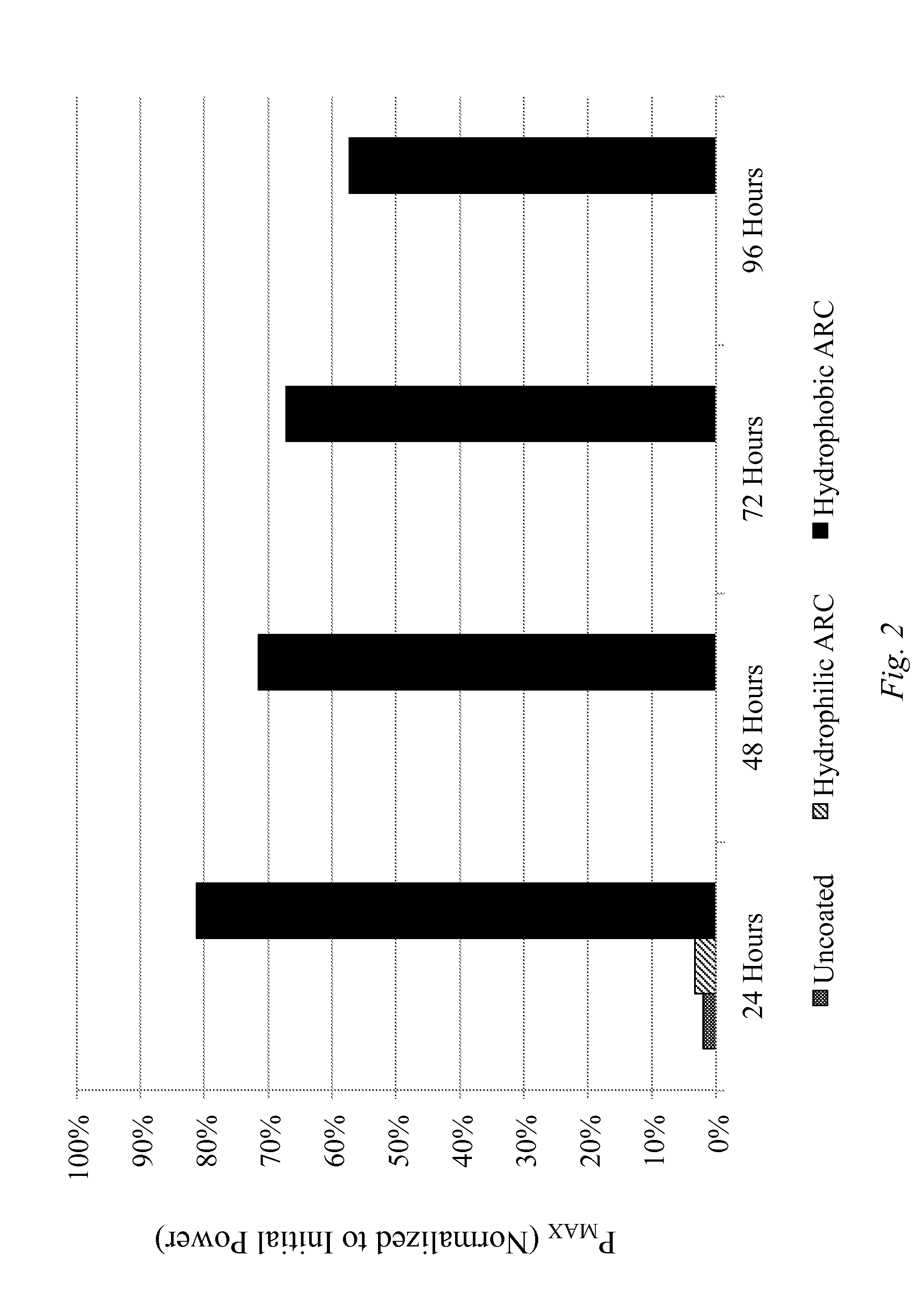
Anti-Reflective and Anti-Soiling Coatings with Self-Cleaning Properties
ActiveUS20120040179A1Evenly distributedUniform depositionLayered productsRecord information storageSoil propertiesSilanes
The embodiments of the invention are directed to coatings and their uses. More particularly, the embodiments of the invention are directed to coating compositions that include silane-based precursors that are used to form coatings through a sol-gel process. The coatings so formed are characterized by anti-reflective, abrasion resistant, and anti-soiling properties. The coatings also have extended weatherability to heat, humidity, and protection against ambient corrosives. The coatings formed from the compositions described herein have wide application, including, for example, use as coatings on the outer glass of solar cells.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Process for PECVD of silicon oxide using TEOS decomposition
InactiveUSRE36623E1Eliminate depositsAvoid failureElectric discharge tubesPretreated surfacesHigh rateSilicon oxide
A high pressure, high throughput, single wafer, semiconductor processing reactor is disclosed which is capable of thermal CVD, plasma-enhanced CVD, plasma-assisted etchback, plasma self-cleaning, and deposition topography modification by sputtering, either separately or as part of in-situ multiple step processing. The reactor includes cooperating arrays of interdigitated susceptor and wafer support fingers which collectively remove the wafer from a robot transfer blade and position the wafer with variable, controlled, close parallel spacing between the wafer and the chamber gas inlet manifold, then return the wafer to the blade. A combined RF / gas feed-through device protects against process gas leaks and applies RF energy to the gas inlet manifold without internal breakdown or deposition of the gas. The gas inlet manifold is adapted for providing uniform gas flow over the wafer. Temperature-controlled internal and external manifold surfaces suppress condensation, premature reactions and decomposition and deposition on the external surface. The reactor also incorporates a uniform radial pumping gas system which enables uniform reactant gas flow across the wafer and directs purge gas flow downwardly and upwardly toward the periphery of the wafer for sweeping exhaust gases radially away from the wafer to prevent deposition outside the wafer and keep the chamber clean. The reactor provides uniform processing over a wide range of pressures including very high pressures. A low temperature CVD process for forming a highly conformal layer of silicon dioxide is also disclosed. The process uses very high chamber pressure and low temperature, and TEOS and ozone reactants. The low temperature CVD silicon dioxide deposition step is particularly useful for planarizing underlying stepped dielectric layers, either alone or in conjunction with a subsequent isotropic etch. A preferred in-situ multiple-step process for forming a planarized silicon dioxide layer uses (1) high rate silicon dioxide deposition at a low temperature and high pressure followed by (2) the deposition of the conformal silicon dioxide layer also at high pressure and low temperature, followed by (3) a high rate isotropic etch, preferably at low temperature and high pressure in the sane reactor used for the two oxide deposition steps. Various combinations of the steps are disclosed for different applications, as is a preferred reactor self-cleaning step.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Active cathode layer for metal-sulfur secondary battery
ActiveUS20160294000A1Perfect sulfur utilization efficiencyIncrease loadElectrode carriers/collectorsSecondary cellsLithiumPolysulfide
A preloaded cathode layer, comprising: (A) An integral porous structure having massive surfaces greater than 100 m2 / g or pores with a size from 1.0 nm to 100 nm, wherein multiple conductive particles, platelets or filaments, without a conductive filler, form a 3-D conductive network; and (B) a metal polysulfide preloaded in the pores or deposited on the massive surfaces, selected from: (a) an MxSy, (x=1-3 and y=1-10) wherein M is a metal element selected from a non-lithium alkali metal, an alkaline metal selected from Mg or Ca, a transition metal, a metal from groups 13 to 17, or a combination thereof, or (b) Li2S6, Li2S7, Li2S8, Li2S9, or Li2S10, wherein the metal polysulfide contains a thin coating or small particles with a thickness or diameter less than 20 nm and occupies a weight fraction of from 1% to 99%.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
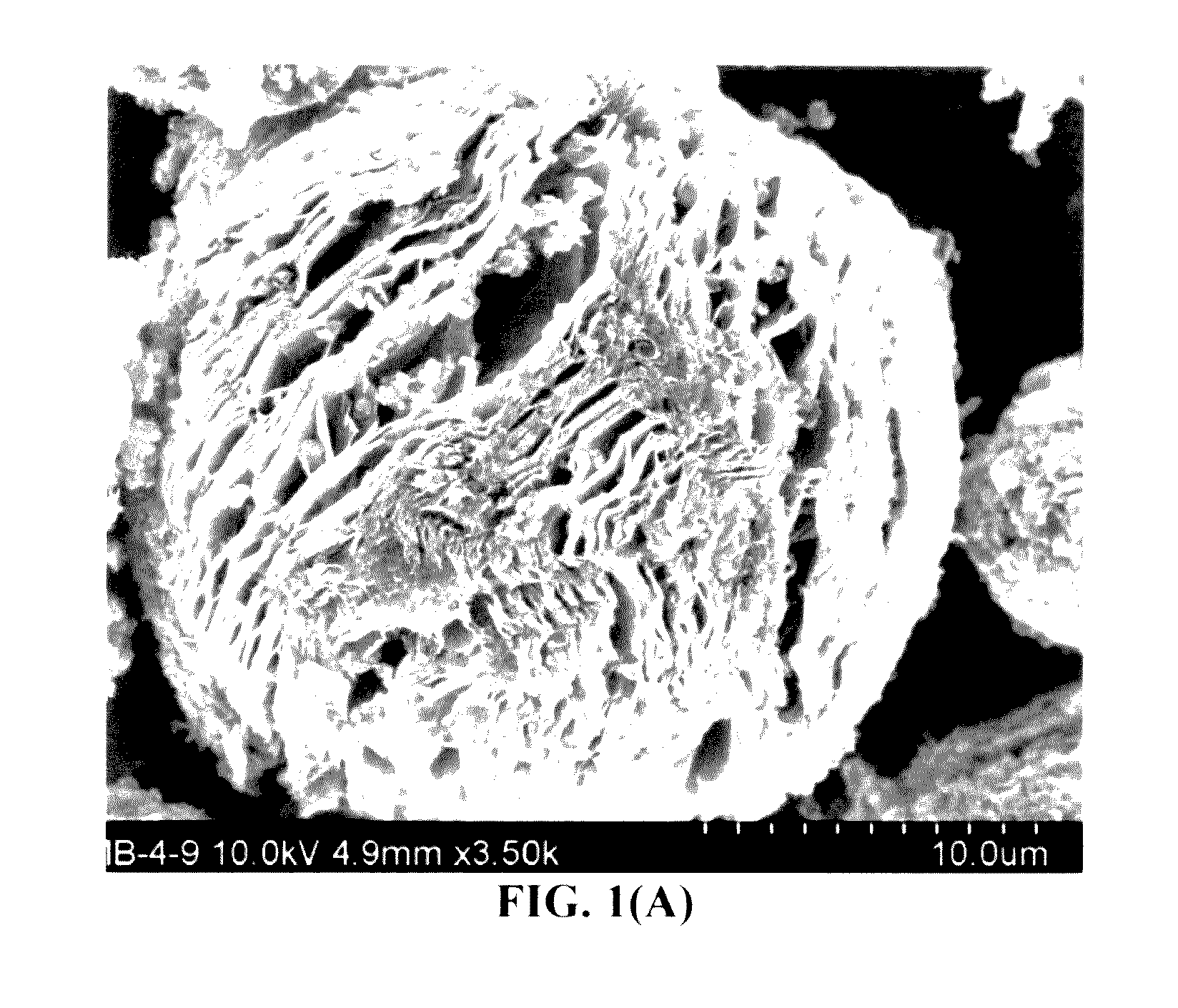
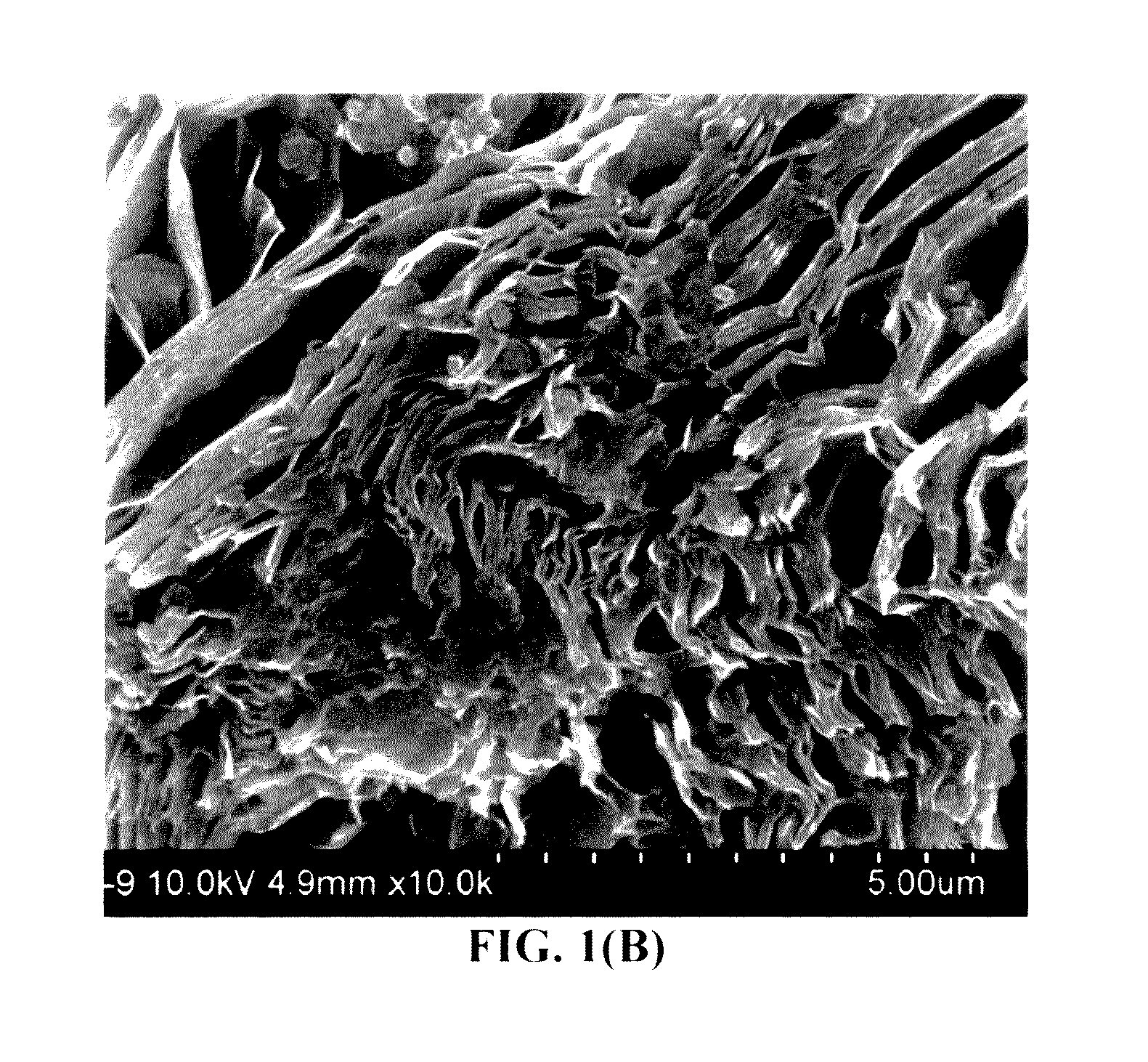
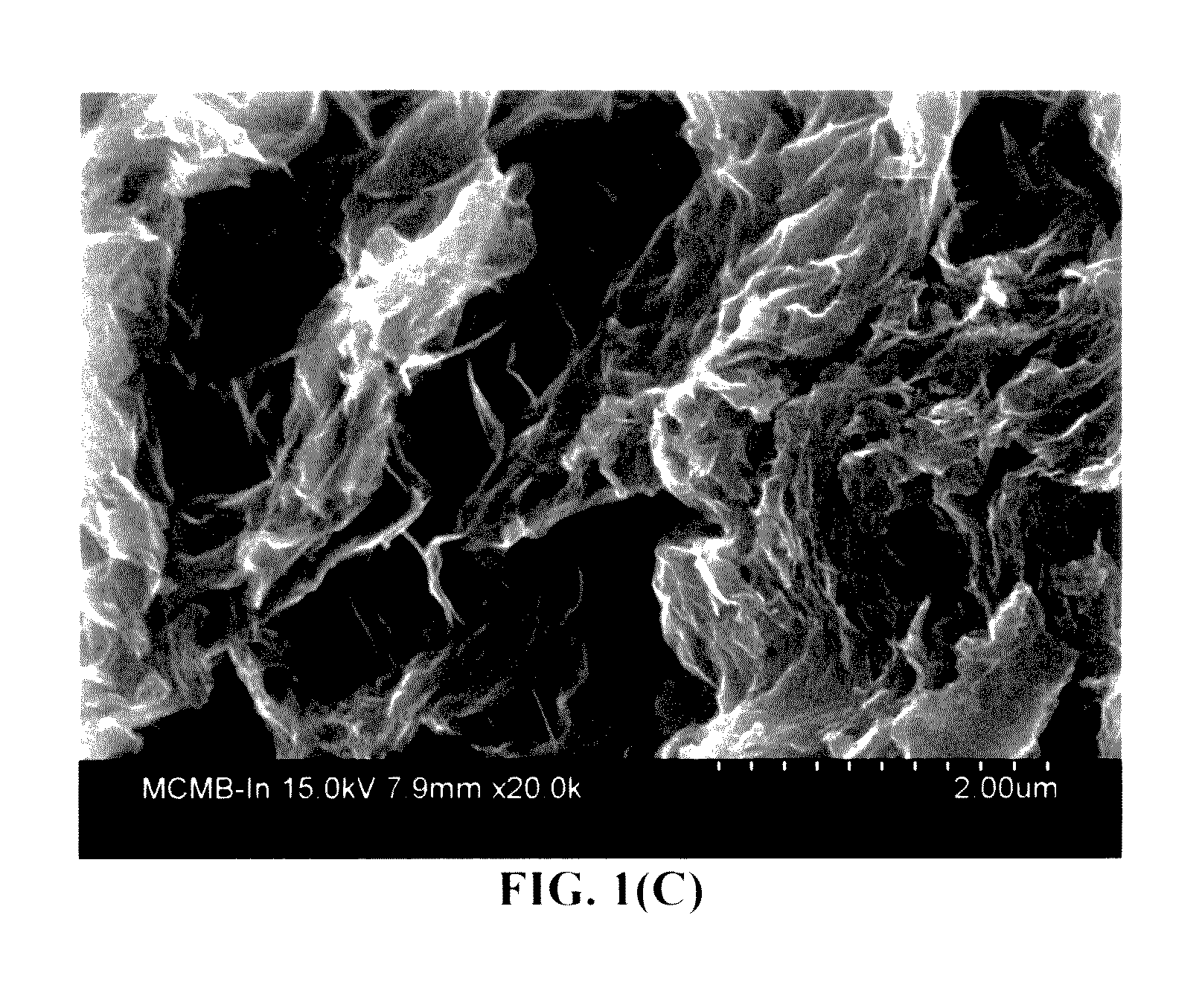
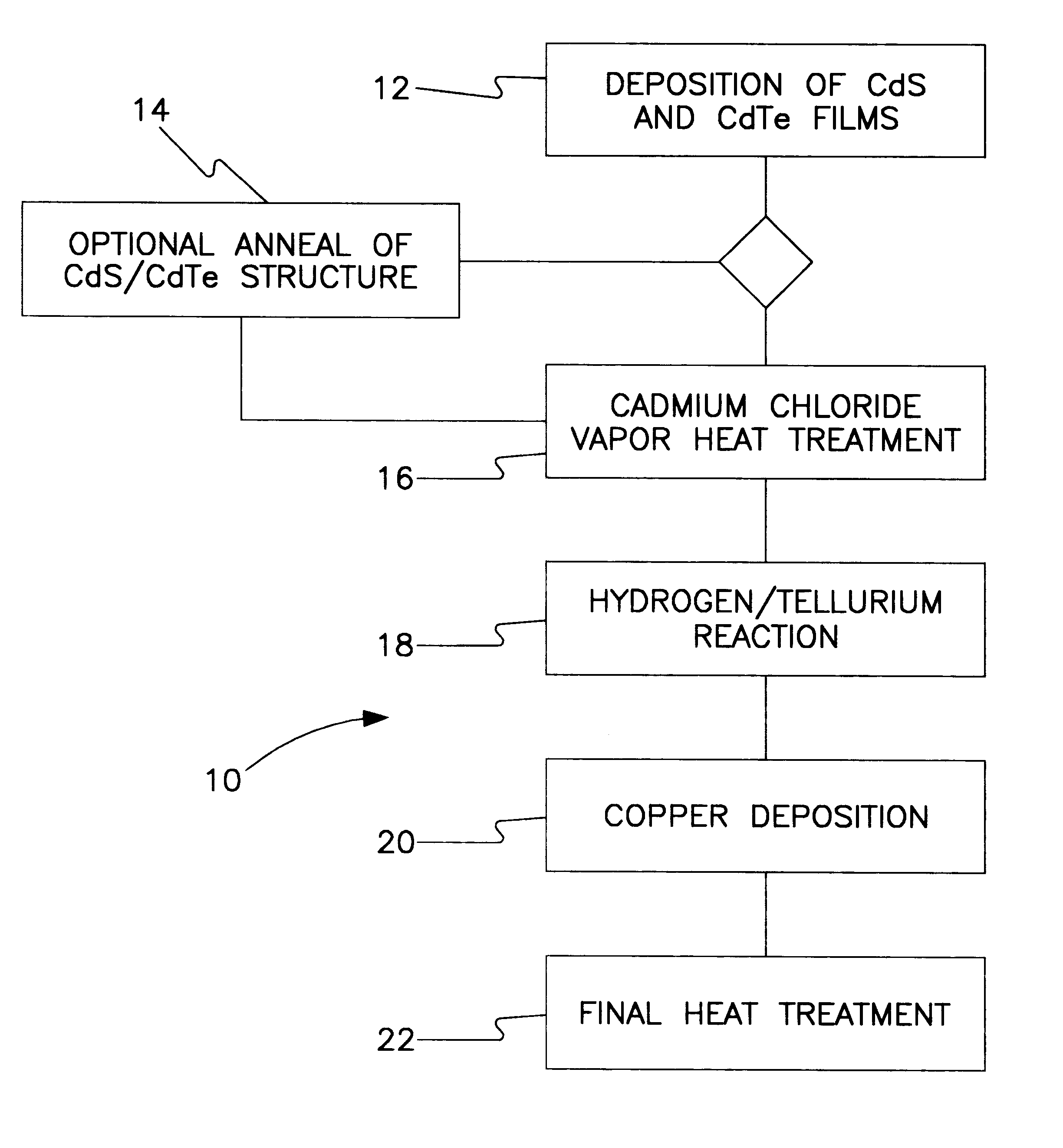
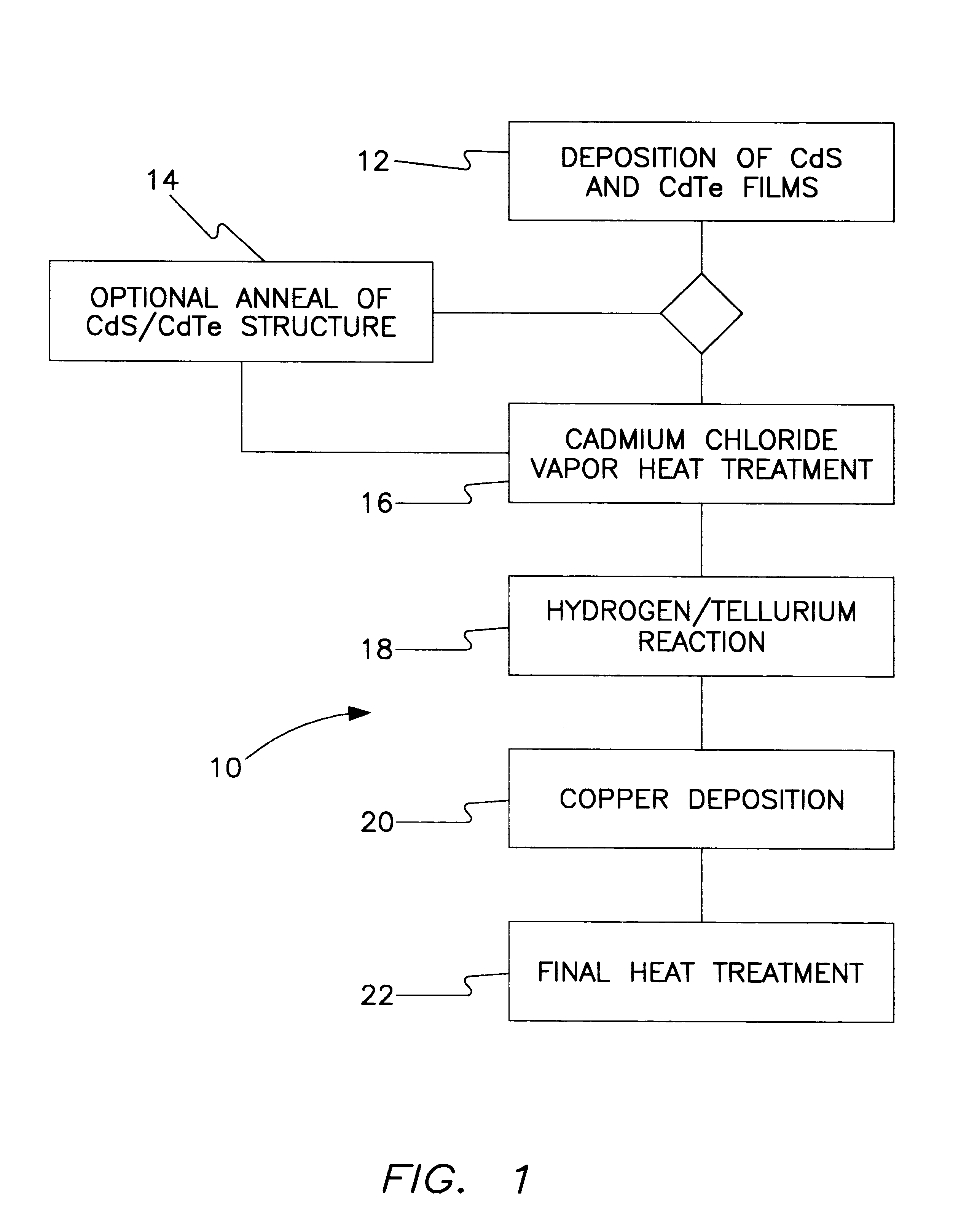
All-vapor processing of p-type tellurium-containing II-VI semiconductor and ohmic contacts thereof
InactiveUS6251701B1Reduce manufacturing costReduce pollutionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactTellurium compounds
An all dry method for producing solar cells is provided comprising first heat-annealing a II-VI semiconductor; enhancing the conductivity and grain size of the annealed layer; modifying the surface and depositing a tellurium layer onto the enhanced layer; and then depositing copper onto the tellurium layer so as to produce a copper tellurium compound on the layer.
Owner:U S DEPT OF ENGERGY
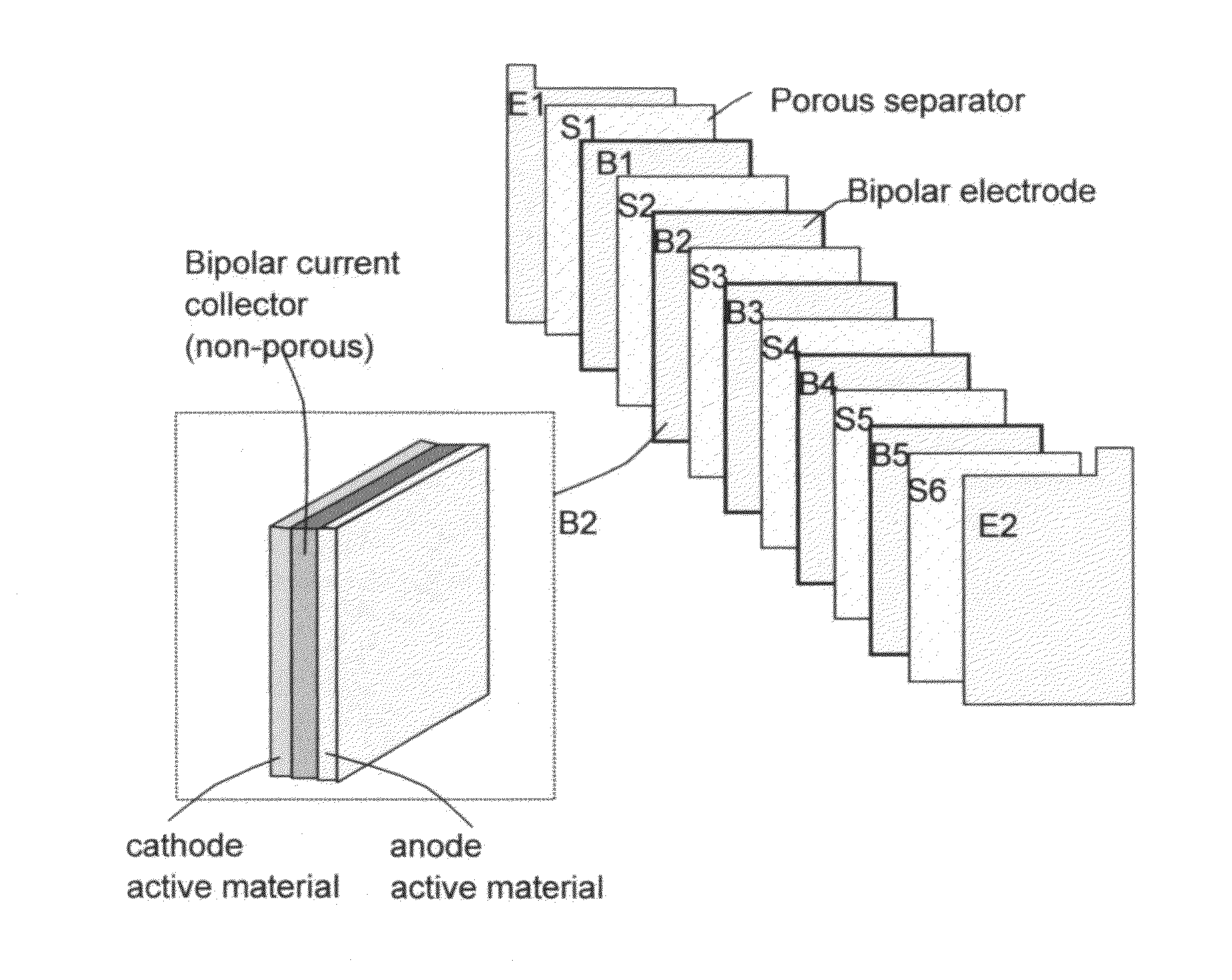
Stacks of internally connected surface-mediated cells and methods of operating same
ActiveUS20130162216A1Improve power densityEasy dischargePrimary cell to battery groupingBatteries circuit arrangementsSupercapacitorEngineering
An energy storage stack of at least two surface-mediated cells (SMCs) internally connected in parallel or in series. The stack includes: (A) At least two SMC cells, each consisting of (i) a cathode comprising a porous cathode current collector and a cathode active material; (ii) a porous anode current collector; and (iii) a porous separator disposed between the cathode and the anode; (B) A lithium-containing electrolyte in physical contact with all the electrodes, wherein the cathode active material has a specific surface area no less than 100 m2 / g in direct physical contact with the electrolyte to receive lithium ions therefrom or to provide lithium ions thereto; and (C) A lithium source. This new-generation energy storage device exhibits the highest power densities of all energy storage devices, much higher than those of all the lithium ion batteries, lithium ion capacitors, and supercapacitors.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC +1
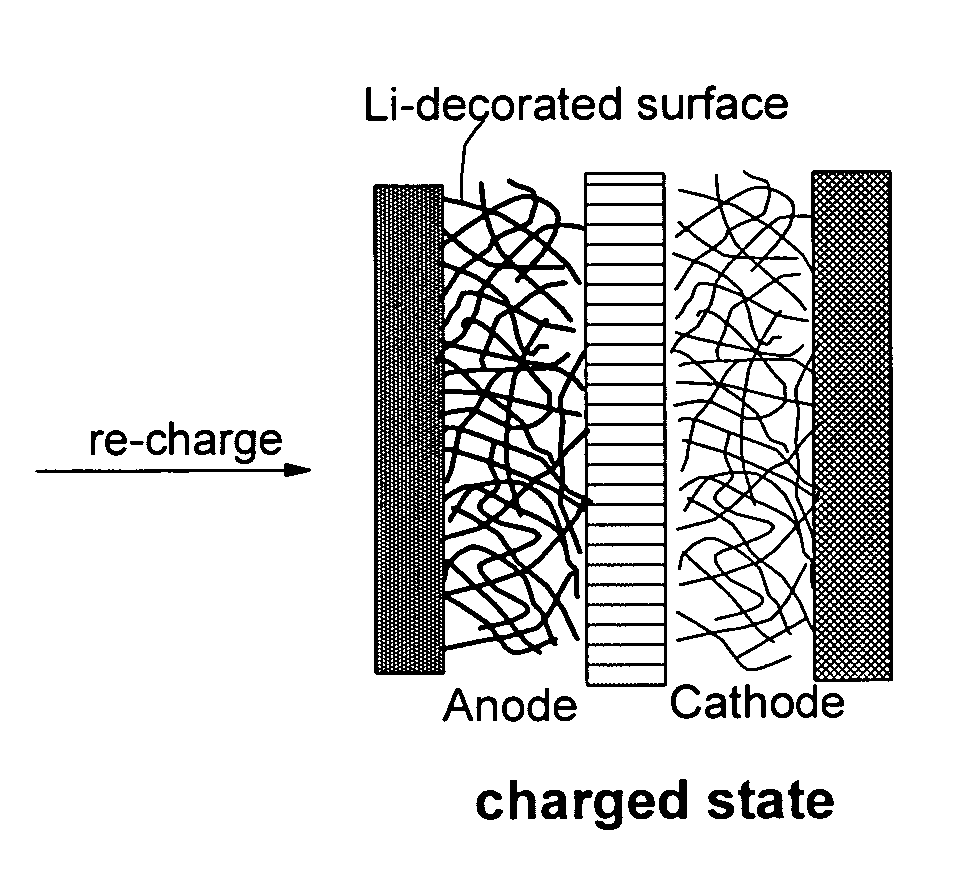
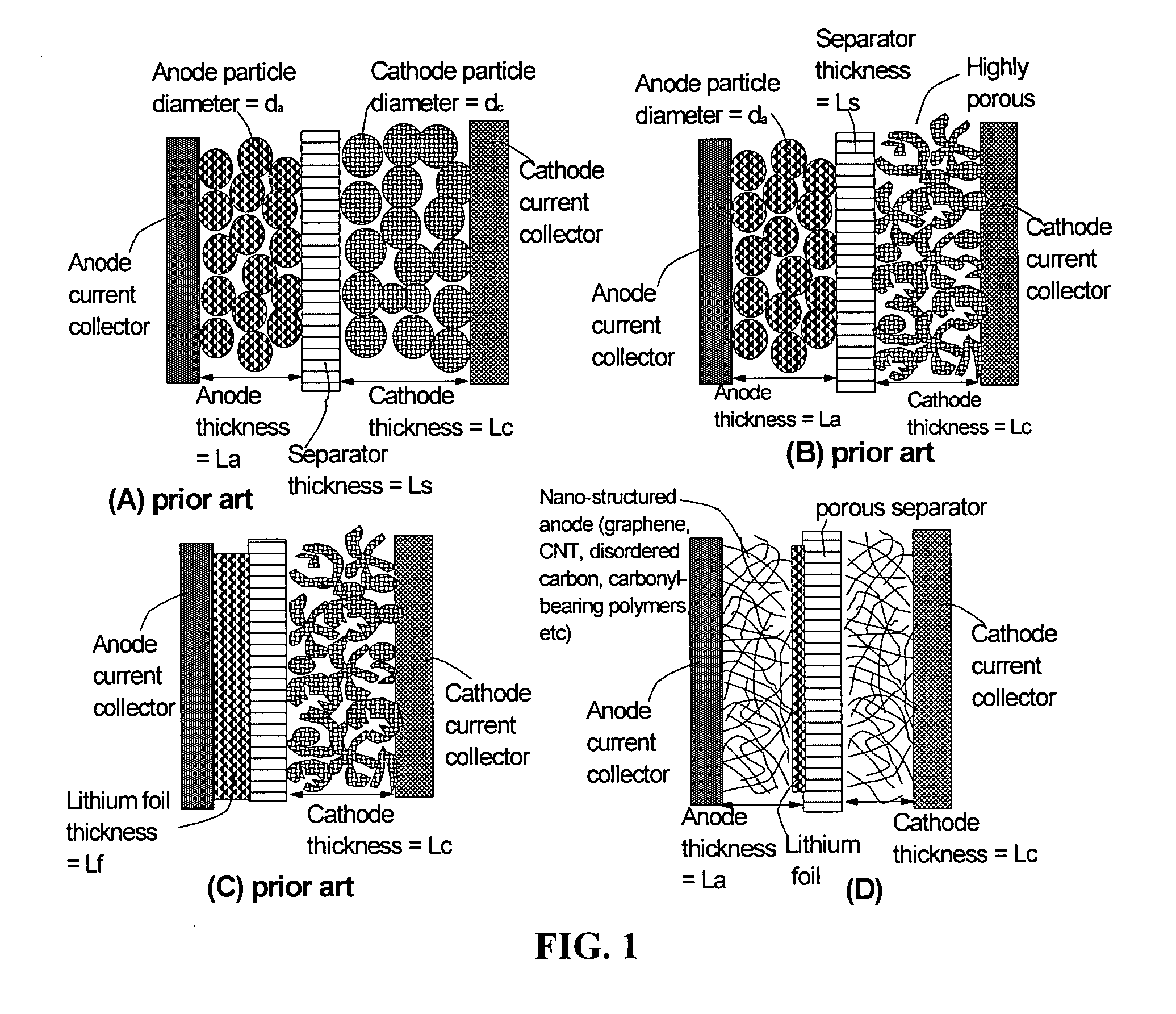
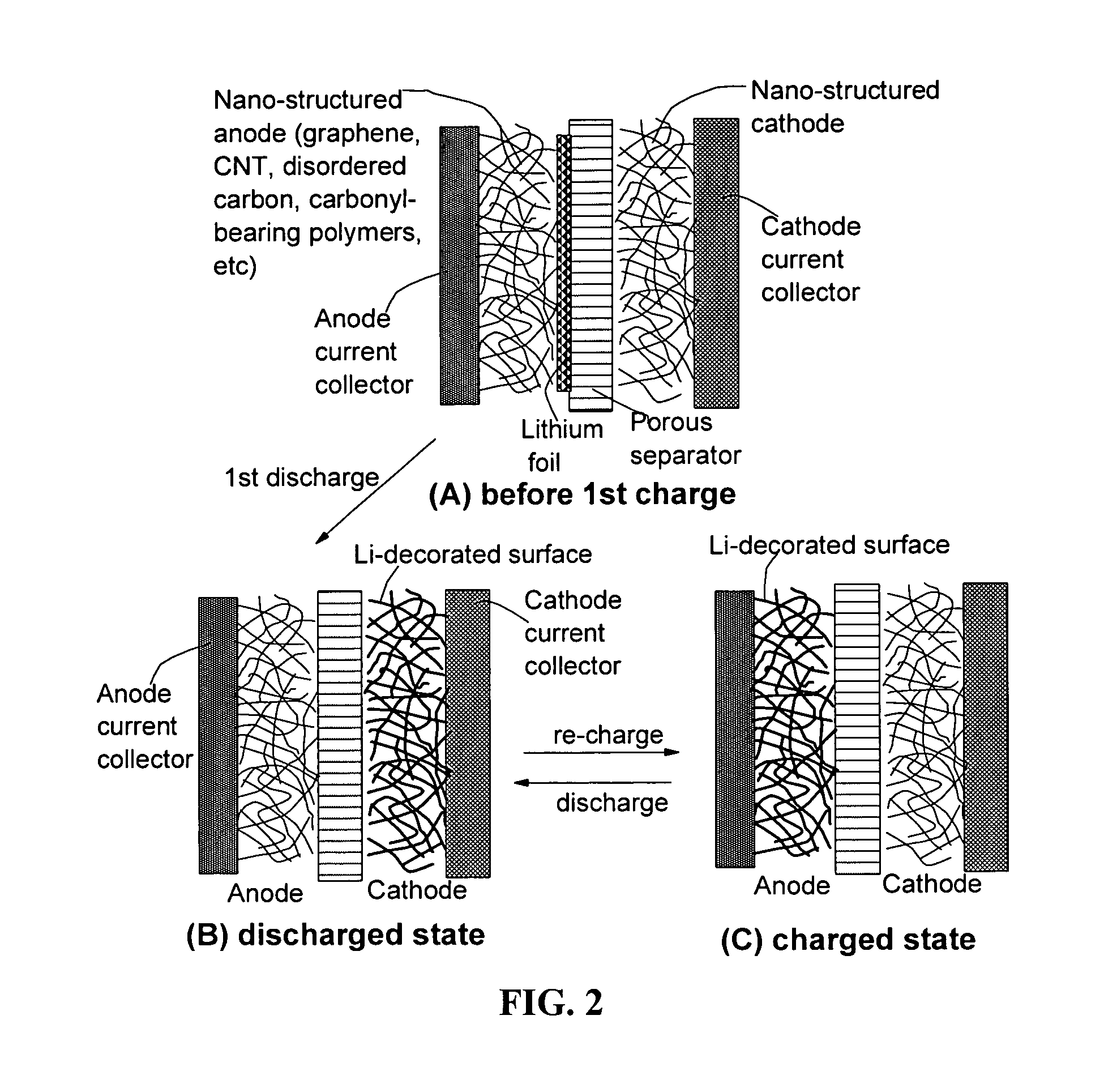
Surface -controlled lithium ion-exchanging energy storage device
ActiveUS20120164539A1Easy to handleShort charging timeAlkaline accumulatorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesElectrical batterySupercapacitor
A surface-controlled, lithium ion-exchanging battery device comprising: (a) A positive electrode (cathode) comprising a first functional material having a first lithium-capturing or lithium-storing surface; (b) A negative electrode (anode) comprising a second functional material having a second lithium-capturing or lithium-storing surface; (c) A porous separator disposed between the two electrodes, and (d) A lithium-containing electrolyte (preferably liquid or gel electrolyte) in physical contact with the two electrodes; wherein at least one of the two electrodes contains therein a lithium source (e.g., lithium foil, lithium powder, stabilized lithium particles, etc) prior to the first charge or the first discharge cycle of the battery device. This new generation of energy storage device exhibits the best properties of both the lithium ion battery and the supercapacitor.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC +1
Method for preparing N-type crystalline silicon solar cell with aluminum-based local emitters on back side
InactiveCN101853897AAvoid damageAvoid Edge Leakage SituationsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesP–n junctionMaterials science
The invention provides a method for preparing an N-type crystalline silicon solar cell with aluminum-based local emitters on the back side. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting N-type silicon wafers to carry out the surface-textured etching process; further forming a front surface field through phosphorous diffusion; depositing a passivating film on the front surface after the phosphorosilicate glass is formed during the removal of diffused phosphorous; carrying out the back-side chemical polishing process on the silicon wafers to remove the N+ layer formed on the back side during the phosphorous diffusion; then, sequentially printing an aluminum layer or a silver-aluminum layer through the passivating film deposited on the back side, local holes or grooves on the back side and screens on the back side; then, printing silver paste on the front surface; and finally, carrying out the one-step sintering process to form a local P+ layer on the back side and allowing the P+ layer to coming into ohmic contact with the electrodes on the front and back surfaces. By using the N-type substrate, forming local aluminum-based P-N junctions on the back side and further using the back-side chemical polishing process to remove the edge junctions, the invention can substitute for the conventional stacking-type plasma etching process, simplify the technological procedures and further bring a series of performance improvement to cells.
Owner:JA YANGZHOU SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC ENG
Method and system for coating internal surfaces using reverse-flow cycling
InactiveUS7541069B2Uniform coatingUniform depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid state diffusion coatingControl systemEngineering
A method and system for coating the internal surfaces of a workpiece is presented. A bias voltage is connected to a workpiece, which functions as a cathode. A gas source and a vacuum source are coupled to each opening through a flow control system. The flow control system is capable of a first mode which enables a first opening to function as a gas inlet and a second opening to function as a vacuum exhaust. The flow control system also has a second mode which enables a first opening to function as a vacuum exhaust and a second opening to function as a gas inlet. The cycling may also be used to coat internal surfaces of a workpiece with a single opening. Cycling the flow control system between the first mode and second mode is performed until a uniform coating along the internal surfaces of the workpiece is achieved.
Owner:SUB ONE TECH
Preparation of hydrogenation catalyst
InactiveCN101298047AEvenly dispersedSmall sizeMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsHigh activationReaction temperature
The invention provides a method for preparing a hydrogenation catalyst with high activation. A disposition method is adopted to carry out step-by-step loading to the active components of the metals of VIB and VIII families; the VIB metal comprises tungsten or molybdenum, while the VIII metal comprises nickel or cobalt; a carrier is alumina. The loading of VIB metal takes a corresponding soluble salt as raw material, an acid solution as a precipitator and a cationic surface active agent as a dispersant. In a hydrothermal condition, the corresponding soluble salt, the acid solution and the cationic surface active agent produce metallic oxide particles by a liquid deposition reaction; the loading of VIII metal also takes a corresponding soluble salt as raw material and carbamide as a precipitator; the adding of the precipitator and the generation of precipitation are separated by controlling reaction temperature in sections and even precipitation is realized to disperse the particles of the active components on the carrier evenly. The hydrogenation catalyst prepared shows good effects in the respects of desulfurization and denitrification activation and can greatly reduce the usage of the active components.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
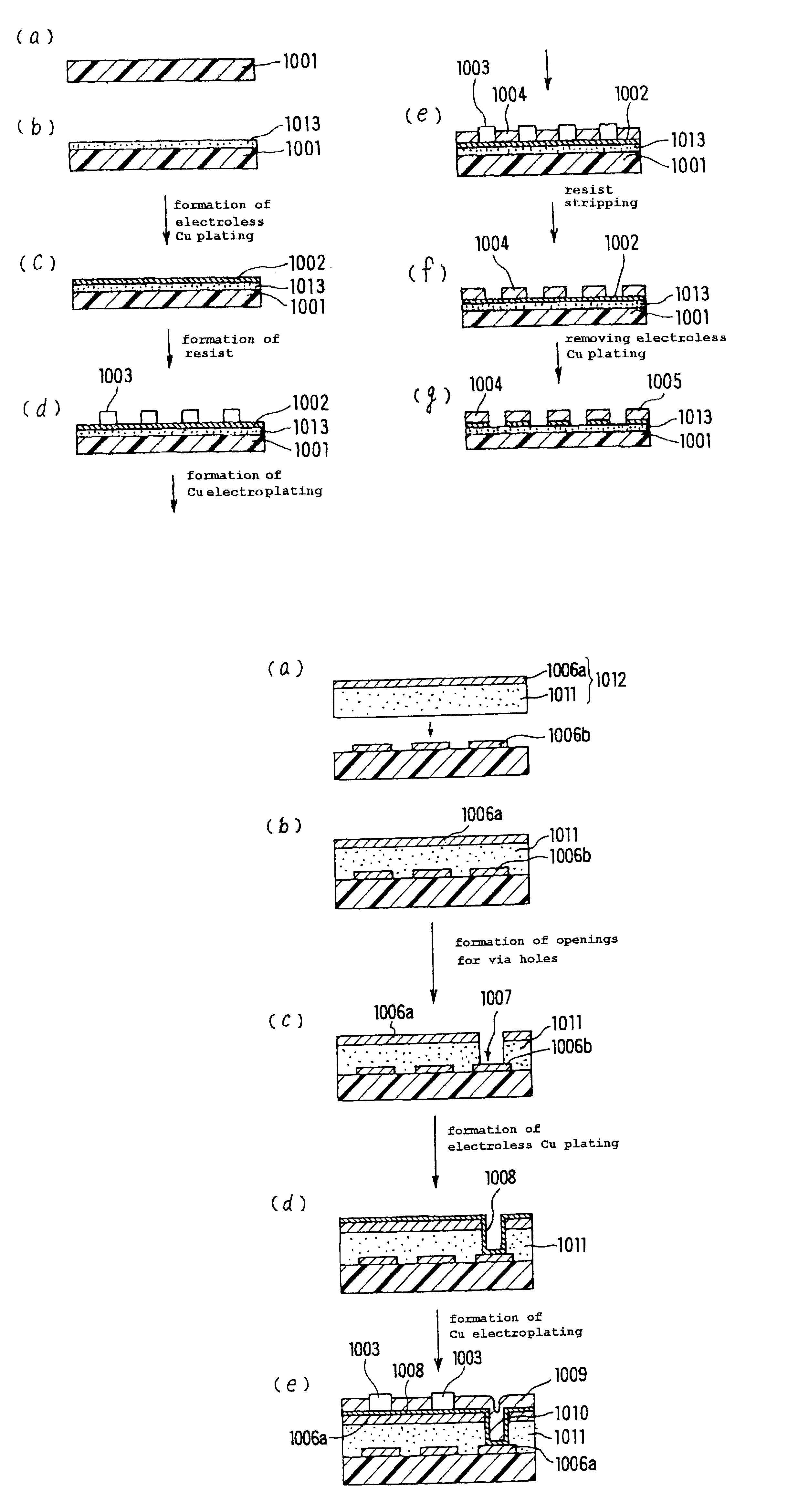
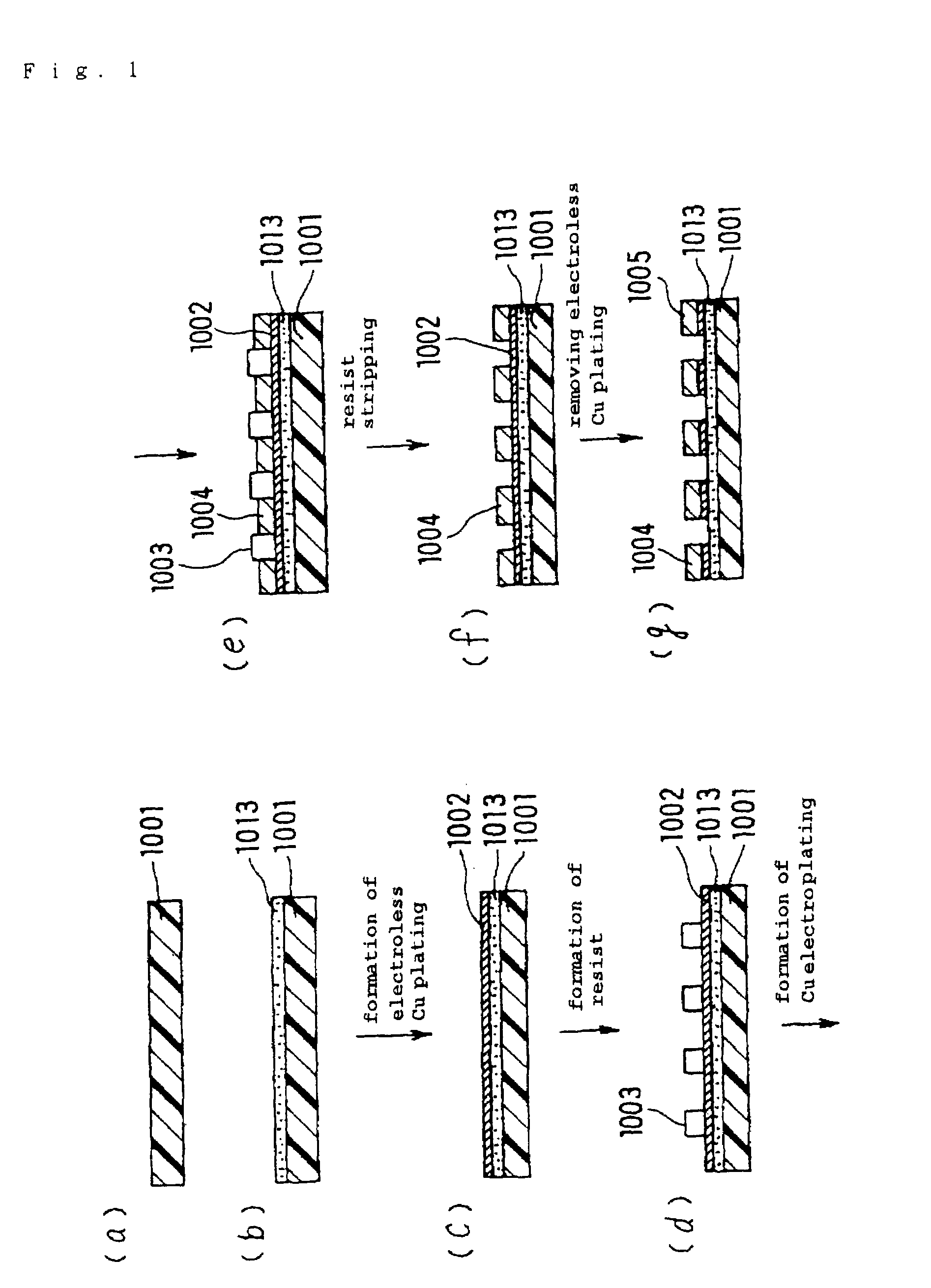
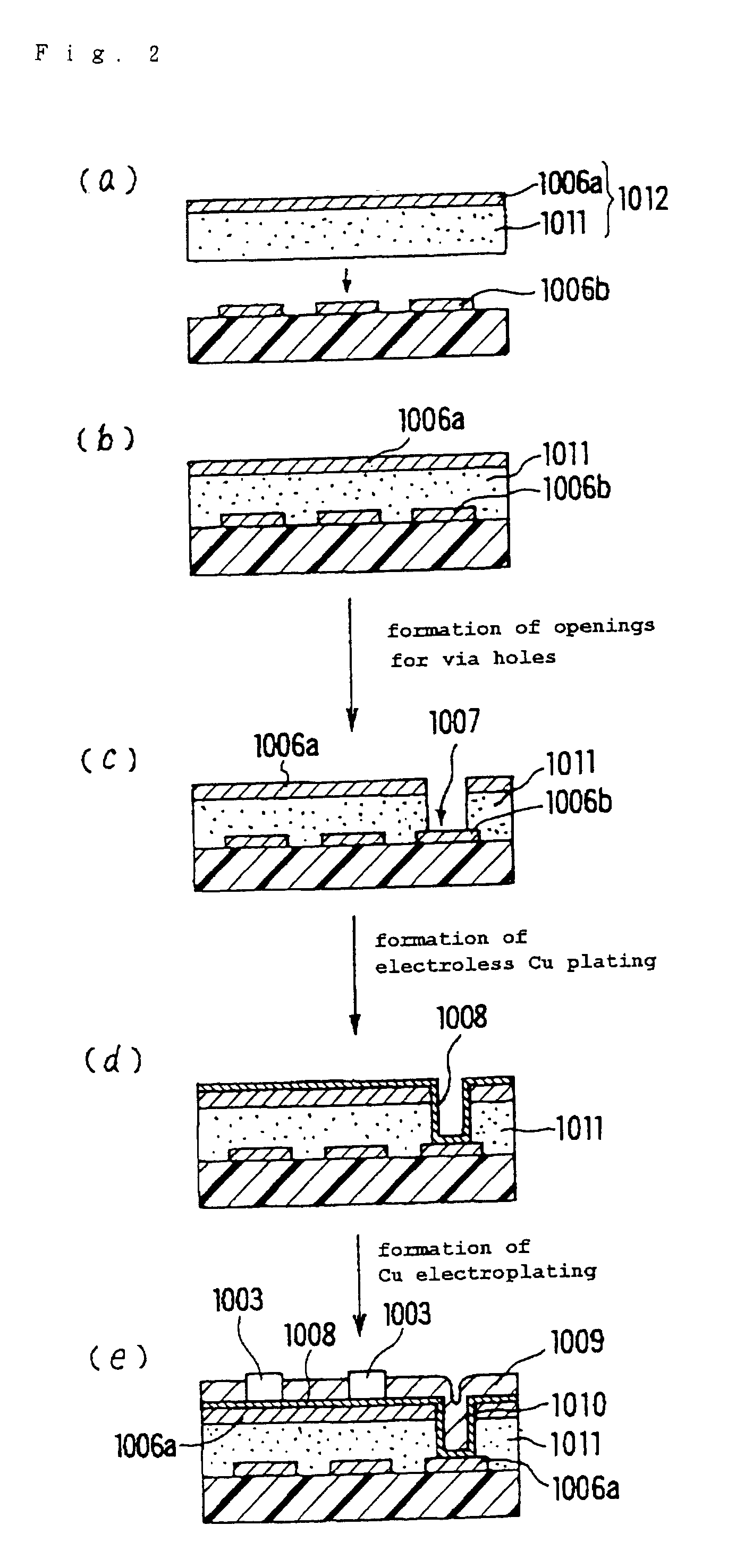
Printed wiring board and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS7230188B1High crystallinityLow equipment costInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorHigh density
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Preparation method of butanediol secondary hydrogenation catalyst by butynediol two-step hydrogenation
ActiveCN101306368AUniform depositionGood dispersionPreparation by hydrogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNickel saltSURFACTANT BLEND
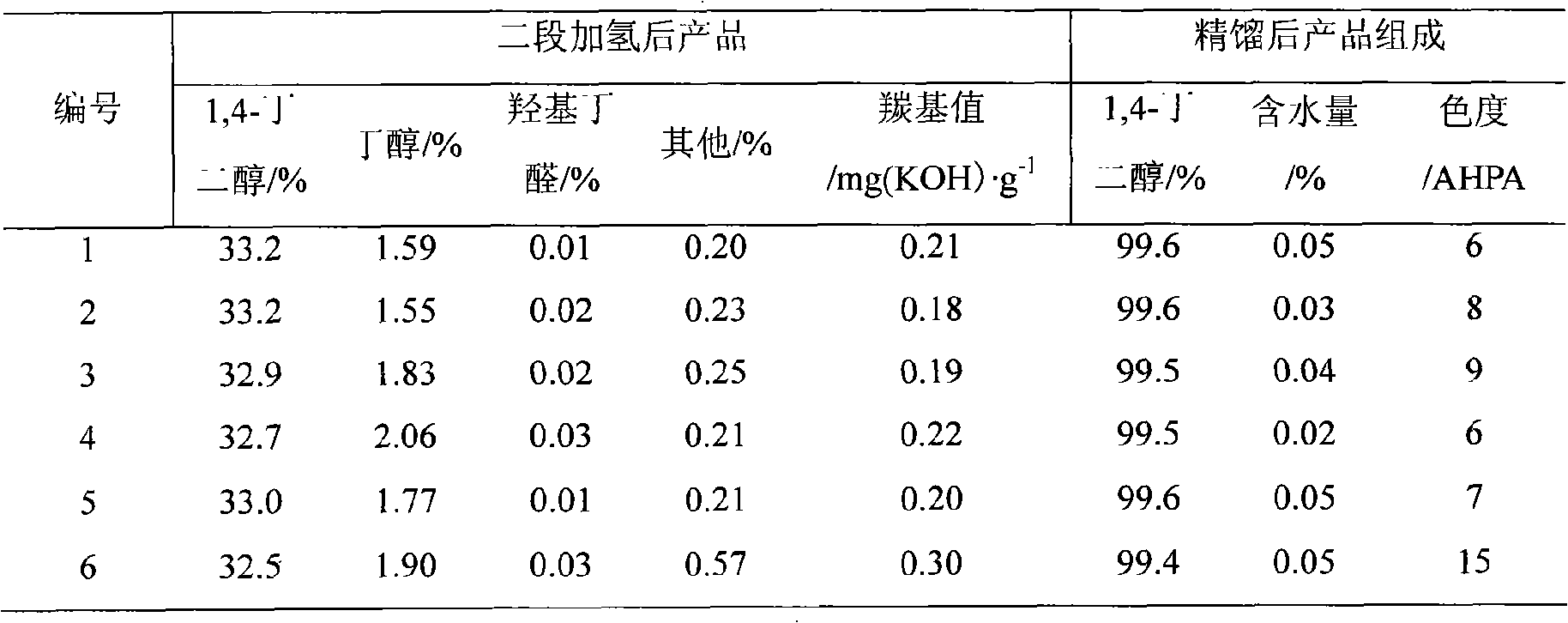
The invention provides a method for preparing a butanediol secondary hydrogenation catalyst through adopting the butynediol two-step hydrotreation, and the method comprises the following steps: an accelerant is introduced into an alumina carrier; the carrier is heated; mixed nickel complex solution containing organic nickel salt, inorganic nickel salt and surfactant is prepared; the mixed nickel salt solution is dipped on the heated carrier, and the catalyst product with the nickel content of 5-25 w% and the accelerant content of 0.001-6 w% can be obtained by drying, baking, deoxidizing and passivating. The catalyst can be used in the process of preparing the butanediol secondary hydrogenation by adopting the butynediol two-step hydrotreation, the carbonyl can be reduced to be lower than 0.2 mg (KOH)*g<-1>, and the contents of acetal and butylene glycol are enabled to be reduced to the lowest level. Through the subsequent rectification, the butylene glycol product with the purity more than or equal to 99.5 percent and the chromaticity lower than or equal to 10 AHPA can be produced.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Method and system for coating sections of internal surfaces
ActiveUS7608151B2Low activation temperatureUniform coatingVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl systemEngineering
A method and system for coating the internal surfaces of a localized area or section of a workpiece is presented. Conductive structures are inserted into one or more openings of a workpiece to define the section to be coated. In some embodiments, a bias voltage is connected to a workpiece section, which functions as a cathode. A gas source and vacuum source are coupled to each conductive structure through a flow control system. The flow control system enables a first opening to function as a gas inlet and a second opening to function as a vacuum exhaust. Only the section encompassed by the conductive structures is coated. When the coating process is completed, a means for varying the conductive structures along the length is utilized to move onto the next section to be coated.
Owner:AGM CONTAINER CONTROLS
Lithium-sulfur secondary battery containing gradient electrolyte
ActiveUS20140342209A1Reduce electrical conductivityLow ionic conductivityElectrode carriers/collectorsTwo electrolyte cellsLithium sulfurBattery cell
A rechargeable lithium-sulfur cell comprising a cathode, an anode, a separator electronically separating the two electrodes, a first electrolyte in contact with the cathode, and a second electrolyte in contact with the anode, wherein the first electrolyte contains a first concentration, C1, of a first lithium salt dissolved in a first solvent when the first electrolyte is brought in contact with the cathode, and the second electrolyte contains a second concentration, C2, of a second lithium salt dissolved in a second solvent when the second electrolyte is brought in contact with the anode, wherein C1 is less than C2. The cell exhibits an exceptionally high specific energy and a long cycle life.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Conductive polyamine-based electrolyte
InactiveUS20060210873A1Facilitated releaseImprove efficiencyAlkaline accumulatorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesIonic liquidPolyamine
Pyrrolidinium based room temperature ionic liquids, and phosphorous and arsenic analogues, are used as electrolytes in energy storage devices including secondary lithium batteries, supercapacitors and asymmetric battery-supercapacitors. The electrolytes preferably contain lithium ions as the charge-carrying species. The electrolytes are in a liquid state at the operating temperature.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
MCrAIY bond coating and method of depositing said MCrAIY bond coating
InactiveUS20050003227A1Enhanced surface roughnessReduce effectInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementLiquid surface applicatorsBond coatingPt element
A method of depositing a bond coating to a surface of an article includes the steps of depositing an inner layer of the bond coating consisting of β-NiAl comprising Fe, Ga, Mo, B, Hf or Zr or γ / β-MCrAlY comprising Fe, Ga, Mo, B, Hf or Zr or γ / γ′- or γ-MCrAlY, and depositing an outer layer of the bond coating, which is more coarse the in the inner layer, consisting of β-NiAl comprising Fe, Ga, Mo, B, Hf or Zr or γ / β-MCrAlY comprising Fe, Ga, Mo, B, Hf or Zr or γ / γ′- or γ-MCrAlY, wherein said elements Fe, Ga, Mo, B, Hf or Zr above mentioned are present individually or in combination. The coating also includes a noble metal selected from the group consisting of platinum, palladium and rhodium in the inner and outer layer or as a separate layer.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Coating materials and methods for enhanced reliability
ActiveUS20160013329A1Reduce trafficHigh surface resistanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPotential induced degradationMoisture
Glass coating materials and methods are disclosed for the coating of glass substrates used in the manufacturer of photovoltaic solar modules such that the coating enhances the reliability of the module by reducing its susceptibility to potential induced degradation (PID). Coating materials are disclosed that reduce soiling on the front surface of the glass; that increase the surface resistivity of the glass and that repel moisture and that seal the surface from the ingress of moisture. Further electrically conductive coatings are disclosed that reduce the electric field between the front and back surfaces of the glass and hence reduce ion mobility within the glass and transport from the interior glass surface to the solar cell. There are additional configuration choices for fine tuning associated with separately optimizing the exterior and interior glass coating. Finally, coating processes and methods are disclosed for coating glass substrates with the disclosed materials.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Process and apparatus for feeding cementitious slurry for fiber-reinforced structural cement panels
ActiveUS20080099171A1Good strength propertiesA large amountNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperEngineeringFibre reinforcement
A head-box for depositing slurry upon a moving web including a main metering roll, a companion roll disposed in closely spaced relation to the metering roll and a vibrating gate which forms a nip between the metering roller and the gate. The nip is arranged to retain a supply of the slurry, and the rolls are driven so slurry retained in the nip progresses over an upper outer peripheral surface of the metering roll to be deposited upon the web. Also, preferably included is a doctor blade disposed in operational relationship to the metering roll for directing the slurry downwardly from the outer metering roll surface to a point above the surface of a carrier for a fiberglass layer upon which the slurry layer is deposited. The vibrating gate and doctor blade may be pivotally mounted to either side of the surfaces of the head-box.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Hydrogenation purification method for siliceous distillate
ActiveCN101343565AIncrease capacityFast inactivationTreatment with hydrotreatment processesPurification methodsHydrogen
The invention relates to a silicon-containing distillate oil hydrofining method, which adopts the method that the silicon-containing distillate oil raw material and hydrogen pass through at least two hydrofining catalyst beds under the hydrofining condition, the silicon-containing distillate oil raw material first passes through a hydrogenising catalyst bed with the silicon catching function, and then passes through a conventional hydrofining catalyst bed; wherein the hydrogenising catalyst with the silicon catching function has a greater pore volume and a specific surface area and a relatively lower metal content. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the process is simple, the good hydrodesulfurization and hydrodedenitrification performance is kept on the premise of enhancing the silicon-containing ability, and the running period of the device is effectively prolonged. The method can be applied to various silicon-containing distillate oil hydrofining processes.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
High-power ion sputtering magnetron
InactiveUS6841051B2Shields heat-sensitive partsAvoid noiseCellsElectric discharge tubesMagnetic heatingDrive shaft
Owner:BUEHLER AG
Method for electrochemical depositing solar cell metallic electrode
ActiveCN101257059AAvoid unevennessAvoid damagePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesElectrochemical responseMetallic electrode
Owner:WUXI SUNTECH POWER CO LTD
Scalable, high-throughput, multi-chamber epitaxial reactor for silicon deposition
ActiveUS20100092697A1Uniform material depositionUniform depositionSolid state diffusion coatingFrom chemically reactive gasesSusceptorVertical edge
One embodiment provides an apparatus for material deposition. The apparatus includes a reaction chamber, and a pair of susceptors. Each susceptor has a front side and a back side, and the front side mounts substrates. The susceptors are positioned vertically in such a way that the front sides of the susceptors face each other, and the vertical edges of the susceptors are in contact with each other, thereby forming a substantially enclosed narrow channel between the substrates. The apparatus also includes a number of gas nozzles for injecting reaction gases. The gas nozzles are controlled in such a way that gas flow directions inside the chamber can be alternated, thereby facilitating uniform material deposition. The apparatus includes a number of heating units situated outside the reaction chamber. The heating units are arranged in such a way that they radiate heat energy directly to the back sides of the susceptors.
Owner:TESLA INC
Zinc negative electrode with zinc ion conductivity interface modification layer, battery and preparation method
ActiveCN111933912AImprove Interface StabilitySolve the large interface impedanceSecondary cellsChemical electrode manufacturingElectrical batteryZinc ion
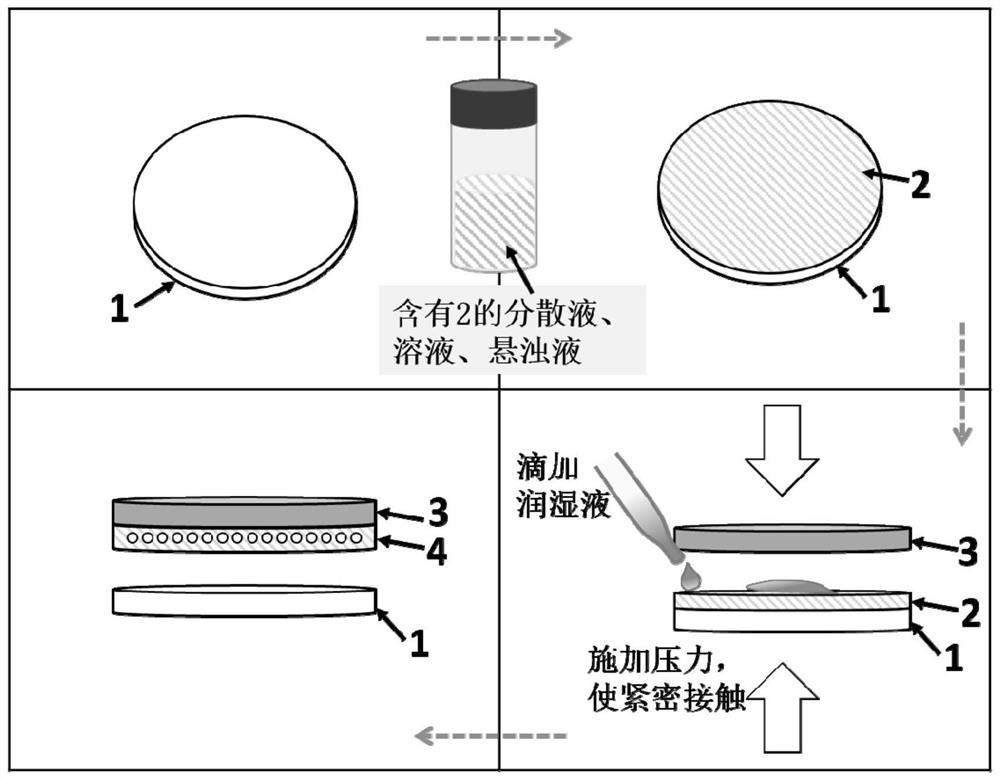
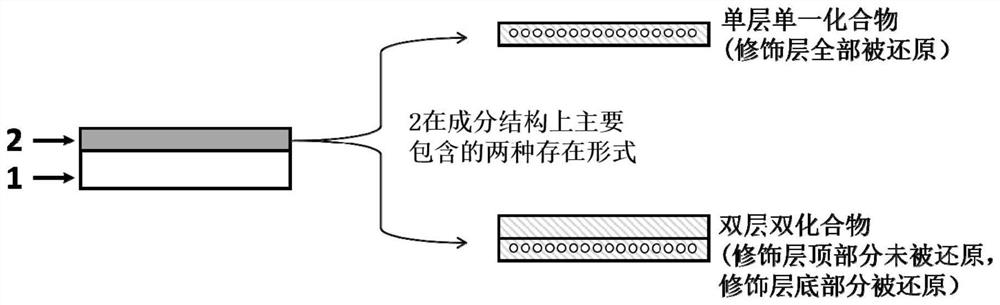
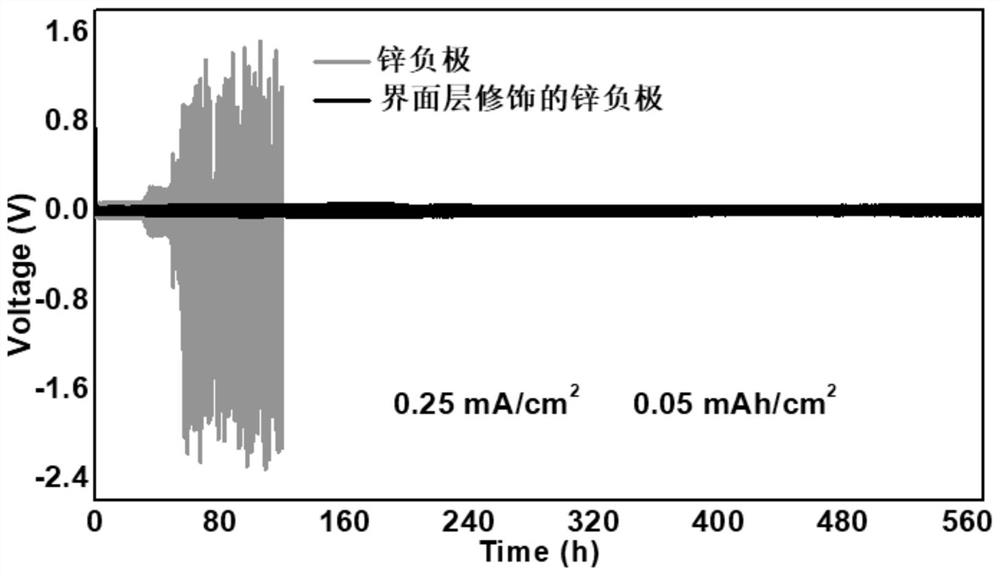
The invention provides a zinc negative electrode with a zinc ion conductivity interface modification layer, a battery and a preparation method, and belongs to the field of aqueous zinc battery metal zinc cathodes. The preparation method comprises: in air atmosphere, pre-constructing an interface modification material M on a base membrane; in a soaking environment by a wetting liquid, the interfacemodification material M layer on the base film being in close contact with the metal zinc to form the short-circuit primary battery, and the contacted interface modification material M and the metalzinc having spontaneous redox reaction, to make the interface modification material convert to ZnxM with zinc ion conductivity from M, meanwhile, transferring the interface modification material layerto the surface of the metal zinc negative electrode from the base film, and finally, obtaining the metal zinc negative electrode with the ZnxM interface modification layer with zinc ion conductivityon the surface. The ZnxM interface modification layer with the zinc ion conductivity can effectively inhibit dendritic crystal growth of a zinc negative electrode during charging and discharging of azinc battery, so that the interface stability of a metal zinc negative electrode is improved, and meanwhile, the cycling stability of a water-based zinc battery is improved. The method is simple and has a good actual effect.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Self-heating type alcohol reforming hydrogen production micro channel reactor with micro-lug boss array structure
The invention discloses a self-heating type alcohol reforming hydrogen production micro channel reactor with the micro-lug boss array structure. Three layers of platy reaction carriers are all provided with micro-lug boss array structures; an upper layer and a lower layer are single-side micro-lug boss array structures; a middle layer is a double-side micro-lug boss array structure; the micro-lug bosses are arranged in the mode of parallel array; the three layers are cascaded to form a reaction channel with an inlet of 90 degrees; both ends of the channel are respectively provided with connector lugs; the gas inlet is provided with a detachable adapter and an outlet is provided with a fixed-type adapter. An upper layer channel is a catalytic reforming hydrogen production channel, and a lower layer channel is a combustion channel. The two layers of channel structures both adopt an open structural type being beneficial for the sediment of the catalytic coating. Fuel gases such as hydrogen and the like are combusted in the combustion channel and generate lot of heat which is transferred into the catalytic reforming hydrogen production channel by the middle layer of the reactor so as to meet the requirement of the steam reforming hydrogen production reaction; the reactor can produce hydrogen in a self-heating type. The invention increases the specific volume of the reactor and increases the yield of the alcohol reforming hydrogen production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com