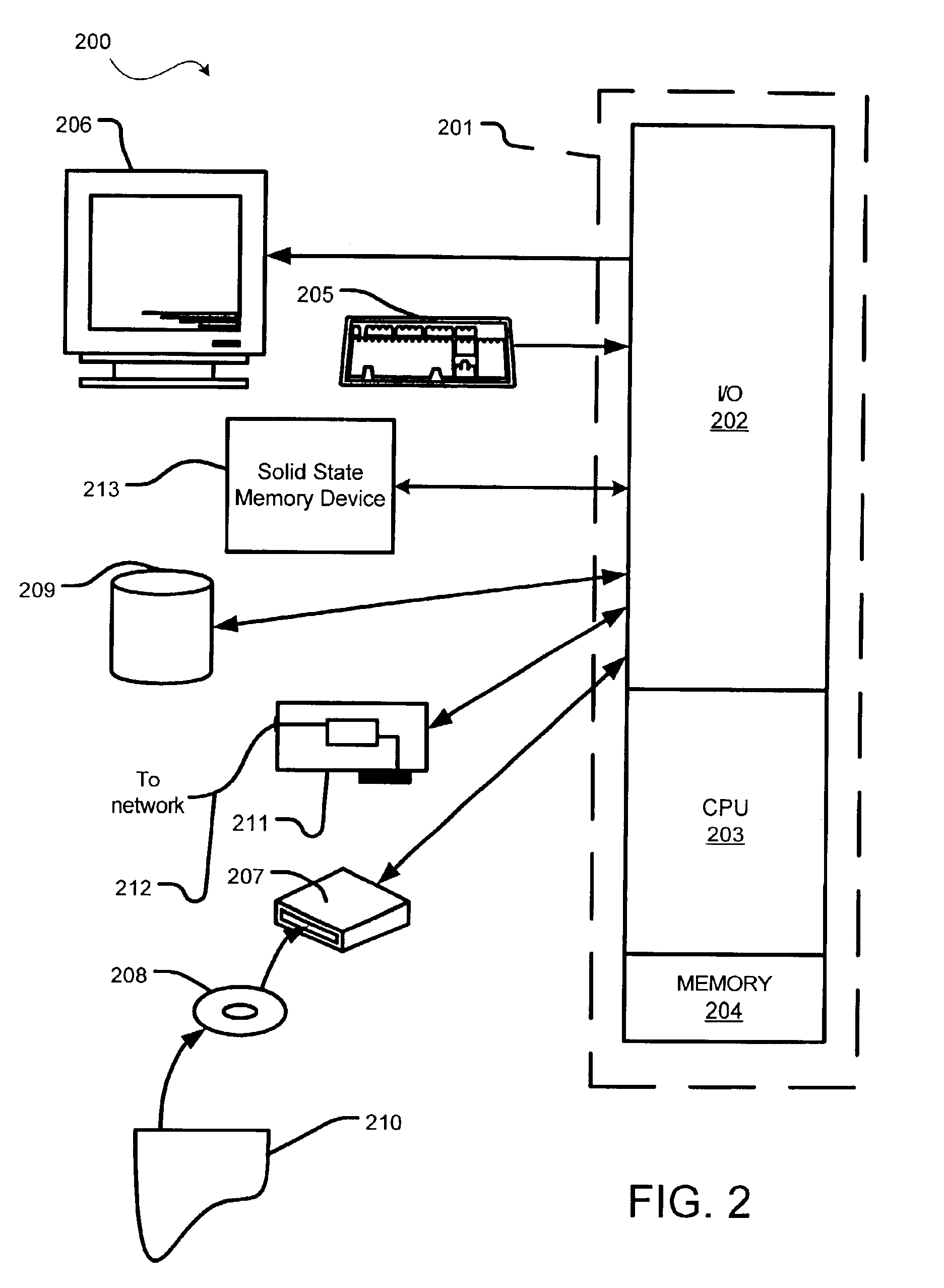
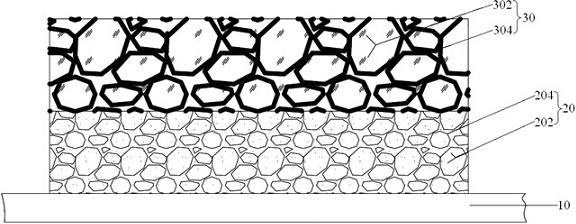
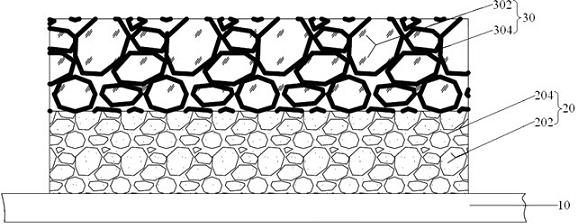
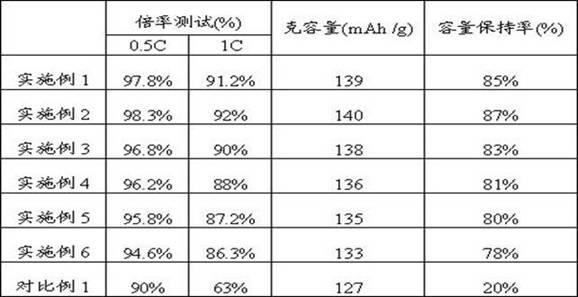
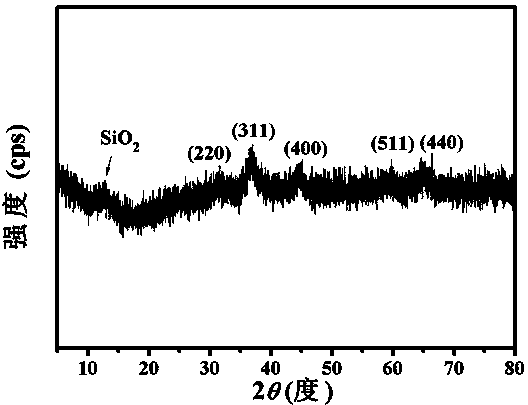
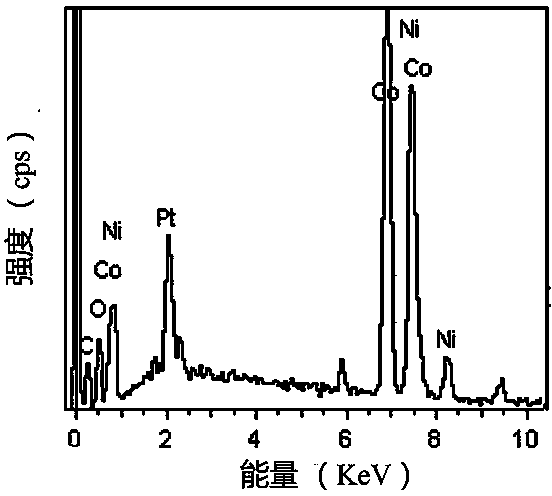
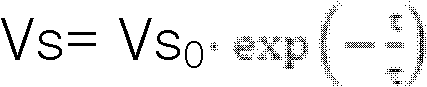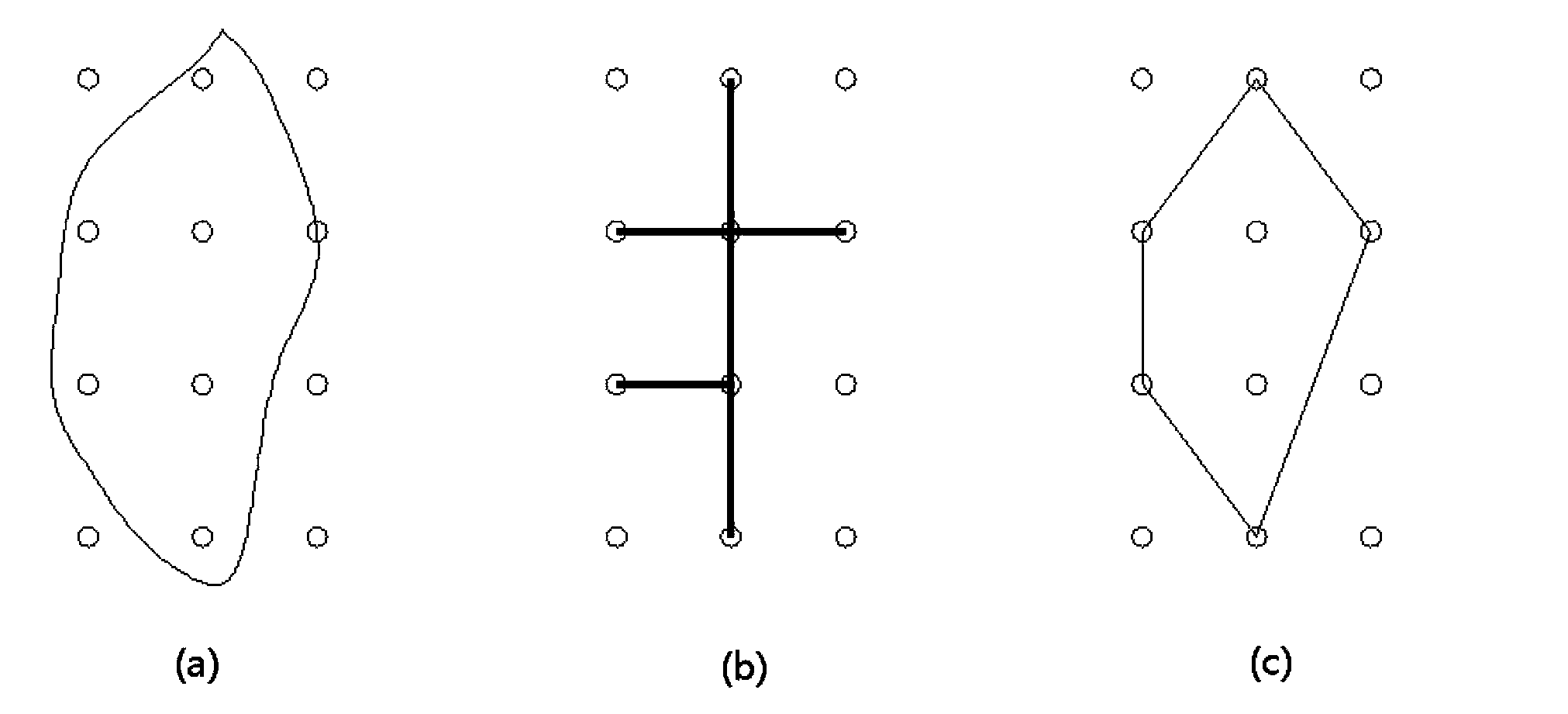Patents
Literature
1087 results about "Conductivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Conductivity (or specific conductance) of an electrolyte solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. The SI unit of conductivity is Siemens per meter (S/m). Conductivity measurements are used routinely in many industrial and environmental applications as a fast, inexpensive and reliable way of measuring the ionic content in a solution. For example, the measurement of product conductivity is a typical way to monitor and continuously trend the performance of water purification systems.
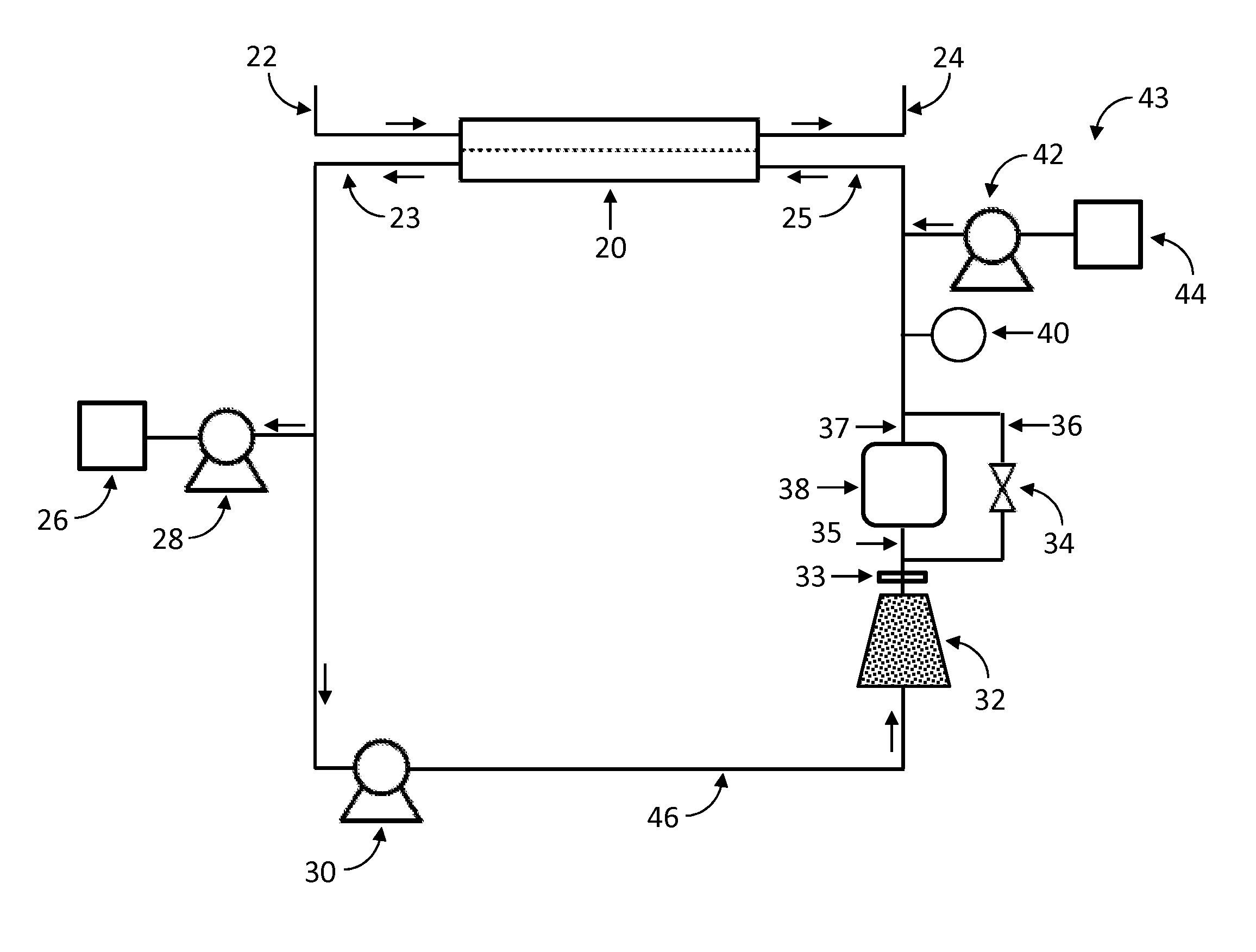
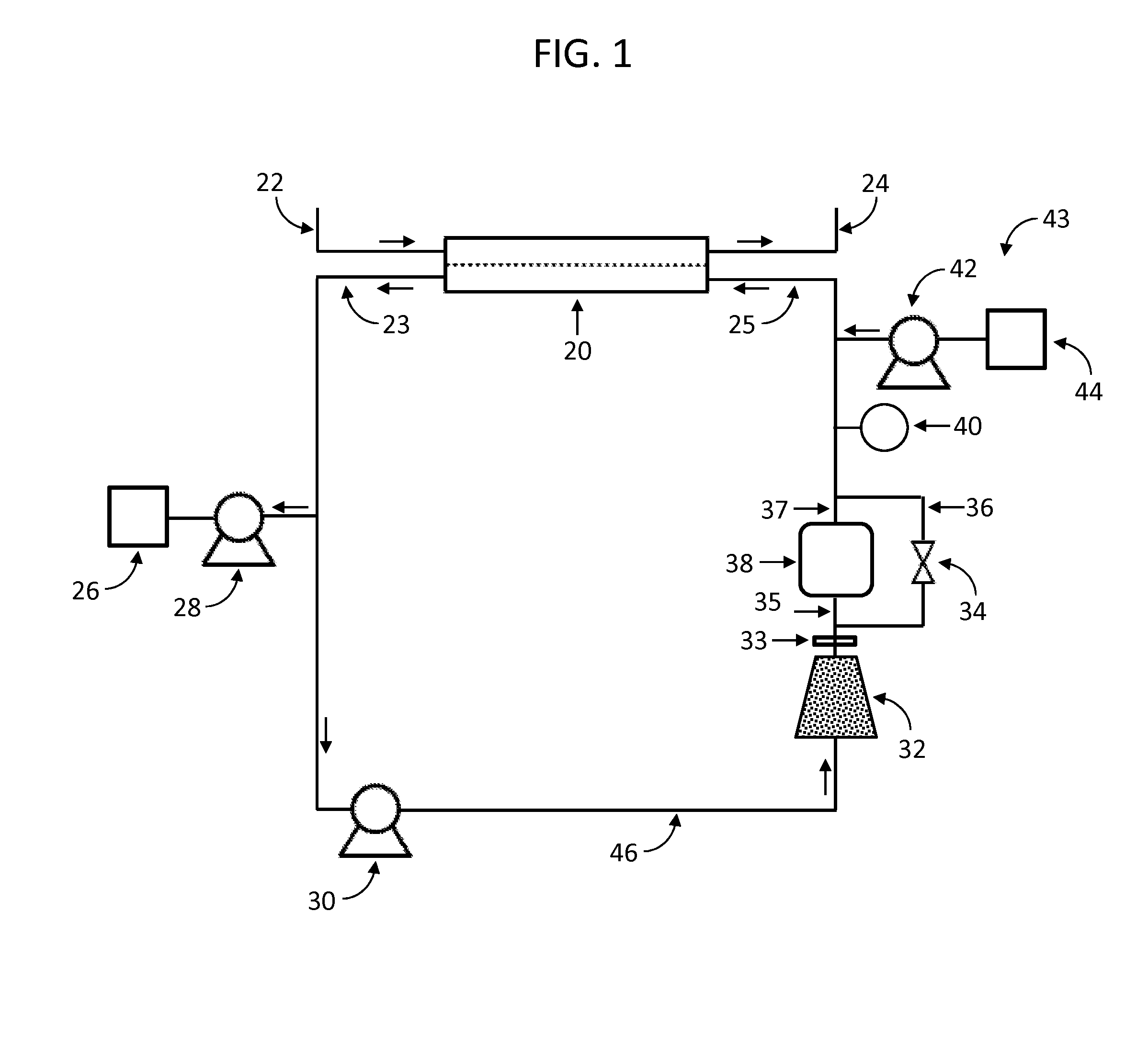
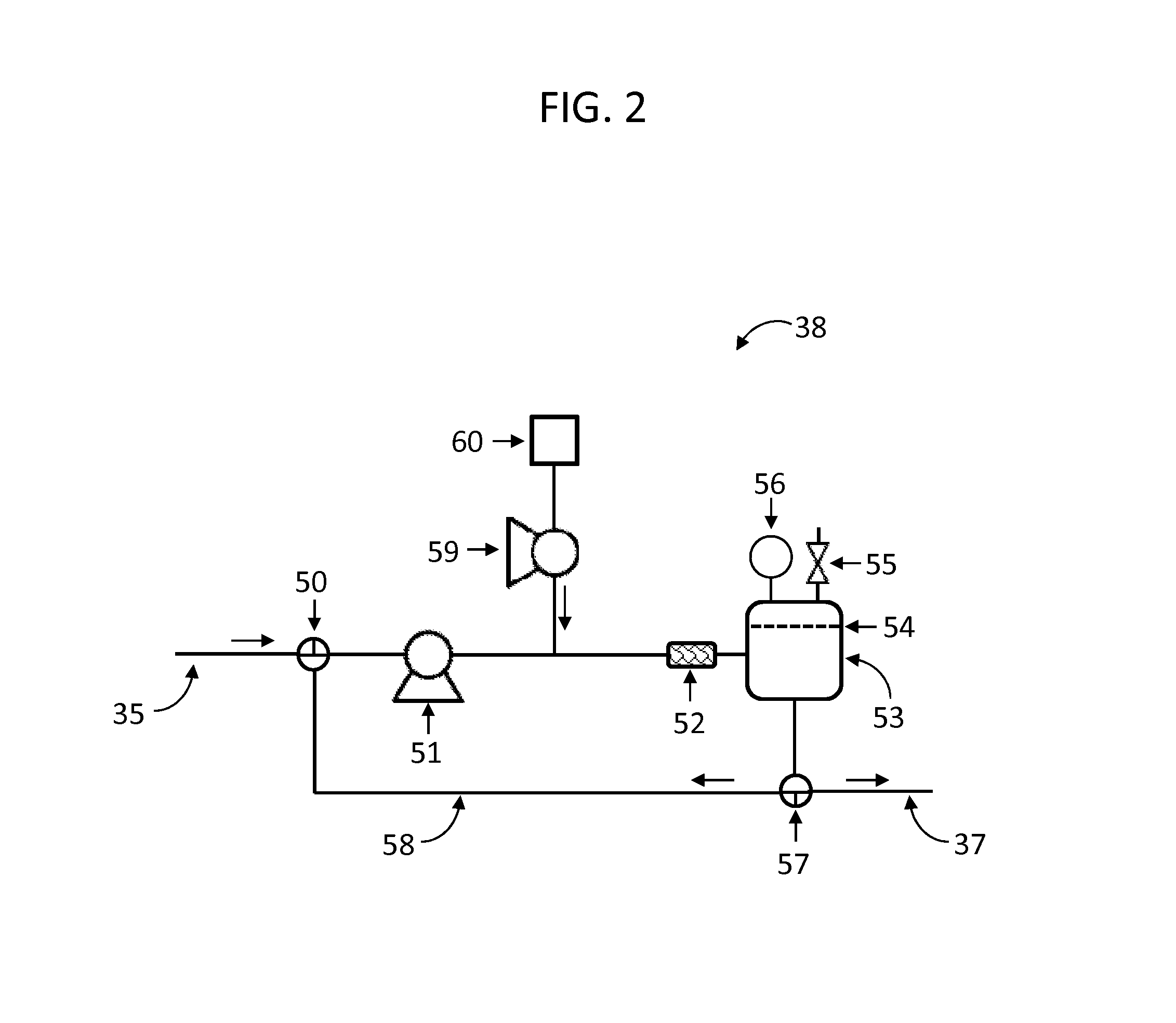
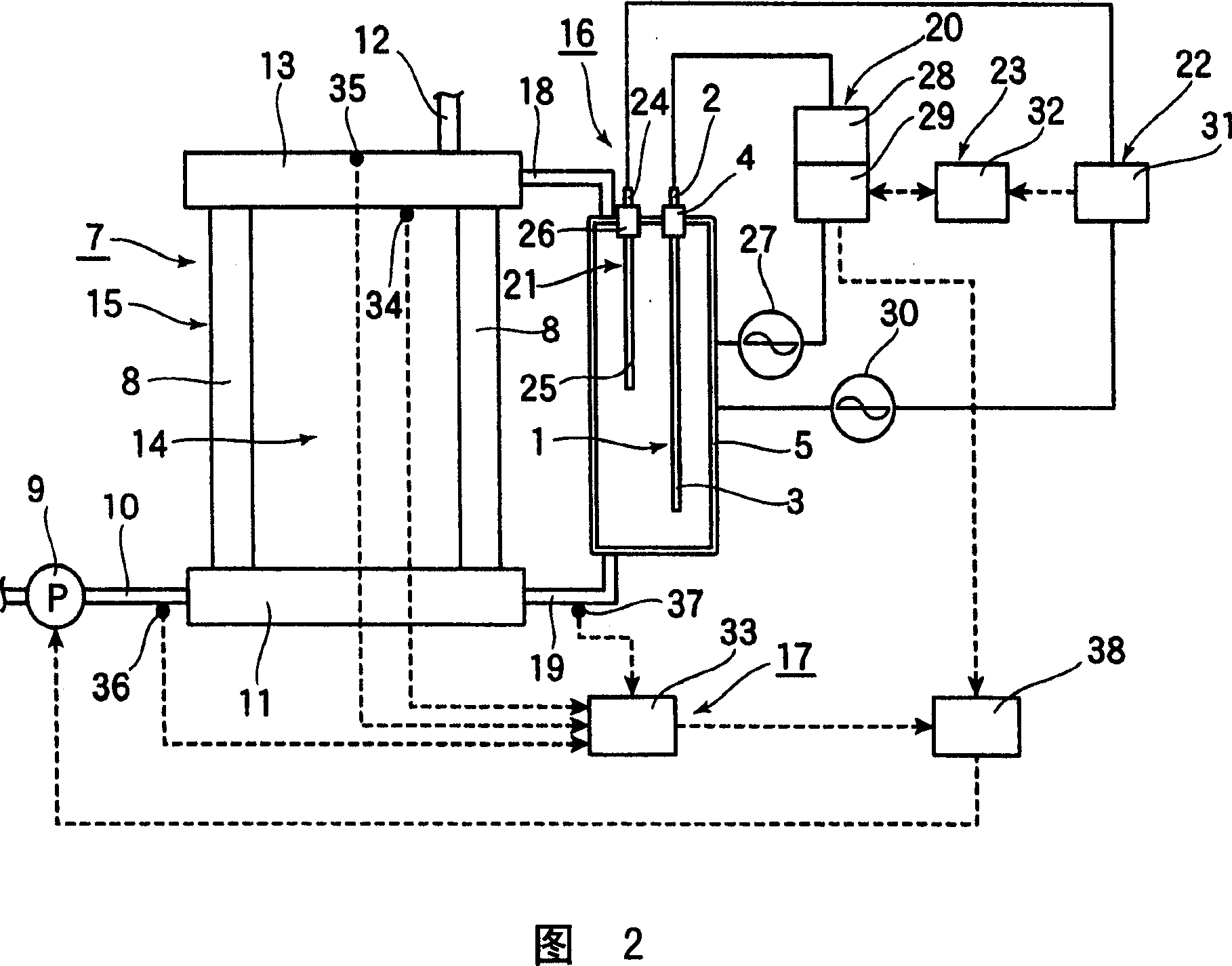
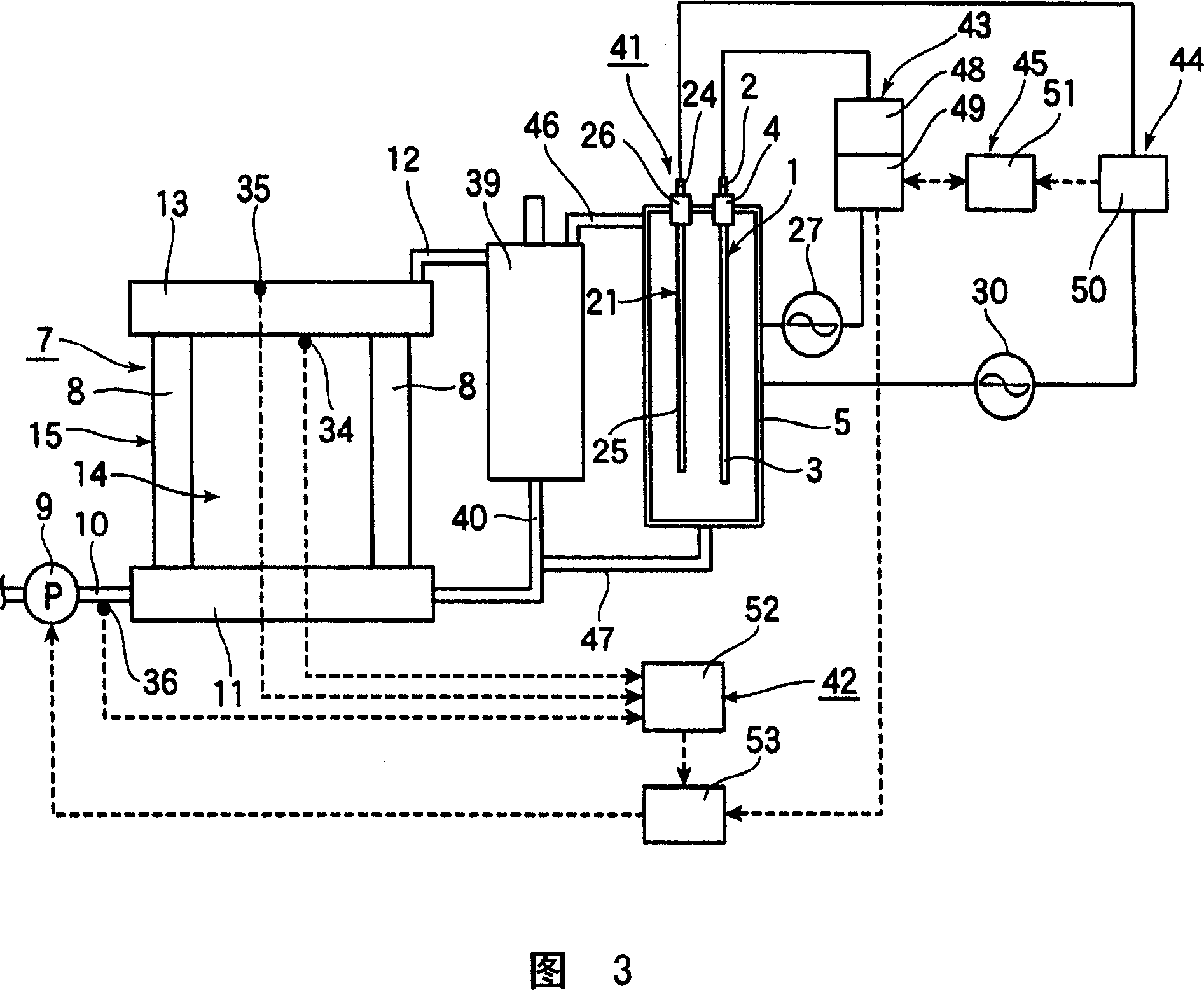
pH BUFFER MEASUREMENT SYSTEM FOR HEMODIALYSIS SYSTEMS
ActiveUS20140220699A1Well mixedSemi-permeable membranesAnalysis using chemical indicatorsThermodynamicsHemodialysis care
A pH-buffer measurement system that has at least one source for modifying the pH of a fluid entering the system, the source selected from an acid source and a base source. The acid source adds an acid equivalent to provide an acid reacted fluid and the base source adds a base equivalent to provide a base reacted fluid. The source is in fluid communication with a flow path and a component for determining a fluid characteristic of the acid reacted fluid or the base reacted fluid. The fluid characteristic that is measured is any one of a gas phase pressure, an electrical conductivity, or thermal conductivity.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
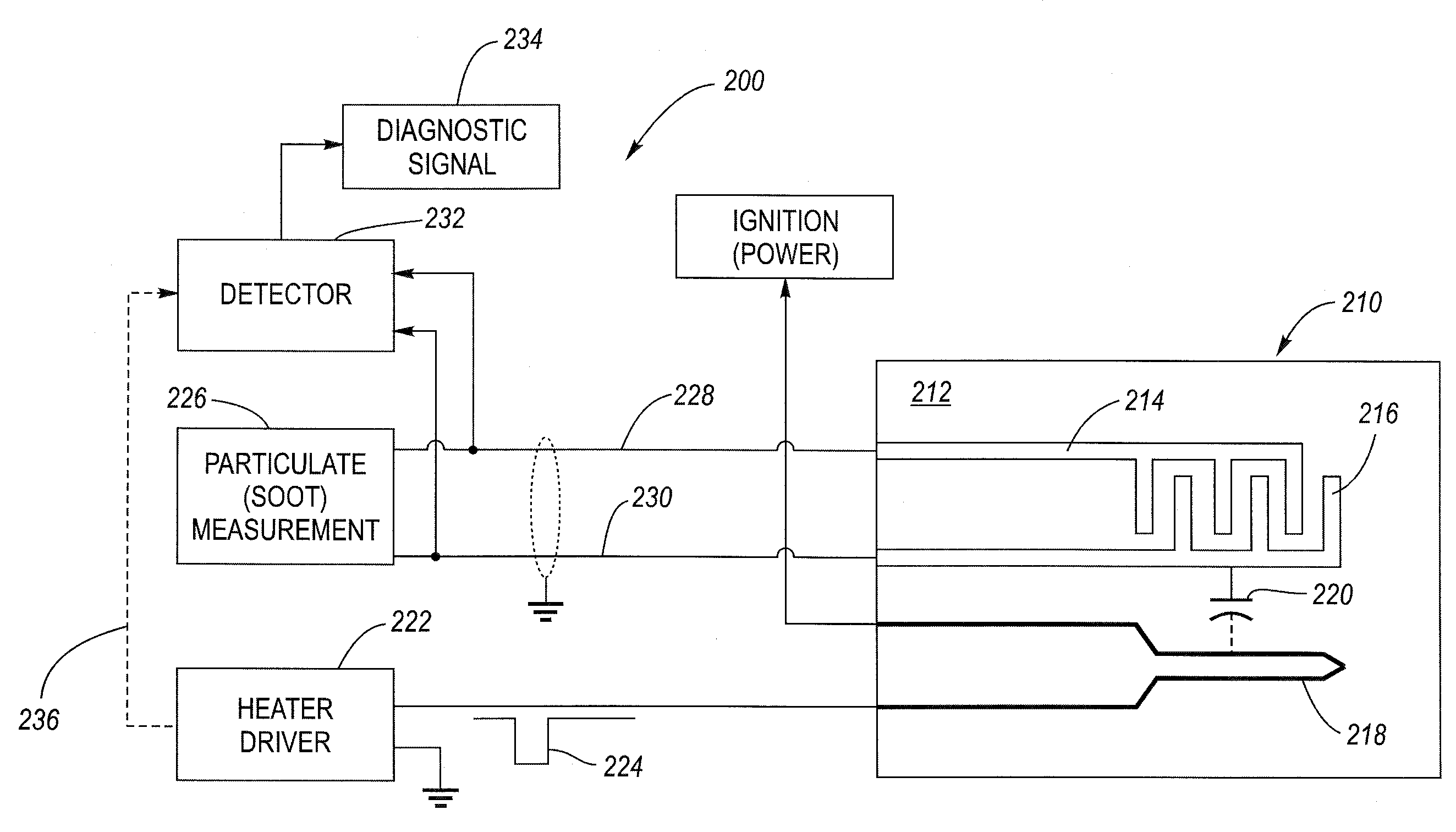
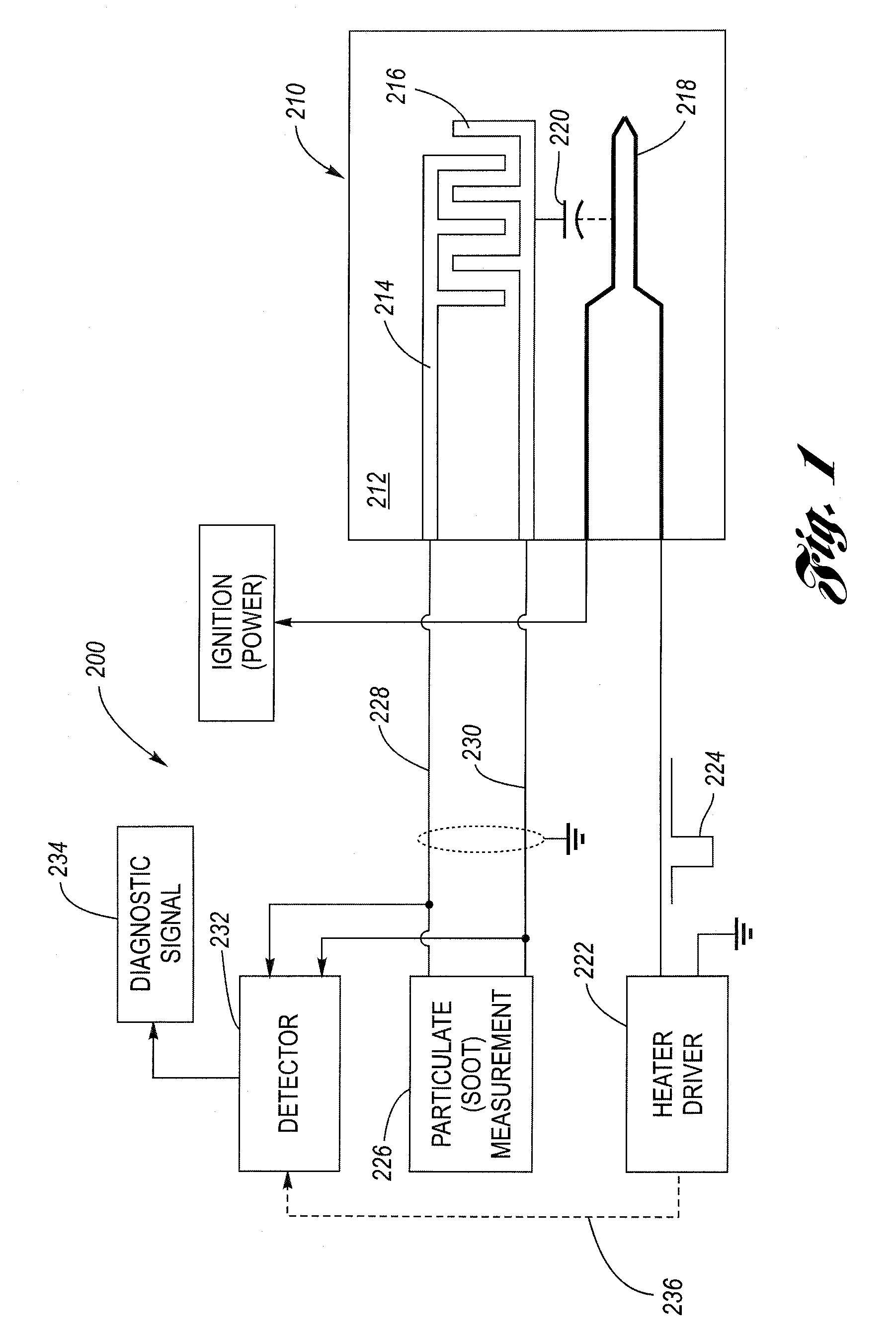
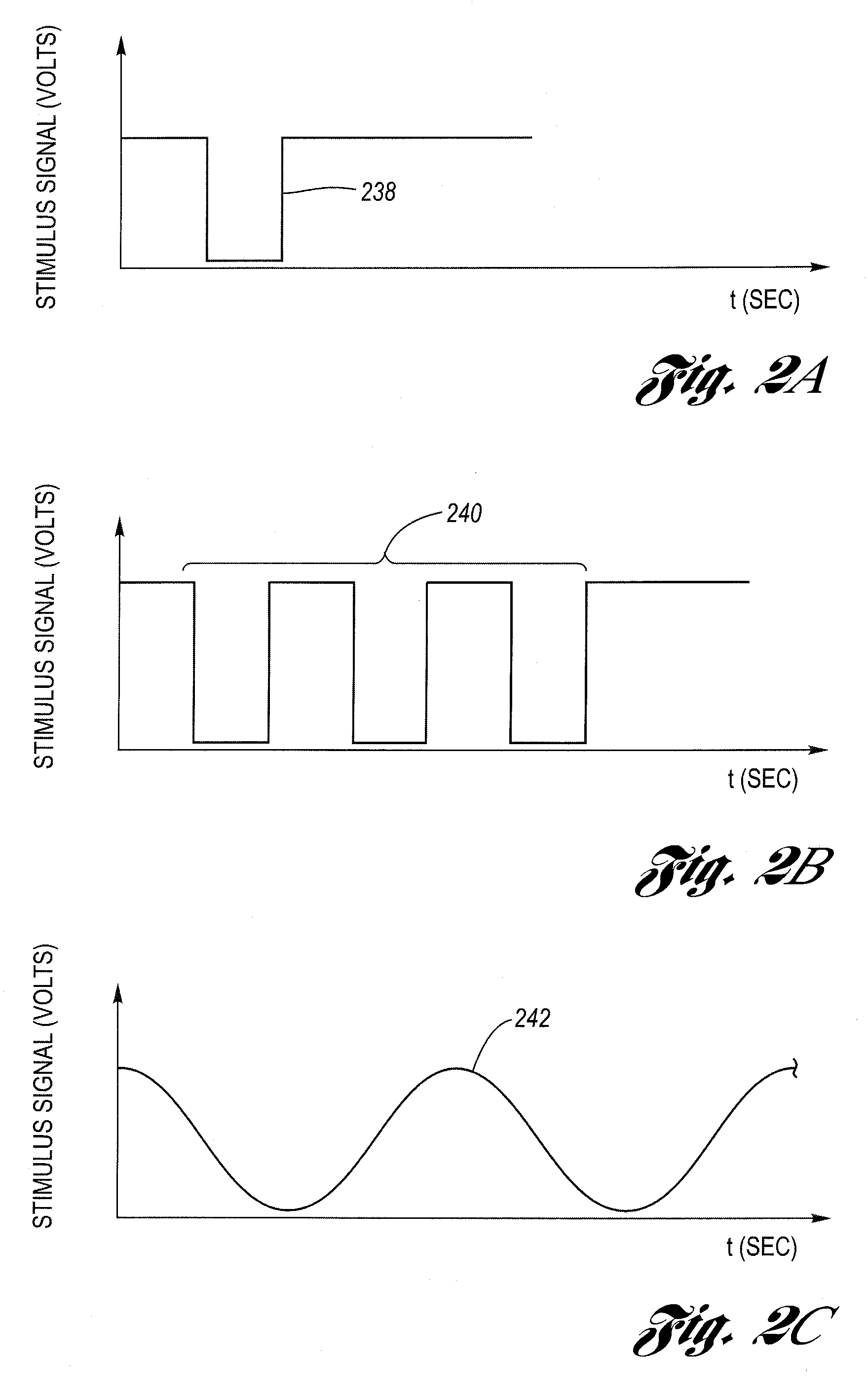
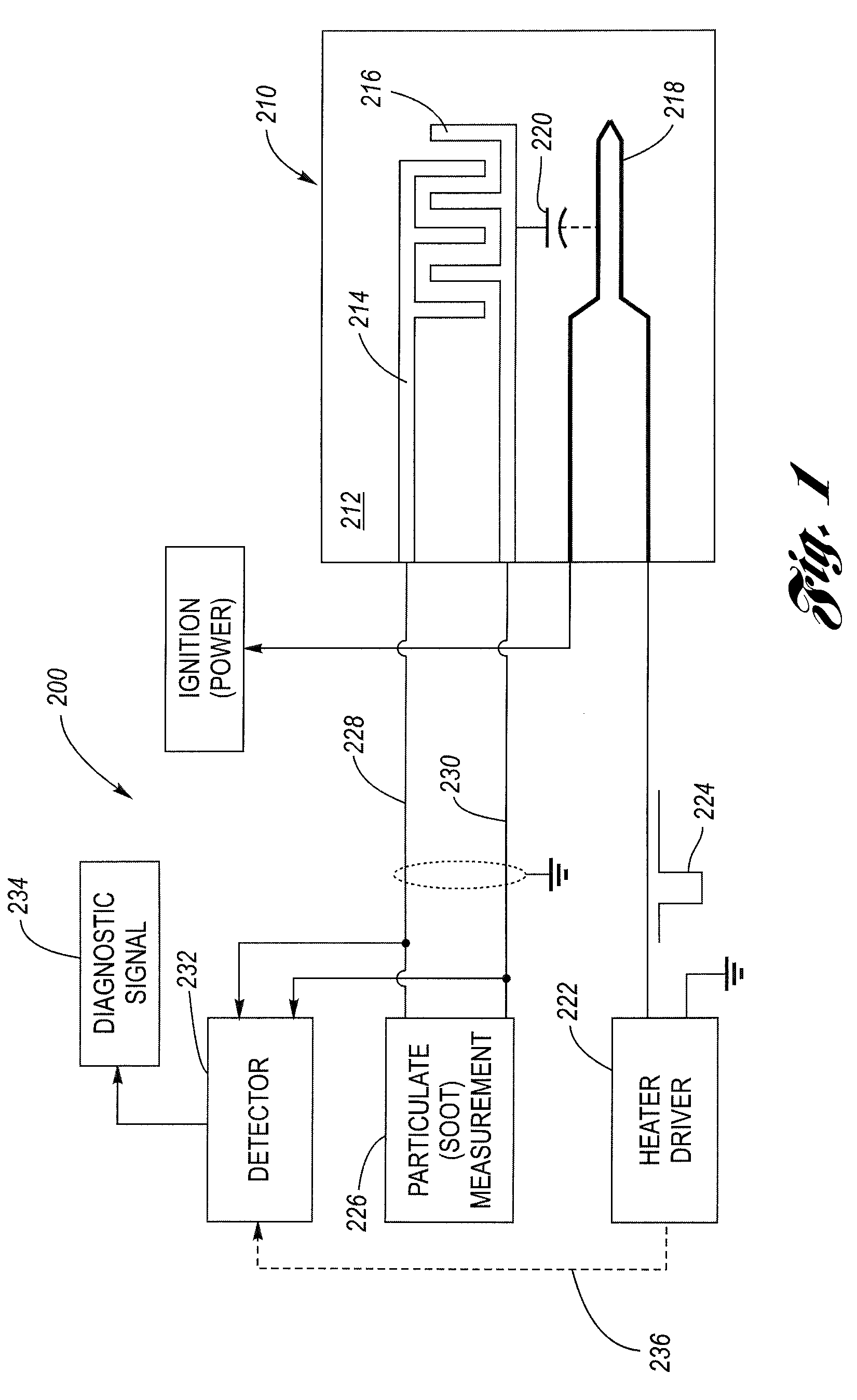
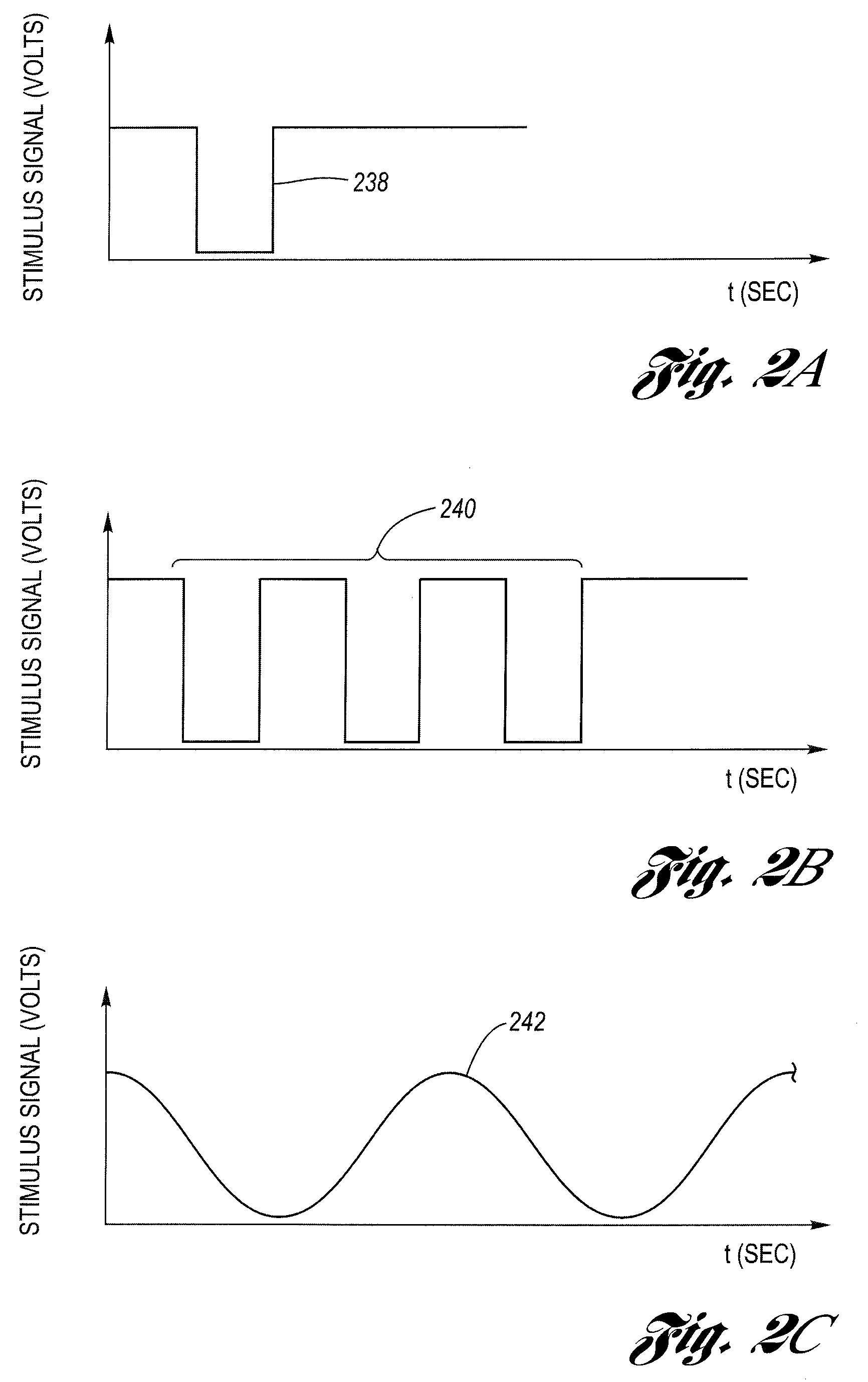
System and method for particulate sensor diagnostic
ActiveUS20090090622A1Fault locationMaterial electrochemical variablesParasitic capacitanceEngineering
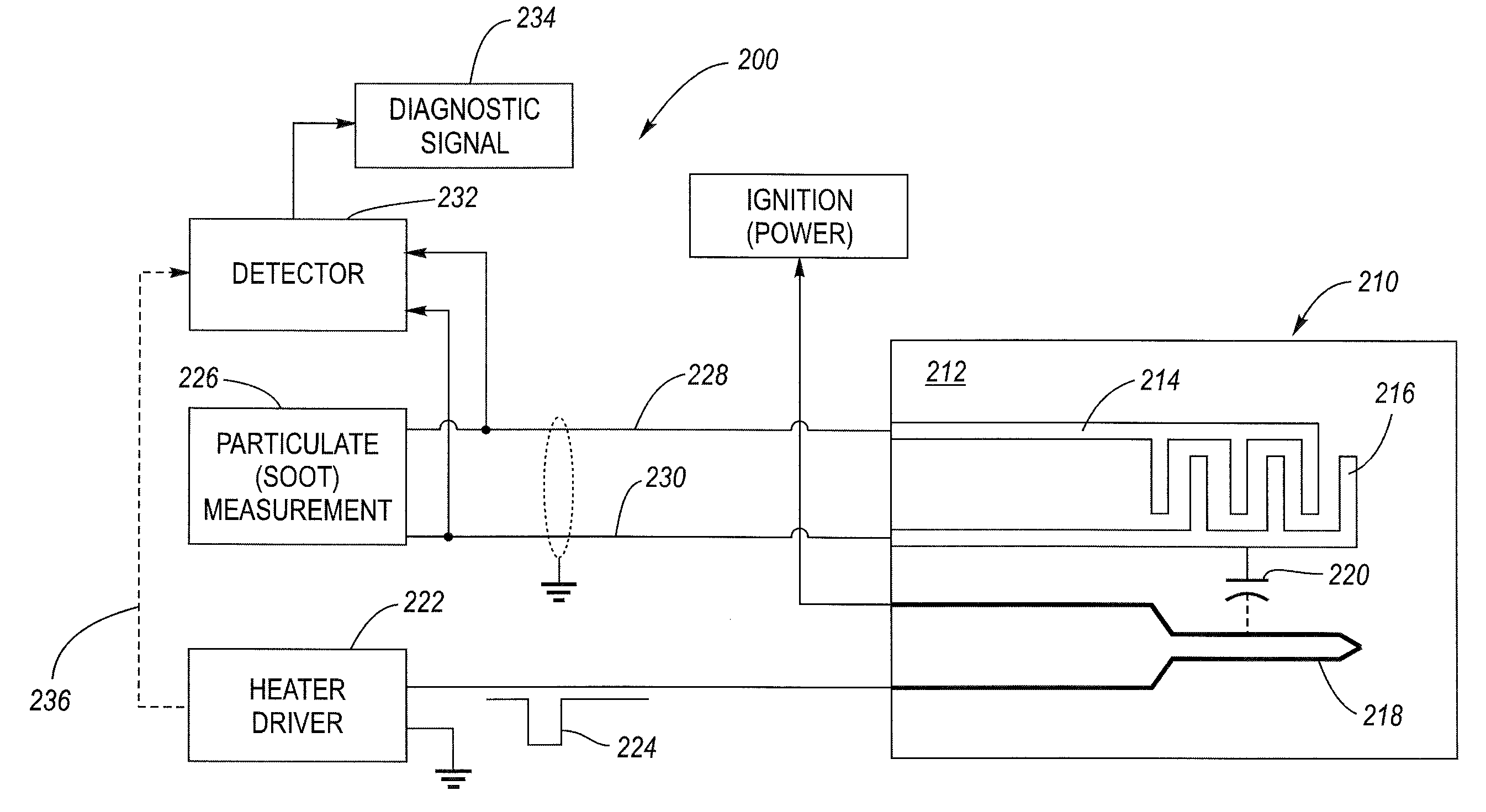
A particulate (soot) sensor system has a diagnostic feature for verifying the integrity of the wiring leads. The sensor system includes a sensor and processing circuitry. The sensor has a substrate, first and second sensing electrodes on the substrate and a heater electrode. The heater electrode is electrically isolated from the first and second sensing electrodes, although there is a parasitic capacitance between them. The processing circuitry includes a heater driver, a measurement circuit connected to the sensing electrodes by wire leads, and a detector. The heater driver, in addition to energizing the heater, produces a stimulus signal that is applied to the heating electrode, which is then coupled via the parasitic capacitance to the sensing electrodes. The detector is coupled to the wiring leads and is configured to detect the stimulus signal when there is electrical conductivity over the leads to the sensing electrodes.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Controlling chemical dispense operations based on conductivity offset
ActiveUS6892143B2Washing controlling processesTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsChemical solutionCompound (substance)
A system and method is disclosed for controlling chemical dispense operations based on a conductivity offset determined for a chemical solution. The chemical dispense operations are performed by or in conjunction with operation of a utility device, such as a warewashing machine. The chemical solution is formed in a solution tank device by combining water with at least one component chemical product. The conductivity offset, which is the conductivity of the water, is used to normalize the conductivity estimated for the chemical solution relative to the component chemical product in the solution. During various points in time during operation of the utility device, the normalized conductivity is compared to a conductivity setpoint, and if the normalized conductivity falls below the conductivity setpoint, a specified volume of the component chemical product is supplied to the solution tank.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Thick electrode with good electrochemical performance and its preparation method
ActiveCN102324493AImproved magnification performanceSolve the problem of concentration polarizationNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesElectrolytic agentEngineering
The invention discloses a thick electrode with a good electrochemical performance. The electrode comprises a current collector and an electrode membrane containing active substances and conductive substances. With a thickness greater than 300 micrometers, the electrode membrane includes an internal membrane layer close to the current collector and an external membrane layer far from the current collector. The conductivity of the electrode membrane decreases from the internal membrane layer to the external membrane layer, while the porosity of the electrode membrane increases from the internal membrane layer to the external membrane layer. The internal membrane layer has great conductivity which can make electrons at the current collector entering or separating from the internal membrane layer rapidly. With great porosity, the external membrane layer can adsorb a lot of electrolyte, thus solving the problem of poor electrolyte wettability of thick electrodes. In addition, the invention also discloses a preparation method of a thick electrode with a good electrochemical performance.
Owner:DONGGUAN AMPEREX TECH +1
Complex monitor for automatically monitoring multiple parameters of water on line
InactiveCN102661923AEconomic savingsNo secondary pollutionColor/spectral properties measurementsMaterial electrochemical variablesPrincipal component analysisUv vis absorbance
The invention discloses a method for automatically monitoring water quality indexes on line and a device for implementing the method. A method of combining an ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy and various sensors is adopted, dozens of water quality indexes including chemical oxygen demand and ammonia nitrogen can be measured at one time, measurement indexes can be configured in a building block mode according to requirements, and chemical agents are not required. According to the device, the constructed digital optical fiber spectrometer is taken as a core, ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrum data of a water sample is processed in a mode of sequentially combining wavelet de-noising, principal component analysis and a support vector machine, and water quality indexes such as chemical oxygen demand and biochemical oxygen demand of water are acquired. Various physical and electrochemical sensors acquire water quality indexes such as ammonia nitrogen, dissolved oxygen and conductivity. All hardware and software for implementing the method is put in a cabinet to form the device, and the device analyzes the introduced water sample under the control of an embedded industrial control computer system, and automatically monitors the water quality indexes in real time.
Owner:SICHUAN BELAM TECH
High resolution resistivity earth imager
ActiveUS7394258B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationDielectricConductivity
Impedance measurements made by a galvanic resistivity tool in a borehole in an earth formation are corrected by a factor that depends on the mud conductivity and the mud dielectric constant. Standoff measurements are not necessary.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped hierarchical porous carbon composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110627033AWidely distributedRich sourcesHybrid capacitor electrodesCarbon preparation/purificationCapacitanceCarbon composites
The invention discloses a nitrogen and sulfur co-doped hierarchical porous carbon composite material, and a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of supercapacitor electrode materials. A natural polymer material which is abundant in the nature, low in price and easy to obtain is used as a carbon source, graphene oxide is added to improve the conductivity, an activator and a doping agent are added in advance, and a general two-step technology (high-temperature carbonization and chemical activation) for preparing a carbon material is simplified into one-step high-temperature annealing, so that the carbon material with a high specific surface area and a hierarchical porous three-dimensional structure is obtained; and nitrogen and sulfur doping improves the electrochemical performances of the material. The composite carbon material has the advantages of high mass specific capacitance, excellent high-current rate capability, ultra-long cycle life,high mass energy density and high power density when used as a high-performance electrode material for a supercapacitor. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, feasibility, low requirements on reaction deices, environmental friendliness, and suitableness for industrial production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Sensor element for detecting a physical measuring variable between bodies exposed to high tribological strain
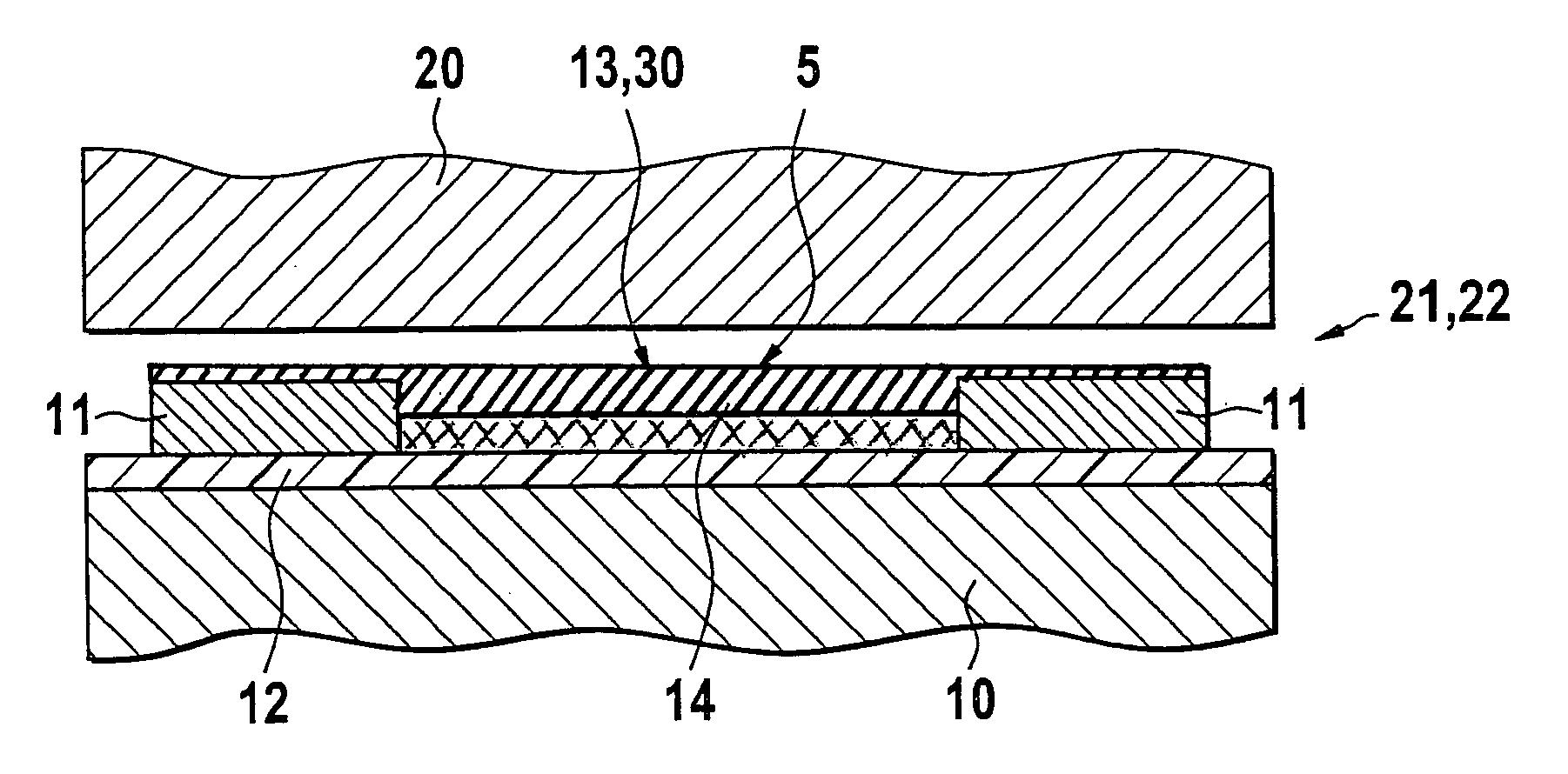
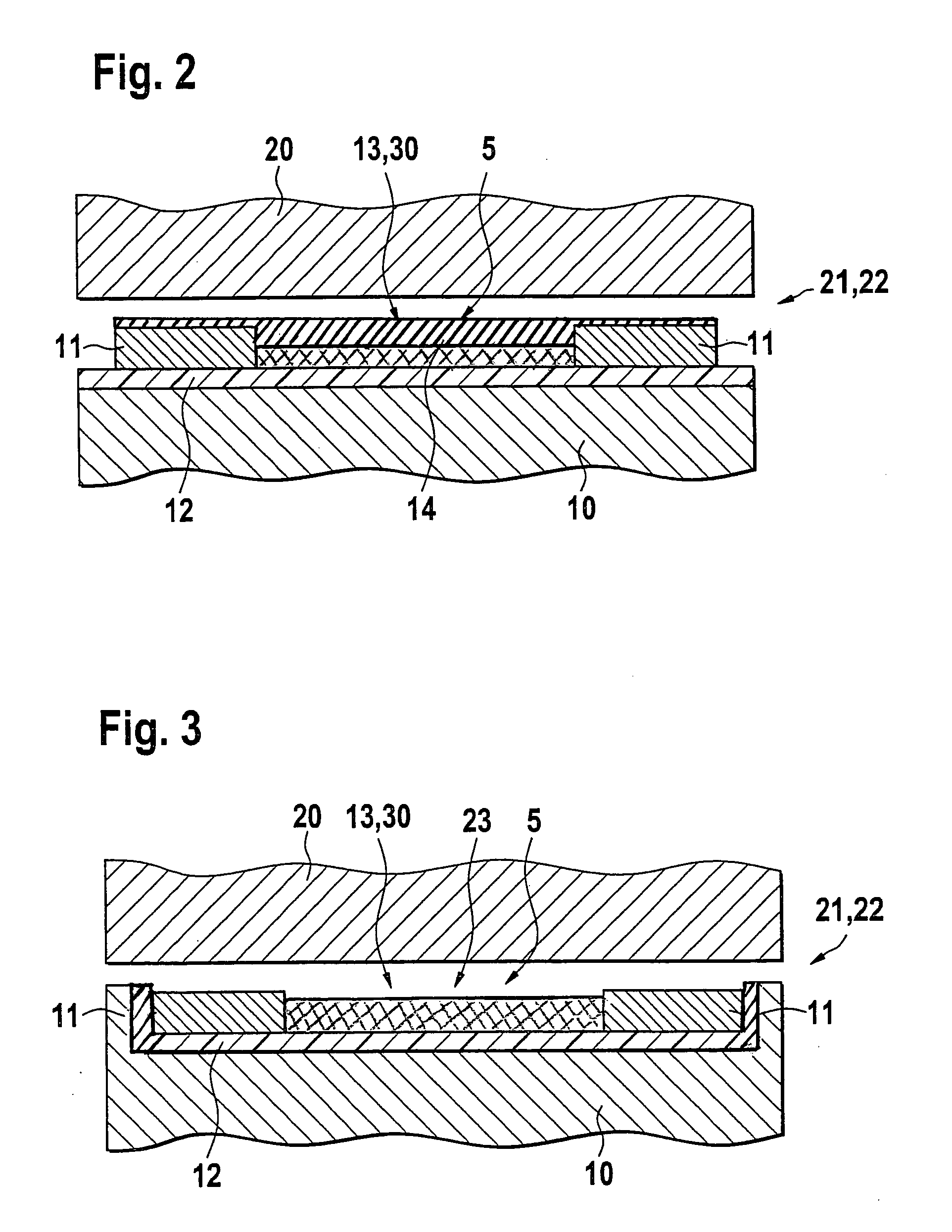
The invention proposes a sensor element (5) for detecting a physical measurement variable such as a pressure, a temperature, a capacitance, or a gap width between two bodies (10, 20) that move in relation to each other during operation and experience high tribological stress. In certain areas between the surfaces of the bodies (10, 20) that move in relation to each other, in a surface region of at least one of the bodies (10), a sensitive layer (13, 30), in particular a sensor segment (13), is provided, which is separated from the body (10) by an insulation layer (12). The insulation layer (12) has at least two component layers (31, 32), wherein one component layer (31) is a layer (31) with at least a low electrical conductivity in comparison to the sensitive layer (13) and wherein one component layer (32) is a layer with a higher tribological stress capacity in comparison to the component layer (31) with the comparatively low electrical conductivity and / or the insulation layer (12) is a layer that is at least essentially comprised of carbon, or contains carbon, oxygen, and silicon. The sensor element (5) proposed is primarily suited for detecting measurement variables in the contact region between lubricated components under high tribological stress.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Contaminant removal apparatus and installation method
InactiveUS20050247571A1High cost-effectiveImprove efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater treatment parameter controlElectrocoagulationElectrical battery
This invention relates to a method of installation of an electrocoagulation (EC) system to remove contaminants from wastewater which includes the steps of: (i) measuring conductivity of the wastewater; (ii) from the result obtained in step (i) determining the number of electrically connected electrodes or unipolar electrodes required in the EC system for efficient removal of the contaminants, and (iii) from step (ii) assessing a range of current and / or voltage to be applied to an EC cell included in the EC system.
Owner:AQUENOX
Method for electromagnetically measuring physical parameters of a pipe
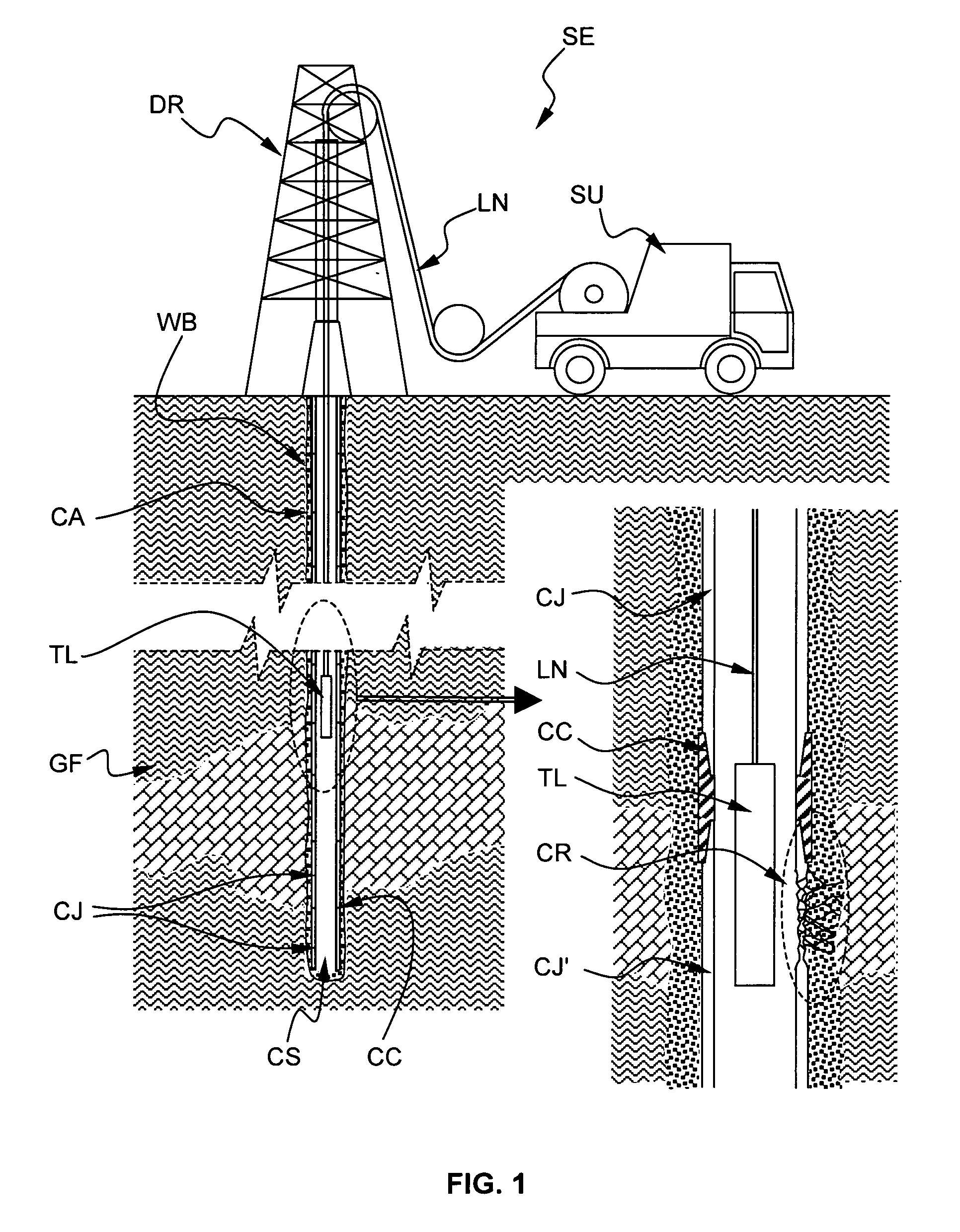
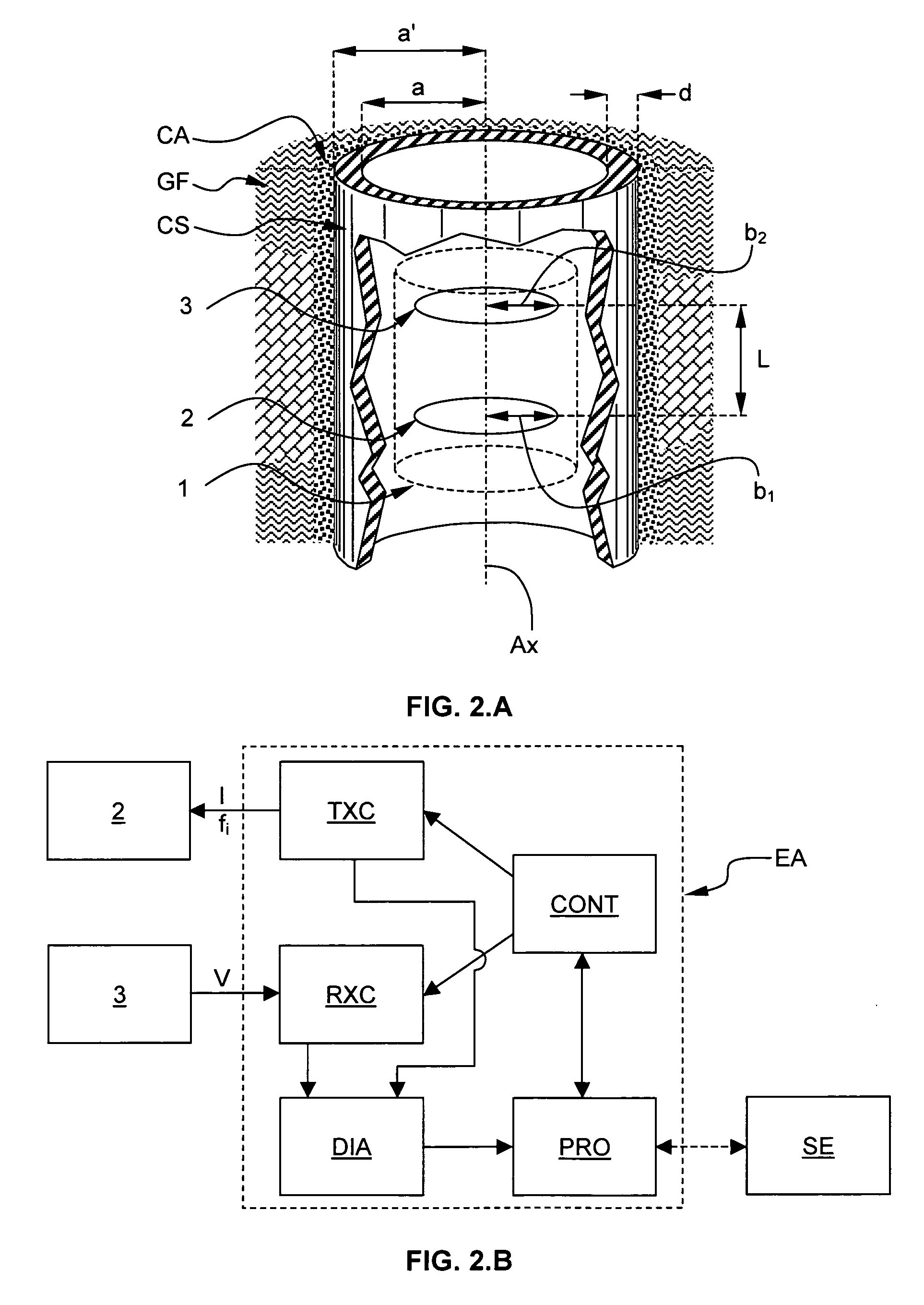
ActiveUS20100017137A1Improve accuracyPlug gaugesElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingTransmitter coilPower flow
The method electromagnetically measures a pipe inner diameter ID and a pipe ratio of magnetic permeability to electrical conductivity μ2 / σ2 by means of a measuring arrangement 1 comprising a transmitter coil 2 and a receiver coil 3, both coils being coaxial to and longitudinally spaced from each other, the measuring arrangement 1 being adapted to be positioned into the pipe CS and displaced through the pipe. The method comprises the steps of:a1) exciting the transmitter coil 2 by means of a transmitter current Ii, the transmitter current having a first excitation frequency f1,a2) measuring a receiver voltage Vi at the receiver coil 3, a3) determining a transimpedance Vi / Ii between the transmitter coil 2 and the receiver coil 3 based on the transmitter current Ii and the receiver voltage Vi, and determining a measurement ratio Mi based on said transimpedance,b) repeating the excitation step a1), the measuring step a2), the transimpedance and the measurement ratio determination step a3) for at least a second excitation frequency f2 so as to define a measurement ratio vector [M1, M2, . . . Mn],c) calculating a prediction function vector [G1, G2, . . . Gn] based on the first and at least the second excitation frequency, a plurality of potential pipe ratio of magnetic permeability to electrical conductivity and a plurality of potential pipe inner diameter ID, andd) applying a minimizing algorithm onto the measurement ratio vector [M1, M2, . . . Mn] and the prediction function vector [G1, G2, . . . Gn] and determining the pipe inner diameter and the pipe ratio of magnetic permeability to electrical conductivity corresponding to a maximum solution of the algorithm.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Multi-parameter water quality monitoring integrated microarray electrodes and preparation method
InactiveCN102495119ARich sourcesMature processing technologyDecorative surface effectsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsInsulation layerWater quality
The invention relates to multi-parameter water quality monitoring integrated microarray electrodes and a preparation method. The invention is characterized in that the microarray electrodes are fabricated on an oxidized wafer. According to the invention, a Pt thin film is used as a substrate of the microarray electrodes, photosensitive polyimide is used as an insulation layer, electrode sites are exposed by using photoetching, and other parts of the microarray electrodes are insulated; an electrochemical modification method is used for electrodeposition of Ag / AgCl and IrOx films on bare electrodes so as to respectively form reference electrodes and pH test electrodes, thereby realizing determination of temperature, oxidation reduction potentials, conductivity and pH values. The preparation method comprises production of the micro-array electrodes, preparation of the Ag / AgCl reference electrodes and preparation of the pH electrodes. Integration and miniaturization of the microarray electrodes provided in the invention are convenient.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
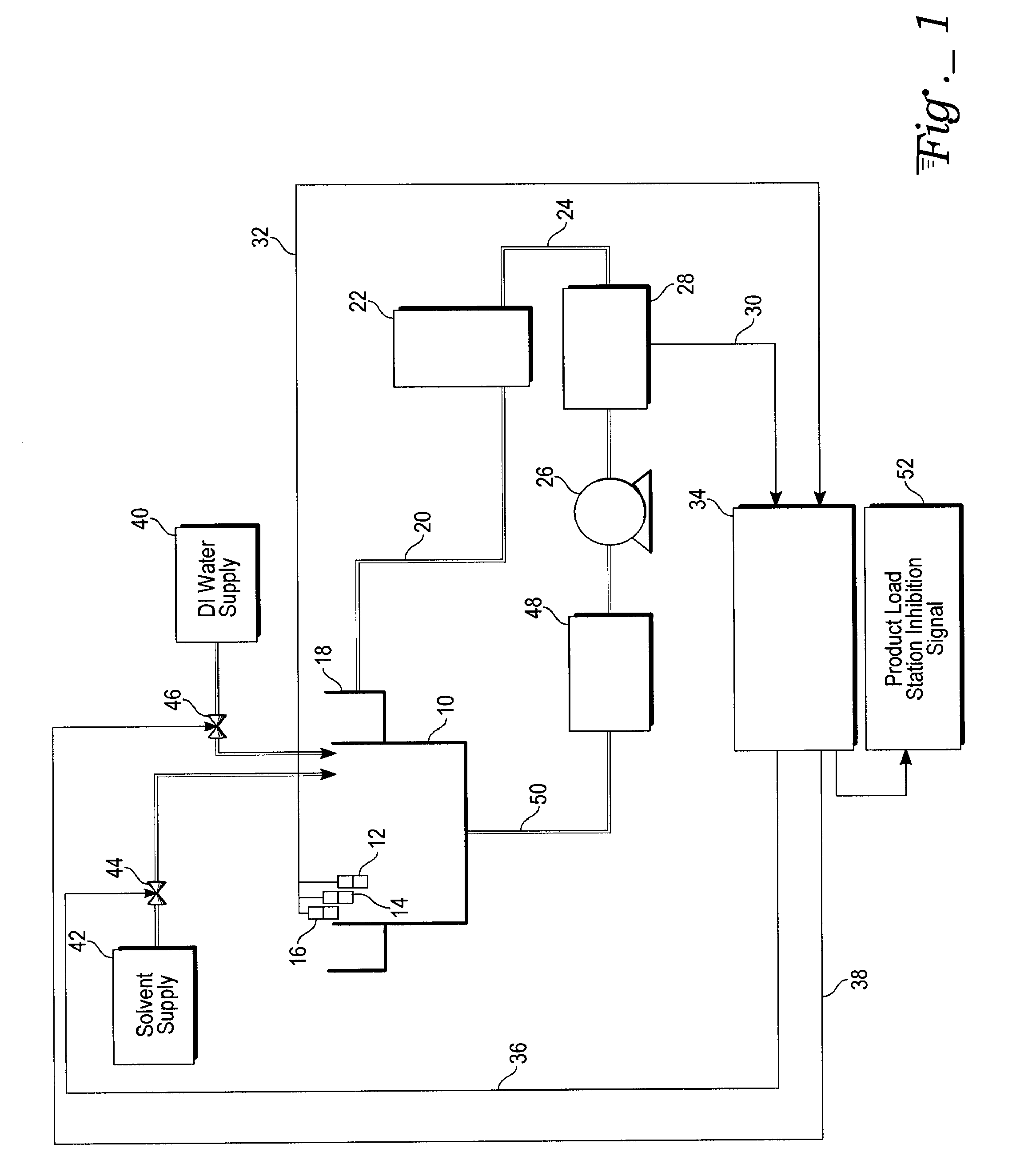
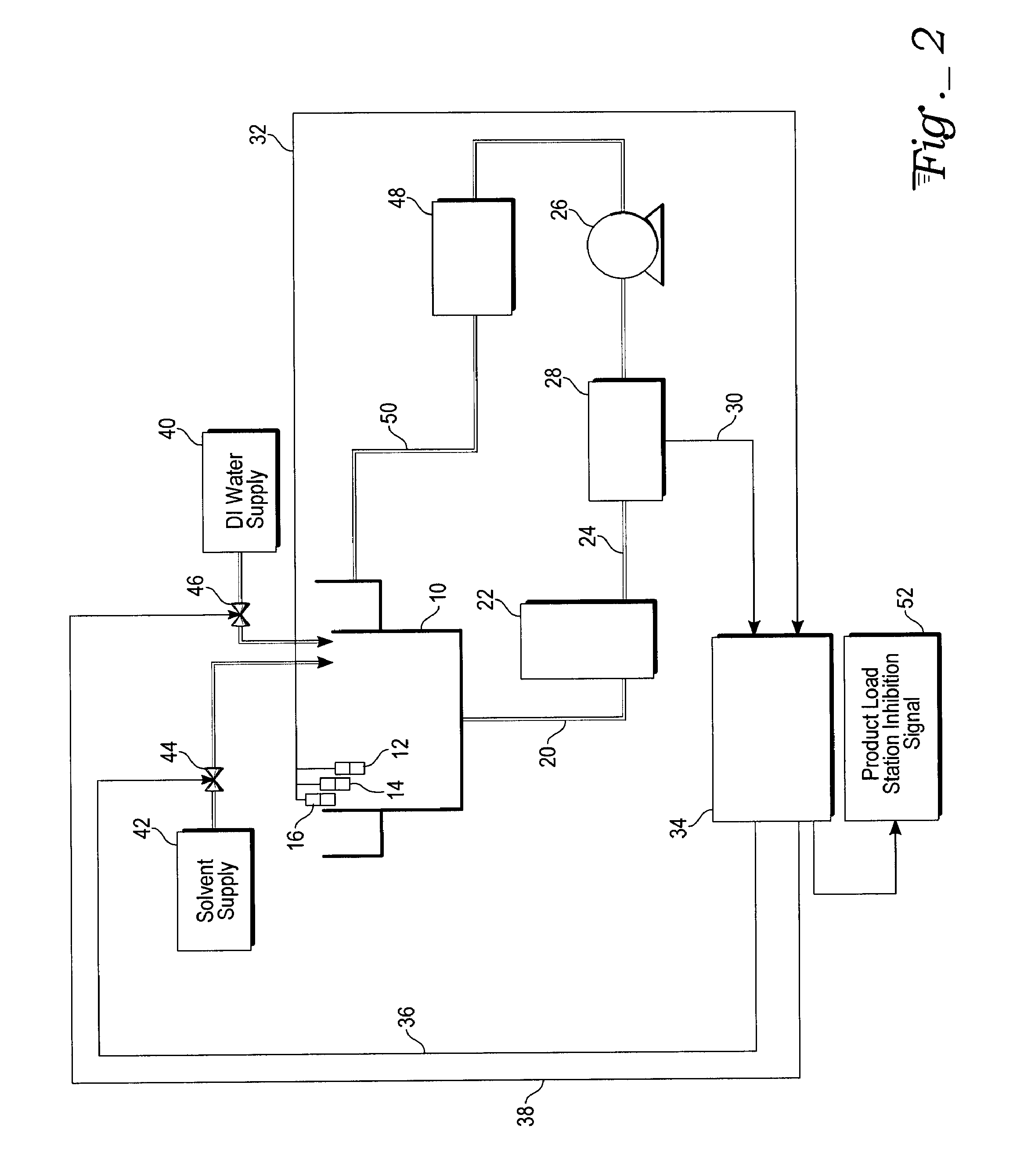
Conductivity control of water content in solvent strip baths
ActiveUS20080023045A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementHollow article cleaningCompound (substance)Process engineering
A system and method for control of water content in a strip bath. The method to control water content in a solvent bath used for cleaning of semiconductor parts in the back end of semiconductor manufacturing requires addition of water to replace evaporated water. This is done by periodically adjusting a conductivity setpoint at least in part based on the elapsed chemical bathlife and at least in part based on the number of semiconductor parts that have been processed in the bath. The conductivity of the strip bath solution is then continuously measured (as by using an electrodeless conductivity probe). Water is added (as by a DI water injection system) into the bath solution whenever the solvent conductivity falls below the conductivity set point.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Method for positioning artificial wetland clogging area through resistivity curve
InactiveCN104049279AContinuous operationGuaranteed uptimeMaterial resistanceElectric/magnetic detectionDielectricConstructed wetland
The invention discloses a method for positioning an artificial wetland clogging area through a resistivity curve. The method includes the steps that first, a direct-current resistivity symmetrical four-pole sounding device is arranged above an artificial wetland, and the apparent resistivity is measured according to the mode that the electrode spacing becomes bigger and bigger; second, a power supply positive electrode A, a power supply negative electrode B, a measurement electrode M and a measurement electrode N of the direct-current resistivity symmetrical four-pole sounding device are all arranged symmetrical about a measurement point, and the apparent resistivity (please see the formula in the specification) of the electrode spacing is calculated every time the power supply electrode spacing is changed; third, the measured apparent resistivity is subjected to inversion, and the resistivity depth measurement curve is drawn according to the resistivity values obtained through inversion; fourth, the non-clogging area of the artificial wetland has the low resistivity characteristic, the clogging area of the artificial wetland has the high resistivity characteristic, and on the resistivity depth measurement curve, the vertical spatial position of the clogging area in the measurement point is determined according to the changing characteristic of the resistivity value. According to the method, on the basis of the conductivity difference of dielectric, the artificial wetland clogging area can be positioned through the resistivity difference.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Combined characterization and inversion of reservoir parameters from nuclear, NMR and resistivity measurements
InactiveUS7157915B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWell logging
A method of determining the distribution of shales, sands and water in a reservoir including laminated shaly sands using vertical and horizontal conductivities derived from nuclear, NMR, and multi-component induction data such as from a Multicomponent Induction Logging Tool
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
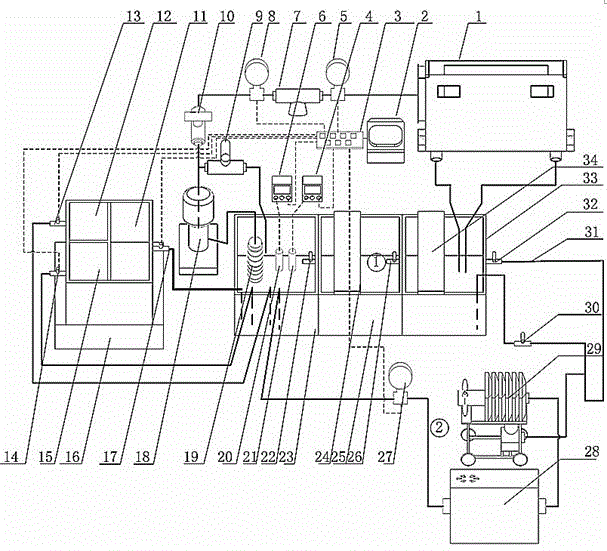
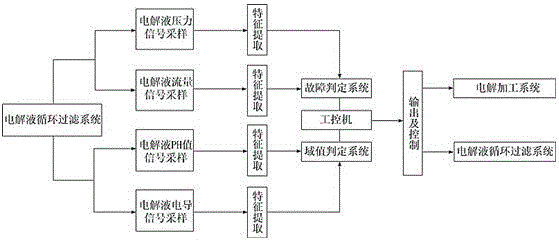
Circulating filtration system for electrochemical machining electrolyte and control method thereof
InactiveCN102873418AImprove cleanlinessImprove operational reliabilityMachining electric circuitsMachining working media supply/regenerationElectrolytic agentSolenoid valve
The invention discloses a circulating filtration system for electrochemical machining electrolyte and a control method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical machining. The circulating filtration system for the electrochemical machining electrolyte comprises an electrolyte tank, an electrolyte circulating device, an electrolyte filtering device, an electrolyte filtering and monitoring device and an electrolyte component control device. According to the circulating filtration system for the electrochemical machining electrolyte, which is disclosed by the invention, two loops are connected in parallel to filter the electrolyte, the electrolyte input to a processing area has a high cleanliness; the electrolyte filtering and monitoring device is adopted to monitor a secondary filter and a plate-and-frame filter press in real time; in an electrolysis processing process, the circulating filtration system for the electrolyte has a high reliability; the electrolyte component control device is used for monitoring the pH (potential of hydrogen) value and the conductivity of the electrolyte in real time; and an industrial personal computer controls a liquid regulation tank to correspond to the on and off of a solenoid valve so as to guarantee the stability of the pH value and the conductivity of the electrolyte in the electrolysis processing process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for manufacturing porous flaky NiCo2O4 and grapheme composite capacitive material
ActiveCN104240972AHigh specific capacitanceImprove electrochemical stabilityHybrid/EDL manufactureAir atmosphereCapacitance
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a porous flaky NiCo2O4 and grapheme composite capacitive material, and belongs to the field of nano composite material manufacturing. According to the method, a graphite oxide, cobalt nitrate and nickel nitrate are dissolved in deionized water in an ultrasonic mode and stirred, a certain amount of hexamethylene tetramine is added, a reflux reaction is carried out for 3-4 hours at the temperature of 90 DEG C, sediments are collected, the collected sediments are calcined in an air atmosphere for 2 hours at the temperature of 330 DEG C, and the porous flaky NiCo2O4 and grapheme nano composite material is obtained. In the manufactured porous flaky NiCo2O4 and grapheme composite capacitive material, porous flaky NiCo2O4 is completely attached to the surface of a grapheme piece. By means of the composite structure, conductivity of the material is improved, and the contact area of the material and an electrolyte solution is greatly improved, so that the composite material has high specific capacitance and good electrochemical stability and can be possibly used as a super-capacitor electrode material.
Owner:江阴智产汇知识产权运营有限公司
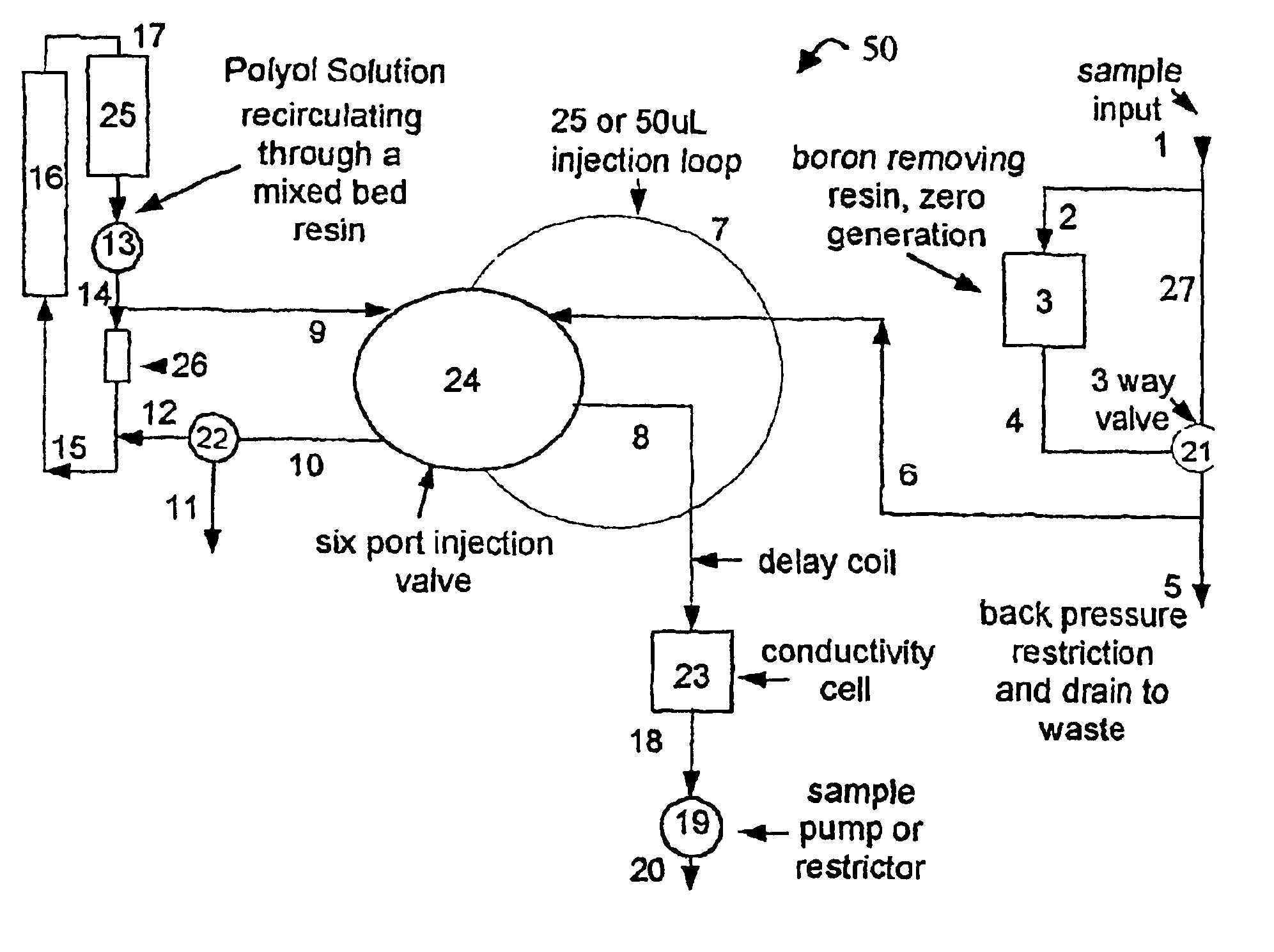
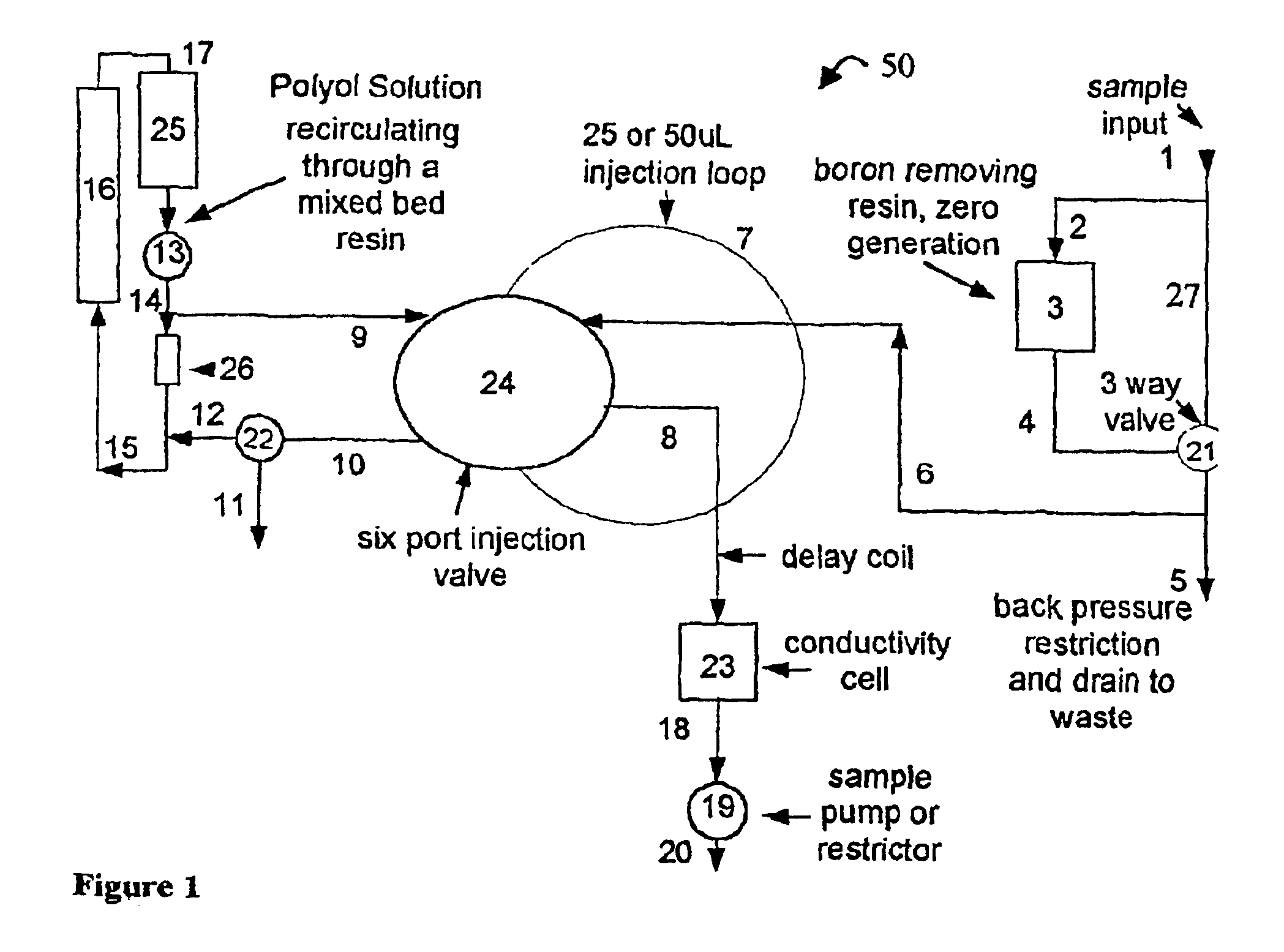
Low-level boron detection and measurement
InactiveUS6884356B2Accurate analysisImprove conductivityIon-exchanger regenerationTesting waterChemical reactionPolyol
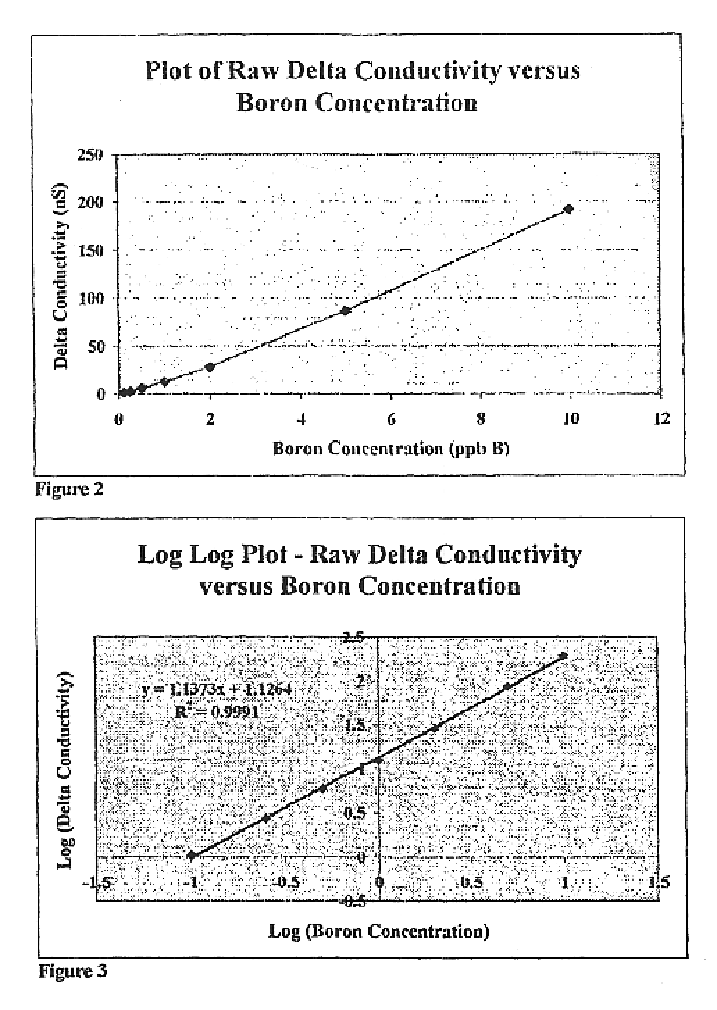
Methods and apparatus (50) are disclosed for accurately measuring low concentrations of boron in deionized water utilizing the chemical reaction of boric acid with a polyol by injecting very small plugs of concentrated polyol into streams of boron containing and non-boron containing water samples to produce an ionized acids product, and then measuring the conductivity difference (delta conductivity), corrected for interfering or extraneous factors which can effect conductivity, between such boron containing and non-boron containing samples using a conductivity and temperature detector (23).
Owner:SIEVERS INSTR
Electrode arrangement for monitoring a bed
ActiveUS8878557B2Lower resistanceSure easySpectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceControl systemElectrical resistivity and conductivity
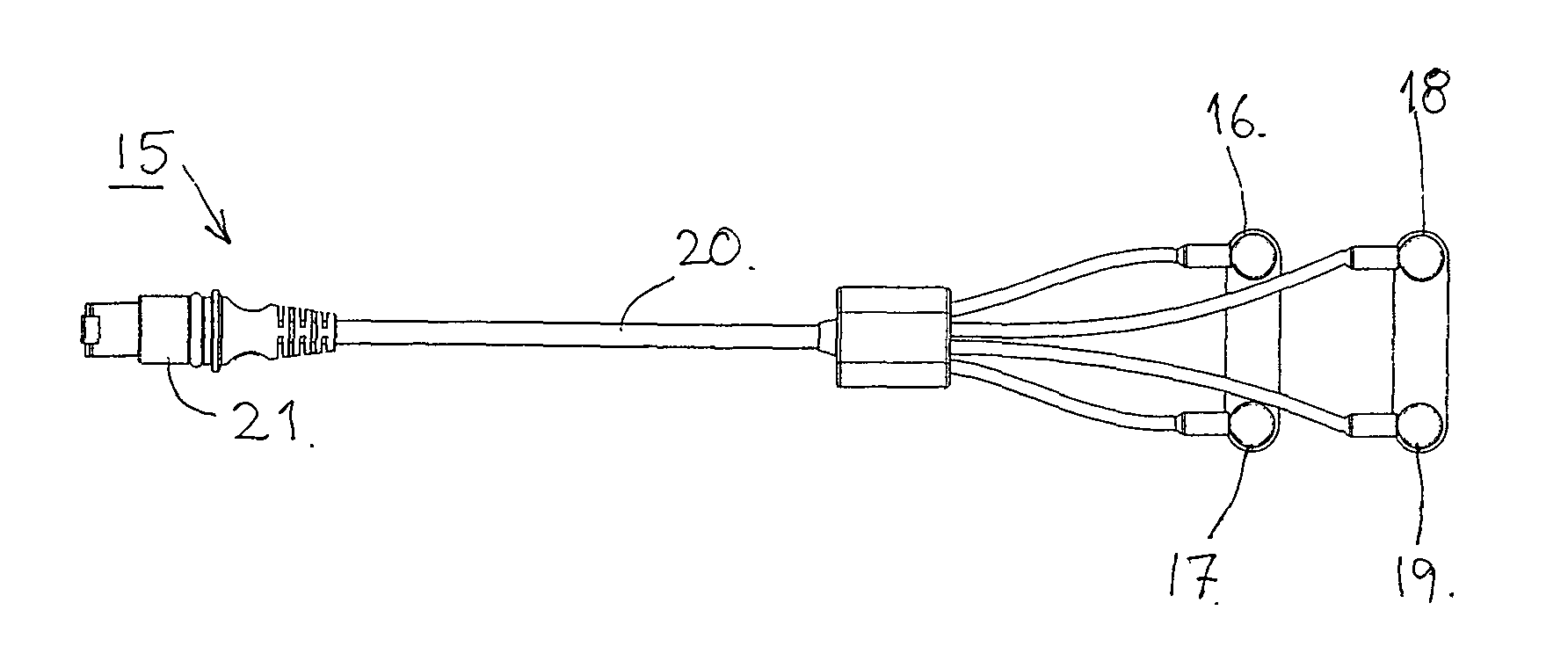
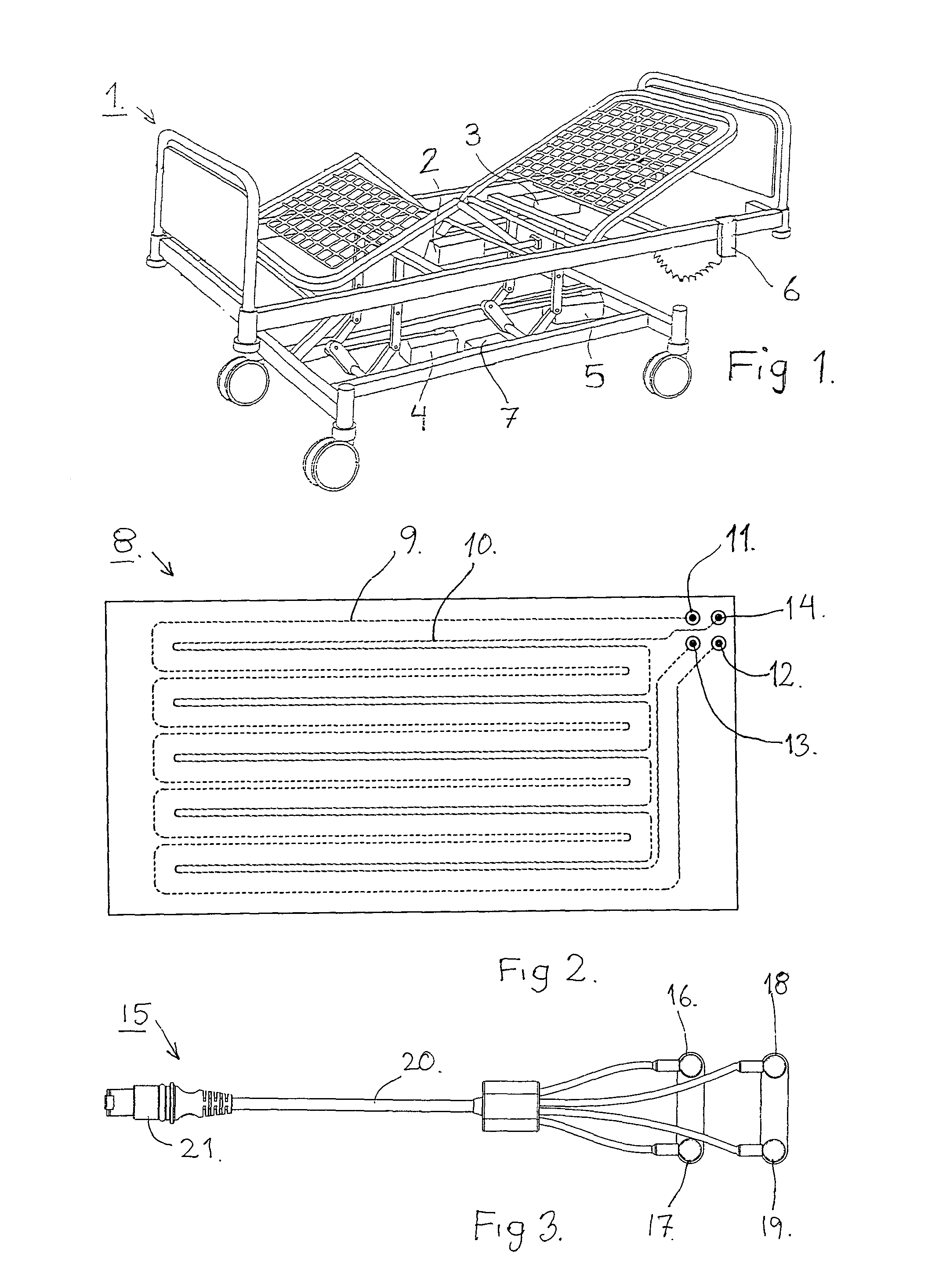
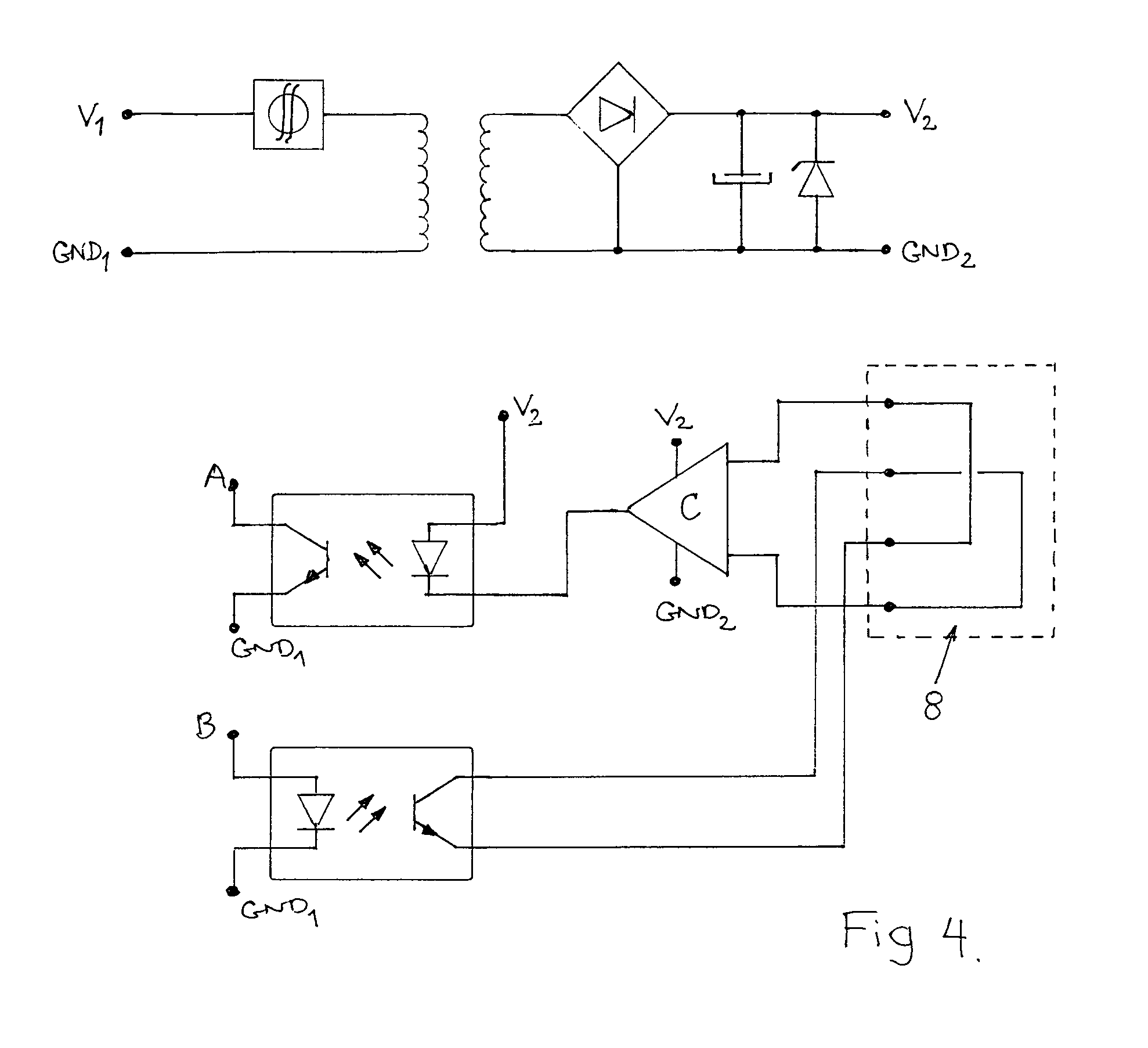
Equipment for indicating a bed-wetting in a bed comprising a bed-wetter sheet and a measuring- and control system. A measuring circuit is furnished to test whether the electrode in the bed-wetter sheet are intact, and afterwards to measure the conductivity in the normal state between the two from each other electrically isolated electrodes whereby the conductivity between the two electrodes will fall drastically by a bed-wetting, human fluids containing salt being spread on the sheet, and indicate the bed-wetting. The measuring circuit is furnished to as a part of a routine to enter into a resting state whereby the measurement is performed with a prearranged fixed time interval.
Owner:LINAK AS
Method and apparatus for producing a conductivity log unaffected by shoulder effect and dip from data developed by a well tool
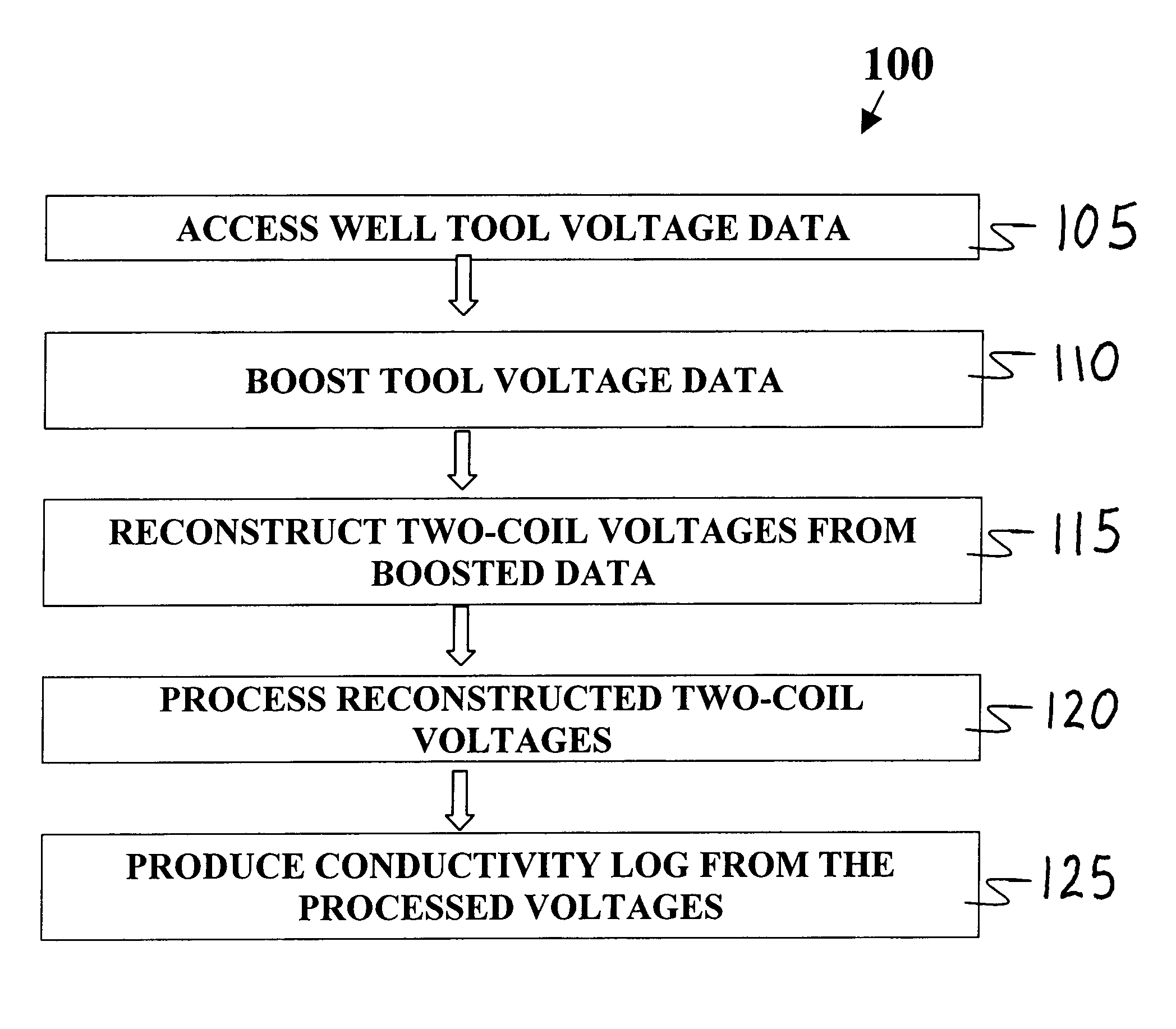
InactiveUS6216089B1Eliminate the effects ofHigh apparent dip angle effectsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingWell loggingComputer science
A method and apparatus for producing a conductivity log, unaffected by shoulder effect and dip, from voltage data developed by a well tool disposed in a borehole. The method involves accessing the voltage data developed by the tool, processing the data, reconstructing two-coil voltage data, and computing differences of the two-coil data, to derive a conductivity profile representative of the formation. The apparatus forms part of a well logging system including a well tool adapted to be moveable through a borehole. The apparatus being coupled to the well tool and adapted with means to access voltage data developed by the receivers disposed on the well tool. The apparatus further adapted with means for boosting the voltage data, means for reconstructing two-coil voltages from the boosted voltage data, means for processing the reconstructed two-coil voltage data, and means for producing a conductivity log from the processed two-coil voltages.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for testing conductivity of medium material
ActiveCN102128985AFacilitated releaseImprove test automationResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringMechanical engineering
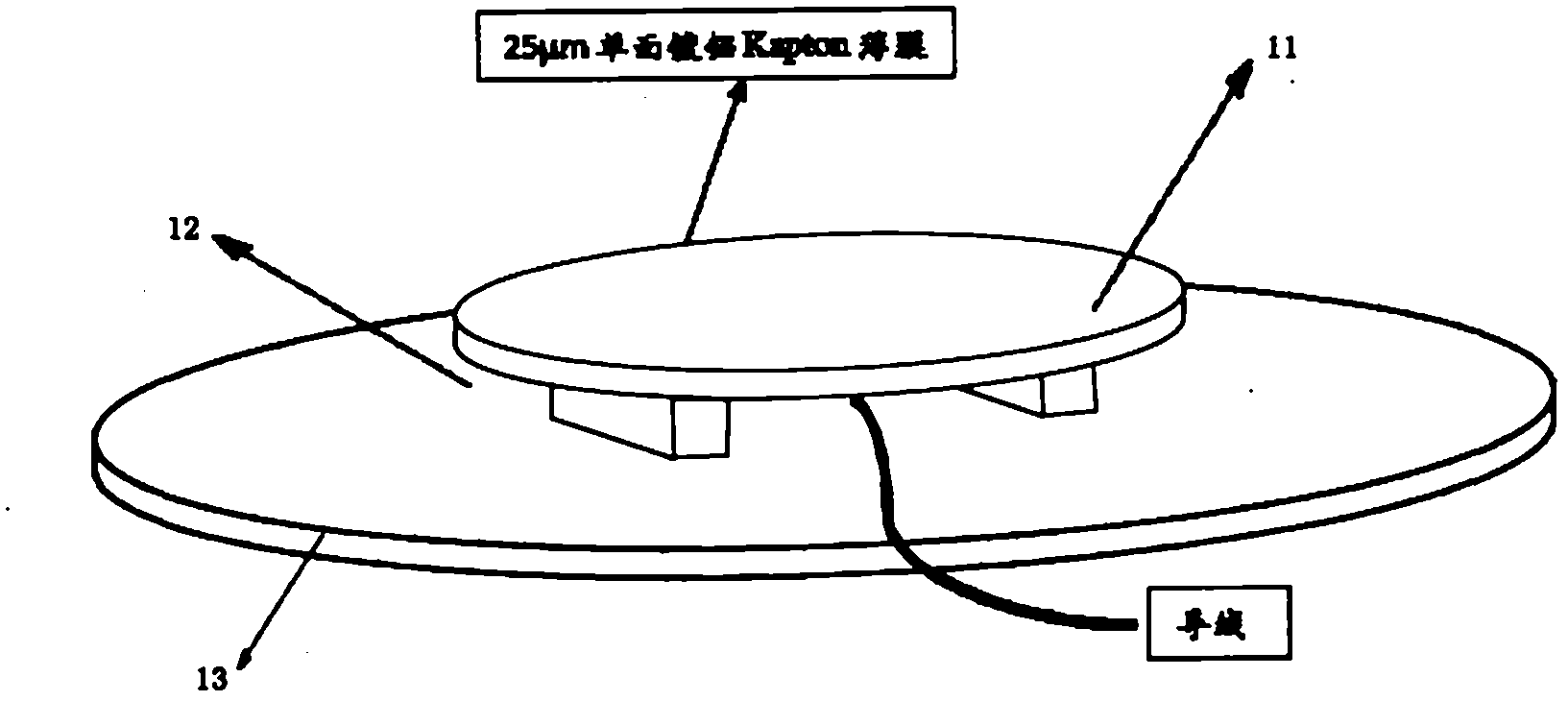
The invention discloses a method for testing conductivity of medium material, wherein the method comprises the following steps of: positioning an electric potential probe at a zero electric potential position above a sample after the preparation before testing is finished; confirming the placing position of the sample, confirming the position coordinate of an electric potential measuring point bya probe driving mechanism, then closing a vacuum jar, turning on the power of an electric gun, and performing electronic irradiation to the sample via a Faraday cut test; quickly descending an electric potential meter probe to the front surface of the sample every 10 minutes to perform inducted non-contact measurement, wherein the data measured by a micro galvanometer and the electric potential probe is waved between negative 0.5% and positive 0.5%, then the charge of the sample is regarded as saturation; turning off the electric gun, attenuating the similar process via a tapping index form in the sample interior electric charge Q and measuring the electric potential decay process of the sample; in a word, the attenuation relationship of the surface electric potential of the sample along time is measured by a surface electric potential probe, and the conductivity of the sample can be calculated according to the sample surface attenuated electric potential at different time. The conductivity testing equipment in the invention can be applied to hazard assessment of deep charging, and also can provide valuable engineering data for the protection of deep charging or discharging.
Owner:NO 510 INST THE FIFTH RES INST OFCHINA AEROSPAE SCI & TECH
Wide-range TOC instrument using plasma oxidation
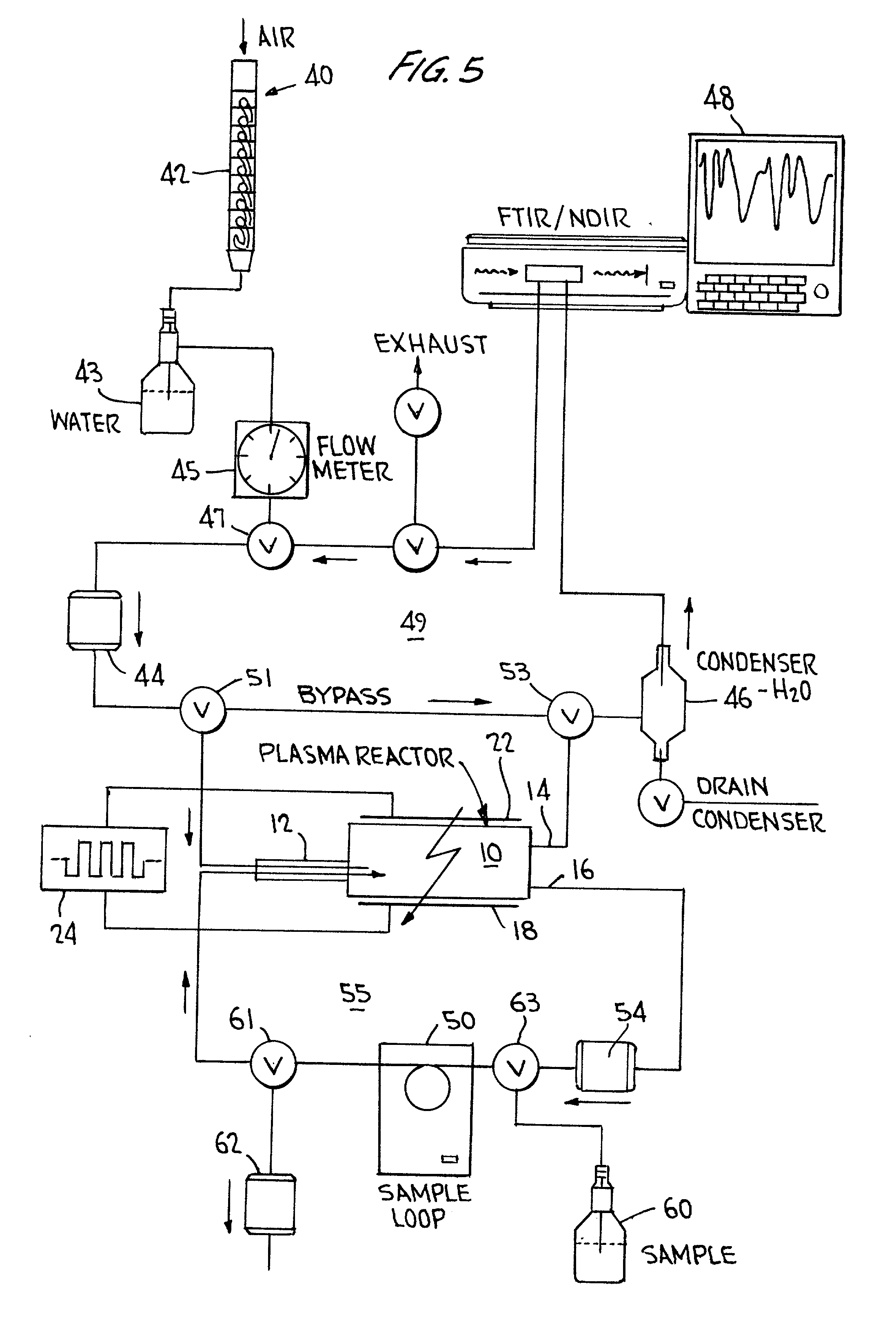
InactiveUS20020068017A1Improve efficiencyShort timeChemical analysis using combustionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationConductivityTotal organic carbon
Total organic carbon in an aqueous or gaseous sample is measured by admitting the sample and an oxidant gas to a cell transparent to plasma, establishing a relatively low energy plasma in the cell, and measuring the CO.sub.2 thus produced using FTIR, NDIR, or conductivity-based techniques.
Owner:HACH CO
Tunnel water leakage detection method and device based on conductivity
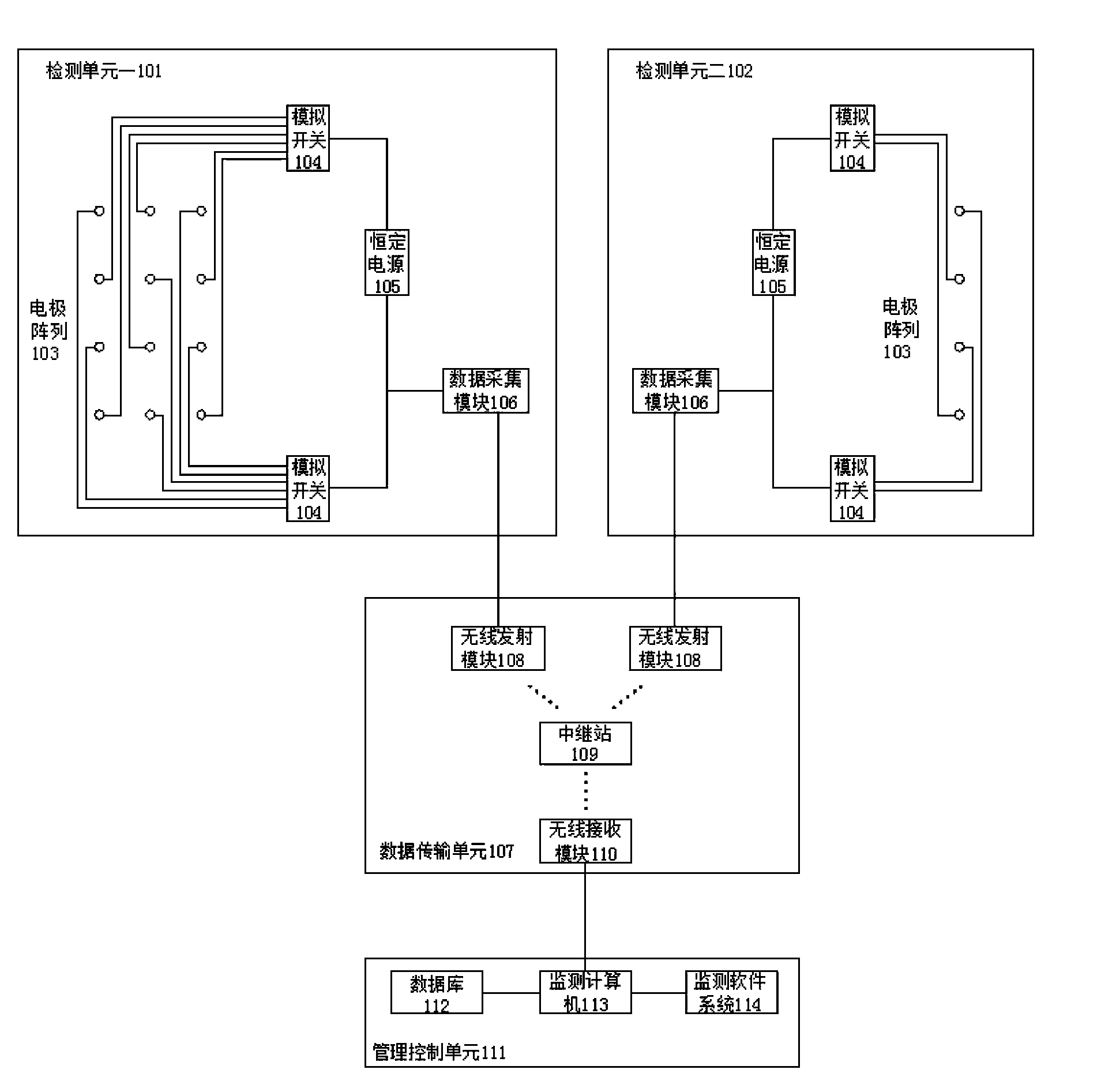
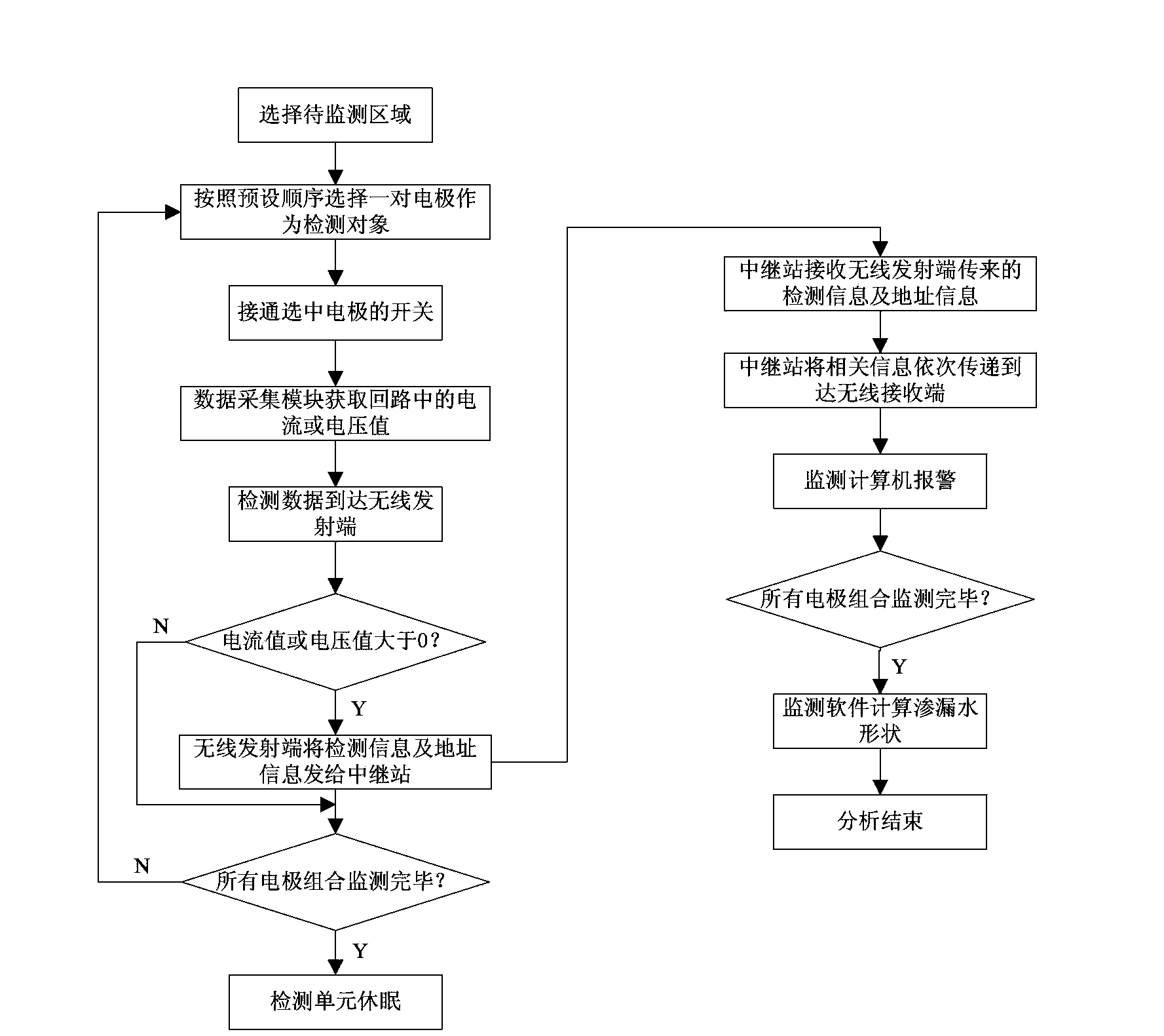
ActiveCN104236812ARealize long-term automatic detectionReduce lossesDetection of fluid at leakage pointElectrode arrayEngineering
The invention relates to a tunnel water leakage detection method and device based on conductivity. By distributing electrode arrays on the inner wall of a tunnel and sequentially applying voltage to every two adjacent electrodes, the wall of a tunnel lining wall and the electrodes can form a power supply loop, whether leakage exists between the electrodes or not is judged according to the current condition in the loop, the detection results of all the electrodes are synthesized, and the shape of the leakage area of the wall of the tunnel can be estimated. Through the method and device, positioning can be performed and an alarm can be given in time when water leakage occurs so that tunnel management staff can find and govern the water leakage damage of the tunnel in the first time. Besides, the development of the existing water leakage damage can be traced for a long time, and observation on the evolution tendency of structural performance of the tunnel can be facilitated.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN INST GRP CO LTD
Atmospheric pressure, glow discharge, optical emission source for the direct sampling of liquid media
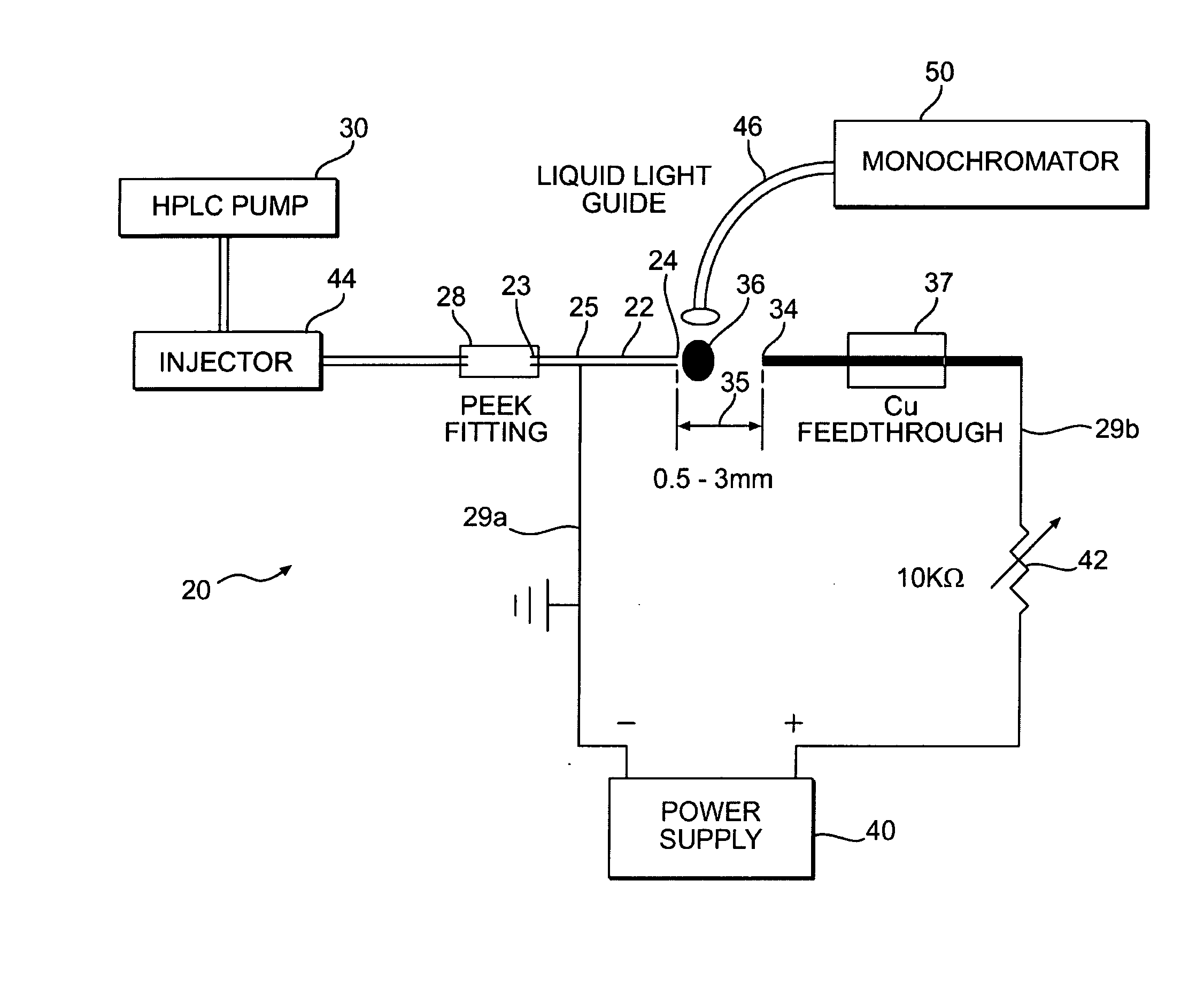
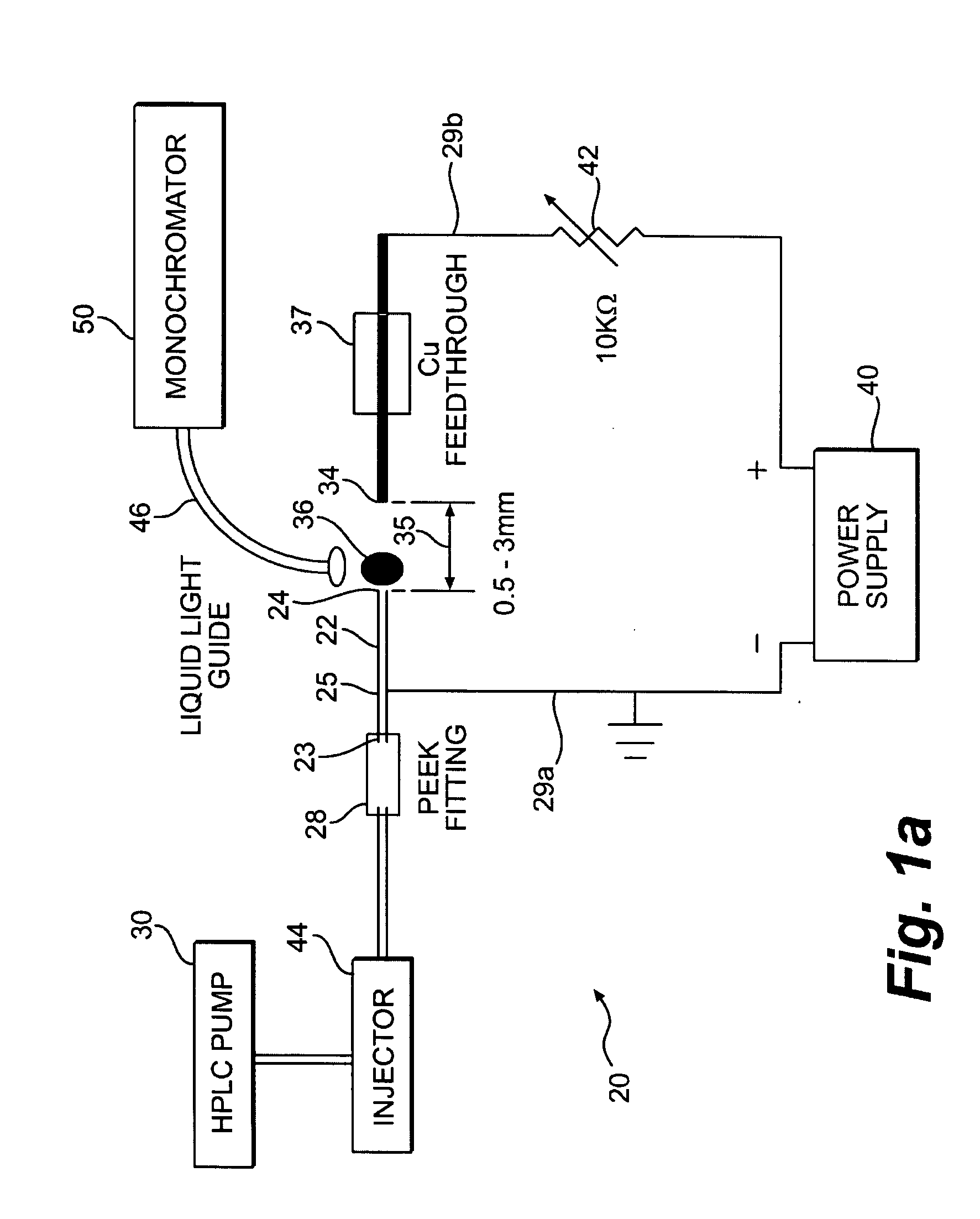
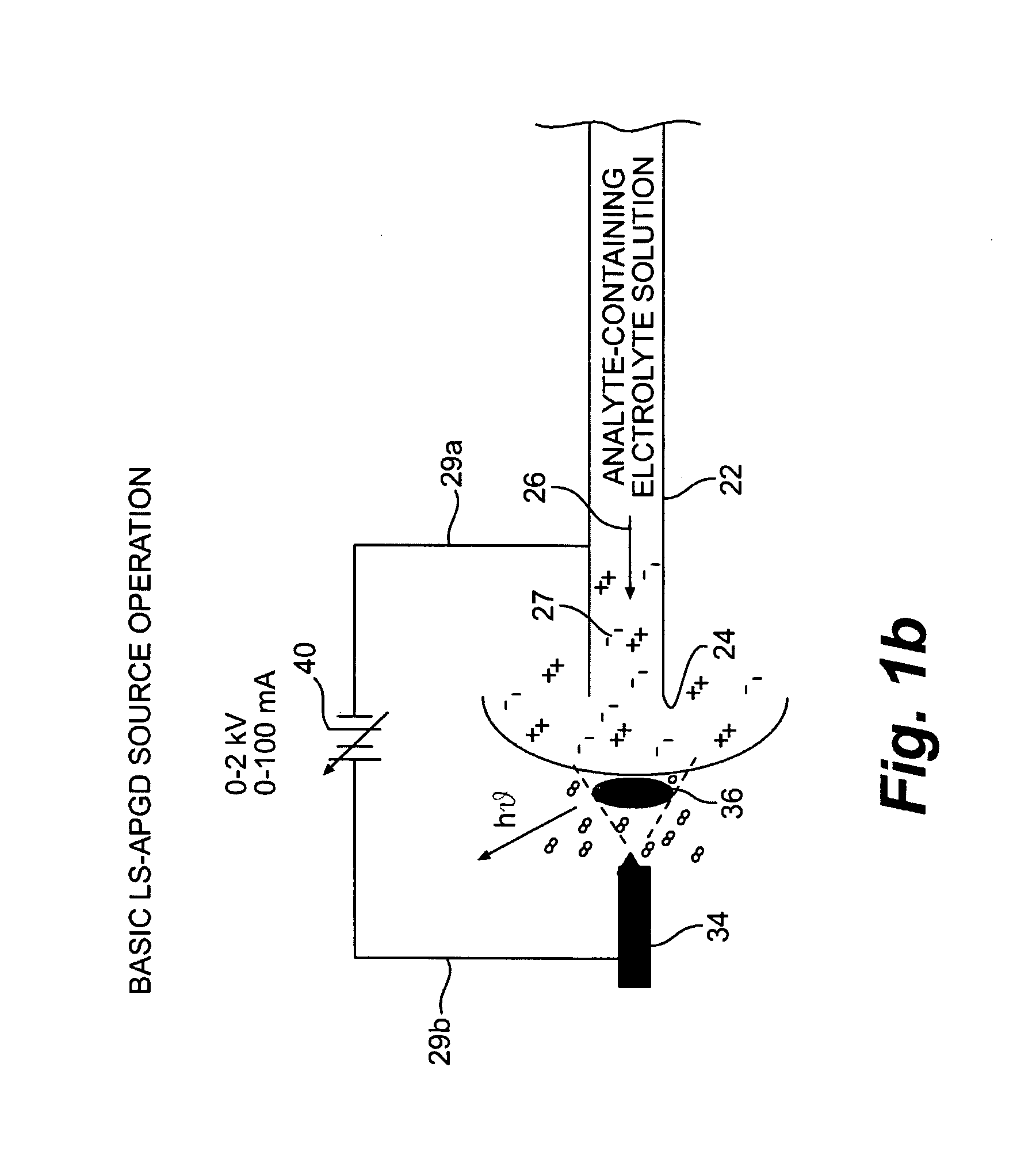
A glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy (GD-OES) source operates at atmospheric pressure. One of the discharge electrodes of the device is formed by an electrolytic solution 27 containing the analyte specimen. The passage of electrical current (either electrons or positive ions) across the solution / gas phase interface causes local heating and the volatilization of the analyte species. Collisions in the discharge region immediately above the surface of the solution results in optical emission that is characteristic of the analyte elements. The device uses the analyte solution as either the cathode or anode. Operating parameters depend on the electrolyte concentration (i.e. solution conductivity) and the gap 35 between the solution surface and the counter electrode. Typical conditions include discharge currents of about 30 to about 60 mA and potentials of about 200 to about 1000 volts. Electrolyte solutions of pH, pNa or pLi values of about 0.5 to about 2 and interelectrode gaps of about 0.5 to about 3 mm produce stable plasmas where the analyte solutions are totally consumed at flow rates of up to about 2.0 mL / min.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIVERSITY
System and method for particulate sensor diagnostic
A particulate (soot) sensor system has a diagnostic feature for verifying the integrity of the wiring leads. The sensor system includes a sensor and processing circuitry. The sensor has a substrate, first and second sensing electrodes on the substrate and a heater electrode. The heater electrode is electrically isolated from the first and second sensing electrodes, although there is a parasitic capacitance between them. The processing circuitry includes a heater driver, a measurement circuit connected to the sensing electrodes by wire leads, and a detector. The heater driver, in addition to energizing the heater, produces a stimulus signal that is applied to the heating electrode, which is then coupled via the parasitic capacitance to the sensing electrodes. The detector is coupled to the wiring leads and is configured to detect the stimulus signal when there is electrical conductivity over the leads to the sensing electrodes.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Method and device for detecting heat conductivity near melting point of phase change energy storage material
InactiveCN102305806ASolve thermal conductivityOvercoming problems such as lattice changesMaterial heat developmentPhase changePhase-change material
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting heat conductivity near the melting point of a phase change energy storage material. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, calculating the approximate value of the heat conductivity near the melting point of the phase change energy storage material according to an analysis formula under the ideal phase change condition; and 2, introducing a numerical simulation correction method to obtain an experiment corrected value, namely the accurate value of the heat conductivity near the melting point of the phase change energy storage material. The method and the device for detecting the heat conductivity near the melting point of the phase change energy storage material are high in test result accuracy and solve the problems that the phase change material has a lattice change when temperature gradient is applied in the conventional measuring method, and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Solid electrolyte
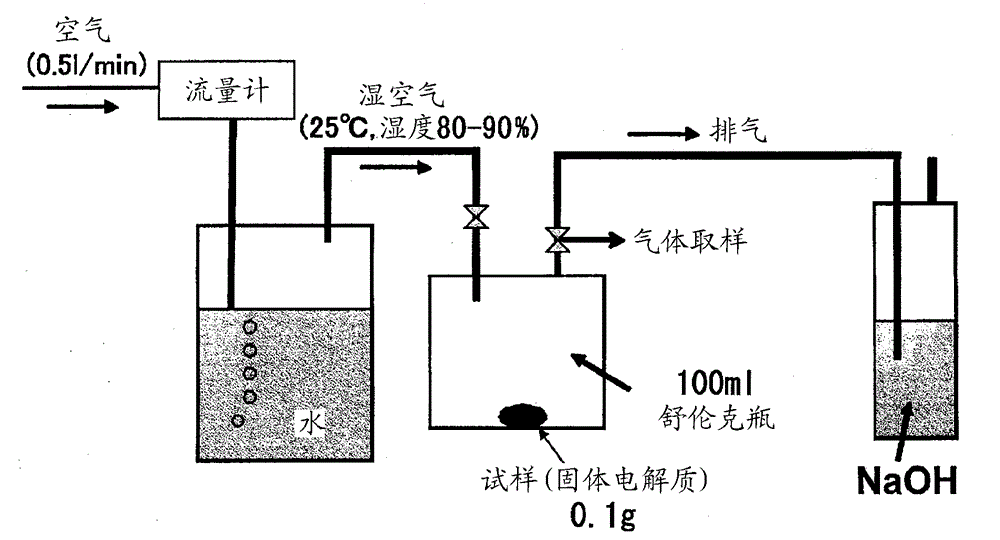
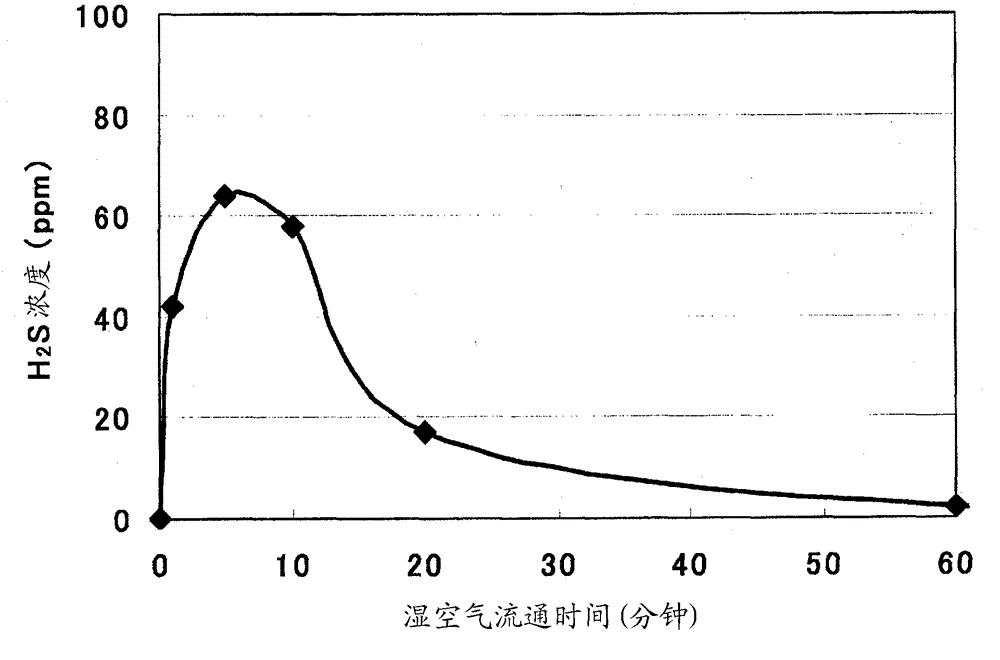
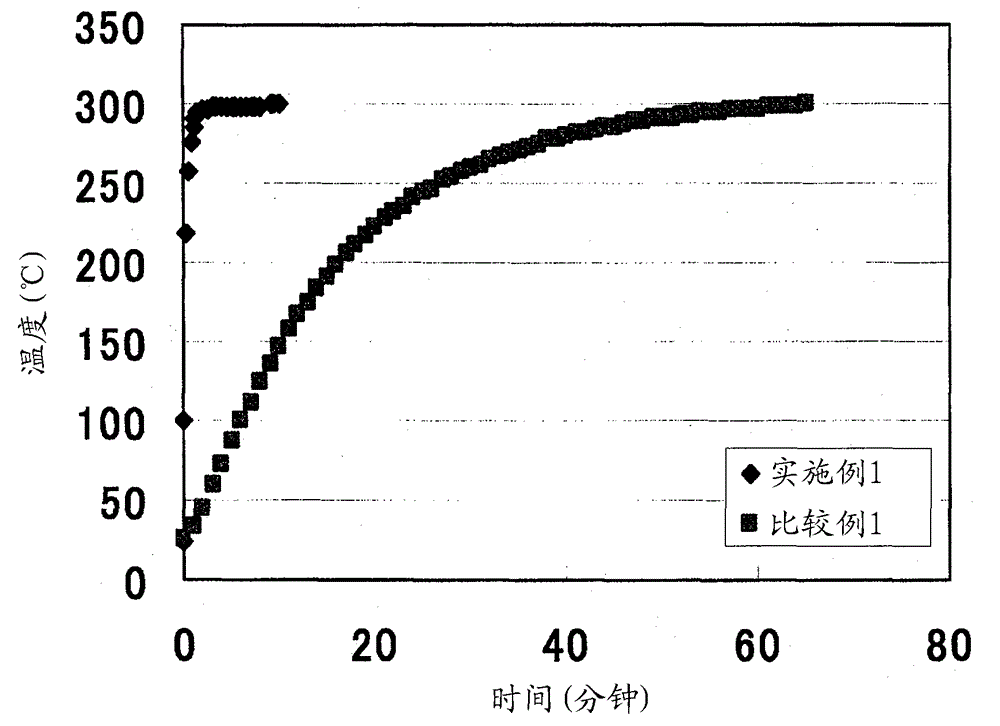
InactiveCN103959546AImprove ionic conductivityNon-metal conductorsCell electrodesConductivityIonic conductivity
This solid electrolyte contains lithium, phosphorus, and sulfur as constituent components, has a peak (first peak) in the region of 81.0-88.0 ppm inclusive in a 31P-NMR spectrum, either does not have a peak in the regions other than the 81.0-88.0 ppm inclusive region or even if there is a peak the peak strength ratio with respect to the first peak is no greater than 0.5, and has an ion conductivity of at least 510-4 S / cm.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
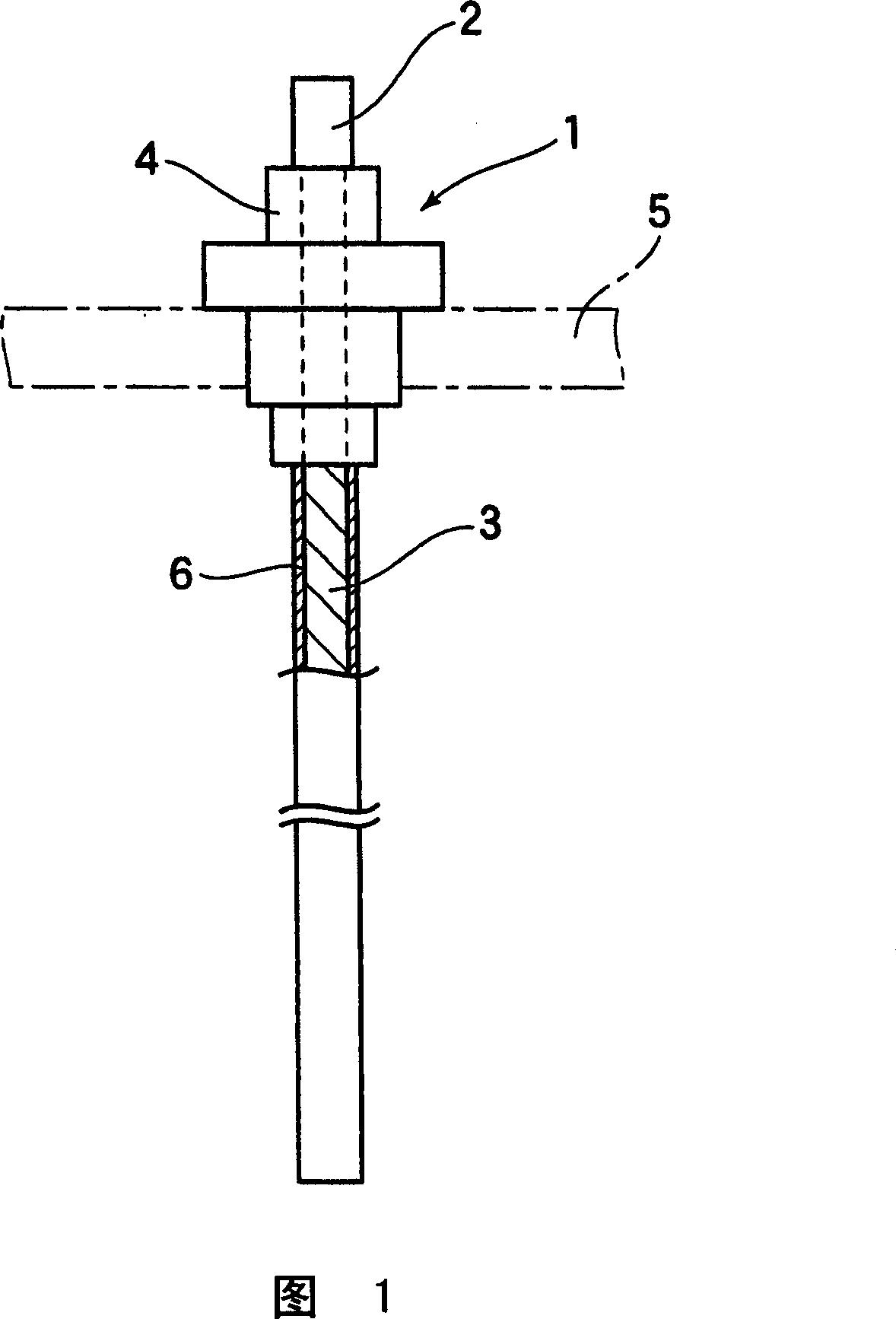
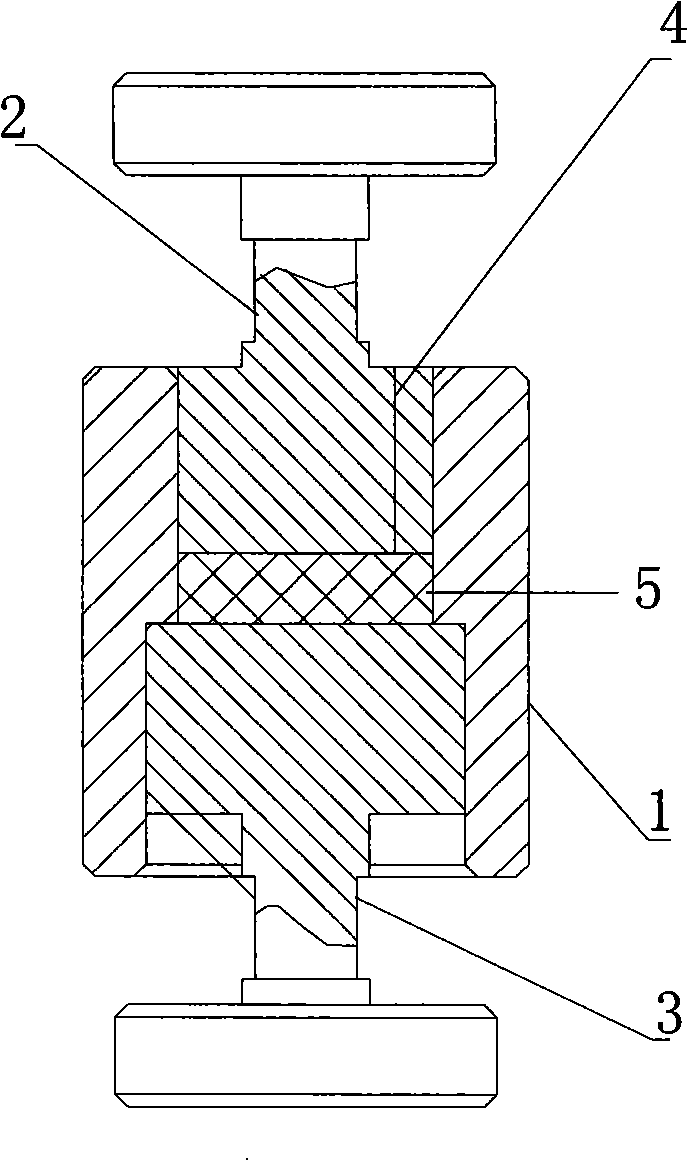
Electrode rod for detecting water-level, method of detecting water-level, and method of controlling water-level
InactiveCN101033997AFunctionAccurate detectionSteam boilersSteam boilers componentsDielectricEngineering plastic
An insulating coating ( 6 ) formed of engineering plastic with high heat resistance, high-pressure resistance, and chemical resistance is formed on a surface of a water-level detecting electrode part ( 3 ) of an electrode rod for detecting water-level ( 1 ) attached to penetrate a metal container ( 5 ) communicating with a boiler ( 7 ) and including an external power supply connecting terminal part ( 2 ) projecting outside the container ( 5 ) and the water-level detecting electrode part ( 3 ) projecting inside the container ( 5 ). One side of a power supply ( 27 ) is connected to the external power supply connecting terminal part ( 2 ), and another side of the power supply ( 27 ) is connected to the container ( 5 ) for energization. An electrostatic capacity between the water-level detecting electrode part ( 3 ) and the container ( 5 ) is measured by using the insulating coating ( 6 ) formed on the surface of the water-level detecting electrode part ( 3 ) as a dielectric. The water-level of water to be brought into contact with the water-level detecting electrode part ( 3 ) in the container ( 5 ) can be detected from the electrostatic capacity. Proportional target water-level in the boiler ( 7 ) is set based on at least one of the burning capacity, vapor pressure, supply water temperature, and electrical conductivity of boiler water, and at least one of the burning capacity, vapor pressure, supply water temperature, and electrical conductivity of boiler water during operation of the boiler ( 7 ) is detected. A difference between the proportional target water-level to be specified by the detected values and actual water-level in the boiler ( 7 ) detected by the electrode rod for detecting water-level ( 1 ) is constantly calculated.
Owner:MIURA COMPANY LIMITED
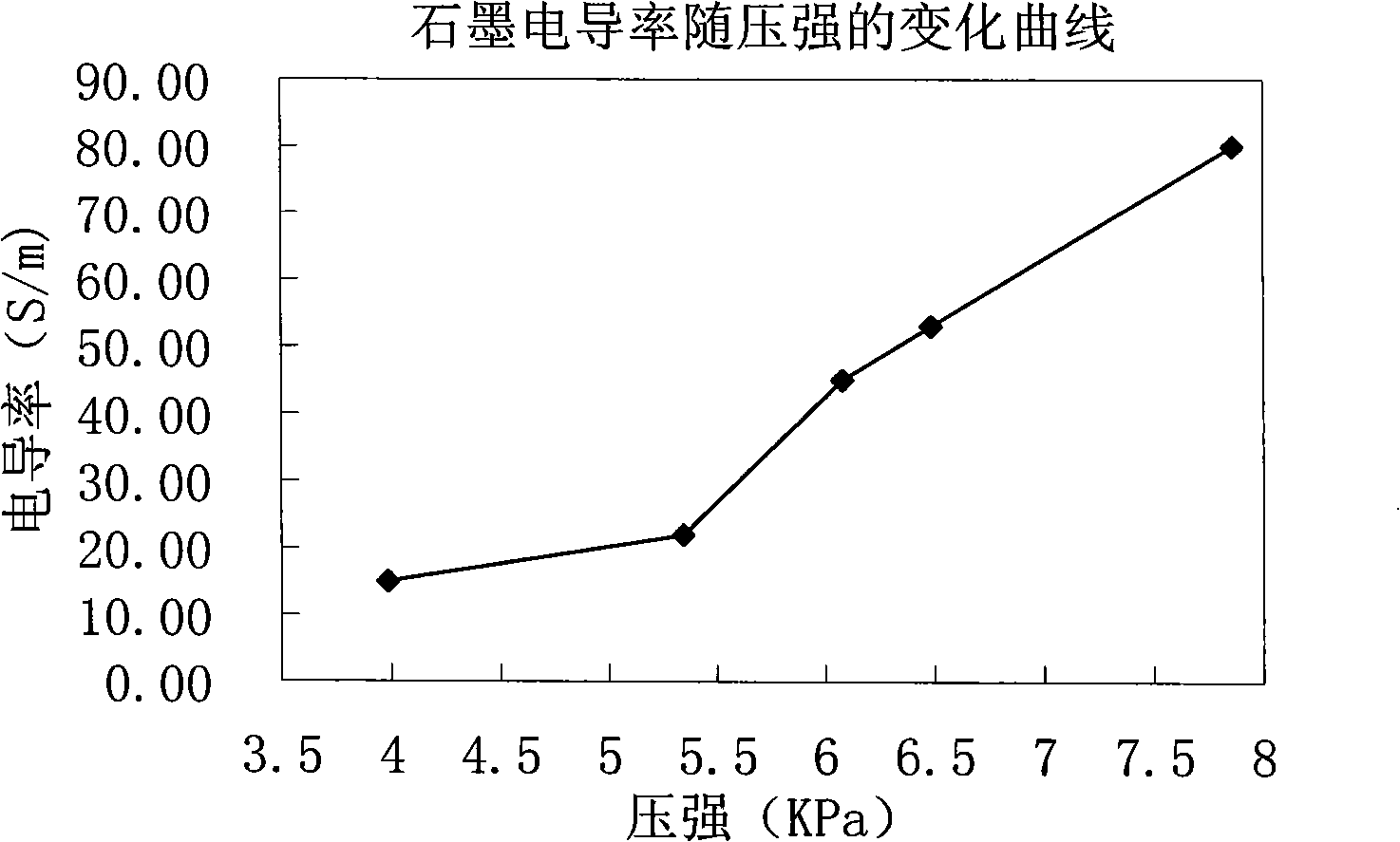
Method for measuring powder body material electric conductivity and electric conductivity measuring apparatus suitable for the method
ActiveCN101324538AHelp optimizeHelp designMaterial impedanceElectrical resistance and conductanceMeasurement device
The invention provides a method for measuring the conductivity of the powder material. The method comprises the following steps: (a) keeping the powder material to be measured in a cylinder shape and applying a certain pressure P to the powder material until the shape of the cylinder powder body can be kept stable; (b) measuring the length L, the cross-sectional area S and the resistance R of thecylinder powder body; and (c) calculating the conductivity of powder material based on the formula that Sigma is equal to L divide (R multiply S). The invention further provides a device for measuring the conductivity, which comprises a powder container, two conductive pistons, a pressure device, and a resistance measuring device. By adopting the method and the device, the conductivity of the powder material to be measured in a pressurized state can be measured, thereby the conductivity of the powder material to be measured in an operating pressure can be quantitatively provided. The relationship of the conductivity of the powder material to be measured varying with the pressure P can be obtained through changing the pressure value of the powder material to be measured and measuring the conductivity thereof. The method facilitates the selection of the electrode material, the optimization of the electrode material formulation and the integrated design of the battery system.
Owner:SHENZHEN BAK POWER BATTERY CO LTD
Preparation method and application of sensor for heavy metal ions Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ built based on alginic acid functionalized graphene
InactiveCN104391030AImprove adsorption capacityIncrease sensor signalMaterial electrochemical variablesPotential differenceAlginic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical analysis or environment monitoring and provides a preparation method of a sensor for heavy metal ions Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ built based on alginic acid functionalized grapheme and a detection method of the heavy metal ions in a water body. The preparation method and the detection method have the benefits that by the utilization of carboxyl richly contained in alginic acid and a hydroxyl functional group, the heavy metal ions can be better absorbed, and in combination with the large specific surface area and the excellent electrical conductivity of the graphene, a sensing signal is enhanced, and the sensitivity is improved; according to potential difference, the different heavy metal ions Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ can be effectively distinguished; the detection method is used for the detection of the heavy metal ions Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+, and the linearity ranges are 0.1-100 <mu>g / L, 0.5-100 <mu>g / L and 0.2-100 <mu>g / L respectively; the limits of detection are 0.021 <mu>g / L, 0.10 <mu>g / L, and 0.041 <mu>g / L respectively; the detection method has an important use value in the quick, sensitive and selective detection of heavy metals.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Device and method for measuring heat conductivity coefficient reduction rate of concrete in uniaxial compression process
ActiveCN105259206AIntegrity guaranteedGuaranteed fitMaterial heat developmentReduction rateUniaxial compression
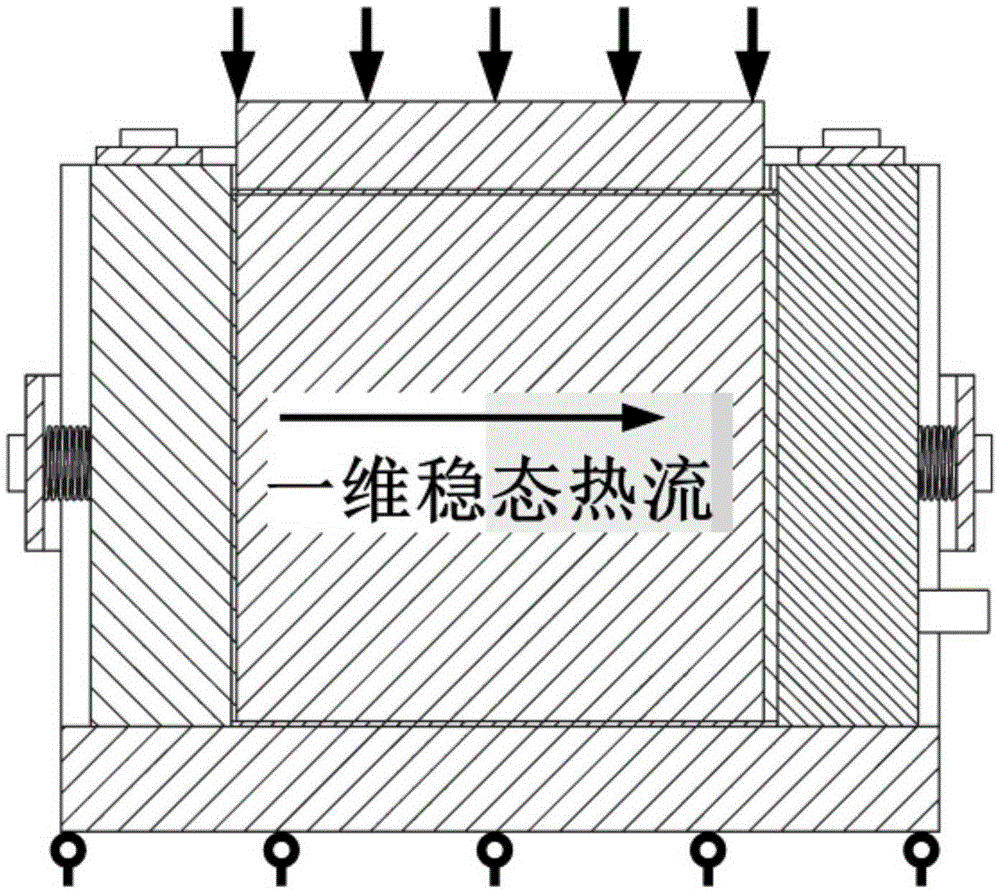
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring the heat conductivity coefficient reduction rate of concrete in a uniaxial compression process. A concrete test sample is put into a bracket to be subjected to a compression load, and meanwhile a heating unit and a refrigerating unit establish a temperature difference between two planes of the concrete test sample; the bracket is used for fixing relative positions of the concrete test sample with the heating unit, the refrigerating unit, a heat insulating material and heat conduction silica gel; the concrete test sample is deformed under pressure, and extrudes the heat insulating material, the heat conduction silica gel, the refrigerating unit and the heating unit in order that the heat insulating material, the heat conduction silica gel, the refrigerating unit and the heating unit move outwards towards the periphery; peripheral support posts of the bracket are used for determining moving tracks of peripheral materials; spring pressing plates and springs on the support posts provide a proper peripheral pressure not influencing mechanics experiments in order to ensure that the refrigerating unit and the heating unit fit the surface of the concrete test sample, thereby reducing a contact thermal resistance as much as possible. Under the situation that the concrete test sample is under a certain compression load, a thermal flow density inside the concrete test sample reaches a steady state, and the temperature is distributed stably in a one-dimensional form in the concrete test sample.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com