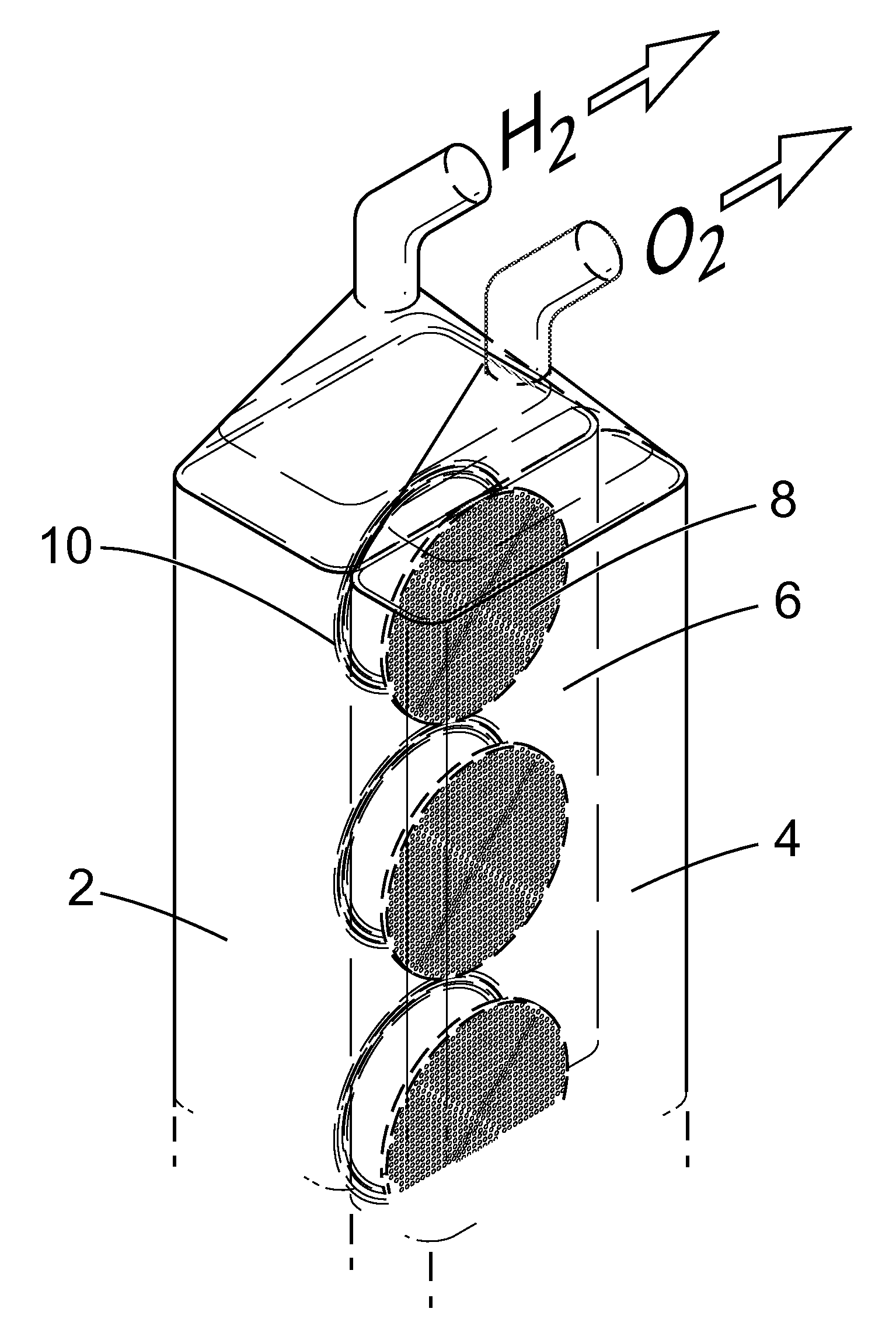
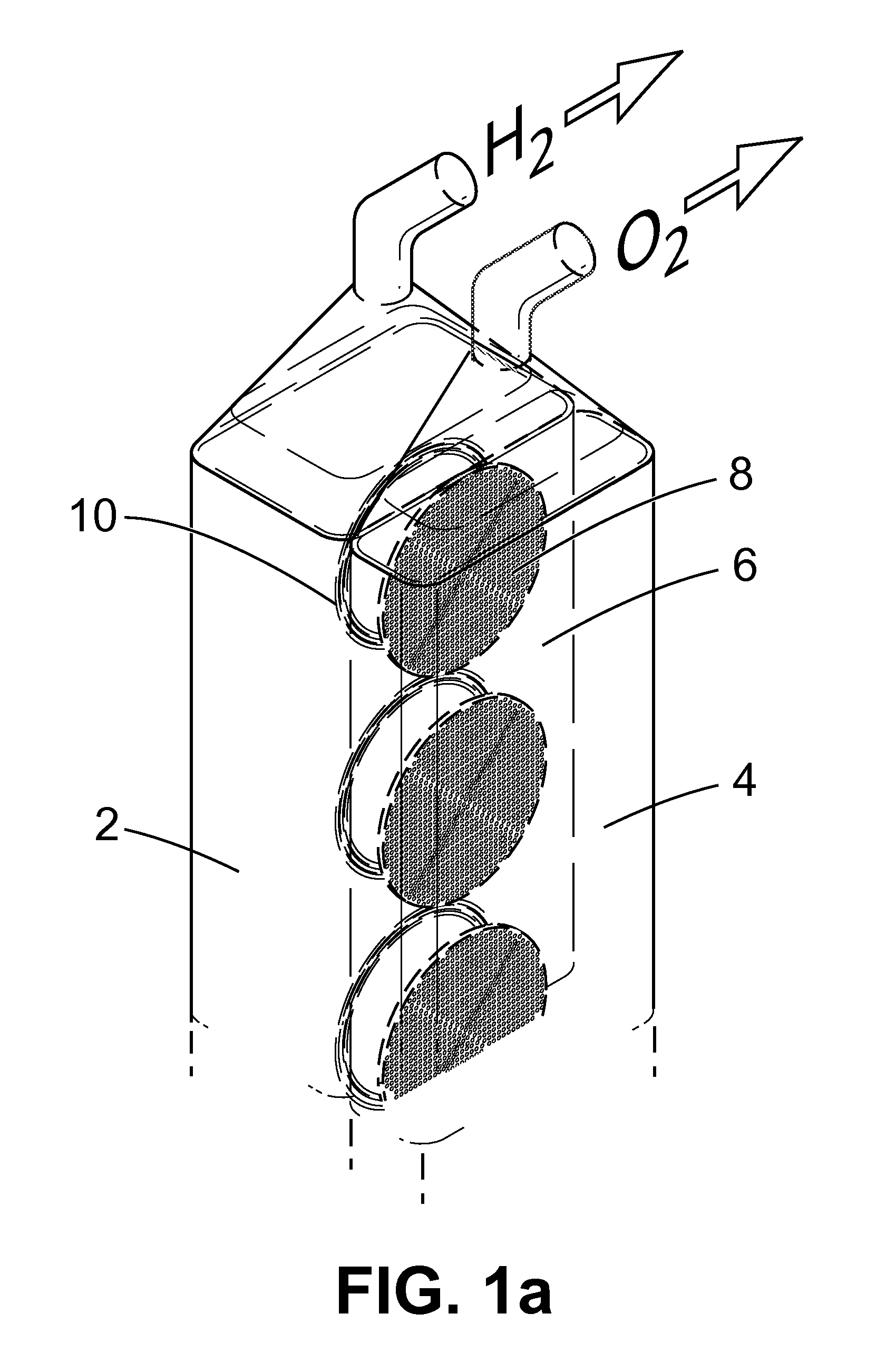
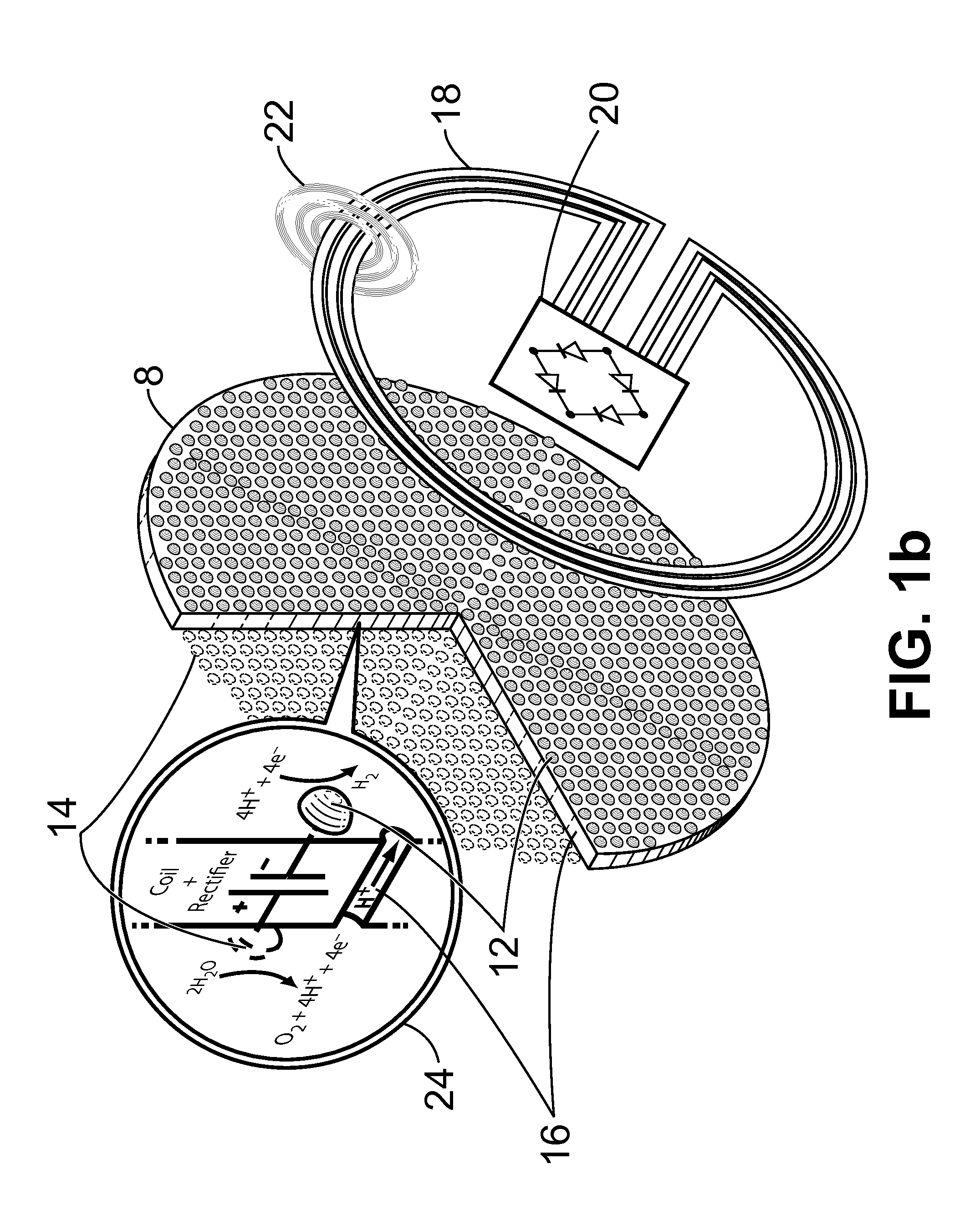
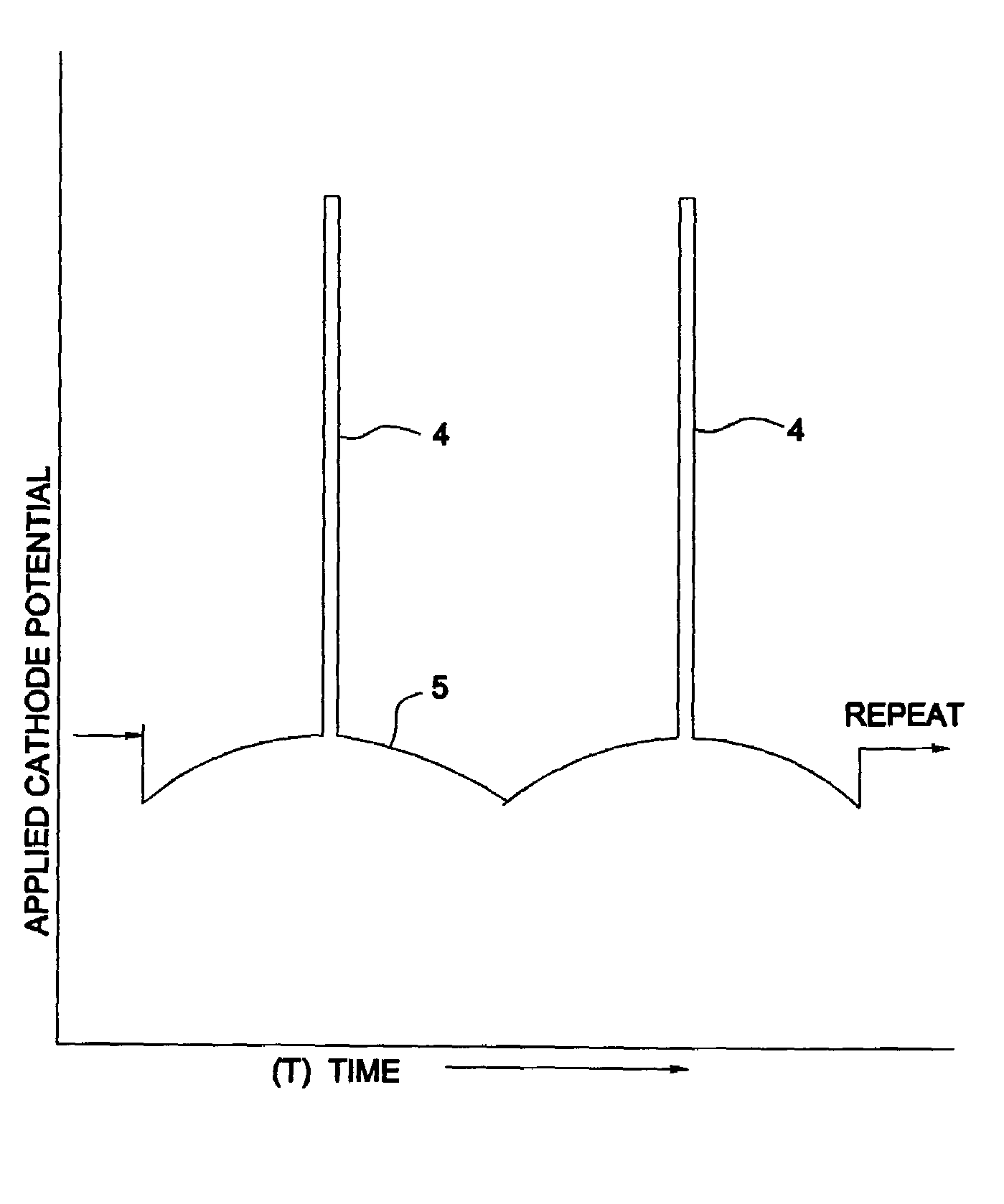
Patents
Literature
760results about "Machining electric circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
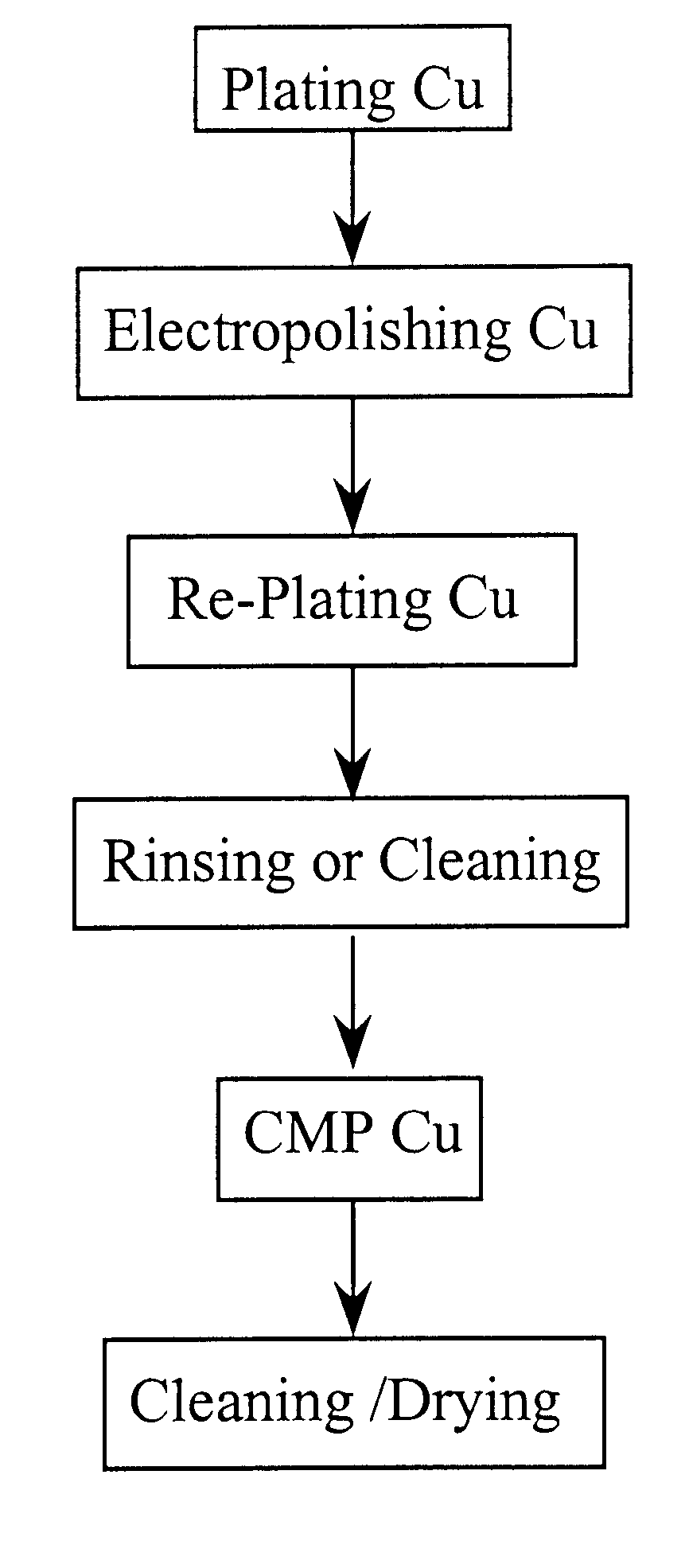
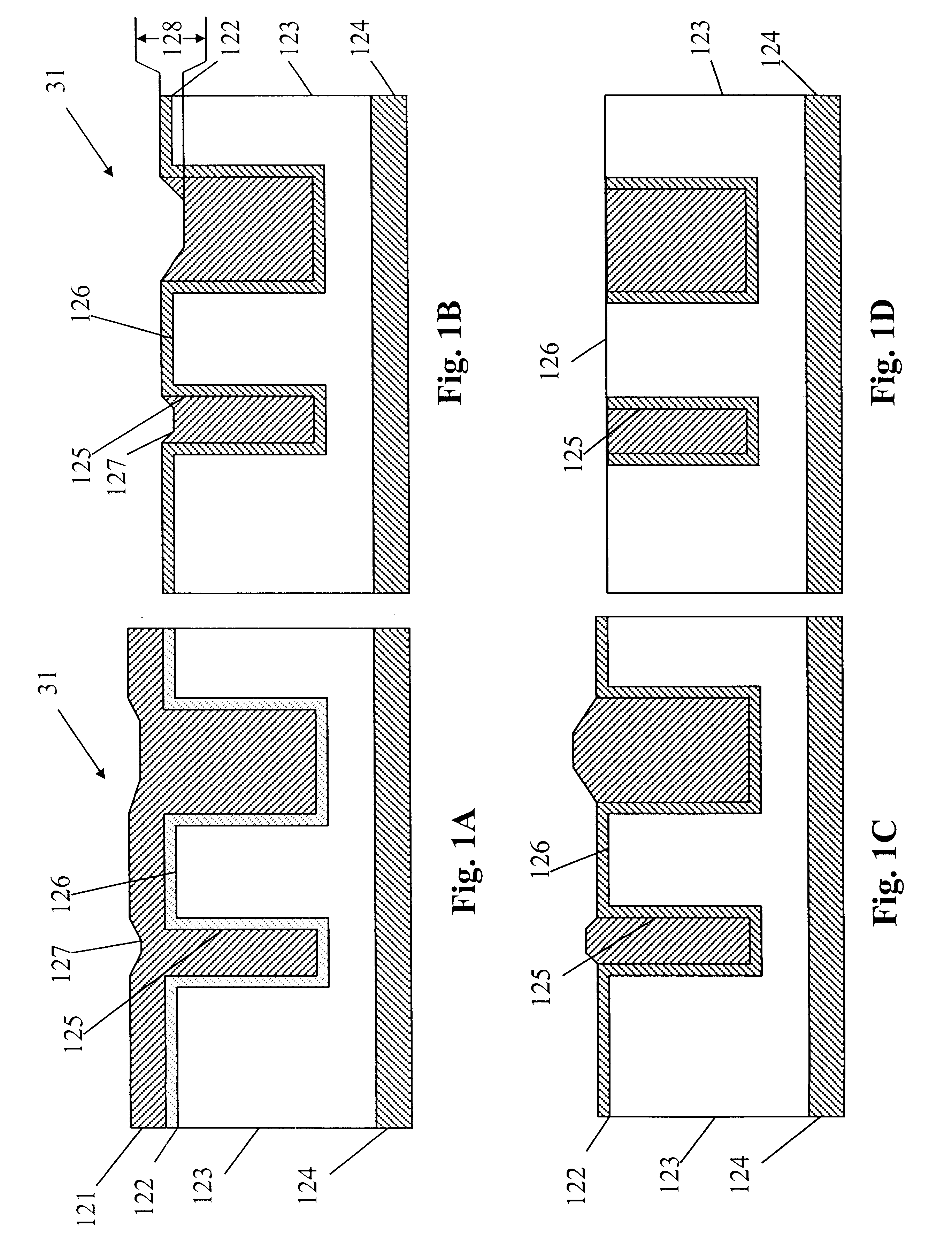
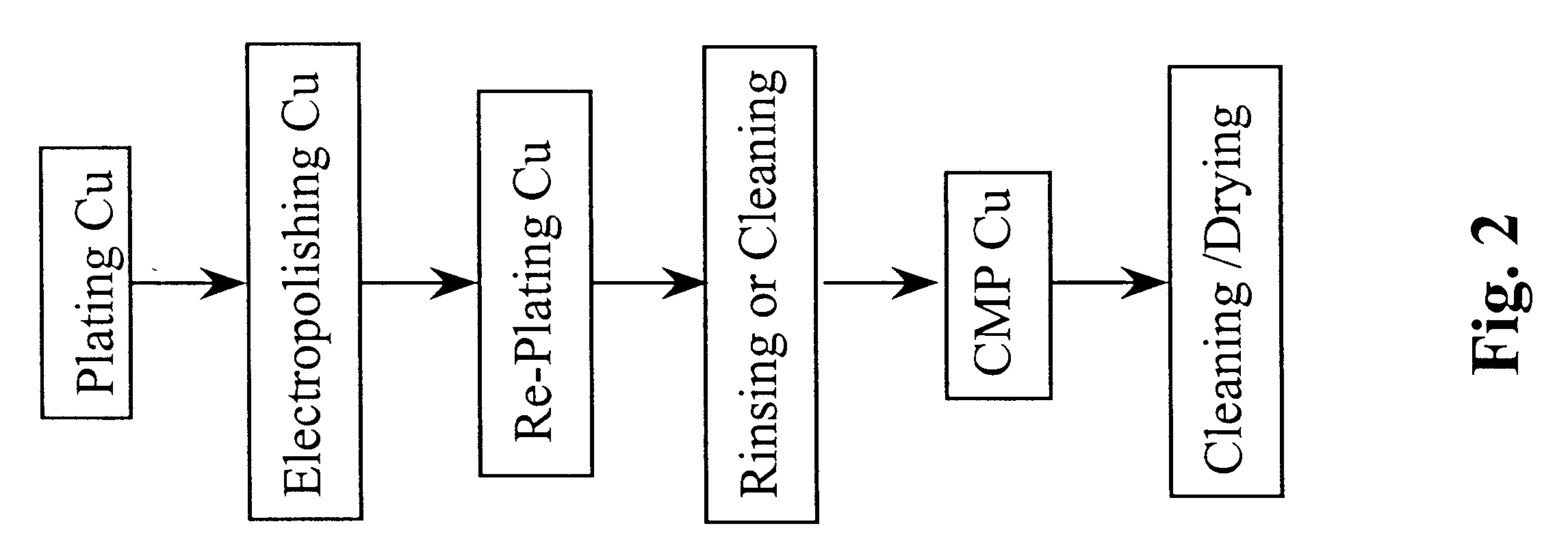
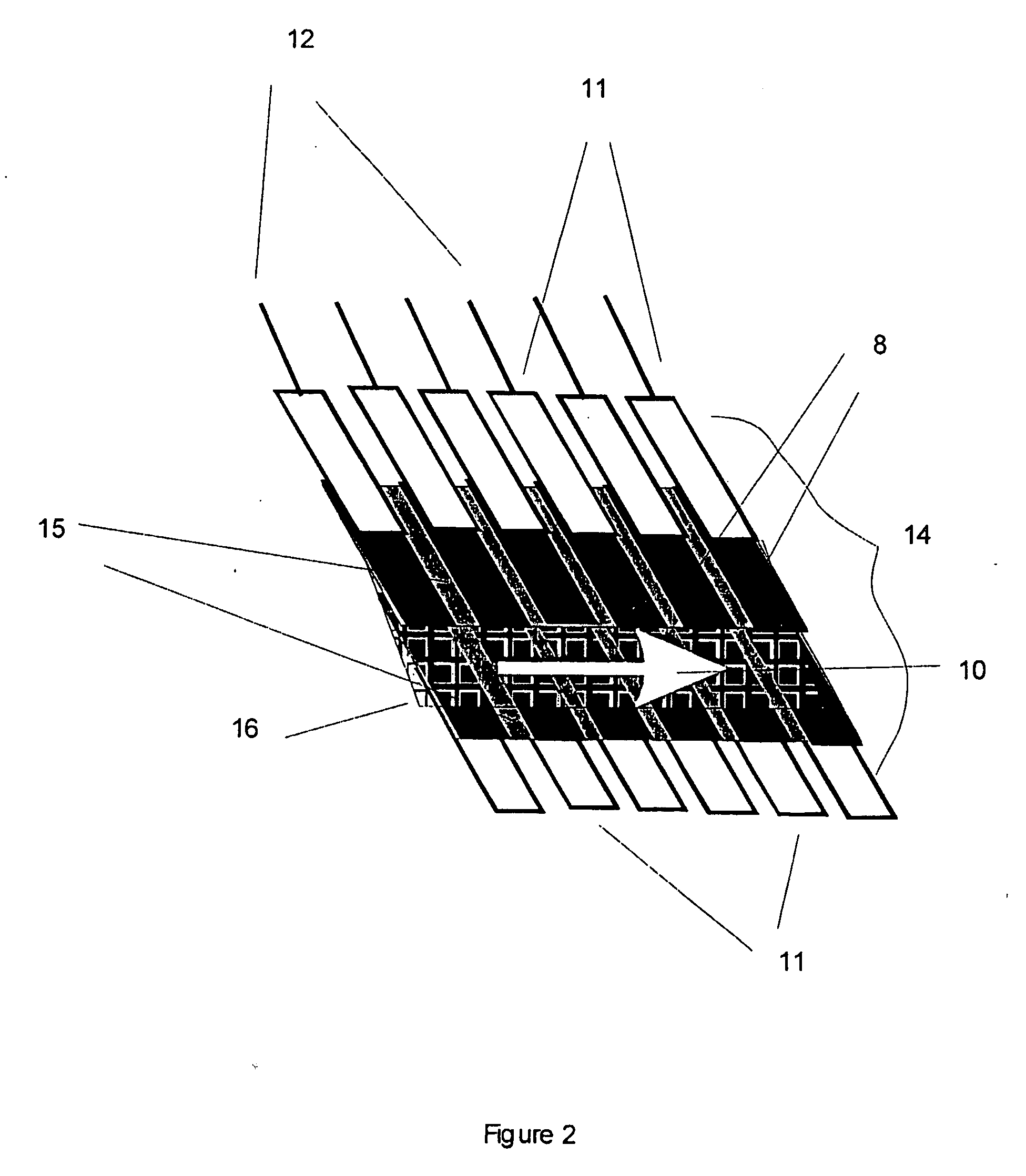
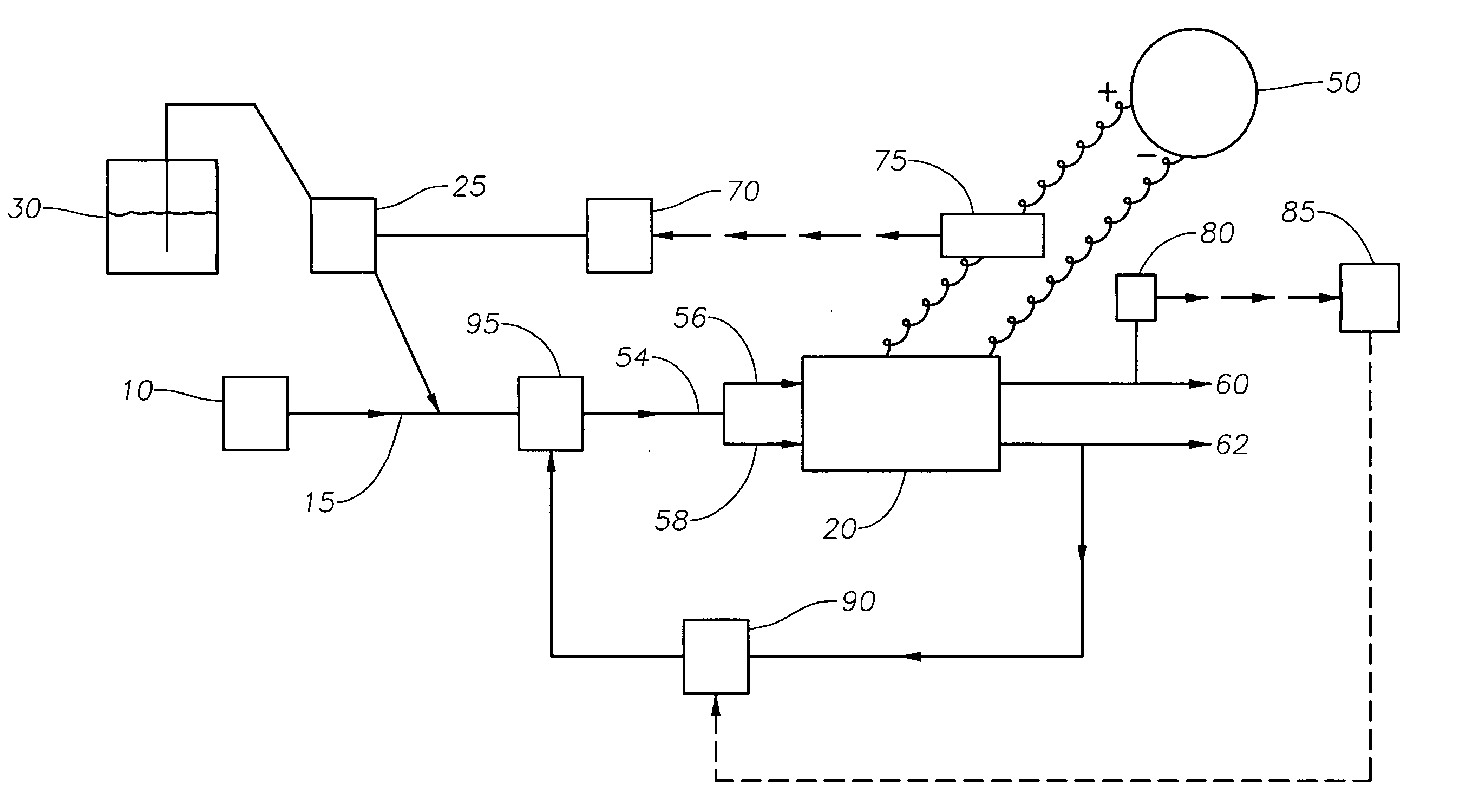
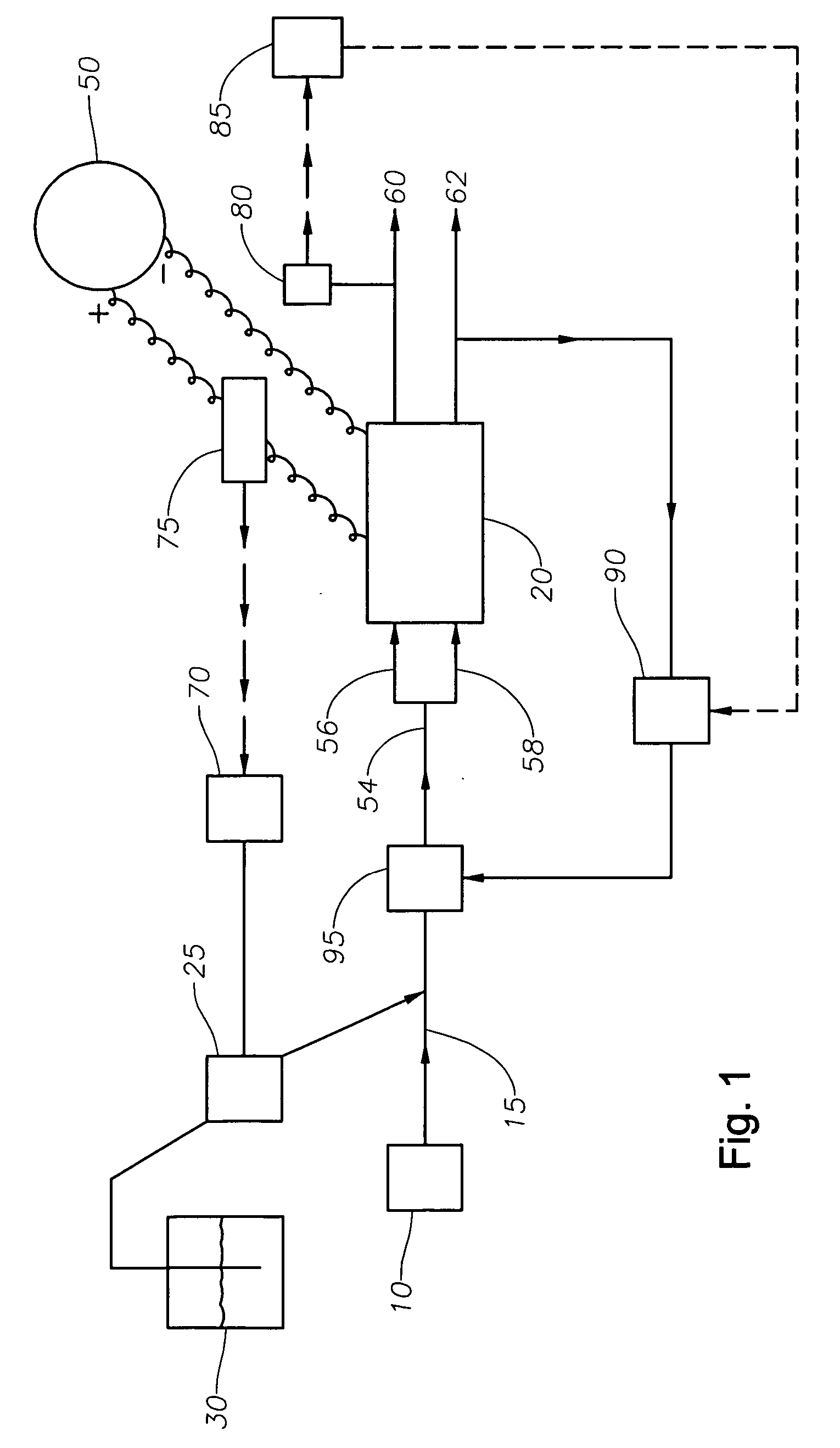
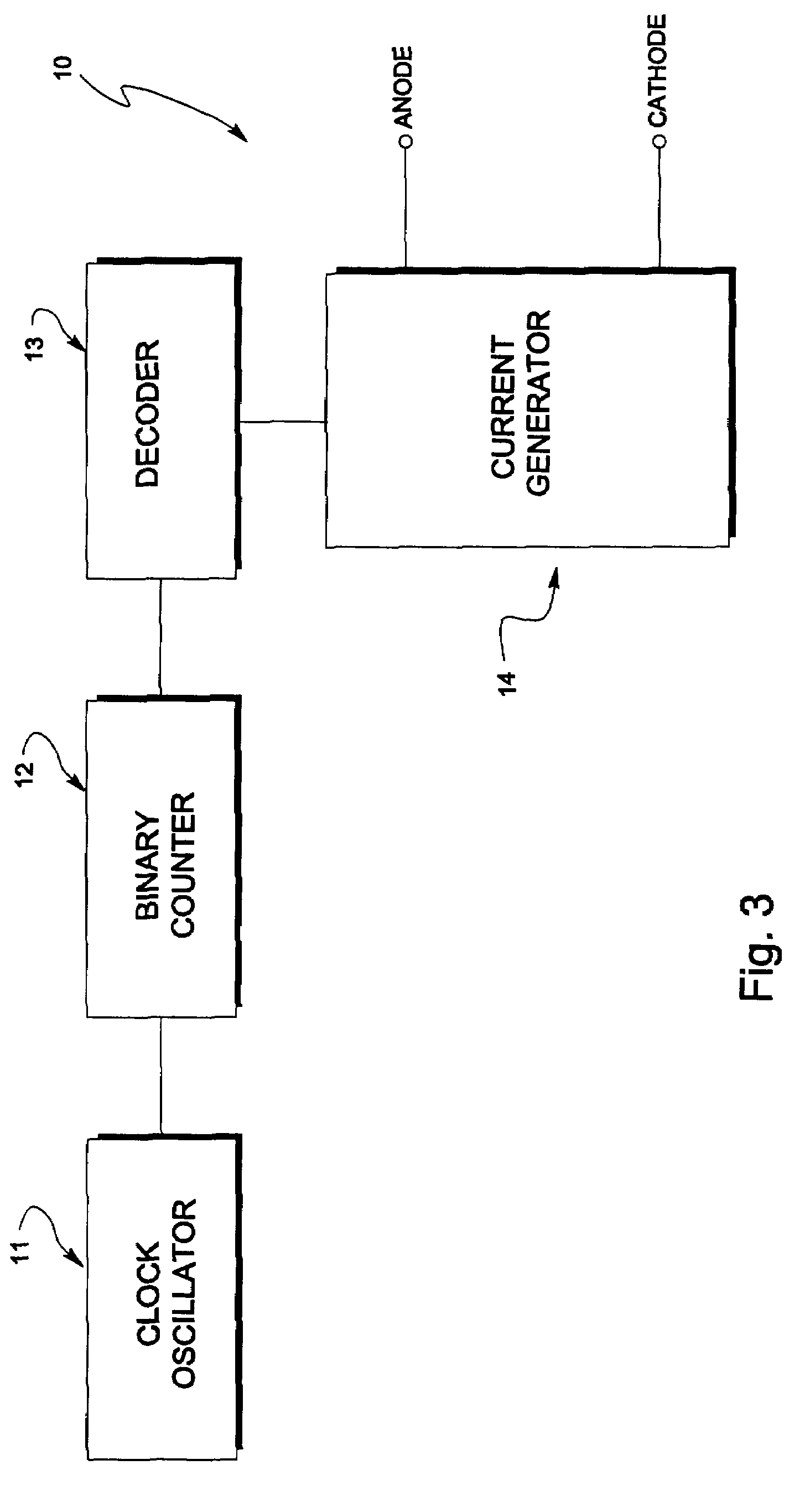
Method for electropolishing metal on semiconductor devices
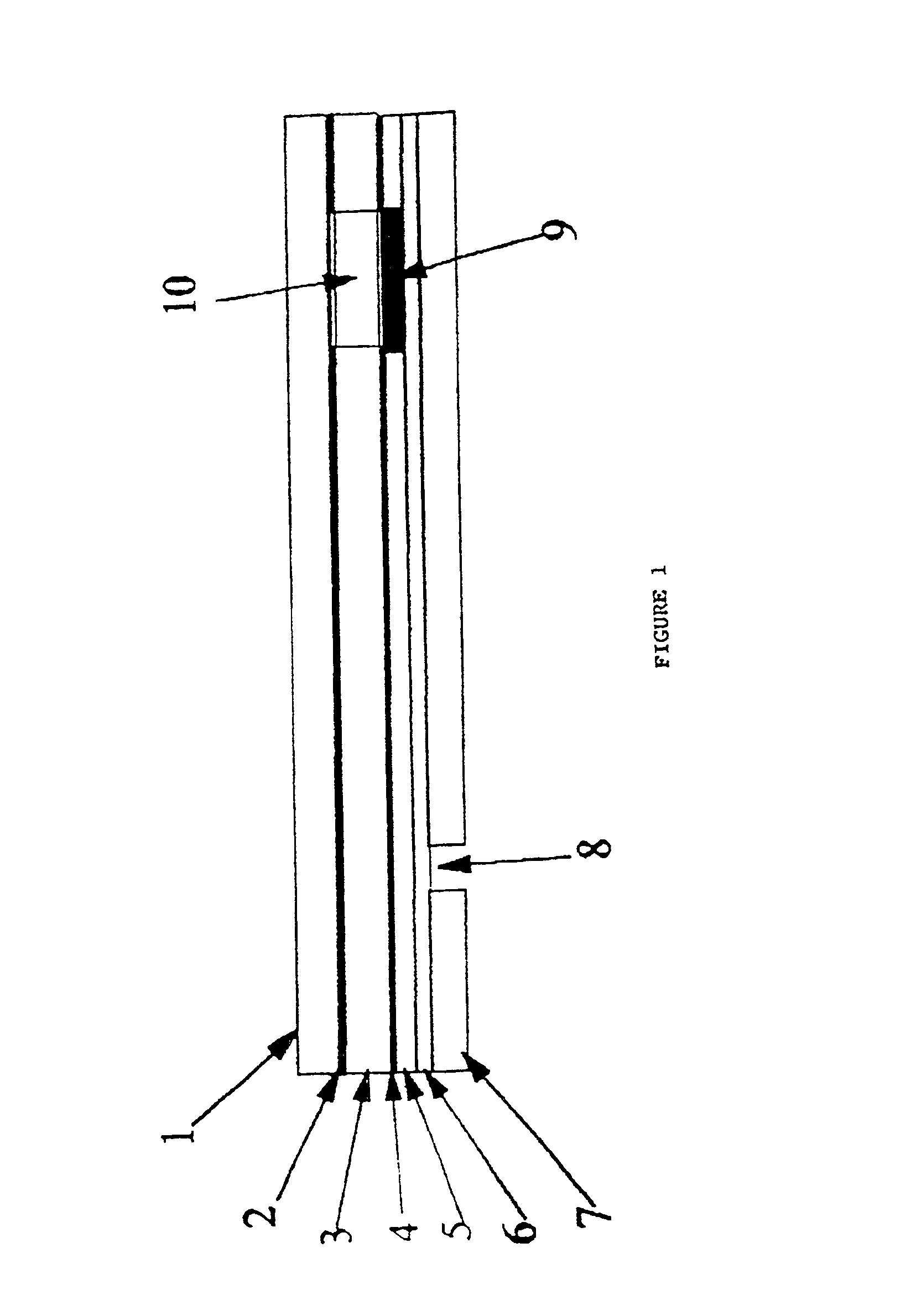
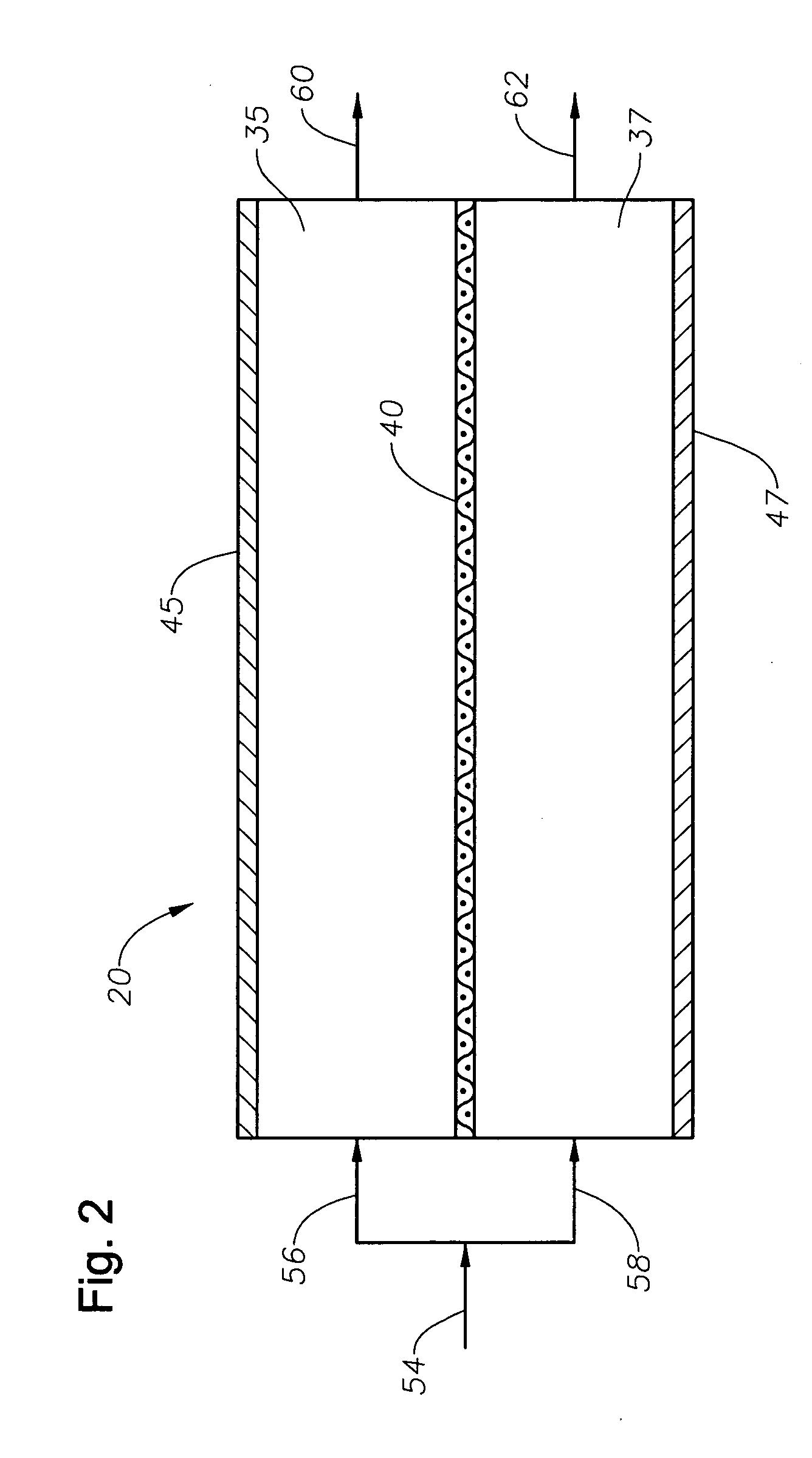
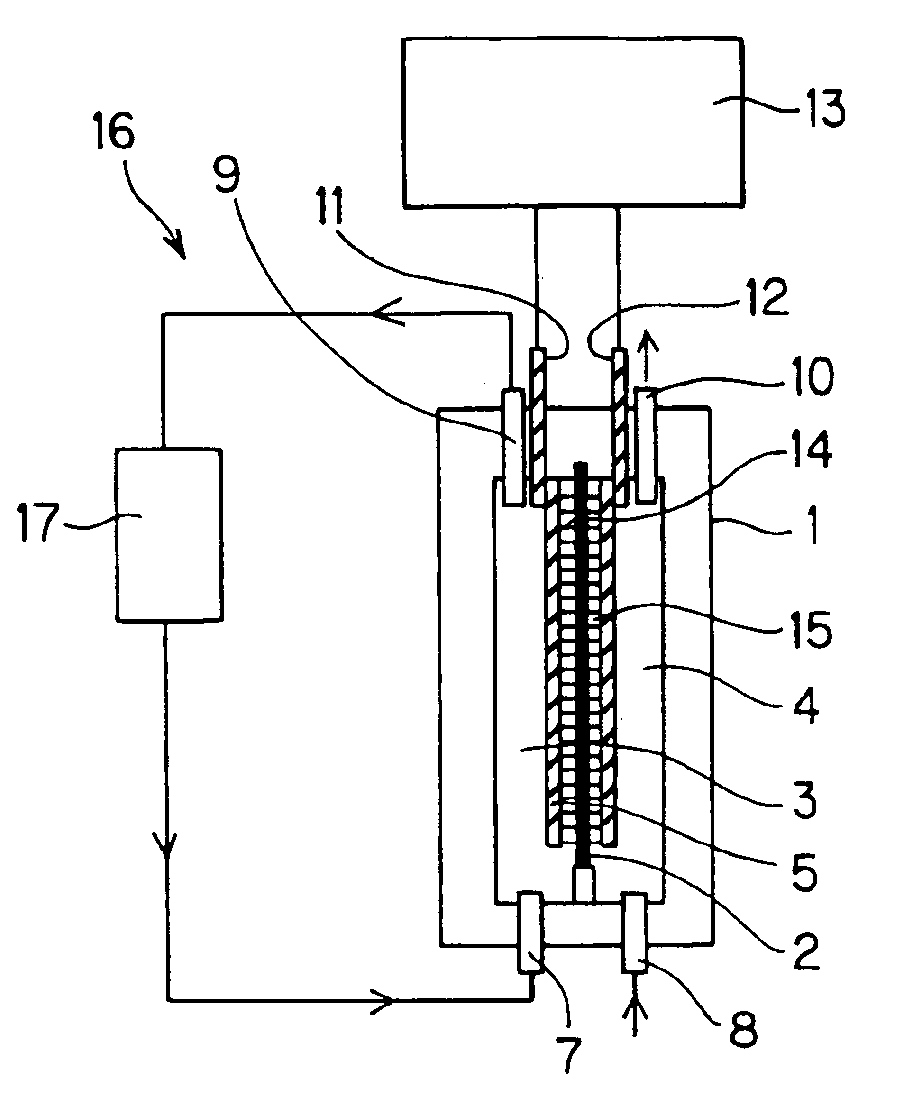
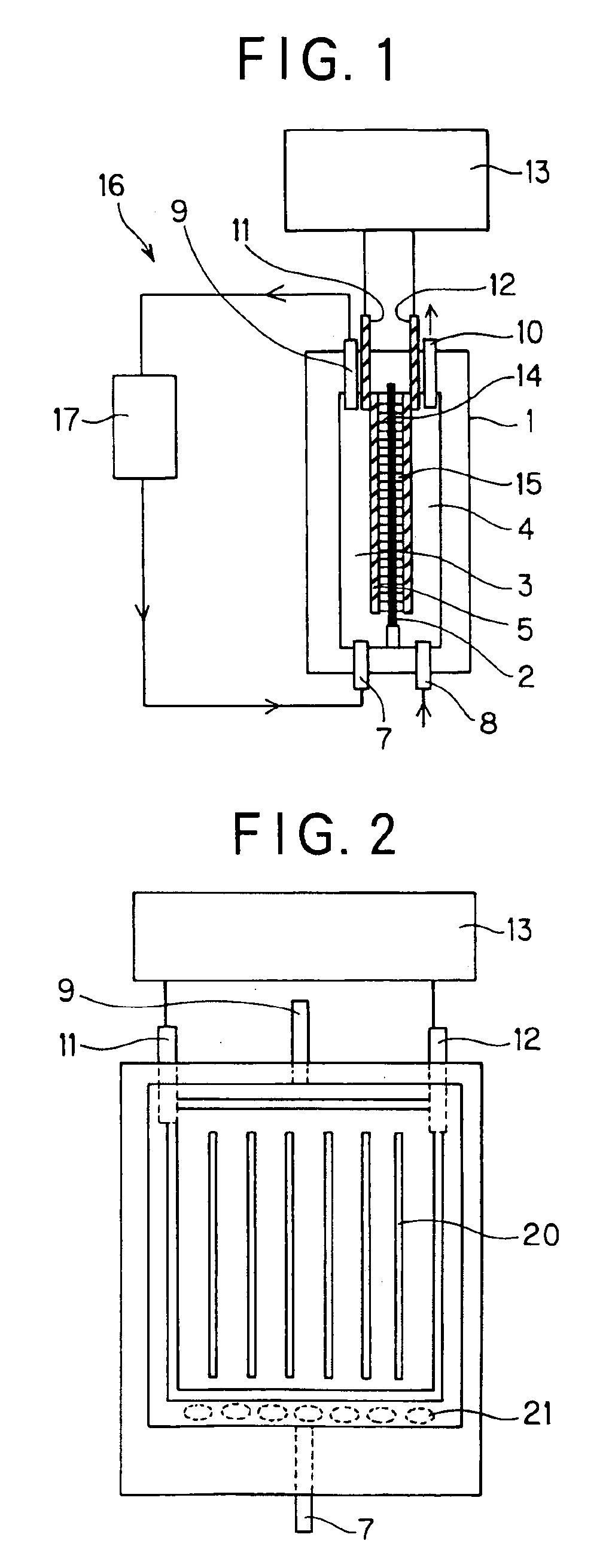
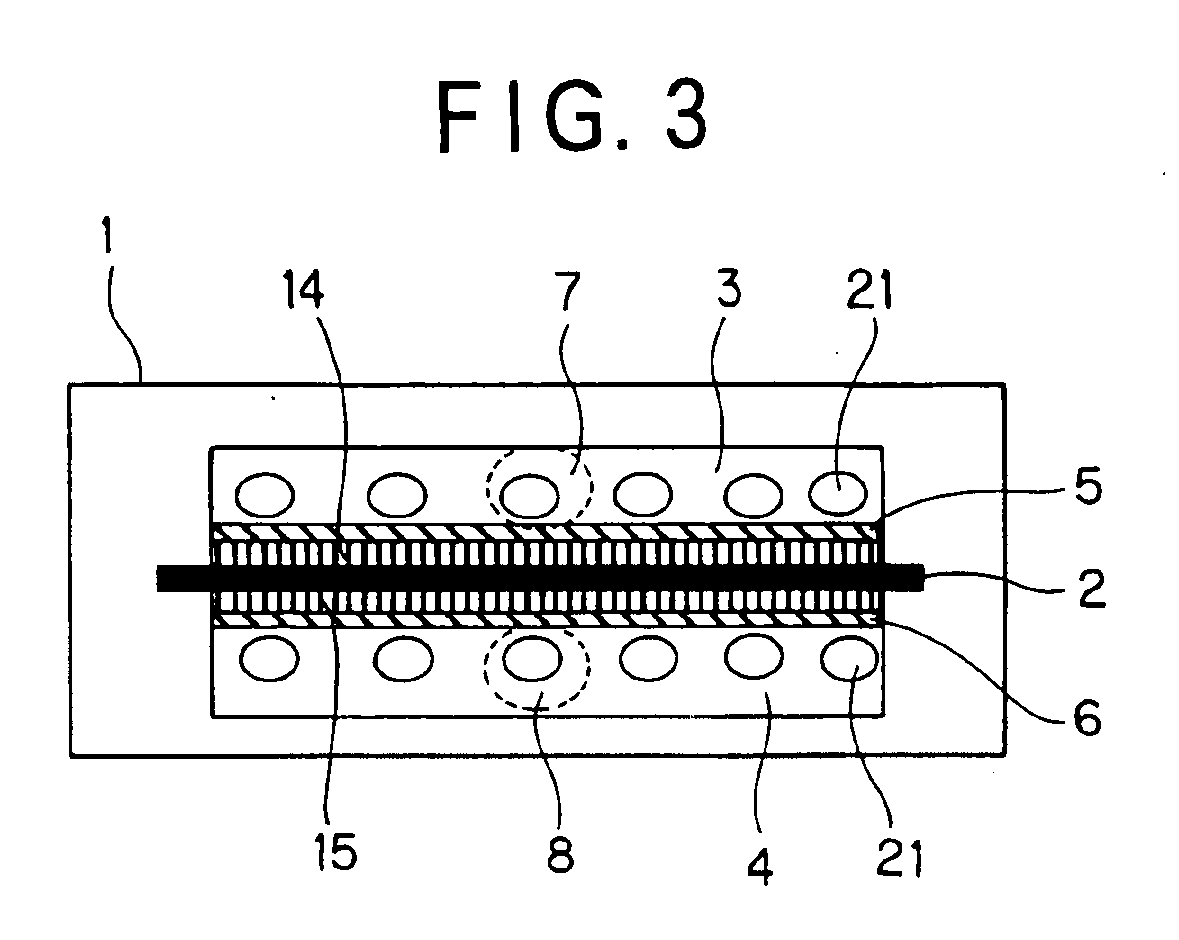
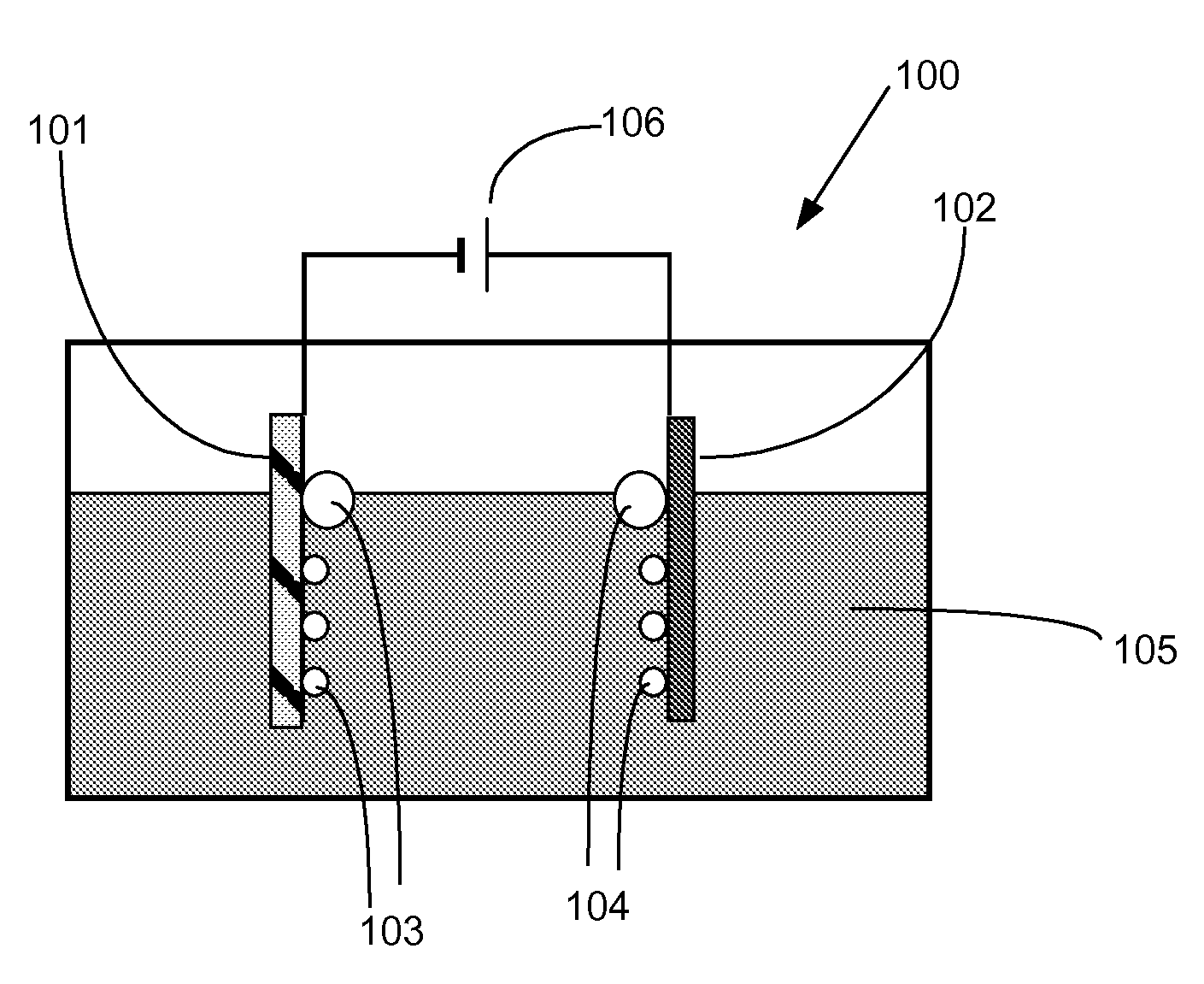
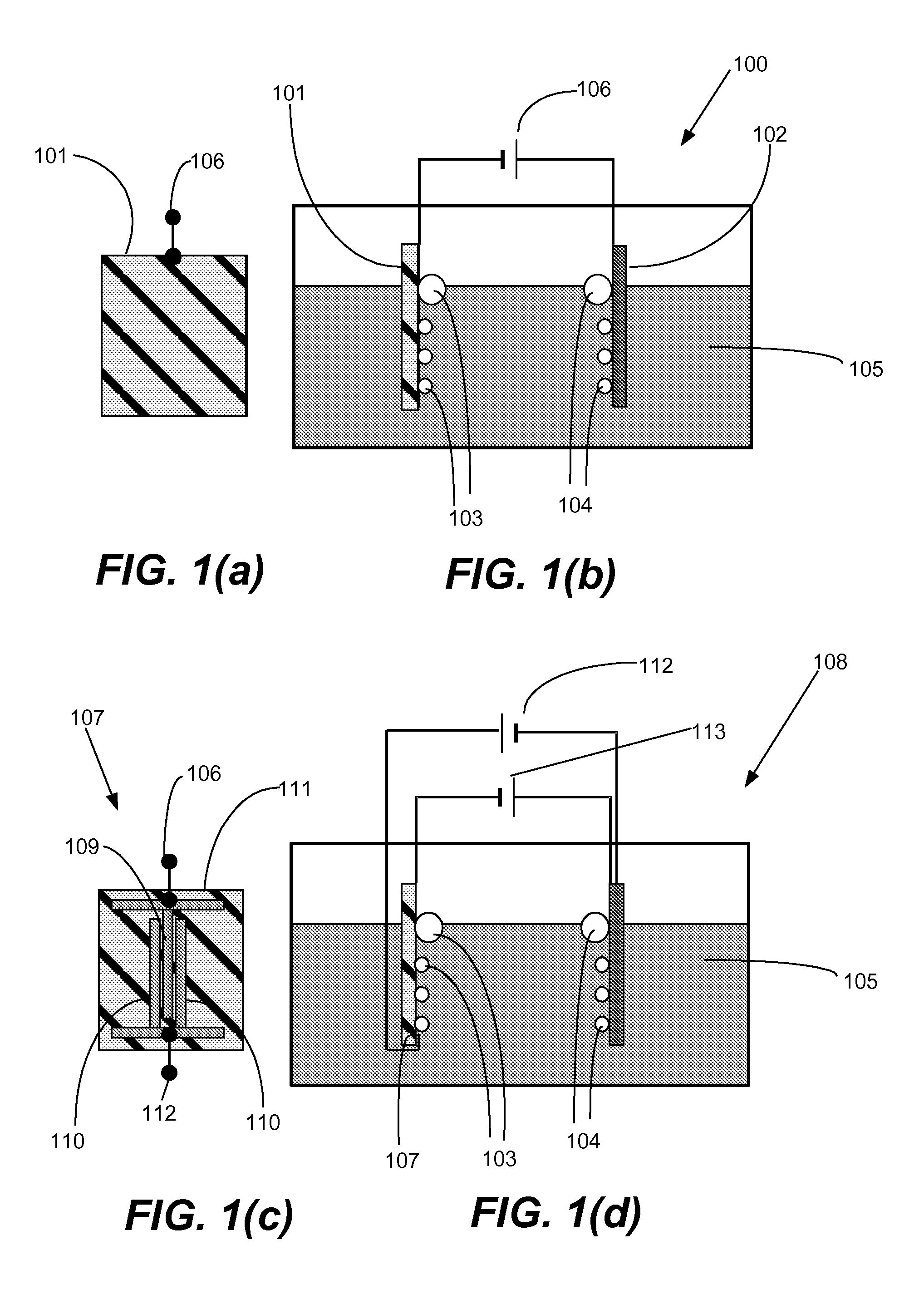
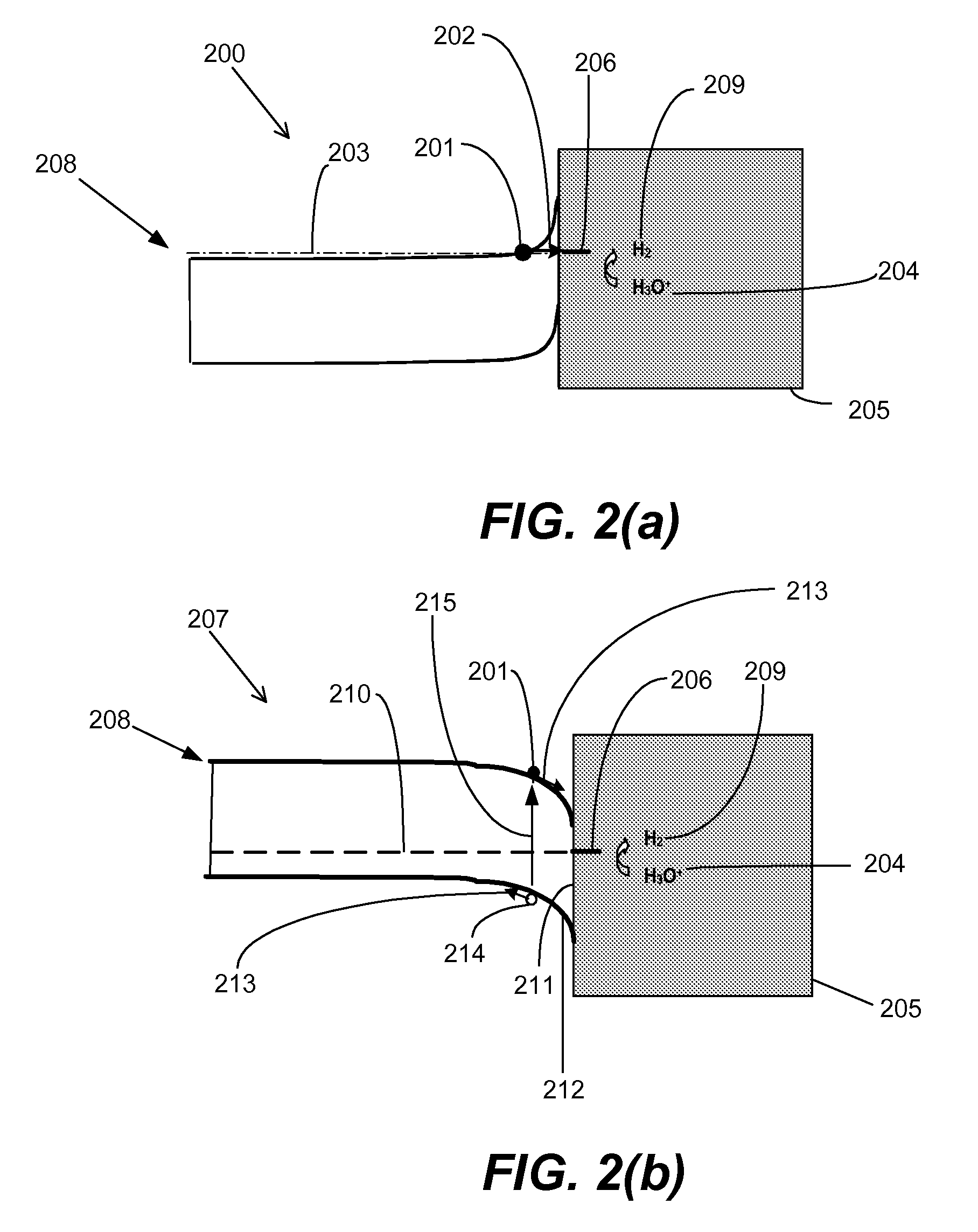
An electropolishing apparatus for polishing a metal layer formed on a wafer (31) includes an electrolyte (34), a polishing receptacle (100), a wafer chuck (29), a fluid inlet (5, 7, 9), and at least one cathode (1, 2, 3). The wafer chuck (29) holds and positions the wafer (31) within the polishing receptacle (100). The electrolyte (34) is delivered through the fluid inlet (5, 7, 9) into the polishing receptacle (100). The cathode (1, 2, 3) then applies an electropolishing current to the electrolyte to electropolish the wafer (31). In accordance with one aspect of the present invention, discrete portions of the wafer (31) can be electropolished to enhance the uniformity of the electropolished wafer.
Owner:ACM RES
Heated electrochemical cell
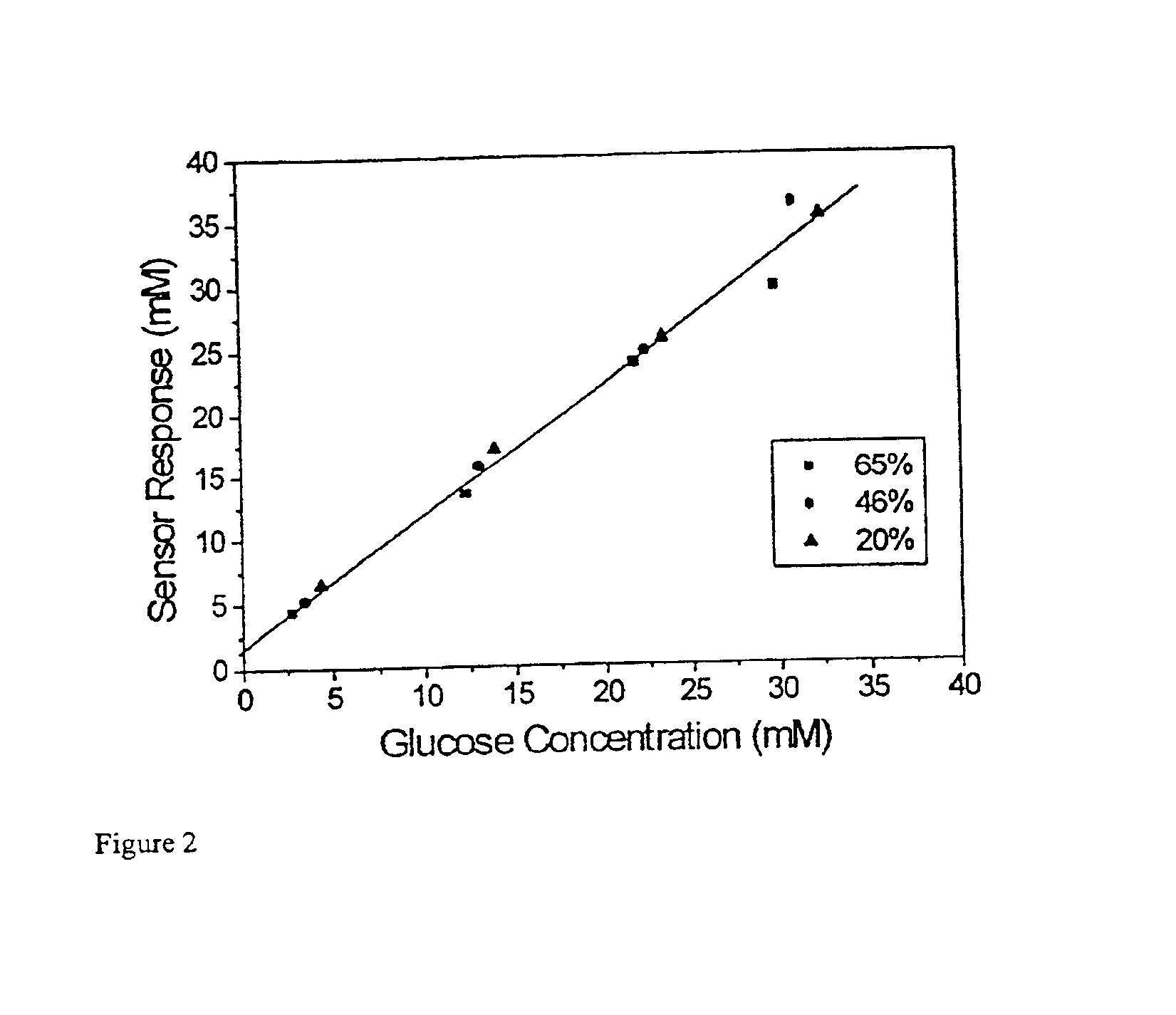
The invention provides a method for determining the concentration of an analyte in a sample comprising the steps of heating the sample and measuring the concentration of the analyte or the concentration of a species representative thereof in the sample at a predetermined point on a reaction profile by means that are substantially independent of temperature. Also provided is an electrochemical cell comprising a spacer pierced by an aperture which defines a cell wall, a first metal electrode on one side of the spacer extending over one side of the aperture, a second metal electrode on the other side of the spacer extending over the side of the aperture opposite the first electrode, means for admitting a sample to the cell volume defined between the electrodes and the cell wall, and means for heating a sample contained within the cell.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
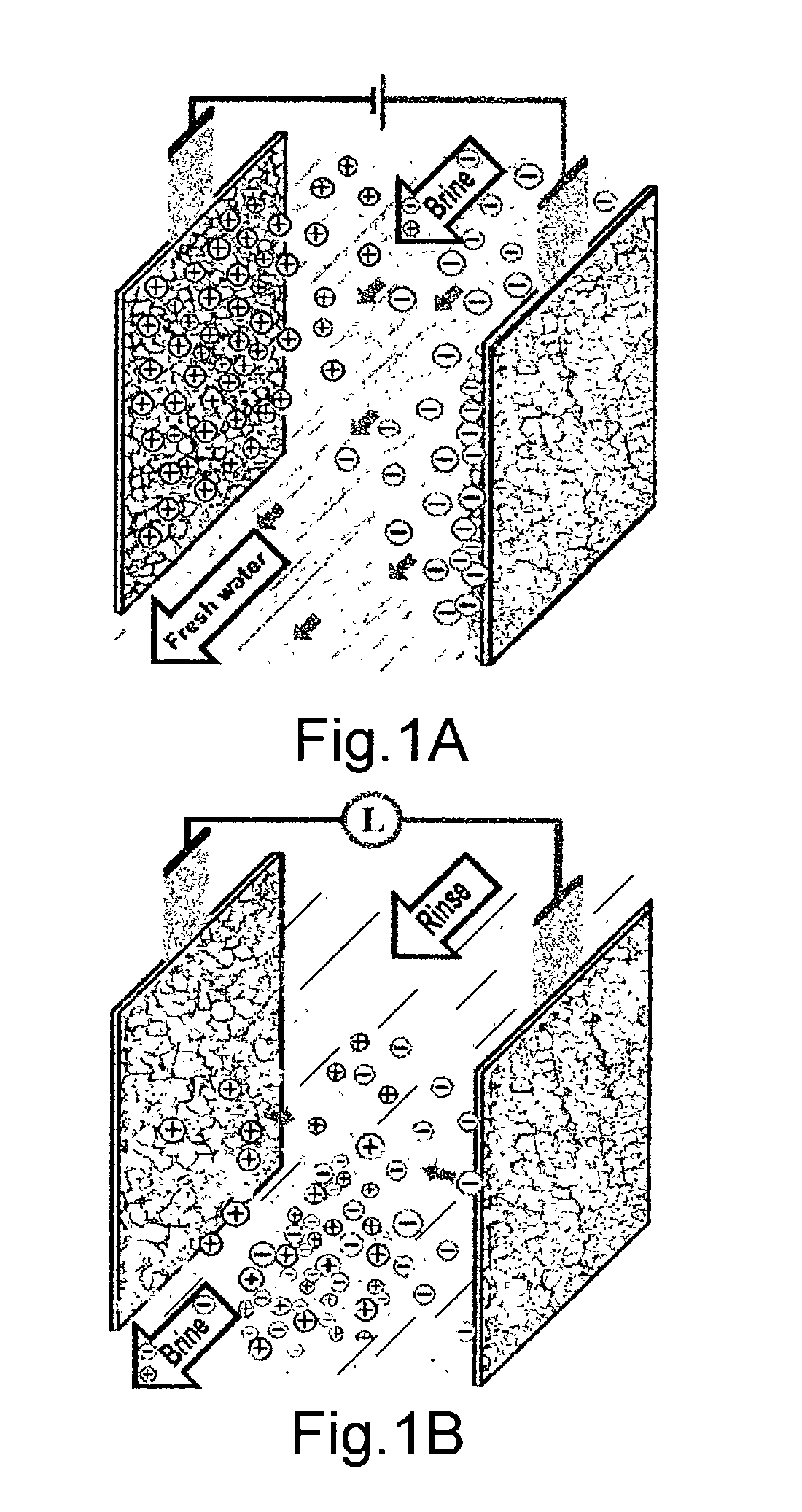
Power efficient flow through capacitor system
InactiveUS20070158185A1Eliminate needRemoval costCellsWater treatment parameter controlPower efficientCapacitor
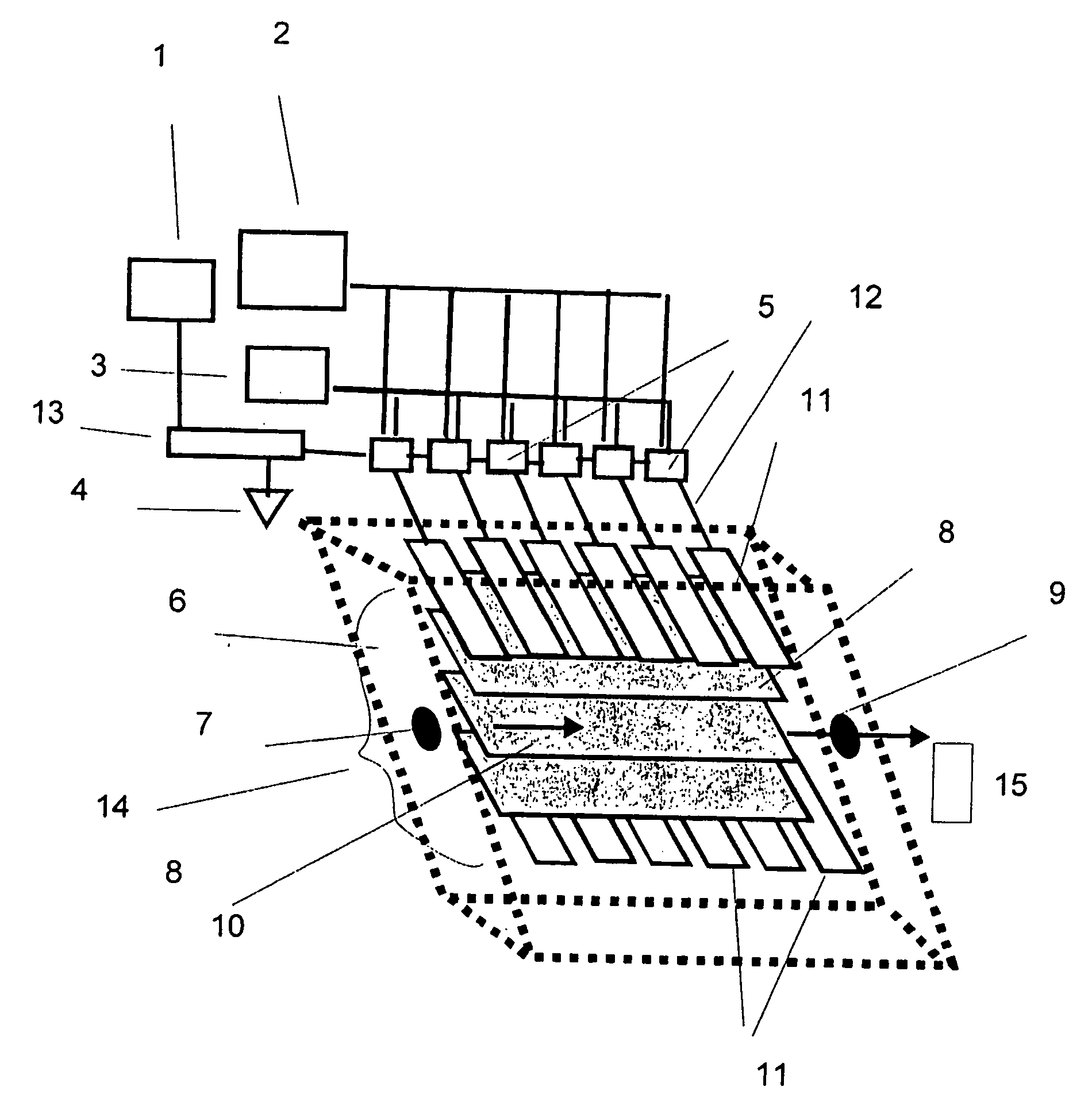
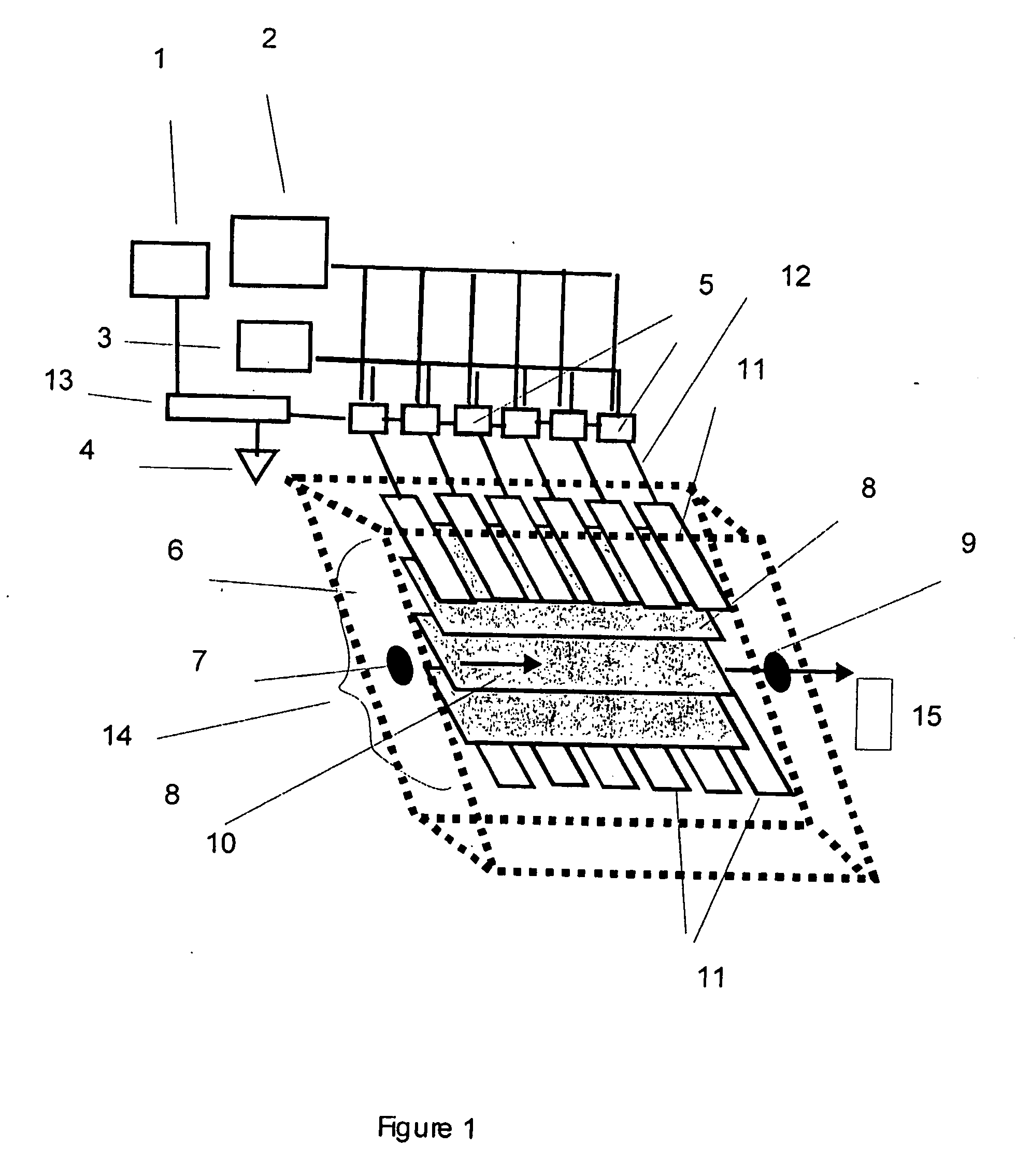
The invention features a flow-through capacitor system that achieves enhanced power efficiency by sequential control and actuation of at least two or more flow-through capacitor cells within the flow-through capacitor system. Alternatively or in addition, power efficiency is enhanced by integrating the purification stages of the system, for example, by placing more than one cell within a single cell casing. Preferably, integrated stage flow-through capacitors are controlled sequentially.
Owner:BIOSOURCE INC
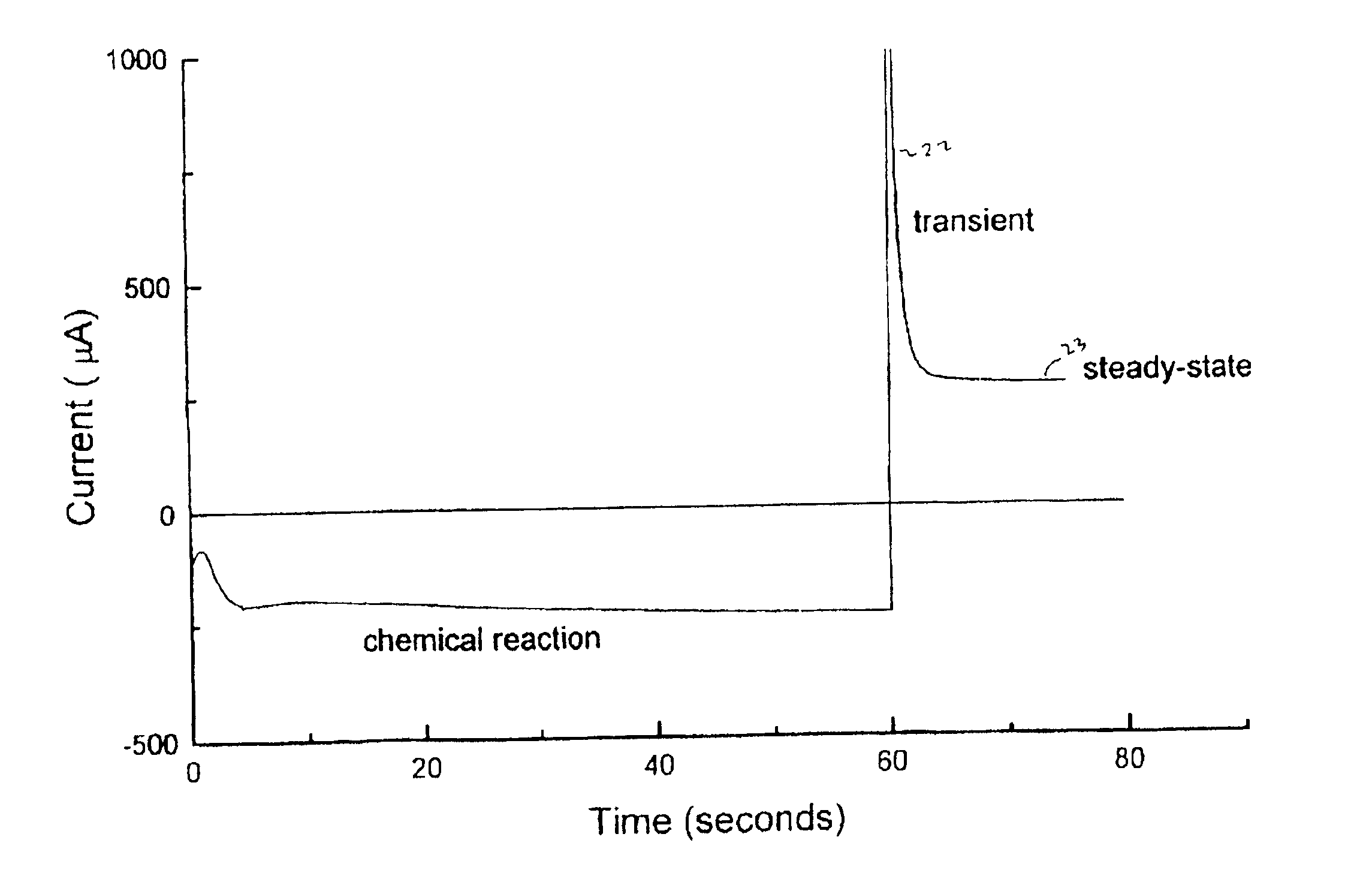
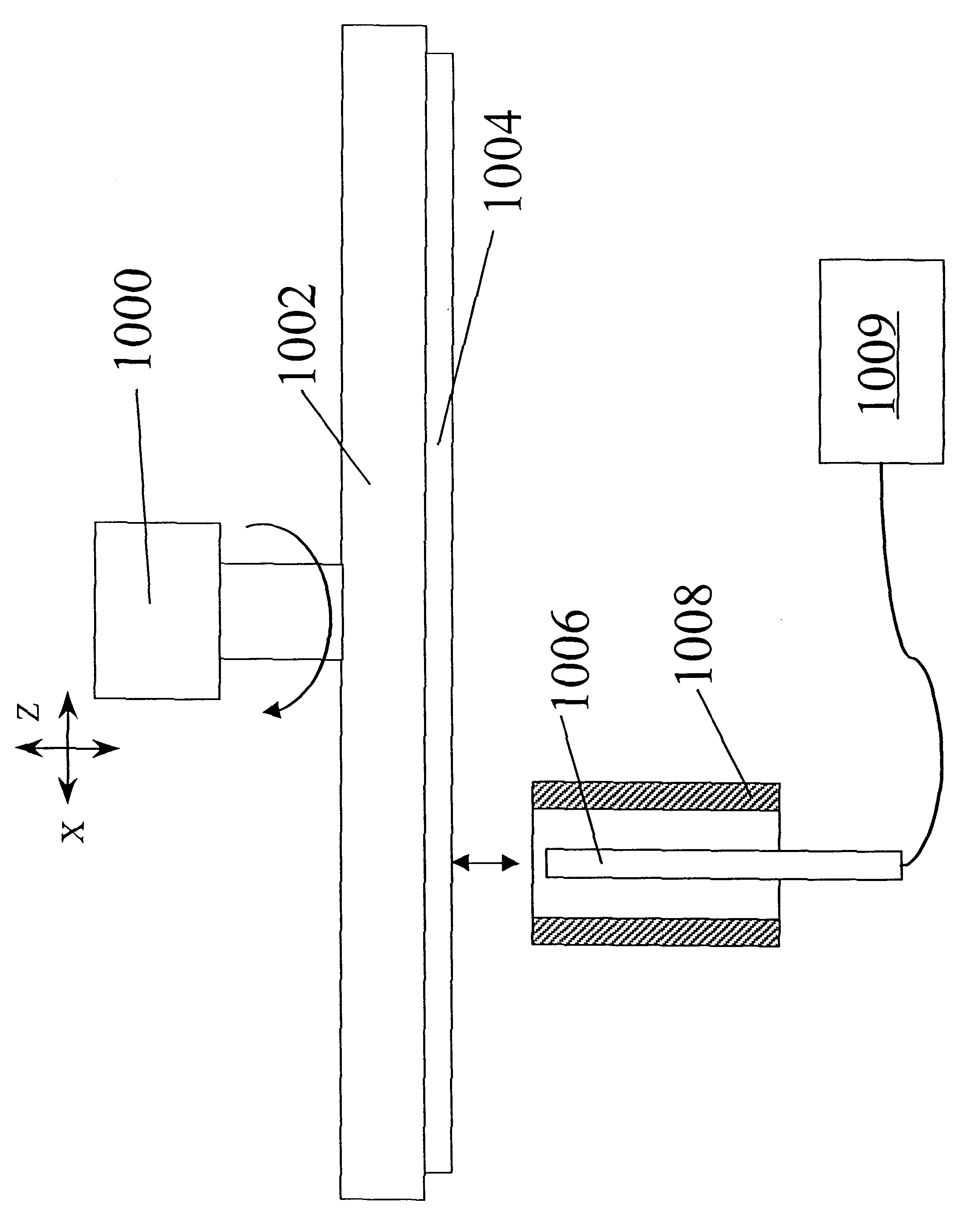
Methods and apparatus for end-point detection
An apparatus for detecting the end-point of an electropolishing process of a metal layer formed on a wafer includes an end-point detector. The end-point detector is disposed adjacent the nozzle used to electropolish the wafer. In one embodiment, the end-point detector is configured to measure the optical reflectivity of the portion of the wafer being electropolished.
Owner:ACM RES
Fully automatic and energy-efficient deionizer
InactiveUS20030098266A1Easy to assembleImprove efficiencyLiquid separation auxillary apparatusSeawater treatmentAutomatic controlComputer module
A fully automatic deionizer comprising five sub-systems for removing ionic contaminants from various liquids at low energy consumption is devised. Based on the charging-discharging principle of capacitors, the deionizer conducts deionization through applying a low DC voltage to its electrodes for adsorbing ions, while more than 30% of the process energy is recovered and stored by discharging the electrodes. At the mean time of discharge, surface of the electrodes is regenerated on site and reset for performing many more cycles of deionization-regeneration till the desirable purification is attained. In one moment, both deionization and regeneration proceed simultaneously on different groups of electrode modules, and in the next moment the electrode modules quickly switch the two processes. Such swift reciprocating actions are engaged in synchronized coordination of sub-systems of electrode modules, energy management, fluid flow, and automatic control.
Owner:GAINIA INTELLECTUAL ASSET SERVICES
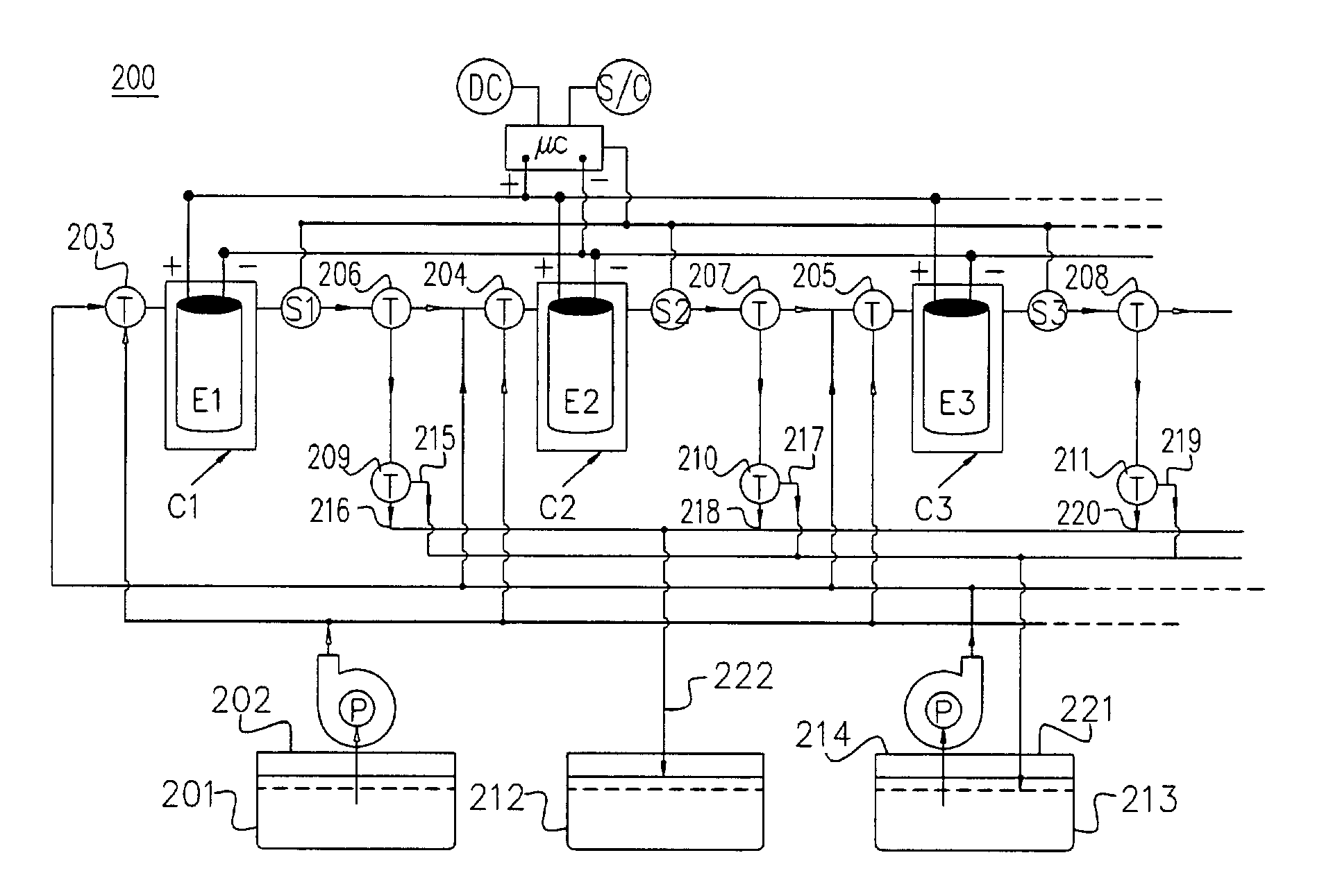
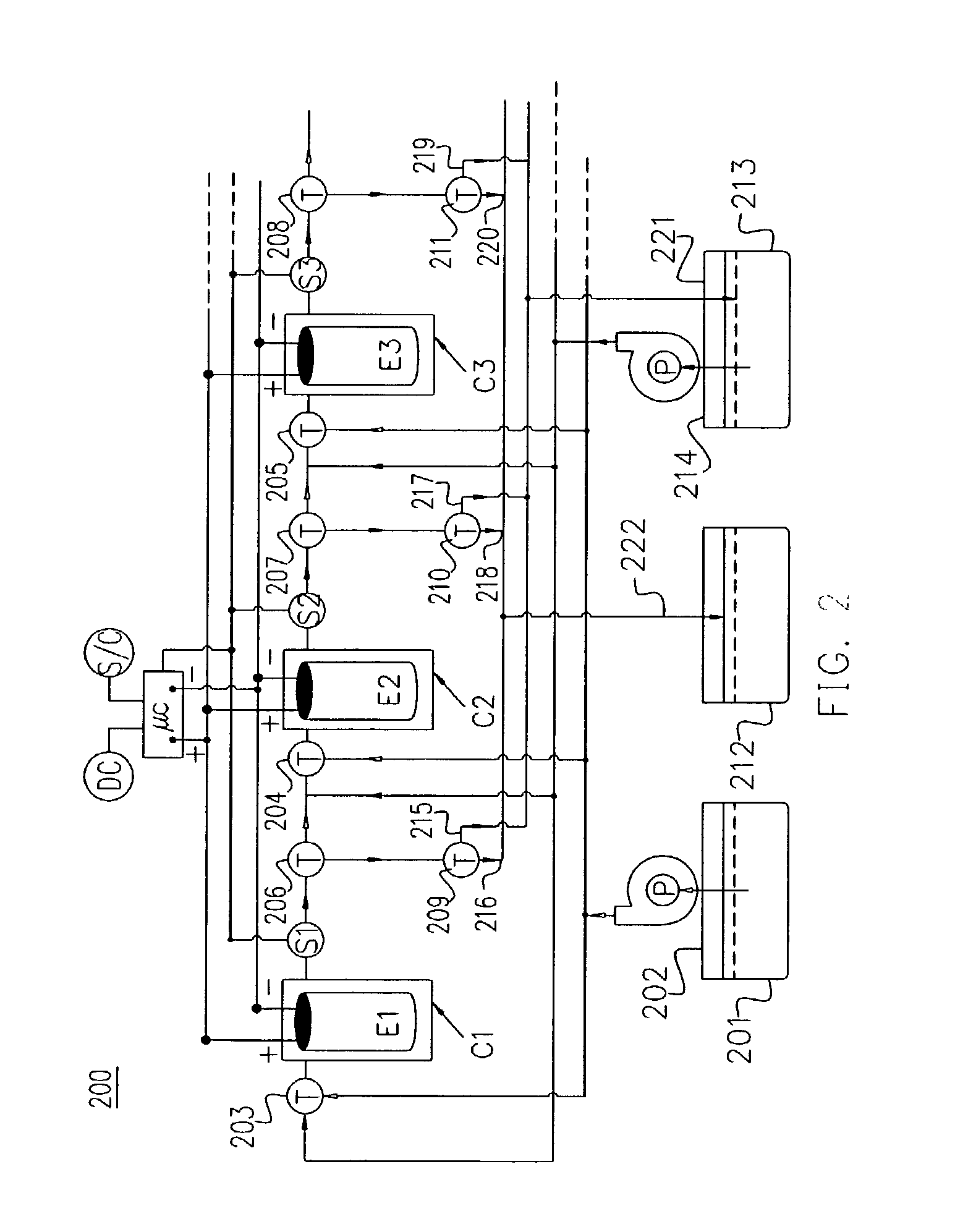
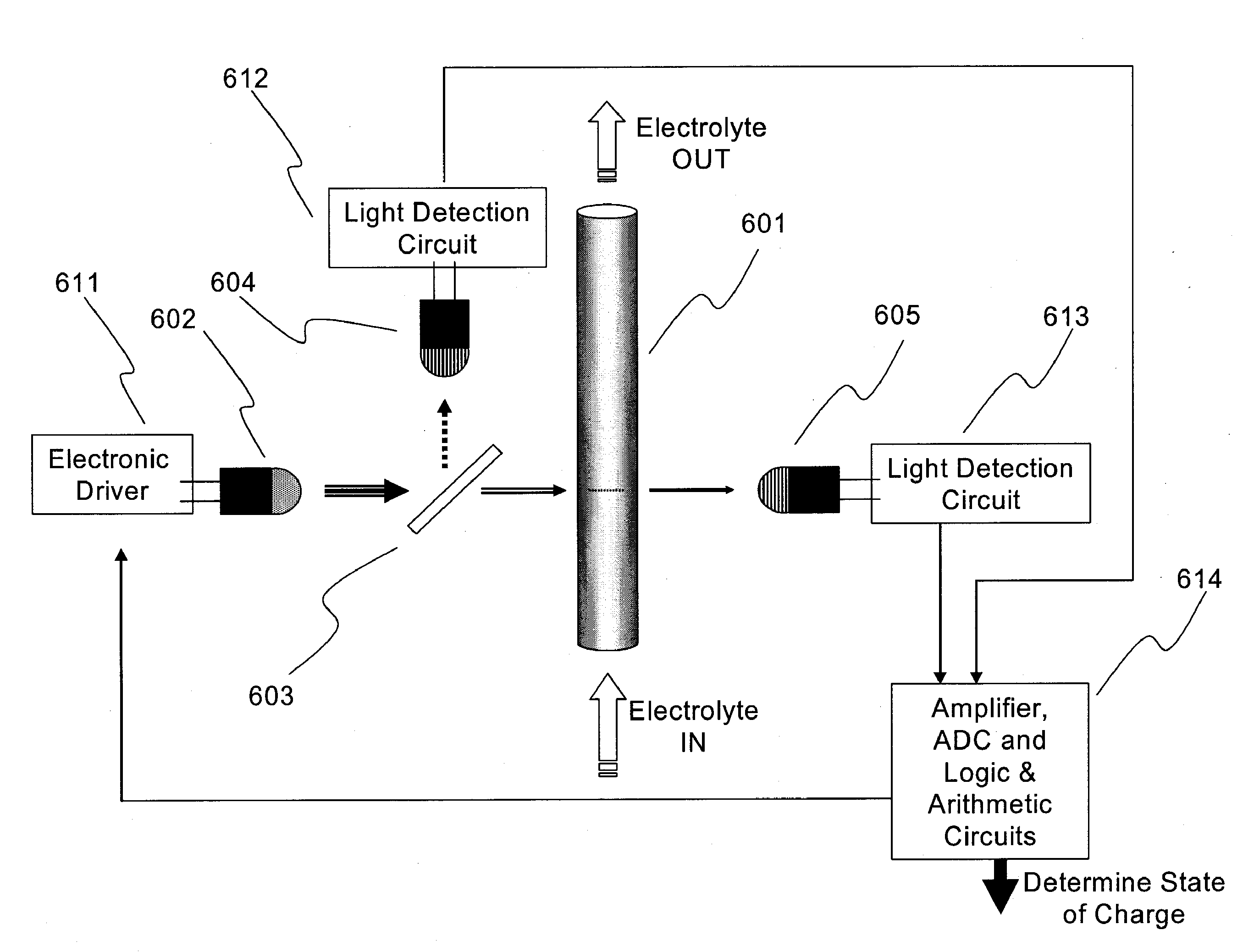
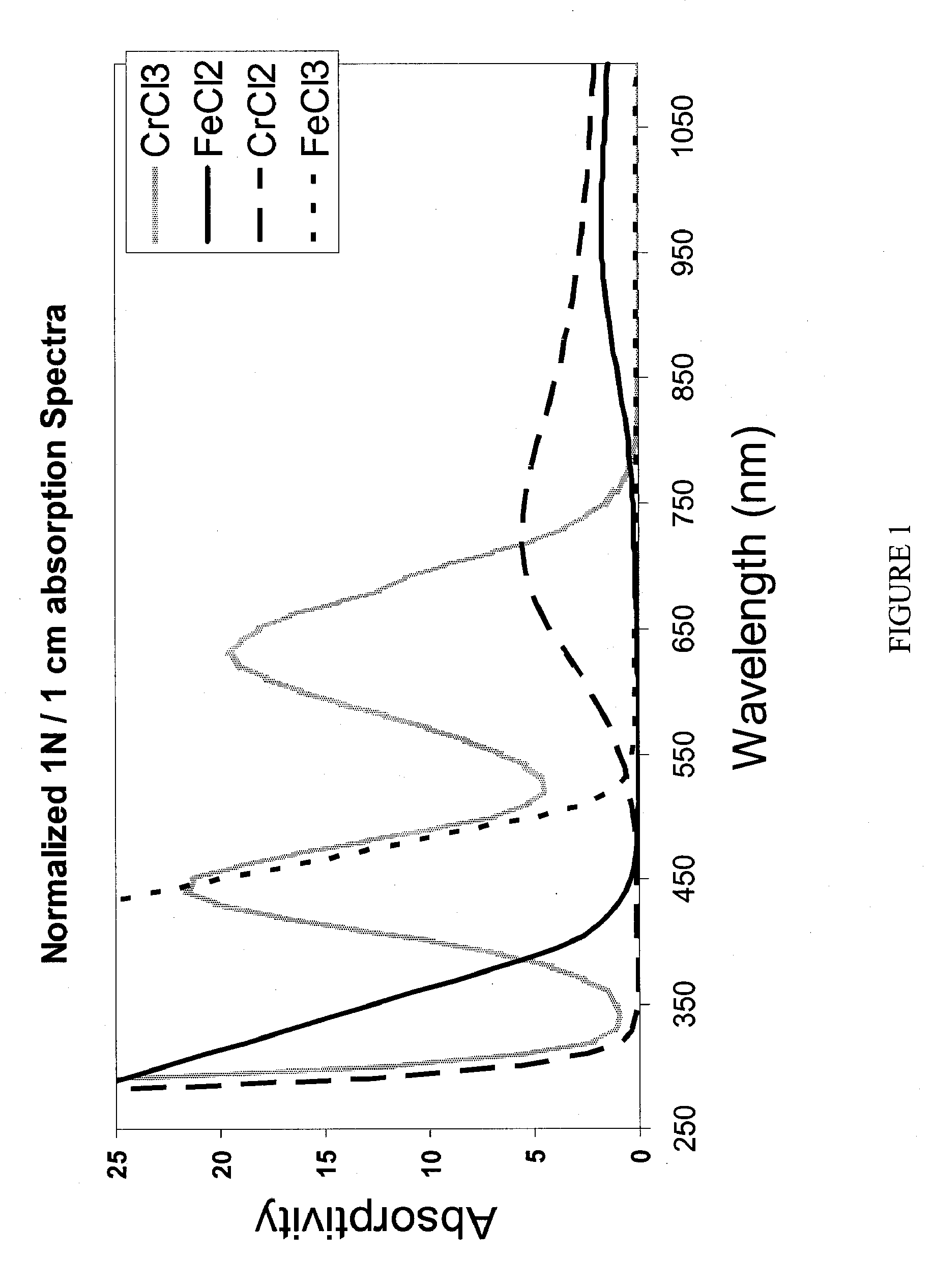
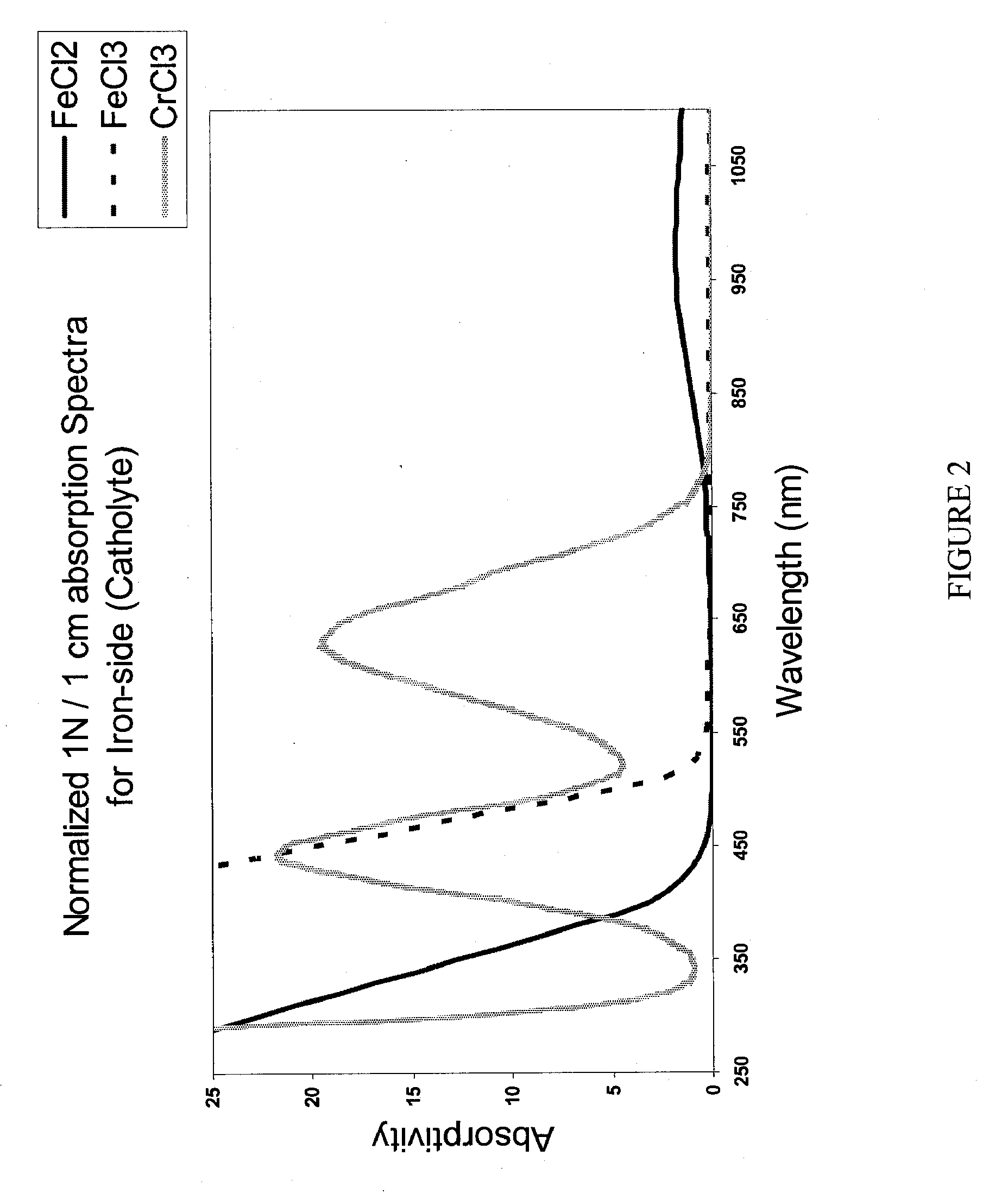
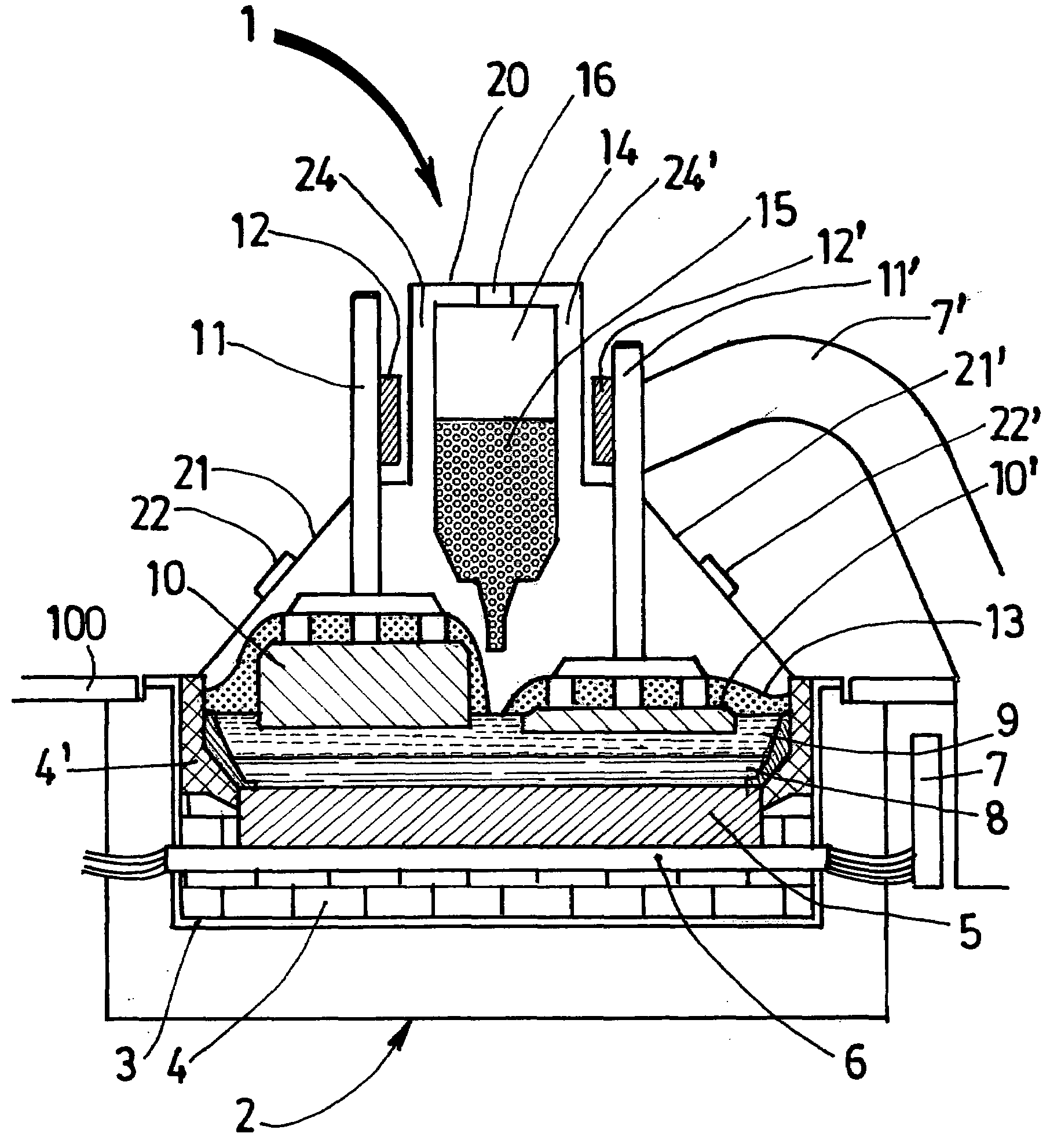
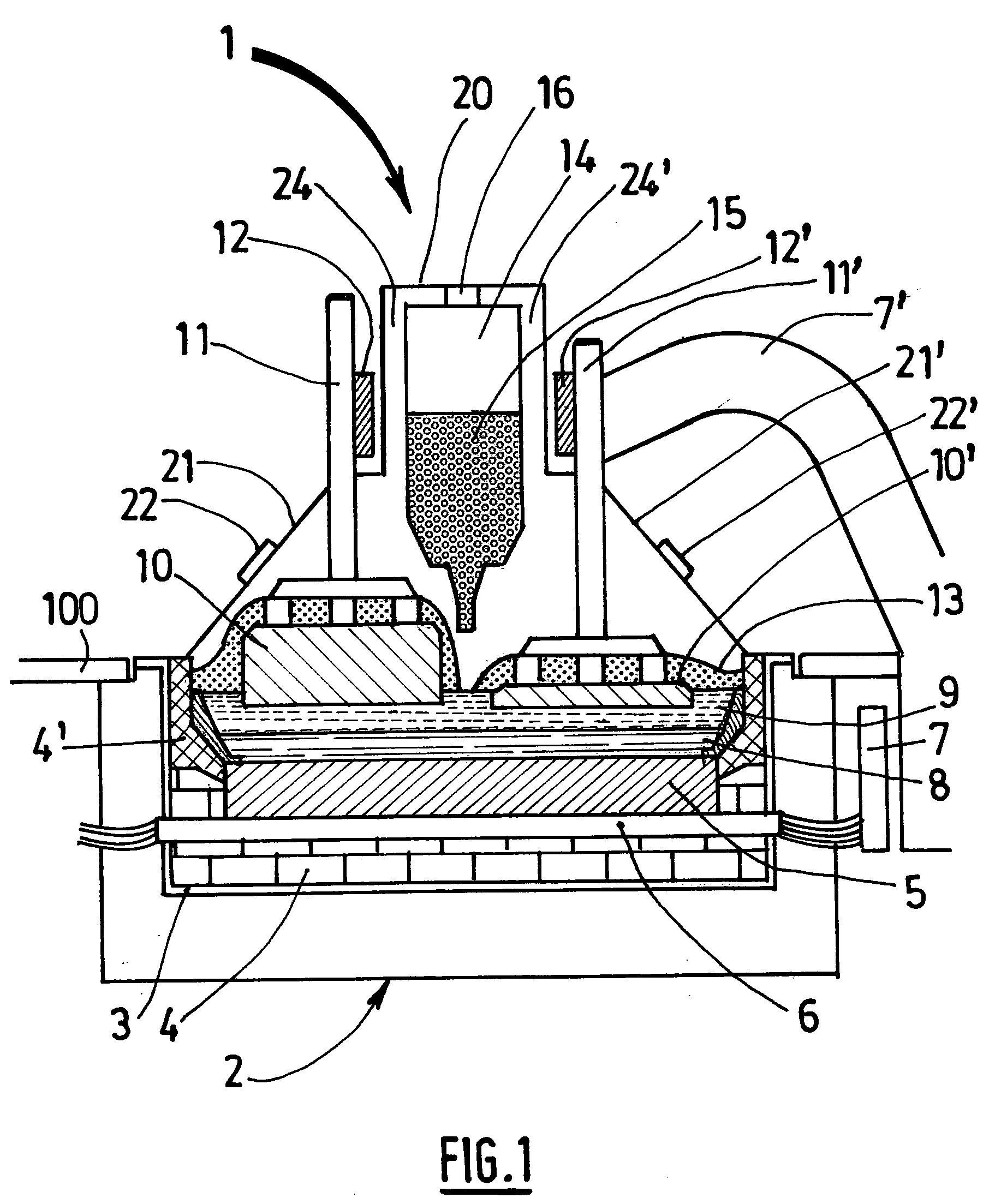
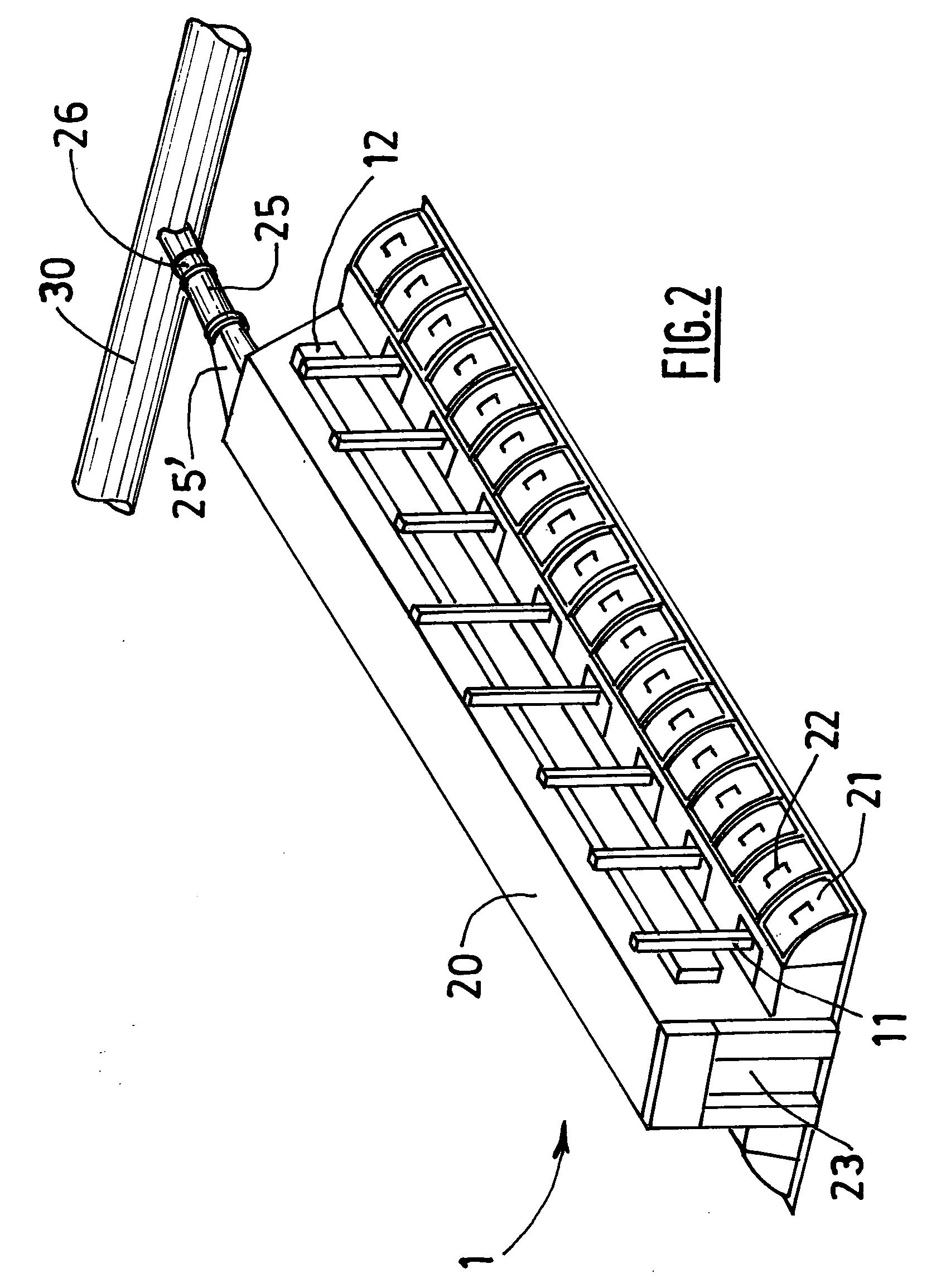
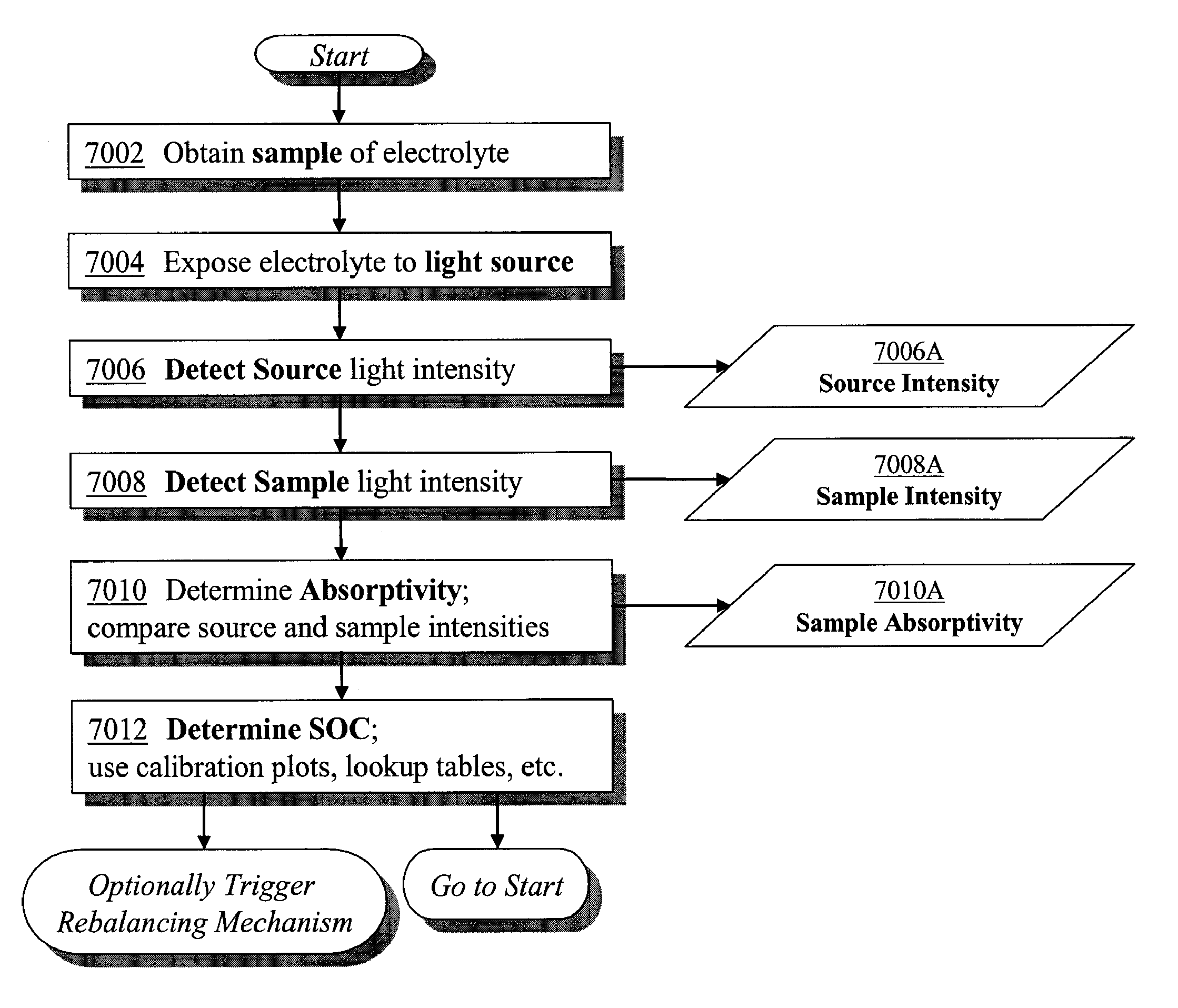
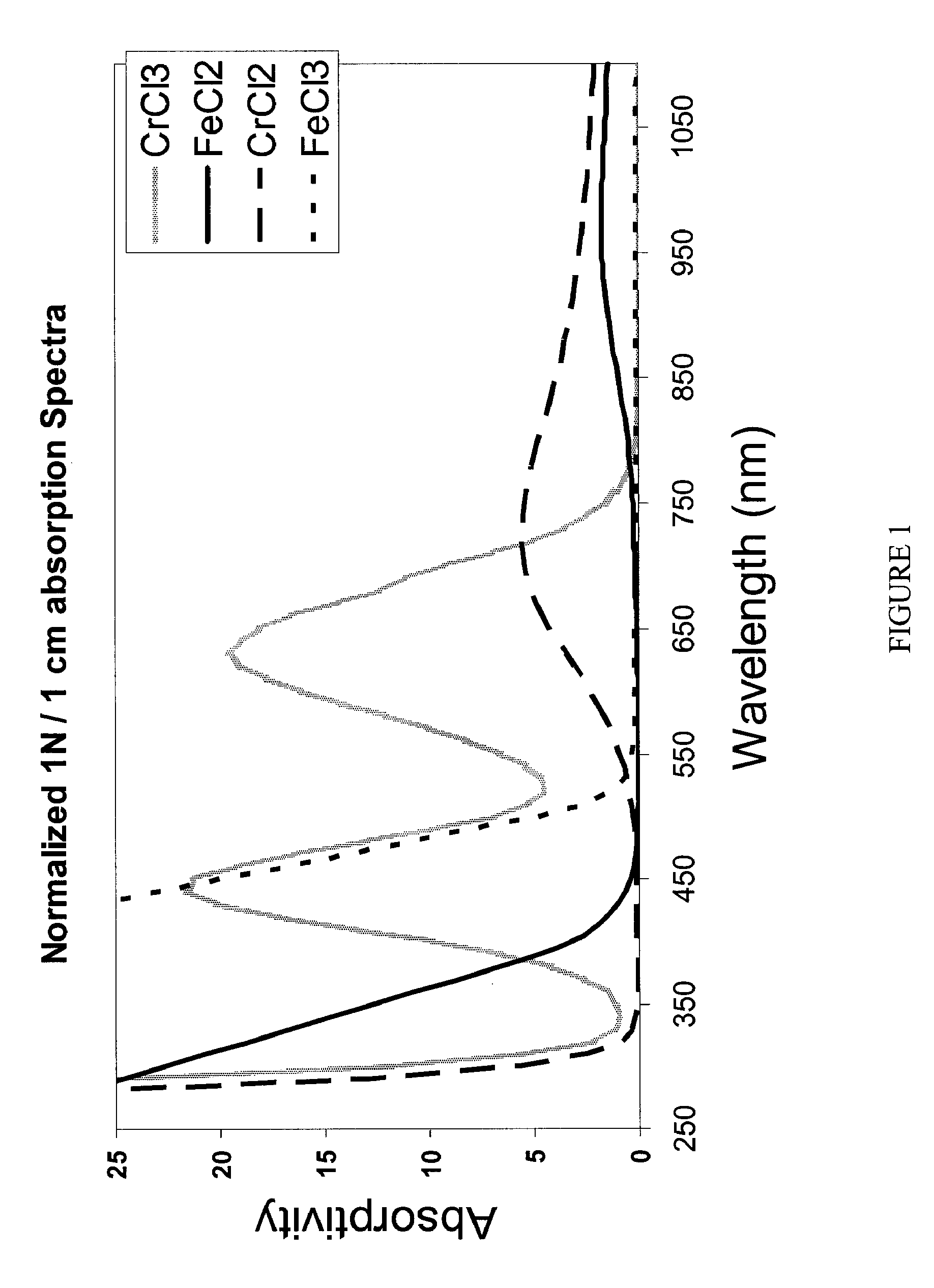
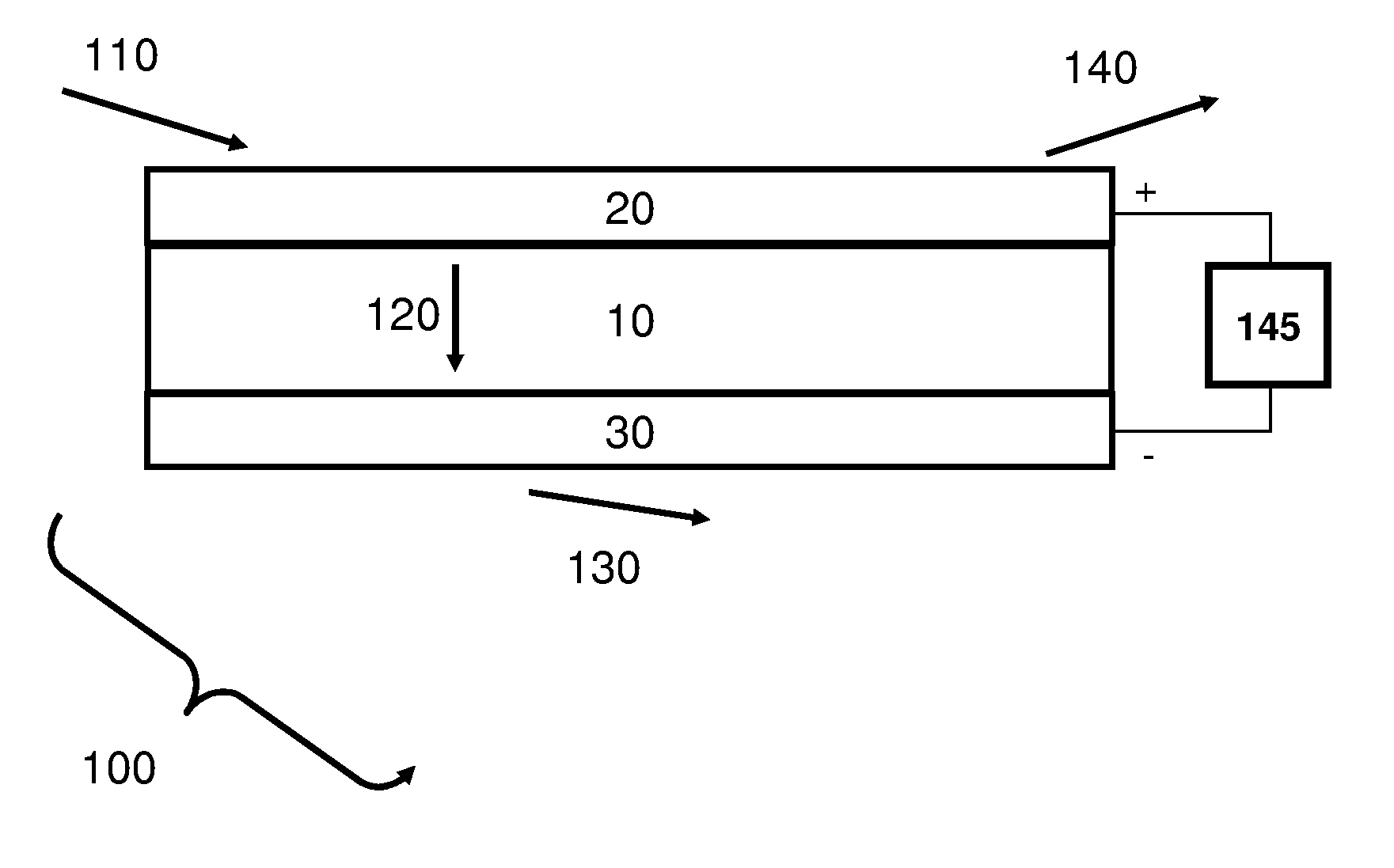
Apparatus and Methods of Determination of State of Charge in a Redox Flow Battery
InactiveUS20080193828A1Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorRedoxState of charge
Apparatus and methods for determining the individual states of charge of electrolytes in a redox battery with mixed or unmixed reactants by optical absorption spectrophotometry are disclosed. The state of charge thus obtained may serve as a gauge for the amount of electro-chemical energy left in the system. Further, the information on anolyte and catholyte charge states may be used for any rebalancing mechanism if the states are different.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
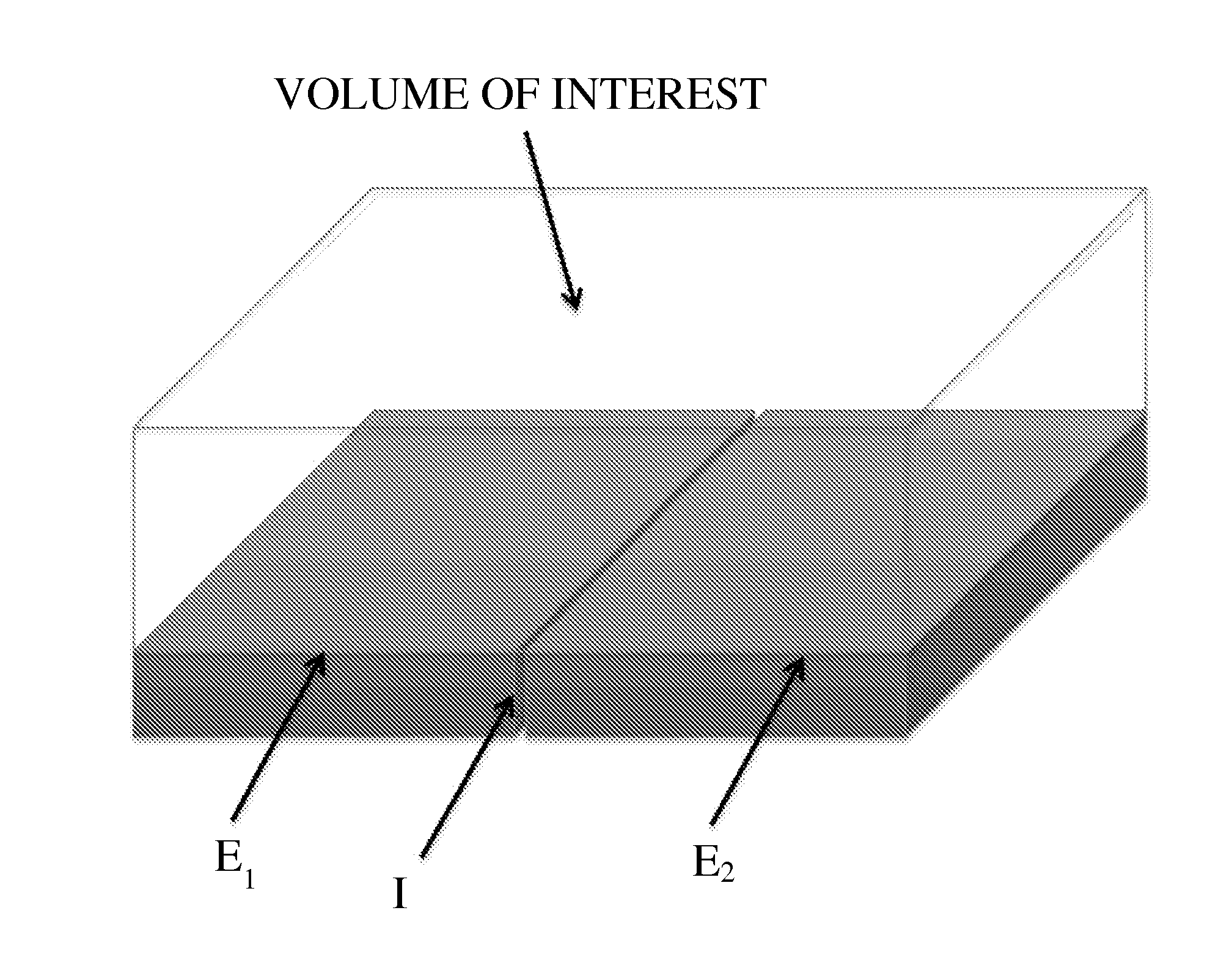
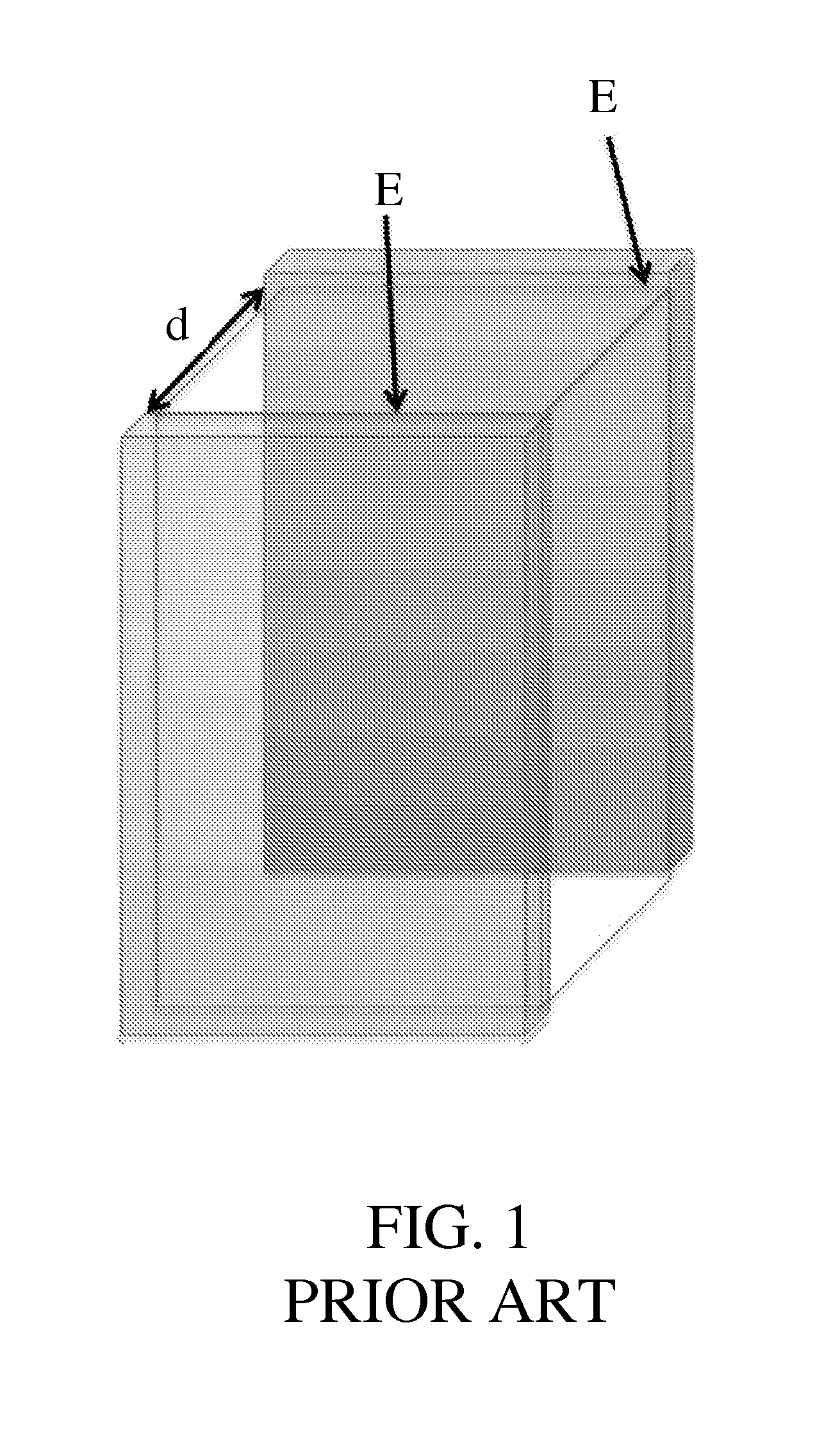
Electroporation electrode configuration and methods
InactiveUS20130196441A1High electric fieldReduce potential differenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsLiquid separation by electricityPotential differenceElectroporation
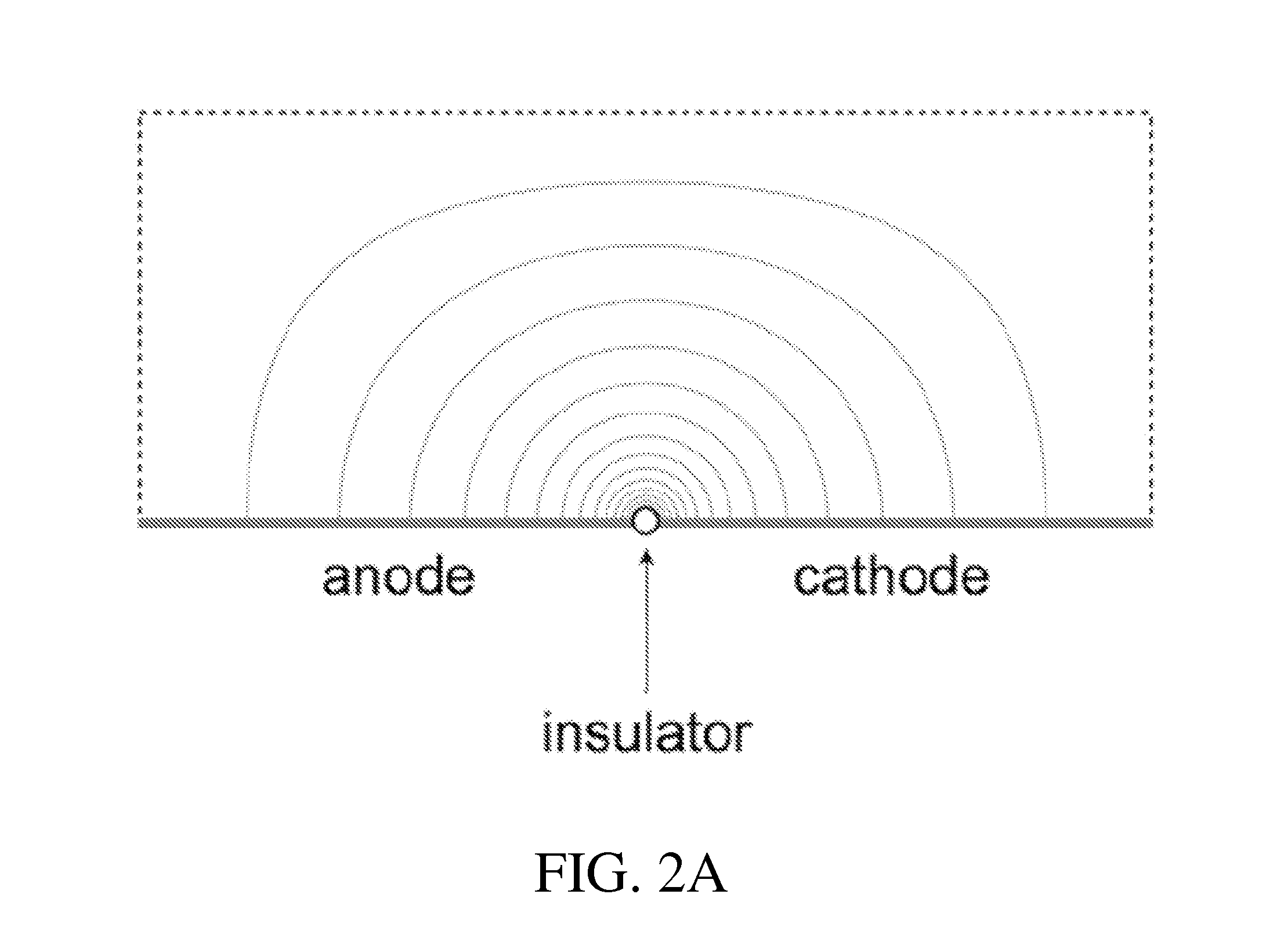
Provided herein are the concept that “singularity-based configuration” electrodes design and method can produce in an ionic substance local high electric fields with low potential differences between electrodes. The singularity-based configuration described here includes: an anode electrode; a cathode electrode; and an insulator disposed between the anode electrode and the cathode electrode. The singularity-based electrode design concept refers to electrodes in which the anode and cathode are adjacent to each other, placed essentially co-planar and are separated by an insulator. The essentially co-planar anode / insulator / cathode configuration bound one surface of the volume of interest and produce desired electric fields locally, i.e., in the vicinity of the interface between the anode and cathode. In an ideal configuration, the interface dimension between the anode and the cathode tends to zero and becomes a point of singularity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Through silicon via filling using an electrolyte with a dual state inhibitor
ActiveUS20110284386A1Faster rateLittle and depositionCellsMachining electric circuitsElectricityElectroplating
A method for electrofilling large, high aspect ratio recessed features with copper without depositing substantial amounts of copper in the field region is provided. The method allows completely filling recessed features having aspect ratios of at least about 5:1 such as at least about 10:1, and widths of at least about 1 μm in a substantially void-free manner without depositing more than 5% of copper in the field region (relative to the thickness deposited in the recessed feature). The method involves contacting the substrate having one or more large, high aspect ratio recessed features (such as a TSVs) with an electrolyte comprising copper ions and an organic dual state inhibitor (DSI) configured for inhibiting copper deposition in the field region, and electrodepositing copper under potential-controlled conditions, where the potential is controlled not exceed the critical potential of the DSI.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
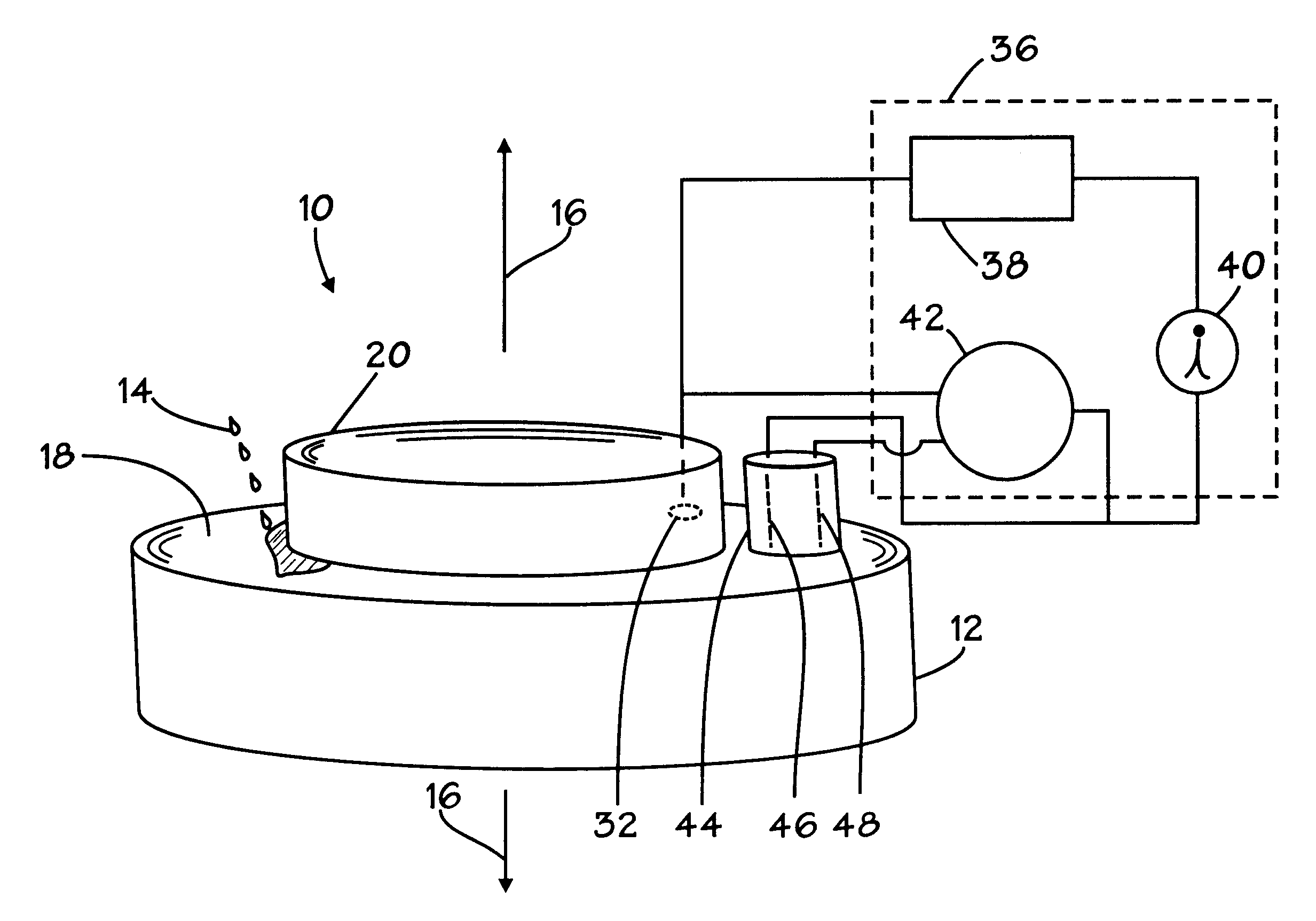
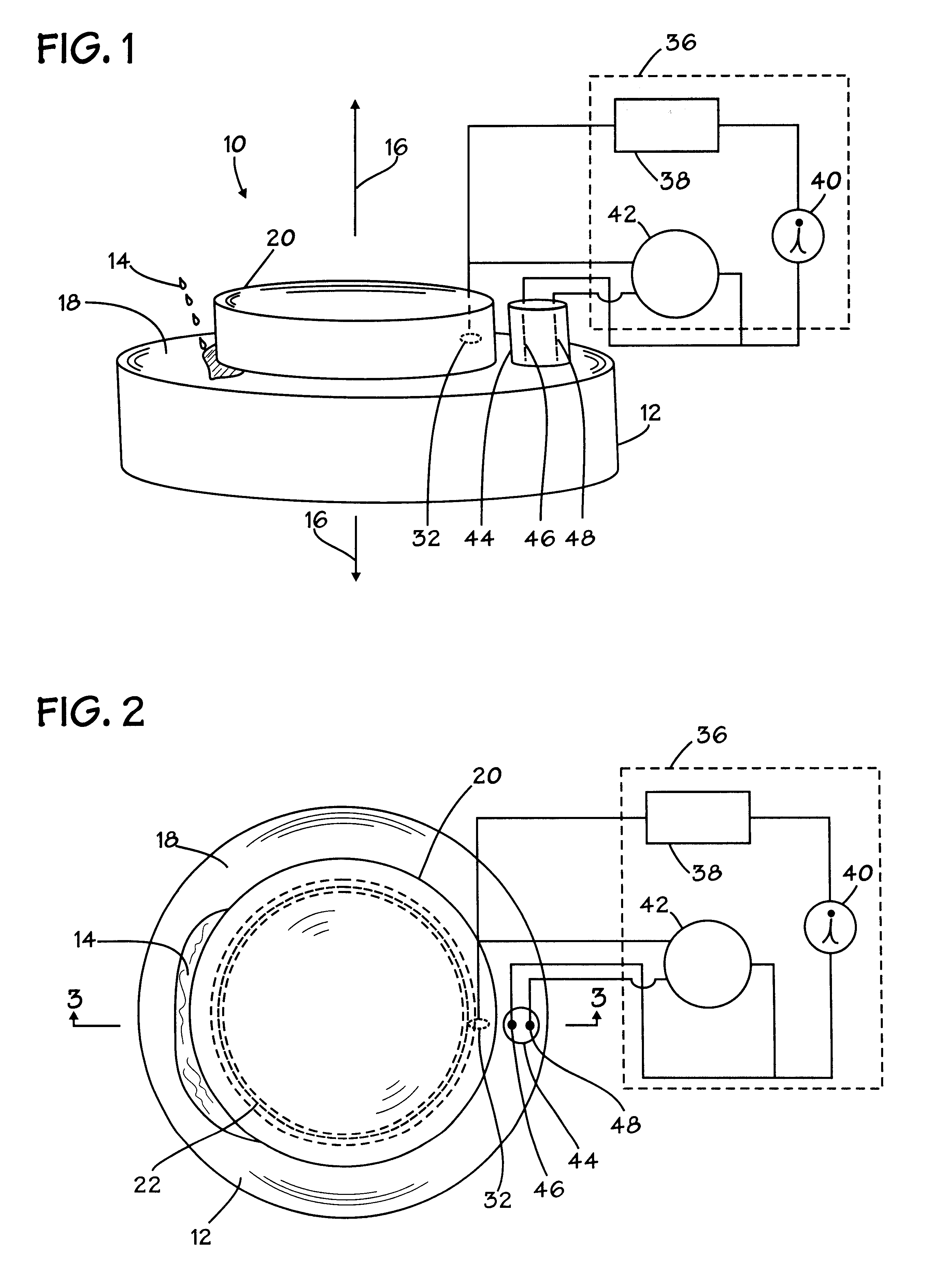
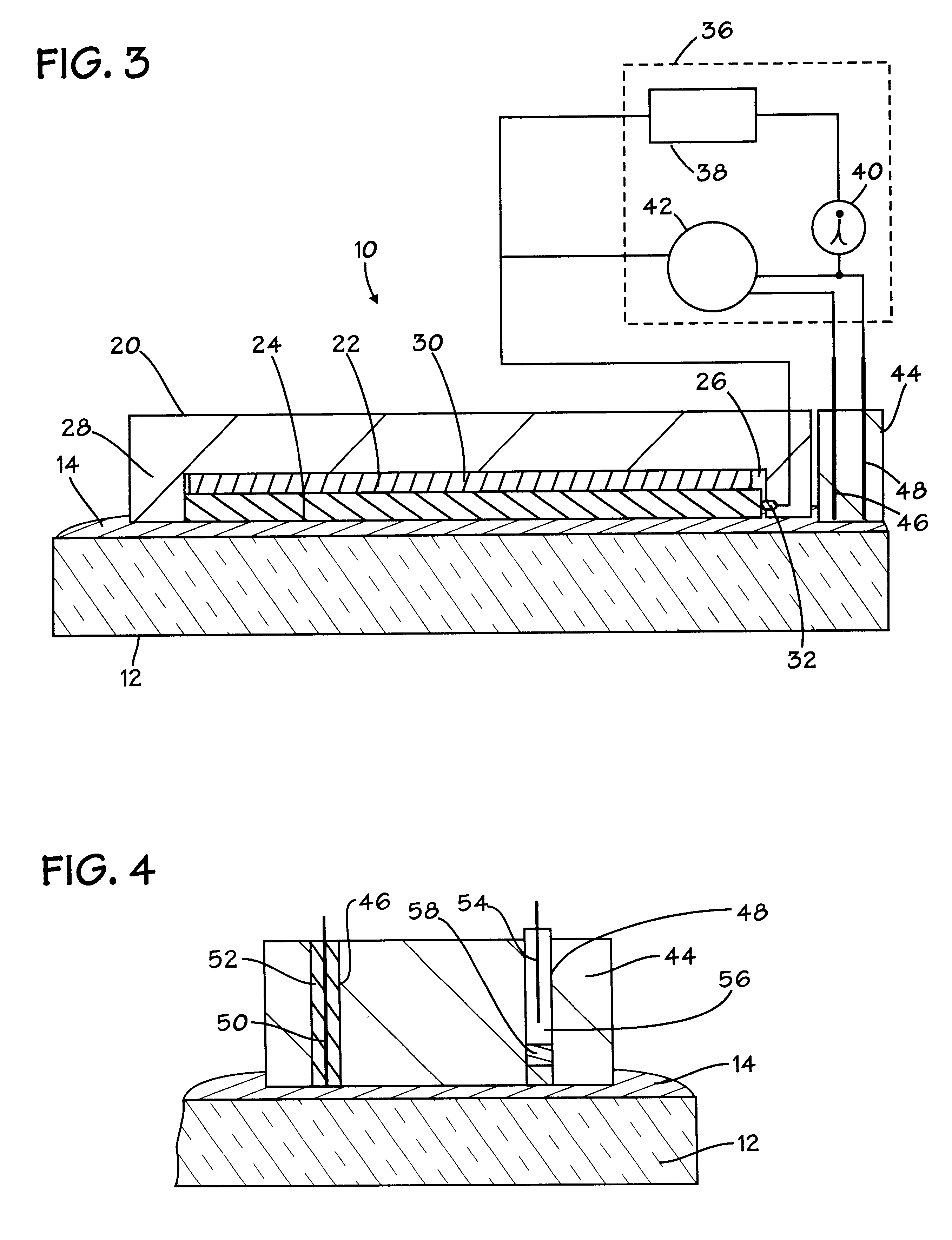
Method and appartus for operation of pool cleaner with integral chlorine generator
ActiveUS20090282627A1Efficiently and effectively distributesUniform concentrationCellsPhotography auxillary processesTime segmentElectrical battery
An automated self-propelled pool cleaner having a housing, a water pump for moving water through the housing, drive means for moving the pool cleaner over the surface of the salt water pool to be cleaned, and an integral electrochemical chlorine generator mounted in the housing, includes a processor / controller that is programmed to activate the chlorine generator, the pump and drive means in predetermined operational sequences that minimize wear and tear on the water pump and drive means, while at the same time distribute and maintain a safe level of sanitizing chlorine in the pool, to thereby obviate the need for an in-line chlorinator or other chemical additive treatments; an optional automated sensor device can be provided to activate a secondary maintenance program which enables the pool cleaner to operate over prolonged periods of time as the sole means for filtering and sanitizing the pool water. An electrochemical cell manual mounting system permits the cell to be secured in place for operation and manually removed for maintenance, repair or replacement by the user without special tools or training.
Owner:AQUA PRODS
Dynamically variable field shaping element
InactiveUS7070686B2Uniform current distributionUniform currentAnodisationMachining electric circuitsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrochemical response
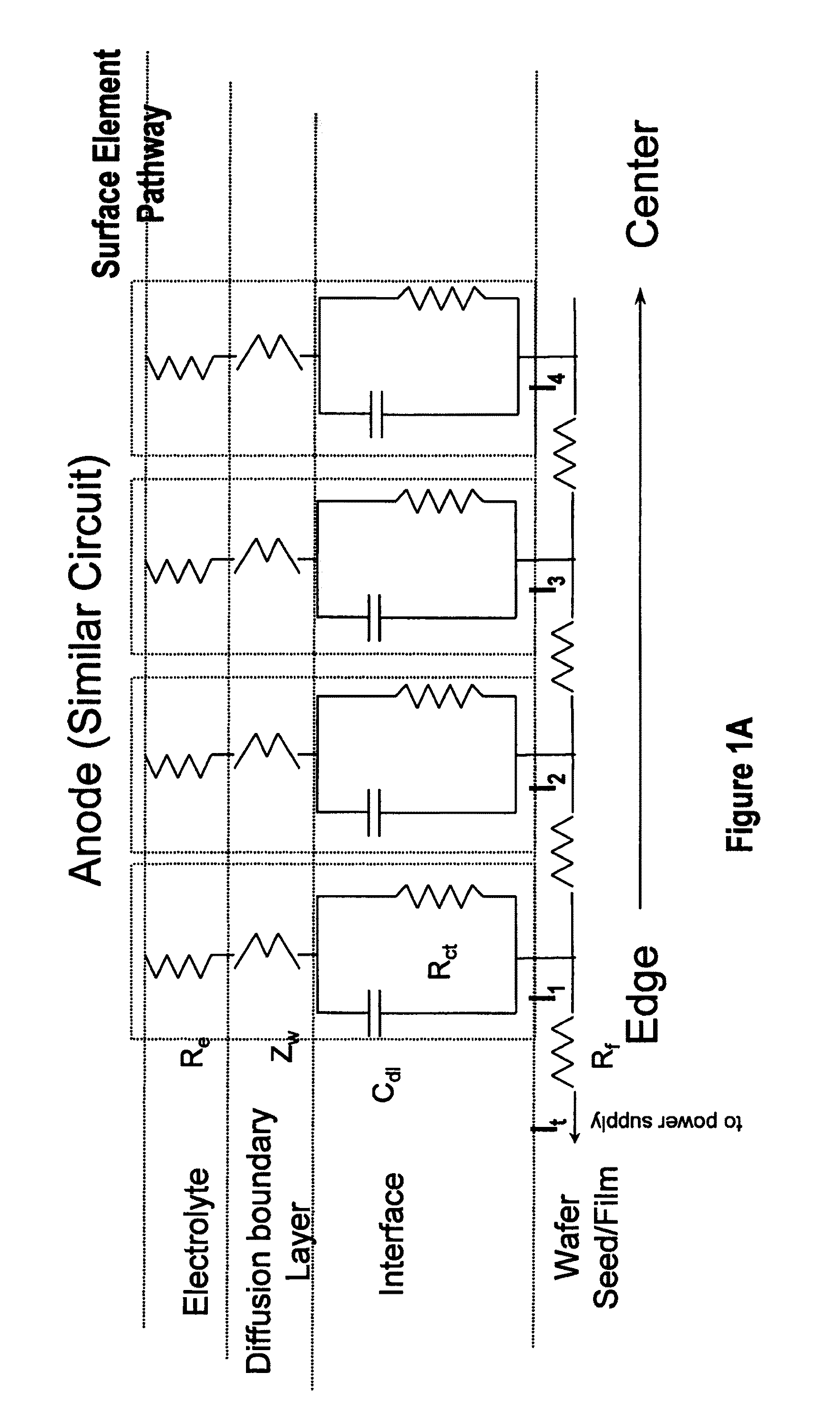
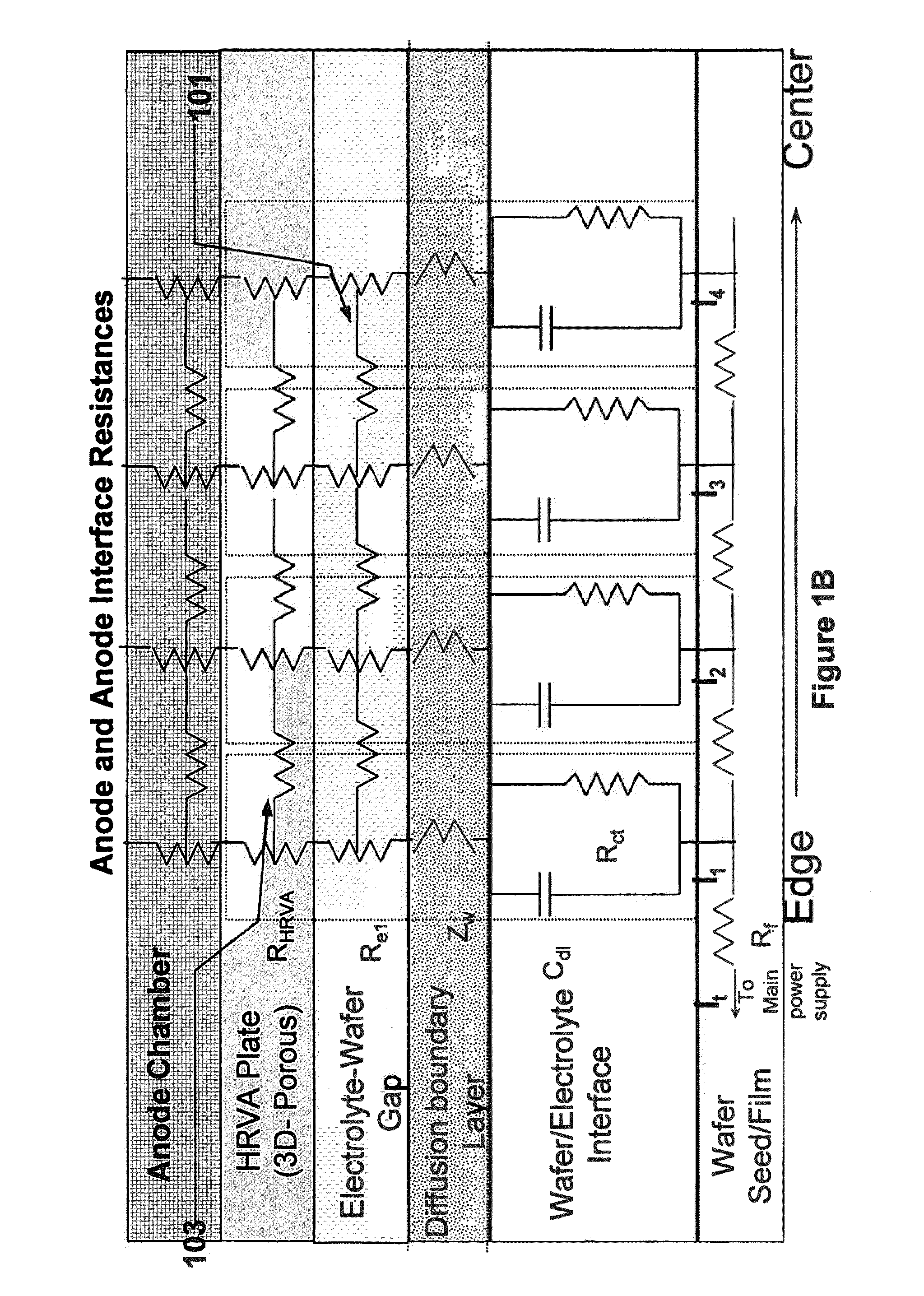
In an electrochemical reactor used for electrochemical treatment of a substrate, for example, for electroplating or electropolishing the substrate, one or more of the surface area of a field-shaping shield, the shield's distance between the anode and cathode, and the shield's angular orientation is varied during electrochemical treatment to screen the applied field and to compensate for potential drop along the radius of a wafer. The shield establishes an inverse potential drop in the electrolytic fluid to overcome the resistance of a thin film of conductive metal on the wafer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Apparatus and method for producing electrolyzed water
An apparatus for producing electrolyzed water includes an electrochemical cell and a solution reservoir containing a solution and having an outlet. An injection pump has an input end in fluid communication with the outlet of the solution reservoir and an output end in fluid communication with the electrochemical cell, wherein the injection pumps an amount of the solution from the solution reservoir to mix with a water solution and enter the electrochemical cell. A current feedback sensor senses a cell current in the electrochemical cell. A current control unit in data communication with the current feedback sensor and the injection pump wherein the current control unit compares the cell current with a preselected current and adjusts the amount of solution pumped from the injection pump responsive to the comparison. The apparatus may also include an automatic control feedback system to monitor and adjust pH.
Owner:EAU TECH
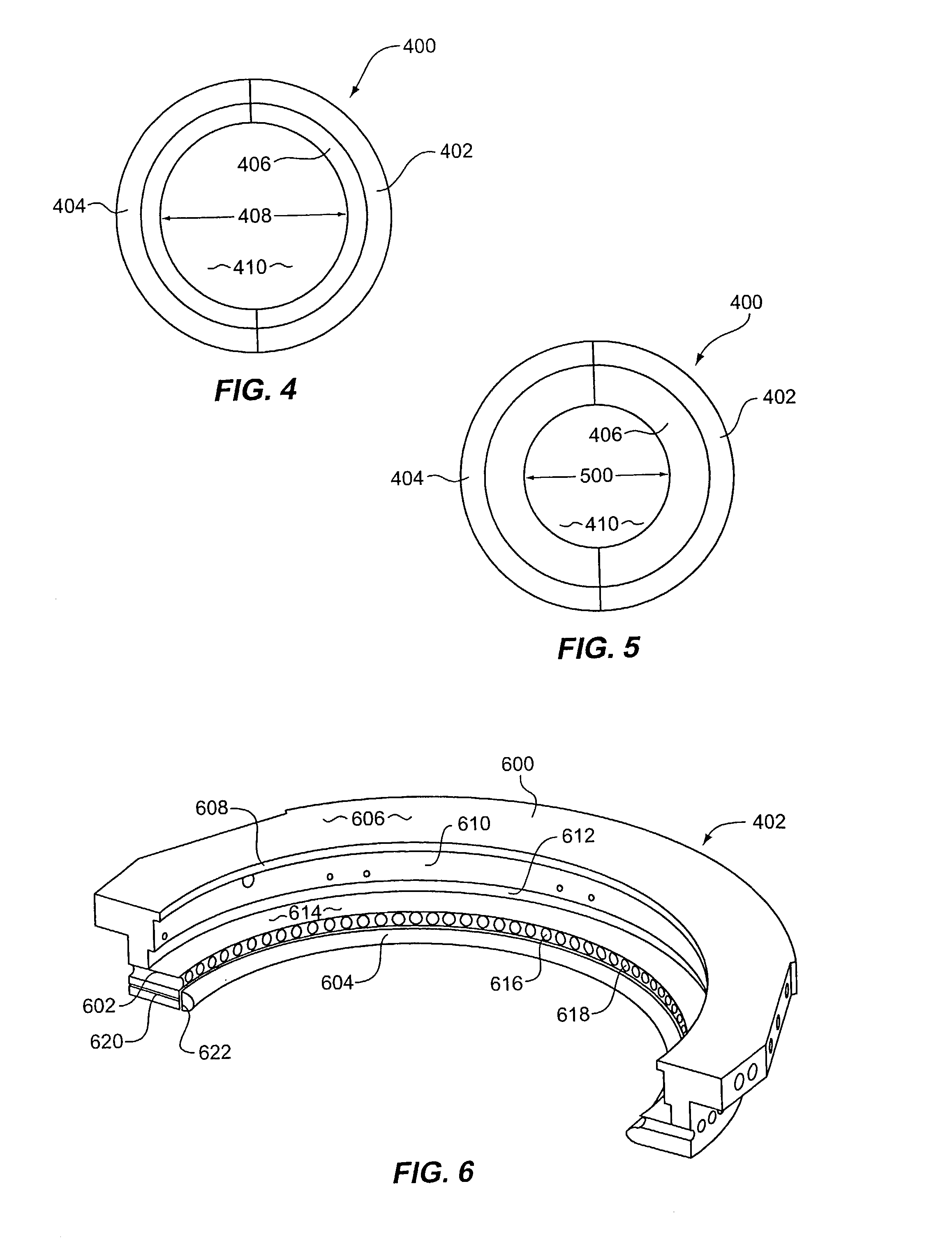
Method and apparatus for electroplating
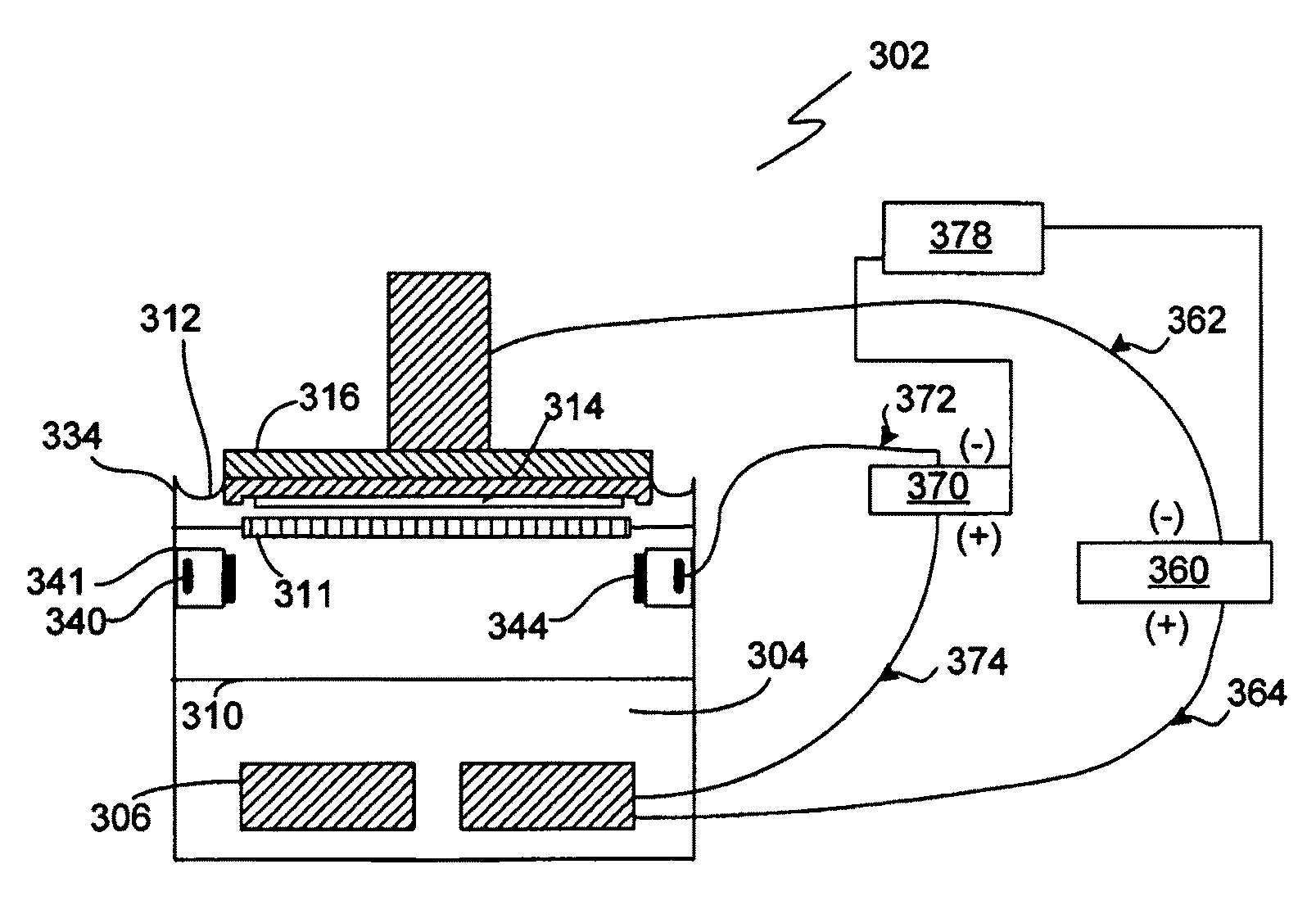
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer and an auxiliary cathode located between the anode and the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface. The auxiliary cathode is configured to shape the current distribution from the anode. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Apparatus for production of strong alkali and acid electrolytic solution
There is provided an apparatus for producing strong alkaline reductive electrolyzed water and acidic water that enables efficient production of electrolyzed water that has excellent washing and sterilizing effects. There is provided an apparatus for producing strong alkaline reductive electrolyzed water and acidic water, which includes an electrolyzer provided with a strong alkaline reductive electrolyzed water-producing chamber, an acidic water-producing chamber and a partitioning membrane, wherein a flow path diffusing device is provided in the electrolyzer, and a gap between the cathode plate and the anode plate of 0.1 mm to 1 mm.
Owner:AQUA ECO
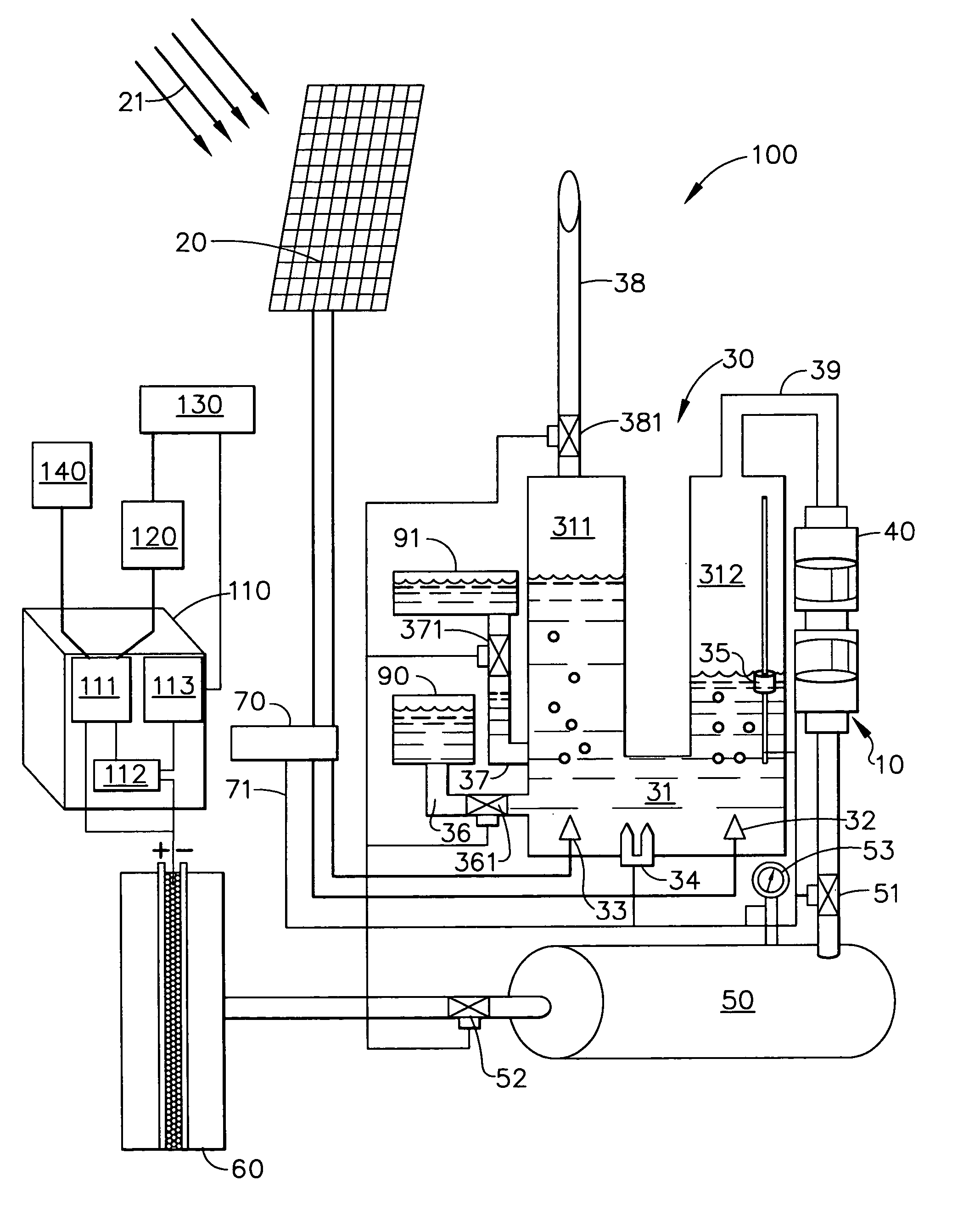
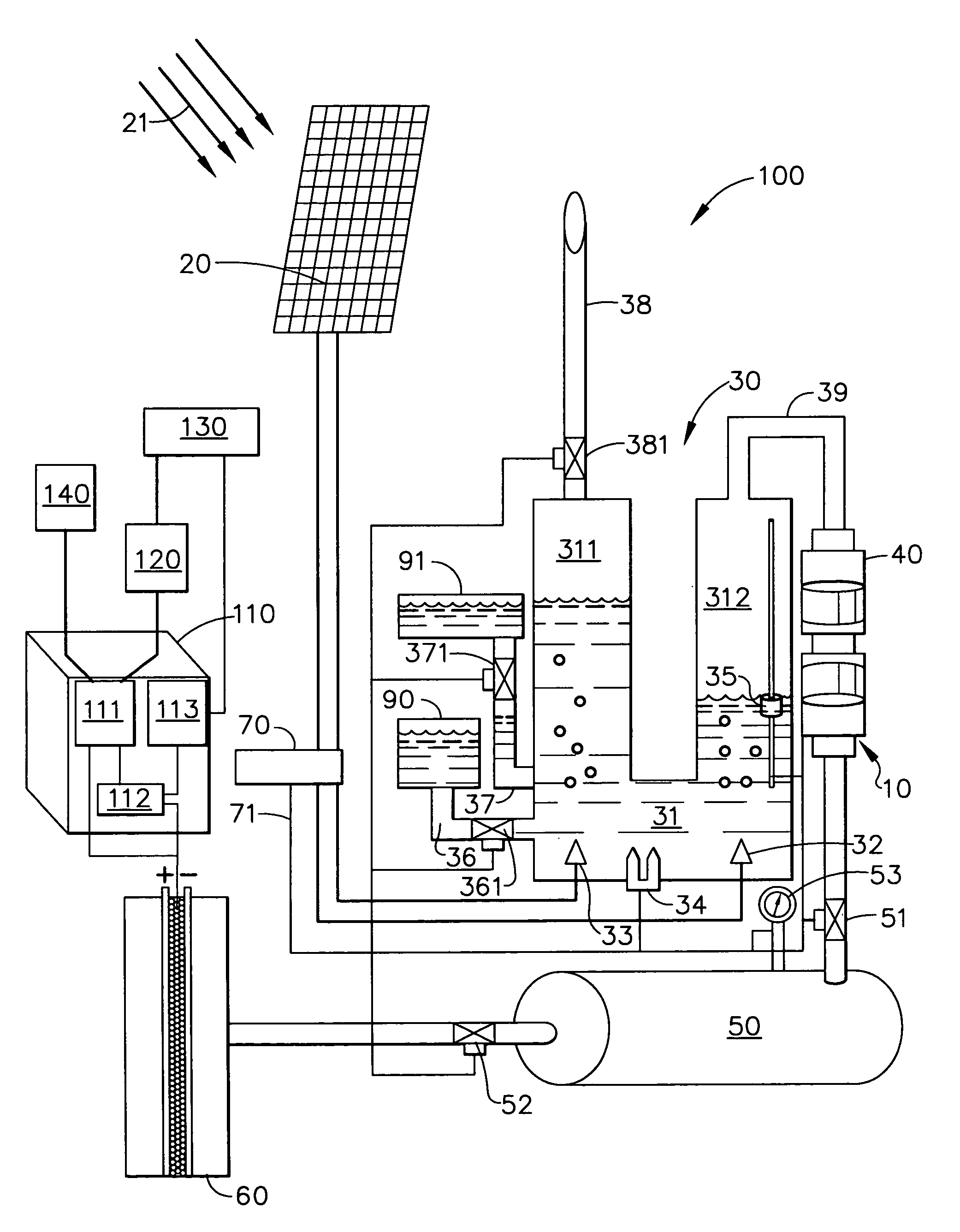
Solar electrolysis power co-generation system
A solar electrolysis power co-generation system includes a solar electrolysis source and a control unit. The solar electrolysis source includes a solar panel, an electrolysis unit, a hermetically sealed compressor, a hydrogen tank, and a hydrogen-powered fuel cell and produces, compresses, and stores hydrogen gas that is used to fuel the fuel cell. The control unit includes an inverter, a microprocessor, and a modem. The control unit connects the solar electrolysis power source with a power grid and with an individual consumer having an electrical load. The power co-generation system utilizes the electrolysis of water and solar energy to power a fuel cell. The energy produced with the fuel cell may be provided to an existing power gird as well as to an individual consumer. Further a method for decentralized power co-generation includes the step of providing a plurality of solar electrolysis power co-generation systems.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
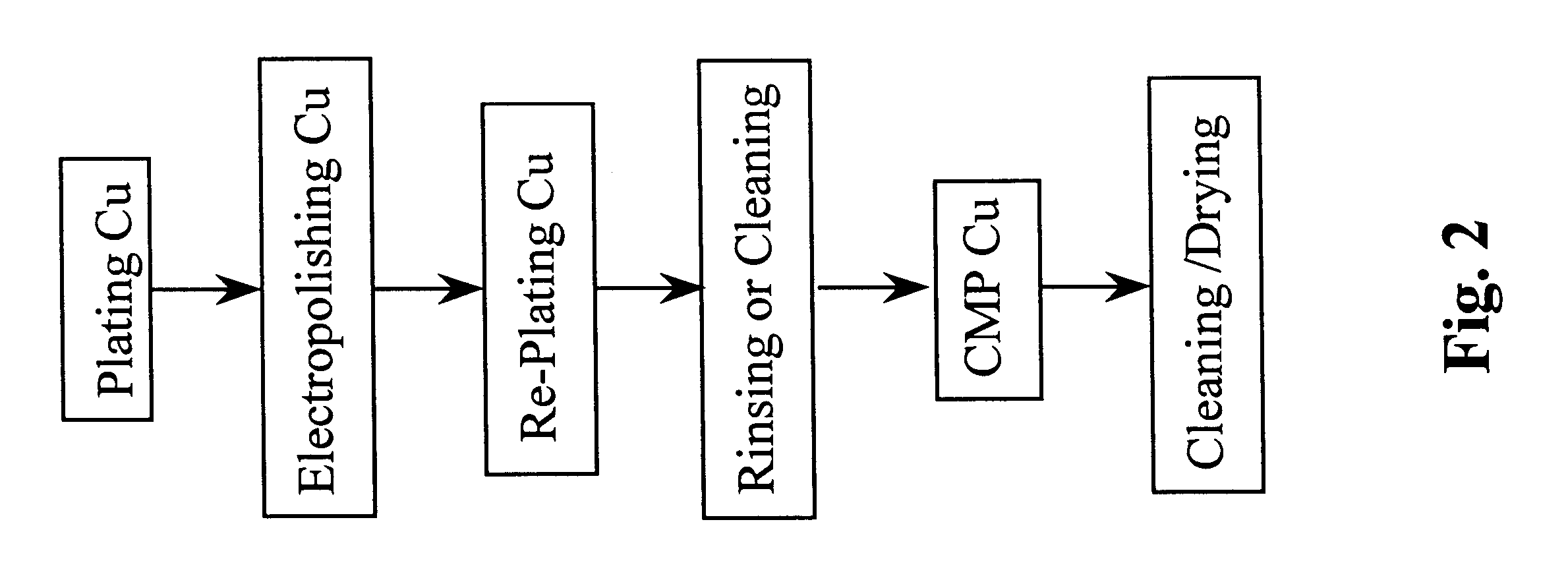
Chemical mechanical polishing with electrochemical control
Various embodiments of a planarization device and methods of using the same are provided. In one aspect, a device for planarizing a surface of a semiconductor workpiece is provided that includes a table for holding a quantity of an electrically conducting solution thereon. A member is included for holding the semiconductor workpiece such that the surface is in contact with the solution and operates as a working electrode. The member has a first conductor for establishing electrical connection with the semiconductor workpiece. A counter electrode is provided for making electrical connection with the solution and a reference electrode is provided for making electrical connection with the solution with a known electrode potential. A power source is operable to control the electric potential between the working electrode and the counter electrode. Slurry consumption may be dramatically reduced and static etch rate due to aborts may be virtually eliminated.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Electroplating apparatus for tailored uniformity profile
ActiveUS20120258408A1Maximizing randomization of flow patternSimple processCellsMachining electric circuitsRadial positionEngineering
Methods of electroplating metal on a substrate while controlling azimuthal uniformity, include, in one aspect, providing the substrate to the electroplating apparatus configured for rotating the substrate during electroplating, and electroplating the metal on the substrate while rotating the substrate relative to a shield such that a selected portion of the substrate at a selected azimuthal position dwells in a shielded area for a different amount of time than a second portion of the substrate having the same average arc length and the same average radial position and residing at a different angular (azimuthal) position. For example, a semiconductor wafer substrate can be rotated during electroplating slower or faster, when the selected portion of the substrate passes through the shielded area.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Cathode for Use in a Wet Capacitor
A cathode containing a metal substrate that possesses a micro-roughened surface imparted by spark anodization is provided. The surface is formed by contacting the substrate with an electrolytic solution and applying a voltage to form a dielectric sub-oxide layer. The voltage is raised to a sufficiently high level to initiate “sparking” at the surface of the substrate, which is believed to create high local surface temperatures sufficient to etch away the substrate. This results in the formation of a “micro-roughened” surface having a plurality elevated regions. These elevated regions can increase the effective surface area and thus allow for the formation of capacitors with increased cathode capacitance for a given size and / or capacitors with a reduced size for a given capacitance. The elevated regions may also exhibit excellent adhesion to additional electrochemically-active materials and provide enhanced stability in certain liquid electrolytes.
Owner:AVX CORP
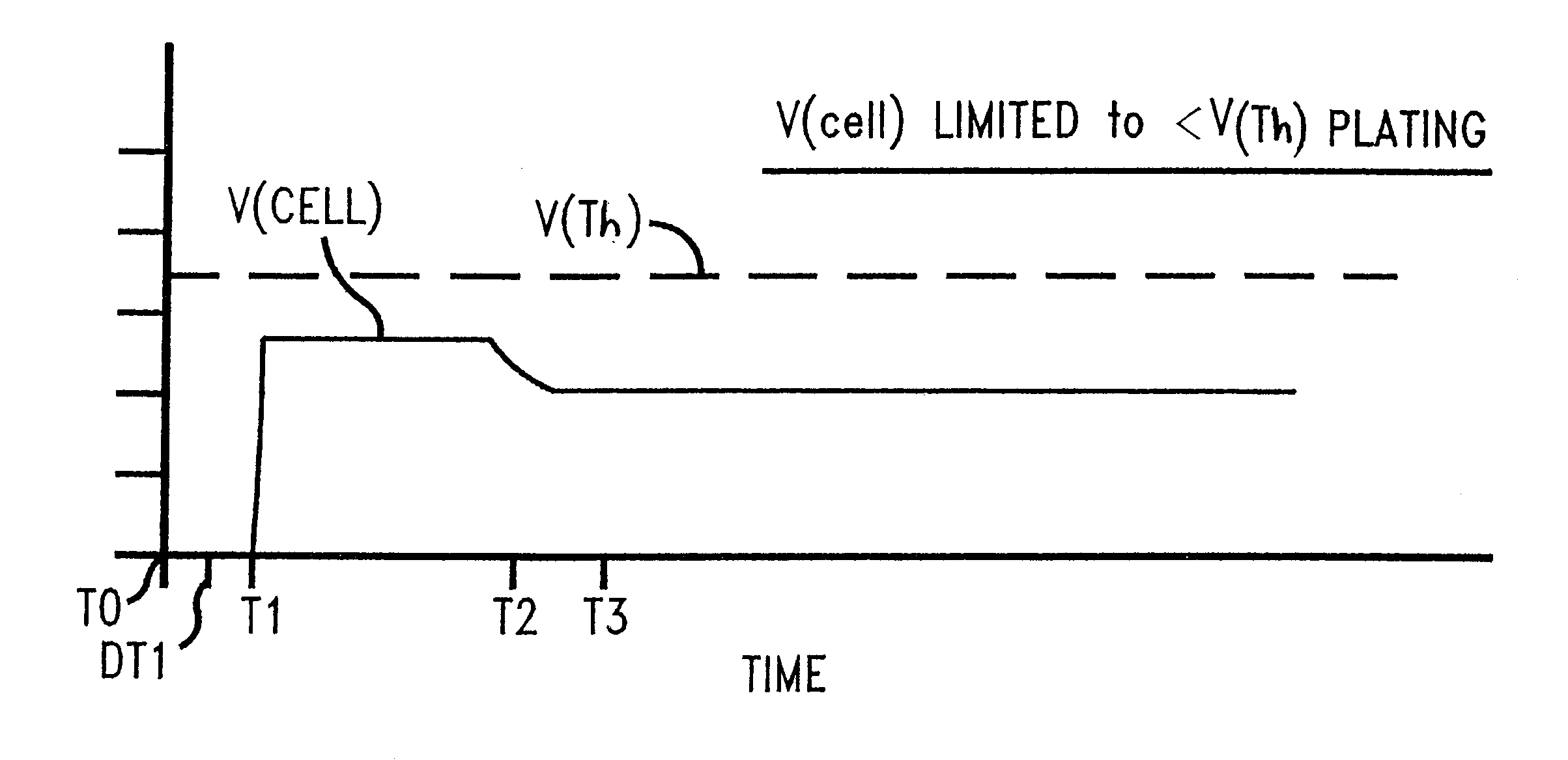
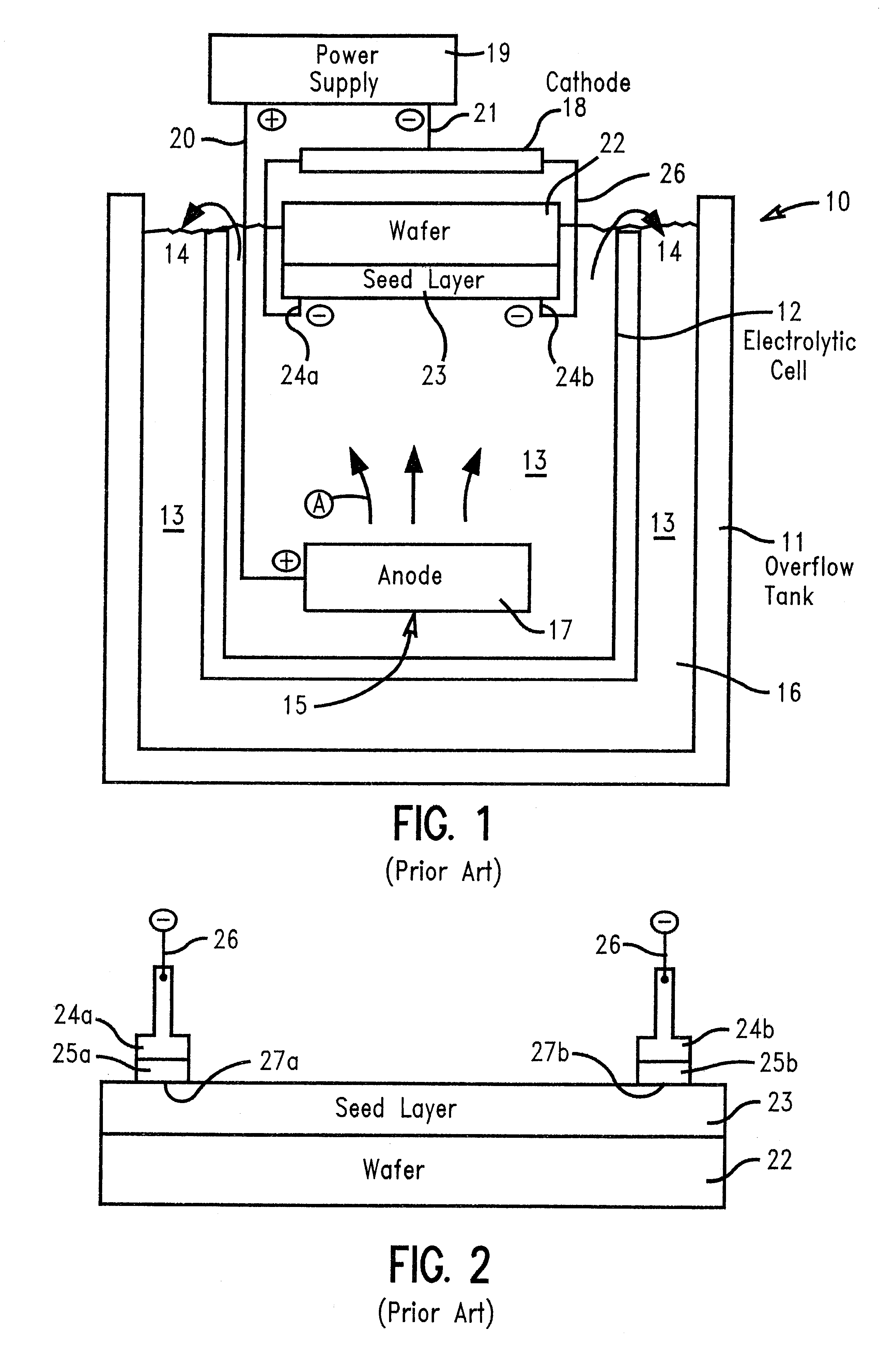
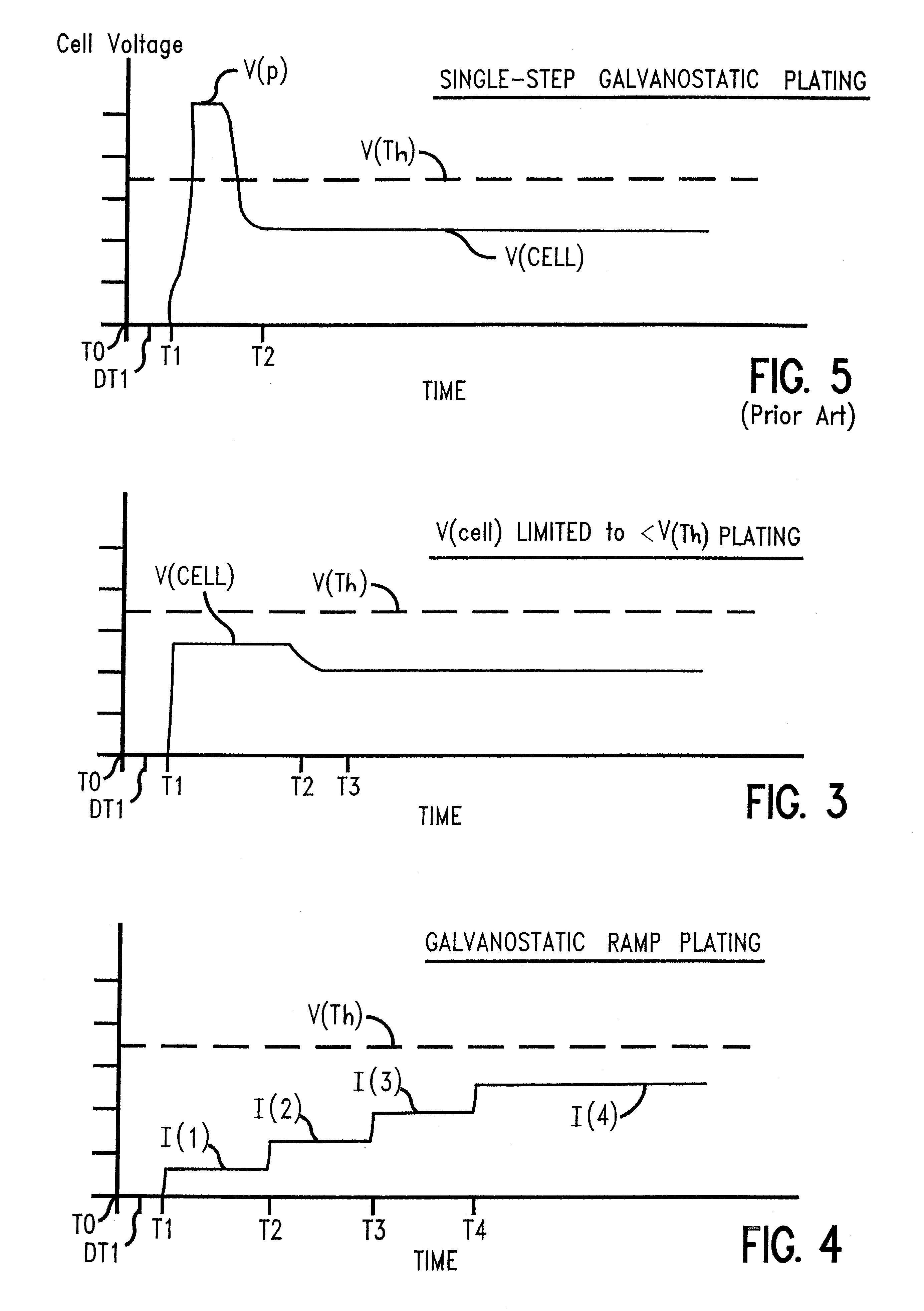
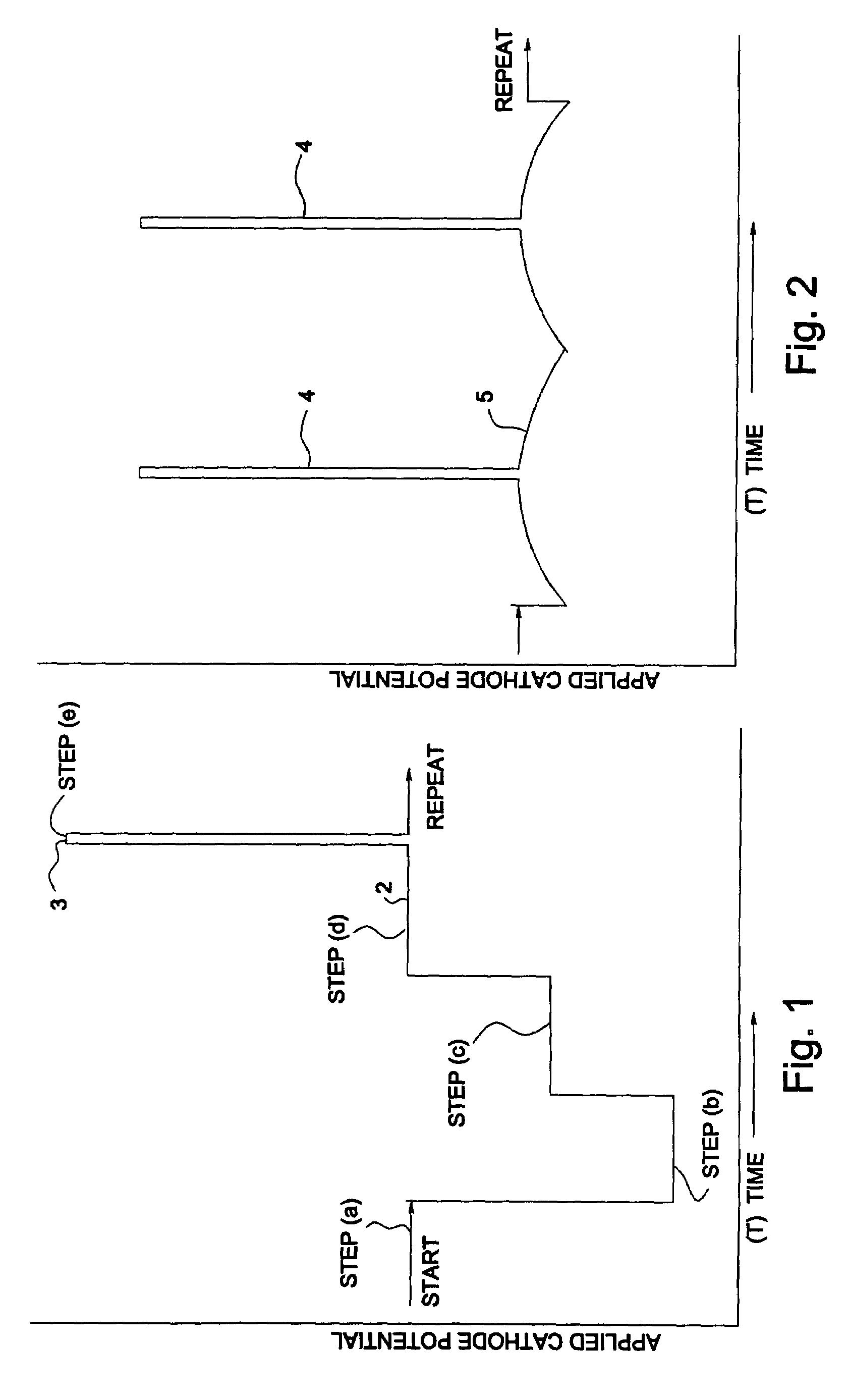
Multi-step potentiostatic/galvanostatic plating control
A method and apparatus are provided for the electroplating of a substrate such as a semiconductor wafer which provides a uniform electroplated surface and minimizes bum-through of a seed layer used on the substrate to initiate electroplating. The method and apparatus of the invention uses a specially defined multistep electroplating process wherein, in one aspect, a voltage below a predetermined threshold voltage is applied to the anode and cathode for a first time period followed by applying a current to the anode and cathode for a second time period the current producing a voltage below the predetermined threshold voltage. In another aspect of the invention, a current is applied to the anode and cathode substrate which current is preprogrammed to ramp up to a current value from a first current value which current produces a voltage below a predetermined threshold voltage. Electroplated articles including copper electroplated semiconductor wafers made using the apparatus and method of the invention are also provided.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
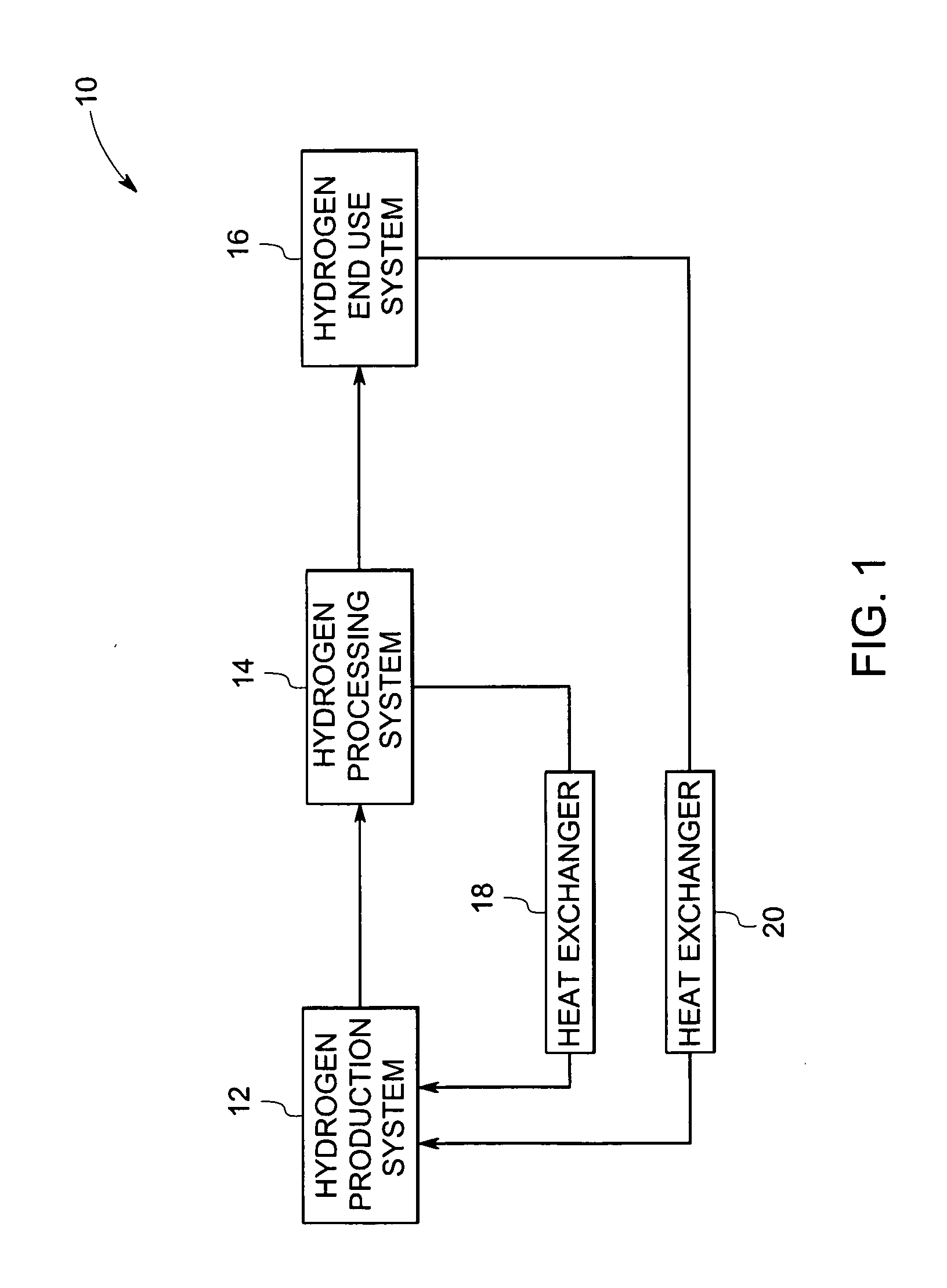
System and sub-systems for production and use of hydrogen
InactiveUS20060065302A1Most efficientSimple designPhotography auxillary processesPV power plantsHydrogenProton
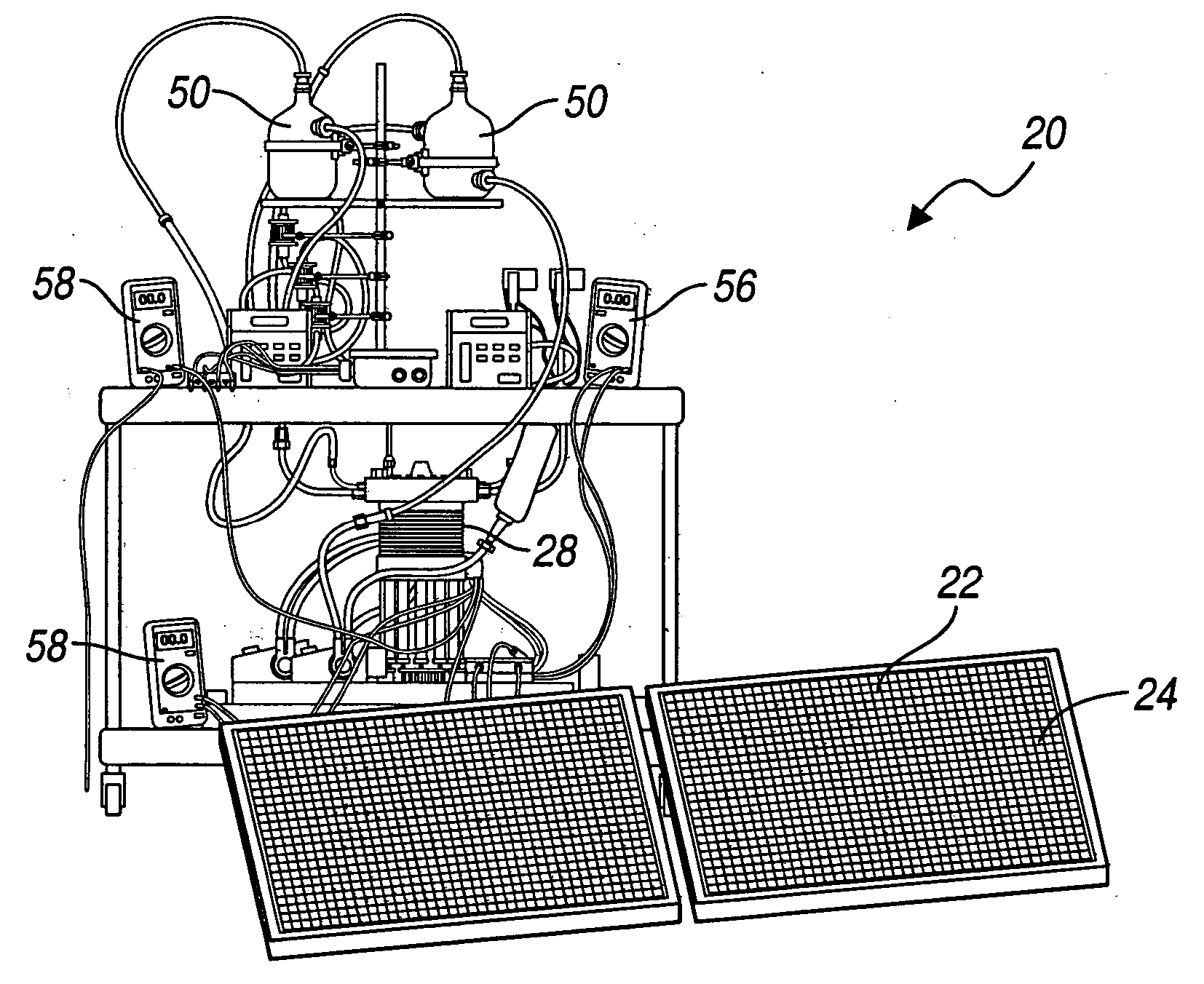
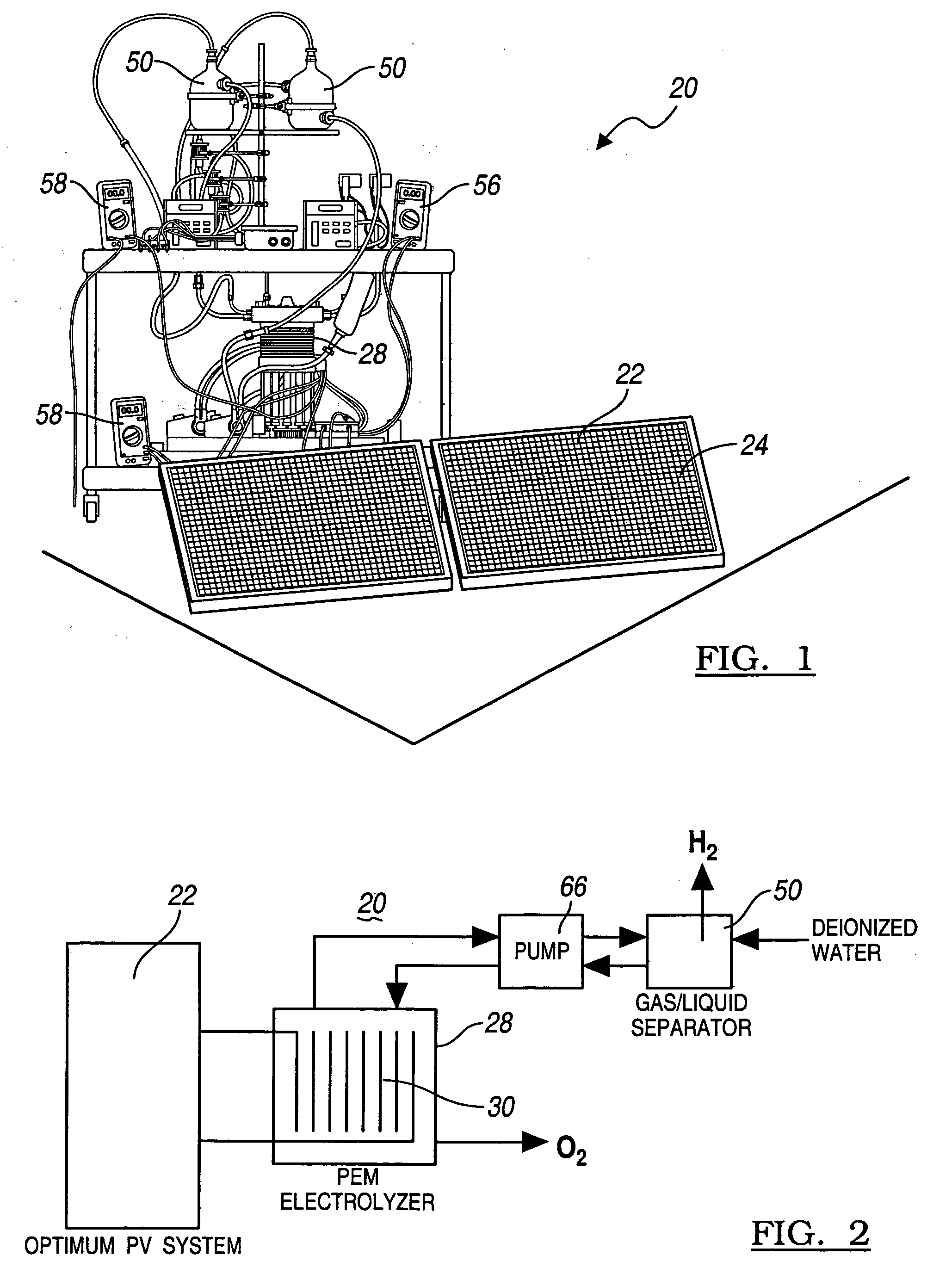
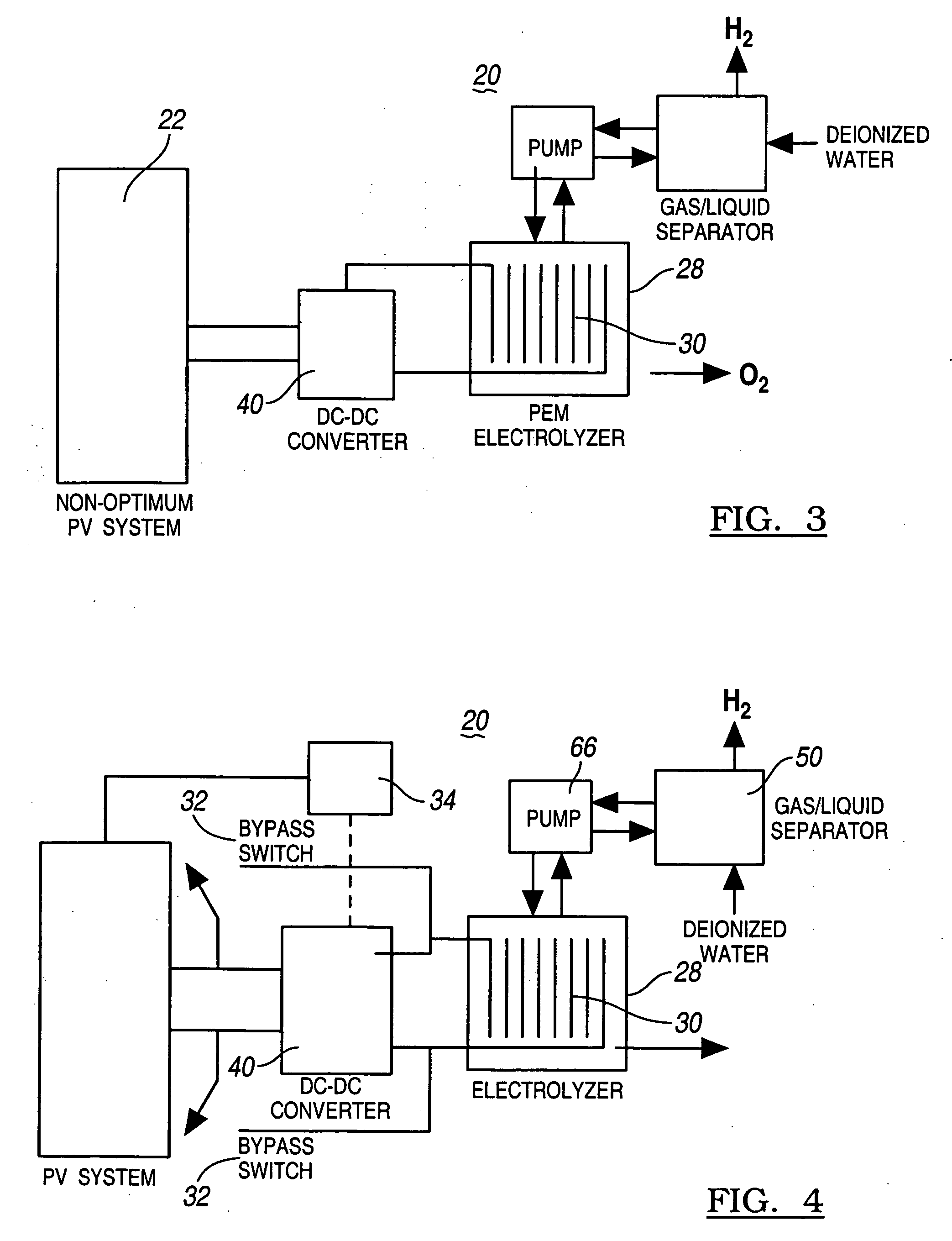
A method for optimizing the efficiency of a solar powered hydrogen generation system is disclosed. The system utilizes photovoltaic modules and a proton exchange membrane electrolyzer to split water into hydrogen and oxygen with an efficiency greater than 12%. This high efficiency for the solar powered electrolysis of water was obtained by matching the voltage generated by photovoltaic modules to the operating voltage of the electrolyzer. Optimizing PV-electrolysis systems makes solar generated hydrogen less expensive and more practical for use as an environmentally clean and renewable fuel.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for treatment of ballast water
ActiveUS20060113257A1Prevent outbreakLiquid separation by electricityAuxillariesHypochloriteHydrogen
A system and method for treating ballast water within an ocean going vessel by generating hypochlorite for treating the ballast water. The system comprises one or more hypochlorite electrolytic cells in fluid communication with a stream of ballast water. A chlorine analyzer is positioned downstream from the electrolytic cells to determine the chlorine concentration of the treated ballast water. A hydrogen separator is connected to the hypochlorite electrolytic cells for venting hydrogen. In the method of this invention, water is taken aboard the ship for ballast in one port. A treatment stream is separated from the ballast water stream and piped to hypochlorite electrolytic cells. Hypochlorite is generated into the treatment stream and the hydrogen byproduct is separated by the hydrogen separators. The treatment stream is then reintroduced to the ballast water to eliminate marine species and pathogenic bacteria from ballast water. The ballast water undergoes de-chlorination prior to being discharged into a new port.
Owner:DE NORA WATER TECH
Apparatus for purifying water
InactiveUS7238278B2Reduce concomitant disadvantageEconomical purification processLiquid solutions solvent extractionLoose filtering material filtersHypohaliteMetal salts
The invention relates to a method for purifying water by forming in an electrolytic cell molecular halogen, hypohalic acid, hypohalite ions or combinations thereof, from halide ions dissolved in the water; and dissolving one or more soluble metal salts in the water to provide corresponding metal ions. The invention also relates to a system for purifying water, having an electrolytic cell comprising a plurality of electrodes sufficient to electrolytically convert halide ion in the water into molecular halogen, hypohalic acid, or hypohalite ions, or combinations thereof; and a metal generator, which provides concentrations of one or more metals to the water.
Owner:ZODIAC POOL SYST LLC
Formation of an emulsion in a fluid microsystem
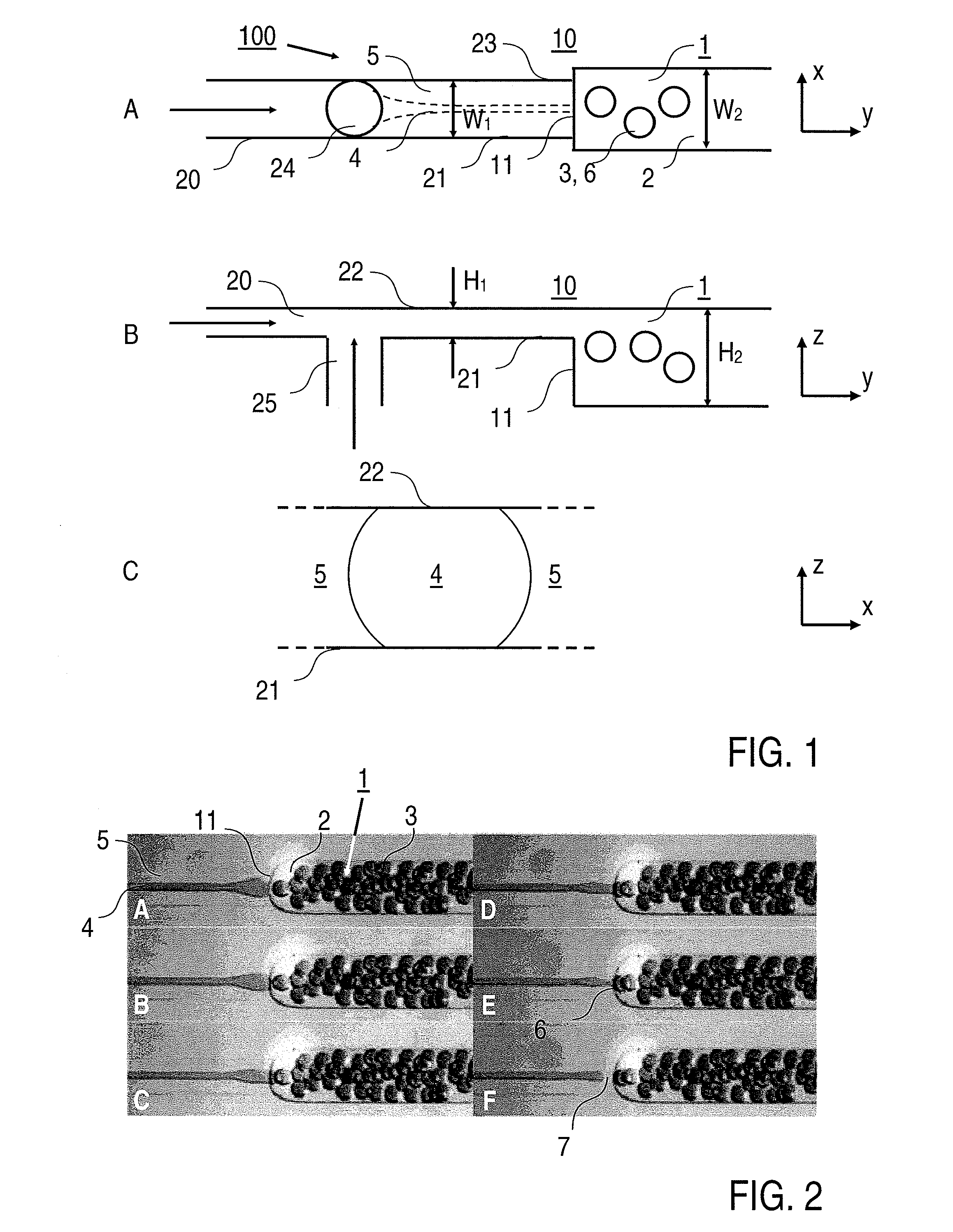
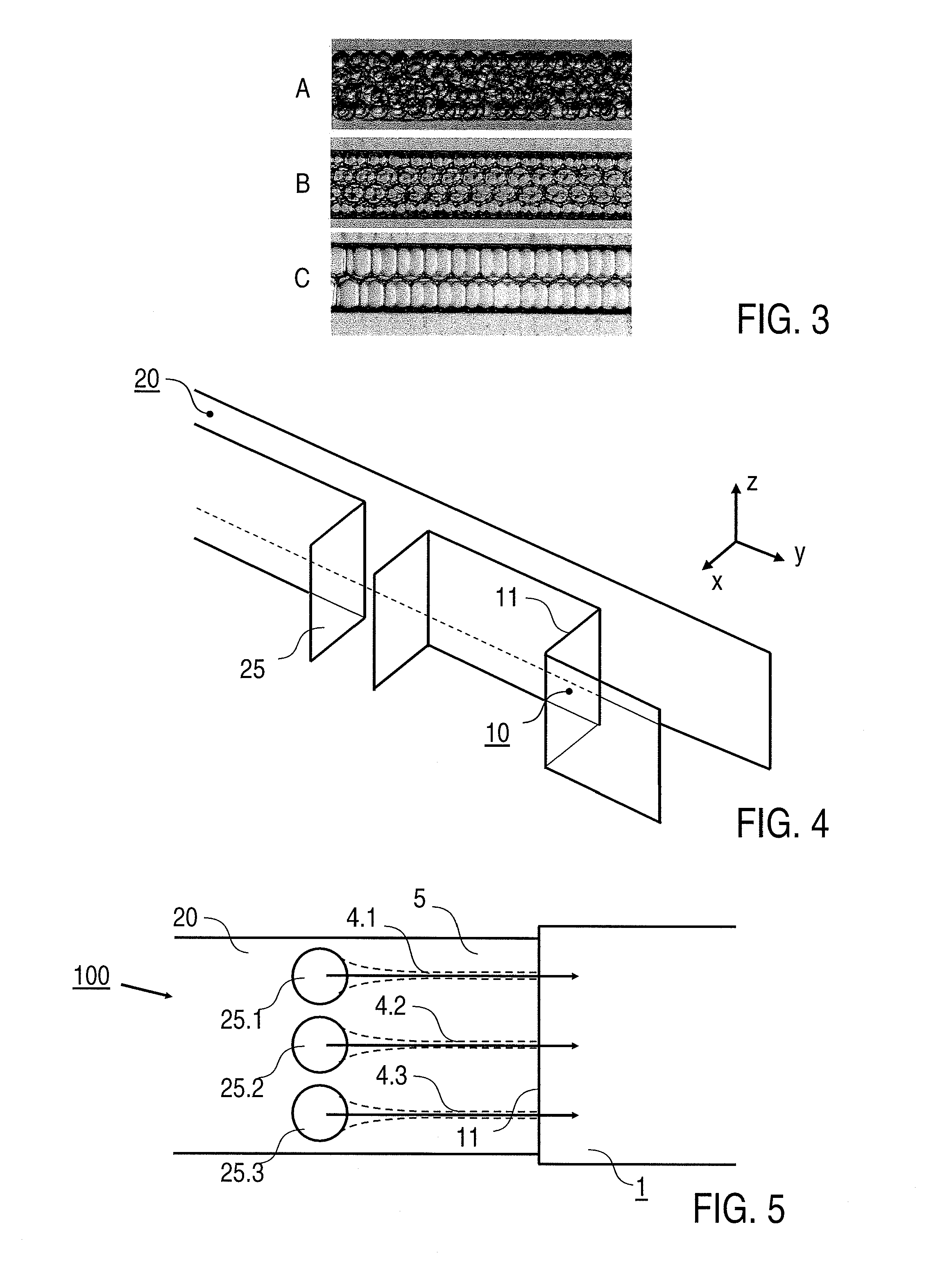
InactiveUS7943671B2Promote fragmentationHigh degreeFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityEmulsionEngineering
There is described a method for forming an emulsion (1) containing at least one dispersed phase (3) and a continuous phase (2) in a fluidic microsystem (100), said method comprising the steps: forming flows (4, 5) of different liquids which flow towards a dispersion region (10), and forming the emulsion (1) from the liquids in the dispersion region (10), wherein the flows (4, 5) run through a common channel (20) to the dispersion region (10) and the flows (4, 5) are arranged next to one another relative to a first reference direction, and wherein the emulsion (1) is produced as the liquids flow through a cross-sectional widening (11) provided in the dispersion region (10), at which the cross section of the channel (20) widens in a second reference direction different from the first reference direction. A fluidic microsystem for forming an emulsion (1) containing a continuous phase (2) and at least one dispersed phase (3) is also described. A fusion of droplets in electric fields is also described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
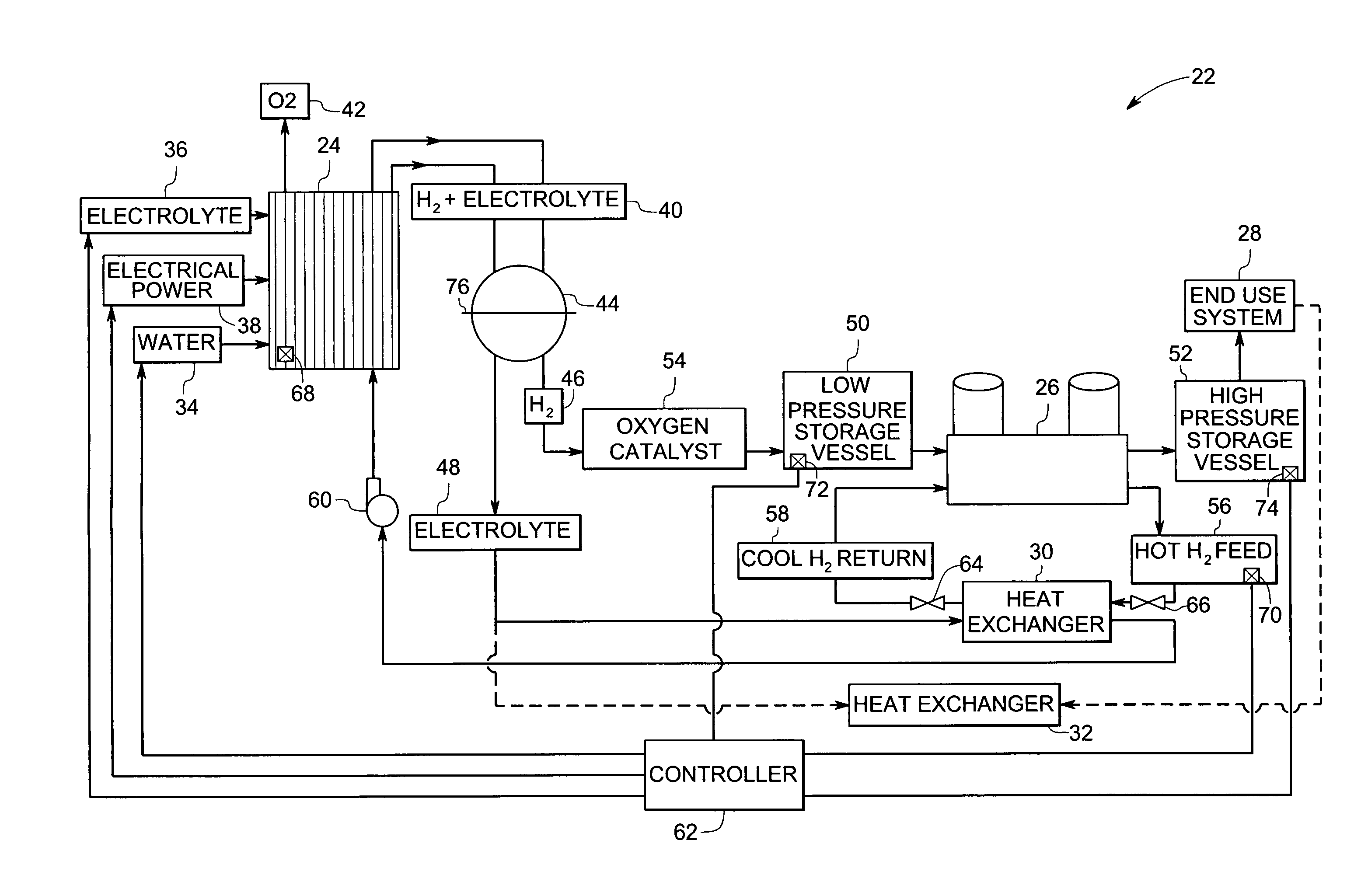
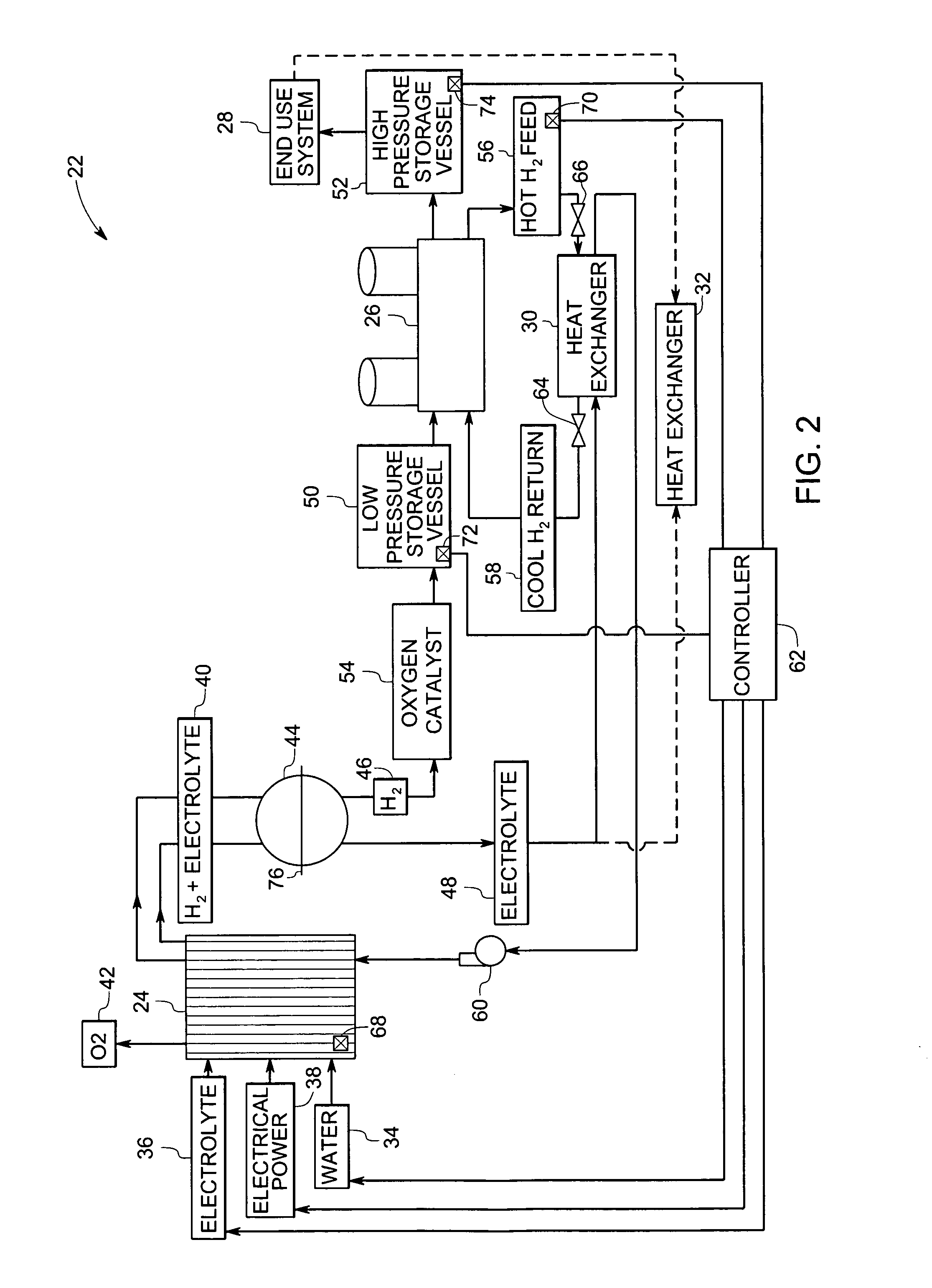
Integrated hydrogen production and processing system and method of operation
InactiveUS20070000789A1Increase temperatureCellsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisProcess engineering
A method of operating an integrated hydrogen production and processing system is provided. The method includes operating an electrolyzer to produce hydrogen from water and utilizing heat generated from the electrolyzer to increase a temperature of an electrolyte in a first mode of operation. The method also includes heating the electrolyte in a second mode of operation by extracting heat from a hydrogen compressor to increase or maintain the temperature of the electrolyte during periods when electrolysis is not performed in the electrolyzer or during startup of the electrolyzer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water
InactiveUS20120149789A1Reduce the amount requiredMaintain efficient productionPhotography auxillary processesHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrogenElectrolysed water
An apparatus for the electrolytic splitting of water into hydrogen and / or oxygen, the apparatus comprising: (i) at least one lithographically-patternable substrate having a surface; (ii) a plurality of microscaled catalytic electrodes embedded in said surface; (iii) at least one counter electrode in proximity to but not on said surface; (iv) means for collecting evolved hydrogen and / or oxygen gas; (v) electrical powering means for applying a voltage across said plurality of microscaled catalytic electrodes and said at least one counter electrode; and (vi) a container for holding an aqueous electrolyte and housing said plurality of microscaled catalytic electrodes and said at least one counter electrode. Electrolytic processes using the above electrolytic apparatus or functional mimics thereof are also described.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Apparatus for electrolysis of water
A method and apparatus are provided for electrolyzing water for enhanced production of oxygen, hydrogen and heat by the steps of (i) providing an electrochemical cell comprising an isotopic hydrogen storage cathode, an electrically conductive anode and an ionically conducting electrolyte comprising water, and (ii) impressing a repeating sequence of voltages across the cathode and anode comprised of at least two cell voltage regimes, a first cell voltage regime consisting of a voltage sufficient to enhance cathodic absorption of hydrogen, and a second cell voltage regime consisting of at least one voltage pulse which is at least two times the voltage of the first cell voltage regime for a total duration no greater than 0.10 seconds.
Owner:LECTRO PRESS
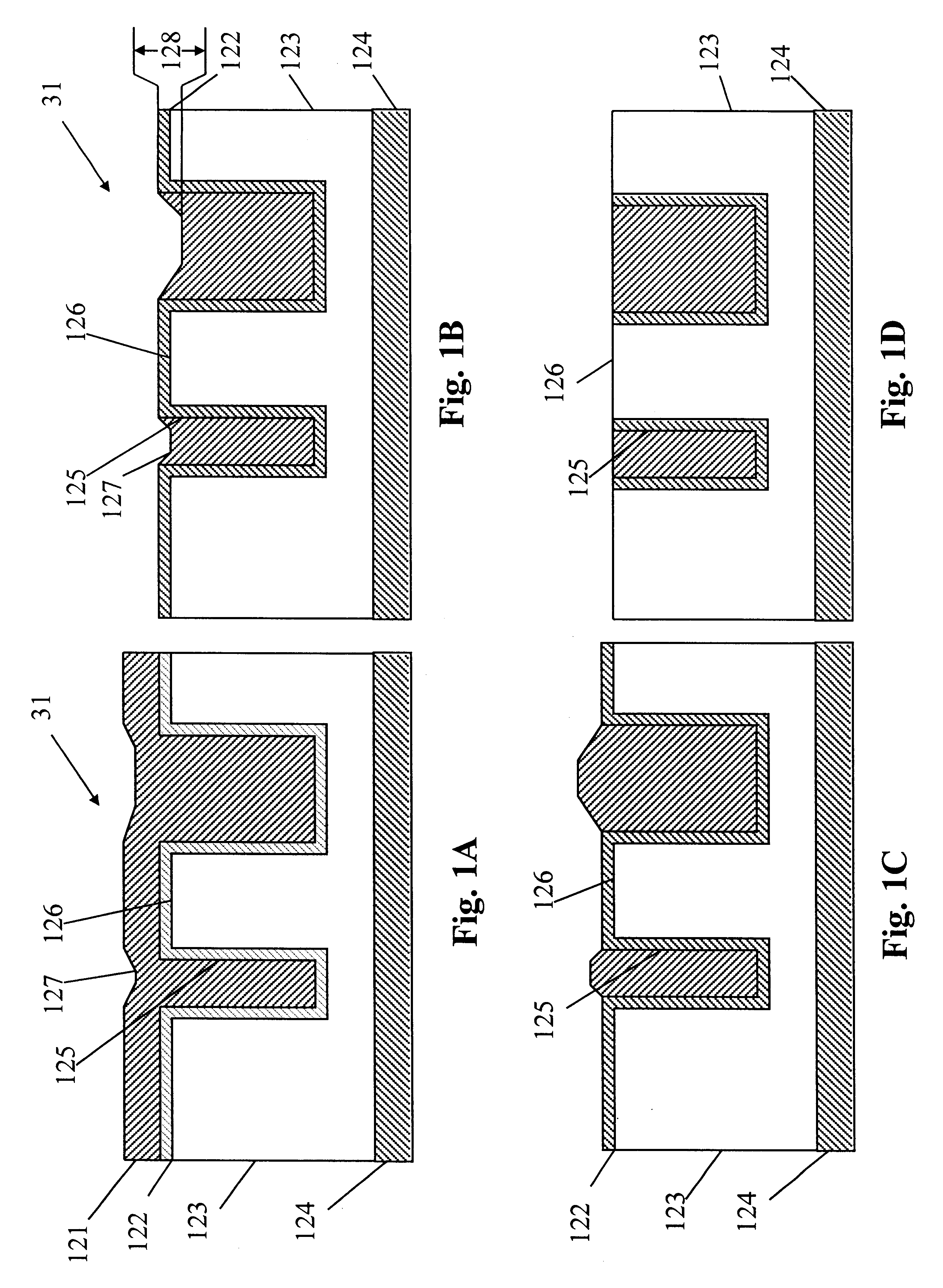
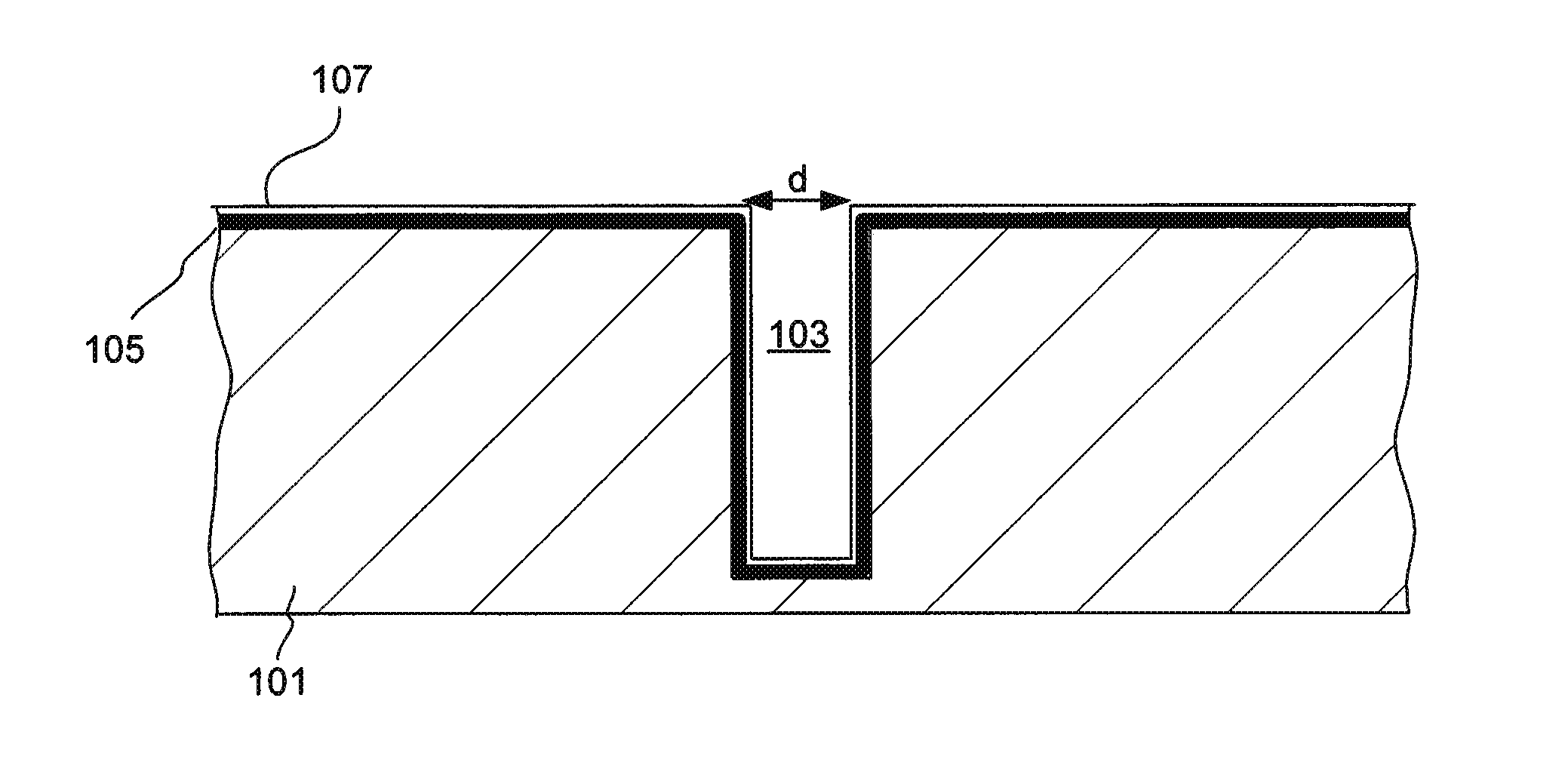
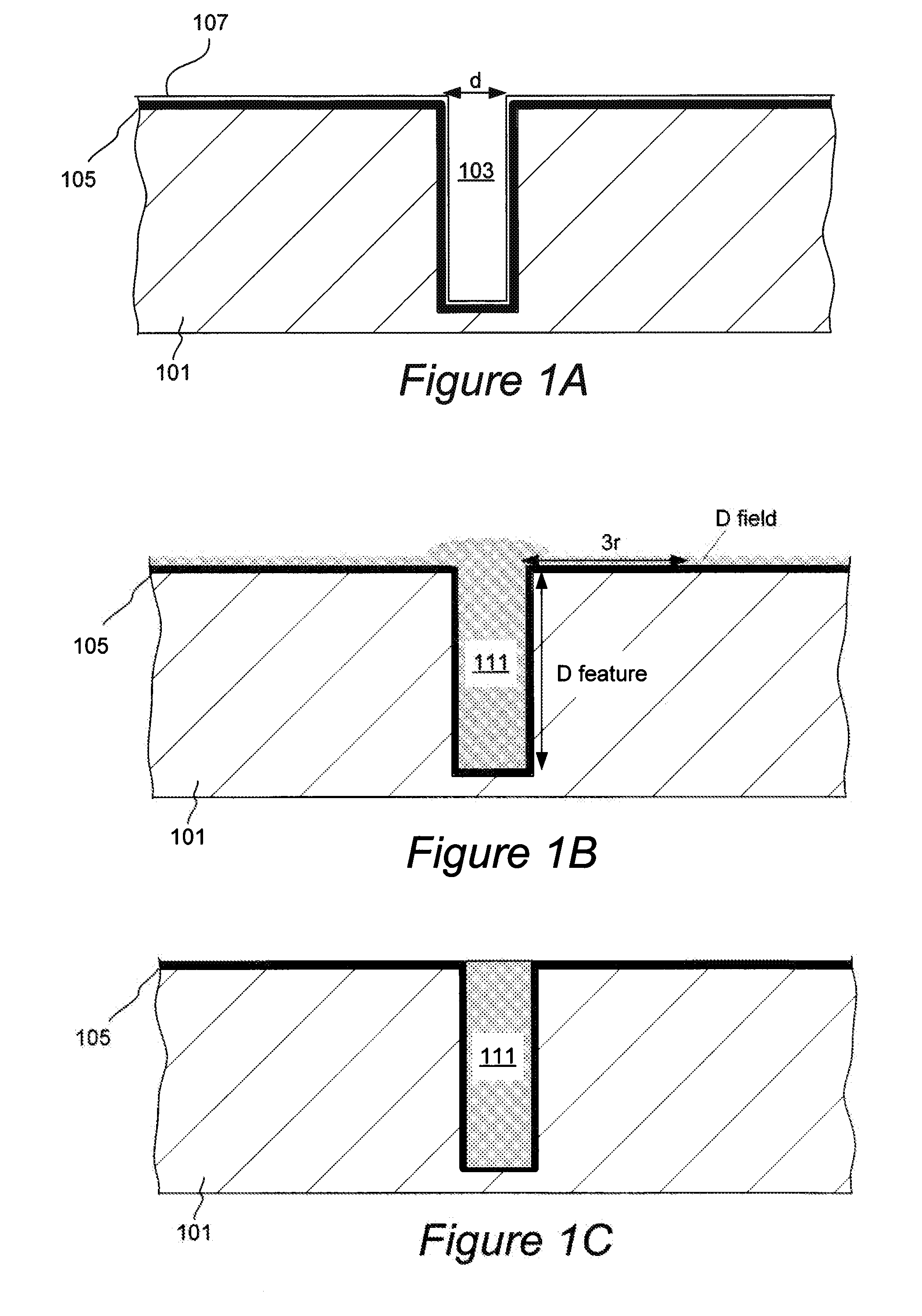
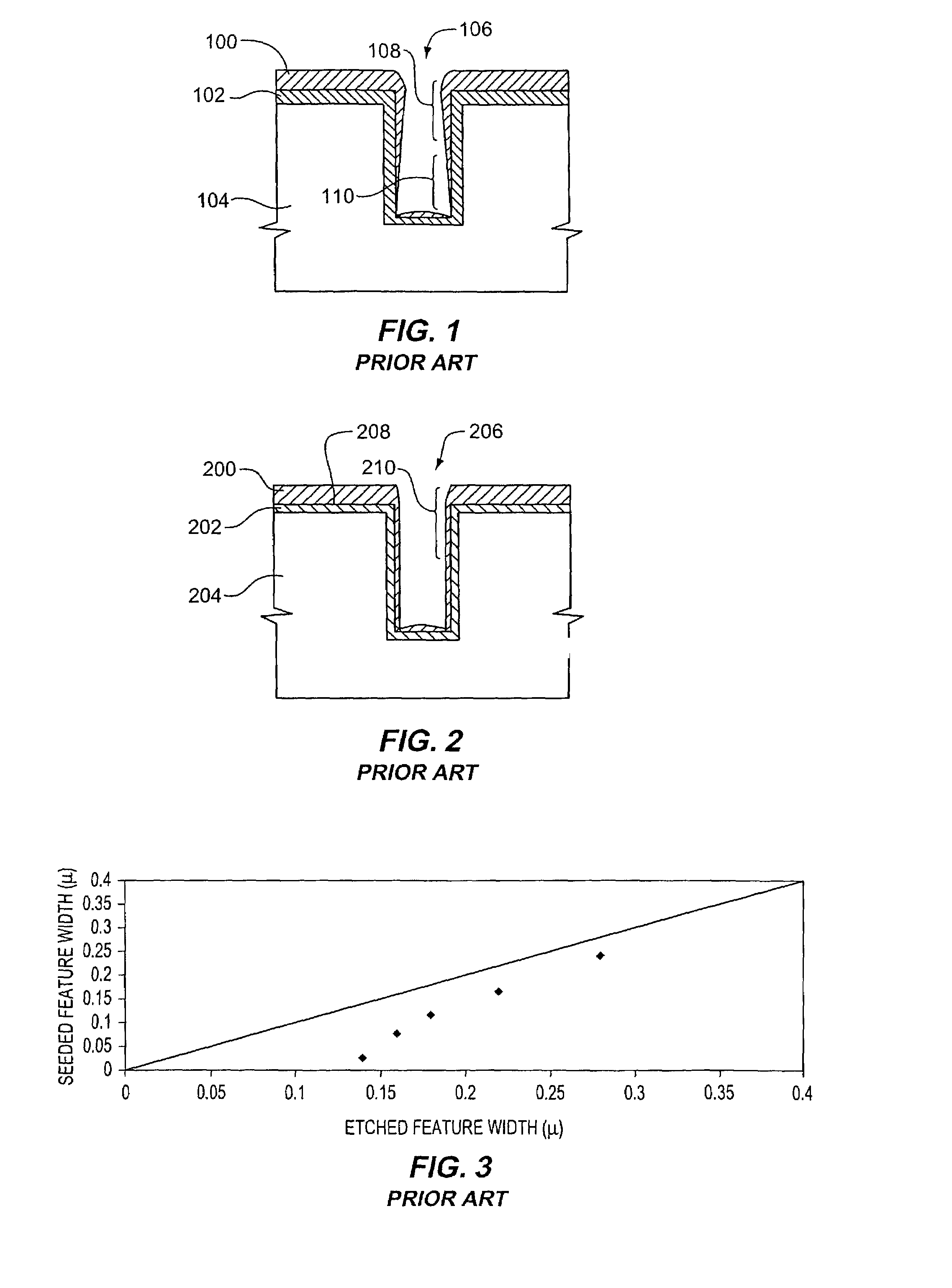
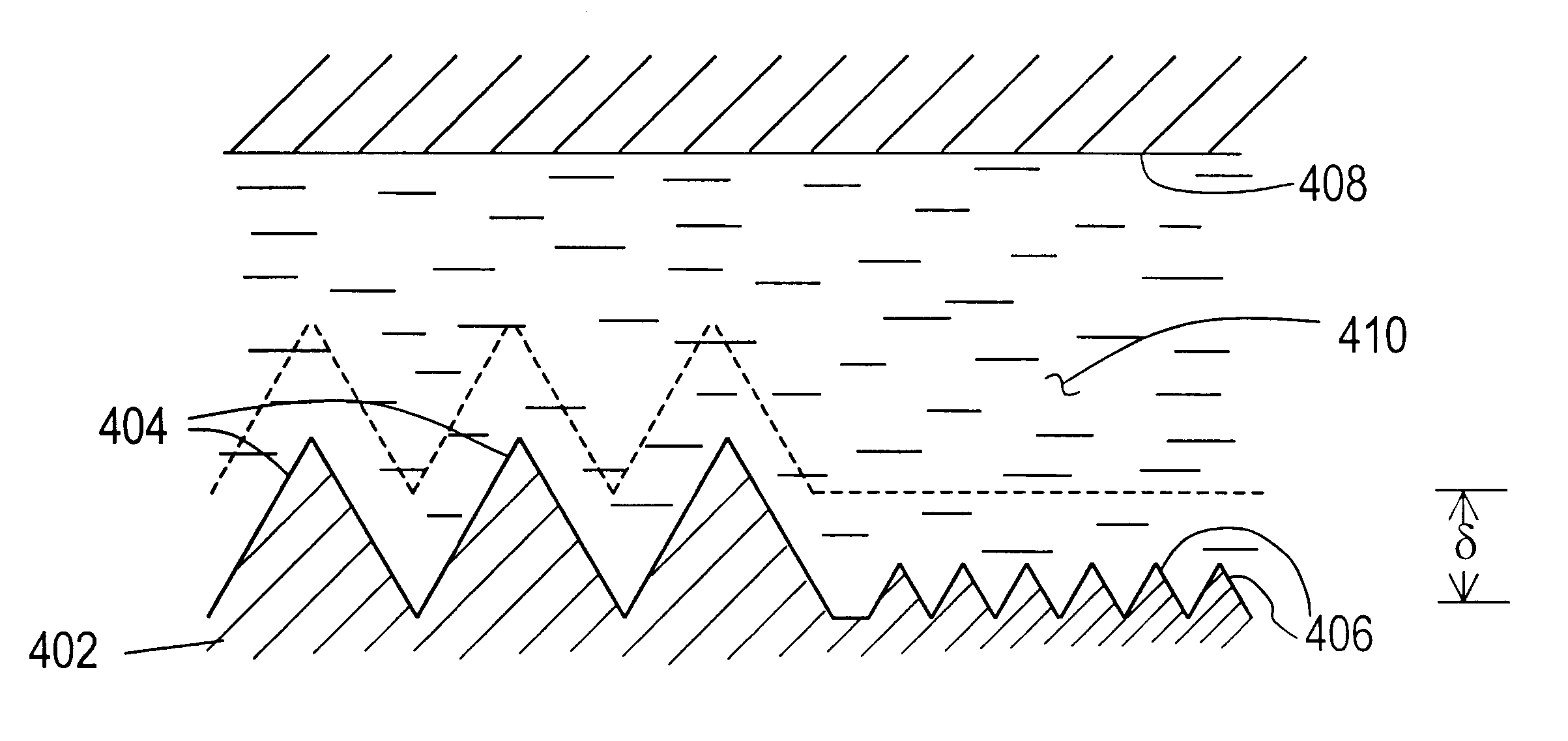
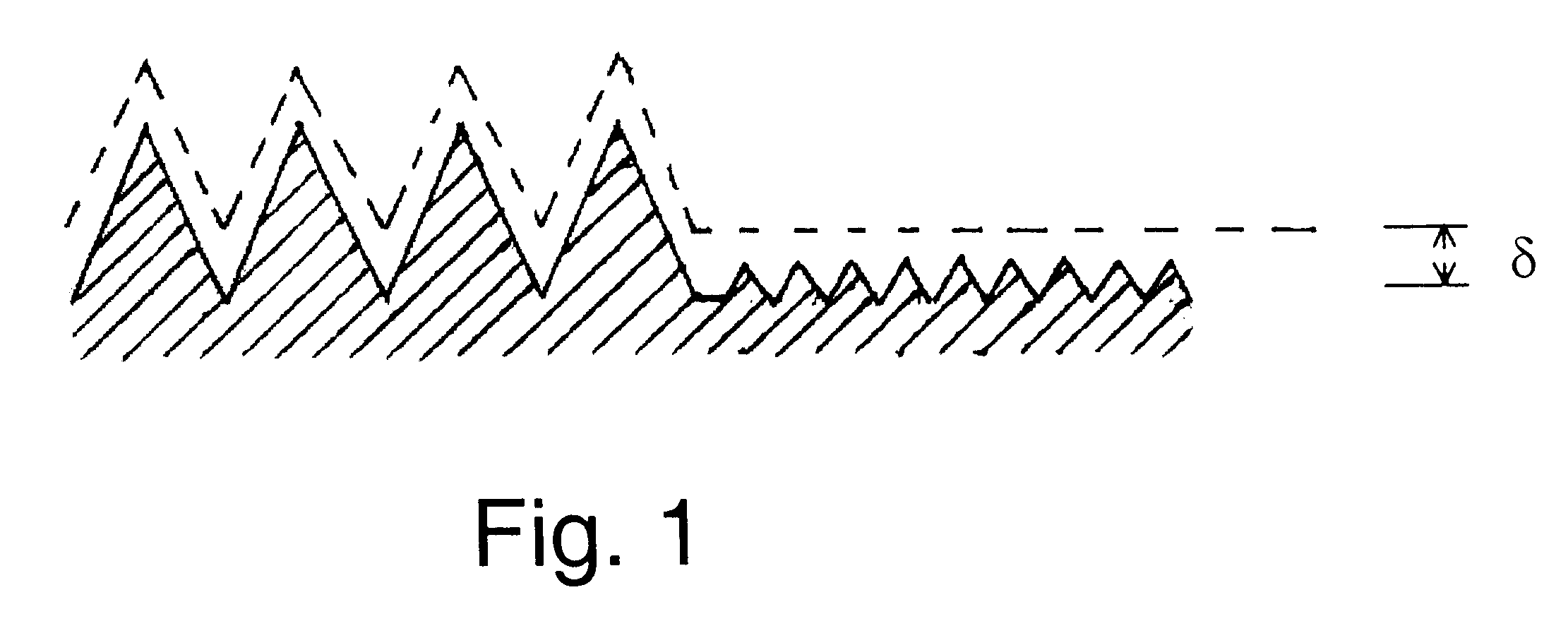
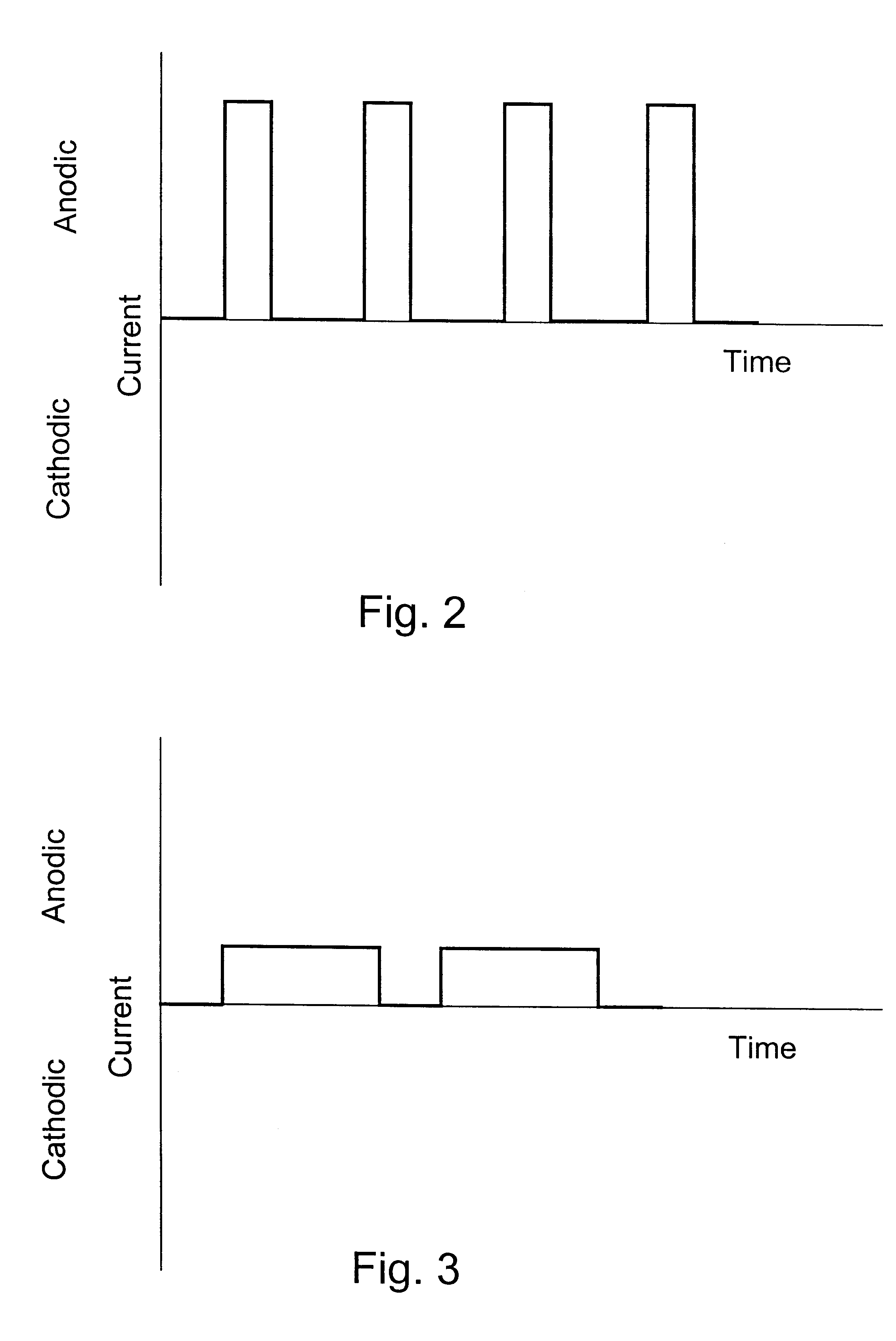
Sequential electromachining and electropolishing of metals and the like using modulated electric fields
A surface of an electrolytically dissolvable material, e.g., an electrolytically dissolvable metal, is smoothed by a two-step electrochemical process wherein a the surface to be smoothed and a counterelectrode are contacted with an electrolyte and an electric current is passed between the substrate and counterelectrode, with the substrate as the anode. In a first step relatively large asperities on the substrate are reduced in height by maintaining a macroprofile regime by using a pulsed electric current with short pulses. In a second step, small asperities and the remainder of the large asperities are reduced or removed by maintaining a microprofile regime by using a pulsed current having longer pulses or a direct current.
Owner:FARADAY TECH INC
Gated electrodes for electrolysis and electrosynthesis
InactiveUS20080116080A1Good effectEnhanced charge transferCellsPhotography auxillary processesOvervoltageElectricity
A gated electrode structure for altering a potential and electric field in an electrolyte near at least one working electrode is disclosed. The gated electrode structure may comprise a gate electrode biased appropriately with respect to a working electrode. Applying an appropriate static or dynamic (time varying) gate potential relative to the working electrode modifies the electric potential and field in an interfacial region between the working electrode and the electrolyte, and increases electron emission to and from states in the electrolyte, thereby facilitating an electrochemical, electrolytic or electrosynthetic reaction and reducing electrode overvoltage / overpotential.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and process for collecting effluents from an electrolytic cell
InactiveUS20090159434A1Increase ratingsStrict controlCellsMachining electric circuitsStreamflowElectrolytic cell
The invention provides a system and a process for collecting effluents produced by an electrolytic cell intended for the production of aluminium and for drawing said effluents away from the cell in a flow of gas. The system comprising a hooding to confine the effluents, at least one outlet channel to collect said flow of gas and suction means to draw said flow of gas away from the cell. The hooding includes removable hoods and, optionally, at least one door to get access to the inside of the hooding. The system further comprises at least one pipe for blowing pressurized air within the outlet channel so as to increase the rate of said flow of gas. Pressurized air supply is activated at a specified pressure Po so as to obtain a specified flow rate Ro.
Owner:ALUMINUM PECHINEY
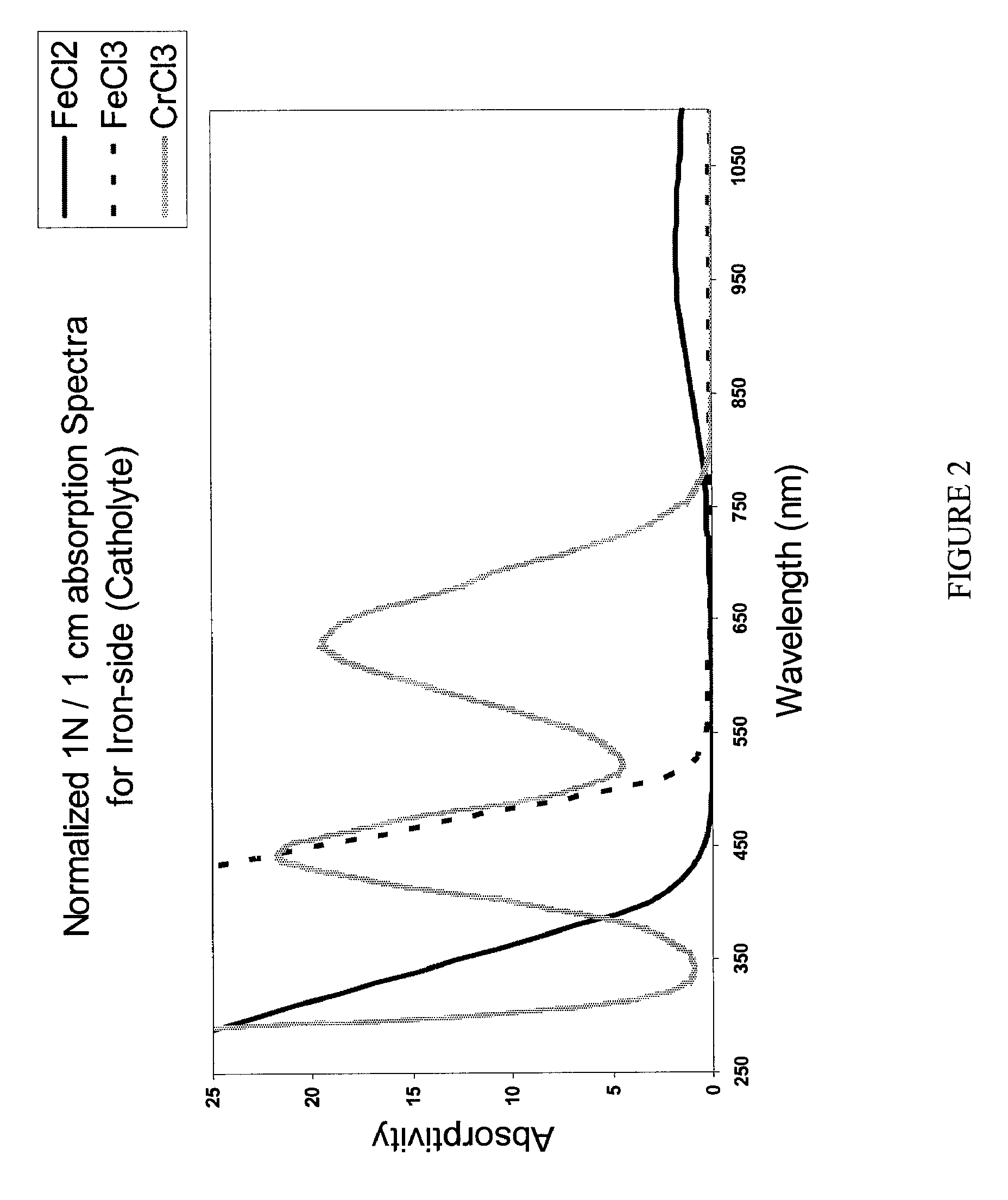
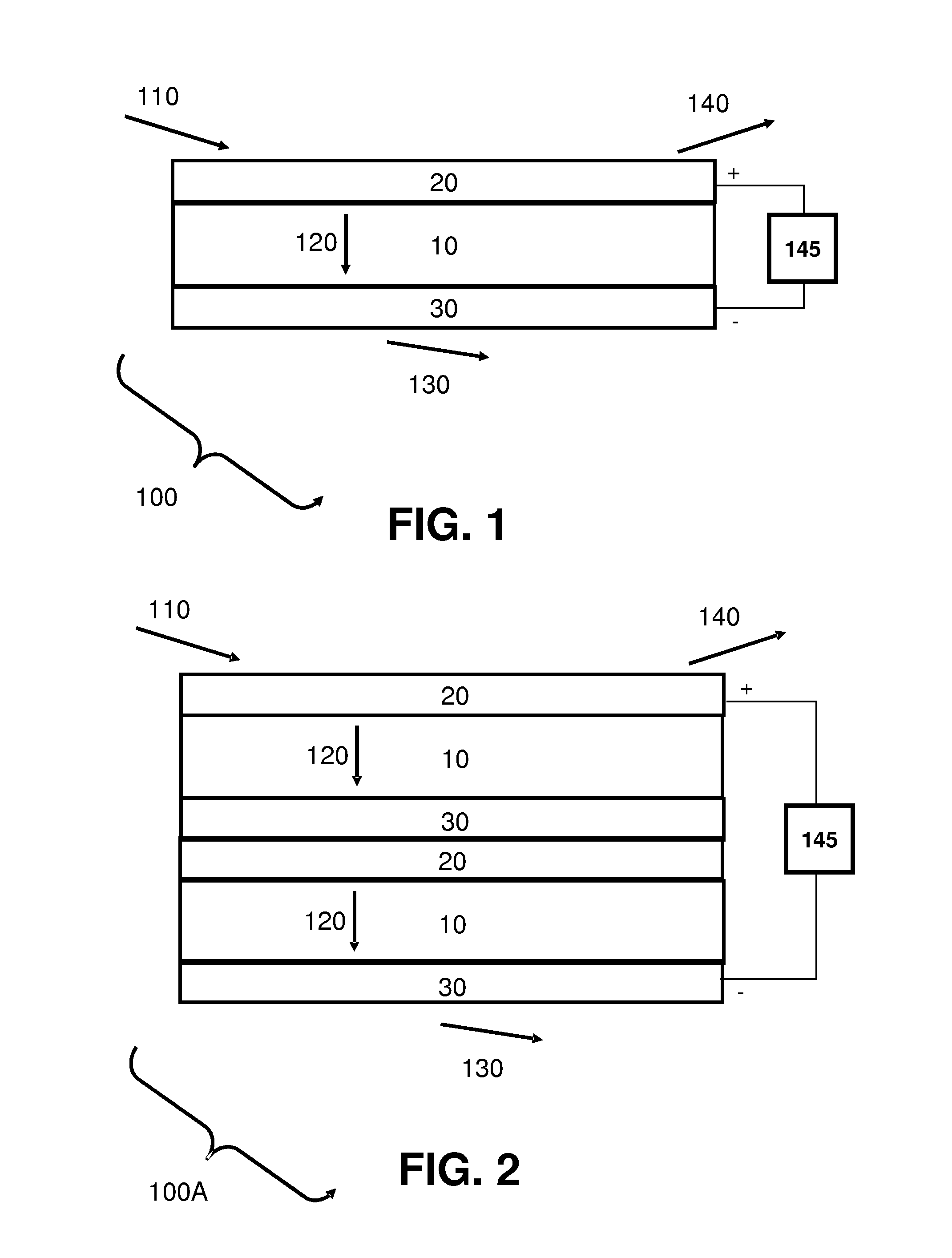
Apparatus and methods of determination of state of charge in a redox flow battery
InactiveUS7855005B2Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorState of chargeRedox
Methods for determining the state of charge of an electrolyte solution in a redox battery by optical absorption spectrophotometry are disclosed. The state of charge thus obtained may serve as a gauge for the amount of electro-chemical energy left in the system.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
Operation Of An Electrolysis Cell
InactiveUS20090325014A1Photography auxillary processesFuel cell auxillariesElectrolysisElectrical battery
An electrolysis cell is controlled for operation under varying electrical power supply conditions. A flow of feed stock to the cell includes an electrolysis reactant at a controlled concentration. A varying amount of electrical power is supplied to the cell to produce an electrolysis reaction that generates a first reaction product at a first side of the cell and a second reaction product at a second side of the cell. The reactant concentration is adjusted as the electrical power varies to substantially maintain the cell at its thermal neutral voltage during cell operation. The cell may be used in an electrolysis system powered by a renewable energy source with varying power output (e.g., wind, solar, etc.).
Owner:ENRG
Popular searches
Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Electric circuits Conductive material chemical/electrolytical removal Electrical-based auxillary apparatus Biological substance pretreatments Sampling Biochemistry cleaning apparatus Material analysis by electric/magnetic means Biomass after-treatment Enzymology/microbiology apparatus
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com