Patents
Literature
1109 results about "Spectrophotometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, spectrophotometry is the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. It is more specific than the general term electromagnetic spectroscopy in that spectrophotometry deals with visible light, near-ultraviolet, and near-infrared, but does not cover time-resolved spectroscopic techniques.
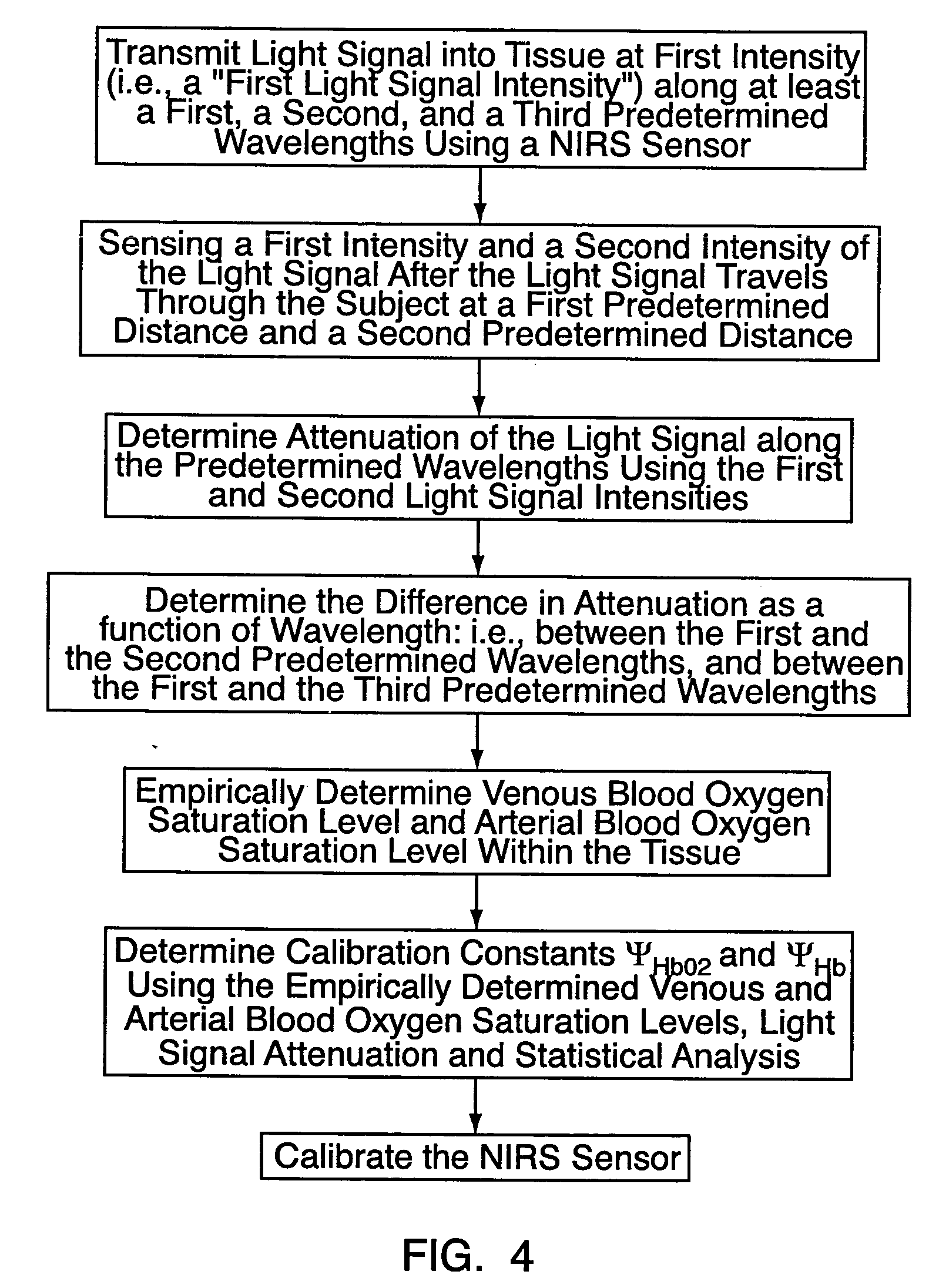
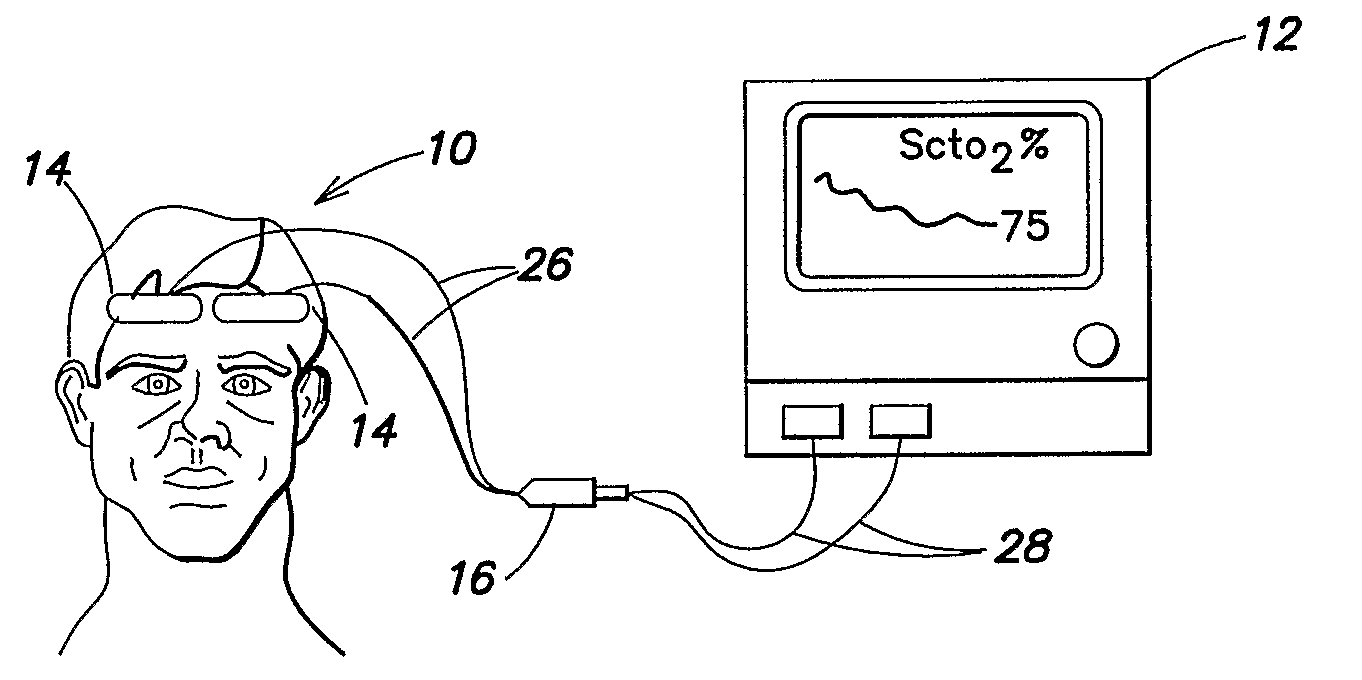
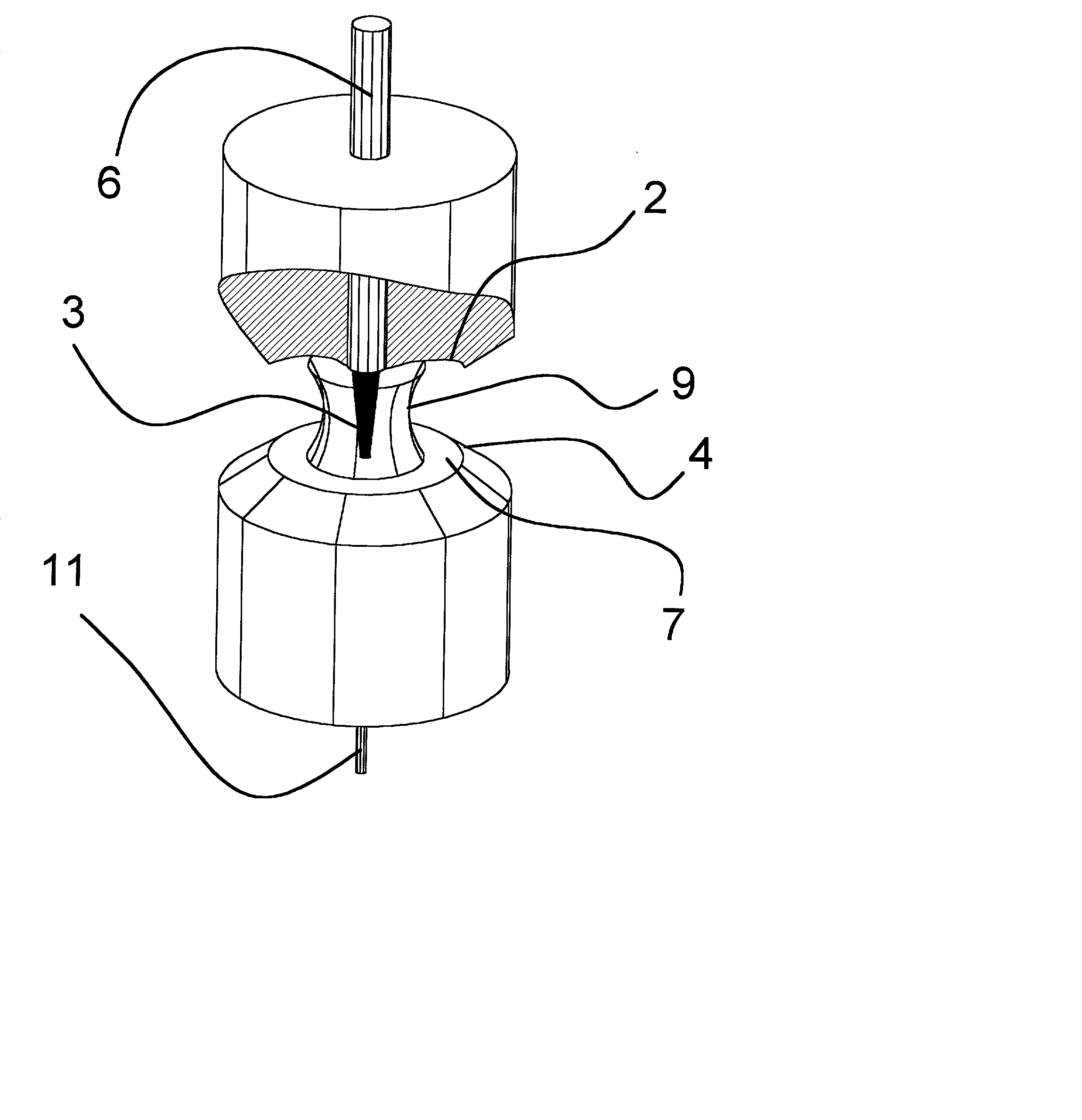
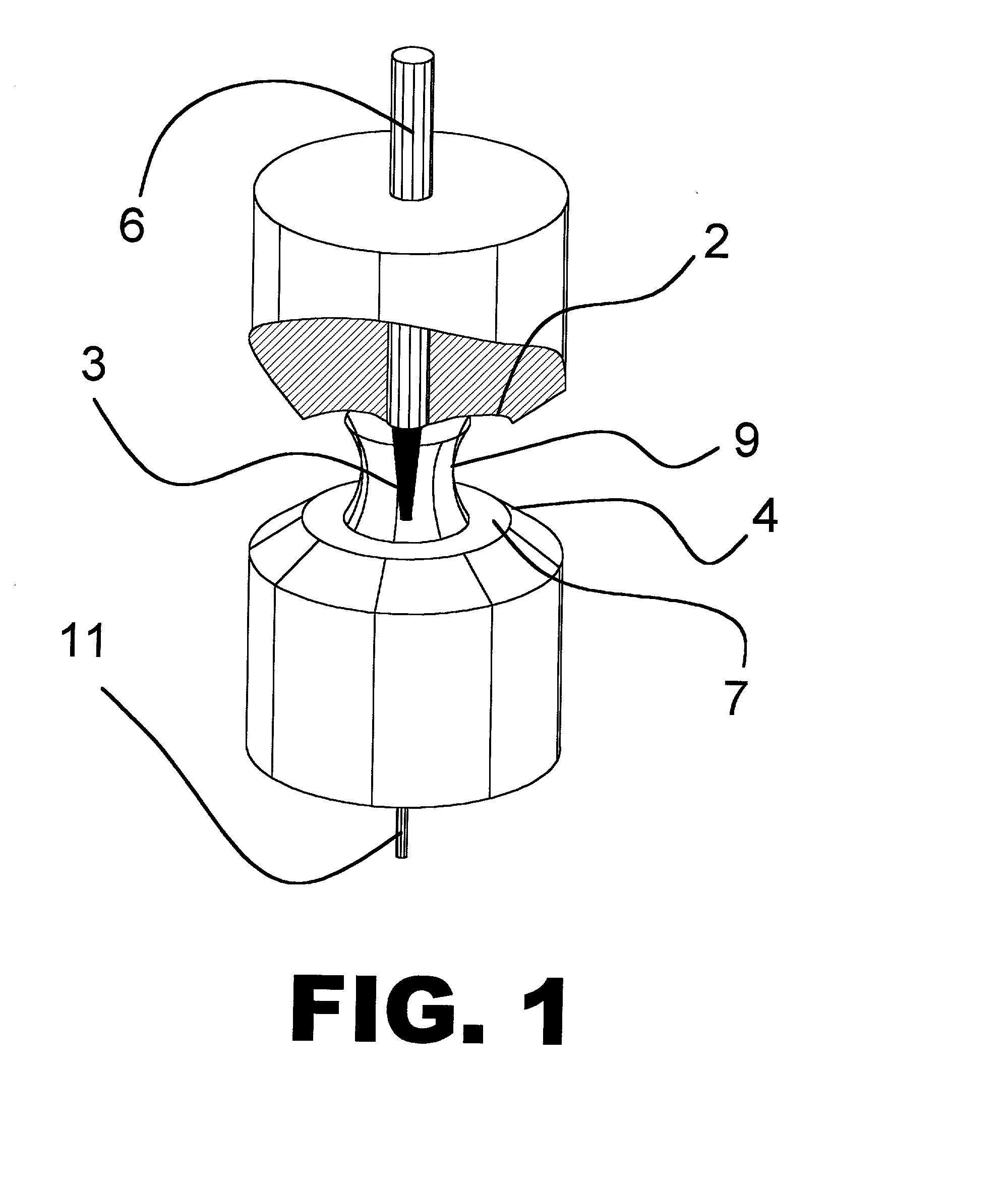
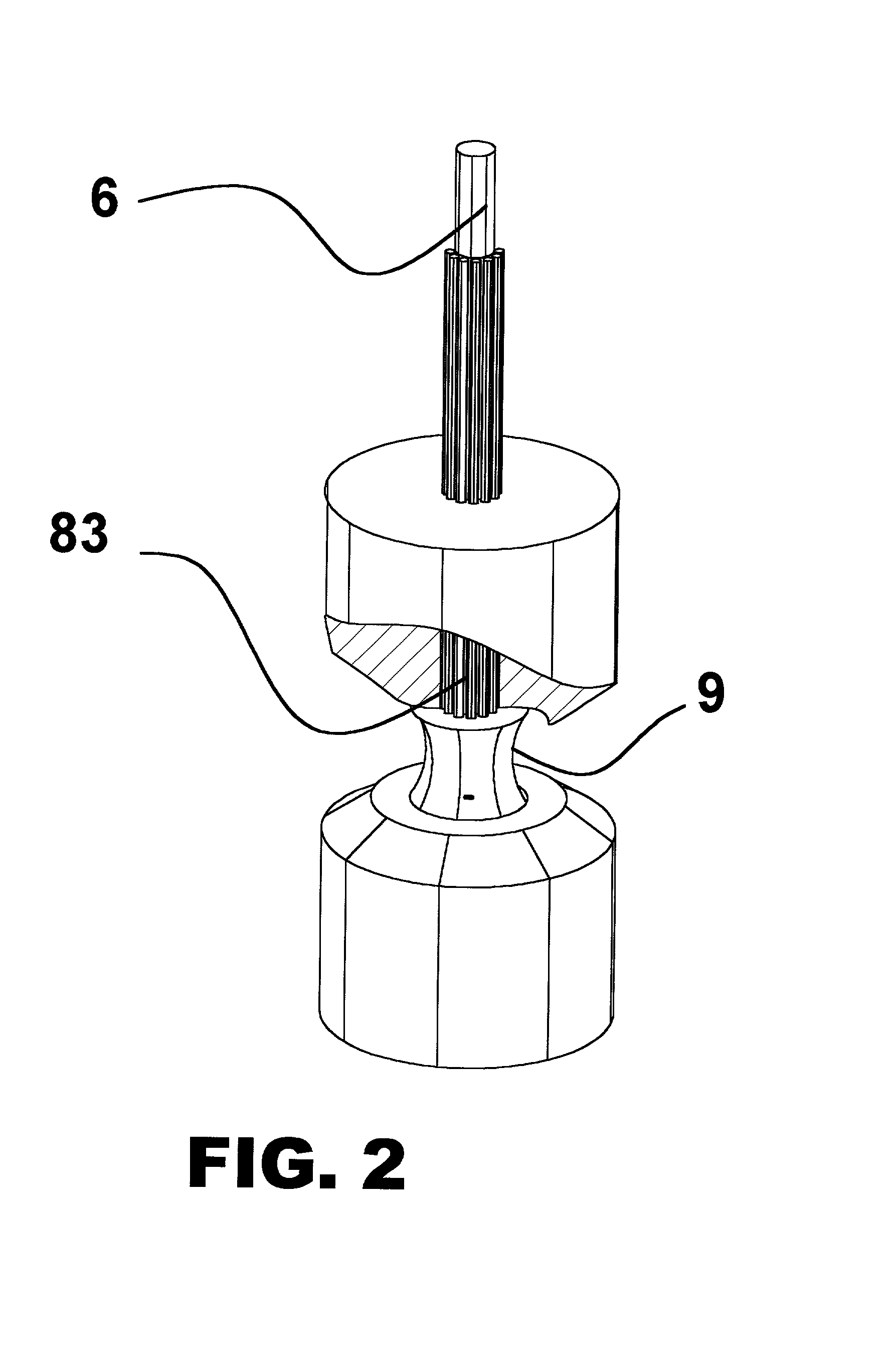
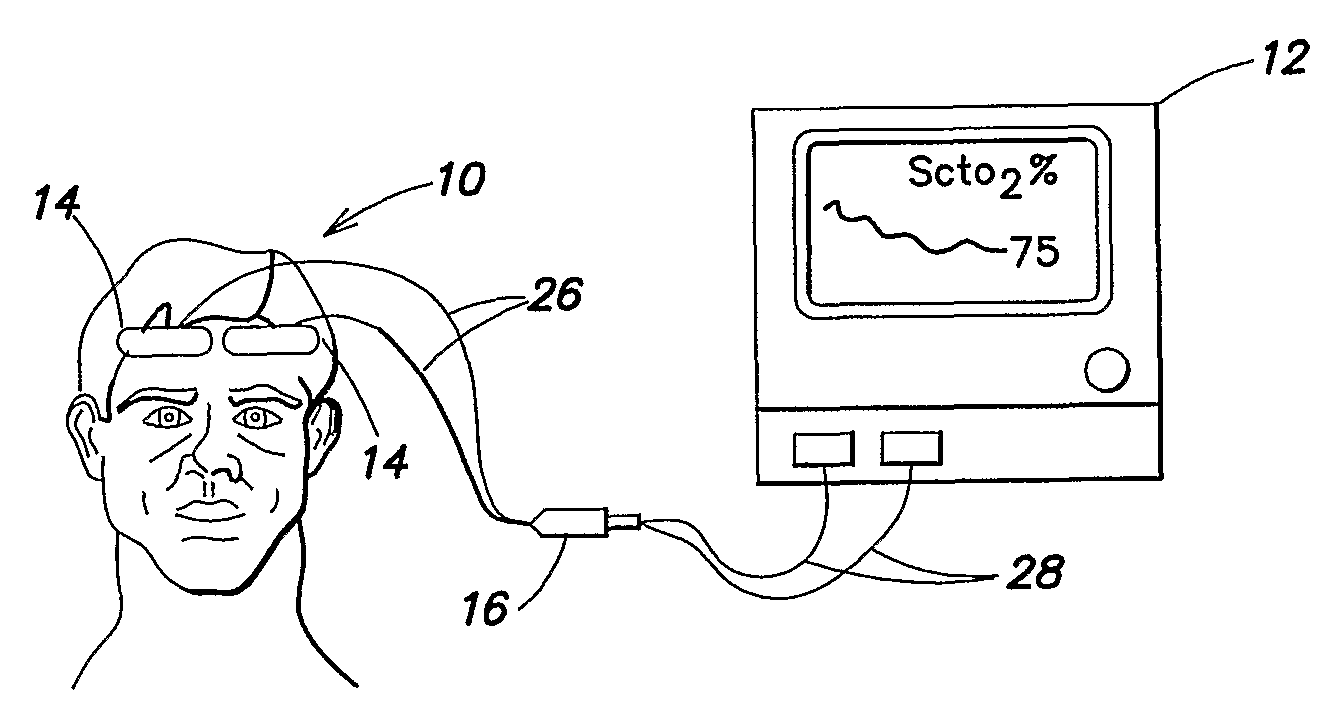
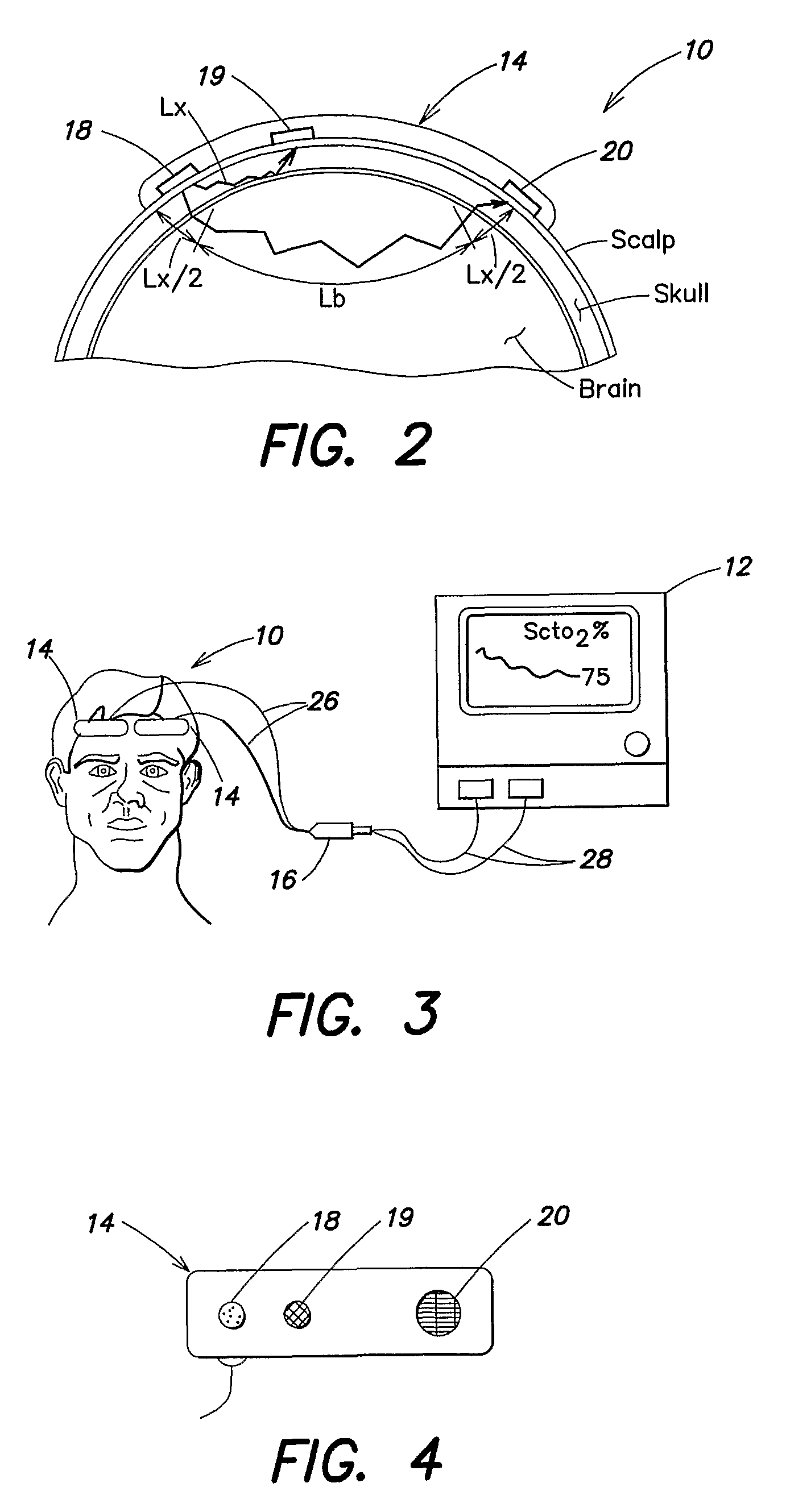
Method for spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
ActiveUS7072701B2Inhibition effectNon-invasive determinationSensorsColor/spectral properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationBlood oxygenation
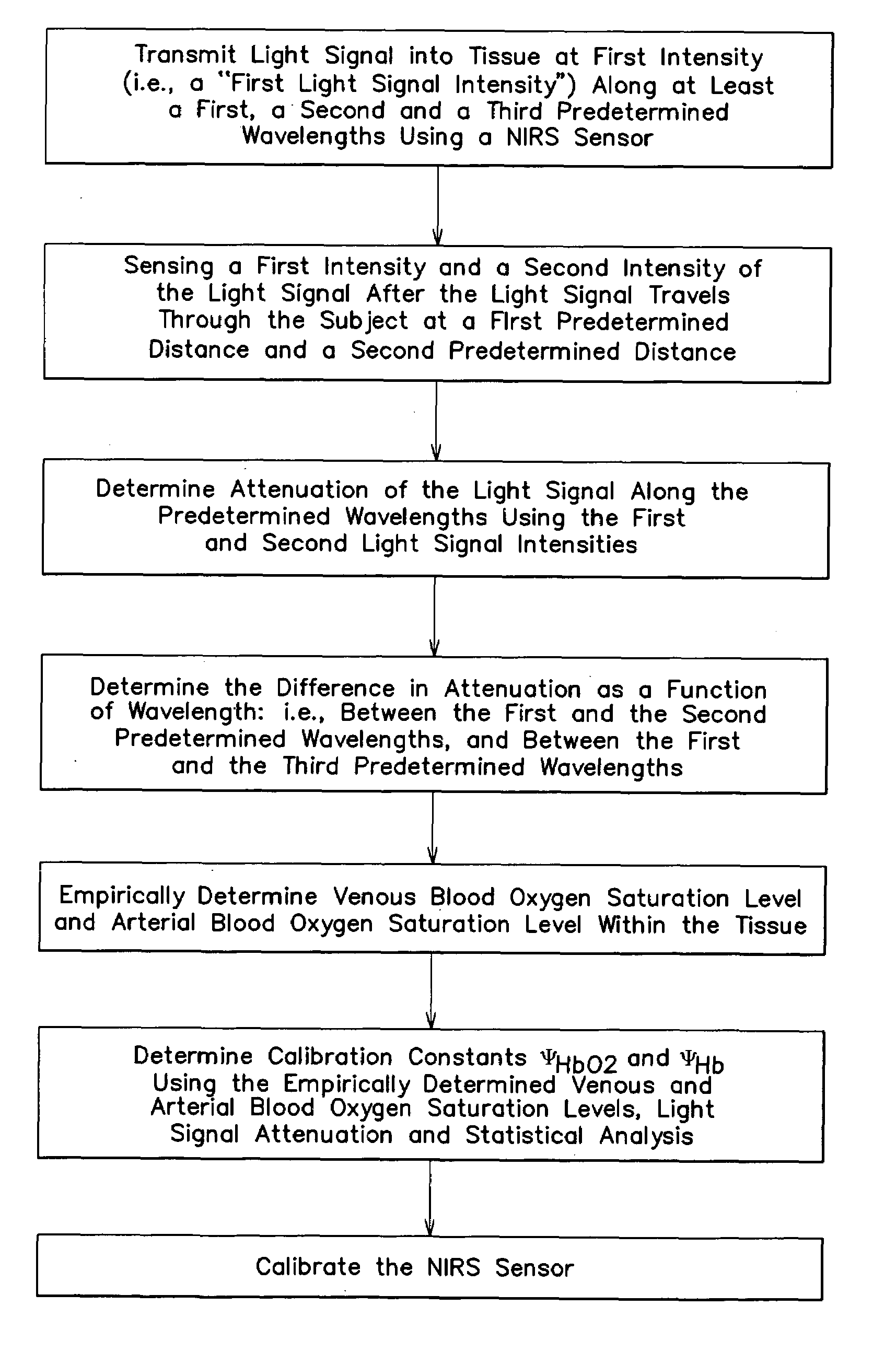
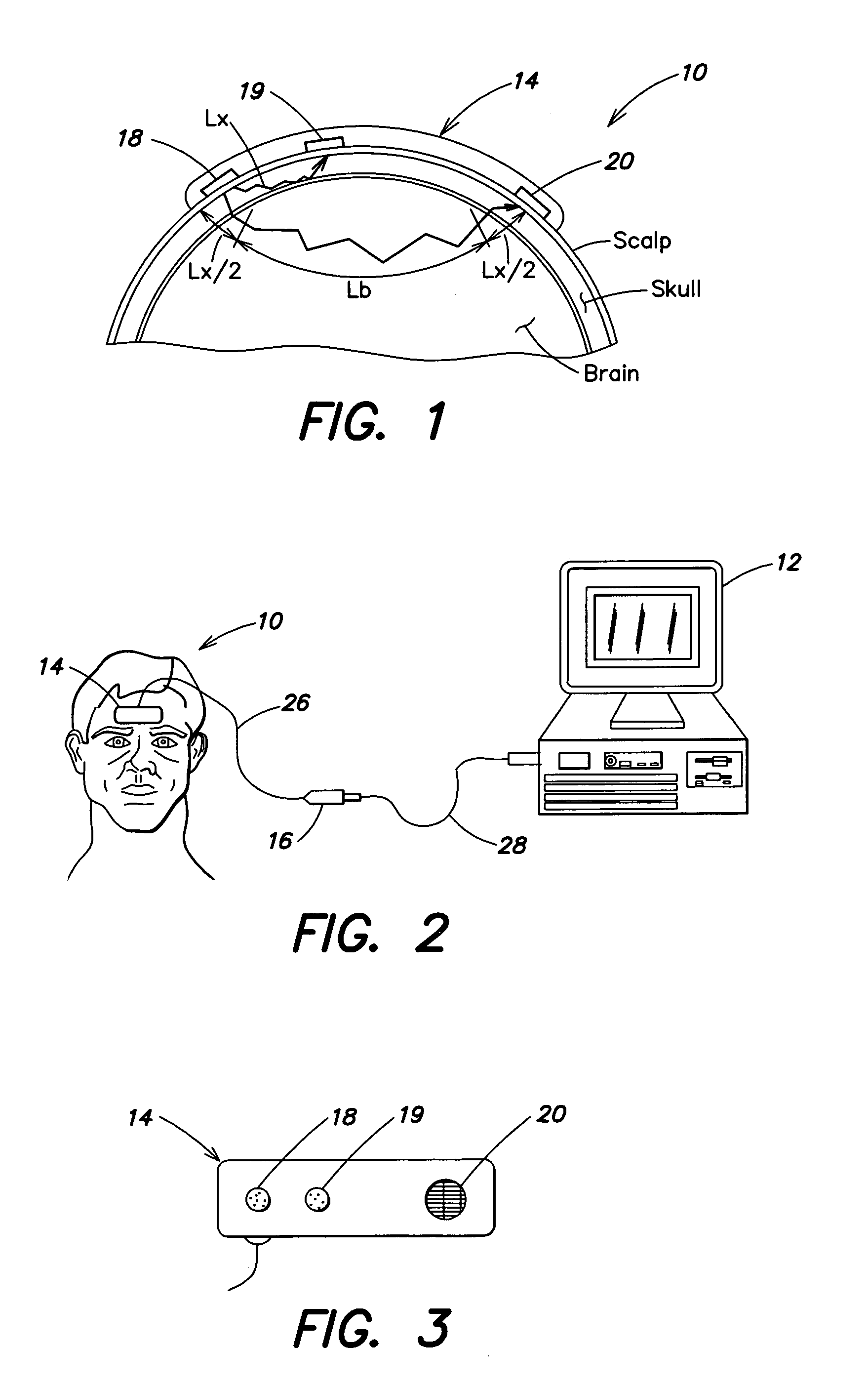
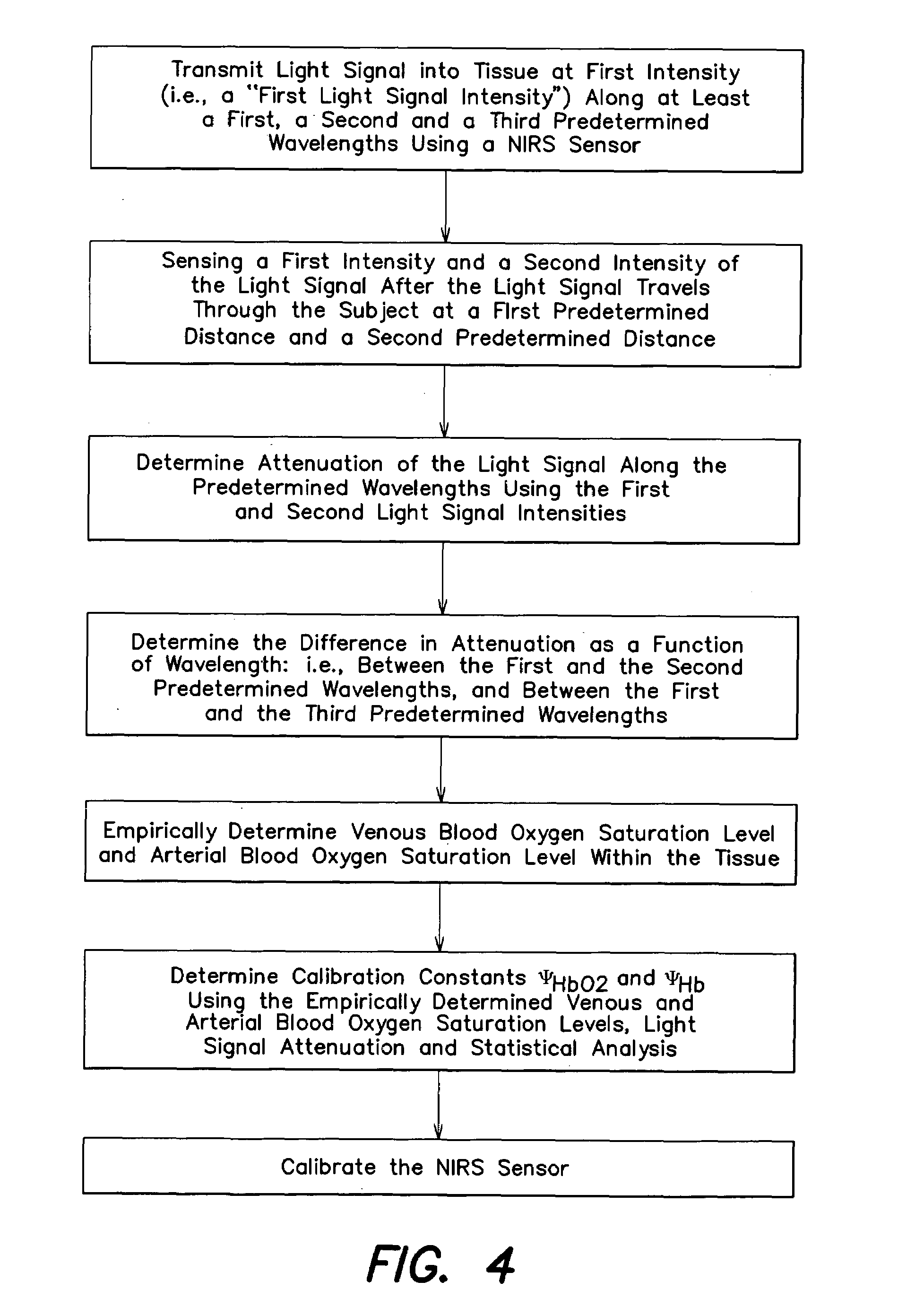
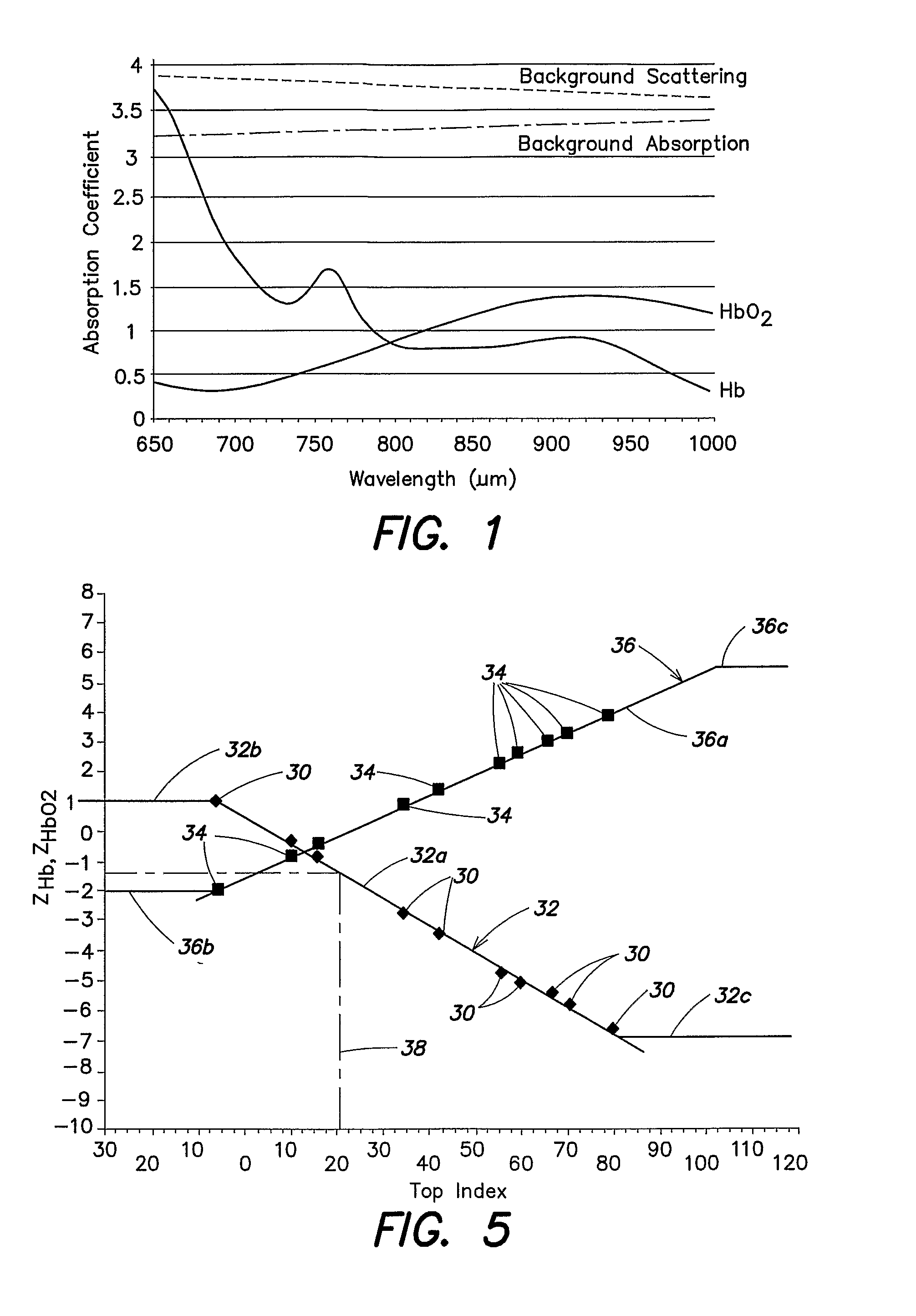
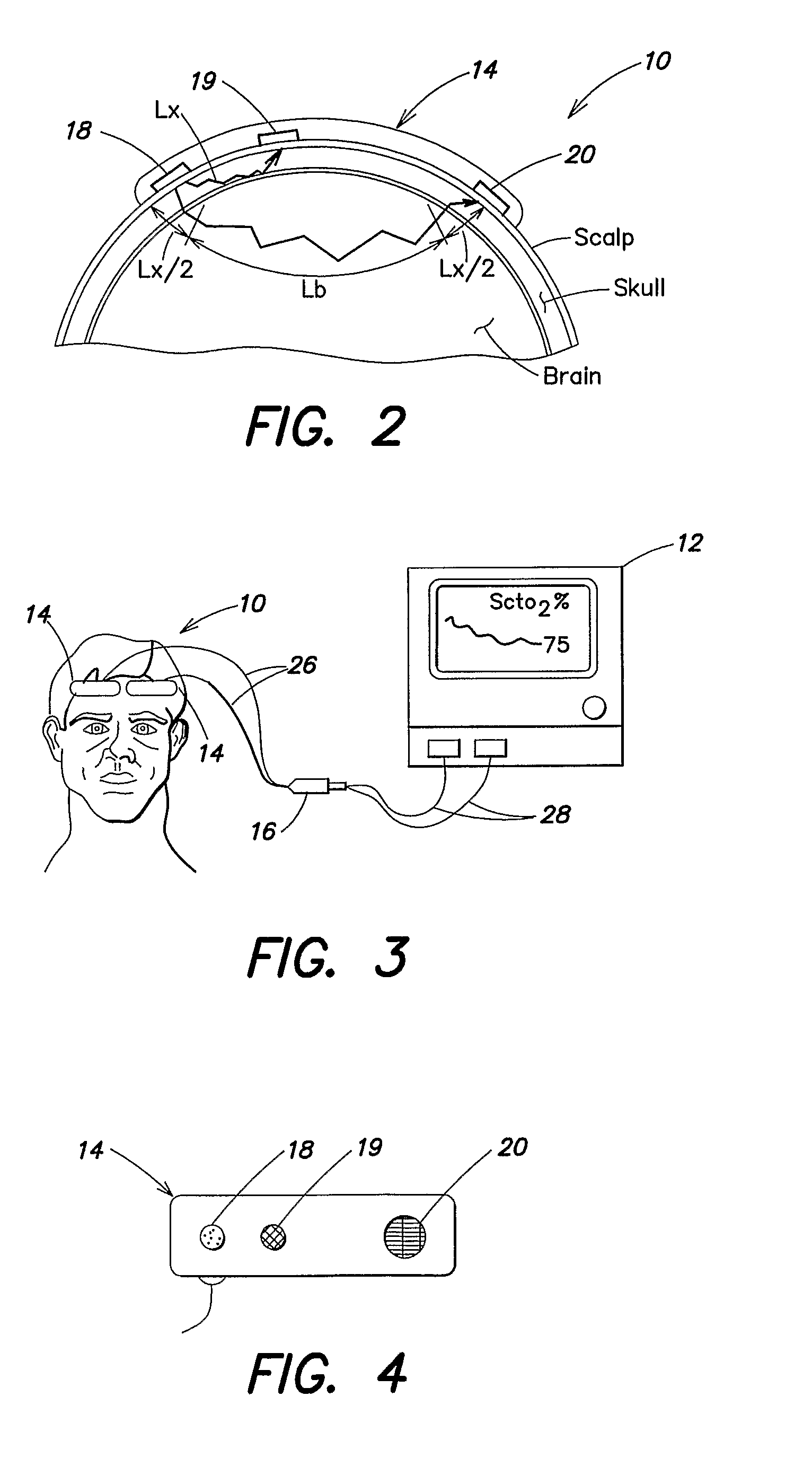
A method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the blood oxygen saturation level within a subject's tissue is provided that utilizes a near infrared spectrophotometric (NIRS) sensor capable of transmitting a light signal into the tissue of a subject and sensing the light signal once it has passed through the tissue via transmittance or reflectance. The method includes the steps of: (1) transmitting a light signal into the subject's tissue, wherein the transmitted light signal includes a first wavelength, a second wavelength, and a third wavelength; (2) sensing a first intensity and a second intensity of the light signal, along the first, second, and third wavelengths after the light signal travels through the subject at a first and second predetermined distance; (3) determining an attenuation of the light signal for each of the first, second, and third wavelengths using the sensed first intensity and sensed second intensity of the first, second, and third wavelengths; (4) determining a difference in attenuation of the light signal between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and between the first wavelength and the third wavelength; and (5) determining the blood oxygen saturation level within the subject's tissue using the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the third wavelength.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for monitoring body fluid and electrolyte disorders
InactiveUS7236811B2Improve measurement reliabilityDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using pressureLipid formationTissue compartment
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Method for spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
ActiveUS20040024297A1Inhibition effectNon-invasive determinationSensorsColor/spectral properties measurementsBlood oxygenationNon invasive
A method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the blood oxygen saturation level within a subject's tissue is provided that utilizes a near infrared spectrophotometric (NIRS) sensor capable of transmitting a light signal into the tissue of a subject and sensing the light signal once it has passed through the transmitting a light signal into the subject's tissue, wherein the transmitted light signal includes a first wavelength, a second wavelength, and a third wavelength; (2) sensing a first intensity and a second intensity of the light signal, along the first, second, and third wavelengths after the light signal travels through the subject at a first and second predetermined distance; (3) determining an attenuation of the light signal for each of the first, second, and third wavelengths using the sensed first intensity and sensed second intensity of the first, second, and third wavelengths; (4) determining a difference in attenuation of the light signal between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and between the first wavelength and the third wavelength; and (5) determining the blood oxygen saturation level within the subject's tissue using the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the third wavelength.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Liquid photometer using surface tension to contain sample
Method and apparatus of spectrophotometry or the like on extremely small liquid samples in which a drop is held between two opposing surfaces by surface tension and one surface is controllably moved toward and away from the other. To provide and transmit exciting energy through the drop for measurement, the optical fibers go through a surface and are finished flush with its surface. One of the surfaces can be swung clear of the other for easy cleaning between tests.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
Sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin compositions
ActiveUS7635773B2Well mixedReduce the amount requiredOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPhosphateEther
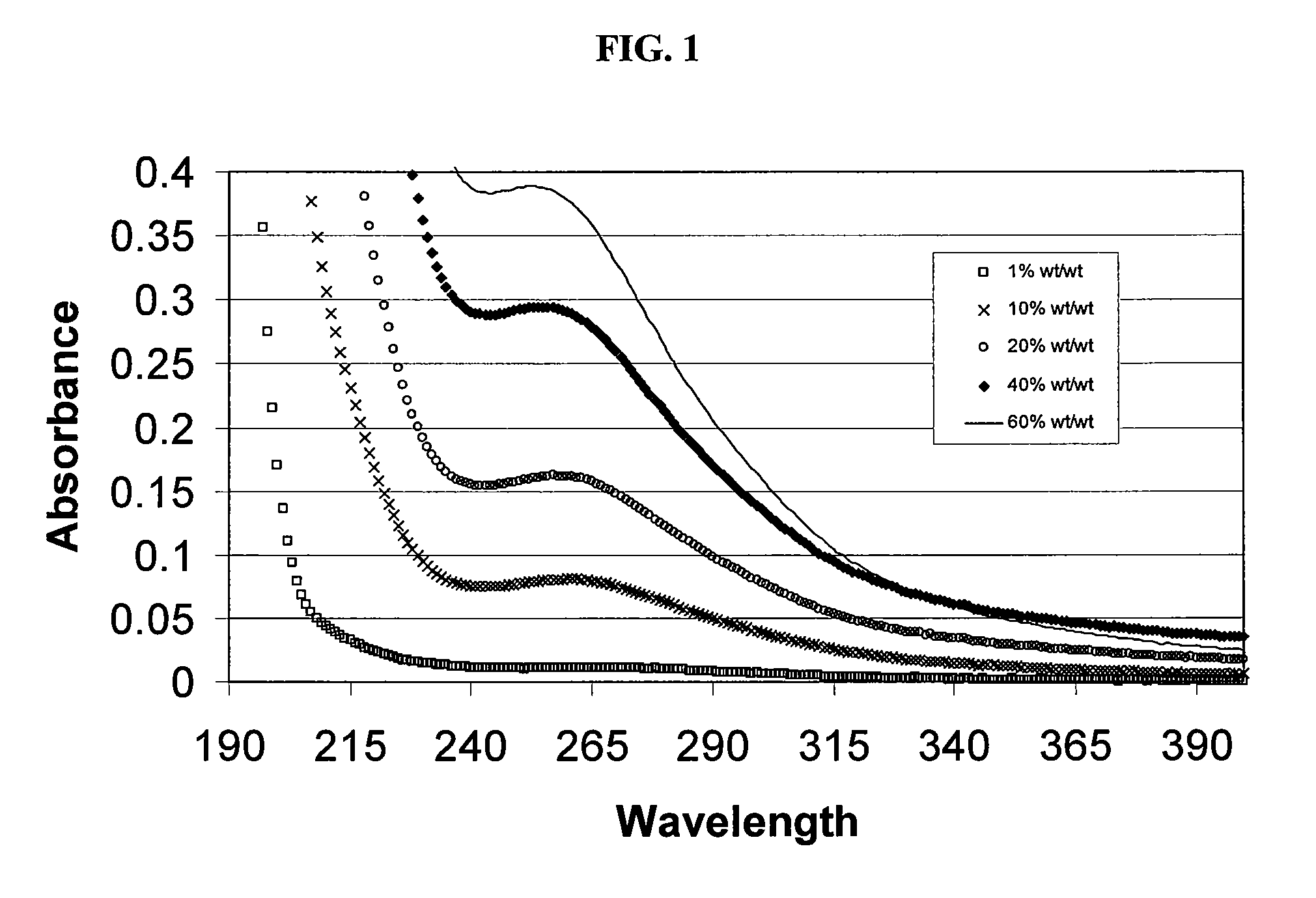
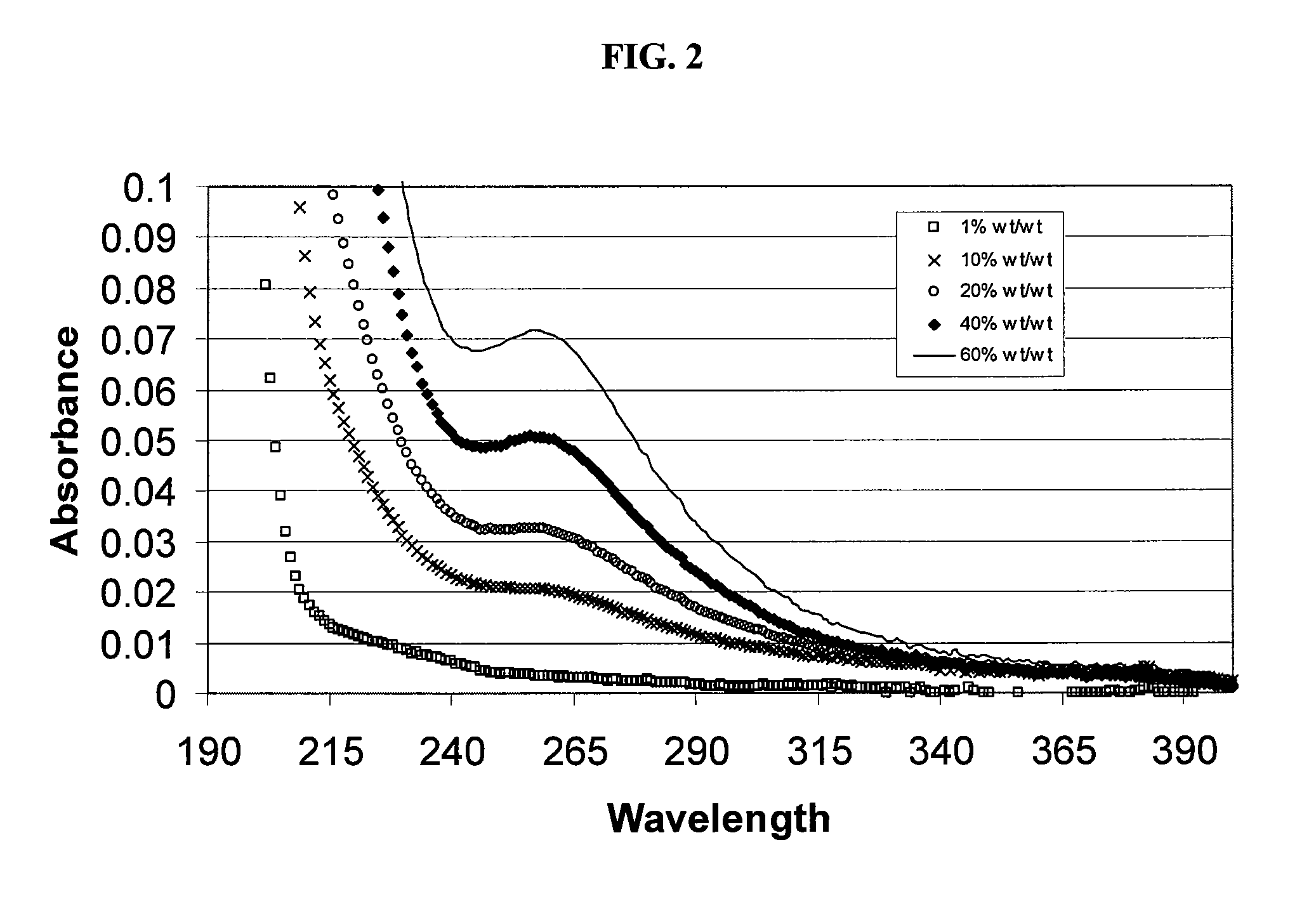
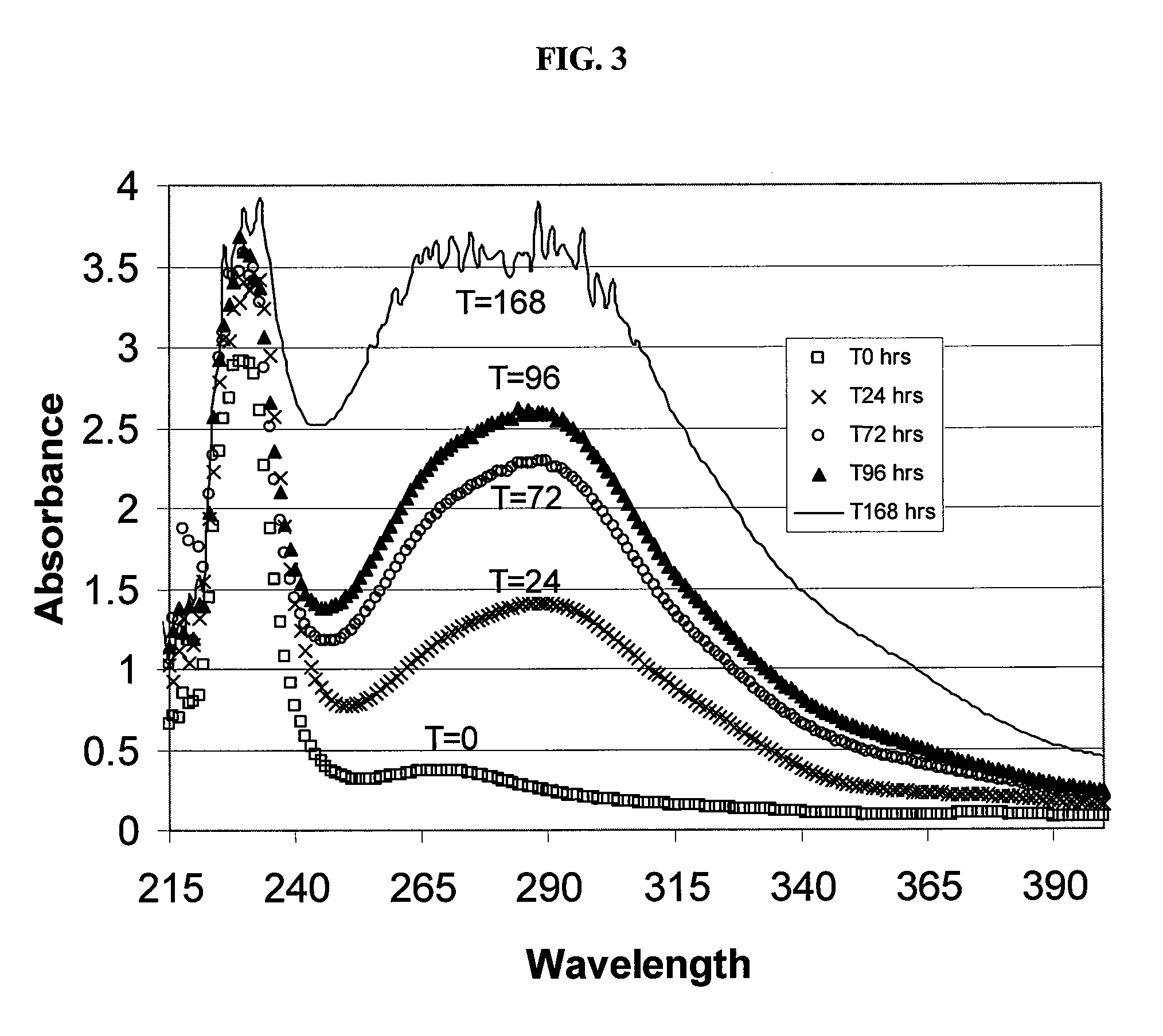
SAE-CD compositions are provided, along with methods of making and using the same. The SAE-CD composition comprises a sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin and less than 100 ppm of a phosphate, wherein the SAE-CD composition has an absorption of less than 0.5 A.U. due to a drug-degrading agent, as determined by UV / vis spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 245 nm to 270 nm for an aqueous solution containing 300 mg of the SAE-CD composition per mL of solution in a cell having a 1 cm path length.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
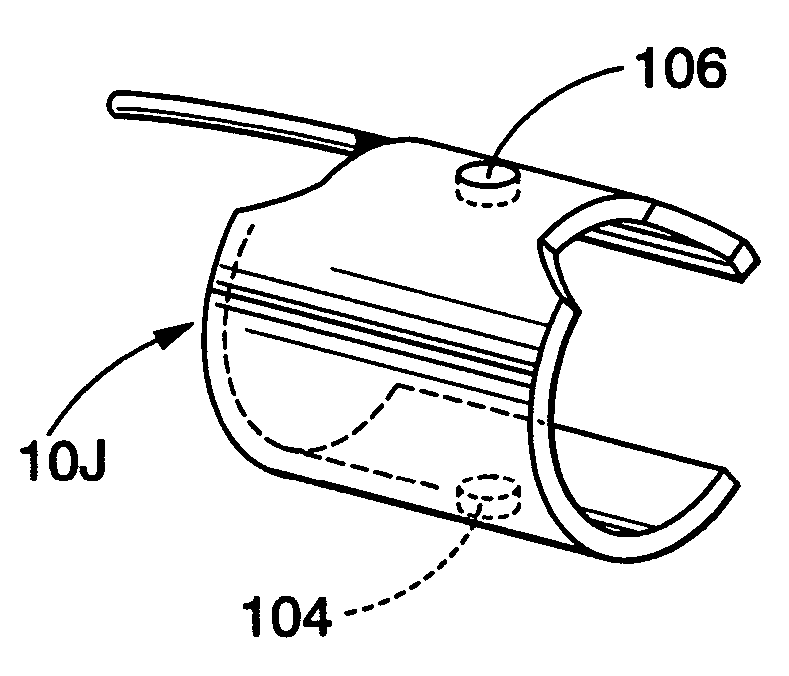
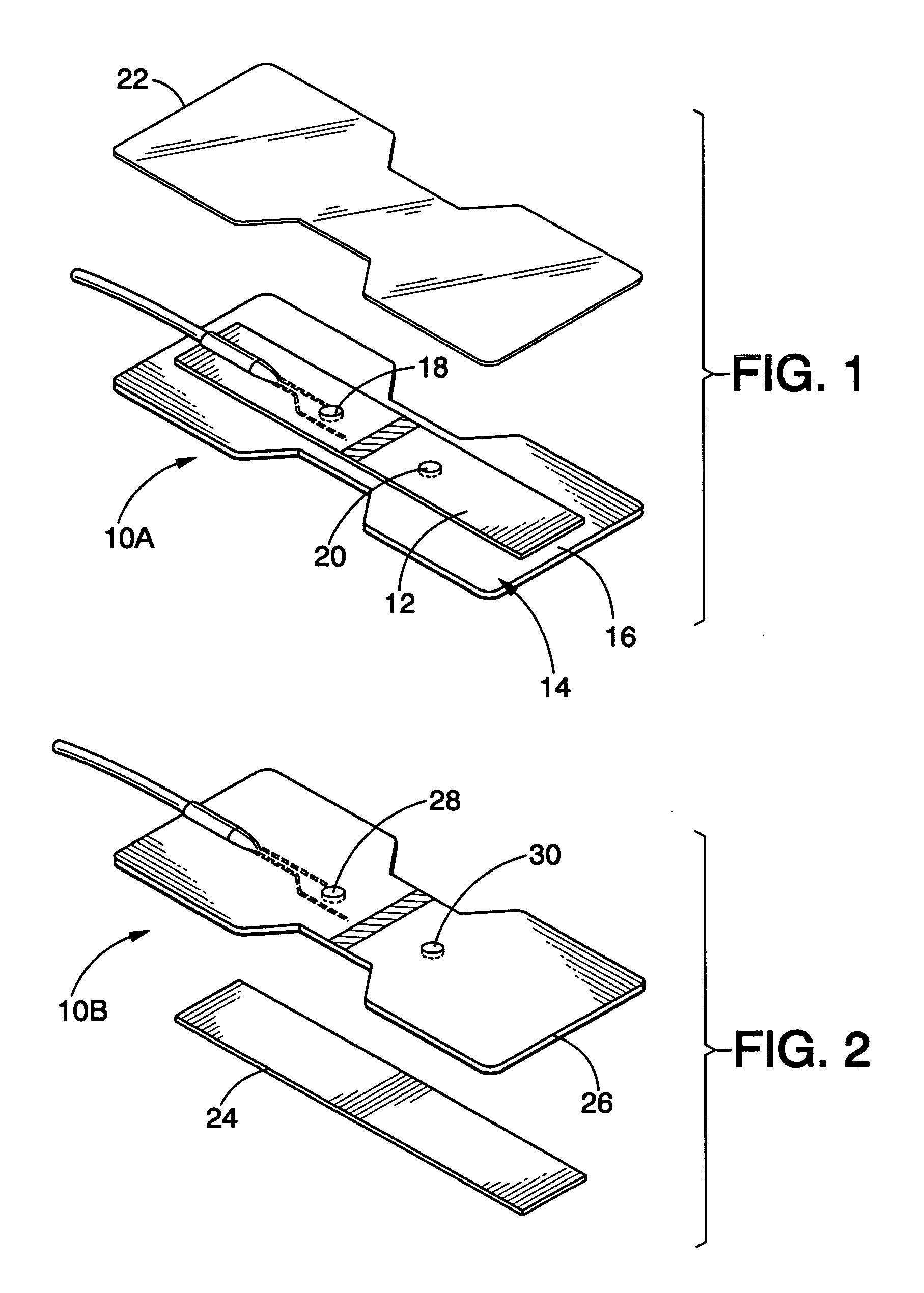
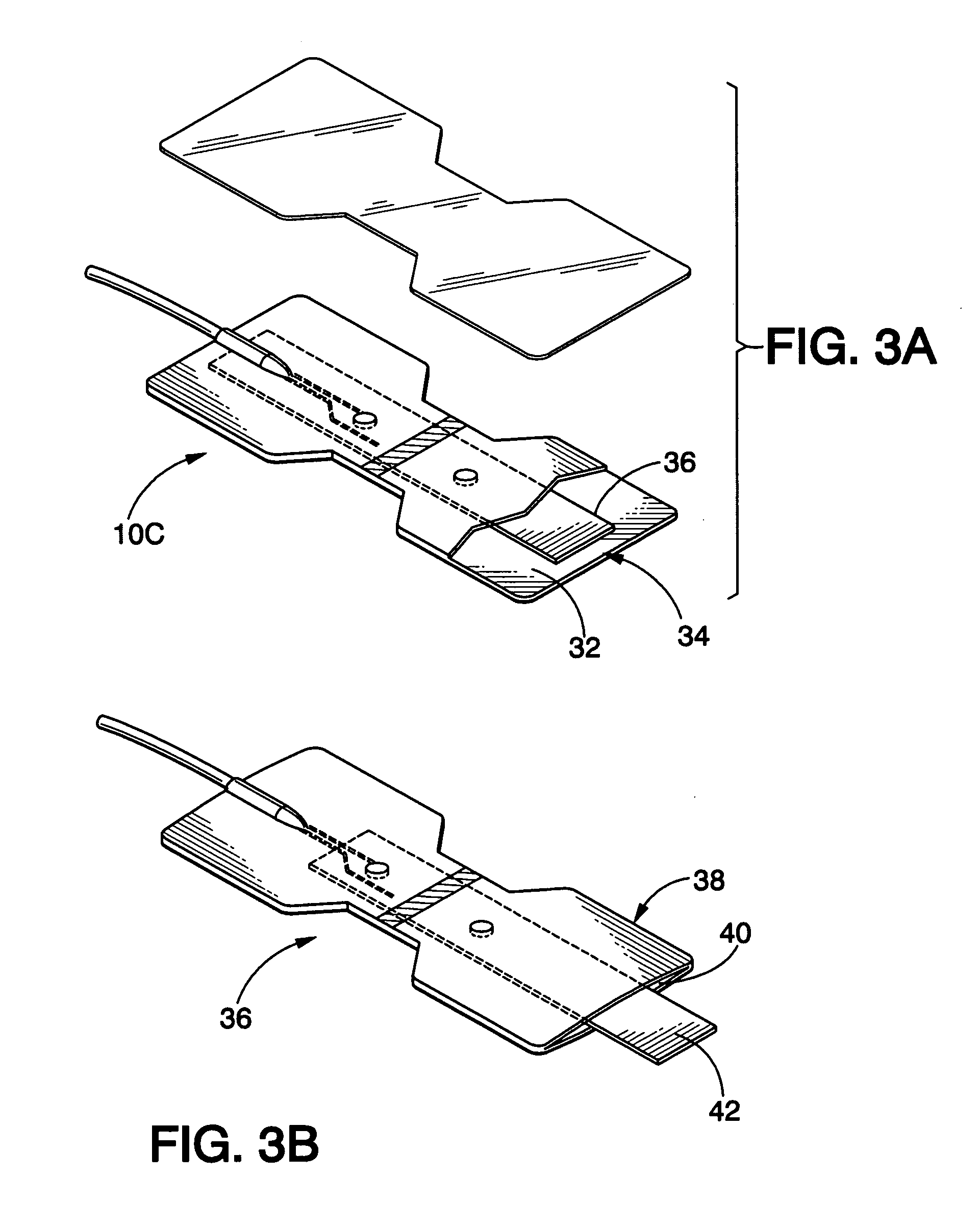
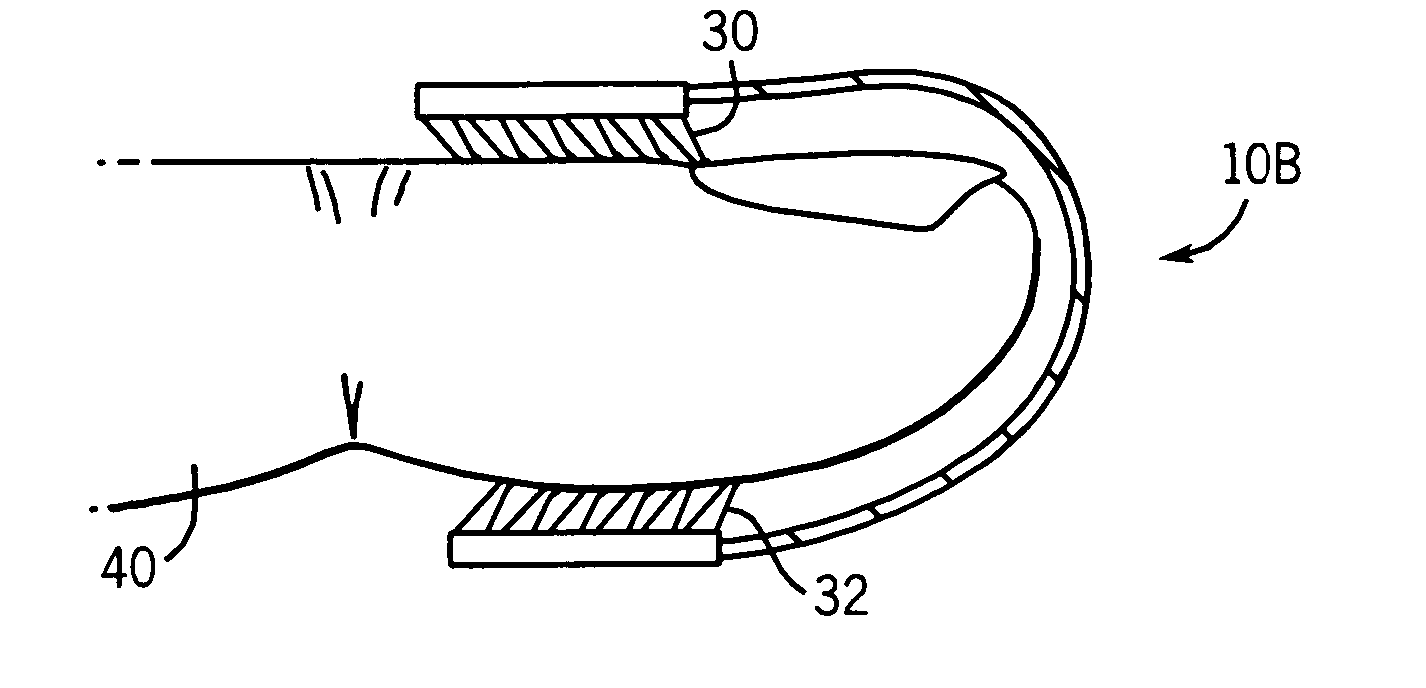
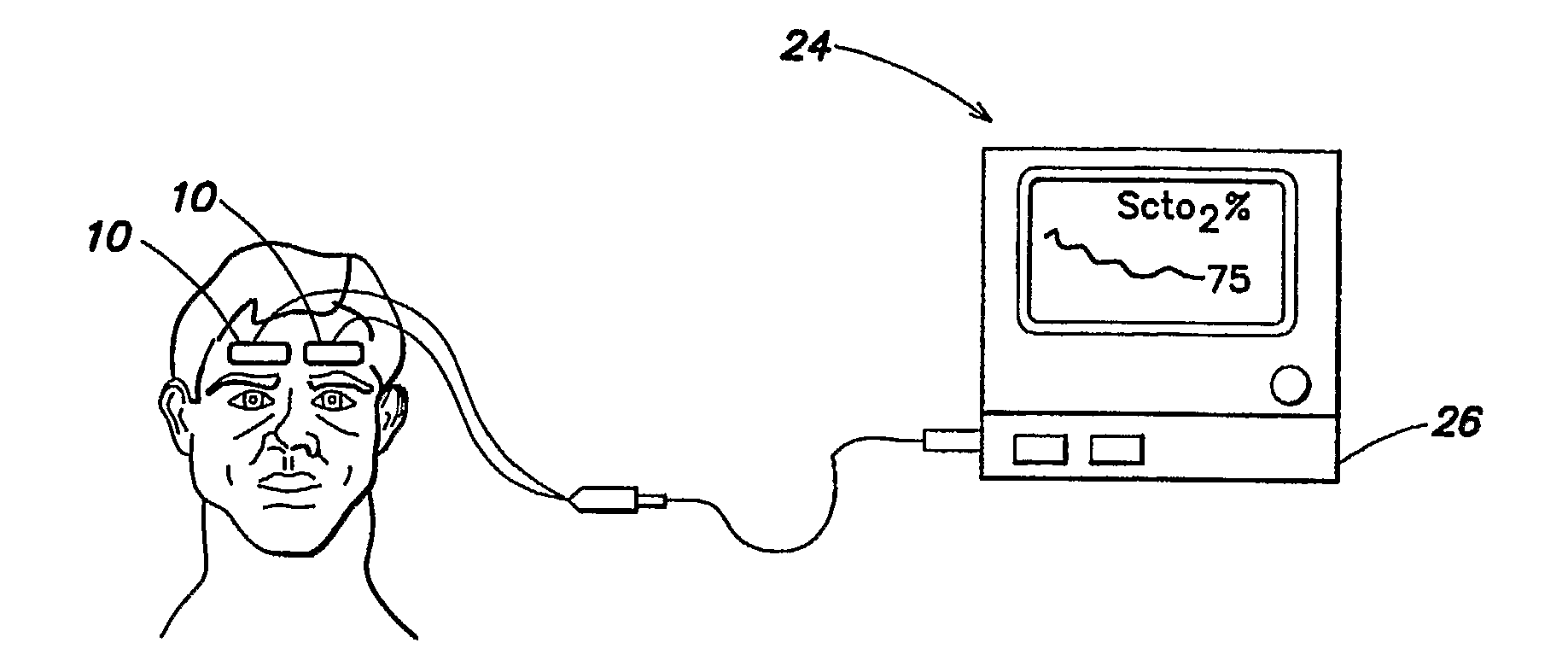
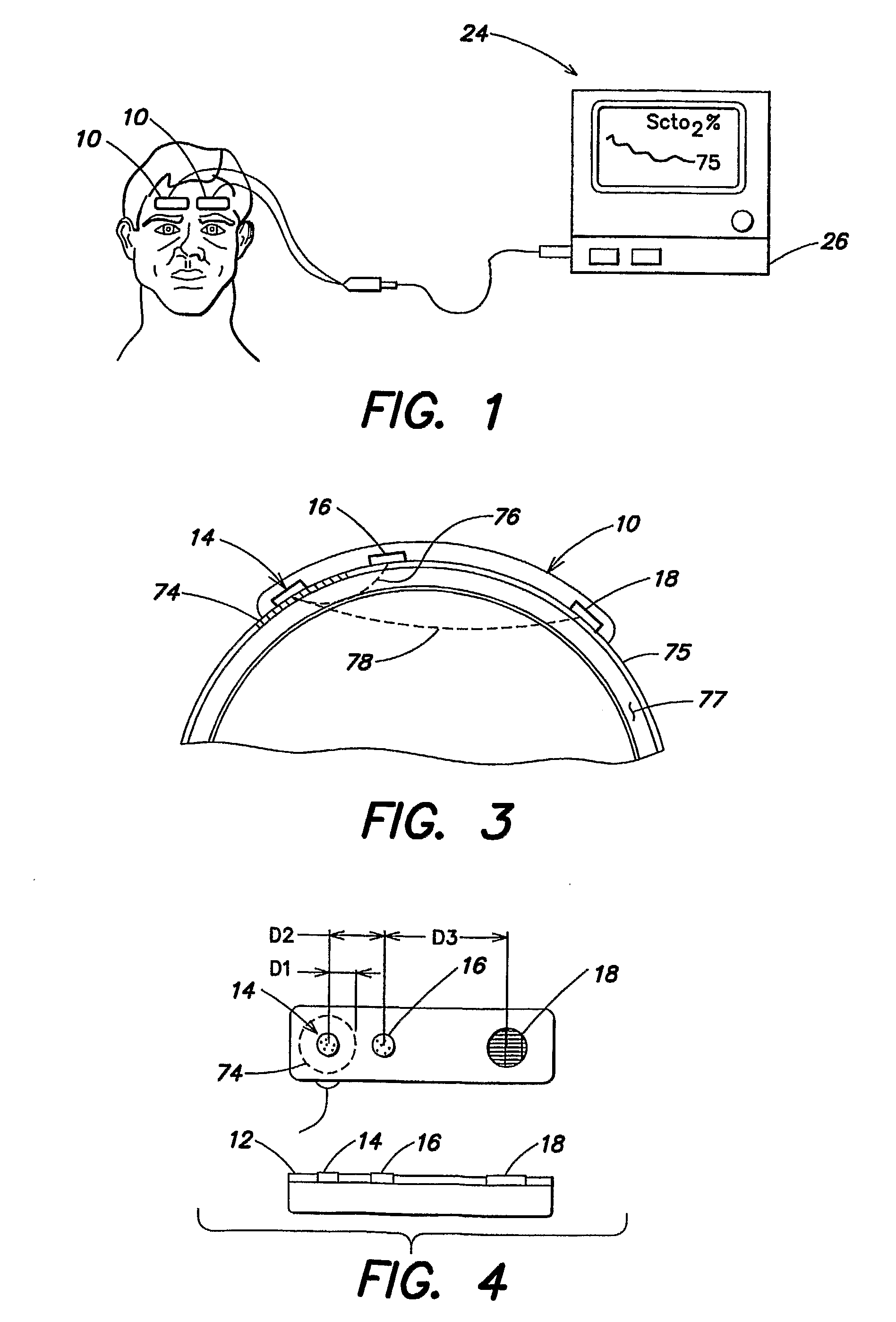
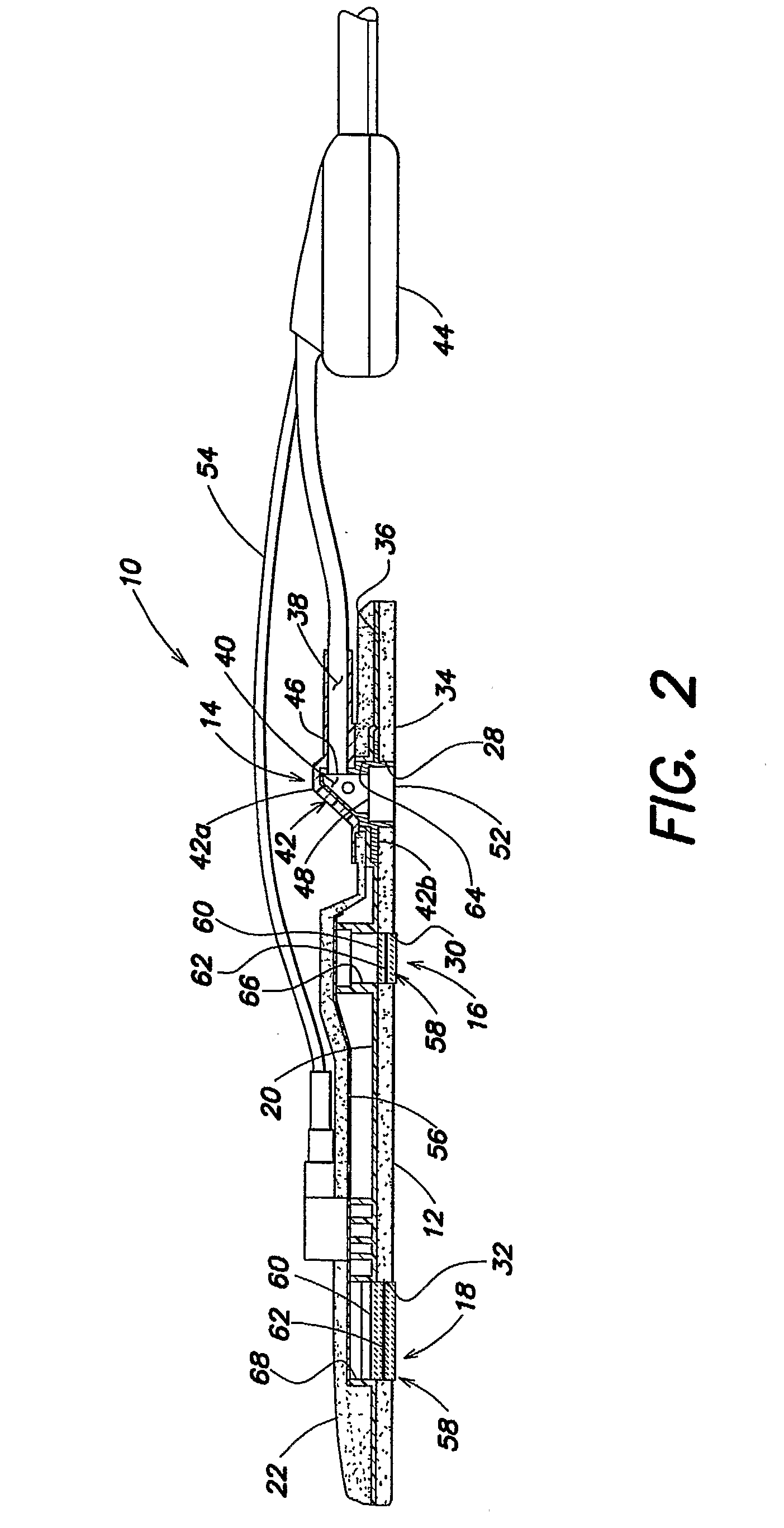
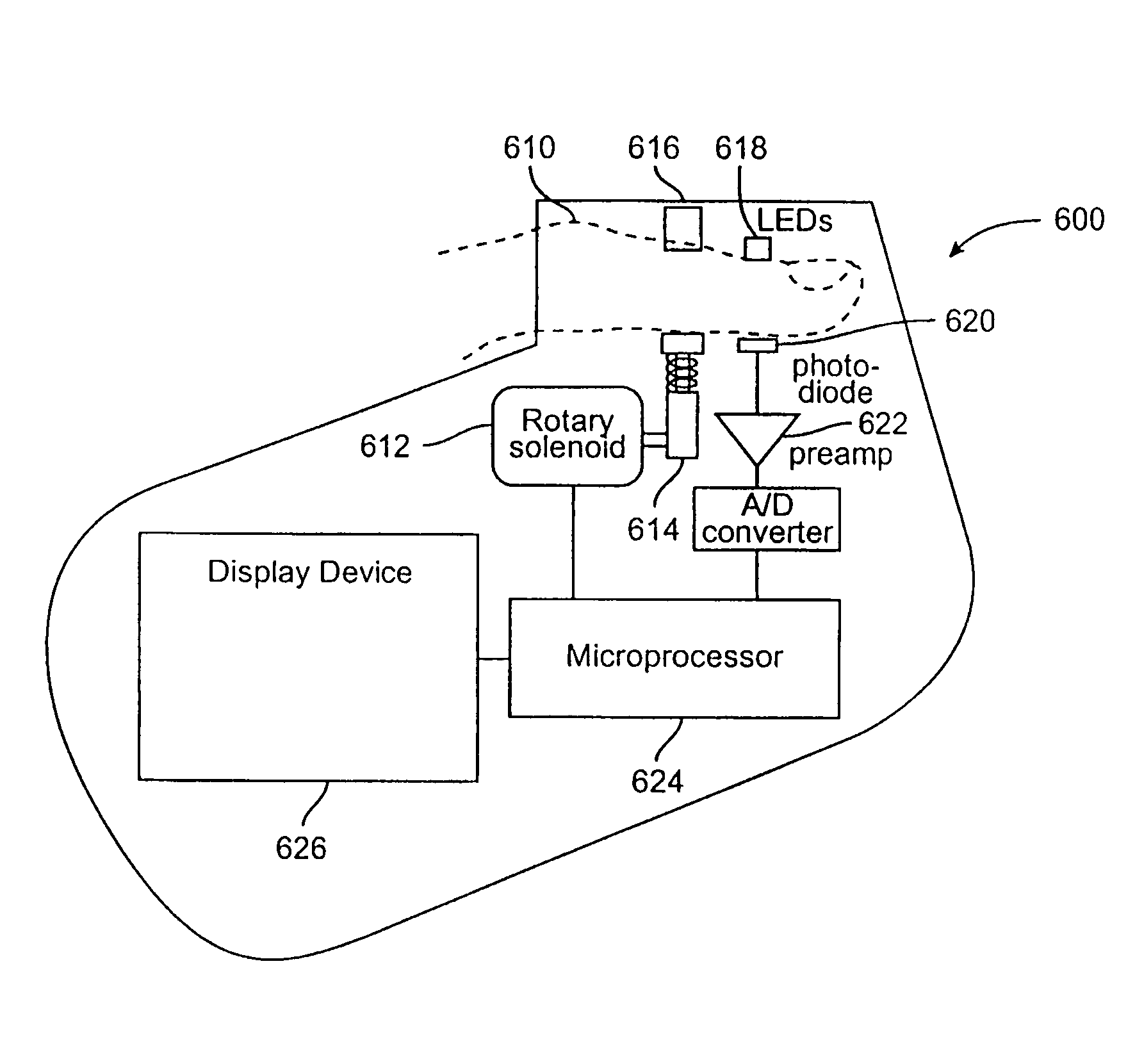
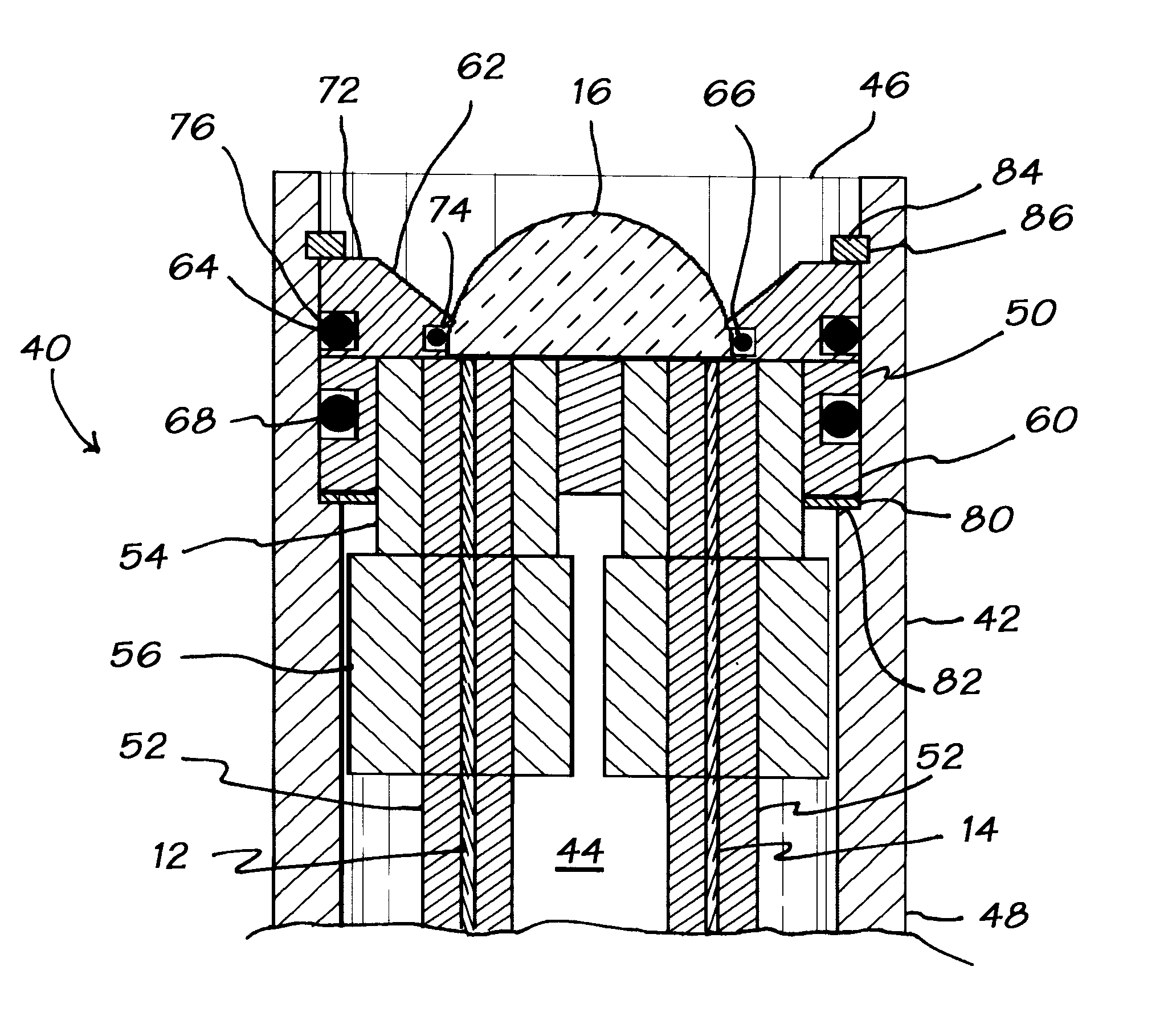
Medical sensor for reducing motion artifacts and technique for using the same
A sensor for pulse oximetry or other applications utilizing spectrophotometry may be adapted to reduce motion artifacts by fixing the optical distance between an emitter and detector. A flexible sensor is provided with a stiffening member to hold the emitter and detector of the sensor in a relatively fixed position when applied to a patient. Further, an annular or partially annular sensor is adapted to hold an emitter and detector of the sensor in a relatively fixed position when applied to a patient. A clip-style sensor is provided with a spacer that controls the distance between the emitter and detector.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
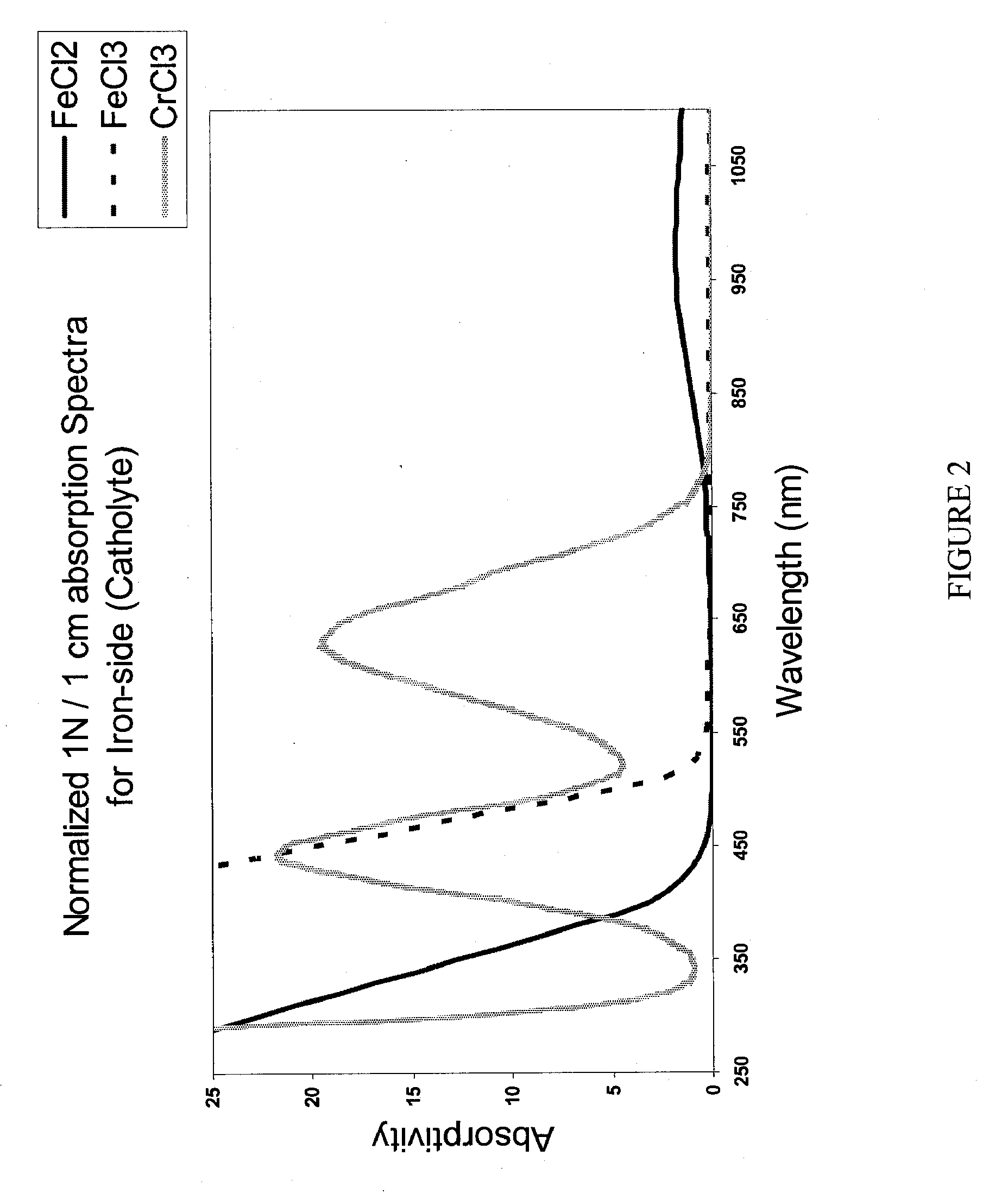
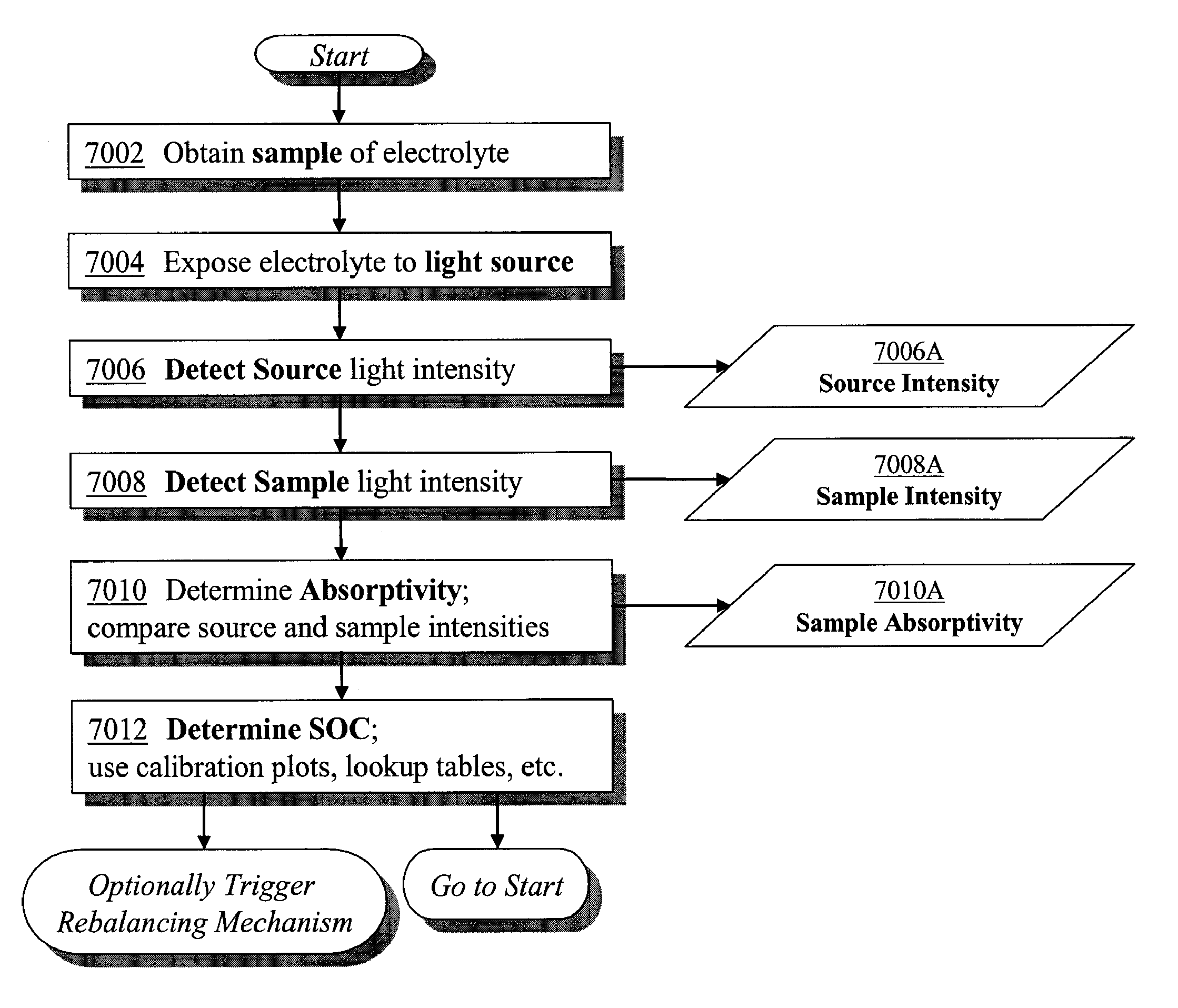
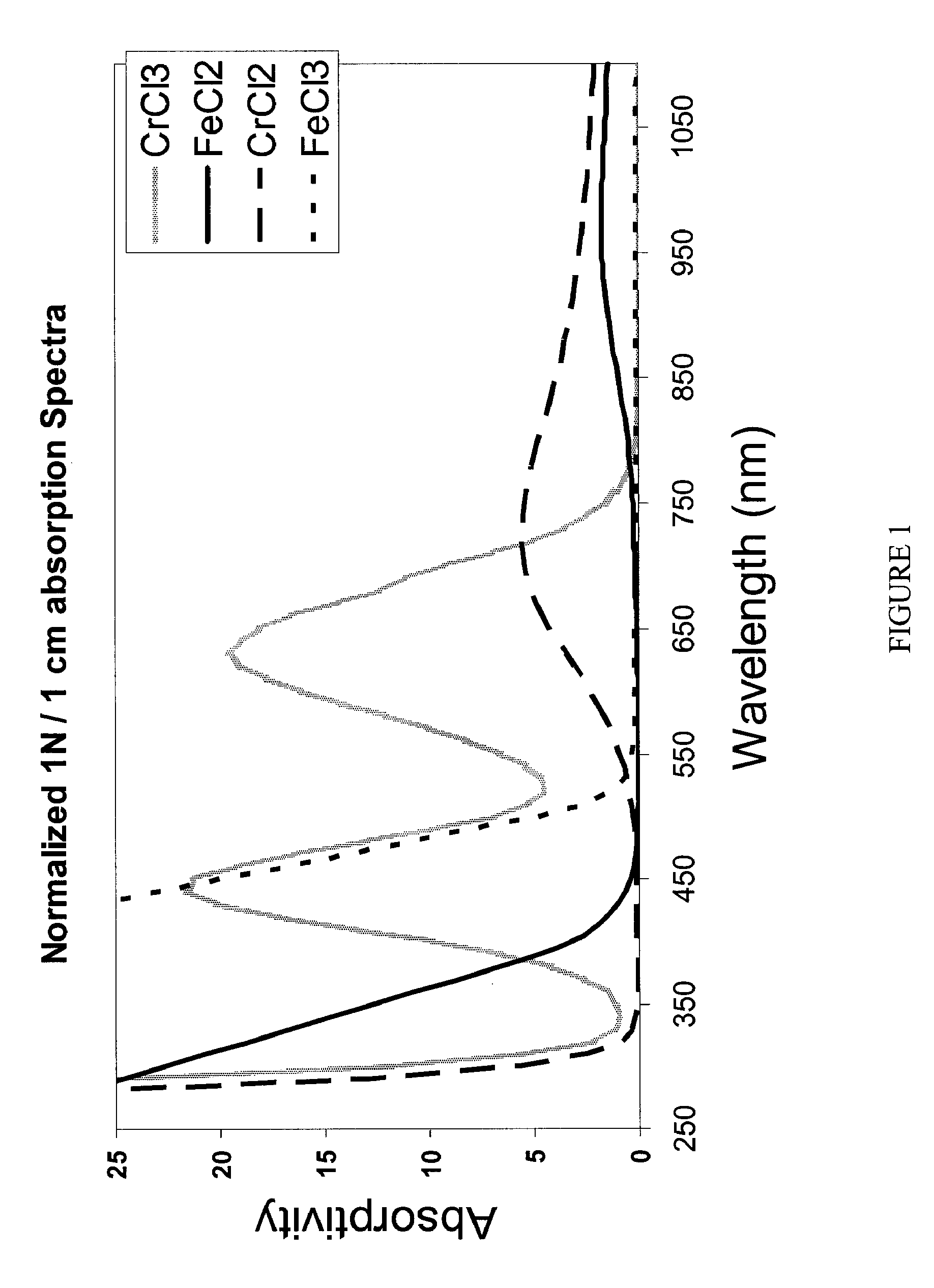
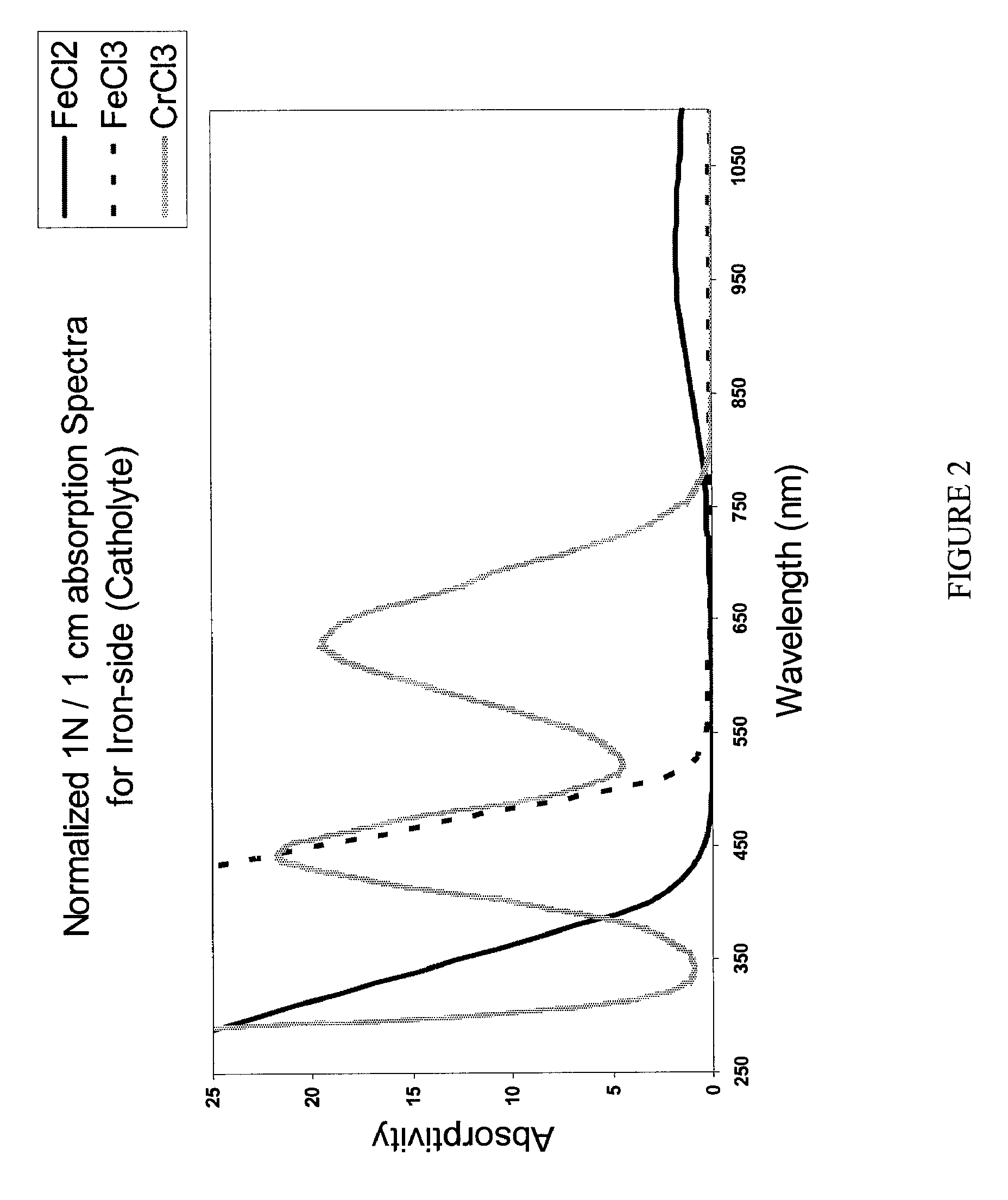
Apparatus and Methods of Determination of State of Charge in a Redox Flow Battery
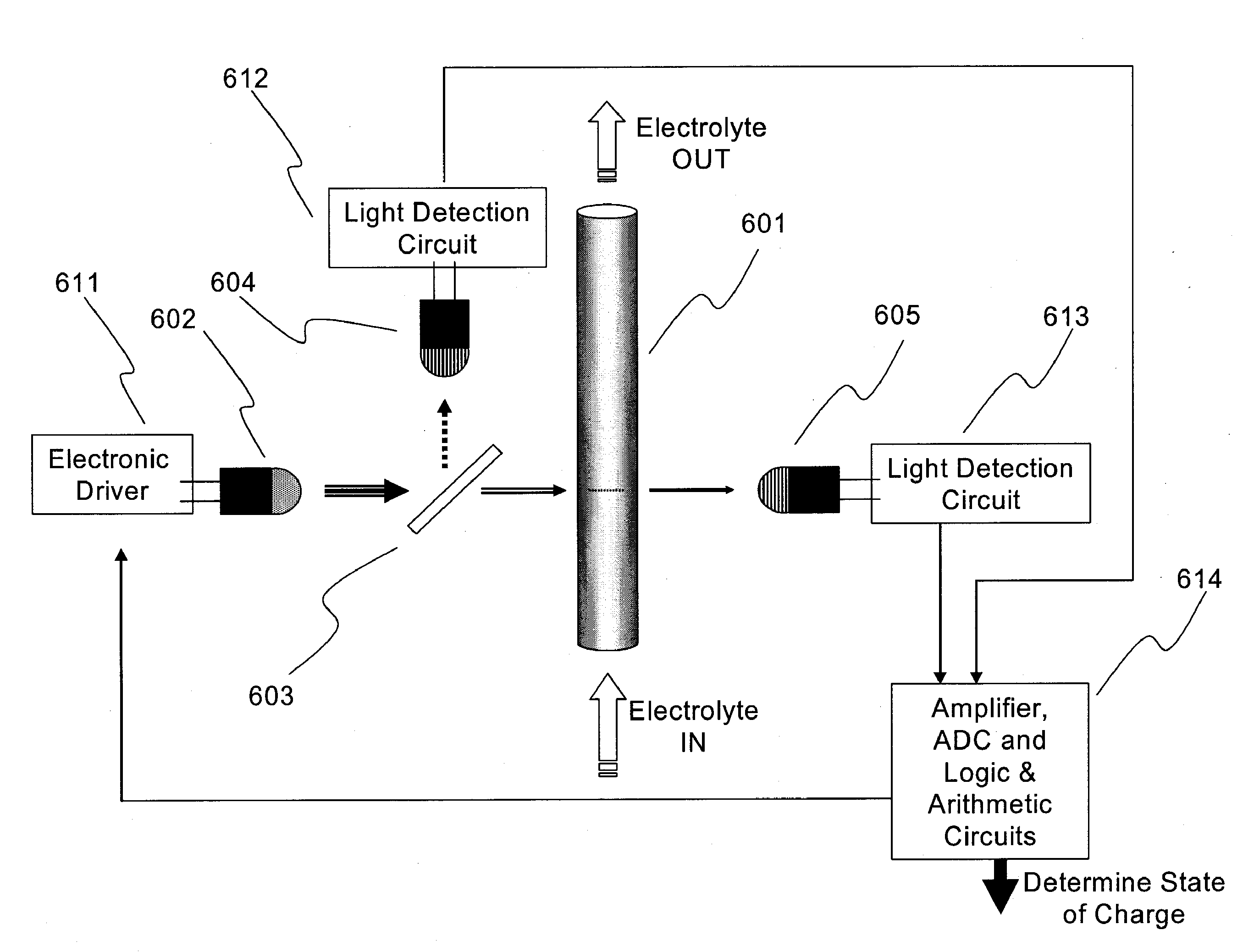
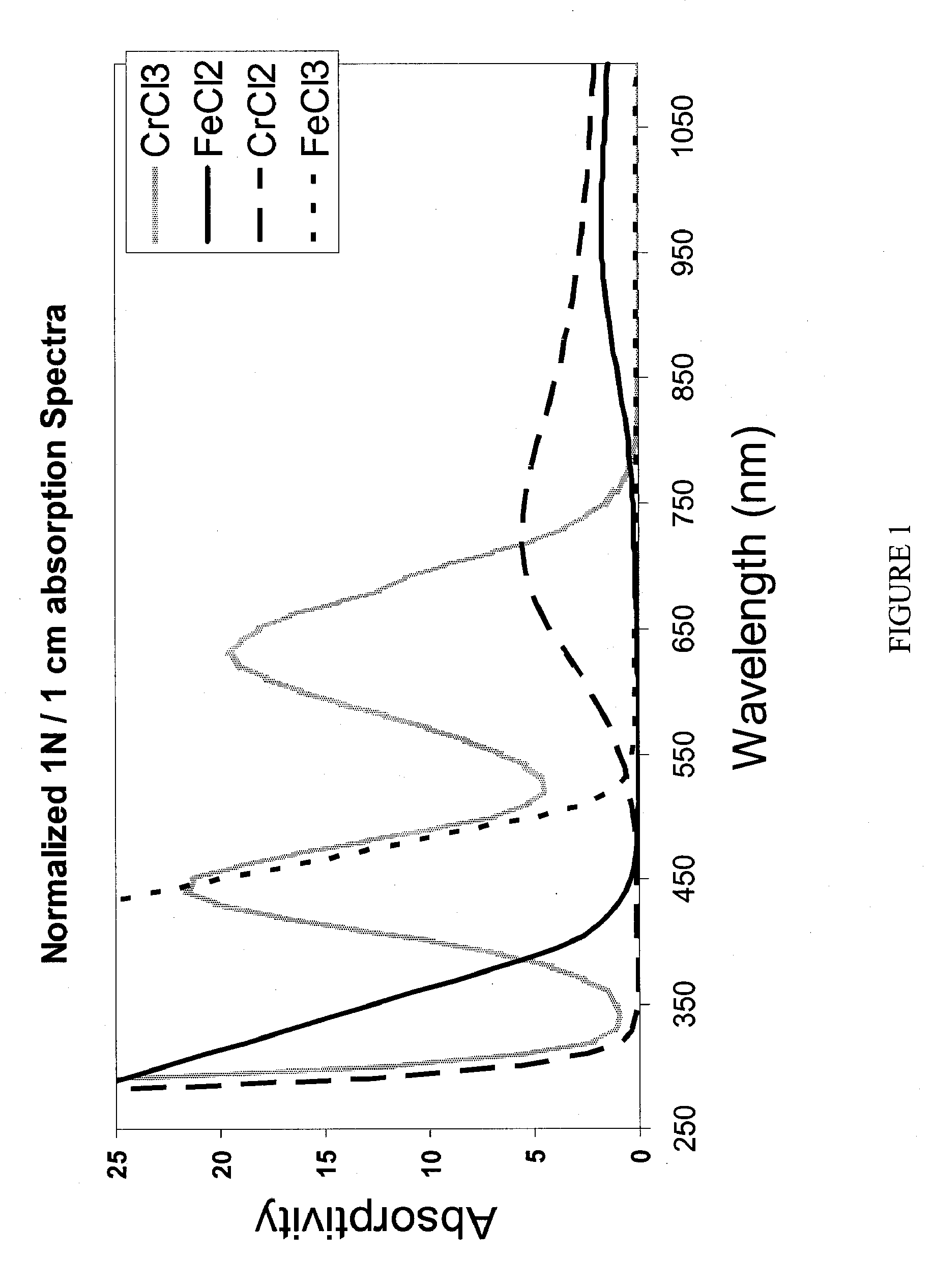
InactiveUS20080193828A1Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorRedoxState of charge
Apparatus and methods for determining the individual states of charge of electrolytes in a redox battery with mixed or unmixed reactants by optical absorption spectrophotometry are disclosed. The state of charge thus obtained may serve as a gauge for the amount of electro-chemical energy left in the system. Further, the information on anolyte and catholyte charge states may be used for any rebalancing mechanism if the states are different.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
Sulfoalkyl Ether Cyclodextrin Compositions
ActiveUS20090270348A1Well mixedReduce the amount requiredOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePhosphateCyclodextrin
SAE-CD compositions are provided, along with methods of making and using the same. The SAE-CD composition comprises a sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin and less than 100 ppm of a phosphate, wherein the SAE-CD composition has an absorption of less than 0.5 A.U. due to a drug-degrading agent, as determined by UV / vis spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 245 nm to 270 nm for an aqueous solution containing 300 mg of the SAE-CD composition per mL of solution in a cell having a 1 cm path length.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Medical sensor for reducing motion artifacts and technique for using the same
A sensor for pulse oximetry or other applications utilizing spectrophotometry may be adapted to reduce motion artifacts by fixing the optical distance between an emitter and detector. A flexible sensor is provided with a stiffening member to hold the emitter and detector of the sensor in a relatively fixed position when applied to a patient. Further, an annular or partially annular sensor is adapted to hold an emitter and detector of the sensor in a relatively fixed position when applied to a patient. A clip-style sensor is provided with a spacer that controls the distance between the emitter and detector.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Medical sensor and technique for using the same
A medical sensor may be adapted to be affixed to a patient's skin. A sensor for pulse oximetry or other spectrophotometric uses is provided with a gripping region that contacts the patient's skin and provides gripping strength to reduce movement of the sensor. Also provided herein is a method of contacting a sensor to a patient's skin and method of manufacturing a sensor.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
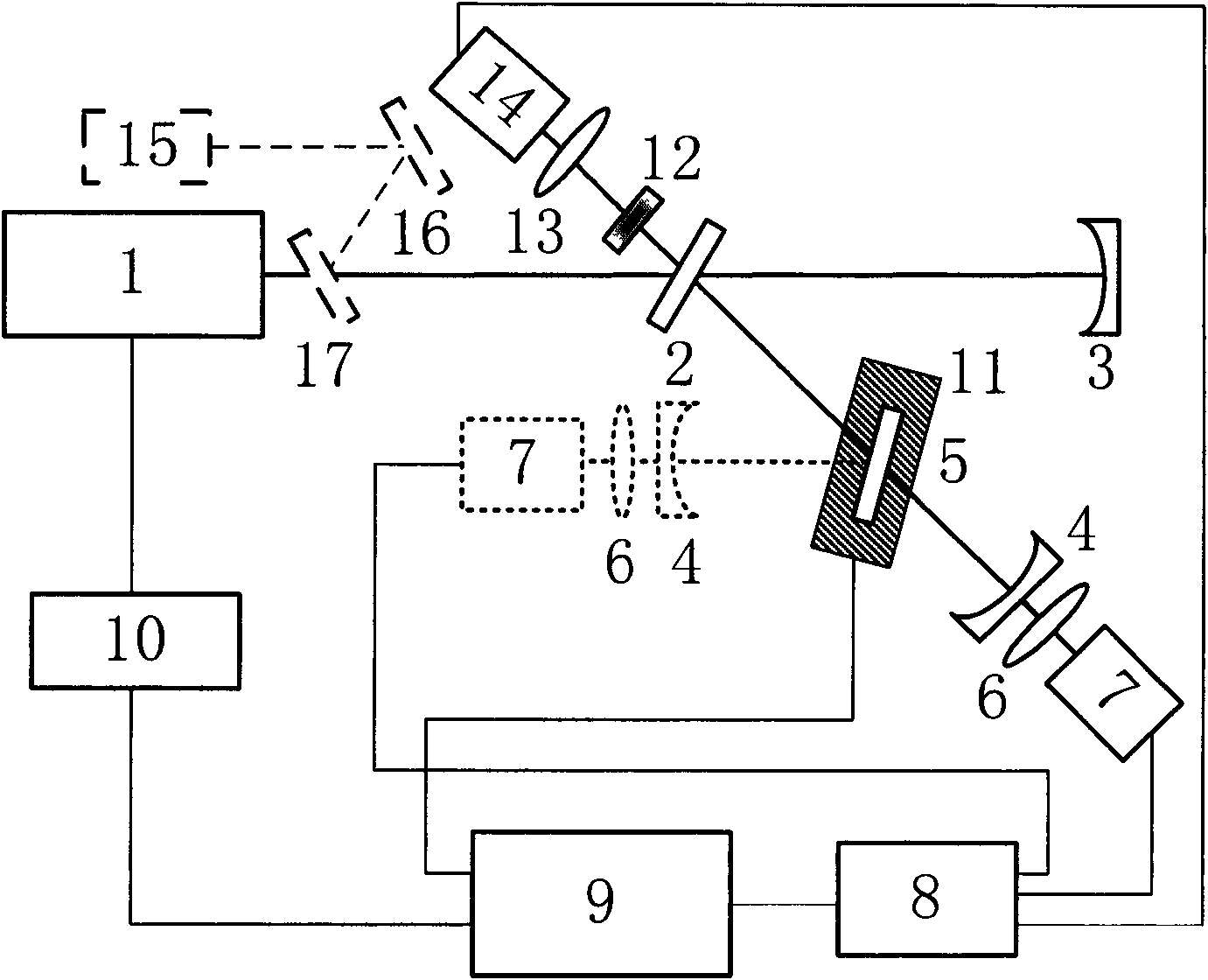
Ultrasensitive spectrophotometer
InactiveUS20060152726A1Lower Level RequirementsRapid fluctuationRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyNoise levelDiffuse reflection
The invention concerns measurements in which light interacts with matter giving rise to changes in light intensity, and preferred embodiment spectrophotometer devices of the invention provide for ultrasensitive measurements through a reflection interaction with matter. The level of light source noise in these measurements can be reduced in accordance with the invention. Preferred embodiments of the invention use sealed housings lacking an internal light source, and reflection based sample and reference cells. In some embodiments a substantially solid thermally conductive housing is used. Other features of preferred embodiments include particular reflection based sample and reference cells. A total internal reflection embodiment includes, for example, a prism including an interaction surface, a detector, a lens that focuses a beam output from the prism onto the detector, and a closed interaction volume having an inlet and an outlet for delivering gas or liquid to the interaction surface. In a specular reflection embodiment, a reflective surface is used instead of a prism. In a diffuse reflection embodiment a matte surface is used instead of a prism and the matte surface produces scattering. Aspects of the invention include identification of noise-contributing components in spectrophotometry and the select set of preferred features in a given embodiment, and noise levels very near the shot noise limit may be realized with application of preferred embodiment devices.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
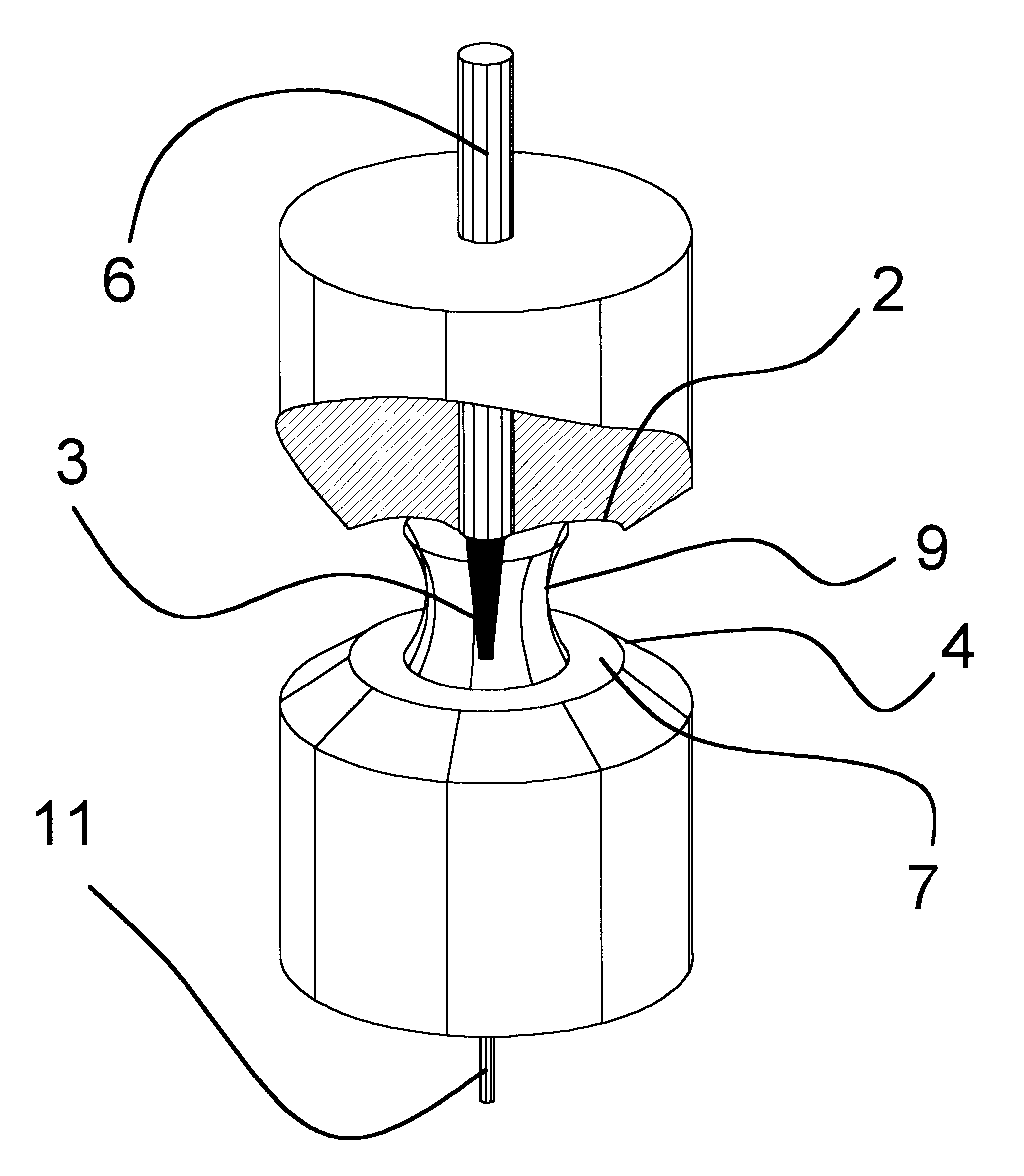
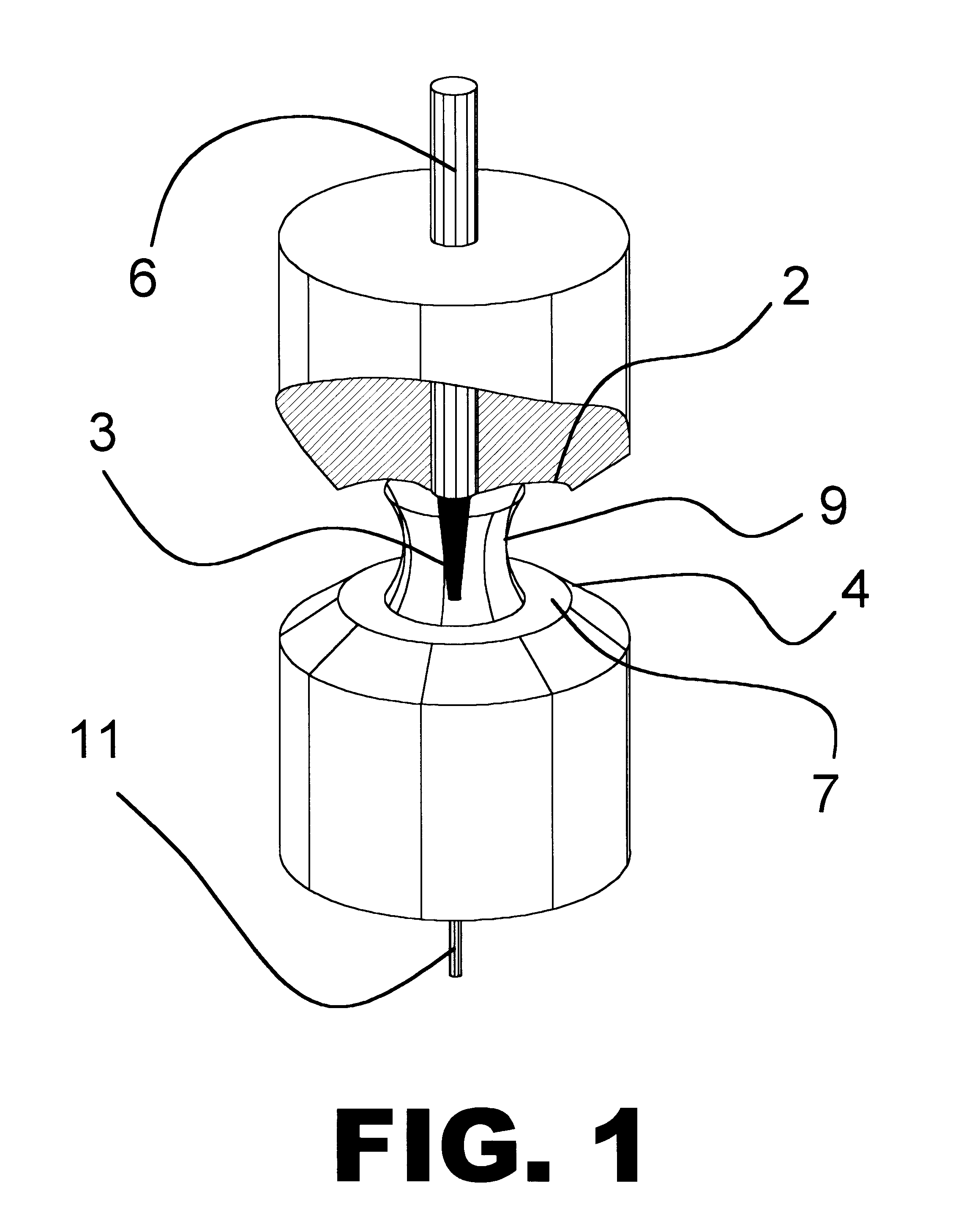
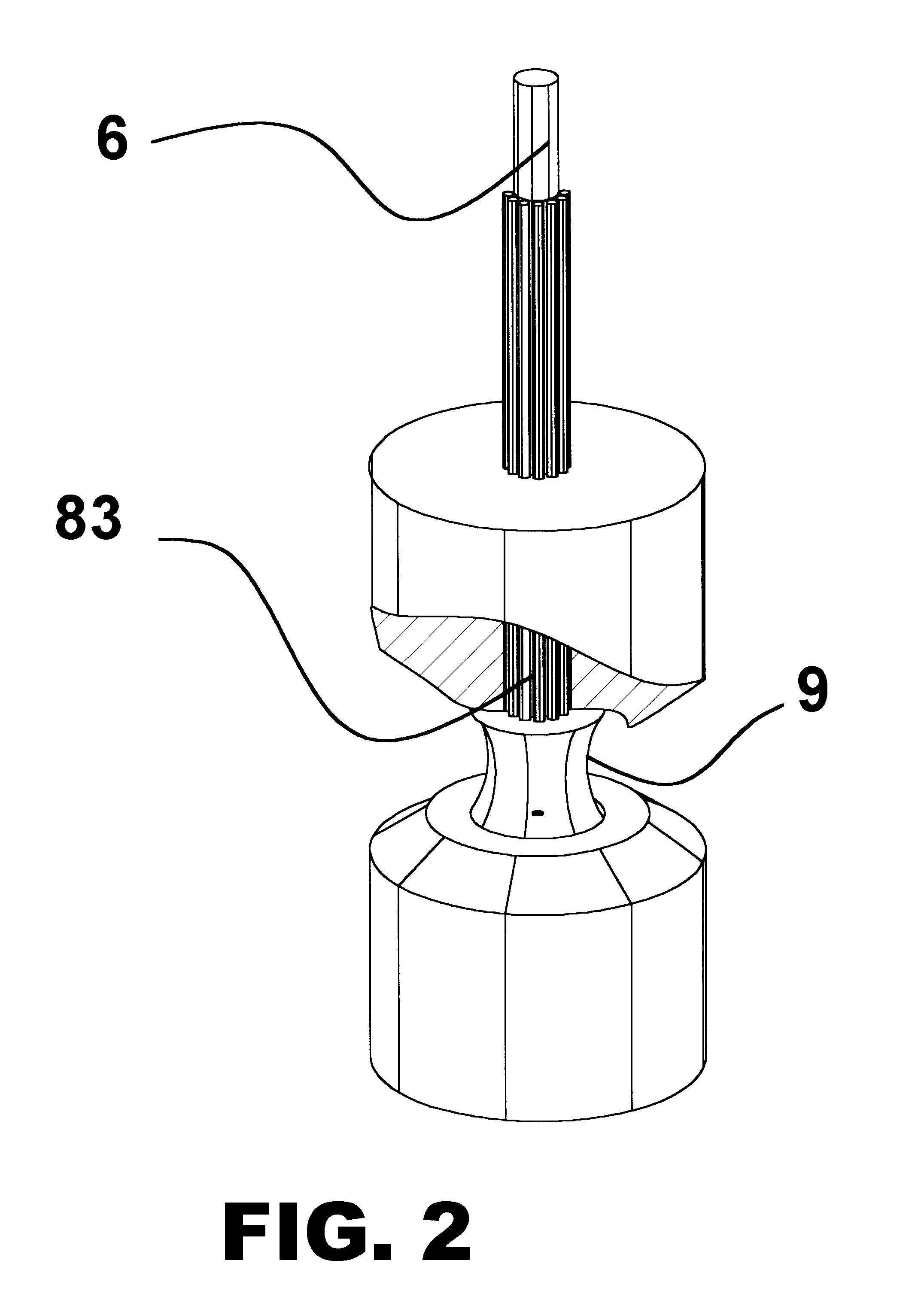
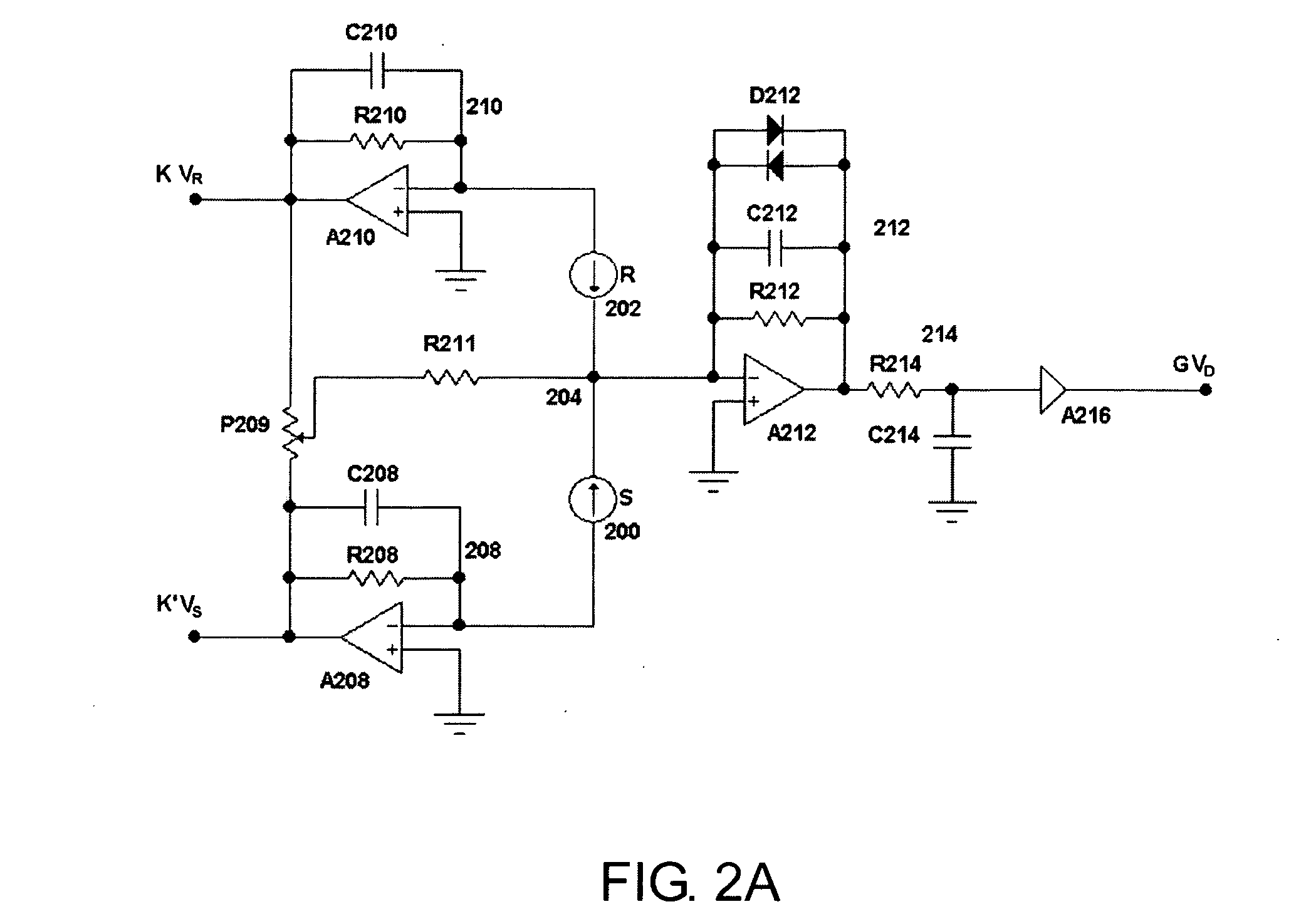
Method and apparatus for spectrophotometric based oximetry
ActiveUS20090182209A1Useful applicationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood oxygenationLength wave
A near infrared spectrophotometric (NIRS) sensor assembly for non-invasive monitoring of blood oxygenation levels in a subject's body is provided that includes a pad, at least one light source, a near light detector, a far light detector, and a cover. The light source is operative to emit near infrared light signals of a plurality of different wavelengths. The near light detector is separated from the light source by a first distance that is great enough to position the first light detector outside of an optical shunt field extending out from the light source. The far light detector is substantially linearly aligned with the near light detector and light source, and is separated from the near light detector by a second distance, wherein the second distance is greater than the first distance.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method for spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
ActiveUS20090281403A1Accurate assessmentImprove accuracyScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound attenuationLight sensing
According to the present invention, a method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the blood oxygen saturation level within a subject's tissue is provided. The method comprises the steps of: 1) providing a near infrared spectrophotometric sensor operable to transmit light along a plurality of wavelengths into the subject's tissue; 2) sensing the light transmitted into the subject's tissue using the sensor, and producing signal data representative of the light sensed from the subject's tissue; 3) processing the signal data to account for physical characteristics of the subject; and 4) determining the blood oxygen saturation level within the subject's tissue using a difference in attenuation between the wavelengths. The apparatus includes a sensor having a light source and at least one light detector, which sensor is operably connected to a processor. The sensor is operable to transmit light along a plurality of wavelengths into the subject's tissue, and produce signal data representative of the light sensed from the subject's tissue. The algorithm is operable to process the signal data to account for the physical characteristics of the subject being sensed.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for monitoring body fluid and electrolyte disorders
InactiveUS7239902B2Rapid and and continuous measurementEasy diagnosisDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using pressureDirect radiationBody fluid
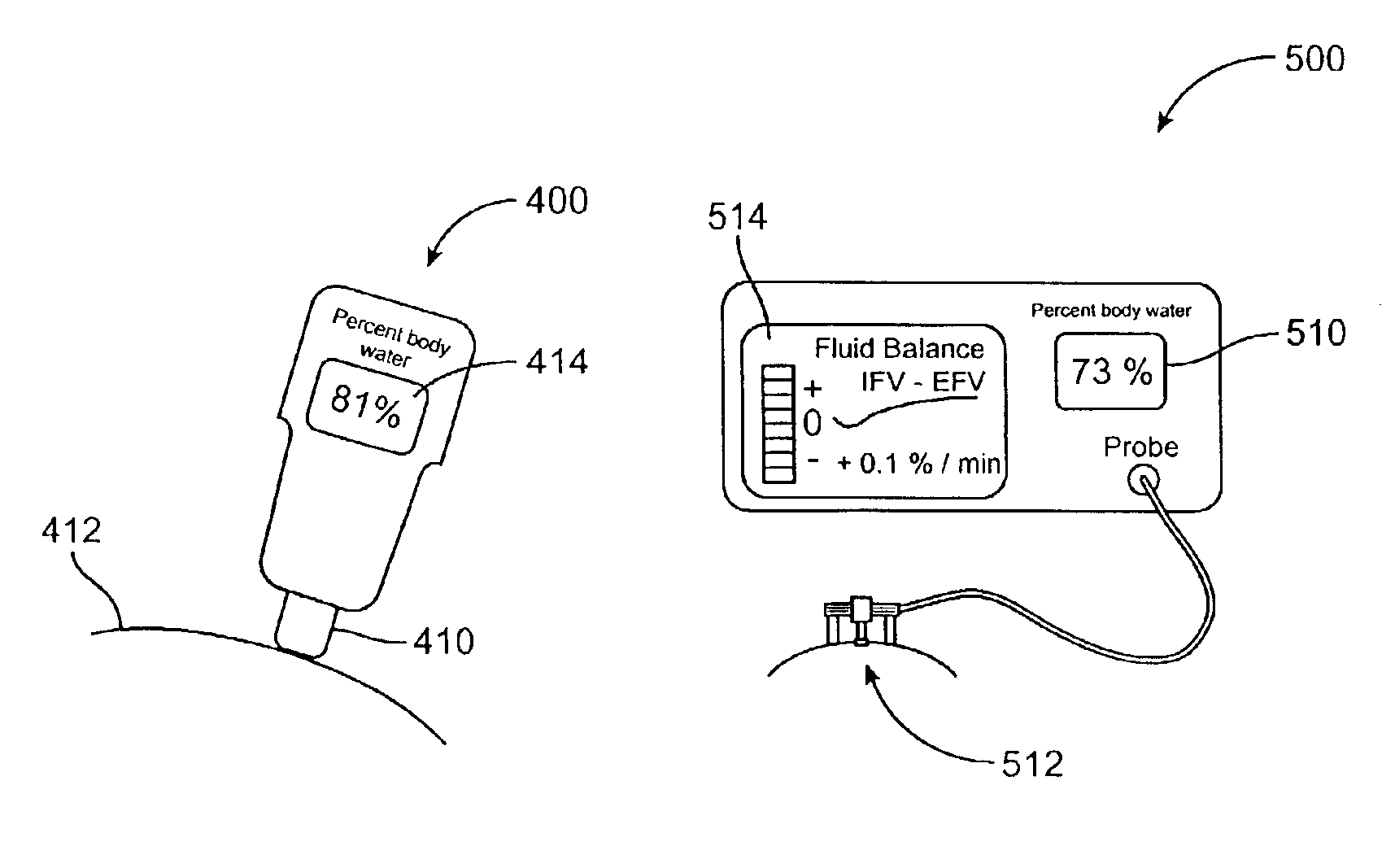
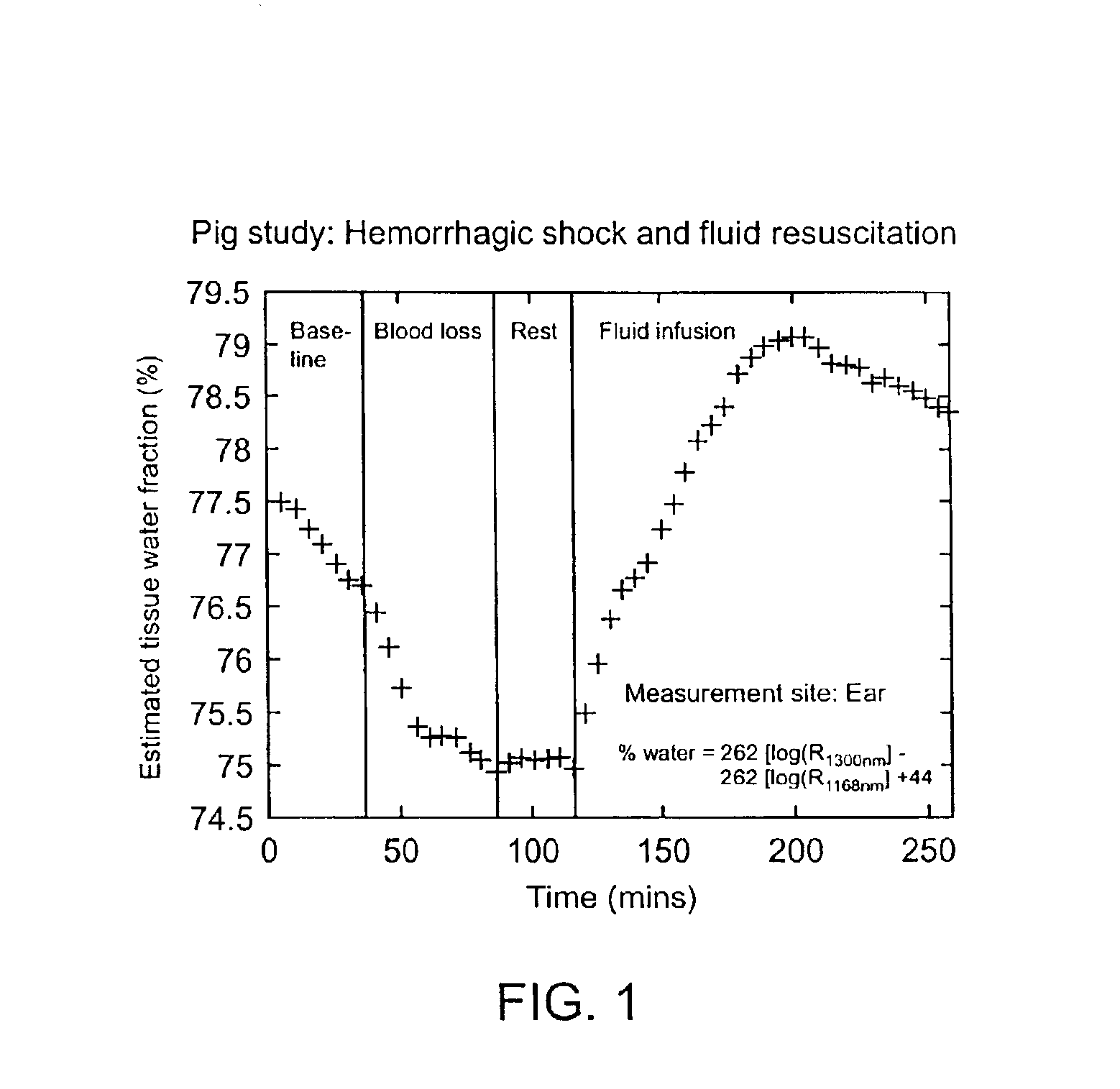
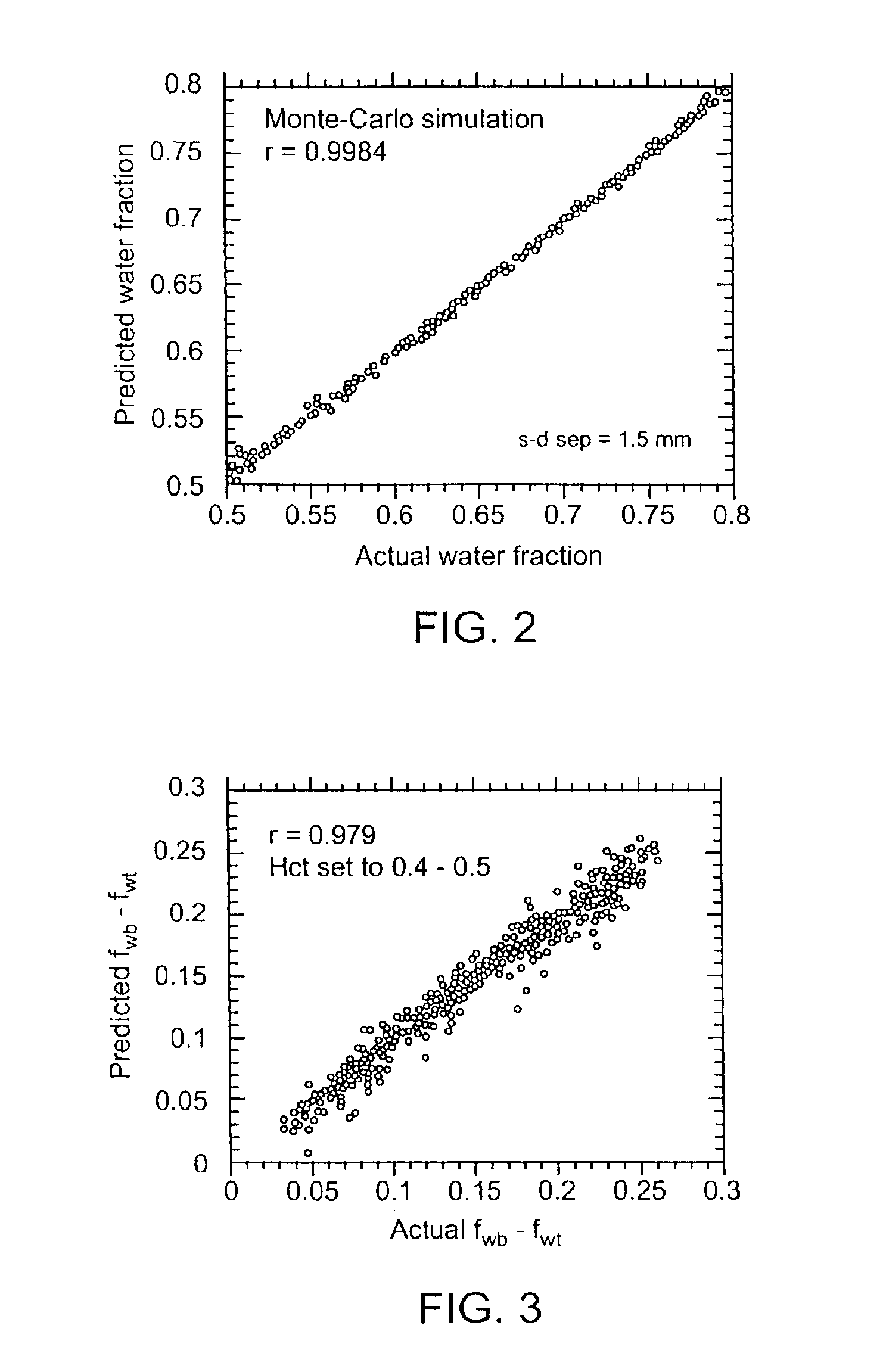
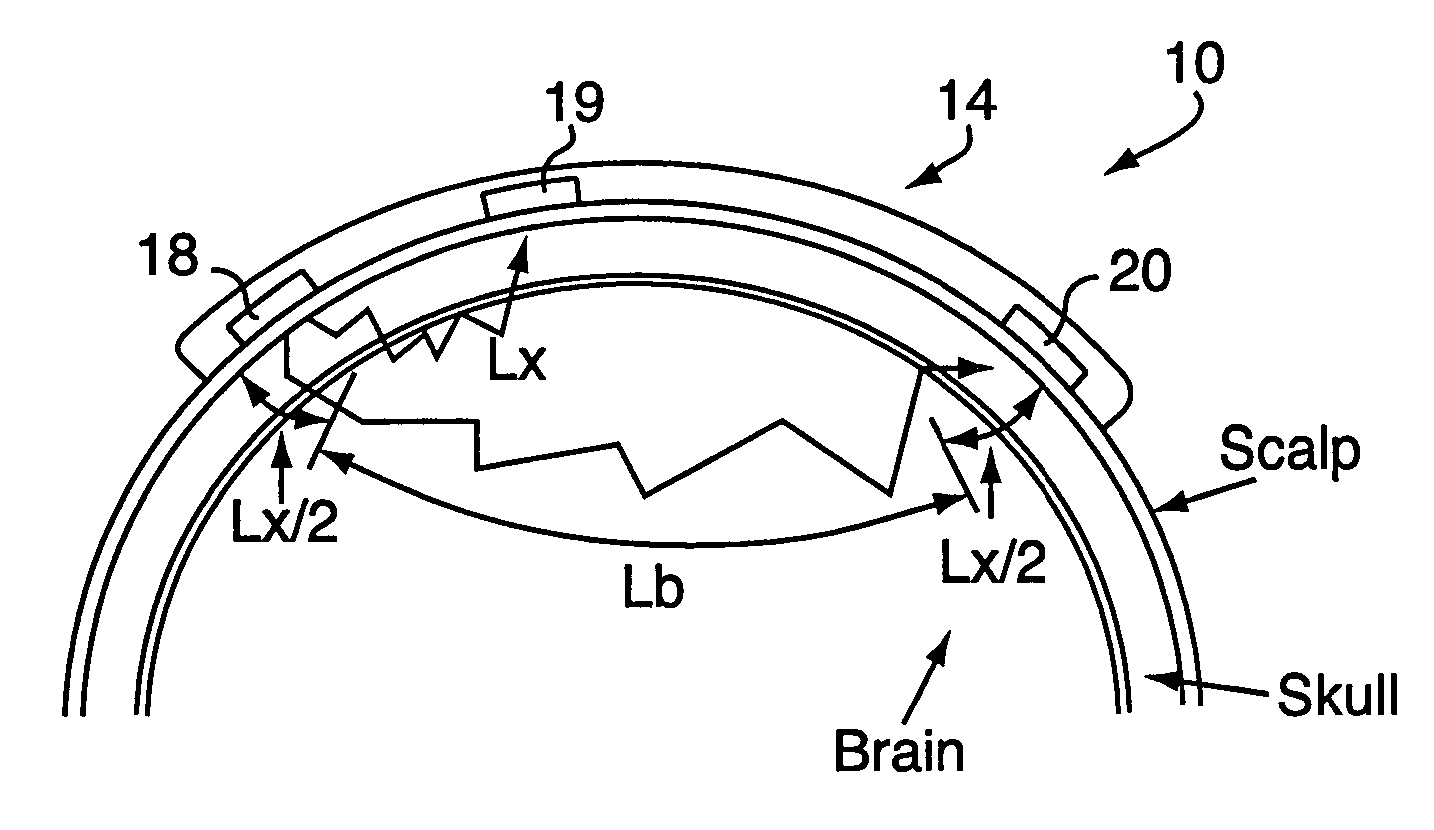
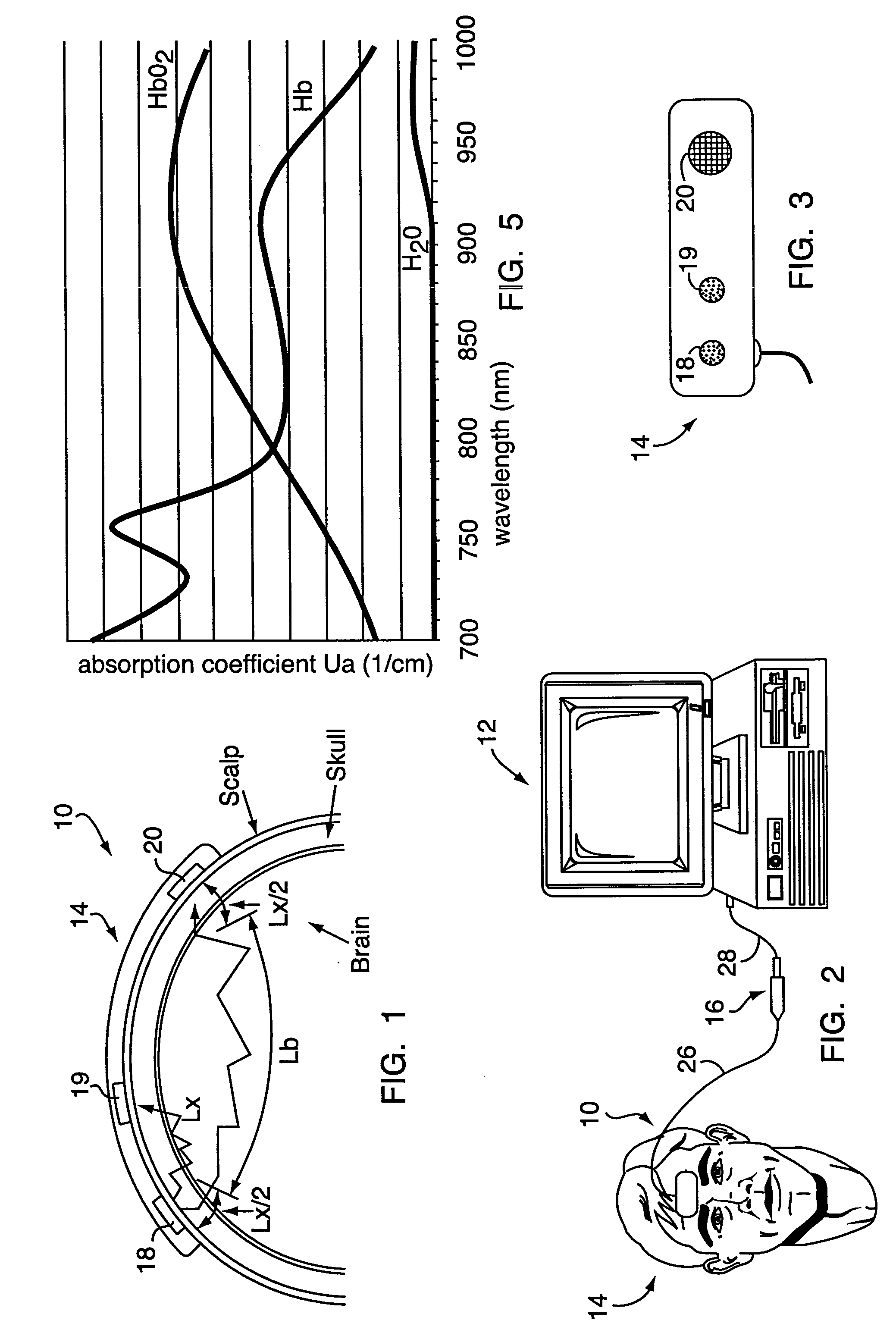
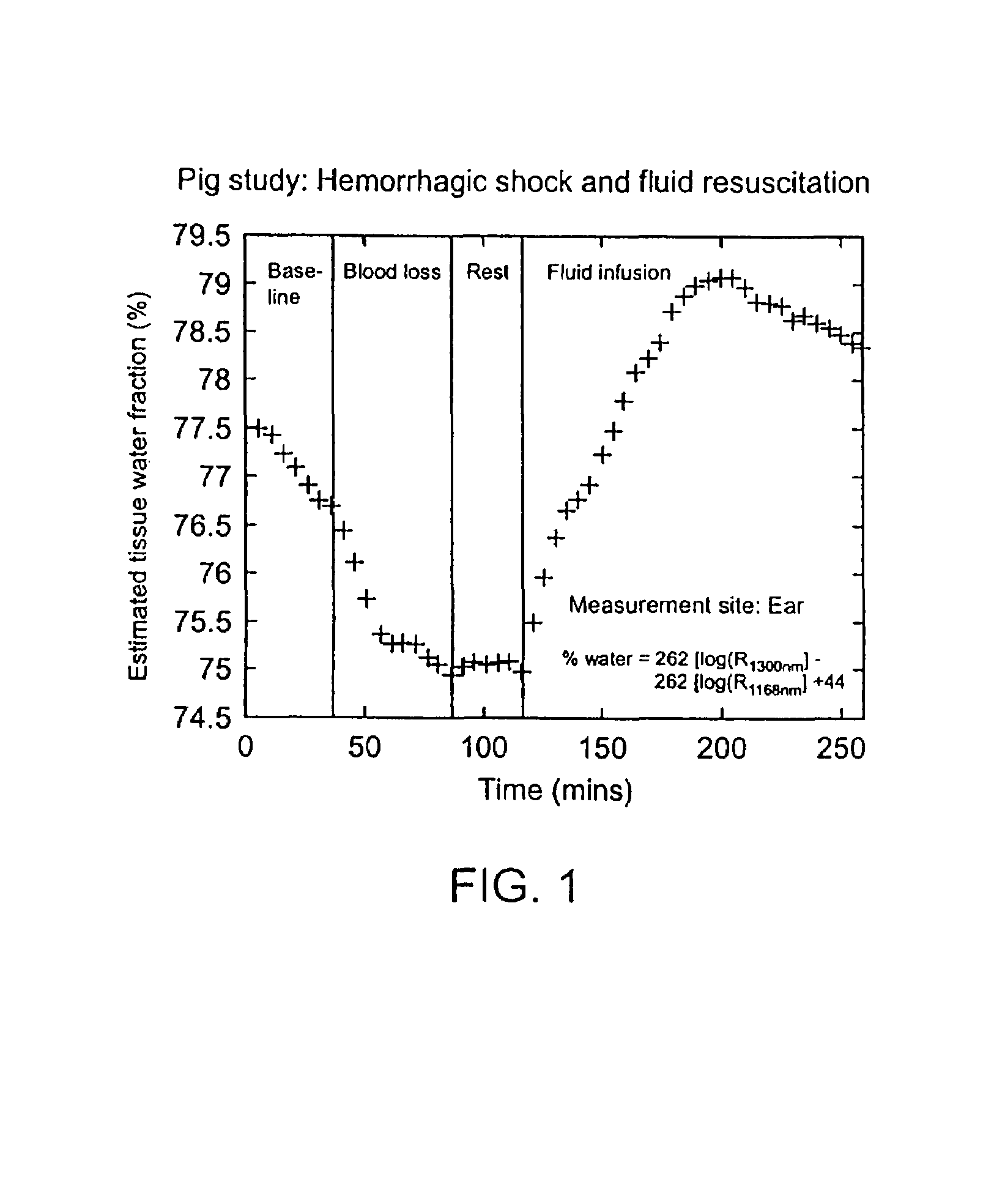
Devices and methods for measuring body fluid-related metric using spectrophotometry that may be used to facilitate diagnosis and therapeutic interventions aimed at restoring body fluid balance. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a device for measuring a body-tissue water content metric as a fraction of the fat-free tissue content of a patient using optical spectrophotometry. The device includes a probe housing configured to be placed near a tissue location which is being monitored; light emission optics connected to the housing and configured to direct radiation at the tissue location; light detection optics connected to the housing and configured to receive radiation from the tissue location; and a processing device configured to process radiation from the light emission optics and the light detection optics to compute the metric where the metric includes a ratio of the water content of a portion of patient's tissue in relation to the lean or fat-free content of a portion of patient's tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
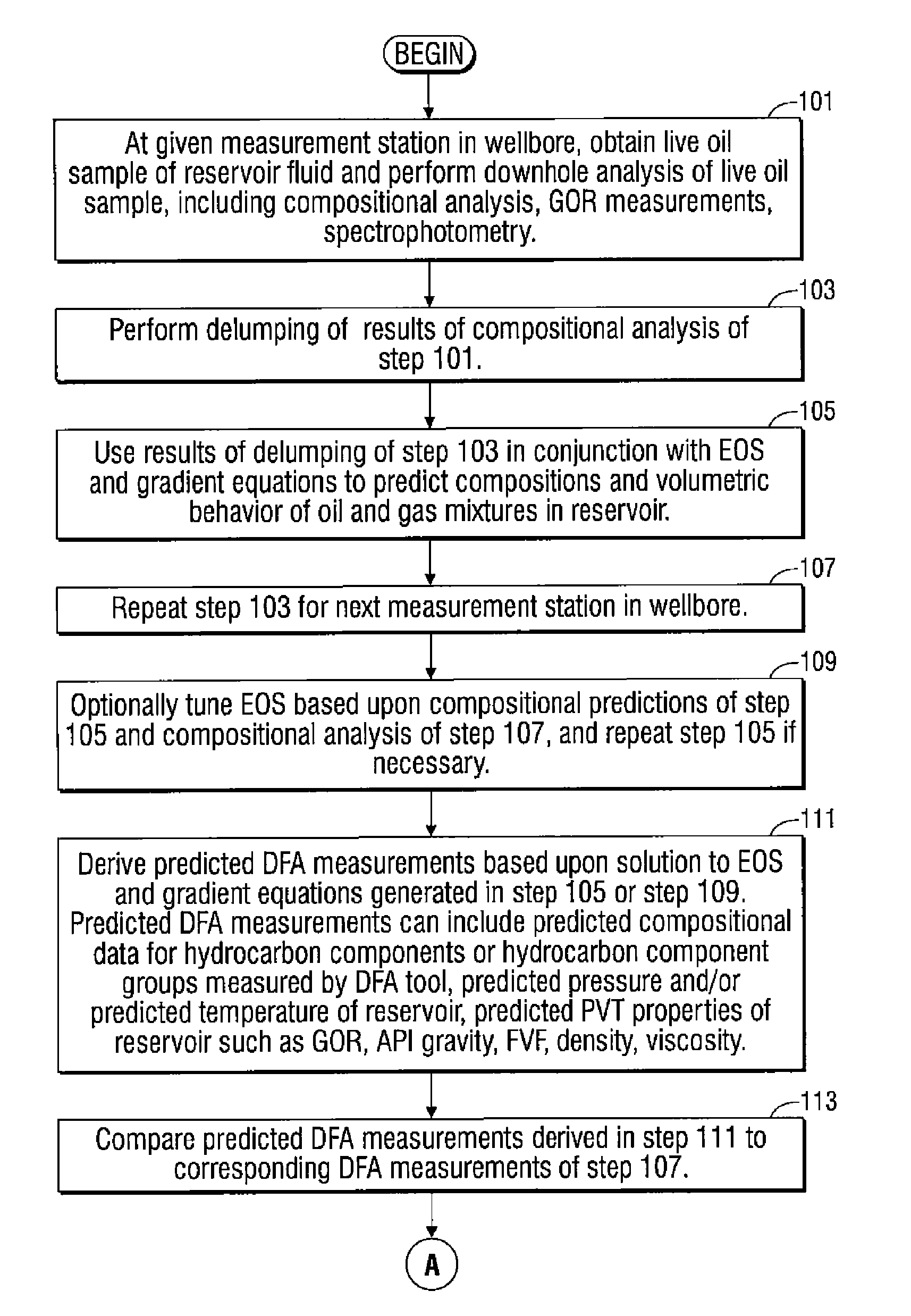
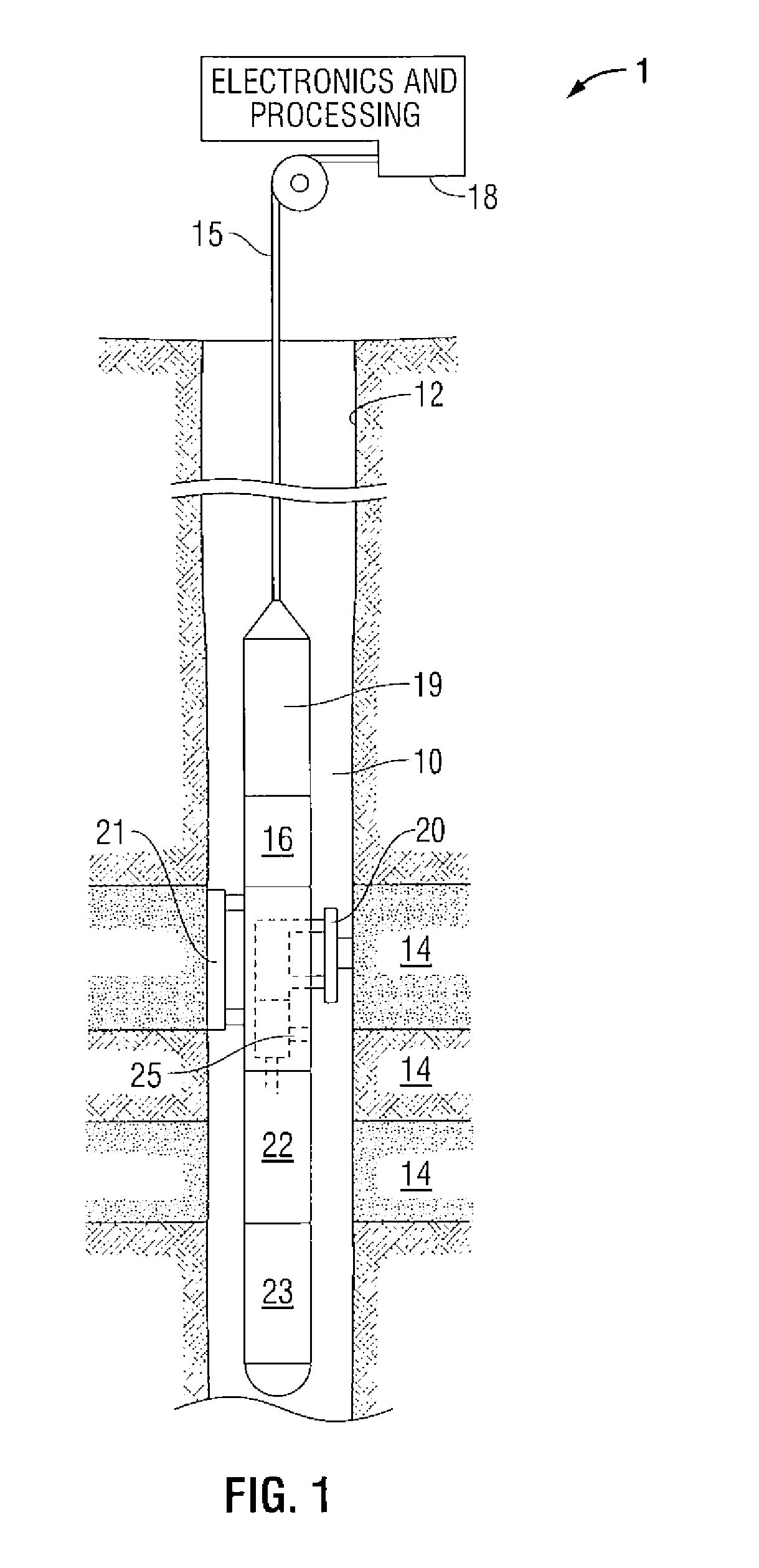
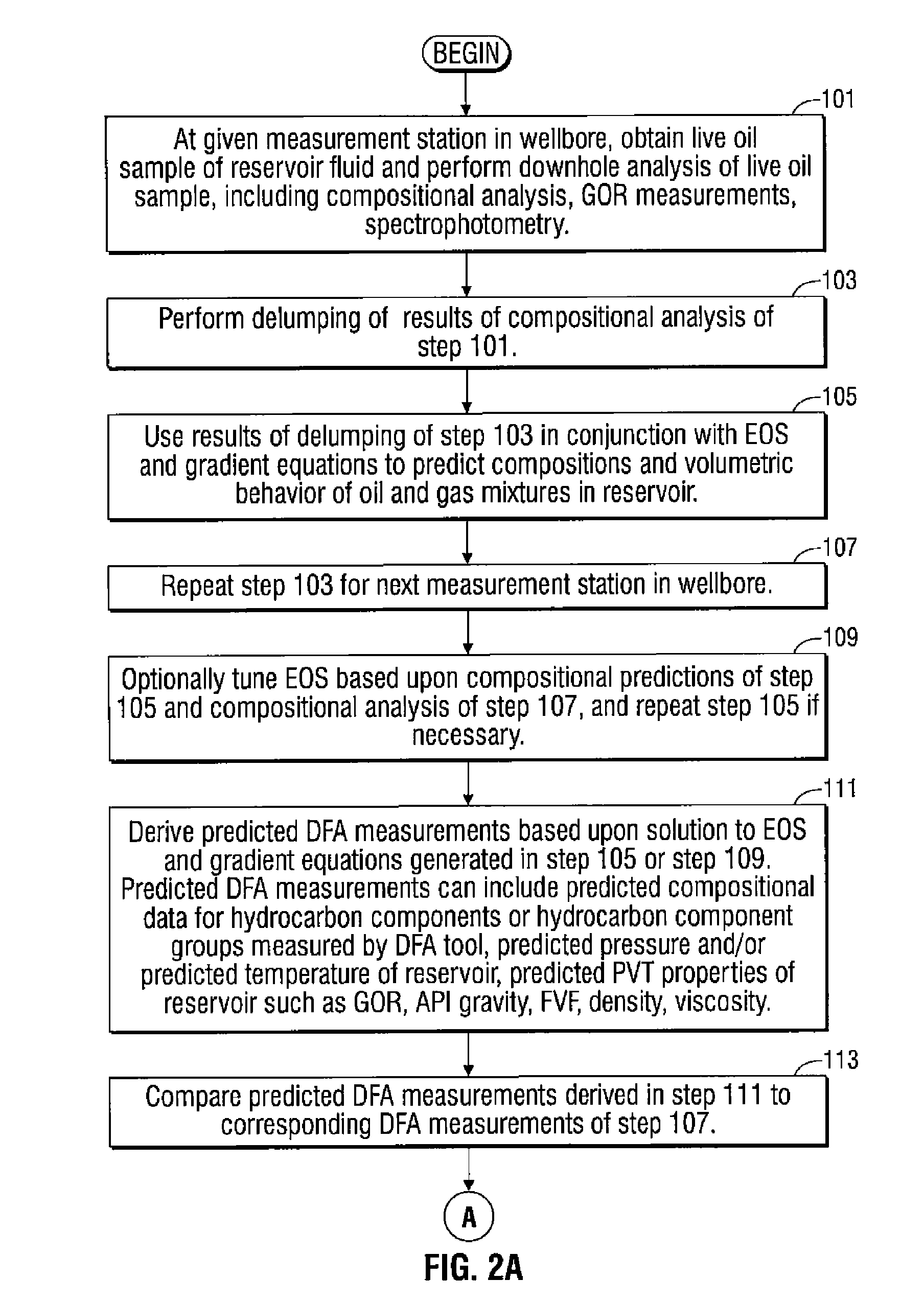
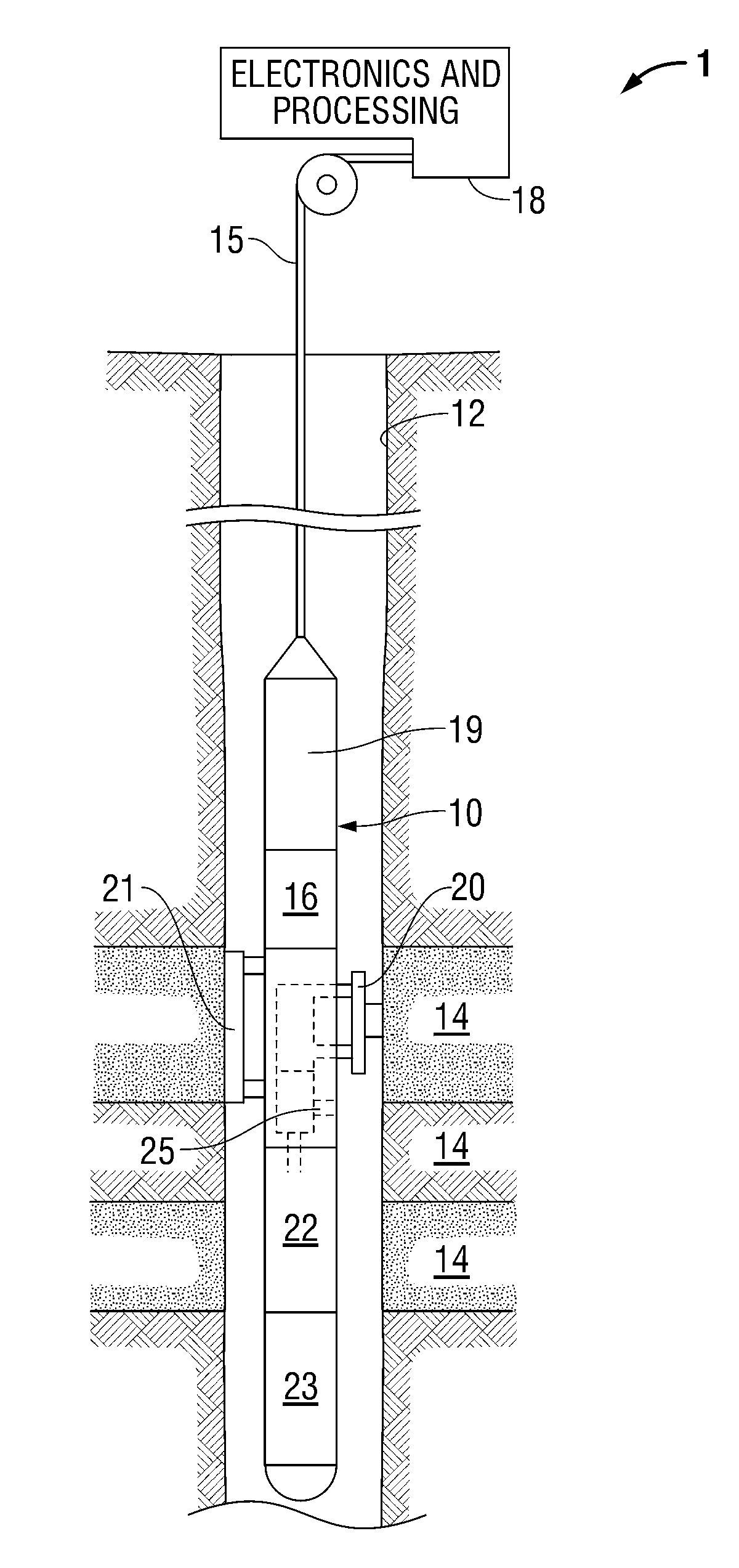
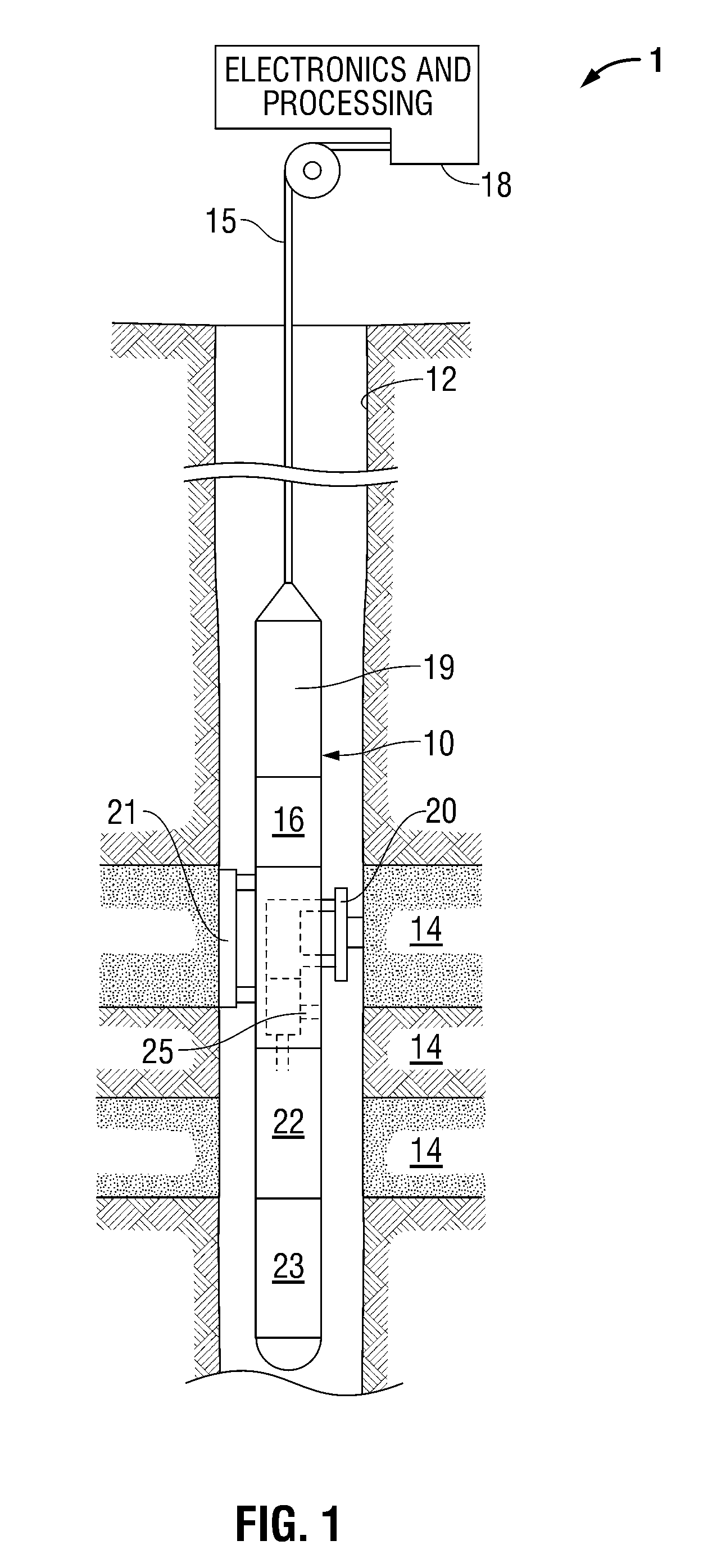
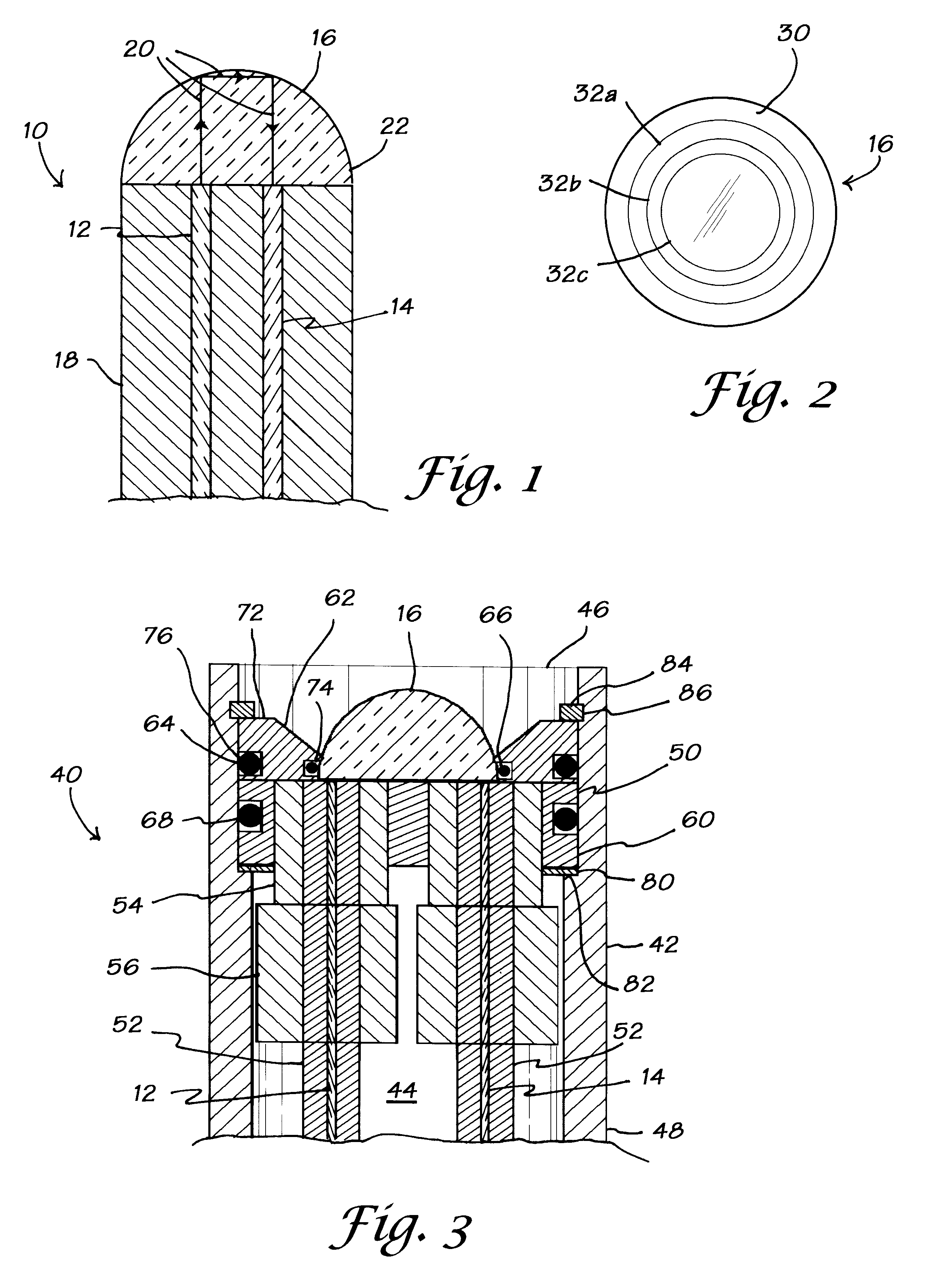
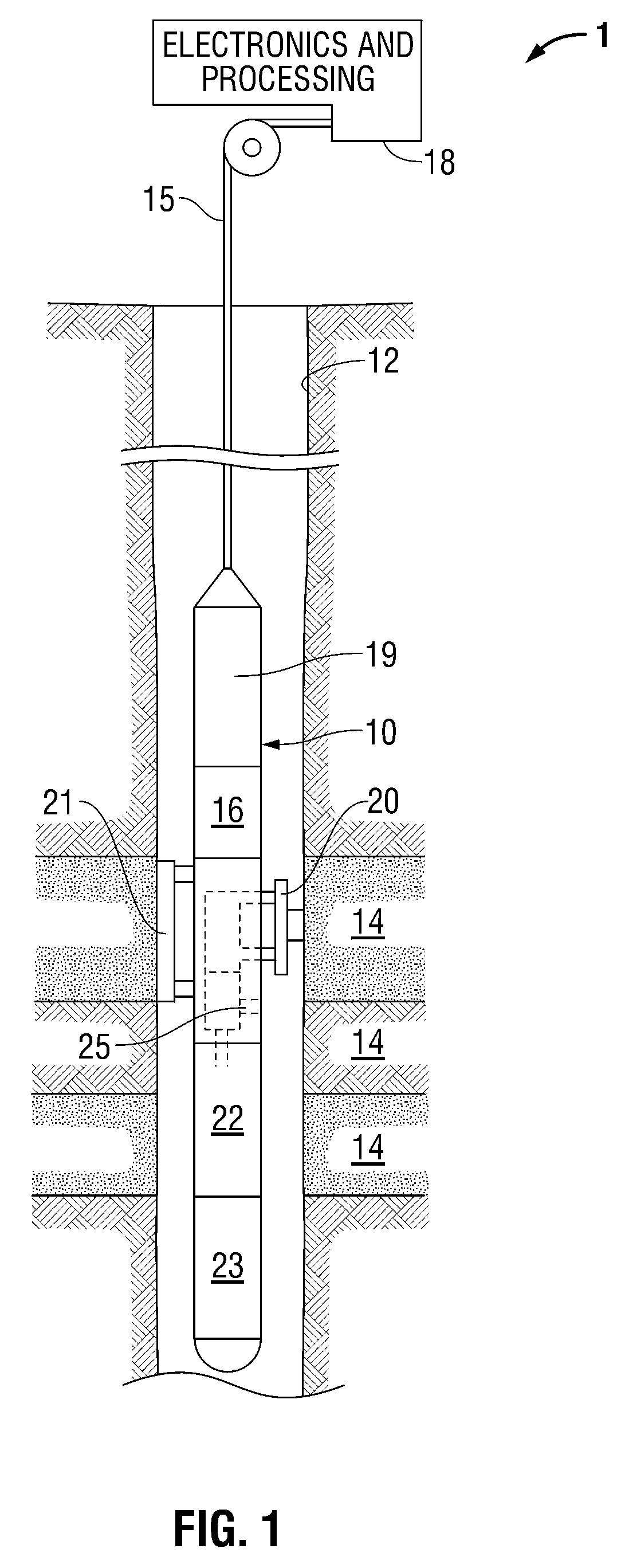
Methods and apparatus for analysis of downhole compositional gradients and applications thereof
ActiveUS7822554B2Accurate divisionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyGas oil ratioSystem usage
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
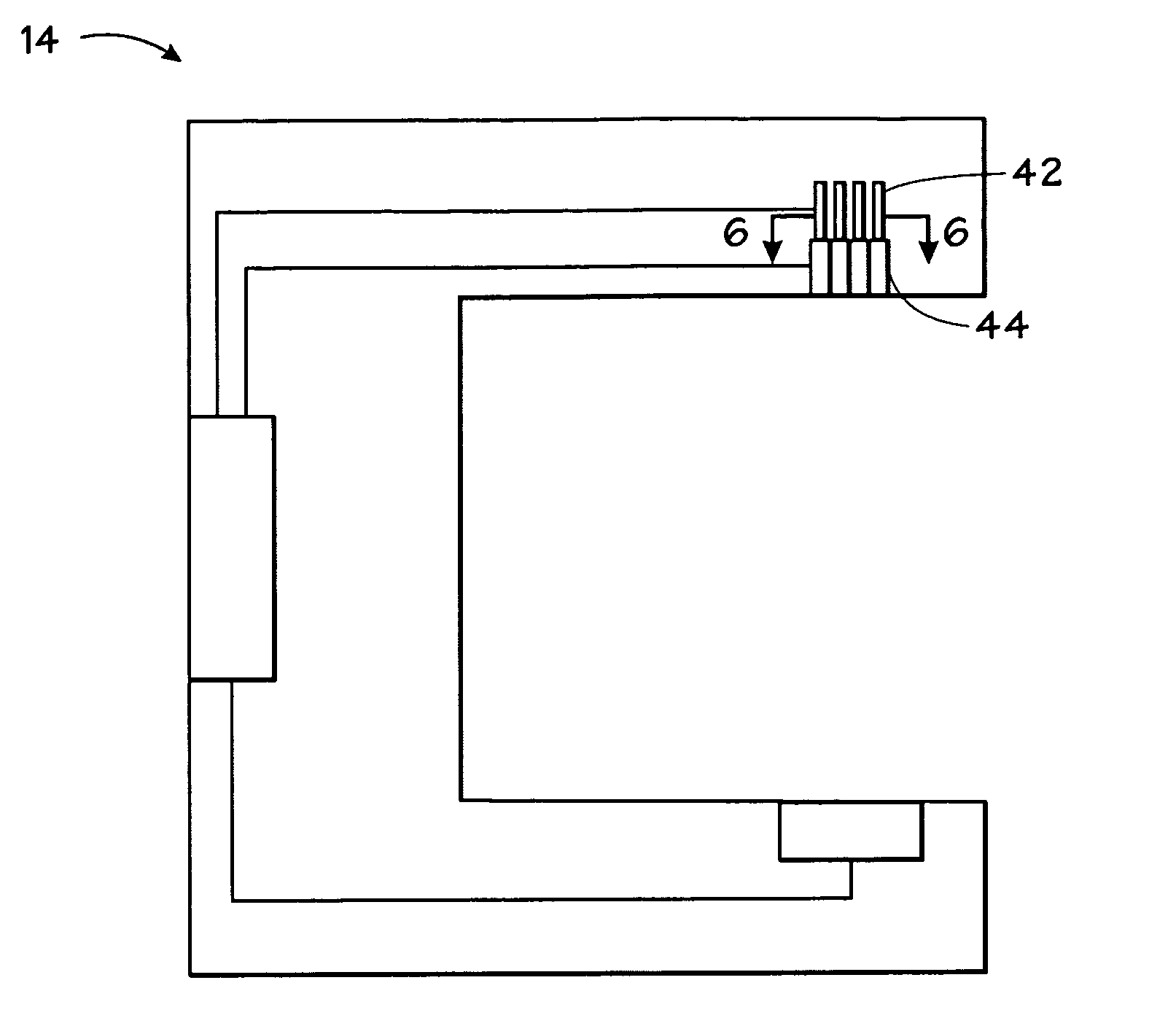
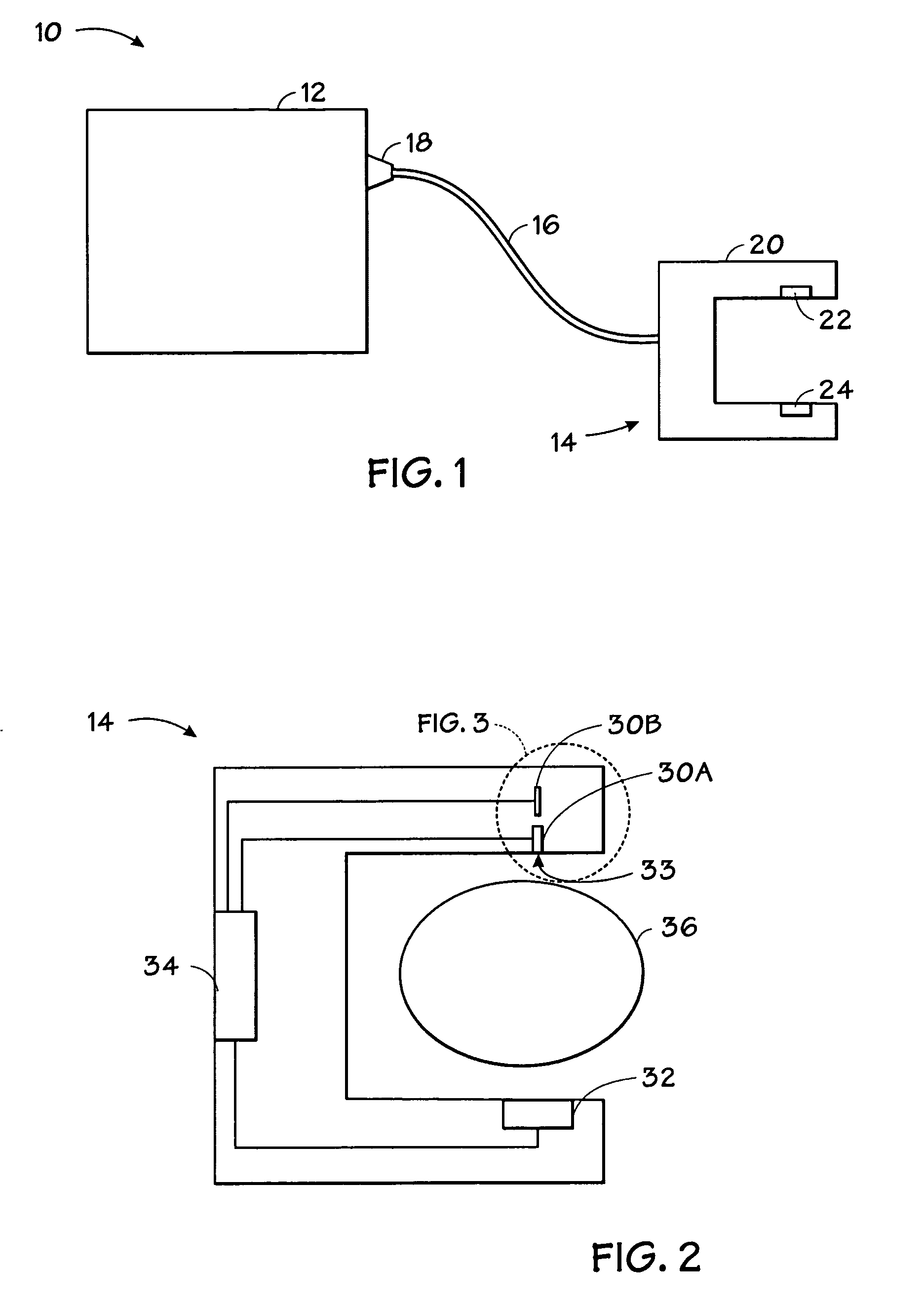
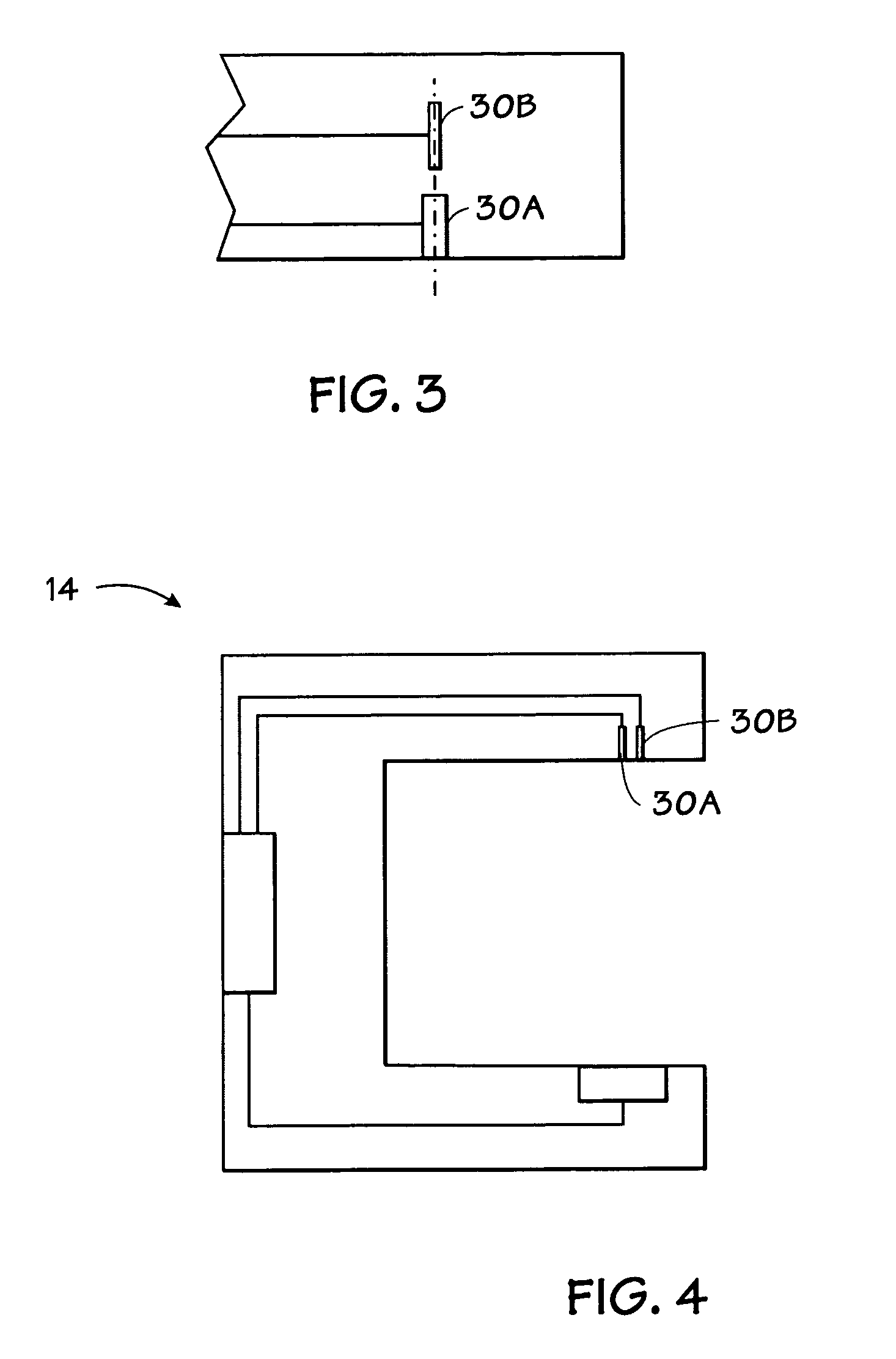
System and method for practicing spectrophotometry using light emitting nanostructure devices
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Apparatus and methods of determination of state of charge in a redox flow battery
InactiveUS7855005B2Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorState of chargeRedox
Methods for determining the state of charge of an electrolyte solution in a redox battery by optical absorption spectrophotometry are disclosed. The state of charge thus obtained may serve as a gauge for the amount of electro-chemical energy left in the system.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
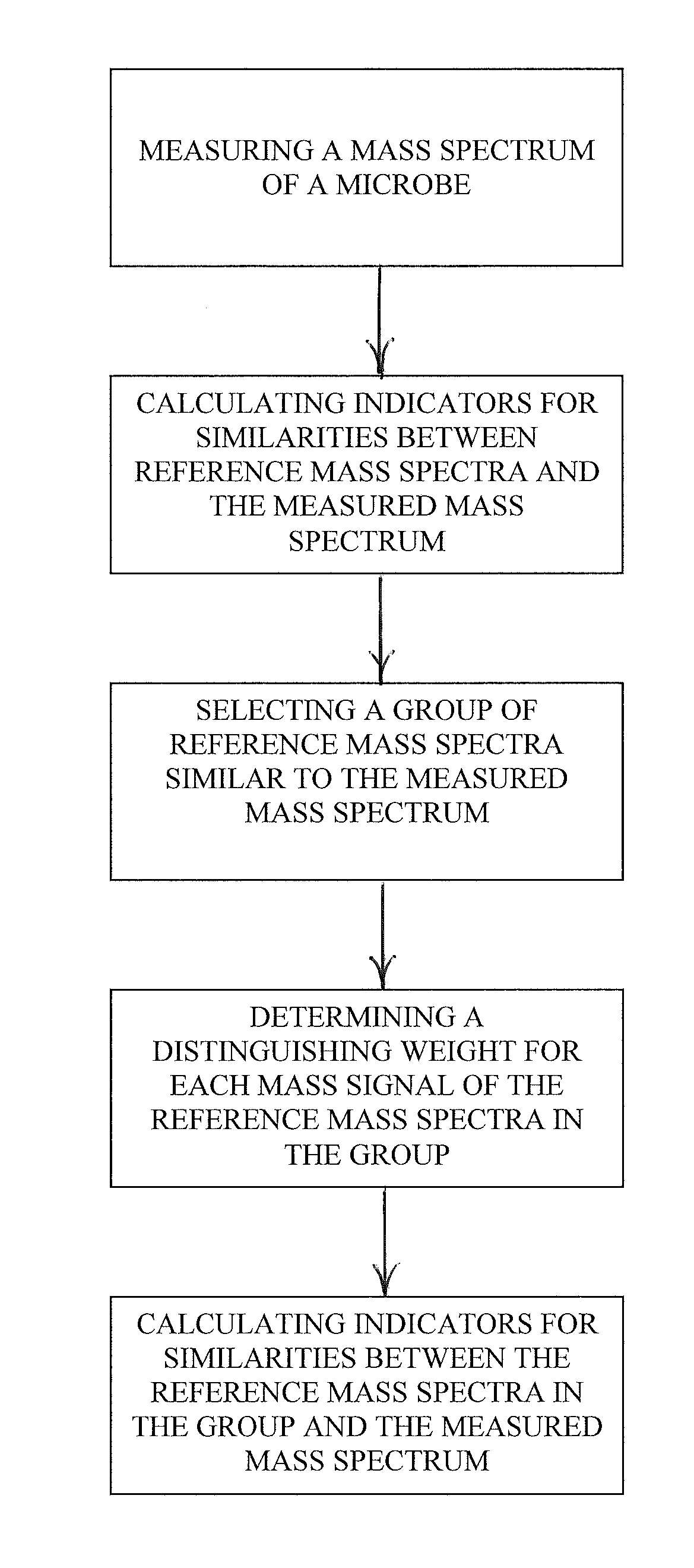
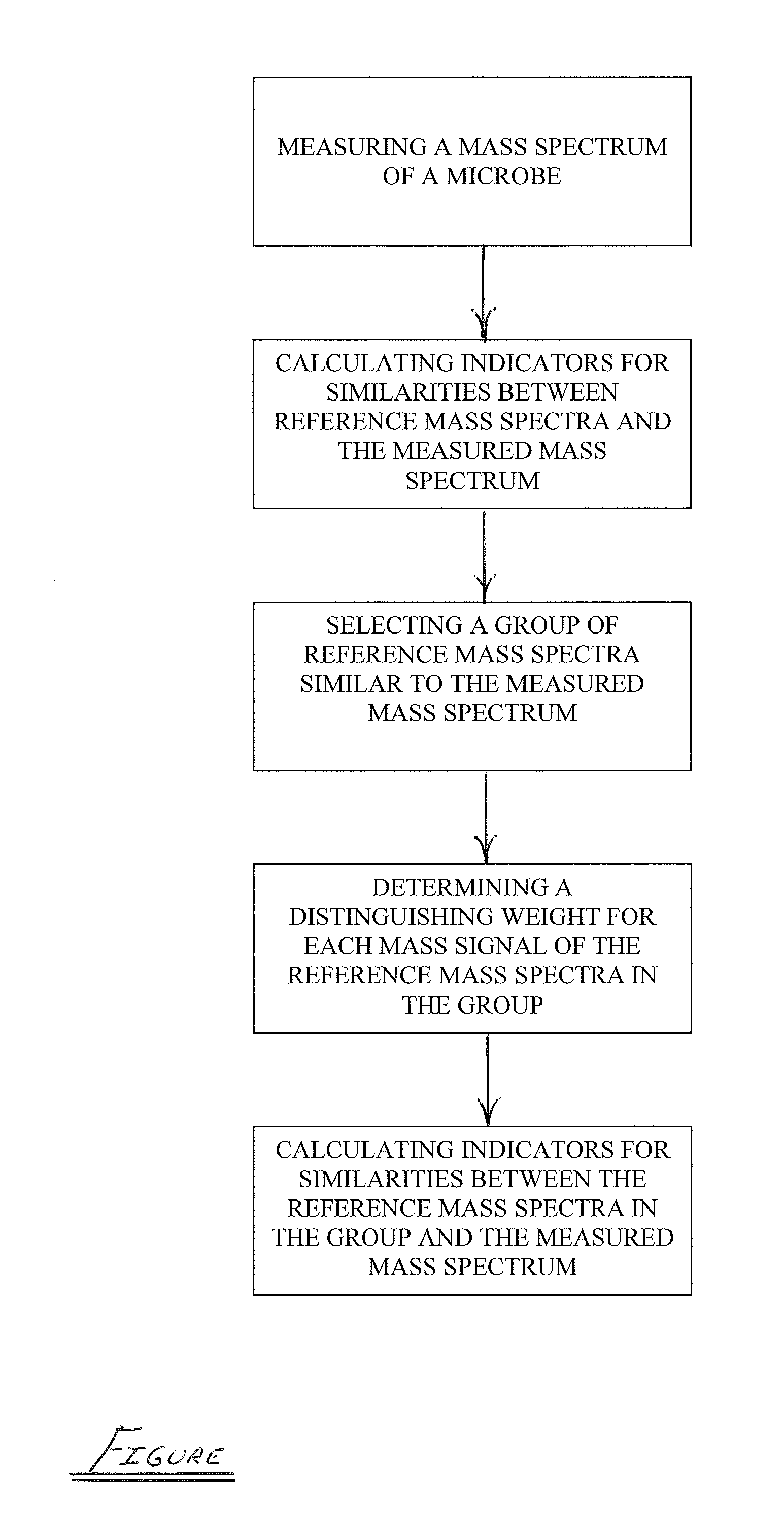
Spectrophotometric identification of microbe subspecies
ActiveUS20110012016A1Particle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismDual stage
A dual-stage method is provided for identifying a microbe by, for example, its species or its subspecies. The method includes measuring a mass spectrum of the microbe using a mass spectrometer, calculating indicators for similarities between reference mass spectra in a library and the measured mass spectrum, selecting a group of reference mass spectra similar to the measured mass spectrum, determining a distinguishing weight for each mass signal of the reference mass spectra in the group, where the distinguishing weights emphasize differences between the reference mass spectra in the group, and calculating indicators for similarities between the reference mass spectra in the group and the measured mass spectrum as a function of the distinguishing weights.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
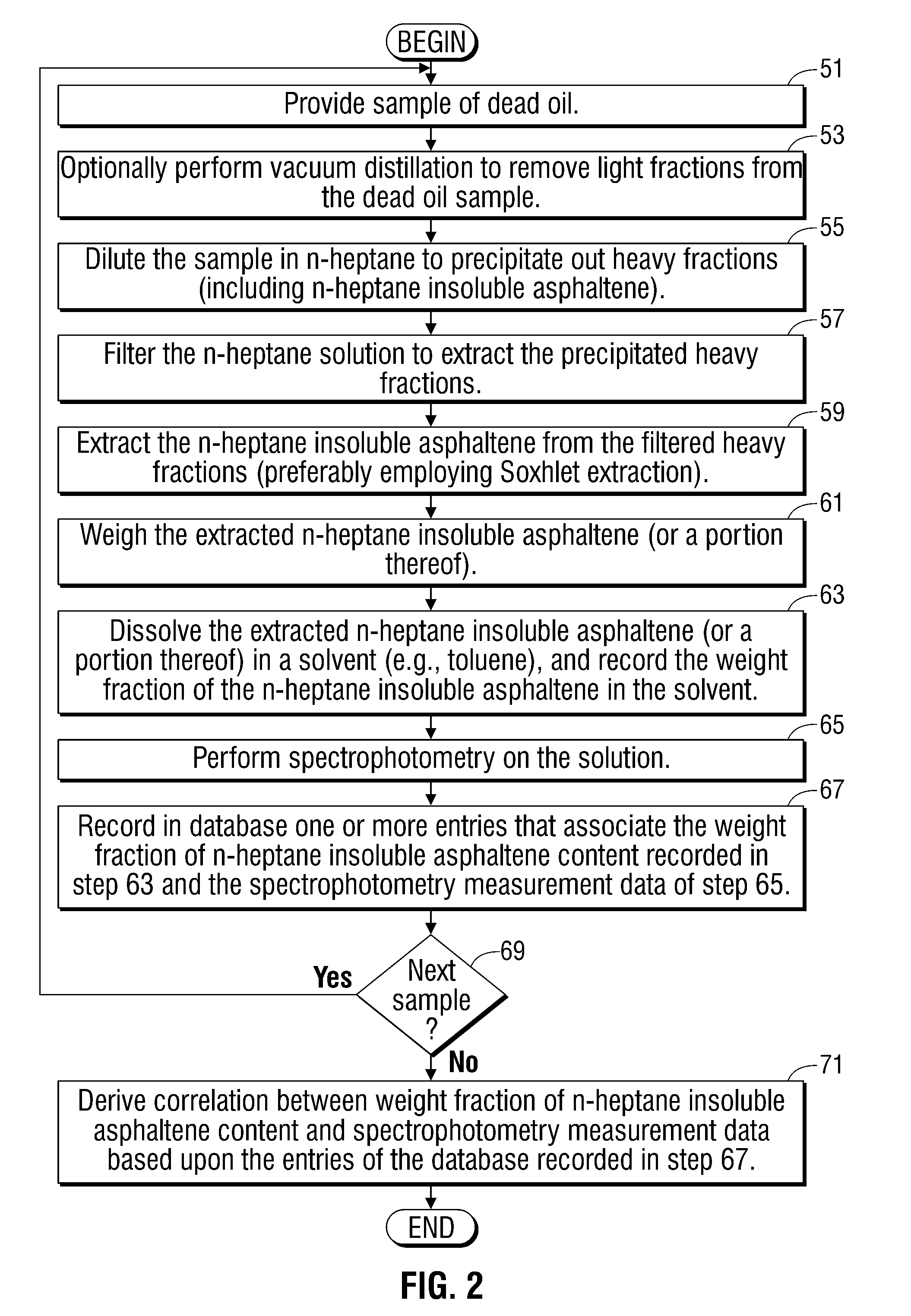
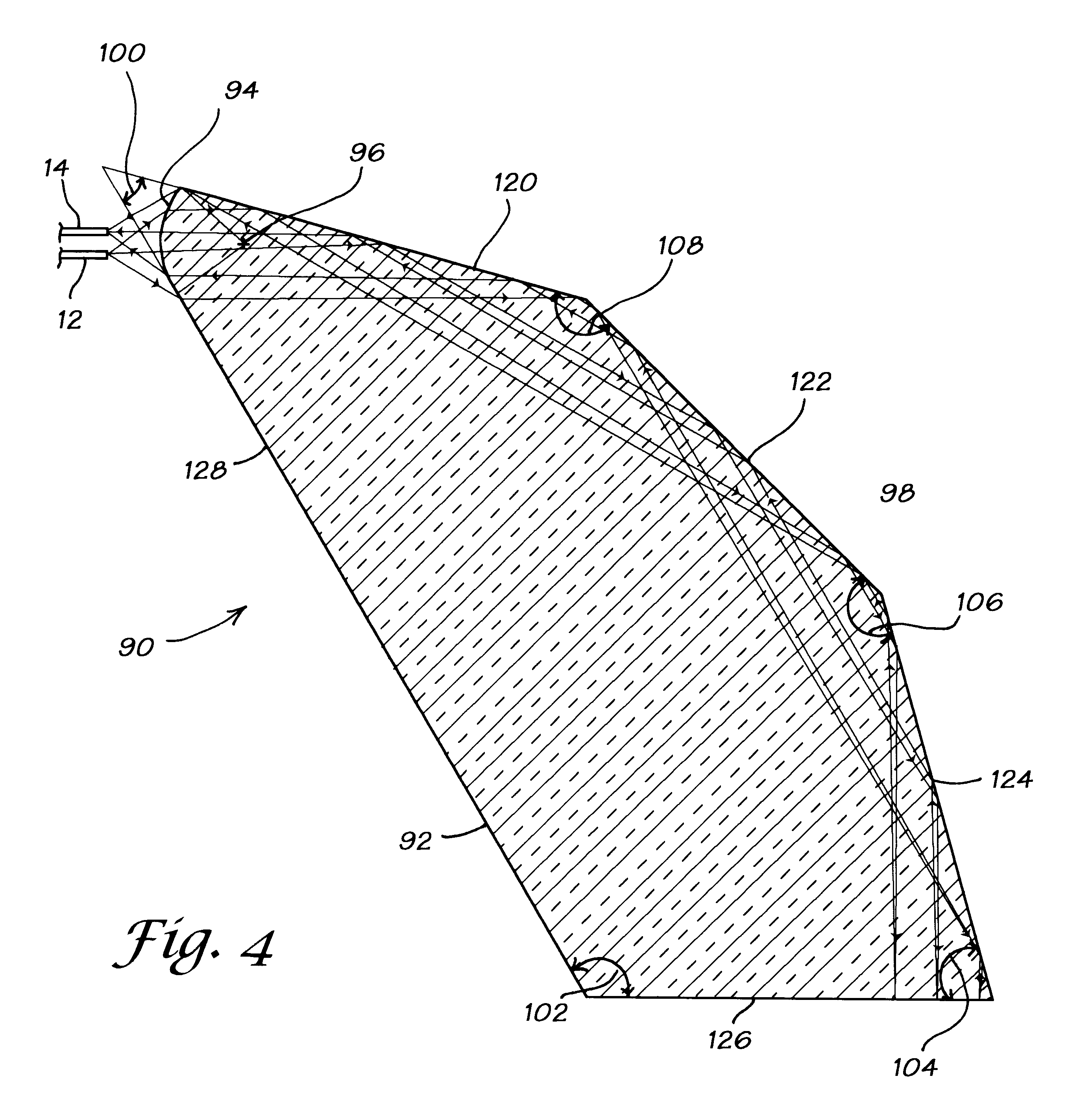
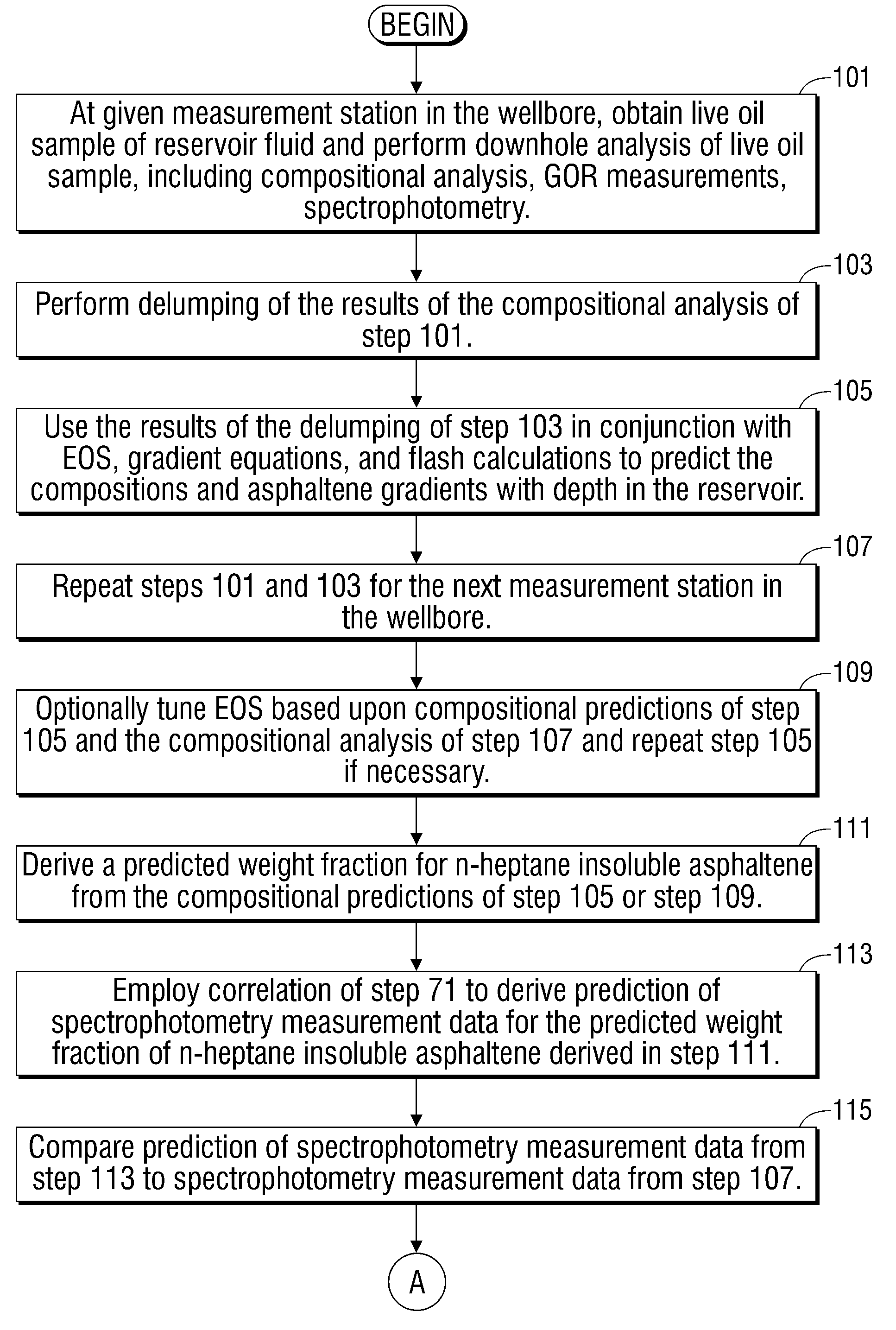
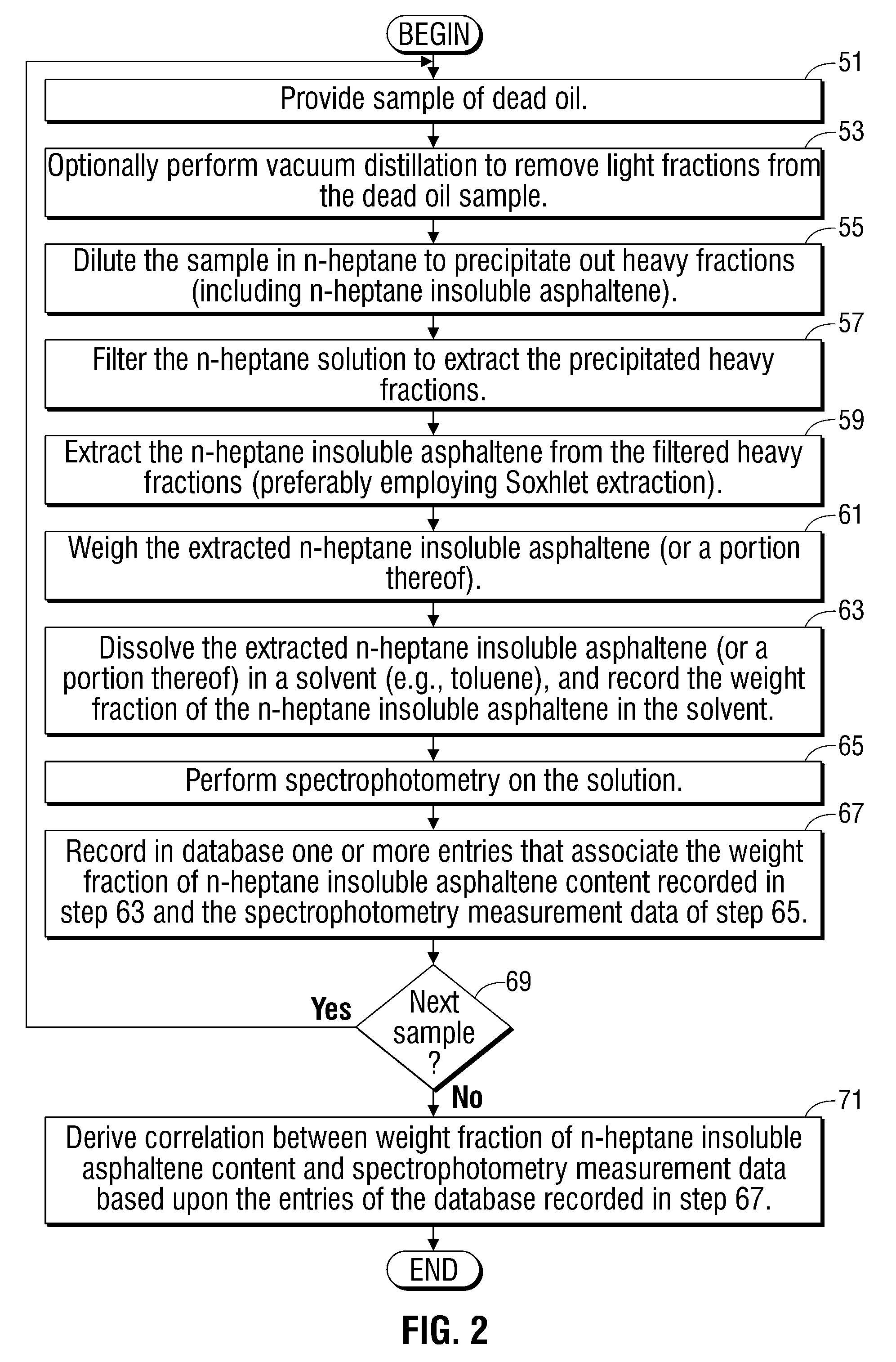
Methods and apparatus for analysis of downhole asphaltene gradients and applications thereof
ActiveUS20090248310A1Accurate divisionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyAsphalteneSpectrophotometry
A method and system for characterizing asphaltene gradients of a reservoir of interest and analyzing properties of the reservoir of interest based upon such asphaltene gradients. The analysis employs a correlation that relates insoluble asphaltene concentration to spectrophotometry measurement data measured at depth.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Liquid photometer using surface tension to contain sample
Method and apparatus of spectrophotometry or the like on extremely small liquid samples in which a drop is held between two opposing surfaces by surface tension and one surface is controllably moved toward and away from the other. To provide and transmit exciting energy through the drop for measurement, the optical fibers go through a surface and are finished flush with its surface. One of the surfaces can be swung clear of the other for easy cleaning between tests.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
Fiber optic probe for attenuated total internal reflection spectrophotometry
InactiveUS6205272B1Scattering properties measurementsCoupling light guidesFiberTotal internal reflection
A fiber optic probe for ATIR (Attenuated Total Internal Reflection) spectrophotometry. The probe includes a housing that contains an optical element or lens, a light-transmitting fiber that directs incident light to the lens, a light-receiving fiber that receives reflected light from the sample interface, a coupler for holding these components in precise alignment, and a flexible armor casing that provides strain relief and protection for the optical fibers. The lens is shaped and dimensioned so that light from the transmitting fiber is reflected at the interface between the lens and the surrounding medium (such as a liquid to be analyzed). The reflected light is transmitted via the transmitting fiber to a suitable spectrophotometer, where the light signal is recorded and analyzed to determine the composition of the sample. The probe is particularly suitable for analyses of fluids and slurries with high optical absorbance.
Owner:INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE
Methods and apparatus for analysis of downhole asphaltene gradients and applications thereof
ActiveUS7996154B2Accurately compartmentalizationAccurate distributionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyAsphalteneSpectrophotometry
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
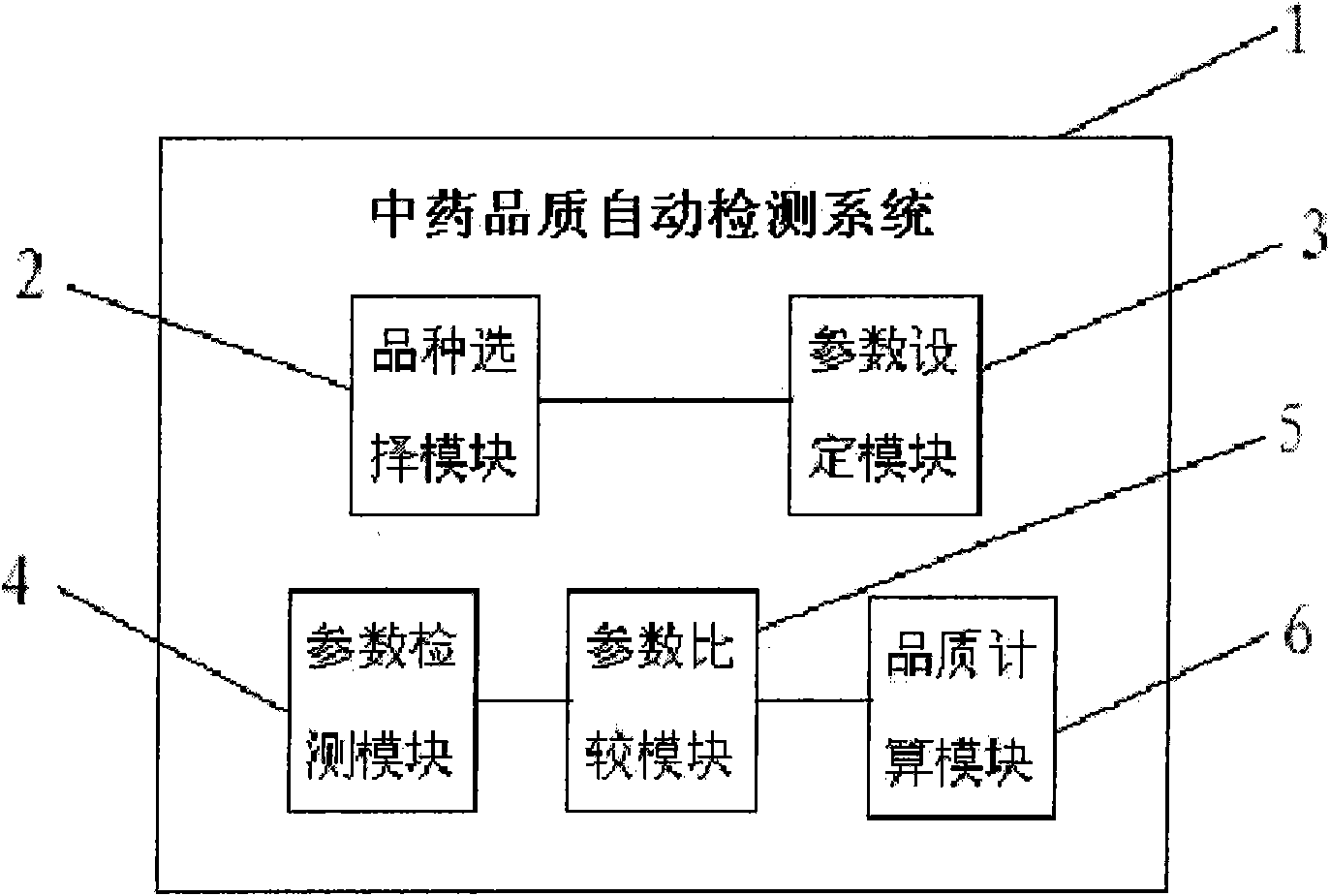
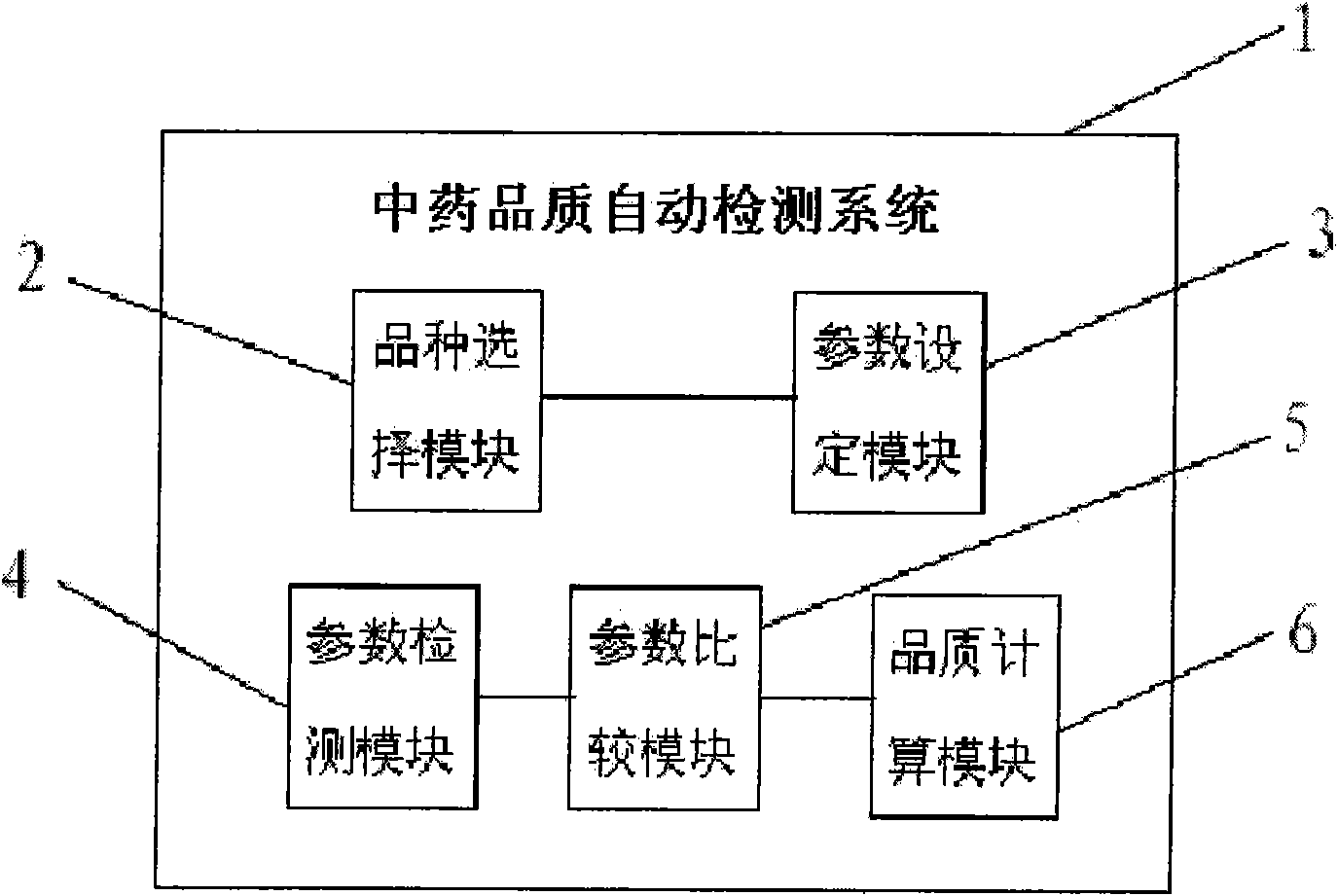
Automatic detecting system for quality of traditional Chinese medicines
InactiveCN101975845AImprove qualityObjective testing standardComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWeight coefficientFood flavor
The invention provides an automatic detecting system for the quality of traditional Chinese medicines. The automatic detecting system comprises a variety selecting module, a parameter setting module, a parameter detecting module, a parameter comparing module and a quality computing module, wherein the variety selecting module is used for selecting the variety of the traditional Chinese medicines to be detected, and determining quality associated parameters to be detected; the parameter setting module is used for setting the characteristic parameters and a parameter quality value of the variety to be detected; the parameter detecting module is used for detecting the parameters of an appearance, color, smell and flavor of the traditional Chinese medicines by an electronic vision system, an electronic nose and an electronic tongue, and detecting content of chemical components, the safe parameters and the general parameters of the traditional Chinese medicines by spectrophotometry or chromatography and a conventional detecting method; the parameter comparing module is used for comparing the detected parameter value with the characteristic parameters and the parameter quality value in the parameter setting module to obtain true and false of the detected variety and the relative parameter quality value; and the quality computing module is used for computing according to the relative parameter quality value and a weighting coefficient to obtain a quality value. The automatic detecting system can automatically detect the quality of the traditional Chinese medicines to obtain an objective and unified detection result.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for comprehensively measuring reflectivity
InactiveCN102169050AAchieving Arbitrary ReflectivityEasy to switchScattering properties measurementsReflective surface testingReflectivity measurementLaser beams
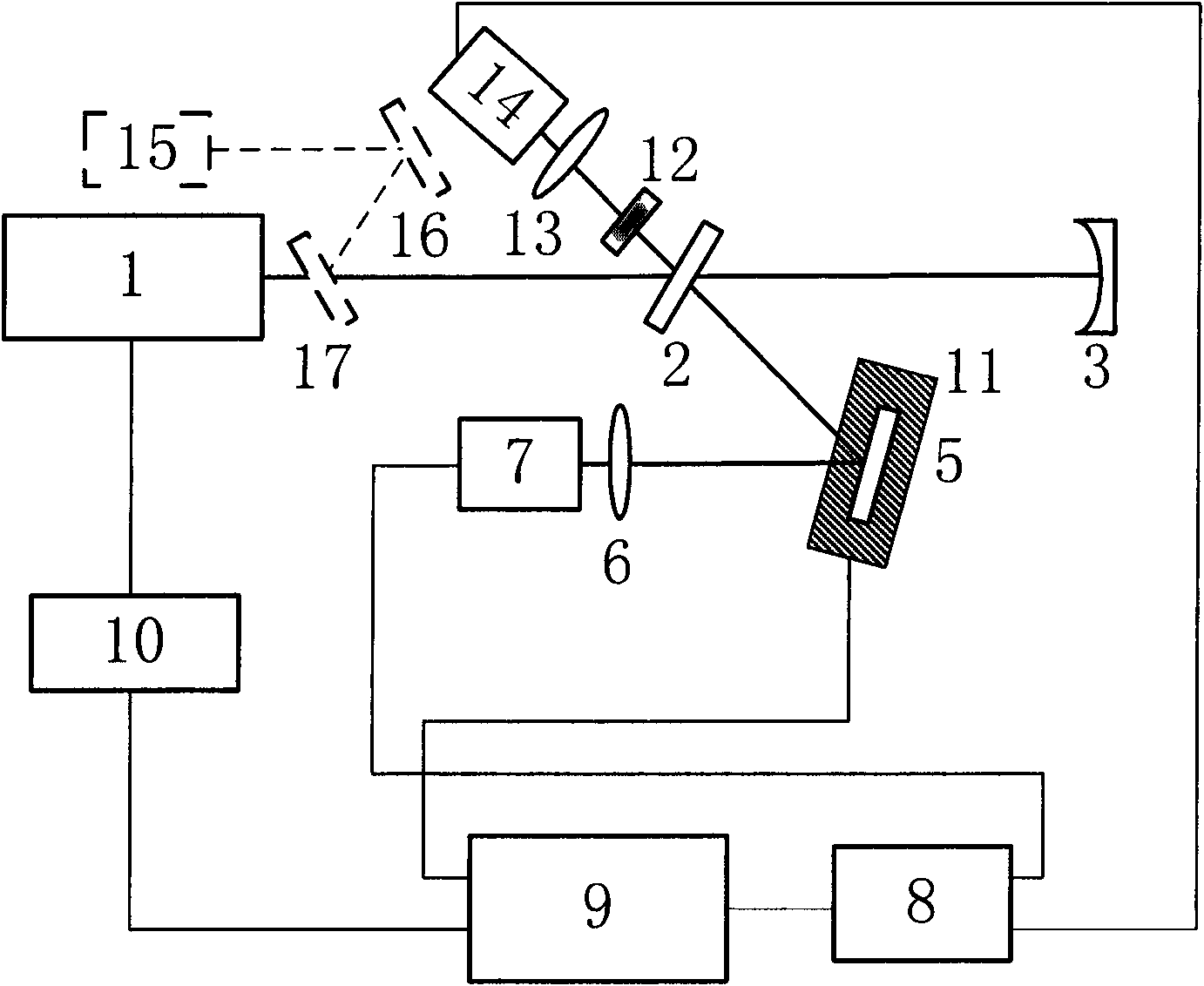
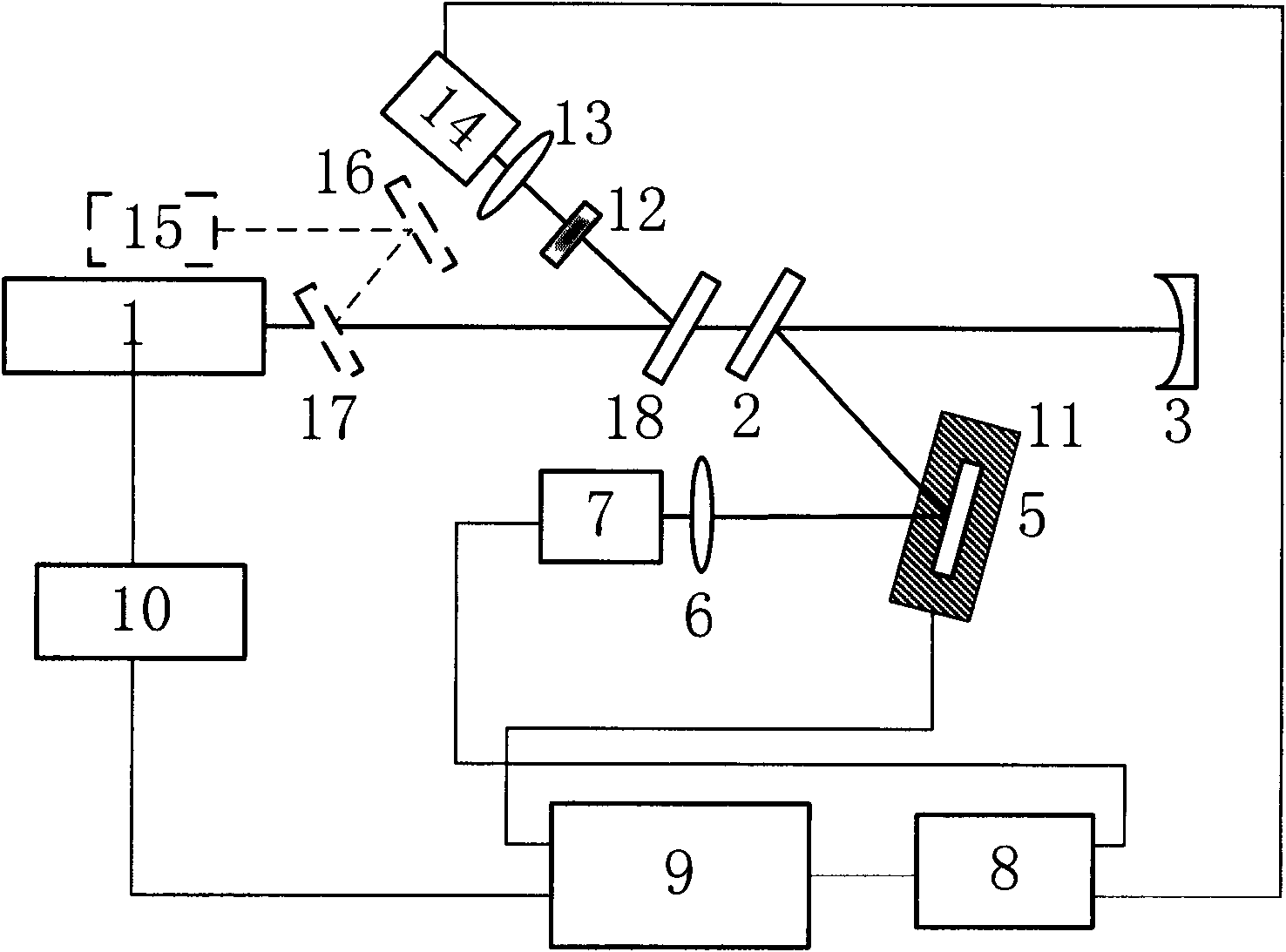
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively measuring reflectivity, which comprises the following steps: dividing continuous incident laser beams into a reference beam and a detection beam, wherein the reference beam is focused on a photoelectric detector for direct detection and the detection beam is injected into an optical resonant cavity; using a cavity ring-down technology to measure an optical element with reflectivity more than 99%, respectively measuring a ring-down time tau 0 of an original optical resonant cavity output signal and a ring-down time tau 1 of the measured optical resonant cavity output signal after an optical element to be measured is added, and calculating the reflectivity R of the optical element to be measured; using the spectrophotometry to measure the reflectivity of the optical element to be measured when the R value is less than 99%; moving away an output cavity mirror; focusing detecting light reflected by a measuring mirror on the photoelectric detector for detecting while recording a light intensity signal ratio of the detection beam to the reference beam; and calibrating to further obtain the reflectivity R of the optical element to be measured. The device for measuring reflectivity can be used for measuring optical elements with any reflectivity and also can be used for realizing the high-resolution two-dimensional imaging of the reflectivity distribution of a large-aperture optical element.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
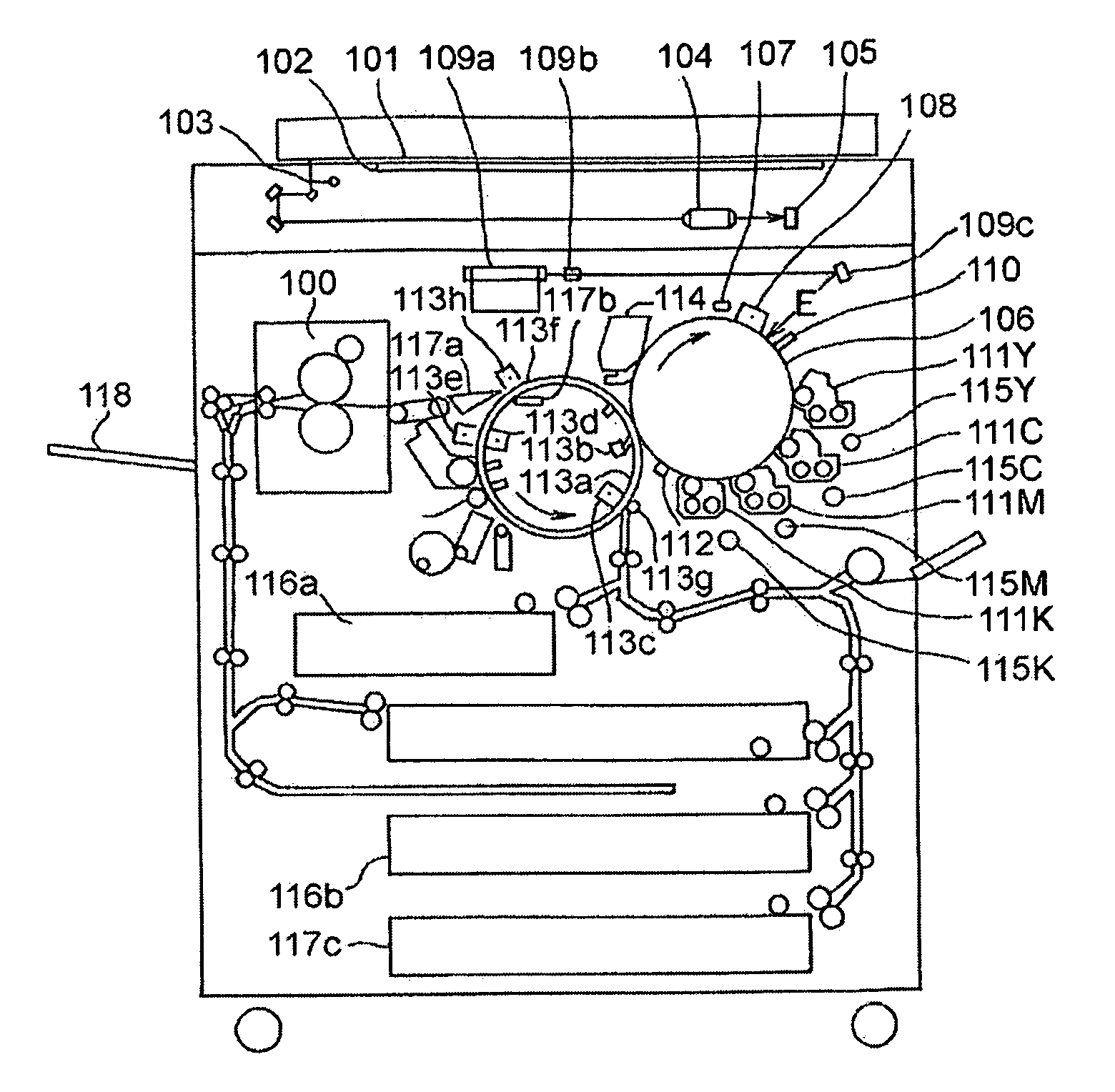
Cyan toner, magenta toner, yellow toner, black toner, and full-color image-forming method
InactiveUS20080247788A1Reduce toner consumptionReduce surface unevennessDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusColor imageEngineering
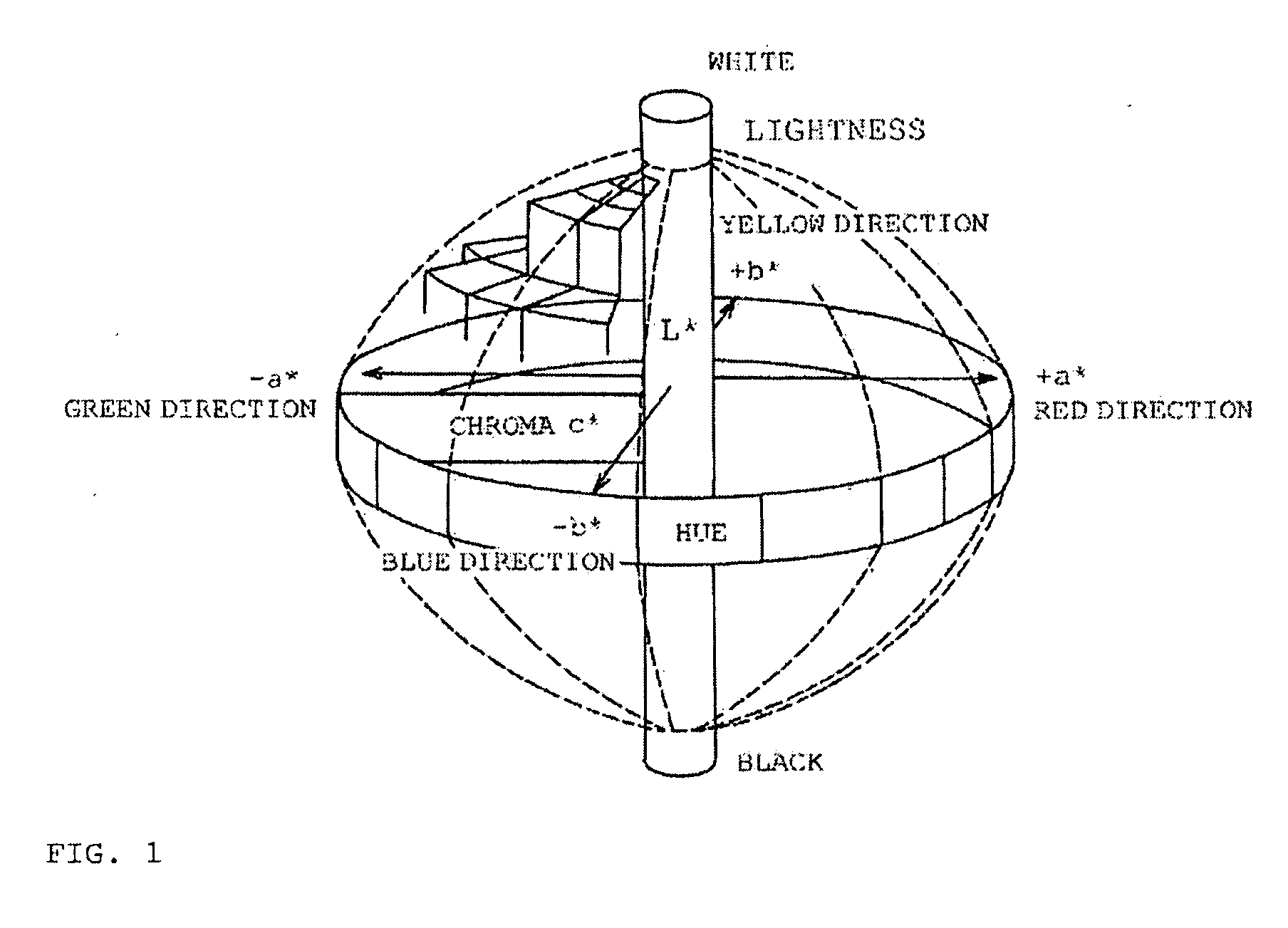
Provided are a toner containing at least a binder resin and a colorant, the toner having a specific hue angle and an absorbance at a specific wavelength in reflectance spectrophotometry, and a full-color image-forming method involving the use of the toner, the method including the steps of: forming an electrostatic image on a charged electrostatic image bearing member; developing the formed electrostatic image with the toner to form a toner image; transferring the formed toner image onto a transfer material; and fixing the transferred toner image to the transfer material to form a fixed image.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
ActiveUS8396526B2Accurate assessmentImprove accuracyScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound attenuationLight sensing
According to the present invention, a method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the blood oxygen saturation level within a subject's tissue is provided. The method comprises the steps of: 1) providing a near infrared spectrophotometric sensor operable to transmit light along a plurality of wavelengths into the subject's tissue; 2) sensing the light transmitted into the subject's tissue using the sensor, and producing signal data representative of the light sensed from the subject's tissue; 3) processing the signal data to account for physical characteristics of the subject; and 4) determining the blood oxygen saturation level within the subject's tissue using a difference in attenuation between the wavelengths. The apparatus includes a sensor having a light source and at least one light detector, which sensor is operably connected to a processor. The sensor is operable to transmit light along a plurality of wavelengths into the subject's tissue, and produce signal data representative of the light sensed from the subject's tissue. The algorithm is operable to process the signal data to account for the physical characteristics of the subject being sensed.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Effective components of rose, its preparing method and use
InactiveCN101002841ASleep longerIncreased incidence of sleepNervous disorderPill deliveryRefluxOrganic solvent
An application of the active component extracted from rose flower in preparing the medicine or health-care food for improving sleep quality is disclosed. Said active component is extracted from dried rose flower through reflux extracting in alcohol, separating by macroreticular resin, and extracting in organic solvent.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for practicing spectrophotometry using light emitting nanostructure devices
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a system and method for practicing spectrophotometry using light emitting nanostructures. Specifically, embodiments of the present invention include a physiologic sensor comprising a sensor body configured for placement adjacent pulsatile tissue of a patient, a first light emitting nanostructure device configured to emit light at a first wavelength through the pulsatile tissue, a second light emitting nanostructure device configured to emit light at a second wavelength through the pulsatile tissue, and a light detector configured to detect the light at the first wavelength and the light at the second wavelength after dispersion through the pulsatile tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Fast detecting method for aftatoxin B1
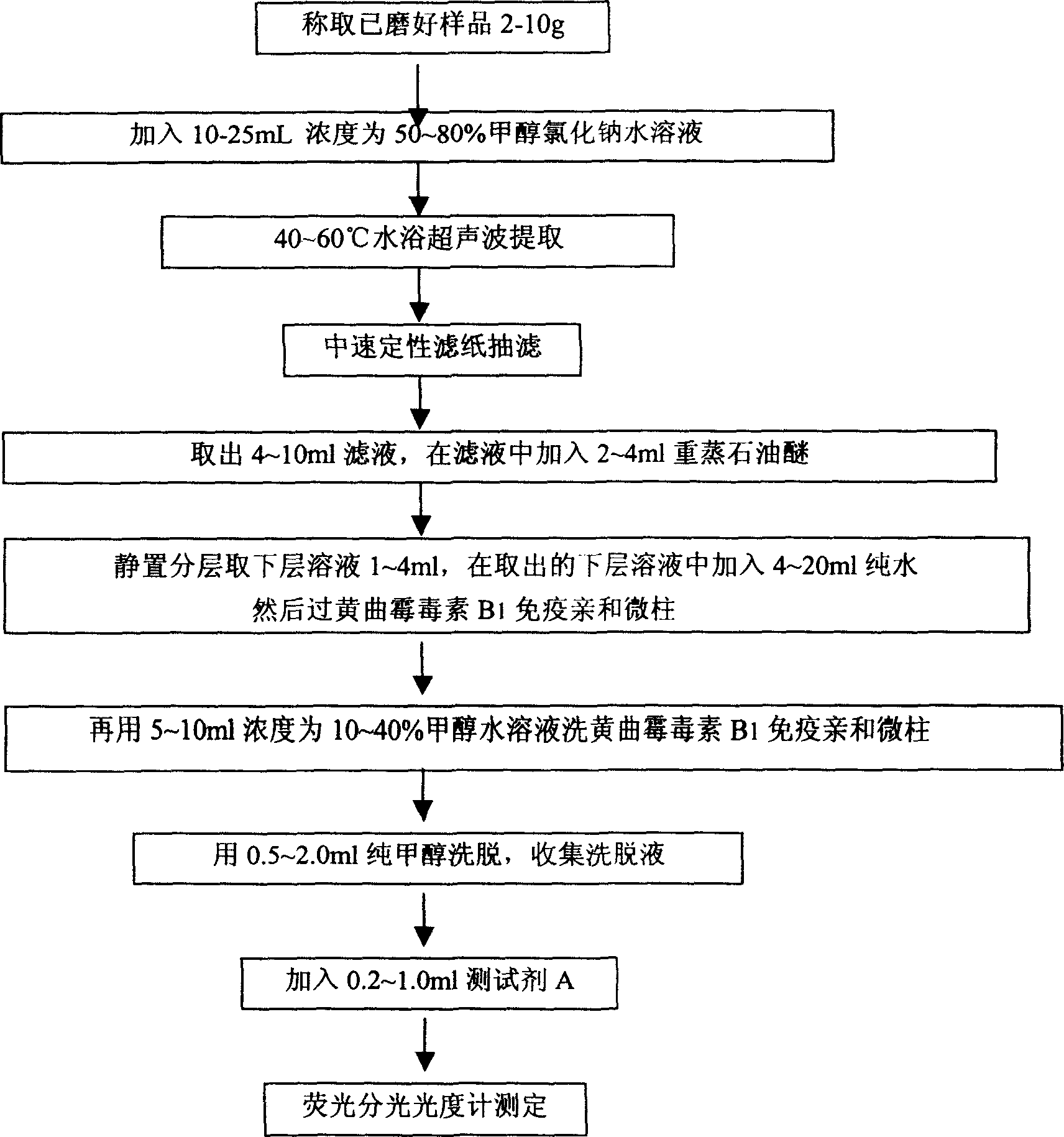
The present invention is fast detection method of aflatoxin B1 in food and feed. The fast detection method includes the following steps: adding ground sample to be tested in 2-10 g in test tube, adding methanol-sodium chloride aqua of 50-80 % concentration in 10-25 ml, ultrasonic extraction in water bath at 40-60 deg.c, and suction filtering to obtain filtrate in 4-10 ml; adding re-distilled petroleum ether in 2-4 ml into the filtrate, shaking, letting stand to laminate, taking the lower layer of solution in 1-4 ml and adding pure water in 4-20 ml; adding to micro immunoaffinity column of aflatoxin B1, washing with methanol aqua of 10-40 % concentration in 5-10 ml, eluting with methanol in 0.5-2.0 ml, collecting the eluted liquid, adding test agent A in 0.2-1.0 ml; and detecting in fluorescent spectrophotometry or similar instrument. The present invention has the features of simple process, high detection precision and stability, fast detection speed and high safety.
Owner:BEIJING CHINAINVENT INSTR TECH +1
Multipoint method for identifying hazardous agents
ActiveUS20090097020A1Radiation pyrometryRaman scatteringSpectral analysisRaman Optical Activity Spectroscopy
The invention relates to apparatus and methods for assessing occurrence of a hazardous agent in a sample by performing multipoint spectral analysis of the sample. Methods of employing Raman spectroscopy and other spectrophotometric methods are disclosed. Devices and systems suitable for performing such multipoint methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com