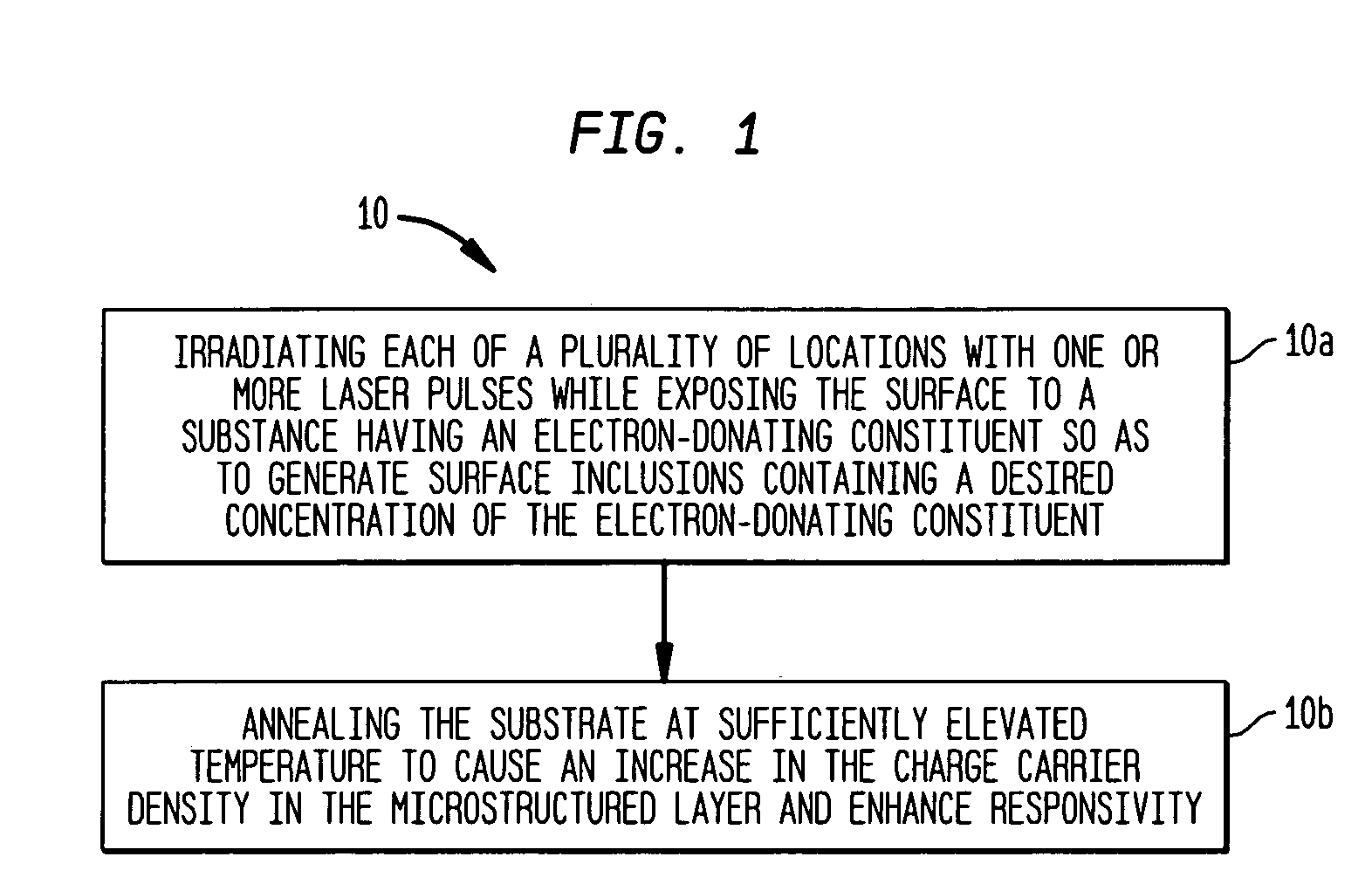
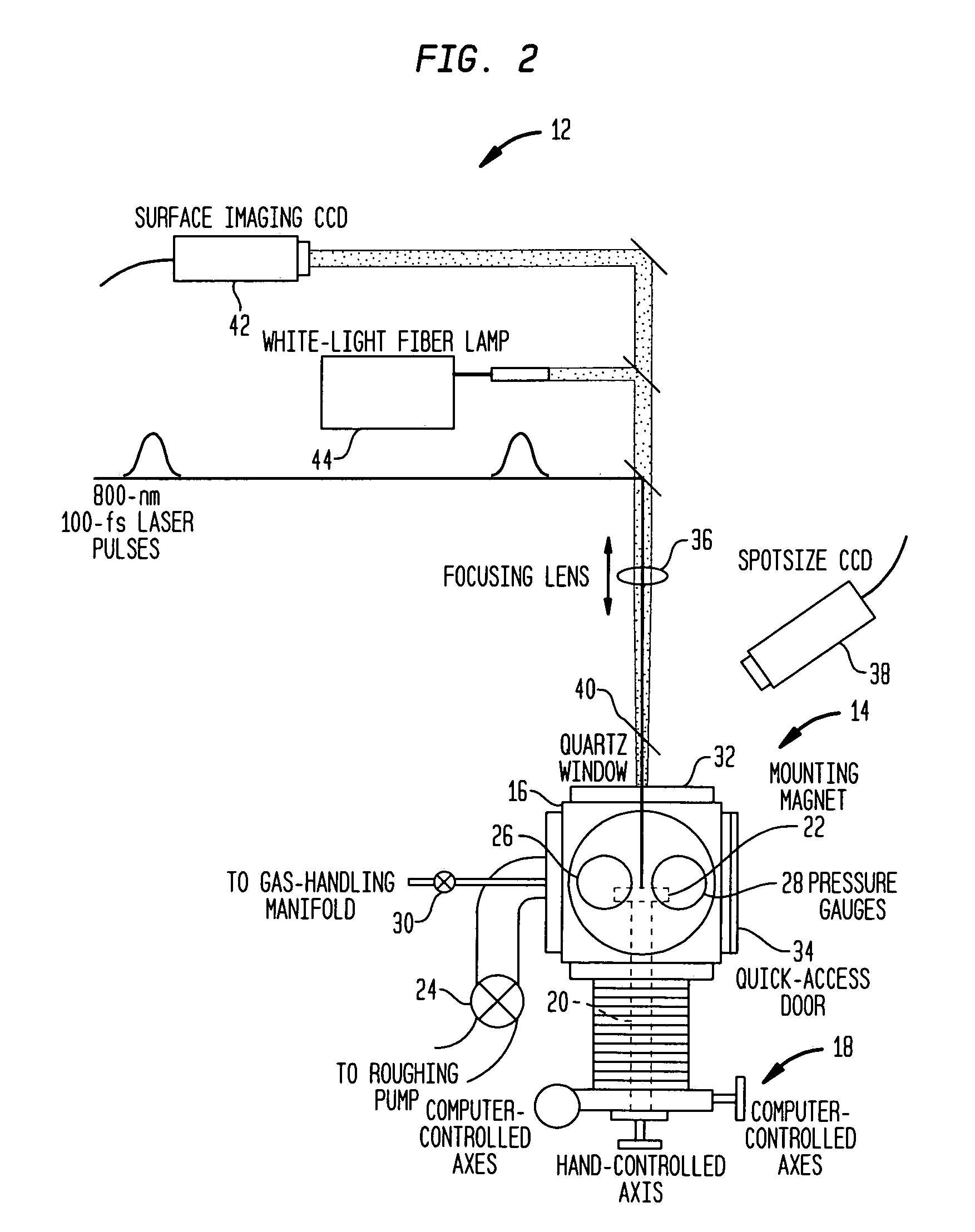
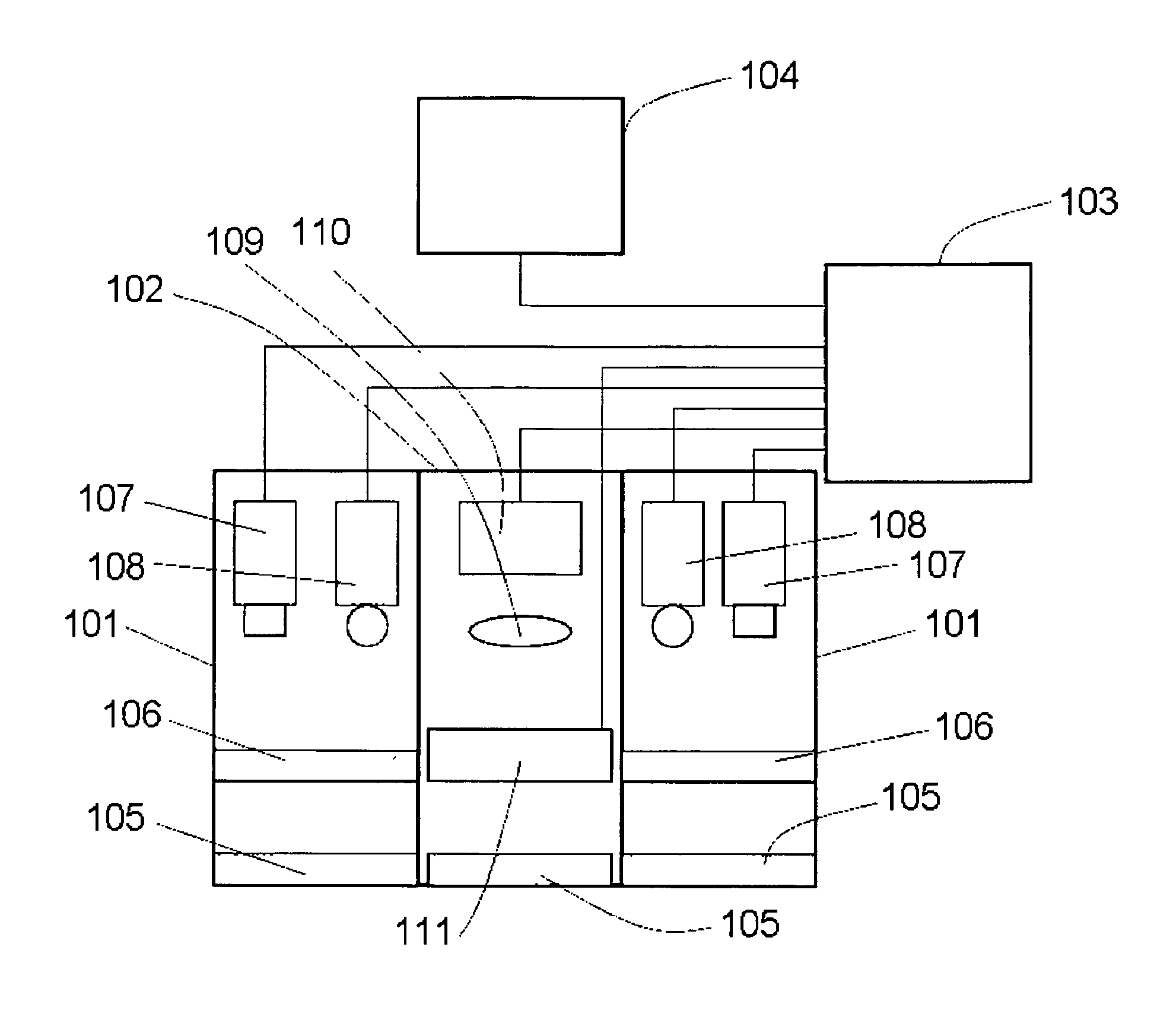
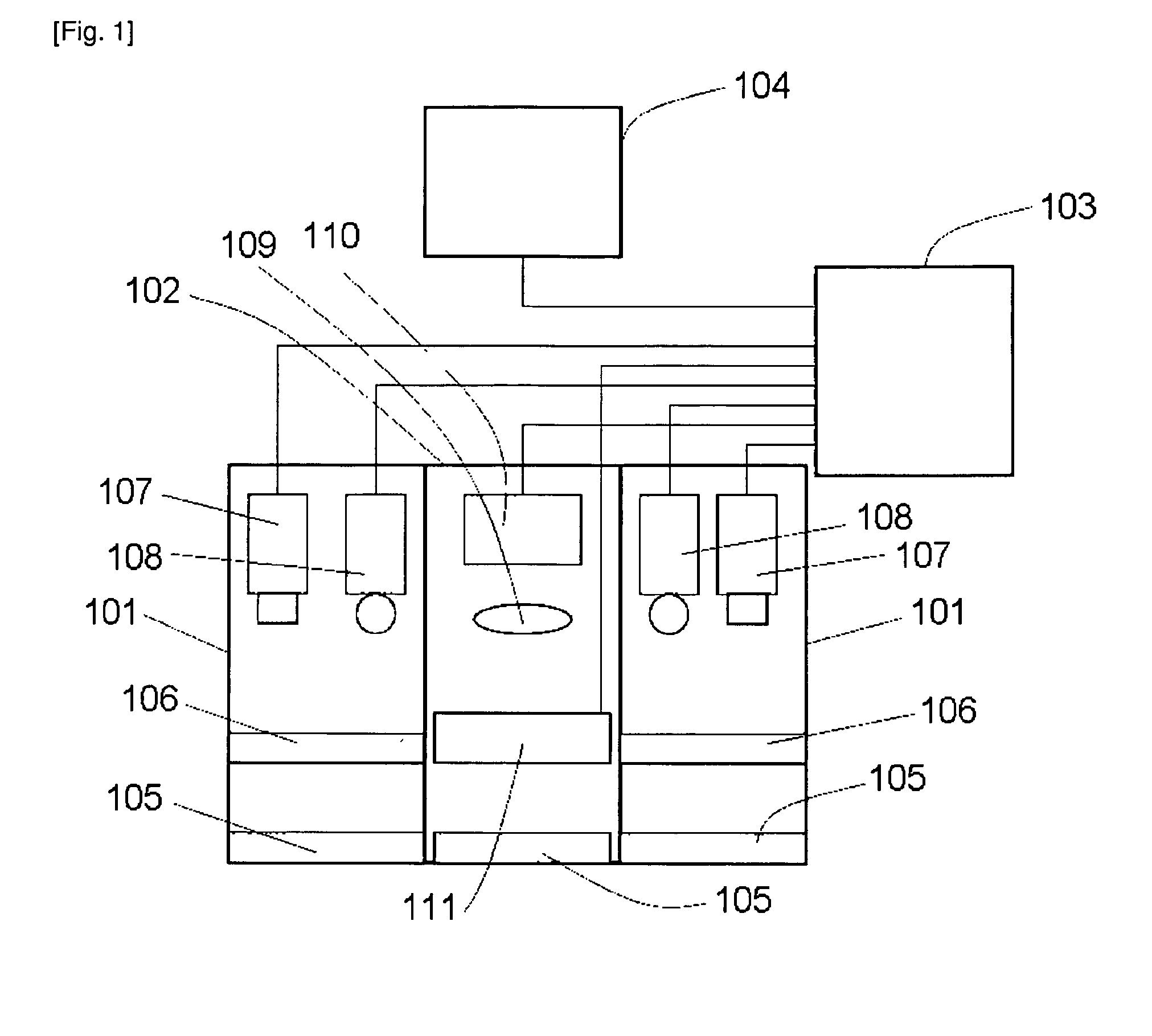
Patents
Literature
4131 results about "Near infrared light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
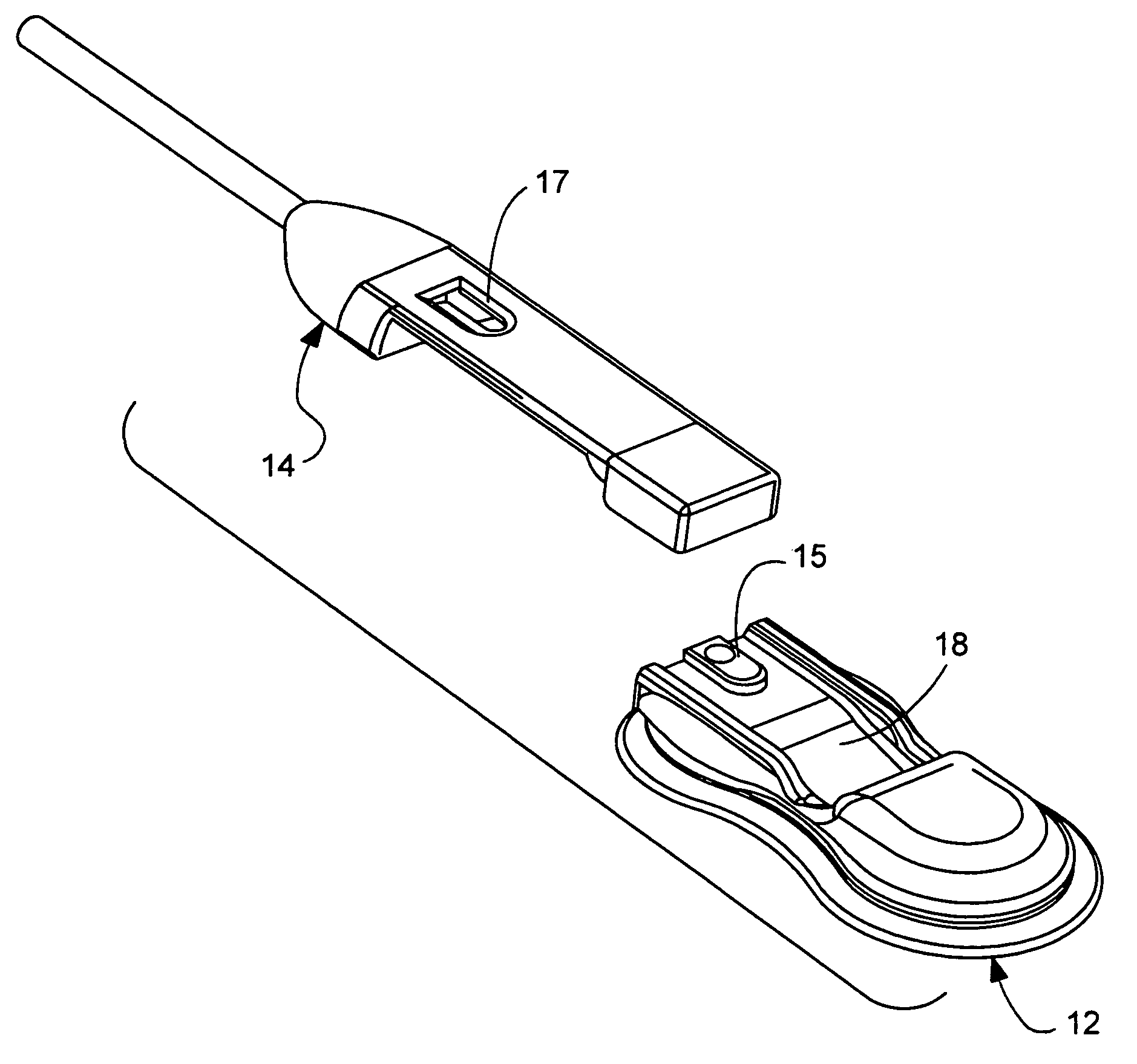
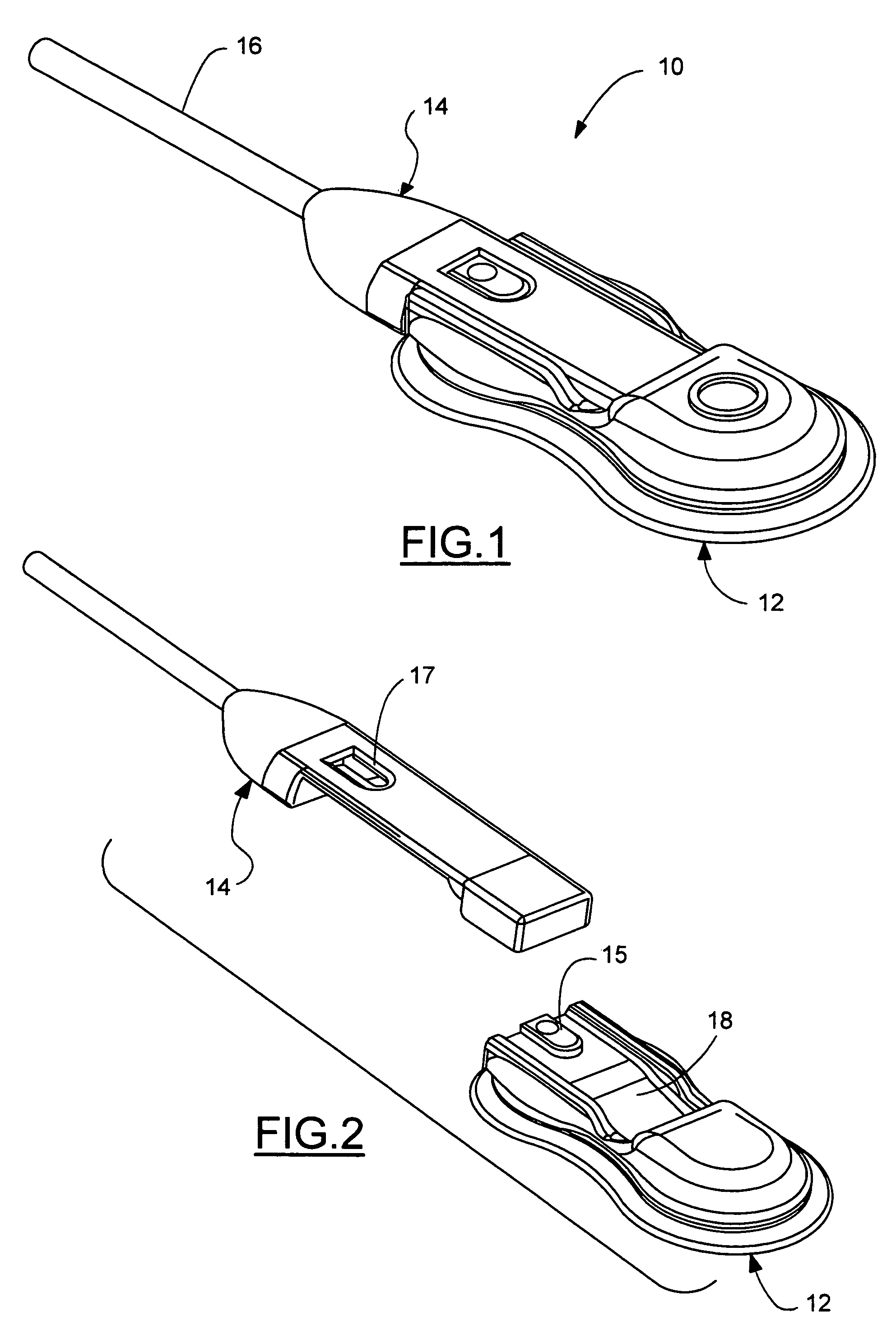
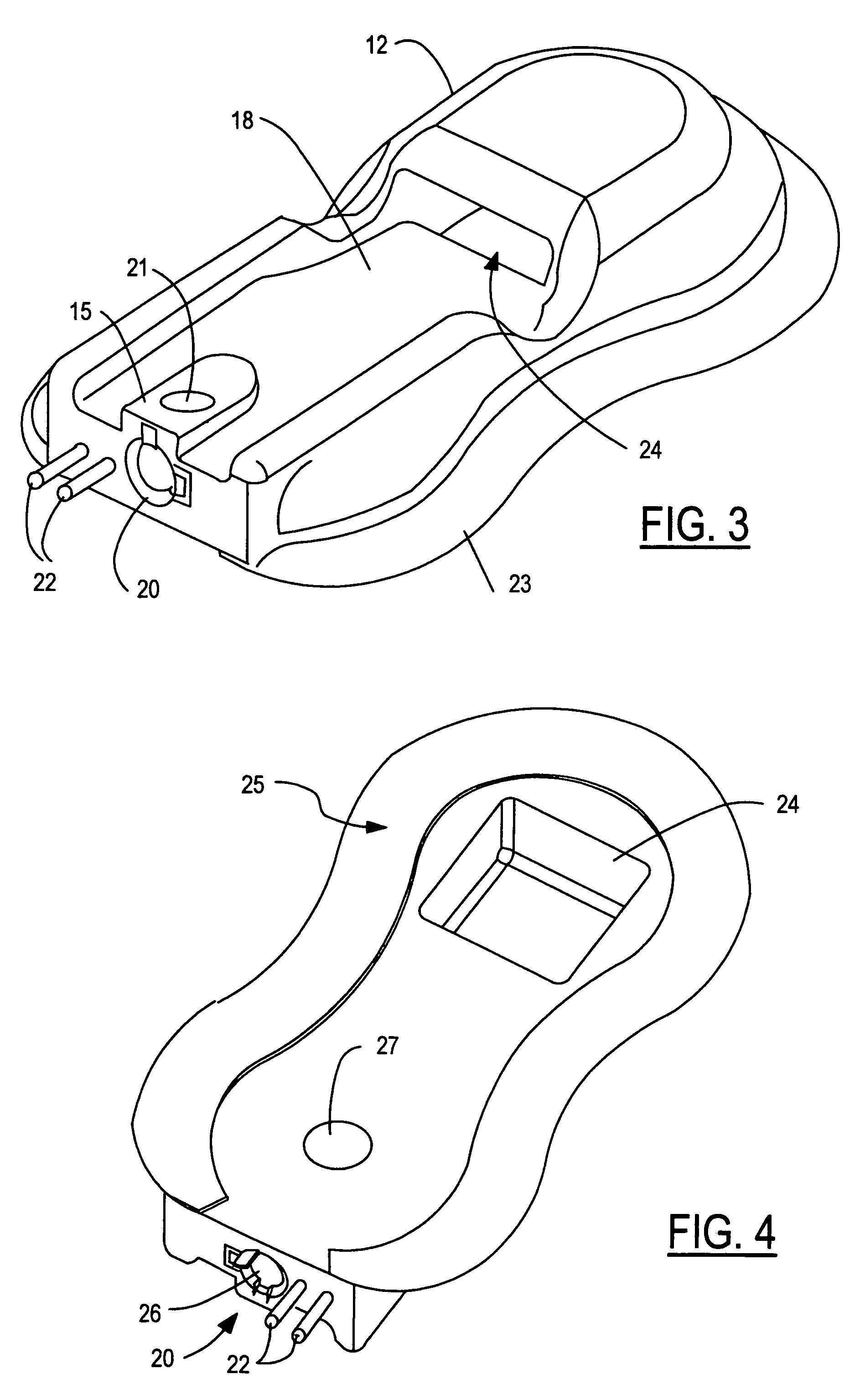
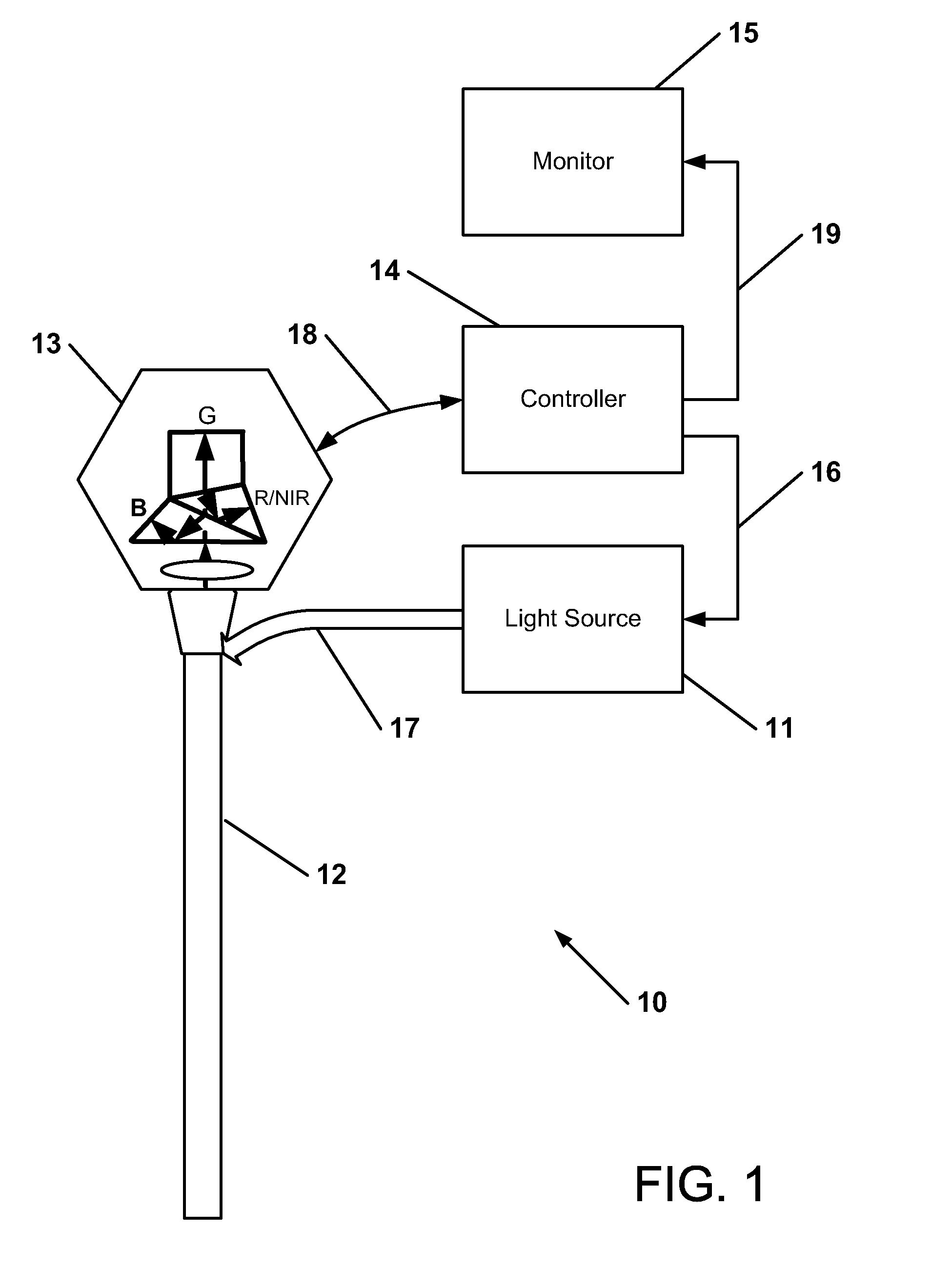
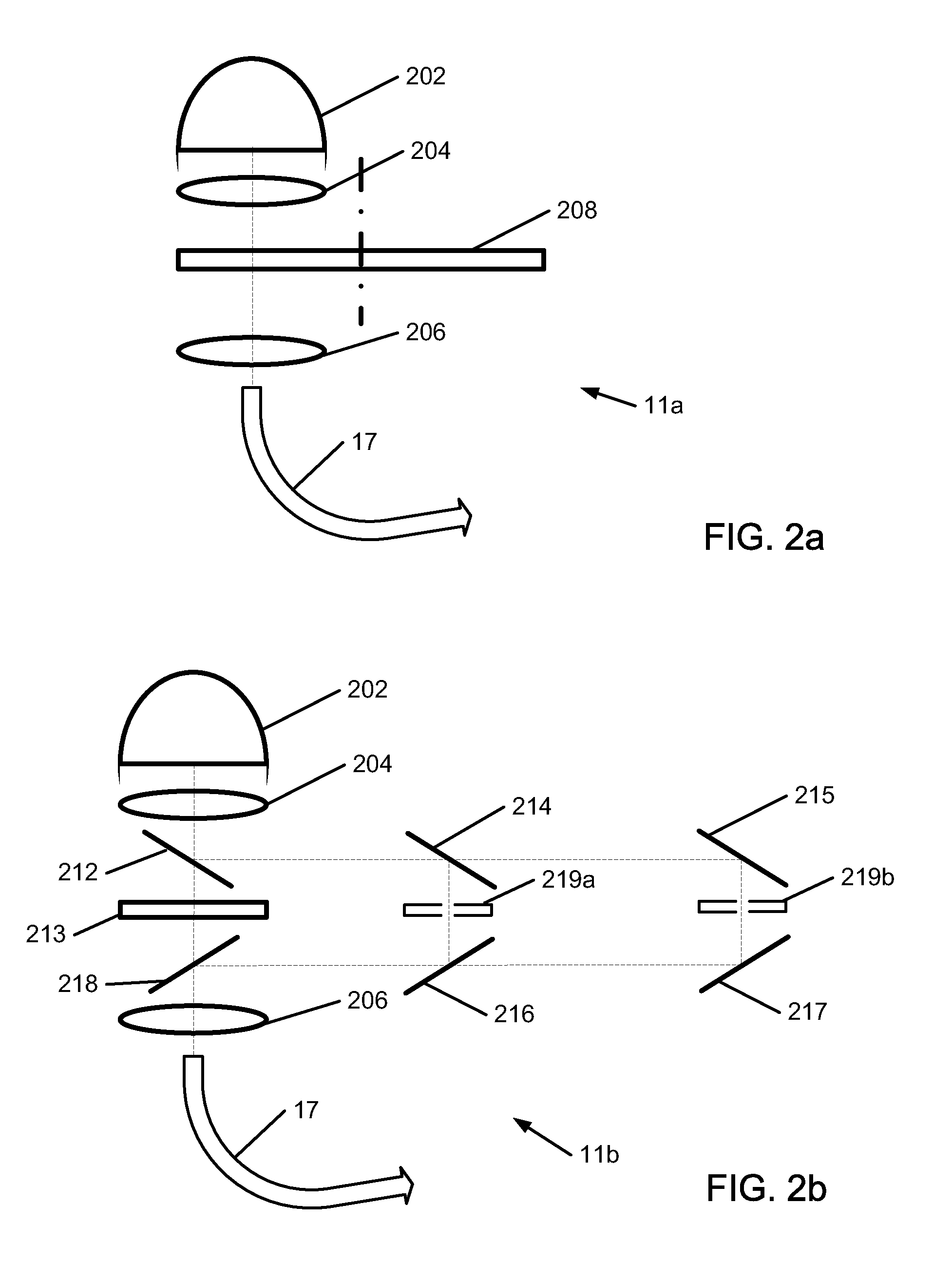
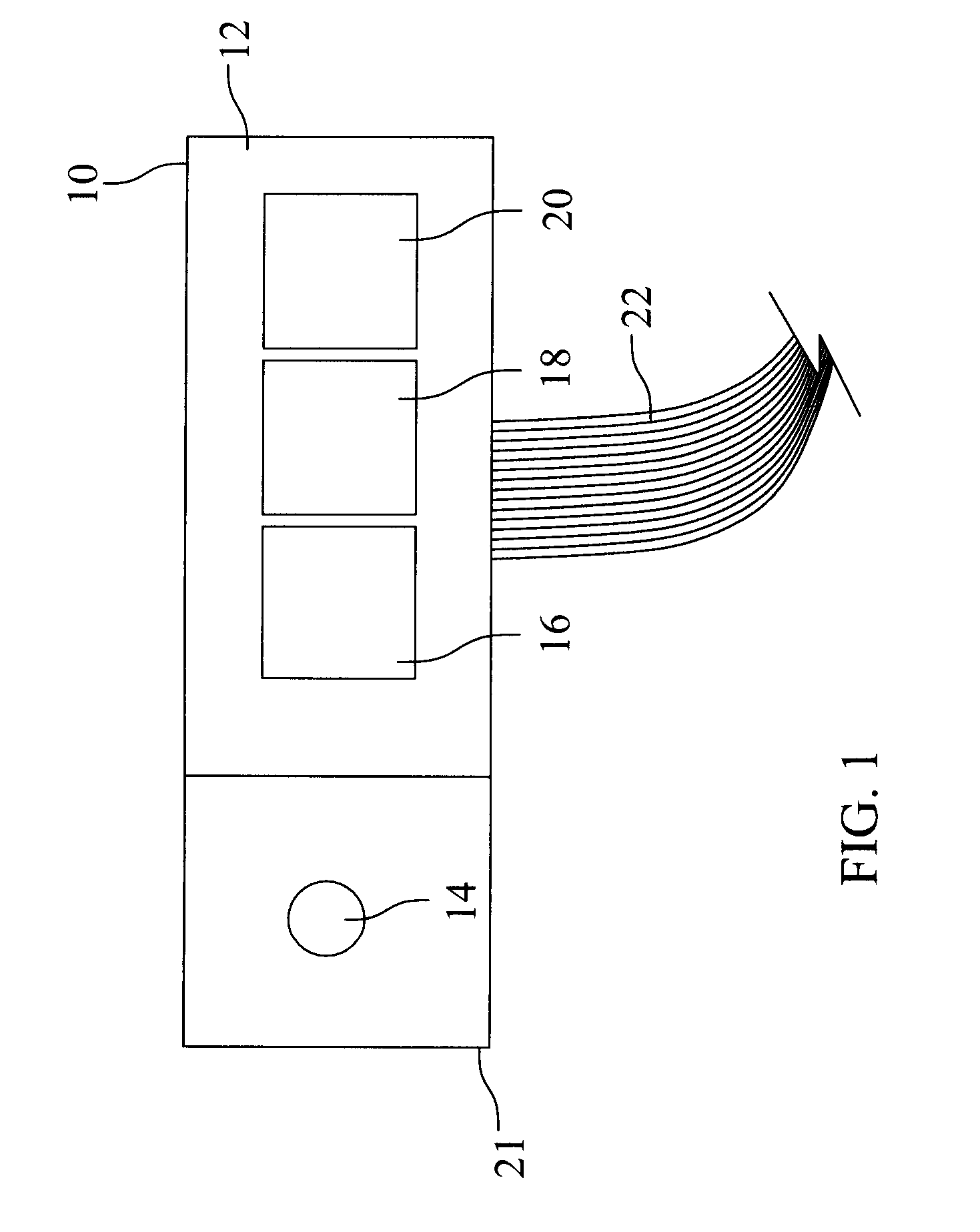
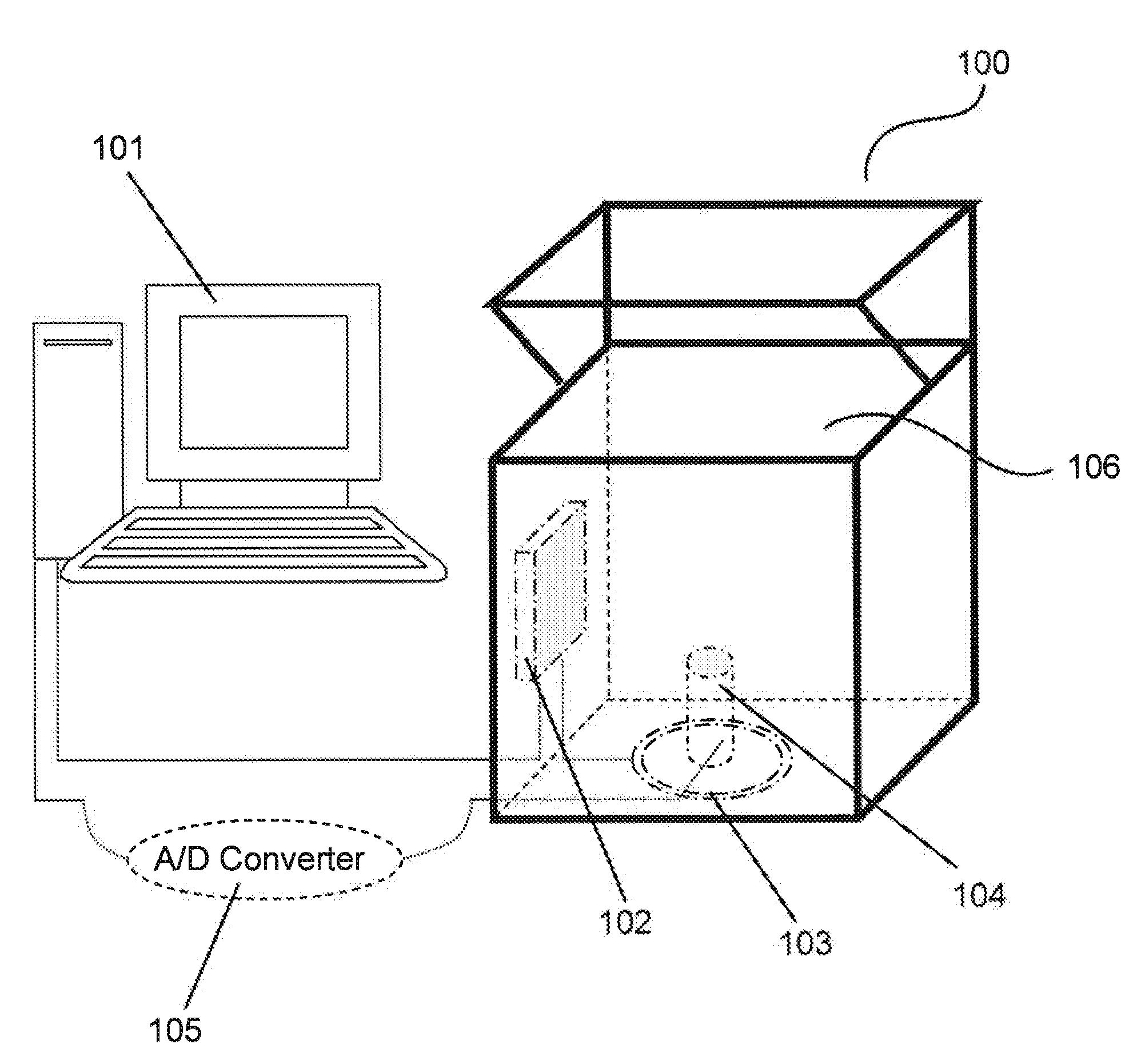
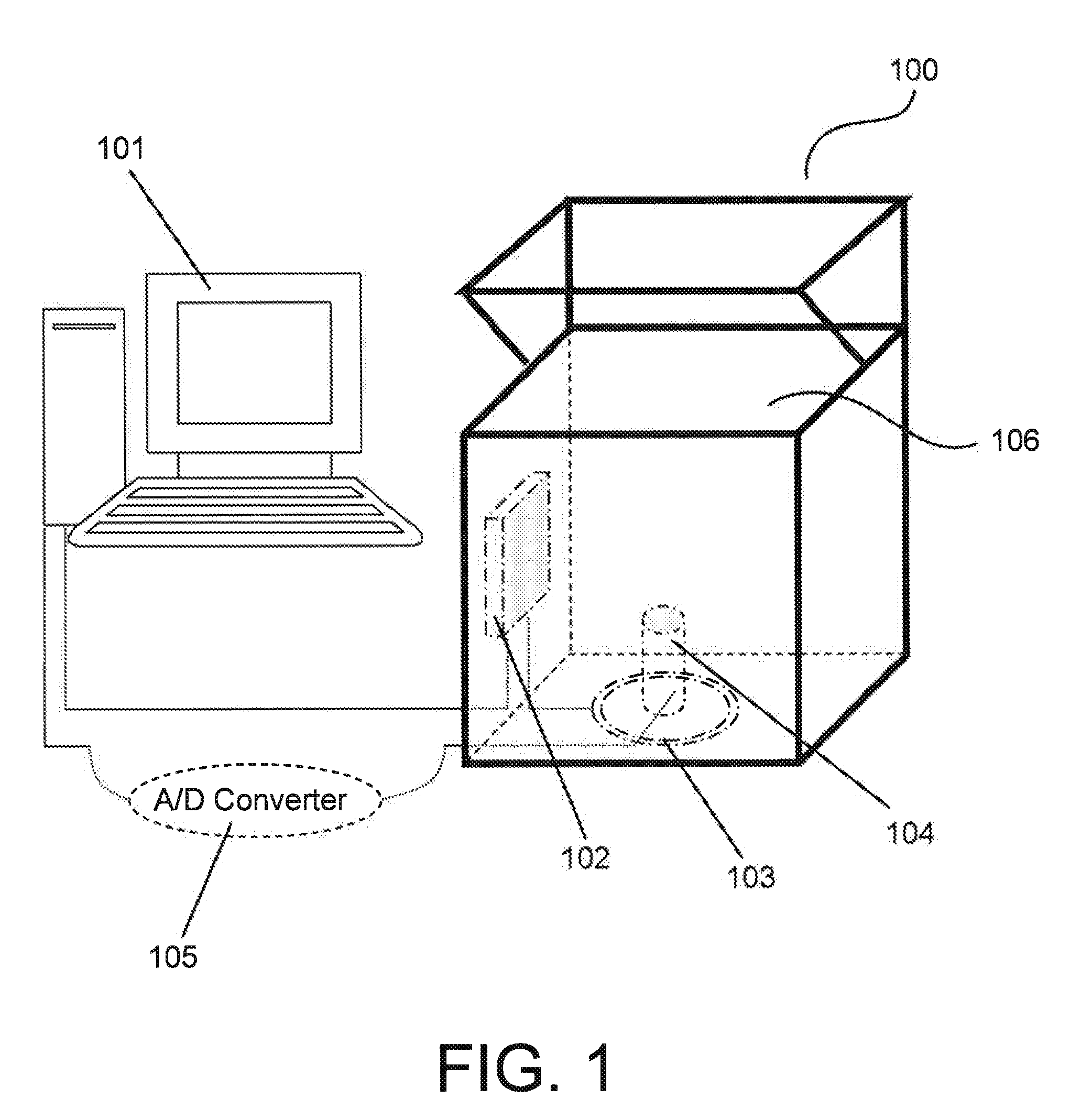
Near infrared spectroscopy device with reusable portion
InactiveUS7706853B2Small sizeFirmly attachedMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical operationHigh energy
A NIRS sensor device for brain monitoring is small in size, provides reliable attachment to a patient, blocks ambient light, is easy to use, is hygienic, and supports data integration with surgical and monitoring systems. The sensor device is coupled to a remote near infrared light source via a hybrid cable. Since the light source is remotely located, a source adapted for providing high energy, short pulses can easily be used so that there is less chance of interference by superficial non-brain tissues and less interference from ambient light. In addition, the remote location avoids changes in output of local light sources experienced in the prior art during hypothermia procedures (e.g., bandwidth shifts in LEDs as a result of lowered temperature). The higher energy may be achieved by the use of laser diodes as opposed to locally-mounted LEDs typically used in the prior art. The sensor device is a two-piece design comprising a reusable portion containing the photodetector(s) and a disposable portion that receives the light from the reusable portion and bends it to direct the light into the brain.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
Silicon-based visible and near-infrared optoelectric devices
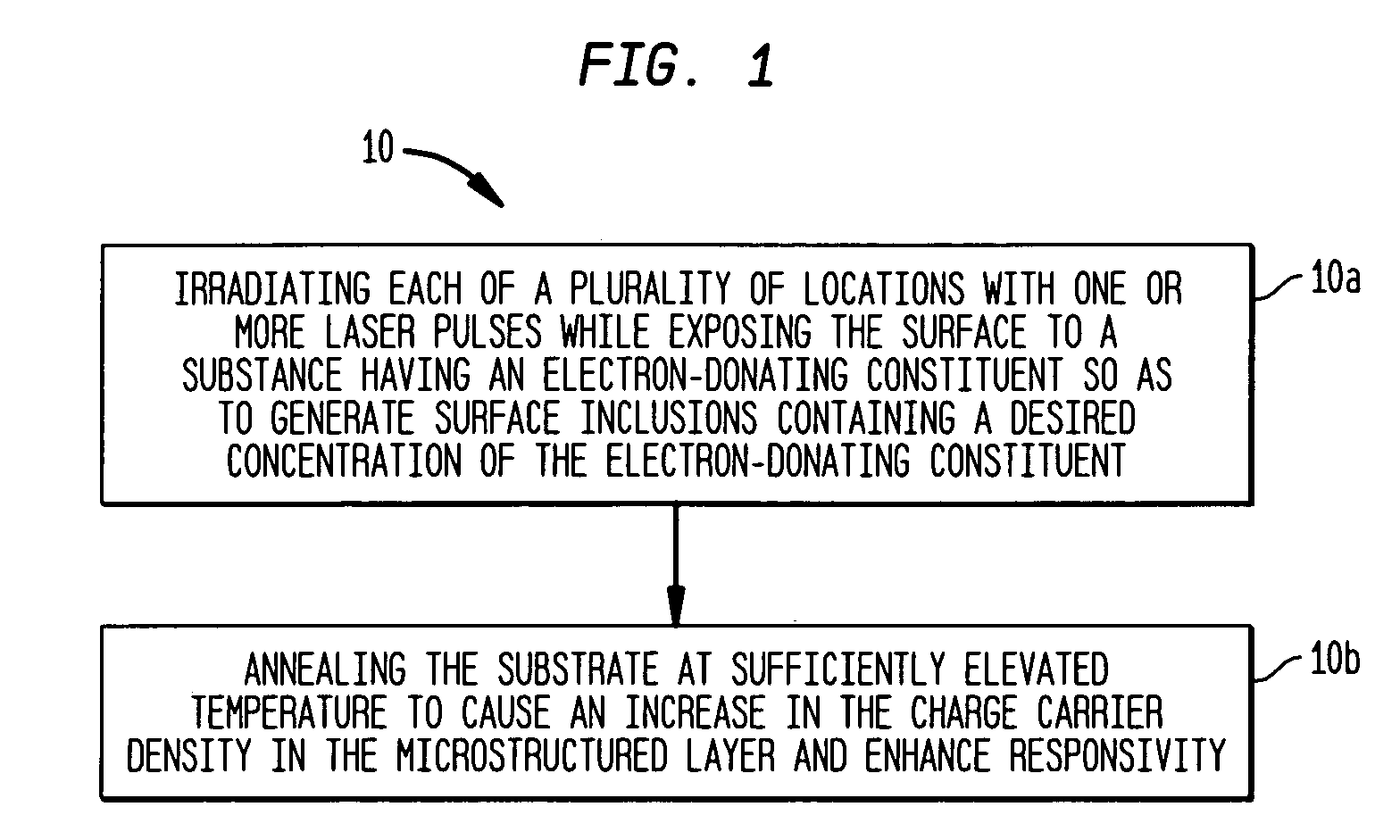
InactiveUS7057256B2Promote generationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsSurface layer
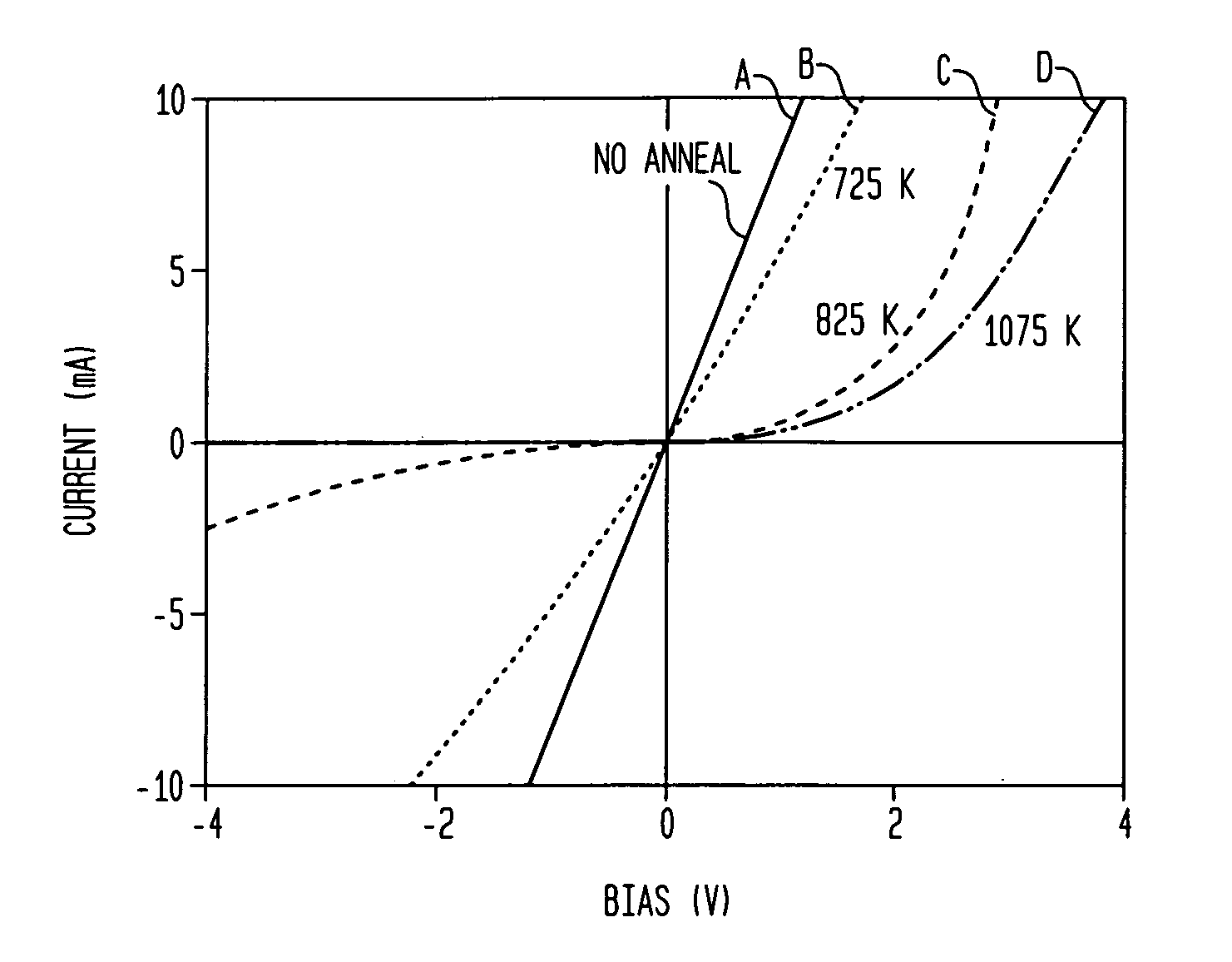
In one aspect, the present invention provides a silicon photodetector having a surface layer that is doped with sulfur inclusions with an average concentration in a range of about 0.5 atom percent to about 1.5 atom percent. The surface layer forms a diode junction with an underlying portion of the substrate. A plurality of electrical contacts allow application of a reverse bias voltage to the junction in order to facilitate generation of an electrical signal, e.g., a photocurrent, in response to irradiation of the surface layer. The photodetector exhibits a responsivity greater than about 1 A / W for incident wavelengths in a range of about 250 nm to about 1050 nm, and a responsivity greater than about 0.1 A / W for longer wavelengths, e.g., up to about 3.5 microns.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method and Apparatus For Facial Image Acquisition and Recognition
InactiveUS20080212849A1Convenient and accurateAccurate and fast face recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionPhotographyInfraredPattern recognition
A method and apparatus for facial image acquisition and / or recognition used for person identification. In infrared face image acquisition, near infrared (NIR) images of a face are captured by an imaging unit with the face illuminated by active NIR lights; an NIR optical filter is used in the imaging unit to minimize visible lights in environments while allowing NIR lights to pass through. NIR face images thus acquired provides good image quality for the purpose of face recognition. In face recognition, eyes are localized in NIR face image(s) quickly and accurately by detecting specular highlight reflection in each eye, whereby face is then localized. The invention effectively problems caused by environmental lights, and leads to accurate and fast face recognition under variable lighting conditions. Moreover, the methods use a non-intrusive and user-friendly way of active lighting for face image acquisition and recognition because the NIR lights are in the invisible spectrum.
Owner:AUTHENMETRIC
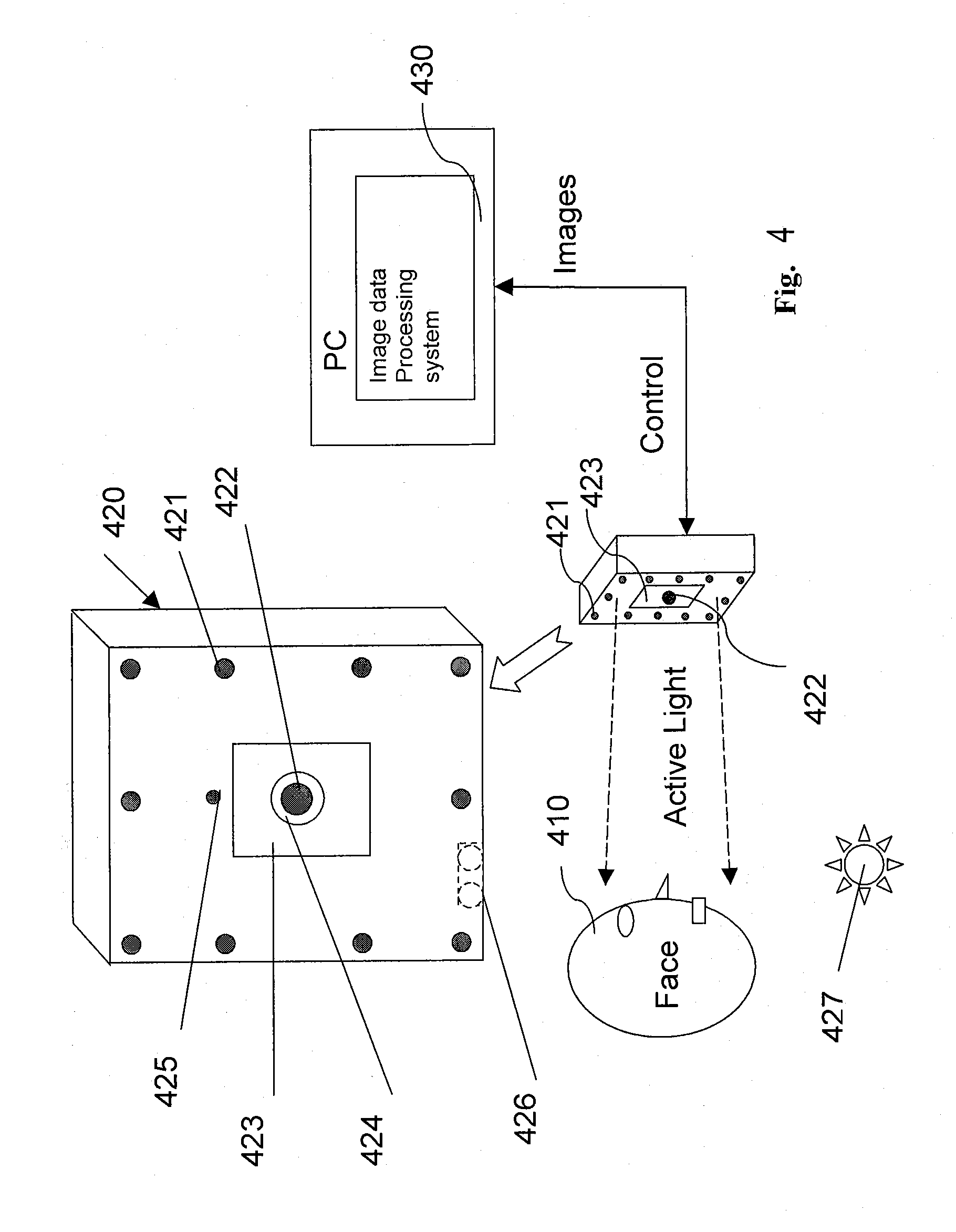
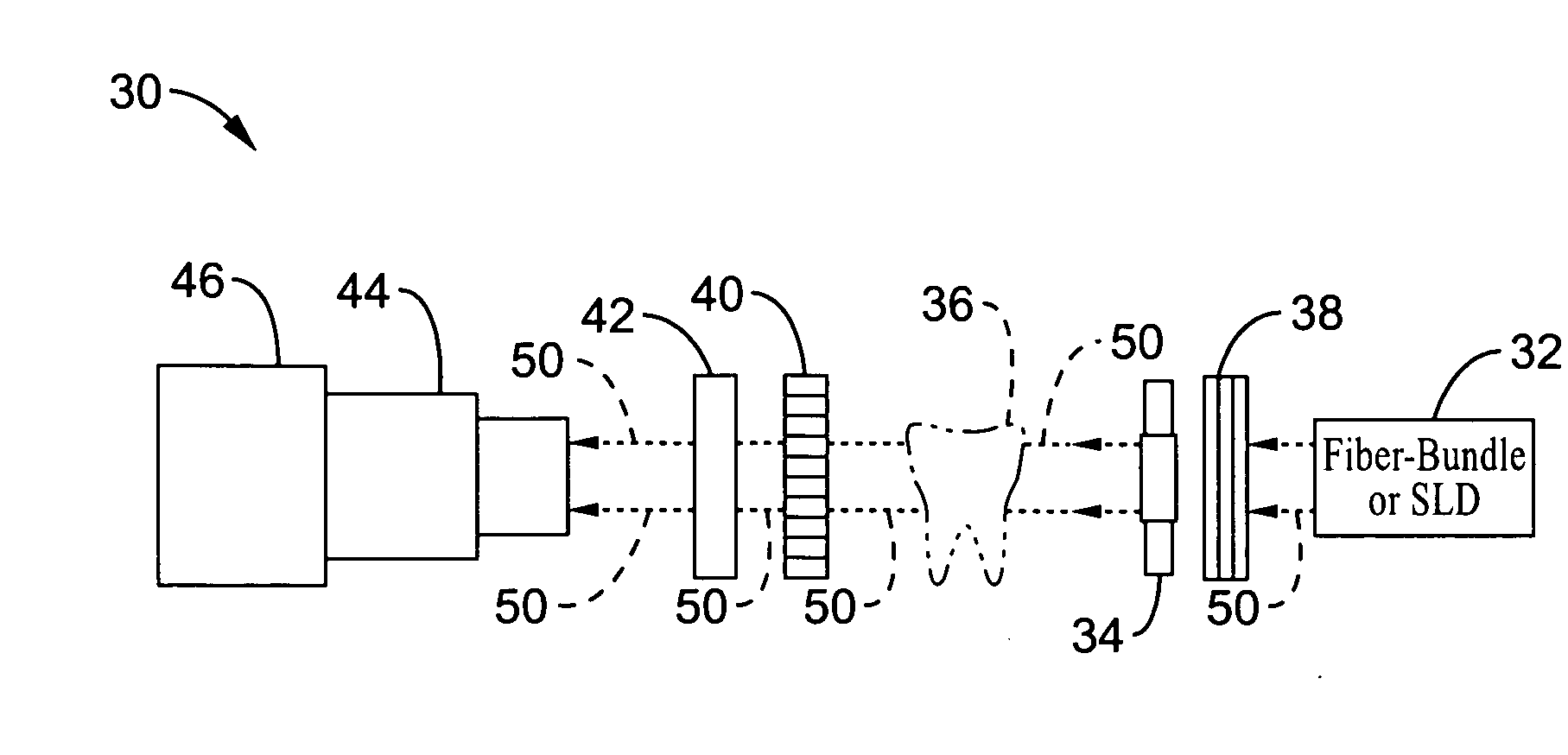
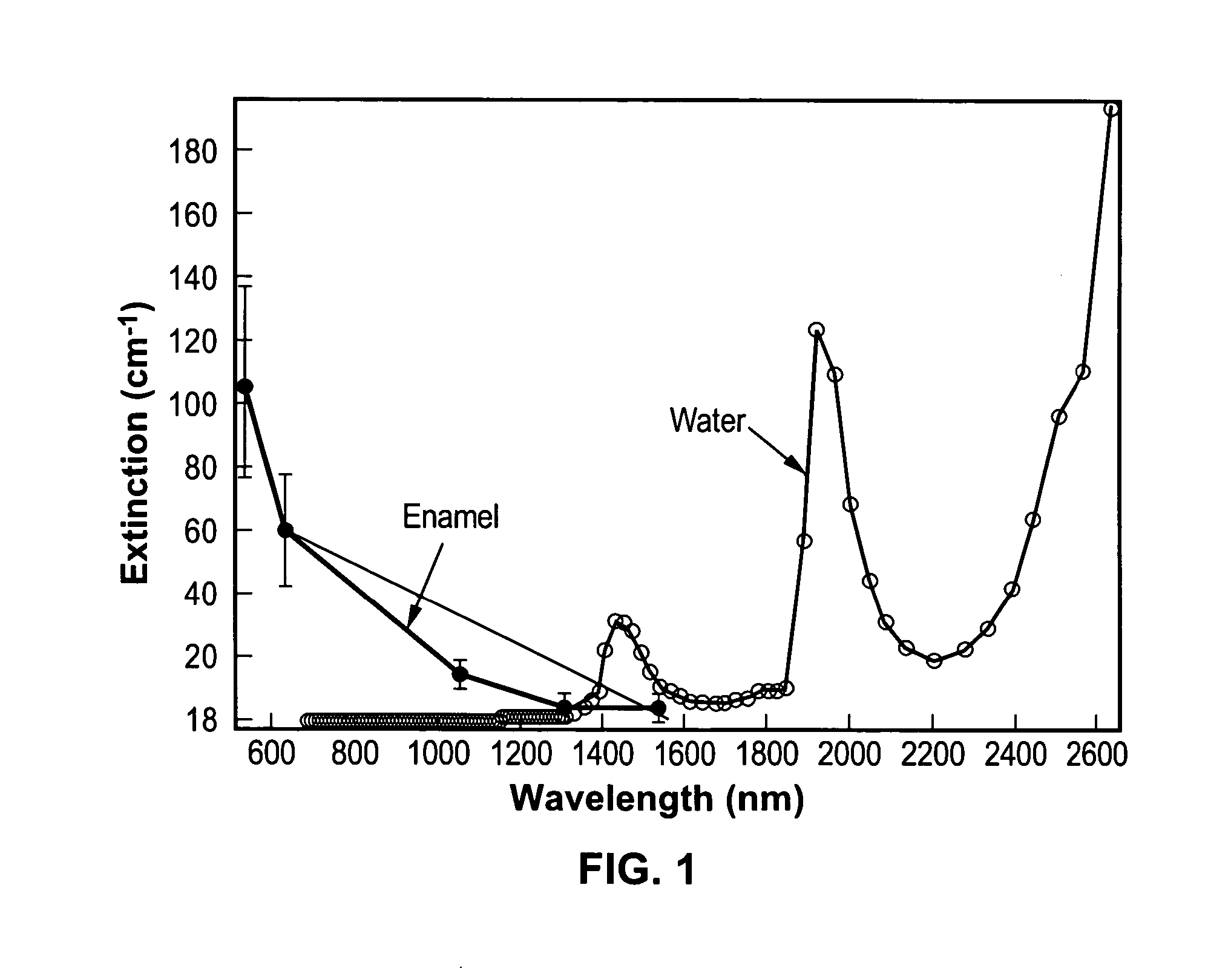
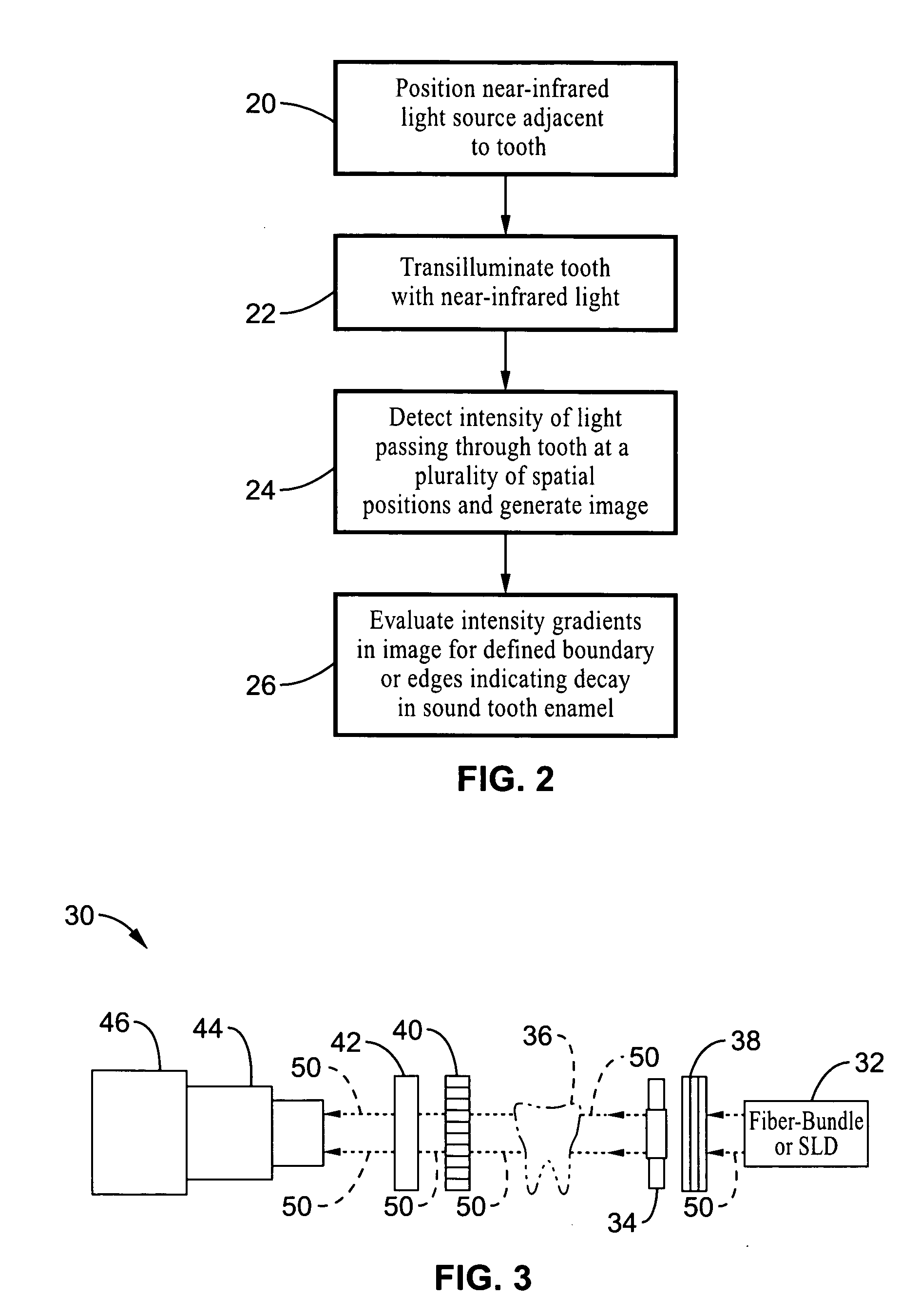
Near-infrared transillumination for the imaging of early dental decay
A method for detecting tooth decay and other tooth anomalies wherein a tooth is transilluminated with a near-infrared light source preferably in the range from approximately 795-nm to approximately 1600-nm, more preferably in the range from approximately 830-nm to approximately 1550-nm, more preferably in the range from approximately 1285-nm to approximately 1335-nm, and more preferably at a wavelength of approximately 1310-nm, and the light passing through the tooth is imaged for determining an area of decay in the tooth. The light source is a fiber-optic bundle coupled to a halogen lamp or more preferably a superluminescent diode, and the imaging device is preferably a CCD camera or a focal plane array (FPA).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
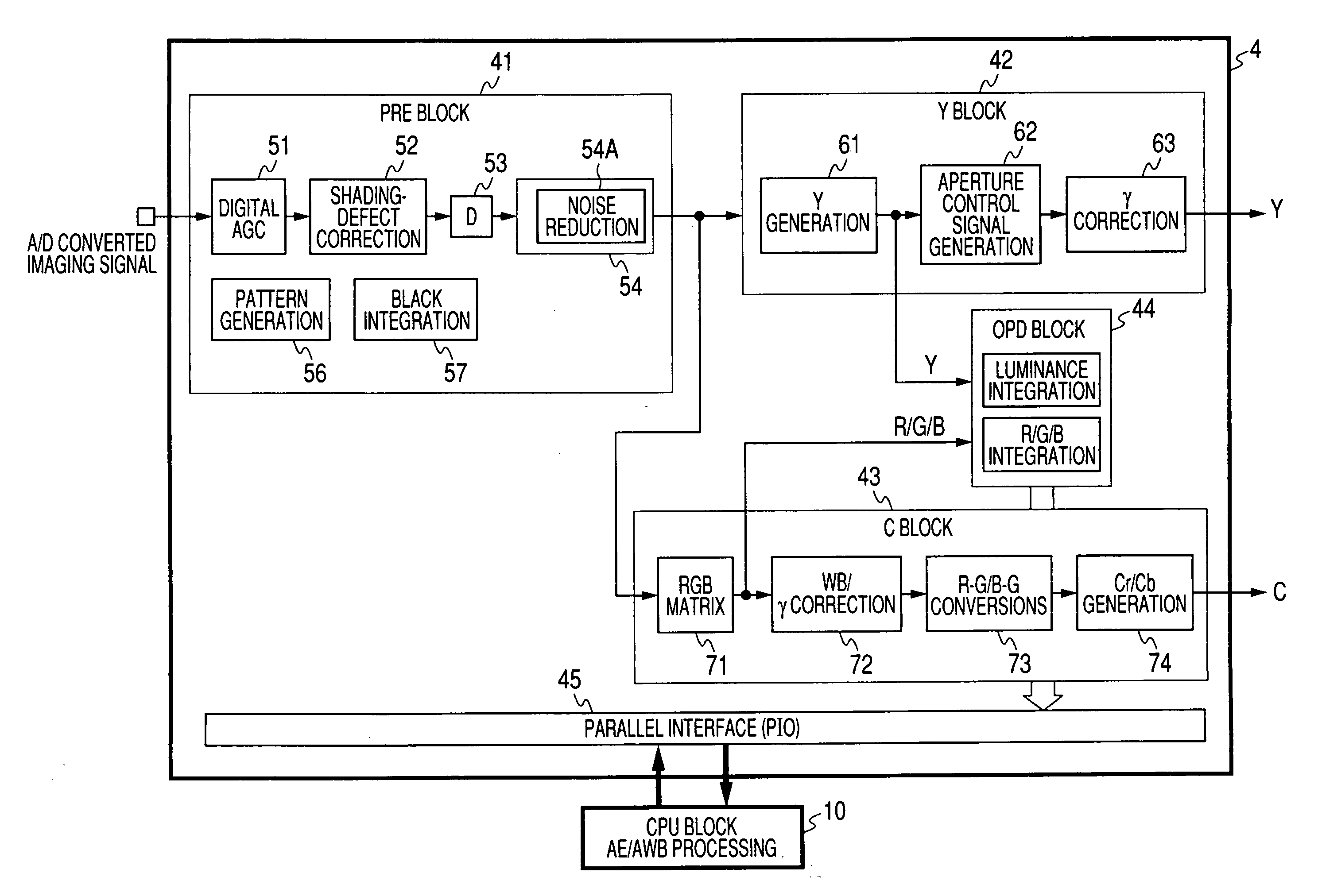
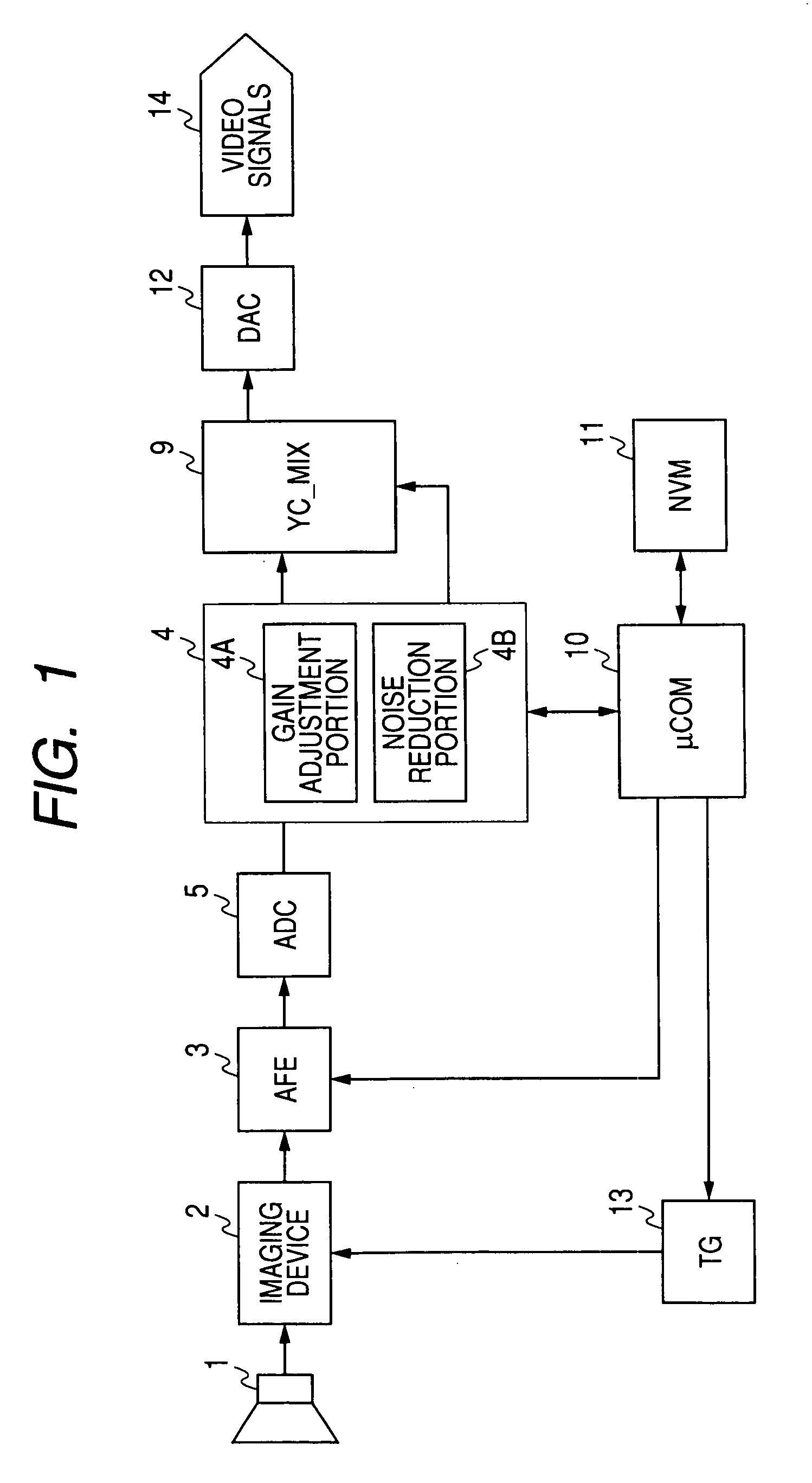
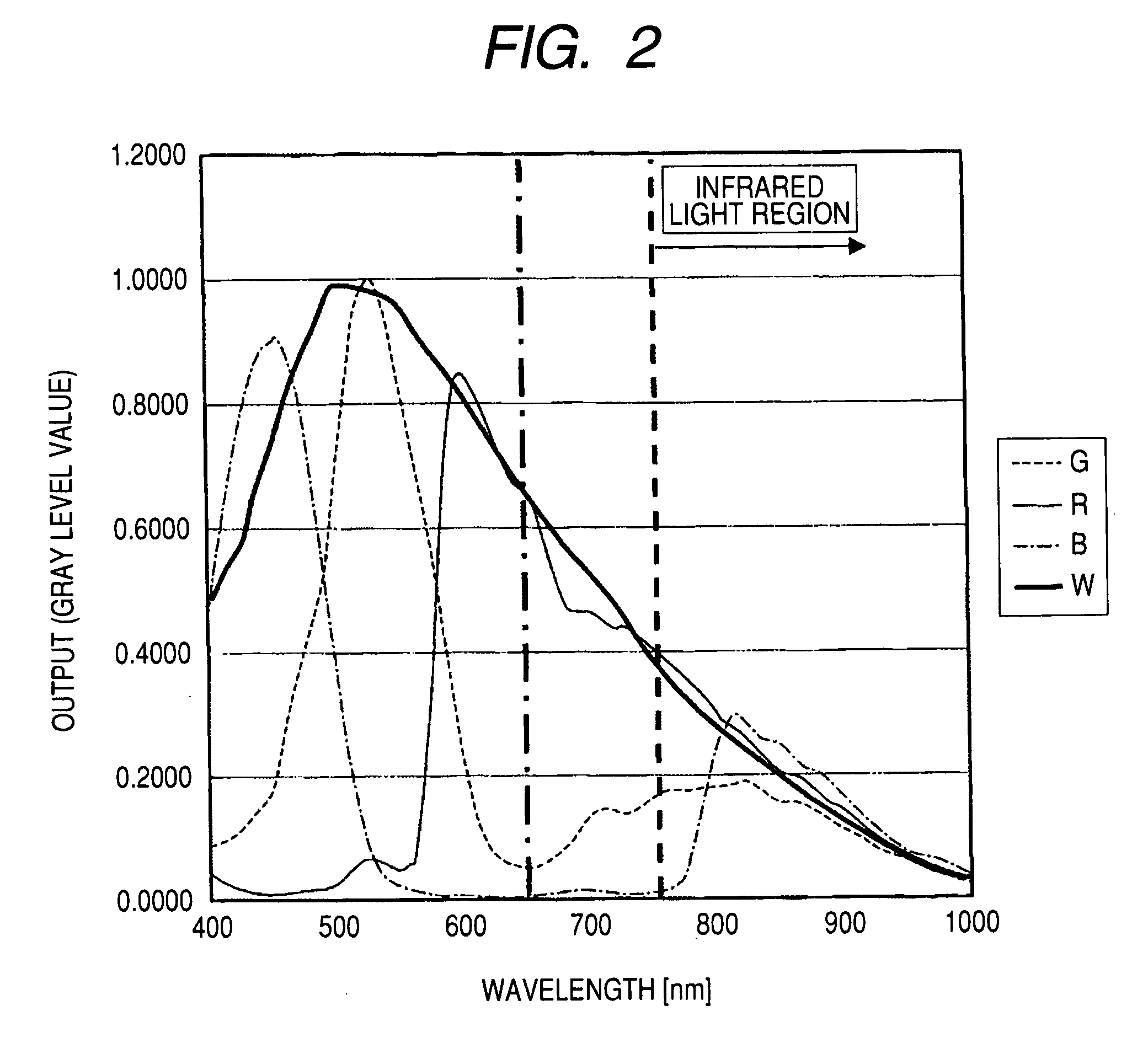
Video input processor, imaging signal-processing circuit, and method of reducing noises in imaging signals
InactiveUS20080284880A1Noise-reducing capability is preventedReduce gainTelevision system detailsSignal generator with single pick-up deviceRelative magnitudeSignal processing circuits
A video input processor is disclosed. The processor includes: an imaging signal-generating portion configured to image a subject and producing first imaging signals containing visible light components and a second imaging signal containing near-infrared light components; a gain adjustment portion configured to adjustably set a maximum gain value according to a relative magnitude between the visible light components and the near-infrared light components and adjust a gain for the first imaging signals at the set maximum gain value; and a noise reduction portion configured to reduce noises in the first imaging signals after the gain has been adjusted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Imaging system for combined full-color reflectance and near-infrared imaging
An imaging system for acquisition of NIR and full-color images includes a light source providing visible light and NIR light to an area under observation, such as living tissue, a camera having one or more image sensors configured to separately detect blue reflectance light, green reflectance light, and combined red reflectance light / detected NIR light returned from the area under observation. A controller in signal communication with the light source and the camera is configured to control the light source to continuously illuminate area under observation with temporally continuous blue / green illumination light and with red illumination light and NIR excitation light. At least one of the red illumination light and NIR excitation light are switched on and off periodically in synchronism with the acquisition of red and NIR light images in the camera.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
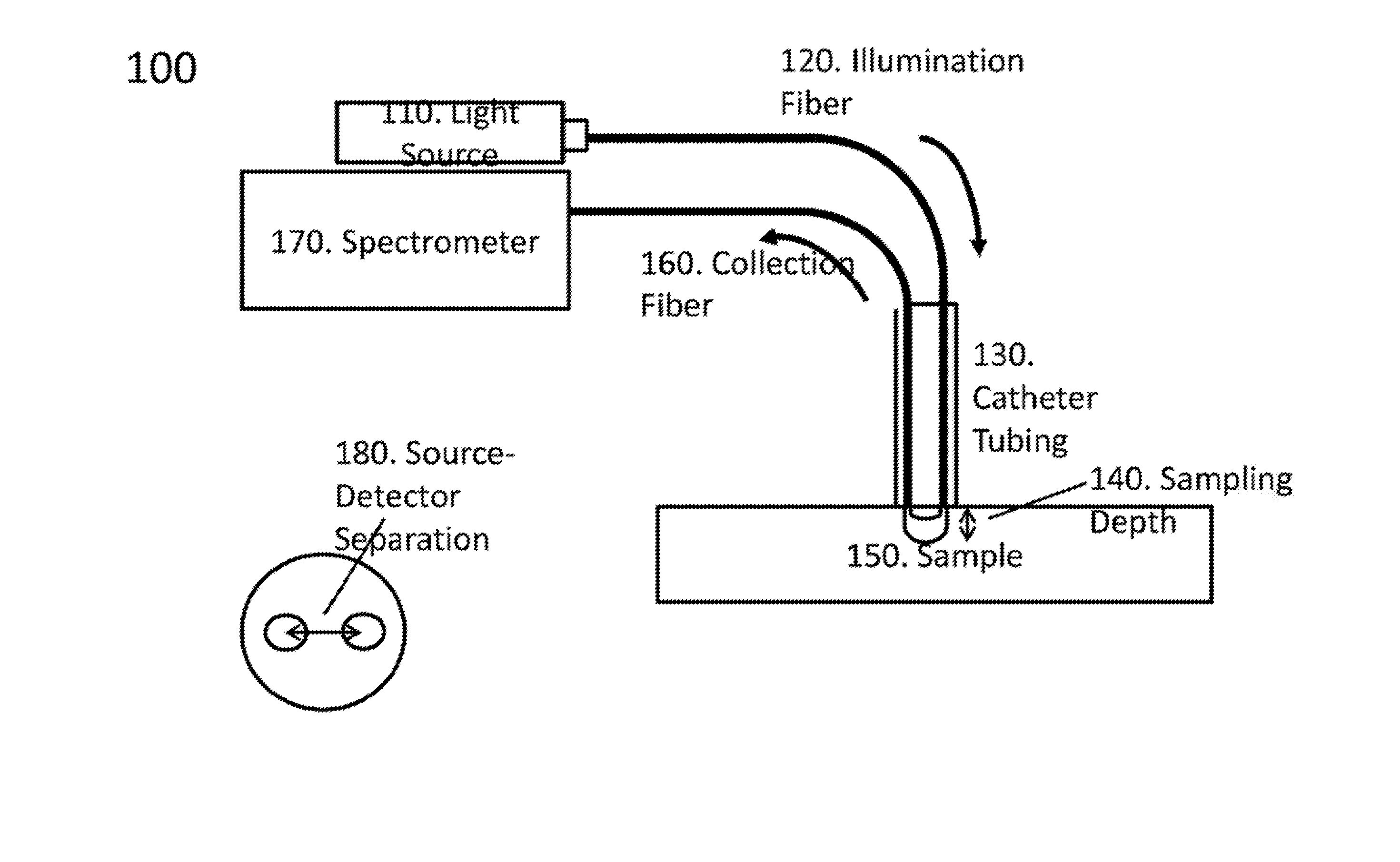
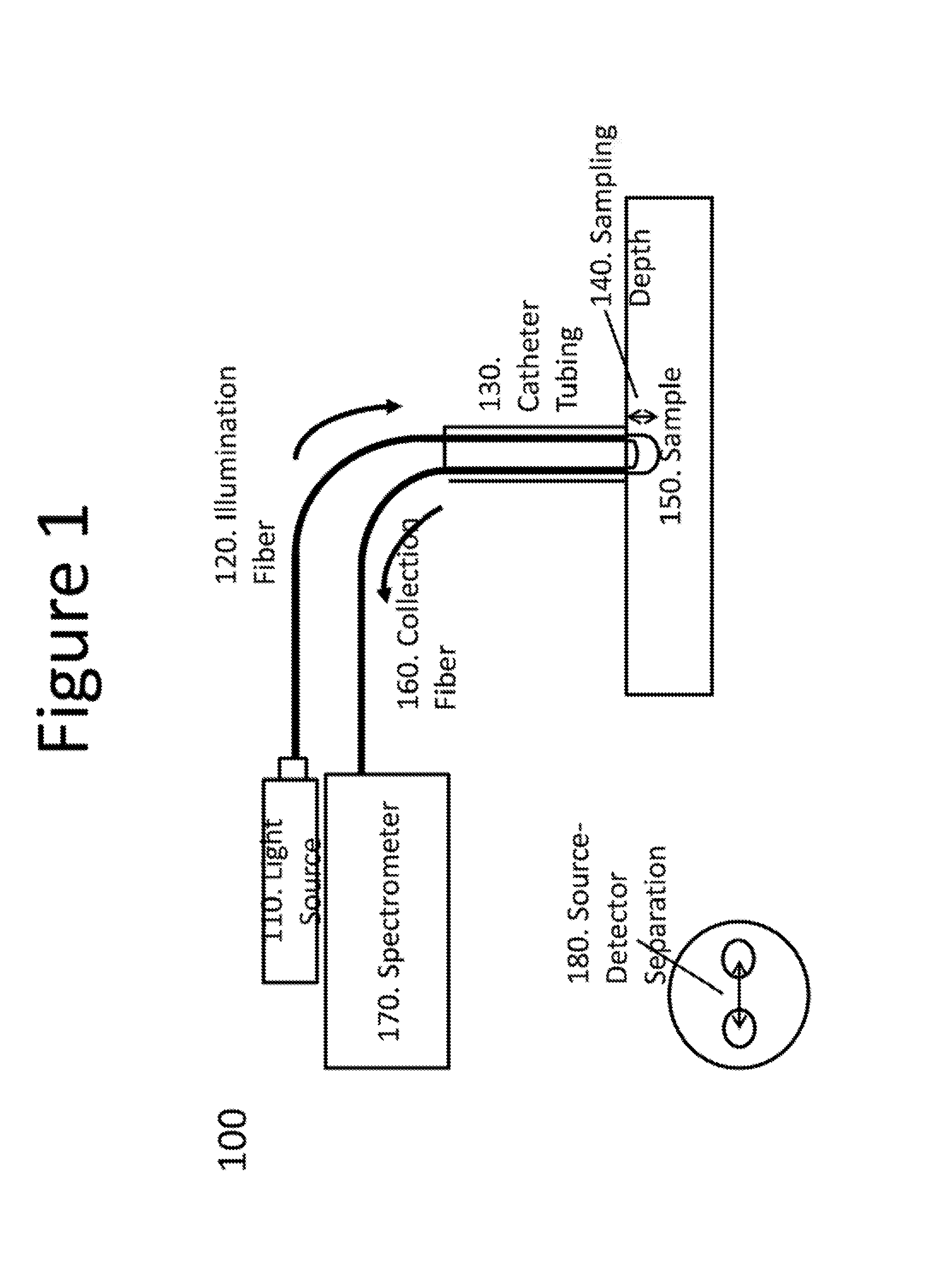
System, method and computer-accessible medium for characterization of tissue
InactiveUS20160235303A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyMedical automated diagnosisDiffuse reflectionNear infrared radiation
An exemplary system, method and computer-accessible medium for determining resultant information about a portion(s) of a tissue(s), can include, for example, receiving initial information which is based on a particular radiation that is returned from the portion(s), the particular radiation can be is based solely on an interaction between the portion(s) and a near-infrared radiation forwarded to the portion(s), and determining the resultant information about the portion(s) of the tissue(s) based on the initial information. The near-infrared radiation can be provided by a near-infrared light optical arrangement that can include a diffusely reflected near-infrared light arrangement. A depth of a lesion to be ablated can be determined by the near-infrared radiation based on the initial information. The initial information can include data corresponding to a reflectance spectrum(s) of the portion(s).
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
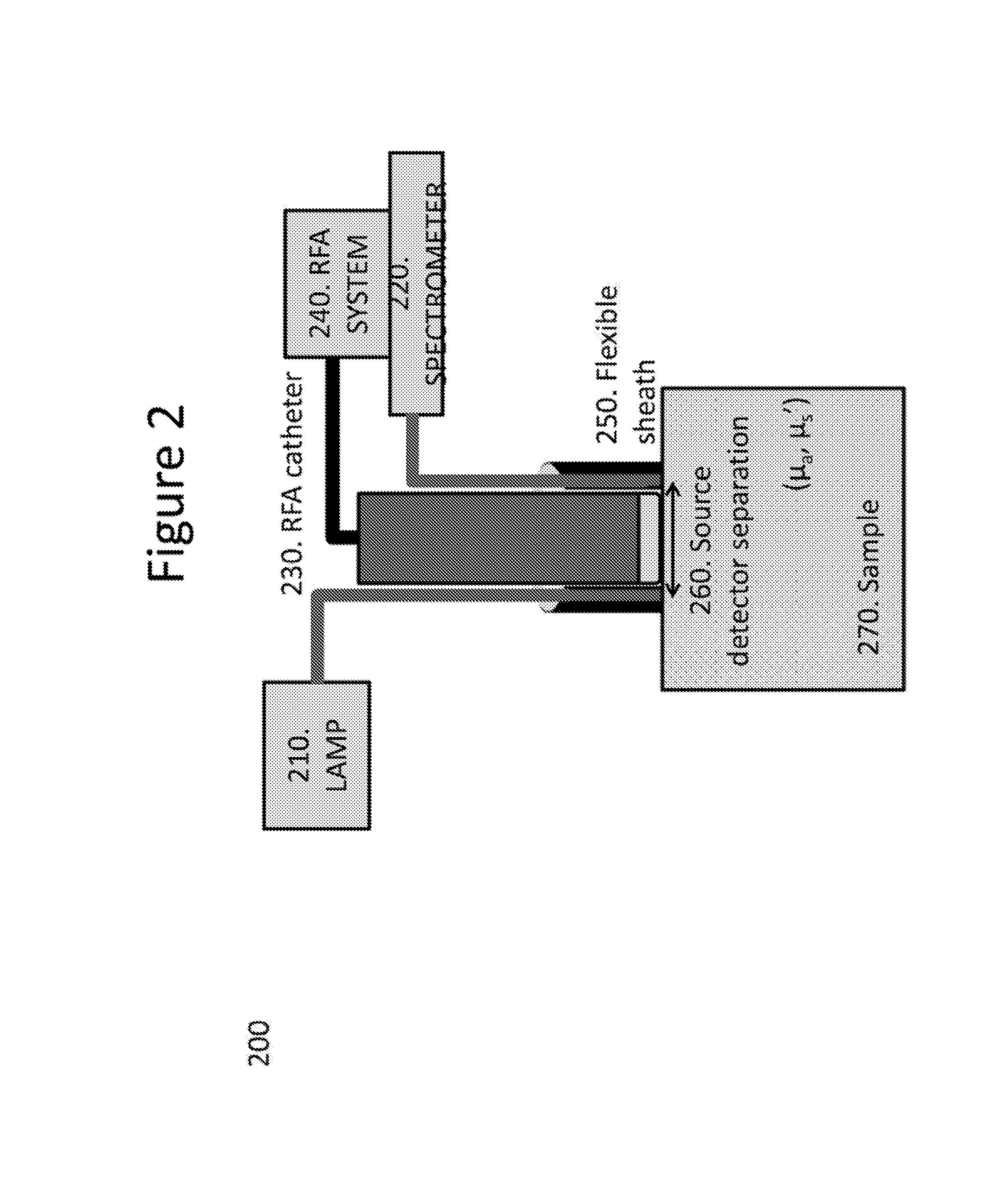
Coronary sinus access catheter with forward-imaging
A coronary access catheter system simplifies the insertion of objects into distal branches of the coronary sinus. The system incorporates a real-time forward-imaging means to view the os and the branches of the coronary sinus. Preferably, the catheter uses near-infrared light as the forward-imaging means, but it could also include ultrasound or electromagnetic transducer. As the image is viewed, the catheter tip can be steered into the coronary sinus os and deflected in a tight radius bend on the distal end to navigate the short radius, right angle turns found in the coronary sinus branches. At that point, a flexible sheath can be placed over the guide catheter or objects such as guidewires can be inserted into channels of the guide catheter. The system consists of a catheter and image acquisition unit, which displays the forward image.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
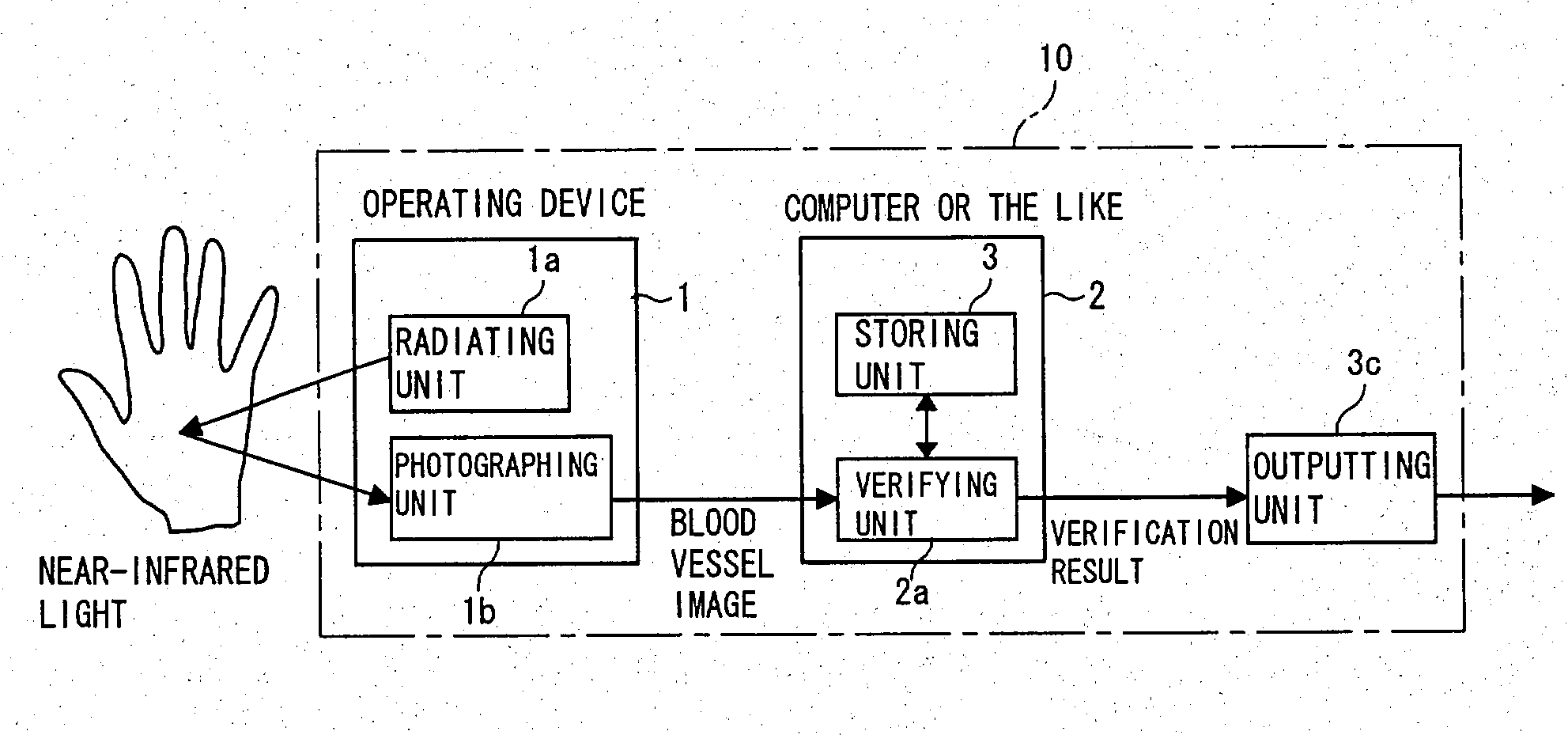
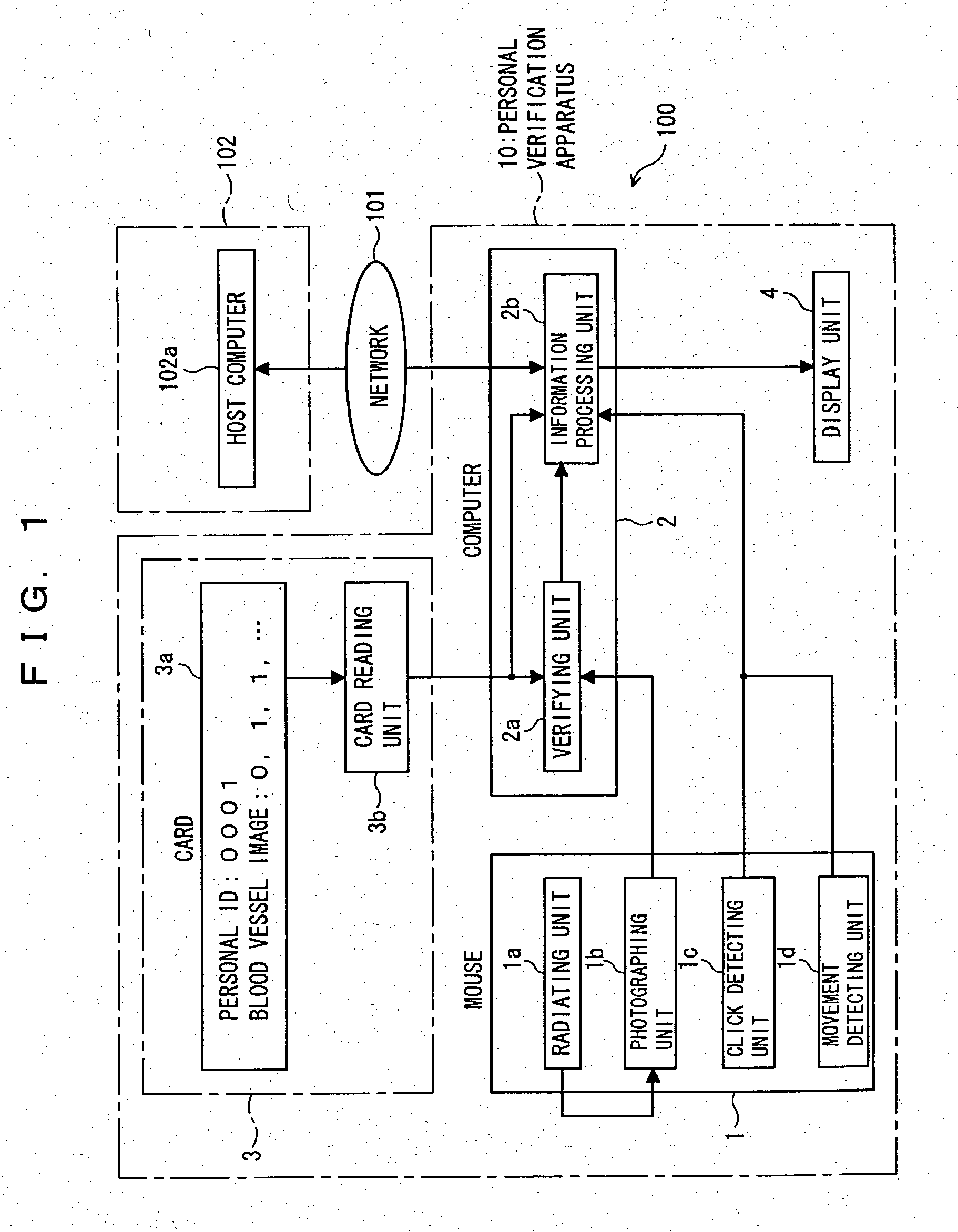
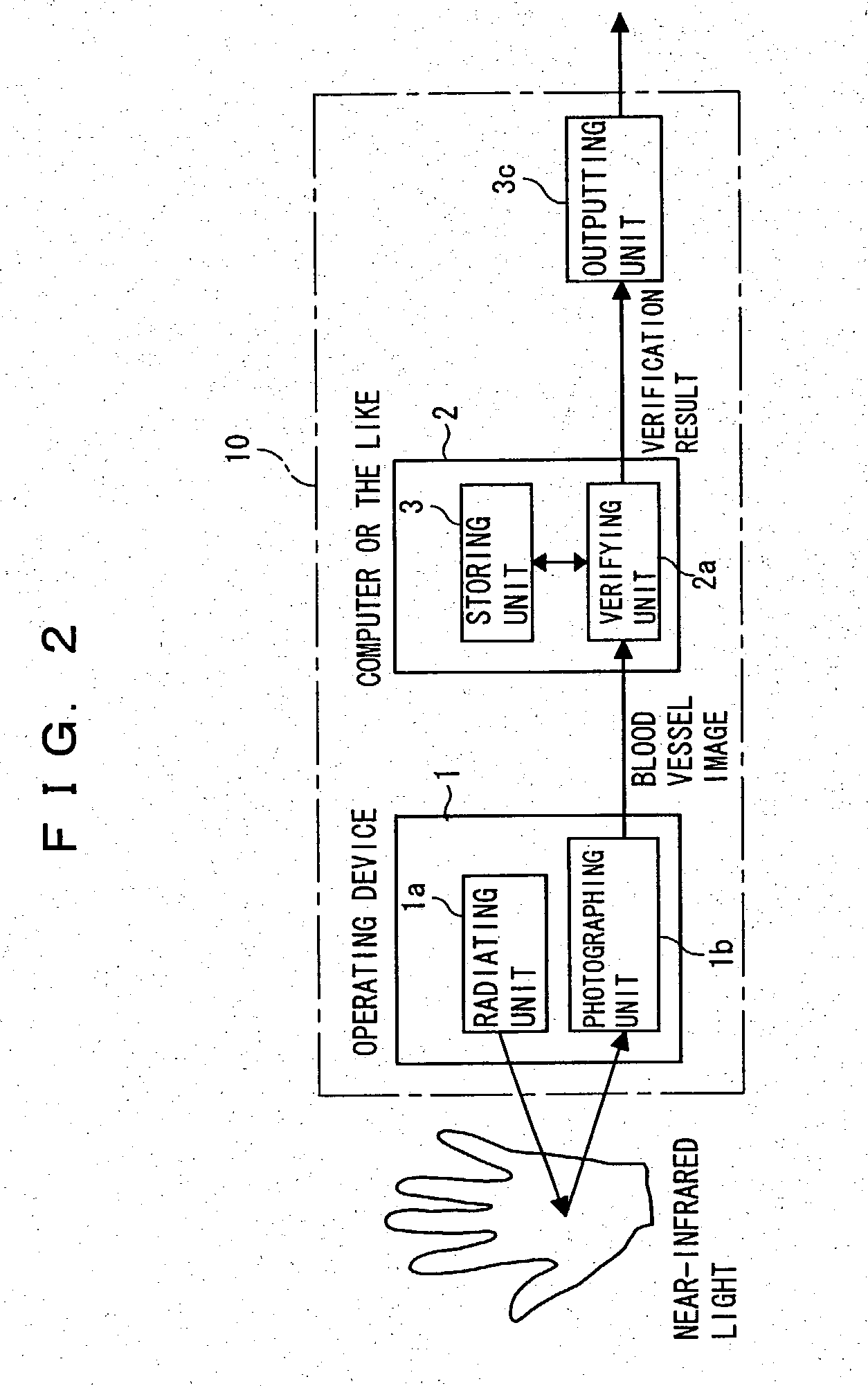
Processor with personal verification function and operating device
InactiveUS20040022421A1Reduce the burden onSave spaceInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisPersonal computerComputer terminal
A processor with a personal verification function has a mouse used by a hand to operate a terminal (personal computer or personal computer main body) and being able to output a photographic blood vessel image obtained by photographing a blood vessel image of the palm of the hand, and a verifying unit carrying out personal verification at a desired time on the basis of the photographic blood vessel image outputted from the mouse and a registration blood vessel image. The mouse has a radiating unit radiating near-infrared light toward the palm of the hand, and a photographing unit photographing the photographic blood vessel image with reflected light from the palm of the hand. The processor with a personal verification function and an operating device make possible personal authentication and personal identification at any time, and are operable within a saved-space without placing a burden on the user.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
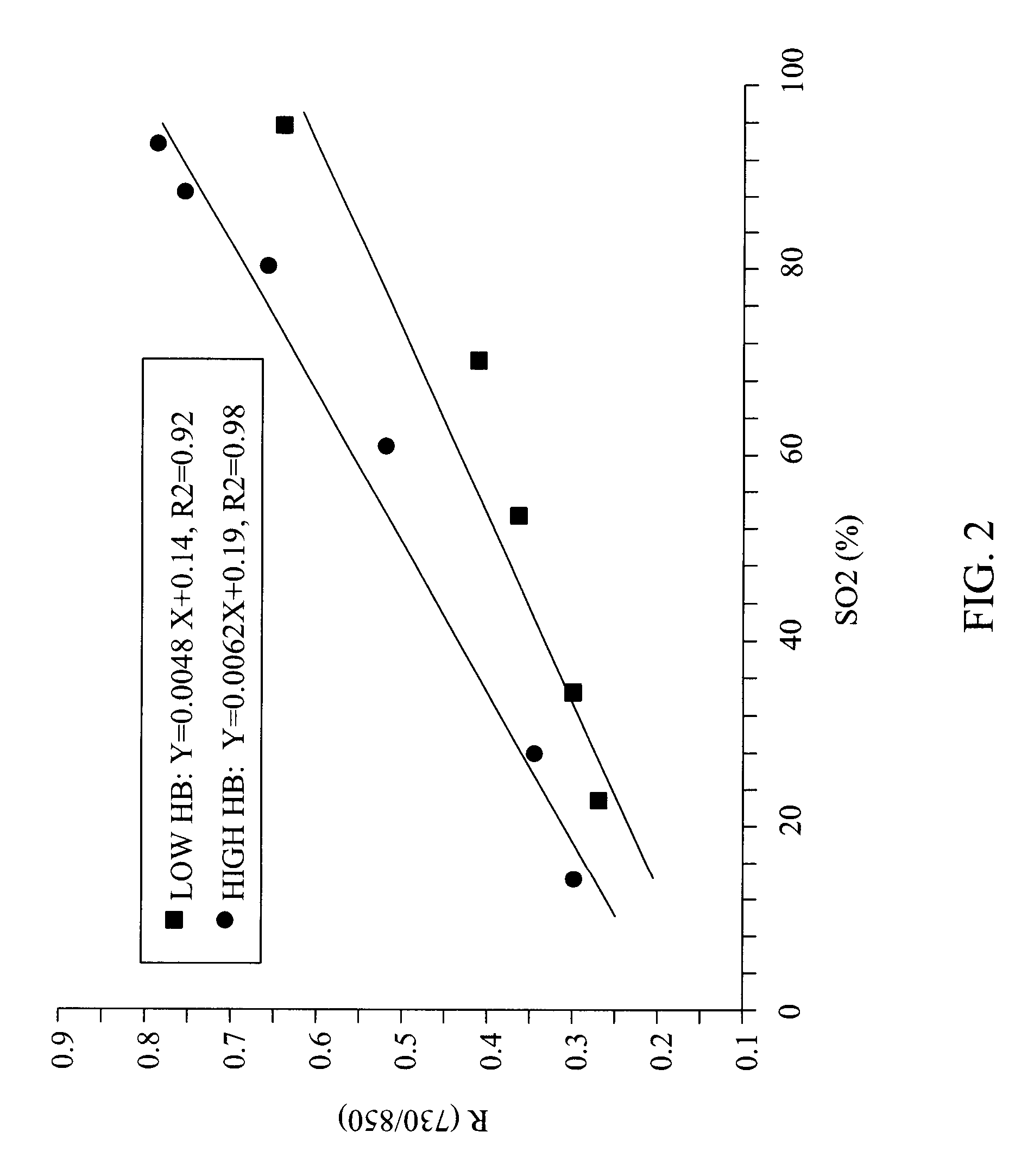
Multi-Wavelength Spatial Domain Near Infrared Oximeter to Detect Cerebral Hypoxia-Ischemia
InactiveUS20080139908A1Material analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringTissue oxygenationMulti wavelength
Methods and apparatus for measuring cerebral O2 saturation and detecting cerebral hypoxia-ischemia using multi-wavelength near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Near-infrared light produced by an emitter is directed through brain tissue. The intensity of the light that passes through the brain tissue is measured using photodiode detectors positioned at distinct distances from the emitter. This process is conducted for at least three wavelengths of near-infrared light. One of the wavelengths used is substantially at an isobestic point for oxy-hemoglobin and deoxy-hemoglobin, but the other two may be any wavelengths within the near-infrared spectrum (700 nm to 900 nm), so long as one of the additional wavelengths is greater than the isobestic point and the other is less than the isobestic point. Tissue oxygenation is calculated using an algorithm derived from the Beer-Lambert law. Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia may be diagnosed using the calculated tissue oxygenation value.
Owner:KURTH CHARLES DEAN
Encoding Free View Point Data in Movie Data Container
ActiveUS20180205963A1Digital video signal modificationSelective content distributionParallaxSound sources
Multiple Holocam Orbs observe a real-life environment and generate an artificial reality representation of the real-life environment. Depth image data is cleansed of error due to LED shadow by identifying the edge of a foreground object in an (near infrared light) intensity image, identifying an edge in a depth image, and taking the difference between the start of both edges. Depth data error due to parallax is identified noting when associated text data in a given pixel row that is progressing in a given row direction (left-to-right or right-to-left) reverses order. Sound sources are identified by comparing results of a blind audio source localization algorithm, with the spatial 3D model provided by the Holocam Orb. Sound sources that corresponding to identifying 3D objects are associated together. Additionally, types of data supported by a standard movie data container, such as an MPEG container, is expanding to incorporate free viewpoint data (FVD) model data. This is done by inserting FVD data of different individual 3D objects at different sample rates into a single video stream. Each 3D object is separately identified by a separately assigned ID.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP +1
Method of detecting biological pattern, biological pattern detector, method of biological certificate and biological certificate apparatus
InactiveUS20050180620A1Reduce adverse effectsEfficient detectionImage enhancementImage analysisOptical propertyPattern detection
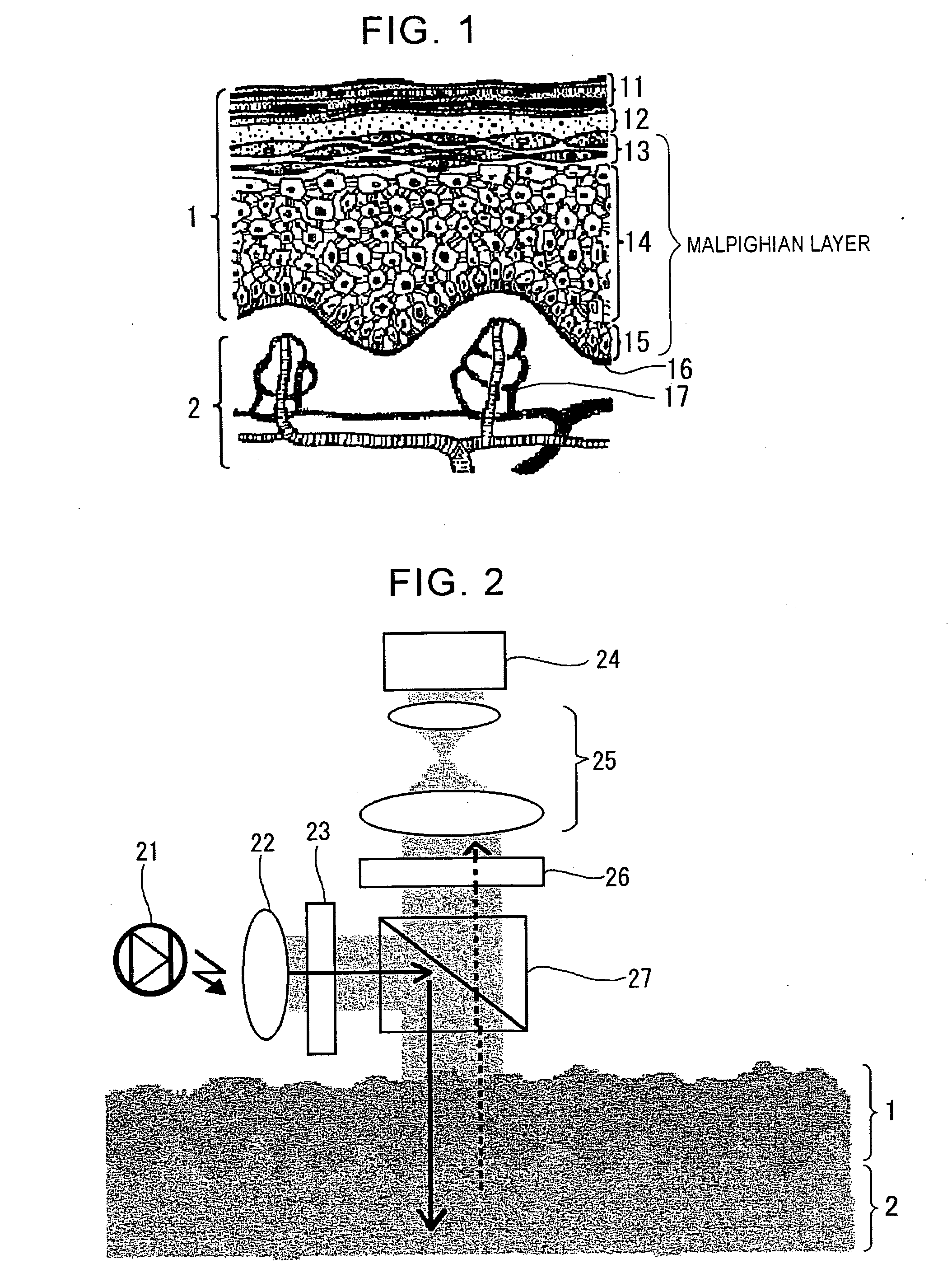
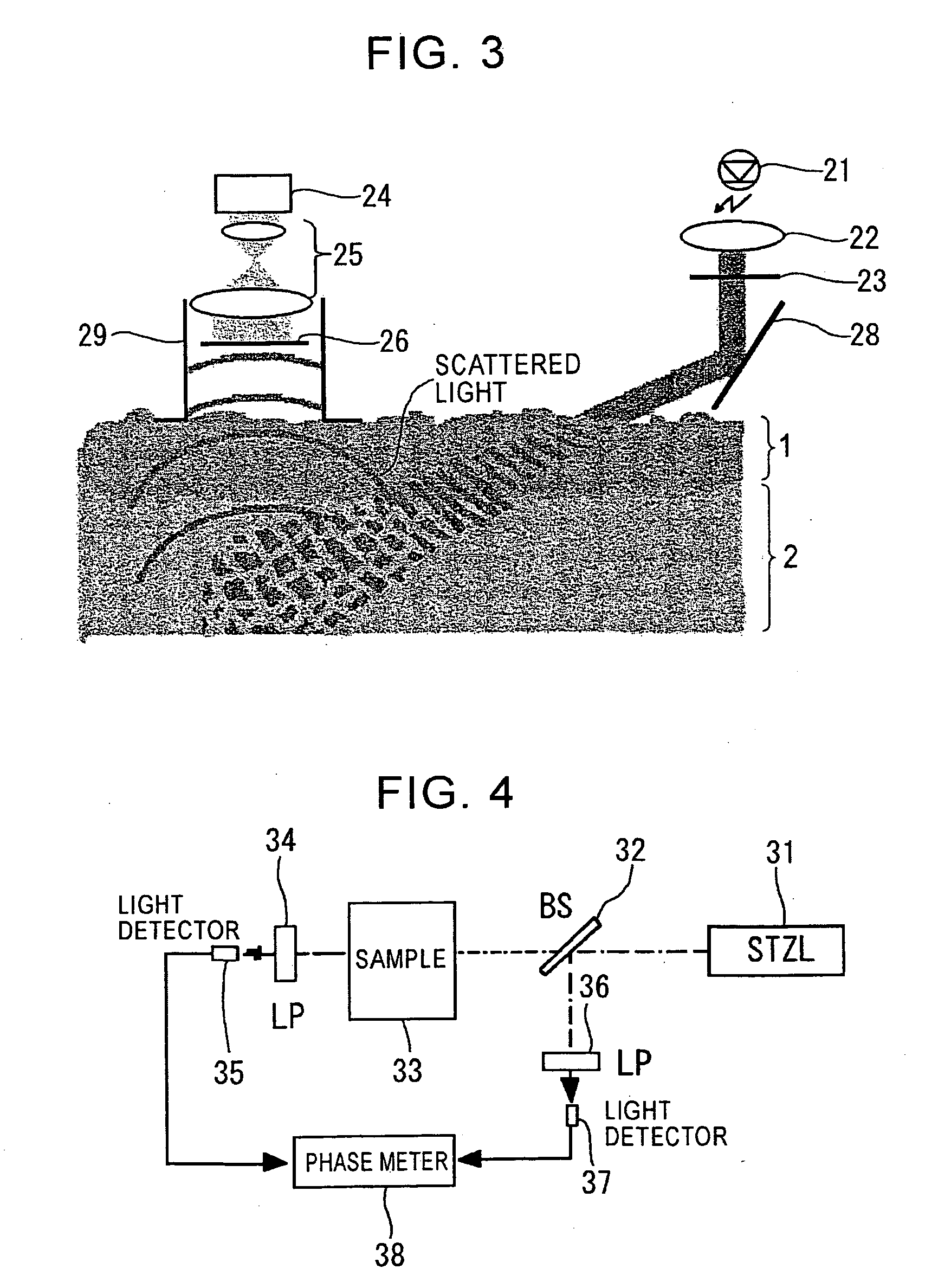
The present invention enables permanent biometric authentication without the risk of forgery or the like. The present invention enables living-tissue discrimination as well as biometric authentication. The roughness distribution pattern of deep-layer tissue of the skin covered with epidermal tissue is detected, thereby extracting a unique pattern of the living tissue. Then, biometric authentication is performed based upon the detected pattern. The roughness distribution pattern of the deep-layer tissue of the skin is optically detected using difference in optical properties between the epidermal tissue and the deep-layer tissue of the skin. In this case, long-wavelength light, e.g., near-infrared light is used as illumination light cast onto the skin tissue. A fork structure of a subcutaneous blood vessel is used as the portion which is to be detected, for example. The portion which is to be detected is determined based upon the structure of the fork structure. In this case, the living-tissue discrimination may be made using the subcutaneous blood vessel.
Owner:SONY CORP
Head-mounted display with an eyeball-tracker integrated system
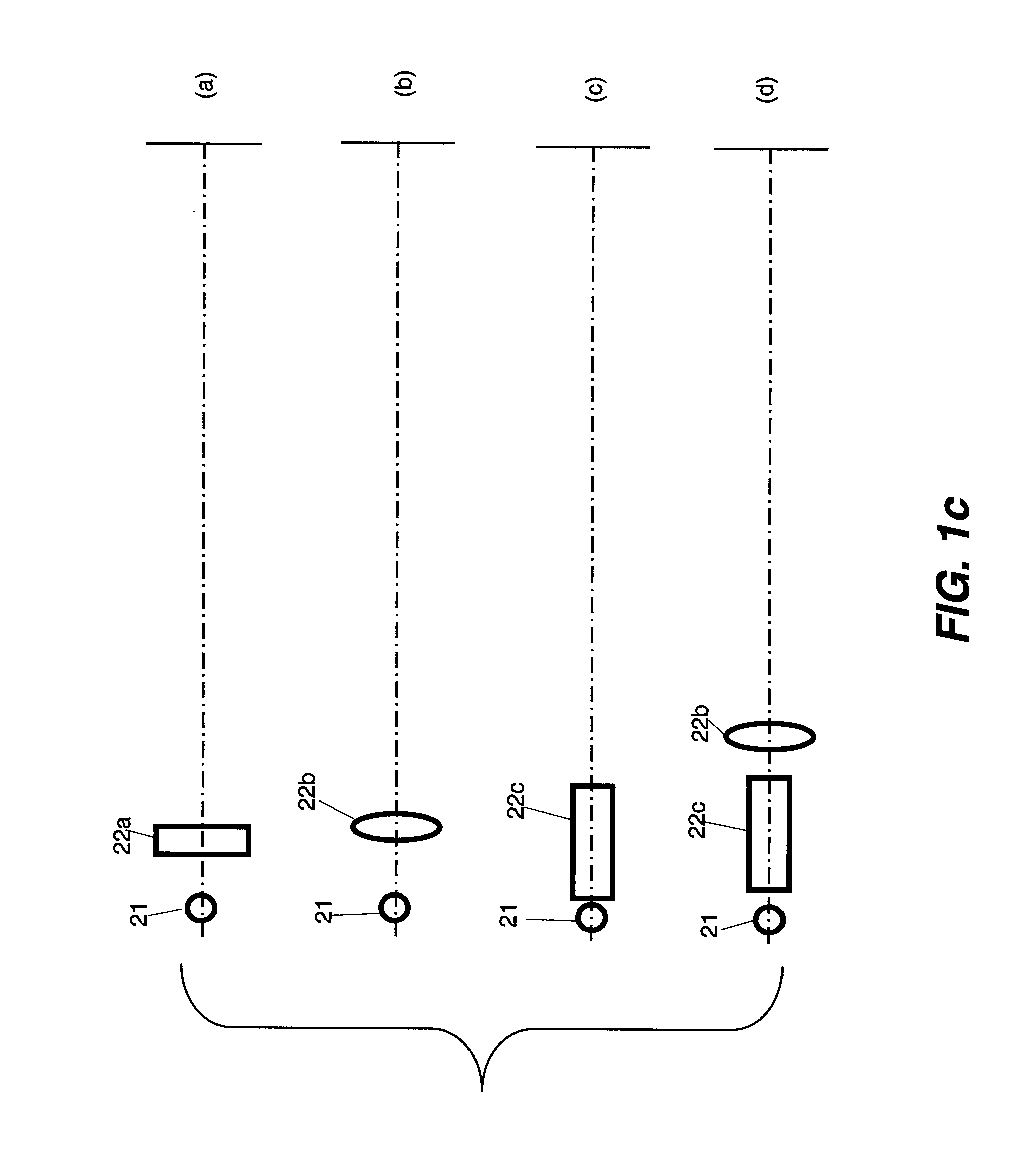
ActiveUS20150138451A1Facilitates exploitationEasy to mergeEye diagnosticsData processing managementTotal internal reflectionDisplay device
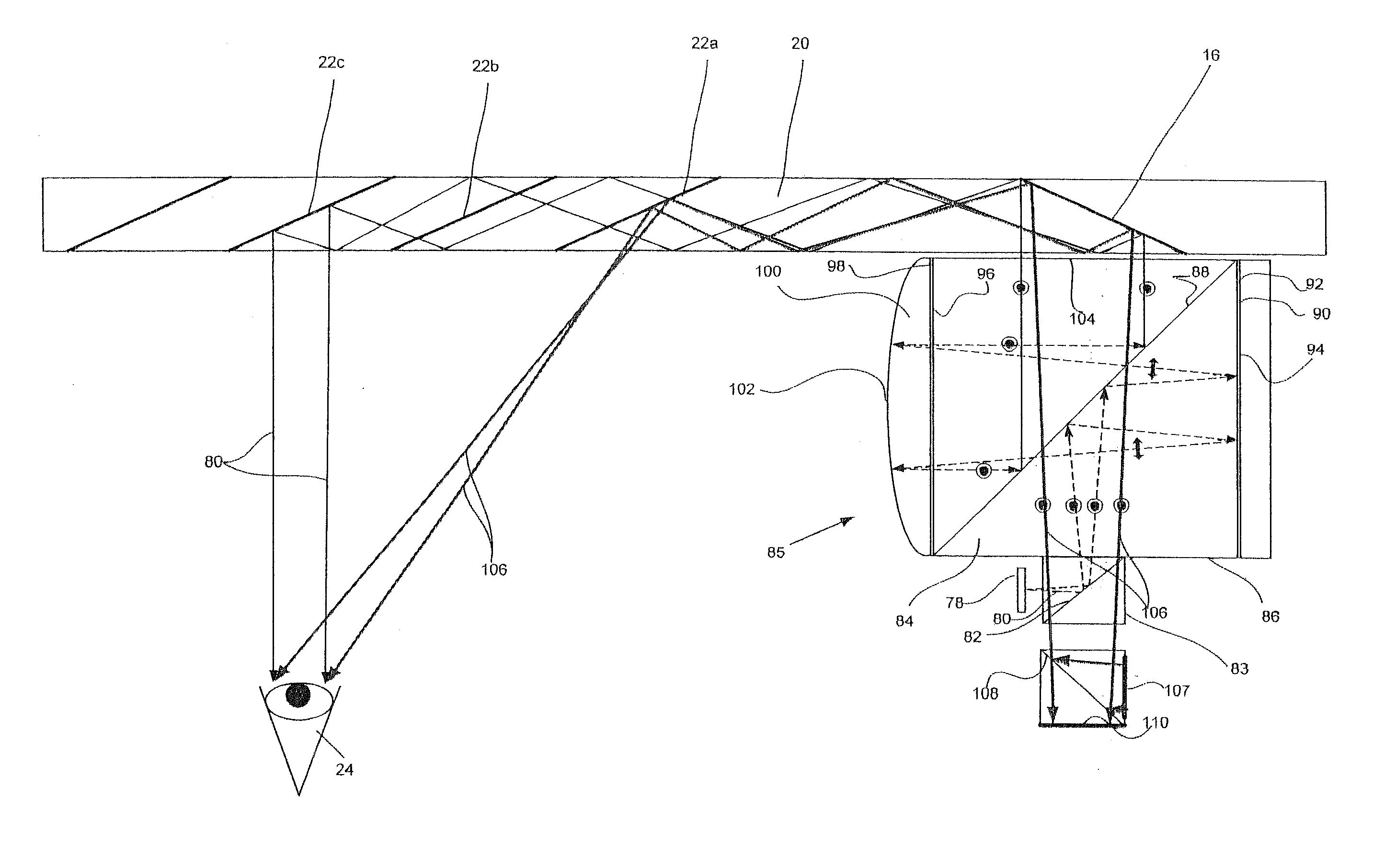
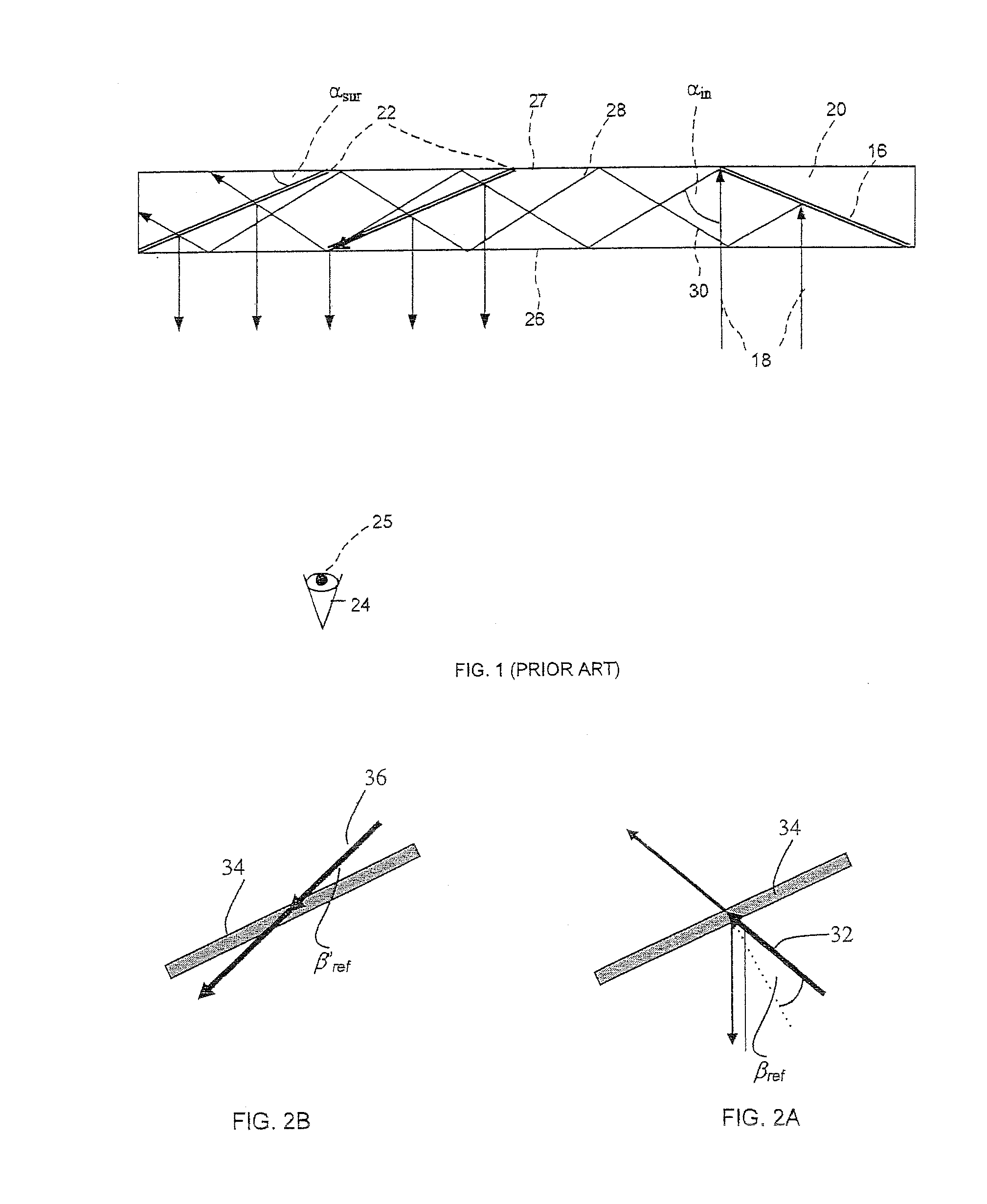
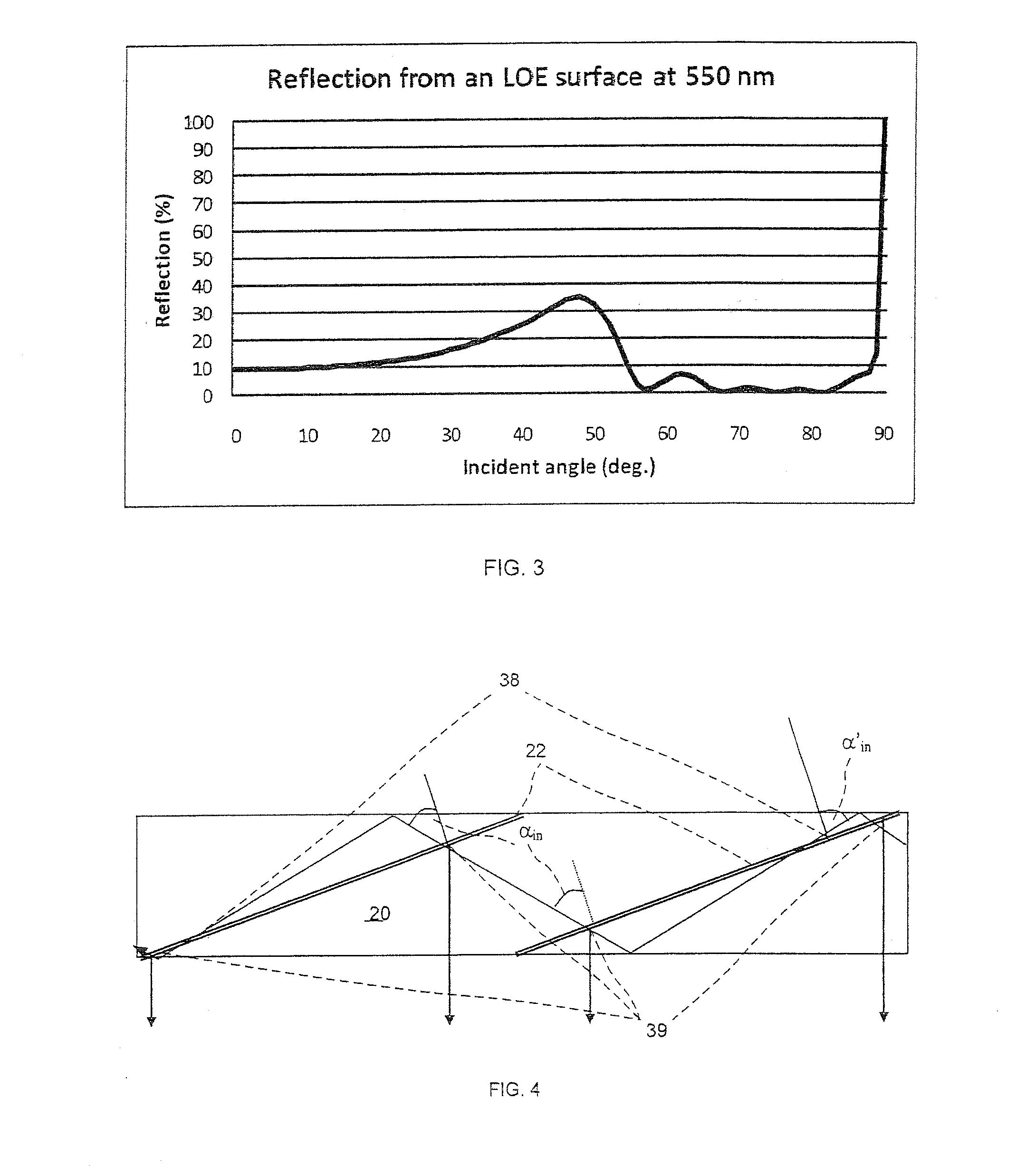
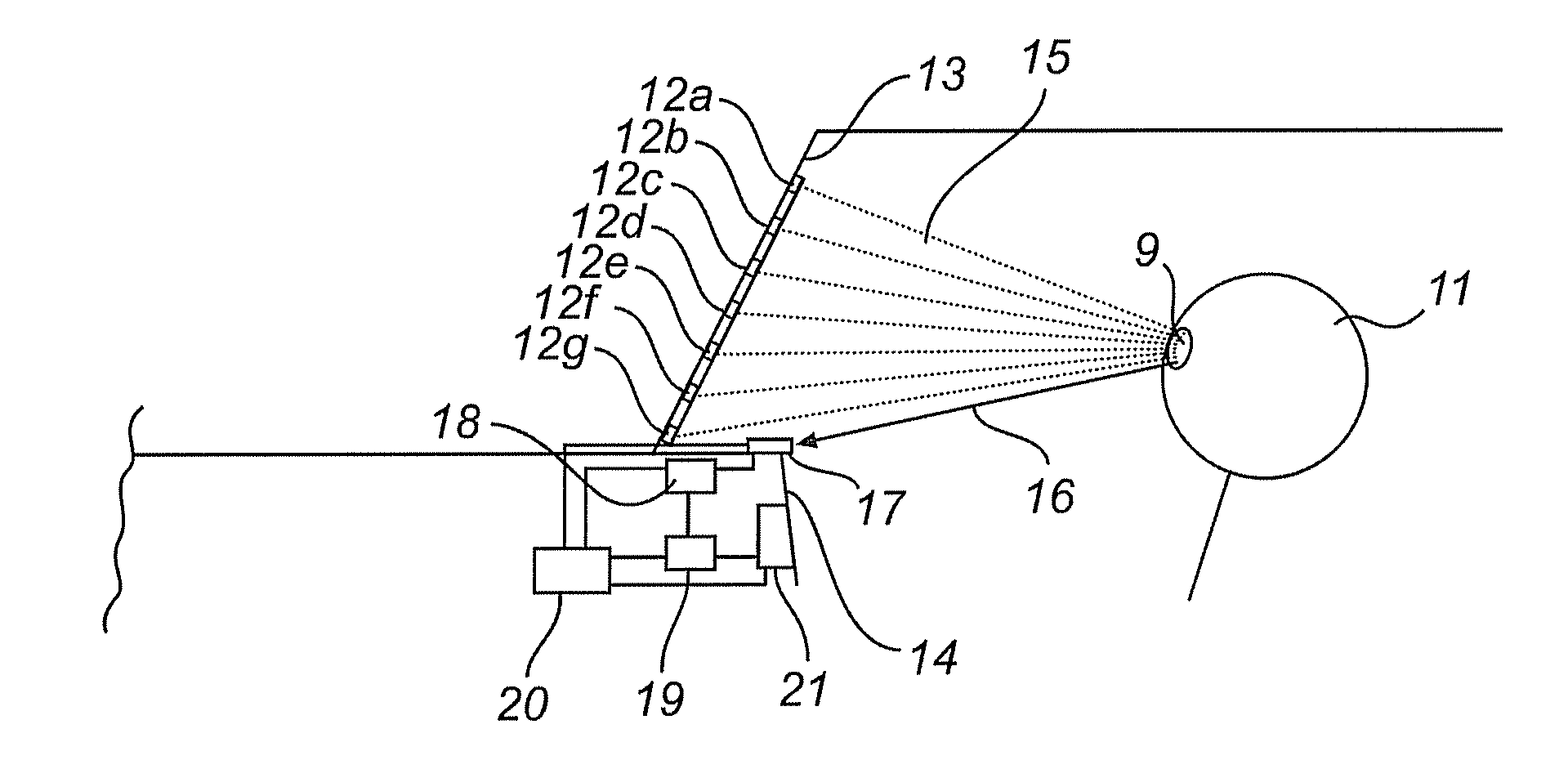
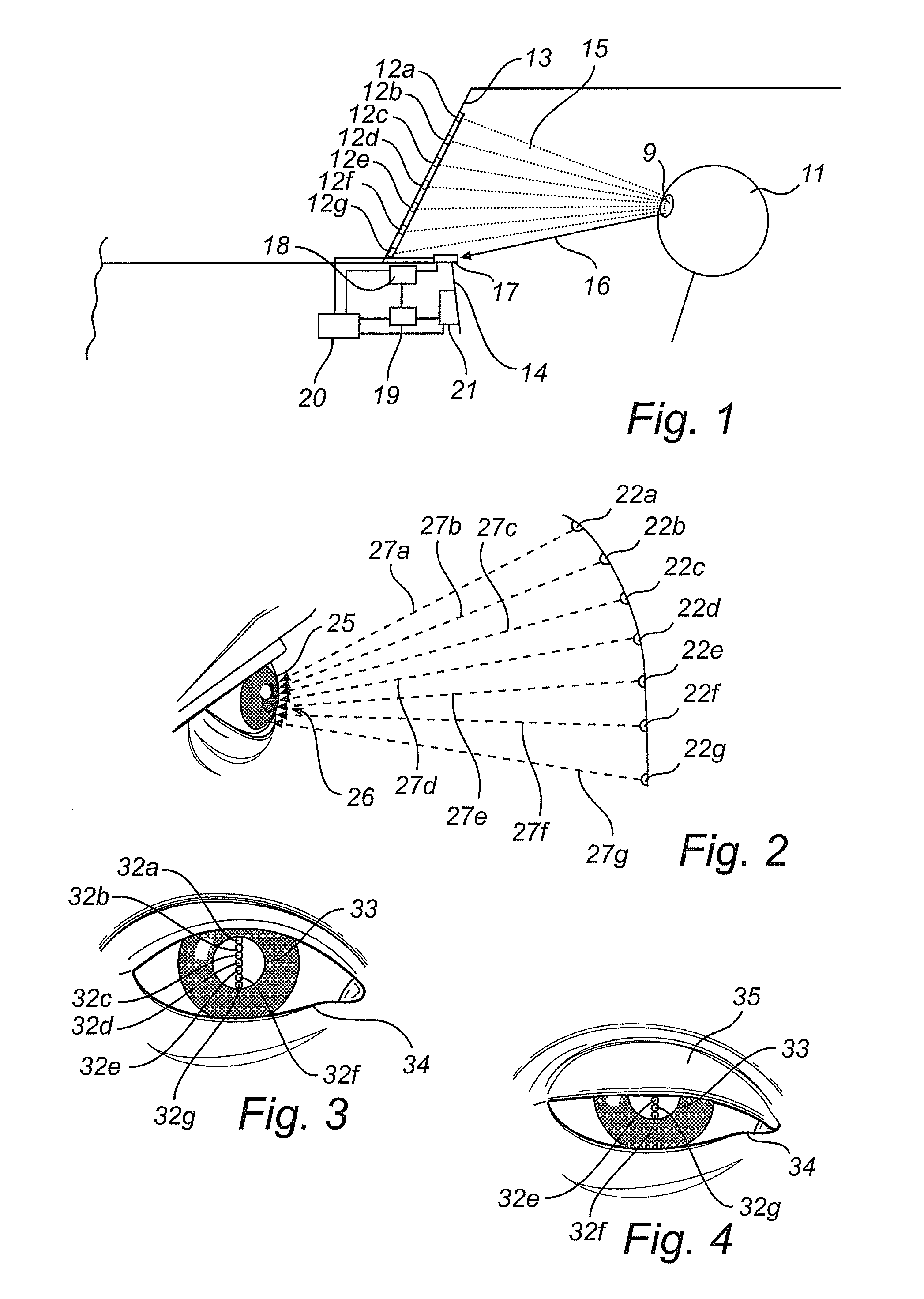
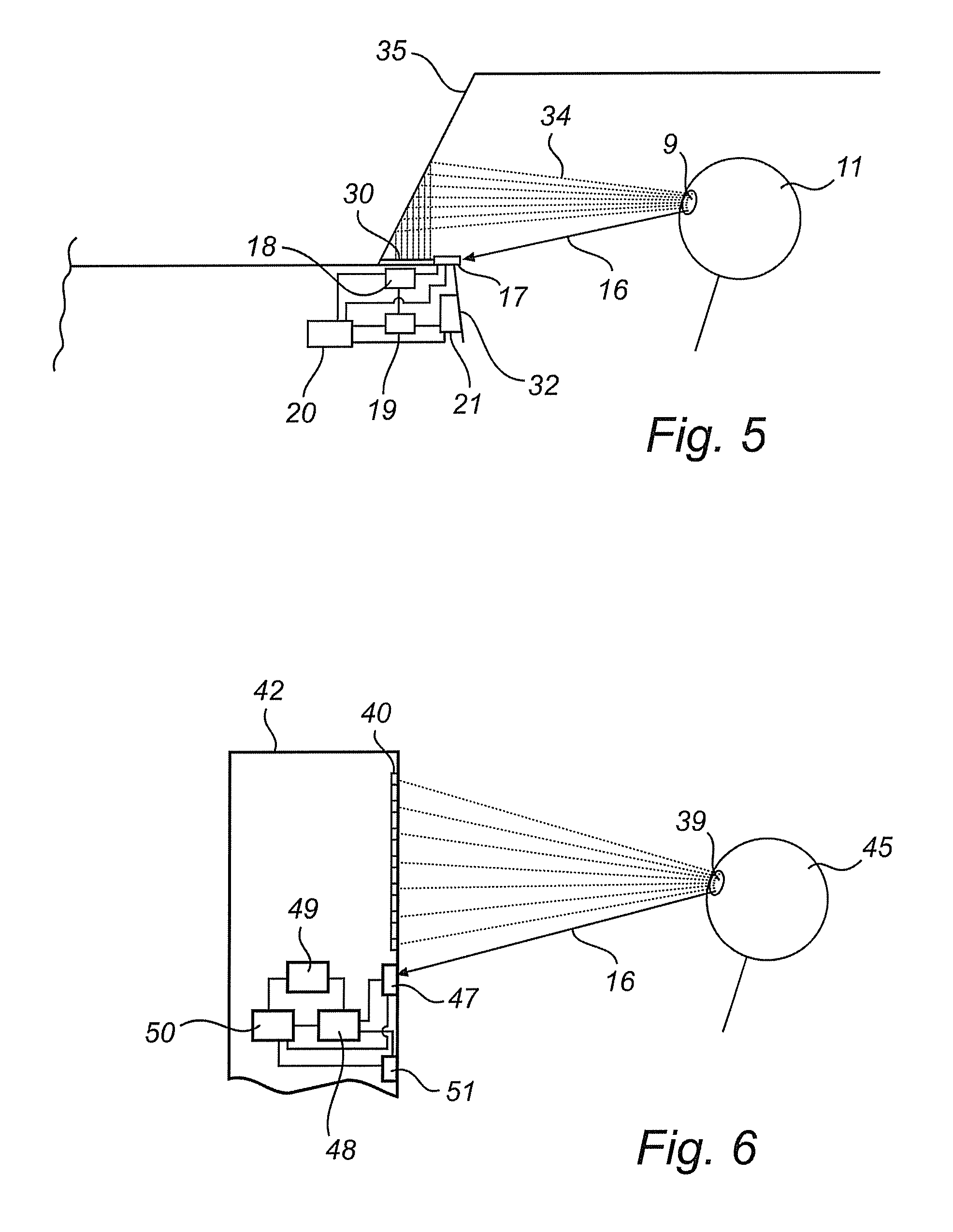
Head-mounted display with an eye-tracking system and including a light-transmitting substrate (20) having two major surfaces and edges, optical means for coupling light into said substrate (20) by total internal reflection, partially-reflecting surfaces (22a-22c) carried by the substrate (20) that are not parallel with the major surfaces of the substrate (20), a near-infrared light source (78) and a display source (92) projecting within the photopic spectrum, wherein light from the light source (78) and light from the display source (92) are coupled into the substrate (20) by total internal reflection.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Silicon-based visible and near-infrared optoelectric devices
InactiveUS20050127401A1Promote generationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface layerPhotovoltaic detectors
In one aspect, the present invention provides a silicon photodetector having a surface layer that is doped with sulfur inclusions with an average concentration in a range of about 0.5 atom percent to about 1.5 atom percent. The surface layer forms a diode junction with an underlying portion of the substrate. A plurality of electrical contacts allow application of a reverse bias voltage to the junction in order to facilitate generation of an electrical signal, e.g., a photocurrent, in response to irradiation of the surface layer. The photodetector exhibits a responsivity greater than about 1 A / W for incident wavelengths in a range of about 250 nm to about 1050 nm, and a responsivity greater than about 0.1 A / W for longer wavelengths, e.g., up to about 3.5 microns.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
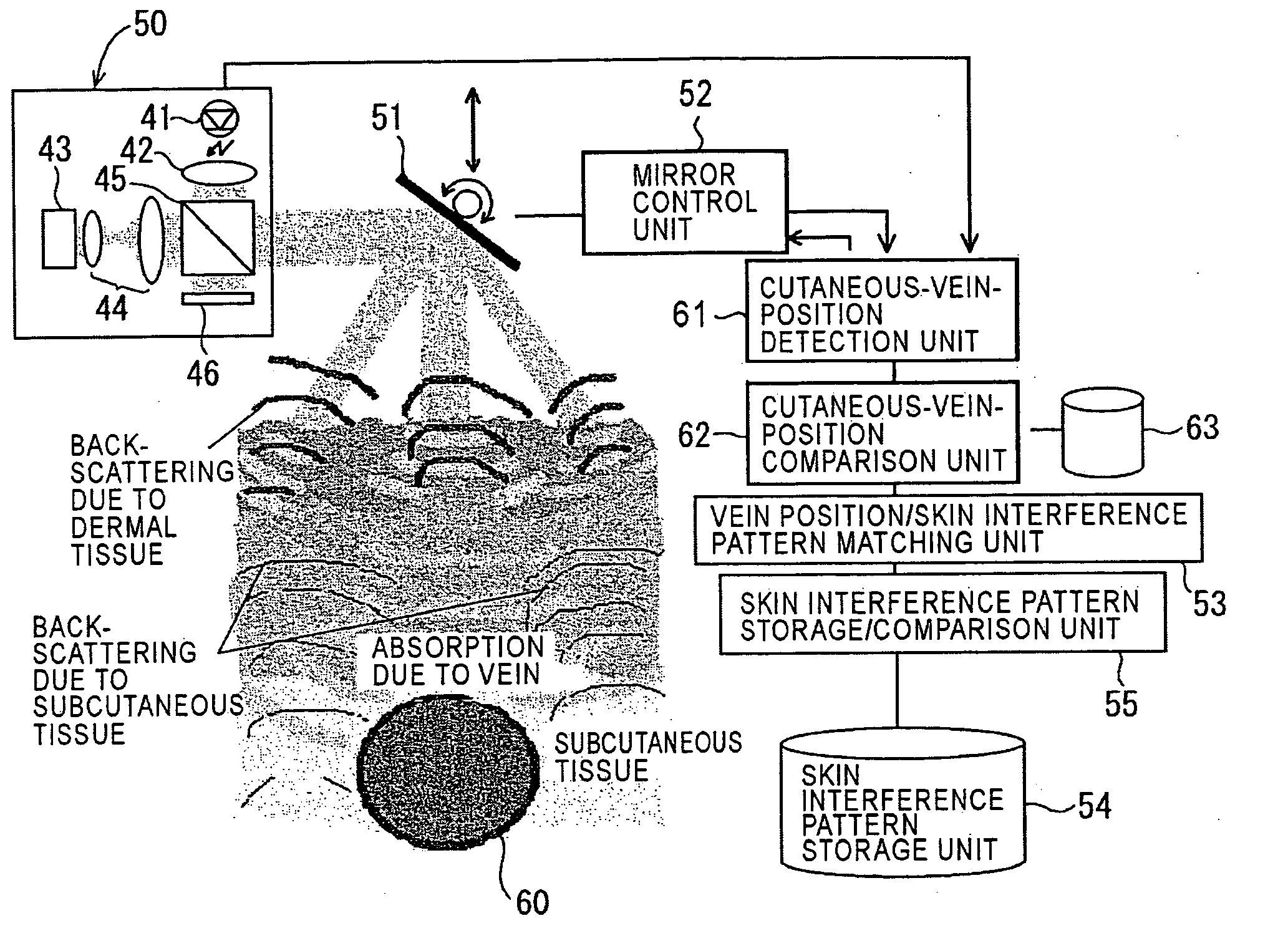
Apparatus and method for recognizing subcutaneous vein pattern
InactiveUS20100061598A1Easy to insertEasy to identifyDiagnostics using lightPerson identificationVeinIlluminance
Owner:INNOZEST
Eye closure detection using structured illumination
ActiveUS20100245093A1High degree of accuracyImprove reliabilityAcquiring/recognising eyesColor television detailsEye closureMonitoring system
A monitoring system monitors and / or predicts drowsiness of a driver of a vehicle or a machine operator. A set of infrared or near infrared light sources is arranged such that an amount of the light emitted from the light source strikes an eye of the driver or operator. The light that impinges on the eye of the driver or operator forms a virtual image of the signal sources on the eye, including the sclera and / or cornea. An image sensor obtains consecutive images capturing the reflected light. Each image contains glints from at least a subset or from all of the light sources. A drowsiness index can be determined based on the extracted information of the glints of the sequence of images. The drowsiness index indicates a degree of drowsiness of the driver or operator.
Owner:TOBII TECH AB
Optical filter and process for producing the same
InactiveUS7025908B1Improve stabilityHigh transparencyTransistorOther chemical processesPhosphoric Acid EstersIon content
The optical filter of the present invention is provided with a near infrared light absorption layer that contains a component composed of copper ions and a phosphoric ester compound expressed by the following Formula (10), in which the phosphorus atom content in the near infrared light absorption layer is 0.4 to 1.3 mol per mole of copper ions, and the copper ion content in the near infrared light absorption layer is 2 to 60 wt %. Thus keeping the phosphorus atom and copper ion content within specific ranges results in good near infrared light absorption and in improved moisture resistance whereby devitrification caused by whitening is suppressed
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
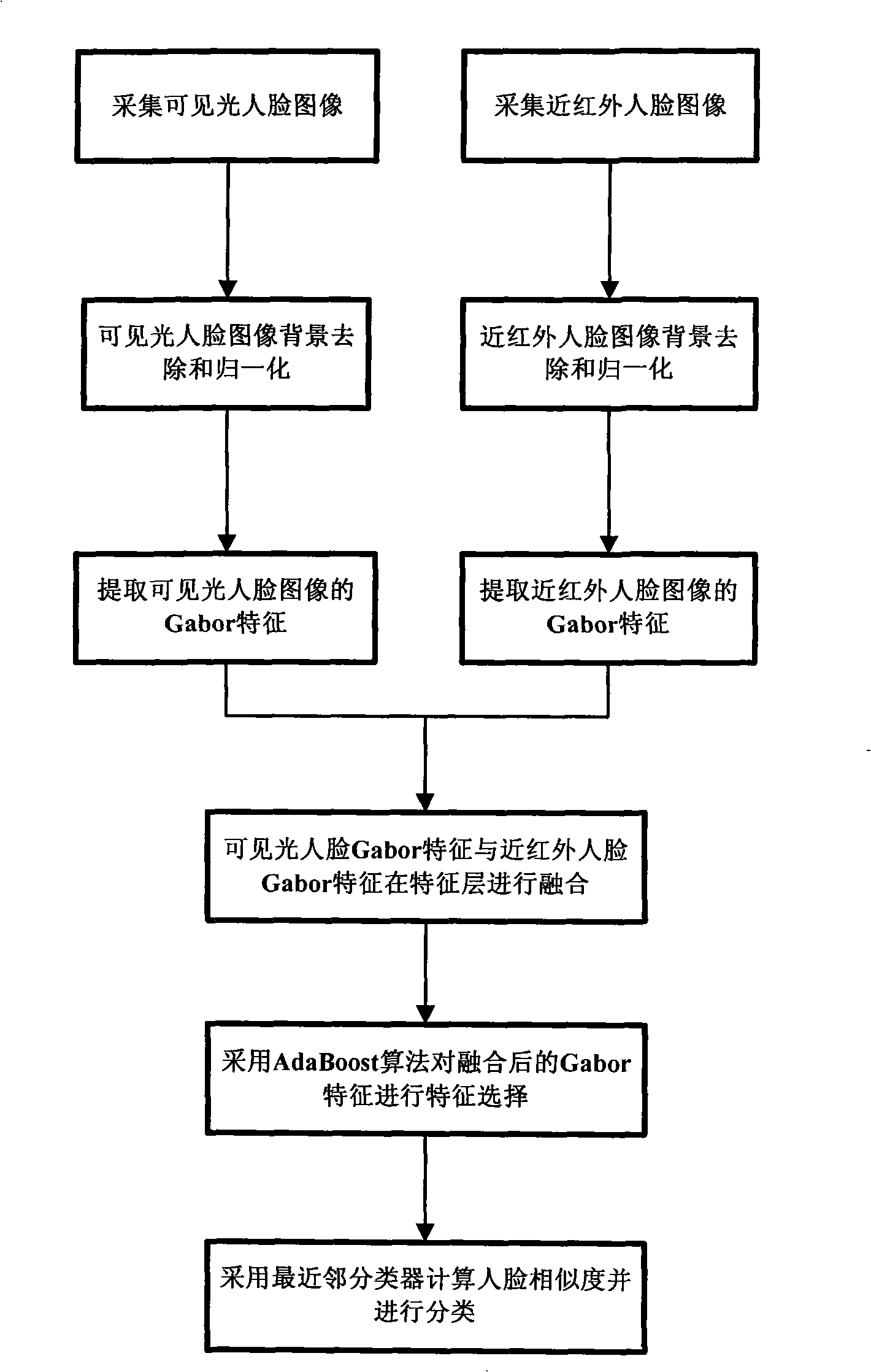
Human face recognition method based on visible light and near-infrared Gabor information amalgamation
InactiveCN101404060AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionInfraredNear neighbor
The invention discloses a human face recognition method which is based on Gabor information fusion of visible light and near-infrared light. The method comprises: human face images under a visible light source and a near-infrared light source are respectively collected, Gabor features of the two images are respectively extracted to be fused at a feature layer; an AdaBoost algorithm is adopted to carry out the feature selection on the feature after the fusion, and the nearest neighbor classification is adopted to carry out the calculation and the classification on the similarity thereof. The human face recognition method has very high accuracy rate and excellent robustness of the impacts of light illumination on the human face recognition; in addition, compared with other methods, the human face recognition method has the advantages of small number of the used features, rapid classification speed, etc.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Image capture apparatus and biometric authentication apparatus
InactiveUS7773870B2Increase the number ofReduce the amount requiredElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisEngineeringImage capture
A biometric authentication apparatus includes an illumination section, an imaging section, a photographic subject placing section, and an authentication section. The illumination section irradiates at least near infrared light onto a biological portion placed in contact with a housing surface. The imaging section images a near infrared light image of the biological portion. The photographic subject placing section is provided in the vicinity of the illumination section, in which at least a part of the light emanation portion of the illumination section on a side where the imaging section is disposed is covered by the photographic subject when the photographic subject is placed. The authentication section performing biometric authentication by making a comparison between a specific pattern extracted from the near infrared light image of the biological portion imaged by the imaging section and a preliminarily registered specific pattern.
Owner:SONY CORP
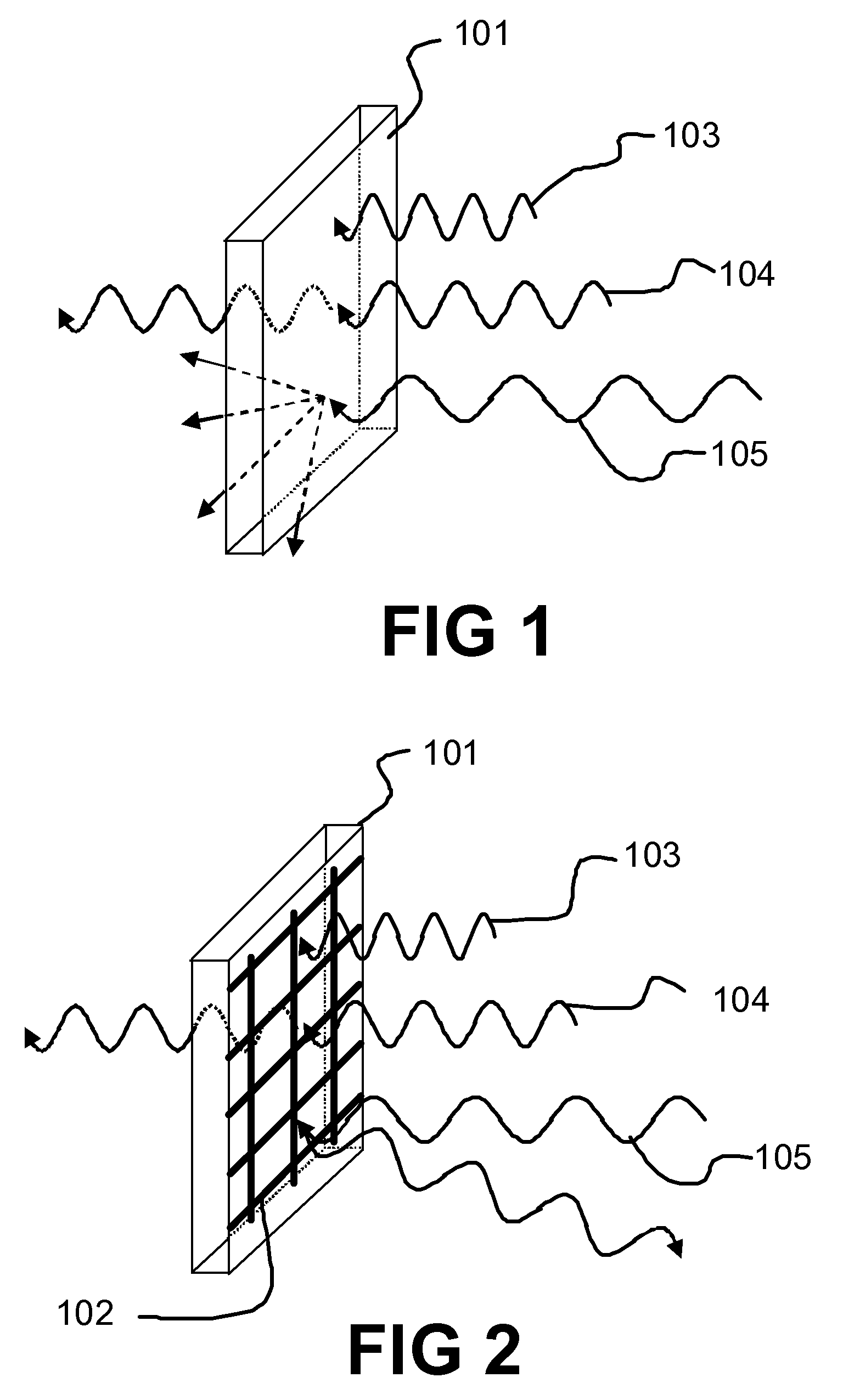
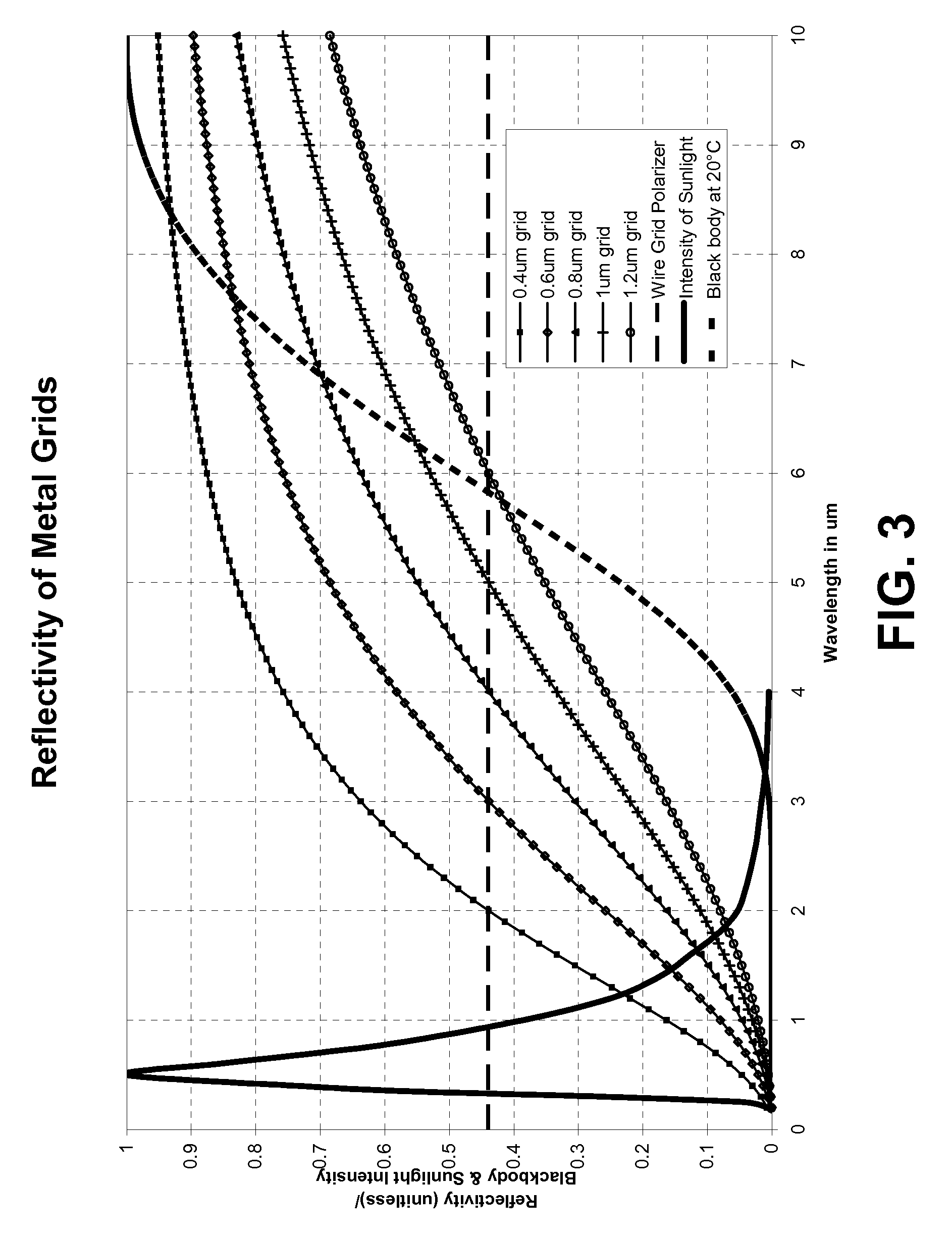
Low-emissivity window films and coatings incorporating nanoscale wire grids
InactiveUS20090128893A1Increasing effective insulation valueDecreased emissivityMirrorsDecorative surface effectsGratingBlack-body radiation
A high-transparency, low-emissivity window film or coating is designed to maximize so-called greenhouse heating. This effect is achieved through the use of conductive grids and / or gratings whose width and spacing has been selected such that the grid appears as a uniform conductive film to long-wavelength infrared (blackbody) radiation. The conductive grid film reflects the blackbody radiation strongly, and such that the grid appears highly transparent to visible and near-infrared light, and therefore transmits it.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
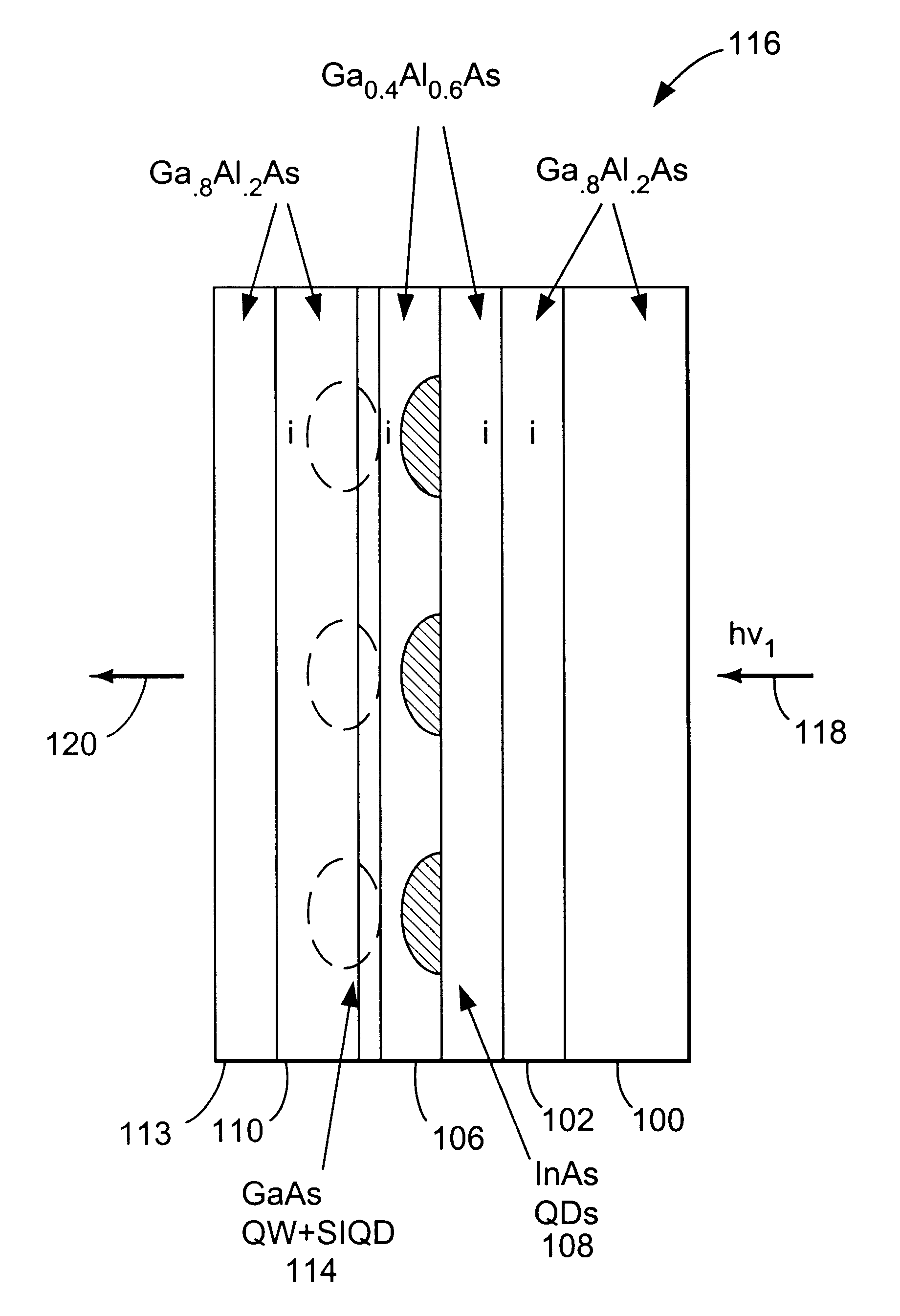
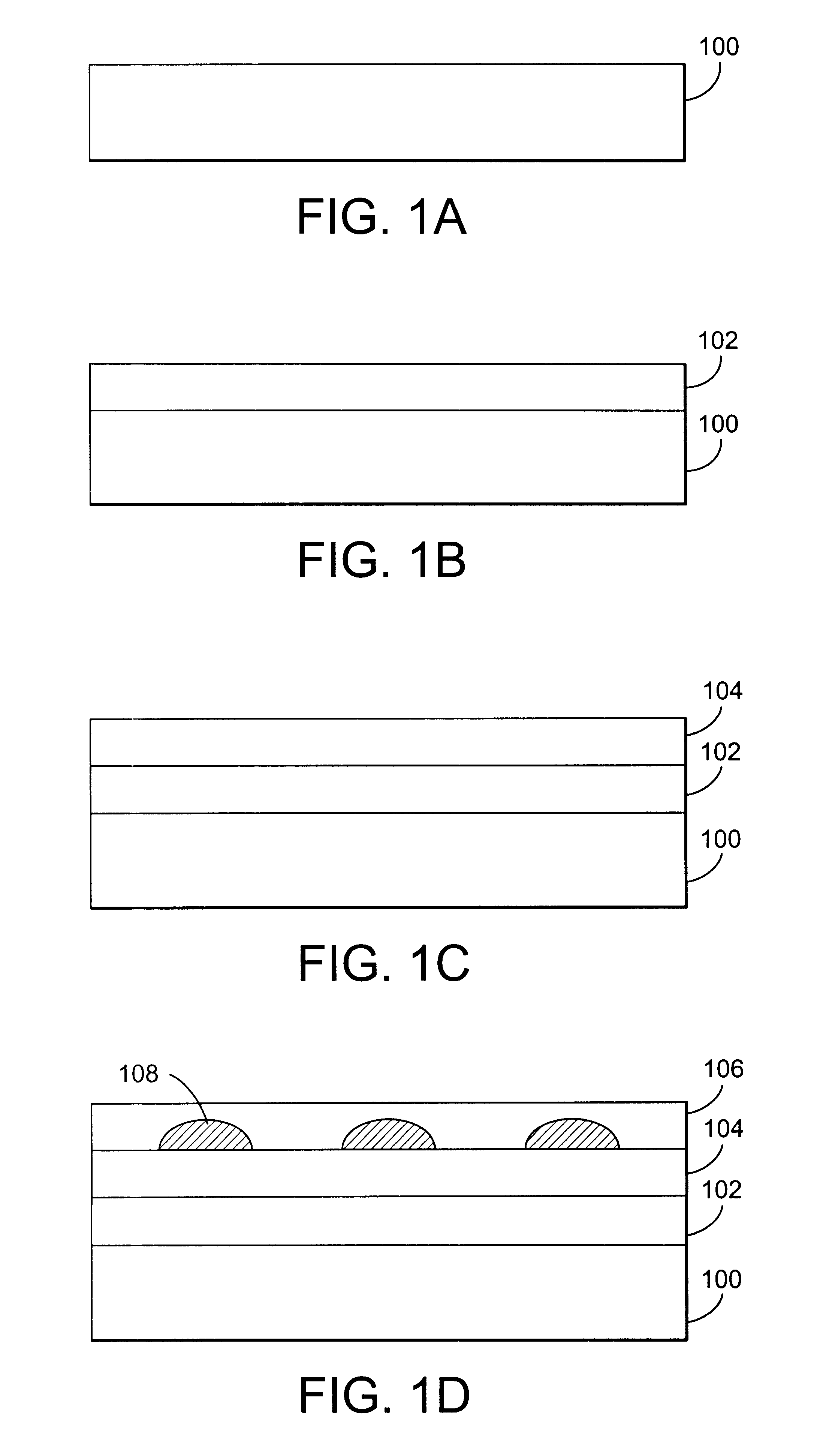
Mid infrared and near infrared light upconverter using self-assembled quantum dots
InactiveUS6541788B2NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStress inducedPhoton
A method and device for converting light from a first wavelength to a second wavelength. The method comprises the steps of exciting an electron in a quantum dot with an incident infrared photon having the first wavelength, the excited electron having a first energy, tunneling the excited electron through a barrier into a stress induced quantum dot, and recombining the excited electron with a hole in the stress induced quantum dot, therein producing a photon having the second wavelength, typically in the visible range. The device comprises a substrate, a spacer layer, coupled to the substrate, a second layer, coupled to the spacer layer, wherein the second layer comprises a different material than the spacer layer, a third layer, coupled to the second layer, wherein the third layer comprises at least one quantum dot, a fourth layer, coupled to the third layer, comprising a quantum well corresponding to each quantum dot in the third layer, a fifth layer, coupled to the fourth layer, wherein the fourth layer and fifth layer comprise a strain induced quantum dot corresponding to each quantum dot in the third layer; and a sixth layer, coupled to the fifth layer, the substrate and the sixth layer for contacting the device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Skin Area Detection Imaging Device
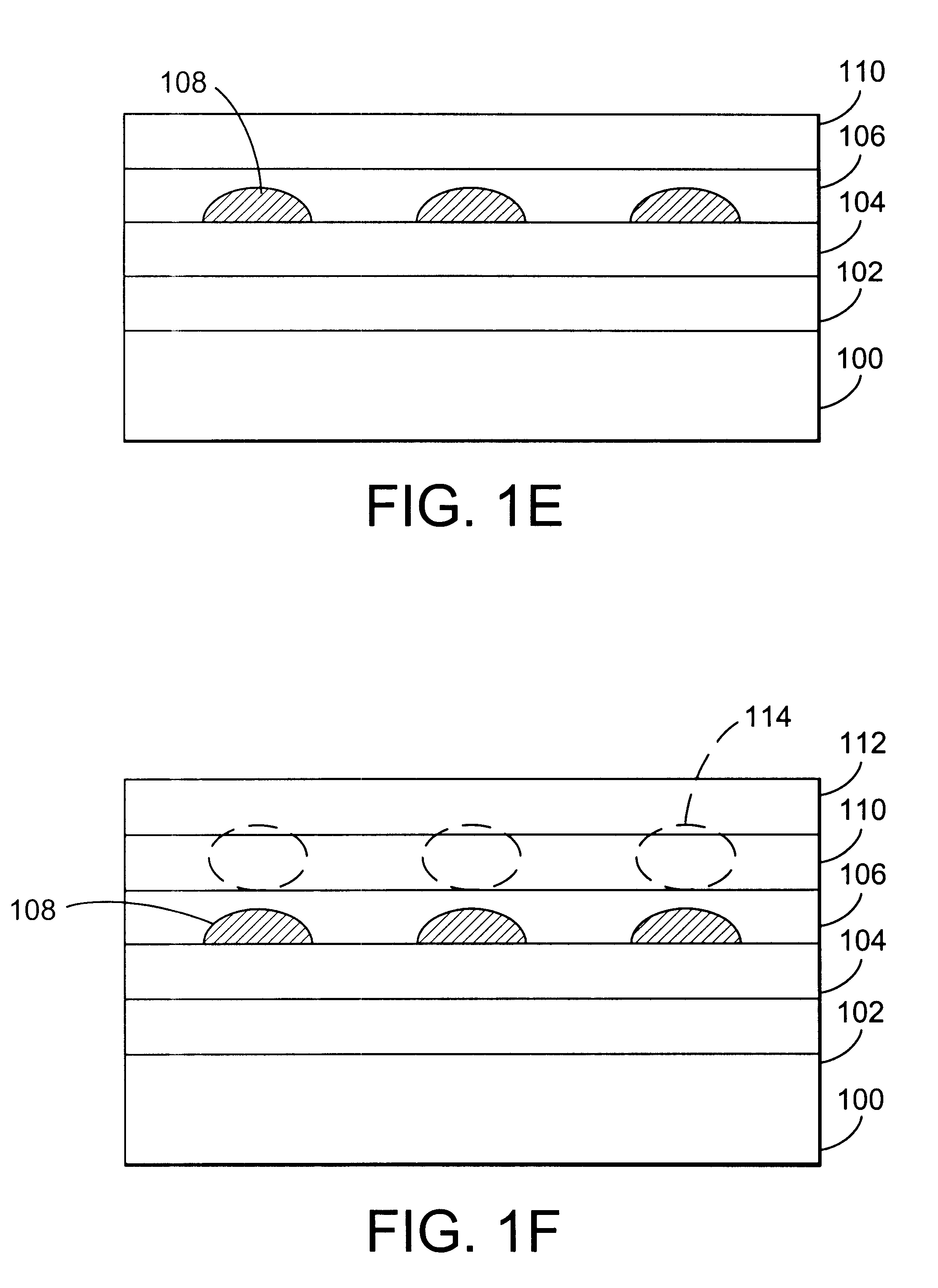
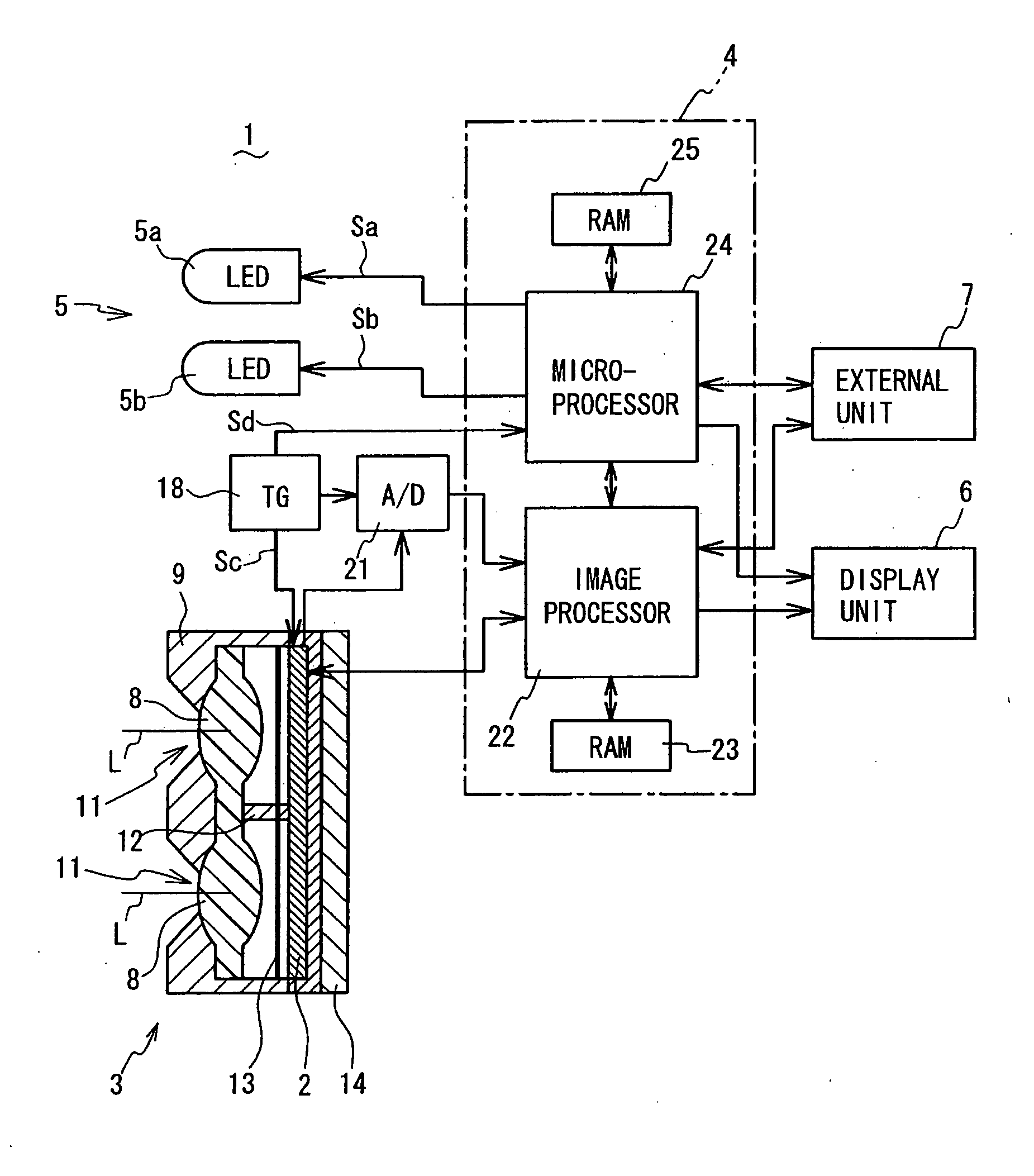
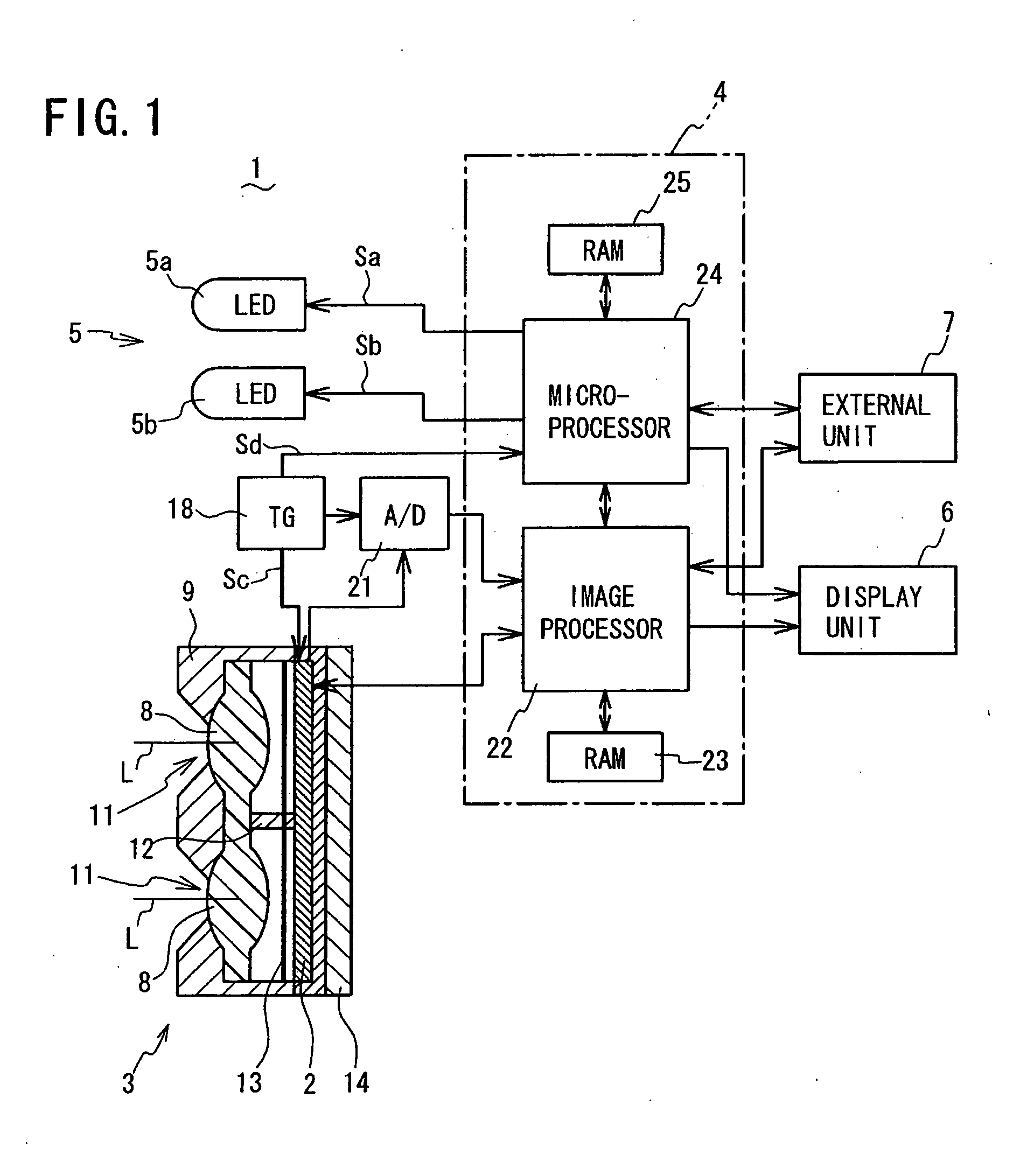
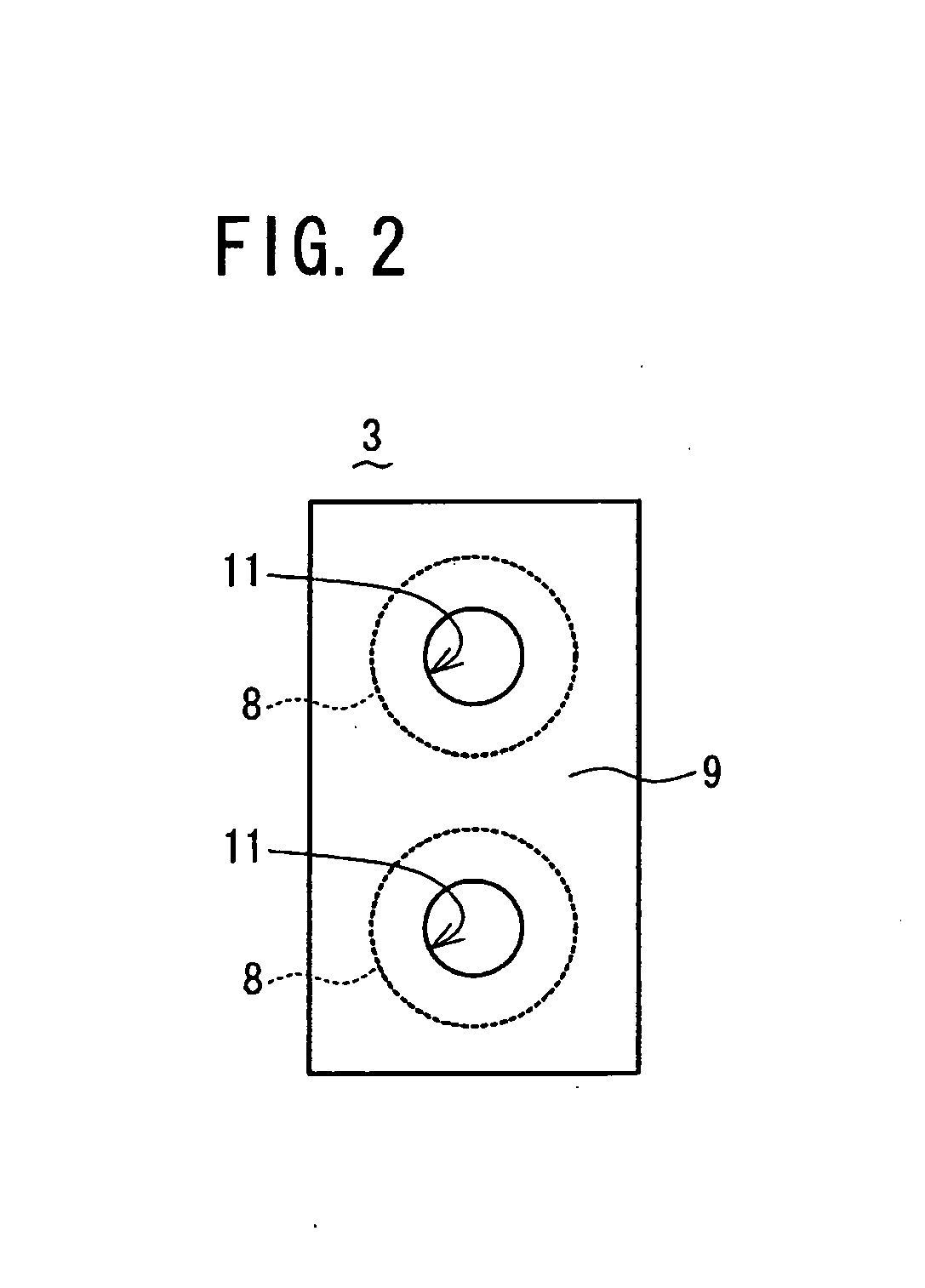
InactiveUS20080177185A1Short timeNo longer be detectedCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringRolling shutterLength wave
A skin area detection imaging device for detecting a skin area of a human body as an object comprises: two optical lenses to form two unit images on an imaging element by collecting light from the object illuminated by near-infrared light; a rolling shutter for sequentially reading the unit images; and two LEDs for emitting lights with different wavelengths (850 nm and 940 nm) in the near-infrared range. A microprocessor switches on the two LEDs when reading the two unit images, respectively. The skin area of one read unit image is displayed with brightness different from that of the other unit image based on difference in reflectance to various wavelengths of near-infrared light. The microprocessor compares the two unit images to determine, as a skin area, an area having difference in brightness larger than a predetermined value. This makes it possible to detect the skin area in a short time.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Transparent thermal insulation anti-ultraviolet coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101899249AHigh solid contentHigh visible light transmittancePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyester coatingsChemical industryThermal insulation
The invention provides a transparent thermal insulation anti-ultraviolet coating and a preparation method thereof, belongs to the technical field chemical industry, materials and environmental protection and relates to the transparent thermal insulation anti-ultraviolet coating which can reduce the transmission of solar energy and ultraviolet and the preparation method thereof. The coating comprises nano-slurry with the thermal insulation anti-ultraviolet function and a film-forming substance, and is combined with the synergistic effects of a wetting dispersant and a hyper-dispersant for preparing the nano-slurry with high solid content and stable dispersion. The preparation process of the coating is simple and can greatly improve the solid content of the coating, ensure the optical effect of a paint film after coating, simultaneously organically combined powder with different functions and obtain the thermal insulation anti-ultraviolet functional coating with satisfactory effects. The coating has the characteristics of low transmission of ultraviolet and near infrared light of solar rays, high transmission of visible light and the like, and can be coated on glass, polycarbonate or organic glass and other transparent materials, and achieve the purposes of energy conservation and protection.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUJIA ADVANCED MATERIALS SCI & TECH
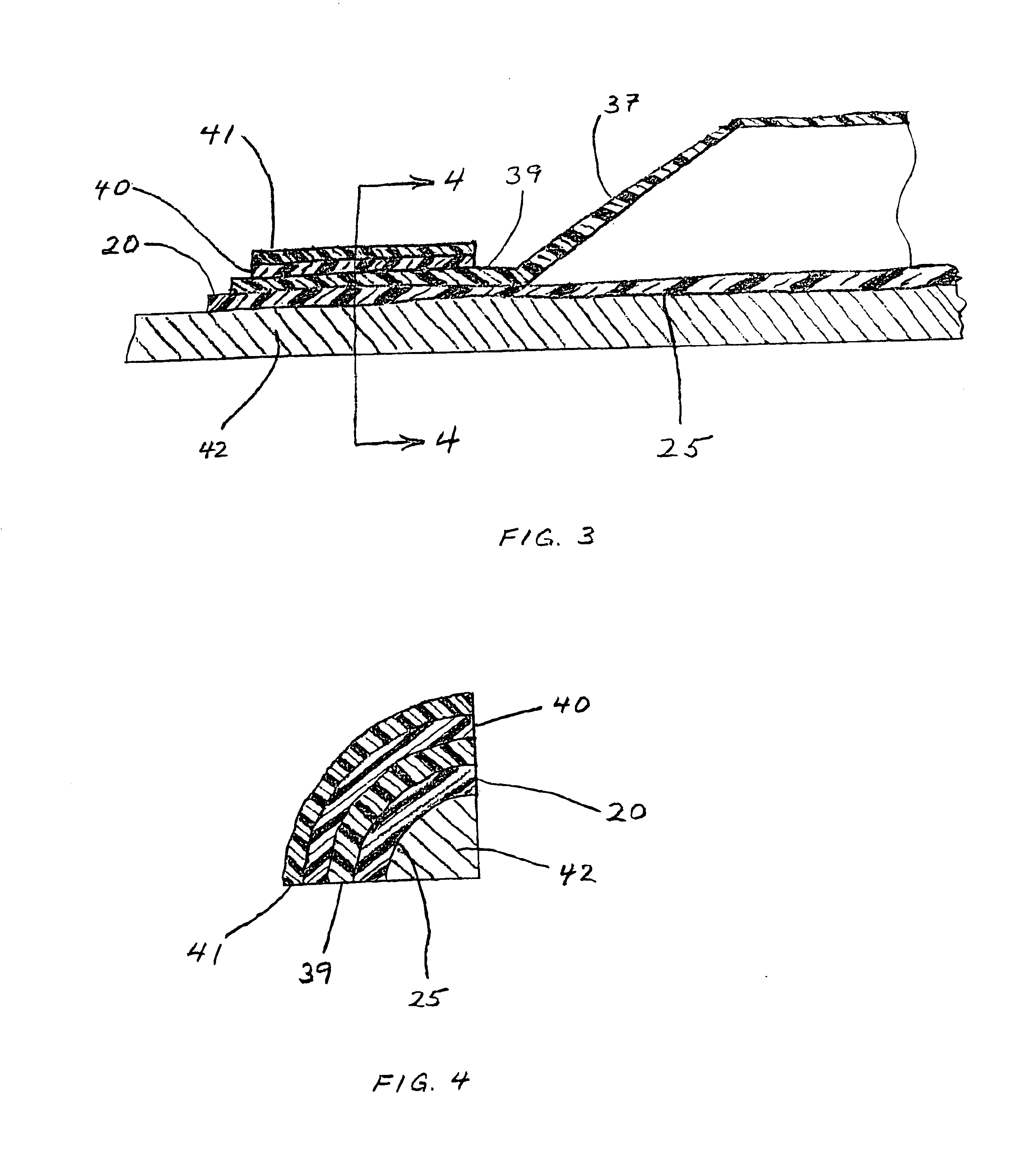
Through-transmission welding of catheter components
InactiveUS6740191B2Easy to controlMinimal damageLamination ancillary operationsSurgeryDistal portionThrough transmission
A process for forming a heat weld between a catheter shaft and a surrounding balloon comprises selecting an elongate catheter shaft formed of thermoplastic polymeric material that is opaque to red and near-infrared light, and selecting a balloon formed of thermoplastic polymeric material that is transparent or translucent to red and near-infrared light. While a neck of the balloon is fitted in close contact around a distal portion of the catheter shaft, a laser beam of red and near-infrared light is applied through the balloon neck to impinge on the underlying opaque distal shaft, which is heated thereby. Heat from the shaft is conducted into the surrounding balloon neck so that adjacent annular portions of both components melt and mix. The molten materials are allowed to cool, forming a secure weld joint between the neck and the shaft. The process yields strong, flexible bonds between balloons and catheter shafts that may be selected from a wide variety of materials.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
Method and Apparatus for Personal Identification Using Palmprint and Palm Vein
ActiveUS20100045788A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsPalm printData library
A method of personal identification includes switching between visible and near infrared light, acquiring palmprint image and palm vein image from a person under the visible and the near infrared light, extracting sub-images from the palmprint image and the palm vein image based on a region of interest, extracting multiple features from the sub-images, and matching the extracted multiple features with stored information in a database to authenticate the person.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
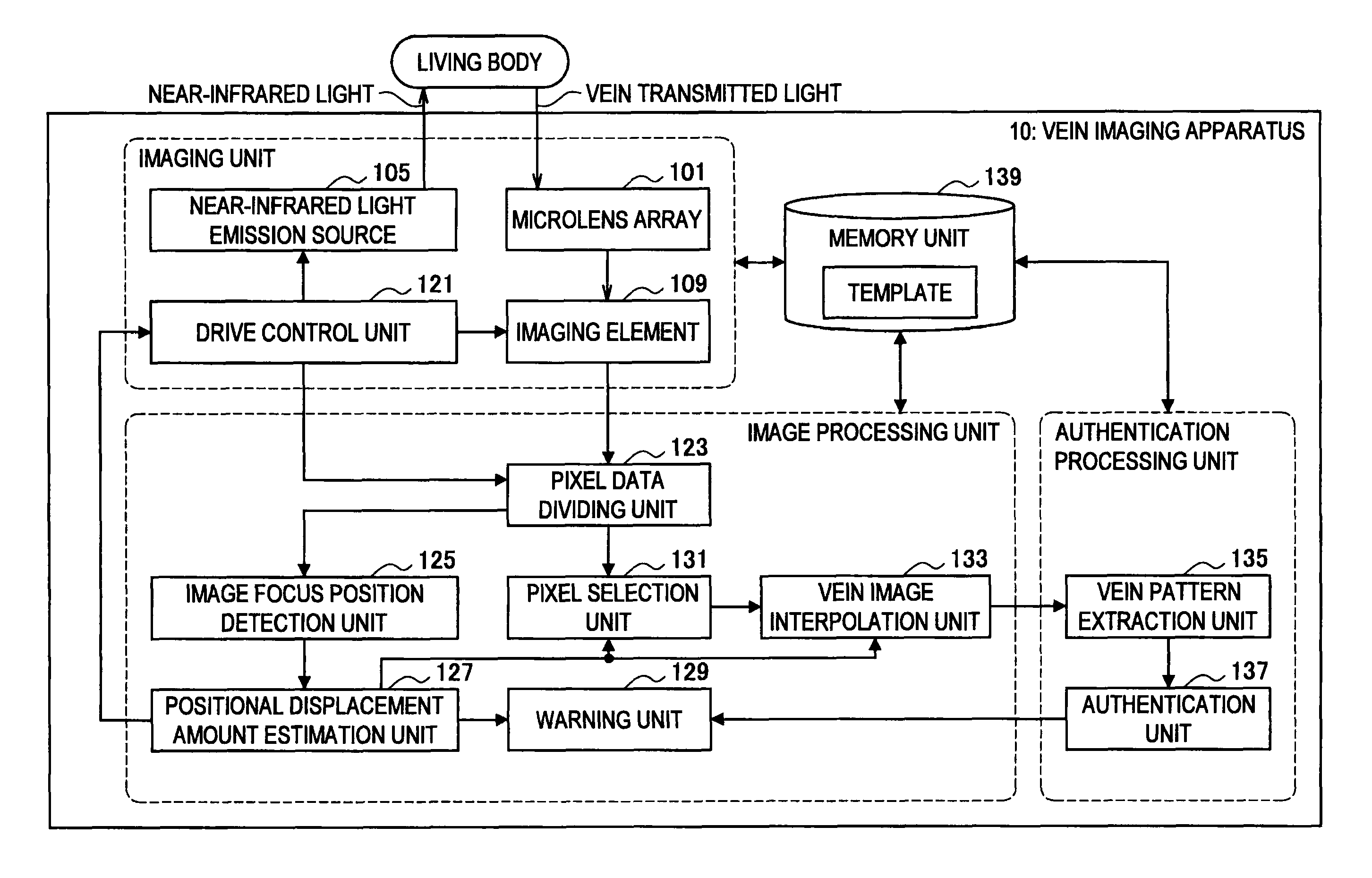
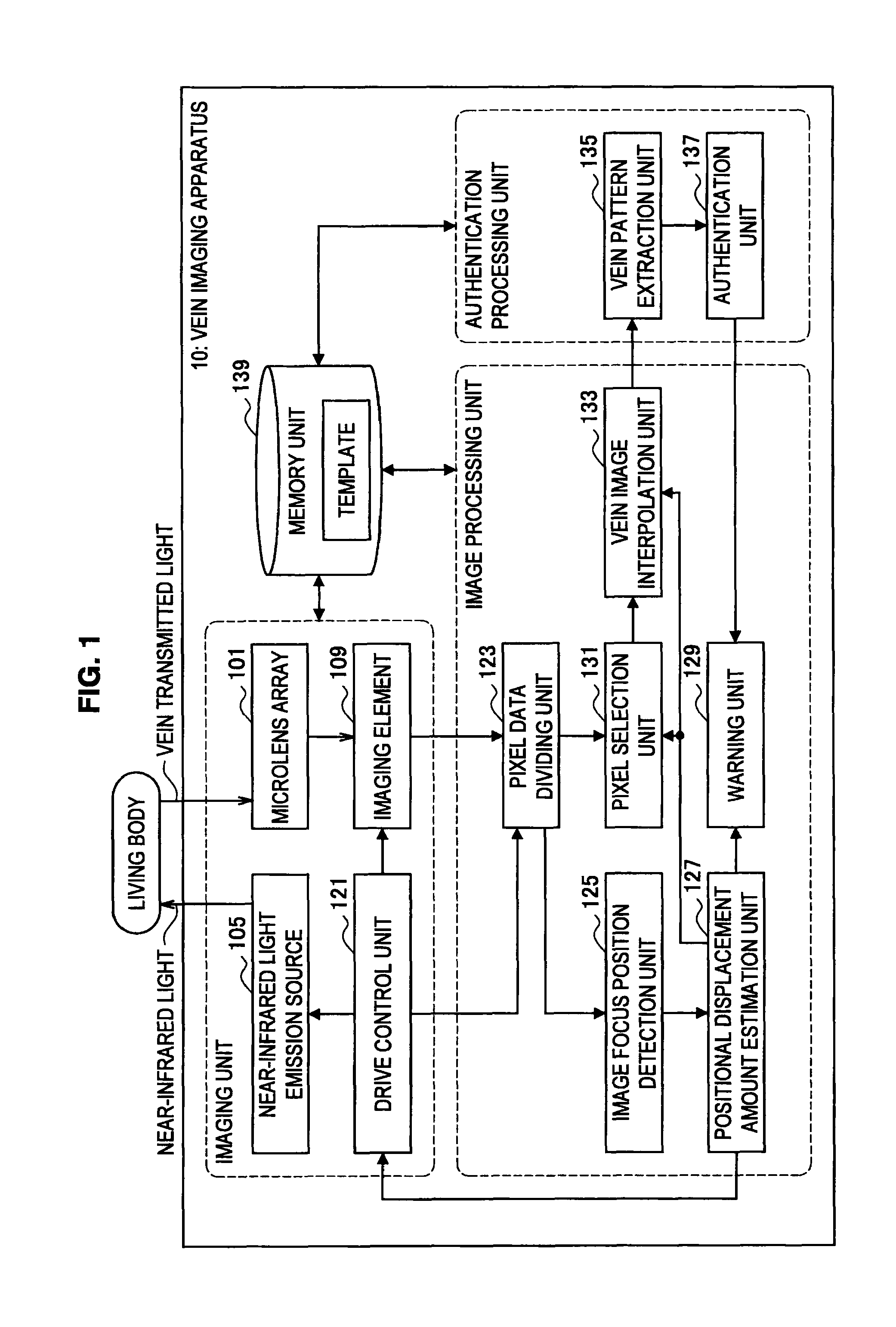
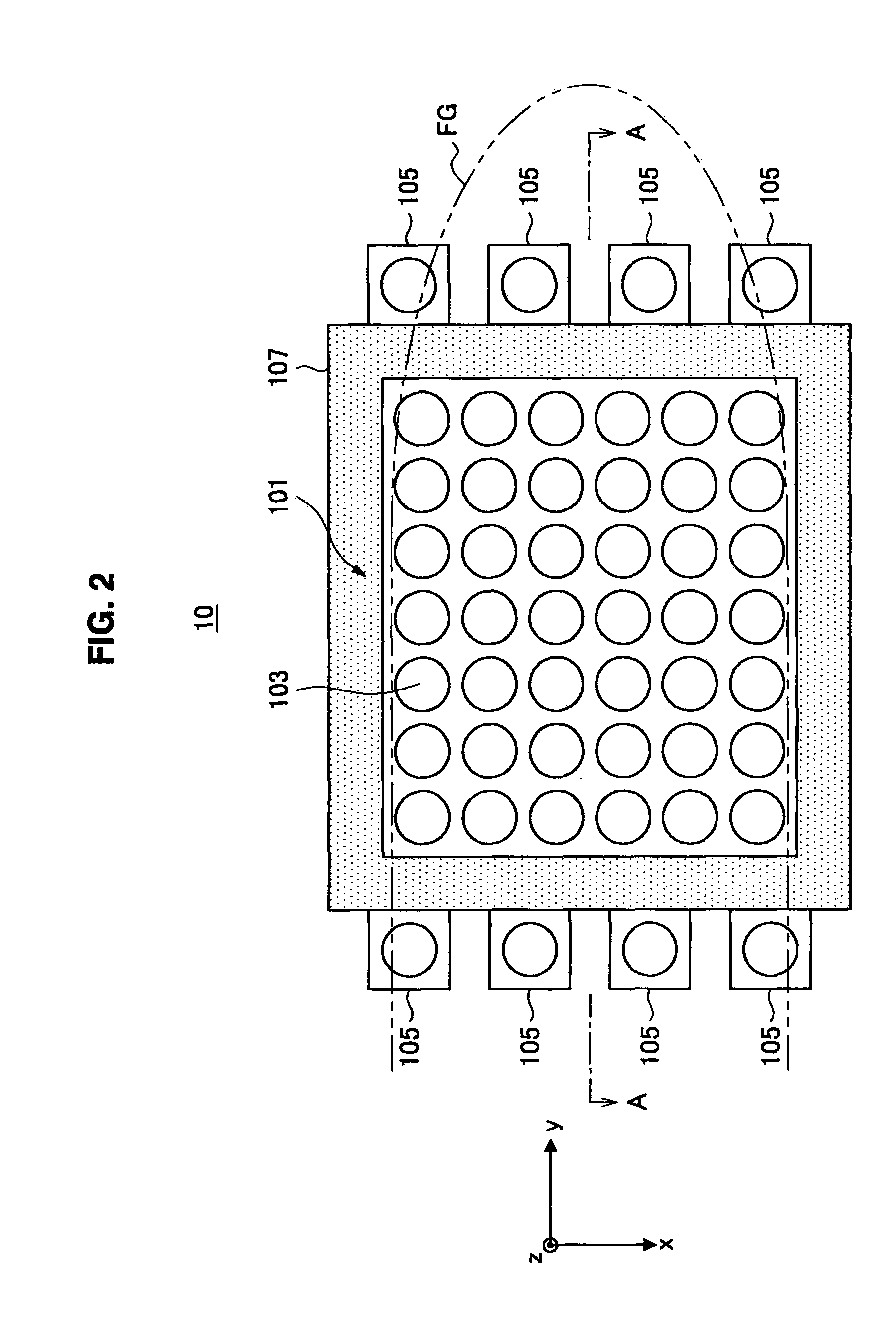
Vein imaging apparatus, positional displacement interpolation method, and program
ActiveUS8320998B2Little has been producedTelevision system detailsDiagnostics using lightVenographyComputer vision
An imaging element of a vein imaging apparatus includes a vein image data generation region generating image data of a vein based a near-infrared light that was condensed by a lens array and that was scattered in a living body and transmitted through the vein and a positional displacement detection data generation region that includes a shielded section in which pixels are shielded from the light and an opening section in which pixels are not shielded from the light, and generates data for detecting positional displacement that is used to detect, based on the light received via the opening section, variation in an image focus position according to an imaging temperature. The vein imaging apparatus detects the image focus position of the light and estimates the amount of positional displacement occurred in the apparatus. The vein imaging apparatus selects a pixel based on the obtained amount of positional displacement.
Owner:MOFIRIA
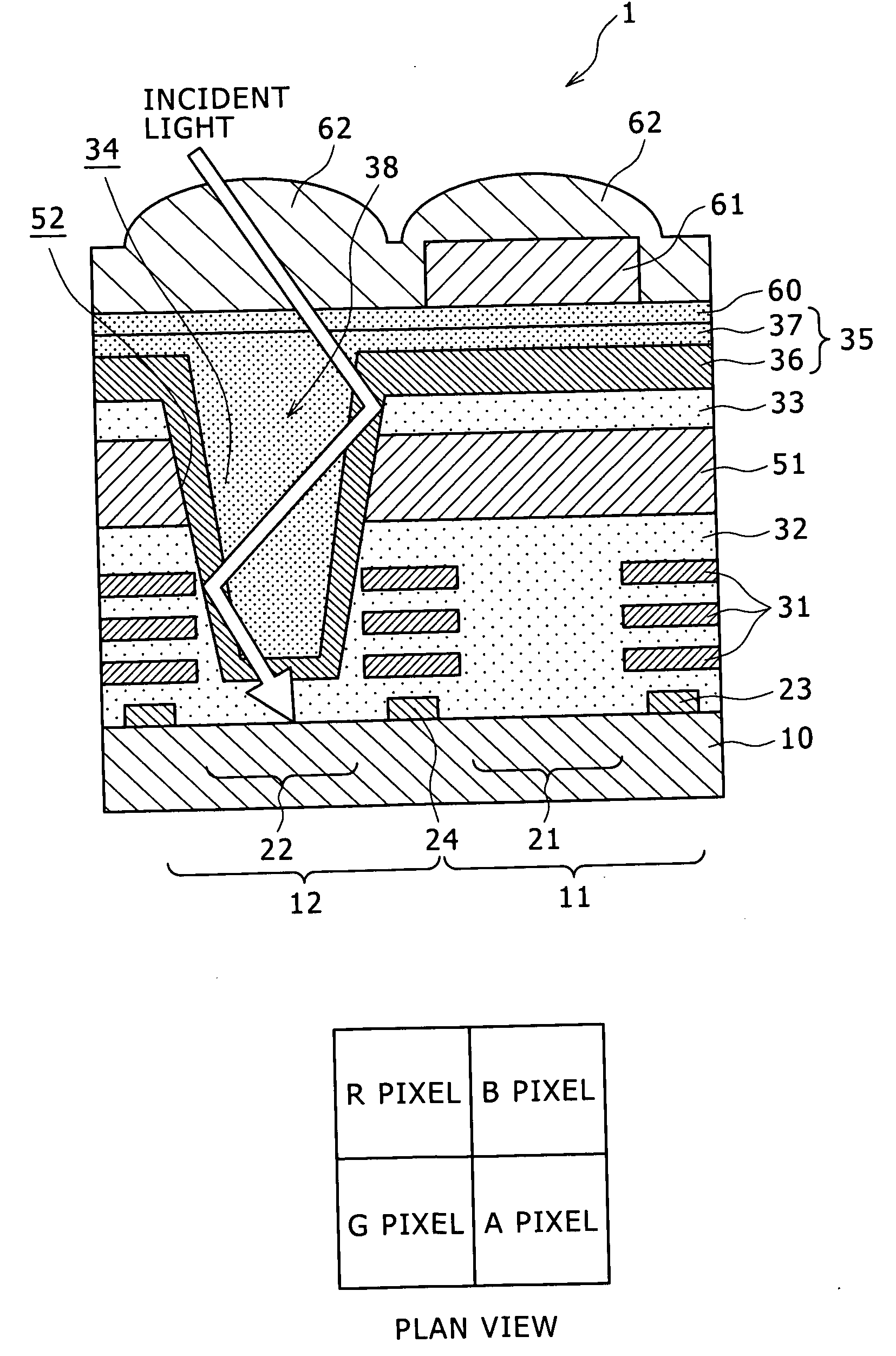
Solid-state image pickup device and a method of manufacturing the same, and image pickup apparatus
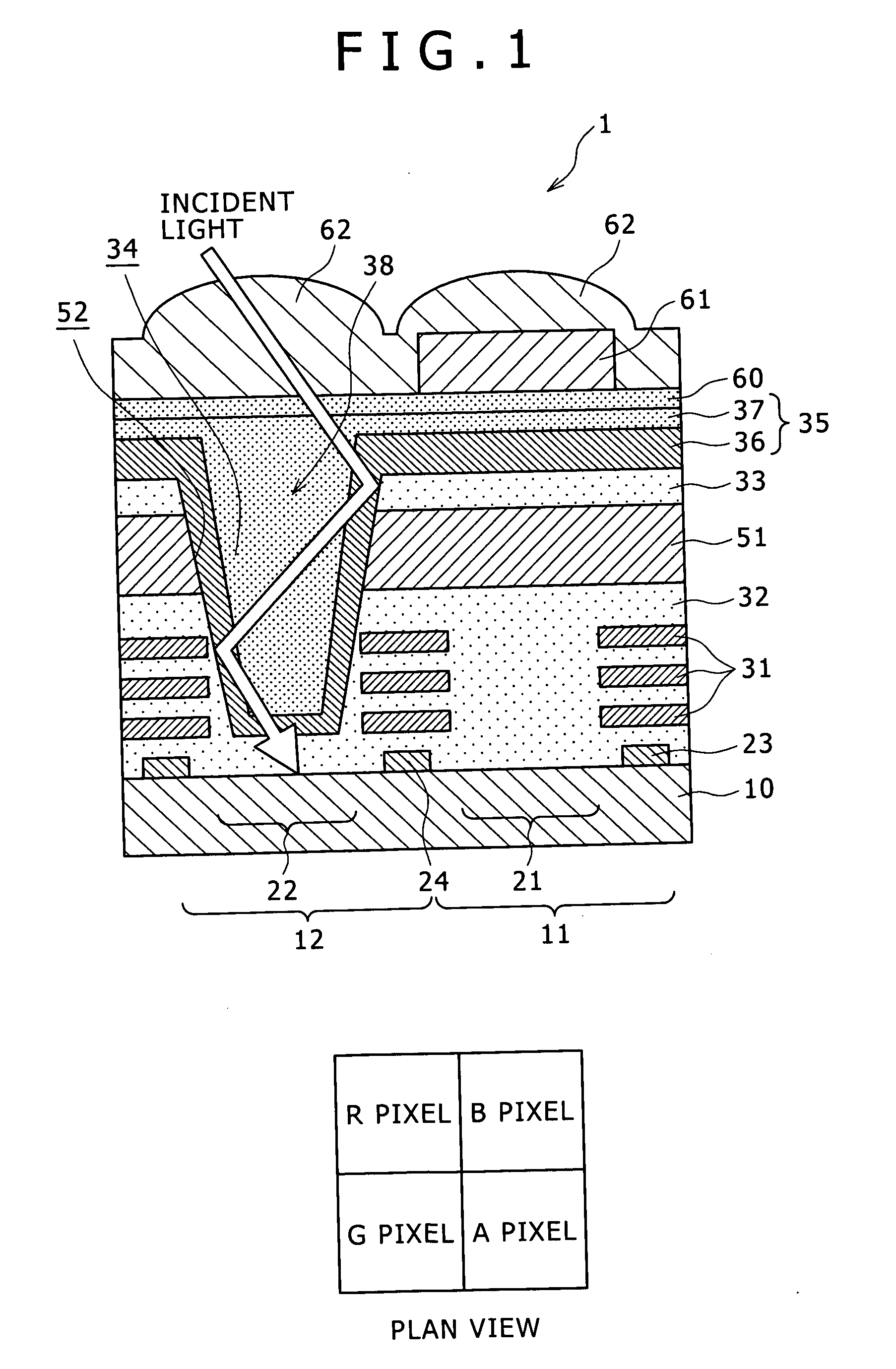
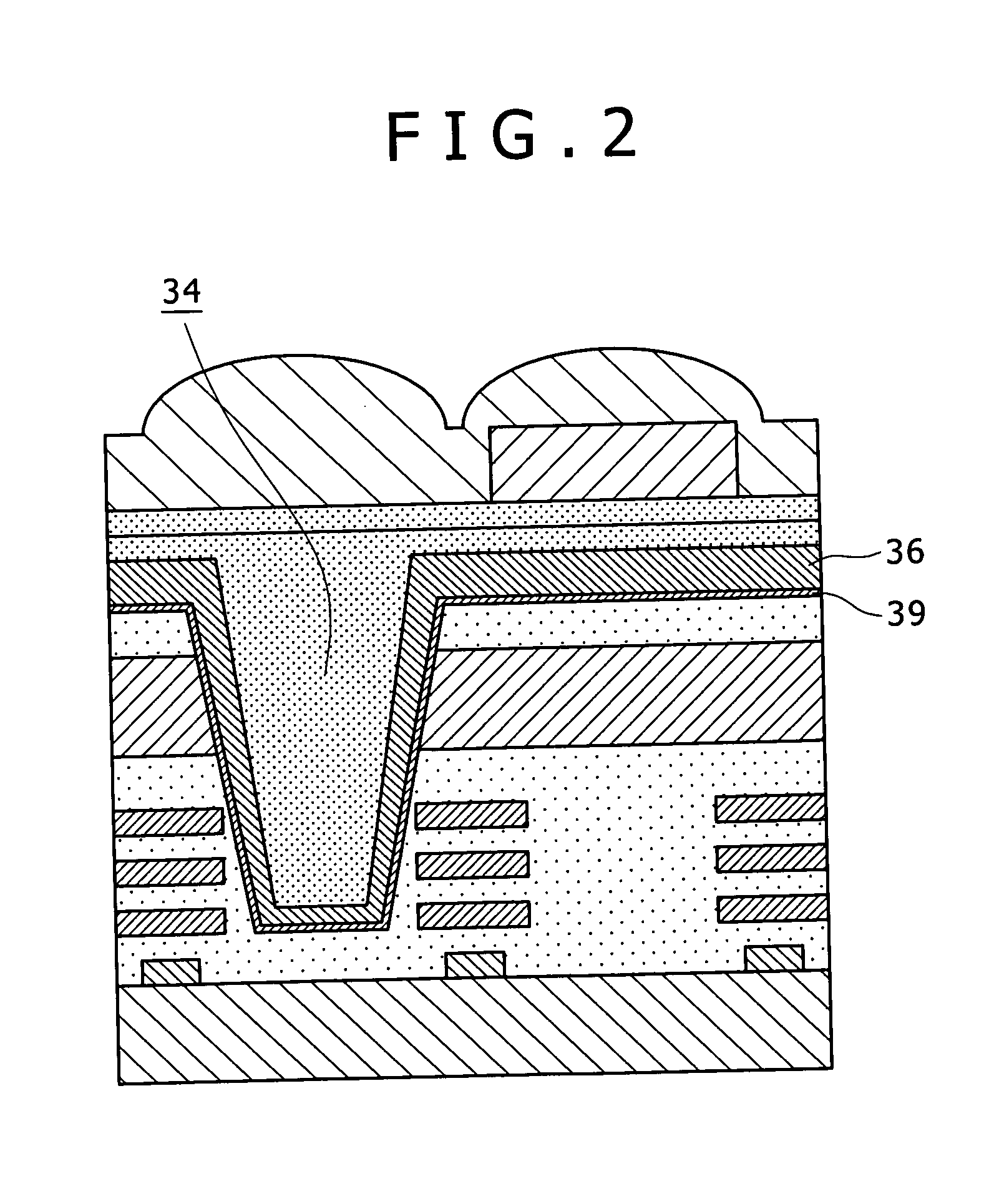
InactiveUS20080283728A1High sensitivityReduce leakageTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesNear infrared lightSolid-state
Disclosed herein is a solid-state image pickup device, including: a first pixel for receiving a visible light of an incident light to subject the visible light to photoelectric conversion; a second pixel for receiving the visible light and a near-infrared light of the incident light to subject each of the visible light and the near-infrared light to the photoelectric conversion; a color filter layer; and an infrared light filter layer for absorbing or reflecting an infrared light, and transmitting the visible light.
Owner:SONY CORP
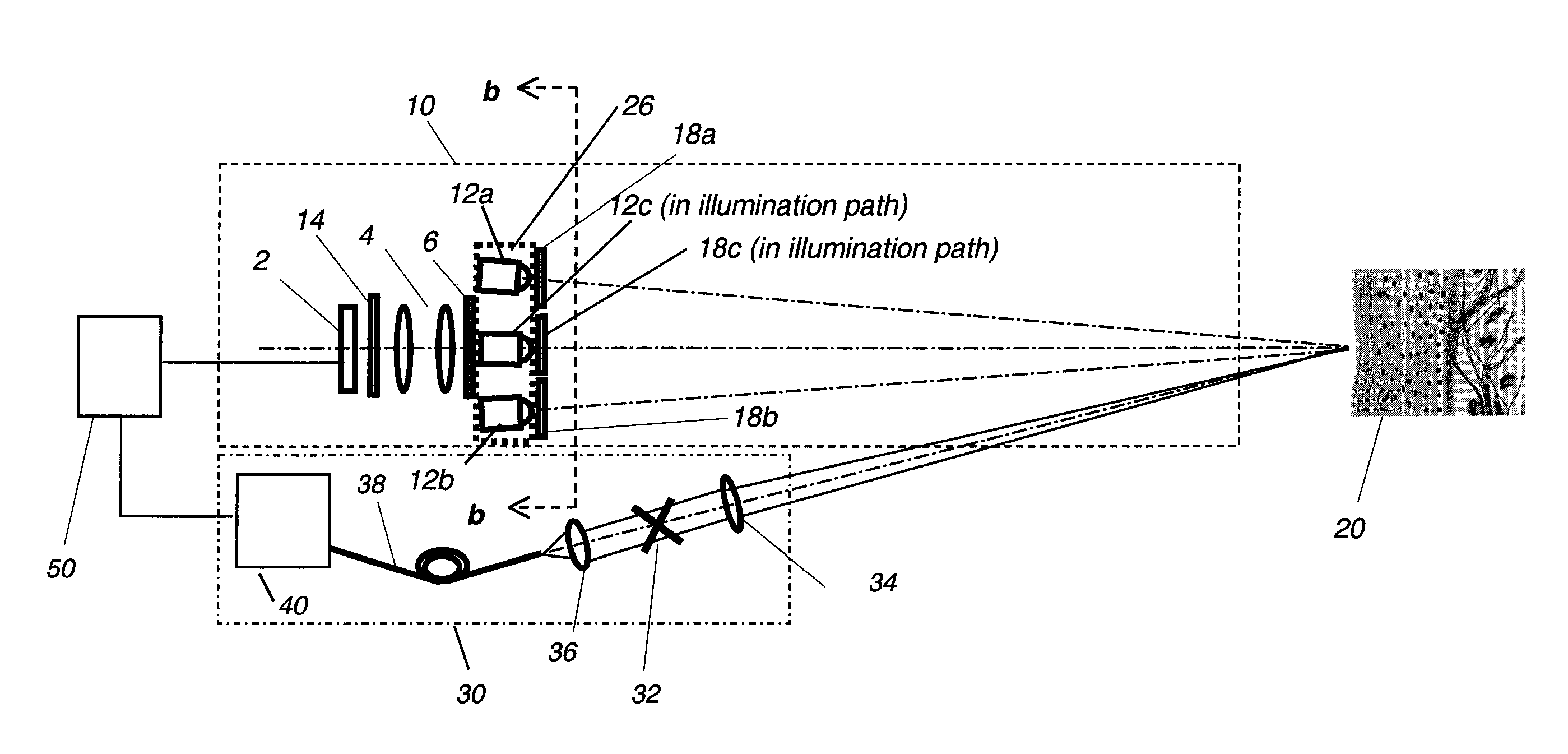
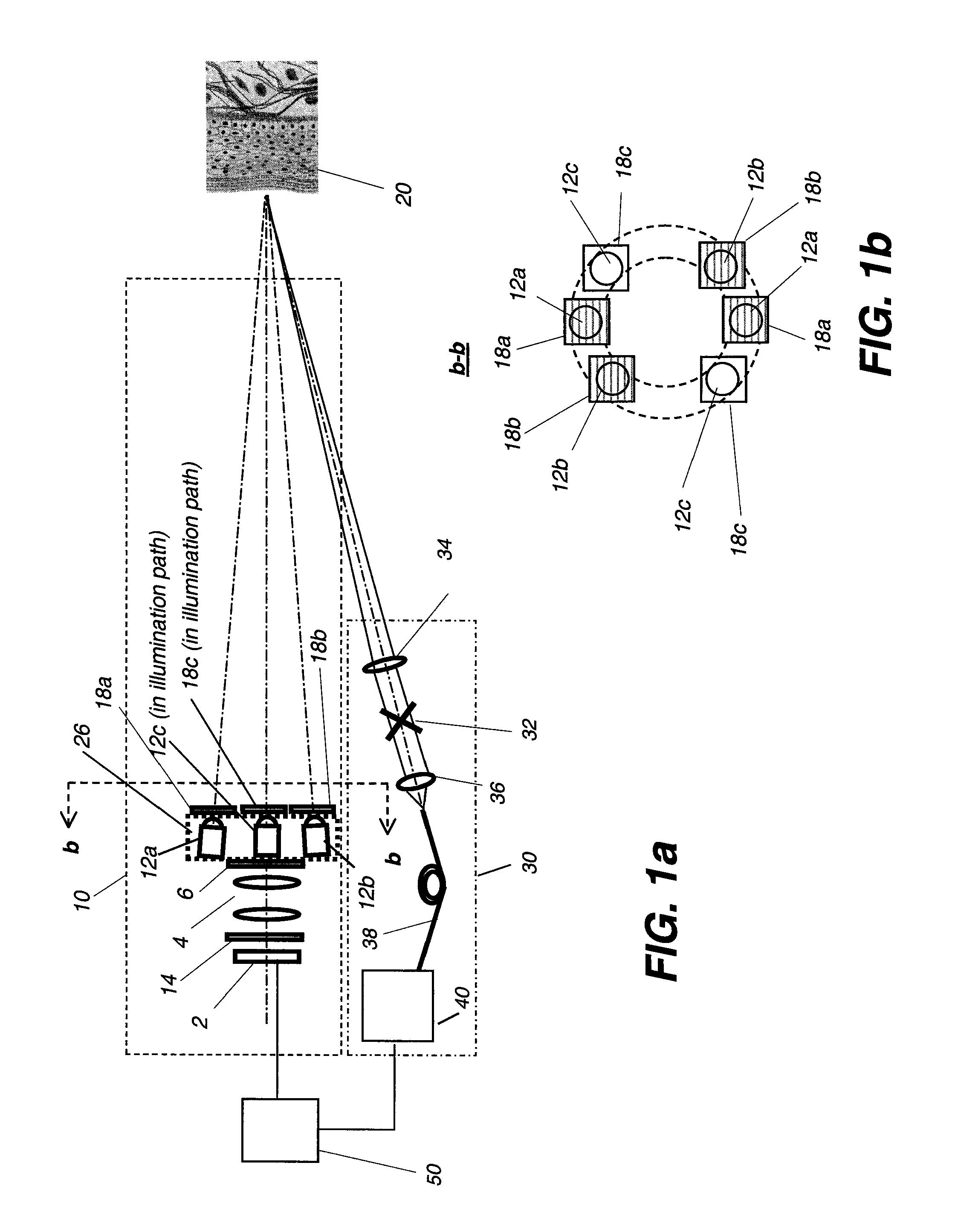
Multimodal imaging system for tissue imaging
InactiveUS20090131800A1Eliminate specular reflectionsEnhance the imageDiagnostics using lightSensorsFluorescenceUltraviolet lights
An apparatus for obtaining area images and optical coherence tomography (OCT) image of a tissue comprises an image sensor, a first illumination means providing broadband polarized polychromatic light, a second illumination means providing narrow-band ultraviolet light, a third illumination means providing Near-Infrared light, an optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging apparatus, one or more polarization elements, and an optical filter. An image processor identifies a region of interest according to area image, which can be a polarized reflectance image, a fluorescence light image, or both for the OCT imaging apparatus to obtain an OCT image over the region of interest.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
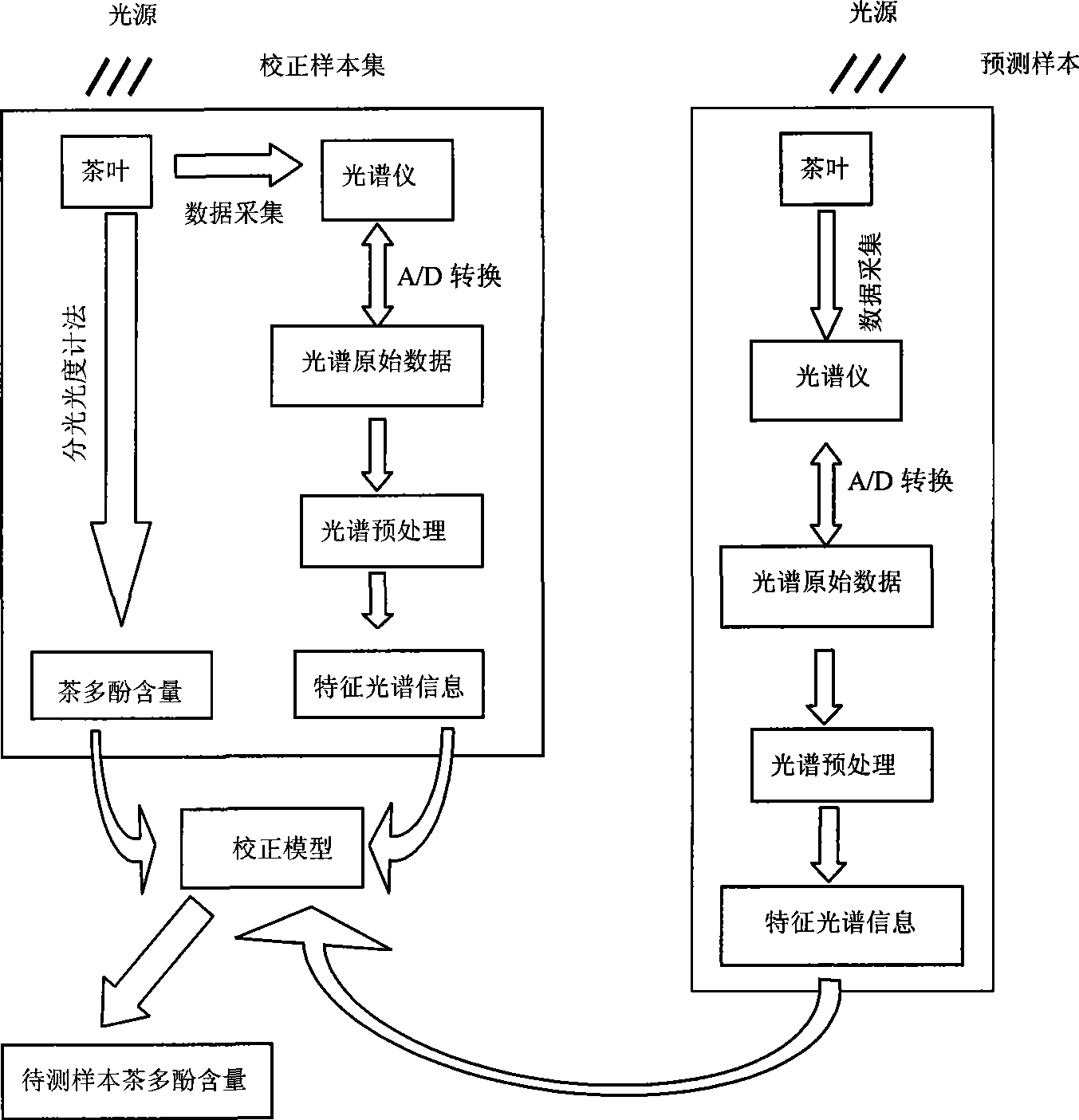
Method for non-destructive measurement for tea polyphenol content of tea based on near infrared spectrum technology
InactiveCN101059426AFast analysisNo pollutionColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsProcess functionPhenolic content in tea
The invention discloses a method for non-damage measuring the tea polyphenol content in tea, based on near-infrared spectrum technique, which comprises that first building a correct model, collecting tea sample as correct sample group, scanning the correct sample group to obtain visible light spectrum and near-infrared light spectrum (325-2500nm), processing spectrum pretreatment on the spectrum data, then using international standard method to measure the tea polyphenol content of correct sample, using multi-element correct regression algorism to build the quantitative relationship between the near-infrared spectrum and the tea polyphenol content of the correct sample, to build the correct model. The invention only needs to scan the near-infrared spectrum of object tea, and input pretreated spectrum data into the correct model which can test the tea polyphenol content. The whole process is controlled by a computer, to realize data pickup, store, display and process functions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Low-light viewing device for displaying image based on visible and near infrared light
A low-light viewing device includes a housing, having mounted thereto: a lens, an electronic camera for receiving light focused by the lens and for providing an output signal; a display for receiving the output signal and displaying an image detected by the camera; a controller for controlling the camera and the display, and a user interface for operating the controller. The lens may be a fixed focus lens having an F number of less than about 1, and a T number of less than about 1.5. The display may have a resolution at least as great as the resolution of the camera. The device may have a processor programmed to provide control signals to the camera and display depending on a selected light environment.
Owner:XENONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com