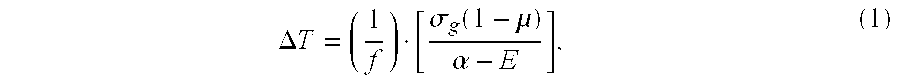Patents
Literature
837 results about "Visible range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The range of visible light starts at about 390 nanometers and ends at 700 nanometers. Nanometers refer to the wavelength of light. Anything straying out of this spectrum is not able to be detected by the human eye.
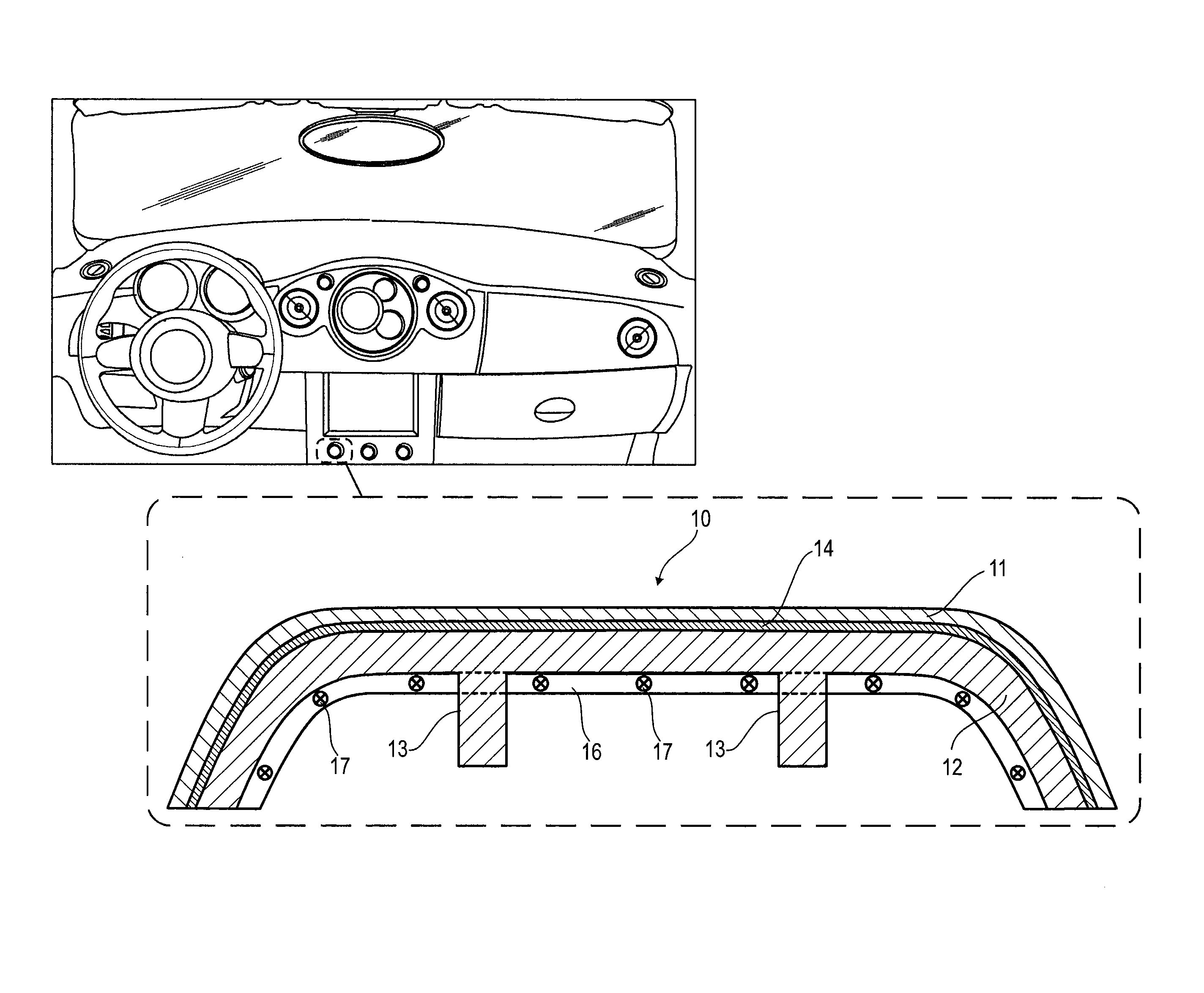
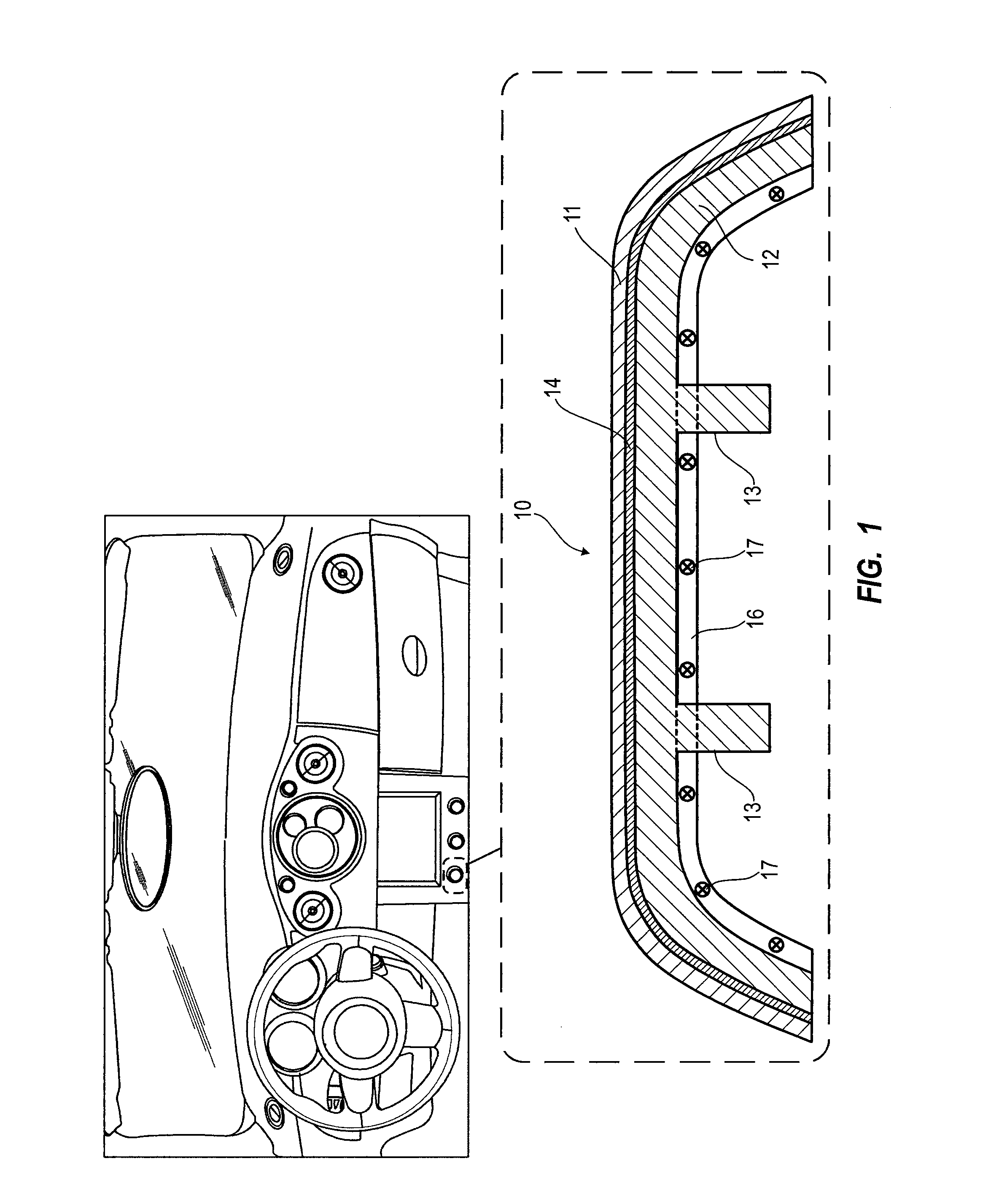
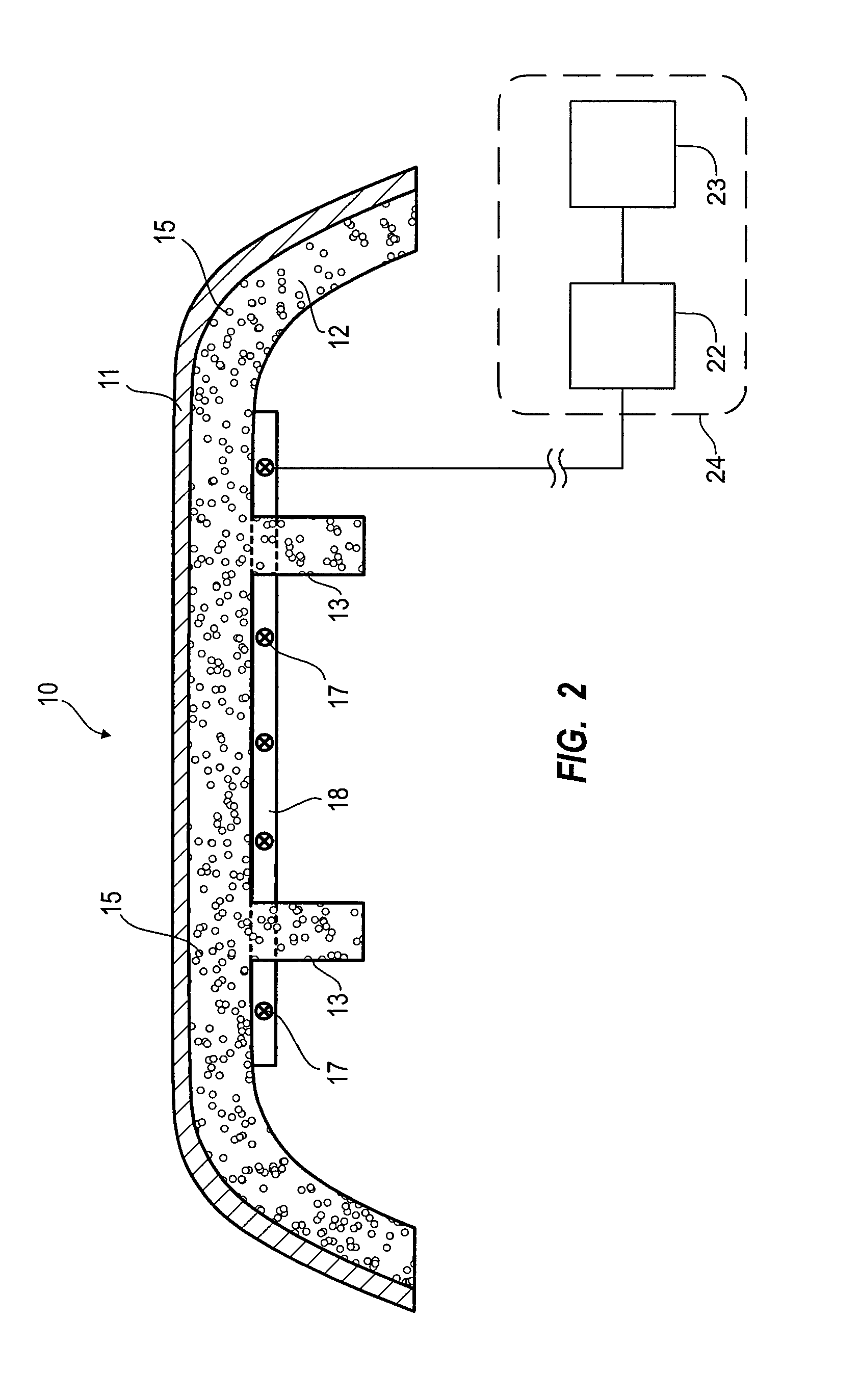
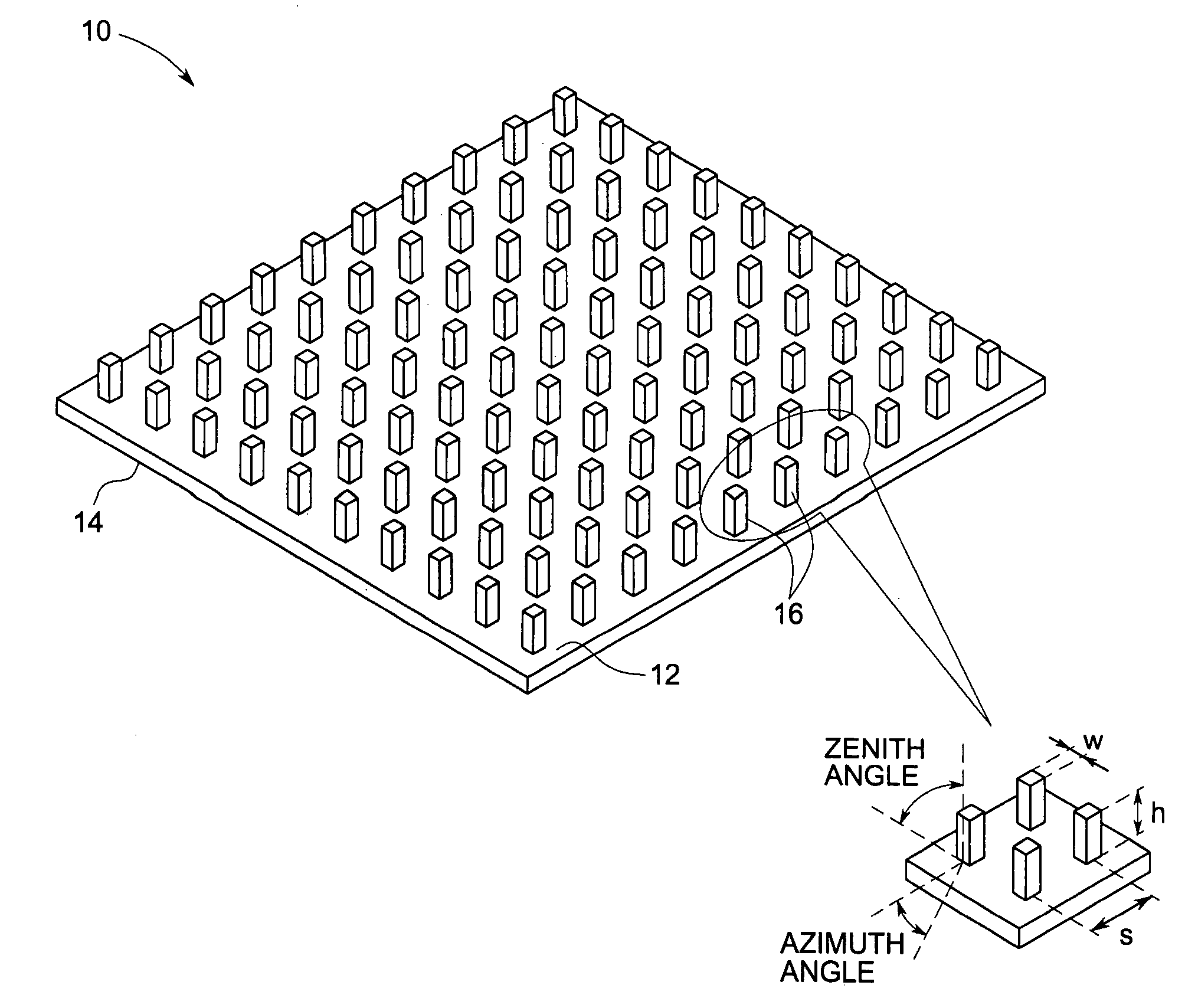
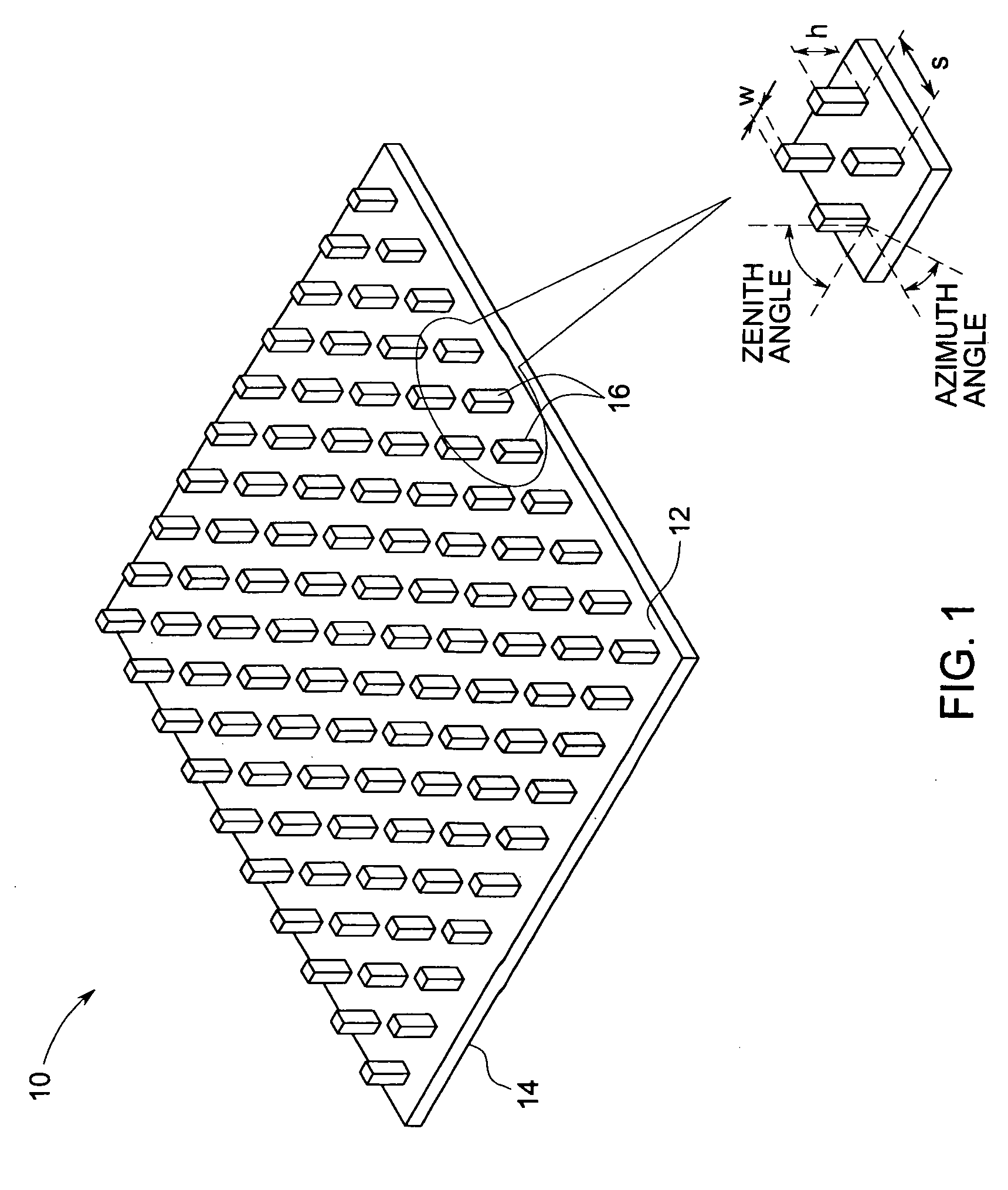
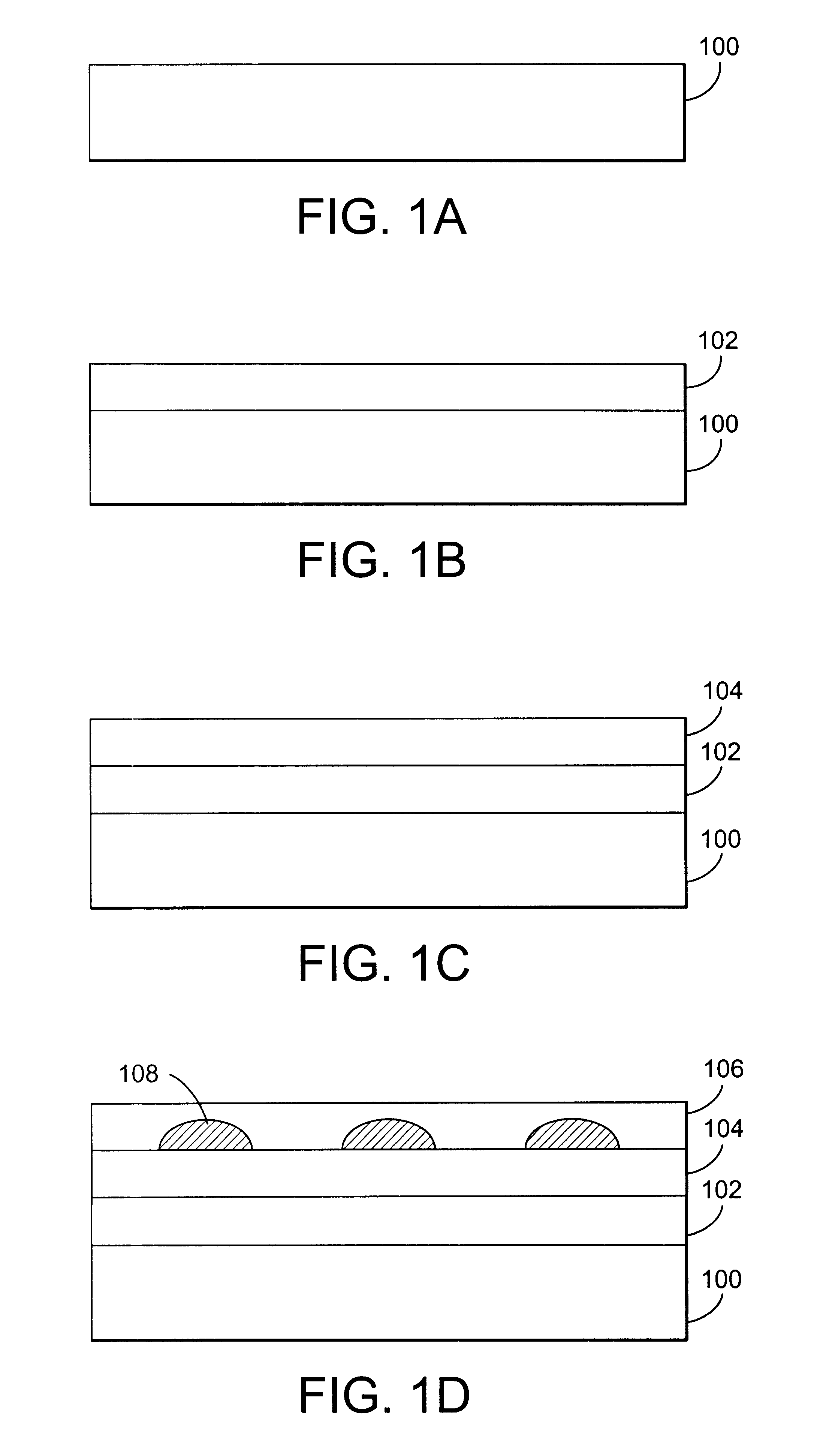
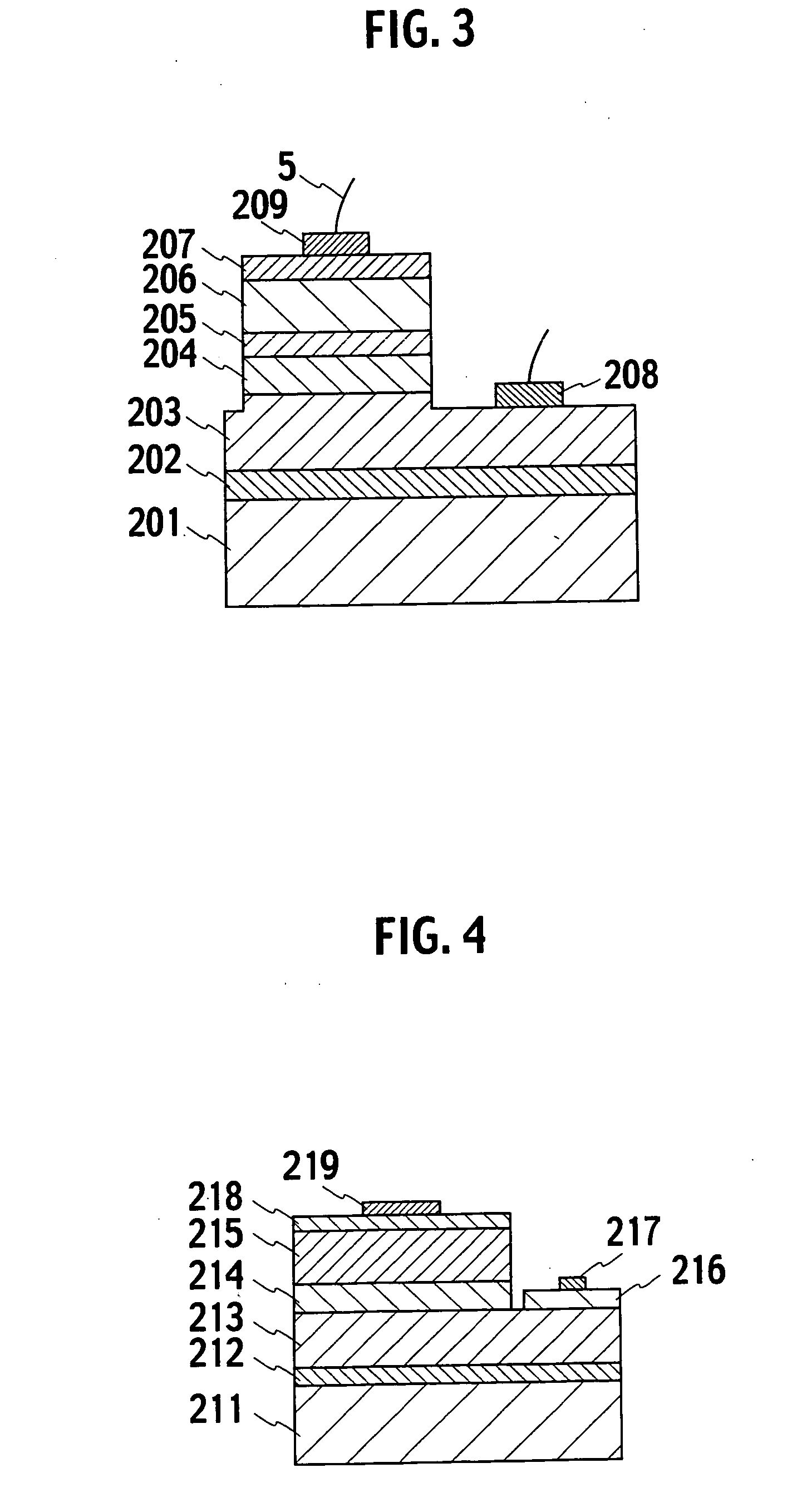
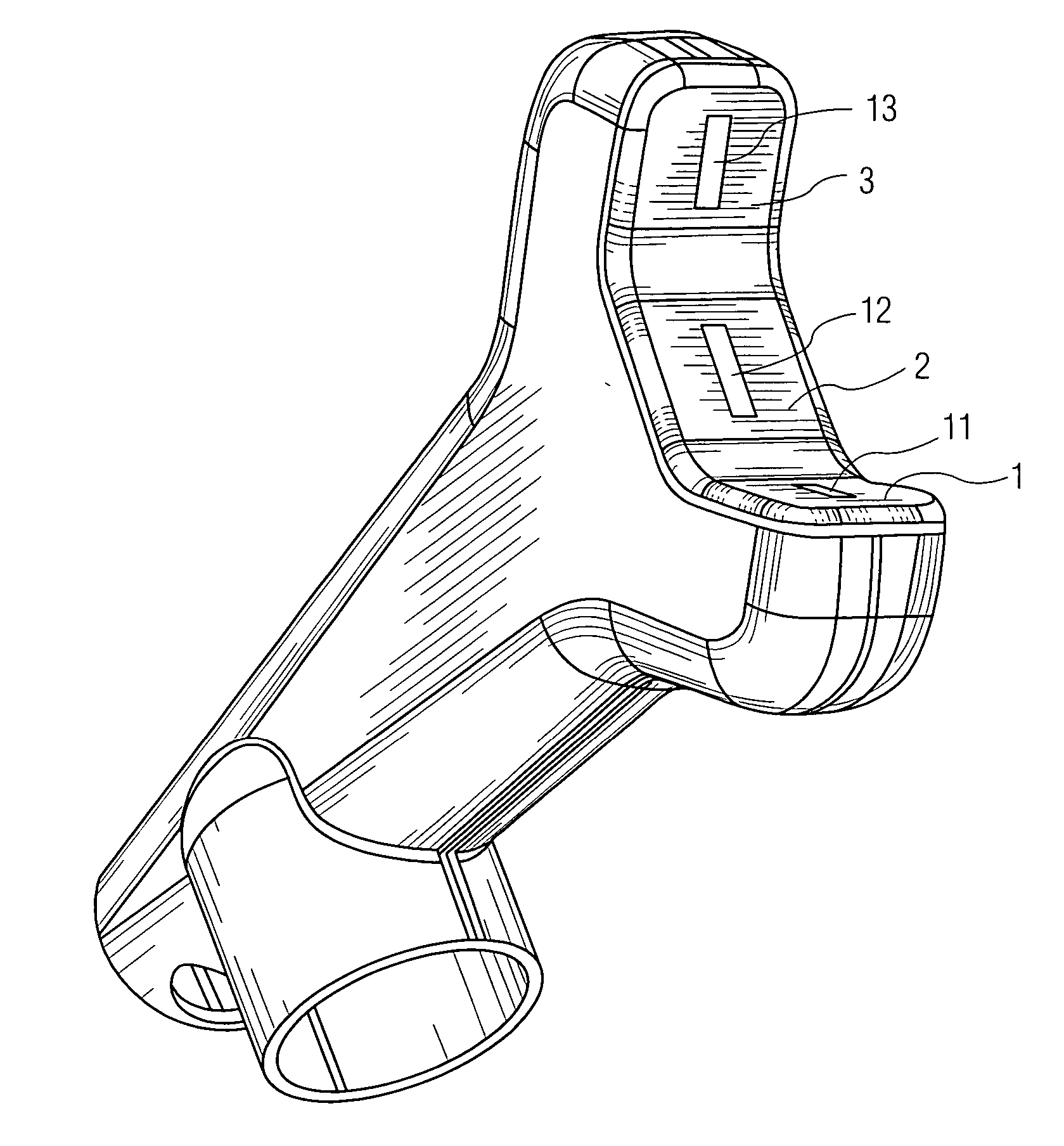
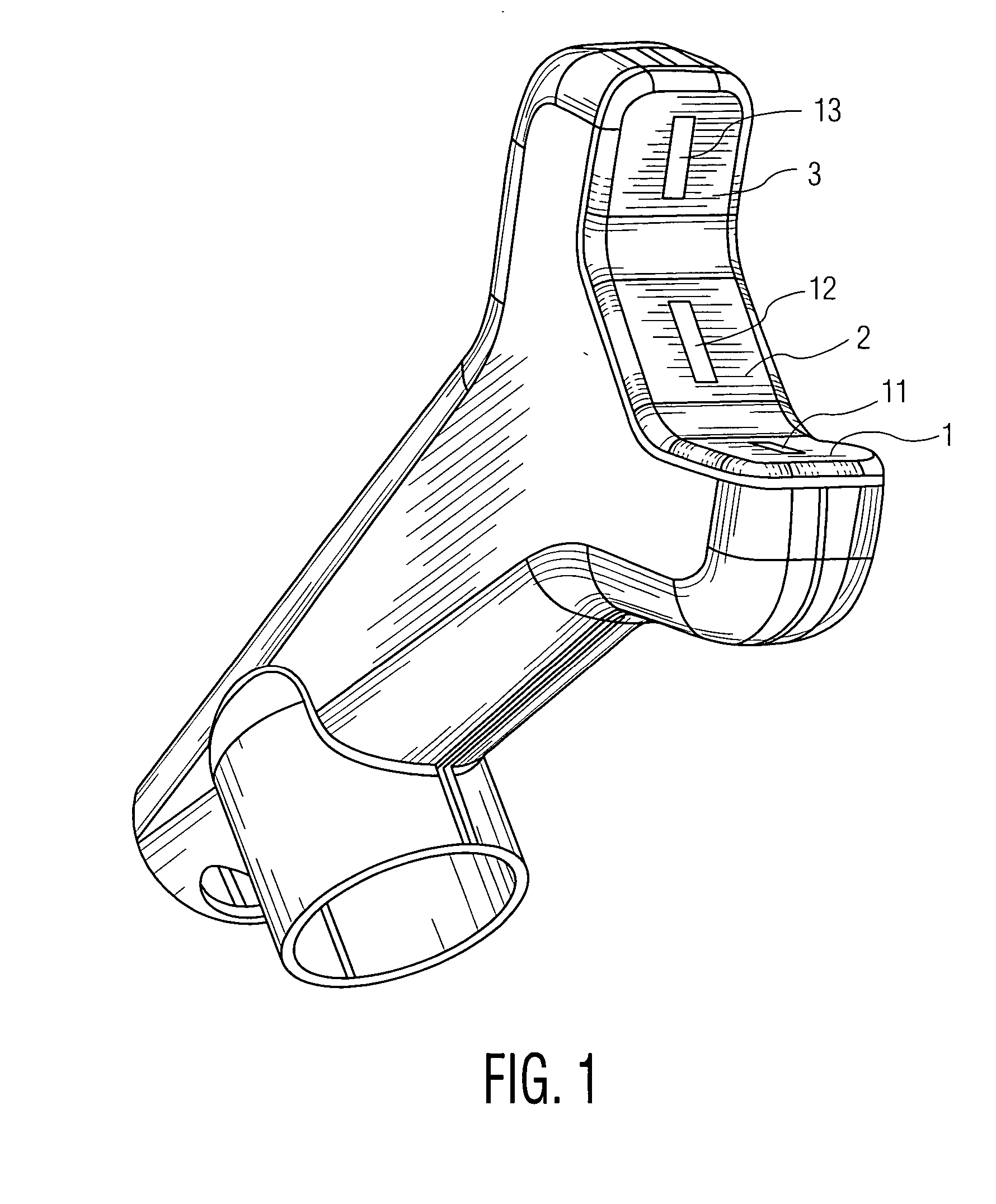
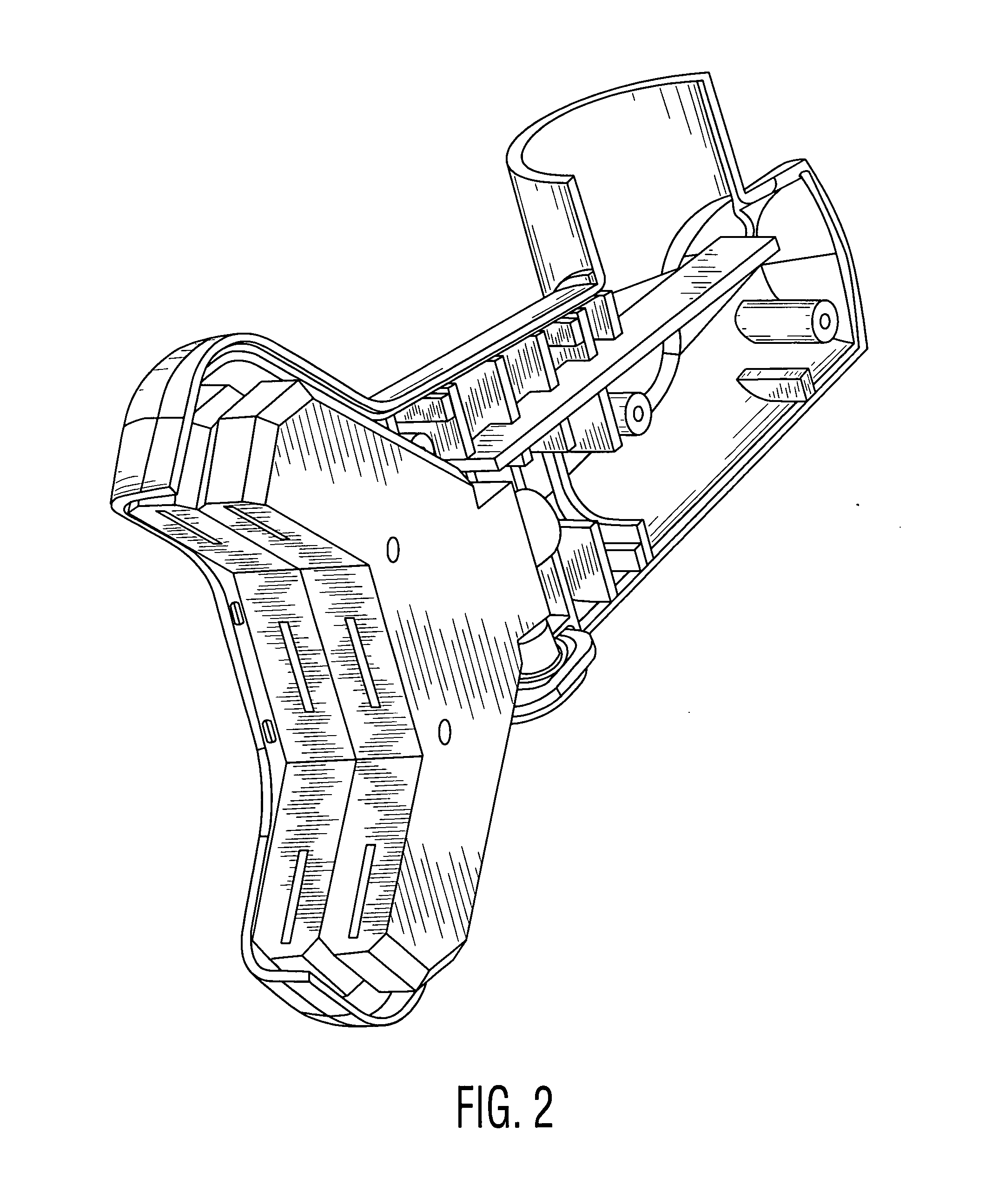
Luminous molded part, in particular a decorative part and/or trim part for a vehicle interior
InactiveUS8016465B2Decorative effectInhibition effectThermometer detailsUV light devicesLuminescent materialVisible range
The invention relates to a molded part, in particular a decorative part and / or a trim part for a vehicle interior. According to the invention, the molded part comprises at least one excitation source for emitting electromagnetic waves and at least one luminescent material which is excitable or excited by the electromagnetic waves emerging from the excitation source or sources to emit light in the visible range.
Owner:NOVEM CAR INTERIOR DESIGN GMBH
Method and tools for oral hygiene
InactiveUS6561808B2Increase motivation for treatmentImprove adhesionCosmetic preparationsImpression capsOral diseasePhotosensitizer
A method and material for self-cleaning of the teeth and mouth using a source of light in the visible range in conjunction with a photosensitive oral hygiene composition possessing a broad absorption spectrum in the visible range. The invention selectively eliminates harmful bacteria by use of a photosensitive agent and a light source. The present invention involves the use of a light-providing dental device to activate a photosensitive agent and destroy harmful bacteria in the oral cavity. It prevents or deters oral diseases, inflammations, and infections.
Owner:BIOLITEC UNTERNEHMENSBETEILLIGUNGS II AG
Information system and method for providing information using a holographic element
ActiveUS20070109619A1Improve relationshipThe relationship is accurateInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsAngle of incidencePhotodetector
In the following, the essential points are summarized again by means of groups of characteristics which each individually and in combination with one another characterize the invention specifically: 1. Information system for providing information in correlation with light incident on an eye, having a holographic element disposed in front of the eye, and an optical scanning device which detects light incident on the eye by way of the holographic element. 2. Information system according to Point 1, wherein the optical scanning device is at a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 3. Information system according to Point 1 or 2, wherein the optical scanning device detects light which is refracted by the holographic element before it impinges on the eye and does not enter the eye. 4. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the optical scanning device detects light which was first reflected back from the eye and was then refracted by the holographic element. 5. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye only at several discrete wavelengths in the visible range before the light impinges on the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device, and refracts light reflected back from the eye only at one discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 6. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye at fewer than 20, fewer than 10 or fewer than 5 discrete wavelengths in the visible range either before the light impinges on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 7. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range either before the light impinges on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 8. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light reflected back by the eye only at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 9. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light of one or several discrete wavelengths, at which the optical scanning device has a high sensitivity. 10. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light a several discrete wavelengths such that the refracted light is guided to a common point, and the angle of incidence of the light on this point permits a clear optionally also wavelength-independent conclusion on the angle of incidence of the light upon the holographic element. 11. Information system according to one of the preceding points, having an optical projection device which projects light into the eye by way of the holographic element. 12. Information system according to Point 11, wherein the light detected by the optical detection device and the light projected in front of the optical projection device run in the opposite direction through a common light guiding lens system and can be focused such by the optical scanning device or projection device that their respective beams describe the same path from or into the eye. 13. Information system for providing information in correlation with information obtained from an eye, having a holographic element disposed in front of the eye, and an optical projection device which projects light into the eye by way of the holographic element. 14. Information system according to one of Points 11 to 13, wherein the optical projection device projects light only at one or several discrete wavelengths in the visible range and / or at a wavelength in the infrared range. 15. Information system according to one of Points 11 to 14, wherein the holographic element refracts the wavelengths of the projected light. 16. Information system according to one of Points 11-15, wherein the optical projection device is in a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 17. Information system according to Point 16, wherein the holographic element comprises one or more optical flags, whose light reflection characteristics can be used by the information system by means of a photodetector for calibrating a projection angle of the optical projection device and / or a light guiding device. 18. Information system according to Point 17, including Point 12, wherein the information system uses the light reflection characteristics of the optical flags for calibrating a scanning angle of the optical scanning device and / or a light guiding device. 19. Information system according to Point 17, wherein the optical flags are generated in that reflecting elements are imaged during the creating of the holographic element such in the holographic element that they (something is missing) reflect light of one or several wavelengths which, corresponding to the predetermined angular ratio with respect to the optical projection device is incident on the holographic element, back along the path of incidence. 20. Information system according to Point 19, wherein the photodetector device has a splitter mirror which is arranged such in the light beam of the optical projection device that it guides a portion of the light, which impinges on the splitter mirror against the projection direction, in the direction of a photodetector which detects in at least two areas situated concentrically around one another. 21. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element has light-refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths, which correspond to a reflection on the concave side of an area constructed according to the curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid. 22. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element has light refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths, which correspond to a refraction on the concave side of an area constructed according to the curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid, which refraction corresponds to a reflection on a respective conical surface which is rotationally symmetrical about the axis of rotation of the ellipsoid and is perpendicular with respect to the ellipsoid at the site of the refraction. 23. Method of providing information in correlation with light incident on an eye, whereby a holographic element is disposed in front of the eye, and an optical scanning device detects the light incident on the eye by means of the holographic element. 24. Method according to Point 23, whereby the optical scanning device is at a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 25. Method according to Point 23 or 24, whereby the optical scanning device detects light which is refracted by the holographic element before impinging on the eye and does not enter the eye. 26. Method according to one of Points 23 to 25, whereby the optical scanning device detects light which was first reflected back from the eye and was then refracted by the holographic element. 27. Method according to one of Points 23 to 26, whereby the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye only at several discrete wavelengths in the visible range before its impinging on the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device and refracts light reflected back from the eye only at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 28. Method according to one of Points 23 to 27, whereby the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye at fewer than 20, fewer than 10 or fewer than 5 discrete wavelengths in the visible range either before its impinging on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 29. Method according to one of Points 23 to 28, whereby the holographic element refracts light originating from the visual field of the eye at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range either before its impinging on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 30. Method according to one of Points 23 to 29, whereby the holographic element refracts light reflected back from the eye only at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 31. Method according to one of Points 23 to 30, whereby the holographic element refracts light of one or several discrete wavelengths, at which the optical scanning device has a high sensitivity. 32. Method according to one of Points 23 to 31, whereby the holographic element refracts light at several discrete wavelengths such that the refracted light is guided to a common point, an the angle of incidence of the light onto this point allows a clear, optionally also wavelength-independent conclusion on the angle of incidence of the light upon the holographic element. 33. Method according to one of Points 23 to 32, whereby an optical projection device projects light by way of the holographic element into the eye. 34. Method according to Point 33, whereby the light detected by the optical scanning device and the light projected in front of the optical projection device run in the opposite direction through a common light guiding lens system and can be focused such by the optical scanning device or projection device that their respective beams describe the same path from or into the eye. 35. Method of providing information in correlation with information obtained from an eye, whereby a holographic element is disposed in front of the eye, and an optical projection device projects light by way of the holographic element into the eye. 36. Method according to points 33 to 35, whereby the optical projection device projects light only at one or several discrete wavelengths in the visible range and / or at a wavelength in the infrared range. 37. Method according to one of Points 33 to 36, whereby the holographic element refracts the wavelengths of the projected light. 38. Method according to one of Points 33 to 37, whereby the optical projection device is in a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 39. Method according to Point 38, whereby the holographic element is equipped with one or more optical flags, whose light reflection characteristics can be used by means of a photodetector device for calibrating a projection angle of the optical projection device and / or a light guiding device. 40. Method according to Point 39, including Point 34, whereby the light reflection characteristics of the optical flags are used for calibrating a scanning angle of the optical scanning device and / or a light guiding device. 41. Method according to Point 39, whereby the optical flags are generated in that reflecting elements are imaged during the creating of the holographic element such in the holographic element that they beam light of one or more wavelengths which, corresponding to the predetermined angular ratio with respect to the optical projection device is incident on the holographic element, back along the incidence path. 42. Method according to Point 41, whereby the photodetector device is equipped with a photodetector detecting in at least two areas situated concentrically around one another, and a splitter mirror which is arranged such in the light beam of the optical projection device that it directs a portion of the light impinging on the splitter mirror against the projecting direction, in the direction of the photodetector. 43. Method according to one of Points 23 to 42, whereby the holographic element has light-refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths which correspond to a reflection on the concave side of an area constructed according to a curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid. 44. Method according to one of Points 23 to 43, whereby the holographic element has light-refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths, which correspond to a refraction on the concave side of an area constructed according to a curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid, which refraction corresponds to a reflection on a respective conical surface rotationally symmetrical about the axis of rotation of the ellipsoid, which conical surface is perpendicular with respect to the ellipsoid at the site of the refraction. While the preceding description with respect to the title is limited to embodiments falling under the initially mentioned generic terms “scanning information system” and “projecting information system”, each individual discussed characteristic of their disclosure can also be used in an embodiment of the systems, devices and methods initially identified by reference to their full content. The applications by the same applicant and / or the same inventors mentioned in the present application should be considered to be a correlated invention complex.
Owner:APPLE INC
Light emitting device having various color temperature
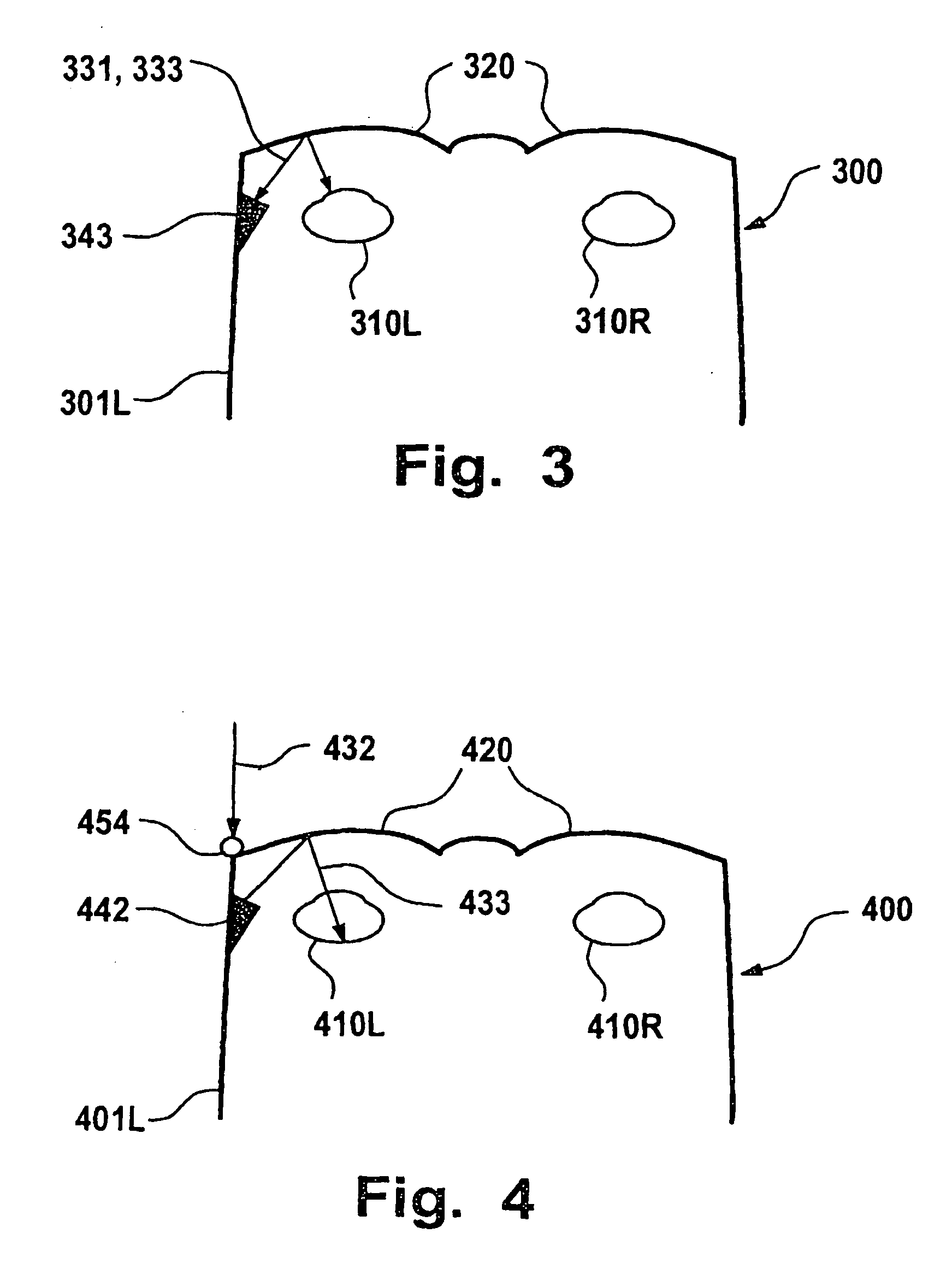
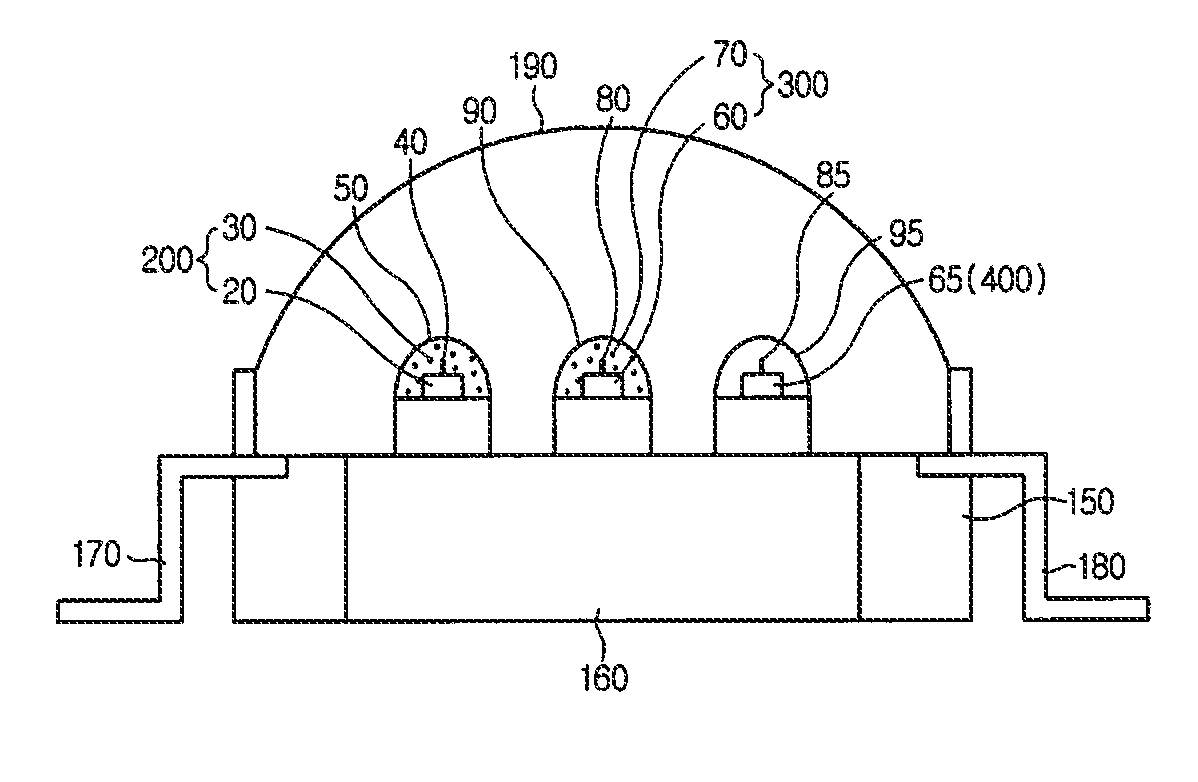
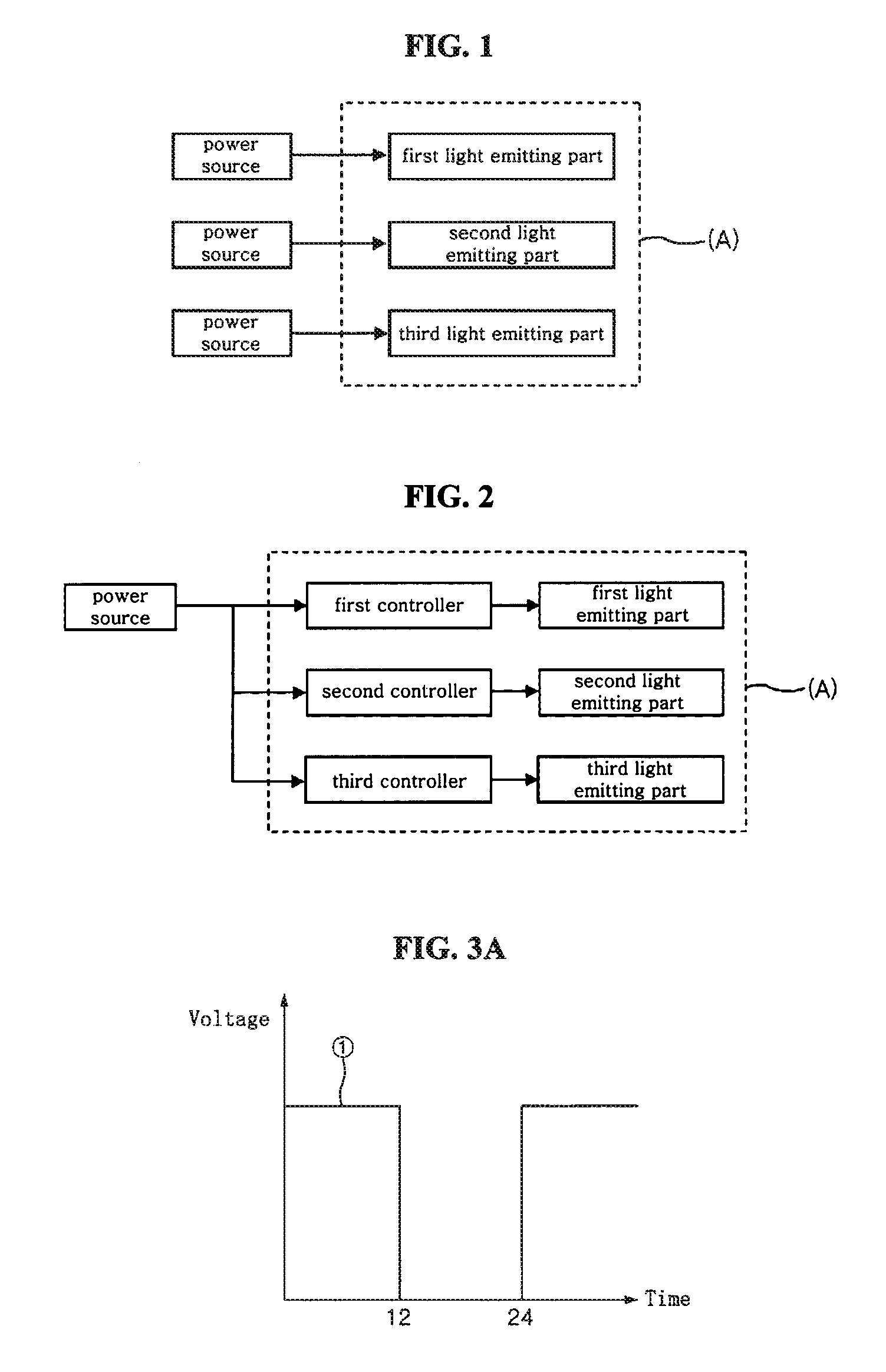
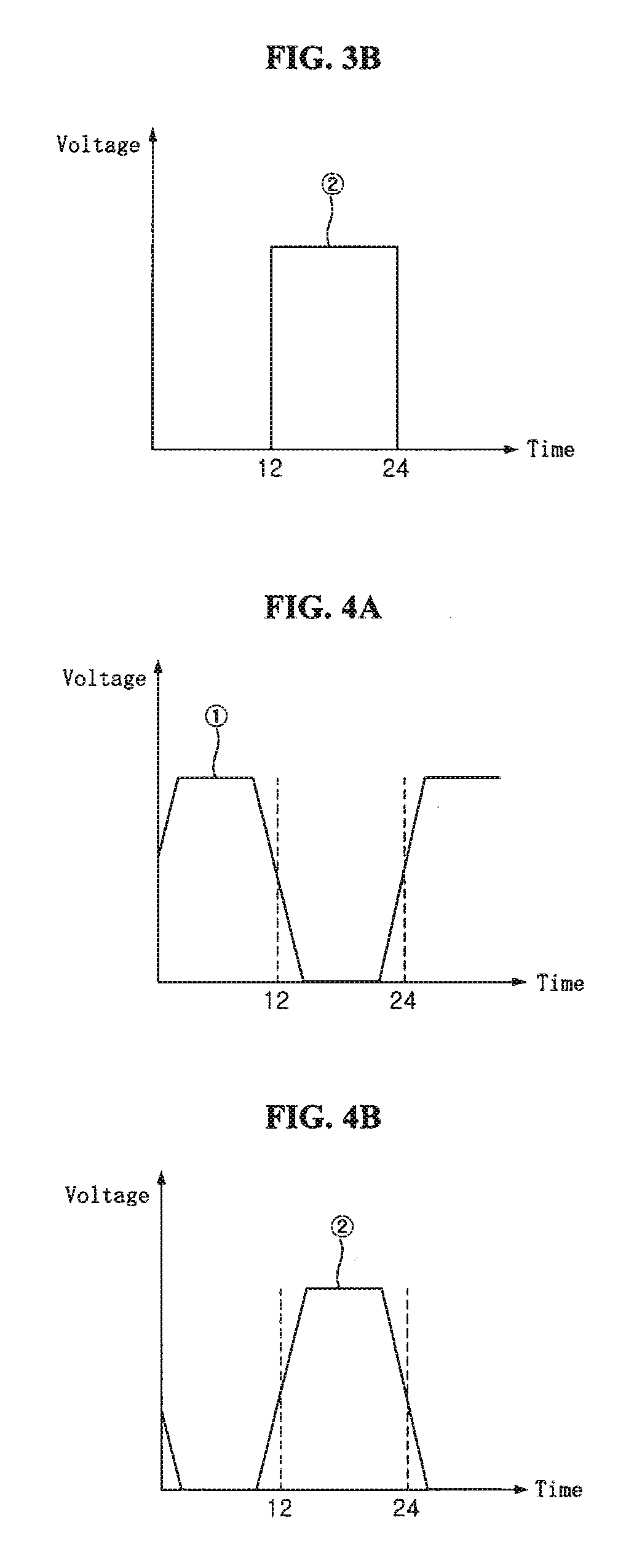
A light emitting device capable of emitting light having various color temperatures is disclosed. The light emitting device includes a first light emitting part emitting a daylight color having a color temperature of 6000 K or more, a second light emitting part emitting white light having a color temperature less than 6000 K, and a third light emitting part emitting light in a visible range of 580 nm or more. The second and third light emitting parts are operable independently of the first light emitting part, and realize a warm white color having a color temperature of 3000 K or less with the white light emitted from the second light emitting part and the light emitted from the third light emitting part. The light emitting device realizes white light of various spectra and color temperatures corresponding to desired mood and utility. The light emitting device is controlled to emit light having a suitable wavelength or a suitable color temperature depending on the circadian rhythm of human, thereby enabling improvement of the user's health.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Articles having low wettability and high light transmission
InactiveUS20070231542A1High light transmittanceIncrease resistanceFouling preventionRecord information storageElectromagnetic radiationLight transmission
An article comprising a surface portion is provided. The surface portion has a plurality of primary features, and the primary features have a height dimension in the range from about I micron to about 500 microns, an aspect ratio in the range from about 0.5 to about 10, and a spacing dimension in the range from about 0.5 to about 50 feature width units. The surface portion comprising the features has a wettability of the surface sufficient to generate, with a reference fluid, a static contact angle of greater than about 120 degrees and a total transmission of at least about 70% in the visible range of electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Image pickup device-equipped rear-view mirror
ActiveUS20090040778A1Reduce reflected light intensityGood anti-glare effectOptical signallingTelevision systemsRefractive indexTransmittance
The present invention is intended to provide an image pickup device-equipped rear view mirror with improved image pickup performance, glare prevention and appearance (design) in addition to improved performance as a vehicle mirror. A mirror element is formed by forming a reflecting film consisting of high refractive index material films and a low refractive index material film on a back surface of a transparent glass substrate. The integrating sphere reflectance of the mirror element in the visible range is 40% to 60% and the near-infrared transmittance is no less than 70% for the whole or part of the band belonging to the near-infrared range within the entire sensitive wavelength range of the near-infrared camera. A black mask member is attached to an entire back surface of the reflecting film. The near-infrared camera is arranged behind the black mask member. The region corresponding to the area for the image-pickup by the near-infrared camera within the entire region of the black mask member is formed of a visible-light absorption and near-infrared transmission filter. The near-infrared transmittance of the visible-light absorption and near-infrared transmission filter is no less than 70% for the whole or part of the band belonging to the near-infrared range within the entire sensitive wavelength range of the near-infrared camera.
Owner:MURAKAMI CORP
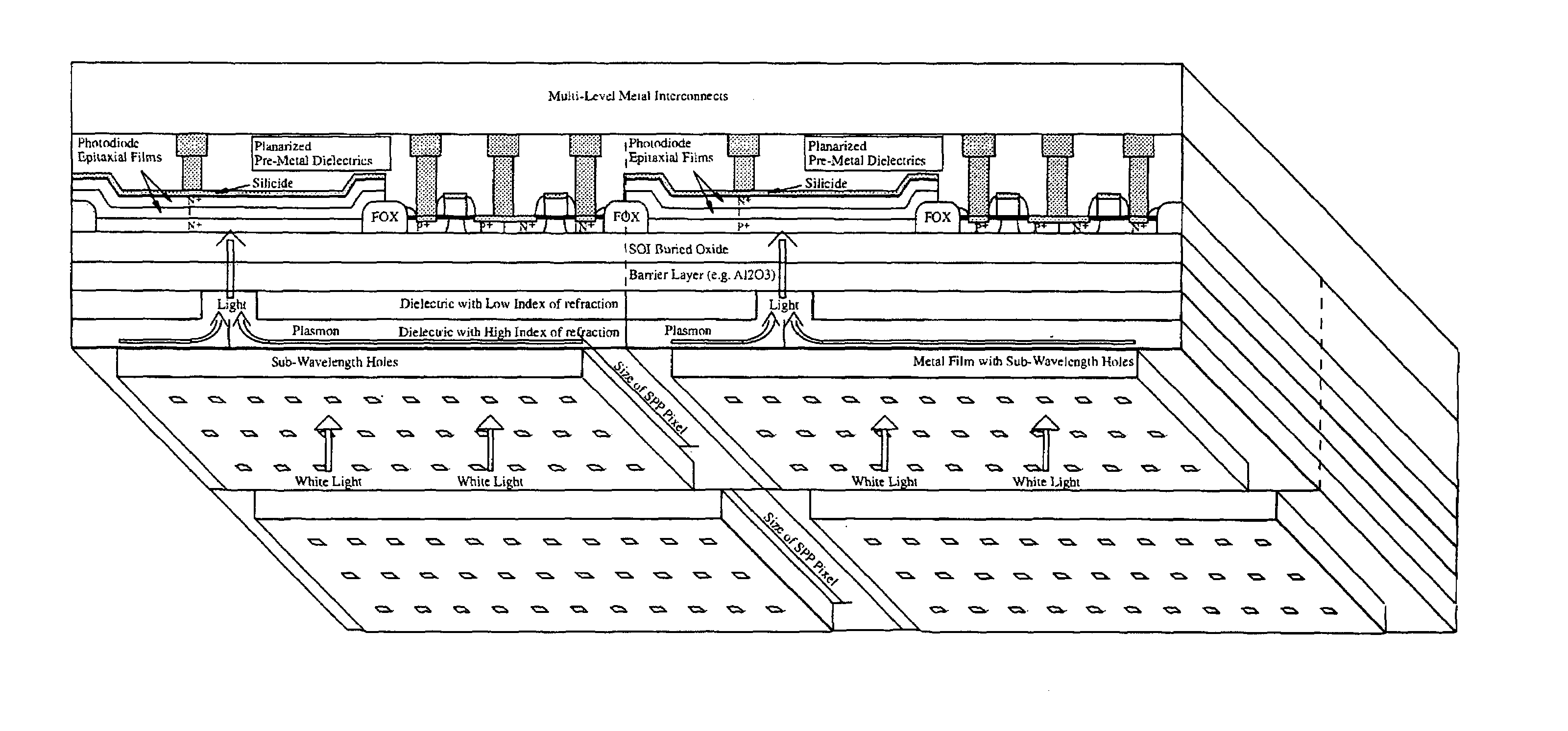
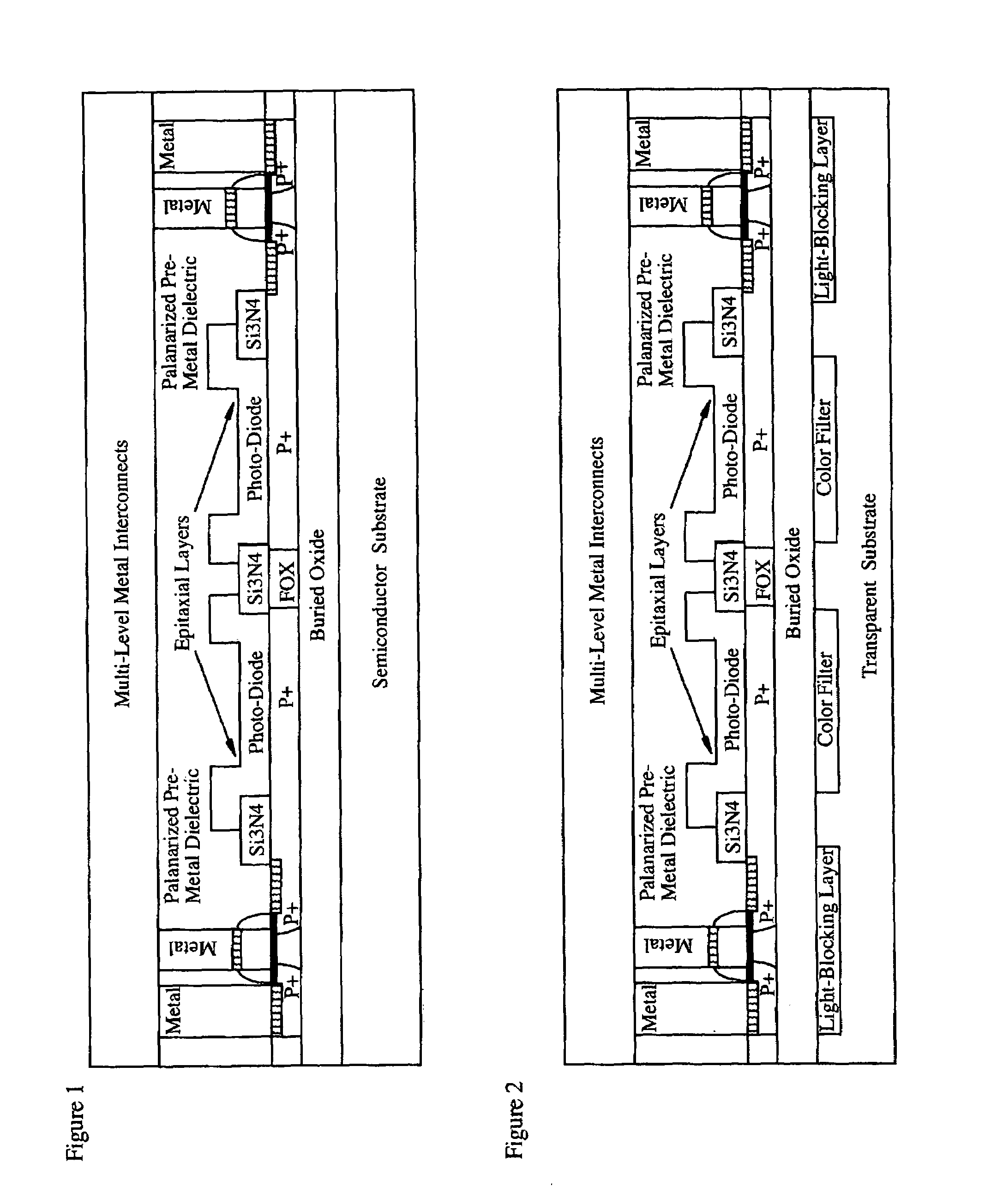
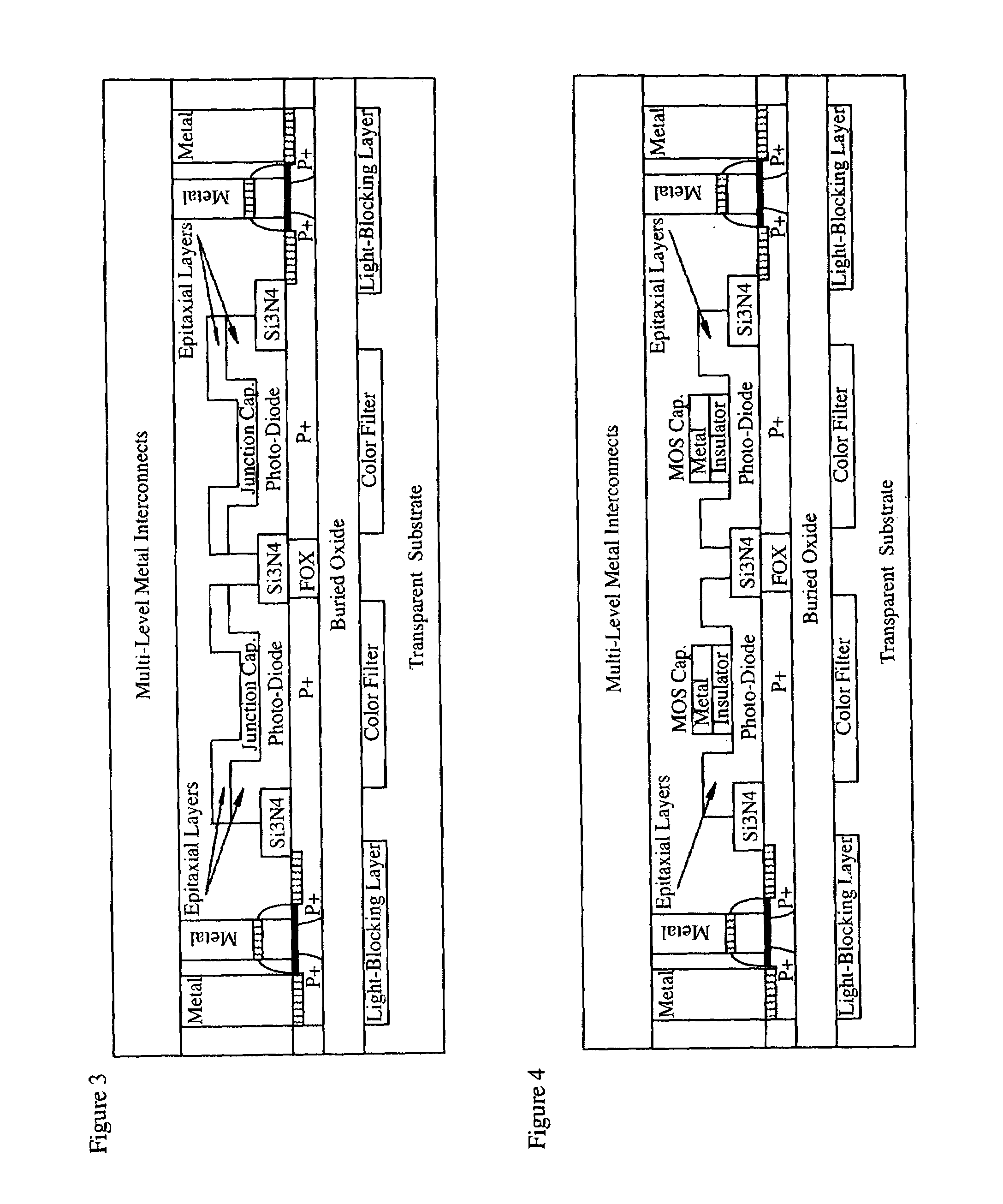
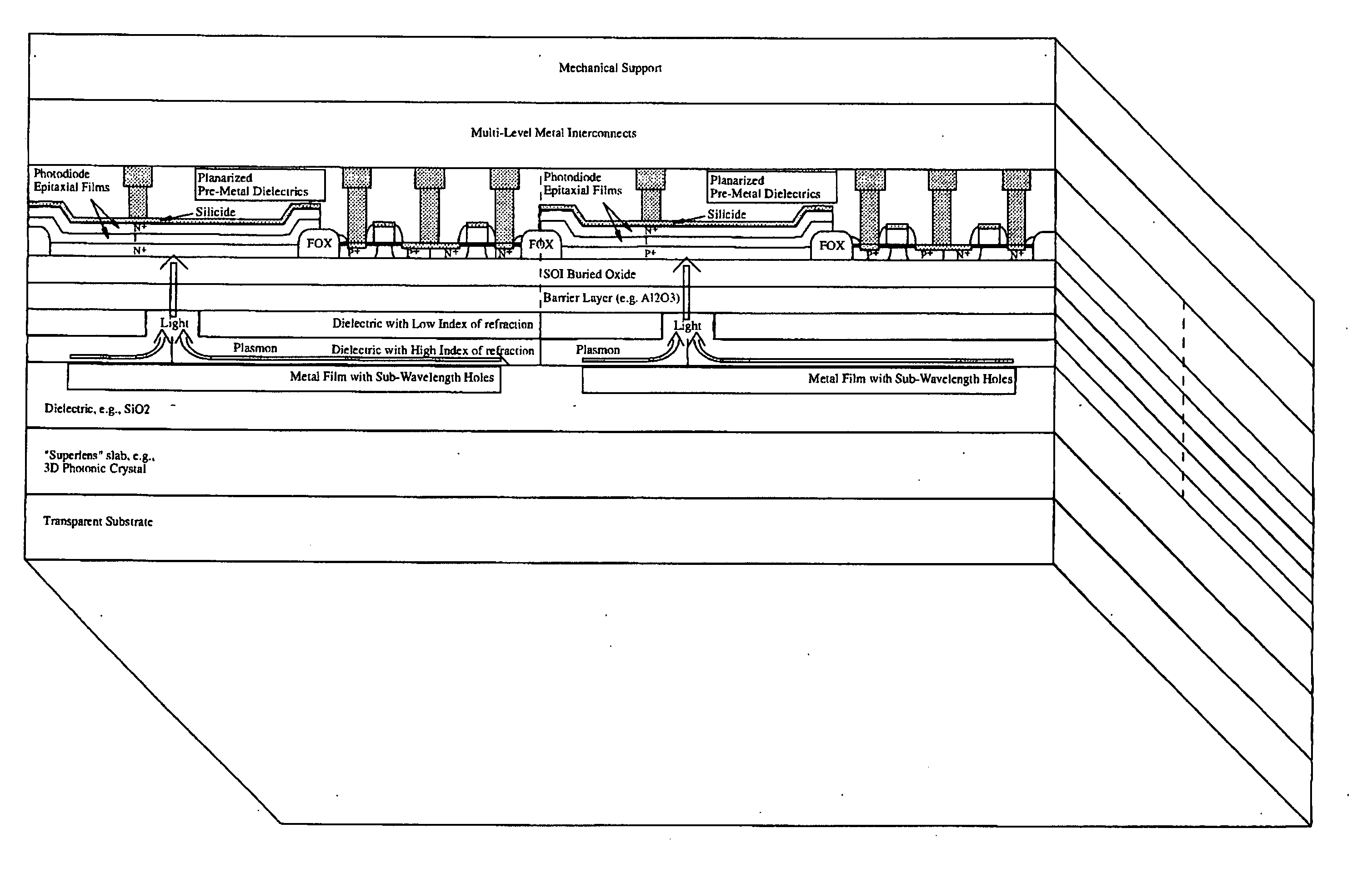
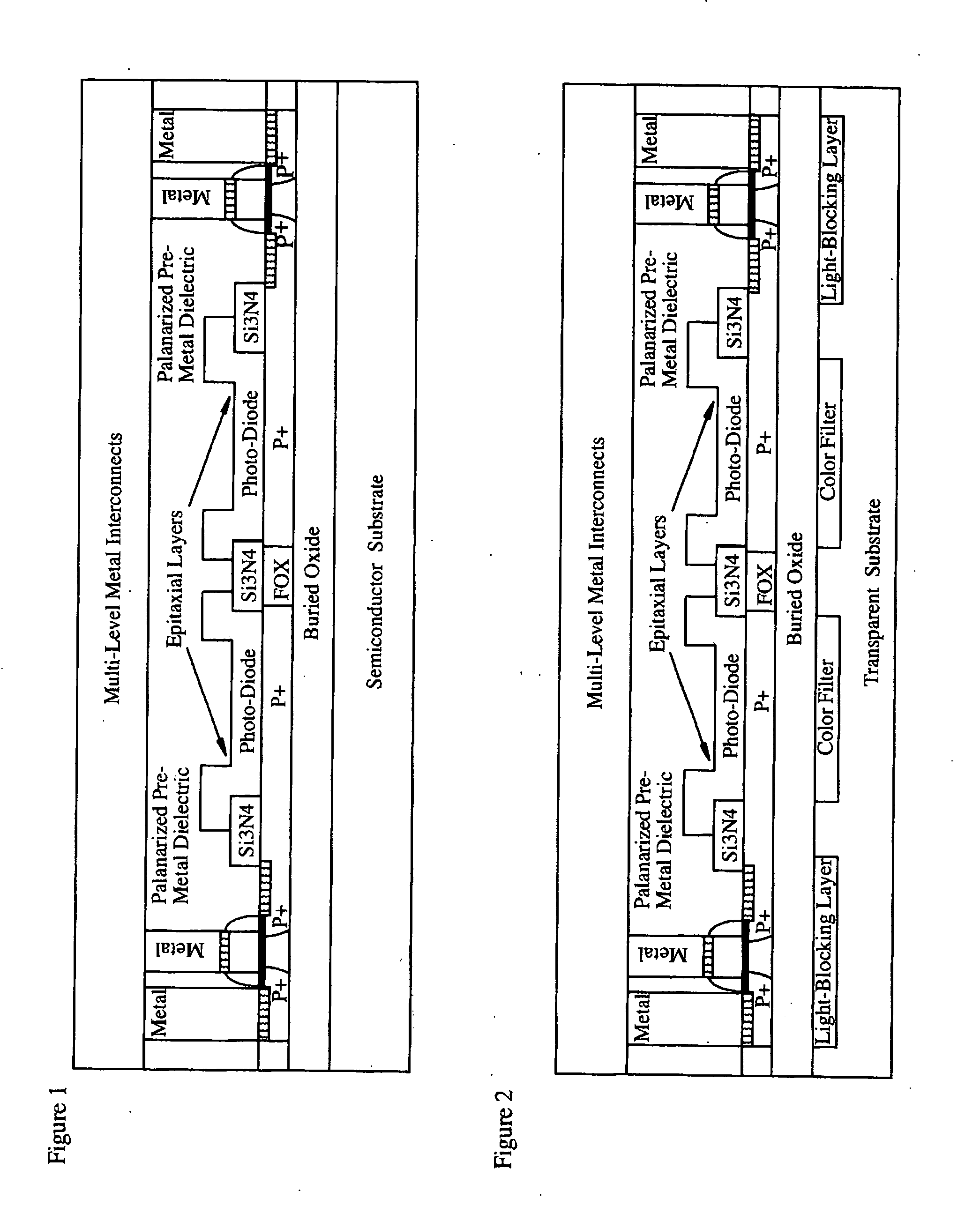
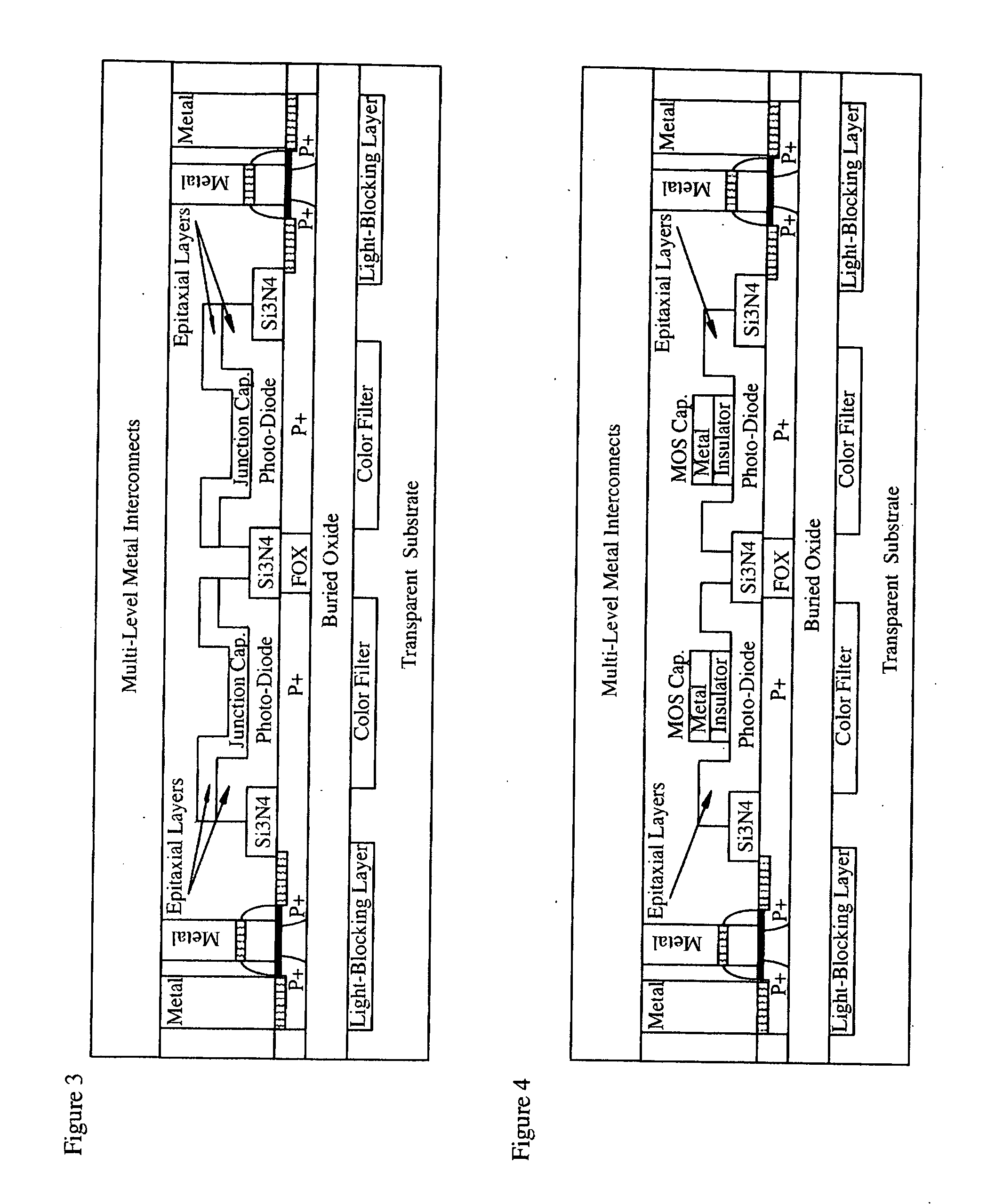
CMOS image sensor
Light sensing devices are monolithically integrates with CMOS devices on Thin-Film Silicon-On-insulator (TF-SOI) or Thin-Film Germanium-On-Insulator (TF-GeOI) substrates. Photo-diode active layers are epitaxially grown on the front-side of the substrate and after full processing of the front-side of the substrate, the substrate material is removed under the buried insulator (buried oxide). Monolithically integrated structures are then fabricated on the back of the buried oxide. The back-side is then bonded to a new substrate that is transparent to the wavelengths of interest. For example, quartz, sapphire, glass, or plastic, are suitable for the visible range. Back-side illumination of the sensor matrix is thereby allowed, with light traveling through the structures fabricated on the back of the substrate, opposite to the side on which CMOS is made.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
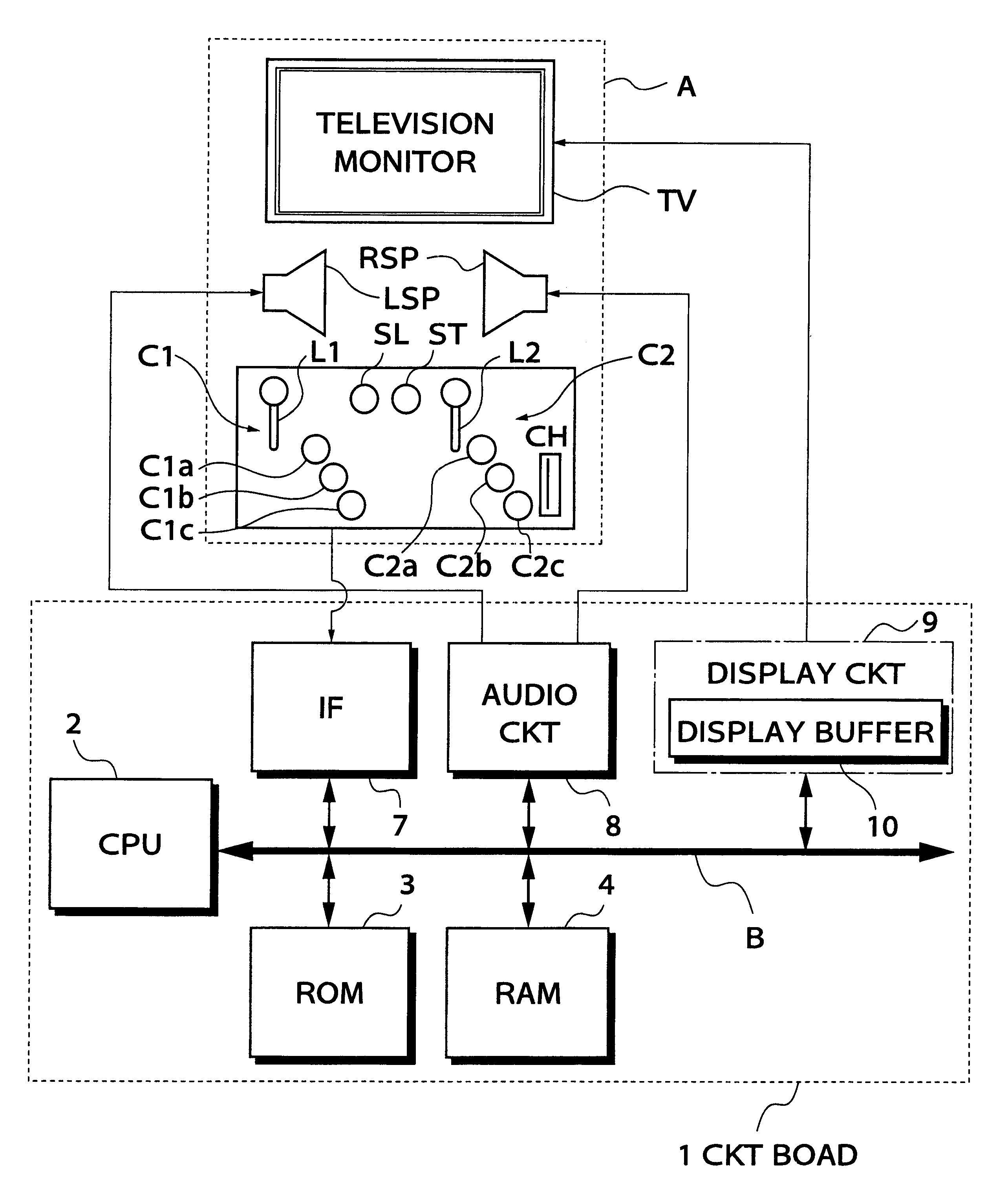
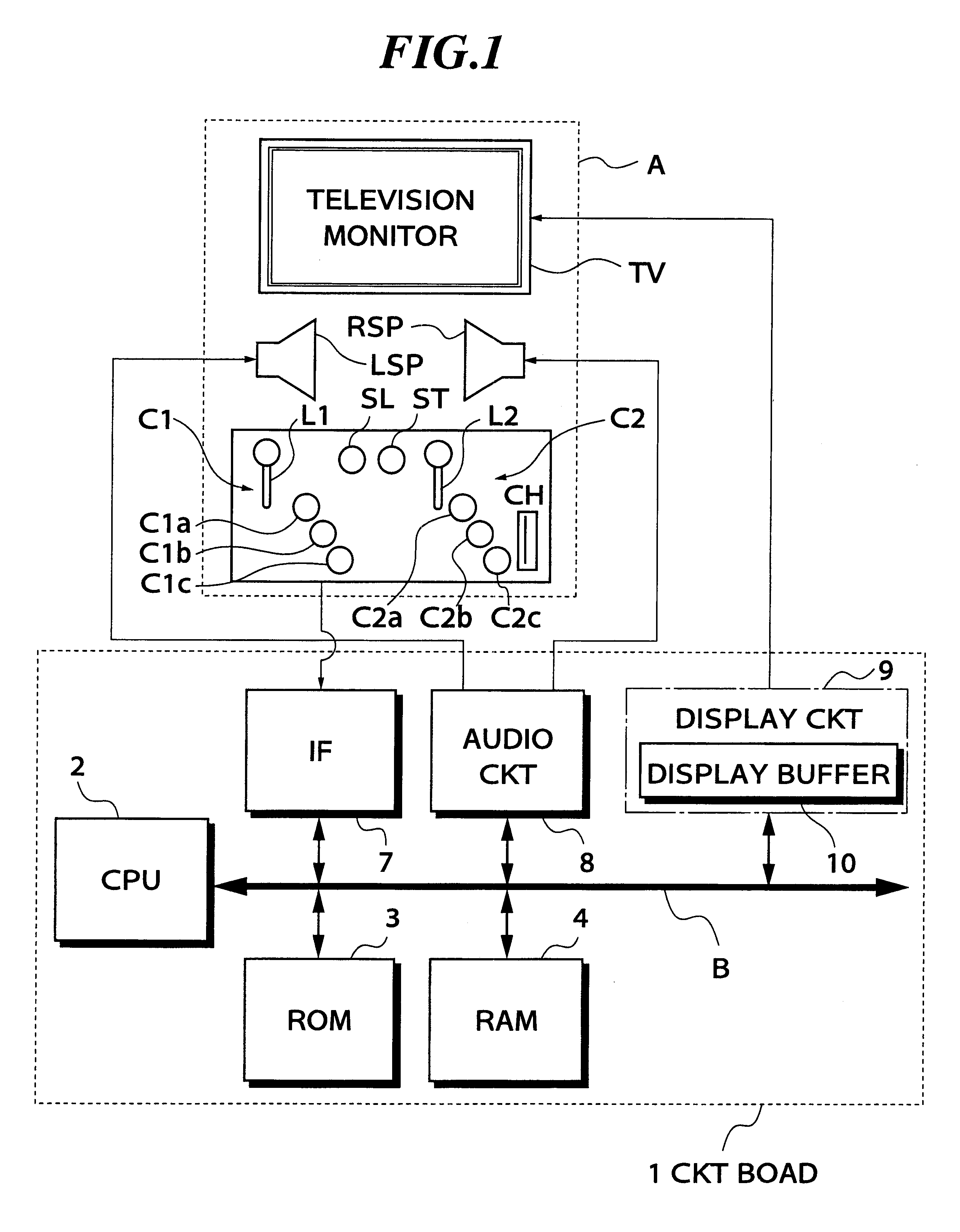
Volleyball video game system
A CPU determines the position of a ball in a virtual game space, and moves a viewpoint based on viewpoint data and the position of the ball. The CPU displays on a monitor TV a portion of a volleyball court in a visible range based on the viewpoint and the direction of an axis thereof. The CPU determines a landing position of the ball, displays a first cursor at the landing position, and displays a player character as it receives the ball when the distance between the player character and the first cursor becomes a predetermined distance before the ball reaches the landing position. When a served ball is received by a player character, the CPU selects a player character to make an attacking action. The CPU assigns a button to the selected player character. When the ball is set by a player character as a setter, the CPU assigns an attack button, and controls the selected player character to perform the attacking action in response to an input signal from the attack button.
Owner:KONAMI DIGITAL ENTERTAINMENT CO LTD
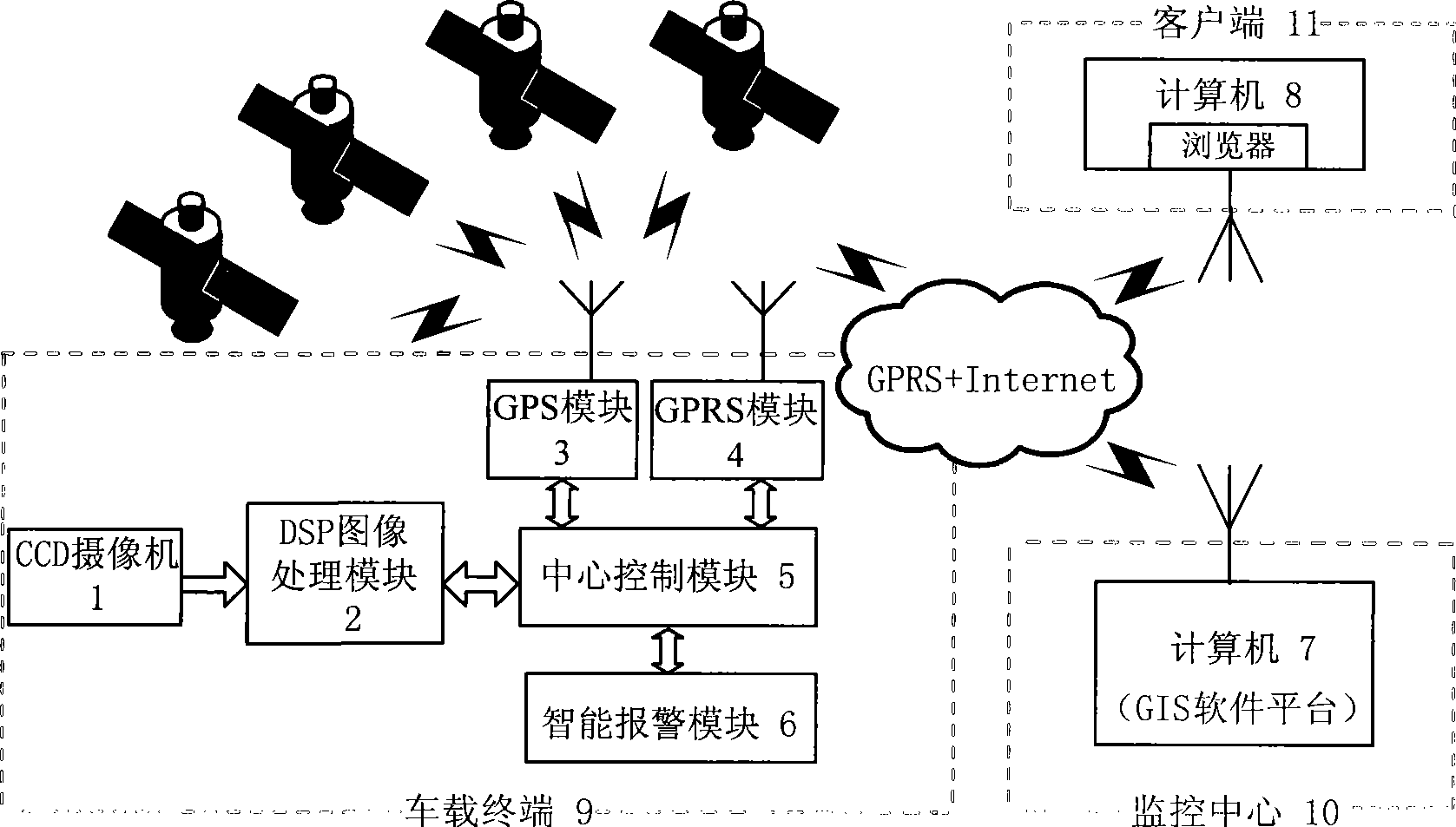
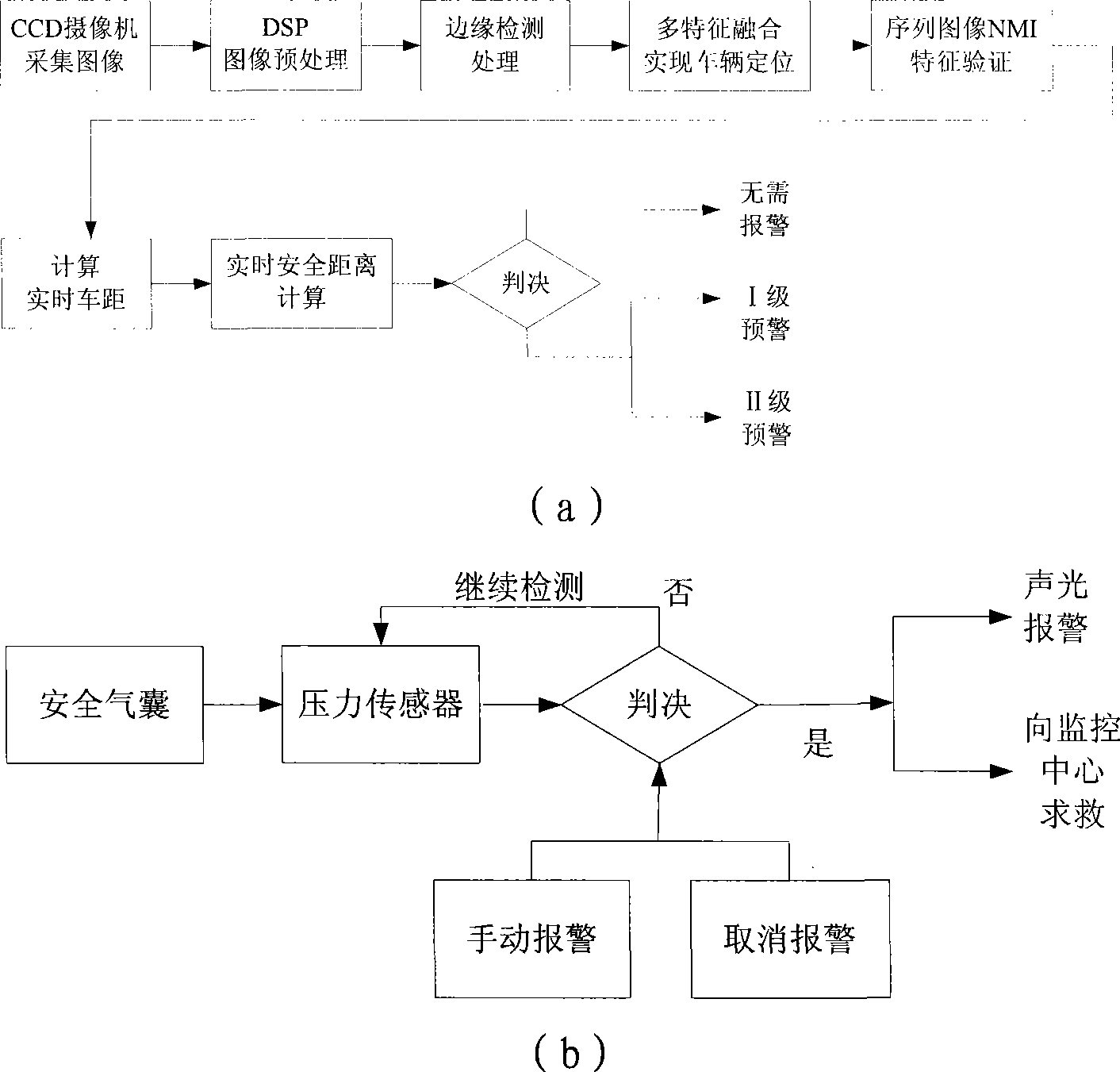
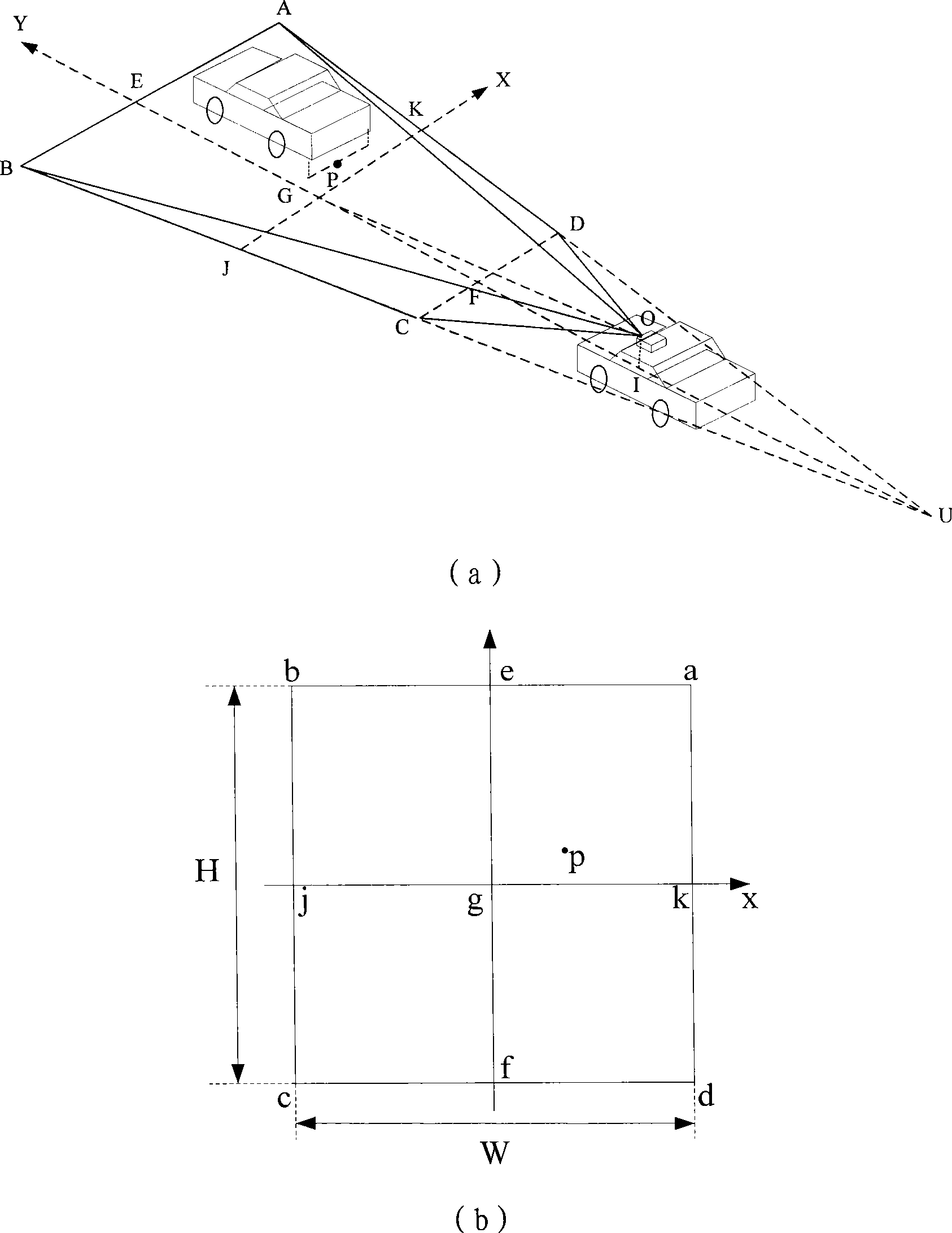
Vehicle intelligent alarming method and device
InactiveCN101391589AImprove securityEfficient detectionPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSignalling/lighting devicesMobile vehicleMachine vision
The invention relates to an on-board intelligent alarming method and a device, wherein, the method combines a longitudinal anti-collision pre-warning method based on the single-eye vision and an accident automatic help-calling method, realizes preventing the rear-end accidents, strives for helping time, reduces injuries and deaths, effectively prevents the collision accidents and personnel deaths caused by the collision, and improves the running safety of the automobile; the device mainly comprises three parts: an on-board terminal, a monitoring center and a user end; the method and the device use the machine vision technique to differentiate the moving vehicles in the front, have high precision and wide visible range, can effectively probe the obstacles, reduce the error reporting possibility and prevent the collision accidents. The method and the device can improve the safety of the vehicle, thus having extremely large application value and prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
CMOS image sensor
Light sensing devices are monolithically integrates with CMOS devices on Thin-Film Silicon-On-insulator (TF-SOI) or Thin-Film Germanium-On-Insulator (TF-GeOI) substrates. Photodiode active layers are epitaxially grown on the front-side of the substrate and after full processing of the front-side of the substrate, the substrate material is removed under the buried insulator (buried oxide). Monolithically integrated structures are then fabricated on the back of the buried oxide. The back-side is then bonded to a new substrate that is transparent to the wavelengths of interest. For example, quartz, sapphire, glass, or plastic, are suitable for the visible range. Back-side illumination of the sensor matrix is thereby allowed, with light traveling through the structures fabricated on the back of the substrate, opposite to the side on which CMOS is made.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Color display device and method for manufacturing the same
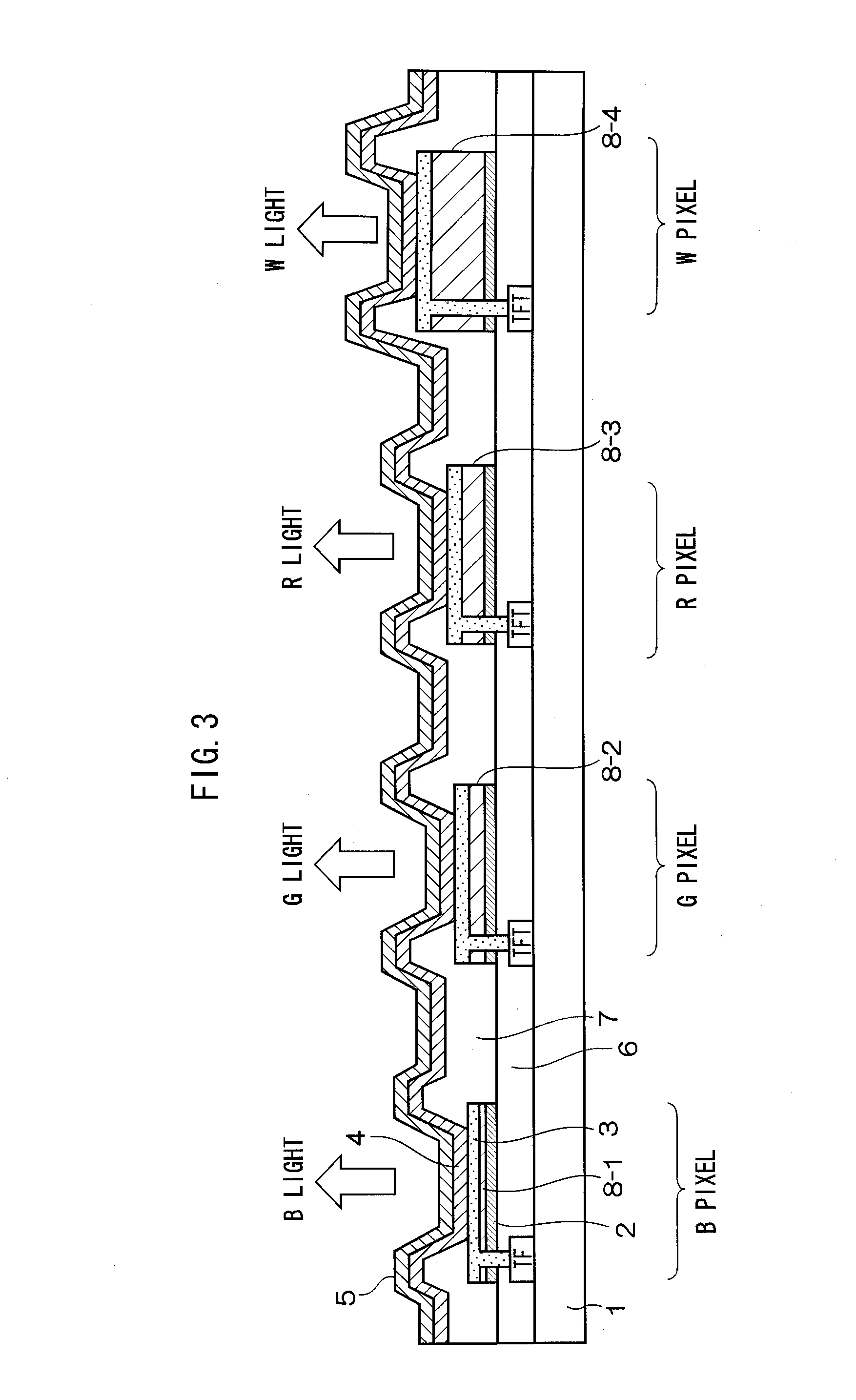
Disclosed is a color display device containing plural pixels on a substrate, each pixel is composed of plural sub-pixels which emit lights different in wavelength in the visible range and a white sub-pixel, the plural sub-pixels and the white sub-pixel each have a white organic electroluminescence layer interposed between an optically semitransparent reflection layer and a light reflection layer, the optical distance between the optically semitransparent reflection layer and the light reflection layer in each of the plural sub-pixels forms a resonator having a distance for resonating emitted light, and the optical distance between the optically semitransparent reflection layer and the light reflection layer in the white sub-pixel is longer than the maximum optical distance between the optically semitransparent reflection layer and the light reflection layer in each of the plural sub-pixels.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Thermochromic laminates and methods for controlling the temperature of a structure
InactiveUS6500555B1Minimize amount of heatMaximizes heat absorption rateSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersTrigger zoneExternal energy
Thermochromic laminates, which predictably vary their ability to absorb or reflect electromagnetic radiation, are provided. Laminates of the invention advantageously possess temperature trigger zones, that is, points or ranges of temperature, which function to decrease or increase the amount of electromagnetic energy, and particularly energy in the UV, infrared and visible ranges, that is reflected from the laminate, or absorbed as heat by the laminate and transmitted to an underlying structure. Laminates of the present invention can be provided in a variety of colors and temperature trigger points or ranges, and require no input of external energy except that of the impinging radiation. Laminates of the invention advantageously can be used in methods alone or combined with other materials such as roofing, siding, heat exchangers and other heat transfer materials and are therefore useful to control the temperature of an underlying structure or object.
Owner:CYGNET WORKS INC
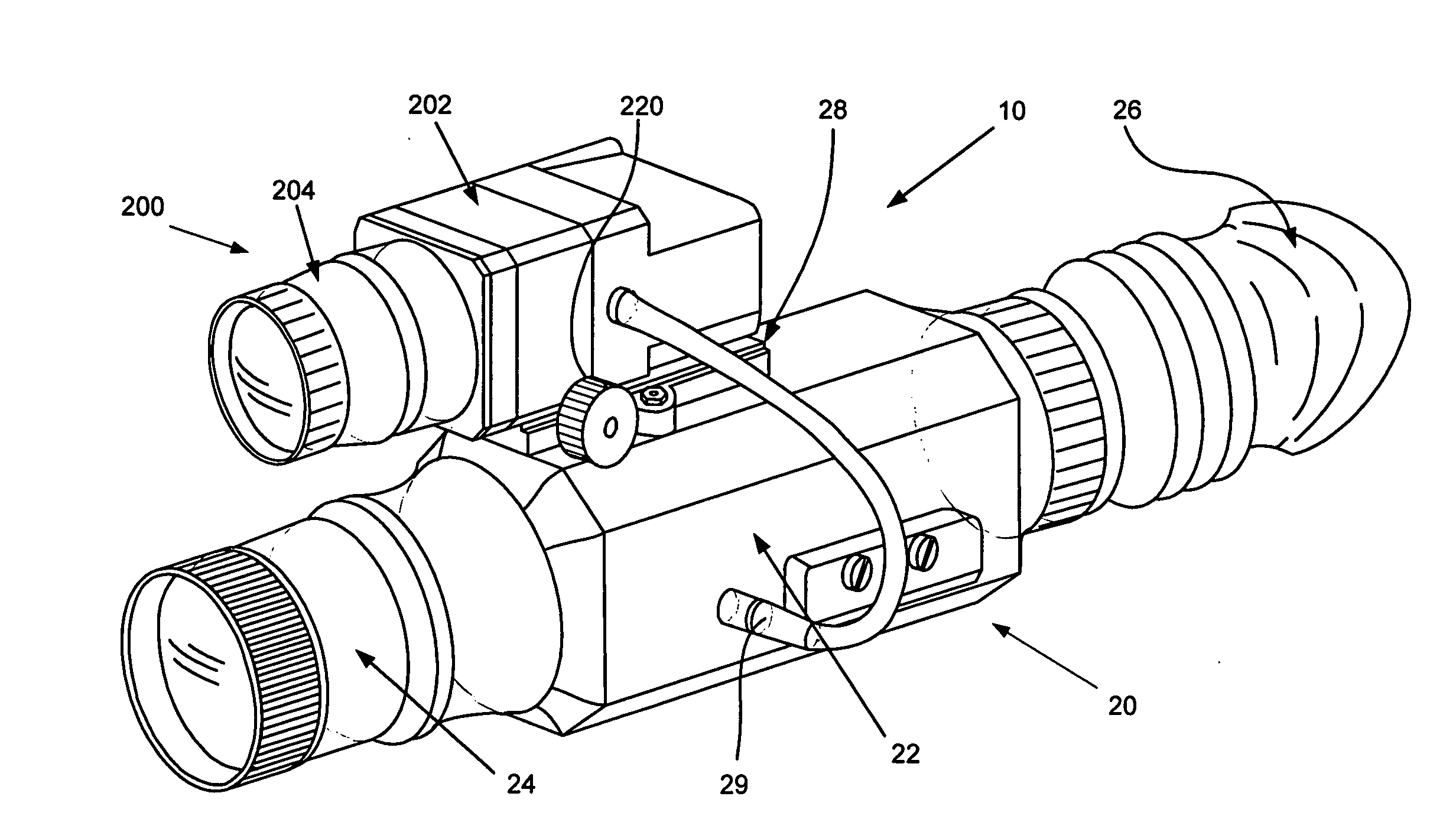
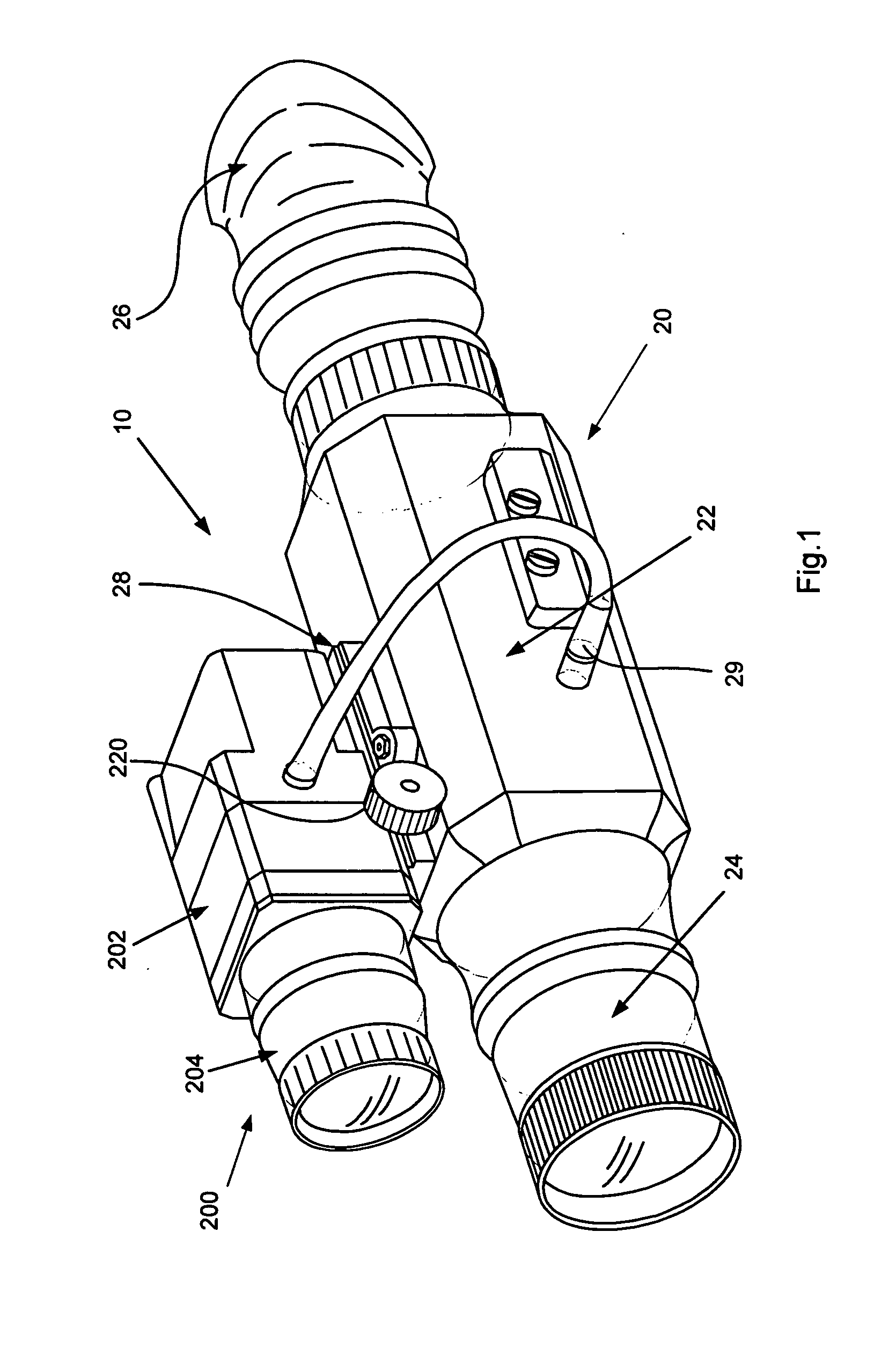
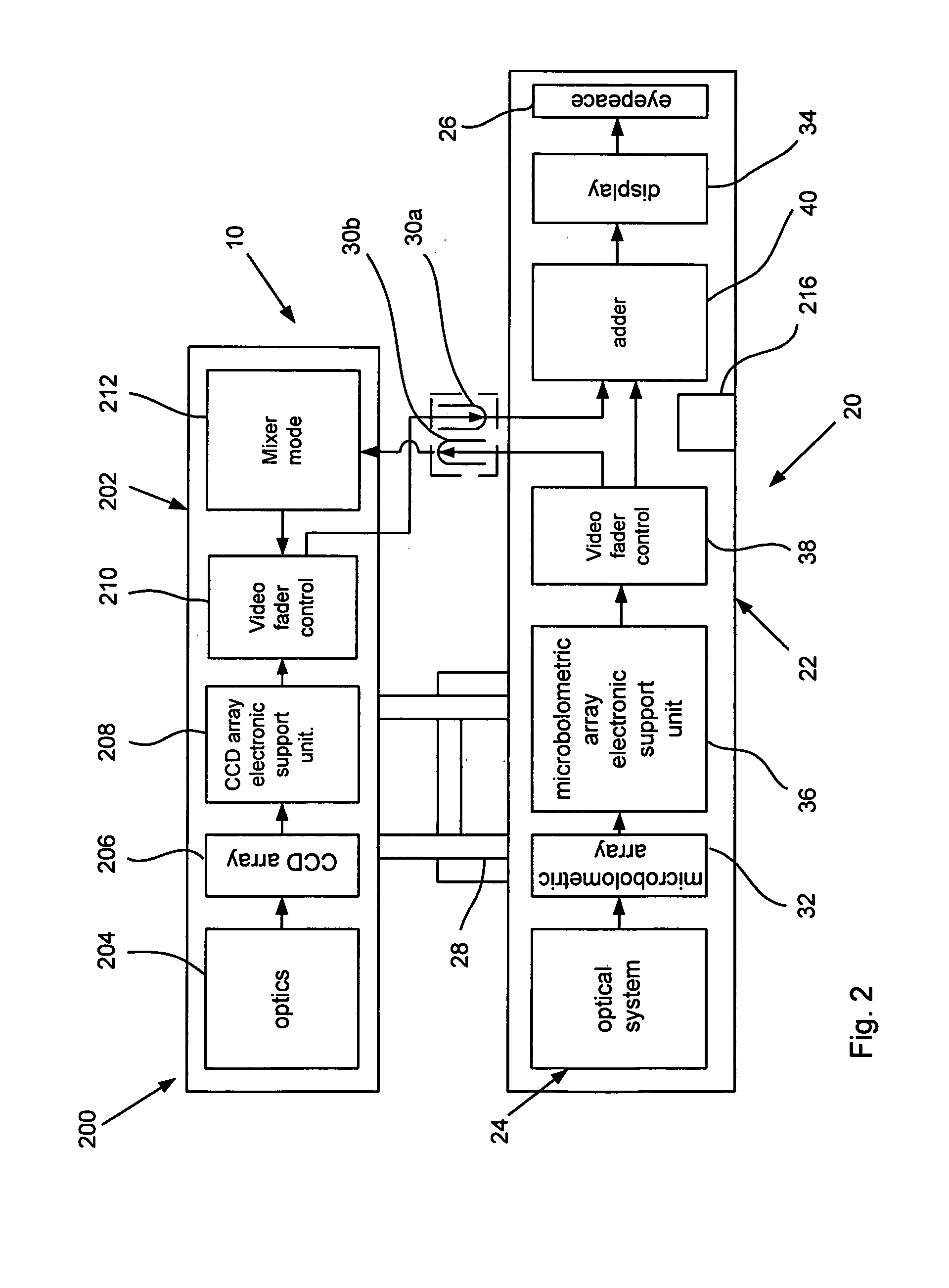
Optical system with automatic mixing of daylight and thermal vision digital video signals
InactiveUS20120019700A1Easy to storeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital videoDisplay device
An optical sight system that comprises a combination of a thermal scope with a CCD visible-range attachment connectable to the thermal scope with a quick-release connector. The system is equipped with a device for automatic interposition of the digital visible image of the CCD visible-range attachment onto the digital thermographic image when the attachment is electrically and mechanically connected to the thermal scope. The CCD is a light-weight device which does not have screen and which is easily attached to the thermal scope by means of a quick-release connection unit. Both digital images are observed on the screen of the thermal-scope display.
Owner:AMERICAN TECH NETWORK
Light emitting device having various color temperature
A light emitting device capable of emitting light having various color temperatures is disclosed. The light emitting device includes a first light emitting part emitting a daylight color having a color temperature of 6000 K or more, a second light emitting part emitting white light having a color temperature less than 6000 K, and a third light emitting part emitting light in a visible range of 580 nm or more. The second and third light emitting parts are operable independently of the first light emitting part, and realize a warm white color having a color temperature of 3000 K or less with the white light emitted from the second light emitting part and the light emitted from the third light emitting part. The light emitting device realizes white light of various spectra and color temperatures corresponding to desired mood and utility. The light emitting device is controlled to emit light having a suitable wavelength or a suitable color temperature depending on the circadian rhythm of human, thereby enabling improvement of the user's health.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
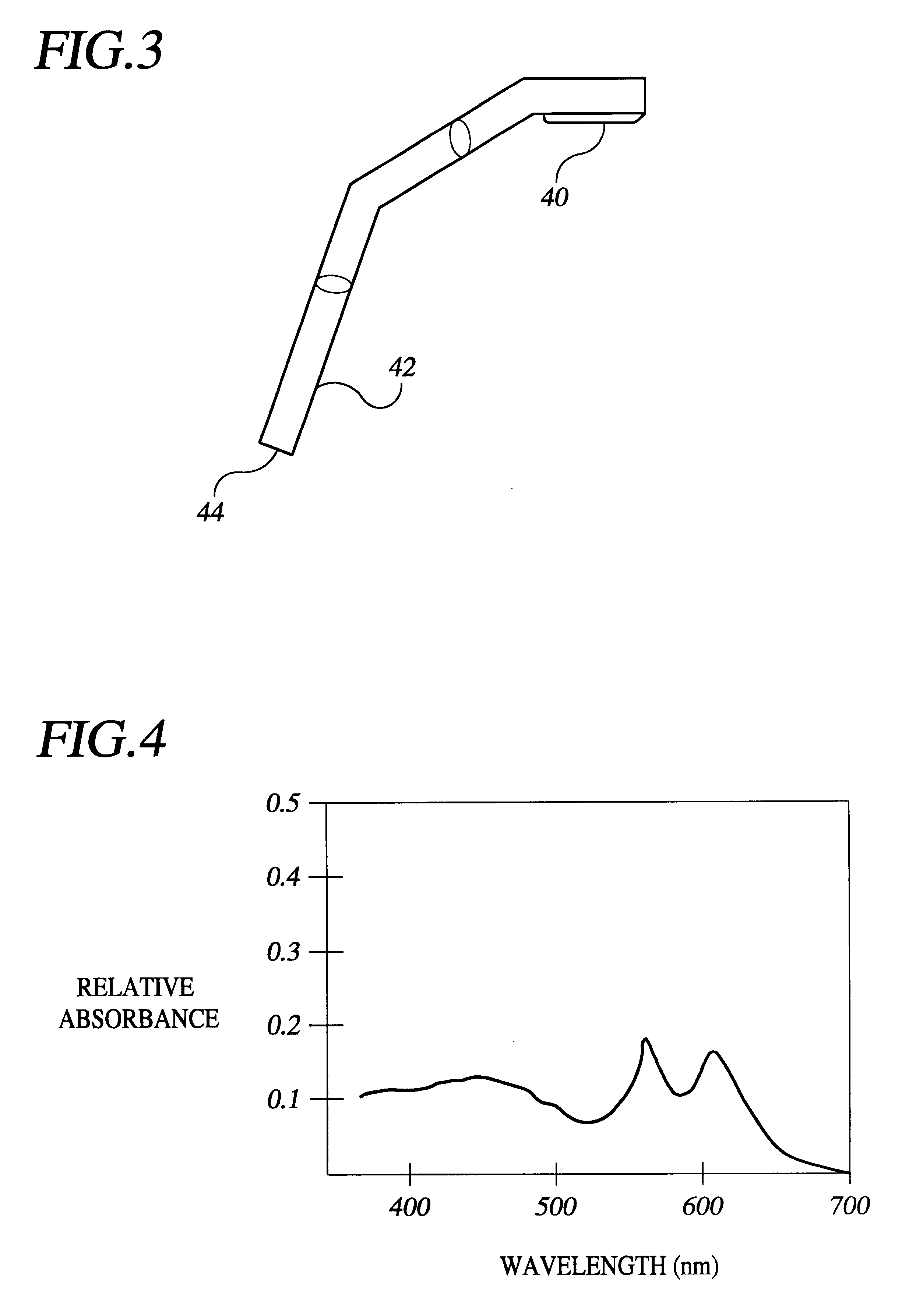
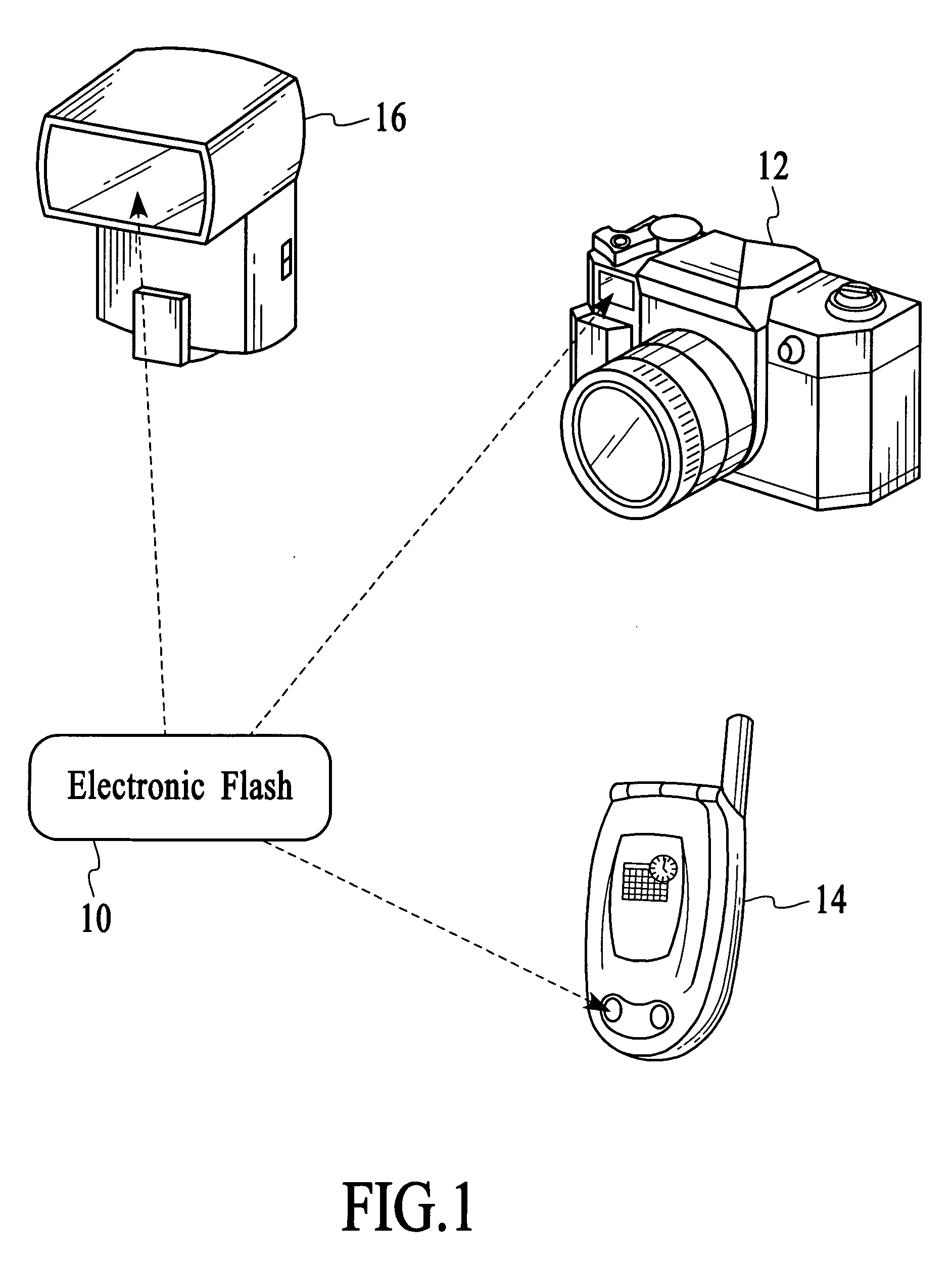
Electronic flash, imaging device and method for producing a flash of light having a wavelength spectrum in the visible range and the infrared range using a fluorescent material
An electronic flash, imaging device and method for producing a flash of light having a wavelength spectrum in the visible wavelength range and the infrared wavelength range uses a fluorescent material to convert at least some of the original light emitted from one or more light sources of the electronic flash to longer wavelength light to produce the flash of light. The light sources may be configured to generate light having a peak wavelength in an ultraviolet-and-visible wavelength range. The fluorescent material may include any combination of red, green, blue and yellow phosphors.
Owner:BENCH WALK LIGHTING LLC
Method and tools for oral hygiene
InactiveUS20030059738A1Enhance the destructive effectSafe for self-treatmentCosmetic preparationsImpression capsOral diseasePhotosensitizer
A method and material for self-cleaning of the teeth and mouth using a source of light in the visible range in conjunction with a photosensitive oral hygiene composition possessing a broad absorption spectrum in the visible range. The invention selectively eliminates harmful bacteria by use of a photosensitive agent and a light source. The present invention involves the use of a light-providing dental device to activate a photosensitive agent and destroy harmful bacteria in the oral cavity. It prevents or deters oral diseases, inflammations, and infections.
Owner:BIOLITEC UNTERNEHMENSBETEILLIGUNGS II AG
Photoelectric conversion device, image pickup device, and method for applying electric field to the same
InactiveUS20060054987A1High color reproductionIncreased durabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoelectric conversionLength wave
A photoelectric conversion device comprises an organic photoelectric conversion film intervening between at least two electrodes, the organic photoelectric conversion film comprising a positive hole transporting photoelectric conversion film and an electron transporting photoelectric conversion film, wherein each of the positive hole transporting photoelectric conversion film and the electron transporting photoelectric conversion film has absorption in a visible range, and a difference in wavelength between longer wavelength ends of absorption of the positive hole transporting photoelectric conversion film and the electron transporting photoelectric conversion film is 50 nm or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Method for manufacturing image display device
ActiveUS20100003425A1Fully curedReduce the amount requiredLiquid crystal compositionsElectric discharge heatingLiquid-crystal displayOptical transmittance
A method for manufacturing an image display device includes the step of forming a cured resin layer 15 by interposing a photo-curable resin composition between a base 2 including an image display unit such as a liquid crystal display panel 8 and a light-transmitting protection member 3 including a light-shielding member 5 and then photo-curing the photo-curable resin composition. In this method, a resin composition having a curing shrinkage ratio of 5% or less, yielding a cured product having a storage elastic modulus at 25° C. of 1.0×107 Pa or less, and forming the cured resin layer having a light transmittance of 90% or more in the visible range is used as the photo-curable resin composition.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Image pickup device-equipped rear-view mirror
The present invention is intended to provide an image pickup device-equipped rear view mirror with improved image pickup performance, glare prevention and appearance (design) in addition to improved performance as a vehicle mirror. A mirror element is formed by forming a reflecting film consisting of high refractive index material films and a low refractive index material film on a back surface of a transparent glass substrate. The integrating sphere reflectance of the mirror element in the visible range is 40% to 60% and the near-infrared transmittance is no less than 70% for the whole or part of the band belonging to the near-infrared range within the entire sensitive wavelength range of the near-infrared camera. A black mask member is attached to an entire back surface of the reflecting film. The near-infrared camera is arranged behind the black mask member. The region corresponding to the area for the image-pickup by the near-infrared camera within the entire region of the black mask member is formed of a visible-light absorption and near-infrared transmission filter. The near-infrared transmittance of the visible-light absorption and near-infrared transmission filter is no less than 70% for the whole or part of the band belonging to the near-infrared range within the entire sensitive wavelength range of the near-infrared camera.
Owner:MURAKAMI CORP
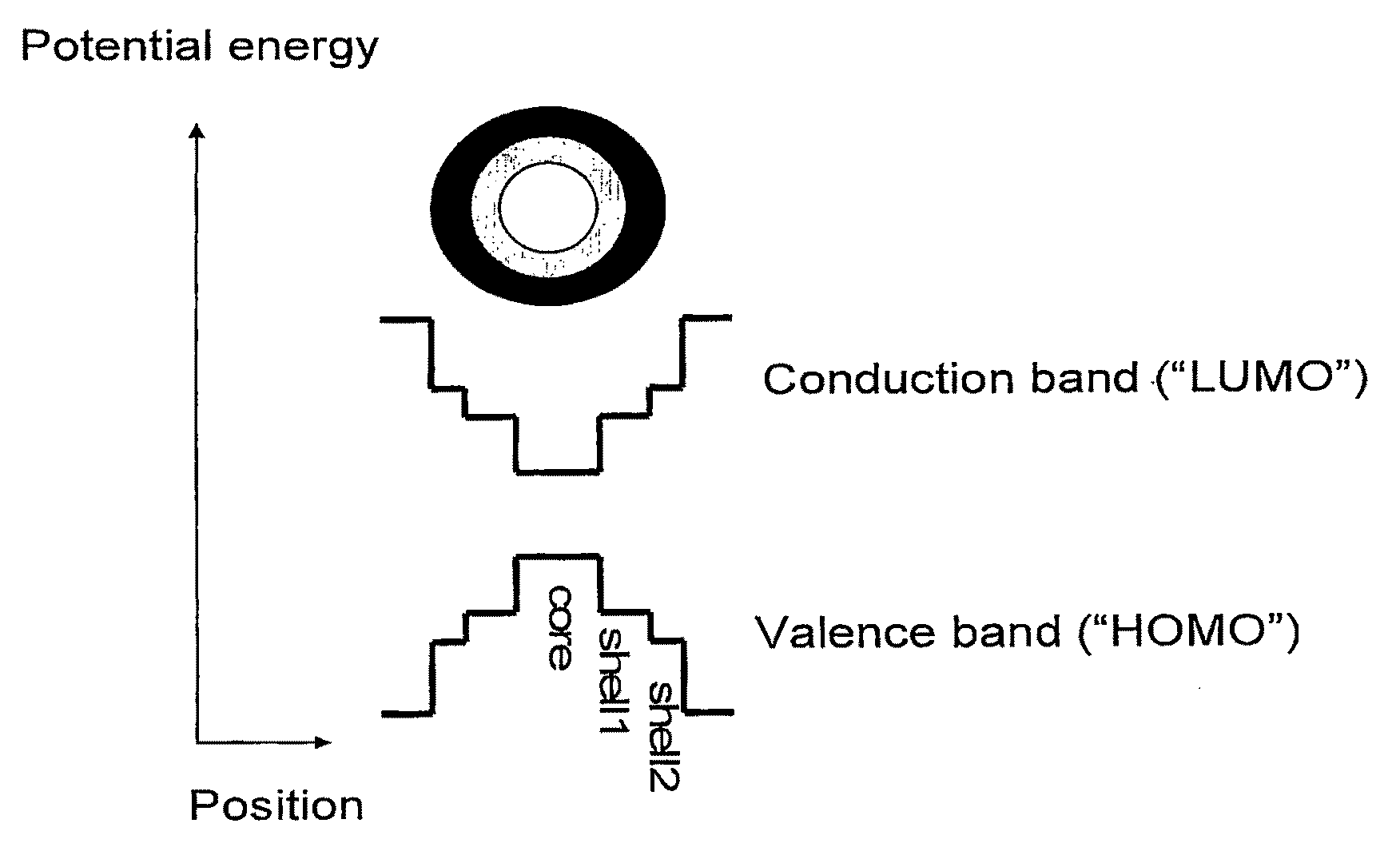
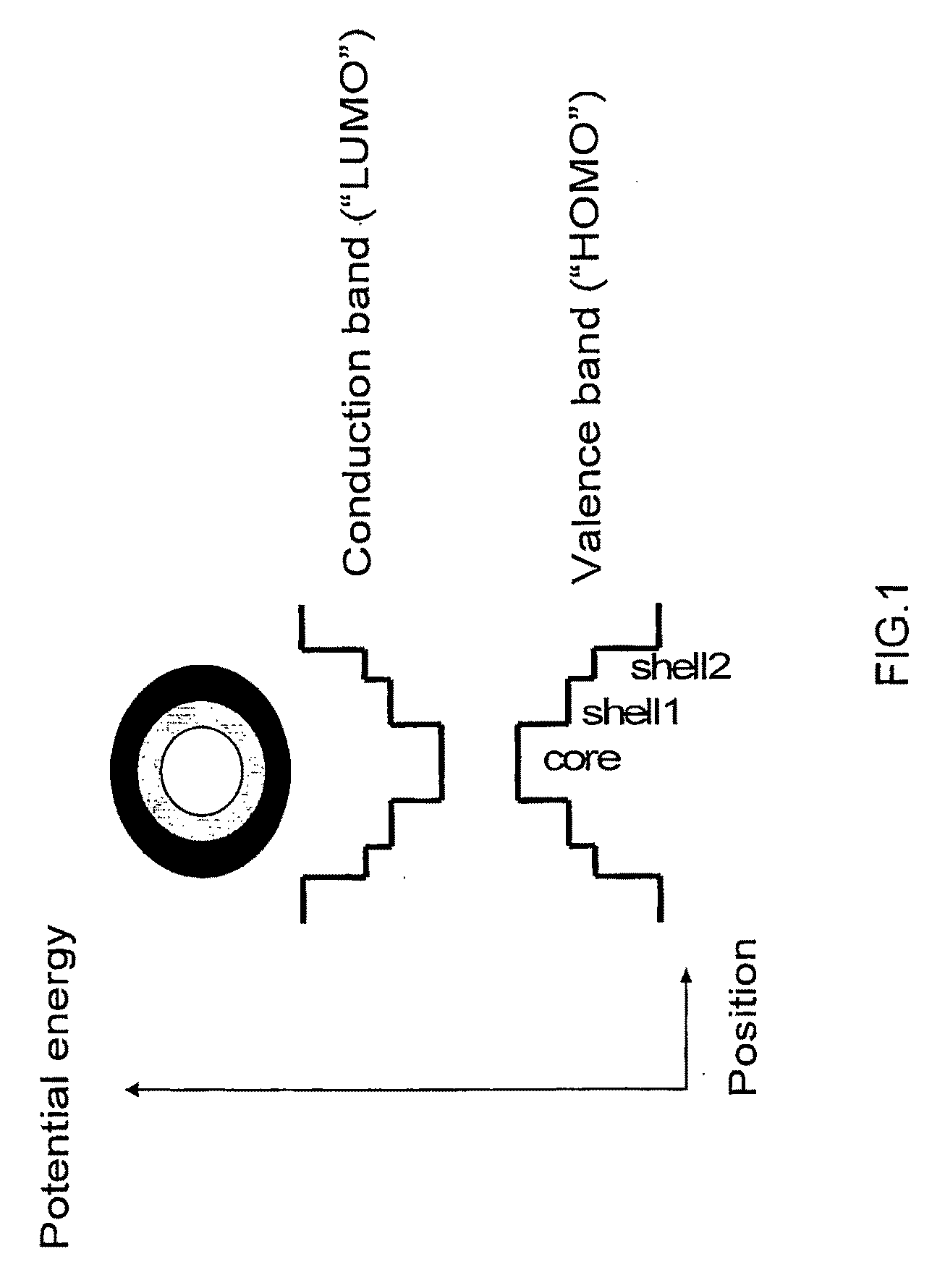
III-V semiconductor core-heteroshell nanocrystals
ActiveUS20090230382A1Improve solubilityHigh quantum yieldMaterial nanotechnologyLaser detailsLuminescence quantum yieldPhotoluminescence
The present invention provides a core / multishell semiconductor nanocrystal comprising a core and multiple shells, which exhibits a type-I band offset and high photoluminescence quantum yield providing bright tunable emission covering the visible range from about 400 nm to NIR over 1600 nm.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
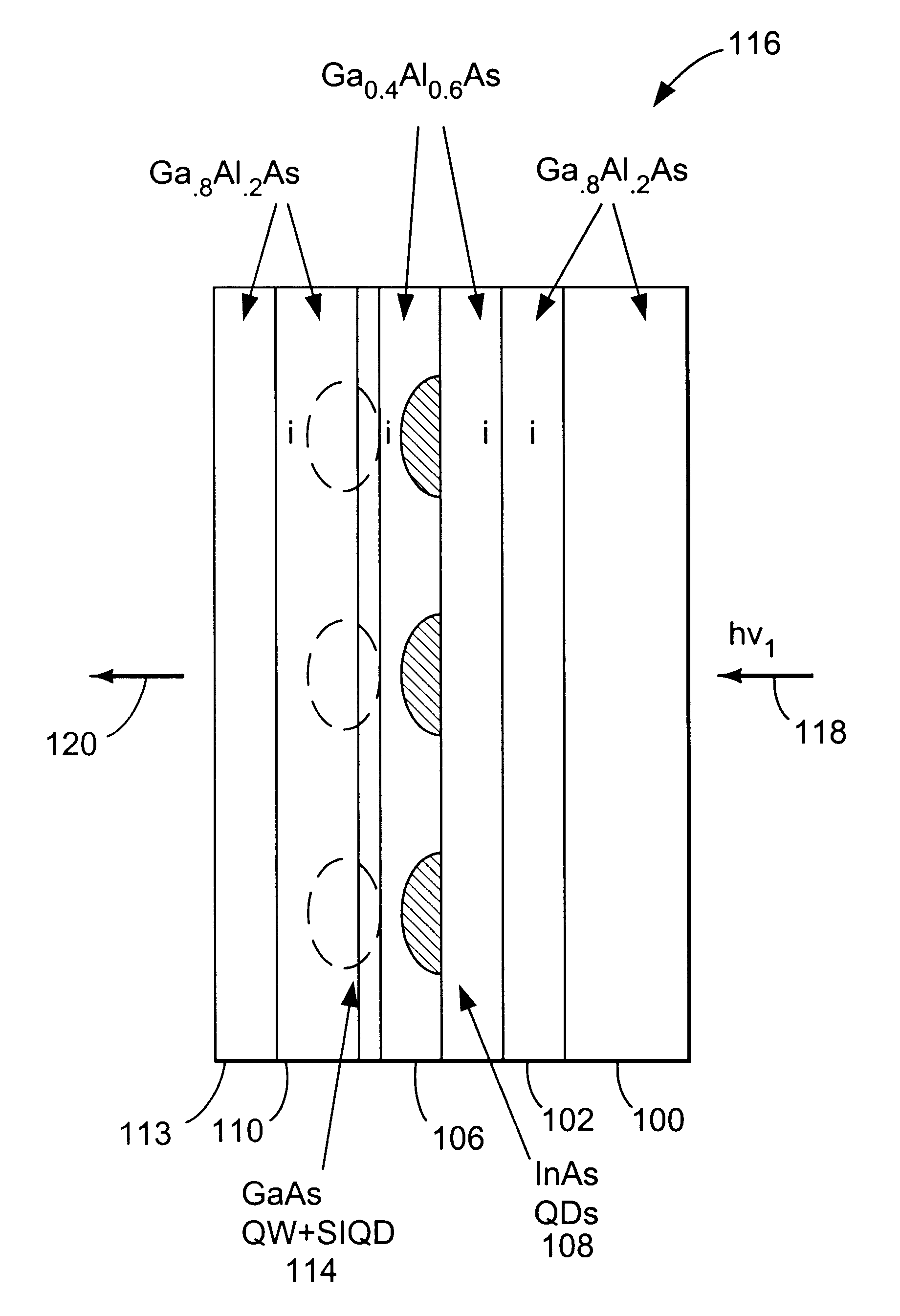
Mid infrared and near infrared light upconverter using self-assembled quantum dots
InactiveUS6541788B2NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStress inducedPhoton
A method and device for converting light from a first wavelength to a second wavelength. The method comprises the steps of exciting an electron in a quantum dot with an incident infrared photon having the first wavelength, the excited electron having a first energy, tunneling the excited electron through a barrier into a stress induced quantum dot, and recombining the excited electron with a hole in the stress induced quantum dot, therein producing a photon having the second wavelength, typically in the visible range. The device comprises a substrate, a spacer layer, coupled to the substrate, a second layer, coupled to the spacer layer, wherein the second layer comprises a different material than the spacer layer, a third layer, coupled to the second layer, wherein the third layer comprises at least one quantum dot, a fourth layer, coupled to the third layer, comprising a quantum well corresponding to each quantum dot in the third layer, a fifth layer, coupled to the fourth layer, wherein the fourth layer and fifth layer comprise a strain induced quantum dot corresponding to each quantum dot in the third layer; and a sixth layer, coupled to the fifth layer, the substrate and the sixth layer for contacting the device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus and method for operating a portable xenon arc searchlight
InactiveUS6896392B2Easily substitutedLong rangeElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsUltravioletEngineering
A xenon arc searchlight or illumination system incorporates a quick change release and assembly so that the lamp, reflector and battery assemblies are easily field replaceable without tools. The lamp, ballast, battery and charger are provided in a single rugged package which can be sealed for field use. The searchlight is combined by an appropriate mounting adaptable with other optical detector devices such as cameras, binoculars and night vision telescopes. The beam output is similarly usable with a combination of filters to allow the most varied intensity and wavelengths for a particular application, such as smoke filled environments, surveillance employing near-infrared or infrared illumination, ultraviolet, underwater illumination or illumination with any color in the visible range.
Owner:XENONICS INC
Translucent or opaque colored glass-ceramic article providing a cooking surface and its use
InactiveUS20050252503A1Minimizing contentEasy resistanceCooking-vessel materialsStoves/ranges foundationsChemical reactionAdditive ingredient
The translucent or opaque colored glass-ceramic article provides a cooking surface and has an adjustable light transmission in a visible range under 15%, as measured for a 4 mm sample thickness; a flaw-free upper surface with an impact resistance of greater than 18 cm breaking height, as tested with a 200 g steel ball in a falling ball test; a temperature difference resistance of greater than 500° C.; a high crystallinity with keatite mixed crystals as principal crystal phase in an interior of the glass-ceramic article and with a residual glass phase fraction of less than 8% by weight; a glassy upper surface layer of from 0.5 to 2.5 μm thick, which is substantially free of high quartz mixed crystals and which inhibits chemical reactions, and a content of enriched ingredients in the residual glass phase in the interior of the glass-ceramic and in the glassy surface layer of ΣNa2O+K2O+CaO+SrO+BaO+F+refining agents of from 0.2 to 1.6% by weight.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Luminescent materials that emit light in the visible range or the near infrared range
InactiveUS20080014463A1Narrow spectral widthEasy to processVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhotoluminescenceElectron donor
Luminescent materials and the use of such materials in anti-counterfeiting, inventory, photovoltaic, and other applications are described herein. In one embodiment, a luminescent material has the formula: [AaBbXxX′x′X″x″][dopants], wherein A is selected from at least one of elements of Group IA; B is selected from at least one of elements of Group VA, elements of Group IB, elements of Group IIB, elements of Group IIIB, elements of Group IVB, and elements of Group VB; X, X′, and X″ are independently selected from at least one of elements of Group VIIB; the dopants include electron acceptors and electron donors; a is in the range of 1 to 9; b is in the range of 1 to 5; and x, x′, and x″ have a sum in the range of 1 to 9. The luminescent material exhibits photoluminescence having: (a) a quantum efficiency of at least 20 percent; (b) a spectral width no greater than 100 nm at Full Width at Half Maximum; and (c) a peak emission wavelength in the near infrared range.
Owner:OMNIPV
Luminescent materials that emit light in the visible range or the near infrared range
InactiveUS7641815B2Narrow spectral widthEasy to processVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhotoluminescenceElectron donor
Luminescent materials and the use of such materials in anti-counterfeiting, inventory, photovoltaic, and other applications are described herein. In one embodiment, a luminescent material has the formula: [AaBbXxX′x′X″x″][dopants], wherein A is selected from at least one of elements of Group IA; B is selected from at least one of elements of Group VA, elements of Group IB, elements of Group IIB, elements of Group IIIB, elements of Group IVB, and elements of Group VB; X, X′, and X″ are independently selected from at least one of elements of Group VIIB; the dopants include electron acceptors and electron donors; a is in the range of 1 to 9; b is in the range of 1 to 5; and x, x′, and x″ have a sum in the range of 1 to 9. The luminescent material exhibits photoluminescence having: (a) a quantum efficiency of at least 20 percent; (b) a spectral width no greater than 100 nm at Full Width at Half Maximum; and (c) a peak emission wavelength in the near infrared range.
Owner:OMNIPV
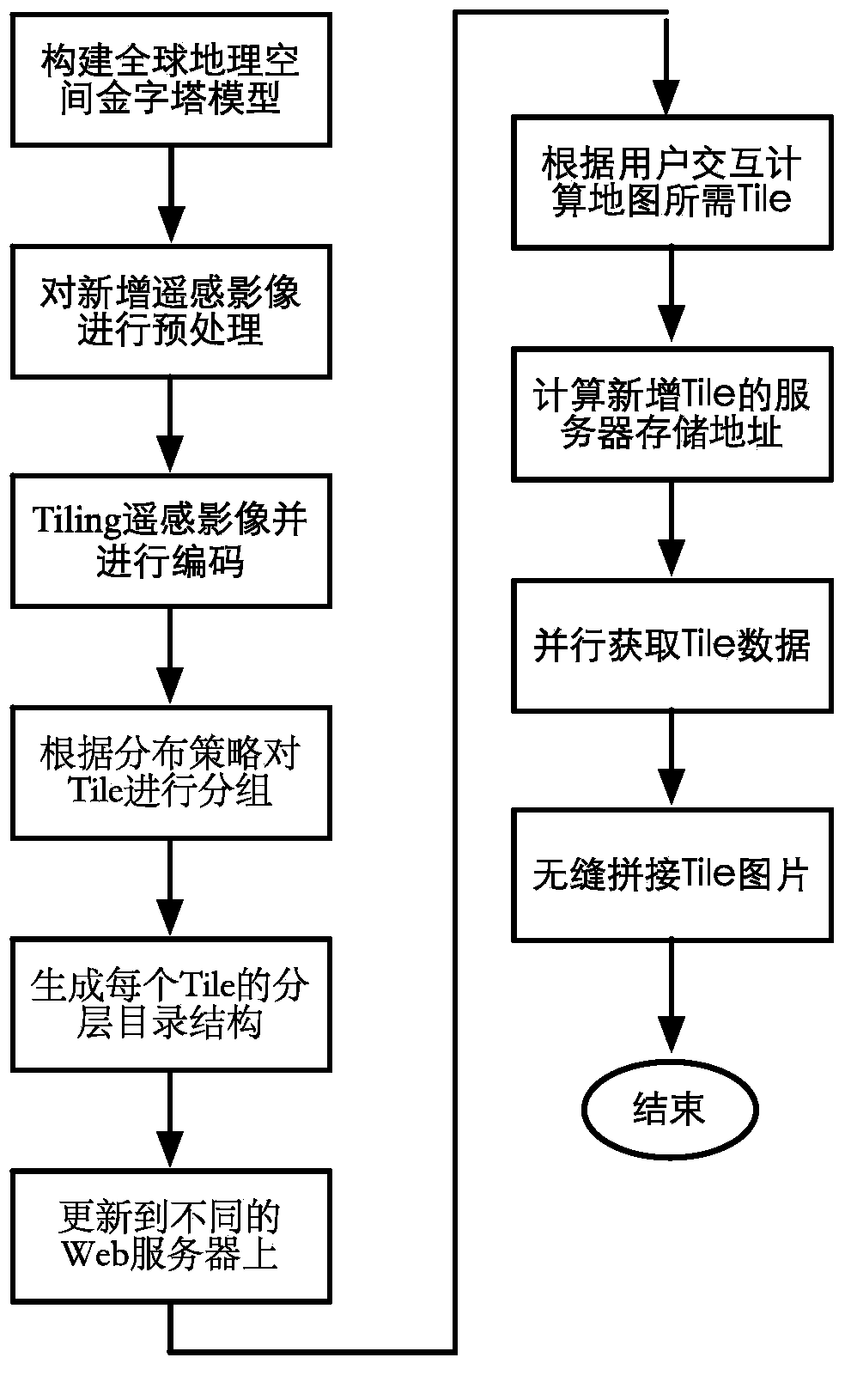
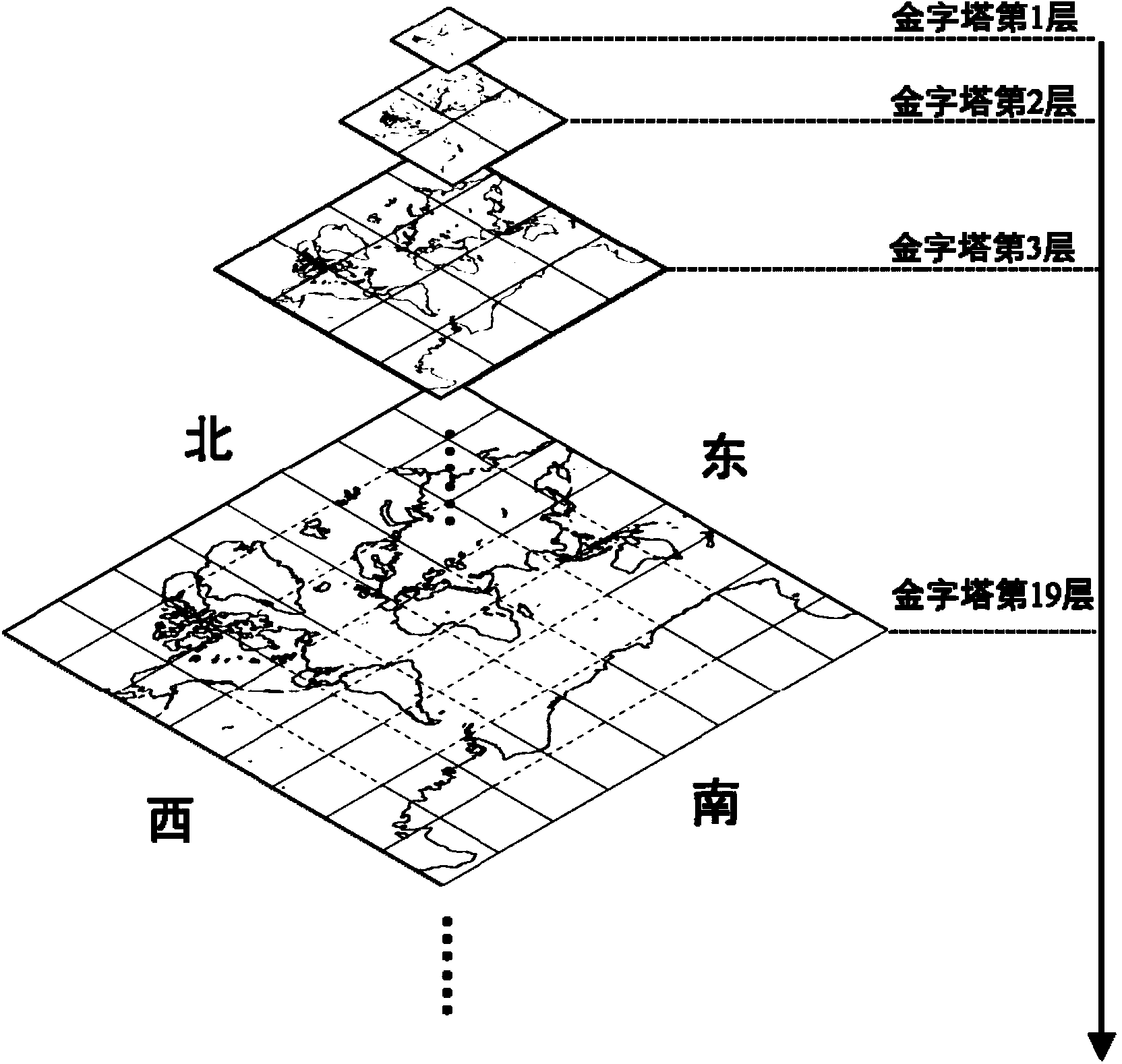
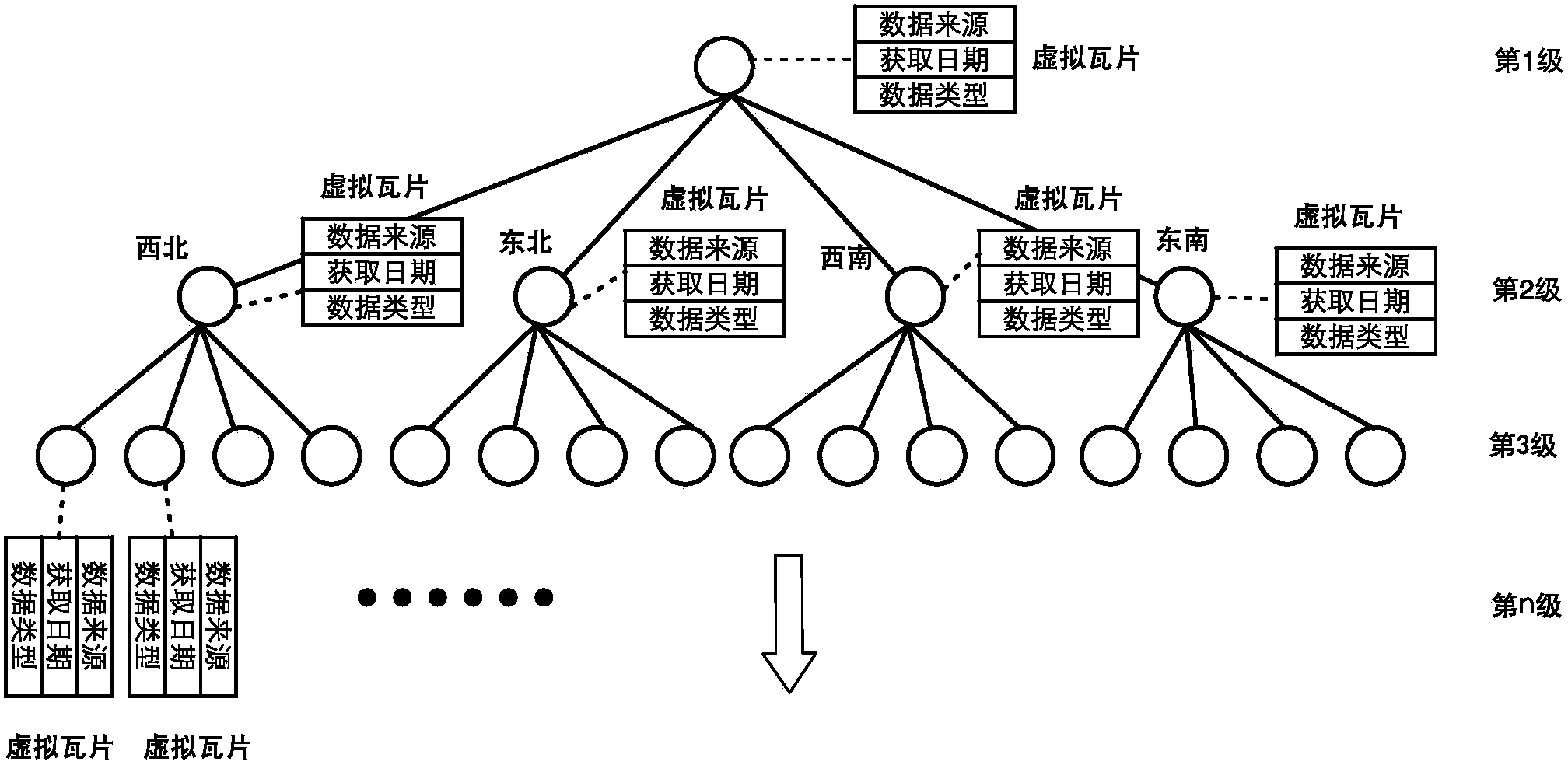
Implement method of lightweight-class global multi-dimensional remote-sensing image network map service
ActiveCN103455624AClear structureEffective organizationSpecial data processing applicationsData centerStructure of Management Information
The invention provides an implement method of lightweight-class global multi-dimensional remote-sensing image network map service. The implement method comprises the following steps: a global geographic space pyramid model is constructed, and a Tile file encoding system is built according to the model; pre-treatment mainly comprising projection transformation, file format conversion and the like is performed on the remote-sensing data so as to cut the remote-sensing data into tiles, and file encoding is performed; according to a distribution strategy, Tile files are grouped to generate a corresponding directory structure, and different images are updated on different Web servers; the visible range of the map requested by a client side is analyzed to calculate the storage paths of all images within the visible range, and the images are loaded and fed back to the client side. According to the invention, the implement method of the light-weight-class global multi-dimensional remote-sensing image network map service can be provided for a remote-sensing data center (such as the China Center for Resources Satellite Data and Application) and can provide remote-sensing data service to users more conveniently.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Heat-absorbing filter and method for making same
InactiveUS6844976B1Reduce manufacturing costRequired propertyLayered productsOptical elementsSurgical teamInfrared reflectance
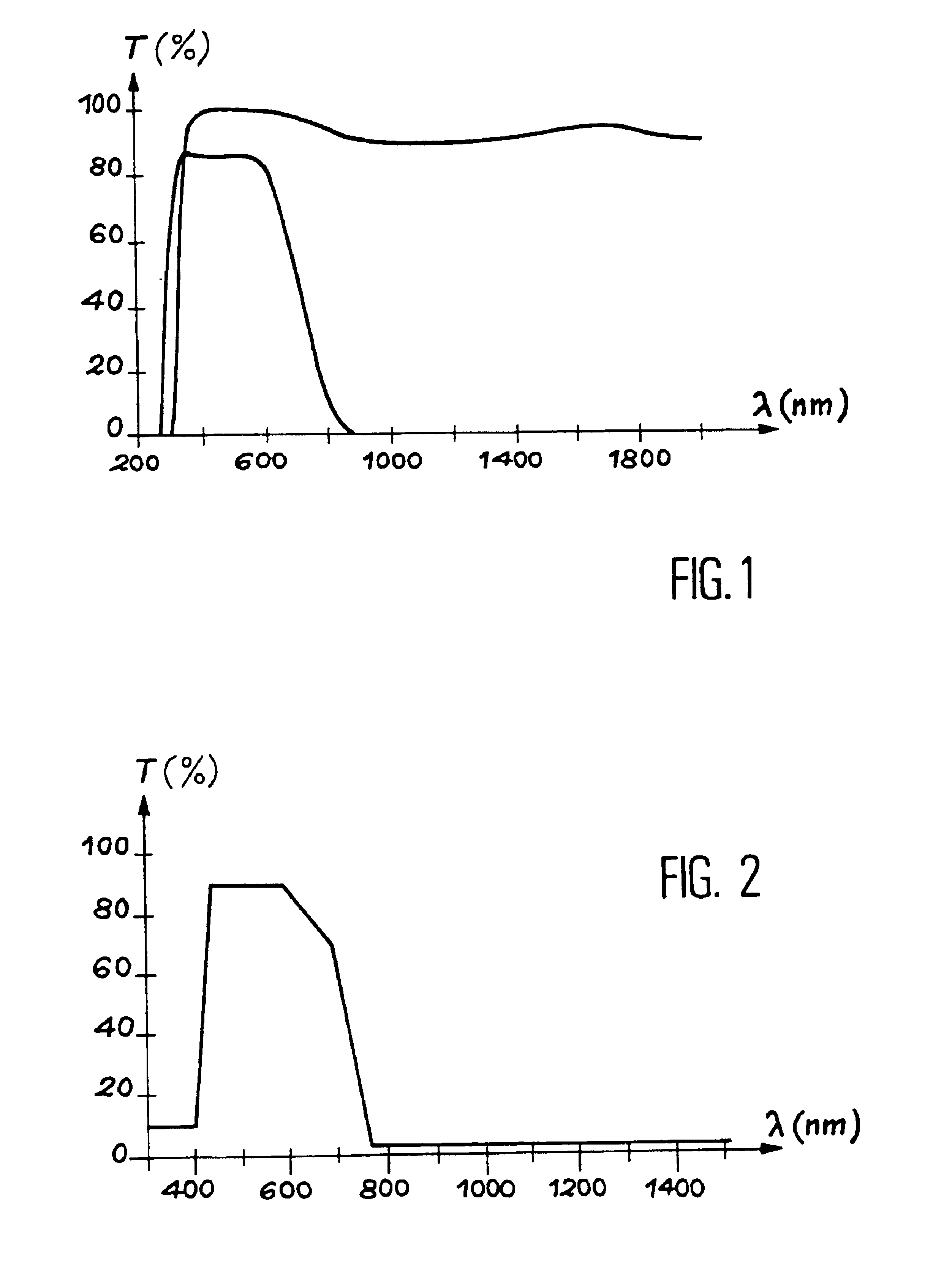
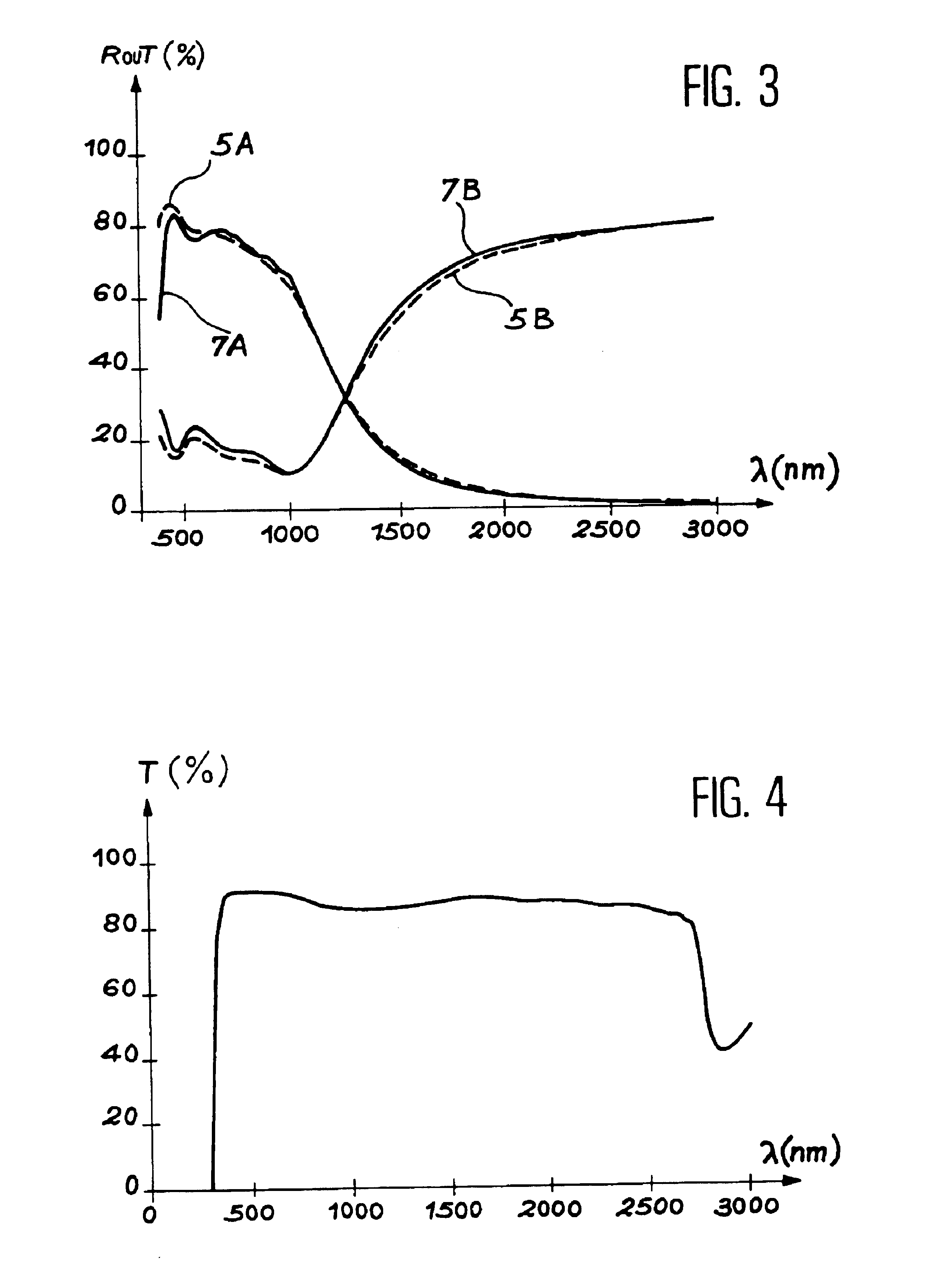
The present invention relates to a heat filter and a process for manufacturing this filter.This heat filter may for example be used to filter surgical or examination lighting composed of a light source which emits energy, or radiation, in the visible and infrared ranges. It allows the light emitted by this source to be filtered so as to prevent infrared radiation from hindering the surgical team or the patient.It includes a substrate, at least one layer of an infrared reflecting material, and a coating forming an interference filter in the visible range.The invention process includes the deposition on a substrate of a layer of an infrared reflecting material and the deposition on this layer of an interference filter in the visible range.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Semiconductor light emitting device
A semiconductor light emitting element includes a semiconductor light emitting element emitting light beams in ultraviolet ranges and visible ranges, and a fluorescent element absorbing the light beams from the semiconductor light emitting element and outputting visible light beams in a light taking-out direction different from a light emitting direction. The light beams emitted from the light emitting element is absorbed within the semiconductor light emitting device.
Owner:ALPAD CORP
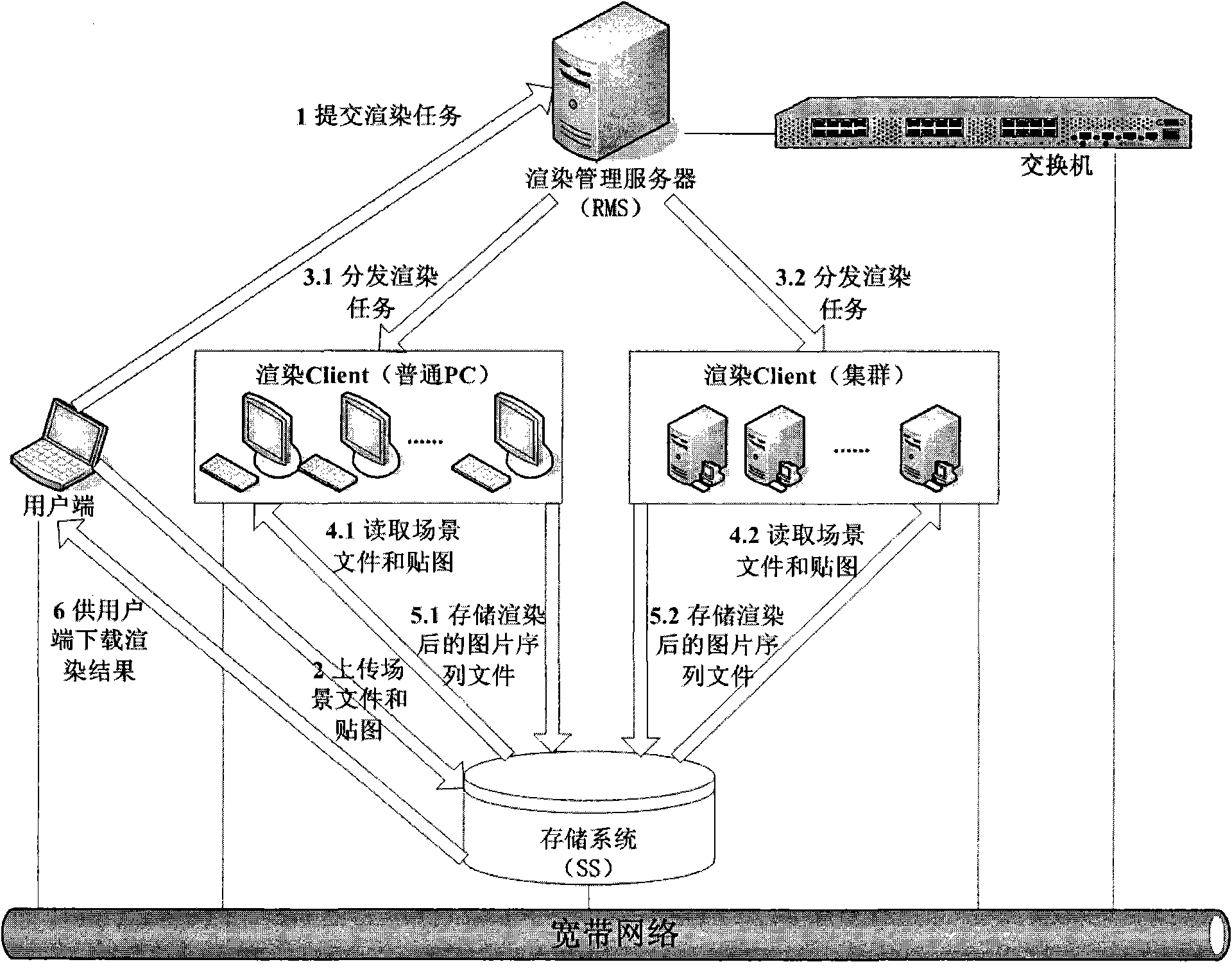
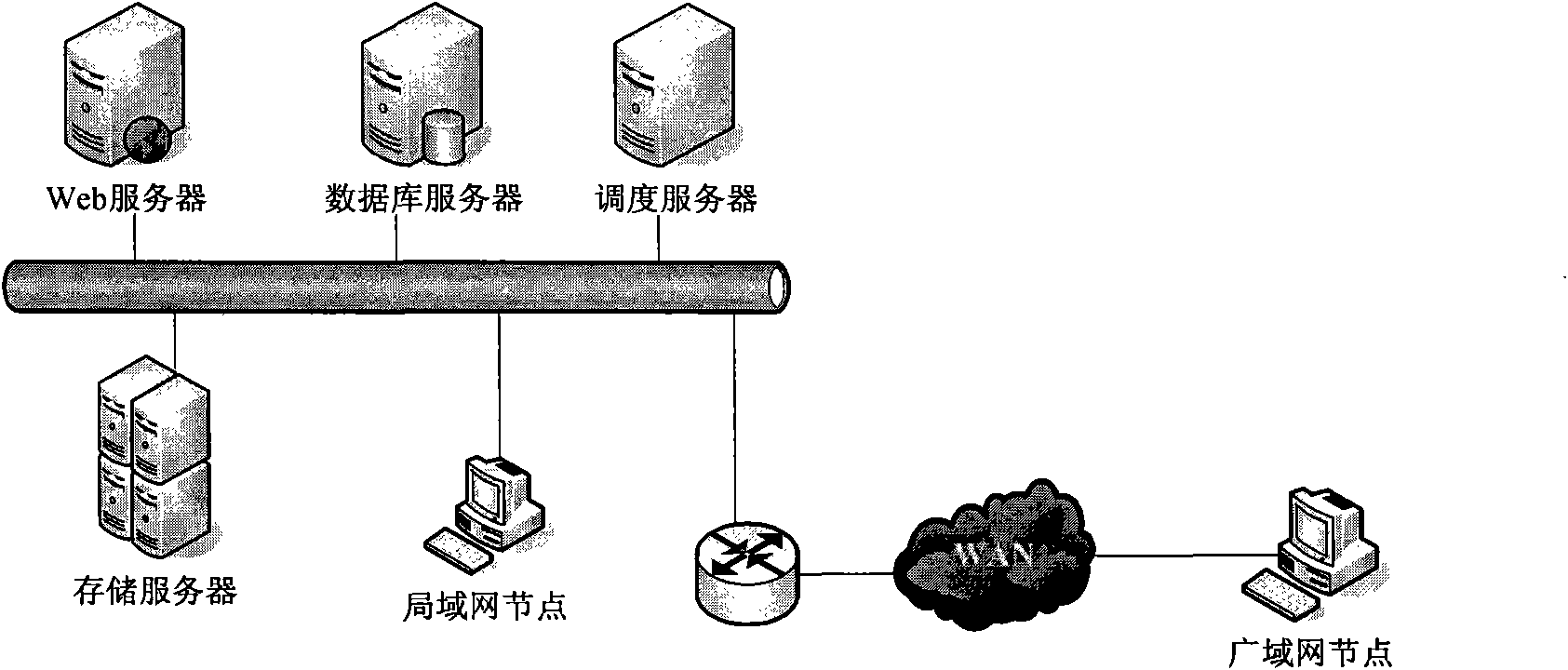
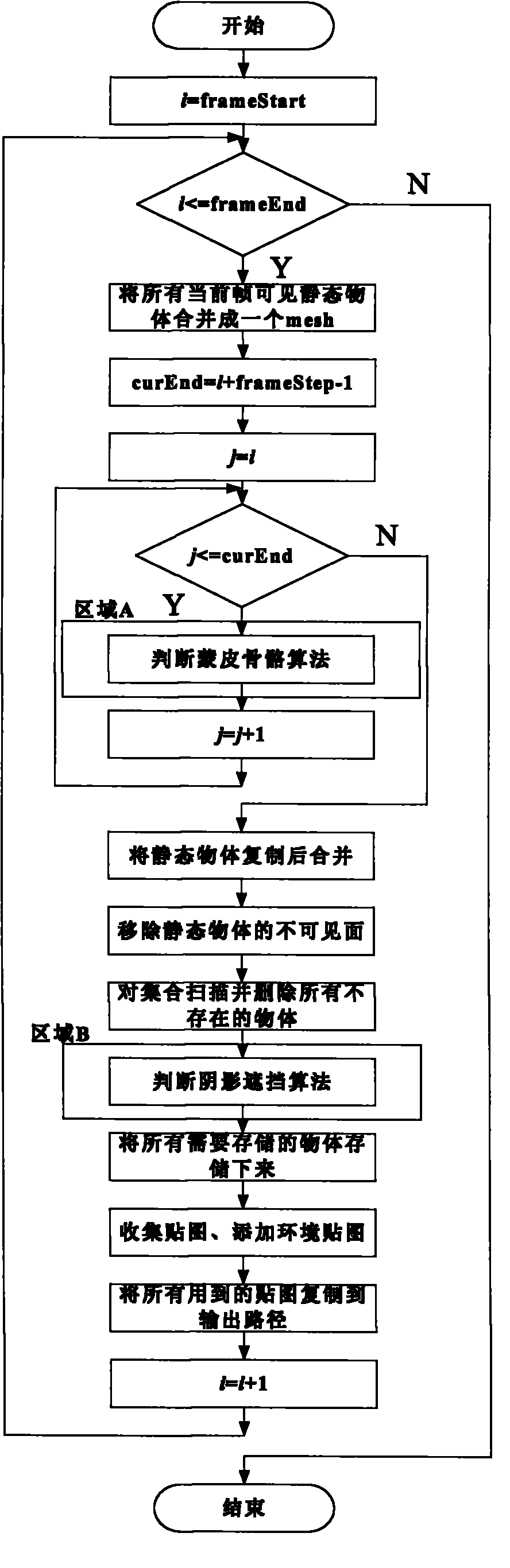
Wide area network-oriented decomposition support method for animation rendering task and implementation method
InactiveCN102088472AImprove efficiencySolve the problem of a large amount of transmitted data occupiedAnimationTransmissionDecompositionAnimation
The invention discloses a wide area network-oriented decomposition support method for an animation rendering task and an implementation method, which belong to the field of computer networks. According to the intensive computation characteristic of the animation rendering task and the characteristic that the transmission rate in a wide area network environment is limited to a network bottleneck bandwidth, the method comprises a visible range-based scene file and picture set splitting method, a node performance assessment method, an operation distribution strategy and integration and process control of the methods. During composition of the rendering task of a user, the scene file and picture set splitting method related to the invention is used and a scene is optimized according to the analysis of objects and pictures which are visible and invisible for the current scene camera, so that the aim of reducing a final rendering file is fulfilled. In a simplified model scene, a transmission data volume in a network can be effectively decreased, equivalent splitting of a scene file and a calculated amount is realized, and the distribution and execution of the fineness of rendering operation are facilitated. By using the method, the computing efficiency of each rendering client is brought into full play, and very high expandability is achieved.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Apparatus for simultaneous illumination of teeth
InactiveUS20060110700A1Improve abilitiesRapid tooth whiteningCosmetic preparationsTeeth fillingUniform fieldMedicine
Owner:DISCUS DENTAL LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com