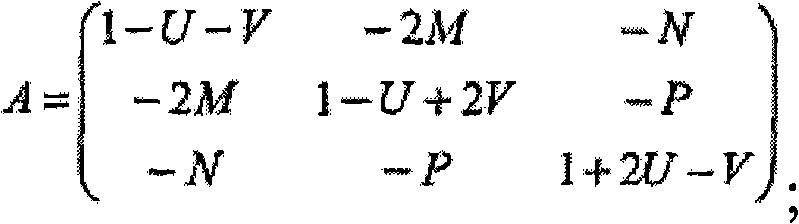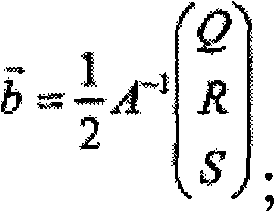Patents
Literature
921 results about "Ellipsoid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere.
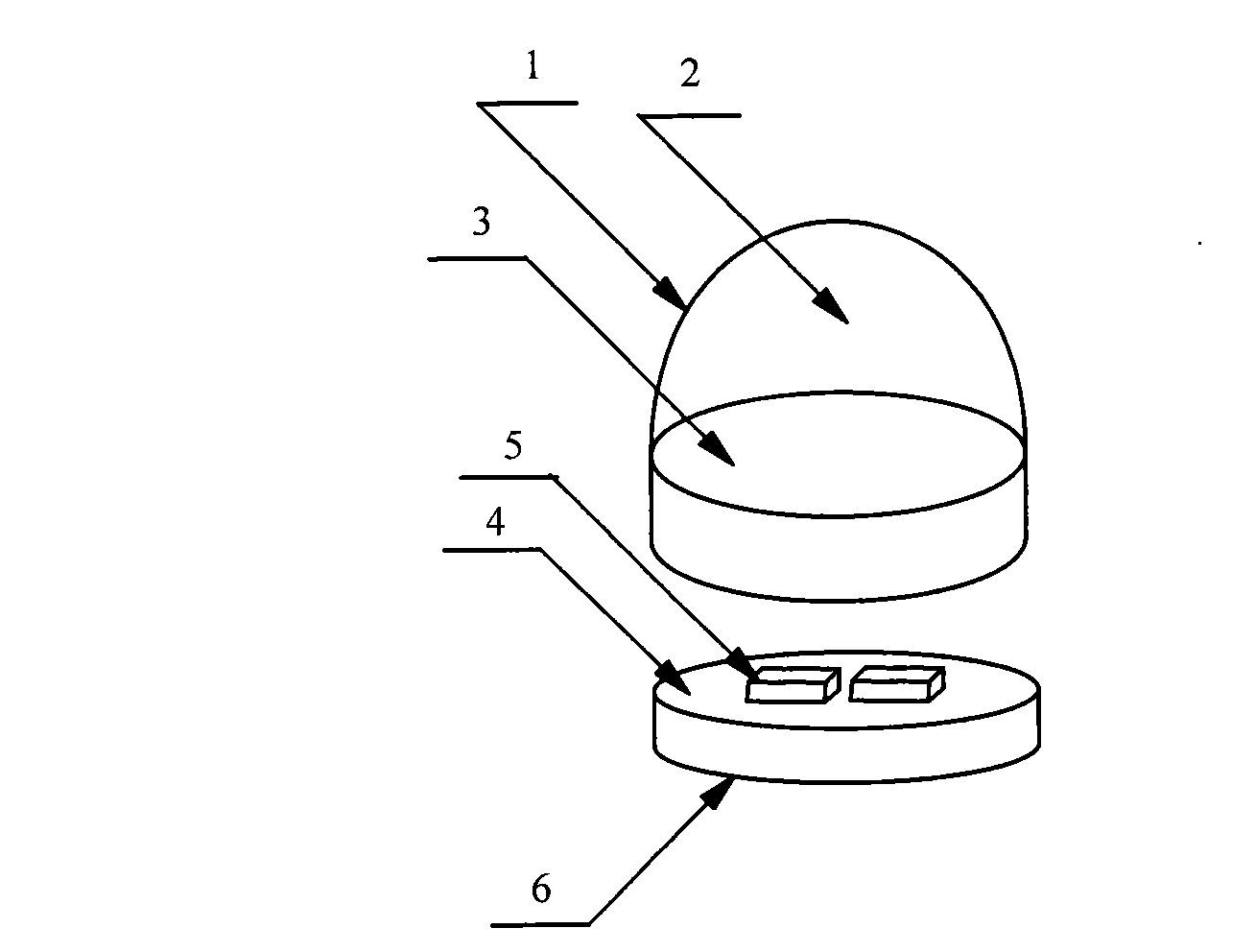
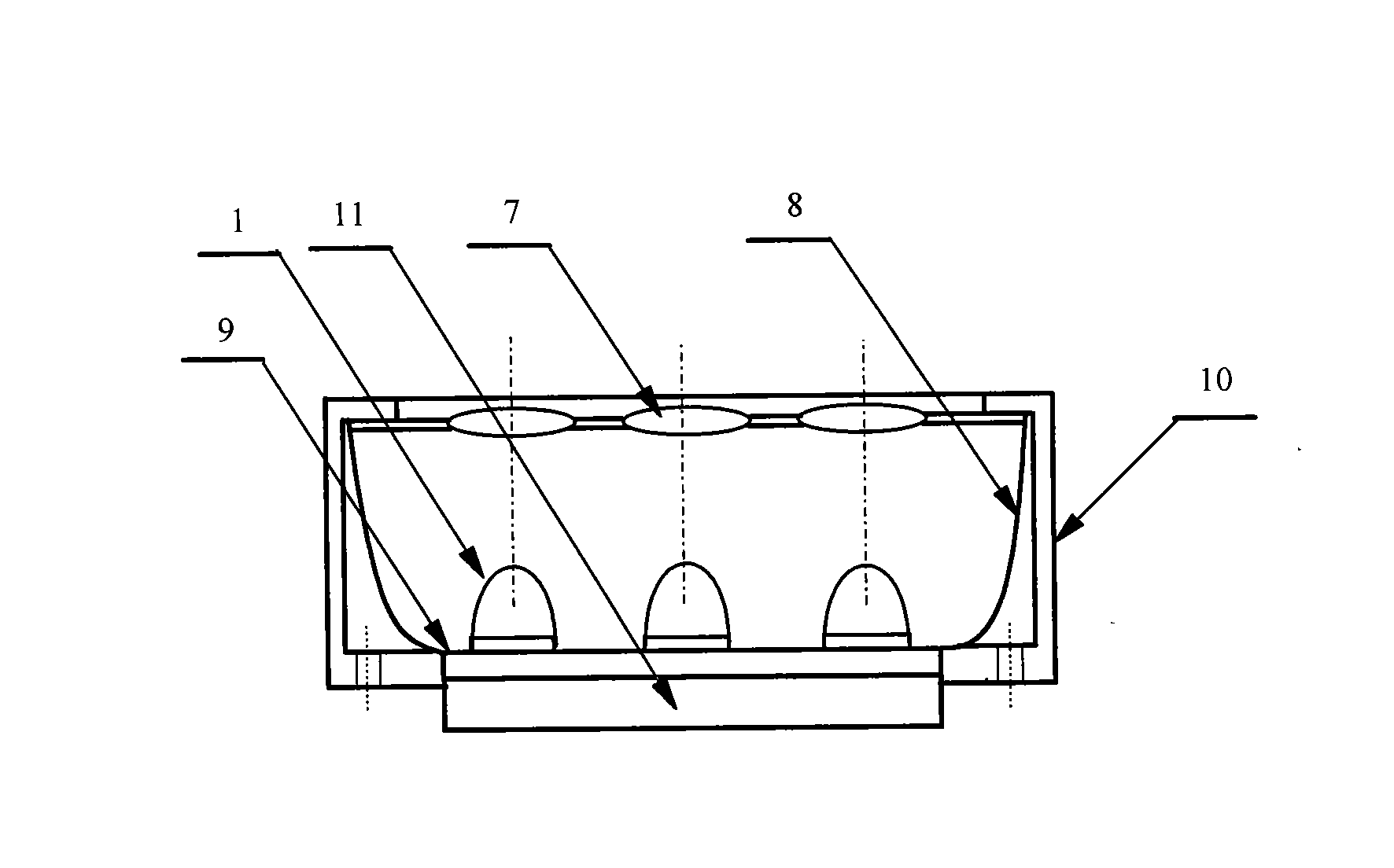
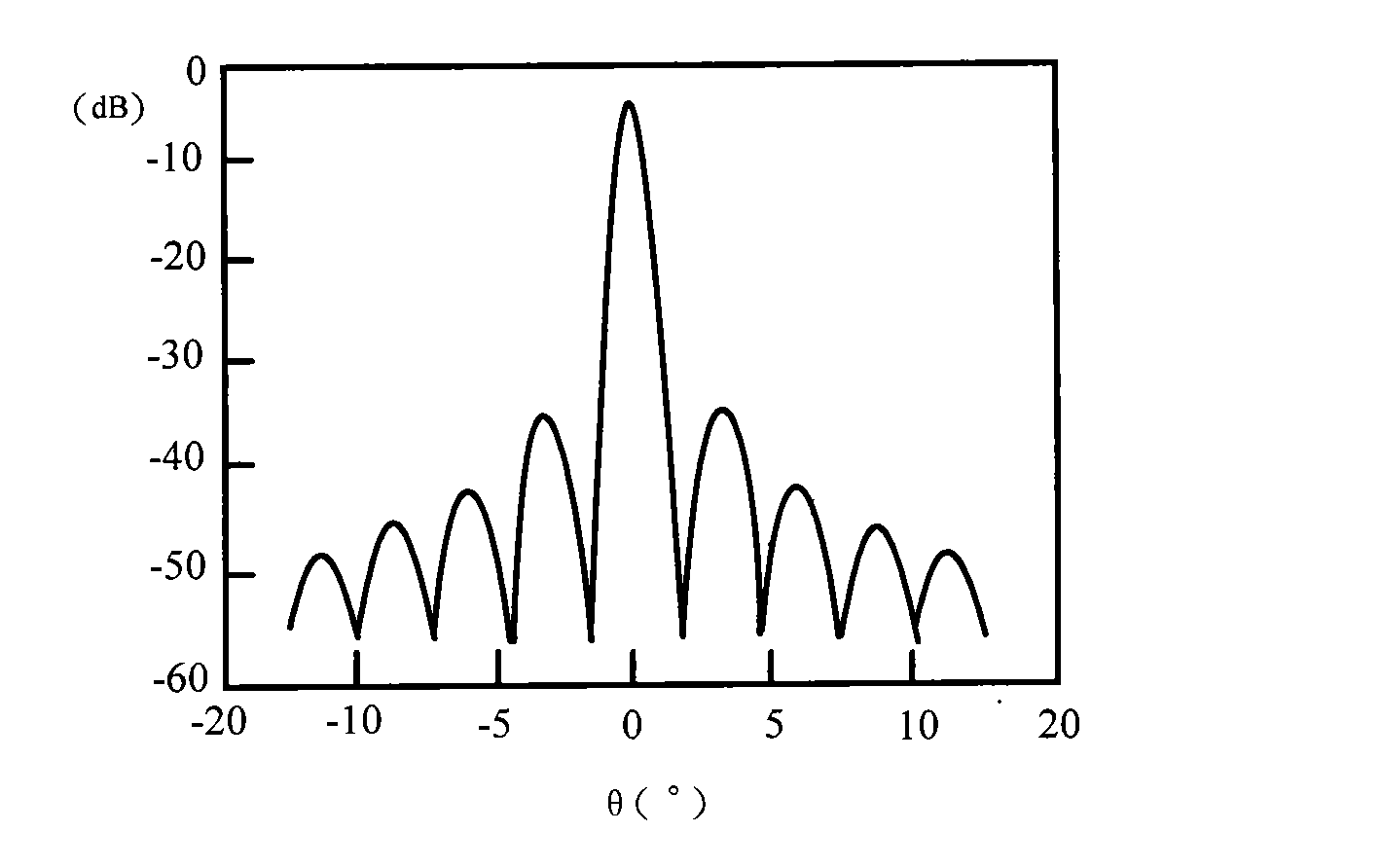
Millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and array thereof
InactiveCN101662076AWith quasi-optical Gaussian beam radiation characteristicsGuaranteed normal transmissionAntenna arraysDielectric resonator antennaDielectric substrate
The invention relates to the technical field of radar, in particular to a millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and an array thereof. The array consists of a microstrip integrated antenna, a dielectric lens, an objective lens, an array base, a reflecting mirror, a protective cover and a beam transfer switch; one end face of the dielectric lens is a hemisphere or an ellipsoid, while the other end face is a cylindrical section; the microstrip integrated antenna is generated by an dielectric substrate, the front surface of the dielectric substrate is closely adhered tothe cylindrical section of the dielectric lens and serves as a feed source, and the back surface is grounded; the hemispherical or ellipsoidal end face of the dielectric lens is an antenna radiating surface; the length of the cylindrical part of the dielectric lens can be changed; the antenna array is arranged into a linear array or an area array; the array base and the reflecting mirror have conical quasi-optical reflecting mirror surfaces; the focus of the objective lens of the linear array or the area array aligns with the central line of the dielectric lens; the protective cover is arranged outside; and the antenna array is controlled by the beam transfer switch. The antenna structure has strong shock resistance and dust prevention, and is suitable for millimeter-wave radars for planes, automobiles and ships, and receiving / emitting sensing of communication equipment.
Owner:阮树成
Millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and array thereof
InactiveCN101662076BWith quasi-optical Gaussian beam radiation characteristicsGuaranteed normal transmissionAntenna arraysDielectric substrateIntegrated antenna
The invention relates to the technical field of radar, in particular to a millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and an array thereof. The array consists of a microstrip integrated antenna, a dielectric lens, an objective lens, an array base, a reflecting mirror, a protective cover and a beam transfer switch; one end face of the dielectric lens is a hemisphere or an ellipsoid, while the other end face is a cylindrical section; the microstrip integrated antenna is generated by an dielectric substrate, the front surface of the dielectric substrate is closely adhered tothe cylindrical section of the dielectric lens and serves as a feed source, and the back surface is grounded; the hemispherical or ellipsoidal end face of the dielectric lens is an antenna radiating surface; the length of the cylindrical part of the dielectric lens can be changed; the antenna array is arranged into a linear array or an area array; the array base and the reflecting mirror have conical quasi-optical reflecting mirror surfaces; the focus of the objective lens of the linear array or the area array aligns with the central line of the dielectric lens; the protective cover is arranged outside; and the antenna array is controlled by the beam transfer switch. The antenna structure has strong shock resistance and dust prevention, and is suitable for millimeter-wave radars for planes, automobiles and ships, and receiving / emitting sensing of communication equipment.
Owner:阮树成
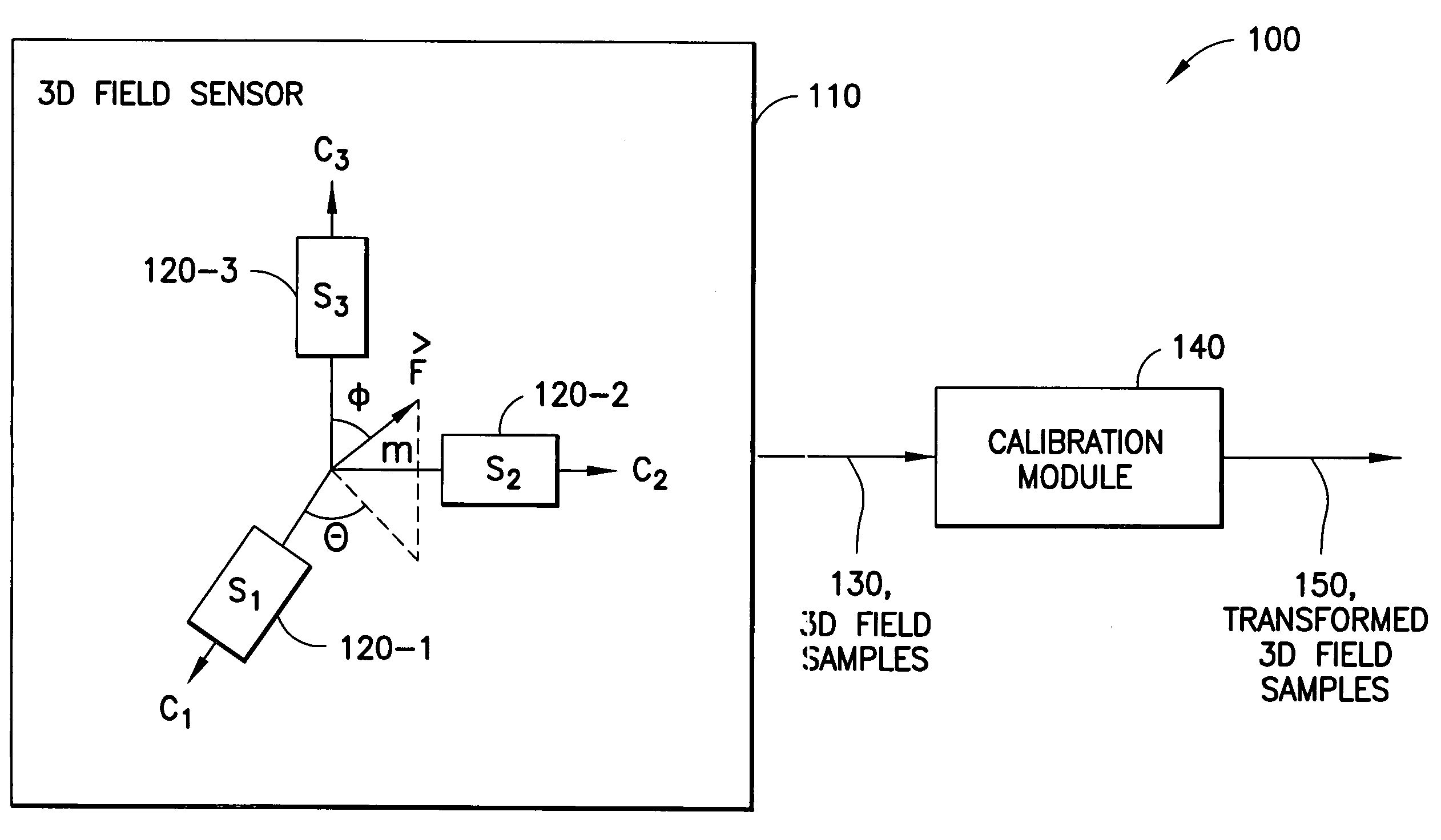
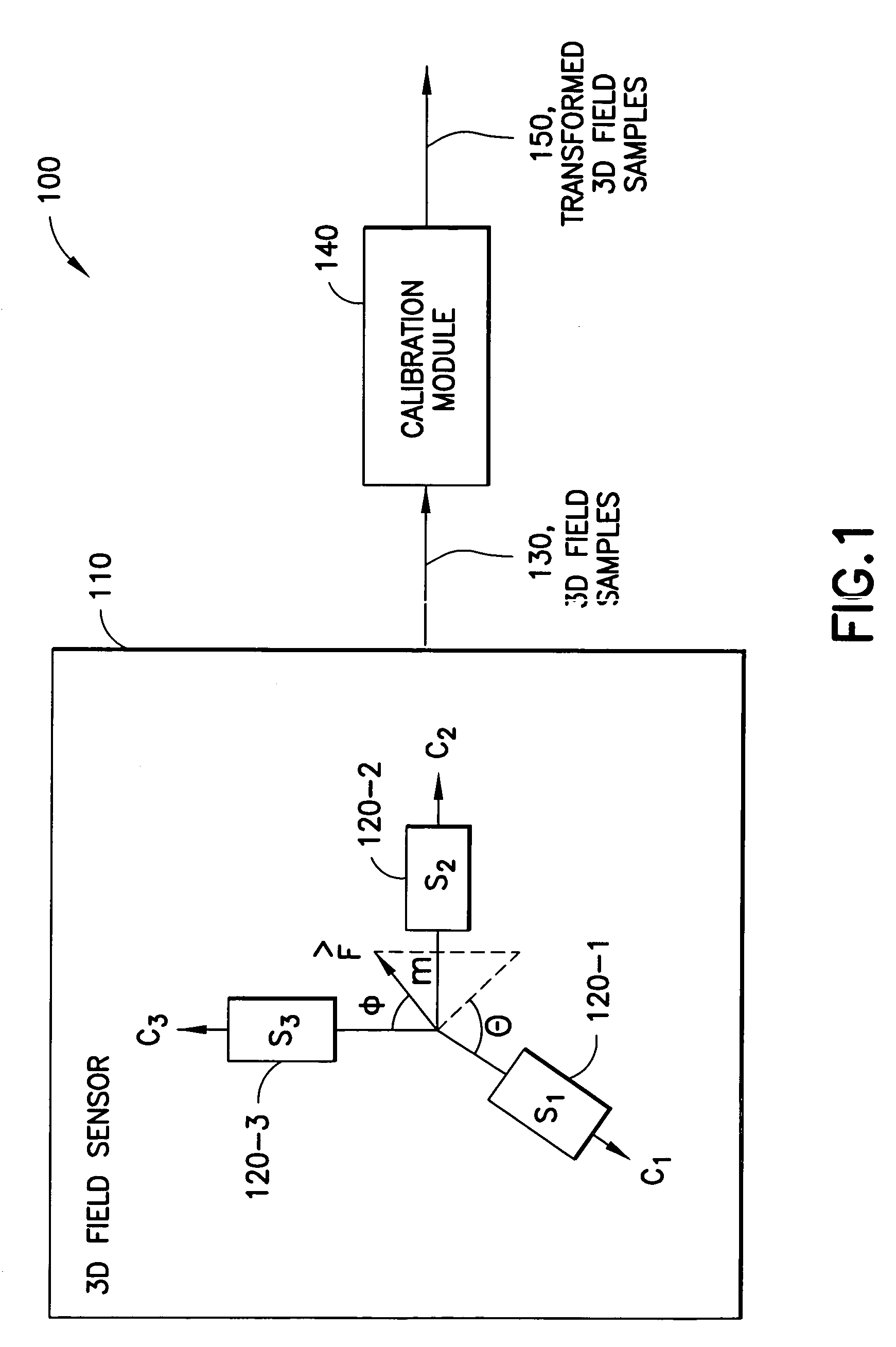
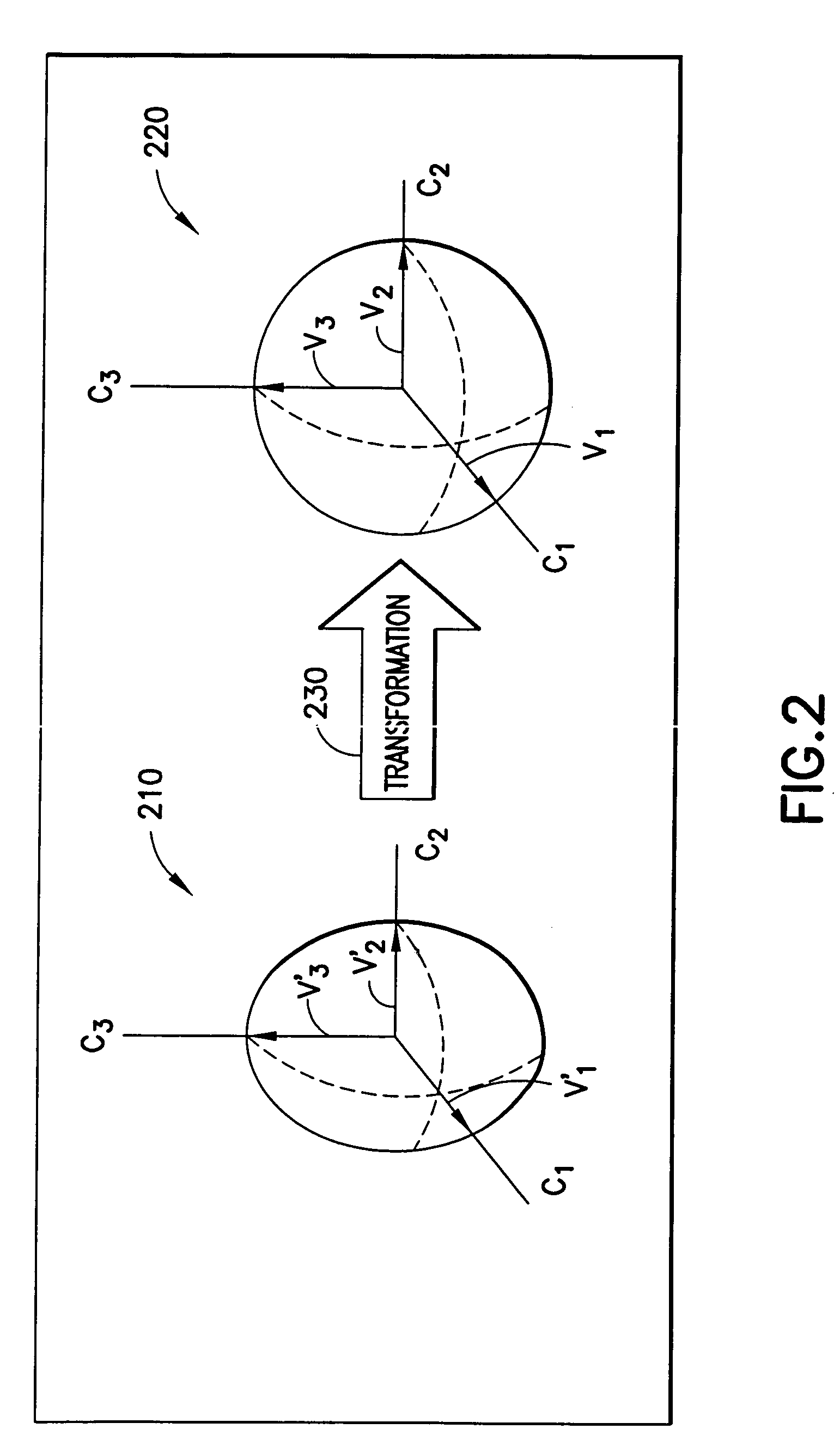
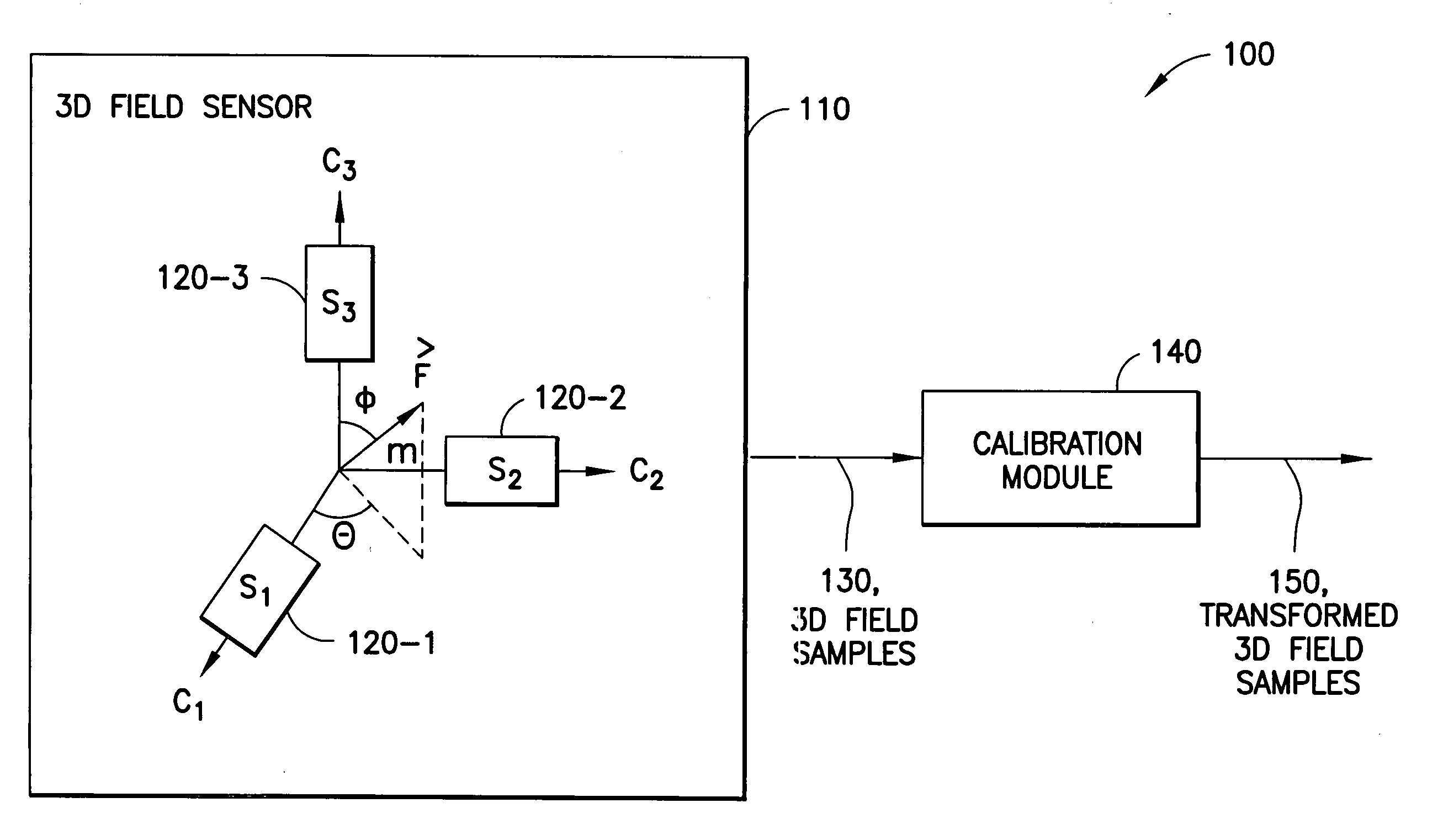
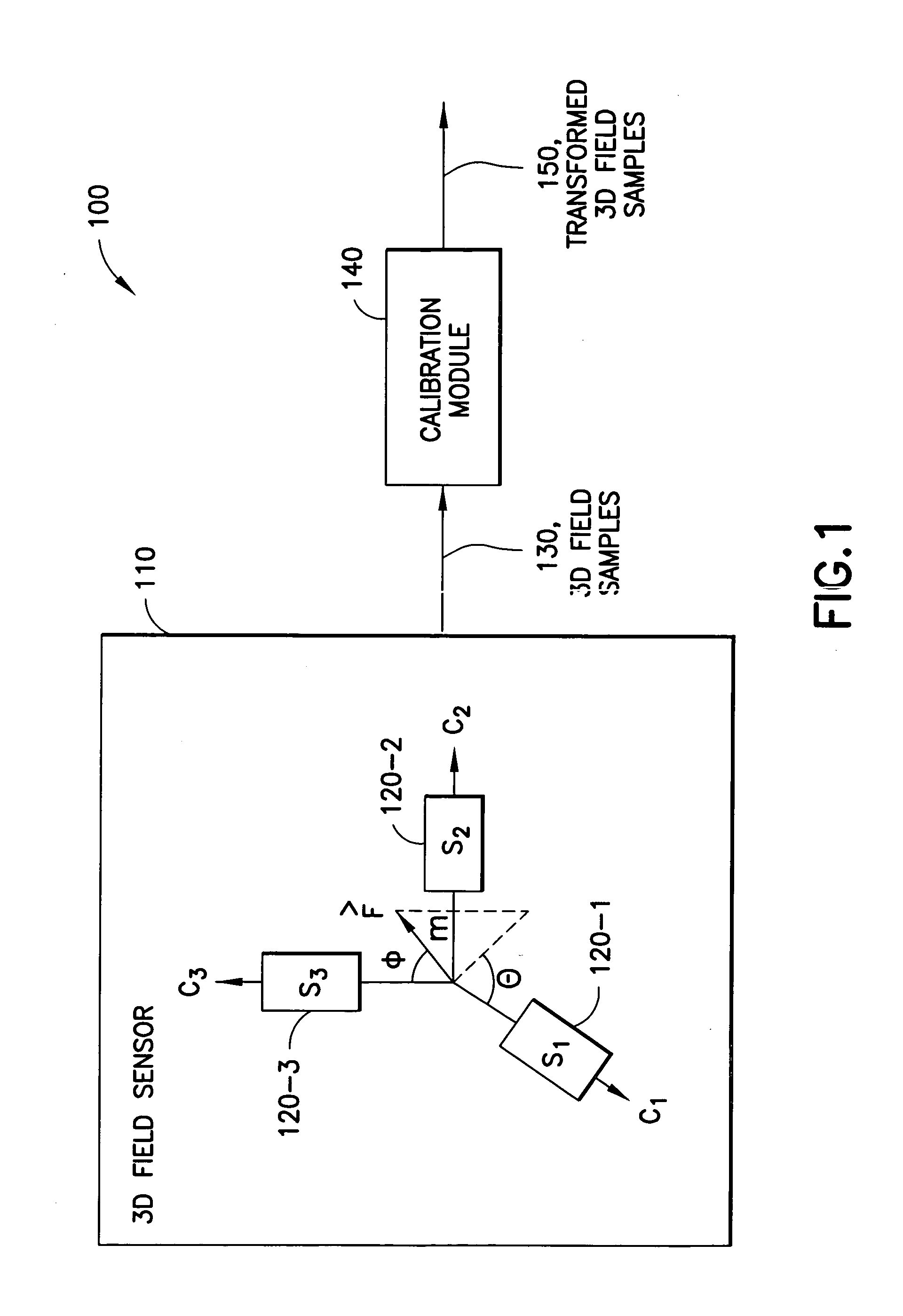
Calibration of 3D field sensors
ActiveUS7275008B2Electrical measurementsTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesCondensed matter physicsEllipsoid
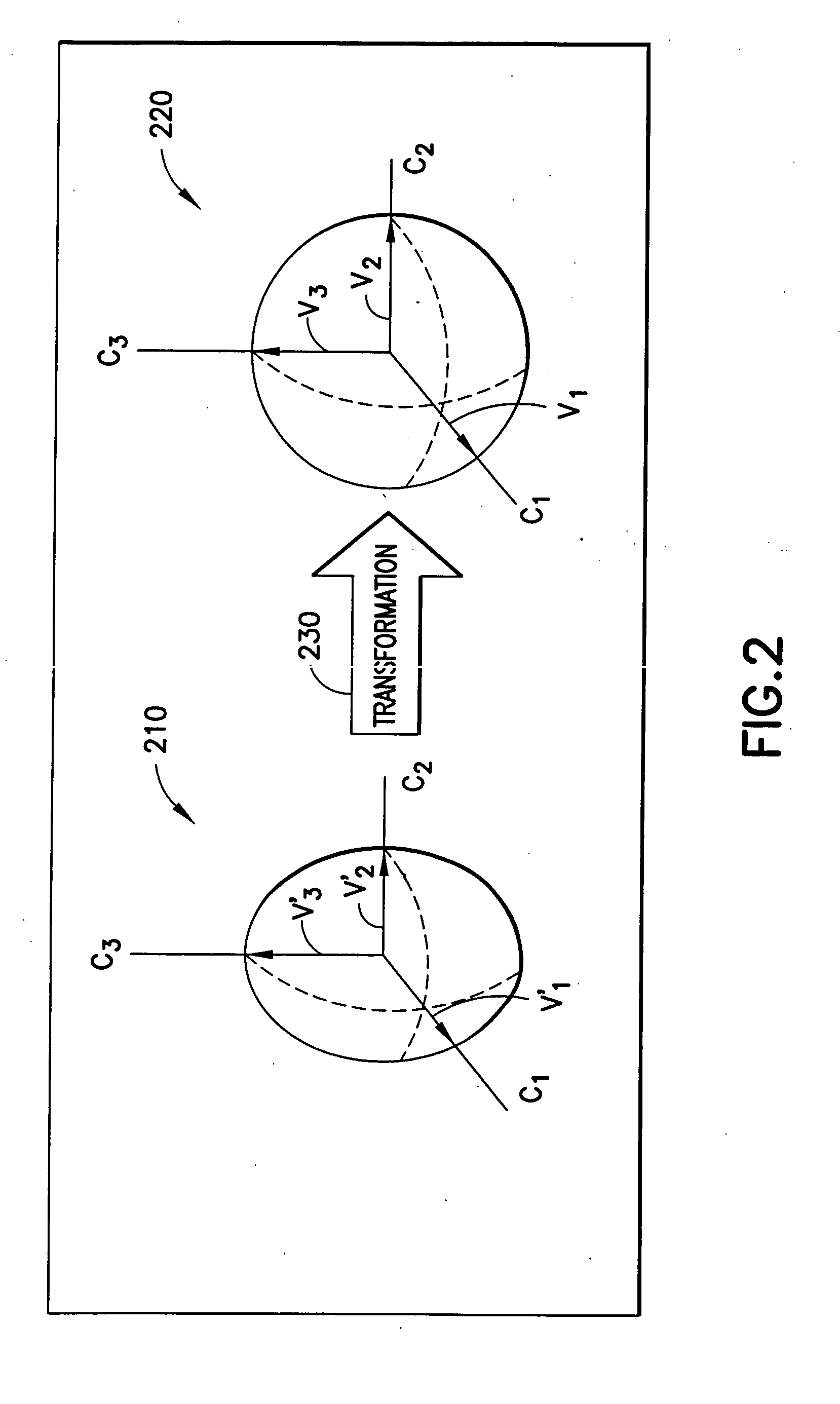
An apparatus-based method is disclosed for calibration of a 3D field sensor. The method includes accessing a plurality of samples, where the samples are from the 3D field sensor. Each sample represents a magnitude and an orientation of a three-dimensional field sensed by the 3D field sensor. Using the plurality of samples, a plurality of parameters is determined of an ellipsoid. The determination of the plurality of parameters is performed so that the ellipsoid fits the plurality of samples. A transformation is determined that transforms the ellipsoid into a sphere. The transformation is applied to a sample to create a transformed sample. Apparatus and signal bearing media are also disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for generating a 2D image having pixels corresponding to voxels of a 3D image
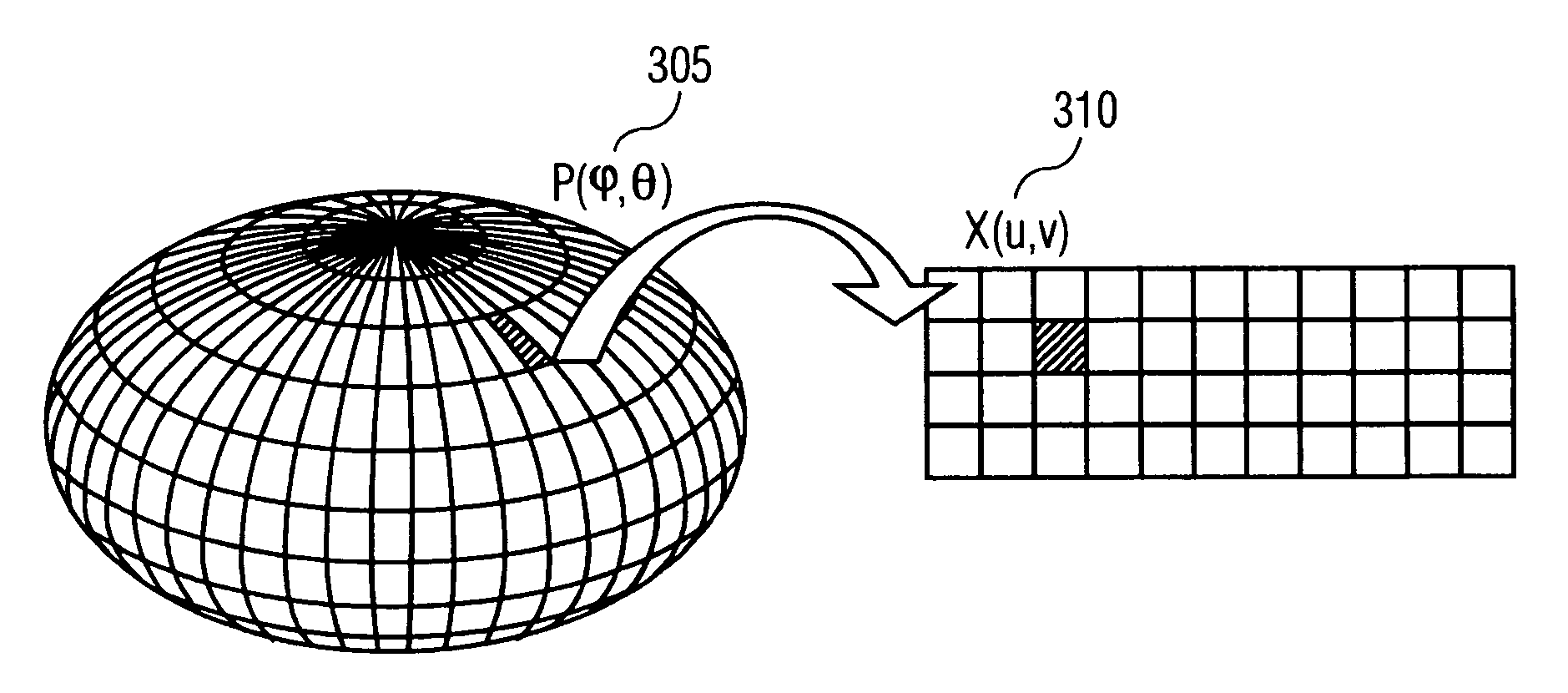
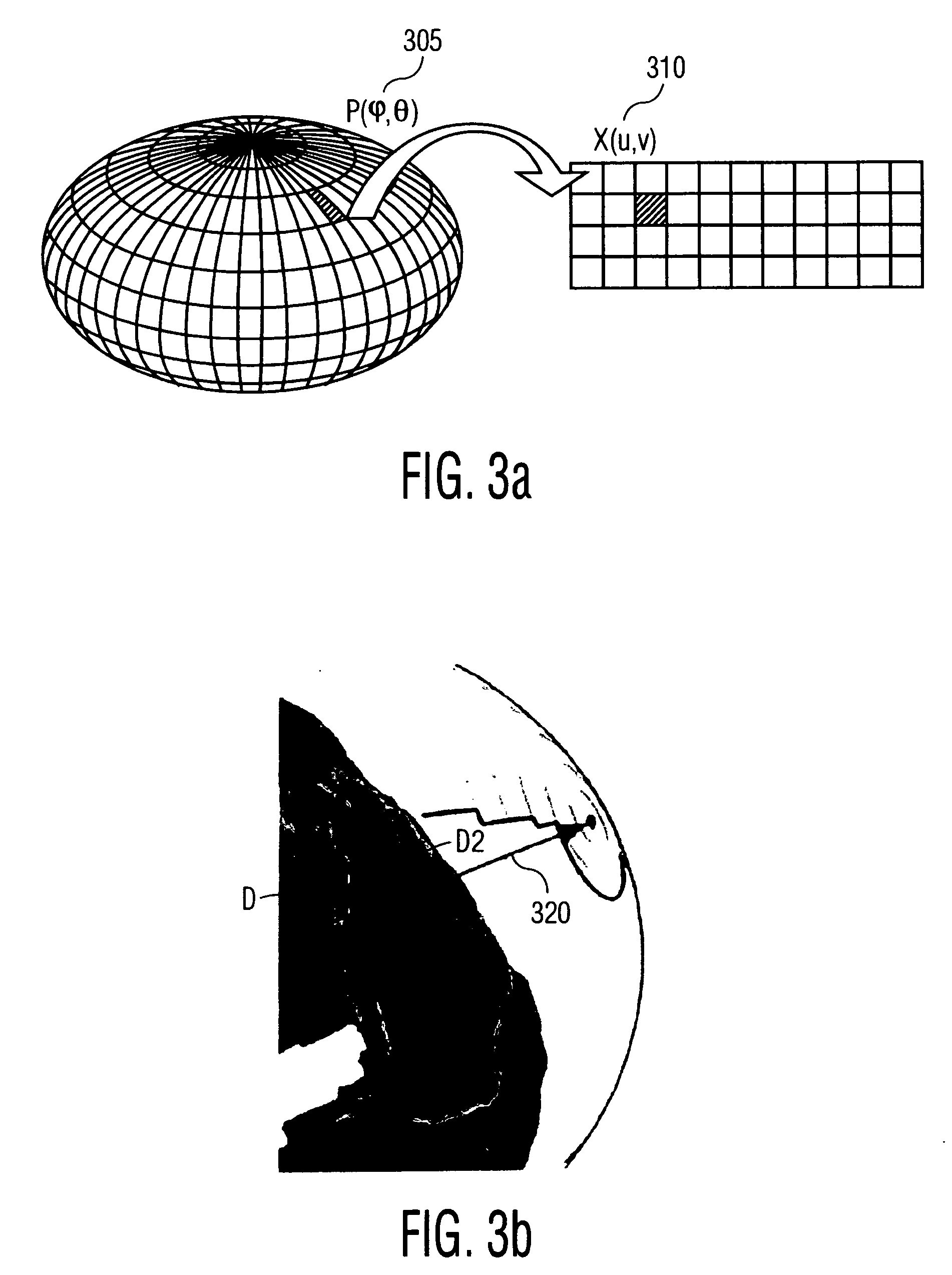
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for generating a two dimensional (2D) image of a structure (e.g., an organ) that has at least one pixel corresponding to at least one voxel of a three dimensional (3D) image of the structure. First, the surface of the structure in the 3D image is modeled by a geometrical volume such as an ellipsoid. Next, normal maximum intensity projection (MIP) rays are cast (i.e., projected) for voxels of the geometrical volume. The 2D image is then generated using the rays. The 2D image has at least one pixel that corresponds to at least one voxel of the 3D image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
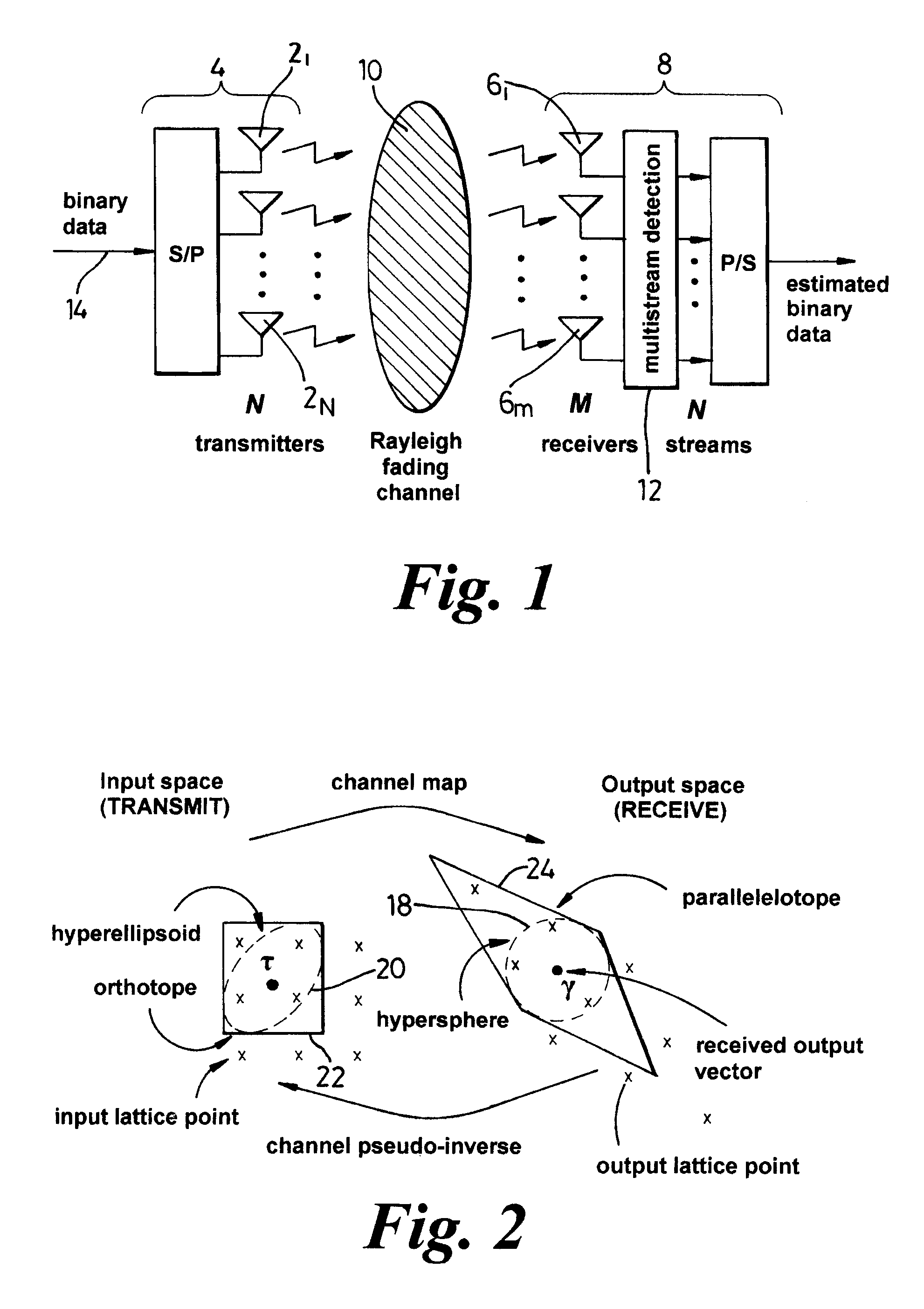
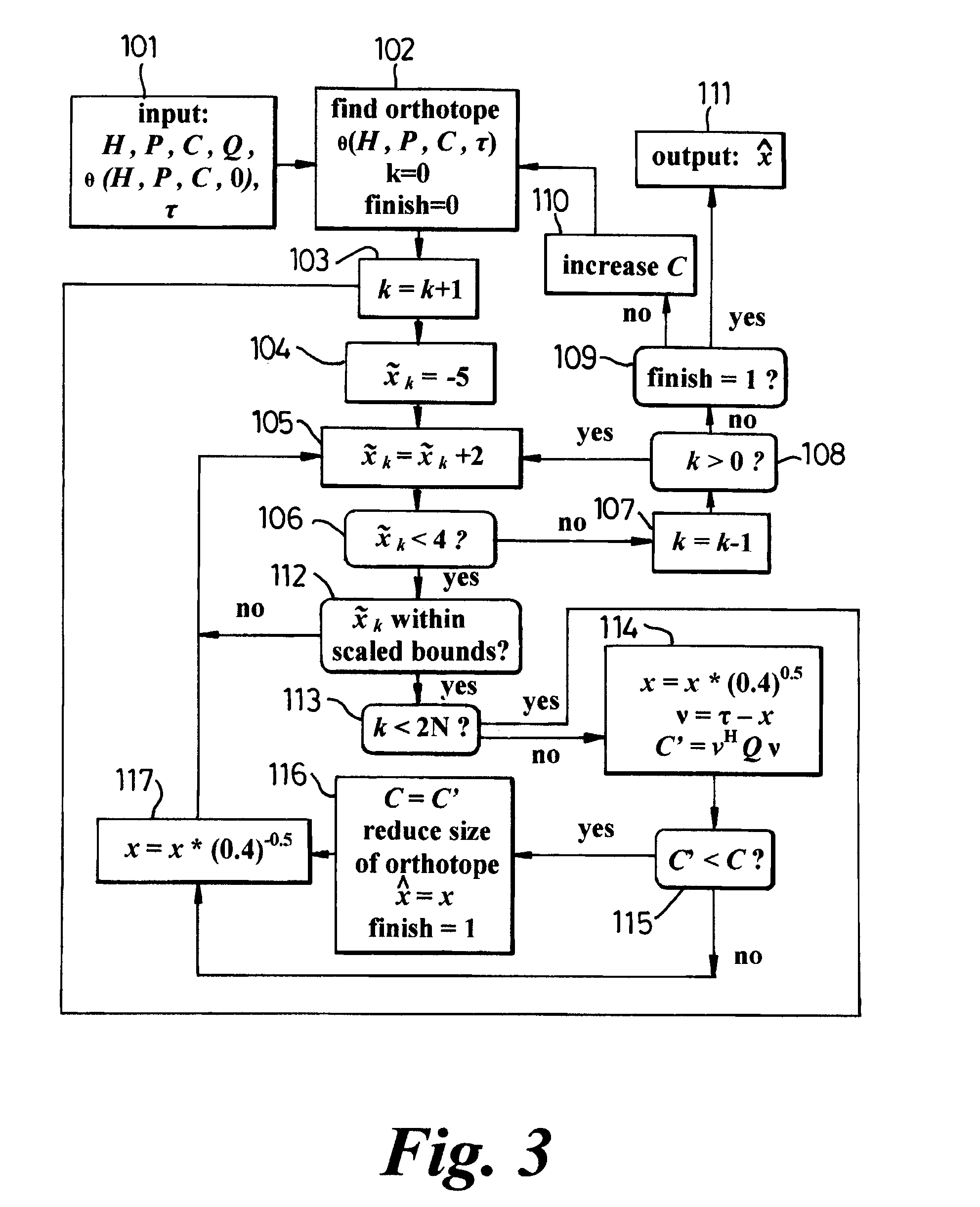
Maximum likelihood decoding
ActiveUS7233634B1Reduce complexityEasy to compareError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemHypersphere
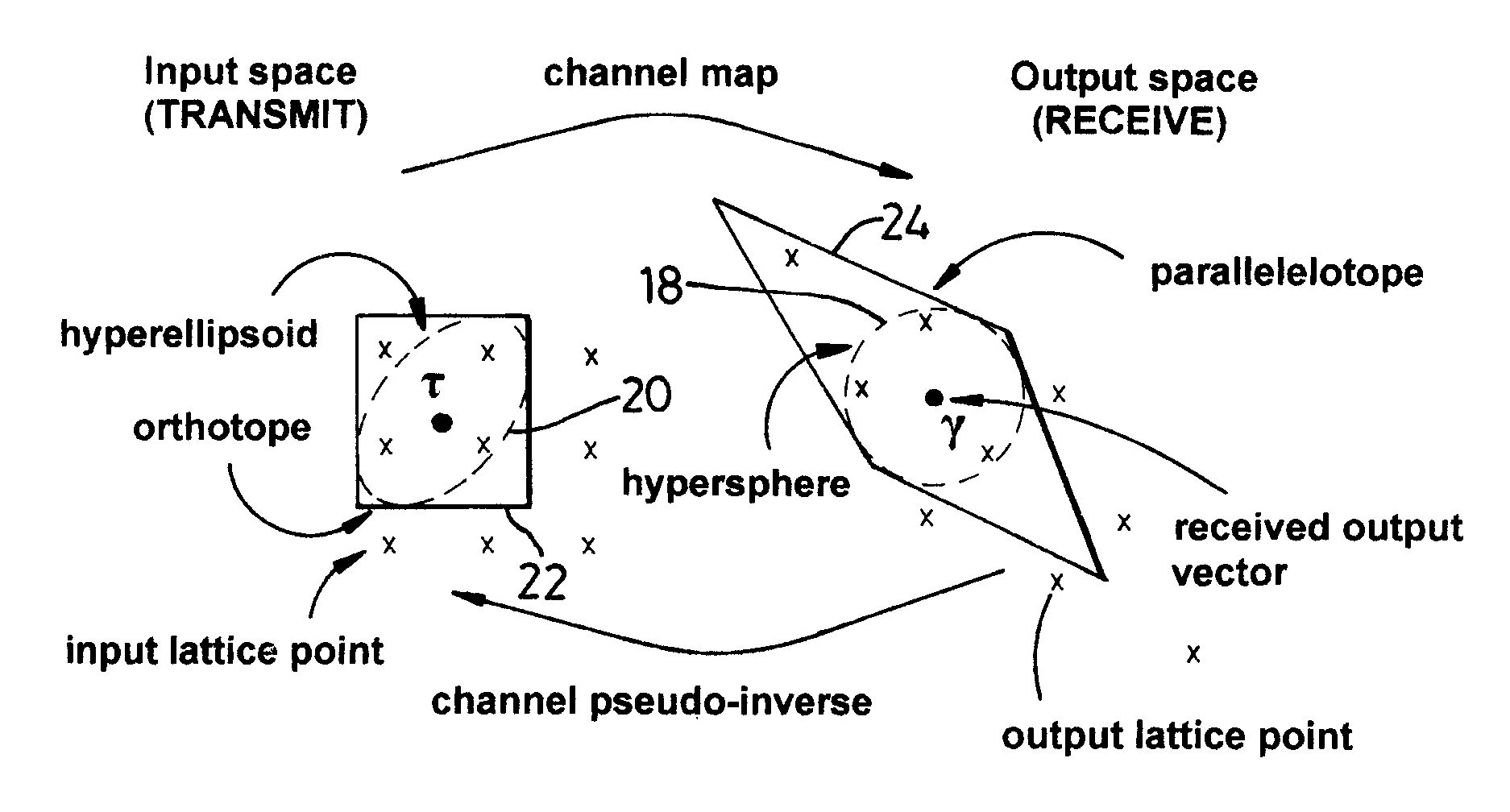
A method of maximum likelihood decoding for detecting the signals transmitted over a Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output (MIMO) channel of a communication system in which there are N co-channel transmit antennas and M co-channel receive antennas. In a first method an orthotope (22) is generated in input signal space centred on an approximate transmit signal point τ which is an inverse mapping from an actual received signal point (y) in output signal space. Only possible transmit points located within the orthotope are considered as candidate points and are transformed into corresponding candidate receive signal points in output signal space. The Euclidean distance between the candidate receive signal points and the actual signal point is calculated and the closest candidate receive signal is selected as the detected received point. In an alternative method, the orthotope is constructed as the smallest such orthotope which can contain a hyperellipsoid (20) in input signal space, which hyperellipsoid is a transformation from output signal space of a hypersphere (18) centred on the actual received signal point (y). Those transmit signal points which lie within the orthotope (22) but outside of the ellipsoid (20) are discarded and the remaining points within the orthotope are considered as candidate points, in the same way as described above.
Owner:APPLE INC
Calibration of 3D field sensors
ActiveUS20070055468A1Electrical measurementsTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesCondensed matter physicsEllipsoid
An apparatus-based method is disclosed for calibration of a 3D field sensor. The method includes accessing a plurality of samples, where the samples are from the 3D field sensor. Each sample represents a magnitude and an orientation of a three-dimensional field sensed by the 3D field sensor. Using the plurality of samples, a plurality of parameters is determined of an ellipsoid. The determination of the plurality of parameters is performed so that the ellipsoid fits the plurality of samples. A transformation is determined that transforms the ellipsoid into a sphere. The transformation is applied to a sample to create a transformed sample. Apparatus and signal bearing media are also disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Textured surface having undercut micro recesses in a surface
InactiveUS20030065401A1Increase the areaDental implantsLayered productsBiomedical engineeringEllipsoid
Owner:TECMET
Conformable thermal pack apparatus, manufacture and method
InactiveUS20070021810A1Easy to manufactureTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingOblate spheroidThermal energy
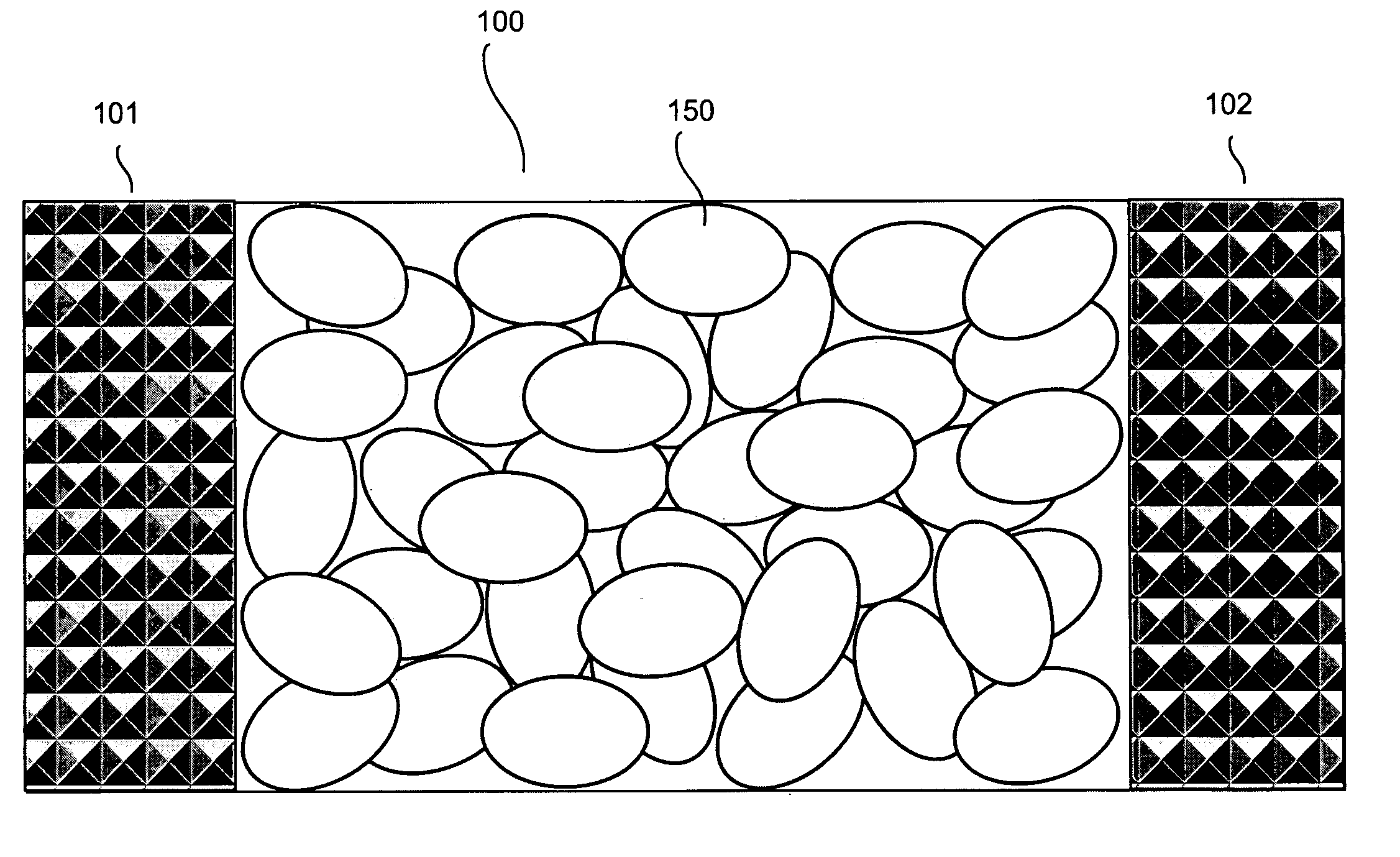
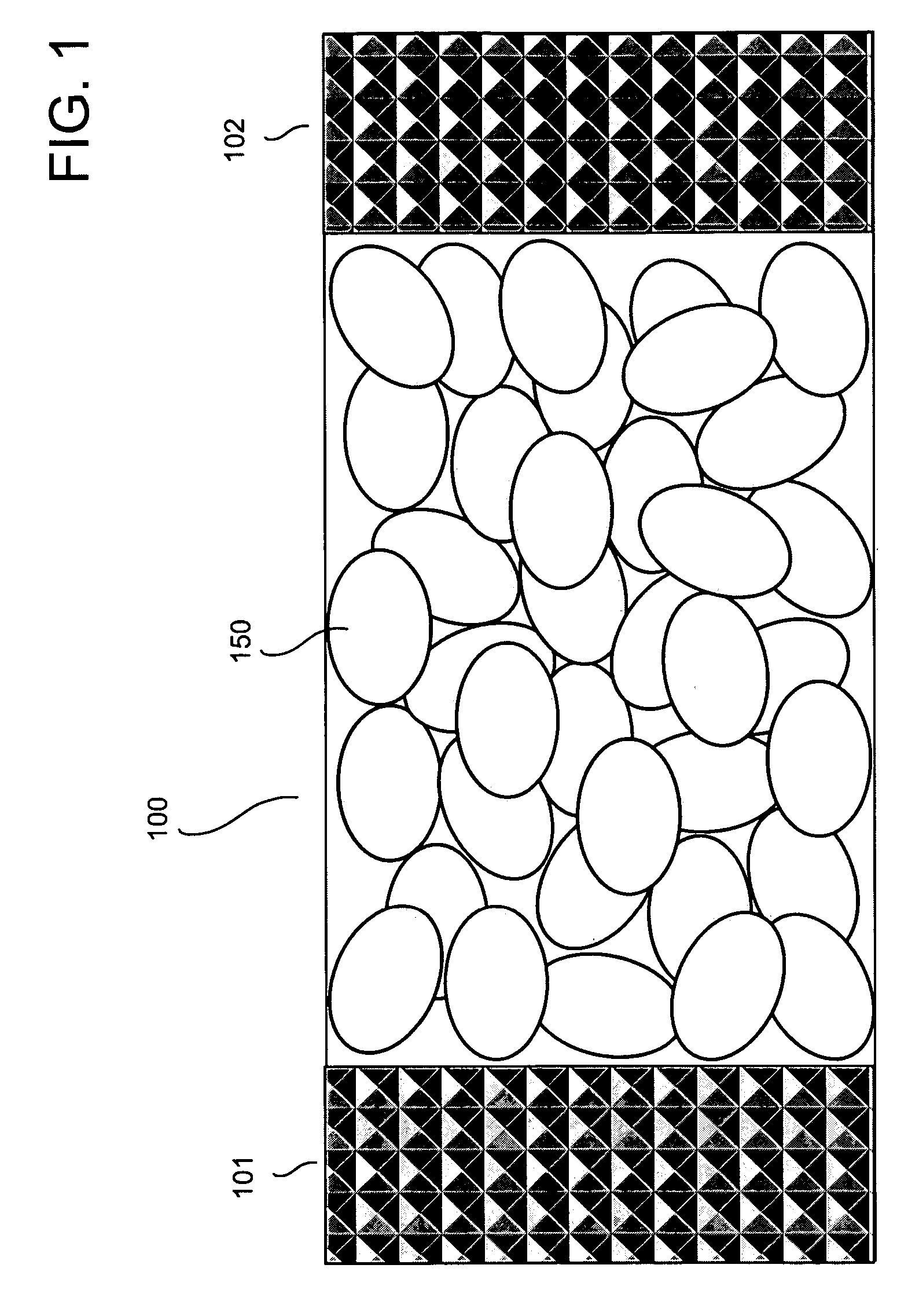
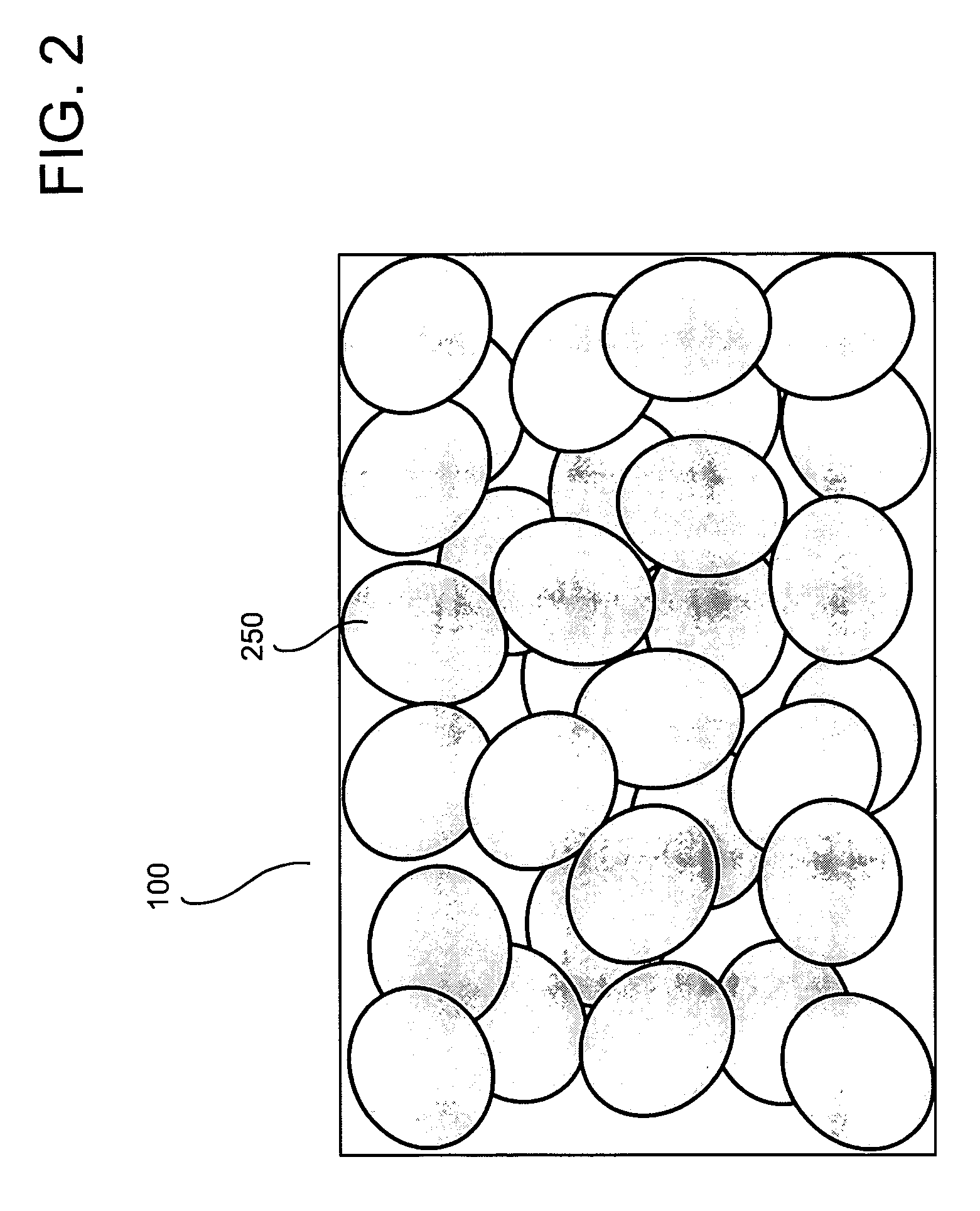
A therapeutic conformable thermal pack having increased thermal energy storage capacity. The apparatus and method enables therapeutic delivery of more stored heat or cold than previously possible to various areas of a treatment area. A new scientific discovery has been made that shows that ellipsoids and oblate spheroids randomly pack more densely than spheres. The thermal pack comprises thermal retaining elements comprising oblate spheroids and / or ellipsoids allowing embodiments to have an improved thermal density and thermal transfer capability.
Owner:PAULIN KATHY WOOD
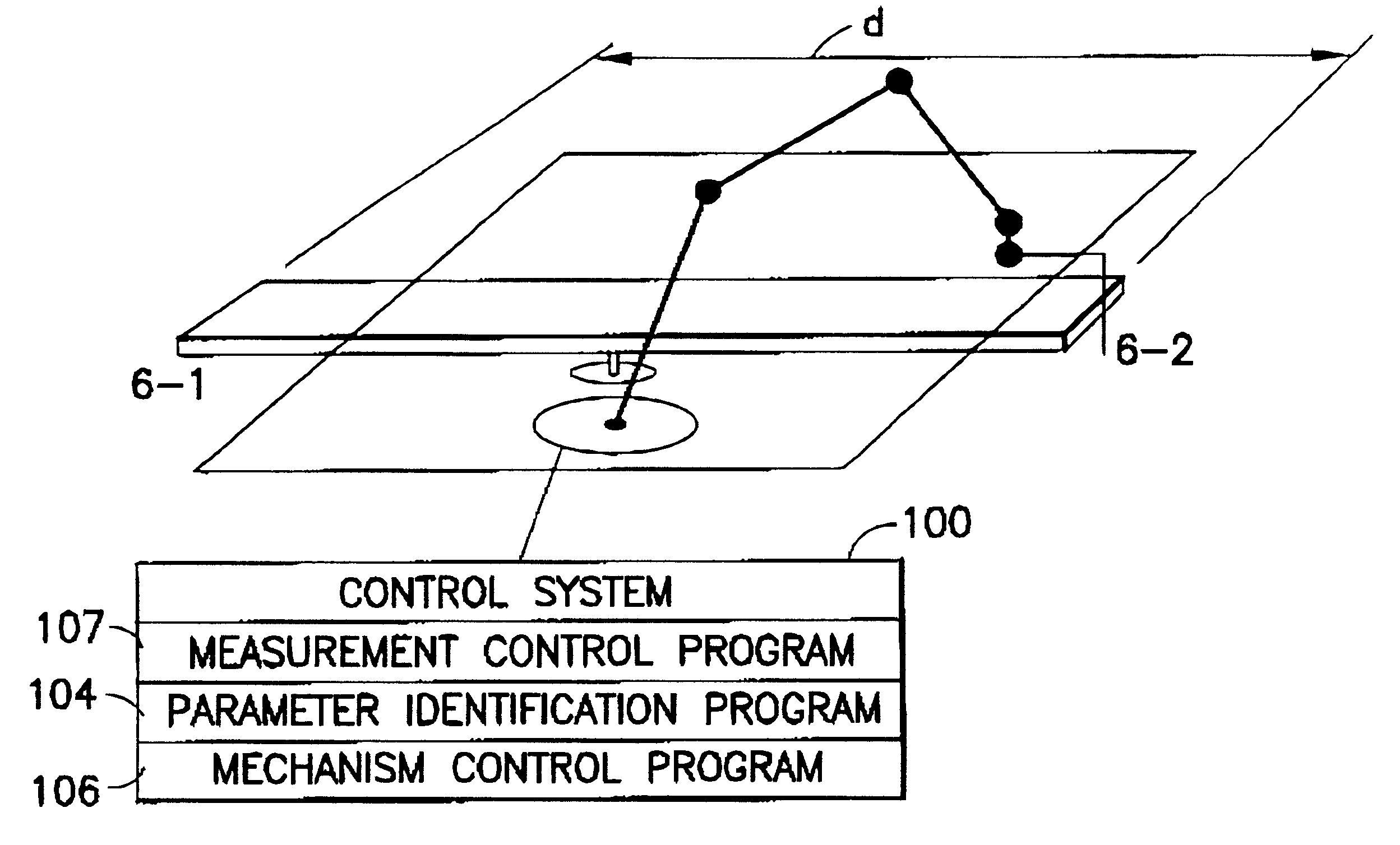
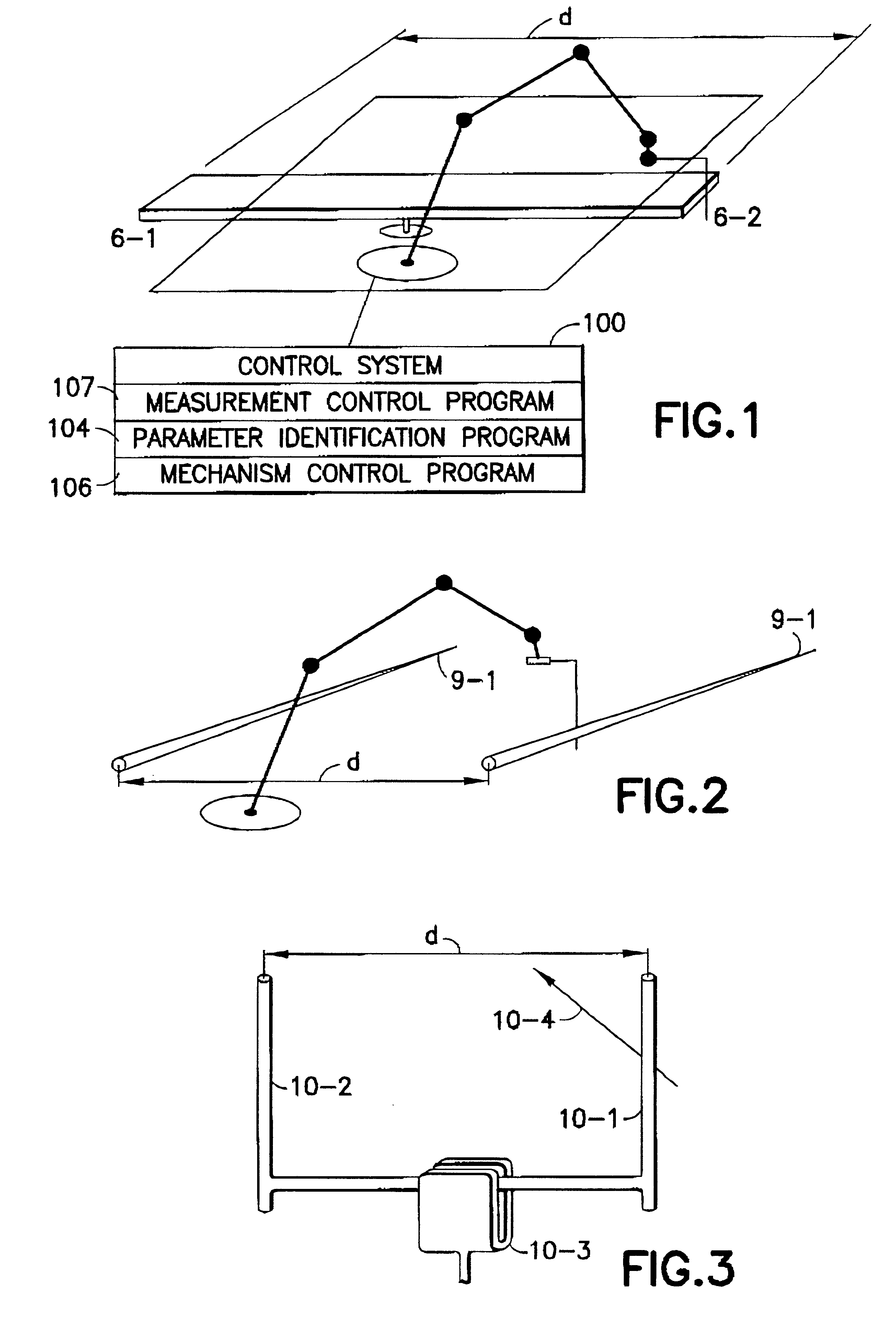
Method and device for the improvement of the pose accuracy of effectors on mechanisms and for the measurement of objects in a workspace
InactiveUS6529852B2Low costHigh precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorMeasurement arrangements for variableInformation processingHyperboloid
A device and a method for measuring the pose of mechanisms includes at least one effector object fixedly joined to a mechanism (e.g., industrial robot, hexapod) in which the at least one effector object moves along one of several axes. The ideal, effective shape of the at least one effector object is a point, a straight line, a plane, an ellipsoid, a cylinder, a hyperboloid or a combination thereof. The movable effector objects interact with reference objects which are arranged in defined positions relative to the mechanism. The interactions are detected by a suitable sensor. The interactions are detected, only the pertaining joint configuration of the mechanism is transmitted to the information processing unit and evaluated and no further continuous values of measuring parameters are required for the evaluation.
Owner:KNOLL ALOIS +1
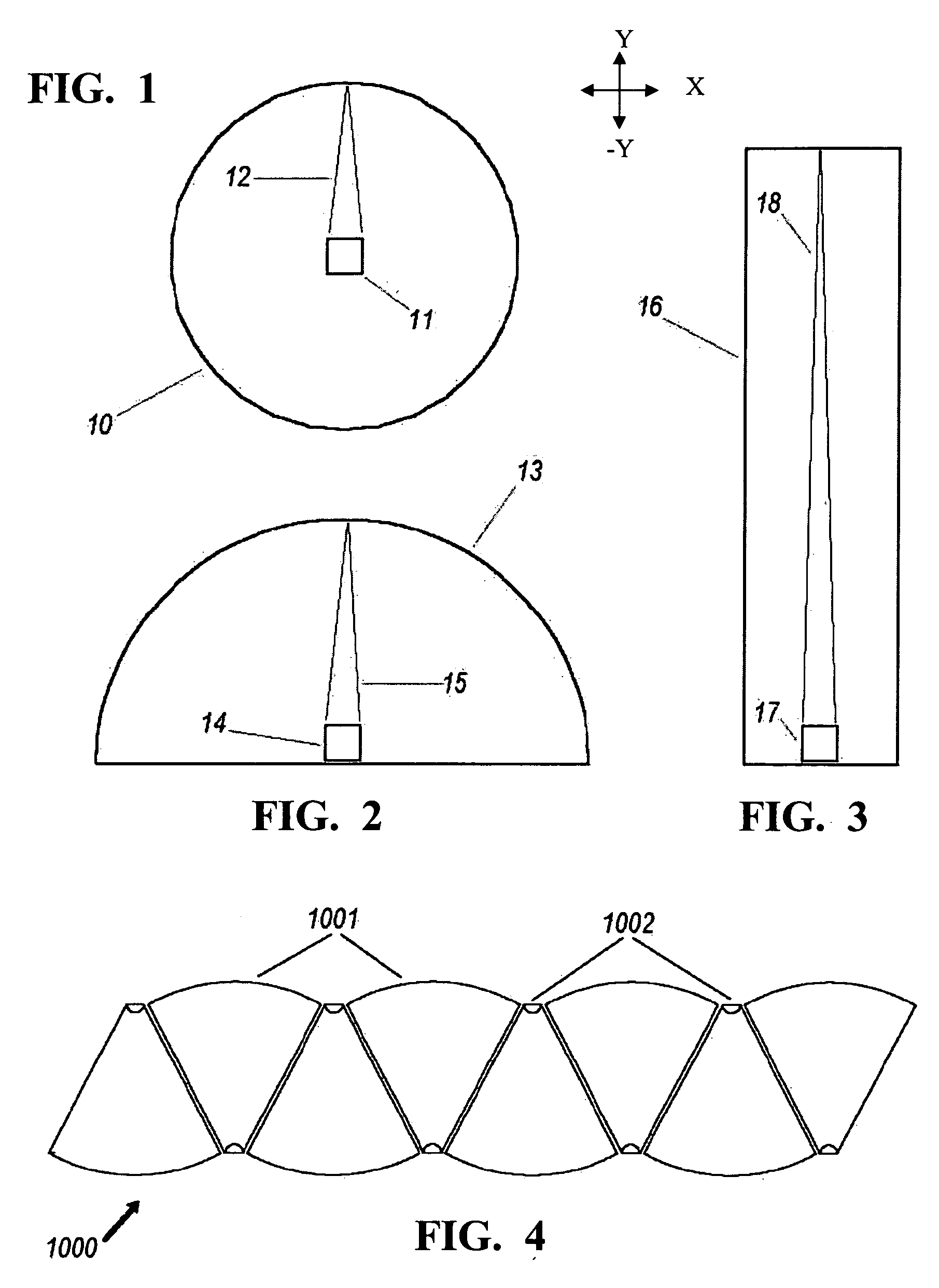
Etendue-squeezing illumination optics
In some embodiments, an apparatus for use generating illumination is provided that comprises a reflective base, a first light source positioned proximate the reflective base, and a reimaging reflector positioned partially about the first light source, where a percentage of light emitted from the first light source is reflected from the reimaging reflector to the reflective base adjacent the first light source establishing a first real image. The reimaging reflector can further comprise a first sector of a first ellipsoid and a second sector of a second ellipsoid, where the first and second sectors establish the first and a second real image. Further embodiments provide a lens that includes a reimaging reflector that receives light and reflects the light establishing a first real image. The reimaging reflector can further comprise a plurality of sectors that reflect light to establish first and second real images.
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
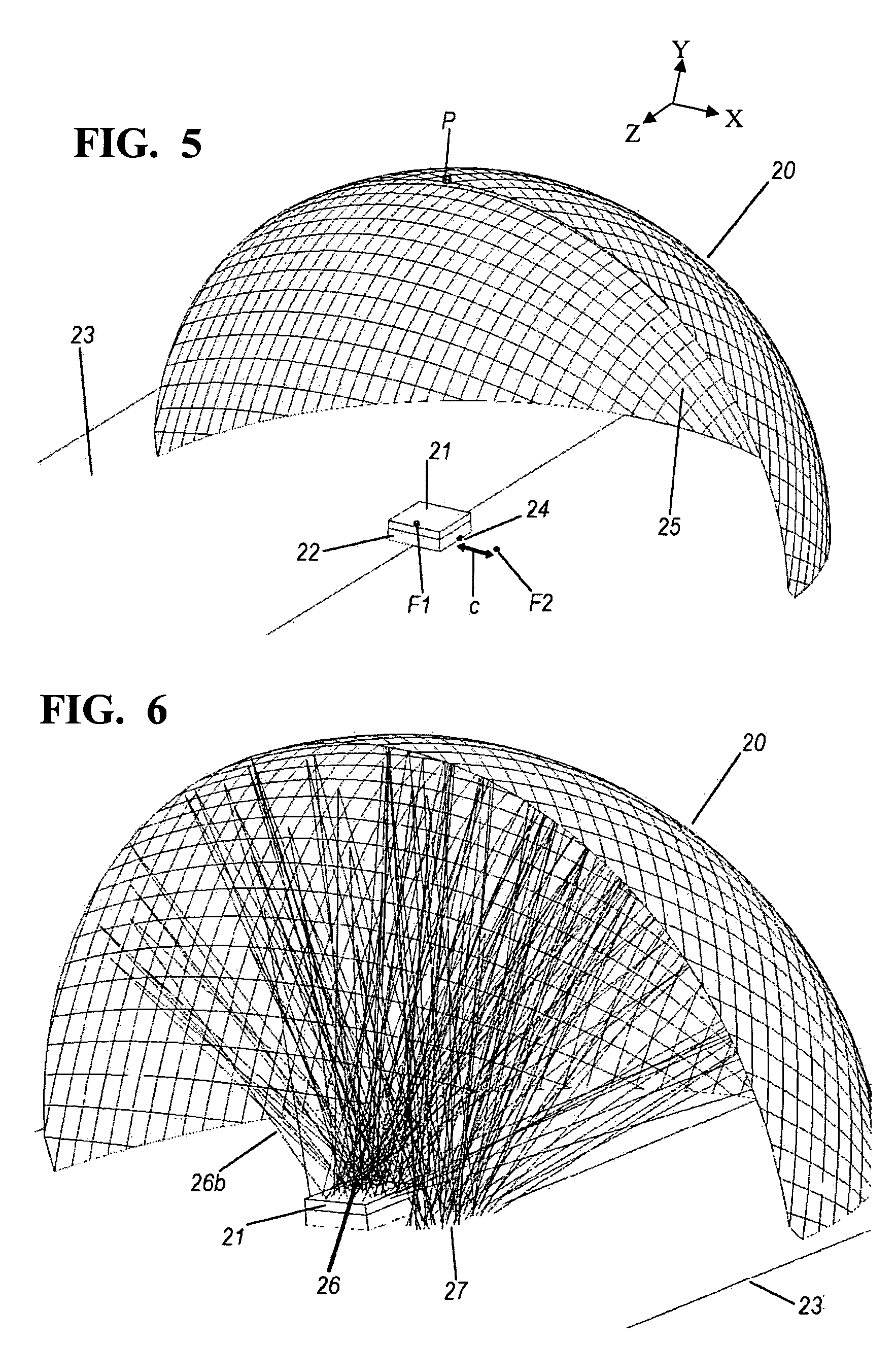
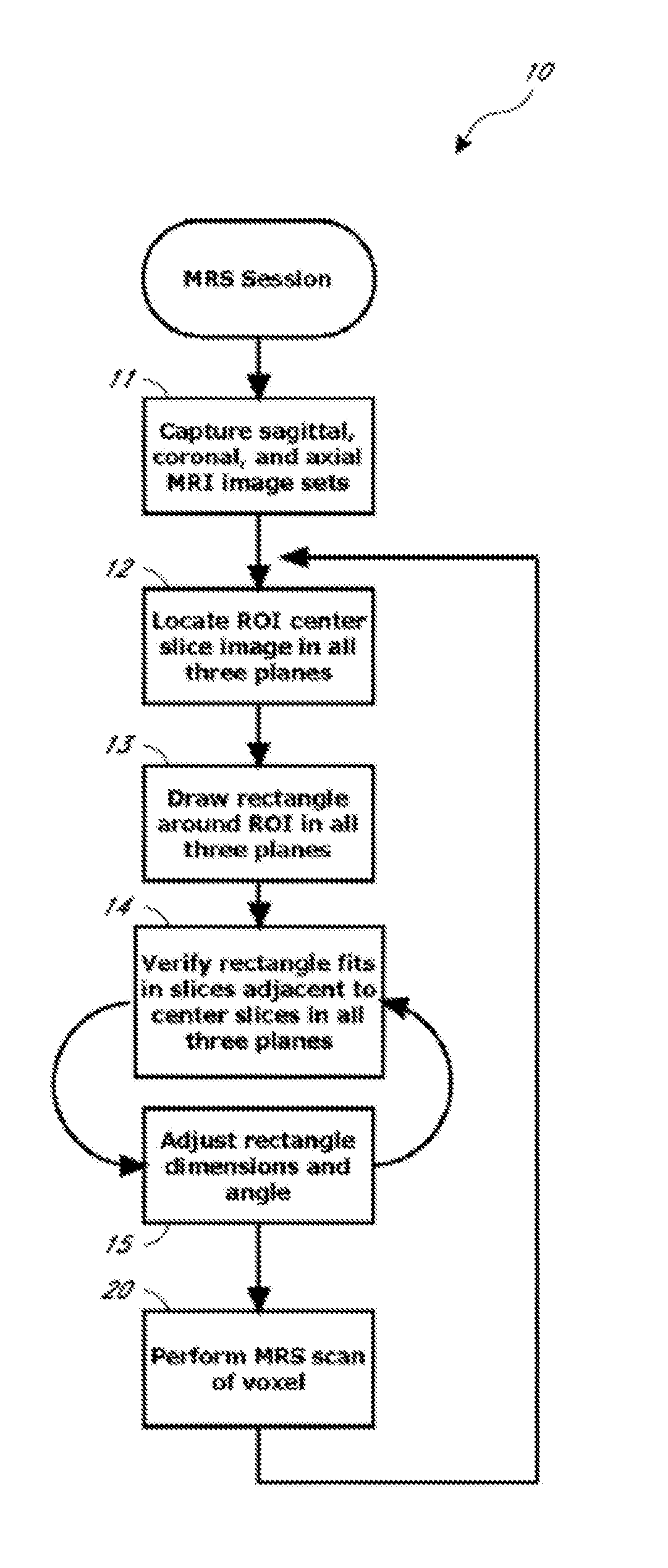
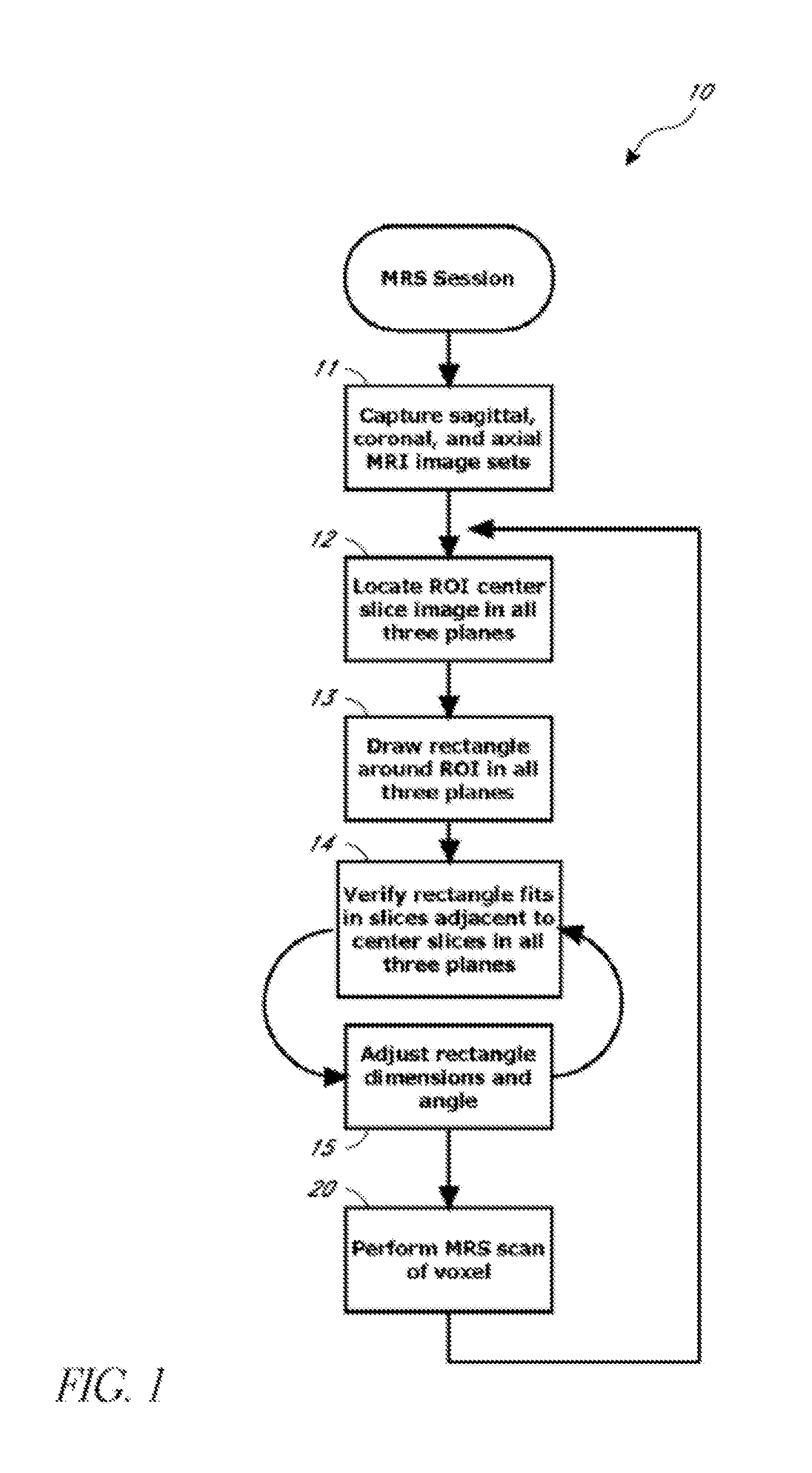
Systems and methods for automated voxelation of regions of interest for magnetic resonance spectroscopy
A system and method for automating an appropriate voxel prescription in a uniquely definable region of interest (ROI) in a tissue of a patient is provided, such as for purpose of conducting magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in the ROI. The dimensions and coordinates of a single three dimensional rectilinear volume (voxel) within a single region of interest (ROI) are automatically identified. This is done, in some embodiments by: (1) applying statistically identified ROI search areas within a field of view (FOV); (2) image processing an MRI image to smooth the background and enhance a particular structure useful to define the ROI; (3) identifying a population of pixels that define the particular structure; (4) performing a statistical analysis of the pixel population to fit a 2D model such as an ellipsoid to the population and subsequently fit a rectilinear shape within the model; (5) repetiting elements (1) through (4) using multiple images that encompass the 3D ROI to create a 3D rectilinear shape; (6) a repetition of elements (1) through (5) for multiple ROIs with a common FOV. A manual interface may also be provided, allowing for override to replace by manual prescription, assistance to identify structures (e.g. clicking on disc levels), or modifying the automated voxel (e.g. modify location, shape, or one or more dimensions).
Owner:ACLARION INC
Etendue-squeezing illumination optics
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
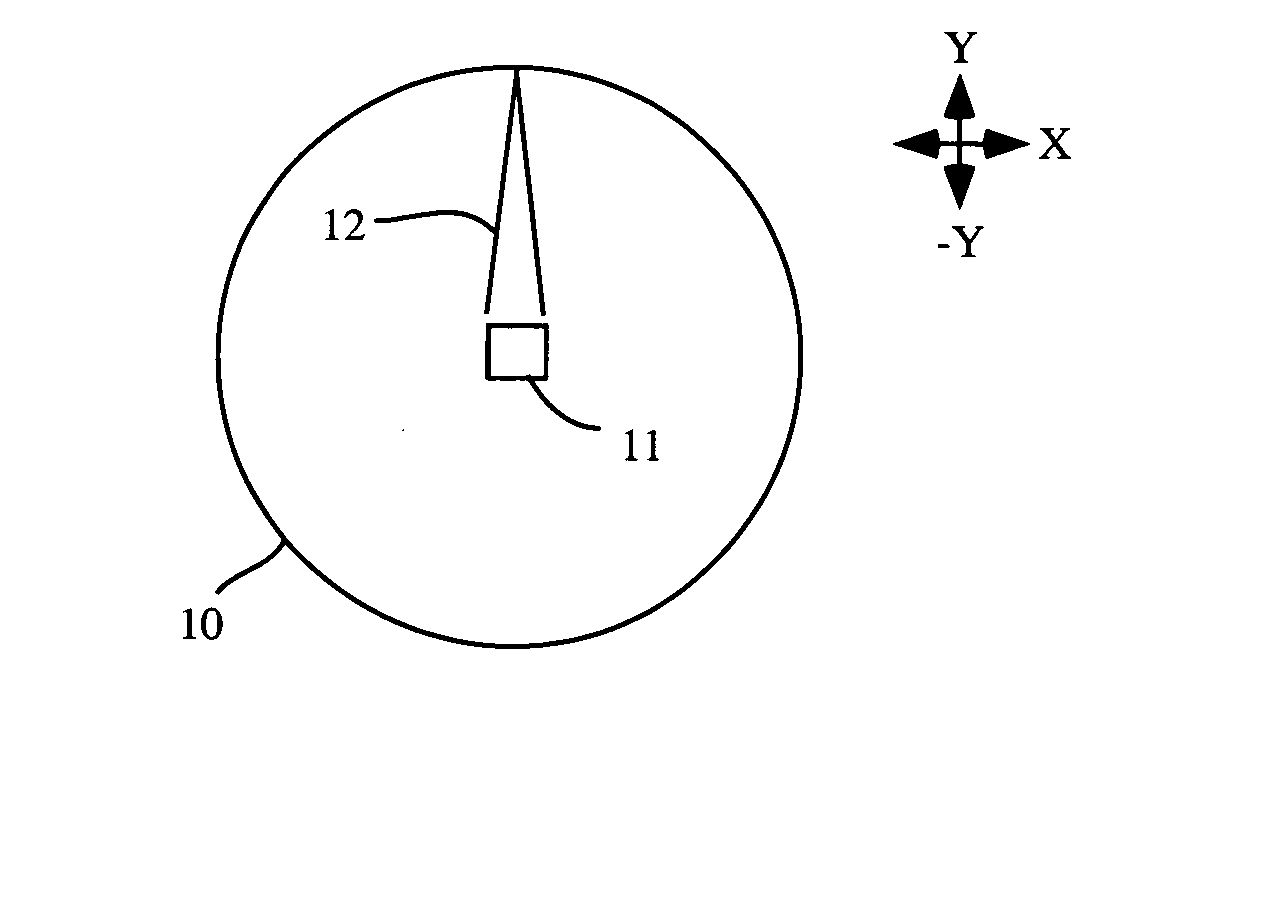
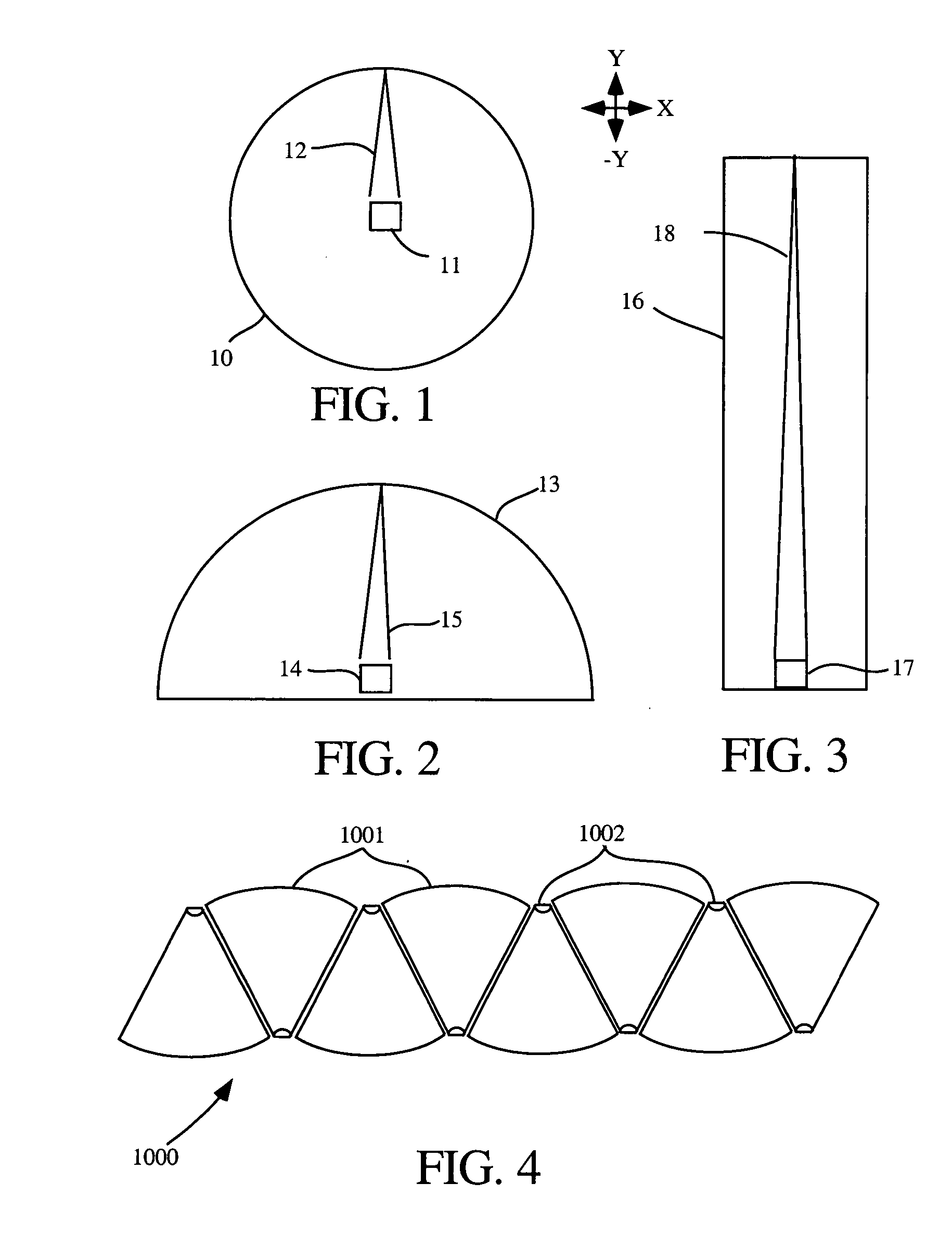
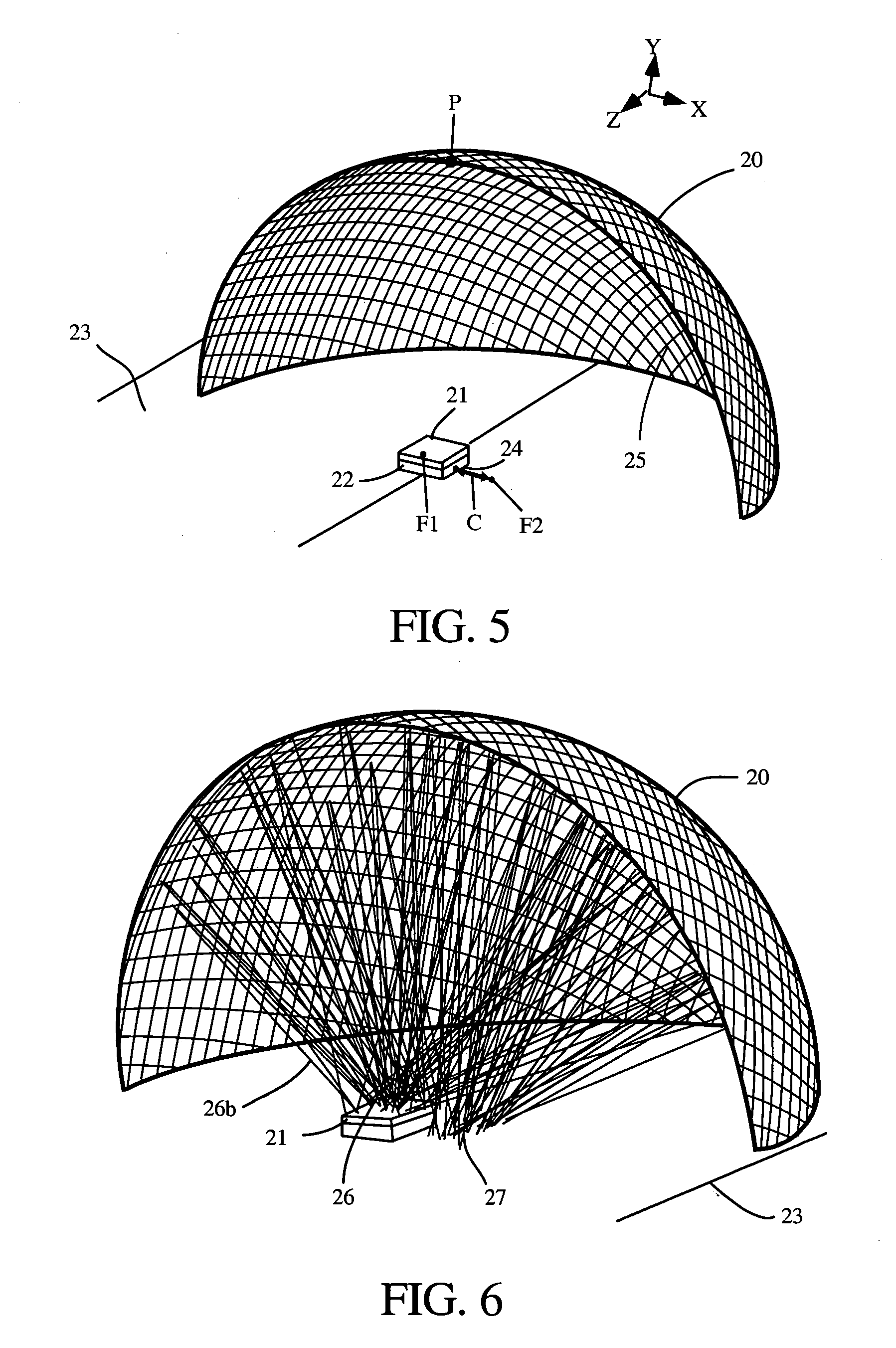
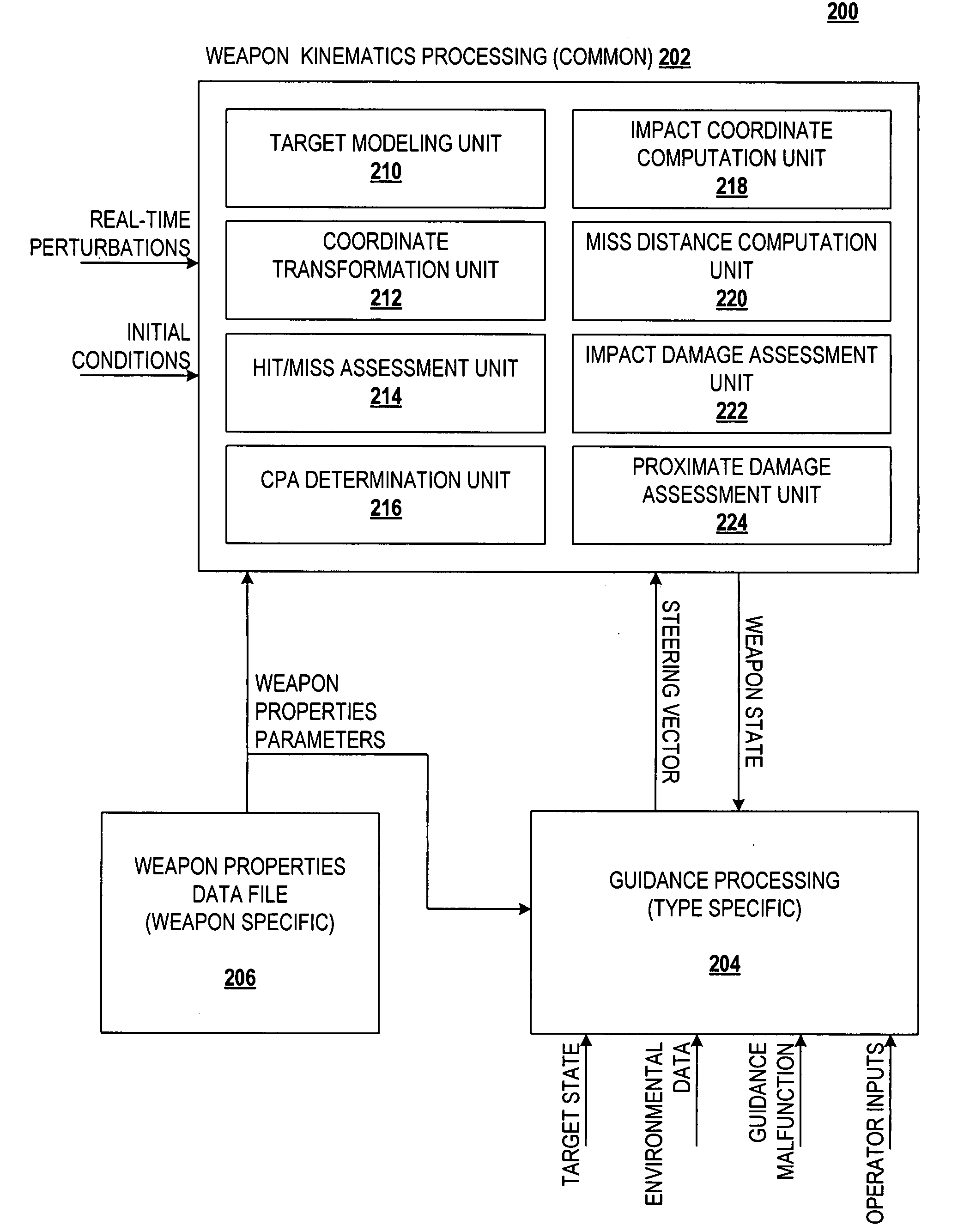
Apparatus, method and computer program product for weapon flyout modeling and target damage assessment
A weapon flyout simulation method, system, and computer program product, includes modeling a target as a plurality of ellipsoidal zones corresponding to a plurality of zones on the target, and performing hit / miss assessment on the target by determining if said trajectory of the weapon interferes with at least one of said plurality of ellipsoids.
Owner:AIRPORTS AUTHORITY OF INDIA
Ellipsoid generator
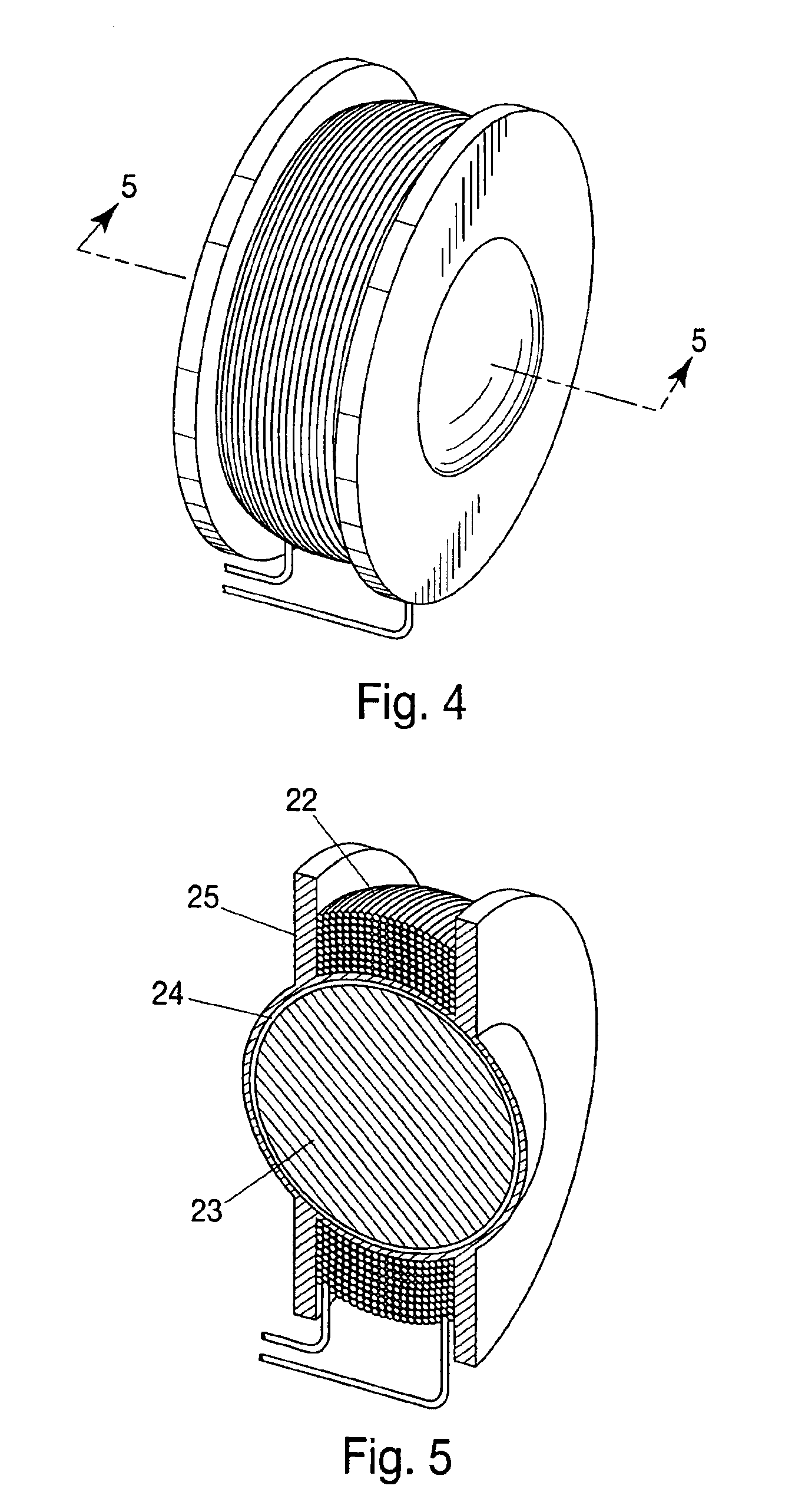
A dynamoelectric device that is highly adaptable to a broad range of applications while providing robust output and energy conversion. The magnetic pole faces of the rotor lie in an ellipsoid. With or without a rotor shaft, the device allows options of either physical connection or contact-less, magnetic coupling. Surrounding the rotor is a brush-less stator having a bobbin-type, axial-centered coil conductor that provides a total capture of magnetic flux emanating from a rotor having an entire surface area of uniform flux density. Devices without a rotor shaft, and those having an air gap filled with ferrofluid, provide a two part generator with remarkable efficiency that is easily waterproofed and mechanically stable.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE INC
Method for calibrating electronic compass of unmanned machine under magnetic environment
ActiveCN102589537AImprove adaptabilitySimplify the calibration stepsCompassesMagnetic disturbanceUncrewed vehicle
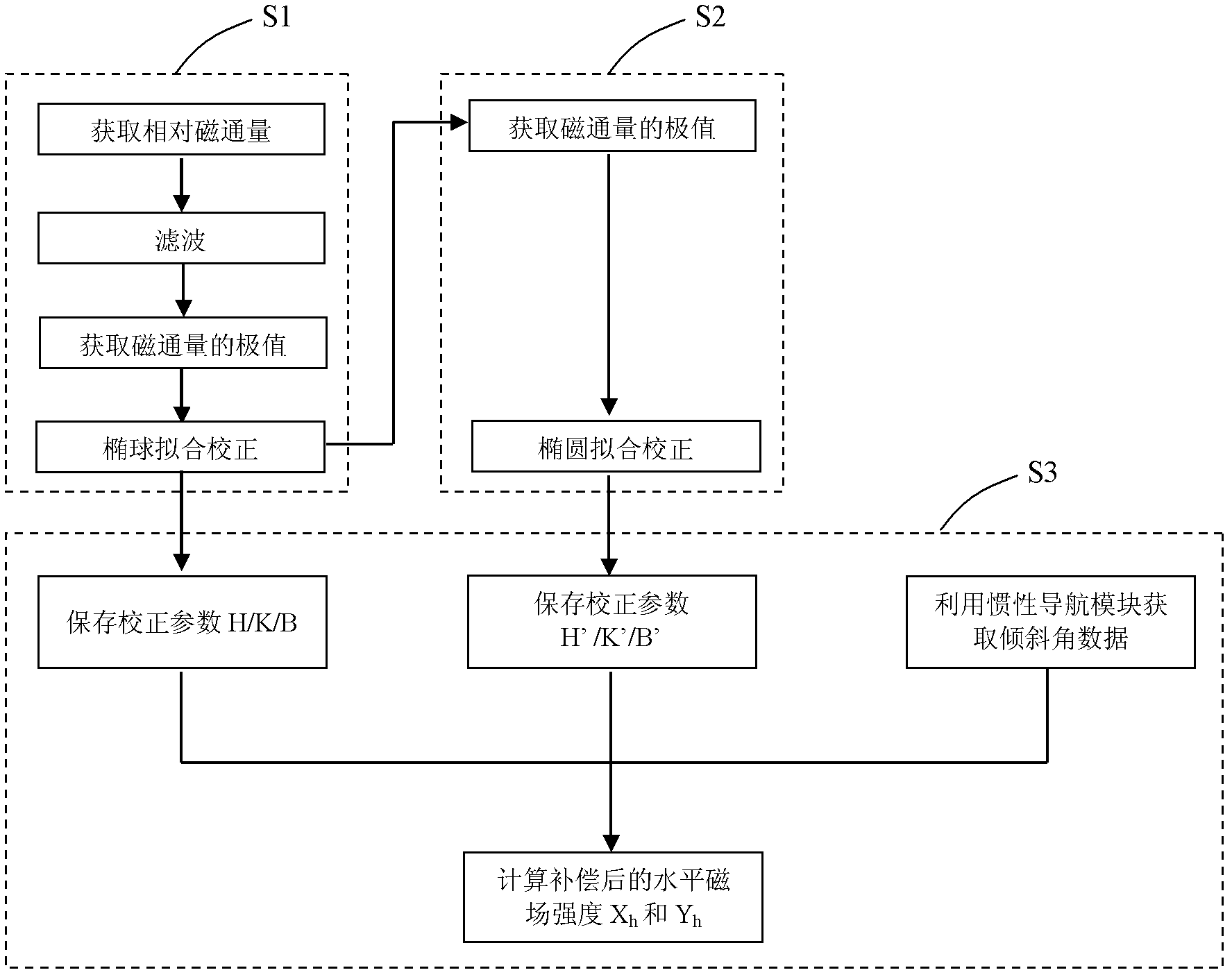
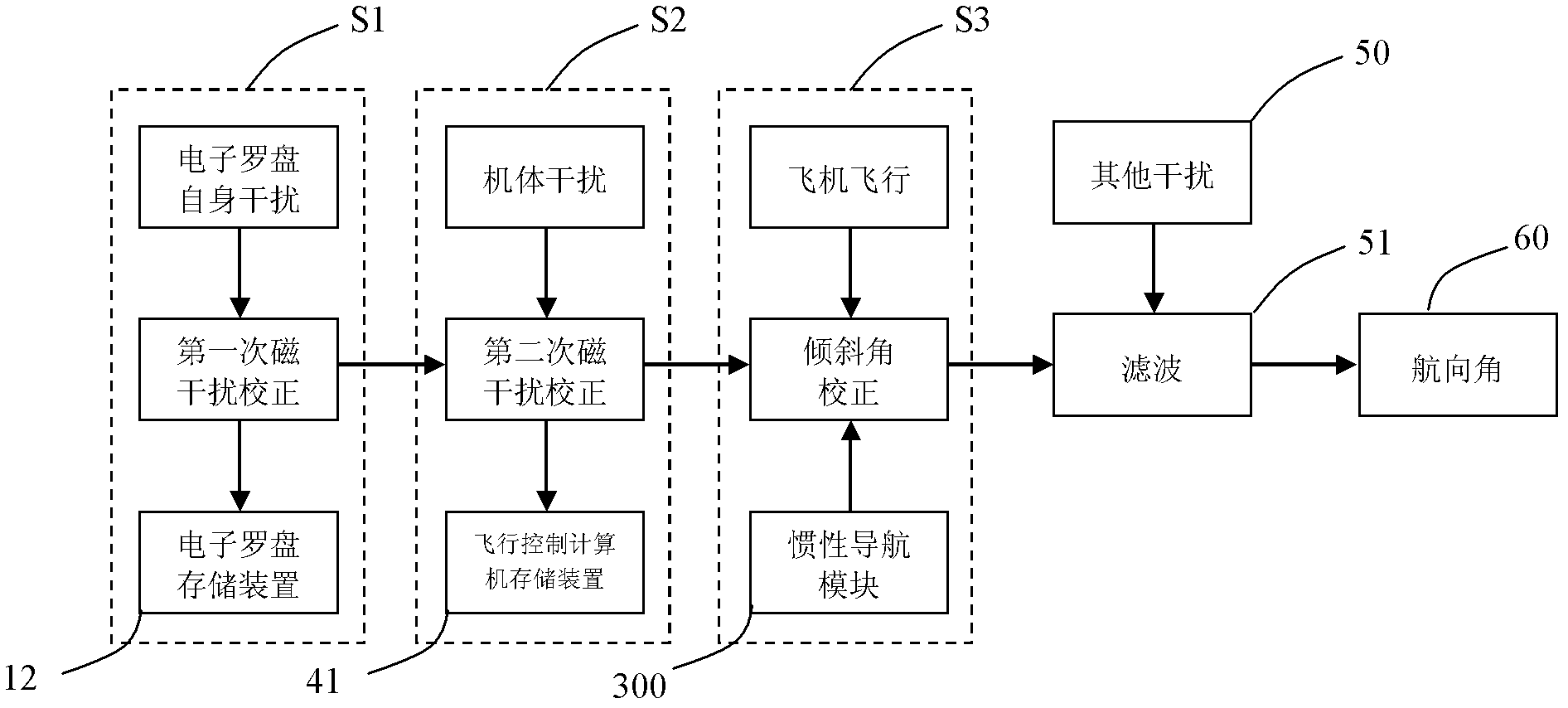
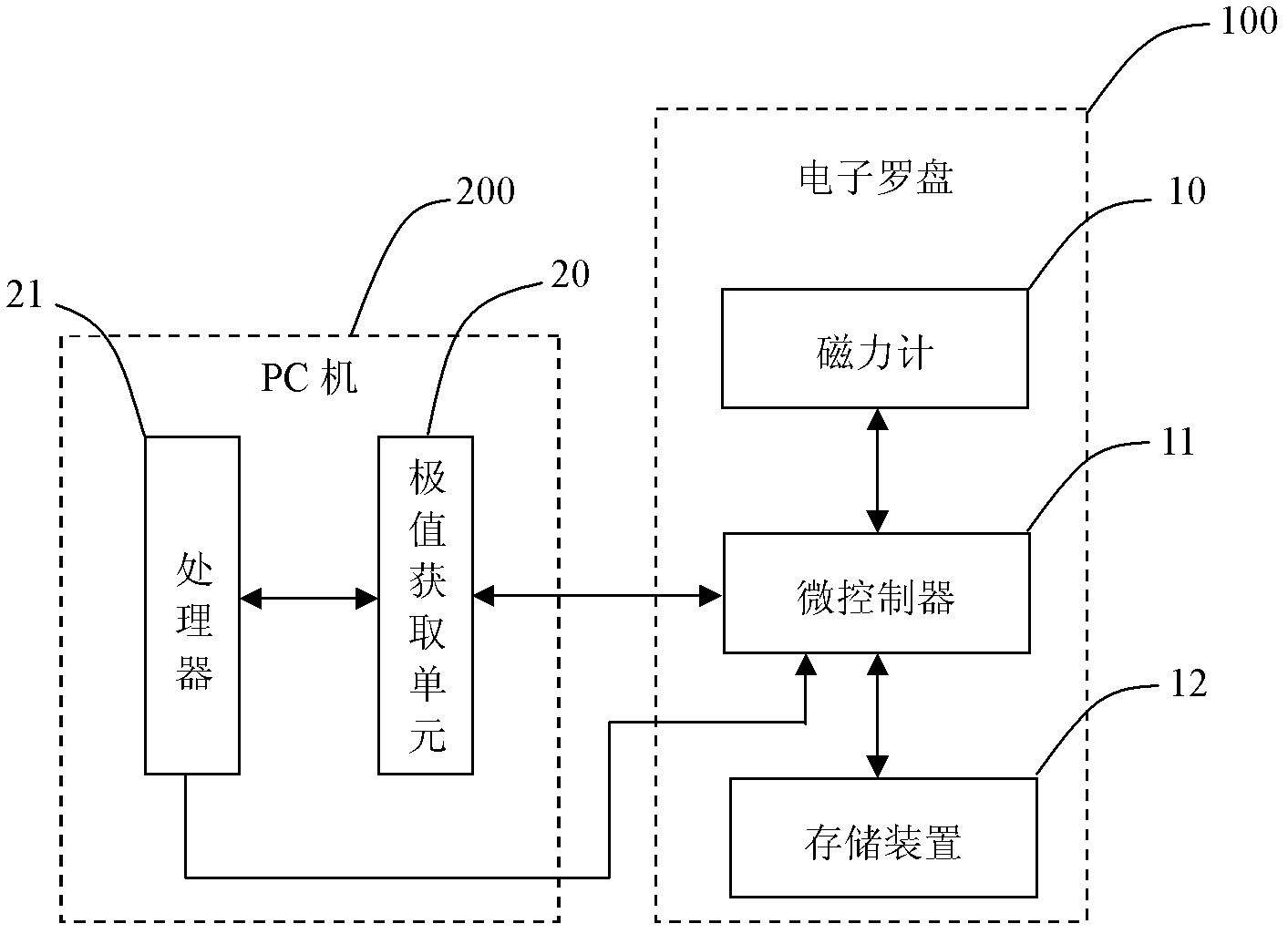
The invention provides a method for calibrating an electronic compass of an unmanned machine under a magnetic environment, which comprises the following steps that: relative magnetic flux of an X-axis, a Y-axis and a Z-axis of the electronic compass is obtained through a magnetometer, ellipsoid fitting calibration on the magnetic flux is carried out after the filter processing, and calibration parameters are stored to a first storage device; an extreme value of the magnetic flux of the X-axis, the Y-axis and the Z-axis of the electronic compass is respectively obtained through the magnetometer, then ellipsoid fitting calibration on the extreme values is performed, and the calibration parameters are stored to a second storage device; obliquity data is obtained through an inertia navigation module, horizontal magnetic field strength Xh and Yh after being compensated are calculated according to the obliquity data and the calibration parameters of step 1 and step 2, so the magnetic interference calibration and obliquity calibration of the electronic compass can be completed. Due to the adoption of the calibration method, the adaptability of the electronic compass can be improved, and the calibration steps can be simplified; and the calibration is unnecessary to perform under the magnetic-free environment, so the requirement on the calibration equipment and the calibration environment is low.
Owner:WUXI HANHE AVIATION TECH
Method for multistatic detection and locating of a mobile craft through the use of digital broadcasting transmitters
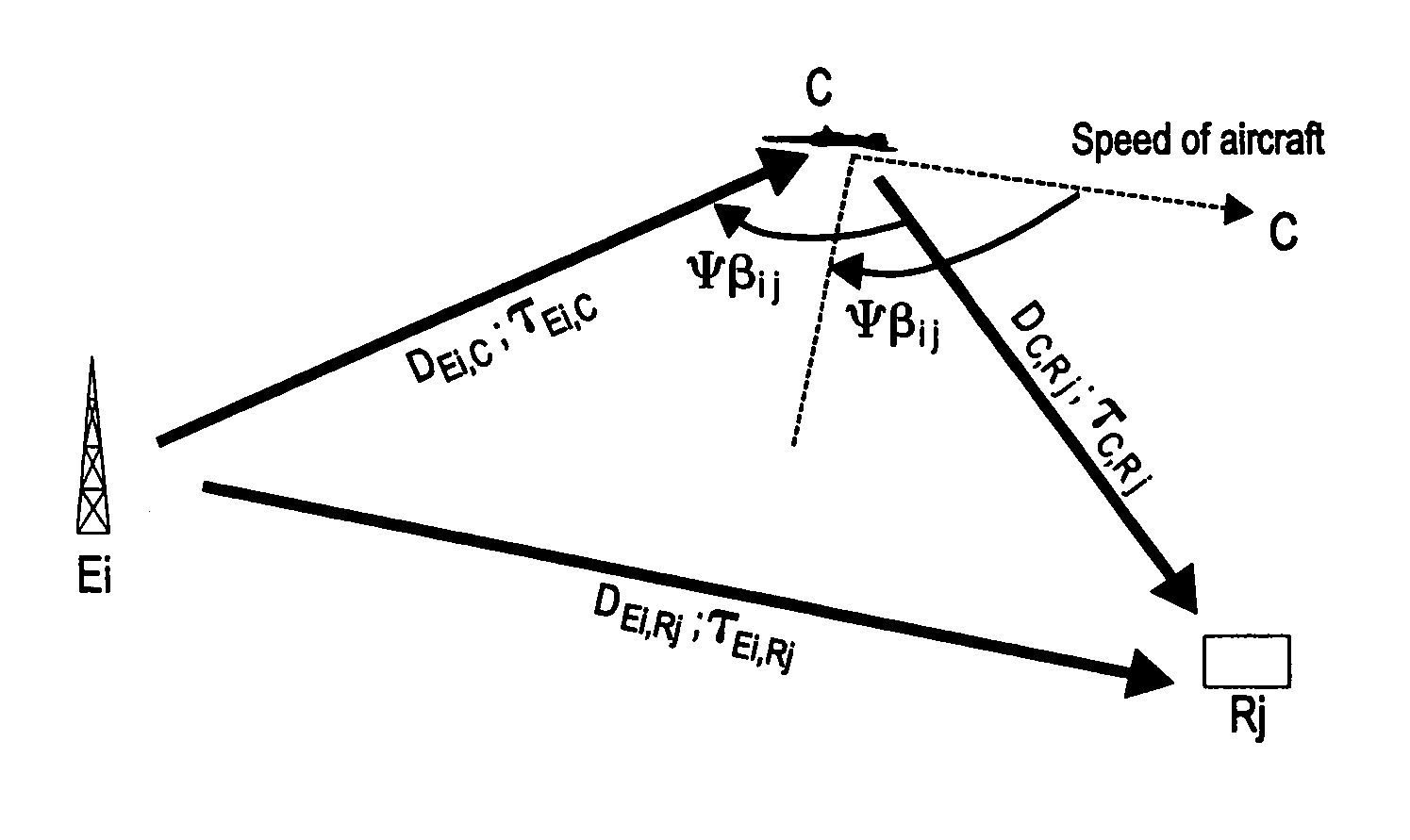
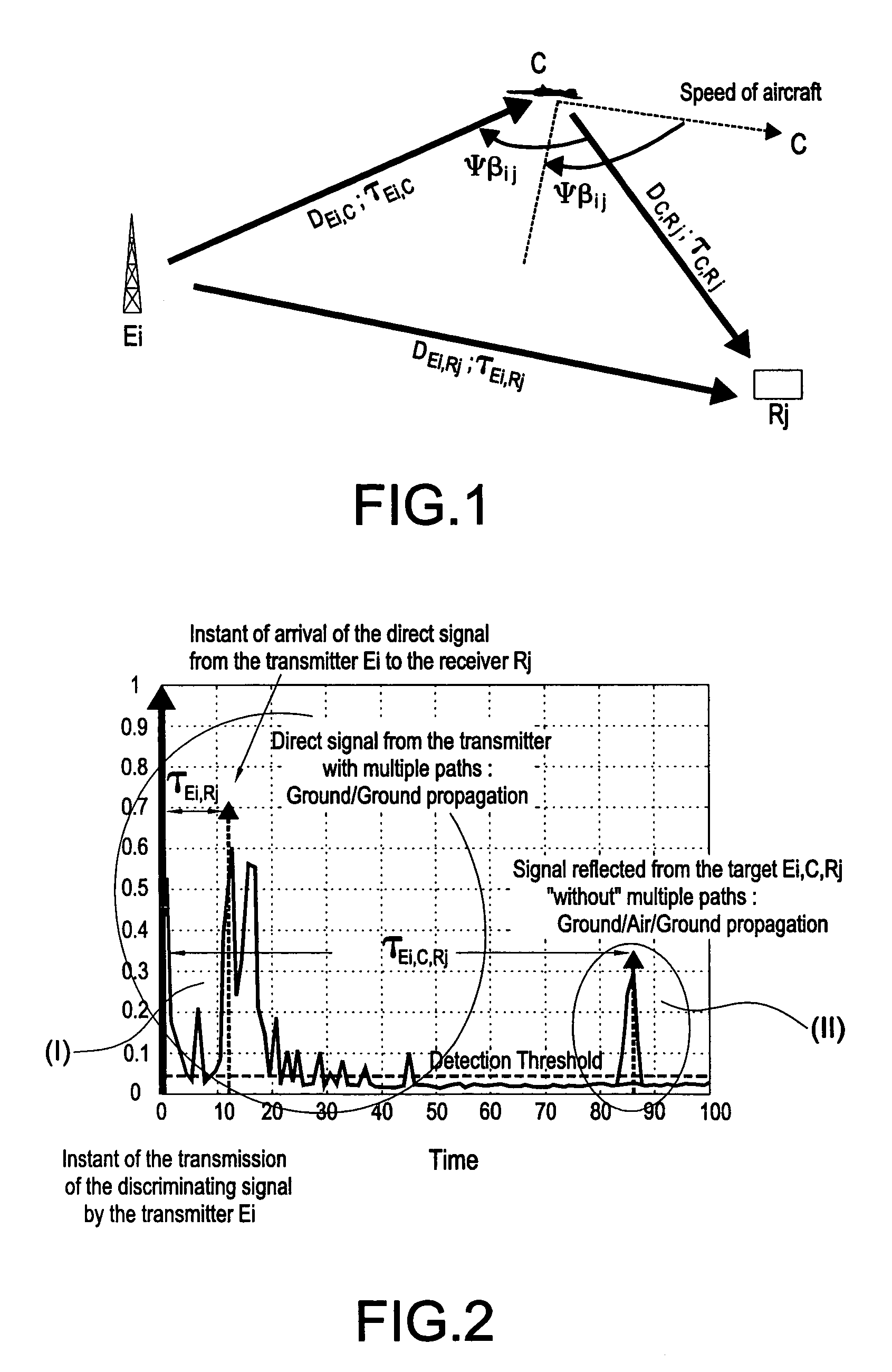
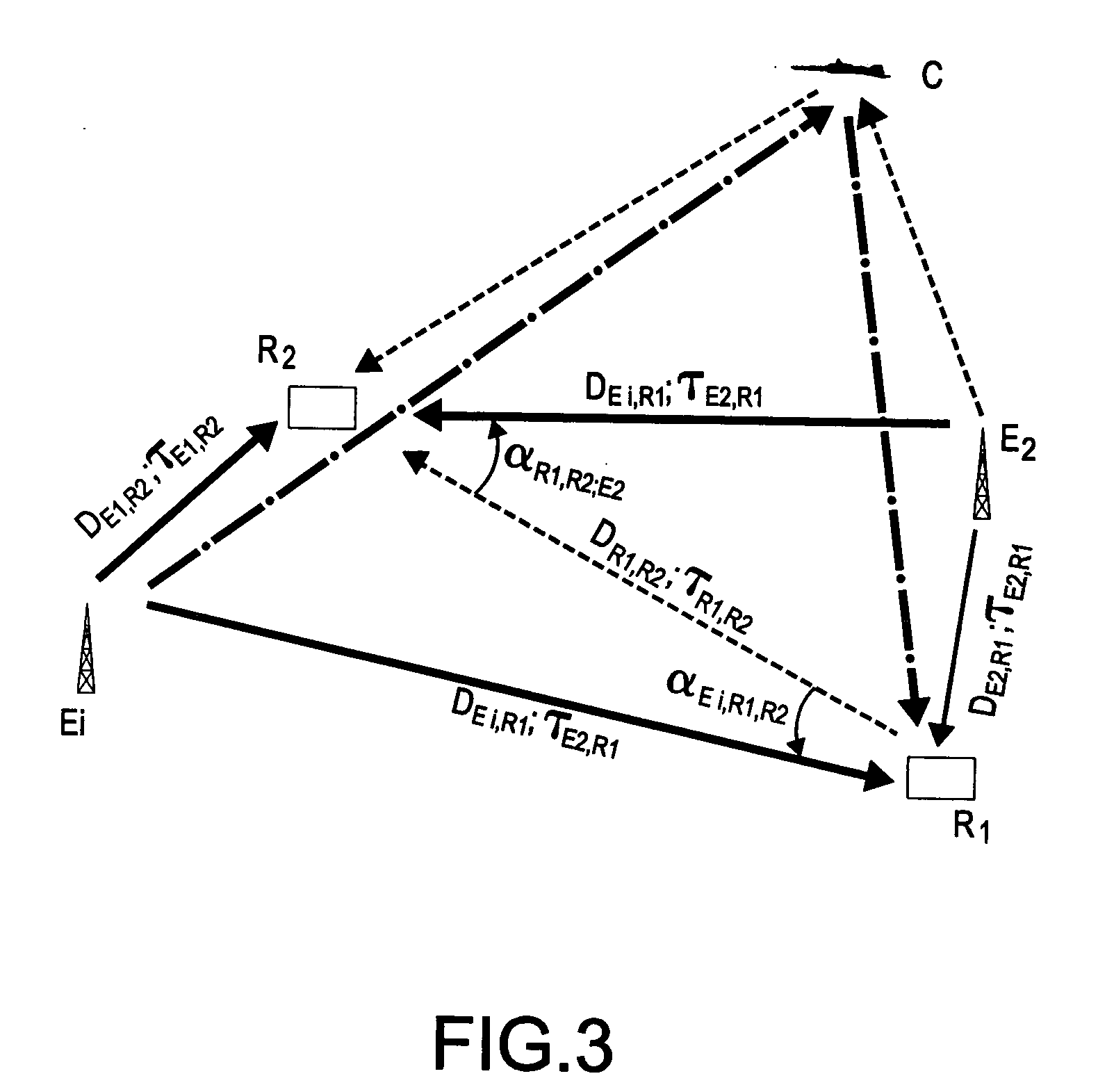
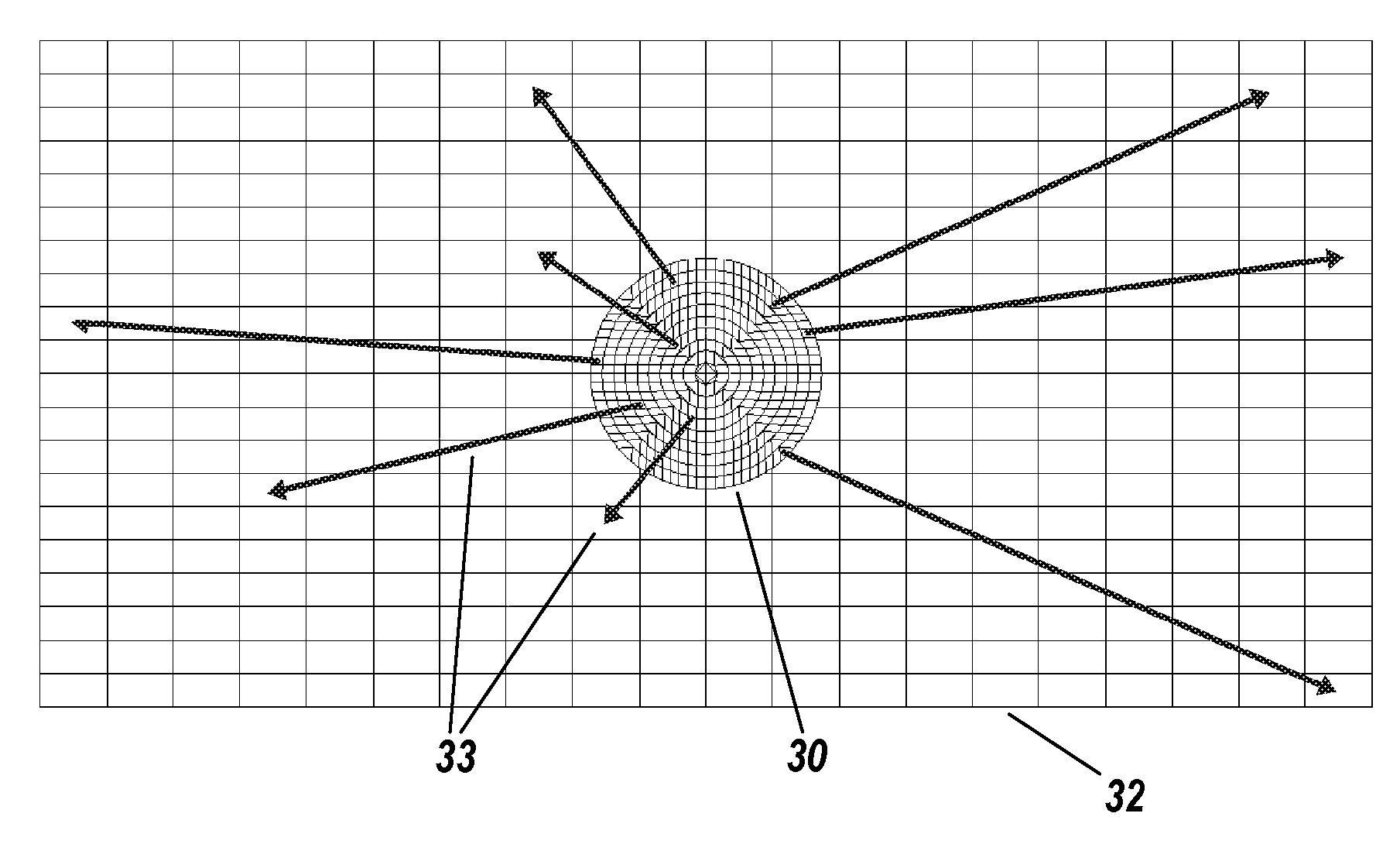
A method to detect and / or locate a mobile craft in a reception system making use of transmitters of opportunity, whose signal comprises elements enabling the synchronization of the receiver, comprises at least the following steps: a) detecting certain “discriminating” sequences of the payload signal; b) separating each transmission present on the carrier frequencies examined by the receiver or receivers by the space / time filtering of the signals in each carrier frequency; c) identifying the transmitters Ei corresponding to the signals received; d) determining the pulse response of the propagation channel for each transmitter Ei and for each detection made on this transmitter;) measuring the instant of arrival of the path reflected by the mobile craft and then its delay relative to the instant of transmission from the transmitter; h) deducing the position of the mobile craft at the intersection of the ellipsoids defined by the foci constituted by the transmitters Ei from which signals are received and the receiver or receivers Rj. The disclosed method can be applied to the detection of an aircraft.
Owner:THALES SA
Free-form lenses for rectangular illumination zones
A light source emits light into a solid angle exceeding pi steradians with a known intensity distribution. An illumination lens has a first surface that receives at least 90% of the light of the known intensity distribution and has a shape that transforms the known intensity distribution into an intermediate intensity distribution within the transparent material of the lens. A second surface receives the intermediate intensity distribution and is shaped to transform the intermediate intensity distribution into a final intensity distribution that produces a prescribed illumination distribution upon a rectangular target zone. At least one of the shapes of the first and second surfaces is non-rotationally symmetric and is approximated by a super-ellipsoid.
Owner:ANTHONY INC
Administration of therapeutic or diagnostic agents using interlabial pad
InactiveUS20020115976A1Loss of some therapeutic efficacyDiscomfortSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLeading edgeDiagnostic agent
A method is disclosed for administering an agent (for example delivering a drug or diagnostic agent) intravaginally or to the interlabial space by positioning an interlabial device, such as an absorbent pad, between the labia. The pad is retained between the labia for a sufficient period of time to deliver an active agent, or allow a reaction with a diagnostic agent. Alternatively, the pad is applied after medication is administered, for example intravaginally or labially or perilabially, to help reduce discomfort to the subject, or loss of medication. The active agent may be carried by the pad itself, or in an intravaginal extension of the pad, or separately in a suppository or other dosage form. In particular examples, the pad has a smaller minor portion superimposed on a larger major portion, and the smaller minor portion is inserted as a leading edge between the labia of the subject to facilitate interlabial insertion. In another example, the pad is placed interlabially after insertion of an agent (such as a medicated suppository) into the vagina, to inhibit loss of the medication from the vagina. The pad can have a variety of shapes, including major and minor portions that are portions of spheres or ellipsoids, or which are elongated and have cross-sections that are circular or ellipsoid, or pads which are folded.
Owner:PREPROGEN LLC
Optical system for imaging distortions in moving reflective sheets
InactiveUS7345698B2Control distortionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsEllipseMagnification
A method and apparatus for detecting and measuring the optical distortion in pieces of glass and other reflective sheets are disclosed. The method inspects the full length and width of large area glass sheets or multiple sheets comprising a load of glass and uses optical magnification of a reflected circular image of precise size. A plurality of circular images is projected onto the glass and reflect as ellipsoids representative of local surface contours. The major and minor axes of the reflected axis define the axis of greatest magnification and demagnification. Distortions in the glass surface are measured in lens power as localized magnification at the elliptical axis. The angle and magnitude of the minor and major axis of the reflected ellipsoids provide data to map the surface profile of the glass. The method measures distortion of random or periodic frequency and measures distortion in all axes.
Owner:LITESENTRY LLC
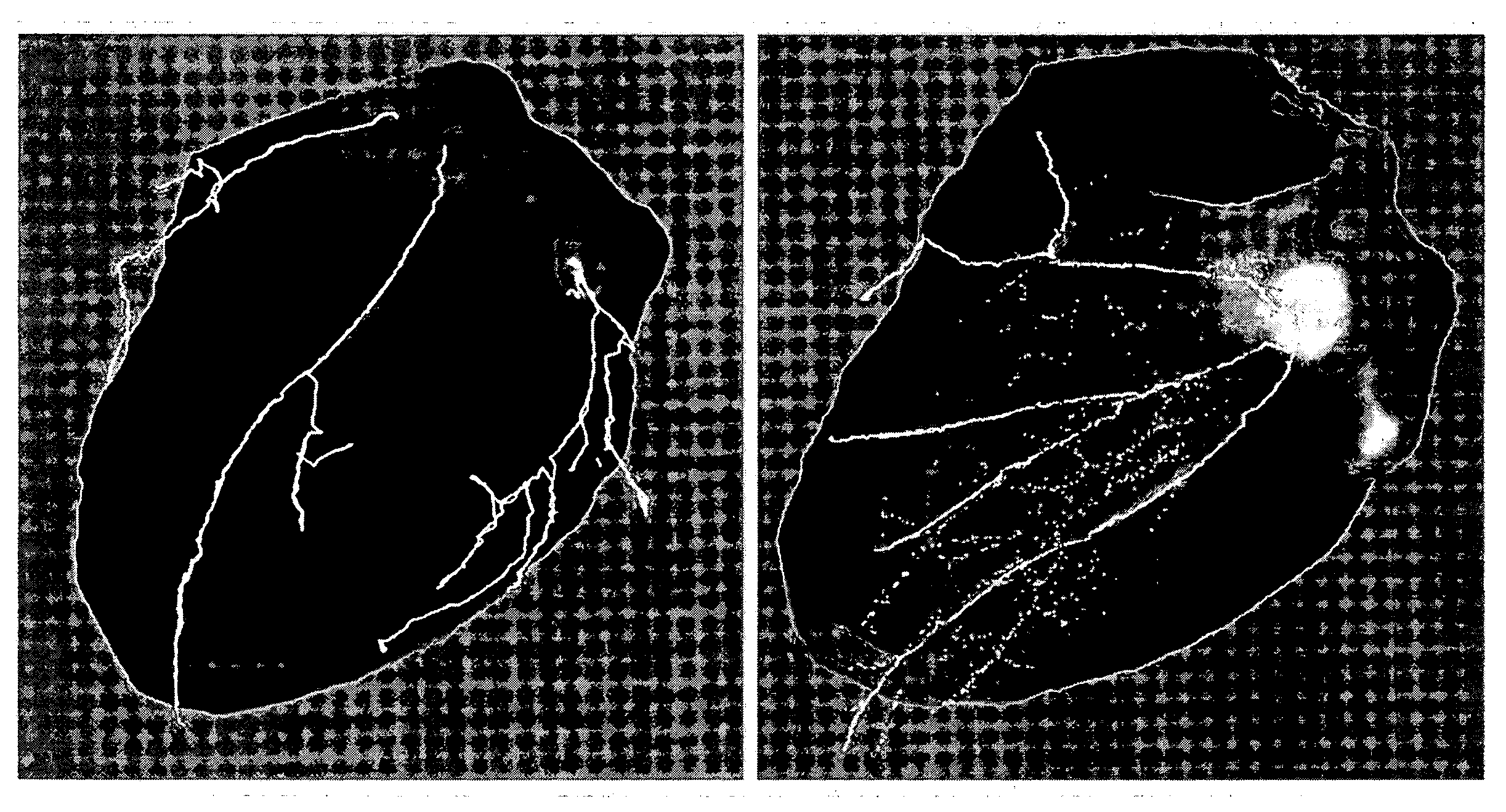
Automatic coronary isolation using a n-MIP ray casting technique
A novel method is presented for detecting coronary arteries as well as other peripheral vessels of the heart. After finding the location of the myocardium through a segmentation method, such as a graph theoretic segmentation method, the method models the heart with a biaxial ellipsoid. For each point of the ellipsoid, a collection of intensities are computed that are normal to the surface. This collection is then filtered to detect the cardiovascular structures. Ultimately, vessel centerline points are detected using a vessel tracking method, and linked together to form a complete coronary artery tree.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
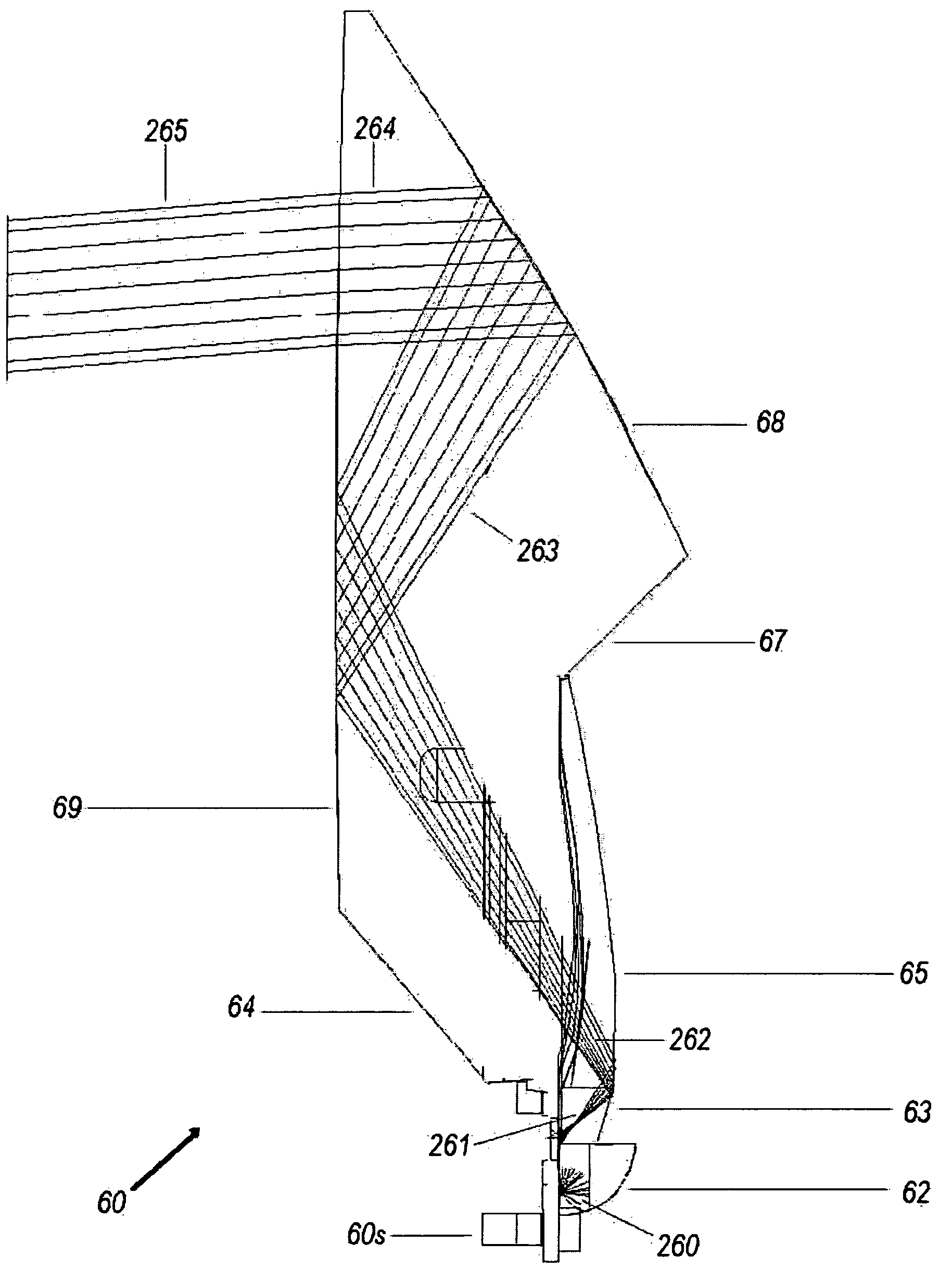
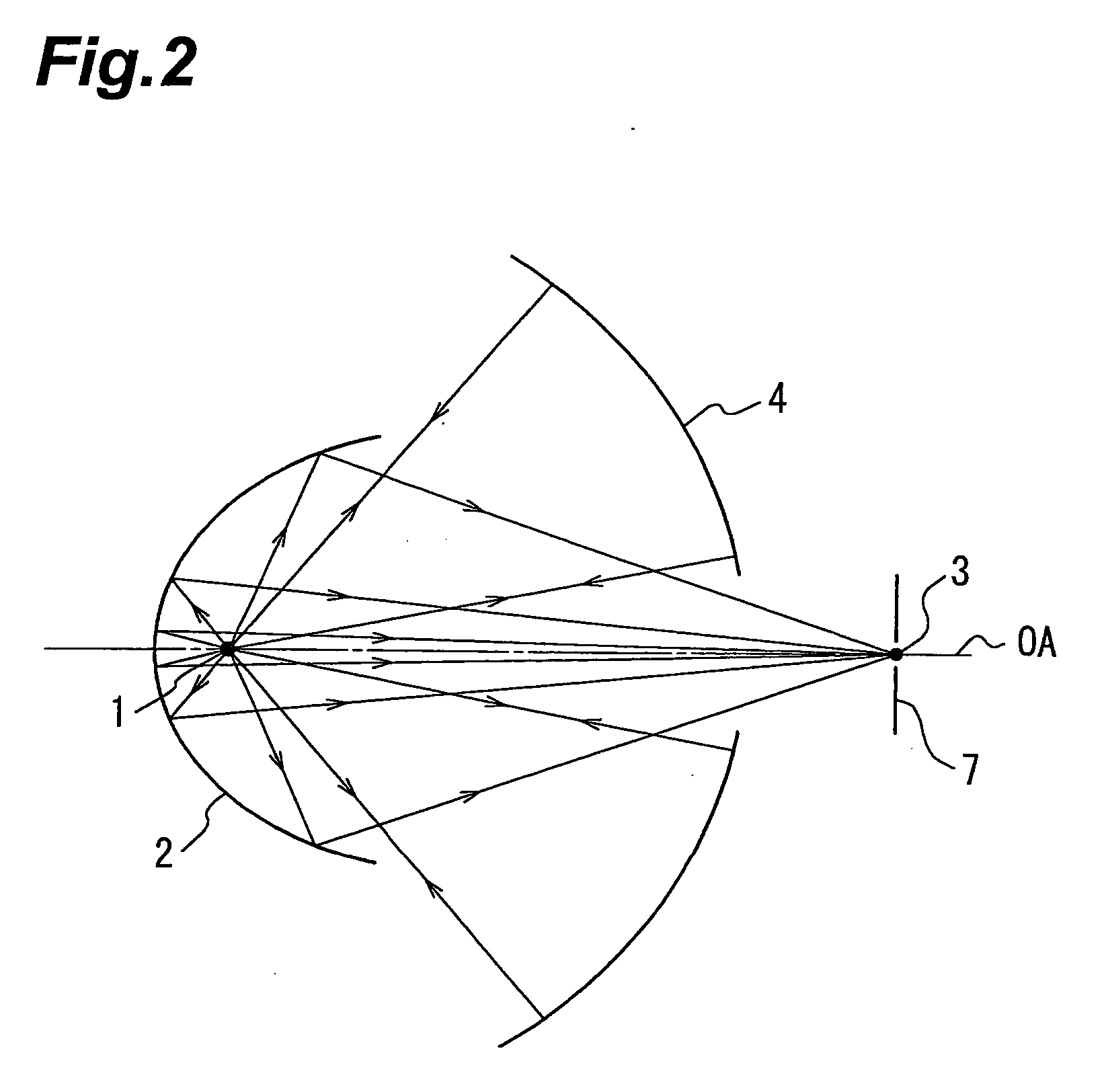
Collector optical system, light source unit, illumination optical apparatus, and exposure apparatus
ActiveUS20060120429A1Improve throughputHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsOptic system
A light source unit of EUV light is provided as a light source unit comprising a plasma light source for emitting EUV light, a collective mirror which has a reflecting surface of an ellipsoid of revolution and at a first focal point of which the plasma light source is located, and an auxiliary collective mirror which has a reflecting surface of a spherical surface and a spherical center of which is located as displaced from a position of the plasma light source.
Owner:NIKON CORP
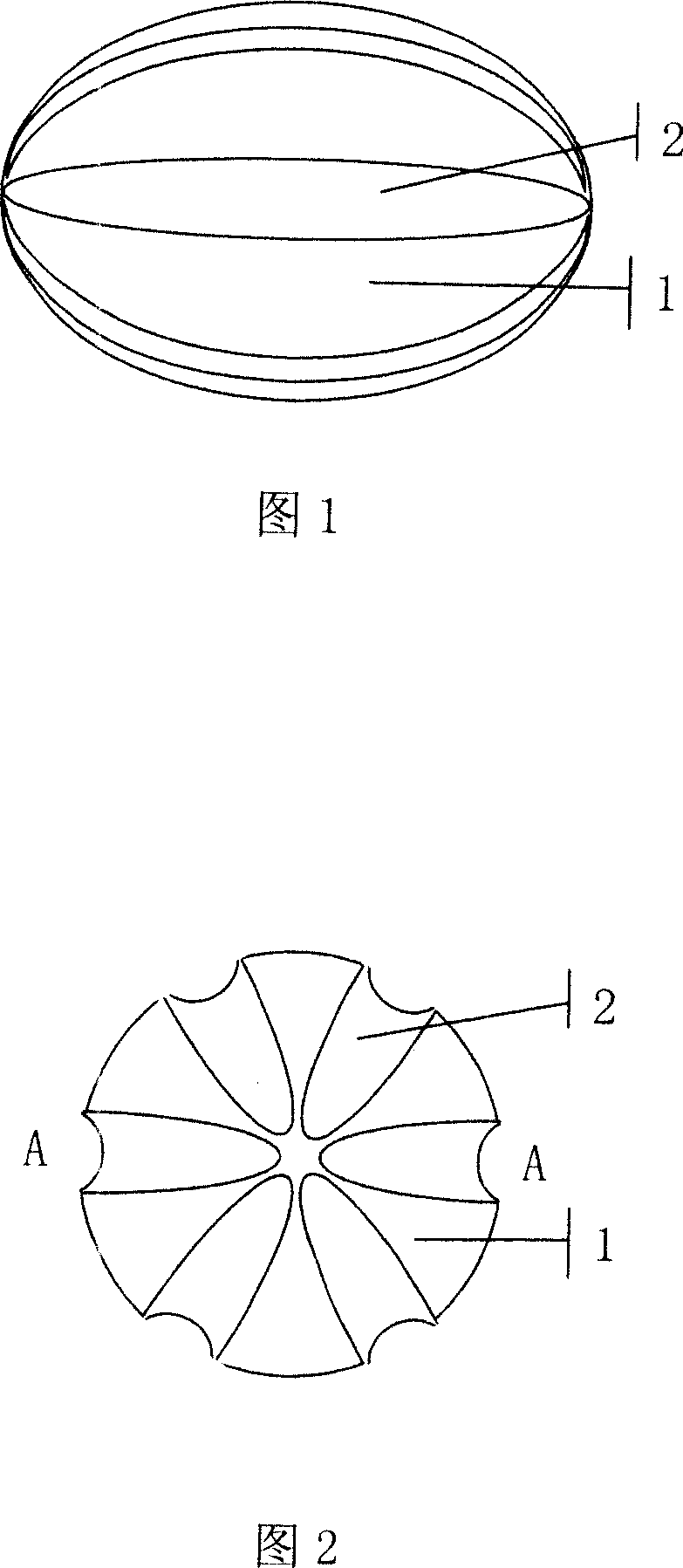
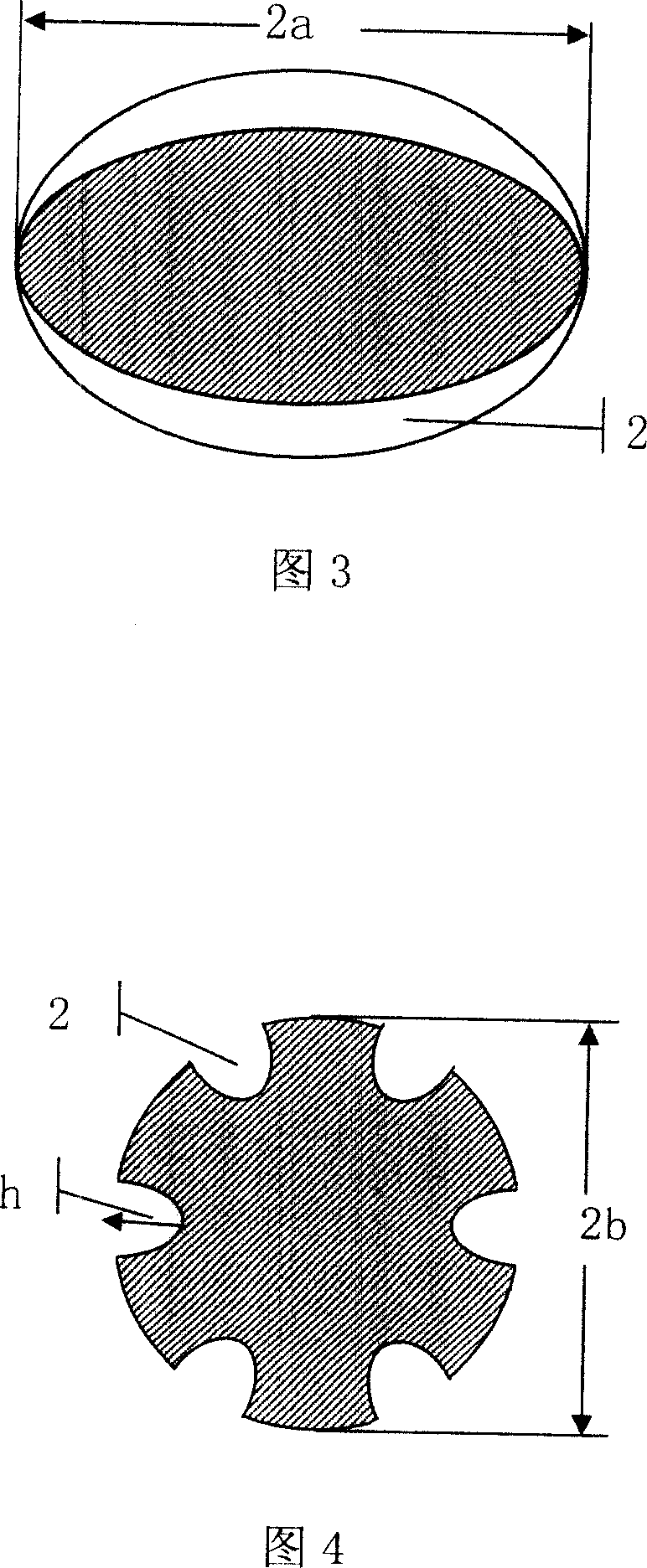
Carrier having a special feature, catalyzer and producing method thereof
ActiveCN101134173AHigh porosityHigh strengthPhysical/chemical process catalystsOil processingSorbent
The present invention is carrier in special shape, catalyst and their preparation process. The carrier is one ellipsoid with the major axis-to-minor axis ratio a / b of 1.05-2.5 and one or several grooves in the major axis direction. The carrier is prepared through pressing the material containing oxide hydrate in a mold to form, and heating the formed matter to convert the oxide hydrate into oxide. The carrier may be applied as adsorbent, catalyst carrier, reactor stuffing, etc. The catalyst prepared with the carrier has relatively great outer surface area and excellent mass transferring process, and may be applied widely in heavy oil processing reaction, etc, especially as hydrogenation activity protectant.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Calibration of 3d field sensors
ActiveCN101292131ATesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesThree-component magnetometersPhysicsEllipsoid
An apparatus-based method is disclosed for calibration of a 3D field sensor. The method comprises accessing a plurality of samples, where the samples are from the 3D field sensor. Each sample represents a magnitude and an orientation of a three-dimensional field sensed by the 3D field sensor. Using the plurality of samples, a plurality of parameters is determined of an ellipsoid. The determination of the plurality of parameters is performed so that the ellipsoid fits the plurality of samples. A transformation is determined that transforms the ellipsoid into a sphere. The transformation is applied to a sample to create a transformed sample. Apparatus and signal bearing media are also disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Super-close optimized collision-avoidance proximity method for failure satellite
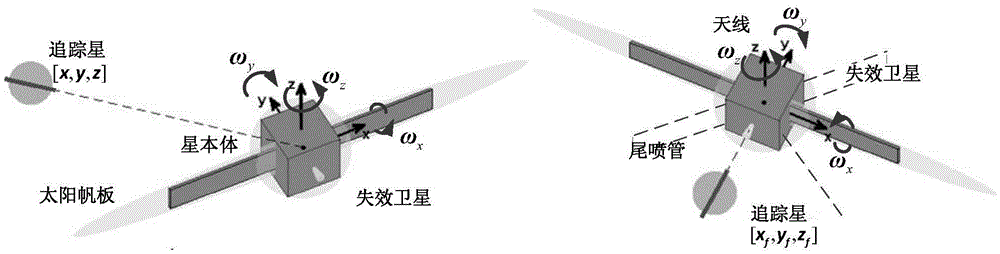
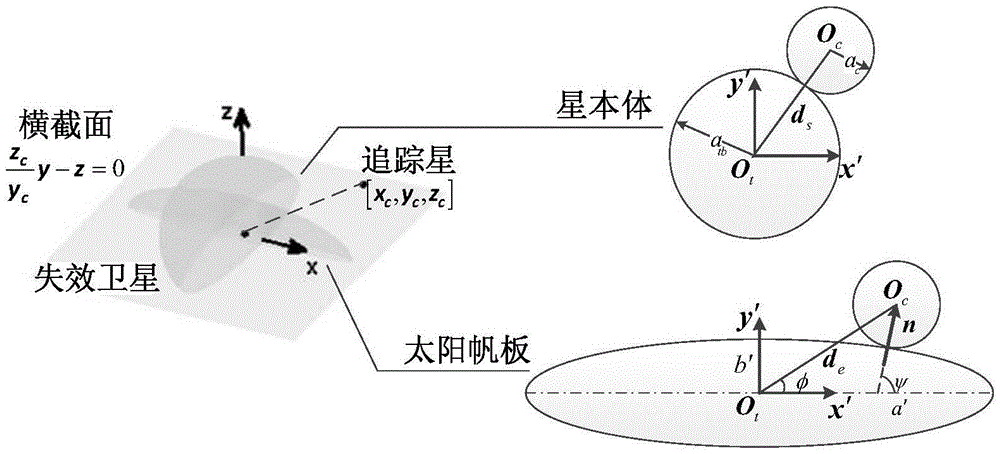
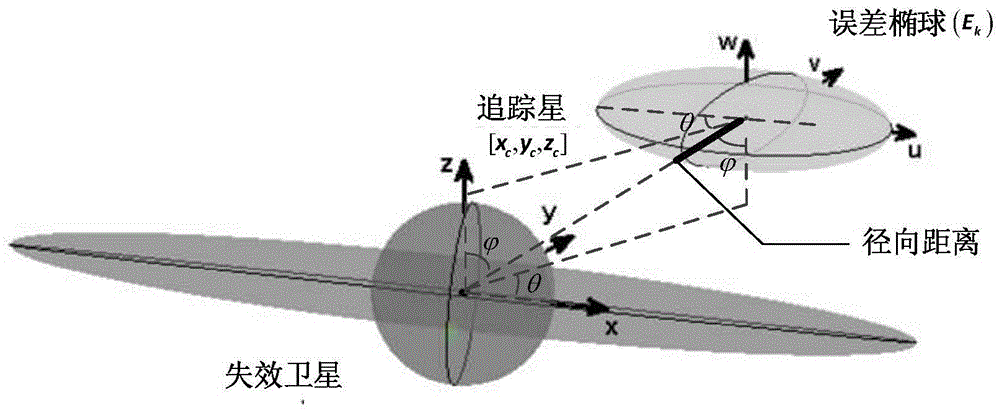
ActiveCN105549606AMeet space constraintsEnsuring safety and collision-free mission requirementsAttitude controlNatural satelliteClosed loop feedback
The invention relates to a super-close optimized collision-avoidance proximity method for a failure satellite, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft encounter. An object, namely the failure satellite, is designed into an envelope model in the sphere and ellipsoid combined form to simplify configuration of the object; posture rolling of the object is considered, a relative dynamic model of the object and a tracked star as well as constraints of the path of the tracked star are derived in the dynamic object system; positional nondeterminacy caused by navigation and measurement errors is considered, and the flight forbidden area of the tracked start is further broadened by combining the collision possibility problem; and a safe collision avoidance path is planned on the basis of the Gauss pseudospectral method, and closed-loop feedback control is carried out. According to the invention, spatial limitation in super-close proximity are considered, and requirements for a safe collision free task can be met; and the posture coupling feature of a close proximity spacecraft is emphasized, and whether the distance between the aircrafts satisfies the constraints can be directly determined.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Vehicular illumination lamp
InactiveUS7178960B2Utilization factor of bundles of raysIncrease profitVehicle headlampsLighting support devicesDistribution controlLight emitting device
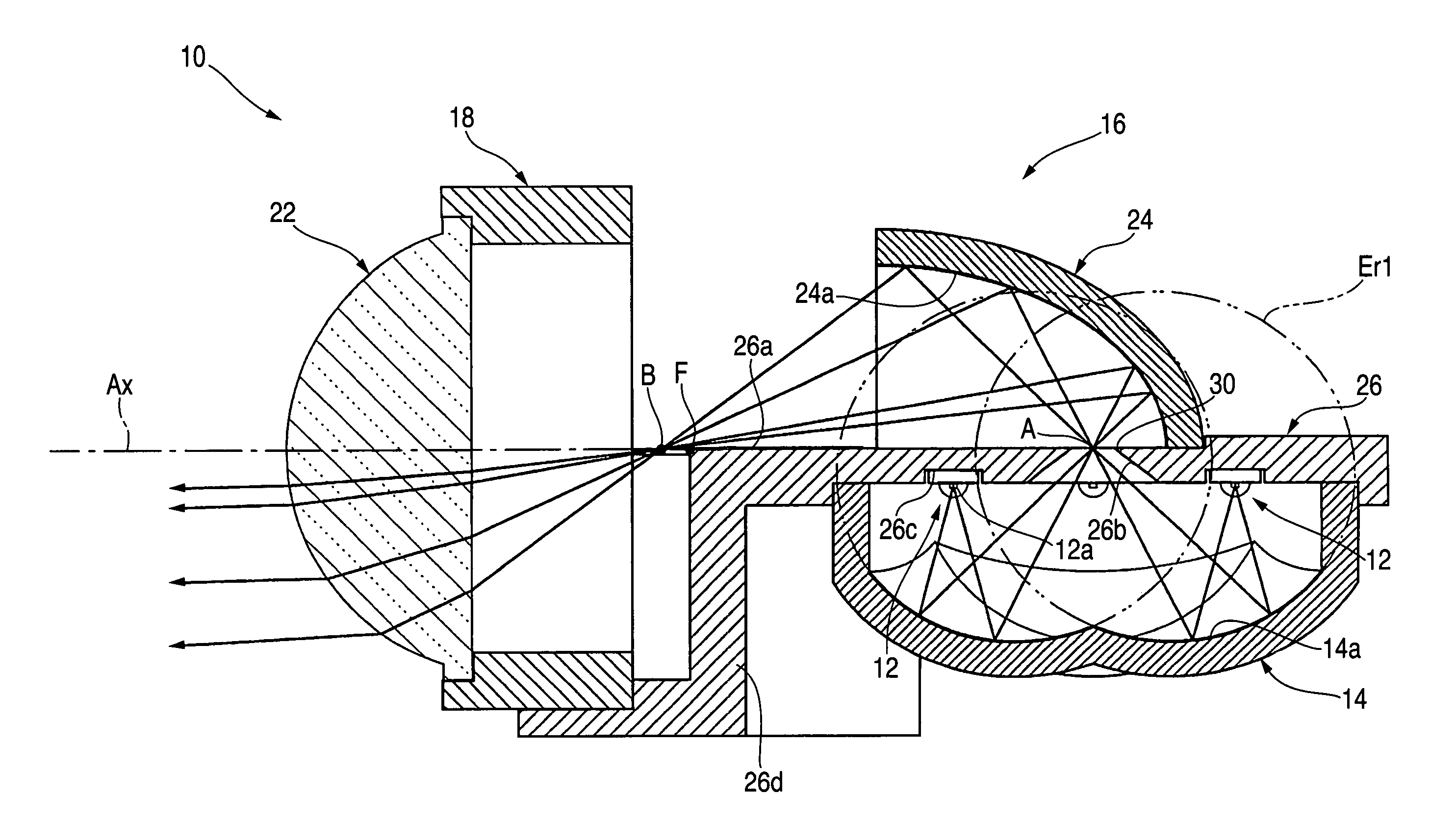
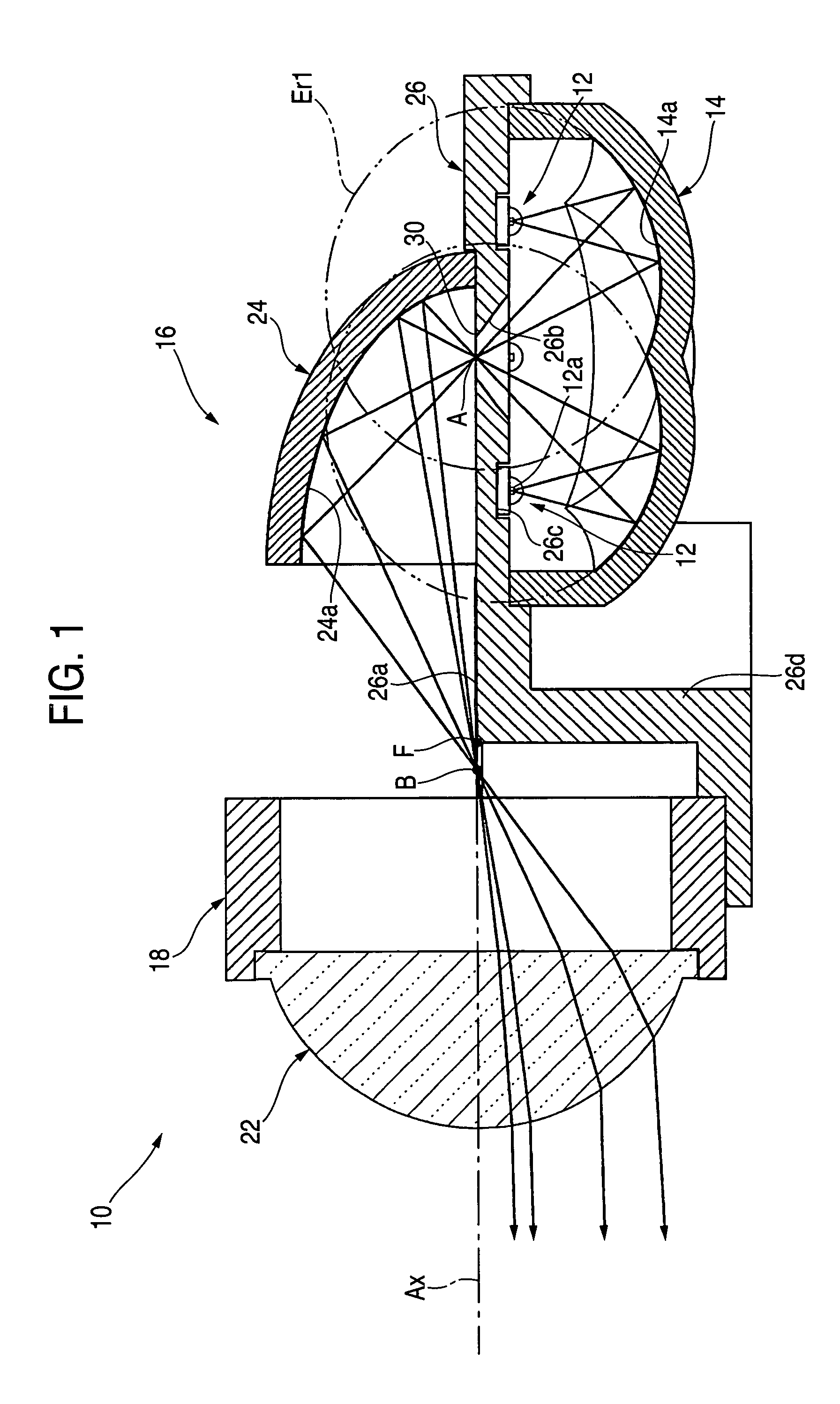
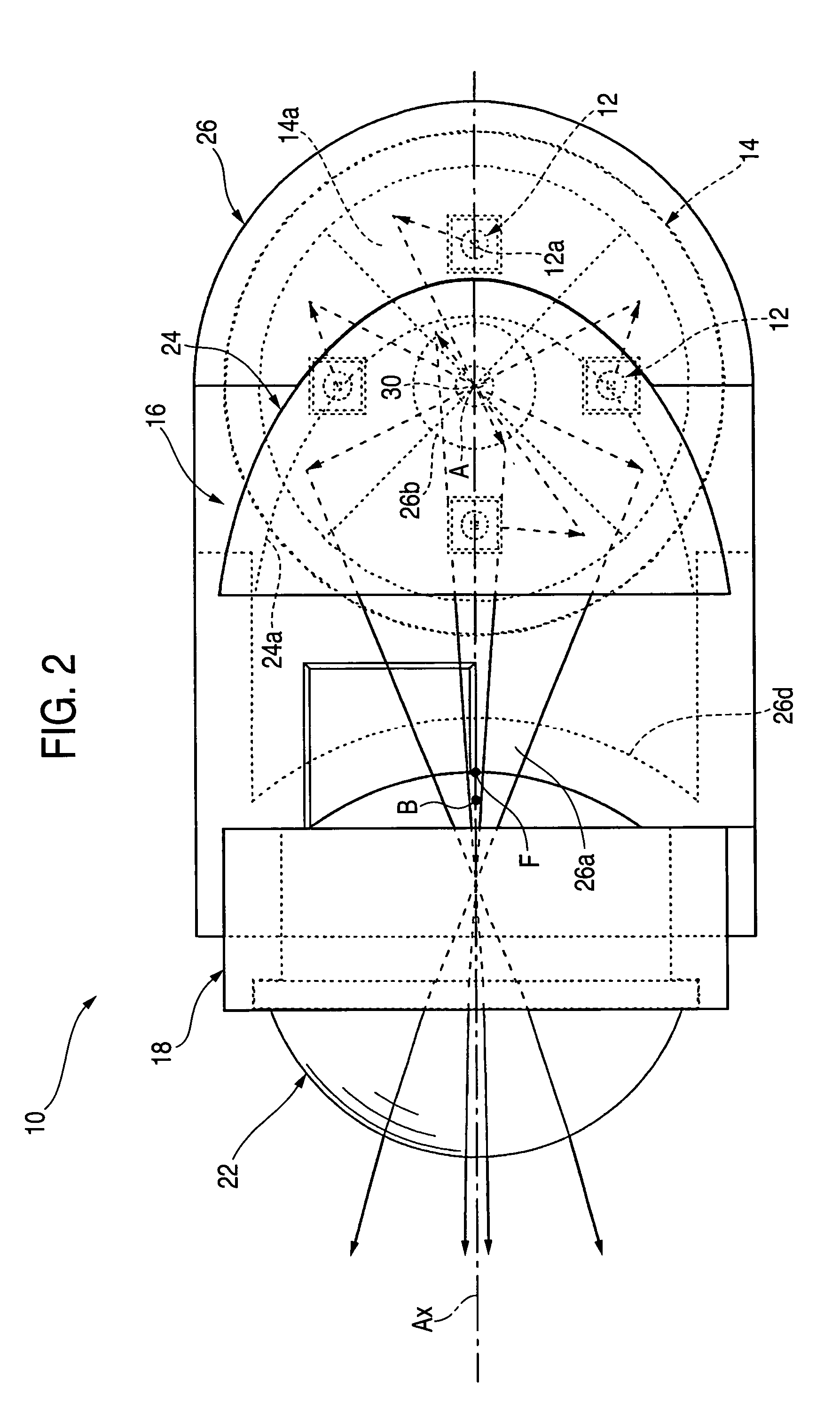
A vehicular illumination lamp, including four light emitting devices 12 which are disposed in such a manner as to spread about a predetermined point A as a center, a reflector 14 having four reflecting surfaces 14a that are made up of ellipsoids of revolution Er1, which take light emitting centers of the respective light emitting devices 12 and the predetermined point A as primary focal points and secondary focal points thereof, respectively, and a light distribution control member 16, which controls the light distribution of light from the respective light emitting devices 12 that is reflected on the reflector 14 so as to cause the light so controlled to traverse to a front of the lamp, whereby light emitted from the respective light emitting devices 12 is made first to be reflected on the respective reflecting surfaces 14a and is then caused to converge on the predetermined point A.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
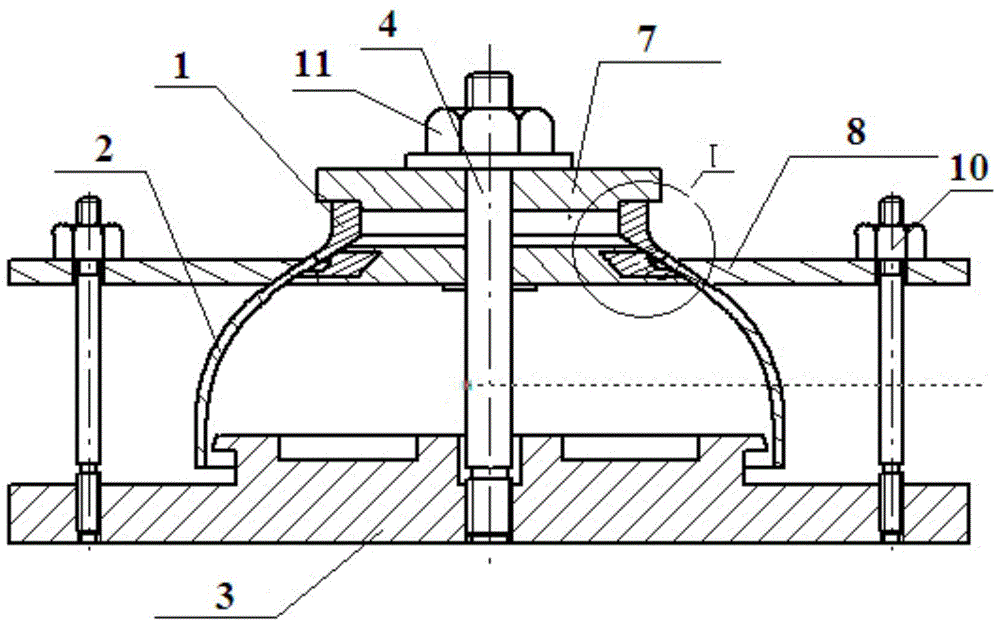
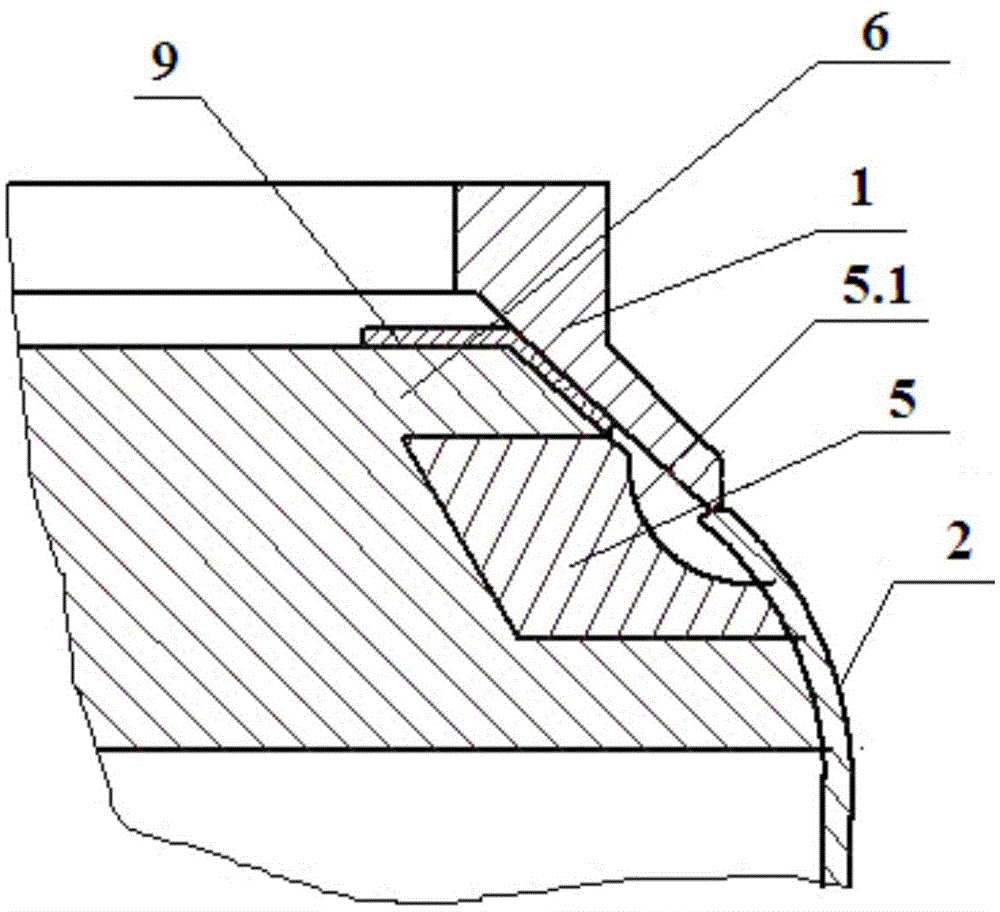
Welding process for ensuring smooth transition and molding of ellipsoidal circular seam and auxiliary welding clamp thereof
InactiveCN104475934AGuaranteed surface shapingControl welding deformation directionWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusCombustion chamberCopper
The invention discloses a welding process for ensuring smooth transmission and molding of an ellipsoidal circular seam. The welding process comprises the following steps: 1) pre-setting a welding groove structure; 2) assembling a joint and an ellipsoid to an auxiliary welding clamp as follows: butting the ellipsoid with a to-be-welded end surface of the joint, adhering the ellipsoid with the lower part of a positioning block fixed on a core rod by virtue of an ellipsoidal pressure plate, adhering the joint with the upper part of the positioning block by virtue of a joint pressure plate, and ensuring a circular seam to-be-welded part of the ellipsoid and the joint to be corresponding to an arc-shaped groove on a ring-shaped copper pad in the middle of the positioning block; 3) respectively performing positioned welding, non-wired backing welding, wired cosmetic welding, non-wired re-melting welding; and 4) slowly cooling and performing annealing thermal treatment. The invention further discloses an auxiliary welding clamp designed for realizing the method. By pre-setting the welding groove structure and the auxiliary welding clamp, dislocation caused by welding shrinkage of the ellipsoidal surface can be balanced out reversely, and the inner surface of the welding seam can be ensured to be molded very well.
Owner:湖北三江航天江北机械工程有限公司
Hot rolled steel sheet having excellent punching workability and fatigue properties, hot dip galvanized steel sheet, and method for producing the same
ActiveCN102333899ALess end face damageExcellent fatigue propertiesFurnace typesMetal rolling arrangementsCarbideBrittle fracture
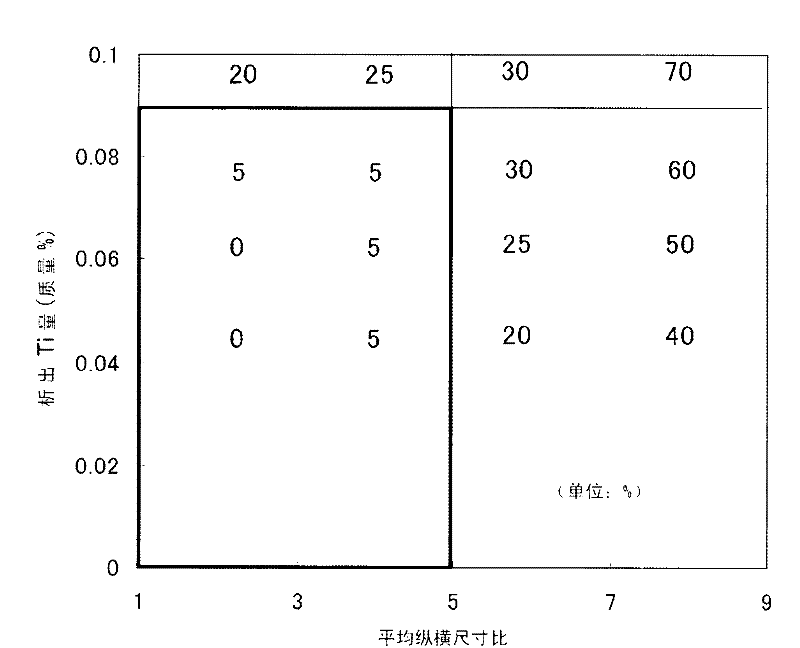
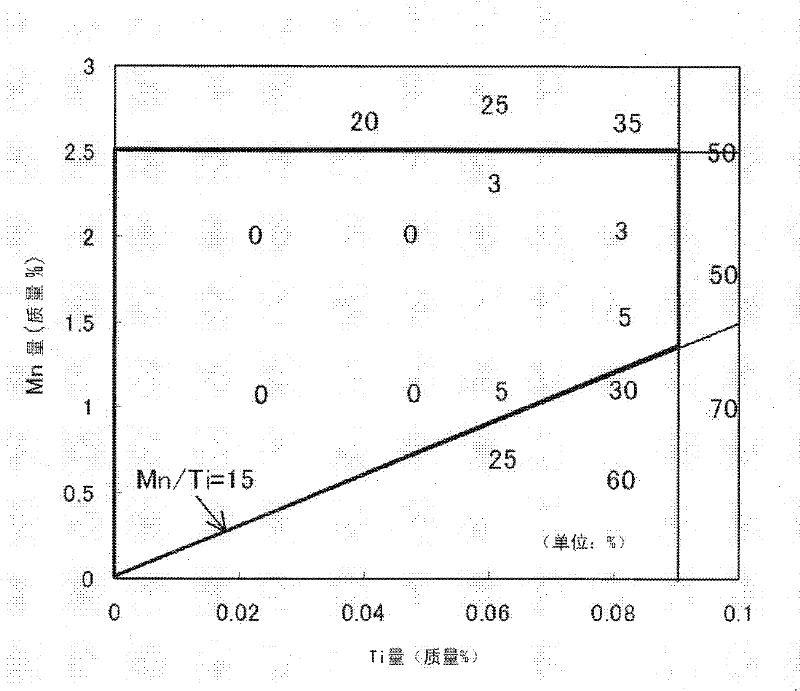
Provided is a hot rolled steel sheet comprising, by mass%, 0.025 to 0.15% of C, 0.01 to 1.0% or less of Si, 1.0 to 2.5% of Mn, 0.02% or less of P, 0.005% or less of S, 0.5% or less of Al, 0.04 to 0.10% of Ti, and 0.007% or less of N, as well as Fe and inevitable impurities as the balance, wherein the Mn / Ti ratio is 15 or greater; Nb is not added; the ferrite volume percentage is 30% or greater and the balance comprises one of or both pearlite and bainite; the average aspect ratio of the crystal grain corresponding ellipsoid is 5 or less; the average distribution density on the ferrite grain boundary surface of Ti carbide having a grain size of 20 nm or greater is 10 grains / [mu]m or less; the brittle fracture rate of surface fractured by punching is less than 20%; and the maximum tensile strength is 590 MPa or greater.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Free-Form Lenses for Rectangular Illumination Zones
ActiveUS20090040769A1Improve efficiencyMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceFree formComputational physics
A light source emits light into a solid angle exceeding pi steradians with a known intensity distribution. An illumination lens has a first surface that receives at least 90% of the light of the known intensity distribution and has a shape that transforms the known intensity distribution into an intermediate intensity distribution within the transparent material of the lens. A second surface receives the intermediate intensity distribution and is shaped to transform the intermediate intensity distribution into a final intensity distribution that produces a prescribed illumination distribution upon a rectangular target zone. At least one of the shapes of the first and second surfaces is non-rotationally symmetric and is approximated by a super-ellipsoid.
Owner:ANTHONY INC
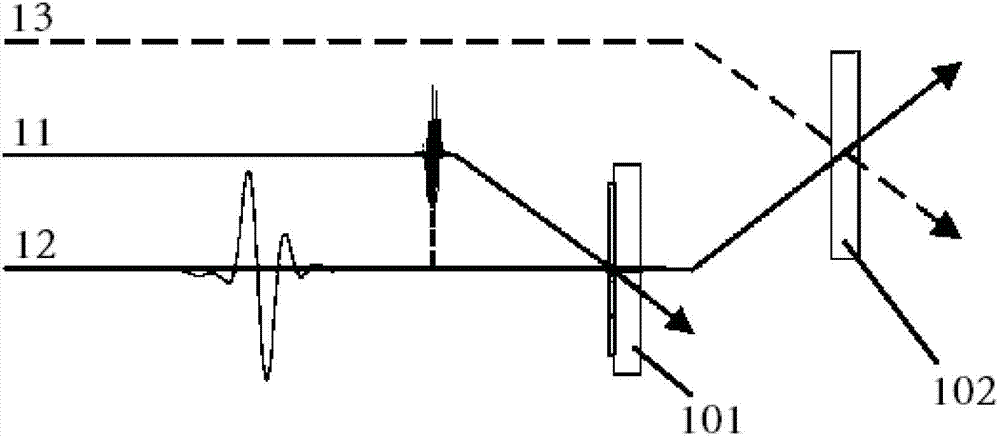
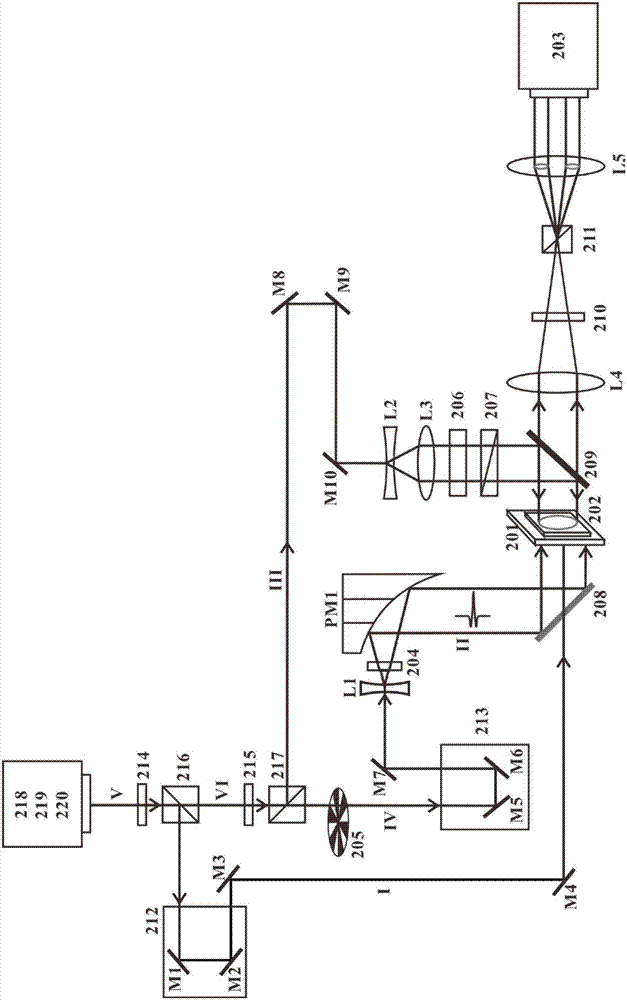
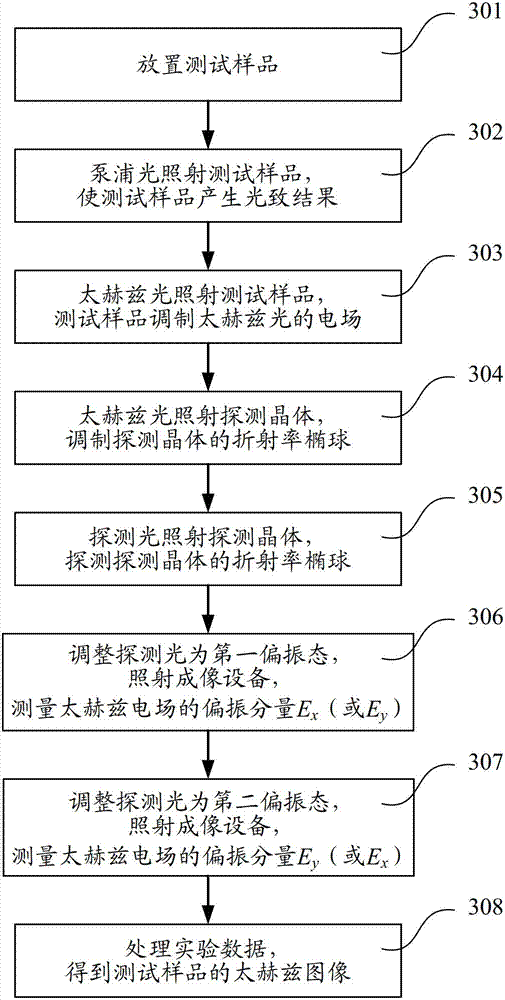
Terahertz time-space resolution imaging system, imaging method and application thereof
The invention relates to a terahertz time-space resolution imaging system. The system comprises a sample placing frame, a detection crystal, a pump light generator, a terahertz light generator, a detection light generator and an imaging device, wherein the detection crystal is located at one side of an exit surface of the sample placing frame; the pump light generator is used for generating a pump light to illuminate a test sample; the terahertz light generator is used for generating a terahertz light to illuminate the test sample, illuminating the detection crystal after acquiring information of the test sample and modulating an index ellipsoid of the detection crystal; the detection light generator is used for generating a detection light to illuminate the detection crystal, detecting the index ellipsoid of the detection crystal and indirectly acquiring the information of the test sample; and the imaging device is located into a light path after the detection light passes through the detection crystal and is used for collecting a terahertz image of the test sample. According to the terahertz time-space resolution imaging system, a terahertz focal plane imaging technique is introduced into a terahertz time resolution spectral measurement system, the time-space resolution imaging measurement on a luminescent property of the test sample is realized, the four-dimensional spectral information is acquired, and the comprehensive and accurate observation on a time-space evolution process of the luminescent property of the test sample is realized.
Owner:BEIJING YUANDA HENGTONG TECH DEV CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com