Patents
Literature
221 results about "Dielectric lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
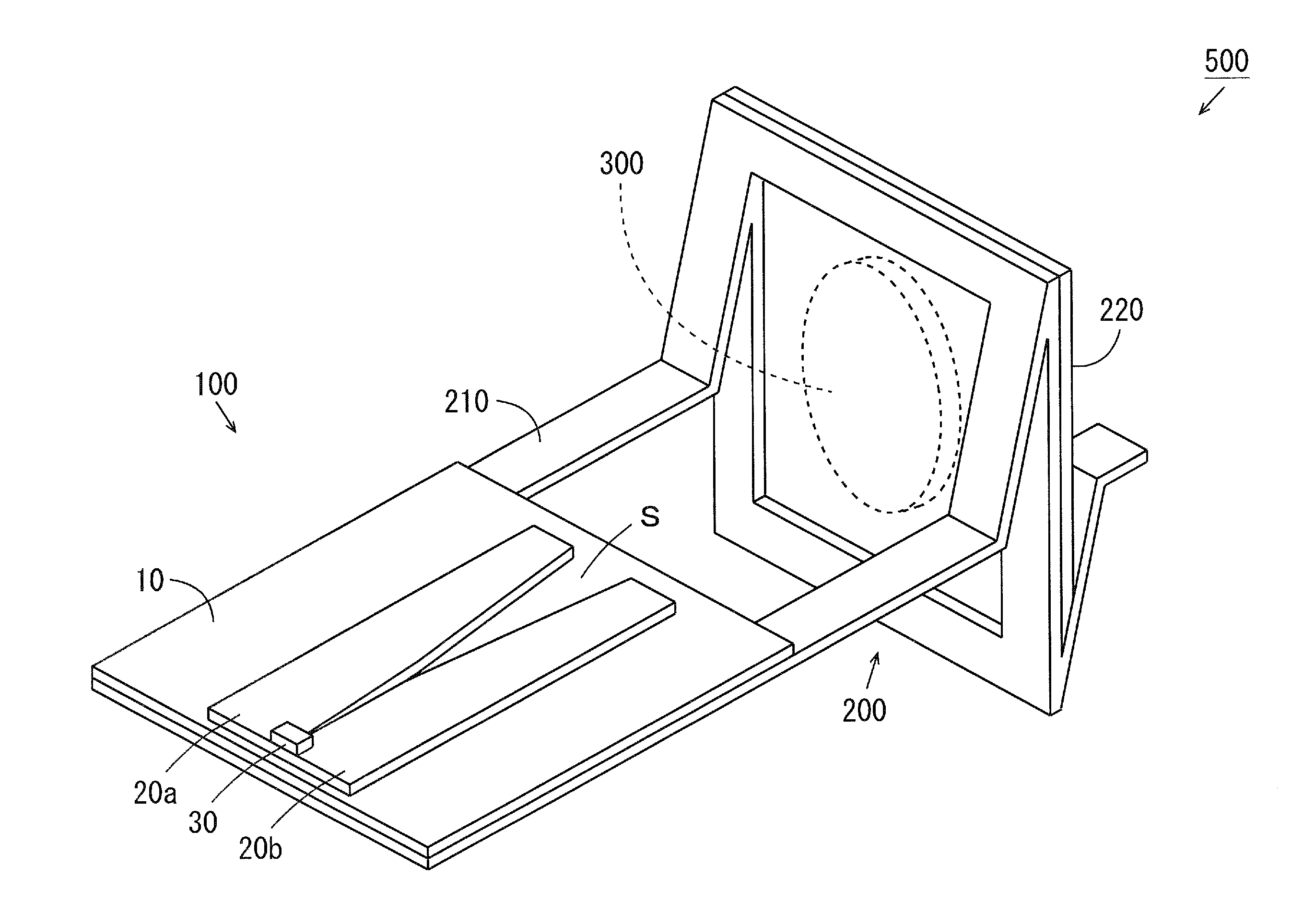
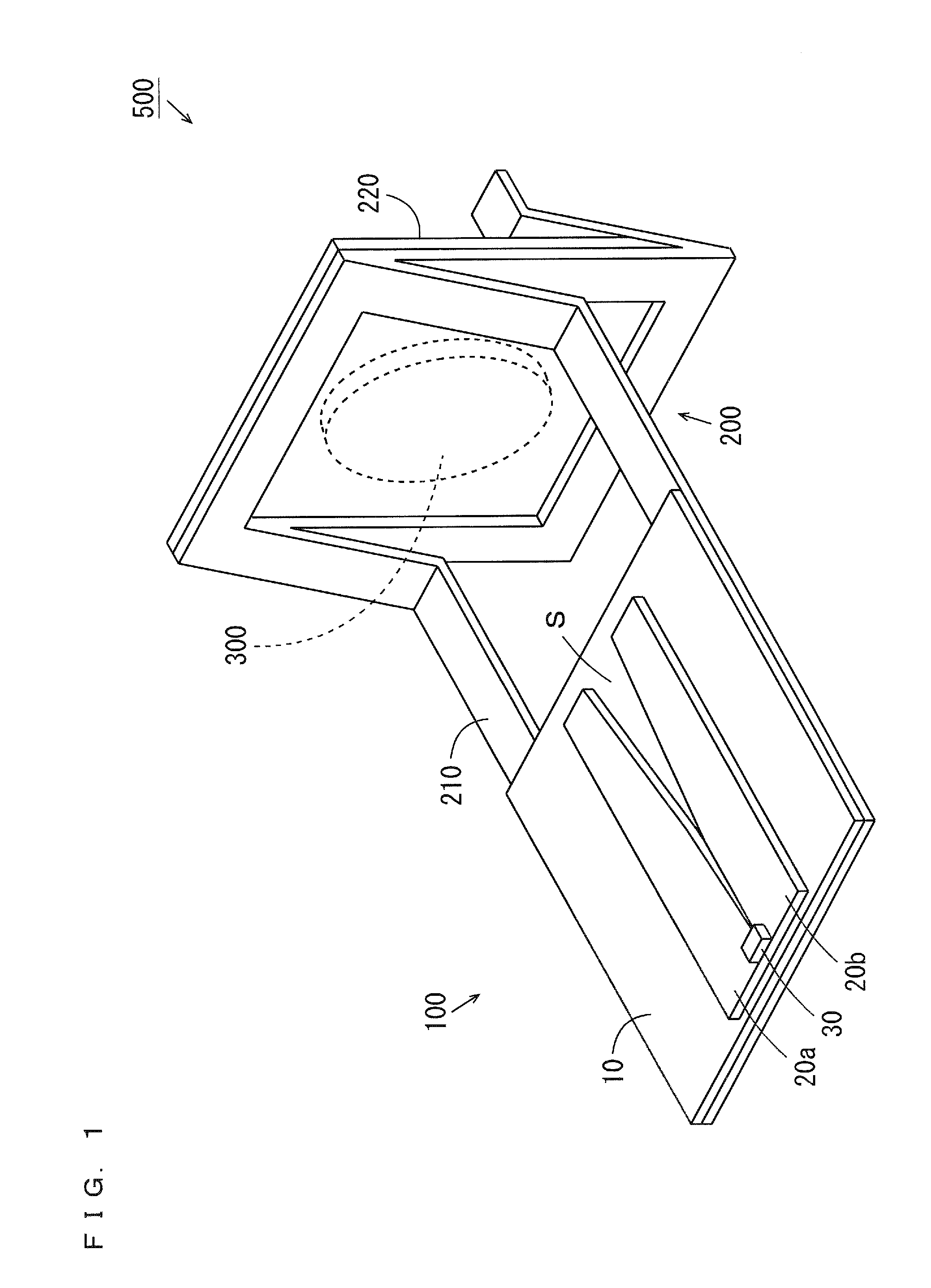
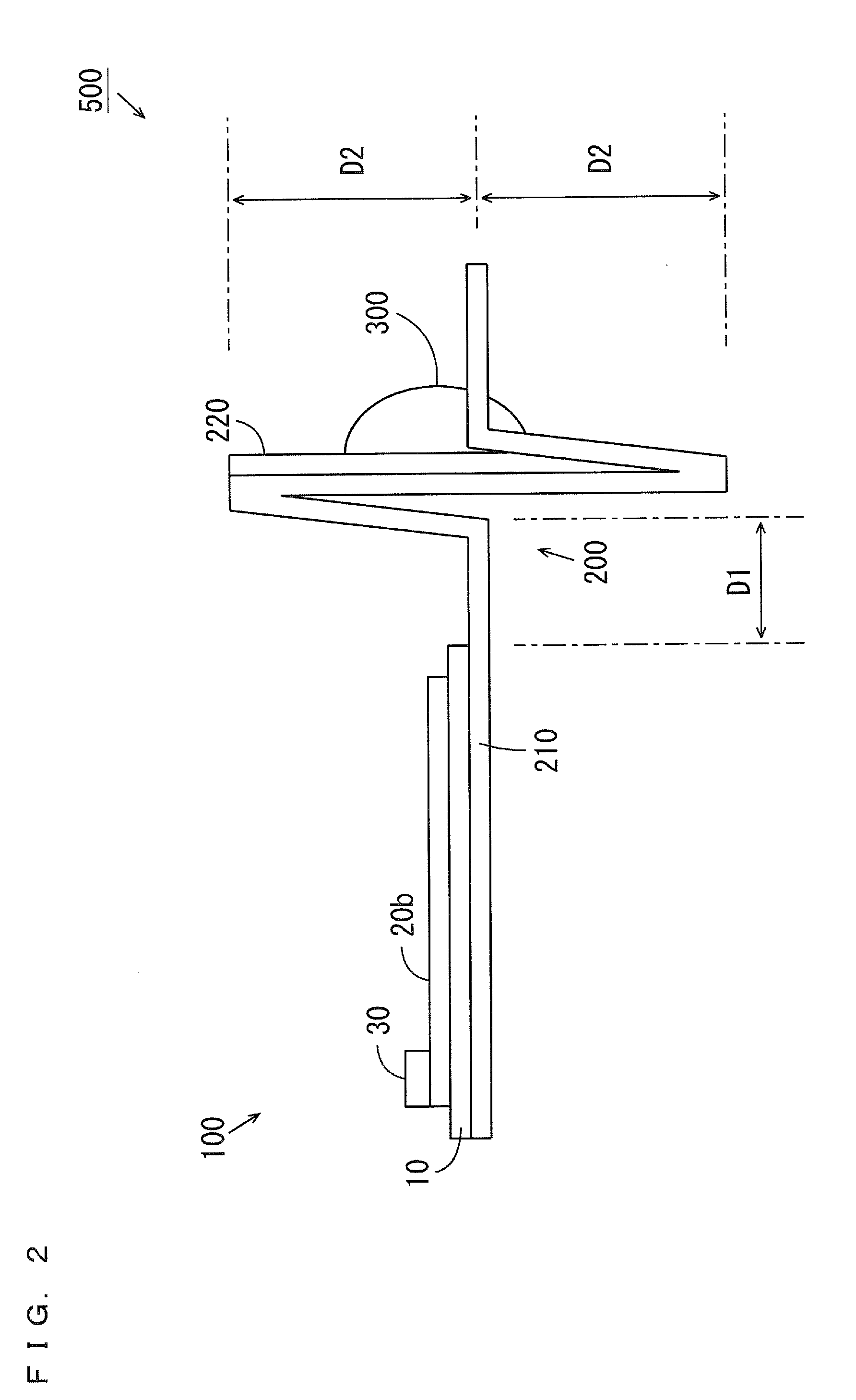
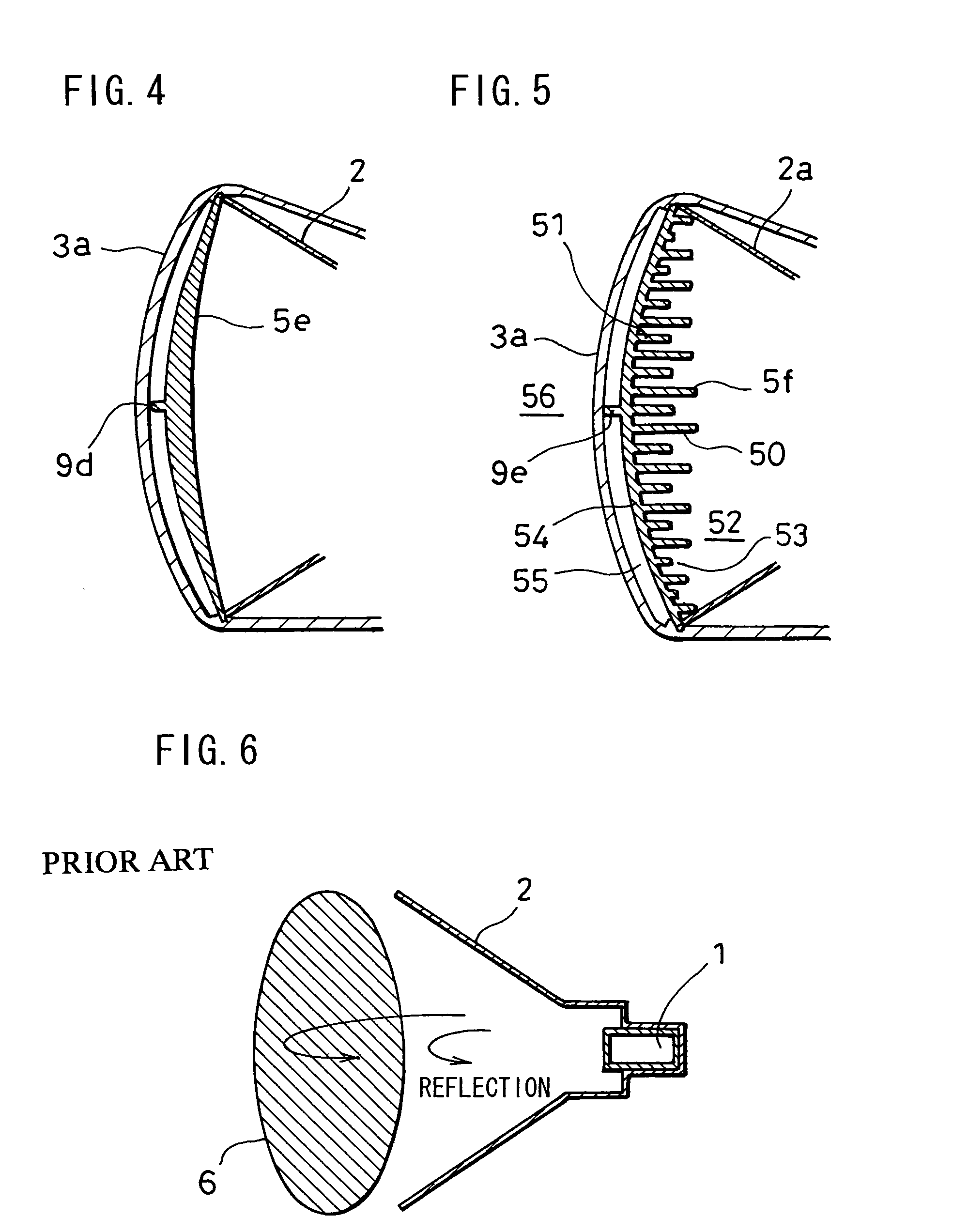
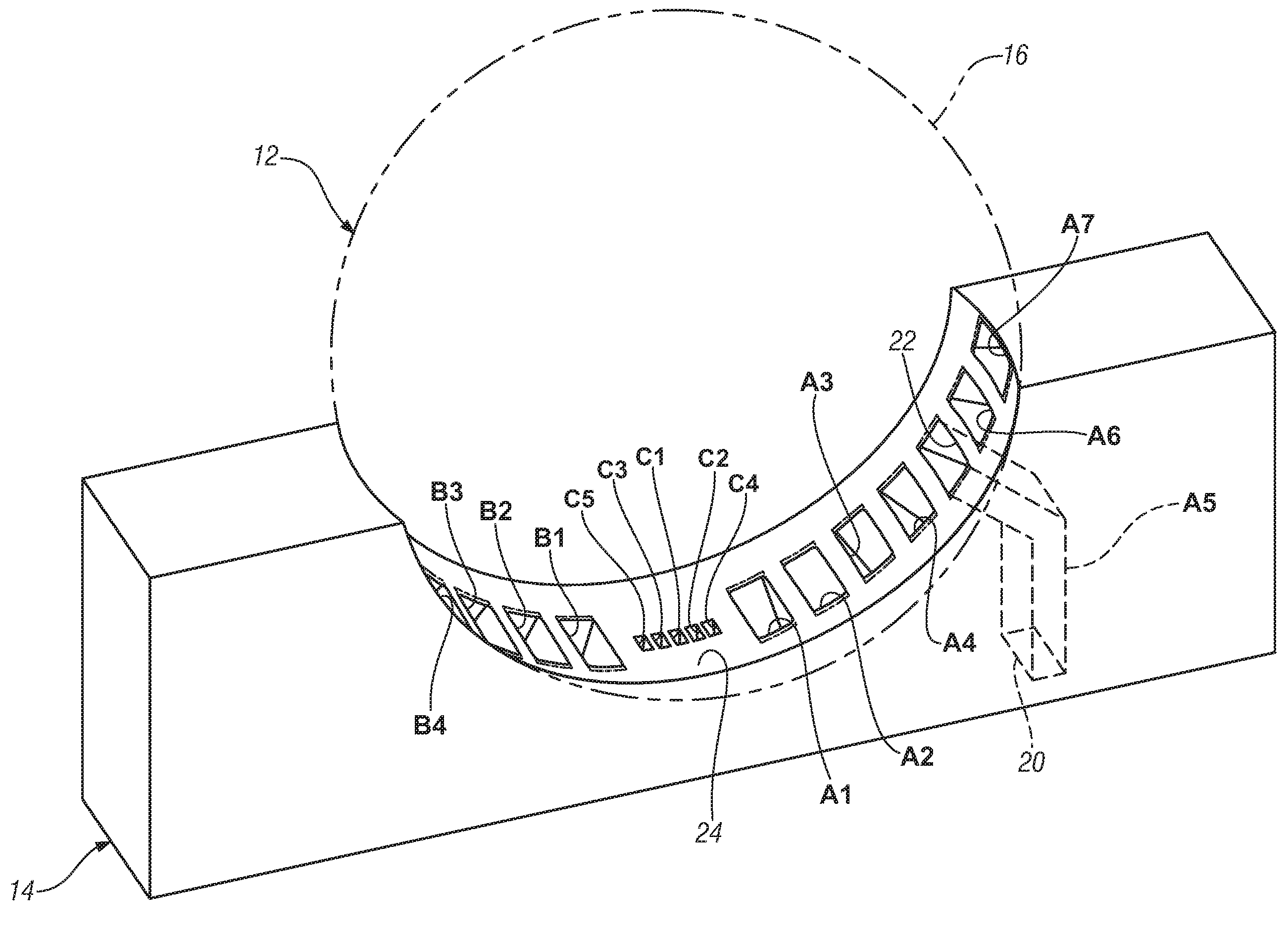
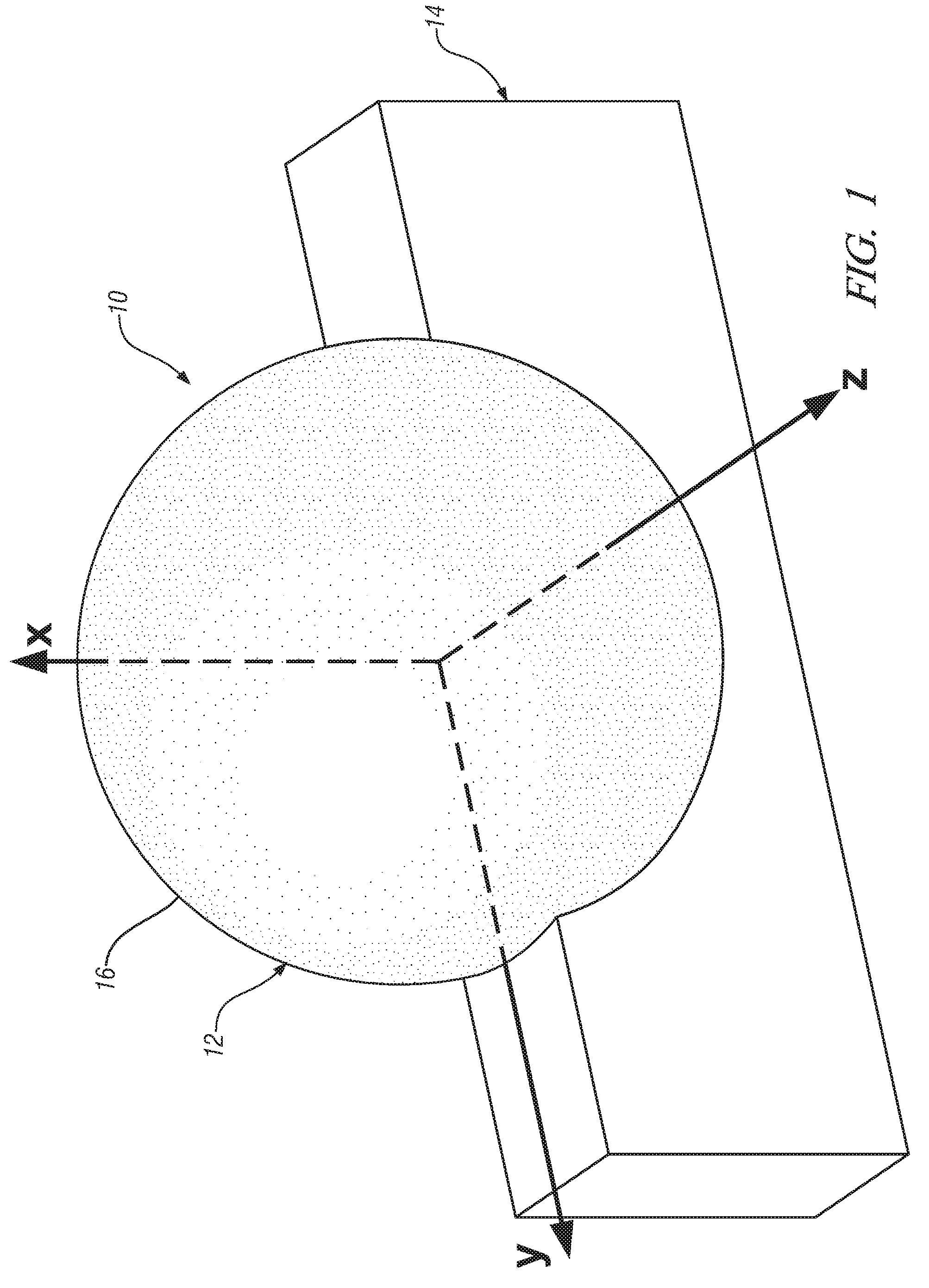
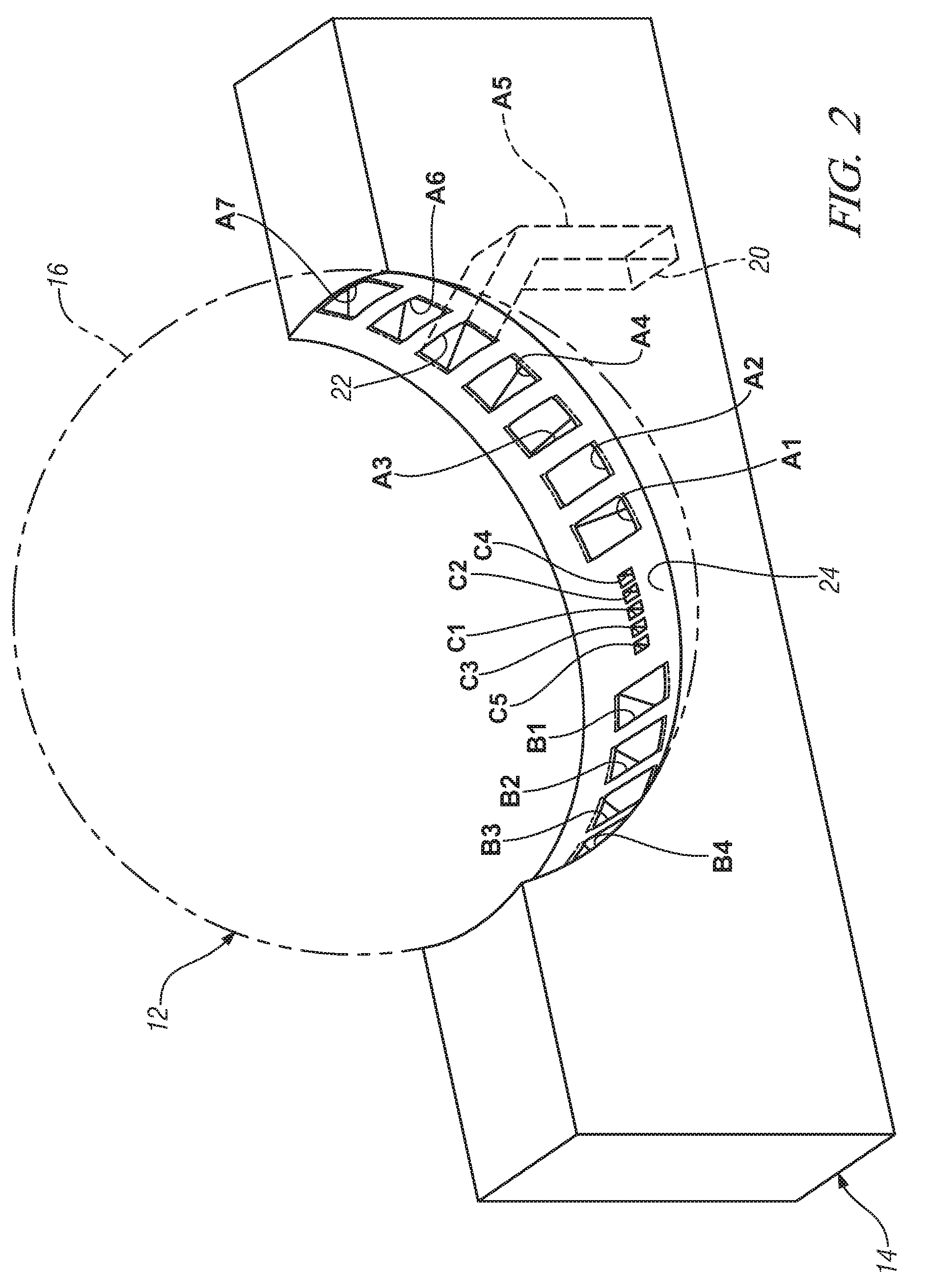
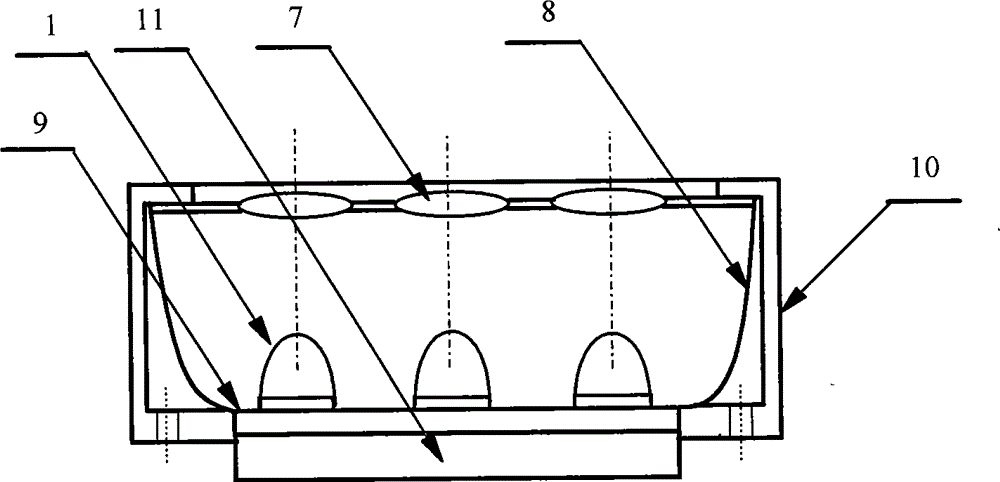
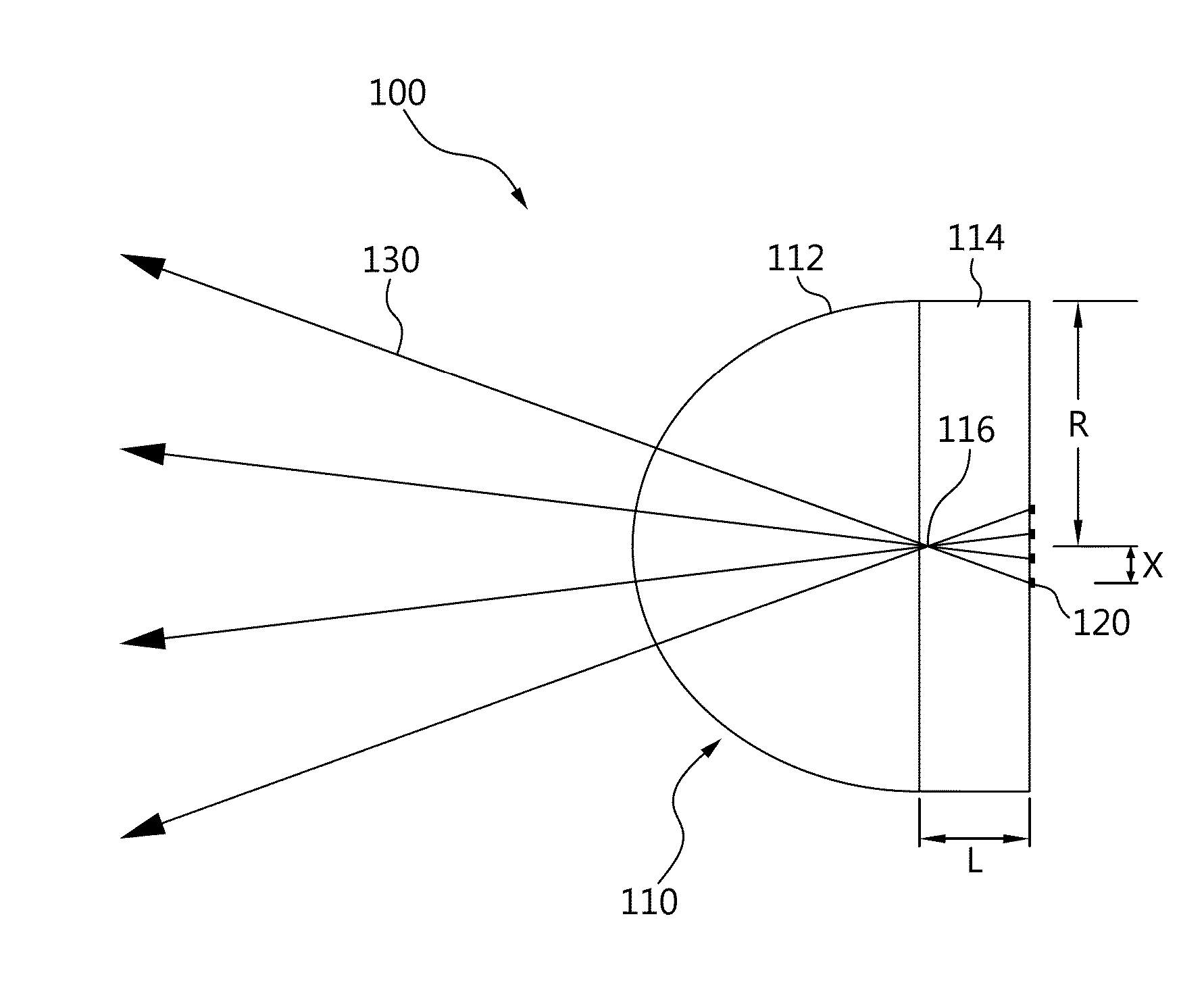
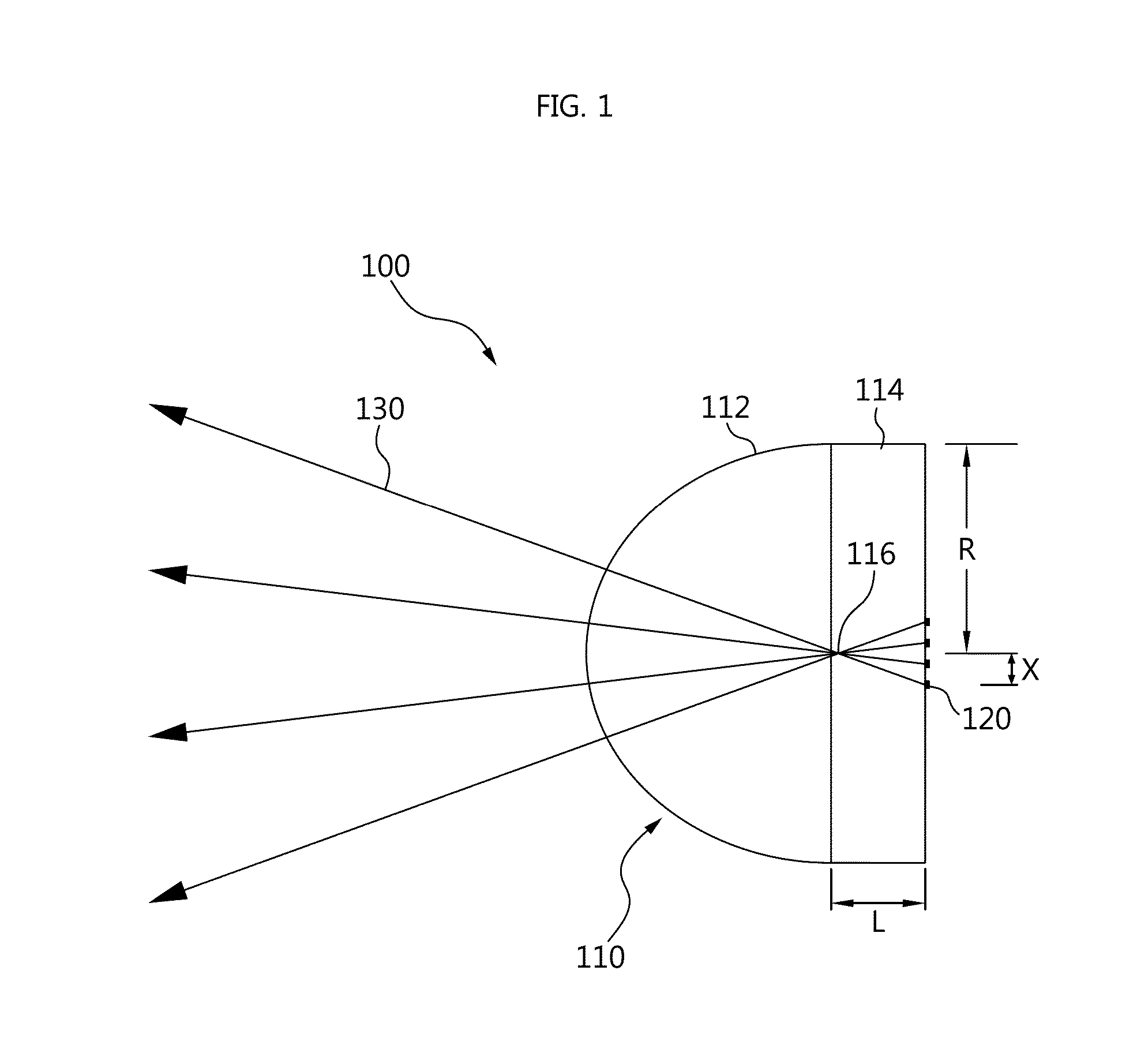
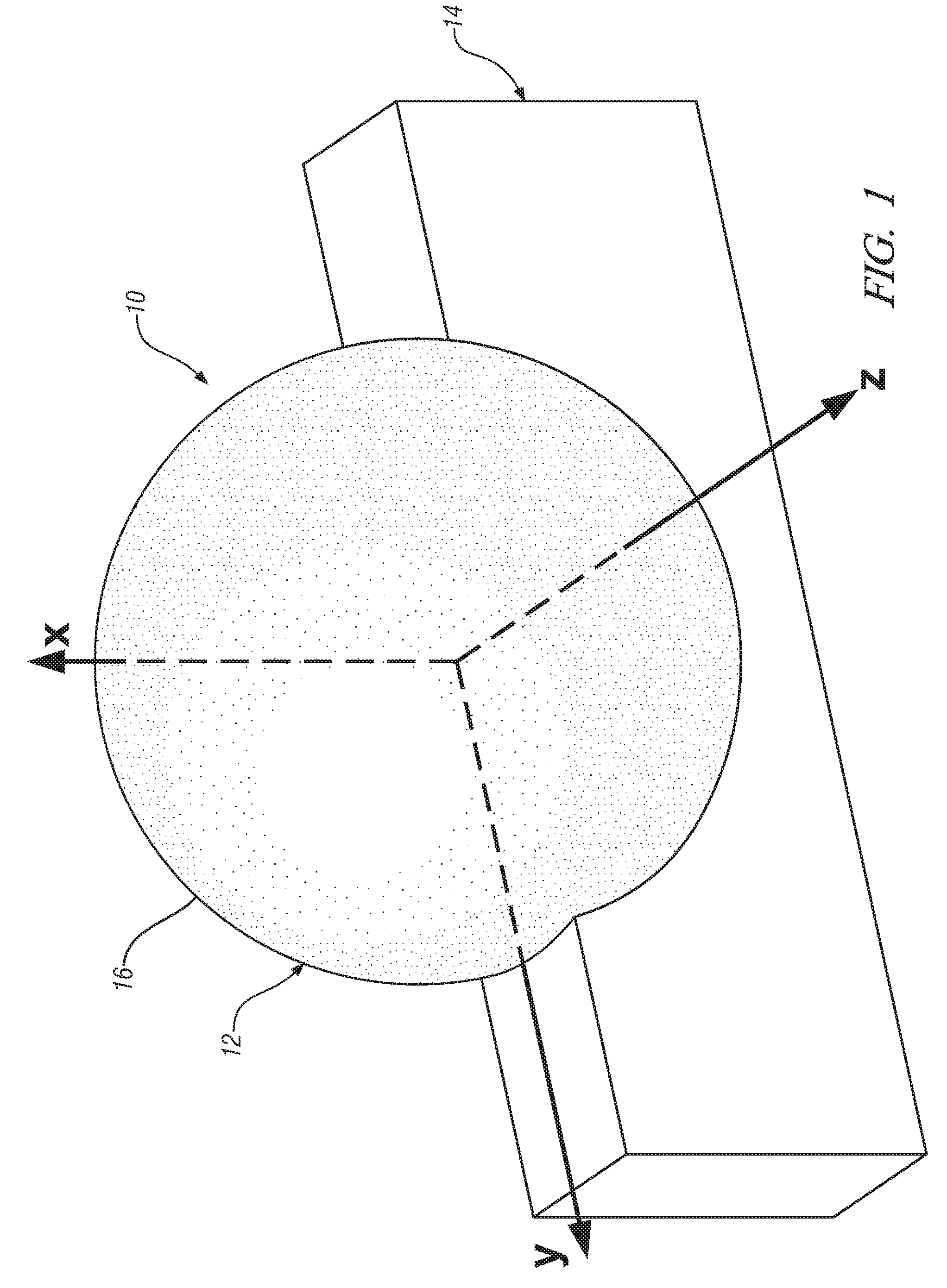
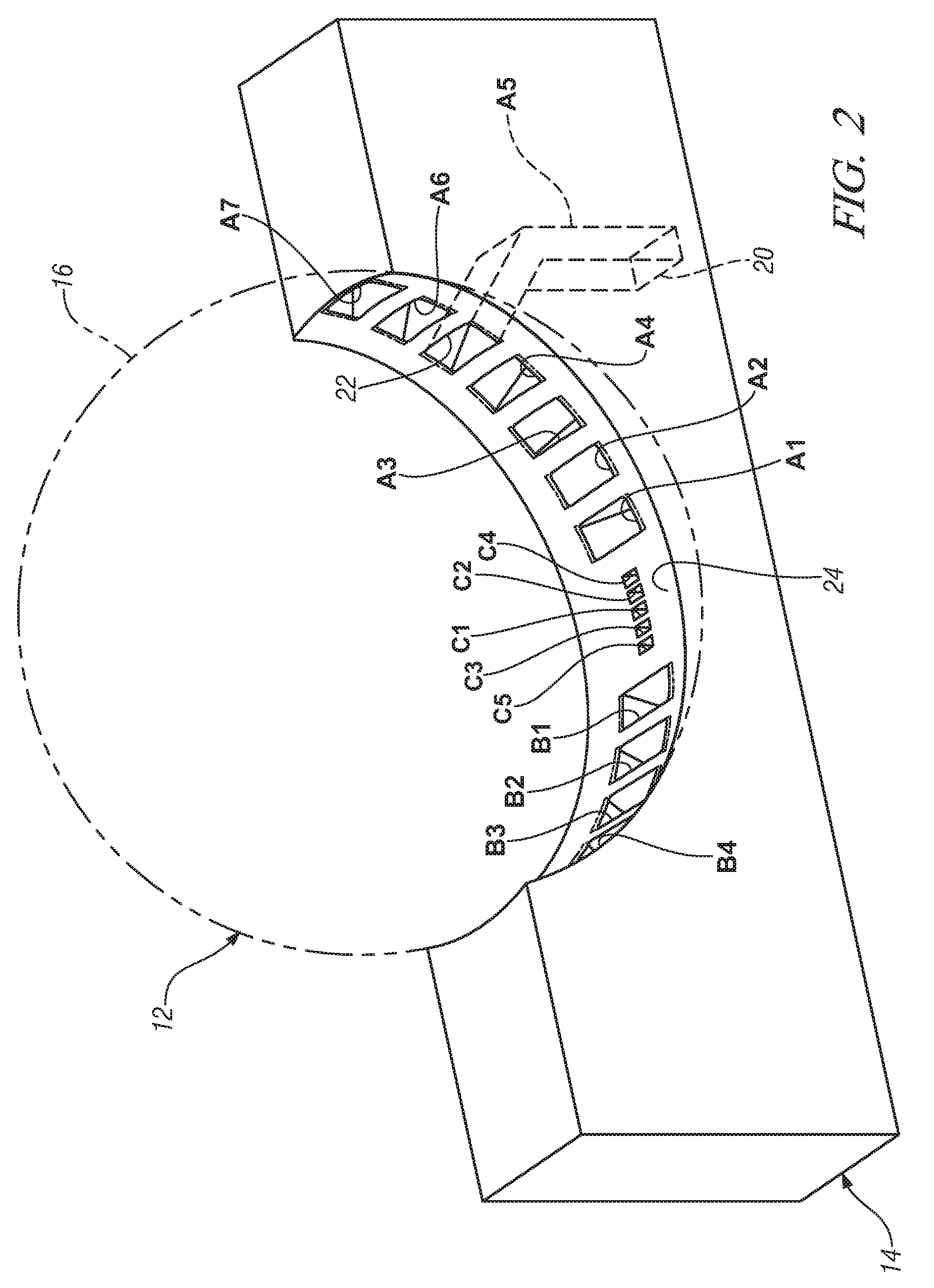
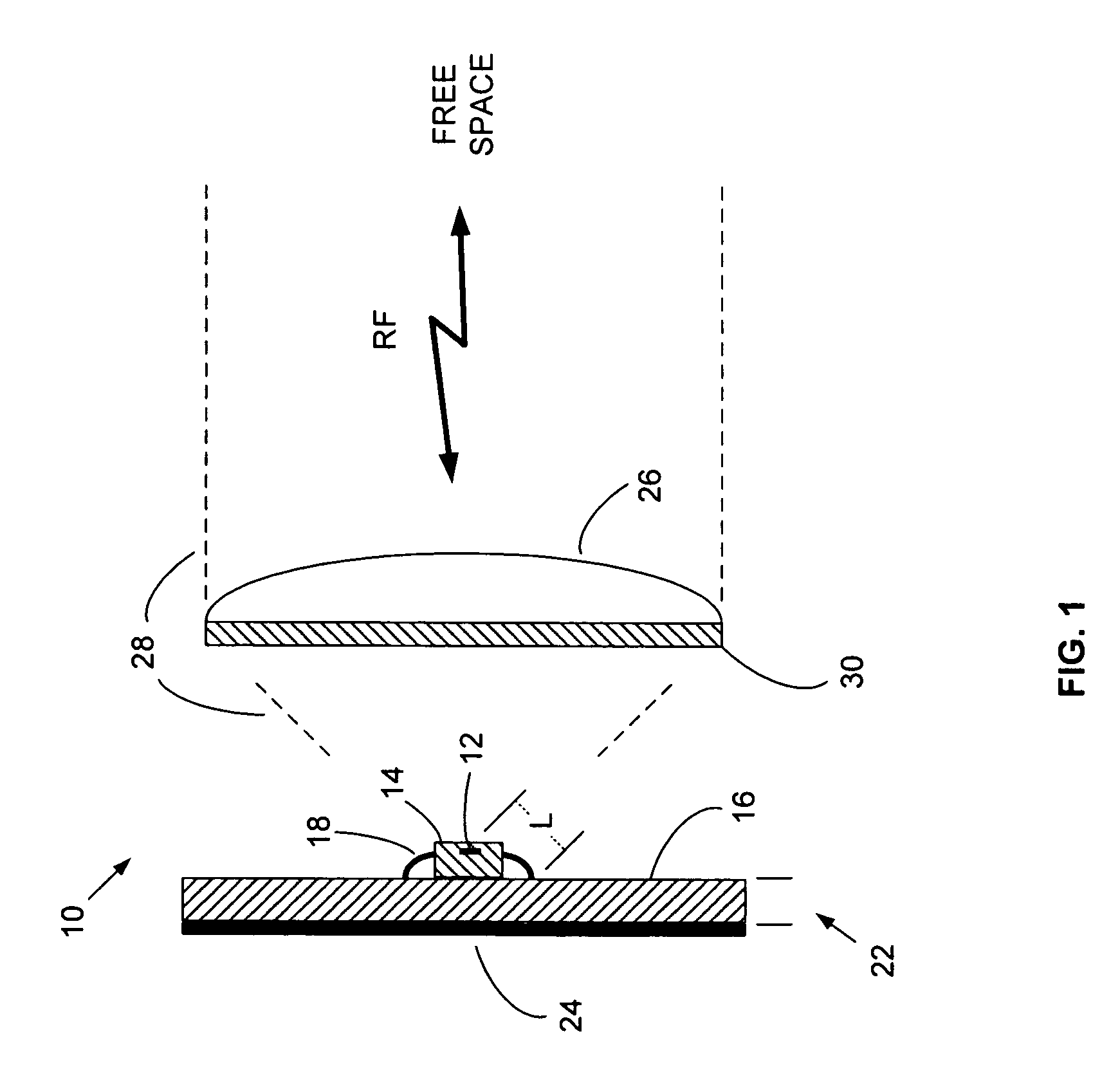
Millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and array thereof
InactiveCN101662076AWith quasi-optical Gaussian beam radiation characteristicsGuaranteed normal transmissionAntenna arraysDielectric resonator antennaDielectric substrate
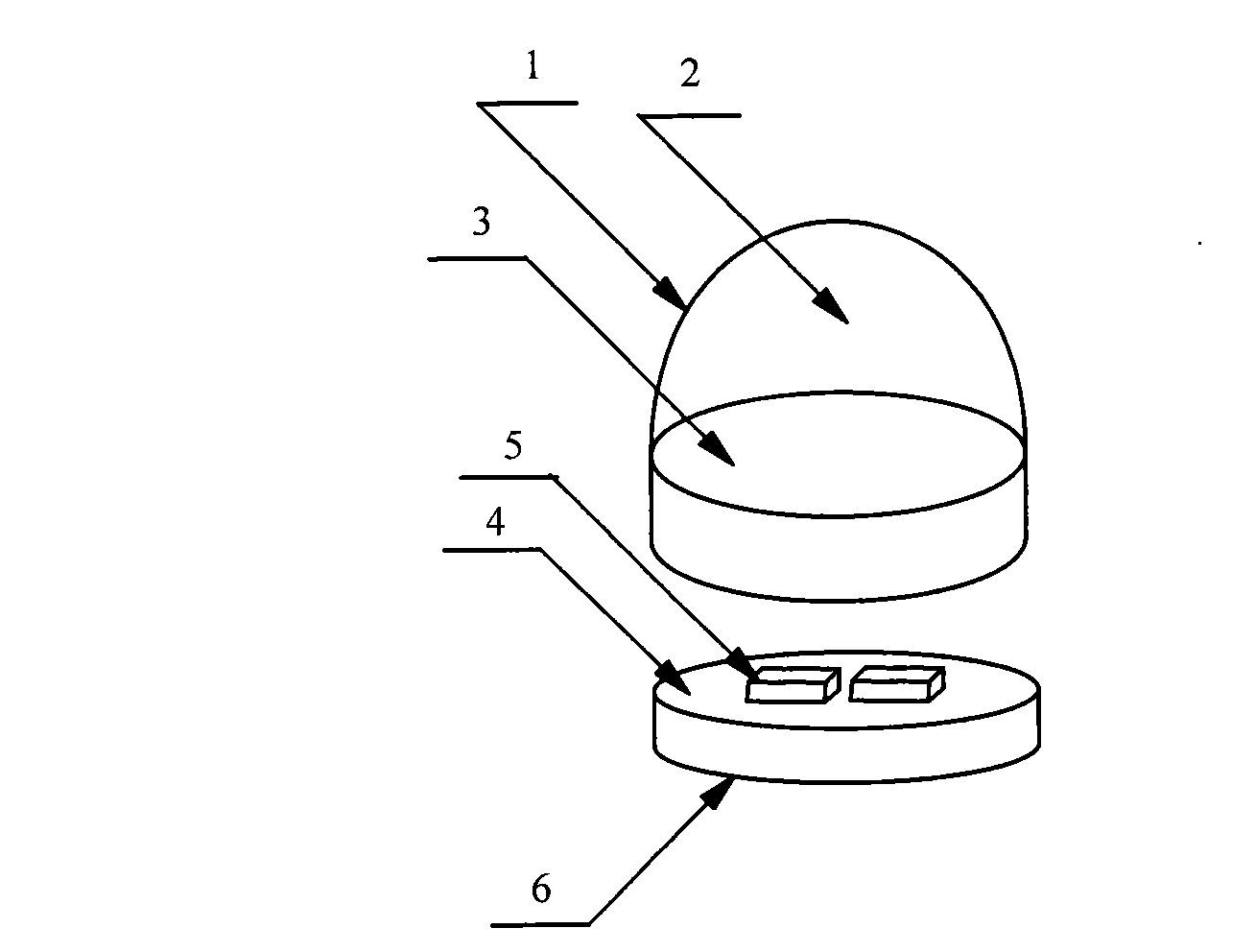
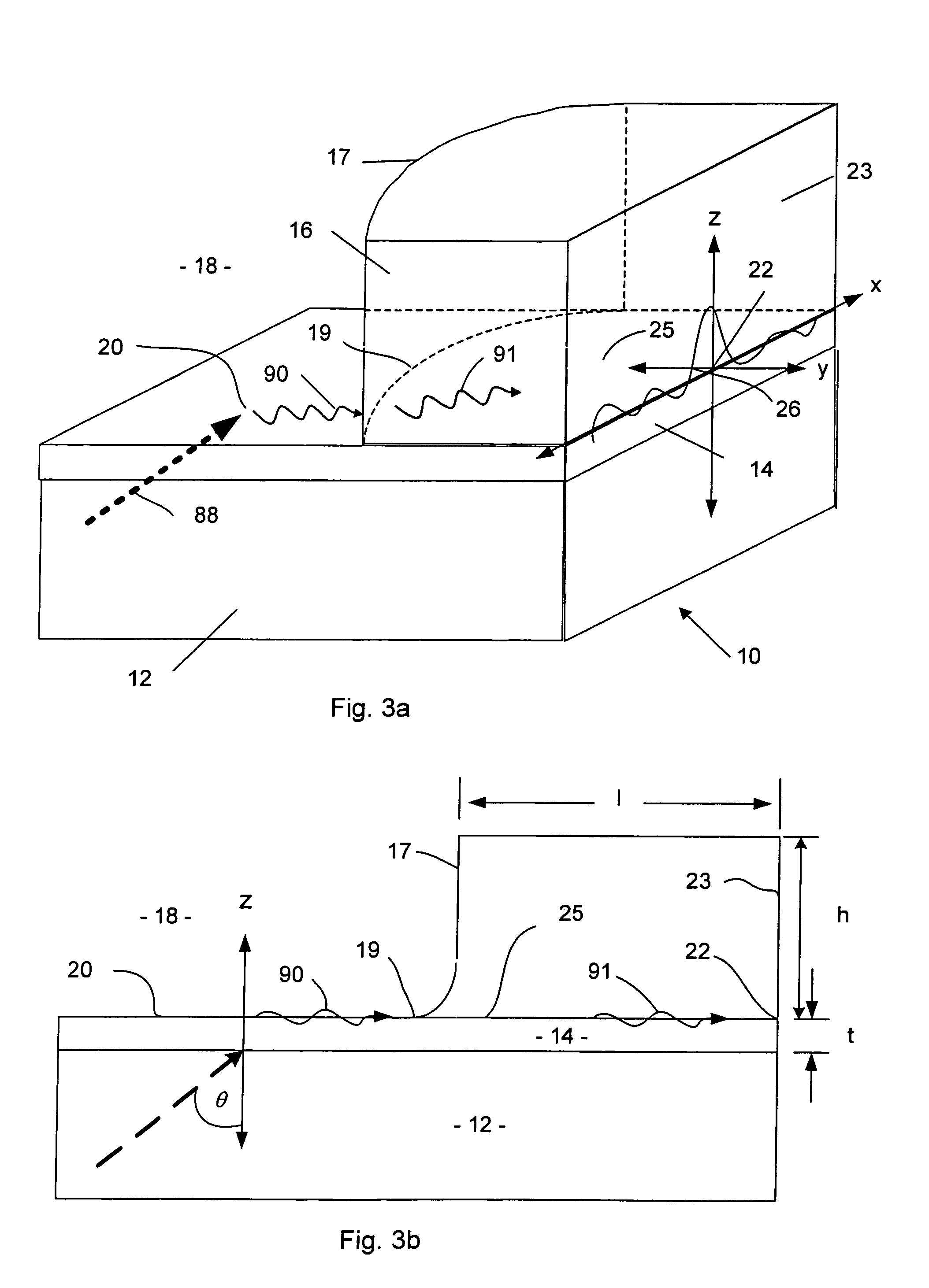
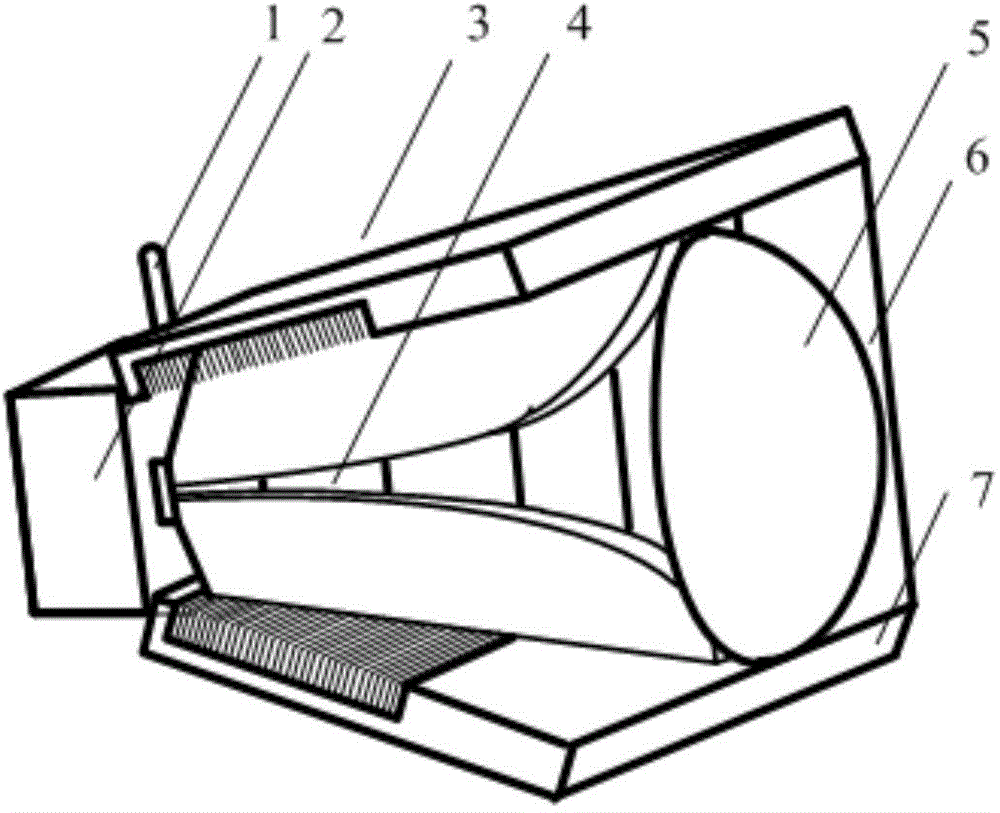
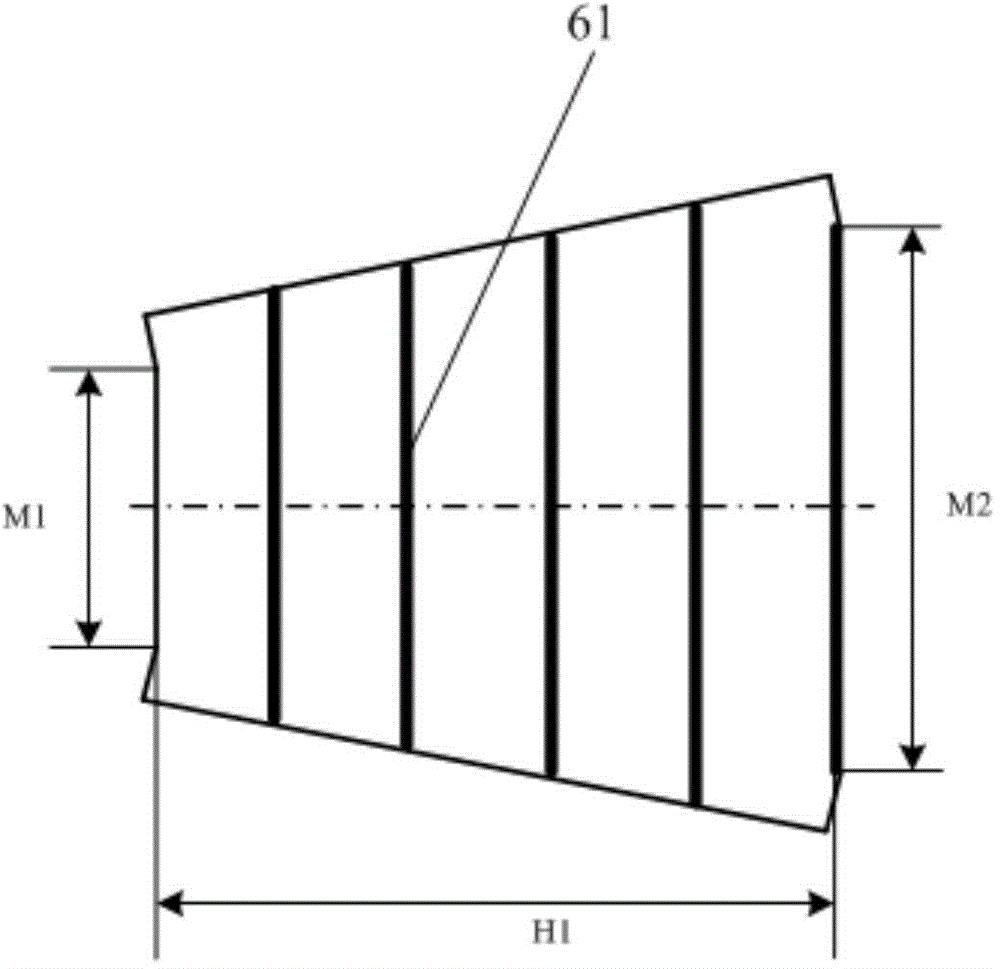
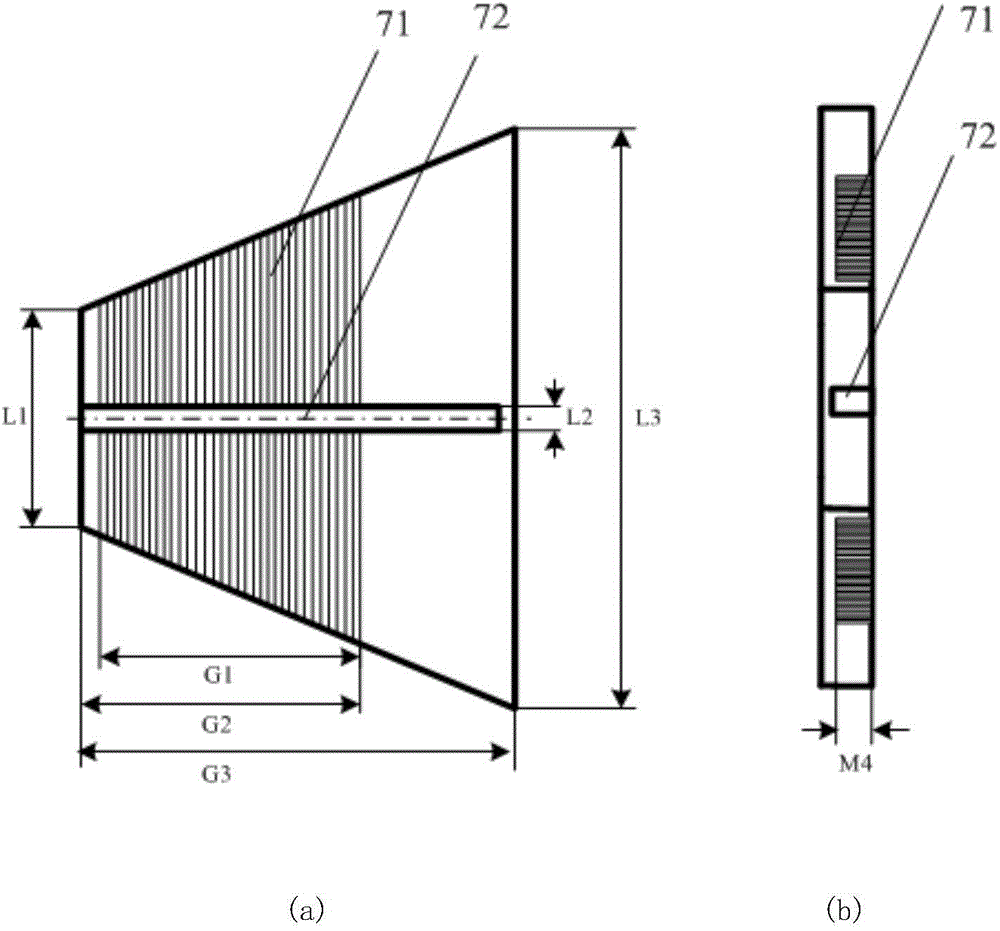
The invention relates to the technical field of radar, in particular to a millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and an array thereof. The array consists of a microstrip integrated antenna, a dielectric lens, an objective lens, an array base, a reflecting mirror, a protective cover and a beam transfer switch; one end face of the dielectric lens is a hemisphere or an ellipsoid, while the other end face is a cylindrical section; the microstrip integrated antenna is generated by an dielectric substrate, the front surface of the dielectric substrate is closely adhered tothe cylindrical section of the dielectric lens and serves as a feed source, and the back surface is grounded; the hemispherical or ellipsoidal end face of the dielectric lens is an antenna radiating surface; the length of the cylindrical part of the dielectric lens can be changed; the antenna array is arranged into a linear array or an area array; the array base and the reflecting mirror have conical quasi-optical reflecting mirror surfaces; the focus of the objective lens of the linear array or the area array aligns with the central line of the dielectric lens; the protective cover is arranged outside; and the antenna array is controlled by the beam transfer switch. The antenna structure has strong shock resistance and dust prevention, and is suitable for millimeter-wave radars for planes, automobiles and ships, and receiving / emitting sensing of communication equipment.
Owner:阮树成
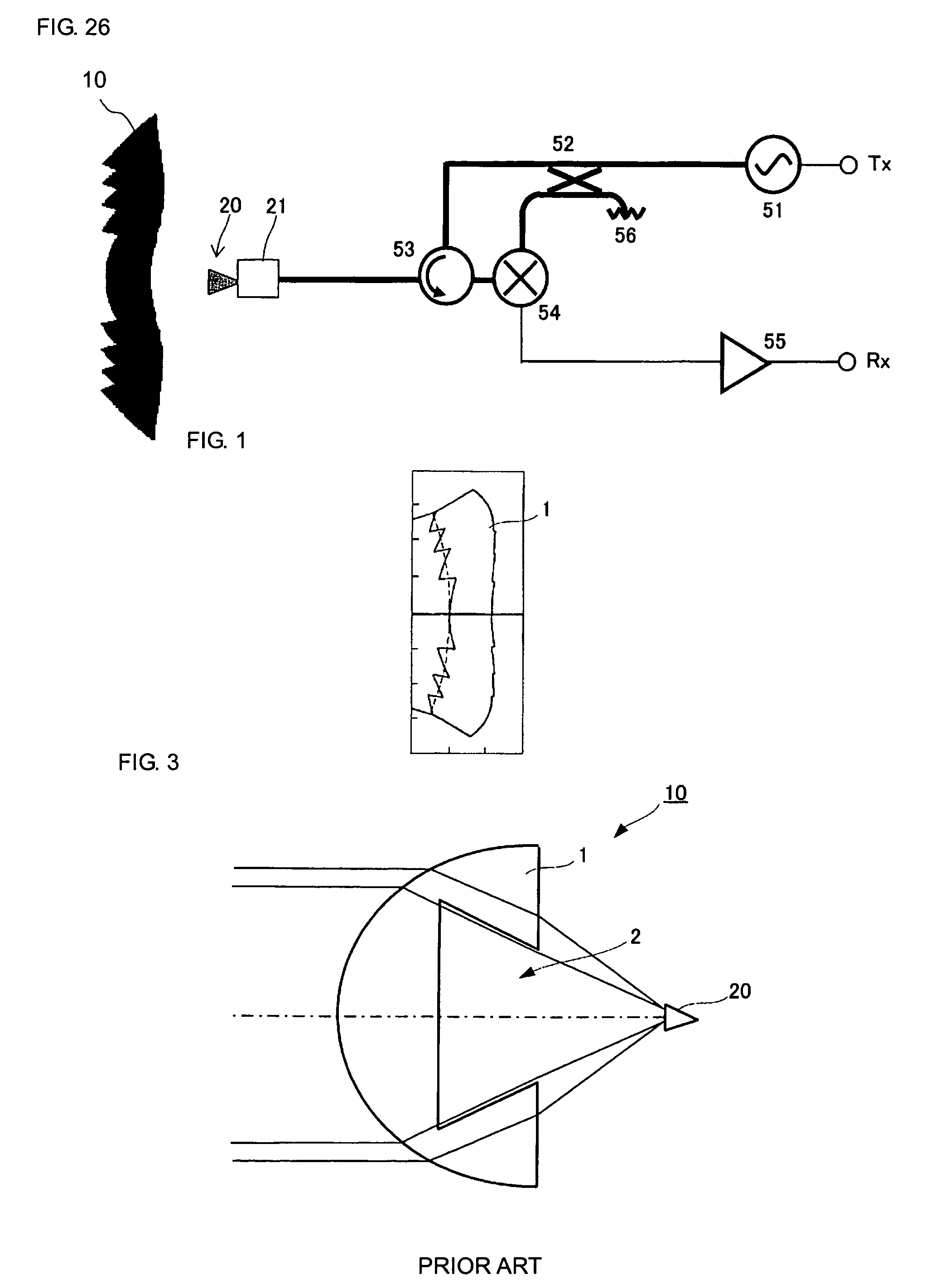
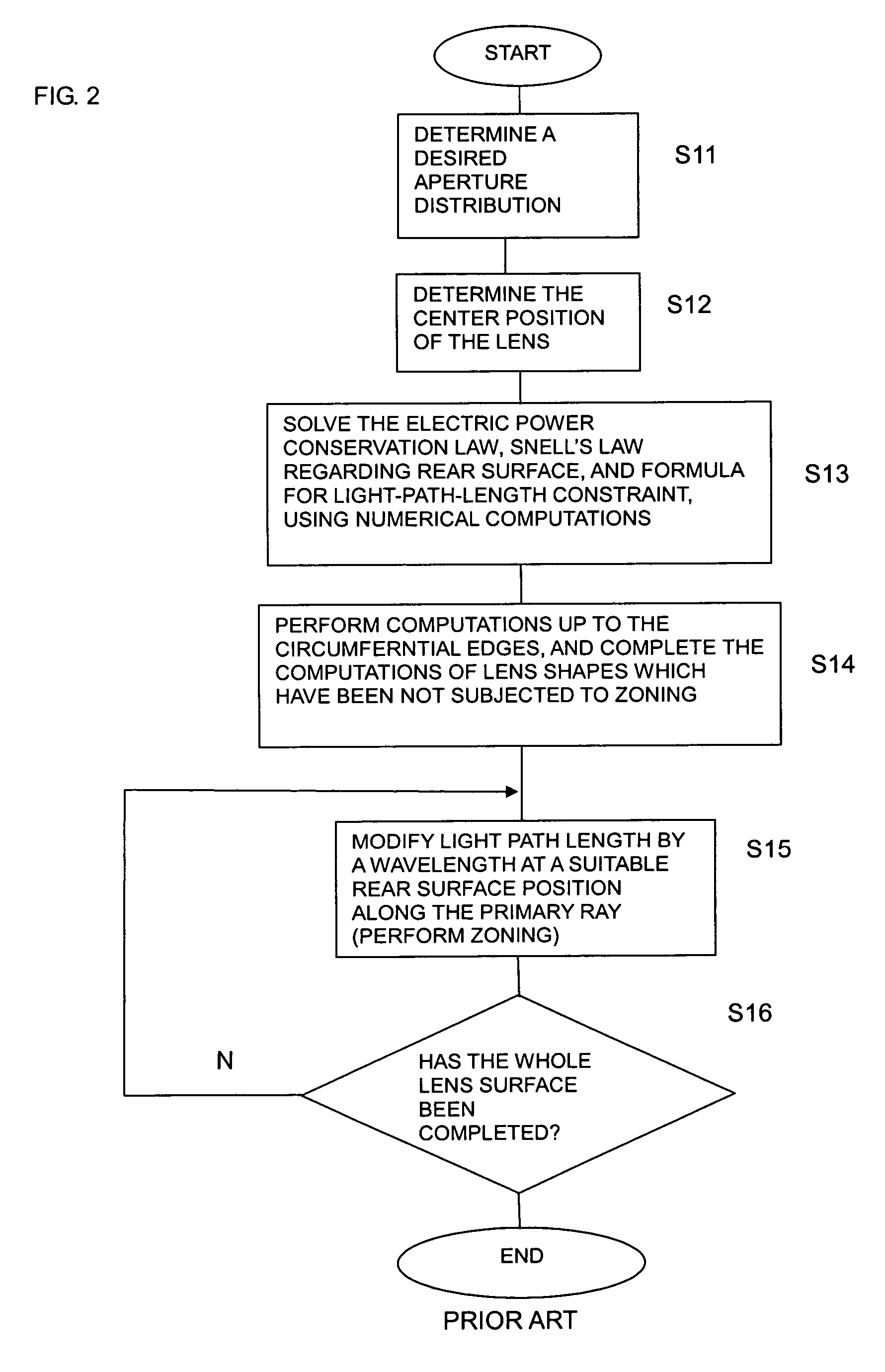
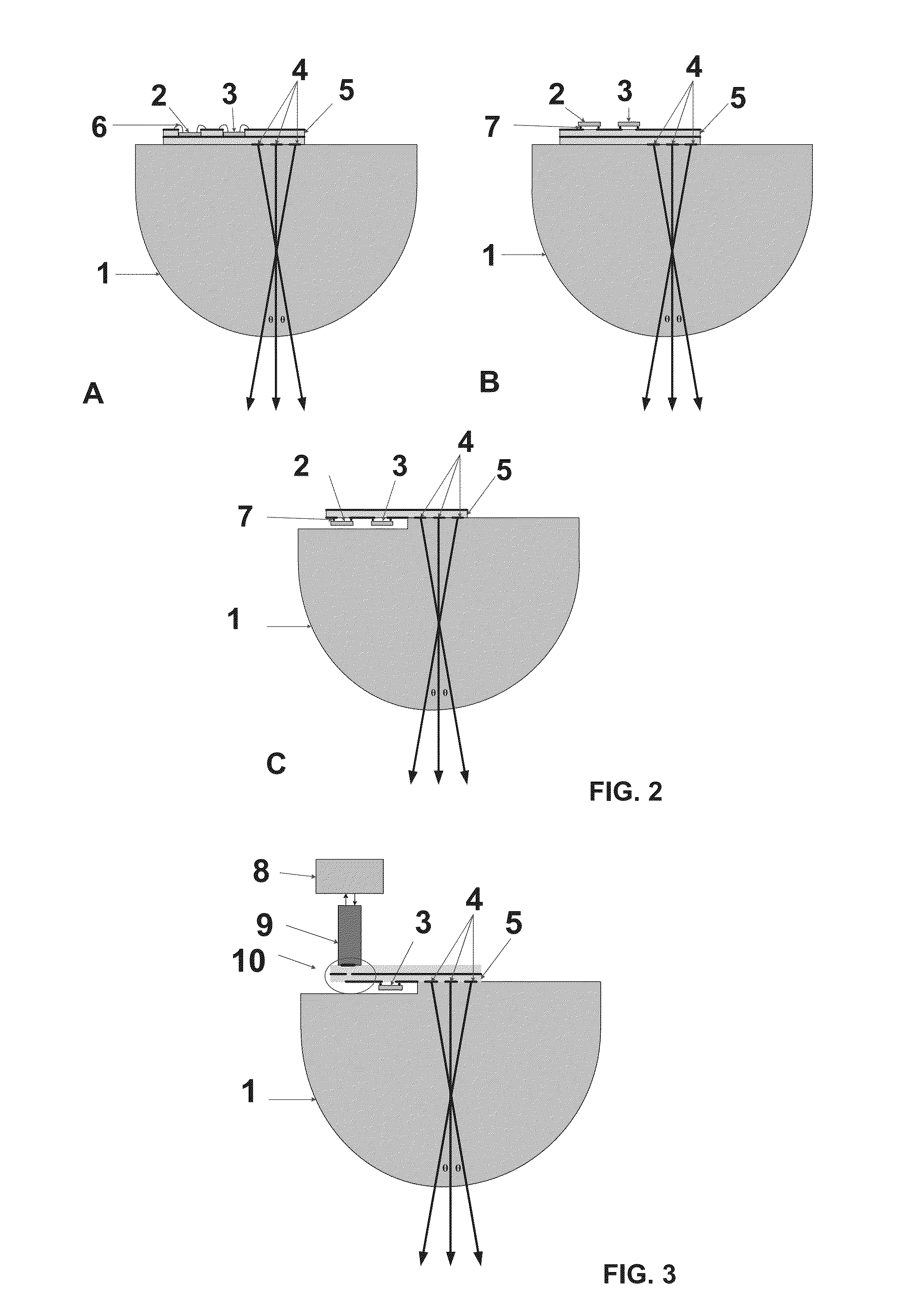
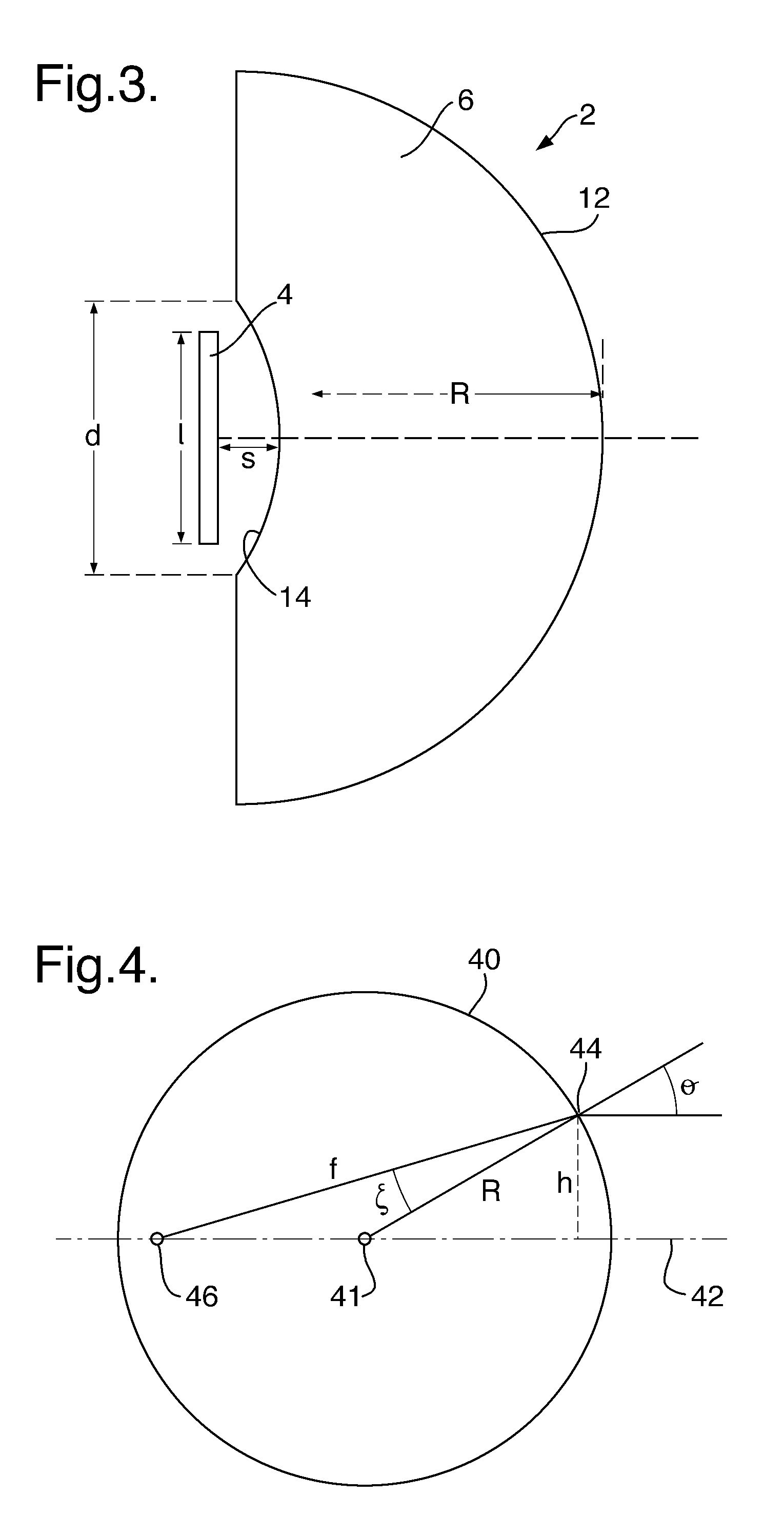
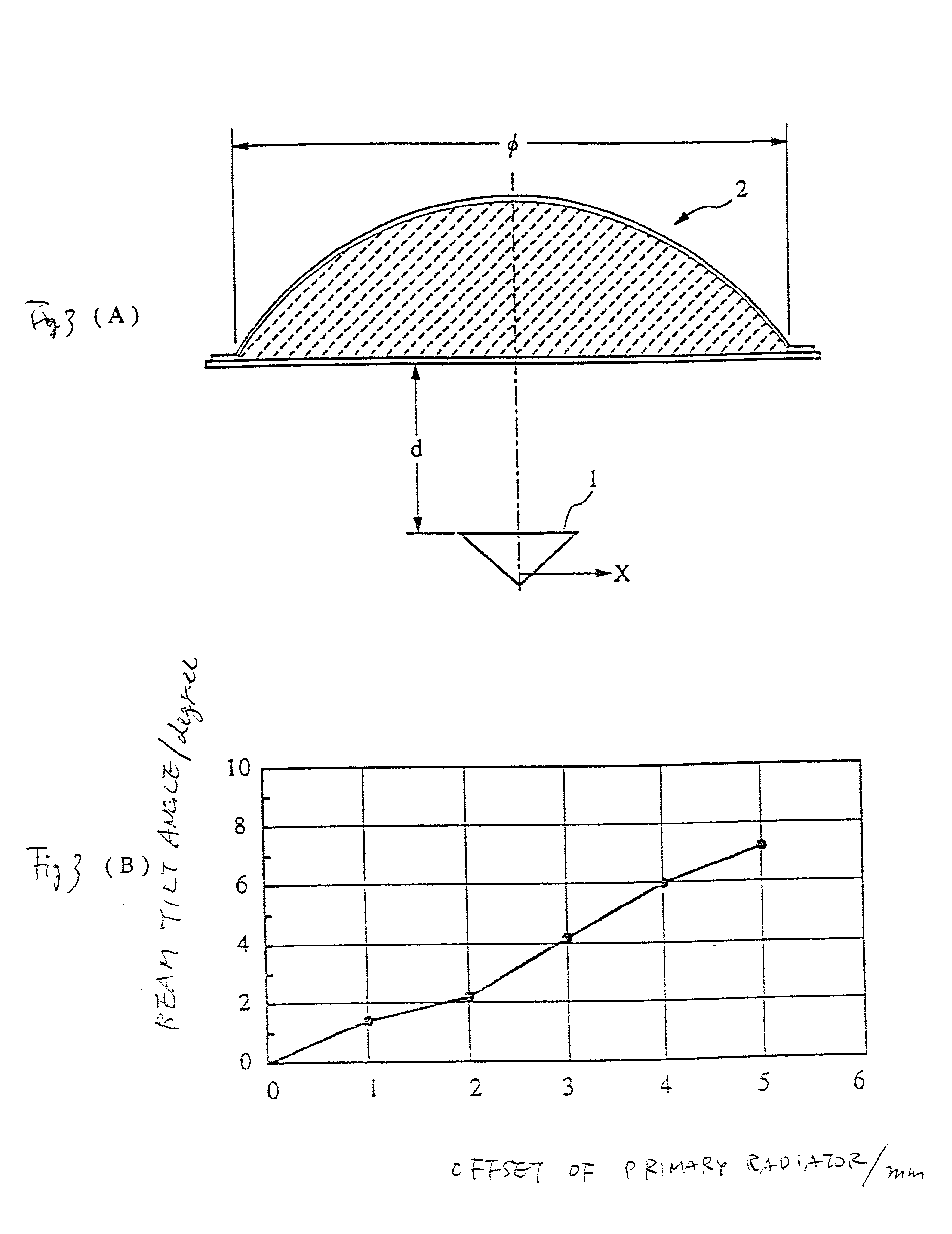
Dielectric lens, dielectric lens device, design method of dielectric lens, manufacturing method and transceiving equipment of dielectric lens
InactiveUS7355560B2Reduce weight and sizeEliminate the problemAntennasPath lengthSimultaneous equations
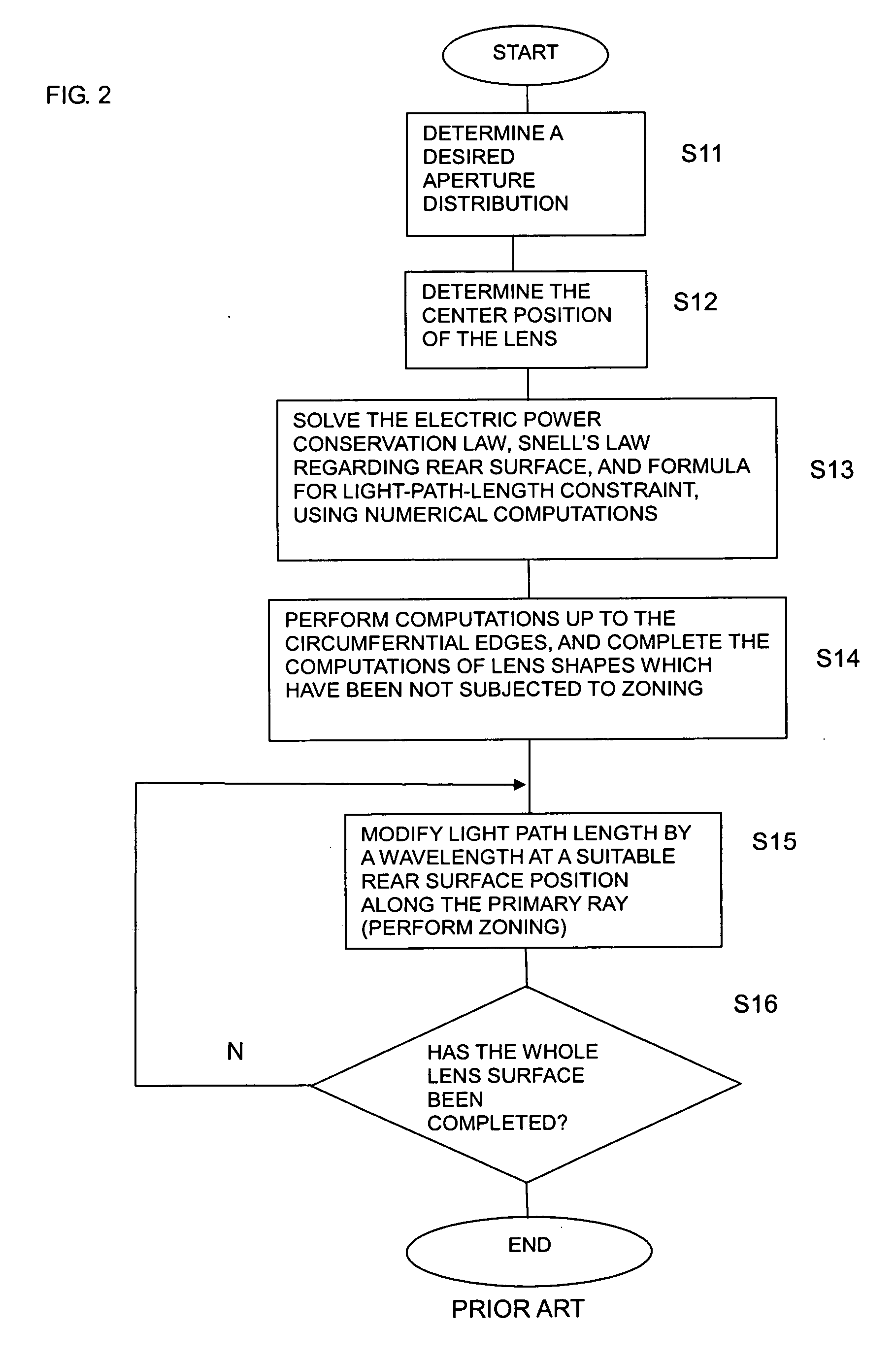
A design process first determines a desired aperture distribution, then converts the electric power conservation law, Snell's law on the rear face side of a dielectric lens, and the formula representing light-path-length constraint, into simultaneous equations, and computes the shapes of the surface and rear face of the dielectric lens depending on the azimuthal angle θ of a primary ray from the focal point of the dielectric lens to the rear face of the dielectric lens, and then reduces the light path length in the formula showing light-path-length constraint by an integral multiple of the wavelength when the coordinates on the surface of the dielectric lens reach a predetermined restriction thickness position. A dielectric lens is designed by sequentially changing the lazimuthal angle θ from its initial value, and also repeating the second and third steps. Thus, downsizing and quantification is realized by zoning while keeping antenna properties at the time of constituting a dielectric lens antenna in a good condition.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Electronically Beam-Steerable Antenna Device
ActiveUS20140077995A1Increase data rateRadio transmissionIndividually energised antenna arraysBeam steeringRadio relay
An electronically beam-steerable antenna device comprises a dielectric lens having at least one flat surface, a high frequency dielectric board, a plurality of at least one primary antenna element with at least one transmission line formed on the high frequency dielectric board, and a switching network electrically connected to the said plurality of at least one primary antenna element and at least one transmission line and adapted to apply electric power to the at least one primary antenna element. The switching network is a semiconductor integrated circuit mounted in or on the high frequency dielectric board, and the high frequency dielectric board with the plurality of at least one antenna element and at least one transmission line formed thereon is adjacent to the flat surface of the dielectric lens.The electronically beam steerable antenna device according to the present invention allows for electronic beam steering in a continuous angle sector while increasing radiation efficiency. The antenna device according to the present invention may be used for providing high data rate point-to-point millimeter-wave communications in radio relay station applications.
Owner:RADIO GIGABIT
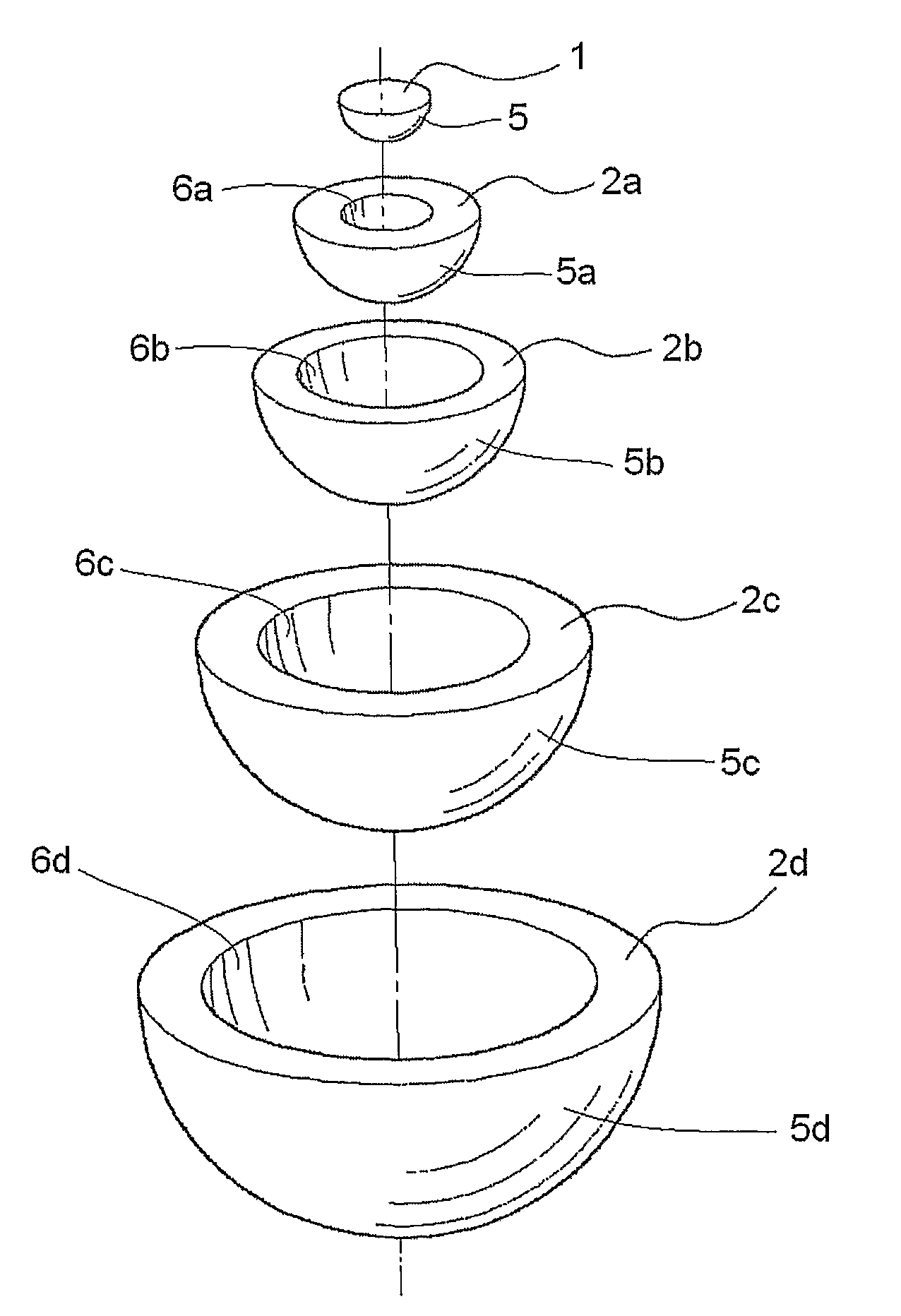
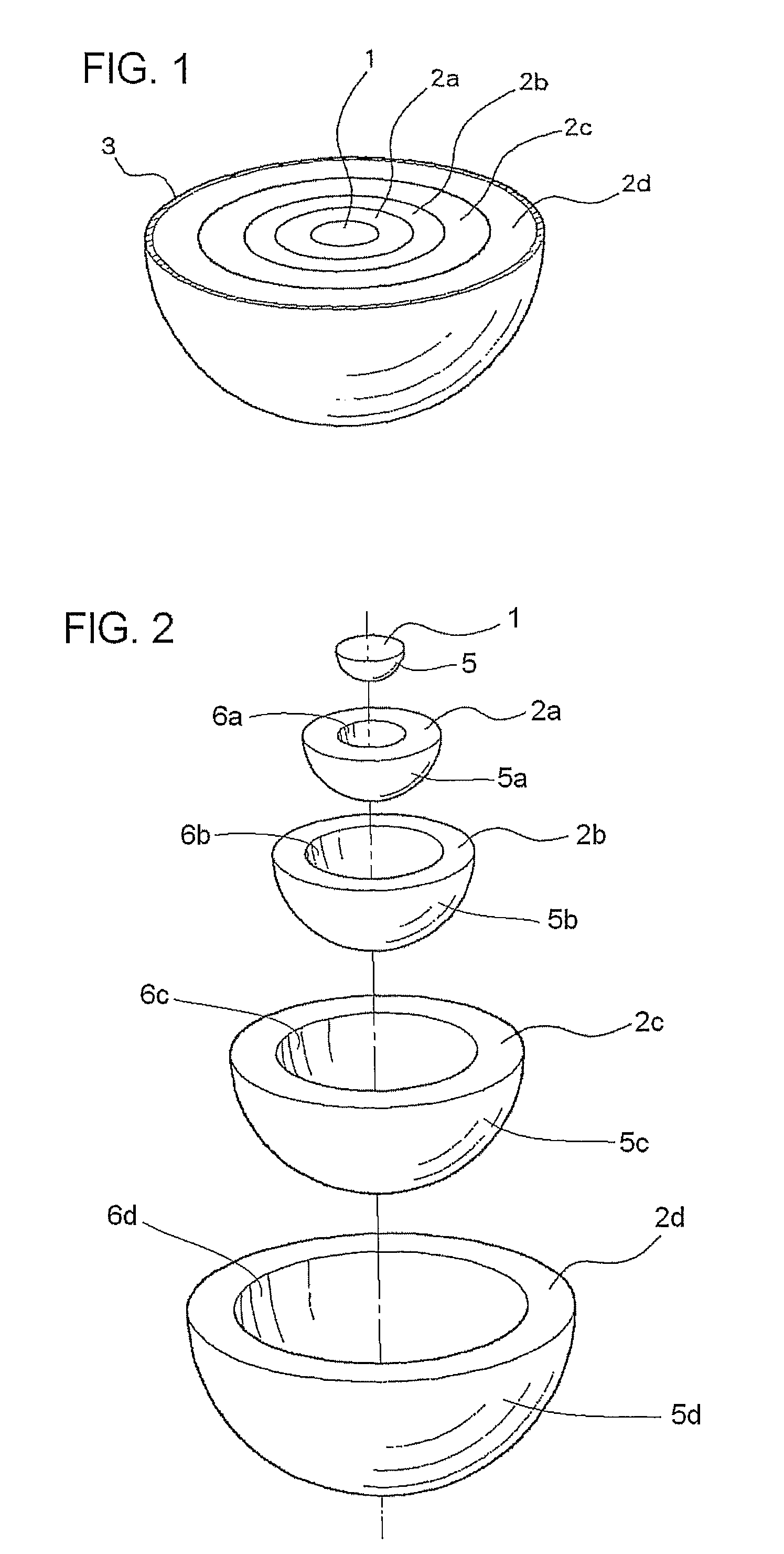
Luneberg dielectric lens and method of producing same
A hemispherical Luneberg dielectric lens including a hemispherical center layer having a hemispherical outer surface, and a plurality of hemispherical dome-shaped layers each having concentric hemispherical inner and outer surfaces, the outer surfaces of the center layer and dome-shaped layers having different diameters and the inner surfaces of said dome-shaped layers having different diameters. The center layer and dome-shaped layers are successively concentrically fitted into one another and integrated into a hemispherical shape. The center layer is a foam molding of ceramic-containing thermoplastic resin expanded beads, while each of said dome-shaped layers is a foam molding of thermoplastic resin expanded beads containing 0 to 80% by weight of a ceramic. The ceramic content per unit volume of the center and dome-shaped layers decreases from the center layer to the outermost dome-shaped layer, and the standard deviation of the apparent density of each of the center and dome-shaped layers is 0.07 g / cm3 or lower.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Antenna module and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20140225129A1Easy to assembleReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
An electrode is formed on at least one surface of first and second surfaces of a dielectric film formed of resin to be capable of receiving or transmitting an electromagnetic wave in a terahertz band. A semiconductor device operable in the terahertz band is mounted on at least one surface of the first and second surfaces of the dielectric film to be electrically connected to the electrode. A portion of a support layer is formed on the first or second surface of the dielectric film, and a dielectric lens is supported by another portion of the support layer. Another portion of the support layer is bent with respect to the portion such that the electromagnetic wave in the terahertz band transmitted or received by the electrode permeates through the dielectric lens.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
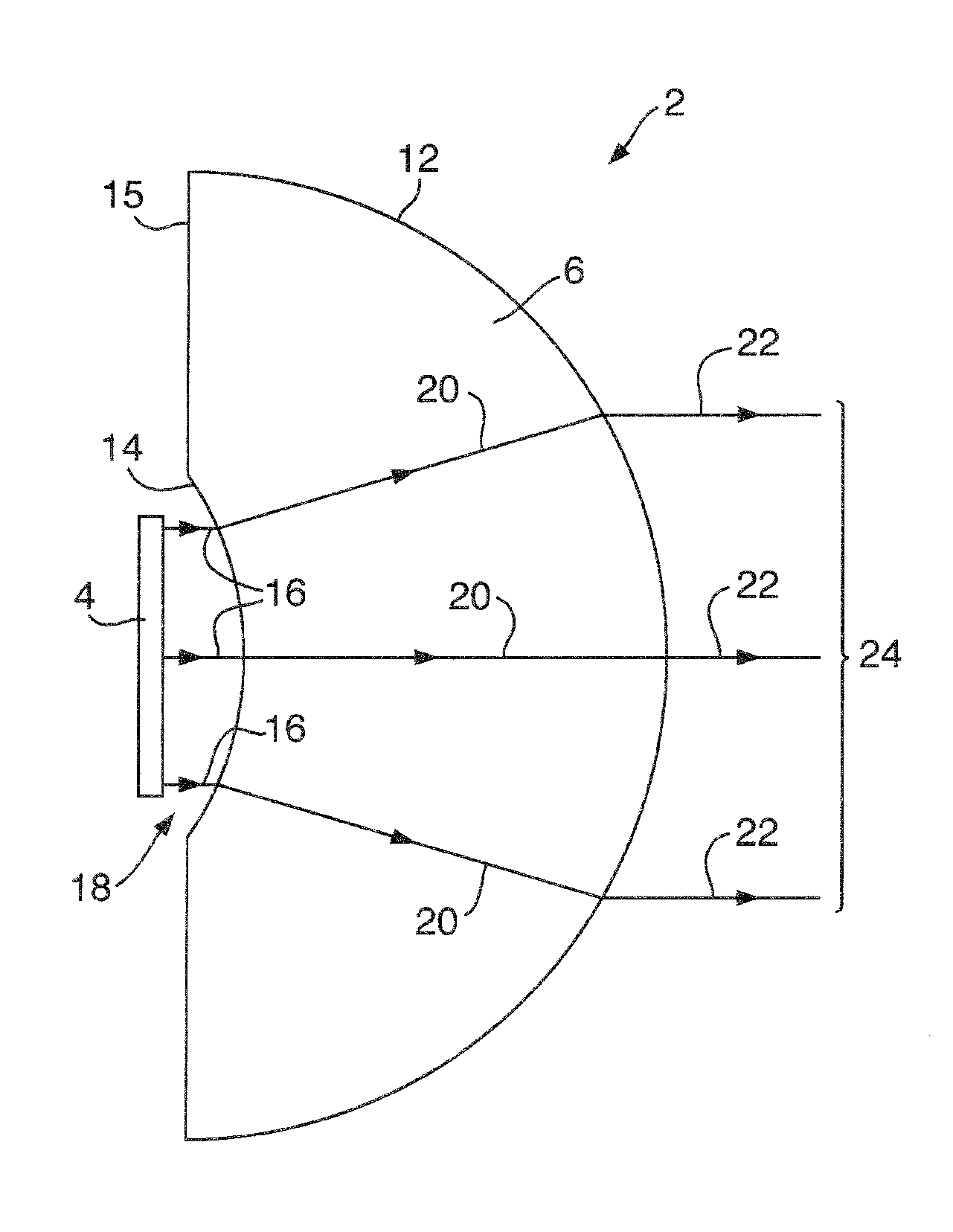
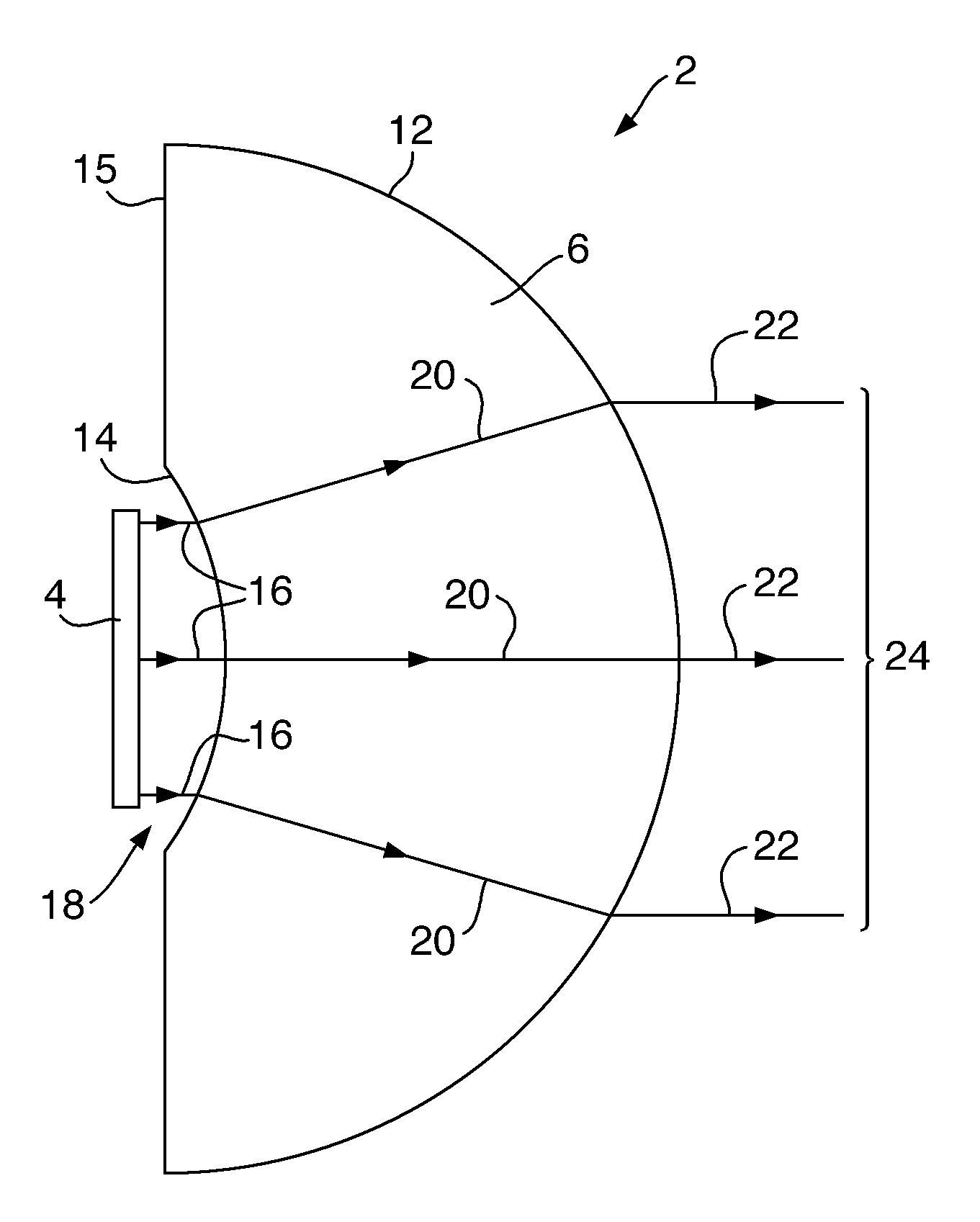
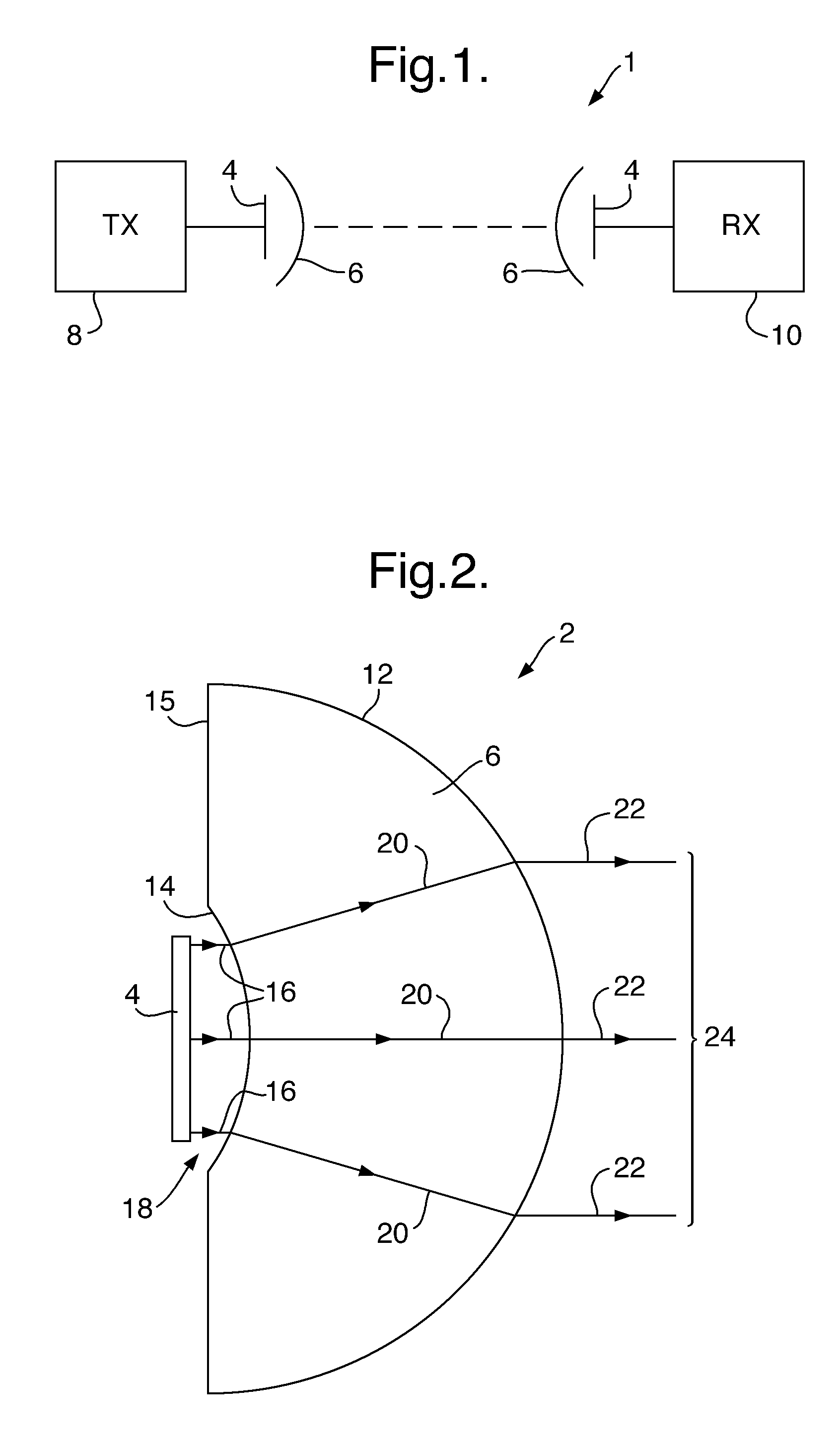
Antenna system
ActiveUS20120306708A1Efficient deploymentIncreasing antenna sizeAntenna arraysLight beamPhase array antenna
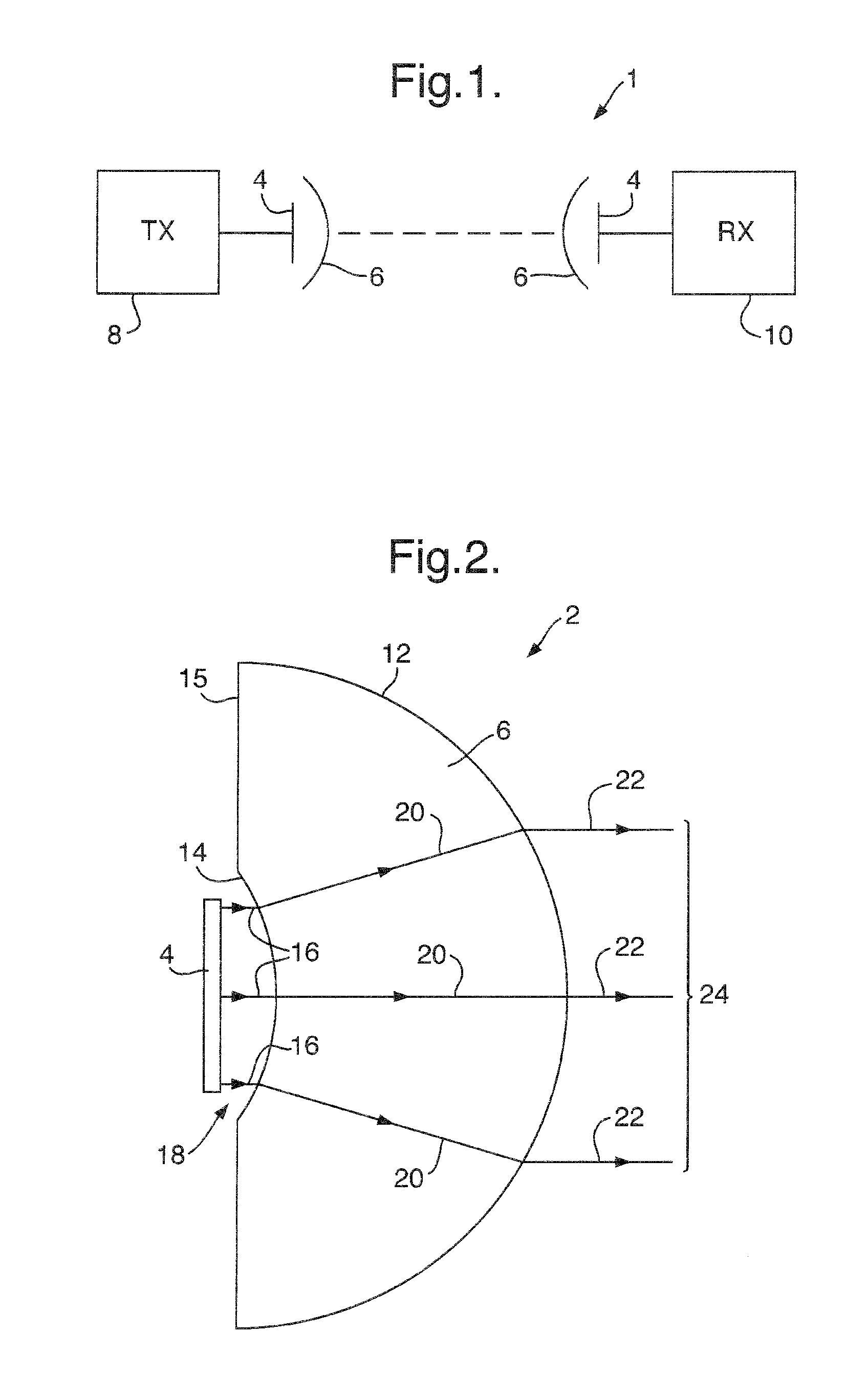
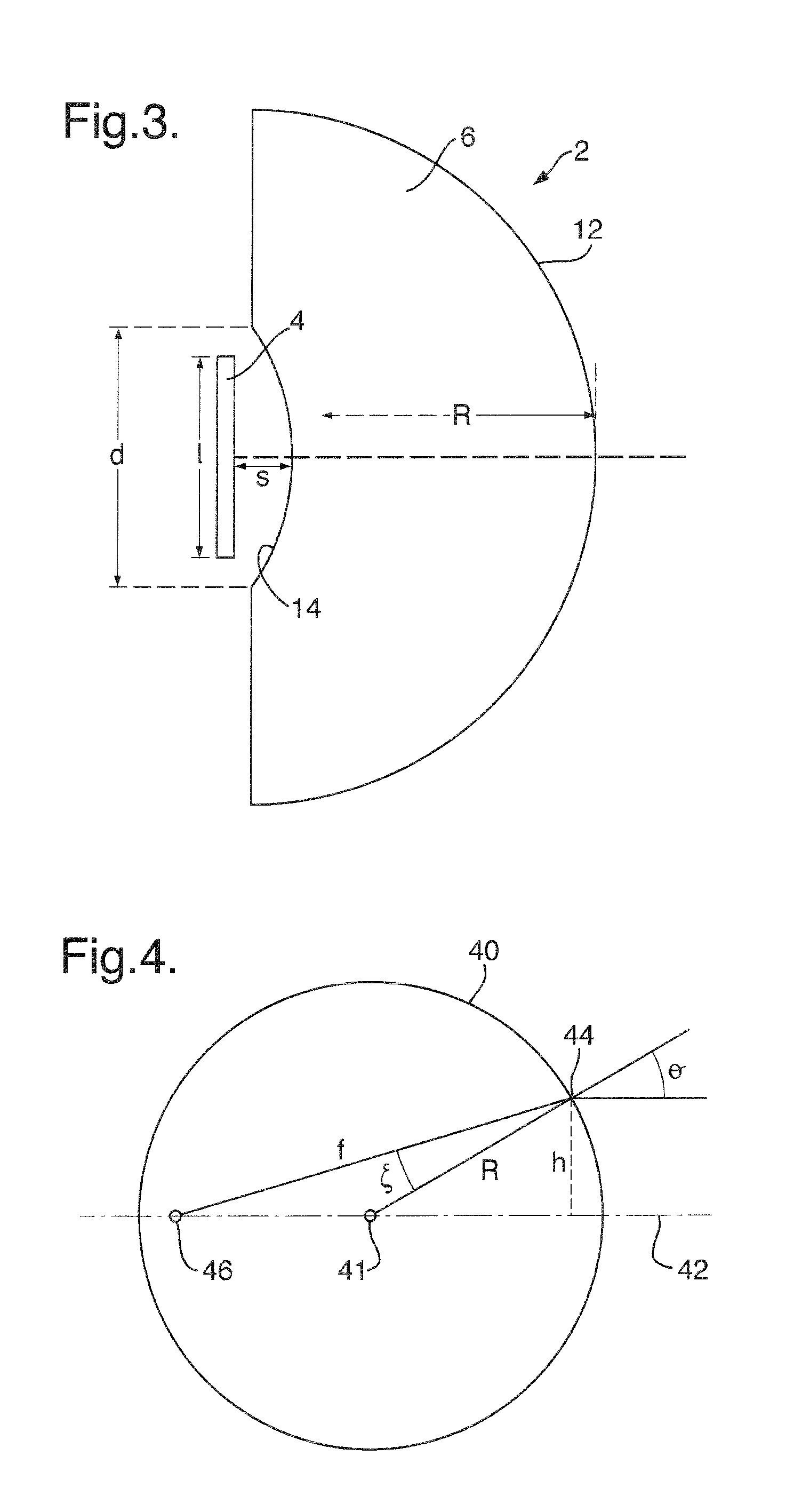
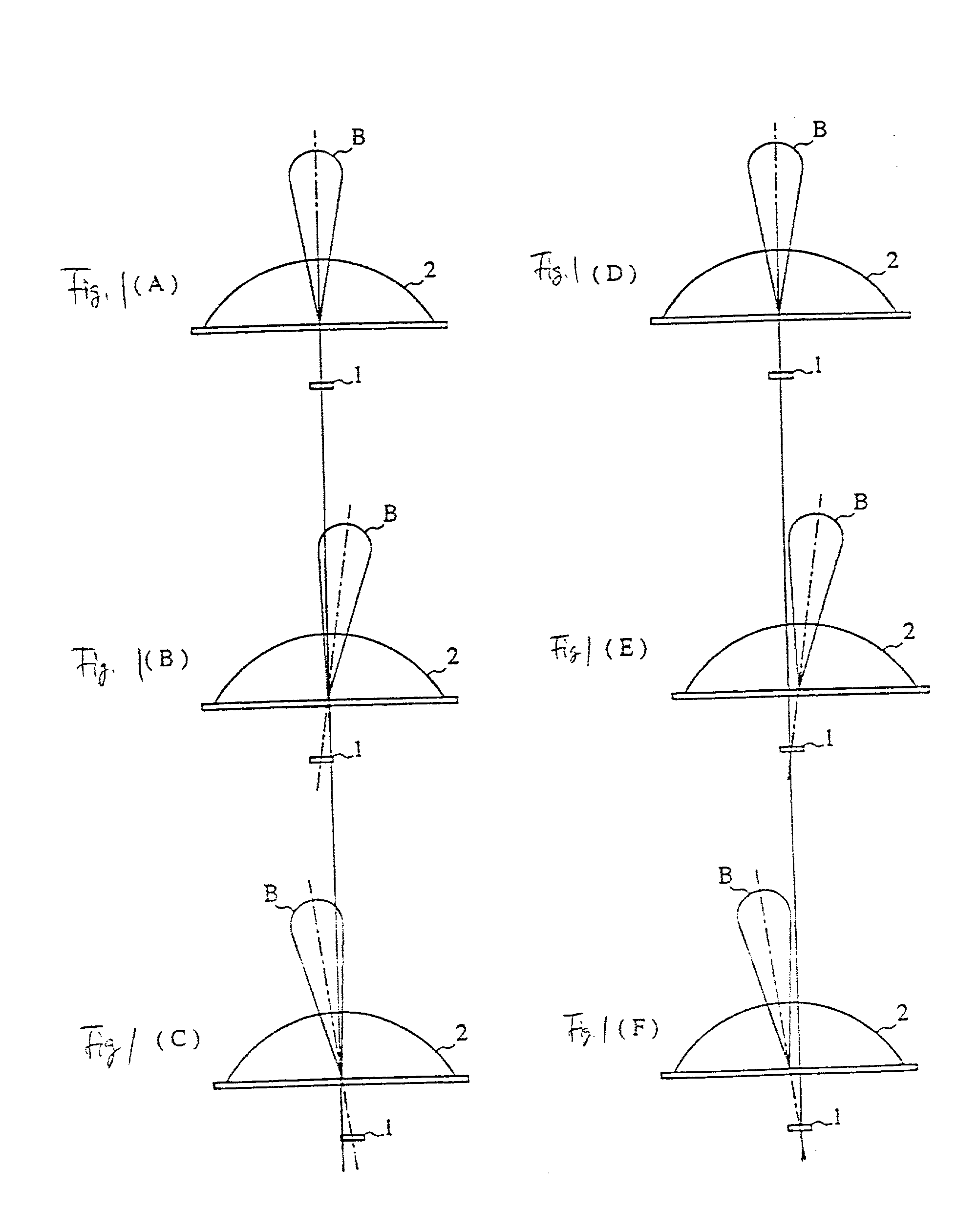
An antenna system, comprising: a phased array antenna (4); and a dielectric lens arrangement (6), for example a single solid dielectric lens (6) comprising a substantially spherical convex surface (12) and a concave surface (14); wherein the dielectric lens arrangement (6) is arranged to magnify the effective aperture of the phased array antenna (4). The concave surface (14) is positioned within the near field of the phased array antenna (4). The phased array antenna (4) is operated at a frequency greater than or equal to 50 GHz. The antenna system retains some ability to electronically scan the beam. The antenna system may be for transmission and / or reception. The antenna system may be used for example for communication between two vehicles.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Fan-beam antenna
InactiveUS7075496B2Simple compositionSmall reflectionWaveguide hornsRadiating element housingsDielectric plateLight beam
An object of the invention is to provide a fan-beam antenna which comprises a flare which is long in a horizontal direction thereof and whose cross section is horn-shaped, and a water-proof box housing components of said antenna, in which a vertical beam width is made narrow without spreading a vertical size to increase gain. Accordingly, this invention is characterized in that a radome radiation surface is constituted of a plurality of dielectric plates equivalently, and at least one of the dielectric plates is made a dielectric lens having a characteristic similar to a convex lens.
Owner:TAIYO MUSEN
Lens antenna
ActiveUS20160087344A1Precise positioningDifferential interacting antenna combinationsRadio relayImpedance matching
Disclosed is a lens antenna comprising a dielectric lens consisting of a collimating part and an extension part, and an antenna element. The extension part of the lens comprises a substantially flat surface crossed by the axis of the collimating part, and the antenna element is rigidly fixed on the surface. The antenna element is formed by a hollow waveguide and comprises a dielectric insert with one end thereof adjacent to said surface; the size of the radiating opening of the waveguide is determined by the predefined width of the main beam and by side lobe levels of the radiation pattern of the lens antenna. The technical result of the invention is an increase in realized gain value due to the use of a waveguide antenna element with a dielectric insert, which provides impedance matching in a wide frequency bandwidth. The present invention can be used in radio-relay point-to-point communication systems, e.g. for forming backhaul networks of cellular mobile communication, in car radars and other radars, in microwave RF tags, in local and personal communication systems, in satellite and intersatellite communication systems, etc.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
Multi-beam antenna with shared dielectric lens
An integrated multi-beam antenna with a shared dielectric lens is disclosed. The antenna is formed by positioning the feed apertures of a plurality of waveguide feeds at positions located on the surface of the shared dielectric lens. The angular direction and shape of radiation beams produced by the waveguide feeds are determined by the physical and dielectric characteristics of the lens, the location of feed apertures of the waveguide feeds on the surface of the lens, and the frequency of electromagnetic energy propagating in the waveguide feeds. The principles of the invention are applied to realize an inexpensive, integrated multi-feed antenna adapted to provide desired angular areas of coverage for both a long range and short range radar in an automotive radar safety system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and array thereof
InactiveCN101662076BWith quasi-optical Gaussian beam radiation characteristicsGuaranteed normal transmissionAntenna arraysDielectric substrateIntegrated antenna
The invention relates to the technical field of radar, in particular to a millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and an array thereof. The array consists of a microstrip integrated antenna, a dielectric lens, an objective lens, an array base, a reflecting mirror, a protective cover and a beam transfer switch; one end face of the dielectric lens is a hemisphere or an ellipsoid, while the other end face is a cylindrical section; the microstrip integrated antenna is generated by an dielectric substrate, the front surface of the dielectric substrate is closely adhered tothe cylindrical section of the dielectric lens and serves as a feed source, and the back surface is grounded; the hemispherical or ellipsoidal end face of the dielectric lens is an antenna radiating surface; the length of the cylindrical part of the dielectric lens can be changed; the antenna array is arranged into a linear array or an area array; the array base and the reflecting mirror have conical quasi-optical reflecting mirror surfaces; the focus of the objective lens of the linear array or the area array aligns with the central line of the dielectric lens; the protective cover is arranged outside; and the antenna array is controlled by the beam transfer switch. The antenna structure has strong shock resistance and dust prevention, and is suitable for millimeter-wave radars for planes, automobiles and ships, and receiving / emitting sensing of communication equipment.
Owner:阮树成
Antenna system
ActiveUS9203149B2Efficient deploymentIncrease powerIndividually energised antenna arraysLight beamPhase array antenna
An antenna system, comprising: a phased array antenna (4); and a dielectric lens arrangement (6), for example a single solid dielectric lens (6) comprising a substantially spherical convex surface (12) and a concave surface (14); wherein the dielectric lens arrangement (6) is arranged to magnify the effective aperture of the phased array antenna (4). The concave surface (14) is positioned within the near field of the phased array antenna (4). The phased array antenna (4) is operated at a frequency greater than or equal to 50 GHz. The antenna system retains some ability to electronically scan the beam. The antenna system may be for transmission and / or reception. The antenna system may be used for example for communication between two vehicles.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
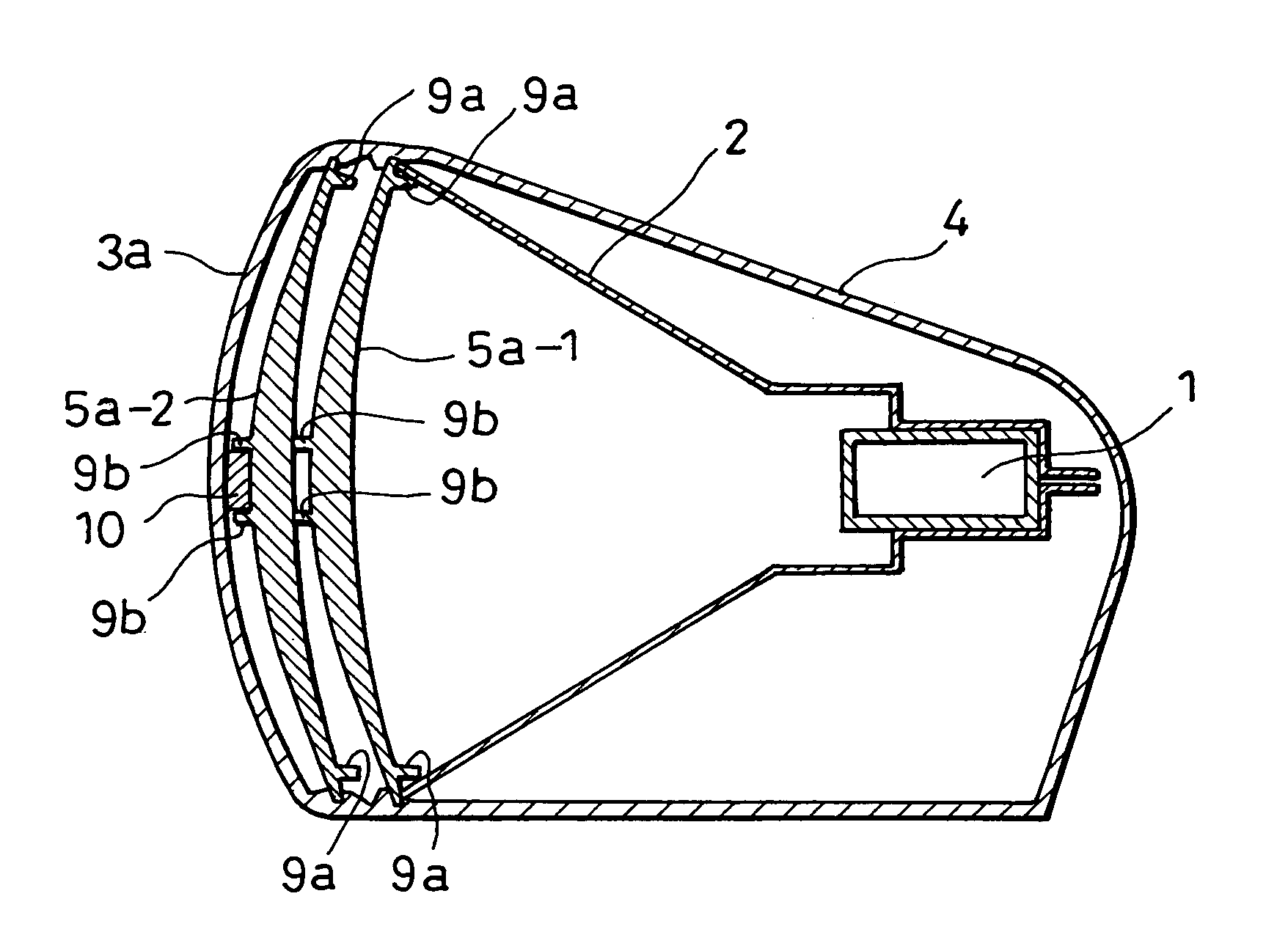
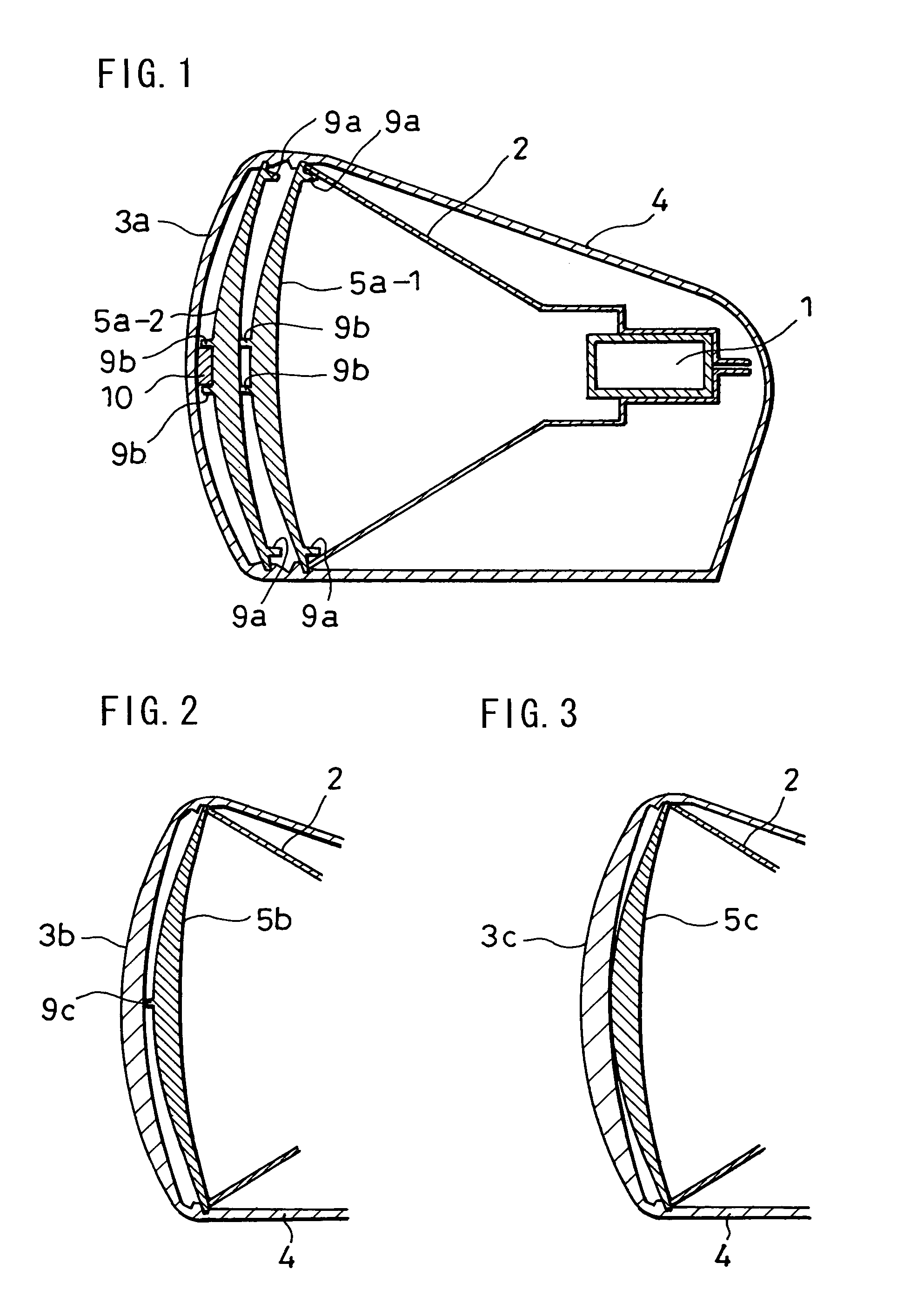
Dielectric lens cone radiator sub-reflector assembly
ActiveUS9105981B2Reduction of sub-reflector spill-overIncrease widthOptical articlesCoupling light guidesWaveguidePhysics
A dielectric cone radiator sub-reflector assembly for a reflector antenna with a waveguide supported sub-reflector is provided as a unitary dielectric block with a sub-reflector at a distal end. A waveguide transition portion of the dielectric block is dimensioned for insertion coupling into an end of the waveguide. A dielectric radiator portion is provided between the waveguide transition portion and a sub-reflector support portion. An outer diameter of the dielectric radiator portion is provided with a plurality of radially inward grooves extending radially inward to a diameter less than an inner diameter of the end of the waveguide and a lens bore extends from a proximal end of the dielectric block towards the distal end of the dielectric block at least to the sub-reflector support portion. The unitary dielectric block may be manufactured as a single contiguous monolithic portion of dielectric material via injection molding.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Controlled lens antenna apparatus and system
Present configuration concerns microelectronics; for instance, compact antenna devices applied in mobile communications and other equipment operating in millimeter range. The controlled lens antenna apparatus may include antenna elements in an integrated circuit configured to transmit beams. The apparatus may also include a dielectric lens antenna configured to generate a plane wave based in the beams transmitted. The apparatus may include a plate configured to deflect the generated plane wave at a random angle.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High gain, multi-beam antenna for 5g wireless communications
ActiveUS20170324171A1Improve directivityImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsFifth generationWeight gain
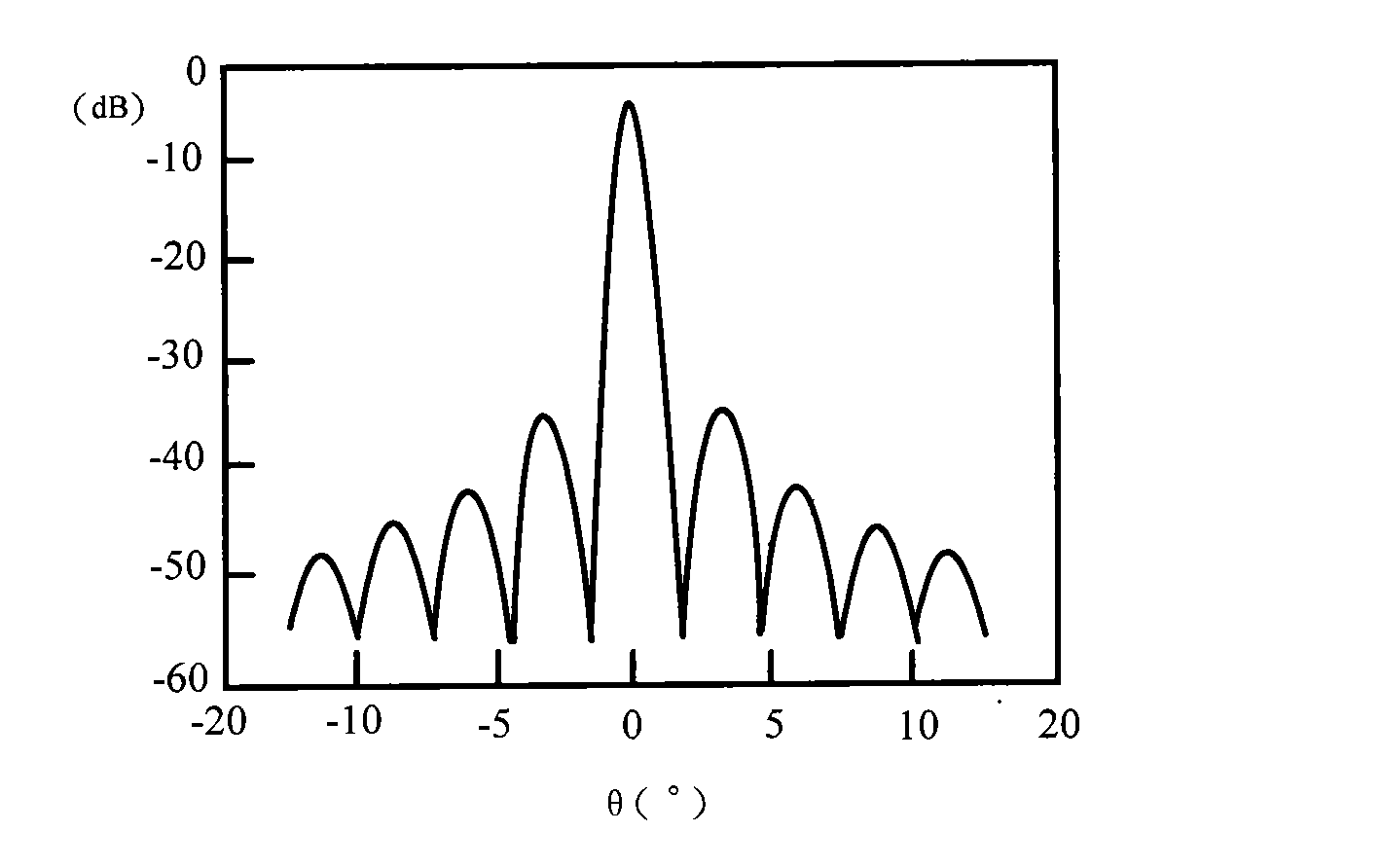
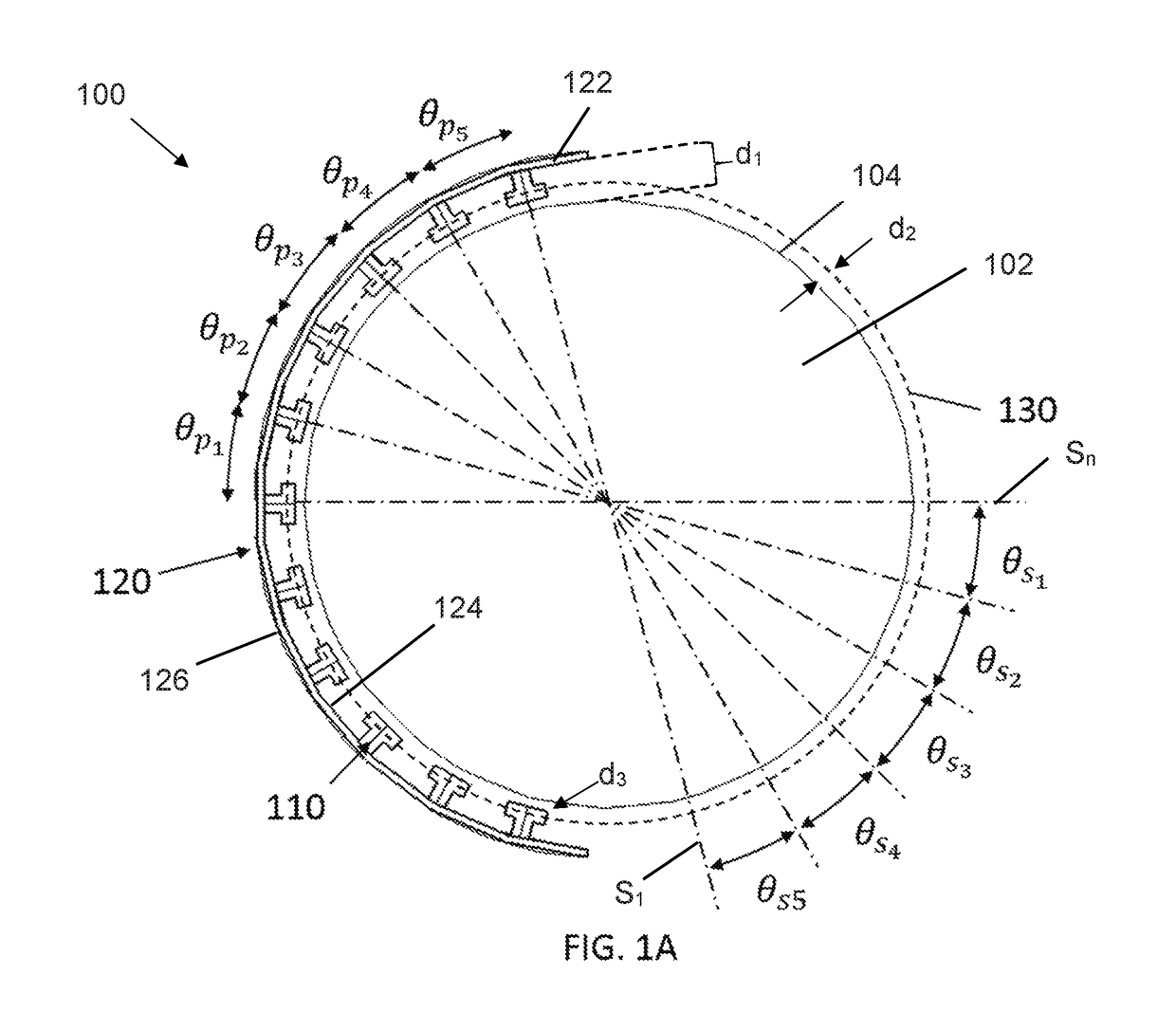
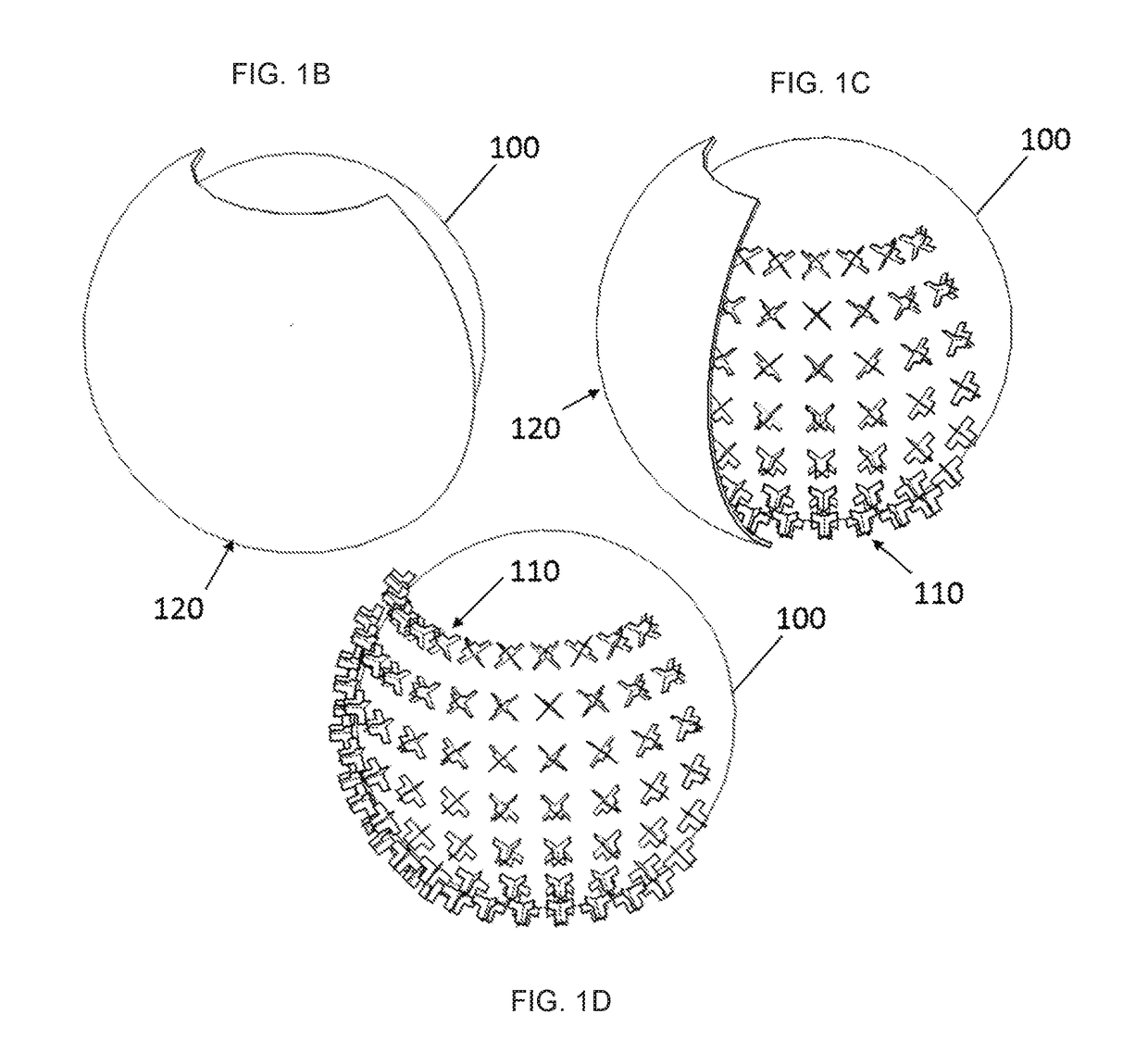
A high gain, multi-beam lens antenna system for future fifth generation (5G) wireless networks. The lens antenna includes a spherical dielectric lens fed with a plurality of radiating antenna elements. The elements are arranged around the exterior surface of the lens at a fixed offset with a predetermined angular displacement between each element. The number of beams and crossover levels between adjacent beams are determined by the dielectric properties and electrical size of the lens. The spherical nature of the dielectric lens provides a focal surface allowing the elements to be rotated around the lens with no degradation in performance. The antenna system supports wideband and multiband operation with multiple polarizations making it ideal for future 5G wireless networks.
Owner:AMPHENOL ANTENNA SOLUTIONS
Dielectric lens, dielectric lens device, design method of dielectric lens, manufacturing method and transceiving equipment of dielectric lens
InactiveUS20060202909A1Preventing antenna propertyAvoiding characteristicAntennasPath lengthSimultaneous equations
A design process first determines a desired aperture distribution, then converts the electric power conservation law, Snell's law on the rear face side of a dielectric lens, and the formula representing light-path-length constraint, into simultaneous equations, and computes the shapes of the surface and rear face of the dielectric lens depending on the azimuthal angle θ of a primary ray from the focal point of the dielectric lens to the rear face of the dielectric lens, and then reduces the light path length in the formula showing light-path-length constraint by an integral multiple of the wavelength when the coordinates on the surface of the dielectric lens reach a predetermined restriction thickness position. A dielectric lens is designed by sequentially changing the lazimuthal angle θ from its initial value, and also repeating the second and third steps. Thus, downsizing and quantification is realized by zoning while keeping antenna properties at the time of constituting a dielectric lens antenna in a good condition.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Millimeter wave marine frequency modulation multichannel anti-collision radar
InactiveCN101373217AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove reliabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency multiplierAcousto-optics
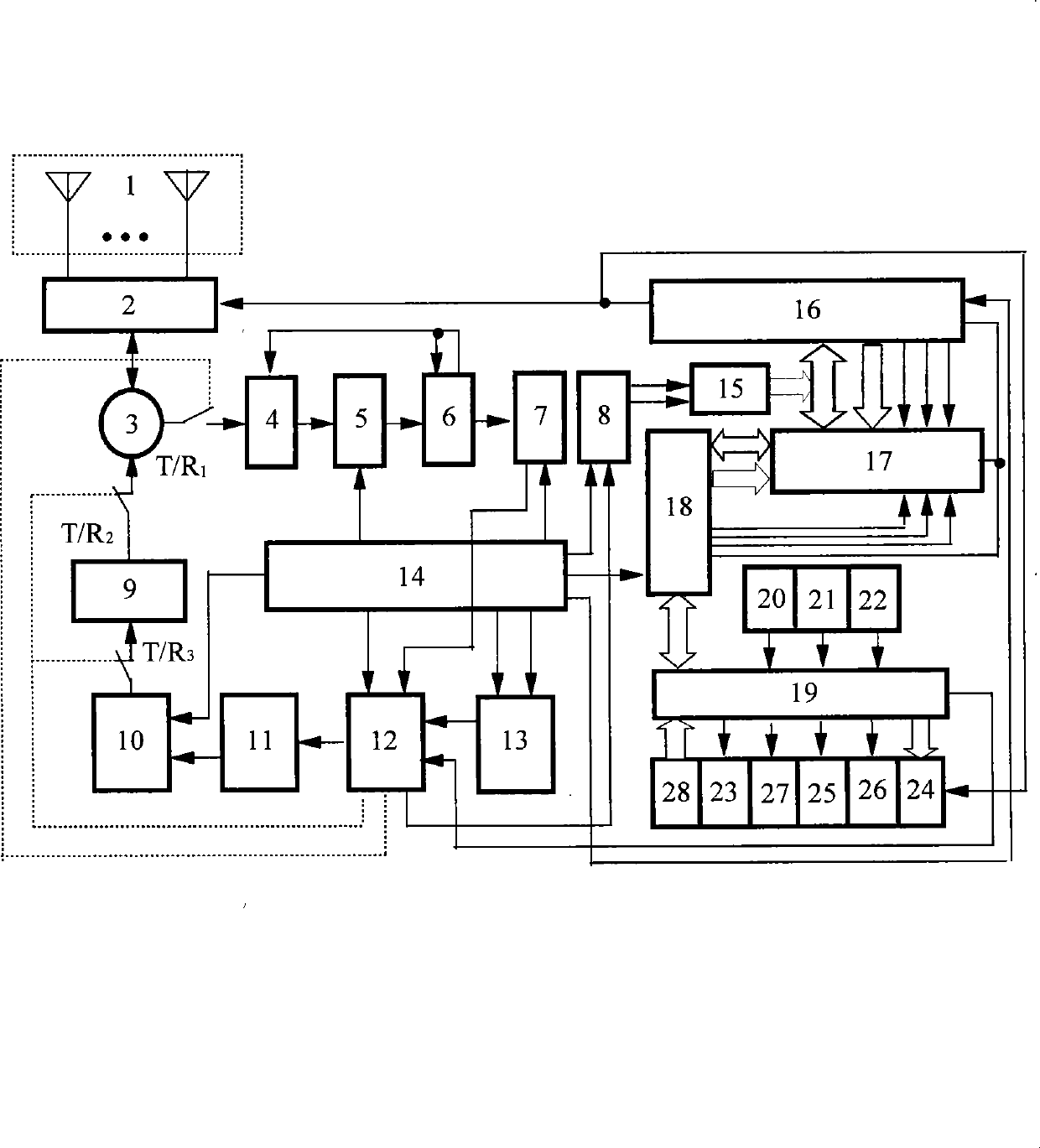
The invention relates to the radio-positioning technical field, particularly a millimeter-wave marine frequency modulation multi-channel anti-collision radar, which is realized through the following steps: adopting the full-phase parameters to receive / transmit reference signals; asynchronously controlling the time division and the time sequence; watching the targets which are prone to collision on the water surface in an omni-directional manner through DSP cyclic scanning wave beams by a quasi-optical dielectric lens antenna circular array; controlling the time division SAW multi-channel passive frequency modulation through a plurality of water surface waterway cameras, an own ship speed sensor, a satellite positioning sensor GPS data MCU; sending to antenna array to transmit through an up-converter, T / R3, a frequency multiplier and a power amplifier, a circulator and T / R2; extracting the SAW multi-channel signals from the returning wave through the antenna array, a wave beam switch, T / R1, the circulator, a high amplifier, a down-converter and a medium amplifier; detecting a plurality of barrier target DSPs so as to confirm the position, the distance and the relative speed; displaying the three-dimensional image on a CRT, wherein the closer the ship gets to the target, the higher the resolution power is; controlling the false-alarm identification and tracing the nearest targets; giving an alarm when the distance is smaller than the safety distance; and intelligently avoiding the barriers or reducing if the distance is close to a risk distance, wherein the control is determined based on the actual condition of the water surface environment combined with the own ship speed and the GPS data, thereby improving the shipping safety.
Owner:阮树成
Apparatus and methods for mapping retinal function
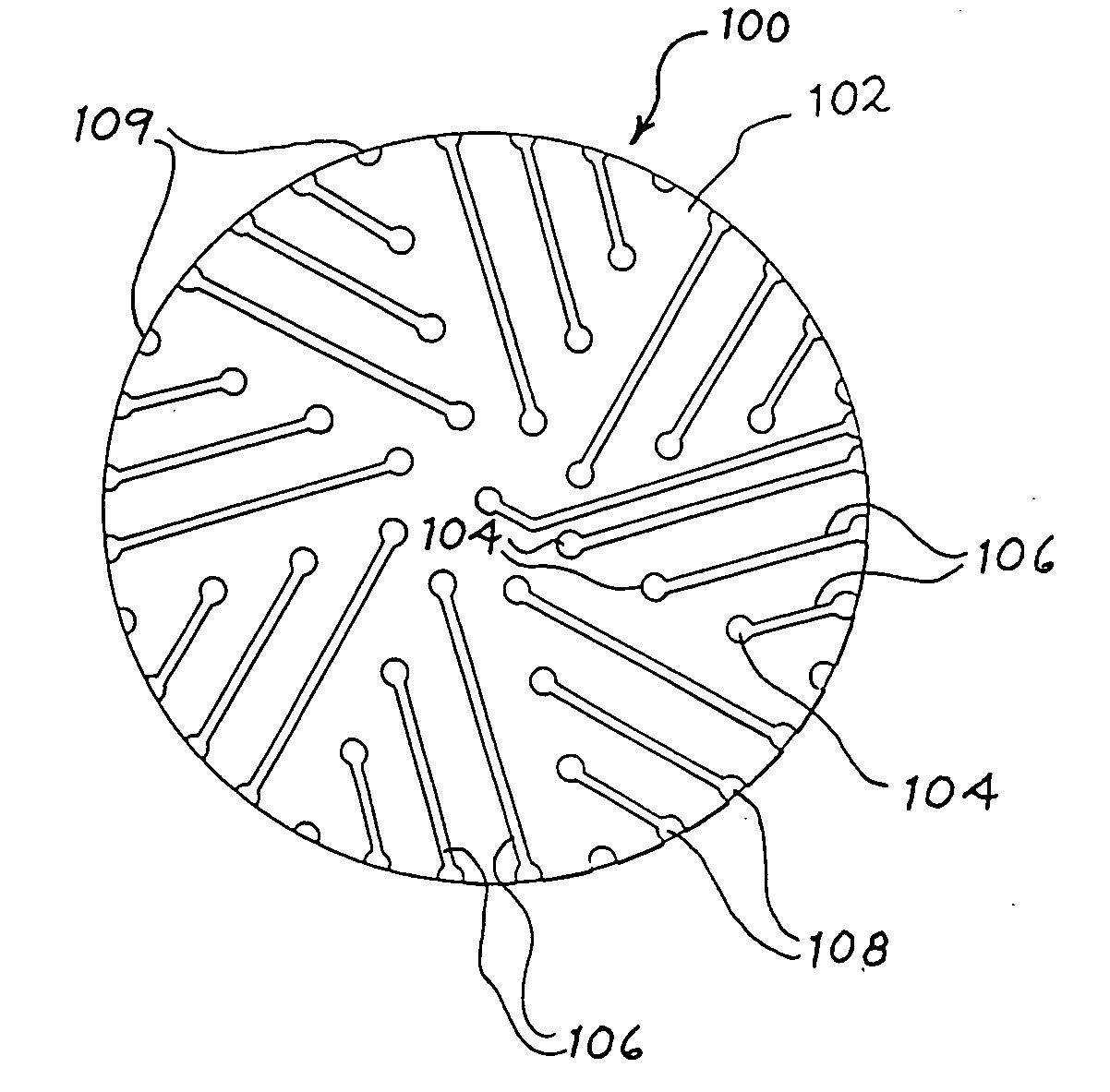
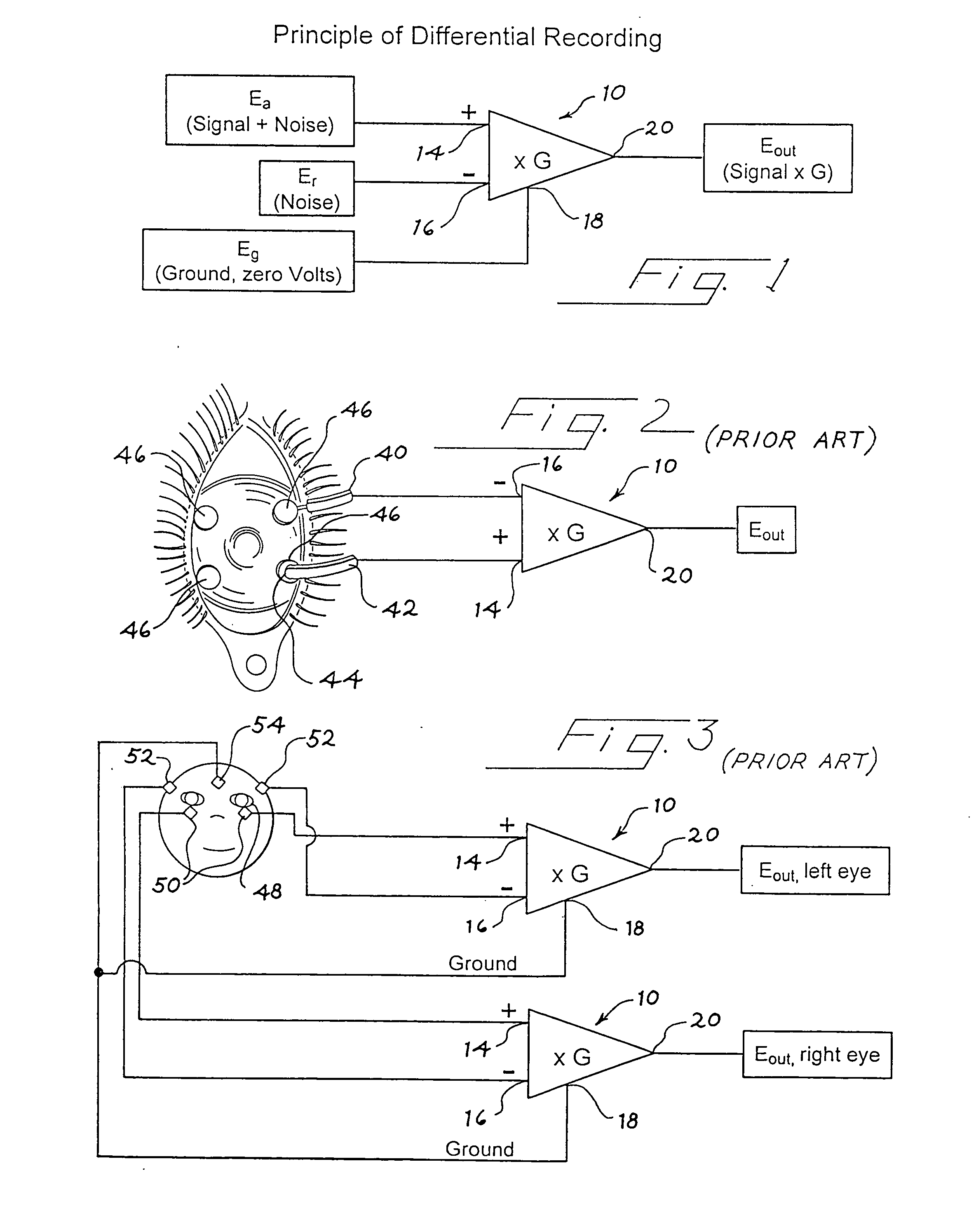
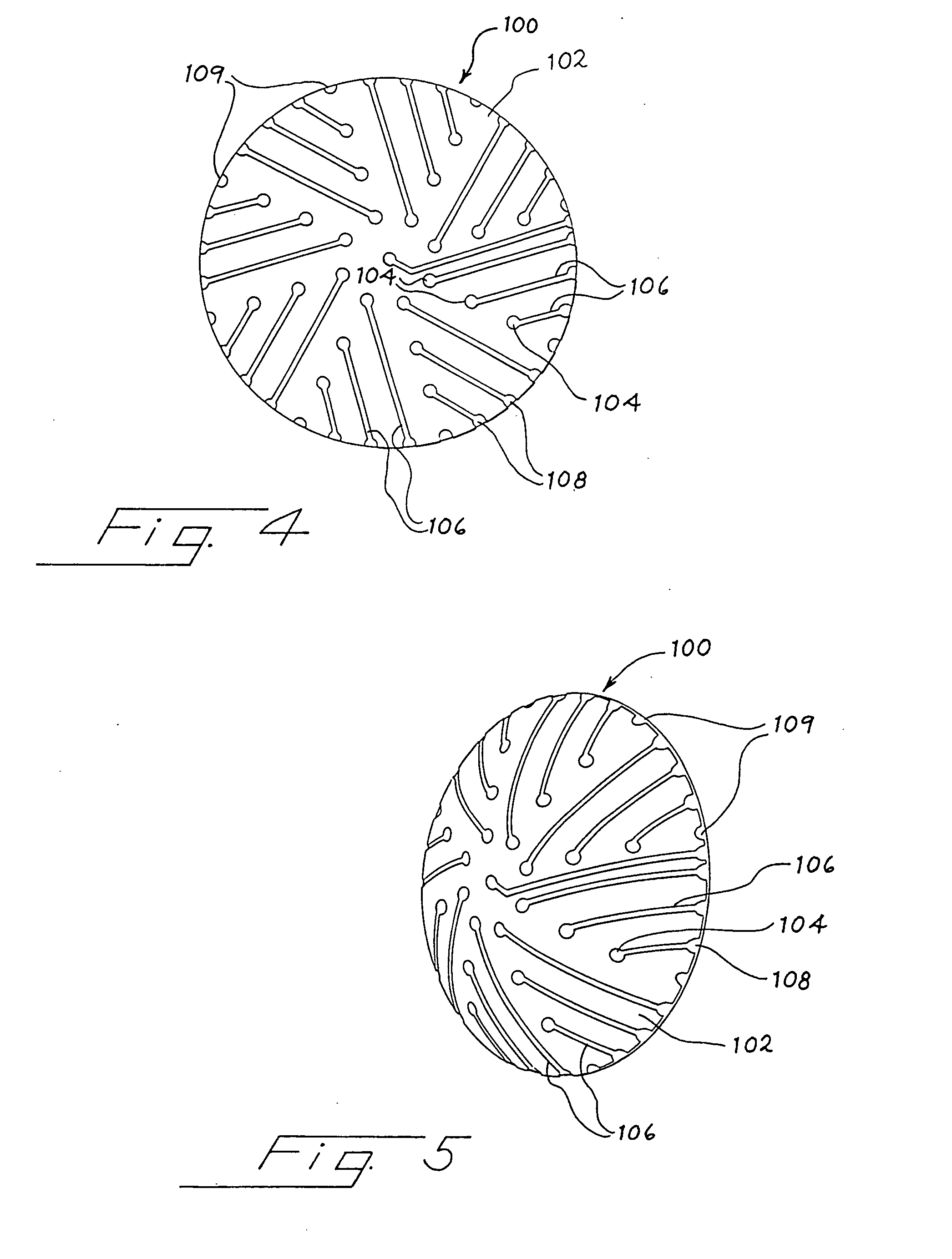
The present invention provides an electrode array device for simultaneously detecting electrical potentials at five or more locations on the anterior surface of an eye. The device comprises a dielectric lens substrate having a concave inner surface conforming to the anterior surface of the eye, and at least five recording electrodes positioned in relation to the inner surface of the lens substrate so as to make electrical connection with the anterior surface of the eye when the lens substrate is placed on the anterior surface of eye. Each recording electrode is in electrically conductive communication with a corresponding conductive contact, there being one conductive contact for each recording electrode. Each conductive contact is adapted for operable connection to signal processor, and each conductive contact is electrically insulated from the anterior surface of the eye. A computational method for analyzing electrophysiological potentials recorded at five or more locations on the anterior surface of the eye, which reflect the spatial distribution of activity of the retina, is also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
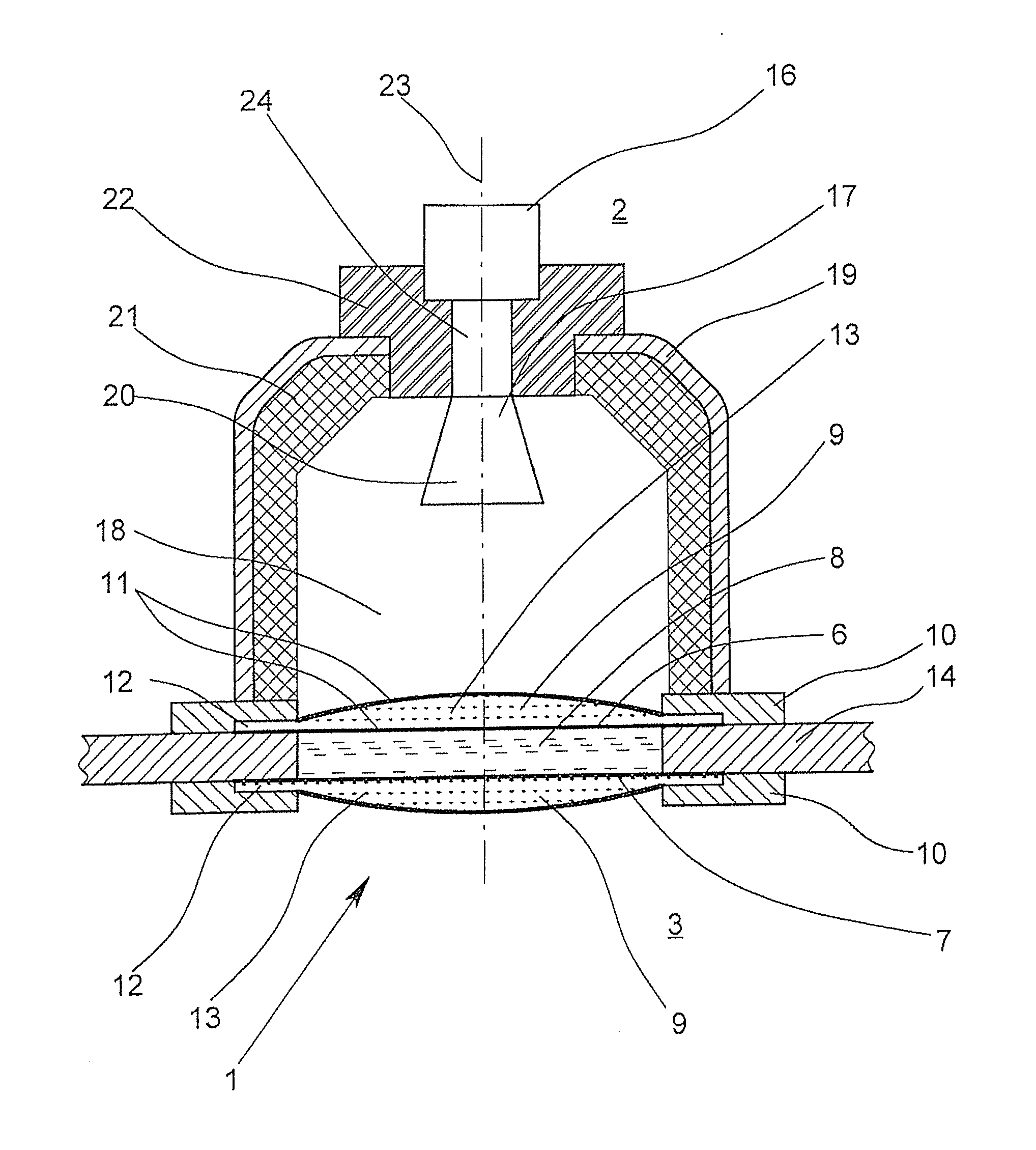
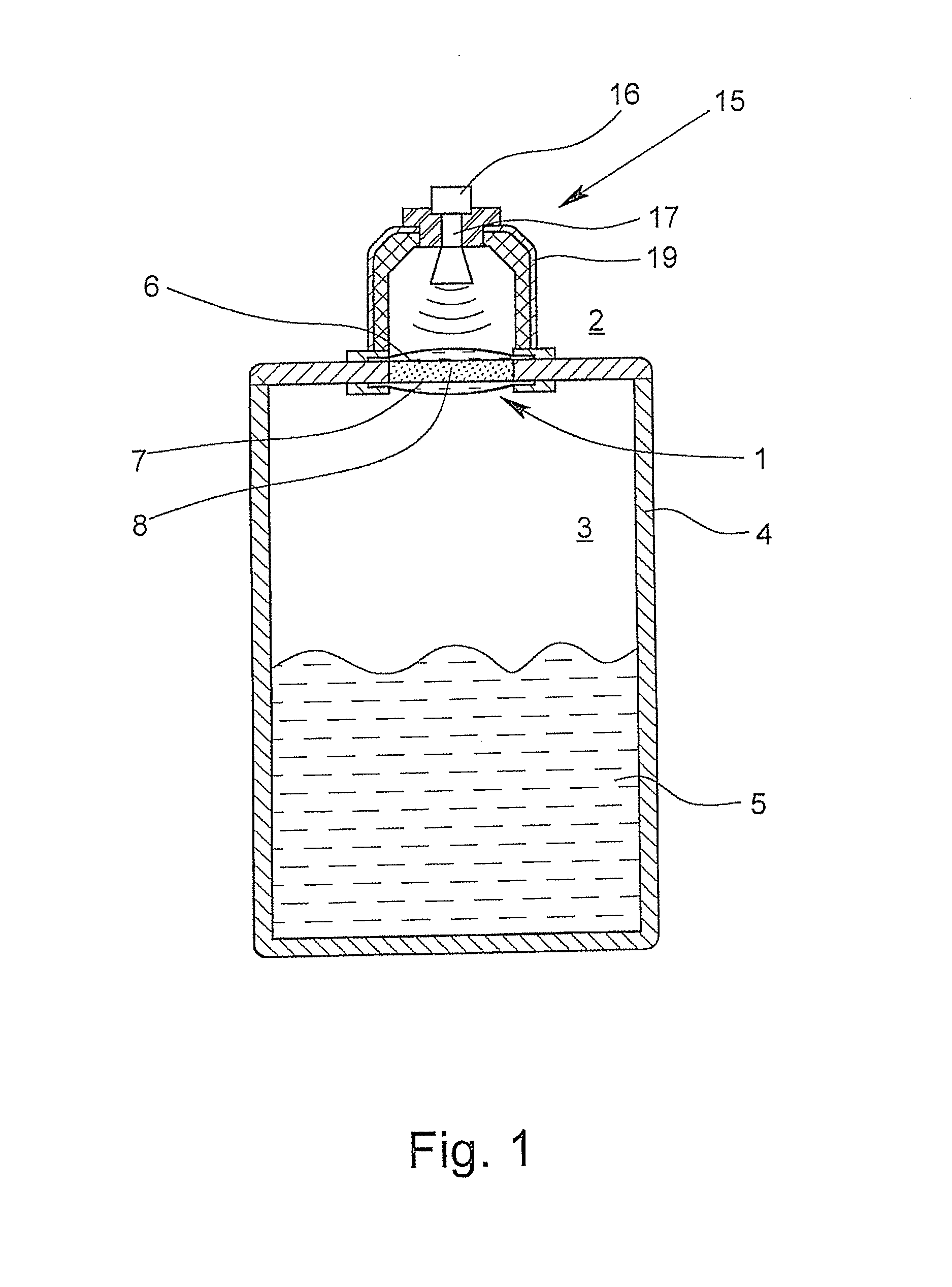
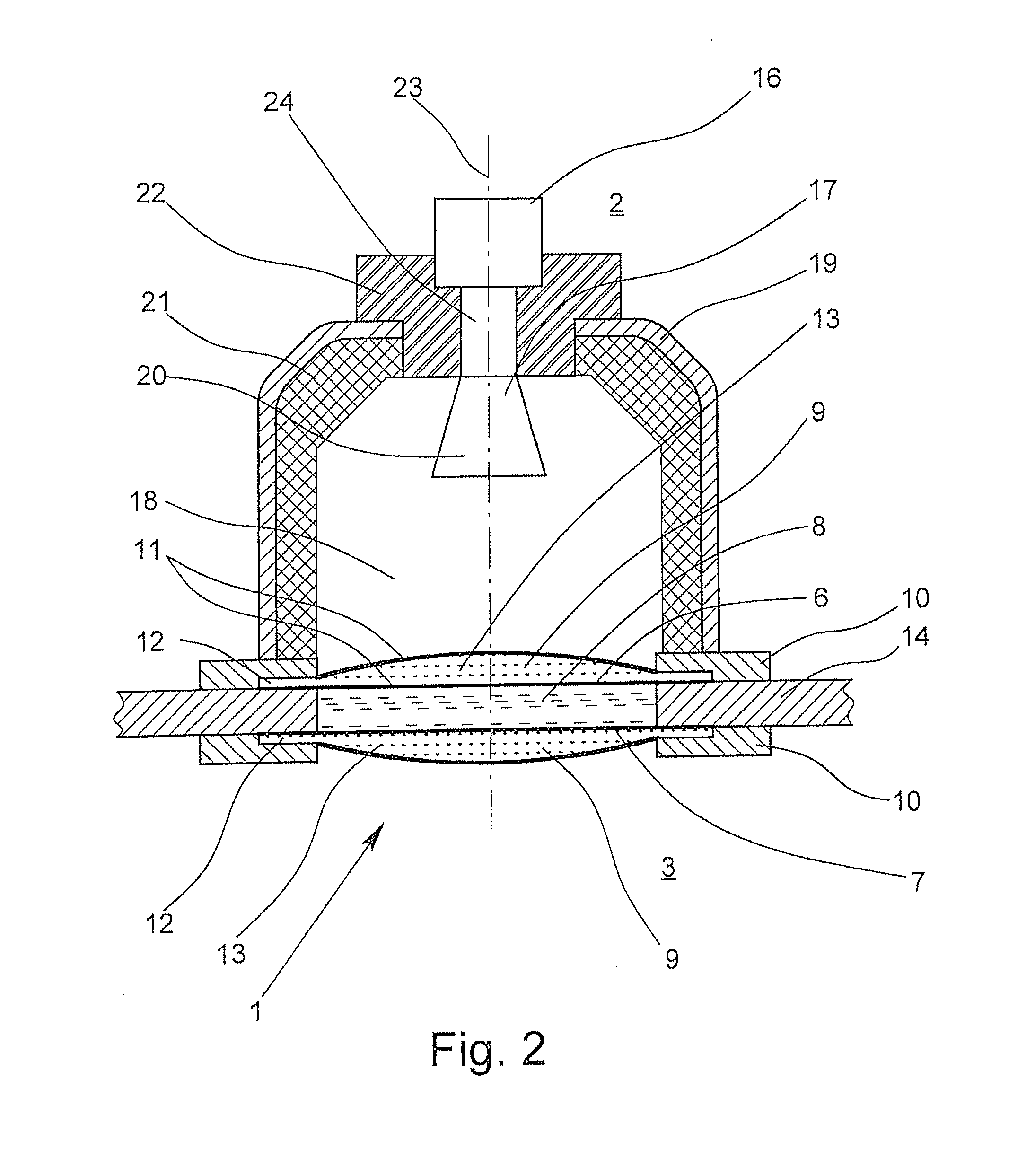
Microwave window and level-measuring system that works according to the radar principle
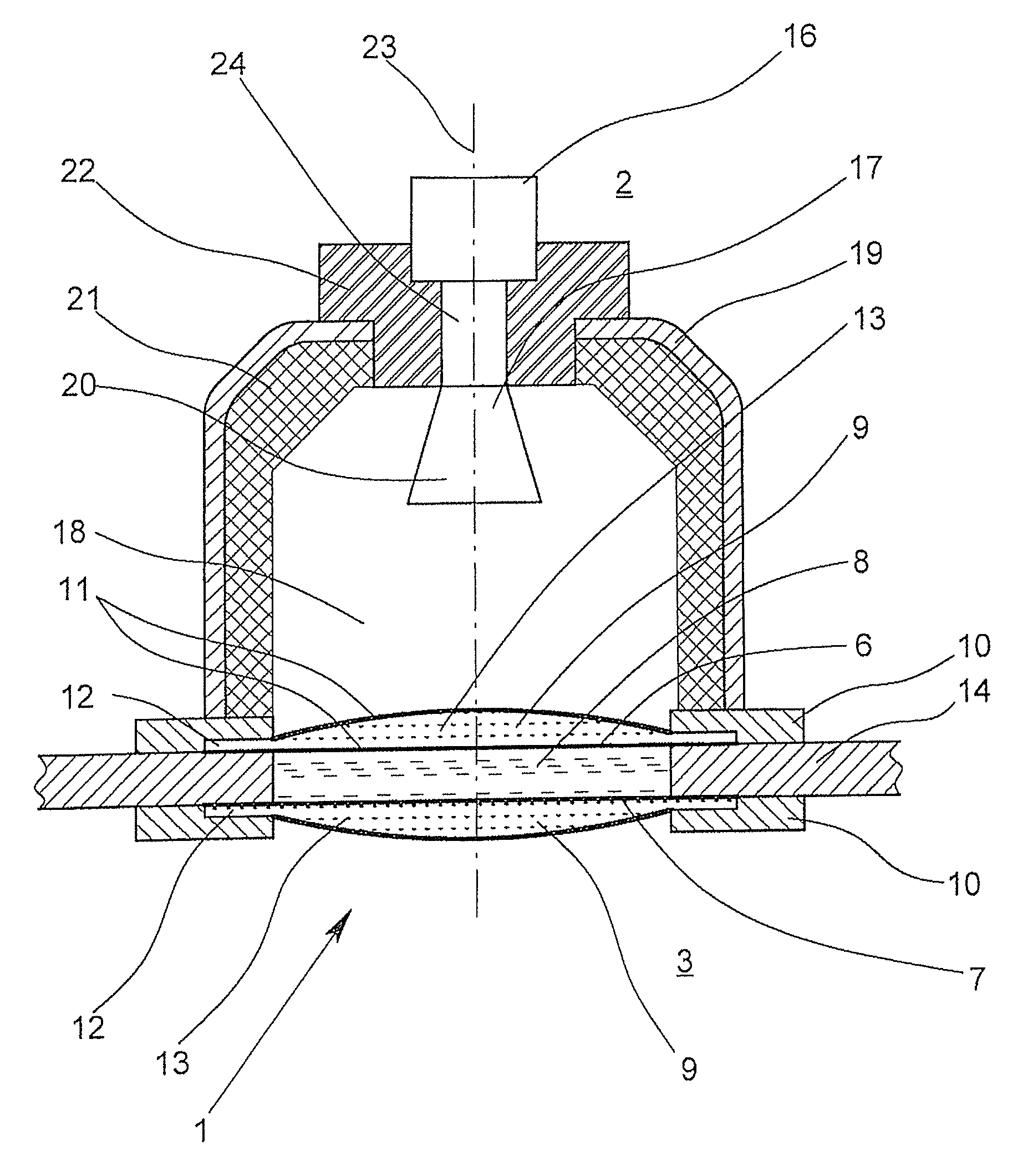
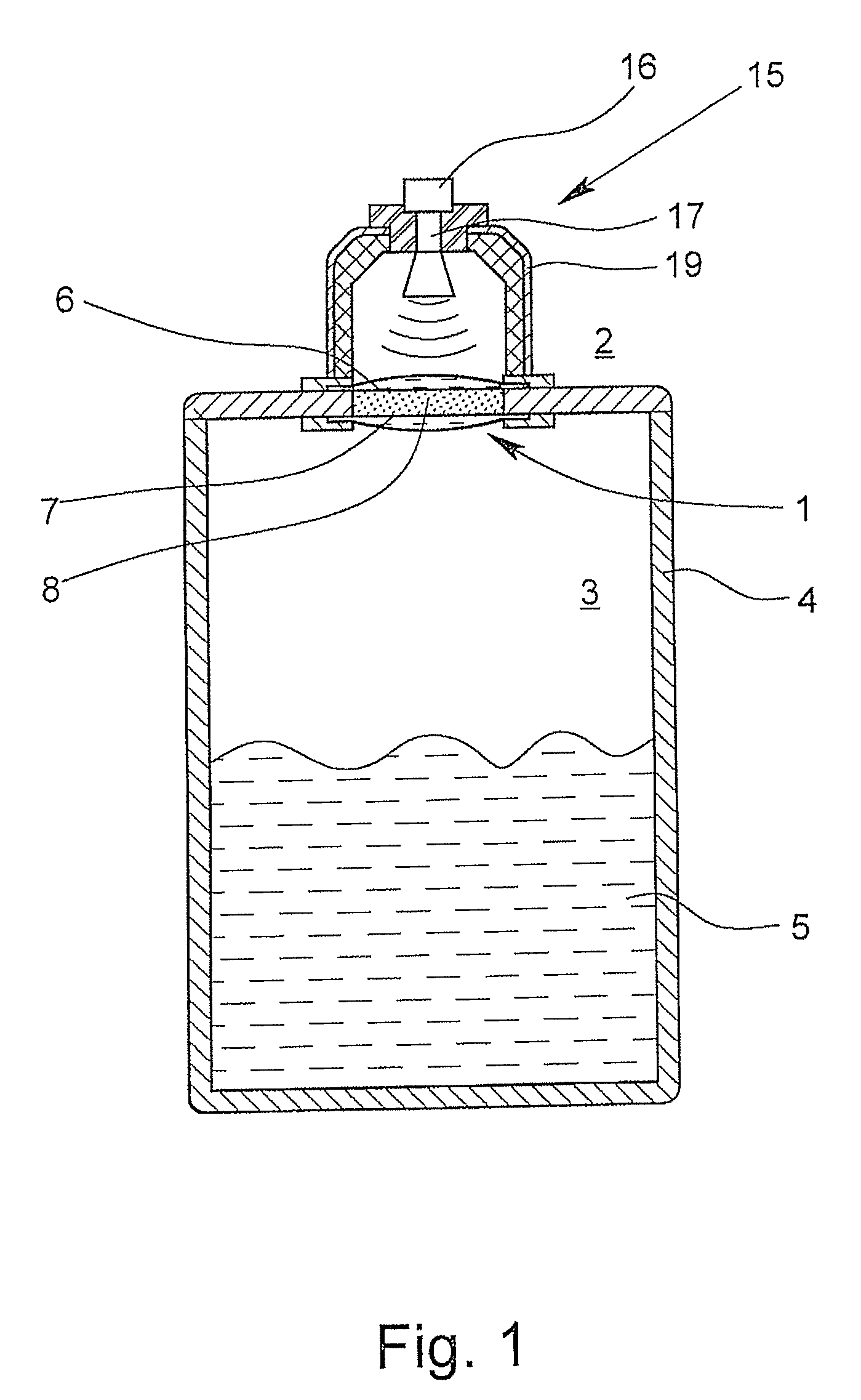
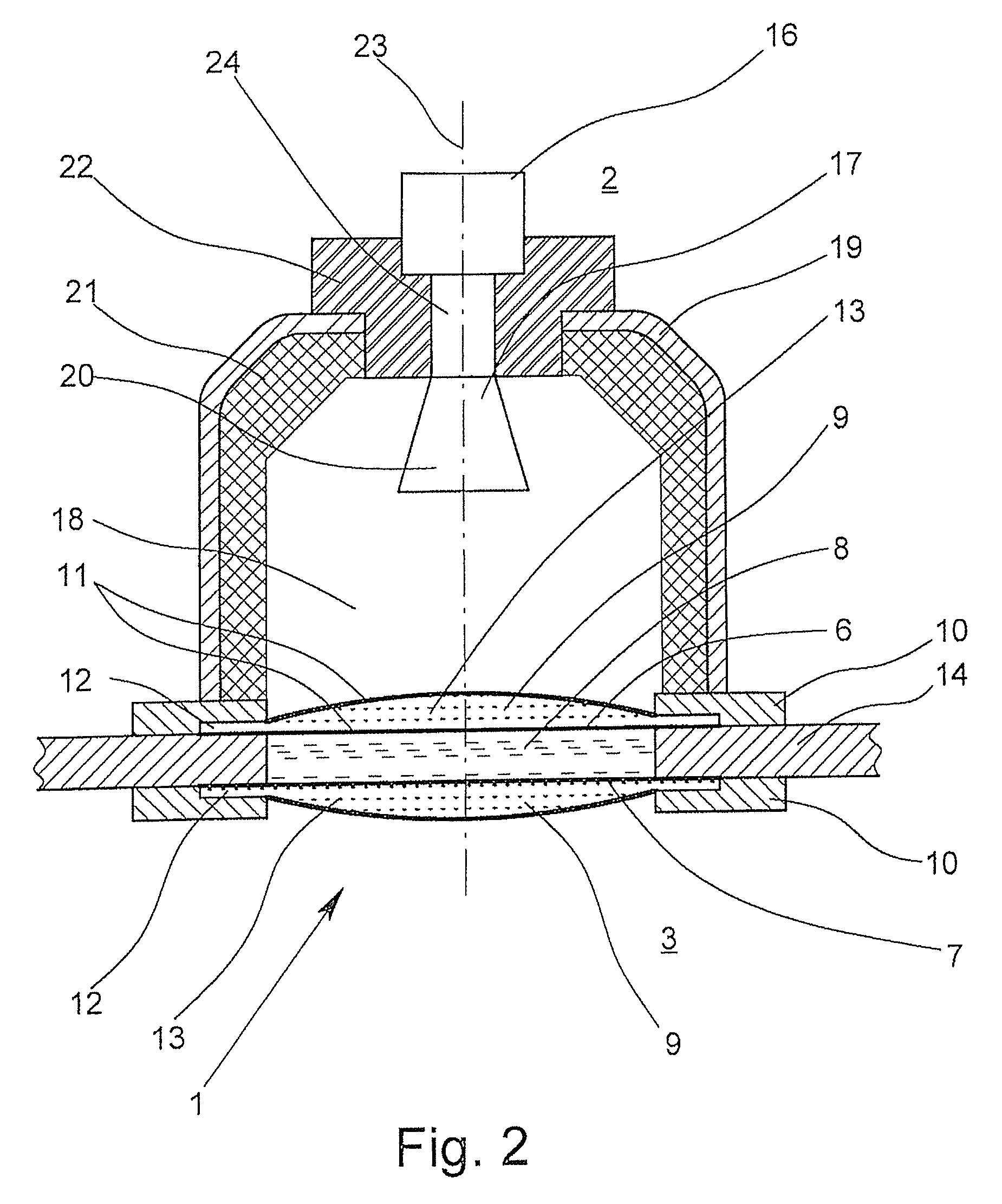
ActiveUS20140047917A1Improve sealingAccurate measurementRadiating element housingsMachines/enginesDiffusionMicrowave
A microwave window for the spatial, pressure-impervious and diffusion-impervious separation and microwave connection of a first space from / to a second space, and a level-measuring system that works according to the radar principle, is provided with a barrier that has two opposite sides and is at least partially permeable to microwaves. To provide a microwave window that makes possible a reliable sealing of a process space and exact measurement, the microwave window has the barrier designed as a disk on at least one side of which at least one plano-convex dielectric lens, which has an essentially homogenous body.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
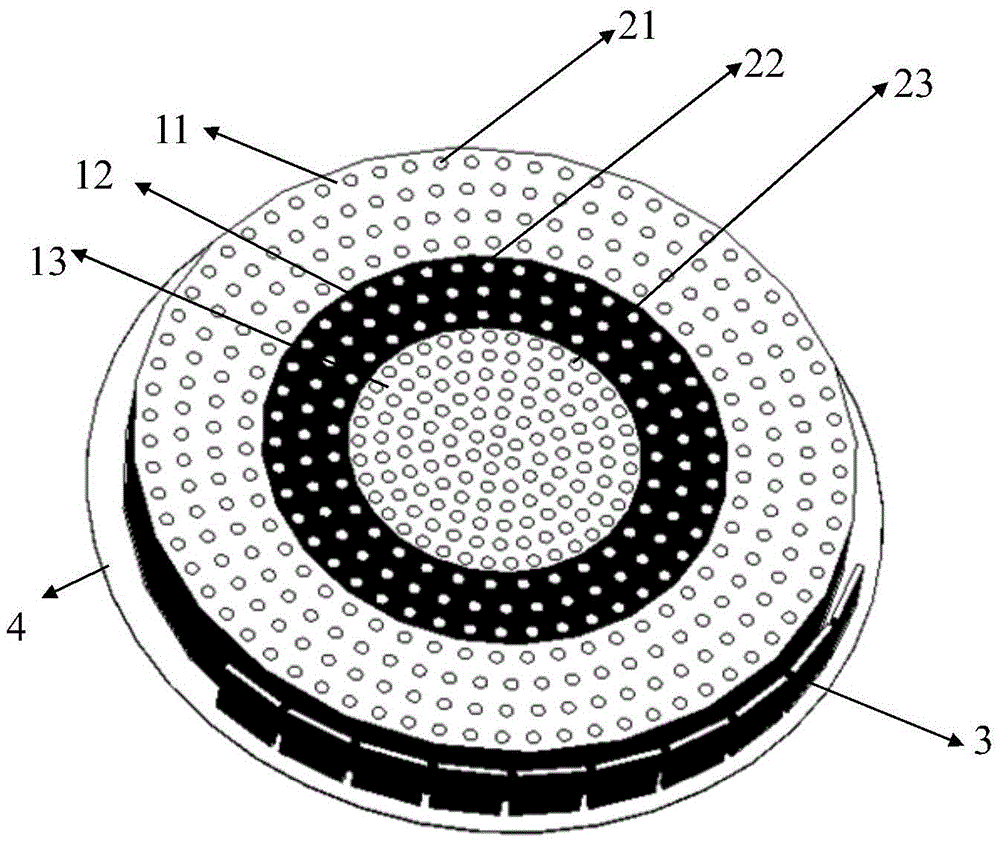
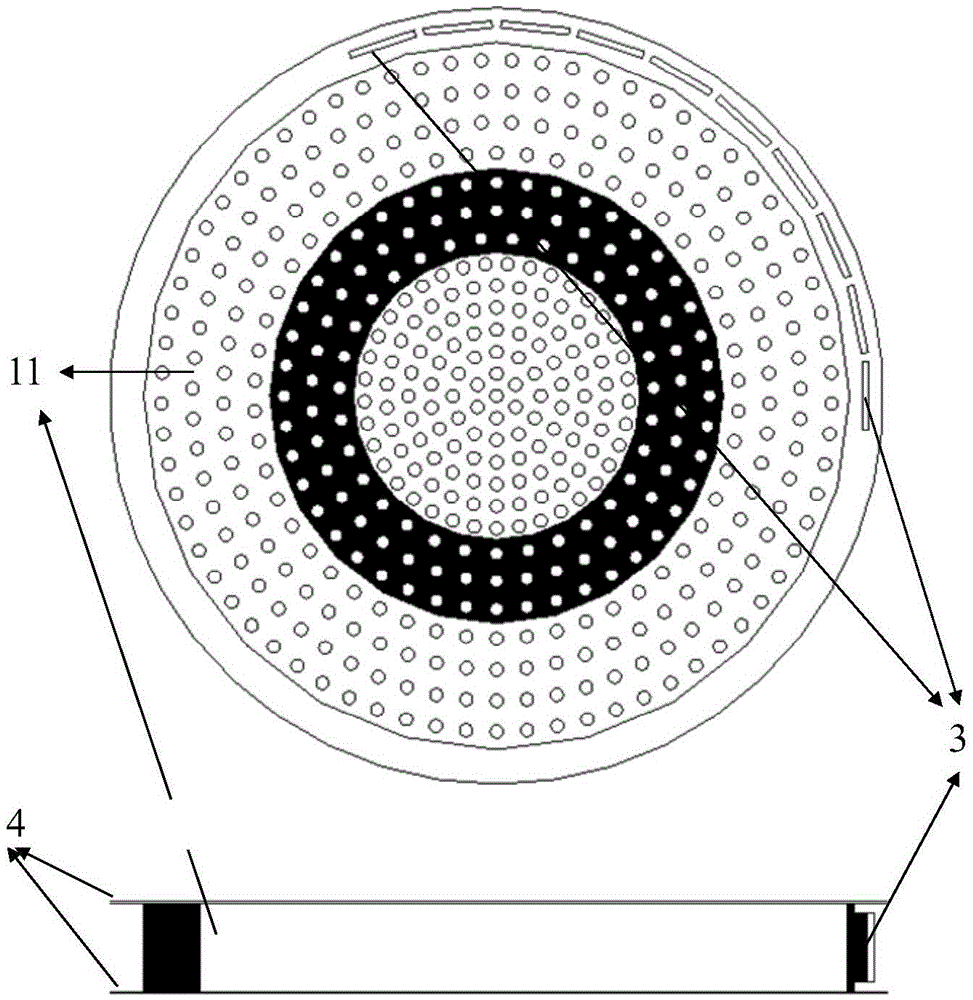
Lightweight dielectric-filled multi-beam cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna
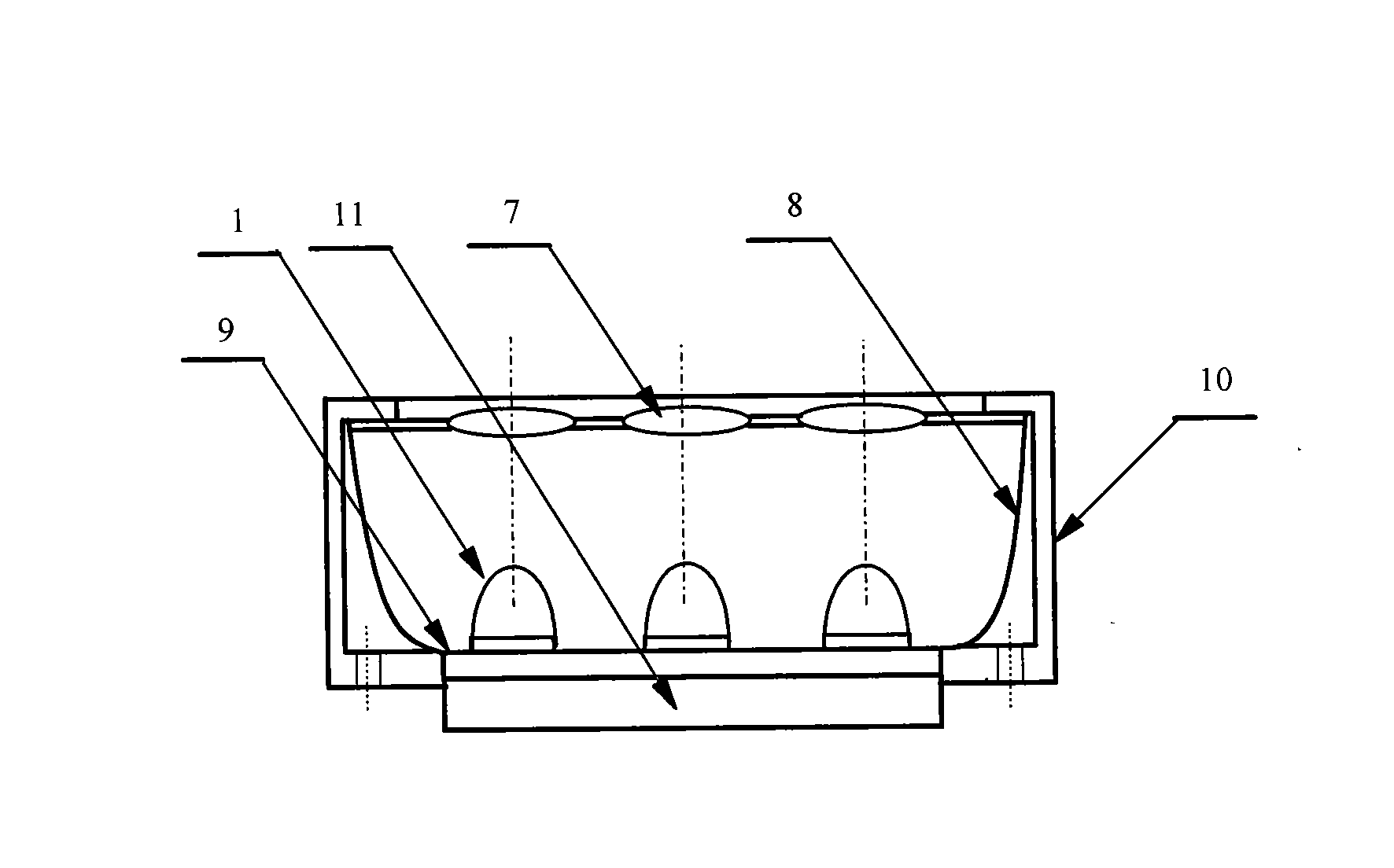
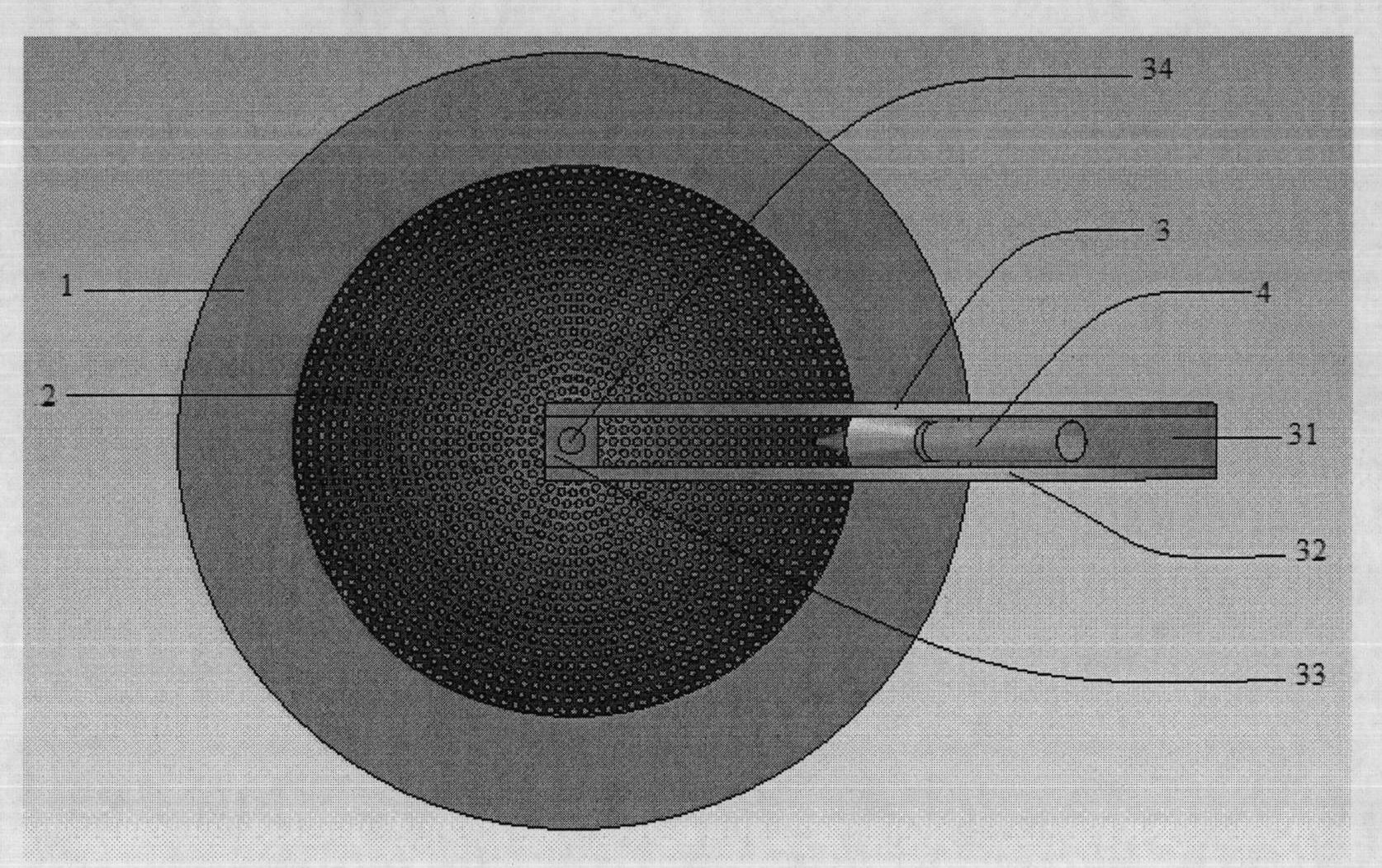
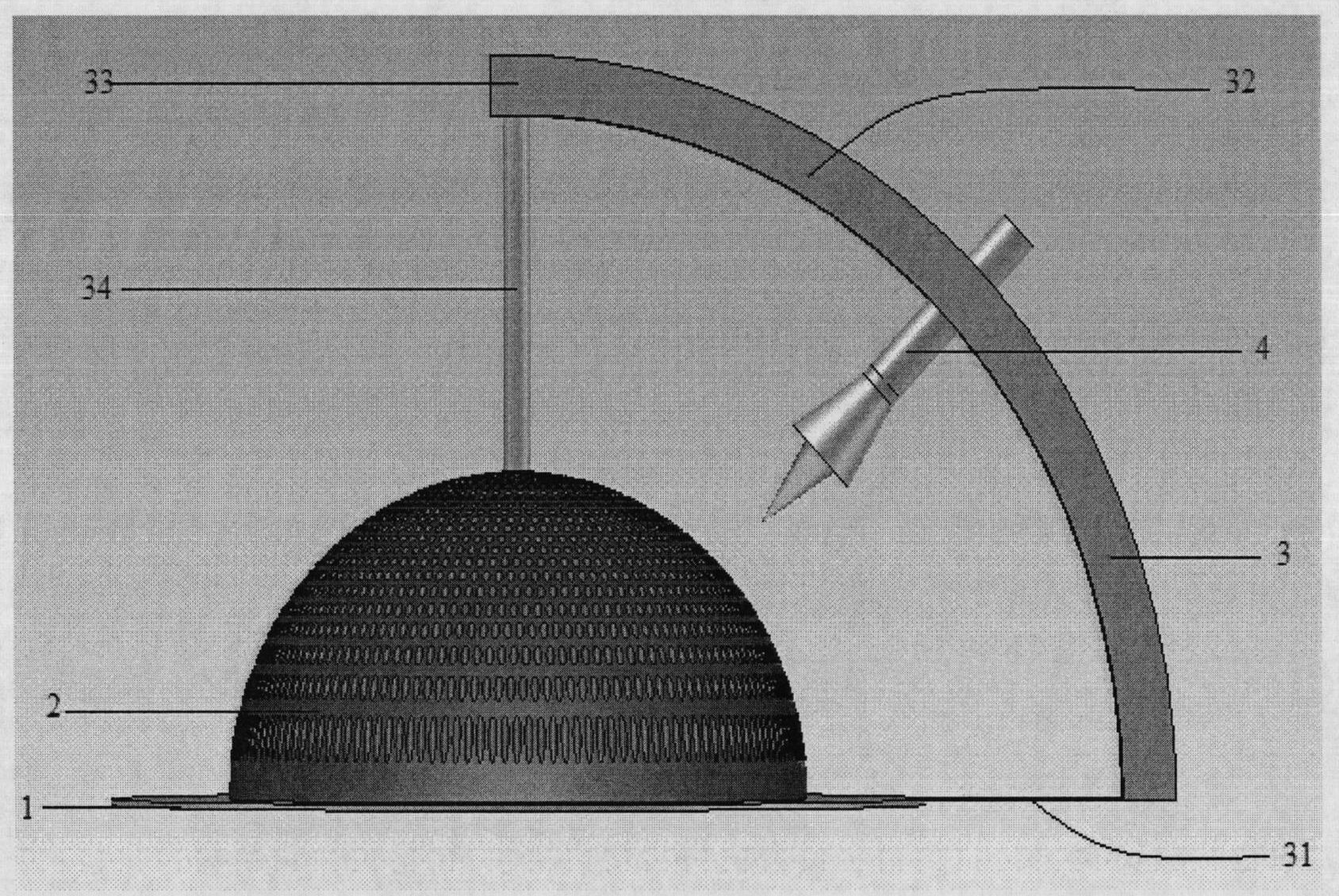
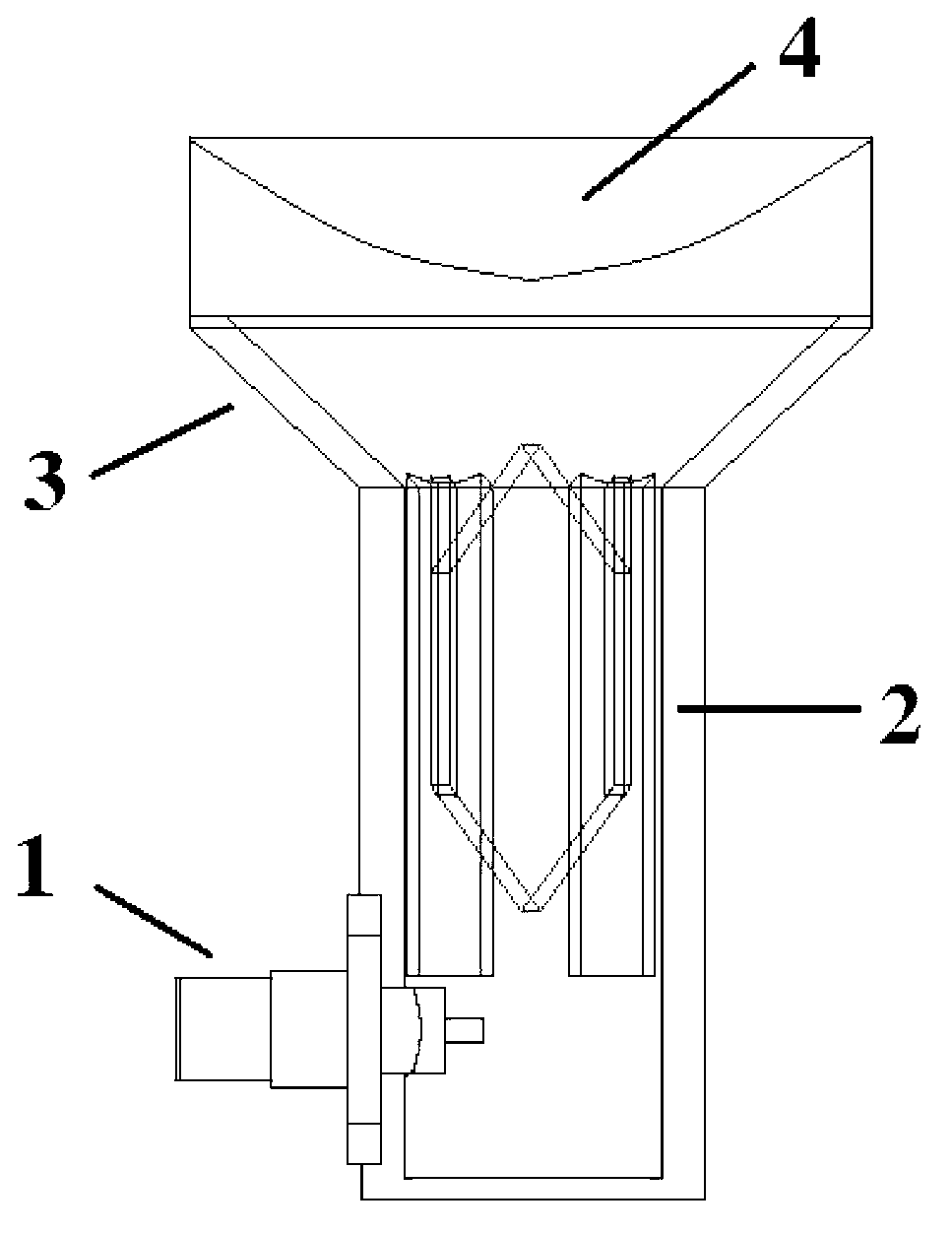
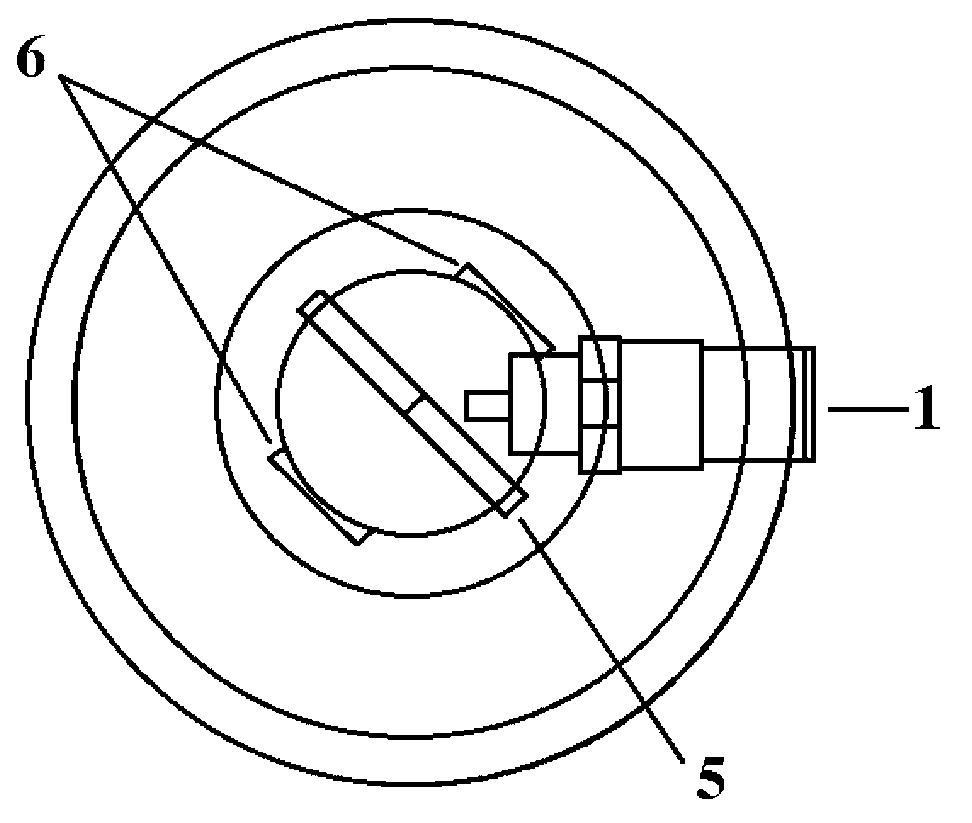
The invention discloses a lightweight dielectric-filled multi-beam cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna applied to multi-beam directional communication and beam scanning. The basic structure of the lightweight dielectric-filled multi-beam cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna comprises a cylindrical Luneberg dielectric lens and a curved array (3), wherein the curved array (3) comprises a plurality of E-shaped microstrip antenna feed sources; the cylindrical Luneberg dielectric lens between two parallel metal plates (4) is divided into three layers, namely an outer layer lens (11), a middle layer lens (12) and an inner layer lens (13); the three layers all adopt lightweight foam with a low dielectric constant as a substrate material; holes are formed in the substrate material and are filled with dielectric rods with high dielectric constants; the holes in the three lenses sequentially become dense from the outside to the inside; and the curved array (3) is fixed between the two parallel metal plates (4). The holes are formed in the substrate material with the low dielectric constant and are filled with a dielectric material with a high dielectric constant, so that required gradient dielectric constant is achieved; and lightweight of the antenna is achieved when the electrical property of the antenna is met.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
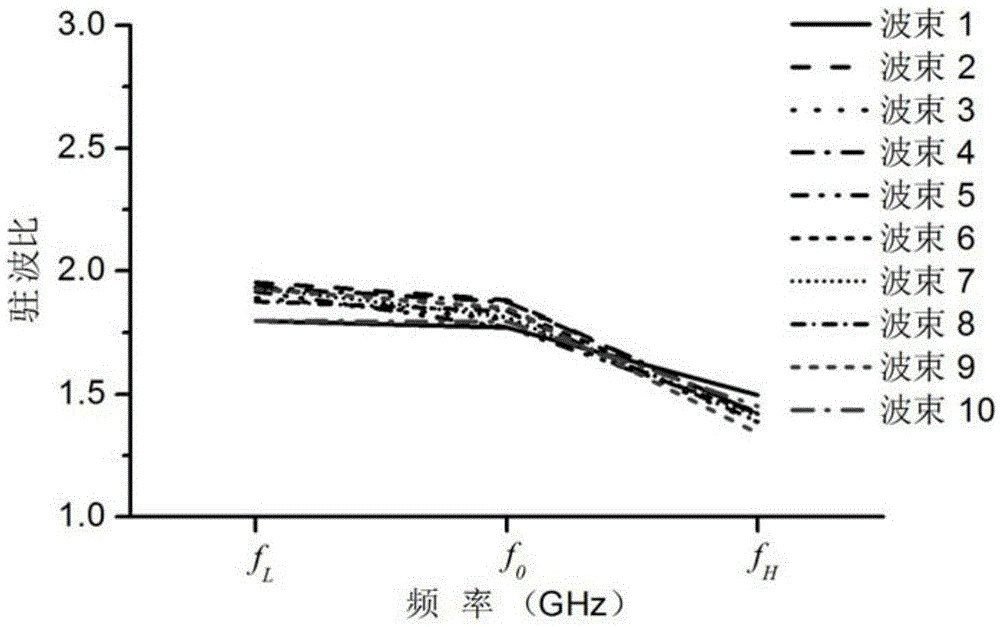
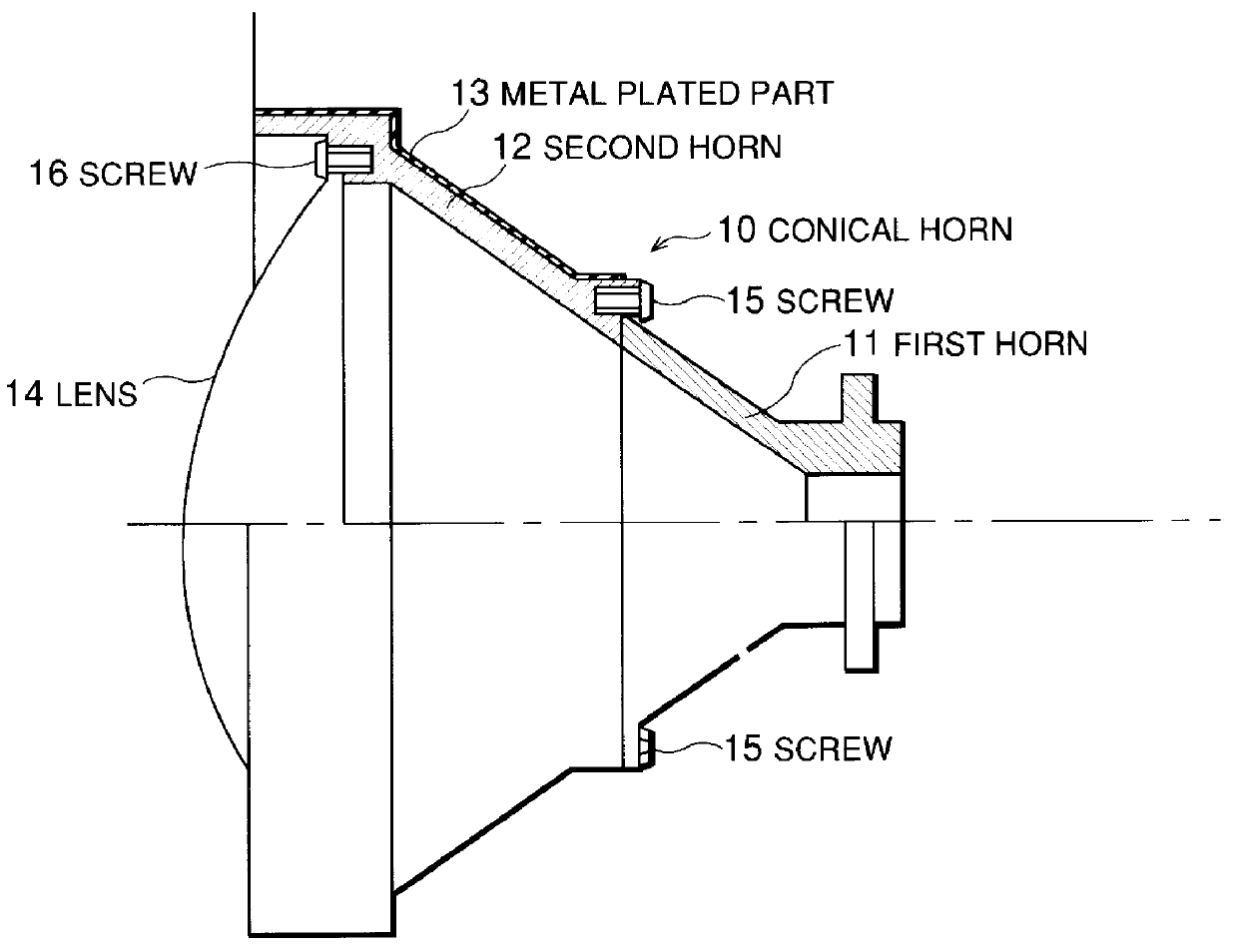
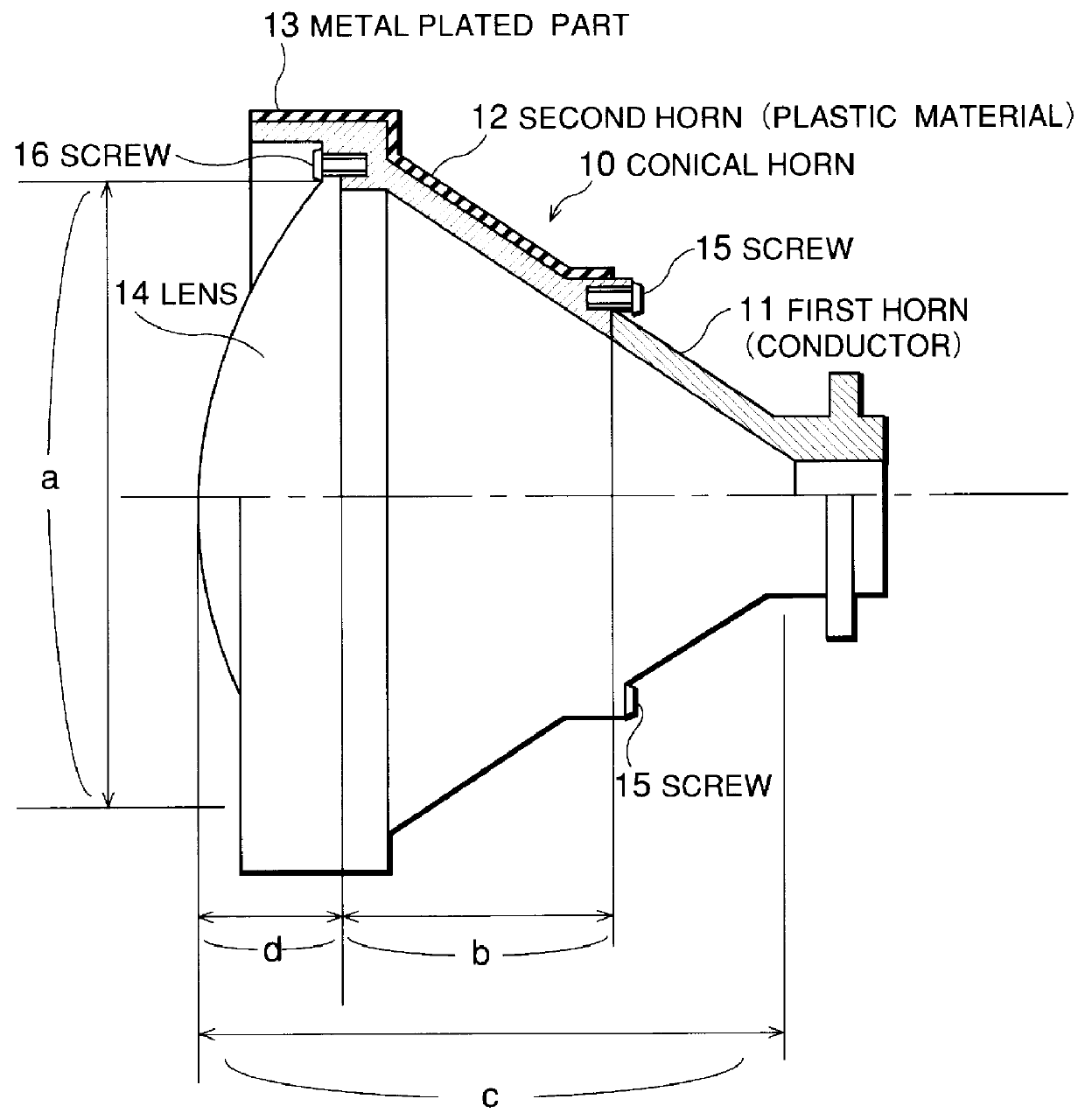
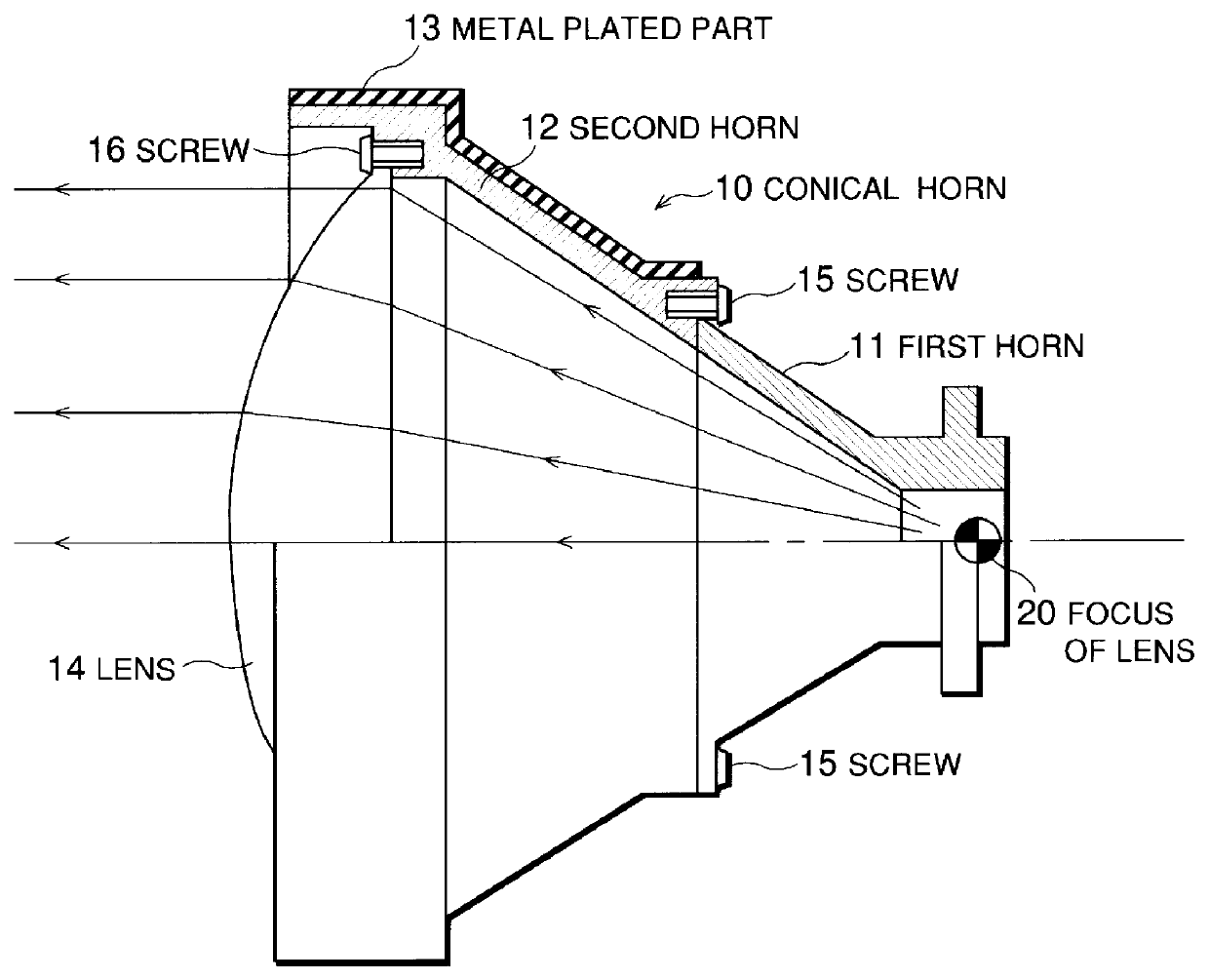
Lens antenna with tapered horn and dielectric lens in horn aperture
A lens antenna having high antenna efficiency, low sidelobe levels, and that is easily assembled. The lens antenna includes a first horn made of a metallic conductor, a second horn made of a high-frequency absorbing plastic material, and a lens for controlling the power distribution at an aperature of the horn. Screws may be used to assemble the first horn, the second horn, and the lens. Though some of the microwave signals input through the circular waveguide of the first horn are reflected on the surface of the lens, most of the microwave signals are absorbed by the second horn. Moreover, because no wave absorber is bonded to an inner wall of a conical horn, nothing screens the microwave signal, the power density distribution at the aperture of the lens is not disrupted. Therefore, it is possible to obtain a desired power density distribution.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multi-beam antenna with shared dielectric lens
An integrated multi-beam antenna with a shared dielectric lens is disclosed. The antenna is formed by positioning the feed apertures of a plurality of waveguide feeds at positions located on the surface of the shared dielectric lens. The angular direction and shape of radiation beams produced by the waveguide feeds are determined by the physical and dielectric characteristics of the lens, the location of feed apertures of the waveguide feeds on the surface of the lens, and the frequency of electromagnetic energy propagating in the waveguide feeds. The principles of the invention are applied to realize an inexpensive, integrated multi-feed antenna adapted to provide desired angular areas of coverage for both a long range and short range radar in an automotive radar safety system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Apparatus for focusing plasmon waves
InactiveUS7106935B2Valid conversionManufacture head surfaceNanoinformaticsMagnetic polesHeat induced
An apparatus for focusing plasmon waves to a spot. The plasmon waves are there converted to light. In one application, the light is used for heat induced magnetic recording. In another application, the light is used as a part of near field scanning microscope. The plasmon waves may be induced on a converging rectangular cone having an aperture. The plasmon waves may also be focused on a flat surface by a curved dielectric lens. In the heat induced magnetic recording embodiment, a magnetic pole structure is integrated into the focusing apparatus, either as one surface of the rectangular cone, or as a layer upon which the curved dielectric lens is formed.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
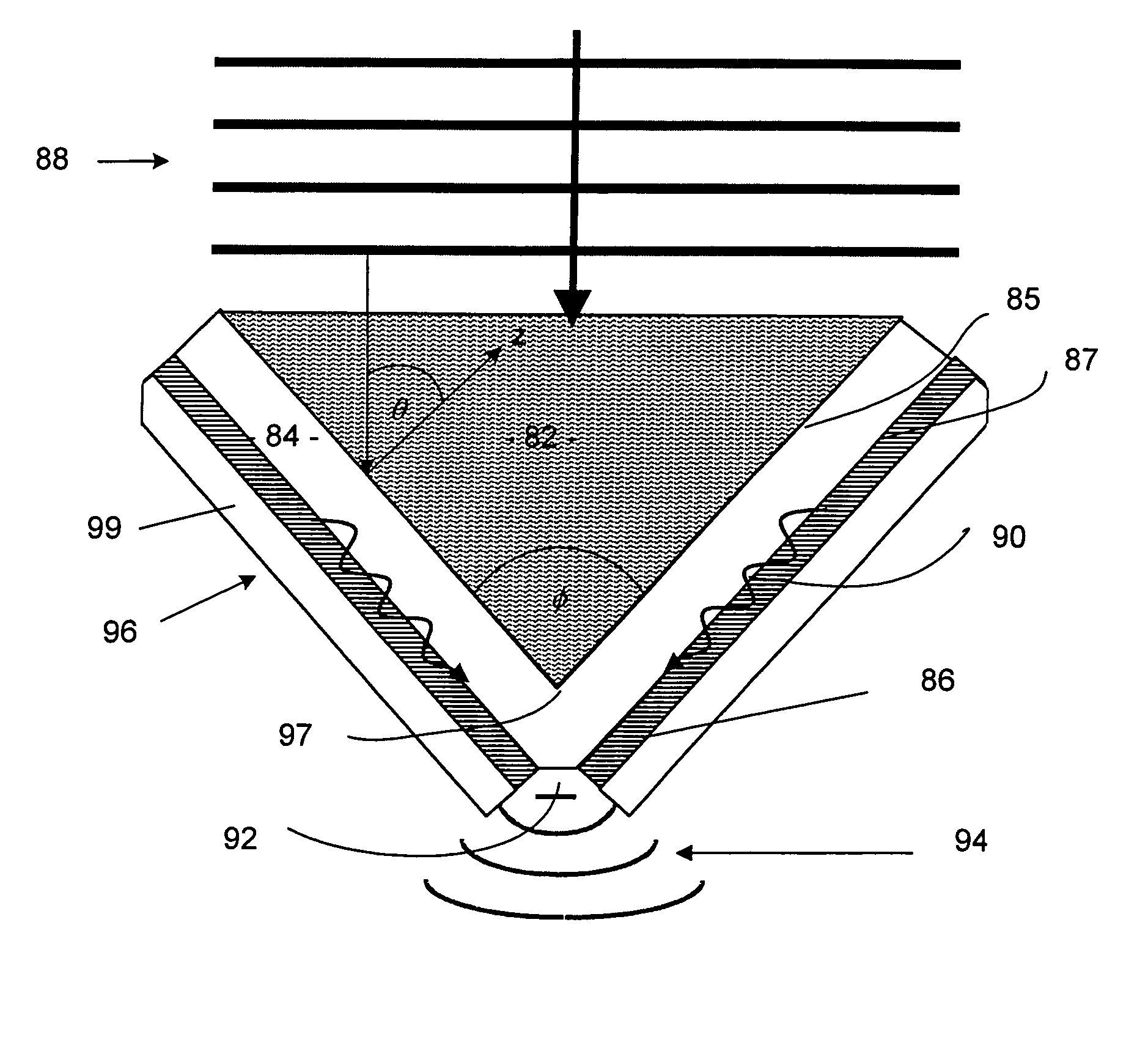
High-efficiency dielectric lens antenna based on novel open-celled structure
InactiveCN101976755AReduce physical sizeEasy to fixAntenna supports/mountingsBeam angleOptoelectronics
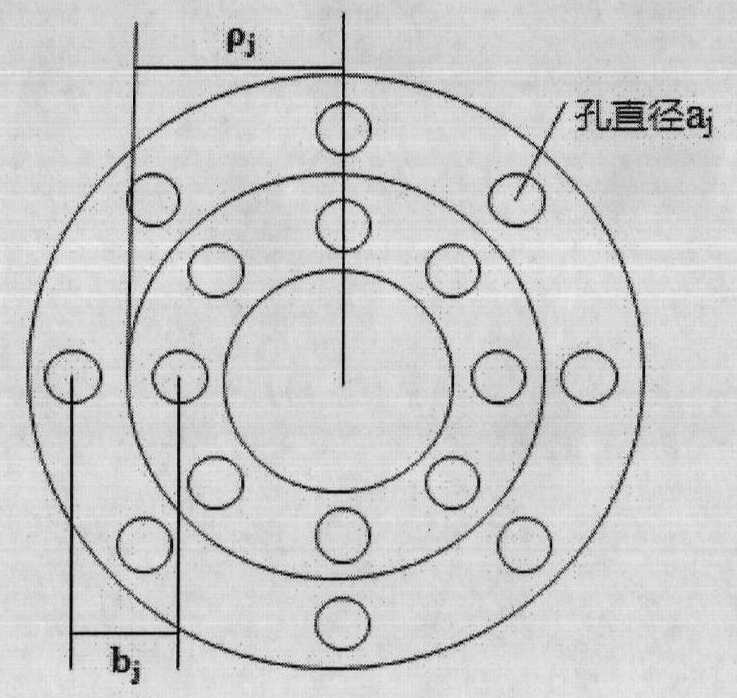
The invention discloses a dielectric lens antenna applied to wireless satellite communication in a luneberg lens antenna system. The basic structure of the dielectric lens antenna comprises a metallic reflecting plate part, a feed-source bracket part, a dielectric lens part and a feed-source part. The metallic reflecting plate part mainly performs shielding and reflecting actions. The dielectric lens part is formed by drilling a cylindrical hole in polytetrafluoroethylene and fixed on the metallic reflecting plate. The feed-source bracket is fixed between the metallic reflecting plate and the dielectric lens, the feed source is fixed on the feed-source bracket, and the incident and emergent foci and the beam angle of the feed source are determined through the slide and the extension of the feed source on the feed-source bracket. Based on the basic structure of the invention, the position, the size and the shape of an air hole are reasonably changed so as to form other concrete embodiments of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
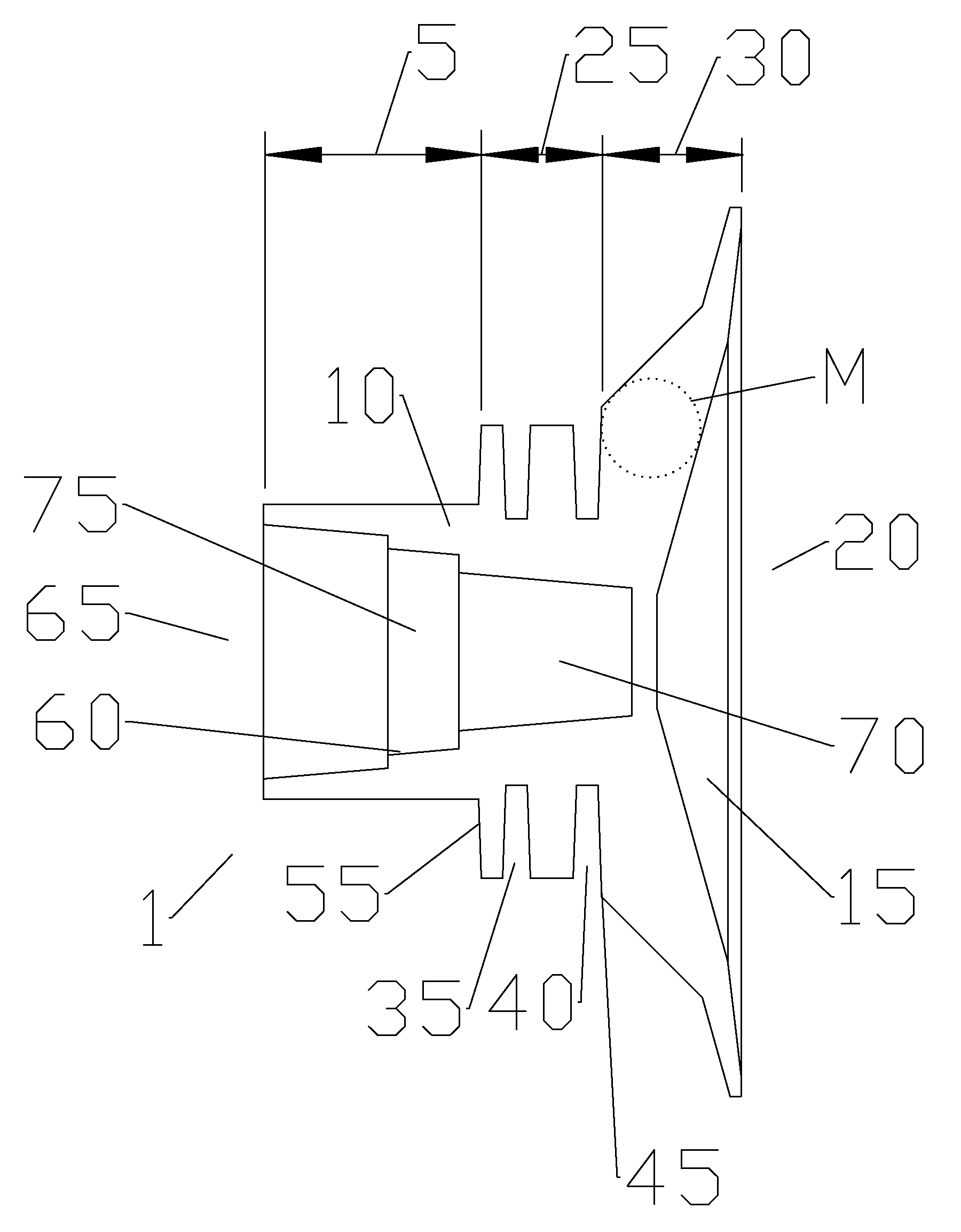
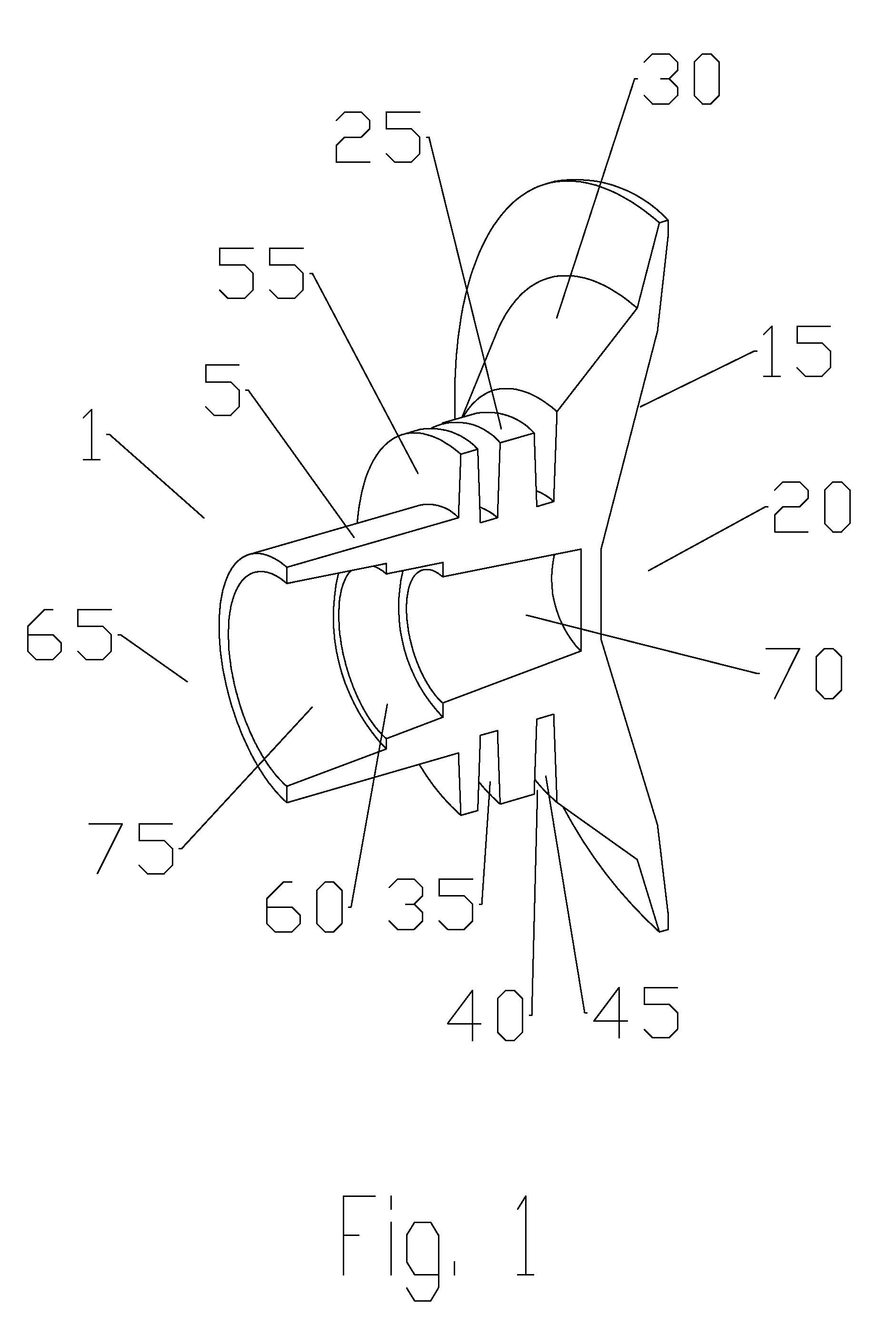
High-gain ultra-wideband corrugated double-ridge horn antenna with loaded lens
The invention provides a high-gain ultra-wideband corrugated double-ridge horn antenna with a loaded lens and belongs to the technical field of microwave antennas. The high-gain ultra-wideband corrugated double-ridge horn antenna is used for solving the problem that the double-ridge horn antenna is low in gain, and a high-frequency directional diagram is disintegrated. The high-gain ultra-wideband corrugated double-ridge horn antenna comprises a coaxial feed connector (1), a rectangular waveguide (2), a corrugated horn (3), a double-ridge waveguide (4) and the dielectric lens (5). The dielectric lens (5) of a hyperbolic structure is arranged at the position of a front port of the corrugated horn (3), the focus of the dielectric lens (5) coincides with the center of an antenna feed, a rear port of the corrugated horn (3) is connected with the rectangular waveguide (2), and the double-ridge waveguide (4) is arranged in the corrugated horn (3). The coaxial feed connector (1) is installed at the upper portion of the rectangular waveguide (2), and plane corrugations are arranged on the surface of the rear portion of the inner side of an upper metal plate (7) and the surface of the rear portion of the inner side of a lower metal plate (7). The high-gain ultra-wideband corrugated double-ridge horn antenna has the advantages that the ultra wide band, the high gain and the stable directional diagram are achieved in the 1-18 GHz area, and the high-gain ultra-wideband corrugated double-ridge horn antenna is suitable for the fields of electromagnetic compatibility tests, reflector antenna feed sources, ultra wide band radars and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Antenna apparatus and transmission and receiving apparatus using the same
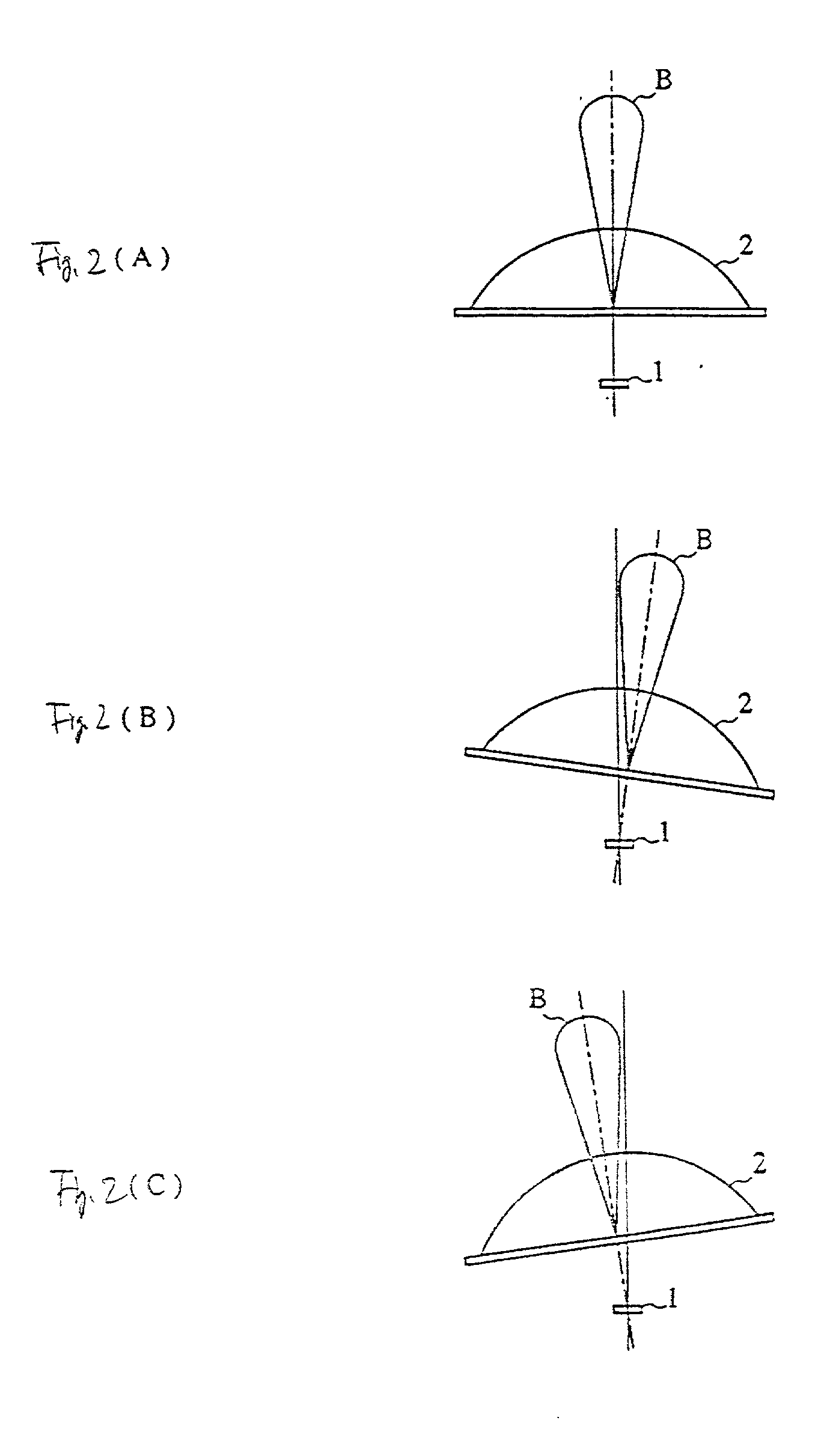
InactiveUS20010013842A1Small sizeIncrease speedAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPhysicsDielectric lens
An antenna apparatus such that a dielectric strip and a dielectric resonator are provided to form a primary vertical radiator, another dielectric strip is provided which is coupled to the dielectric strip to form a directional coupler, and a radiation beam is tilted by changing the relative position of the primary radiator with respect to the dielectric lens by displacing the primary vertical radiator in the directional coupler.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
RF transceiver having a directly radiating transistor
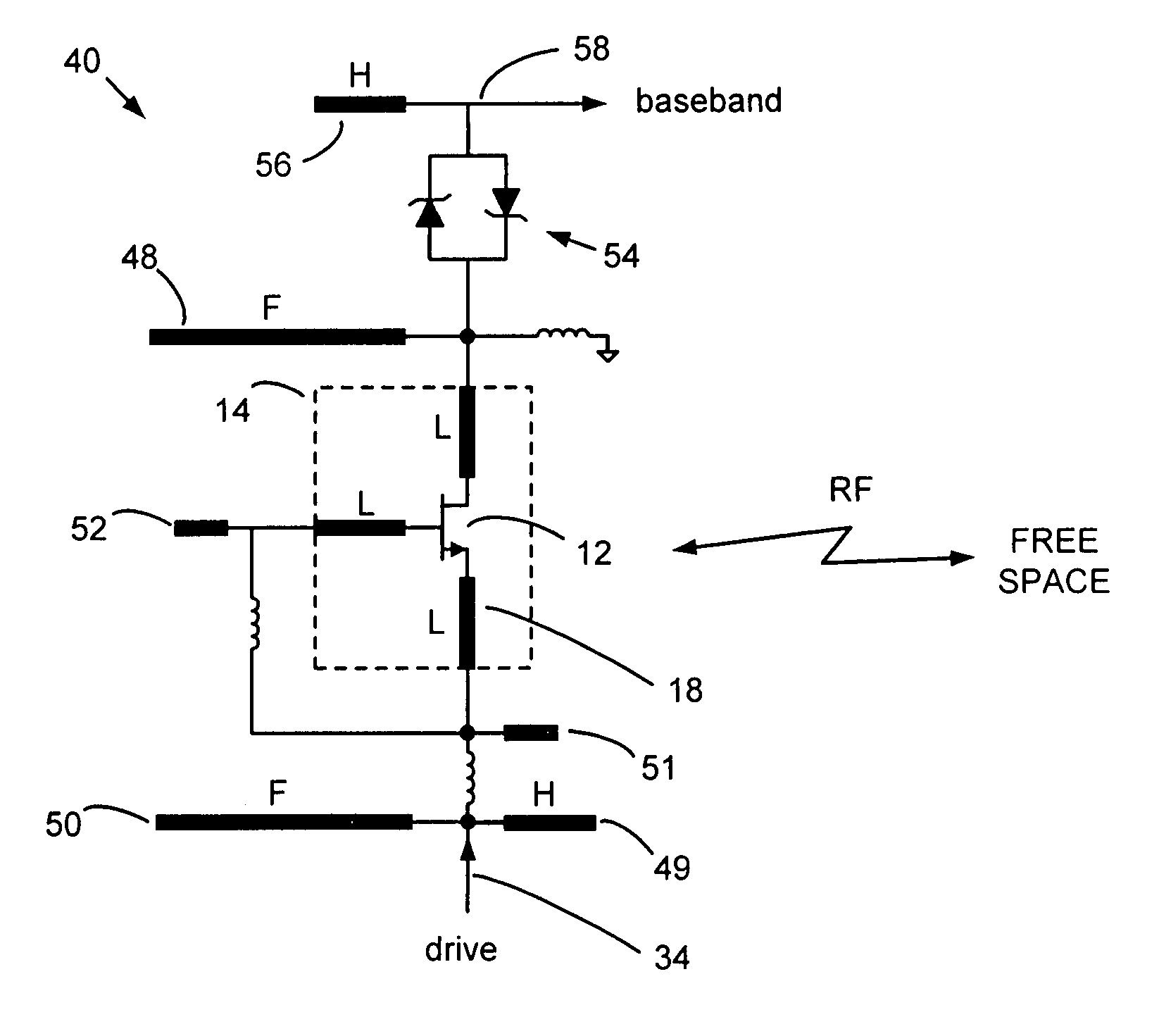
InactiveUS7224944B2Antenna equipments with additional functionsRadio transmissionUltra-widebandTransceiver
Transistor package leads form quarter-wave antenna elements that directly radiate RF energy into free space without the need for a separate antenna. The transistor operates at a fundamental frequency and radiates a harmonic, thereby allowing radiation at frequencies normally considered “beyond cutoff” for a packaged transistor. This technique enables an additional 20 GHz of spectrum for use by surface mount technology. The transistor may be mounted on 1.6 mm thick glass-epoxy circuit board that also forms a quarter-wave reflector at 26 GHz. An optional dielectric lens produces a narrow beam and an optional planar filter rejects spurious fundamental emissions. A 26 GHz ultra-wideband (UWB) pulse-echo radar rangefinder implementation provides a low-cost upgrade to ultrasound.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
Dielectric lens antenna having heating body and radio equipment including the same
InactiveUS6175335B1Antenna supports/mountingsRadiating element housingsRadio equipmentDielectric resonator antenna
A dielectric lens antenna having a lens comprising a dielectric material and a heating body disposed on a surface of the lens. The dielectric lens antenna has a snow-melting function, which prevents degradation in lens-efficiency.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Microwave window and level-measuring system that works according to the radar principle
ActiveUS9091584B2Improve sealingIndependently manufacturedAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating element housingsDiffusionMicrowave
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Radar sensor
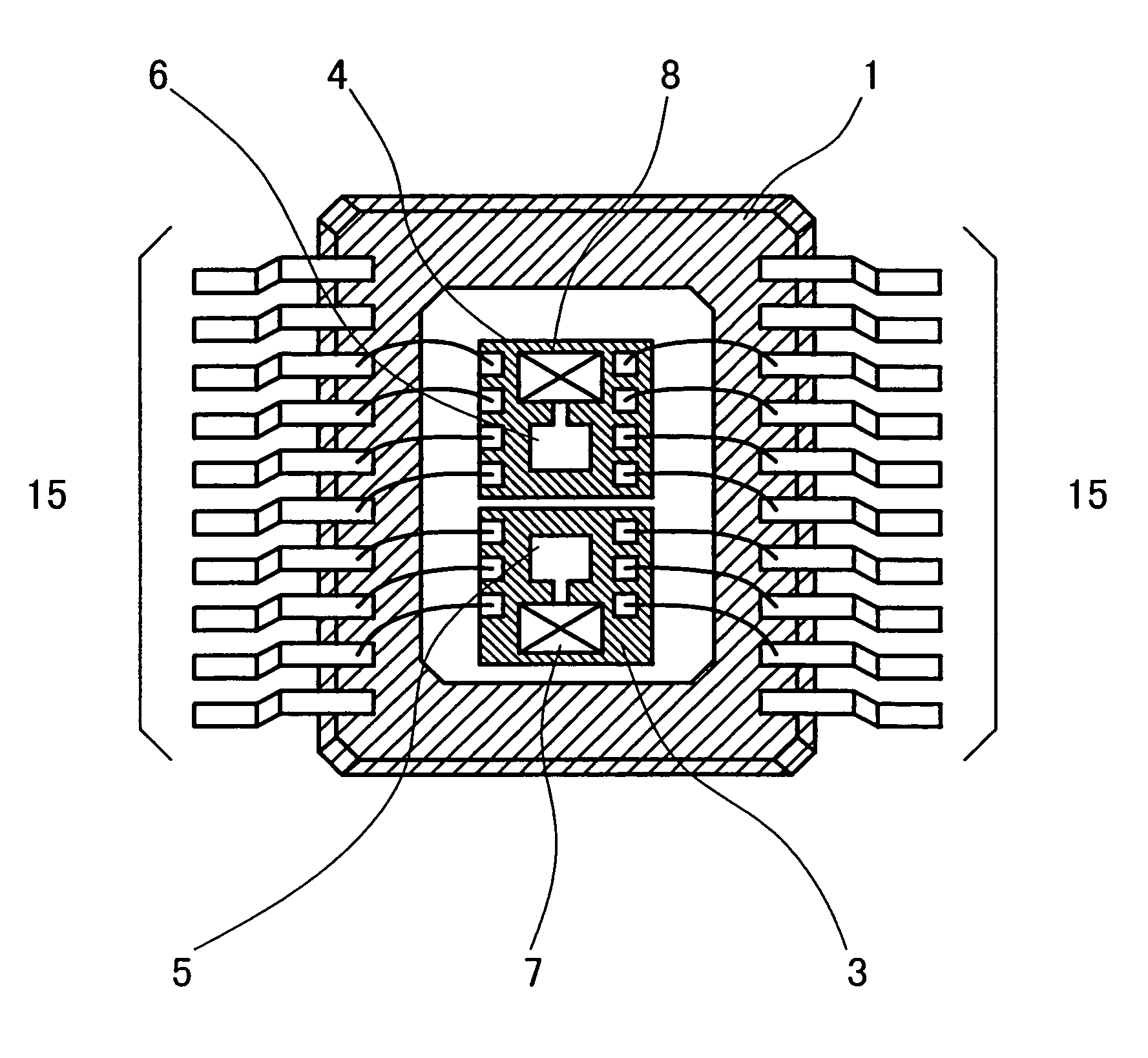
InactiveUS7154432B2Reduce manufacturing costLow costAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadarFrequency mixer
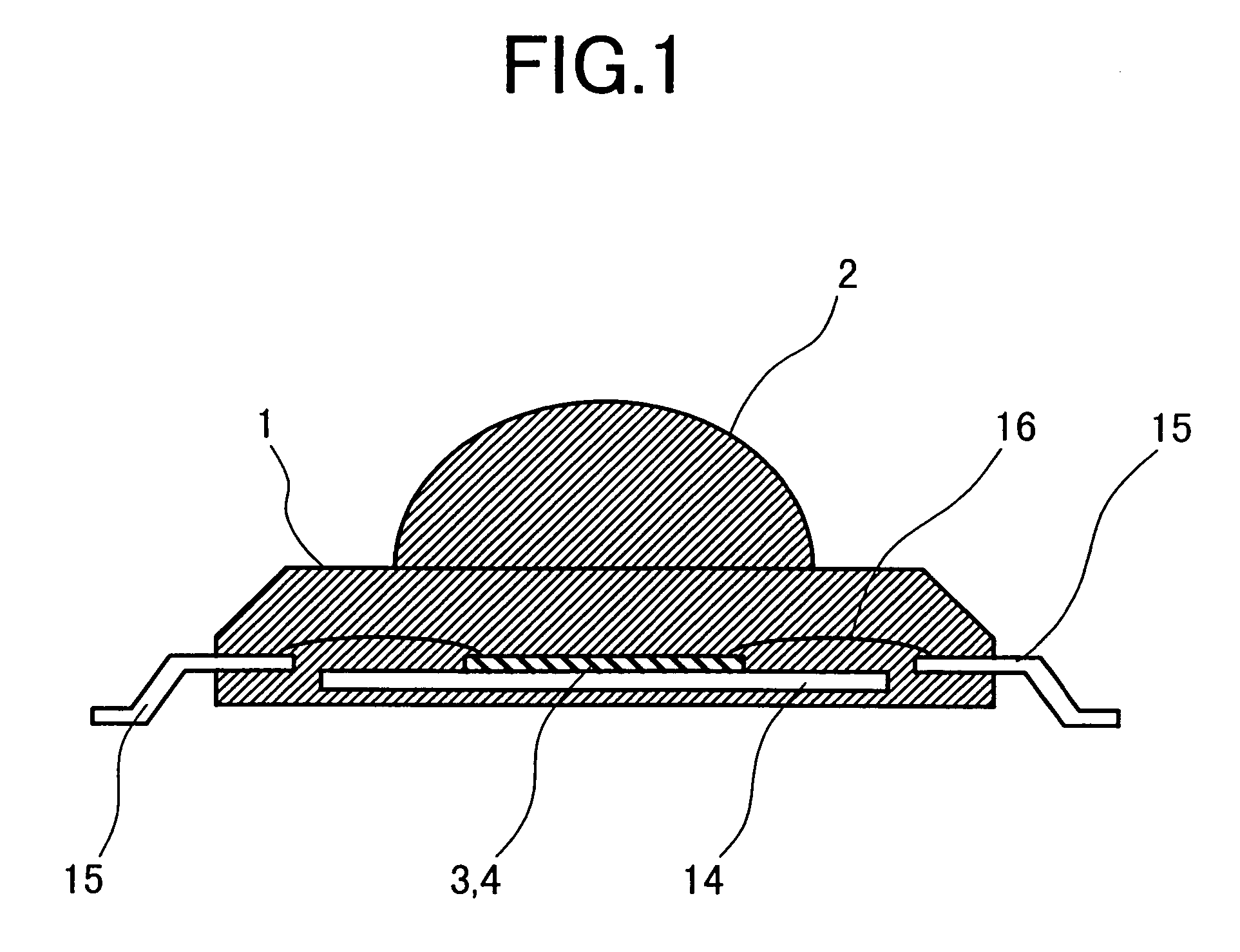
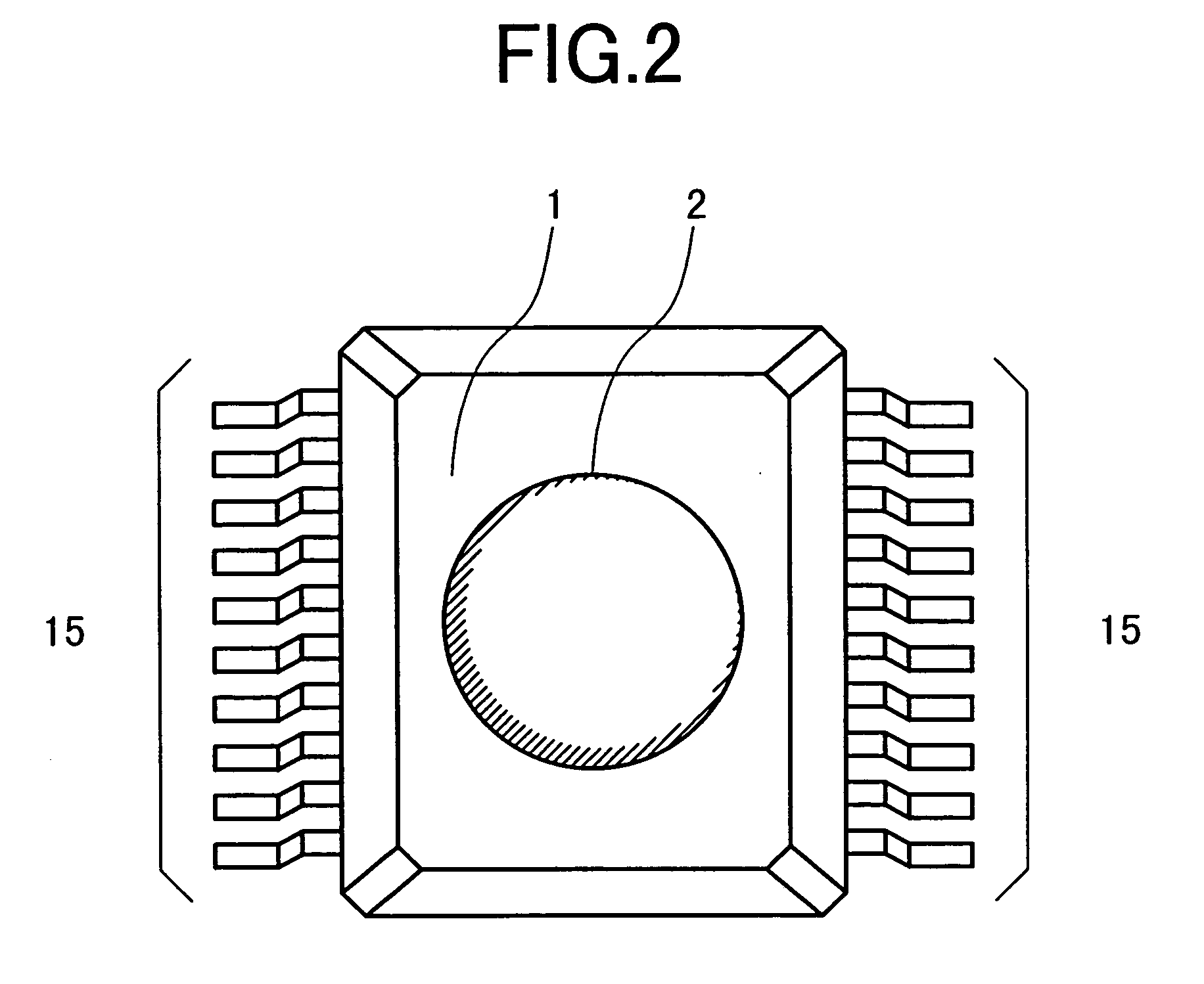
The invention intends to provide a sensor module suitable for miniaturization and reduction in costs, in the radar sensor that uses a millimeter or sub-millimeter wave signal of which frequency is more than 20 GHz. To accomplish this problem, the radar sensor is integrated into a one chip MMIC, in which an active circuit including an oscillator and a mixer is formed with an antenna on one semiconductor substrate. Further, the MMIC is sealed with a resin package. A dielectric lens is formed on the resin package over the antenna to attain a desired beamwidth. Thereby, the lens and the resin package can integrally be formed by a metal mold, thus reducing the cost.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Small circularly-polarized horn antenna
InactiveCN103236586AGood radiation characteristicsImprove stabilityWaveguide hornsHorn antennaPolarizer
The invention discloses a small circularly-polarized horn antenna and mainly solves the problem that the prior art cannot simultaneously meet requirements of high power, high gain, wide band and circular polarization. The small circularly-polarized horn antenna comprises a coaxial-circular waveguide converter (1), a circular polarizer (2), a conical horn (3), a dielectric lens (4) and a circular waveguide (7), the circular polarizer (2) is mounted inside the circular waveguide (7) which is directly connected with the conical horn (3), the dielectric lens (4) is fixed in front of the conical horn (3), the conical-circular waveguide converter is mounted on the side wall of the circular waveguide (7), the circular polarizer (2) is composed of a symmetric hexagonal dielectric inserting piece (5) and two rectangular compensation grooves (6) which are fixed inside the circular waveguide (7), and the two compensation grooves are symmetrically arranged right above and right below of the dielectric inserting piece (5) inside the circular waveguide (7). The small circularly-polarized horn antenna has the advantages of wide band, good stability, high gain, large power capacity and good circular polarization characteristic.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com