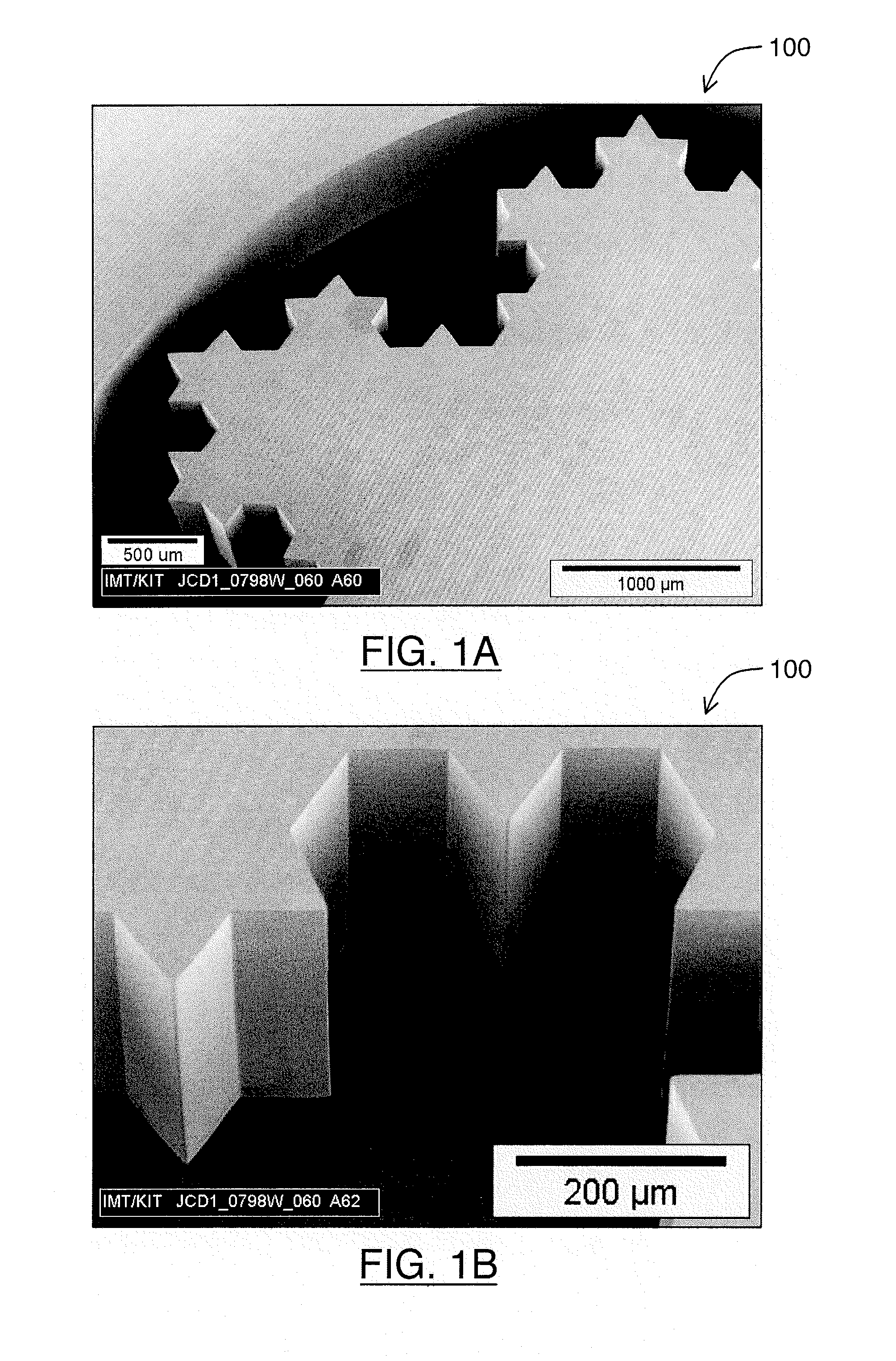
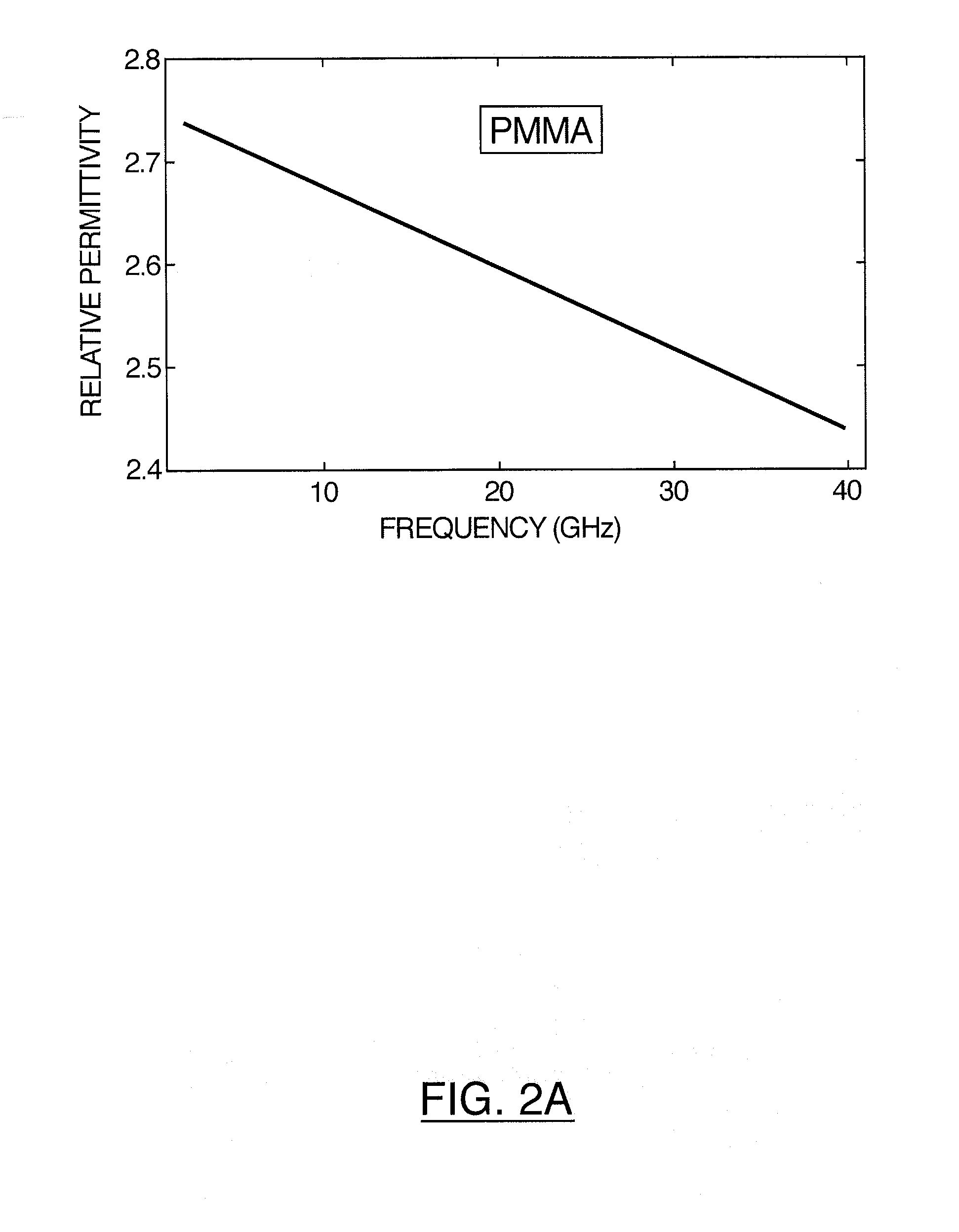
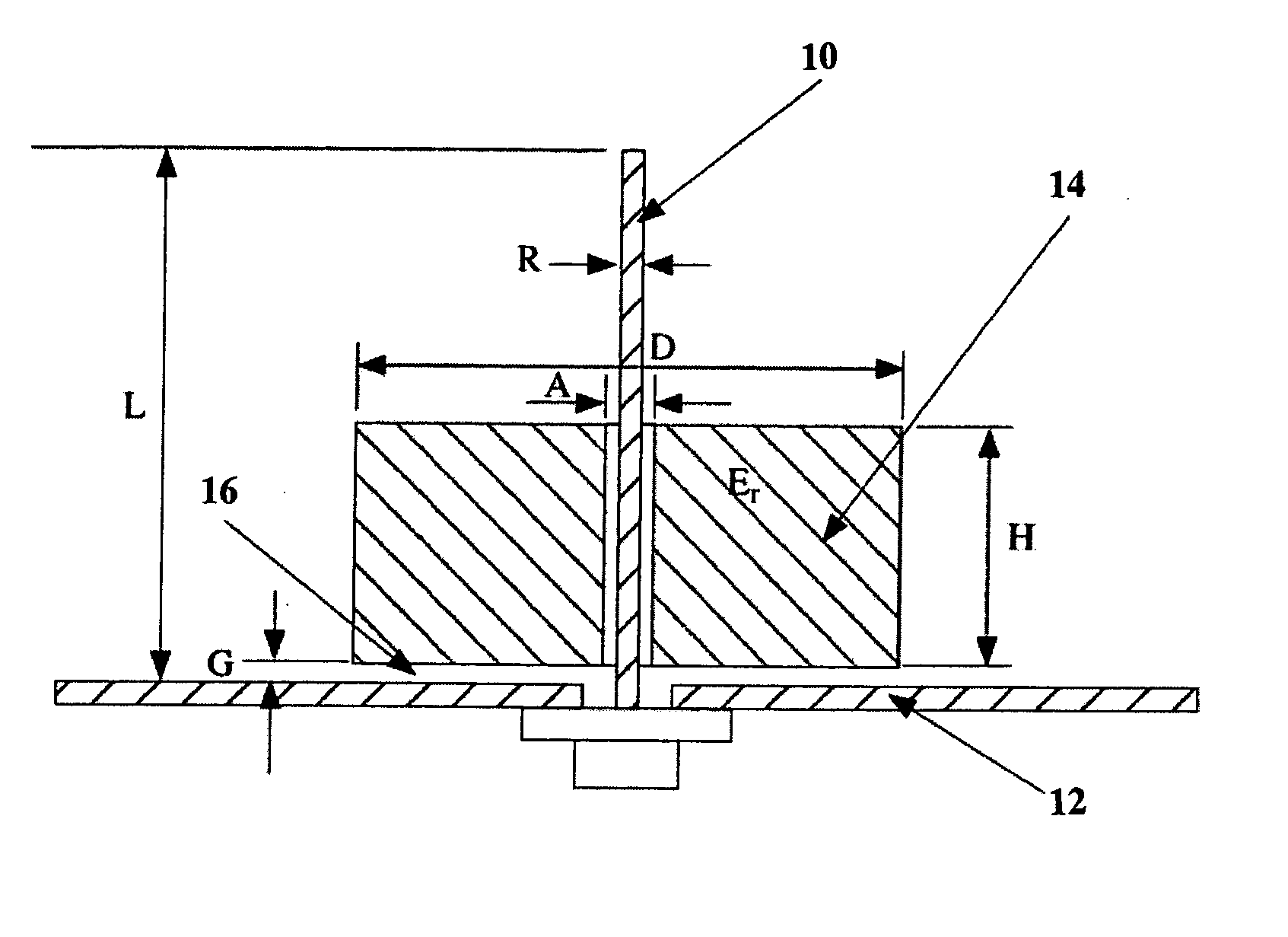
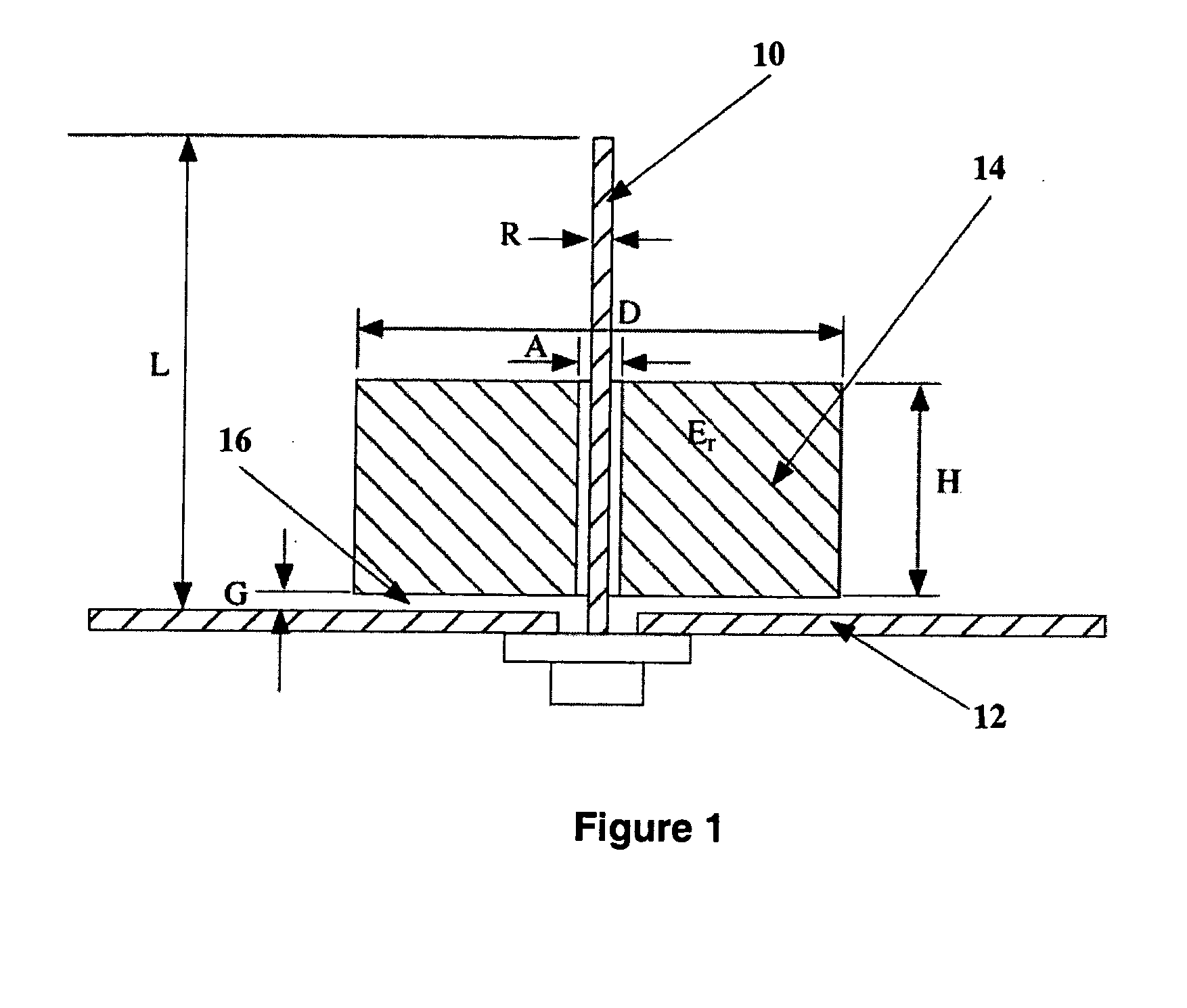
Patents
Literature
363 results about "Dielectric resonator antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
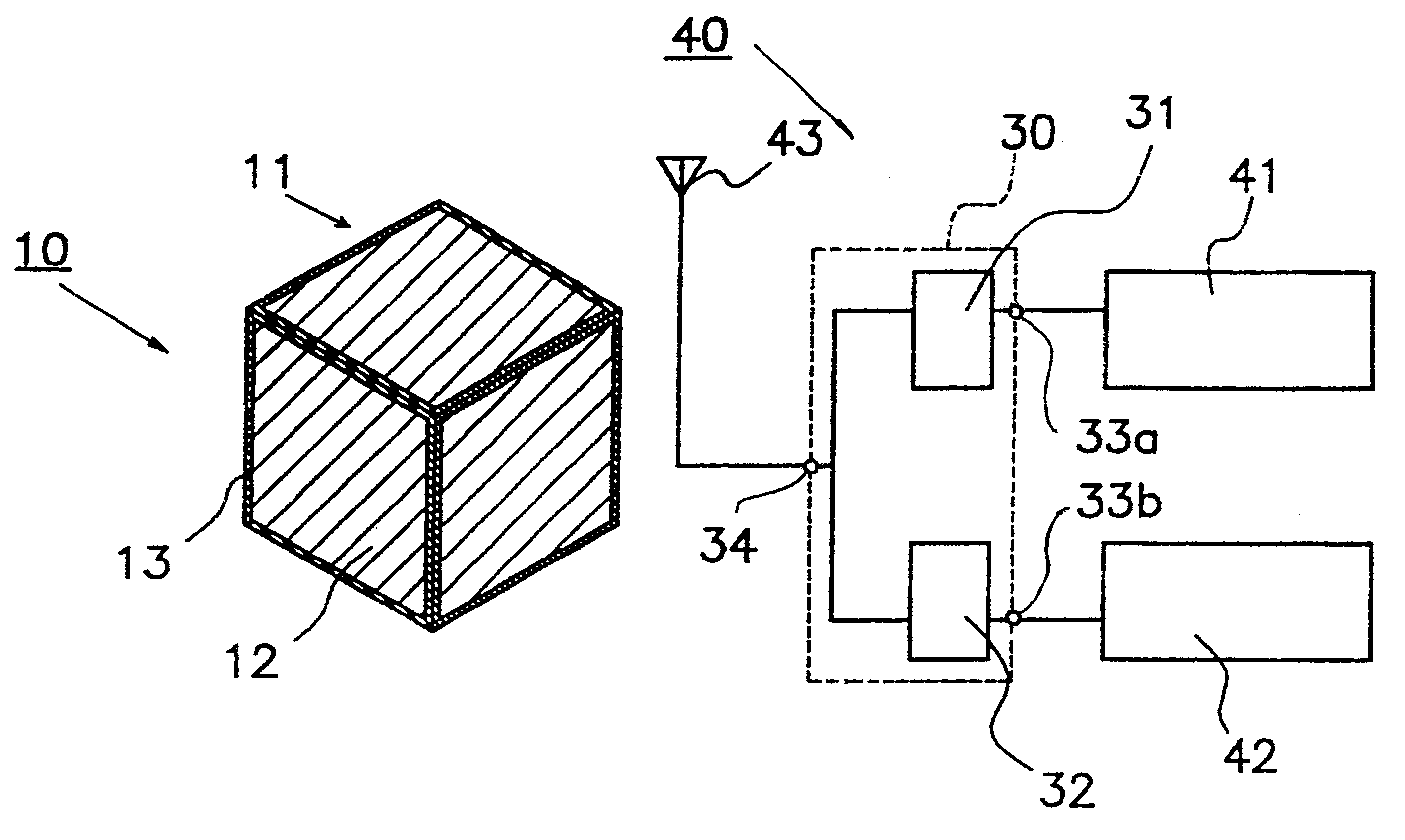
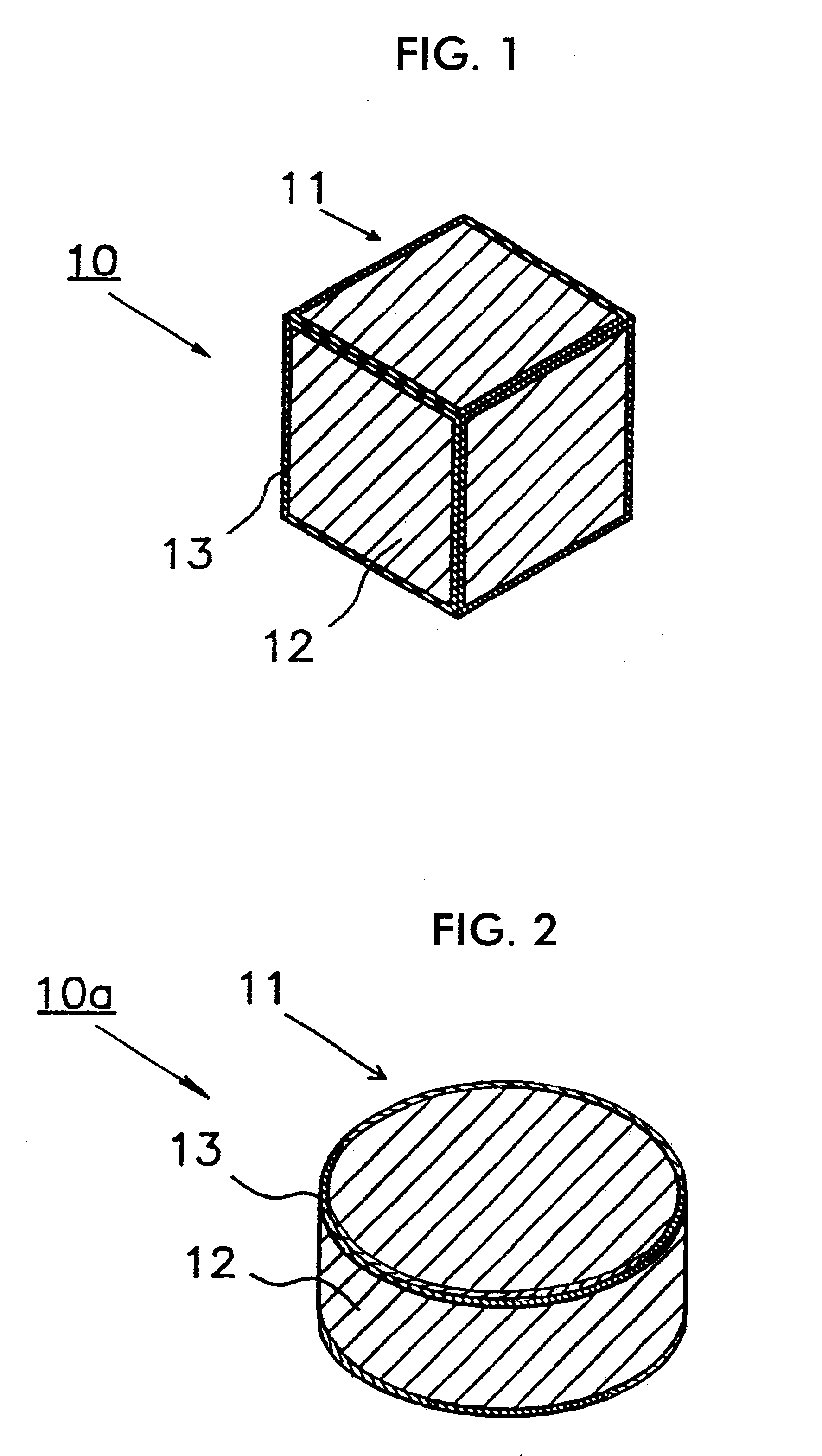
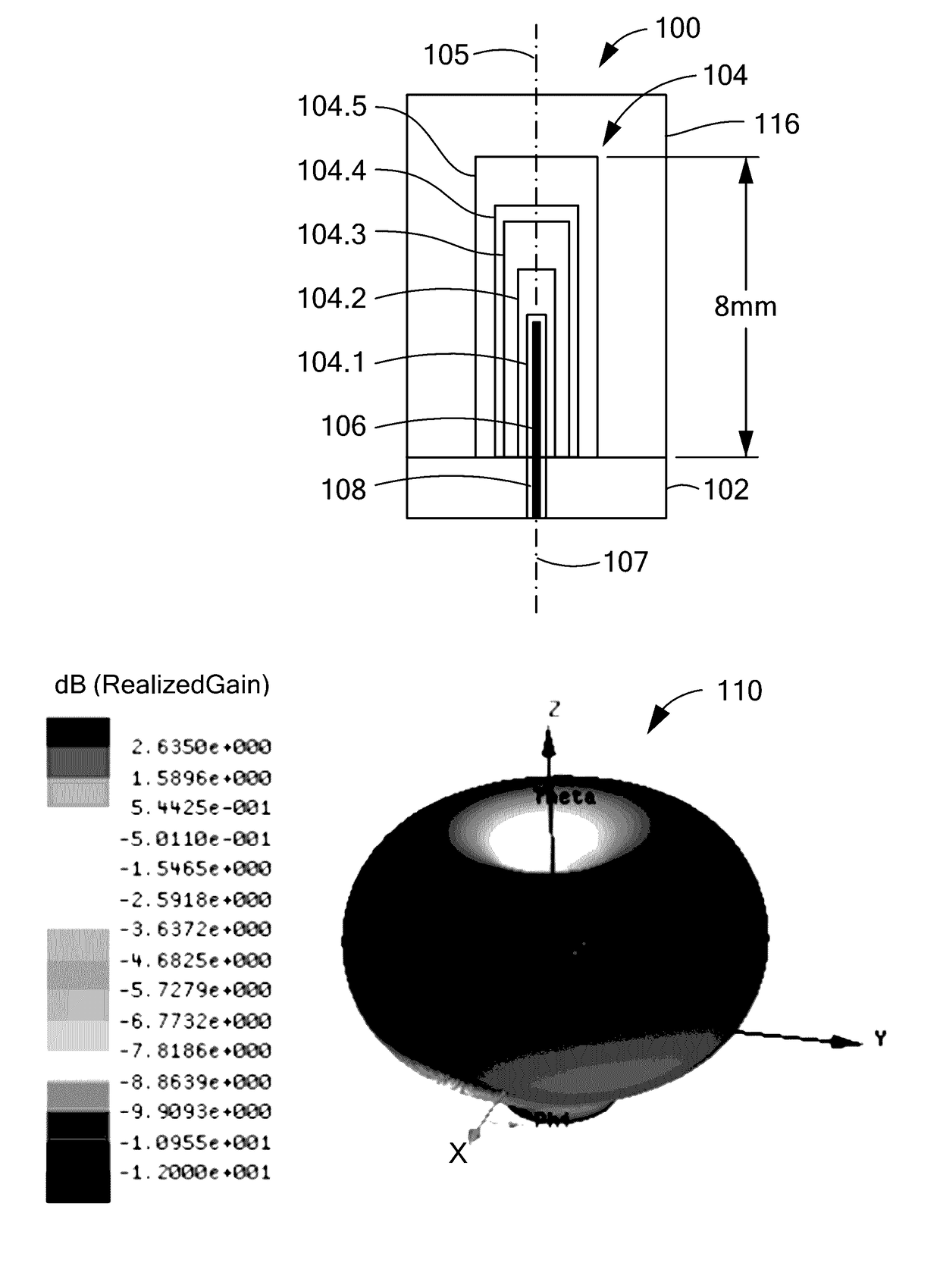
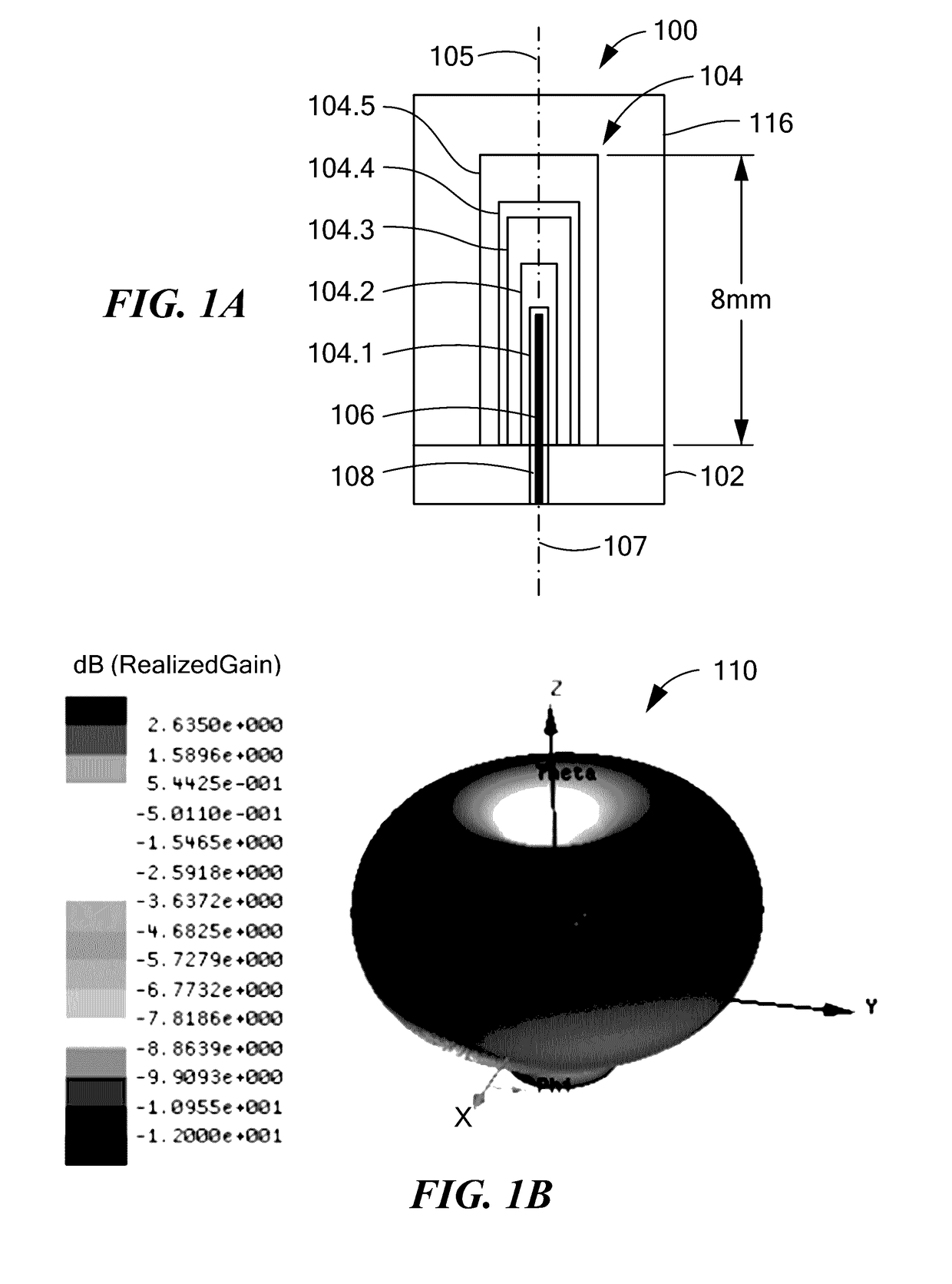
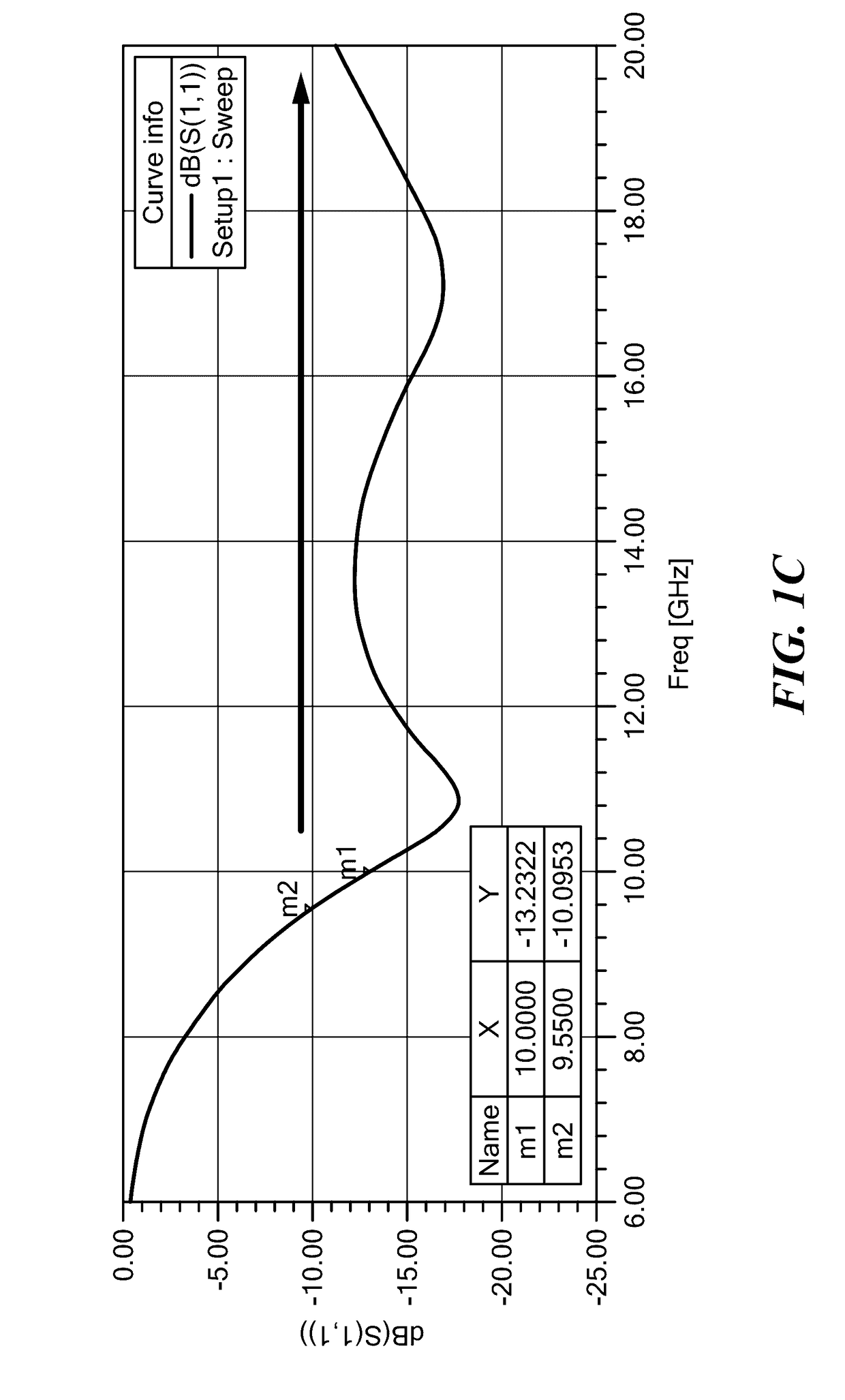
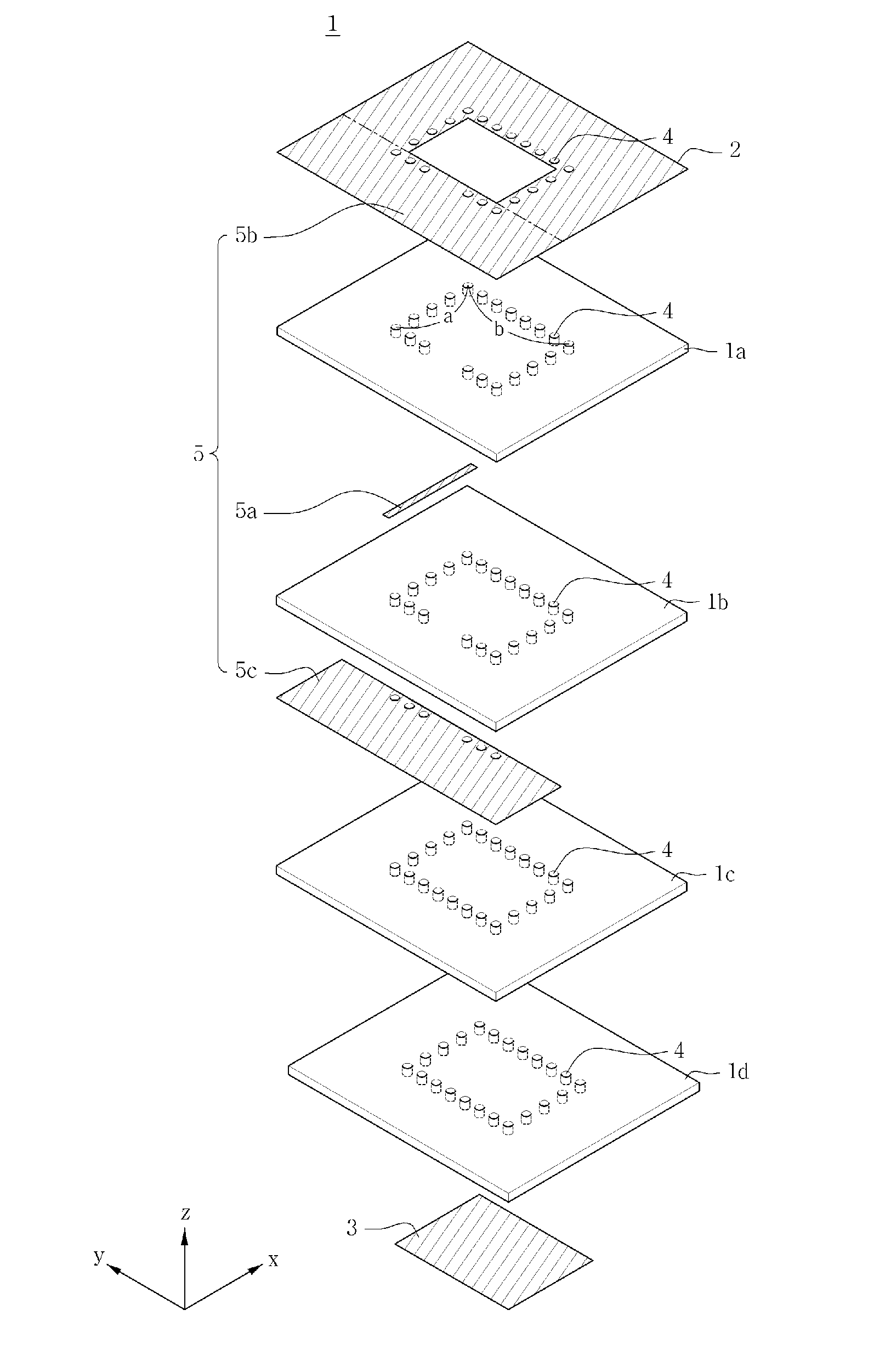
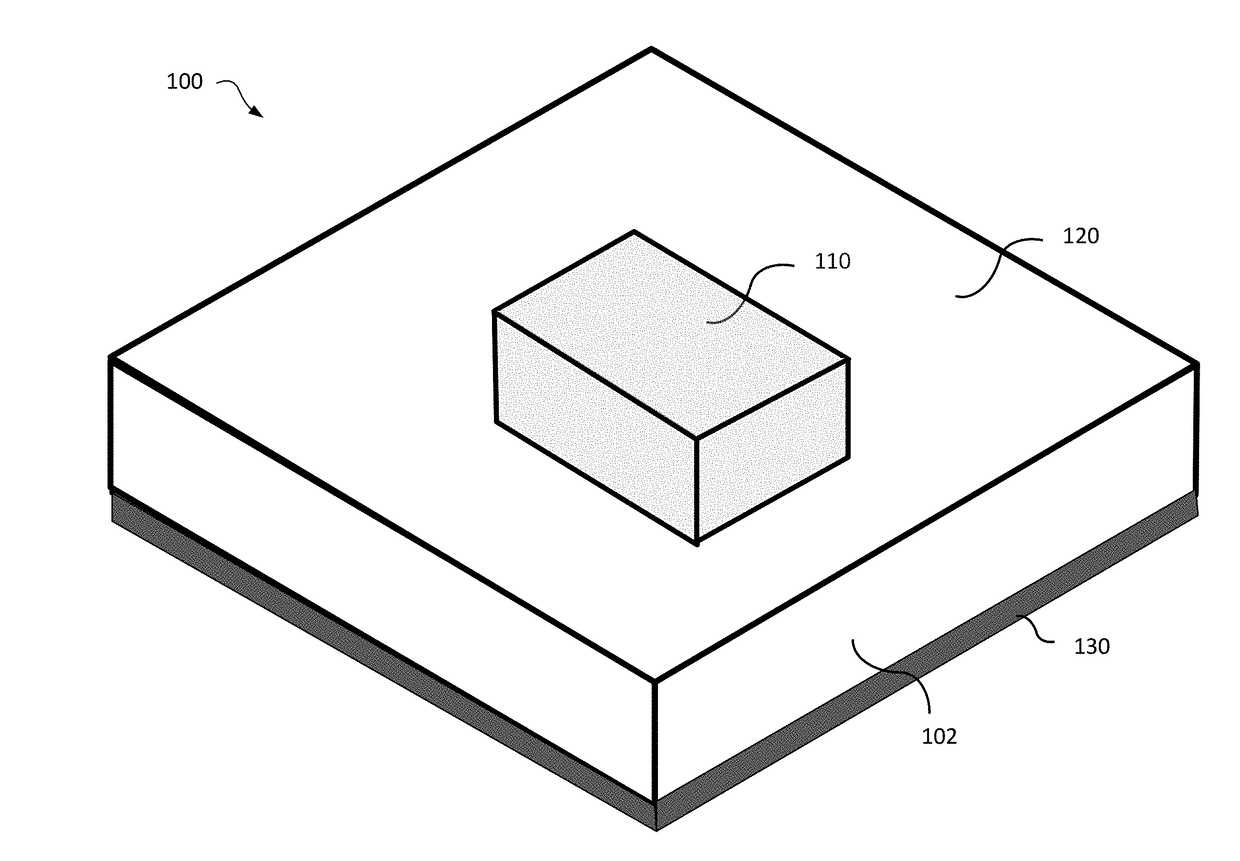
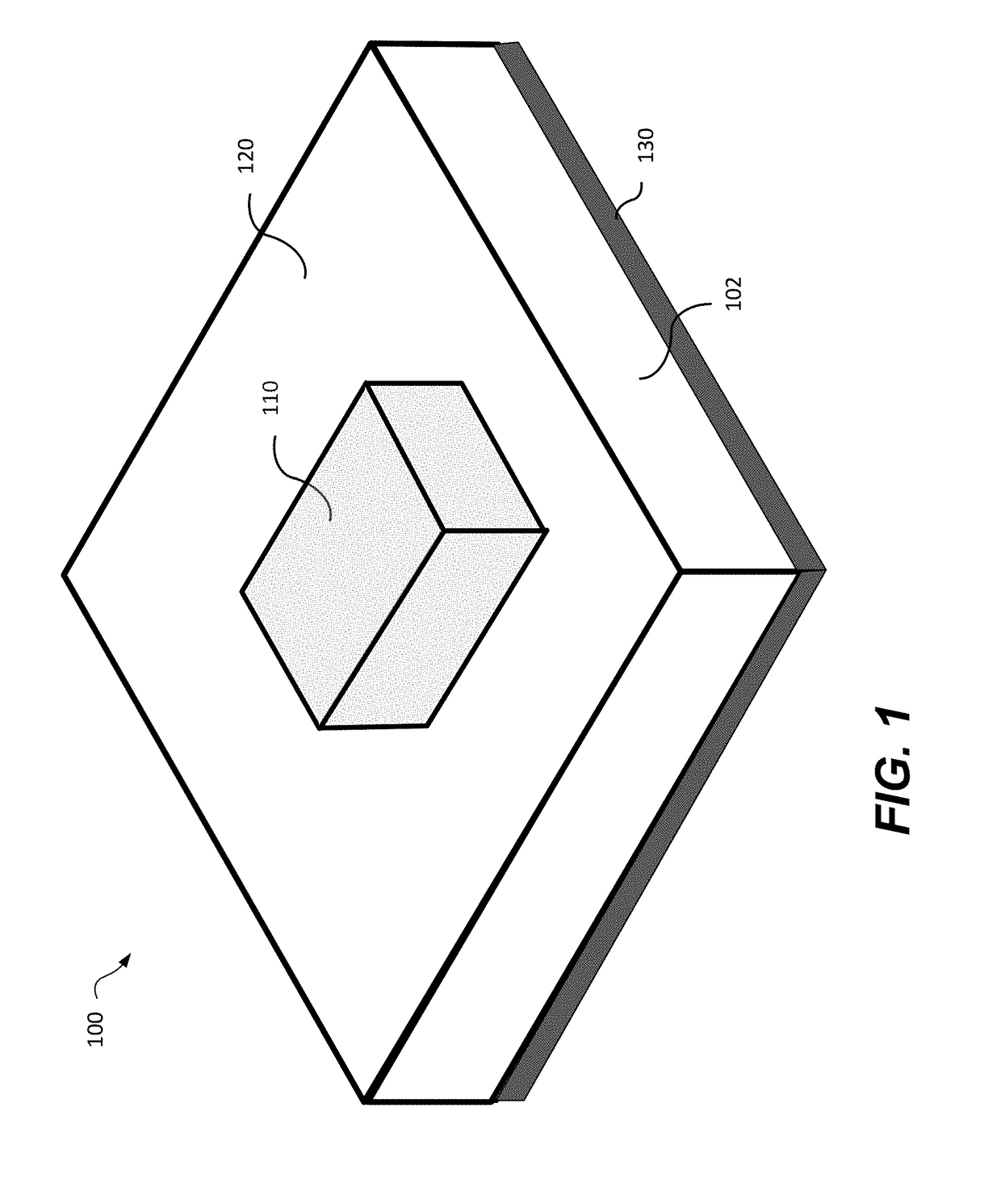
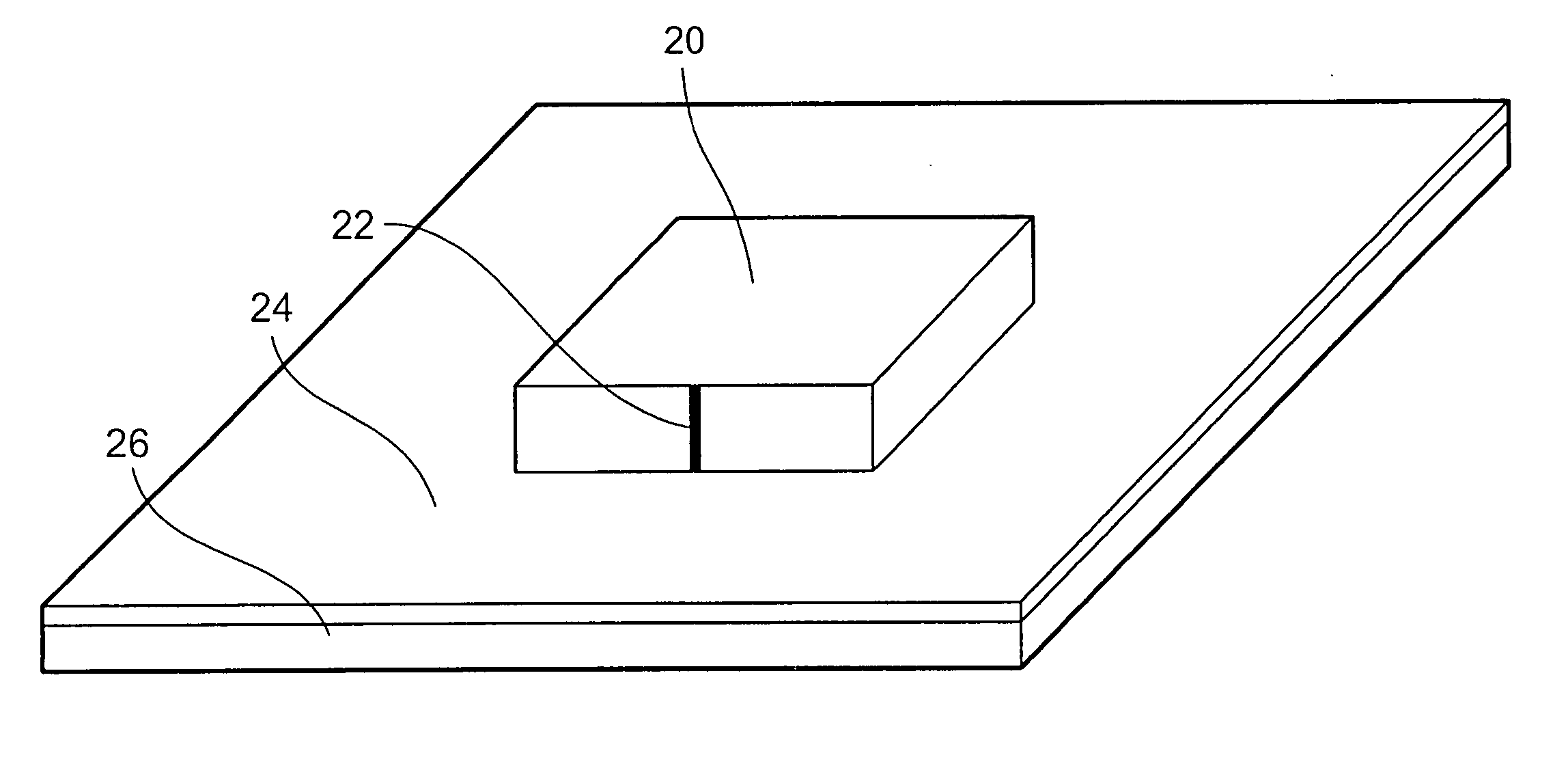
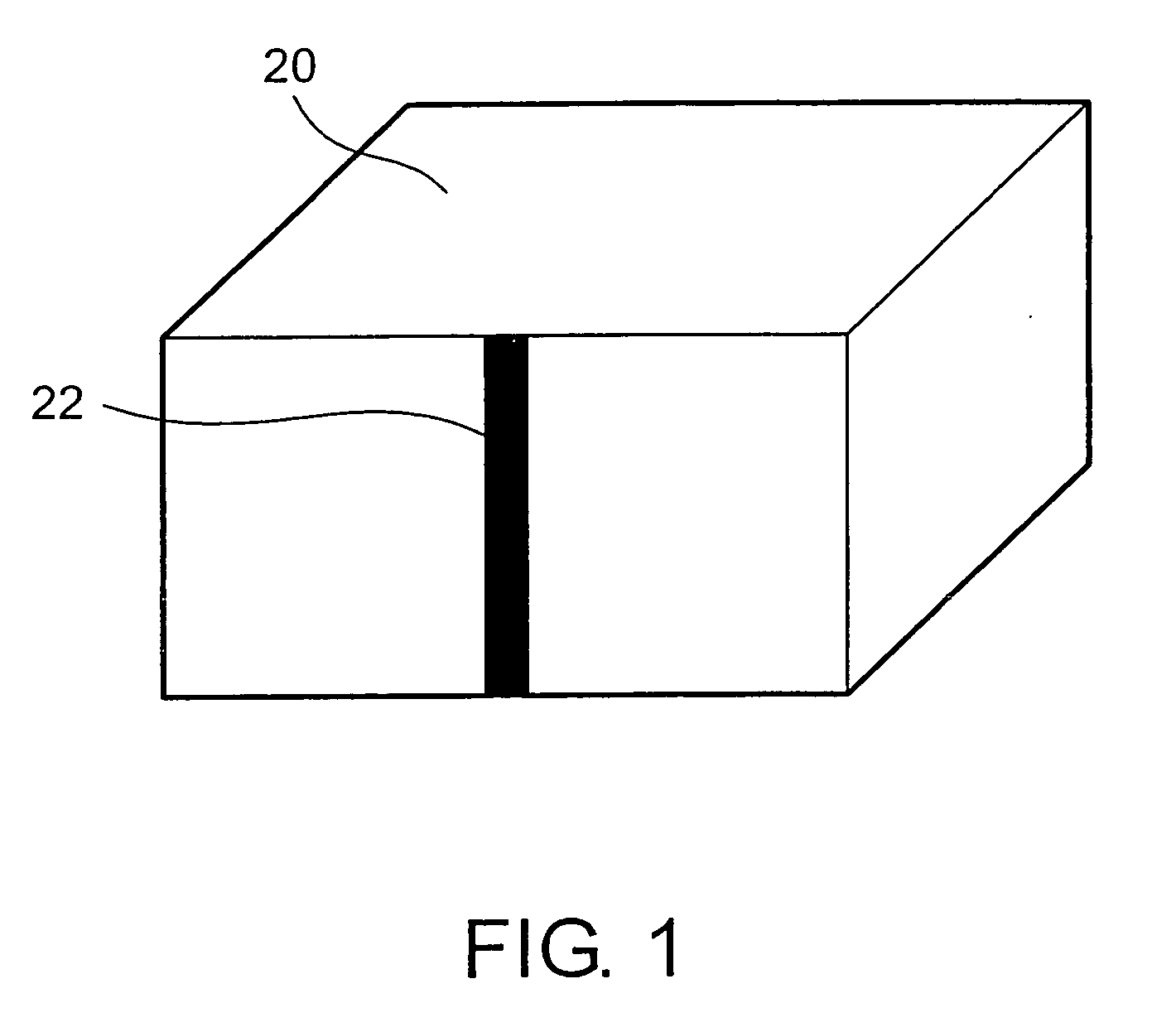
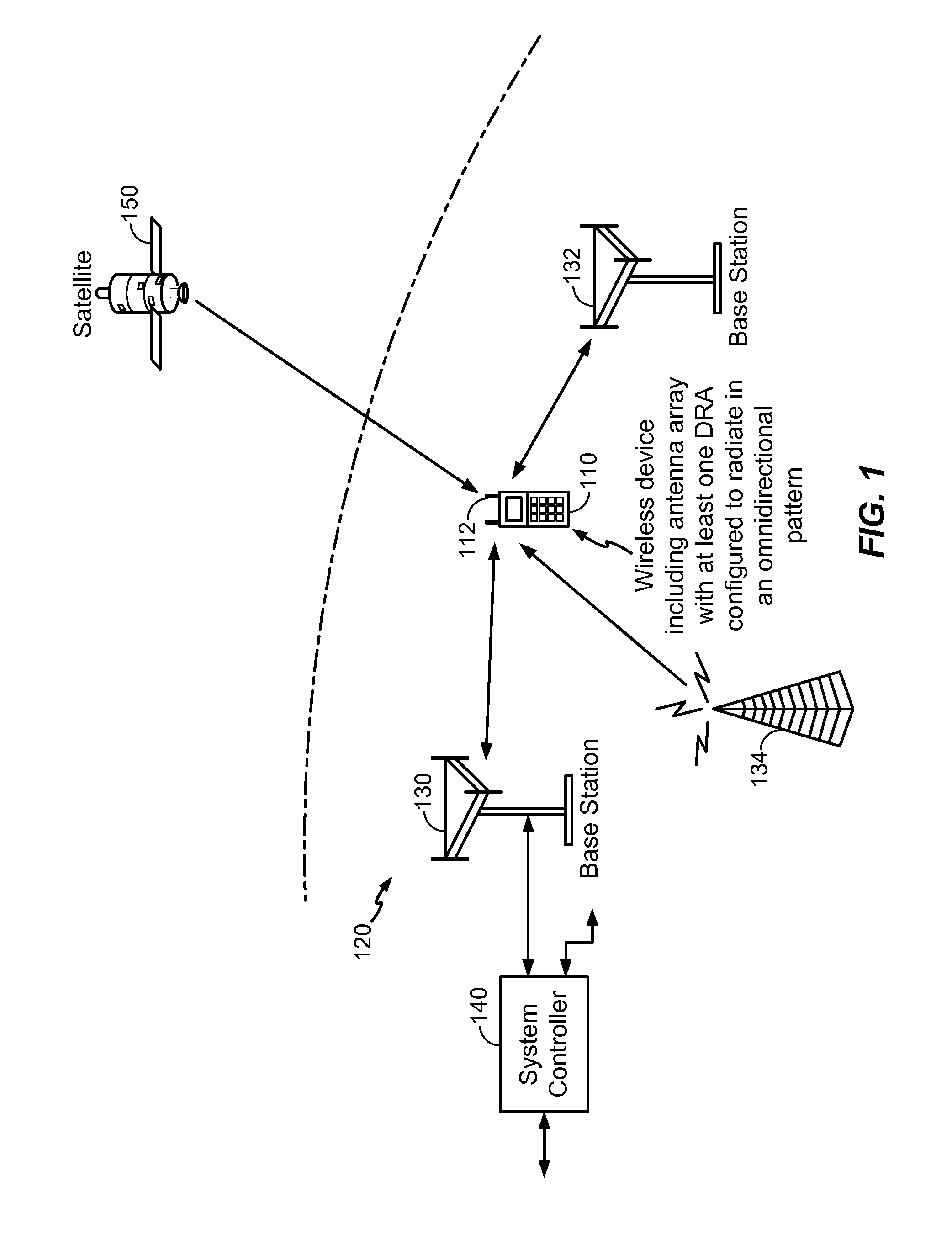
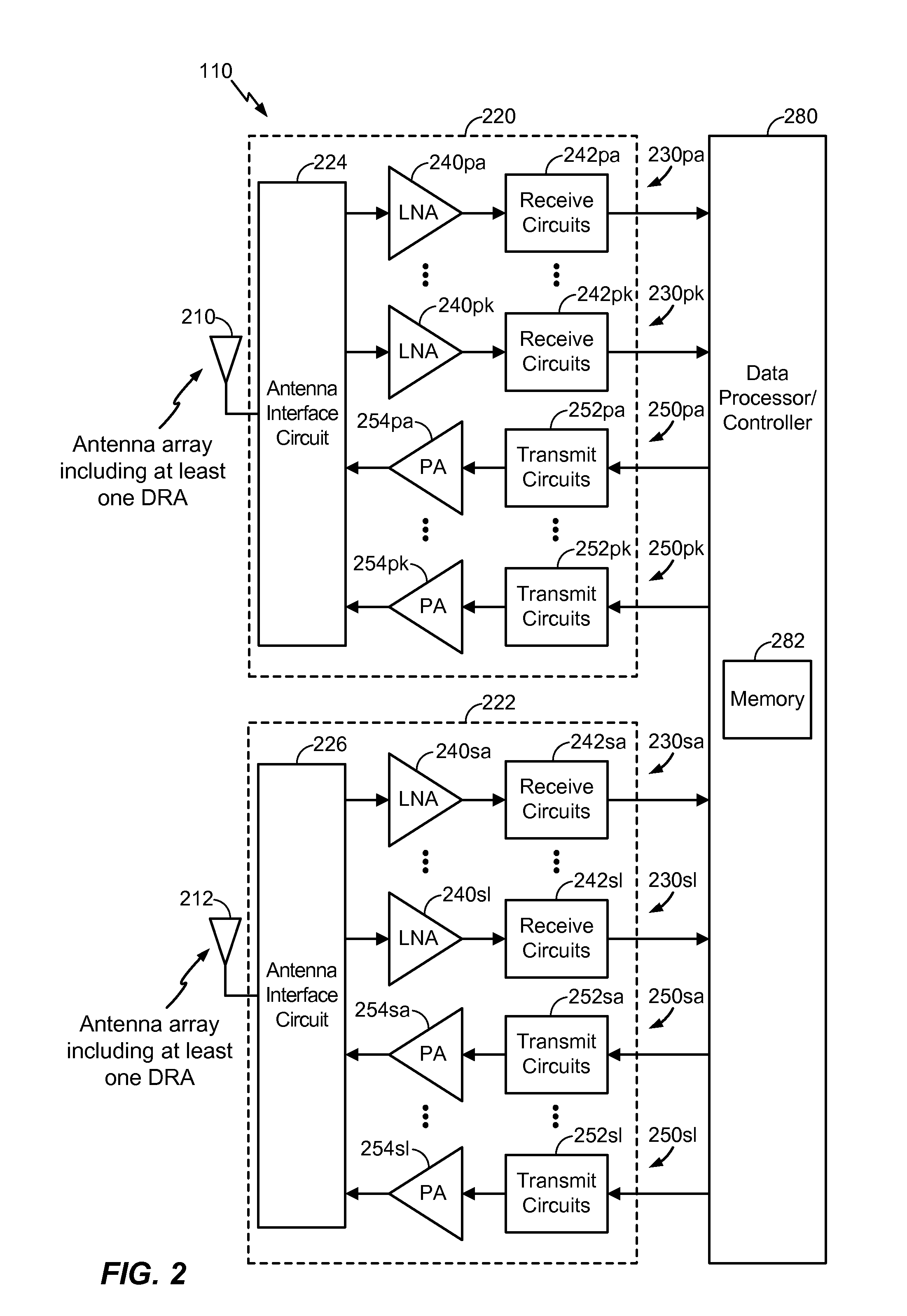
A dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) is a radio antenna mostly used at microwave frequencies and higher, that consists of a block of ceramic material of various shapes, the dielectric resonator, mounted on a metal surface, a ground plane. Radio waves are introduced into the inside of the resonator material from the transmitter circuit and bounce back and forth between the resonator walls, forming standing waves. The walls of the resonator are partially transparent to radio waves, allowing the radio power to radiate into space.
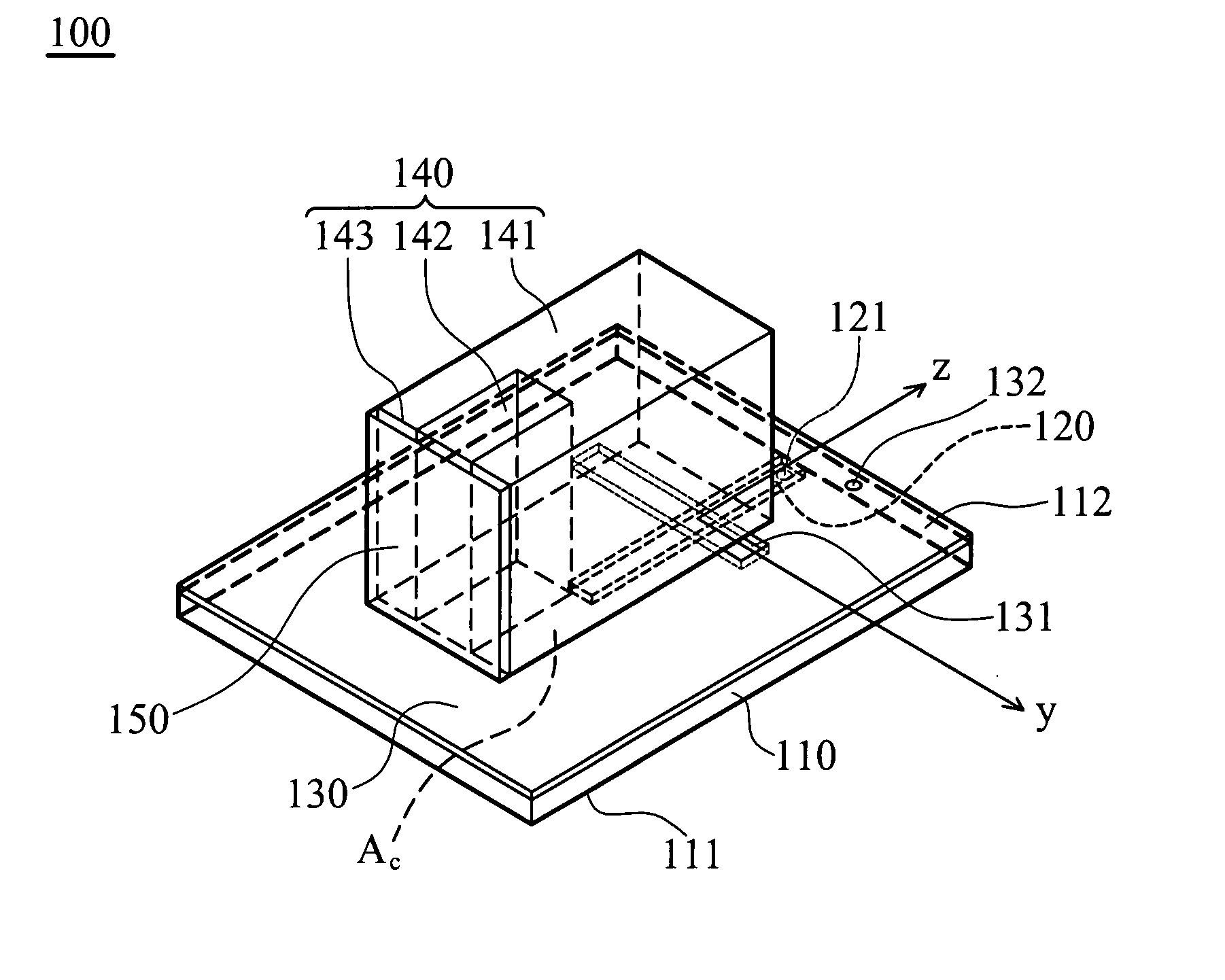
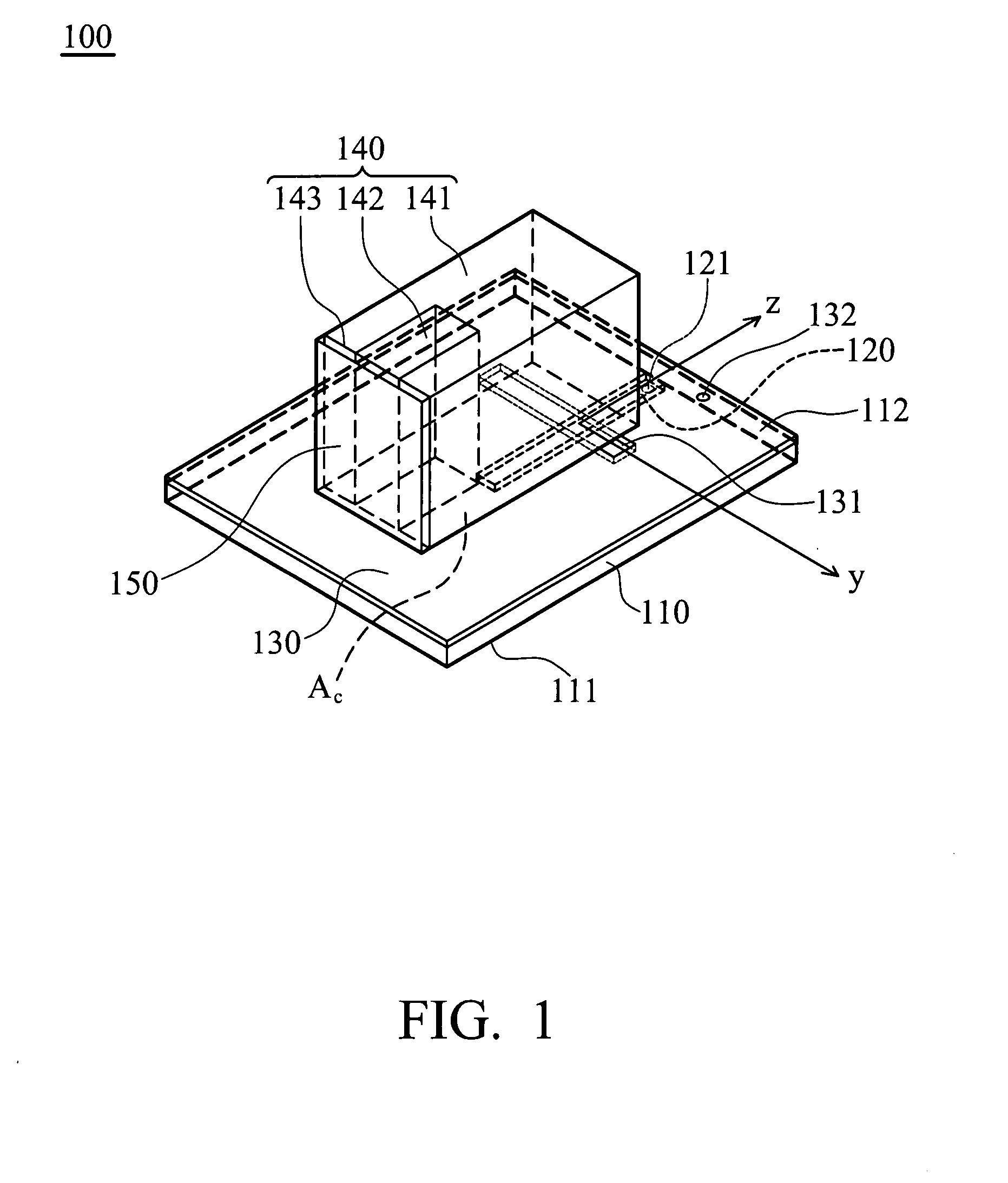
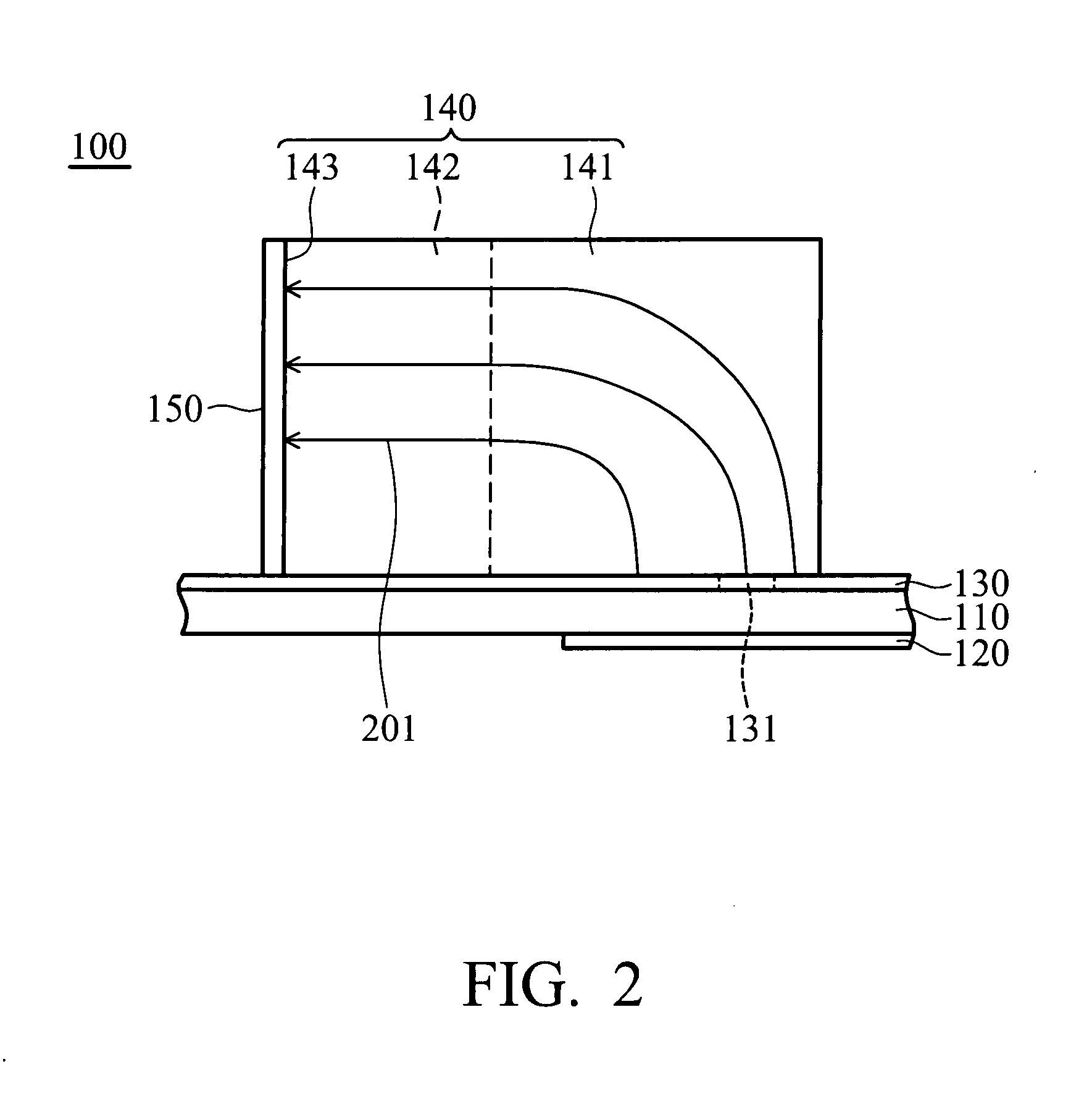
Wideband dielectric resonator antenna
InactiveUS20080278378A1Easy to manufactureReduces attrition rateSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric resonator antennaGround plane
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
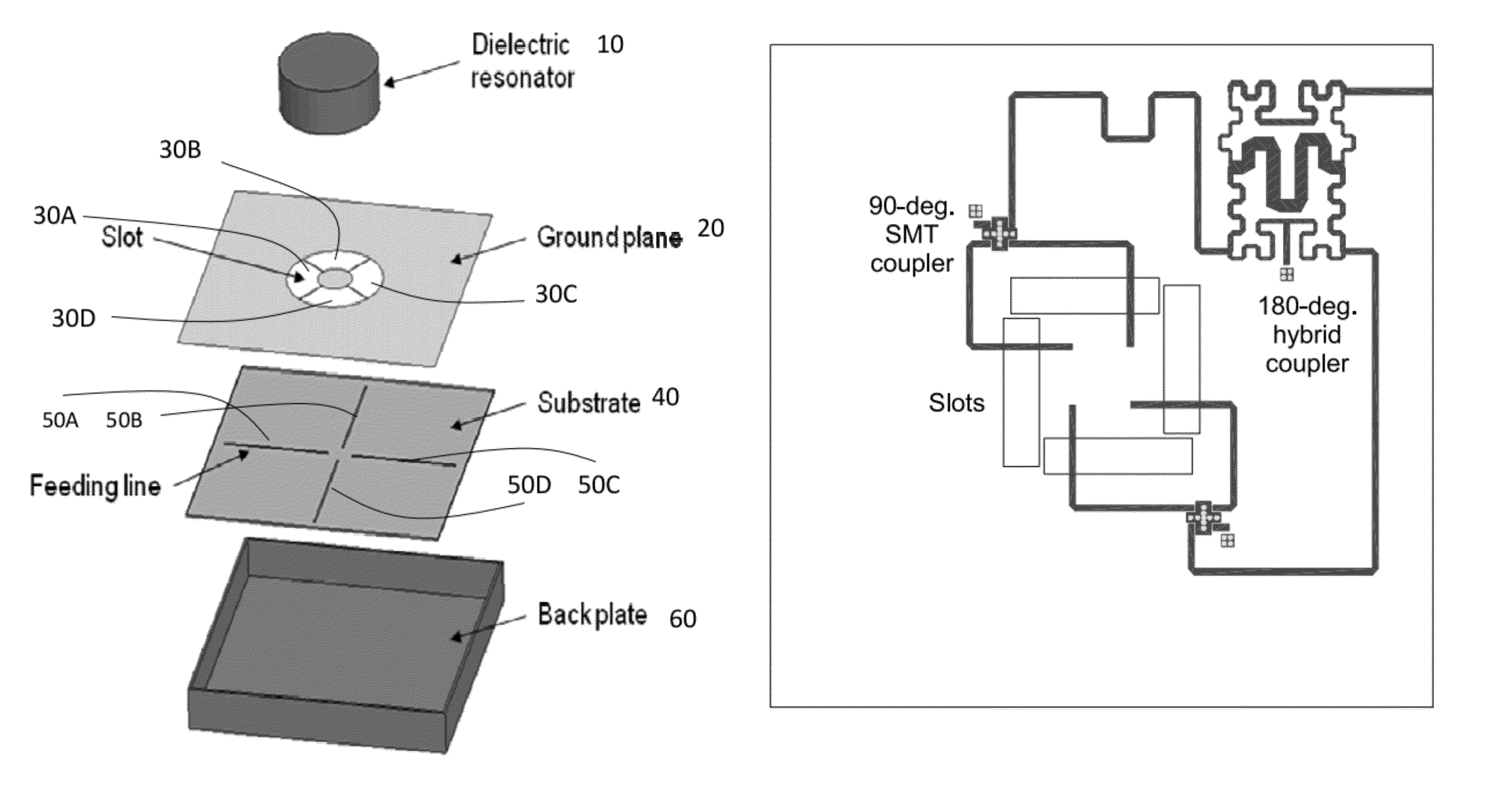
Wideband circularly polarized hybrid dielectric resonator antenna
ActiveUS8928544B2High bandwidthCompact geometryAntenna supports/mountingsAntennas earthing switches associationDielectric resonator antennaPhase difference
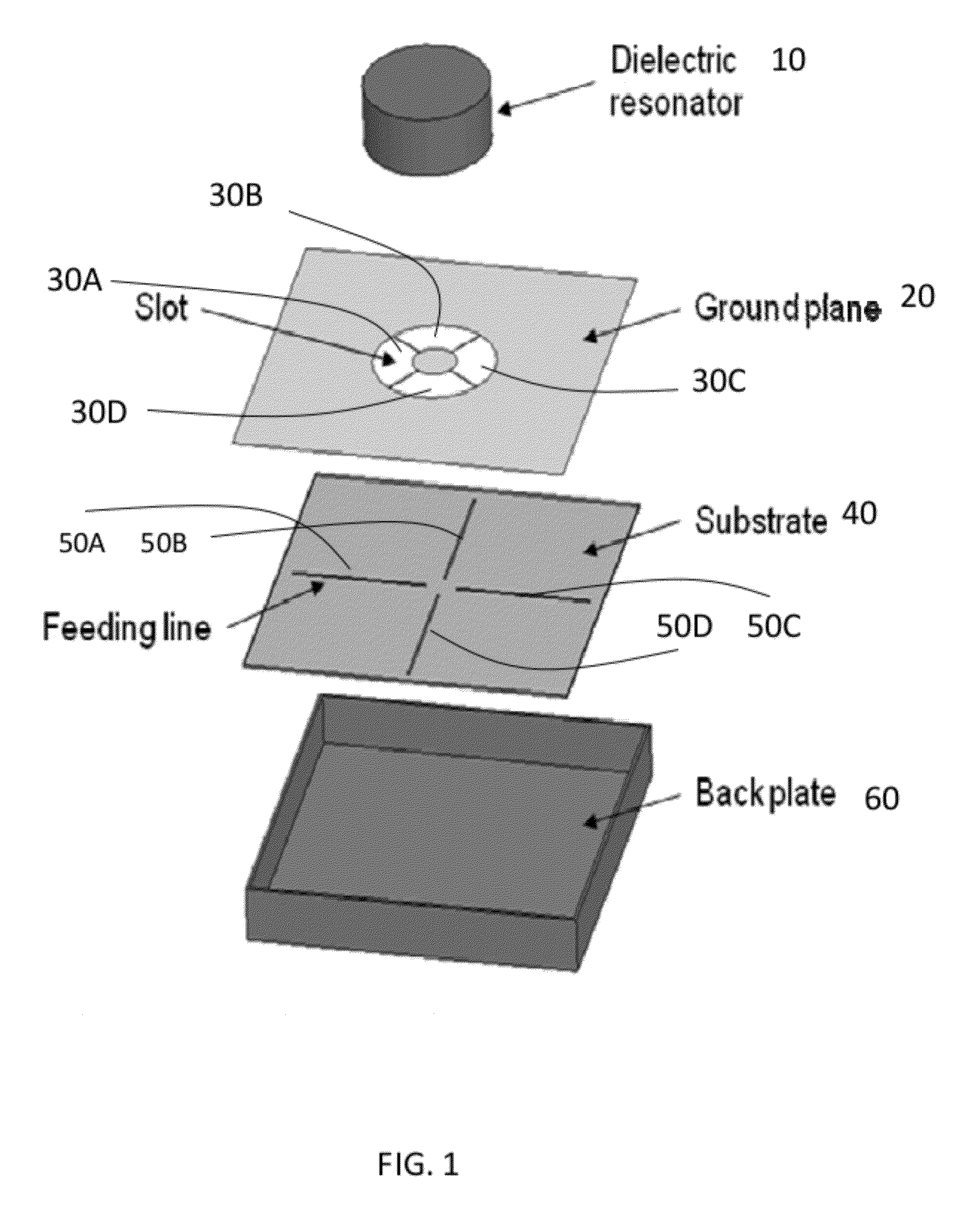
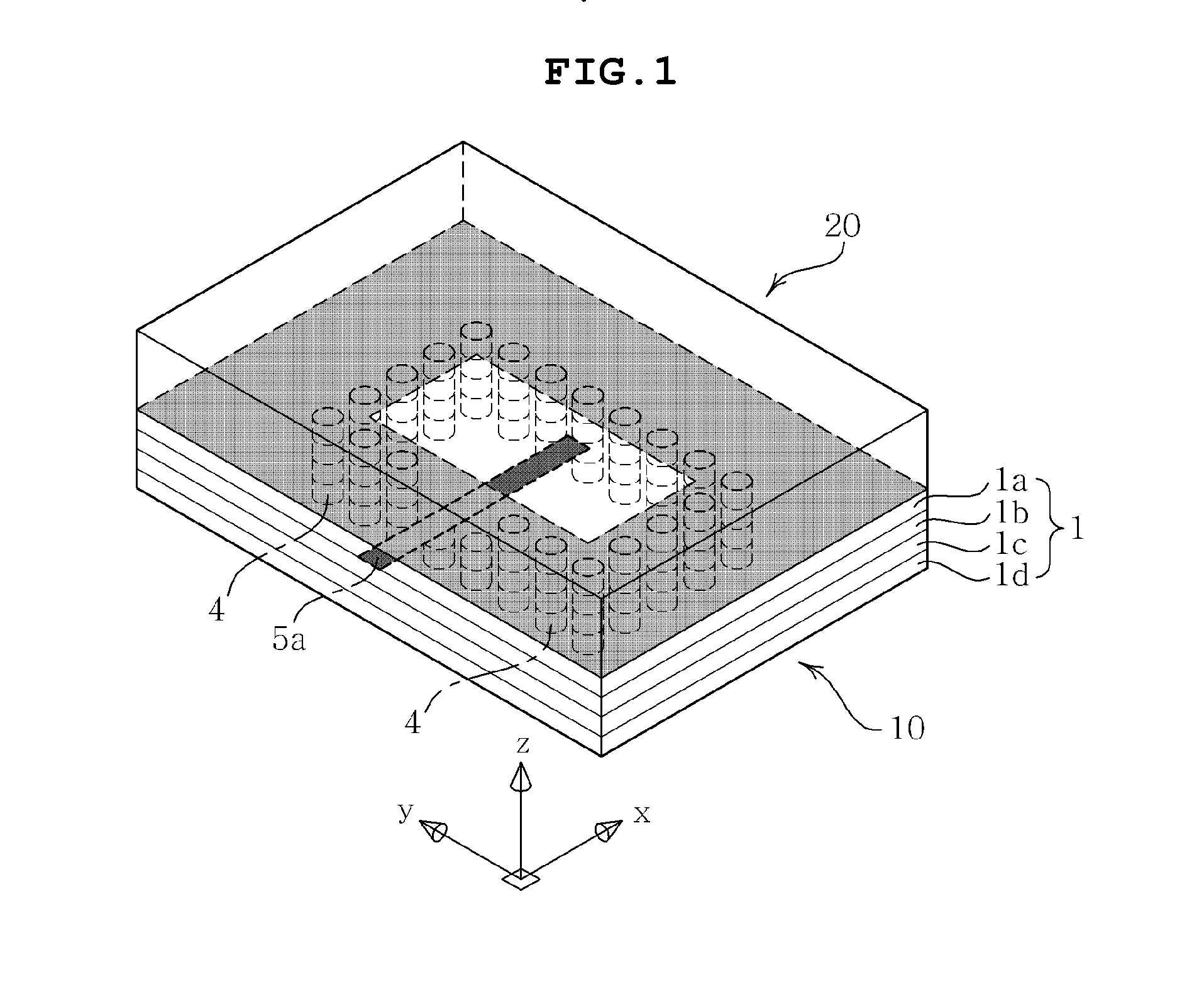
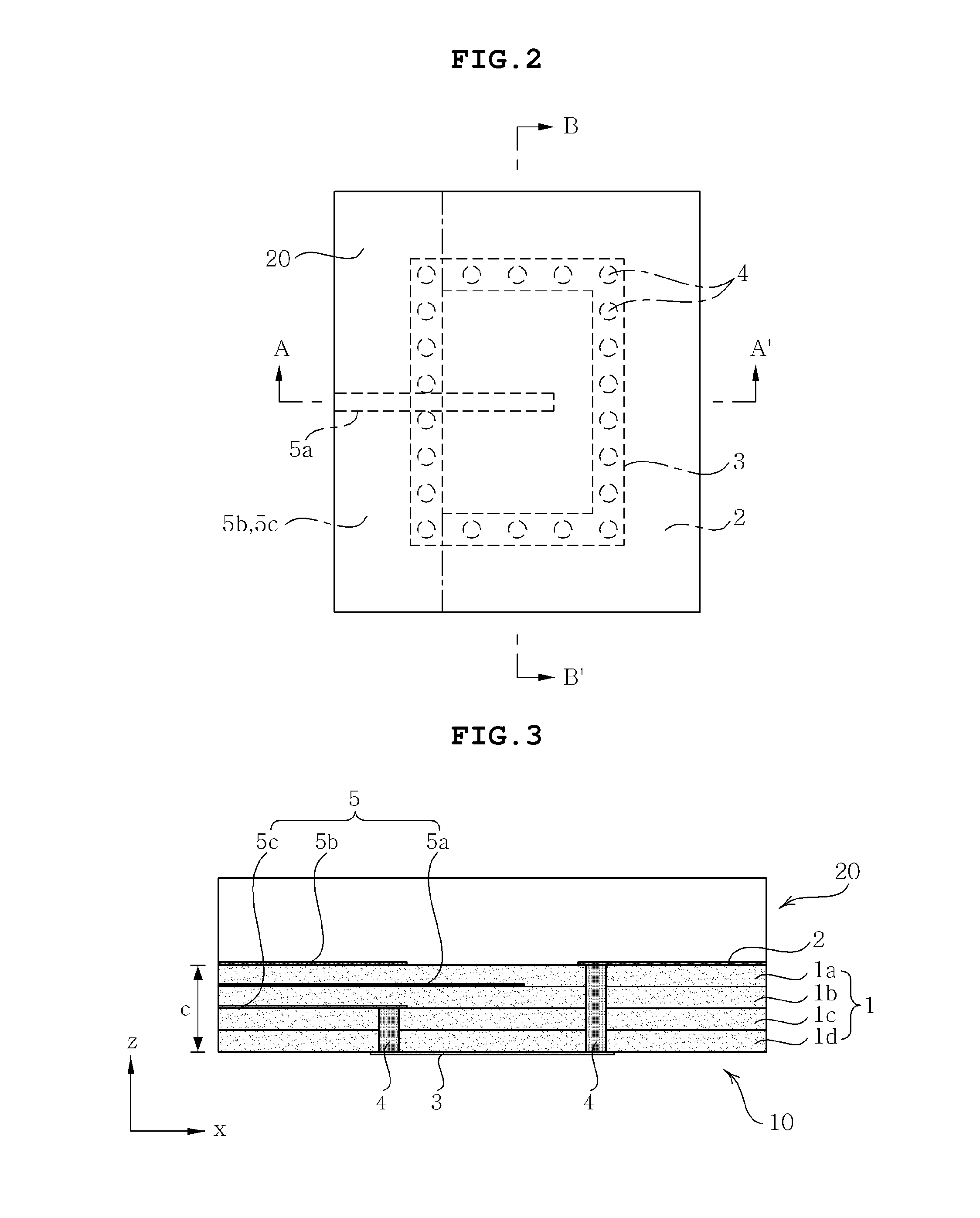
The present invention provides a dielectric resonator antenna comprising: a dielectric resonator; a ground plane, operatively coupled with the dielectric resonator, the ground plane having four slots; and a substrate, operatively coupled to the ground plane, having a feeding network consisting of four microstrip lines; wherein the four slots are constructed and geometrically arranged to ensure proper circular polarization and coupling to the dielectric resonator; and wherein the antenna feeding network combines the four microstrip lines with a 90 degree phase difference to generate circular polarization over a wide frequency band.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
Dielectric resonator array antenna
InactiveUS20140043189A1Improve featuresIndividually energised antenna arraysElectrically short antennasTime delaysDielectric resonator antenna
Disclosed herein is a dielectric resonator array antenna including one or more series-feed type array elements installed to be arranged in parallel in a multilayer substrate, wherein first high frequency signals having the same or different phases or time delays are adjusted to be applied to the respective series-feed type array elements and respective radiated 1D array beams are individually used or combined to adjust beamforming of 2D array beams. Also, since the series-feed type array element is configured by connecting a plurality of dielectric resonator antennas in series, it can be easily and simply fed in series through coupling generated by the intervals between the feeding lines of the pertinent feeding unit of the plurality of dielectric resonator antennas connected in series. In addition, the broadband characteristics can be obtained by using the plurality of dielectric resonator antennas, whereby the overall antenna performance can be enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
Millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and array thereof
InactiveCN101662076AWith quasi-optical Gaussian beam radiation characteristicsGuaranteed normal transmissionAntenna arraysDielectric resonator antennaDielectric substrate
The invention relates to the technical field of radar, in particular to a millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and an array thereof. The array consists of a microstrip integrated antenna, a dielectric lens, an objective lens, an array base, a reflecting mirror, a protective cover and a beam transfer switch; one end face of the dielectric lens is a hemisphere or an ellipsoid, while the other end face is a cylindrical section; the microstrip integrated antenna is generated by an dielectric substrate, the front surface of the dielectric substrate is closely adhered tothe cylindrical section of the dielectric lens and serves as a feed source, and the back surface is grounded; the hemispherical or ellipsoidal end face of the dielectric lens is an antenna radiating surface; the length of the cylindrical part of the dielectric lens can be changed; the antenna array is arranged into a linear array or an area array; the array base and the reflecting mirror have conical quasi-optical reflecting mirror surfaces; the focus of the objective lens of the linear array or the area array aligns with the central line of the dielectric lens; the protective cover is arranged outside; and the antenna array is controlled by the beam transfer switch. The antenna structure has strong shock resistance and dust prevention, and is suitable for millimeter-wave radars for planes, automobiles and ships, and receiving / emitting sensing of communication equipment.
Owner:阮树成
Dielectric-resonator array antenna system
InactiveUS20060082516A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDielectric resonator antennaLight beam
A dielectric resonator element array (DRA) antenna system and method for using same is disclosed. The dielectric resonator antenna system includes a ground plain, a feed structure, an array of dielectric resonator elements electrically coupled to the feed structure, each dielectric element having a relatively high permittivity, a radome close to or in contact with the array of dielectric resonator elements, an object mounting apparatus for mounting the antenna system on an object, and a beam shaping and steering controller, the beam shaping and steering controller controlling the feed structure to thereby control excitation phases of the dielectric resonator elements.
Owner:STRICKLAND PETER C
Dielectric resonant antenna using a matching substrate
ActiveUS20110248891A1Low dielectric constantReduce sensitivitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric resonator antennaDielectric resonator
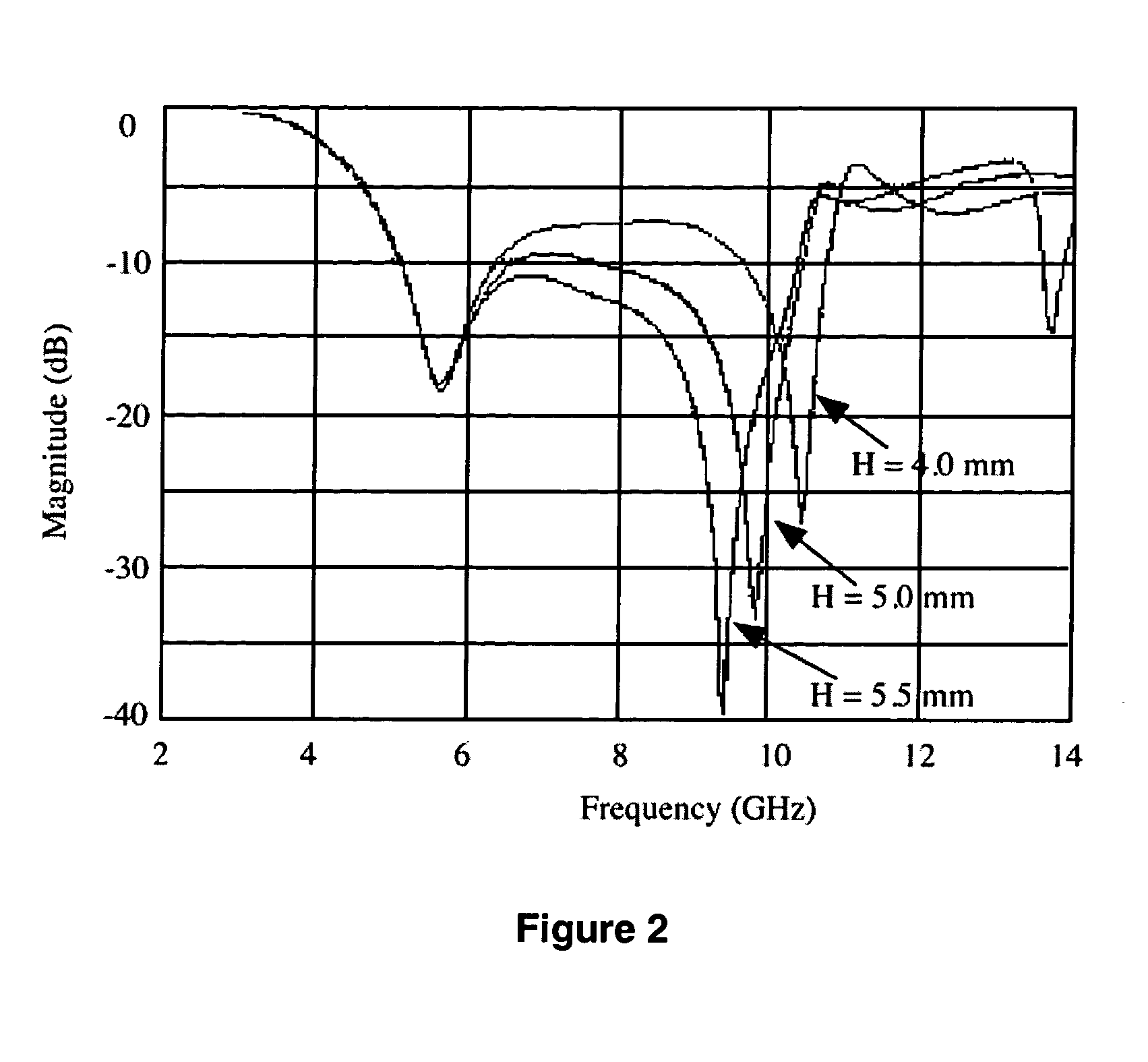
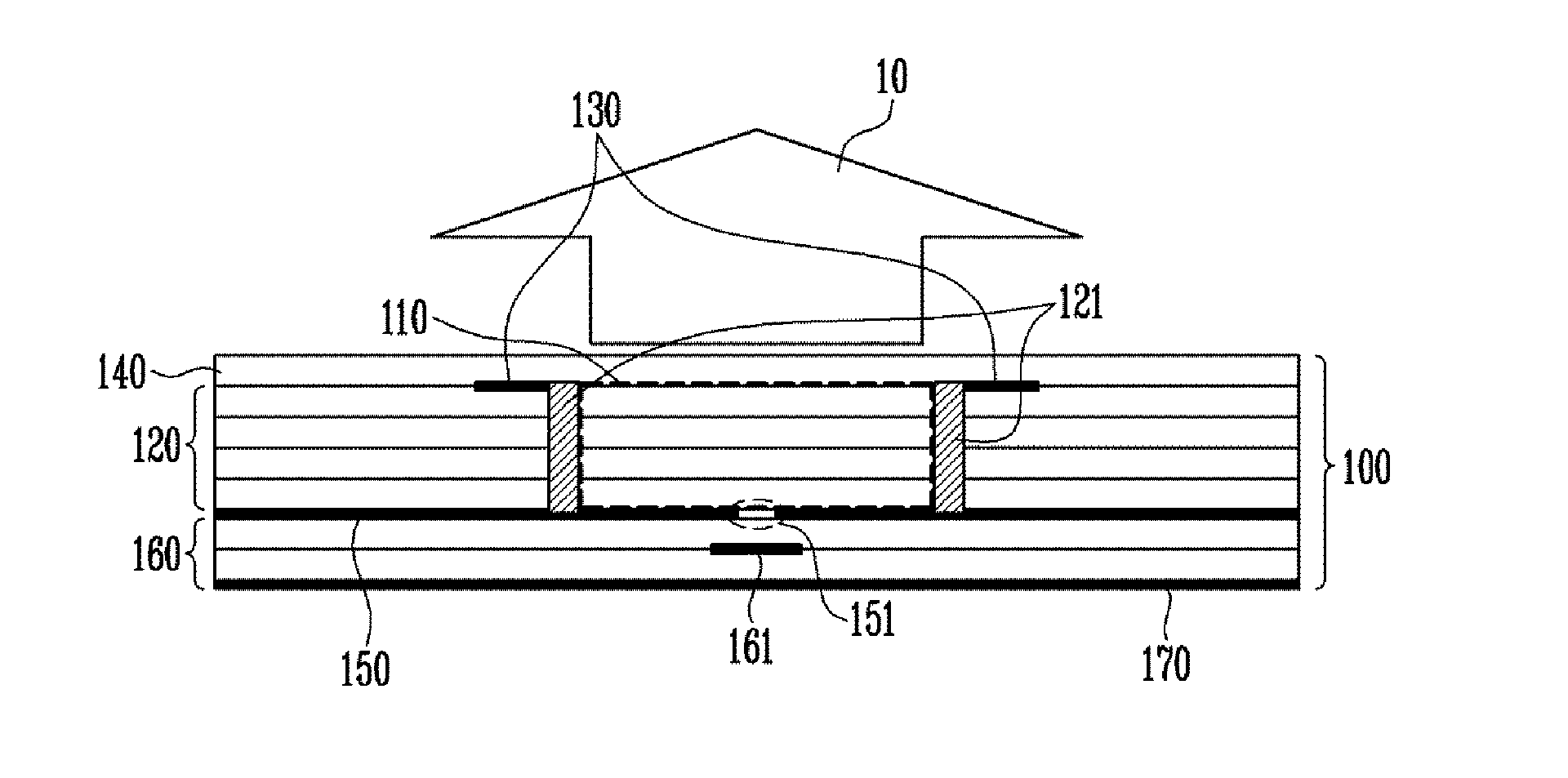
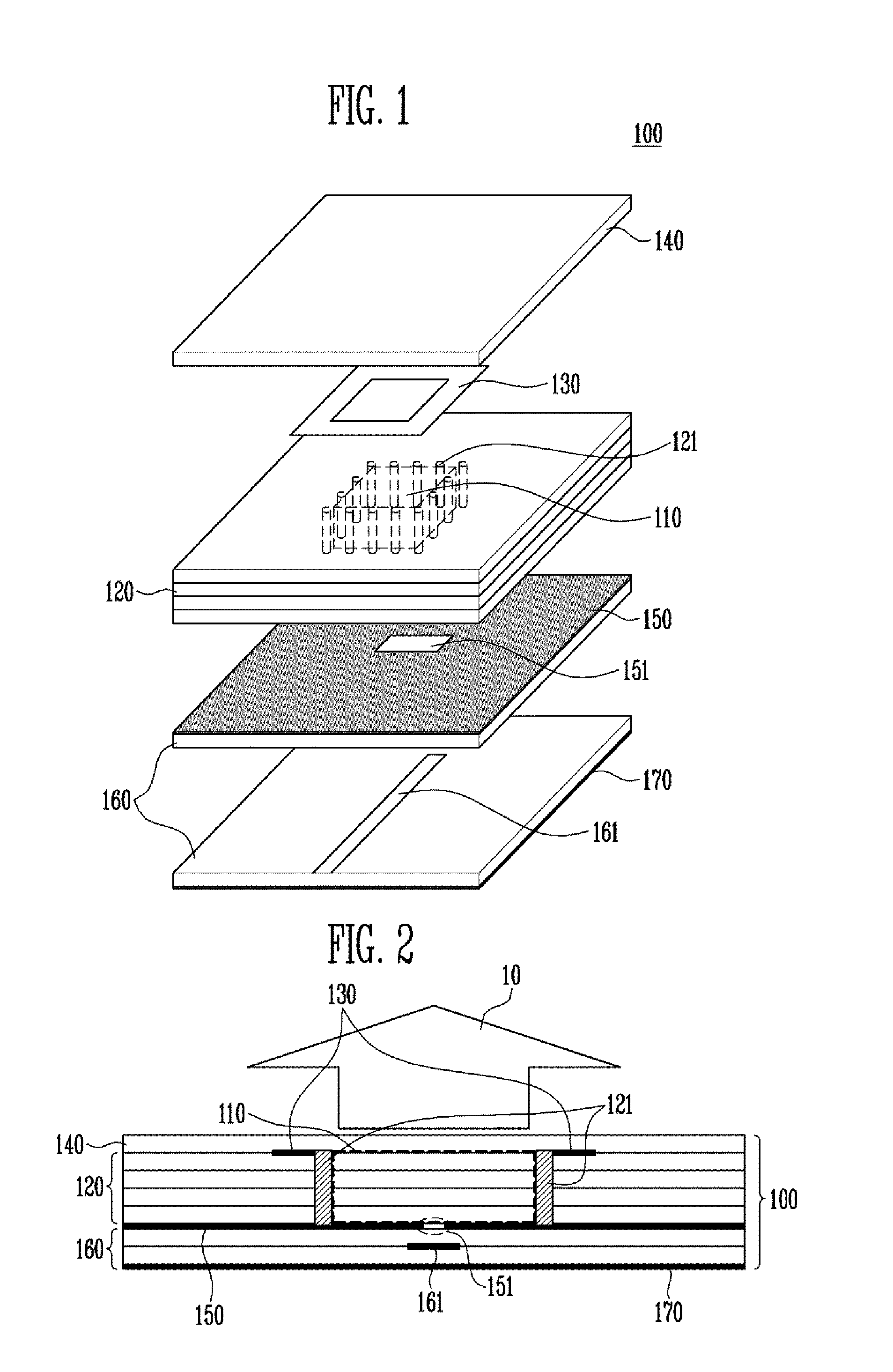
Disclosed herein is a dielectric resonator antenna using a matching substrate in order to improve a bandwidth. The dielectric resonator antenna includes: a dielectric resonator body part that is embedded in a multi-layer substrate and has an opening part on the upper portion thereof; and at least one matching substrate that is stacked on the opening part and includes an an insulating layer having a dielectric constant smaller than that of the multi-layer substrate but larger than that of air, thereby making it possible to improve the bandwidth without adjusting the size of the dielectric resonator body part and to prevent loss and change in the radiation pattern due to the substrate mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
Wideband circularly polarized hybrid dielectric resonator antenna
ActiveUS20120212386A1High bandwidthCompact geometryPolarised antenna unit combinationsAntennas earthing switches associationDielectric resonator antennaPhase difference
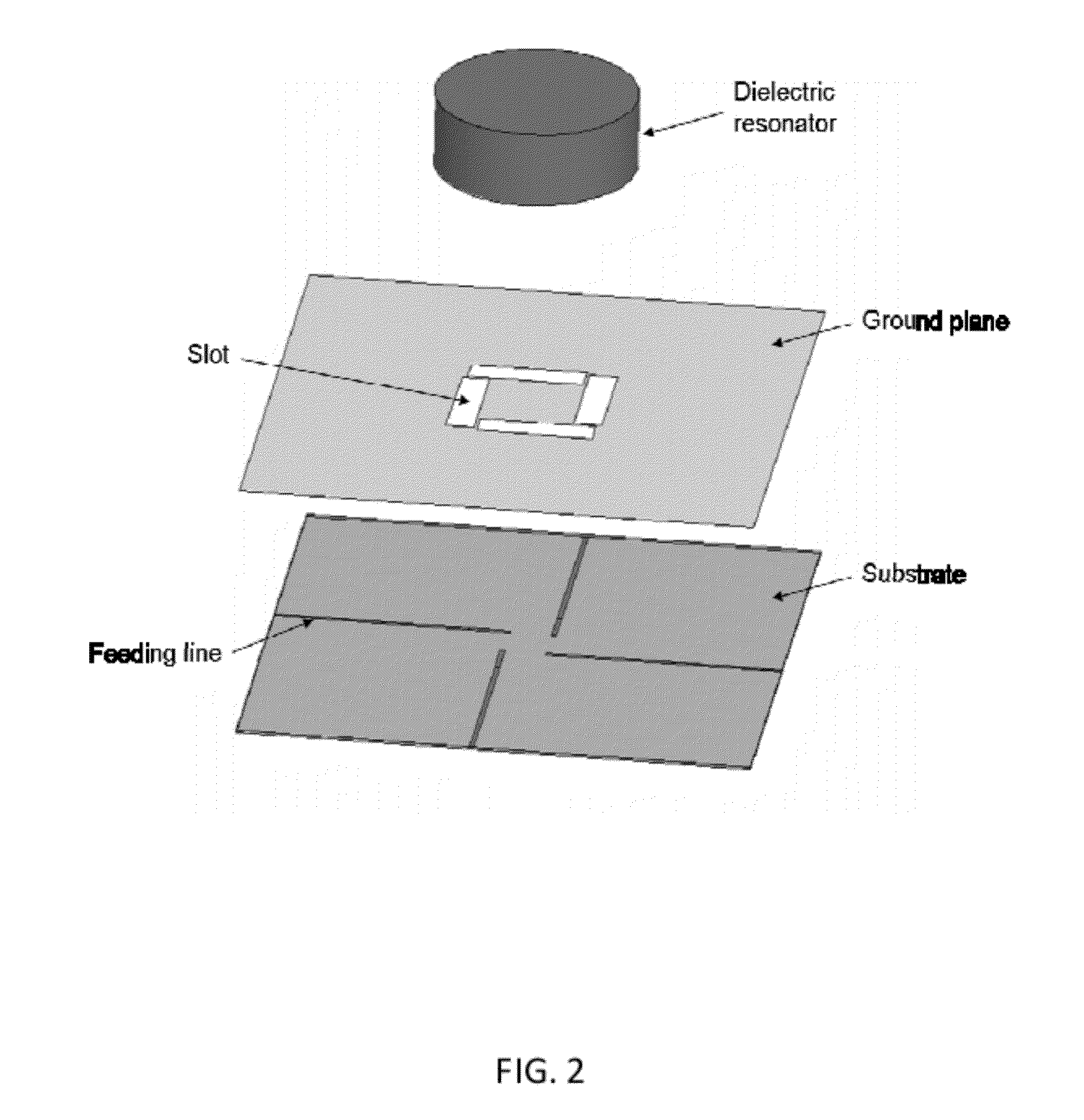
The present invention provides a dielectric resonator antenna comprising: a dielectric resonator; a ground plane, operatively coupled with the dielectric resonator, the ground plane having four slots; and a substrate, operatively coupled to the ground plane, having a feeding network consisting of four microstrip lines; wherein the four slots are constructed and geometrically arranged to ensure proper circular polarization and coupling to the dielectric resonator; and wherein the antenna feeding network combines the four microstrip lines with a 90 degree phase difference to generate circular polarization over a wide frequency band.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
Light transmissible resonators for circuit and antenna applications
ActiveUS20110122036A1Increase currentHigh voltageElectrically short antennasDielectric resonator antennaSolar cell
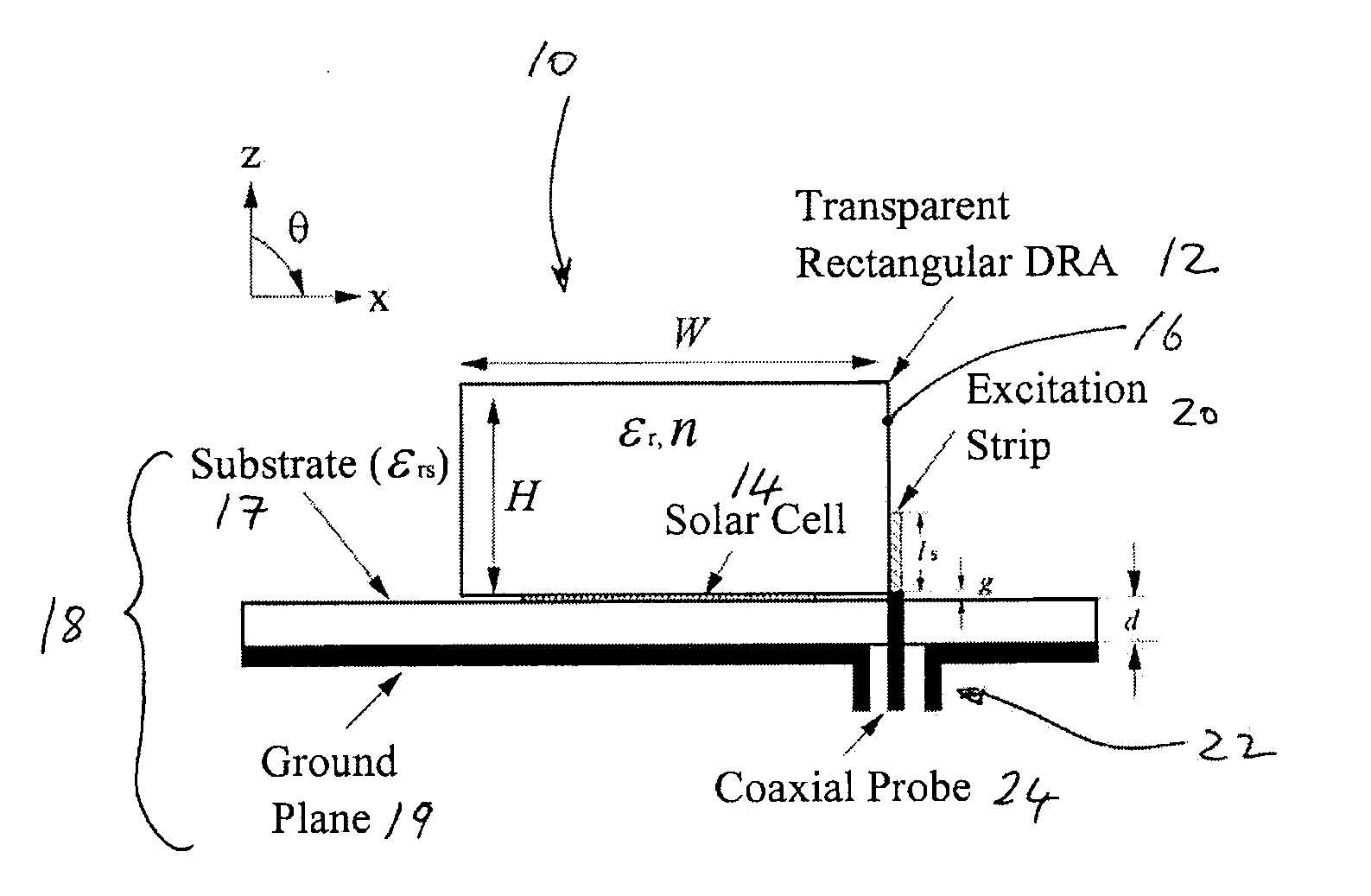
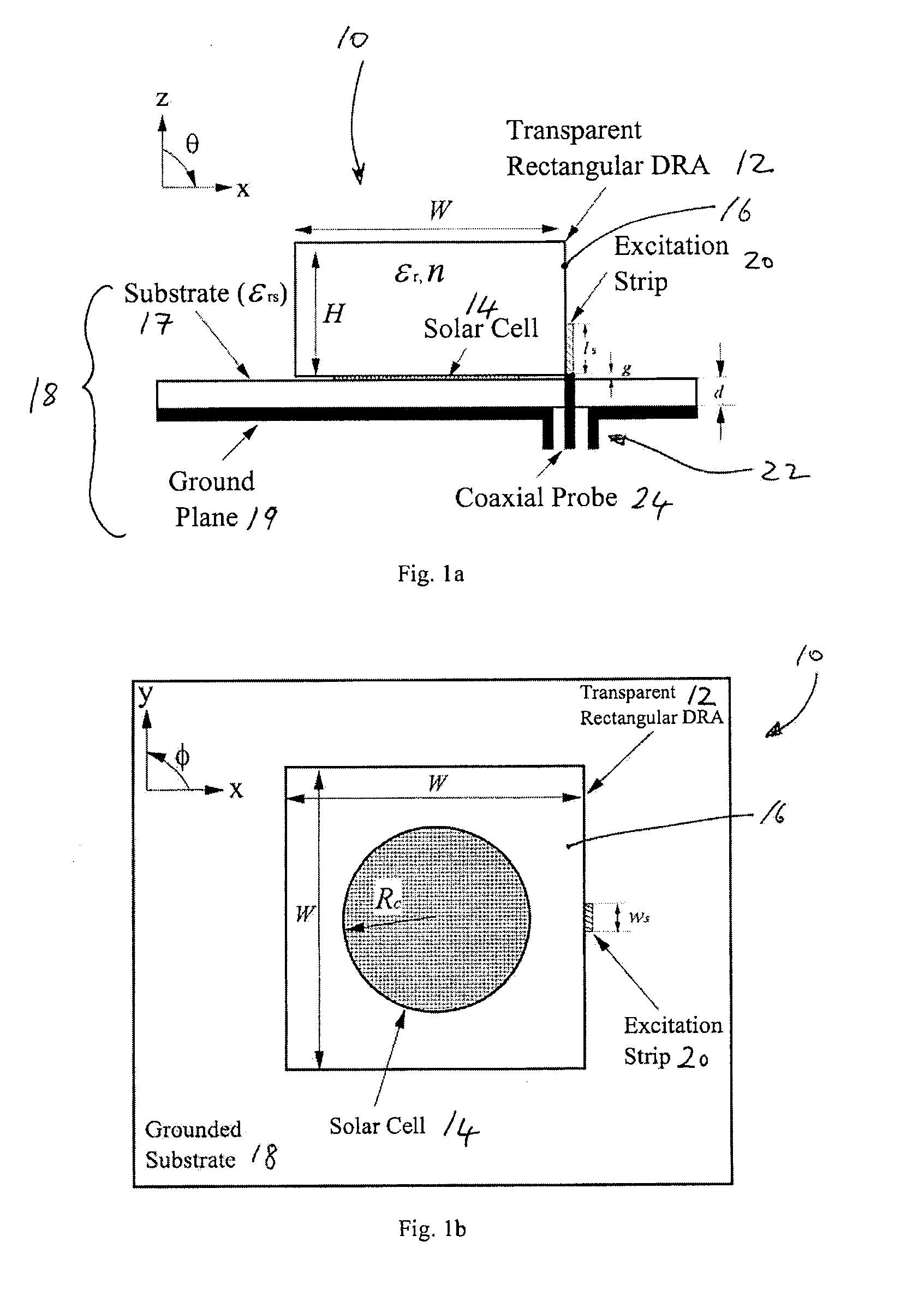
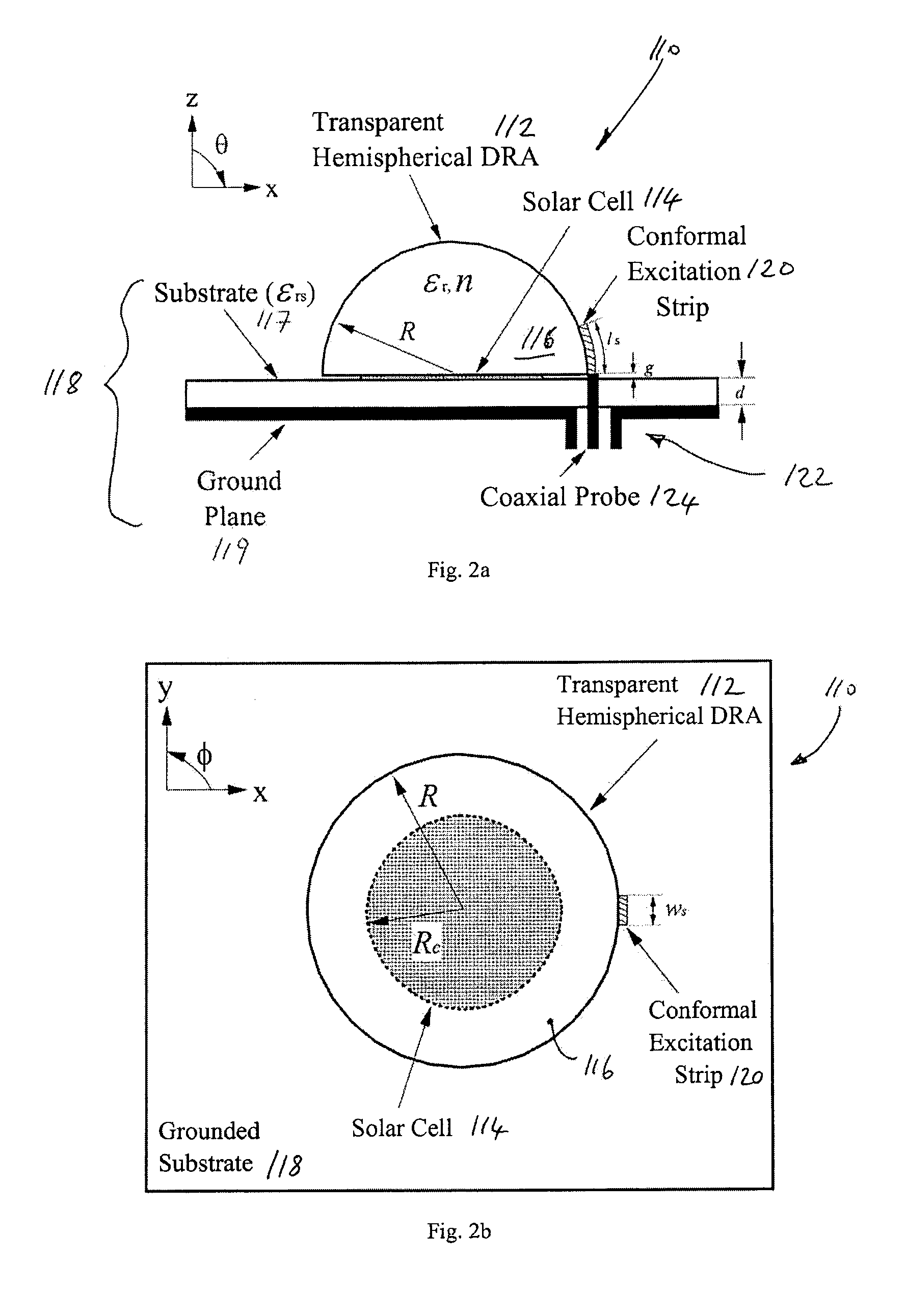
Provided is a circuit for an electronic device having a non-planar transparent resonator. The transparent resonator is mounted on said circuit so as to at least partially occupy a footprint of another component of the circuit. The transparent resonator forms part of a light pathway on said circuit for transmitting light to or from said another component. Also provided is a transparent dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) for optical applications. Since the DRA is transparent, it can let light pass through itself and, thus, the light can be utilized by an optical part of a system or device. The transparent DRA can be placed on top of a solar cell. Since the DRA does not block the light, the light can reach the solar cell panel and power can be generated for the system or device. The system or device so obtained is very compact because no extra footprint is needed within the system or device for the DRA. It finds application in compact wireless applications that need a self-sustaining power device.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Adjusted directivity dielectric resonator antenna
InactiveUS6344833B1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric resonator antennaDual band antenna
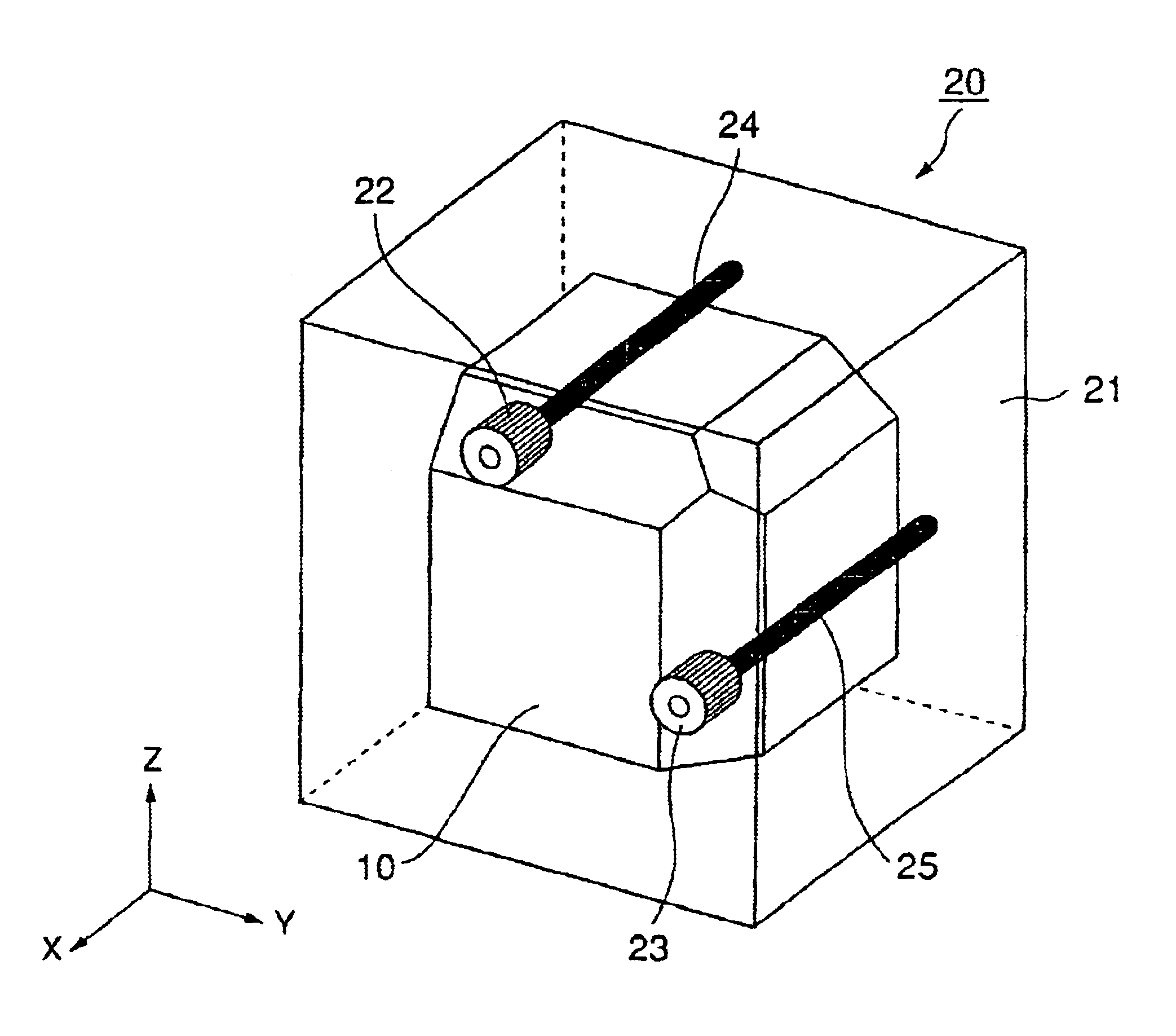
A dielectric resonator antenna having a resonator formed from a dielectric material mounted on a ground plane with a conductive skirt. The ground plane is formed from a conductive material. First and second probes are electrically coupled to the resonator for providing first and second signals, respectively, to or receiving from the resonator. The first and second probes are spaced apart from each other. The first and second probes are formed of conductive strips that are electrically connected to the perimeter of the resonator and are substantially orthogonal with respect to the ground plane. A dual band antenna can be constructed by positioning and connecting two dielectric resonator antennas together. Each resonator in the dual band configuration resonates at a particular frequency, thereby providing dual band operation. The resonators can be positioned either side by side or vertically. Further advantage is obtained by mounting the dual antenna stack within a radome.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
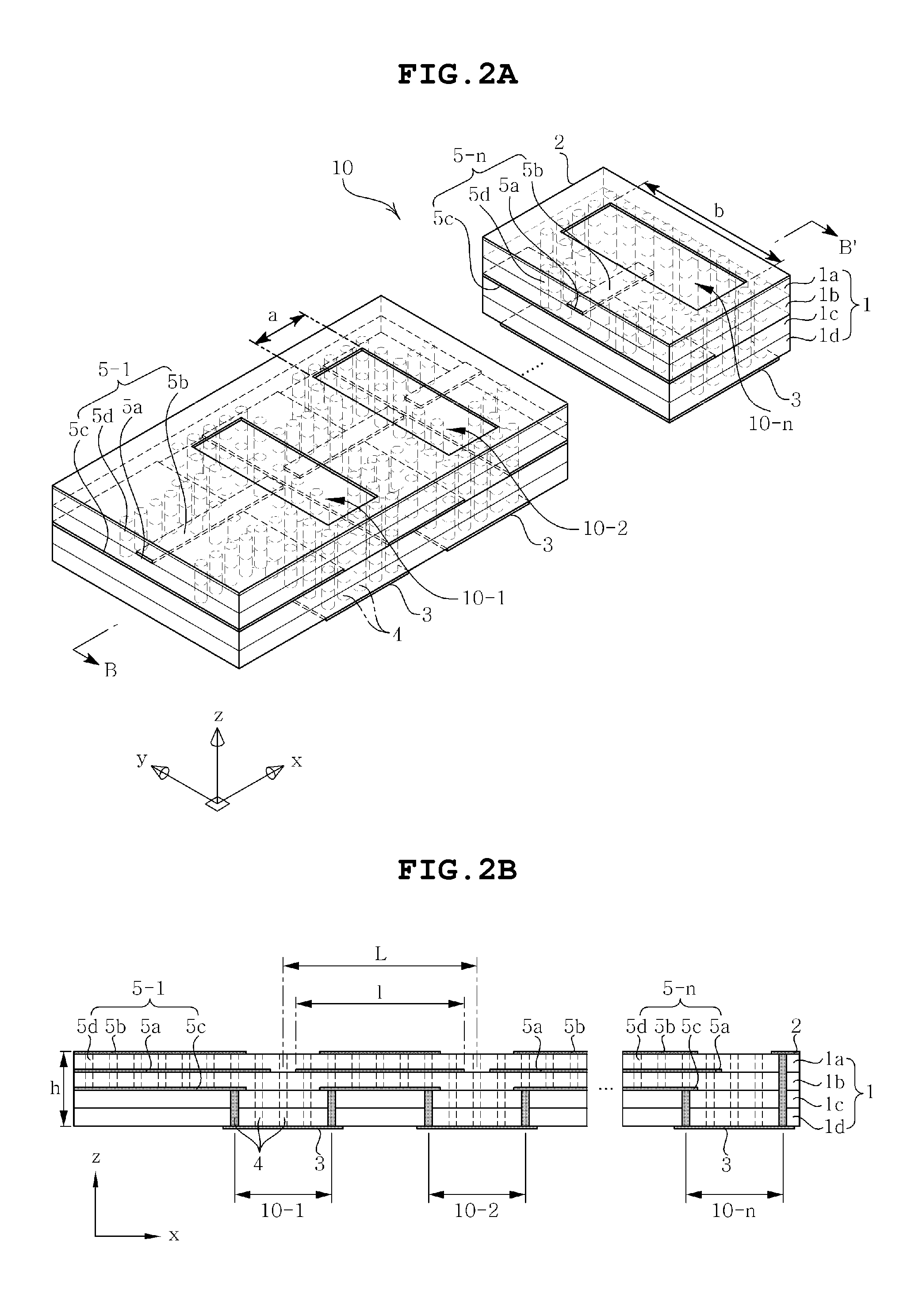
Dielectric resonator antenna embedded in multilayer substrate for enhancing bandwidth
ActiveUS20110248890A1Easy to manufactureMinimize changesSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric resonator antennaDielectric resonator
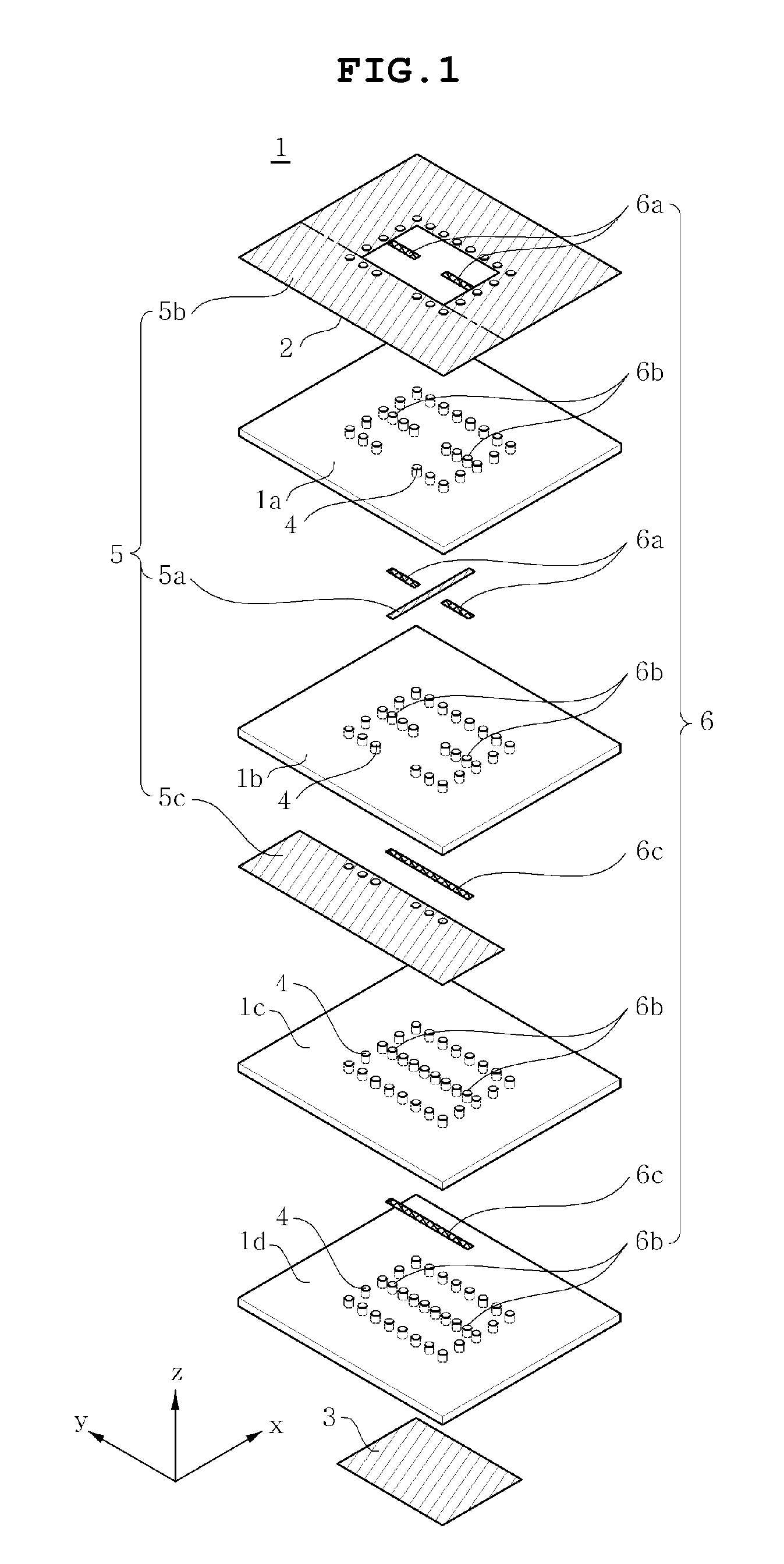
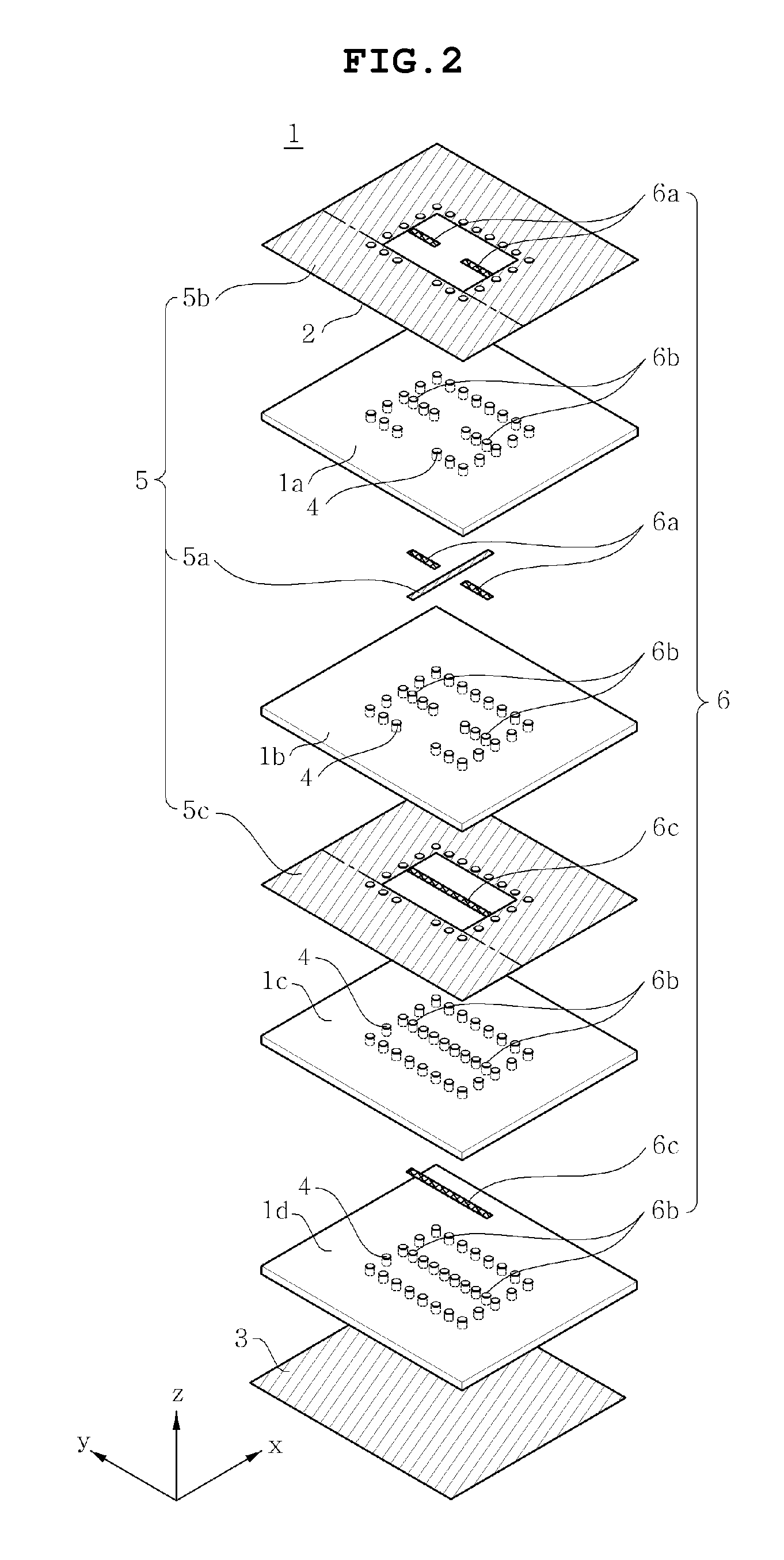
Disclosed herein is a dielectric resonator antenna embedded in a multilayer substrate for enhancing bandwidth. The dielectric resonator antenna includes a multilayer substrate, a first conductive plate, a second conductive plate, a plurality of first metal via holes, a feeding part configured to feed a dielectric resonator, and a conductive pattern part inserted into the dielectric resonator so that a vertical metal interface is formed in the dielectric resonator. Accordingly, the dielectric resonator antenna has low sensitivity to fabrication errors and an external environment, and can enhance the radiation characteristics of the antenna when multiple resonances occur.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Electronic part, dielectric resonator, dielectric filter, duplexer, and communication device comprised of high TC superconductor
InactiveUS6470198B1Superconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectrical conductorSilver electrode
In a dielectric resonator, a superconductor is formed on two neighboring surfaces of a cubic dielectric body, and the superconductors formed on each two neighboring surfaces are connected by a silver electrode formed in the vicinity of the edge where the neighboring two surfaces join.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Dielectric-patch resonator antenna
InactiveUS6292141B1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric resonator antennaConductive materials
A dielectric-patch resonator antenna having a resonator formed from a dielectric material mounted on a ground plane with a conductive skirt, and a patch element disposed inbetween. The ground plane and patch are formed from conductive materials. First and second probes are electrically coupled to the resonator for providing first and second signals, respectively, to or receiving from the resonator. The first and second probes are spaced apart from each other. The first and second probes are formed of conductive strips that are electrically connected to the perimeter of the resonator and are substantially orthogonal with respect to the ground plane. A dual band antenna can be constructed by positioning and connecting two dielectric resonator antennas together. Each resonator in the dual band configuration resonates at a particular frequency, thereby providing dual band operation. The resonators can be positioned either side by side or vertically.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Broadband multiple layer dielectric resonator antenna and method of making the same
ActiveUS20170125908A1Additive manufacturing apparatusSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectric resonator antennaBroadband
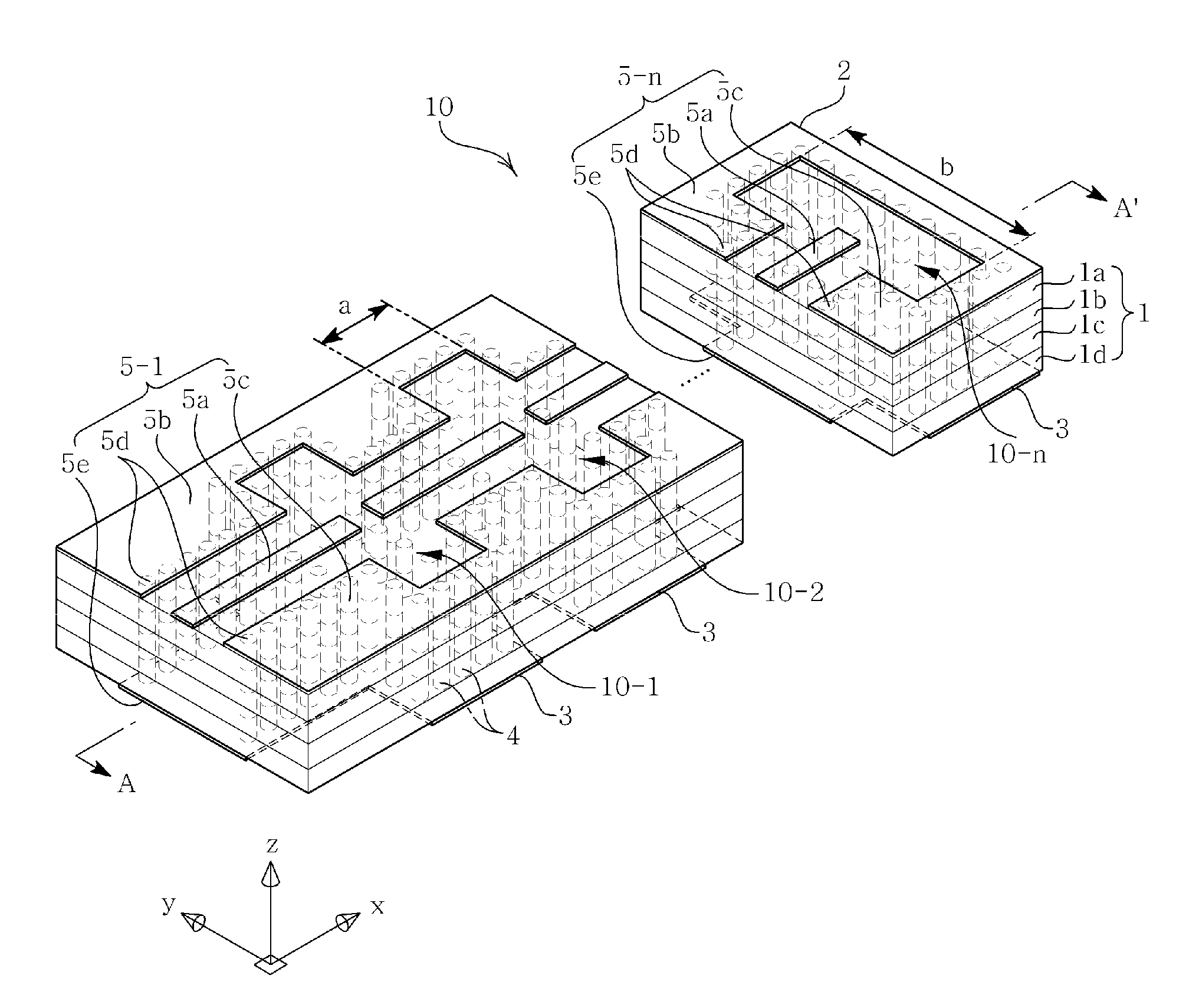
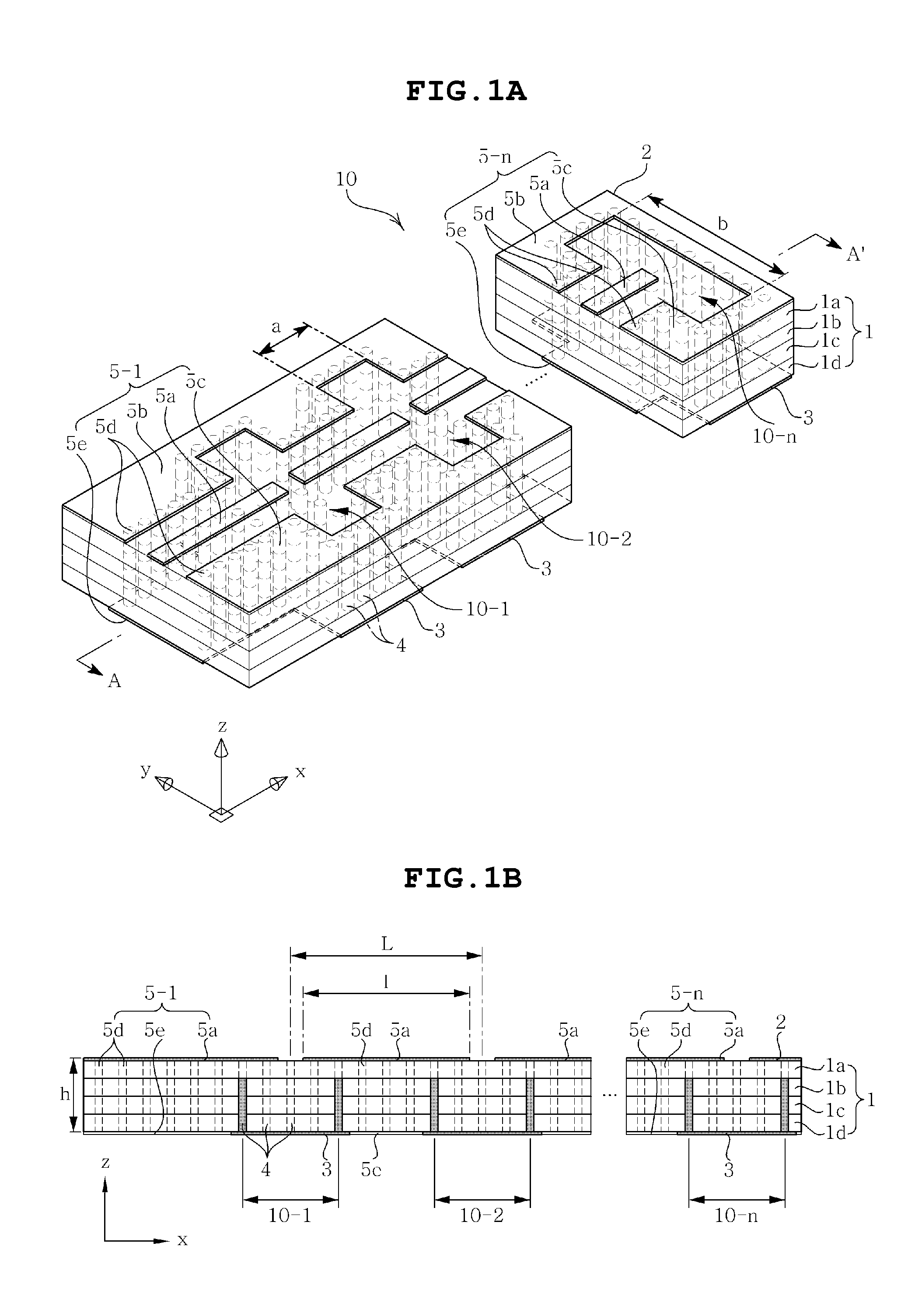
A dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) includes: an electrically conductive ground structure; a plurality of volumes of dielectric materials disposed on the ground structure comprising N volumes, N being an integer equal to or greater than 3, disposed to form successive and sequential layered volumes V(i), i being an integer from 1 to N, wherein volume V(1) forms an innermost volume, wherein a successive volume V(i+1) forms a layered shell disposed over and at least partially embedding volume V(i), wherein volume V(N) at least partially embeds all volumes V(1) to V(N−1); and a signal feed disposed and structured to be electromagnetically coupled to one or more of the plurality of volumes of dielectric materials.
Owner:ROGERS CORP
Dielectric resonator antenna embedded in multilayer substrate
InactiveUS20110133991A1Easy to makeLittle changeSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric resonator antennaDielectric resonator
Disclosed is a dielectric resonator antenna embedded in a multilayer substrate, which includes a multilayer substrate, a first conductor plate having an opening, a second conductor plate formed on the bottom of a lowermost insulating layer resulting from stacking at least two insulating layers downward from the first conductor plate, a plurality of metal via holes passing through around the opening at a predetermined interval, and a feeder for transmitting a frequency signal to the dielectric resonator embedded by the metal boundaries defined by the first conductor plate, the second conductor plate and the plurality of metal via holes, thus exhibiting low sensitivity to fabrication error and the external environment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Multi-band single feed dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) array
ActiveUS20170271772A1Antenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsMulti bandDielectric resonator antenna
A multi-band single feed dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) and DRA array are provided. The DRA is made of a dielectric material having a first and second antenna regions wherein the second antenna region has a different dielectric constant than the first antenna region. The dielectric material is supported by a feeding substrate. The feeding substrate has a top surface ground plane having a slot positioned below the first antenna region of the dielectric material and a microstrip feeding line on the bottom surface in alignment with the slot on the top surface ground plane.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Aesthetic dielectric antenna and method of discretely emitting radiation pattern using same
ActiveUS20130234898A1Satisfies needRadiating elements structural formsAntenna equipments with additional functionsElectricityDielectric resonator antenna
An aesthetic dielectric antenna (e.g., a dielectric resonator antenna) includes an aesthetically shaped decoration having at least one dielectric with a dielectric constant of more than one. A waveguide, feedline, probe or other means of excitation is electronically coupled to the dielectric to emit a radiation pattern for carrying analog or digital information.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Dielectric-patch resonator antenna
InactiveUS20020196190A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric resonator antennaGround plane
A dielectric-patch resonator antenna having a resonator formed from a dielectric material mounted on a ground plane with a conductive skirt, and a patch element disposed inbetween. The ground plane and patch are formed from conductive materials. First and second probes are electrically coupled to the resonator for providing first and second signals, respectively, to or receiving from the resonator. The first and second probes are spaced apart from each other. The first and second probes are formed of conductive strips that are electrically connected to the perimeter of the resonator and are substantially orthogonal with respect to the ground plane. A dual band antenna can be constructed by positioning and connecting two dielectric resonator antennas together. Each resonator in the dual band configuration resonates at a particular frequency, thereby providing dual band operation. The resonators can be positioned either side by side or vertically.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Polymer-based resonator antennas
ActiveUS20140327597A1Improve the effective dielectric constantPhotosensitive material processingAntennas earthing switches associationDielectric resonator antennaDielectric resonator
Dielectric resonator antennas suitable for use in compact radiofrequency (RF) antennas and devices, and methods of fabrication thereof. Described are dielectric resonator antennas fabricated using polymer-based materials, such as those commonly used in lithographic fabrication of integrated circuits and microsystems. Accordingly, lithographic fabrication techniques can be employed in fabrication. The polymer-based dielectric resonator antennas can be excited using tall metal vertical structures, which are also fabricated using techniques adapted from integrated circuit and microsystems fabrication.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN +1
Ultra wideband antenna
ActiveUS20050017903A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesUltra-widebandDielectric resonator antenna
An ultra-wideband antenna for operating in a frequency is disclosed wherein a monopole antenna extends from a ground plane. The monopole has an effective length L of one quarter wavelength at the lowest frequency f1. A dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) surrounds the monopole antenna for resonating at substantially between or at two and three times the lowest frequency f1. the DRA is of a height of less than ¾ L and is disposed in such a manner as being above the ground plane and either contacting or spaced therefrom by a gap G, wherein 0≦G≦0.2 H. The ultra-wideband antenna is of a much greater bandwidth than the sum of bandwidth of the monople or the DRA alone.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C +1
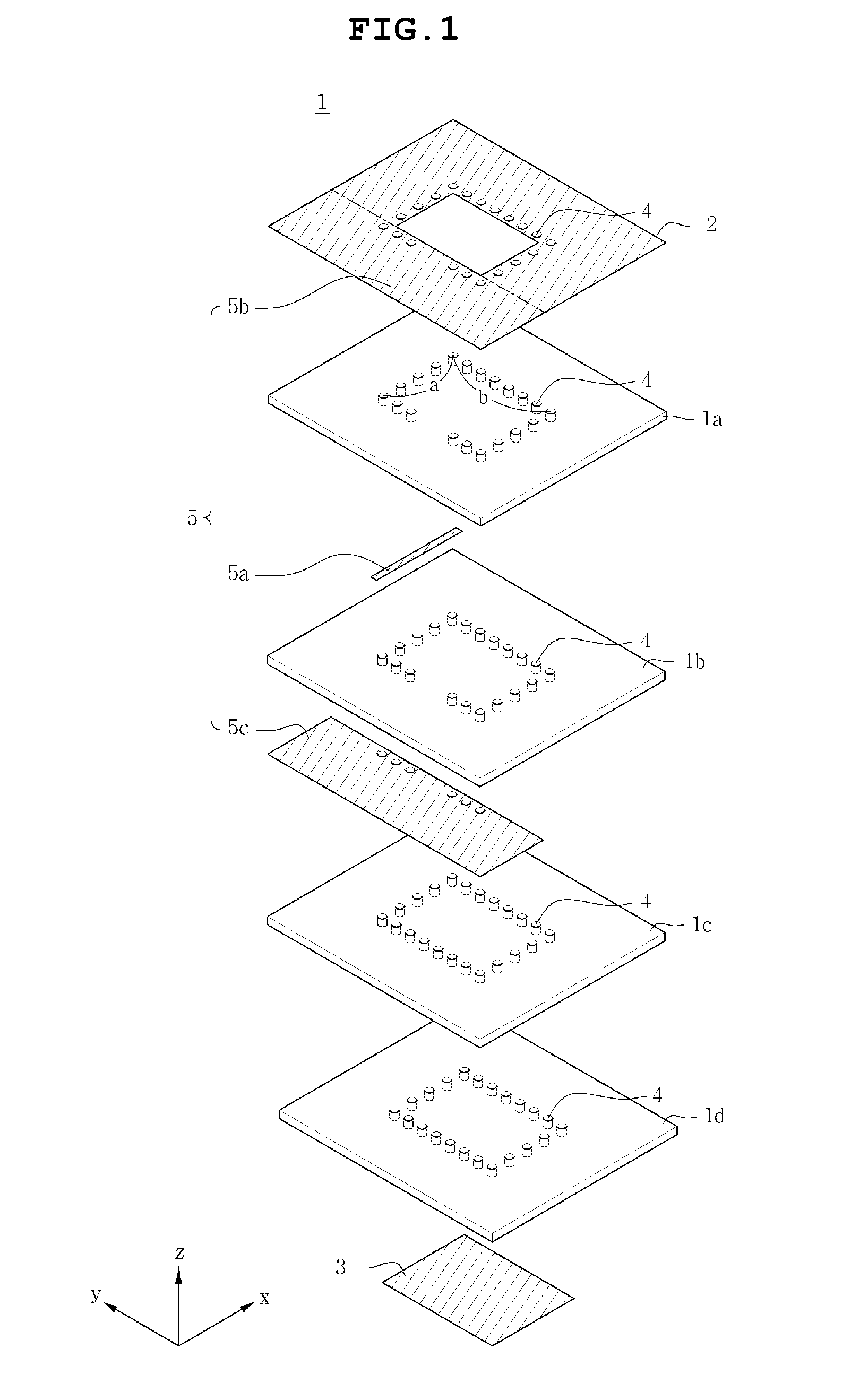
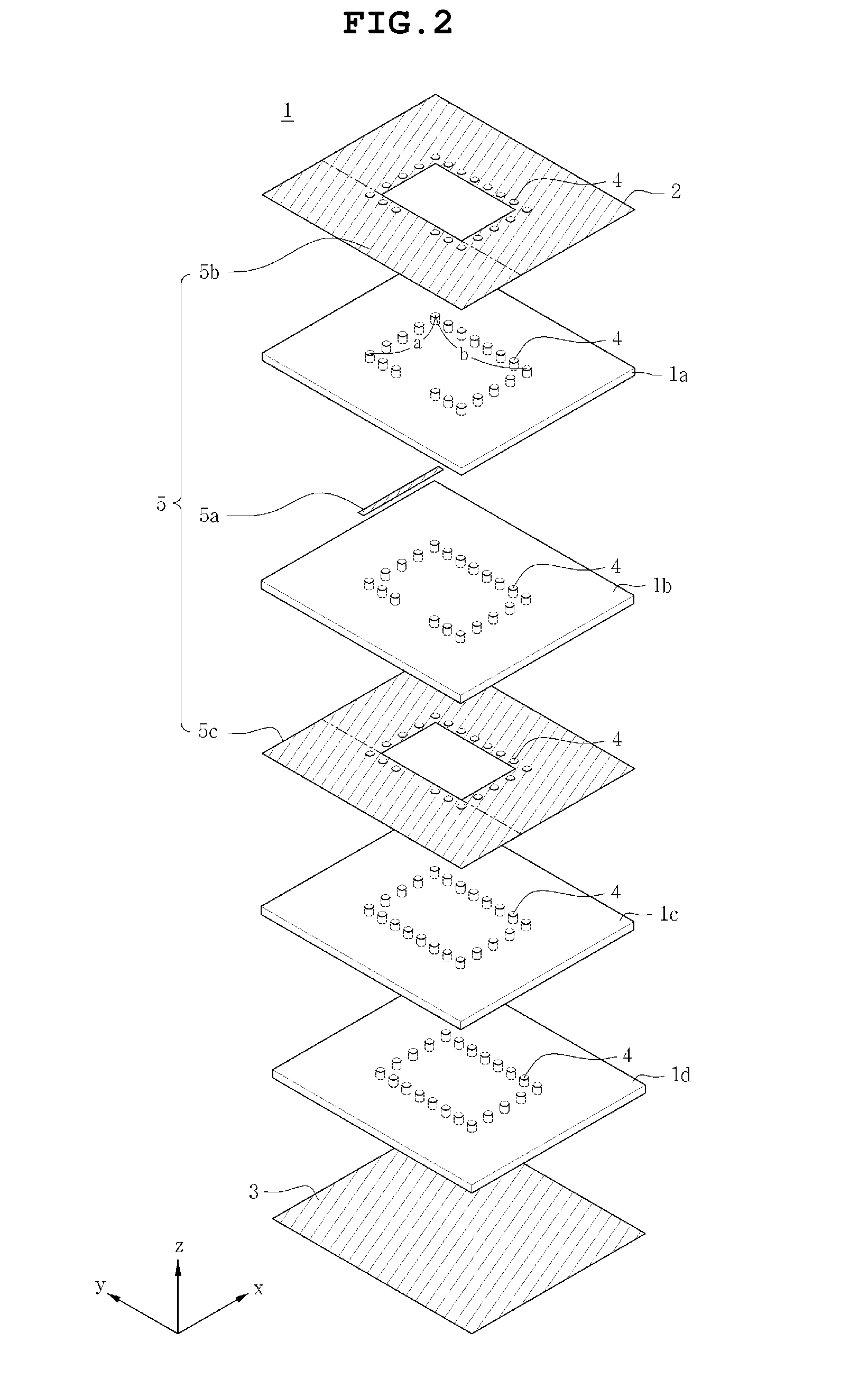
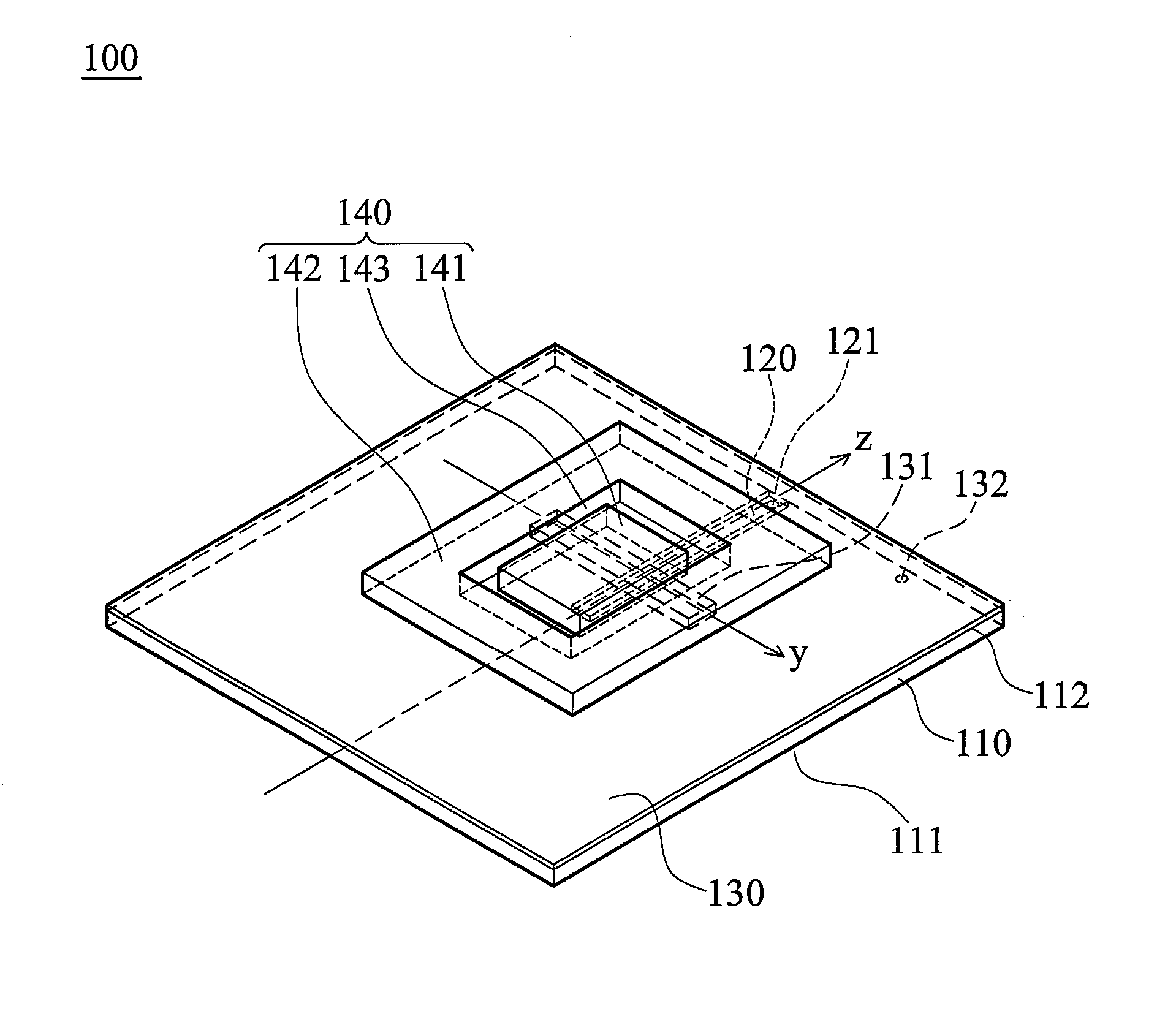
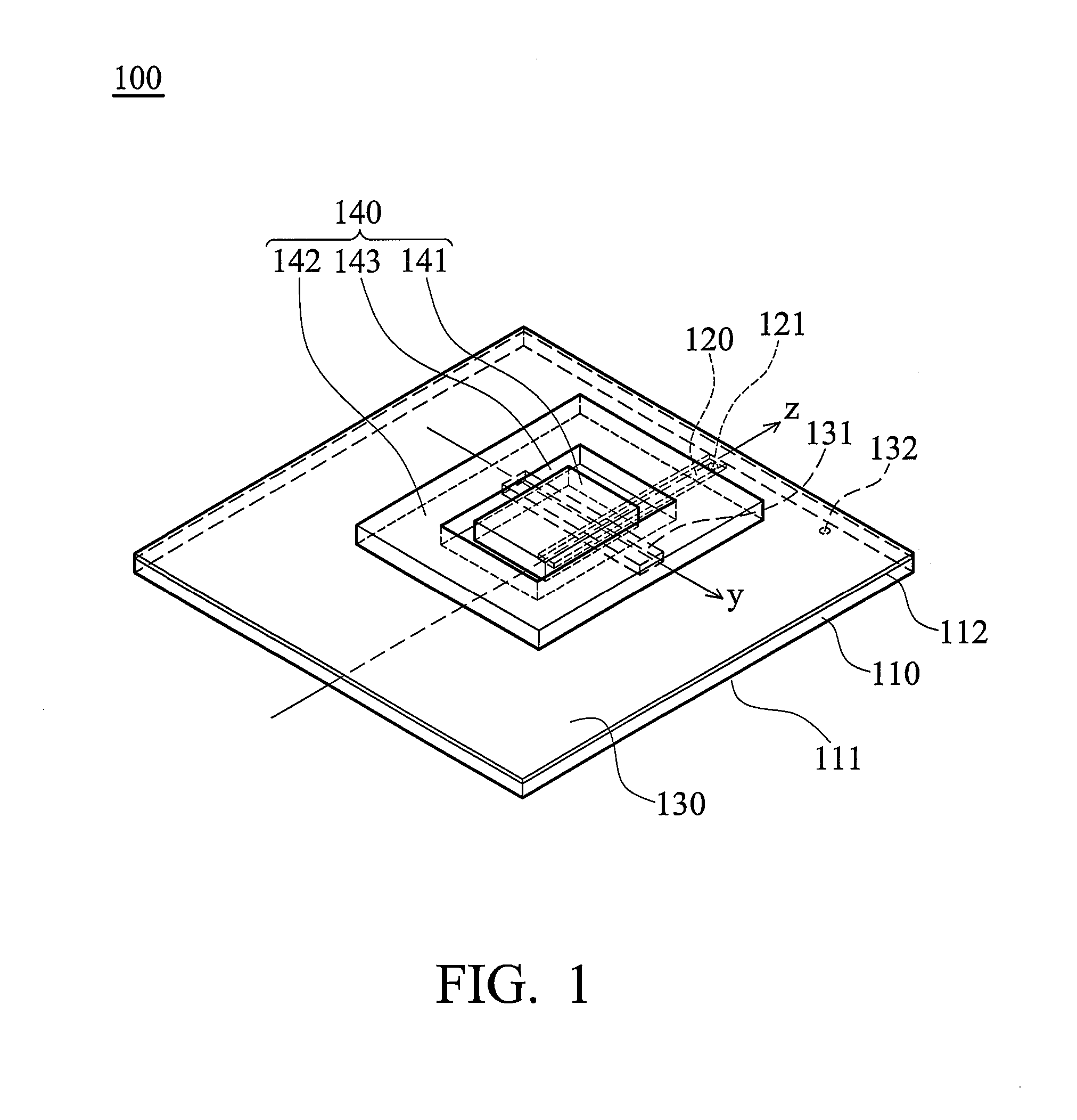
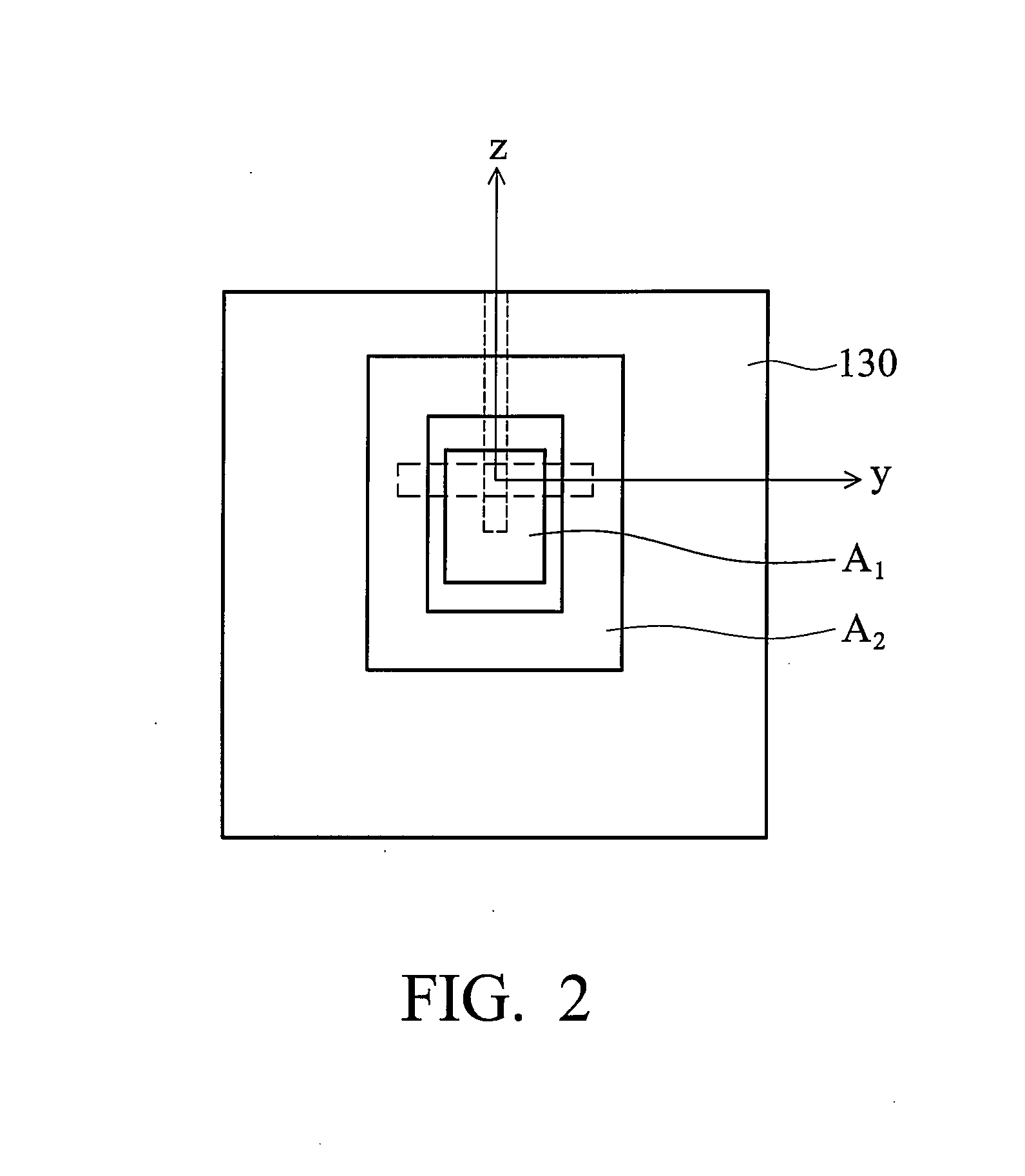
Dielectric resonator antenna
InactiveUS20150207233A1Reduce processing costsReduce manufacturing costAntenna earthingsAntennas earthing switches associationCouplingDielectric resonator antenna
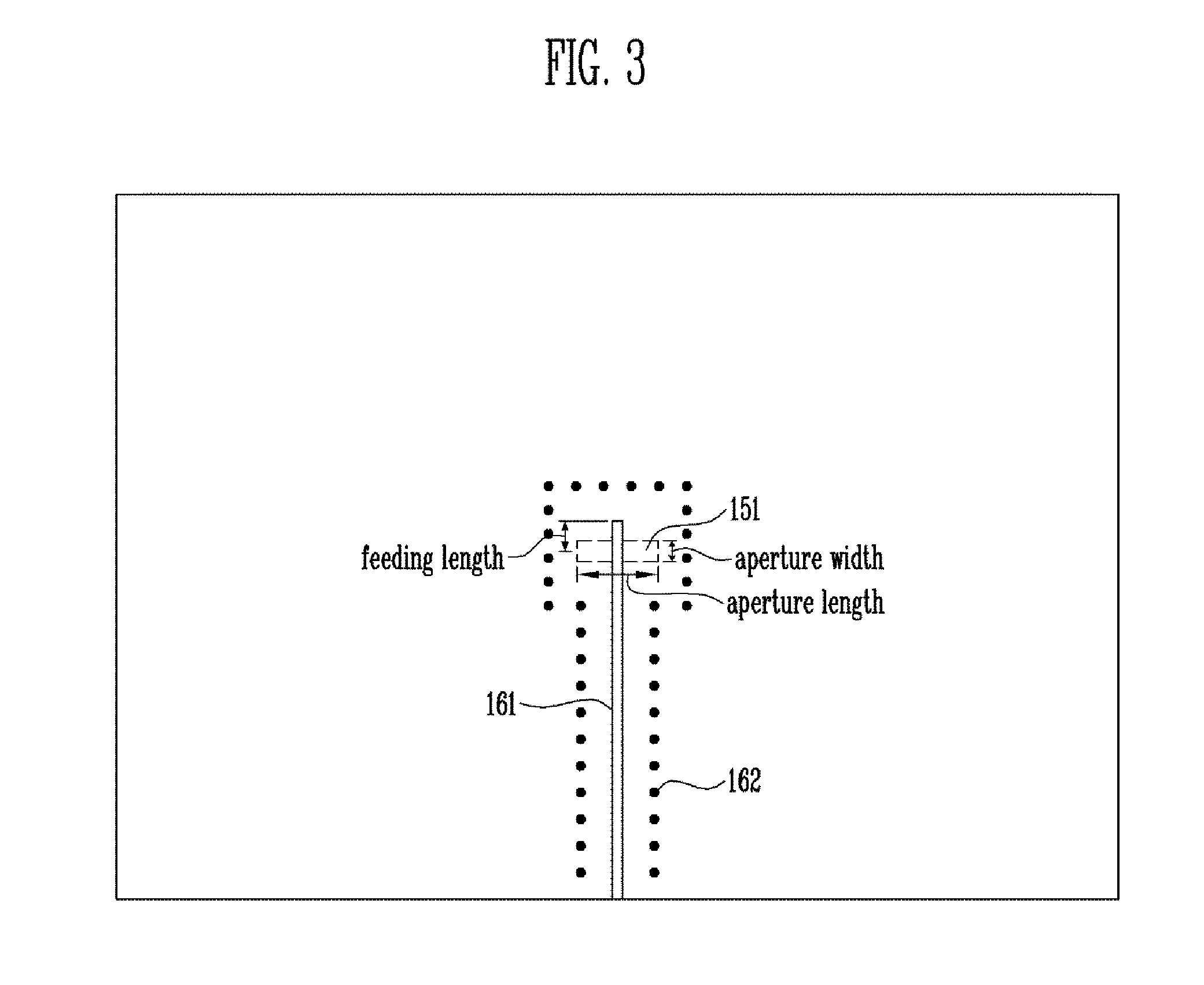
Disclosed is a dielectric resonator antenna. The dielectric resonator antenna includes: a dielectric resonator; an antenna layer formed inside the dielectric resonator, and including a plurality of vias positioned at a surrounding area of the dielectric resonator; a metal pattern forming an opened surface in an upper portion of the antenna layer; a dielectric layer configured to cover the metal pattern on the dielectric resonator; an internal ground pattern including a coupling aperture for inputting a signal into the dielectric resonator under the dielectric resonator; and a feeding layer including a strip transmission line for transmitting a signal to the dielectric resonator, and positioned under the antenna layer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Broadband dielectric resonator antenna embedding moat and design method thereof
InactiveUS20080272963A1Small heightLow costSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric resonator antennaBroadband
An antenna is provided comprising a substrate, a feed conductor, a ground layer and a resonator body. The substrate comprises a first surface and a second surface. The feed conductor is formed on the first surface. The ground layer is formed on the second surface comprising an opening. The resonator body comprises a first resonator structure and a second resonator structure. The first resonator structure is disposed on the ground layer. The second resonator structure is disposed on the ground layer surrounding the first resonator structure, wherein a groove is formed between the first and the second resonator structures.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
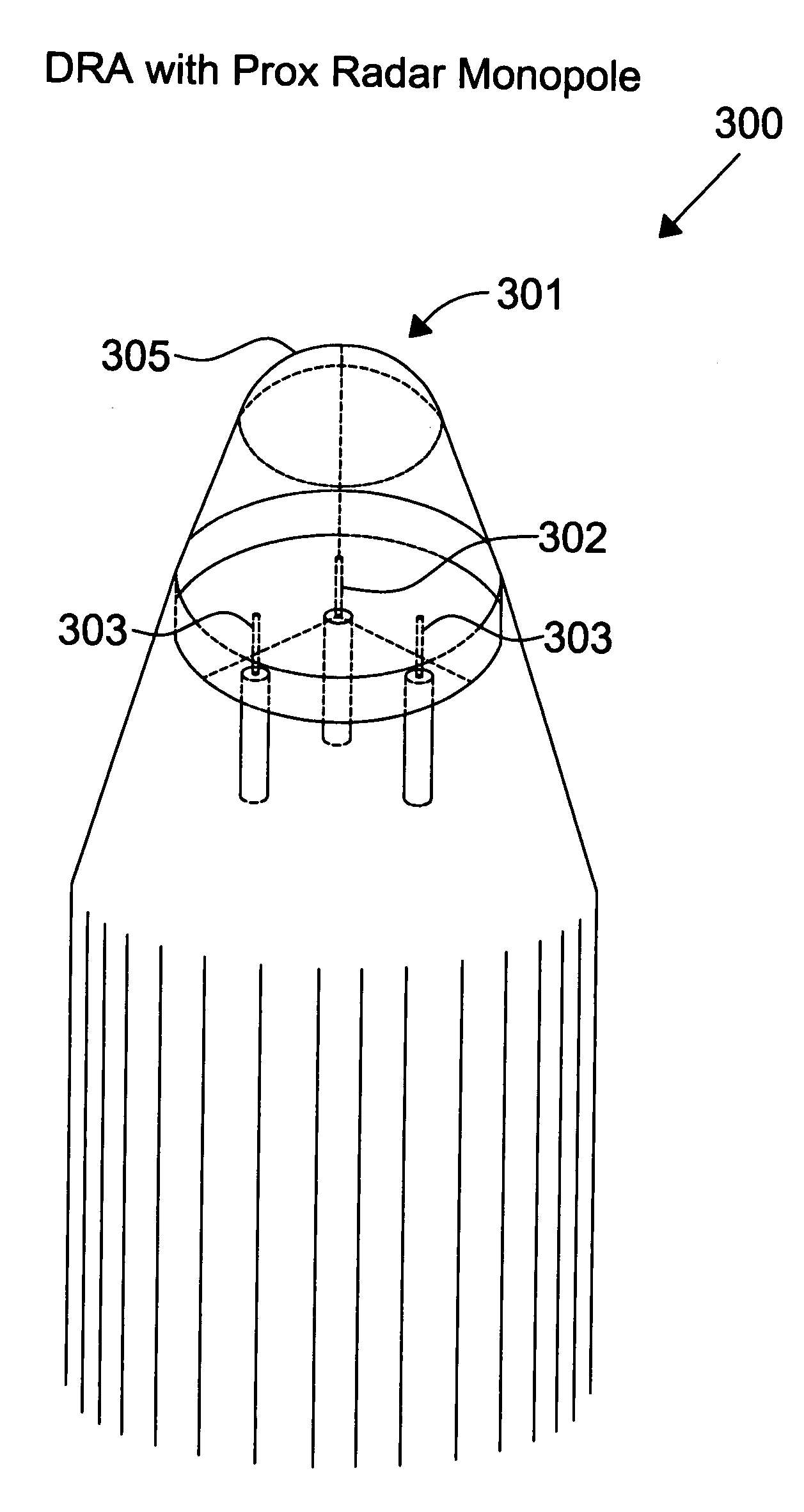
Proximity radar antenna co-located with GPS DRA fuze
ActiveUS7498969B1Improve approachReduce the amount requiredDirection controllersAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadar antennasDielectric resonator antenna
The present invention is directed to a fuze application capable of GPS (Global Positioning System) and proximity radar functionality by co-locating a proximity radar antenna with a GPS DRA (Dielectric Resonator Antenna) fuze. The GPS DRA fuze has a HE11δ mode structure resulting in an E-field null at the center. The monopole proximity radar antenna is mounted in the E-field null center and is thus electrically isolated from the GPS DRA fuze. The high dielectric constant permits the GPS DRA fuze to operate in the L1 frequency and the electrically shortened proximity radar antenna to resonate in the C-Band within a small form factor. The GPS DRA fuze maintains a forward-looking CP (circular polarization) pattern while proximity antenna maintains a desirable monopole pattern. Nesting allows mounting of both GPS and proximity radar antennas on the fuze nose while reducing the total space occupied.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Dielectric resonator antenna with a caved well
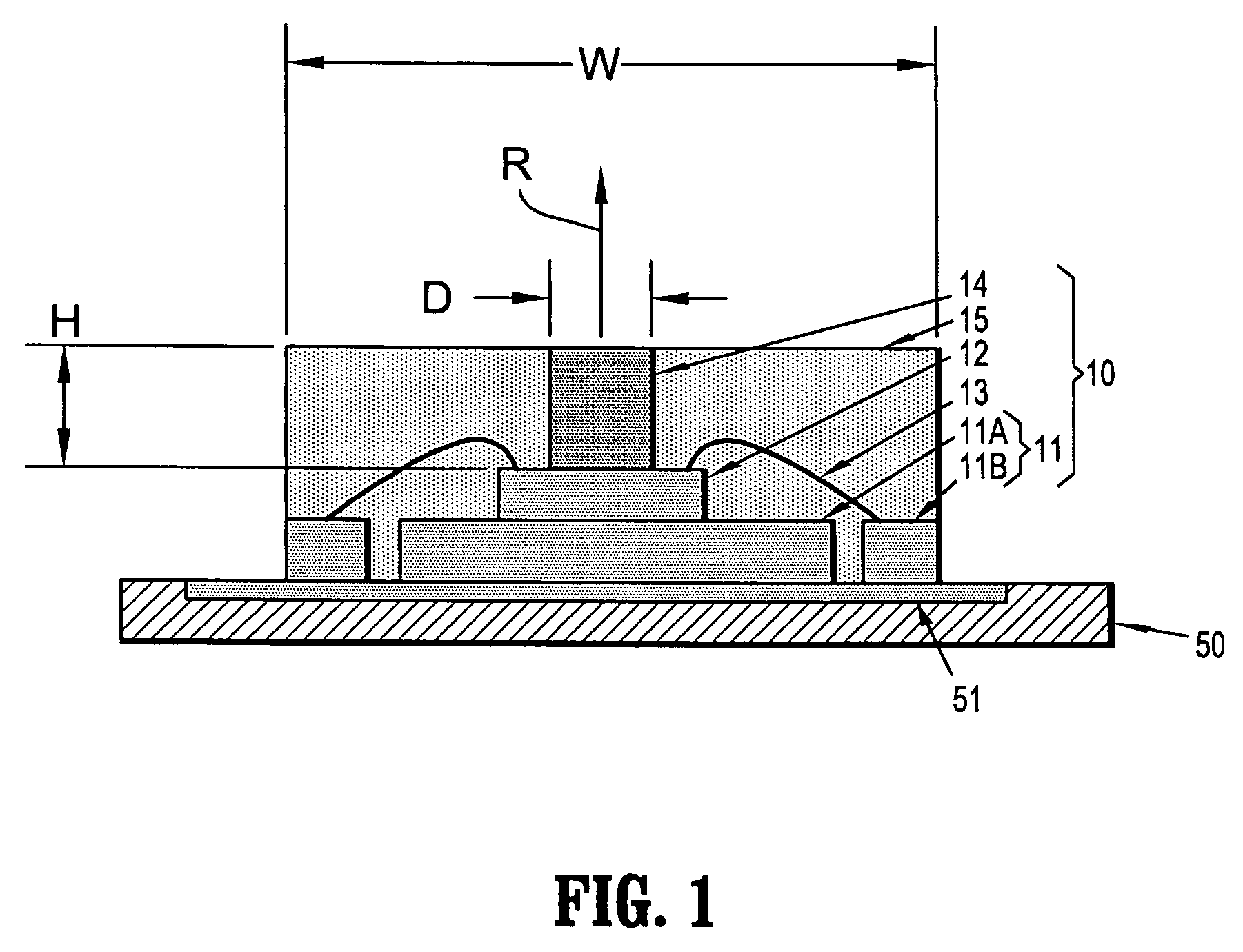
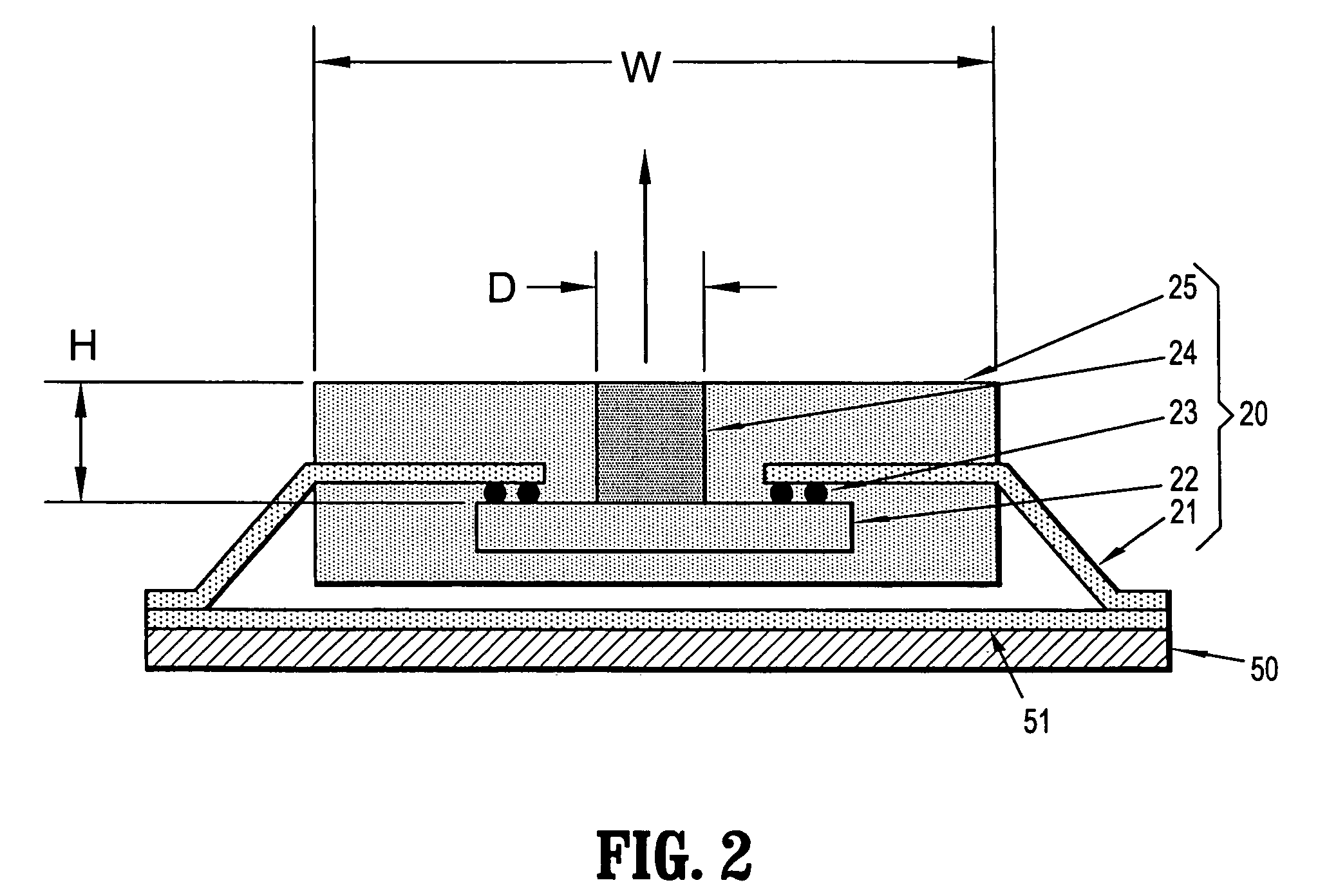
InactiveUS7292204B1Small sizeSimple structureAntenna earthingsElectrically short antennasDielectric resonator antennaDielectric substrate
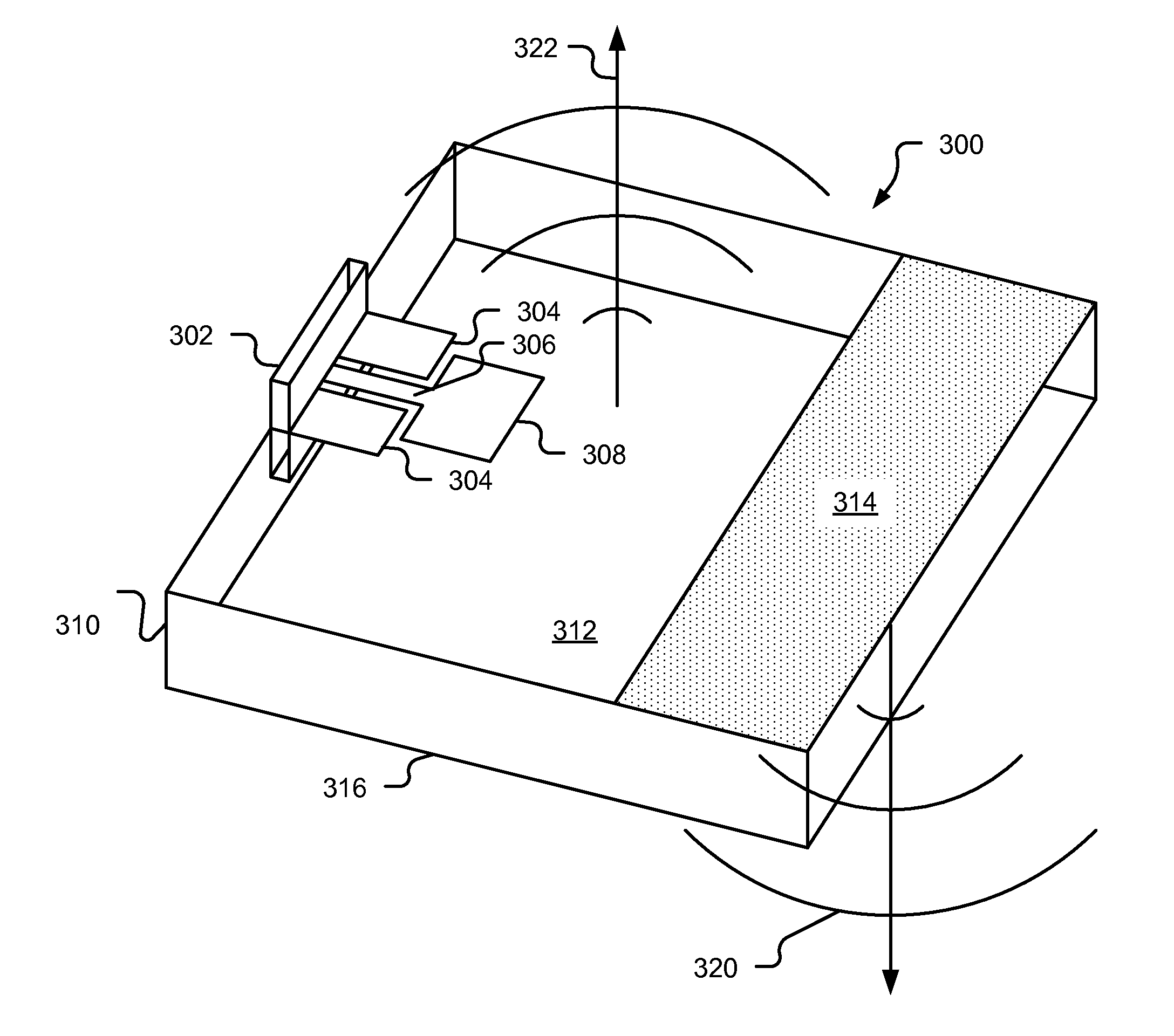
A dielectric resonator antenna is a dielectric resonator mounted on a feed-in / feed-out component. The dielectric resonator is a rectangular parallelepiped made of a dielectric, and has a caved well passing through from the top surface to the bottom surface thereof. The feed-in / feed-out component includes a dielectric substrate, a ground metal layer and a strip metal layer coated on the top surface and the bottom surface, respectively, of the dielectric substrate. An etched part is provided on the ground metal layer. Wherein, the dielectric resonator with the caved well is mounted on the ground metal layer of the feed-in / feed-out component.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Broadband multiple layer dielectric resonator antenna and method of making the same
ActiveUS20170125909A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating element housingsDielectric resonator antennaBroadband
A method for the manufacture of a dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) or array of DRA's, the DRA having: an electrically conductive ground structure; a plurality of volumes of dielectric materials disposed on the ground structure having N volumes, N being an integer equal to or greater than 3, disposed to form successive and sequential layered volumes V(i), i being an integer from 1 to N, wherein volume V(1) forms an innermost volume, wherein a successive volume V(i+1) forms a layered shell disposed over and at least partially embedding volume V(i), wherein volume V(N) at least partially embeds all volumes V(1) to V(N−1); and, a signal feed disposed and structured to be electromagnetically coupled to one or more of the plurality of volumes of dielectric materials. The method including molding at least one of the plurality of volumes of the dielectric material, or all of the volumes of the dielectric material.
Owner:ROGERS CORP
Antenna for portable terminal and portable terminal using same
InactiveUS20060119518A1Increase heightLow dielectric constantSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsResonanceDielectric resonator antenna
A dielectric resonator antenna which emits an electric wave by having a dielectric body resonate is disclosed. A magnetic material is contained in the electric body, thereby increasing the relative permeability to more than 1 and lowering the relative permittivity. Consequently, the Q-value of the resonance can be lowered while maintaining the rate of wavelength shortening. With this technique, a broadband dielectric resonator antenna can be realized.
Owner:OHMI TADAHIRO
Apparatus and methods for packaging dielectric resonator antennas with integrated circuit chips
InactiveUS7504721B2Reduce lossLow dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCommunications systemDielectric resonator antenna
Apparatus and methods are provided for integrally packaging antenna devices with semiconductor IC (integrated circuit) chips, wherein IC chips are packaged with dielectric resonators antennas that are integrally constructed as part of a package molding (encapsulation) process, for example, to form compact integrated radio / wireless communications systems for millimeter wave applications.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Broadband multiple layer dielectric resonator antenna and method of making the same
ActiveUS20170125910A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating element housingsDielectric resonator antennaBroadband
A dielectric resonator antenna (DRA), includes: an electrically conductive ground structure; a plurality of volumes of dielectric materials disposed on the ground structure having N volumes, N being an integer equal to or greater than 3, disposed to form successive and sequential layered volumes V(i), i being an integer from 1 to N, wherein volume V(1) forms an innermost volume, wherein a successive volume V(i+1) forms a layered shell disposed over and at least partially embedding volume V(i), wherein volume V(N) at least partially embeds all volumes V(1) to V(N−1); and a signal feed disposed and structured to be electromagnetically coupled to one or more of the plurality of volumes of dielectric materials.
Owner:ROGERS CORP
Dielectric resonator antenna and method of making the same
ActiveUS20180115072A1Individually energised antenna arraysAntenna earthingsElectricityDielectric resonator antenna
A dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) includes a plurality of volumes of dielectric materials having N volumes, N being an integer equal to or greater than 3, disposed to form successive and sequential layered volumes V(i), i being an integer from 1 to N, and a signal feed disposed to produce a main E-field component having a defined direction, Ē, in the DRA. The N volumes include a non-gaseous dielectric material, and have an inner region with a dielectric constant that is less than the dielectric constant of the non-gaseous dielectric material. The inner region has a cross sectional overall height Hr, and a cross sectional overall width Wr in a direction parallel to Ē, and the volume of non-gaseous dielectric material has a cross sectional overall height Hv, and a cross sectional overall width Wv in a direction parallel to Ē, wherein Hr is greater than Wr / 2.
Owner:ROGERS CORP
Dielectric resonator and dielectric filter
InactiveUS6762658B1Simple compositionLow insertion lossResonatorsDielectric resonator antennaDielectric resonator
A dielectric resonator (10) having three surfaces formed by chamfering three ridged portions sharing an apex of a dielectric block and another three surfaces adjacent respectively thereto, in which each of the chamfered surfaces and the adjacent surfaces thereto offers an angle of 45 degrees and an area ratio of the chamfered surfaces with respect to the adjacent surfaces is 45% is mounted in a cut-off waveguide of a generally rectangular parallelopiped (21) and feeding probe (24) and (25) are provided for composing a dielectric filter.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Surface wave launched dielectric resonator antenna
InactiveUS20150207234A1Antenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectric resonator antennaPrinted circuit board
An apparatus includes a printed circuit board having a first surface and a second surface opposite the first surface. The apparatus includes a surface launcher of a dielectric resonator antenna (DRA). The surface launcher is coupled to the first surface of the printed circuit board. A metal structure is coupled to the first surface and configured to direct a portion of a wave of the DRA through the second surface.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com