Light transmissible resonators for circuit and antenna applications
a technology of transmissible resonators and antennas, applied in the direction of electrically short antennas, antennas, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the antenna gain from about 5 dbi to 0 dbi, increasing the cost of reducing the transparency of the antenna, and challenging the problem of high conducting transparent films
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
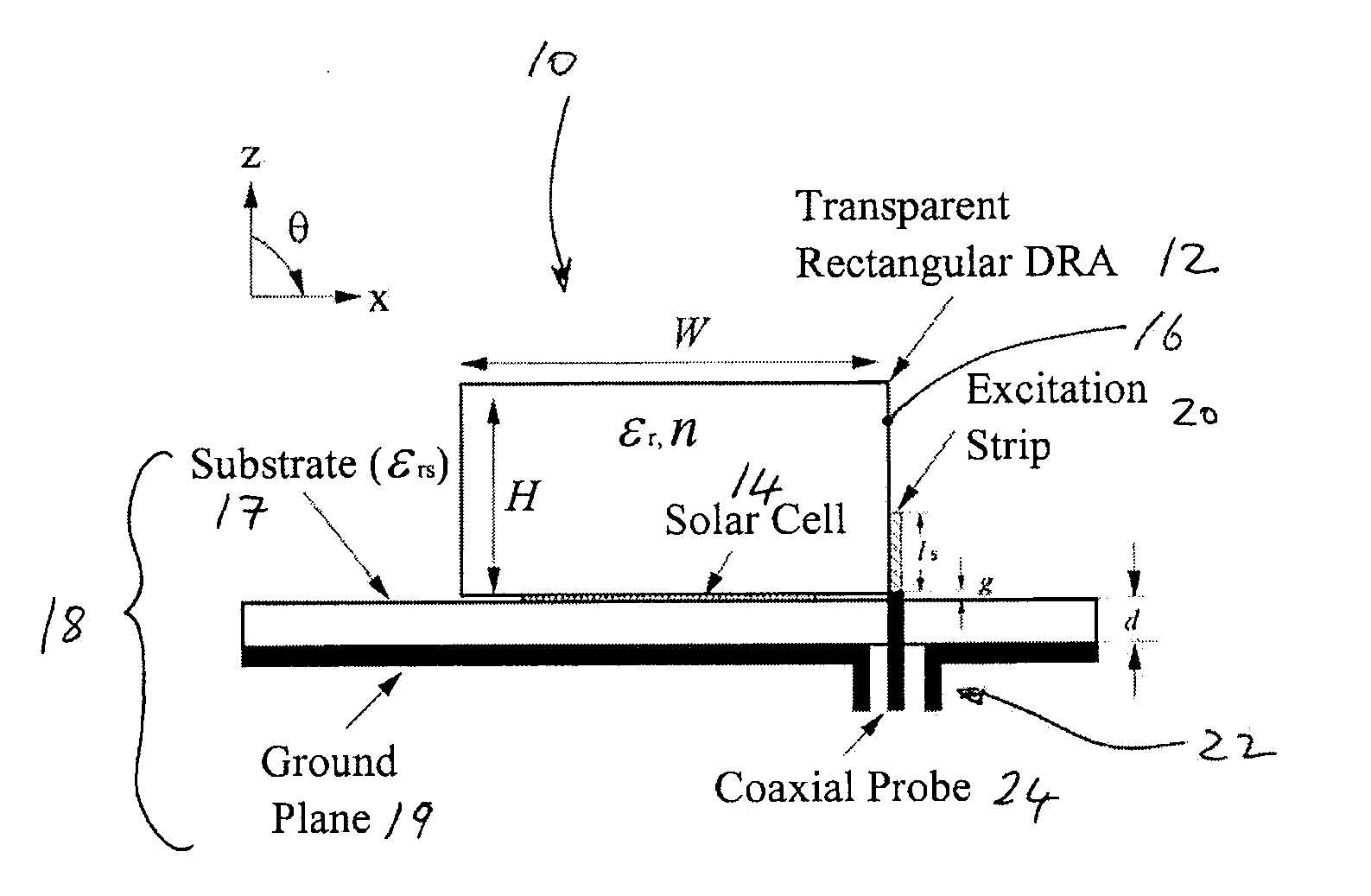
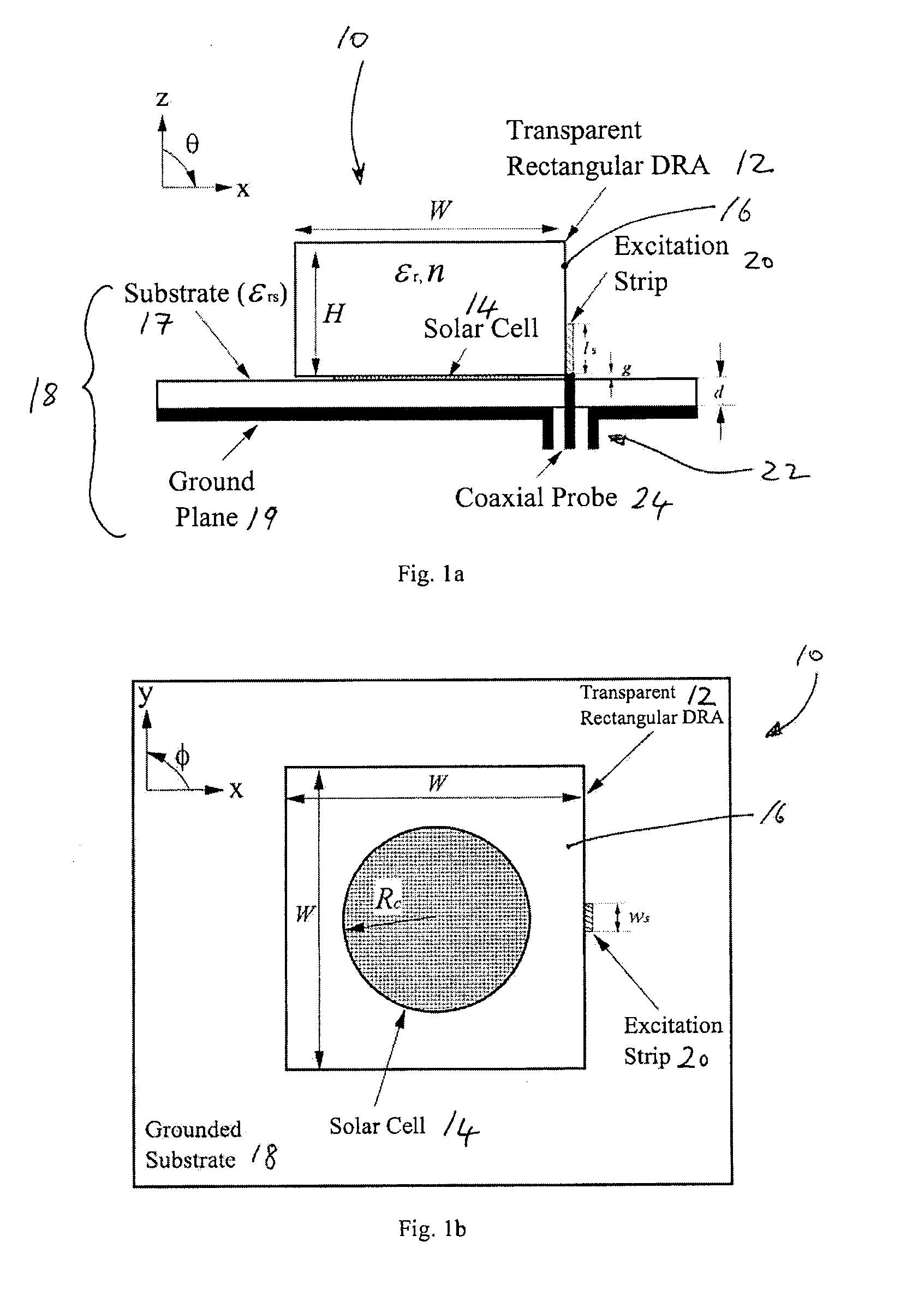
[0051]Referring to FIGS. 1a and 1b, a circuit 10 including a DRA 12 in accordance with the invention is described. This embodiment of a DRA 12 comprises a non-focusing transparent rectangular DRA 12. As a rectangular DRA is mechanically easier to fabricate than other shapes, it is of great interest to antenna engineers.
[0052]In this case, the DRA 12, in addition to serving as an antenna, serves as a protective cover for an underlaid solar cell 14. As the DRA 12 is transparent, it does not deter the solar cell 14 from collecting sunlight or ambient light. In addition, high compactness can be easily achieved by placing the solar cell panel 14 beneath the DRA 12 in order to reduce or minimize the footprint occupied by the combined components. The DRA 12 comprises a dielectric resonator (DR) element 16; a ground plane or grounded substrate 18 comprising a non-conductive substrate 17 and a conductive ground plane layer 19; and a strip feedline (conformal strip) 20 for exciting the DR ele...
second embodiment
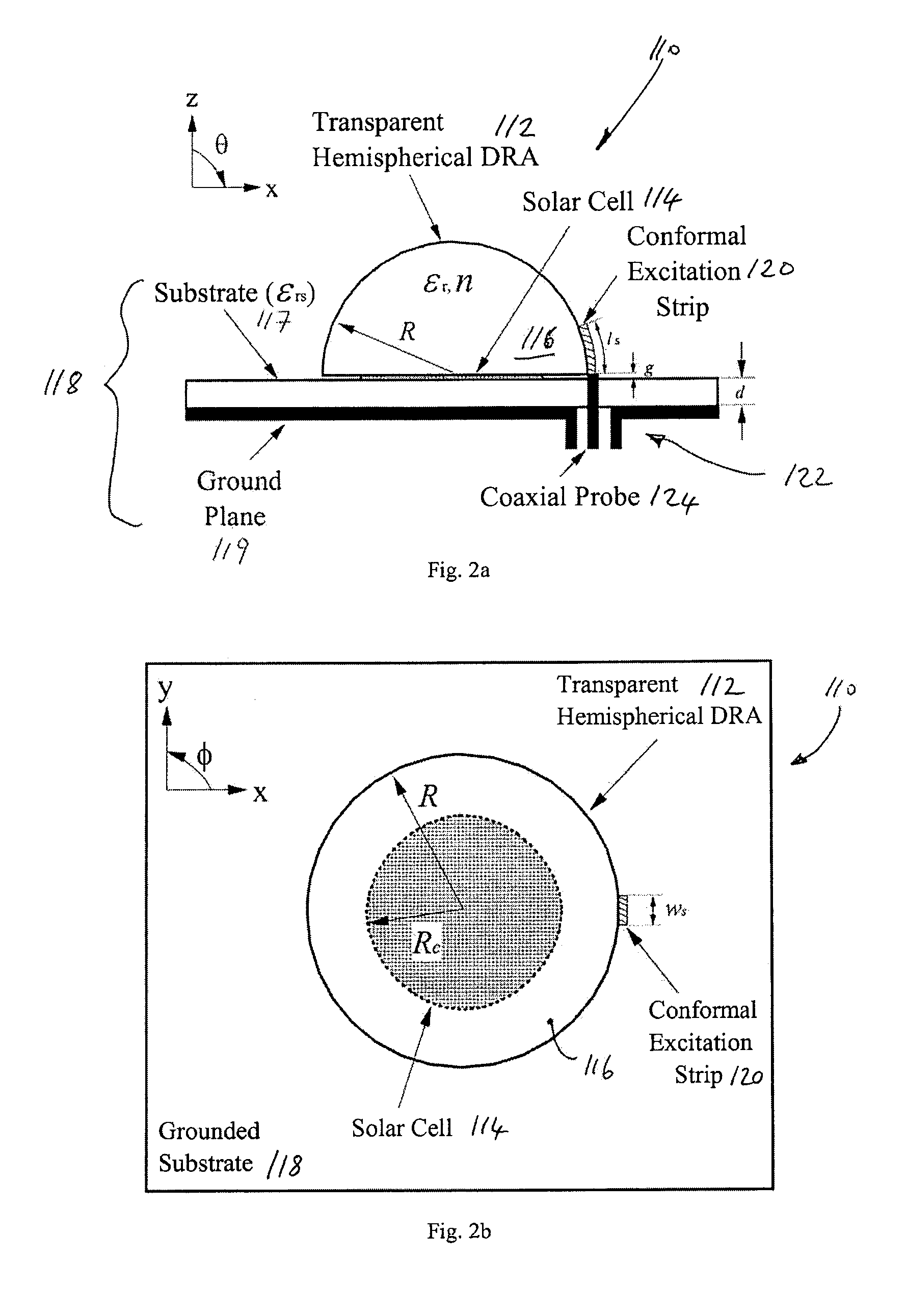
[0056]Referring to FIGS. 2a and 2b, a DRA 112 in accordance with the invention is described. This embodiment of a DRA 112 is mounted on a circuit 110 of an electronic device or system (not shown) and comprises a focusing transparent DRA 112 which is shaped to focus light impinging on its upper surface and to convey the focused light to a selected region on a lower surface thereof adjacent an underlaid solar cell. The selected region may be chosen as a region that maps to or overlaps a light receiving part of the solar cell 114 when the DRA 112 is mounted on the circuit 110 above the solar cell 114.
[0057]In this case, the DRA 112, in addition to serving as an antenna and a protective cover for the underlaid solar cell 114, also acts to focus captured light onto a light receiving part of the solar cell 114 thereby enhancing performance of the solar cell whilst preserving a compact form by sharing a footprint with the solar cell 114. In this embodiment, the DRA 112 also comprises a die...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com