Patents
Literature
2893results about How to "Increase opening ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
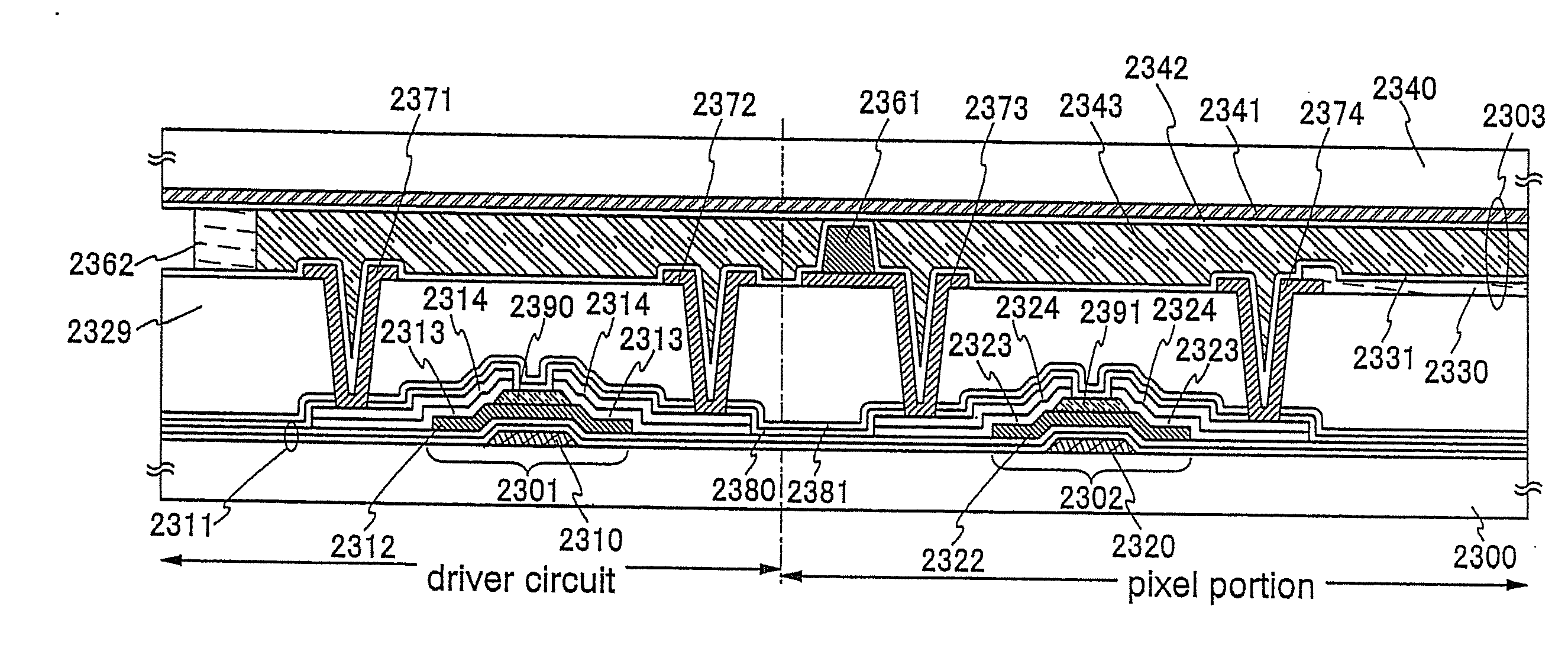
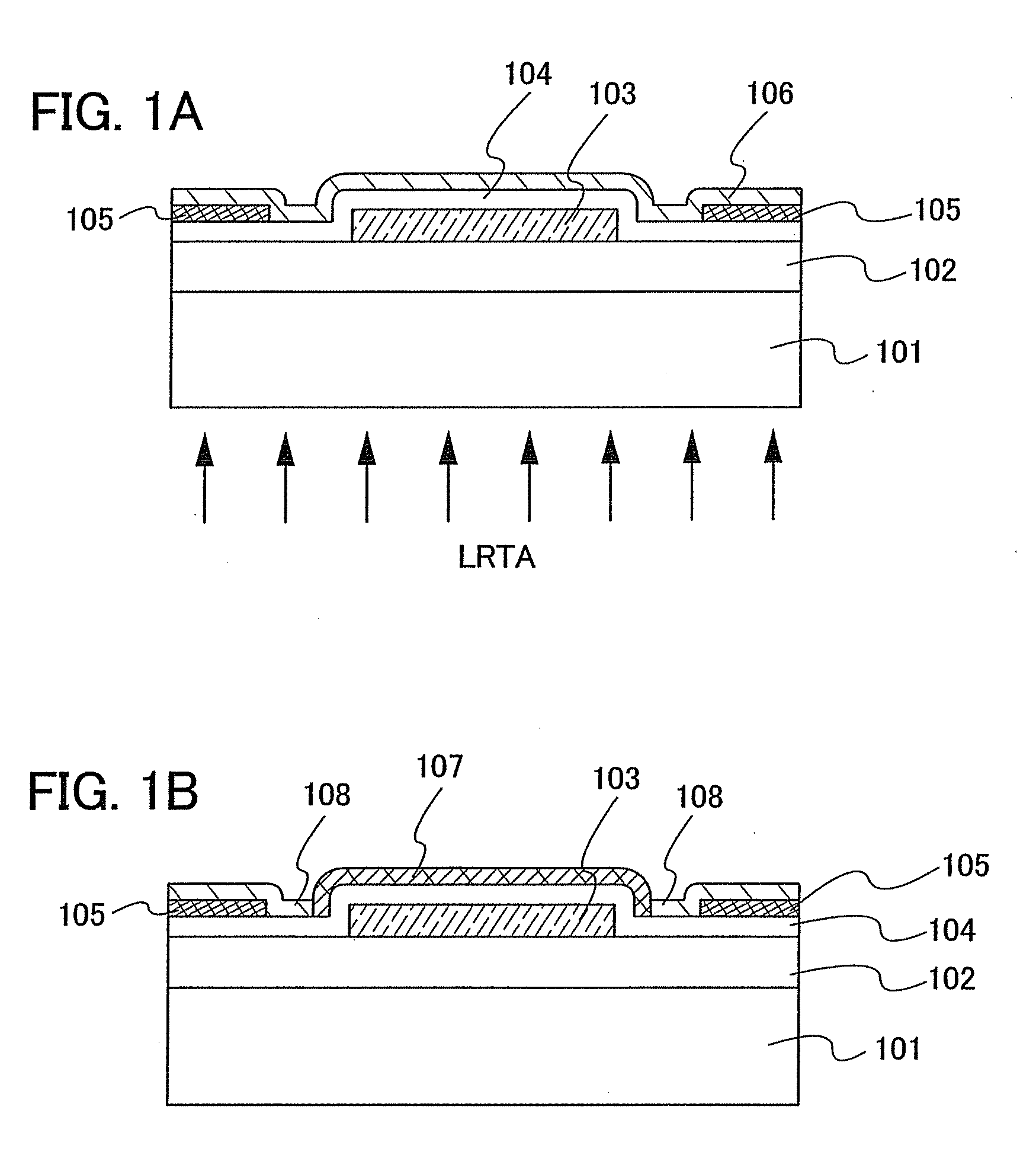
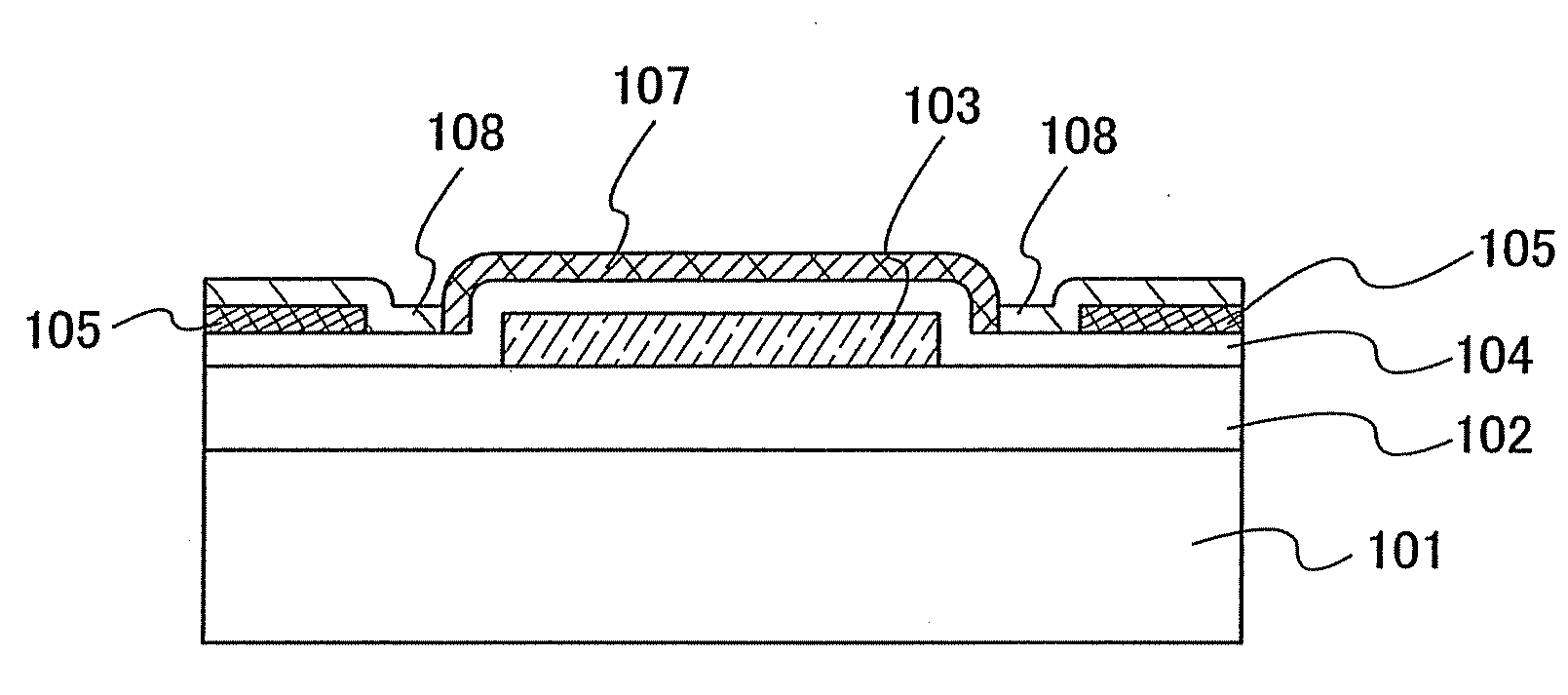
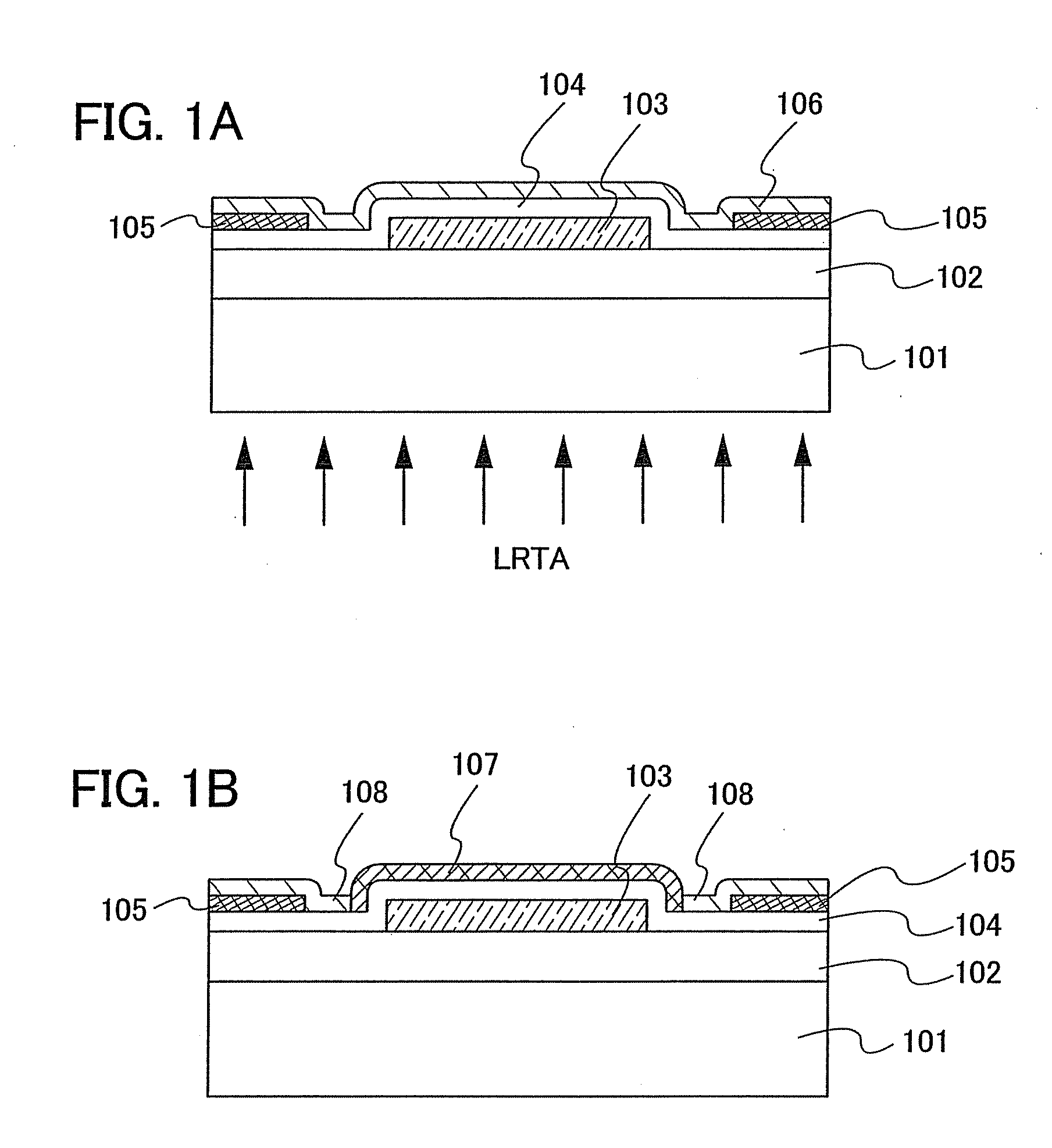
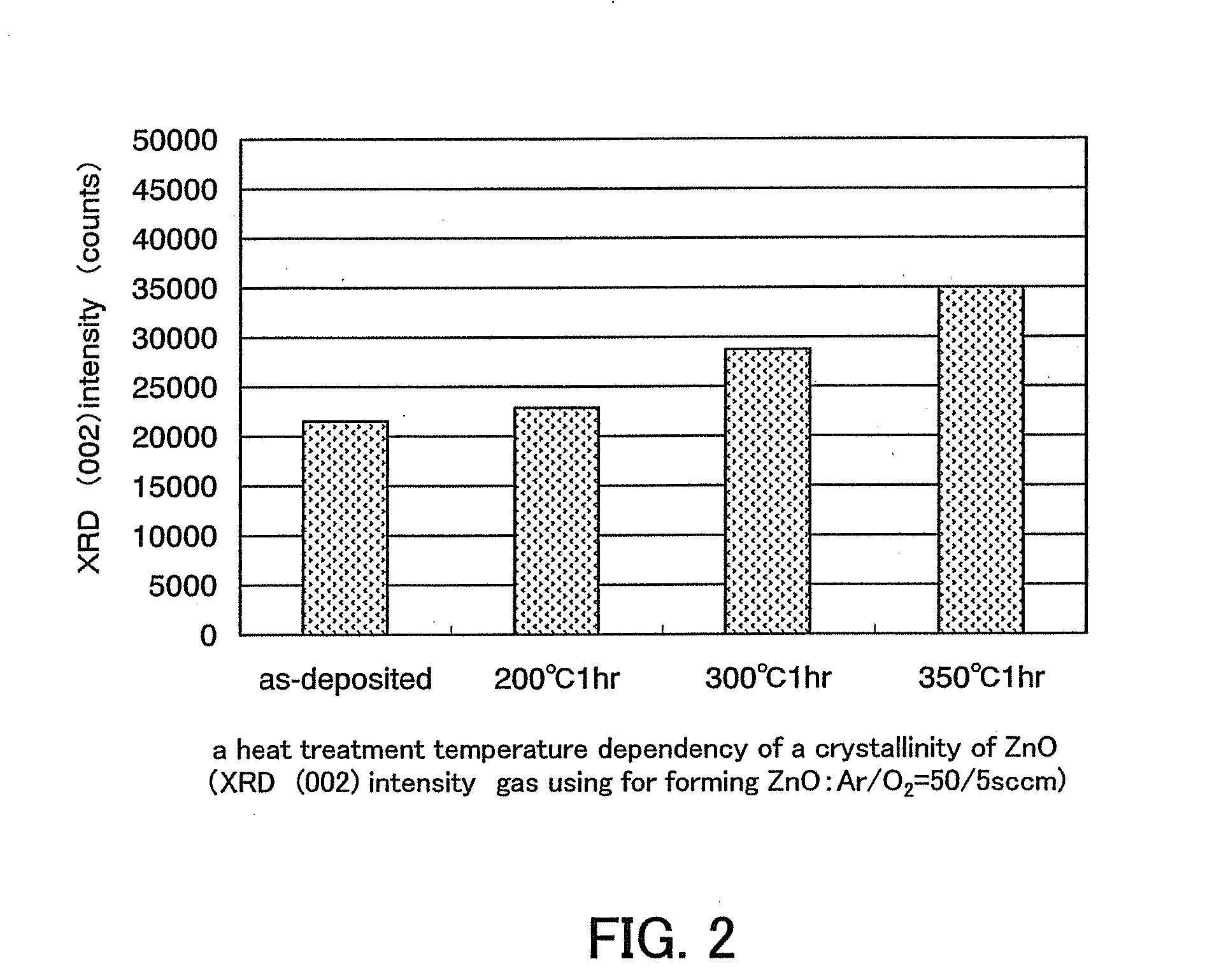
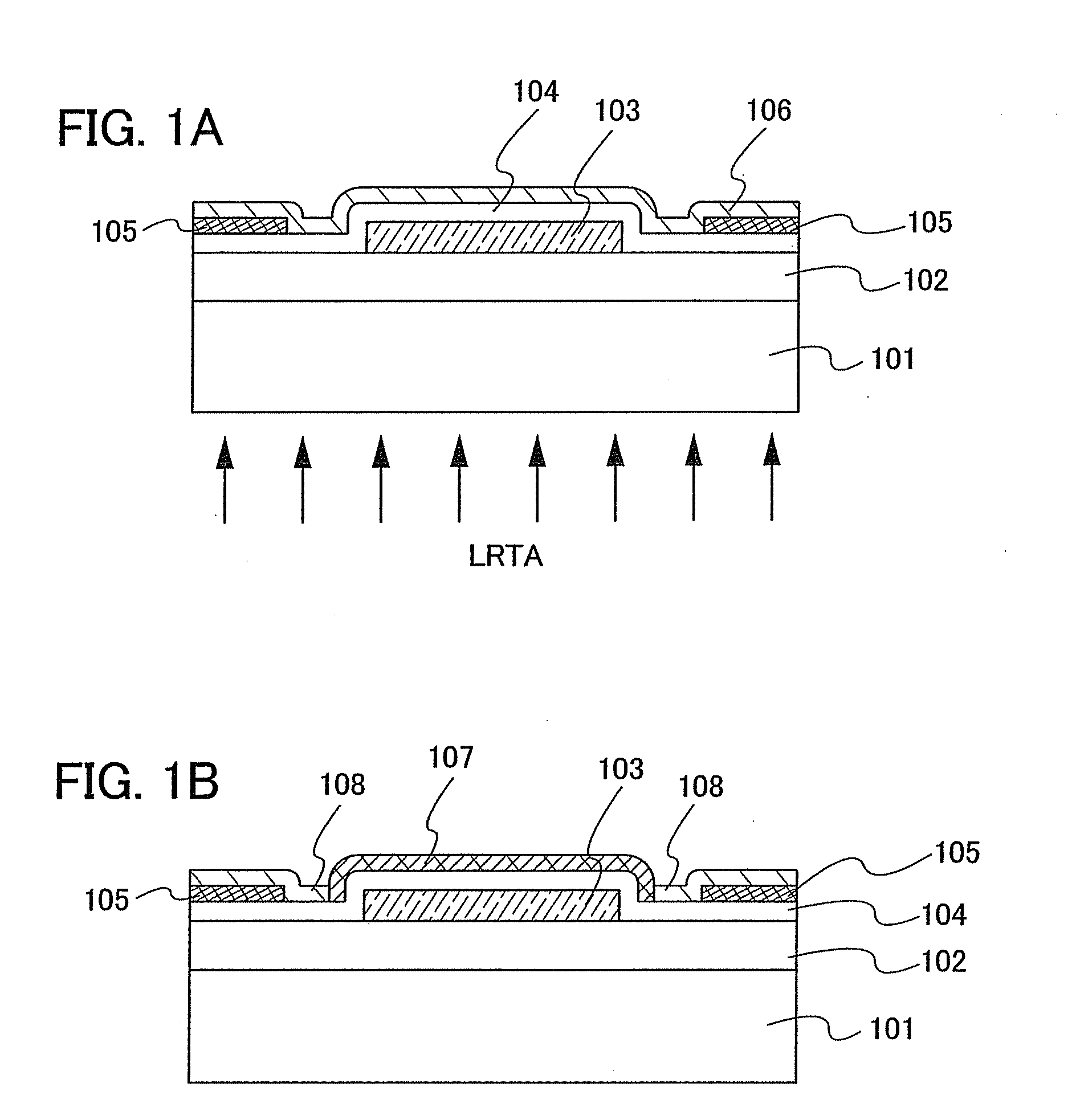
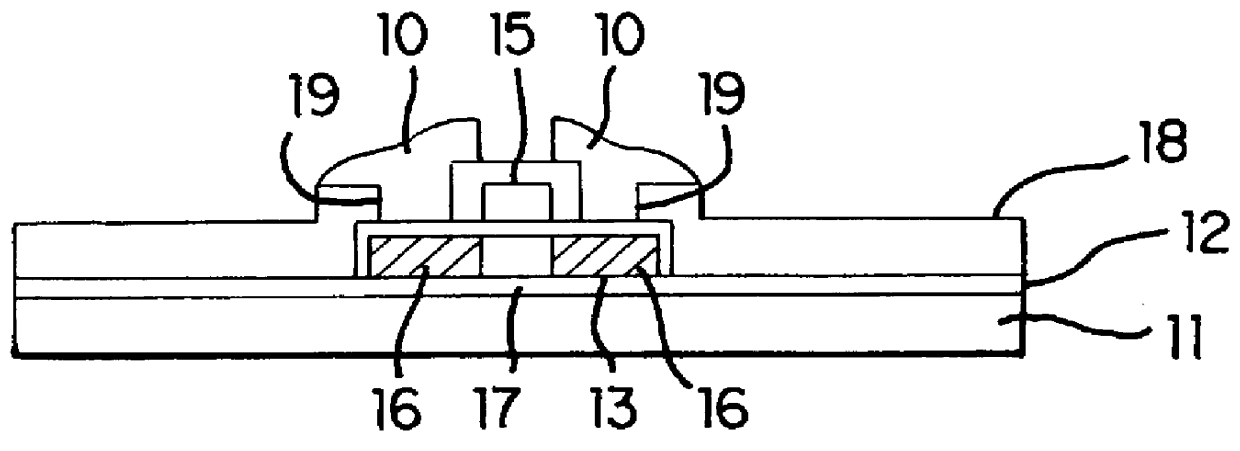
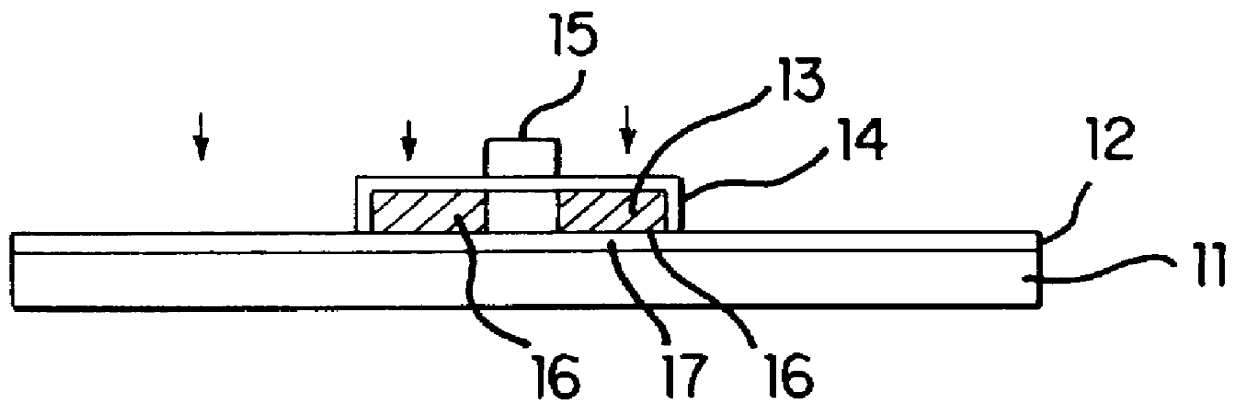
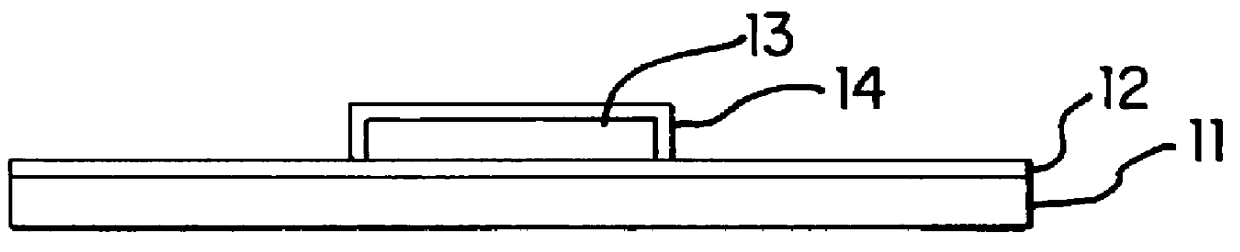
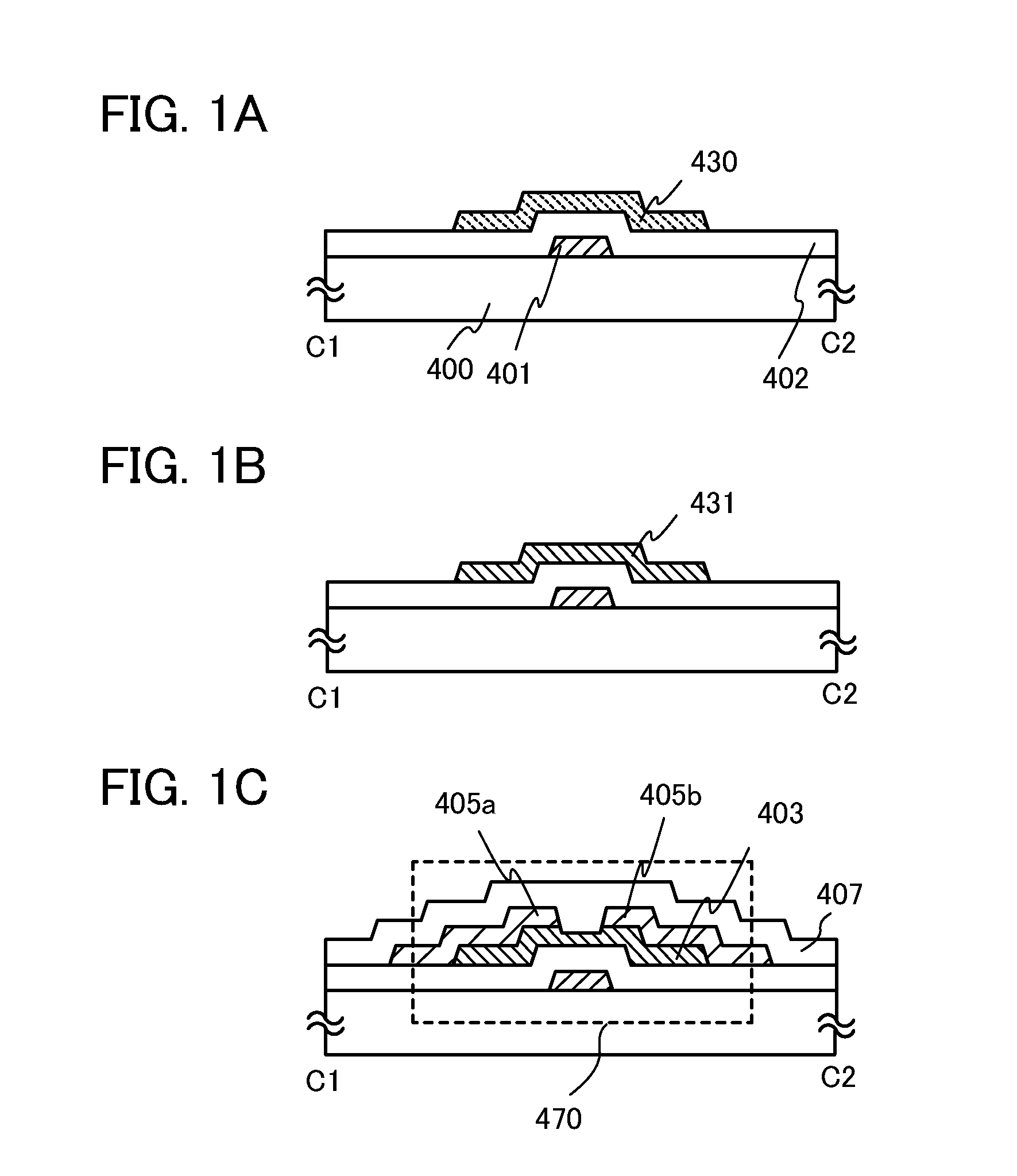
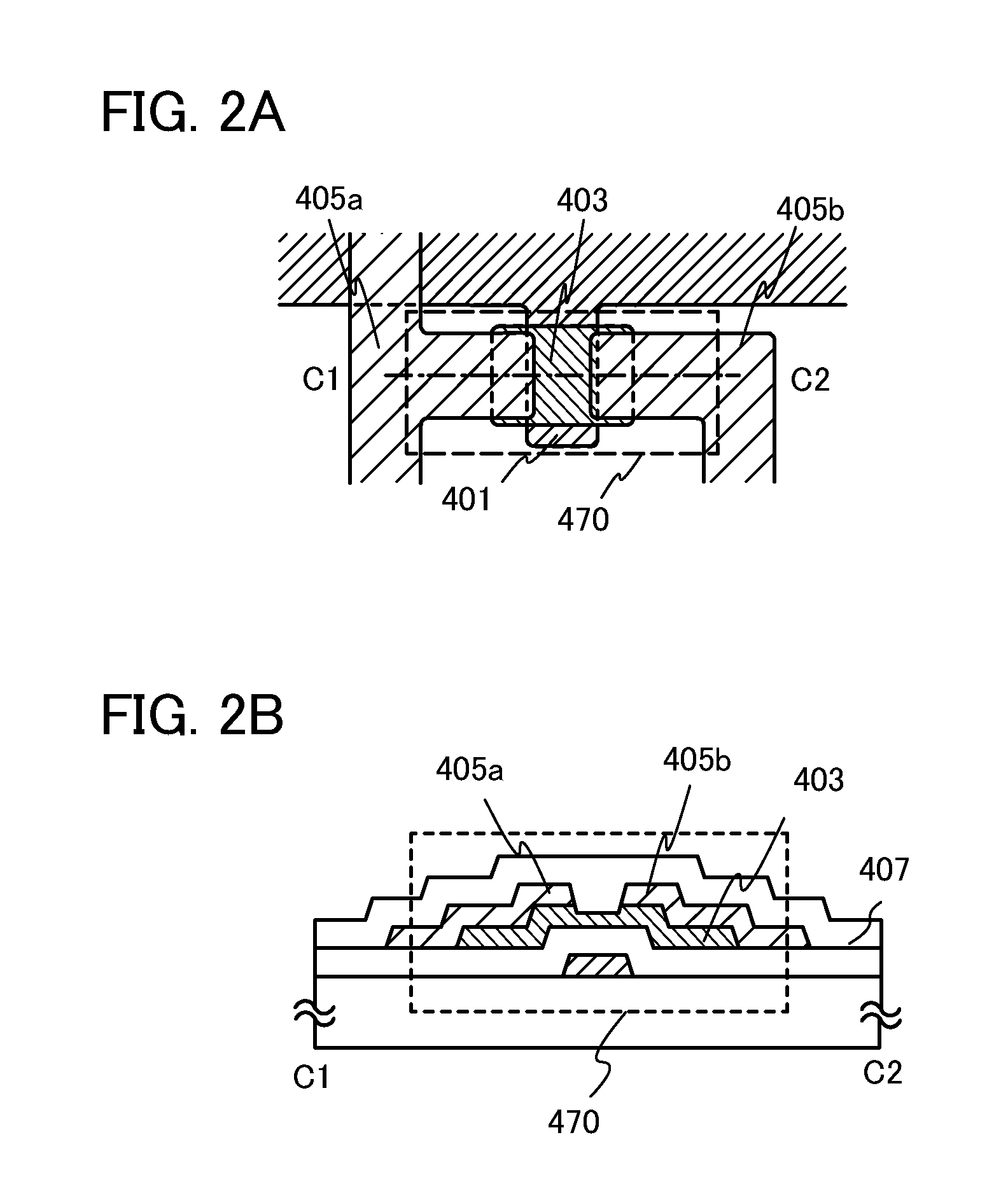
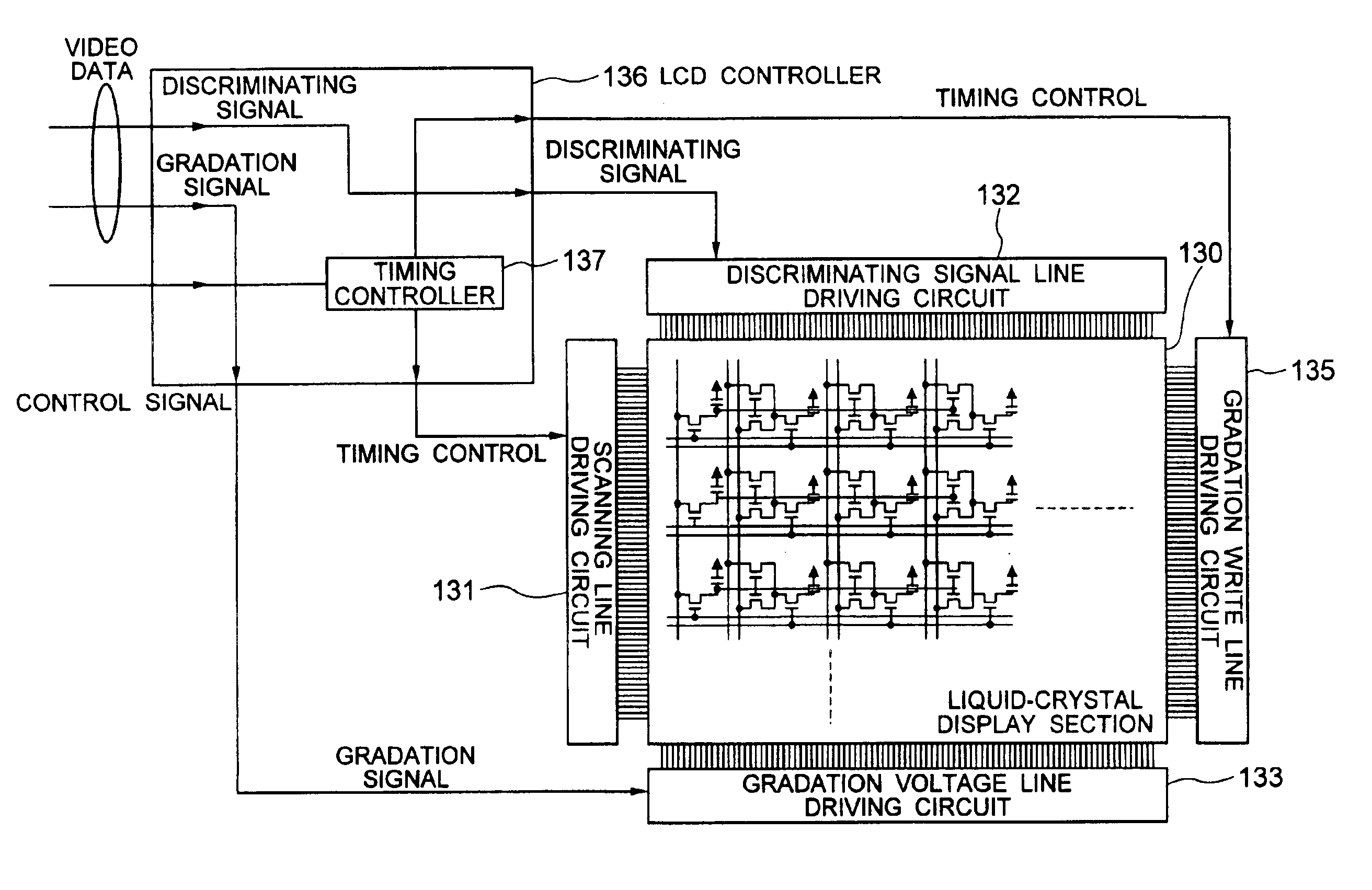
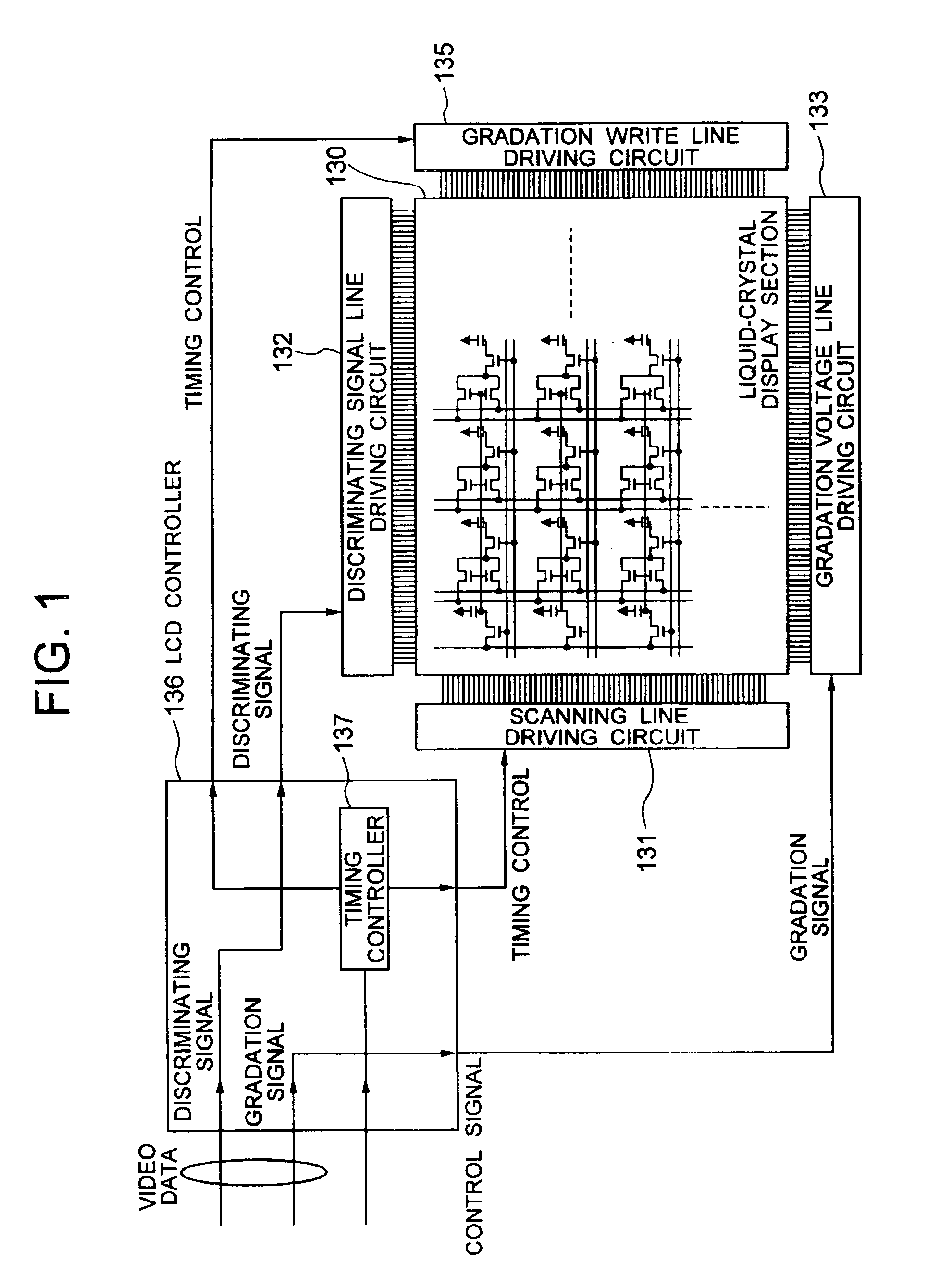
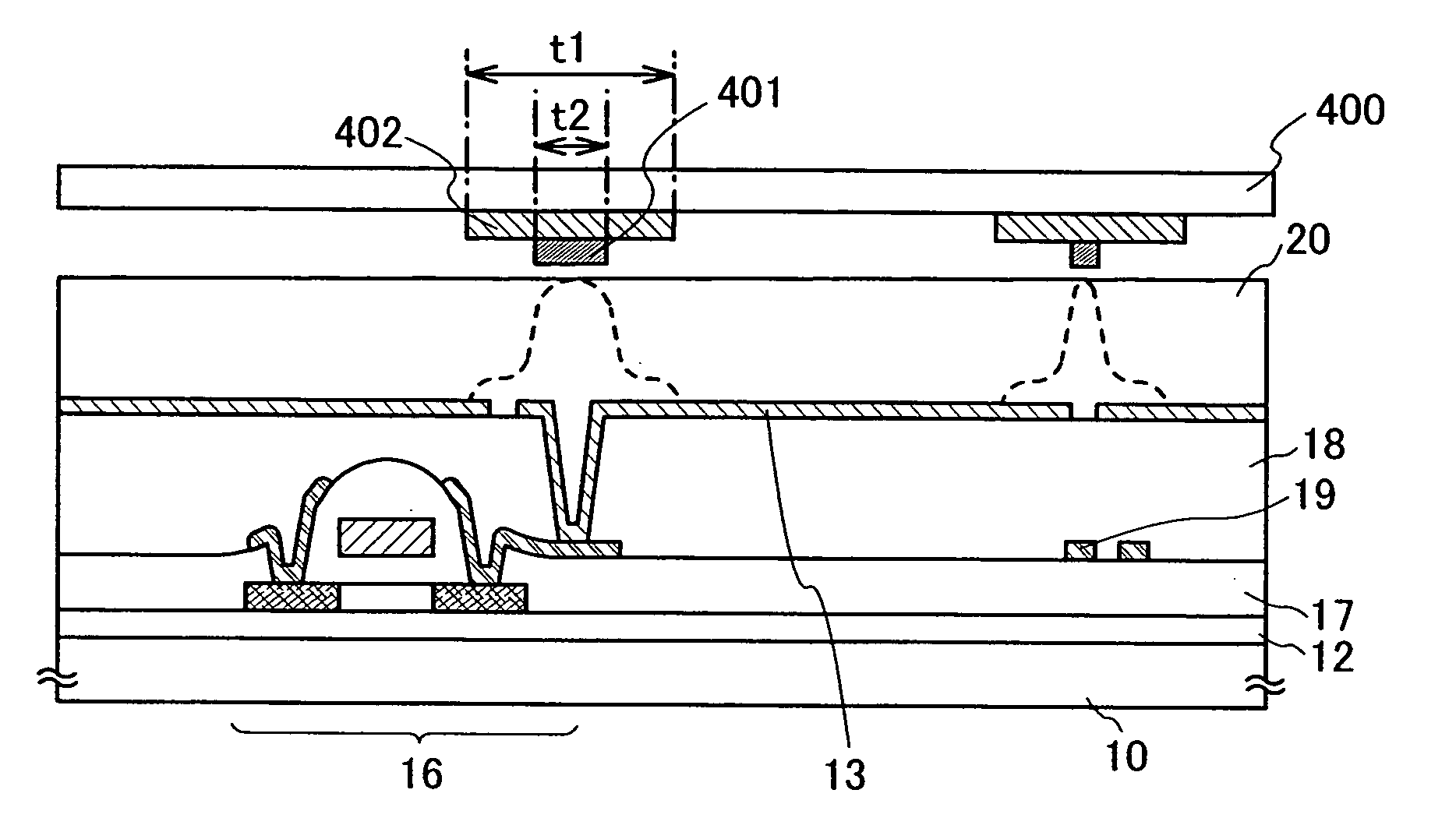
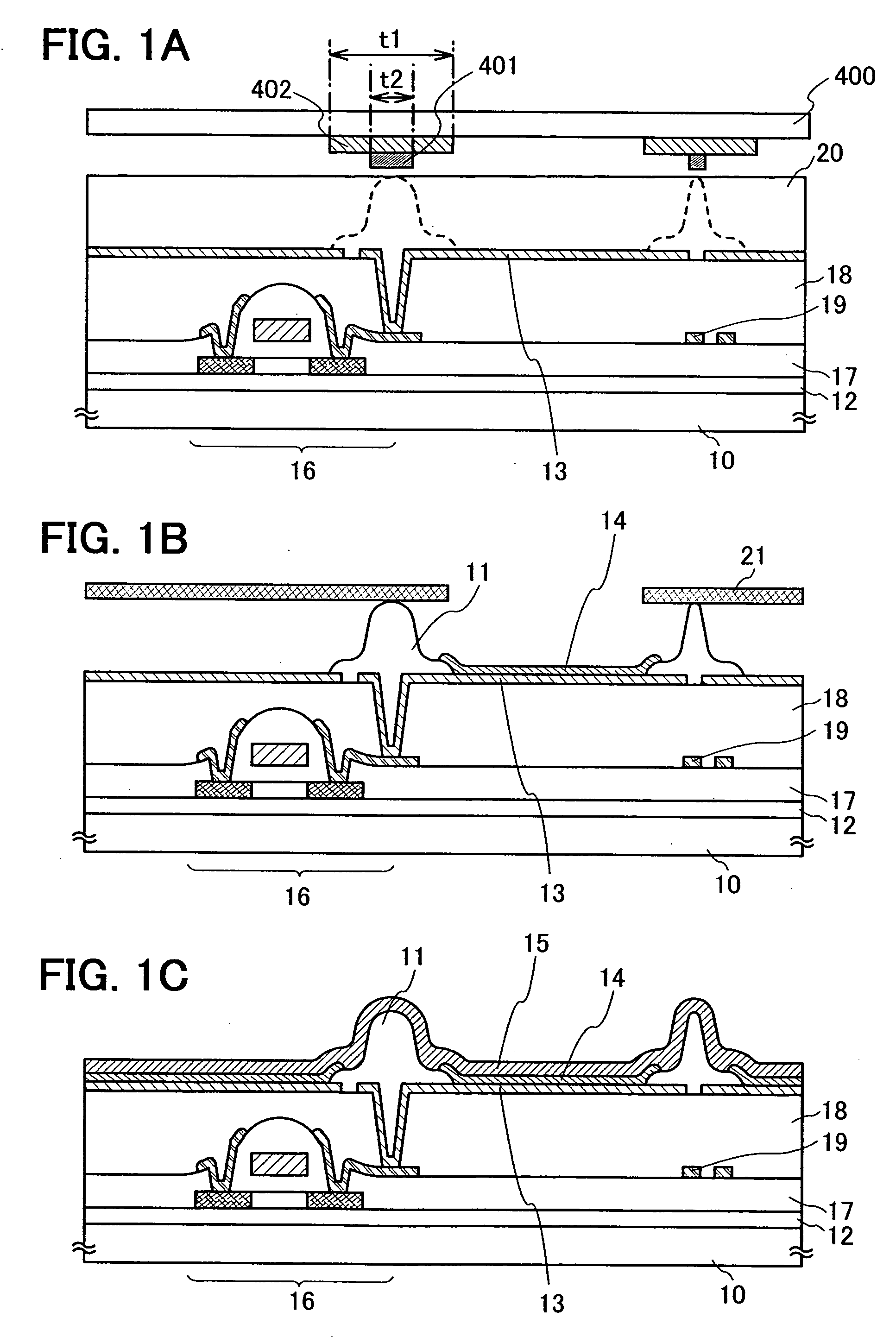
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
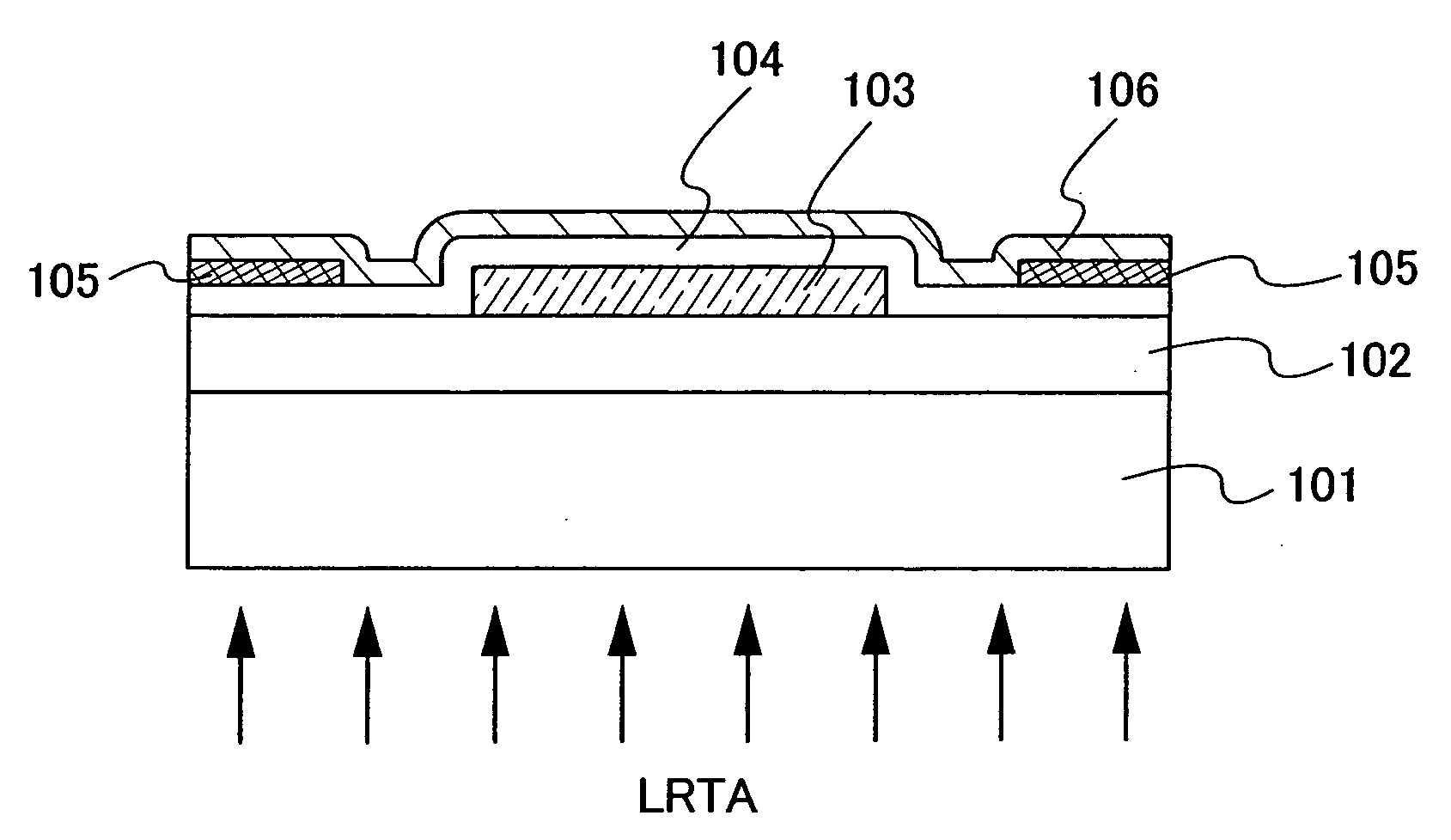
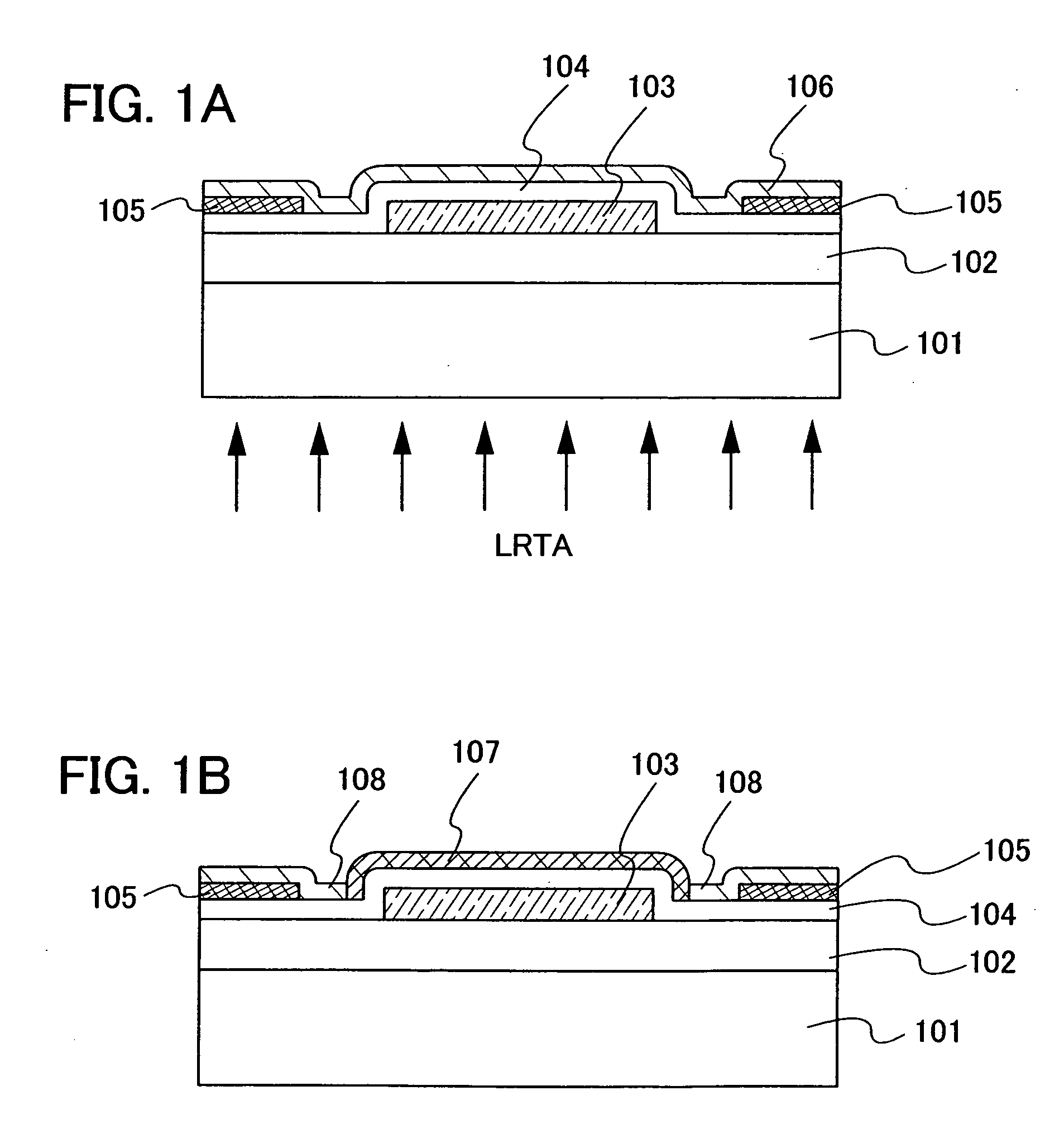
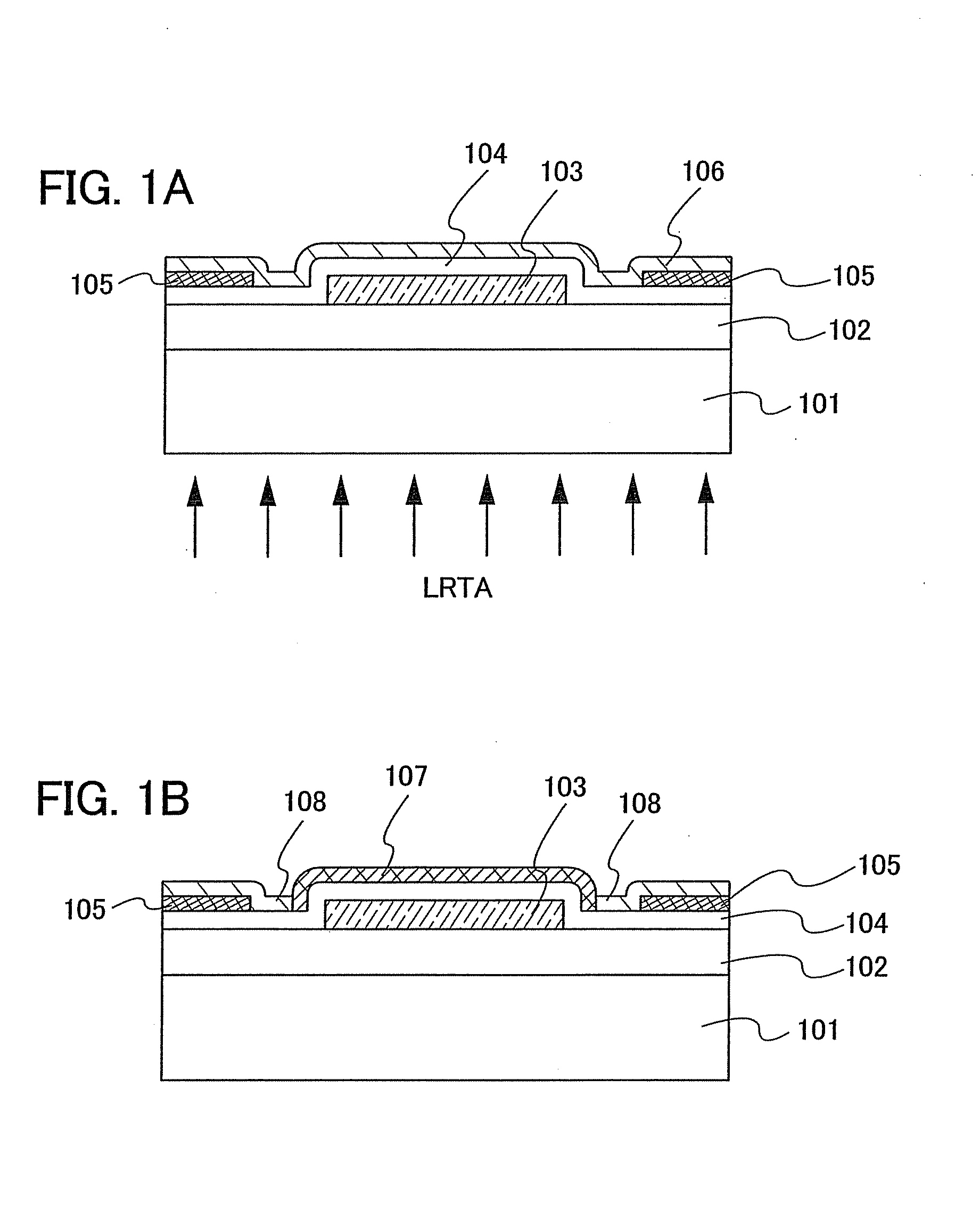
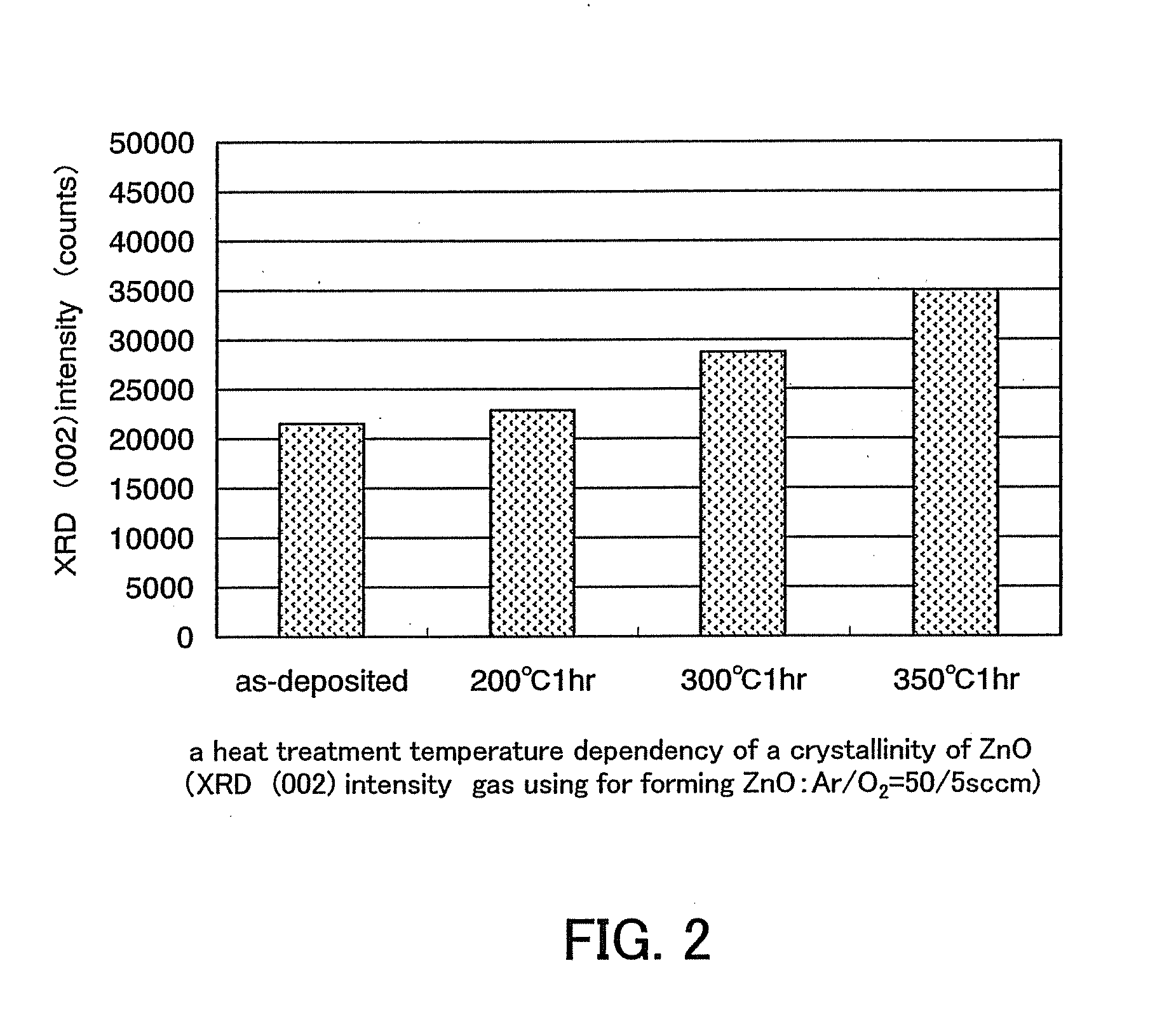
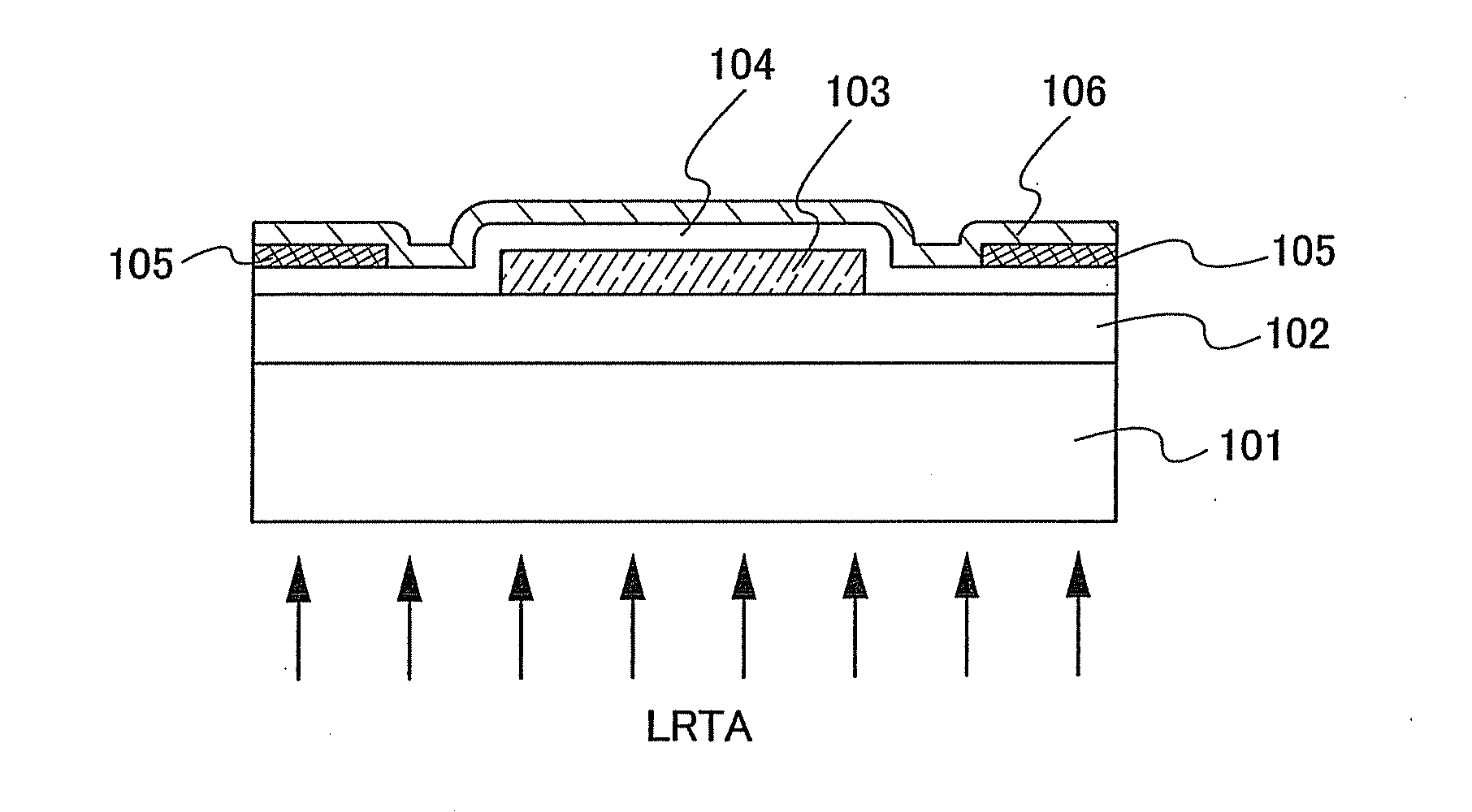
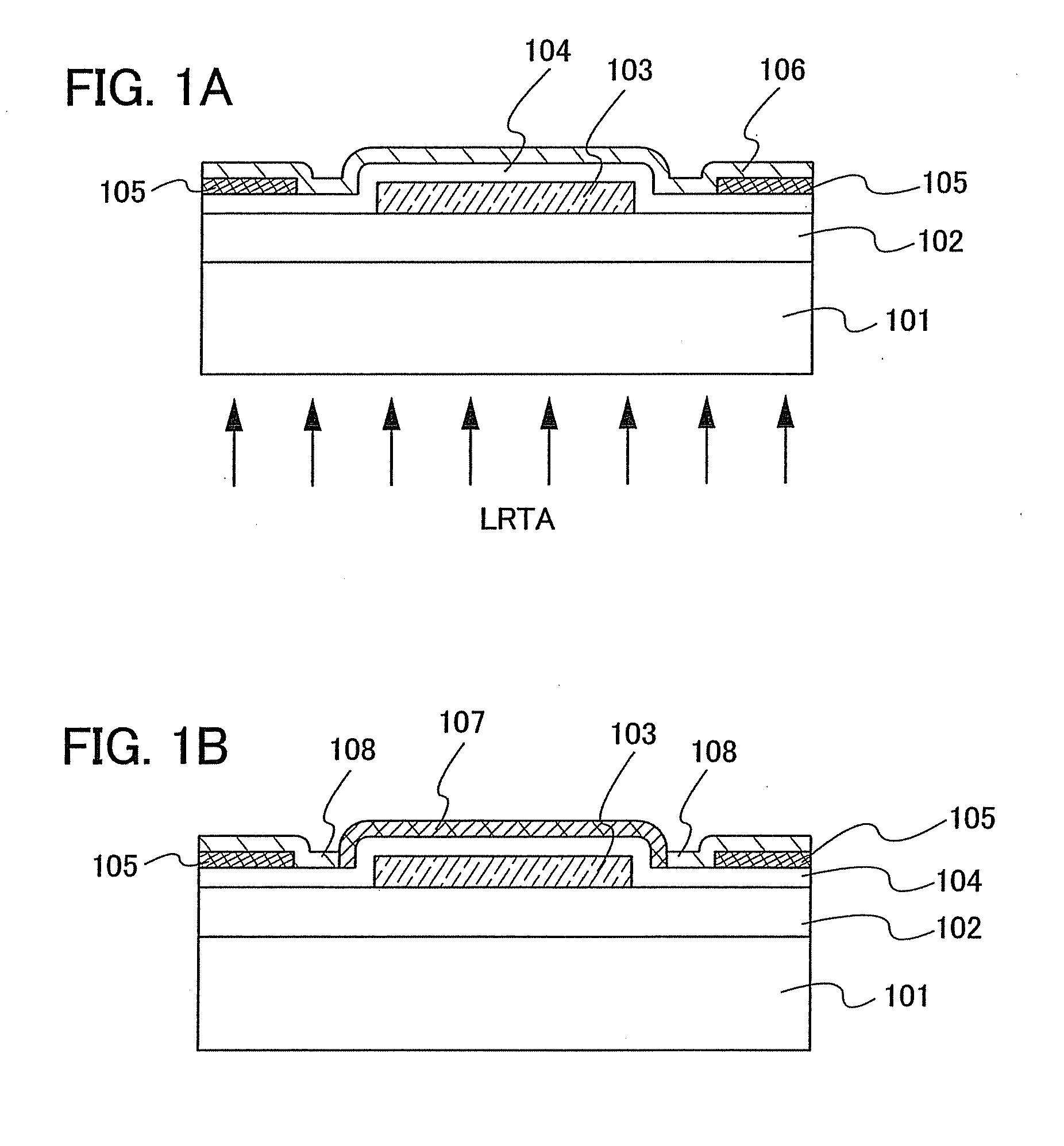
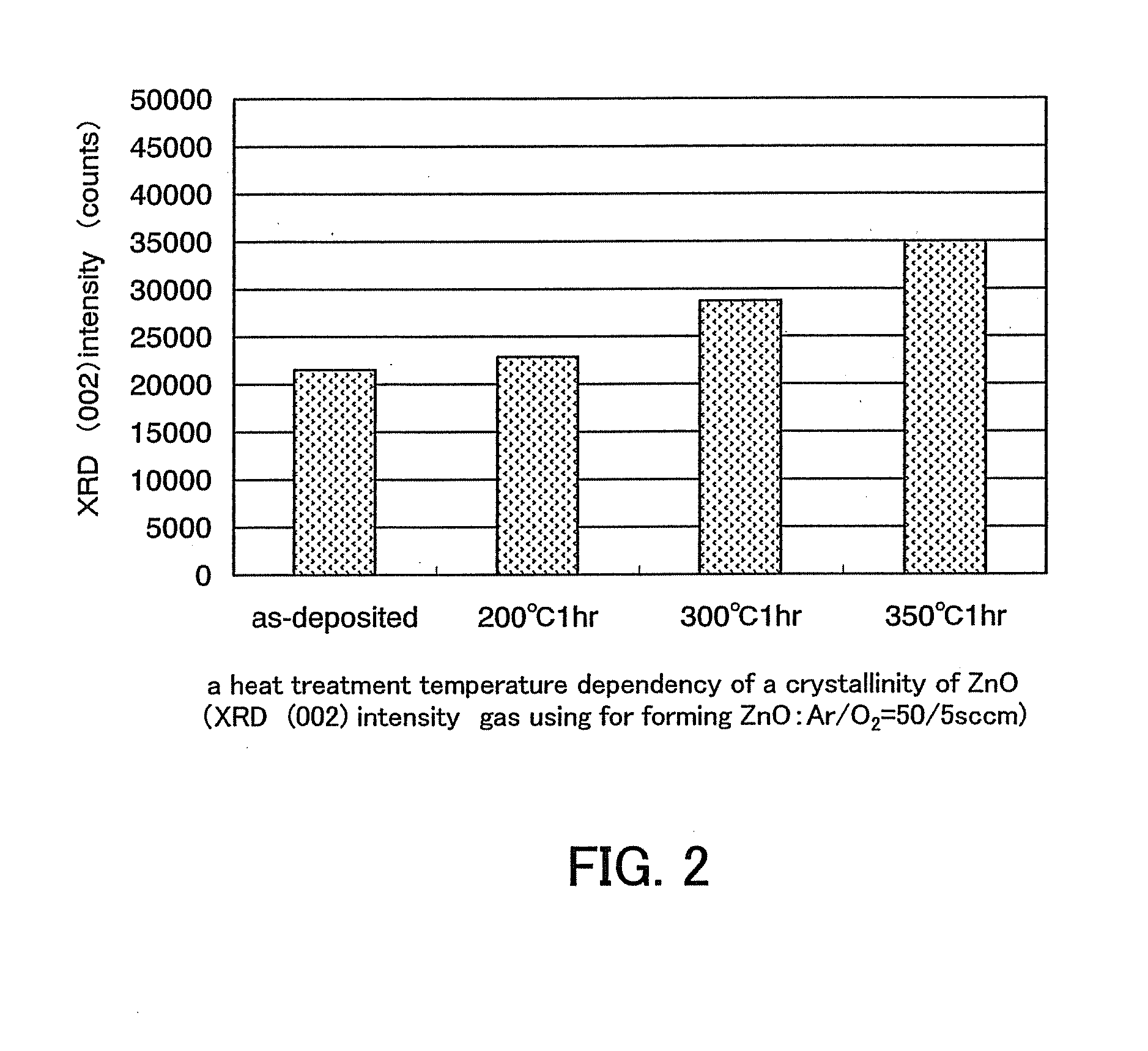
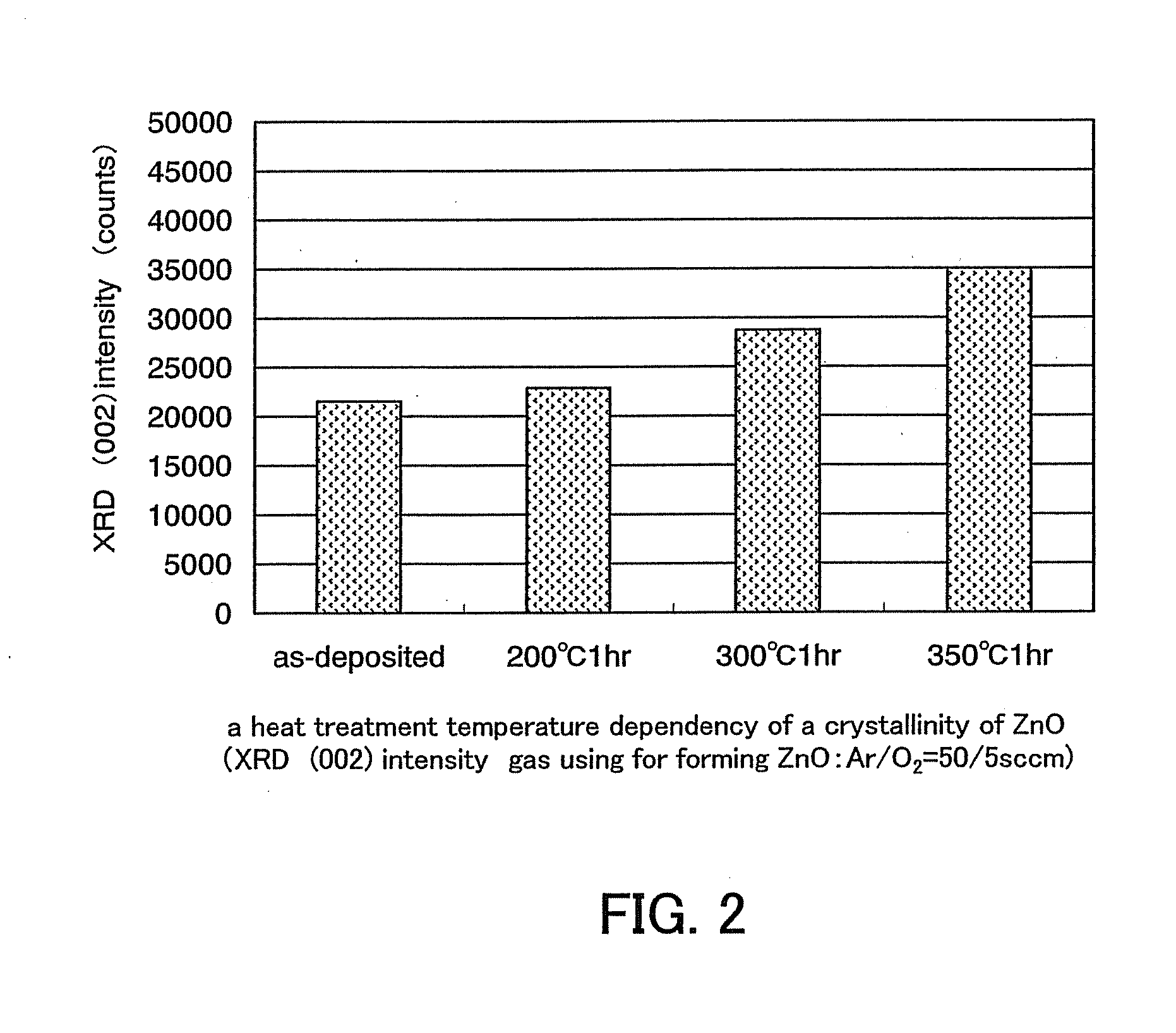
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080308797A1High yieldReduce the ratioTransistorDischarge tube luminescnet screensEngineeringZinc
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
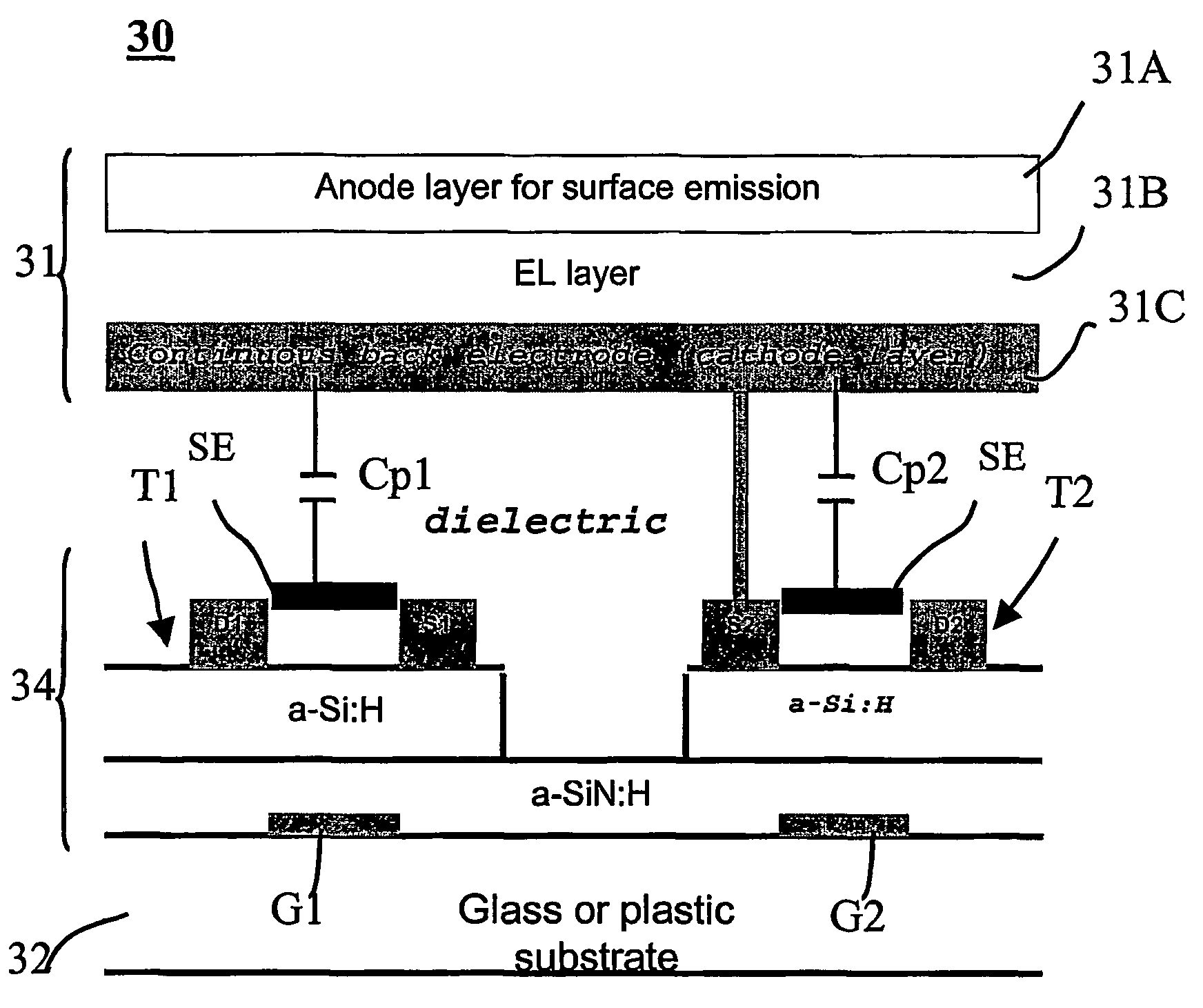
Organic light emitting diode display having shield electrodes
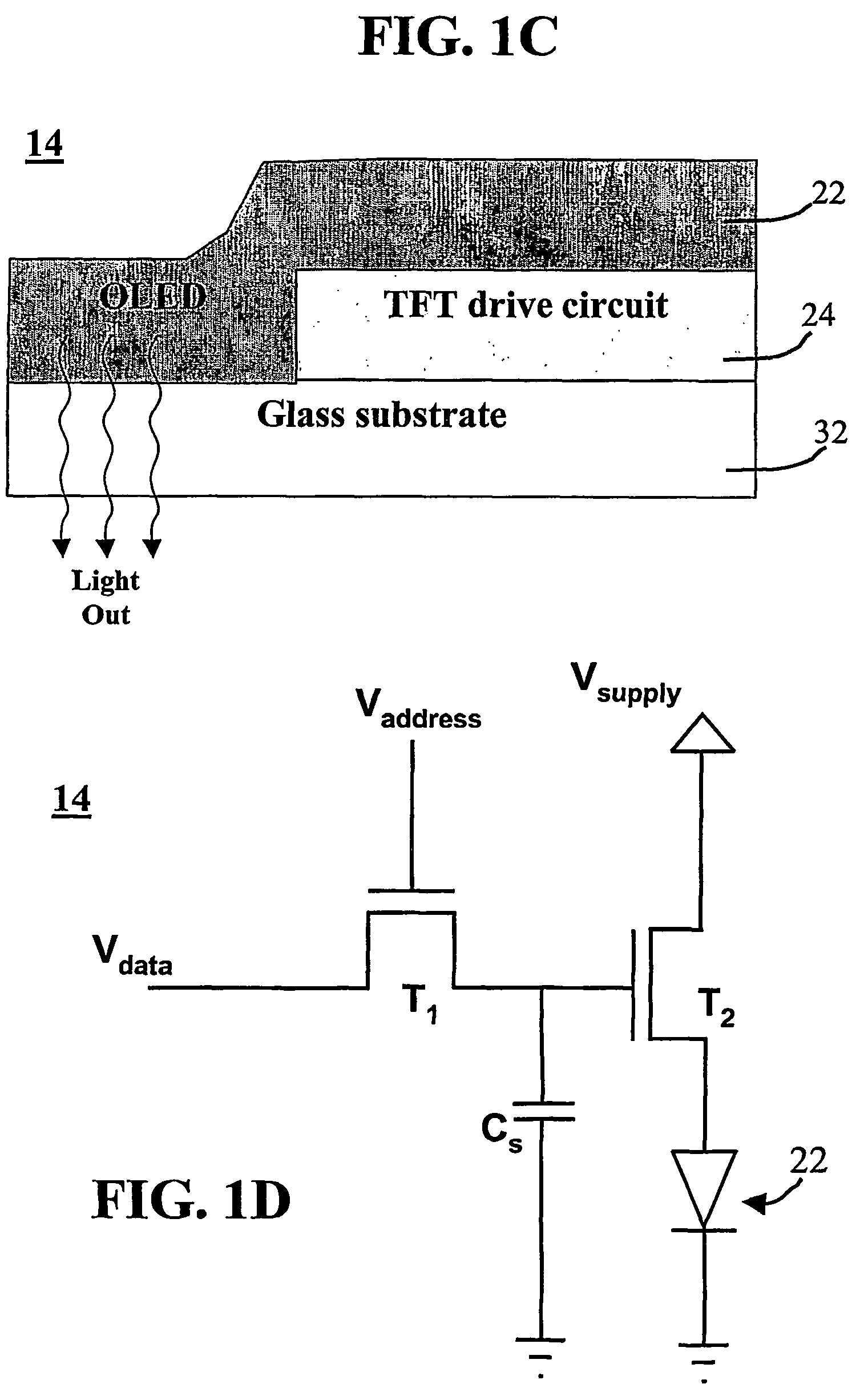
InactiveUS7248236B2Minimize parasitic capacitanceImprove performanceTransistorStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
An organic light emitting diode (OLED) display includes at least one shield electrode between a cathode layer and an OLED drive circuit. The OLED drive circuit has at least one thin-film transistor (TFT), and the shield electrode is disposed to correspond to the thin-film transistor and closer to the cathode layer, covering an entire region between the source and drain of the thin-film transistor. The shield electrode is either grounded or tied to the gate of the thin-film transistor, to thereby minimize parasitic capacitances in the pixels of the display to enhance the display performance. The presented architecture enables high density drive circuit integration in amorphous silicon or other technologies, yet preserving a high display aperture ratio.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
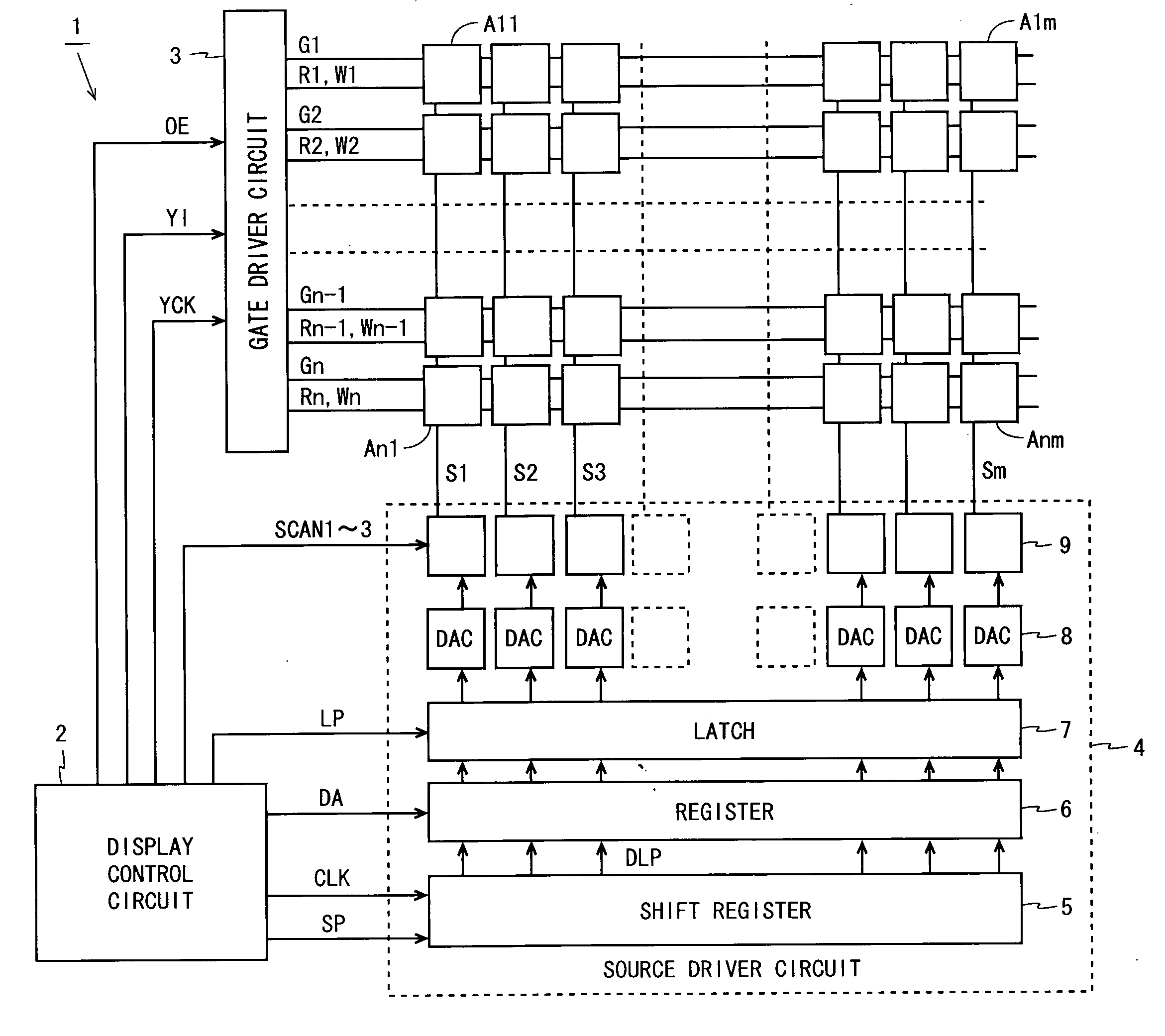
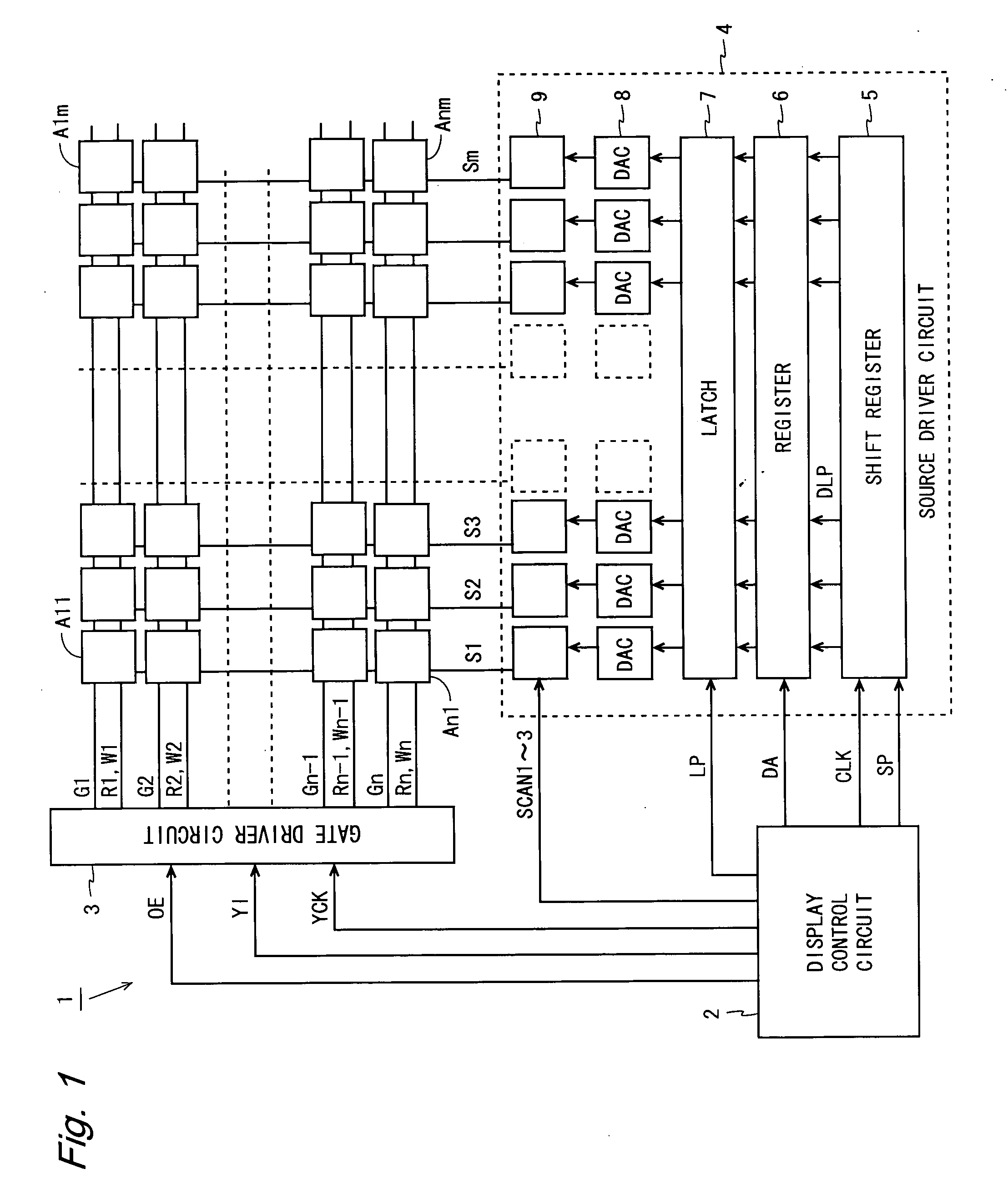
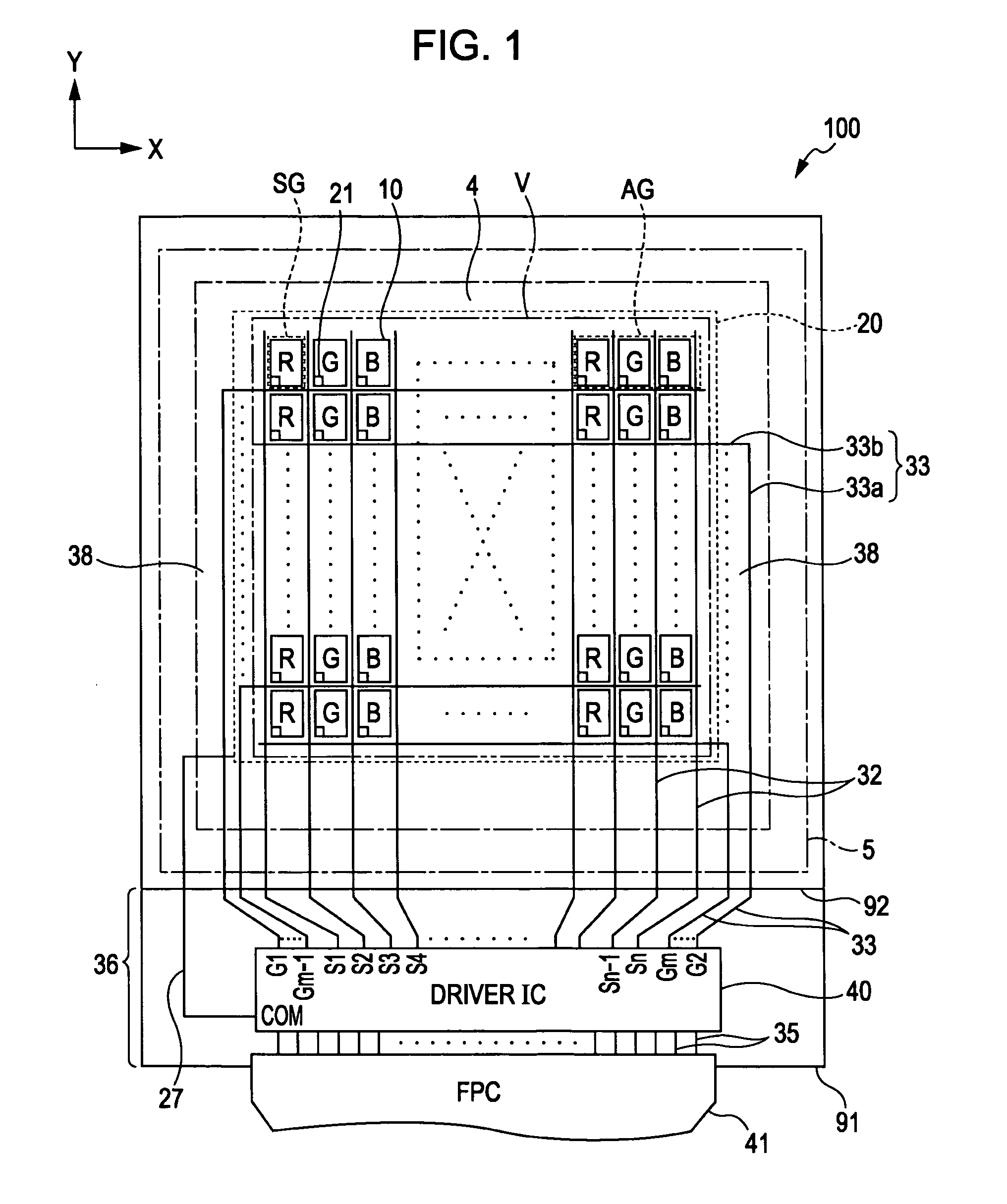
Display device and driving method thereof
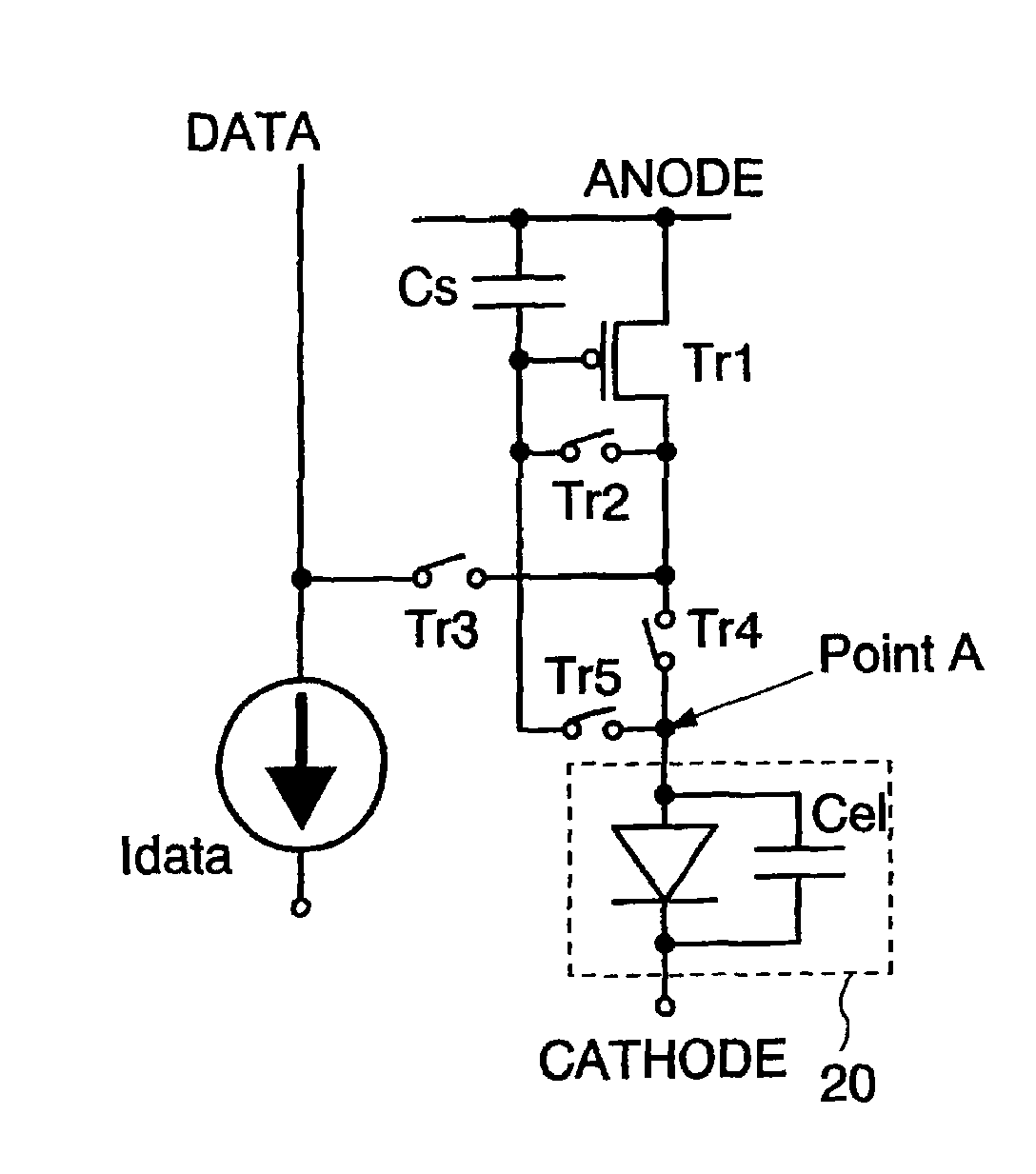
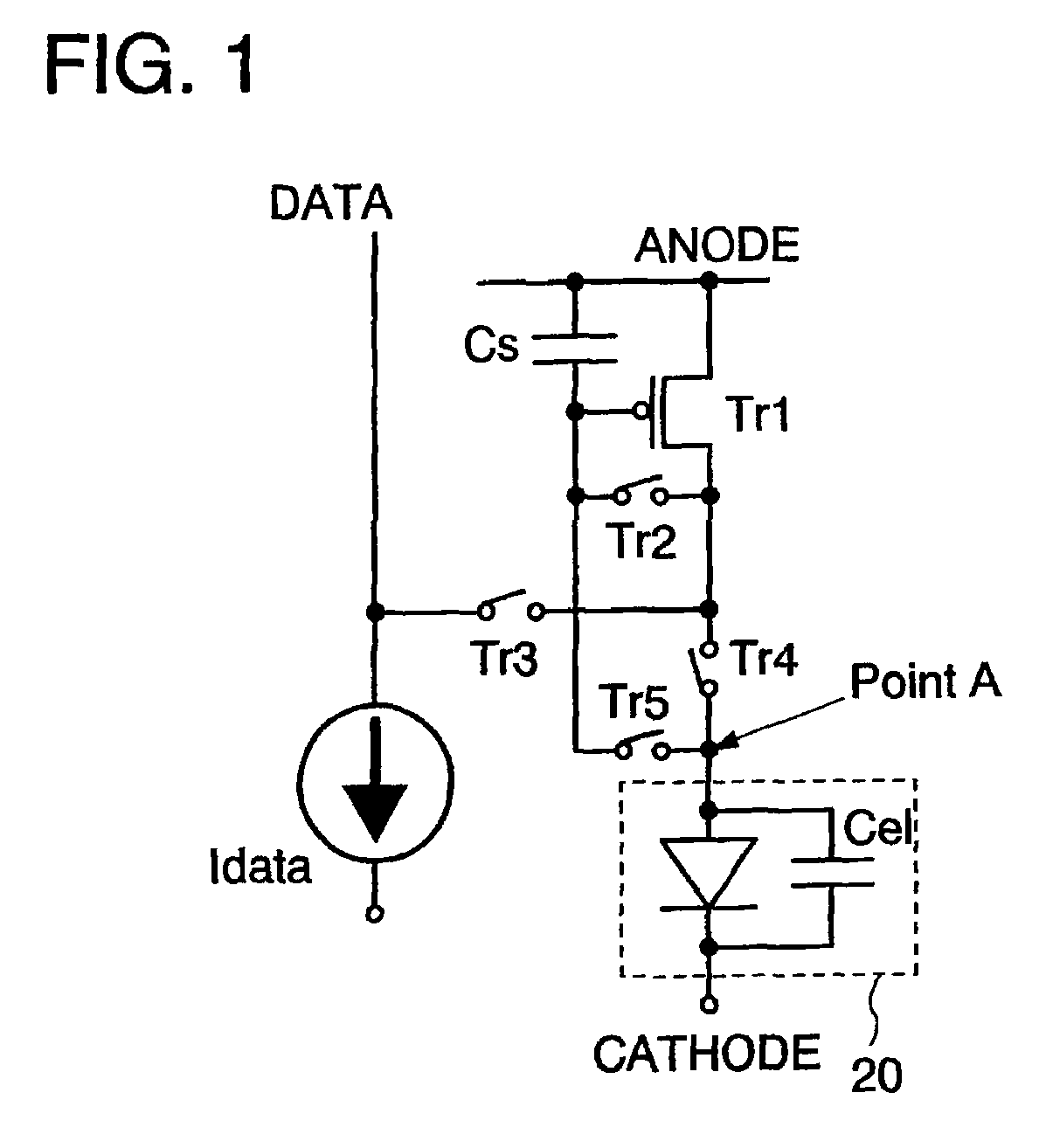
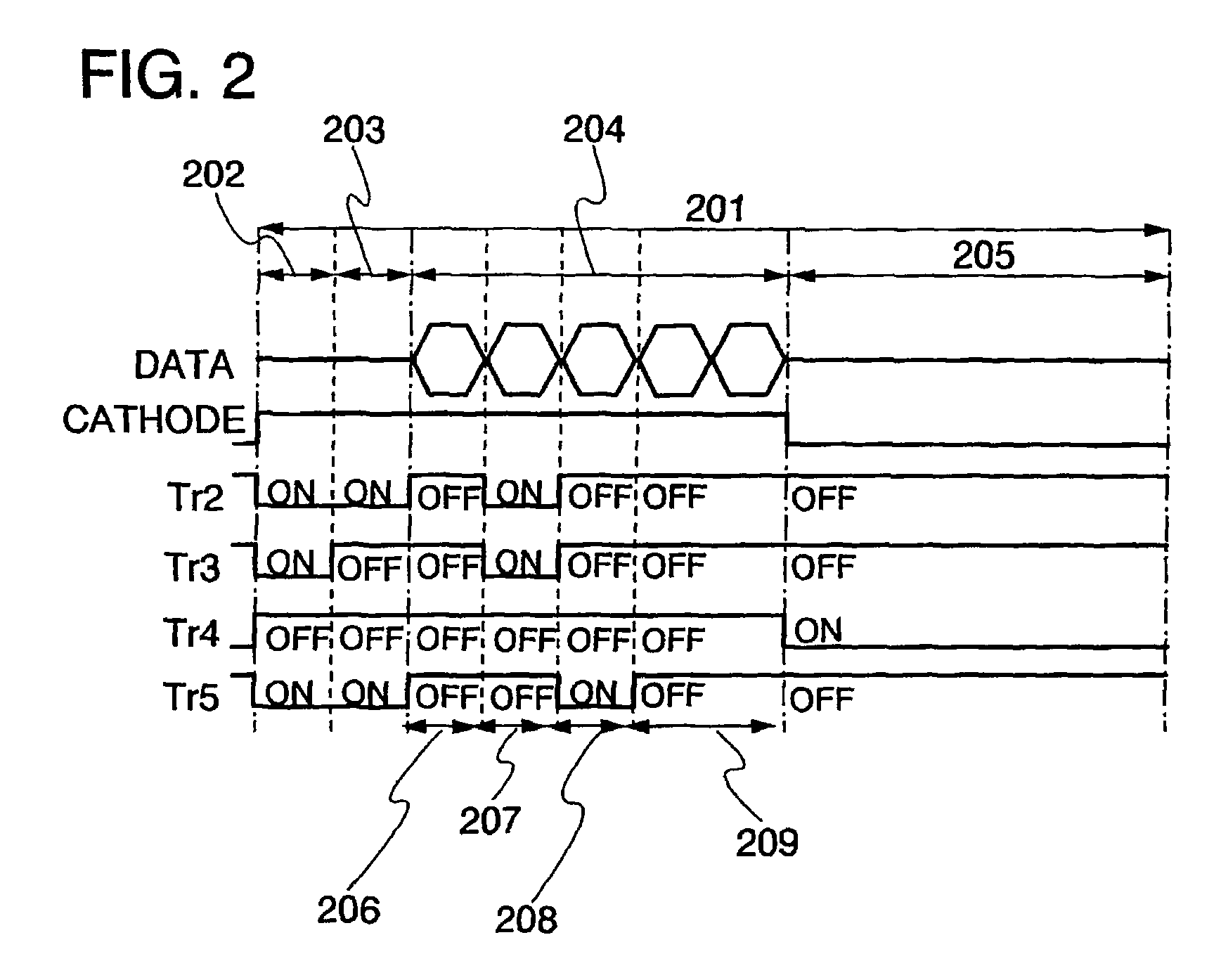
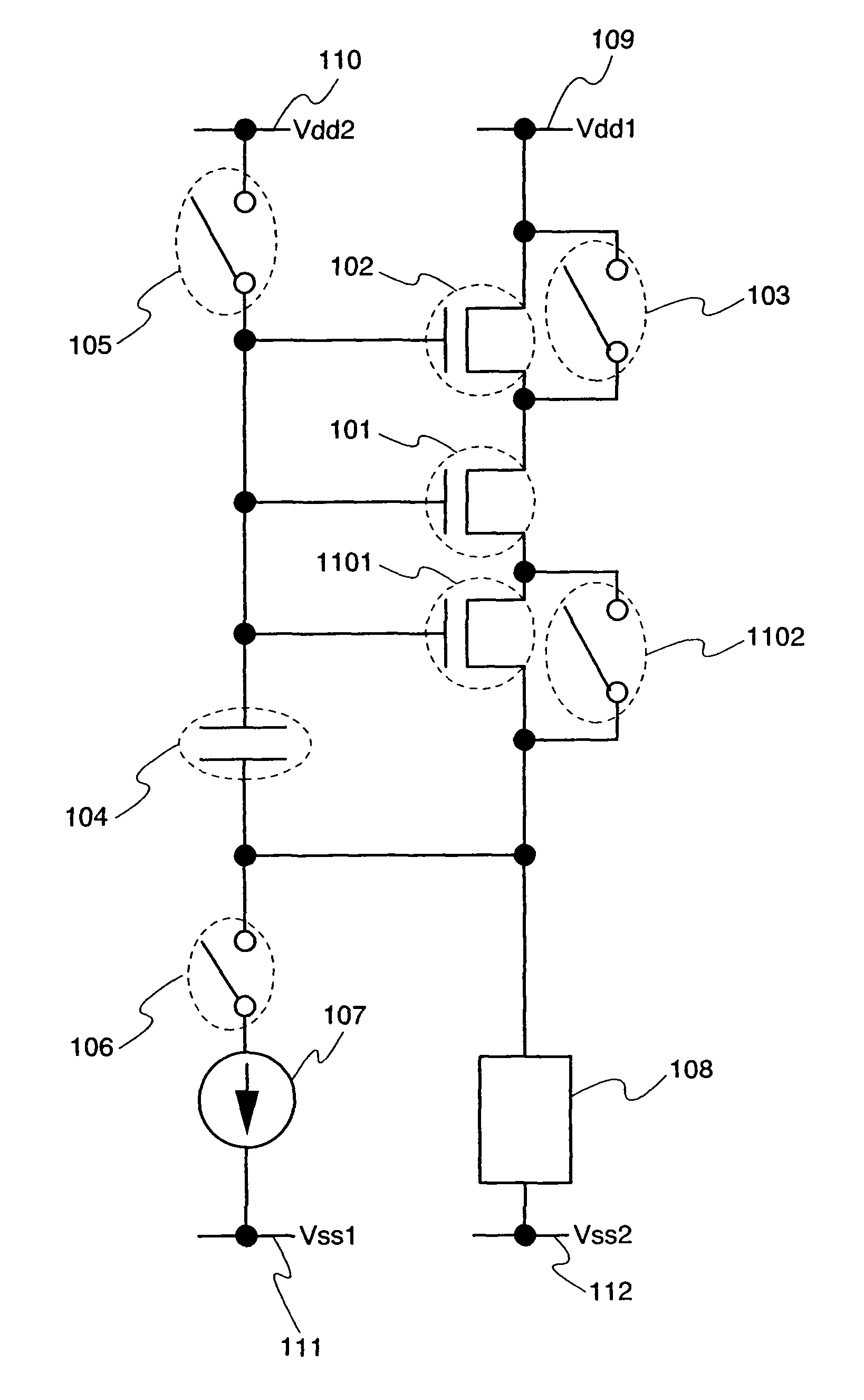
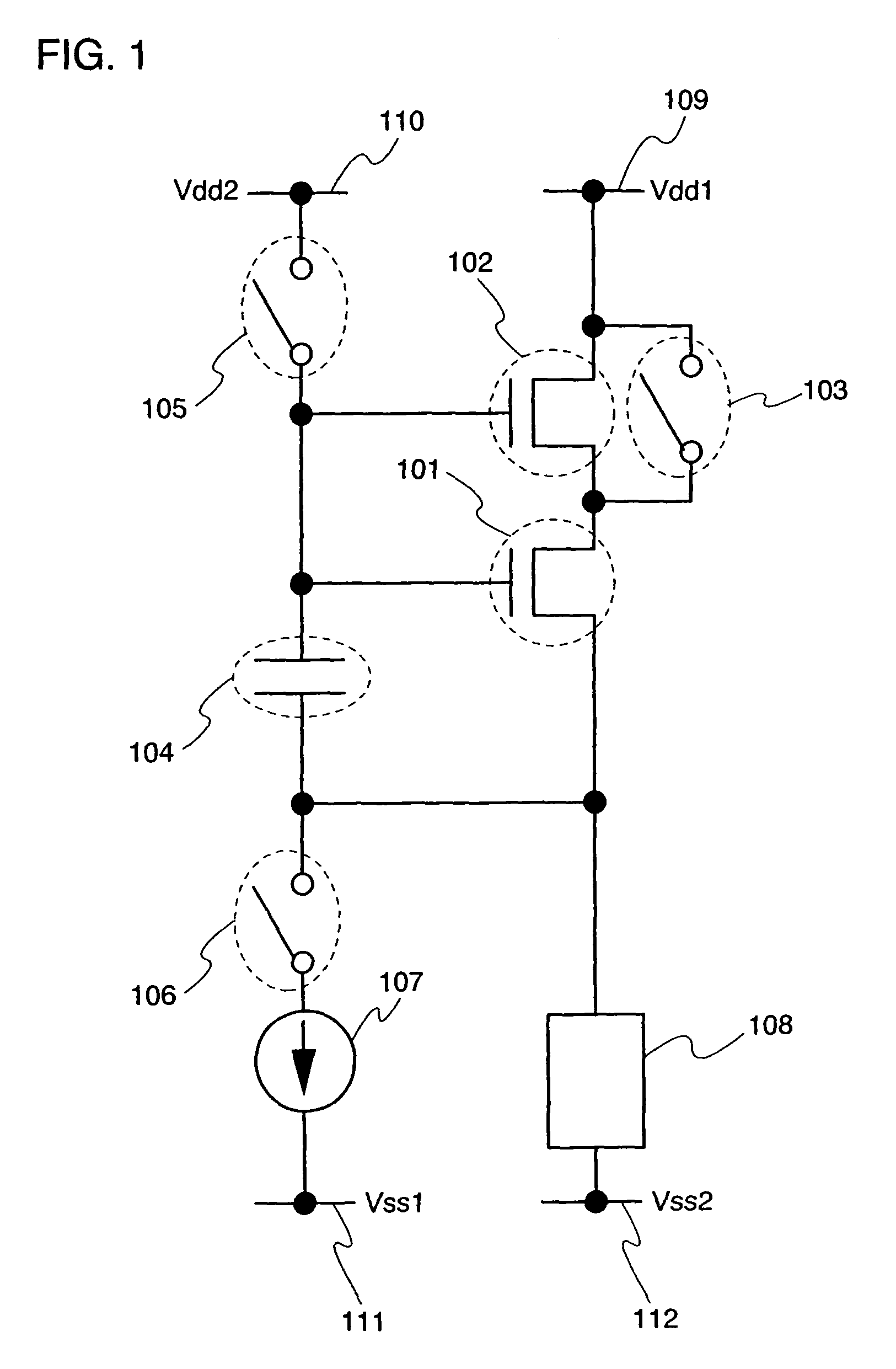
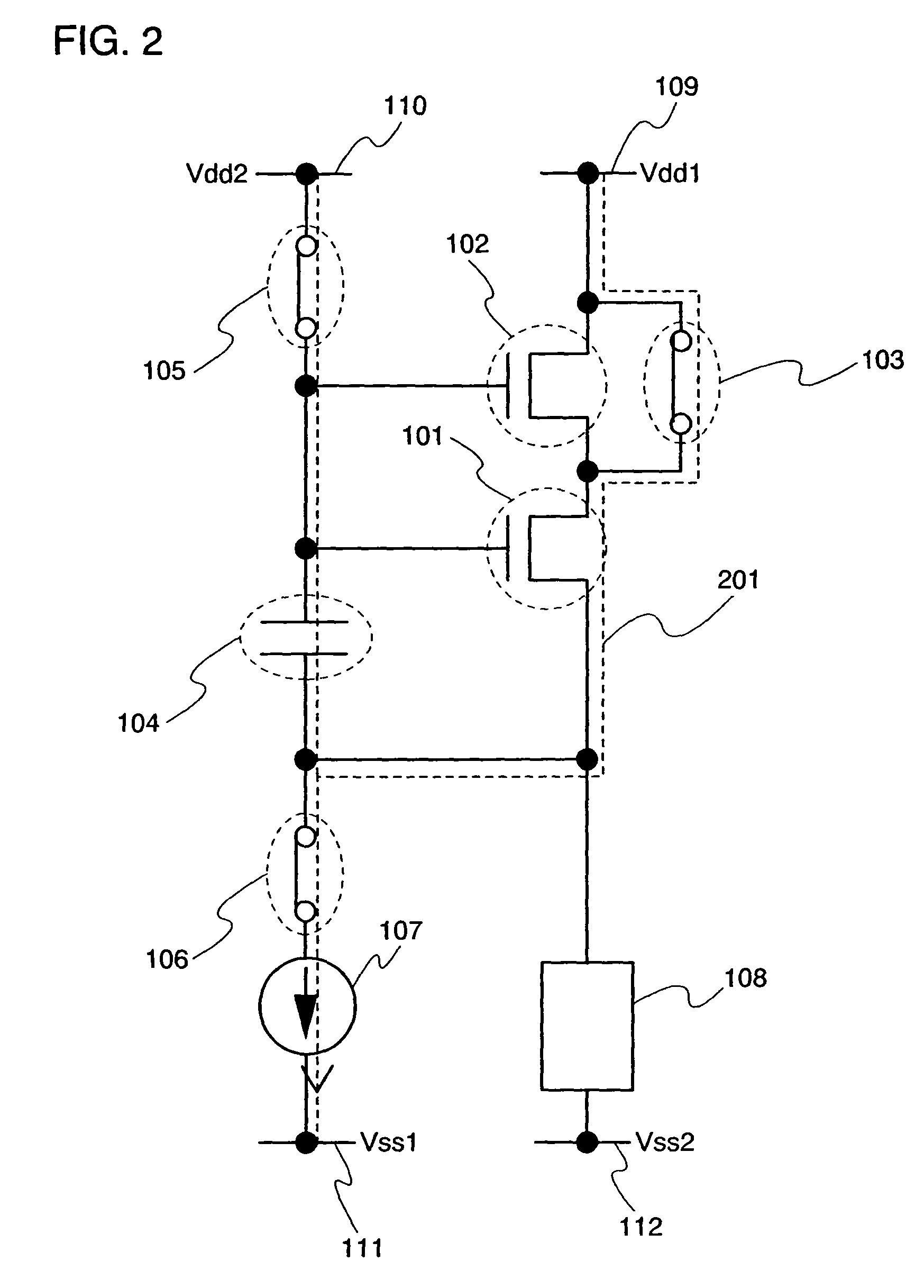
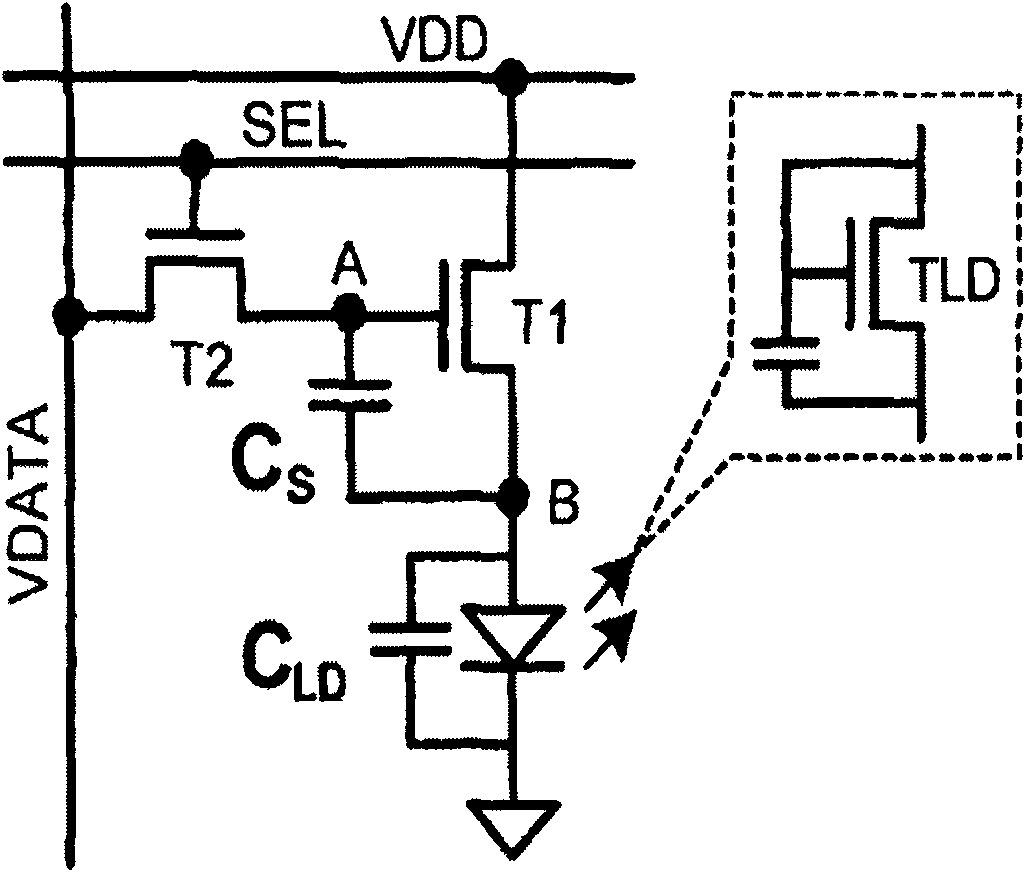
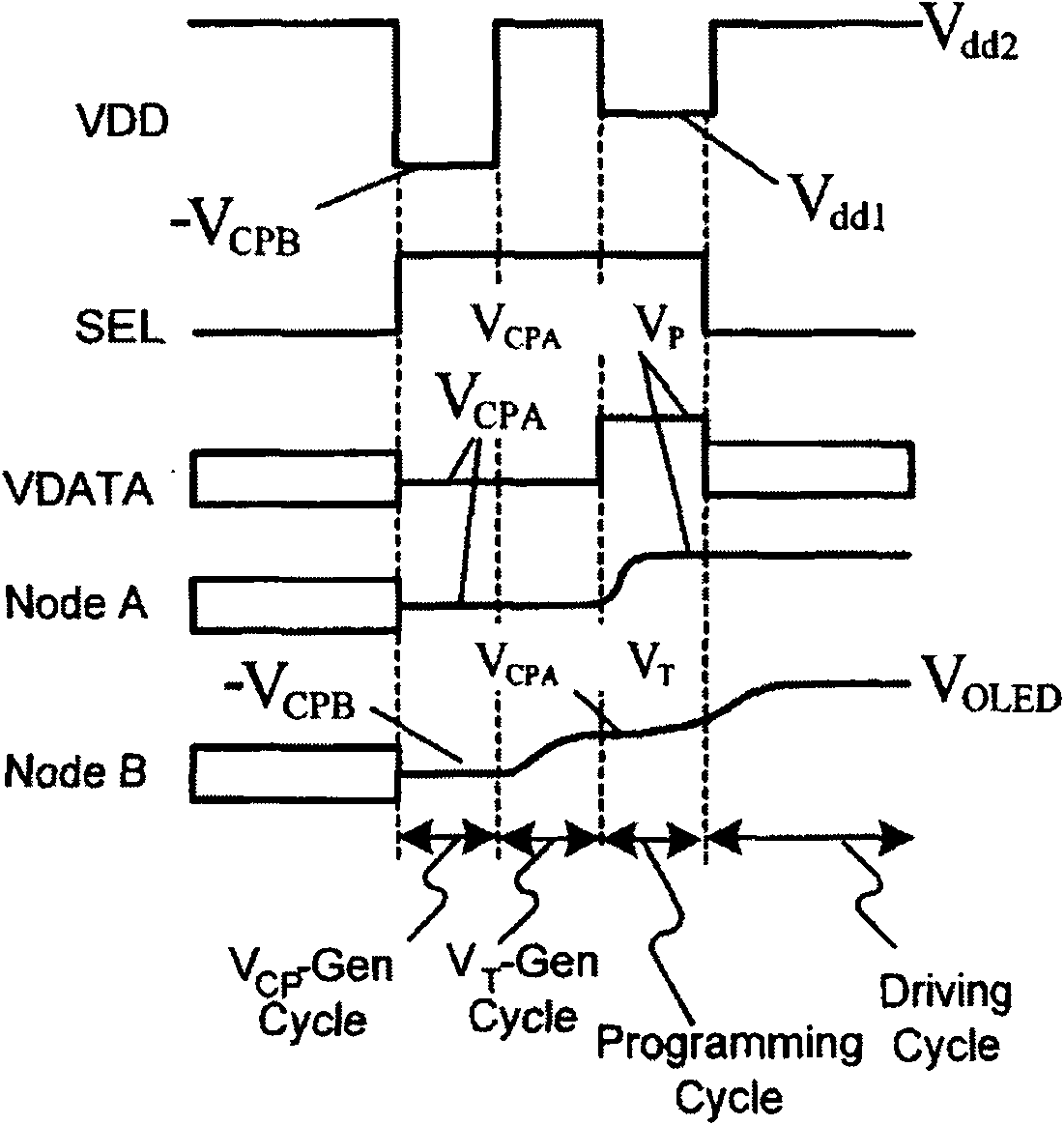
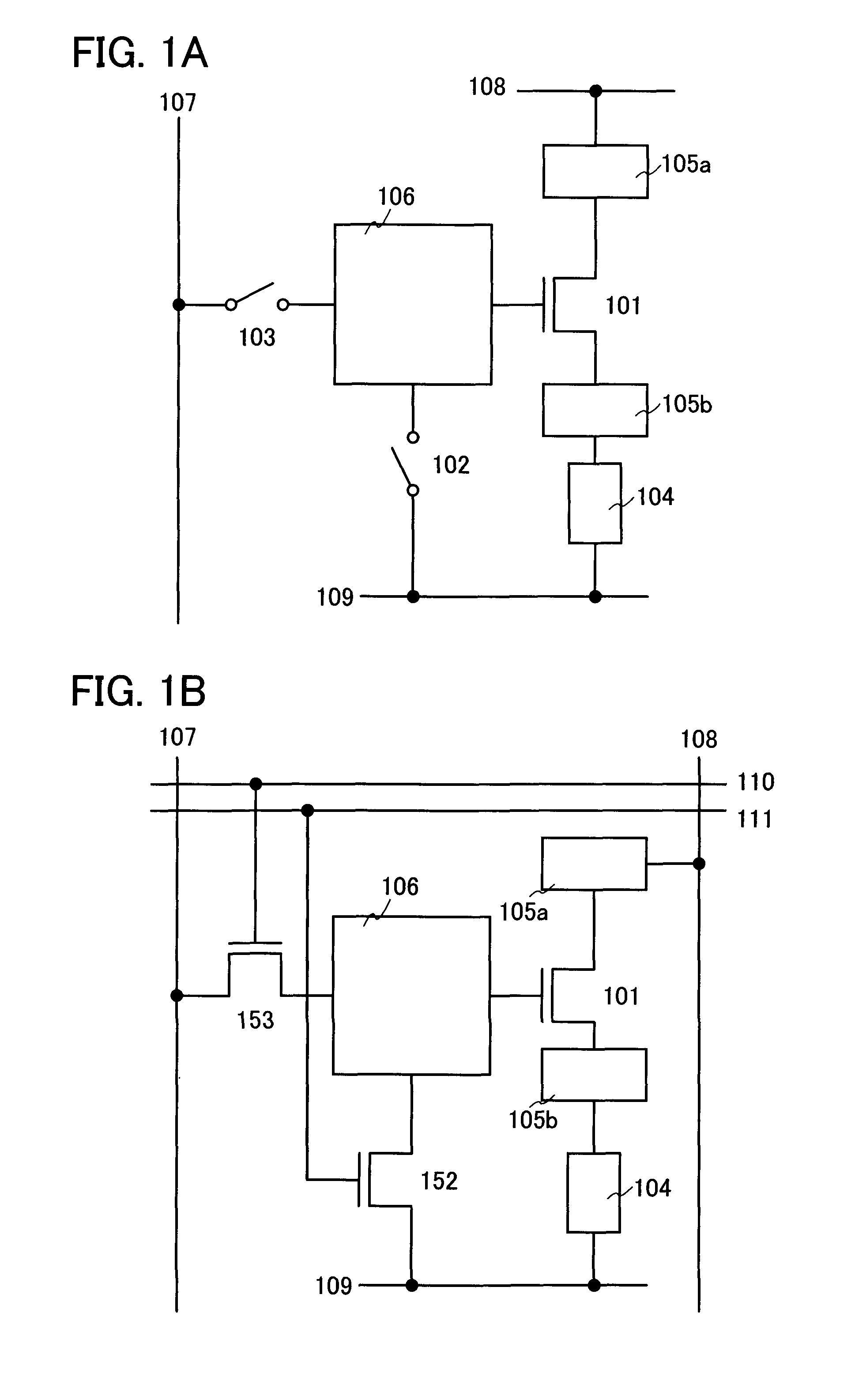
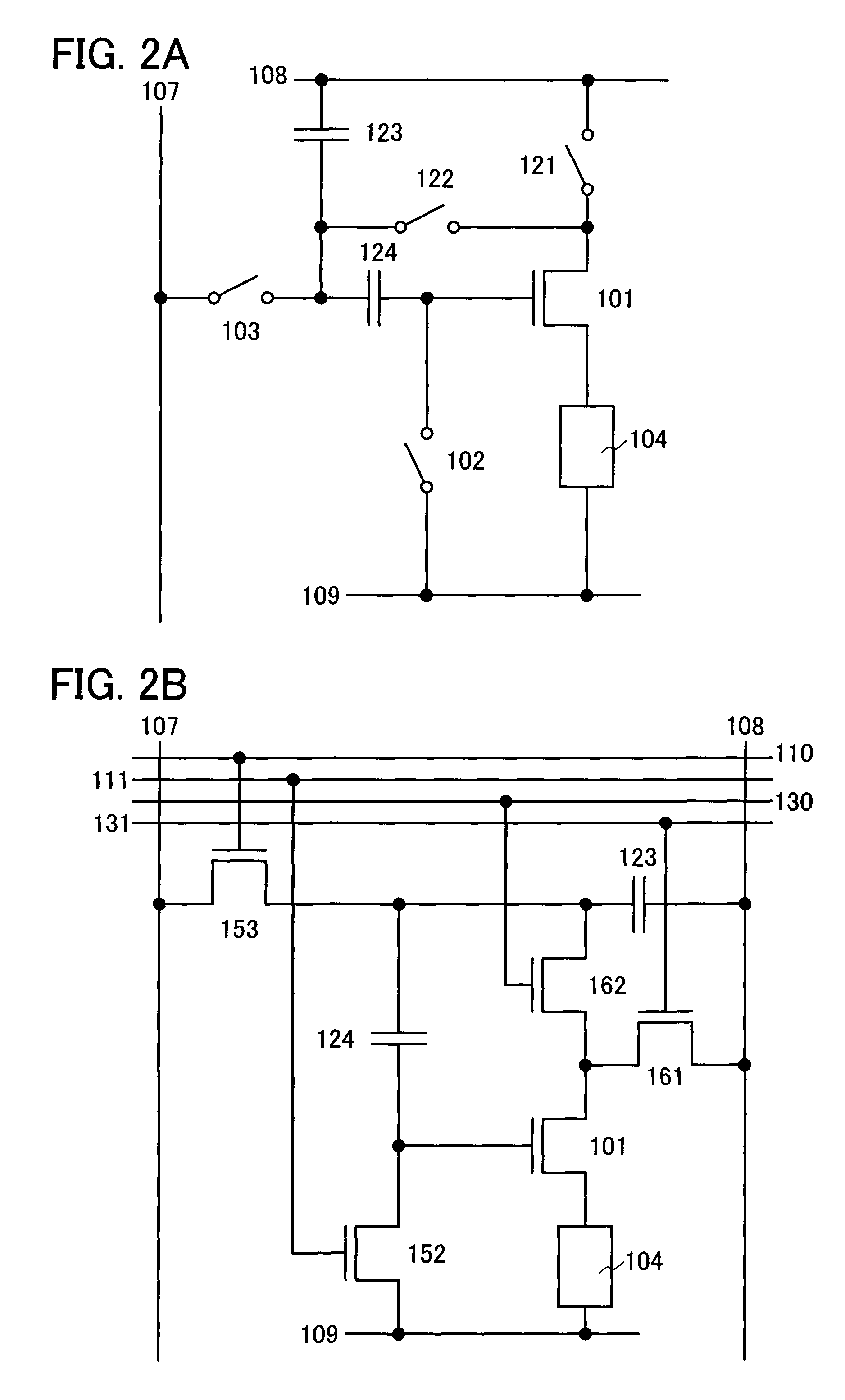
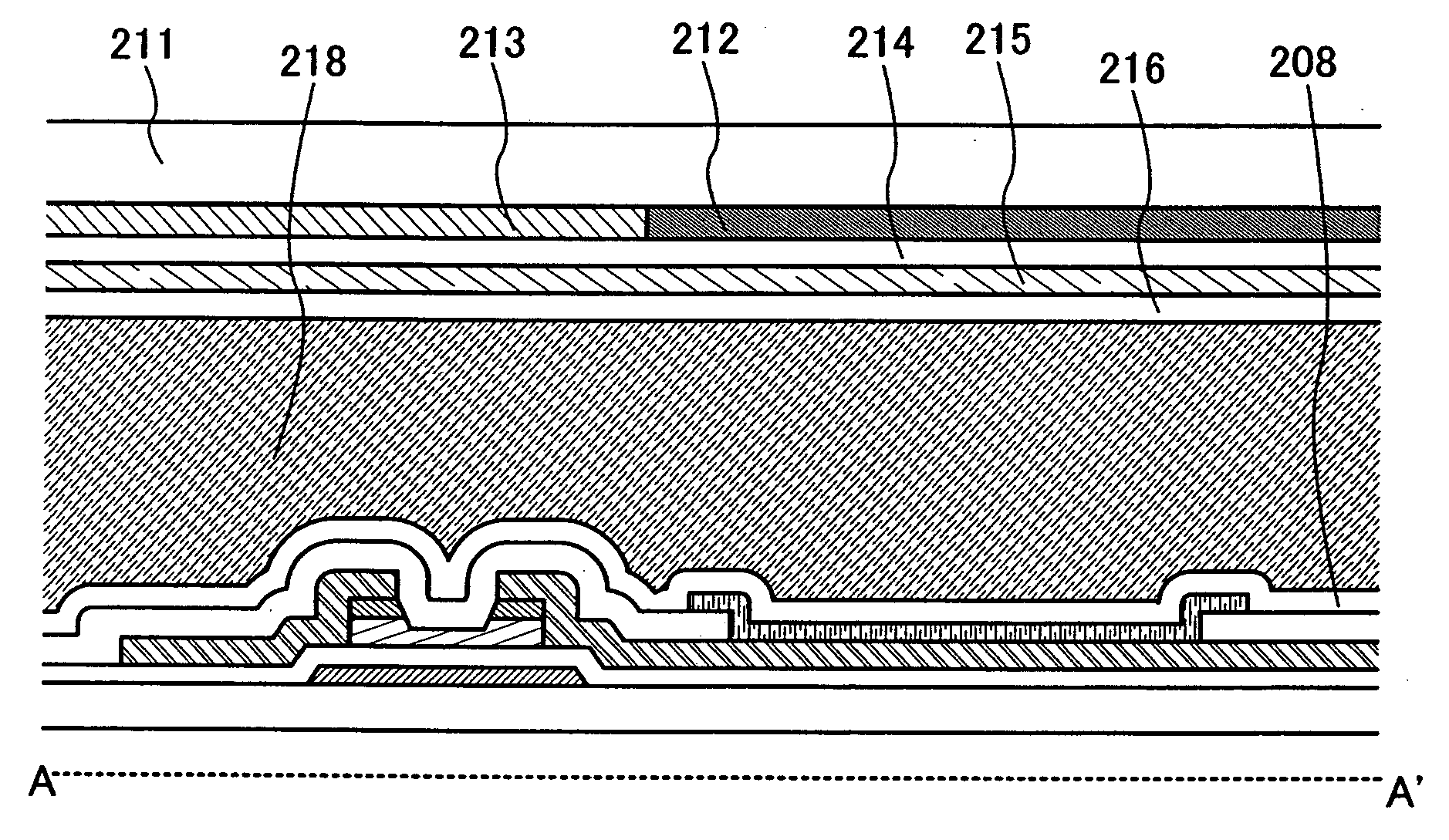
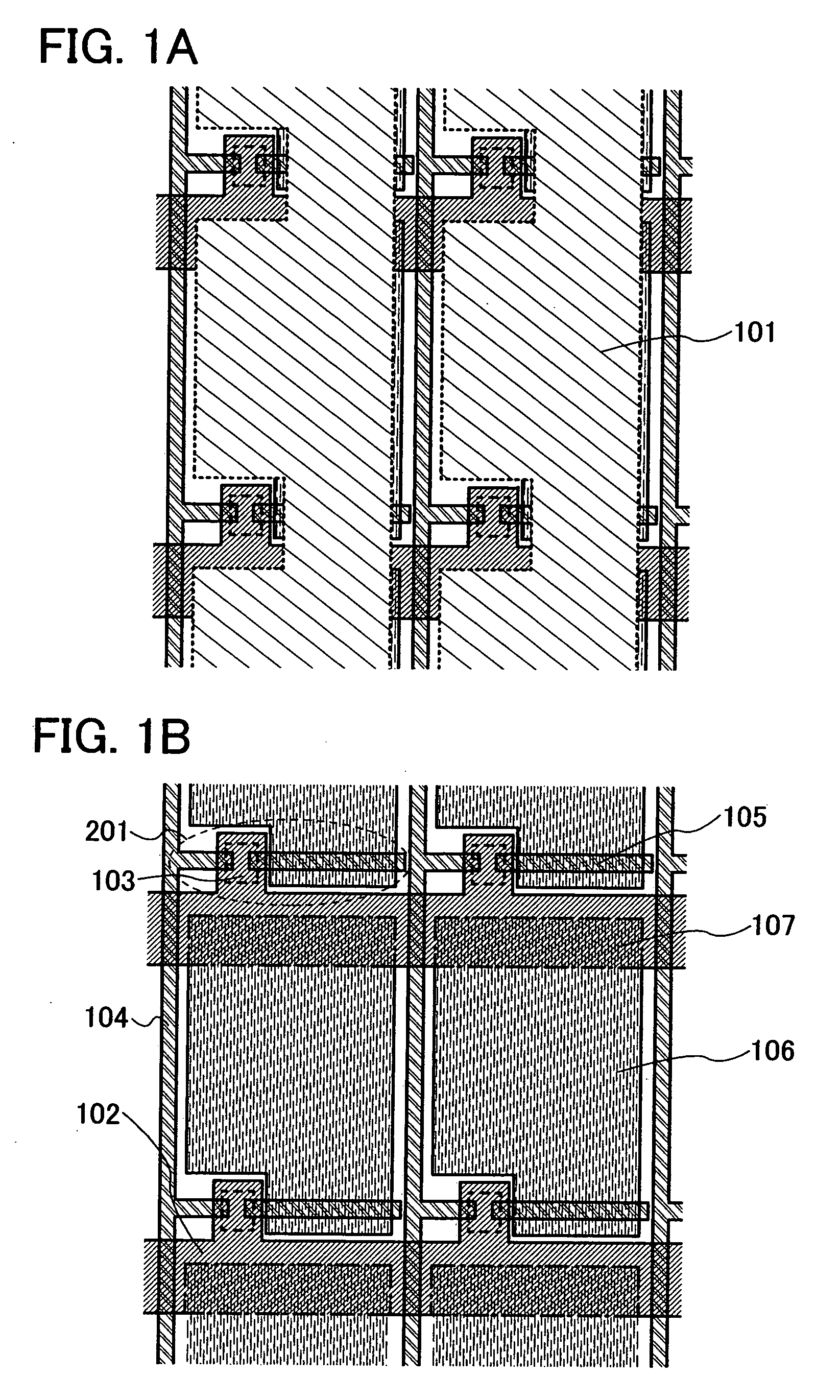
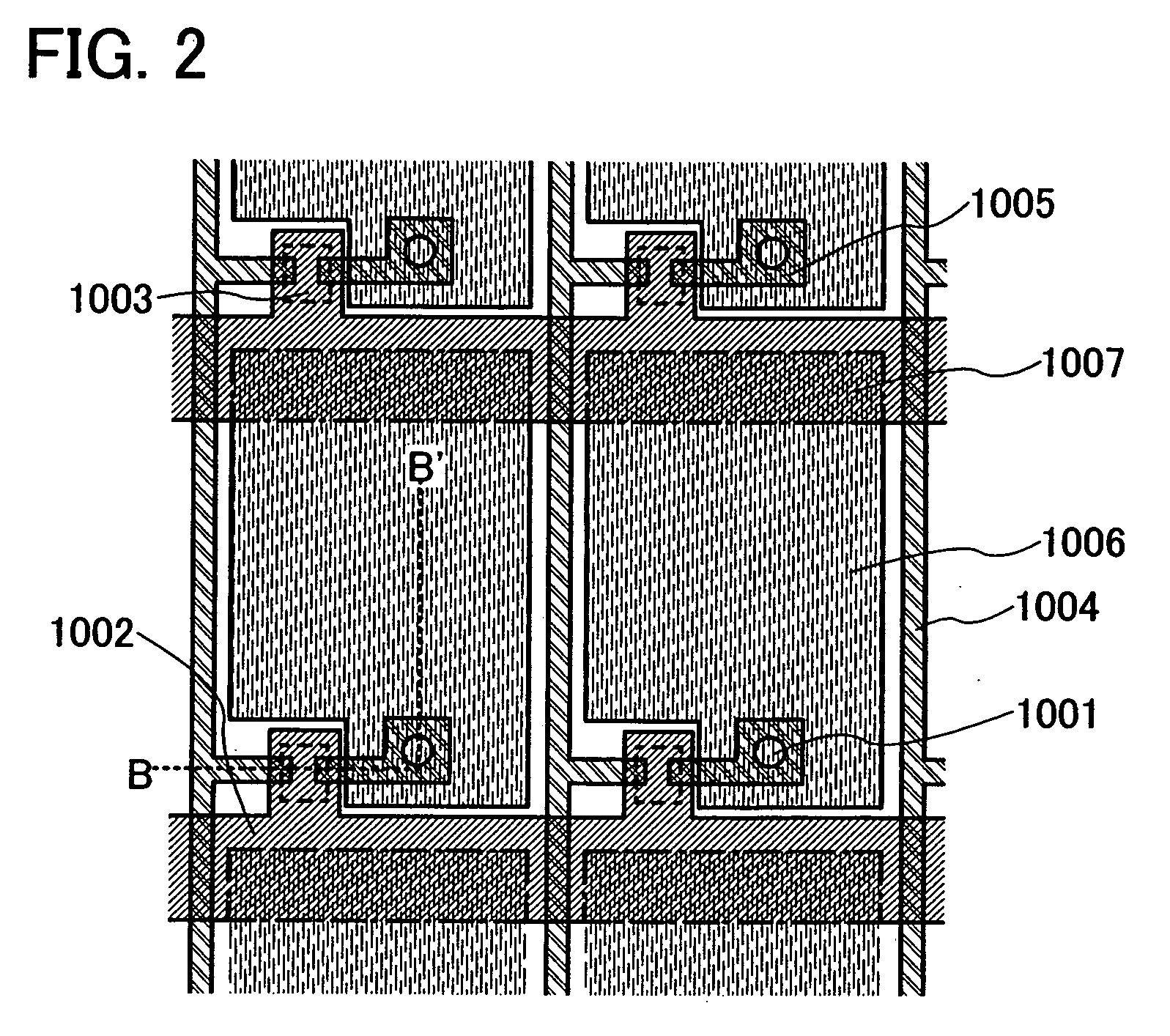
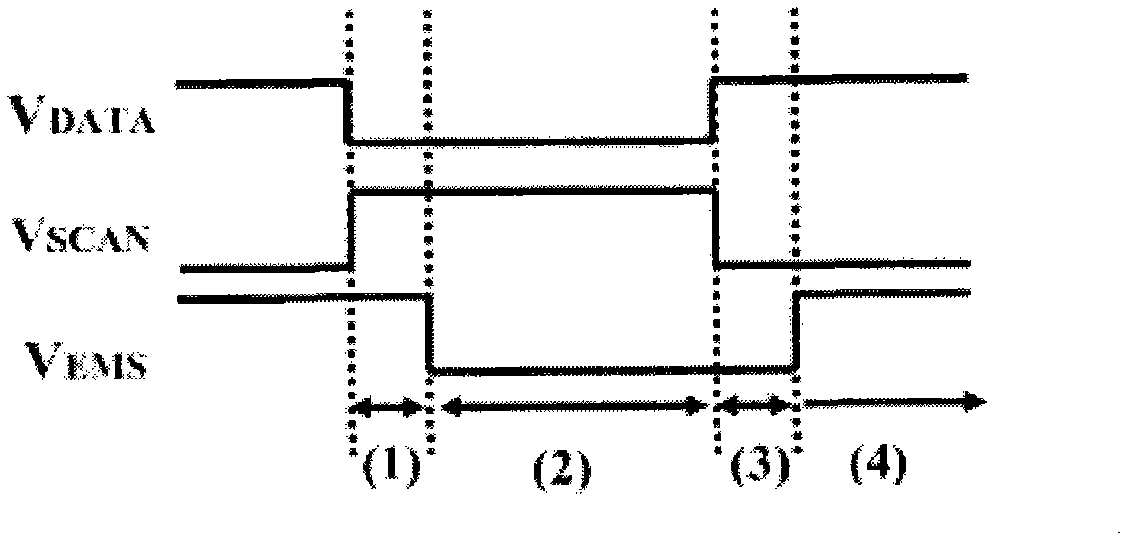
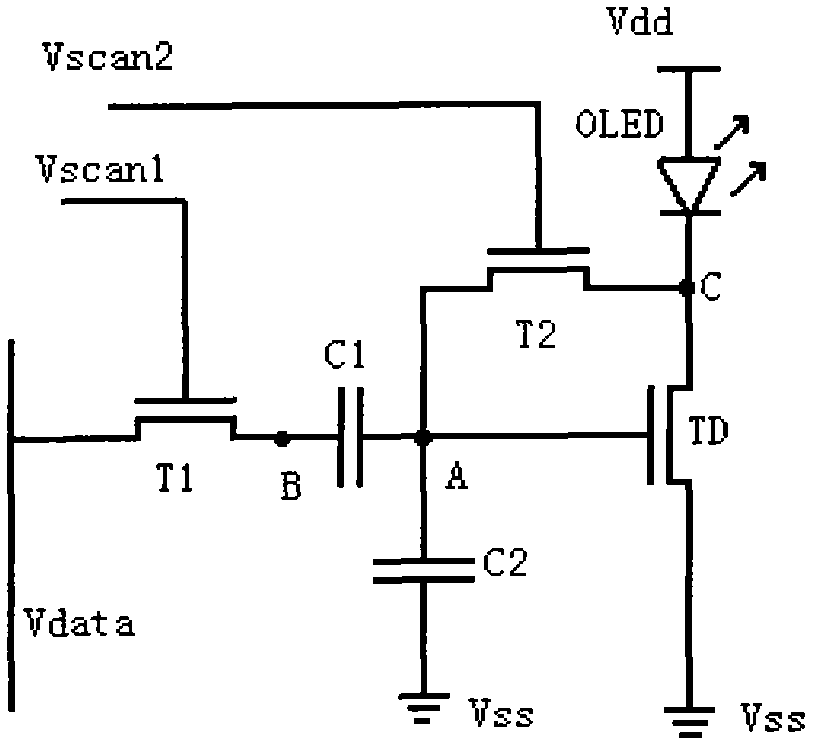
ActiveUS7969390B2Short timeIncrease opening ratioStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceAperture ratio
To solve the lack of program time, which is a problem of a display device including an EL element, and to provide a display device including a pixel circuit with a high aperture ratio and a driving method thereof. In a circuit including a driving transistor, a capacitor, a display element which can be used as a capacitor, a first power supply line and a second power supply line, potentials of the first power supply line and the second power supply line are set to be almost the same, thereby a threshold voltage of the driving transistor is held in the display element, and after that, a charge is divided into the display element and the capacitor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
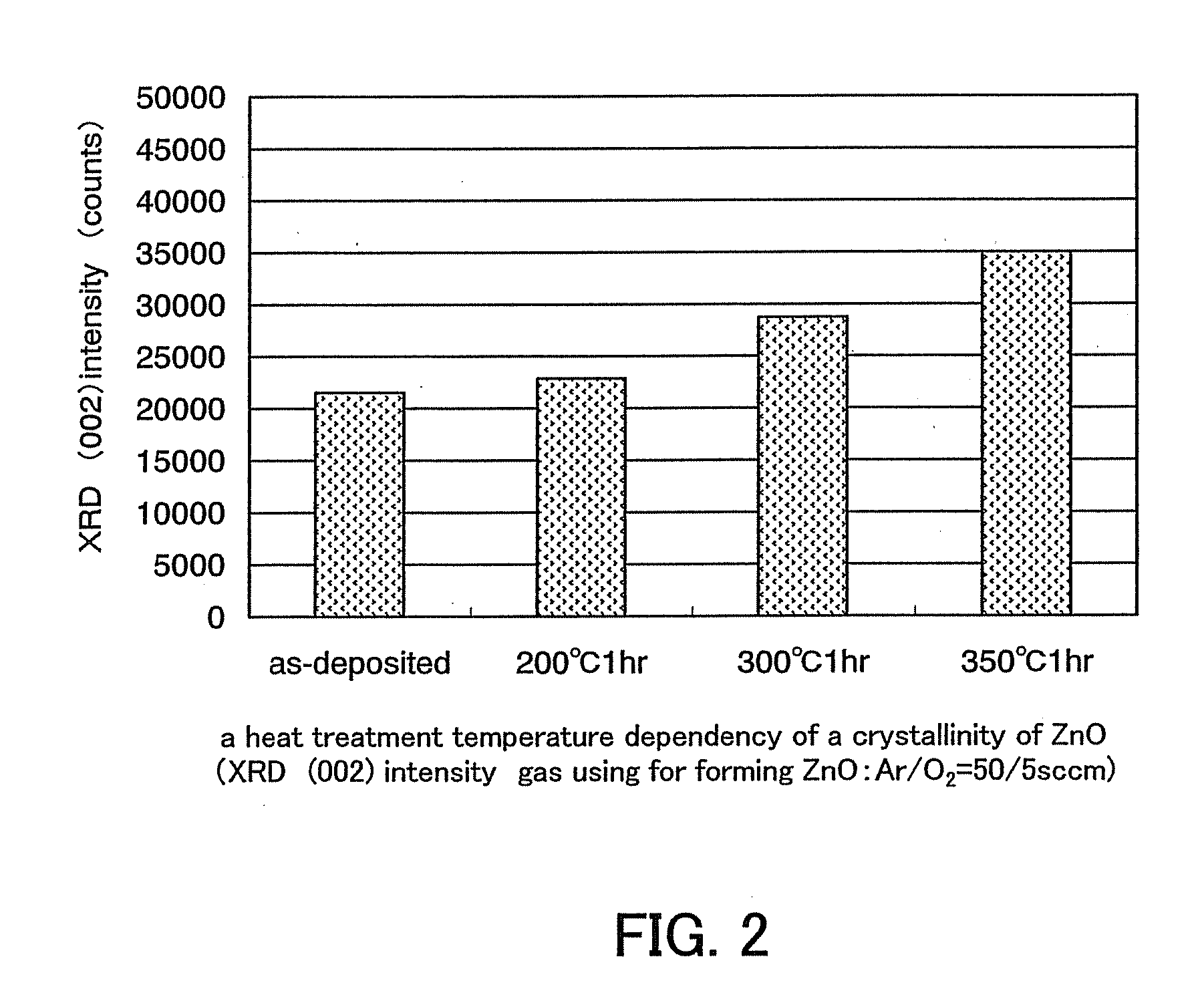
Method for forming crystalline semiconductor layers, a method for fabricating thin film transistors, and method for fabricating solar cells and active matrix liquid crystal devices
InactiveUS6066516AGreat fabricationImprove mobilityTransistorFinal product manufactureActive matrixSolar cell
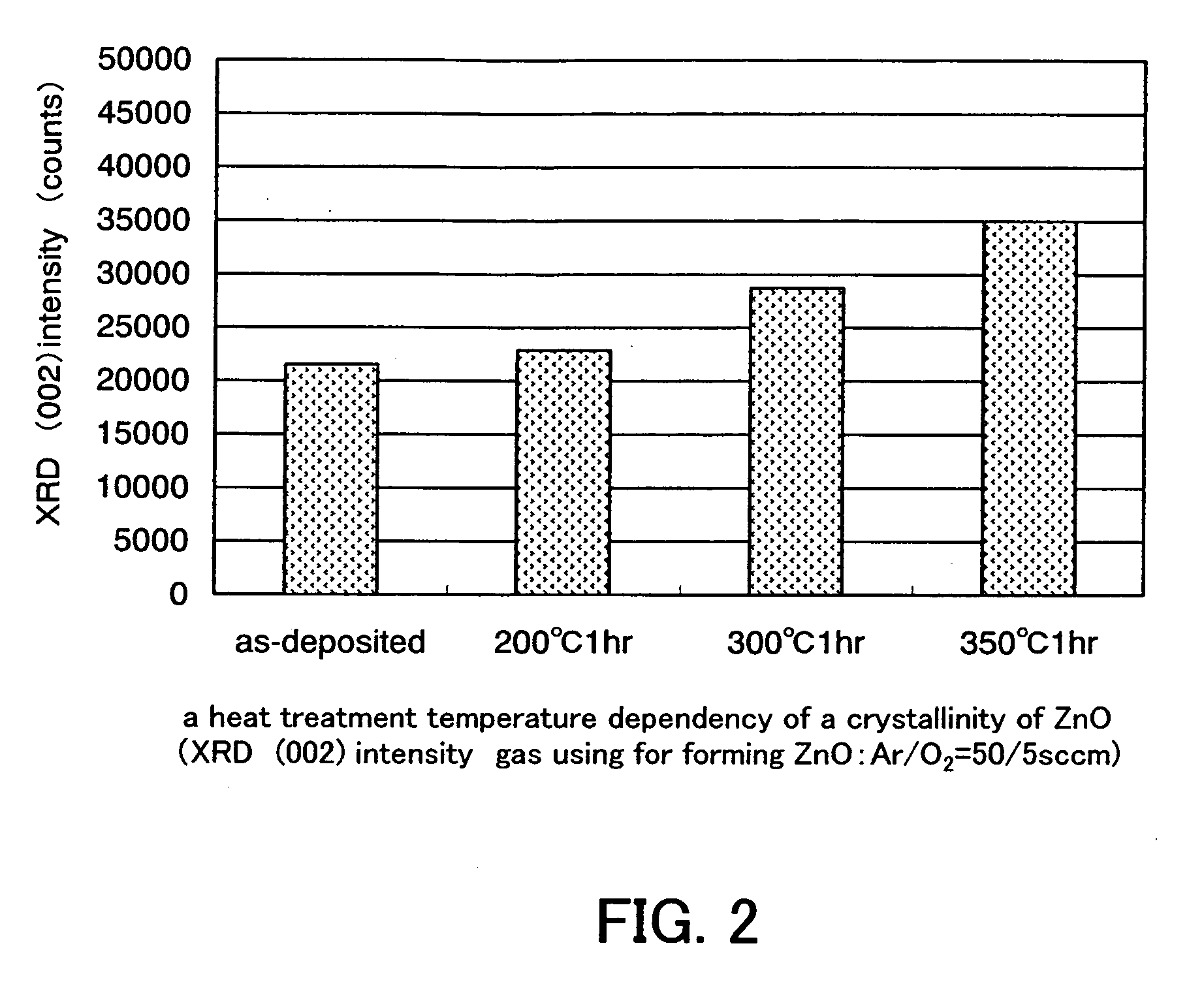
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 01775 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 31, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 31, 1997 PCT Filed Jun. 26, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 01863 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 16, 1997A crystalline semiconductor layer can be formed by forming a semiconductor film on an inexpensive conventional substrate. Next, perform a first annealing process in which nearly the entire surface of the semiconductor film is exposed to laser irradiation or other forms of irradiation, and then perform a second annealing process consisting of rapid thermal annealing. This enables the formation of a high quality crystalline semiconductor film with high throughput but without subjecting the substrate to undue thermal stress. When this invention is applied to thin film transistors, good transistors having high performance are easily fabricated. When this invention is applied to solar cells, energy conversion efficiency is increased.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
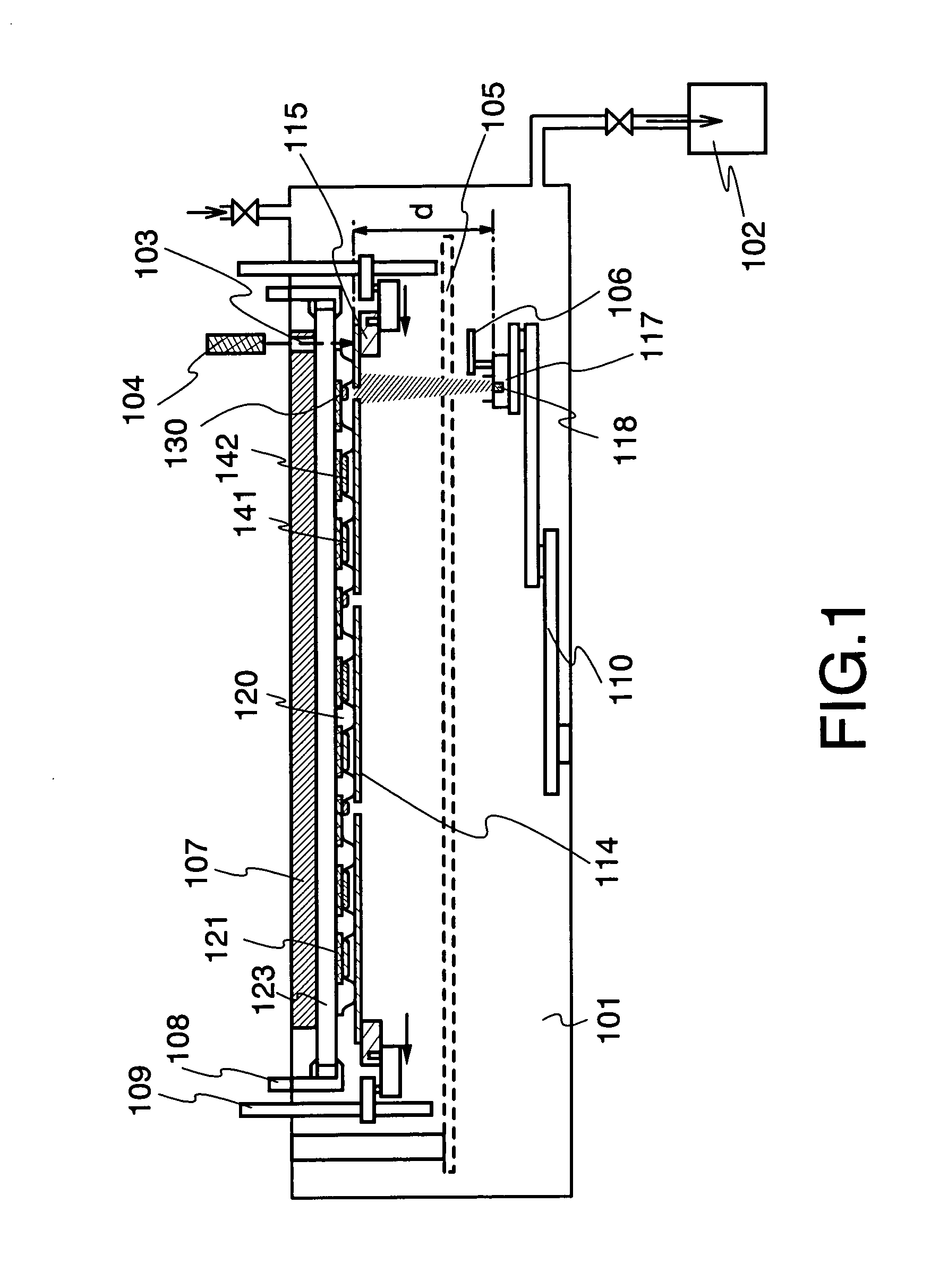
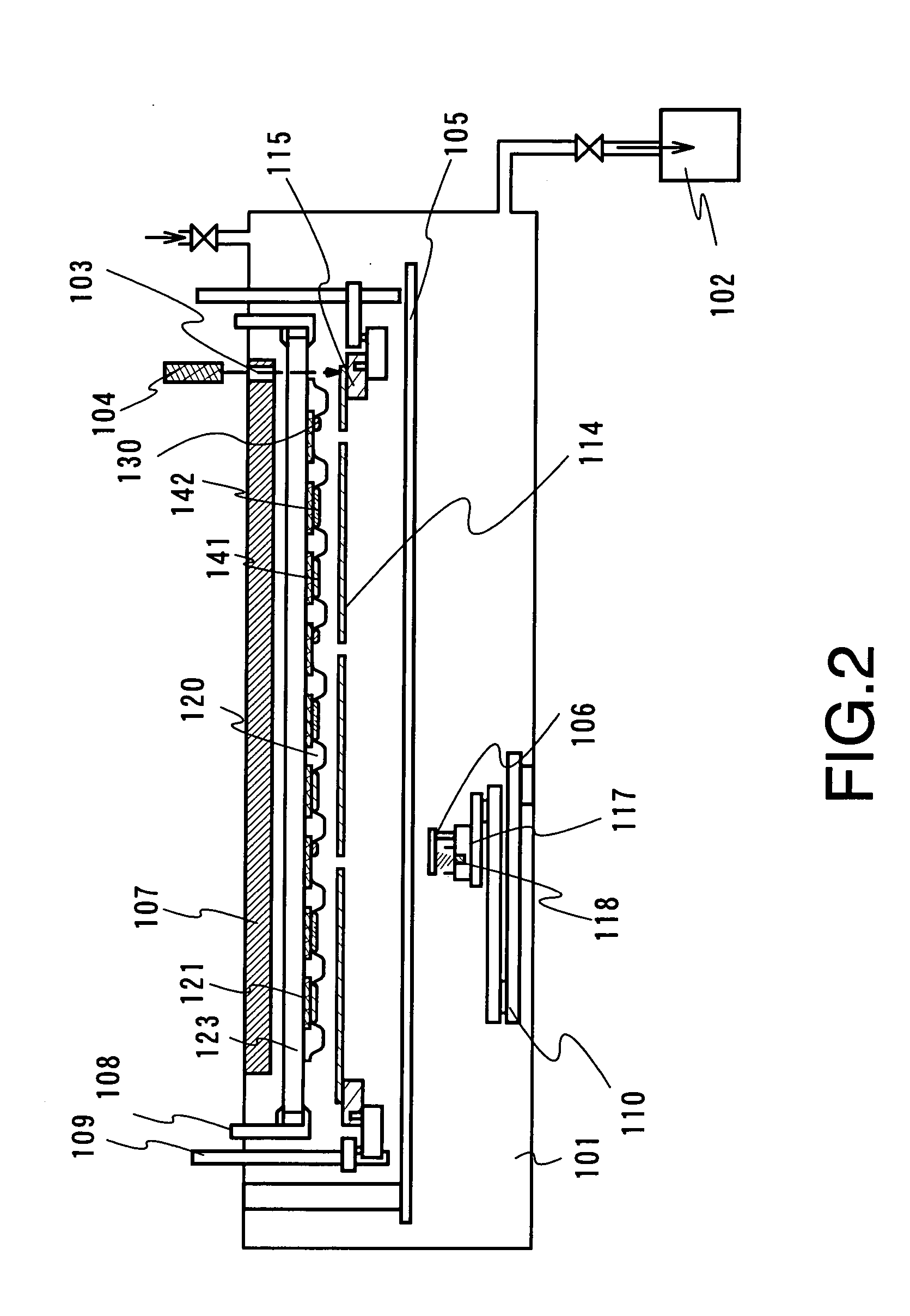
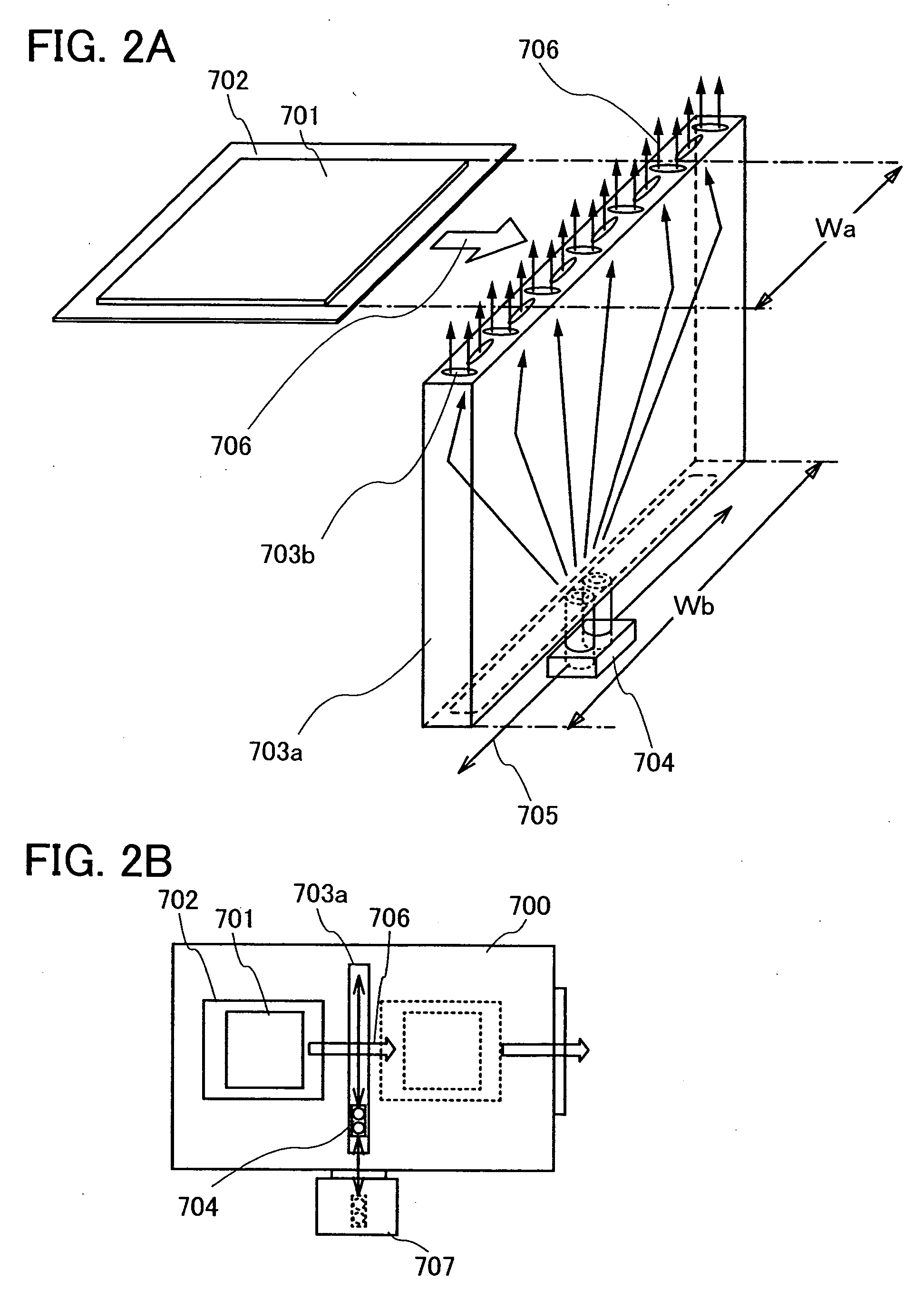
Manufacturing apparatus
InactiveUS20060011136A1High definitionIncrease opening ratioVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingManufacturing cost reductionGas phase
It is an object of the present invention to provide a manufacturing apparatus that reduces a manufacturing cost by enhancing efficiency in the use of an EL material and that is provided with a vapor deposition apparatus which is one of manufacturing apparatuses superior in uniformity in forming an EL layer and in throughput in the case of manufacturing a full-color flat panel display using emission colors of red, green, and blue. According to one feature of the invention, a mask having a small opening with respect to a desired vapor deposition region is used, and the mask is moved accurately. Accordingly, a desired vapor deposition region is vapor deposited entirely. In addition, a vapor deposition method is not limited to movement of a mask, and it is preferable that a mask and a substrate move relatively, for example, the substrate may be moved at a μm level with the mask fixed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display device and its driving method
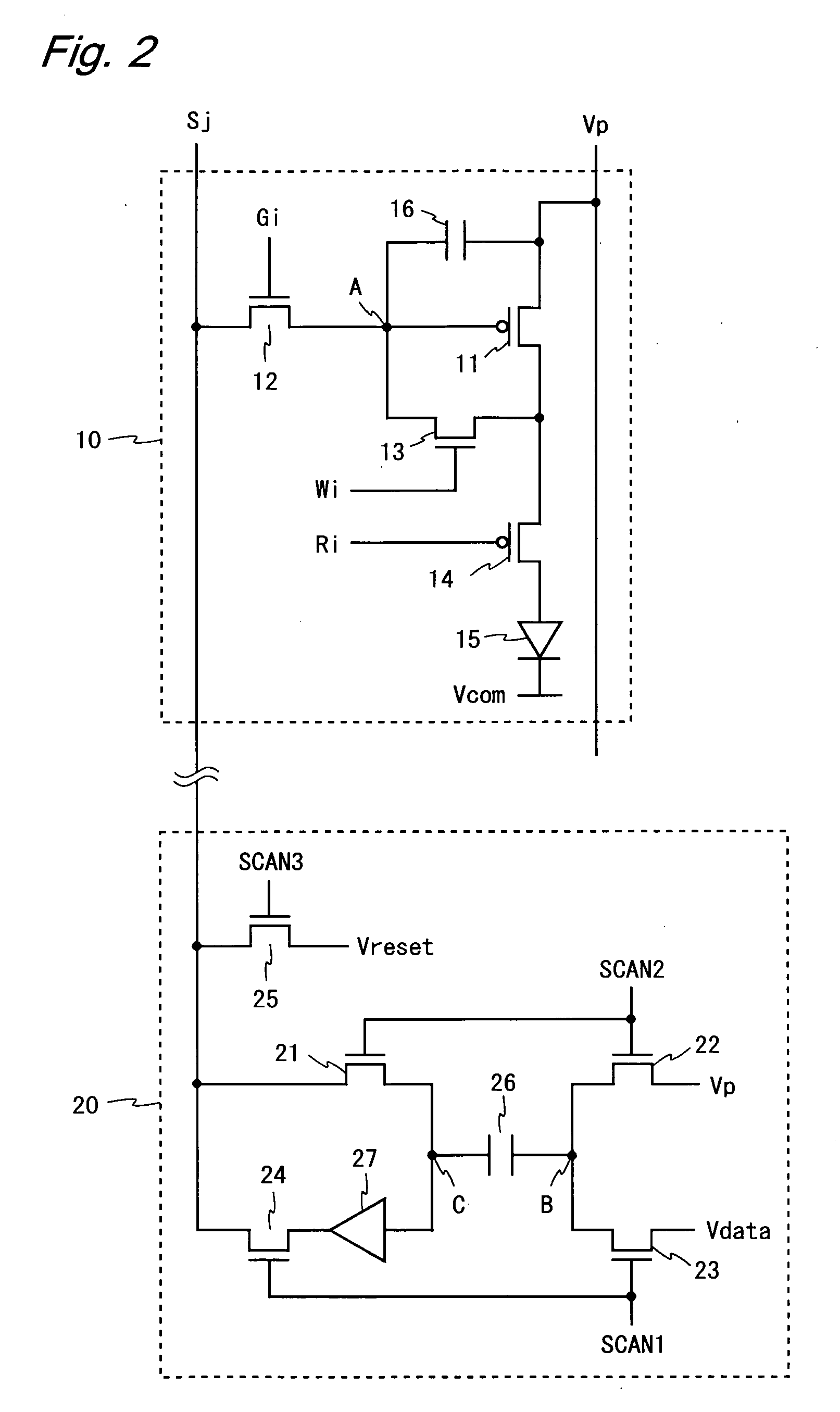
ActiveUS20100045646A1Reduce scaleReduce areaCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriver circuitDisplay device
In a pixel circuit 10, TFTs 12 and 13 are turned on while a TFT 14 is turned off, and a voltage (VDD+Vx) which depends on a threshold voltage Vth of a driving TFT 11 is read onto a data line Sj. Moreover, switches 21 and 22 in a source driver circuit are turned on, and a voltage Vx is held at a capacitor 26. Next, the TFT 13 is turned off, states of switches 21 to 24 are switched, and a voltage (Vdata+Vx) is applied to the data line Sj. Further, the TFT 12 is turned off while the TFT 14 is turned on. An amount of an electric current flowing through an organic EL element 15 after the turn-on of the TFT 14 is determined from the voltage (Vdata+Vx) of a gate terminal of the driving TFT 11. Thus, it is possible to efficiently utilize an amplitude of a data voltage and compensate variations in threshold voltage of the driving TFT 11 with high accuracy, without increasing a scale of the pixel circuit 10.
Owner:SHARP KK
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20100140613A1Improve efficiencyReduce the ratioSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsSemiconductorOxide semiconductor
A semiconductor device includes an oxide semiconductor layer provided over a substrate having an insulating surface; a gate insulating film covering the oxide semiconductor layer; a first conductive layer and a second conductive layer laminated in this order over the gate insulating film; an insulating film covering the oxide semiconductor layer and a gate wiring including a gate electrode (the first and second conductive layers); and a third conductive layer and a fourth conductive layer laminated in this order over the insulating film and electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor layer. The gate electrode is formed using the first conductive layer. The gate wiring is formed using the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer. A source electrode is formed using the third conductive layer. A source wiring is formed using the third conductive layer and the fourth conductive layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device, display device and electronic device equipped with the semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070035340A1Reduce power consumptionAvoid flowImpedence convertorsElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention provides a semiconductor device which can prevent a current from flowing into a display element at a signal writing operation, without increasing power consumption and without changing a potential of a power supply for supplying a current to a load in each row. When a predetermined current is supplied to a transistor to set a gate-source voltage of the transistor, a potential of a gate terminal of the transistor is adjusted so as to prevent a current from flowing into a load which is connected to a source terminal of the transistor. Thus, a potential of a wire connected to the gate terminal of the transistor is made different from that of a wire connected to a drain terminal of the transistor. At that time, an operation of a transistor is shifted so as to allow a large amount of current to flow, and influences by intersection capacitance parasitic to a wire or the like or wire resistance are hardly caused, and a set operation is conducted quickly.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
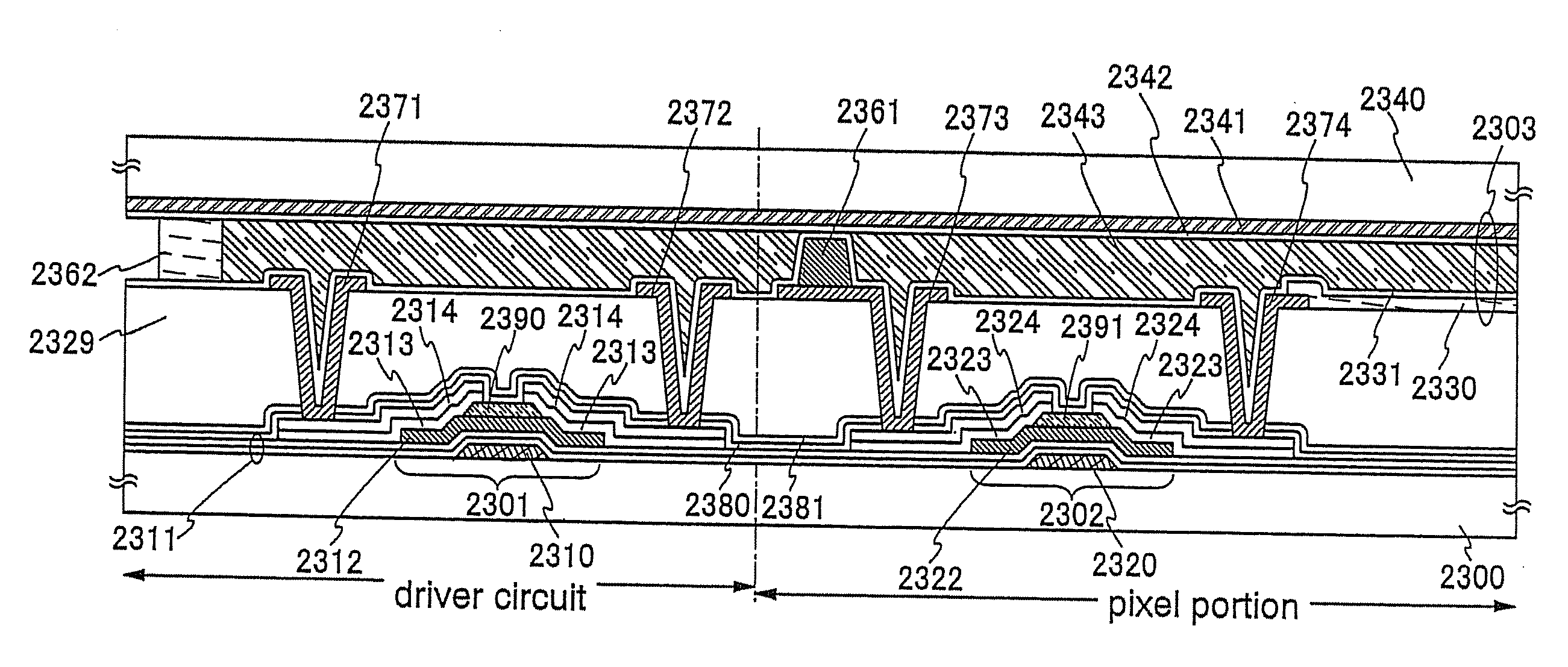
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110006302A1Easily brokenIncrease opening ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceMoisture
It is an object to manufacture and provide a highly reliable display device including a thin film transistor with a high aperture ratio which has stable electric characteristics. In a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device having a thin film transistor in which a semiconductor layer including a channel formation region is formed using an oxide semiconductor film, a heat treatment for reducing moisture and the like which are impurities and for improving the purity of the oxide semiconductor film (a heat treatment for dehydration or dehydrogenation) is performed. Further, an aperture ratio is improved by forming a gate electrode layer, a source electrode layer, and a drain electrode layer using conductive films having light transmitting properties.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
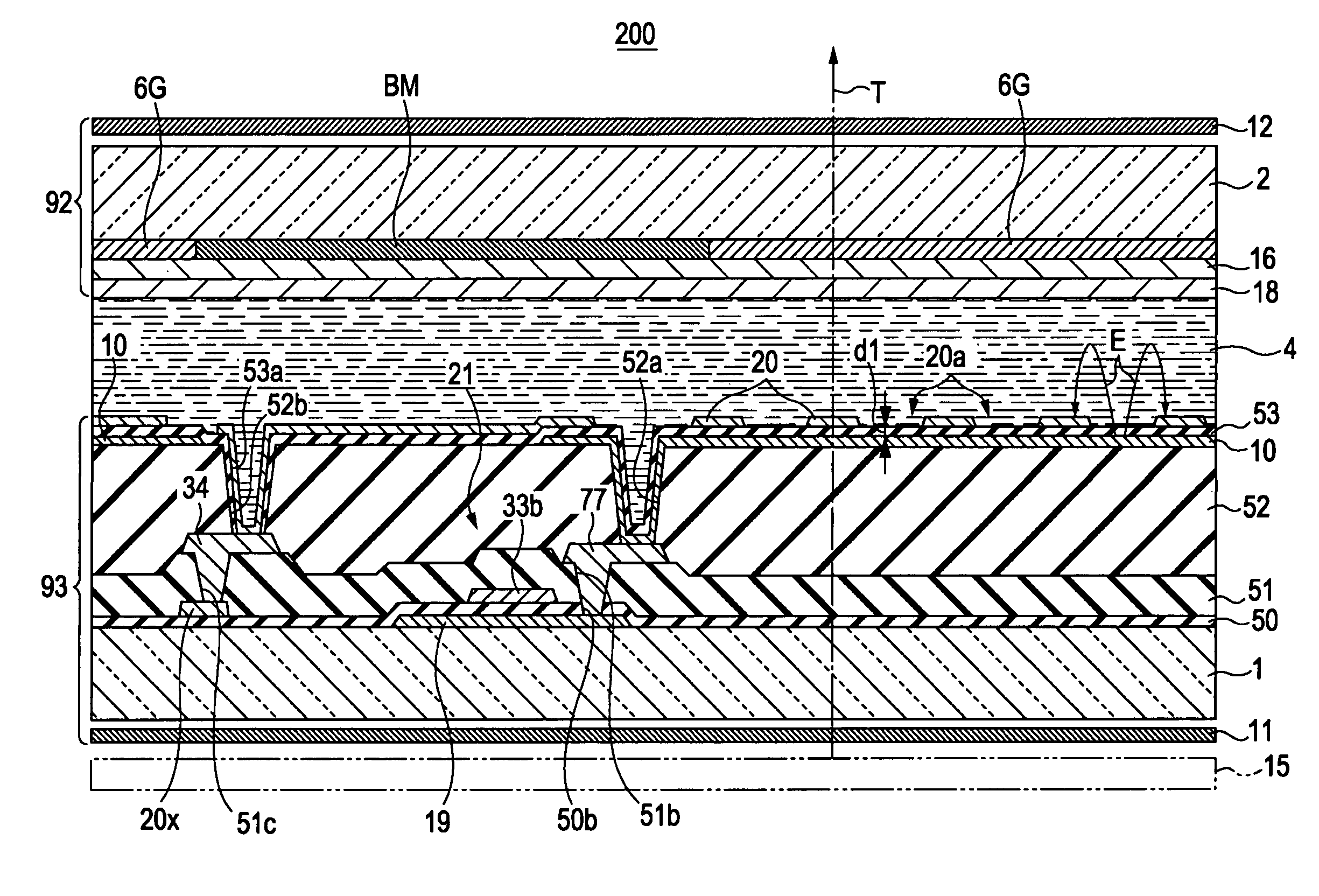
Liquid crystal apparatus and electronic device
A liquid crystal apparatus includes a substrate that retains liquid crystal, a switching element provided in the substrate, a first insulating film above the switching element, a first electrode above the first insulating film, a second insulating film above the first electrode, and a second electrode above the second insulating film. The second electrode has a plurality of slits and produces an electric field between the first electrode and the second electrode via each of the slits.
Owner:EPSON IMAGING DEVICES CORP
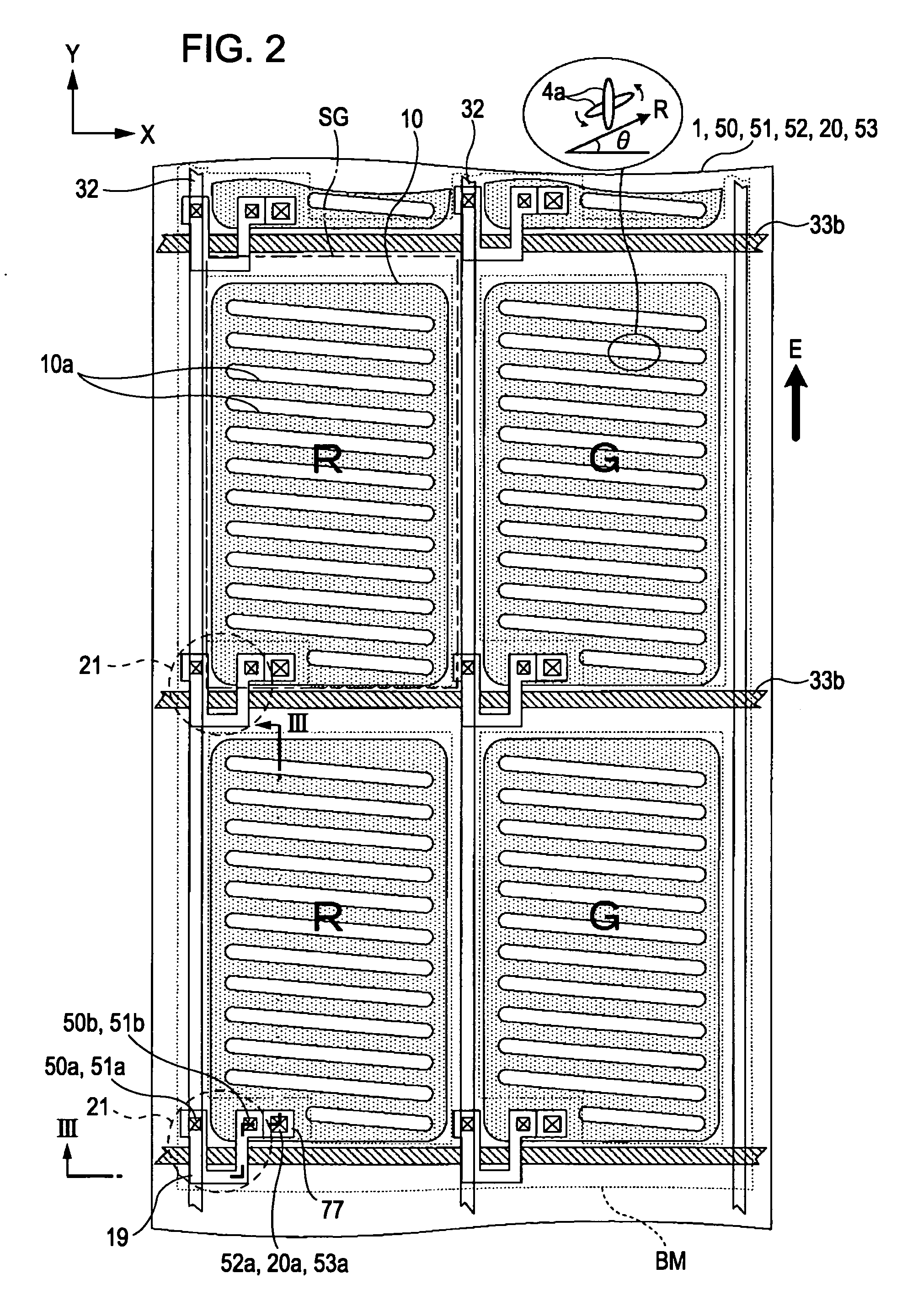
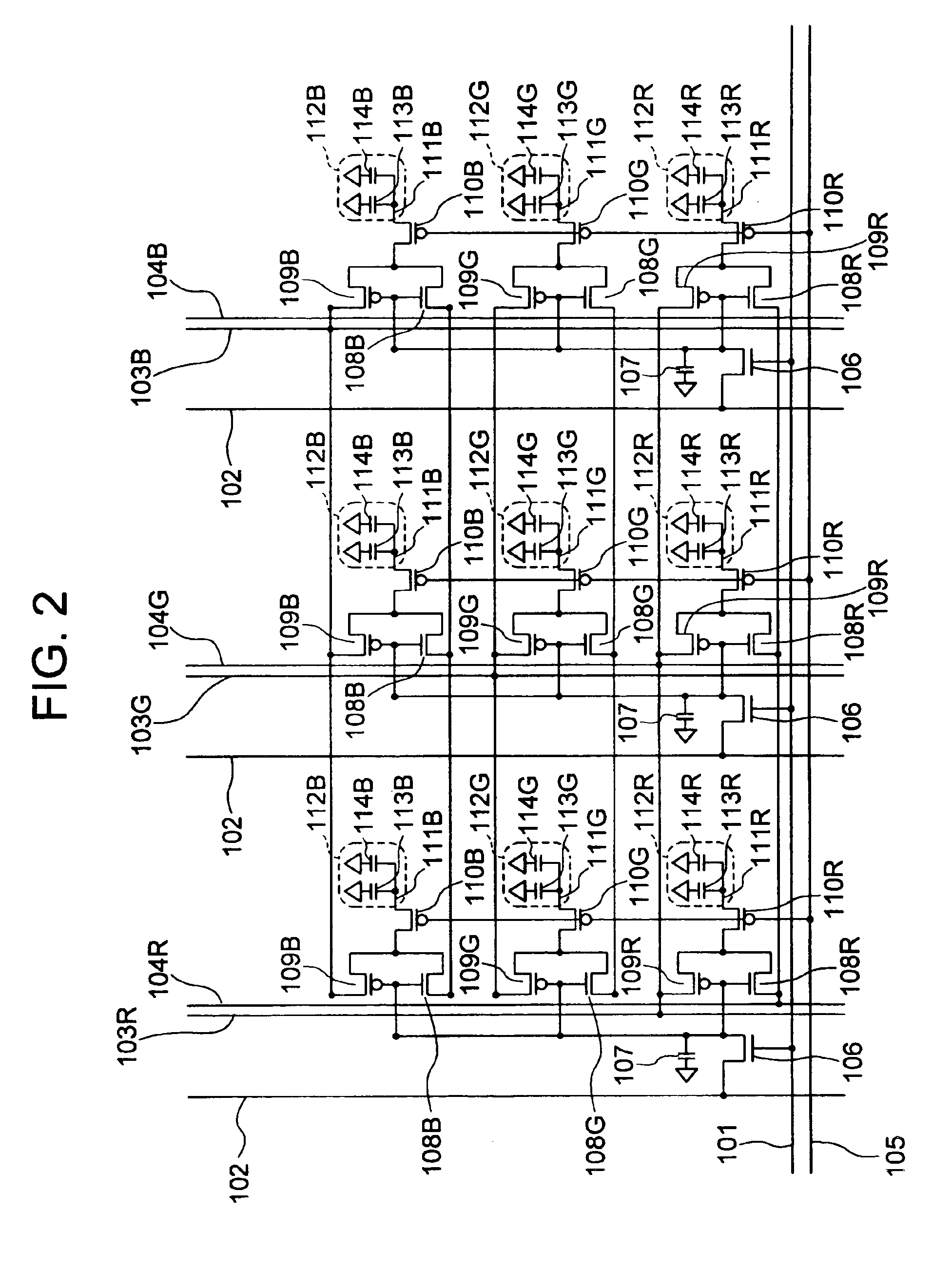
Array substrate comprising semiconductor contact layers having same outline as signal lines
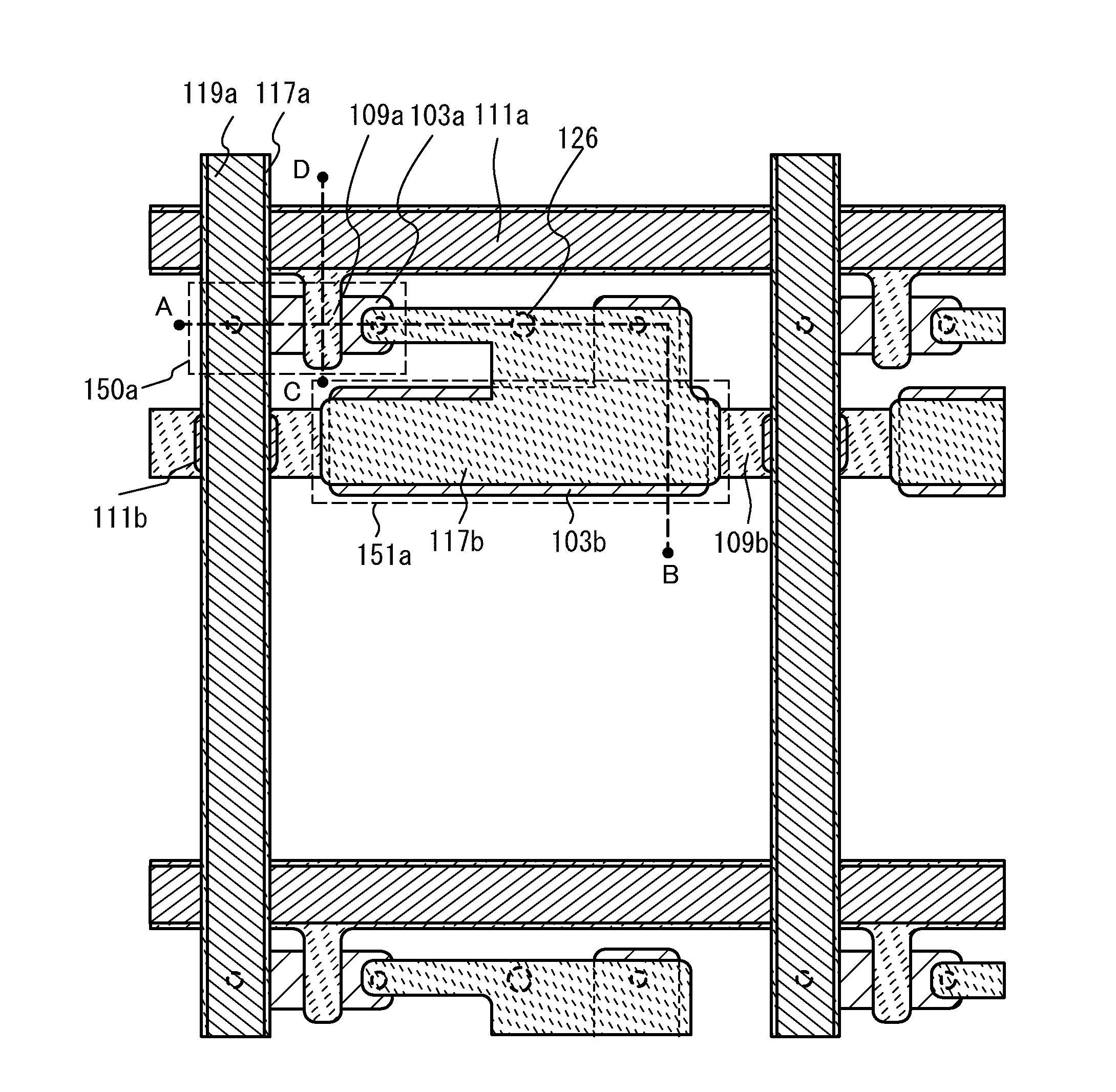
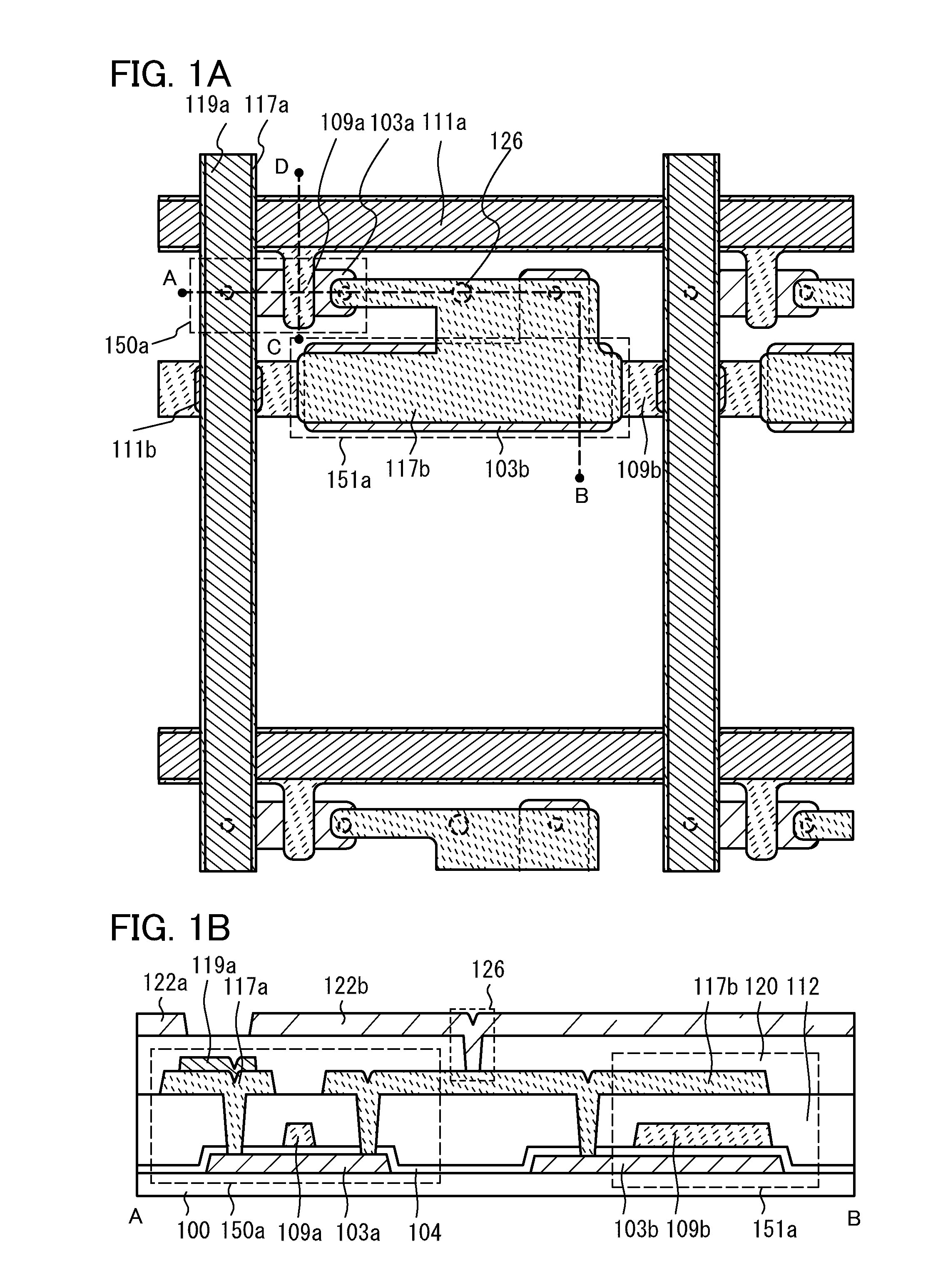
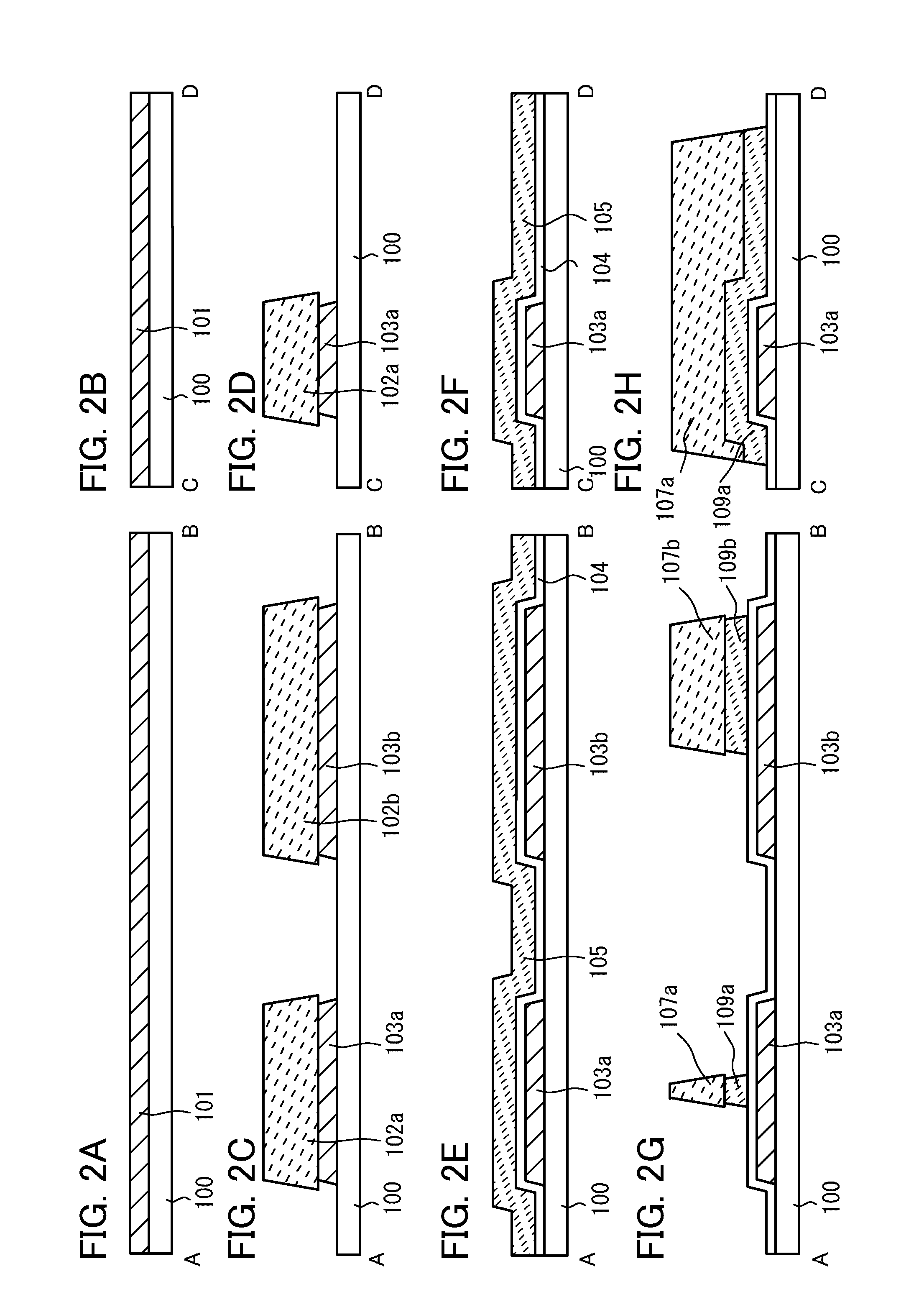
InactiveUS6078366AImprove eliminationReduce the ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact layerAperture ratio
An array substrate includes plural scanning lines (111); a thin film transistor (112) having a first dielectric film (115), (117), a semiconductor film (120) thereon, and a source electrode (126b) electrically coupled to the semiconductor film (120) and a drain electrode (126a); a signal line (110) as taken out of the drain electrode (126a) to extend at substantially right angles to the scanning lines (111); and a pixel electrode (131) electrically connected to the source electrode (126b), wherein the pixel electrode (131) is electrically connected to the source electrode (126b) through a second dielectric film (127) as disposed on at least the signal line (110) while the pixel electrode (131) overlaps an elongate region (113) from its neighboring scanning line (111) through the first and second dielectric films (115), (117), (127). With such an arrangement, an appropriate storage capacitor can be formed by causing the scanning lines and pixel electrode to overlap each other without having to decrease the manufacturing yield while enabling achievement of high aperture ratio.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY CENTRAL CO LTD
Pixel driving circuit for active organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display and driving method thereof
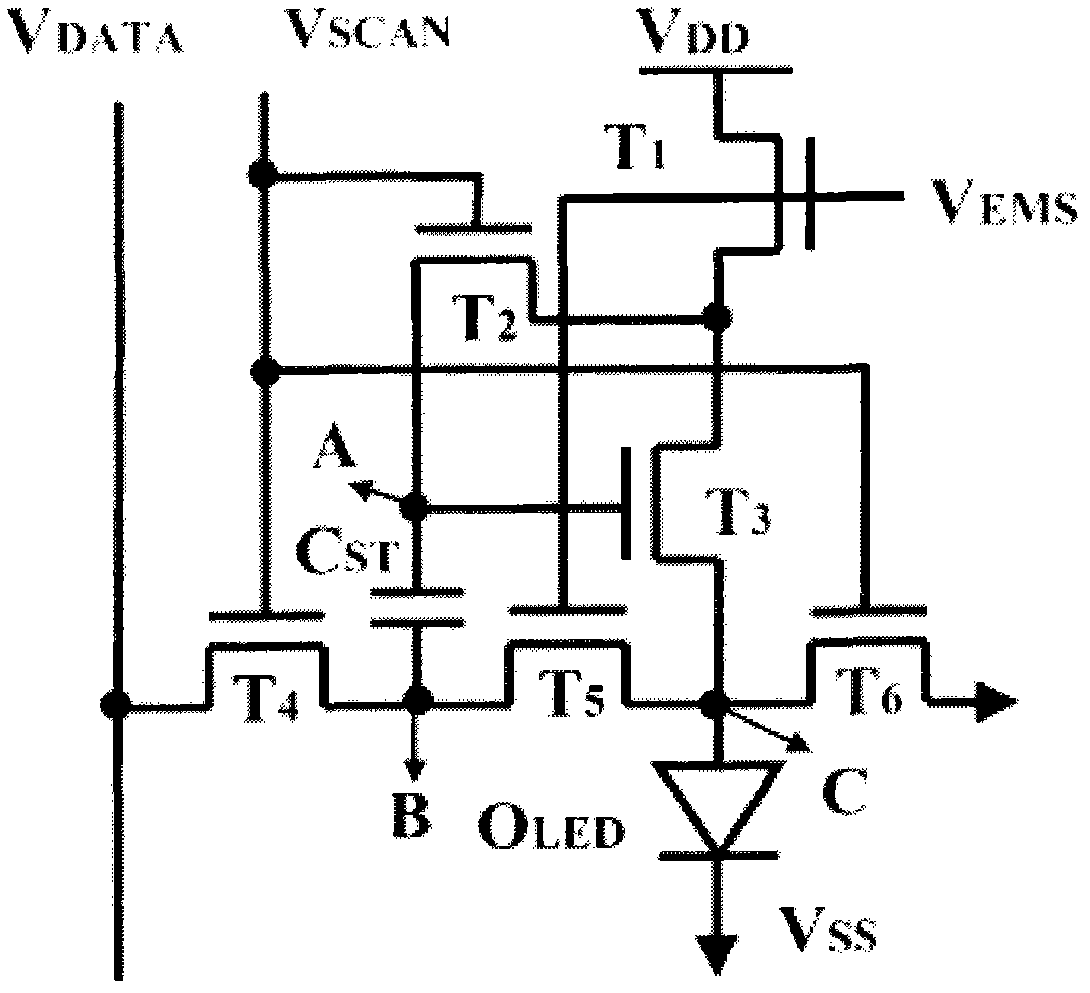
InactiveCN101986378ACompensation for brightness non-uniformityIncrease contrastStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceDisplay device
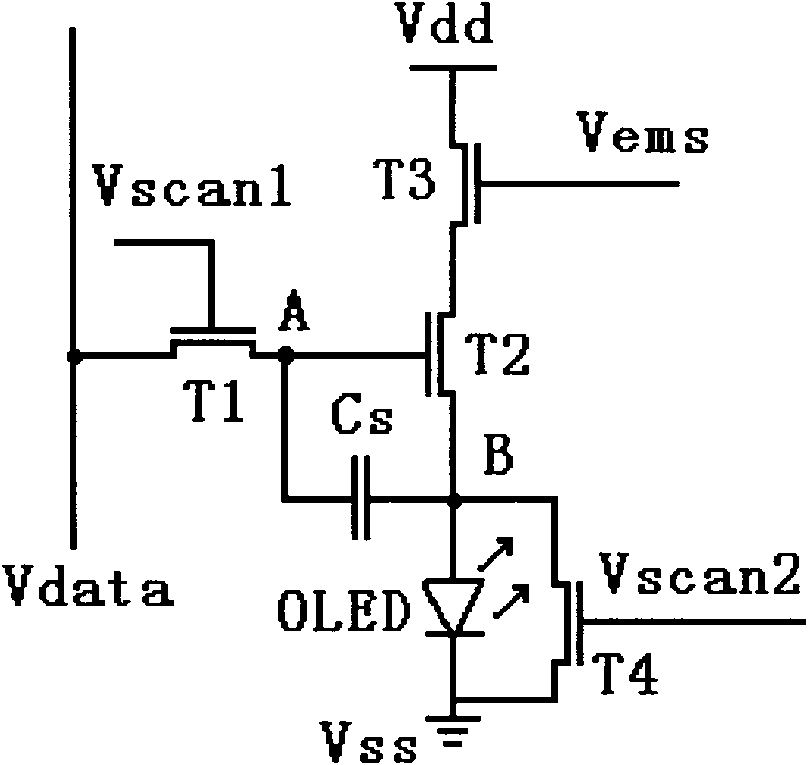
The invention discloses a pixel driving circuit for an active organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display and a driving method thereof. The pixel driving circuit comprises a driving transistor, three switch transistors, a storage capacitor and an OLED, wherein the drain electrode of a first transistor is connected with a data line; the grid electrode of the first transistor is connected with a first scanning control line; the source electrode of the first transistor is connected with the end A of the storage capacitor; the drain electrode of a second transistor is connected with the source electrode of a third transistor; the grid electrode of the second transistor is connected with the end A of the storage capacitor; the source electrode of the second transistor is connected with the drain electrode of a fourth transistor and the end B of the storage capacitor and is grounded through the OLED; the drain electrode of the third transistor is connected with a power wire; the grid electrode of the third transistor is connected with a light-emitting control line; the grid electrode of the fourth transistor is connected with a second scanning control line; and the source electrode of the fourth transistor is grounded. The pixel driving circuit of the invention can effectively compensate the non-uniformity of threshold voltages of the transistors and the degradation of a starting voltage of the OLED so as to realize uniform display screen brightness of the OLED and high contrast ratio.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
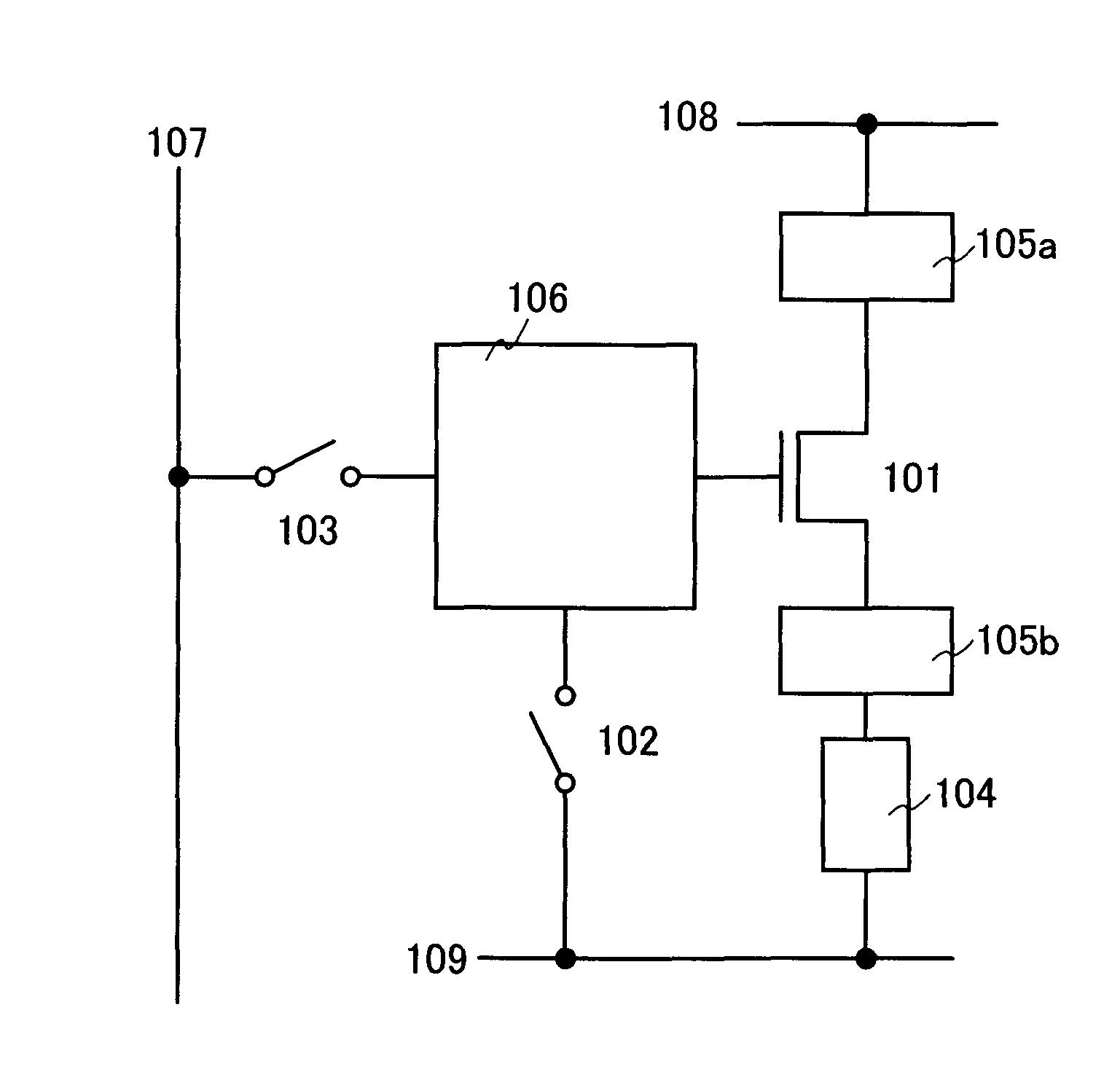
Precision Surgical System
InactiveUS20070173870A2Extended speed rangeIncrease speedEye surgeryEndoscopic cutting instrumentsNoise generationElectricity
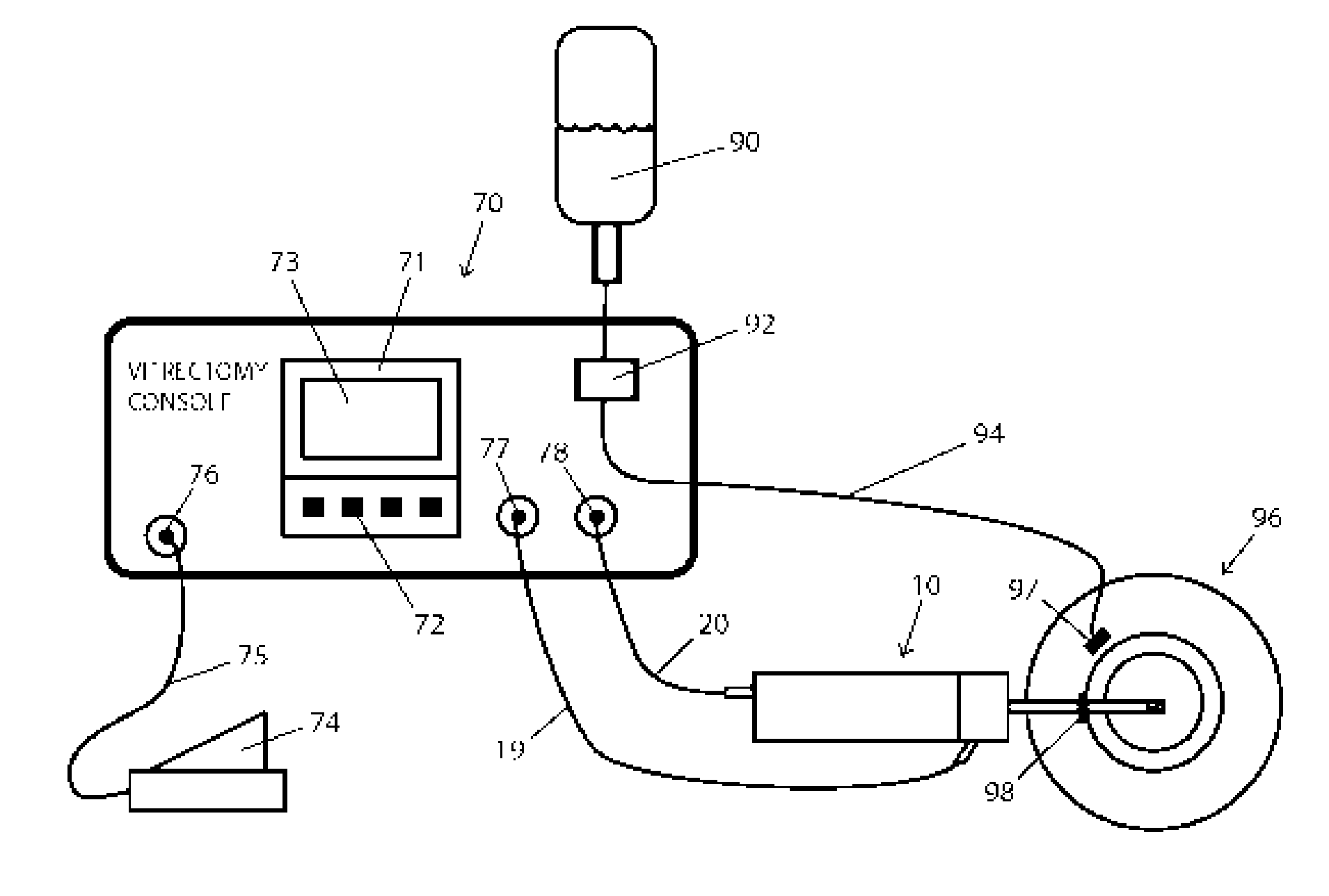
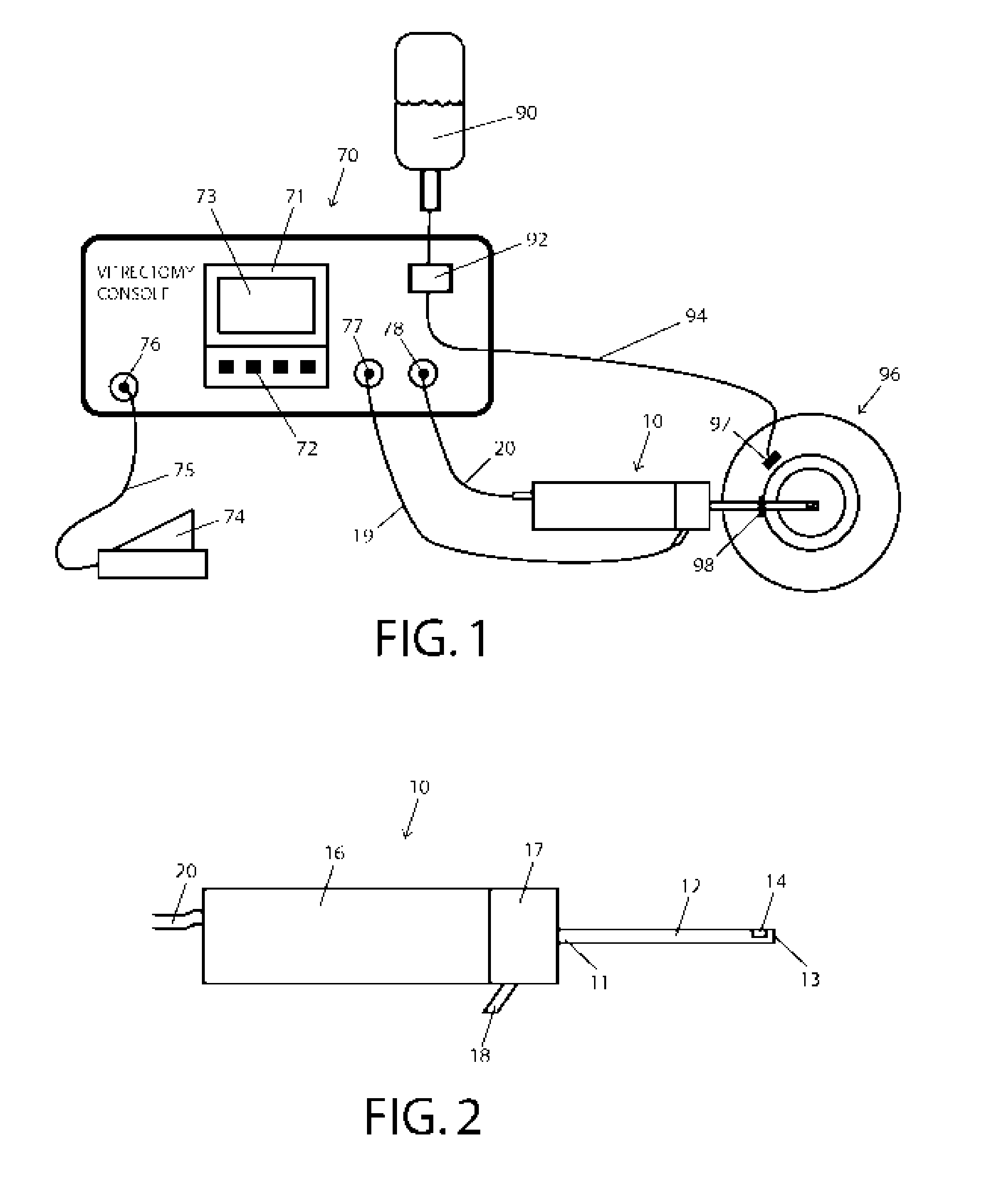
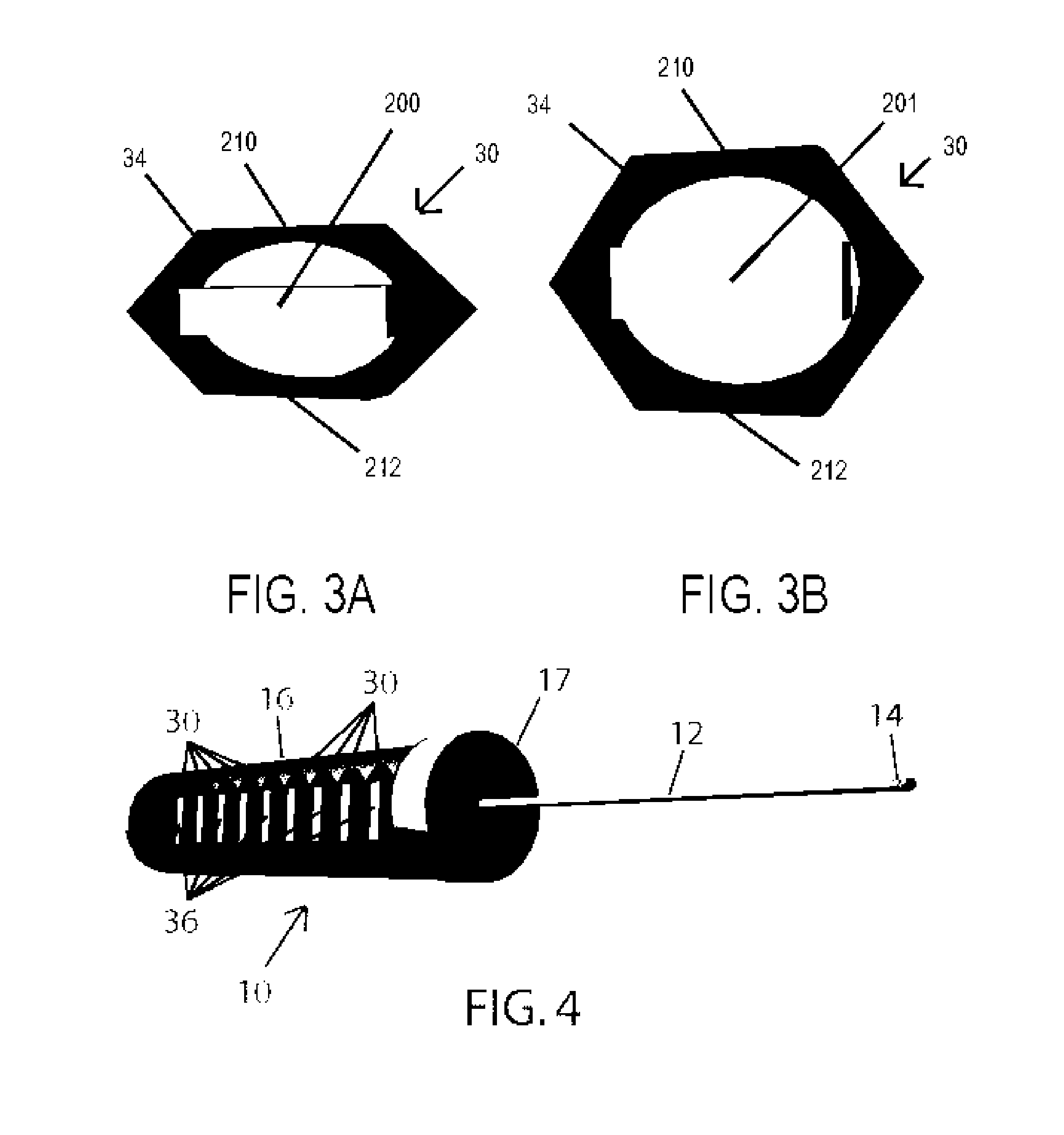
A high-speed surgical handpiece (10) suitable for vitreoretinal surgery having a cutter (42) and actuators (36). The cutter (42) is a guillotine-type cutter activated by an array of leveraged piezoelectric actuators (30) that receive a driving signal from a driving controller. The controller can have control and display units with a plurality of input mechanisms receiving input from a user who selects a desired cutting rate and frequency for the cutter. The control unit produces a piezoelectric actuator output signal based on the inputs received. Fast cutting rates with reduced duty cycle as well as a proportional mode of operation are available, allowing slow controlled cutting action, for example proportional to depression of a foot-pedal (74). Low degrees of vibration and noise generation are produced.
Owner:DR ZACHARIAS JAIME
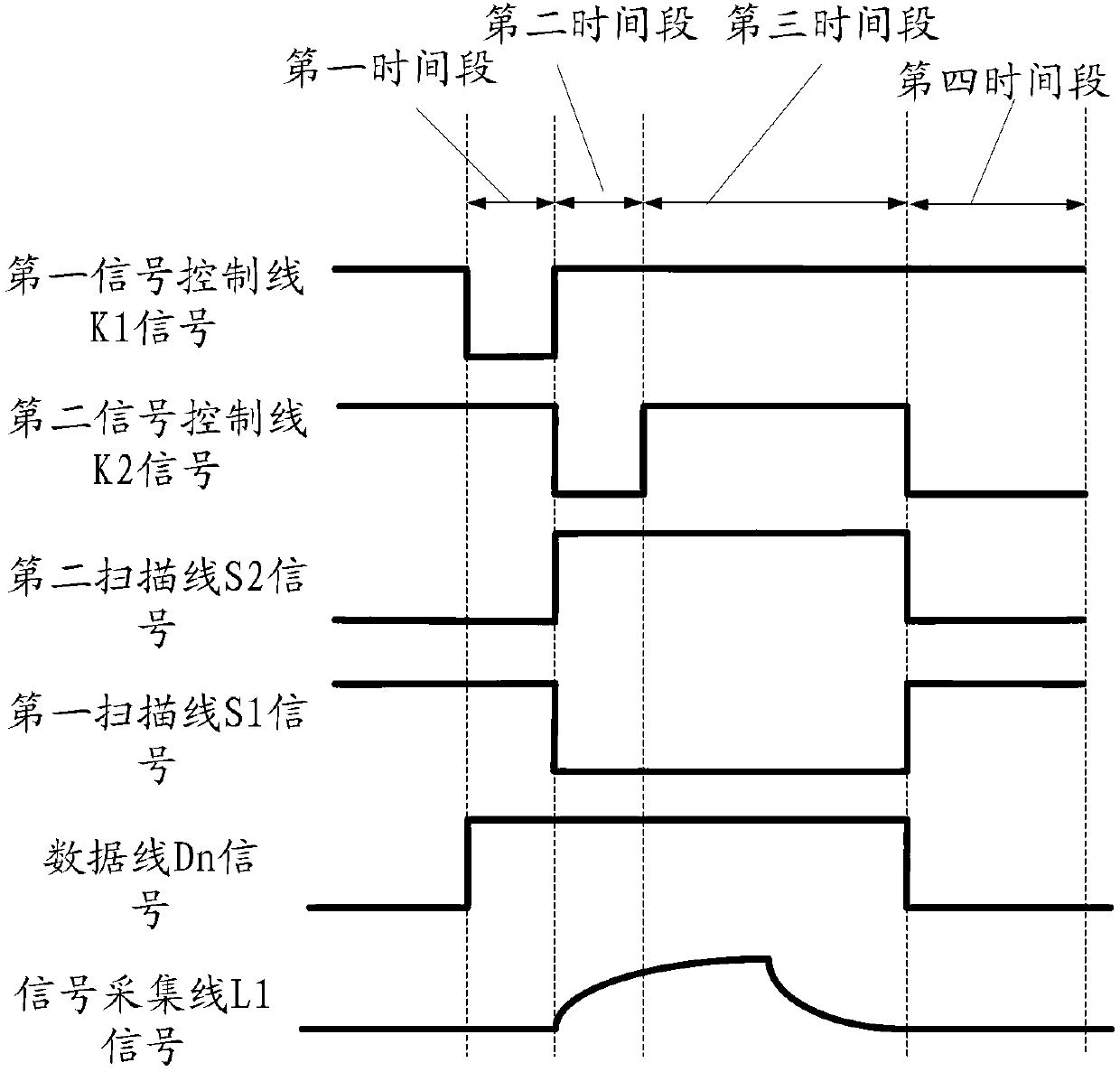
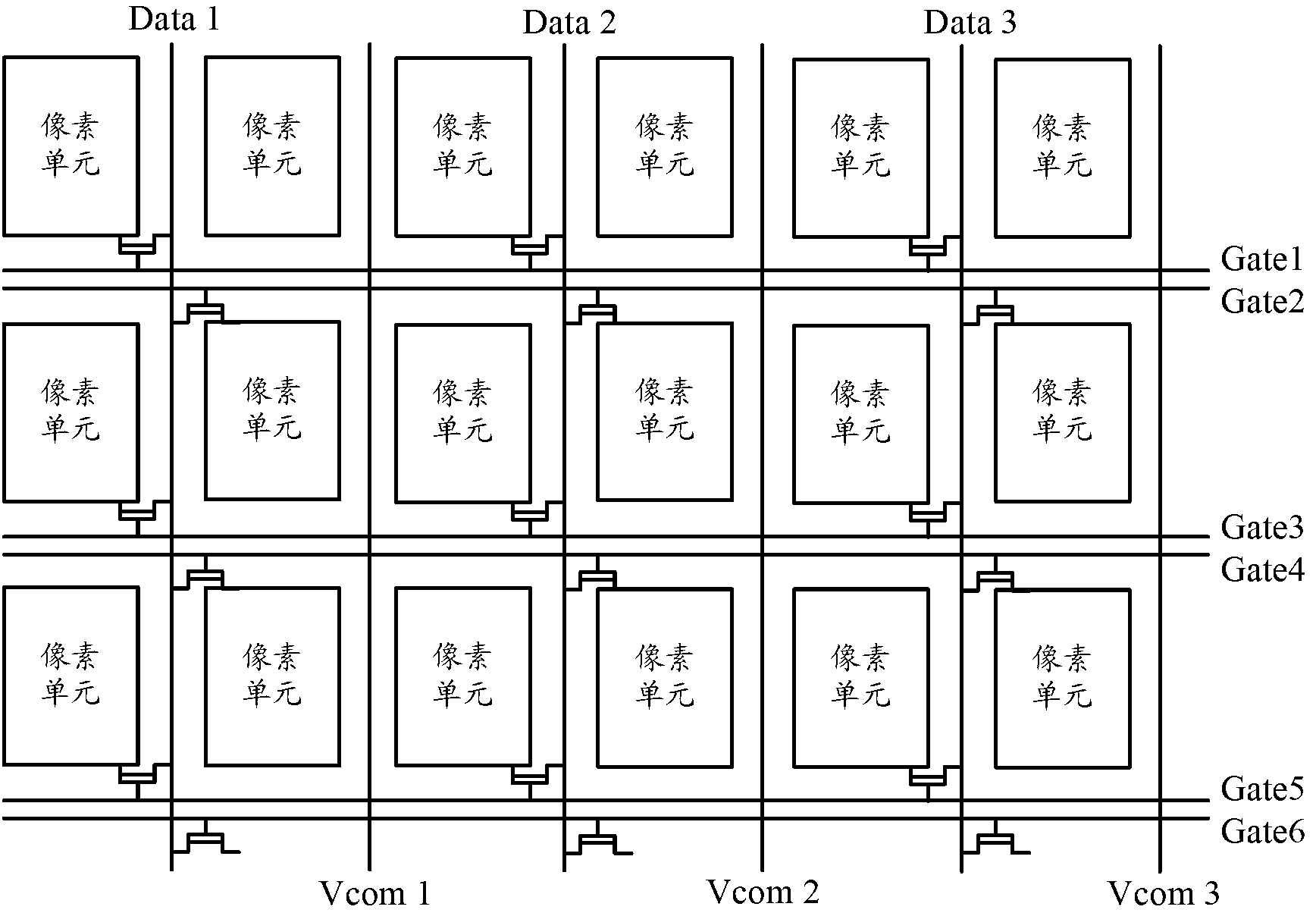
Touch control display circuit structure and driving method, array substrate and display device thereof
ActiveCN103135846AReduce process technologyLow costStatic indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingControl lineData lines
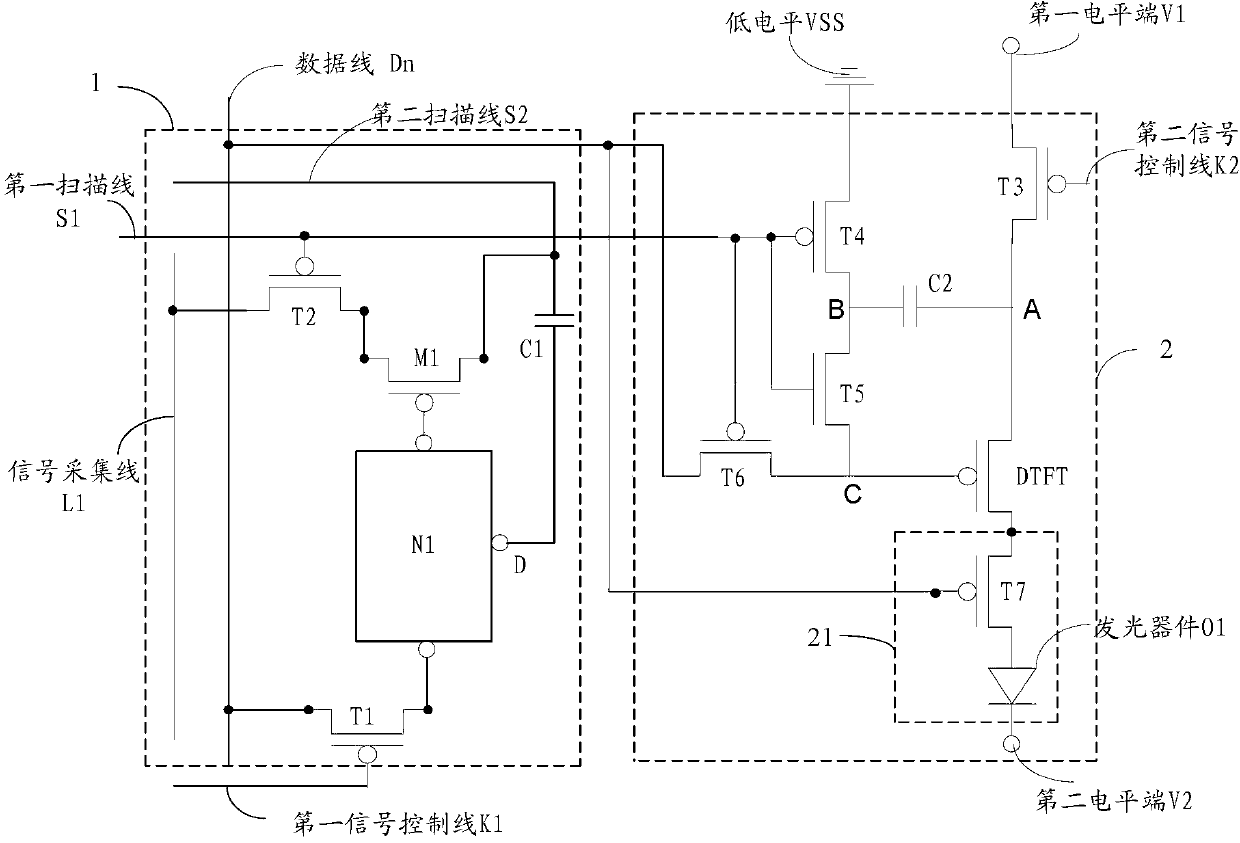
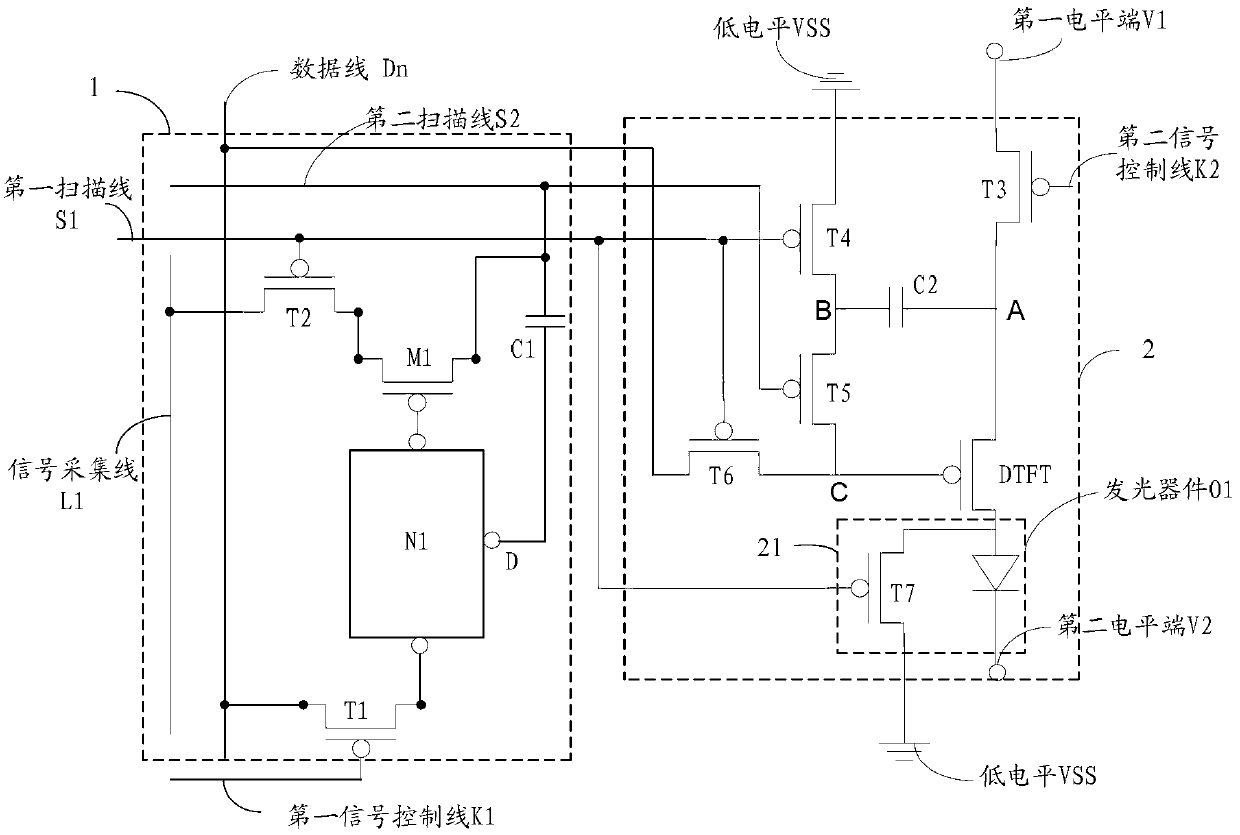
The invention discloses a touch control display circuit structure and a driving method, an array substrate and a display device thereof, and relates to the field of displayer manufacture. The touch control display circuit structure can reduce manufacturing processes during touch display product producing process, improves aperture opening ratio, and improves product additional value. The touch control display circuit structure comprises a touch control unit, a display unit, a data line, a first scanning line, a second scanning line, a signal collection line, a first signal control line, another one data line, another one first scanning line, another one second scanning line and another one signal control line, wherein the data line, the first scanning line, the second scanning line, the signal collection line and the first signal control line are connected with the touch control unit, and the another one data line, the another one first scanning line, the another one second scanning line and the another one signal control line are connected with the display unit. The touch control display circuit structure is applied to displayer manufacture.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
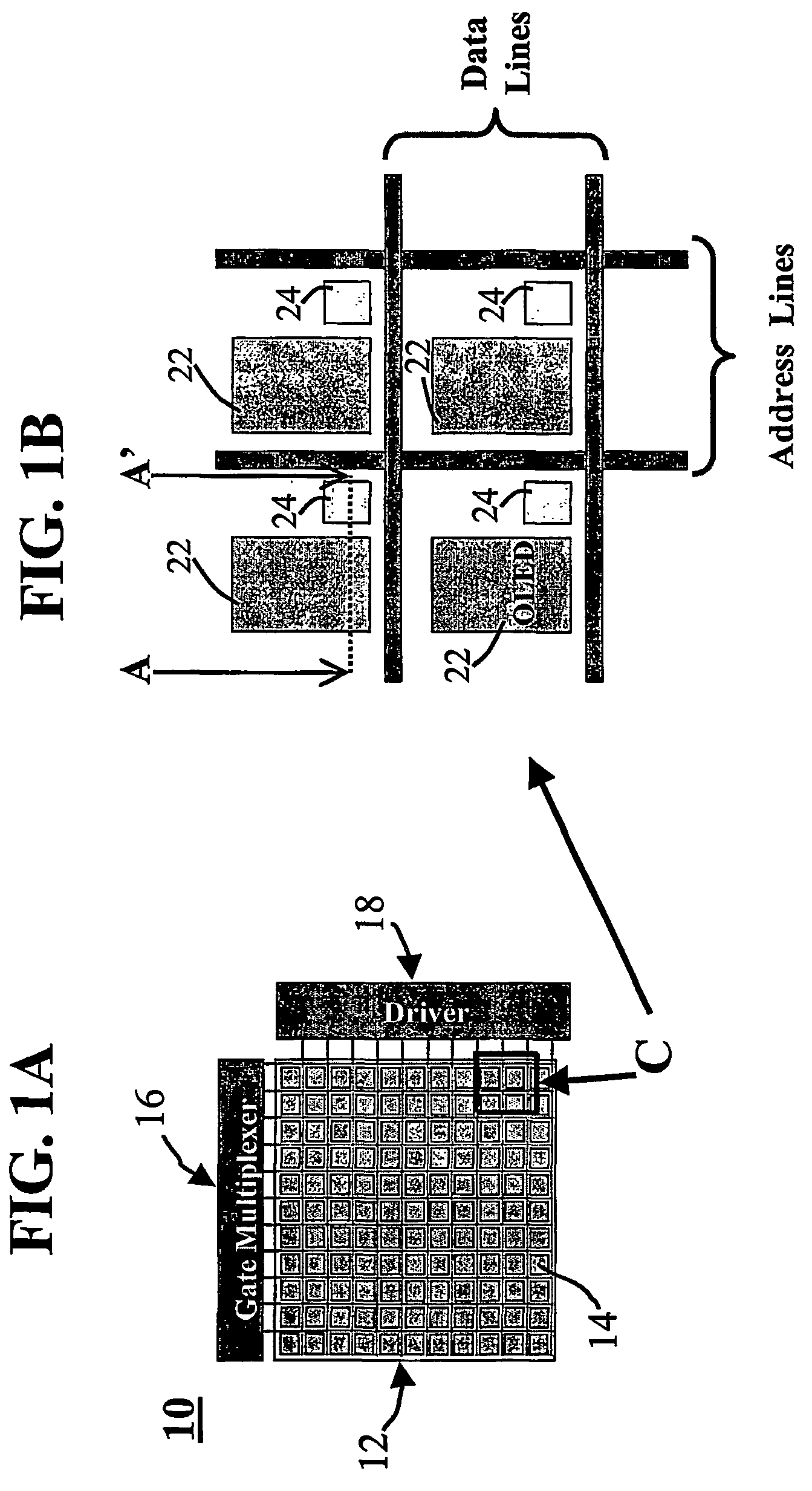
Display device for decompressing compressed image data received
InactiveUS6909442B2Improve transmission performanceImprove data performanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceImage signal
A display device including a plurality of blocks of pixels each of which includes a red subpixel, a green subpixel, and a blue subpixel, each of the blocks including pixels in a form of a matrix having N rows and M columns includes a first active element shared among three subpixels of each pixel and a second active element connected to a second active element formed in each subpixel connected to the first active element. Ma gradation voltage lines (Ma is an integer; M≧Ma≧2) respectively of red, green, and blue subpixels in a direction of the column are commonly connected. The display device directly displays a compressed image signal without developing the image signal into a bit map in which each subpixel has gradation information.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
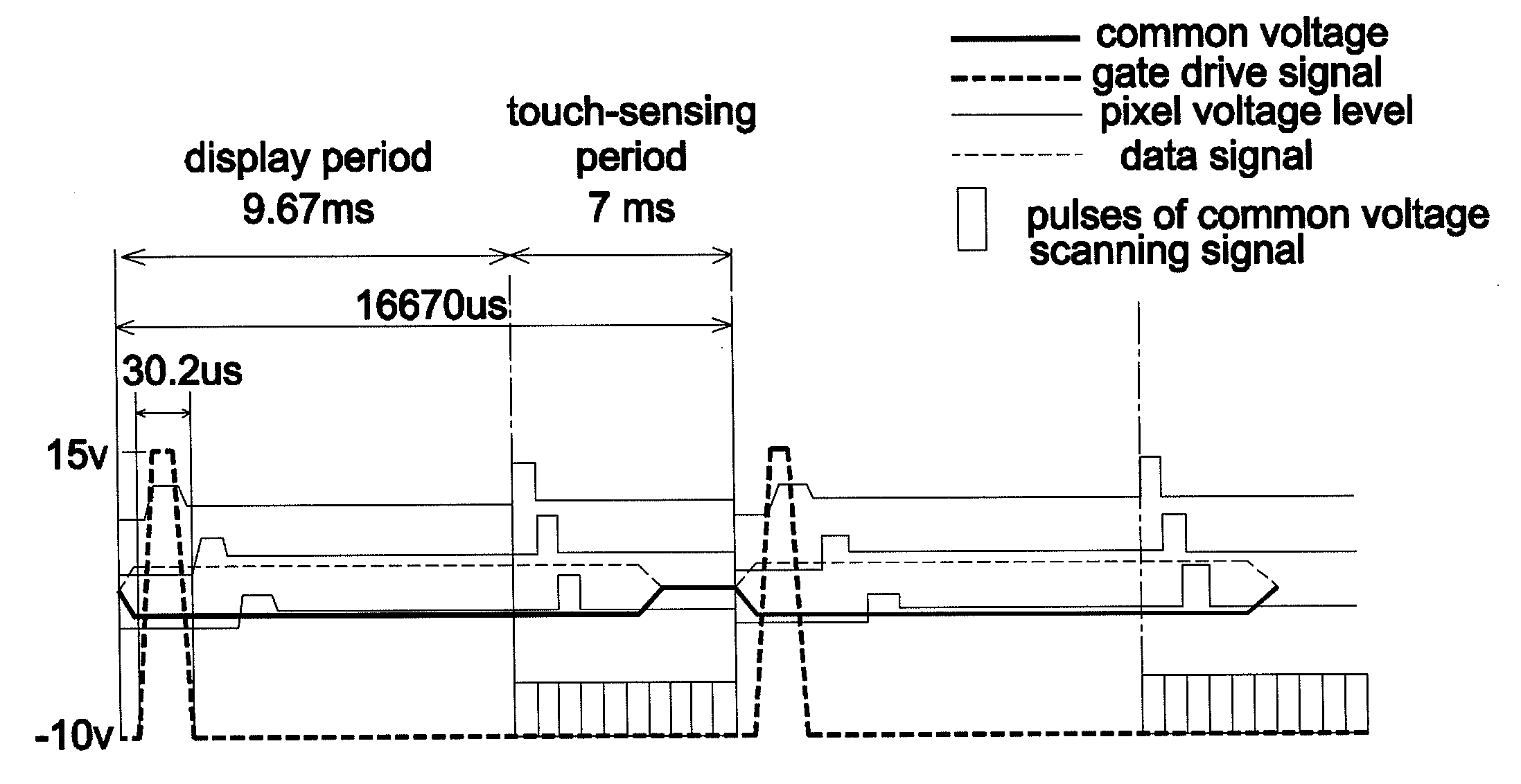
Touch-sensing display device
InactiveUS20120206403A1Increase opening ratioReduce signal interferenceNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceTouch Senses
A touch-sensitive display device includes a color filter substrate, an array substrate, a liquid crystal layer, and a touch-sensing structure. The touch-sensing structure is disposed on the color filter substrate and includes at least one first sensing series and at least one second sensing series overlapped with and spaced apart from the first sensing series. During a touch-sensing operation, the first sensing series receives a common voltage scanning signal, and the second sensing series receives a sensing signal to sense coupling capacitance formed as a result of a touch action when the common voltage scanning signal drives the first sensing series.
Owner:WINTEK CORP
Display device
InactiveUS20070120785A1Reduce the ratioIncrease the number ofStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesProduction rateElectricity
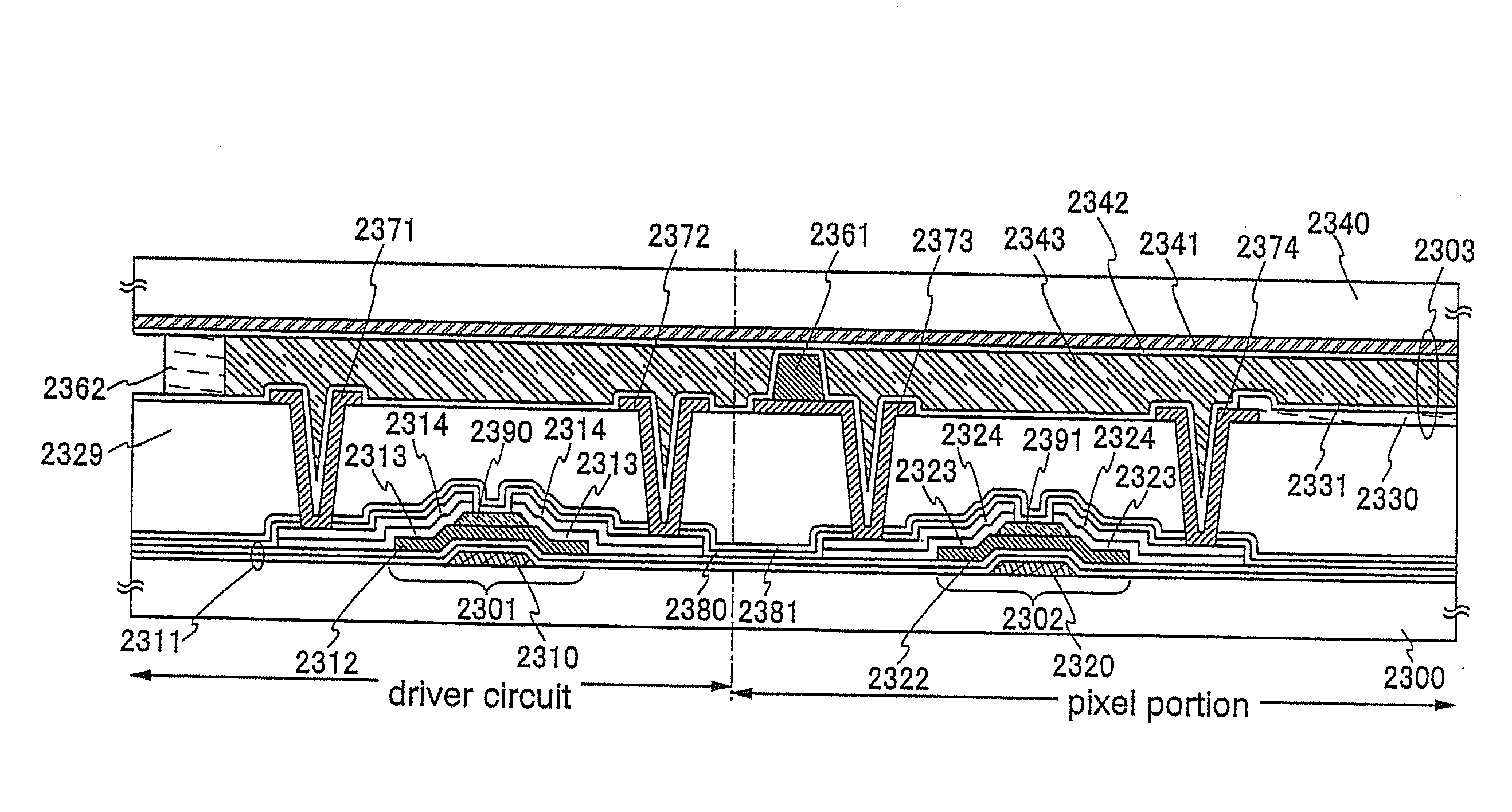
To provide a high-performance and highly reliable display device with a high aperture ratio, including light-emitting elements, and a manufacturing method thereof, and a technique for manufacturing such a display device at a low cost with high productivity. A compensating circuit, a light-emitting element, a switch, and a transistor are included, in which one terminal of the switch is electrically connected to the compensating circuit, a gate of the transistor is electrically connected to the compensating circuit, one of a source and a drain of the transistor is electrically connected to a first electrode of the light-emitting element, the other of the source and the drain of the transistor is maintained at a certain potential, and a second electrode of the light-emitting element and the other terminal of the switch are electrically connected to the same wire.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Solid imaging element and manufacturing method thereof
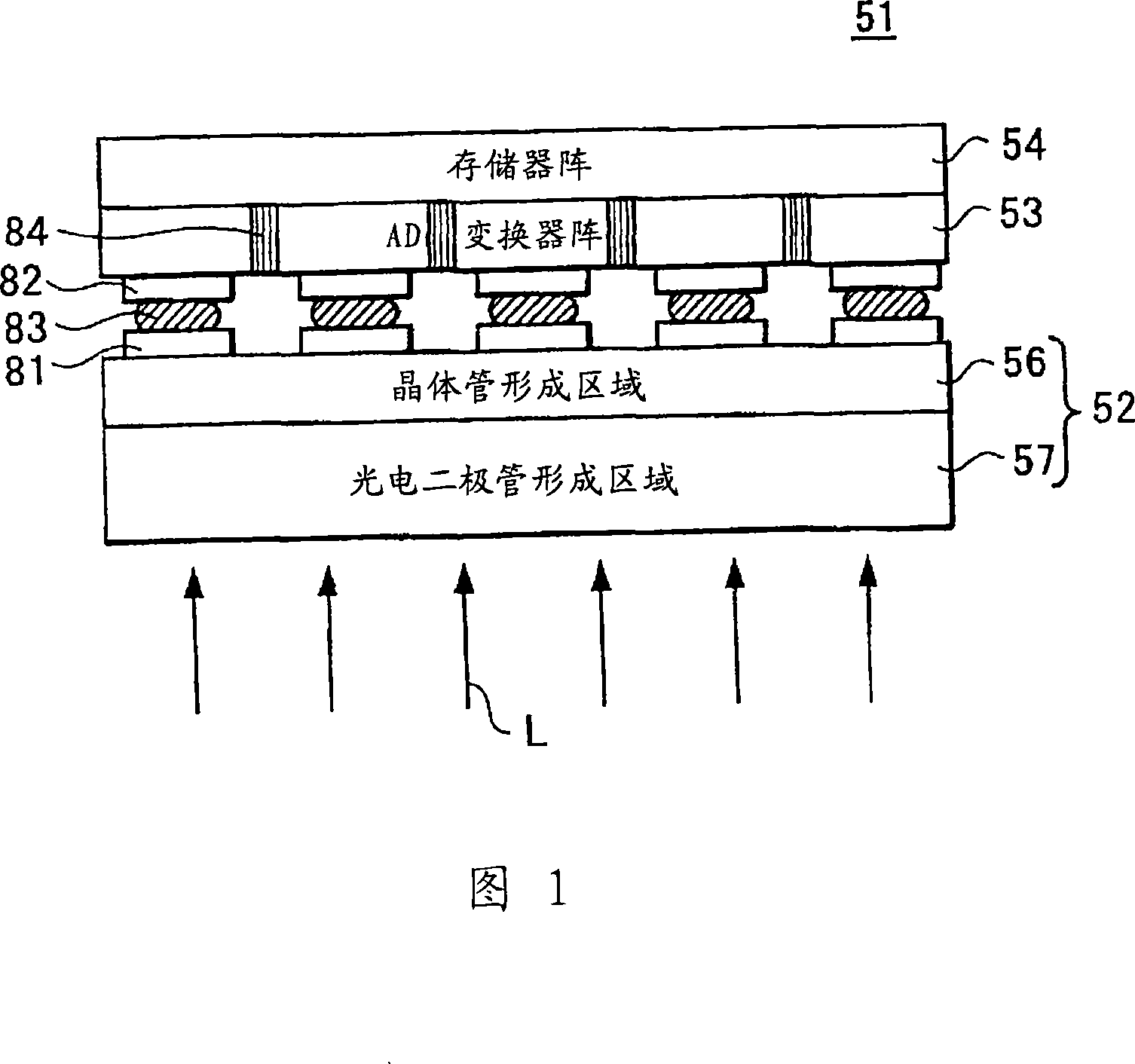
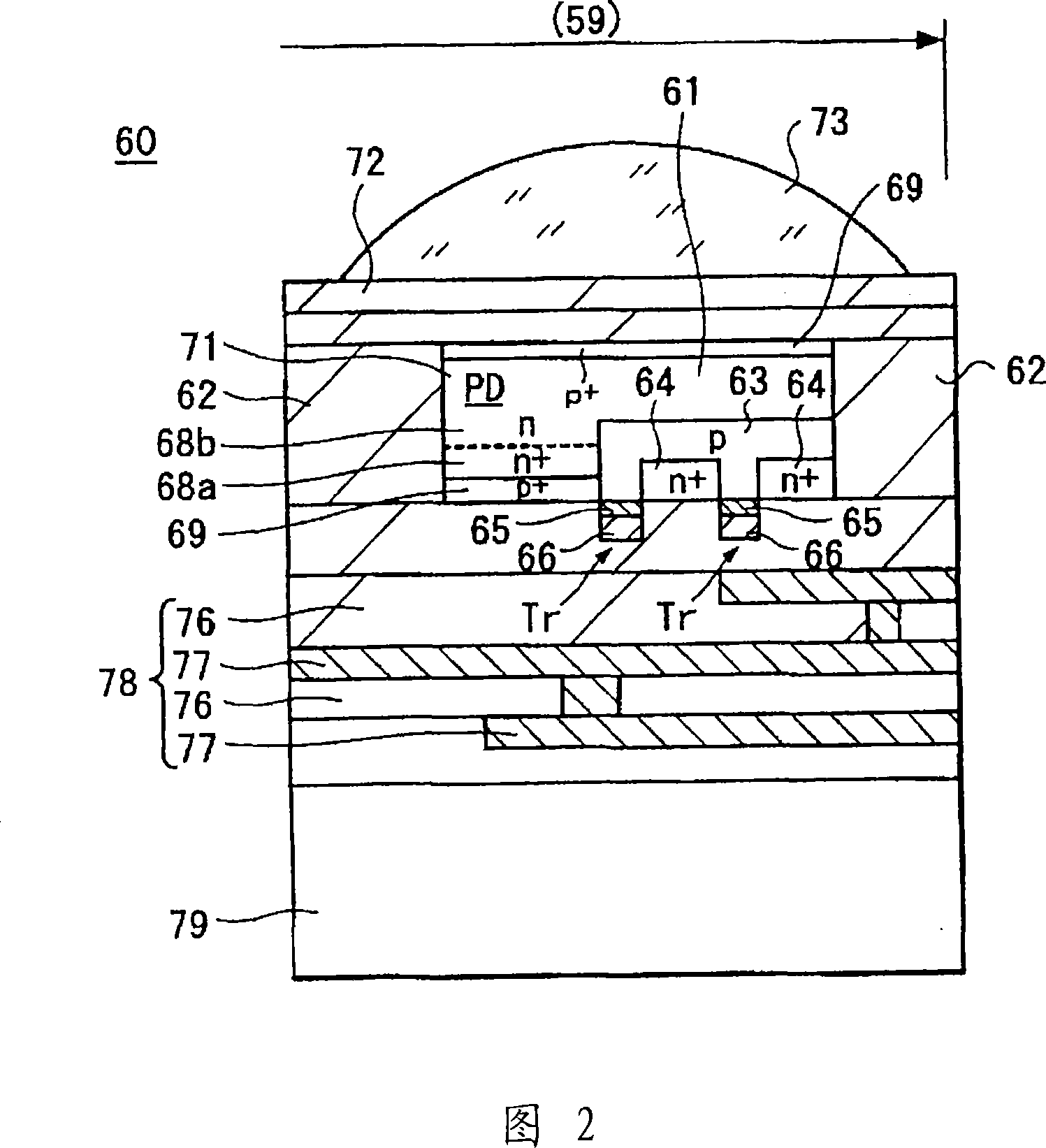
InactiveCN101228631AImprove photoelectricityIncrease profitTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSImage sensor
A CMOS type semiconductor image sensor module wherein a pixel aperture ratio is improved, chip use efficiency is improved and furthermore, simultaneous shutter operation by all the pixels is made possible, and a method for manufacturing such semiconductor image sensor module are provided. The semiconductor image sensor module is provided by stacking a first semiconductor chip, which has an image sensor wherein a plurality of pixels composed of a photoelectric conversion element and a transistor are arranged, and a second semiconductor chip, which has an A / D converter array. Preferably, the semiconductor image sensor module is provided by stacking a third semiconductor chip having a memory element array. Furthermore, the semiconductor image sensor module is provided by stacking the first semiconductor chip having the image sensor and a fourth semiconductor chip having an analog nonvolatile memory array.
Owner:SONY CORP
Synchronous and asynchronous bi-gate thin film transistor (TFT)-organic light emitting diode (OLED) pixel drive circuit and drive method thereof
The invention discloses a synchronous and asynchronous bi-gate thin film transistor (TFT)-organic light emitting diode (OLED) pixel drive circuit and a drive method thereof. The pixel drive circuit comprises a first transistor, a second transistor, a storage capacitor and a light emitting diode, wherein, the first transistor is a synchronous bi-gate TFT and the second transistor is an asynchronous bi-gate TFT. A synchronous bi-gate structure and an asynchronous bi-gate structure are introduced in on the basis of the traditional 2T1C circuit and a precharging voltage and a feedback line are added to the pixel drive circuit. Thus, the maintaining effect to data voltage at a non-gating stage of the storage capacitor is effectively improved. In addition, the threshold voltage compensation of the driving transistors is effectively realized. Thus, the uniformity and the stability of the luminance of displays are ensured. Compared with most pixel drive circuits which are adopted to realize data maintaining and threshold compensation, the transistors, the capacitors and the control lines are saved and the circuit structure is greatly simplified. Thus, the opening ratio and the resolution ratio are increased and the cost is reduced.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20070085475A1Reduce the number of stepsAvoid defectsDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesEvaporationMiniaturization
As a result of miniaturization of a pixel region associated with an improvement in definition and an increase in a substrate size associated with an increase in area, defects due to precision, bending, and the like of a mask used at the time of evaporation have become issues. A partition including portions with different thicknesses over a pixel electrode (also referred to as a first electrode) in a display region and in the vicinity of a pixel electrode layer is formed, without increasing the number of steps, by using a photomask or a reticle provided with an auxiliary pattern having a light intensity reduction function made of a diffraction grating pattern or a semi-transmissive film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
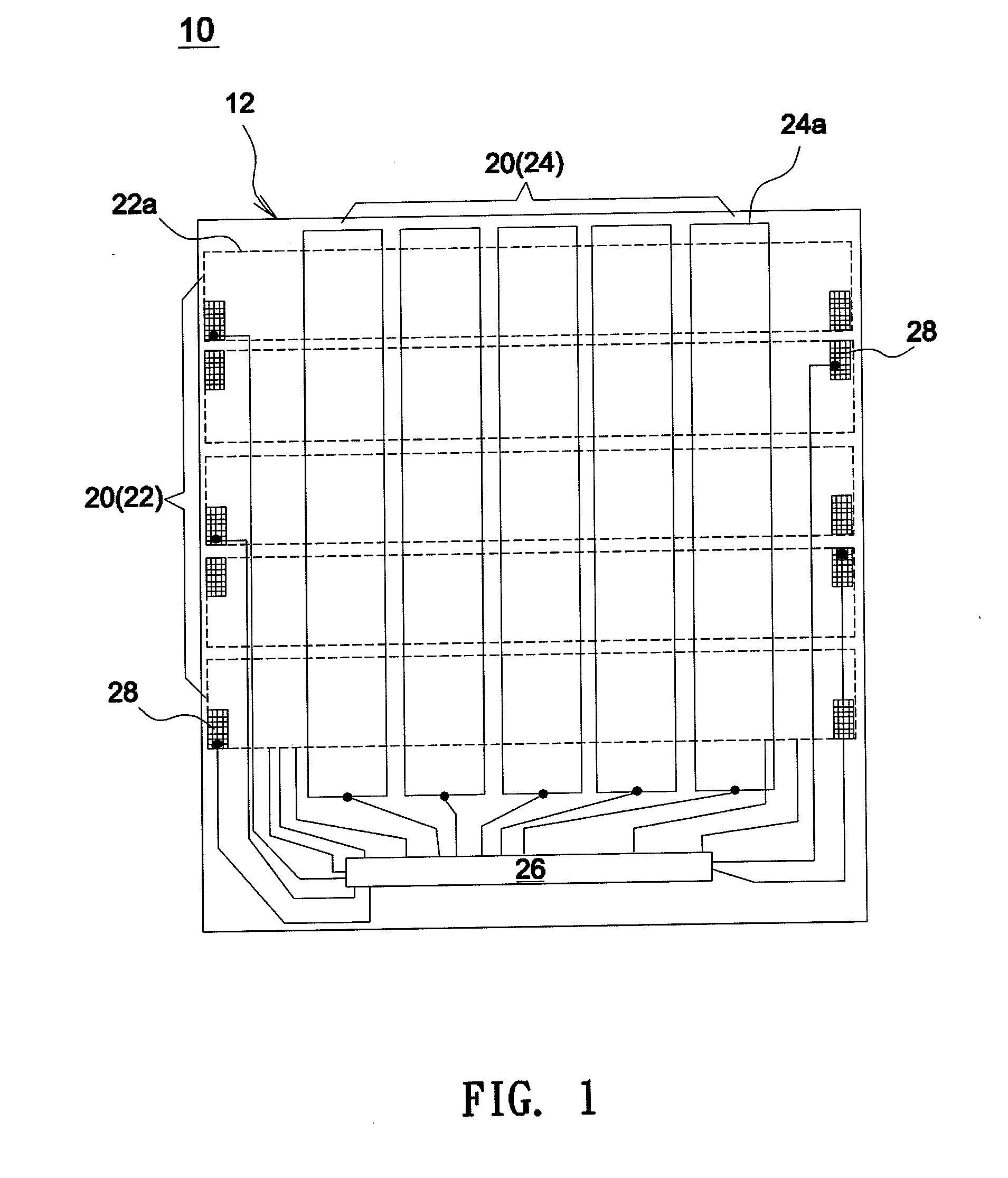
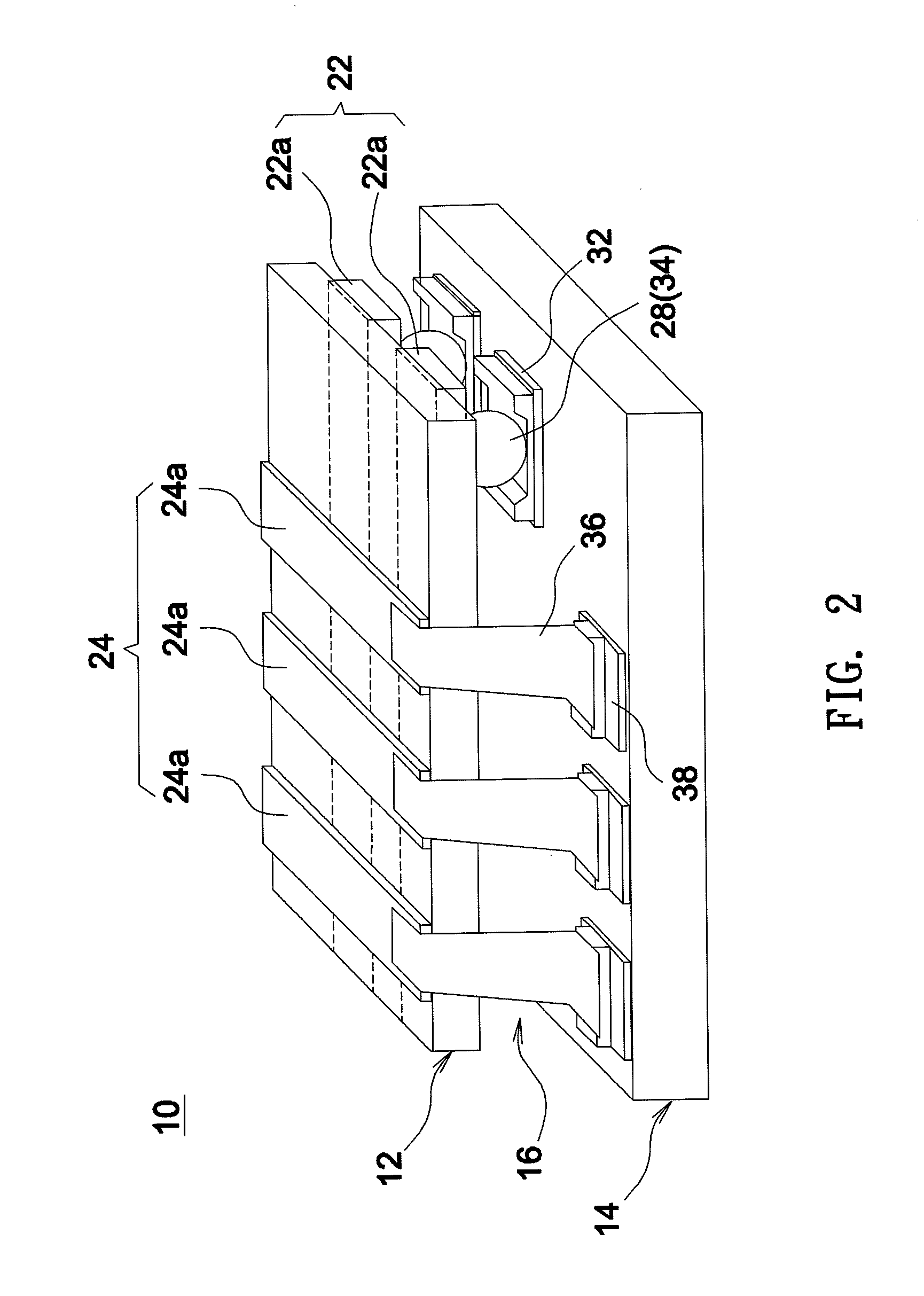
Capacitance-type embedded touch screen, driving method thereof and display device
ActiveCN102937852AIncrease opening ratioSave spaceStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsCapacitanceLarge aperture
The invention discloses a capacitance-type embedded touch screen, a driving method thereof and a display device. A touch sensing electrode extending along the line direction of pixel units is arranged on a color film substrate; on a TFT (Thin Film Transistor) array substrate, a double grid structure is adopted, i.e., two grid signal lines are arranged between the adjacent pixel units, and every two adjacent rows of pixel units form a group of pixel unit rows and share a data signal line between the two rows of pixel units, thus saving the position of part of data signal lines. Therefore, touch driving electrodes for realizing a touch function can be arranged on the saved positions of the grid signal lines, i.e., the touch driving electrodes are arranged at clearances between adjacent pixel units, so that not only can the precision of required by touch be ensured, but also less aperture area of the pixel units is occupied, and the relatively large aperture ratio of the touch screen can be ensured.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS7098086B2Improve the display effectIncrease opening ratioTransistorTelevision system detailsDielectricEngineering
To provide a liquid crystal display device having high quality display by obtaining a high aperture ratio while securing a sufficient storage capacitor (Cs), and at the same time, by dispersing a load (a pixel writing-in electric current) of a capacitor wiring in a timely manner to effectively reduce the load. A scanning line is formed on a different layer from a gate electrode and the capacitor wiring is arranged so as to be parallel with a signal line. Each pixel is connected to the individually independent capacitor wiring via a dielectric. Therefore, variations in the electric potential of the capacitor wiring caused by a writing-in electric current of a neighboring pixel can be avoided, whereby obtaining satisfactory display images.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organic lighting element color pixel array mode and its forming method
InactiveCN101051648AIncrease opening ratioReduced Alignment DifficultySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEffect lightLuminescence
A color display panel has an array with a plurality of pixels, each pixel comprises a first sub pixel, a second sub pixel and a third sub pixel, and a red luminescence zone, green luminescence zone and blue luminescence zone. The display panel comprises pixel arrangement of the red luminescence zone, green luminescence zone and blue luminescence zone, which forms a triangle, geometry center of each luminescence zone is positioned at different vertexes of the triangle, such that a side of the triangle substantially is in parallel with on of row direction and column direction, arbitrary luminescence zones bothering with different colors of the row direction are defined to have a distance gap, and arbitrary luminescence zones bothering with different colors of the column direction are defined to have a distance gap, the two gaps distance is substantially or almost equal. The invention can reduce the contraposition difficulty of mask manufacturing technique, besides can increase the opening ratio of the luminescence area of sub pixel, to avoid the color blending circumstance of full color OLED display panel.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20070146566A1Reduce contact resistanceHigh light transmittanceSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsTectorial membraneElectrical resistance and conductance
It is an object to obtain a liquid crystal display device in which a contact defect is reduced, increase in contact resistance is suppressed, and an opening ratio is high. The present invention relates to a liquid crystal display device having a substrate; a thin film transistor provided over the substrate, which includes a gate wiring, a gate insulating film, an island-shaped semiconductor film, a source region, and a drain region; a source wiring which is provided over the substrate and is connected to the source region; a drain electrode which is provided over the substrate and is connected to the drain region; an auxiliary capacitor provided over the substrate; a pixel electrode connected to the drain electrode; and a protective film formed so as to cover the thin film transistor and the source wiring, where the protective film has an opening, and the auxiliary capacitor is formed in the area where the opening is formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Pixel drive circuit of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) display and drive method thereof
InactiveCN101976545AProblems Compensating for Brightness Non-UniformityIncrease opening ratioStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceHemt circuits
The invention discloses a pixel drive circuit of an OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) display and a drive method thereof. The pixel circuit comprises a drive transistor, two switching transistors, a coupling capacitor, a storage capacitor and an OLED, wherein the drain electrode of the first switching transistor is connected with a data line, the grid electrode is connected with a first scanning control line, and the source electrode is connected with the end B of the coupling capacitor; the drain electrode of the second switching transistor is connected with the storage capacitor and the end A of the coupling capacitor, the grid electrode is connected with a second scanning control line, and the source electrode is connected with the drain electrode of the drive transistor and is connected with a power line through the OLED; and the grid electrode of the drive transistor is connected with the storage capacitor and the end A of the coupling capacitor, and the source electrode is grounded. The circuit can be used for effectively compensating the heterogeneity of threshold voltage of a thin film transistor and the degeneration of the cut-in voltage of the OLED to improve the picture brightness homogeneity of the OLED display screen.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com