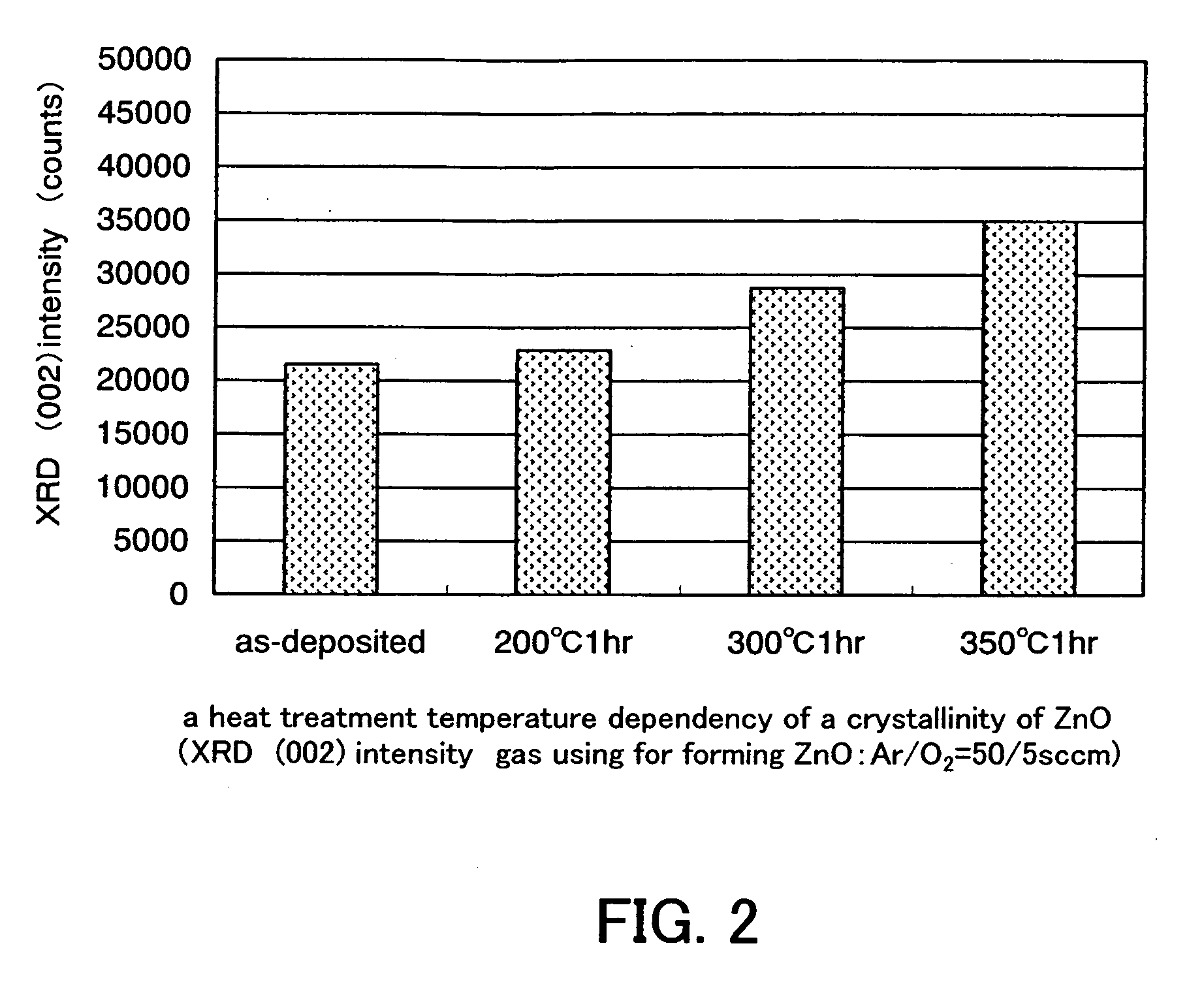
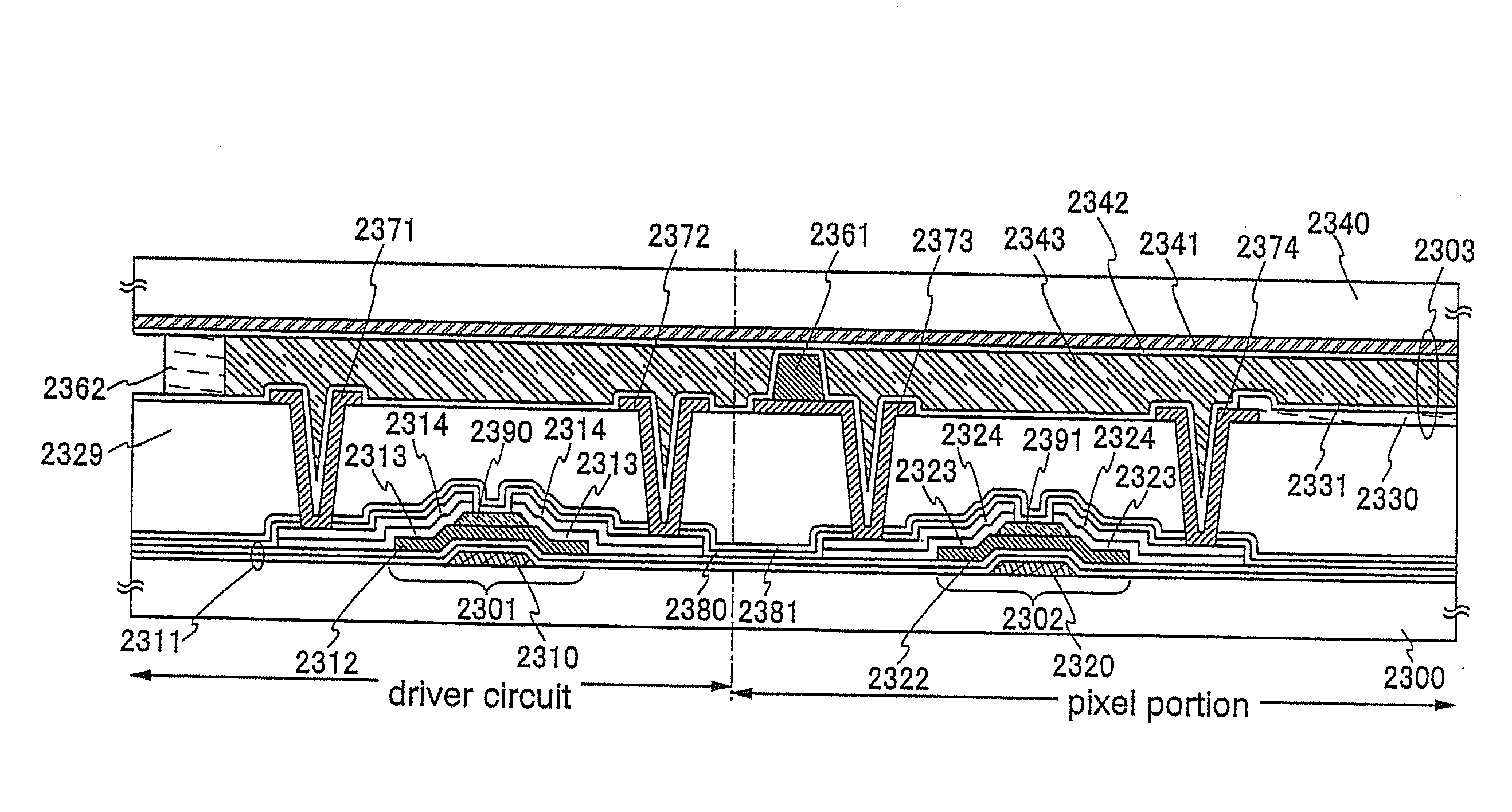
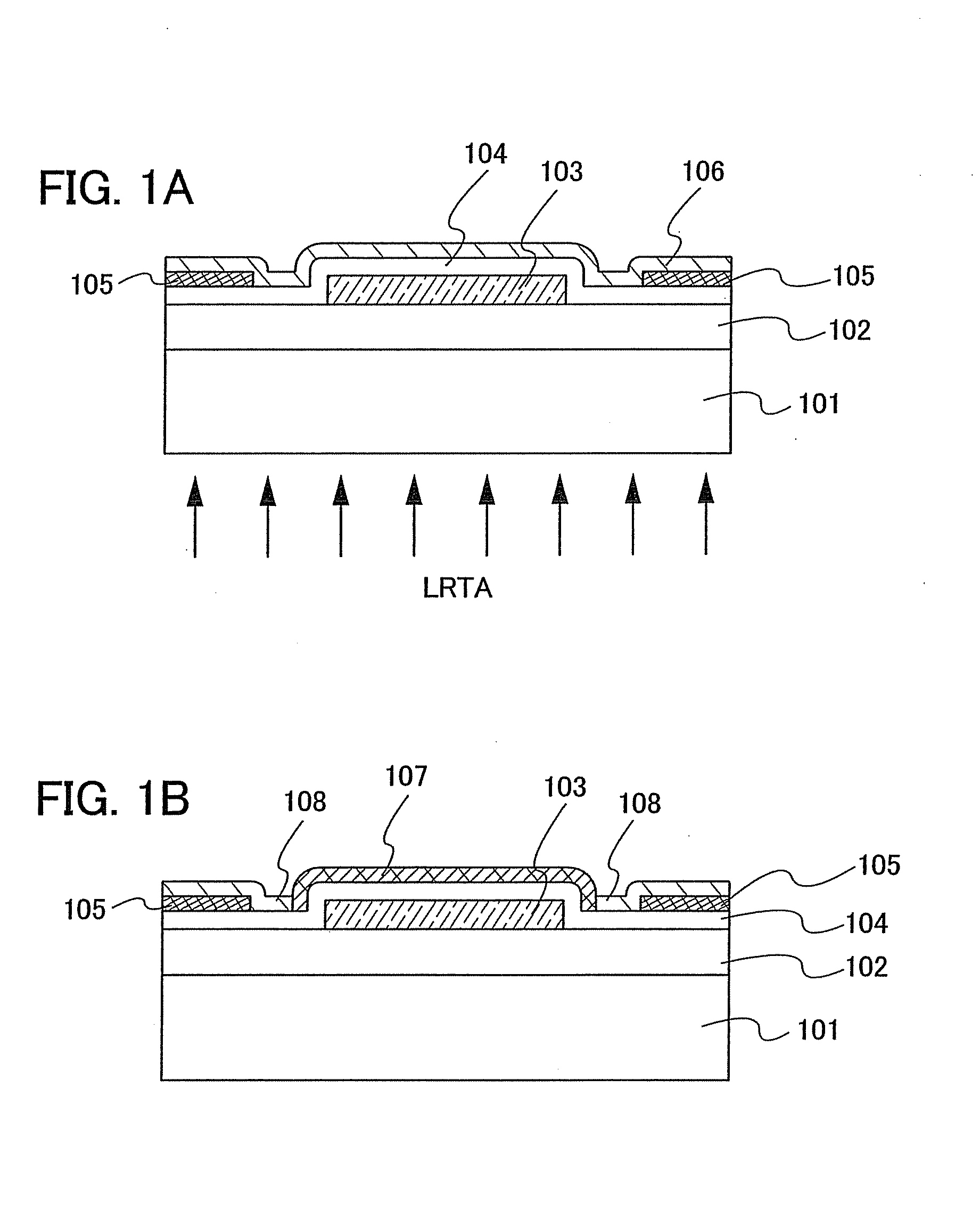
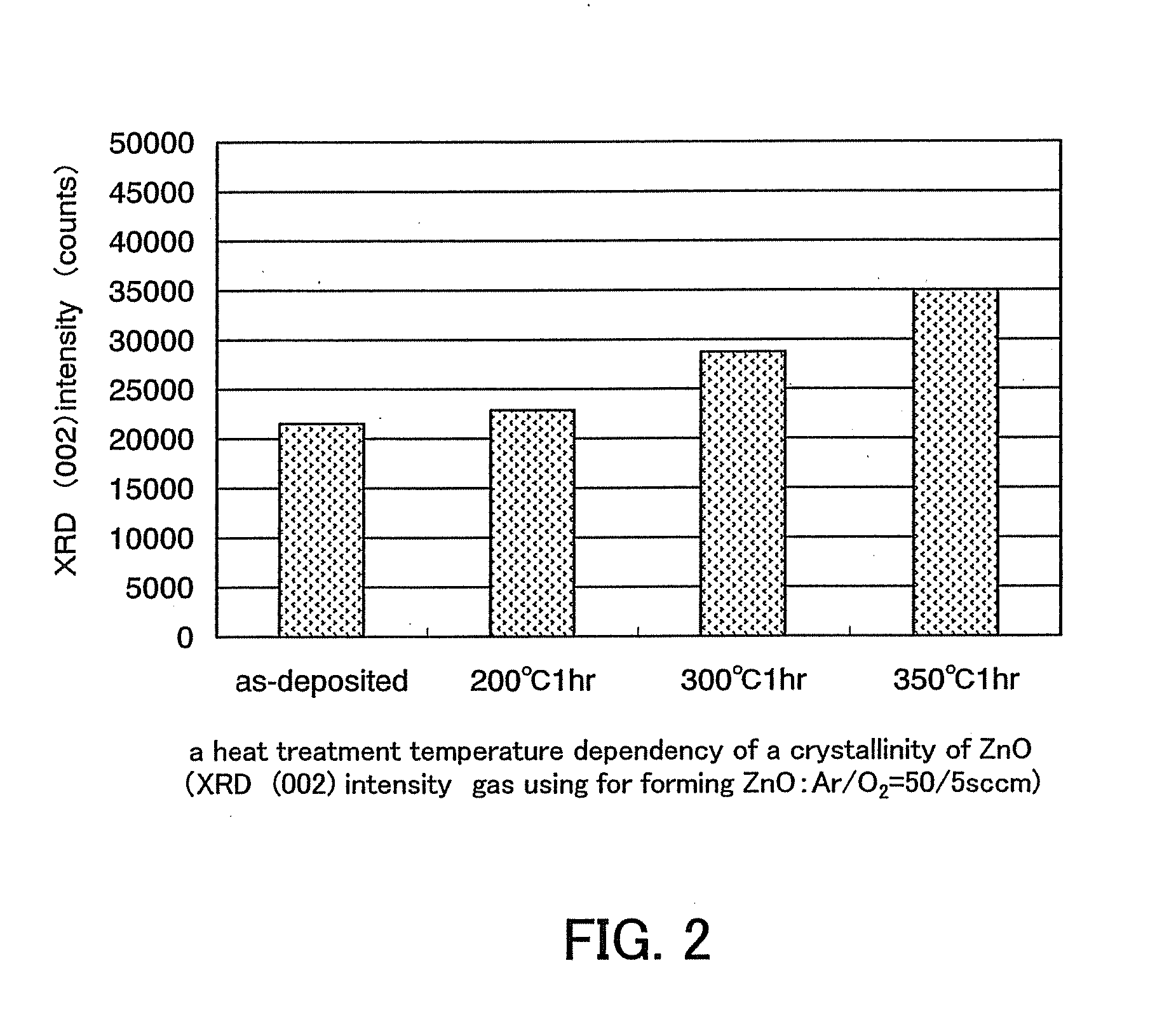
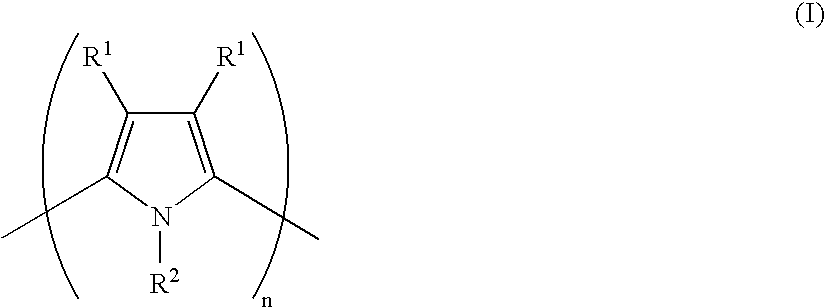Patents
Literature
25533 results about "Thin-film transistor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special kind of MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) made by depositing thin films of an active semiconductor layer as well as the dielectric layer and metallic contacts over a supporting (but non-conducting) substrate. A common substrate is glass, because the primary application of TFTs is in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). This differs from the conventional bulk MOSFET transistor, where the semiconductor material typically is the substrate, such as a silicon wafer.
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method, and electronic device
ActiveUS20060244107A1Stabilize element propertyEasy to manufactureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface levelIntrinsic resistance
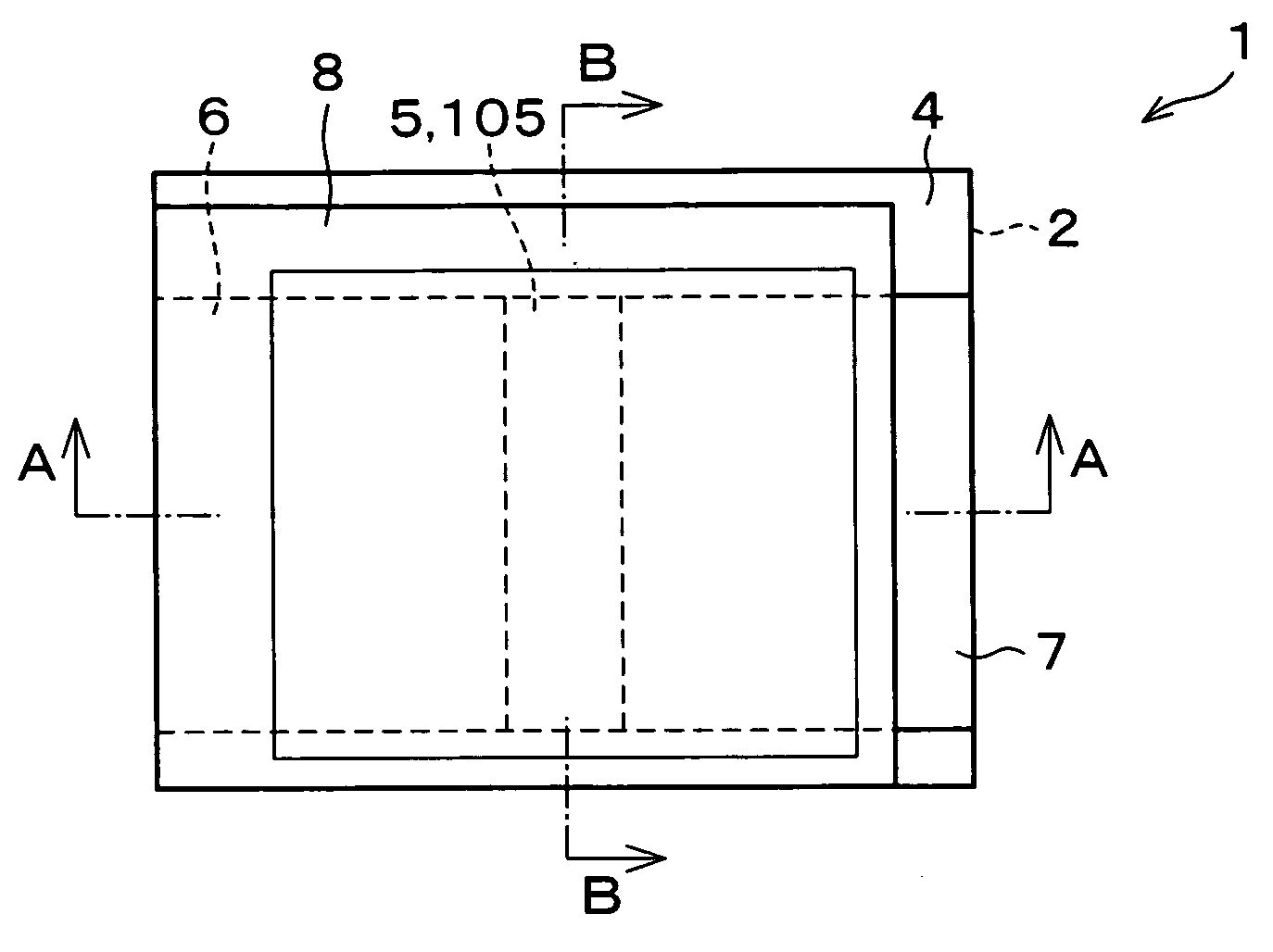
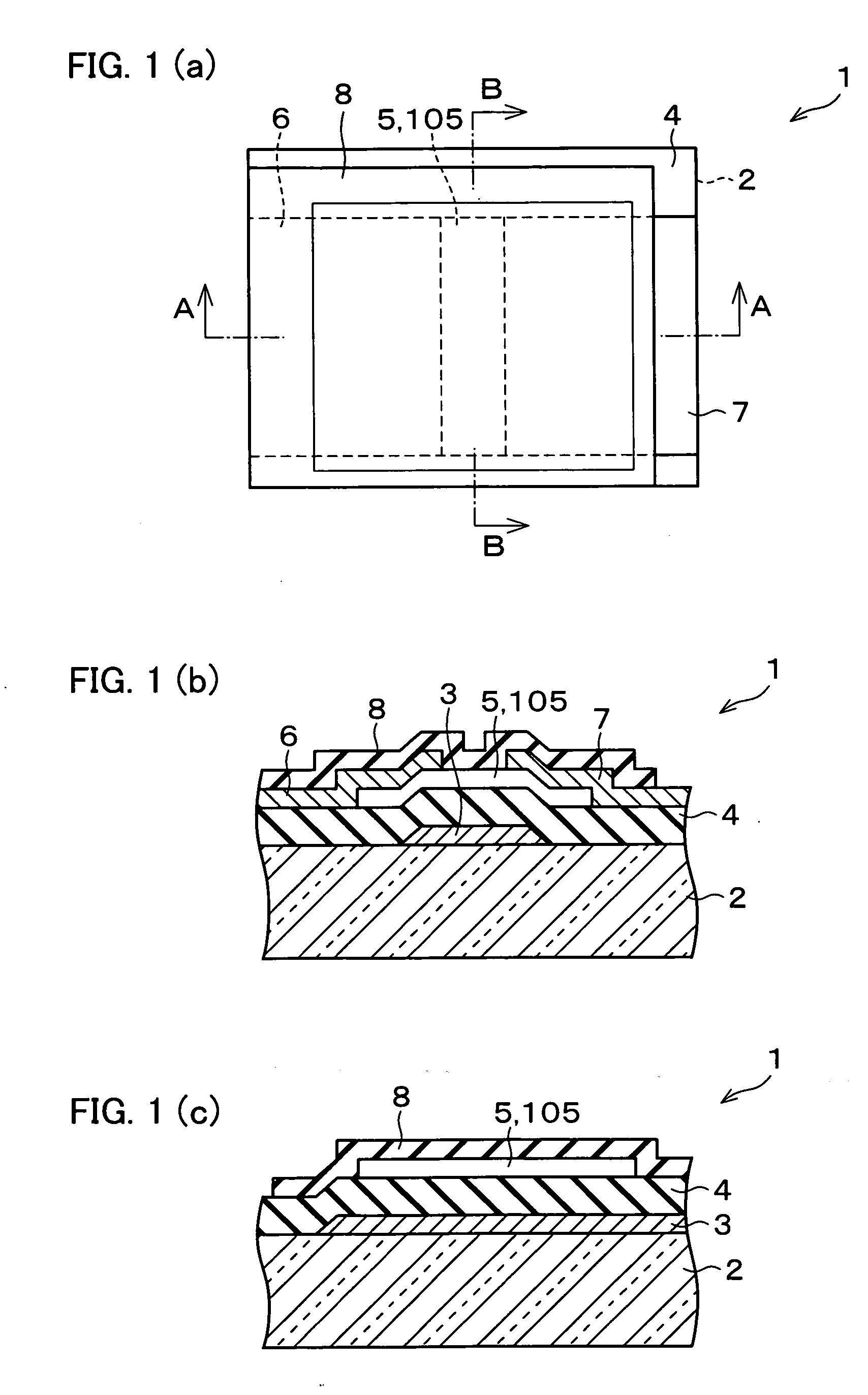
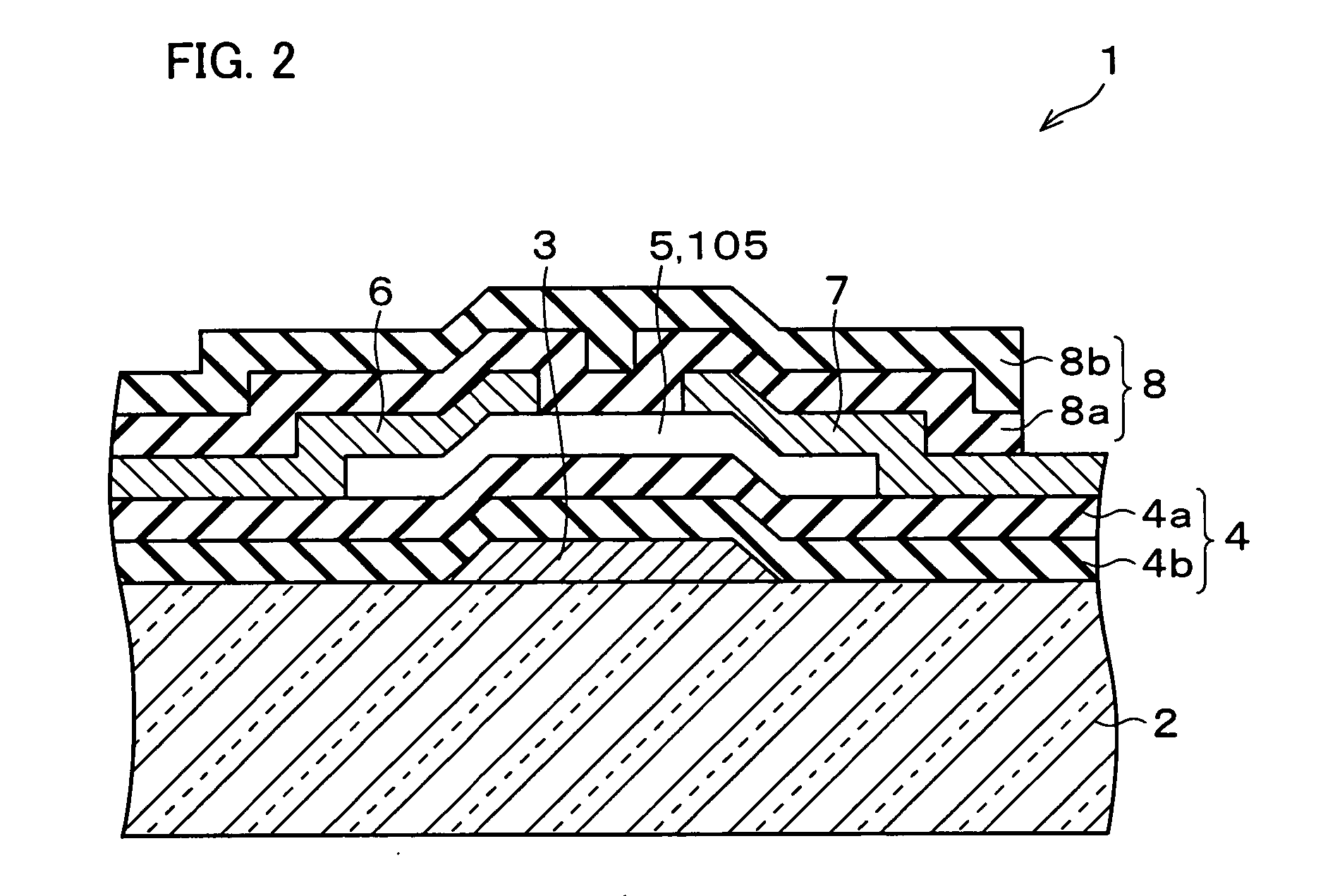
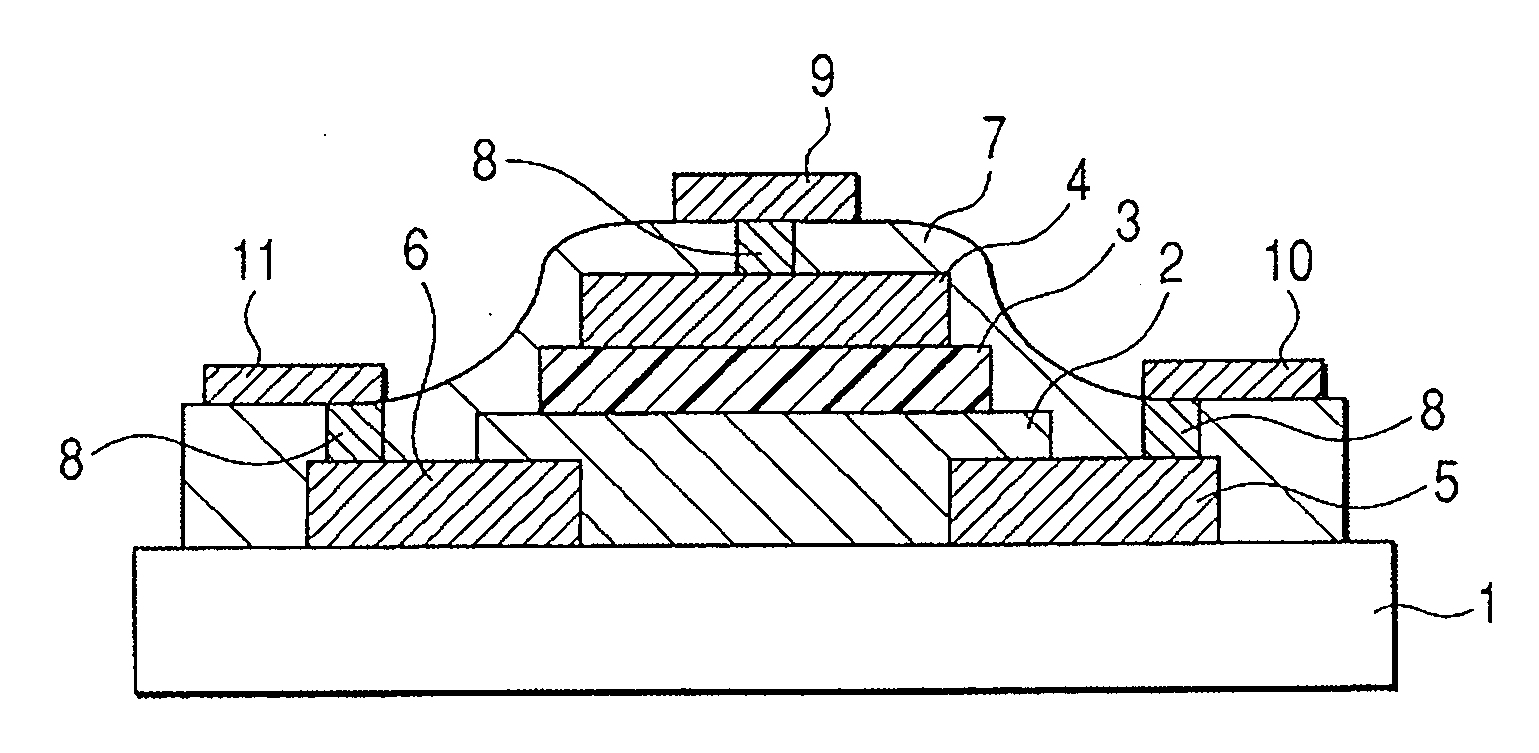
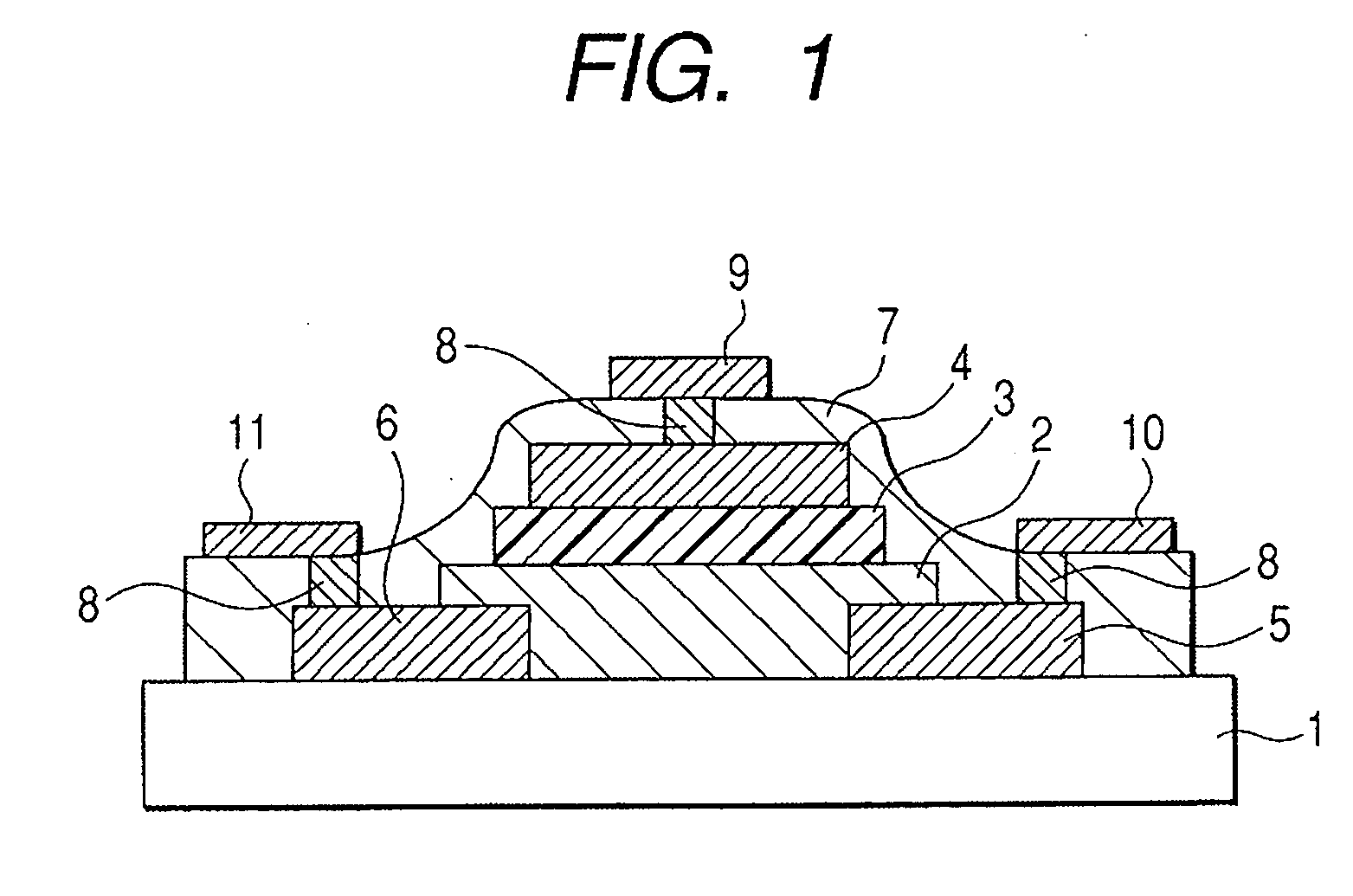
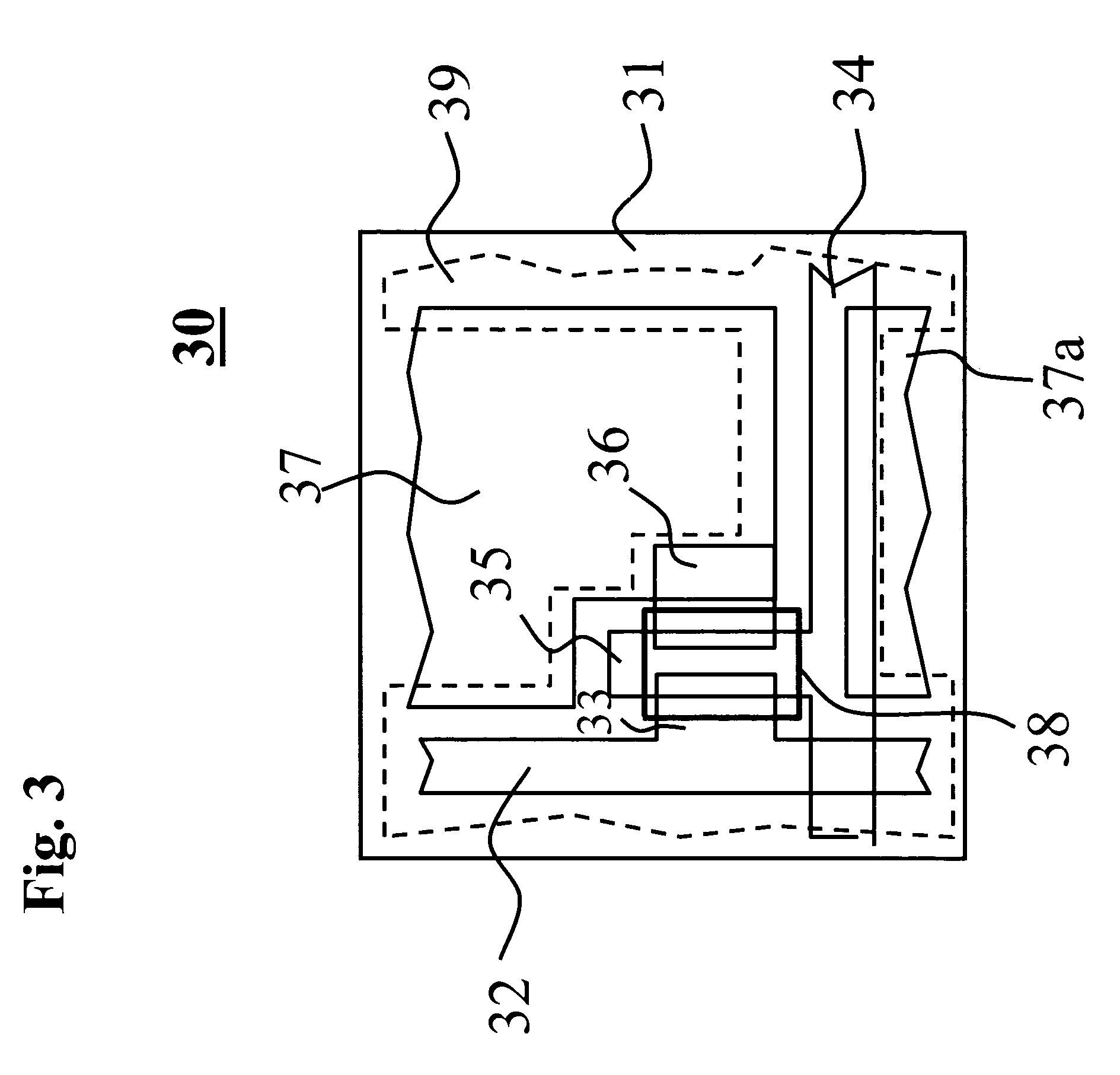
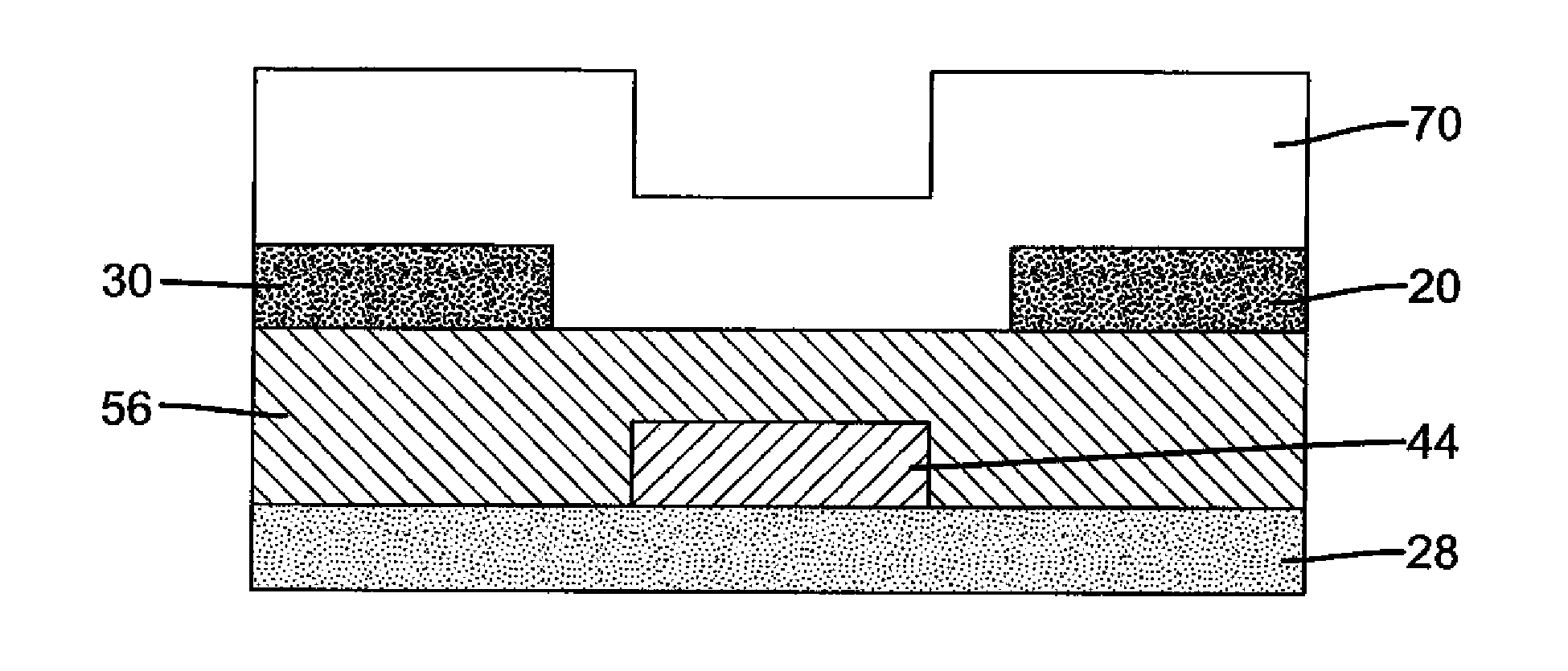
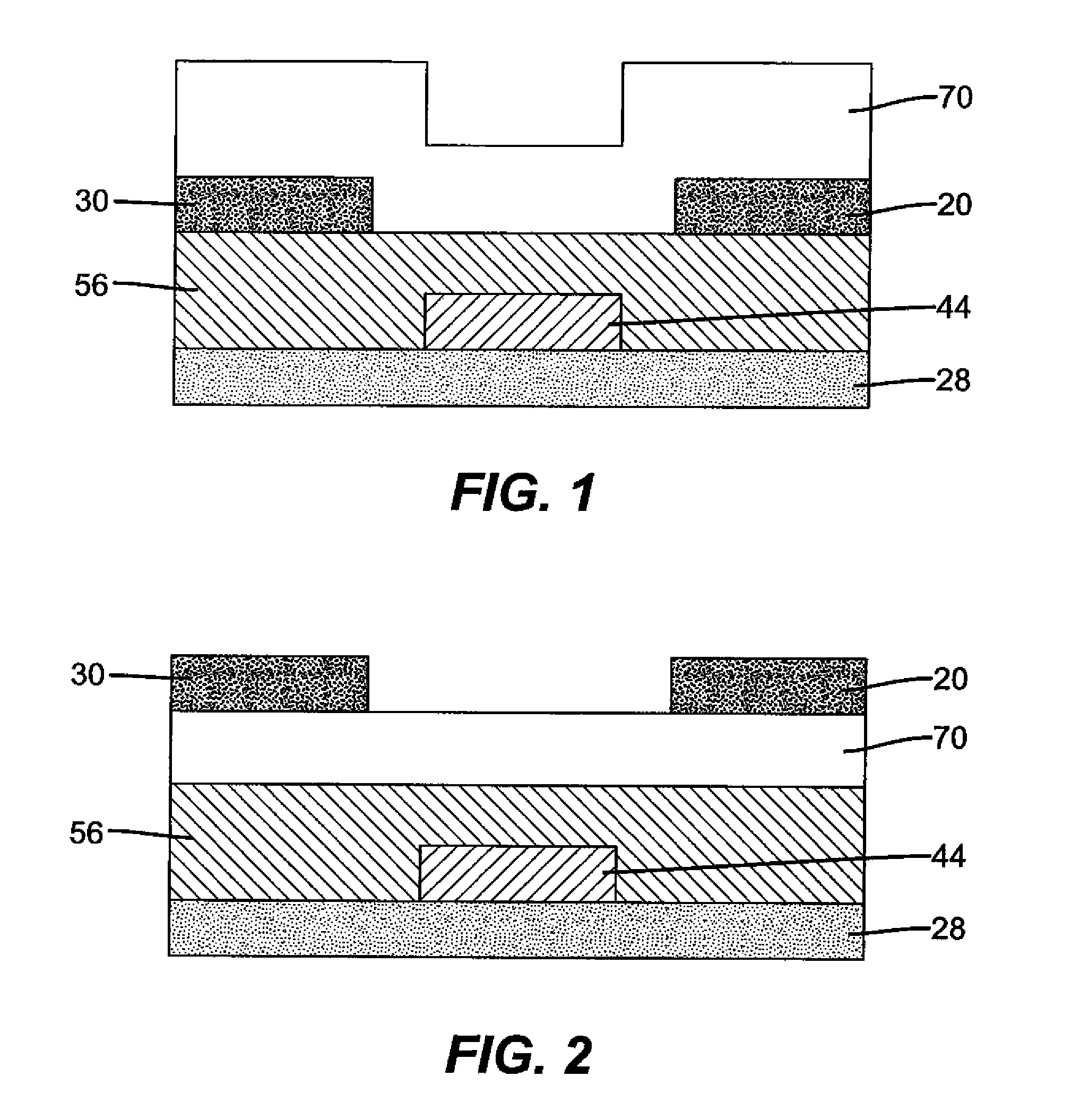
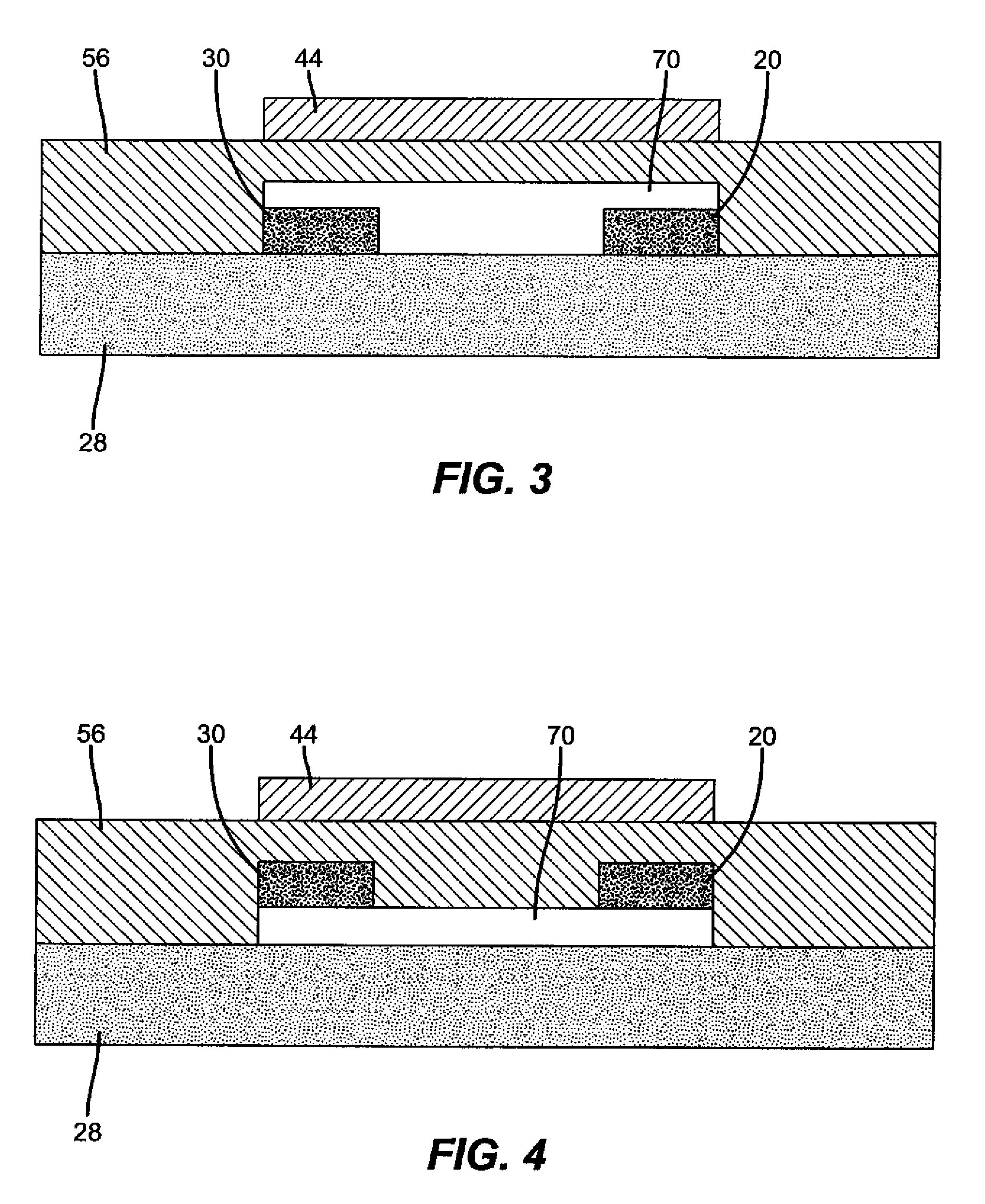
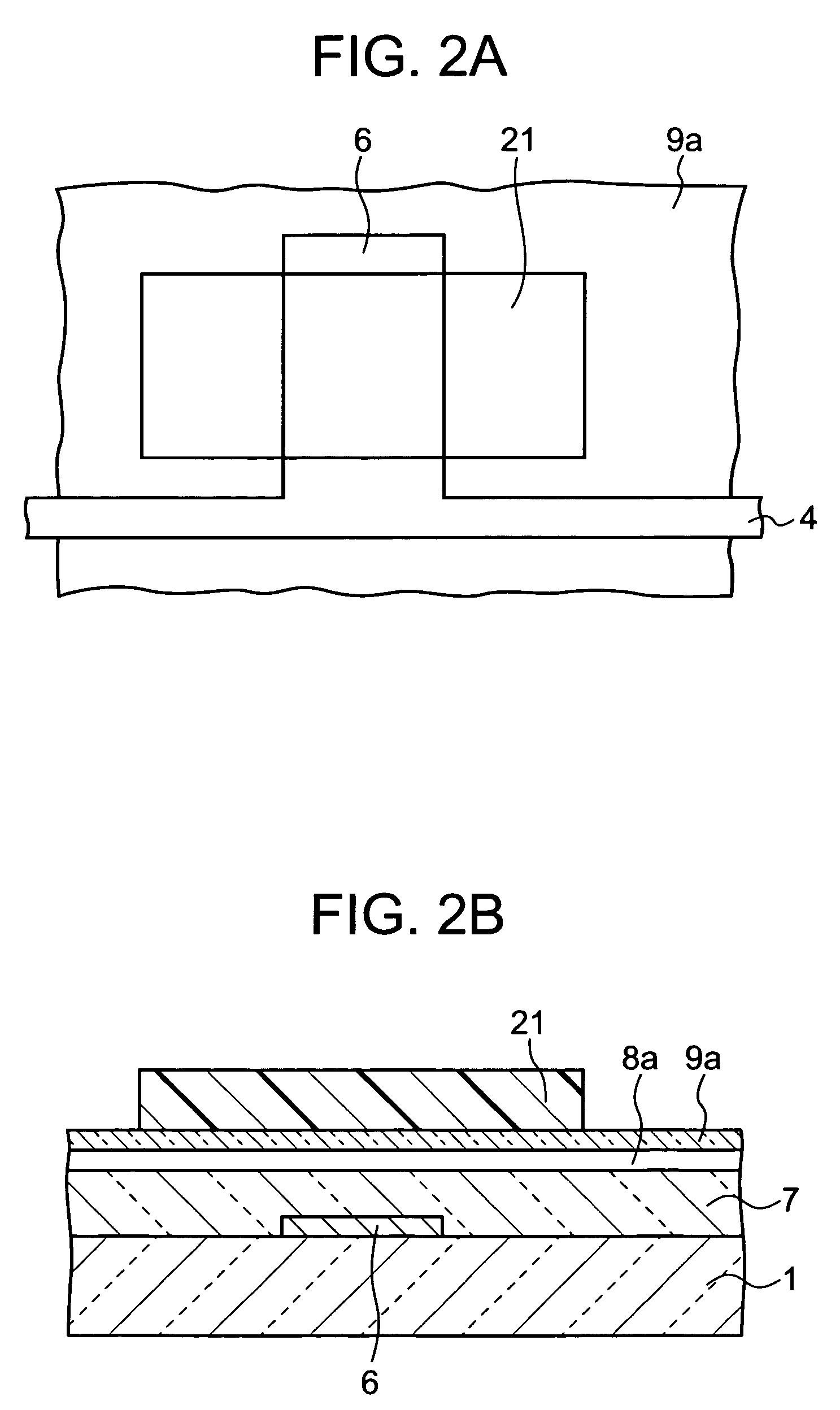
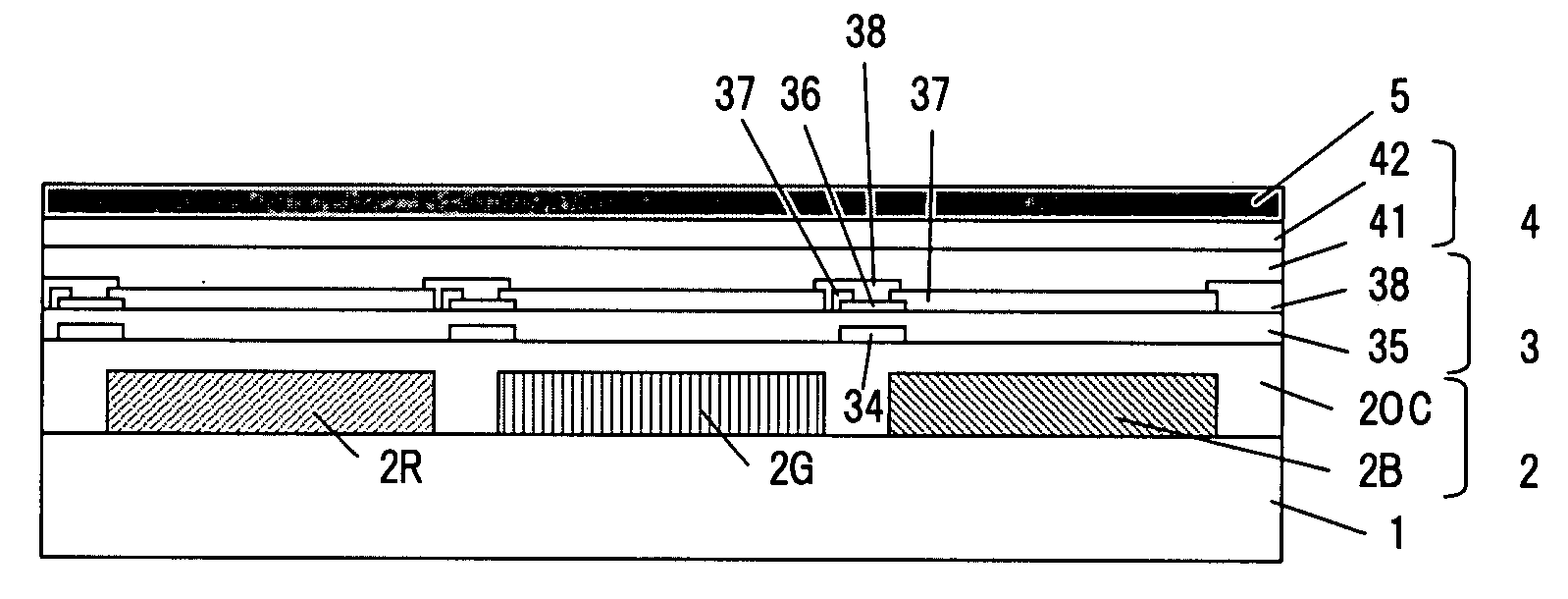
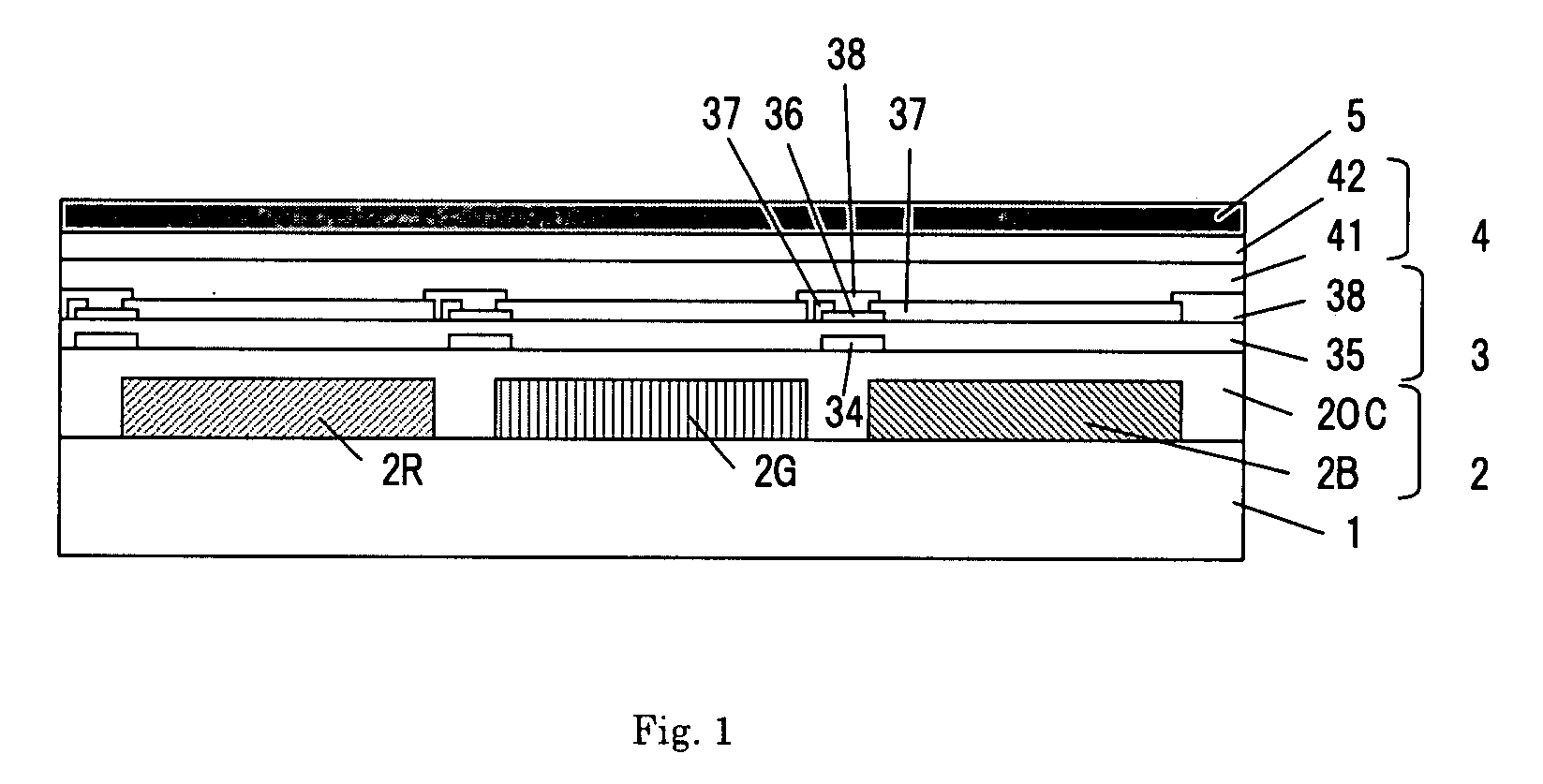
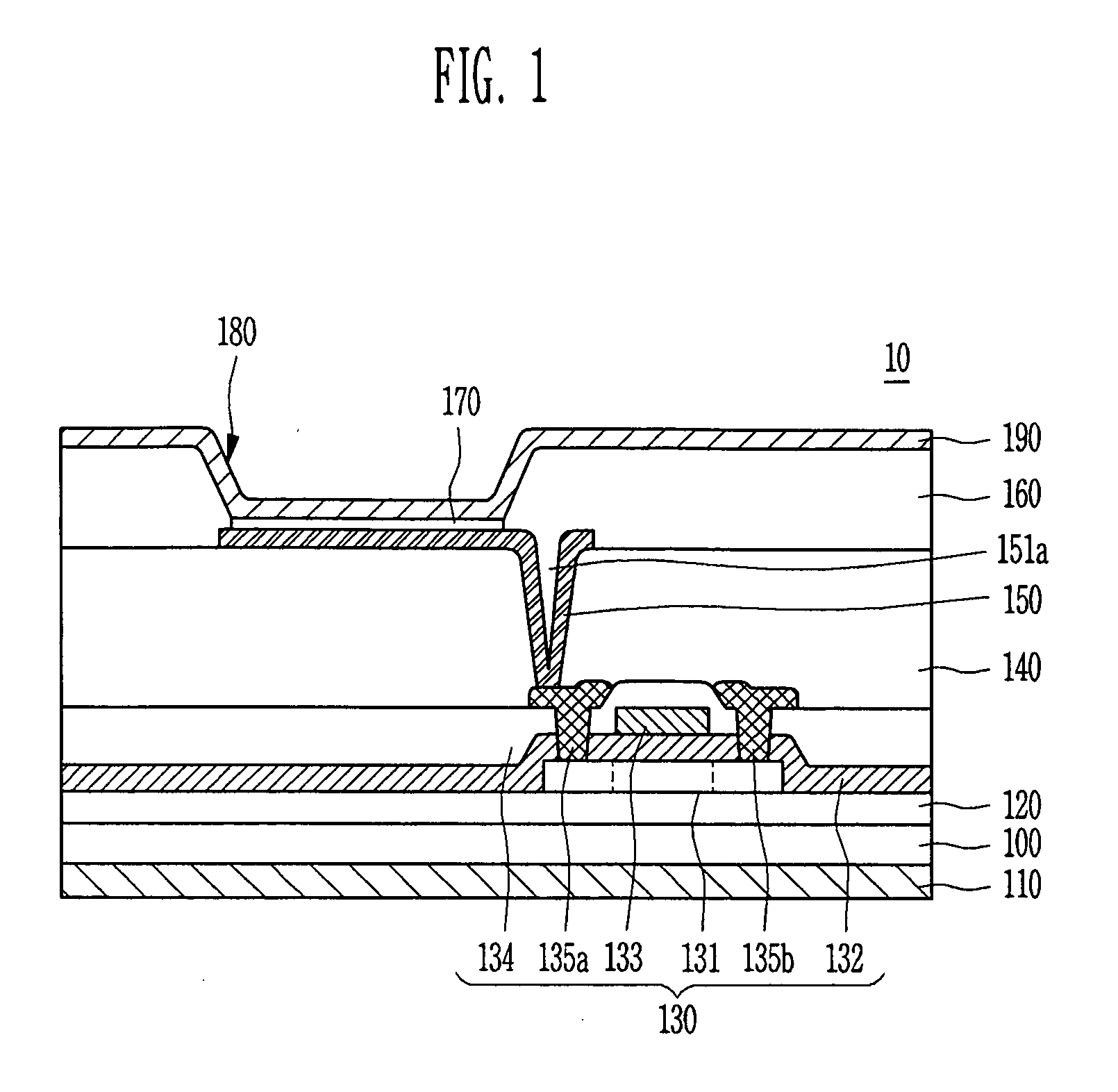
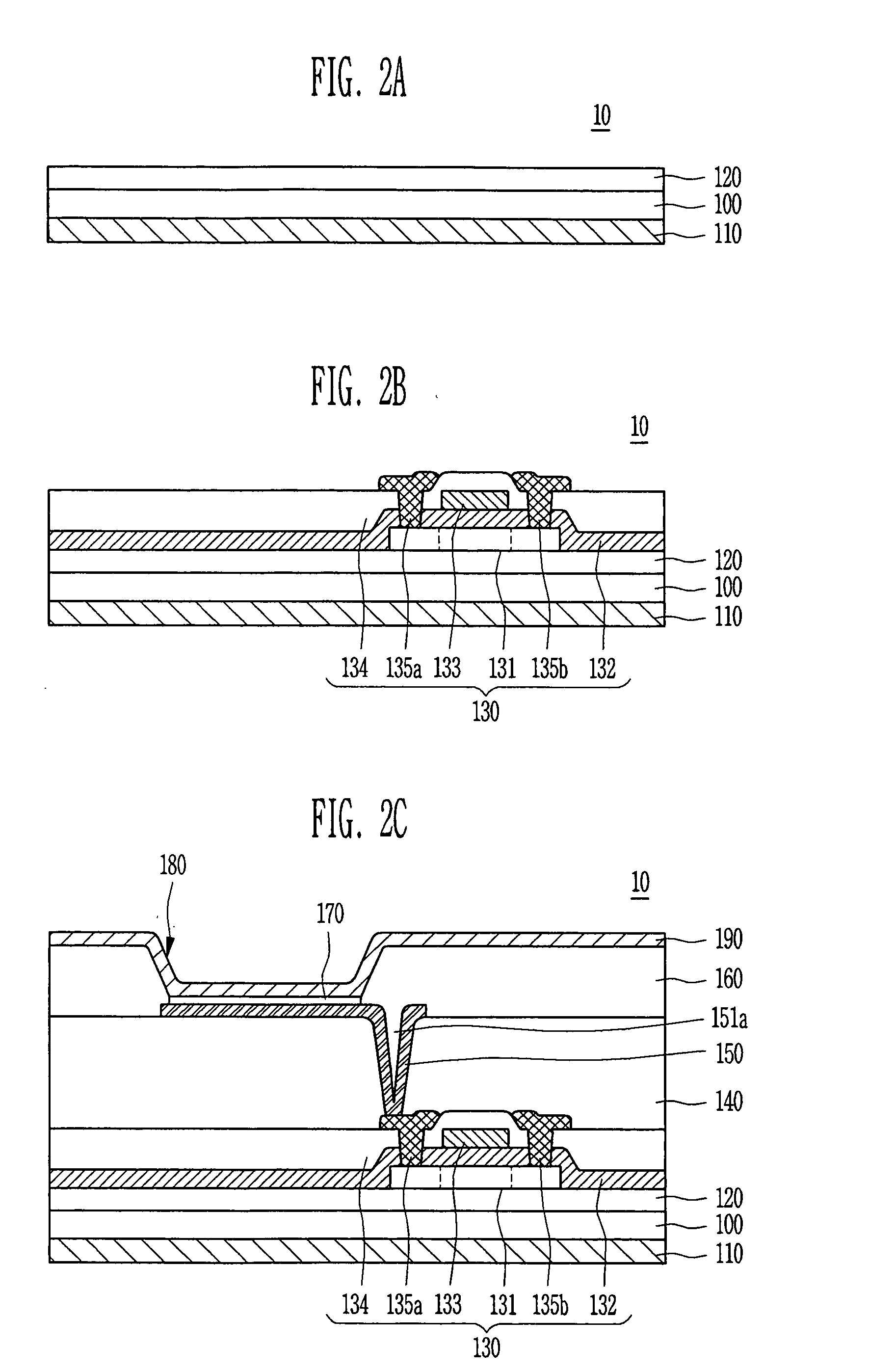
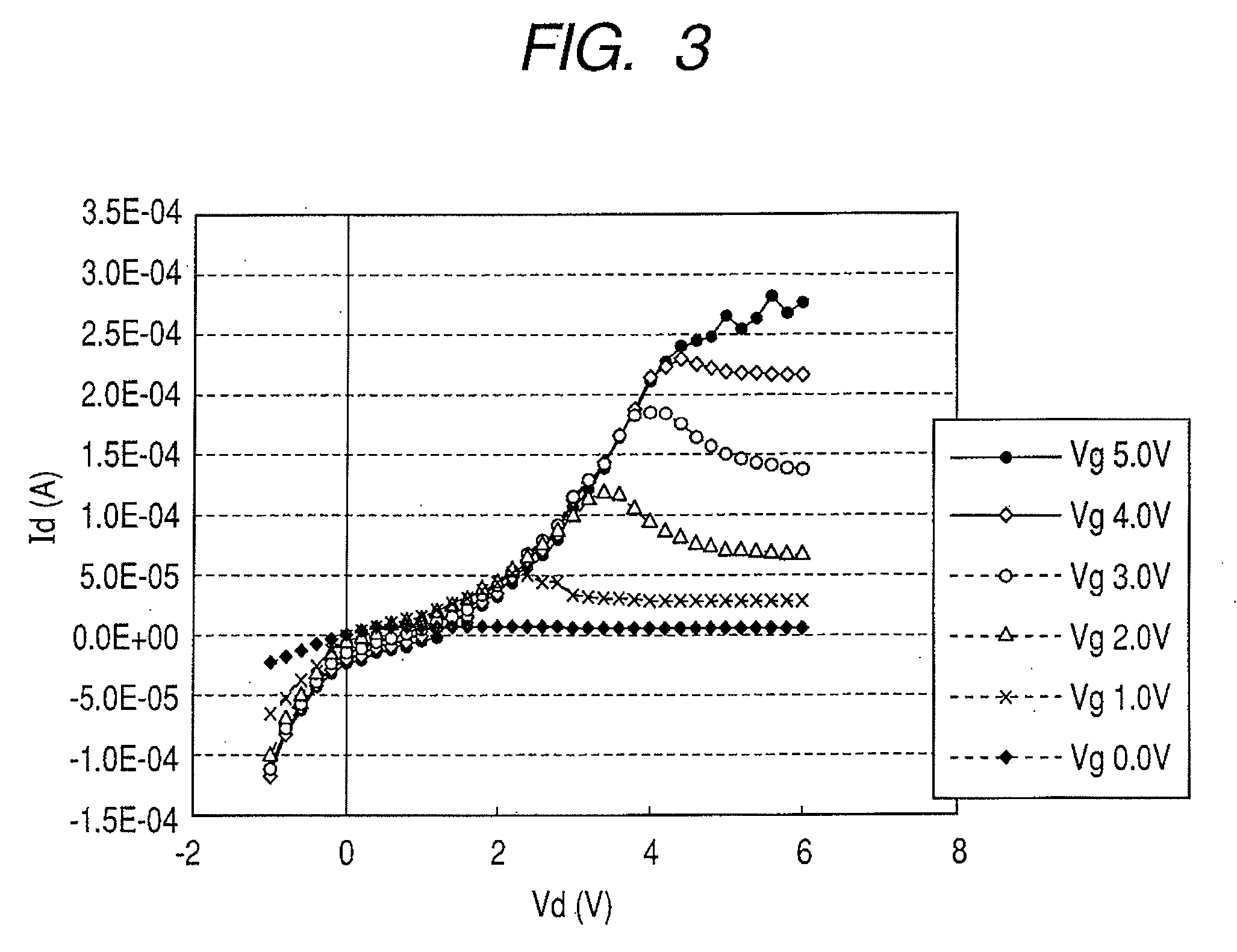
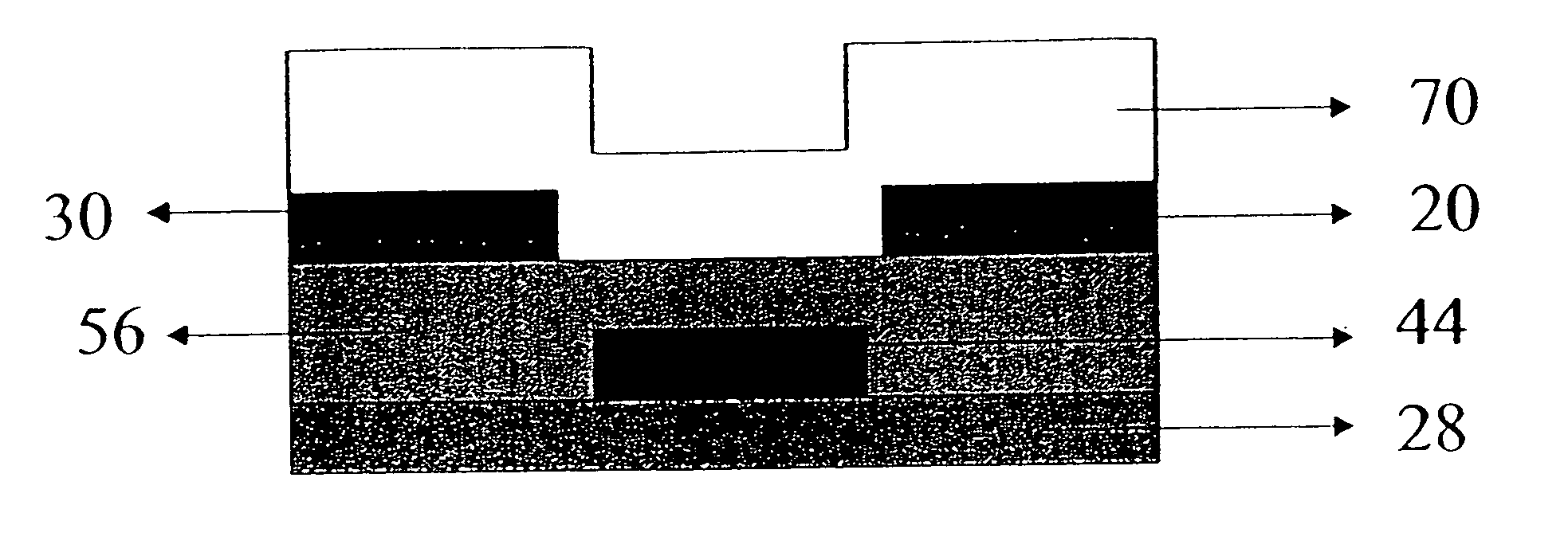
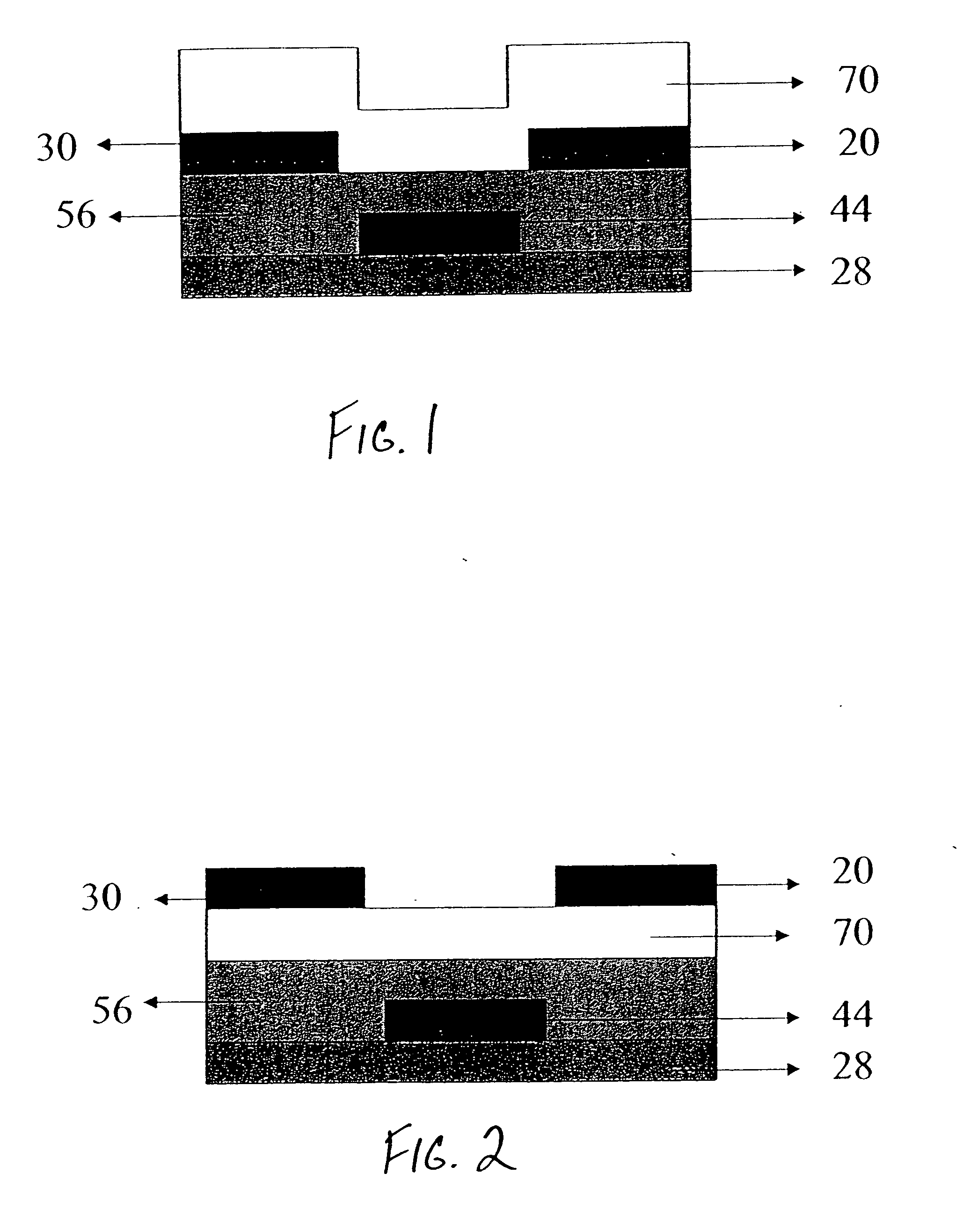
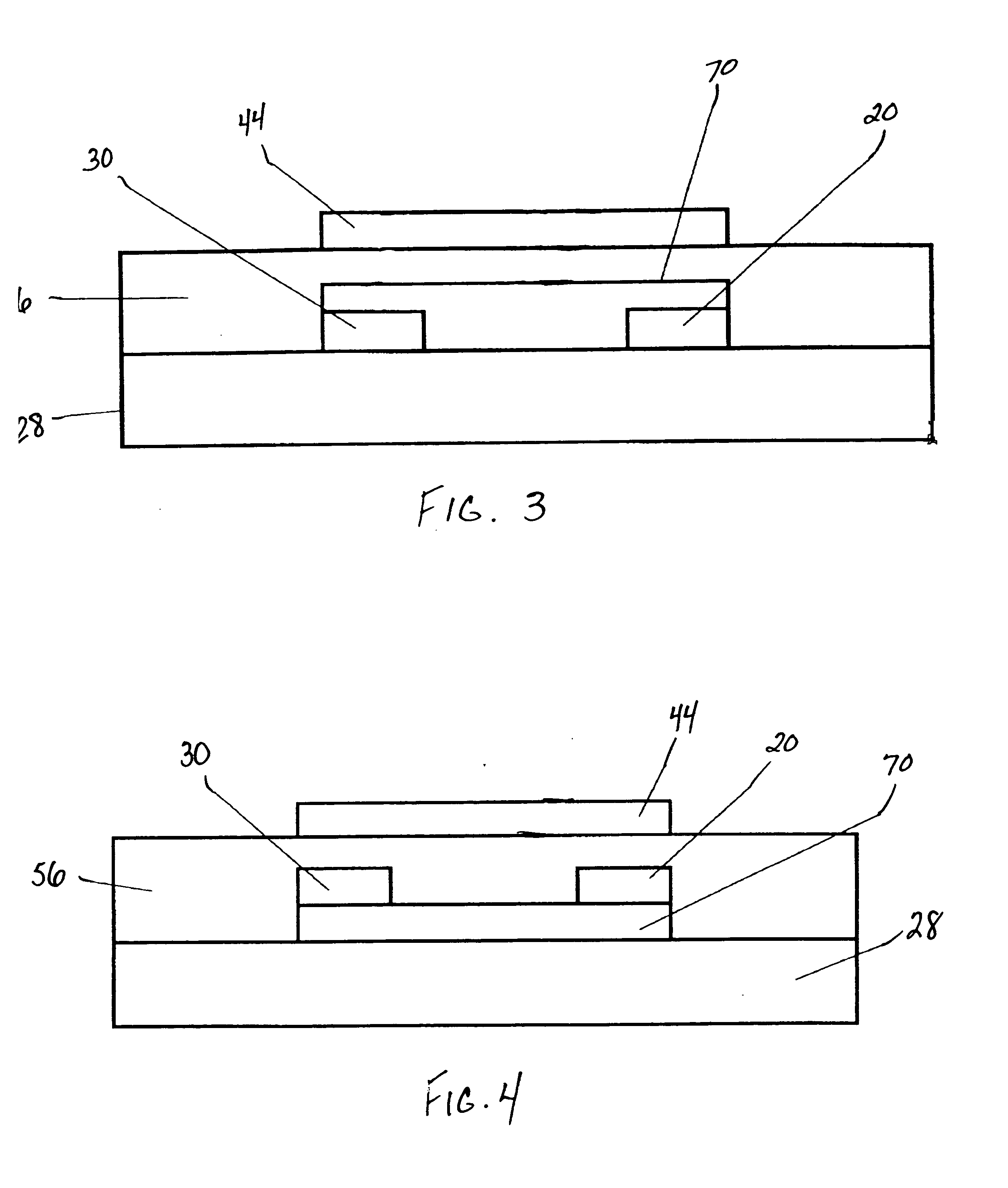
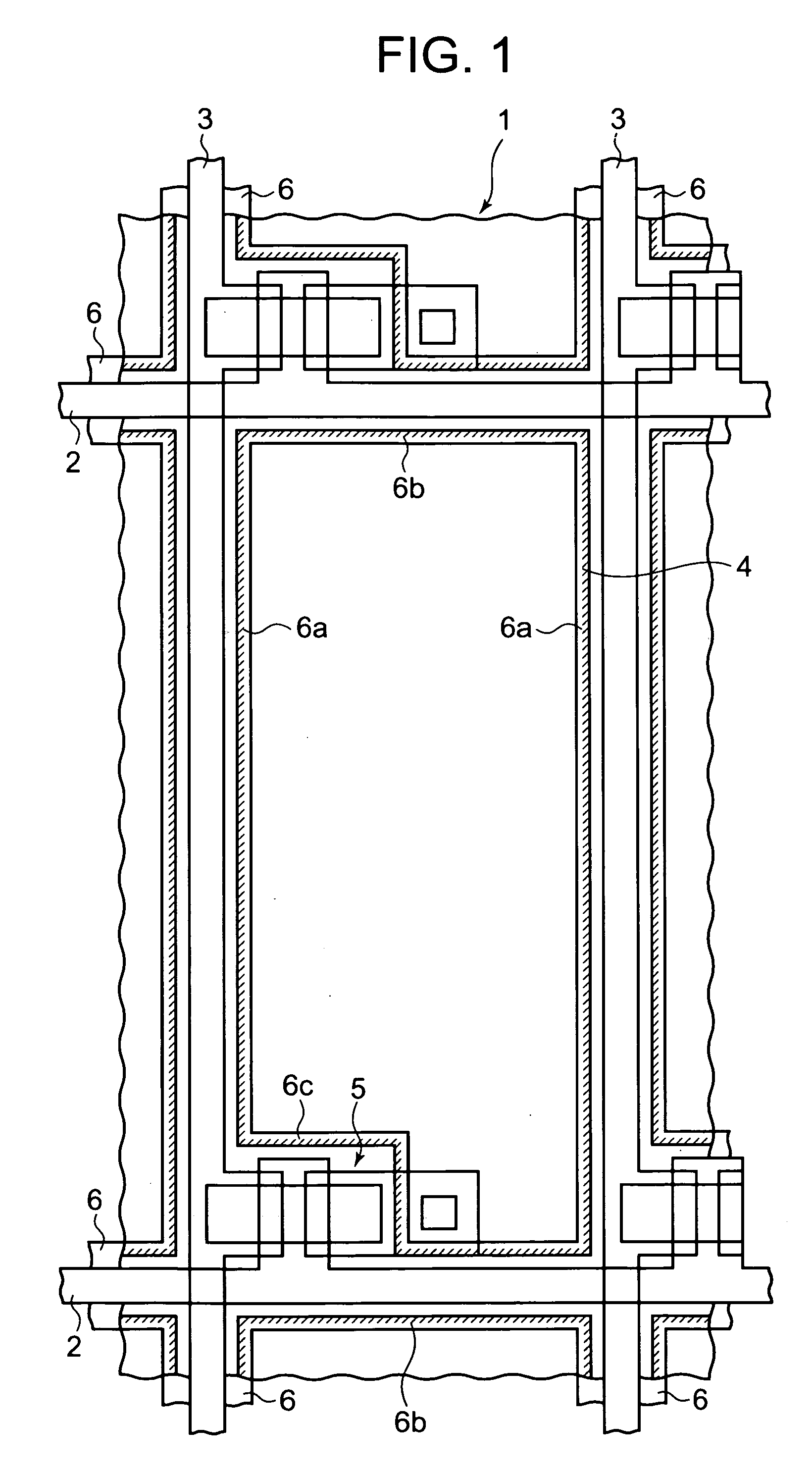
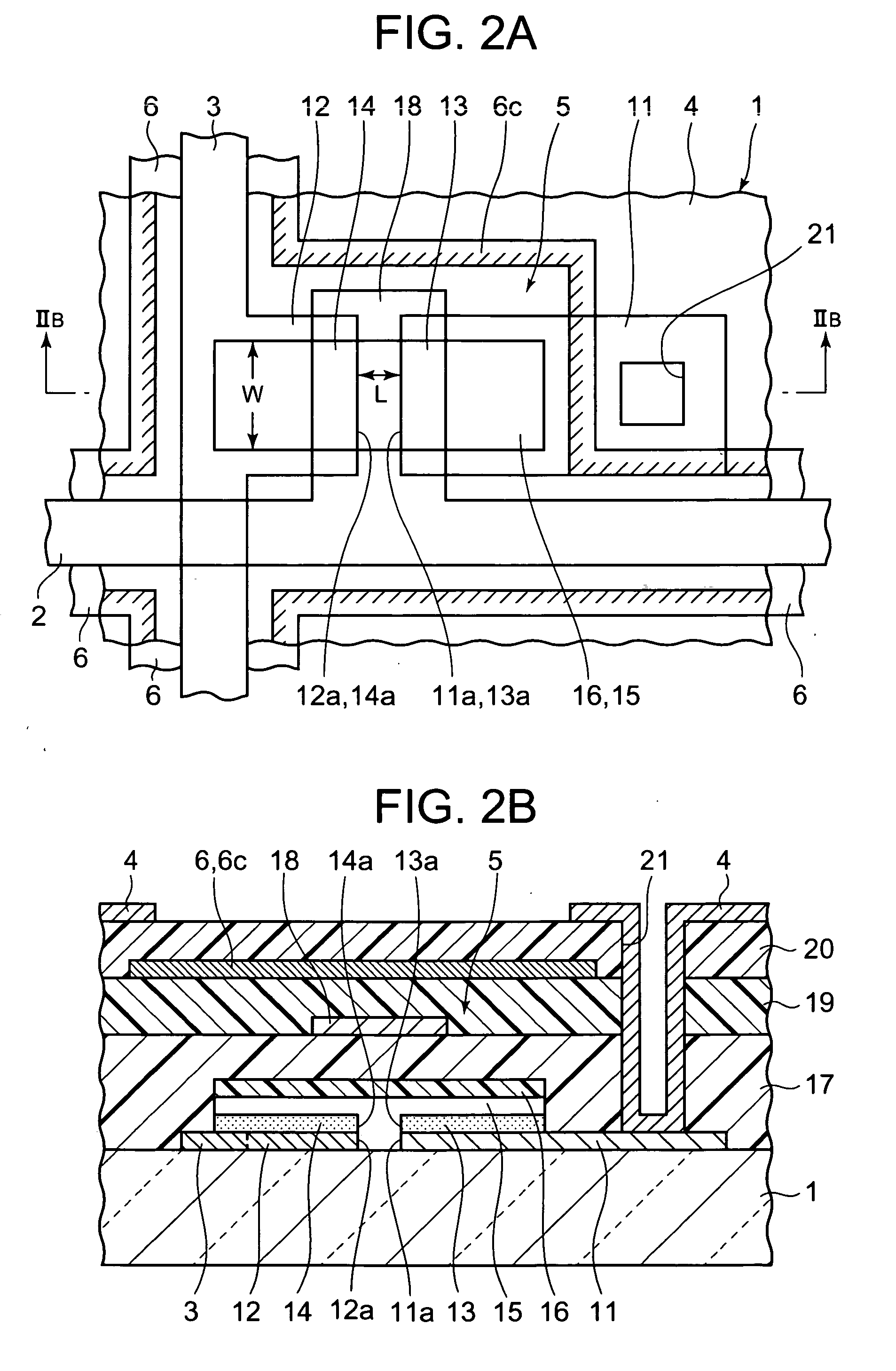
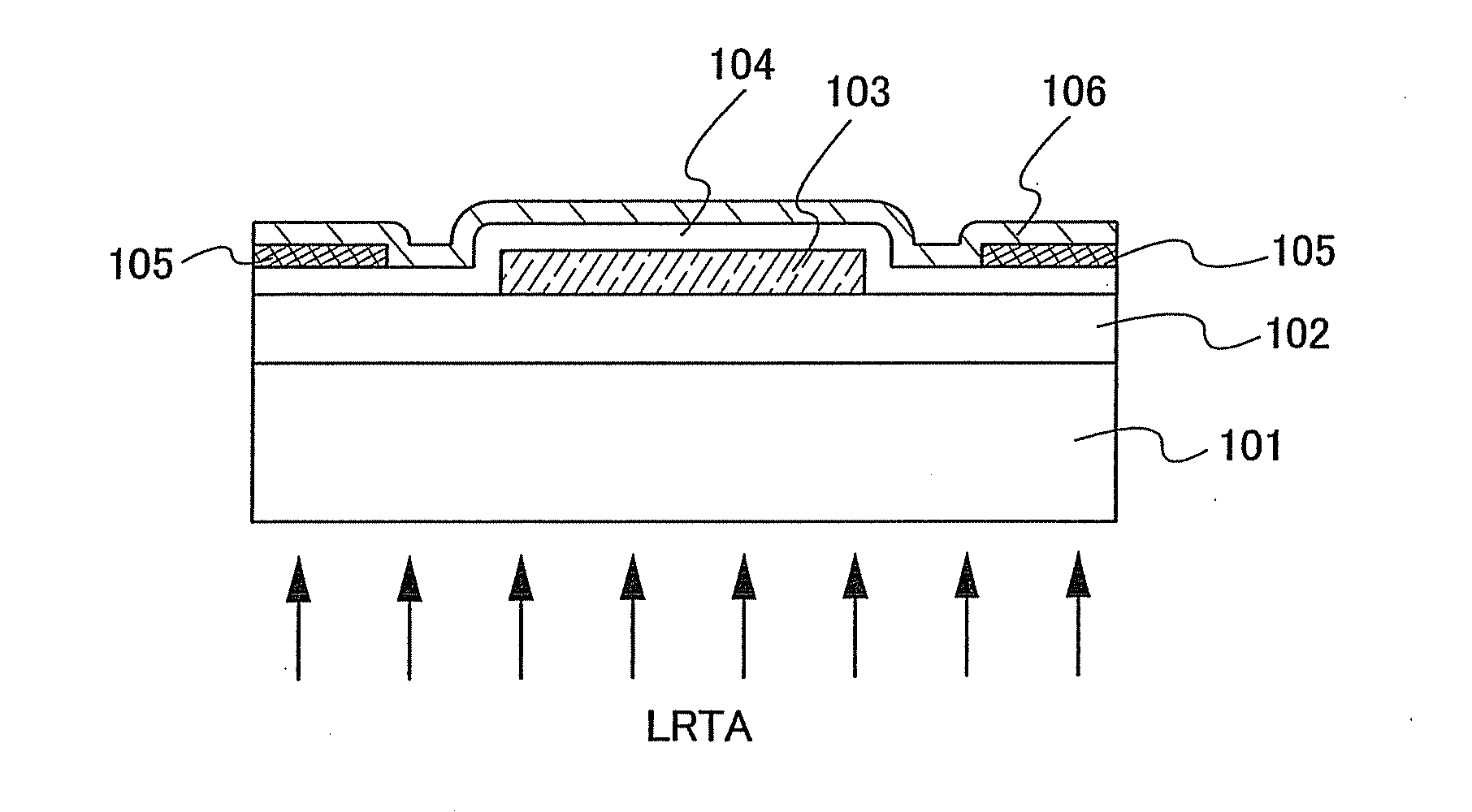
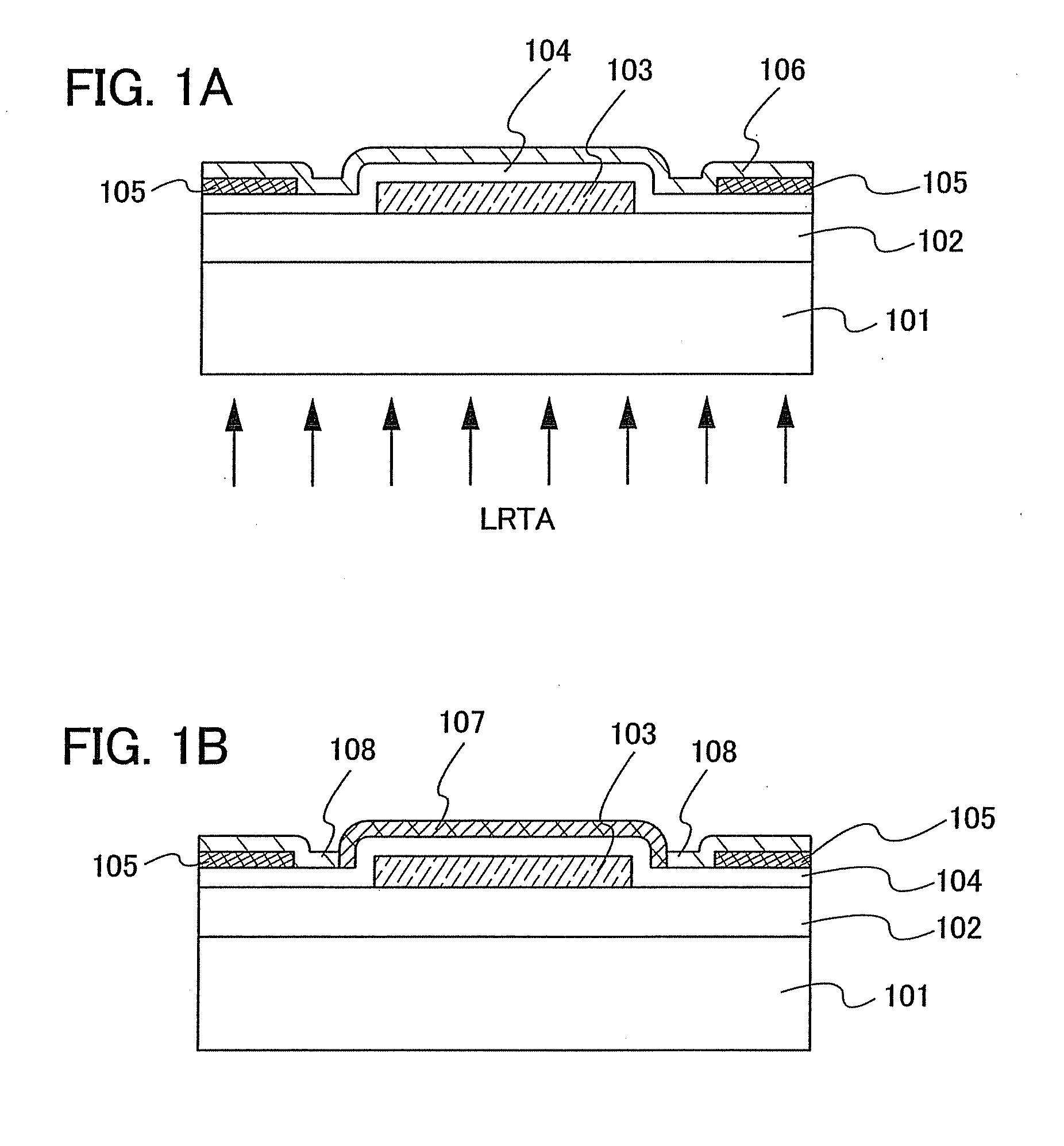
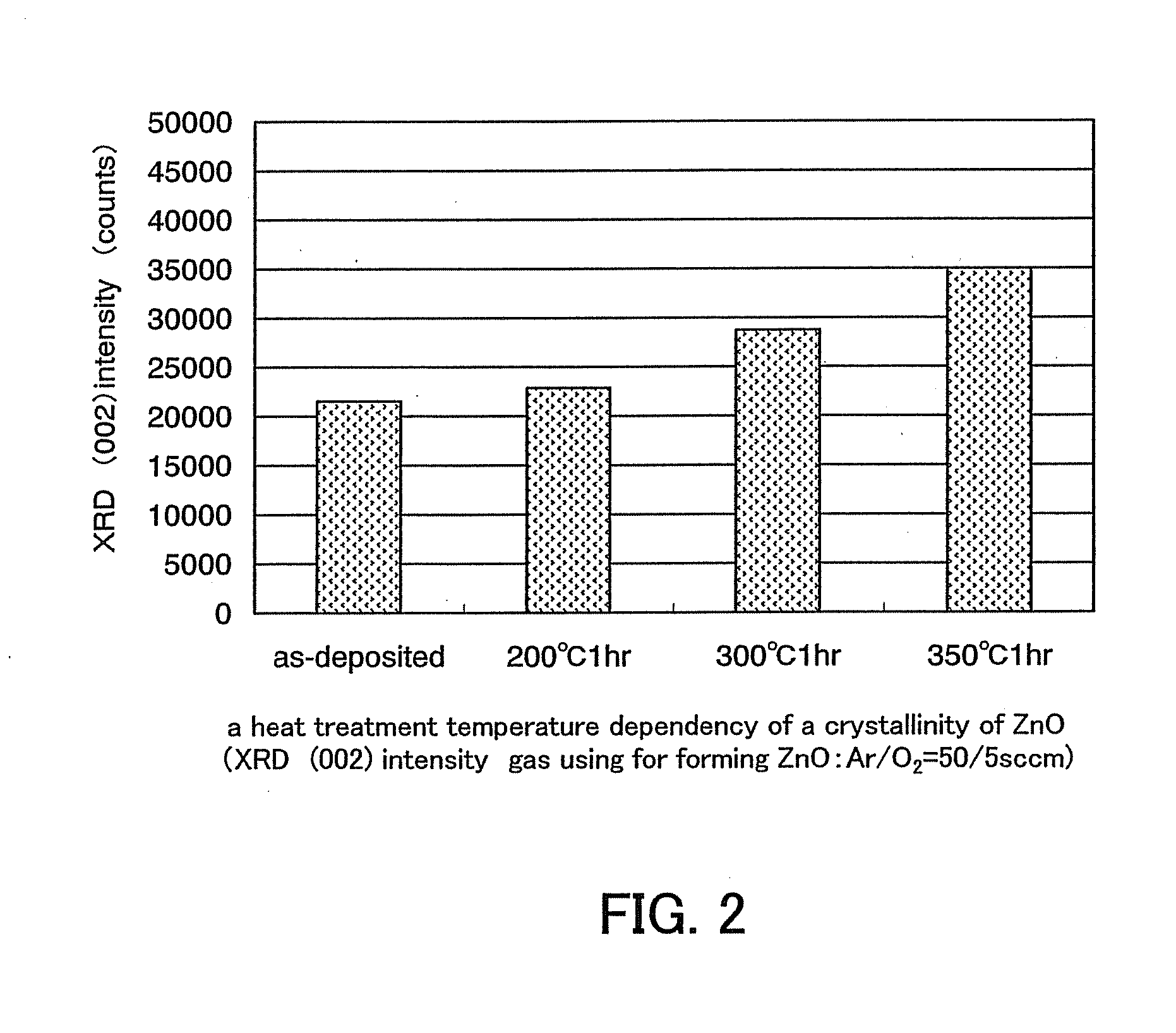
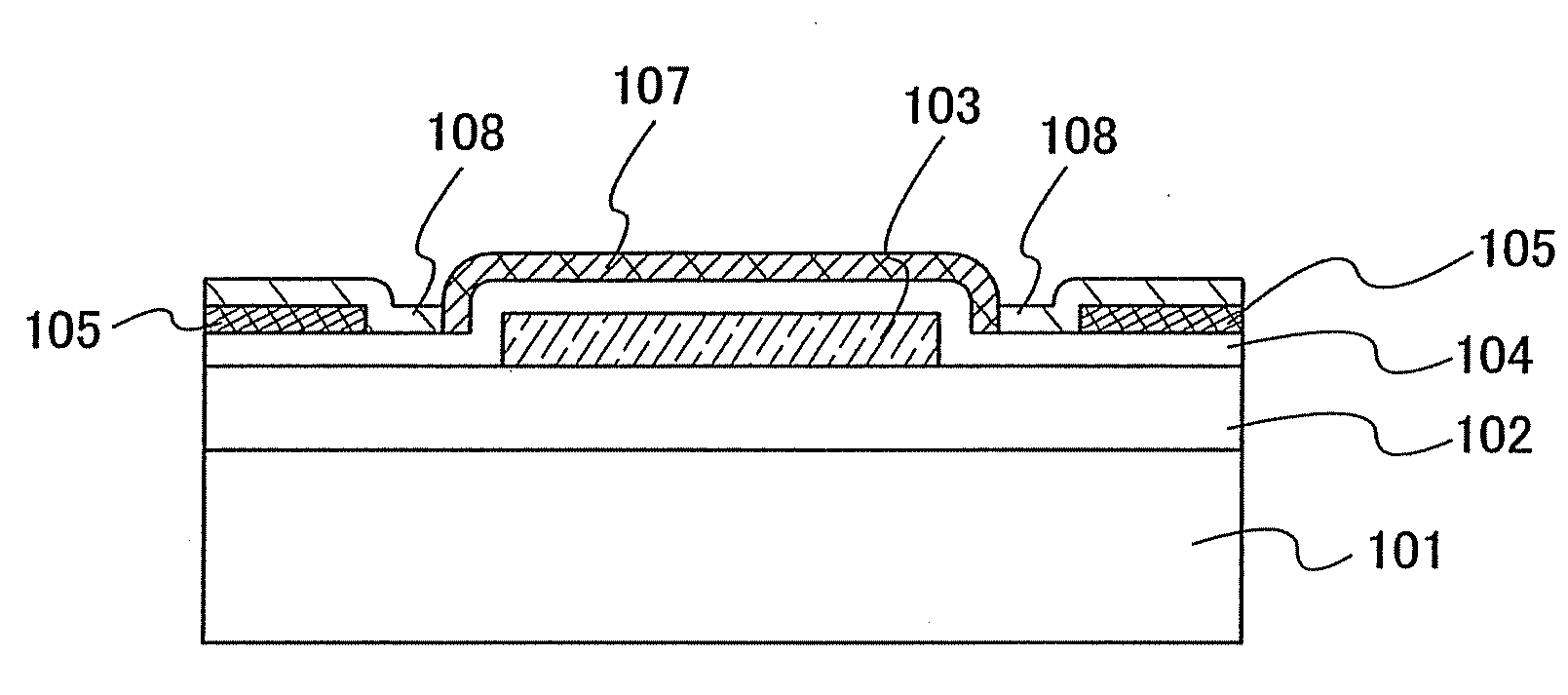
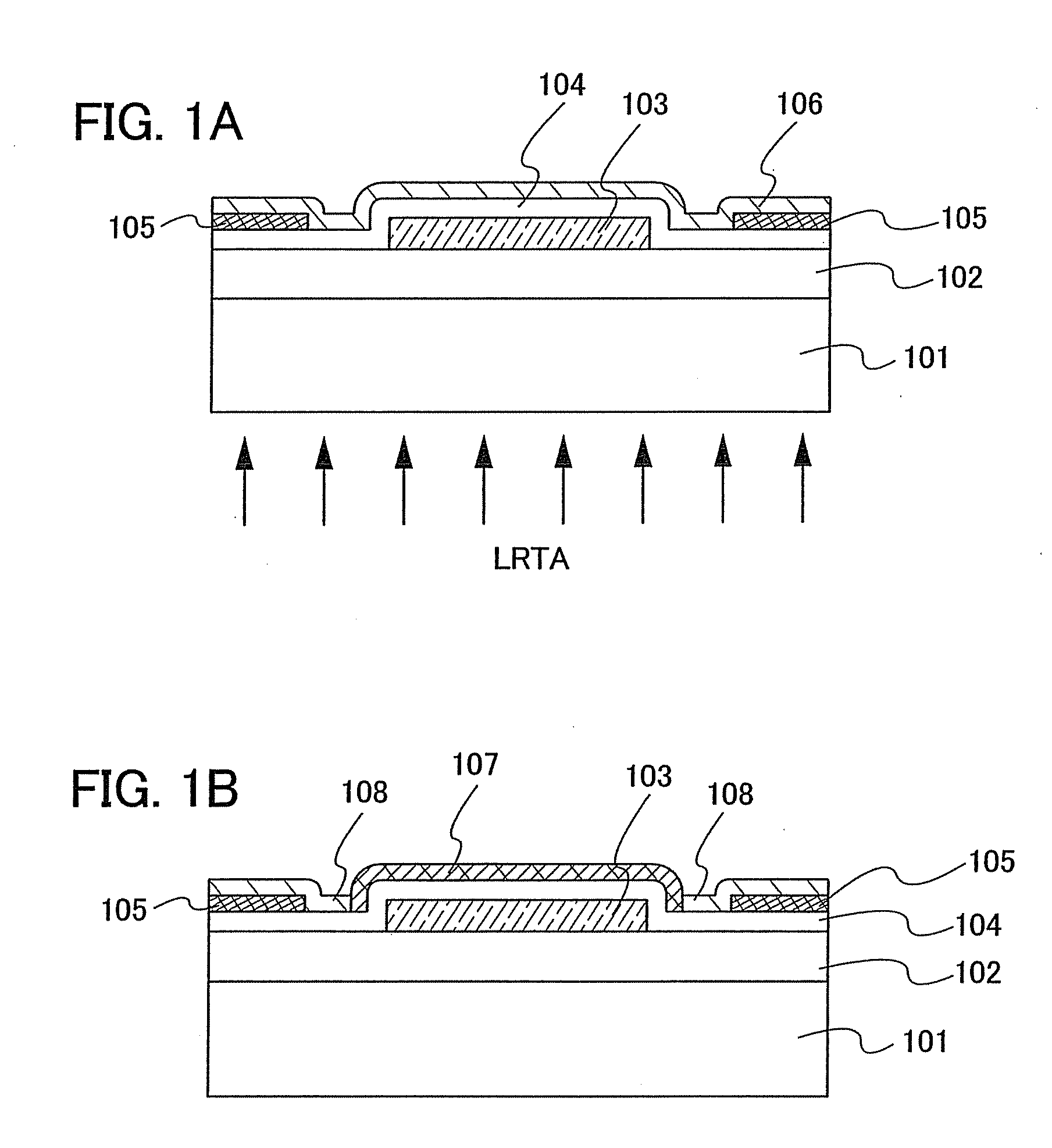
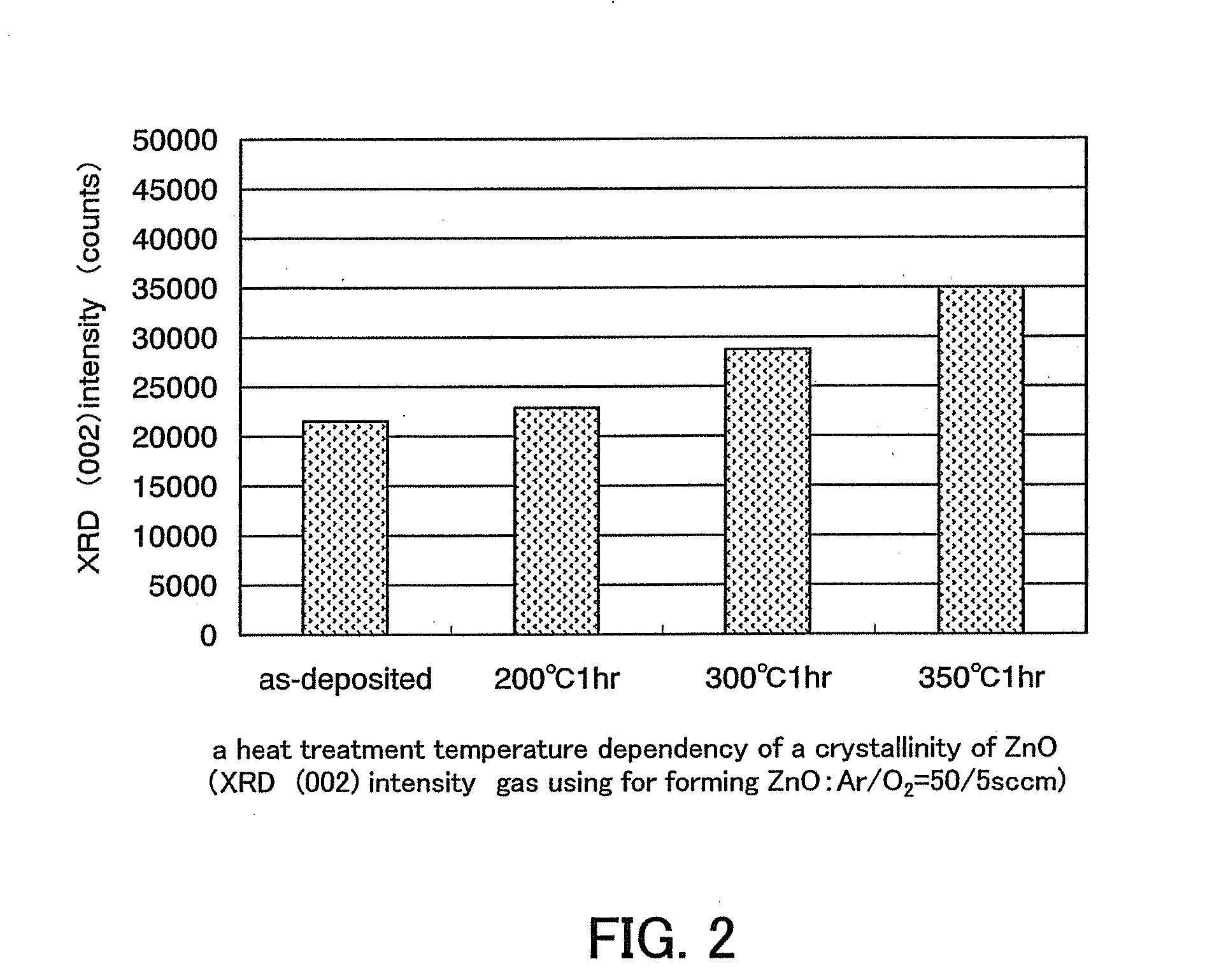
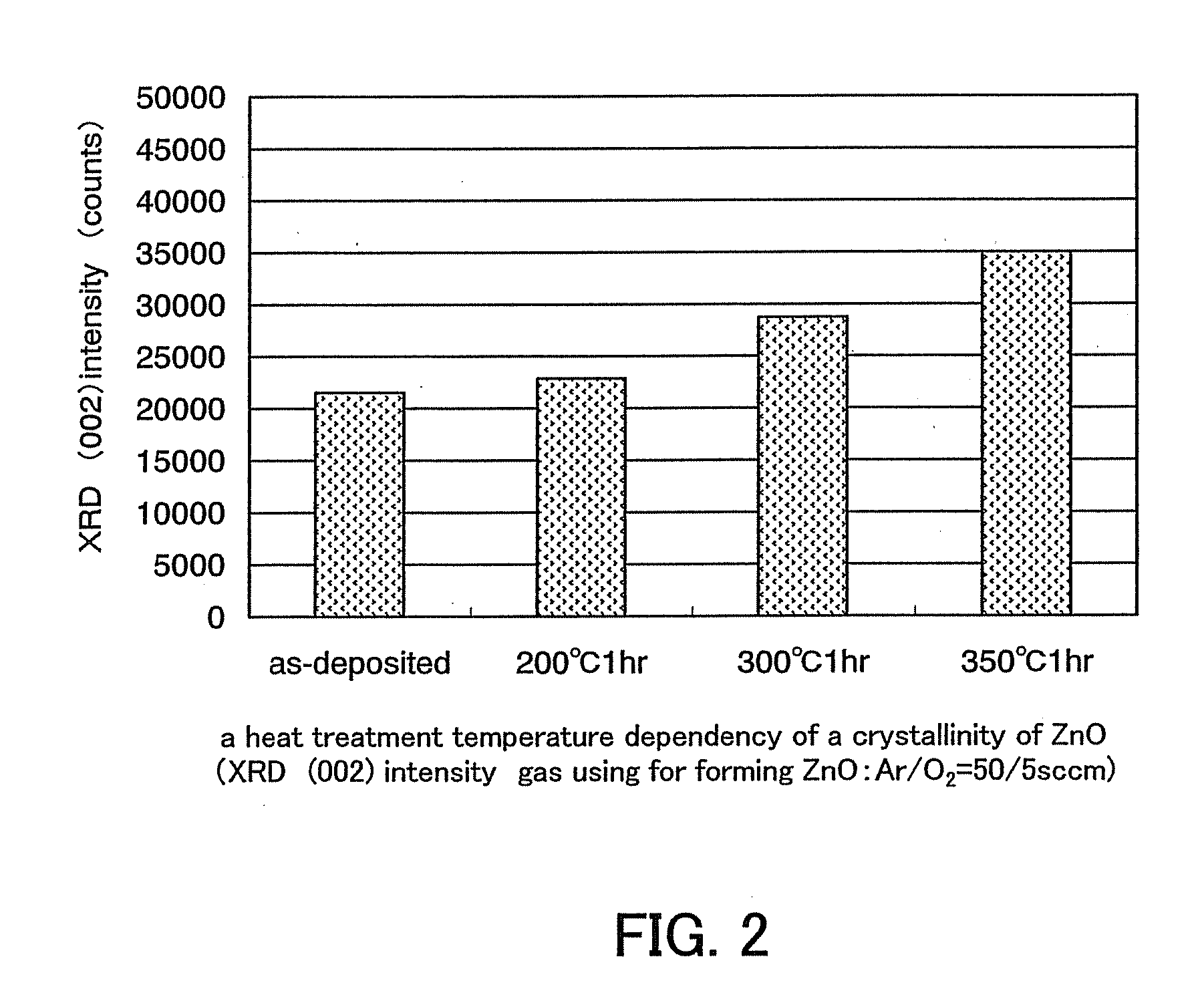
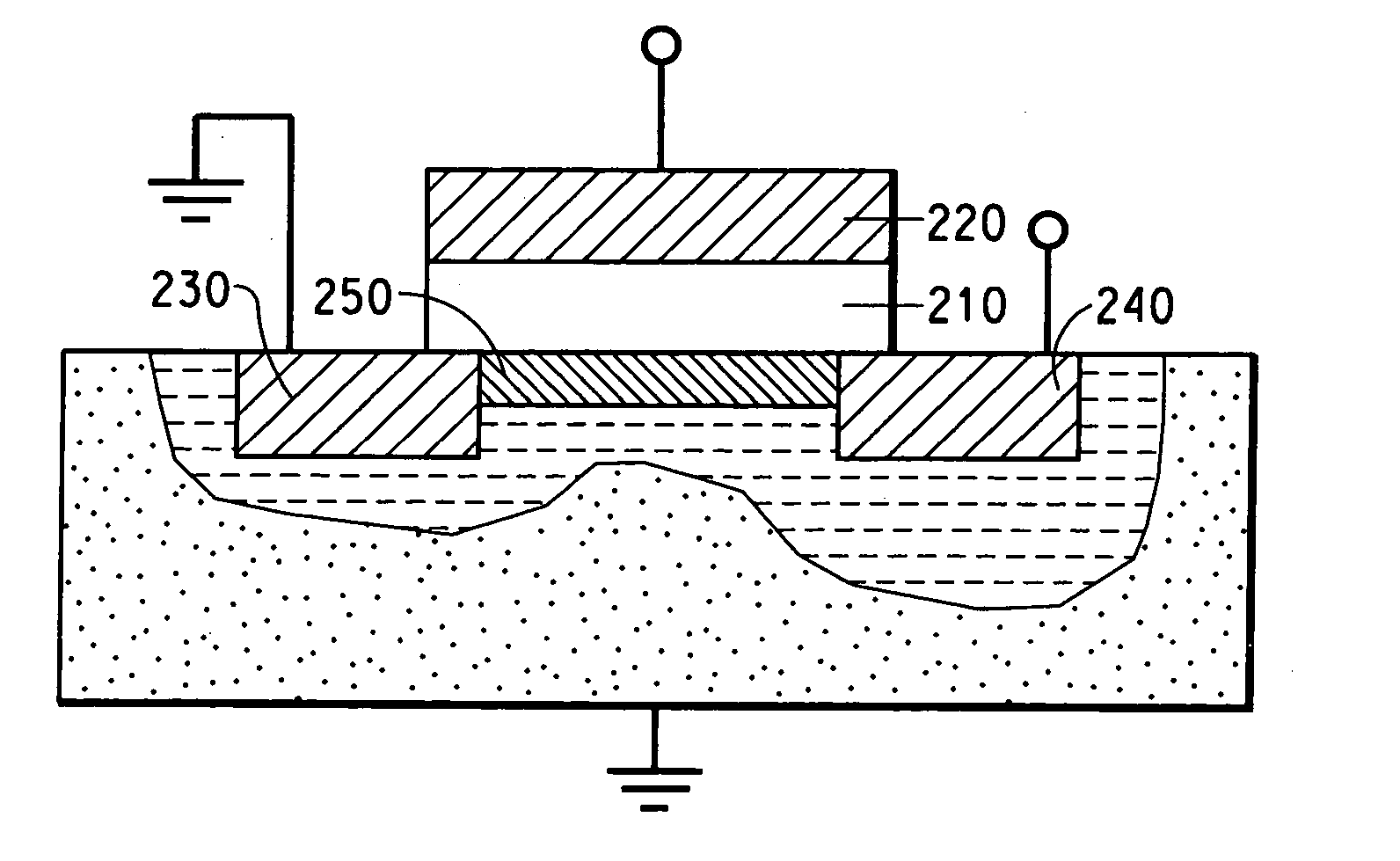
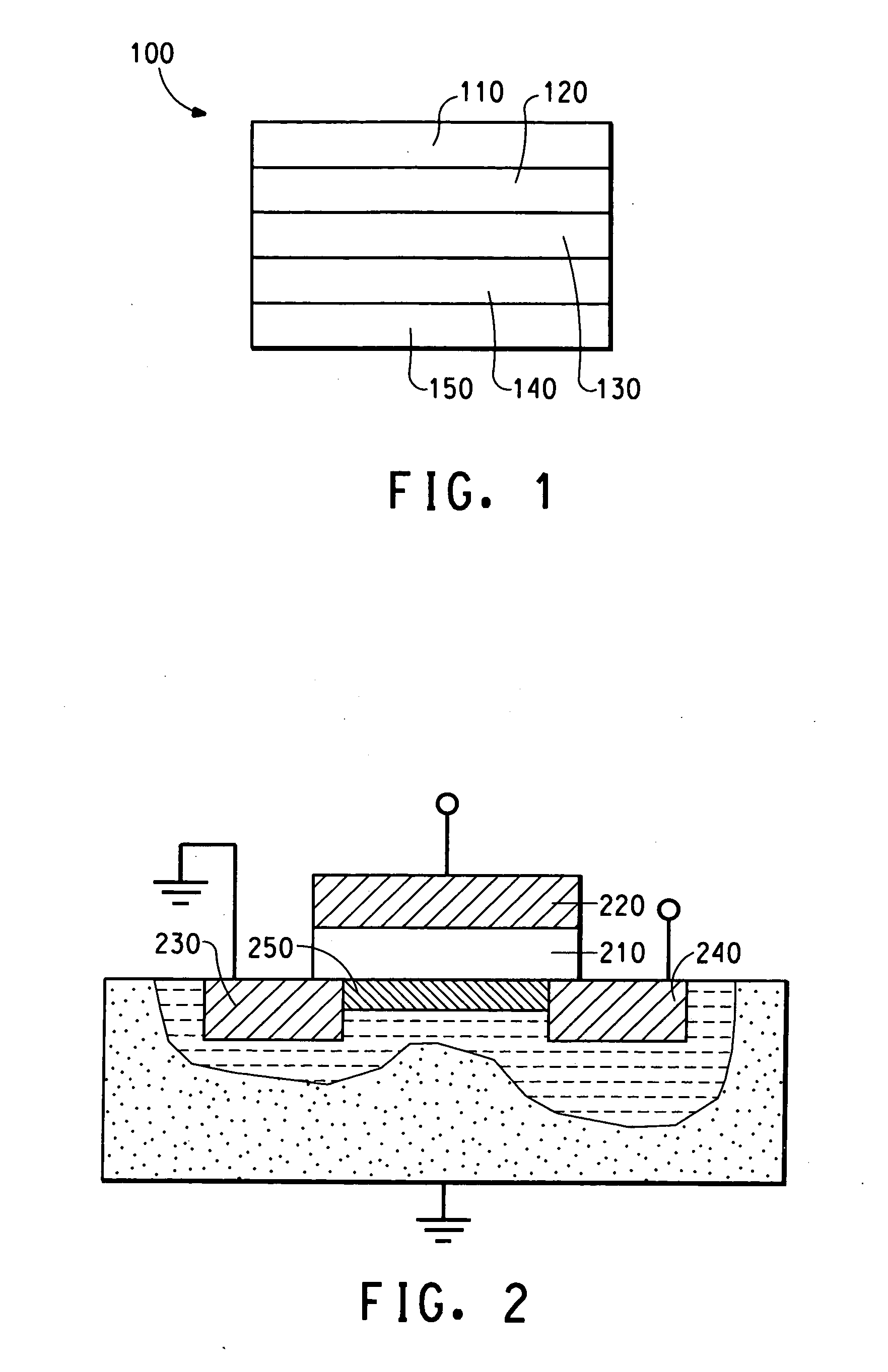
In a thin film transistor (1), a gate insulating layer (4) is formed on a gate electrode (3) formed on an insulating substrate (2). Formed on the gate insulating layer (4) is a semiconductor layer (5). Formed on the semiconductor layer (5) are a source electrode (6) and a drain electrode (7). A protective layer (8) covers them, so that the semiconductor layer (5) is blocked from an atmosphere. The semiconductor layer (5) (active layer) is made of, e.g., a semiconductor containing polycrystalline ZnO to which, e.g., a group V element is added. The protective layer (8) thus formed causes decrease of a surface level of the semiconductor layer (5). This eliminates a depletion layer spreading therewithin. Accordingly, the ZnO becomes an n-type semiconductor indicating an intrinsic resistance, with the result that too many free electrons are generated. However, the added element works on the ZnO as an accepter impurity, so that the free electrons are reduced. This decreases a gate voltage required for removal of the free electrons, so that the threshold voltage of the thin film transistor (1) becomes on the order of 0V. This allows practical use of a semiconductor device which has an active layer made of zinc oxide and which includes an protective layer for blocking the active layer from an atmosphere.
Owner:SHARP KK +2
Oxide semiconductor thin film transistor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070052025A1Improve reliabilityUnstability of may lessenSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Provided is a thin film transistor comprising a channel layer comprised of an oxide semiconductor containing In, M, Zn, and O, M including at least one selected from the group consisting of Ga, Al, and Fe. The channel layer is covered with a protective film.
Owner:CANON KK
Indium oxide-based thin film transistors and circuits
In electronic displays or imaging units, the control of pixels is achieved by an array of transistors. These transistors are in a thin film form and arranged in a two-dimensional configuration to form switching circuits, driving circuits or even read-out circuits. In this invention, thin film transistors and circuits with indium oxide-based channel layers are provided. These thin film transistors and circuits may be fabricated at low temperatures on various substrates and with high charge carrier mobilities. In addition to conventional rigid substrates, the present thin film transistors and circuits are particularly suited for the fabrication on flexible and transparent substrates for electronic display and imaging applications. Methods for the fabrication of the thin film transistors with indium oxide-based channels are provided.
Owner:SHIH YI CHI +3
Transparent oxide semiconductor thin film transistors
This invention relates to novel, transparent oxide semiconductor thin film transistors (TFT's) and a process for making them.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Methods of making thin film transistors comprising zinc-oxide-based semiconductor materials and transistors made thereby
ActiveUS7402506B2NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsZinc
A thin film transistor comprises a zinc-oxide-containing semiconductor material. Such transistors can further comprise spaced apart first and second contact means or electrodes in contact with said material. Further disclosed is a process for fabricating a thin film transistor device, wherein the substrate temperature is no more than 300° C. during fabrication.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
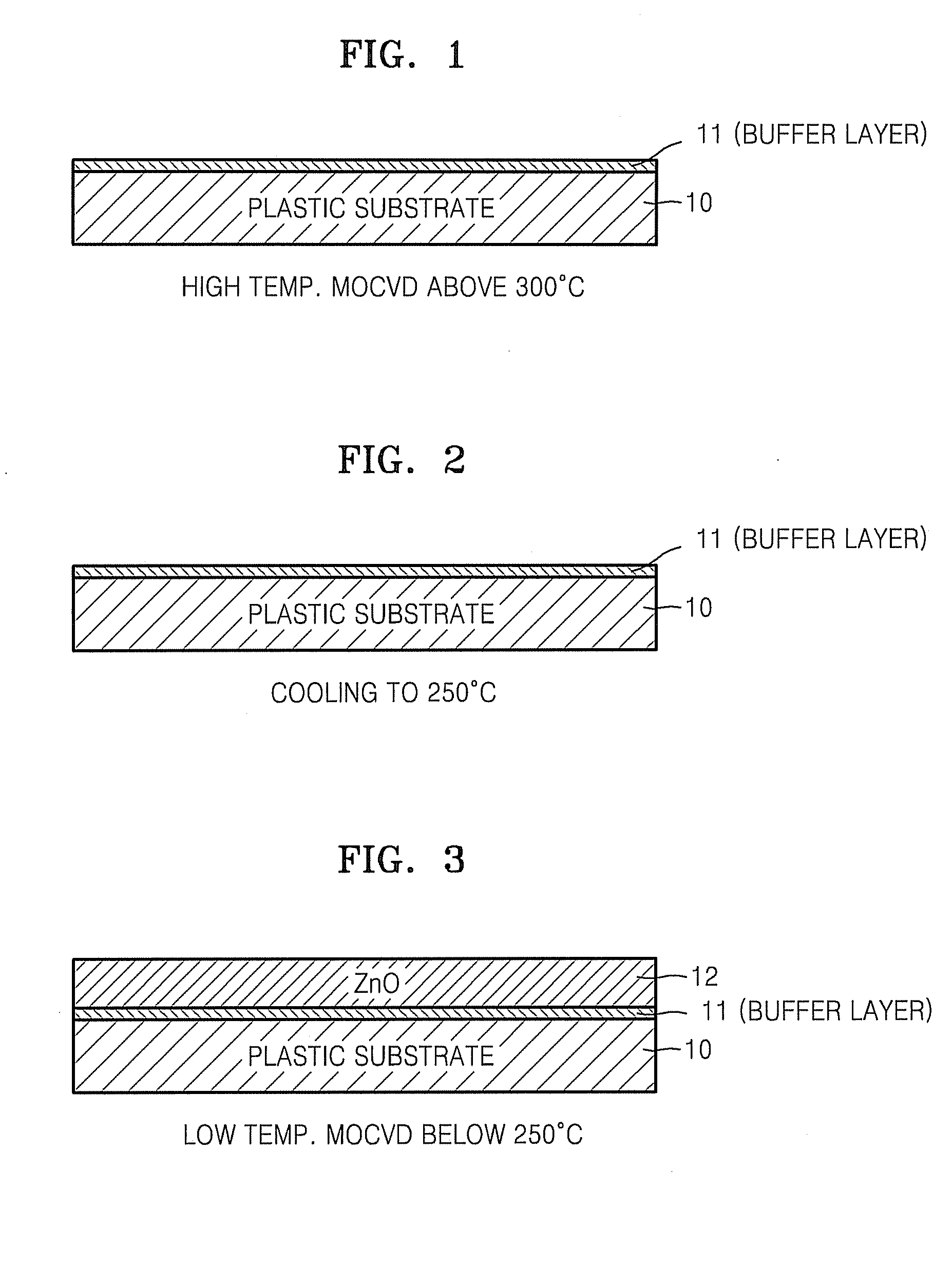
METHOD OF FABRICATING ZnO FILM AND THIN FILM TRANSISTOR ADOPTING THE ZnO FILM
InactiveUS20070172591A1Liquid surface applicatorsChemical vapor deposition coatingChemical vapor depositionMetal
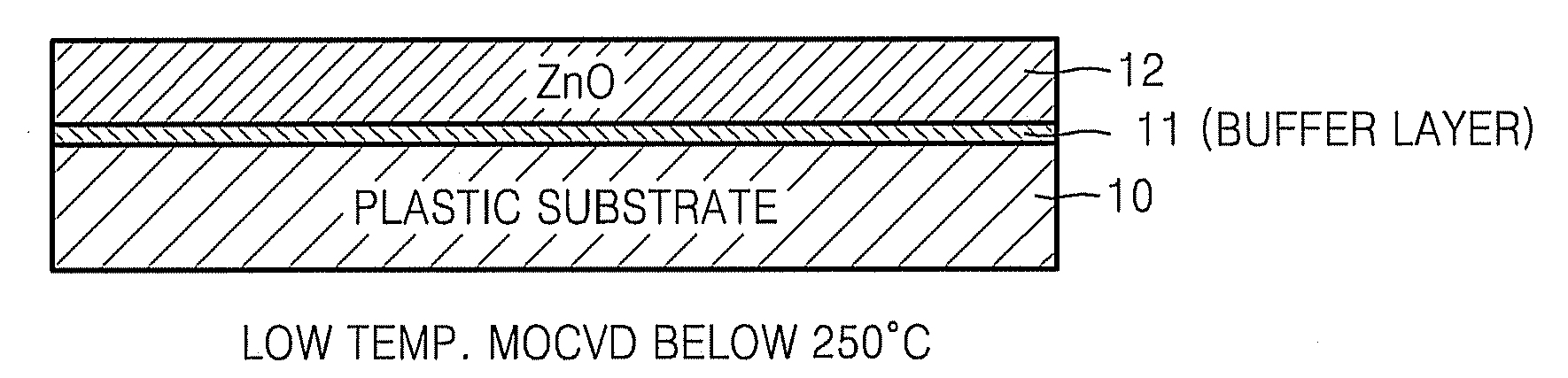
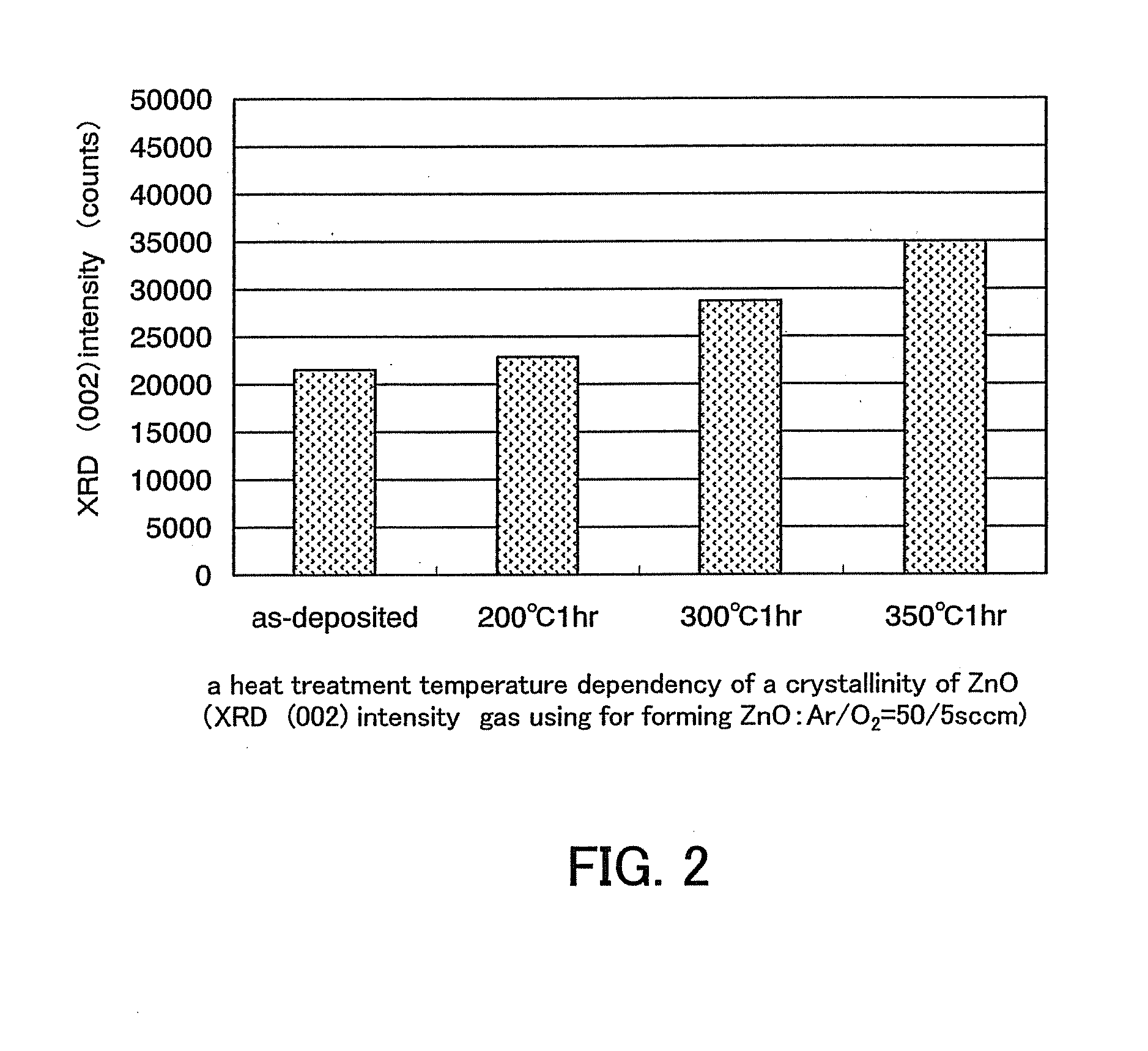
Provided is a method of fabricating a low temperature ZnO polycrystalline film and a thin film transistor (TFT) adopting the low temperature ZnO polycrystalline film. The method includes growing ZnO on a substrate at a first temperature for a first time using Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) to form a ZnO buffer layer, and heating the substrate at a temperature lower than the first temperature to grow ZnO on the ZnO buffer layer for a second time longer than the first time so as to form a ZnO film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Thin film transistor having an etching protection film and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7385224B2Improve machining accuracySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor thin films
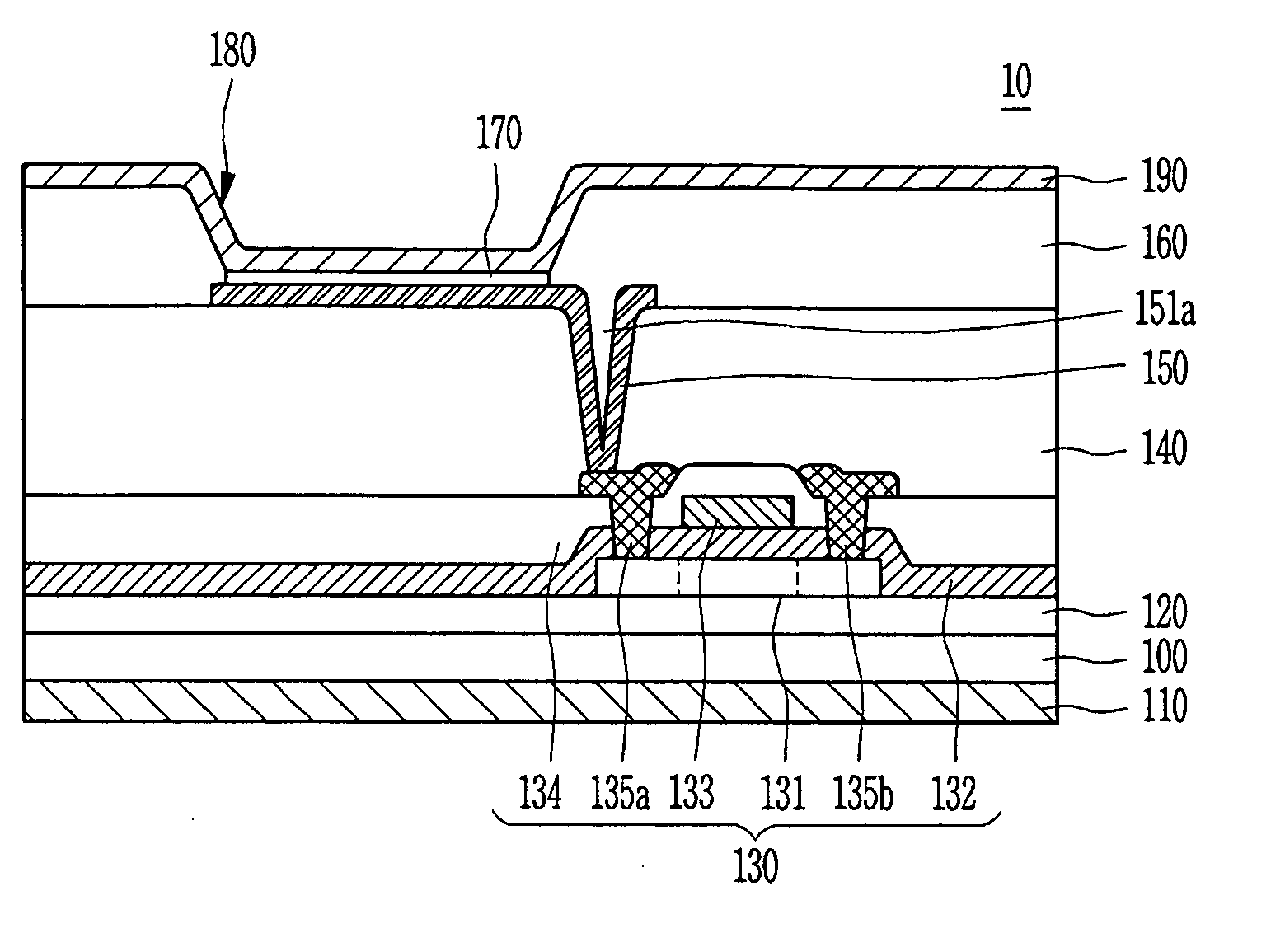
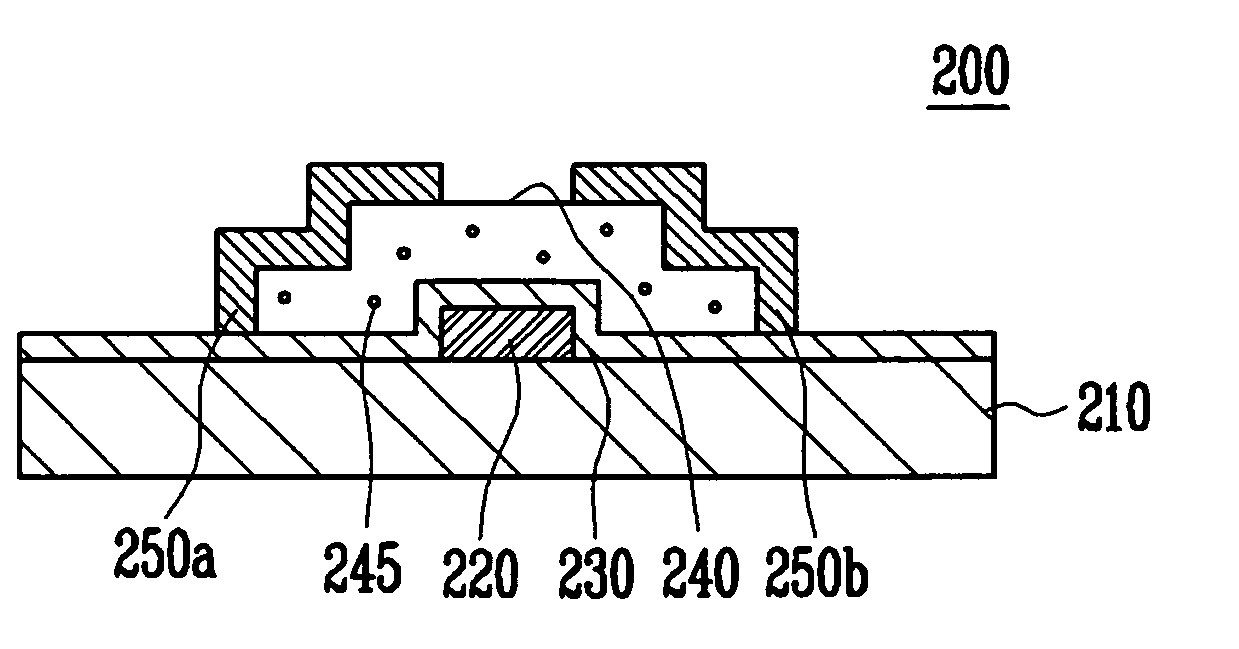
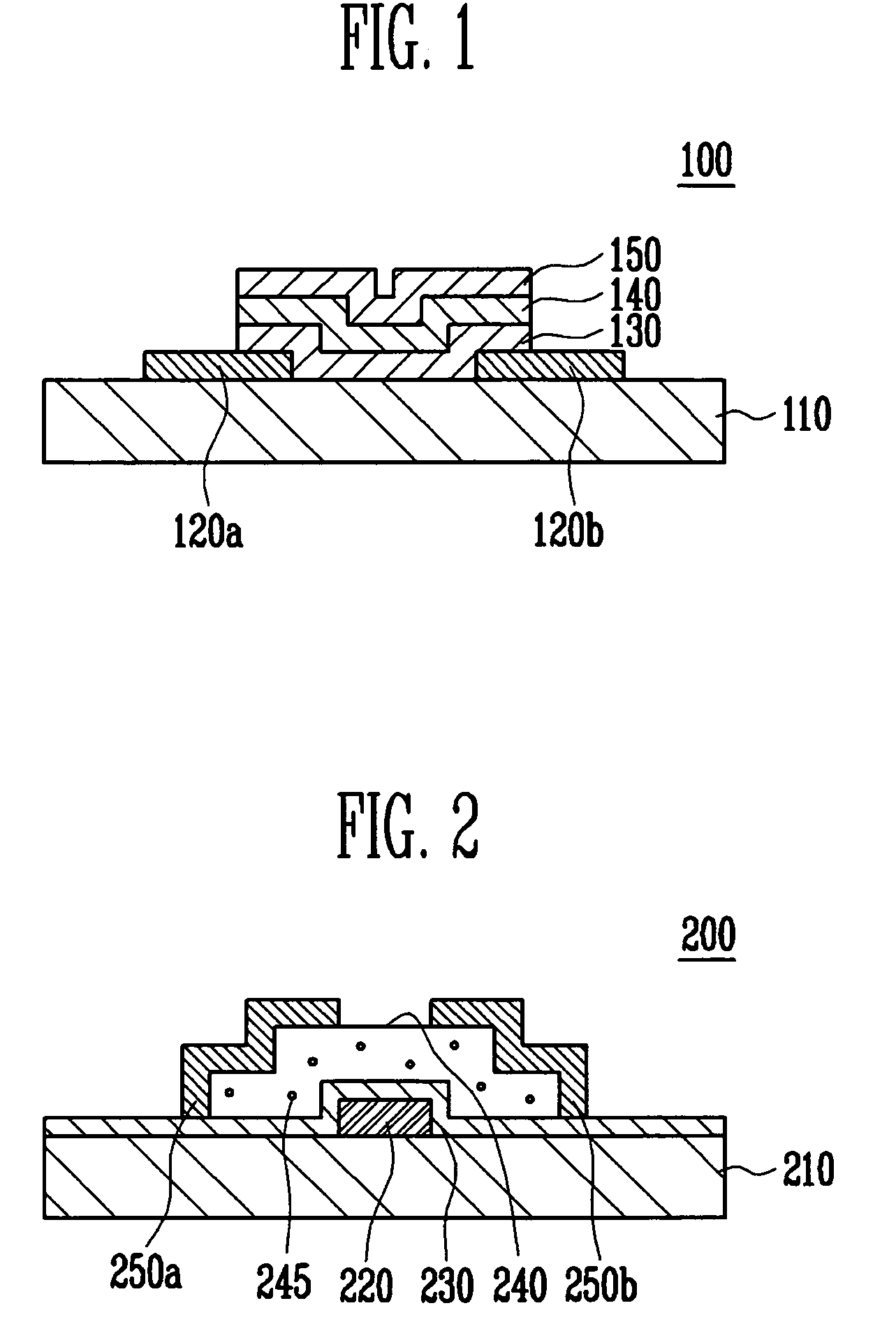
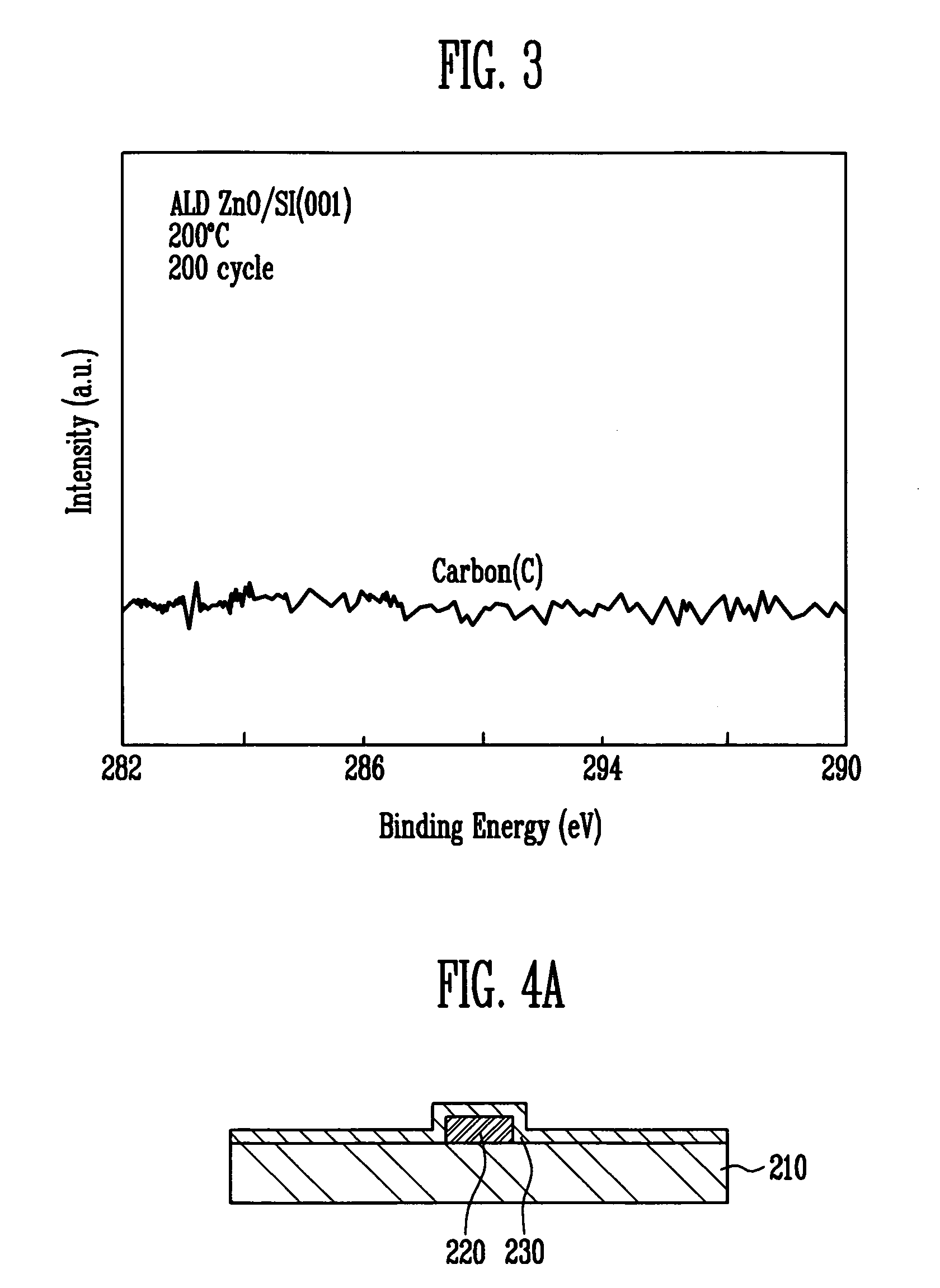
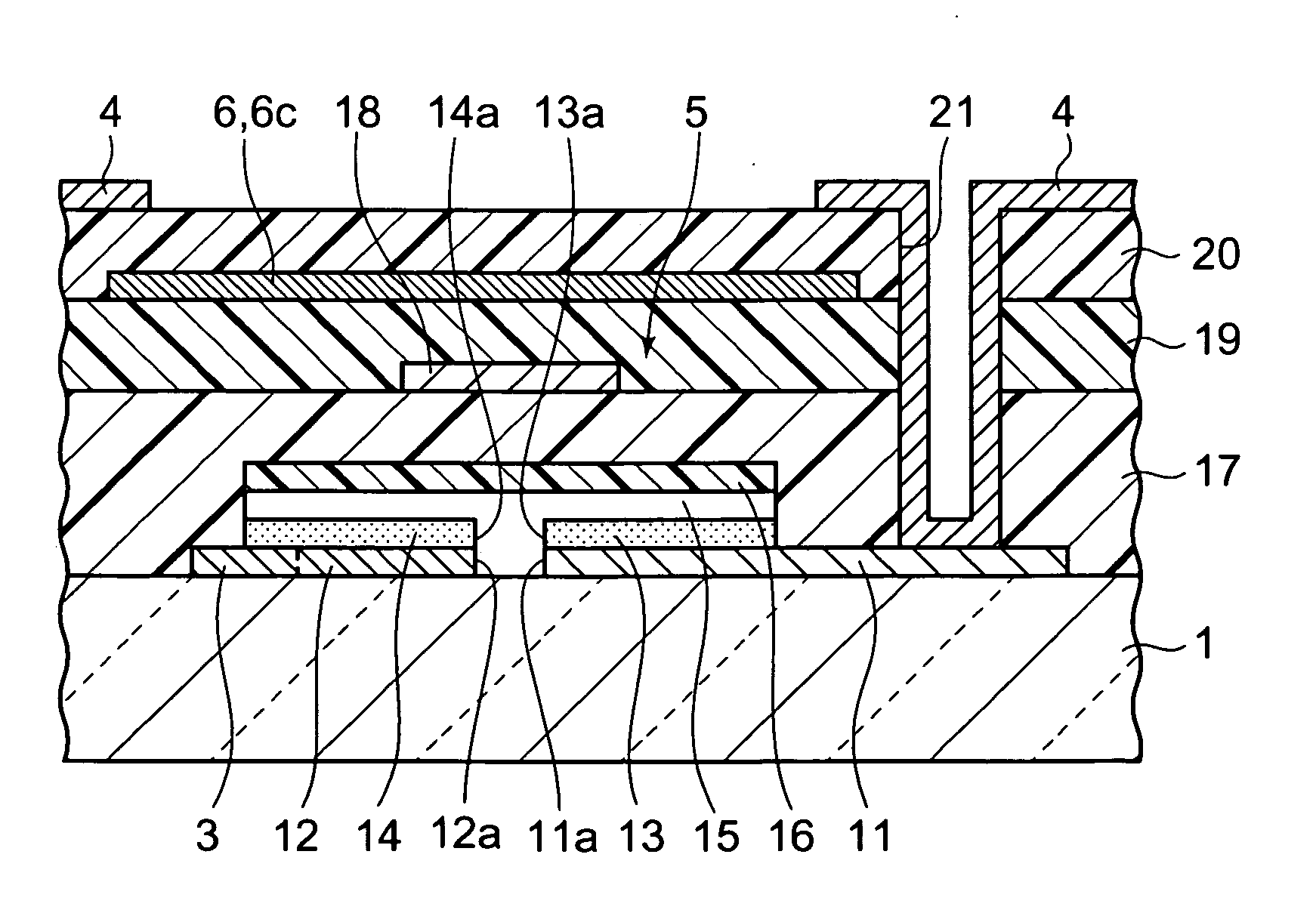
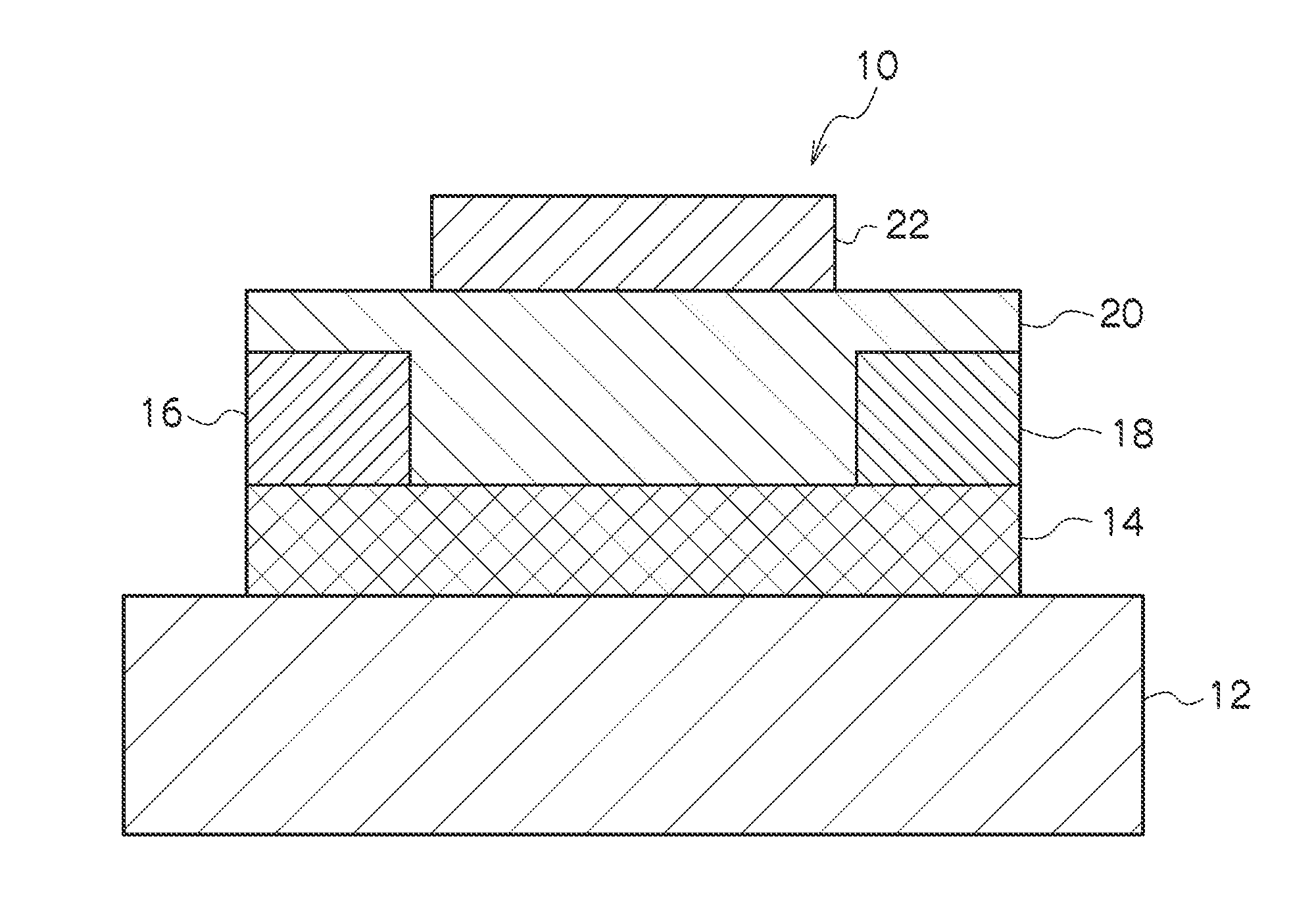
A thin film transistor of the present invention includes a semiconductor thin film (8); a gate insulating film (7) formed on one surface of the semiconductor thin film (8); a gate electrode (6) formed to be opposite to the semiconductor thin film (8) through the gate insulating film (7); a source electrode (15) and a drain electrode (16) electrically connected to the semiconductor thin film (8); a source region; a drain region; and a channel region. The thin film transistor further includes an insulating film (9) formed on a peripheral portion corresponding to at least the source region and the drain region of the semiconductor thin film (8), and having a contact hole (10, 11) through which at least a part of each of the source region and the drain region is exposed wherein the source electrode (15) and the drain electrode (16) are connected to the semiconductor thin film (8) through the contact hole (10, 11).
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
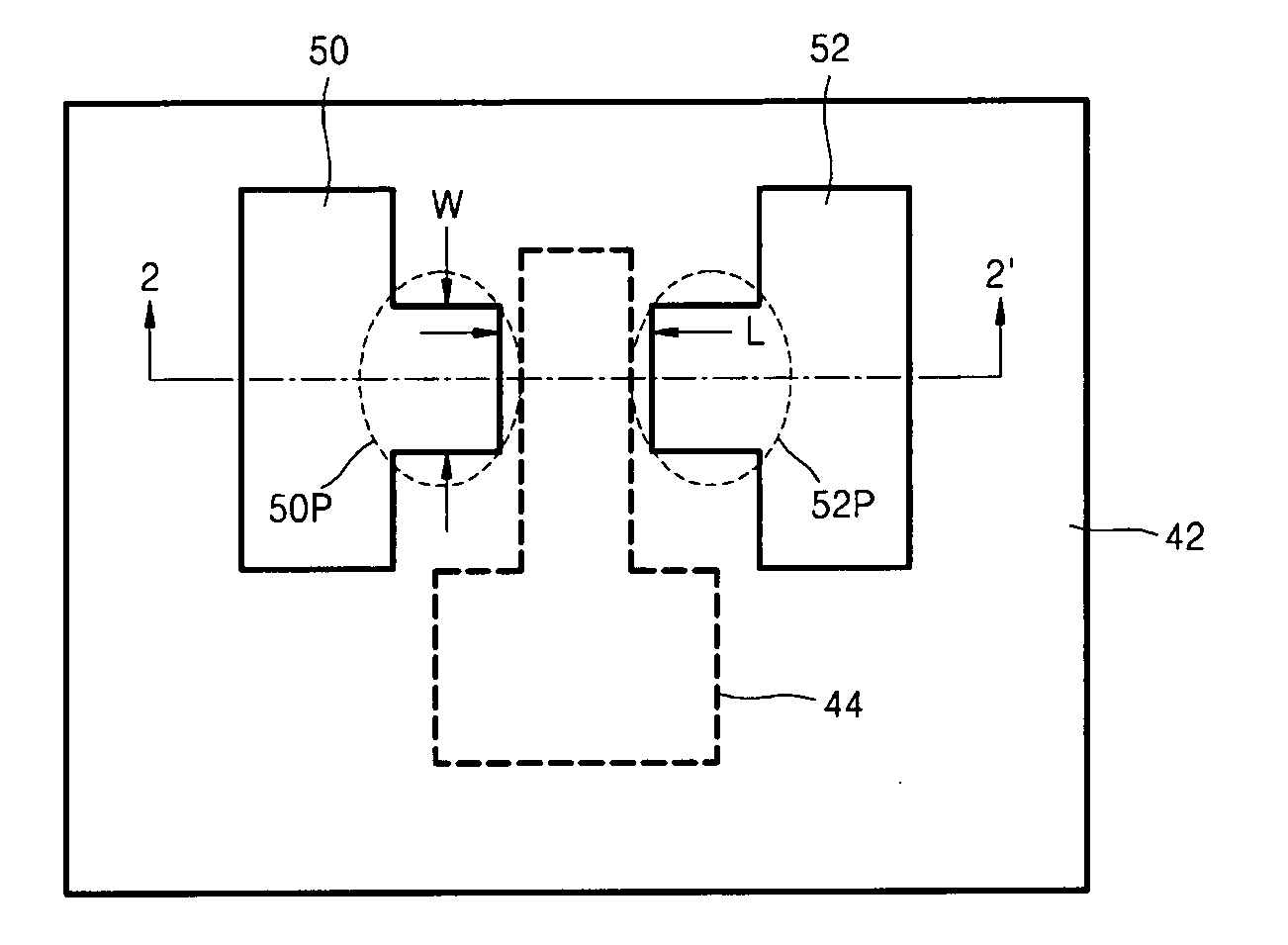
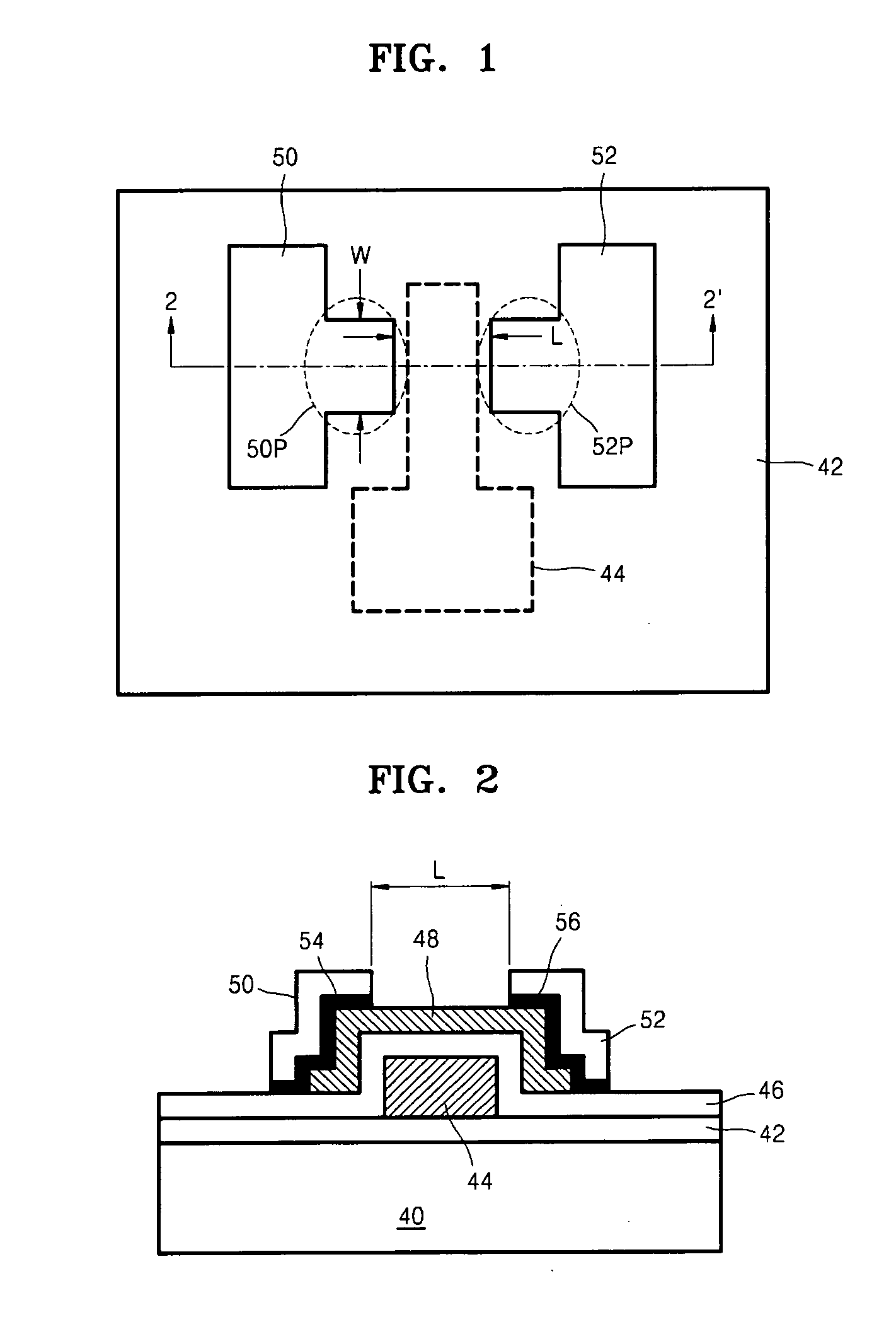
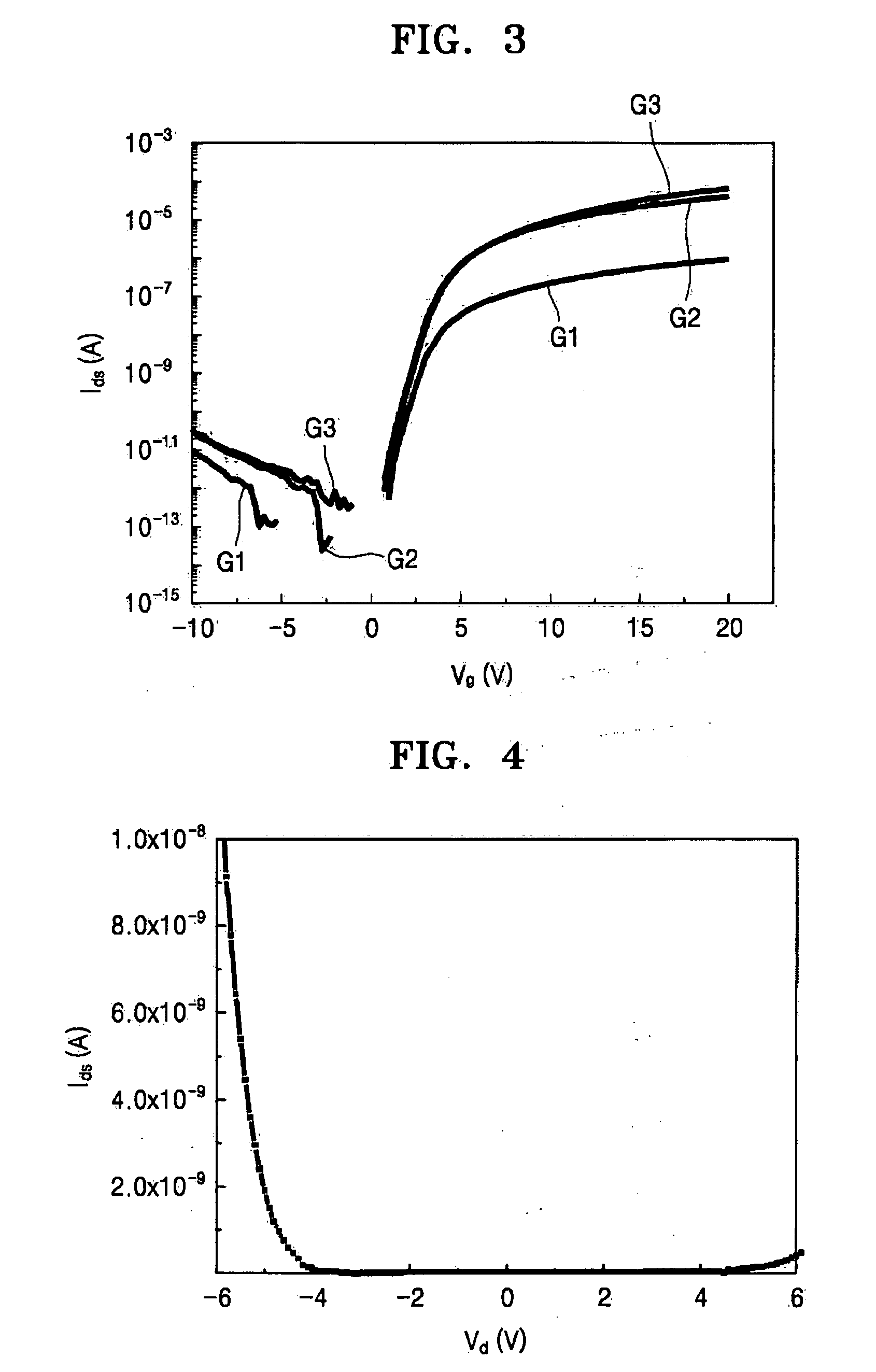
Thin film transistor including selectively crystallized channel layer and method of manufacturing the thin film transistor
ActiveUS20080258140A1Stable contact characteristicHigh carrier mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringIon implantation
Provided are a thin film transistor (TFT) including a selectively crystallized channel layer, and a method of manufacturing the TFT. The TFT includes a gate, the channel layer, a source, and a drain. The channel layer is formed of an oxide semiconductor, and at least a portion of the channel layer contacting the source and the drain is crystallized. In the method of manufacturing the TFT, the channel layer is formed of an oxide semiconductor, and a metal component is injected into the channel layer so as to crystallize at least a portion of the channel layer contacting the source and the drain. The metal component can be injected into the channel layer by depositing and heat-treating a metal layer or by ion-implantation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Color el display and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20080129195A1Quality improvementHigh color purityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention is a color EL display characterized in that at least color filters, a thin film transistor circuit, an organic EL layer, and a common electrode are laminated in this order on a transparent substrate. Another embodiment of the invention is a method for producing a color EL display comprising the steps of forming color filters or a transparent substrate; forming a thin film transistor circuit; forming an organic EL layer; and forming a common electrode, wherein process temperatures of the steps of forming the thin film transistor circuit and subsequent steps are 200° C. or less.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Organic light emitting display (OLED) and its method of fabrication
ActiveUS20070024187A1Improve visibilityIncrease contrastDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic light emitting deviceOptoelectronics
An Organic Light Emitting Display (OLED) and its method of fabrication includes: a transparent substrate; a photochromatic layer formed on a first surface of the transparent substrate; at least one transparent Thin Film Transistor (TFT) formed on a first surface of the transparent substrate, and an organic light emitting device formed on and electrically connected to the transparent TFT.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090114910A1Uniform and high stabilityIncrease productionTransistorSolid-state devicesIn planeDevice material
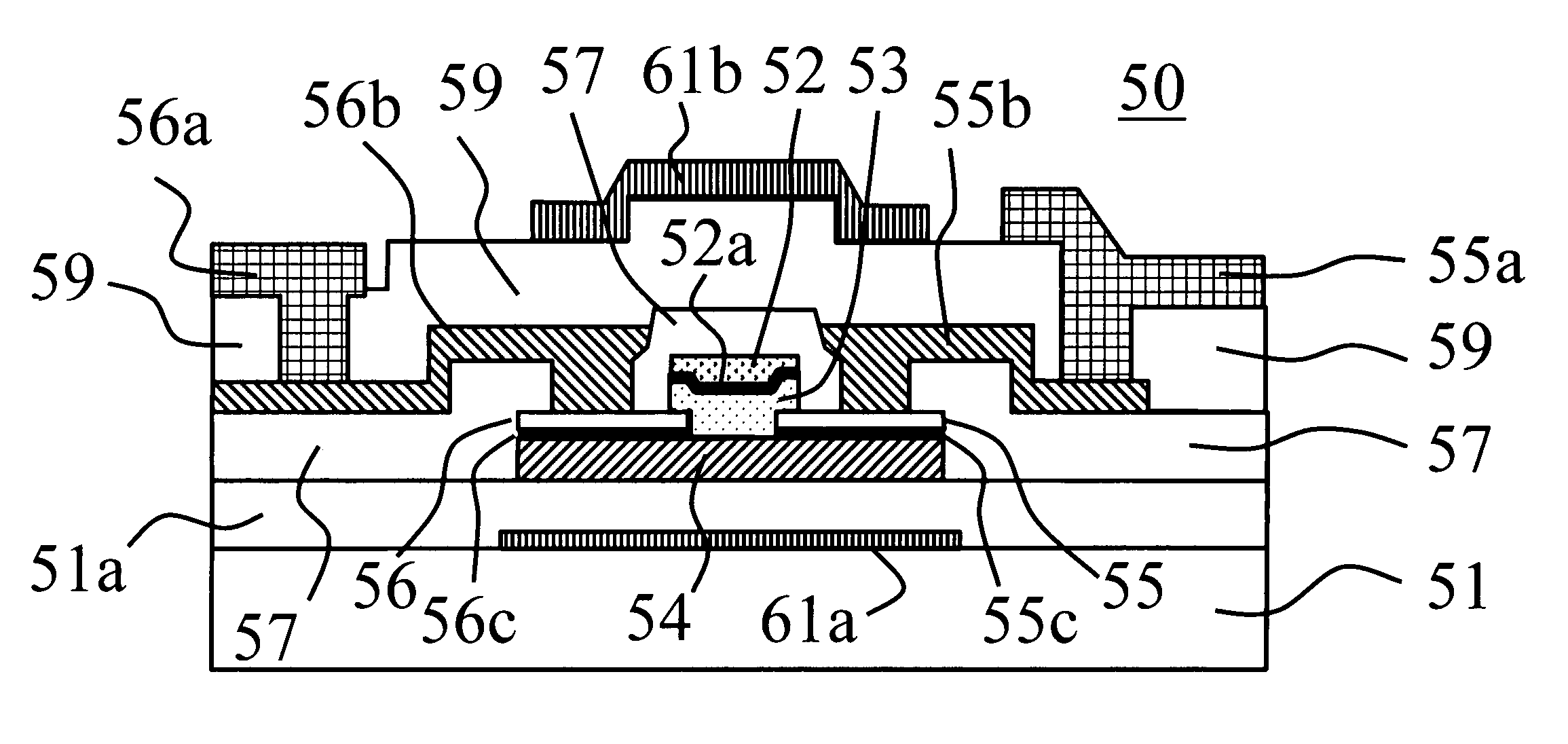
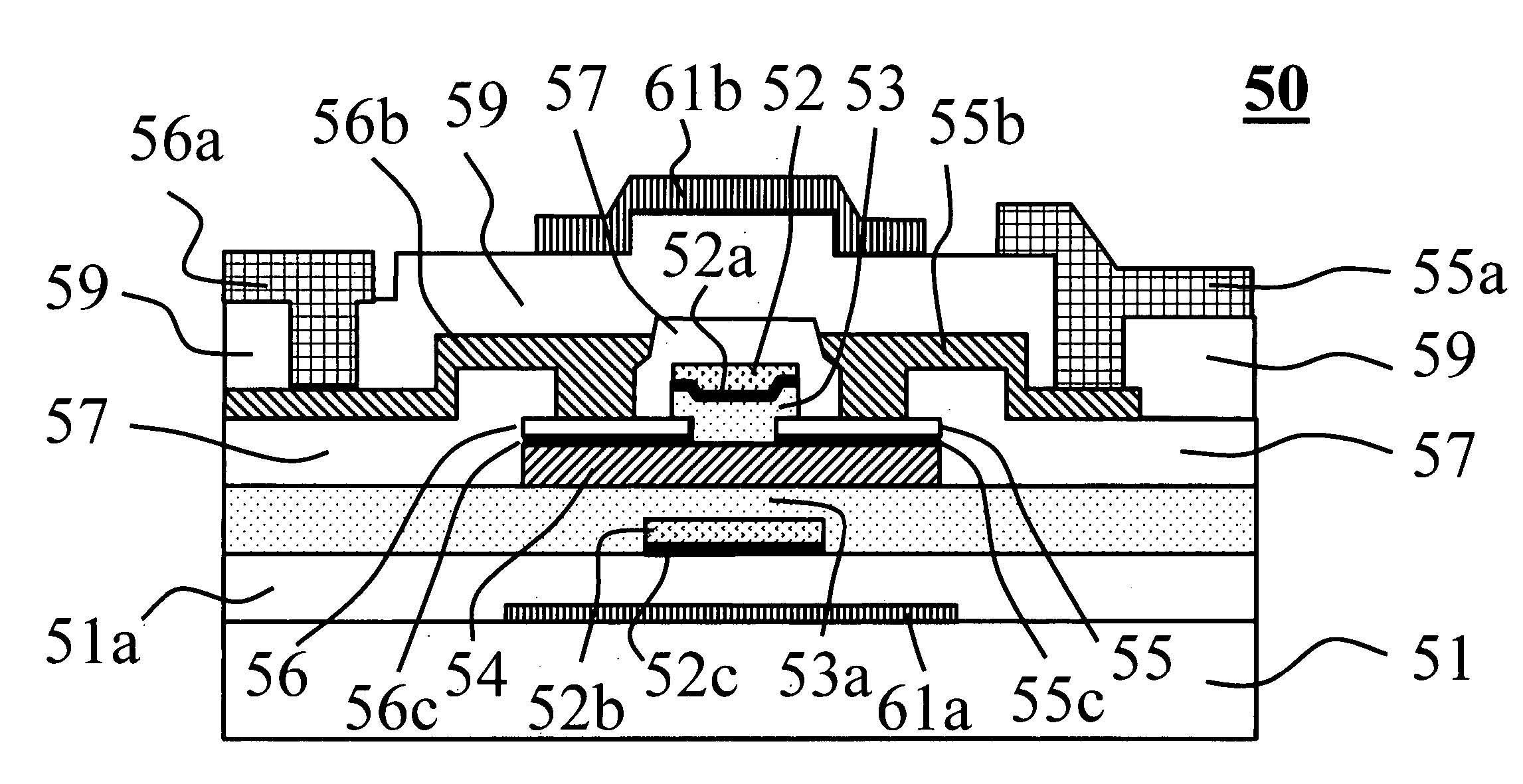
In the present invention, a thin film transistor is formed on a plastic film substrate (1) having anisotropy of thermal shrinkage rate or coefficient of thermal expansion in in-plane directions of the substrate. A channel is formed such thatthe direction (7) in which the thermal shrinkage rate or the coefficient of thermal expansion of the substrate is largest is nonparallel tothe direction (8) of a current flowing through the channel of the thin film transistor. Then, a thin film transistor having stable and uniform electrical characteristics, which is formed on the plastic film substrate, is provided.
Owner:CANON KK
Thin film transistor and organic light-emitting display device having the thin film transistor
InactiveUS20080224133A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenDisplay device
Disclosed is a thin film transistor including a P-type semiconductor layer, and an organic light-emitting display device having the thin film transistor. The present invention provides a thin film transistor including a substrate, a semiconductor layer, and a gate electrode and a source / drain electrode formed on the substrate, wherein the semiconductor layer is composed of P-type ZnO:N layers through a reaction of a mono-nitrogen gas with a zinc precursor, and the ZnO:N layer includes an un-reacted impurity element at a content of 3 at % or less.
Owner:SAMSUNG MOBILE DISPLAY CO LTD
Methods of making thin film transistors comprising zinc-oxide-based semiconductor materials and transistors made thereby
A thin film transistor comprises a zinc-oxide-containing semiconductor material. Such transistors can further comprise spaced apart first and second contact means or electrodes in contact with said material. Further disclosed is a process for fabricating a thin film transistor device, wherein the substrate temperature is no more than 300° C. during fabrication.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Thin film transistor having oxide semiconductor layer and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060284172A1Etch resistance of resist is lowPromote meltingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZincSemiconductor
A thin film transistor has a semiconductor thin film including zinc oxide, a protection film formed on entirely the upper surface of the semiconductor thin film, a gate insulating film formed on the protection film, a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film above the semiconductor thin film, and a source electrode and drain electrode formed under the semiconductor thin film so as to be electrically connected to the semiconductor thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
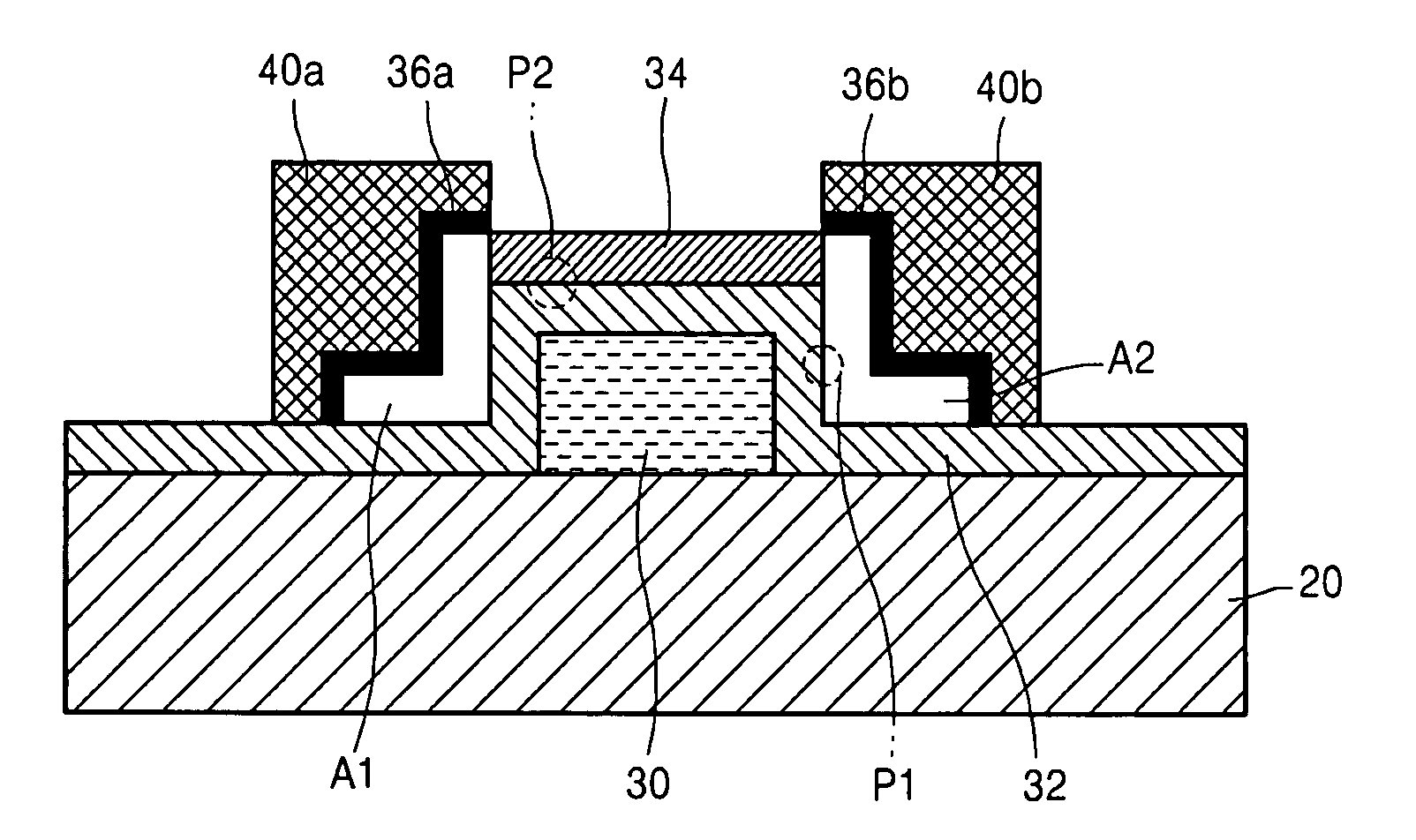
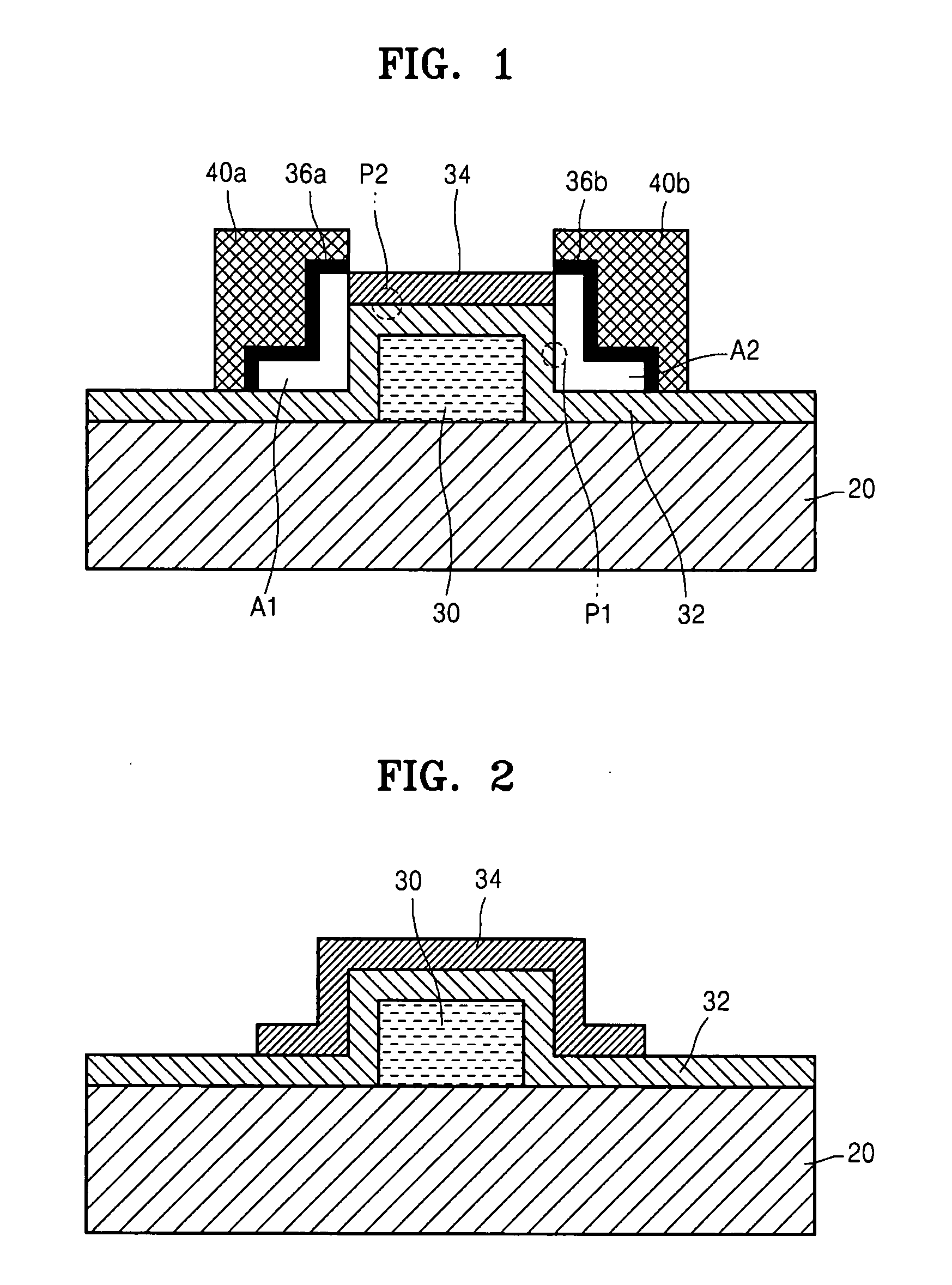
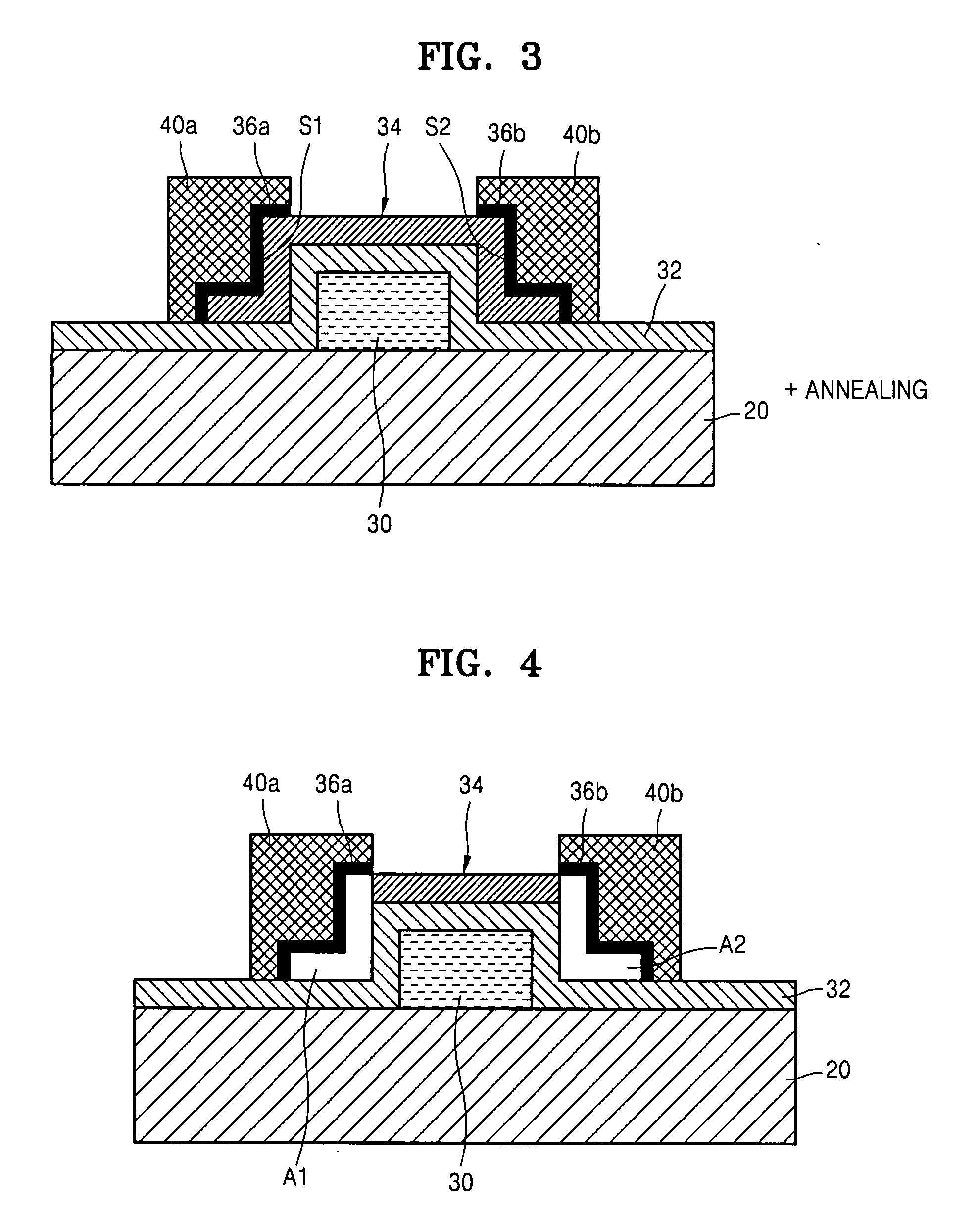
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method and apparatus for integrating manual input
InactiveUS6888536B2Simple methodEasy to learnInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisLow noiseBiomechanics
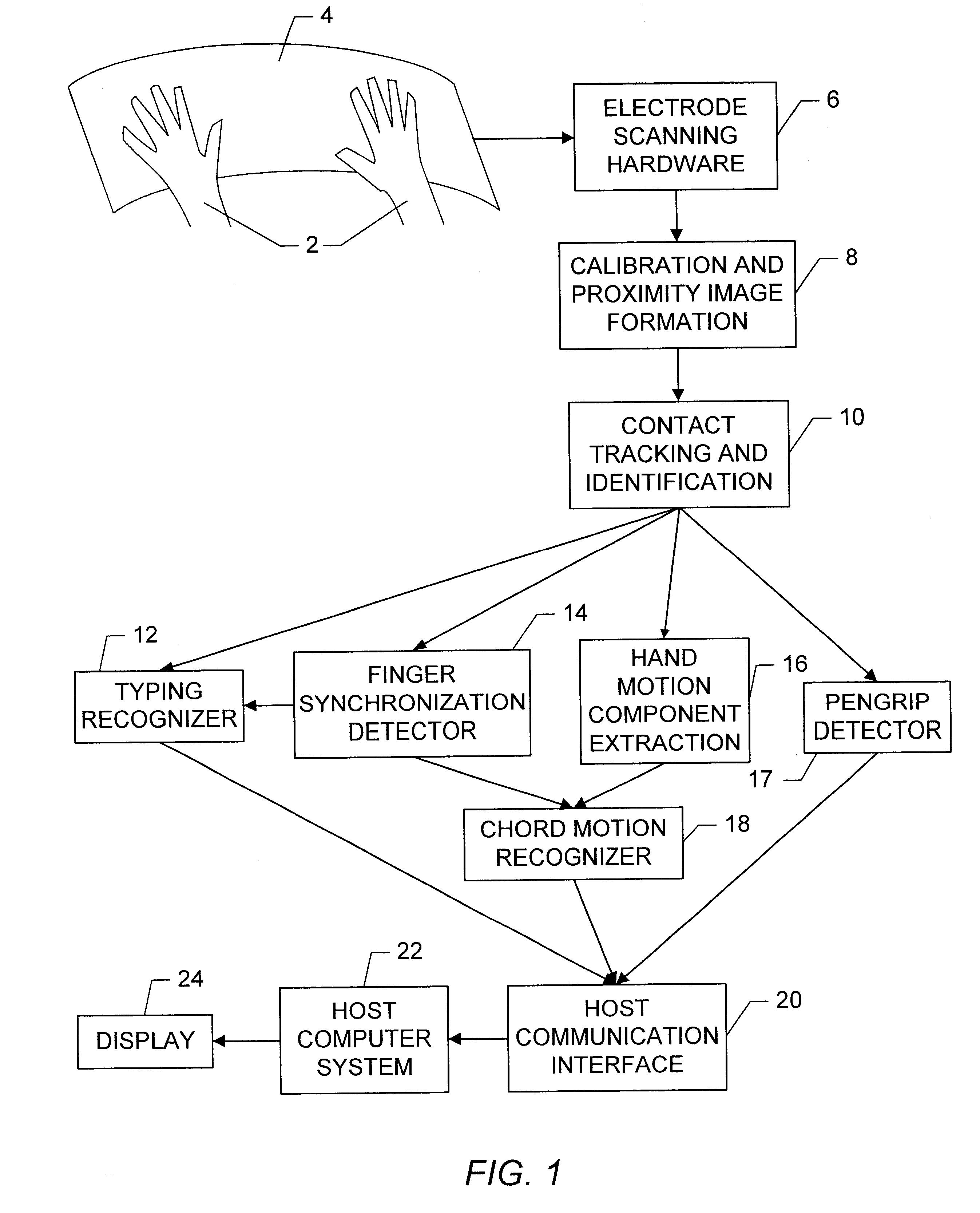
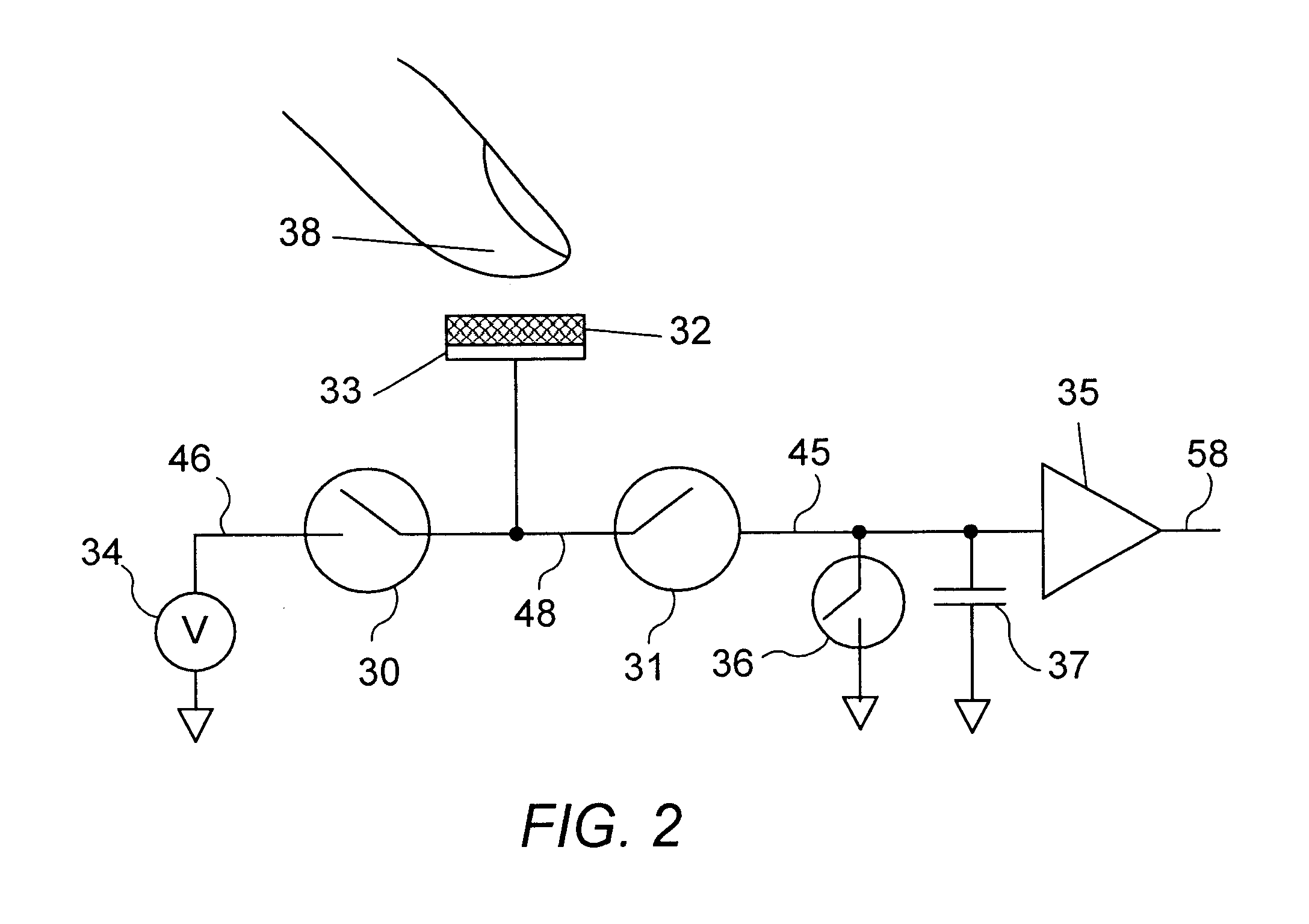
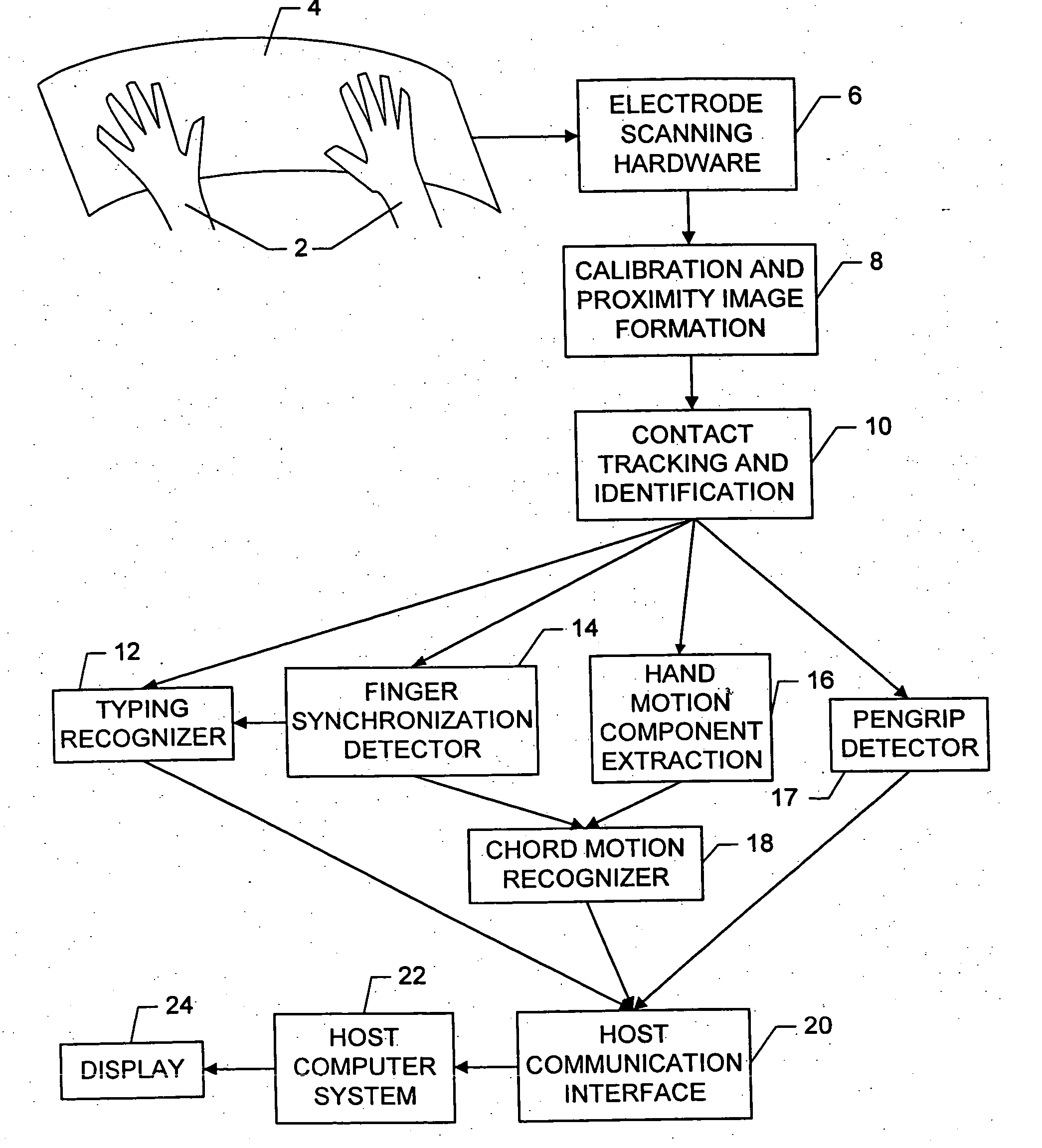
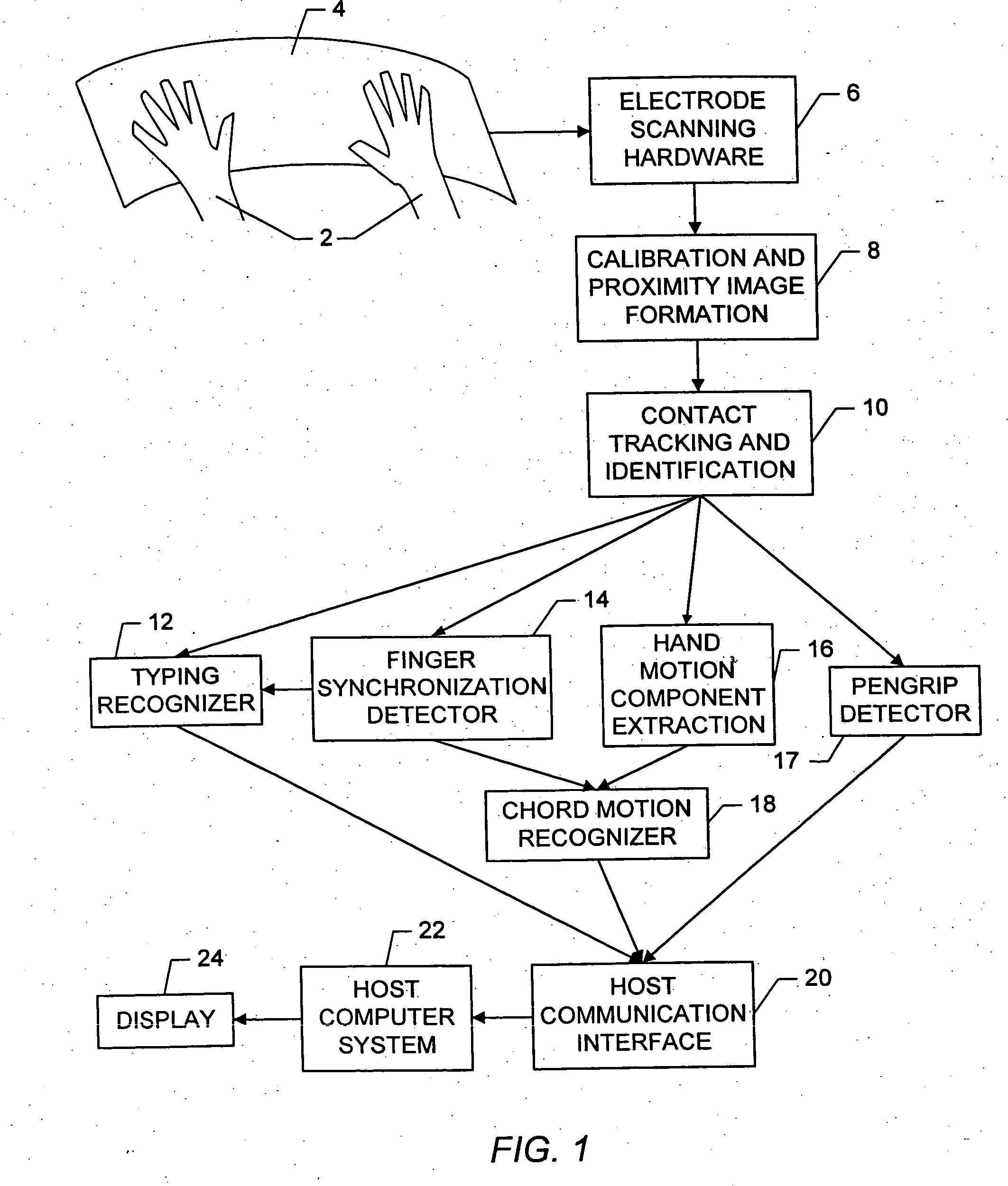
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for simultaneously tracking multiple finger and palm contacts as hands approach, touch, and slide across a proximity-sensing. compliant, and flexible multi-touch surface. The surface consists of compressible cushion, dielectric, electrode, and circuitry layers. A simple proximity transduction circuit is placed under each electrode to maximize signal-to-noise ratio and to reduce wiring complexity. Such distributed transduction circuitry is economical for large surfaces when implemented with thin-film transistor techniques. Scanning and signal offset removal on an electrode array produces low-noise proximity images. Segmentation processing of each proximity image constructs a group of electrodes corresponding to each distinguishable contact and extracts shape, position and surface proximity features for each group. Groups in successive images which correspond to the same hand contact are linked by a persistent path tracker which also detects individual contact touchdown and liftoff. Combinatorial optimization modules associate each contact's path with a particular fingertip, thumb, or palm of either hand on the basis of biomechanical constraints and contact features. Classification of intuitive hand configurations and motions enables unprecedented integration of typing, resting, pointing, scrolling, 3D manipulation, and handwriting into a versatile, ergonomic computer input device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080308797A1High yieldReduce the ratioTransistorDischarge tube luminescnet screensEngineeringZinc
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Indium oxide-based thin film transistors and circuits
In electronic displays or imaging units, the control of pixels is achieved by an array of transistors. These transistors are in a thin film form and arranged in a two-dimensional configuration to form switching circuits, driving circuits or even read-out circuits. In this invention, thin film transistors and circuits with indium oxide-based channel layers are provided. These thin film transistors and circuits may be fabricated at low temperatures on various substrates and with high charge carrier mobilities. In addition to conventional rigid substrates, the present thin film transistors and circuits are particularly suited for the fabrication on flexible and transparent substrates for electronic display and imaging applications. Methods for the fabrication of the thin film transistors with indium oxide-based channels are provided.
Owner:SHIH YI CHI +3
Current drive circuit and display device using the same, pixel circuit, and drive method
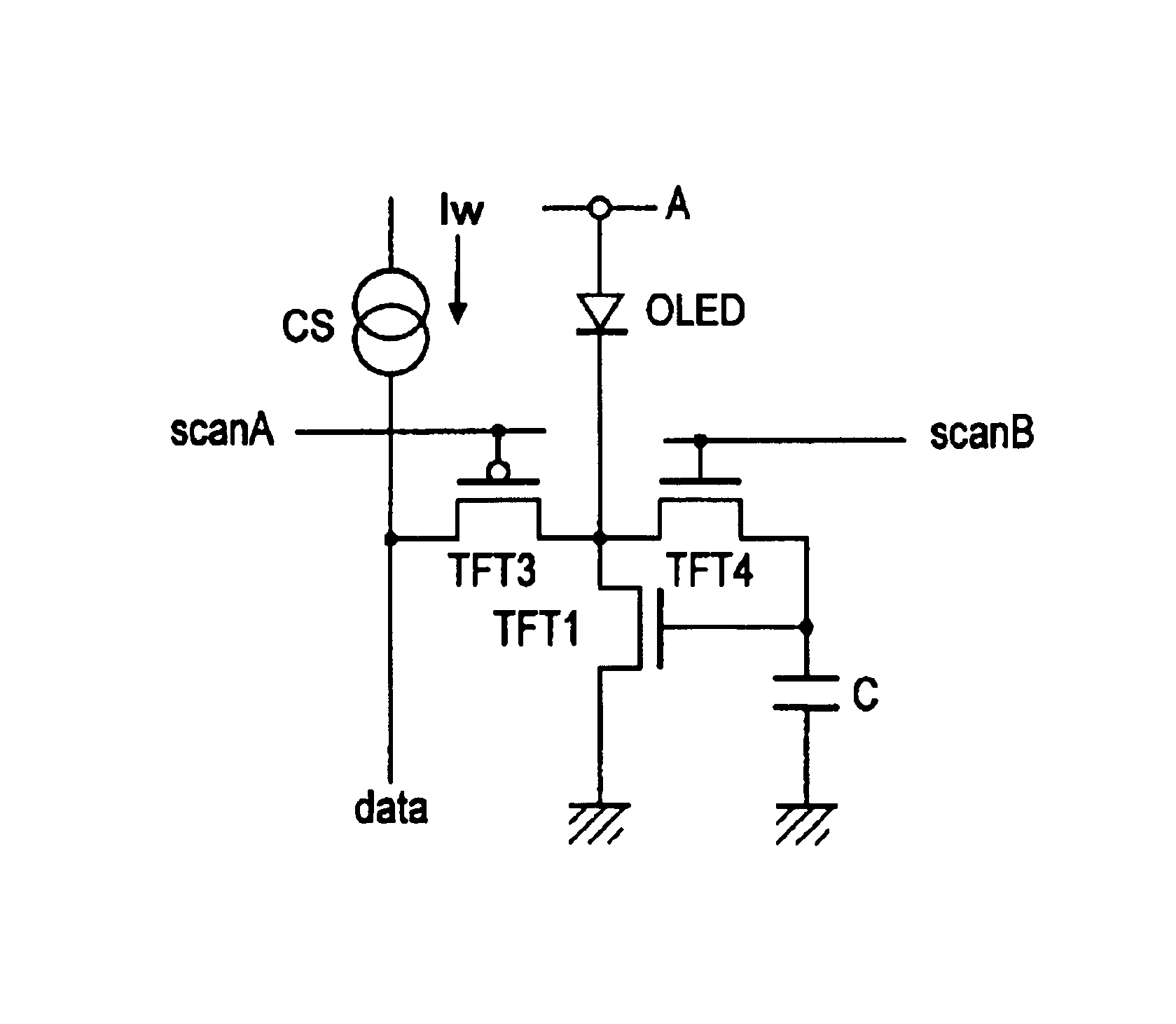
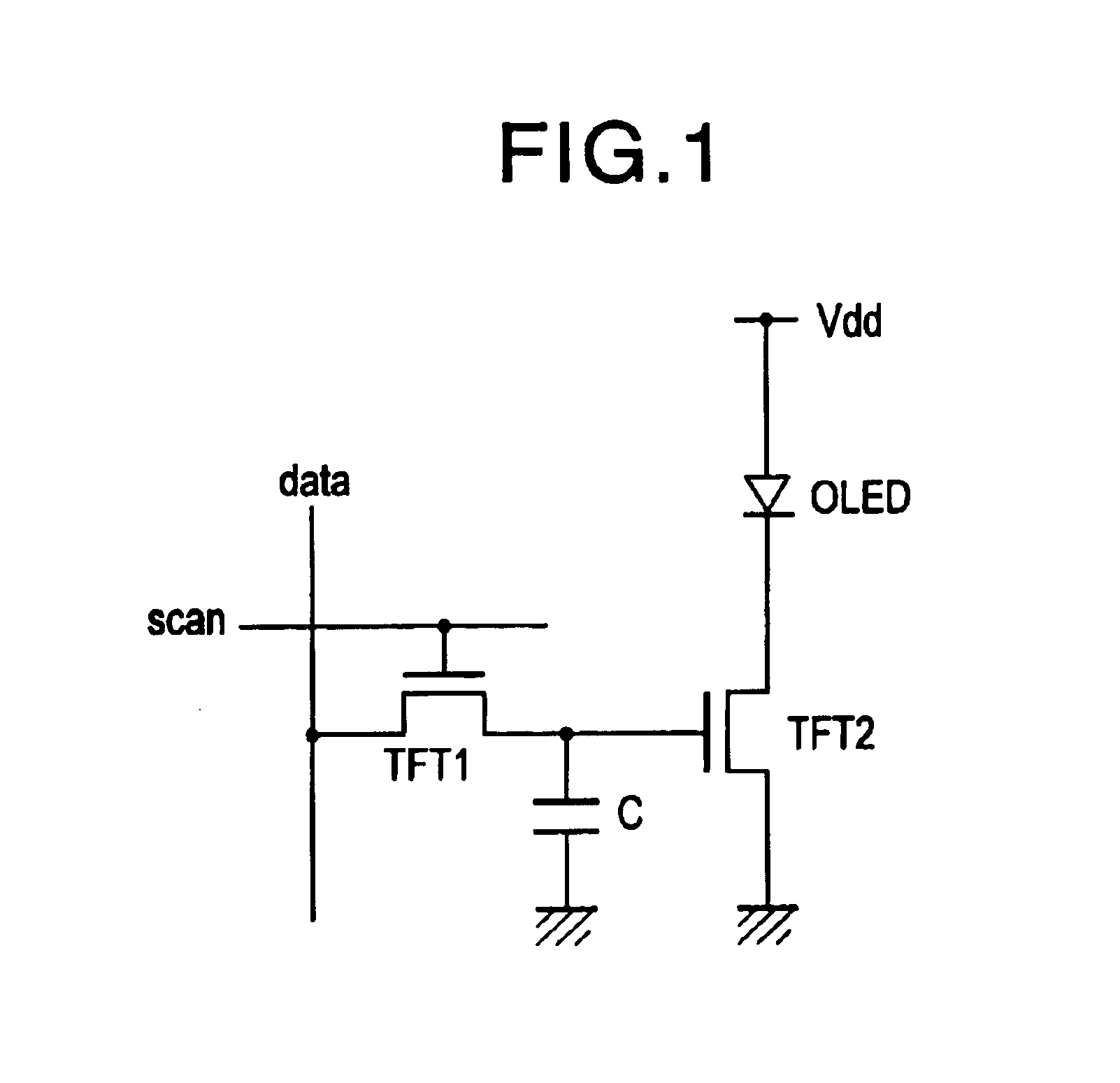
InactiveUS6859193B1Stably and accurately supplyingHigh quality imagingSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriving currentDisplay device
A display including a current drive circuit capable of supplying a desired current to a light-emitting element in each pixel stably and accurately irrespective of the characteristic variations of active elements in the pixel, thereby providing a high-definition image. Each pixel is composed of a receiving transistor (TFT3) for receiving a signal current (1w) from a data ine (data) when a scanning line (scanA) is selected, a converting transistor (TFT1) for converting the current level of the received signal current (1w) to a voltage level and holding the voltage level, and a driving transistor (TFT3) for allowing a drive current having a current level corresponding to the held voltage level to flow through light-emitting element (OLED). The converting thin film transistor (TFT1) generates the converted voltage level at its gate by allowing the signal current (Iw) through its channel, and a capacitor (C) holds the voltage level at the gate of the transistor (TFT1). The transistor (TFT2) allows the drive current having a current level corresponding to the voltage level held by the capacitor (C) to flow through the light-emitting element (OLED).
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing the same and flat panel display device having the same
ActiveUS8148779B2Improve featuresAvoid chargingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrappingEngineering
A thin film transistor (TFT) using an oxide semiconductor as an active layer, a method of manufacturing the TFT, and a flat panel display device having the TFT include a gate electrode formed on a substrate; an active layer made of an oxide semiconductor and insulated from the gate electrode by a gate insulating layer; source and drain electrodes coupled to the active layer; and an interfacial stability layer formed on one or both surfaces of the active layer. In the TFT, the interfacial stability layer is formed of an oxide having a band gap of 3.0 to 8.0 eV. Since the interfacial stability layer has the same characteristic as a gate insulating layer and a passivation layer, chemically high interface stability is maintained. Since the interfacial stability layer has a band gap equal to or greater than that of the active layer, charge trapping is physically prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Thin film transistor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080203387A1Improve featuresSmooth connectionTransistorSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsMaterials science
Provided are a thin film transistor and a method of manufacturing the same. The thin film transistor may include a gate; a channel layer; a source and a drain, the source and the drain being formed of metal; and a metal oxide layer, the metal oxide layer being formed between the channel layer and the source and the drain. The metal oxide layer may have a gradually changing metal content between the channel layer and the source and the drain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Thin film transistor and method of producing thin film transistor
ActiveUS20100320459A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin membraneCrystal structure
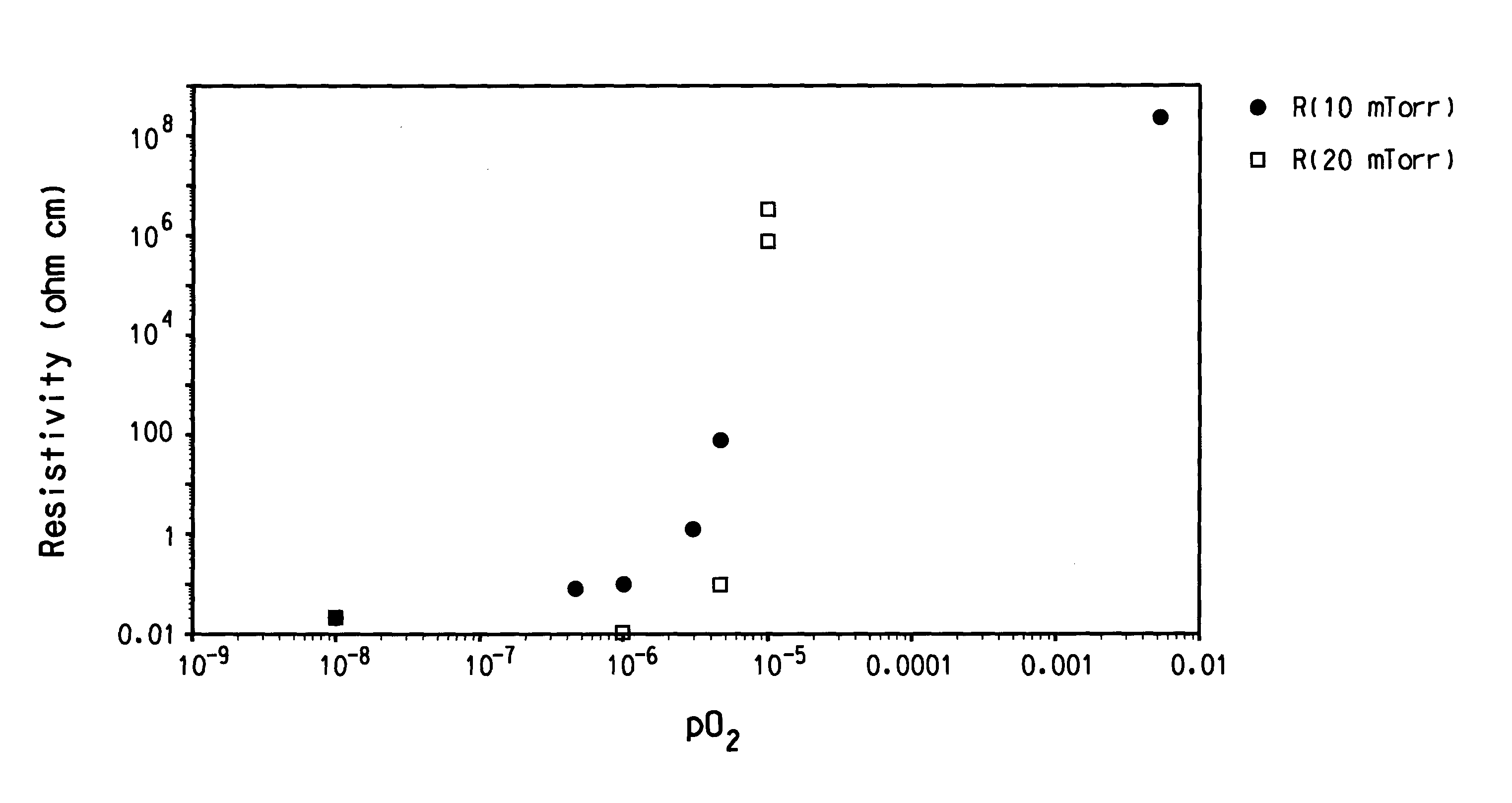
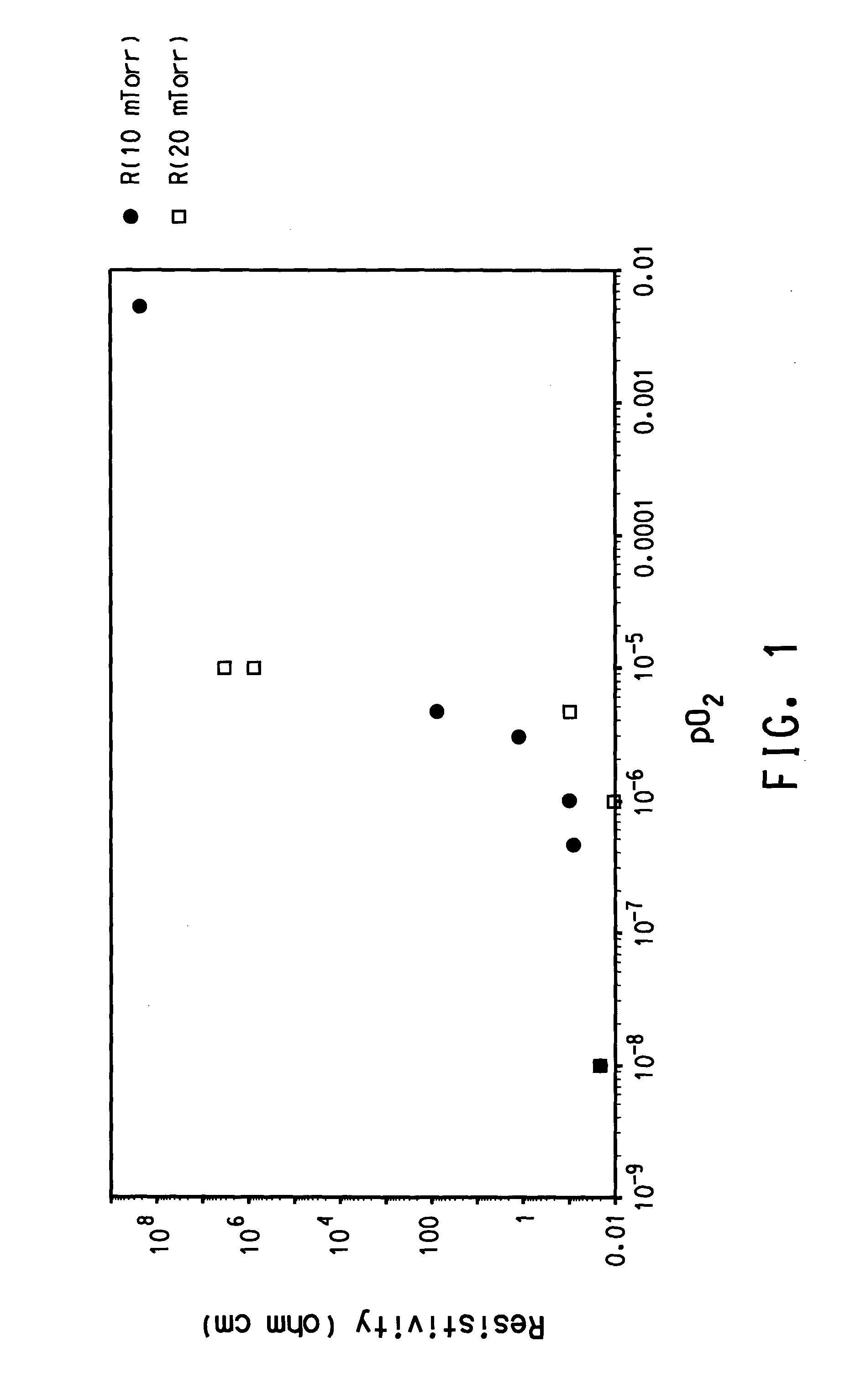
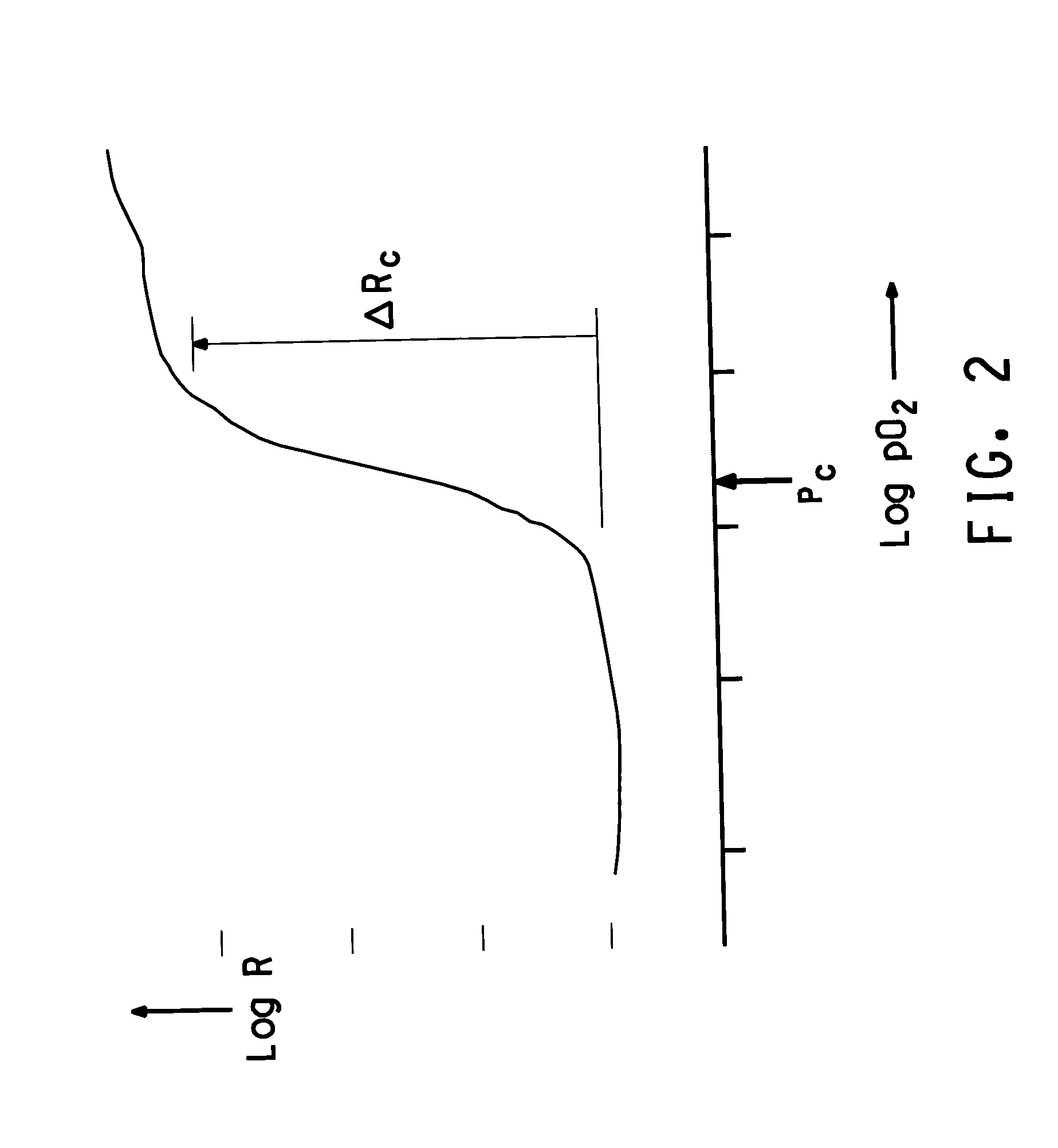
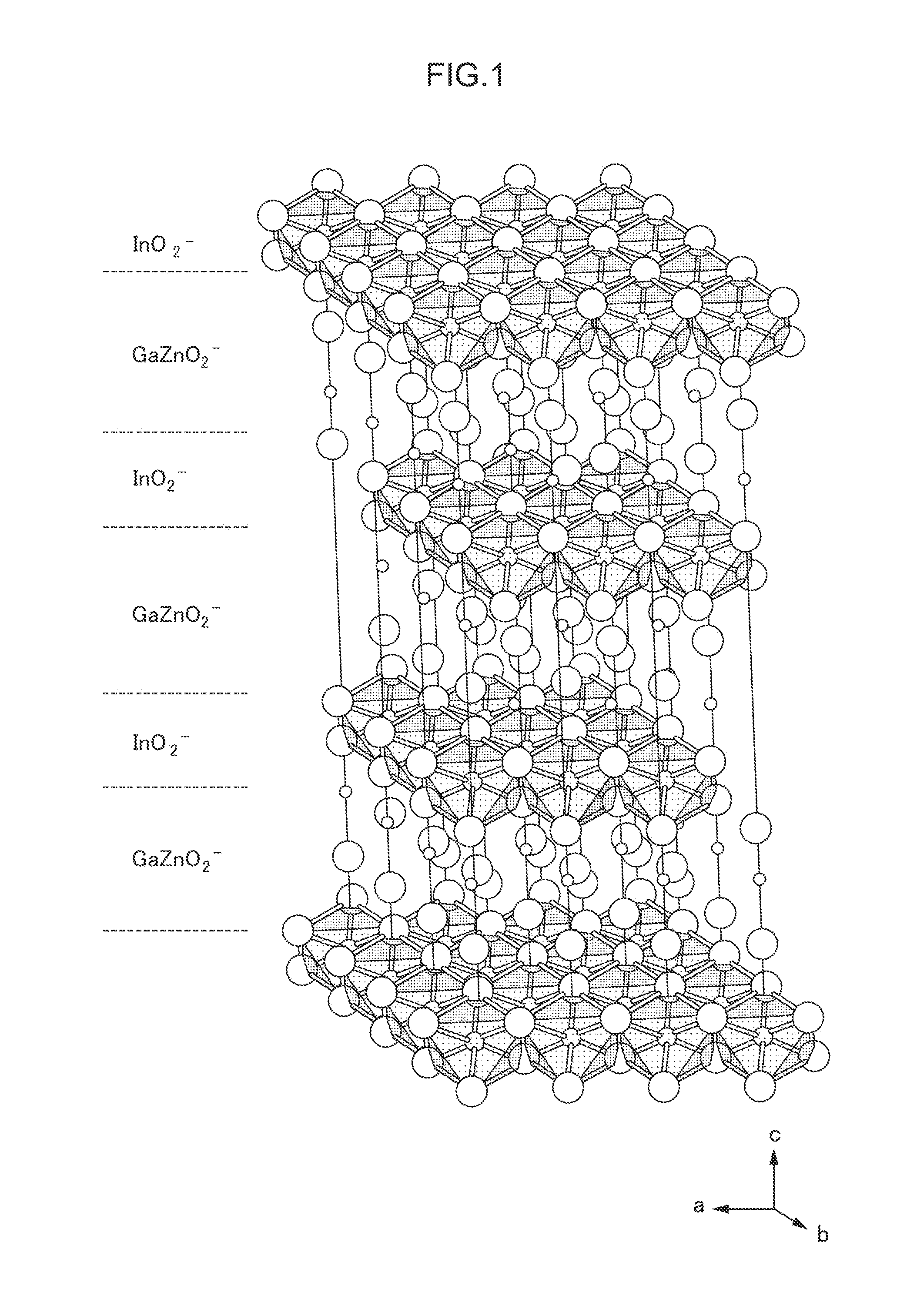
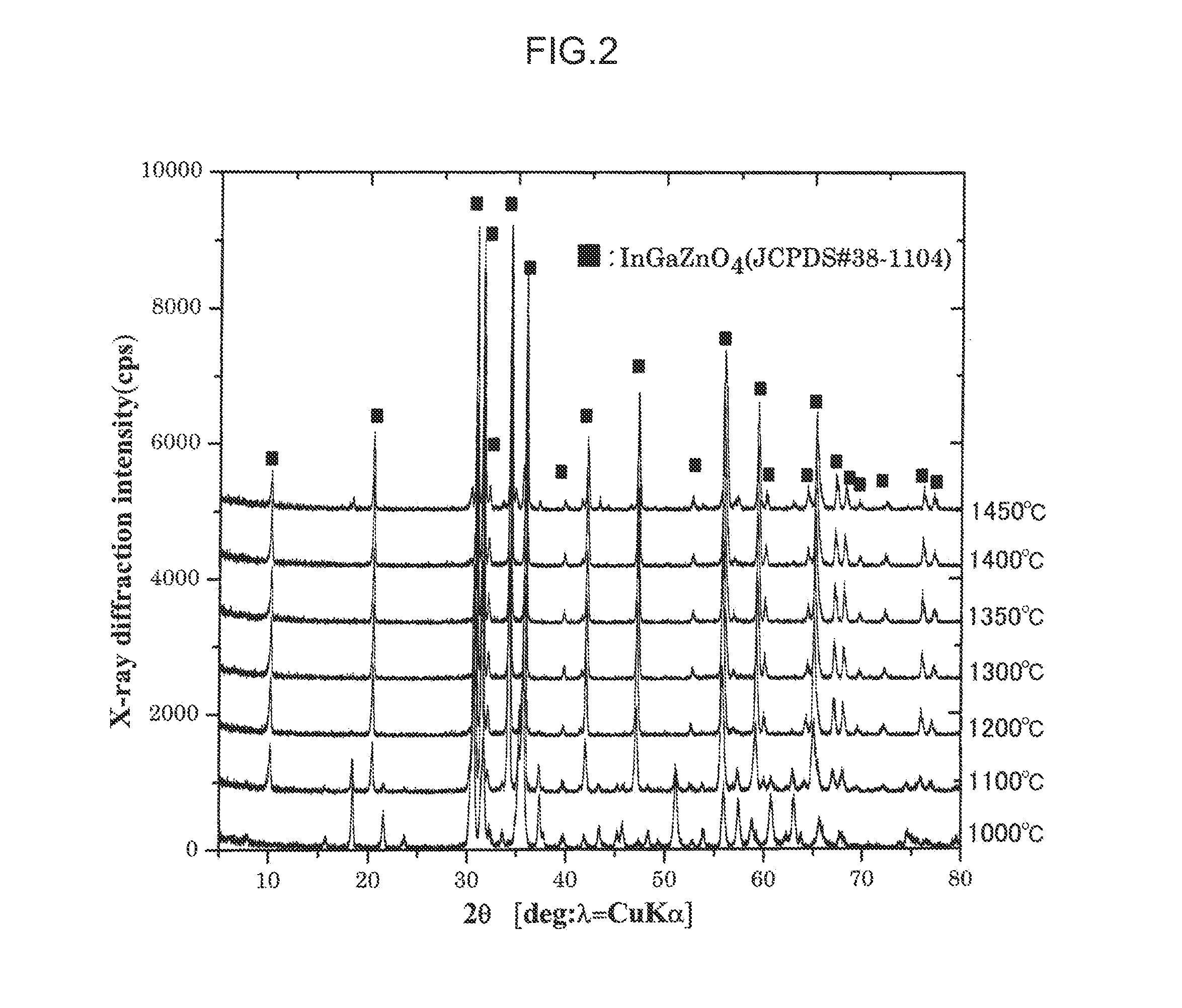
The invention provides a thin film transistor comprising an active layer, the active layer comprising an IGZO-based oxide material, the IGZO-based oxide material being represented by a composition formula of In2-xGaxZnO4-δ, where 0.75<x<1.10 and 0<δ≦1.29161×exp(−x / 0.11802)+0.00153 and being formed from a single phase of IGZO having a crystal structure of YbFe2O4, and a method of producing the thin film transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method and apparatus for integrating manual input
InactiveUS20050104867A1Easy to learnEasy to identifyInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisLow noiseDielectric
Owner:APPLE INC
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100051949A1Small currentHigh on-off ratioTransistorStatic indicating devicesMetallic materialsOxygen deficient
A thin film transistor structure in which a source electrode and a drain electrode formed from a metal material are in direct contact with an oxide semiconductor film may lead to high contact resistance. One cause of high contact resistance is that a Schottky junction is formed at a contact plane between the source and drain electrodes and the oxide semiconductor film. An oxygen-deficient oxide semiconductor layer which includes crystal grains with a size of 1 nm to 10 nm and has a higher carrier concentration than the oxide semiconductor film serving as a channel formation region is provided between the oxide semiconductor film and the source and drain electrodes.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Water dispersible polypyrroles made with polymeric acid colloids for electronics applications
InactiveUS20050205860A1Material nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrolytesWater dispersiblePolypyrrole
Compositions are provided comprising aqueous dispersions of at least one polypyrrole and at least one colloid-forming polymeric acids at methods of making such compositions. The new compositions are useful in electronic devices including organic electronic devices such as organic light emitting diode displays, memory storage, electromagnetic shielding, electrochromic displays,and thin film transistors, field effect resistance devices.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
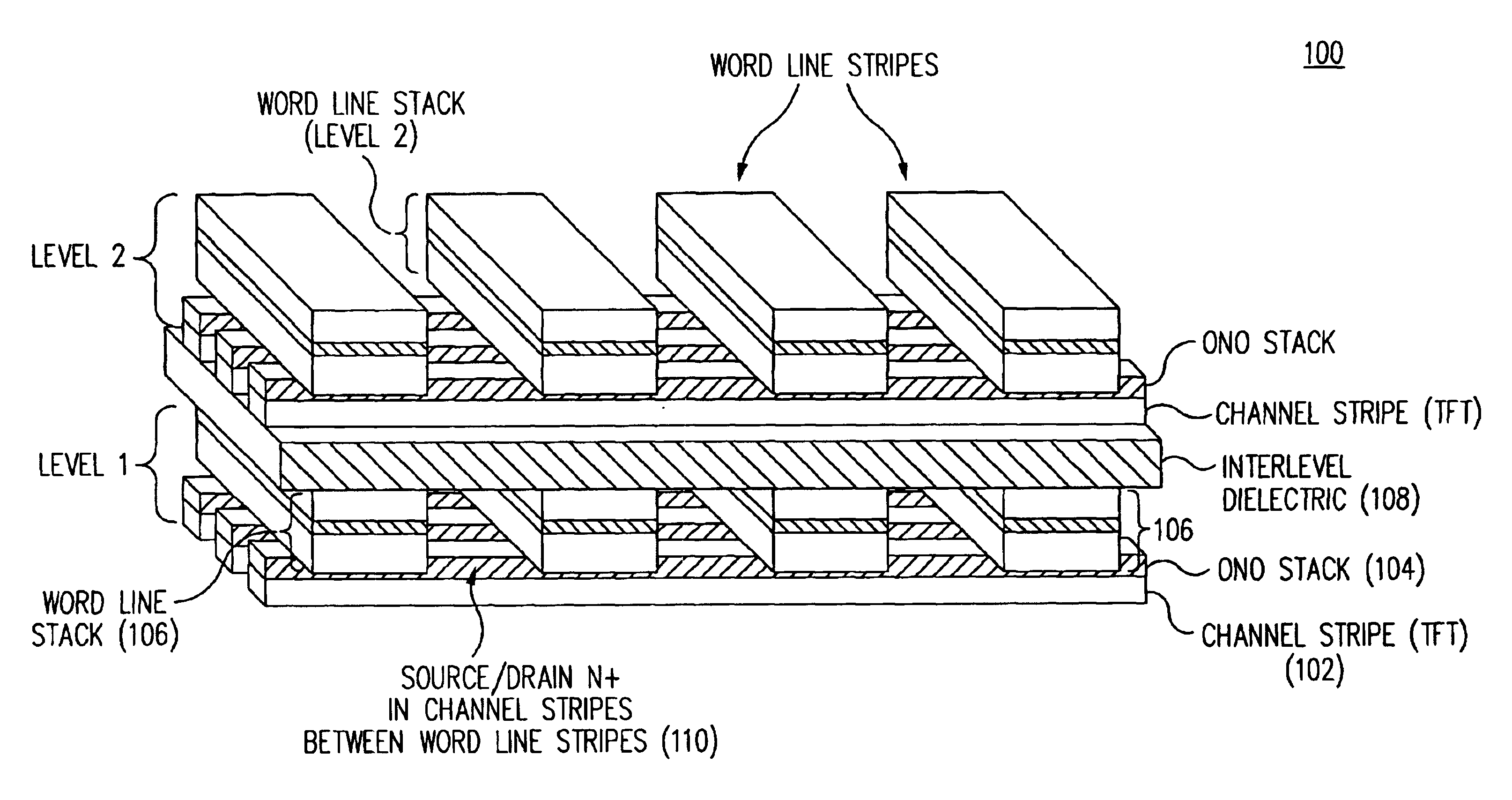
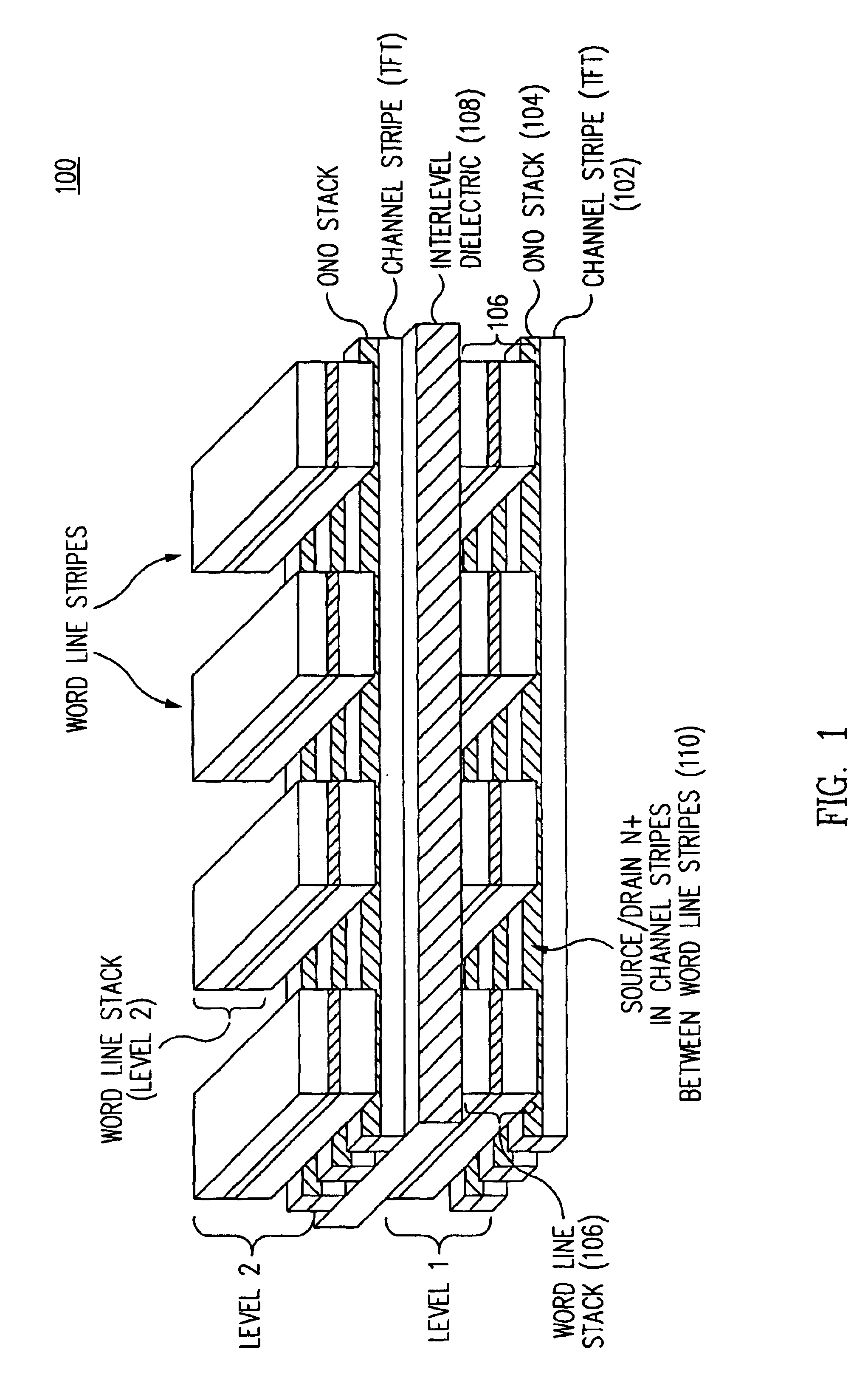
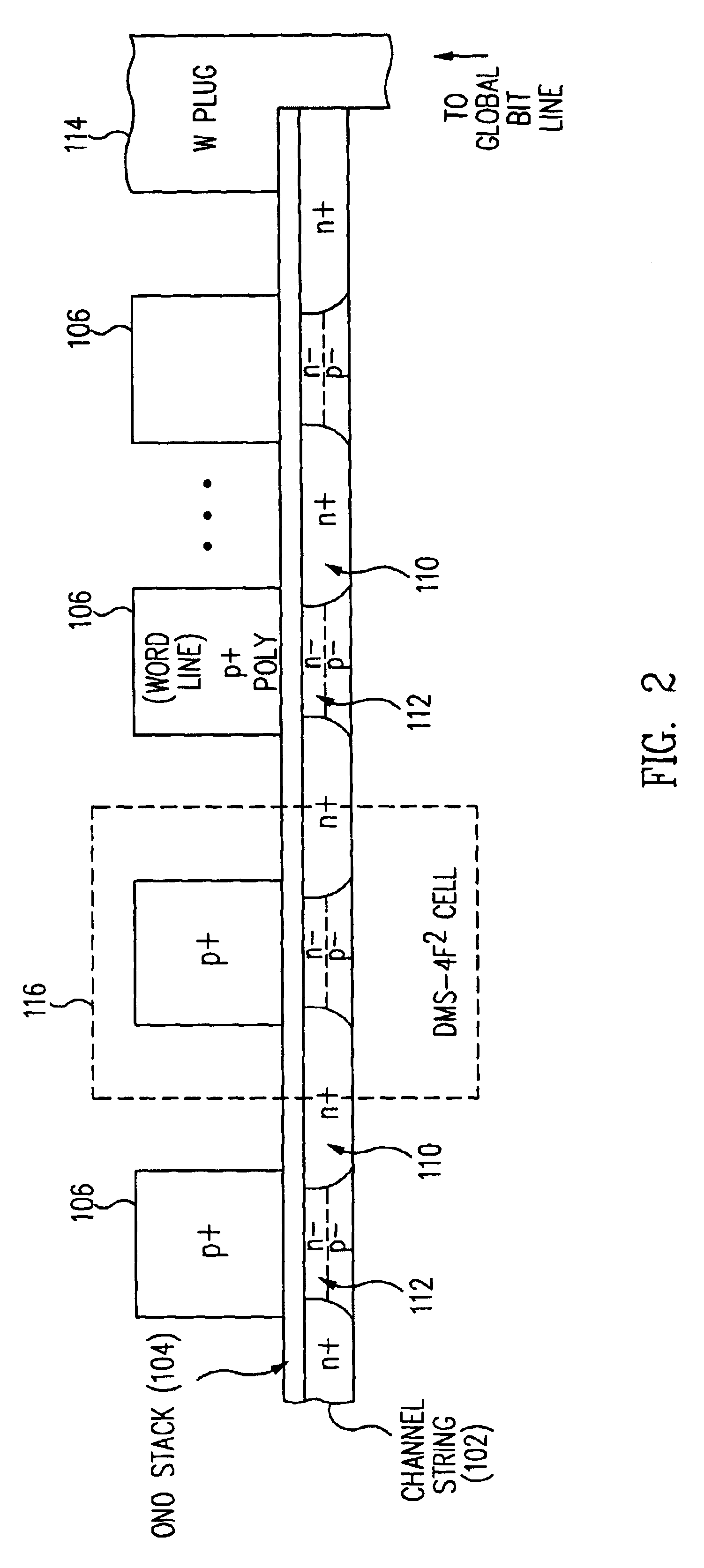
Method for fabricating programmable memory array structures incorporating series-connected transistor strings
InactiveUS7005350B2Reduce in quantityDense memory arraySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineComputer architecture
A three-dimensional flash memory array incorporates thin film transistors having a charge storage dielectric arranged in series-connected NAND strings to achieve a 4F2 memory cell layout. The memory array may be programmed and erased using only tunneling currents, and no leakage paths are formed through non-selected memory cells. Each NAND string includes two block select devices for respectively coupling one end of the NAND string to a global bit line, and the other end to a shared bias node. Pairs of NAND strings within a block share the same global bit line. The memory cells are preferably depletion mode SONOS devices, as are the block select devices. The memory cells may be programmed to a near depletion threshold voltage, and the block select devices are maintained in a programmed state having a near depletion mode threshold voltage. NAND strings on more than one layer may be connected to global bit lines on a single layer. By interleaving the NAND strings on each memory level and using two shared bias nodes per block, very little additional overhead is required for the switch devices at each end of the NAND strings. The NAND strings on different memory levels are preferably connected together by way of vertical stacked vias, each preferably connecting to more than one memory level. Each memory level may be produced with less than three masks per level.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com